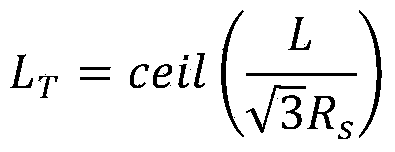Patents
Literature
159 results about "Comparison area" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
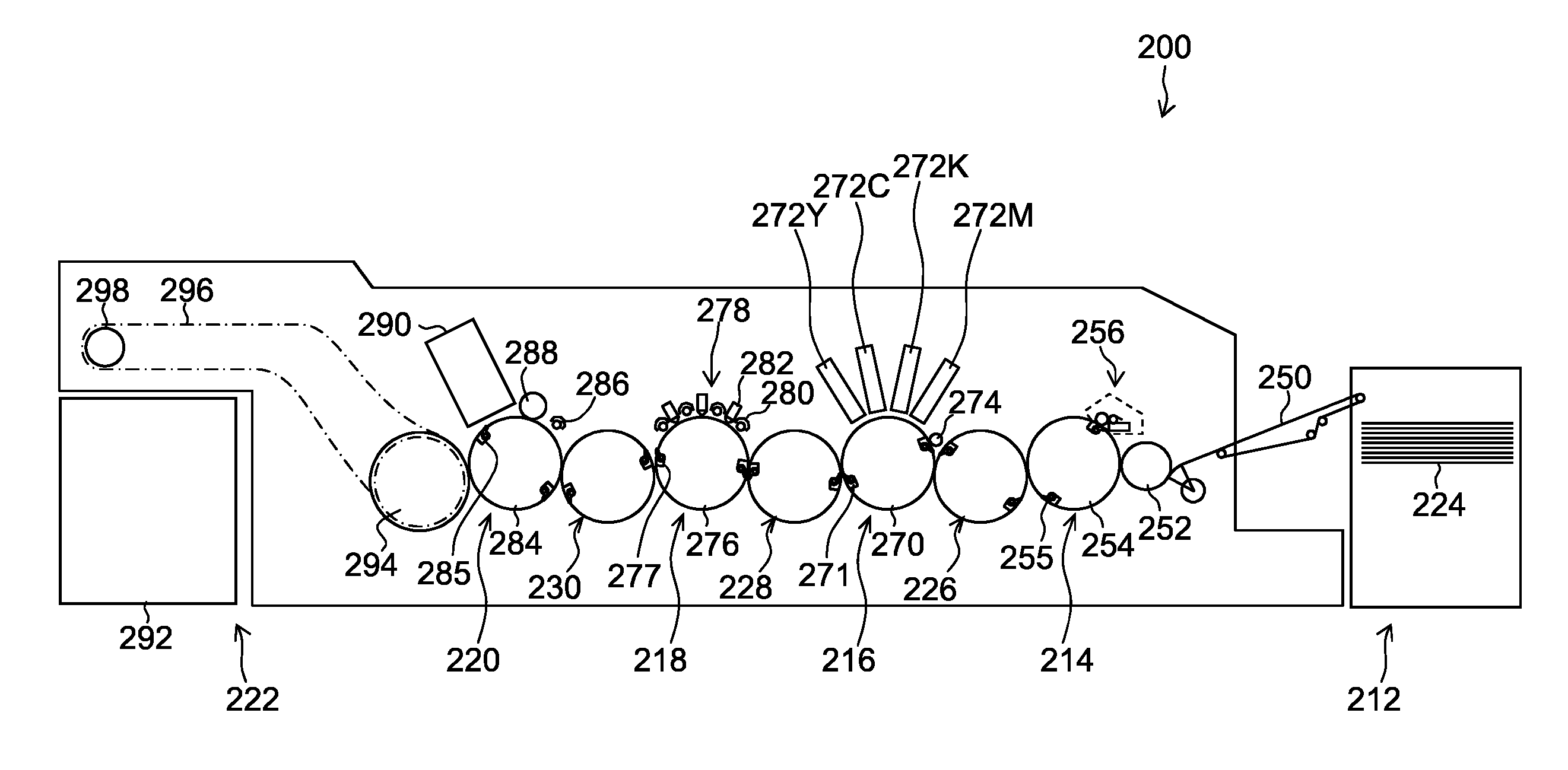
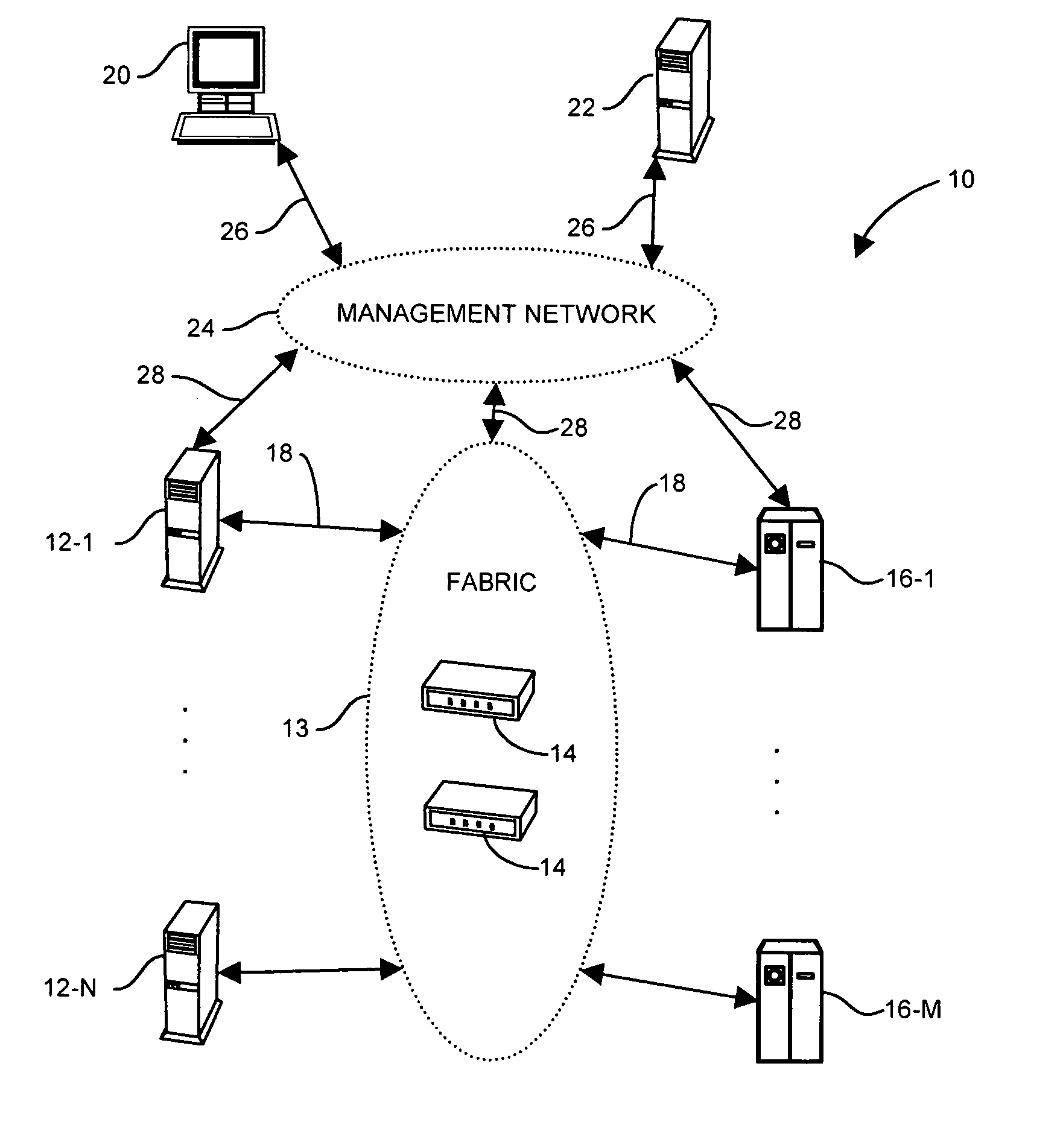
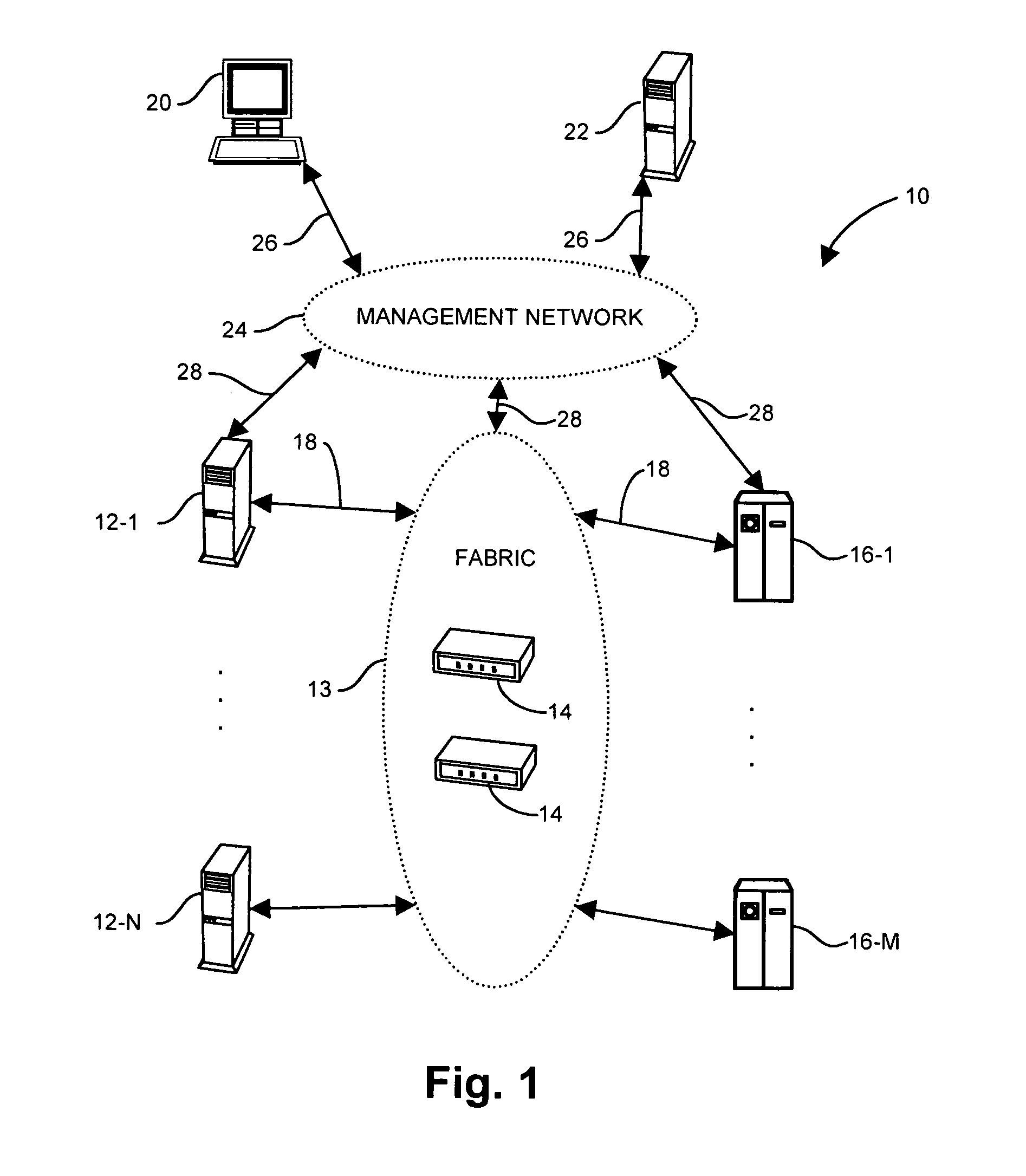
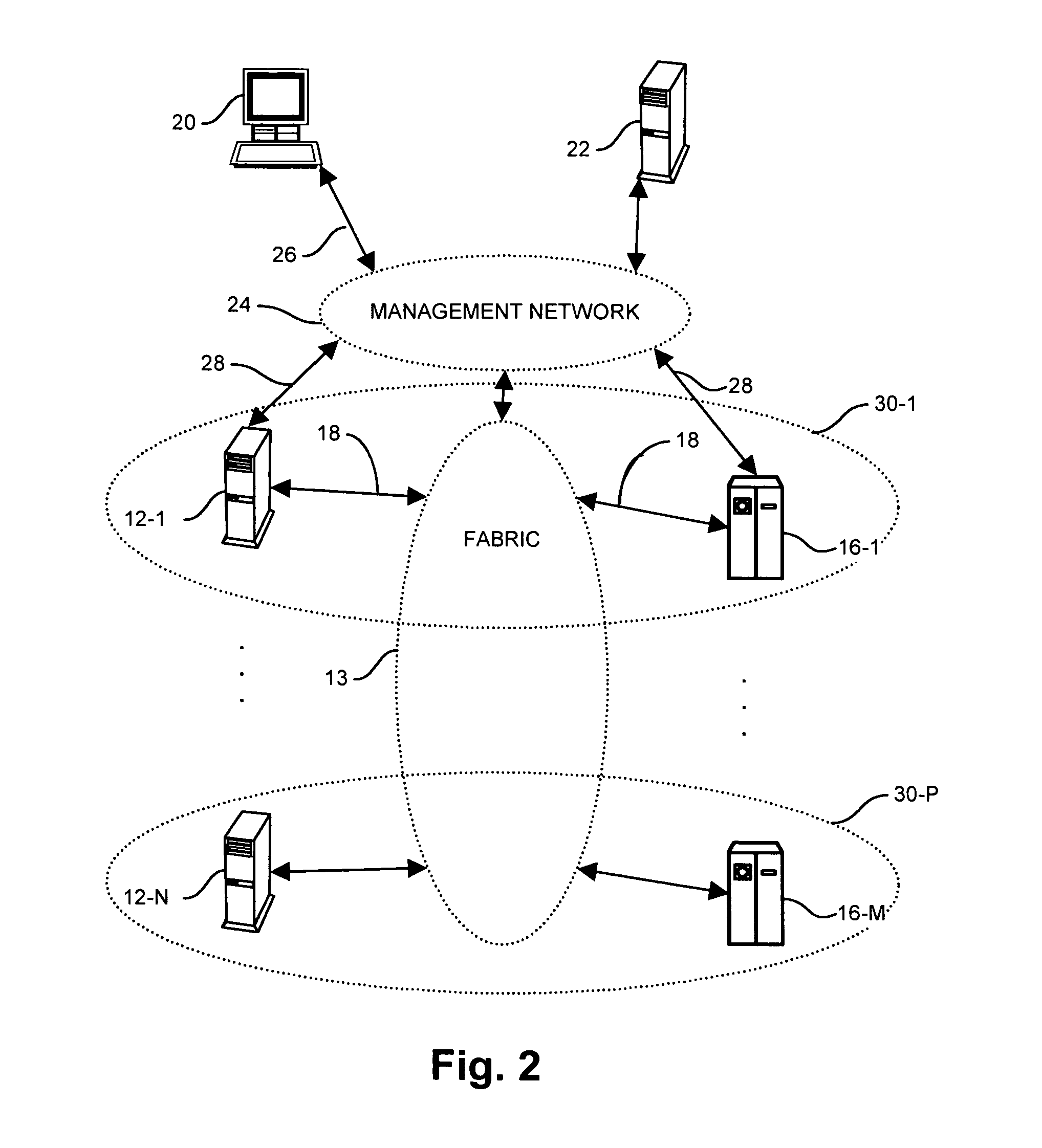
Patient positioning device and patient positioning method
InactiveUS7212608B2Improve accuracyAvoid accuracyBuilding locksPatient positioning for diagnosticsPattern matchingX-ray
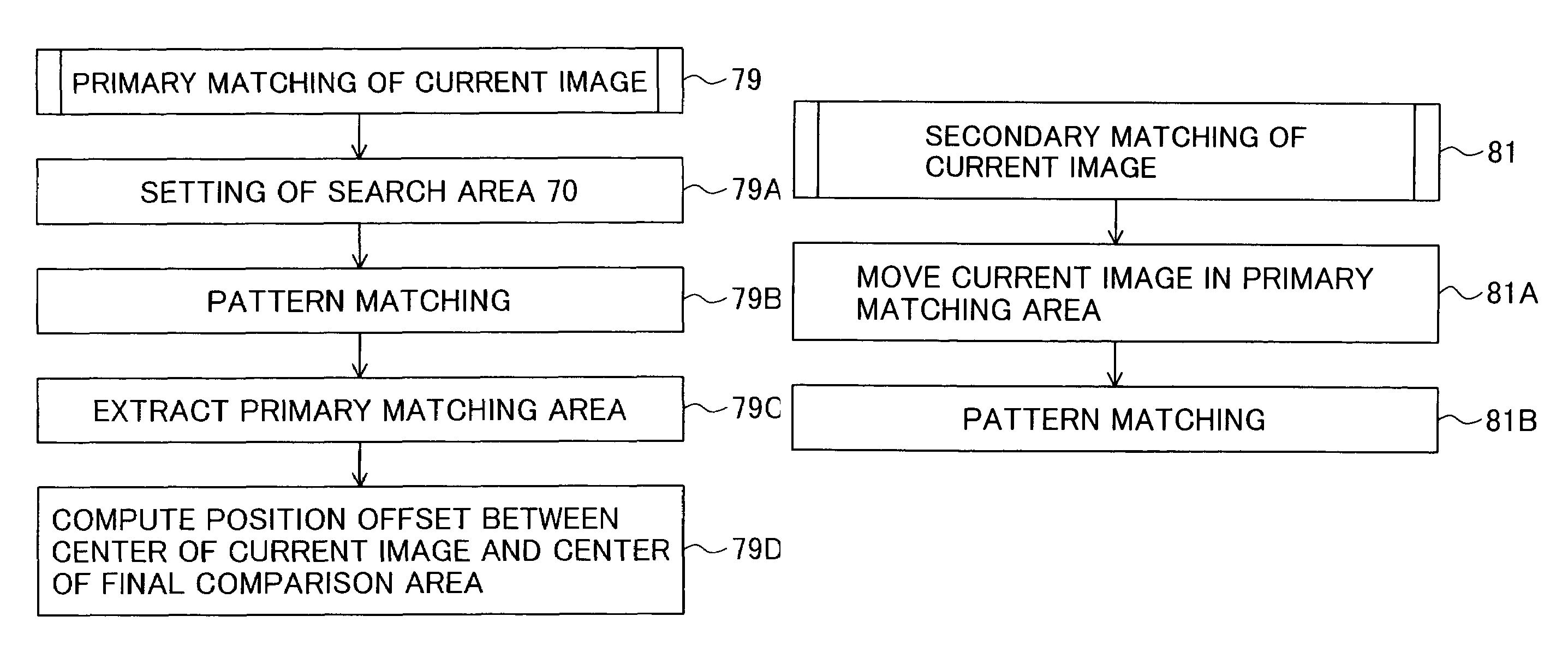
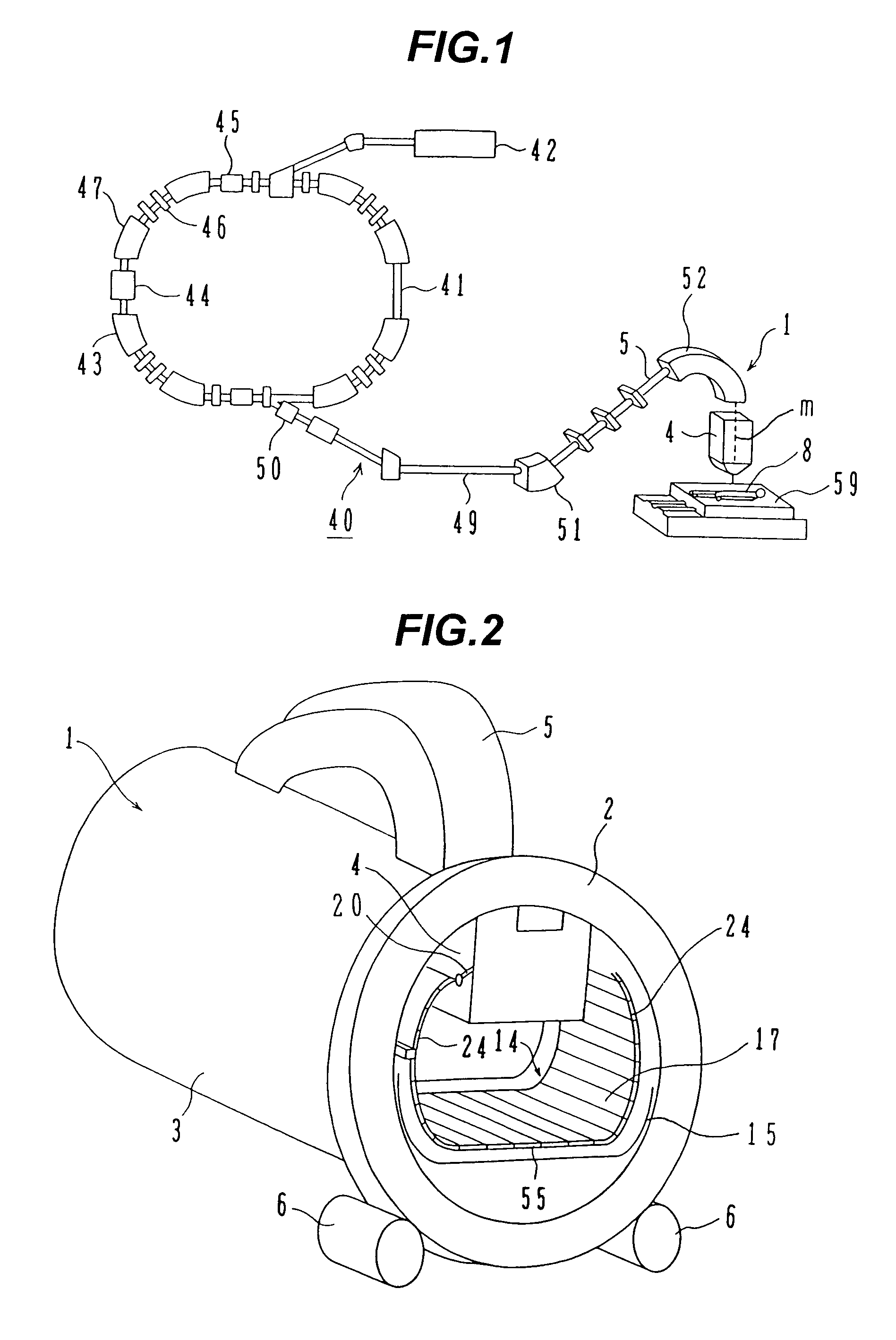
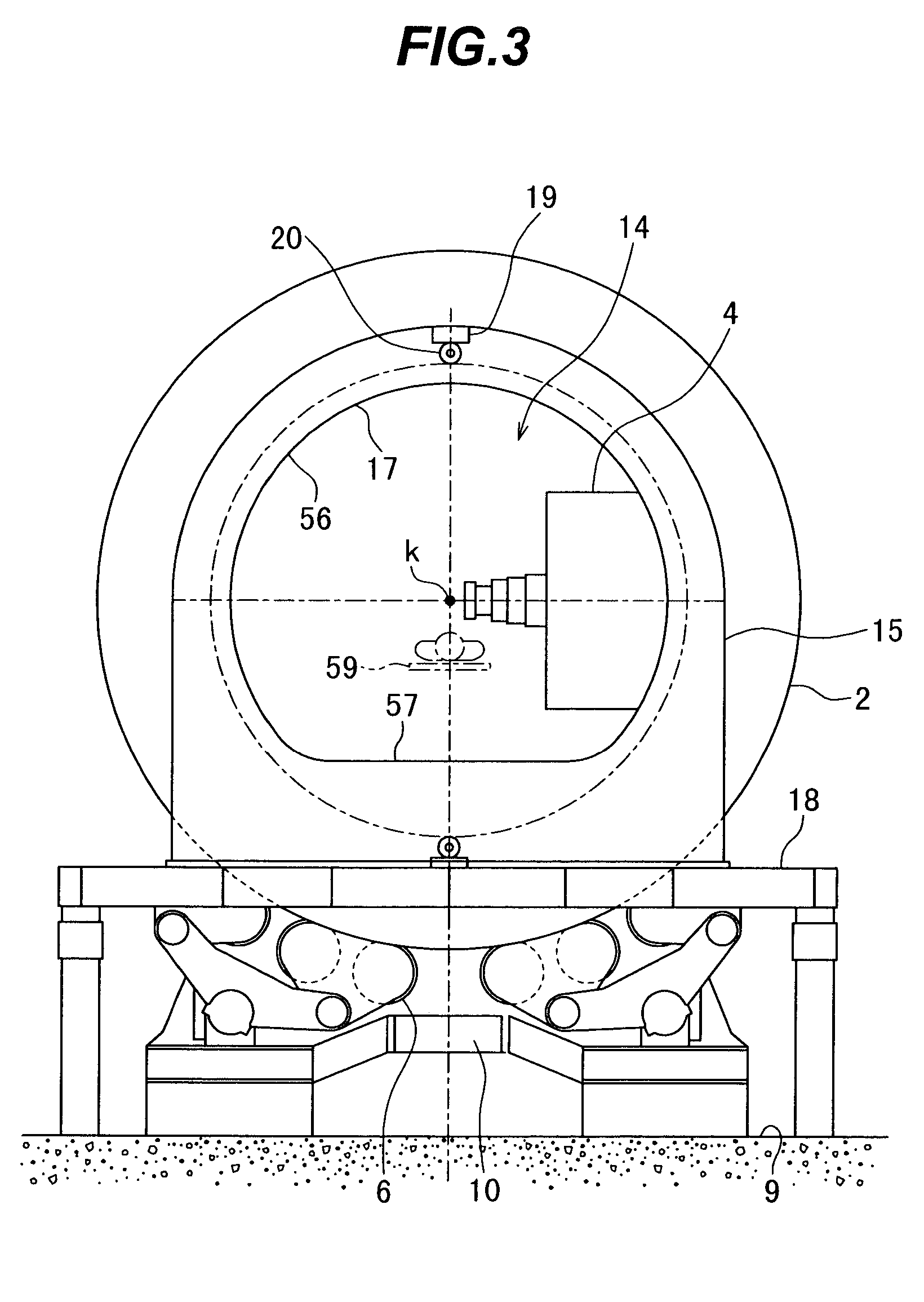
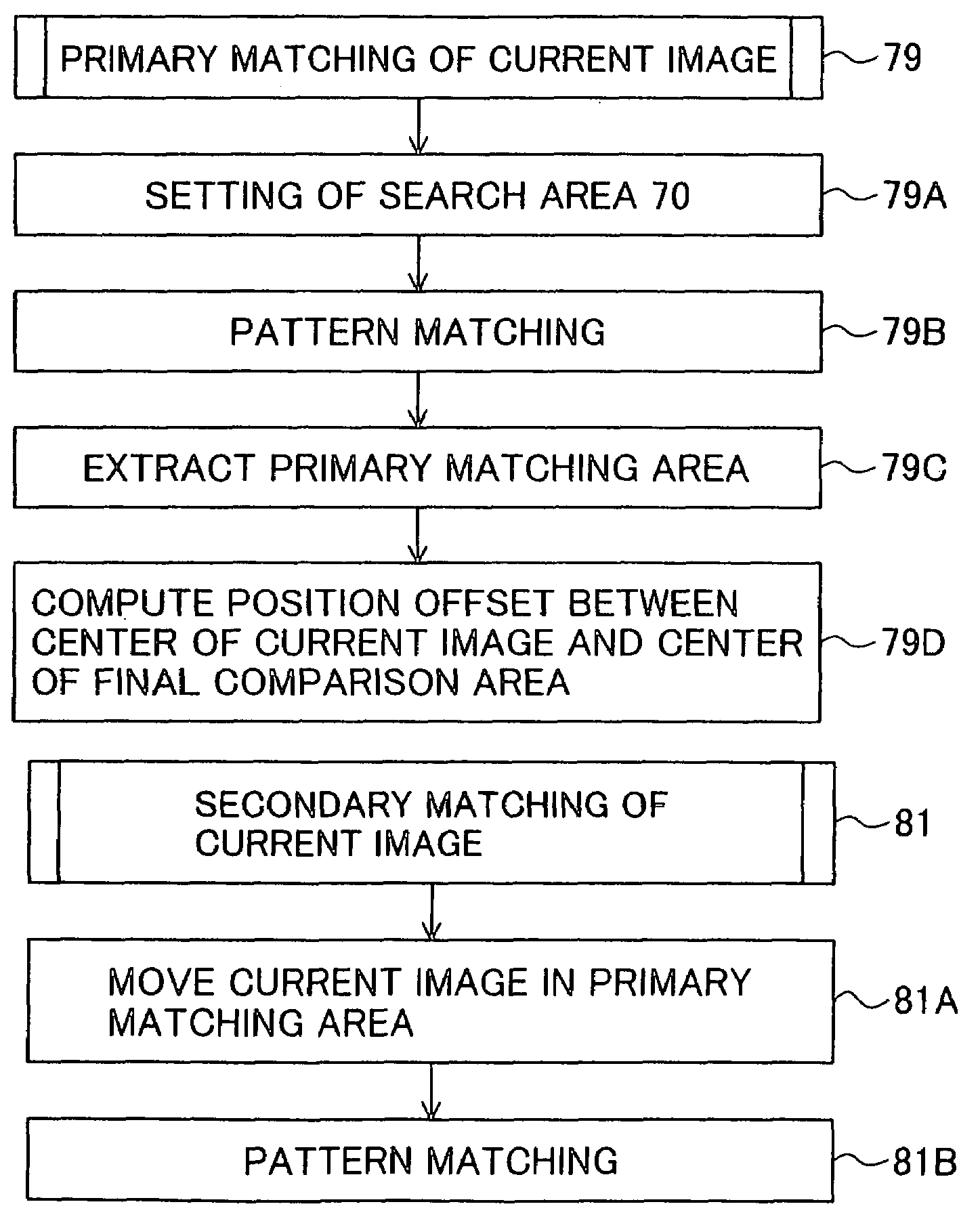
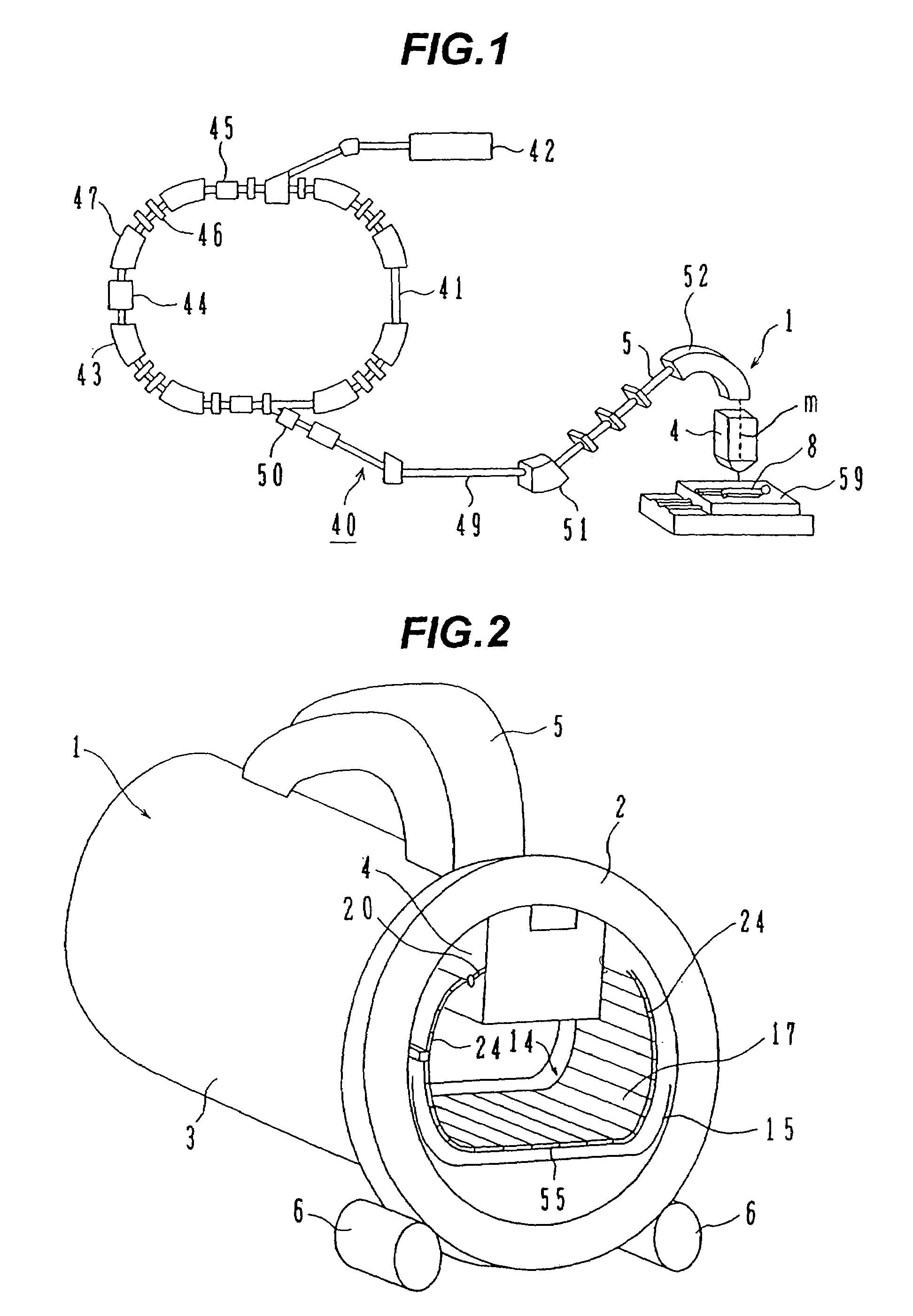
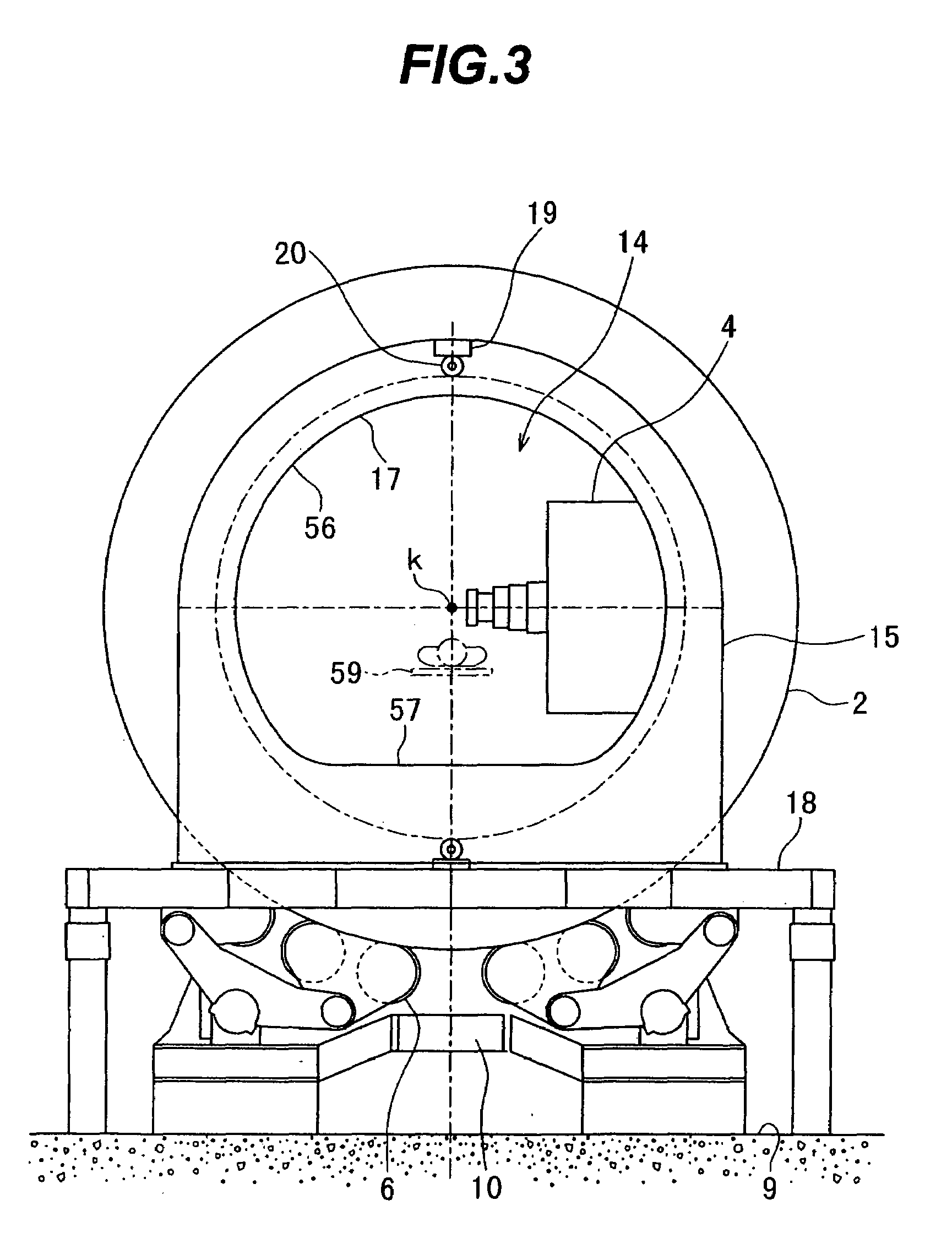
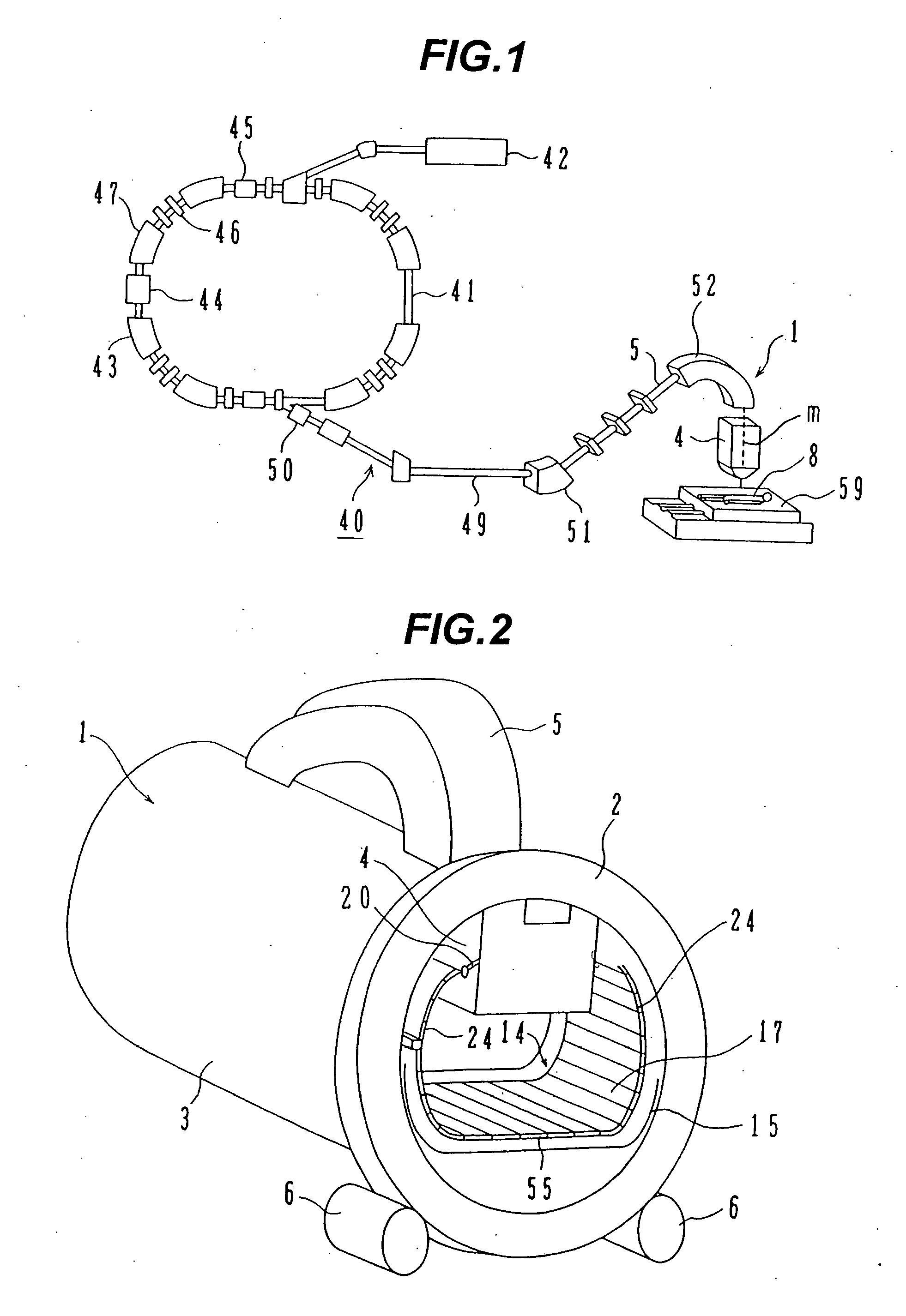
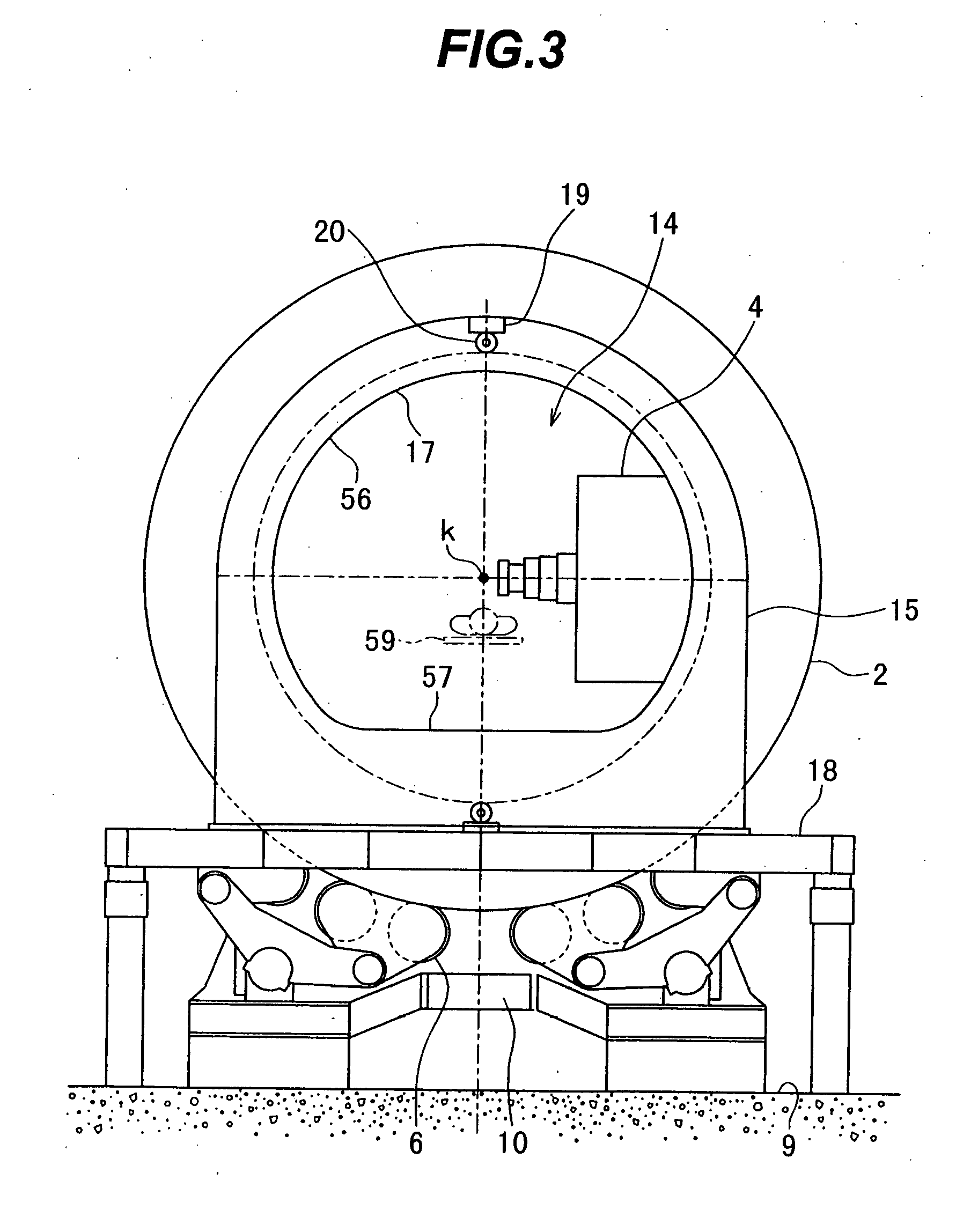
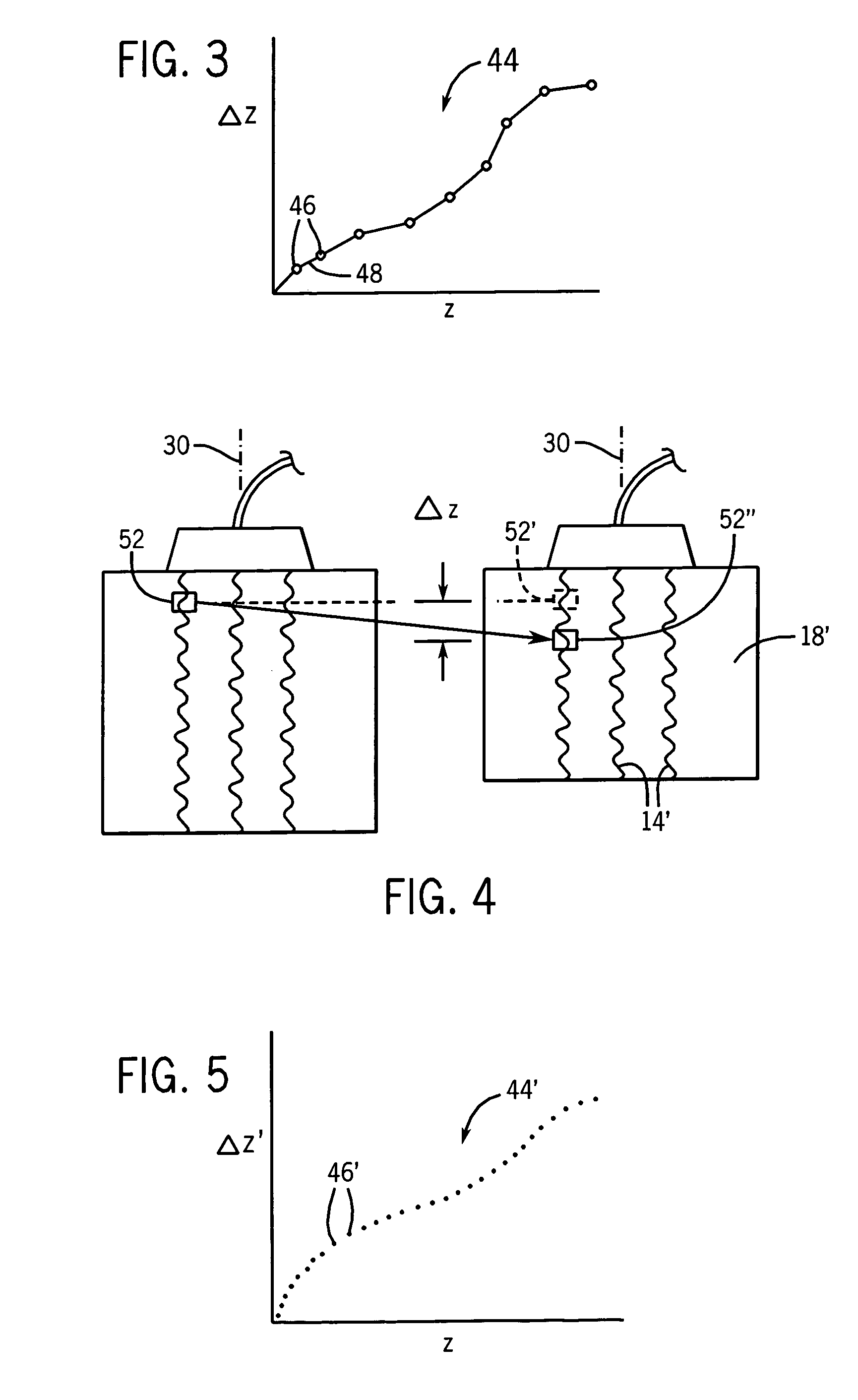
The invention is intended to always ensure a sufficient level of patient positioning accuracy regardless of the skills of individual operators. In a patient positioning device for positioning a patient couch 59 and irradiating an ion beam toward a tumor in the body of a patient 8 from a particle beam irradiation section 4, the patient positioning device comprises an X-ray emission device 26 for emitting an X-ray along a beam line m from the particle beam irradiation section 4, an X-ray image capturing device 29 for receiving the X-ray and processing an X-ray image, a display unit 39B for displaying a current image of the tumor in accordance with a processed image signal, a display unit 39A for displaying a reference X-ray image of the tumor which is prepared in advance, and a positioning data generator 37 for executing pattern matching between a comparison area A being a part of the reference X-ray image and including an isocenter and a comparison area B or a final comparison area B in the current image, thereby producing data used for positioning of the patient couch 59 during irradiation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Patient positioning device and patient positioning method
InactiveUS7212609B2Improve accuracyAvoid accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPattern matchingX-ray
The invention is intended to always ensure a sufficient level of patient positioning accuracy regardless of the skills of individual operators. In a patient positioning device for positioning a patient couch 59 and irradiating an ion beam toward a tumor in the body of a patient 8 from a particle beam irradiation section 4, the patient positioning device comprises an X-ray emission device 26 for emitting an X-ray along a beam line m from the particle beam irradiation section 4, an X-ray image capturing device 29 for receiving the X-ray and processing an X-ray image, a display unit 39B for displaying a current image of the tumor in accordance with a processed image signal, a display unit 39A for displaying a reference X-ray image of the tumor which is prepared in advance, and a positioning data generator 37 for executing pattern matching between a comparison area A being a part of the reference X-ray image and including an isocenter and a comparison area B or a final comparison area B in the current image, thereby producing data used for positioning of the patient couch 59 during irradiation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
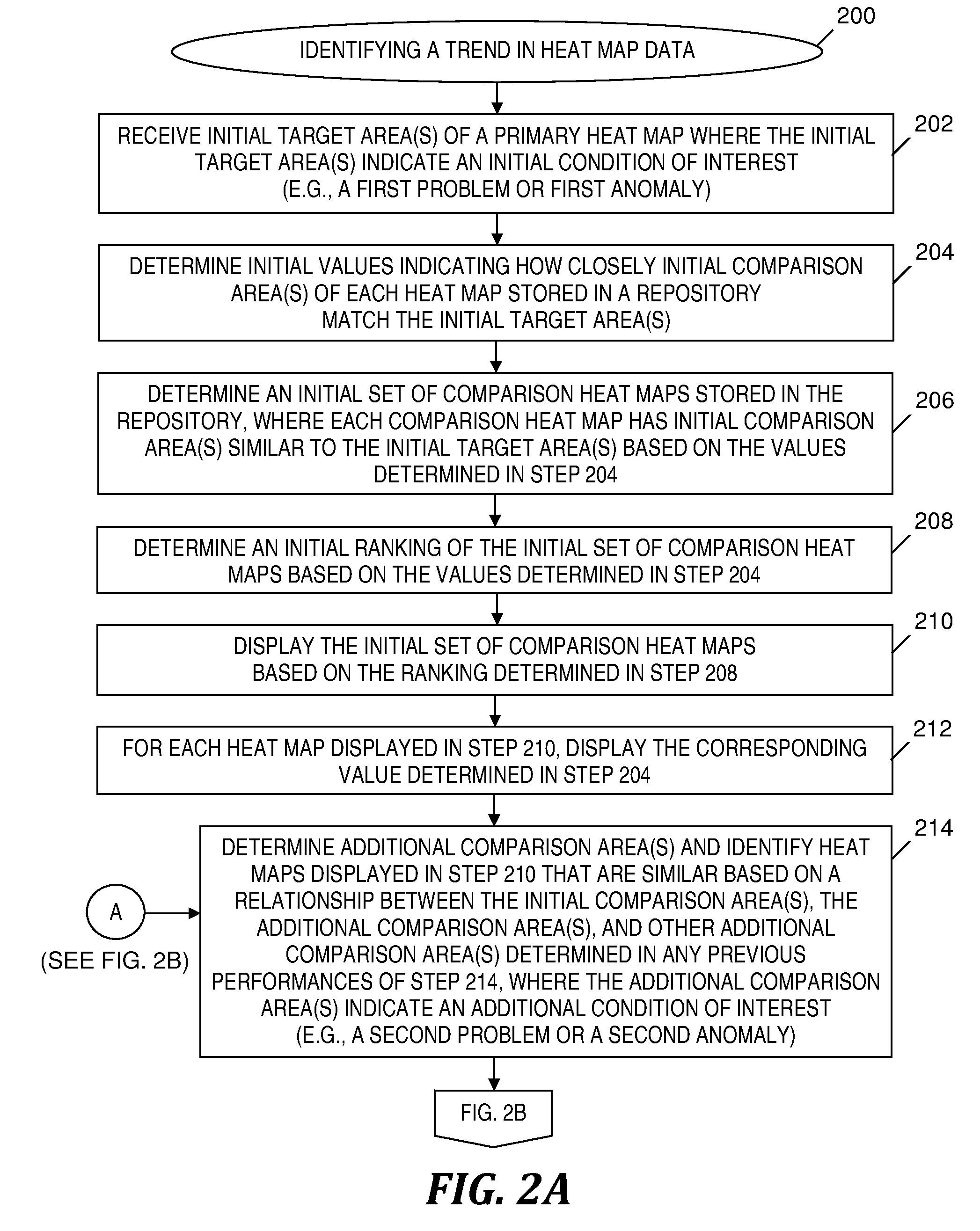
Interactive data visualization for trend analysis
InactiveUS20130013248A1Easy to identifyEasy to useThermometer detailsError detection/correctionData visualizationThematic map
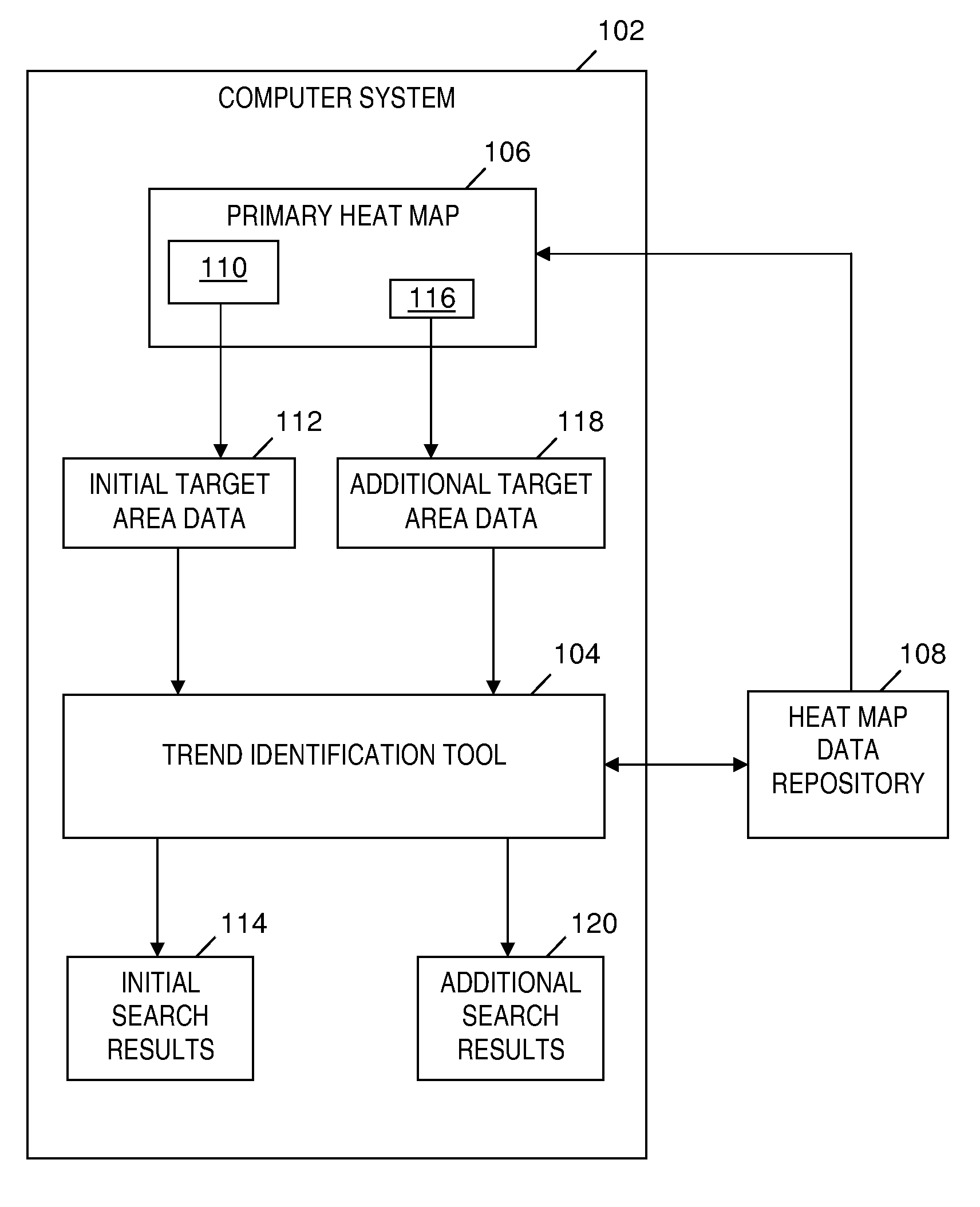
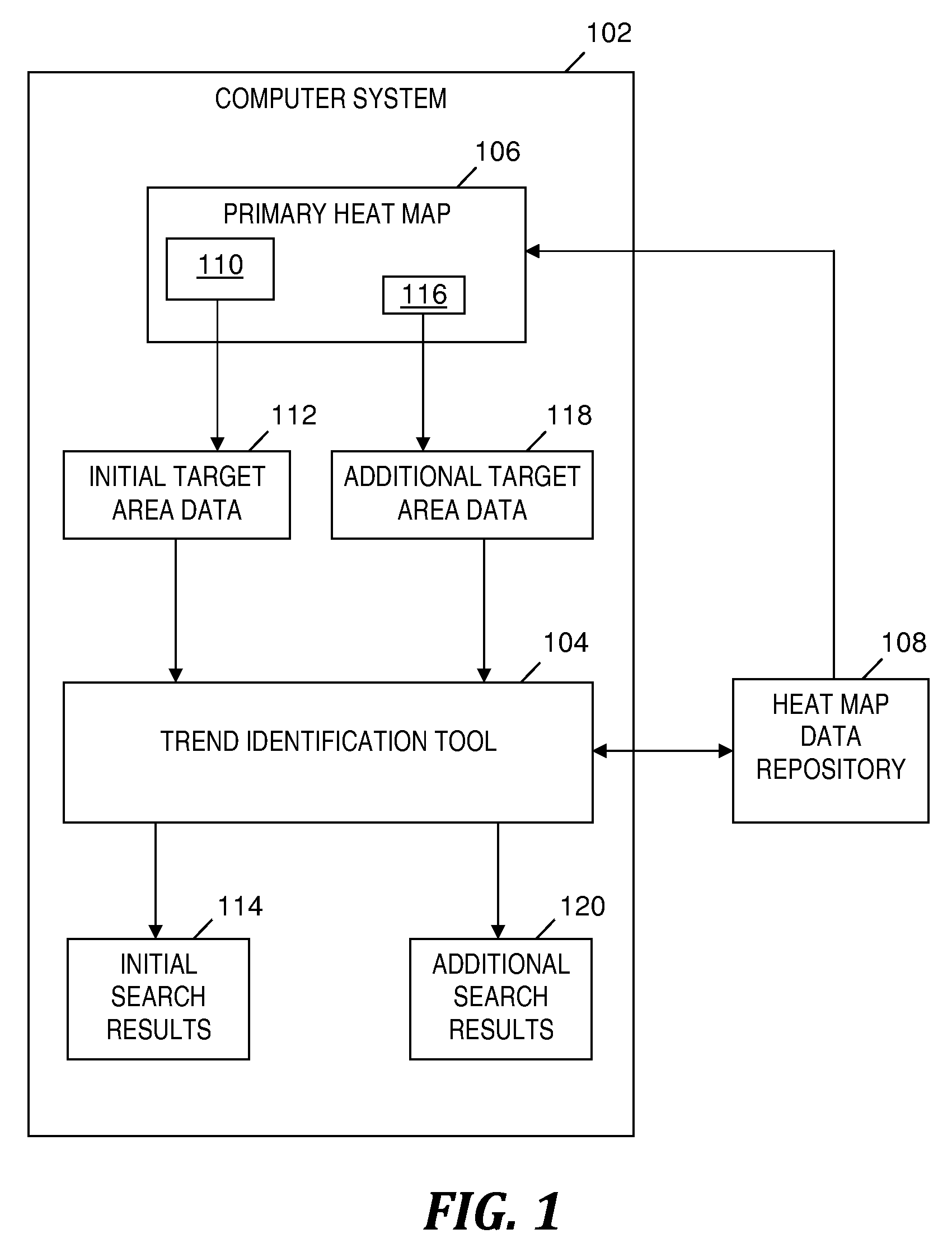
A method and system for identifying a trend in data of heat maps. An initial set of comparison heat maps included in the repository is determined and displayed based on how closely initial comparison area(s) of each comparison heat map match initial target area(s) of a first heat map. A review of the initial set of comparison heat maps determines additional comparison area(s) corresponding to additional target area(s) of the first heat map. In an iterative process, an additional set of comparison heat maps is determined and displayed based on how closely initial and additional comparison areas match respective initial and additional target areas of the first heat map. A trend relating initial and additional target areas is identified based on the displayed additional set of comparison heat maps and based on how closely comparison areas match their respective target areas.
Owner:IBM CORP
Image processing methods, image management systems, and articles of manufacture
Image processing methods, image management systems, and articles of manufacture are described. According to one embodiment, an image processing method includes accessing image data of a plurality of images, defining a plurality of regions in individual ones of the images, wherein the regions individually comprise a plurality of image forming elements having a common characteristic, comparing a region of one of the images with respect to regions of a plurality of others of the images, and providing information indicative of similarities of the one image relative to the others of the images using results of the comparing.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Mutual information and interaction-based medical image splicing method
ActiveCN103236048AAccurate splicingStrong robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisMutual informationComparison area
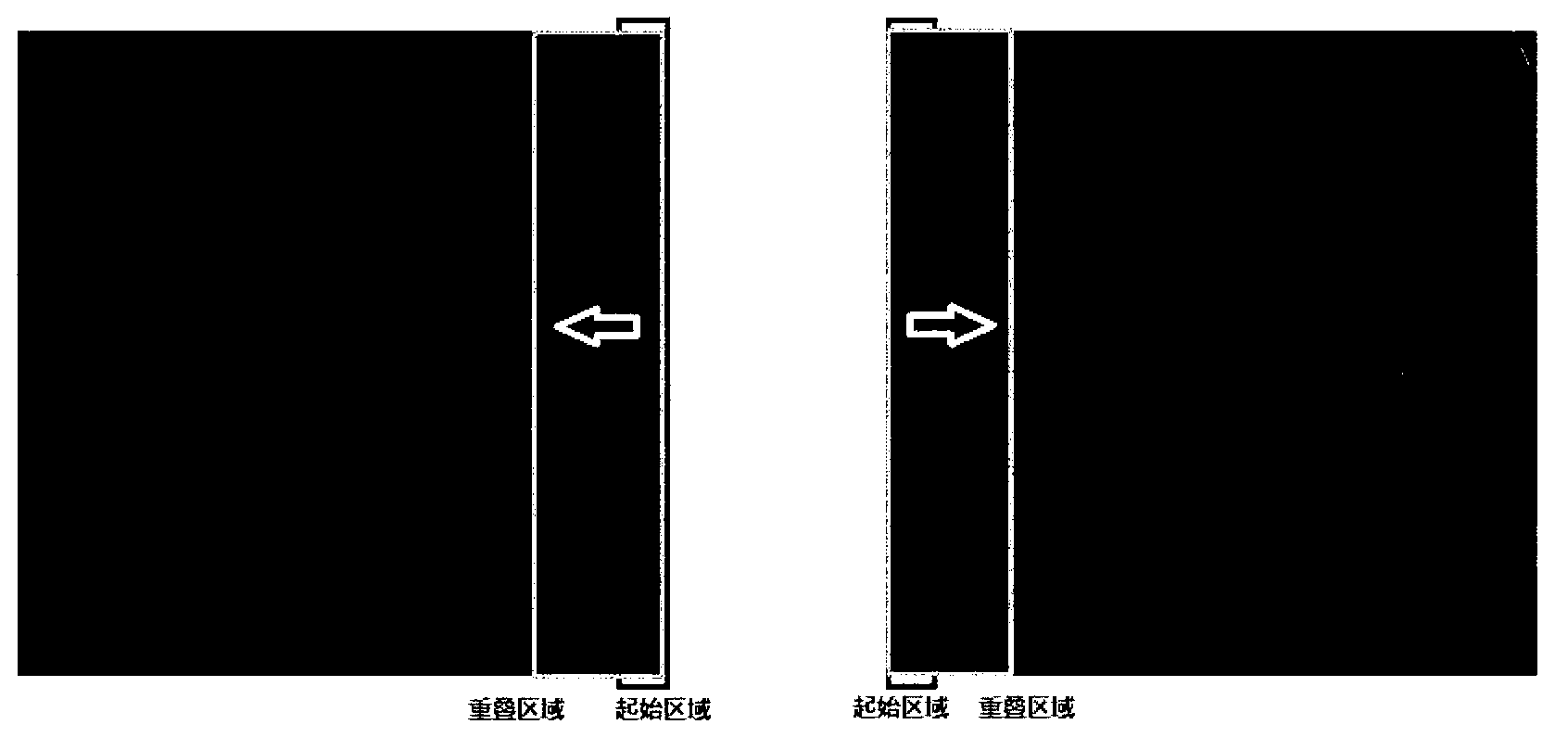
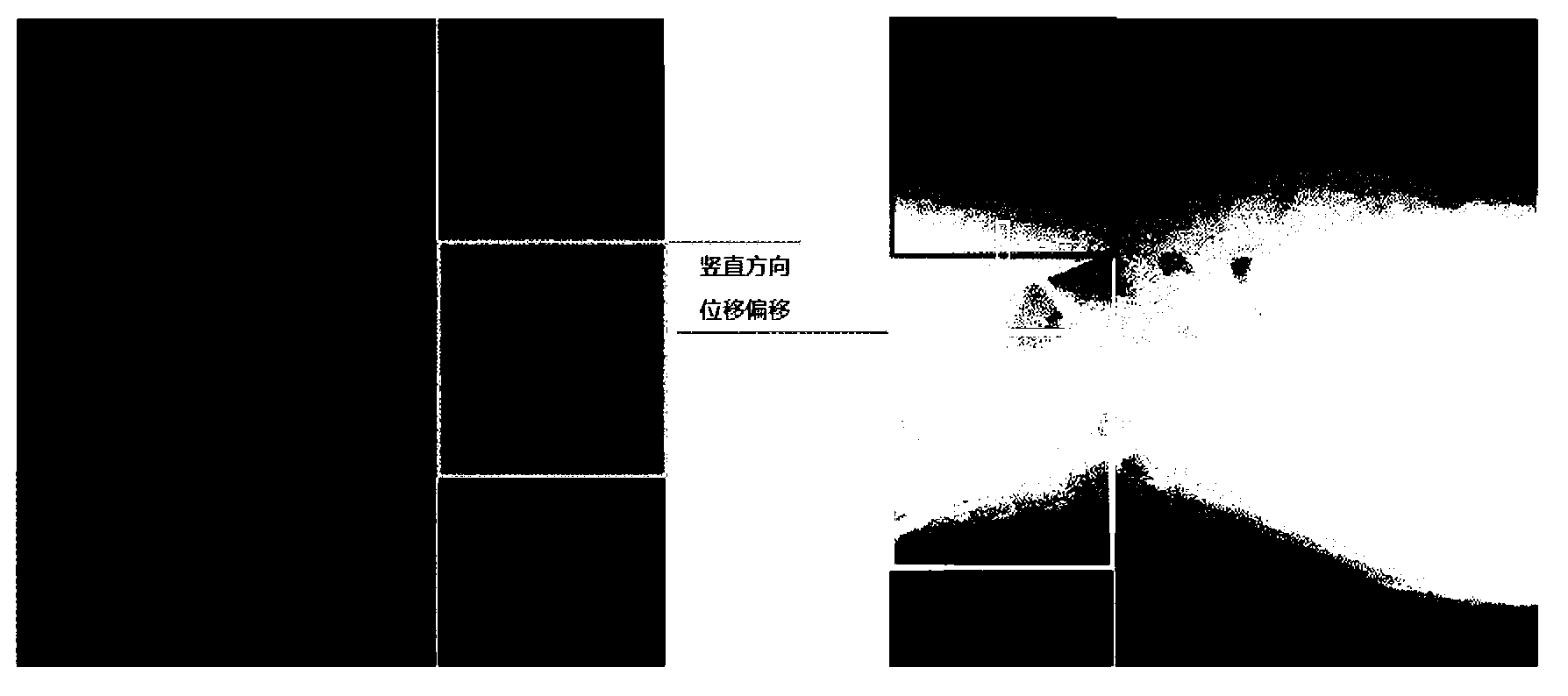
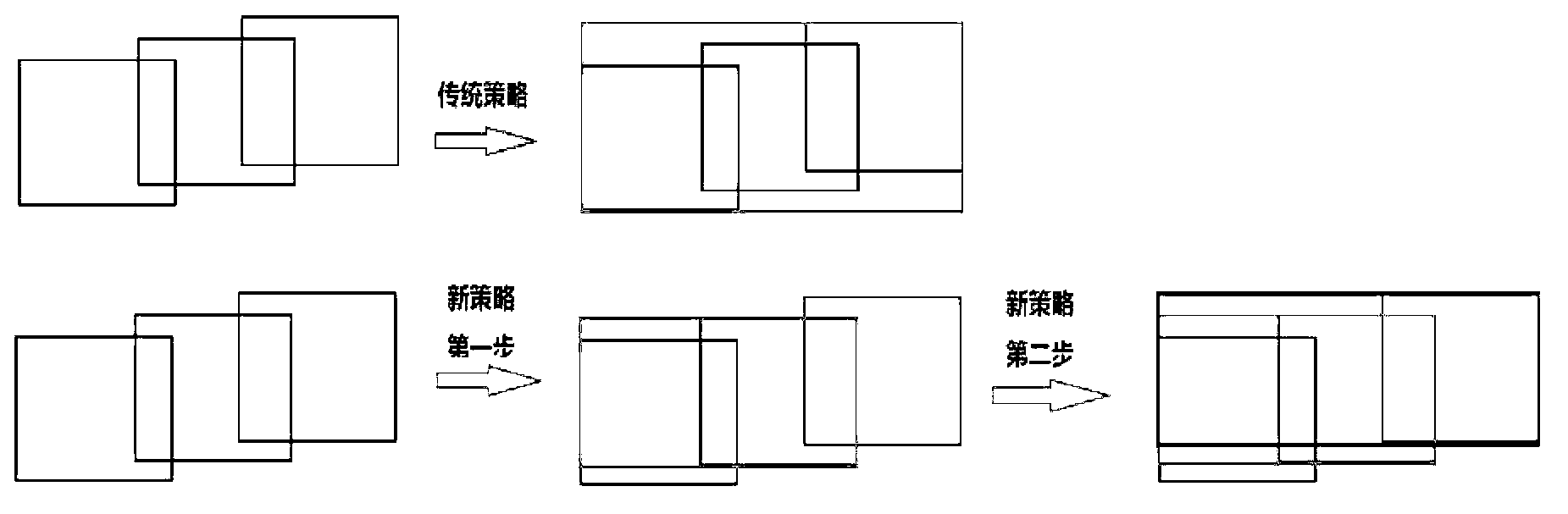
The invention provides a mutual information and interaction-based medical image splicing method. According to the method, a strategy for searching for an image registration parameter is improved in a way that a target area and a comparison area are simultaneously enlarged, images are sequentially registered in a horizontal direction and a vertical direction, and are fused and seamlessly processed according to the obtained registration parameter, a linear weighting function is used for smoothly transiting an overlapped area, and a strategy for determining the size of the area of a spliced result image is also improved to realize the automatic and seamless splicing of images in any number to finally obtain an extra large-viewing angle medical image. In addition, in order to increase splicing speed and meet the requirements of a doctor, interaction with the doctor is added when the method is implemented, the doctor can manually divide an area to be matched, and a splicing process can be simplified according to needs. Experiments prove that a satisfactory splicing result can be obtained by the method and that the method has high clinical application value and is significant for researches.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for implementing zone control of digital television
InactiveCN101431655AReduce usageSave resourcesAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsNetwork packetSmart card
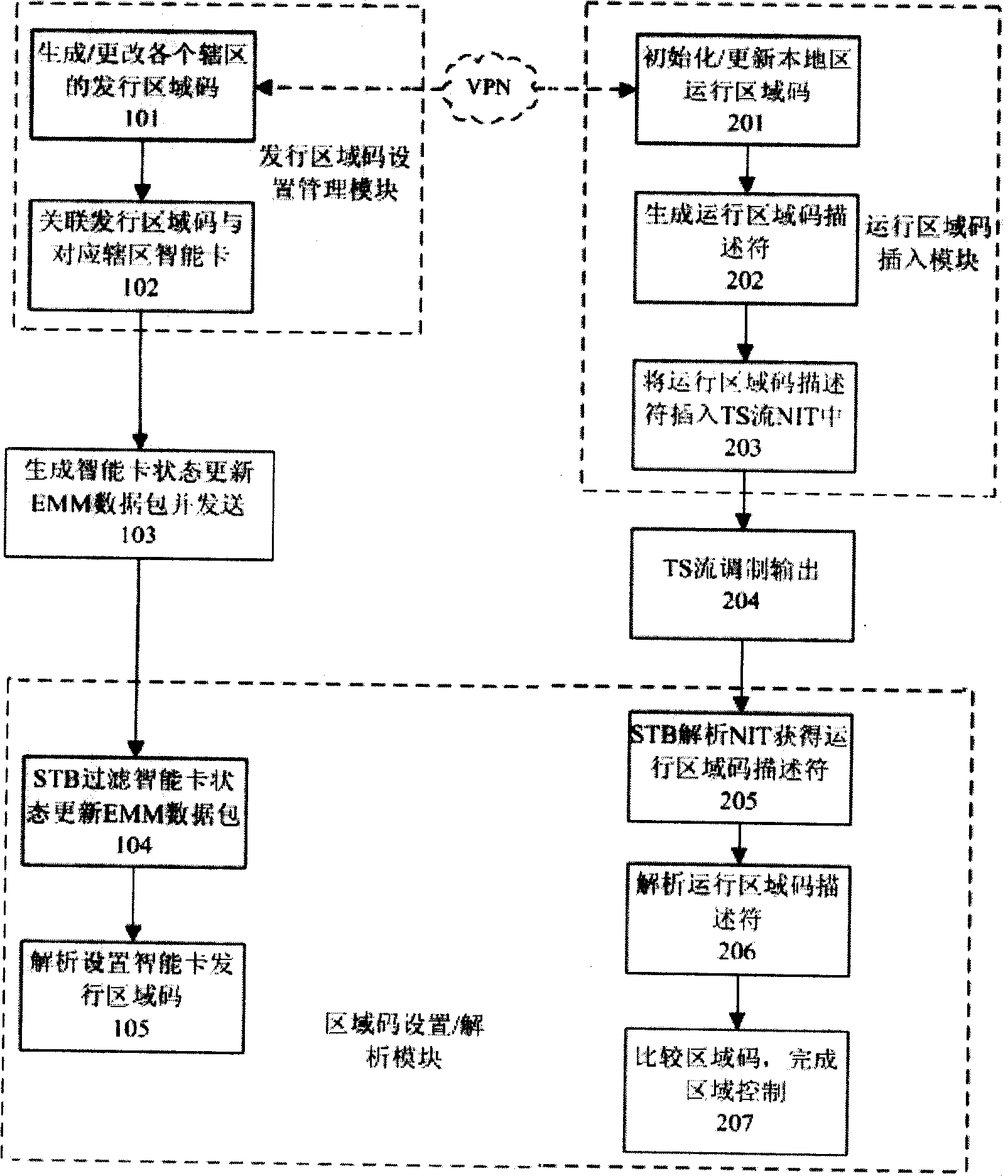
The invention relates to a method for realizing control to a digital TV region. The invention discloses the method for realizing control to the digital TV region which has little cost and occupies less system resource. The technical scheme is summed up in that: setting and changing an initiation state of an smart card issue region code; generating / changing the issue region code of each region; associating the issue region code and corresponding region smart card; generating update EMM data package of the smart card and sending; STB filtering the smart card state and updating EMM data package; analytically setting the smart card issue region code; initializing native region operating code; generating the operation region code description code; inserting the operating region code description signal into TS flow NIT; modulation outputting TS flow; analytically NIT and obtaining the operation region code description signal; analytically the operation region code description signal; comparing the region code and finishing the region control. The invention reduces use of the hardware equipment, reduces cost and occupies less system resource without needing NIT table distribution center.
Owner:SICHUAN CHANGHONG ELECTRIC CO LTD
System and method for detecting electronic element on circuit board
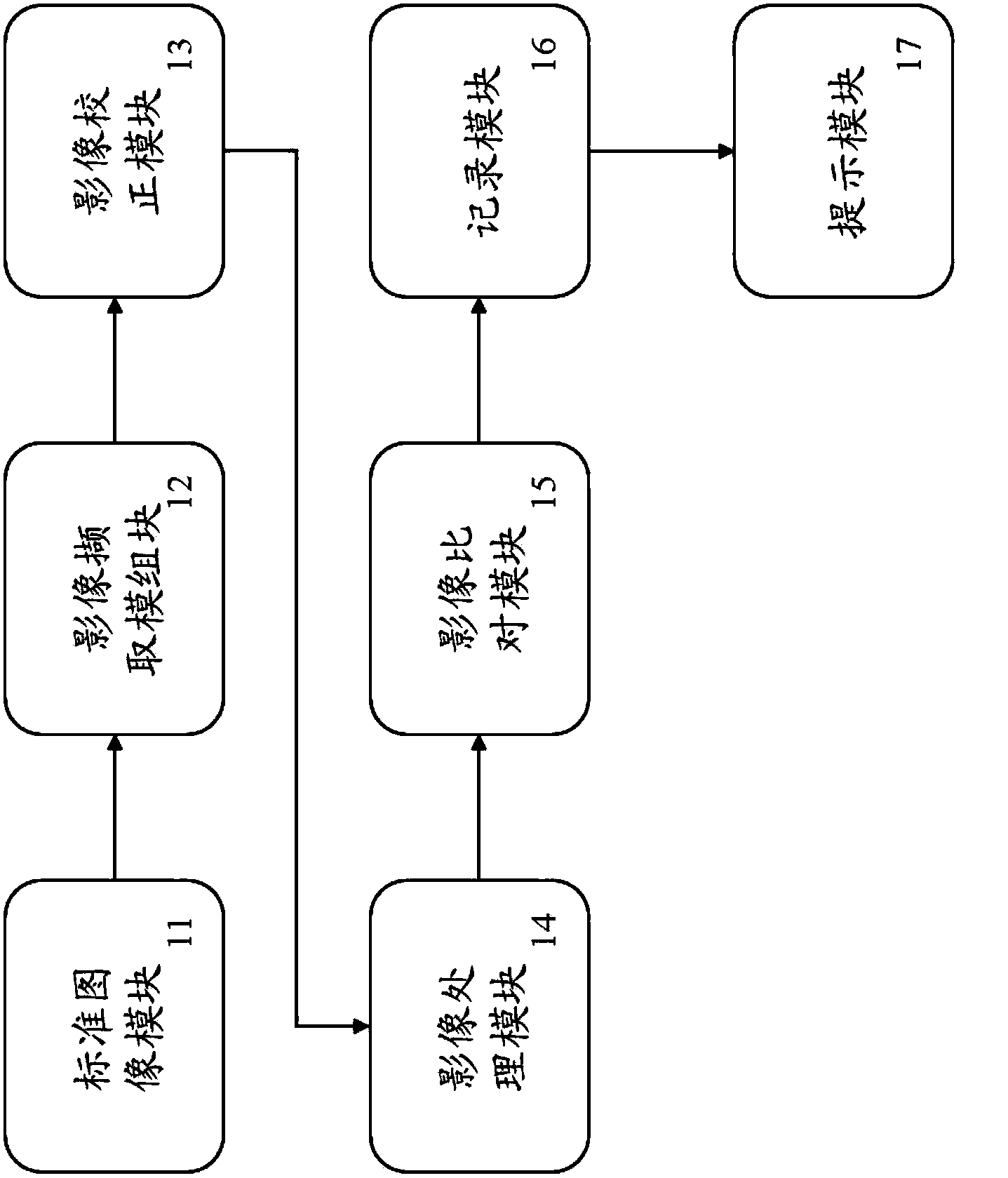
InactiveCN103674959AImprove detection efficiencyOptically investigating flaws/contaminationImaging processingImage calibration
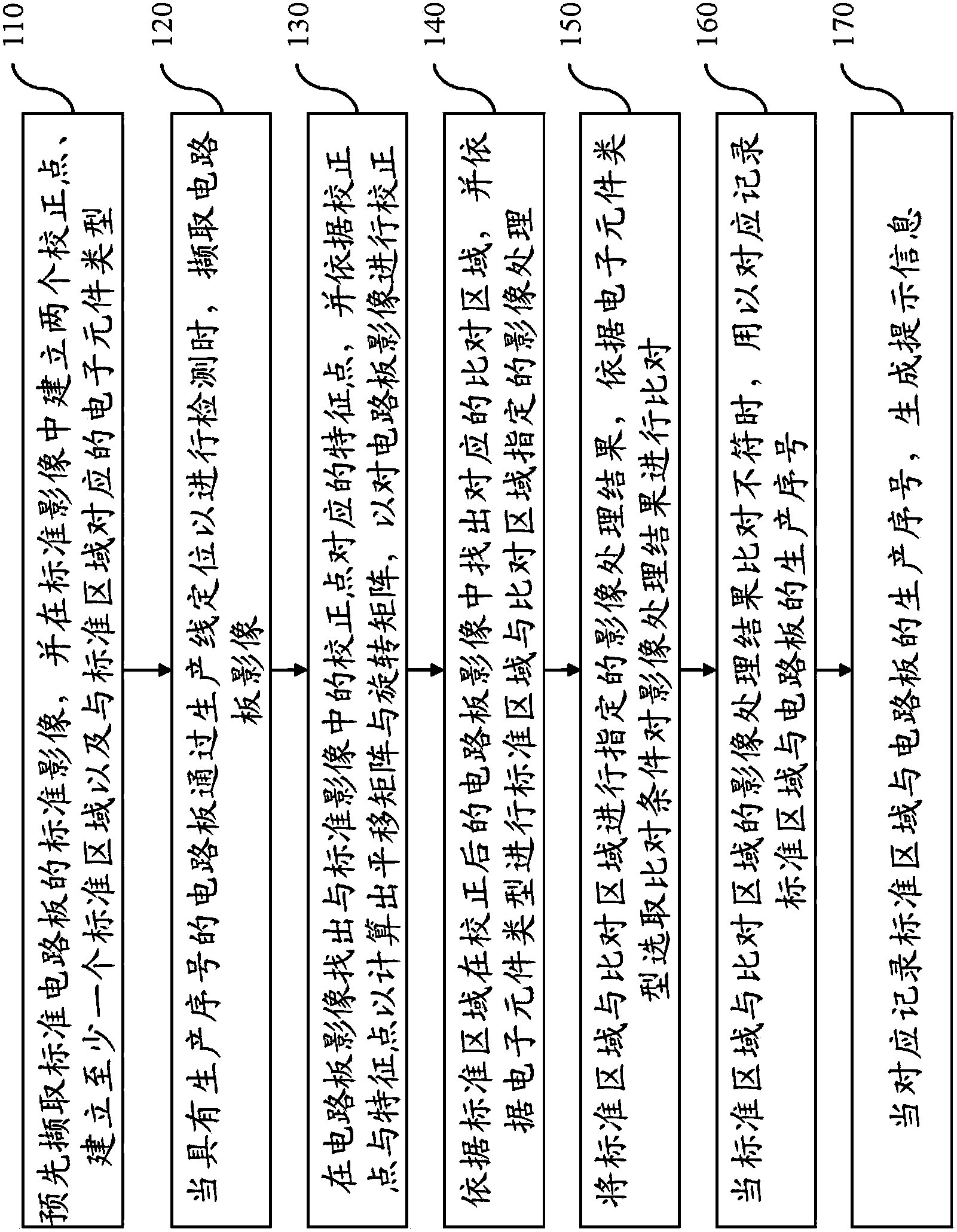
The invention relates to a system and a method for detecting an electronic element on a circuit board. The method comprises the steps of pre-building a standard image with a calibration point and a standard area, capturing an image of the circuit board to be detected, correcting the circuit board image according to the calibration point, finding a corresponding comparison area in the corrected circuit board image according to the standard area, performing designated image treatment and image comparison on the standard area and the comparison area according to the type of the electronic element, and correspondingly recording production sequence numbers of the standard area and the circuit board to generate a prompt message when the image processing results of the standard area and the comparison area are not matched. Therefore, the technical effect that the efficiency of detecting the electronic element on the circuit board is improved can be achieved.
Owner:INVENTEC PUDONG TECH CORPOARTION +1
Patient positioning device and patient positioning method
InactiveUS20060203958A1Improve accuracyAvoid accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingAbnormal tissue growthPattern matching
The invention is intended to always ensure a sufficient level of patient positioning accuracy regardless of the skills of individual operators. In a patient positioning device for positioning a patient couch 59 and irradiating an ion beam toward a tumor in the body of a patient 8 from a particle beam irradiation section 4, the patient positioning device comprises an X-ray emission device 26 for emitting an X-ray along a beam line m from the particle beam irradiation section 4, an X-ray image capturing device 29 for receiving the X-ray and processing an X-ray image, a display unit 39B for displaying a current image of the tumor in accordance with a processed image signal, a display unit 39A for displaying a reference X-ray image of the tumor which is prepared in advance, and a positioning data generator 37 for executing pattern matching between a comparison area A being a part of the reference X-ray image and including an isocenter and a comparison area B or a final comparison area B in the current image, thereby producing data used for positioning of the patient couch 59 during irradiation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
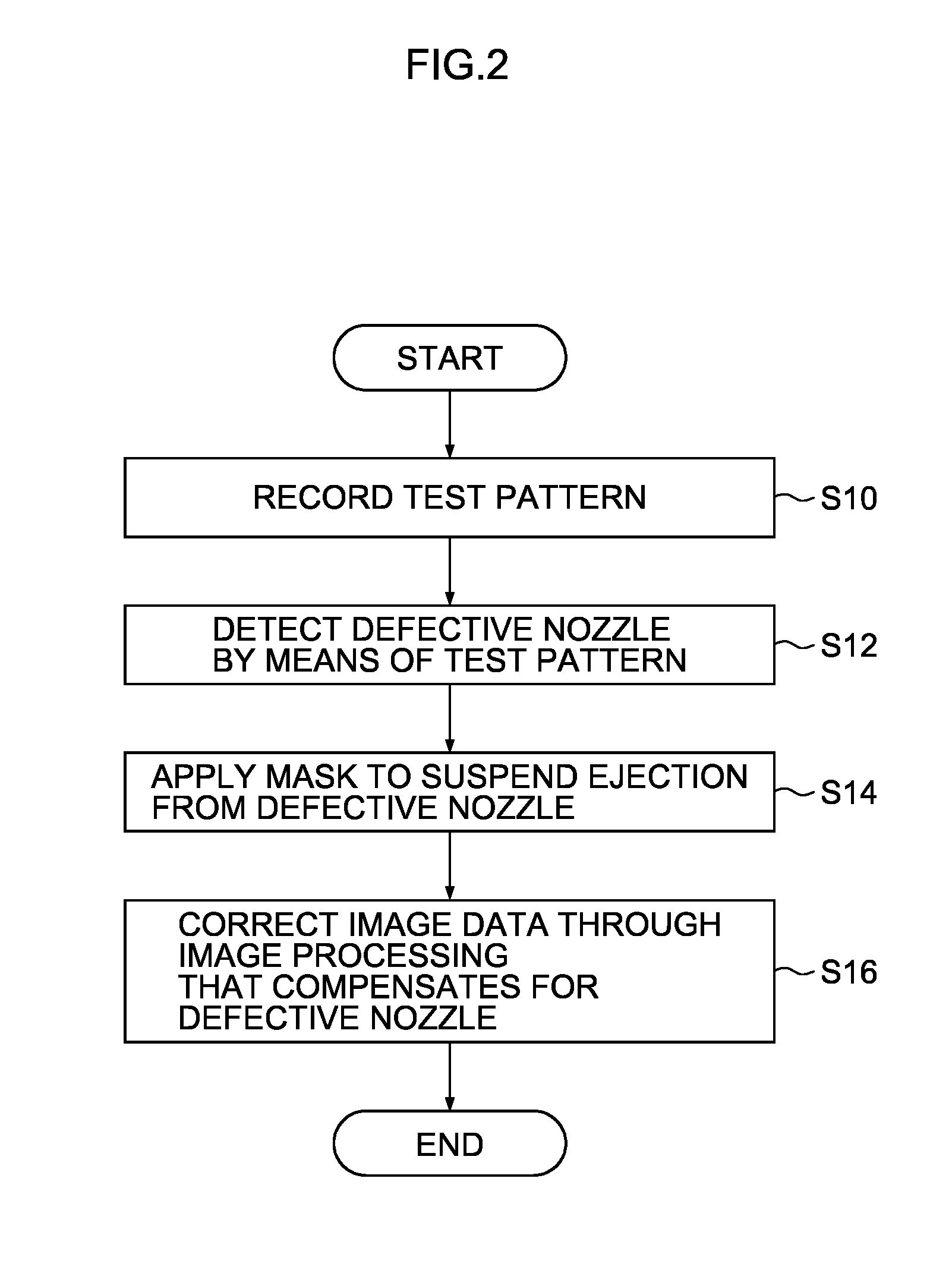
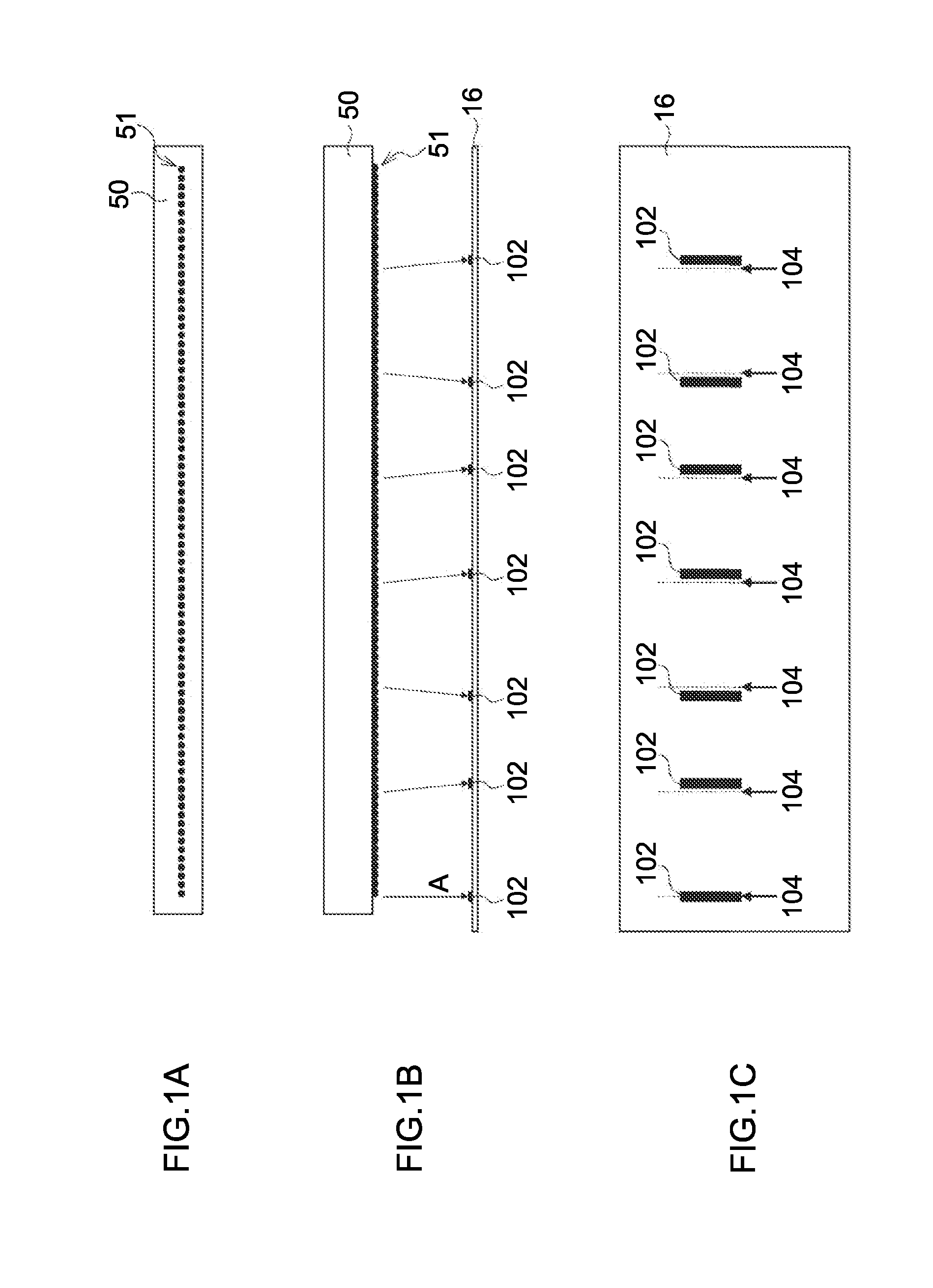
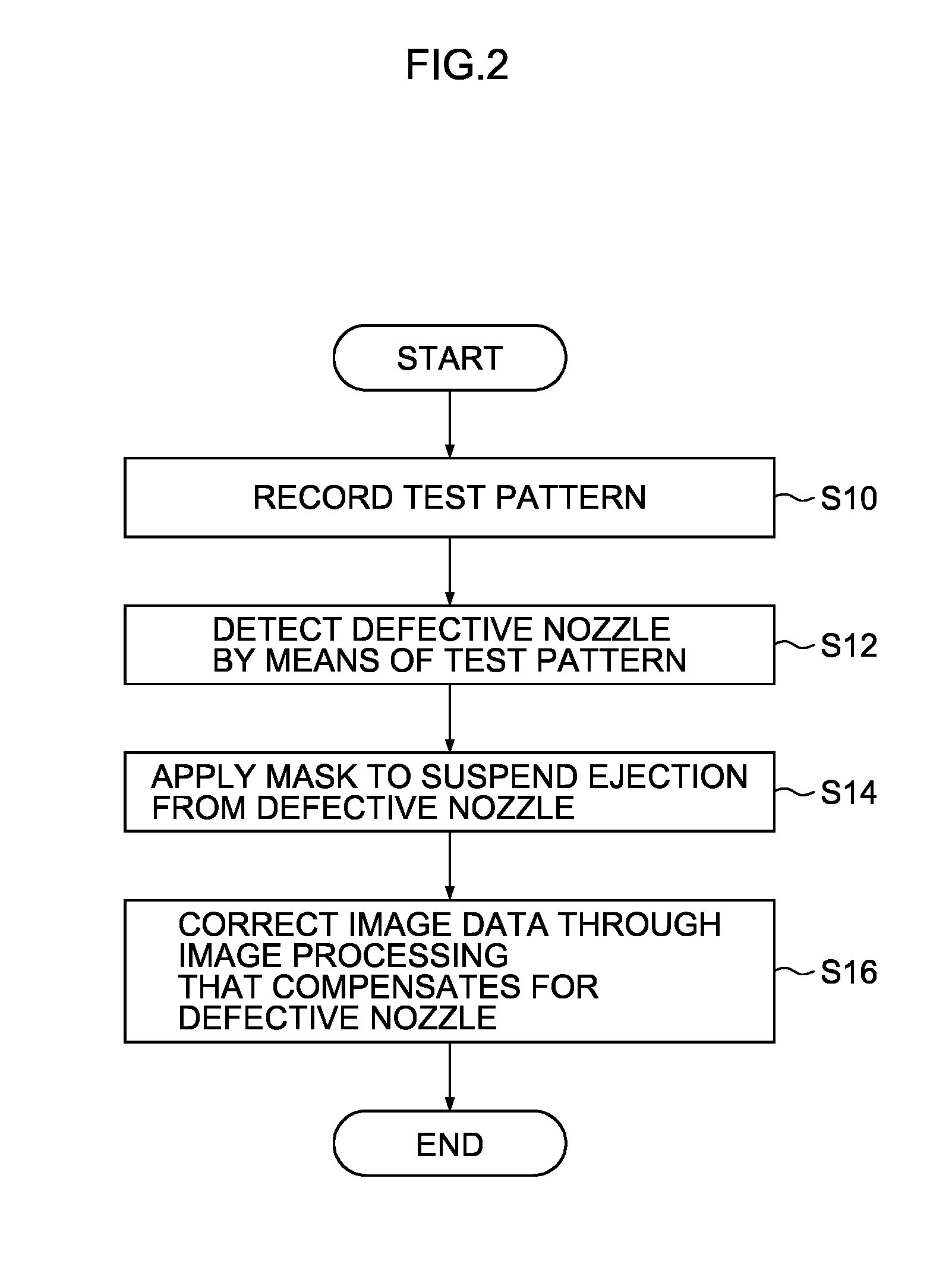
Defective recording element detecting apparatus and method, and image forming apparatus and method
InactiveUS8891128B2Accurate identificationEffective correctionDigitally marking record carriersVisual representation by matrix printersComputer hardwareRecord element
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
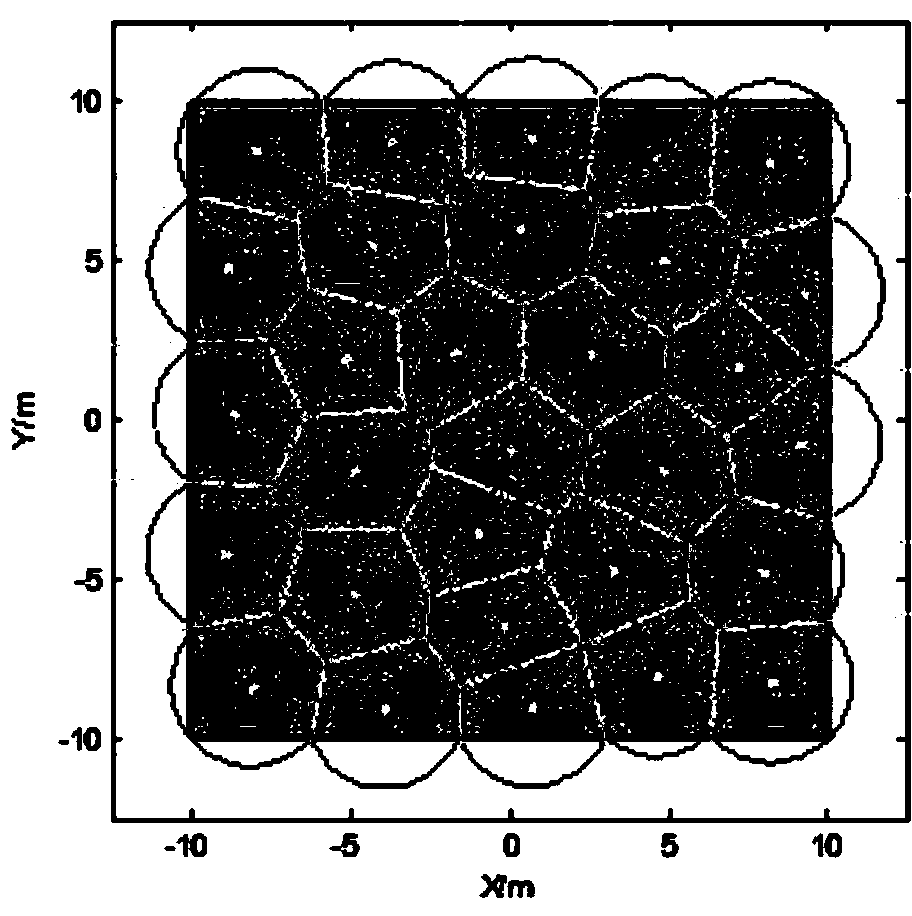
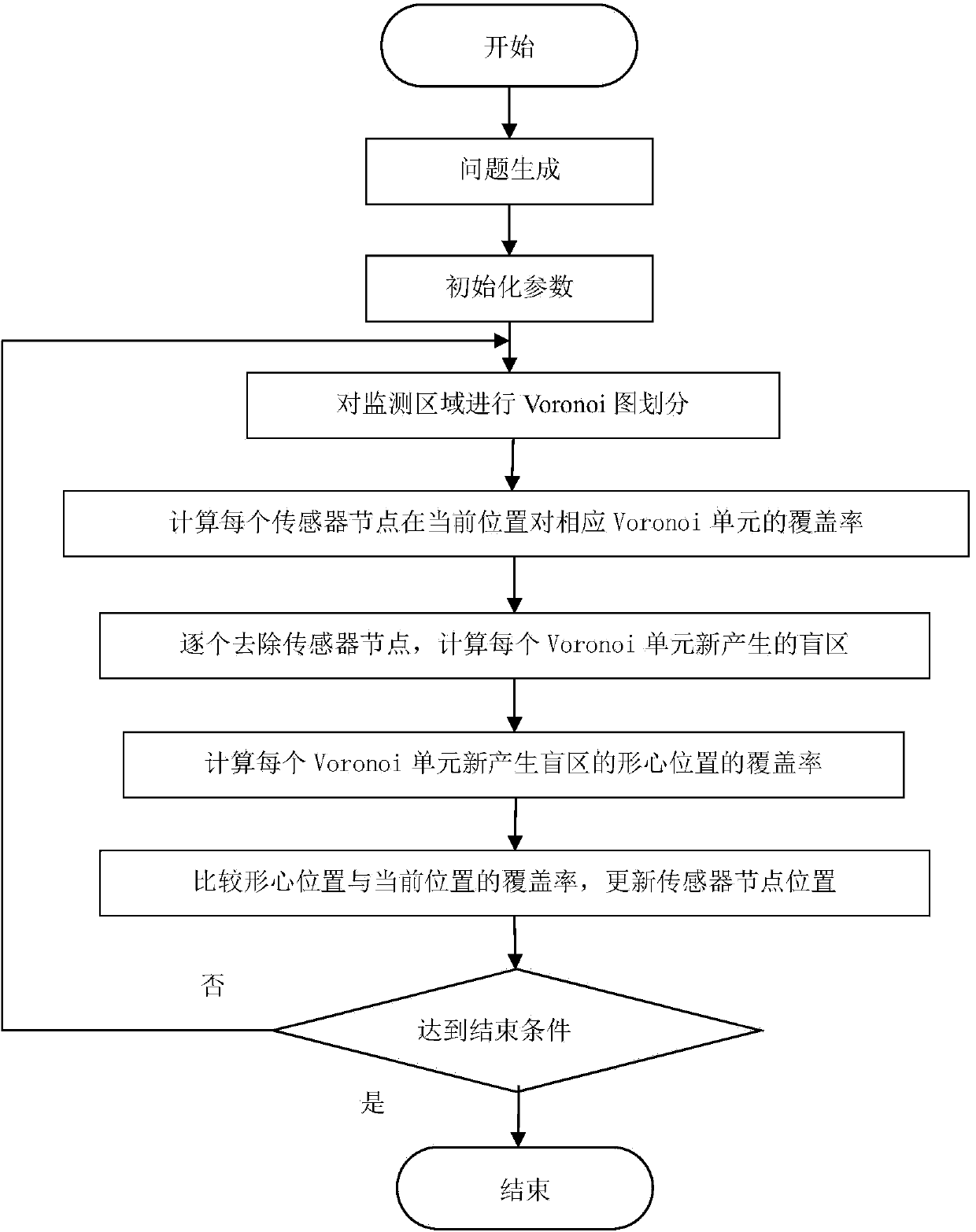
Wireless sensor network node coverage optimization method based on Voronoi diagram for blind area
ActiveCN104159236AIncrease coverageGuaranteed uniformityNetwork topologiesNetwork planningLine sensorNODAL
The invention applies a Voronoi diagram to wireless sensor network node coverage optimization and provides a coverage mechanism based on a Voronoi diagram blind area type new arithmetic. The coverage mechanism is used for providing an optimal solution to a problem of the wireless sensor network node coverage. The problem of the wireless sensor network node coverage is defined as a problem of disk coverage, a wireless sensor is idealized, and the position of a sensor node is regarded as a center of circle, thereby sensing a standard circle with a radius. By means of the Voronoi diagram, an area under monitoring is divided into multiple Voronoi units; a method of removing nodes in the Voronoi units one by one is adopted; and newly-generated geometric centers of the Voronoi units are calculated. A result is assessed by comparing "coverage rate", "node distribution uniformity" and "coverage efficiency" of the area (in order to prevent experimental chance, repeat operation for 30 times and then take the average). Through simulation experiments, validity and high effectiveness of the algorithmic provided by the invention are verified.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Defective recording element detecting apparatus and method, and image forming apparatus and method
InactiveUS20120154837A1Accurate identificationEffective correctionDigitally marking record carriersVisual presentation using printersComputer hardwareRecord element
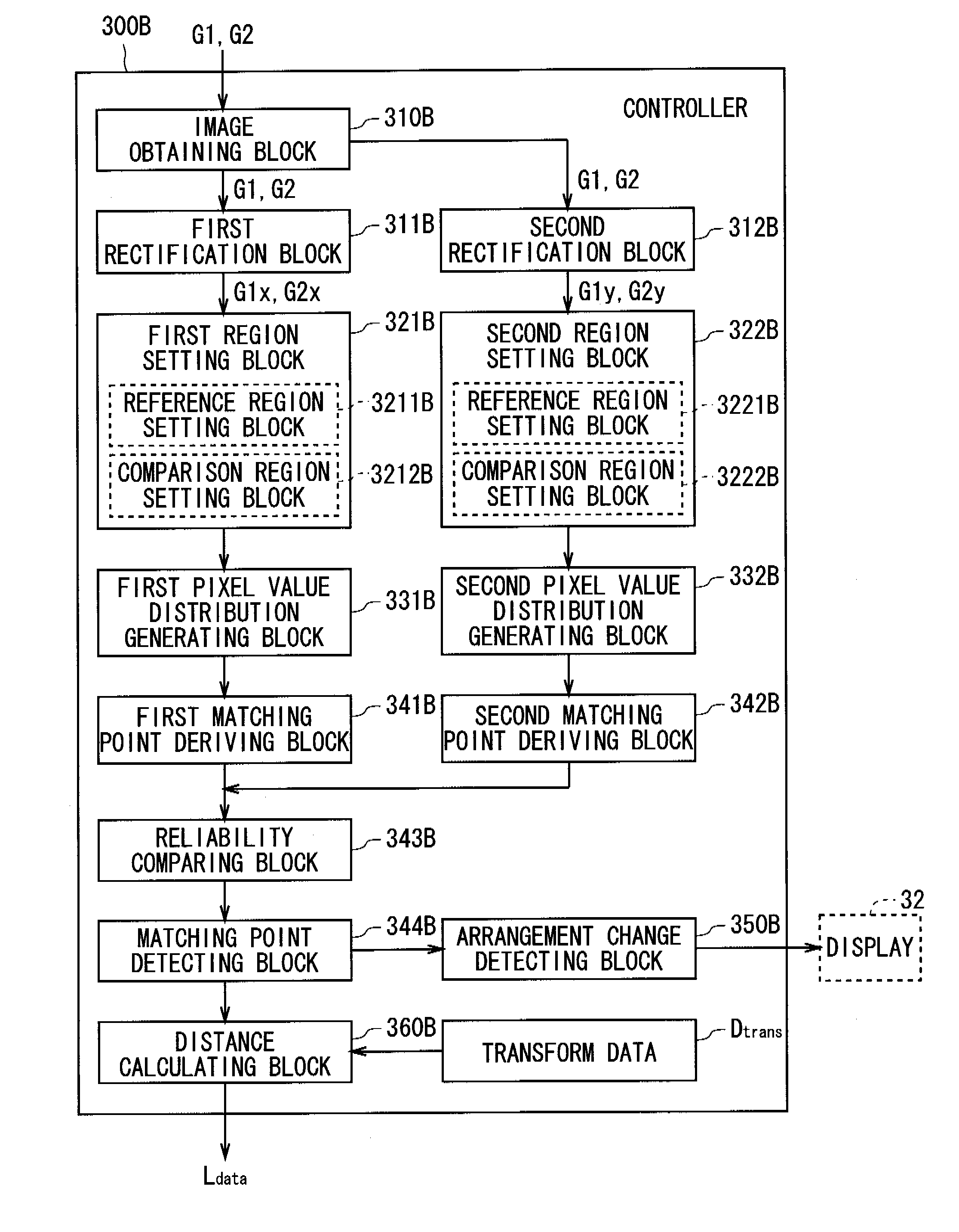
A defective recording element detecting apparatus includes: a read image data acquiring device which acquires read image data of a test pattern recorded on a recording medium by a recording head having recording elements; a reference area setting device which sets a reference area including a part of the test pattern on a read image representing image contents of the read image data; a comparison area setting device which sets a comparison area on the read image; a correlation operation device which performs a correlation operation between the comparison area and the reference area; a distortion correction value determining device which determines a distortion correction value, from a result of the correlation operation; an image distortion correcting device which corrects image distortion of the read image using the distortion correction value; and a defective recording element determining device which identifies a defective recording element according to the corrected read image.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
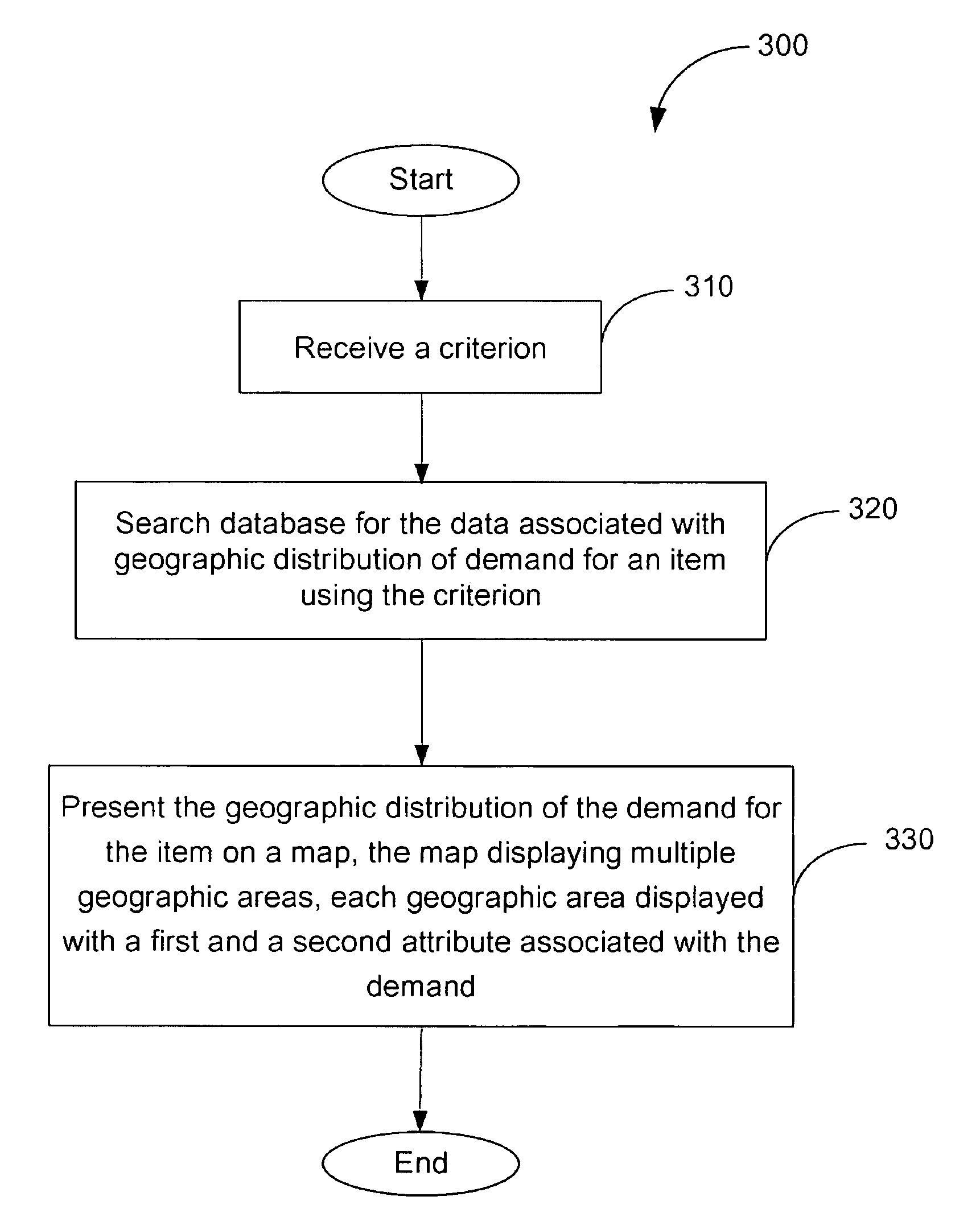
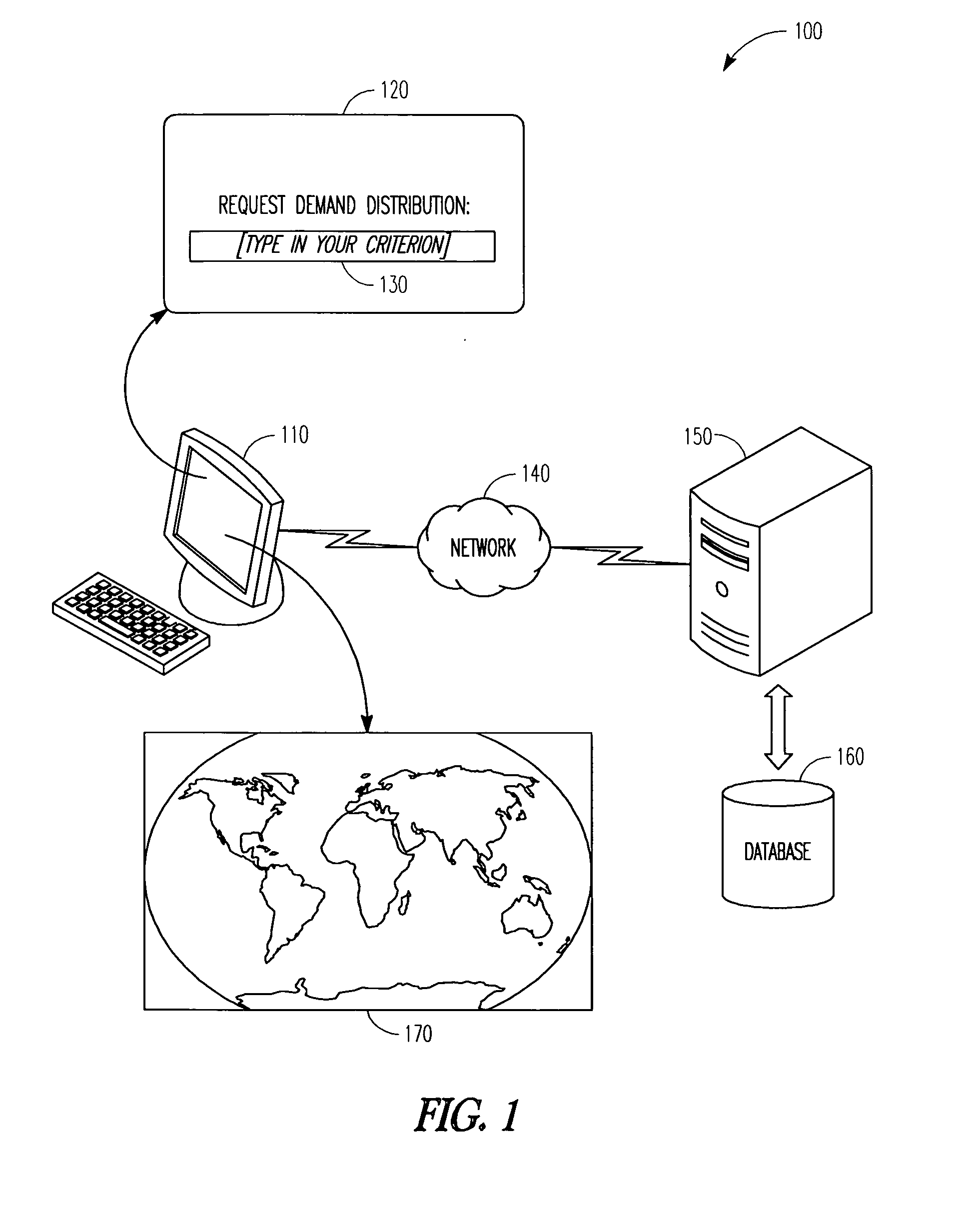
Regional demand and supply comparison
InactiveUS20100070342A1Digital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsData miningGeographic distribution
A computerized method and a system for comparing regional demand and supply are provided. Example embodiments may include receiving a criterion to identify an item and searching a database for data associated with demand and / or supply for the item identified by the criterion. The computerized method may also include presenting a geographic distribution of demand, supply, and / or net-demand for the item on a map. The map may display multiple geographic areas; each one of the multiple geographic areas may be displayed with a first and a second attribute. The first and the second attributes may be associated with the demand, supply, and / or the net-demand.
Owner:EBAY INC
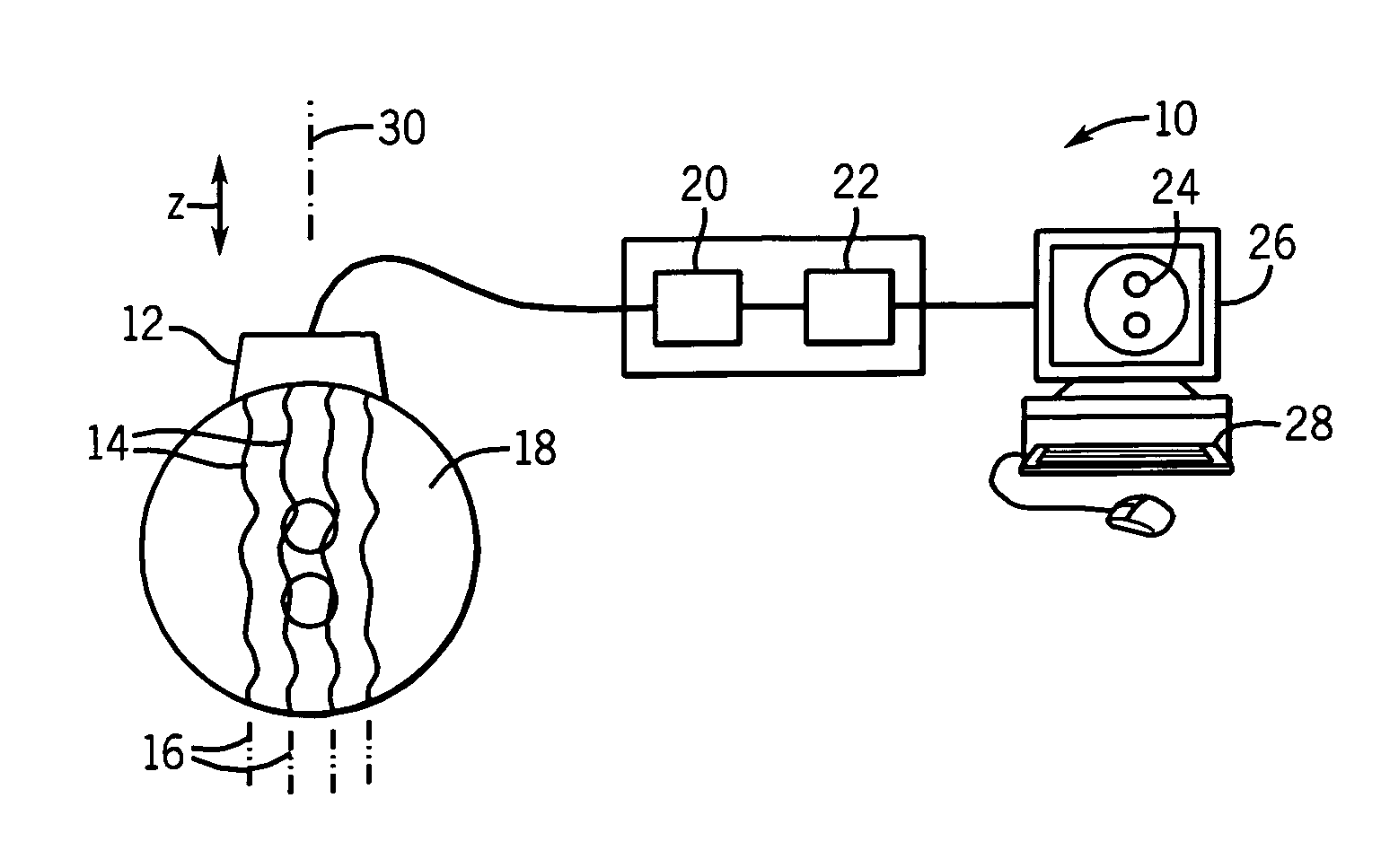
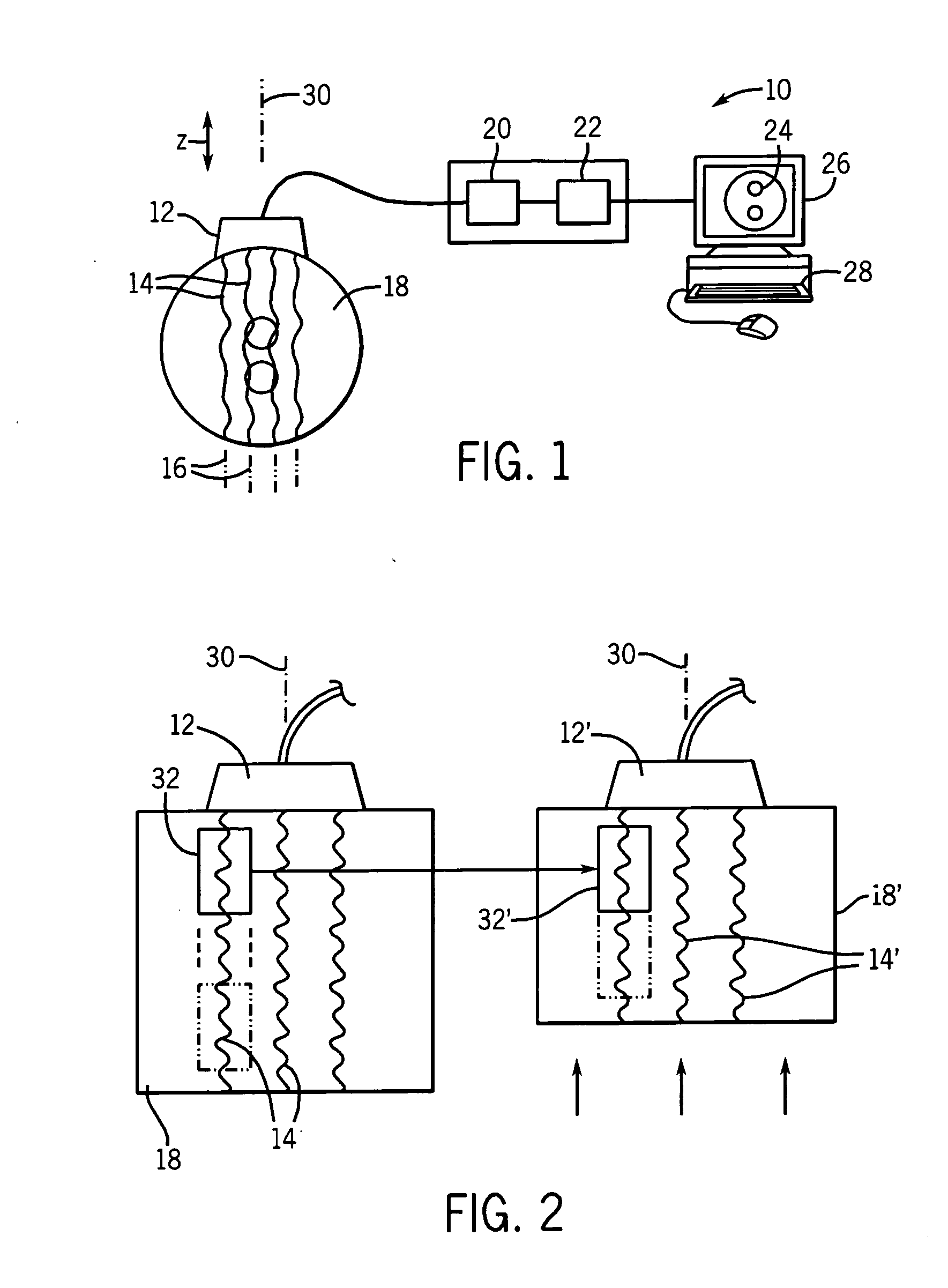
High resolution elastography using two step strain estimation
ActiveUS20070083113A1Reduce riskAvoid problemsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesImage enhancementStrain estimationComparison area
High-resolution elastography employs a multiple-step process in which successively finer samplings of data and smaller areas of data are evaluated to provide increasingly accurate displacement measurements, wherein each displacement measurement guides the determination of corresponding regions of comparison used in the next displacement evaluation.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Image processing apparatus, information processing system, and image processing method
InactiveUS20110026773A1High precisionReduce sizeImage analysisOptical rangefindersInformation processingImaging processing
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
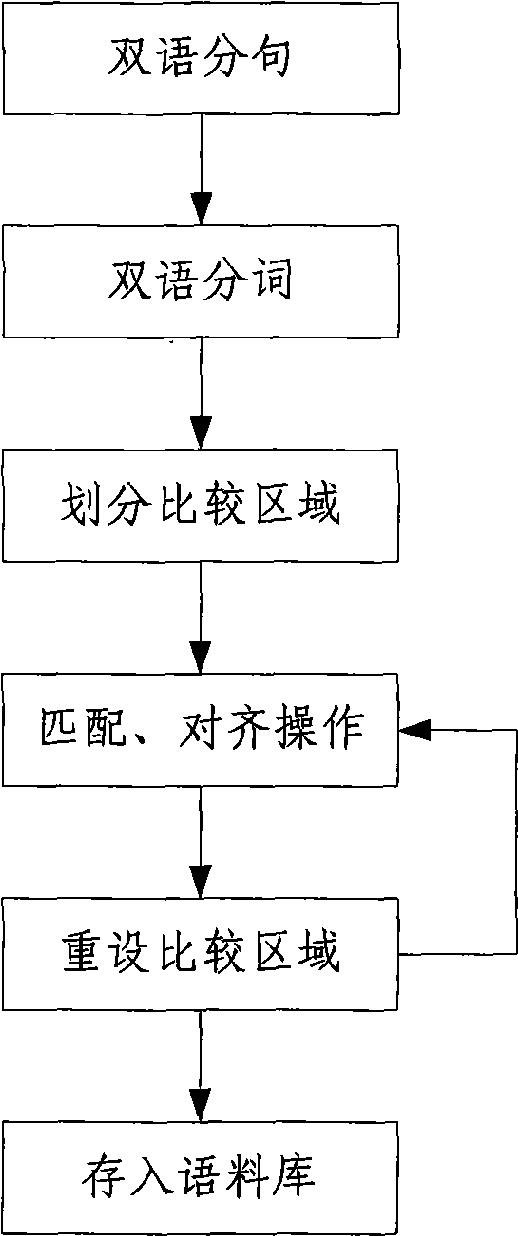
Double-language sentence alignment method and device
ActiveCN101488126AFast constructionImprove the efficiency of alignmentSpecial data processing applicationsComparison areaParticiple
The invention discloses a bilingual sentence alignment method which comprises a clause step, a participle step, an alignment step, a matching step and an execution step; wherein, the alignment step concretely comprises: a region division step which respectively divides the first language and the second language requiring alignment into a plurality of comparing regions containing sentences of the first language and the second language according to prearranged region division rules; in the matching step, the mutual matching rate of every pair of sentences in the comparing region of every pair of the first language and the corresponding second language is calculated and the combinations of the mutually matched sentences of the first language and the second language according to the mutual matching rate is determined; in the execution step, the alignment operation on the combination of the sentences of the first language and the second language with the biggest mutual matching rate is executed. A corresponding bilingual sentence alignment device is also disclosed by the invention. The invention can greatly improve the aligning efficiency and accelerate the constructing speed of corpuses.
Owner:深圳市点通数据有限公司
Defective recording element detecting apparatus and method, and image forming apparatus and method
InactiveCN102555473AAccurate identificationOther printing apparatusPictoral communicationComputer hardwareRecord element
The invention provides a defective recording element detecting apparatus and method, and an image forming apparatus and method. The defective recording element detecting apparatus includes: read image data acquiring means adapted to acquire read image data of a test pattern recorded on a recording medium by a recording head having a plurality of recording elements; reference area setting means adapted to set a reference area including a part of the test pattern on a read image; comparison area setting means adapted to set a comparison area on the read image; correlation operation means adapted to perform a correlation operation between the comparison area and the reference area while making the comparison area to conduct relative translation relative to the reference area; distortion correction value determining means adapted to determine a distortion correction value so as to correct the offset of the image in the comparison area relative to that of the reference area; image distortion correcting means adapted to correct image distortion of the read image using the distortion correction value; and defective recording element determining means adapted to identify a defective recording element according to the corrected read image.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Optimization techniques during processing of print jobs
InactiveUS20050213142A1Visual presentation using printersDigital computer detailsGraphicsComputer printing
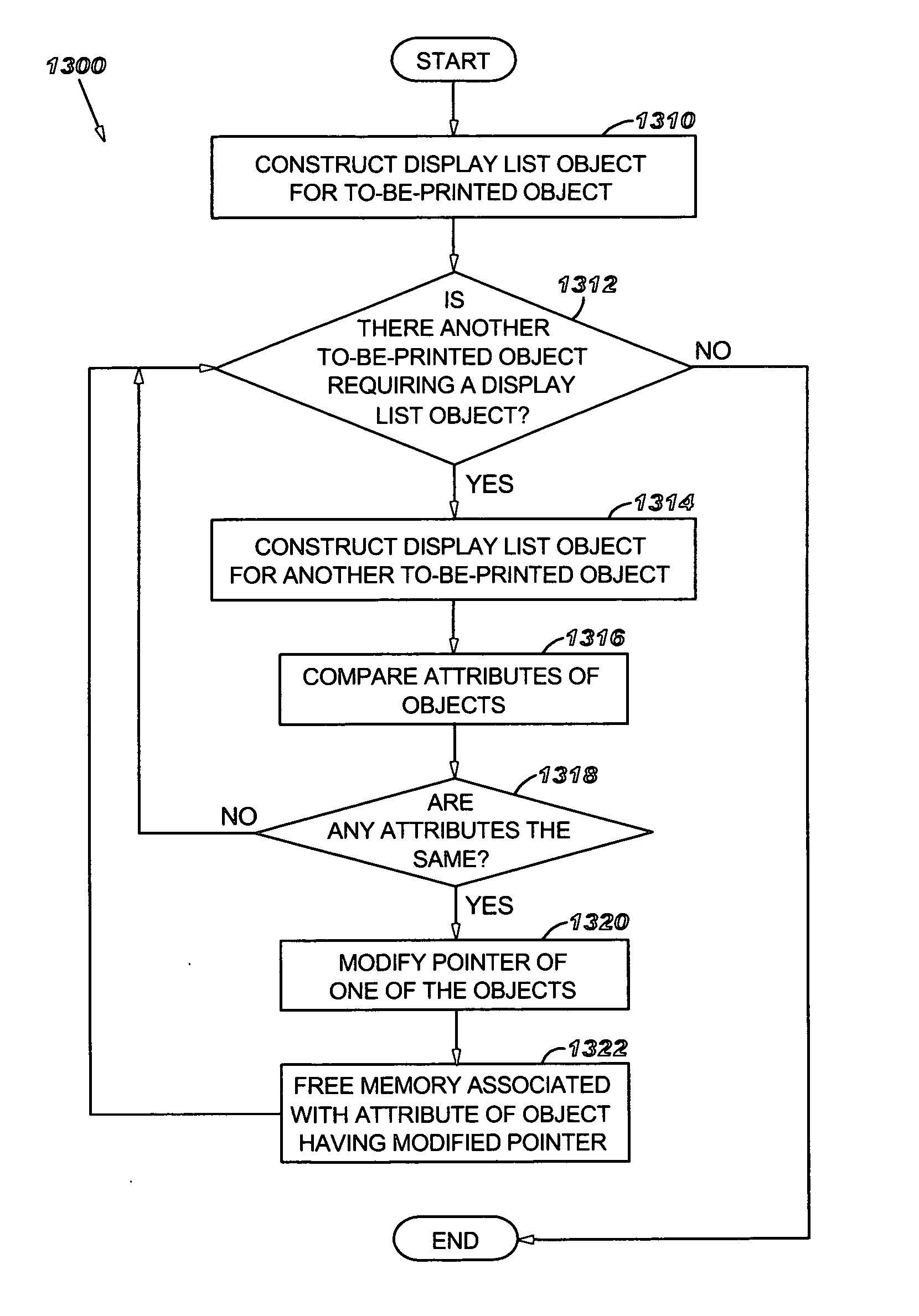
Methods for processing print jobs in rendering devices include constructing display list objects for to-be-printed objects and comparing attributes thereof for sameness and compatibility. If same or compatible, attributes become shared and memory locations with redundant information are freed for use with other processing operations. In one aspect, the invention allows sharing of attributes for adjacent objects, for any two objects or for all objects. Pointers of the objects having shared attributes may become modified to point to a new location or eliminated altogether. The object itself may also become eliminated. Preferably, attribute comparison includes comparing color values of ink attributes for exactness and comparing vector drawing commands of region attributes for comparability. Individual objects on the display list can be linked together and a root may precede the first object. Computer readable media and graphics engines in laser printers are preferred structures for comparing attributes.
Owner:MCARDLE JOHN J JR
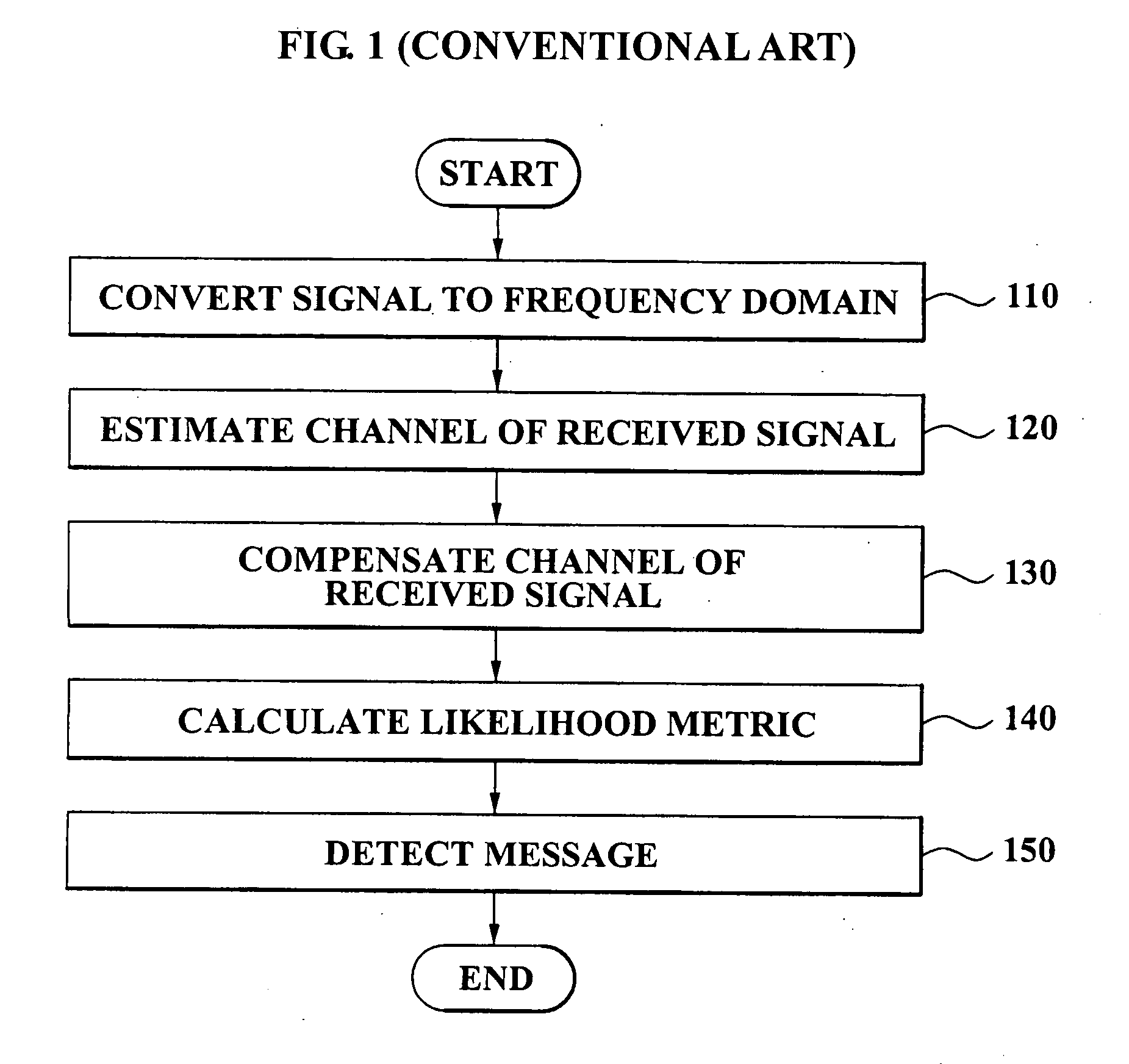
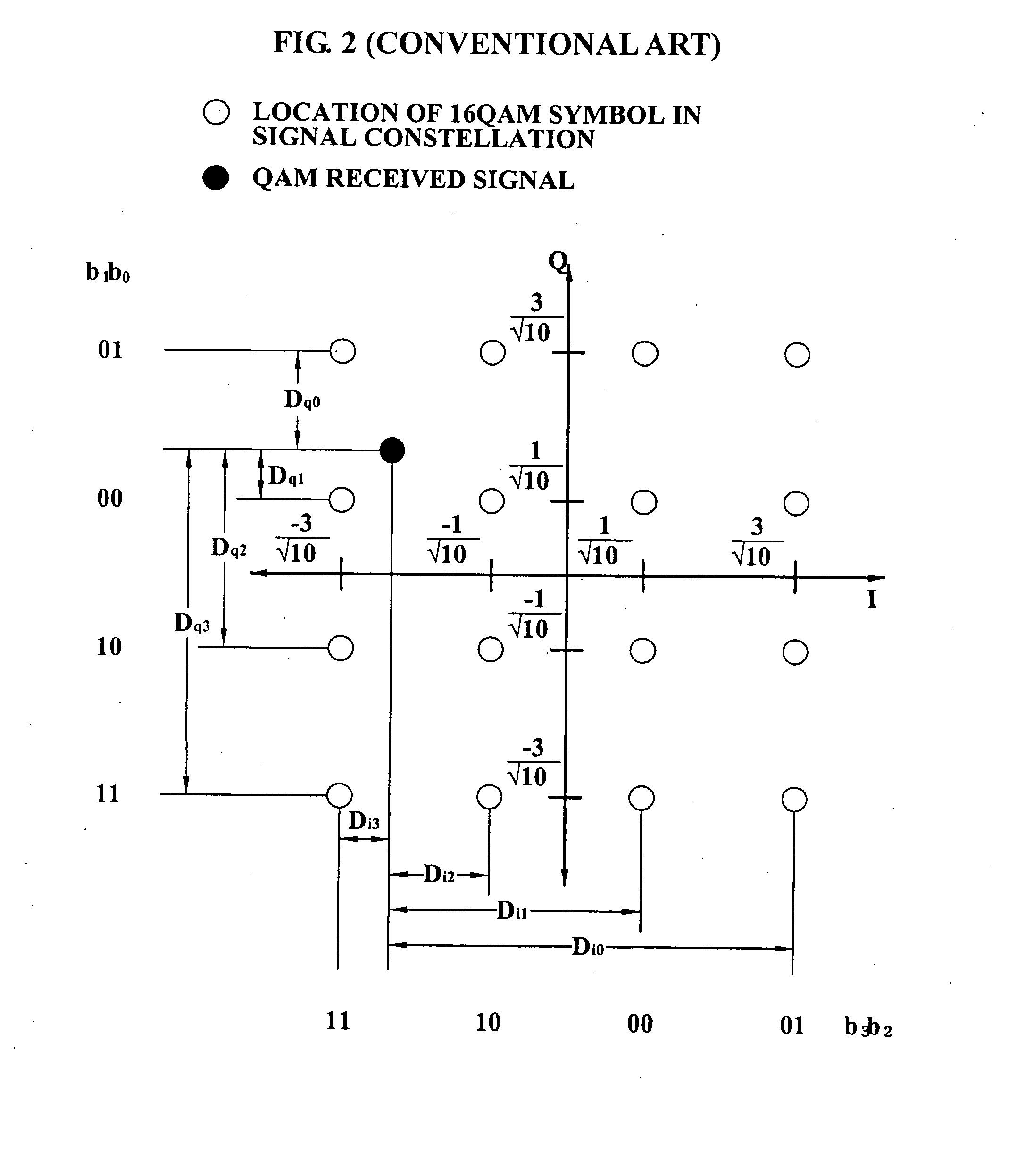
Method and apparatus for calculating likelihood metric of a received signal in a digital communication system
InactiveUS20070217536A1Reduce complexityImprove accuracyData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionCommunications systemComputer science
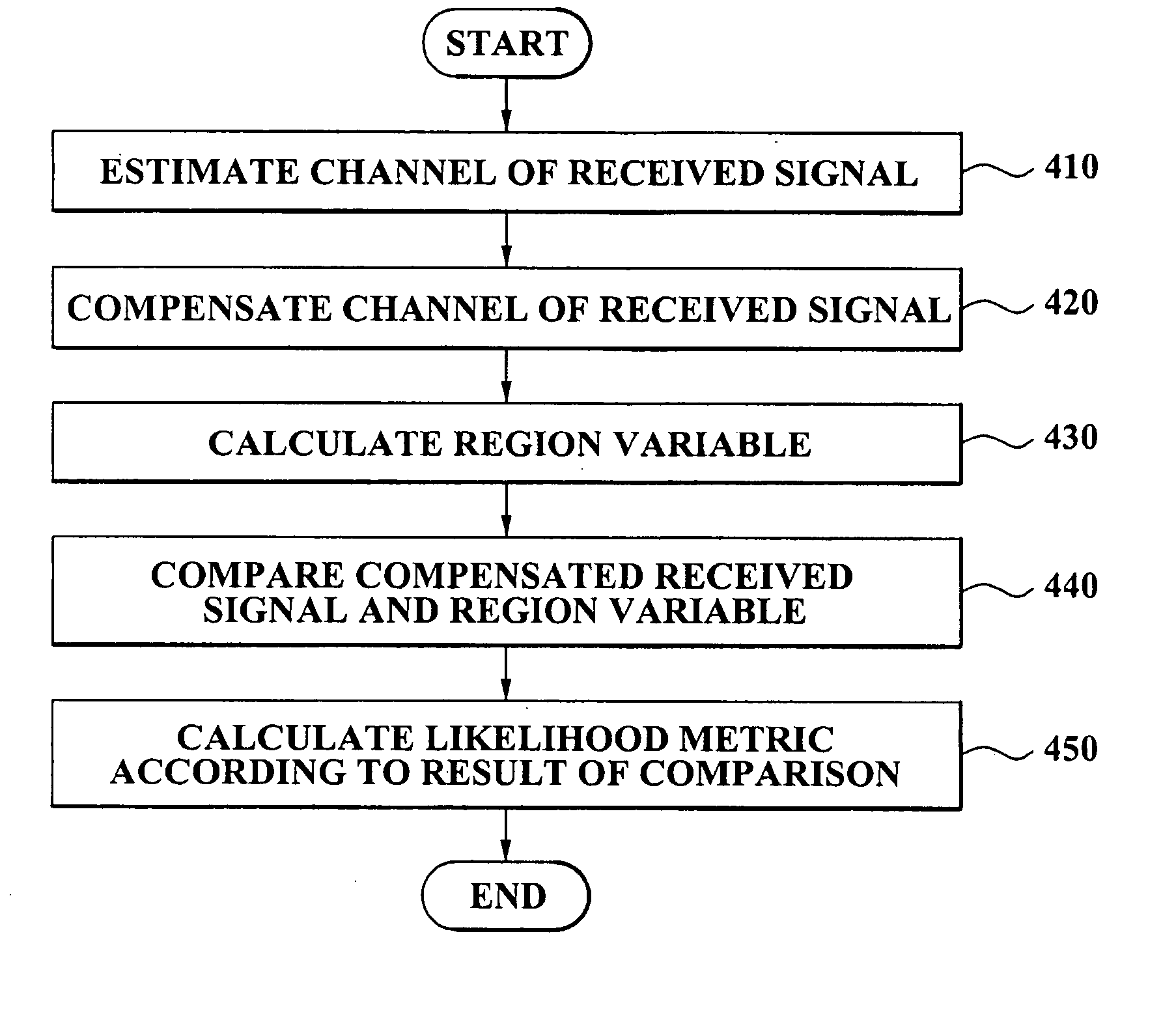
A likelihood metric calculation method including: estimating a channel of a received signal and generating a channel estimate; compensating a channel of the received signal according to the channel estimate; calculating a region variable according to the channel estimate; and comparing the region variable and a magnitude of the compensated received signal and calculating a likelihood metric of the received signal according to a result of the comparison. An apparatus for calculating a likelihood metric including: a channel estimation unit estimating a channel of the received signal and generating a channel estimate; a channel compensation unit compensating a channel of the received signal according to the channel estimate; a region variable calculation unit calculating a region variable according to the channel estimate, the region variable being a value obtained by scaling a symbol coordinate value in a signal constellation corresponding to the received signal utilizing the channel estimate; a comparison unit comparing a magnitude of the compensated received signal and the region variable; and a bit metric calculation unit calculating a likelihood metric with respect to each bit of the compensated received signal according to a result of the comparison. According to the present invention, it is possible to reduce a complexity in the compensating of the channel and the calculating of the likelihood metric. Also, since effects caused by the channel variation are reflected as a weighting factor in the calculating of the likelihood metric, it is possible to improve a message detection performance of the entire system.
Owner:POS DATA CO LTD
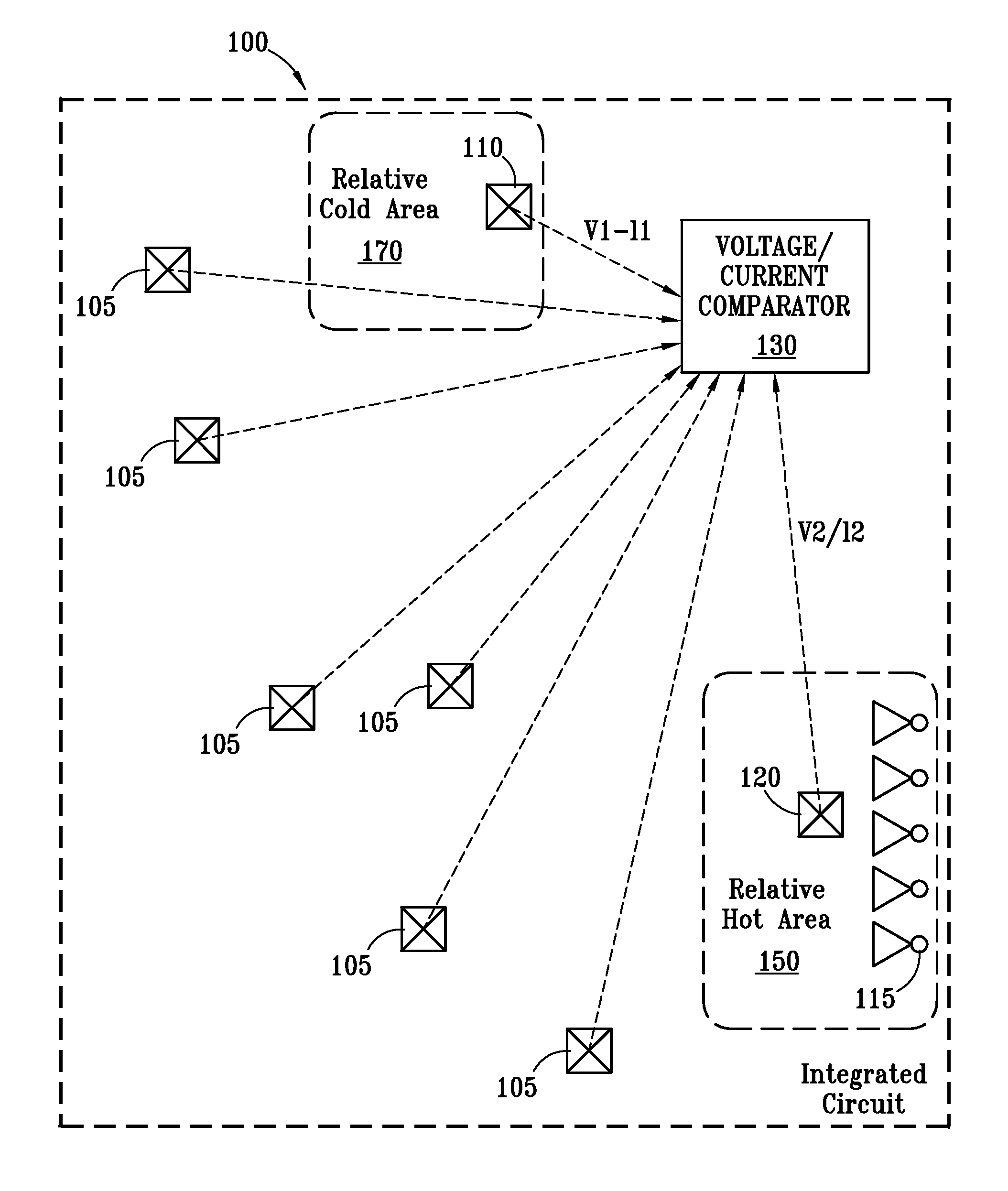
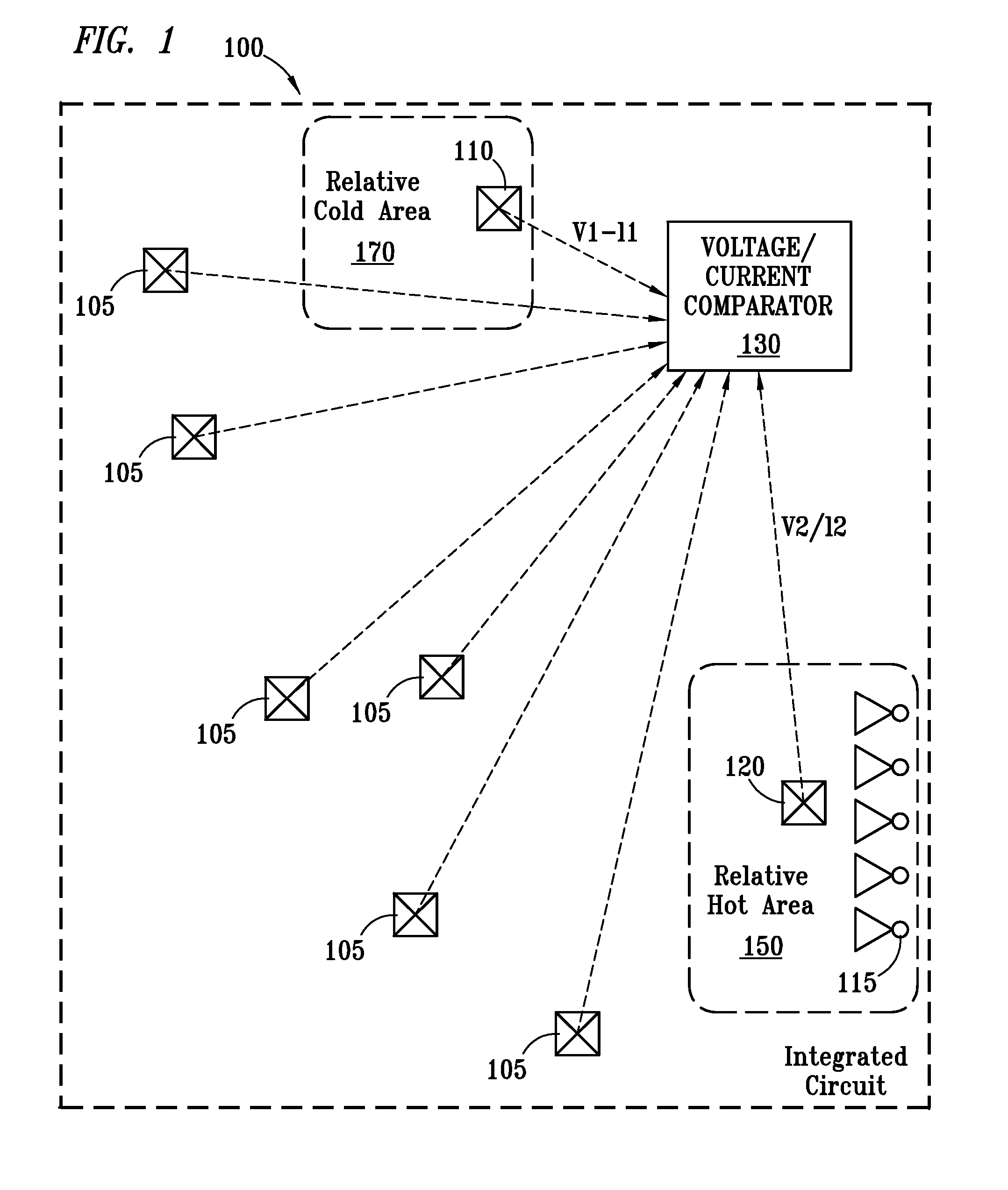
Thermal sensing method and system
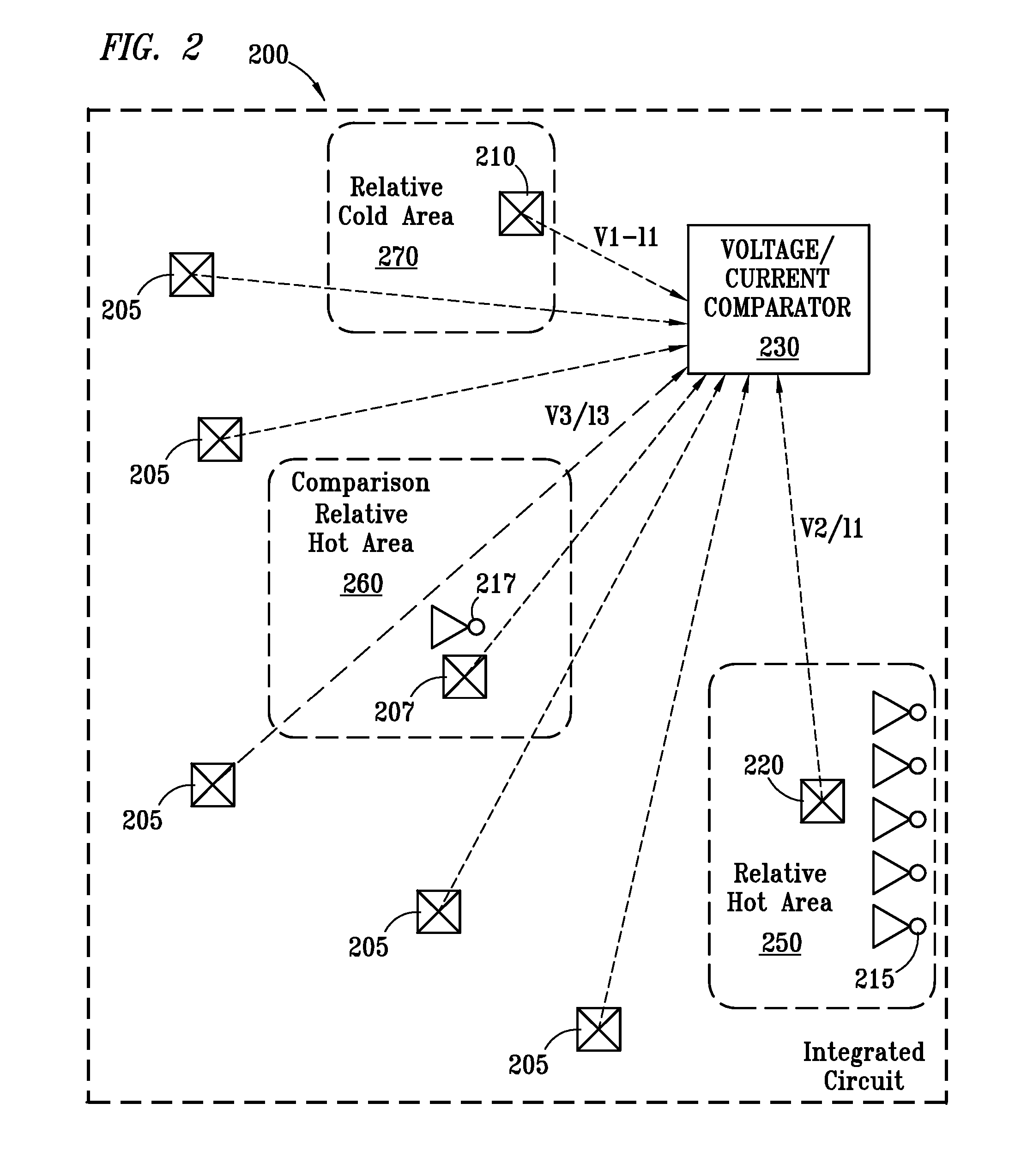
InactiveUS20070150225A1Thermometer detailsThermometers using value differencesComparison areaIntegrated circuit
The present invention provides a method for determining a hot area of an integrated circuit. A first temperature sensor in a first area of a chip is read, the chip comprising a plurality of chip areas, wherein the first area is a comparison area. The comparison area comprises at least one I / O device that is controlled to simulate other functional I / O devices on the chip. A second temperature sensor in a second area of a chip is read. The readings of the first temperature sensor and the second temperature sensor are compared. If the difference between the first temperature reading and the second temperature reading exceeds a threshold, a first error condition is indicated.
Owner:BOERSTLER DAVID WILLIAM +1
Preparation of Mn-base metal oxide catalyst through H2O2 quick reduction method and application of Mn-base metal oxide catalyst to volatile organic chemicals (VOCs) low-temperature catalytic combustion
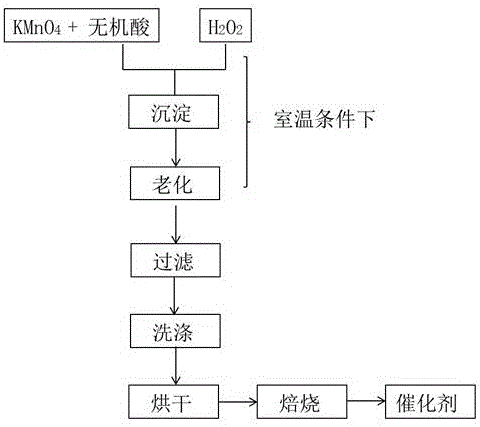
ActiveCN105921146AGood dispersionImprove adsorption capacityCatalyst activation/preparationIncinerator apparatusPrecipitationHigh heat
The invention discloses a novel preparation method of a Mn-base metal oxide (MnOx) catalyst and application of the MnOx catalyst to the field of volatile organic chemicals (VOCs) low-temperature catalytic combustion. The method comprises the steps that KMnO4 and inorganic liquid acid are dissolved to a certain volume of deionized water to form a solution 1; a certain amount of H2O2 is diluted by deionized water to form a solution 2; on the room temperature condition, the solution 2 is added into the solution 1 dropwise; generated sediment is filtered, washed, dried and roasted at the high temperature after being aged and passing the night, and then the needed MnOx catalyst can be obtained. The method has the advantages that simpleness and quickness are achieved; the problems that the synthetic temperature is high, time is long and the amount of waste water and the number of waste residues are large in a hydrothermal synthesis method and a direct precipitation method can be avoided; a MnOx material of a multilevel structure can be synthesized, and the large comparison area is beneficial for a VOCs catalytic combustion reaction on the surface of the MnOx catalyst. In methylbenzene and methanol low-temperature combustion, the synthesized MnOx has an ideal catalyzing effect.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Four-dimensional analysis-based biological feature recognition method and four-dimensional analysis-based biological feature recognition system
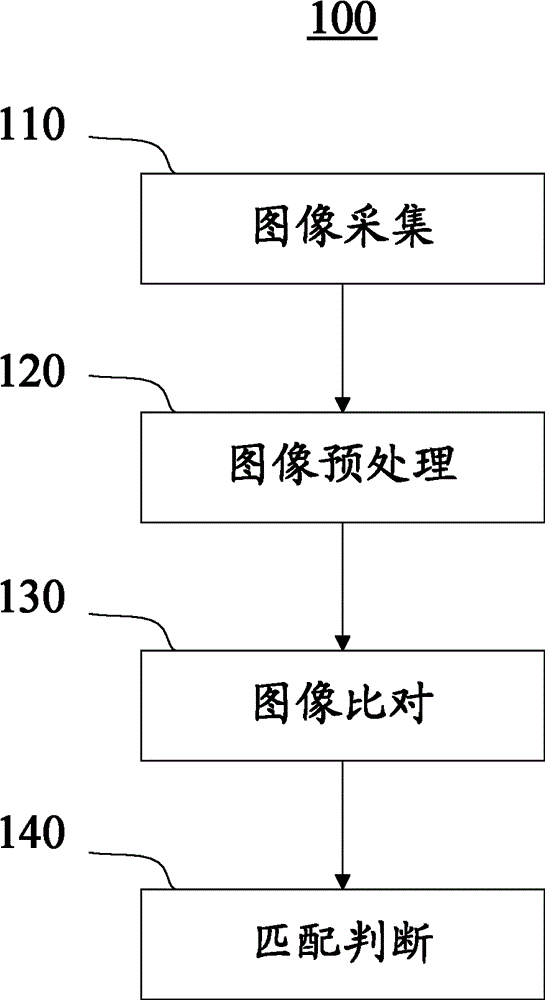
The invention aims at providing a four-dimensional analysis-based biological feature recognition method and a four-dimensional analysis-based biological feature recognition system. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of acquiring an image with biological features to serve as a target image; preprocessing the target image; performing image comparison on the preprocessed target image and a reference image preregistered so as to obtain an image energy residual value between the target image and the reference image, wherein the image comparison comprises comparison between a designated comparison area in the target image and a corresponding comparison area in the reference image; when the image energy residual value is less than or equal to a preset threshold value, determining that the target image and the reference image are matched, and otherwise, determining that target image and the reference image are unmatched.
Owner:EYESMART TECH
System and method for managing zoning in a storage area network by comparing zone sets and identifying differences between zone sets
InactiveUS7774445B1Reduce the possibilityDigital computer detailsTransmissionDifference listStorage area network
In a storage area network (SAN), first and second zone sets are compared to identify differences, including zones appearing in one zone set but not the other, and zones in both zone sets but having different contents in each. A zone comparison user interface (UI) window is displayed on a SAN management computer system via user selection from a pop-up menu appearing when a SAN object is selected from a hierarchical object display. The UI window includes a differences display area to display zone set differences and includes fields for identifying a type of zone difference, a zone identifier, and identifiers of host computers and storage devices of a zone. Based on differences identified between the first and second zone sets, identifiers of those zones of the first and second zone sets having a predetermined difference type are displayed. Also displayed, for each such zone, are (i) identifiers of the host computers and storage devices of the zone, and (ii) a difference type indicator indicating which of the difference types applies to the zone.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
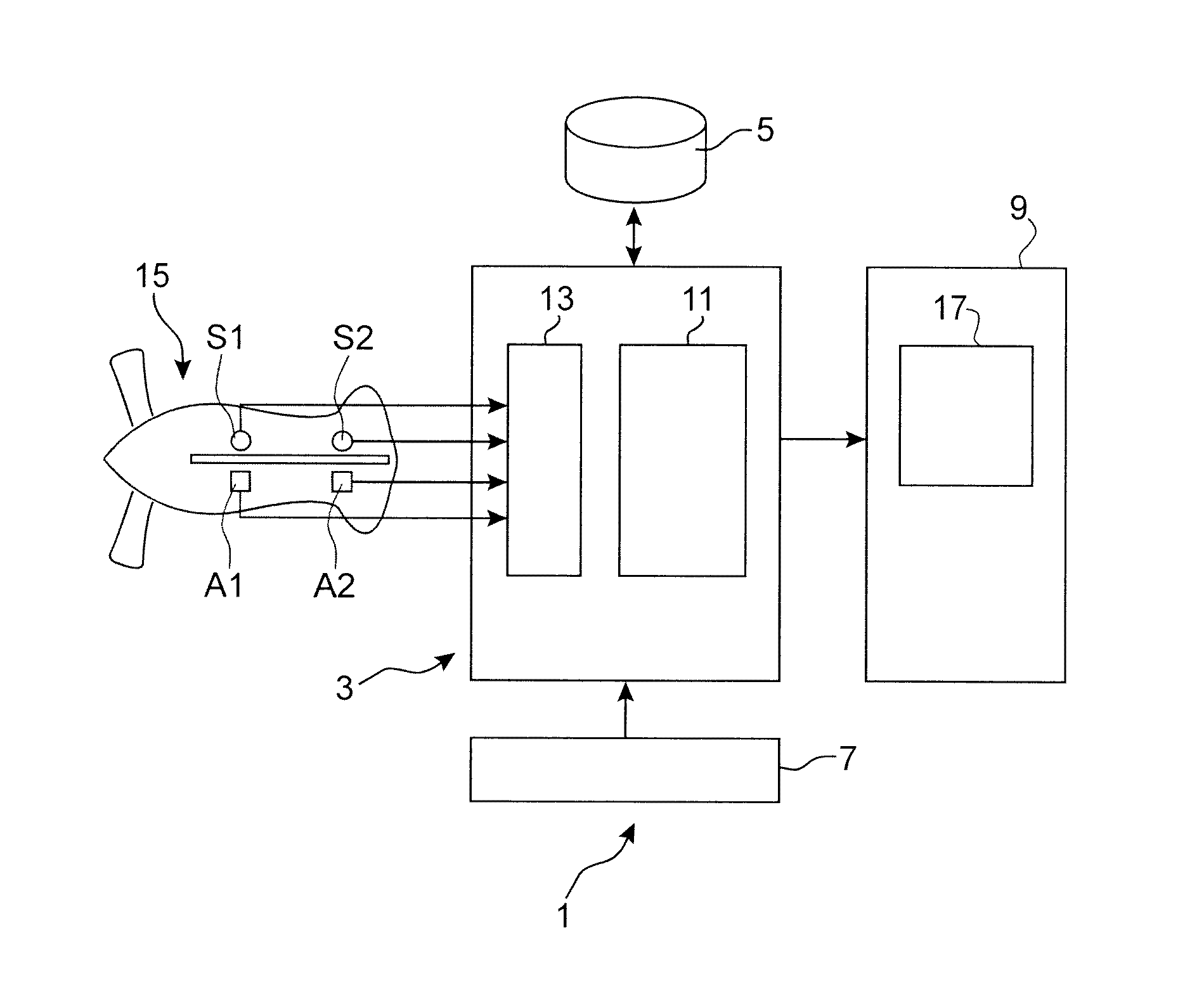
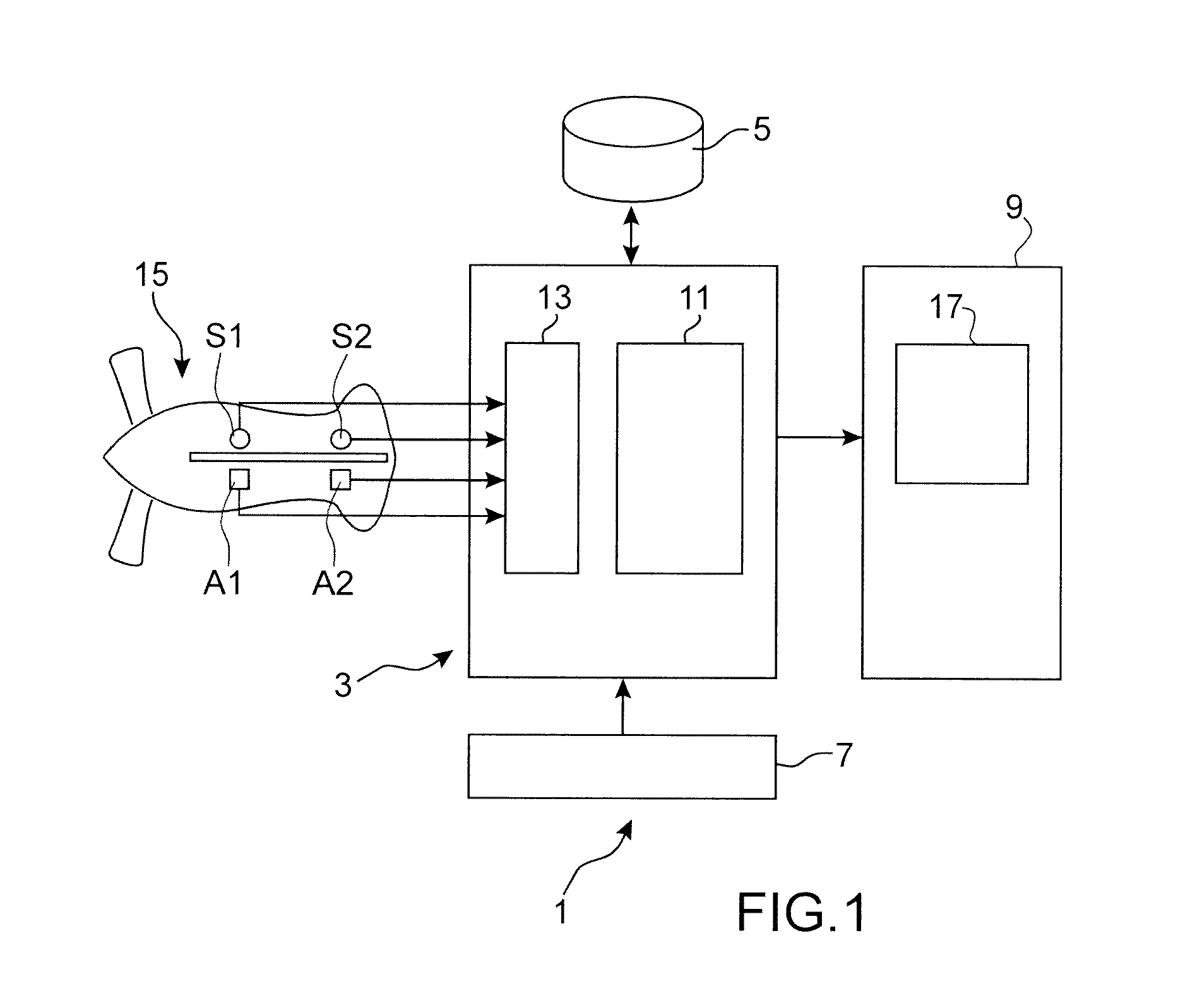
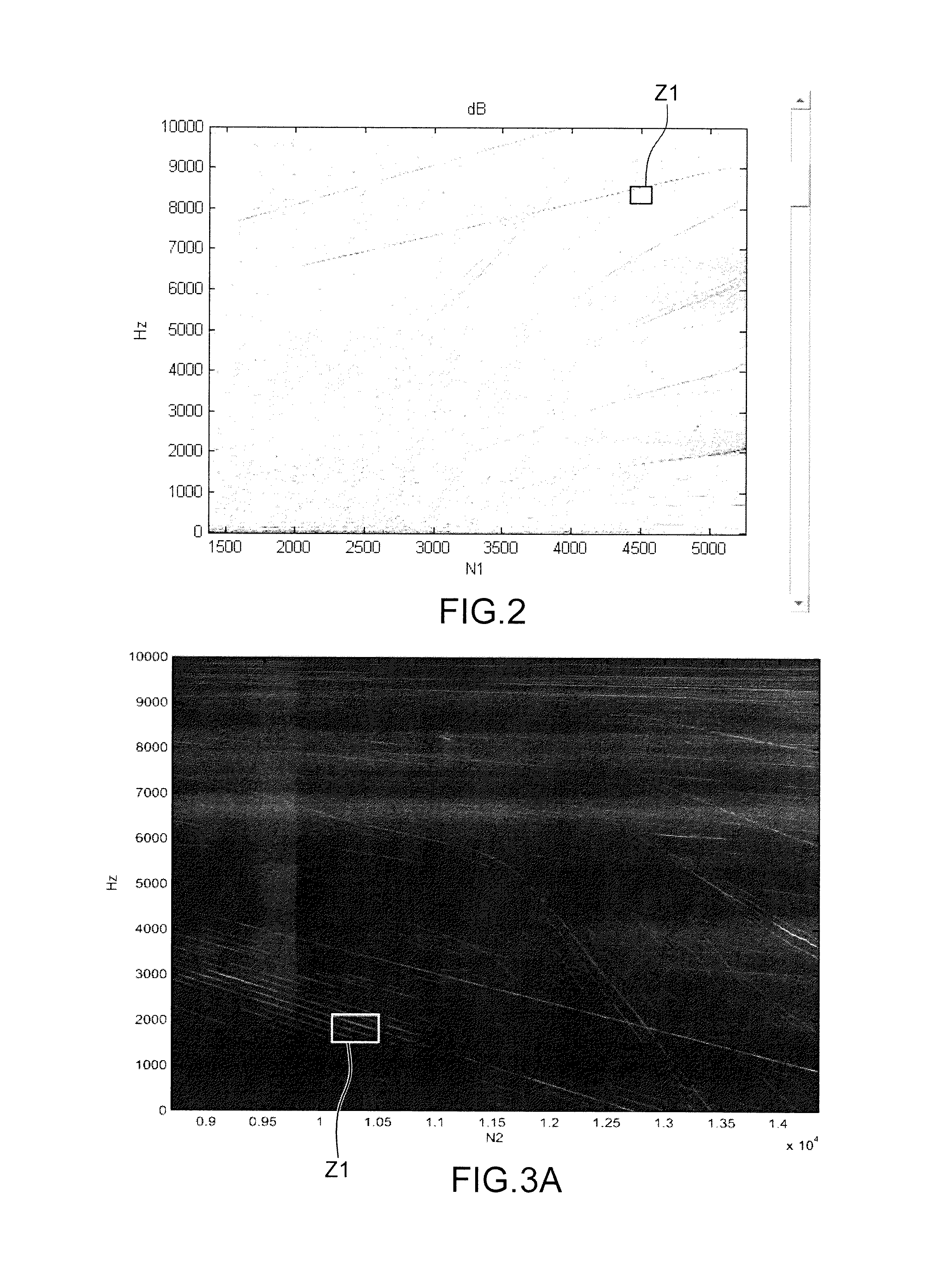
Method and system for the vibration analysis of an engine
ActiveUS20160103038A1Easy diagnosisInternal-combustion engine testingTesting/monitoring control systemsFrequency spectrumReference database
A method and a system for the vibration analysis of an engine, including acquiring vibration signals relating to the engine and in order to form at least one spectrogram that represents an operating state of the engine, selecting at least one zone of interest in at least one spectrogram, comparing each zone of interest with a set of corresponding comparison zones belonging to annotated spectrograms recorded in a reference database, and determining a subset of comparison zones that have vibration behaviours similar to those of the zone of interest, and displaying the subset of comparison zones and annotations associated with the subset of comparison zones.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
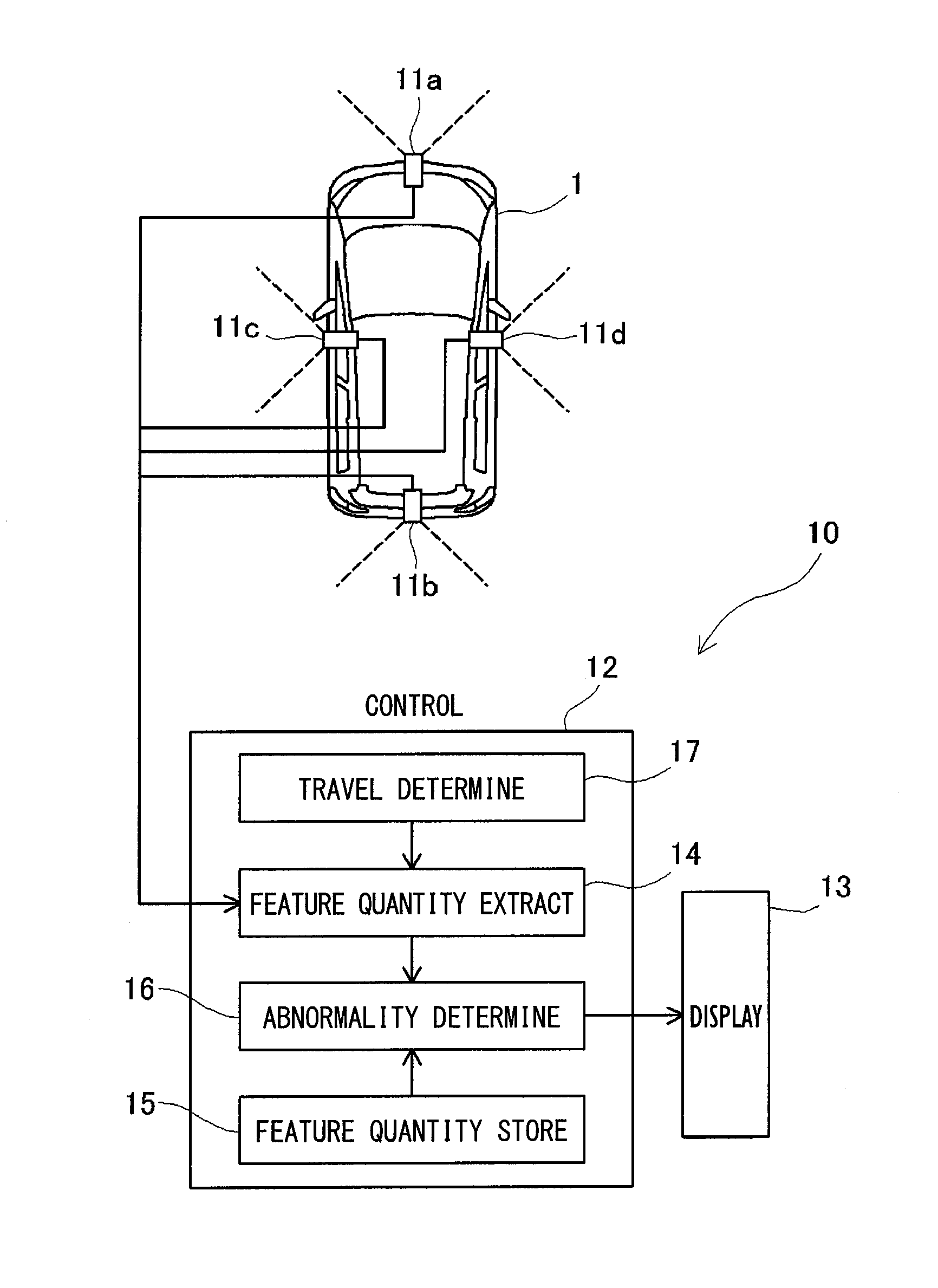
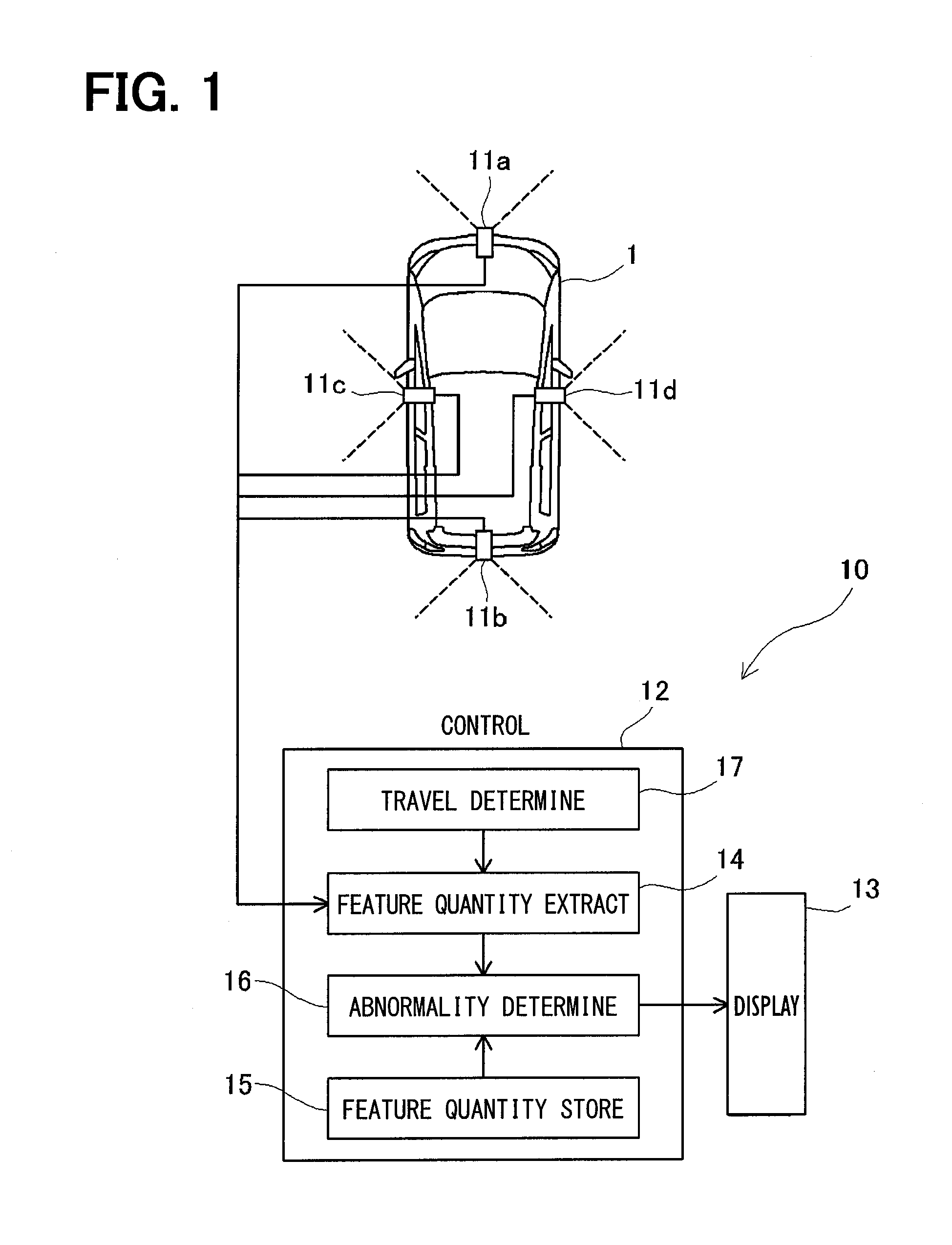
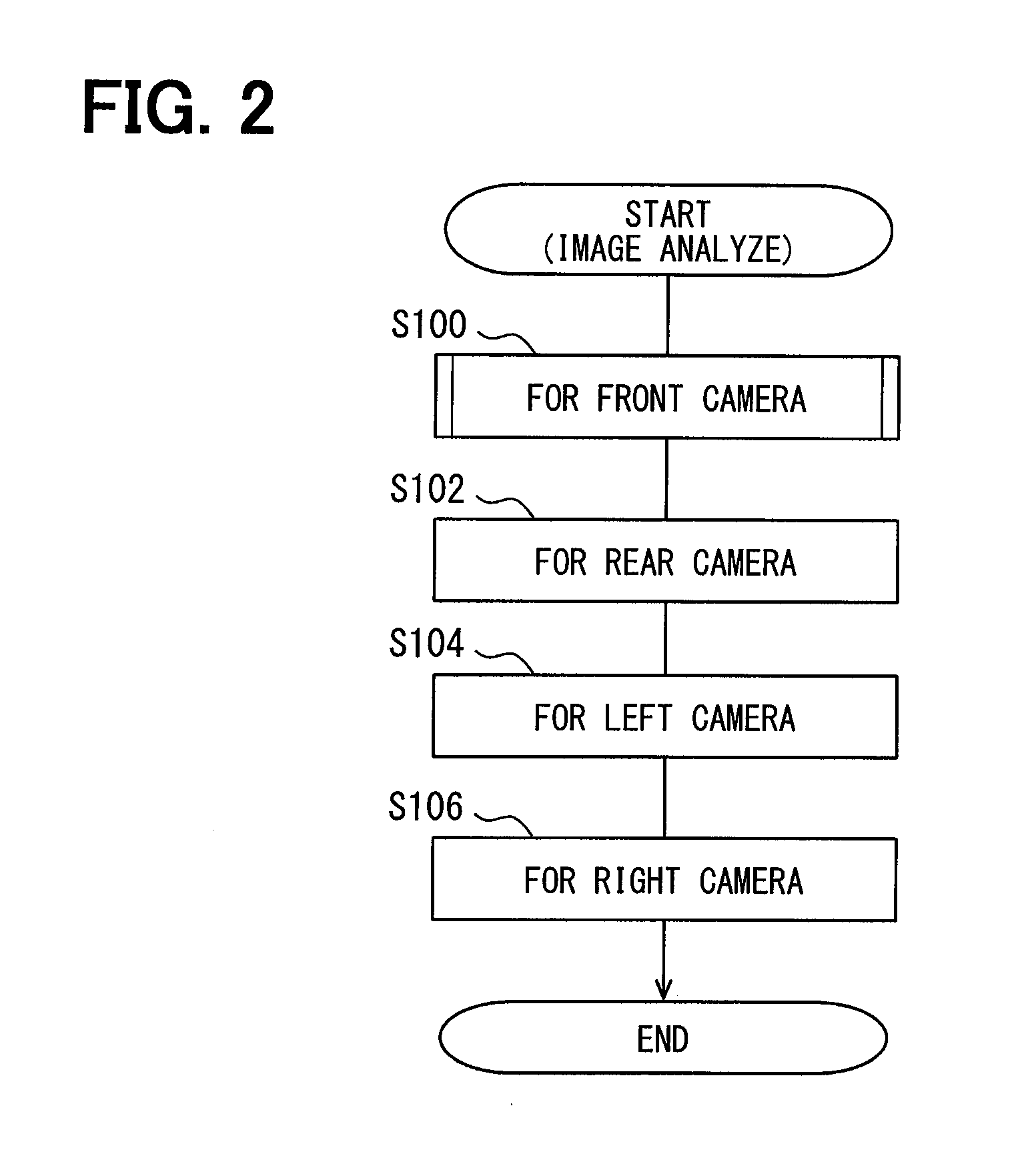
Image analysis apparatus and image analysis method
An image analysis apparatus is applied to an on-vehicle camera that captures an image of a predetermined monitoring region oriented in a predetermined direction referenced to a vehicle, to analyze an image captured by the on-vehicle camera. The image analysis apparatus includes (i) a storage section that stores a feature quantity of a monitoring region image obtained when an image of the monitoring region is captured by the on-vehicle camera, (ii) an extraction section that acquires an image captured by the on-vehicle camera and extracts a feature quantity of the image captured by the on-vehicle camera, and (iii) a notification section that compares the feature quantity of the image captured by the on-vehicle camera against the feature quantity of the monitoring region image to perform determination whether the on-vehicle camera is mounted in an abnormal position, and notifies a result of the determination.
Owner:DENSO CORP
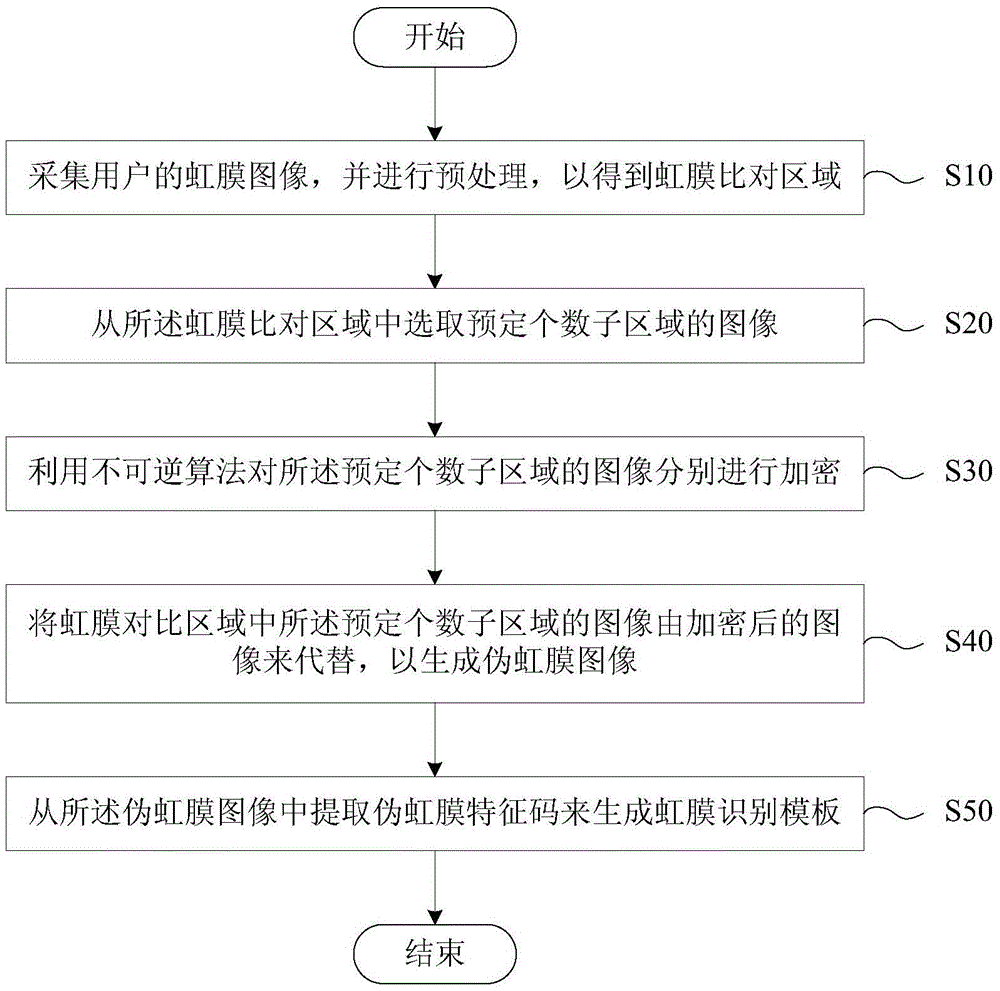
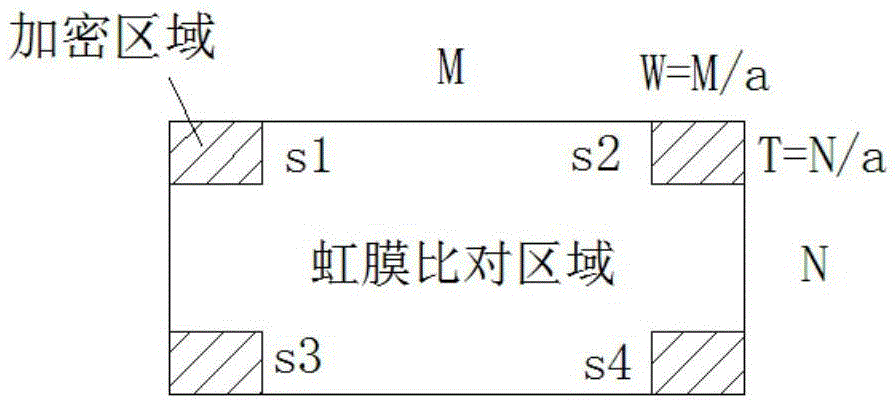
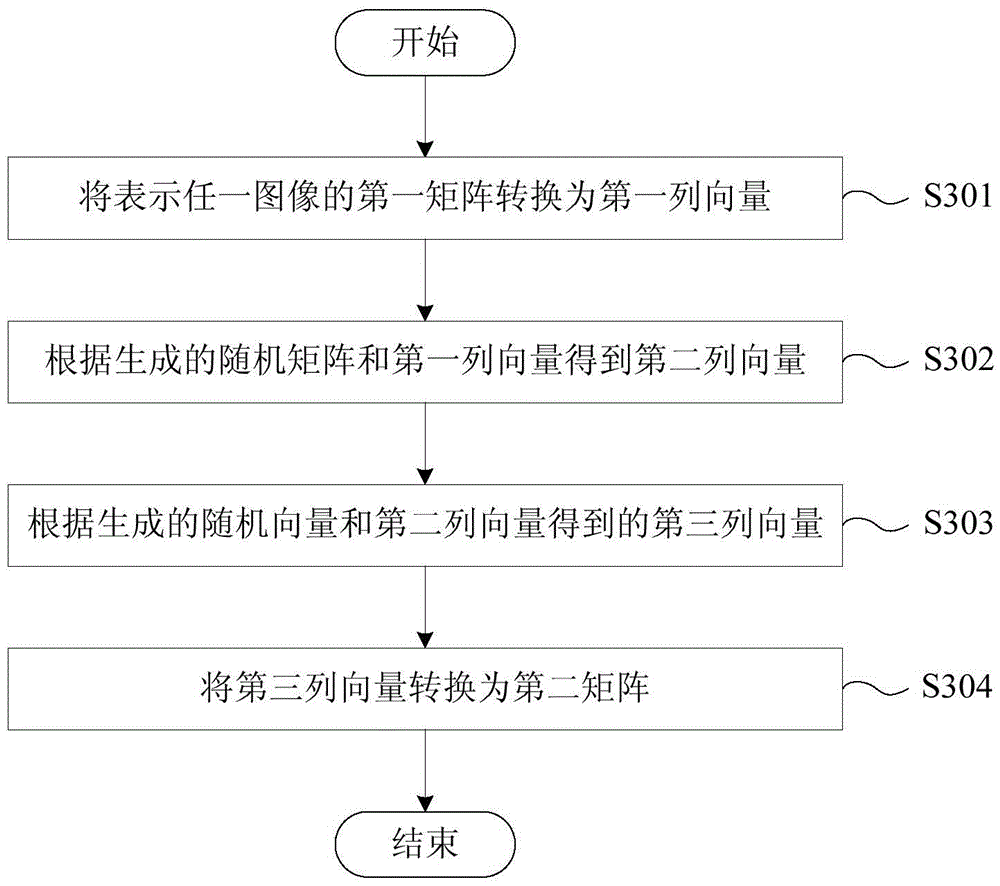
Production method and equipment of fake iris template and identity authentication method and equipment
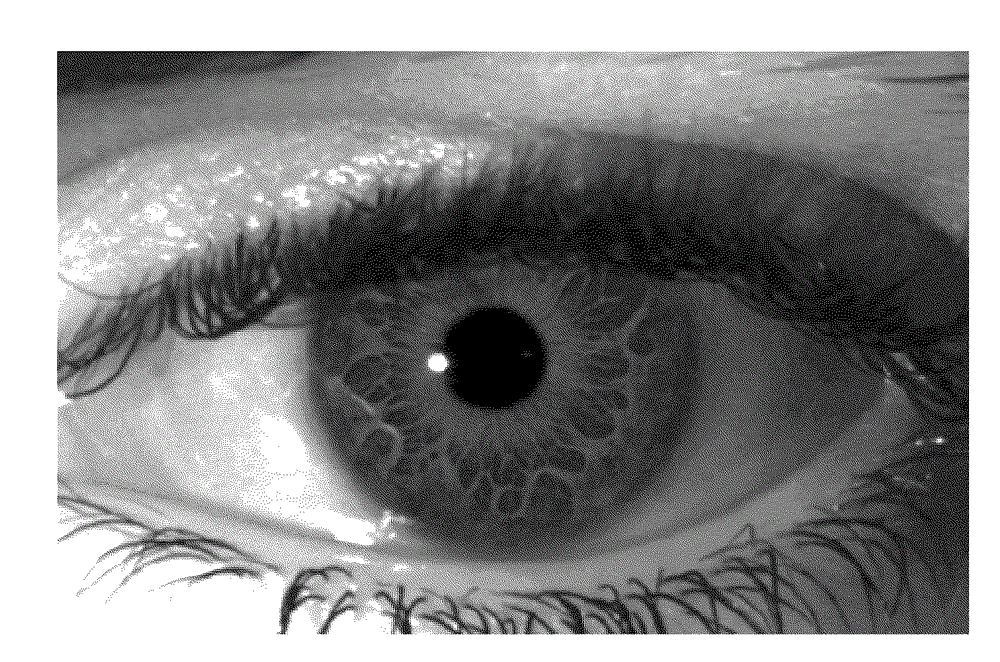
ActiveCN105488377AImprove securityProtect personal privacyCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital data authenticationComputer hardwareIris image
The invention provides a production method and equipment of a fake iris template and an identity authentication method and equipment. The production method of the fake iris template comprises the following steps: (A) collecting the iris image of a user, and preprocessing the collected iris image to obtain an iris comparison area; (B) selecting the images of a preset number of subareas from the iris comparison area; (C) utilizing a non-invertible algorithm to independently encrypt the images of the preset number of subareas; (D) replacing the images of the preset number of subareas in the iris comparison area with the encrypted image to generate a fake iris image; and (E) extracting fake iris feature codes from the fake iris image to generate the fake iris template. The above fake iris template does not reflect the truly complete iris, can effectively protect individual privacy and improves iris identification safety.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Method and apparatus for issuing mobile telecommunication information
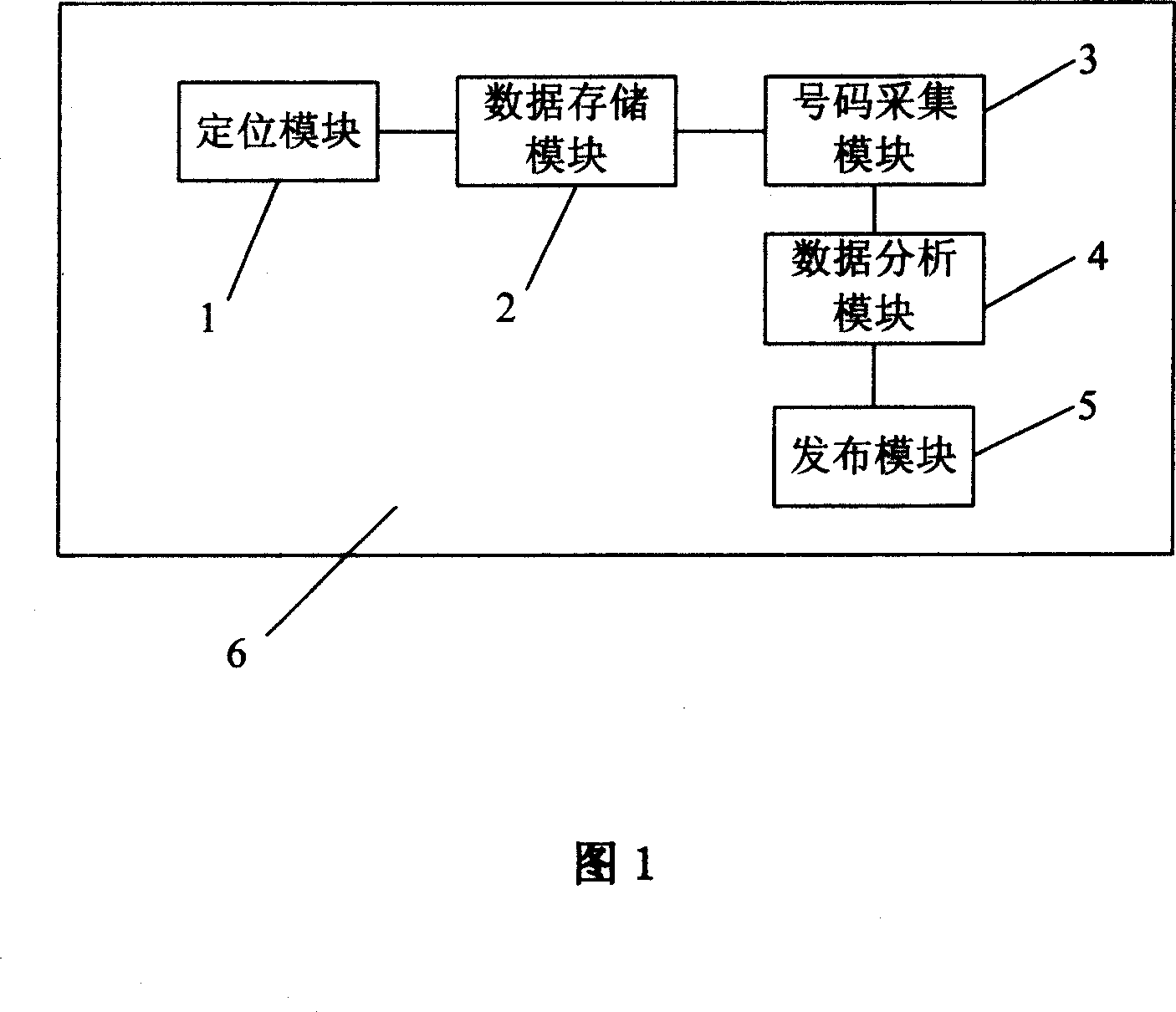
InactiveCN101076136AGood release effectRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsLocation information based serviceTime informationComputer science
The method comprises: the mobile terminal communicates with the mobile communication network to get its own geographic coordinate and saves the data; the mobile terminal enters into the area taking its own geographic coordinate as center and collects the geographic coordinate data of other mobile terminals; comparing the data of both; if the geographic data of the later is at the comparison area, getting the number of the mobile terminal, and according to the acquired number, getting the location and time information of the number to create the database; finally, sending the dedicate information to the mobile terminal. The apparatus comprises: a location module, a data storage module, a number collecting module, a data analysis module, and an information releasing module.
Owner:谭书敬
Method for preparing porous nanofiber
ActiveCN104233491ATo achieve the effect of hole makingCoexistent mesoporous structureMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentSynthetic polymer filament chemical after-treatmentFiberHydrogen fluoride
The invention discloses a method for preparing a porous nonofiber, and the method comprises the following steps of: dissolving spinning materials into a solvent, adding polyvinyl pyrrolidone, and uniformly stirring to prepare nanofiber polymer solution; adding SiO2 nano-particles into the nanofiber polymer solution, magnetically stirring to an uniform state as spinneret solution; injecting the spinneret solution into an ejector, spinning under the additional electric field, preparing the nanofiber containing the SiO2 nano-particles by controlling spinning time and moving a receiving screen, and finally calcining; soaking the nanofiber solution containing the SiO2 nano-particles with HF (Hydrogen Fluoride) solution, slowly stirring, cleaning and drying to prepare the porous nanofiber fabric. In the method, particles are doped in removal to prepare pores in the nanofiber, as a result, the dyeing property is improved by adopting the provided fabric comparison area.
Owner:湖州菱创科技有限公司
Graphical analysis system and graphical analysis method
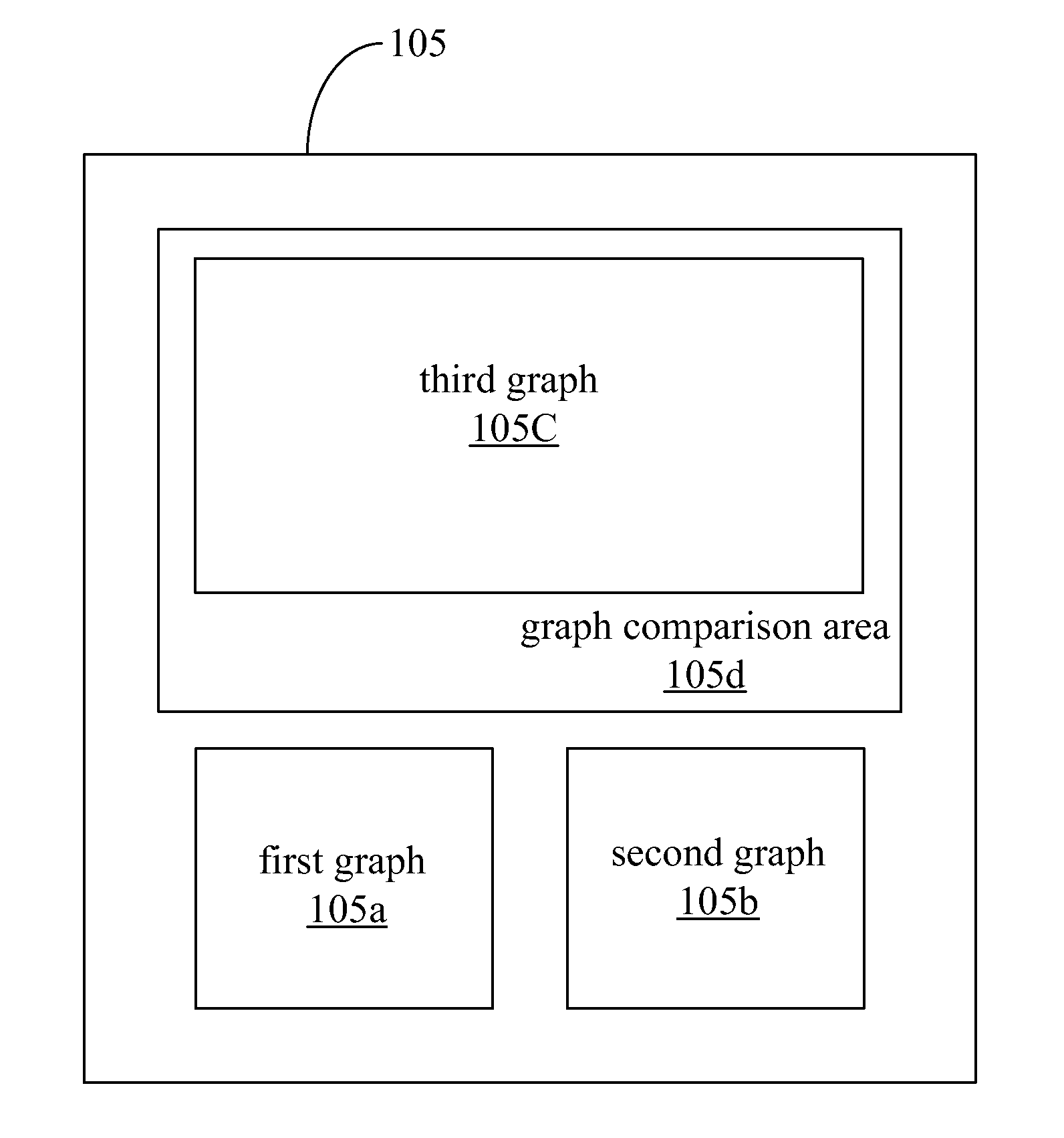
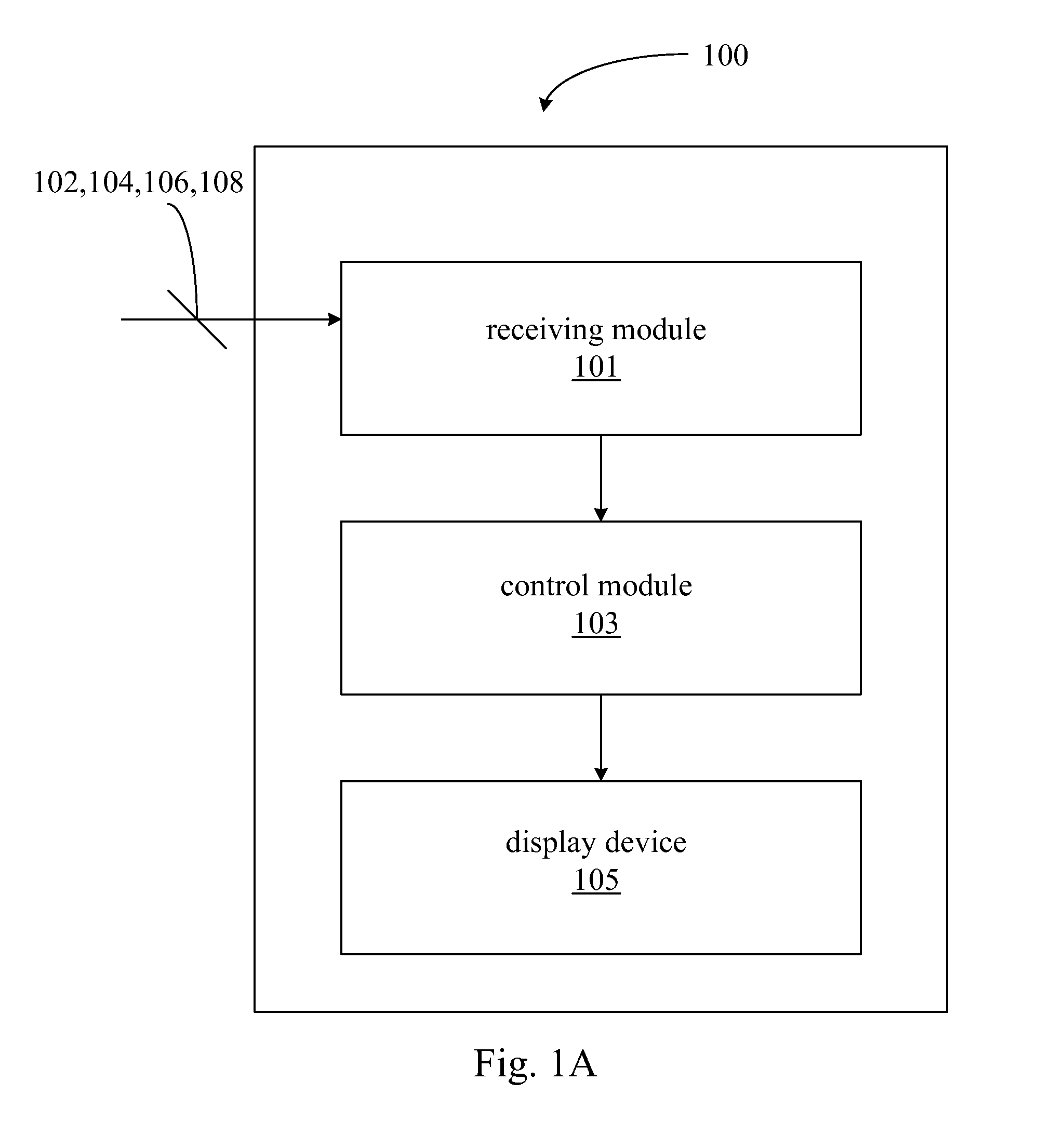
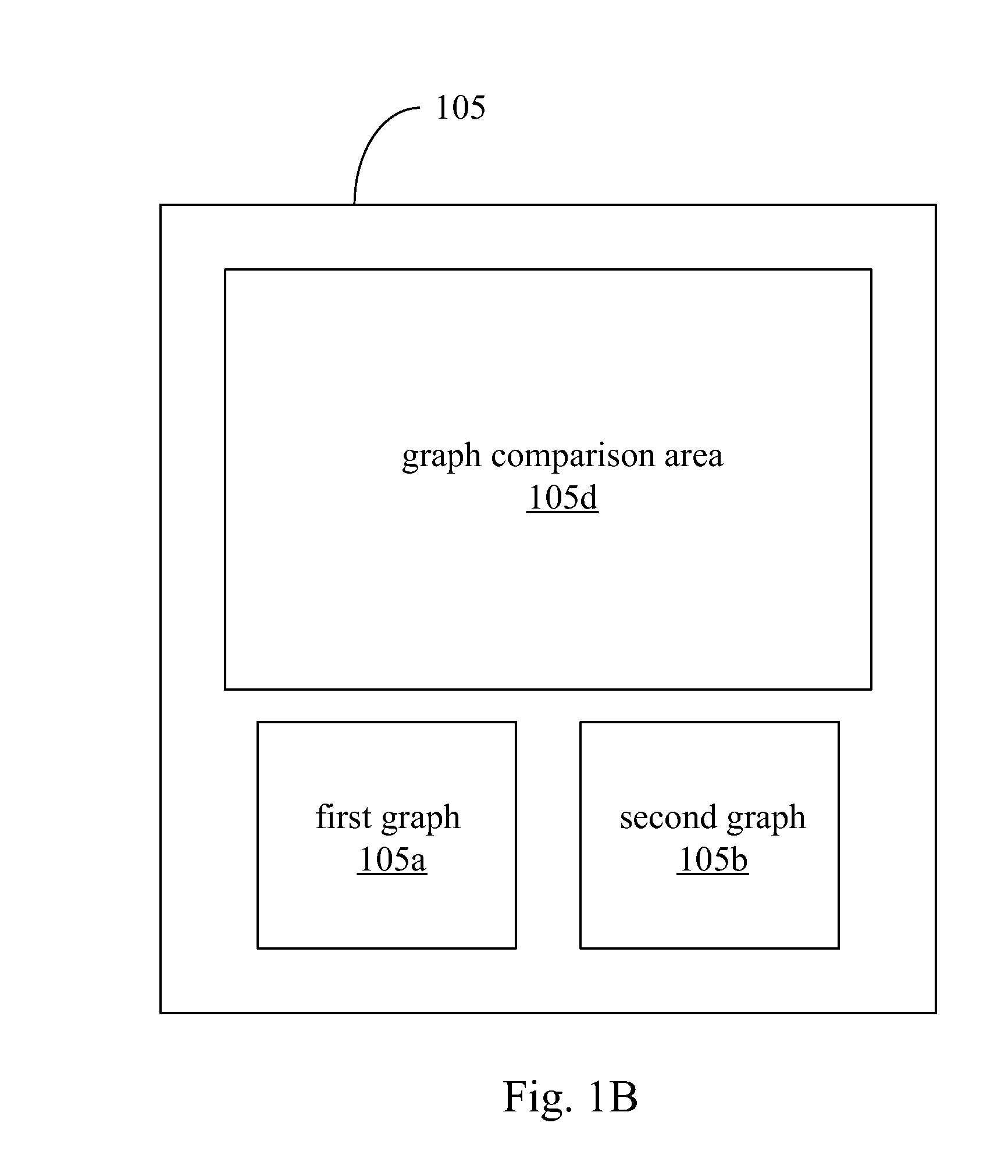
InactiveUS20150178963A1Drawing from basic elementsInput/output processes for data processingComputer hardwareData display
A graphical analysis system and a graphical analysis method are disclosed. The graphical analysis system includes a display device, a receiving module, and a control module. The display device is configured to display a first graph, a second graph, and a graph comparison area, in which the display device displays the first graph according to first data and displays the second graph according to second data. The receiving module is configured to receive a first and second input commands. The control module is configured to respond to the first and second input commands. When the first and second input commands are configured to drag and drop the first graph and the second graph into the graph comparison area respectively, the control module controls the display device to display a third graph and display the corresponding data of the first data and the second data in juxtaposition in the third graph.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
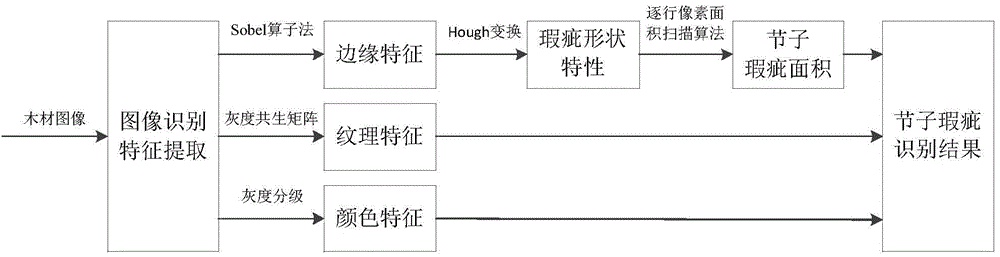
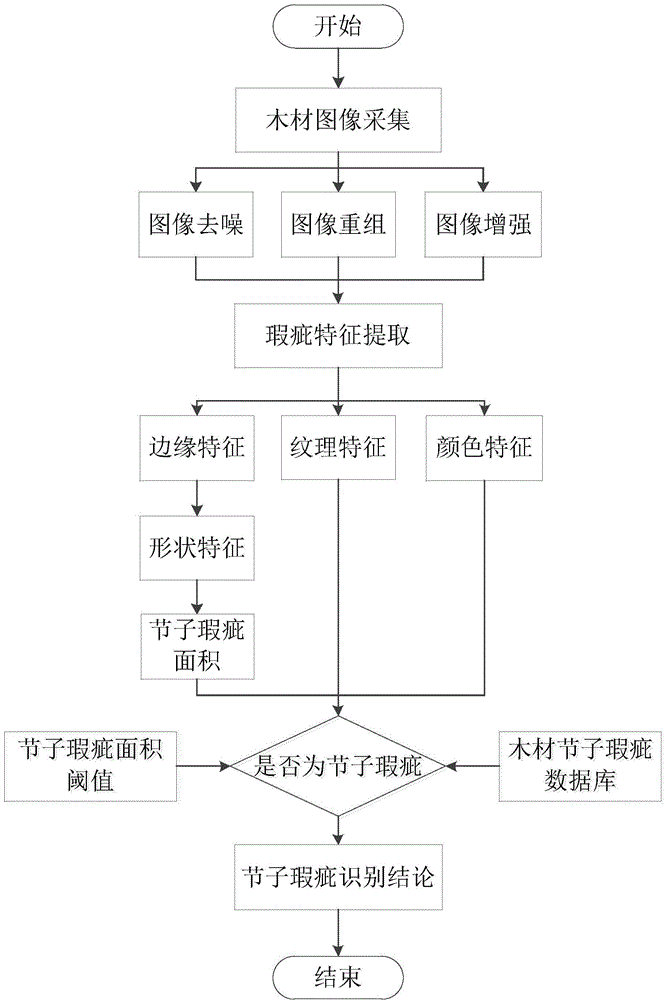
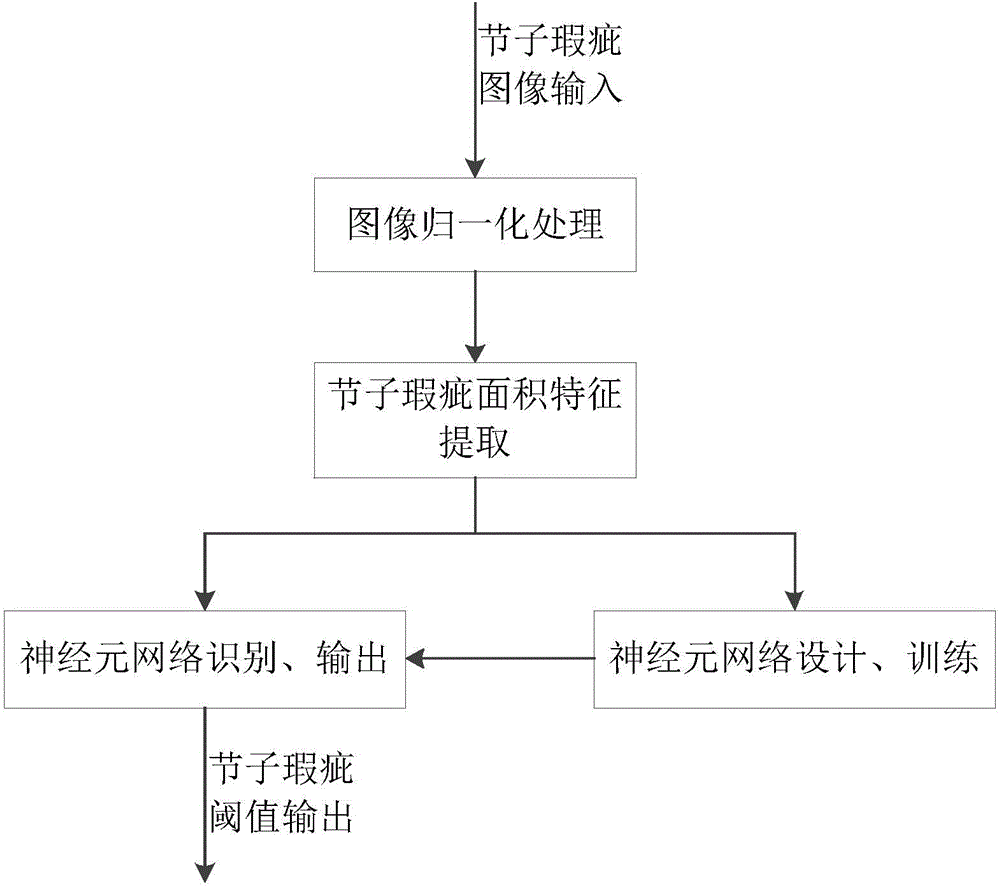
Computer image based automatic identification method of timber knot flaws
InactiveCN104700417AOvercoming distractionsOvercoming processabilityImage analysisImage denoisingFeature extraction
The invention discloses a computer image based automatic identification method of timber knot flaws. The method comprises the major steps of firstly, acquiring timber images by use of digital cameras, secondly, performing preprocessing, such as image recombination, image denoising and image enhancement, on the acquired timber images, thirdly, performing characteristic extraction on the preprocessed images by use of an image digital processing algorithm, fourthly, judging the quasi-circle or ellipse shape features of the timber flaws by virtue of Hough transformation according to flaw edge characteristics and determining candidate regions, fifthly calculating the area of knot flaws by use of a line-by-line pixel area scanning algorithm, and sixthly, identifying the timber knot flaws by use of a comparison area threshold and characteristic parameters. The method is used for identifying the timber knot flaws by use of the image identification technique, and is high in identification accuracy, high in speed and simple to operate; the method is capable of meeting the requirements of the modern timber processing industry on the knot flaw identification speed and quality, and also capable of accurately locating the knot flaws to facilitate high-speed automatic cutting of the knot flaws.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com