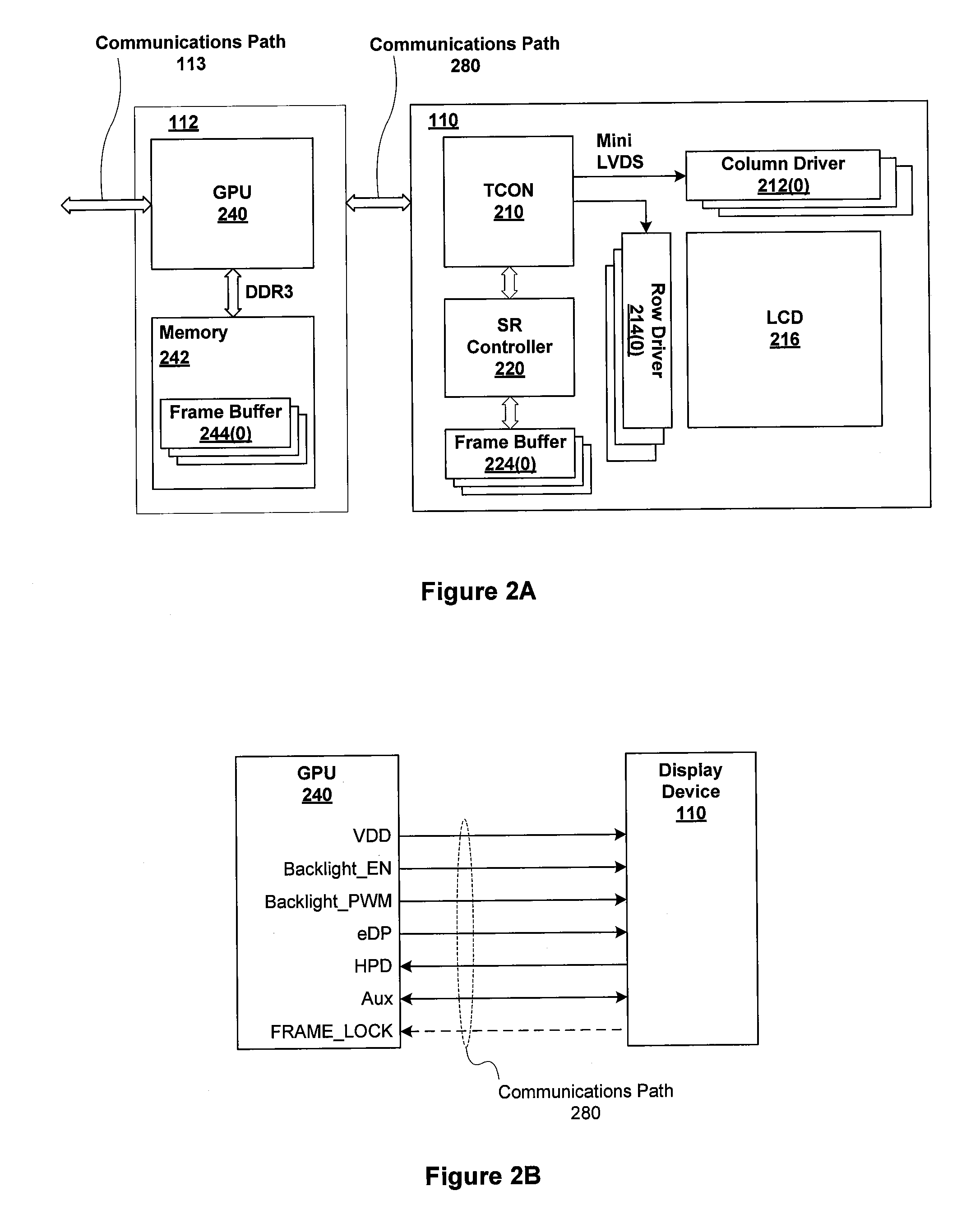
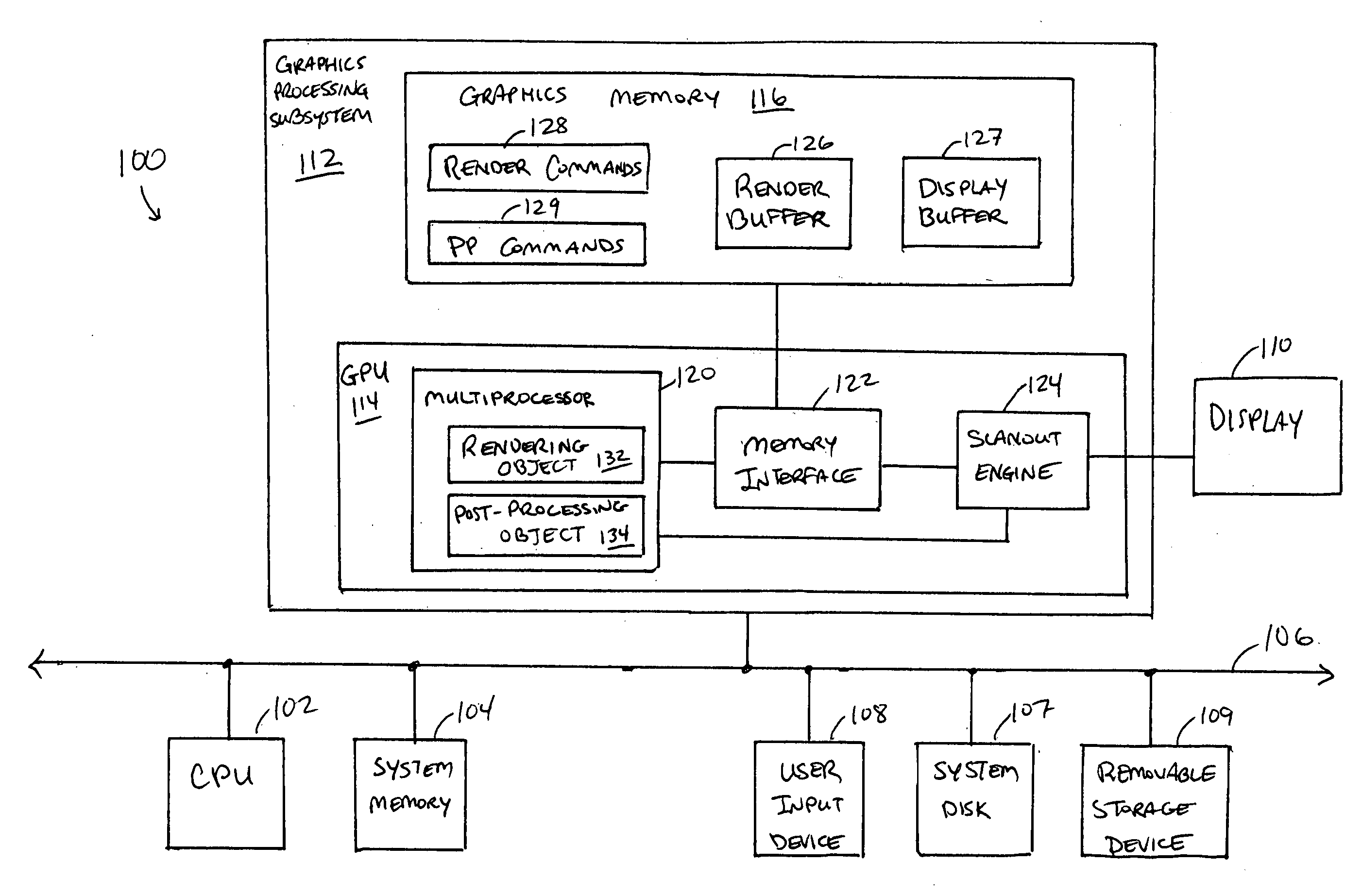
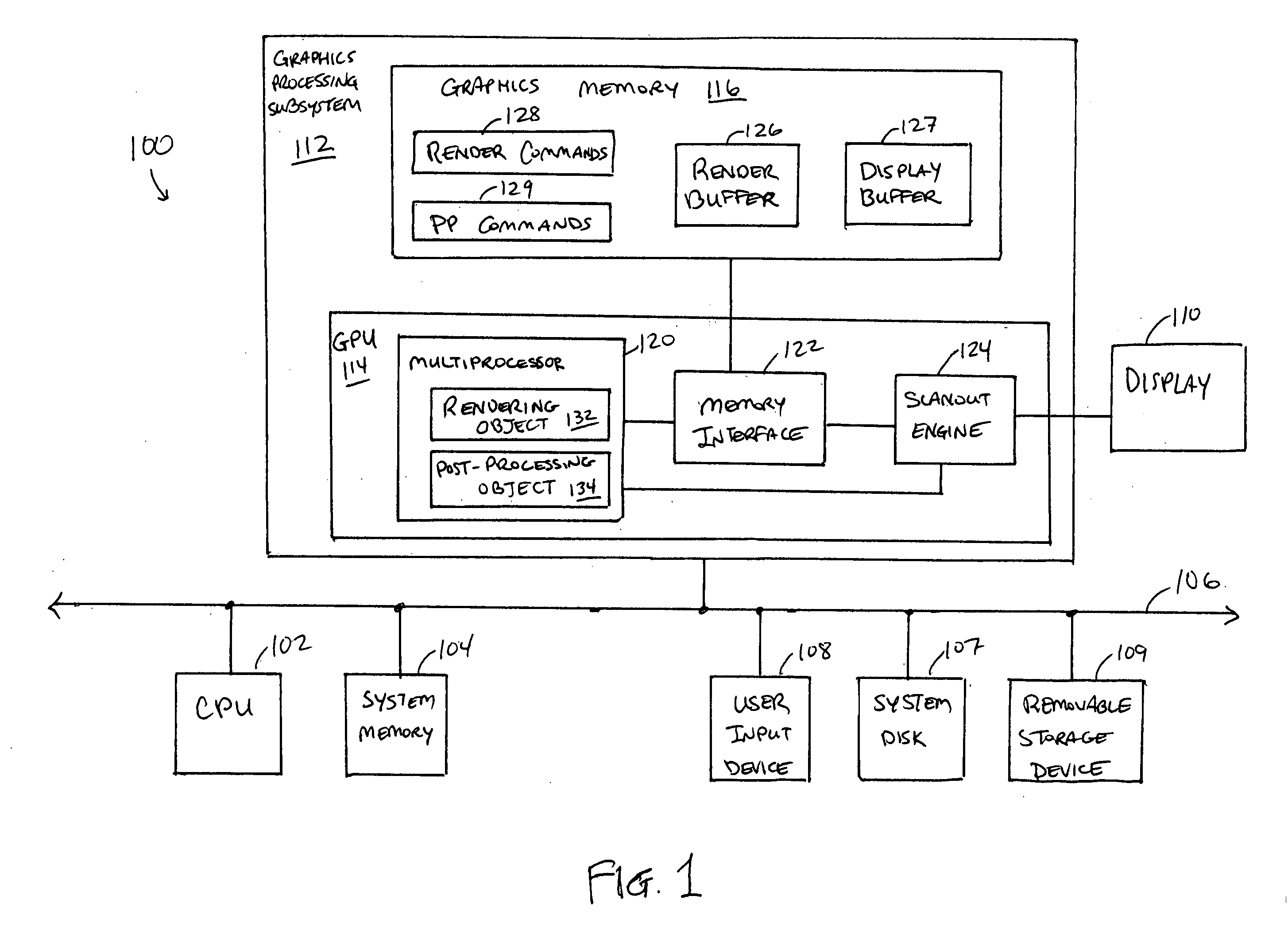
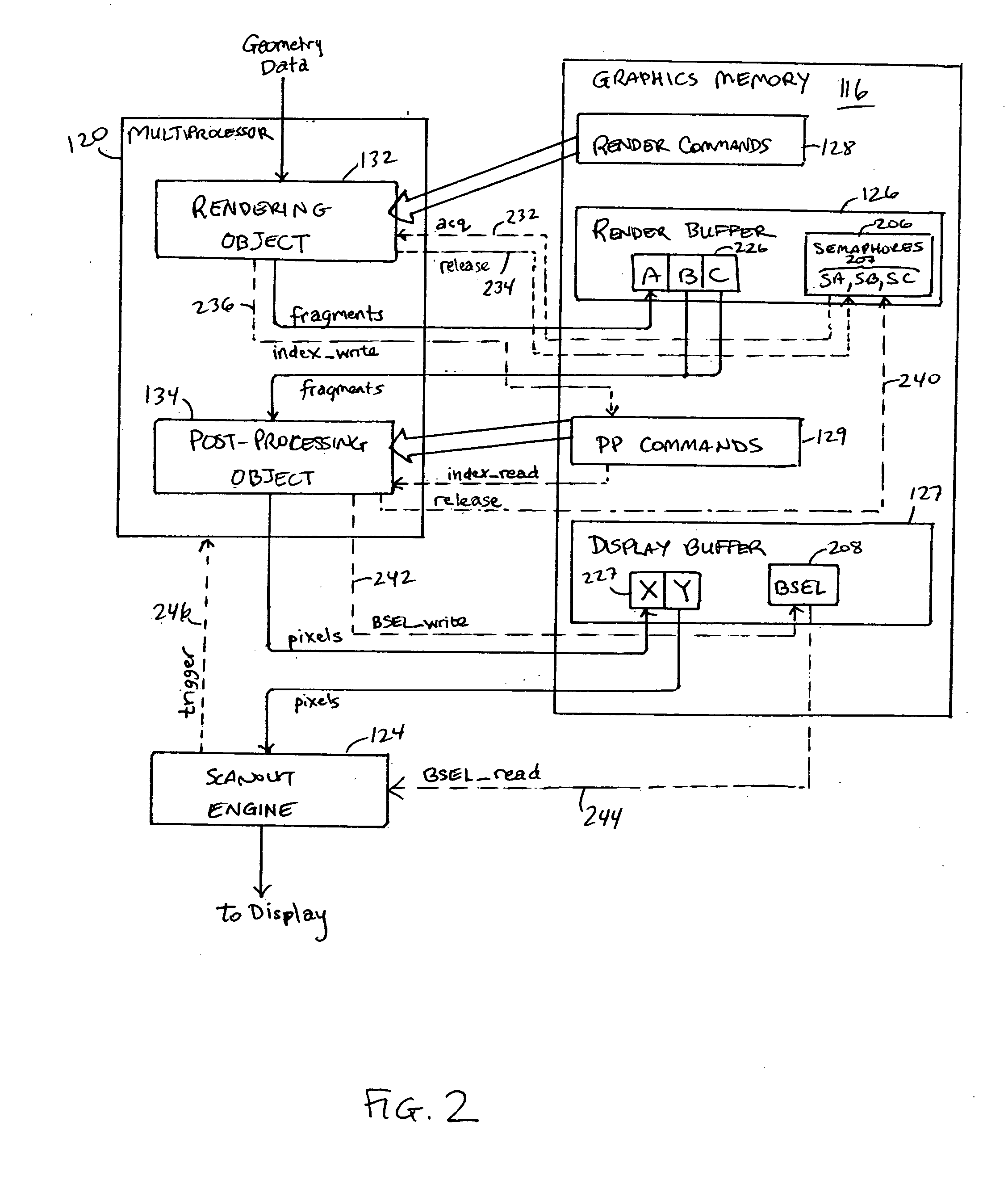
Patents
Literature
583 results about "Framebuffer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
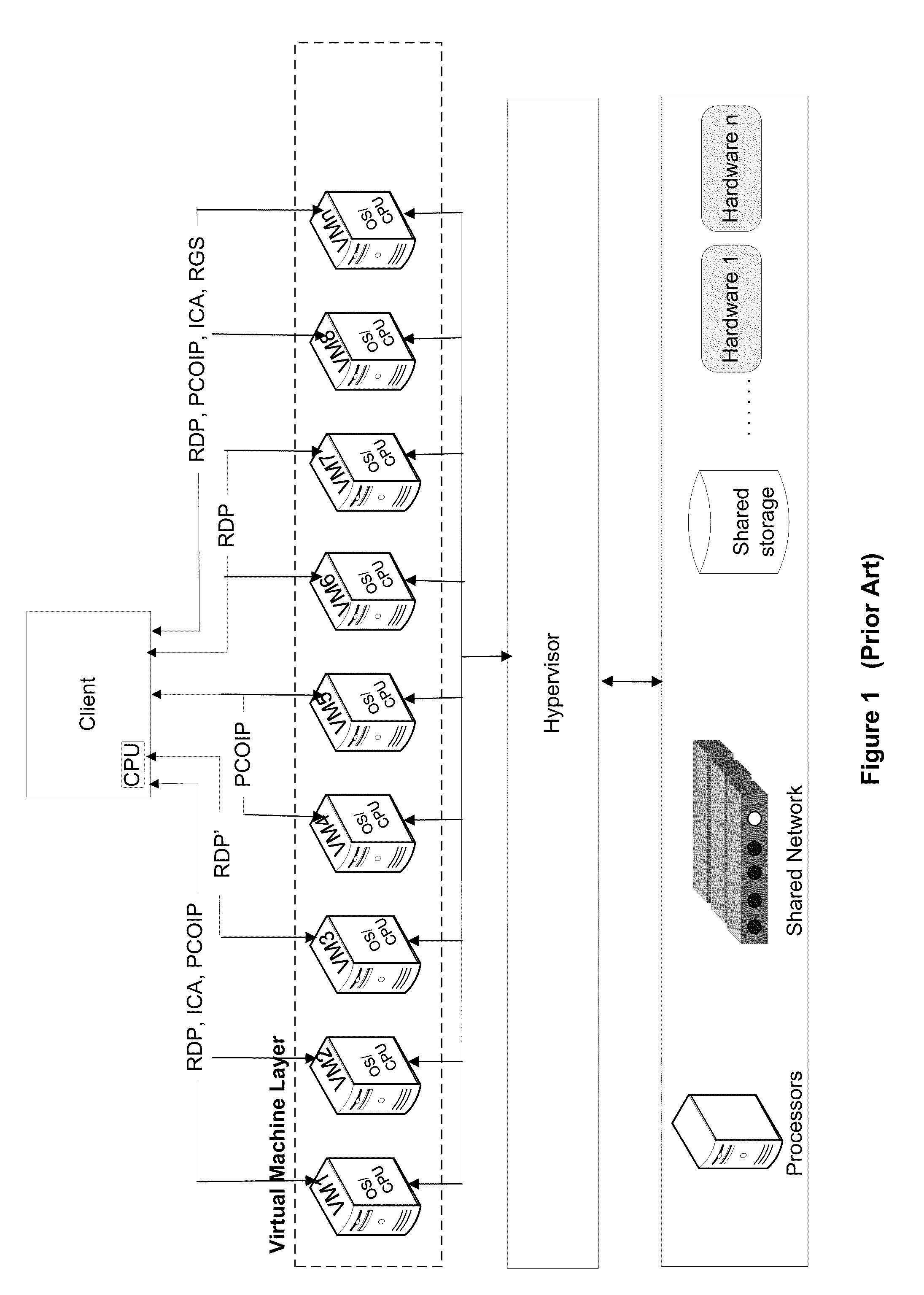
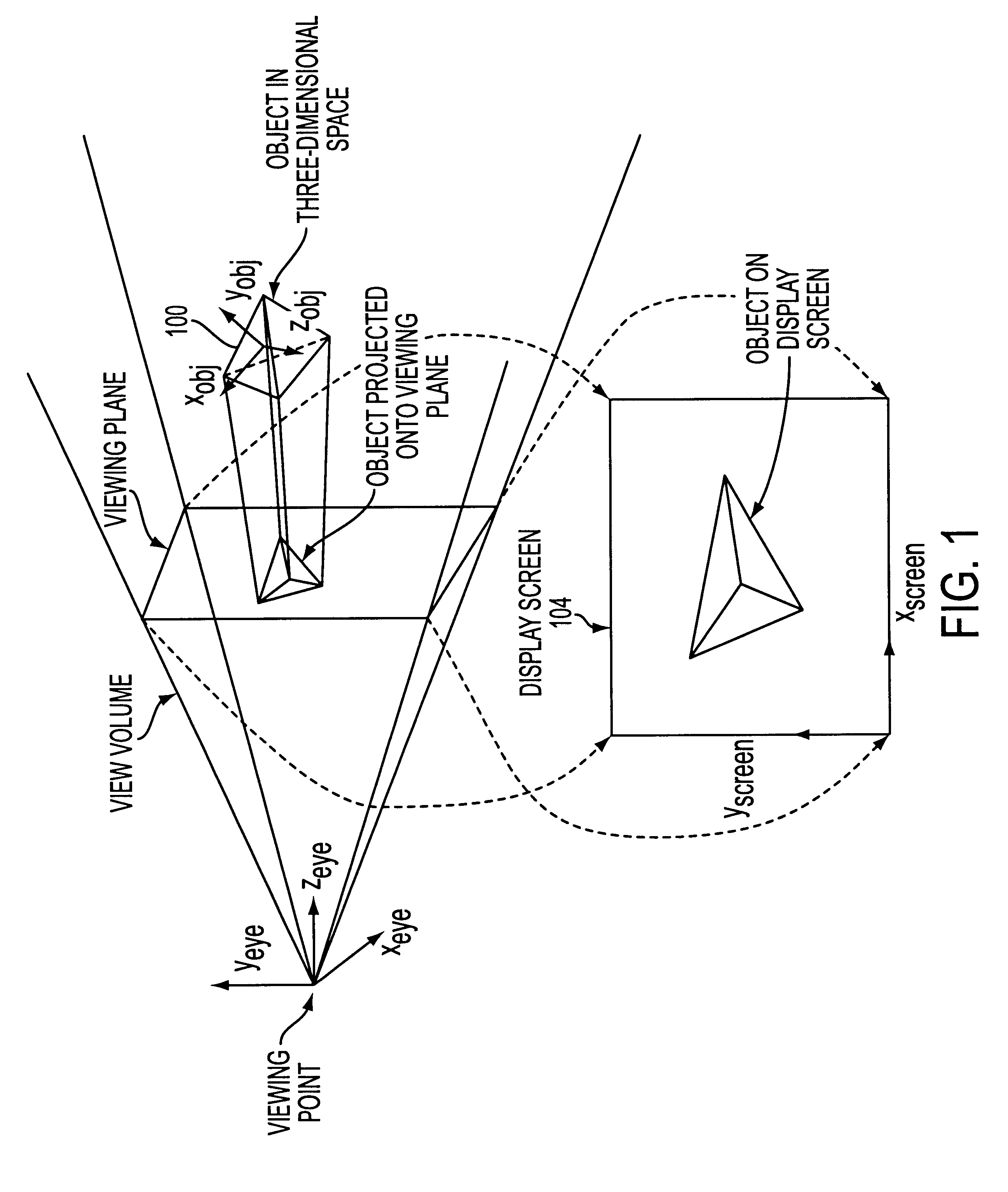
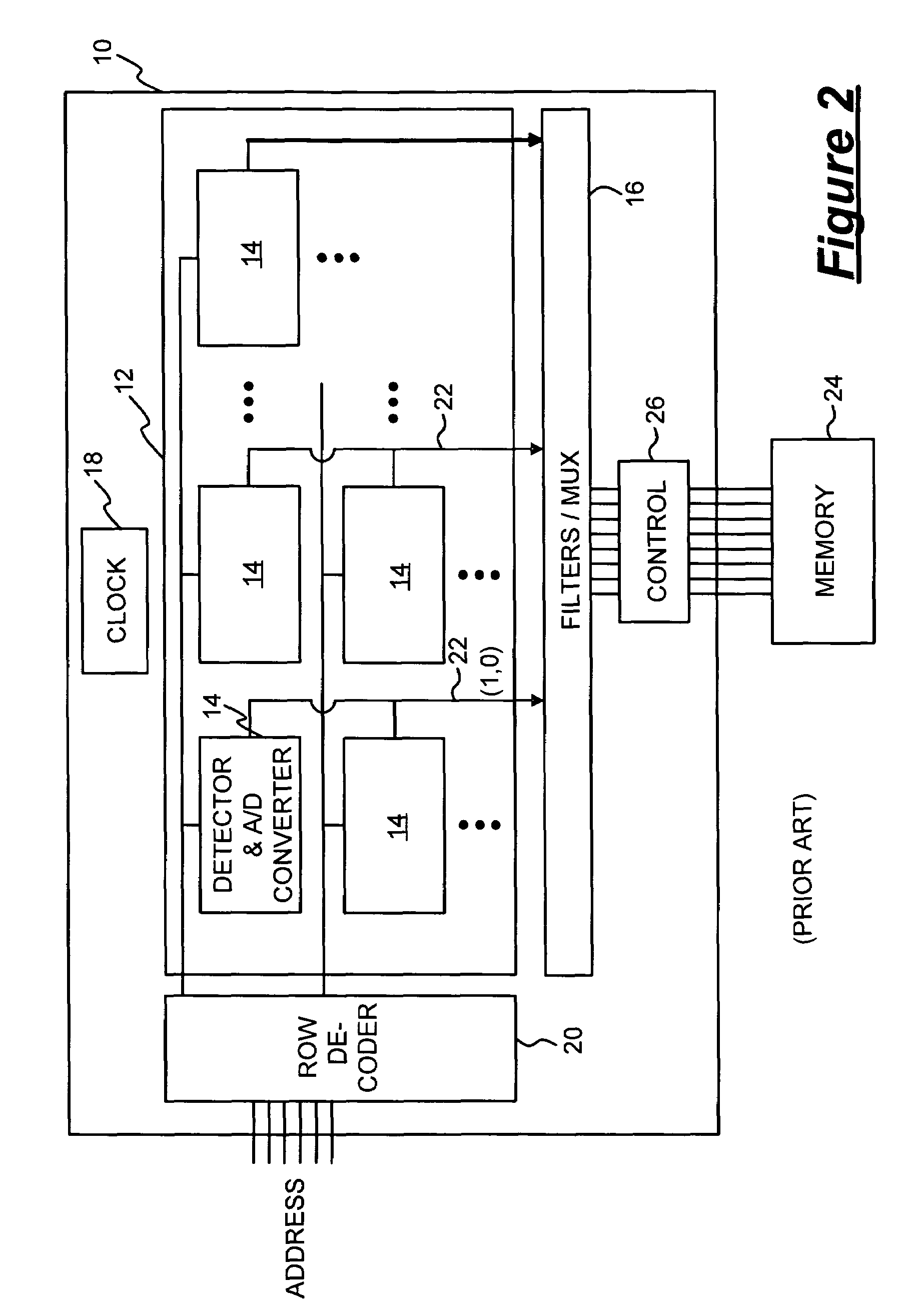
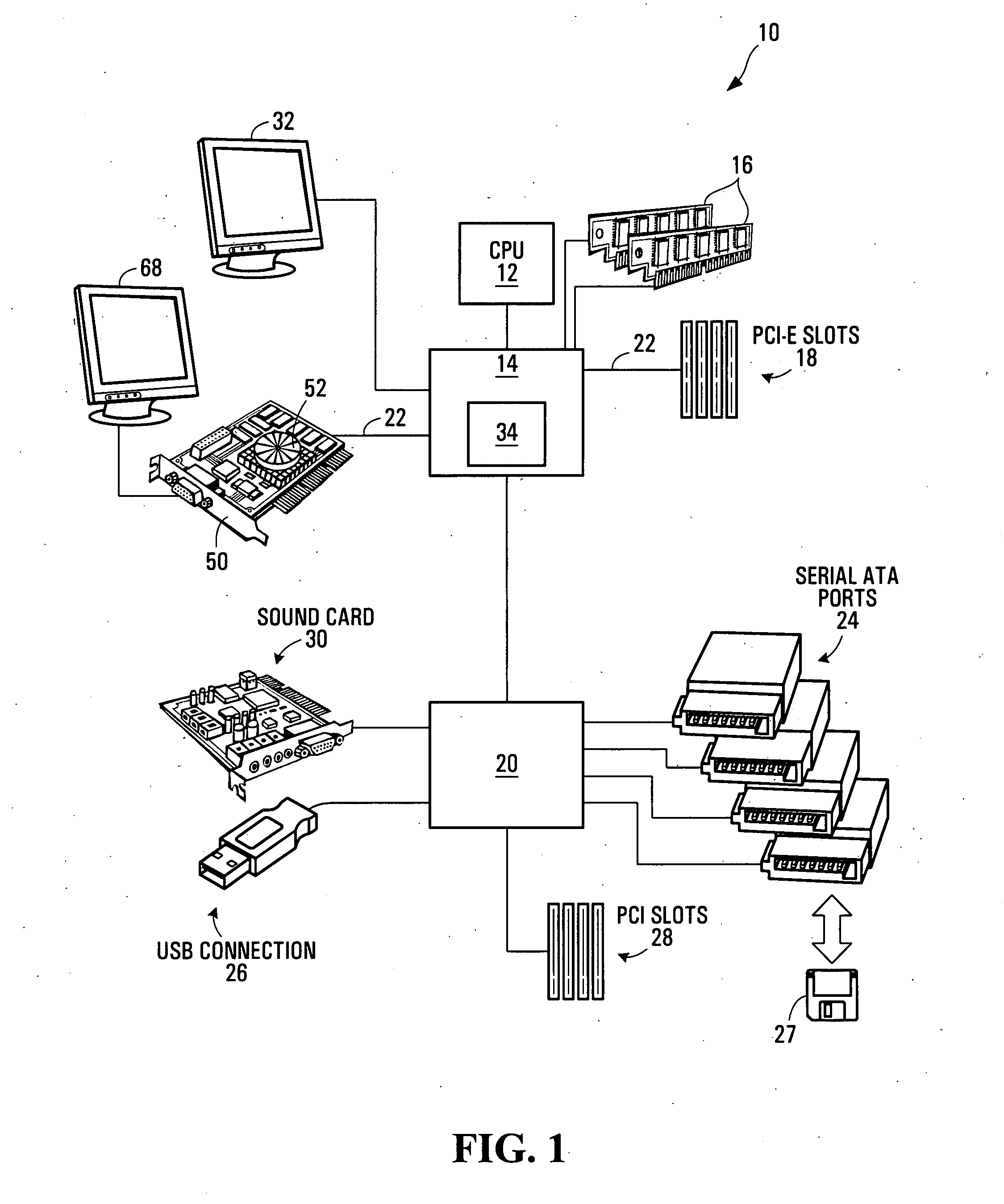
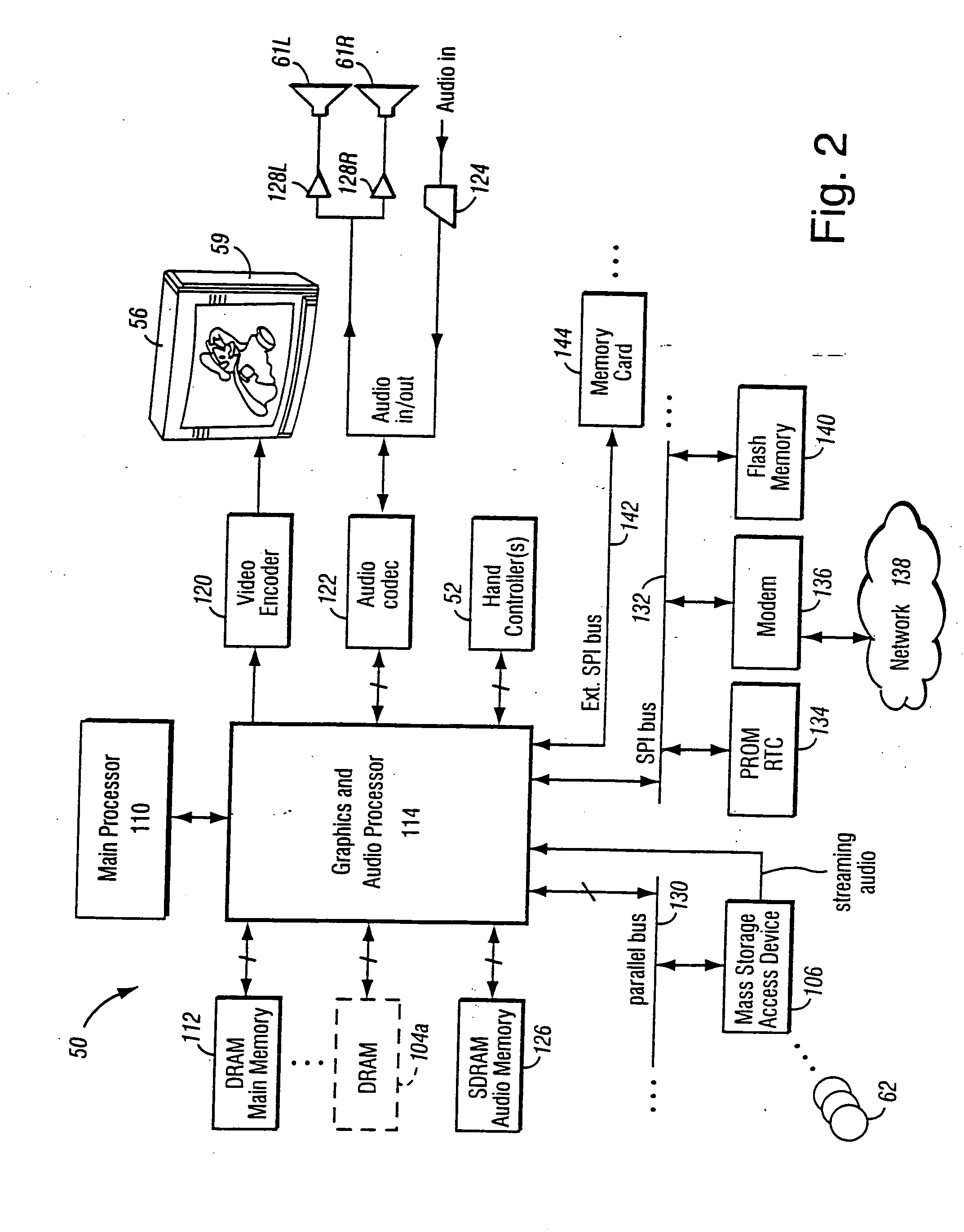
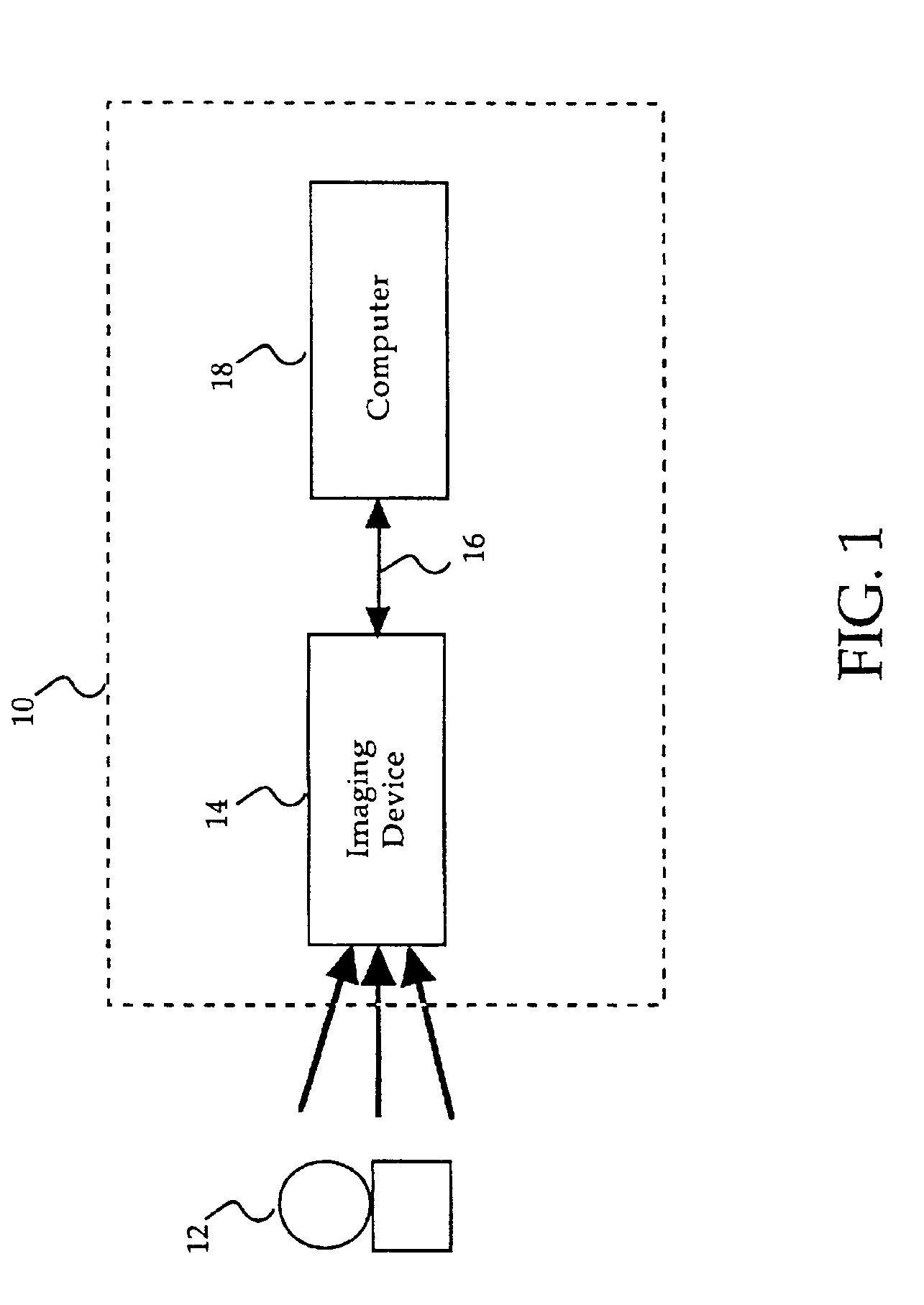
A framebuffer (frame buffer, or sometimes framestore) is a portion of RAM containing a bitmap that drives a video display. It is a memory buffer containing a complete frame of data. Modern video cards contain framebuffer circuitry in their cores. This circuitry converts an in-memory bitmap into a video signal that can be displayed on a computer monitor.
Super-resolution overlay in multi-projector displays
InactiveUS20040239885A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsProgram codeFourier transform
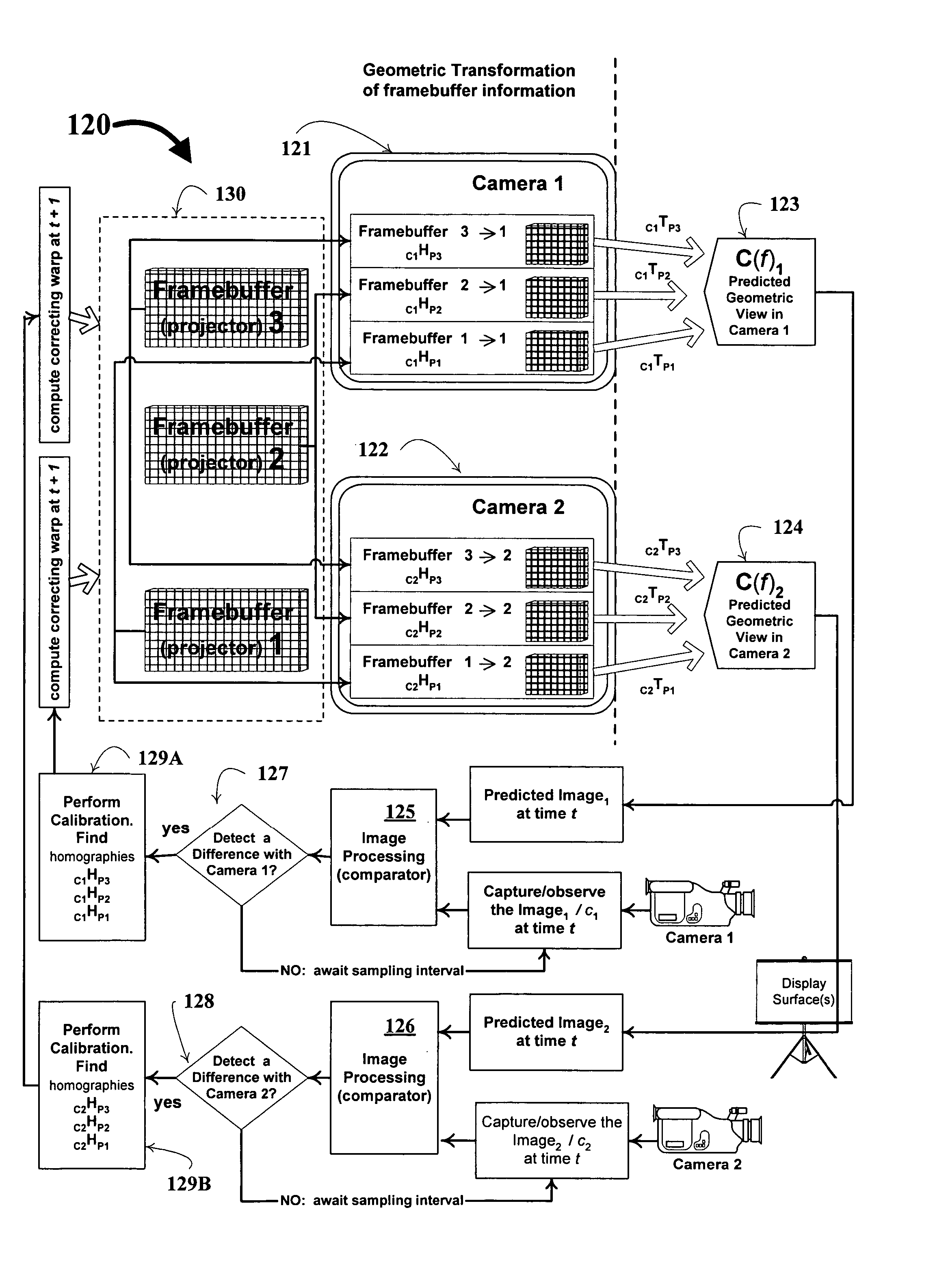
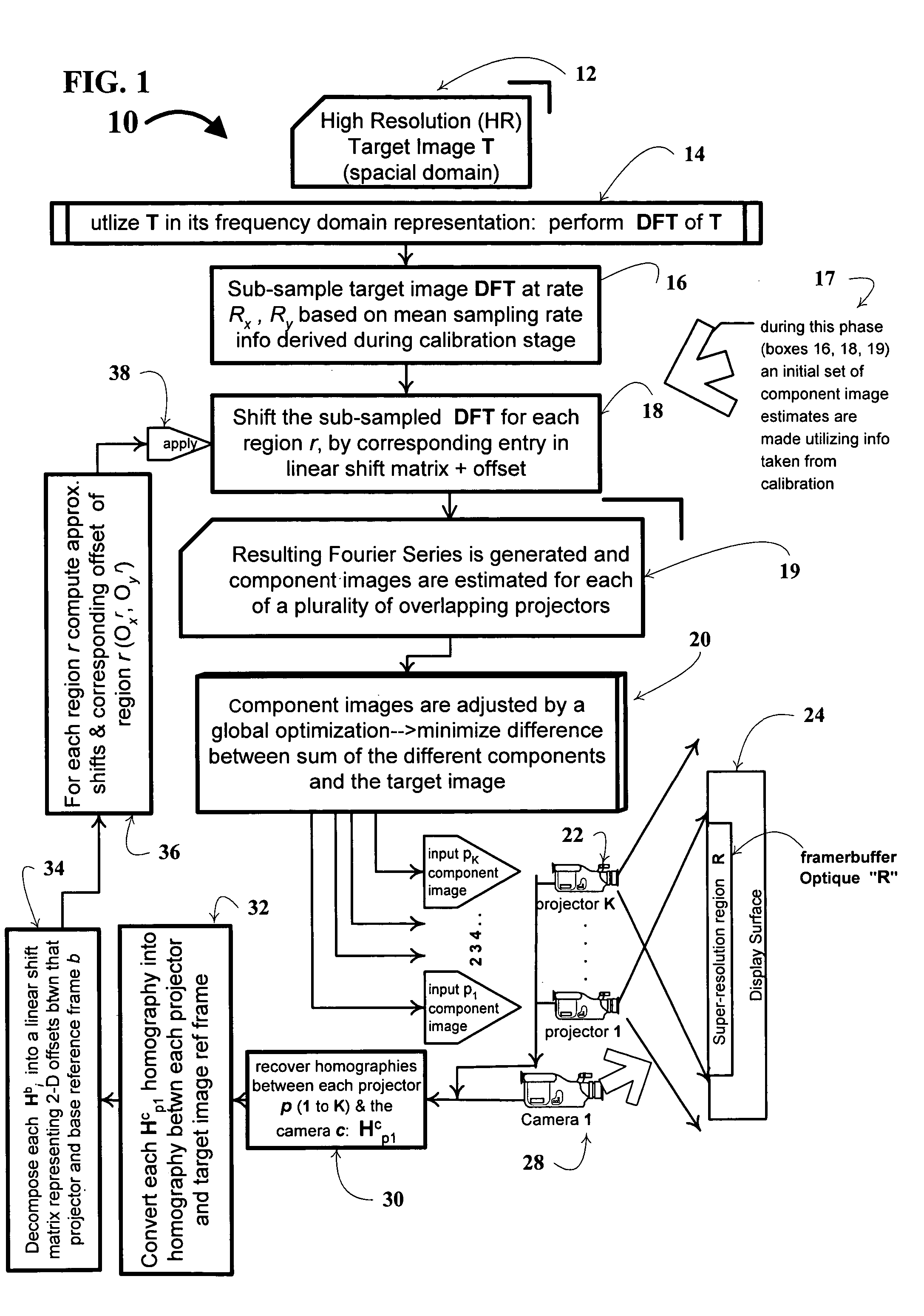
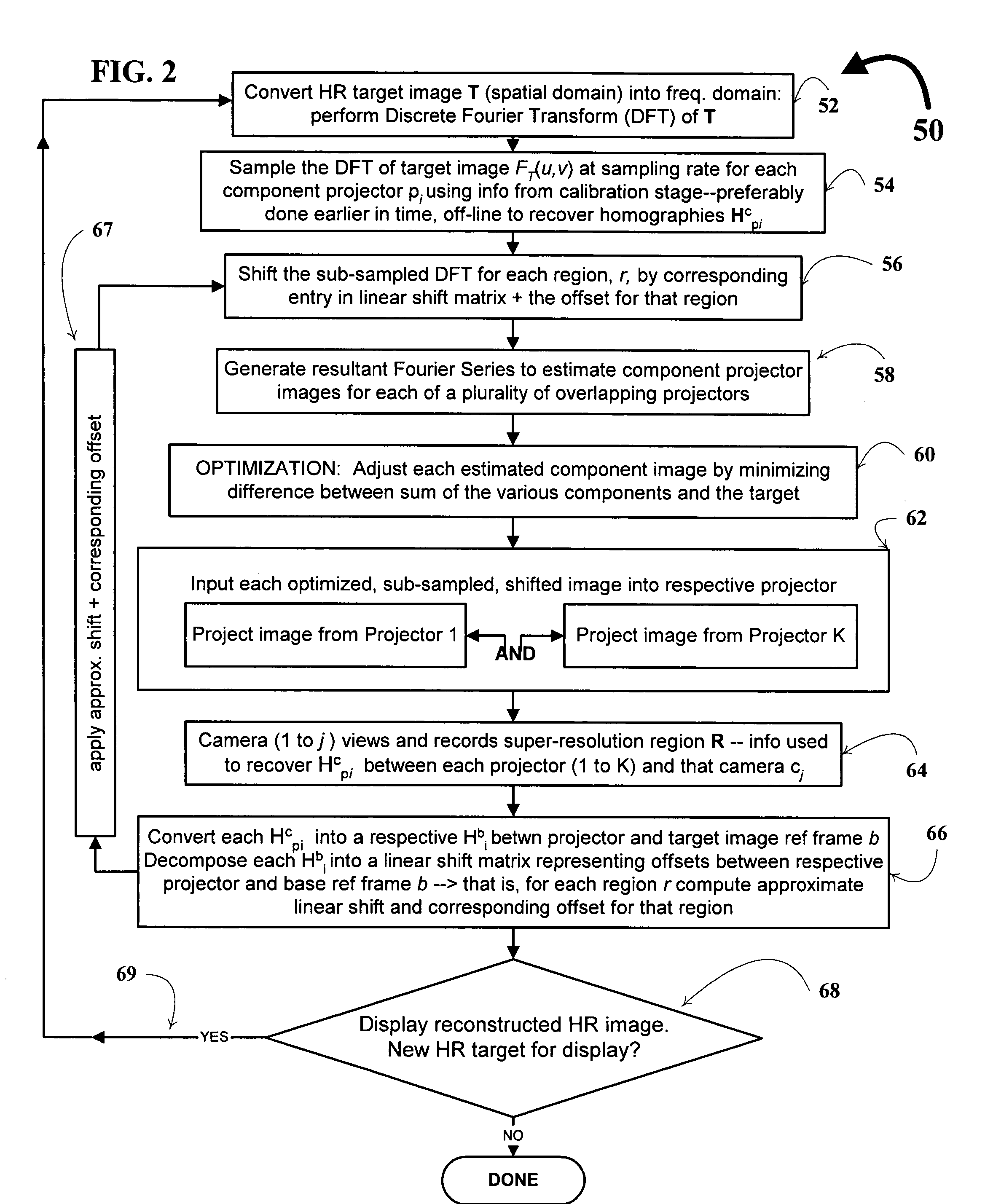
A technique, associated system and computer executable program code, for projecting a superimposed image onto a target display surface under observation of one or more cameras. A projective relationship between each projector being used and the target display surface is determined using a suitable calibration technique. A component image for each projector is then estimated using the information from the calibration, and represented in the frequency domain. Each component image is estimated by: Using the projective relationship, determine a set of sub-sampled, regionally shifted images, represented in the frequency domain; each component image is then composed of a respective set of the sub-sampled, regionally shifted images. In an optimization step, the difference between a sum of the component images and a frequency domain representation of a target image is minimized to produce a second, or subsequent, component image for each projector. Here, a second set of frequency domain coefficients for use in producing a frequency domain representation of the second component image for each projector is identified. Taking the inverse Fourier transform of the frequency domain representation of the second component image, converts the information into a spatial signal that is placed into the framebuffer of each component projector and projected therefrom to produce the superimposed image.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
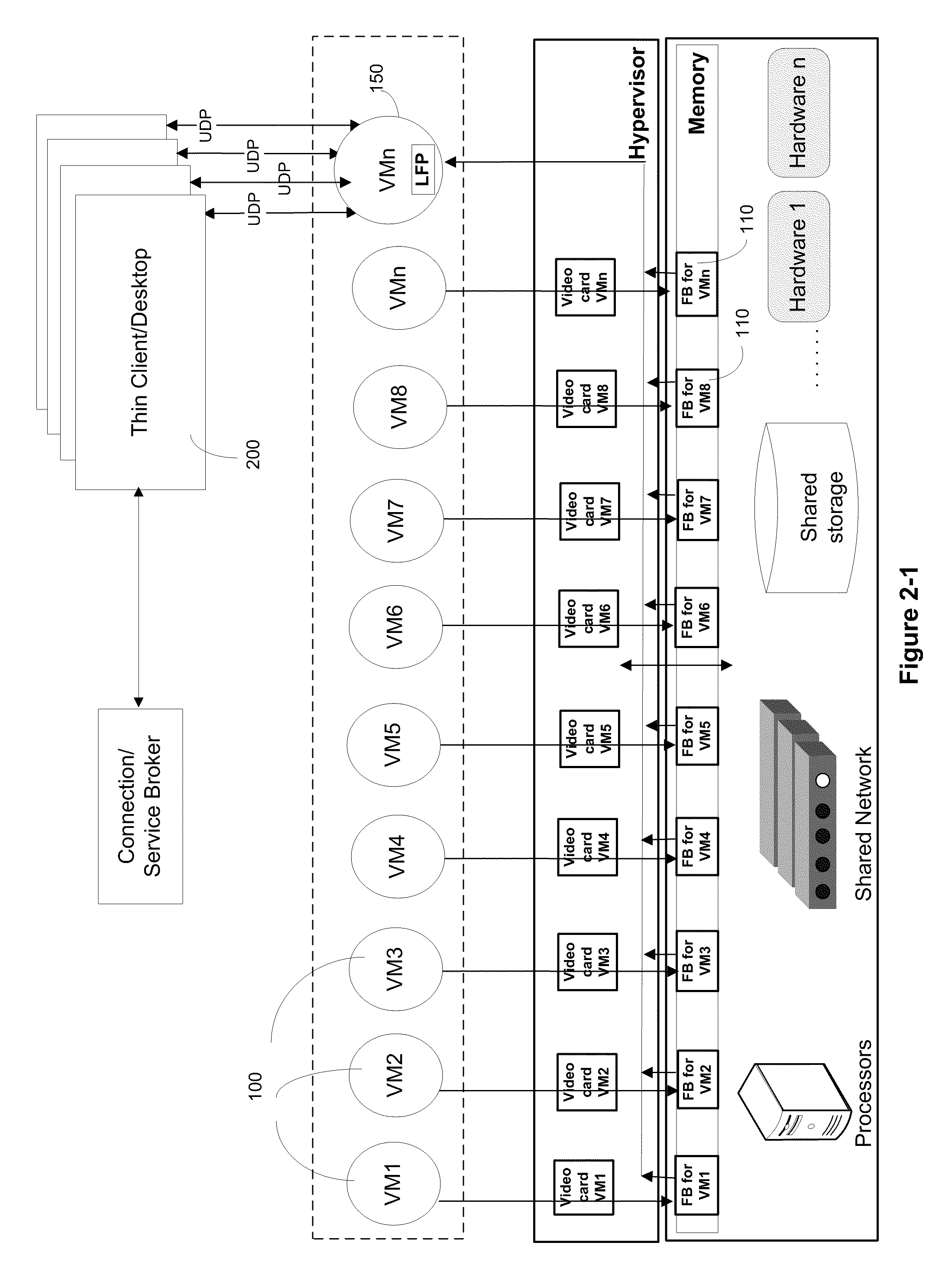
Systems and Algorithm For Interfacing With A Virtualized Computing Service Over A Network Using A Lightweight Client
ActiveUS20110126110A1High performance imageEasy to decompressInterprogram communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsVirtual memoryNetwork packet
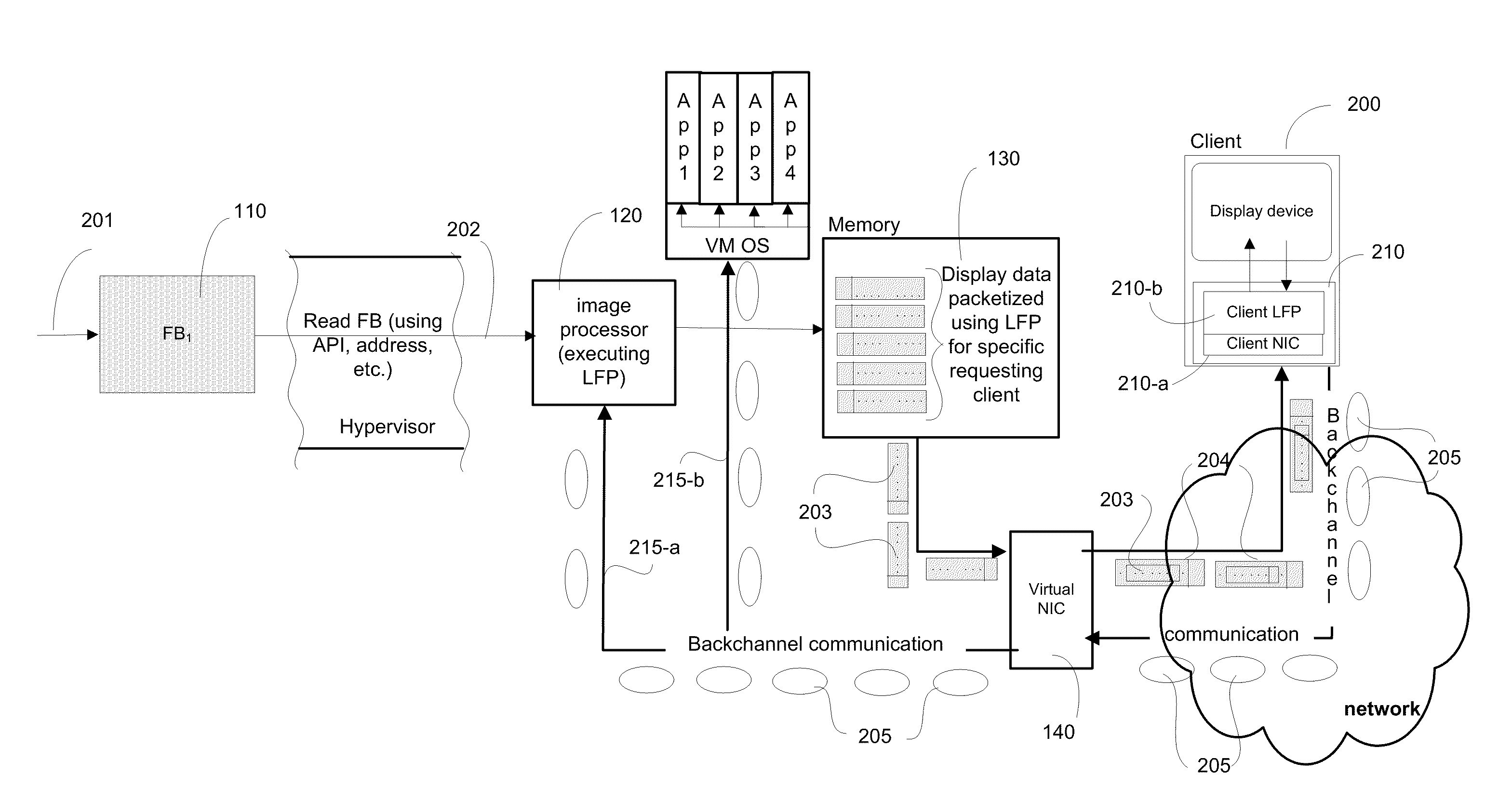
Systems and algorithm for controlling a virtualized computer service remotely through a client includes defining a virtual infrastructure in which a plurality of virtual machines are running on a hypervisor with at least one of the virtual machine executing an image processor algorithm. The image processor algorithm is configured to receive a connection request from the client for controlling the virtualized computer service (or simply, virtual service) available at a specific virtual machine. The request includes a plurality of connection parameters that describe the connection requirements of the client and is received at the virtual machine that is equipped with the image processor algorithm. The connection parameters are interrogated using the image processor algorithm to identify a specific virtual machine that provides the requested virtualized computer service. A framebuffer data for the identified virtual machine located in virtual memory is accessed and read directly through a hypervisor. The framebuffer data is processed into a plurality of image data packets using the image processor algorithm and transmitted to the client for presenting on a display device associated with the client. The image data packet grammar is tailored to the client and represents an image of the virtual machine display for the identified virtual machine.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
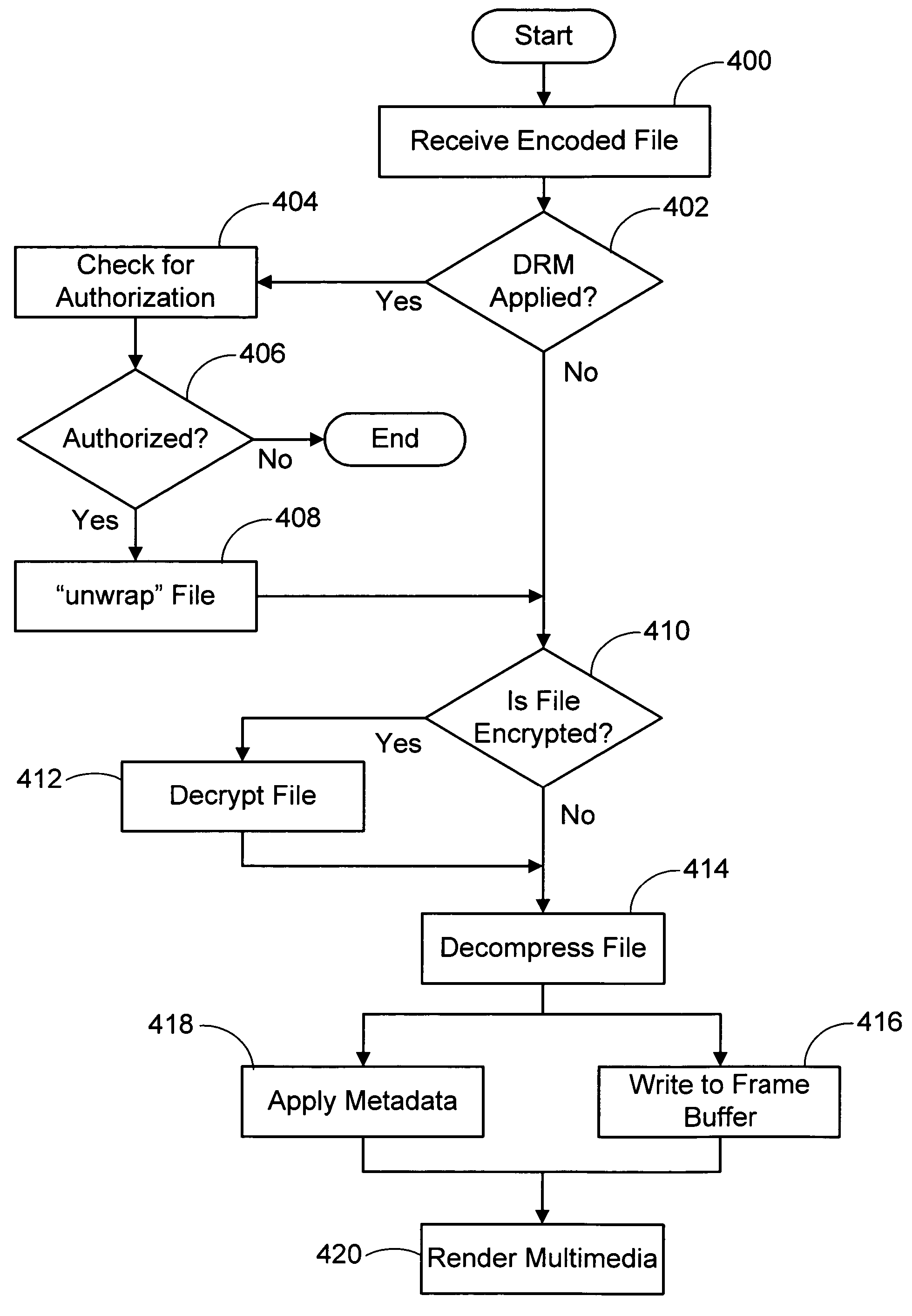
Method and apparatus to decode a streaming file directly to display drivers
InactiveUS20050195205A1Eliminating intermediate processingEliminating storage stepCathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital video signal modificationLiquid-crystal displayComputer graphics (images)
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System for transforming streaming video data
InactiveUS7143432B1Decreased bit depthAttenuation bandwidthPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningImage resolutionComputer graphics (images)
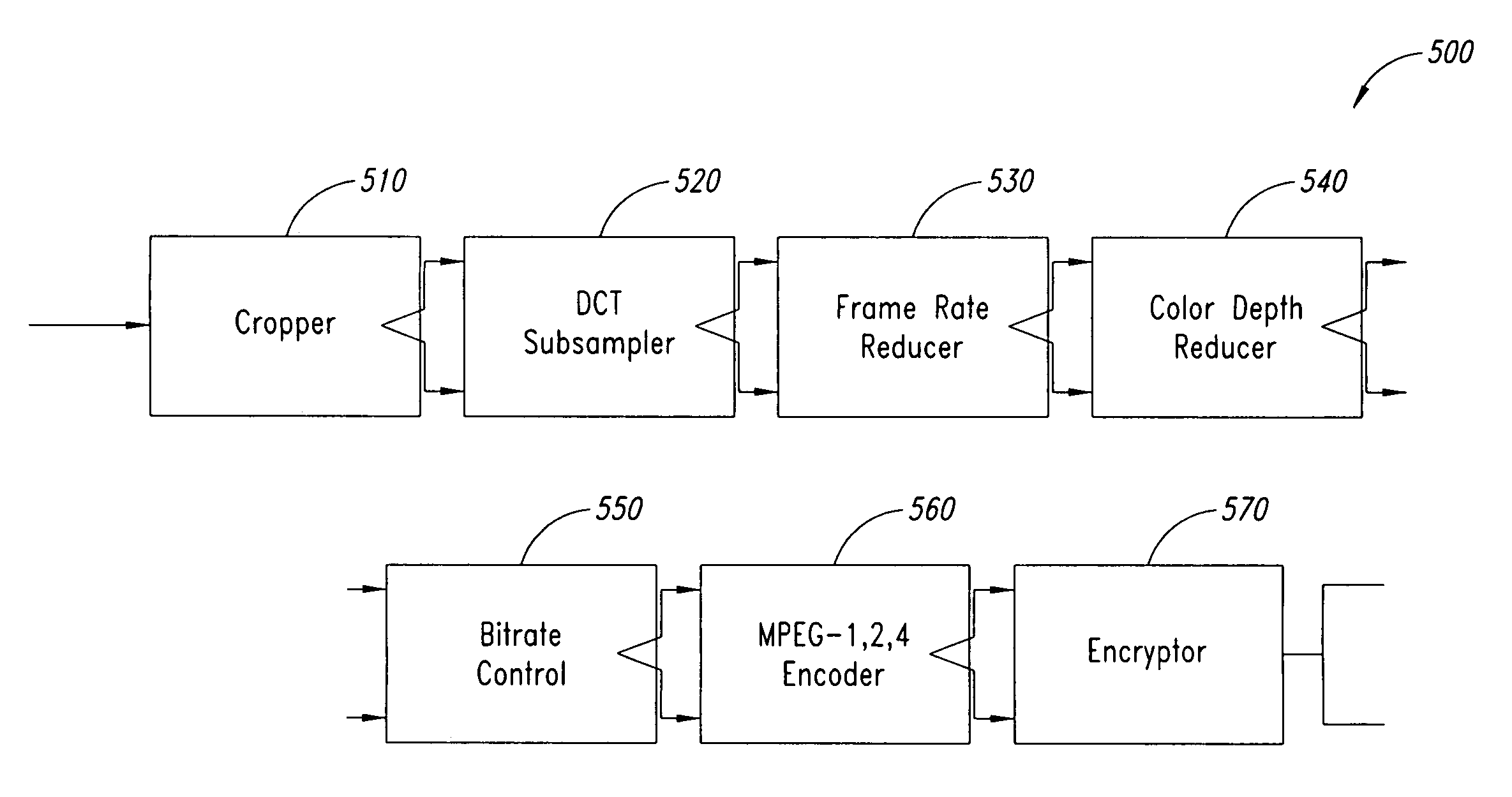
According to one embodiment, a circuit configured to form an output video stream includes a resolution modification circuit configured to receive a plurality of video frames from a frame buffer, and configured to modify resolution of the plurality of video frames, when the desired resolution for the output video stream is different than a resolution of the input video stream, the plurality of frames of data derived from an input video stream, a frame reducing circuit coupled to the resolution reducing circuit configured to reduce a number of video frames in the plurality of video frames from the resolution reducing circuit, when a desired frame rate for the output video stream is different than a frame rate of the input video stream, a depth reduction circuit coupled to the frame reducing circuit configured to reduce bit depth of the plurality of video frames from the frame reducing circuit, when a desired bit depth for the output video stream is different than a bit depth of the input video stream, and a rate reduction circuit coupled to the depth reduction circuit, configured to scale the plurality of video frames from the depth reduction circuit, in response to a desired bit rate for the output video stream, and an encoder coupled to the rate reduction circuit, configured to encode the plurality of video frames from the rate reduction circuit into the output video stream is also contemplated.
Owner:ADAPTIVE STREAMING INC
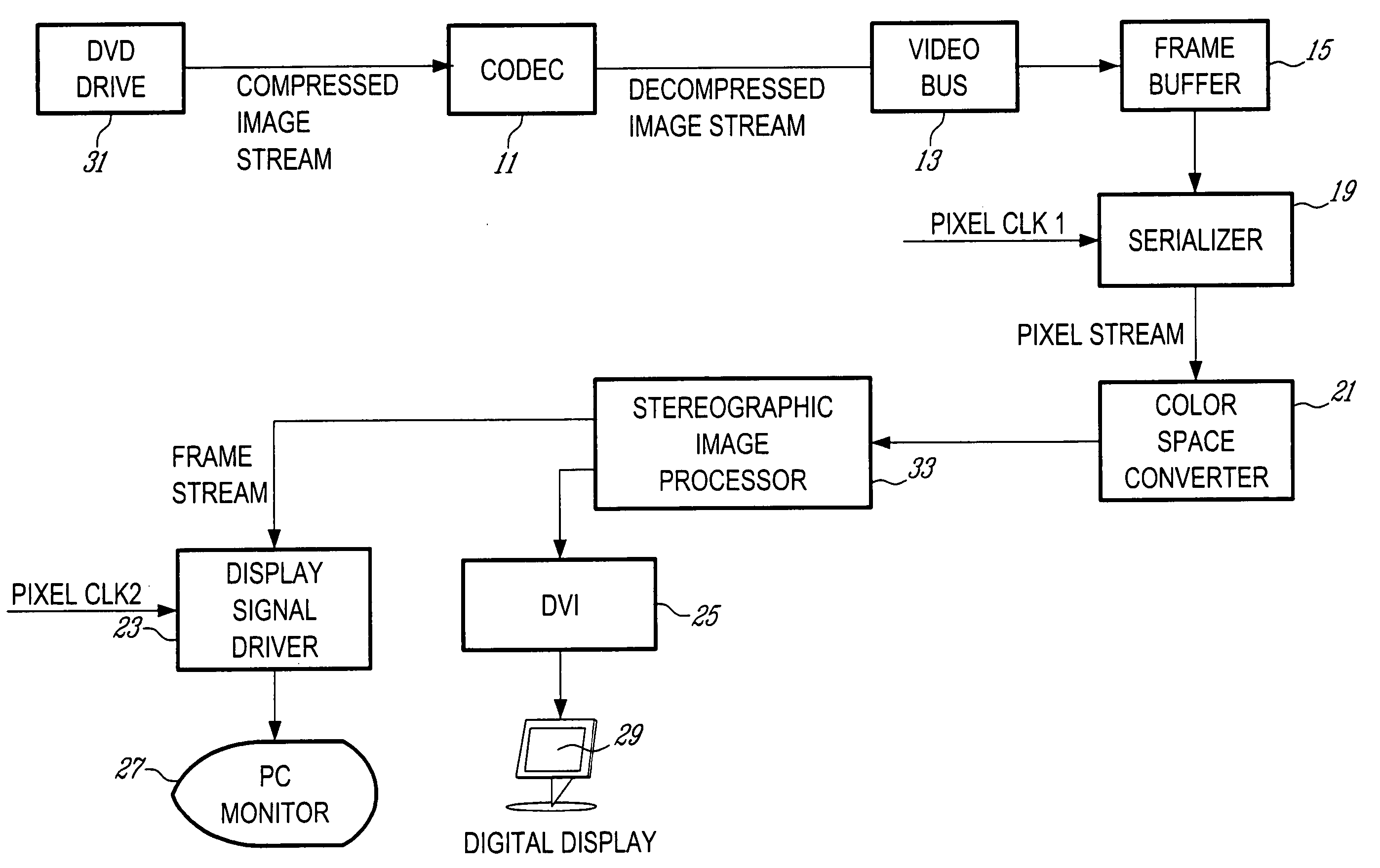
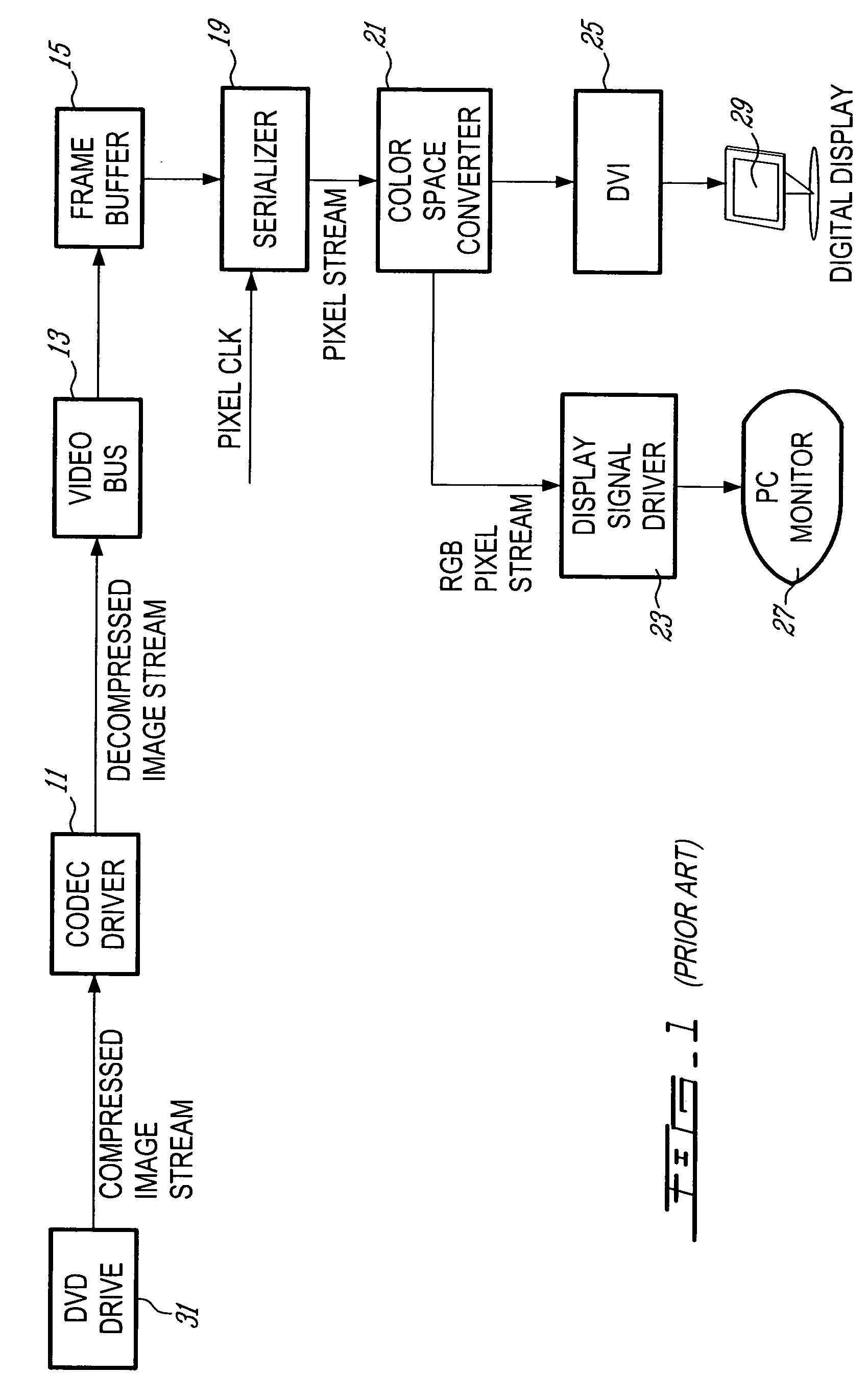
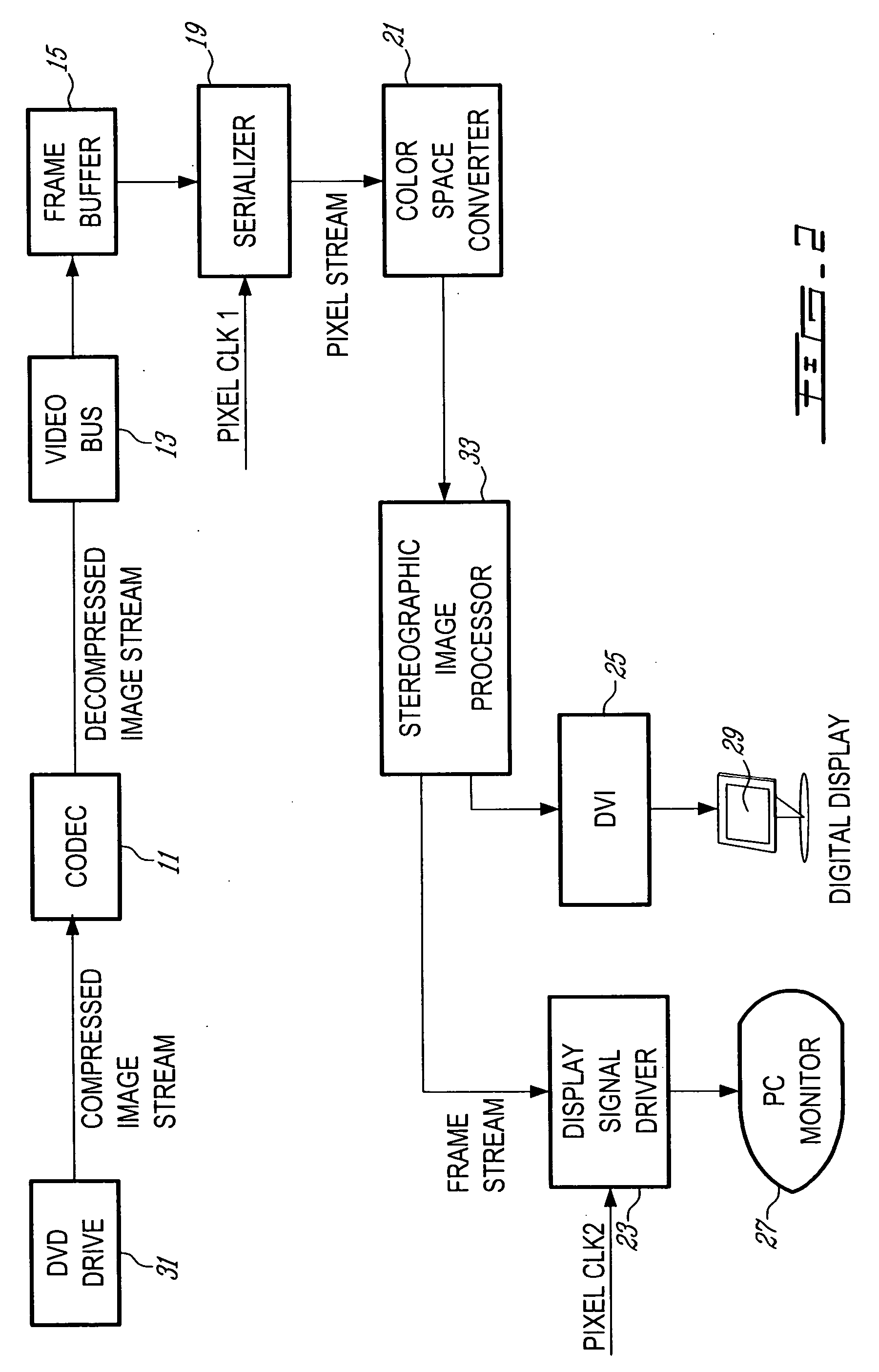
Apparatus for processing a stereoscopic image stream
ActiveUS20050117637A1High visual quality reproductionElimination substantialImage analysisDetails involving 3D image dataComputer visionSignal generator
A system is provided for processing a compressed image stream of a stereoscopic image stream, the compressed image stream having a plurality of frames in a first format, each frame consisting of a merged image comprising pixels sampled from a left image and pixels sampled from a right image. A receiver receives the compressed image stream and a decompressing module in communication with the receiver decompresses the compressed image stream. The left and right images of the decompressed image stream are stored in a frame buffer. A serializing unit reads pixels of the frames stored in the frame buffer and outputs a pixel stream comprising pixels of a left frame and pixels of a right frame. A stereoscopic image processor receives the pixel stream, buffers the pixels, performs interpolation in order to reconstruct pixels of the left and right images and outputs a reconstructed left pixel stream and a reconstructed right pixel stream, the reconstructed streams having a format different from the first format. A display signal generator receives the stereoscopic pixel stream to provide an output display signal.
Owner:3DN
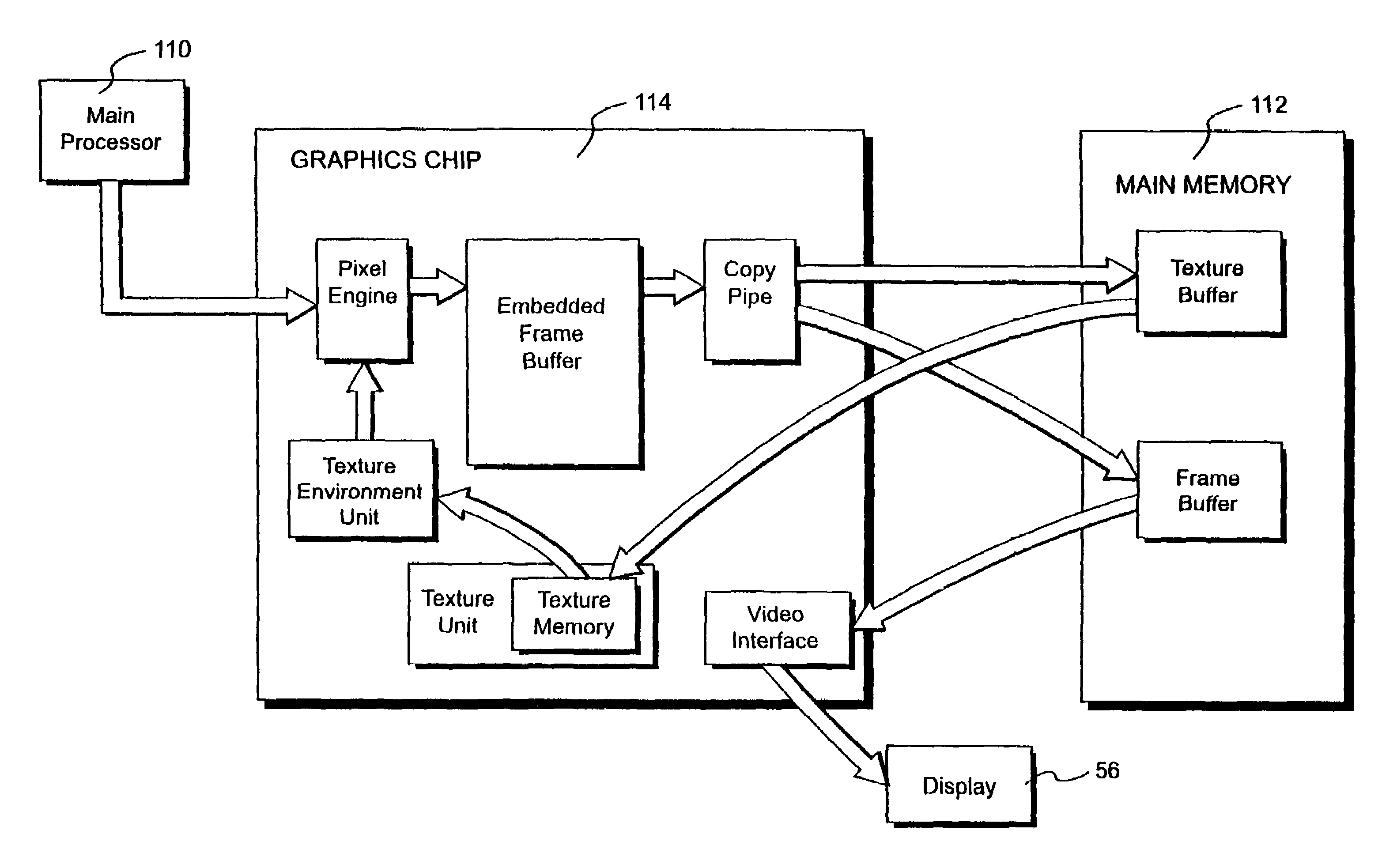
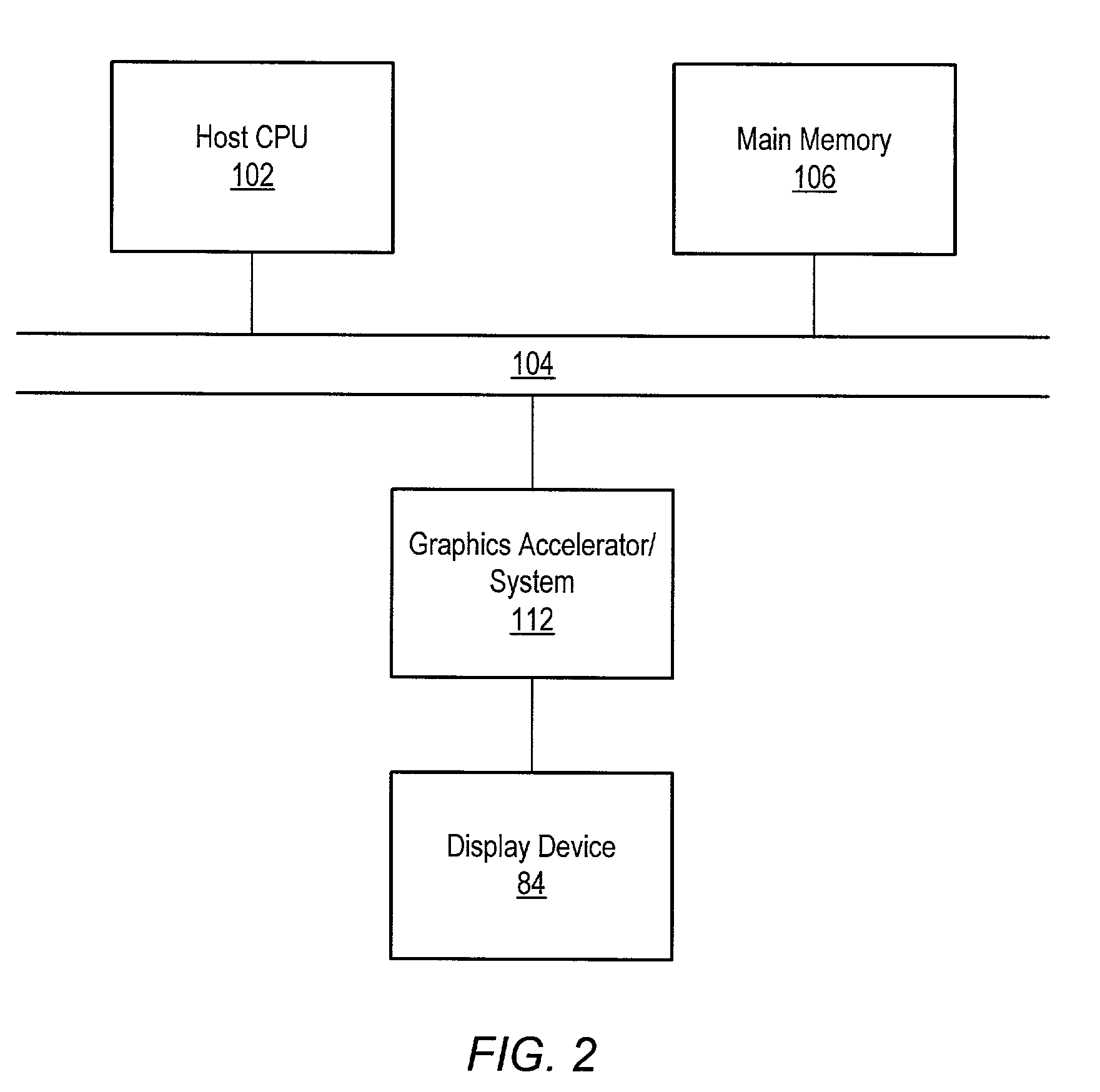
Graphics system with copy out conversions between embedded frame buffer and main memory
InactiveUS7184059B1Improve system flexibilityEasy to useImage memory managementCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphic systemGraphics processing unit
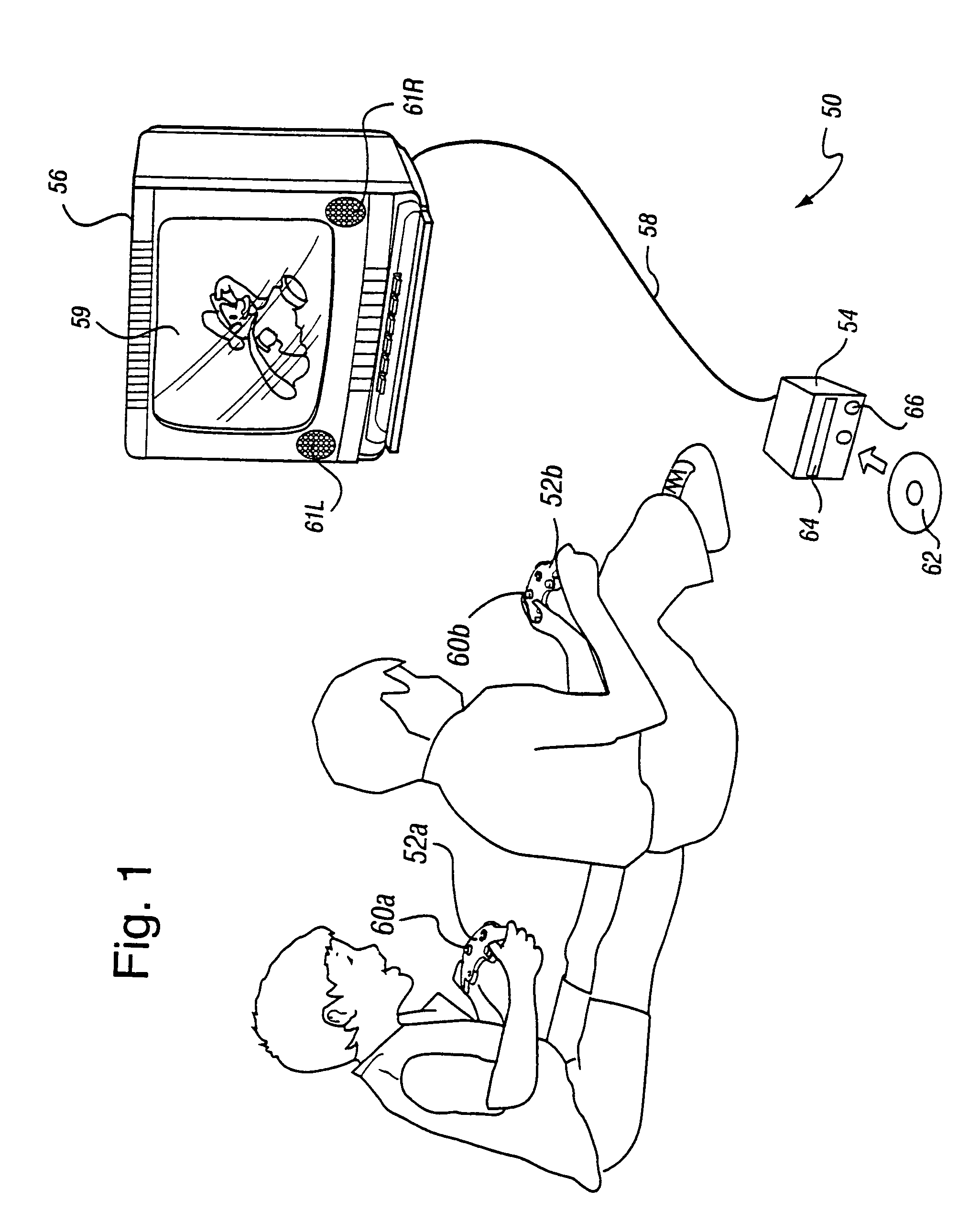
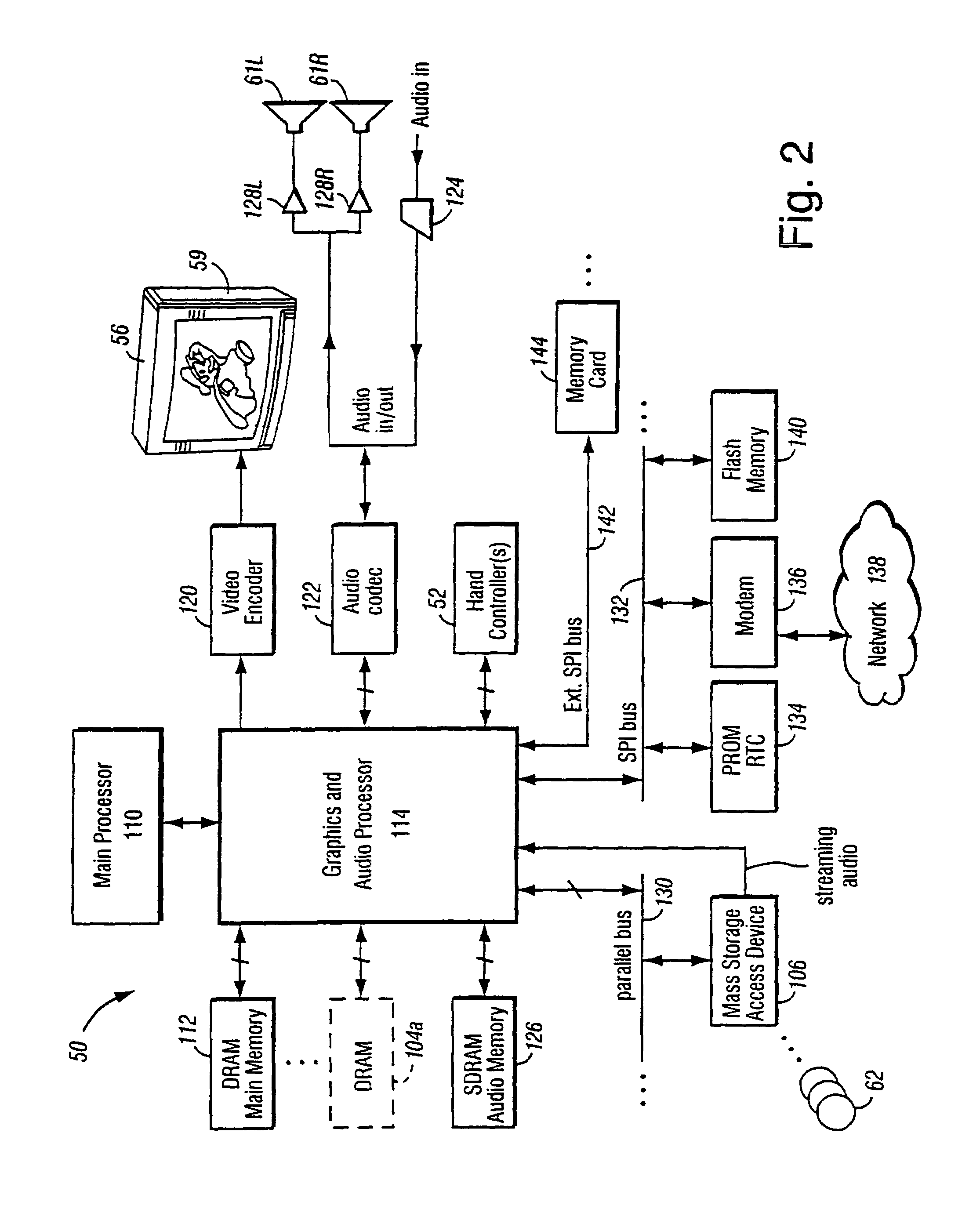
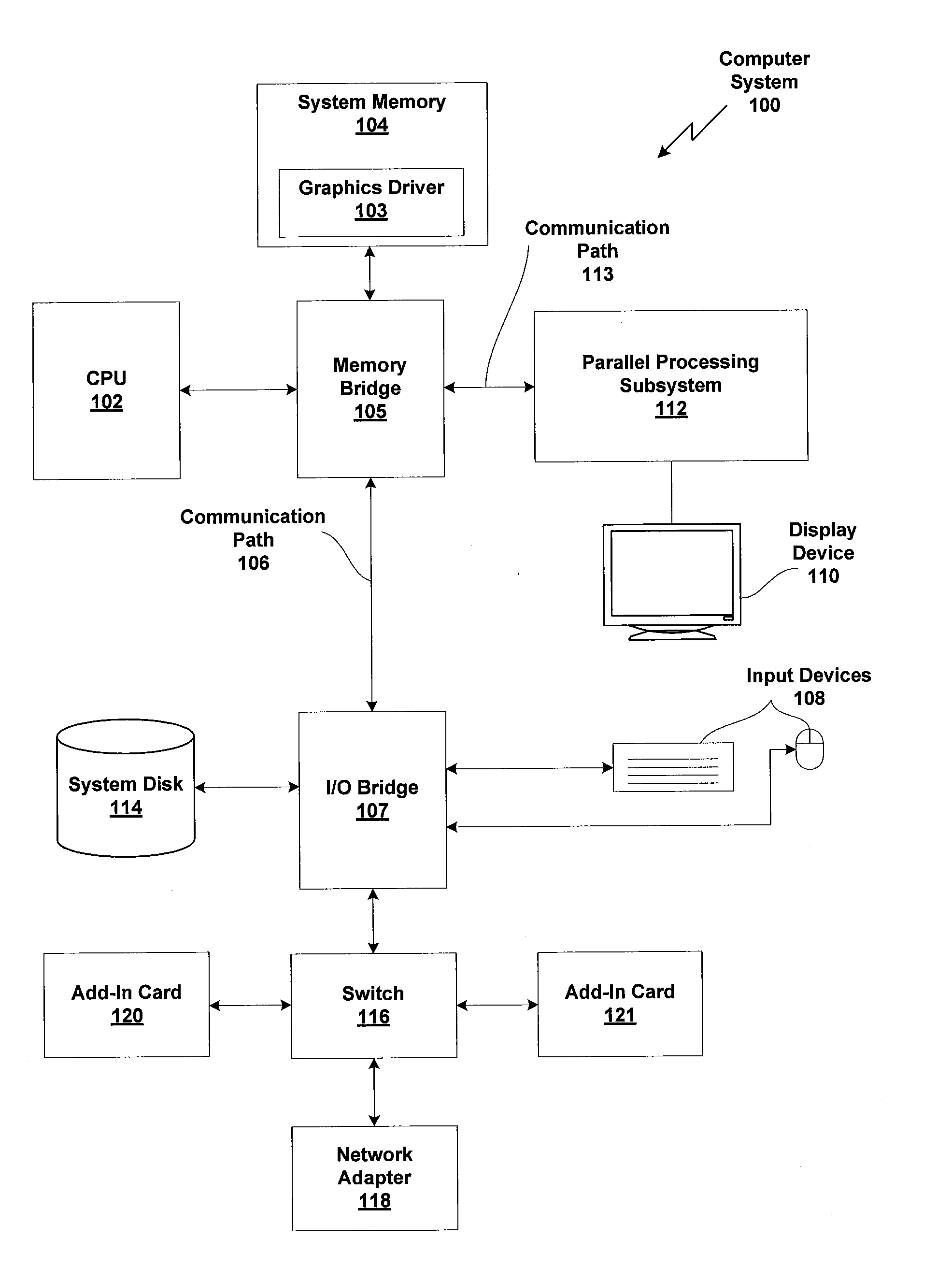
A graphics system including a custom graphics and audio processor produces exciting 2D and 3D graphics and surround sound. The system includes a graphics and audio processor including a 3D graphics pipeline and an audio digital signal processor. The graphics processor includes an embedded frame buffer for storing frame data prior to sending the frame data to an external location, such as main memory. A copy pipeline is provided which converts the data from one format to another format prior to writing the data to the external location. The conversion may be from one RGB color format to another RGB color format, from one YUV format to another YUV format, from an RGB color format to a YUV color format, or from a YUV color format to an RGB color format. The formatted data is either transferred to a display buffer, for use by the video interface, or to a texture buffer, for use as a texture by the graphics pipeline in a subsequent rendering process.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
System and method for handling display device requests for display data from a frame buffer
InactiveUS20030169262A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphic systemMemory bank
A graphics system may include a frame buffer, a processing device coupled to access data in the frame buffer, a frame buffer interface coupled to the frame buffer, and an output controller configured to assert a request for display data to provide to a display device. The frame buffer interface may receive the request for display data from the output controller and delay providing the request for display data to the frame buffer if the processing device is currently requesting access to a portion of the frame buffer targeted by the request for display data. For example, if the frame buffer includes several memory banks and the request for display data targets a first bank, the frame buffer interface may delay providing the request for display data to the frame buffer if the processing device is currently requesting access to the first bank.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
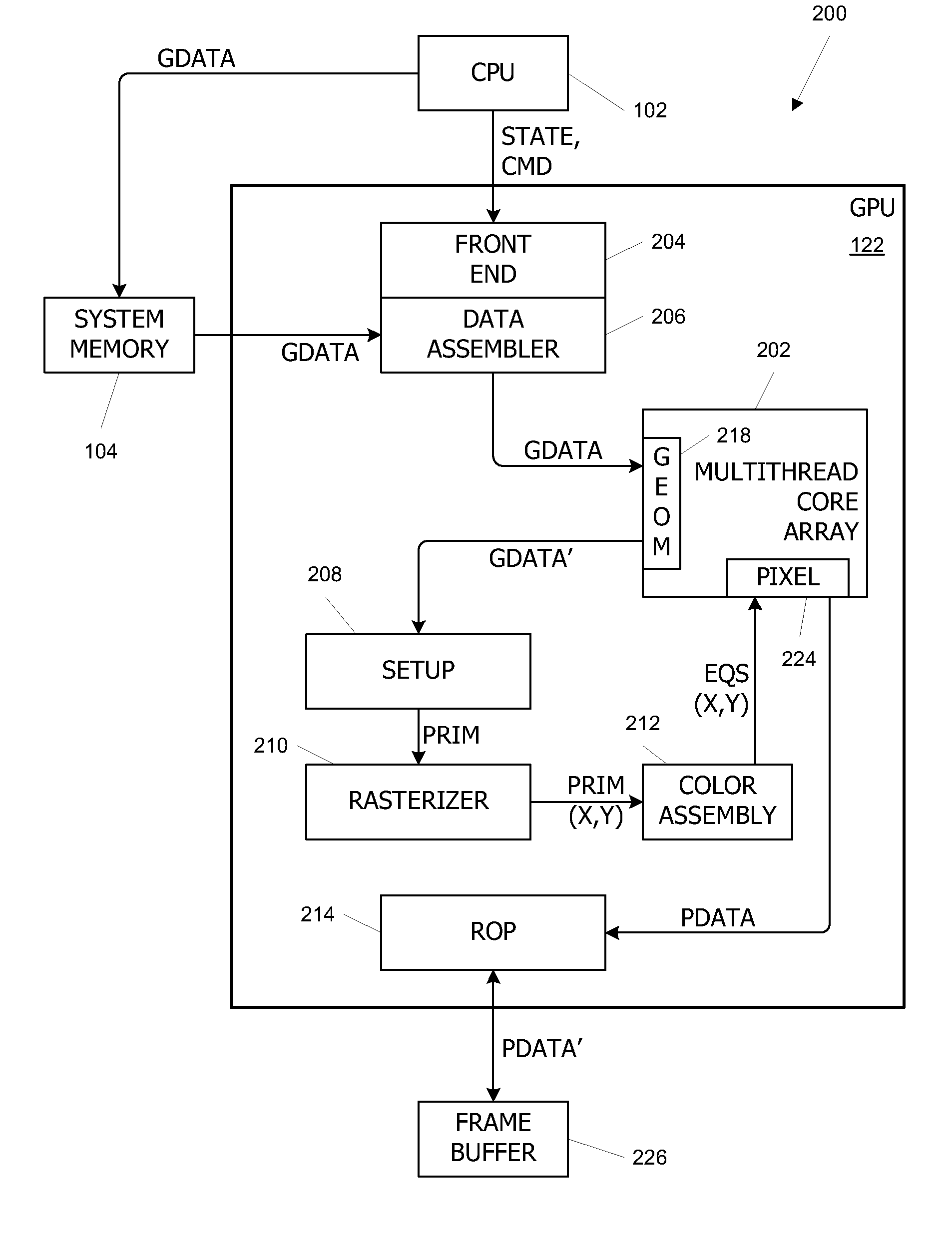
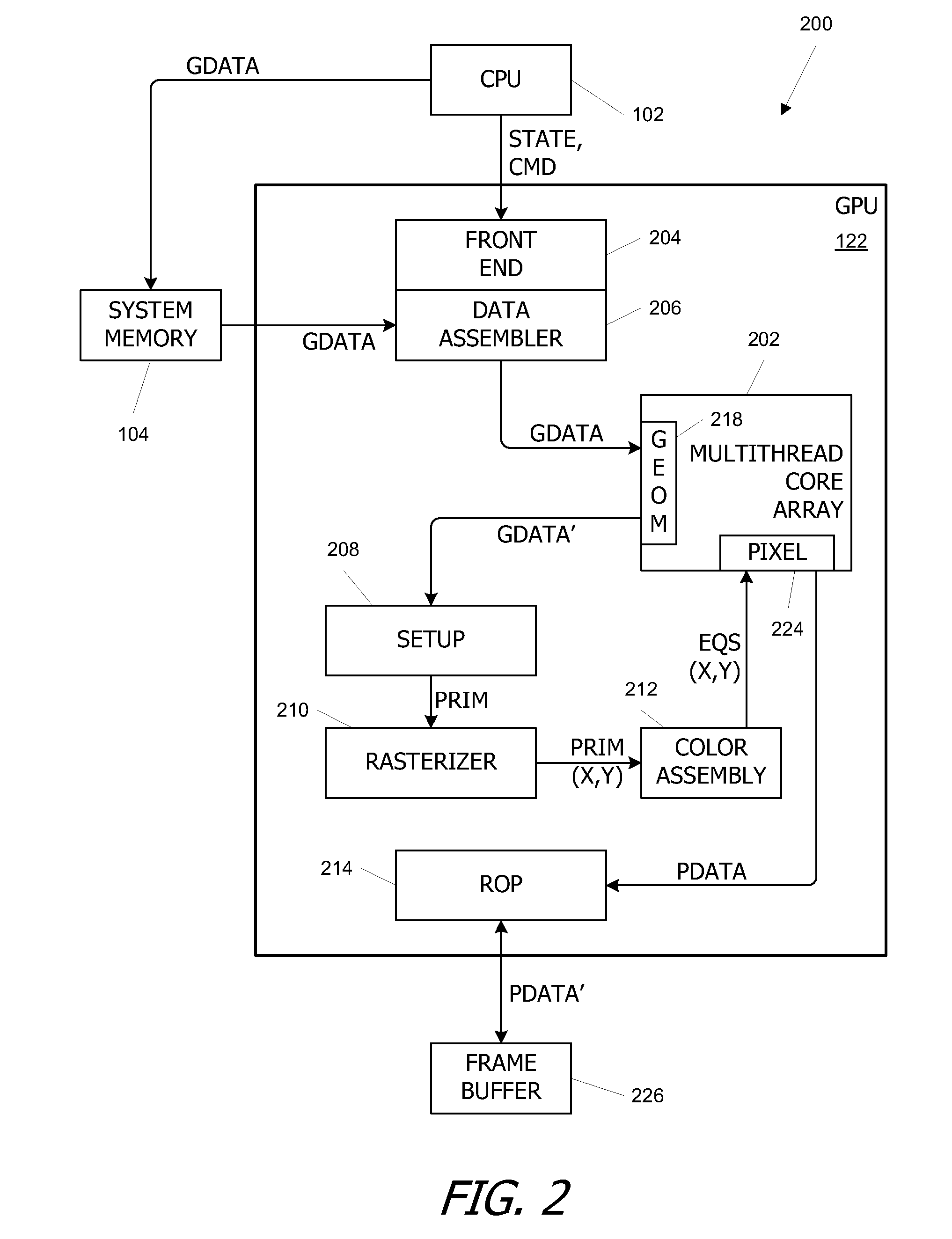
Parallel Array Architecture for a Graphics Processor
InactiveUS20070159488A1Improving memory localityImprove localitySingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsCathode-ray tube indicatorsProcessing coreParallel computing
A parallel array architecture for a graphics processor includes a multithreaded core array including a plurality of processing clusters, each processing cluster including at least one processing core operable to execute a pixel shader program that generates pixel data from coverage data; a rasterizer configured to generate coverage data for each of a plurality of pixels; and pixel distribution logic configured to deliver the coverage data from the rasterizer to one of the processing clusters in the multithreaded core array. The pixel distribution logic selects one of the processing clusters to which the coverage data for a first pixel is delivered based at least in part on a location of the first pixel within an image area. The processing clusters can be mapped directly to the frame buffers partitions without a crossbar so that pixel data is delivered directly from the processing cluster to the appropriate frame buffer partitions. Alternatively, a crossbar coupled to each of the processing clusters is configured to deliver pixel data from the processing clusters to a frame buffer having a plurality of partitions. The crossbar is configured such that pixel data generated by any one of the processing clusters is deliverable to any one of the frame buffer partitions.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
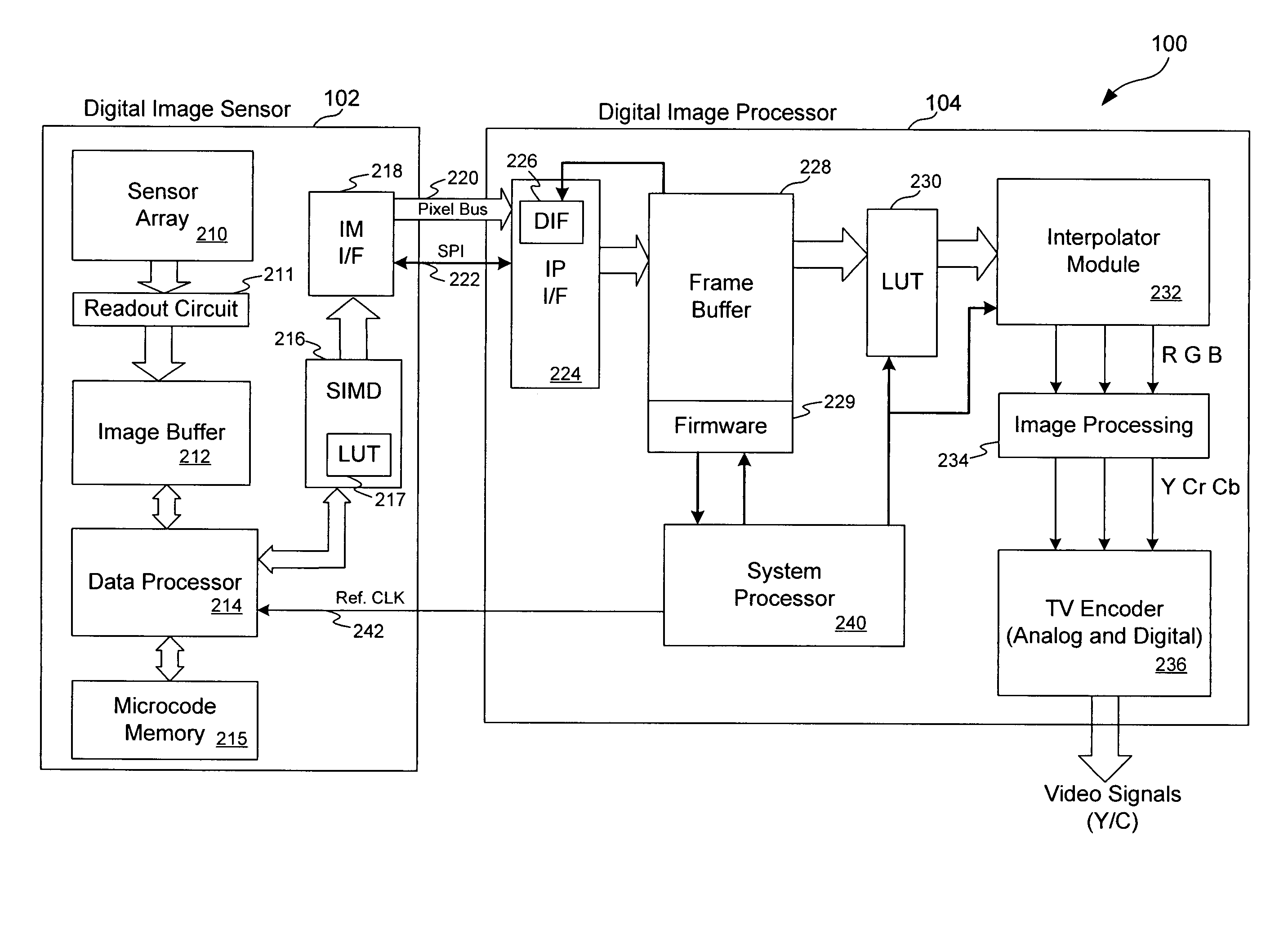
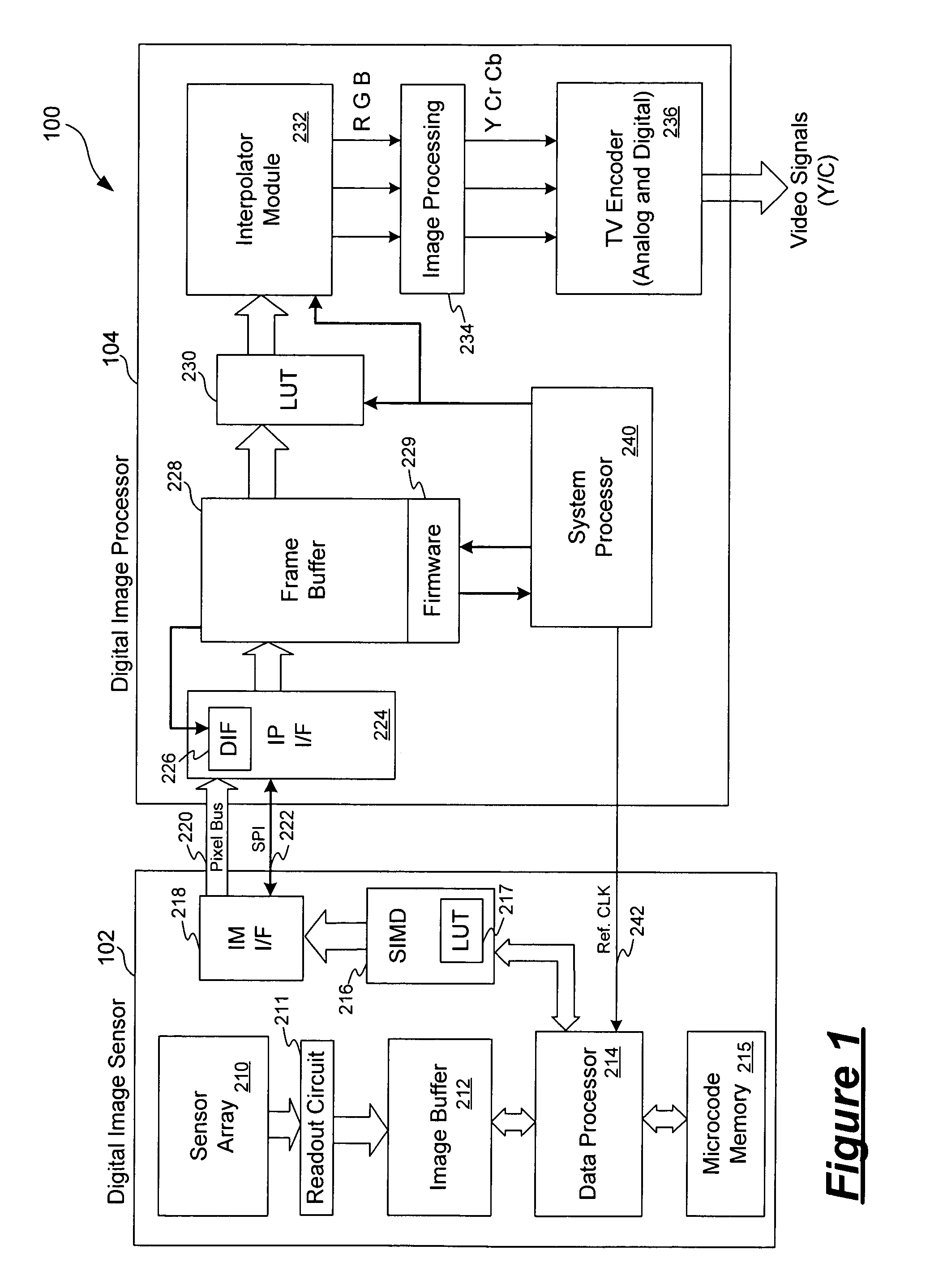
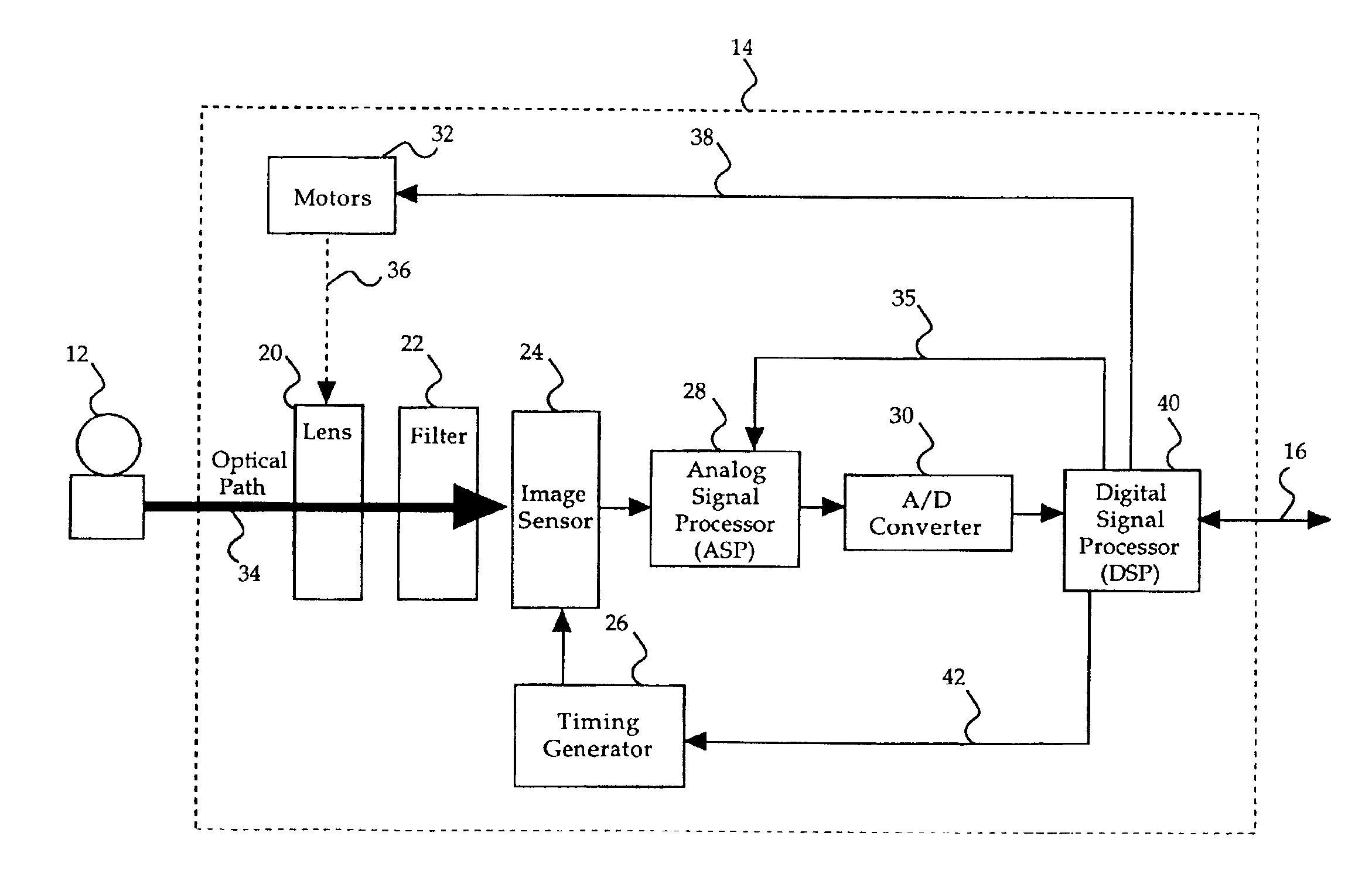
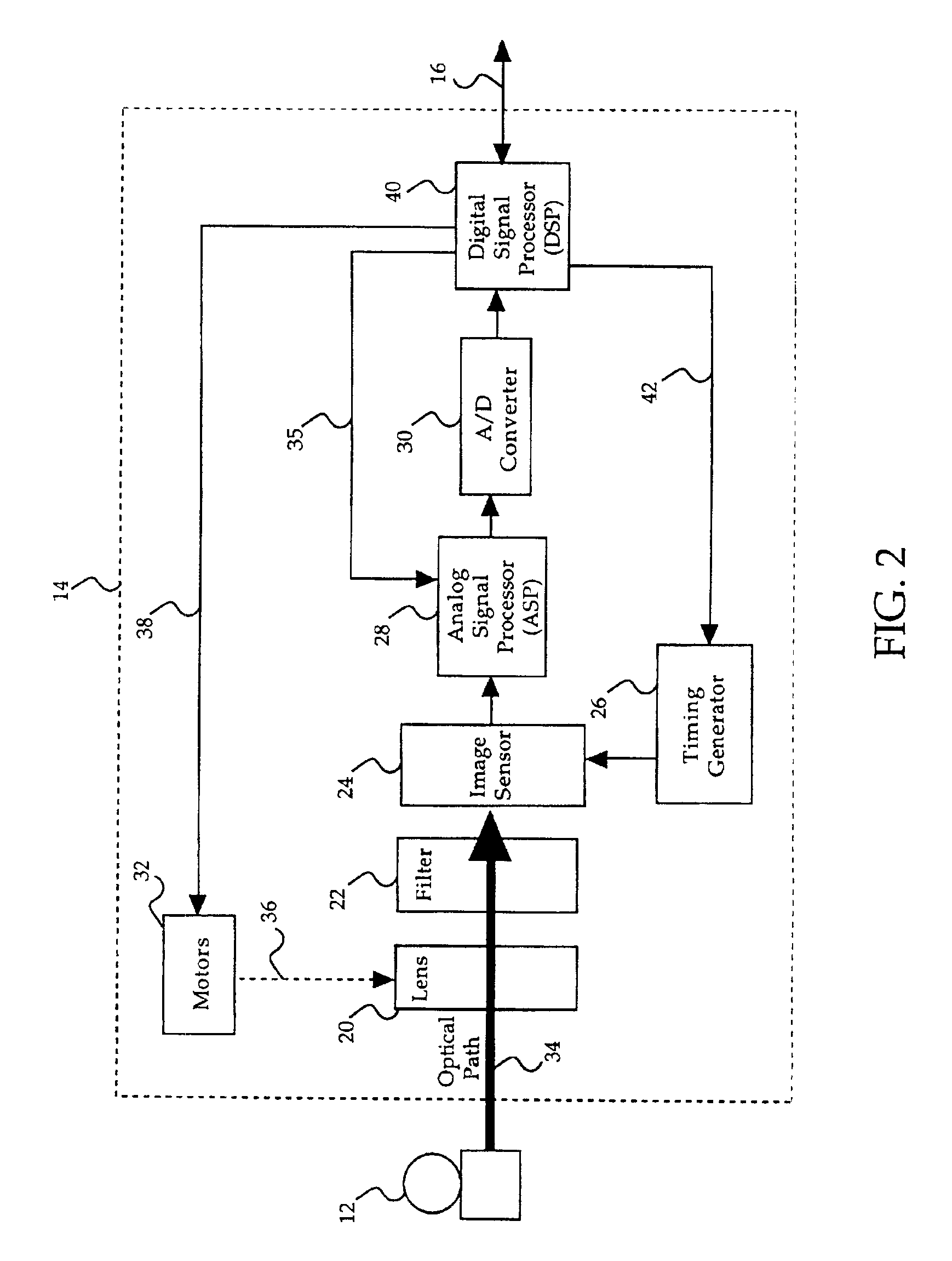
Video imaging system including a digital image sensor and a digital signal processor
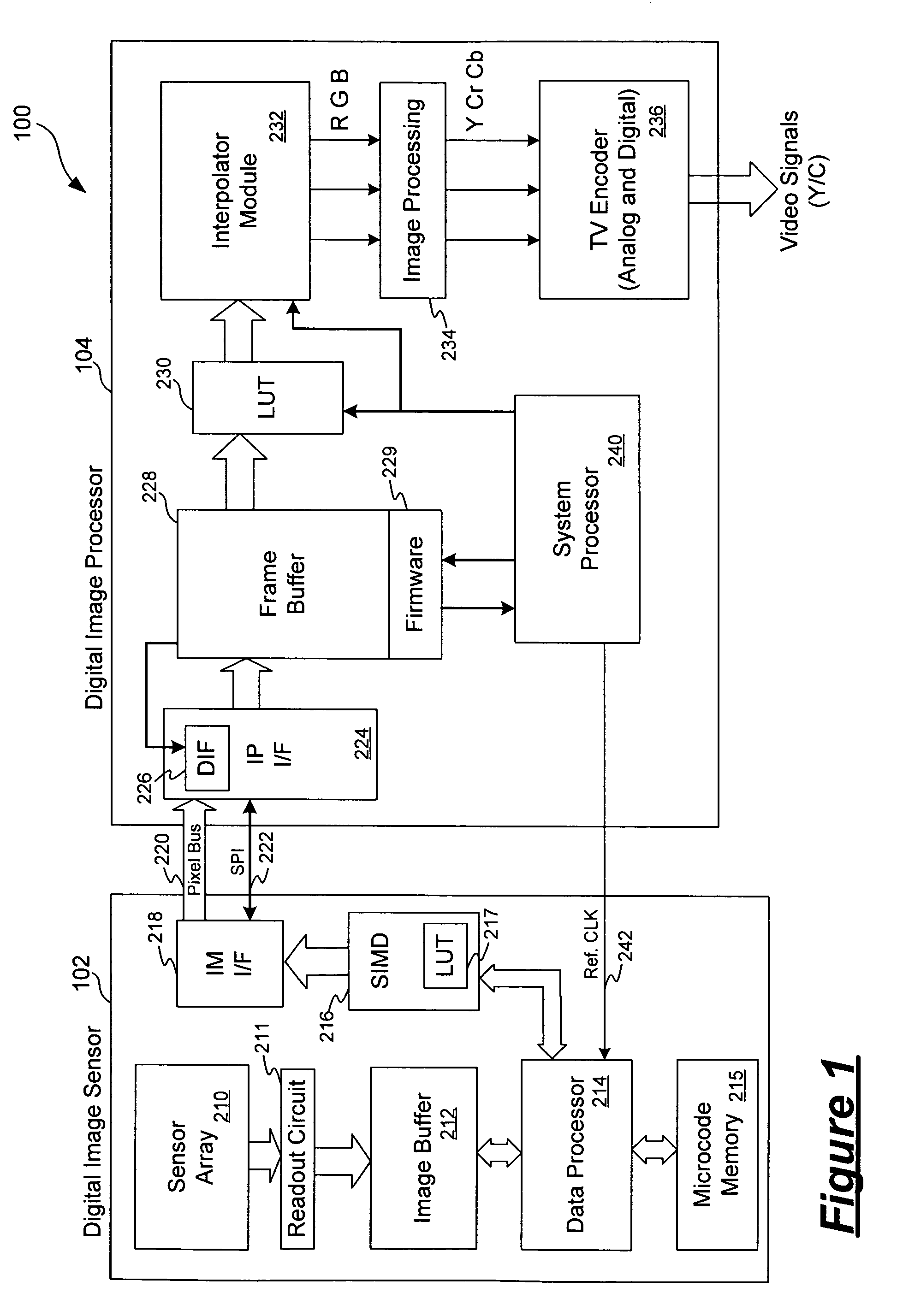
ActiveUS7483058B1Reduce noiseRemove random noiseTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSensor arrayDigital signal processing
A video imaging system includes a digital image sensor for performing image capture operations and a digital image processor for performing image processing operations. The digital image sensor includes a sensor array outputting digital pixel data, an image buffer for storing the pixel data, a first processor and a first interface circuit for transferring the pixel data onto a pixel bus. The digital image processor includes a second interface circuit coupled to receive the pixel data from the pixel bus, a frame buffer coupled to store the pixel data, an image processing pipeline for processing the pixel data stored in the frame buffer into video data, and a second processor. The digital image sensor and the digital image processor transfer control information over a control interface bus and the digital image sensor performs the image capture operations independent of the image processing operations performed by the digital image processor.
Owner:PIXIM
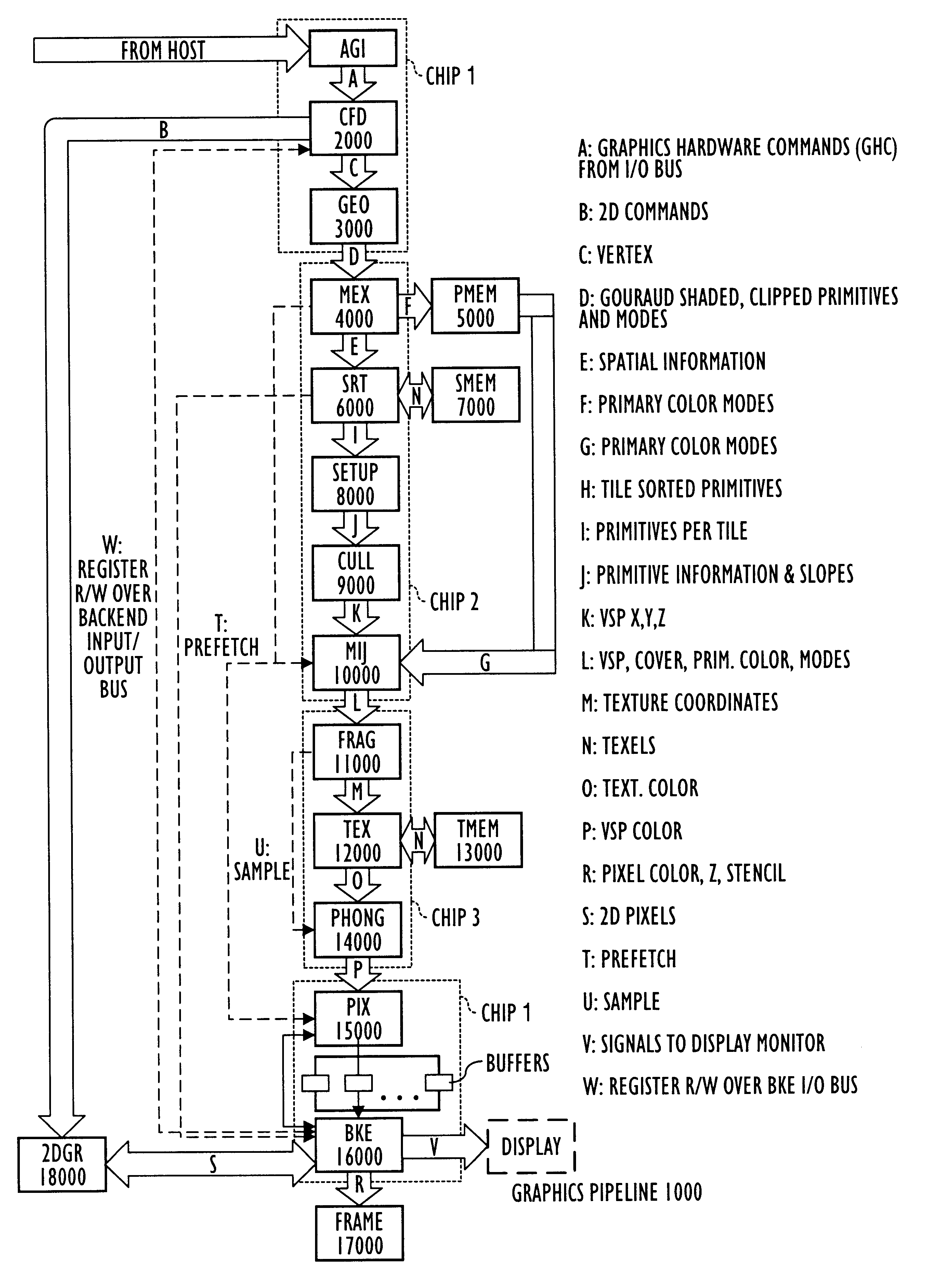
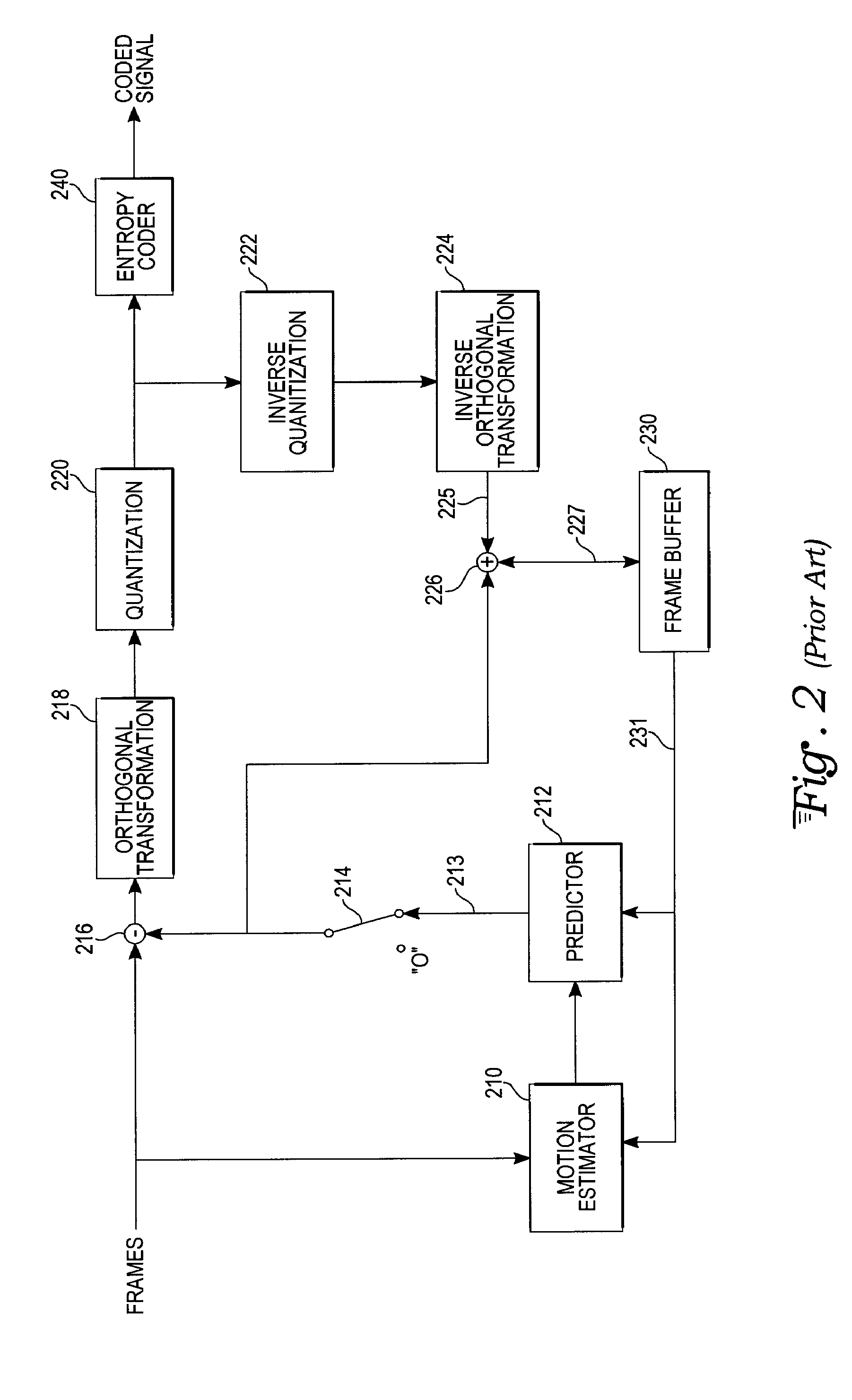
Deferred shading graphics pipeline processor
InactiveUS6268875B1Attenuation bandwidthTexturing/coloringImage memory managementPhong shadingComputer graphics (images)
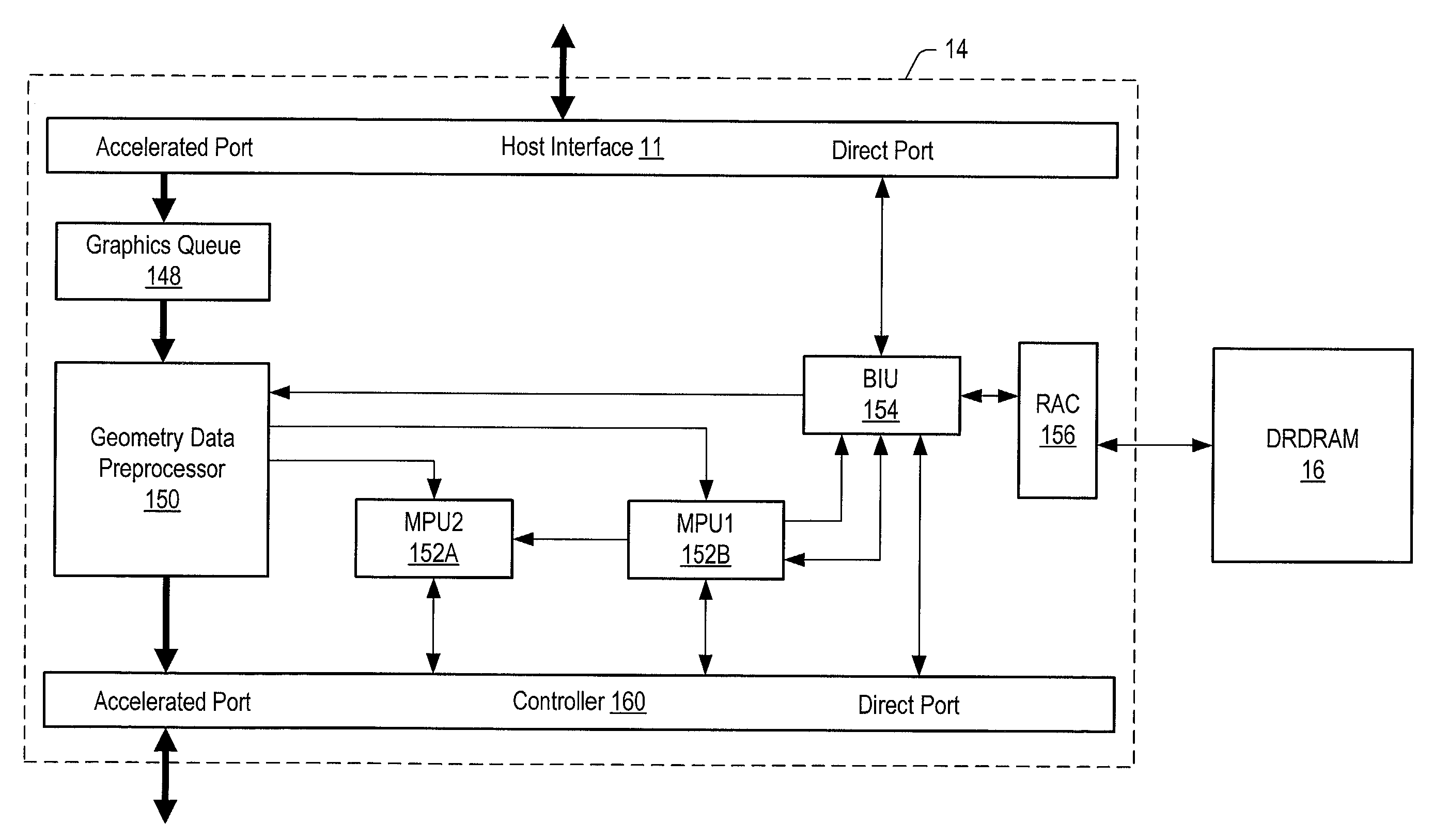
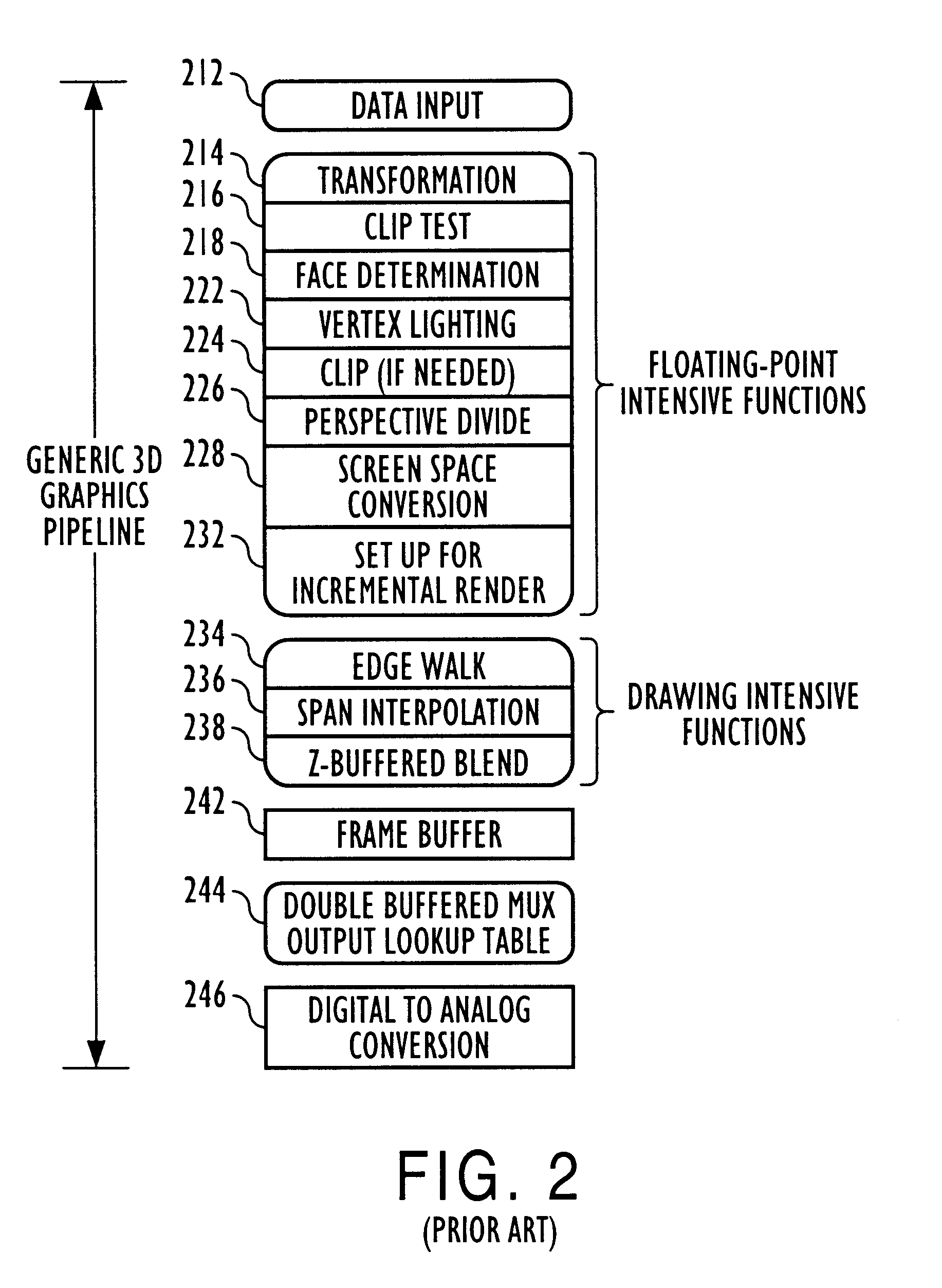
Three-dimensional computer graphics systems and methods and more particularly to structure and method for a three-dimensional graphics processor and having other enhanced graphics processing features. In one embodiment the graphics processor is a Deferred Shading Graphics Processor (DSGP) comprising an AGP interface, a command fetch & decode (2000), a geometry unit (3000), a mode extraction (4000) and polygon memory (5000), a sort unit (6000) and sort memory (7000), a setup unit (8000), a cull unit (9000), a mode injection (10000), a fragment unit (11000), a texture (12000) and texture memory (13000) a phong shading (14000), a pixel unit (15000), a backend unit (1600) coupled to a frame buffer (17000). Other embodiments need not include all of these functional units, and the structures and methods of these units are applicable to other computational processes and systems as well as deferred and non-deferred shading graphical processors.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and apparatus for performing burst refresh of a self-refreshing display device
ActiveUS20130021352A1Reduce power consumptionExtend battery lifeCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectric digital data processingDisplay deviceFramebuffer
A method and apparatus for performing display image refresh in bursts to a display device. A buffered refresh controller includes capabilities to drive the display based on video signals generated from a local frame buffer at a first rate. The graphics controller may optimally be configured to burst a new frame of pixel data to the buffered refresh controller at a second rate to replace the previous frame of pixel data in the local frame buffer. The second rate is different than the first rate. Additionally, the graphics controller may send frames only when they contain new pixel data. By enabling the graphics controller to selectively transmit the new frame of pixel data at the second rate, higher than the first rate, the graphics controller may be placed in a power-saving state during at least a portion of each frame update.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Real-time display post-processing using programmable hardware
ActiveUS20060132491A1Image memory managementMultiprogramming arrangementsDisplay deviceProgrammable hardware
In a graphics processor, a rendering object and a post-processing object share access to a host processor with a programmable execution core. The rendering object generates fragment data for an image from geometry data. The post-processing object operates to generate a frame of pixel data from the fragment data and to store the pixel data in a frame buffer. In parallel with operations of the host processor, a scanout engine reads pixel data for a previously generated frame and supplies the pixel data to a display device. The scanout engine periodically triggers the host processor to operate the post-processing object to generate the next frame. Timing between the scanout engine and the post-processing object can be controlled such that the next frame to be displayed is ready in a frame buffer when the scanout engine finishes reading a current frame.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
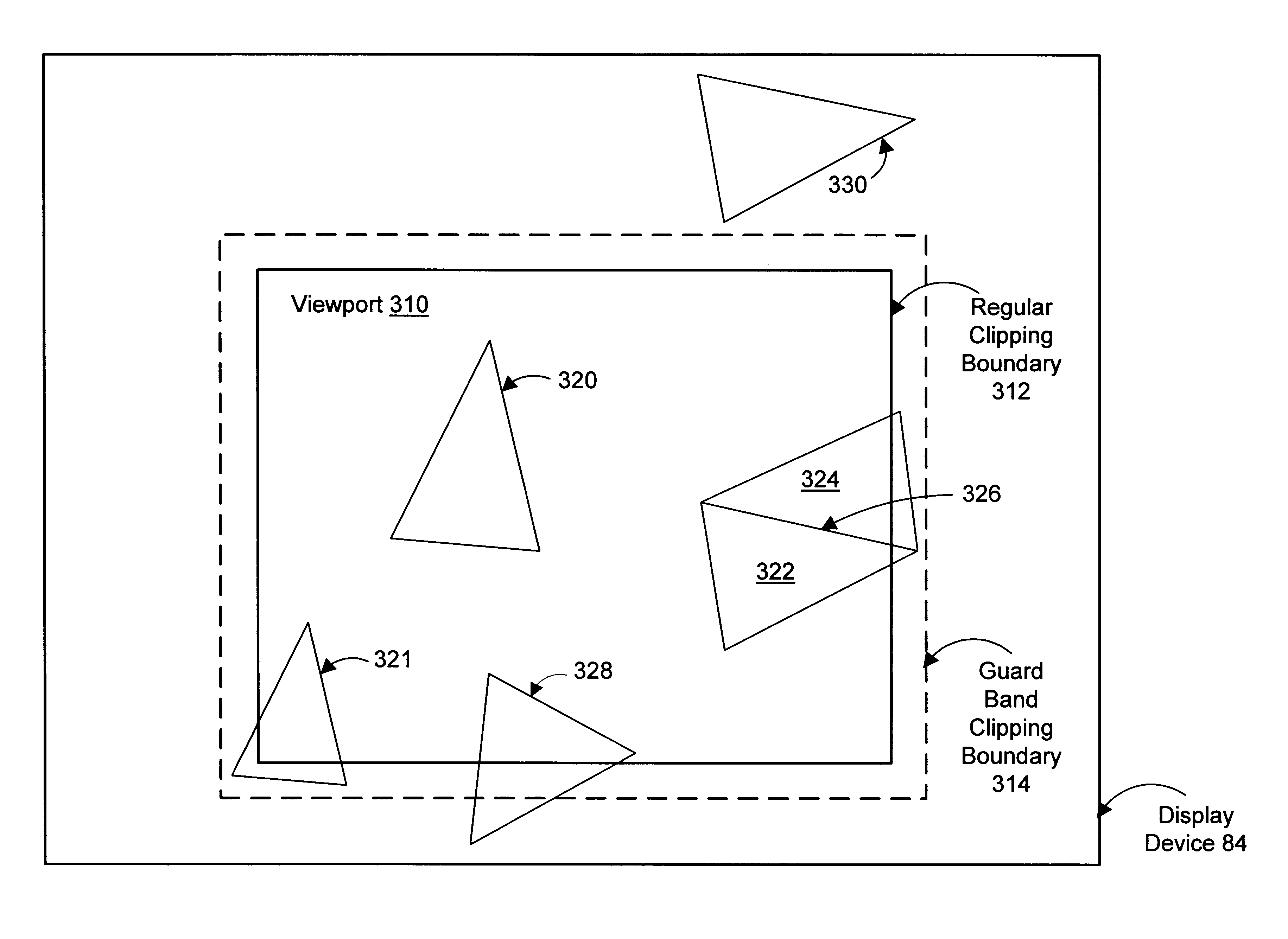
Graphics system using clip bits to decide acceptance, rejection, clipping
A method and computer graphics system for clip testing using clip bits stored in a general-purpose register for each vertex of a geometric primitive. In one embodiment, a rendering unit or other processor sets bits in a clip bits register for each vertex of a geometric primitive. Each bit indicates whether the vertex is inside or outside of a clipping boundary with respect to a particular clipping plane. A frame buffer controller or other graphics processor performs clip testing on the entire geometric primitive by performing Boolean operations on the clip bits. The frame buffer controller may trivially accept or trivially reject the primitive based on the clip testing. If the primitive cannot be trivially rejected or trivially accepted, then the frame buffer controller sends an interrupt to the rendering unit. The rendering unit reads an exception register to determine that the reason for the interrupt is the need to clip the primitive. The rendering unit reads the vertices from the frame buffer controller, clips the primitive, and sends the new vertices to the frame buffer controller. The frame buffer controller clears the interrupt and resumes its graphics processing.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
System and method for performing high-precision, multi-channel blending using multiple blending passes
A high-precision multi-channel blending operation replaces a single pass blending operation to overcome distortions resulting from an insufficient number of bits available per pixel in a hardware frame buffer. A desired frame buffer configuration, with a fewer number of channels, and a larger number of bits available per channel than available for a single pass blending operation, is specified and allocated in memory. The same, fewer number of channels from a destination image are written into the frame buffer. The frame buffer is configured for blending, and the same, fewer number of channels from the source image are blended into the frame buffer. The contents of the frame buffer is written into a memory location. The above steps are repeated, until all of the channels have been blended and written into different parts of memory. The channel information from the memory locations are combined to form an image having a user-desired bit resolution.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
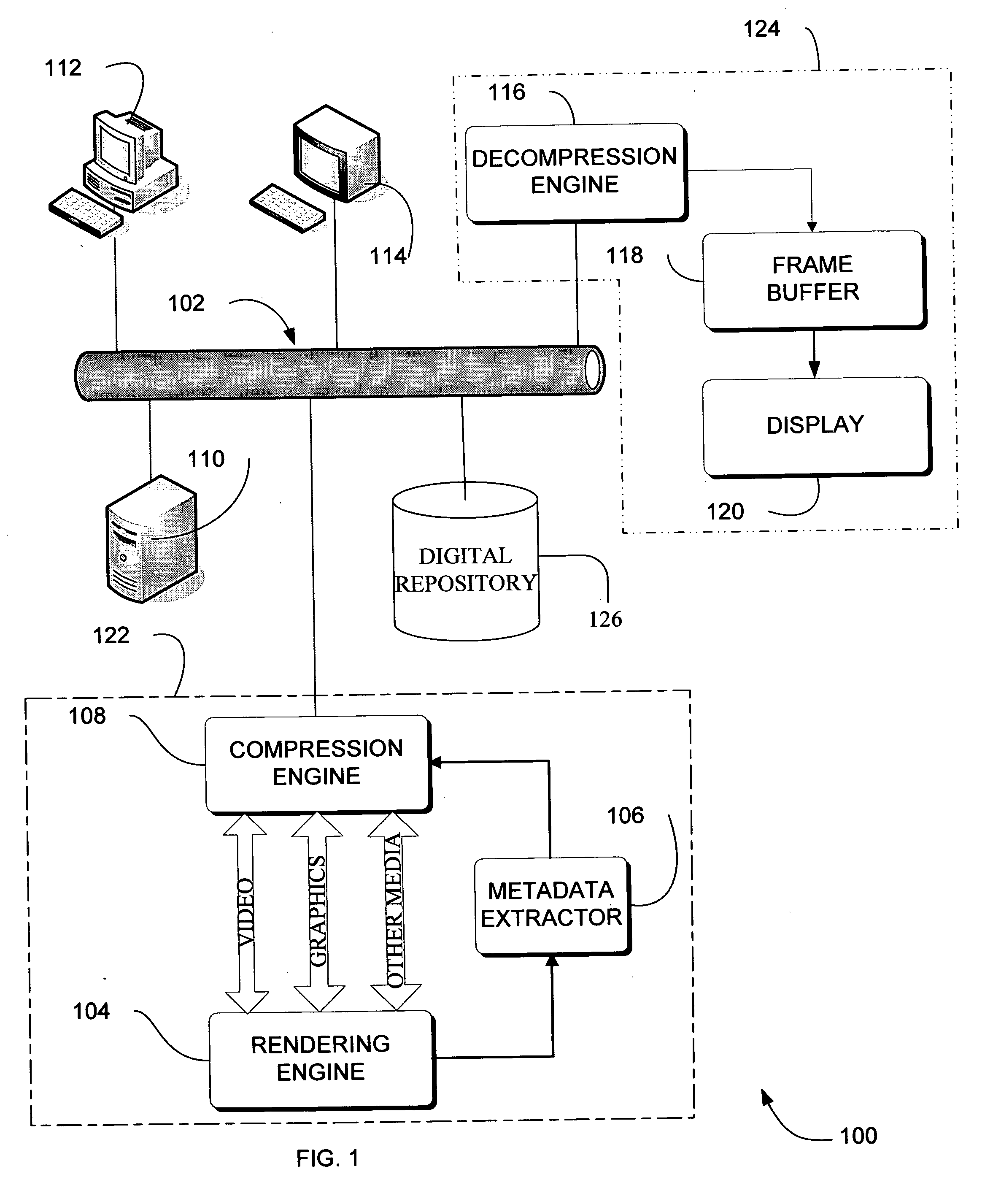
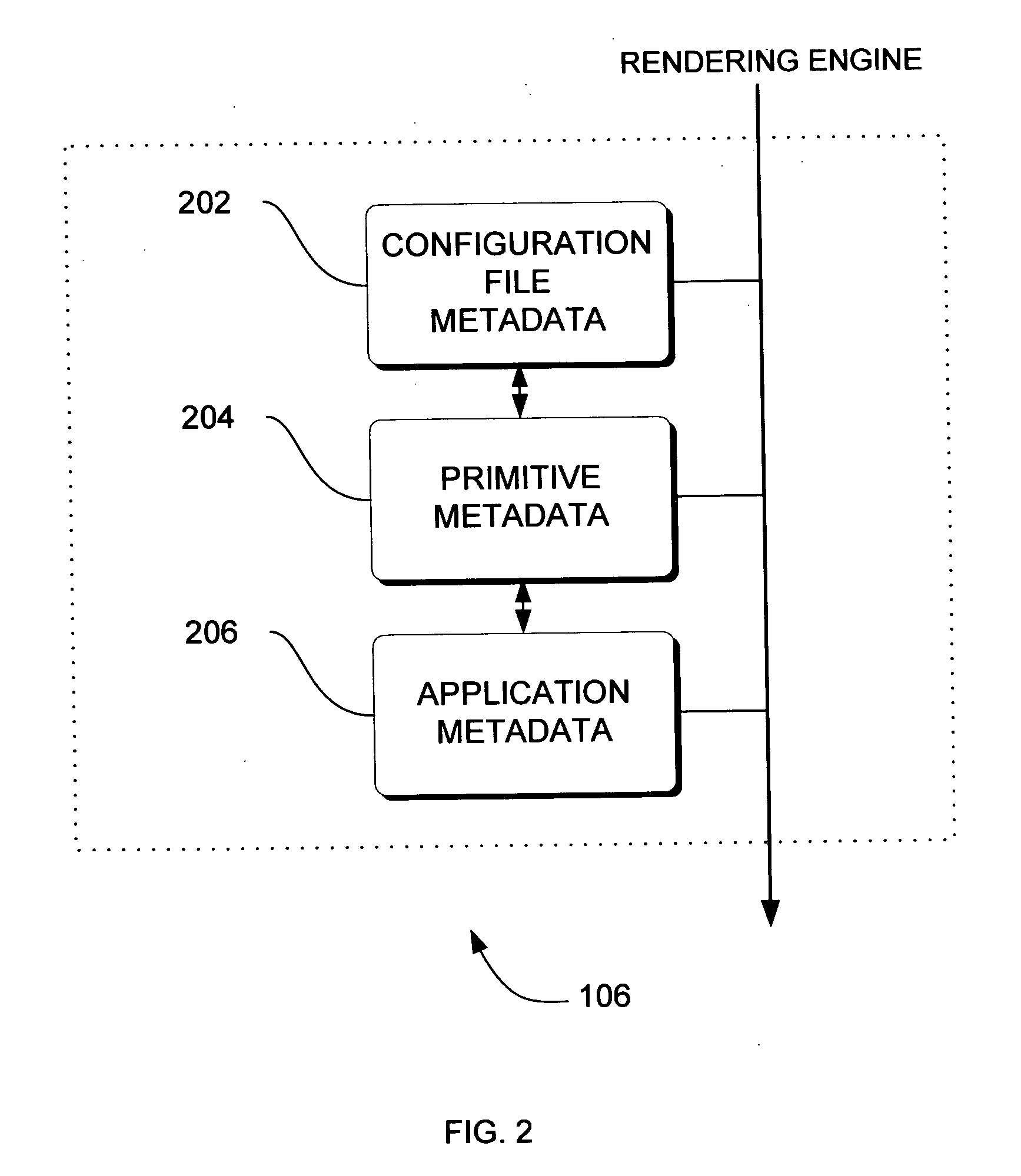
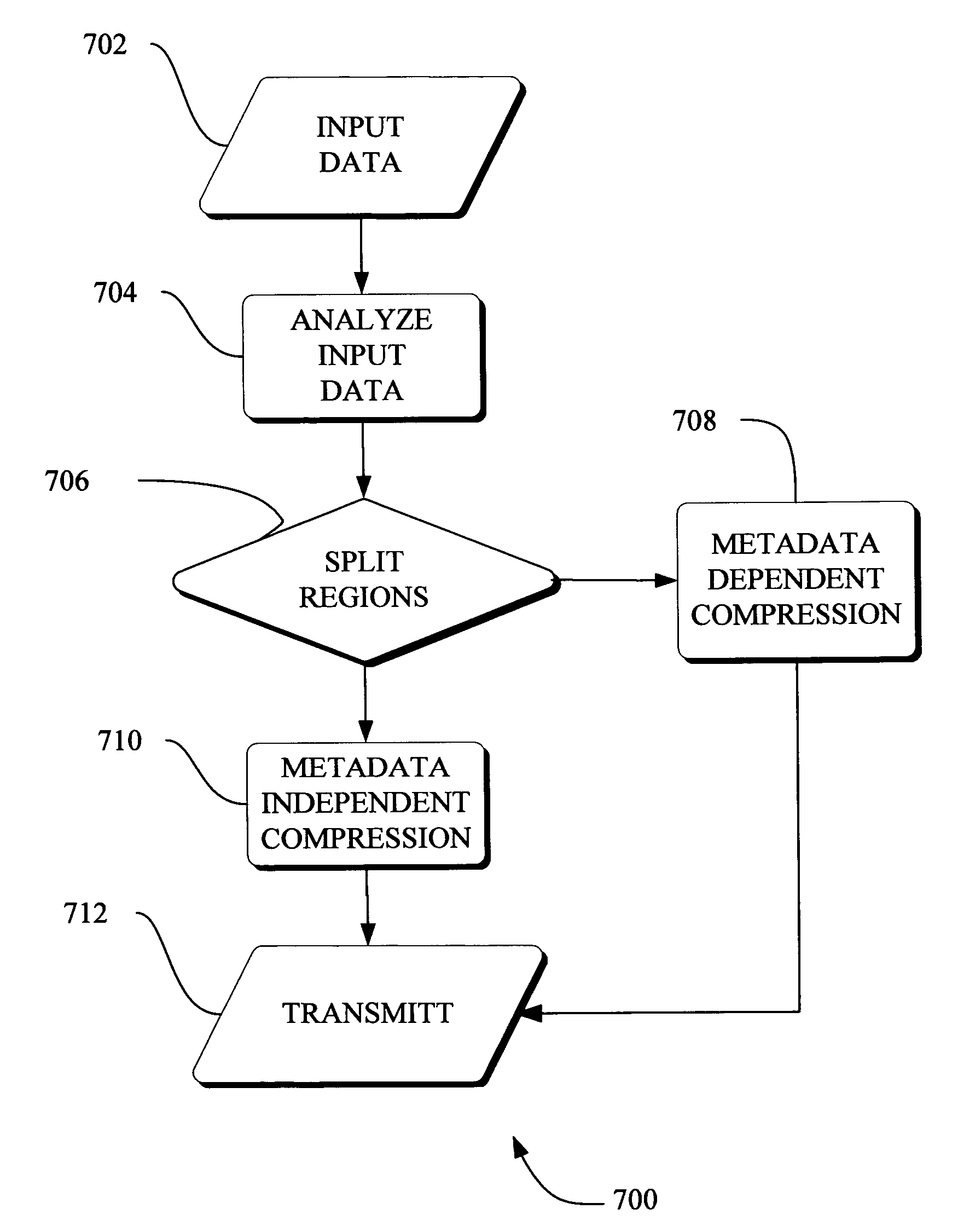
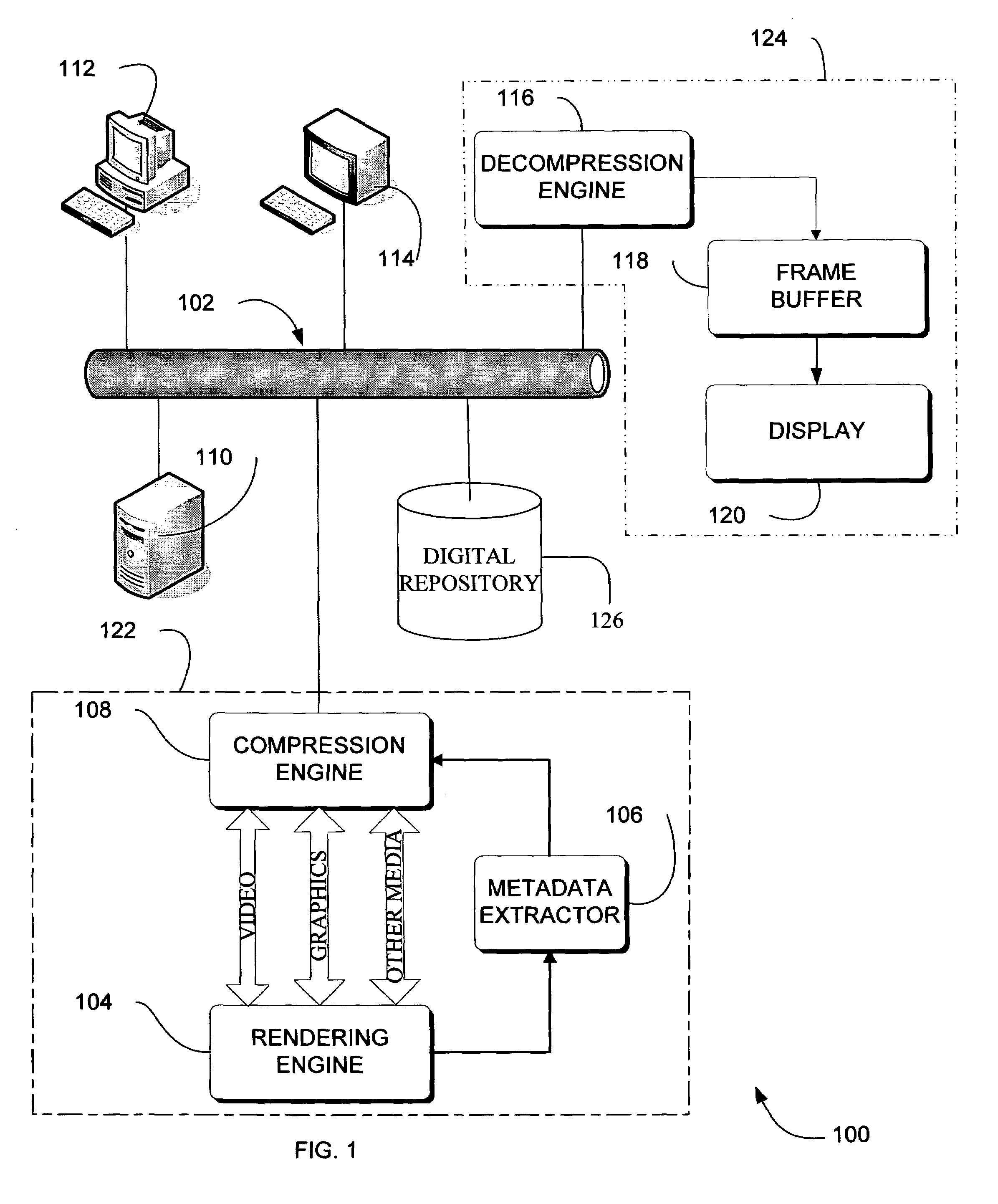
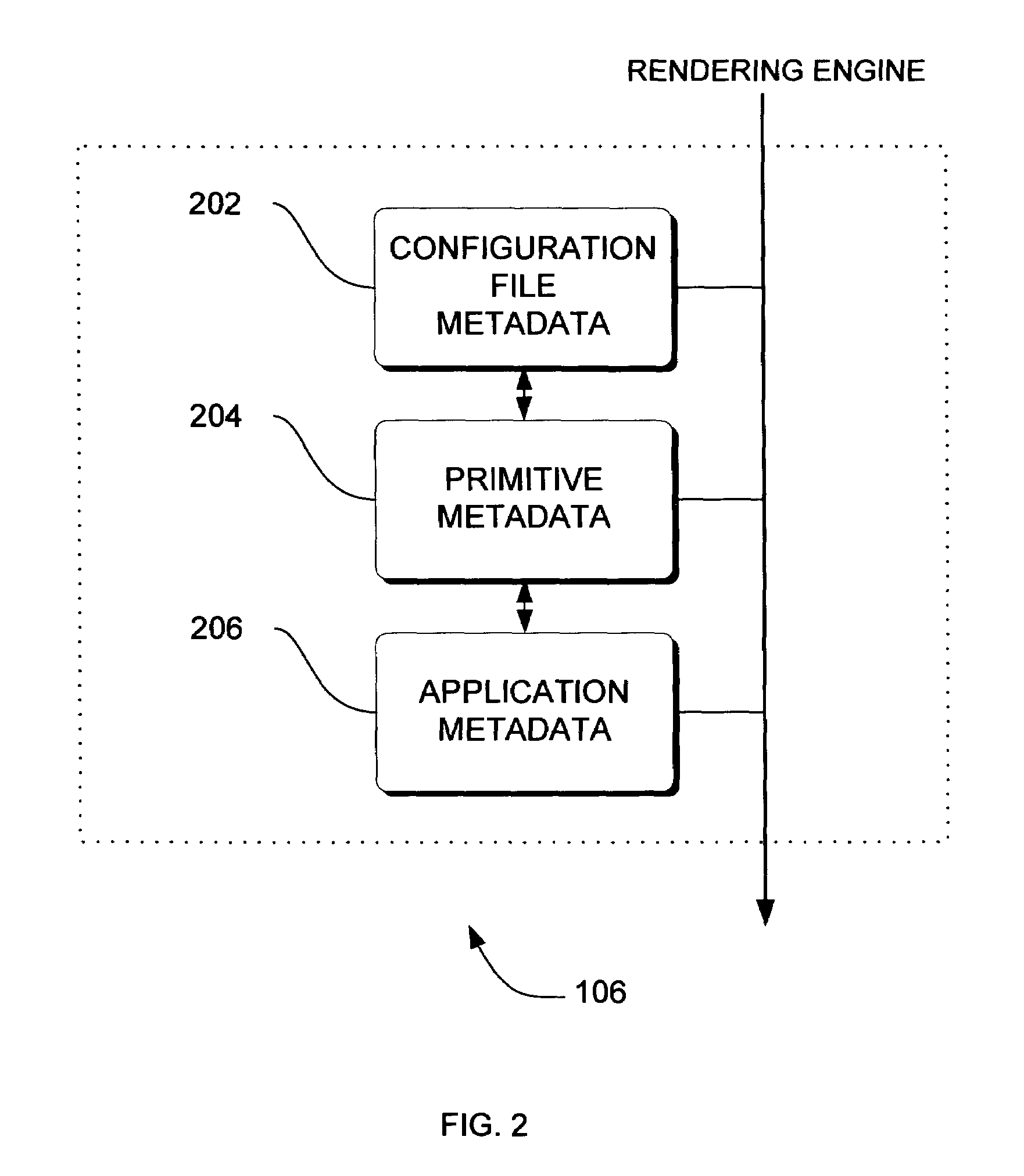
Adaptive video compression of graphical user interfaces using application metadata
InactiveUS20060294125A1Digital data processing detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionData streamDisplay device
Systems, methods and computer accessible medium are provided through which an input data stream consisting one or more media regions before entering a network to be rendered by a display coupled a remote video frame buffer is compressed on the basis of one or more configuration file metadata, source primitive metadata, and application high-level metadata of identified media regions. The input data stream is compressed by using one or more MPEG compression, JPEG compression, vector graphics compression, Huffman coding, or user defined compression scheme.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for controlling a self-refreshing display device coupled to a graphics controller
InactiveUS20120206461A1Reduce generationDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsDisplay deviceData storing
A method and apparatus for controlling a self-refreshing display device coupled to a graphics controller are disclosed. A self-refreshing display device has a capability to drive the display based on video signals generated from a local frame buffer in the display device. A graphics controller coupled to the display device may optimally be placed in one or more power saving states when the display device is operating in a panel self-refresh mode. The graphics controller detects one or more progressive levels of idleness in the graphics controller and the pixel data stored in a frame buffer. Based on the detected idleness, the graphics controller signals the display device to enter or exit the panel self-refresh mode and enters a power saving state. When exiting the panel self-refresh mode, the display device and / or graphics controller ensure that the video signals generated by the local controller and the graphics controller are aligned.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
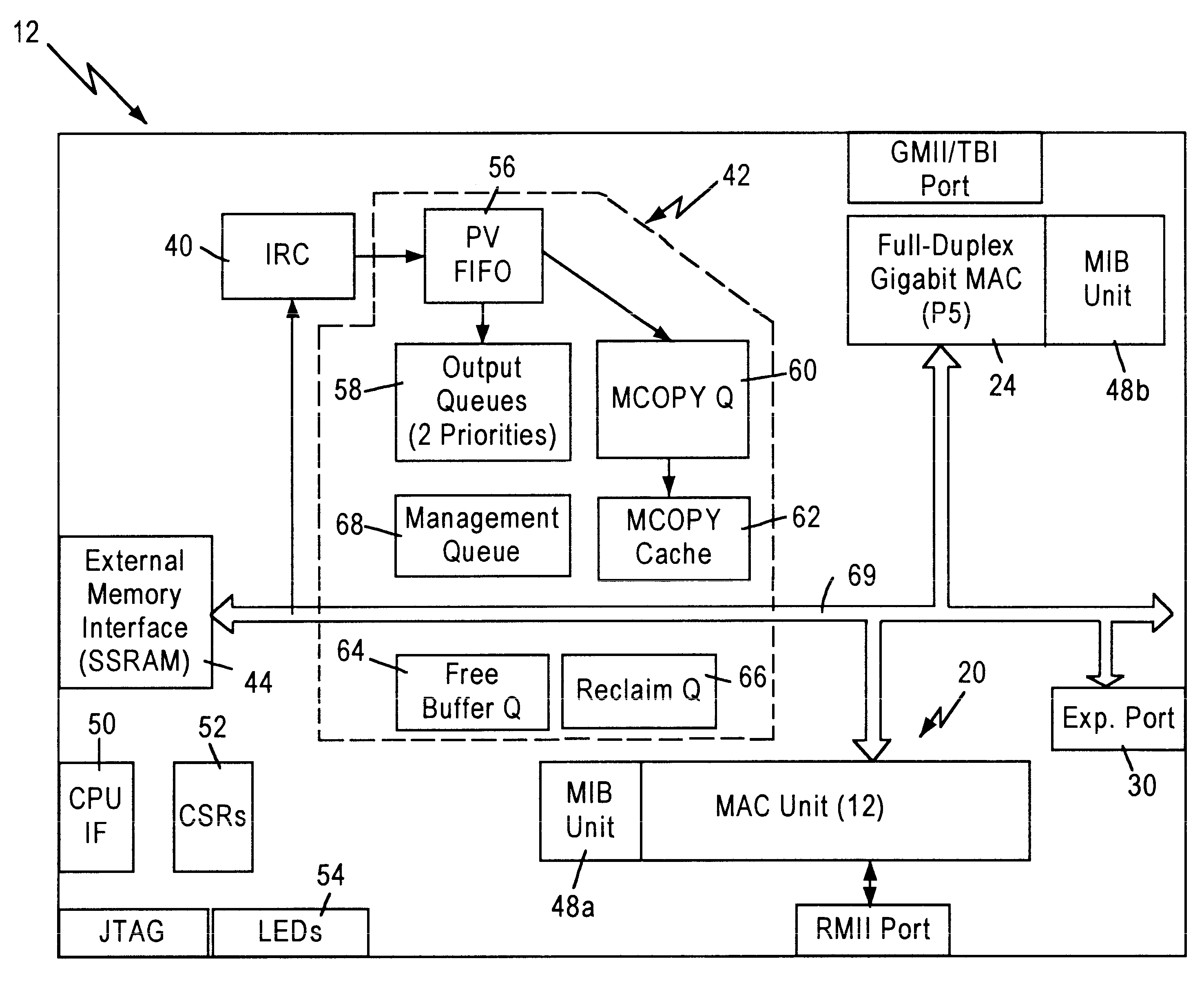
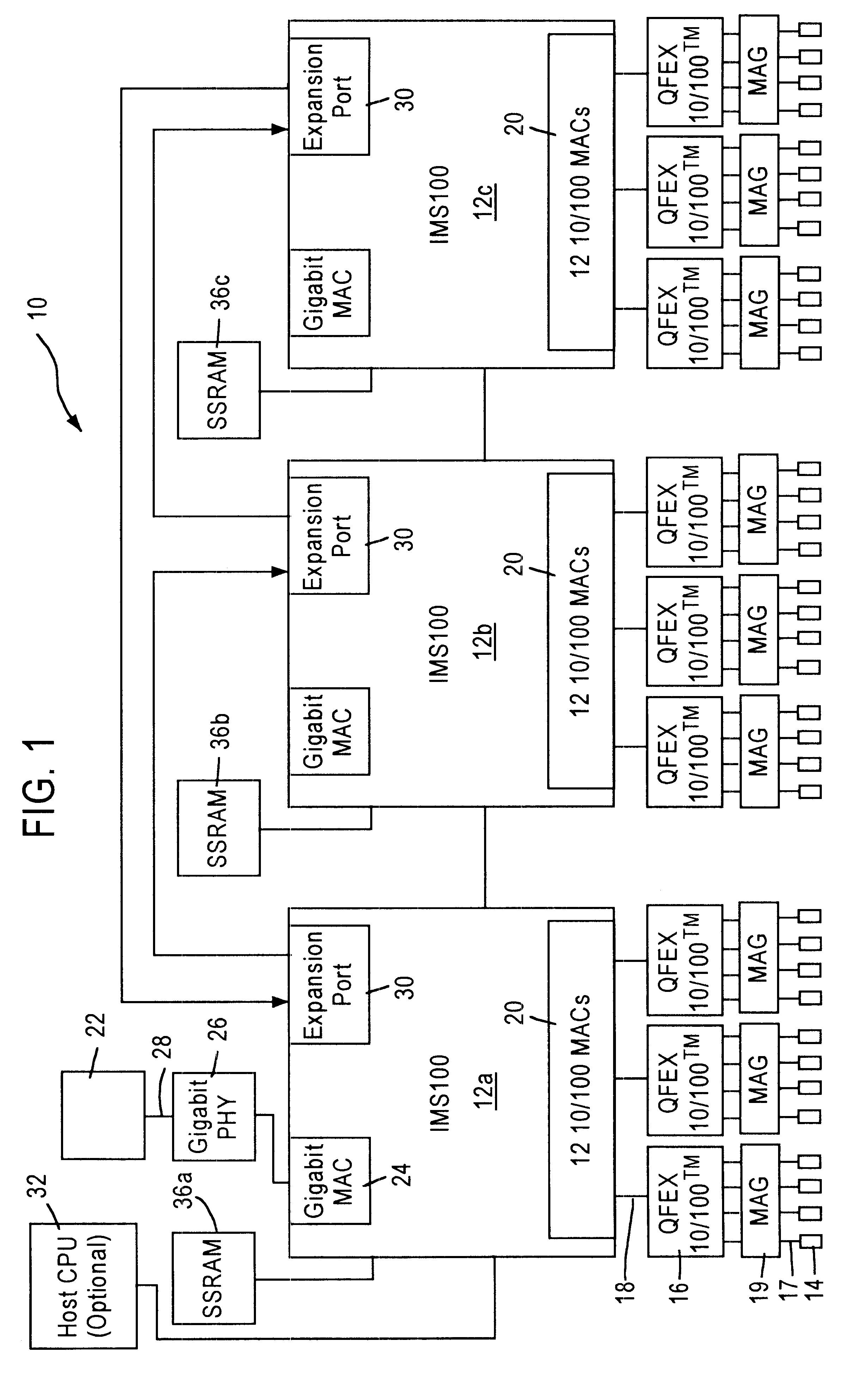
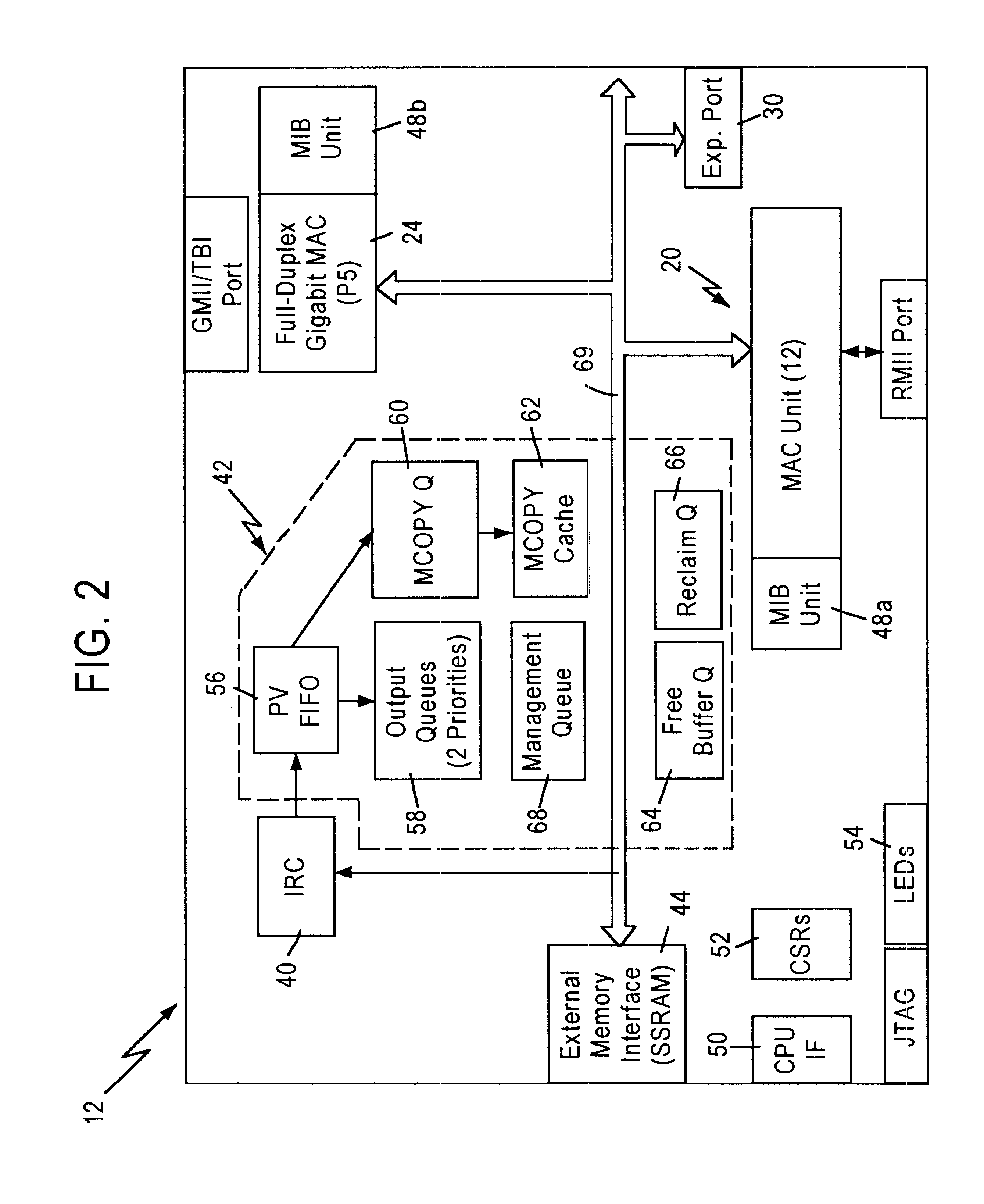
Method and apparatus for reclaiming buffers using a single buffer bit
InactiveUS6504846B1Efficient recyclingSpecial service provision for substationNetworks interconnectionExternal storageMultiple frame
A method and apparatus are disclosed for reclaiming frame buffers used to store data frames received by a network switch. The apparatus includes a multicopy queue for queuing entries corresponding to received data frames which must be transmitted by multiple output ports of the network switch, a free buffer queue for queuing frame pointers that identify locations in an external memory where reclaimed frame buffers are located, and a multicopy circuit that retrieves entries from the multicopy queue and determines if all copies of a received data frame have been transmitted by the specified output ports. The multicopy circuit also reclaims one or more frame buffers, based on the size of the received data frame. The present invention allows efficient reclaiming of frame buffers regardless of whether the received data frame is stored in a single frame buffer or multiple frame buffers.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
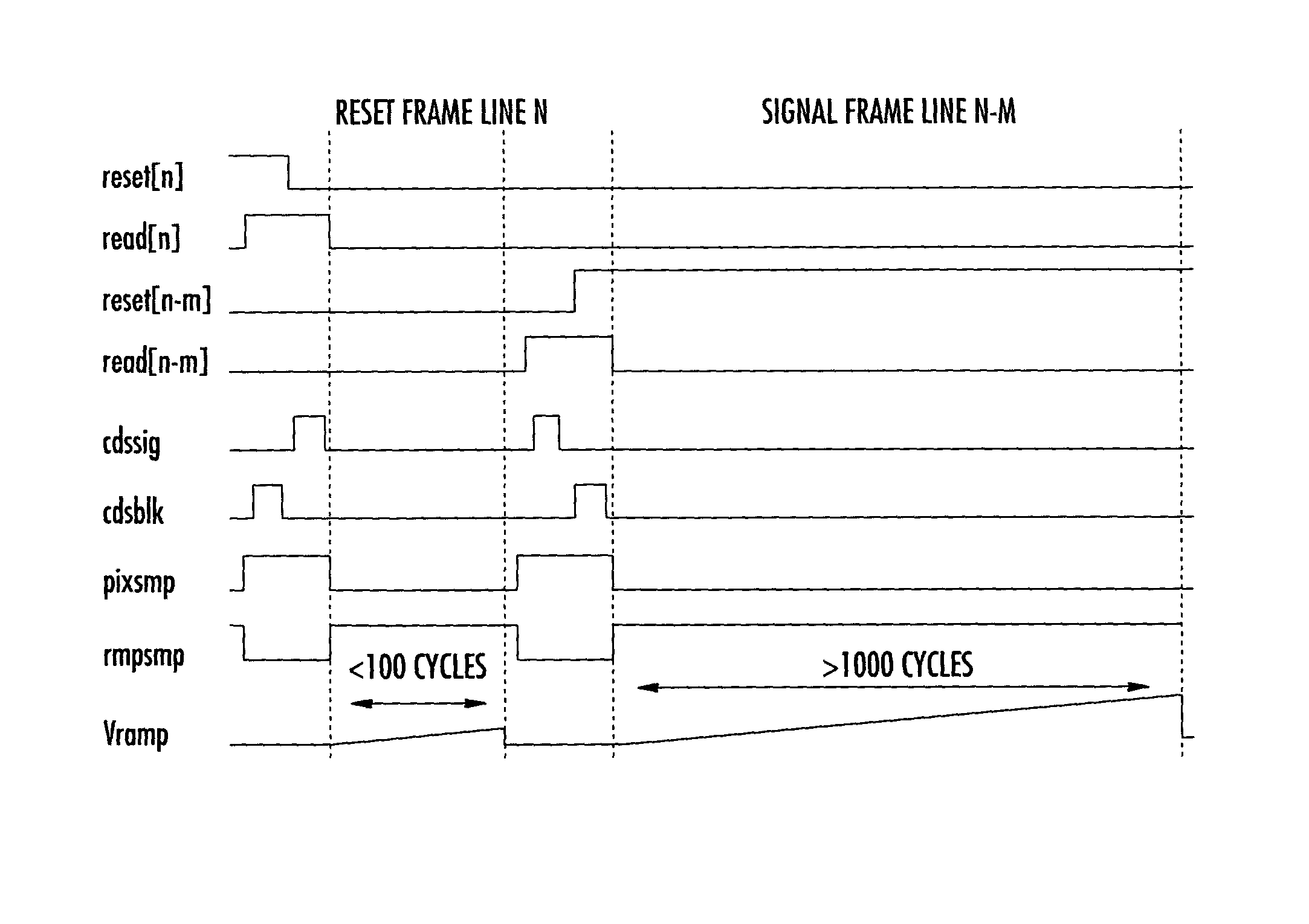
Image sensor reading during reset and reading on release from reset
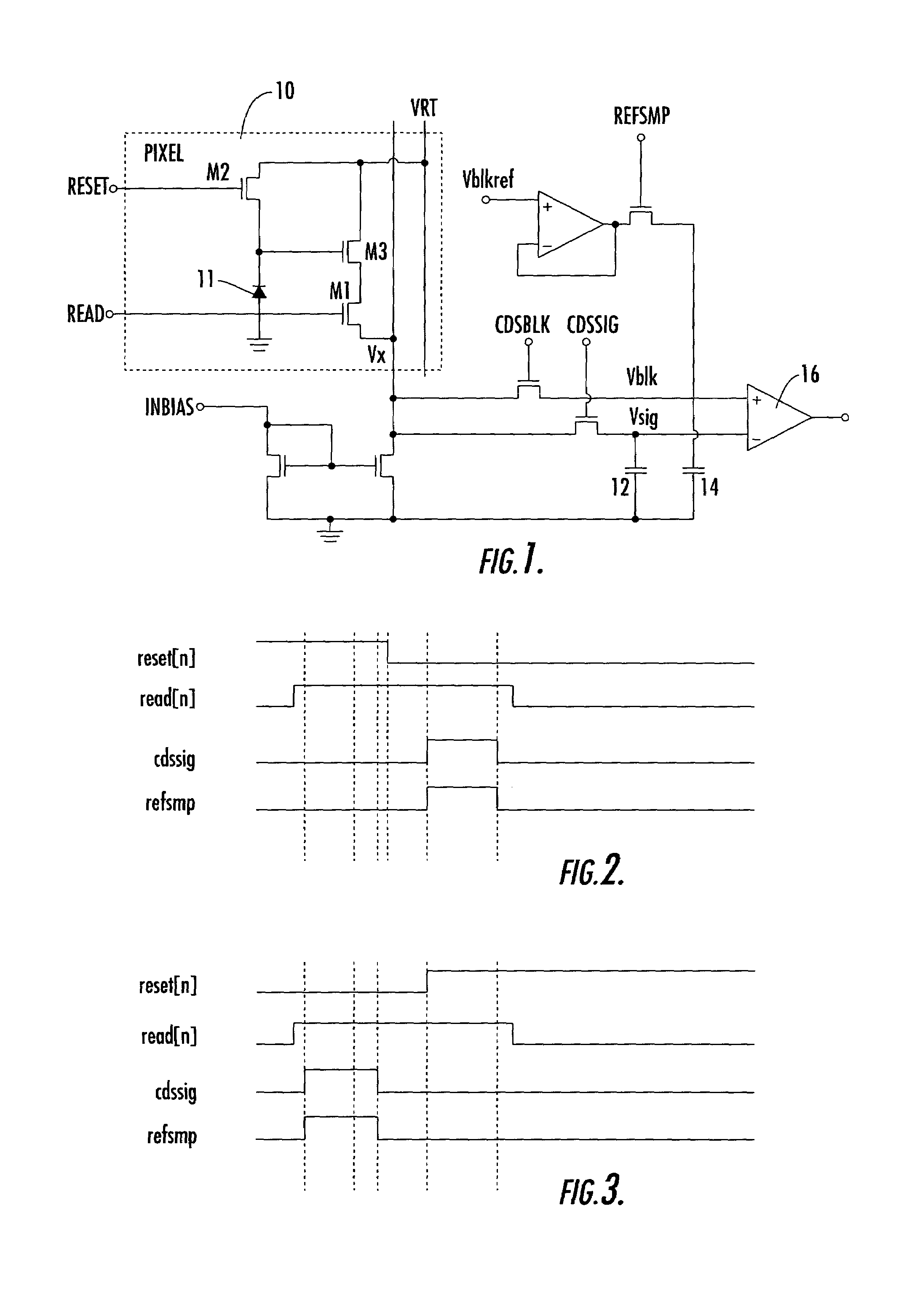
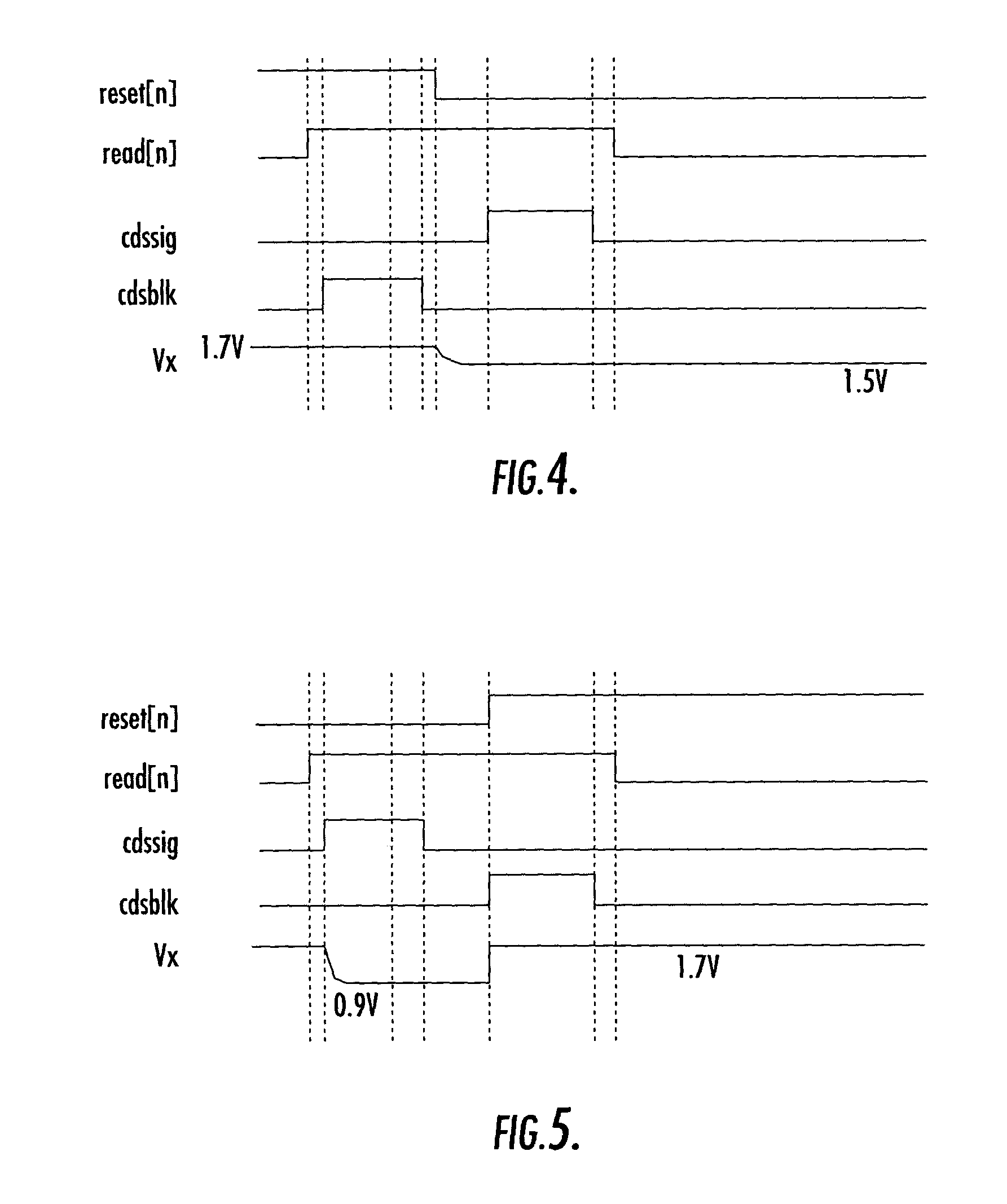
ActiveUS7280140B2Reducing frame buffer sizeSmall sizeTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsComputer scienceCapacitor
A solid state image sensor has an array of pixels in which each column has a reset voltage line and a read line. The sensor is reset and read a row at a time, with reset-related values held in a frame buffer for subsequent subtraction from read values. Reset-related values are derived in each column by sampling the voltage during reset on one capacitor and the voltage on release of reset on a second capacitor, and differencing these values to provide an output for the frame buffer. This provides a reduction in the size of frame buffer which would otherwise be required.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS LTD
Image processor with noise reduction circuit
ActiveUS7265784B1Reduce noiseRemove random noiseTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDigital imagingRandom noise
A digital imaging system includes an image sensor, an interface circuit, a frame buffer and an image processor. The image sensor includes a two-dimensional array of pixel elements and outputs digital signals on a pixel bus as pixel data representing an image of a scene. The interface circuit is coupled to receive the pixel data from the pixel bus. The frame buffer is coupled to store pixel data provided by the interface circuit. The image processor operates to process the pixel data stored in the frame buffer to generate image data for displaying the image of the scene. The interface circuit includes a noise reduction circuit operated to perform signal processing on the pixel data received on the pixel bus for noise reduction. Thus, random noise such as readout noise can be eliminated as pixel data are being transferred from the image sensor and stored in the frame buffer.
Owner:PIXIM
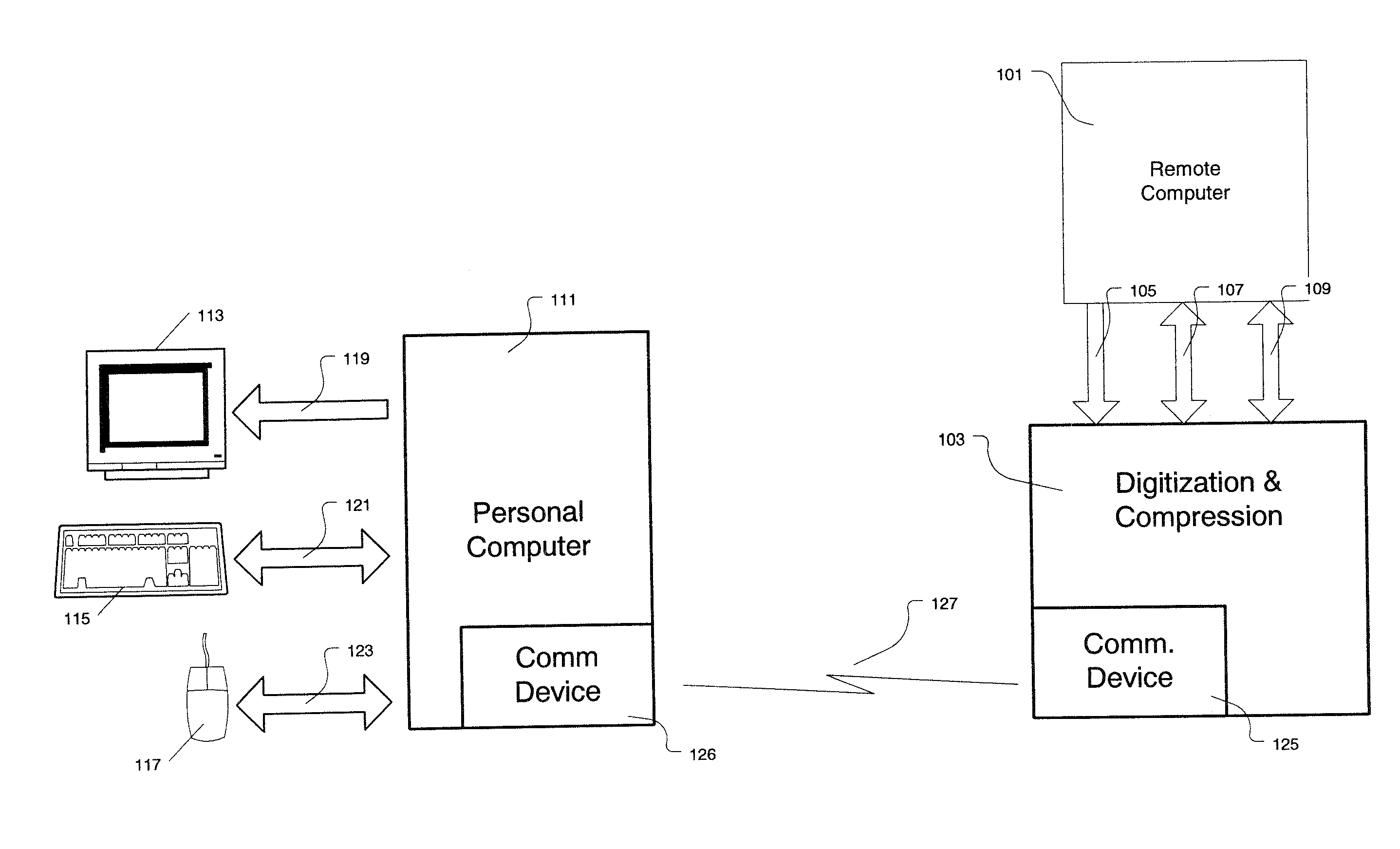
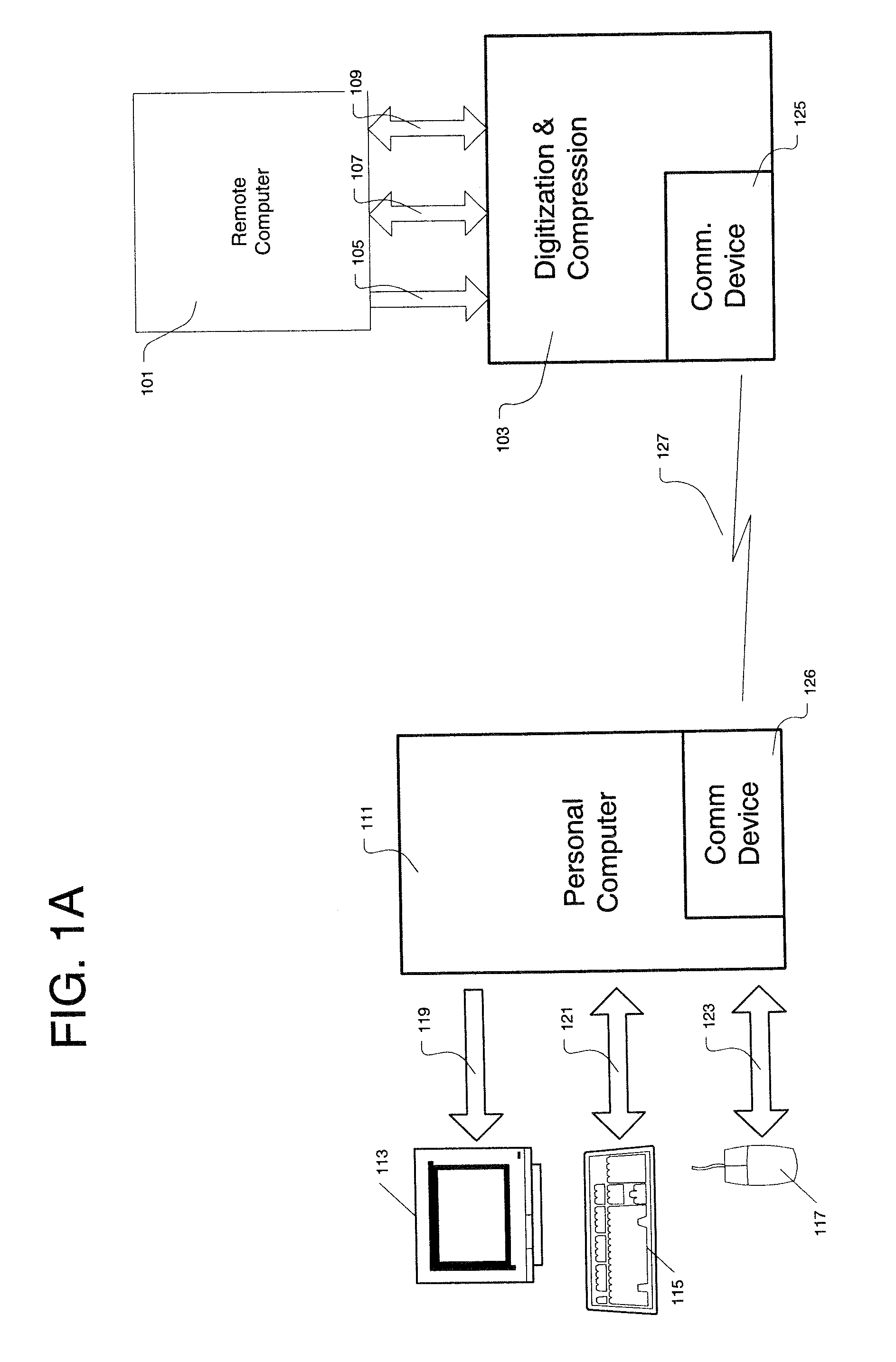
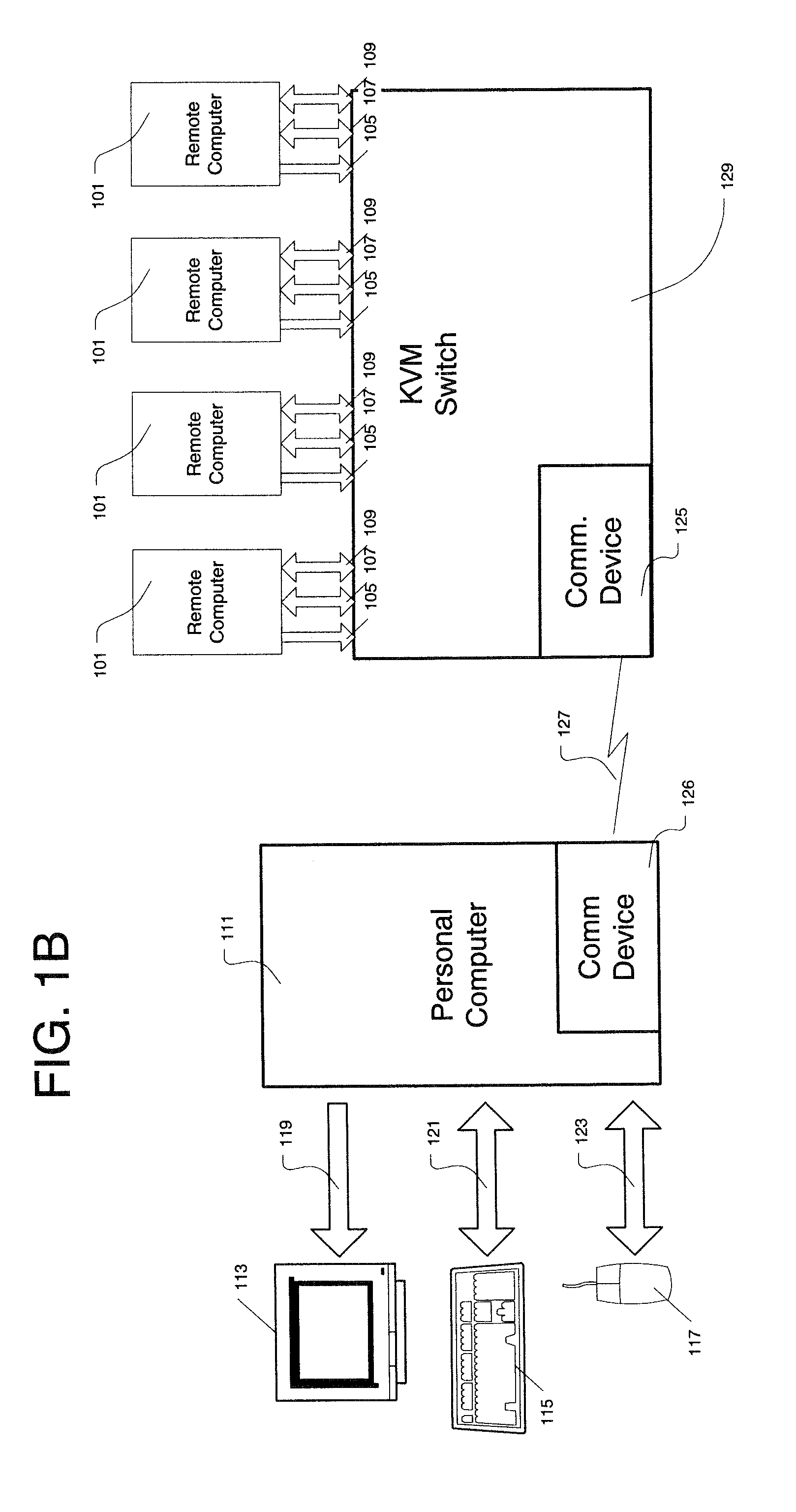
Method And Apparatus For Digitizing And Compressing Remote Video Signals
InactiveUS20100225658A1Guaranteed normal transmissionEfficient use of bandwidthPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningRemote computerCompression method
A method and apparatus for digitizing and compressing video signals for transmitting the signals between a remotely located computer and a host or local computer. The digitization and compression method and apparatus is capable of dividing frame buffers into cells and comparing image data from previously captured frame buffers to create synchronized video signals and transmit the video signals over an extended range by limiting the portions of the transmission bandwidth of pixel data transferred between the remote computer and the local computer. In an alternate embodiment of the present invention, a keyboard video mouse switch is disposed between the remotely located computer and the local computer.
Owner:COLEMAN SCOTT
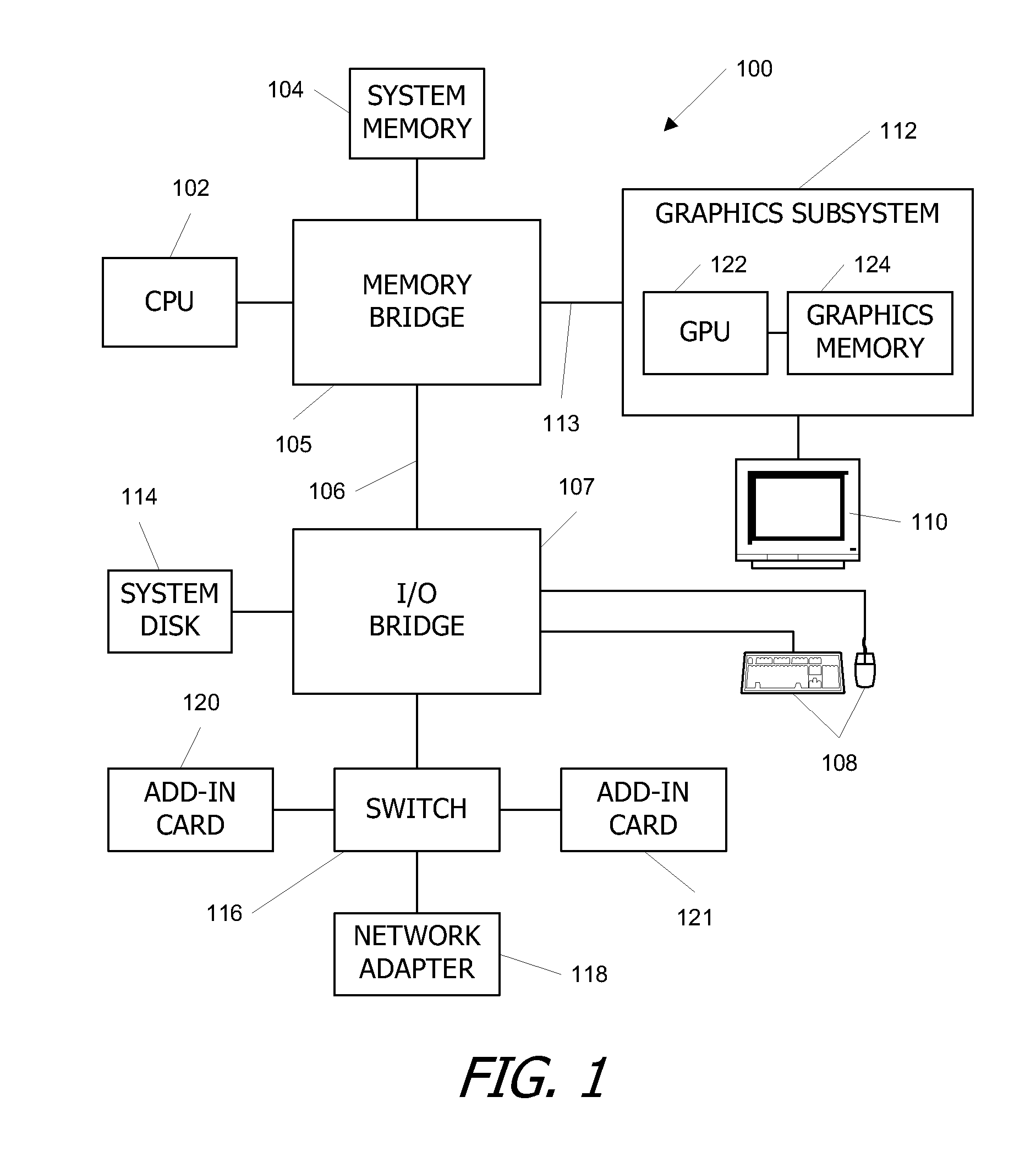
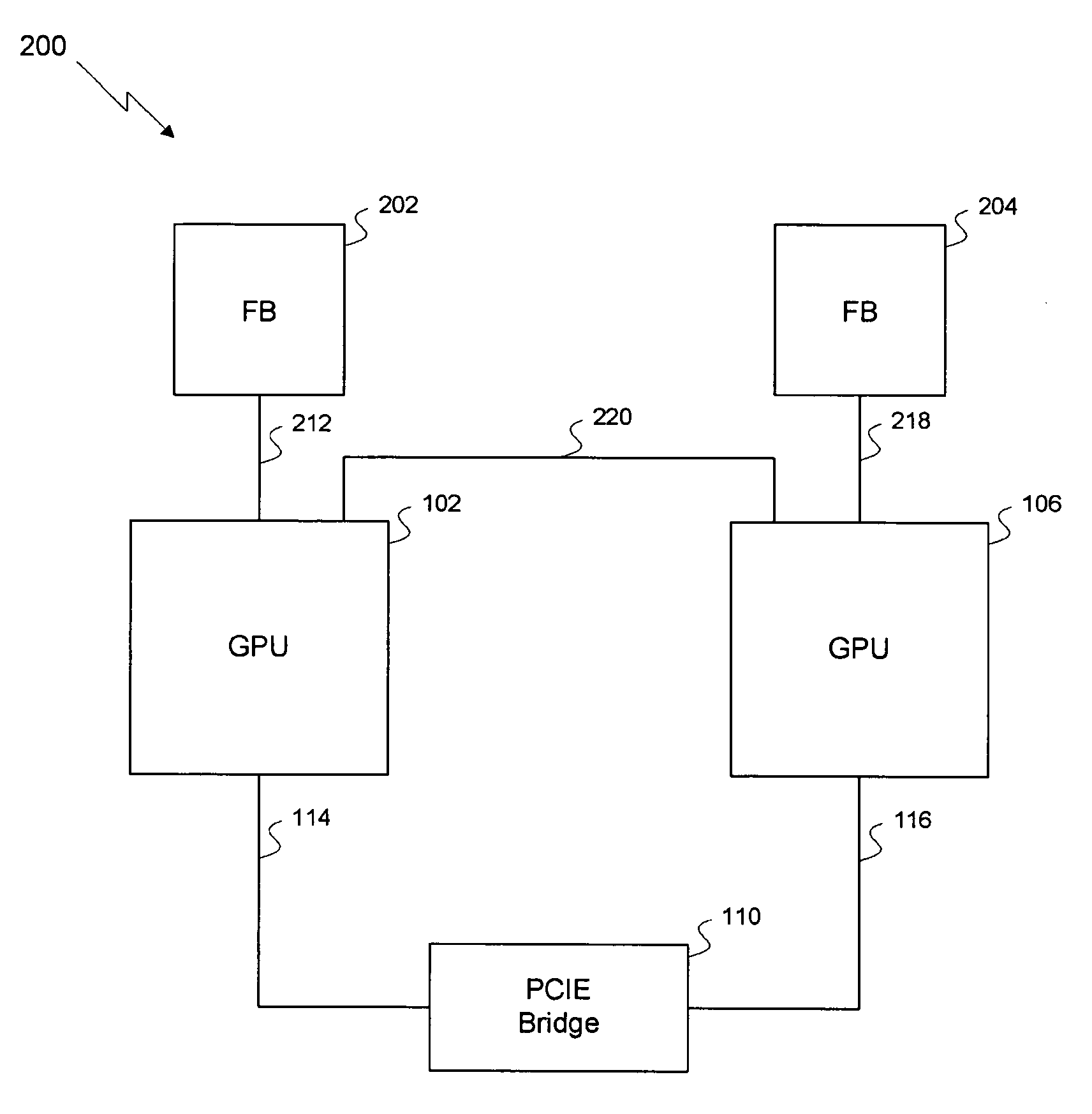
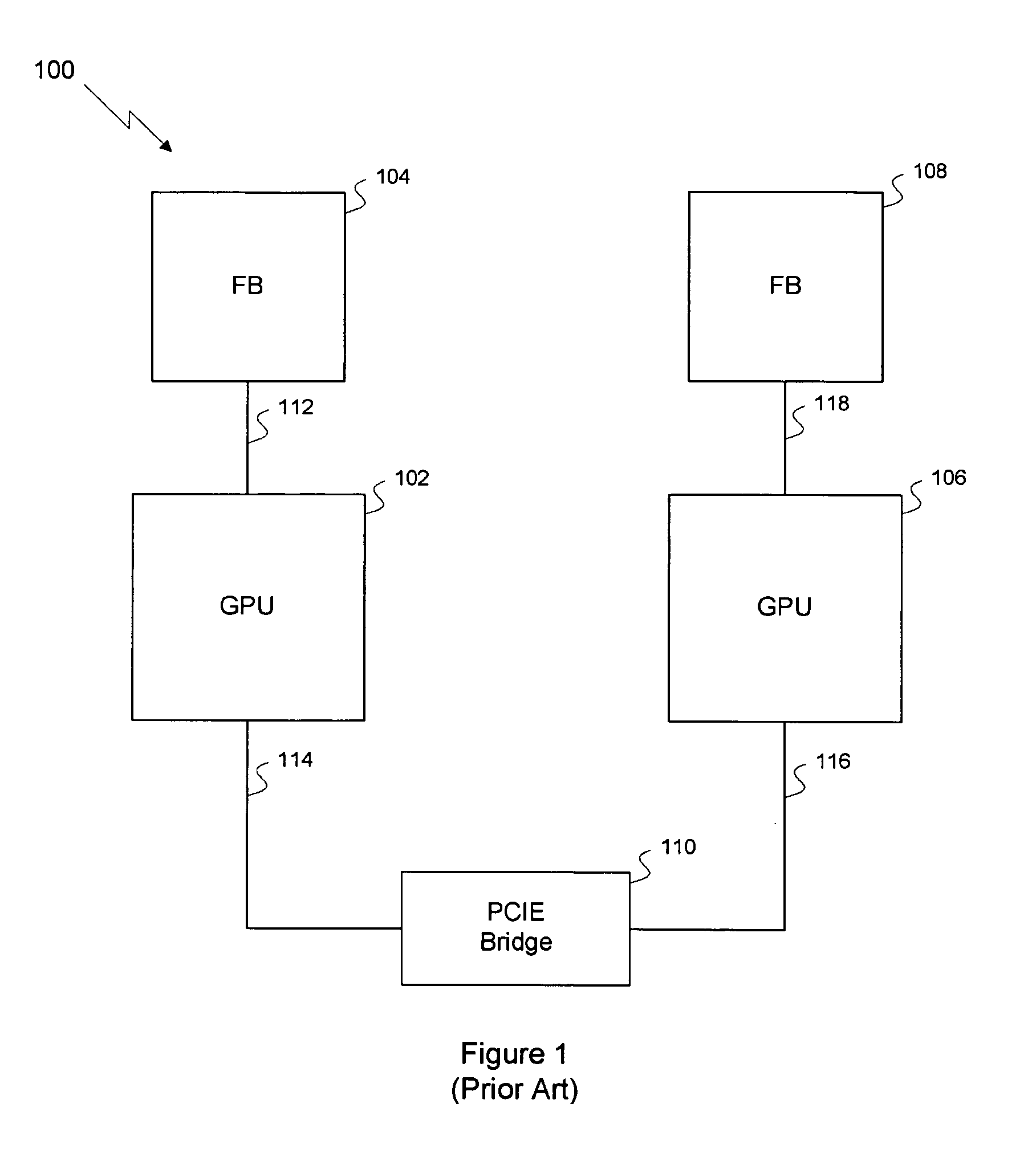
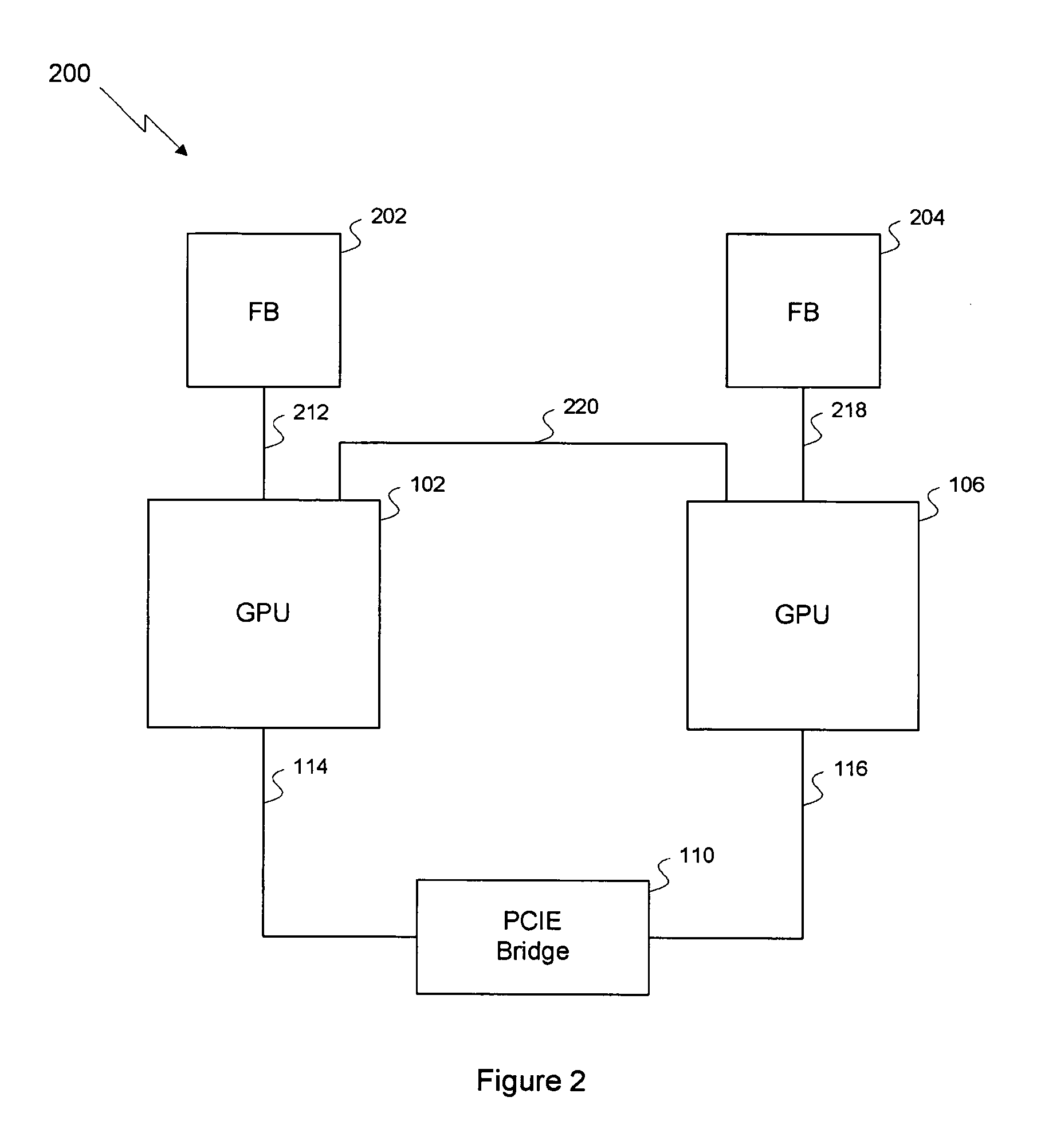
Efficient multi-chip GPU
ActiveUS7616206B1Raise the ratioMore scalableCathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsData compressionExtensibility
One embodiment of the invention sets forth a technique for efficiently combining two graphics processing units (“GPUs”) to enable an improved price-performance tradeoff and better scalability relative to prior art multi-GPU designs. Each GPU's memory interface is split into a first part coupling the GPU to its respective frame buffer and a second part coupling the GPU directly to the other GPU, creating an inter-GPU private bus. The private bus enables higher bandwidth communications between the GPUs compared to conventional communications through a PCI Express™ bus. Performance and scalability are further improved through render target interleaving; render-to-texture data duplication; data compression; using variable-length packets in GPU-to-GPU transmissions; using the non-data pins of the frame buffer interfaces to transmit data signals; duplicating vertex data, geometry data and push buffer commands across both GPUs; and performing all geometry processing on each GPU.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Programmable sample filtering for image rendering
A graphics system configured to perform programmable filtering of samples to generate pixel values. The graphics system comprises a frame buffer, an accelerator unit and a video output processor. The accelerator unit receives graphics primitives, renders samples for the graphics primitives, and stores the rendered samples into a sample area of the frame buffer. The accelerator unit subsequently reads the samples from the sample area of the frame buffer, and filters the samples with a programmable filter having a programmable support region. The resulting pixel values are stored in a pixel area of the frame buffer. The video output processor reads the pixel values from the pixel area and converts the pixel values into a video signal which is provided to a video output port.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
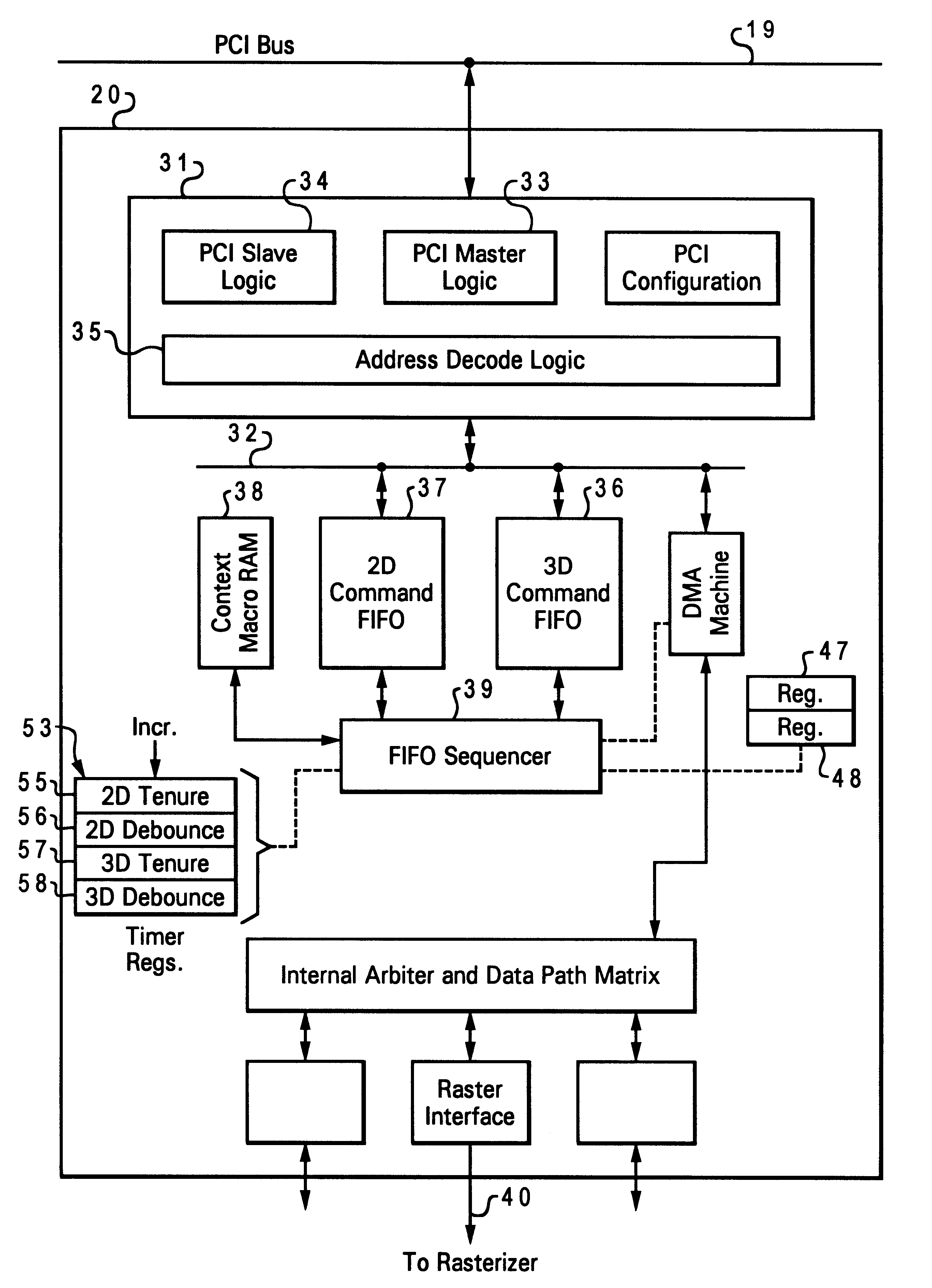
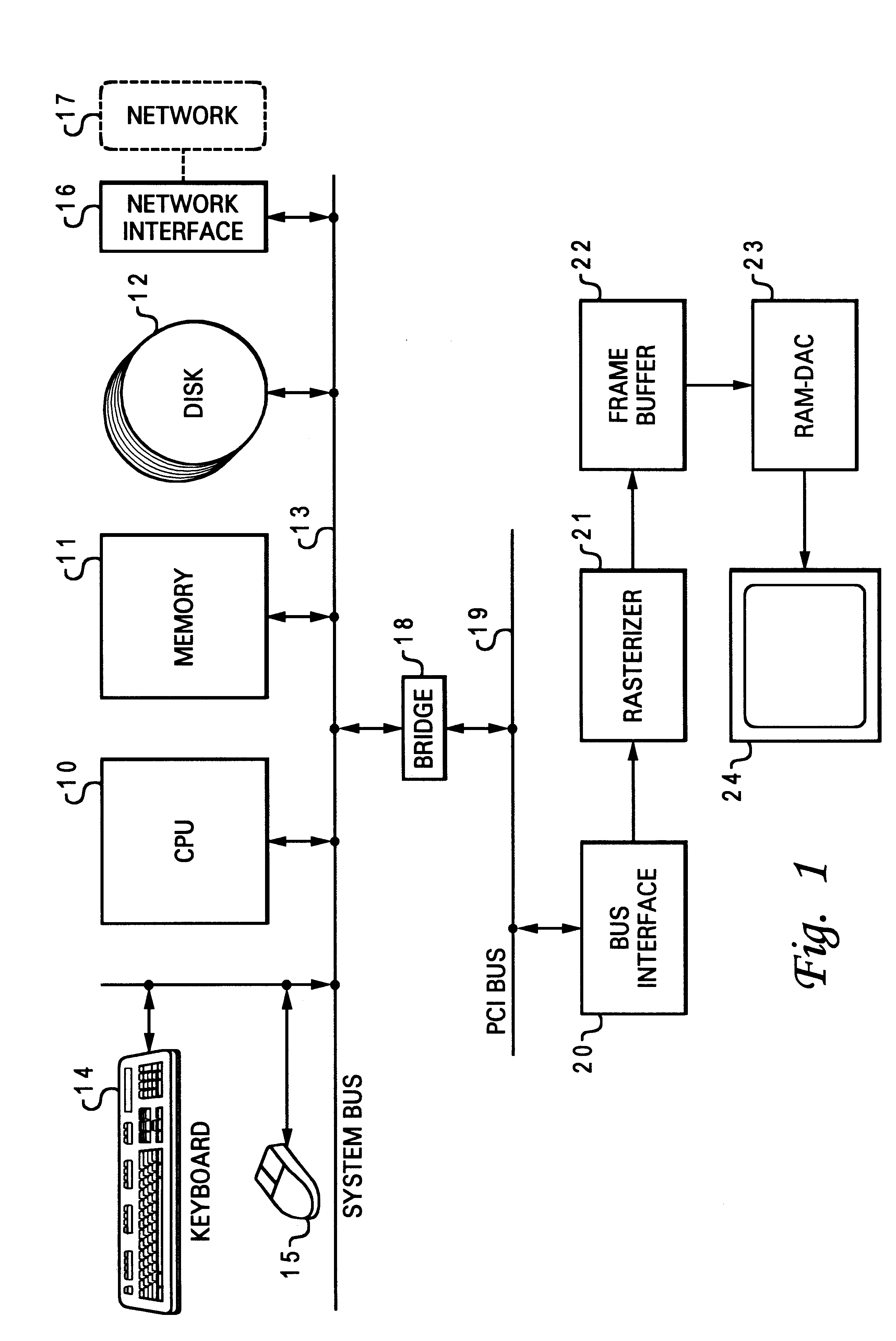
Computer graphics system with dual FIFO interface
InactiveUS6252600B1Minimum delayEasy to useImage memory managementCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphic systemComputerized system
A computer system has a graphics subsystem employing a rasterizer and a frame buffer, with a digital-to-analog converter for producing drive signals to a video display. A bus interface acts as a gateway between a PCI bus and the graphics subsystem; this interface manages commands and DMAs passing between the host processor and various parts of the graphics subsystem. Within the interface, two command FIFOs are employed, one for storing commands / data sent from the host for 2D display (window management) and another for 3D applications. Using two command FIFOs eliminates the need for host semaphore, FIFO draining, and the latency associated with these operations. Timers are provided in the interface, associated with the two command FIFOs, to manage and regulate the frequency with which the system automatically switches between 2D and 3D FIFO processing. Host intervention is minimized by use of a context macro store for holding locally the sequences for context save and context restore which are used repeatedly.
Owner:IBM CORP
Adaptive video compression of graphical user interfaces using application metadata
InactiveUS7548657B2Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationData streamDisplay device
Systems, methods and computer accessible medium are provided through which an input data stream consisting one or more media regions before entering a network to be rendered by a display coupled a remote video frame buffer is compressed on the basis of one or more configuration file metadata, source primitive metadata, and application high-level metadata of identified media regions. The input data stream is compressed by using one or more MPEG compression, JPEG compression, vector graphics compression, Huffman coding, or user defined compression scheme.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
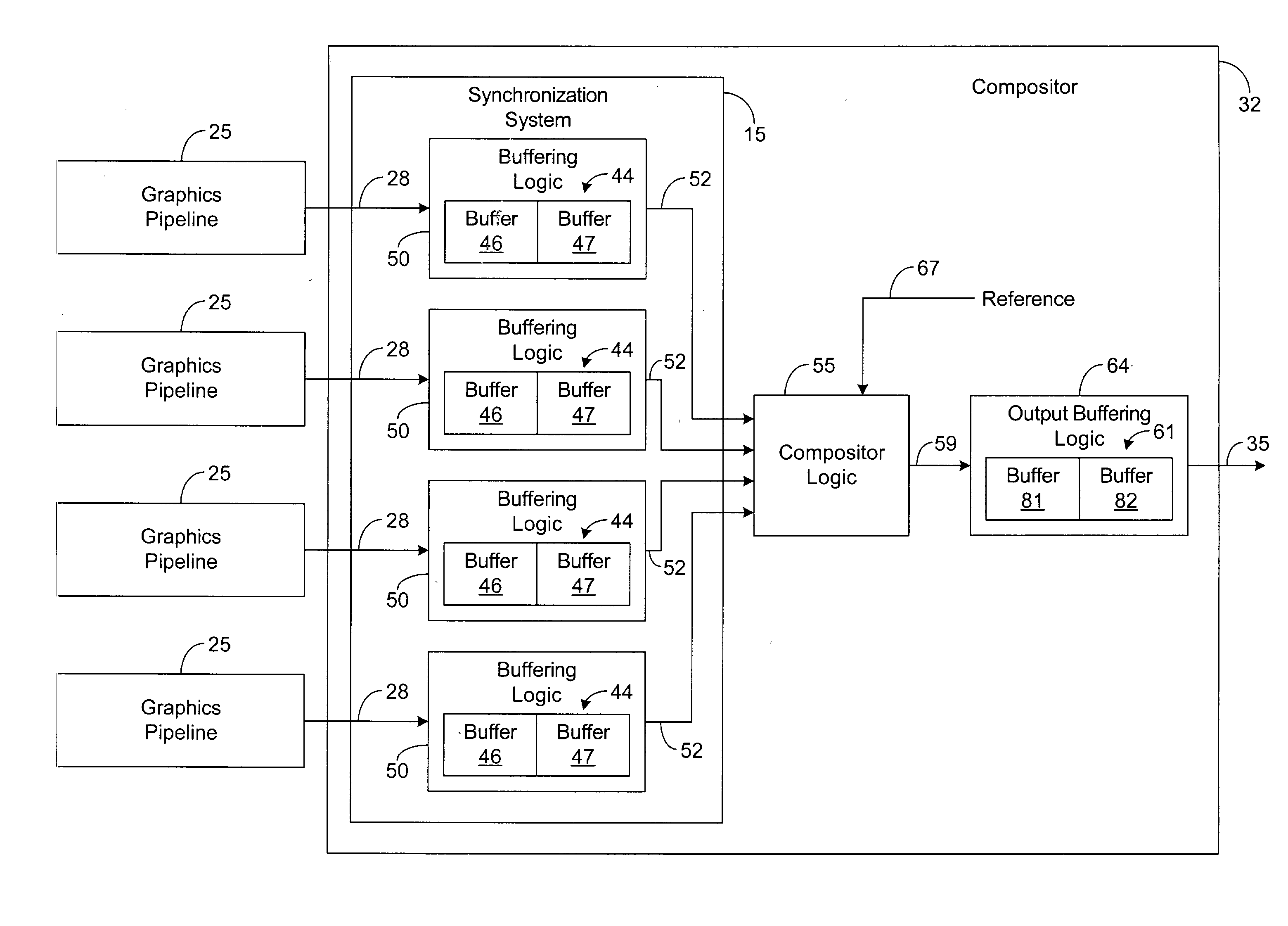
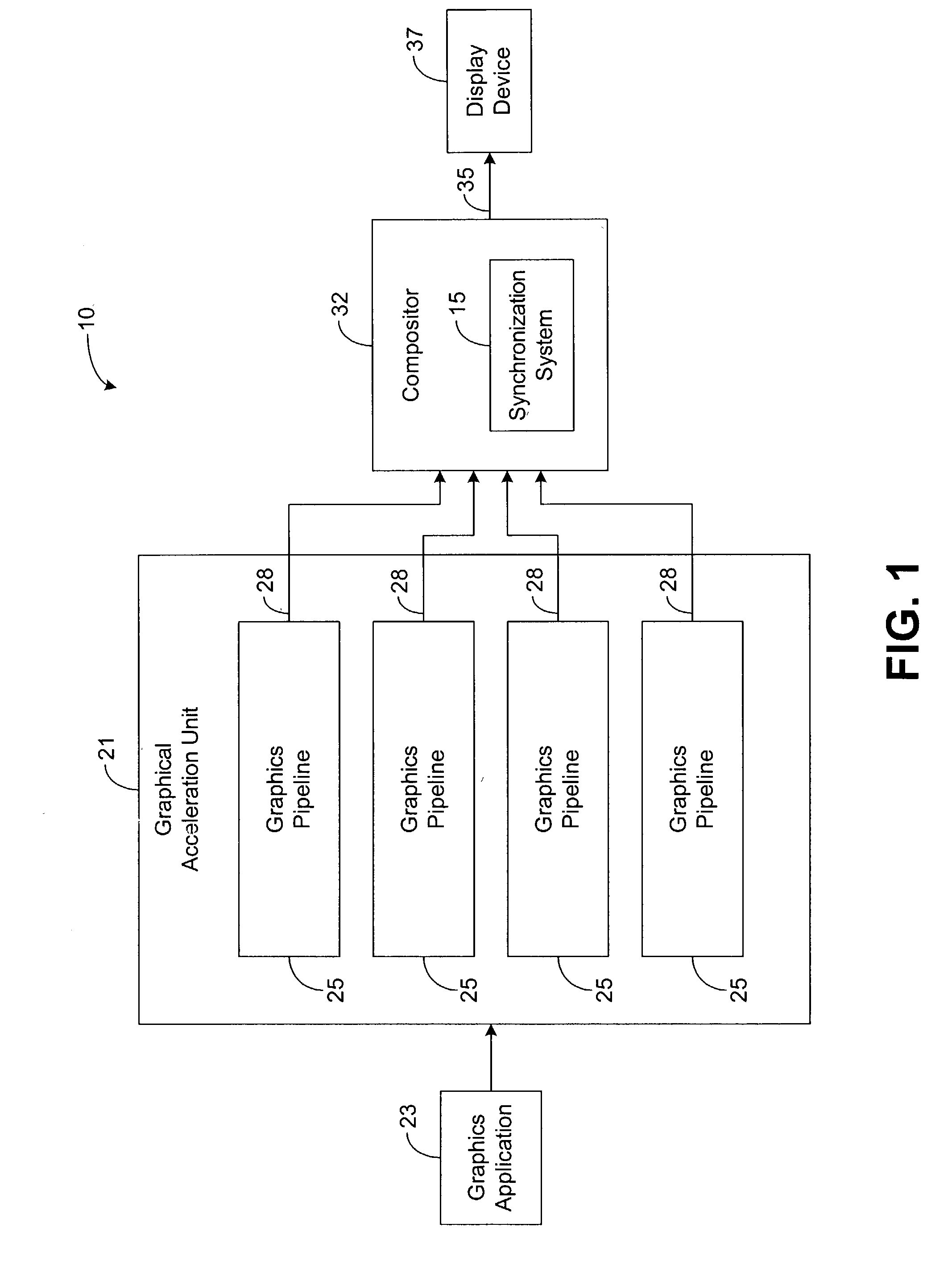
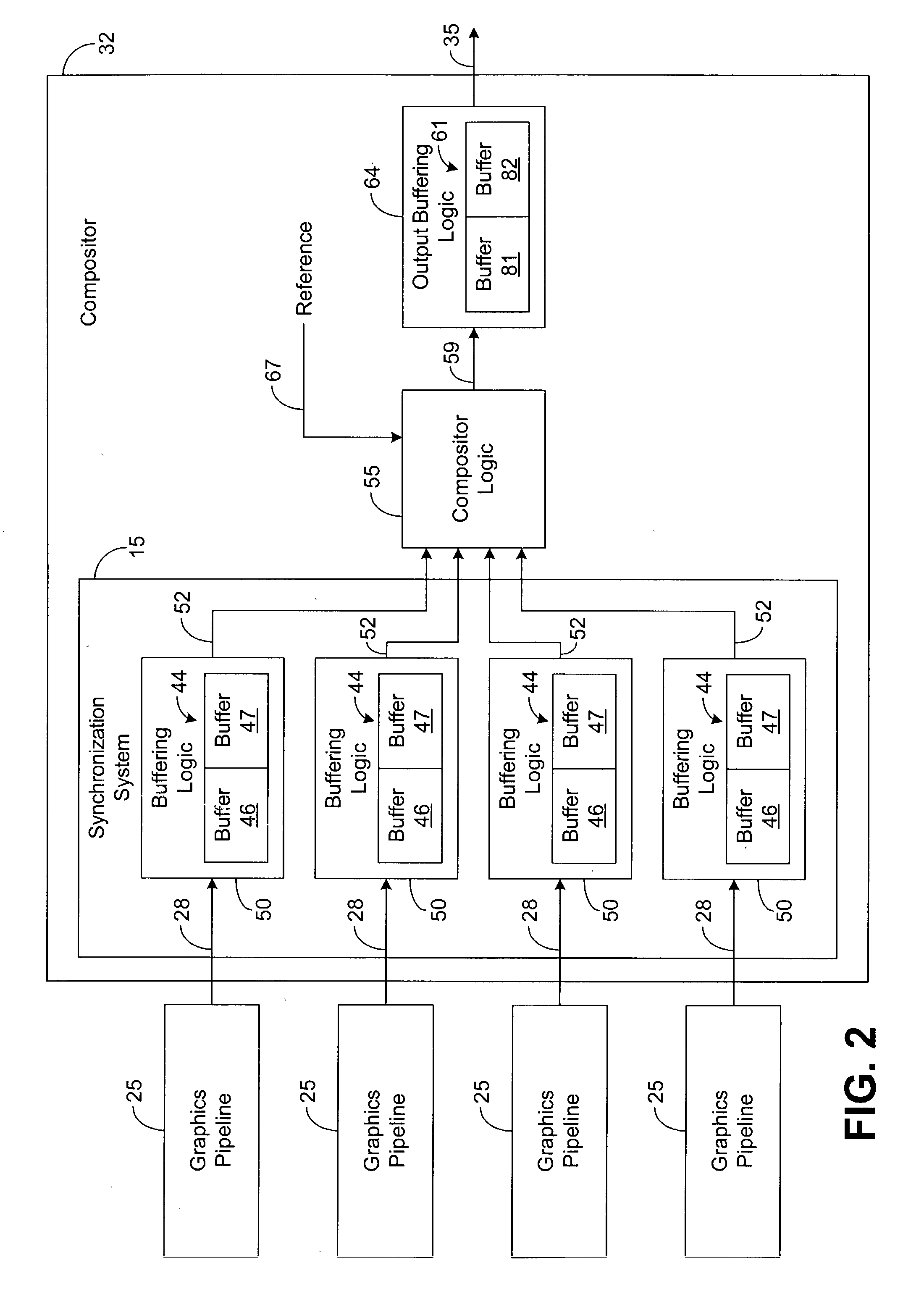
System and method for sychronizing video data streams
InactiveUS20030227460A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital output to display deviceData streamData buffer
A system for synchronizing video data streams utilizes a plurality of buffer pairs and buffering logic. The buffering logic is configured to receive image frames from a plurality of asynchronous video data streams and to perform comparisons between frame identifiers associated with the image frames. The buffering logic is further configured to double buffer the image frames via the plurality of frame buffer pairs based on the comparisons and to synchronously output the image frames from the frame buffer pairs.
Owner:HANGZHOU HIKVISION DIGITAL TECH
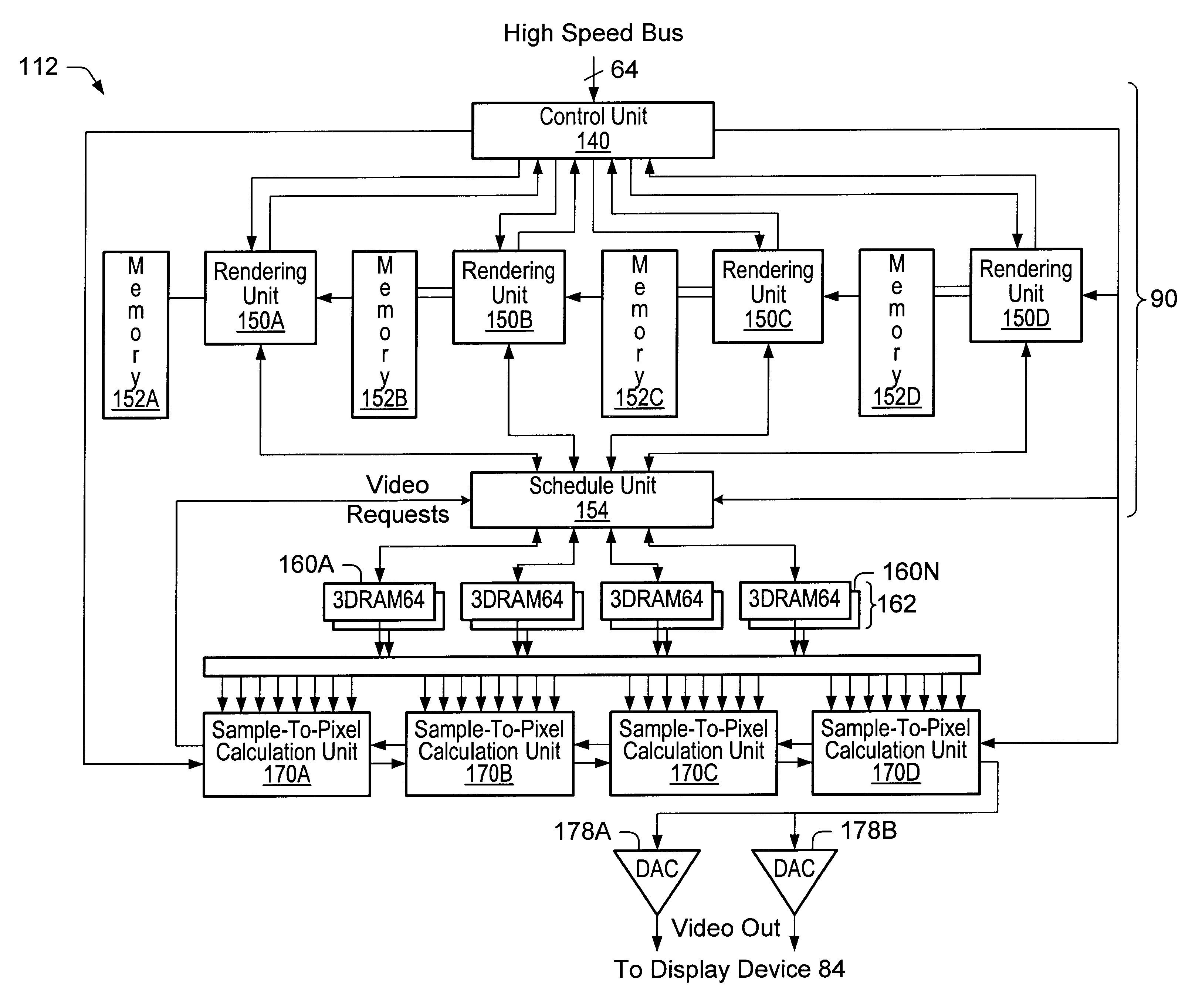
Video rendering across a high speed peripheral interconnect bus
InactiveUS20080143731A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsDisplay deviceHigh velocity
Graphics generated by one graphics processor are transferred across a high speed interconnect bus to a frame buffer. The rendered frames from the frame buffer are presented on a display by way of a display interface in communication with the frame buffer. The display interface of another existing (e.g. integrated) graphics adapter / subsystem may be used to present the rendered frames on an interconnected display.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
Graphics system with embedded frame buffer having reconfigurable pixel formats
InactiveUS20060197768A1Improve system flexibilityEasy to useCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingGraphic systemSignal processing
A graphics system including a custom graphics and audio processor produces exciting 2D and 3D graphics and surround sound. The system includes a graphics and audio processor including a 3D graphics pipeline and an audio digital signal processor. The graphics system has a graphics processor includes an embedded frame buffer for storing frame data prior to sending the frame data to an external location, such as main memory. The embedded frame buffer is selectively configurable to store the following pixel formats: point sampled RGB color and depth, super-sampled RGB color and depth, and YUV (luma / chroma). Graphics commands are provided which enable the programmer to configure the embedded frame buffer for any of the pixel formats on a frame-by-frame basis.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
Distributed rendering of texture data
ActiveUS7969444B1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsDisplay deviceWorkload
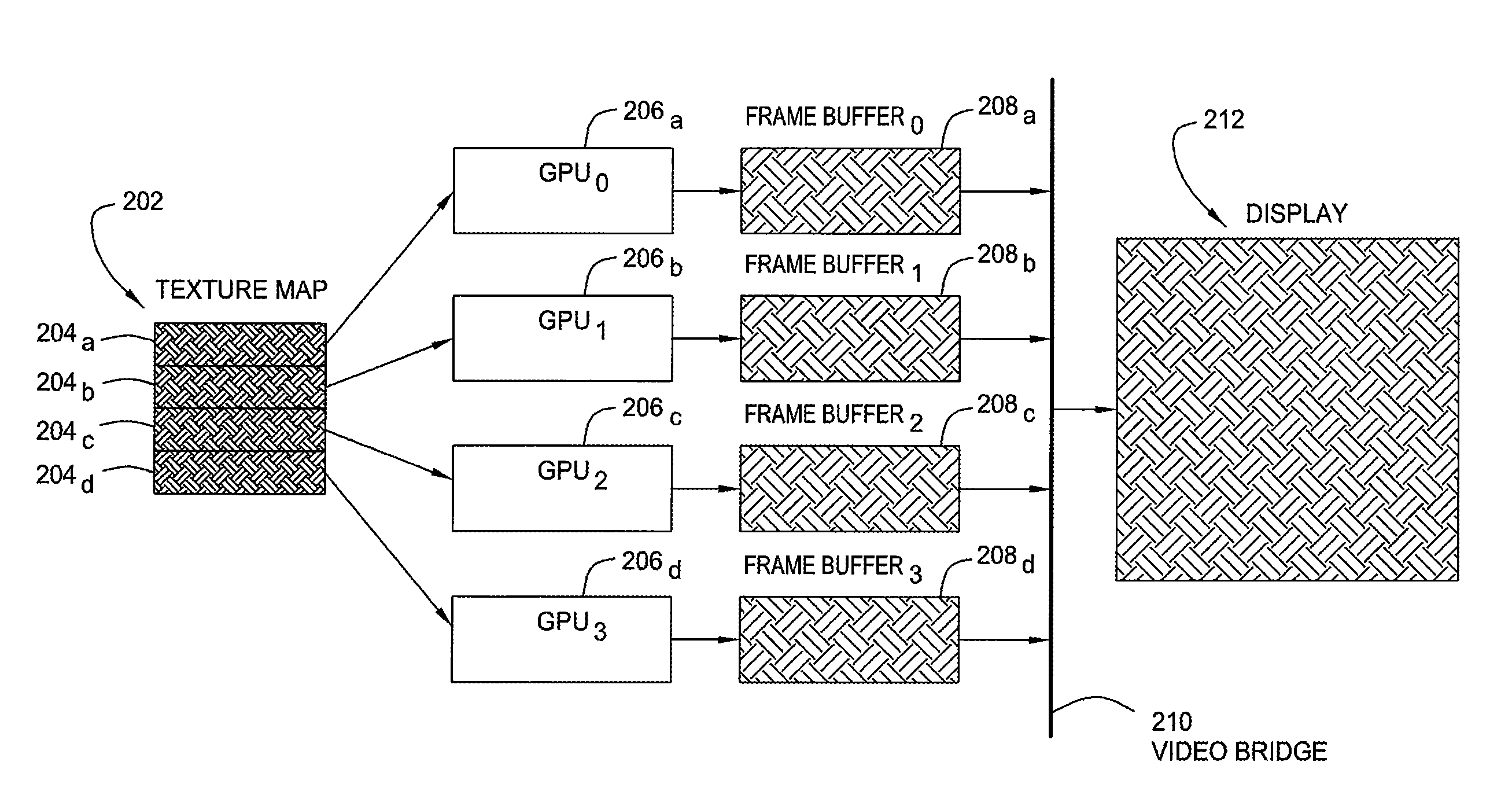
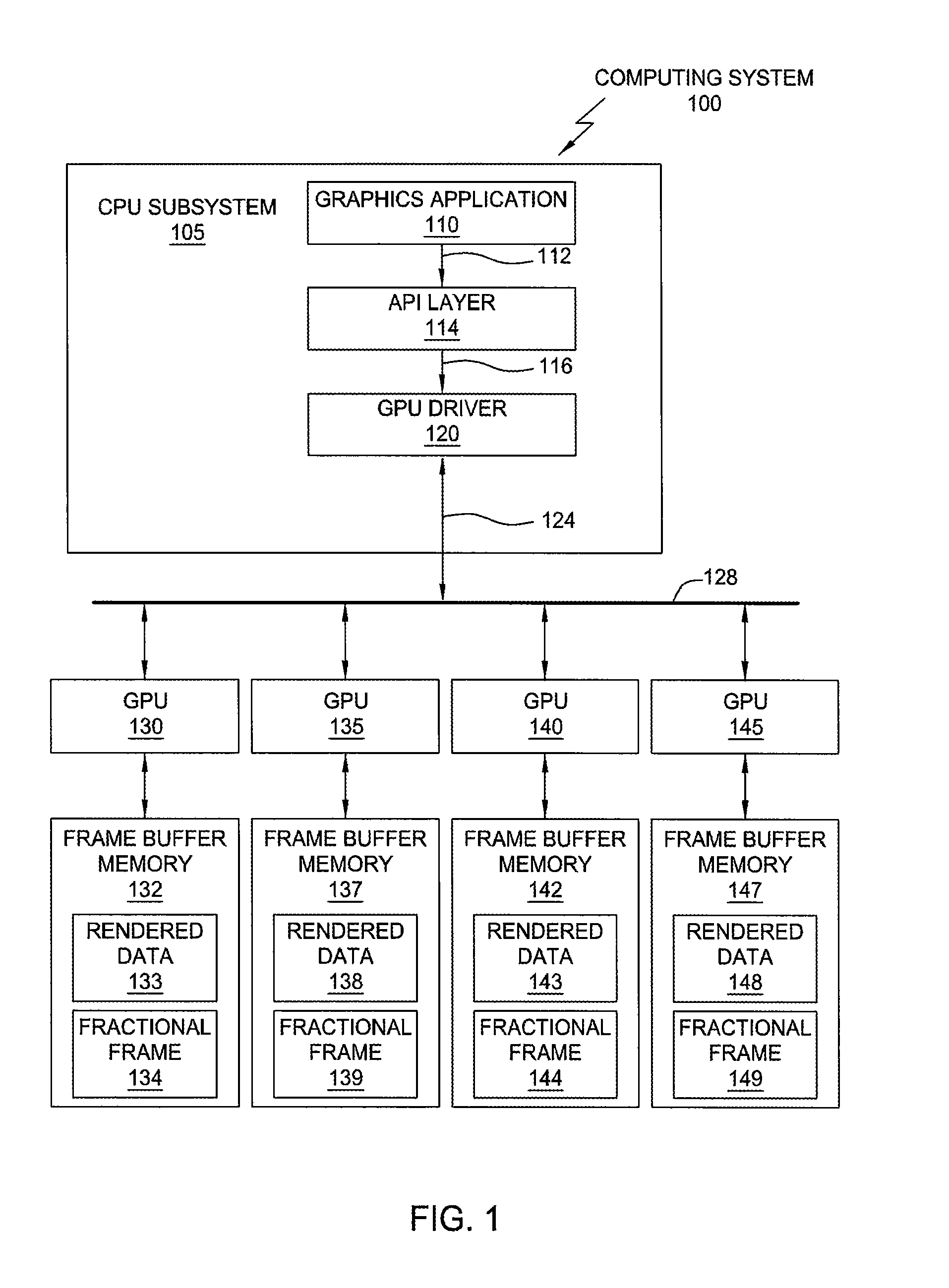
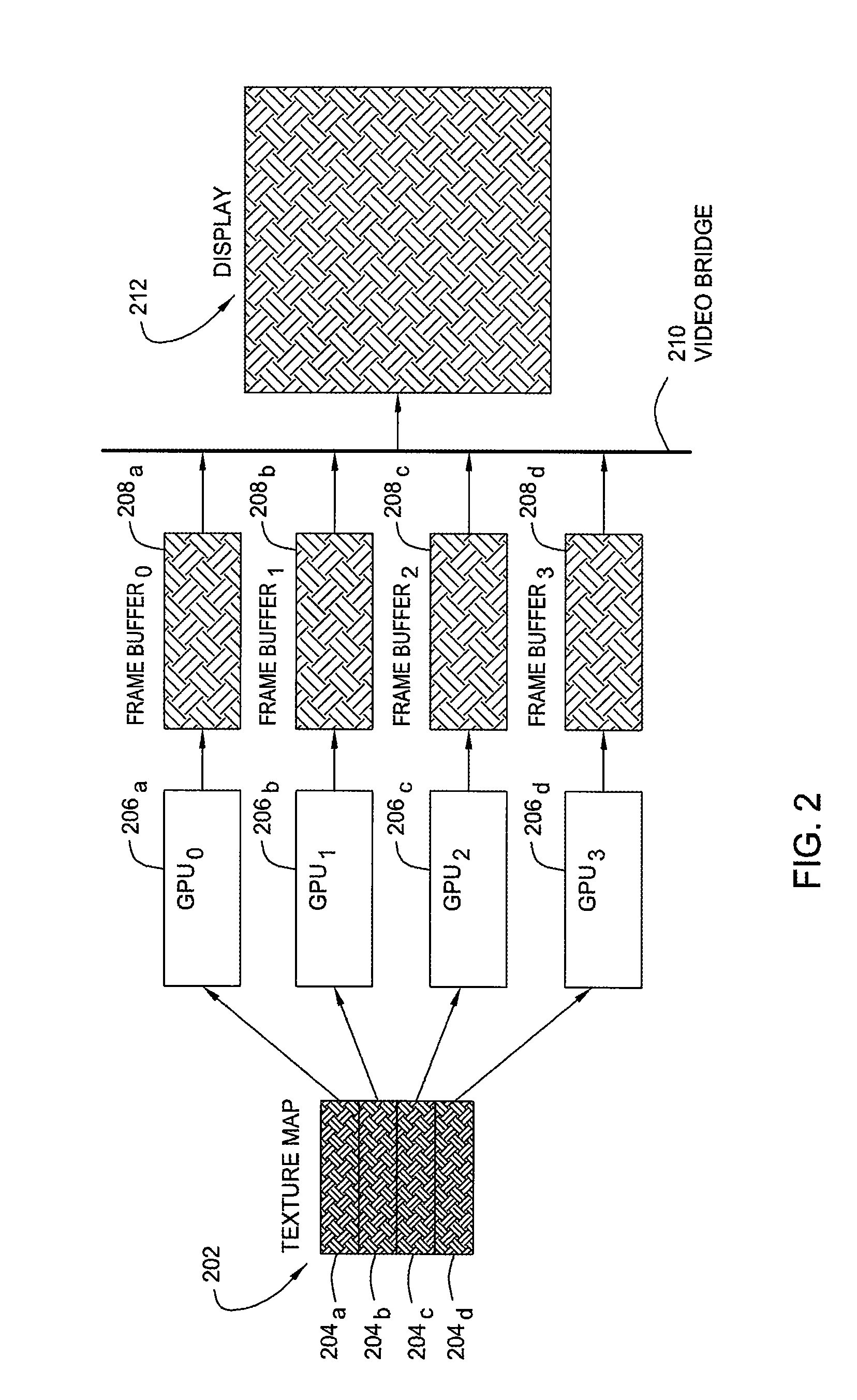
A method and apparatus for distributing the workload of rendering an image where texture mapping is involved among multiple graphics processing units (GPUs) are provided. The method generally entails dividing a texture map among multiple GPUs, performing texture mapping in each GPU to render image data in each GPU's frame buffer, combining the image data from each frame buffer, and scanning out the combined image to a display.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
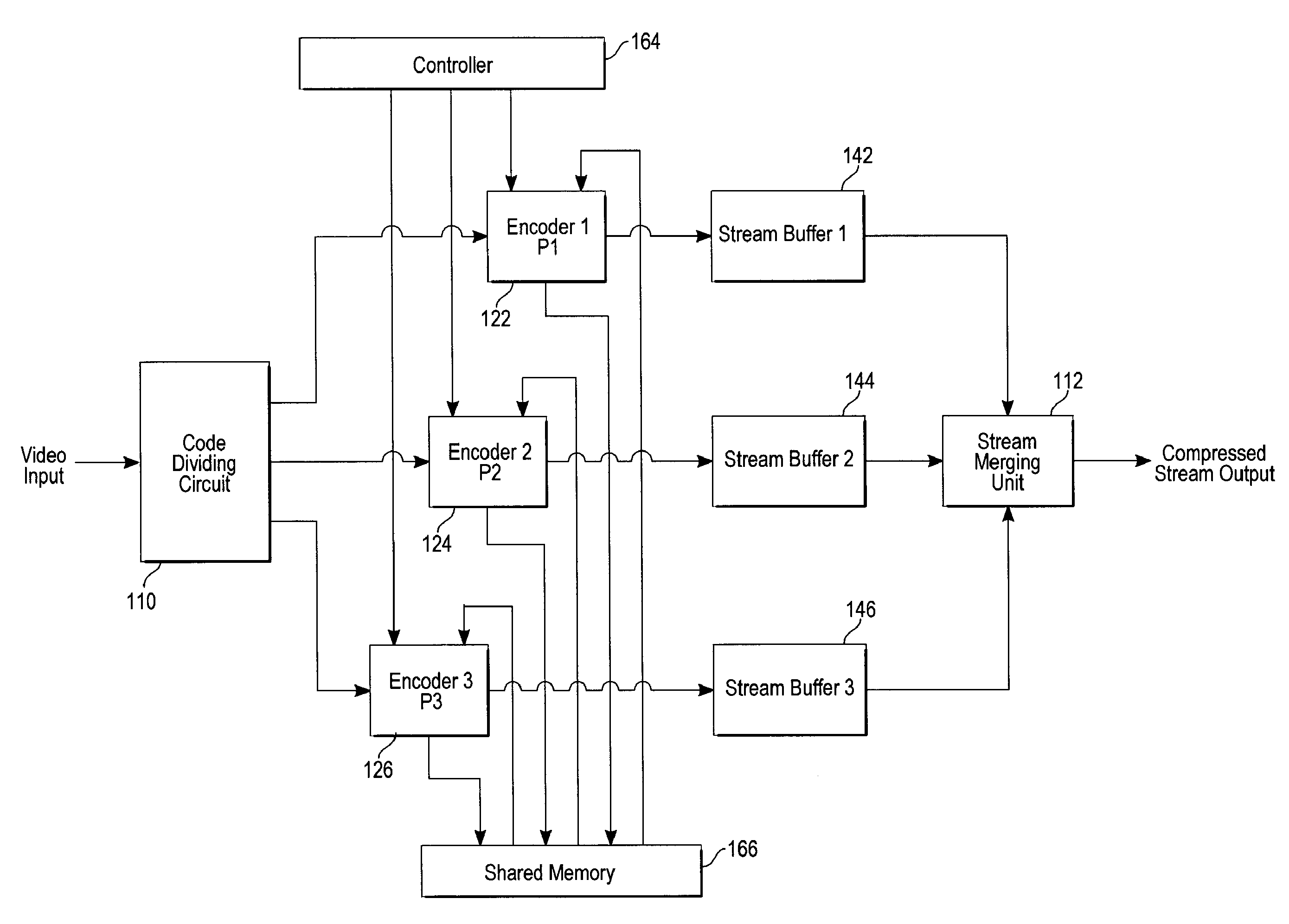
Method and apparatus for encoding and decoding of video streams
InactiveUS20080152014A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionFramebufferComputer hardware
A method and processor to encode and / or decode a video stream exploiting frame-level parallelism. Frames of the video stream are encoded and / or decoded using M processing units where each processing unit processes one different frame at a time. Each processing unit writes the reconstructed frame to a frame buffer. A processing unit can start the encoding and / or decoding process once sufficient data of the previous reconstructed frame are available.
Owner:ON DEMAND MICROELECTRONICS
Apparatus and method for increasing a digital camera image capture rate by delaying image processing
InactiveUSRE39213E1Increasing image capture rateSlow imaging processTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
An apparatus for increasing a digital camera image capture rate comprises an imaging device for capturing raw image data, a frame buffer for receiving the image data, a first RAM spooler for transferring the raw image data to a RAM disk, a first flash spooler for transferring the raw image data from the RAW disk to a flash memory, an image processor for processing and compressing the raw data, a second RAM spooler for storing the compressed image data into the RAM disk, and a second flash spooler for transferring the compressed image data from the RAM disk to the flash memory.
Owner:APPLE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com