Patents
Literature
216 results about "Rate reduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A rate reduction is a reduction in premium and it is frequently made retroactive either in the form of a cash refund or a credit available for application against future premiums. A retroactive rate reduction is, thus, very similar to a dividend.
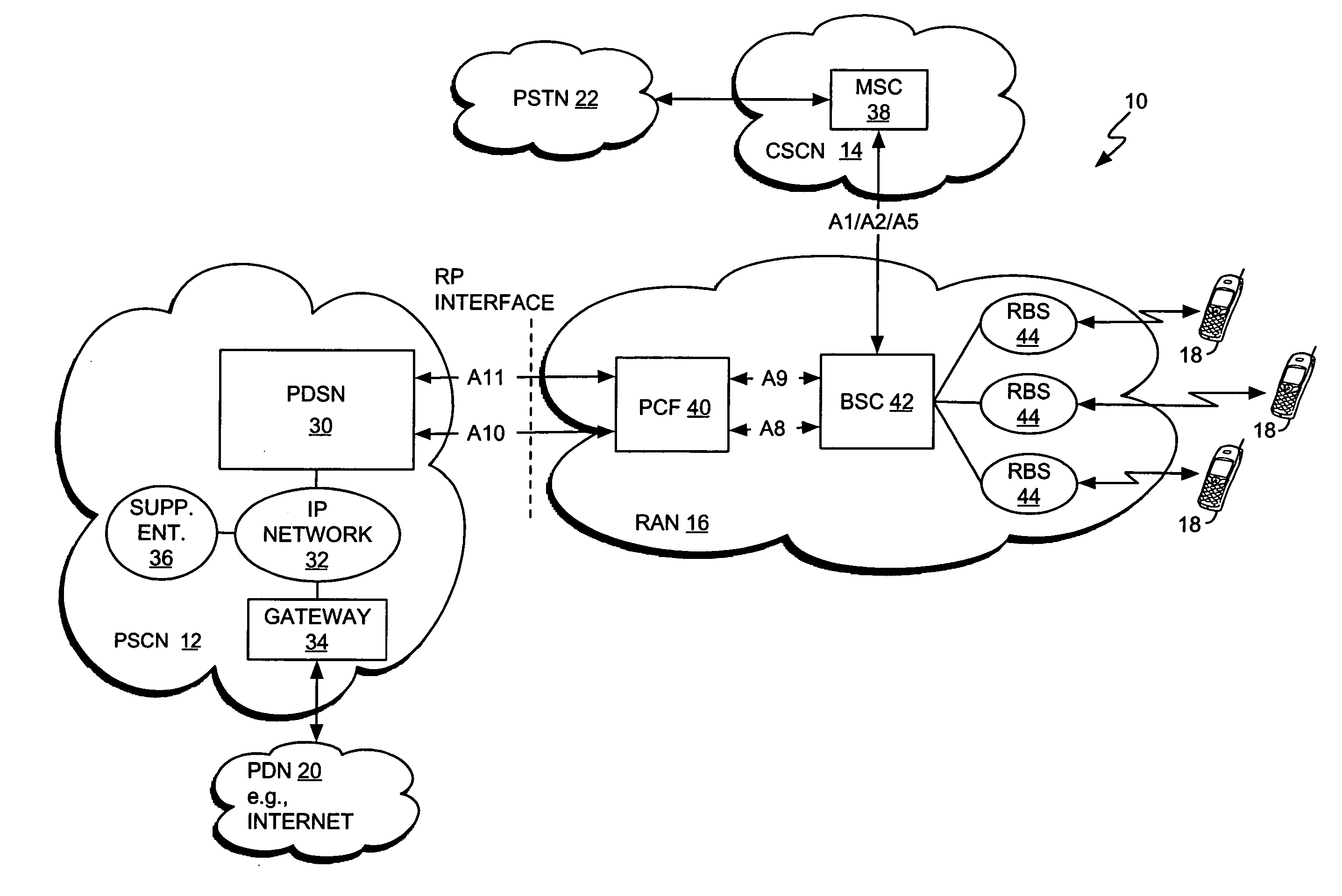
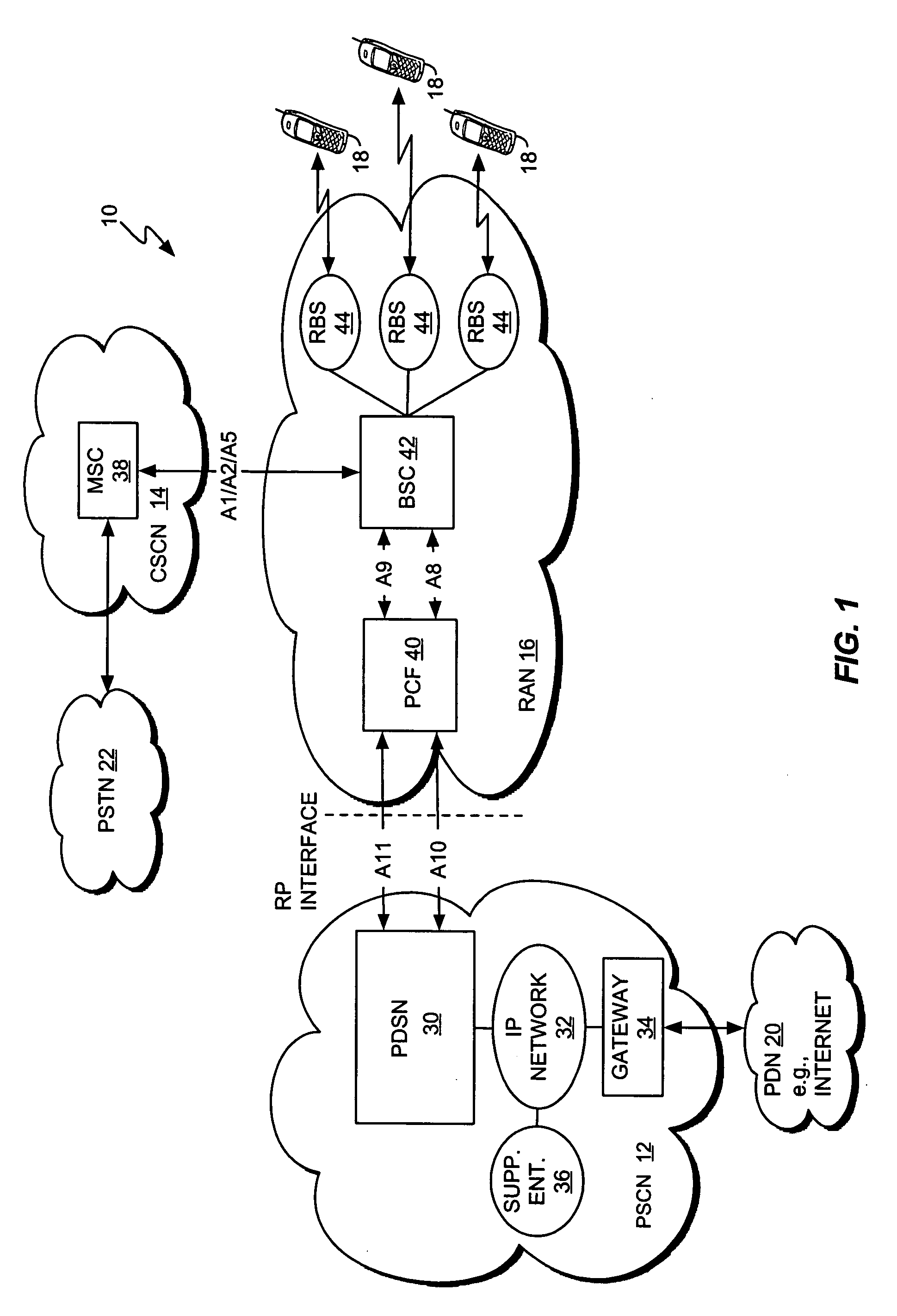
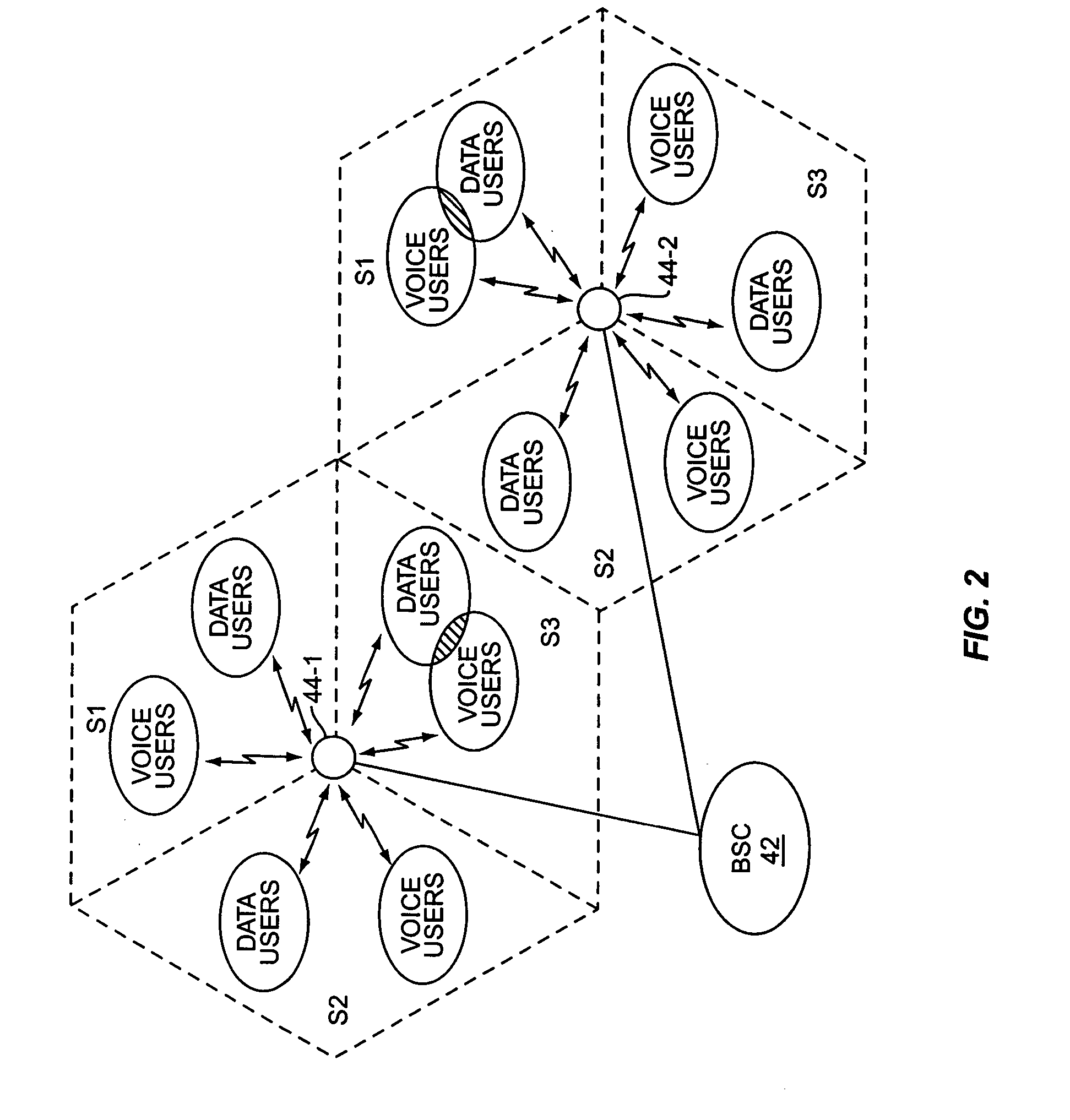
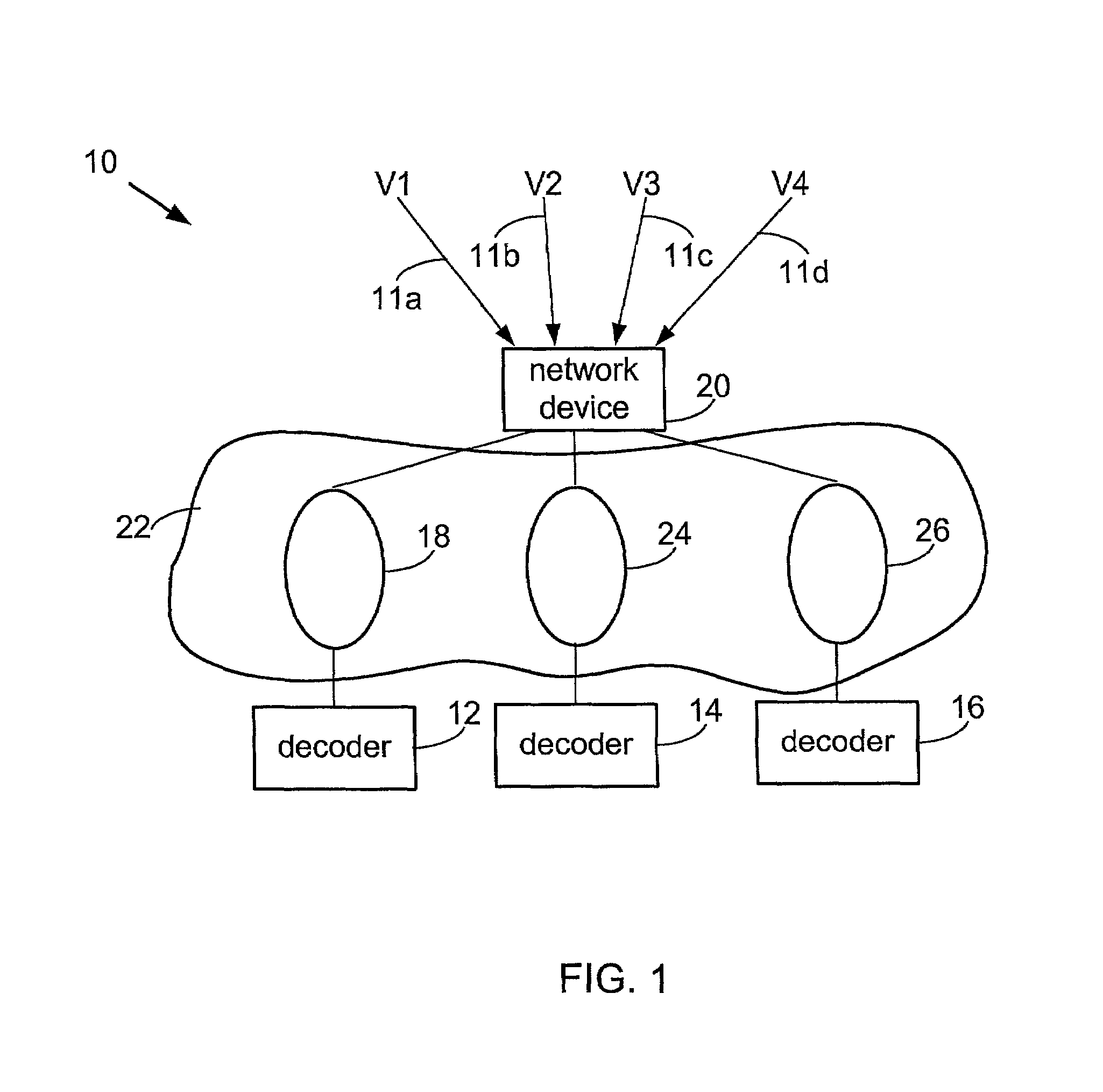
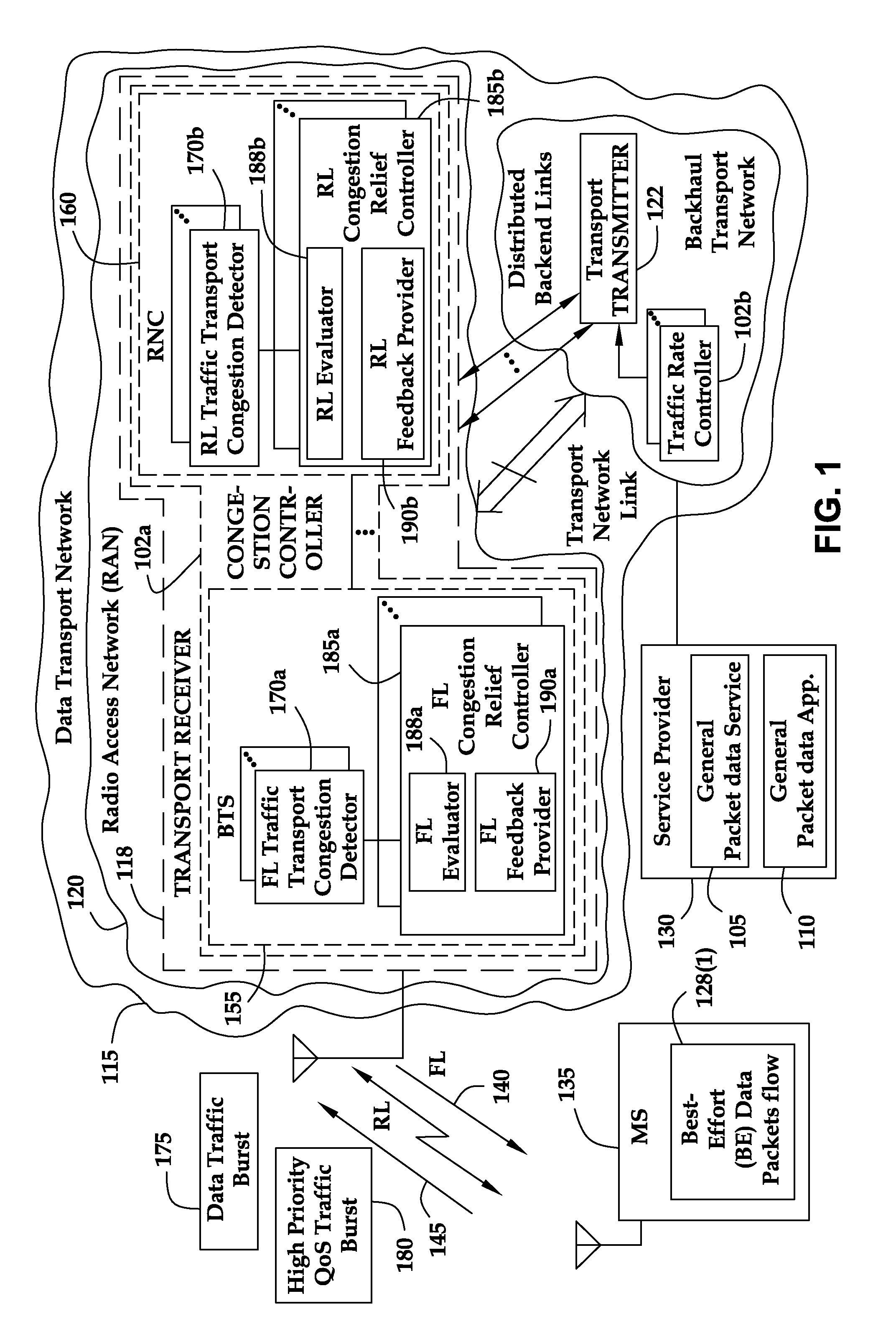
Dynamic voice over data prioritization for wireless communication networks
InactiveUS20050107091A1Reduce overheadIncrease network resource availableError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsData rateRate reduction
In a wireless communication network providing voice and data services, one or more entities in the network, such as a base station controller and / or radio base station, can be configured to reduce data services overhead responsive to detecting a congestion condition, thereby increasing the availability of one or more network resources for voice services. In one or more exemplary embodiments, one or more current data services users are targeted for modification of their ongoing data services to effect the reduction in data services overhead. Modifications can include, but are not limited to, any one or more of the following: forward or reverse link data rate reductions, and shifting of forward or reverse link traffic from dedicated user channels to shared user channels. Targeting of users for service modification can be based on reported channel quality information. For example, users reporting poor radio conditions can be targeted first for service modifications.
Owner:IDTP HLDG
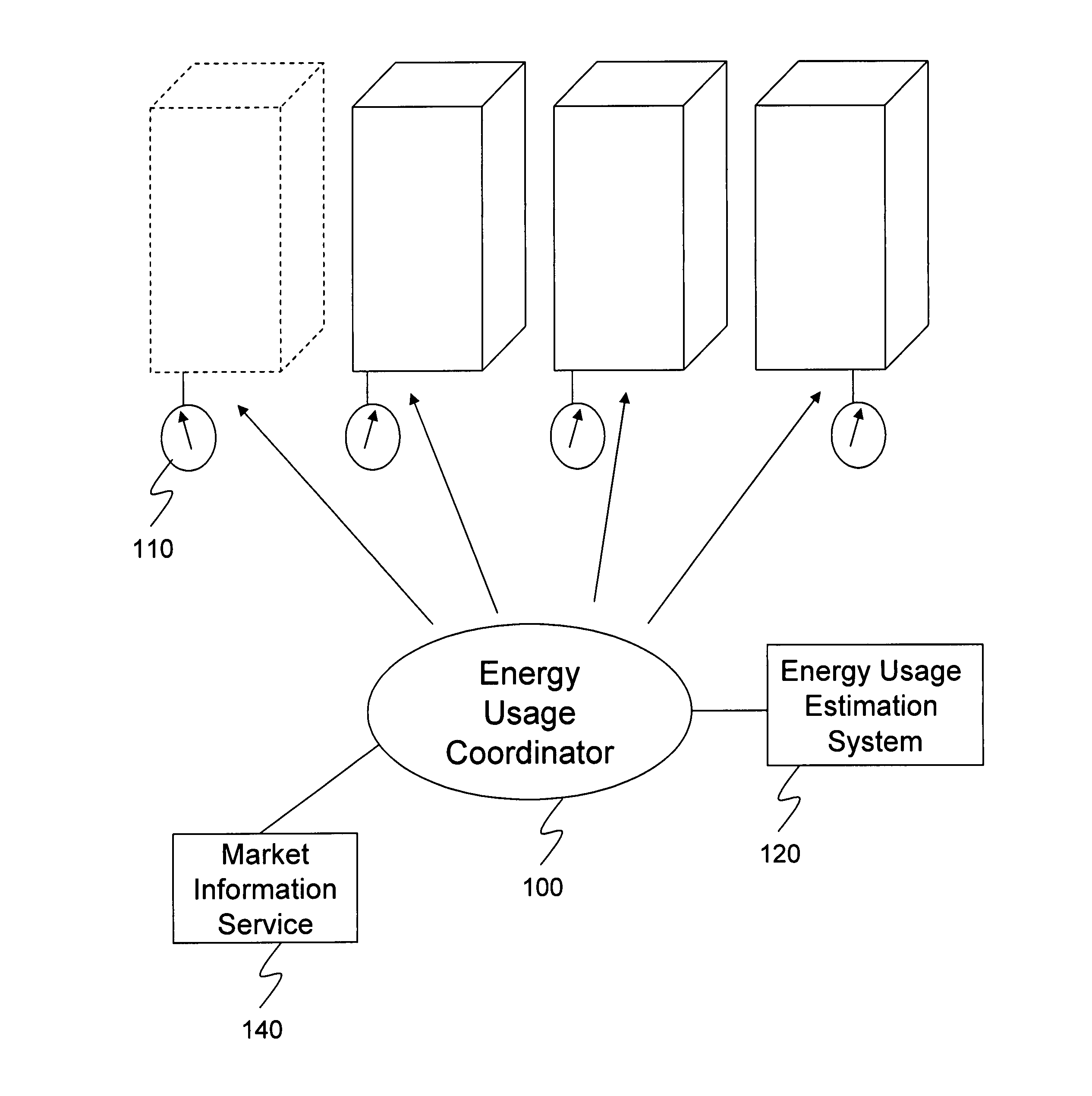
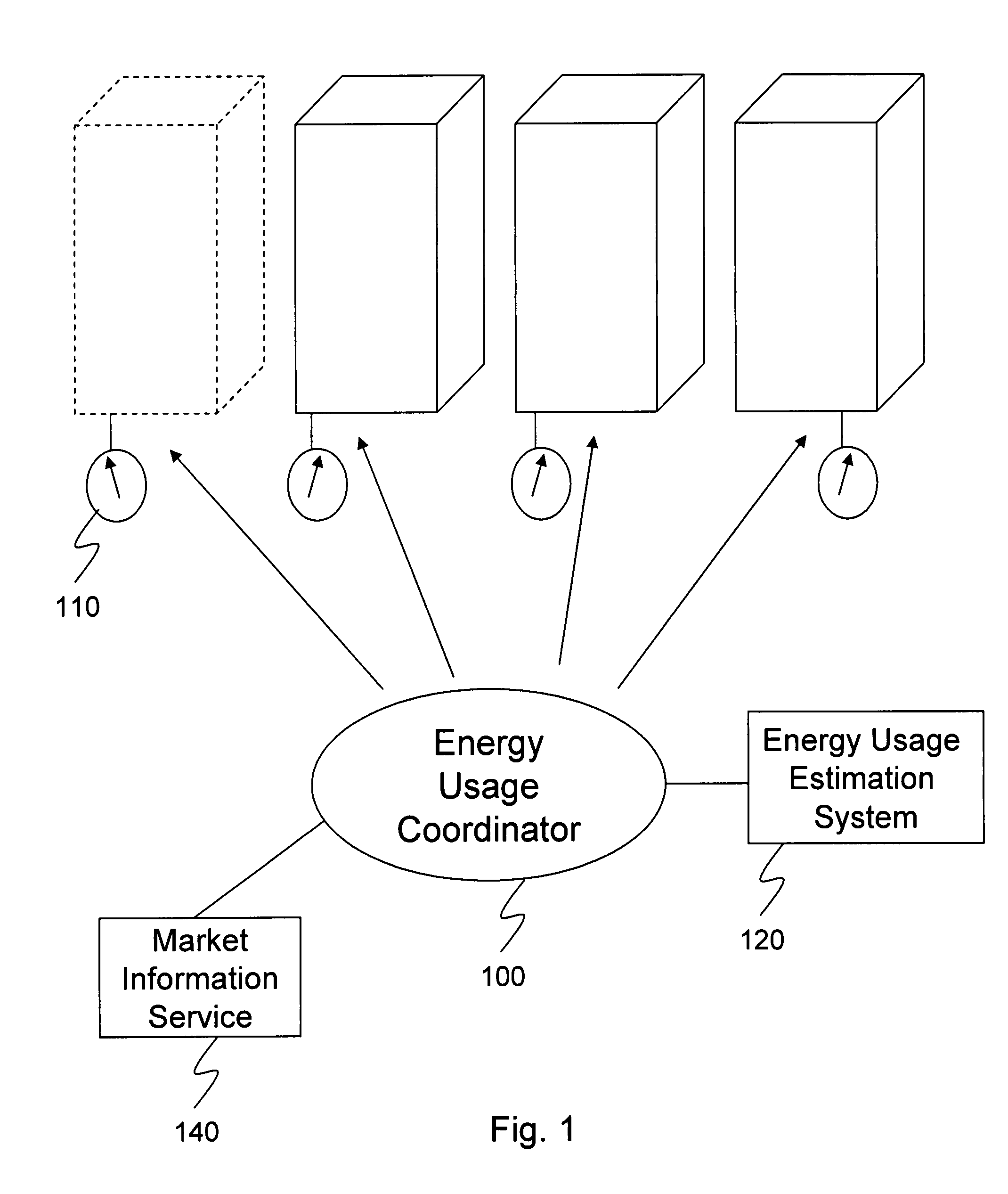
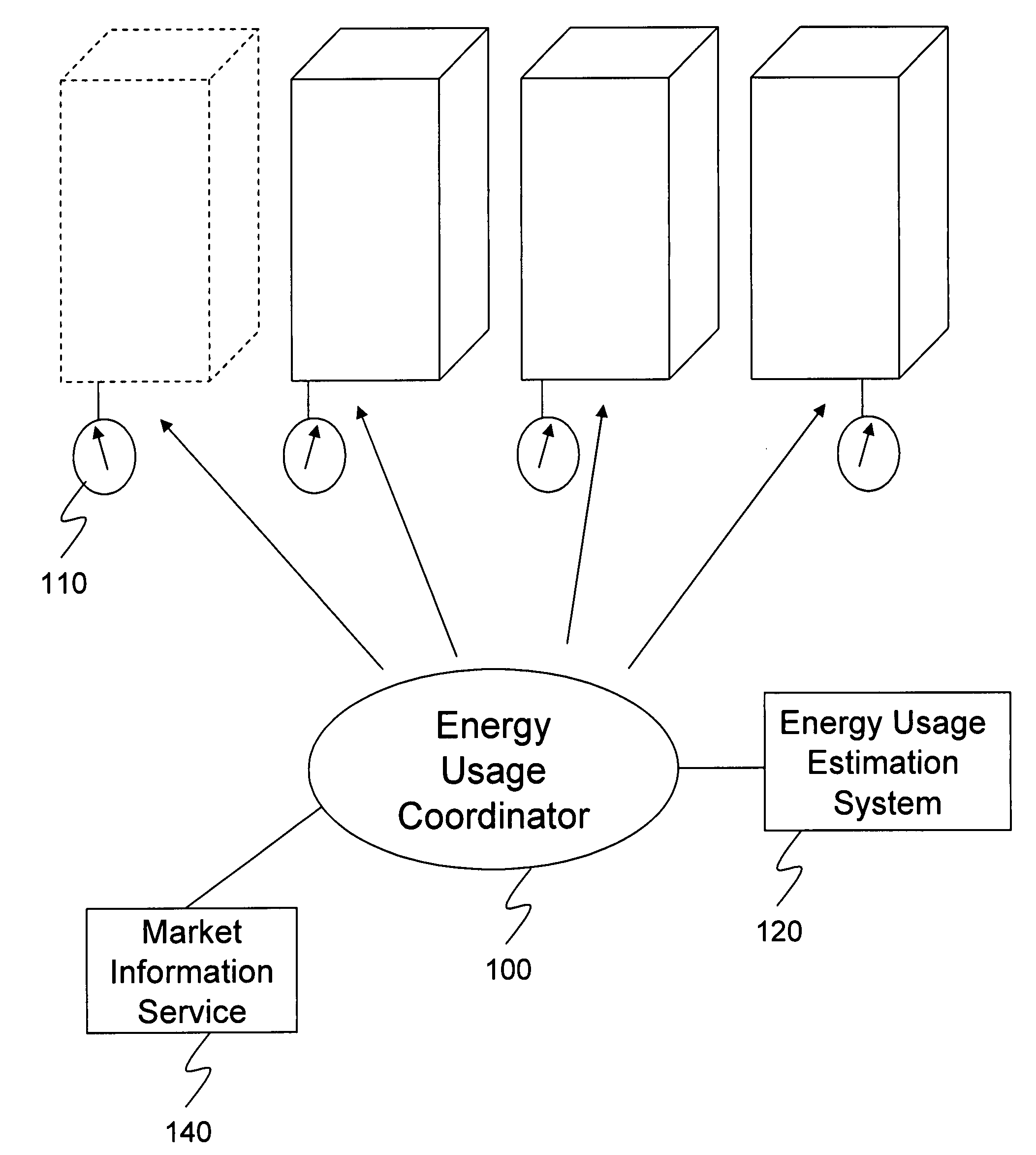
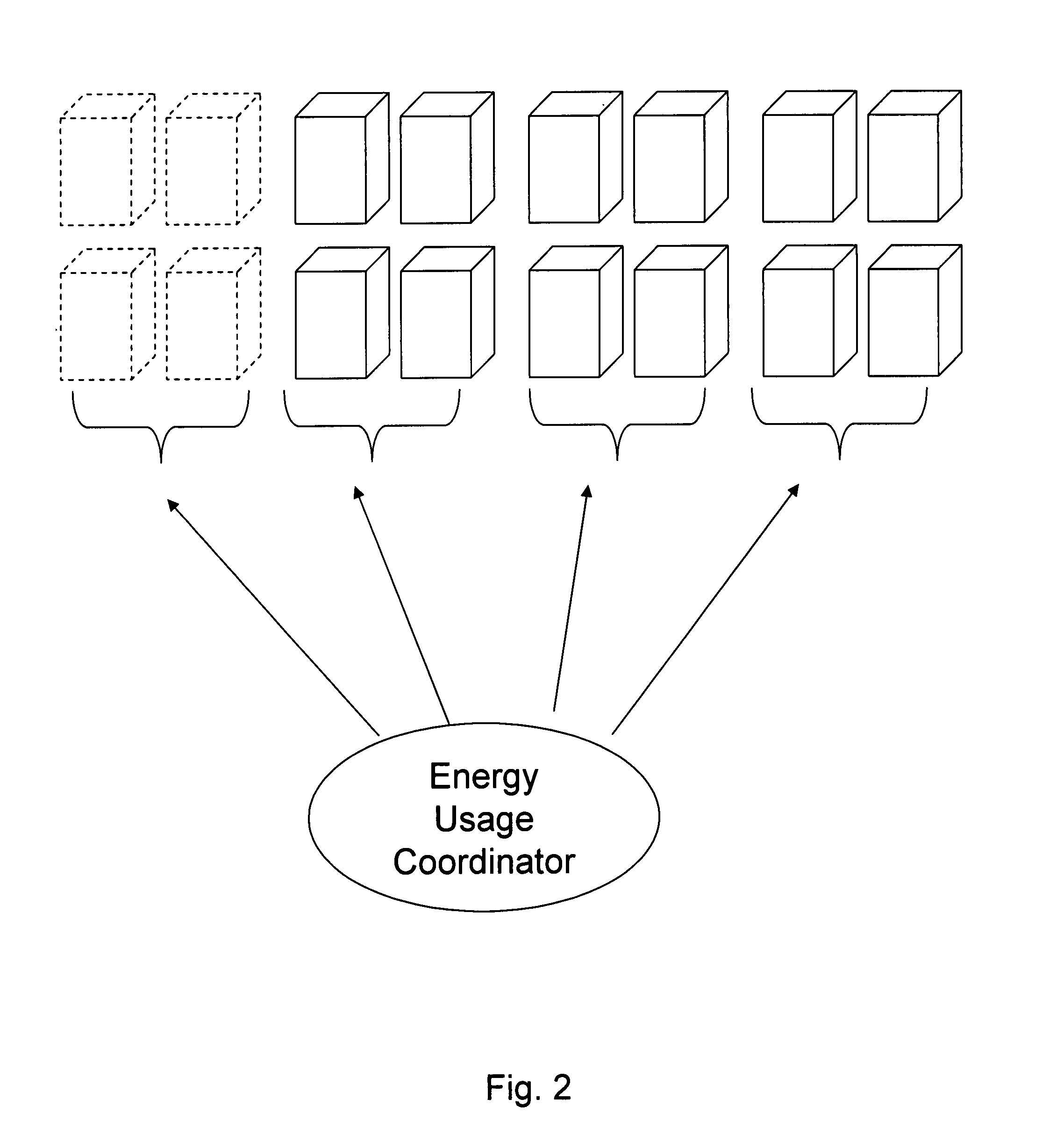
Multi-building control for demand response power usage control
An energy usage coordinator controls the energy usage of individual buildings of a group (or portfolio) of buildings in one or more load zones. These buildings have all contracted with an energy company which controls (directly or indirectly) the energy usage coordinator. By agreeing to lower energy usage during times of peak usage (when the energy company may otherwise have to pay very high prices on the spot or short term market), the owners or managers of the buildings receive a preferential energy rate from the energy company. Such a preferential rate may be in the form of a fixed rate reduction or a variable rate reduction. Alternatively, the energy company may determine that the energy is currently selling for twice what its building portfolio has contracted to pay for it so it requests some portion of the portfolio to reduce usage so that it can sell the excess / saved energy in the market.
Owner:CONSTELLATION NEWENERGY
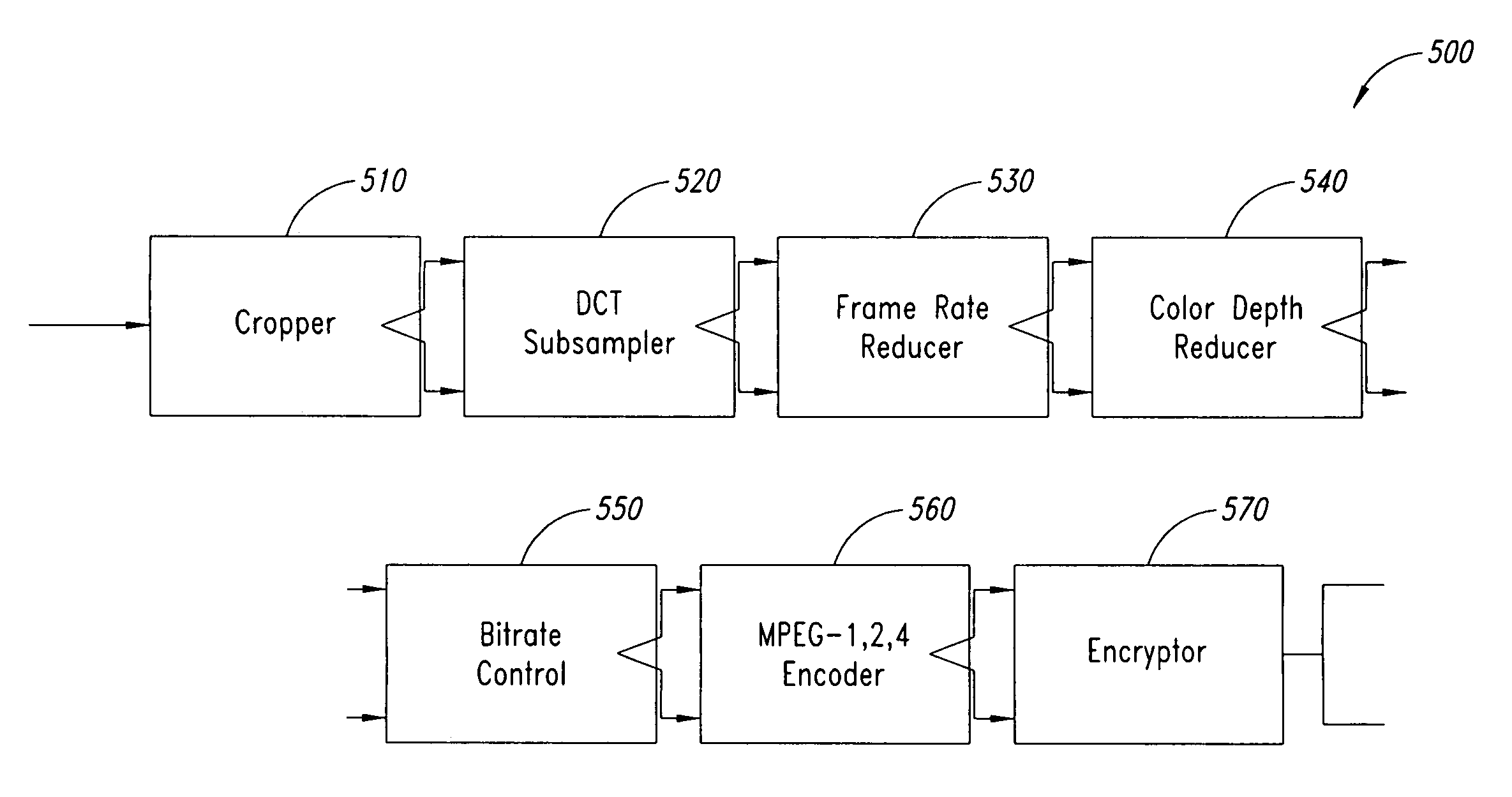
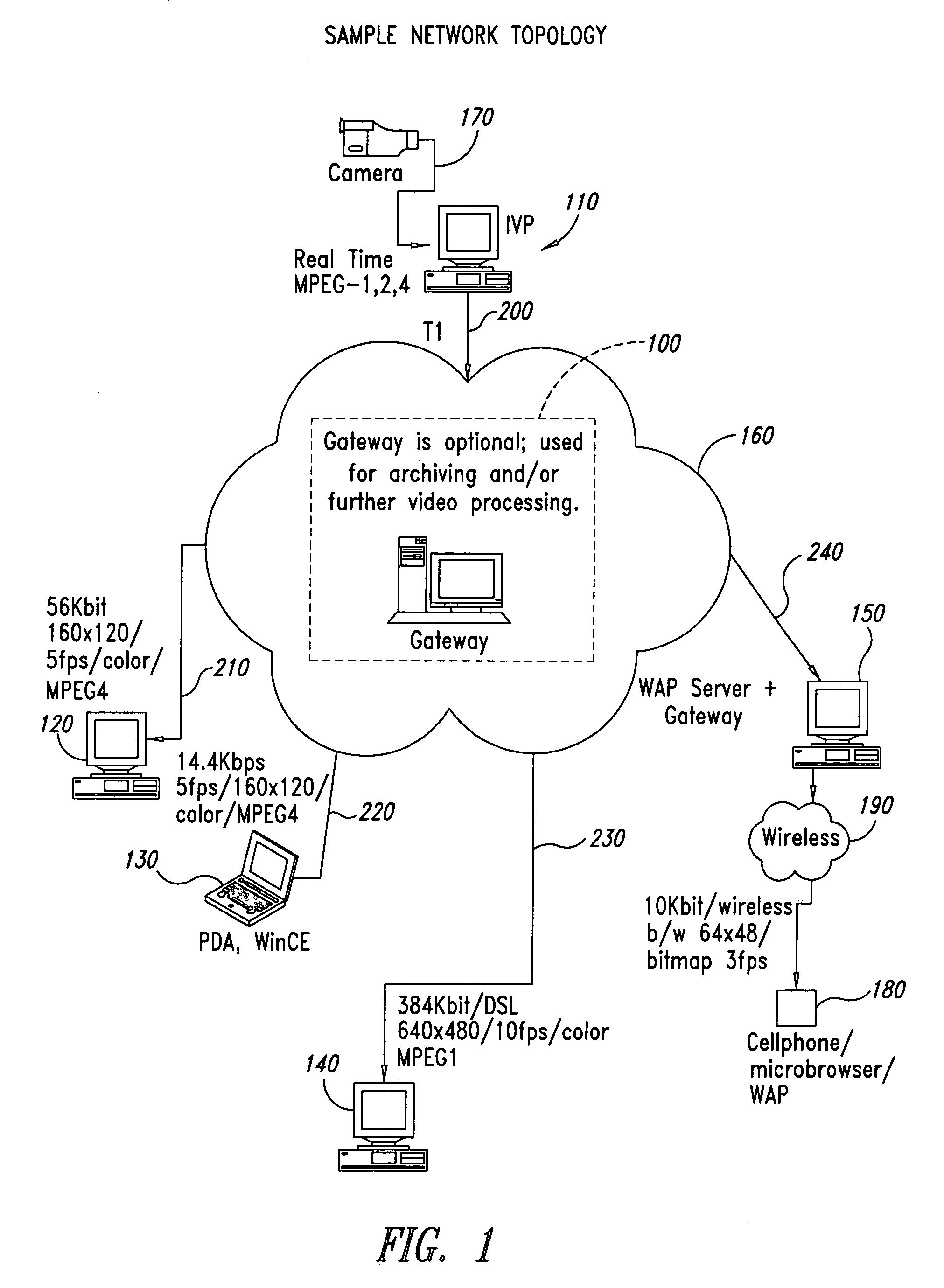
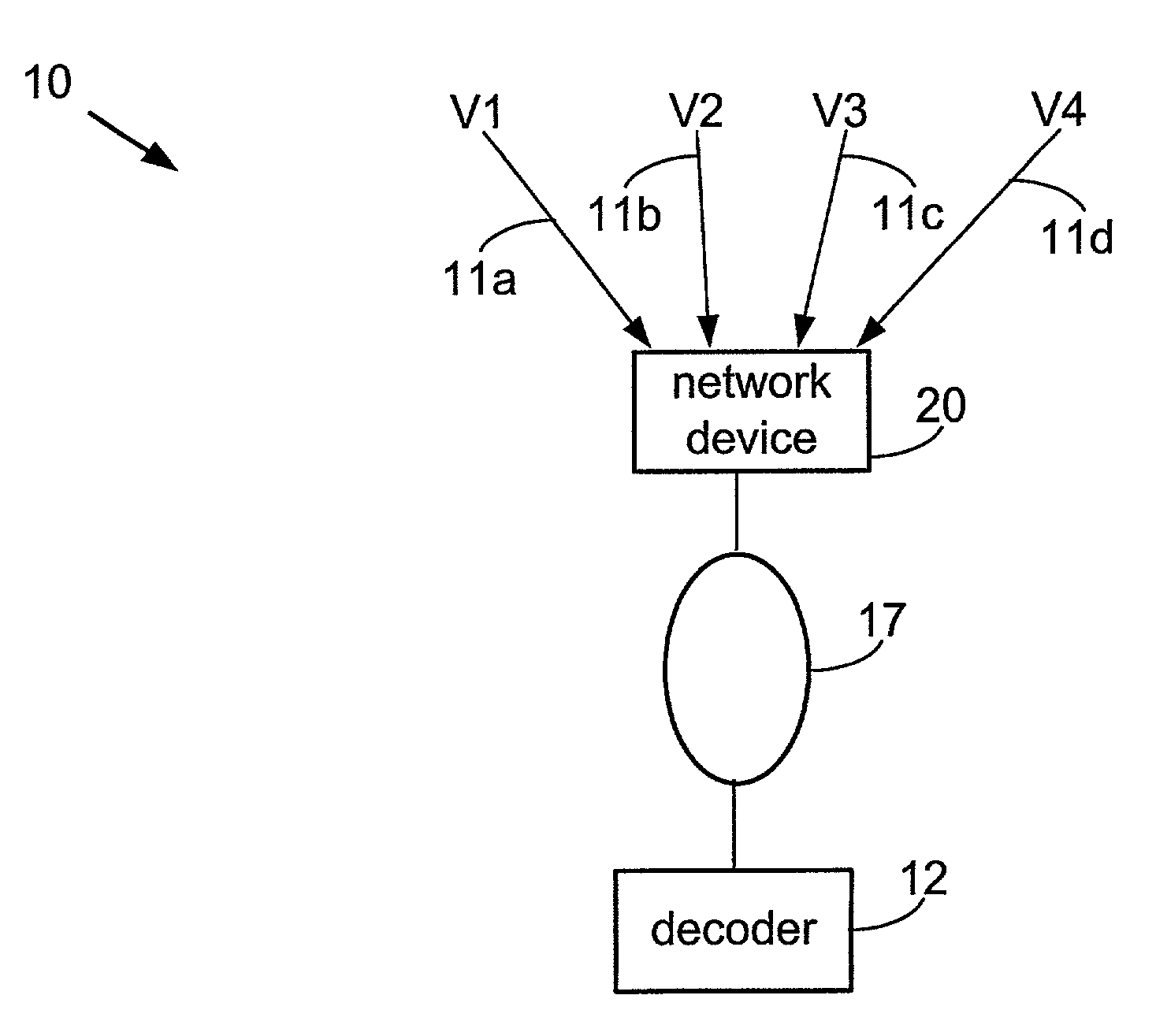
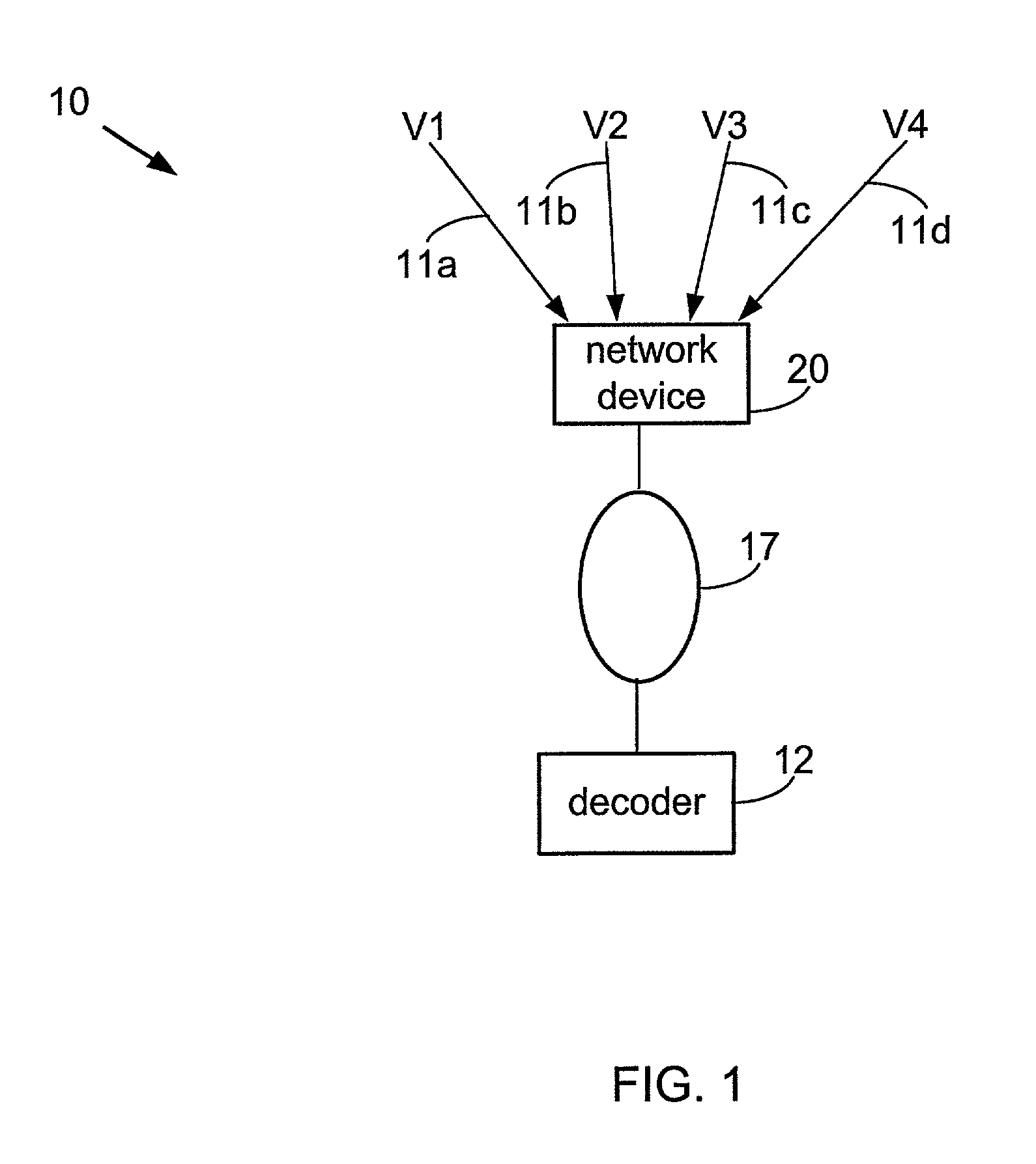
System for transforming streaming video data
InactiveUS7143432B1Decreased bit depthAttenuation bandwidthPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningImage resolutionComputer graphics (images)
According to one embodiment, a circuit configured to form an output video stream includes a resolution modification circuit configured to receive a plurality of video frames from a frame buffer, and configured to modify resolution of the plurality of video frames, when the desired resolution for the output video stream is different than a resolution of the input video stream, the plurality of frames of data derived from an input video stream, a frame reducing circuit coupled to the resolution reducing circuit configured to reduce a number of video frames in the plurality of video frames from the resolution reducing circuit, when a desired frame rate for the output video stream is different than a frame rate of the input video stream, a depth reduction circuit coupled to the frame reducing circuit configured to reduce bit depth of the plurality of video frames from the frame reducing circuit, when a desired bit depth for the output video stream is different than a bit depth of the input video stream, and a rate reduction circuit coupled to the depth reduction circuit, configured to scale the plurality of video frames from the depth reduction circuit, in response to a desired bit rate for the output video stream, and an encoder coupled to the rate reduction circuit, configured to encode the plurality of video frames from the rate reduction circuit into the output video stream is also contemplated.
Owner:ADAPTIVE STREAMING INC
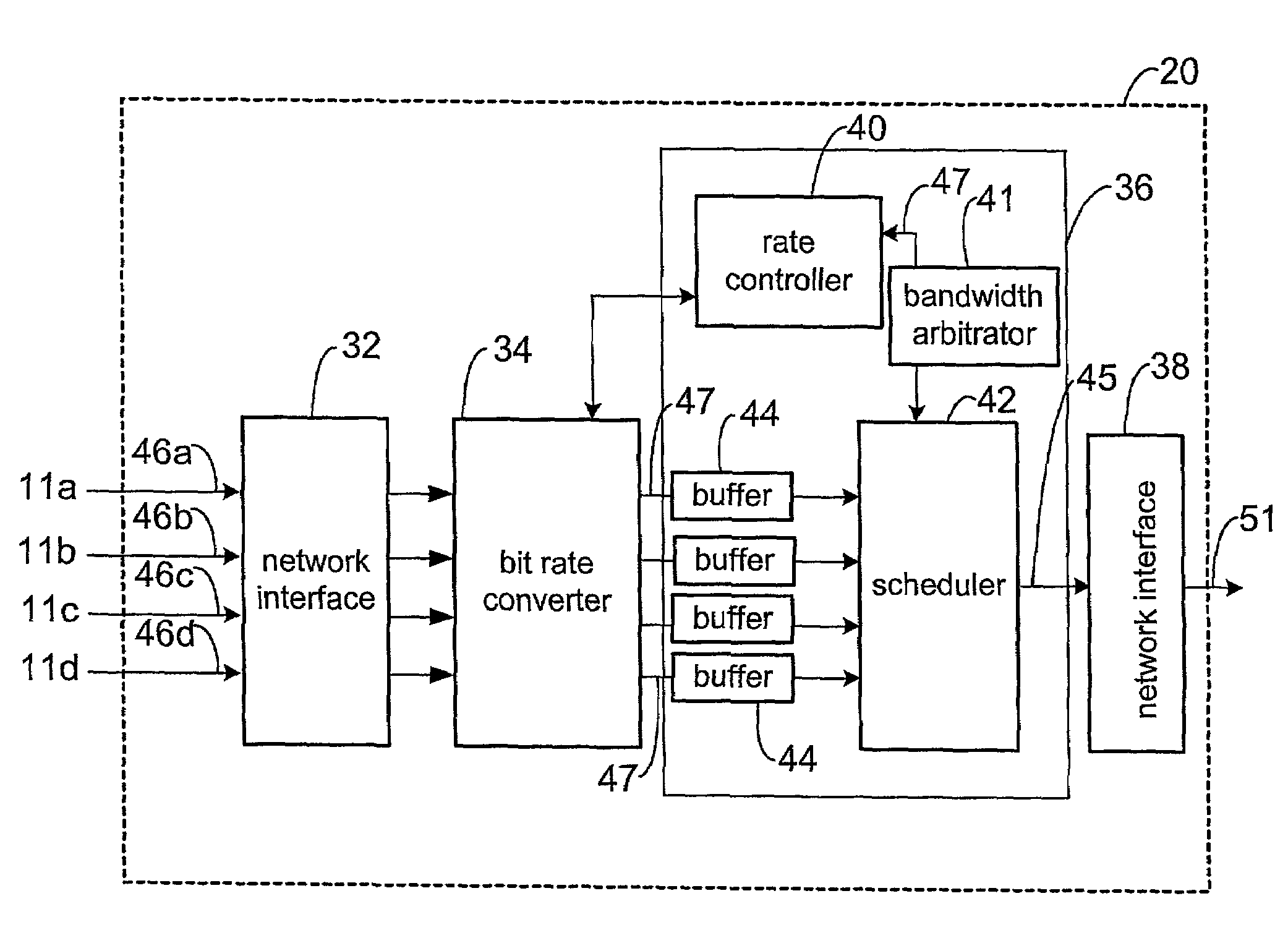
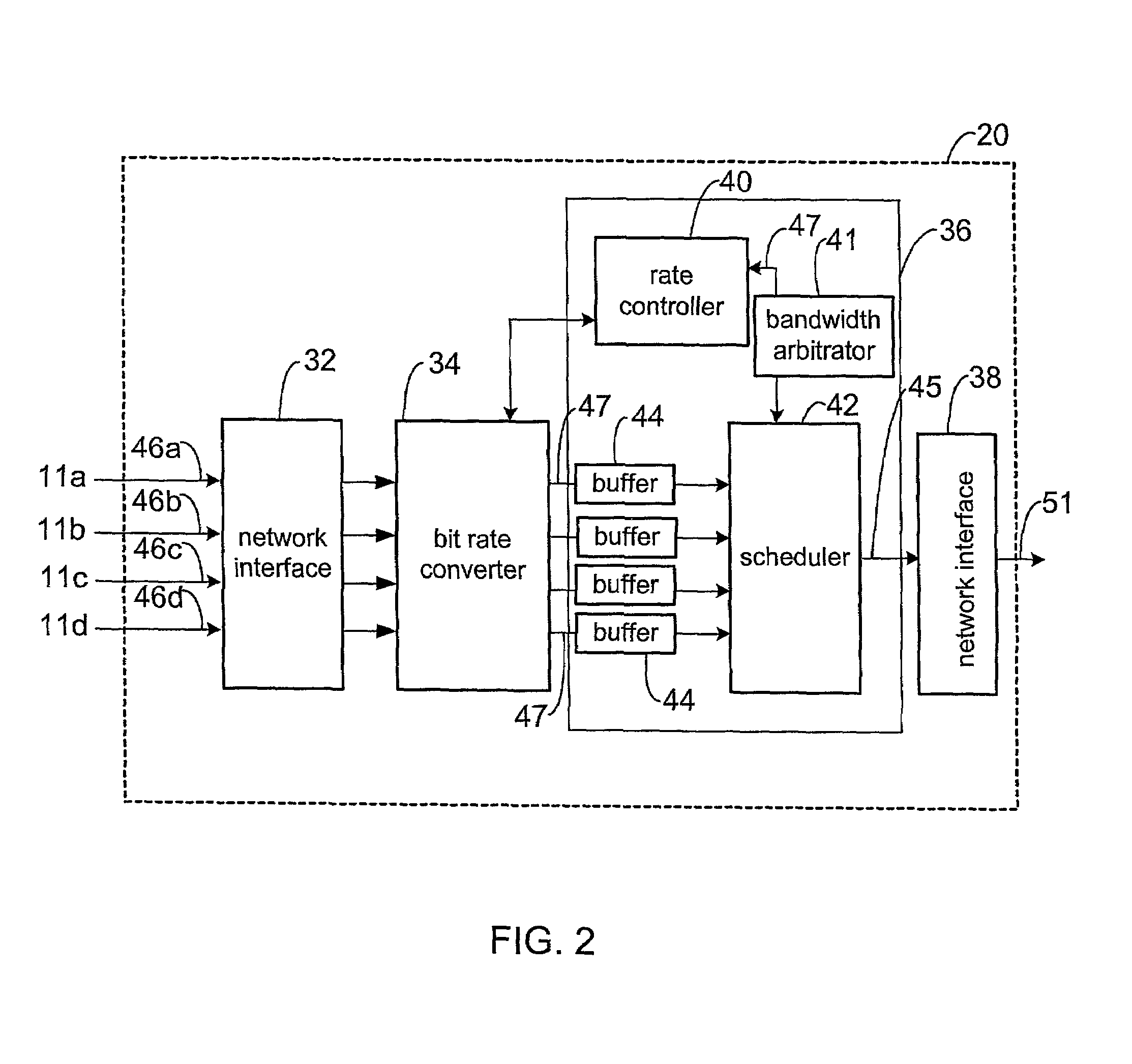
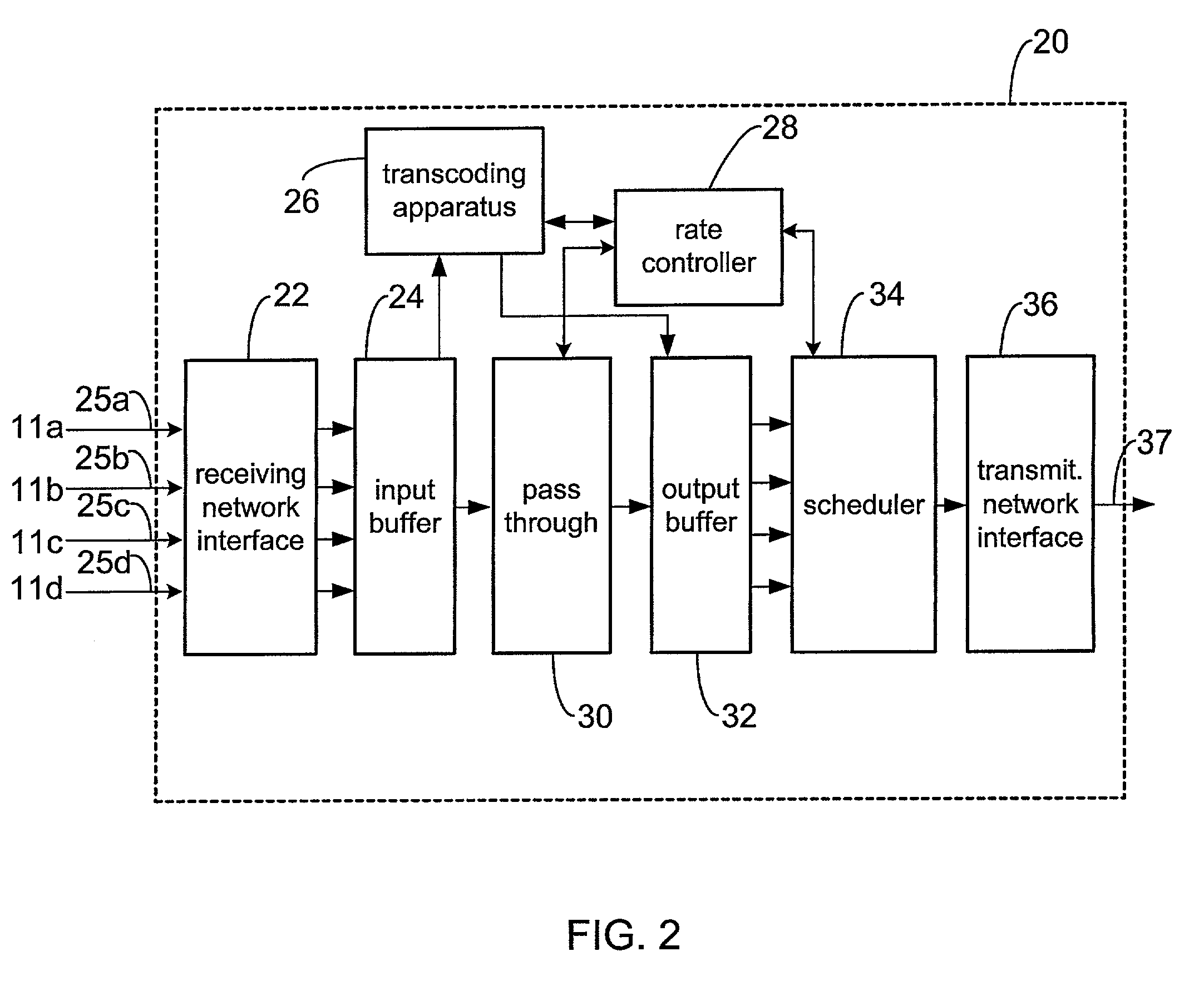
Efficient available bandwidth usage in transmission of compressed video data
InactiveUS7292602B1Minimizing rateIncrease downstream decoder buffer levelColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMultiplexingVideo transmission
Described herein are systems and methods for multiplexing and transmitting video data. The systems and methods use excess bandwidth in a channel available after meeting minimum transmission requirements for all bitstreams. A network device of the invention flexibly allocates this available bandwidth to minimize further rate reduction. More specifically, the network device periodically determines the available bandwidth, and divides the available bandwidth among multiple incoming bitstreams being multiplexed in order to increase downstream decoder buffer levels. By maintaining increased decoder buffer levels, future rate reduction of the video data may be avoided or applied to a lesser degree. Minimizing rate reduction in this manner improves bandwidth usage efficiency, and thus improves video data transmission and end-user output video quality.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
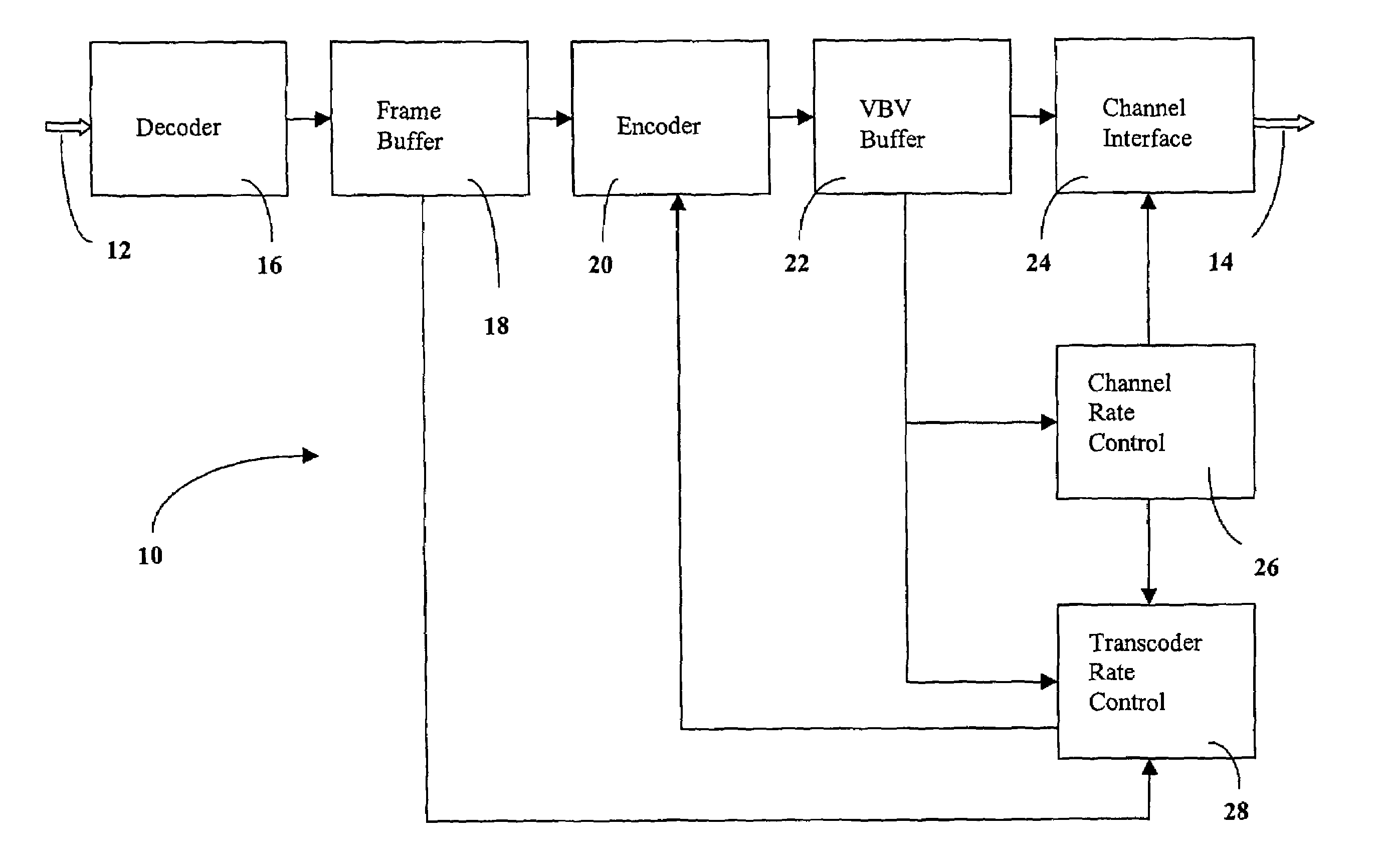
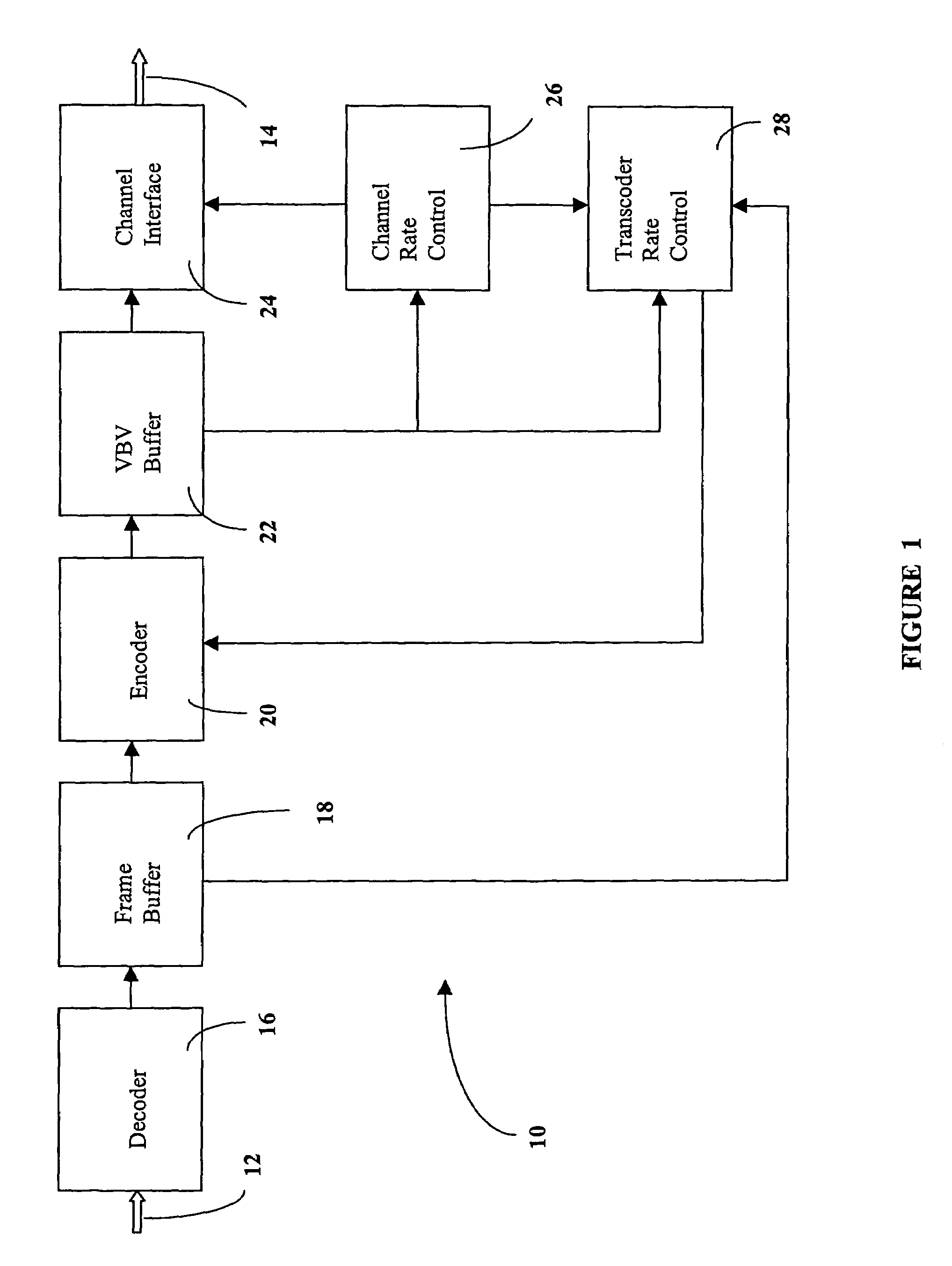
Rate control method for video transcoding
InactiveUS7170938B1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureTranscoding
The present invention discloses a system and method for rate control of MPEG video streams to achieve a target bit rate in a transcoder at the best visual quality possible. The invention monitors video buffer fullness for selecting the amount of rate reduction necessary to achieve a target bit rate. The invention also utilizes a method for selective requantization of DCT coefficients to assure visual quality.
Owner:CISCO SYST CANADA
System, apparatus, and method for uplink resource allocation
InactiveUS20060120321A1Easy to useIncrease data rateNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionTelecommunicationsHigh rate
A system, method and apparatus for managing uplink radio resources. The RRAM employs selective rate reduction to ensure resources for subscriber stations depending on individual QoS requirements. In response to a request for a new DDCH, the RRAM can drop a subscriber station at a low data rate and no media reservations. In response to traffic measurement reports from the subscriber stations, the RRAM attempts to increase or decrease the data rate of a subscriber station. When there are insufficient uplink resources, RRAM tries to lower the rate of a higher rate subscriber station. Searching for subscriber stations to lower, RRAM starts at the highest rate and continues to search lower data rates until a suitable candidate is found. RRAM also reserves resources for subscriber stations that will not be reallocated to other subscriber stations.
Owner:WI LAN INC
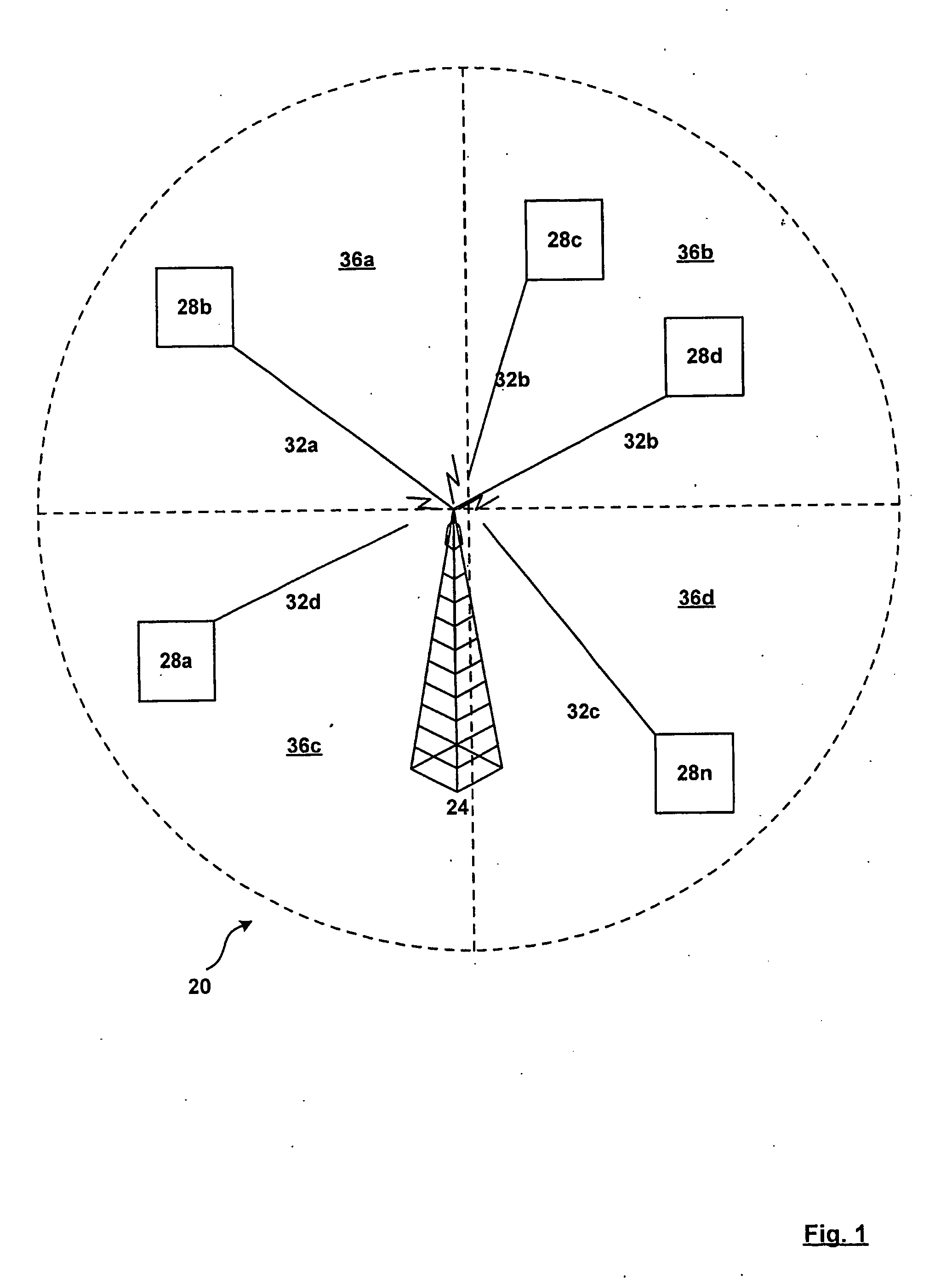
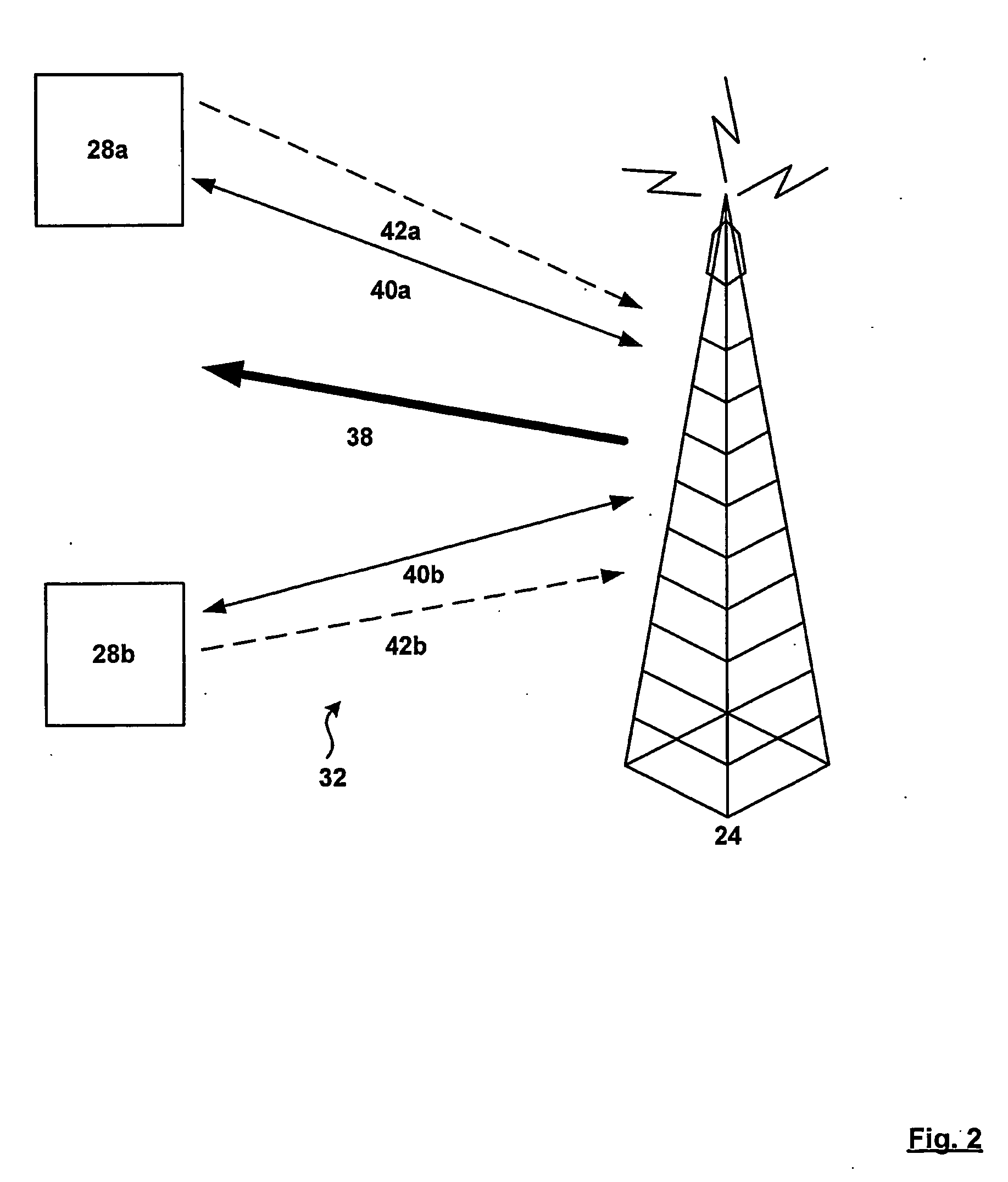
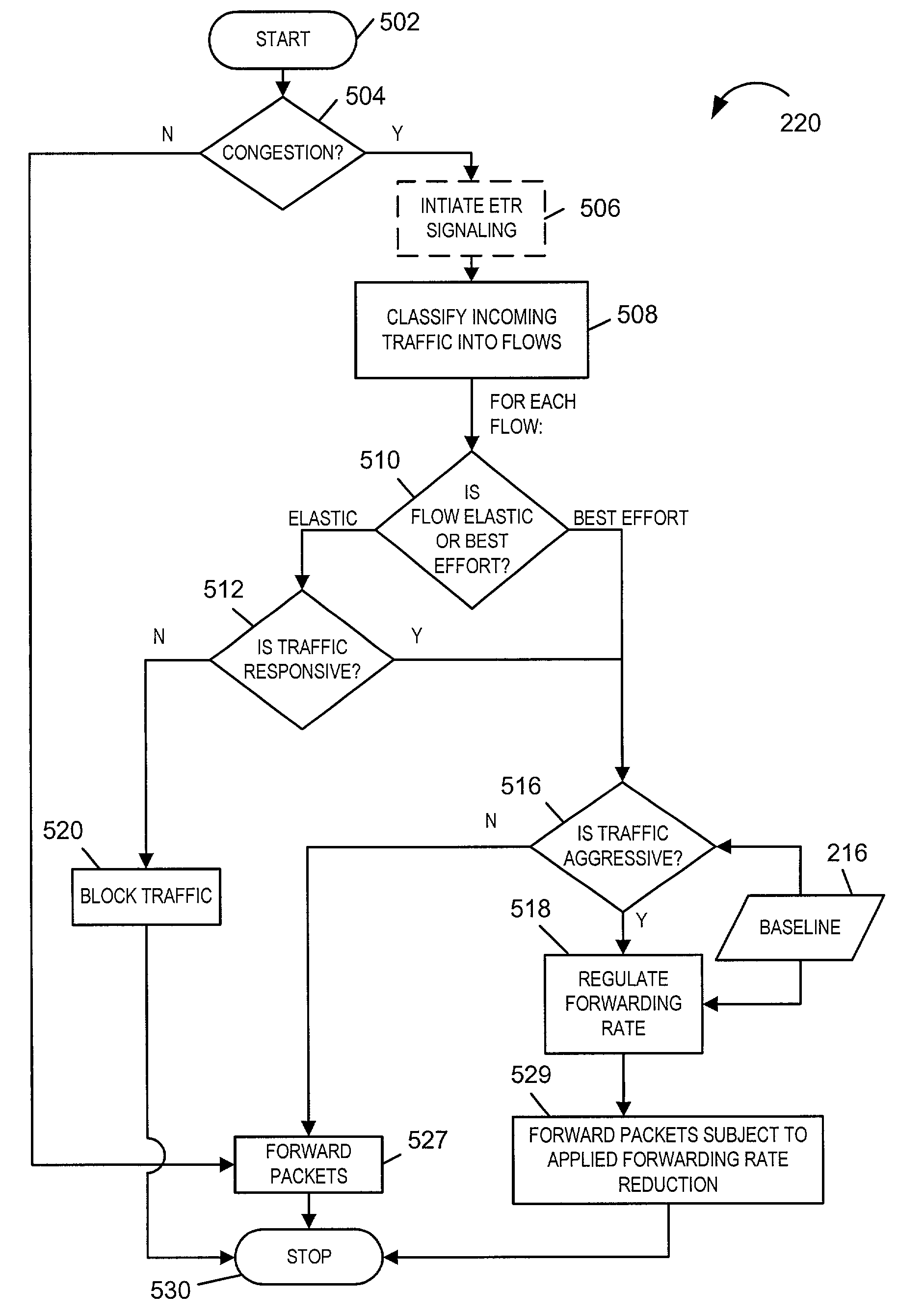
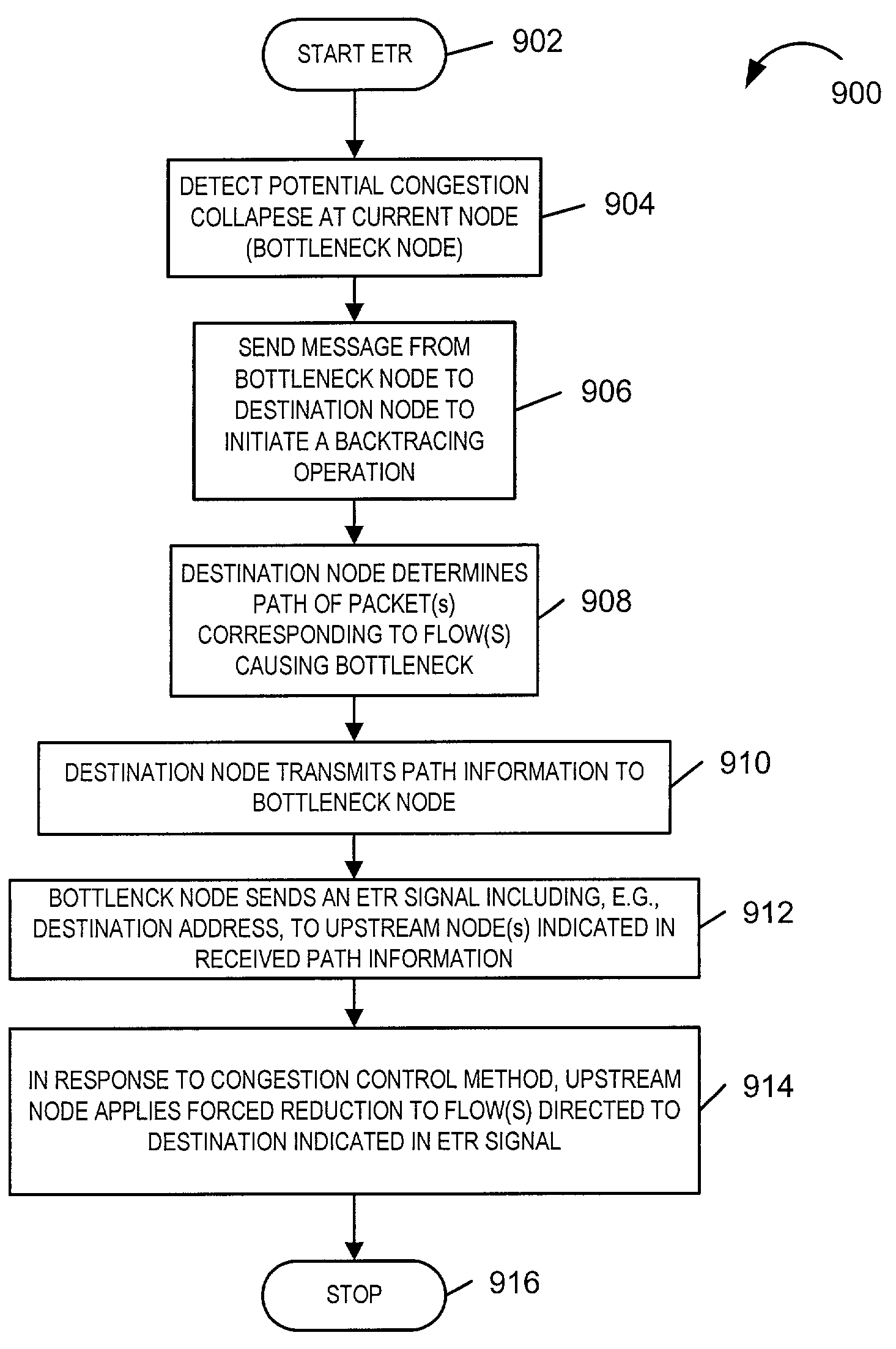
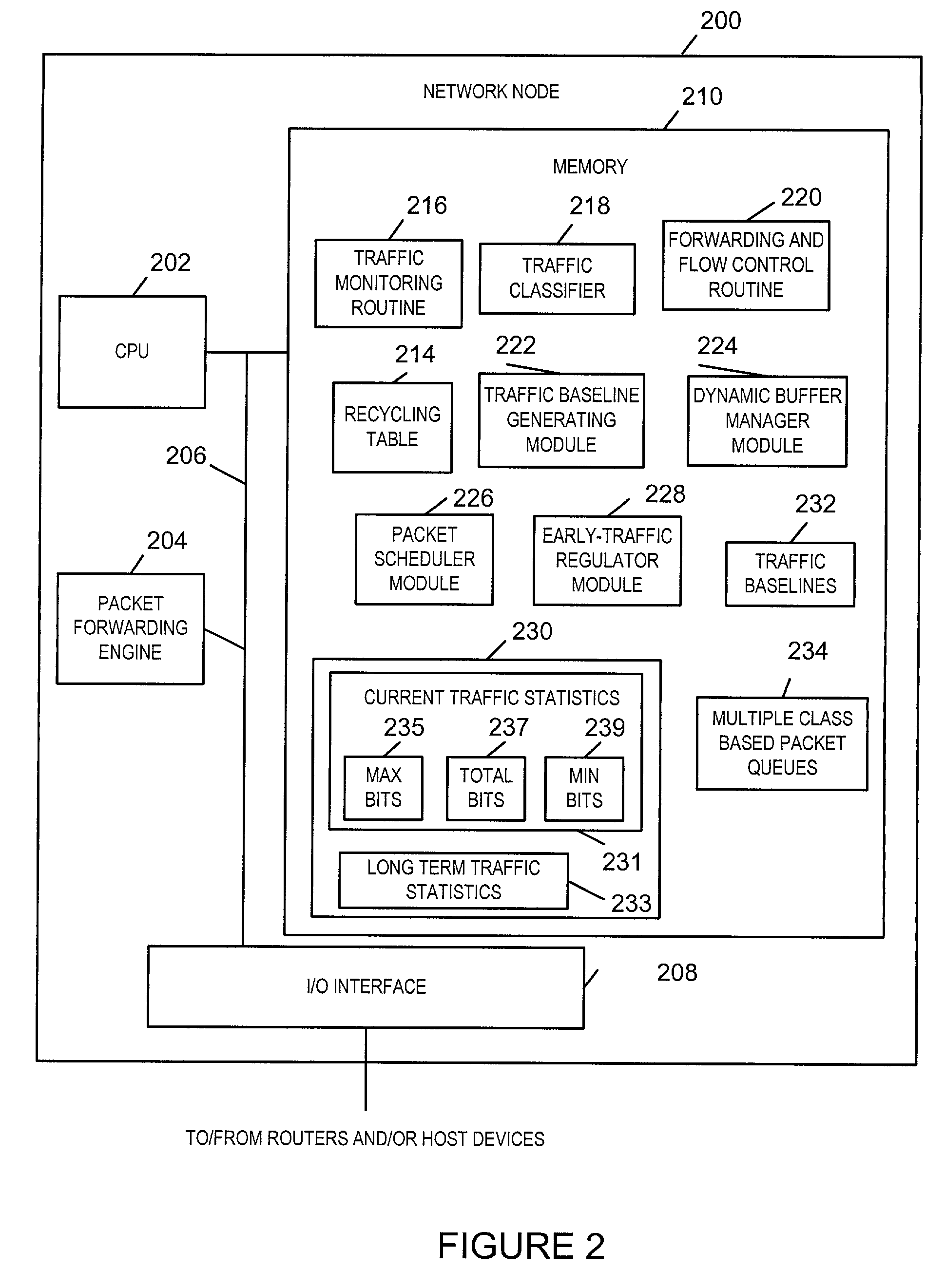
Anti-flooding flow-control methods and apparatus
ActiveUS7092357B1Reducing flow of trafficReduce processing burdenError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityData stream
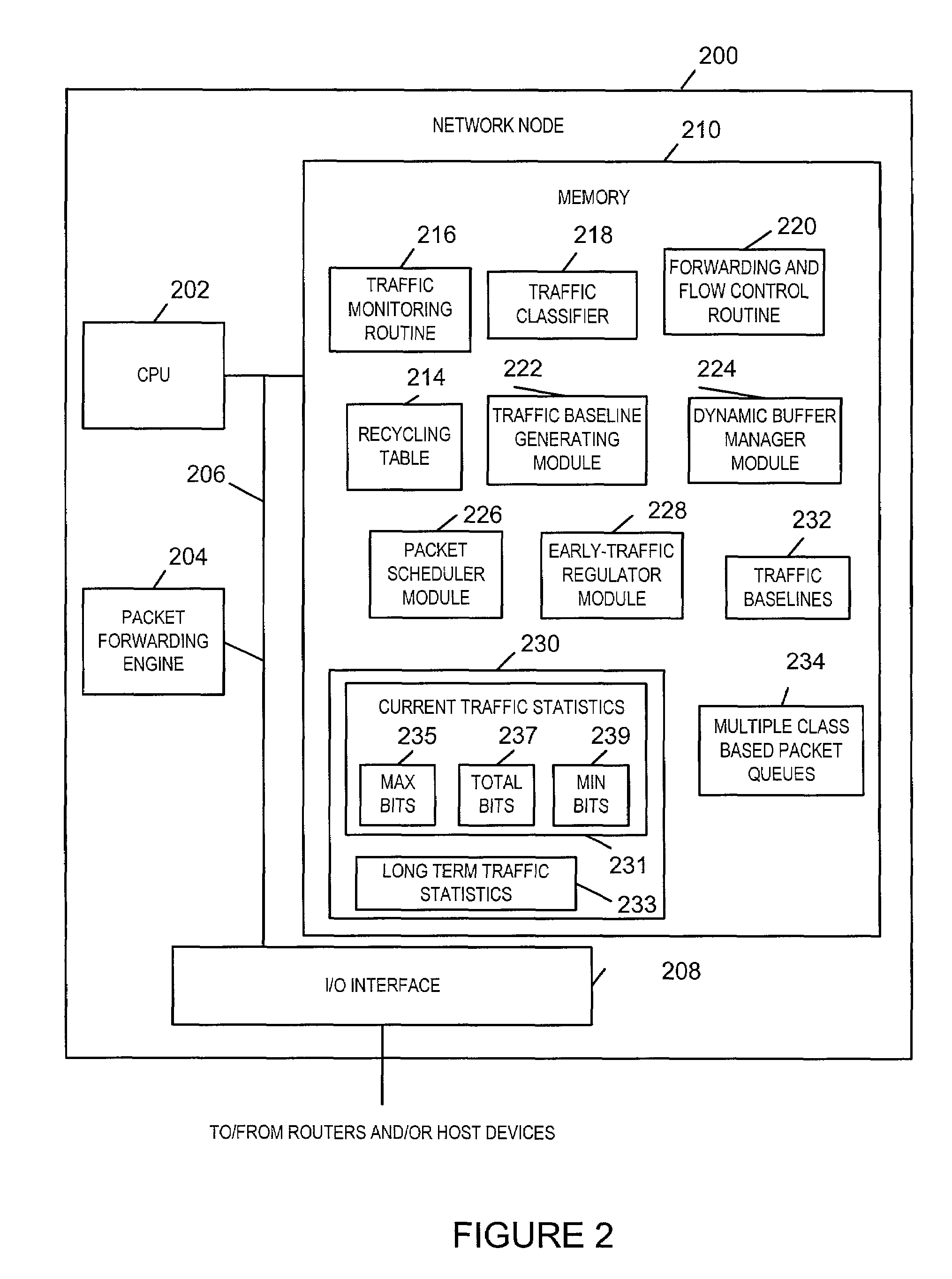
Methods and apparatus for providing an Anti-Flooding Flow-Control (AFFC) mechanism suitable for use in defending against flooding network Denial-of-Service (N-DoS) attacks is described. Features of the AFFC mechanism include (1) traffic baseline generation, (2) dynamic buffer management, (3) packet scheduling, and (4) optional early traffic regulation. Baseline statistics on the flow rates for flows of data corresponding to different classes of packets are generated. When a router senses congestion, it activates the AFFC mechanism of the present invention. Traffic flows are classified. Elastic traffic is examined to determine if it is responsive to flow control signals. Flows of non-responsive elastic traffic is dropped. The remaining flows are compared to corresponding class baseline flow rates. Flows exceeding the baseline flow rates are subject to forced flow rate reductions, e.g., dropping of packets.
Owner:PALO ALTO NETWORKS INC
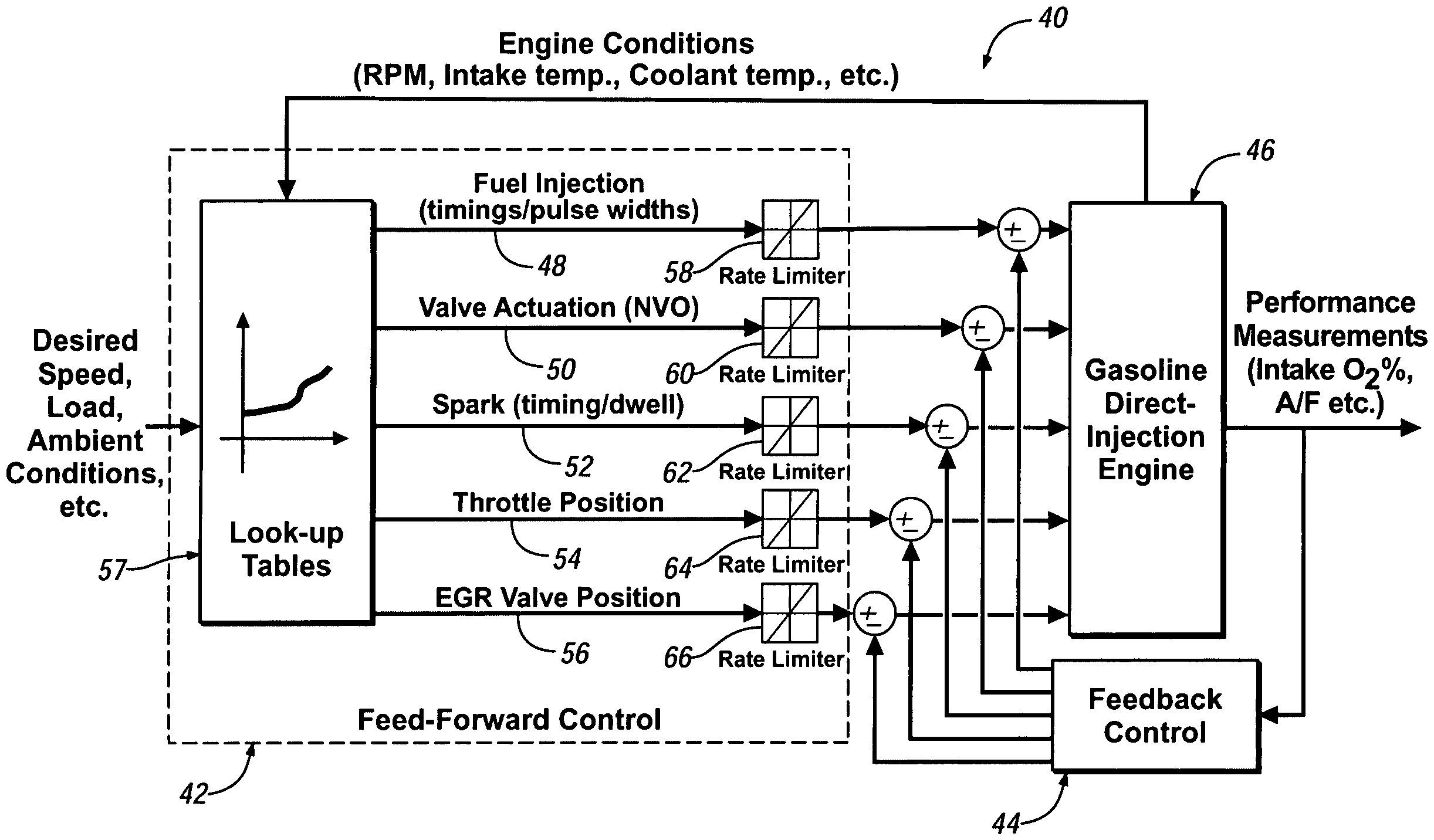
Load transient control methods for direct-injection engines with controlled auto-ignition combustion
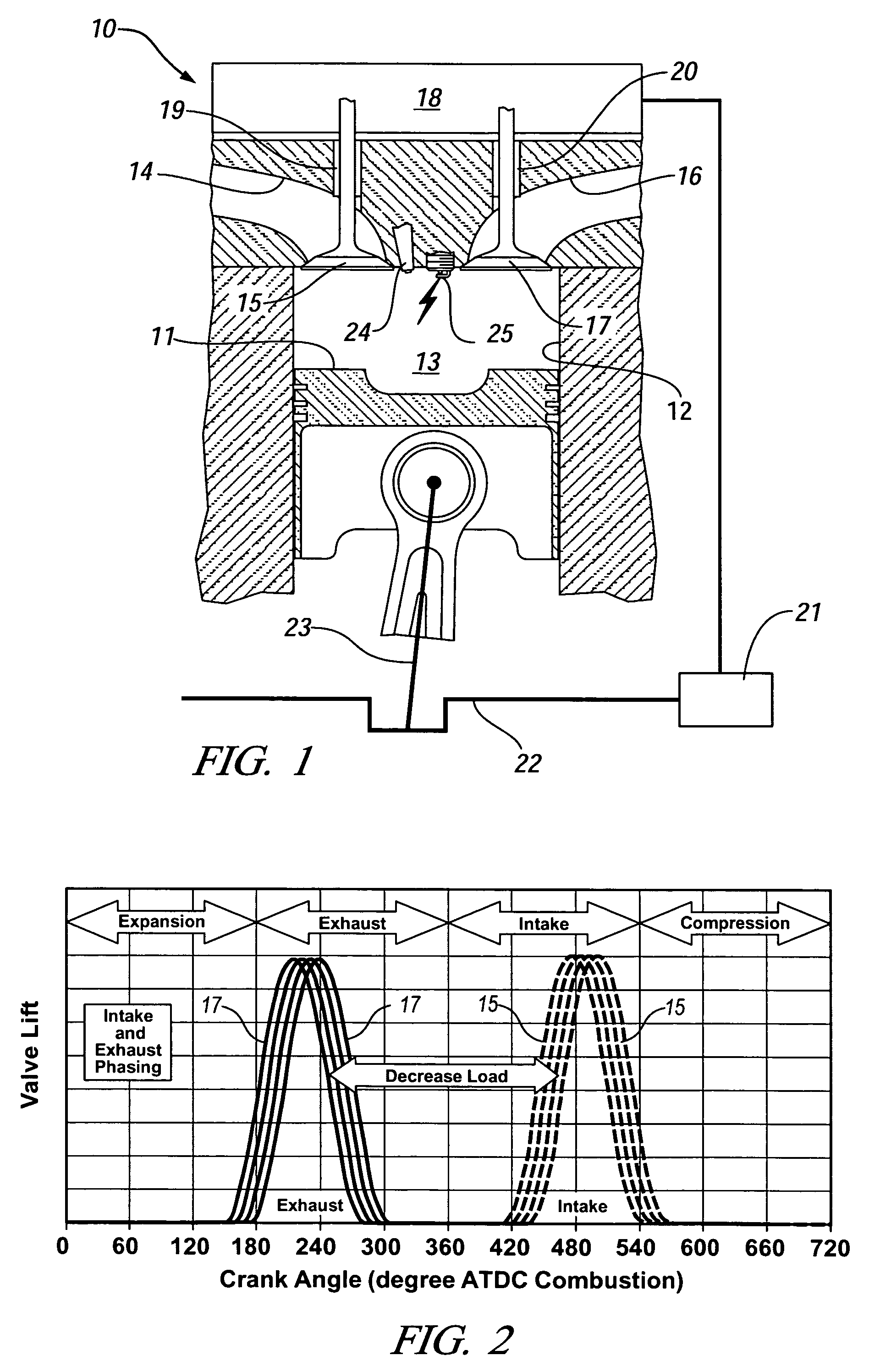
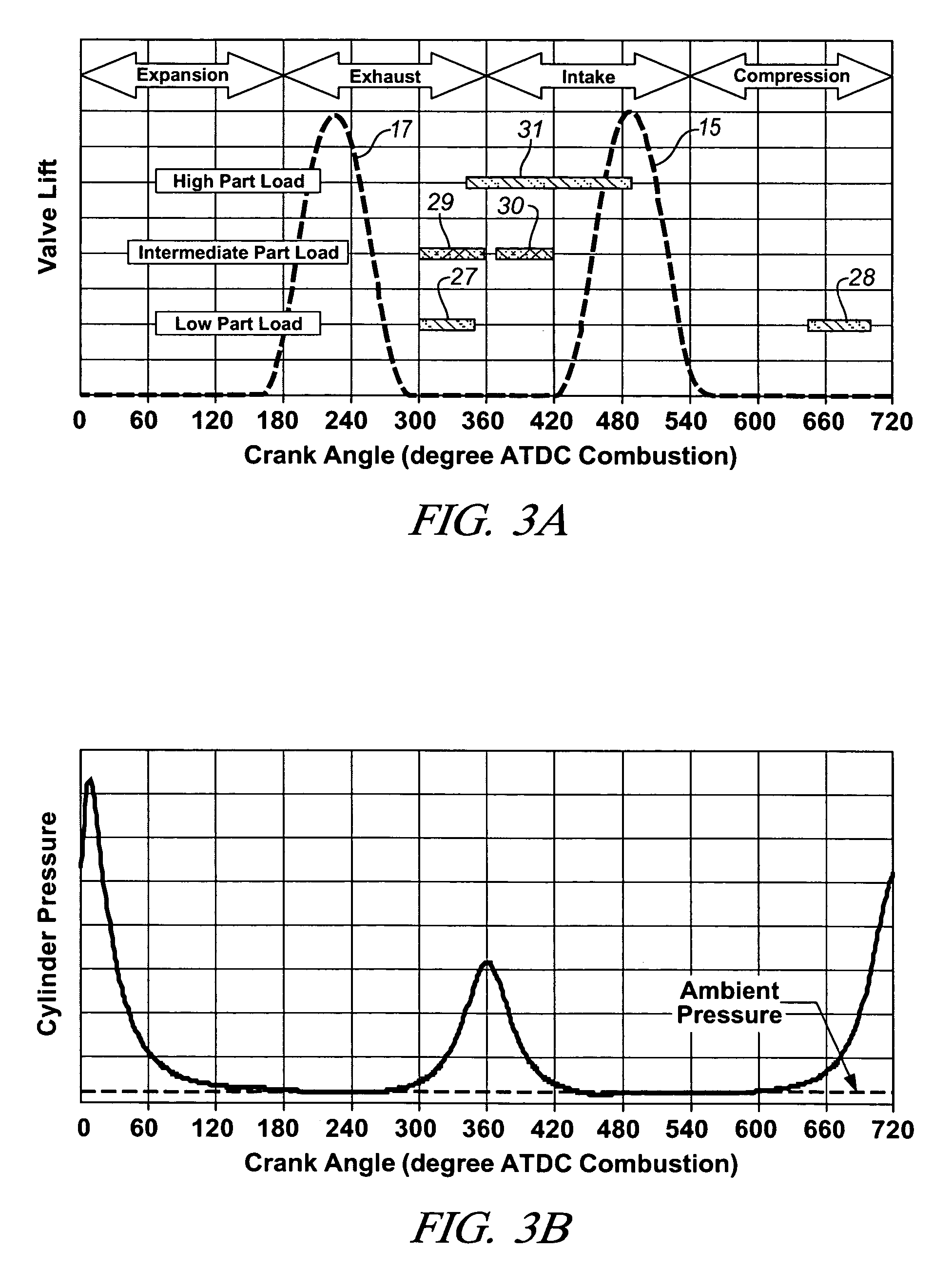
InactiveUS20060196467A1Electrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelHomogeneous charge compression ignitionLow load
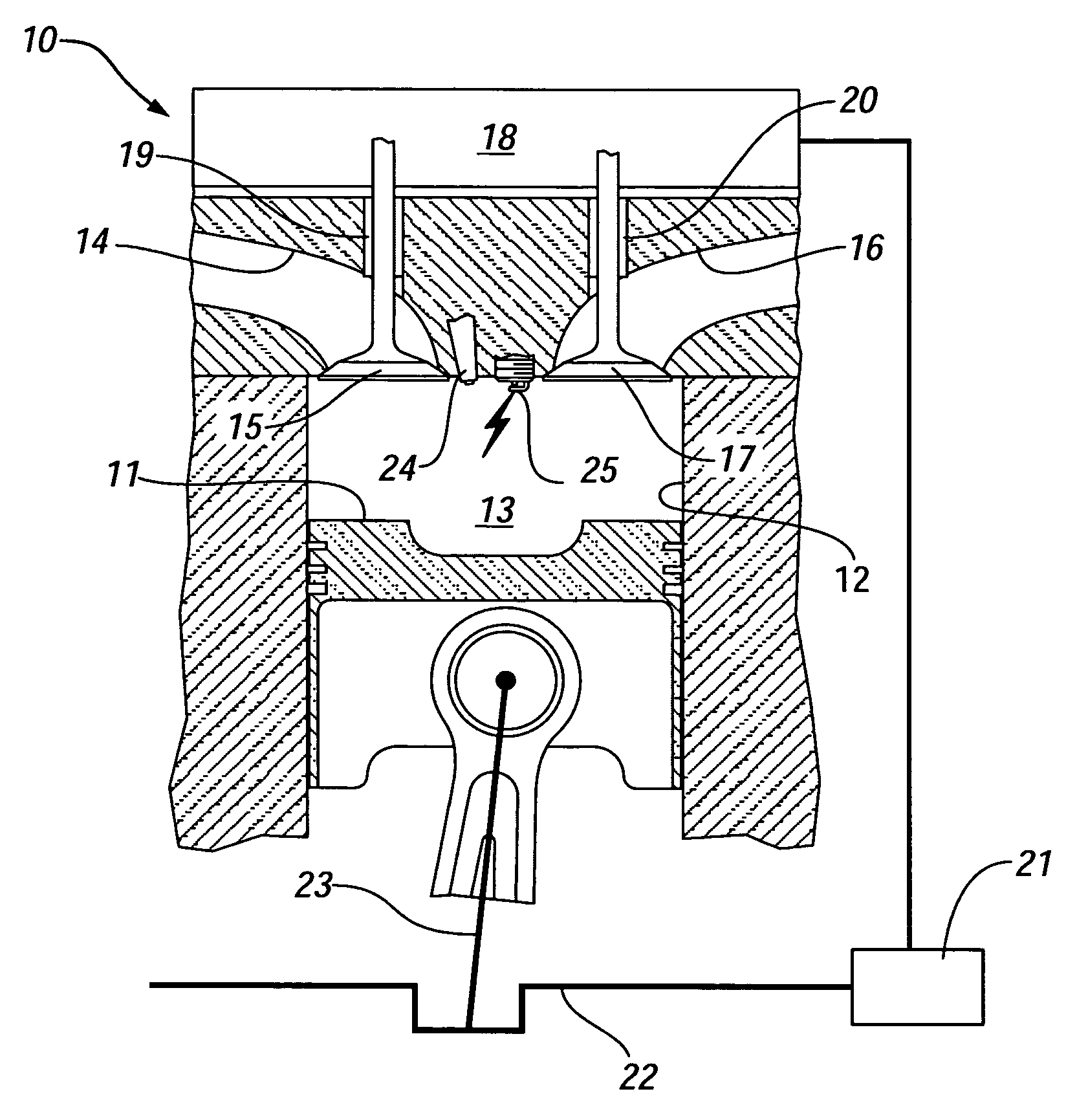
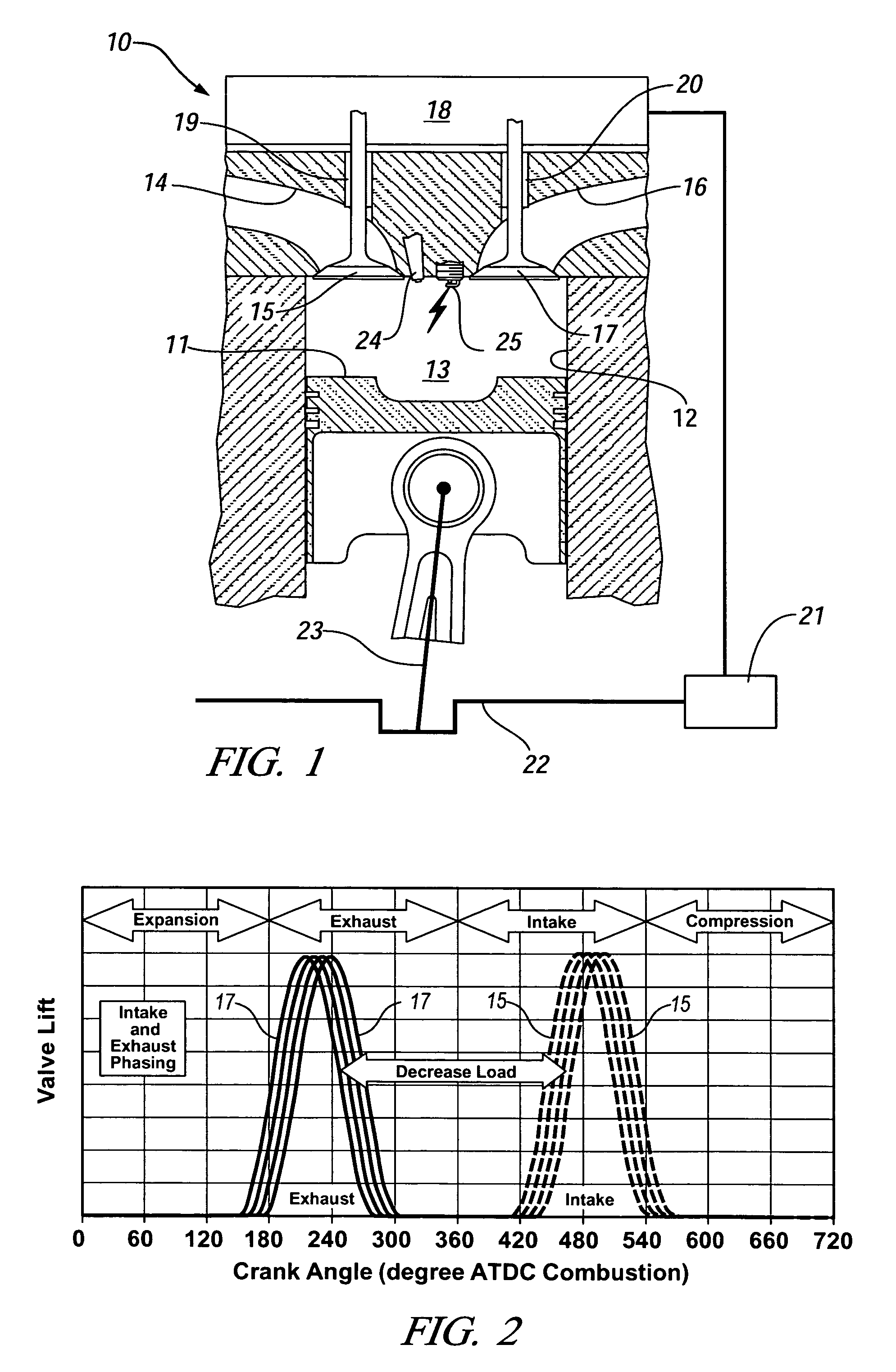
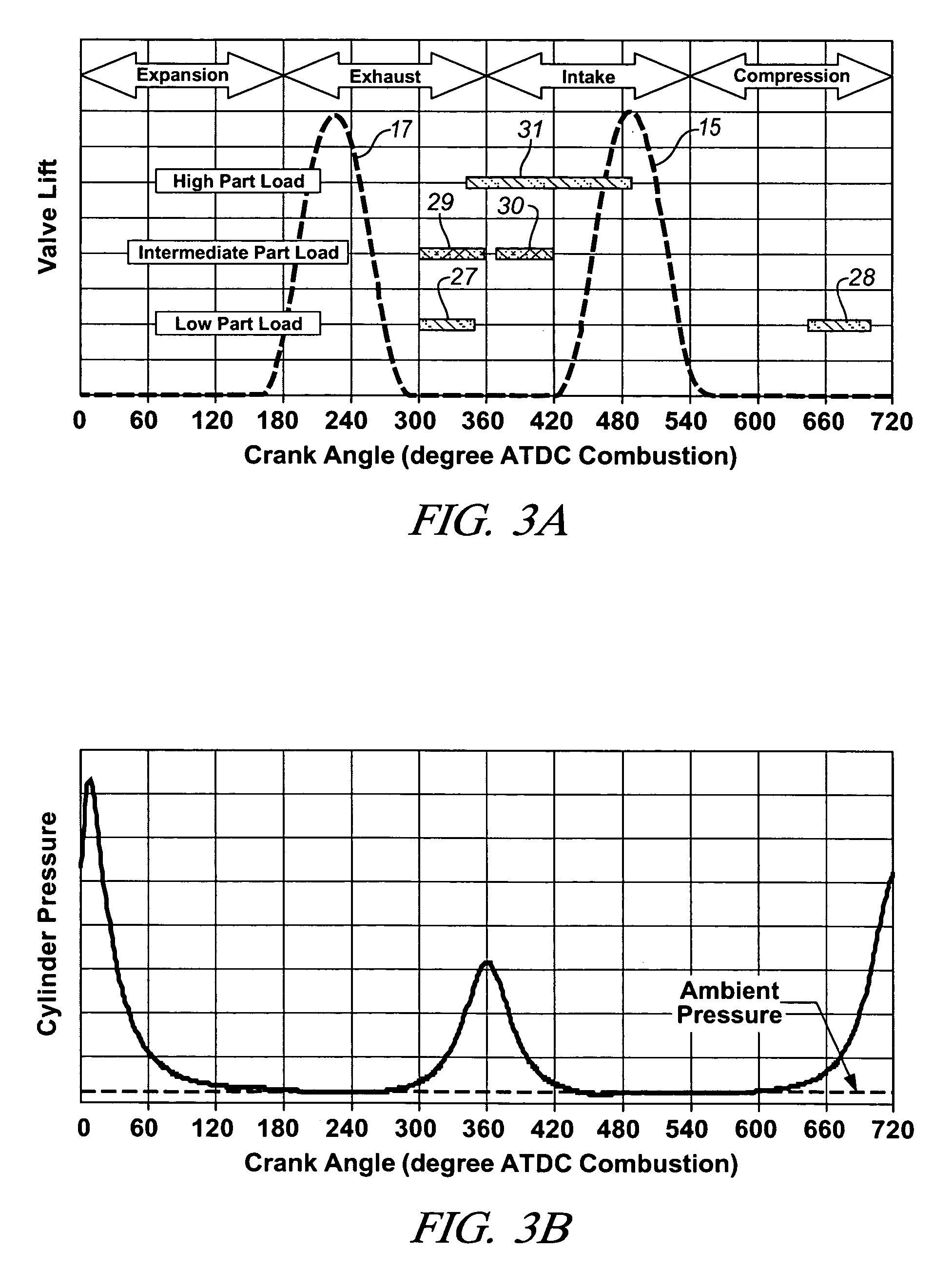
A direct injection controlled auto-ignition engine is operated at steady state, within a homogeneous charge compression-ignition (HCCI) load range and with fuel-air-diluent mixtures at predetermined conditions, for each speed and load, of engine control inputs, including at least fueling mass flow rate, injection timing (FI), spark timing (SI) and exhaust recompression obtained by negative valve overlap (NVO). During load change rates below a predetermined threshold, SI, FI and NVO change rates are synchronized to current changes in the fueling mass flow rate. For fast load increases above the threshold, the cylinder charge is temporarily enriched by increasing the percentage of residual gas or reducing the percentage of fresh air mass in the charge sufficiently to maintain auto-ignition temperature during the load change. This may be done by delaying NVO action for a predetermined speed-dependent number of engine cycles. At very low loads, stable fuel rate reduction may require an alternate method involving deceleration fuel cut-off followed by a step change during refire.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Early traffic regulation techniques to protect against network flooding
ActiveUS7295516B1Reducing flow of trafficReduce processing burdenError preventionTransmission systemsRoad traffic controlTraffic capacity
Methods and apparatus for providing an Anti-Flooding Flow-Control (AFFC) mechanism suitable for use in defending against flooding network Denial-of-Service (N-DoS) attacks is described. Features of the AFFC mechanism include (1) traffic baseline generation, (2) dynamic buffer management, (3) packet scheduling, and (4) optional early traffic regulation. Baseline statistics on the flow rates for flows of data corresponding to different classes of packets are generated. When a router senses congestion, it activates the AFFC mechanism of the present invention. Traffic flows are classified. Elastic traffic is examined to determine if it is responsive to flow control signals. Flows of non-responsive elastic traffic is dropped. The remaining flows are compared to corresponding class baseline flow rates. Flows exceeding the baseline flow rates are subject to forced flow rate reductions, e.g., dropping of packets.
Owner:PALO ALTO NETWORKS INC
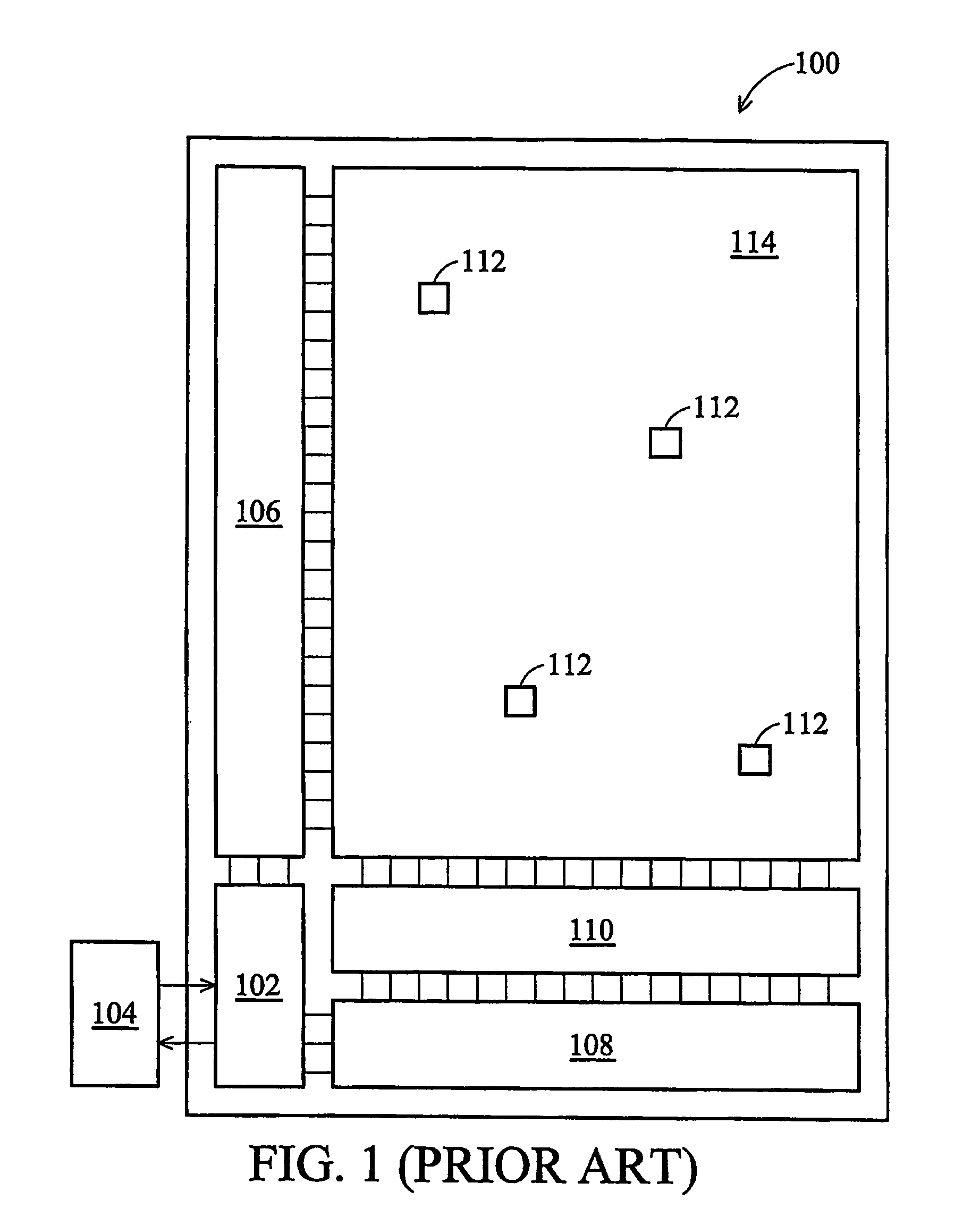
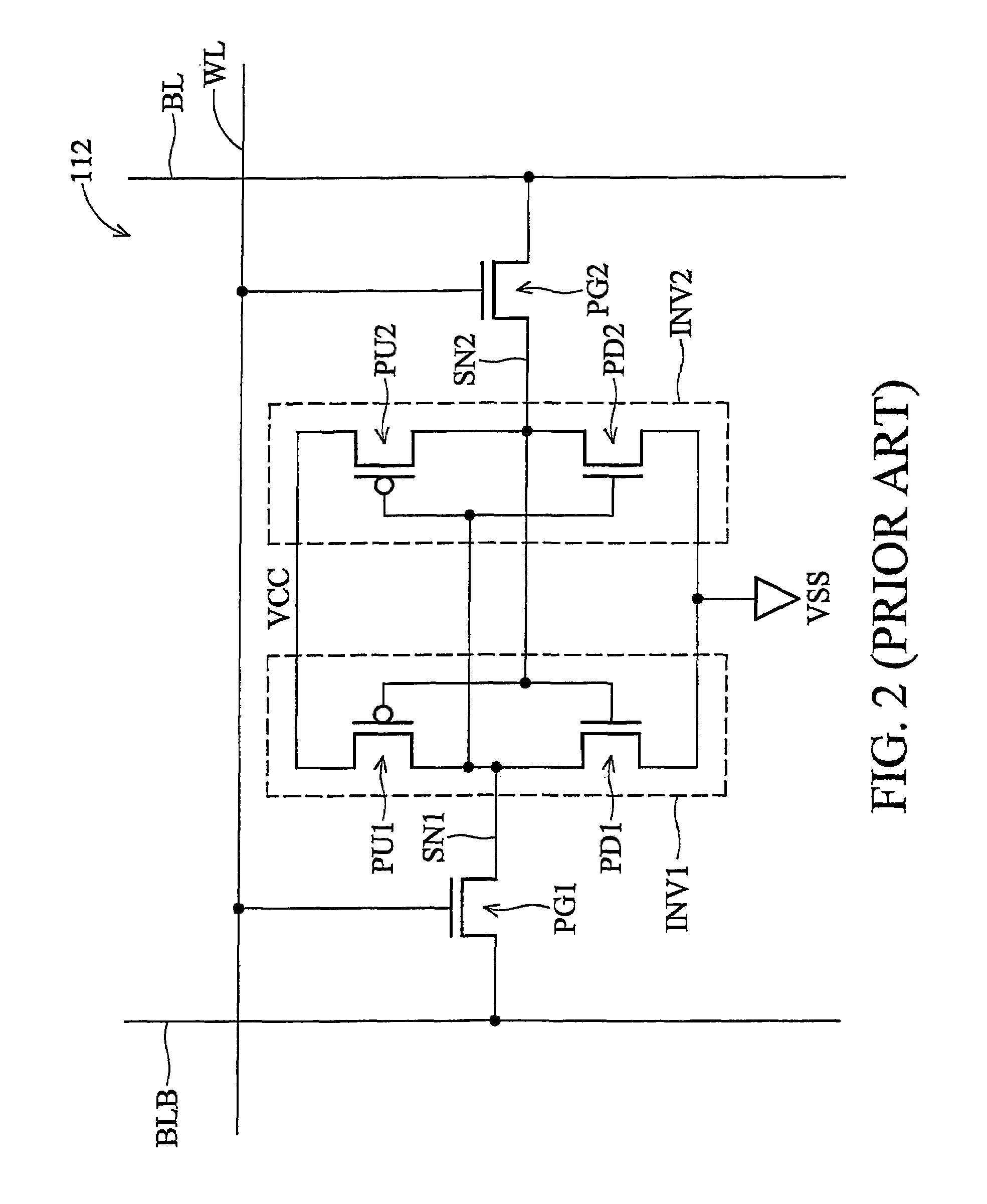
SRAM cell for soft-error rate reduction and cell stability improvement
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
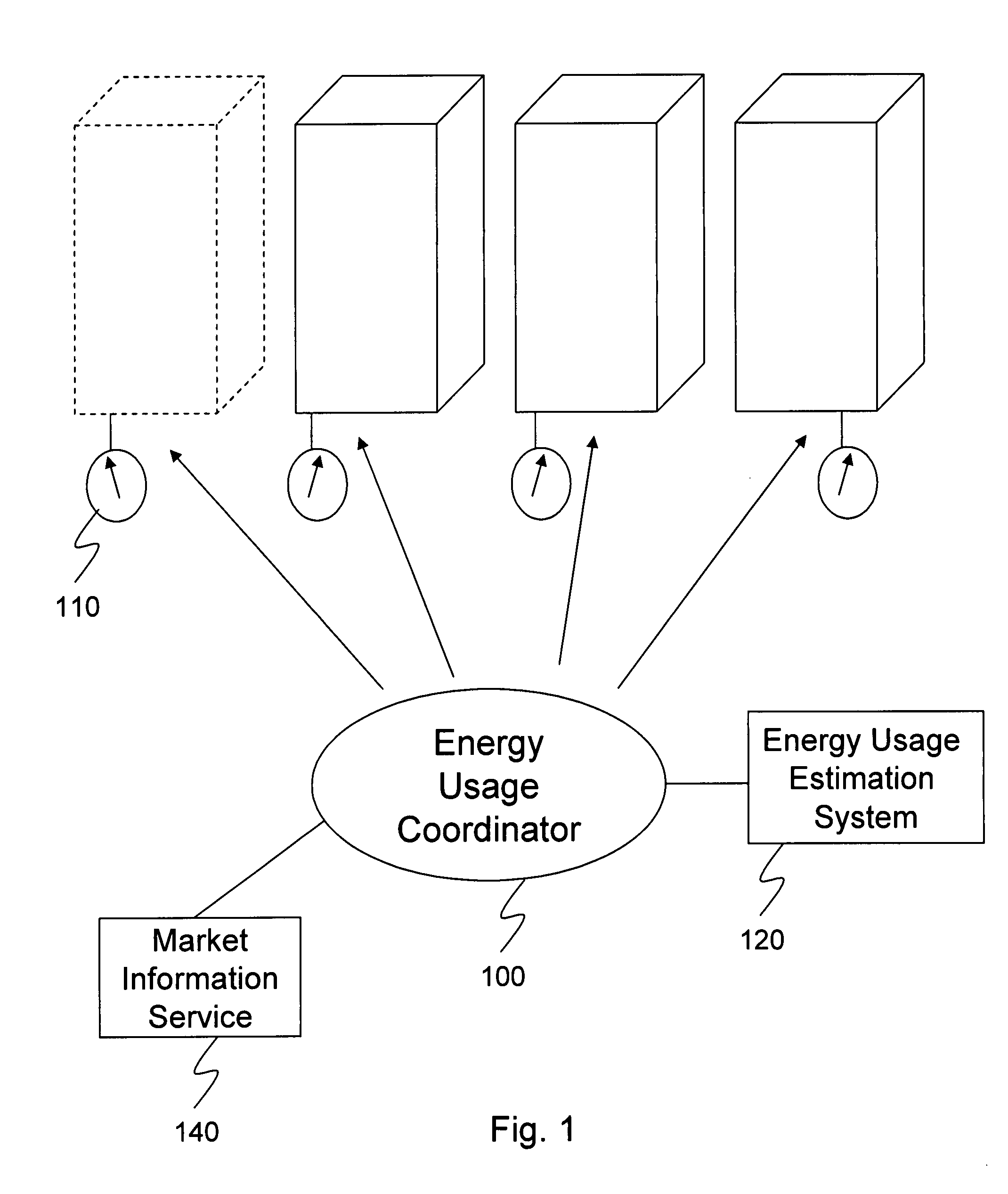
Multi-building control for demand response power usage control
An energy usage coordinator controls the energy usage of individual buildings of a group (or portfolio) of buildings in one or more load zones. These buildings have all contracted with an energy company which controls (directly or indirectly) the energy usage coordinator. By agreeing to lower energy usage during times of peak usage (when the energy company may otherwise have to pay very high prices on the spot or short term market), the owners or managers of the buildings receive a preferential energy rate from the energy company. Such a preferential rate may be in the form of a fixed rate reduction or a variable rate reduction. Alternatively, the energy company may determine that the energy is currently selling for twice what its building portfolio has contracted to pay for it so it requests some portion of the portfolio to reduce usage so that it can sell the excess / saved energy in the market.
Owner:CONSTELLATION NEWENERGY
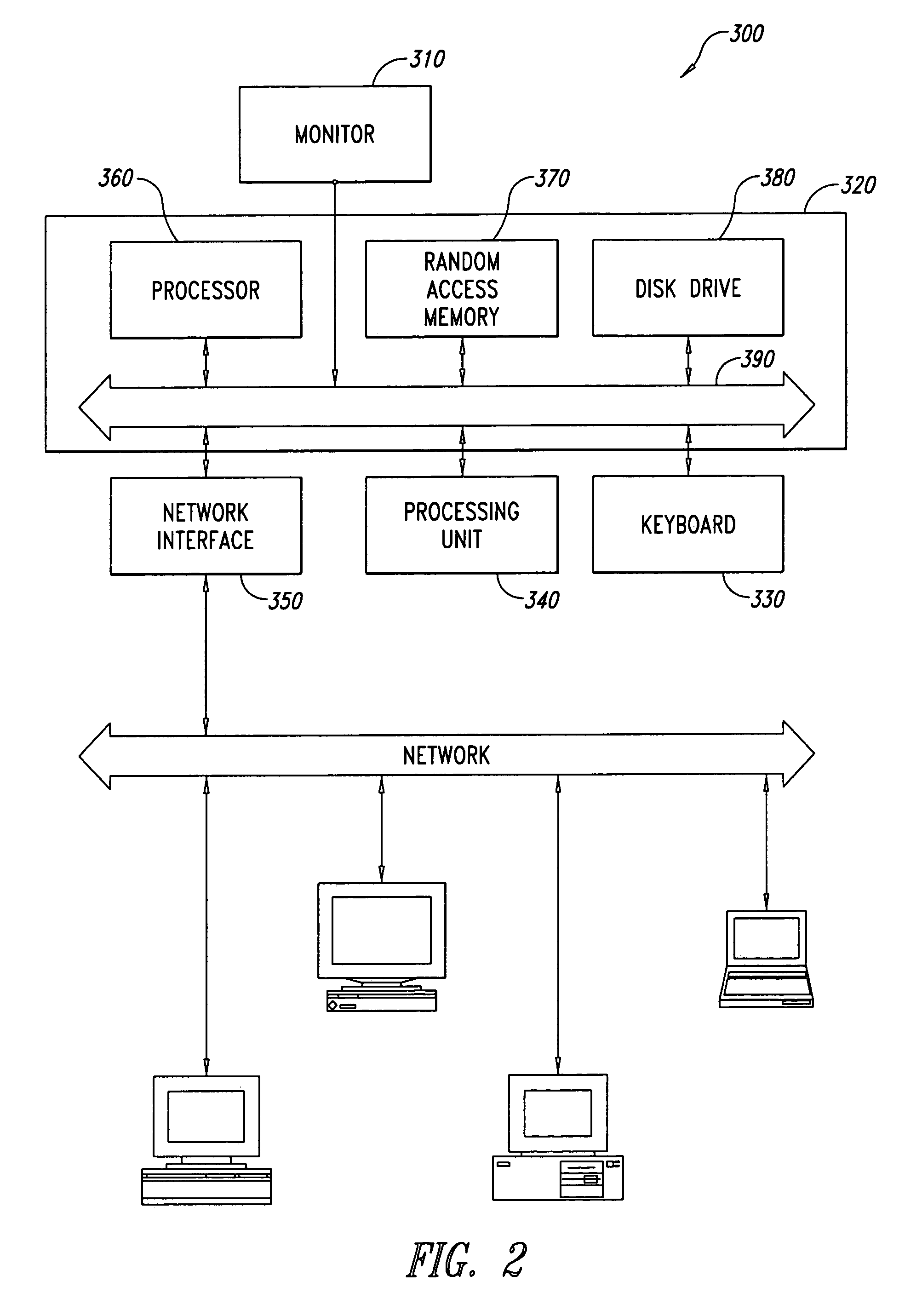
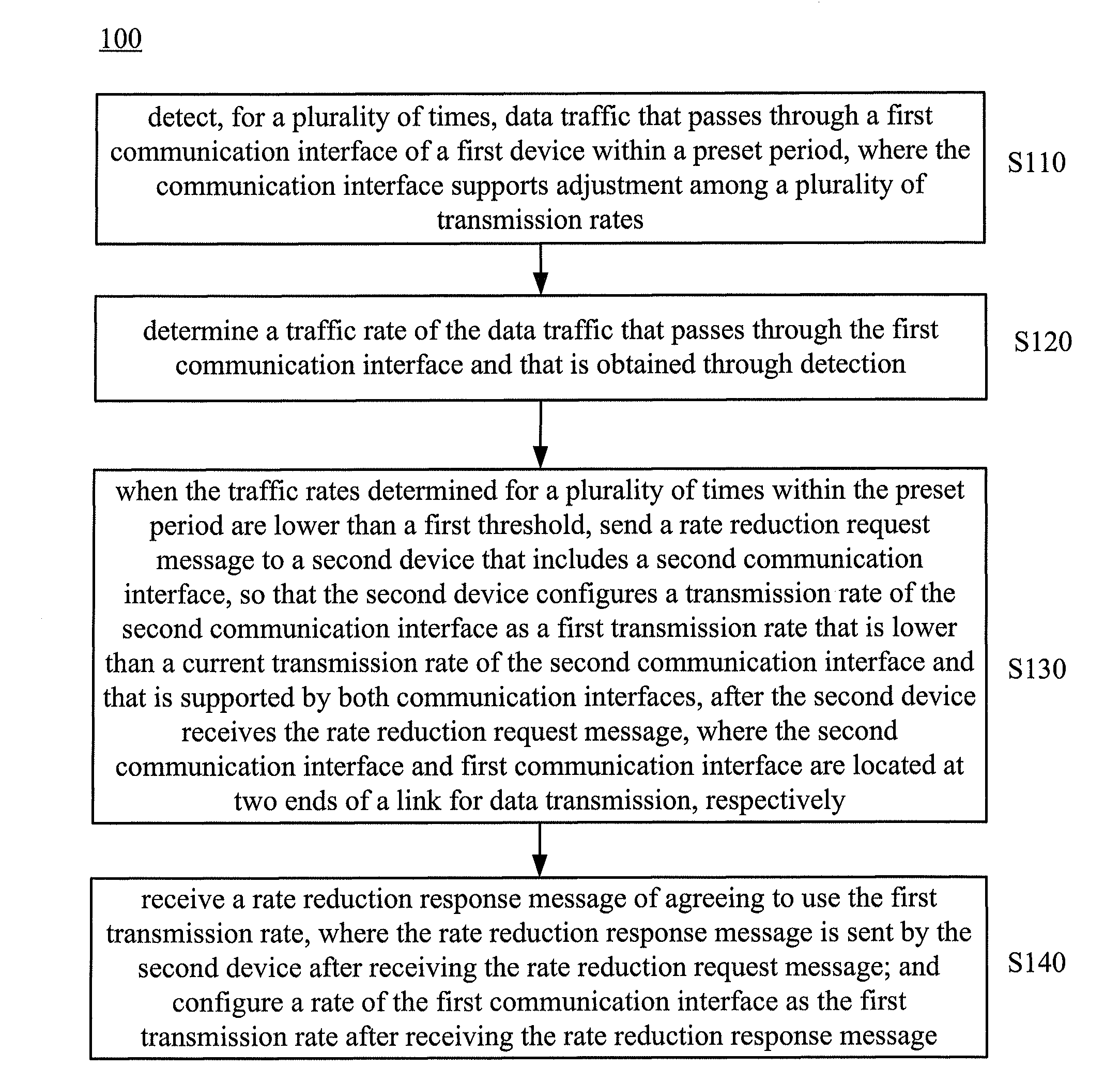
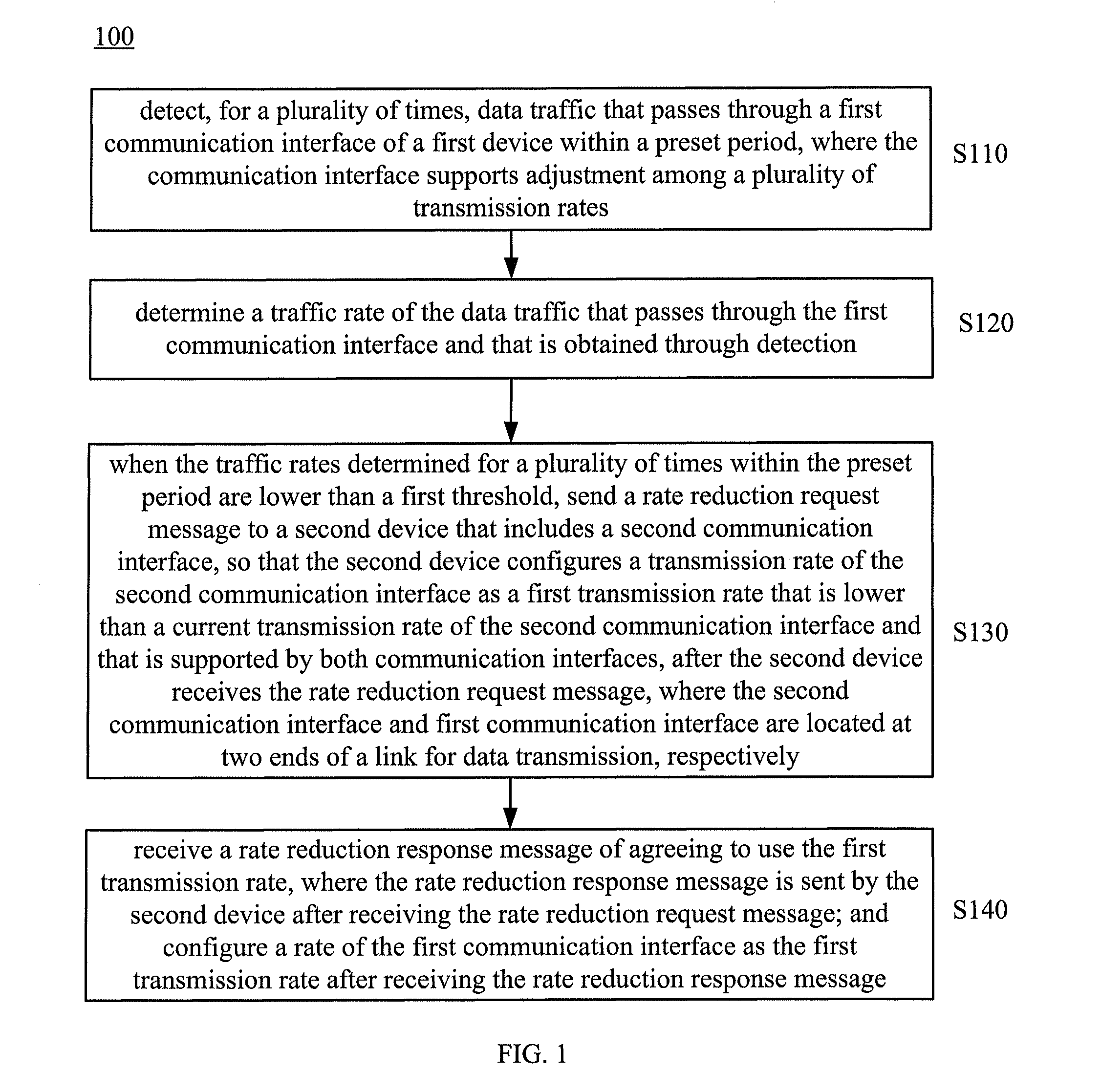
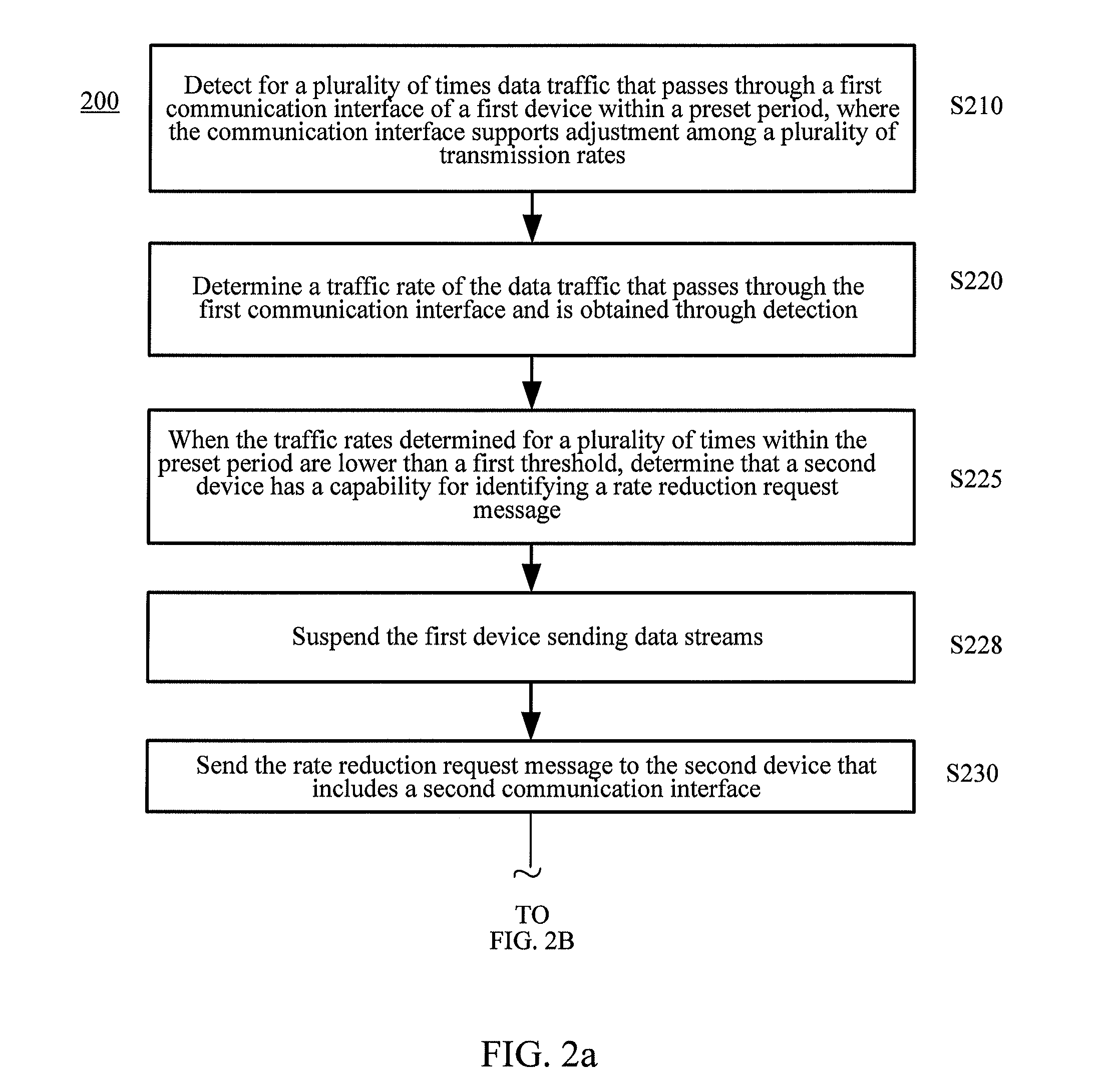
Method and network device for controlling transmission rate of communication interface
ActiveUS20130138830A1Save energyLow transfer rateEnergy efficient ICTMultiple digital computer combinationsCommunication interfaceTraffic capacity
A method for controlling a transmission rate of a communication interface includes detecting, for a plurality of times, data traffic that passes through a first communication interface of a first device within a preset period; when the traffic rates at which the data traffic passes through the first communication interface within the preset period are lower than a first threshold, sending a rate reduction request message to a second device that includes a second communication interface, so that the second device configures a rate of the second communication interface as a first transmission rate that is lower than a current transmission rate of the second communication interface and that is supported by both communication interfaces after receiving the rate reduction request message. In this way, power consumption of the communication interface may be reduced.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
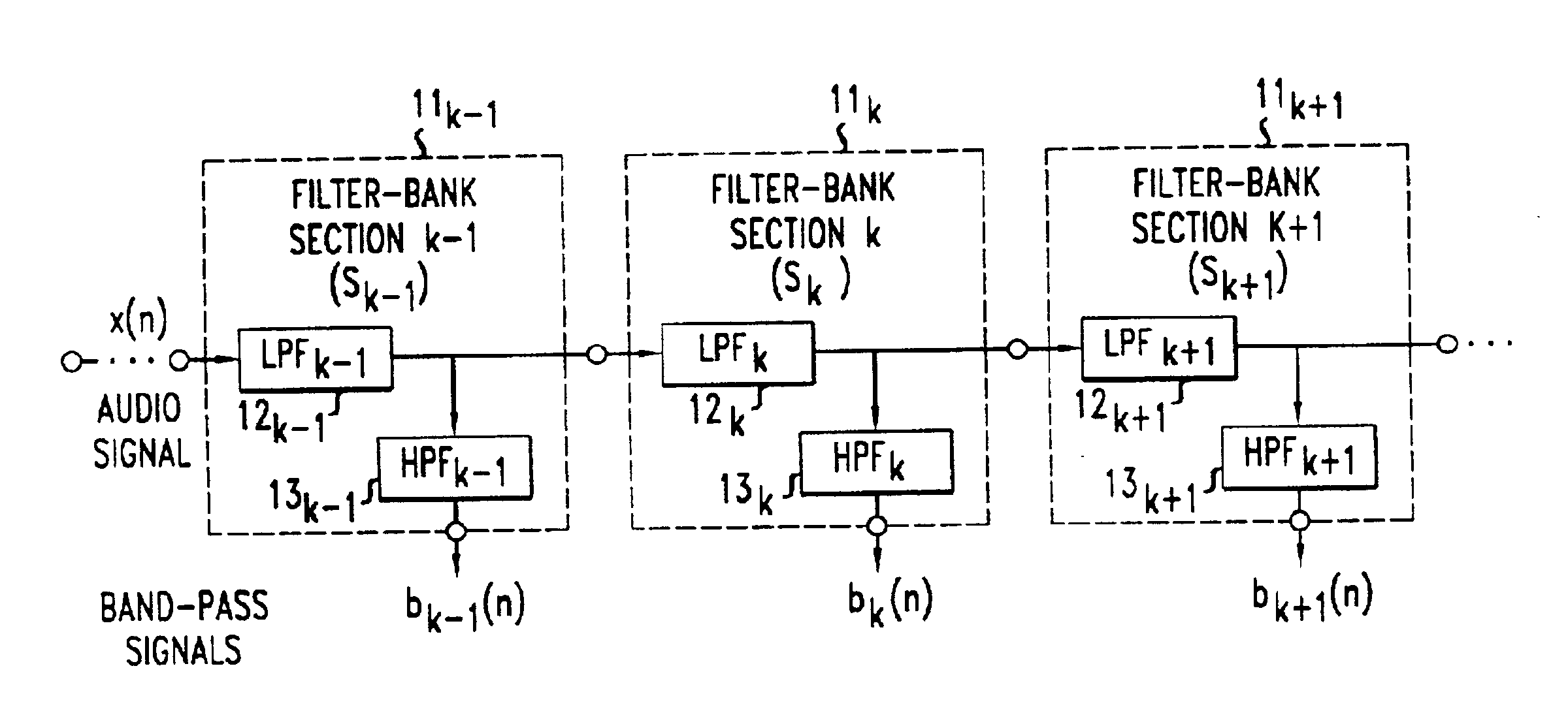
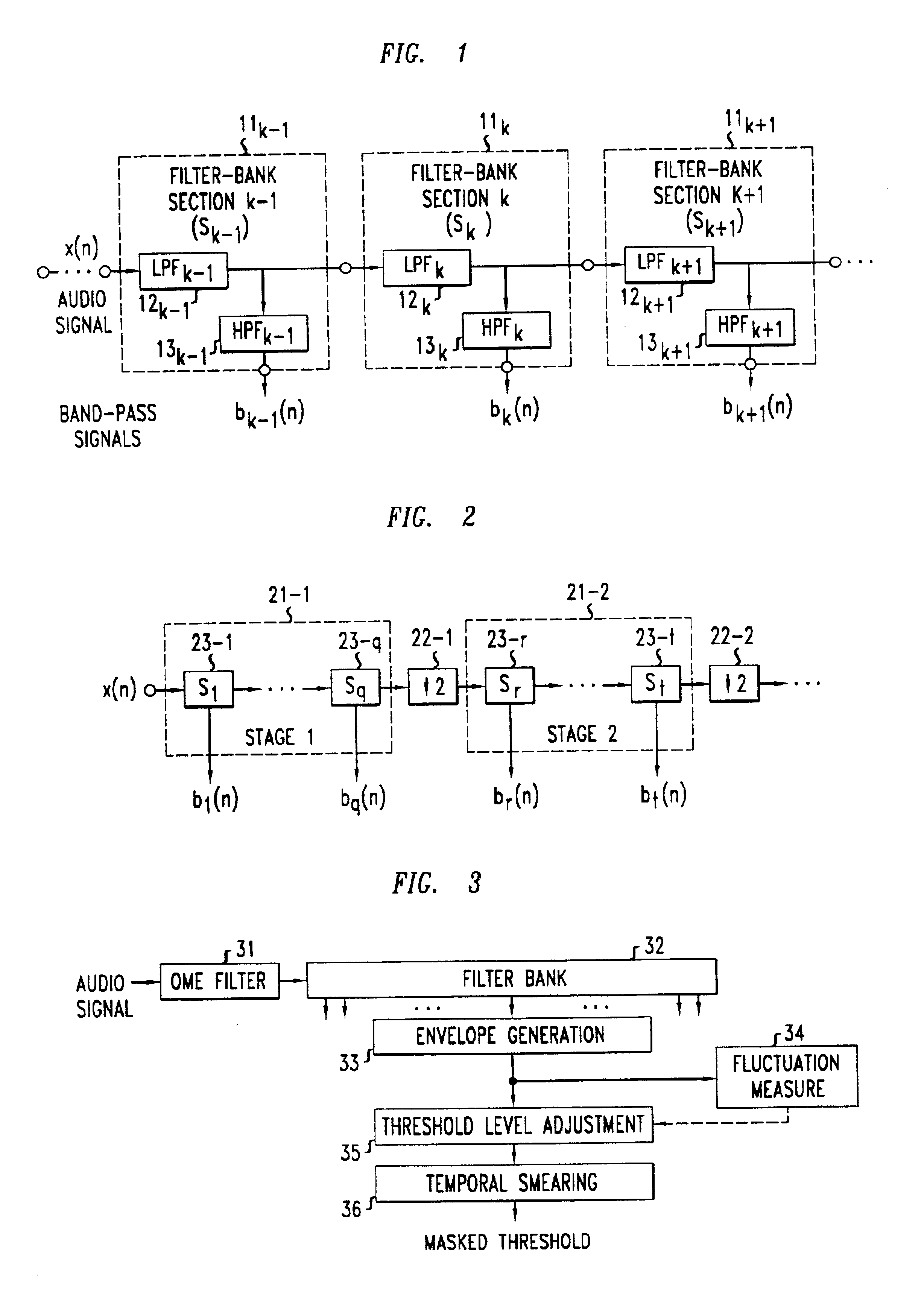
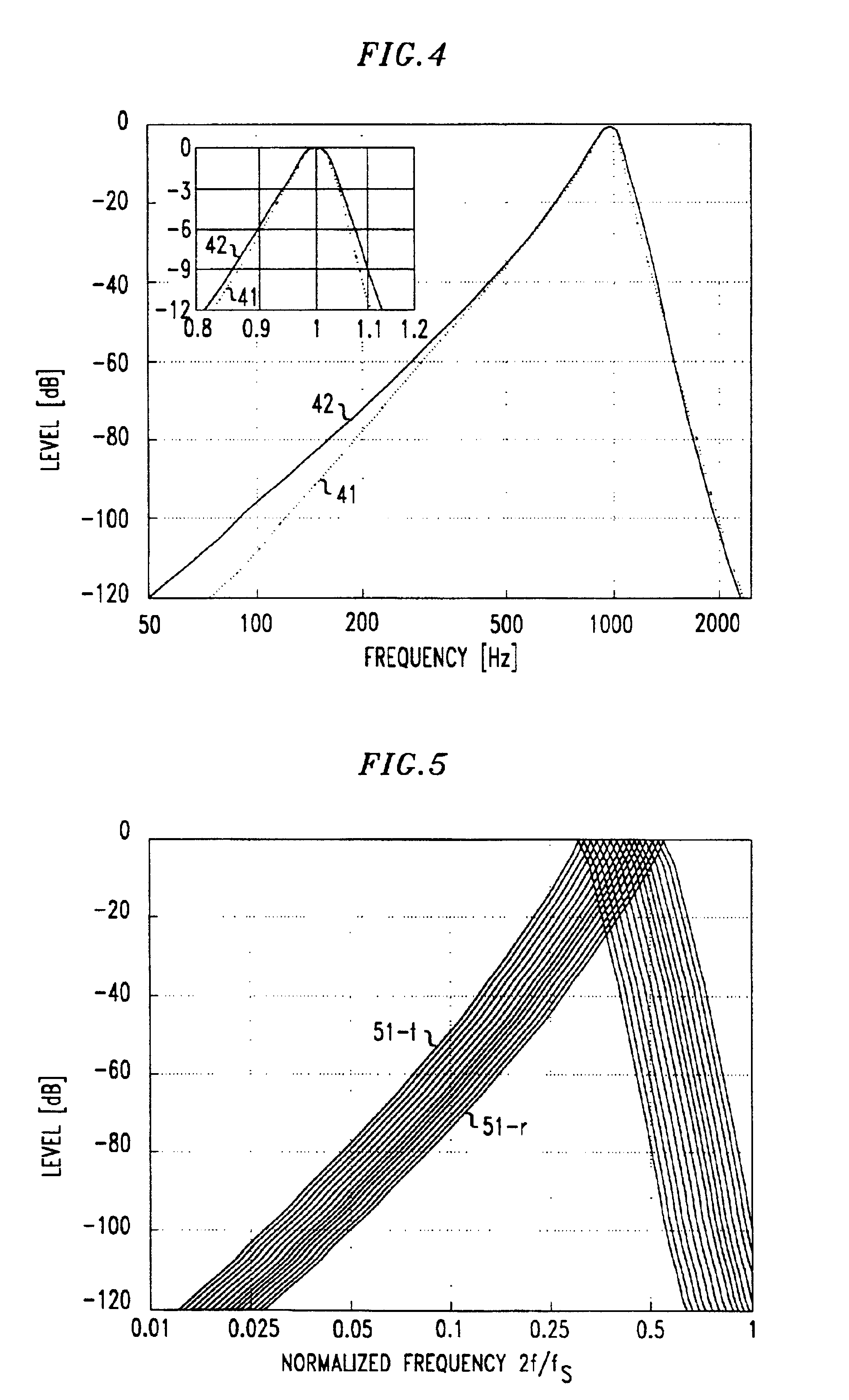
Cochlear filter bank structure for determining masked thresholds for use in perceptual audio coding
InactiveUS6915264B2Reduced sampling rate requirementsSimple modelSpeech analysisComplex mathematical operationsIir filteringEngineering
A method and apparatus for determining masked thresholds for a perceptual auditory model used, for example, in a perceptual audio coder, which makes use of a filter bank structure comprising a plurality of filter bank stages which are connected in series, wherein each filter bank stage comprises a plurality of low-pass filters connected in series and a corresponding plurality of high-pass filters applied to the outputs of each of the low-pass filters, and wherein downsampling is advantageously applied between each successive pair of filter bank stages. In accordance with one illustrative embodiment, the filter bank comprises low order IIR filters. The cascade structure advantageously supports sampling rate reduction due to the continuously decreasing cutoff frequency in the cascade. The filter bank coefficients may advantageously be optimized for modeling of masked threshold patterns of narrow-band maskers, and the generated thresholds may be advantageously applied in a perceptual audio coder.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Photon/energy identifying x-ray and gamma ray imaging device ("pid") with a two dimensional array of pixels and system therefrom
ActiveUS20120280131A1Reduce the amount of dataReduce data rateTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesSoft x rayDigital signal processing
An photon (energy) identifying radiation imaging device, for imaging x-ray, gamma ray and charged radiation in medical, dental and industrial applications. The imaging device includes a detector substrate and a readout substrate. The detector substrate has a plurality of detector pixels and the readout substrate has a plurality of corresponding pixel readout circuits. Each pixel readout circuit has circuitry for processing an input analog signal and also has one or more buffers for temporarily storing values corresponding to the signal of at least two individual incoming radiation events. The readout substrate includes a digital controller having digital processing units for carrying out off-pixel digital signal processing and data / rate reduction prior to readout.
Owner:OY AJAT LTD
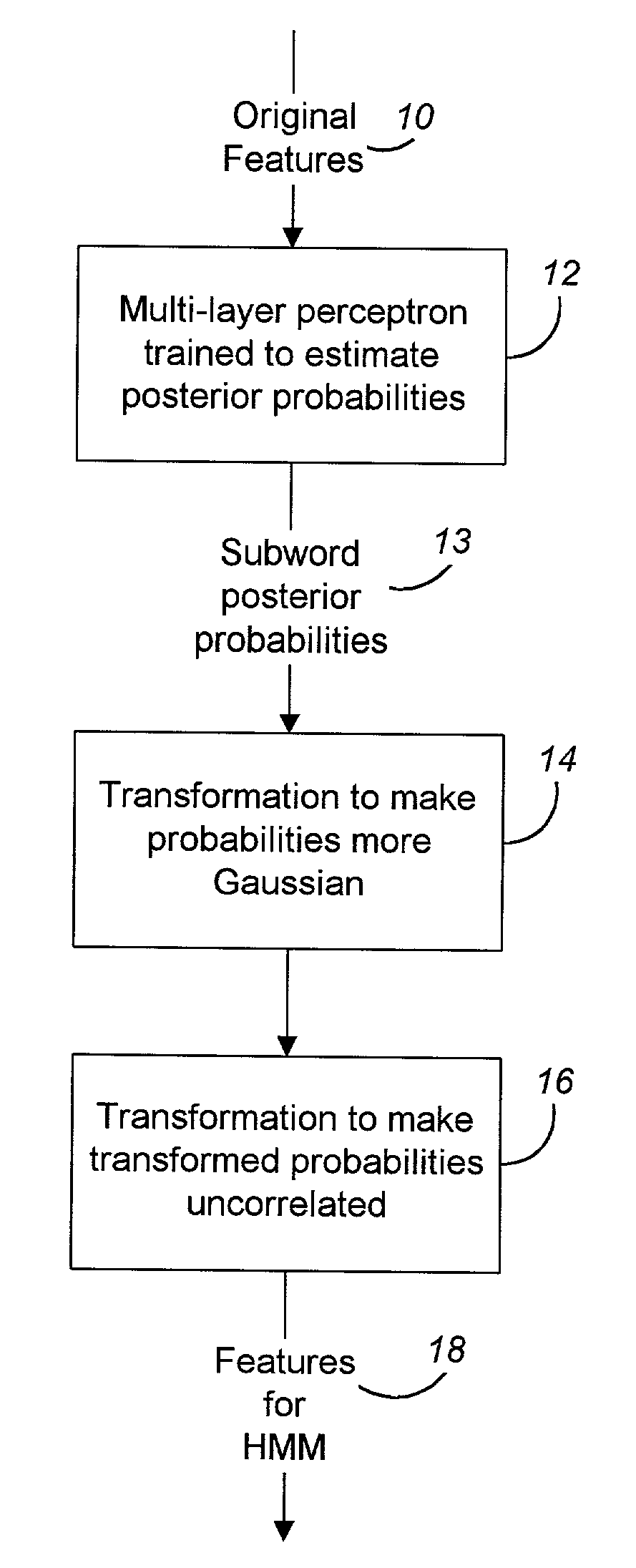
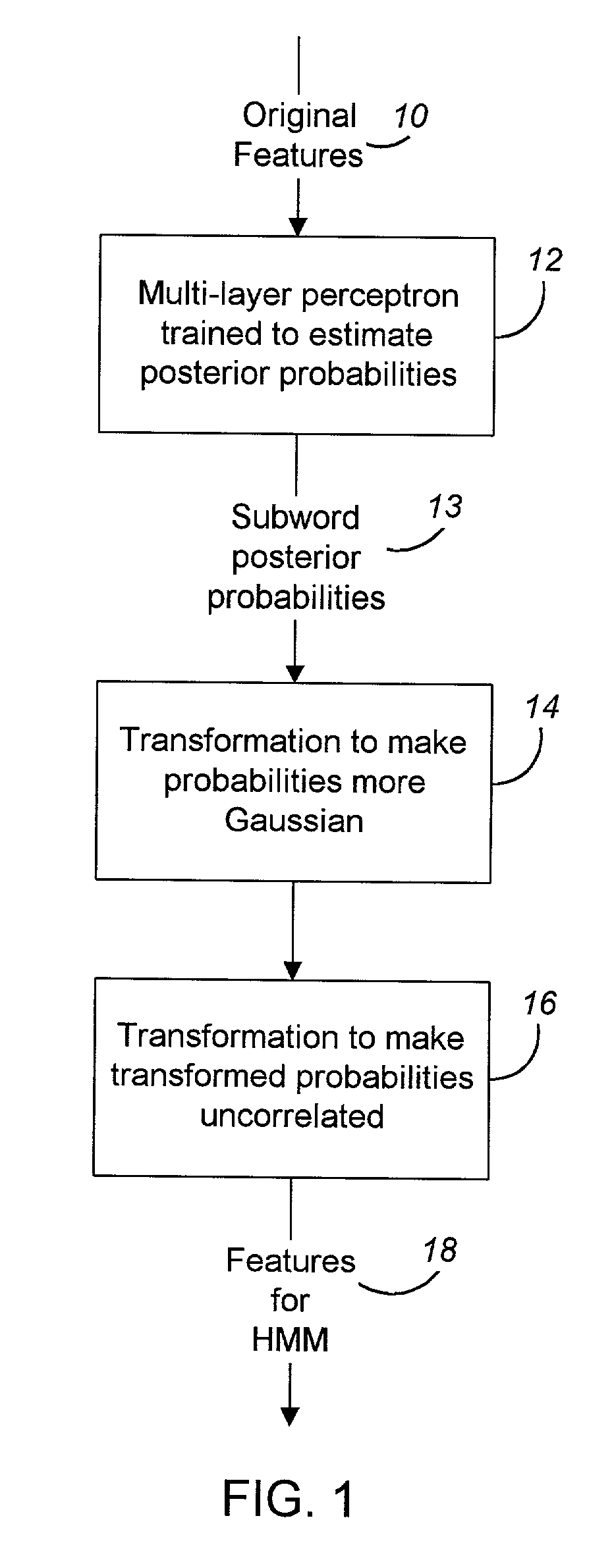
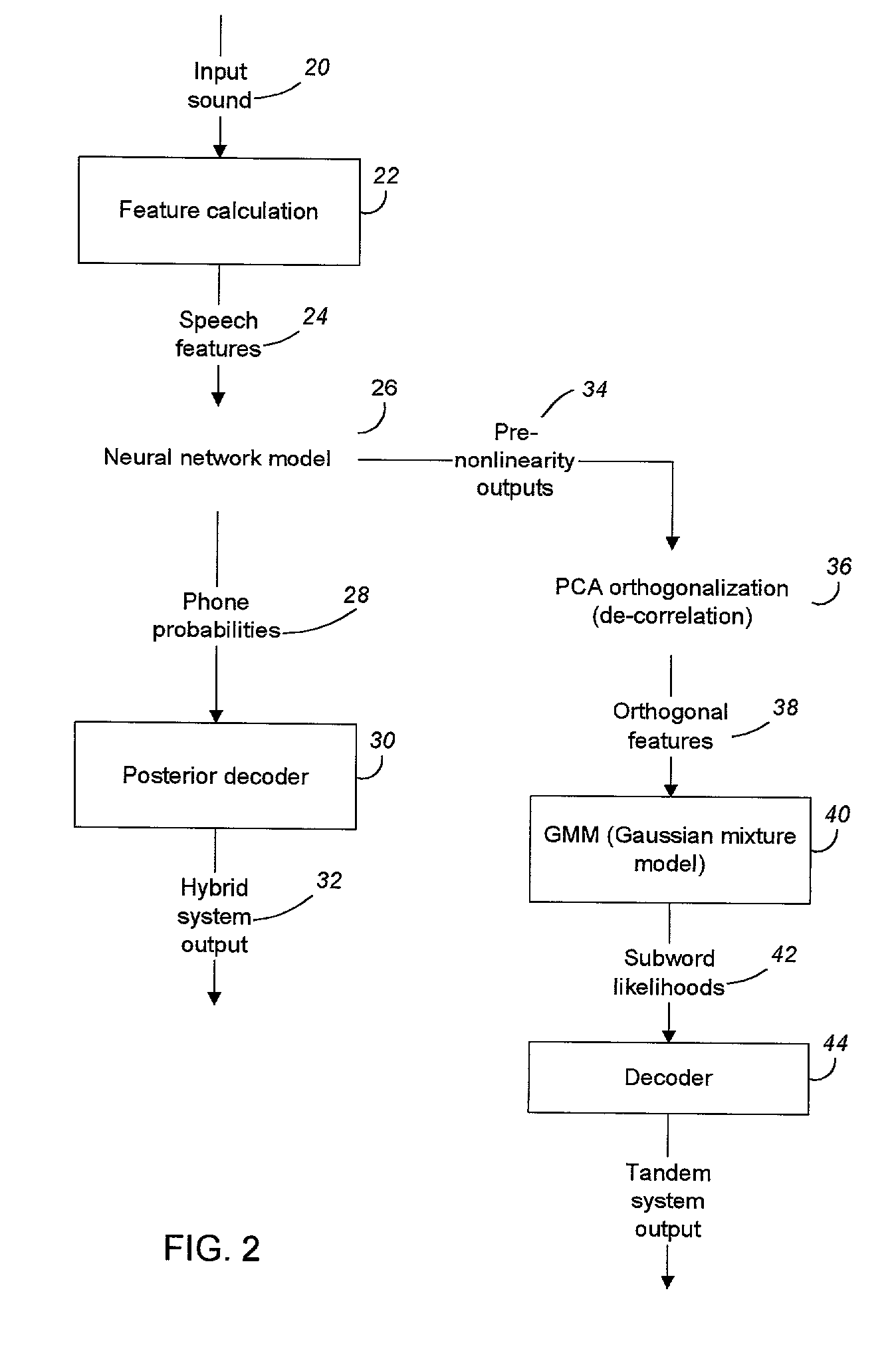
Nonlinear mapping for feature extraction in automatic speech recognition
The present invention successfully combines neural-net discriminative feature processing with Gaussian-mixture distribution modeling (GMM). By training one or more neural networks to generate subword probability posteriors, then using transformations of these estimates as the base features for a conventionally-trained Gaussian-mixture based system, substantial error rate reductions may be achieved. The present invention effectively has two acoustic models in tandem—first a neural net and then a GMM. By using a variety of combination schemes available for connectionist models, various systems based upon multiple features streams can be constructed with even greater error rate reductions.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL COMPUTER SCIENCE INSTITUTE
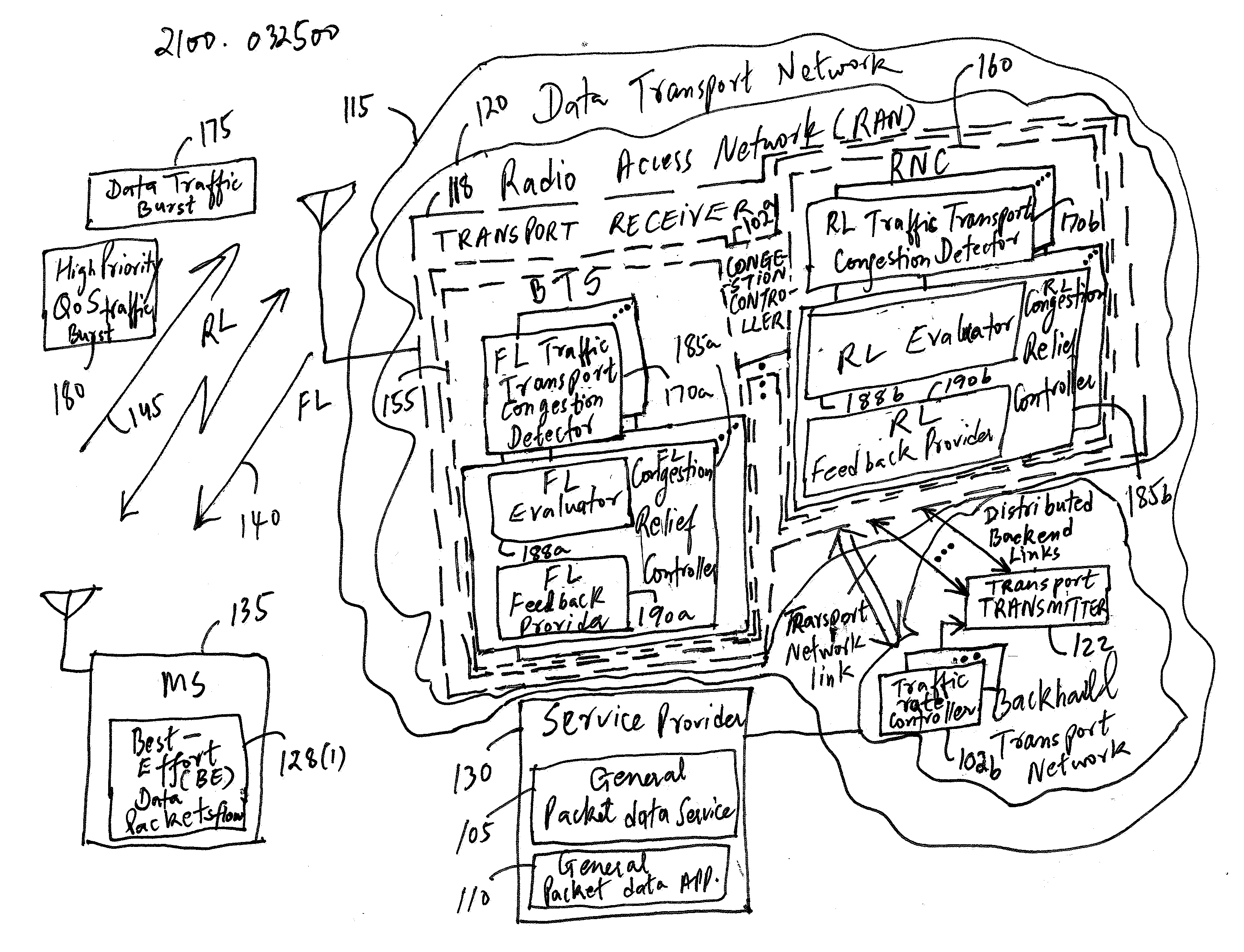
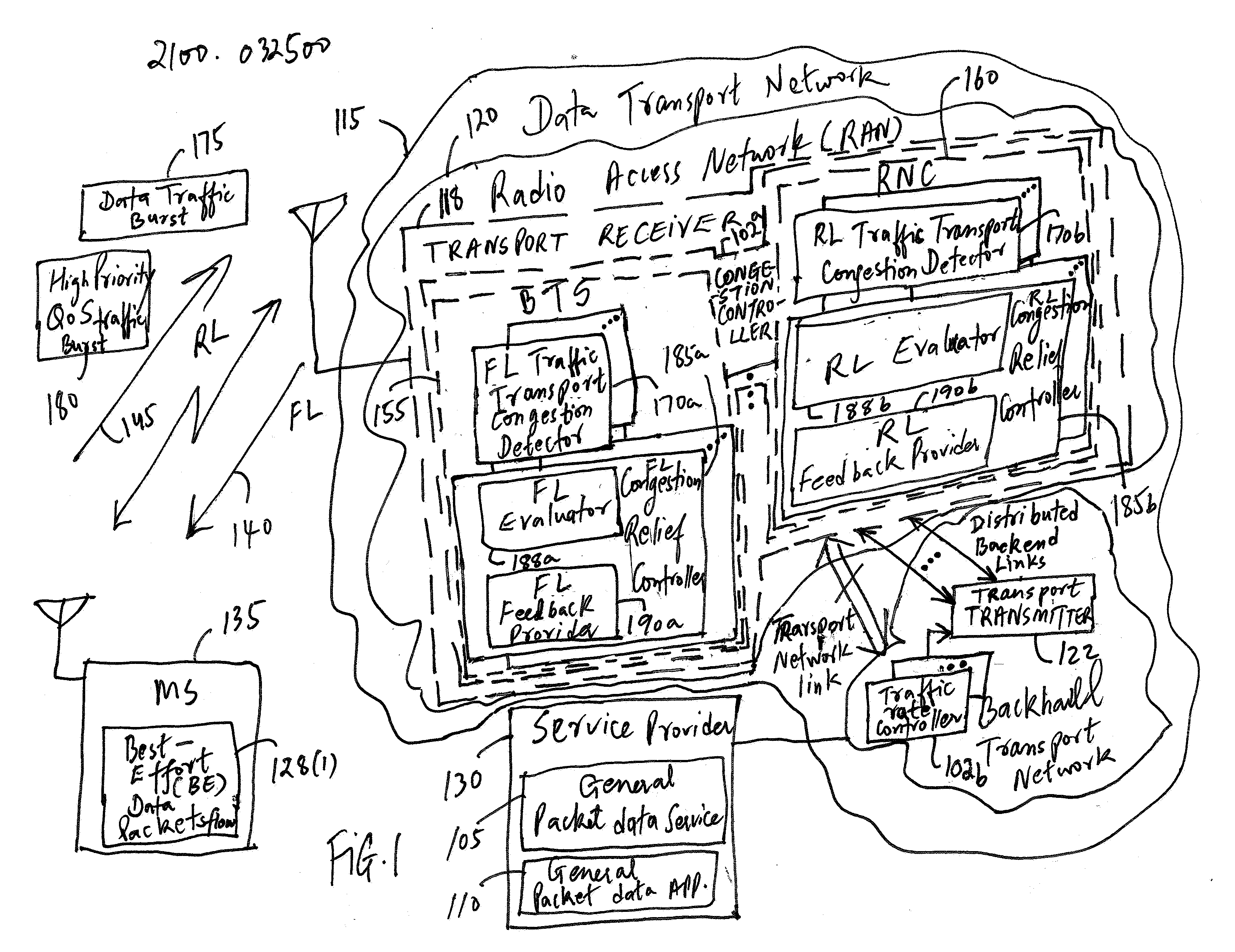
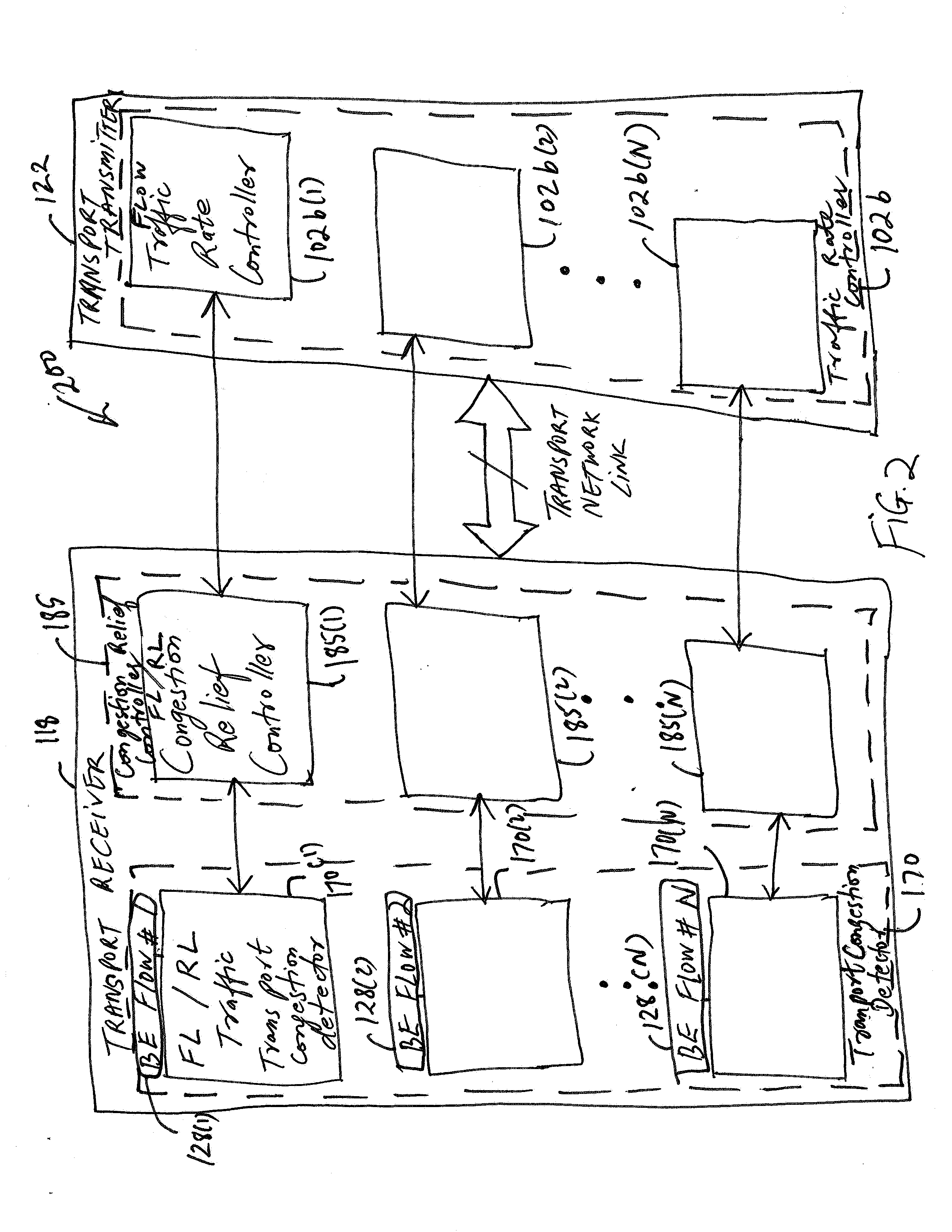
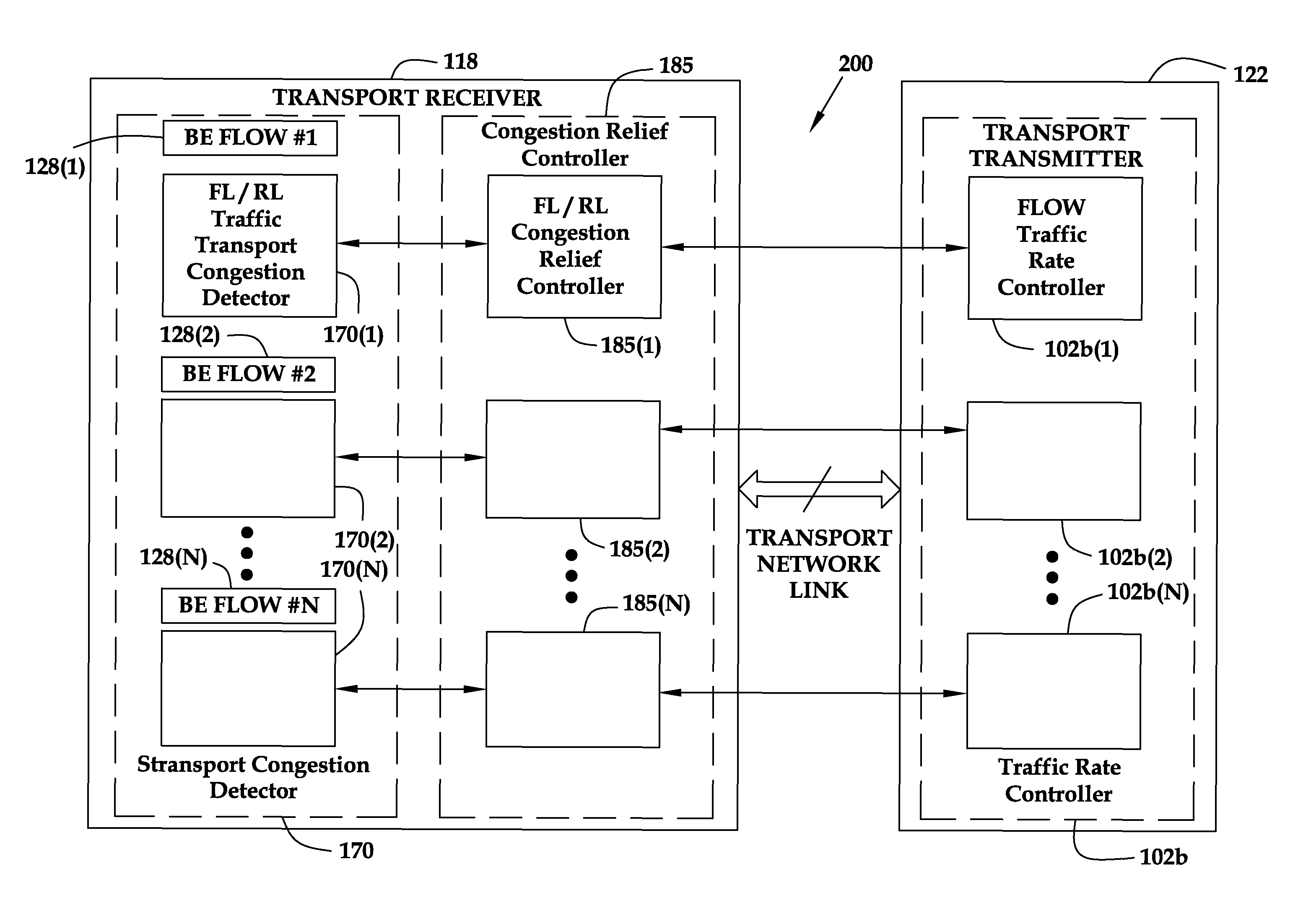
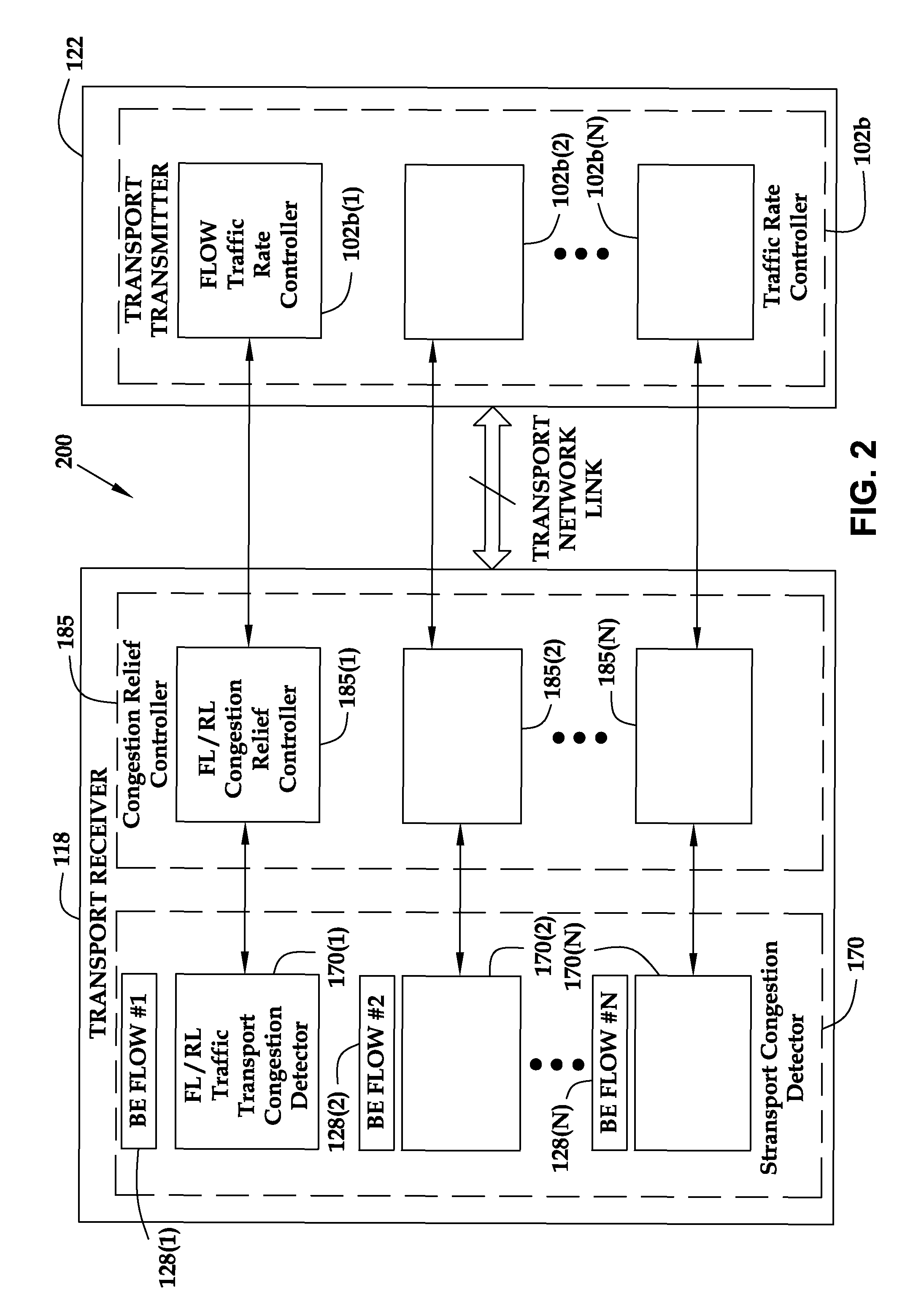
Reducing packet loss for a packet data service during congestion in a transport network
ActiveUS20080008092A1Reducing for data serviceReduce flow rateEnergy efficient ICTError preventionTraffic capacityTransmission congestion
A method and an apparatus for reducing packet loss for a packet data service during congestion in a transport network are provided. The method comprises measuring a packet loss rate over a time period in one or more flows of data traffic packets associated with the packet data service to determine whether the one or more flows of data traffic packets are experiencing a variation in a desired traffic performance level at a particular time duration during the congestion in the time period. The method further comprises triggering a request to reduce a flow rate of at least one of the one or more flows of data traffic packets based on the packet loss rate if the at least one of the one or more flows of data traffic packets experiences the variation in the desired traffic performance level. By using a distributed transport congestion control, for example, only such Best Effort data traffic packet flows that generate bursty traffic at a specific moment of congestion sense the congestion and thus trigger an associated rate reduction action. However, other flows that do not experience the congestion may not be affected.
Owner:RPX CORP
Sub-picture level pass through
InactiveUS6950464B1Improves and expedites compressed video data deliveryPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningComputer graphics (images)Transcoding
The invention described herein improves and expedites compressed video data delivery by providing systems and methods for transcoding and pass through on a sub-picture level. For example, in MPEG embodiments described herein, transcoding and compressed video data pass through may occur on a macroblock or slice level. This permits portions of a picture that need no rate reduction to be passed through without transcoding. The invention may also implement pass through on a picture by picture basis. Accordingly, the invention may determine transcoding or pass through for each picture or picture subregion. Thus, systems and methods described herein provide flexible compressed video data transcoding and pass through, as determined by varying bit rate demands of compressed video data transmission.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Load transient control methods for direct-injection engines with controlled auto-ignition combustion
InactiveUS7370633B2Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHomogeneous charge compression ignitionLow load
A direct injection controlled auto-ignition engine is operated at steady state, within a homogeneous charge compression-ignition (HCCI) load range and with fuel-air-diluent mixtures at predetermined conditions, for each speed and load, of engine control inputs, including at least fueling mass flow rate, injection timing (FI), spark timing (SI) and exhaust recompression obtained by negative valve overlap (NVO). During load change rates below a predetermined threshold, SI, FI and NVO change rates are synchronized to current changes in the fueling mass flow rate. For fast load increases above the threshold, the cylinder charge is temporarily enriched by increasing the percentage of residual gas or reducing the percentage of fresh air mass in the charge sufficiently to maintain auto-ignition temperature during the load change. This may be done by delaying NVO action for a predetermined speed-dependent number of engine cycles. At very low loads, stable fuel rate reduction may require an alternate method involving deceleration fuel cut-off followed by a step change during refire.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
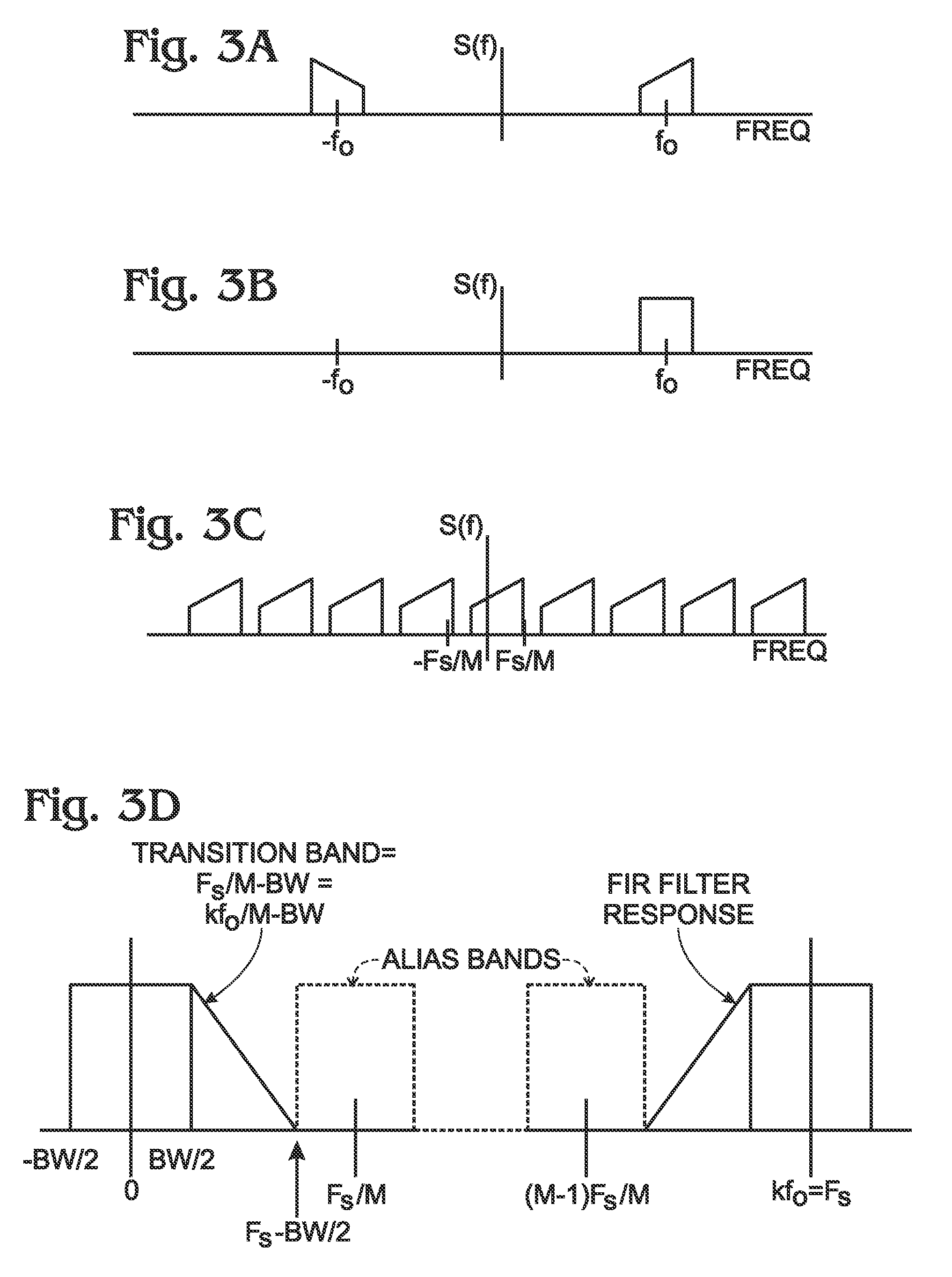
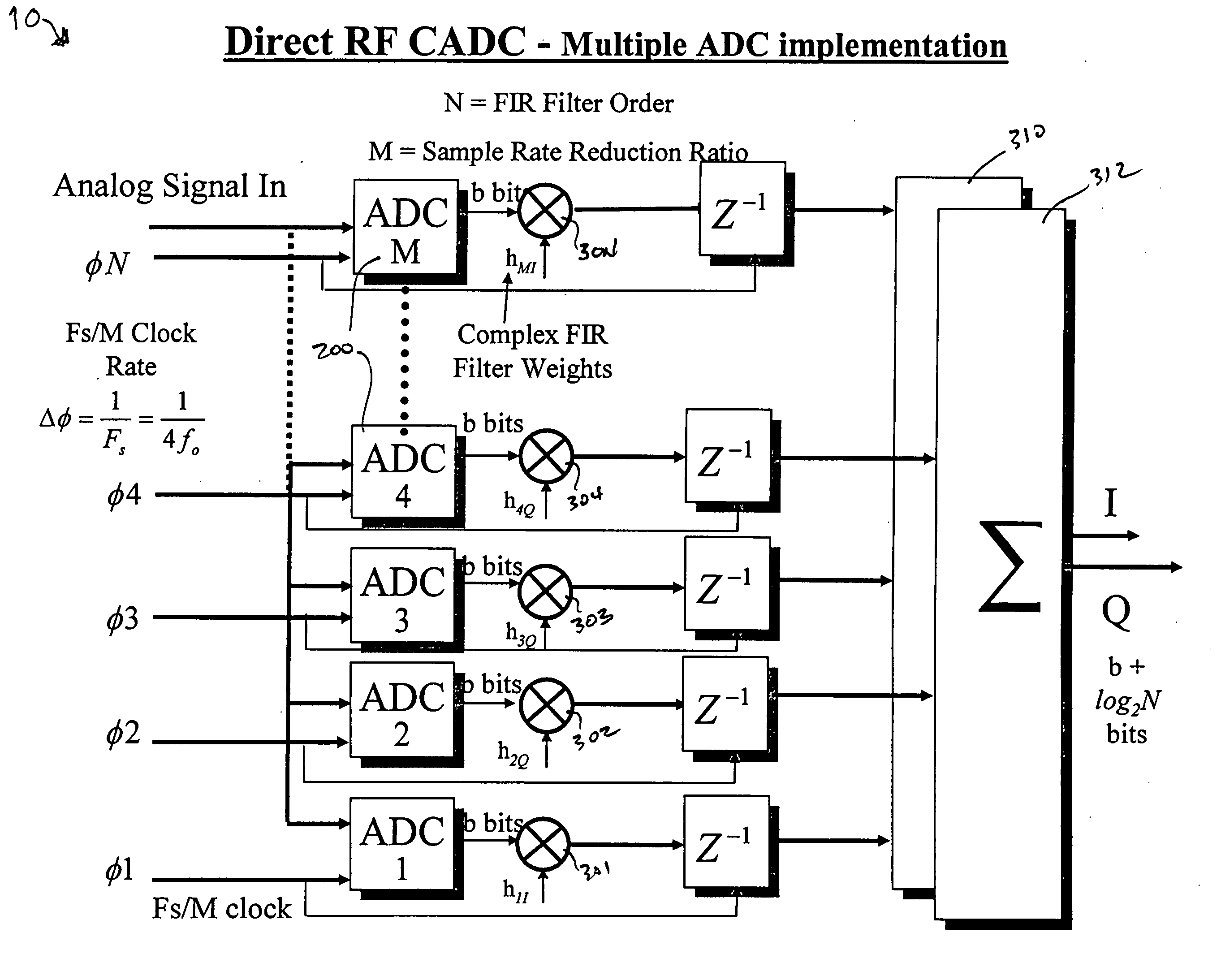
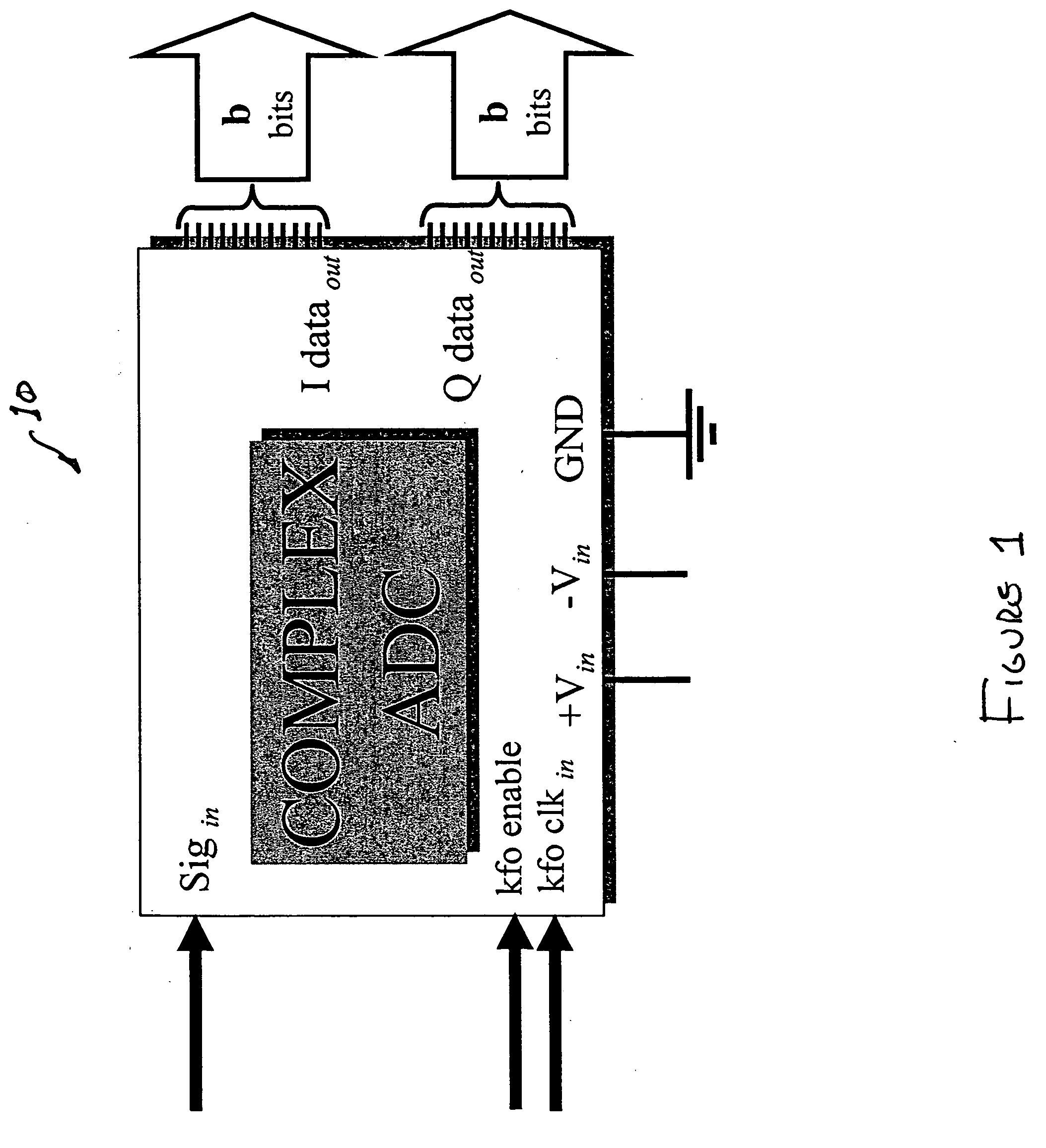
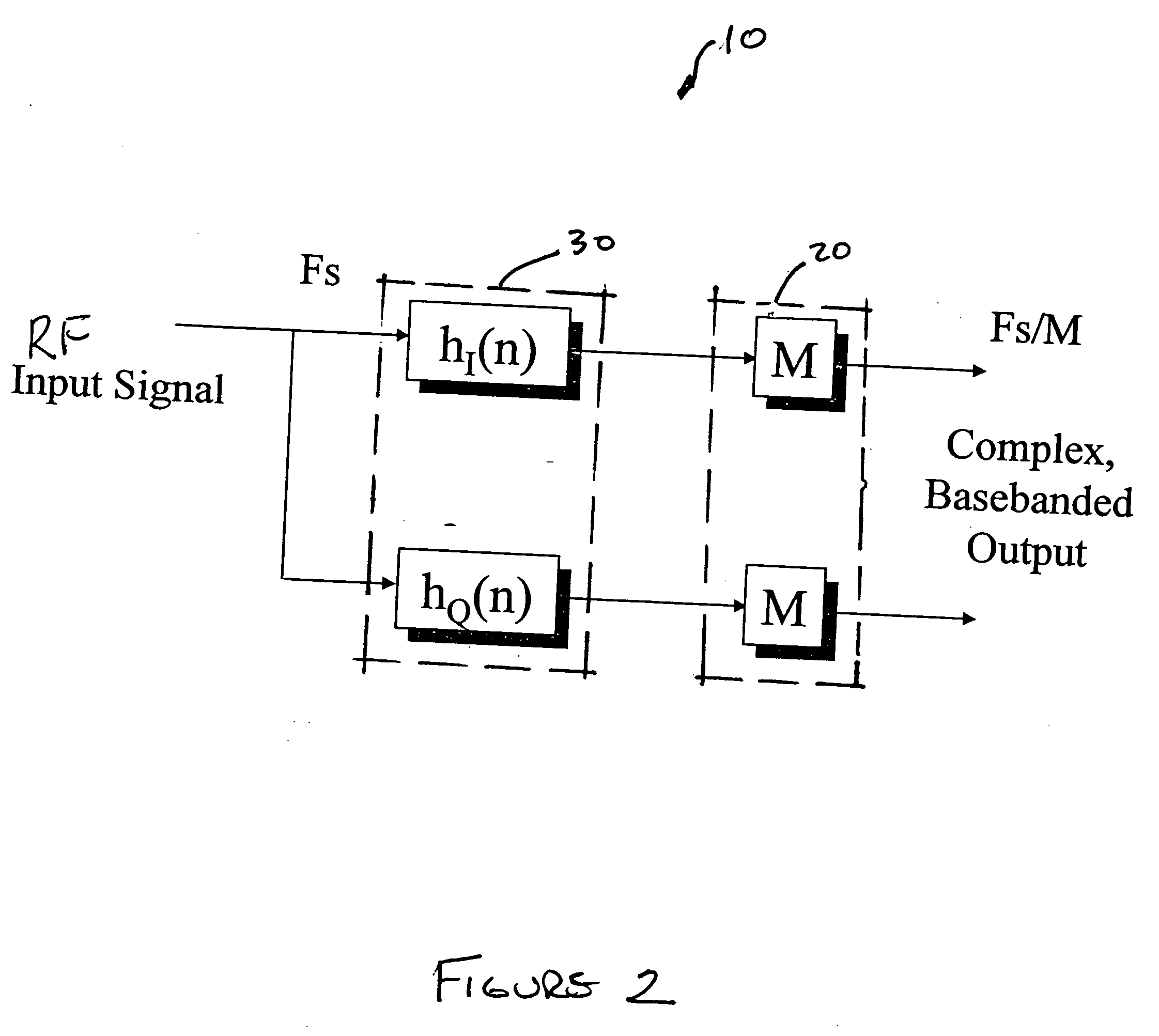
Direct RF complex analog to digital converter
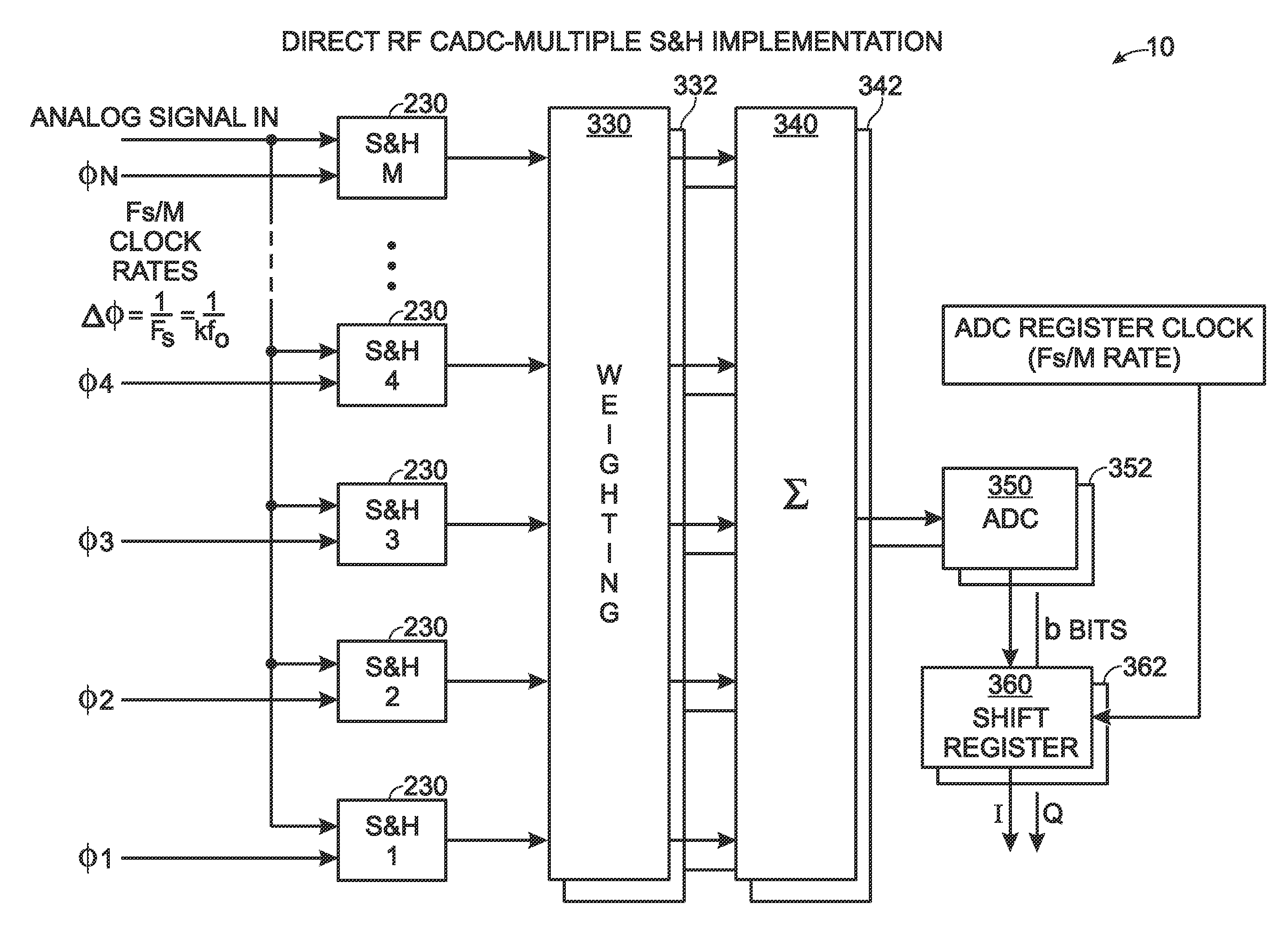
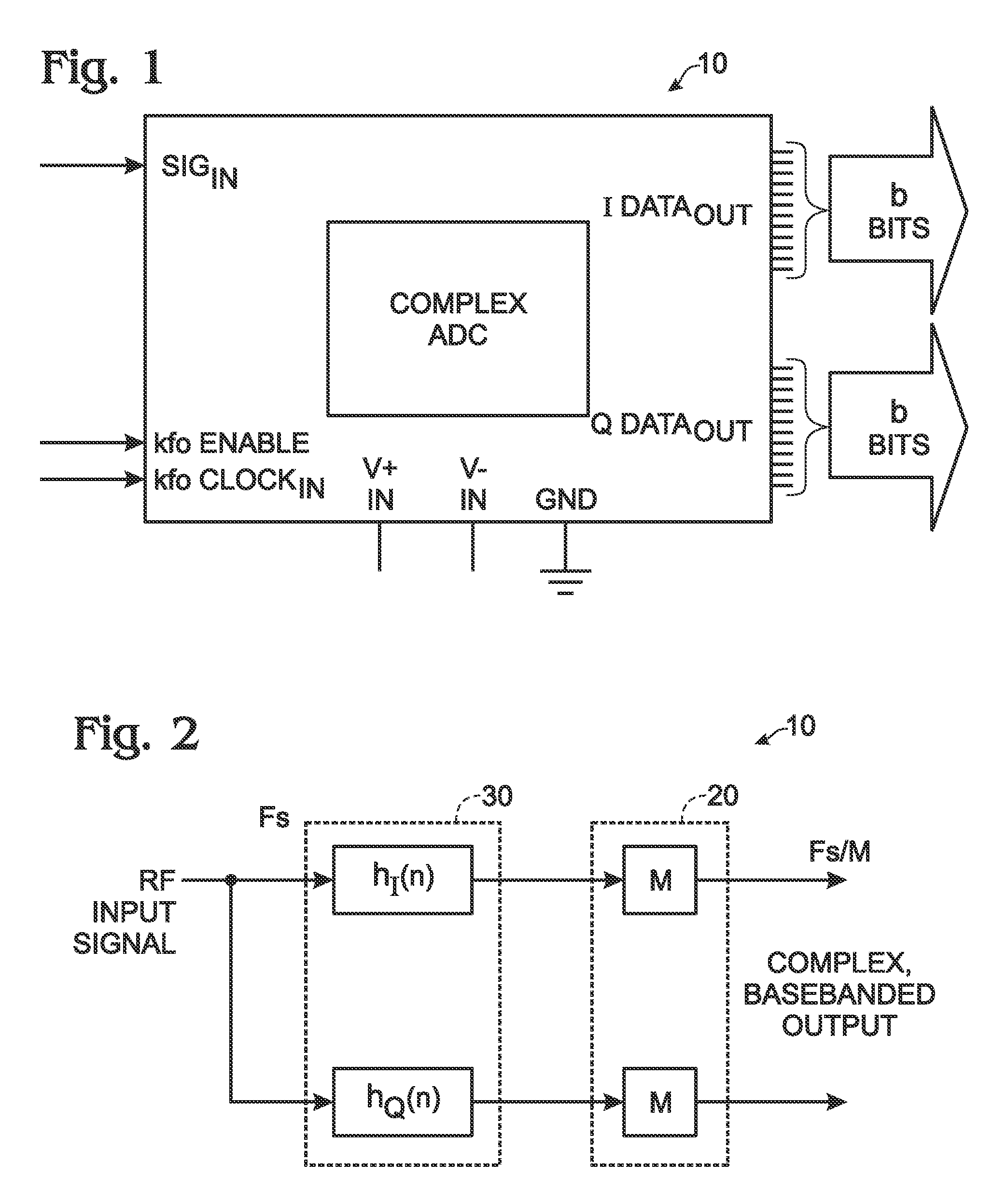
InactiveUS7532684B2Lose weightLess-expensivePhase-modulated carrier systemsAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionBandpass filteringDigital down converter
An analog to digital converter device that includes a sample rate reduction system configured to sample a radio frequency (RF) signal. The RF signal has a bandwidth centered at a first frequency. The sample rate reduction system is configured to directly sample the RF signal at a sampling rate that is an integer multiple of the first frequency. The sample rate reduction system also is configured to provide M-sample outputs, each of the M-sample outputs being sampled at a reduced sampling rate equal to the sampling rate divided by M. M is an integer sample rate reduction value. An Nth order complex bandpass filter is coupled to the sample rate reduction system. The complex bandpass filter is configured to filter each of the M-sample outputs to obtain a plurality of complex baseband signals.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Entitative coal seam gas drainage drilling hole double-pipe drainage method
ActiveCN103075179AIncreased extraction flowIncreased extraction spaceGas removalSealing/packingGeomorphologyDrainage flow
The invention provides an entitative coal seam gas drainage drilling hole double-pipe drainage method, which is particularly applicable to a coal mine underground entitative coal seam long-distance and large-aperture gas drainage drilling hole. A gas drainage pipe is sent into the drainage drilling hole to the hole bottom, a flexible sleeve pipe with the diameter being twice the diameter of the gas drainage pipe is sheathed at the back part of the gas drainage pipe, a 3-4m pattern hole is formed at the front end of the flexible sleeve pipe, a first polyurethane double-material hole sealing bag and a second polyurethane double-material hole sealing bag are respectively and fixedly arranged in positions with distances being 4 to 5m and 22 to 23m from the front end of the flexible sleeve pipe by adhesive tapes, and the flexible sleeve pipe is sent into the drainage drilling hole after the hole sealing bags are extruded so that the second polyurethane double-material hole sealing bag is 2 to 3m away from the hole opening of the drilling hole; after the polyurethane is cured, cement mortar is filled between the two polyurethane hole sealing sections; and after the cement mortar is cured, the flexible sleeve pipe is connected into a gas drainage net for gas drainage. The method has the advantages that the structure is simple, the operation is convenient, and the problem of gas drainage flow rate reduction can be effectively solved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Direct RF complex analog to digital converter
InactiveUS20060165198A1Improve system reliabilityLarge digital word sizePhase-modulated carrier systemsAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionBandpass filteringA d converter
An analog to digital converter device that includes a sample rate reduction system configured to sample a radio frequency (RF) signal. The RF signal has a bandwidth centered at a first frequency. The sample rate reduction system is configured to directly sample the RF signal at a sampling rate that is an integer multiple of the first frequency. The sample rate reduction system also is configured to provide M-sample outputs, each of the M-sample outputs being sampled at a reduced sampling rate equal to the sampling rate divided by M. M is an integer sample rate reduction value. An Nth order complex bandpass filter is coupled to the sample rate reduction system. The complex bandpass filter is configured to filter each of the M-sample outputs to obtain a plurality of complex baseband signals.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Reducing packet loss for a packet data service during congestion in a transport network
A method and an apparatus for reducing packet loss for a packet data service during congestion in a transport network are provided. The method comprises measuring a packet loss rate over a time period in one or more flows of data traffic packets associated with the packet data service to determine whether the one or more flows of data traffic packets are experiencing a variation in a desired traffic performance level at a particular time duration during the congestion in the time period. The method further comprises triggering a request to reduce a flow rate of at least one of the one or more flows of data traffic packets based on the packet loss rate if the at least one of the one or more flows of data traffic packets experiences the variation in the desired traffic performance level. By using a distributed transport congestion control, for example, only such Best Effort data traffic packet flows that generate bursty traffic at a specific moment of congestion sense the congestion and thus trigger an associated rate reduction action. However, other flows that do not experience the congestion may not be affected.
Owner:RPX CORP
Real estate finance instrument
InactiveUS20050021453A1Monthly paymentReduce paymentFinanceSpecial data processing applicationsPaymentRate reduction
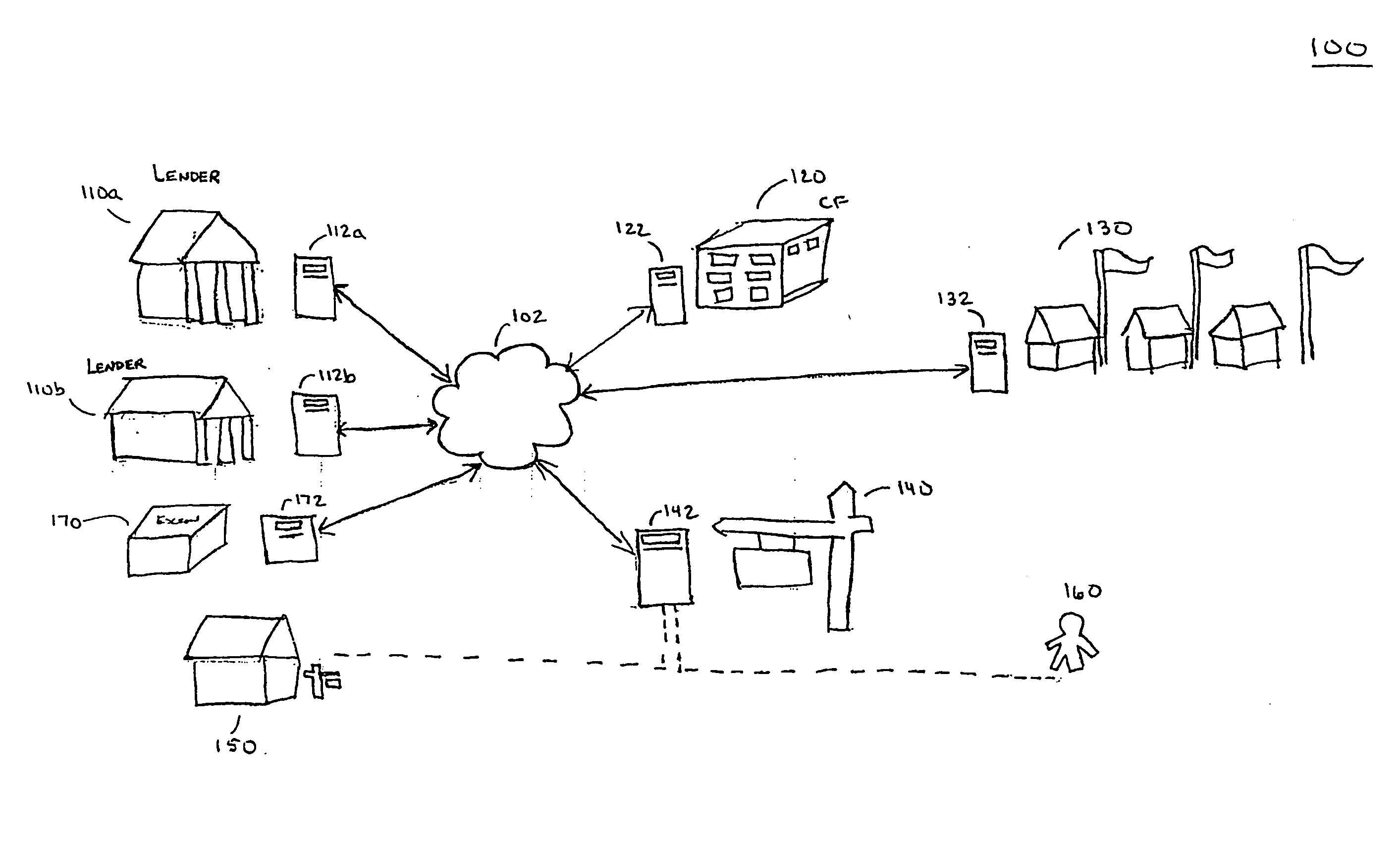
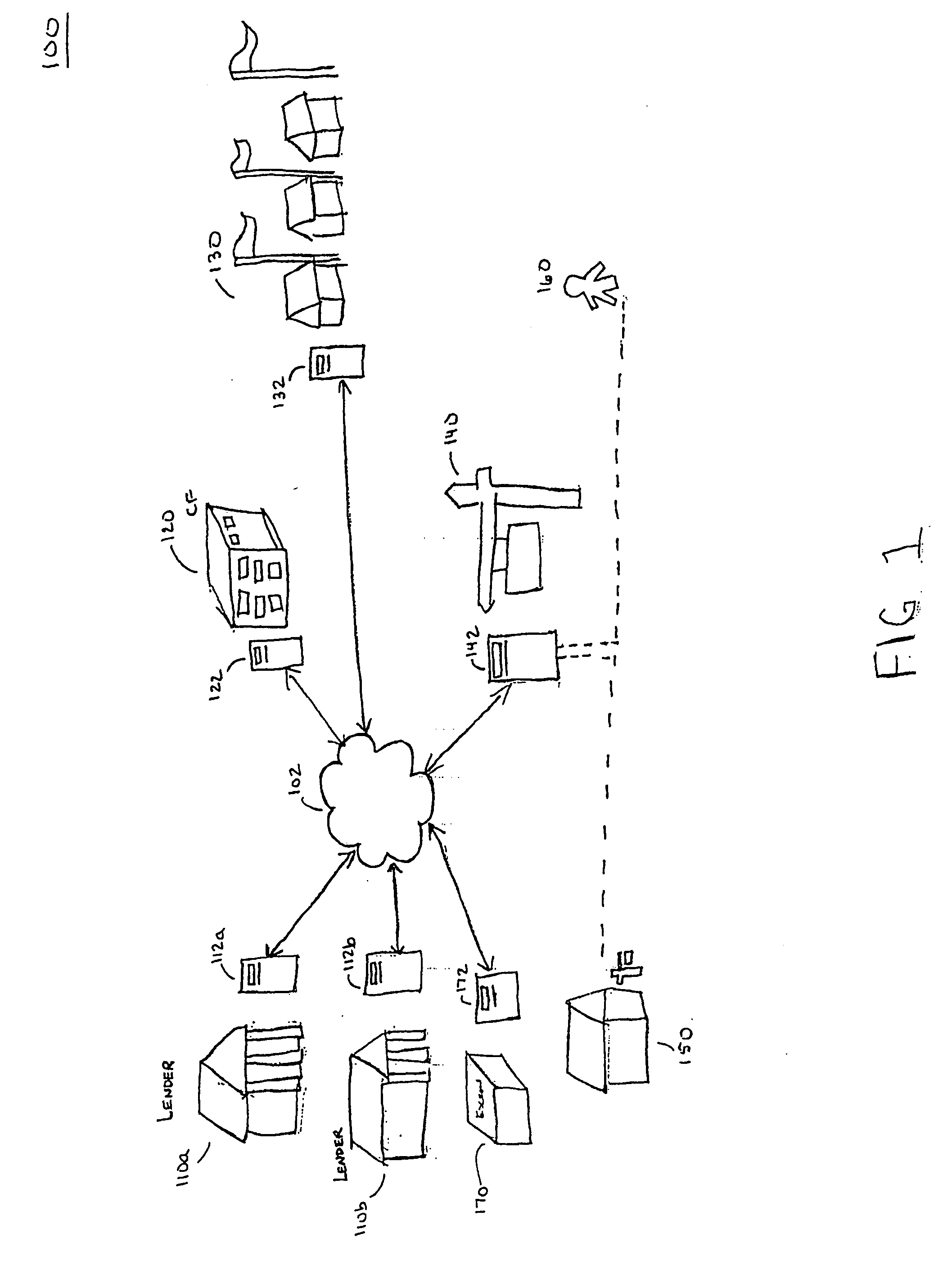
A system and method of structuring and financing a real estate transaction, such as a residential real estate transaction. A seller can maximize a selling price while minimizing the loan payments of the buyer over a predetermined period of time. A seller can purchase a financial instrument as seller paid points that can result in a reduction in the effective interest rate for the buyer. The interest rate reduction can be effective over a predetermined period of time, usually less than or equal to five years. The buyer can present the financial instrument to a lender when applying for a mortgage. The lender can redeem the financial instrument for the amount of seller paid points and supplement any mortgage. The lender can then reduce the buyer's loan payments over the predetermined period of time, based on the amount of seller paid points.
Owner:LYMAN GERALD G
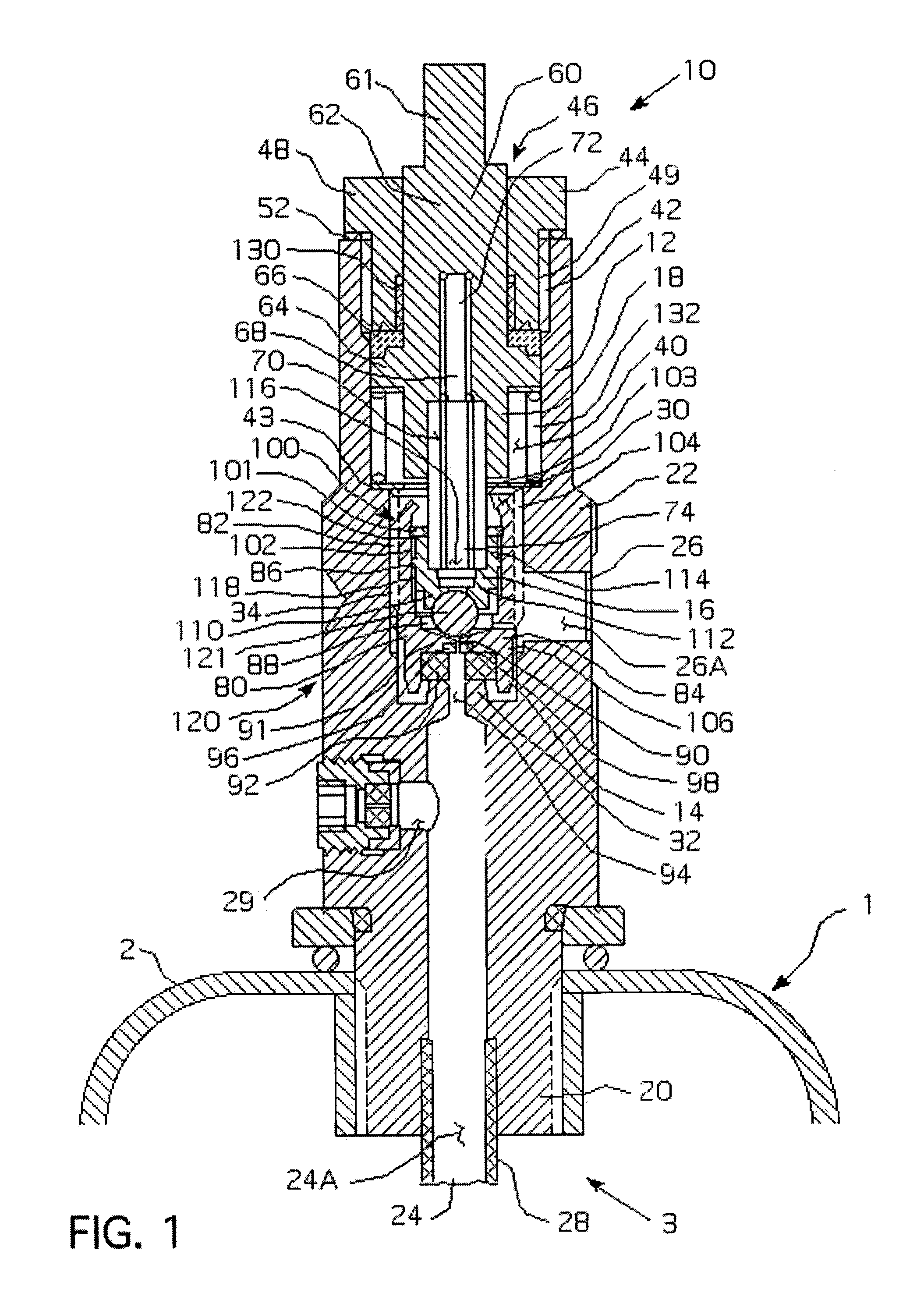
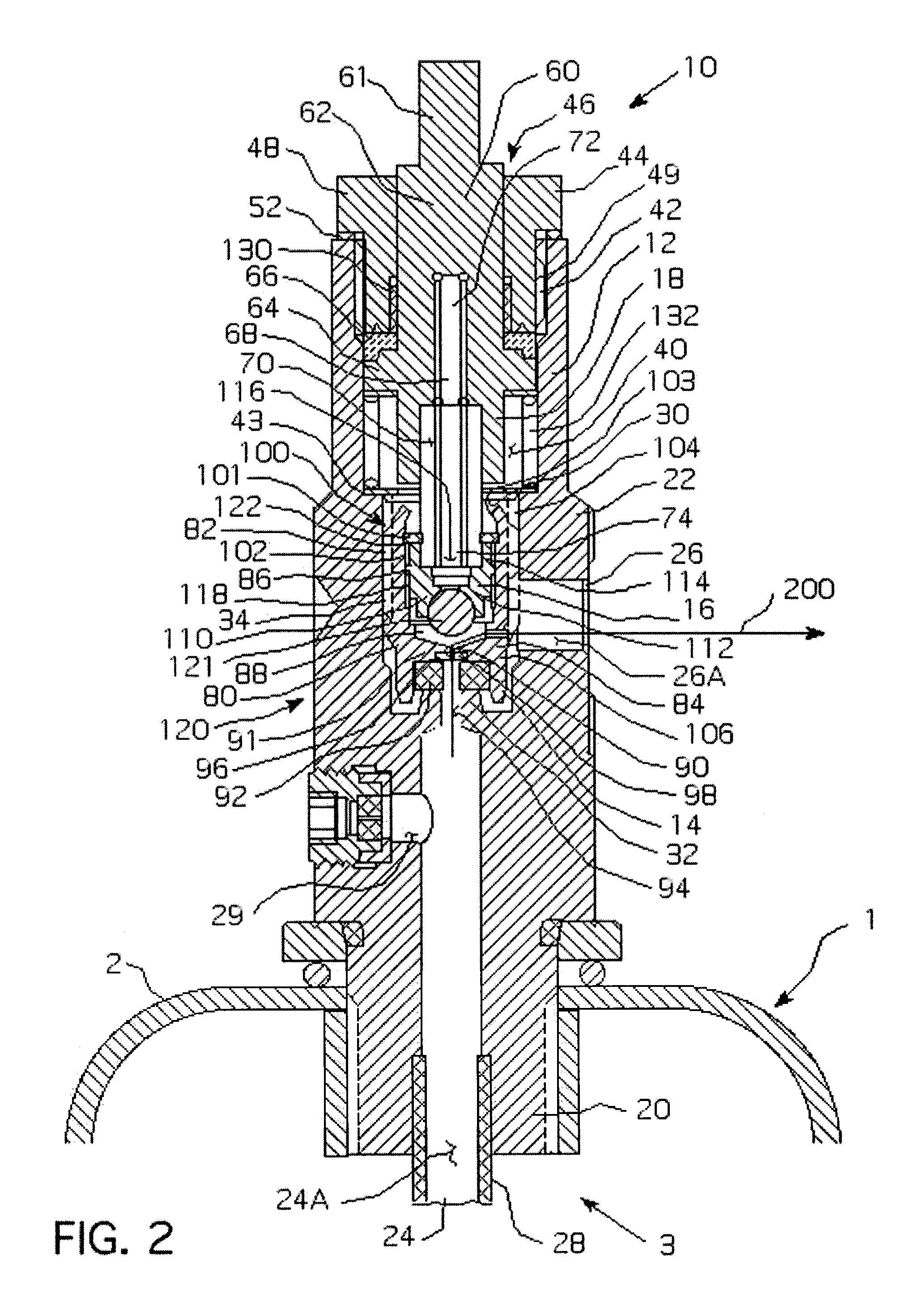
Valve with pressurization rate reduction device
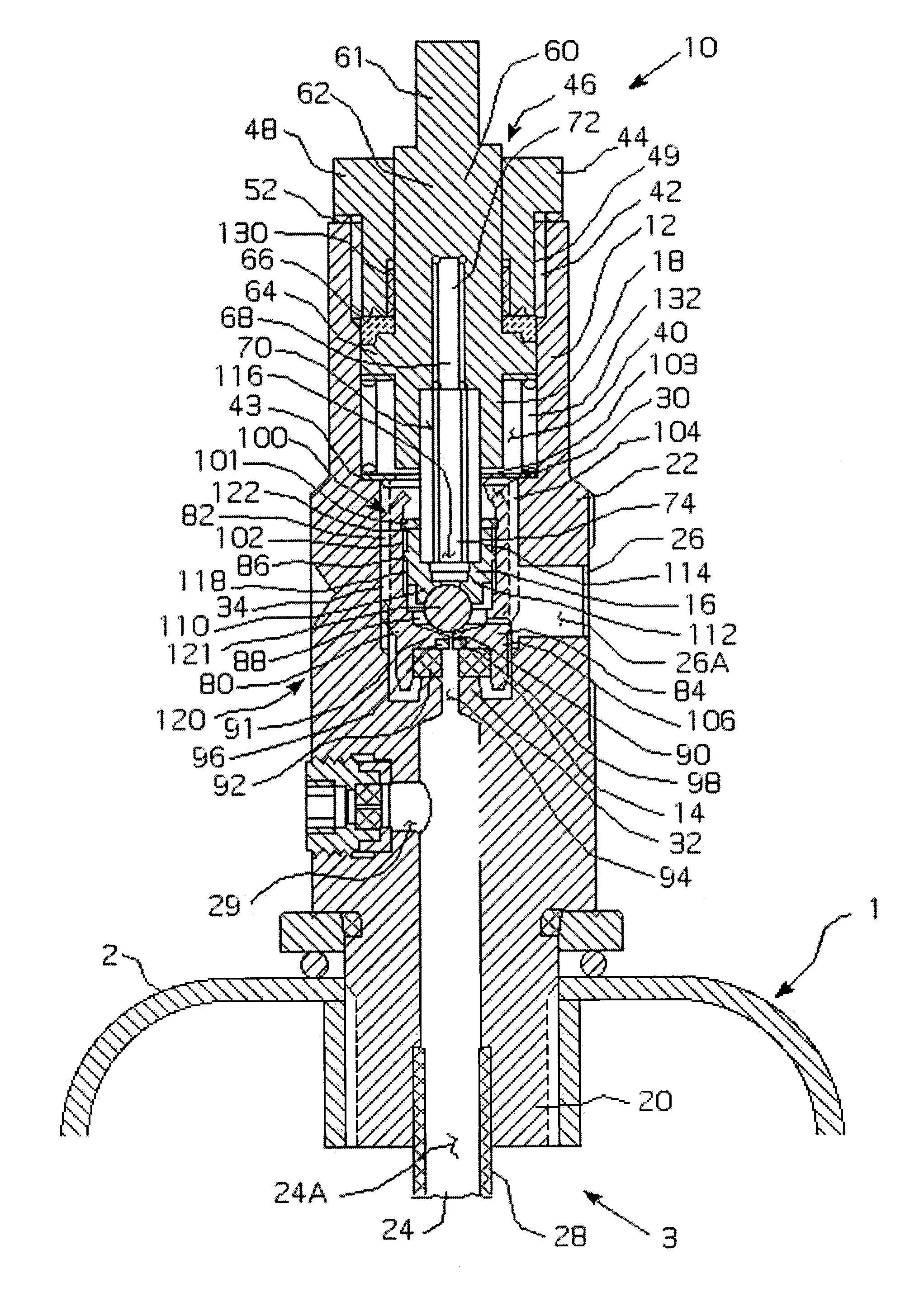
ActiveUS6957661B1Reduce chanceReduce and eliminate and compressionOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPressure relieving devices on sealing facesEngineeringRate reduction
A valve includes a housing assembly, a stem assembly and a surge suppression device. The surge suppression device includes an initial flowpath between the valve inlet and the outlet, a primary flowpath between the inlet and the outlet, a first valve assembly and a second valve assembly. The first valve assembly is coupled to the stem assembly and threadably engages the housing assembly and structured to move between a first, closed position wherein the primary flowpath is blocked and a second, open position wherein the primary flowpath is not blocked. The second valve assembly is threadably coupled to the housing assembly and structured to move between a first, closed position wherein the initial flowpath is blocked and a second, open position wherein the initial flowpath is not blocked.
Owner:SHERWOOD VALVE
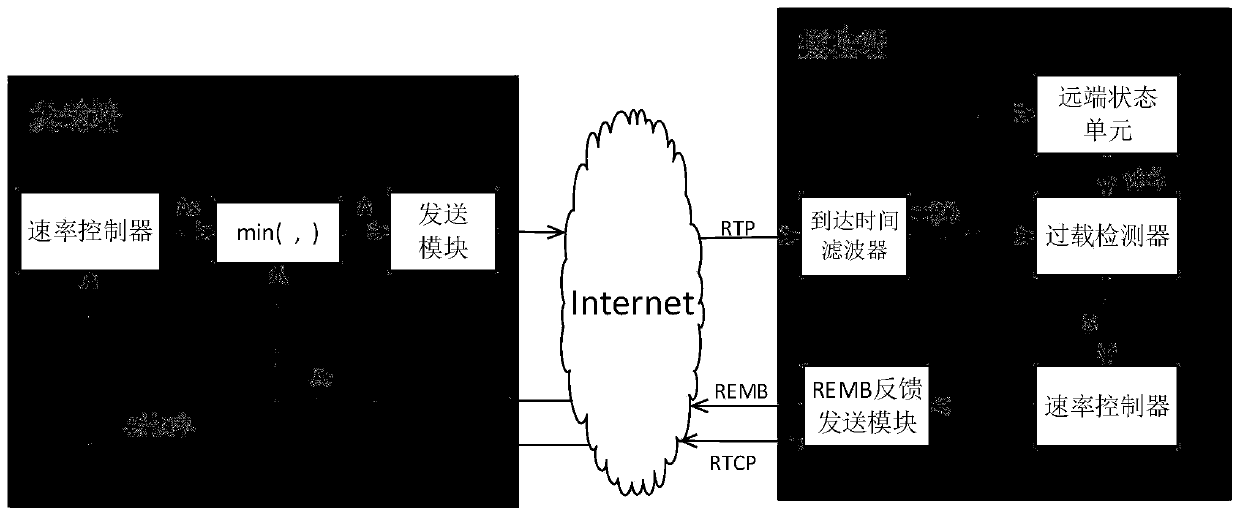
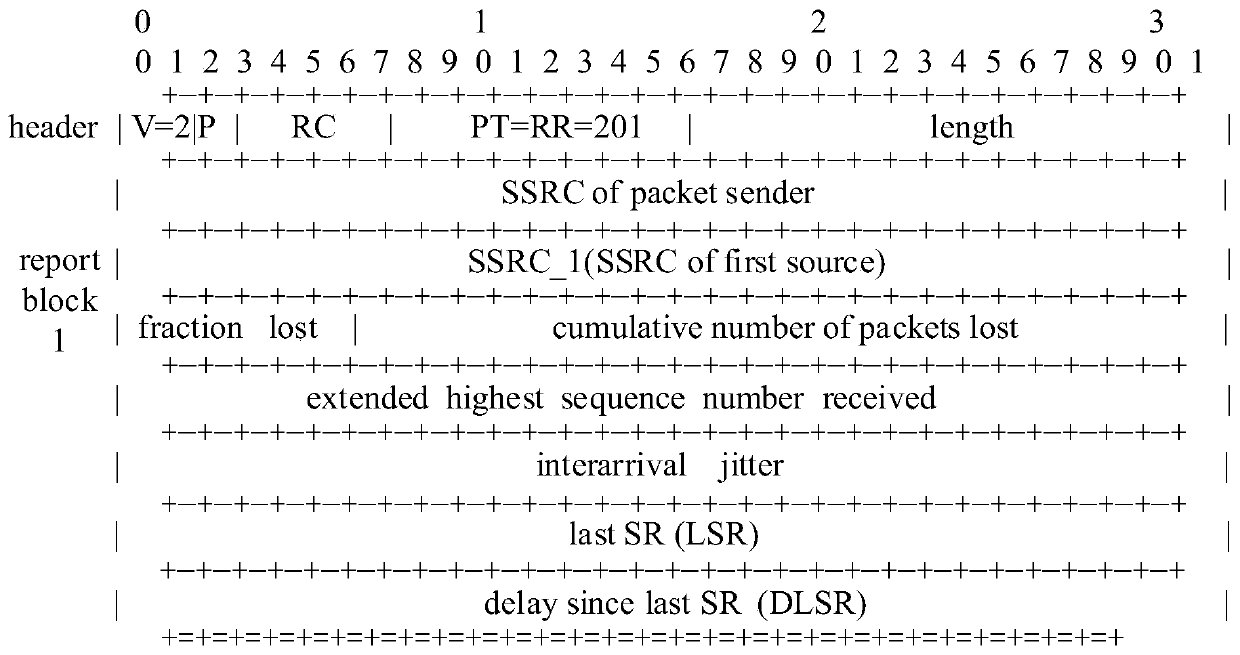
Rate reduction parameter optimization method based on a congestion degree factor
InactiveCN109905326AMeet optimization needsHigh real-time requirementsData switching networksTime delaysReal time communication systems
The invention discloses a rate reduction parameter optimization method based on a congestion degree factor. The rate reduction parameter optimization method is applied to a point-to-point multimedia real-time communication system based on an RTP / RTCP protocol. The method comprises the following steps of the receiving end adaptively selects a congestion threshold value according to the inter-frametime delay change condition, generates a state signal S by combining the queuing time delay change condition of the current frame and the congestion threshold value, and adjusts the sending rate according to the state signal. When the network is congested, the congestion degree is quantified, a rate reduction parameter is calculated according to the congestion degree, and the sending rate is controlled to be reduced as the step length; and finally,the final sending rate is calaculated by combining the estimated values of the rate control modules of the sending end and the receiving end to thesending rate. Compared with the prior art, the method can be suitable for various network environments, the incoming rate can be increased, the packet loss rate and the network delay can be reduced, and more stable and smooth multimedia real-time communication service can be brought to users.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
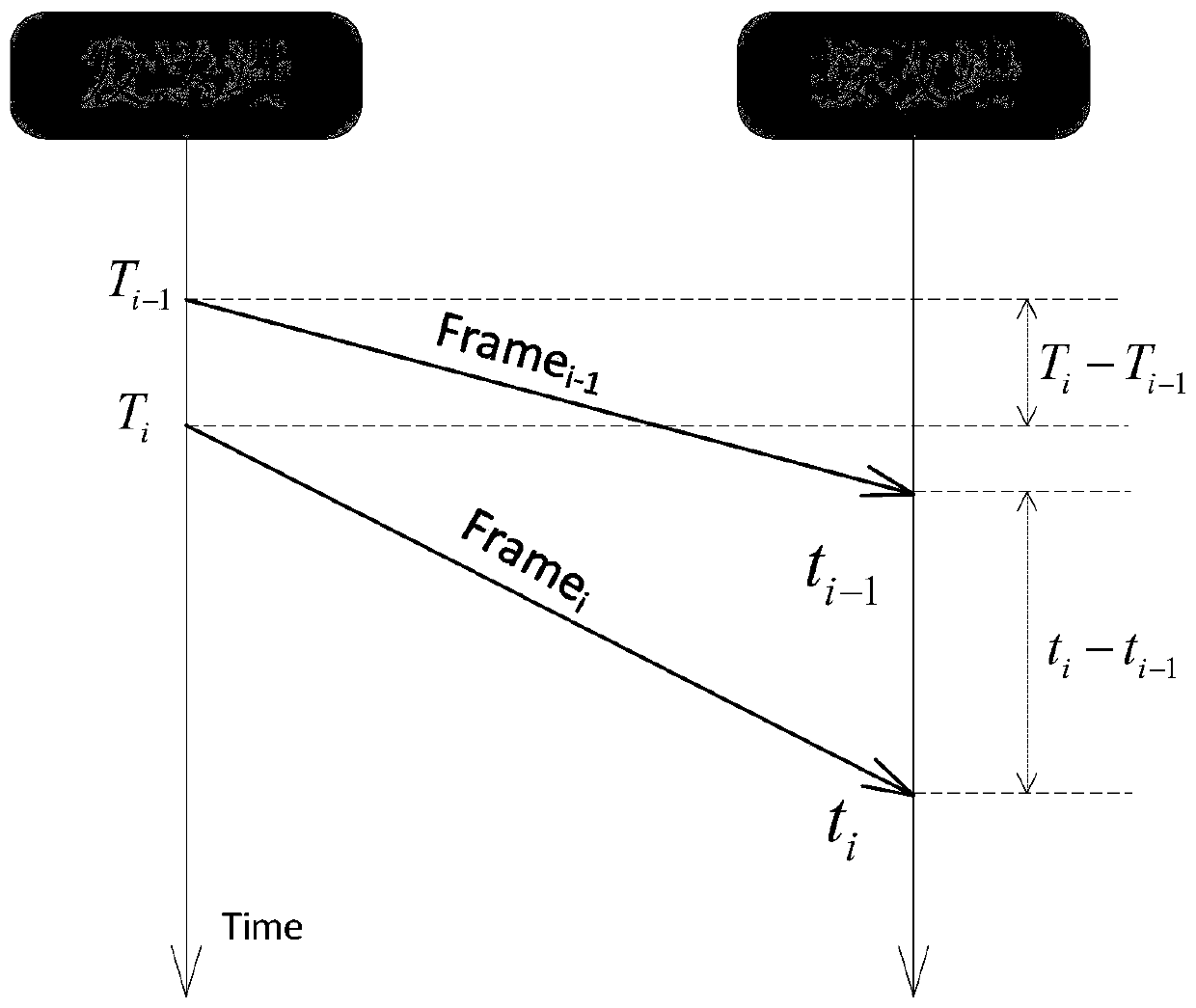
Dynamic updating of scheduling hierarchy in a traffic manager of a network processor
ActiveUS20120020368A1Reducing scheduling rateData switching by path configurationMemory systemsTraffic capacityData stream
Described embodiments provide for dynamically controlling a scheduling rate of each node in a scheduling hierarchy of a network processor. A traffic manager generates a tree scheduling hierarchy having a root scheduler and N scheduler levels. The network processor generates tasks corresponding to received packets. A traffic manager enqueues received tasks in a queue of the scheduling hierarchy associated with a data flow. The queue has a parent scheduler at each level of the hierarchy up to the root scheduler. The traffic manager maintains one or more scheduling data structures for each node in the scheduling hierarchy. If the traffic manager receives a rate reduction request corresponding to a given node of the scheduling hierarchy, the traffic manager updates one or more indicators in the scheduling data structure corresponding to the given node and removes the given node from the scheduling hierarchy, thereby reducing the scheduling rate of the node.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and system for processing communication signal
InactiveCN101262456AFully understandSpatial transmit diversityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksSingular value decompositionChannel state information
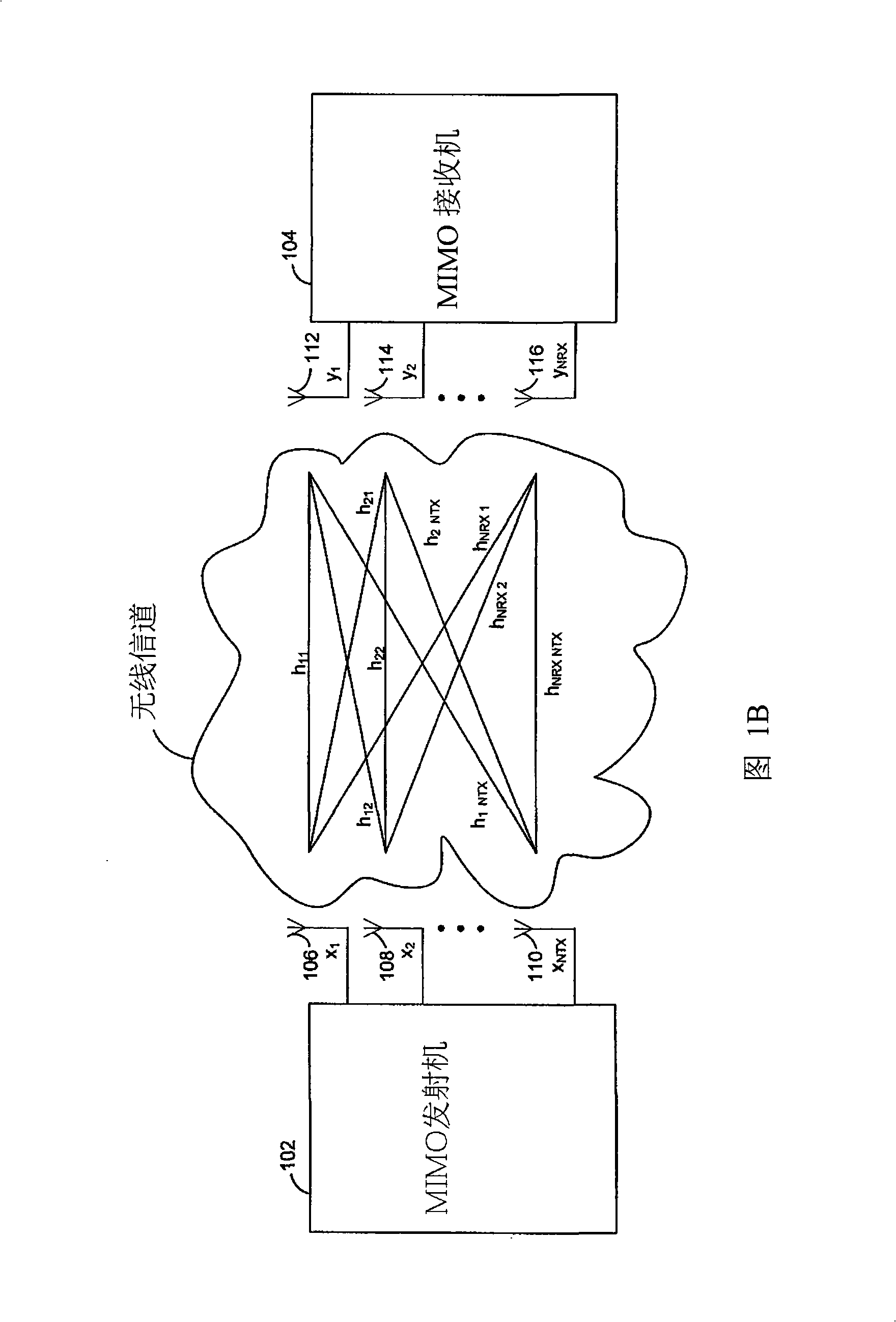
The invention discloses a method and a system for processing communication signal. Aspects of a method and system for a delta quantizer for rate reduction pre-coding matrices may include quantizing a change in channel state information in a MIMO pre-coding system onto a codebook and generating a pre-coding matrix based on at least the channel state information. The channel state information may be a matrix V and one or more associated singular values. The matrix V may be generated using Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) or Geometric Mean Decomposition (GMD). One or more columns of the matrix V may be selected based on the one or more associated singular values and may be combined to enable the generation of the pre-coding matrix. The codebook may comprise one or more unitary matrices. An index of an element of the codebook, onto which the change in channel state information is quantized, may be transmitted from a receiver to a transmitter.
Owner:BROADCOM CORP
Photon/energy identifying X-ray and gamma ray imaging device (“PID”) with a two dimensional array of pixels and system therefrom
ActiveUS9310495B2Mitigate such drawbackReduce the amount requiredTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansDigital signal processingRadiation imaging
An photon (energy) identifying radiation imaging device, for imaging x-ray, gamma ray and charged radiation in medical, dental and industrial applications. The imaging device includes a detector substrate and a readout substrate. The detector substrate has a plurality of detector pixels and the readout substrate has a plurality of corresponding pixel readout circuits. Each pixel readout circuit has circuitry for processing an input analog signal and also has one or more buffers for temporarily storing values corresponding to the signal of at least two individual incoming radiation events. The readout substrate includes a digital controller having digital processing units for carrying out off-pixel digital signal processing and data / rate reduction prior to readout.
Owner:OY AJAT LTD
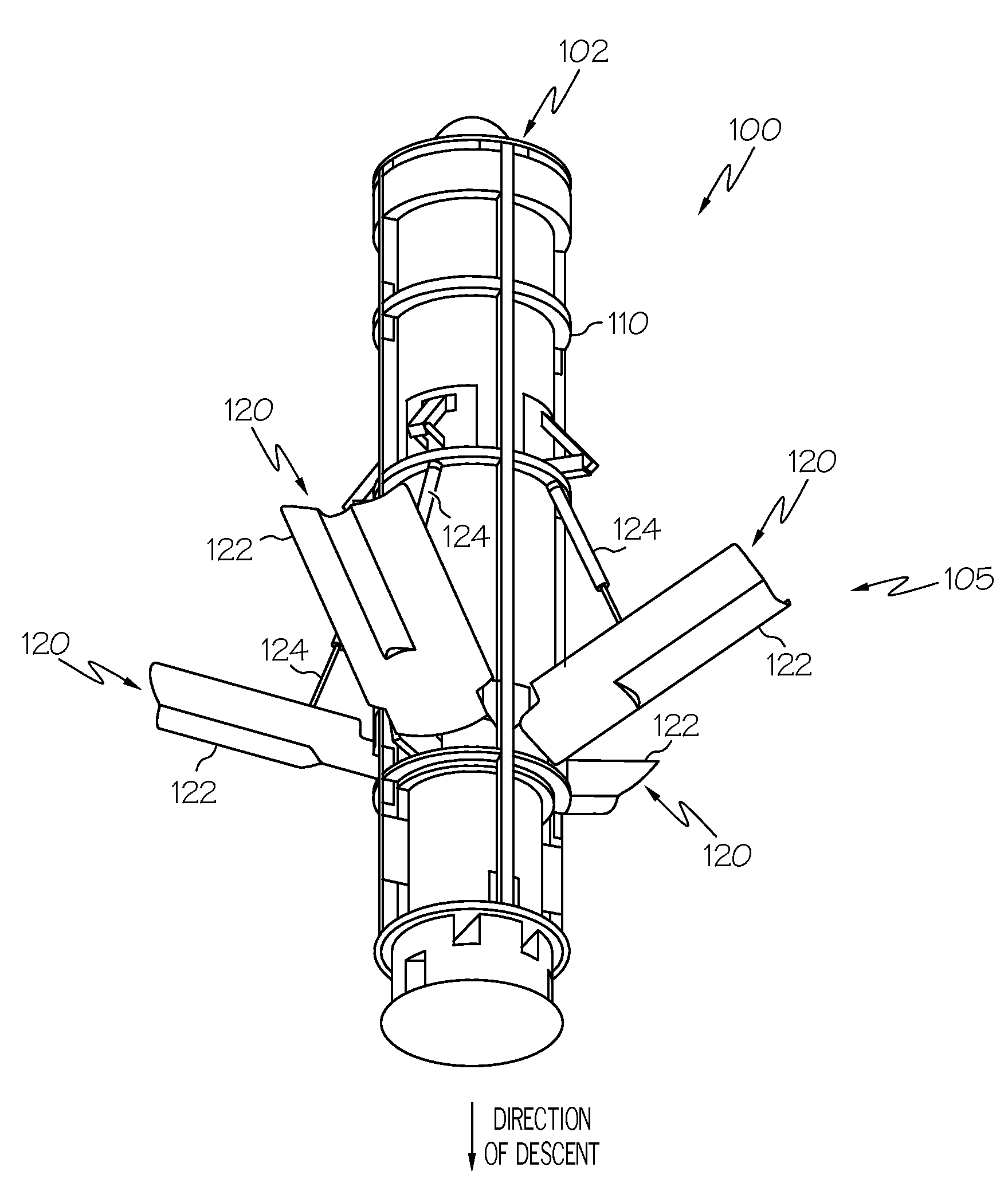
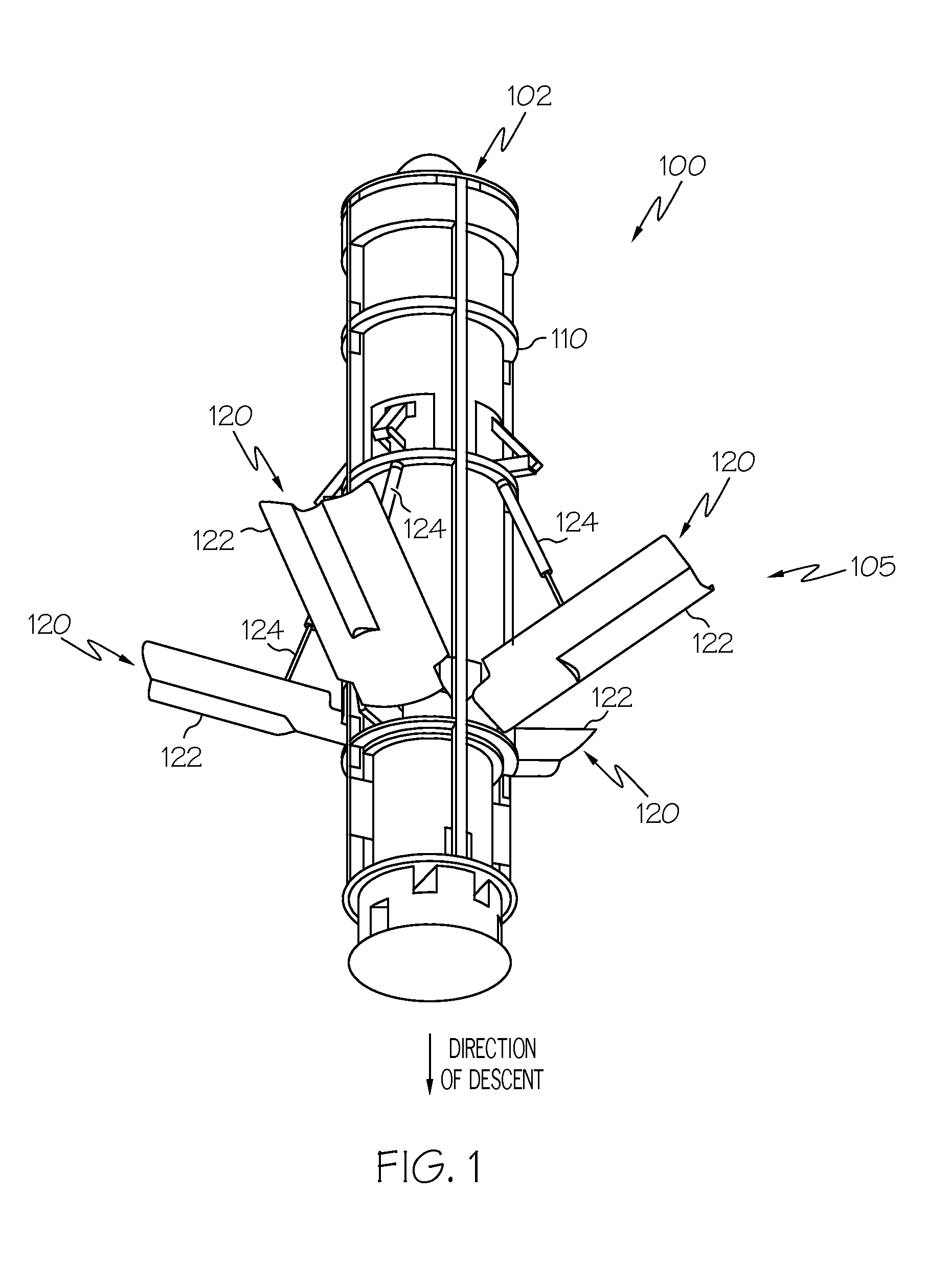
Systems and methods for underwater descent rate reduction
ActiveUS20110041754A1Reduce probabilityDefensive equipmentDepth chargesDelivery vehicleHydrostatic pressure
Systems and methods for underwater descent rate reduction are provided. In one embodiment, a method for underwater descent rate reduction for an underwater delivery vehicle is provided. The method comprises: opening a first valve based on a first hydrostatic pressure to permit water to flow into a first chamber of a hydrostatic pressure driven piston assembly; developing a pressure differential across a piston head separating the first chamber from a second chamber of the hydrostatic pressure driven piston assembly; pushing the piston head into the second chamber to extend a piston rod from the hydrostatic pressure driven piston assembly; and pivoting a deflecting flap downward into a direction of vehicle descent as the piston rod extends.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
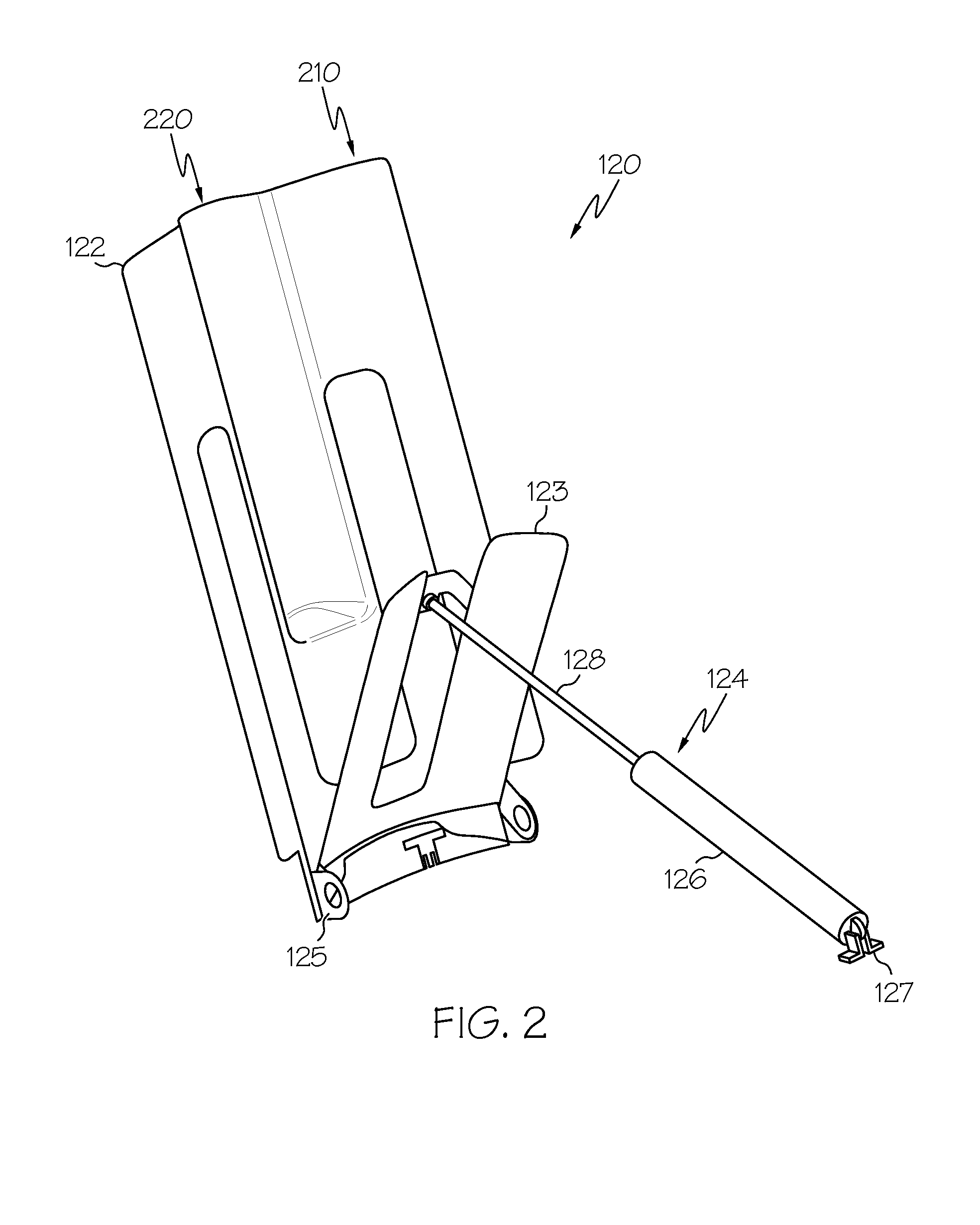
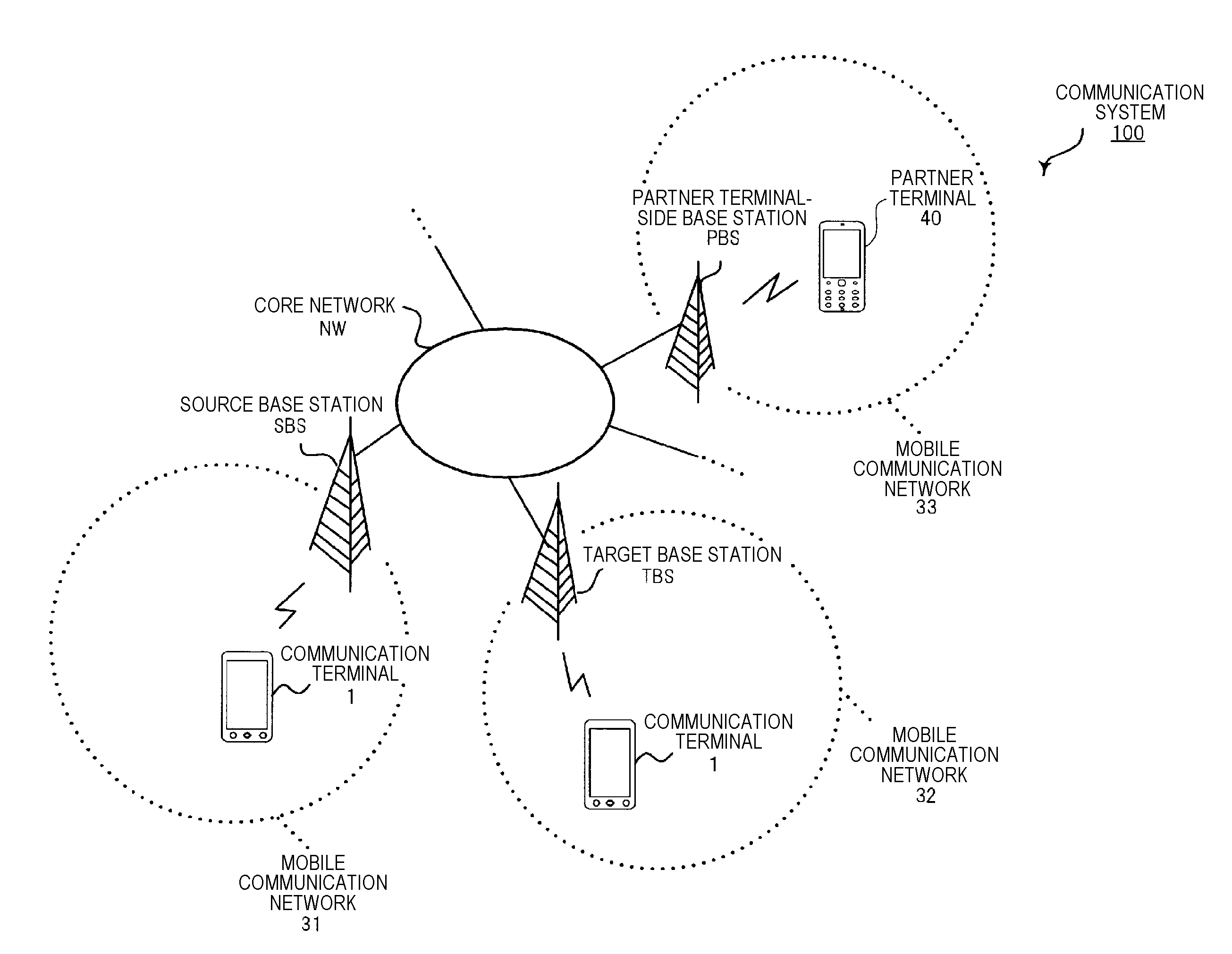
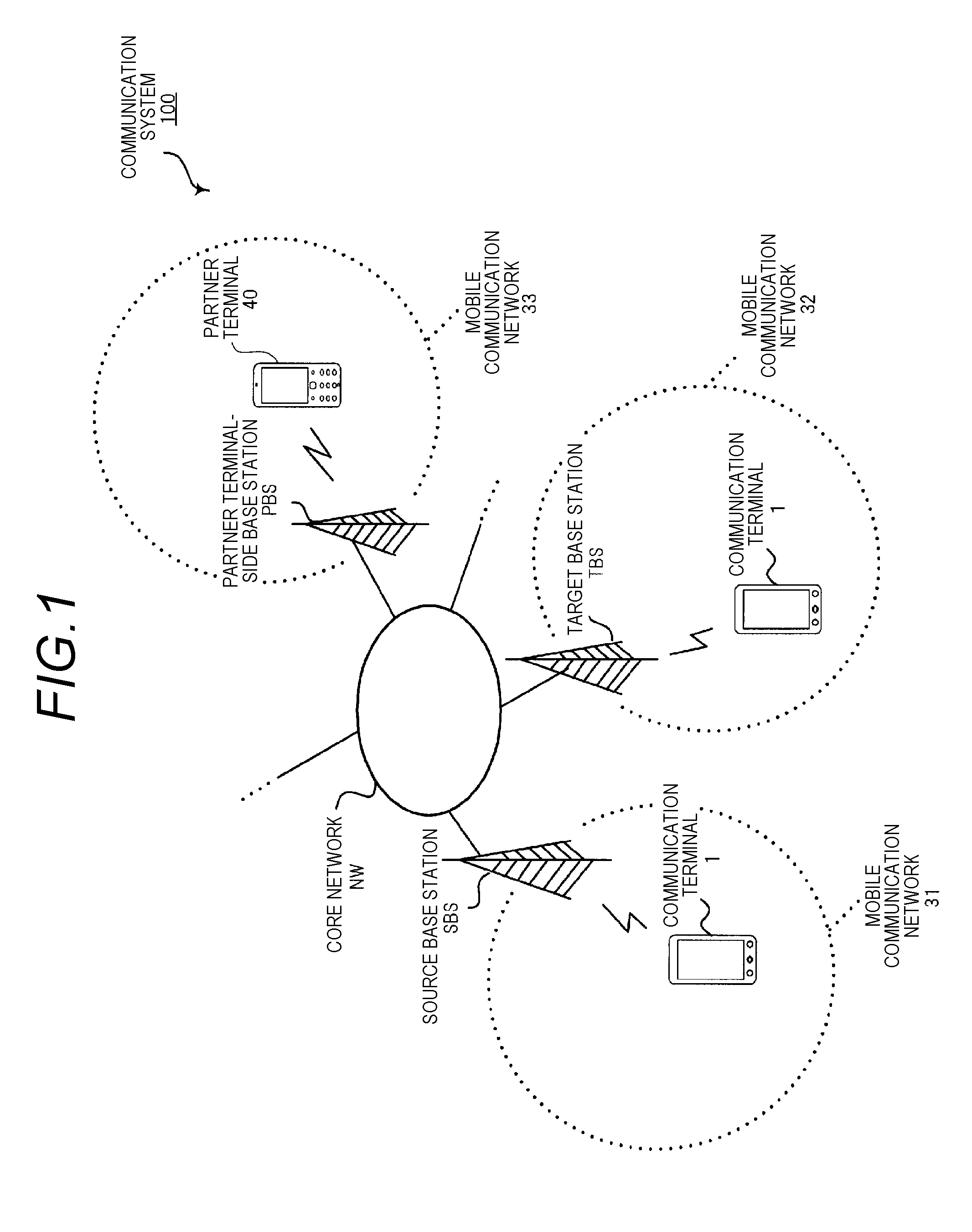
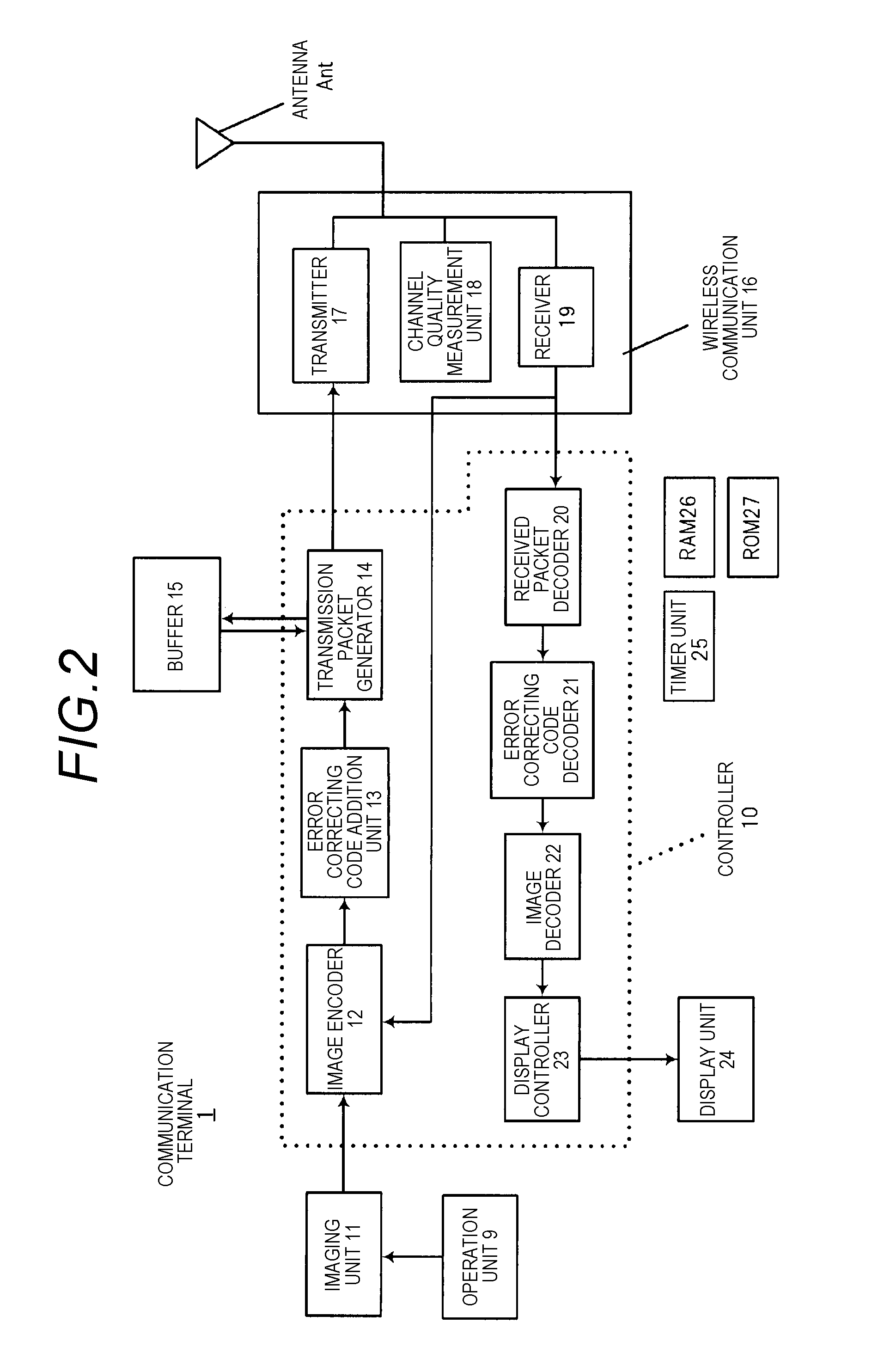
Communication terminal and encoding rate reduction method
ActiveUS20140219251A1Reduce probabilityWireless commuication servicesCommunication unitComputer terminal
A communication terminal includes a communication unit to be connected to a first base station and a second base station in different communication protocols, and an encoder which encodes data at an encoding rate determined according to the first base station or the second base station for each predetermined time T and outputs the encoded data to the communication unit. When a connection destination is changed from the first base station to the second base station in a period when the communication unit is being connected to the first base station, the communication unit transmits change information to the encoder before the change of the connection to the second base station is completed. The encoder changes the encoding rate determined according to the first base station to the encoding rate determined according to the second base station when received the change information.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com