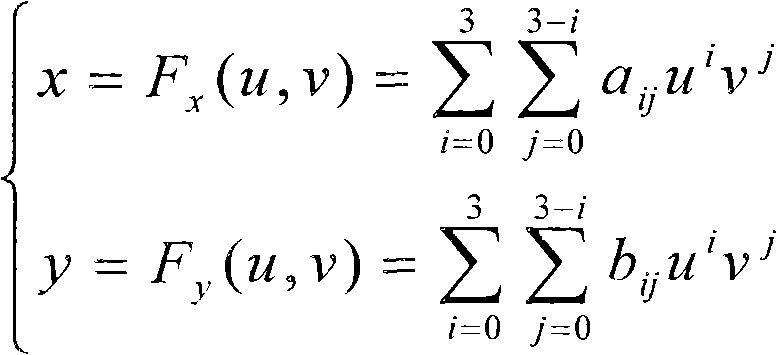Patents
Literature
480 results about "Geometric distortion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
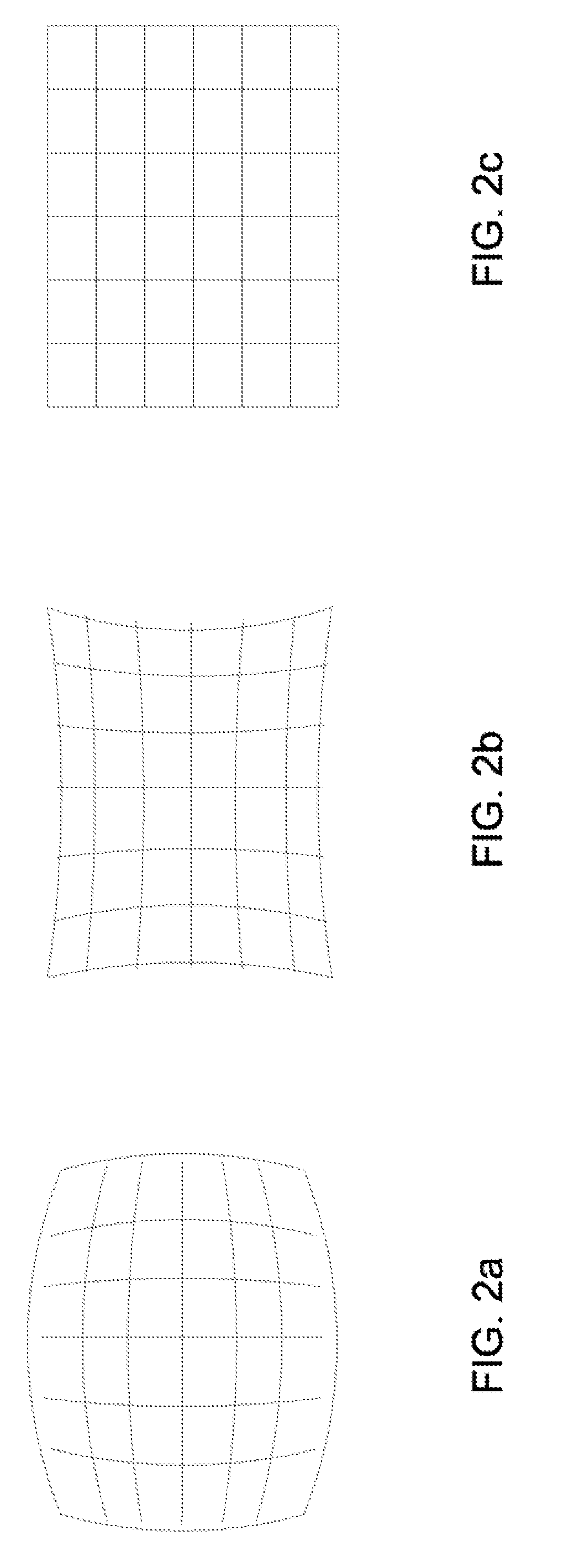
In geometric optics, distortion is a deviation from rectilinear projection; a projection in which straight lines in a scene remain straight in an image.
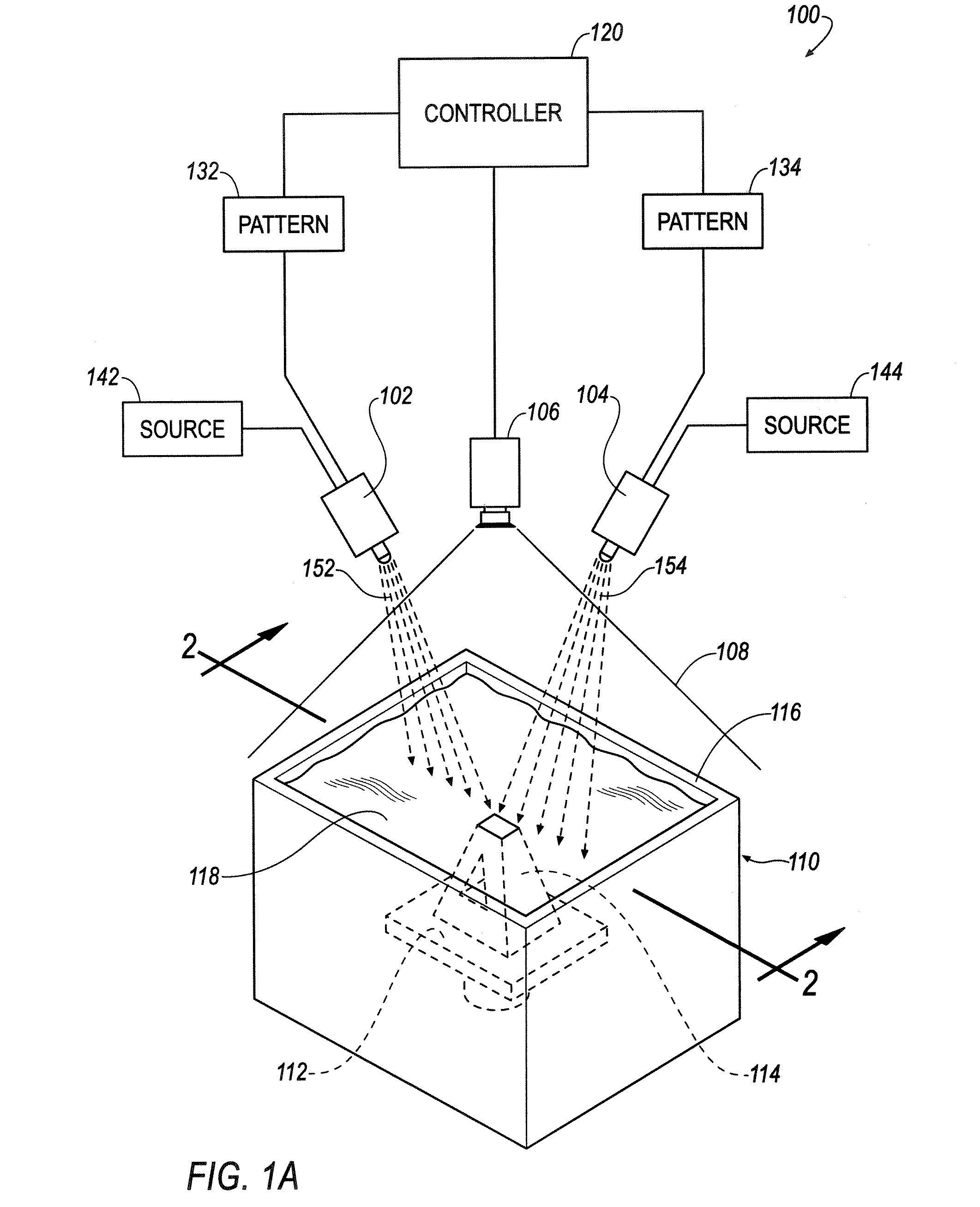
System and Method for Manufacturing
ActiveUS20100125356A1Image enhancementAdditive manufacturing apparatusComputer graphics (images)Reactive material
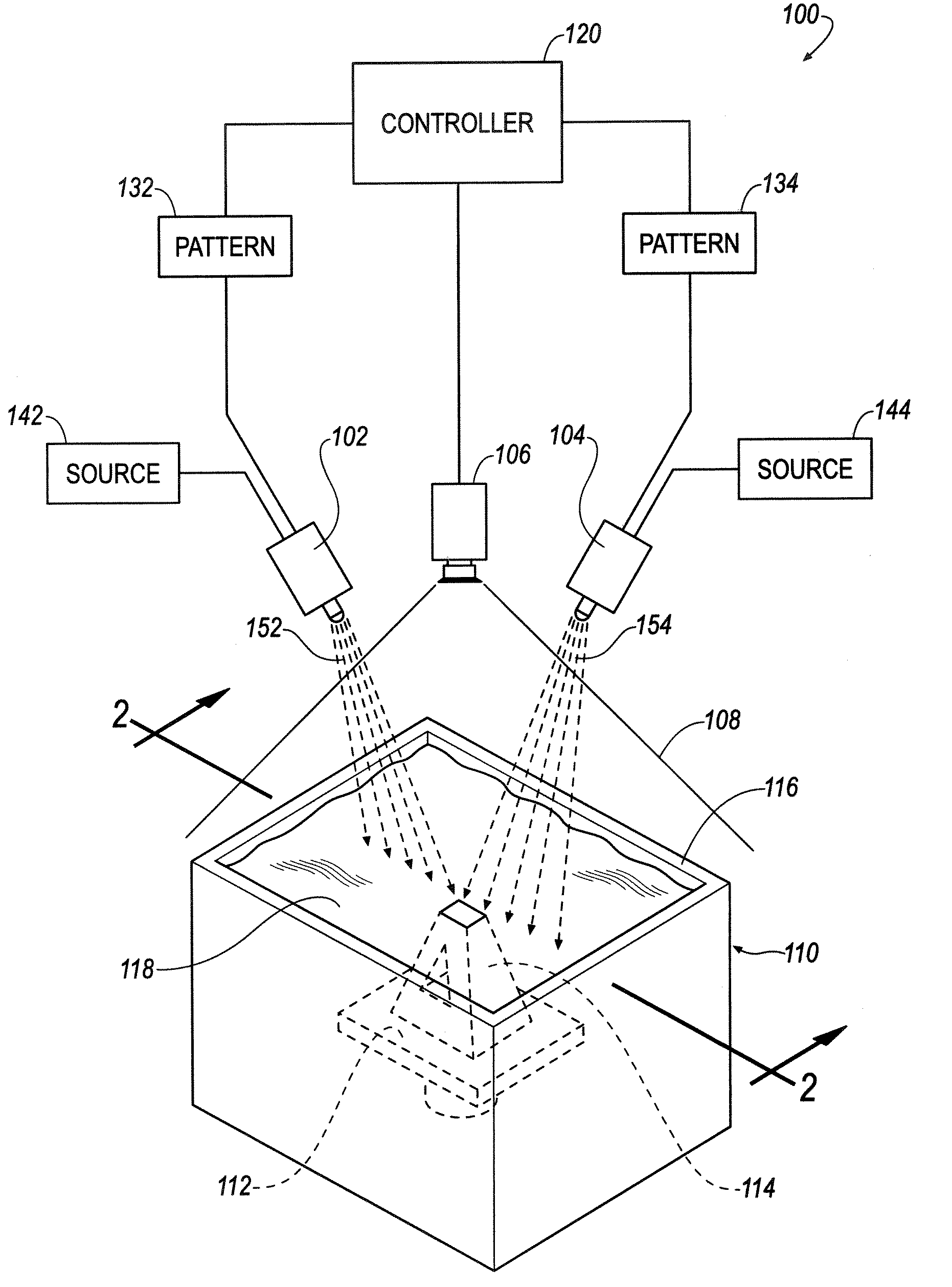
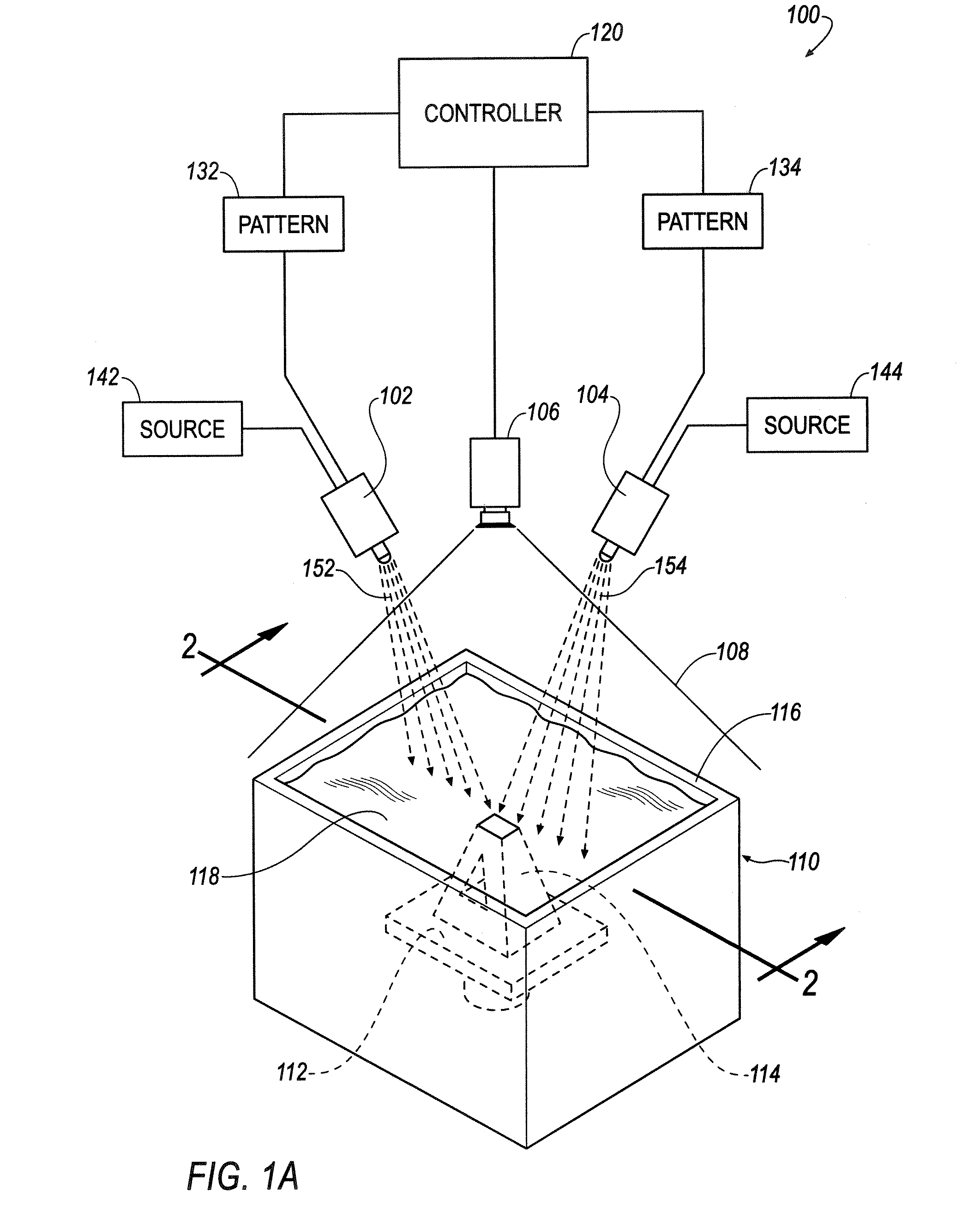
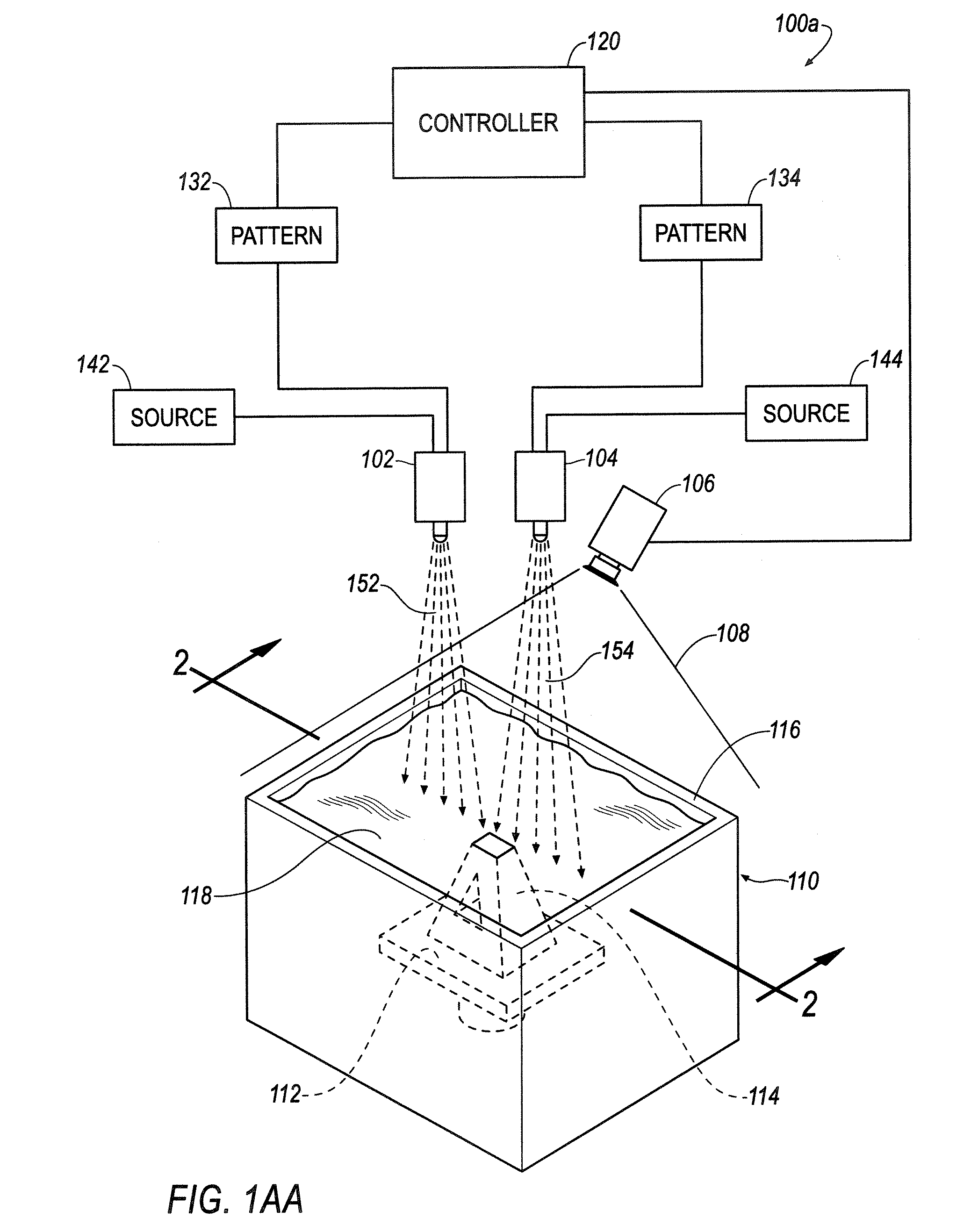
A method includes receiving a predetermined object pattern representing a portion of a three-dimensional object, modifying the predetermined object pattern to correct for geometric distortion of a pattern generator, and generating the modified pattern using the pattern generator. The generated pattern interacts with a reactive material to form the portion of the three-dimensional object defined by the predetermined object pattern.
Owner:GLOBAL FILTRATION SYST
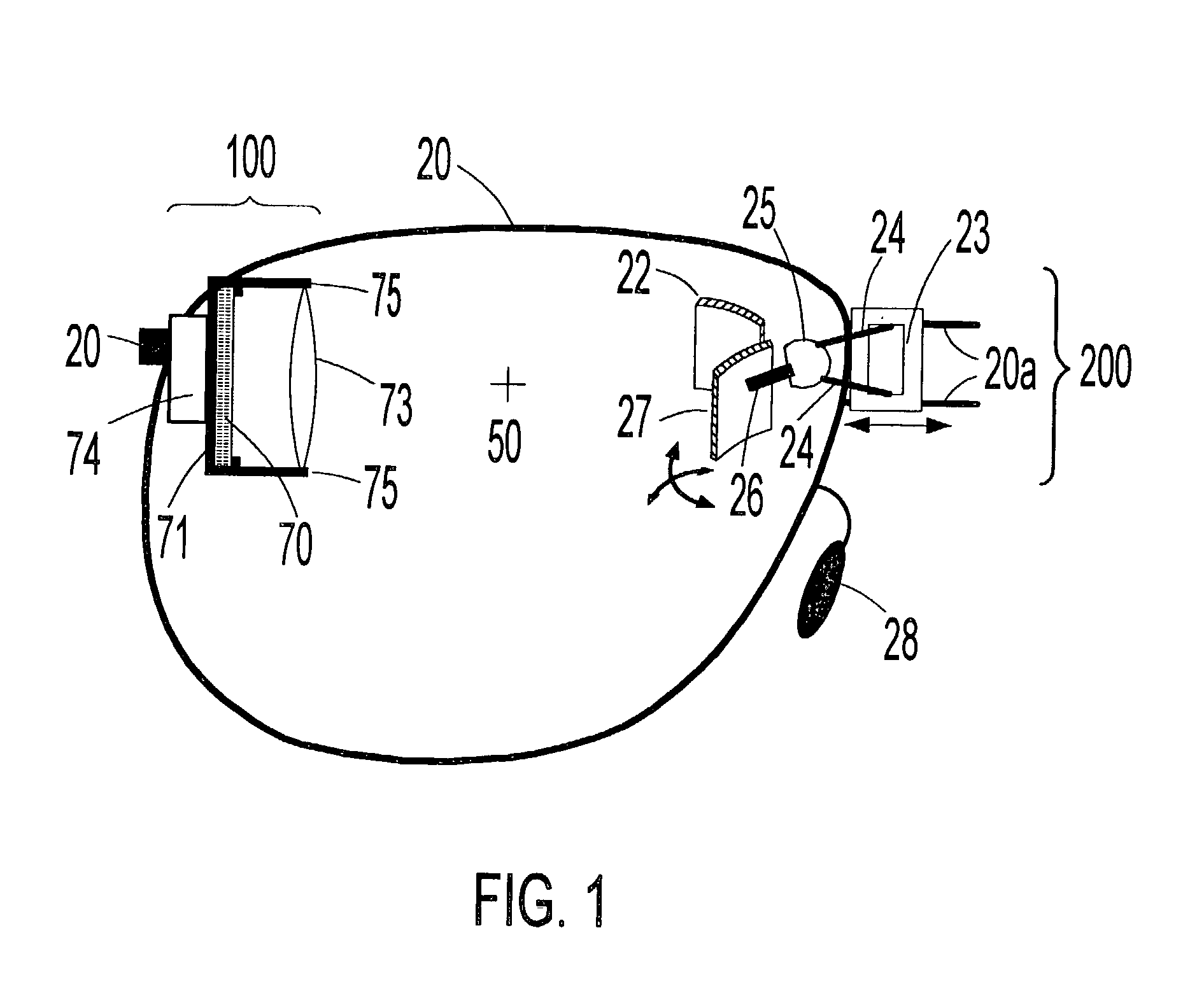
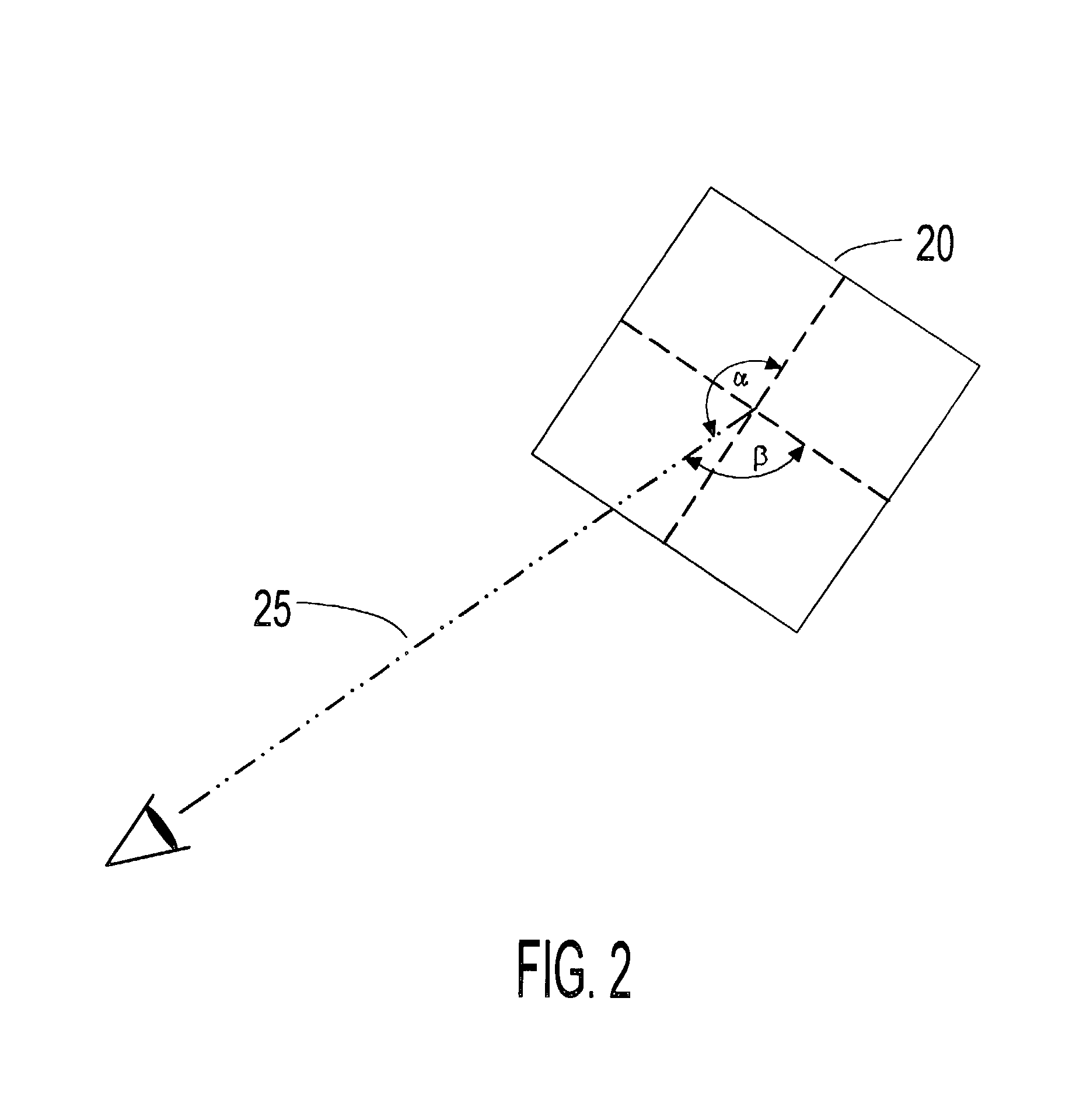
Virtual display apparatus for mobile activities
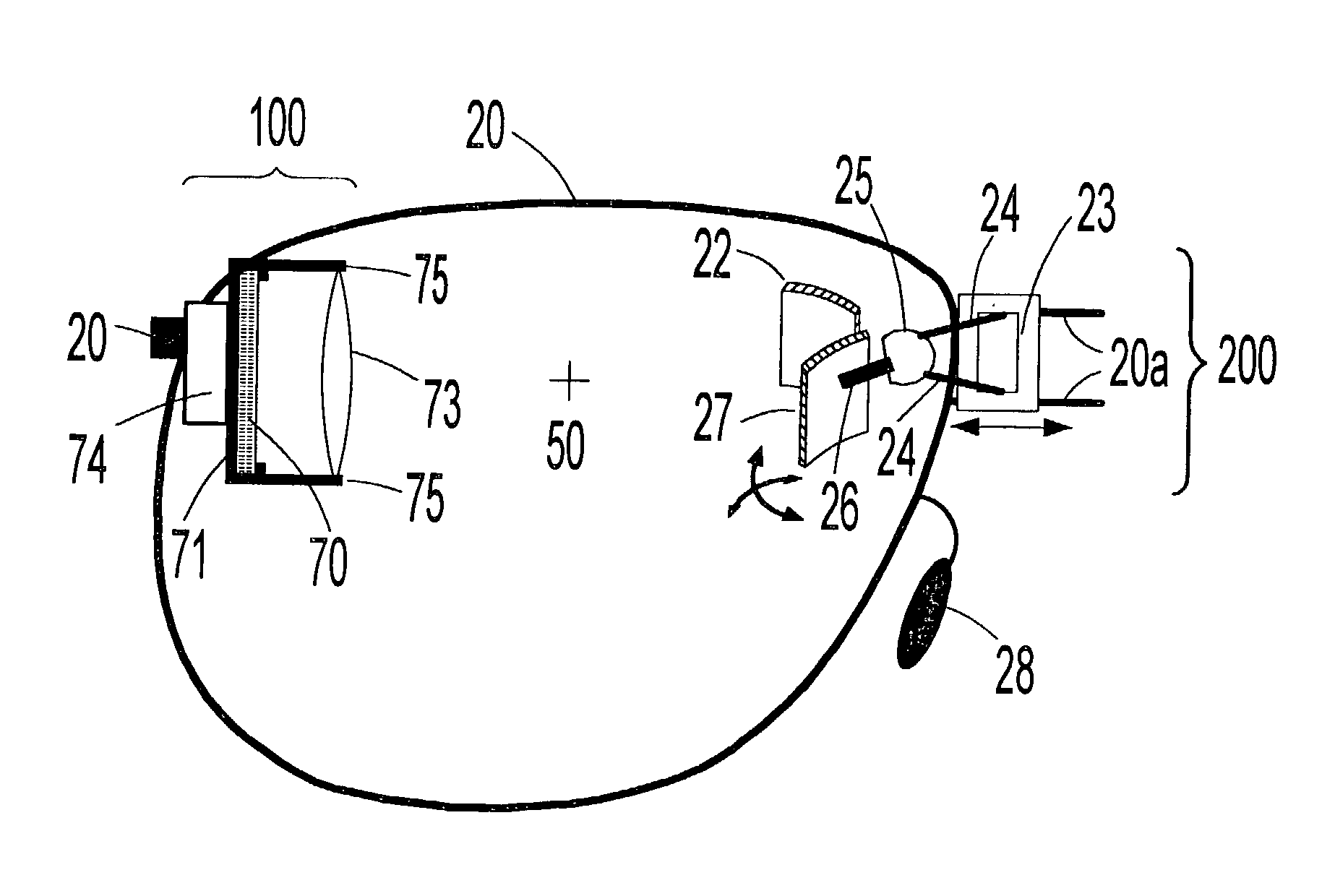
InactiveUS20030030597A1Prevent slippagePrevent dislodgingCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical elementsComputer scienceField of view
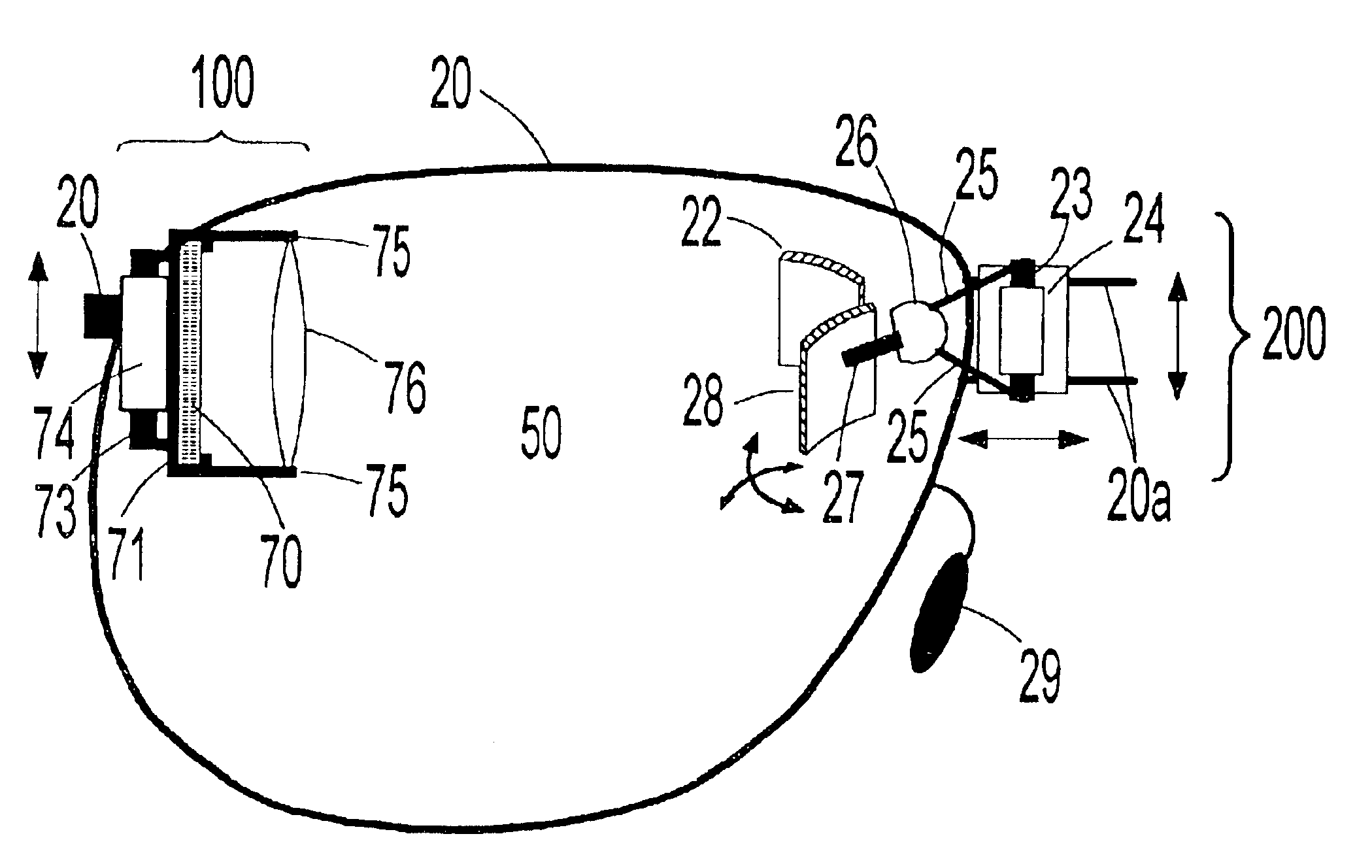
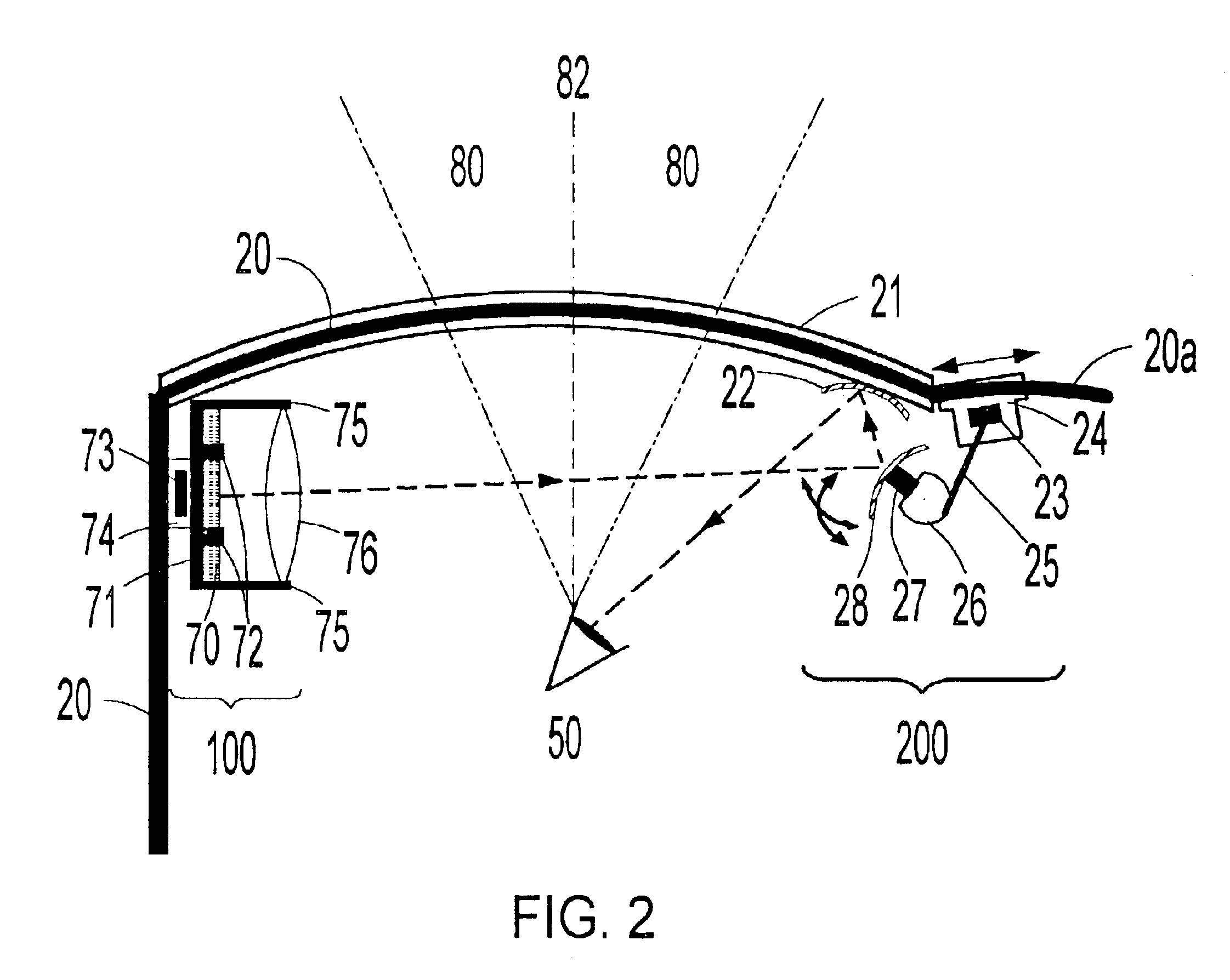
The present invention teaches a method of constructing head-mounted virtual display apparatuses for mobile activities based on a non-cross-cavity optical configuration, which simultaneously provides the user with "look toward" access to an inset virtual image and an unobstructed forward field of view of at least 35 degrees. In one embodiment, a pair of light deflecting elements and associated adjustment means project a light path from the normal peripheral field of view towards the eye without geometric distortion of the virtual image associated image plane tilt.
Owner:GEIST RICHARD EDWIN
Image warping and lateral color correction
Color or grayscale images having optical elements induced geometric distortions can be corrected on individual color image component by creating correction image component having the complementary distortion; and applying the correction image component to the corresponding distorted color image component.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Head-mounted virtual display apparatus with a near-eye light deflecting element in the peripheral field of view
InactiveUS6771423B2Minimize and eliminate geometric distortionMinimizing fatigueCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-optical partsVisual field lossDisplay device
The present invention is a head-mounted virtual display apparatus based on a cross-cavity optical configuration, in which a near-eye light deflecting element (LDE) is located in the peripheral field of view. Positioning of the near-eye LDE in the peripheral field of view provides the user simultaneously with "look toward" access to an inset magnified image of a miniature display and an unobstructed forward field of view of at least 35 degrees. Active and passive alignment means, including articulating connections and image warping electronics, allow correction of geometric distortion arising from folding of the optical train and / or embodiments based on off-axis optical configurations.
Owner:GEIST RICHARD
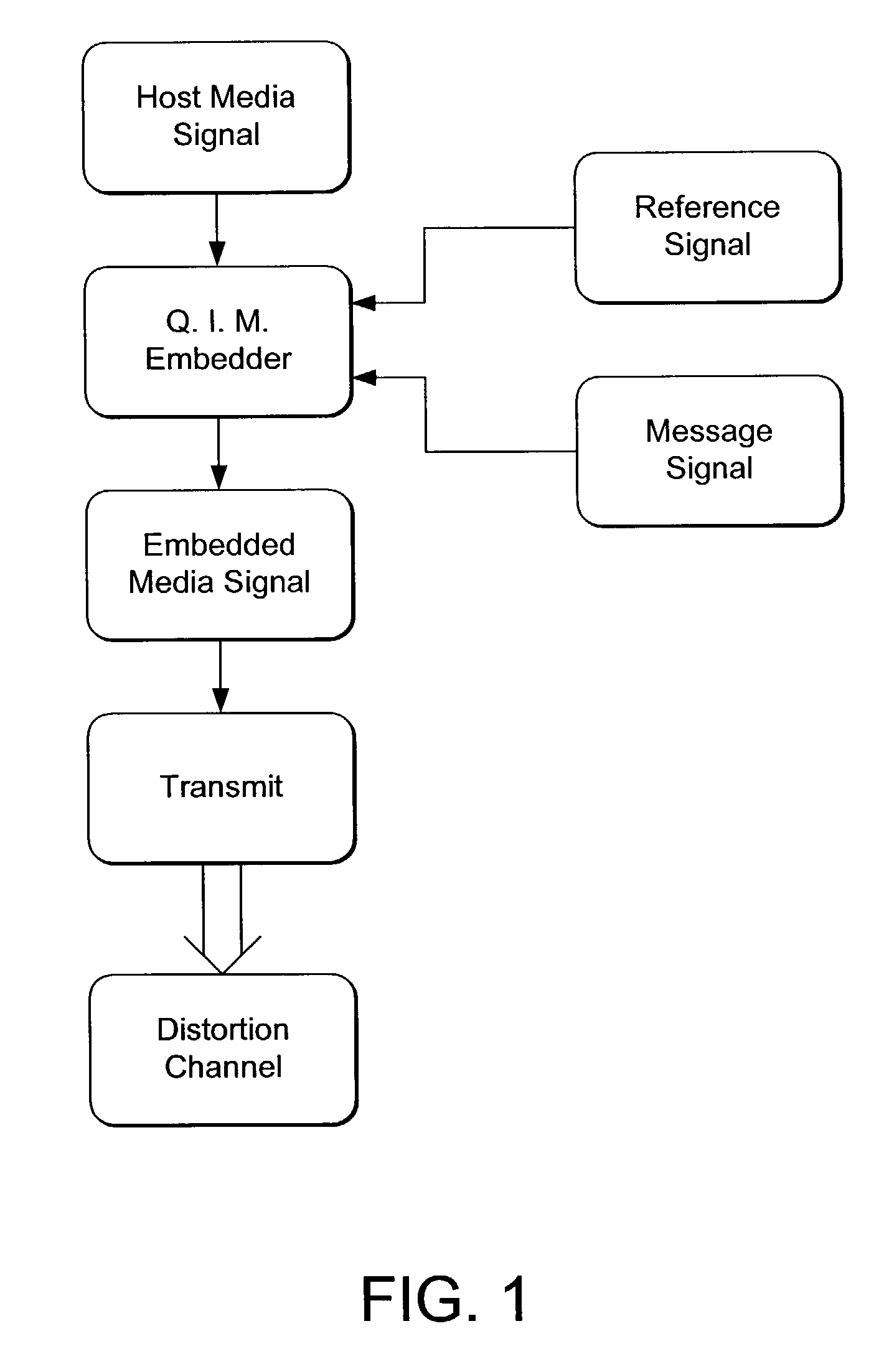
Media signal filtering for use in digital watermark reading
InactiveUS7076082B2Reduce errorsReduce the impactSpeech analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionCircular referenceCurve fitting
A curve fitting method is used to synchronize a reader of embedded data in a media signal. A circular reference signal is embedded in the media signal. After geometric distortion of the media signal, the reference signal is distorted, yet still detectable. The amount of distortion is derived by detecting the reference signal, and applying a curve fitting method from which the distortion is calculated.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP (FORMERLY DMRC CORP)
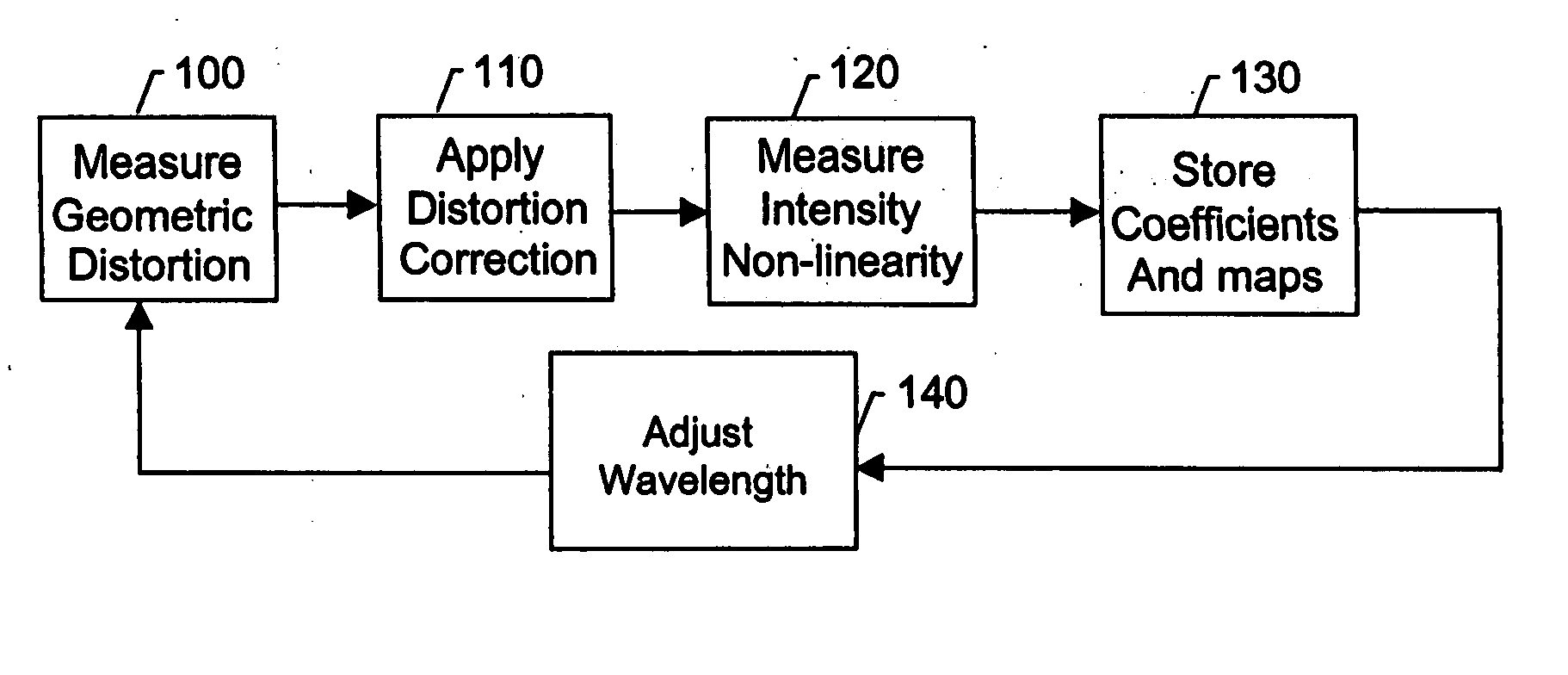
Calibration and error correction in multi-channel imaging
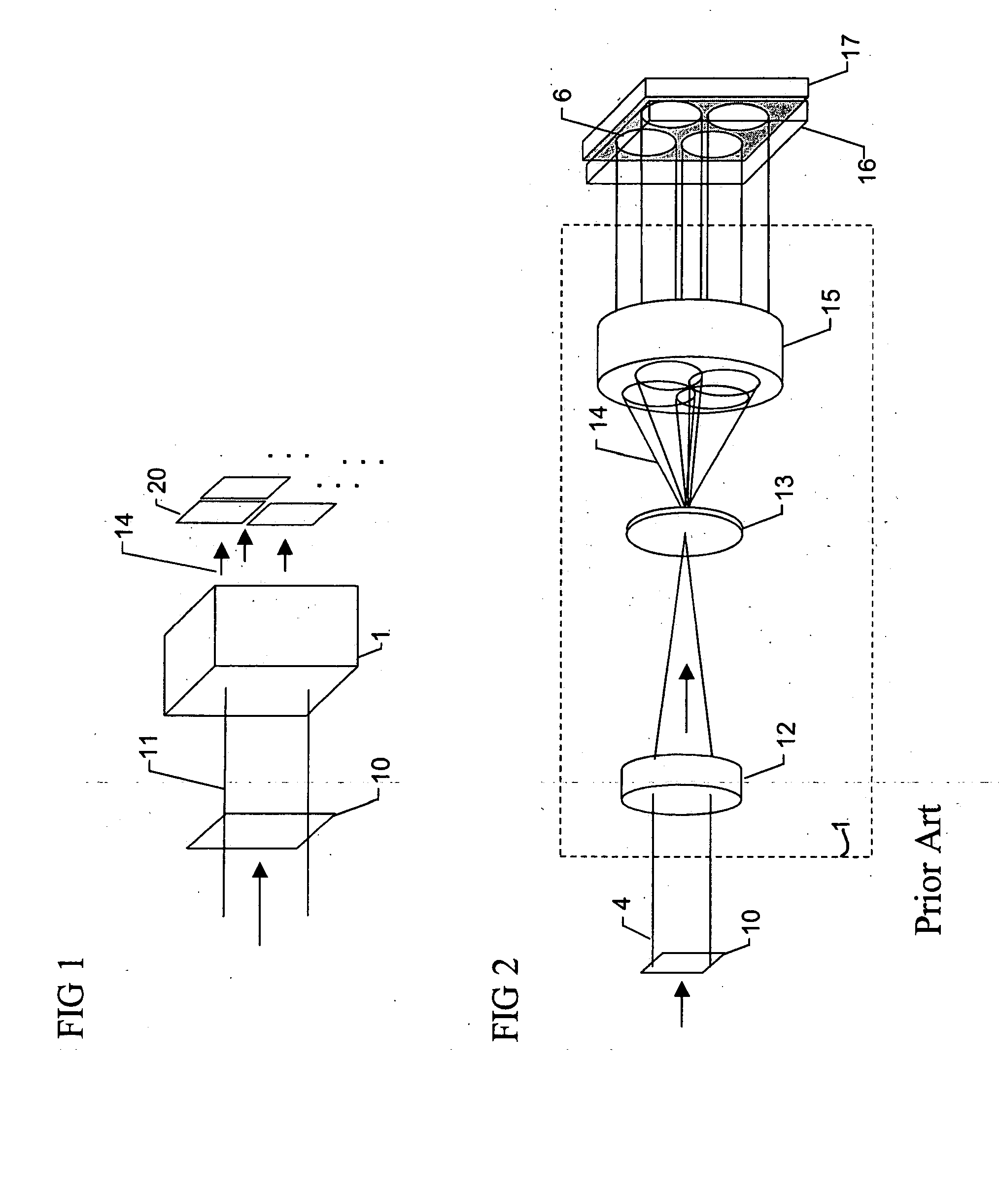
ActiveUS20050083531A1Reducing phase-dependent systematic measurement errorMeasure can be takenImage enhancementOptical measurementsPhase correlationPath length
A multi-channel imaging system is calibrated by measuring the geometric distortion in each sub-image, generating corresponding correction factors, and applying such factors to correct subsequent image data. In addition, intensity transfer-function arrays are measured at each pixel, and further used to correct for system and detector nonlinearities and nonuniformity between images. The procedure is repeated over a range of wavelengths to produce a complete set of correction coefficients and transfer functions. When the system is used for interferometric phase measurements, multiple measurements are preferably taken and a random phase offset in the reference path length is introduced at each measurement. The multiple phase data so derived are then averaged to reduce phase-dependent systematic measurement errors.
Owner:ONTO INNOVATION INC
Method for stitching partial radiation images to reconstruct a full image
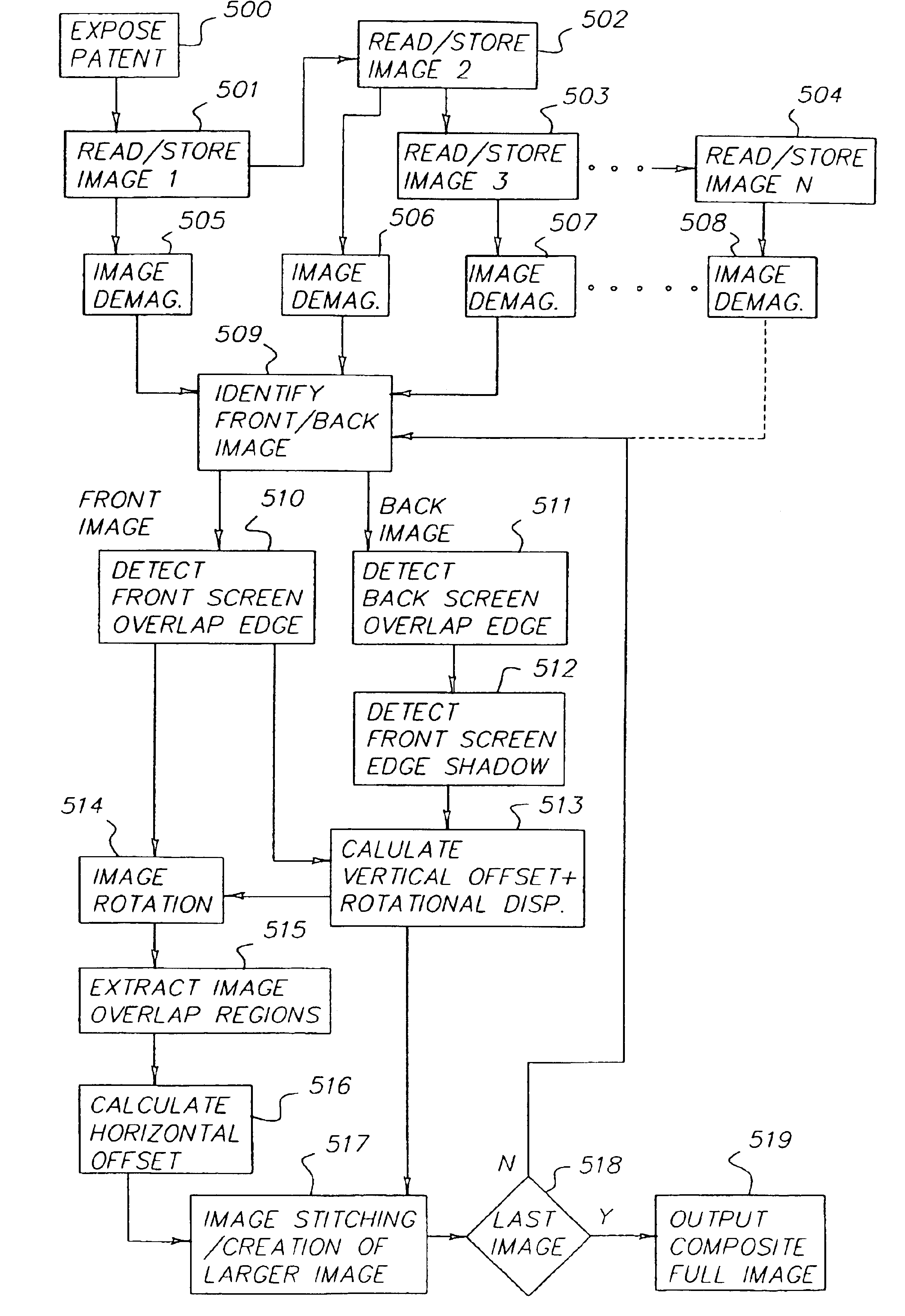
InactiveUS6895106B2High geometric accuracyImprove image qualityCharacter and pattern recognitionImage data processing detailsComputer graphics (images)Radiology
A method of forming a composite digital image comprising: providing 1-N digital images formed from 1-N contiguous segments of a larger radiographic image recorded in 1-N overlapping storage phosphor screens wherein N is equal to or greater than 2 and wherein the image content in the overlapped region of contiguous images is the same, and the end edge of a screen nearest an x-ray source is present in both contiguous images; selecting a pair of contiguous digital images, wherein one image is closer to said x-ray source than said other image; correcting for any geometric distortion if applicable in said pair of digital images based on the distance between x-ray source and said storage phosphor screen; determining any rotational displacement and any vertical displacement between said pair of digital images by matching said end edge of said one image present in said pair of images correcting for image orientation if applicable based on any said rotational displacement; determining any horizontal displacement between said pair of digital images by correlating the image content in said overlapping regions of said pair of digital images; stitching said pair of digital images together to form a larger composite digital image along said one image edge based on any said horizontal and vertical displacement; and repeating said correcting for any geometric distortion to said stitching with the larger composite image and the next consecutive overlapping digital image until all N digital images are stitched together to form a full composite image.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
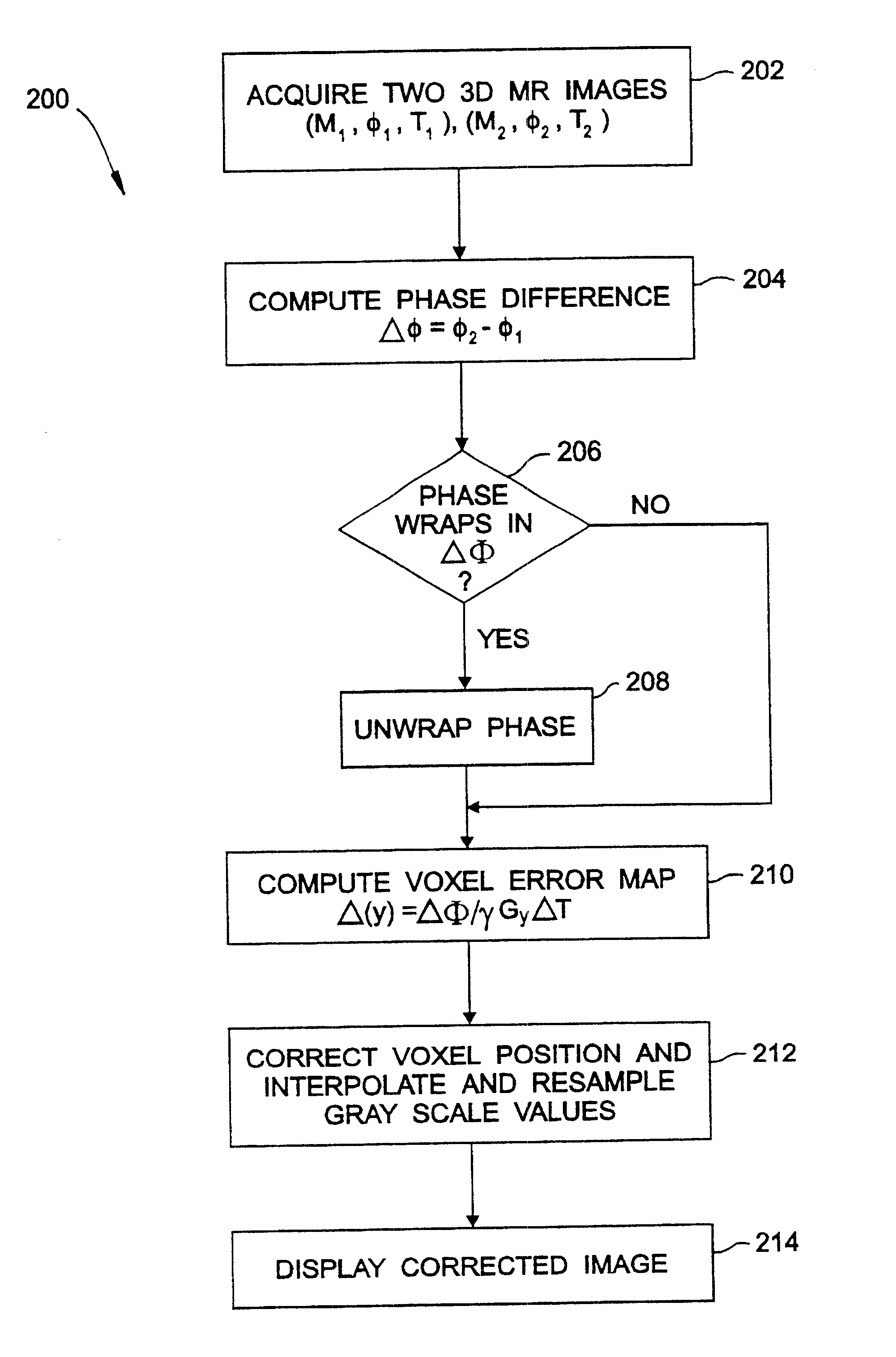
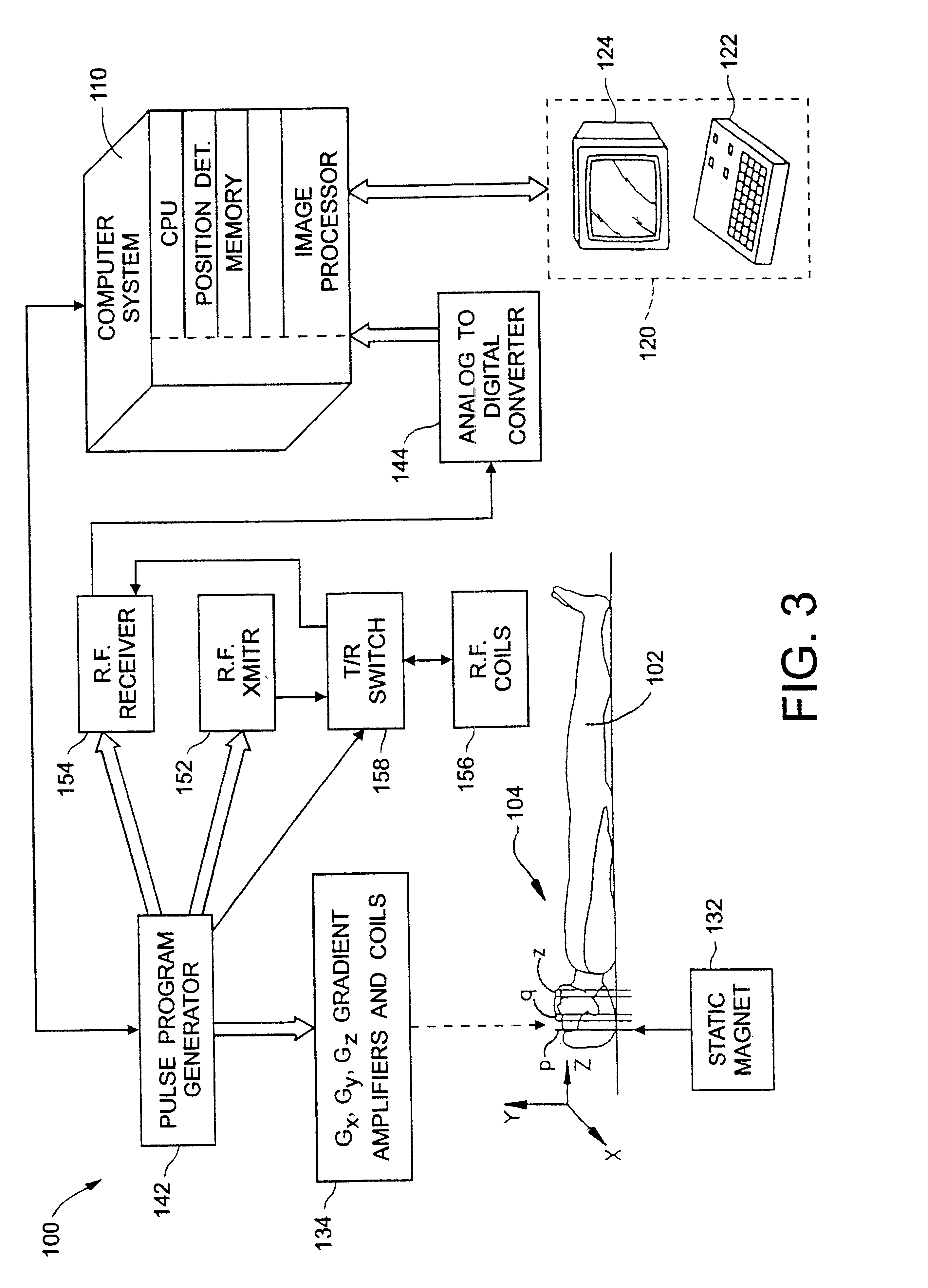
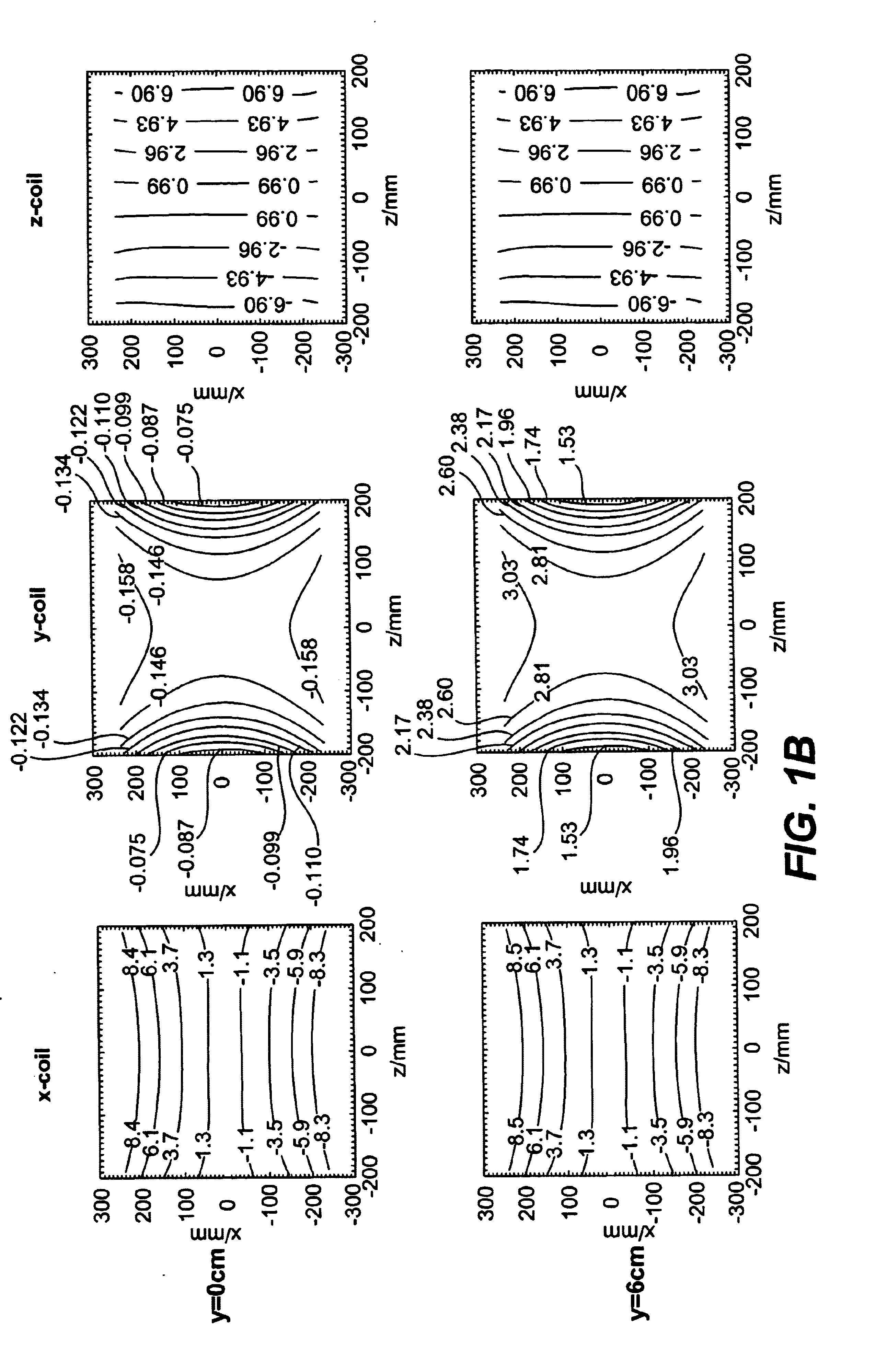
Geometric distortion correction in magnetic resonance imaging
A three dimensional (3D) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system (100) performs object-induced geometric distortion correction. The MRI system performs (202) a 3D MRI pulse sequence to acquire a first 3D MR image of an examination region containing at least a portion of a subject and performs (202) the 3D MRI pulse sequence a second time to acquire a second 3D MR image of the examination region A computer system (110) computes (210) a voxel error map based on a phase difference between the first and second 3D MR images and corrects (212) voxel positions in one of the 3D MR images in accordance with the voxel error map.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
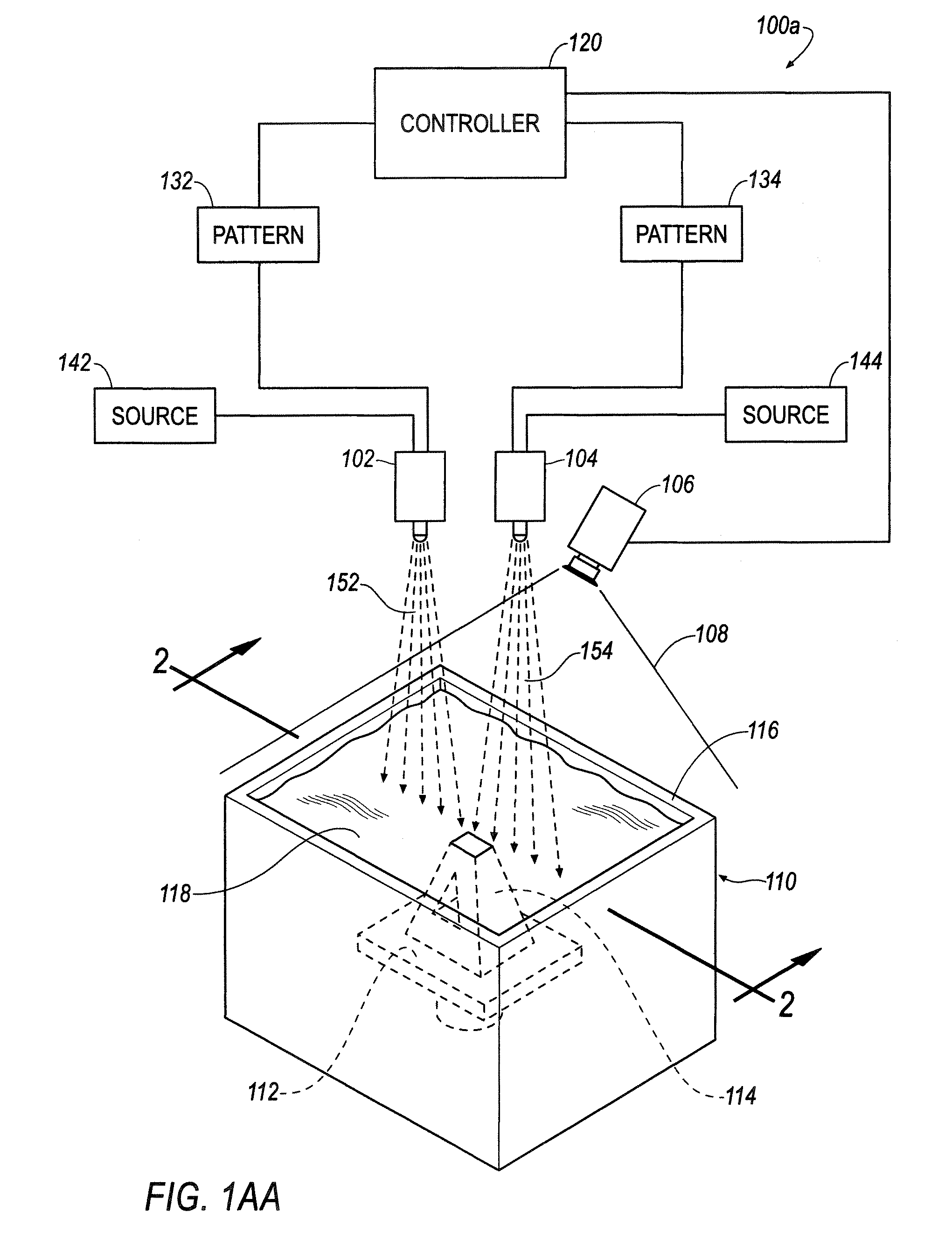
System and method for manufacturing
ActiveUS8666142B2Image enhancementAdditive manufacturing apparatusComputer graphics (images)Reactive material
Owner:GLOBAL FILTRATION SYST
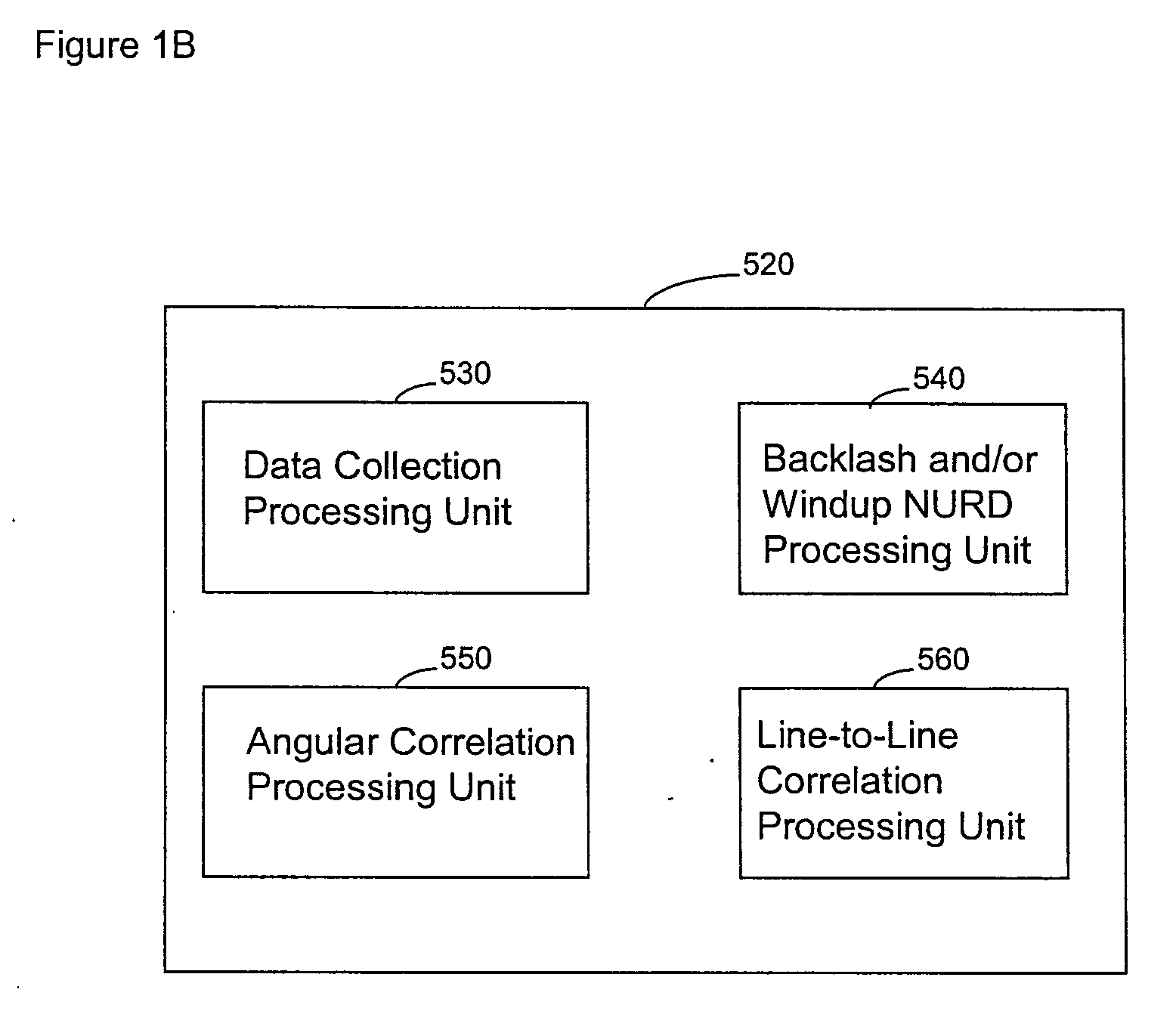
System and method for reducing angular geometric distortion in an imaging device
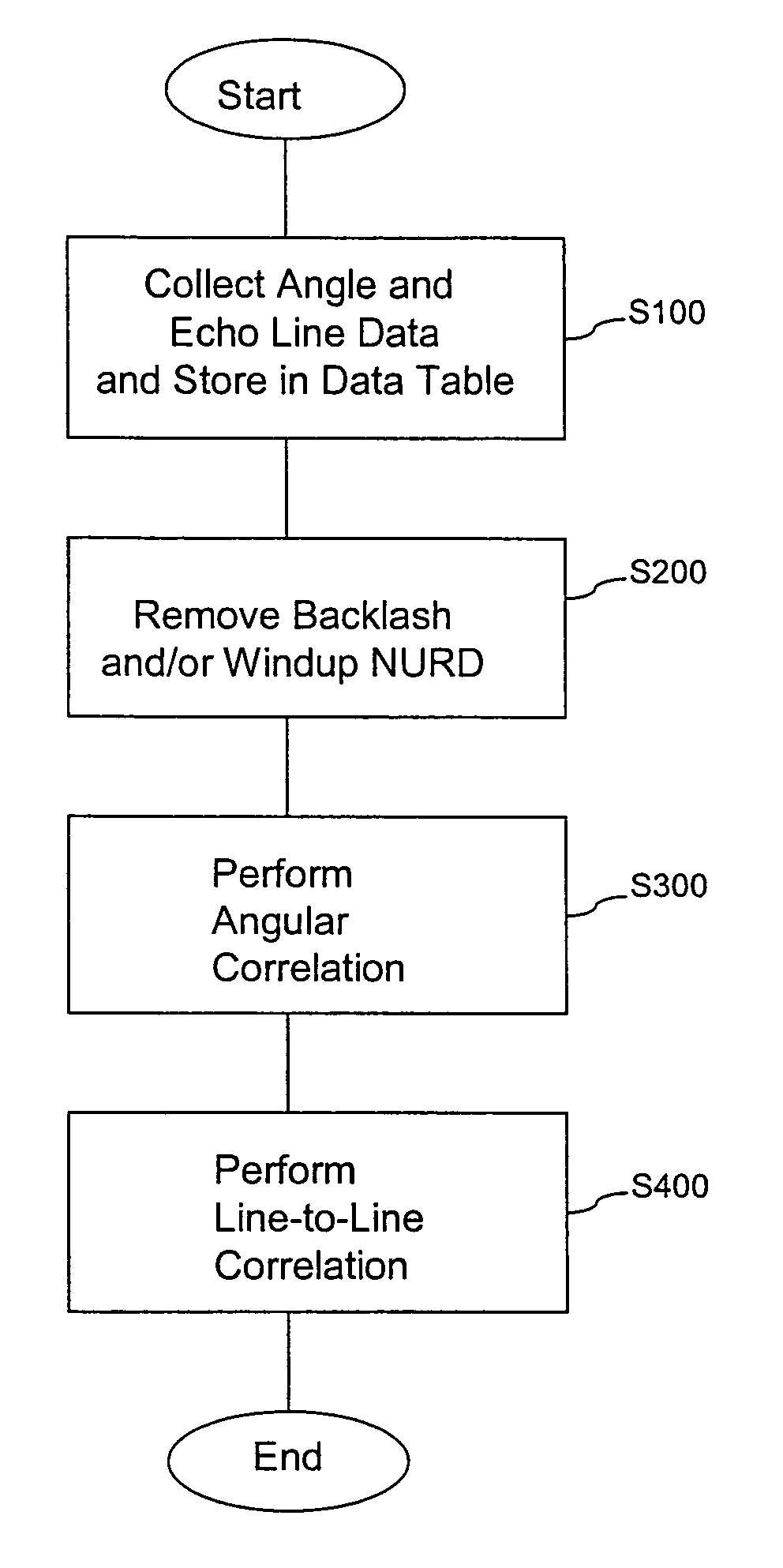
ActiveUS20070106155A1Reduce geometric distortionReduce and substantially eliminate angular geometric distortionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterTreatment choicesTreatment options
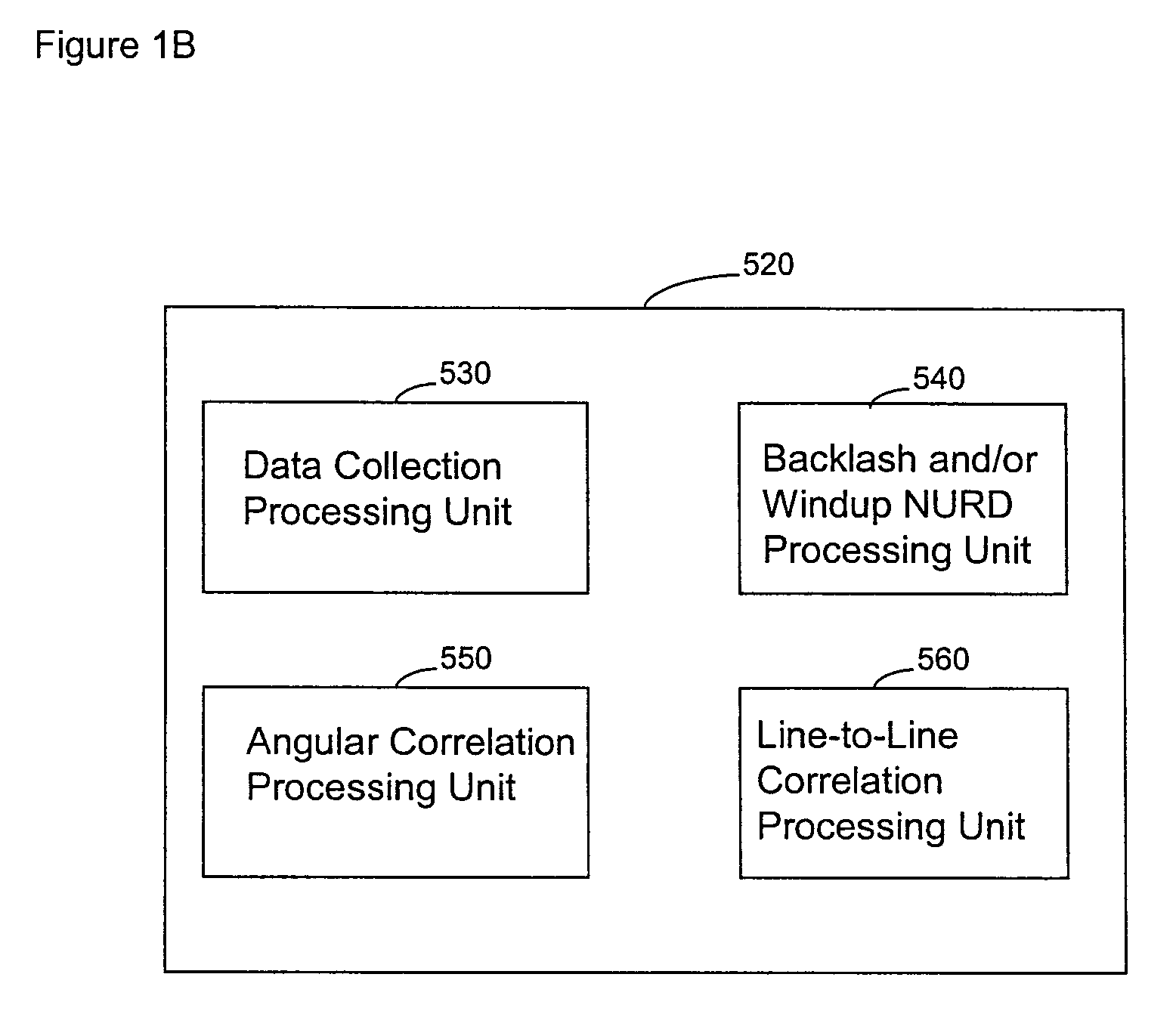
A system and method are provided for significantly reducing or substantially eliminating angular geometric distortions in devices designed for imaging and / or inspection of an interior portion or surface of a cavity. A series of processing steps or methods may be employed to eliminate Non-Uniform Rotational Distortion (NURD) in such devices, for example, unidirectional and bi-directional intravascular ultrasonic (IVUS) imaging systems. The system may include a processor and an electronic module which control operation of a transducer assembly provided at a distal end of a catheter assembly. The system invokes a first processing step or method to collect and store raw angle and line data, as well as one or more of second and third processing steps or methods which adjust for NURD experienced during backlash of a bi-directional imaging system and a fourth processing step or method which performs a line-to-line correlation function. The system and method provide more accurate and reliable angular orientations of anomalies identified during imaging and / or inspection of the interior portion or surface of the cavity, thus facilitating diagnosis and treatment options.
Owner:VOLCANO CORP
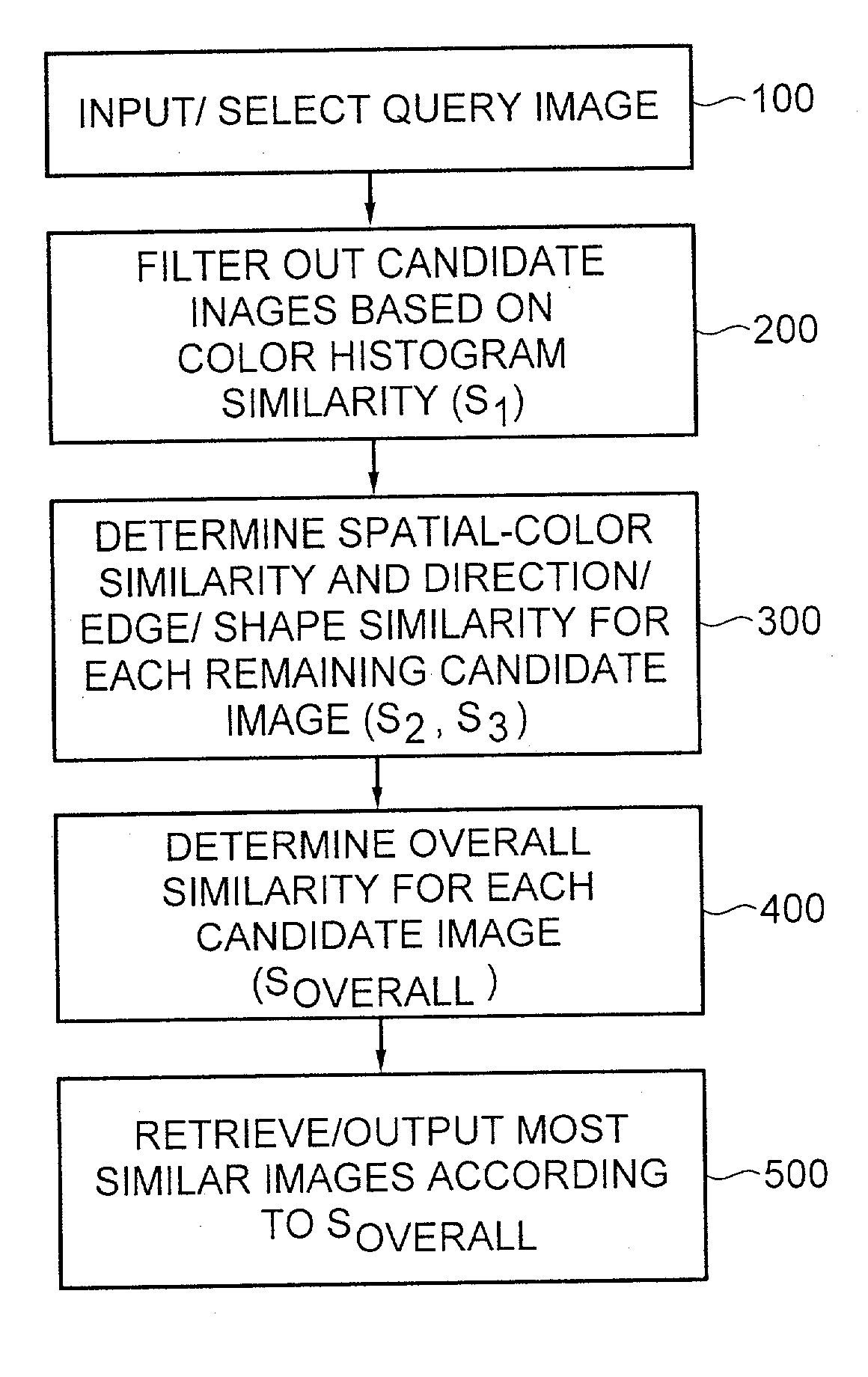
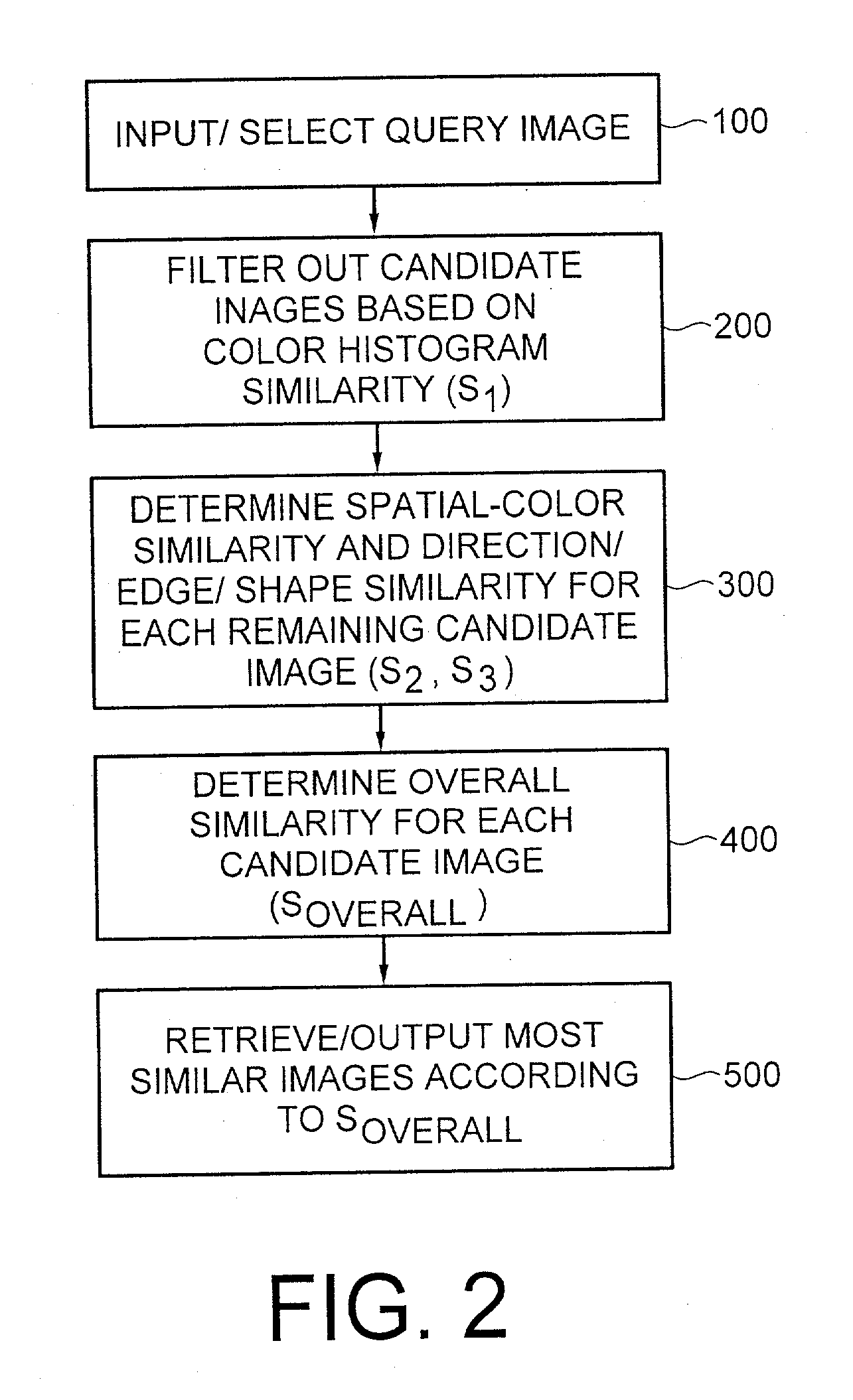
Method for automatic retrieval of similar patterns in image databases
InactiveUS20030179213A1Fast and accurate imageCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsDecompositionDatabase index
An image retrieval system and method that combines histogram-based features with Wavelet Frame decomposition features, as well as two-pass progressive retrieval process. The proposed invention is robust against illumination changes as well as geometric distortions. During the first round of retrieval, moment features of image histograms in the Karhunen-Loeve color space are derived and used to filter out most of the dissimilar images. During the second round of retrieval, multi-resolution WF decomposition is recursively applied to the remaining images. A set of coefficients of low-pass filtered subimages at the coarsest level, after being mean-subtracted and normalized, are utilized as features containing spatial-color information. Modulus and direction coefficients are calculated from the high-pass filtered X-Y directional subimages at each level, and central moments are derived from the direction histogram of the most significant direction coefficients to obtain TRSI direction / edge / shape features. Since the proposed invention is fast and robustness against illumination and geometric distortions, the invention is quite appealing for real-time image / video database indexing and retrieval applications.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
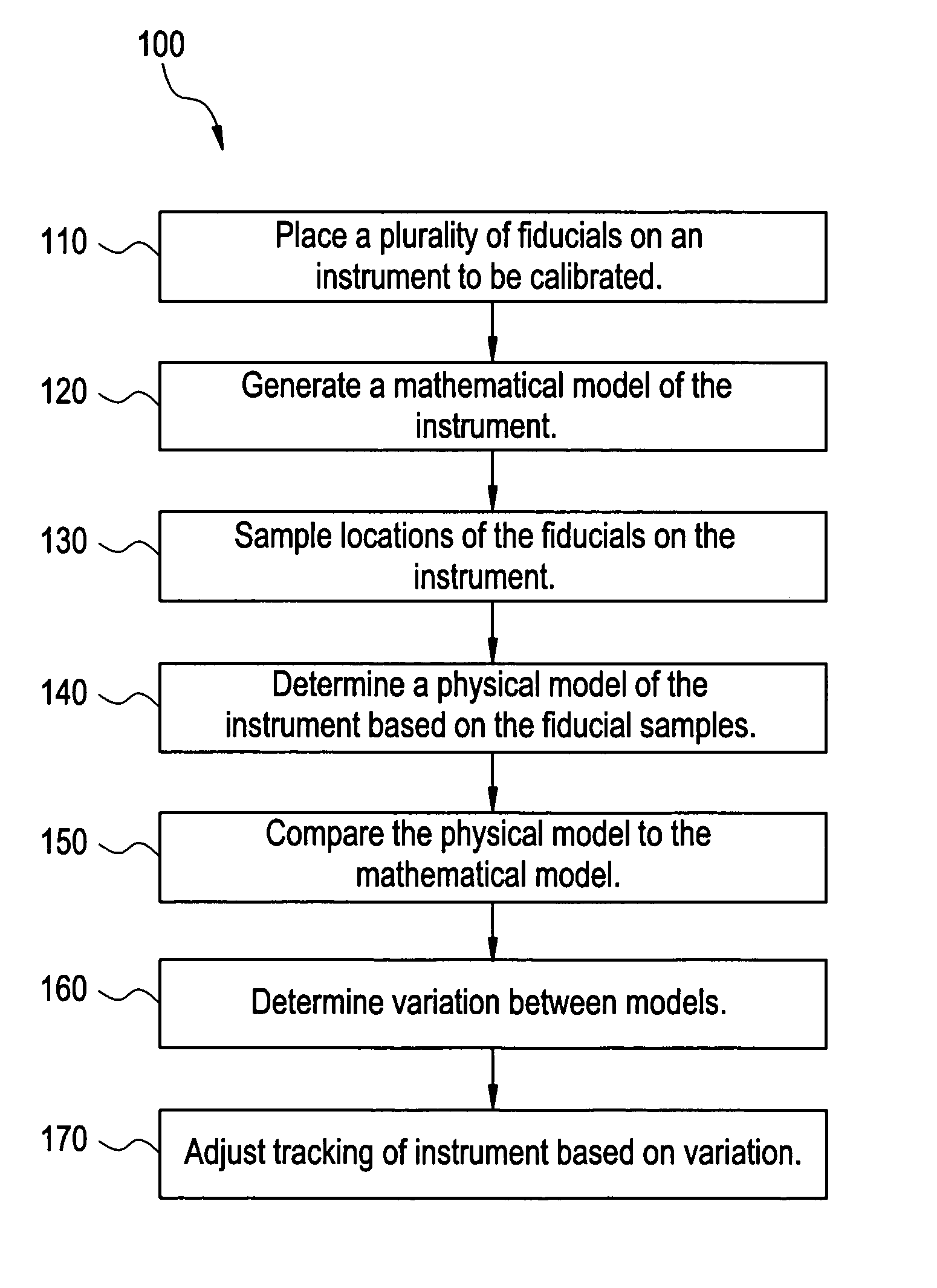
Method and system for geometric distortion free tracking of 3-dimensional objects from 2-dimensional measurements
InactiveUS20050228270A1Easy to trackSurgical navigation systemsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsData setImaging data
Certain embodiments of the present invention provide a method and system for improved tracking of an internal object, such as an implant or part of the anatomy, during an image-guided operation. In an embodiment, the method may include obtaining a plurality of fiducials for an internal object from a plurality of projection views, obtaining a plurality of measurements for the internal object using the plurality of fiducials, forming a three-dimensional model of the internal object using the plurality of measurements from a plurality of projection views for use in tracking the internal object, and performing an image-guided operation using an image data set and a three-dimensional representation of the internal object. The fiducials may be indentations, curves, grooves and / or identifying features in the internal object. In an embodiment, the representation of the internal object is compared to a computer-generated model of the internal object.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
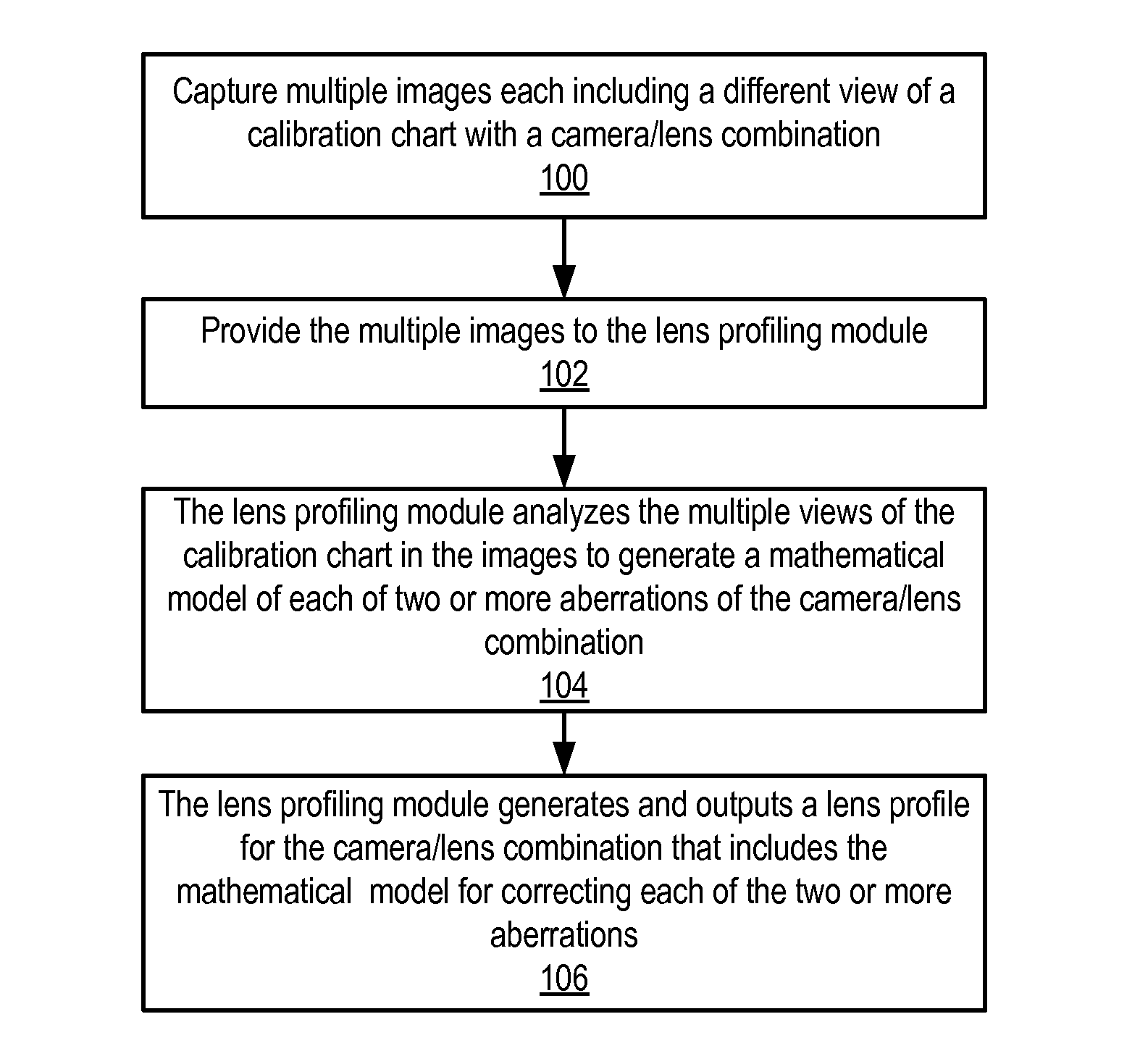
Methods and apparatus for camera calibration based on multiview image geometry
ActiveUS8368762B1Relaxes camera calibration setupSimple working processTelevision systemsMathematical modelIntrinsics
Methods and apparatus for camera calibration based on multiview image geometry. A lens profiling module may estimate two or more mathematical models for correcting aberrations in images in a single pass from a set of calibration images captured with a camera / lens combination. For example, the module may estimate the lens aberrations of geometric distortion, lateral chromatic aberration, and vignette models in a single pass. The module may determine point correspondences, 3D transformations, and camera intrinsics for views of calibration charts captured in the images. The module estimates the mathematical models for the two or more types of aberrations from the information determined from the views of the calibration charts. The module may automatically determine an optimal model complexity when estimating the mathematical models. The estimated models may be written or appended to a lens profile for the camera / lens combination used to captured the calibration images.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Head-mounted virtual display apparatus for mobile activities
InactiveUS7145726B2Minimize and eliminate geometric distortionPassively minimizing or eliminating image degrading factorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical axisDisplay device
The present invention is a head-mounted virtual display apparatus based on a non-cross-cavity optical configuration, in which a near-eye light deflecting element (LDE) is located in the peripheral field of view. Positioning of the near-eye LDE in the peripheral field of view provides the user with simultaneous access to an inset magnified image of a miniature display and an unobstructed forward field of view of at least 35 degrees. Active and passive alignment means, including articulating connections and image warping electronics, allows for correction of geometric distortion arising from folding of the optical train, and orthogonal alignment of the virtual image plane with the optical axis between the user's eye and the virtual image plane.
Owner:GEIST RICHARD
Method and apparatus for evaluating integrated circuit packages having three dimensional features
The present invention provides for methods and an apparatus for evaluating objects having three dimensional features. One method involves using both two dimensional data sets to improve the processing of three dimensional data sets. The two dimensional data set can be used to pre-qualify the three dimensional data set, or may be used to locate that data within the three dimensional data set that is characteristic of the three dimensional feature. The invention may include a sensor configured to capture both three dimensional and two dimensional data. The present invention provides for an efficient technique to evaluate three dimensional data. The present invention also solves heretofore unrecognized problems associated with geometric distortion.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Image correction apparatus
InactiveUS7072527B1Accurate detectionEasy to detectImage enhancementImage data processing detailsImage correctionOutput device
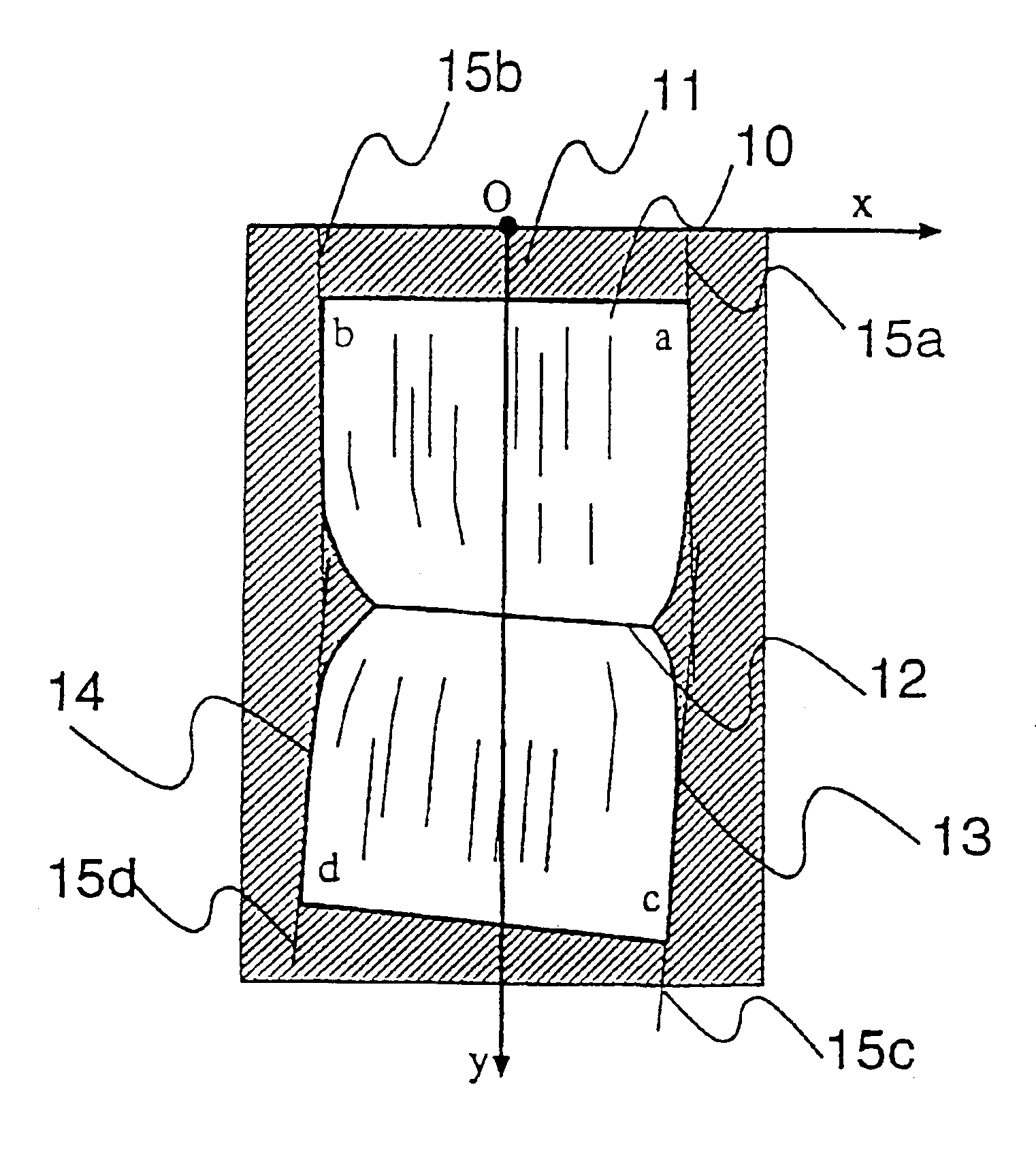
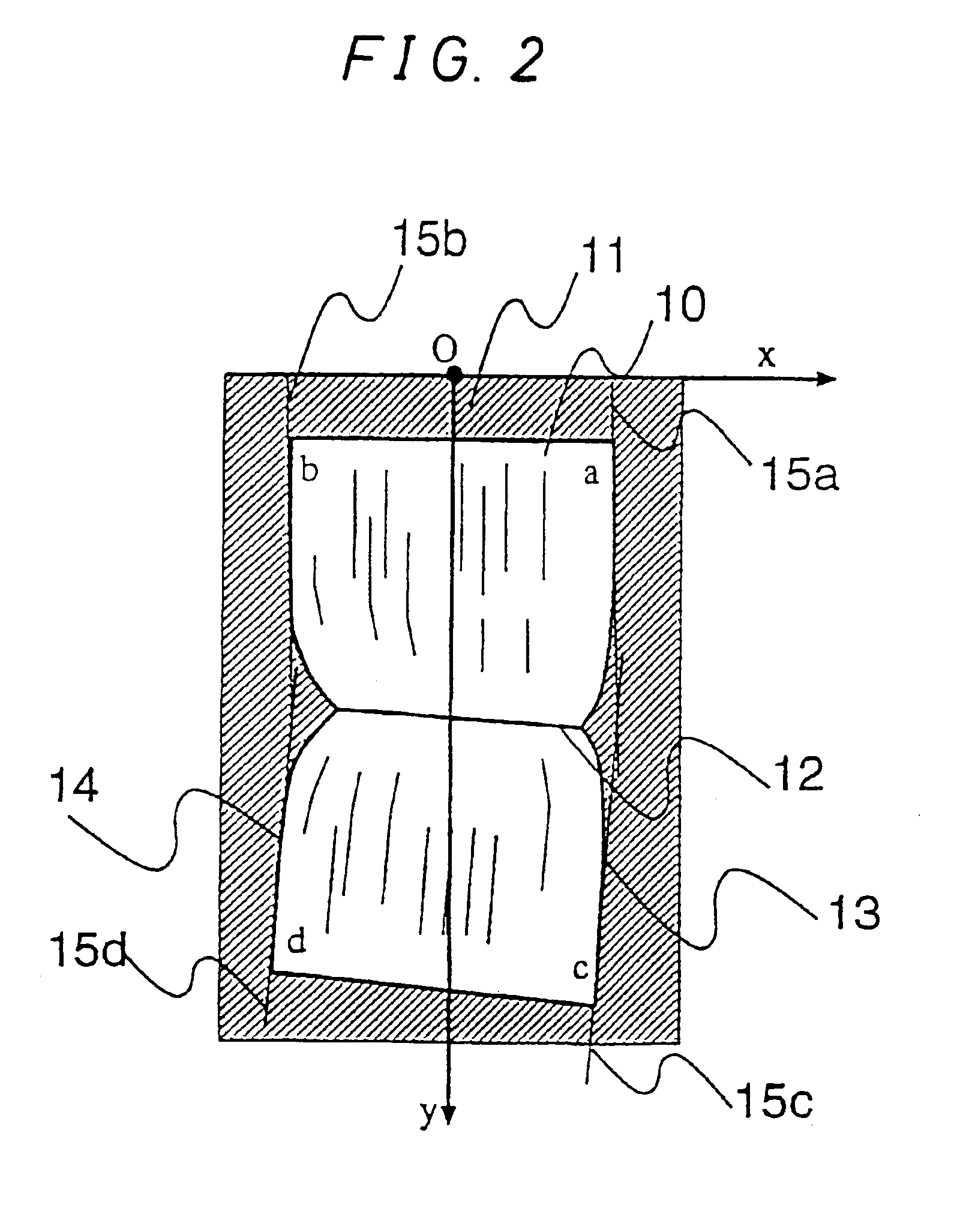
An image correction apparatus 1 includes an image input device 3, a memory device 4, a central processing unit 2, and and image output device 5. In the image correction apparatus 1, a locally wrinkled document or a document with a binding portion lifted differently between the top and bottom of the document is read from the image input device 3 and, using a program which is run on the central processing unit 2, an input image is corrected for the geometric distortion and luminance variations caused due to the upper and lower sides of the document making a slope with respect to a document platen, and thereby, a flat document image is restored.
Owner:SHARP KK
Bar code image identification method
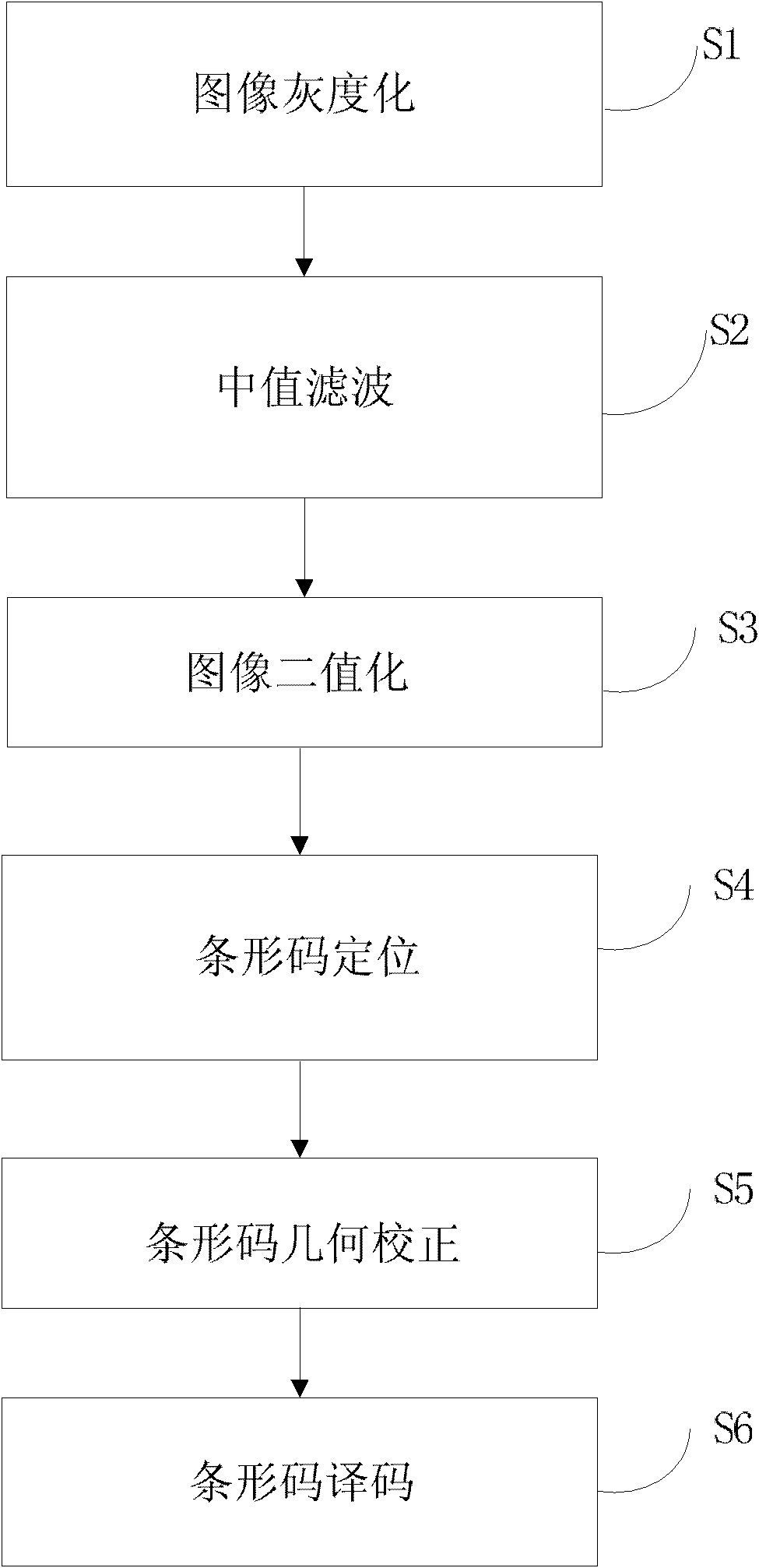
InactiveCN102136058ARealize binary segmentationImprove adaptabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing by electromagnetic radiationBarcodeImage identification
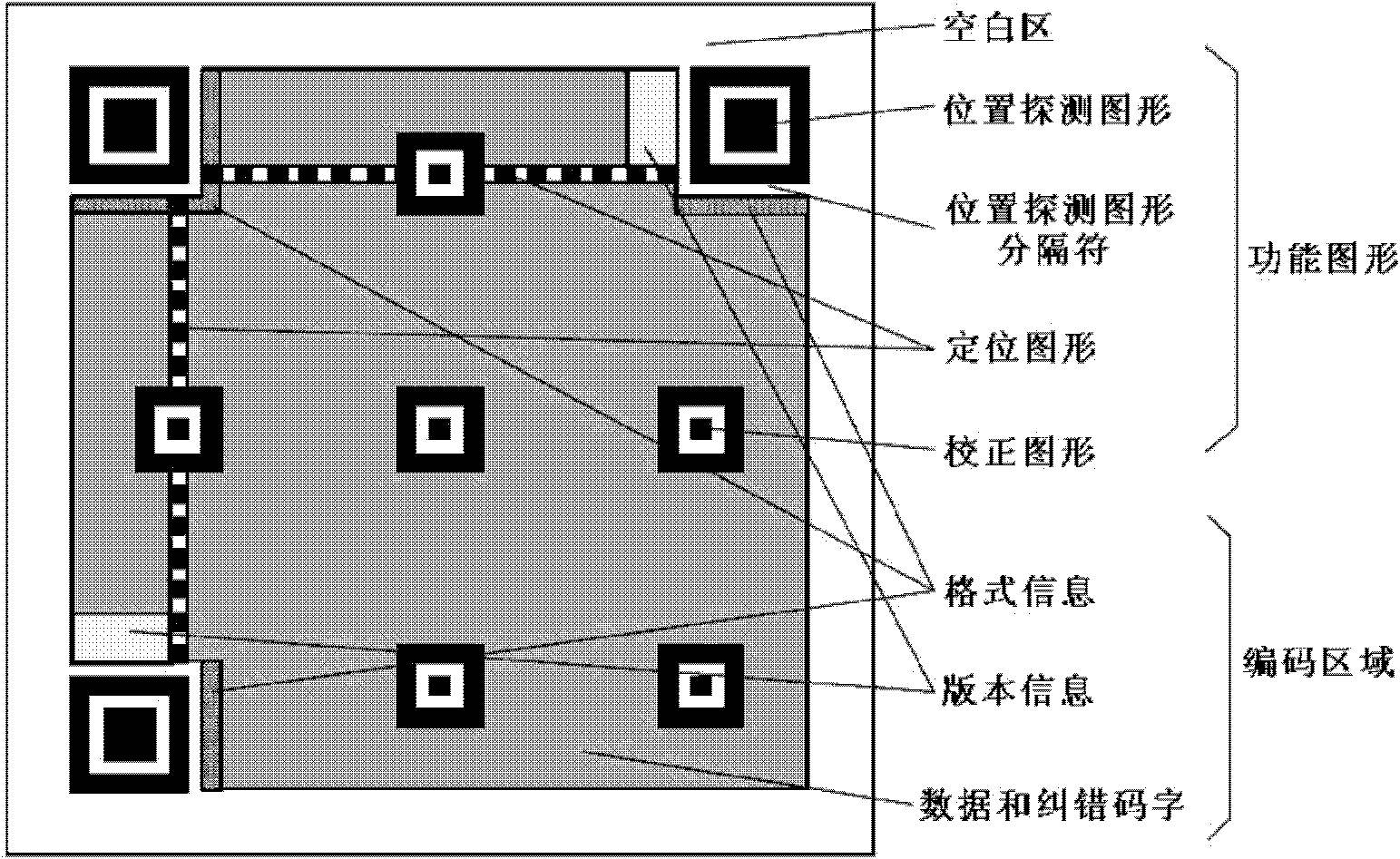
The invention disclose a bar code image identification method, belonging to the field of computer information automatic identification technology, the method comprises the following steps: S1. carrying out gradation to a colored image which is captured by an Android mobile phone camera, wherein the colored image is a bar code image; S2. conducting median filtering processing to a grayed image; S3. conducting binaryzation processing to the image which carries out the median filtering processing; S4. conducting bar code positioning to the image which carried out the binaryzation processing; S5. conducting geometric distortion correction to the positioned image; and S6. decoding the corrected image, so as to obtain a code word of the image. In the invention, the precision of the bar code identification is improved and the complexity is reduced.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Correction of the effect of spatial gradient field distortions in diffusion-weighted imaging
ActiveUS6969991B2Convenient distanceMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionField of viewIsocenter
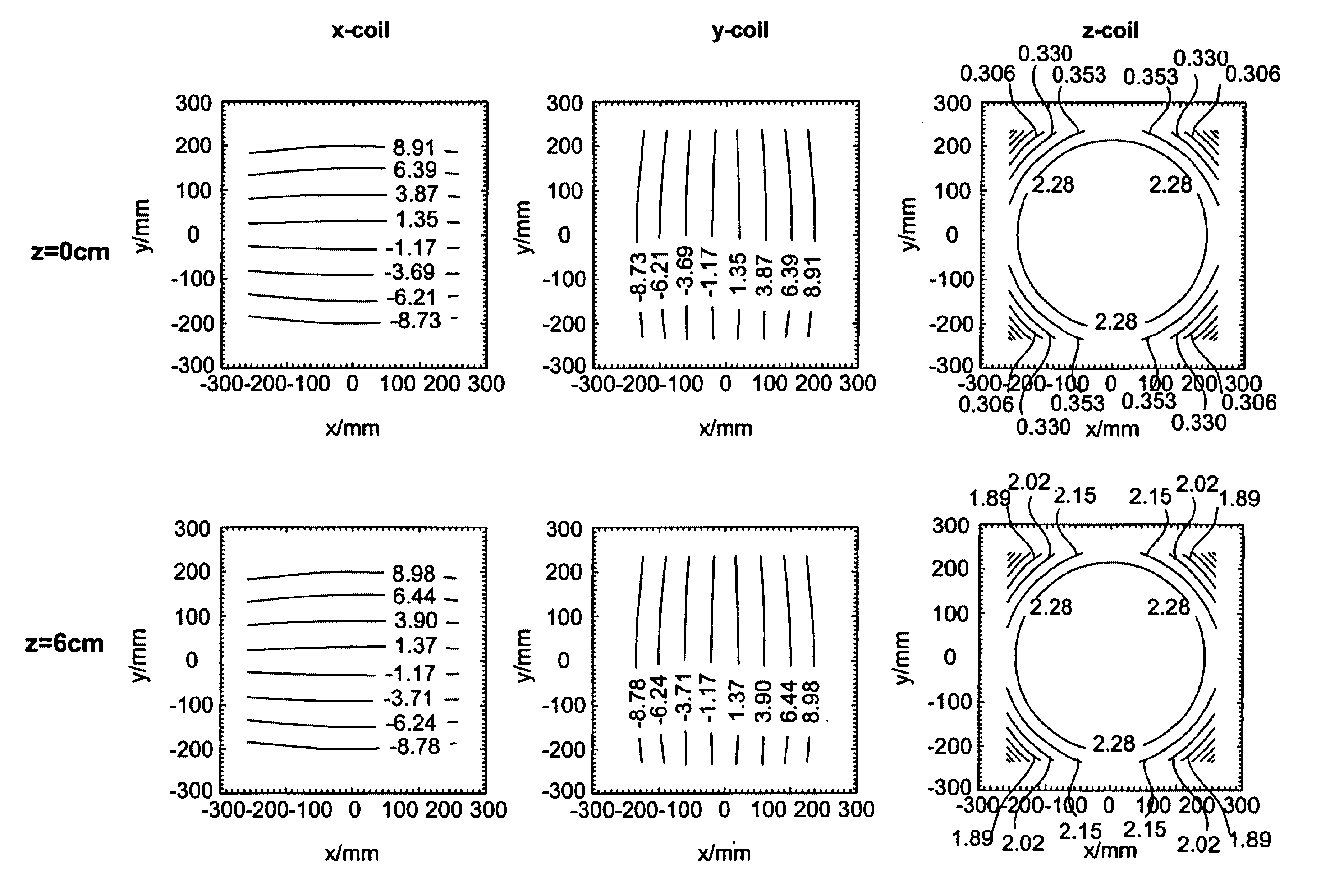
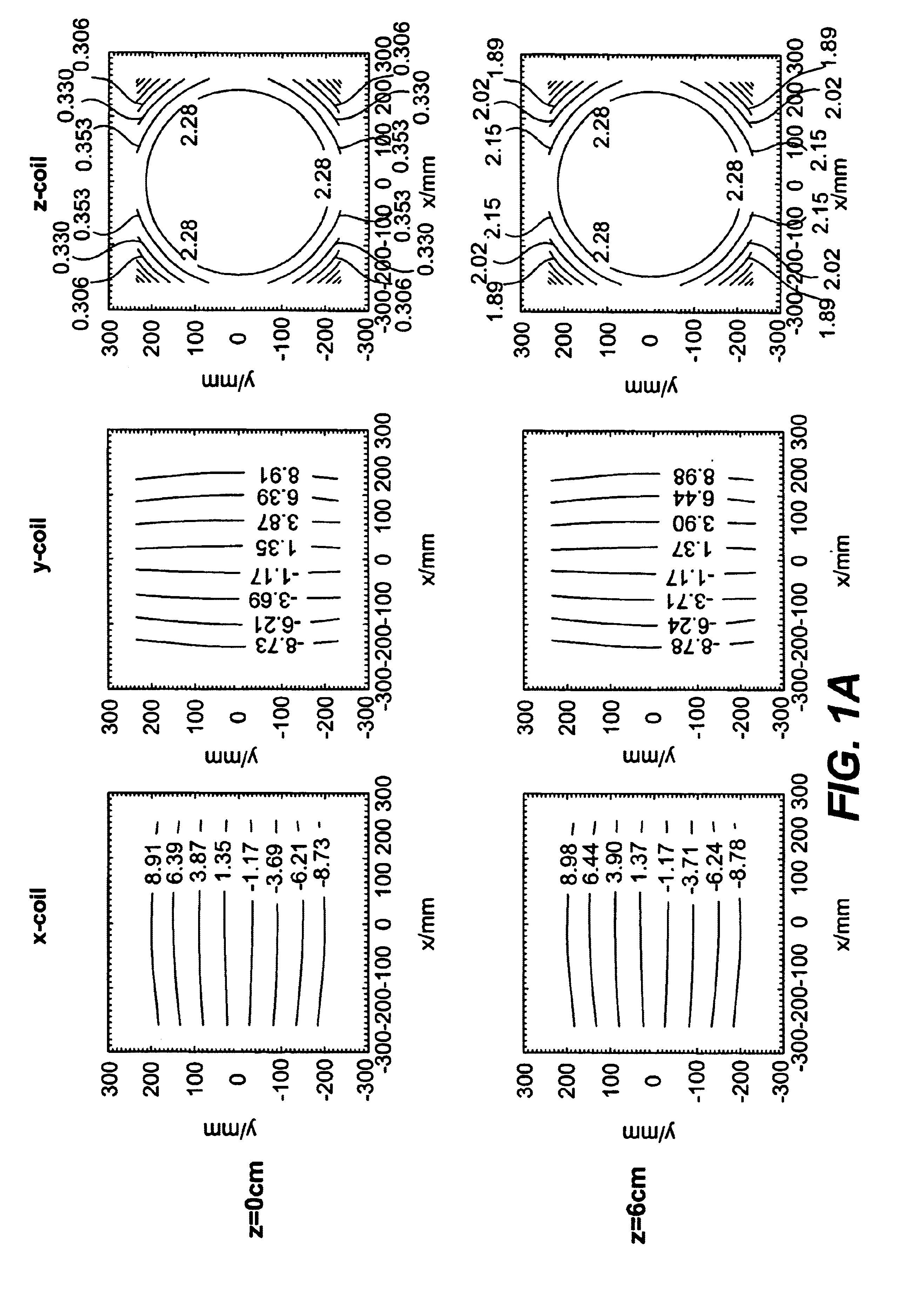
A general mathematical framework is formulated to characterize the contribution of gradient non-uniformities to diffusion tensor imaging in MRI. Based on a model expansion, the actual gradient field is approximated and employed, after elimination of geometric distortions, for predicting and correcting the errors in diffusion encoding. Prior to corrections, experiments clearly reveal marked deviations of the calculated diffusivity for fields of view generally used in diffusion experiments. These deviations are most significant with greater distance from the magnet's isocenter. For a FOV of 25 cm the resultant errors in absolute diffusivity can range from approximately −10 to +20 percent. Within the same field of view, the diffusion-encoding direction and the orientation of the calculated eigenvectors can be significantly altered if the perturbations by the gradient non-uniformities are not considered. With the proposed correction scheme most of the errors introduced by gradient non-uniformities can be removed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method and apparatus for expanding a color gamut
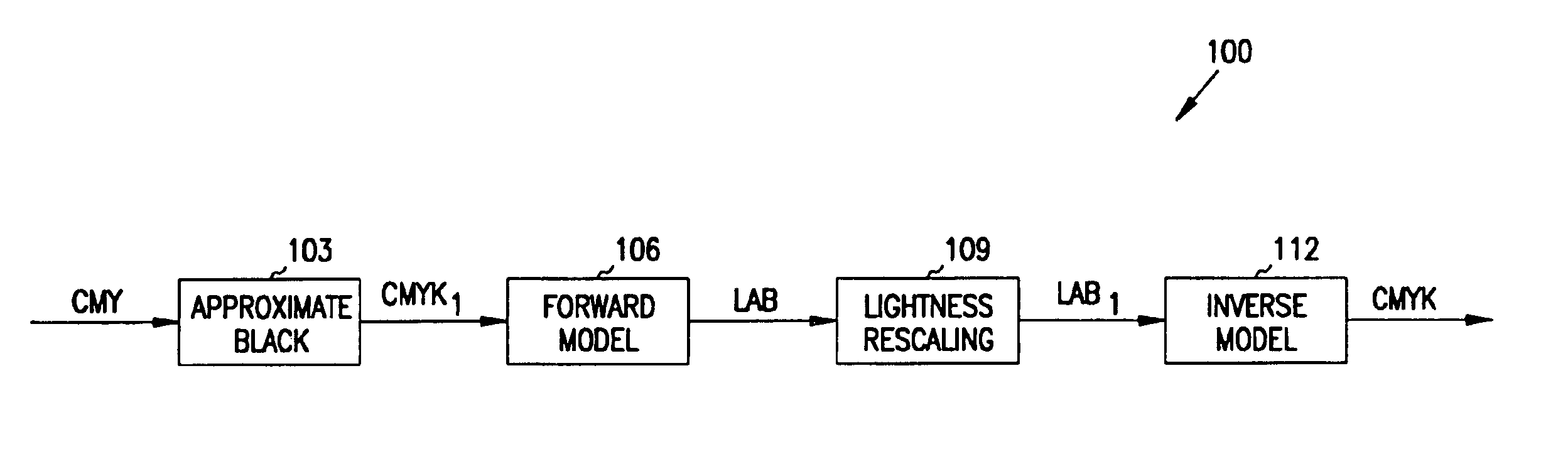
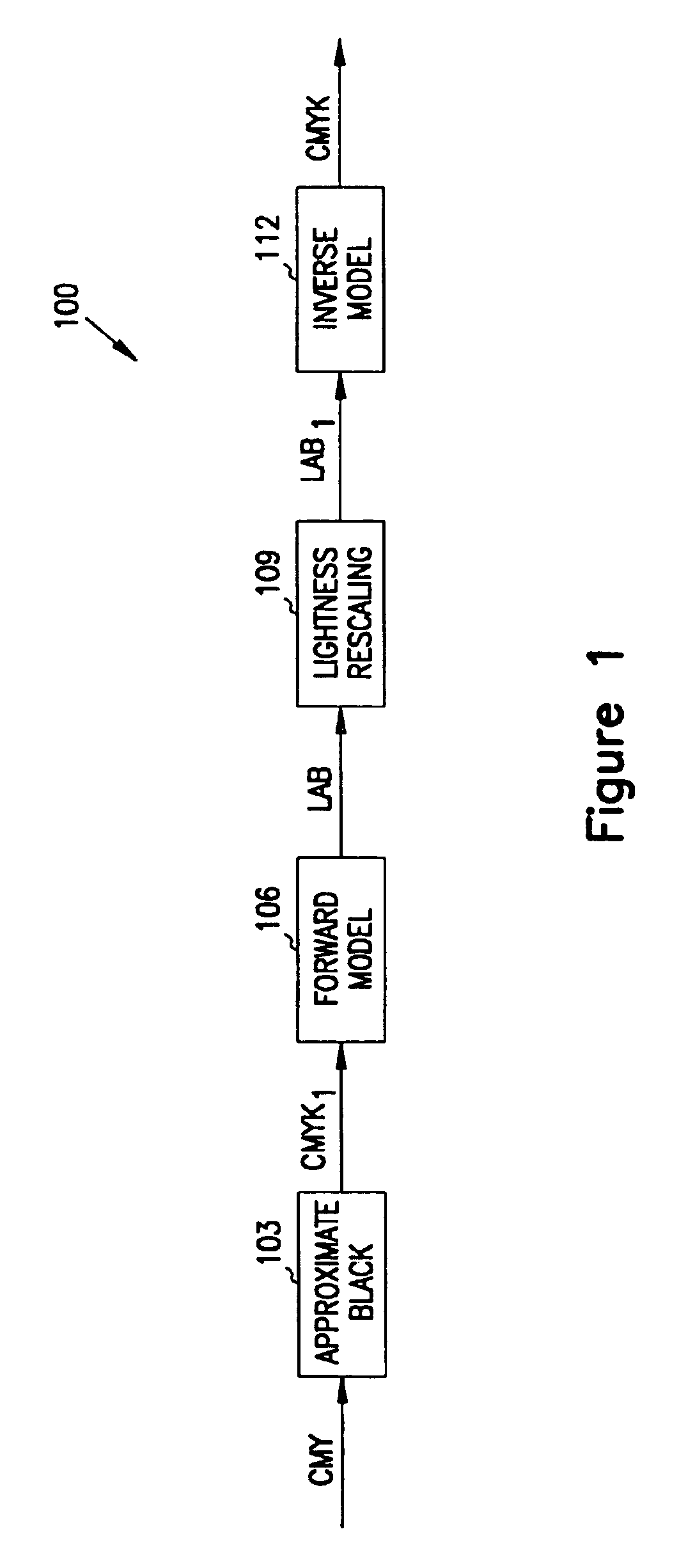
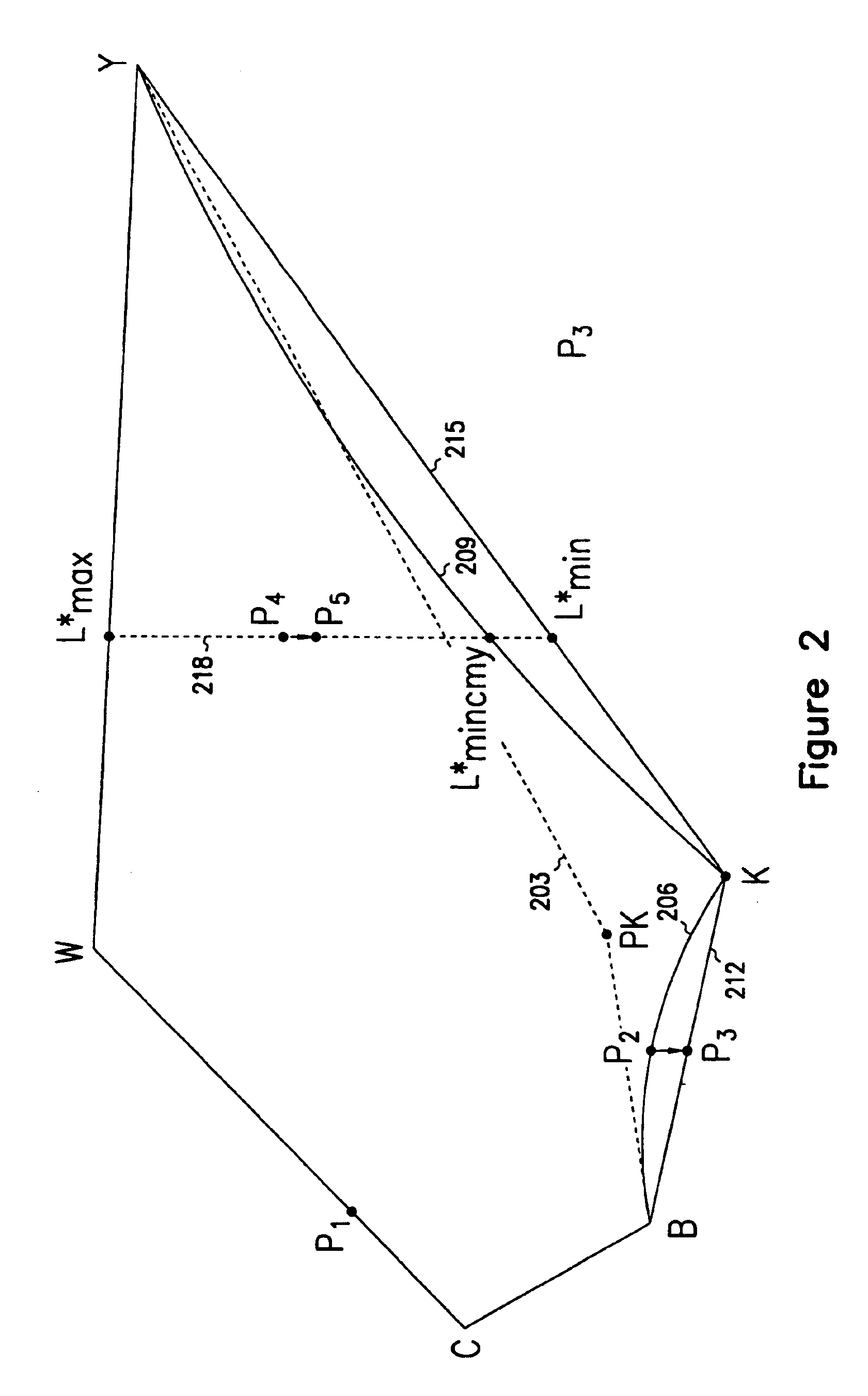
InactiveUS6867883B1Upper surfaceLower surfaceDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsGamutGeometric distortion
A color gamut in a first color space is expanded to utilize a larger gamut in a second color space. The gamut in the first color space is first converted by black generation or geometric distortion to a gamut in a second color space. The gamut in the second color space is converted by forward mapping to a gamut in a third color. The gamut in the third color space is expanded by linear rescaling. Finally, the linearly rescaled gamut is mapped to a gamut in the second color space through inverse modeling to form a final color gamut. The final color gamut utilizes the gamut available in the second color space, which is larger than the gamut available in the first color space.
Owner:LEXMARK INT INC
System and method for reducing angular geometric distortion in an imaging device
ActiveUS8047996B2Reducing angular geometric distortionRemove geometric distortionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterComputer moduleCorrelation function
Owner:VOLCANO CORP
Identification method of two-dimensional barcode image on high-reflect light cylindrical metal
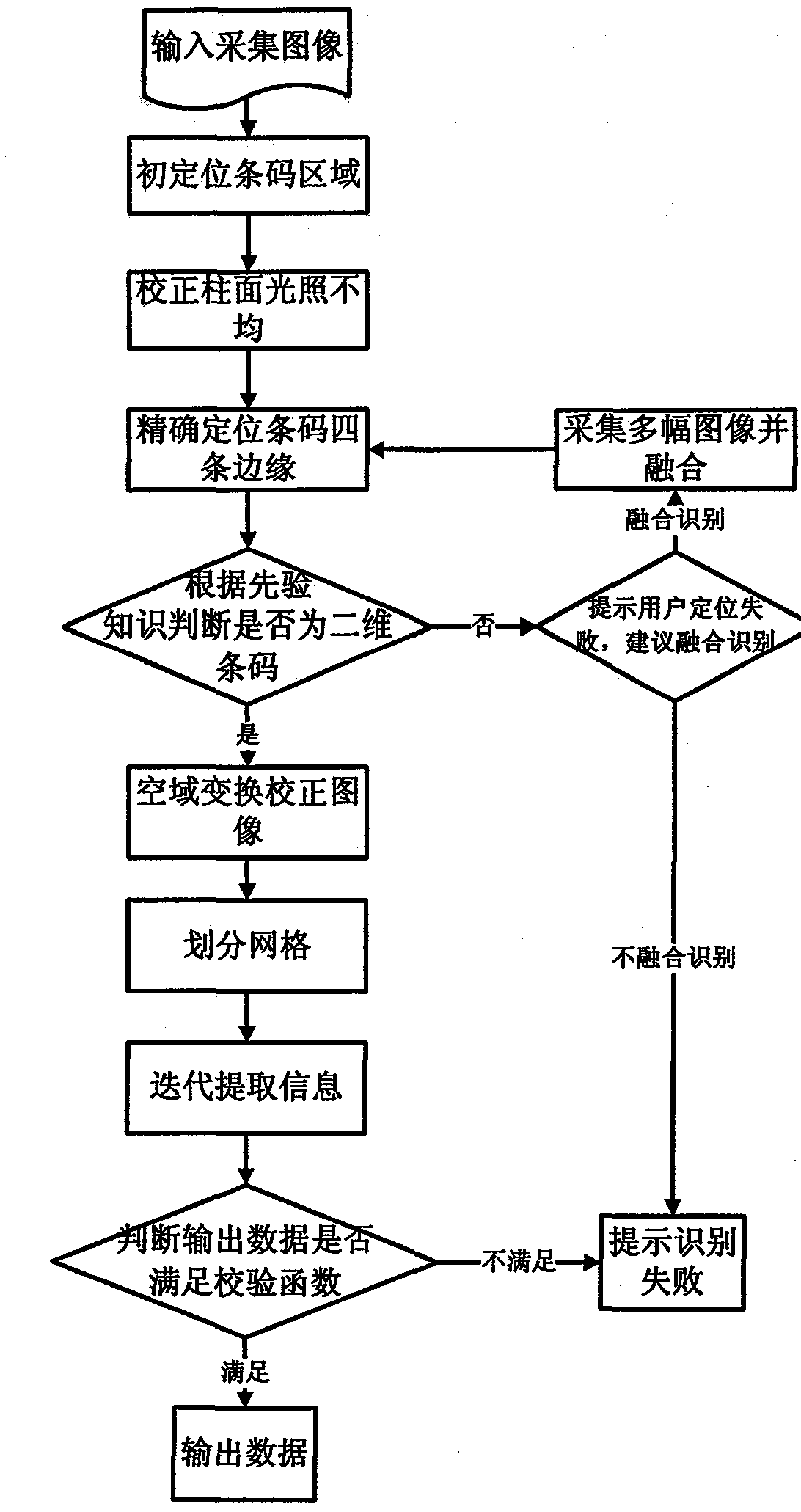
InactiveCN102354363AImprove recognition rateSensing by electromagnetic radiationBarcodeComputer science
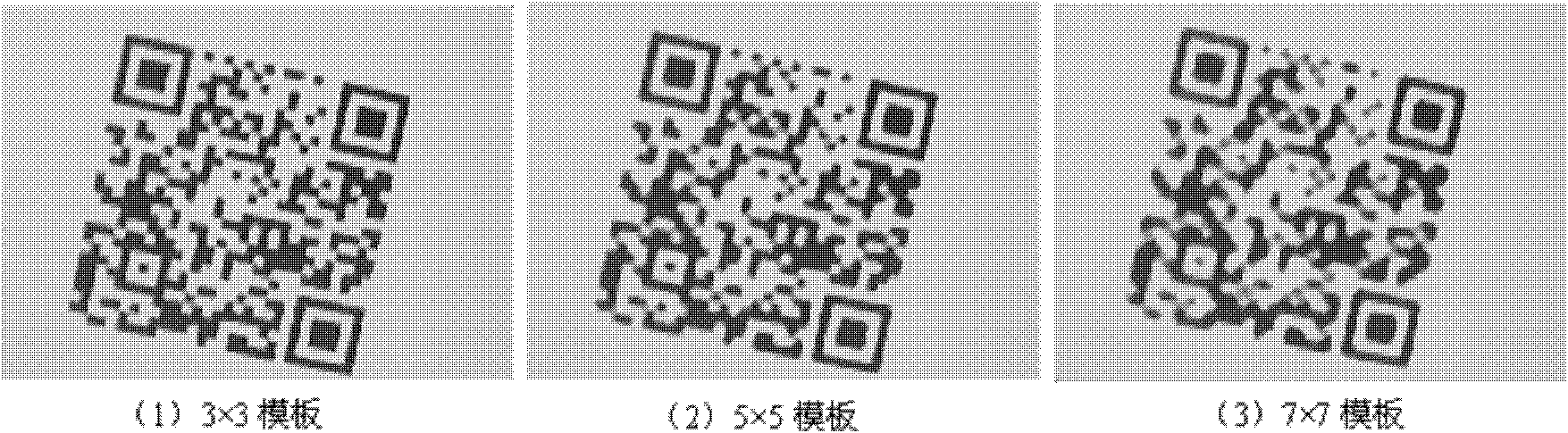
The invention discloses an identification method of a two-dimensional barcode image on a high-reflect light cylindrical metal, comprising the steps of: correcting the unevenness of cylindrical illumination by primarily positioning a two-dimensional barcode area; exactly positioning four edges of a barcode; judging whether output data meet a check function; acquiring and blending a plurality of images; correcting the images by means of affine transformation; dividing a grid; and extracting information in an iteration way and the like to obtain an information matrix of a two-dimensional barcode module. The identification method is higher in identification rate to the two-dimensional barcode on the metal which is capable of being rotated and tilted at optional angles, mild or moderate in geometric distortion, mild or moderate in uneven illumination, not high in contrast ratio, and mild or moderate in attrition.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
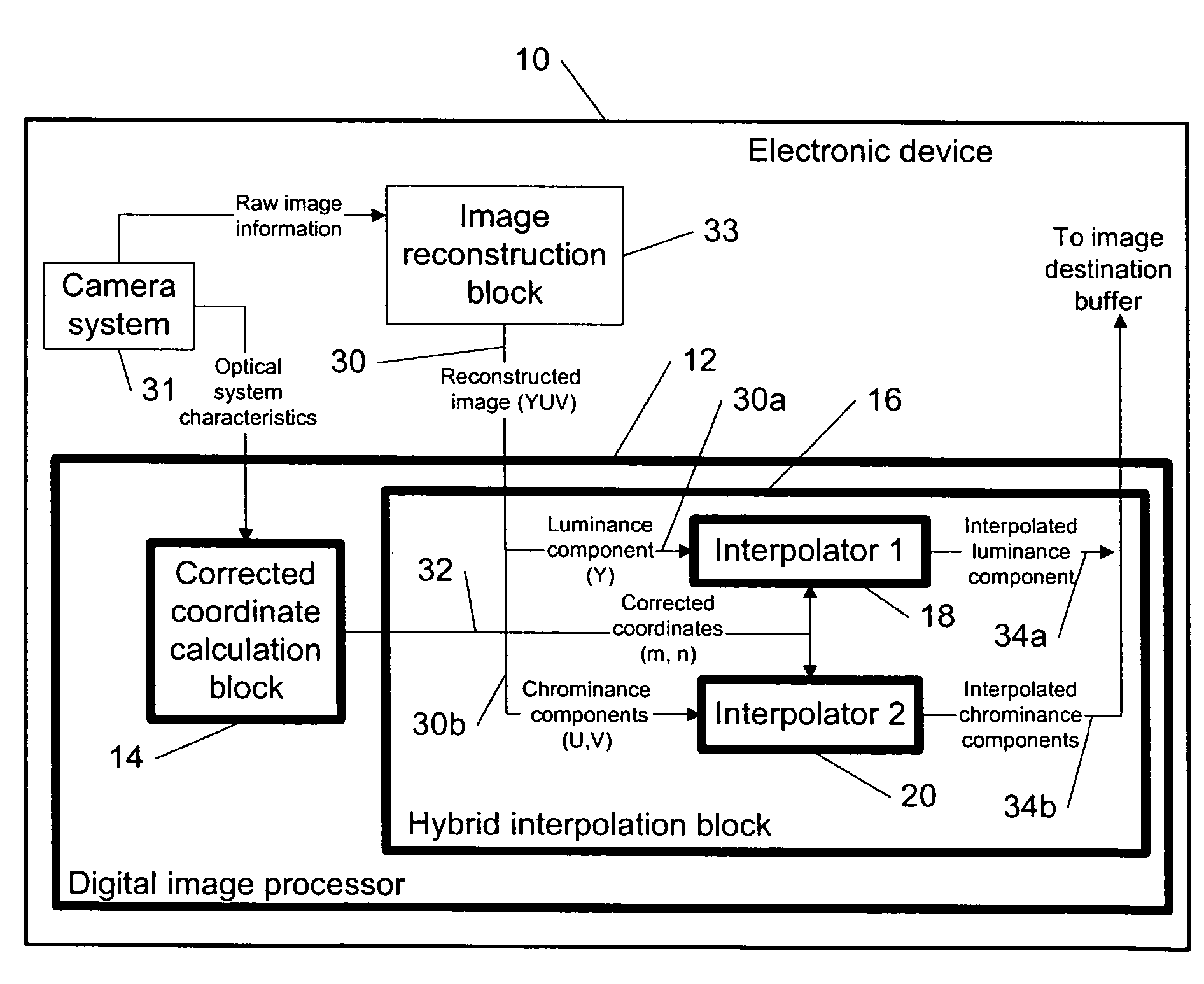
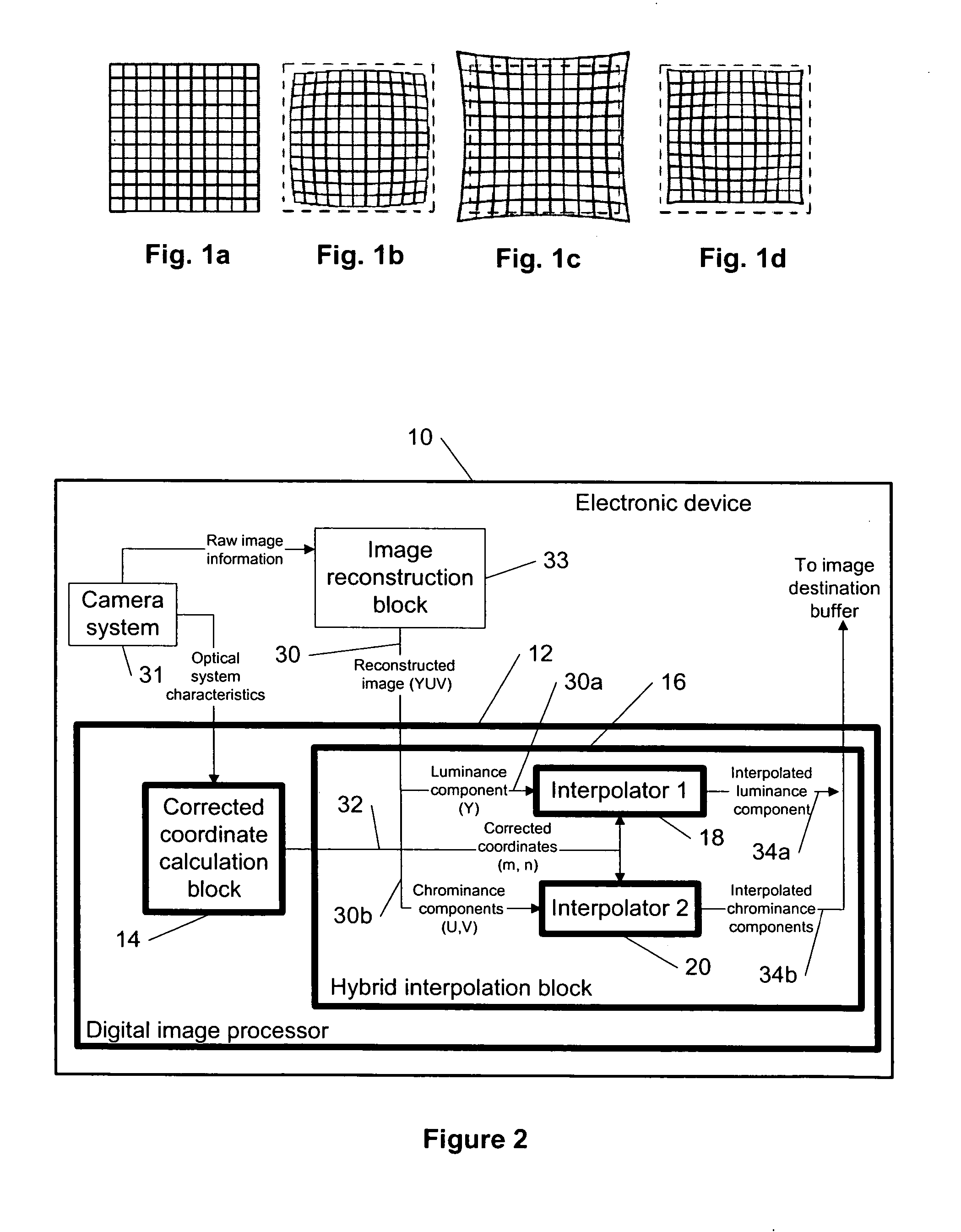
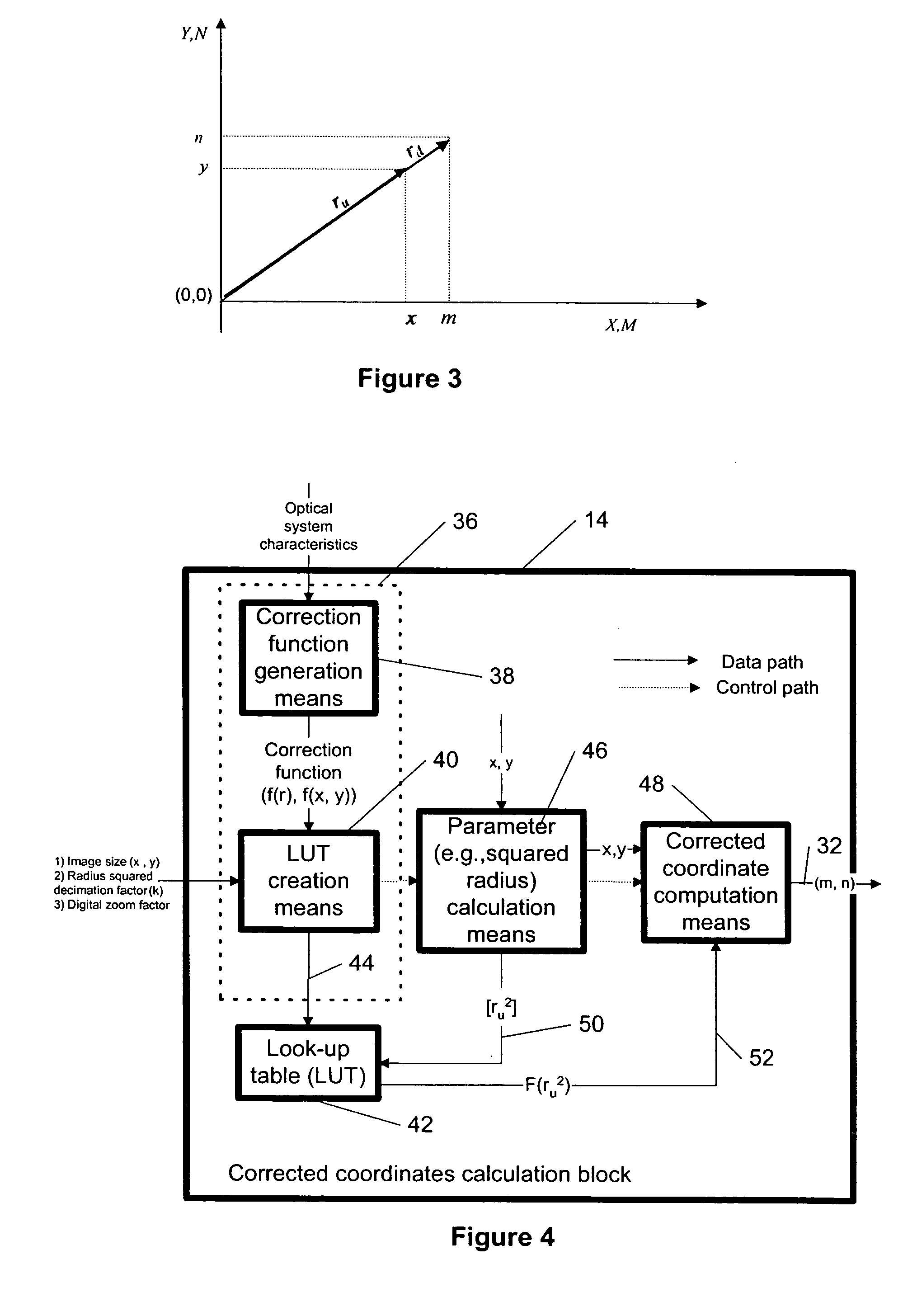
Distortion correction of images using hybrid interpolation technique
The specification and drawings present a new method, system, apparatus and software product for correcting a geometrical distortion of an image using a hybrid interpolation technique by a digital image processor. After calculating corrected coordinates of pixels in the image, the interpolation of color components of the pixels can be performed by using the corrected coordinates, wherein at least one color component is interpolated using a quality interpolator which is different from quality interpolators used for other color components.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
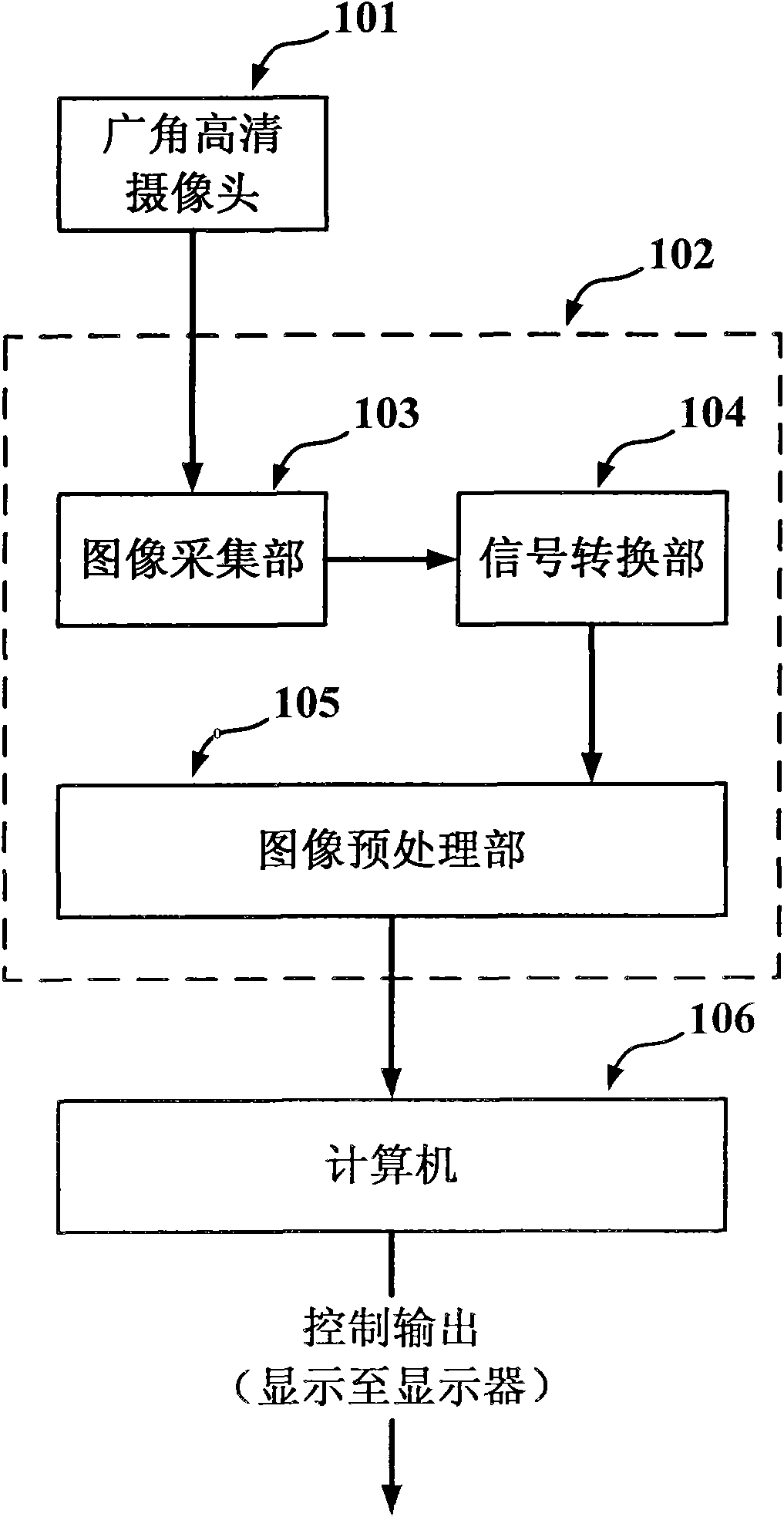
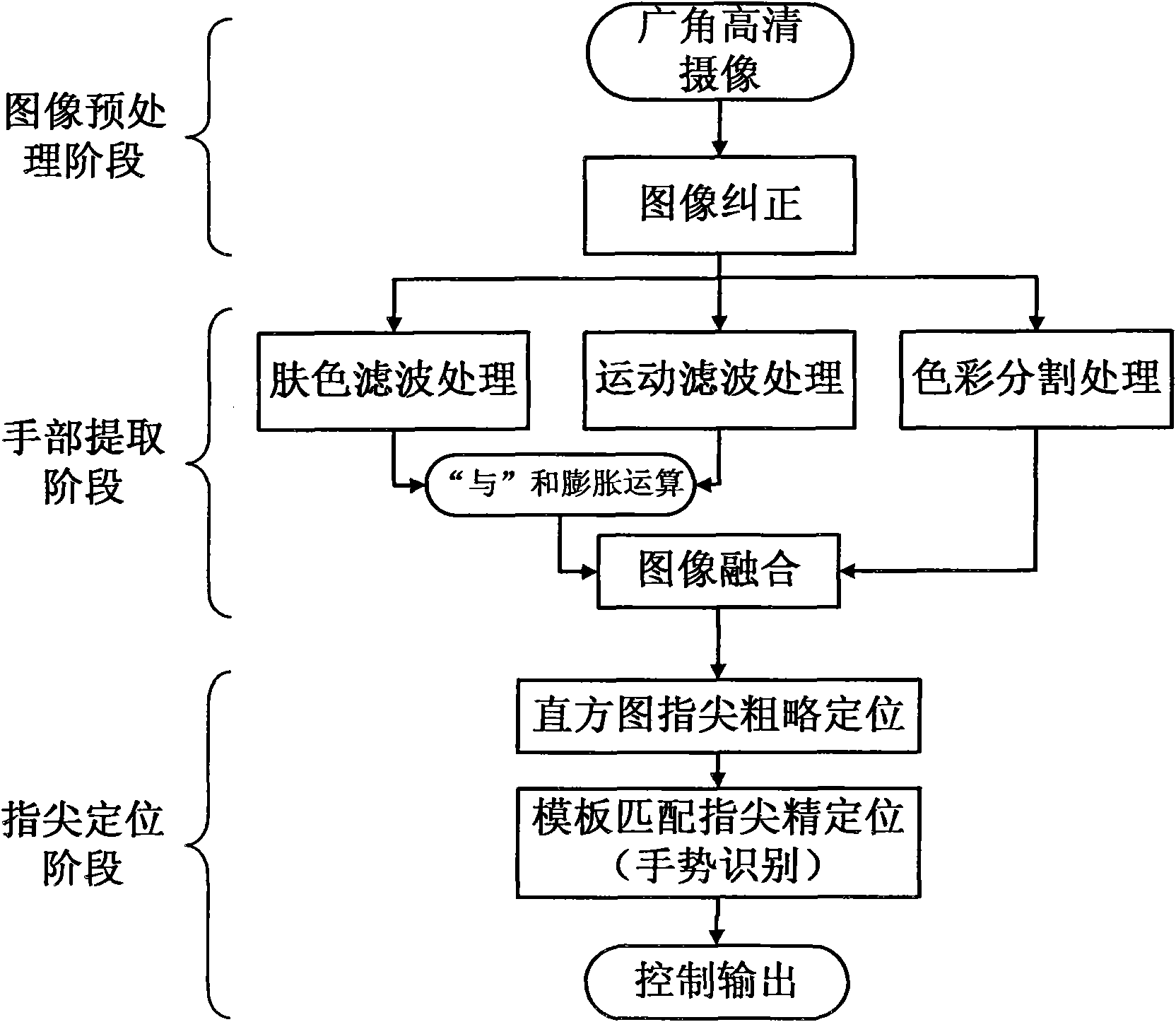
Method for quick-speed human-computer interaction based on finger tip tracking
InactiveCN101593022AImprove perceived efficiencyEasy to detectInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionTip positionFinger tracking
The invention discloses a method for quick human-computer interaction based on finger tip tracking, which comprises the following steps: firstly, preprocessing an image, adopting a wide-angle high-definition camera to perform high-resolution image pick-up on an indoor area, and performing image geometric distortion correction on the obtained images; secondly, extracting hand images, processing the obtained corrected images by a skin color filter, a motion filter and a color splitter, merging the results, and splitting the hand images out of the obtained corrected images; and finally, performing finger tip positioning: applying a histogram to perform rough finger tip positioning, using the rough position of a finger tip as a center to construct a searching window, and performing precise finger tip positioning through template matching. The method effectively improves the perceiving efficiency of scene images, achieves finger detection and positioning in a large range, judges the image distance between two eyes as a basis to perform the finger tip positioning without prior knowledge of the environment, and has outstanding distance robustness.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
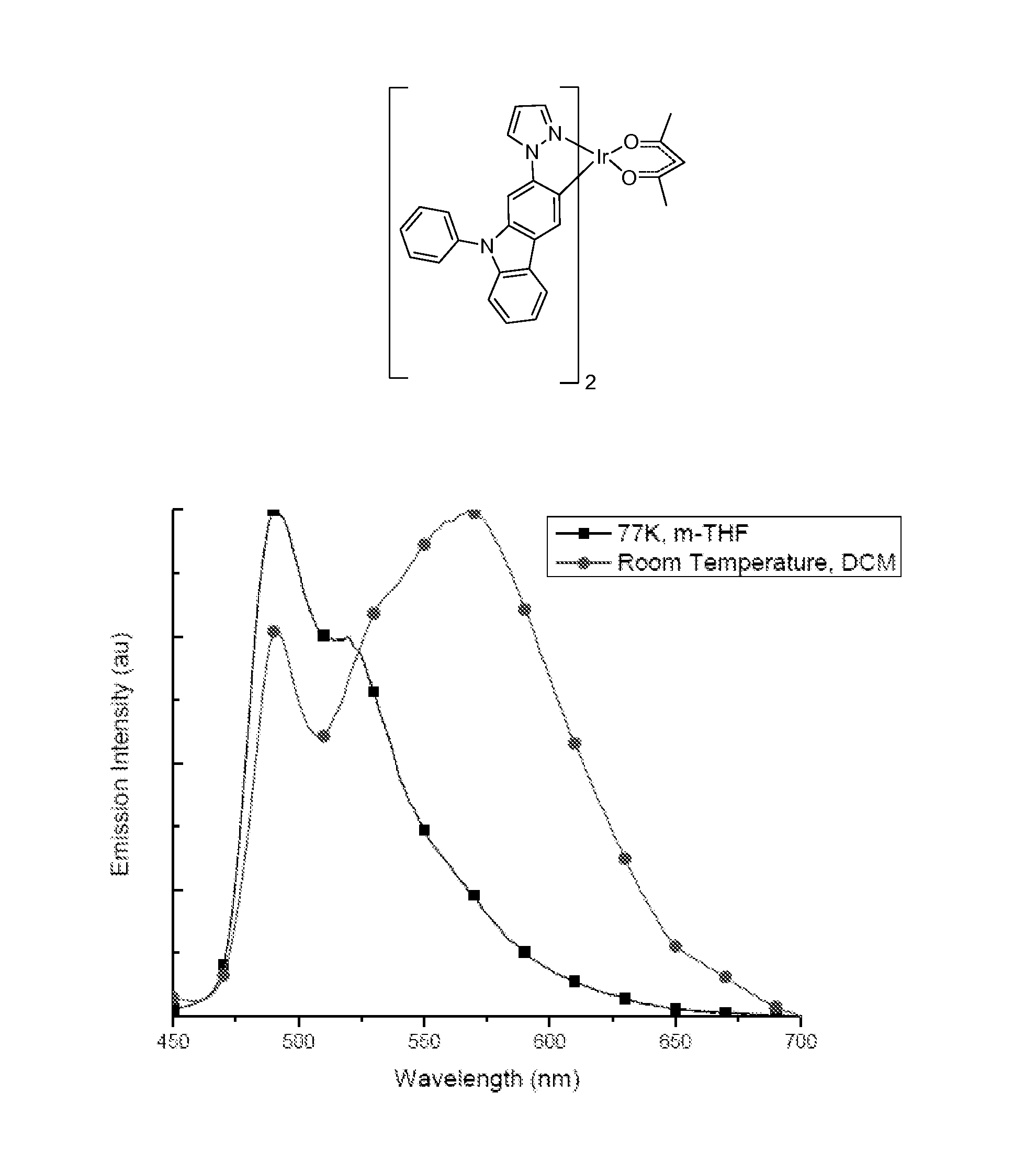
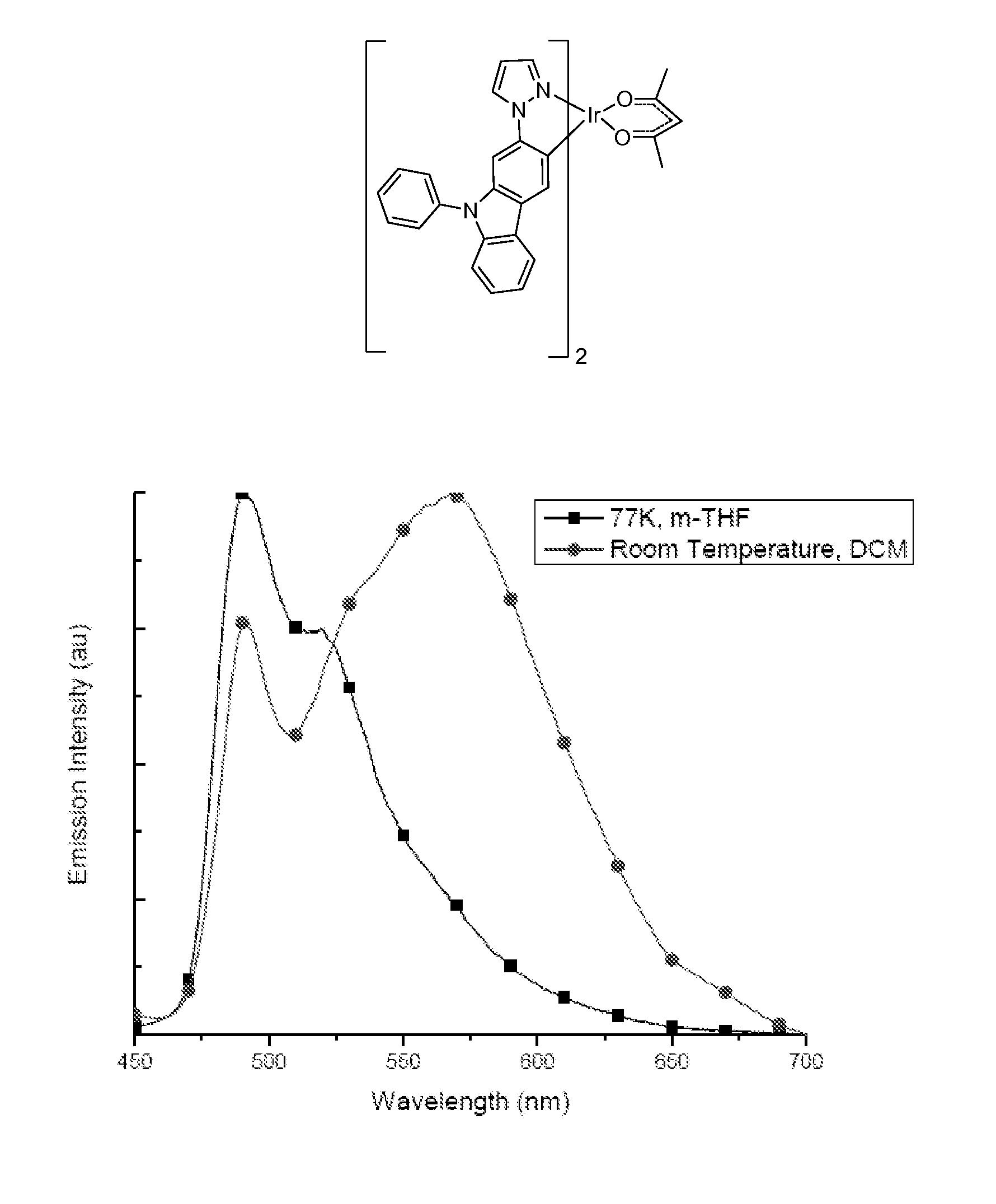
Iridium complexes demonstrating broadband emission through controlled geometric distortion and applications thereof
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Correction method of fisheye image distortion on basis of cubic projection
InactiveCN101726855AOvercome geometric deformationIn line with intuitive feelingOptical elementsViewpointsFisheye lens
The invention belongs to the field of advanced manufacturing technology, relating to a correction method of fisheye image distortion on the basis of cubic projection. The correction method comprises the following steps: 1. using a fisheye lens to obtain an imaging model, and calibrating the fisheye lens according to the imaging model to obtain a calibration parameter; 2. according to the collected fisheye image, determining a viewpoint, taking the viewpoint as the original point of a coordinate system, and building a cubic perspective projection model to obtain the cubic perspective projection of a spatial point; 3. building a mapping relation between the cubic perspective projection of the spatial point and the fisheye image; and 4. using bilinearity interpolation to realize the distortion correction of the fisheye image. The invention utilizes a cubic projection model to correct distorted fisheye images and can effectively overcome the geometric distortion existing in the original fisheye images, and the corrected image conforms to the intuitional feeling of people and has strong sense of reality.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
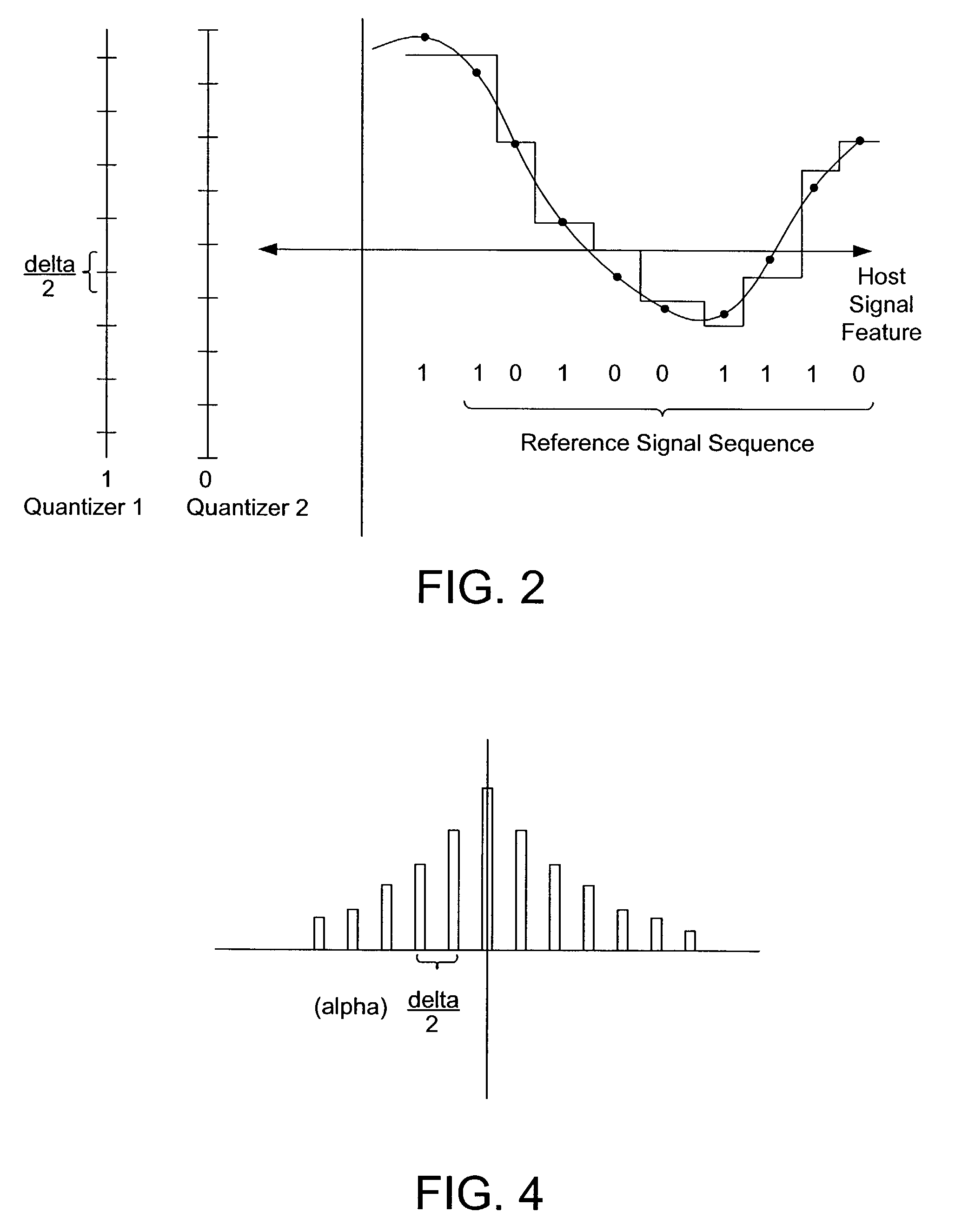
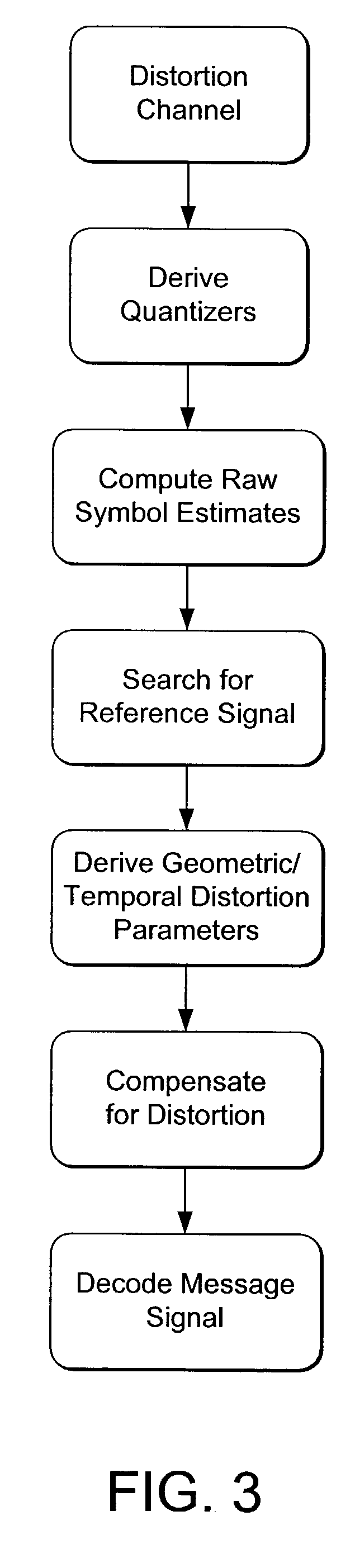
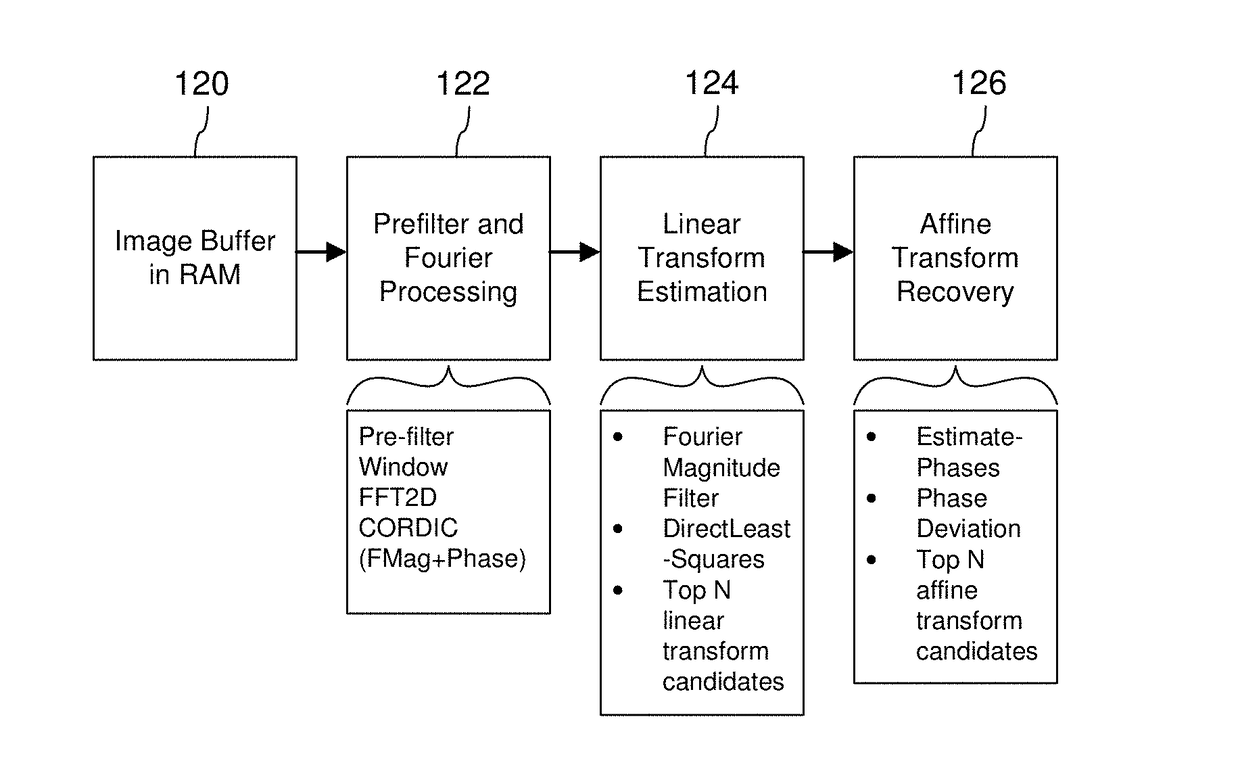
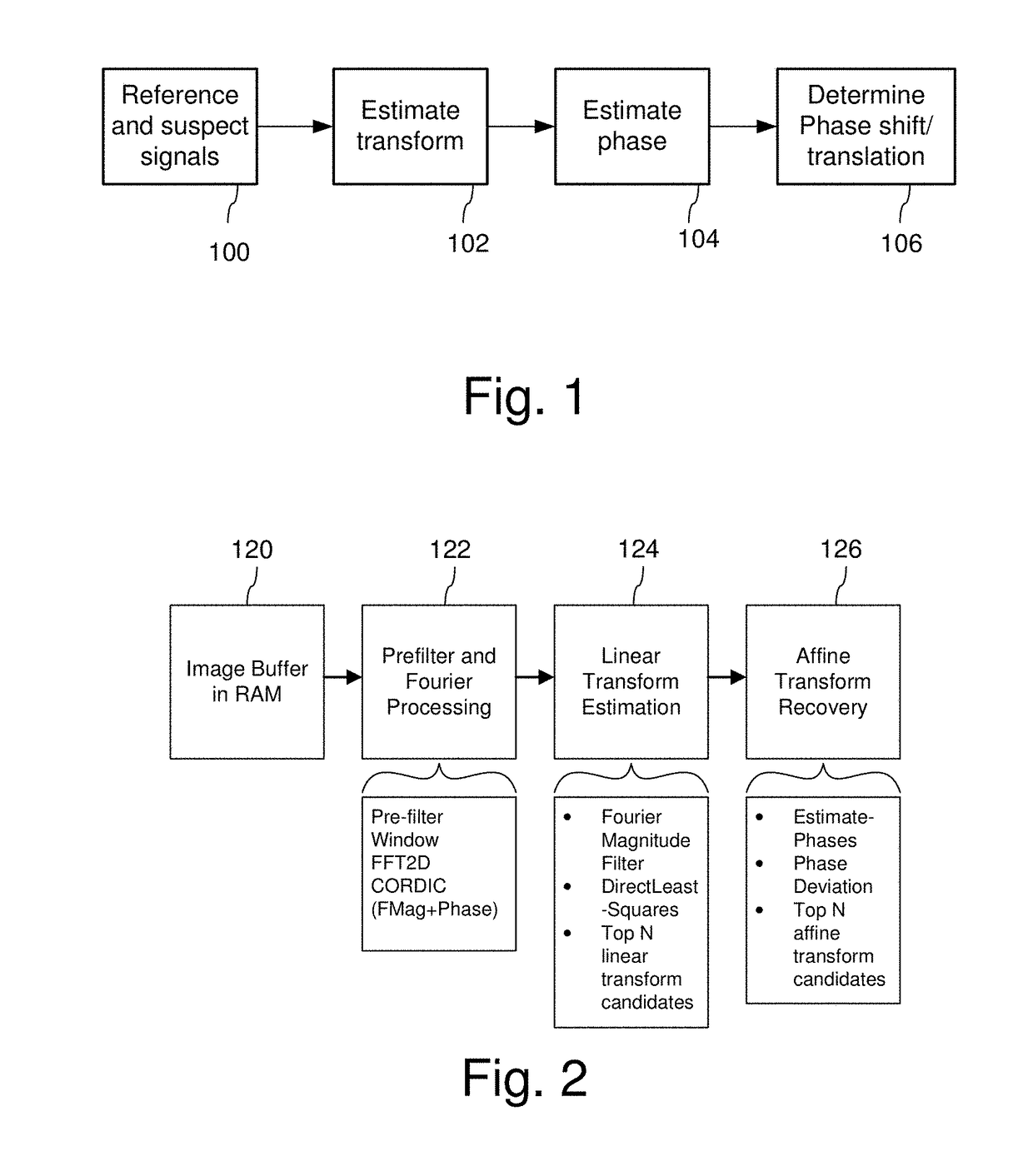
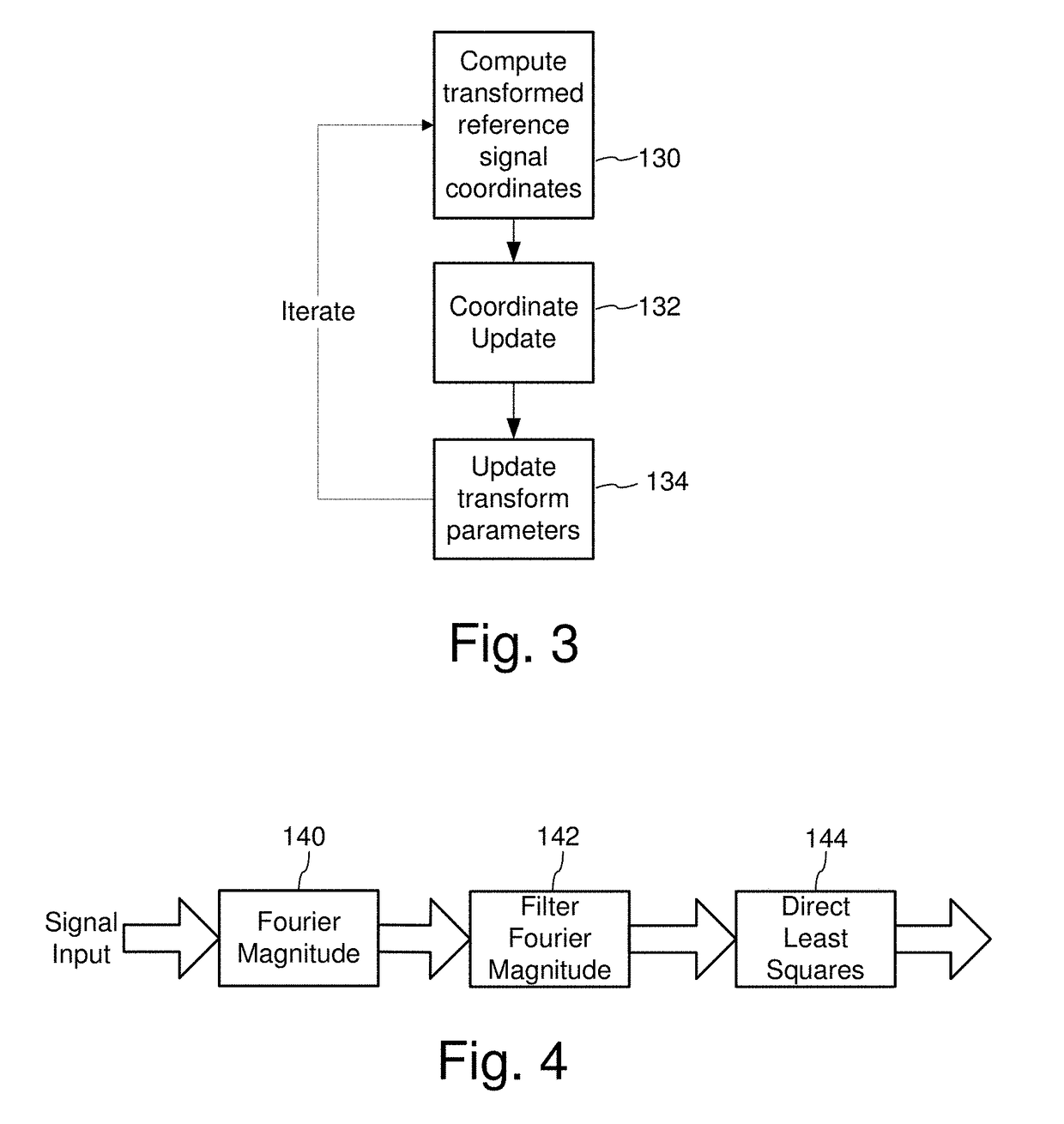
Signal Processors and Methods for Estimating Geometric Transformations of Images for Digital Data Extraction
ActiveUS20170193628A1Accurate measurementAccurate locationGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital dataConfidence metric
Signal processing devices and methods estimate a geometric transform of an image signal. From a seed set of transform candidates, a direct least squares method applies a seed transform candidate to a reference signal and then measures correlation between the transformed reference signal and an image signal in which the reference signal is encoded. Geometric transform candidates encompass differential scale and shear, which are useful in approximating a perspective transform. For each candidate, update coordinates of reference signal features are identified in the image signal and provided as input to a least squares method to compute an update to the transform candidate. The method iterates so long as the update of the transform provides a better correlation. At the end of the process, the method identifies a geometric transform or set of top transforms based on a further analysis of correlation, as well as other results. Phase characteristics are exploited in the process of updating coordinates and measuring correlation. The geometric transform is used as an approximation of the geometric distortion of an image after digital data is encoded in it, and is used to compensate for this distortion to facilitate extracting embedded digital messages from the image. Due to the errors in the approximation, a signal confidence metric is determined and used to weight message symbol estimates extracted from the image.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
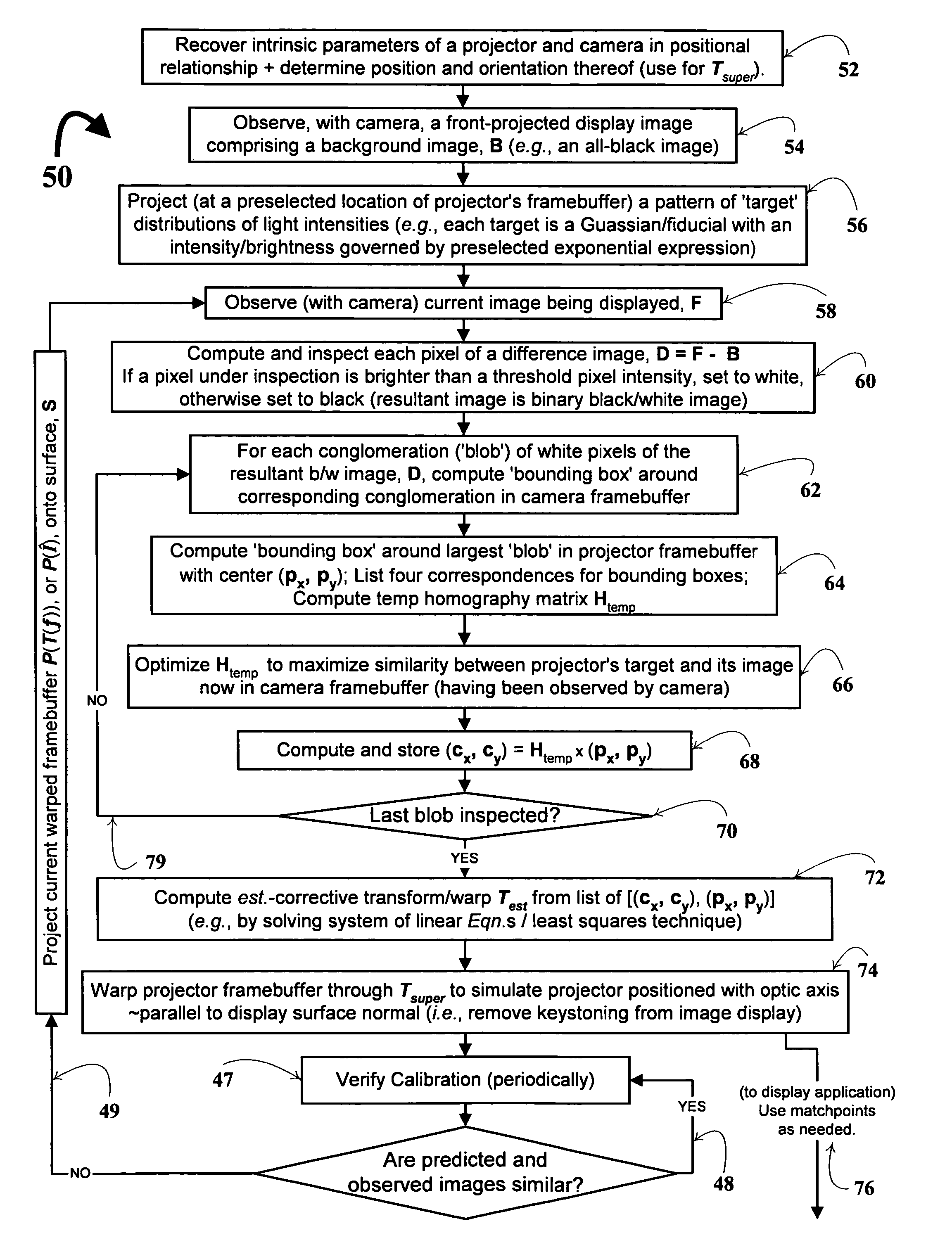
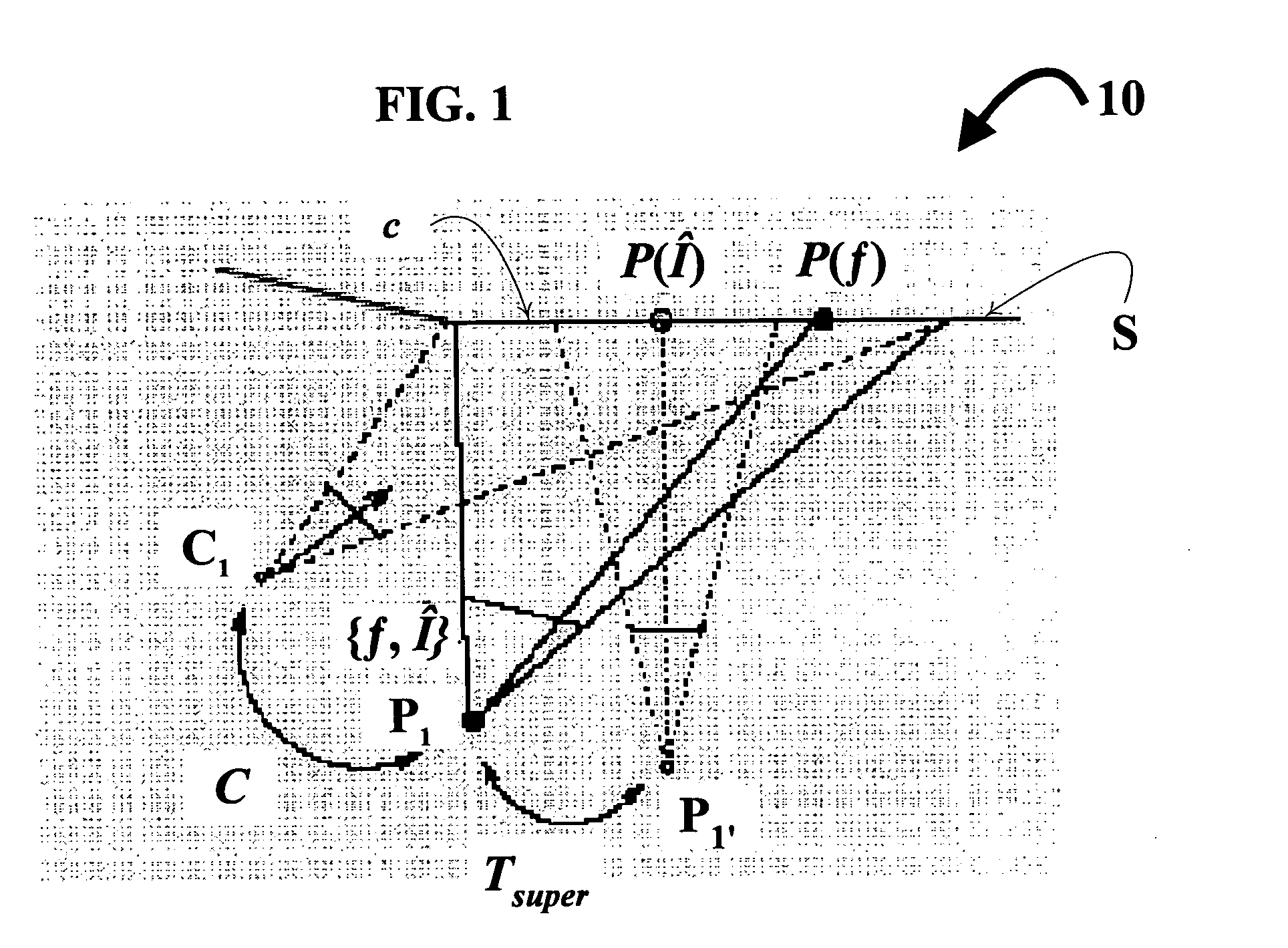
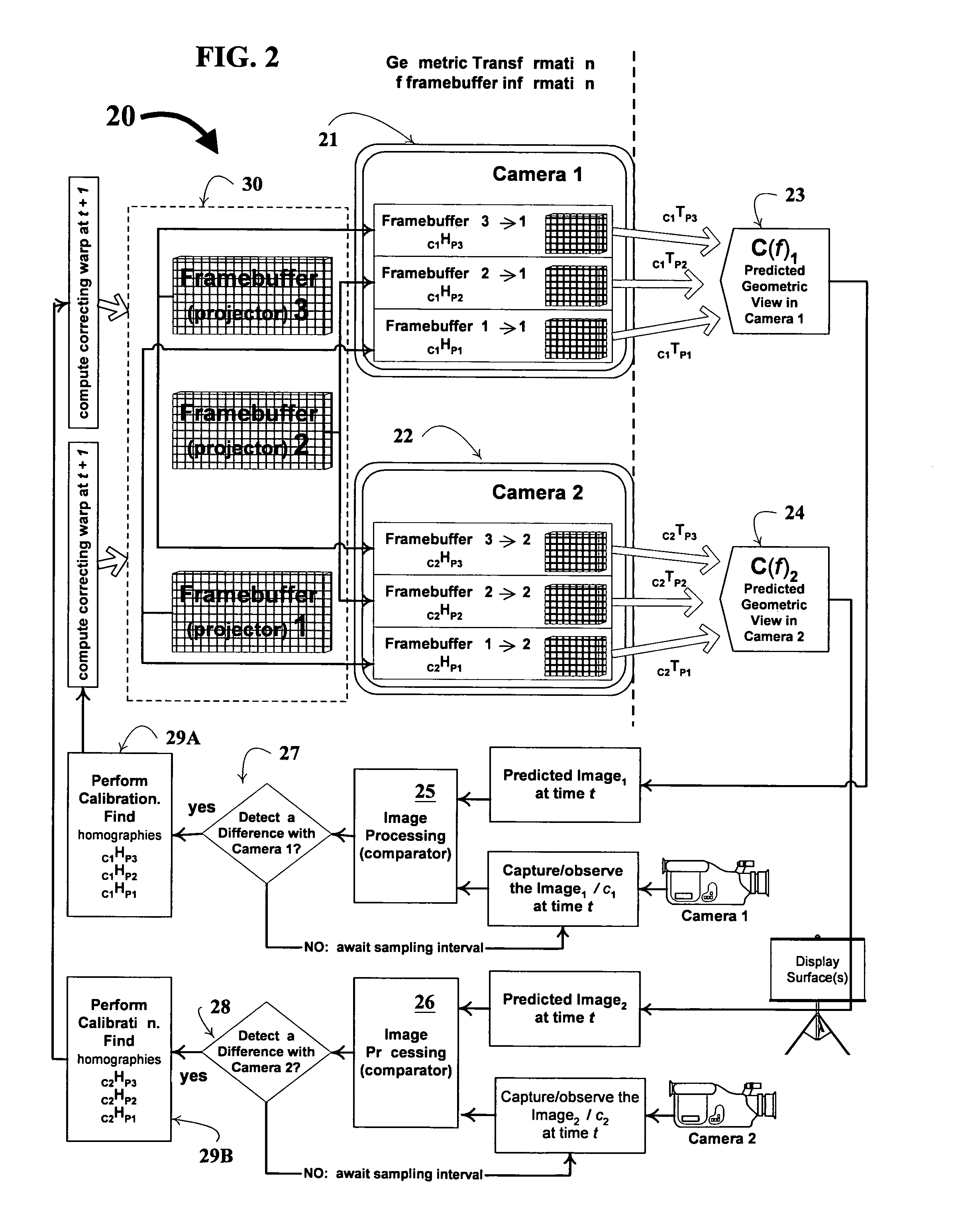
Monitoring and correction of geometric distortion in projected displays
InactiveUS7119833B2Easy to operateCorrect distortionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDisplay deviceTarget distribution
A technique, and associated system and computer executable program code on a computer readable storage medium, for automatically correcting distortion of a front-projected display under observation by at least one camera. The technique may be employed in a myriad of front-projected display environments, e.g., single or multiple projectors and cameras are used. The technique includes: observing a first image, projected from at least one projector, comprising at least one target distribution of light intensities; for each conglomeration of white pixels of a difference image, compute a bounding box comprising a corresponding conglomeration of pixels in a framebuffer information of the camera, compute a bounding box comprising a corresponding conglomeration of pixels in a framebuffer information of the projector, compute an initial homography matrix, Htemp, mapping pixels of the projector's bounding box to those of the camera's bounding box, optimize the initial homography matrix, compute a central location, (Cx, Cy), of the camera's bounding box using the initial homography matrix; and using a plurality of correspondence values comprising the correspondence, compute a corrective transform to aid in the automatic correcting of the display.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
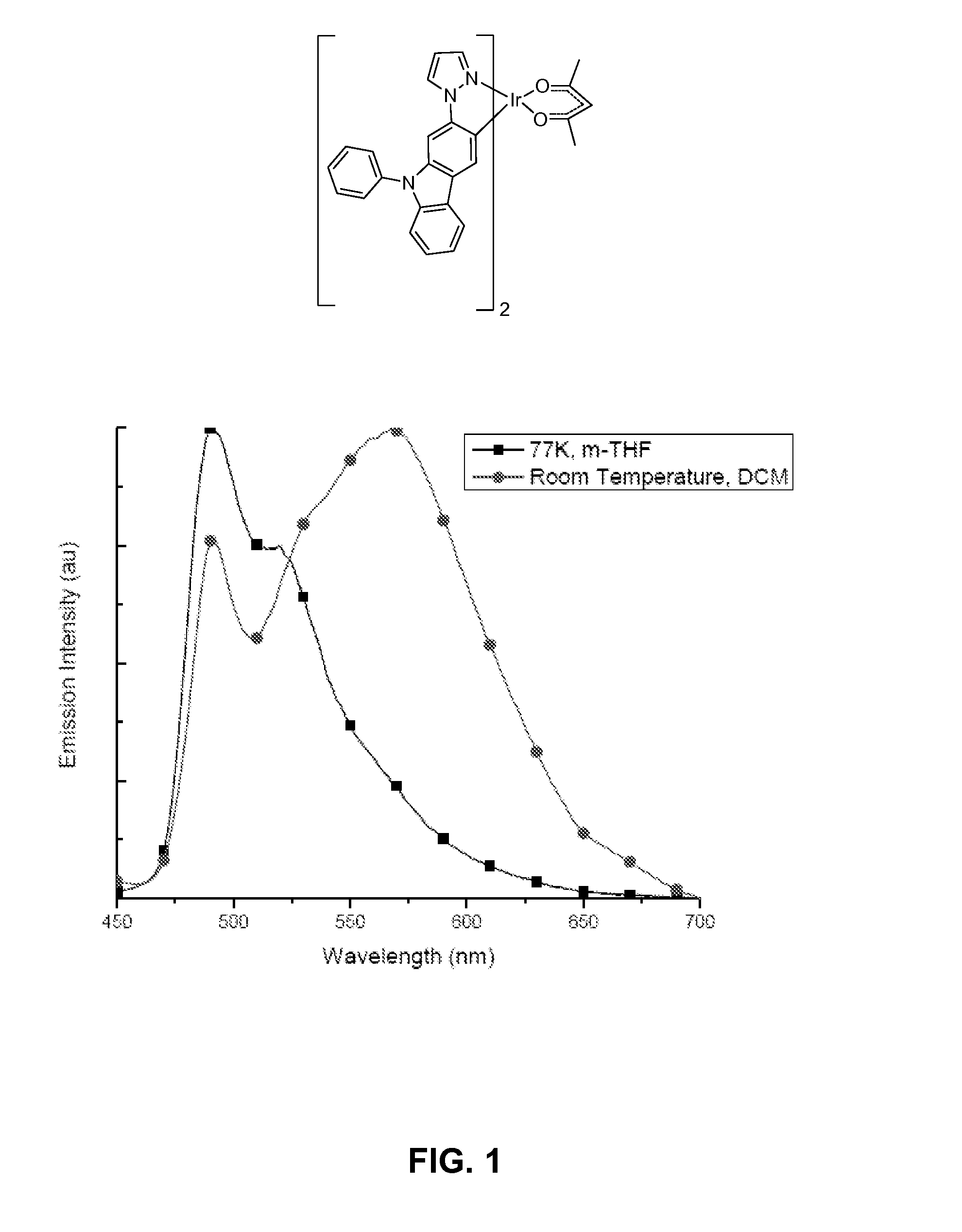
Iridium complexes demonstrating broadband emission through controlled geometric distortion and applications thereof
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for visualization of geo-located media contents in 3D rendering applications
ActiveUS20160335796A1Input/output processes for data processing3D-image renderingComputer visionMetadata
An approach is provided for accurate processing and registering of media content for rendering in 3D maps and other applications. The approach includes determining at least one first pixel of at least one image that geometrically corresponds to at least one second pixel of at least one rendered three-dimensional map. Further, the approach includes processing and / or facilitating a processing of (a) the at least one first pixel; (b) the at least one second pixel; (c) metadata associated with at least one of the at least one first pixel and the second pixel; or (d) a combination thereof to determine at least one confidence value, wherein the at least one confidence value is indicative of an estimated level of geometric distortion resulting from projecting the at least one first pixel onto the at least one second pixel. Furthermore, the approach includes determining whether to cause, at least in part, a rendering of the at least one first pixel onto the at least one rendered three-dimensional map based, at least in part, on the confidence value.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
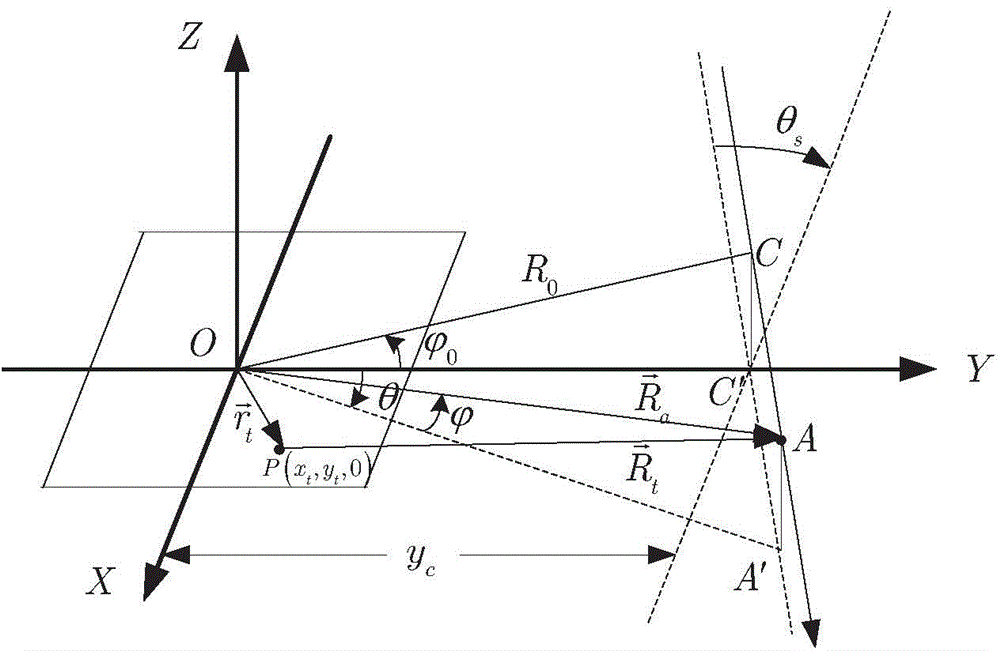
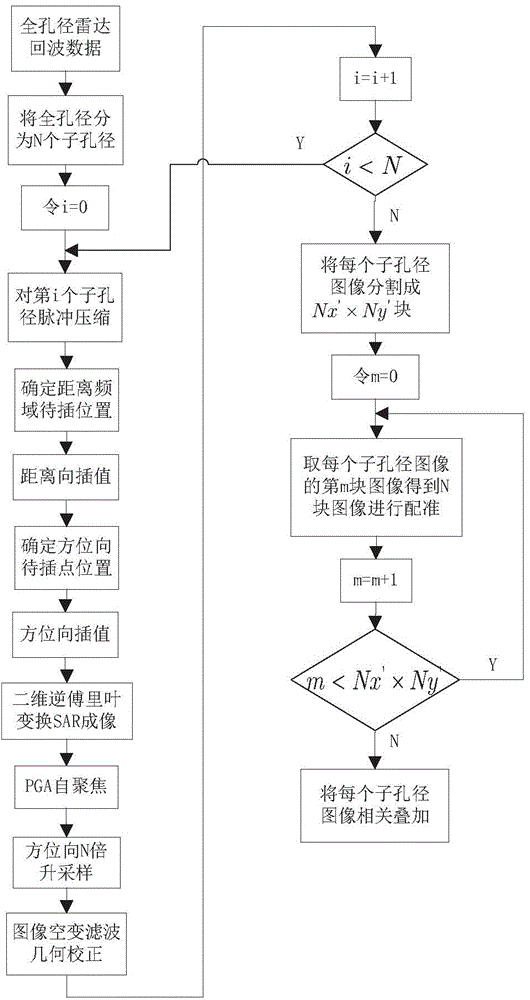
Sub-aperture partition PFA (Polar Format Algorithm) radar imaging method
ActiveCN104391297AAchieve registrationRealize seamless splicingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImaging processingRadar imaging
The invention discloses a sub-aperture partition PFA (Polar Format Algorithm) radar imaging method, and belongs to the technical field of radar imaging. All apertures are partitioned into a plurality of sub-apertures; the sub-apertures are processed by using PFA to obtain azimuthal low-resolution images; movement error of the sub-aperture images is eliminated by using PGA (Phase Gradient Autofocus) processing; geometric distortion is eliminated through azimuthal up-sampling, space varying filter and geometric correction; partitioned sub-blocks with overlapped images of all the sub-aperture images obtained by the geometric correction are subjected to image registration; finally all the registered sub-aperture images are fused to obtain a final SAR image. The full-aperture data of a large block is partitioned into sub-aperture data of small blocks for processing, so that the imaging processing efficiency is improved; the partitioned sub-blocks with overlapped images are registered during implementation of the sub-aperture image registration, so that the registration of the entire images can be realized better and seamless splicing of the sub-blocks can also be realized after registration.
Owner:南京六季光电技术研究院有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com