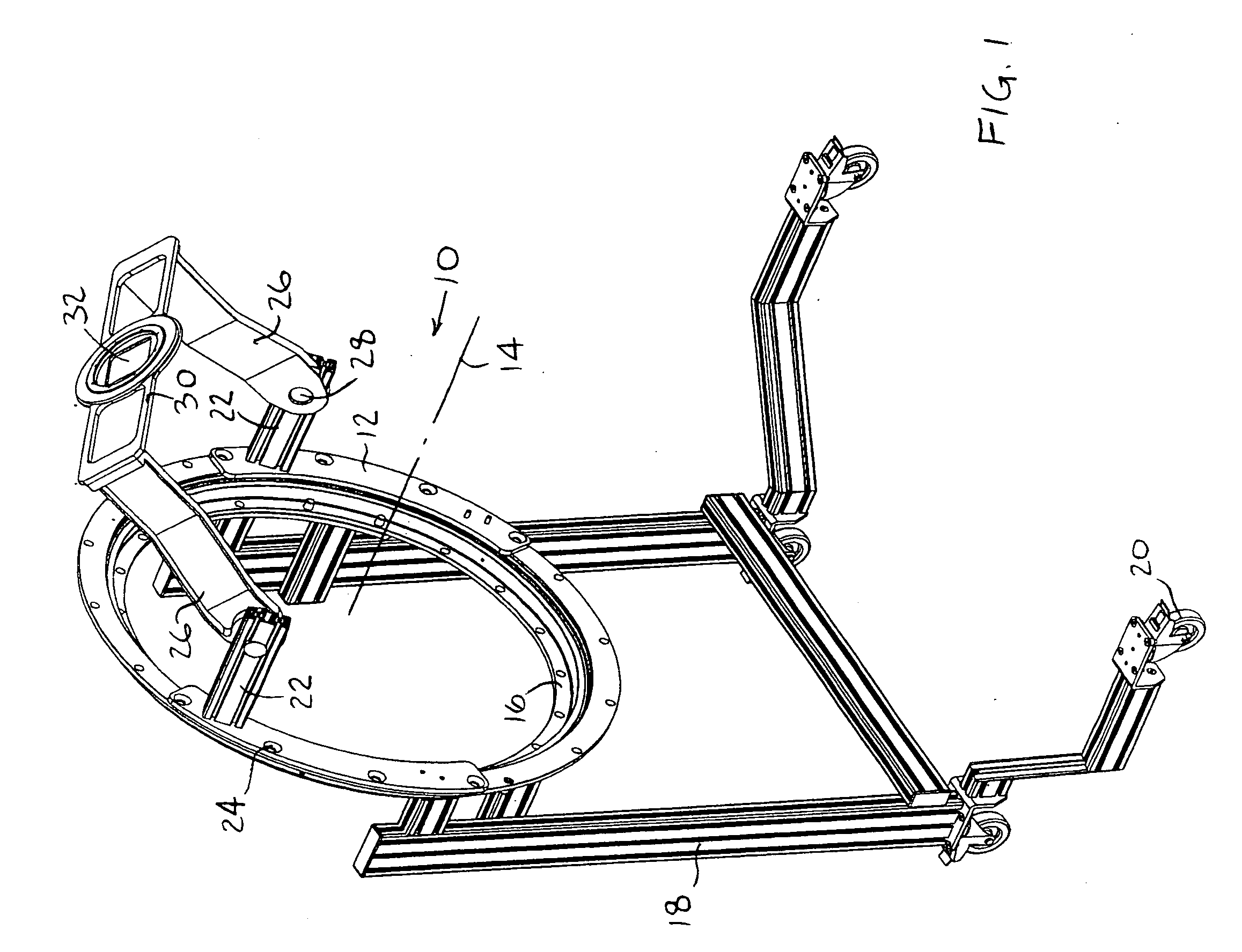
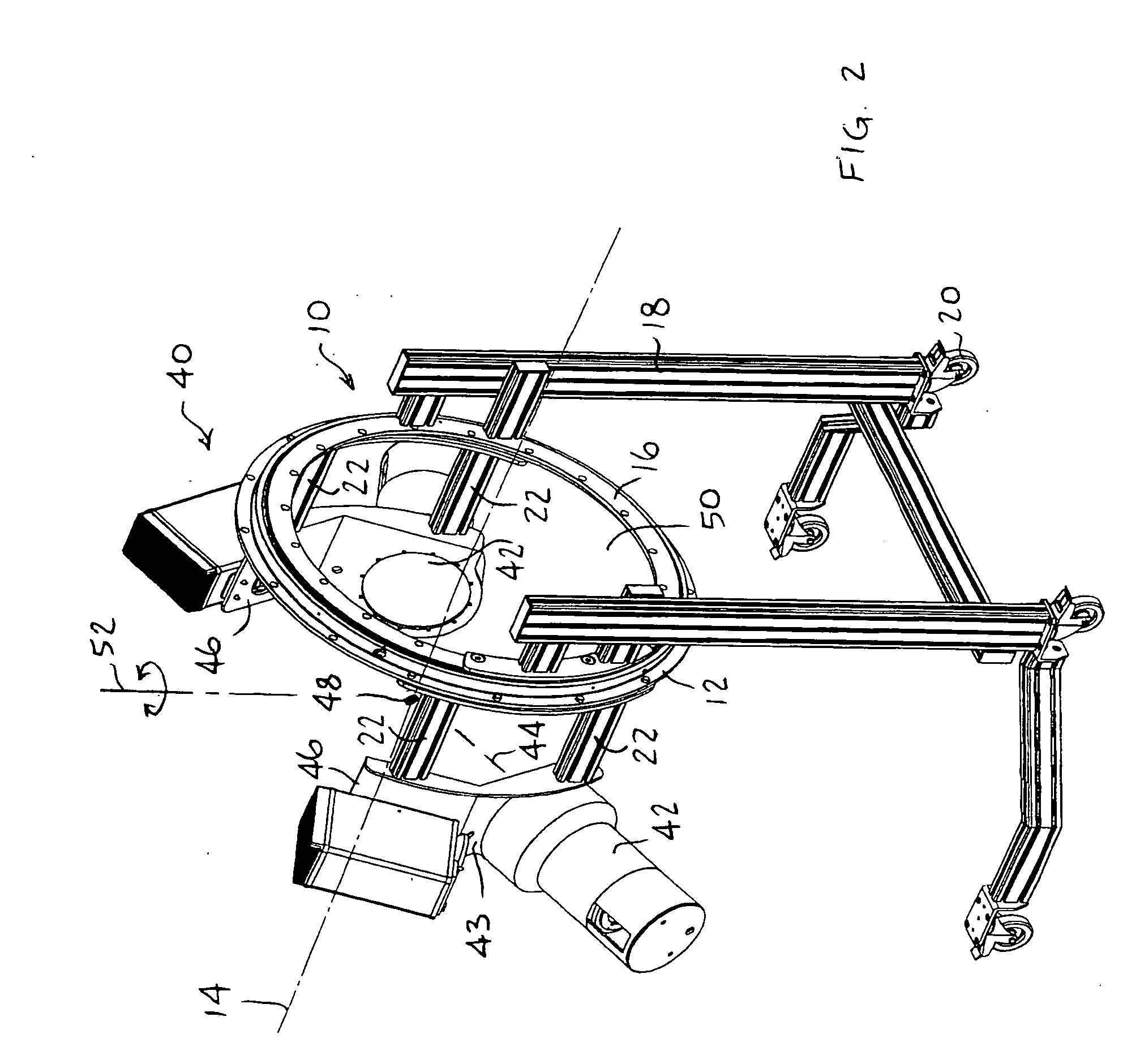
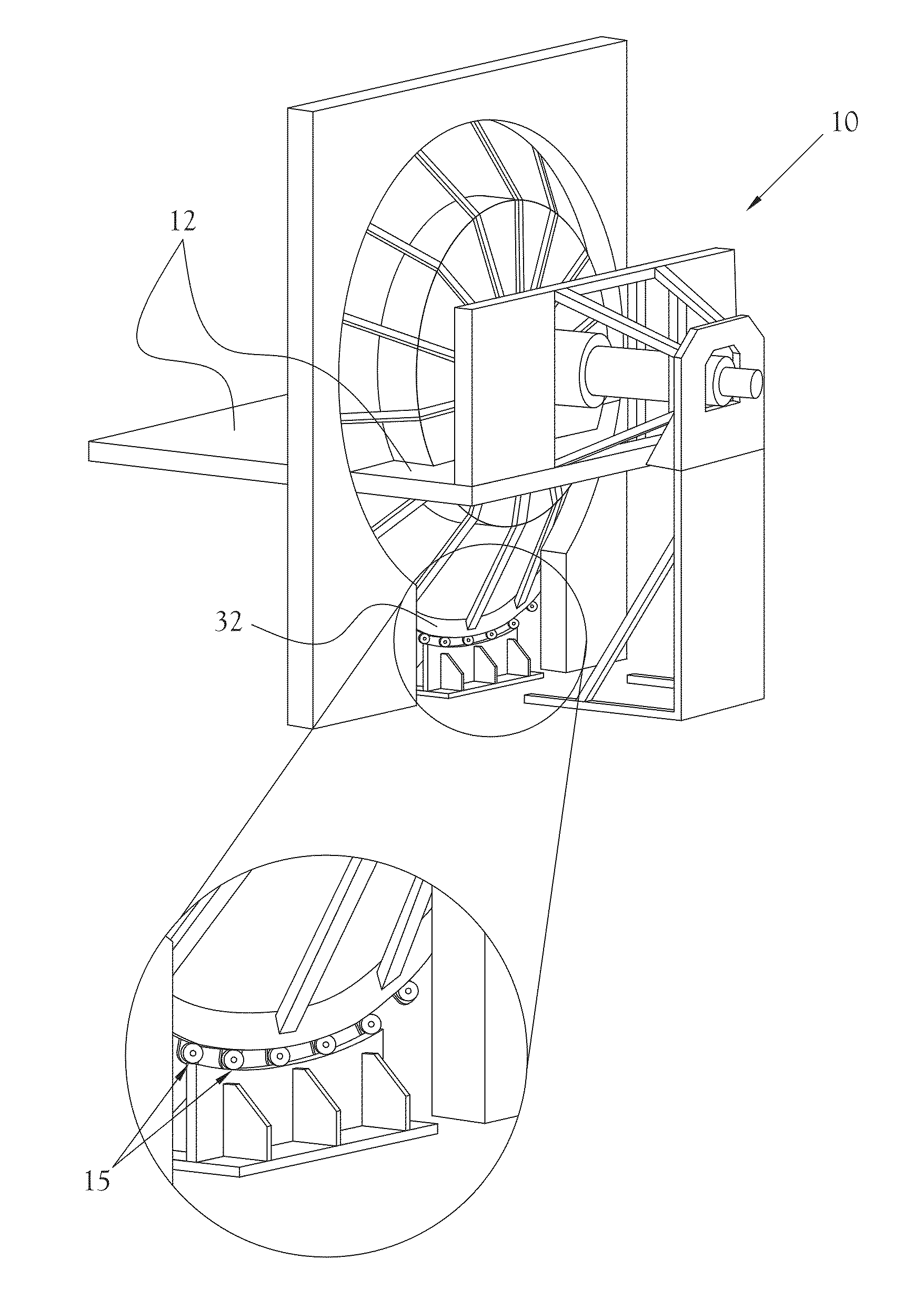
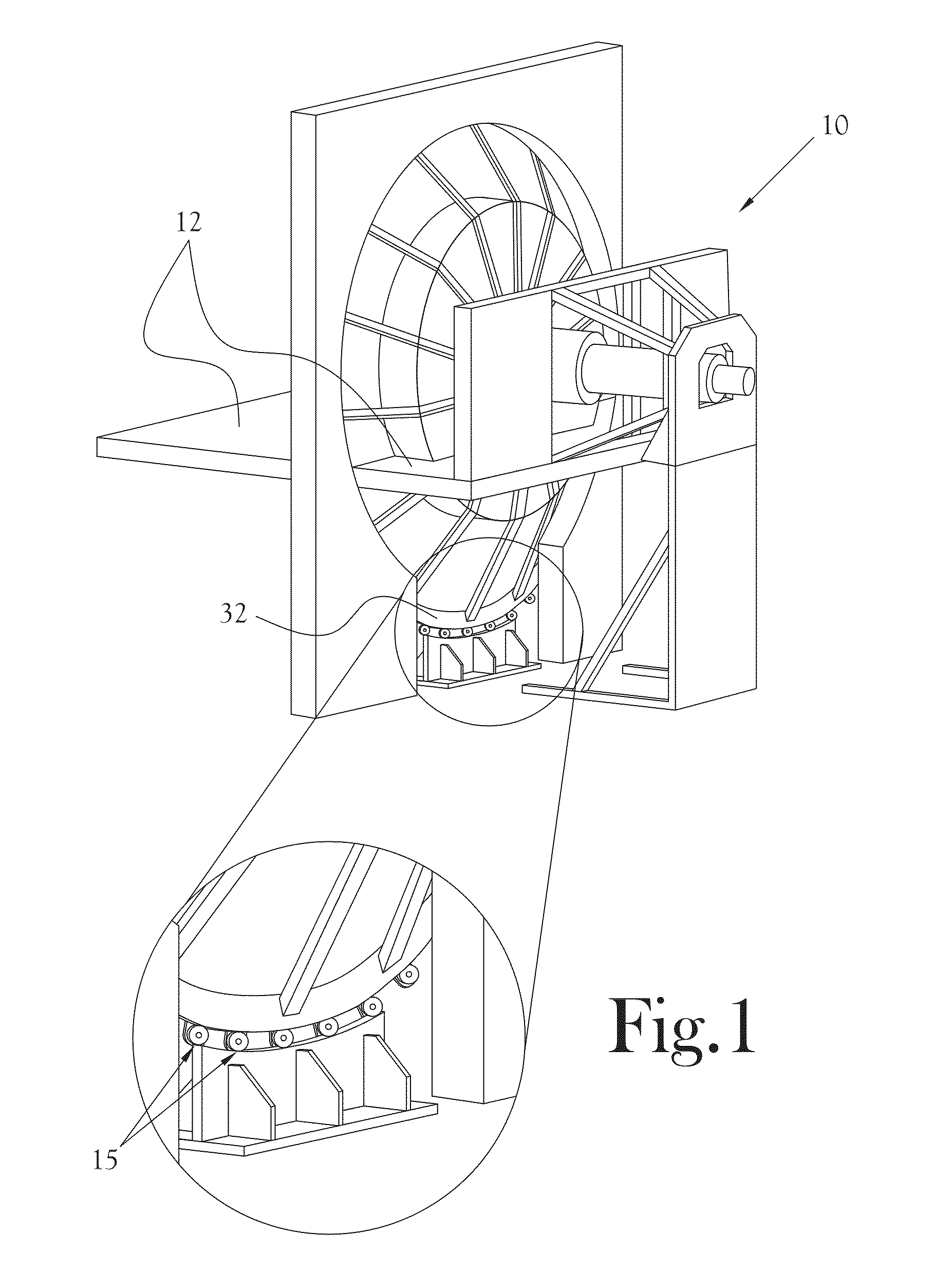
Patents
Literature
181 results about "Isocenter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
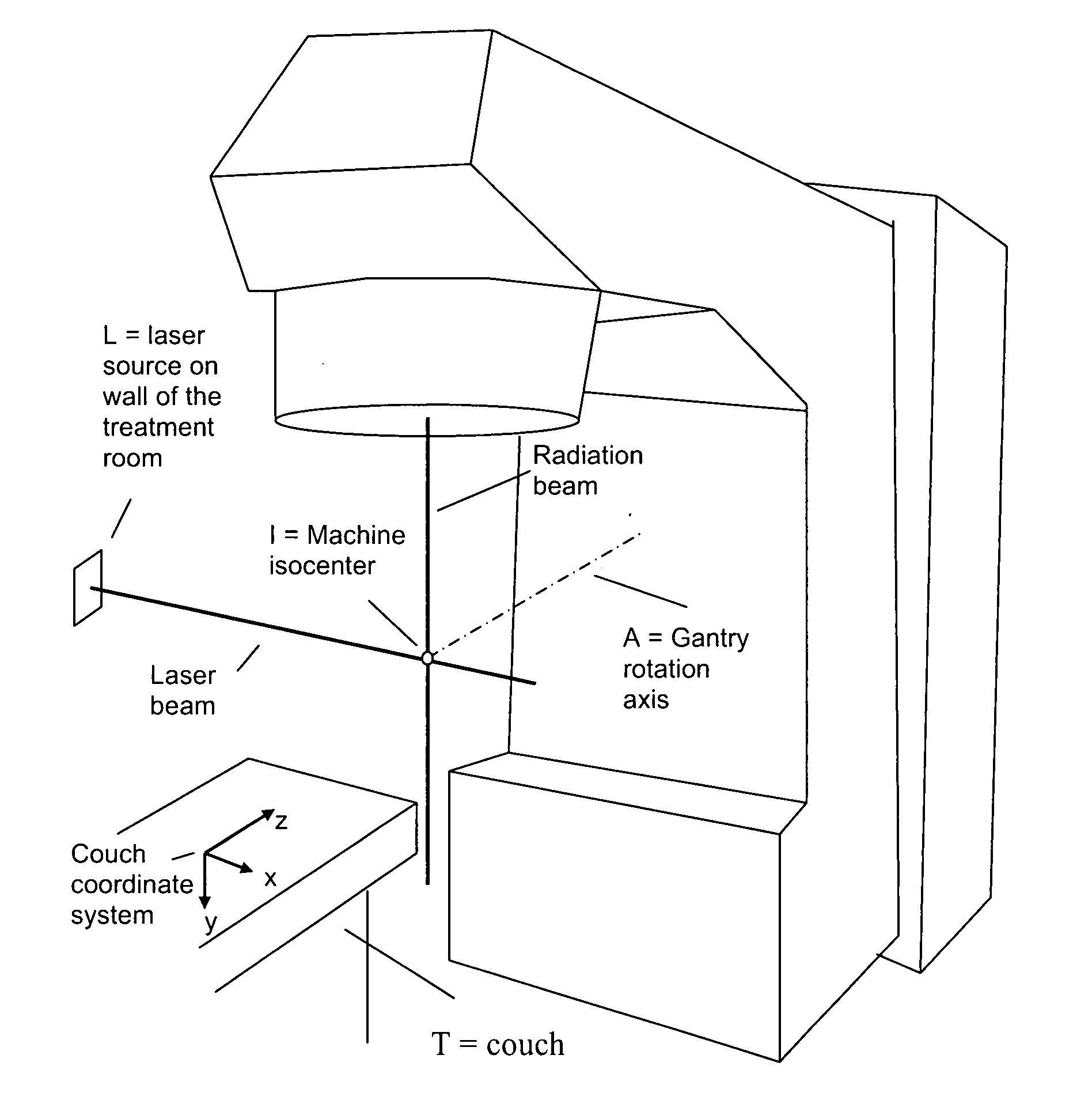
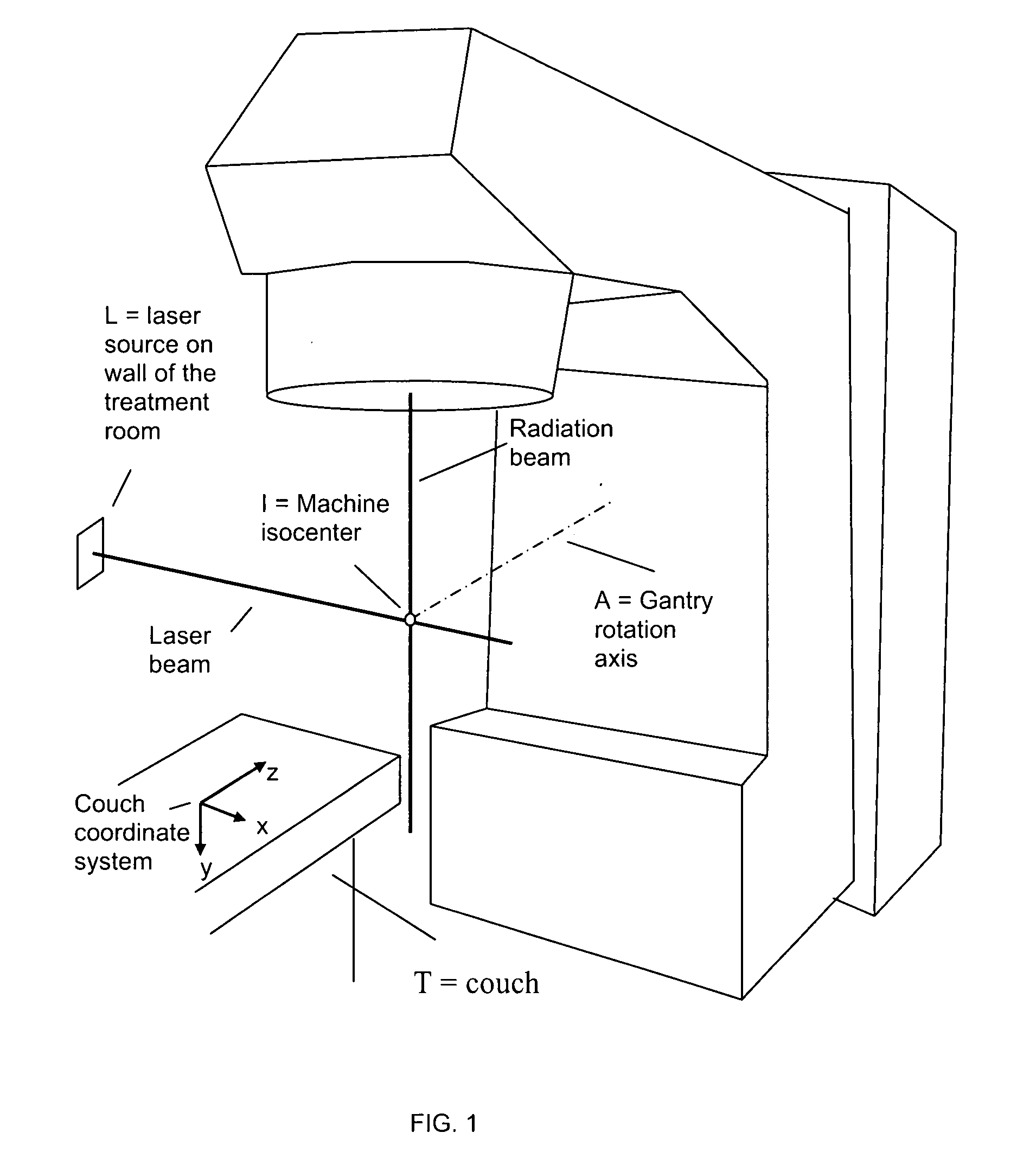
Isocenter in aerial photography: it is a point where a line cuts an angle of 90 degree of tier/2. It is the point on the aerial photo platform that directly falls on a line half-way between the Principal point and the Nadir point. In imaging physics and radiation oncology, the isocenter is termed as the point in space through which the central rays of the radiation beams pass.
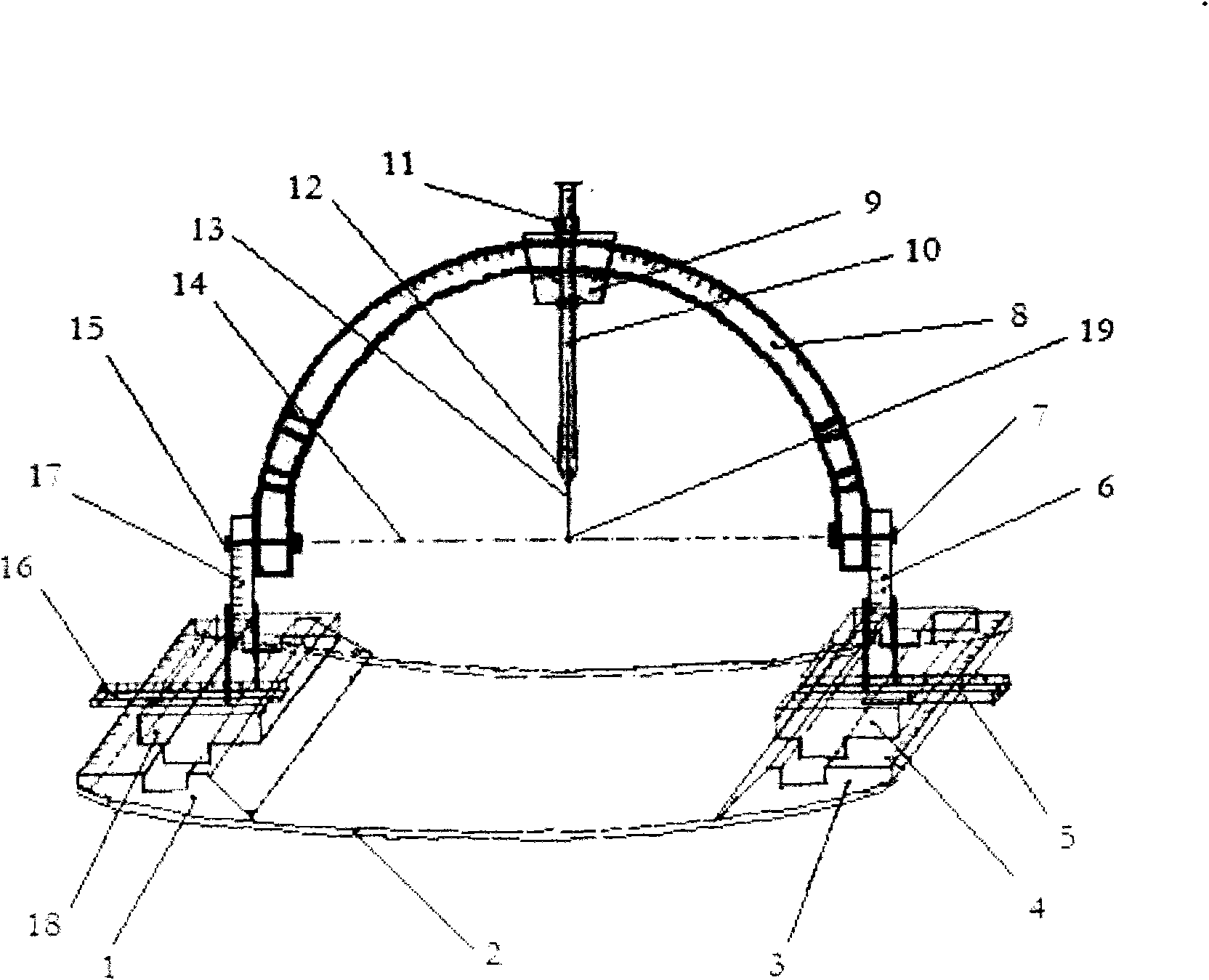
Guided Radiation Therapy System
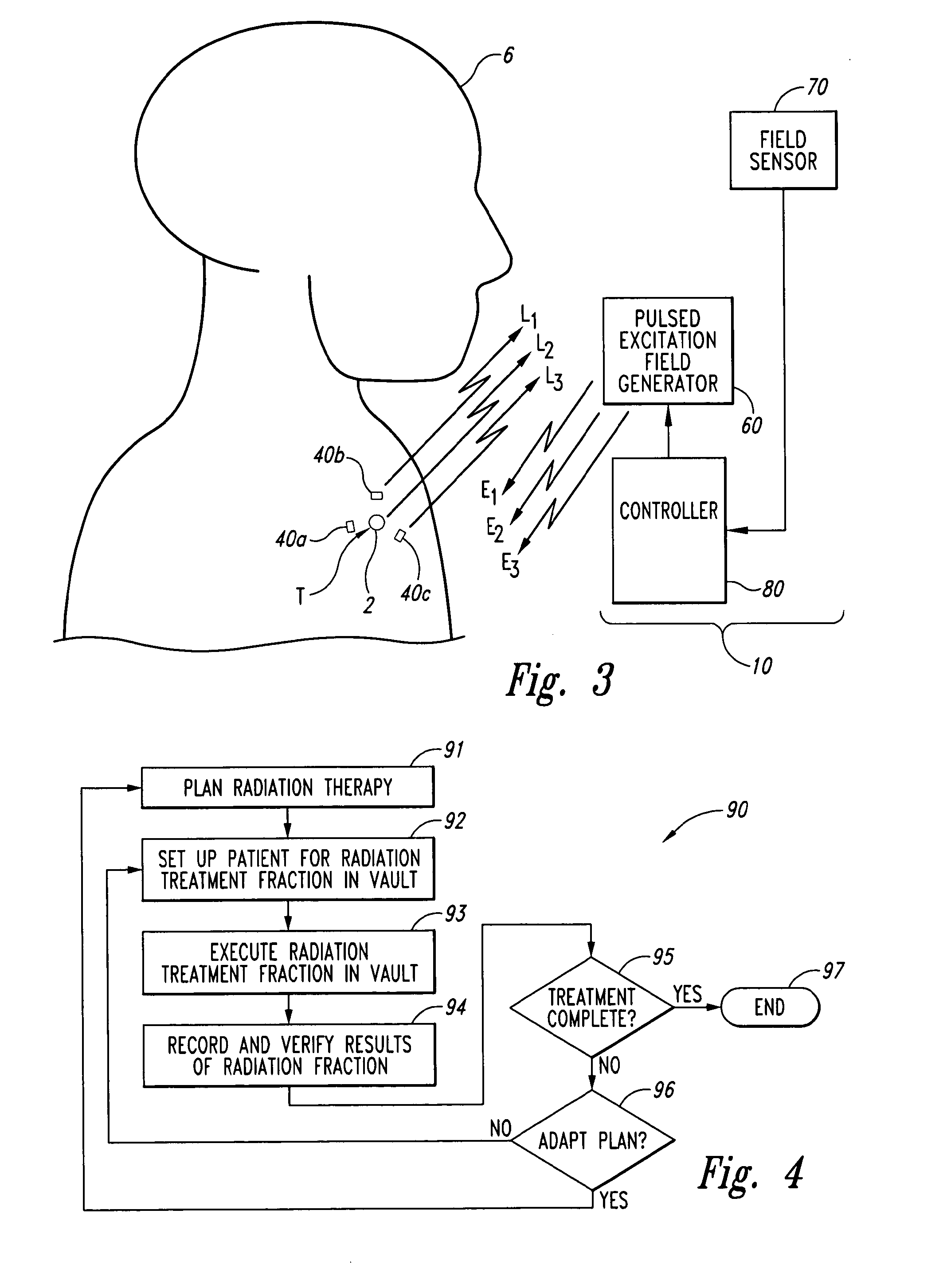
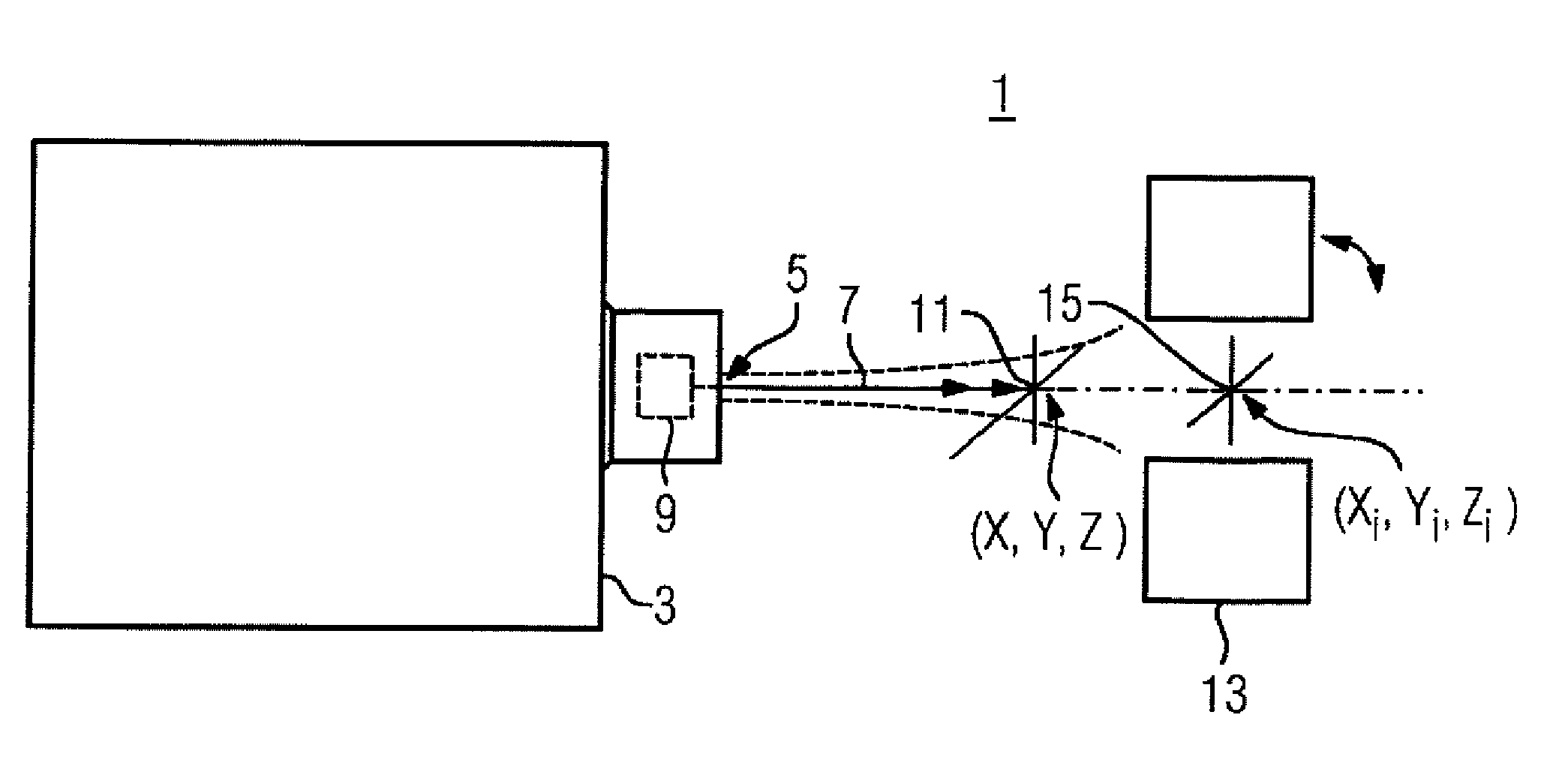
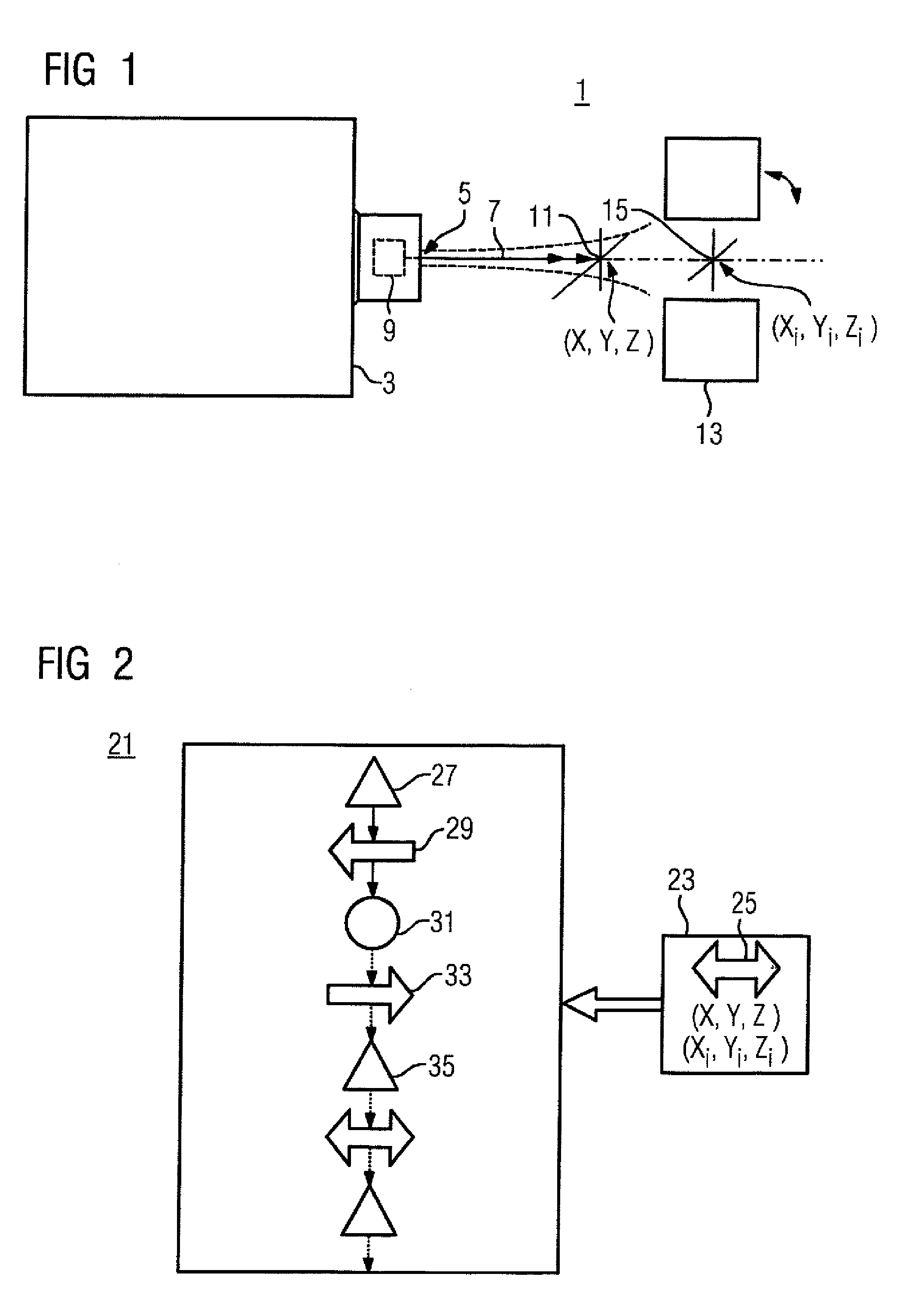
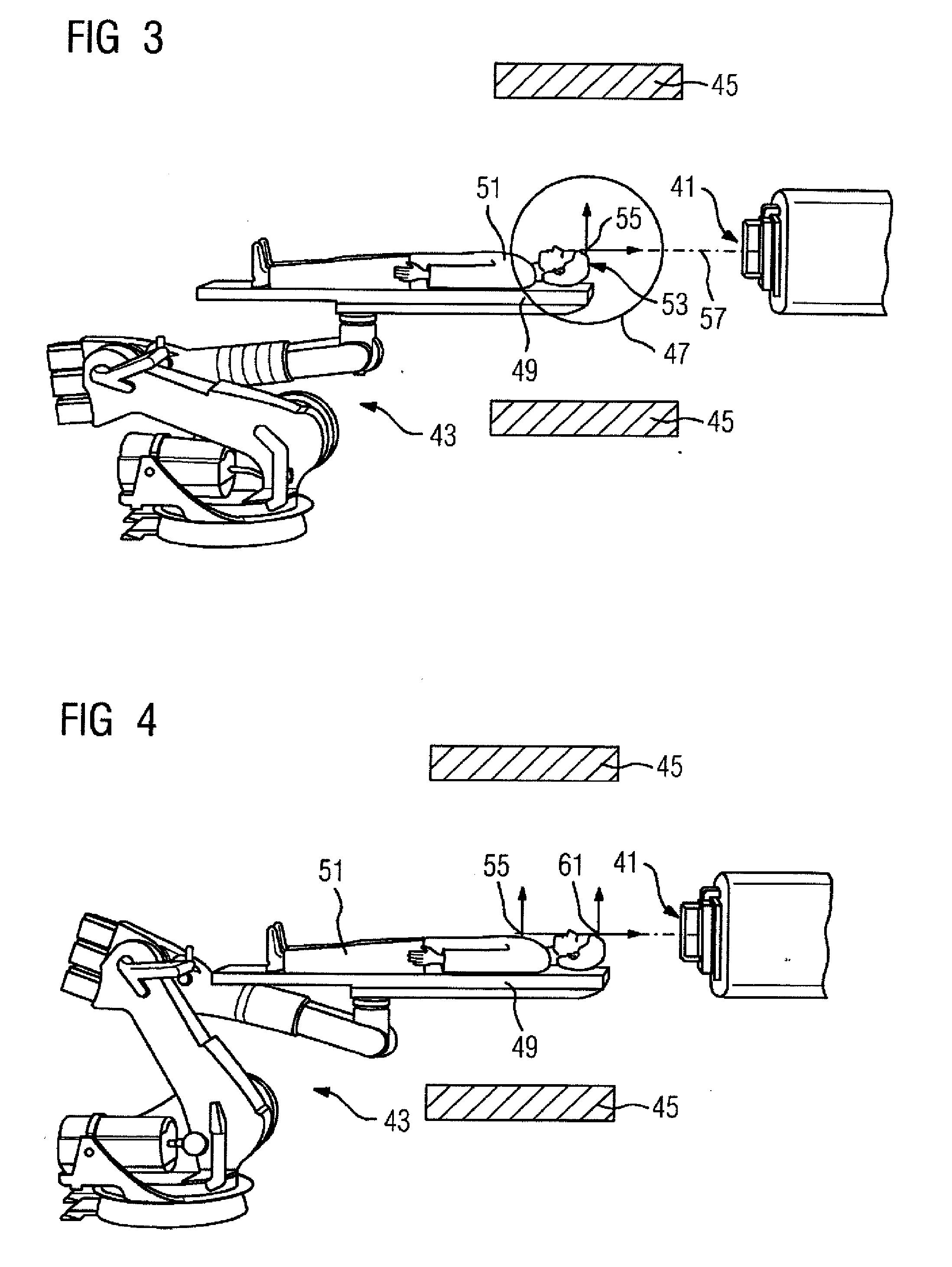
InactiveUS20020193685A1Accurate locationAccurate trackingSurgical navigation systemsPosition fixationMonitoring systemIsocenter
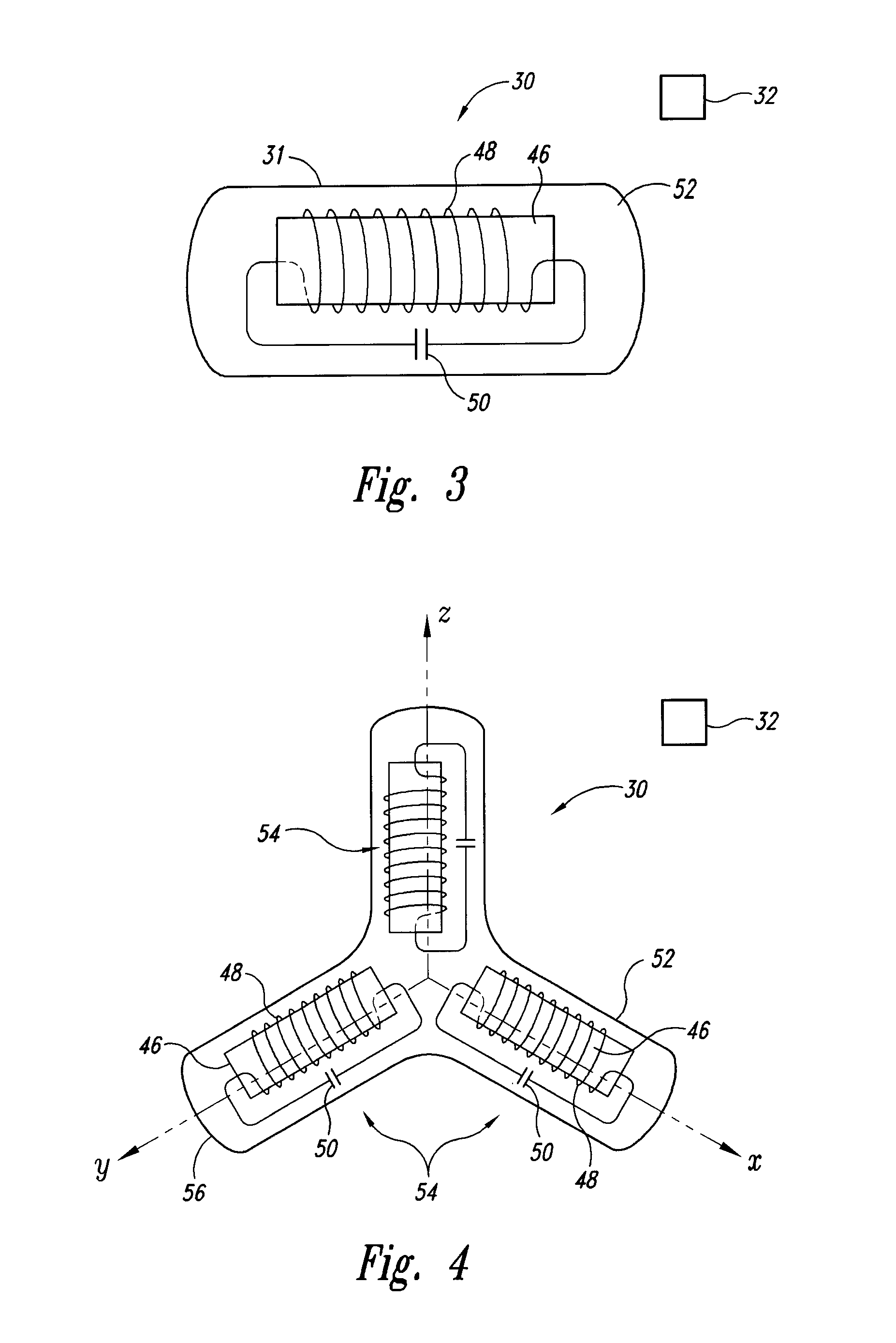
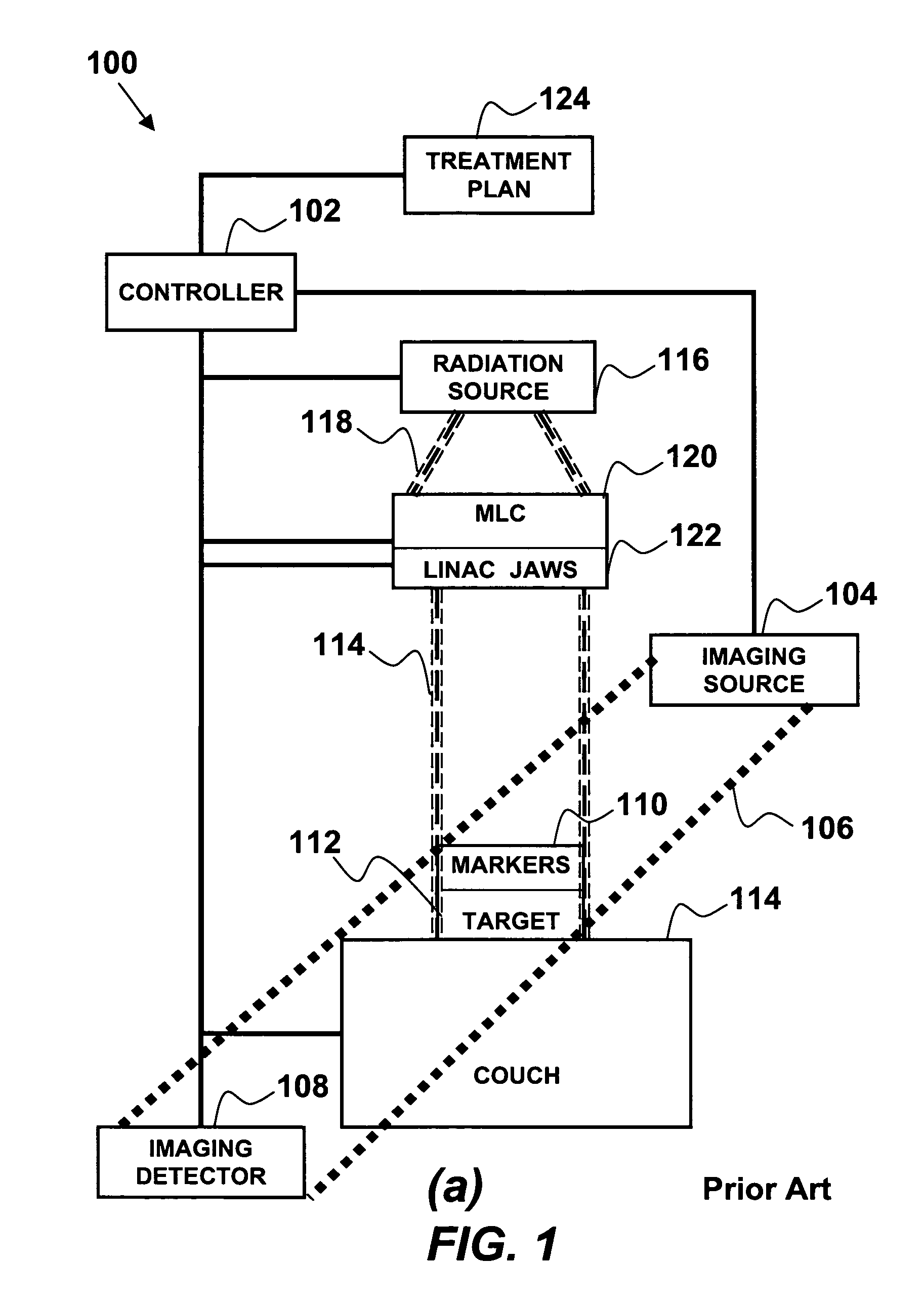
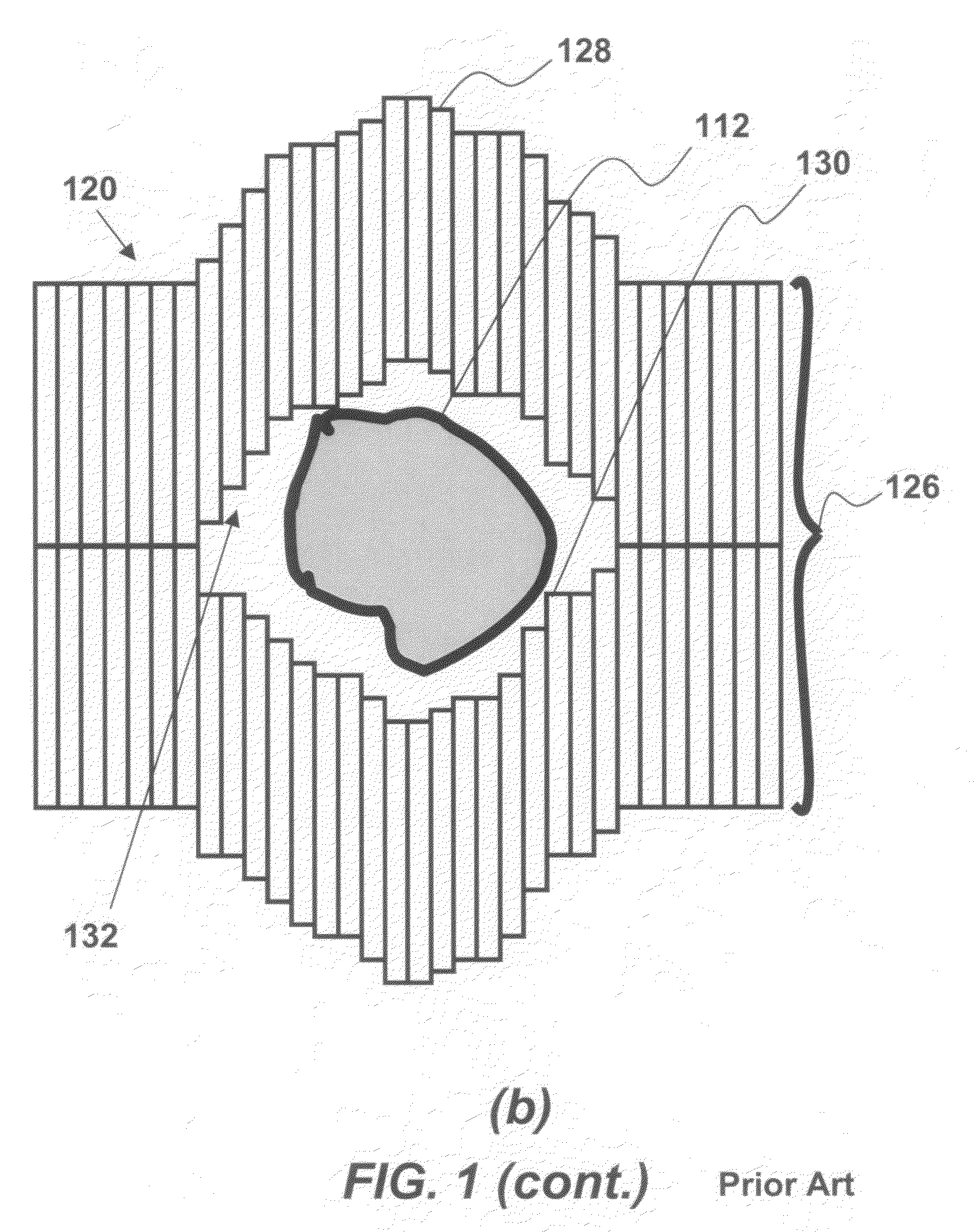
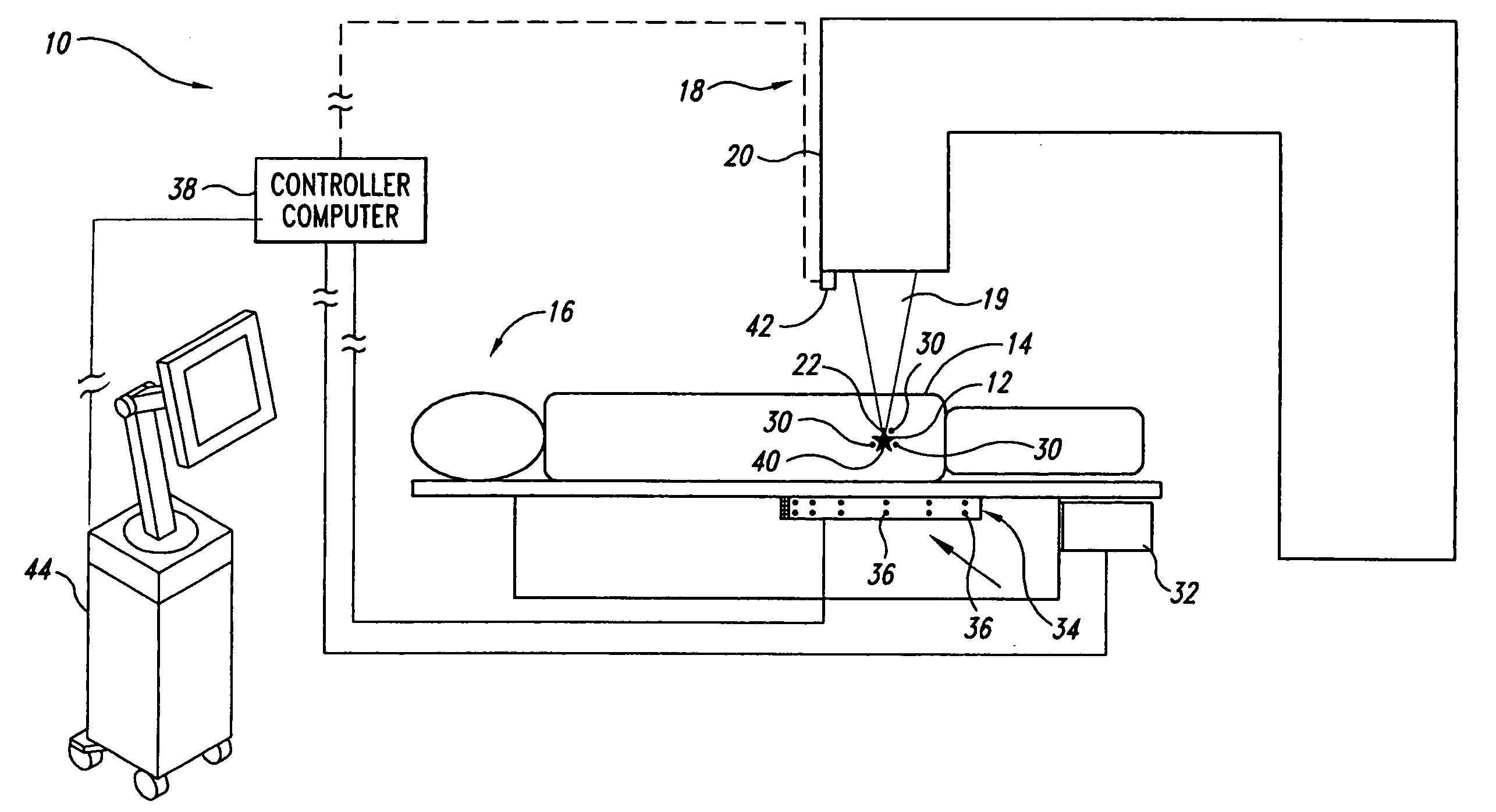
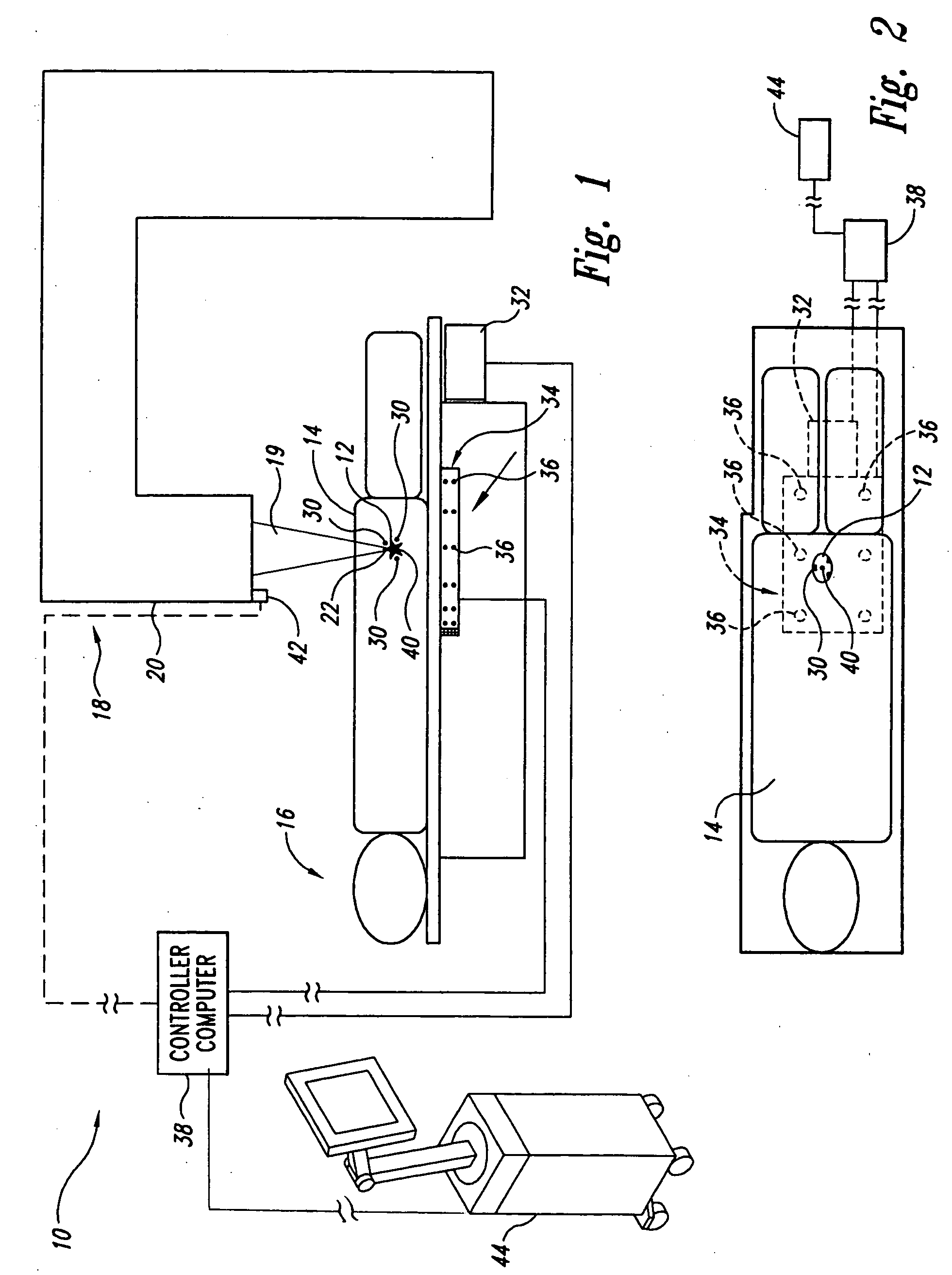
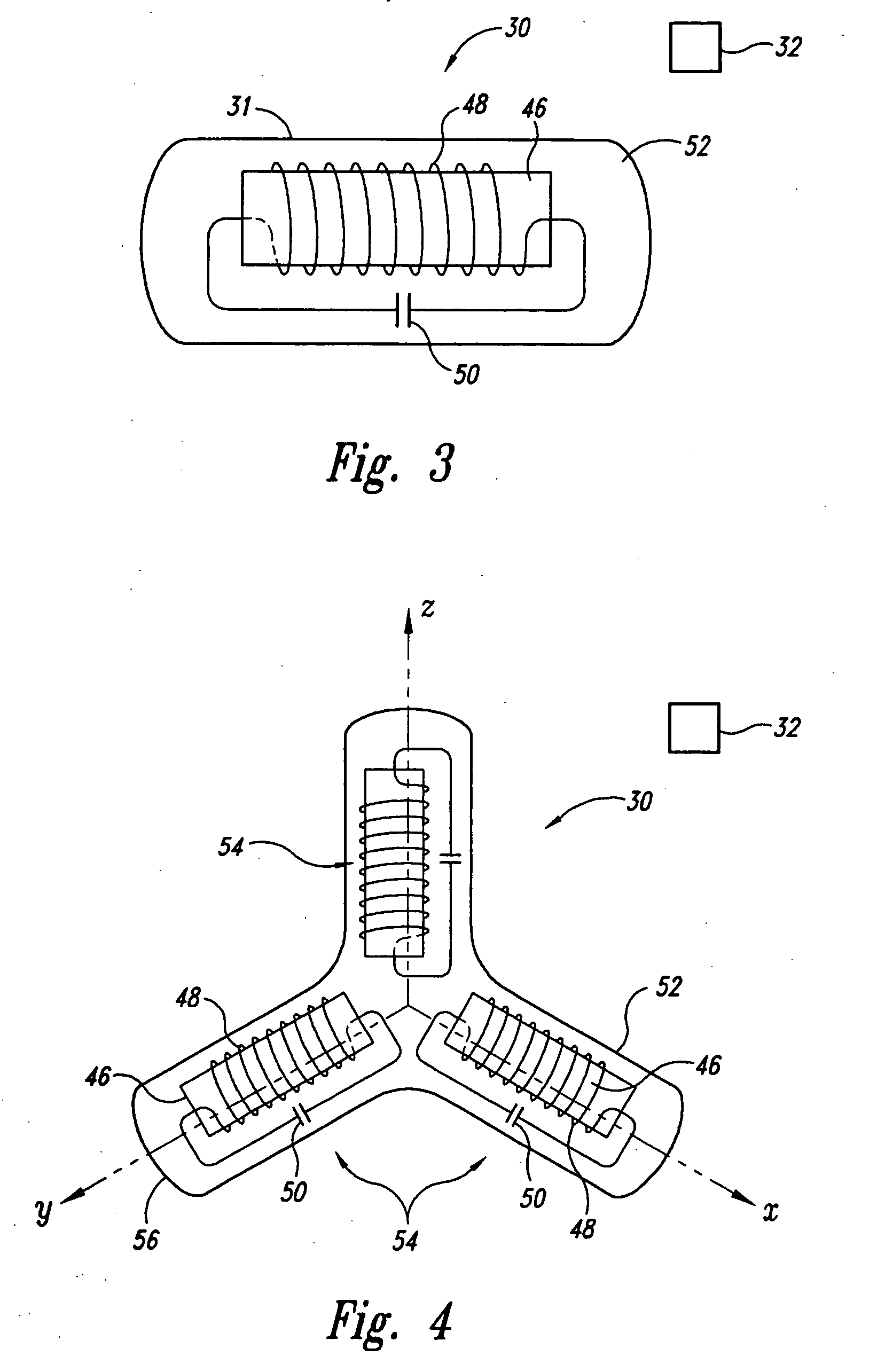
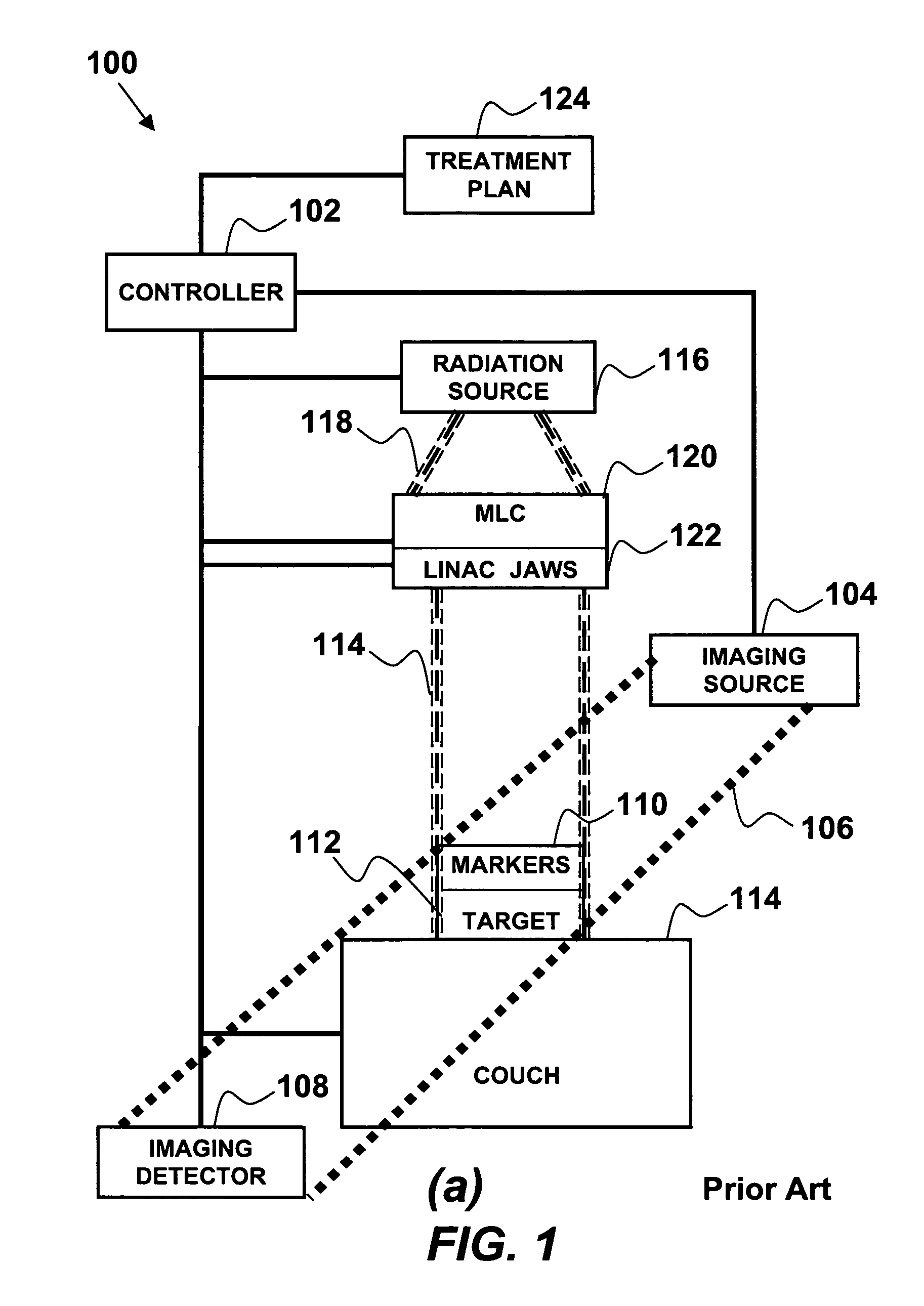
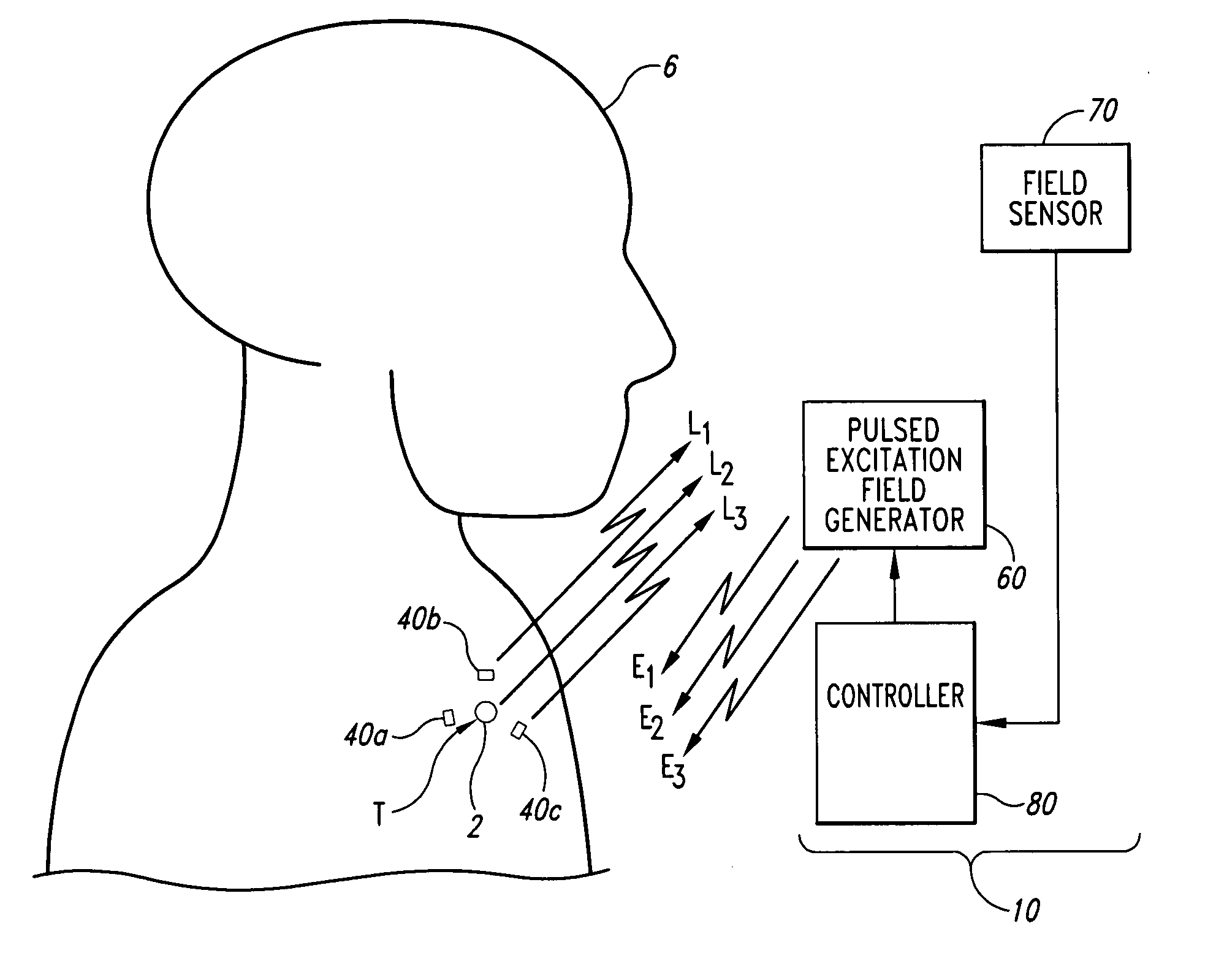
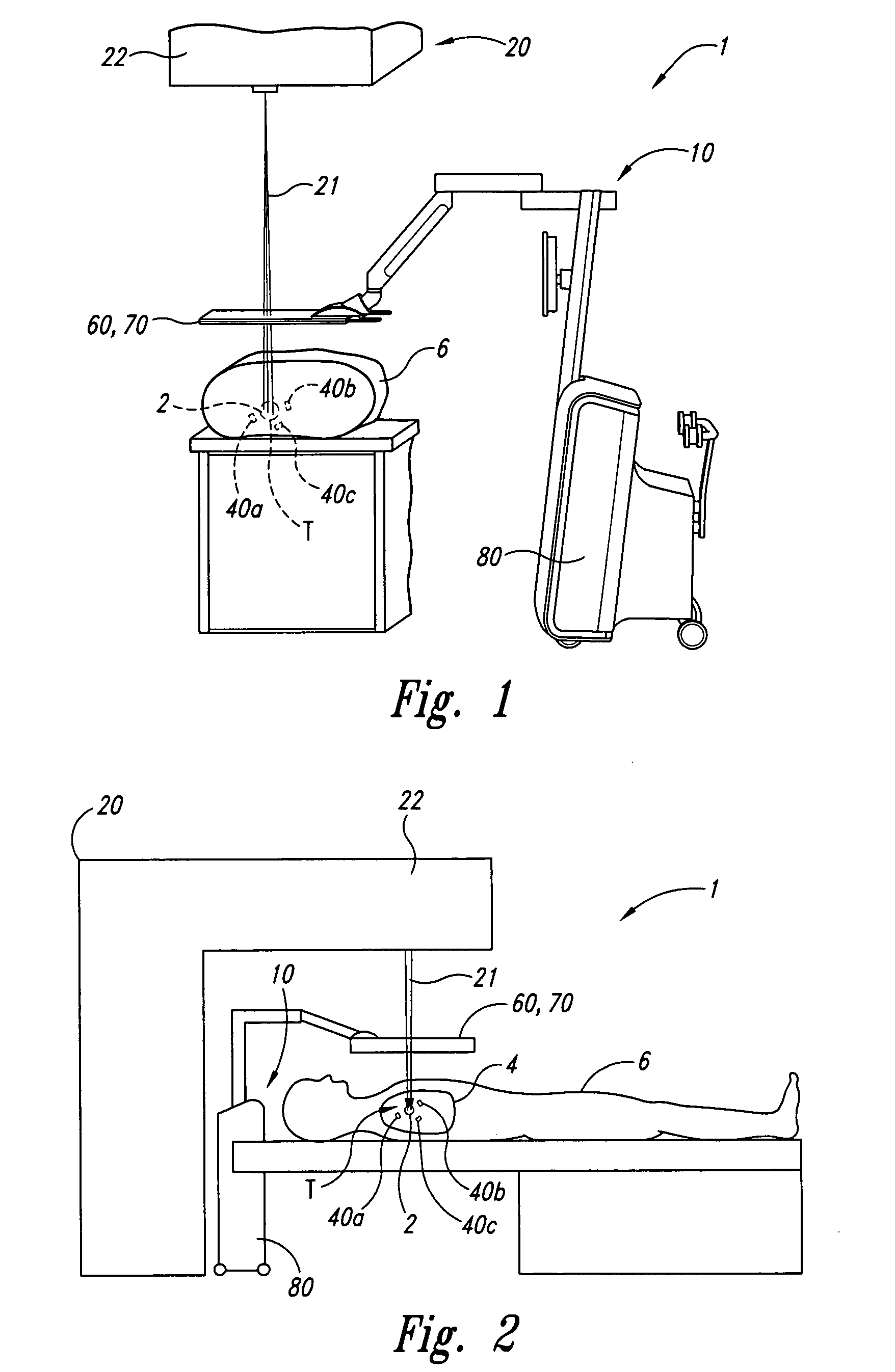
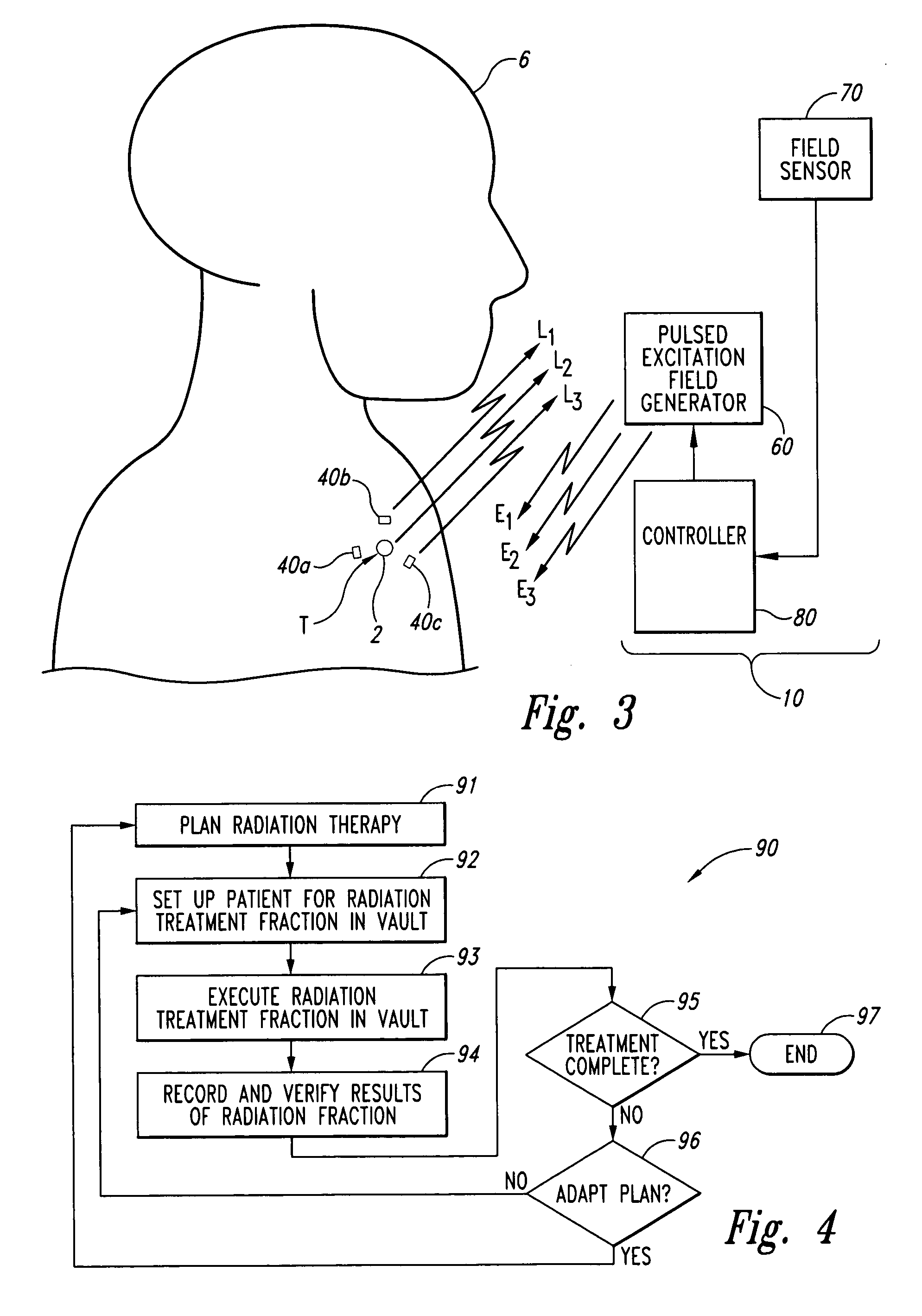
<heading lvl="0">Abstract of Disclosure< / heading> A system and method for accurately locating and tracking the position of a target, such as a tumor or the like, within a body. In one embodiment, the system is a target locating and monitoring system usable with a radiation delivery source that delivers selected doses of radiation to a target in a body. The system includes one or more excitable markers positionable in or near the target, an external excitation source that remotely excites the markers to produce an identifiable signal, and a plurality of sensors spaced apart in a known geometry relative to each other. A computer is coupled to the sensors and configured to use the marker measurements to identify a target isocenter within the target. The computer compares the position of the target isocenter with the location of the machine isocenter. The computer also controls movement of the patient and a patient support device so the target isocenter is co-incident with the machine isocenter before and during radiation therapy.
Owner:CALYPSO MEDICAL +1
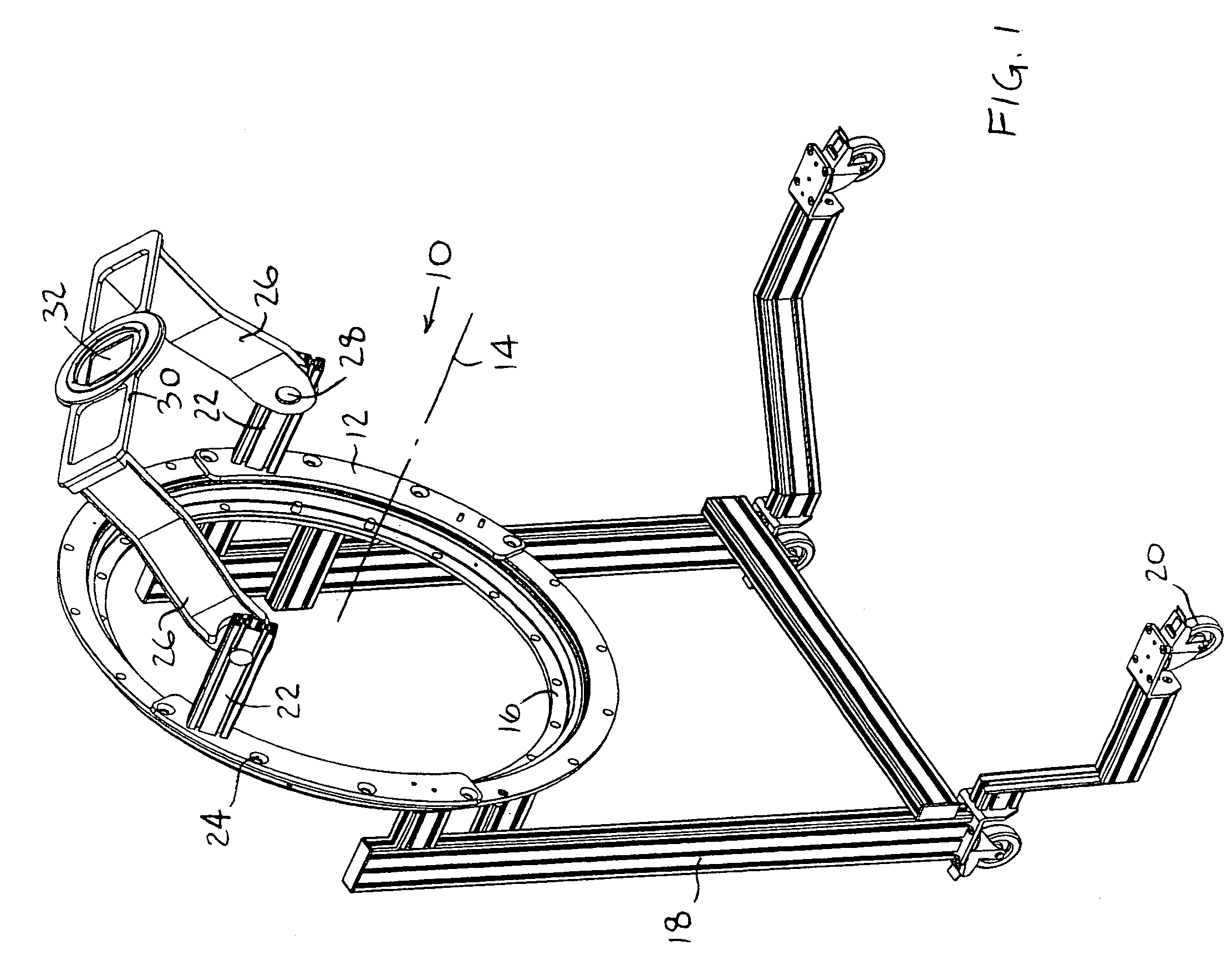
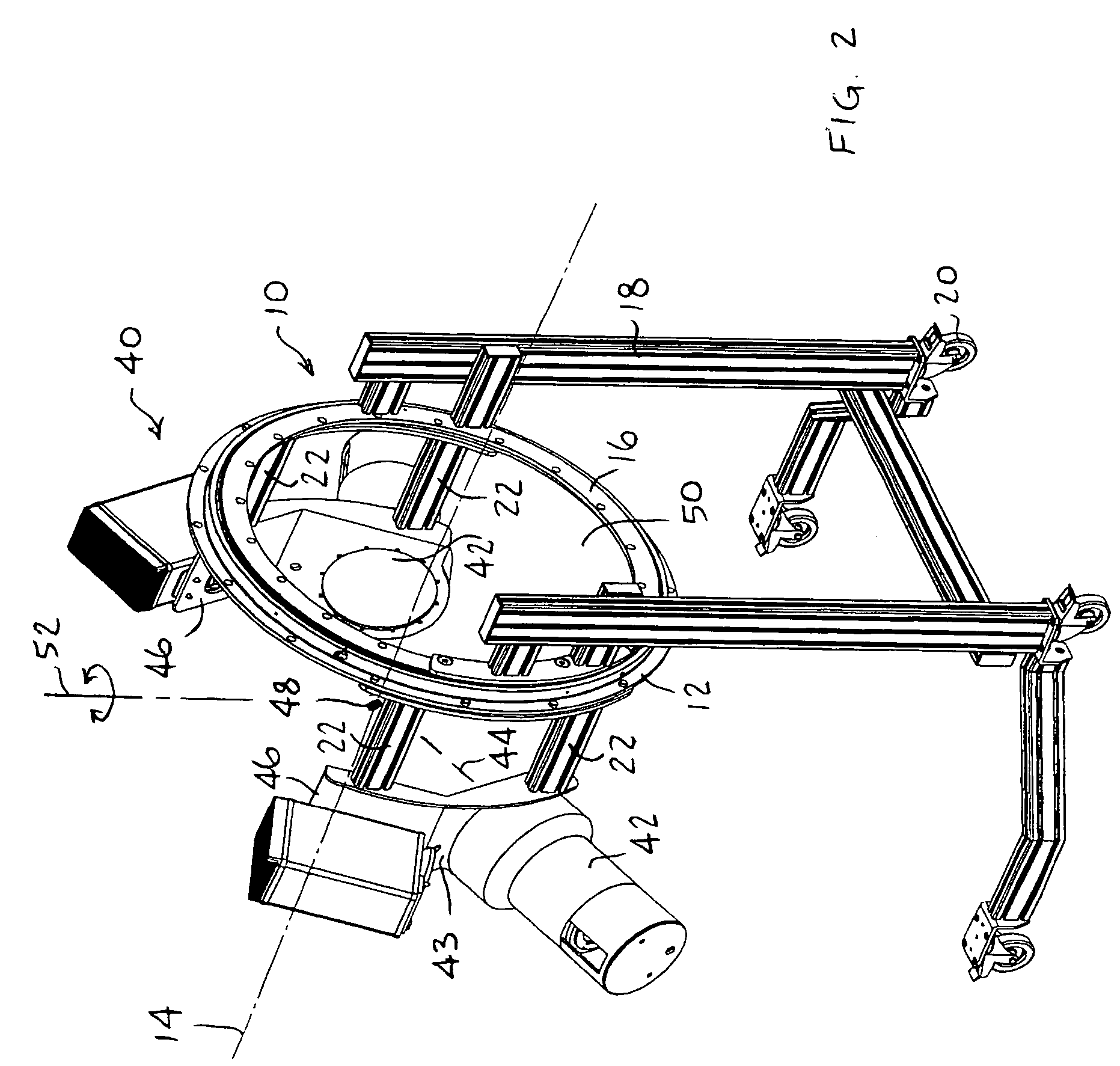
Patient positioning device and patient positioning method
InactiveUS7212608B2Improve accuracyAvoid accuracyBuilding locksPatient positioning for diagnosticsPattern matchingX-ray
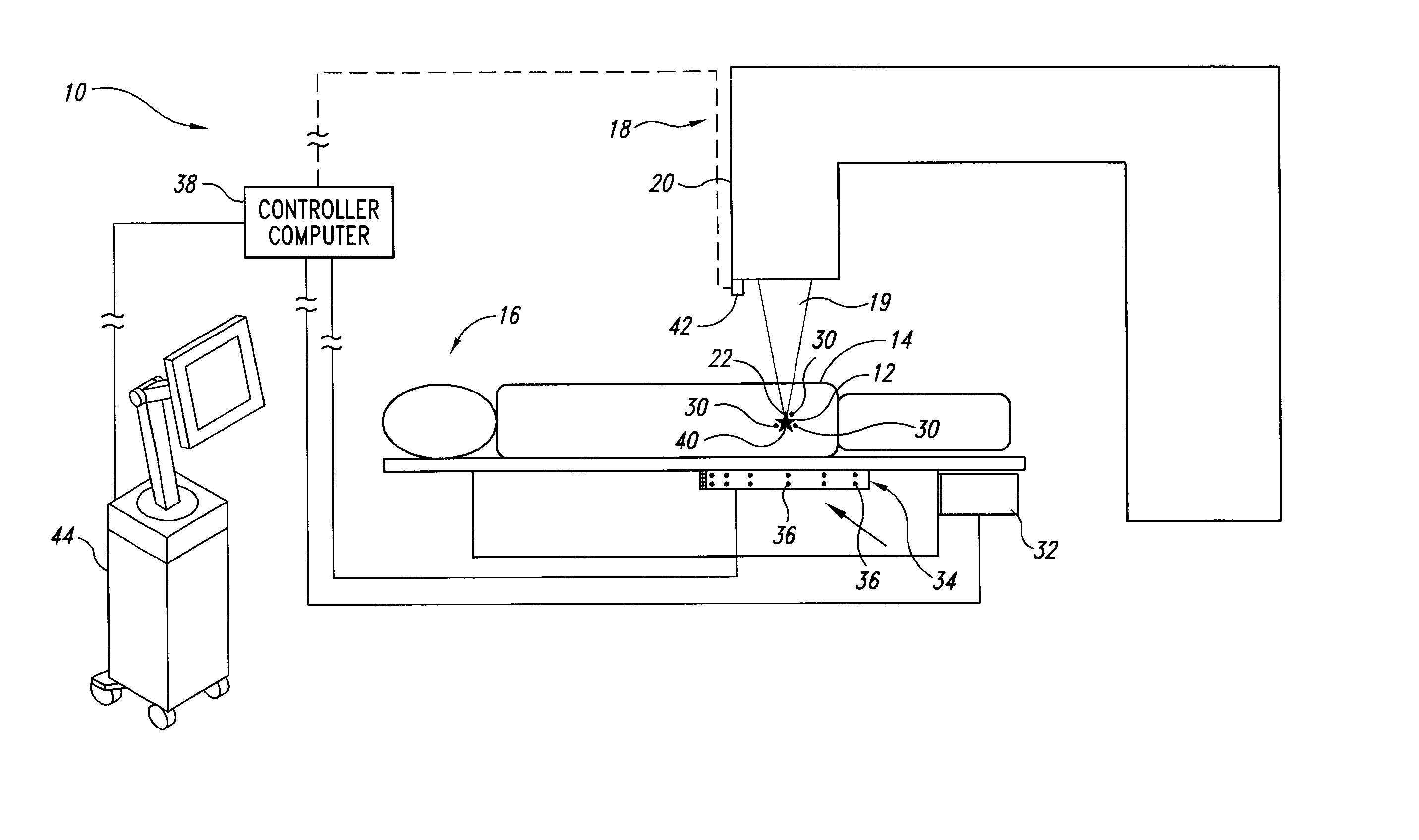
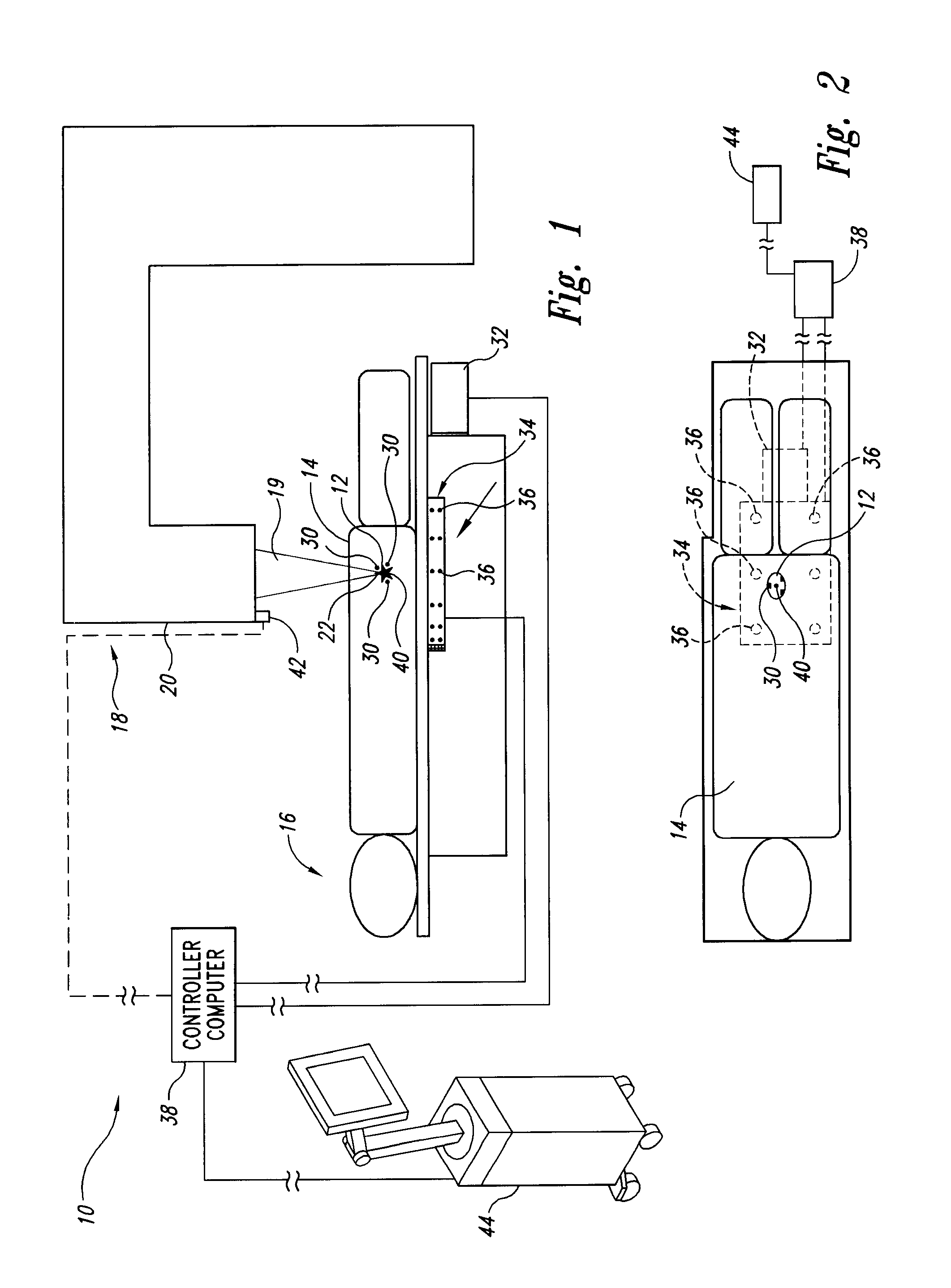
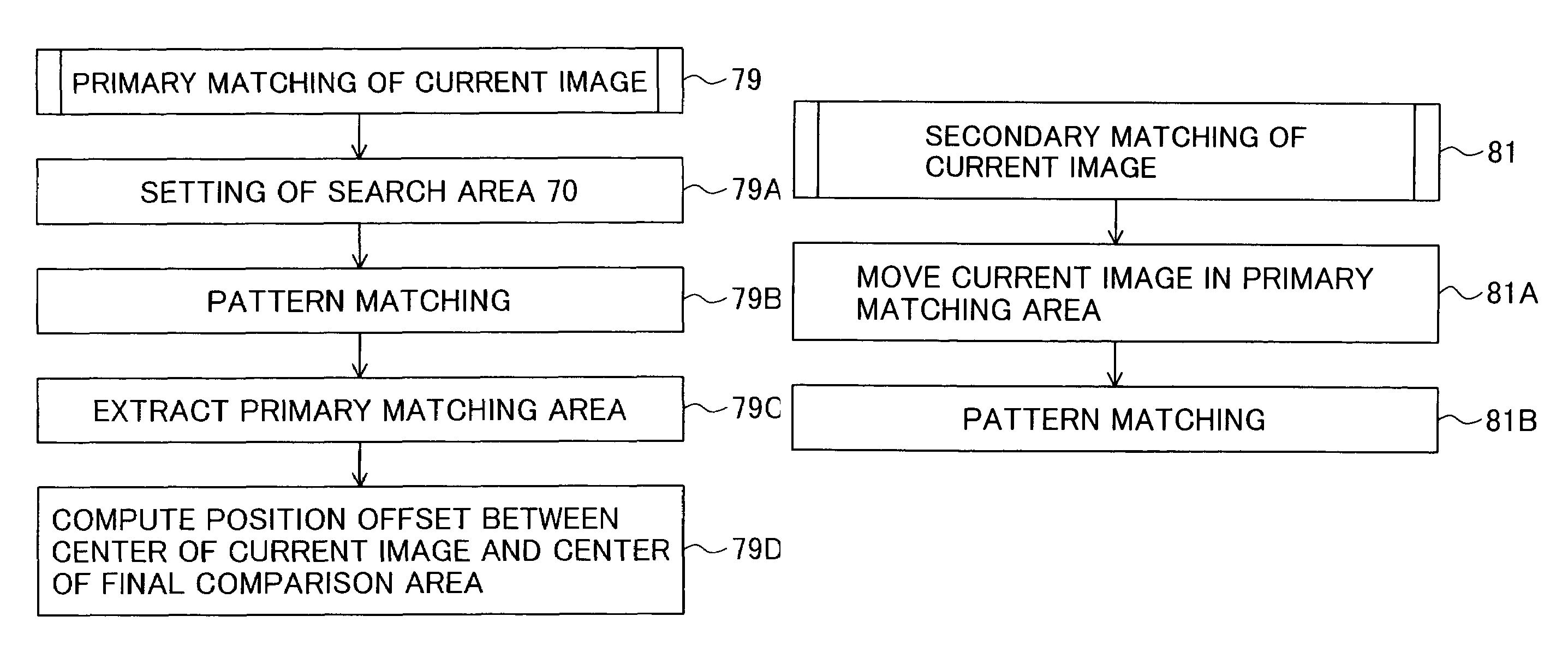
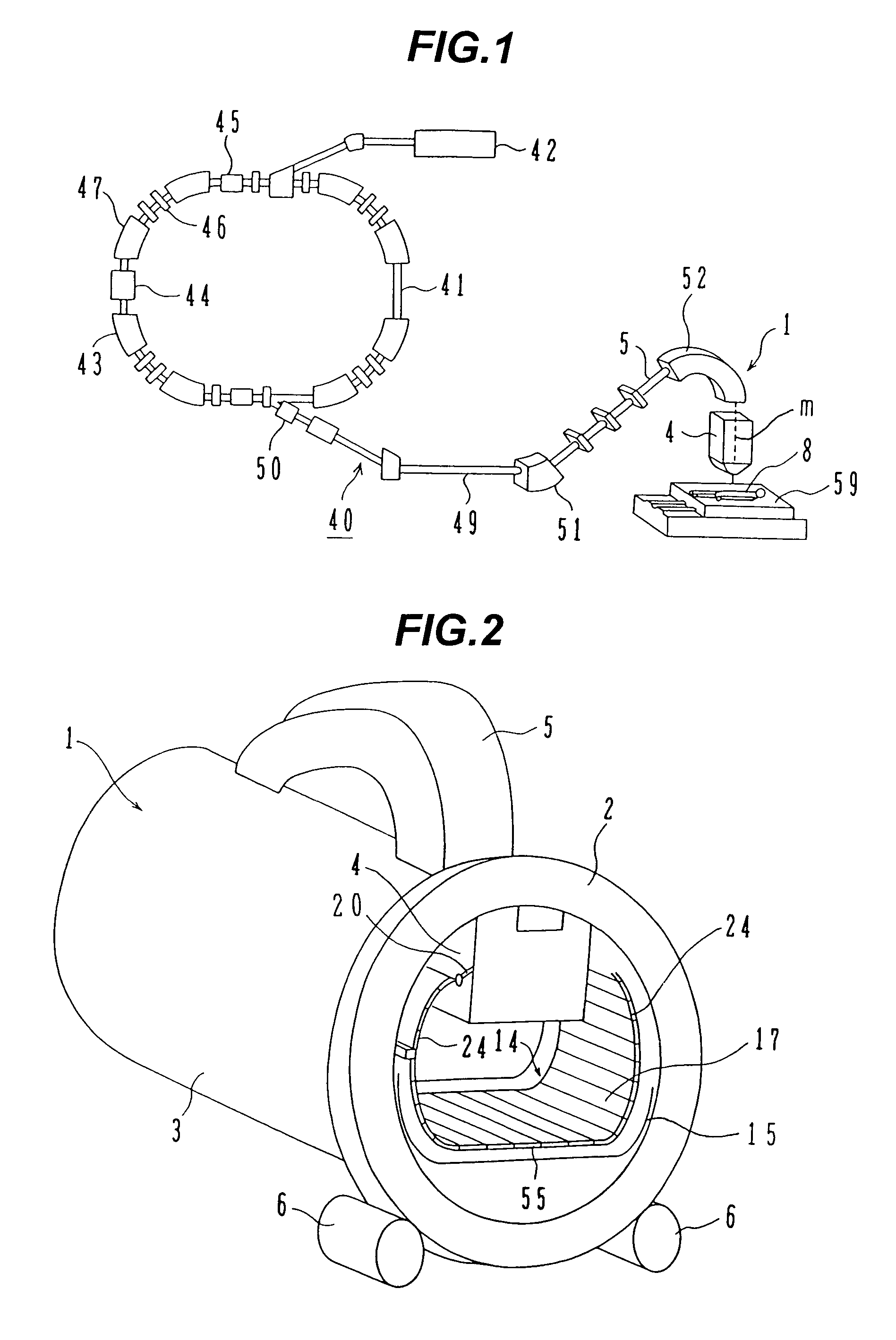
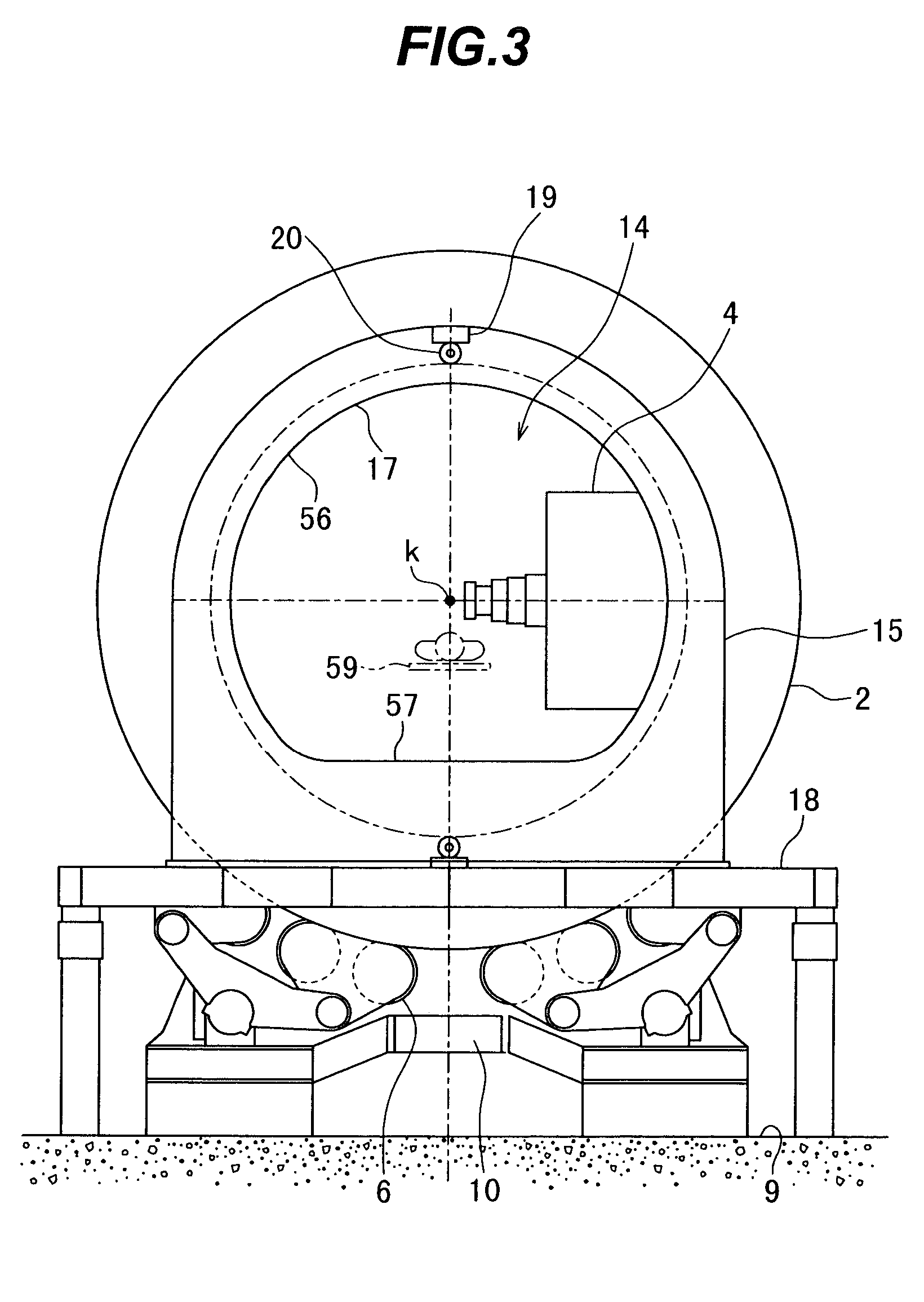
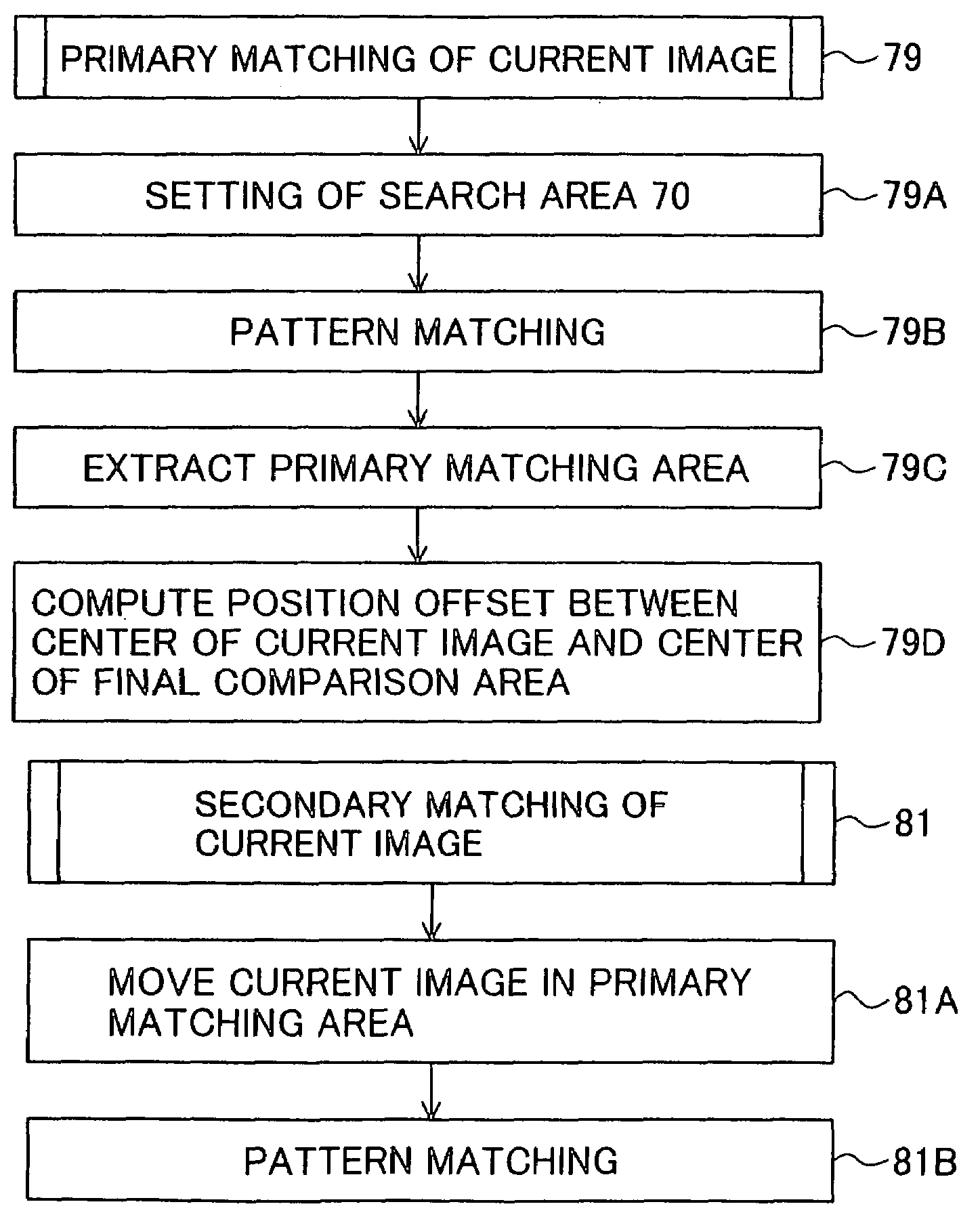
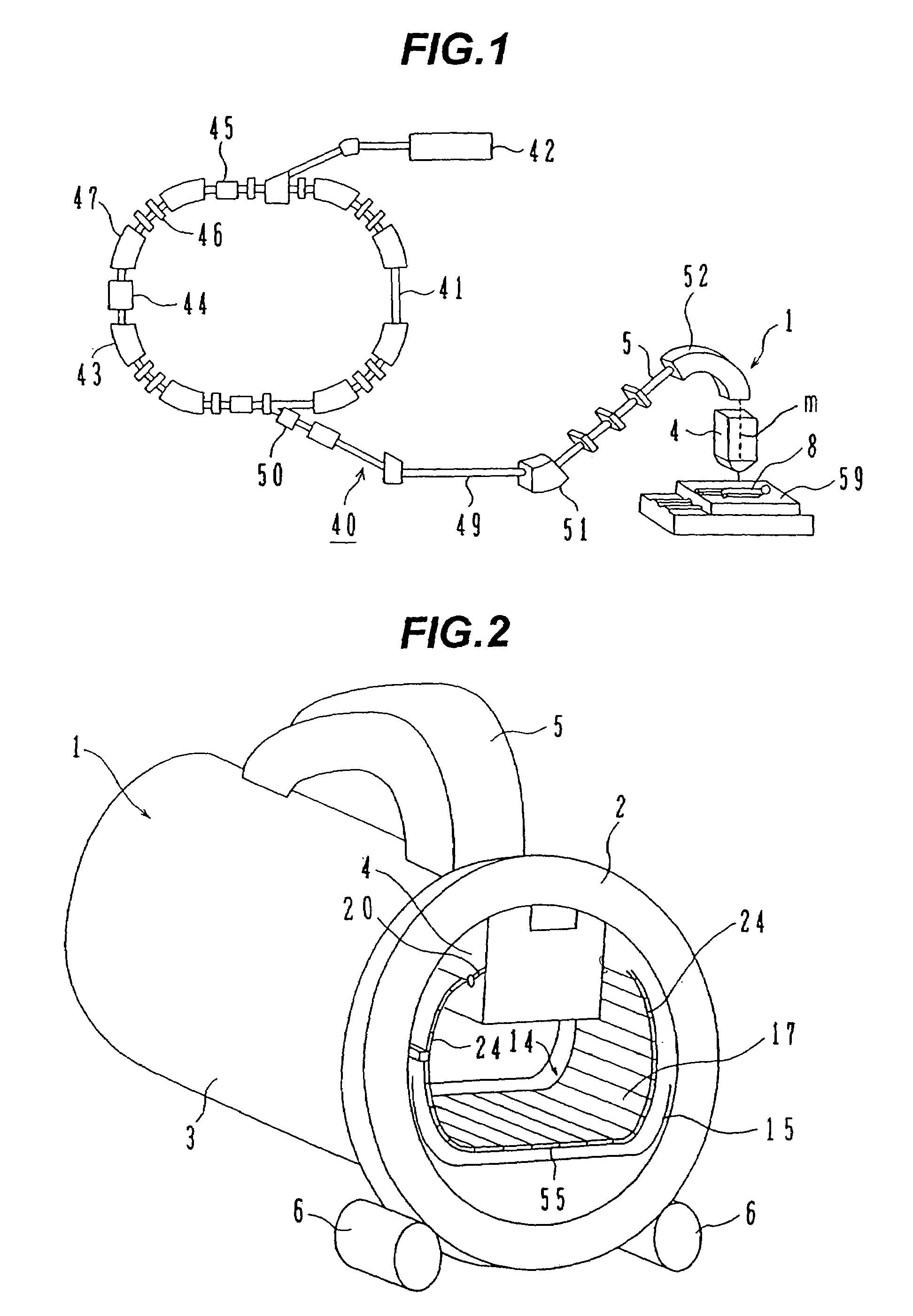
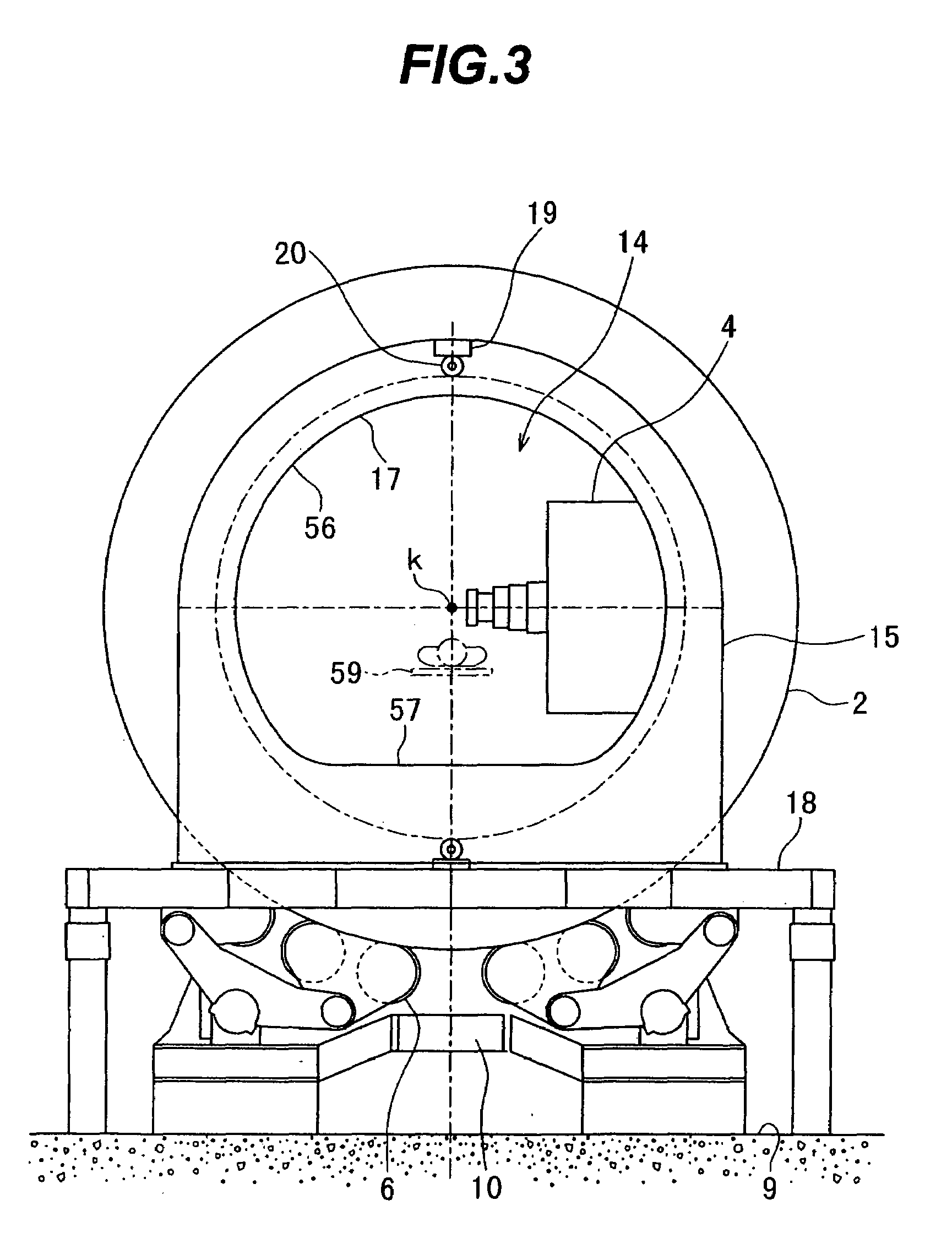
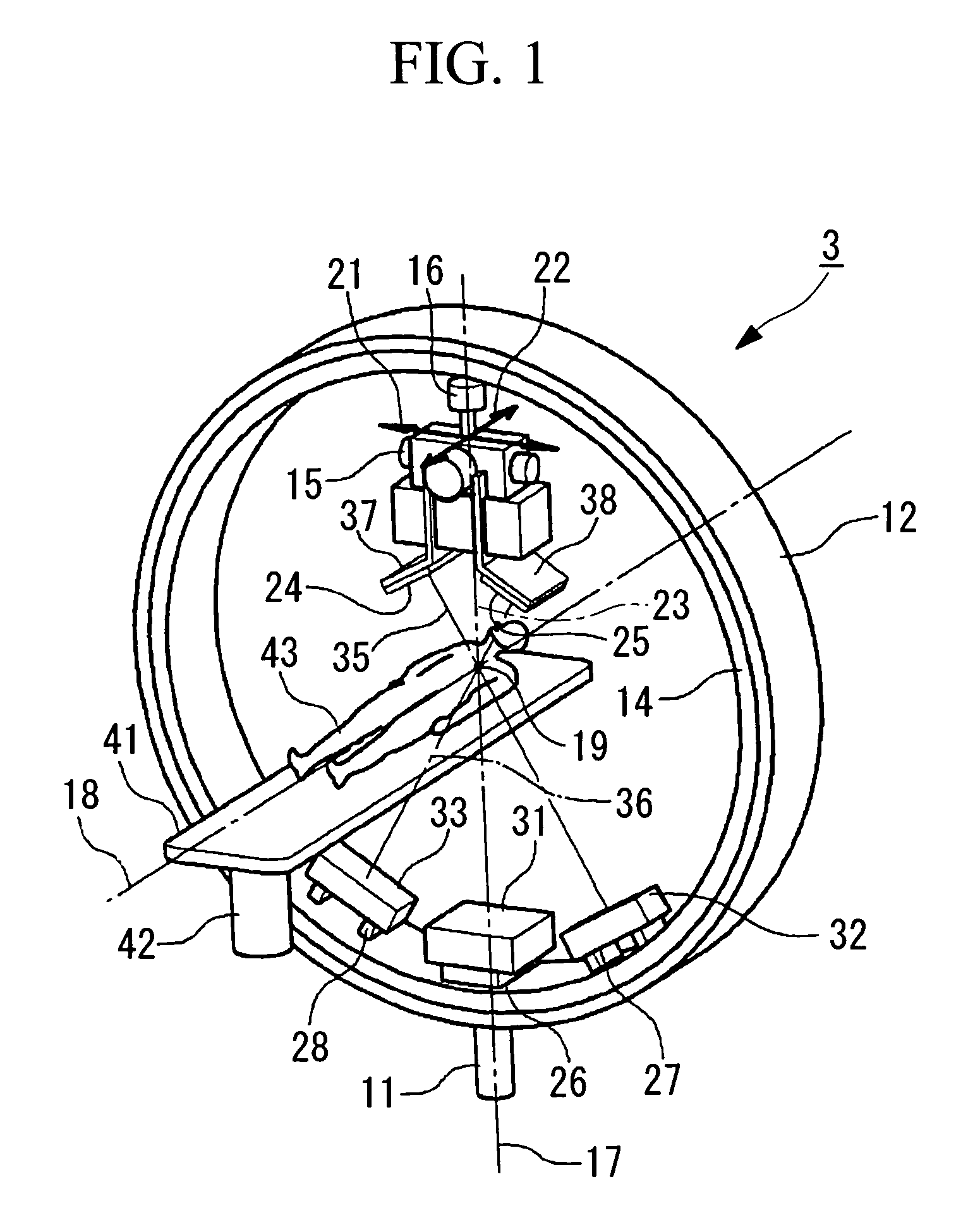
The invention is intended to always ensure a sufficient level of patient positioning accuracy regardless of the skills of individual operators. In a patient positioning device for positioning a patient couch 59 and irradiating an ion beam toward a tumor in the body of a patient 8 from a particle beam irradiation section 4, the patient positioning device comprises an X-ray emission device 26 for emitting an X-ray along a beam line m from the particle beam irradiation section 4, an X-ray image capturing device 29 for receiving the X-ray and processing an X-ray image, a display unit 39B for displaying a current image of the tumor in accordance with a processed image signal, a display unit 39A for displaying a reference X-ray image of the tumor which is prepared in advance, and a positioning data generator 37 for executing pattern matching between a comparison area A being a part of the reference X-ray image and including an isocenter and a comparison area B or a final comparison area B in the current image, thereby producing data used for positioning of the patient couch 59 during irradiation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Patient positioning device and patient positioning method
InactiveUS7212609B2Improve accuracyAvoid accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPattern matchingX-ray
The invention is intended to always ensure a sufficient level of patient positioning accuracy regardless of the skills of individual operators. In a patient positioning device for positioning a patient couch 59 and irradiating an ion beam toward a tumor in the body of a patient 8 from a particle beam irradiation section 4, the patient positioning device comprises an X-ray emission device 26 for emitting an X-ray along a beam line m from the particle beam irradiation section 4, an X-ray image capturing device 29 for receiving the X-ray and processing an X-ray image, a display unit 39B for displaying a current image of the tumor in accordance with a processed image signal, a display unit 39A for displaying a reference X-ray image of the tumor which is prepared in advance, and a positioning data generator 37 for executing pattern matching between a comparison area A being a part of the reference X-ray image and including an isocenter and a comparison area B or a final comparison area B in the current image, thereby producing data used for positioning of the patient couch 59 during irradiation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method to track three-dimensional target motion with a dynamical multi-leaf collimator
InactiveUS20080159478A1Radiation beam directing meansX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPrediction algorithmsMulti leaf collimator
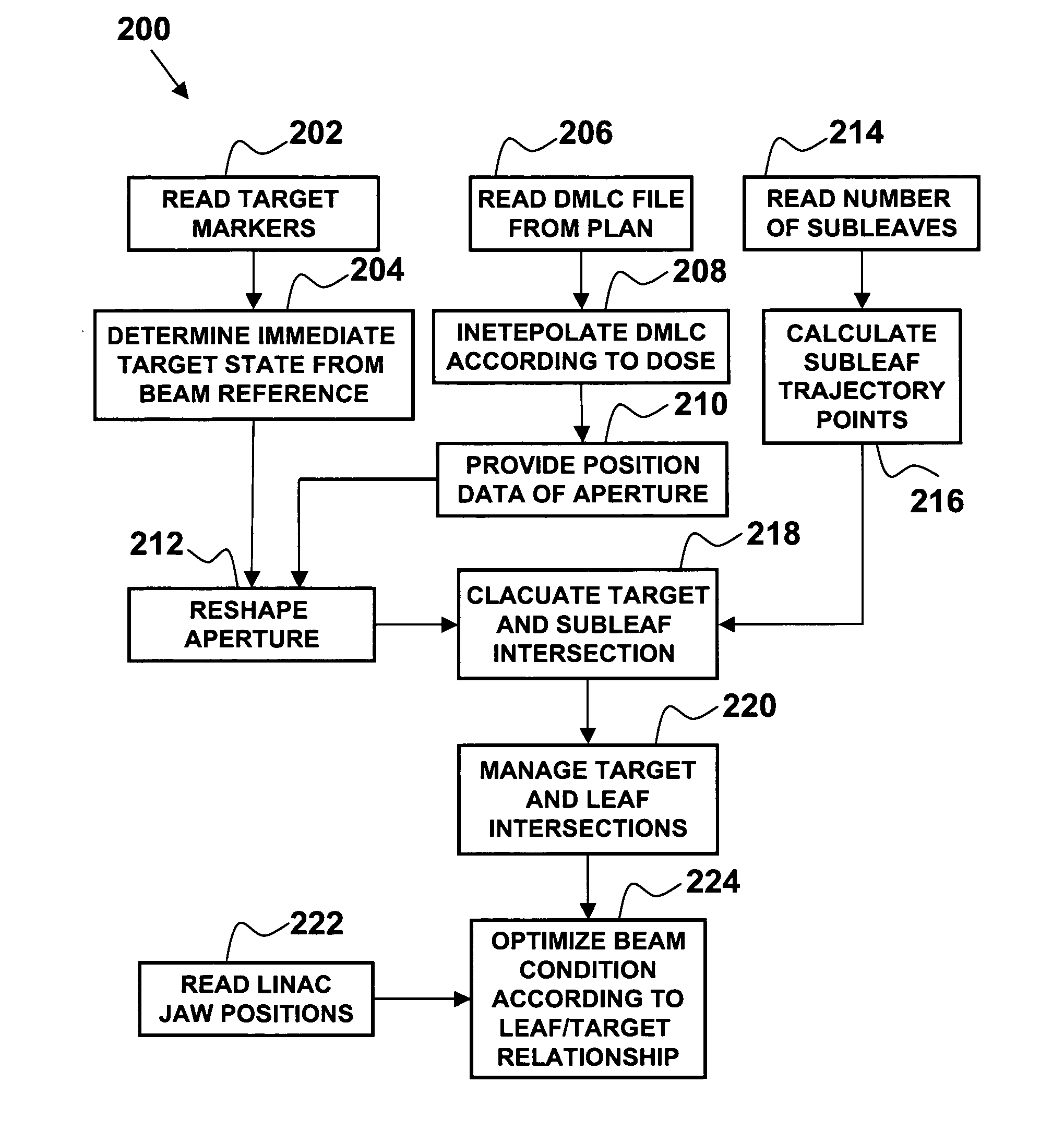
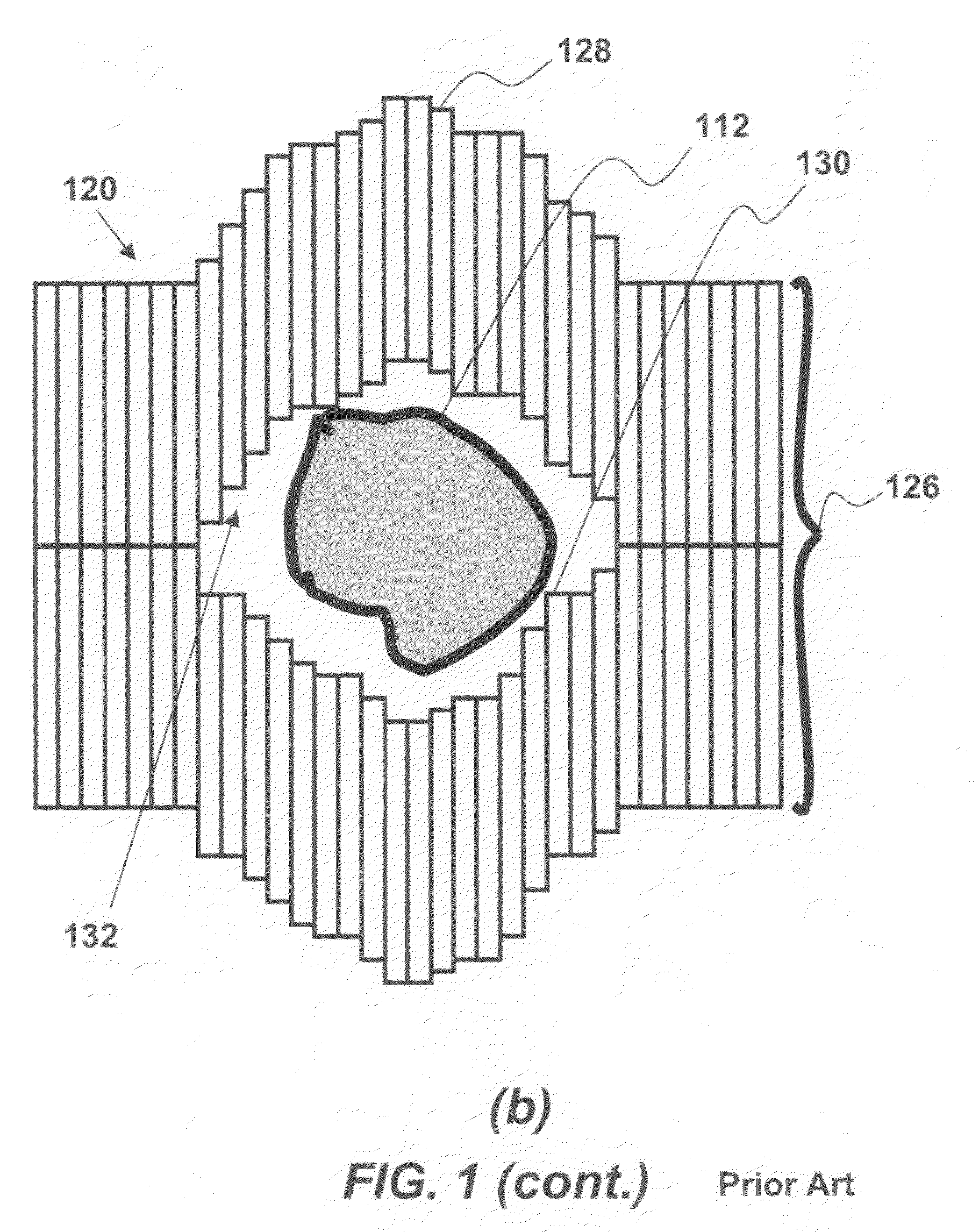
A method of continuous real-time monitoring and positioning of multi-leaf collimators during on and off radiation exposure conditions of radiation therapy to account for target motion relative to a radiation beam is provided. A prediction algorithm estimates future positions of a target relative to the radiation source. Target geometry and orientation are determined relative to the radiation source. Target, treatment plan, and leaf width data, and temporal interpolations of radiation doses are sent to the controller. Coordinates having an origin at an isocenter of the isocentric plane establish initial aperture end positions of the leaves that is provided to the controller, where motors to position the MLC midpoint aperture ends according to the position and target information. Each aperture end intersects a single point of a convolution of the target and the isocenter of the isocentric plane. Radiation source hold-conditions are provided according to predetermined undesirable operational and / or treatment states.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS +1
Guided radiation therapy system
A system and method for accurately locating and tracking the position of a target, such as a tumor or the like, within a body. In one embodiment, the system is a target locating and monitoring system usable with a radiation delivery source that delivers selected doses of radiation to a target in a body. The system includes one or more excitable markers positionable in or near the target, an external excitation source that remotely excites the markers to produce an identifiable signal, and a plurality of sensors spaced apart in a known geometry relative to each other. A computer is coupled to the sensors and configured to use the marker measurements to identify a target isocenter within the target. The computer compares the position of the target isocenter with the location of the machine isocenter. The computer also controls movement of the patient and a patient support device so the target isocenter is coincident with the machine isocenter before and during radiation therapy.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Method to track three-dimensional target motion with a dynamical multi-leaf collimator
InactiveUS7469035B2Radiation beam directing meansX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPrediction algorithmsMulti leaf collimator
A method of continuous real-time monitoring and positioning of multi-leaf collimators during on and off radiation exposure conditions of radiation therapy to account for target motion relative to a radiation beam is provided. A prediction algorithm estimates future positions of a target relative to the radiation source. Target geometry and orientation are determined relative to the radiation source. Target, treatment plan, and leaf width data, and temporal interpolations of radiation doses are sent to the controller. Coordinates having an origin at an isocenter of the isocentric plane establish initial aperture end positions of the leaves that is provided to the controller, where motors to position the MLC midpoint aperture ends according to the position and target information. Each aperture end intersects a single point of a convolution of the target and the isocenter of the isocentric plane. Radiation source hold-conditions are provided according to predetermined undesirable operational and / or treatment states.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS +1
Guided radiation therapy system
ActiveUS7657301B2Surgical navigation systemsPosition fixationAbnormal tissue growthMonitoring system
A system and method for accurately locating and tracking the position of a target, such as a tumor or the like, within a body. In one embodiment, the system is a target locating and monitoring system usable with a radiation delivery source that delivers selected doses of radiation to a target in a body. The system includes one or more excitable markers positionable in or near the target, an external excitation source that remotely excites the markers to produce an identifiable signal, and a plurality of sensors spaced apart in a known geometry relative to each other. A computer is coupled to the sensors and configured to use the marker measurements to identify a target isocenter within the target. The computer compares the position of the target isocenter with the location of the machine isocenter. The computer also controls movement of the patient and a patient support device so the target isocenter is coincident with the machine isocenter before and during radiation therapy.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
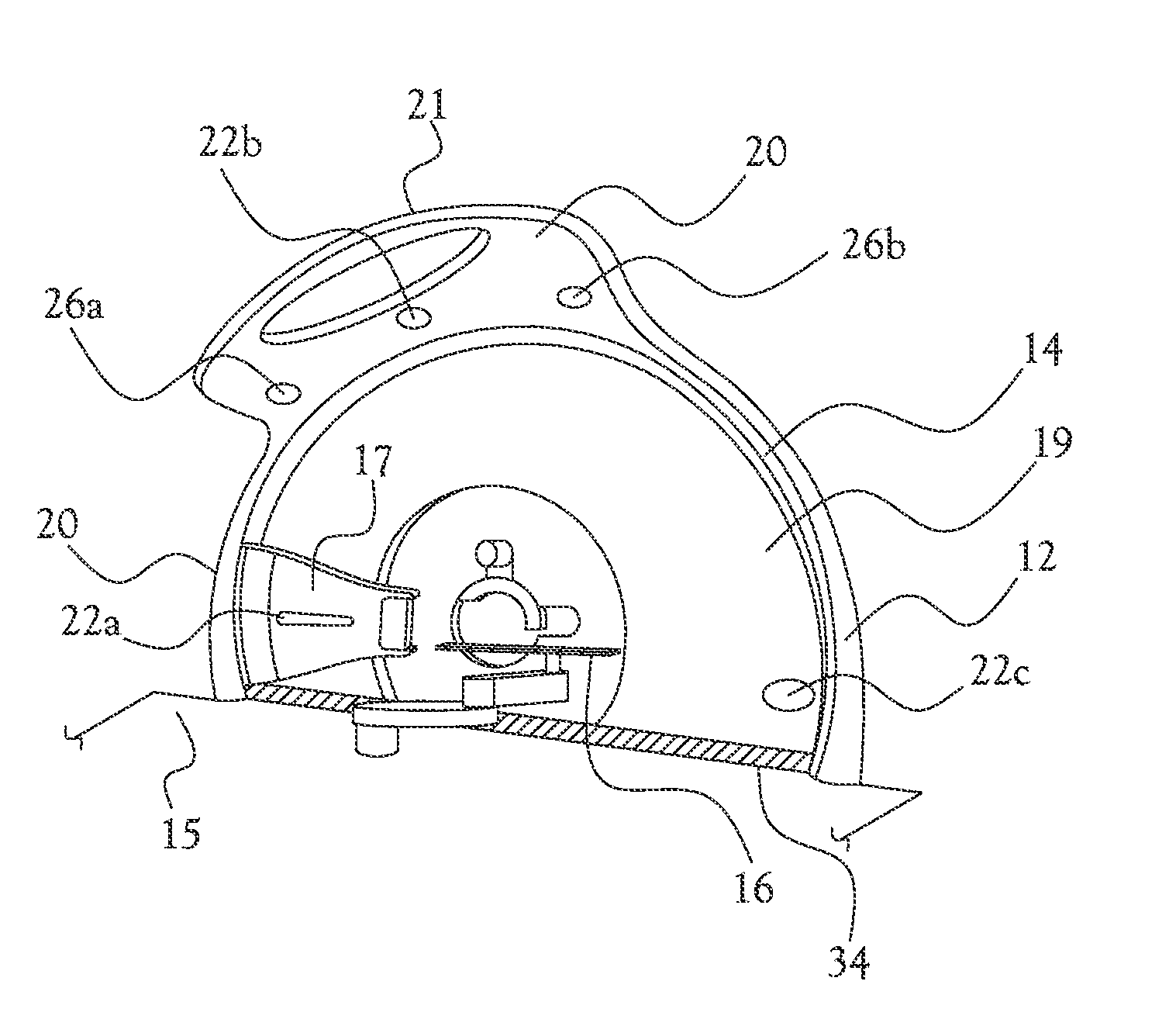
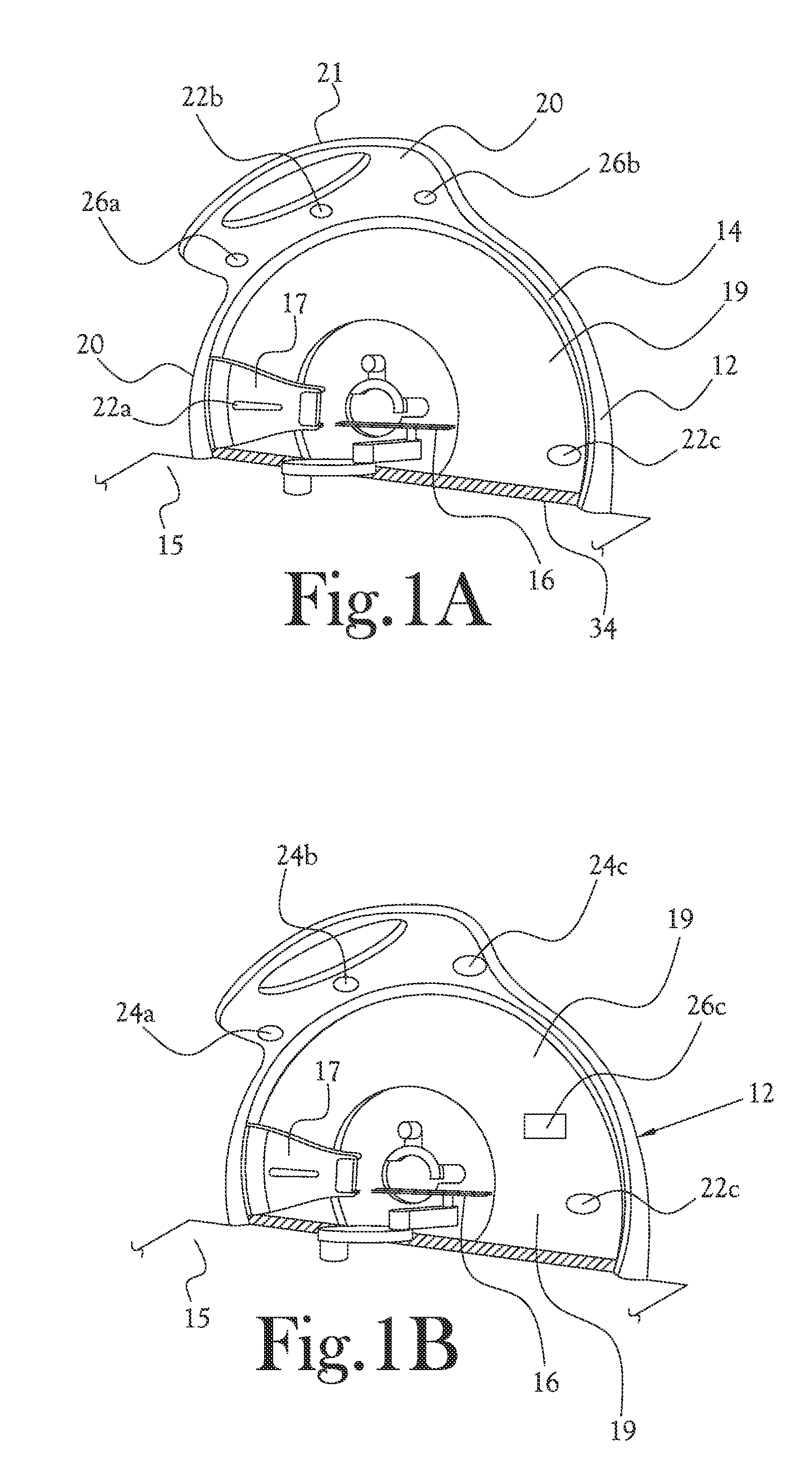
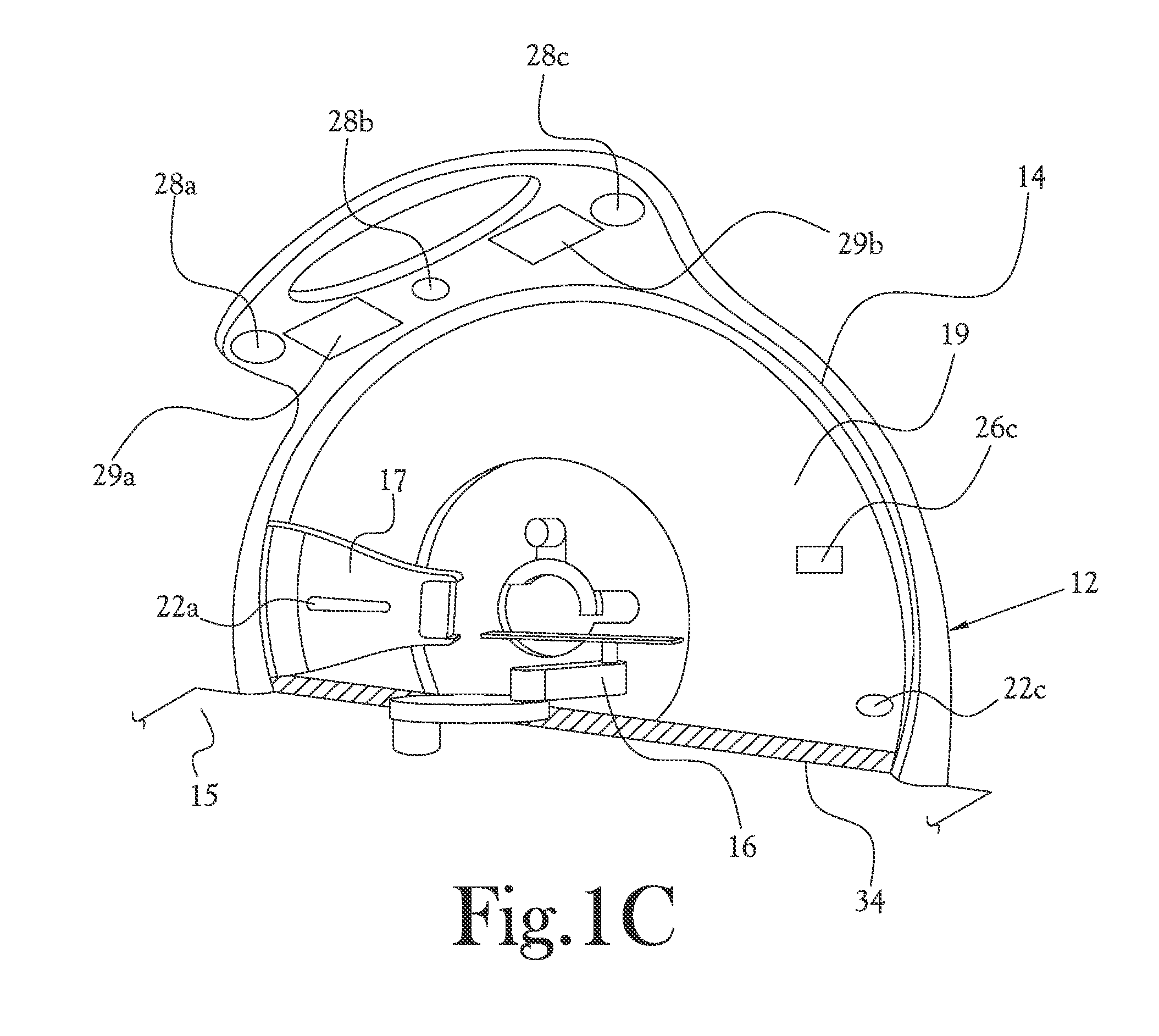
Medical device
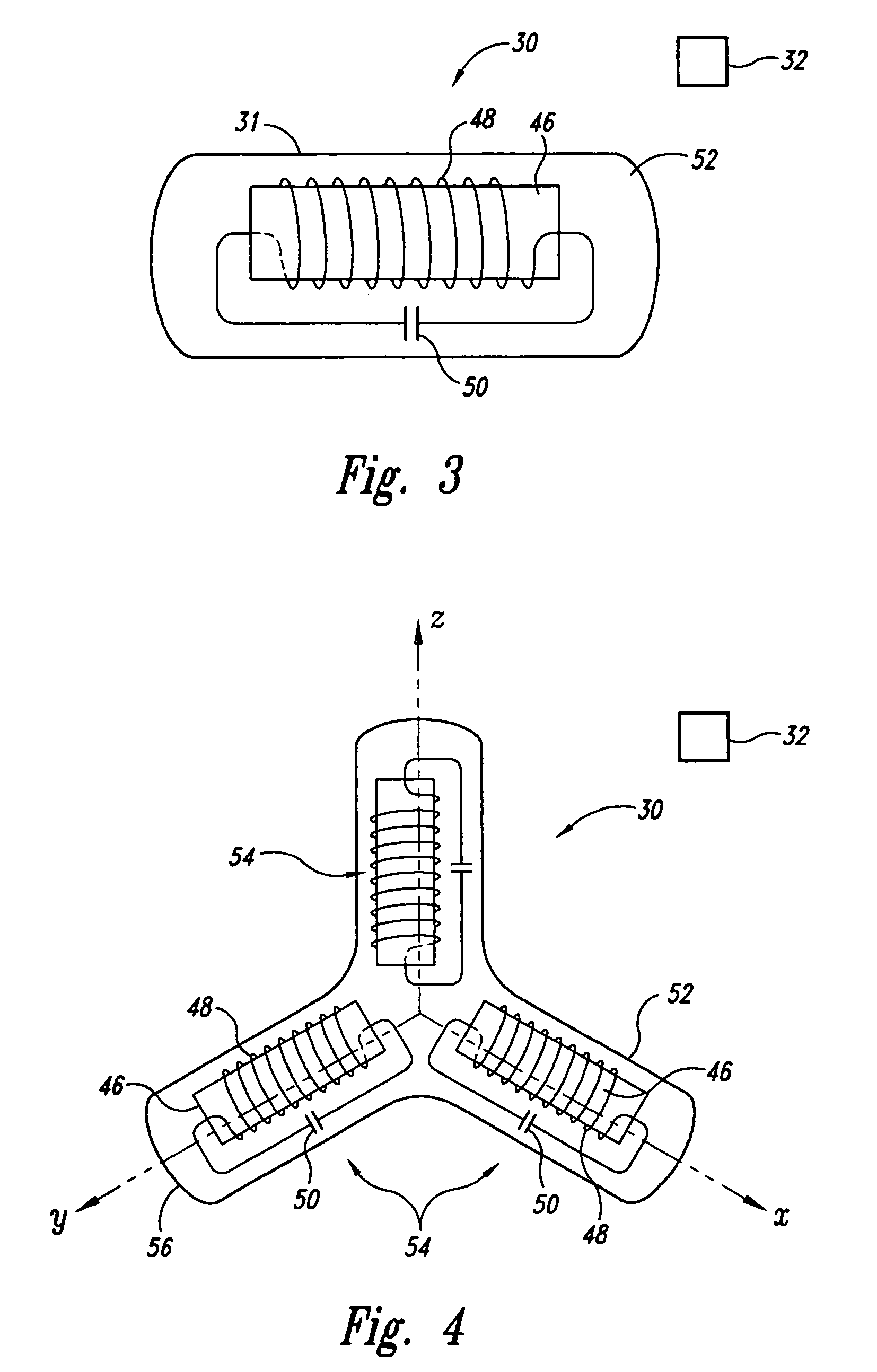
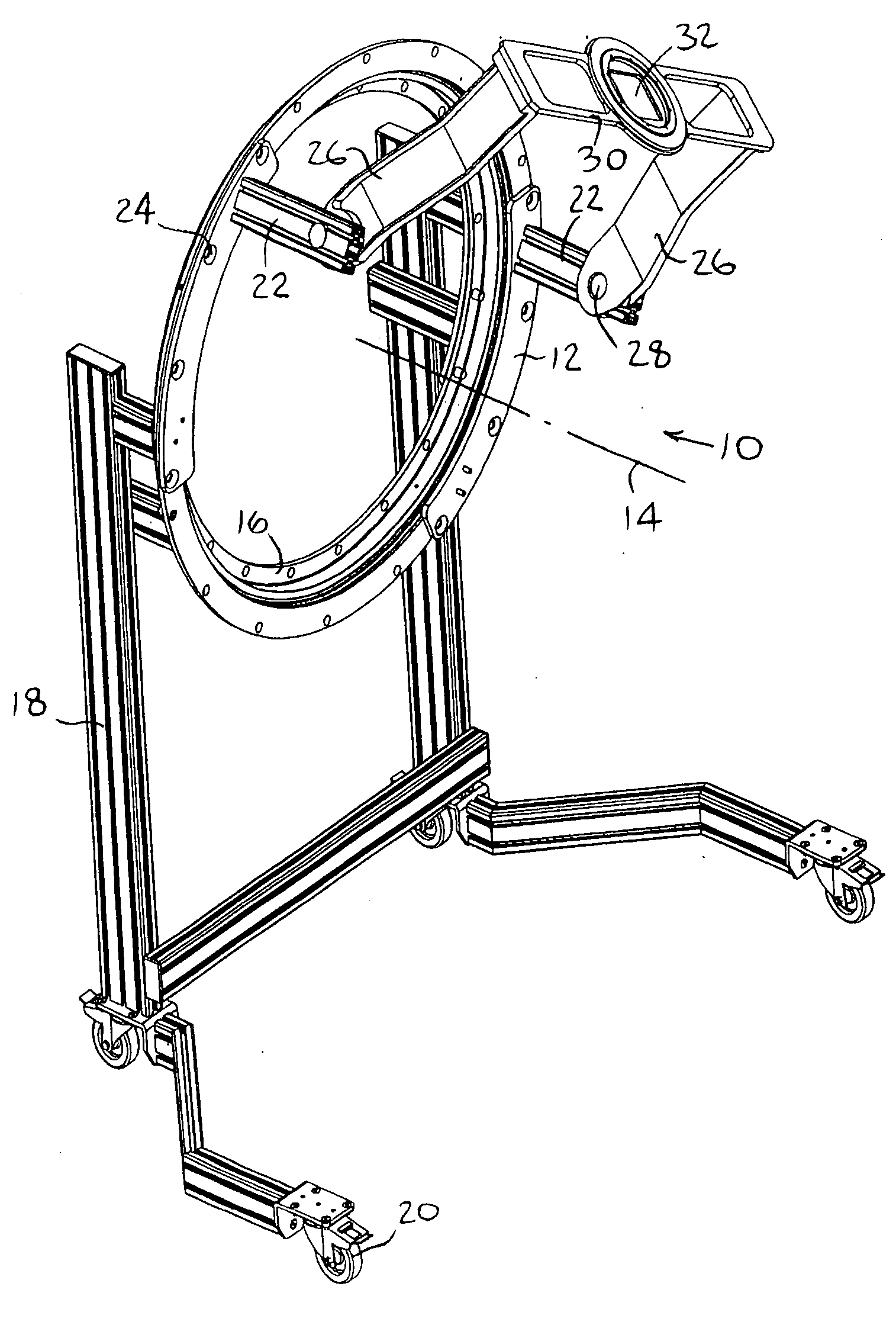
ActiveUS7679073B2Low experience requirementIncrease spacingRadiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsLight beamIsocenter
A medical device can perform treatment and diagnosis without causing a sense of unease to the patient. The medical device includes a substantially ring-shaped support frame provided in such a manner that a central axis through which an isocenter passes is disposed substantially horizontally; a substantially ring-shaped moving gantry which slides relative to the support frame and which has an opening at the isocenter side thereof a radiation emitter configured to emit a beam towards the isocenter; and a protective cover which covers the radiation emitter and an inner circumferential side of the moving gantry and which moves together with the moving gantry.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Systems and methods for real time tracking of targets in radiation therapy and other medical applications
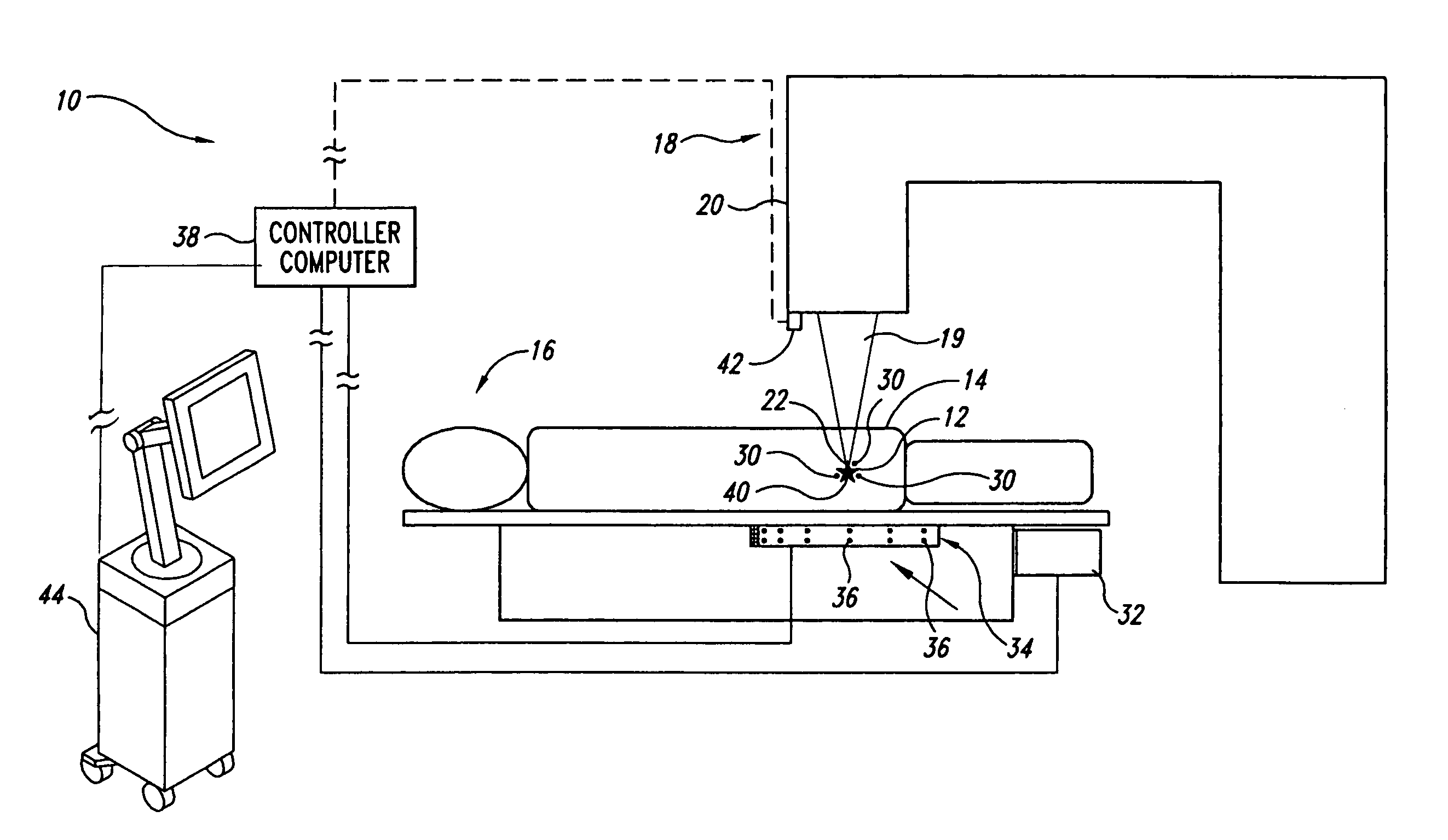
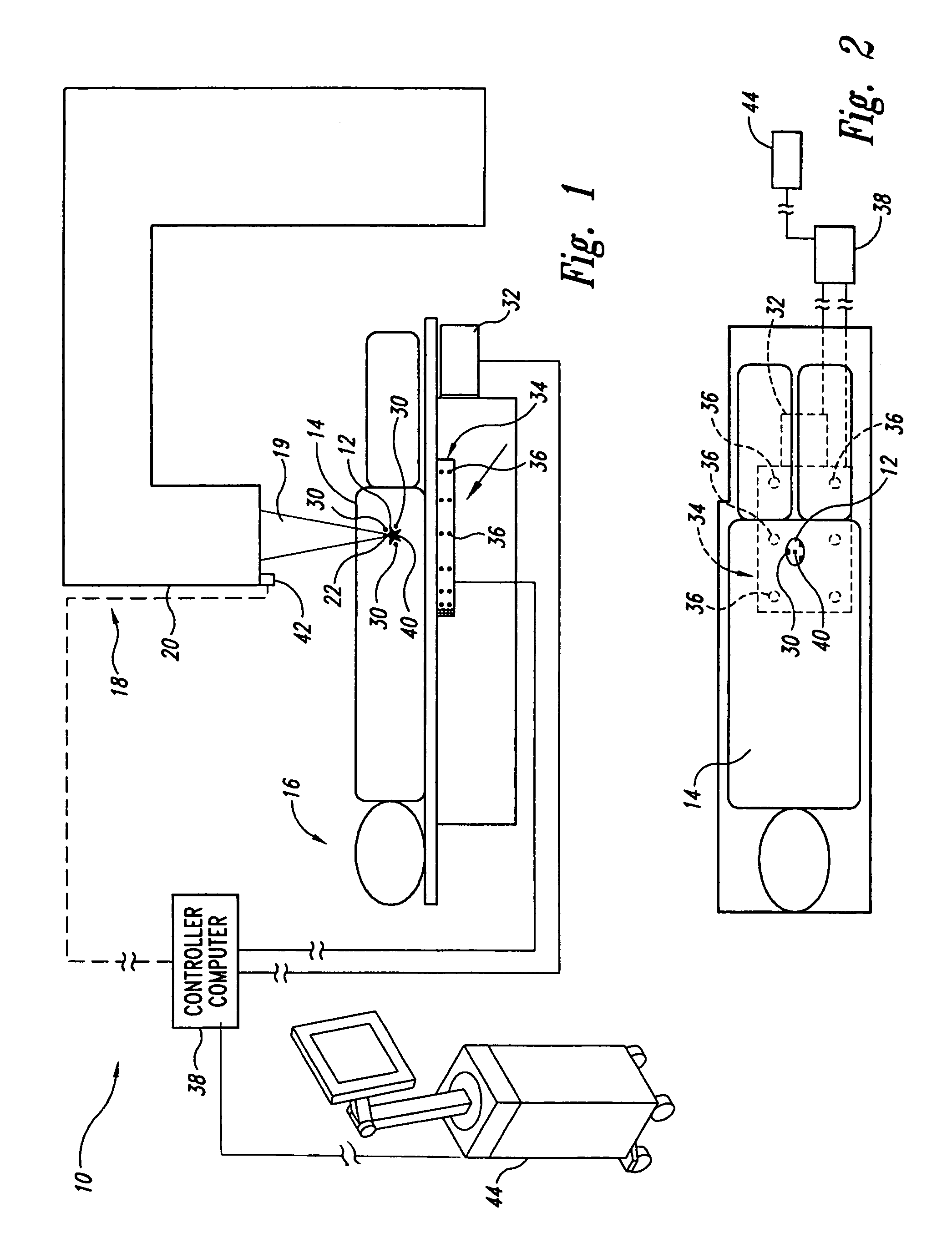
InactiveUS20060079764A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsComputer scienceIsocenter
Systems and methods for tracking targets in real time for radiation therapy and other applications. In one embodiment, a method includes collecting position information of a marker implanted within a patient at a site relative to the target at a time tn, and providing an objective output indicative of the location of the target based on the position information collected at time tn. The objective output is provided to a memory device, user interface, and / or radiation delivery machine within 1 ms to 2 seconds of the time tn when the position information was collected. This embodiment of the method can further include providing the objective output at a periodicity of 10-200 ms during at least a portion of a treatment procedure. For example, the method can further include generating a beam of ionizing radiation and directing the beam to a machine isocenter, and continuously repeating the collecting procedure and the providing procedure every 10-200 ms while irradiating the patient with the ionizing radiation beam.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Correction of the effect of spatial gradient field distortions in diffusion-weighted imaging
ActiveUS6969991B2Convenient distanceMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionField of viewIsocenter
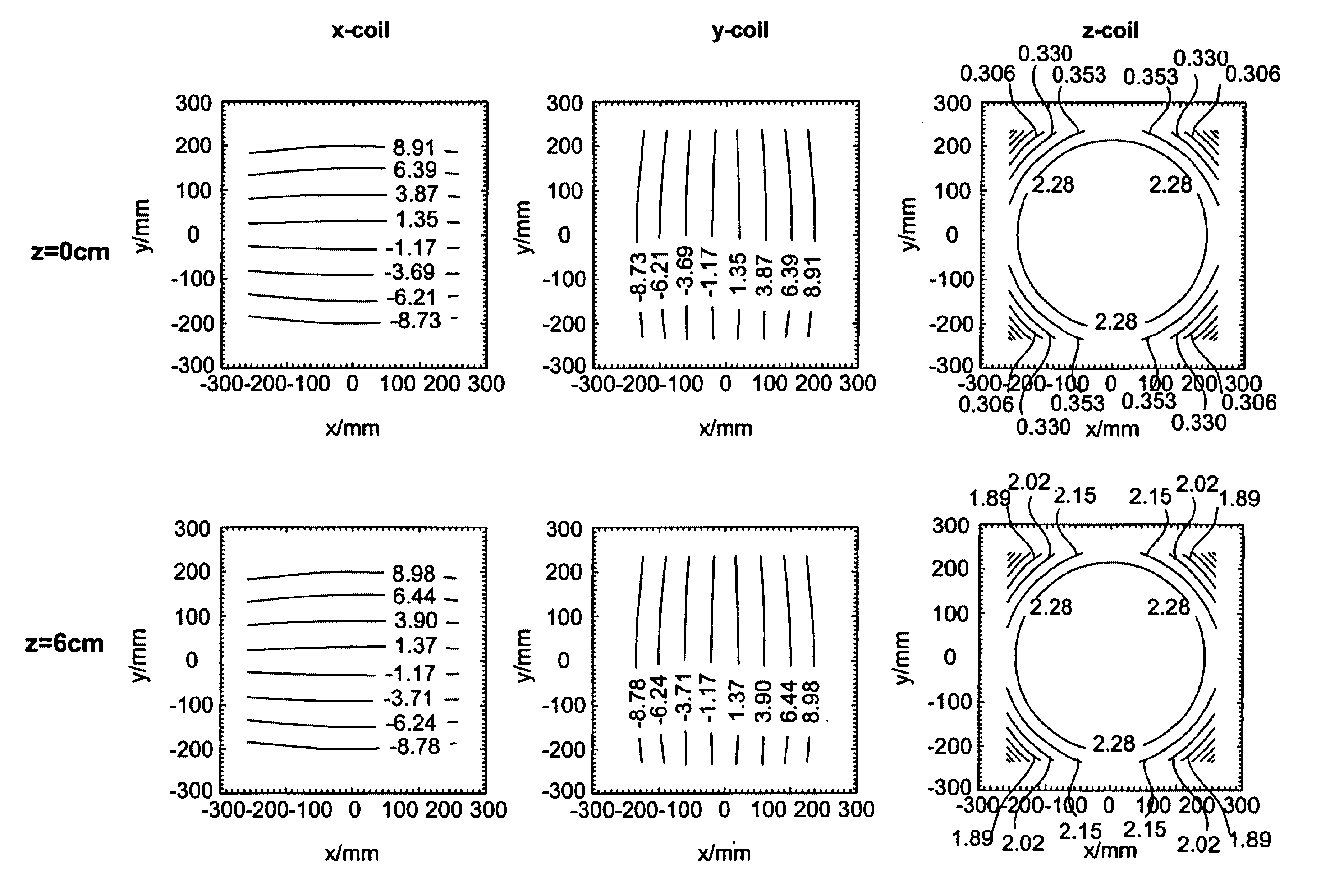
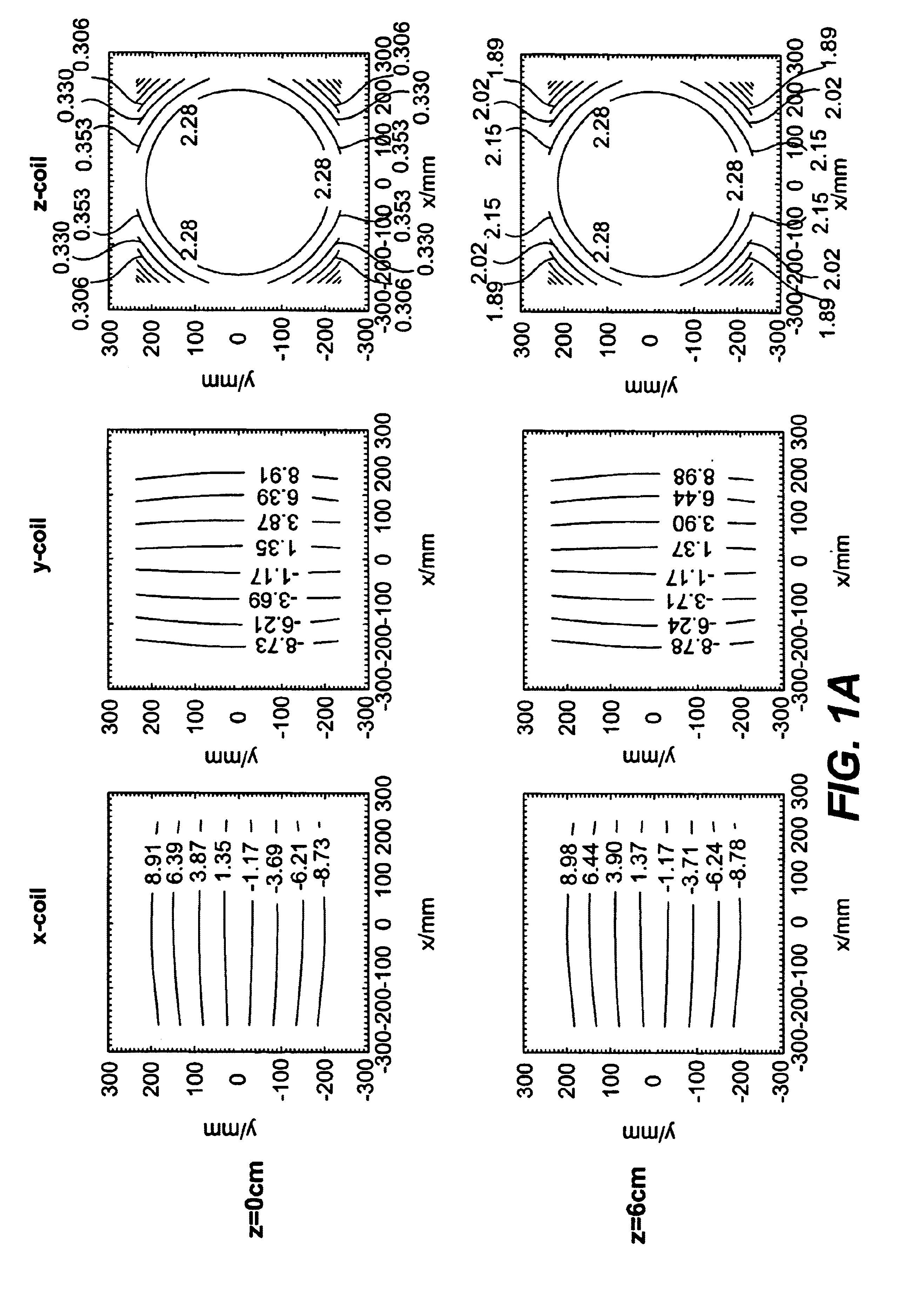
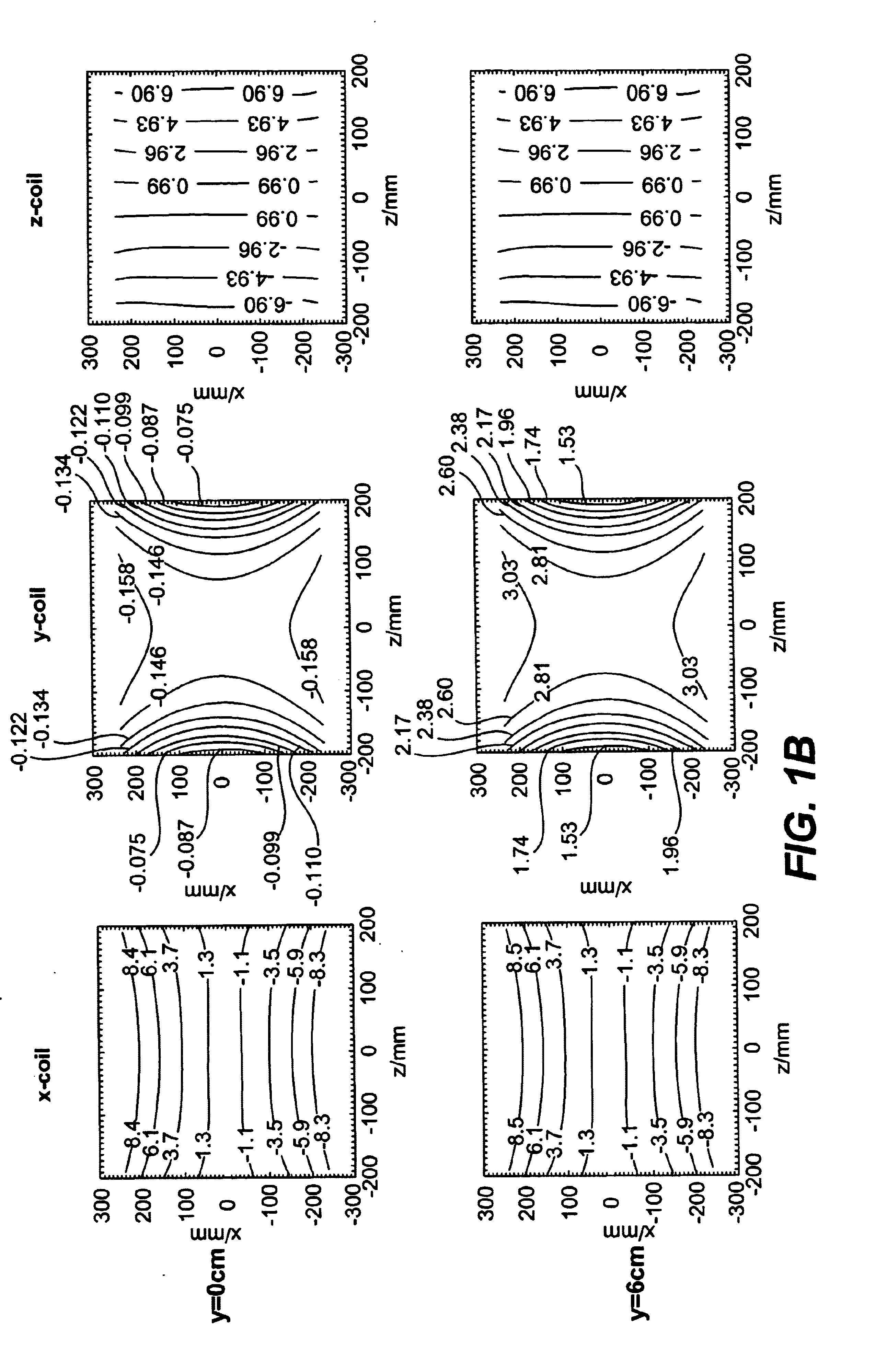
A general mathematical framework is formulated to characterize the contribution of gradient non-uniformities to diffusion tensor imaging in MRI. Based on a model expansion, the actual gradient field is approximated and employed, after elimination of geometric distortions, for predicting and correcting the errors in diffusion encoding. Prior to corrections, experiments clearly reveal marked deviations of the calculated diffusivity for fields of view generally used in diffusion experiments. These deviations are most significant with greater distance from the magnet's isocenter. For a FOV of 25 cm the resultant errors in absolute diffusivity can range from approximately −10 to +20 percent. Within the same field of view, the diffusion-encoding direction and the orientation of the calculated eigenvectors can be significantly altered if the perturbations by the gradient non-uniformities are not considered. With the proposed correction scheme most of the errors introduced by gradient non-uniformities can be removed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
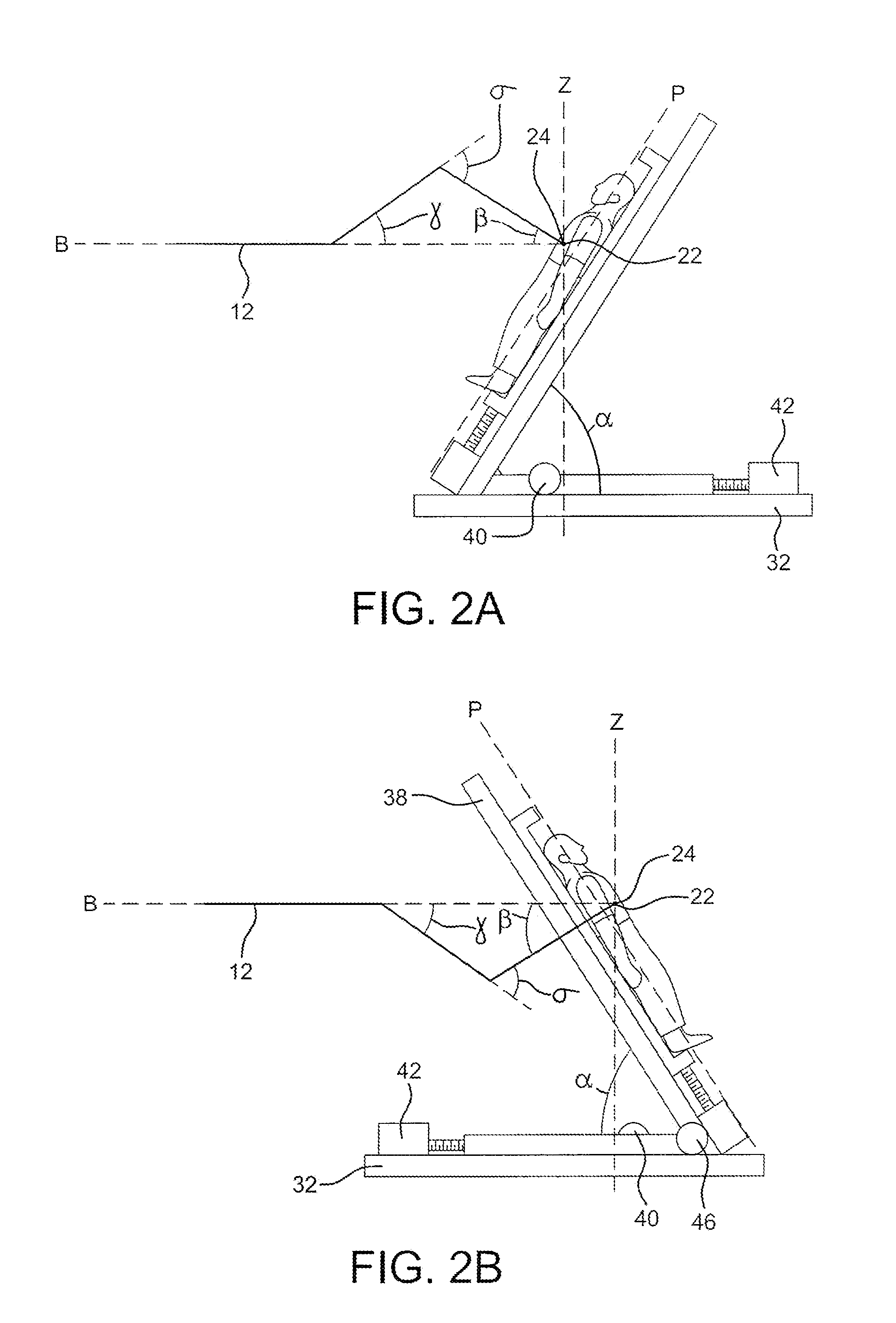
Device and method for administering particle beam therapy
ActiveUS8053745B2Thermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsParticle beamLight beam
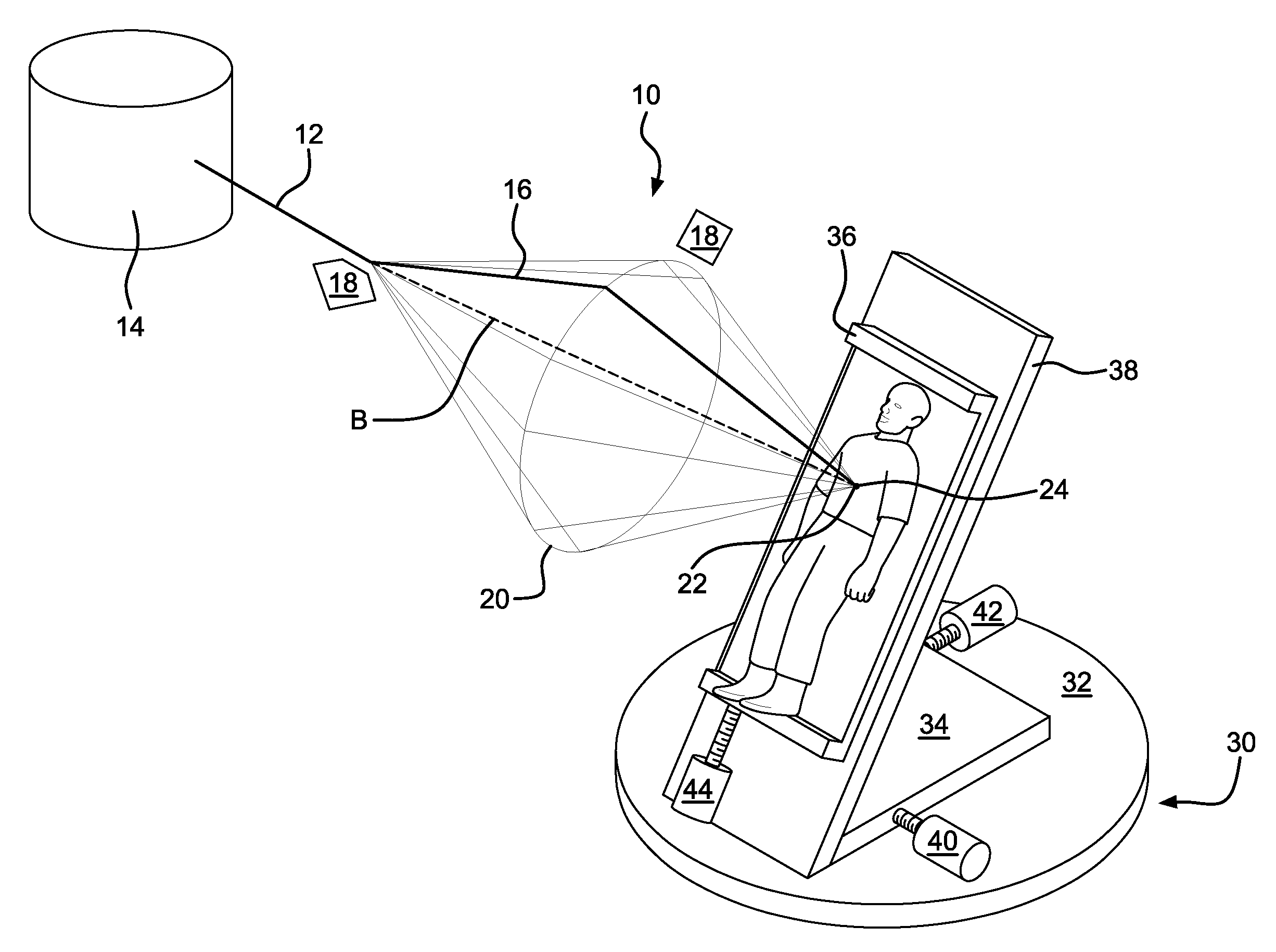
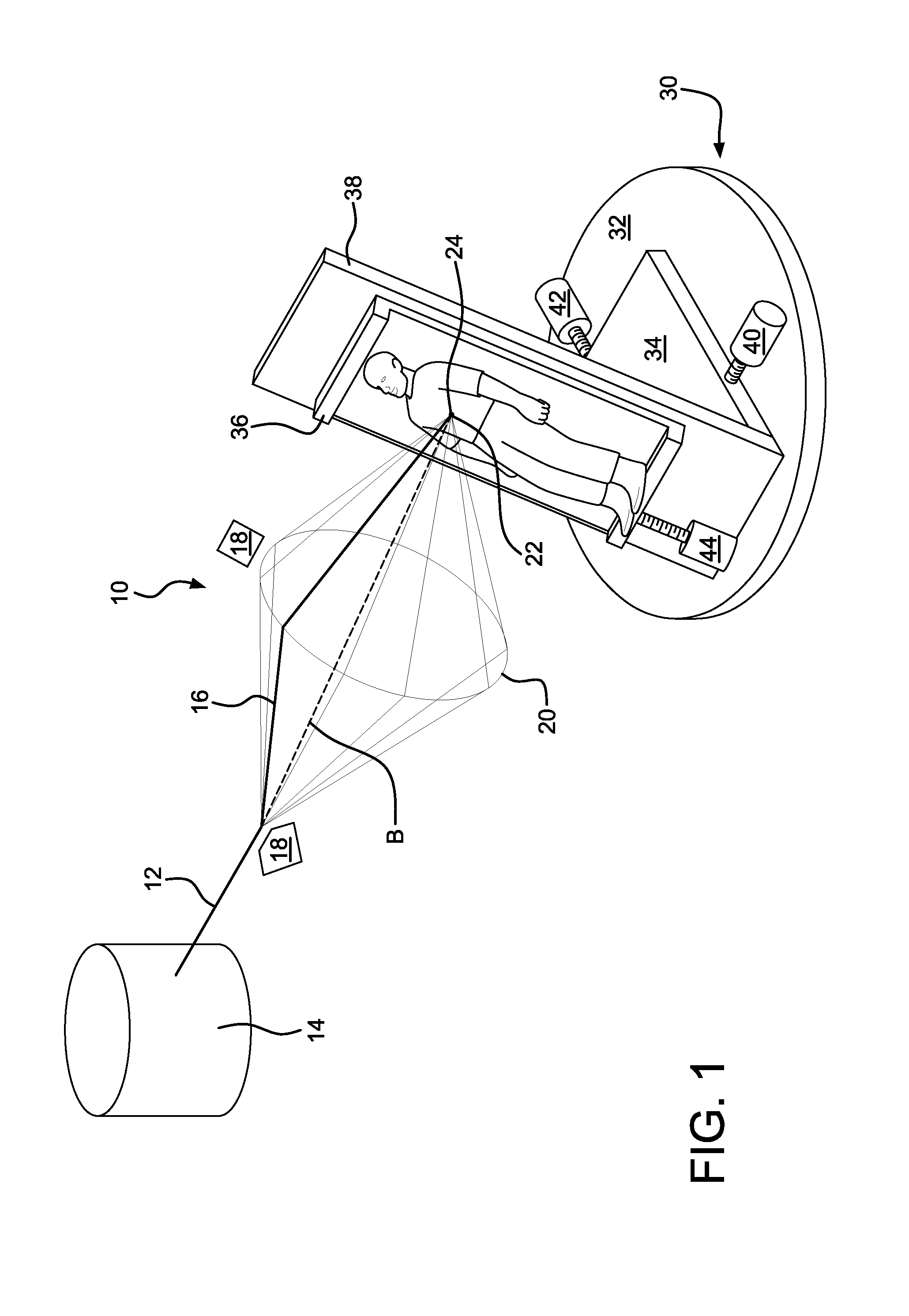
A device for circumscribing a target site with a beam. The target site is located within a target body. The path of the beam is varied rotationally so as to form a cone with an isocenter at the cone's apex. The isocenter is fixed on the approximate center of the target site. The target body is rotated about a vertical axis passing approximately through the center of the target site, and the rates of rotation of the beam path and body, respectively correspond so that the beam intersects an axis passing through the target site at an approximately constant angle.
Owner:MOORE FAMILY PROPERTIES LLC
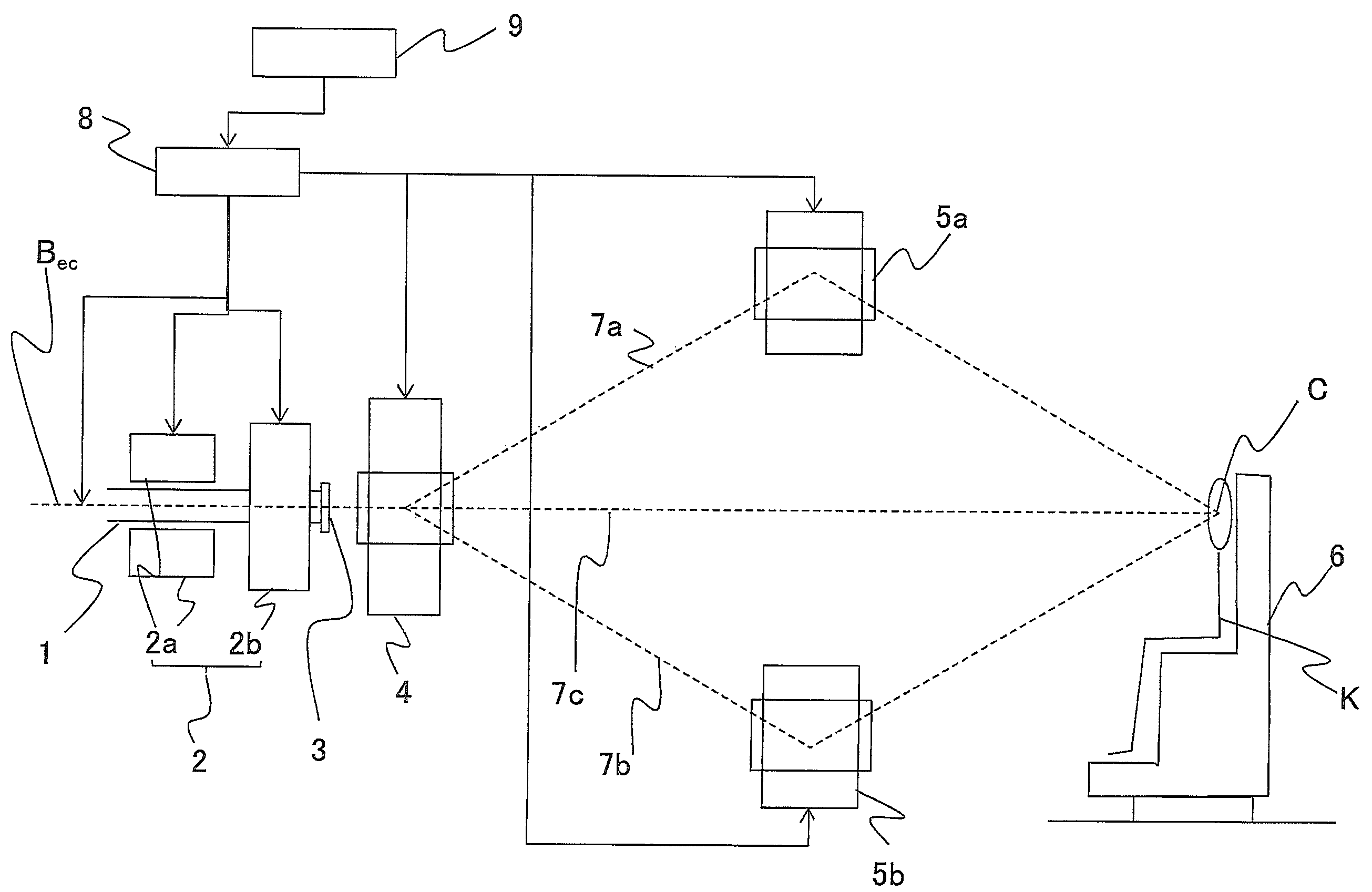
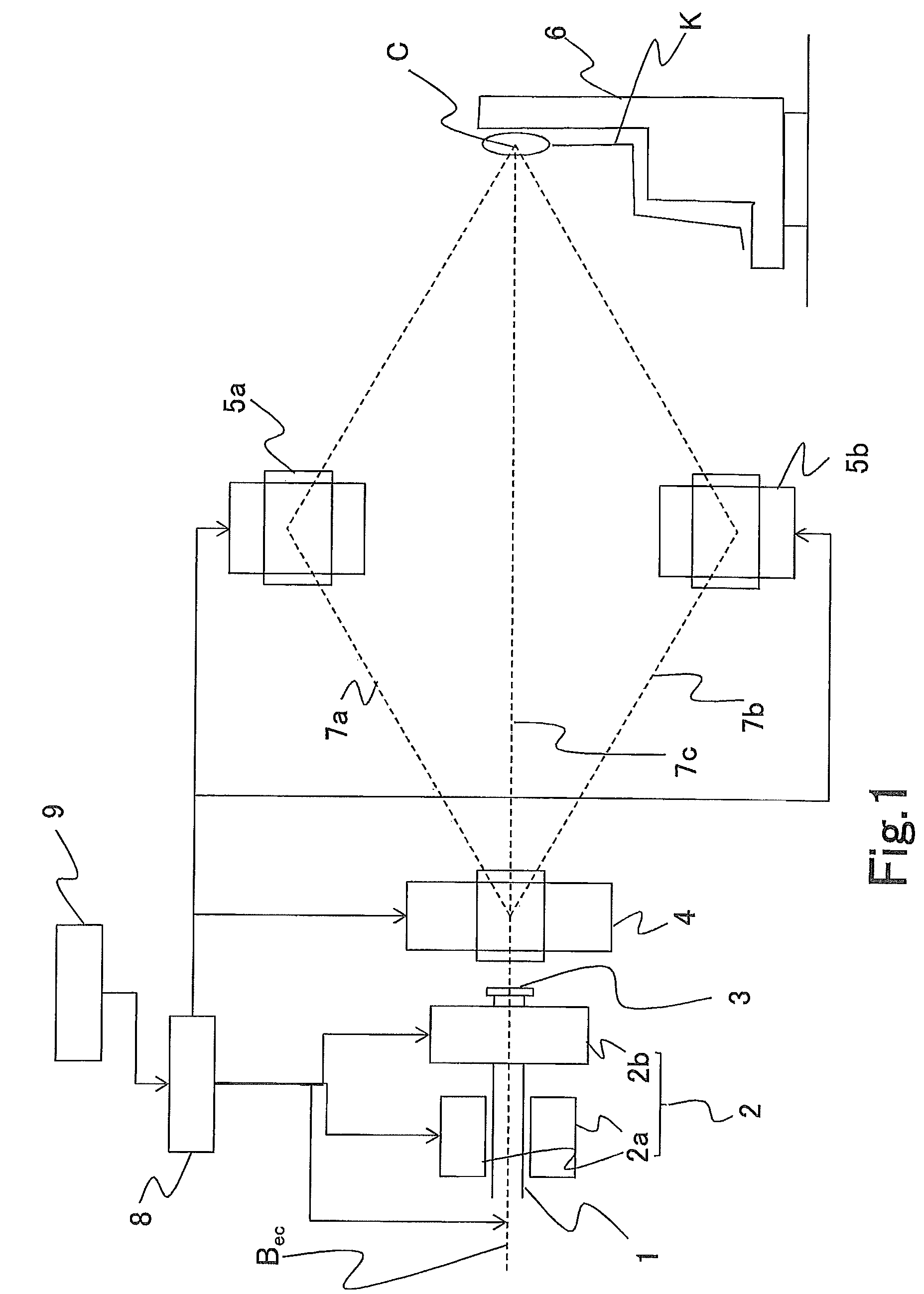
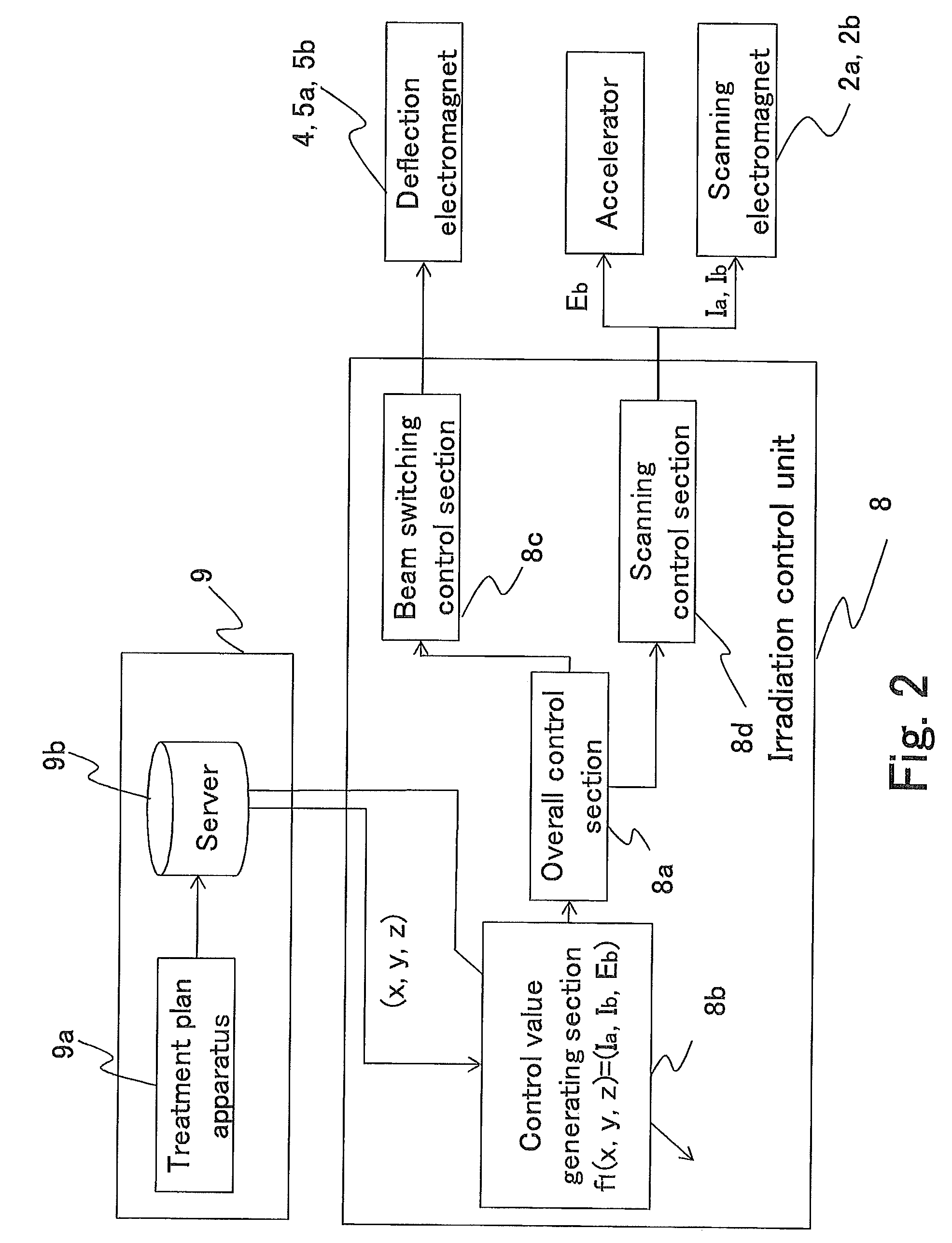
Particle beam therapy system and adjustment method for particle beam therapy system
ActiveUS8389949B2Reduce the amount requiredDivergence distance of a charged particle beam longerThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersParticle beamLight beam
The objective is to obtain a particle beam therapy system, the irradiation flexibility of which is high and that can reduce the amount of irradiation onto a normal tissue. There are provided a scanning electromagnet that performs scanning and outputting in such a way that a supplied charged particle beam is formed in a three-dimensional irradiation shape based on a treatment plan; and deflection electromagnets that switch the orbits for the charged particle beam in such a way that the charged particle beam with which scanning and outputting are performed by the scanning electromagnet reaches an isocenter through a single beam orbit selected from a plurality of beam orbits established between the isocenter and the scanning electromagnet. The distance between the scanning electromagnet and the isocenter is made long.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method for radiation therapy delivery at varying source to target distances
A method for providing radiation therapy to target tissue in a patient provides for adjustment of the vertical position of the patient couch to account for errors introduced by the weight supported by the couch at its desired positions for treatment. The method further contemplates determining the initial location of the center of the target tissue with respect to the immobilization frame supporting the patient, to eliminate errors introduced by collateral position sensing equipment. The method is particularly suited for extended distance treatments wherein, in one embodiment, a tare is established based on the actual isocenter of the gantry and then a subsequent adjustment of couch position is made with respect to movement of the couch to position the target tissue at the virtual isocenter.
Owner:CHIEN STANLEY +2
Imaging and treatment system
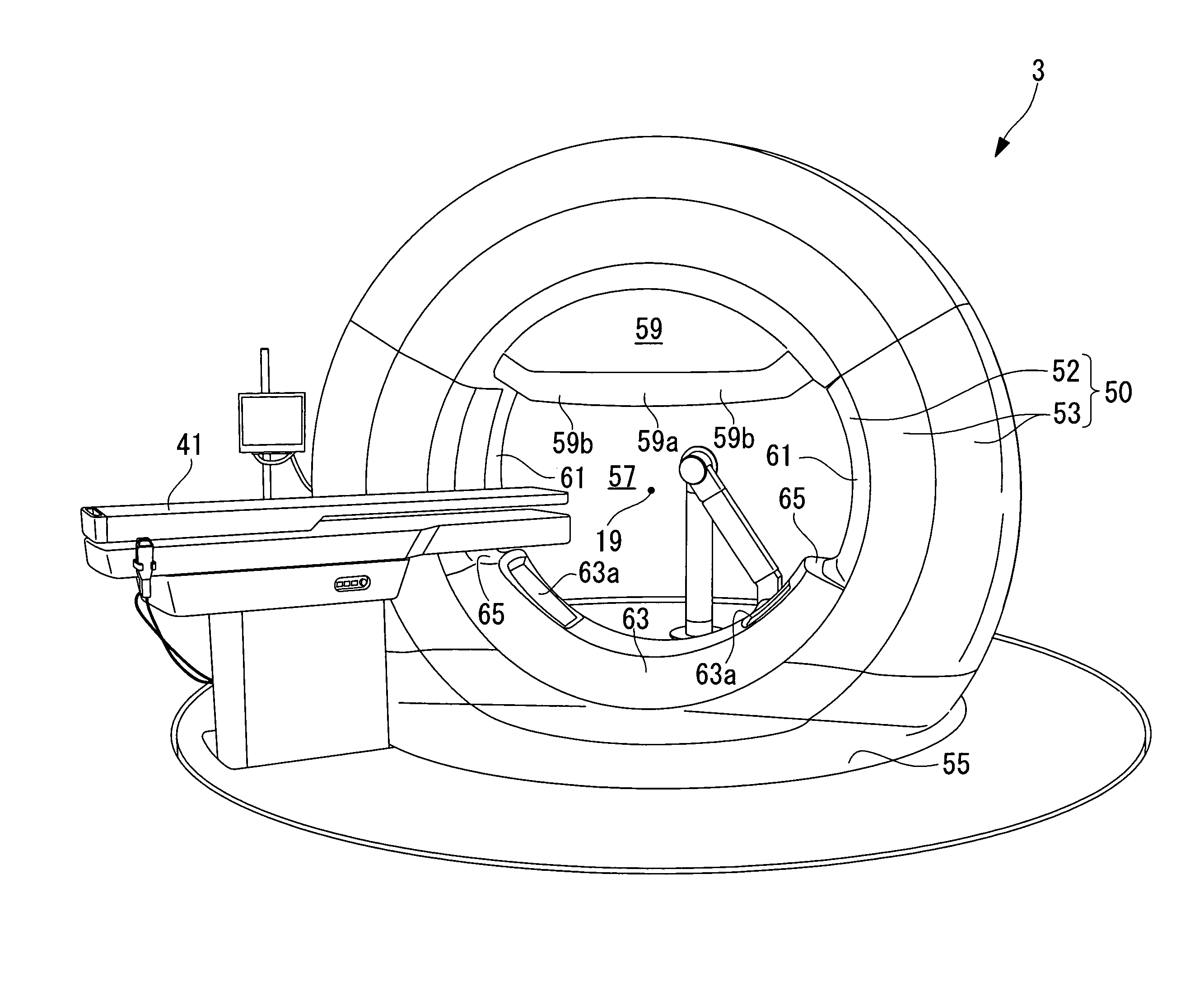
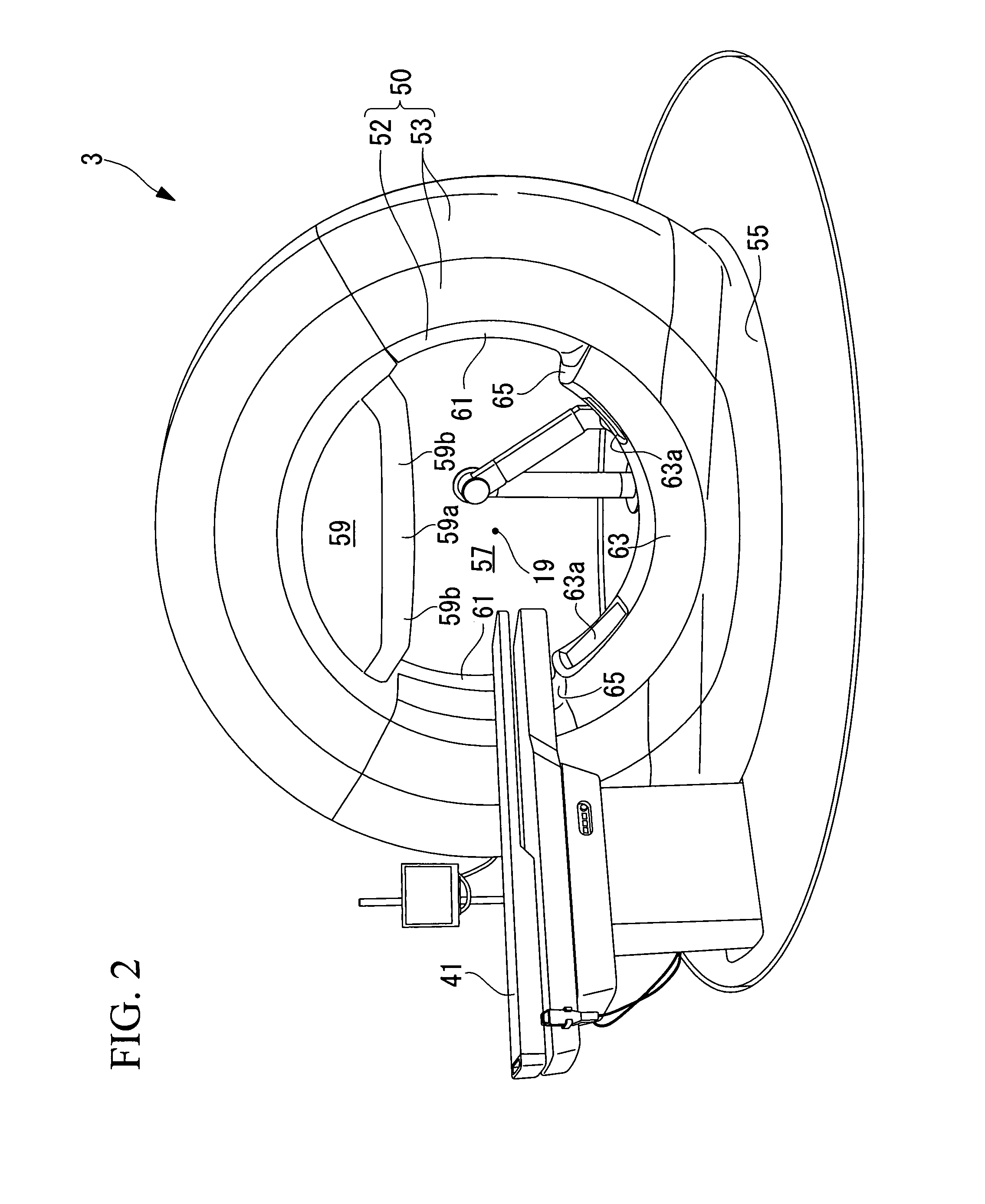
An imaging device including a rotator having a hollow bore for a patient to move therein and thereout, the rotator being rotatable about a longitudinal axis, at least one linkage arm extending outwards from the rotator, and imaging apparatus mounted on the at least one linkage arm, the imaging apparatus including an imaging source that emits an imaging beam to an imaging detector aligned therewith along an imaging direction, the at least one linkage arm capable of full axial rotation about an imaging isocenter along an entire length of the patient, the isocenter lying along a longitudinal axis, and wherein the imaging apparatus is operative to rotate and to capture images of the patient along the imaging direction as the patient is positioned at an angle in a range of about 0-90° inclusive with respect to the longitudinal axis.
Owner:EIN GAL MOSHE
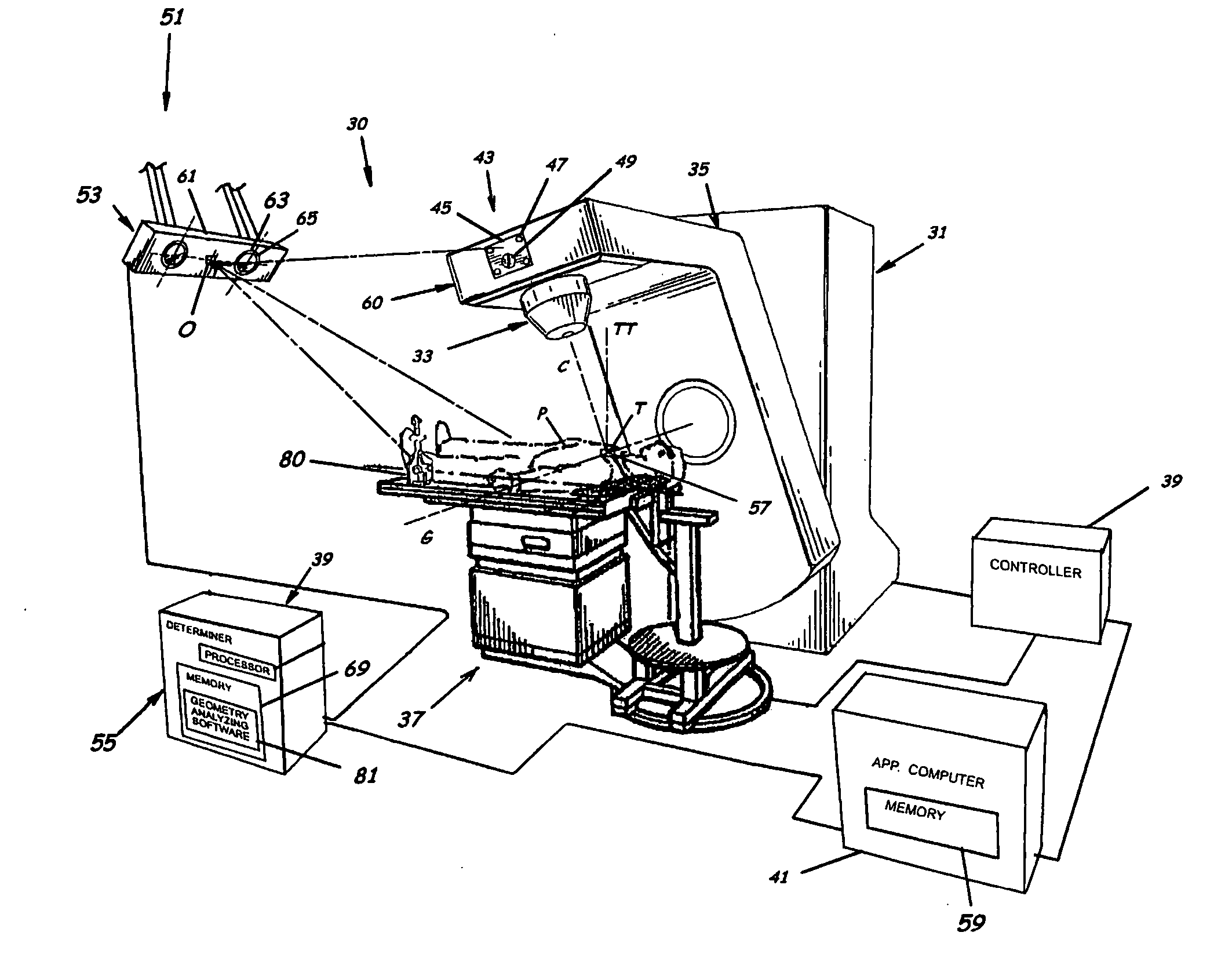
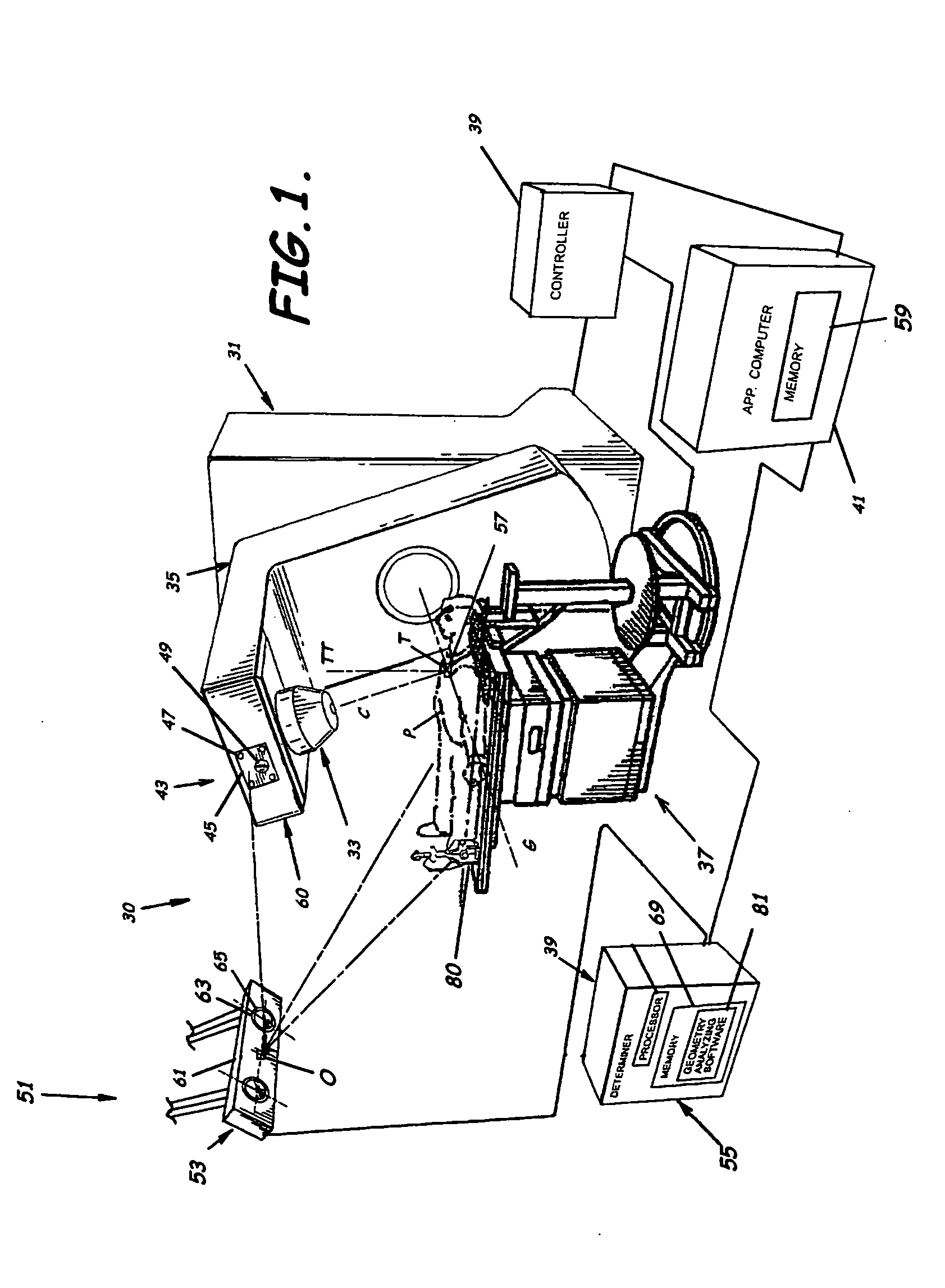
System for monitoring the geometry of a radiation treatment apparatus, trackable assembly, program product, and related methods
ActiveUS20060215813A1Accurate CalibrationPrecise applicationRadiation beam directing meansX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTreatment deliveryApplication computers
A system to monitor a geometry of a treatment apparatus, an apparatus, a trackable assembly, program product, and methods are provided. The system includes a treatment apparatus having a radiation emitter, a rotating assembly controlled by a controller, and an application computer, which provides treatment delivery instructions to the controller. The system can also include a trackable assembly connected to the rotating assembly and having a fixedly connected first trackable body which functions as a reference fixture and a pivotally connected second trackable body which provides data used to determine a rotation angle of the rotating assembly. The system also includes an apparatus to track a trackable body which has a trackable body detector to detect a position of the indicators carried by the first and the second trackable bodies and a determiner to determine and verify the location of the origin of an isocenter coordinate system and to determine rotational path data about the rotating assembly.
Owner:BEST MEDICAL INT
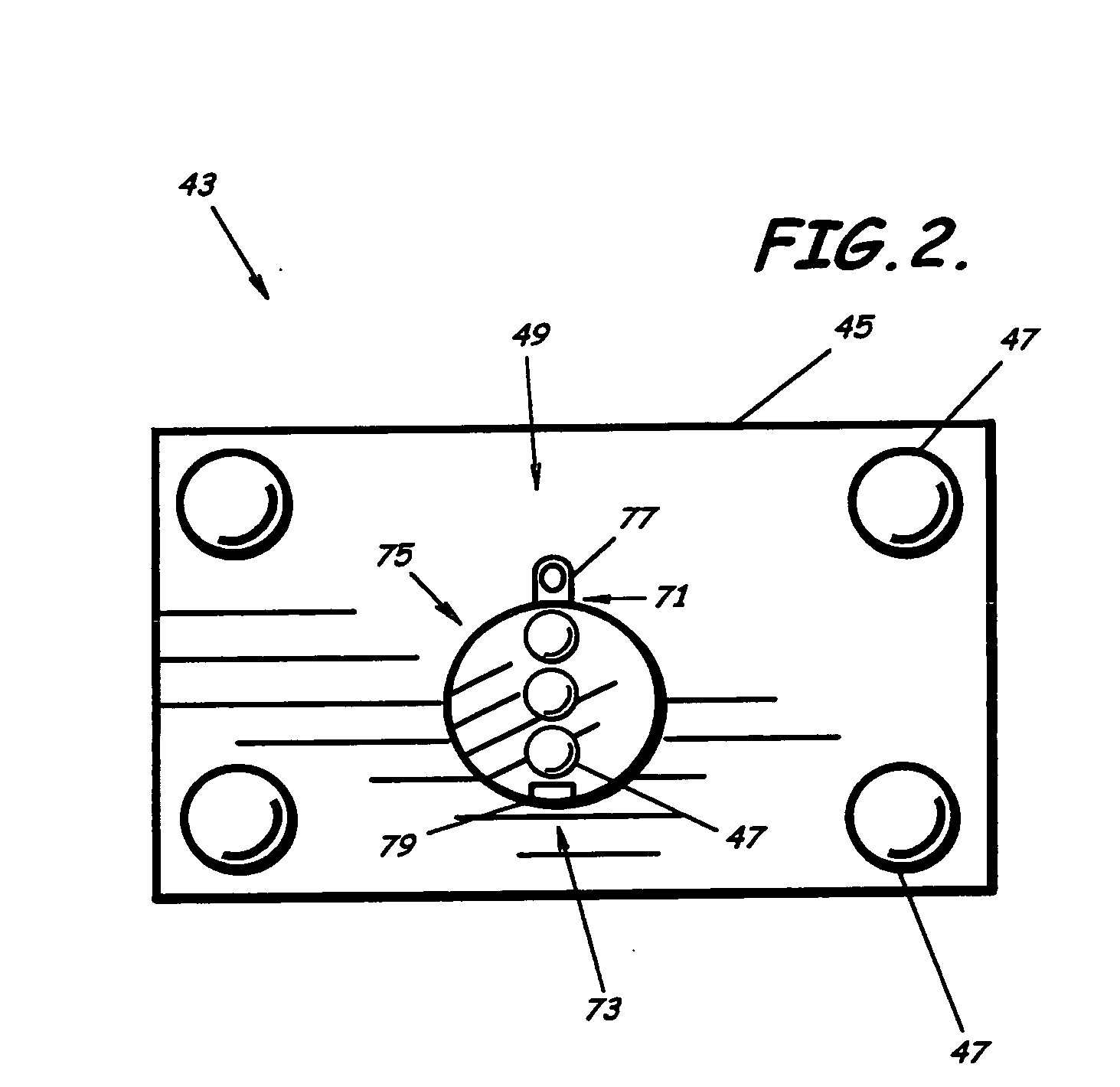
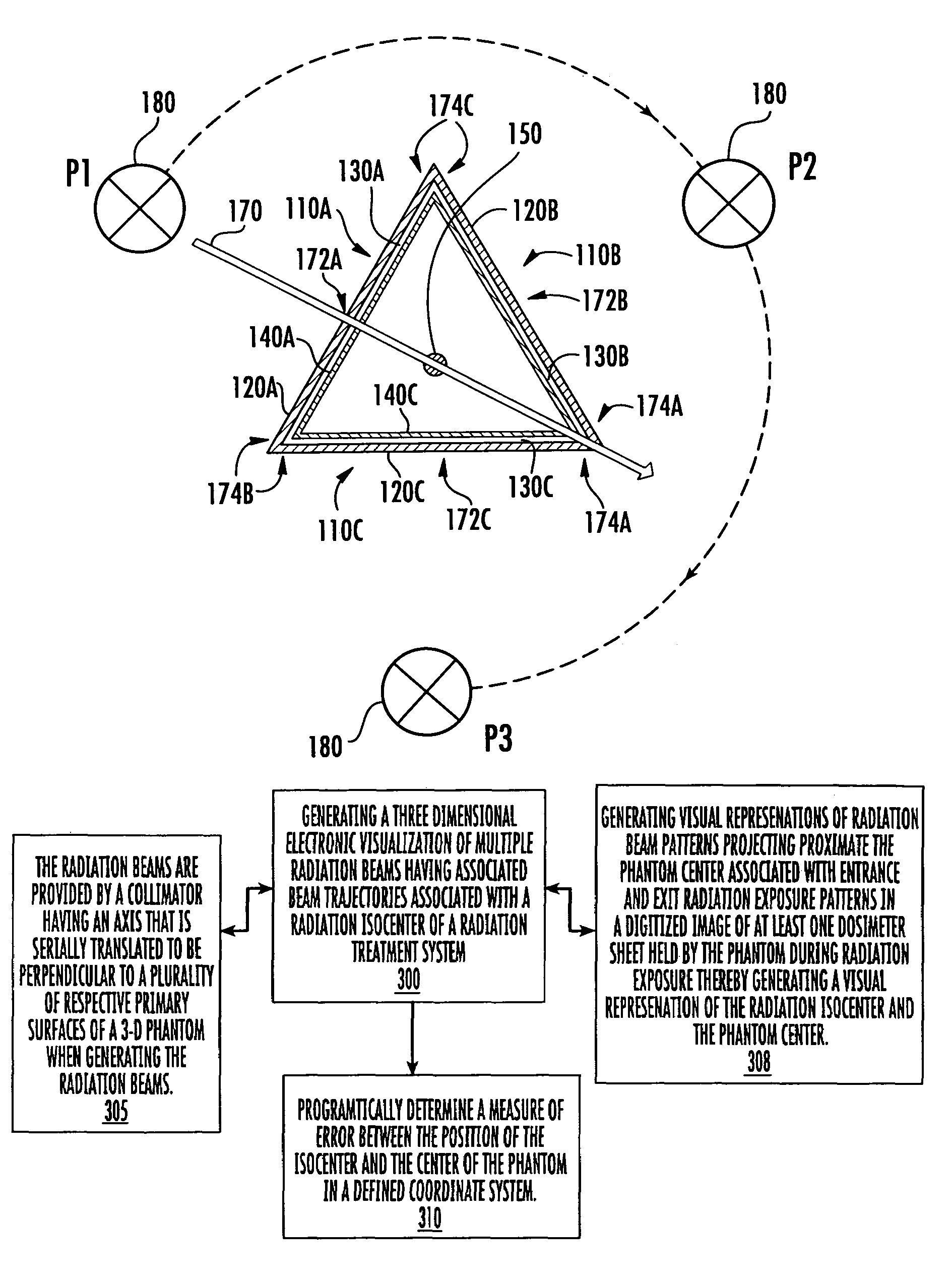
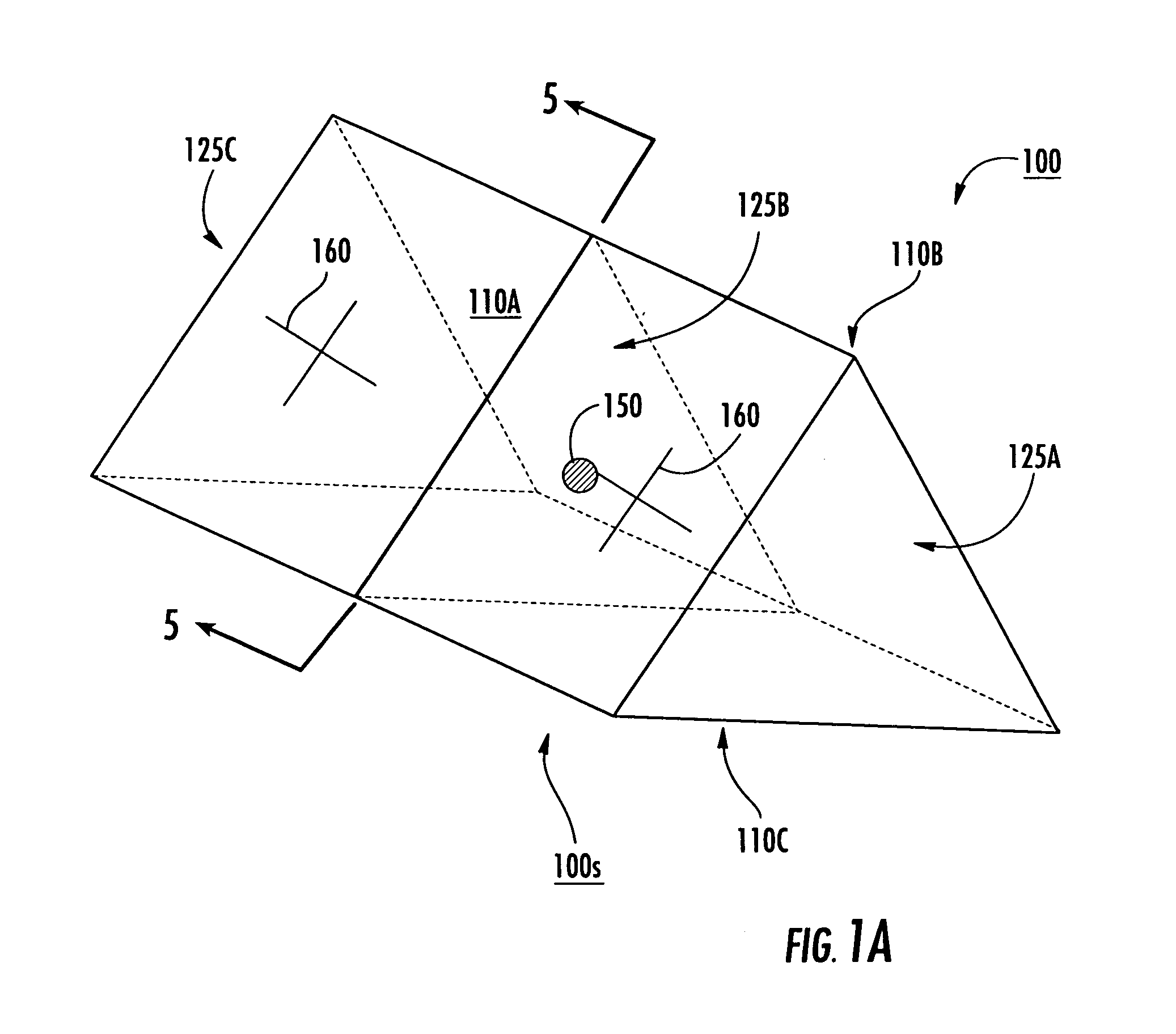
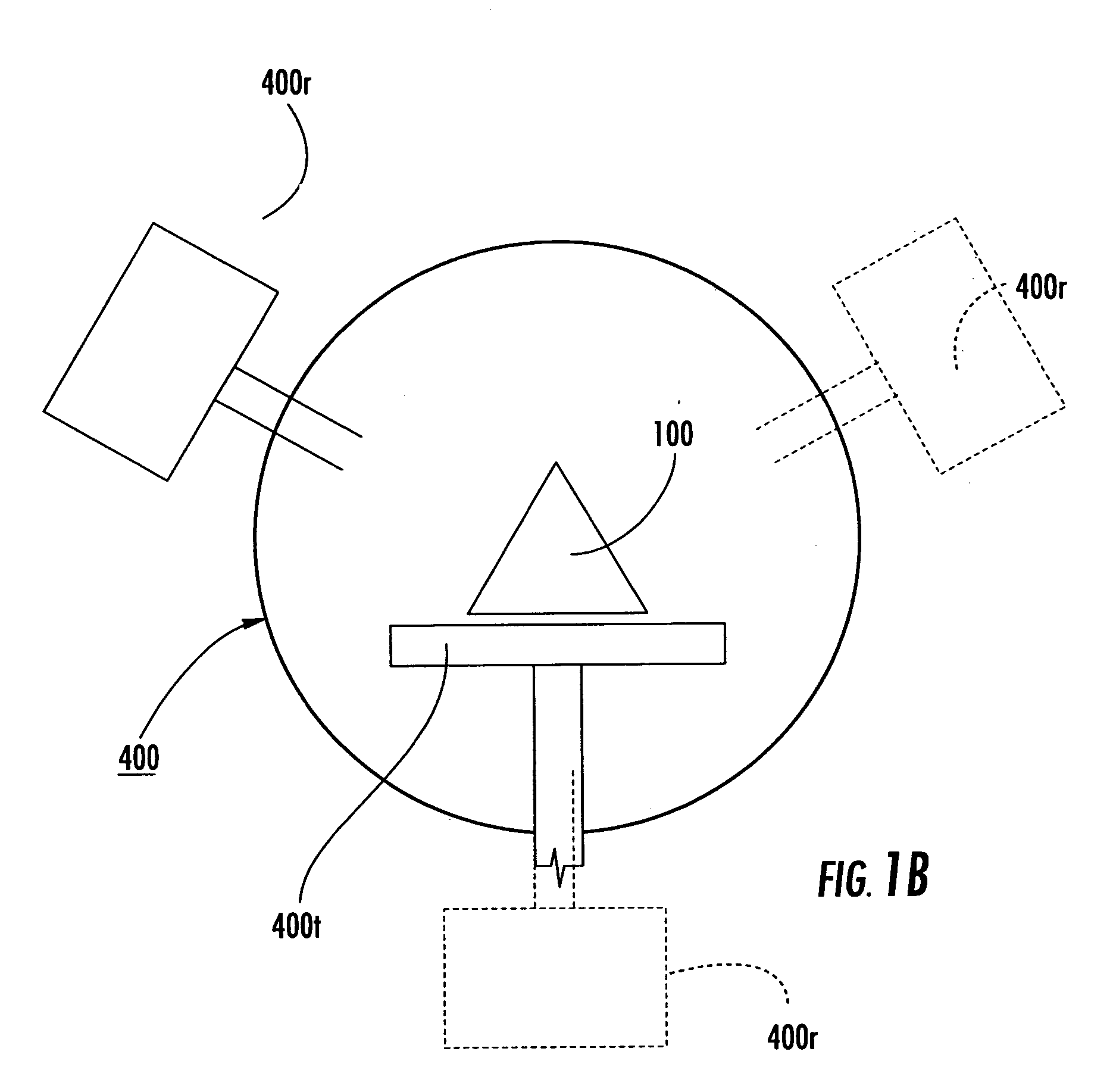
Radiation isocenter measurement devices and methods and 3-D radiation isocenter visualization systems and related methods
A three-dimensional phantom assembly for use with a radiation treatment device includes a three-dimensional support member having at least two, spaced apart opposed surfaces configured to hold at least one generally planar radiation sensitive dosimeter sheet such that the dosimeter sheet generally conforms to a shape defined by the two opposed surfaces. During irradiation, a radiation beam trajectory passes through the two opposed surfaces. Related systems methods for determining a radiation isocenter and / or generating a 3-D visualization of the radiation isocenter using radiation patterns obtained using a phantom are also described.
Owner:EAST CAROLINA UNIVERISTY
Positioning method and device, upper computer and radiotherapy system
ActiveCN108635681APositioning to achieveCause some damagesSurgeryDiagnostic markersComputer scienceIsocenter
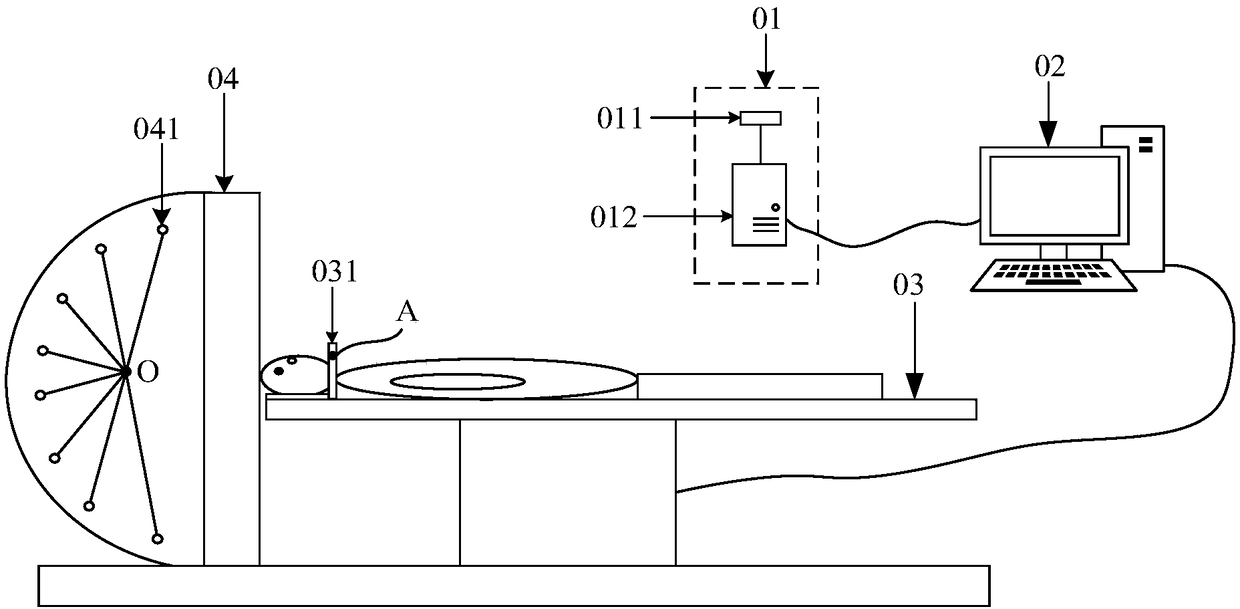
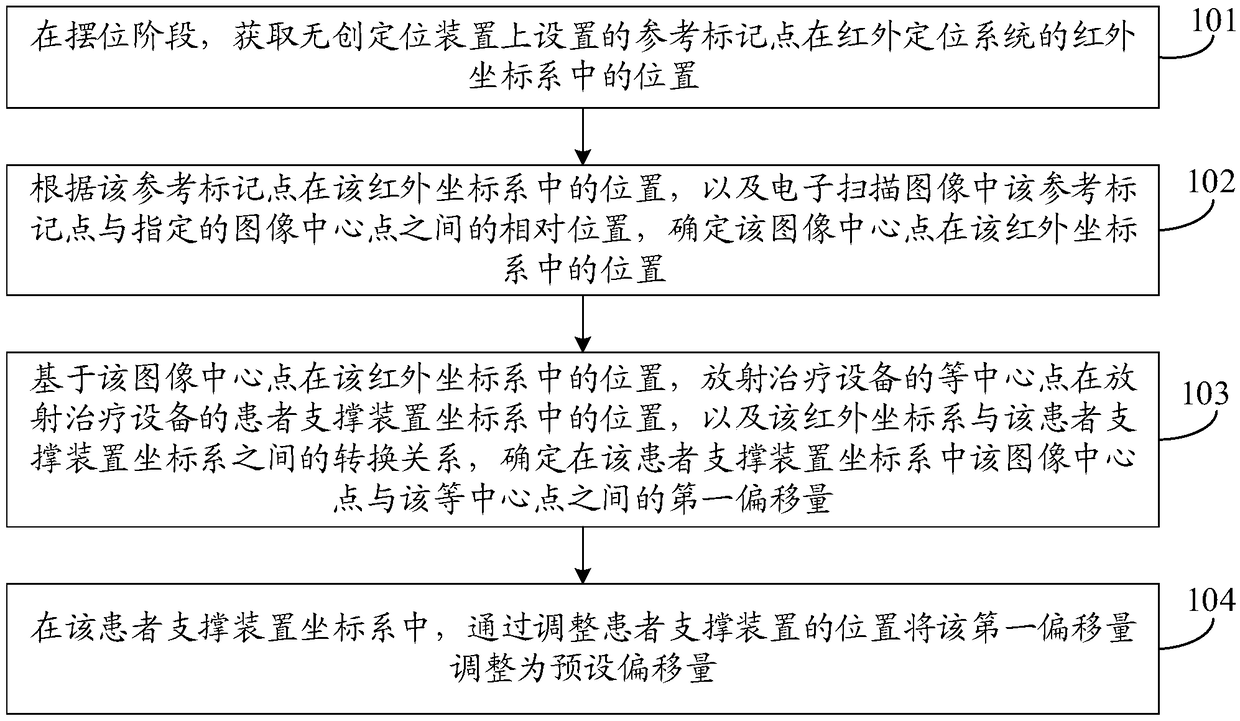
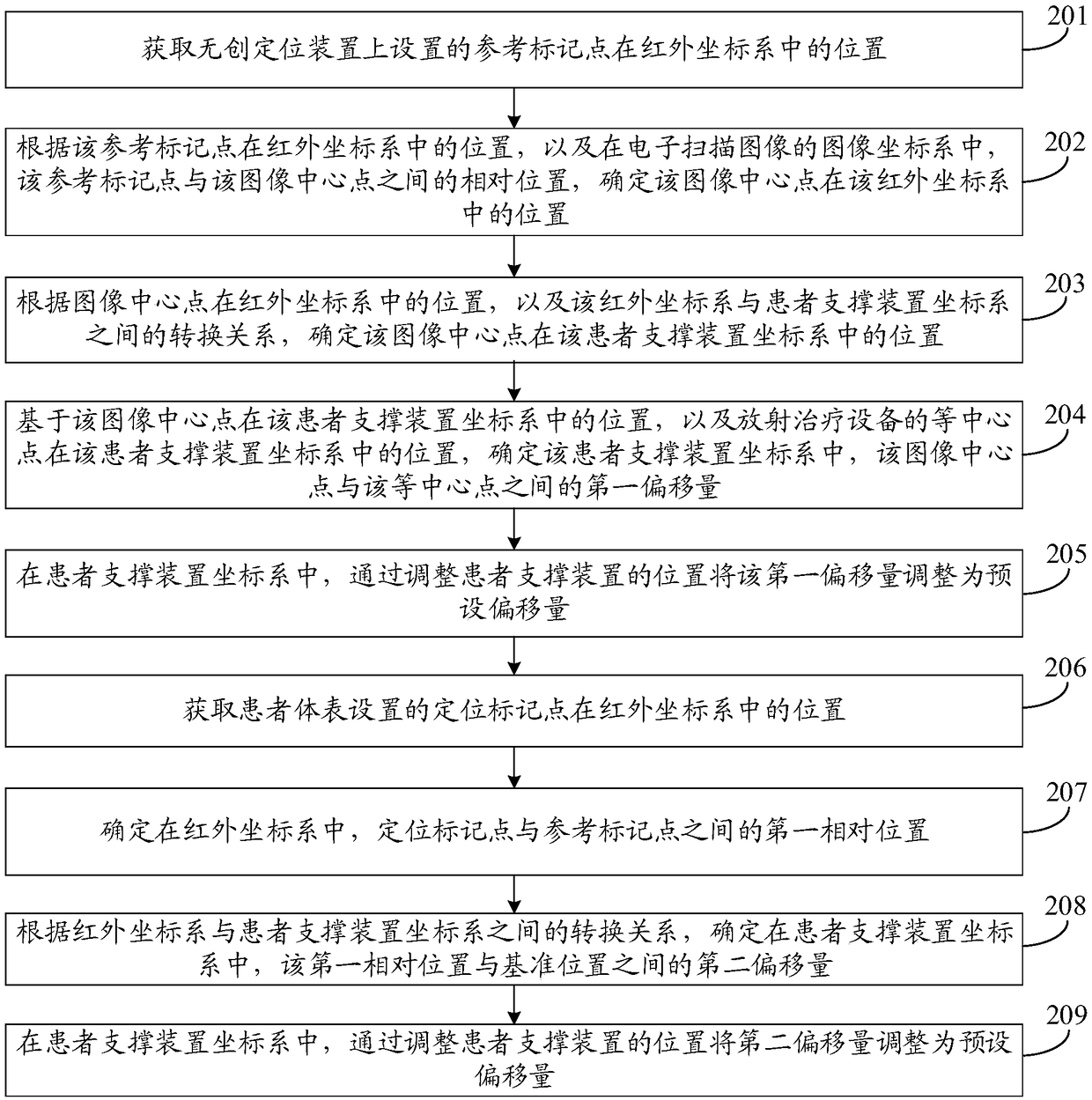
The invention discloses a positioning method and device, an upper computer and a radiotherapy system, and belongs to the field of radiotherapy. The positioning method comprises the steps that the positions, in an infrared coordinate system, of reference mark points arranged on a noninvasive positioning device are obtained; according to the positions of the reference mark points in the infrared coordinate system and the relative positions between reference mark points in an electronic scanning image and a designated image center point, the position of the image center point in the infrared coordinate system is determined; on the basis of the position of the image center point in the infrared coordinate system, the position of an isocenter point of radiotherapy equipment in a patient supporting device coordinate system, and the conversion relation between the infrared coordinate system and the patient supporting device coordinate system, the first offset amount between the image center point and the isocenter point in the patient supporting device coordinate system is determined; and in the patient supporting device coordinate system, the first offset amount is adjusted to the presetoffset amount by adjusting the position of a patient supporting device. The positioning method is low in cost, and a patient is not harmed.
Owner:CYBERMED TECH XIAN +1
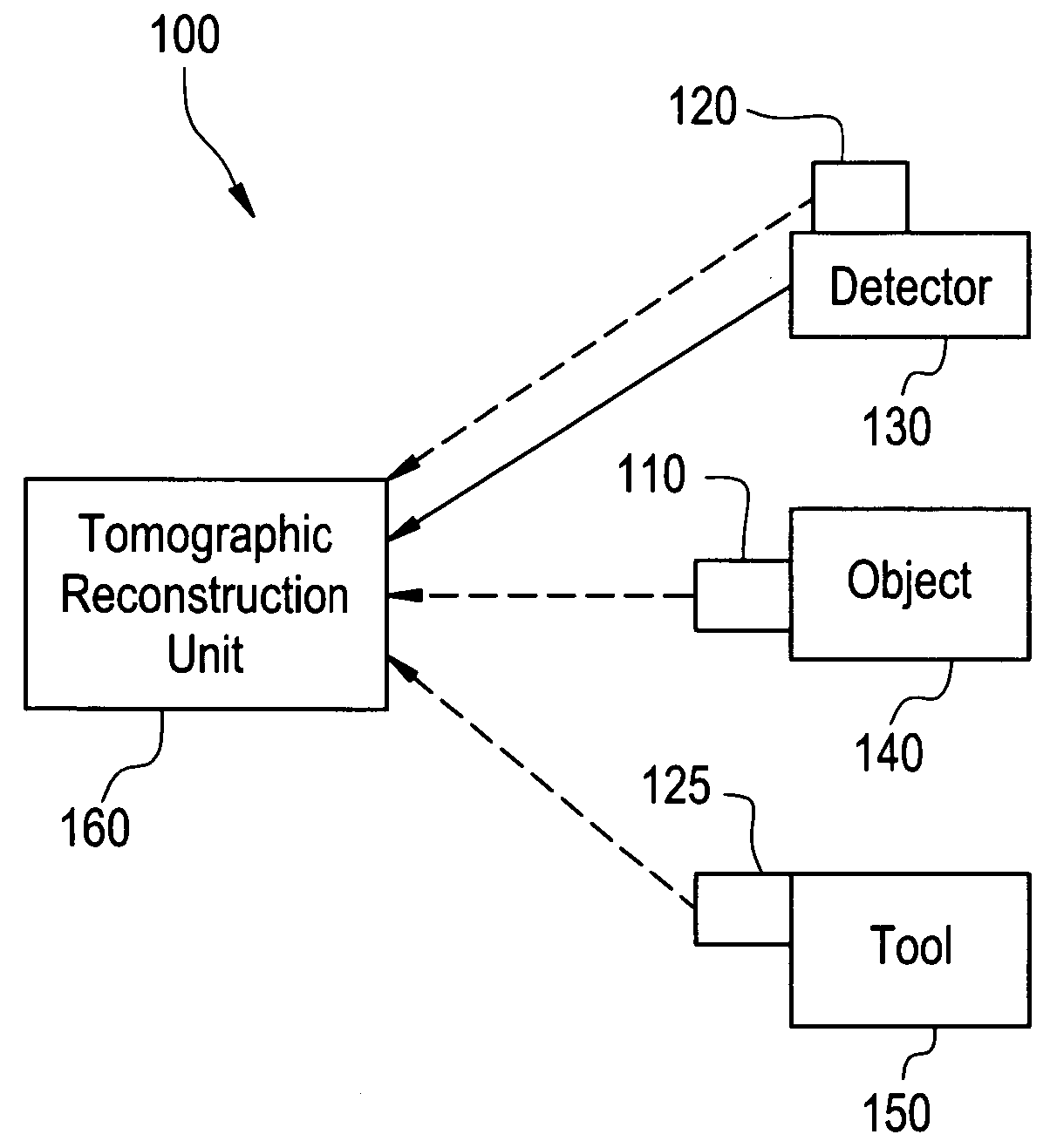
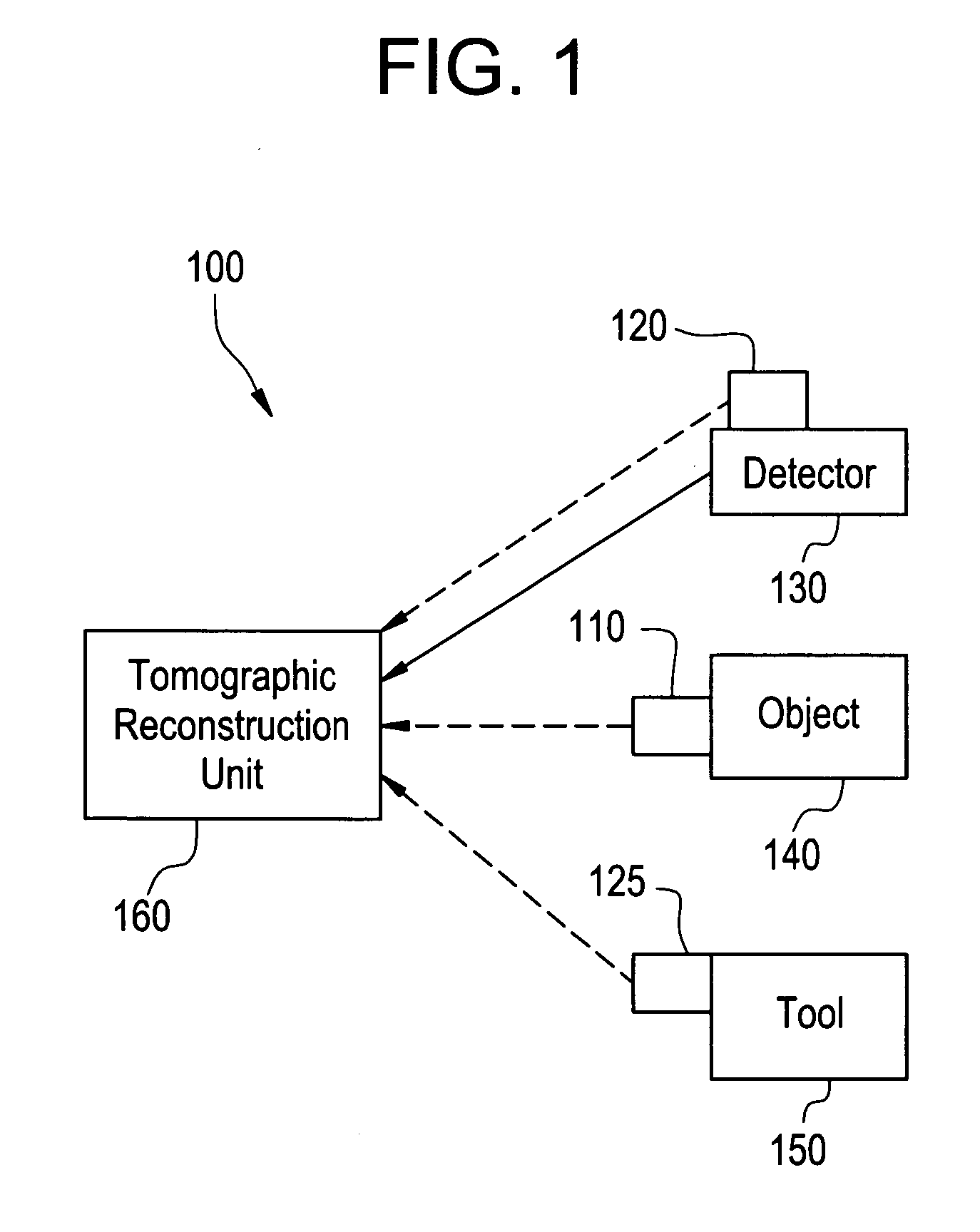
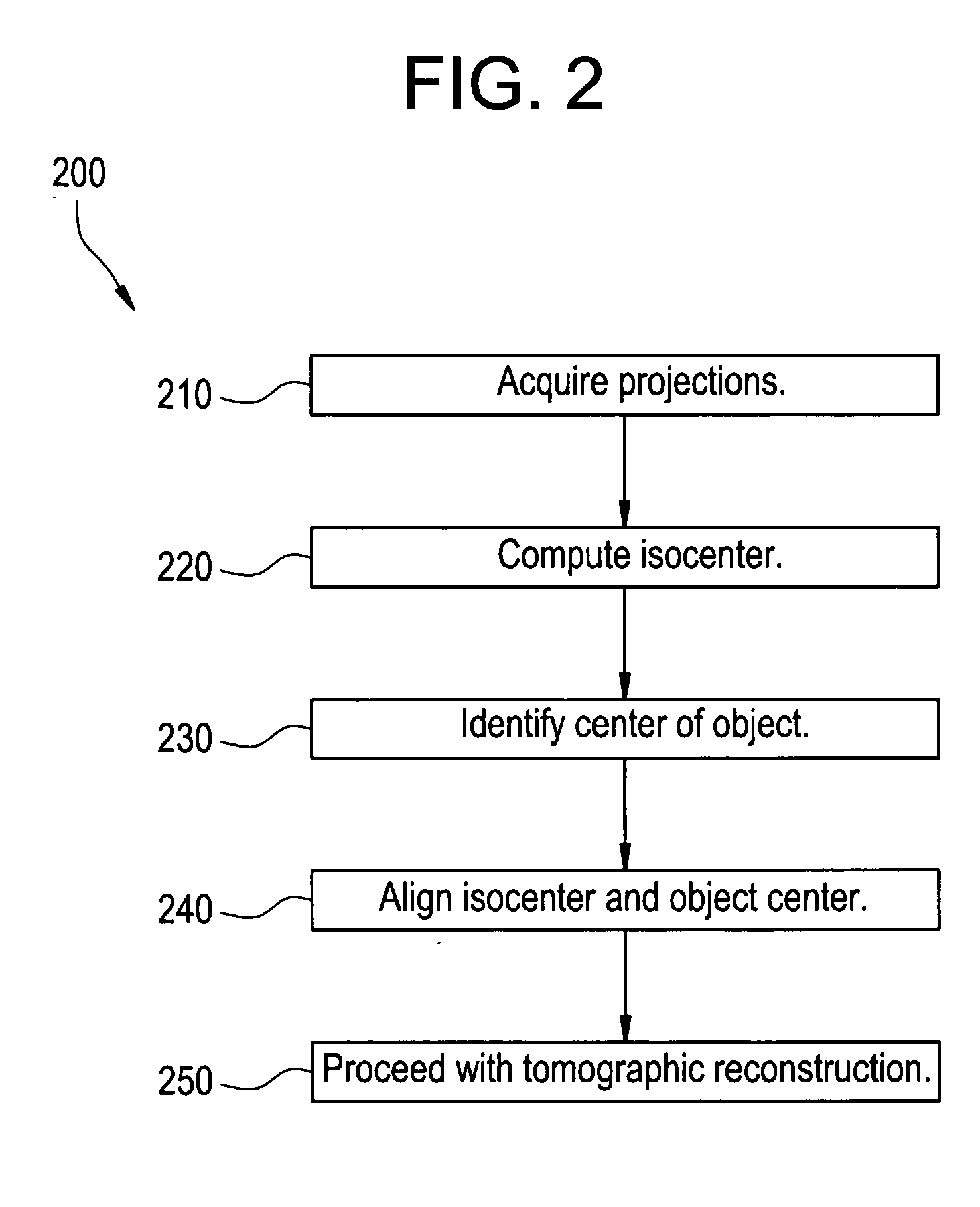
Method and apparatus for positioning an object with respect to the isocenter of an acquisition system
Certain embodiments of the present invention relate to a system and method for object and isocenter alignment in an imaging system. The system includes an electromagnetic, an electromagnetic receiver, and an imaging unit for determining an isocenter of an imaging scanner based on information from the electromagnetic receiver. The imaging unit identifies the isocenter based on a plurality of electromagnetic position measurements. The imaging unit identifies a center of an object to be imaged based on information from a second electromagnetic receiver. The imaging unit repositions the object based on the isocenter. In an embodiment, the emitter is located on the object, the first receiver is located on a detector, and the second receiver is located on a tool for identifying a center of the object or a portion of the object.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Systems and methods for real-time tracking of targets in radiation therapy and other medical applications
InactiveUS20100317968A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsLight beamIsocenter
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
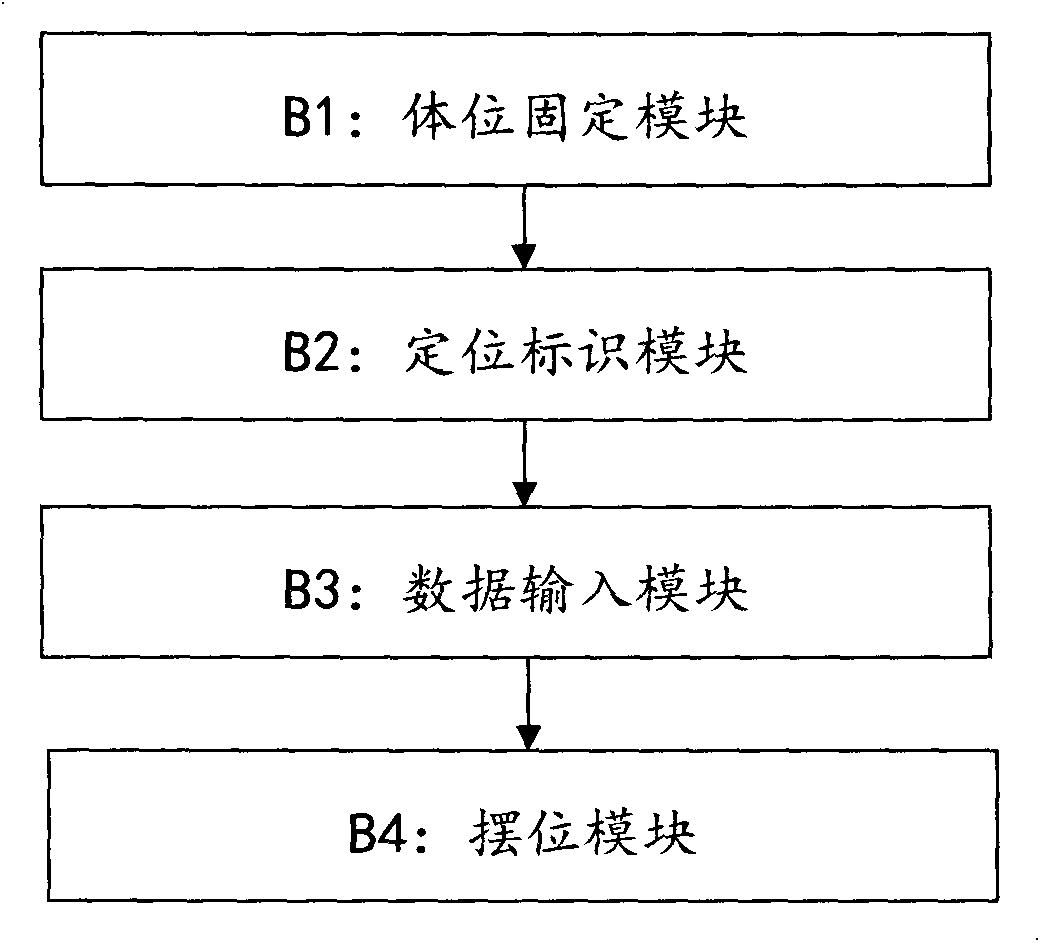
Rapid and accurate tumor positioning method
InactiveCN104338238AReduce work intensitySimplify the radiotherapy positioning operation processTomographyRadiation diagnosticsAbnormal tissue growthComputer science
A method to accurately and rapidly locate tumor, comprising the steps of using a immobilization module to ensure the consistency of patient positioning, verification and the position of each treatment; using a locating and marking module comprising a locating and marking tool for locating and marking; using a data input module to obtain the data required for a calculation of Optical Positioning System in radiotherapy; and using a positioning module to calculate the deviation between the planned isocenter and the machine isocenter, and to provide prompts of patient positioning.
Owner:NANJING CHENGDA MEDICAL TECH
Method and apparatus for employing multiple axial-sources
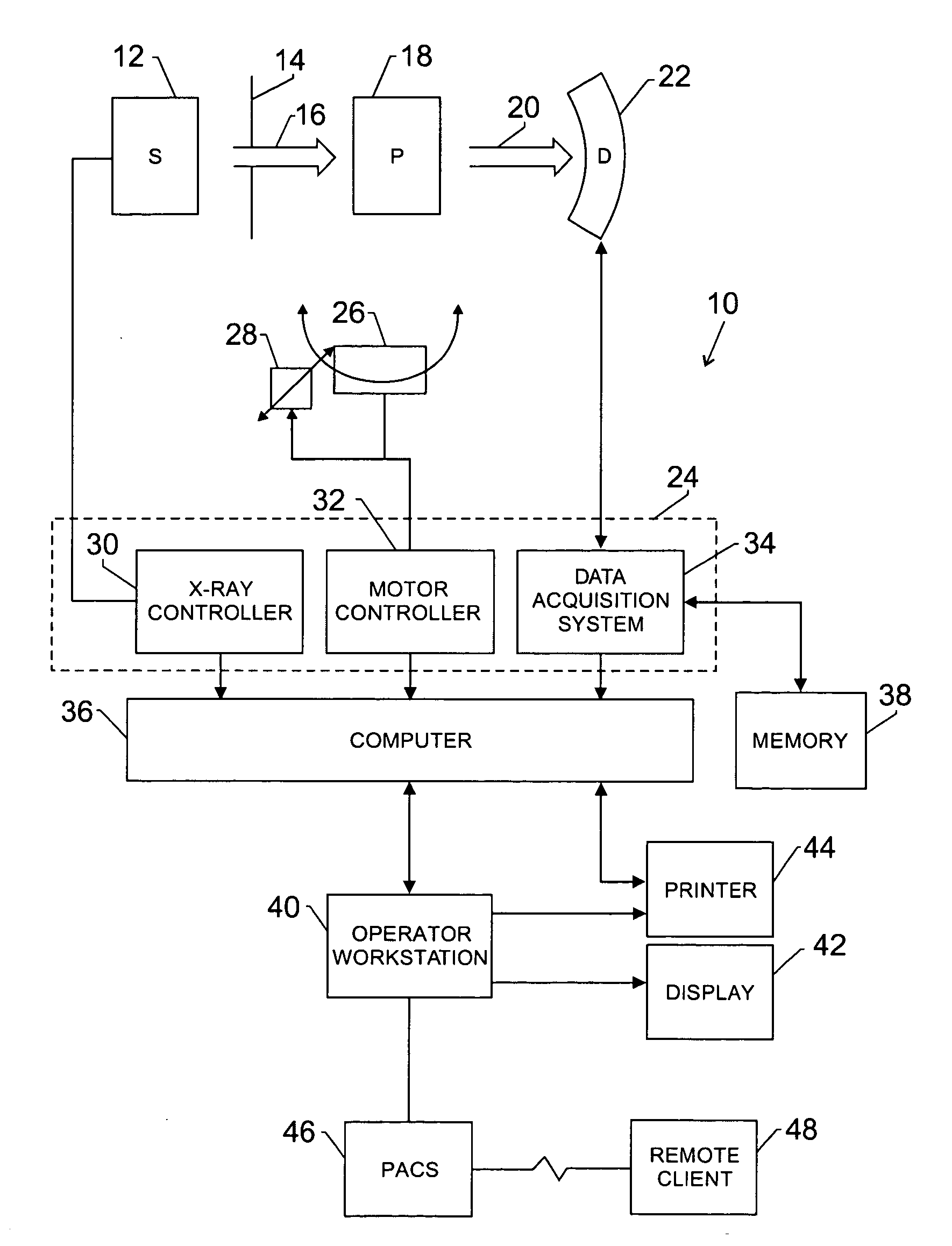
InactiveUS7639774B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray tube electrodesX-rayField of view
A technique is provided for improving z-axis coverage and / or reducing cone beam artifacts during CT imaging. Multiple X-ray emission points are provided along the z-axis. Some or all of the emission points may be concurrently active. X-rays from concurrently active emission points are collimated so that X-rays from two or more emission points do not overlap on the detector. In addition, different groups of concurrently activated emission points may be sequentially or alternately activated, in conjunction with collimation, to prevent the overlap of X-rays from different emission points on the detector. In this manner, The X-rays may be timed and collimated such that the respective streams of radiation become adjacent at different locations, such as at the detector, the isocenter, or edge of the field of view.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for recording images of a definable region of an examination object using a computed tomography facility
InactiveUS7500783B2Precise rotationReduce radiation loadTomographyRadiation beam directing meansSoft x rayObject based
There is described a method for recording images of a definable region of an examination object using an x-ray diagnostics facility for producing computed tomography recordings comprising an image recording facility comprising at least one radiation source and at least one radiation detector for the rotating recording of individual images, on the basis of which an image suitable for outputting is produced, comprising the following steps: Recording of images of the entire examination region by rotating the image recording facility about a first isocenter with a first measuring field, a first resolution and a first dose, and generating an overview image of the examination object; Defining the region in the examination object based on the overview image and defining the location of a second isocenter as a function of the location and / or geometry of the region.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Tumor isocenter multi-angle non-planar percutaneous puncture method
InactiveCN102755195AHighly dependent on experienceHigh technology dependenceSurgical needlesComputerised tomographsFungating tumourSmall tumors
The invention discloses a tumor isocenter multi-angle non-planar percutaneous puncture method belonging to a novel method that a doctor carries out tumor percutaneous puncture on a tumor patient under the guidance of CT in the technical field of medical treatment, and solving the problems of high dependence on experiences and techniques of an operator, easy generation of larger puncture errors, long occupation time of puncture, large difficulty in puncturing smaller tumors or deeper tumors in early stage, and low success rate in the tumor percutaneous puncture technology. The technical scheme is as follows: the tumor isocenter multi-angle non-planar percutaneous puncture method comprises the steps of sharing an isocenter by a center point of a semi-circular piercer and a center point of a tumor through coordinate system transfer, and driving a puncture needle for realizing multi-angle non-planar puncture through sliding of an arrow rest and rotating of the piercer. The tumor isocenter multi-angle non-planar percutaneous puncture method has the advantages that the problems of high dependence on experiences and techniques of the operator, easy generation of larger puncture errors, long occupation time of puncture, large difficulty in puncturing smaller tumors or deeper tumors in early stage, and low success rate in the tumor percutaneous puncture technology are solved, vital organs, puncture taboo organs and taboo focuses can be effectively avoided, the tumor percutaneous puncture error can be shortened to 2mm under the guidance of the CT, and the highest tumor percutaneous puncture precision at home and abroad is achieved.
Owner:陈德路
Treatment theater for proton therapy
InactiveUS20150087883A1Simplifies traditional designImprove the treatment experienceX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyMedicineProton
A theater system for a proton treatment system, including a tunnel structure configured around an isocenter of a proton treatment system, and one or more devices mounted on the tunnel structure to communicate with a patient located on a treatment bed of the proton treatment system.
Owner:PRONOVA SOLUTIONS
Particle therapy
InactiveUS20090114847A1Keep distanceChemical conversion by chemical reactionX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPatients positionIsocenter
The invention relates to a treatment room for a particle therapy system that has a treatment room isocenter, which can be set variably during treatment and forms an origin of a coordinate system, and a patient positioning apparatus for automatically positioning the patient with reference to the set treatment room isocenter.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Imaging and treatment system
An imaging device including a rotator having a hollow bore for a patient to move therein and thereout, the rotator being rotatable about a longitudinal axis, at least one linkage arm extending outwards from the rotator, and imaging apparatus mounted on the at least one linkage arm, the imaging apparatus including an imaging source that emits an imaging beam to an imaging detector aligned therewith along an imaging direction, the at least one linkage arm capable of full axial rotation about an imaging isocenter along an entire length of the patient, the isocenter lying along a longitudinal axis, and wherein the imaging apparatus is operative to rotate and to capture images of the patient along the imaging direction as the patient is positioned at an angle in a range of about 0-90° inclusive with respect to the longitudinal axis.
Owner:EIN GAL MOSHE
Systems and methods of adjusting a rotating gantry system
ActiveUS20150126801A1Error minimizationRolling contact bearingsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyEngineeringBearing surface
A gantry wheel adjustment system and method to adjust a gantry wheel of a proton treatment system, including an estimation unit to estimate a bearing adjustment value for each of the adjustable bearings based on a stiffness parameter of each adjustable bearing, the stiffness parameter being a function of a force applied at each adjustable bearing and a deflection of the gantry wheel associated with the force applied at each adjustable bearing, the bearing adjustment value corresponding to a nominal position value for each adjustable bearing to compensate for gantry wheel flexing when the gantry wheel is rotated from a first angular position to a second angular position, the adjustable bearings being configured to support the gantry wheel on the bearing surface and maintain the proton beam at the isocenter of the gantry wheel during gantry wheel rotation.
Owner:PRONOVA SOLUTIONS
C-arm x-ray device
ActiveUS7048440B2Easy and cost-effectiveX-ray apparatusRadiation diagnosticsX-rayHorizontal and vertical
The invention concerns a C-arm x-ray device with a non-isocentric C-arm on which an x-ray source is positioned and that can be orbitally or angularly rotated, whereby the C-arm x-ray device comprises a device fashioned to horizontally adjust the C-arm (which enables an adjustment of the C-arm within the plane of the C-arm) and a device fashioned to vertically adjust the C-arm, where the horizontal adjustment device and the vertical adjustment device are fashioned such that they can automatically move the central x-ray beam of the x-ray source back into the isocenter, given an orbital or angulatory rotation of the C-arm via the horizontal and vertical adjustment device. An appertaining method is also provided.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
Prevention of setup errors in radiotherapy
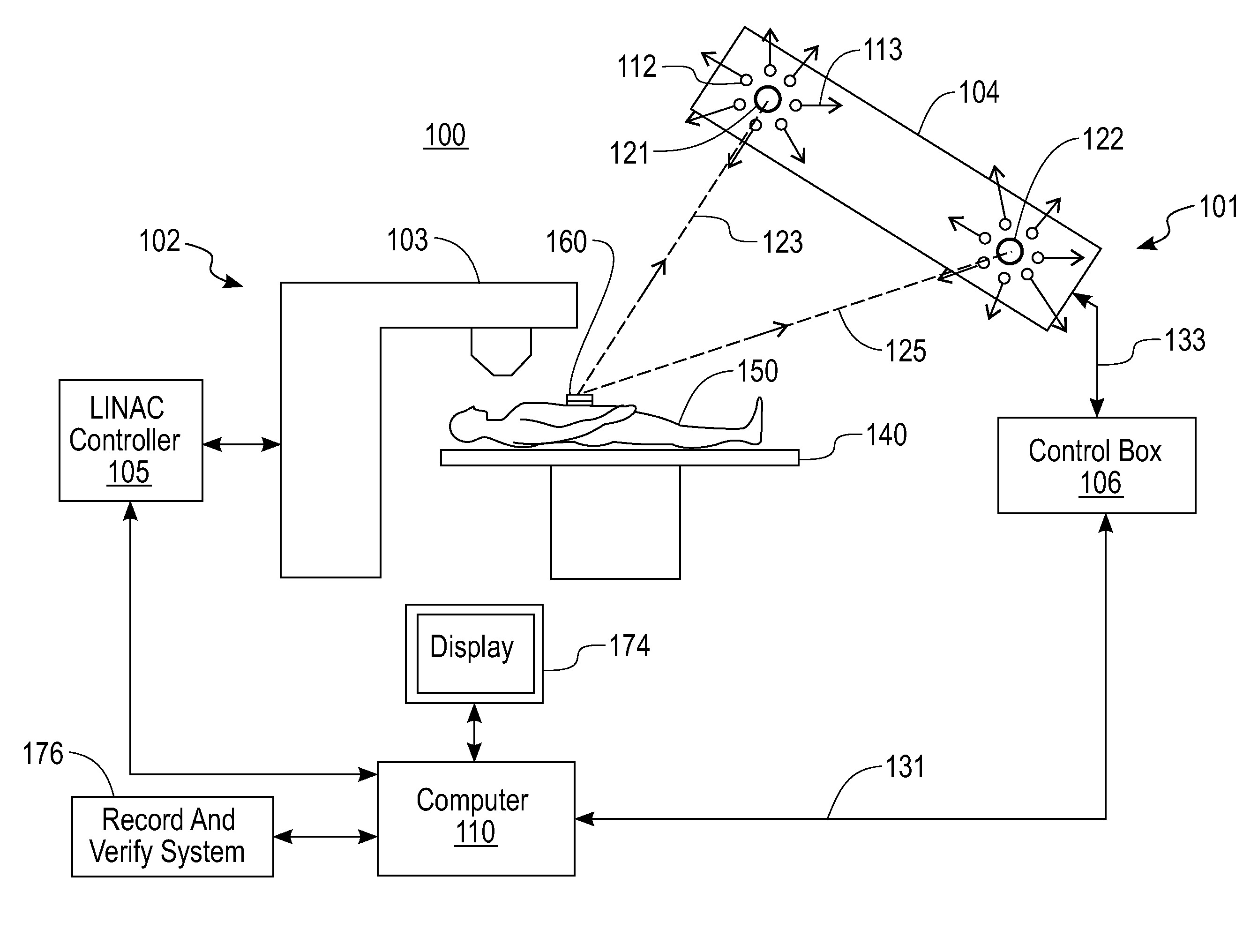
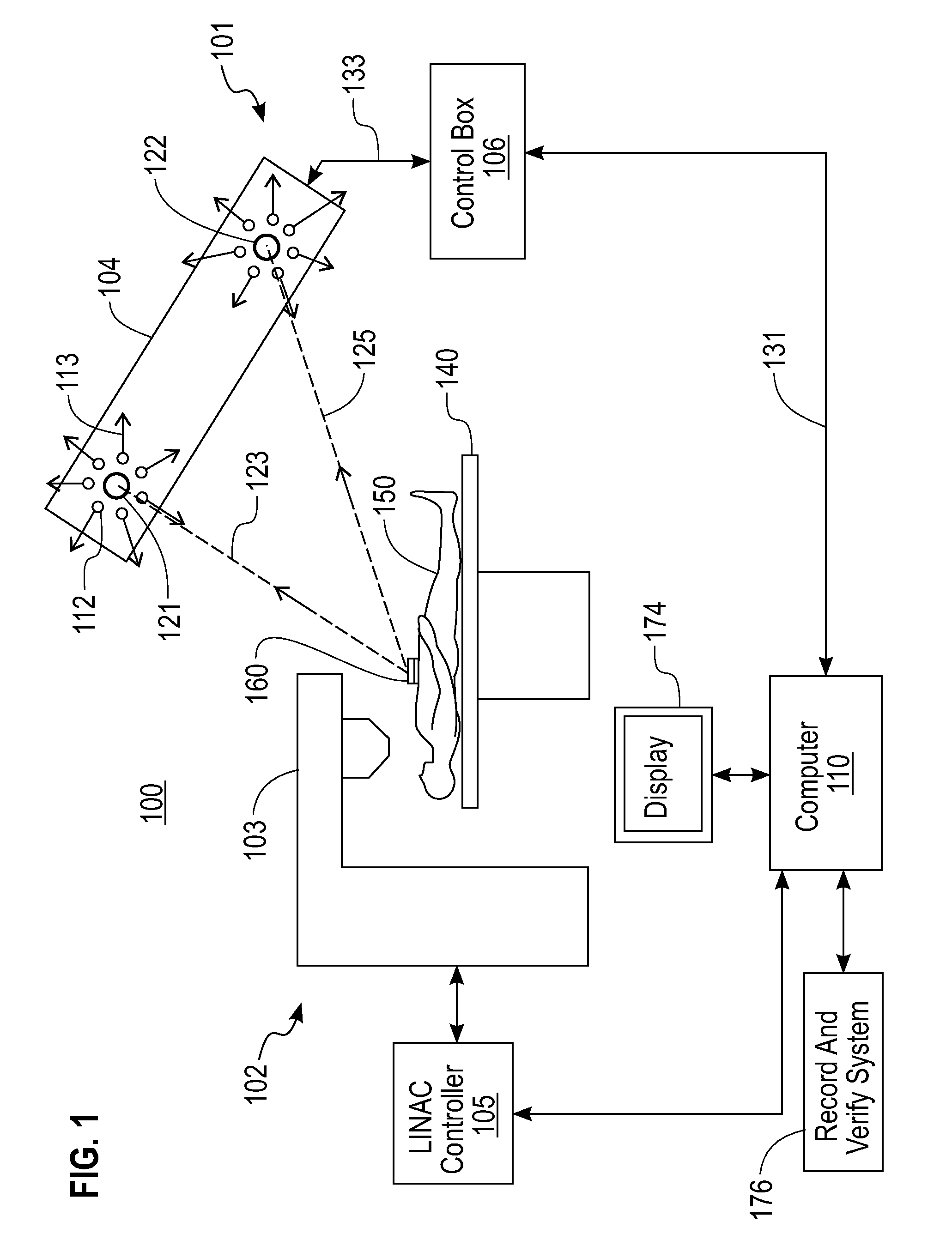
A patient safety system (PSS) (100) uses optical tracking in a linear accelerator treatment room to prevent gross setup errors. A patient (150) undergoes a computed tomography (CT) treatment-simulation scan while a CT ball bearing (BB) is on patient's surface. The CT BB is replaced with an infrared reflective marker (IRRM) (160) before radiotherapy treatment starts. Coordinates of the CT BB relative to an isocenter of the treatment room are used as reference for tracking. The coordinate system of an optical tracking system is converted to a coordinate system of the treatment room. The PSS evaluates setup accuracy for a radiotherapy session by comparing real-time position of the single IRRM determined by the optical tracking technology with a predicted reference position, and displays results on a graphical user interface. The PSS stops radiation when a deviation between real-time coordinates and predicted coordinates of the IRRM (160) exceeds a predefined threshold.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Rapid dosage verifying method based on X-ray imaging flat panel detector
InactiveCN106215331AOvercoming time consumingOvercoming the lack of effortX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyFlat panel detectorClinical dosimetry
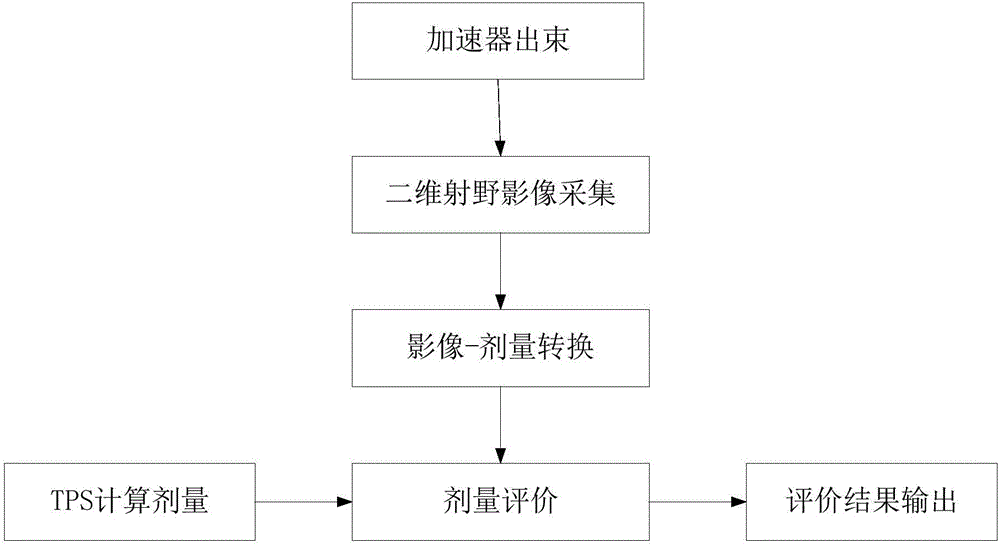
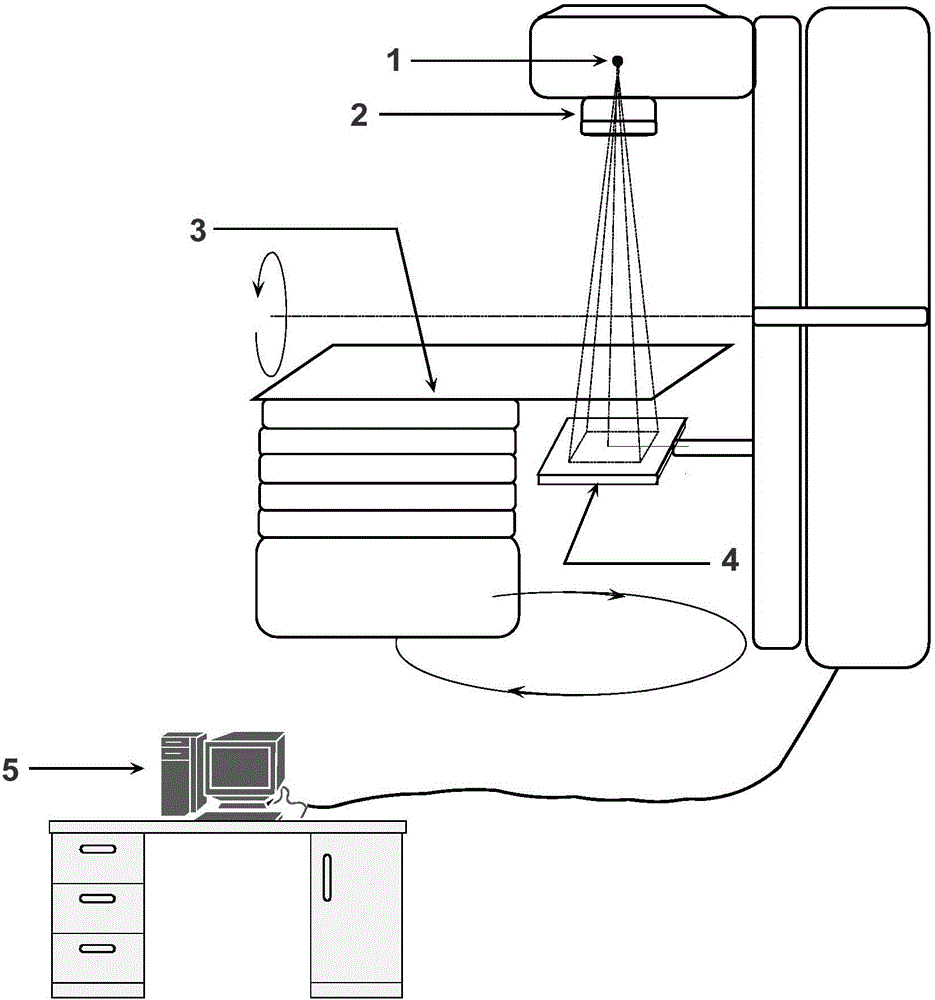
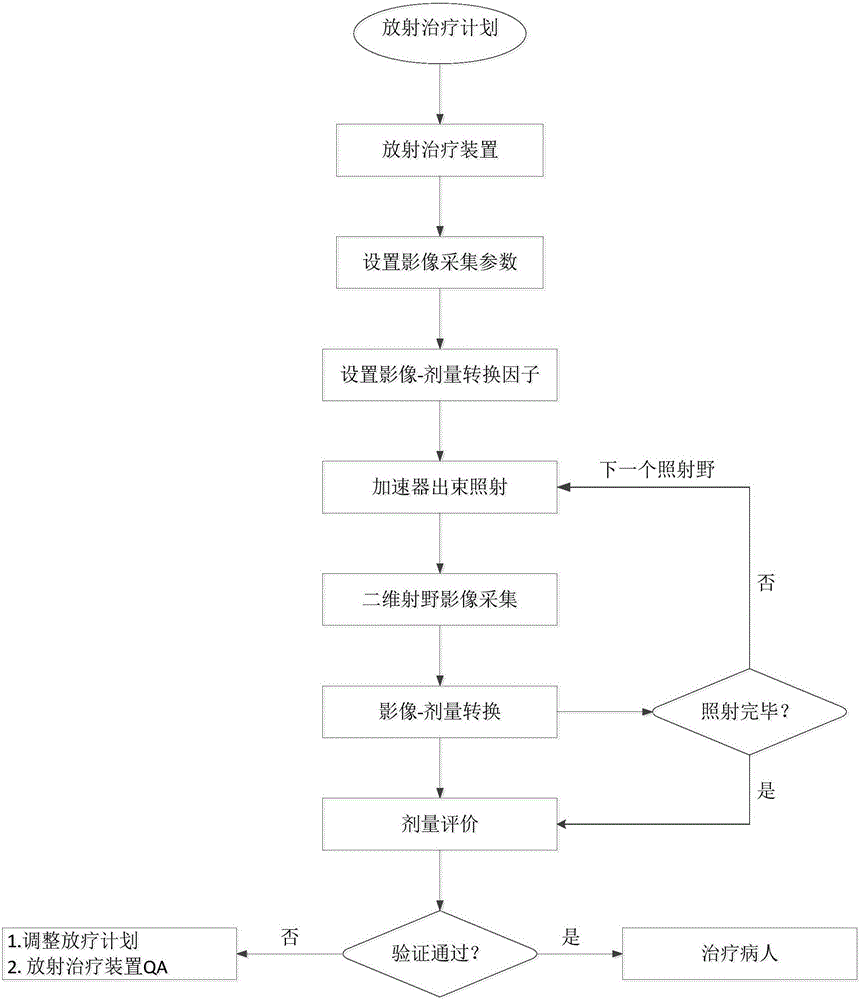
The invention relates to a rapid dosage verifying method based on an X-ray imaging flat panel detector, and the method comprises the steps: enabling a radiotherapy device to carry out irradiation according to all irradiation field parameters of a radiotherapy plan before the radiotherapy, and enabling the X-ray imaging flat panel detector to collect two-dimensional X-ray irradiation field images at the same time; converting the two-dimensional X-ray irradiation field images into the two-dimensional plane dosage distribution of a specific equivalent water depth, carrying out the reverse calculation of a two-dimensional plane dosage of an isocenter, and achieving the dosage verification of the radiotherapy plan before radiotherapy through the comparison and evaluation of the two-dimensional plane dosage calculated by a radiotherapy plan system and an actual measured two-dimensional plane dosage. The method irons out the defects that a conventional clinic dosage verification technology consumes a large amount of time and labor and needs to turn the irradiation field angle to zero, alleviates the burden of a clinic medical physic doctor, can achieve the precise and quick verification of dosage, and is high in applicability.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com