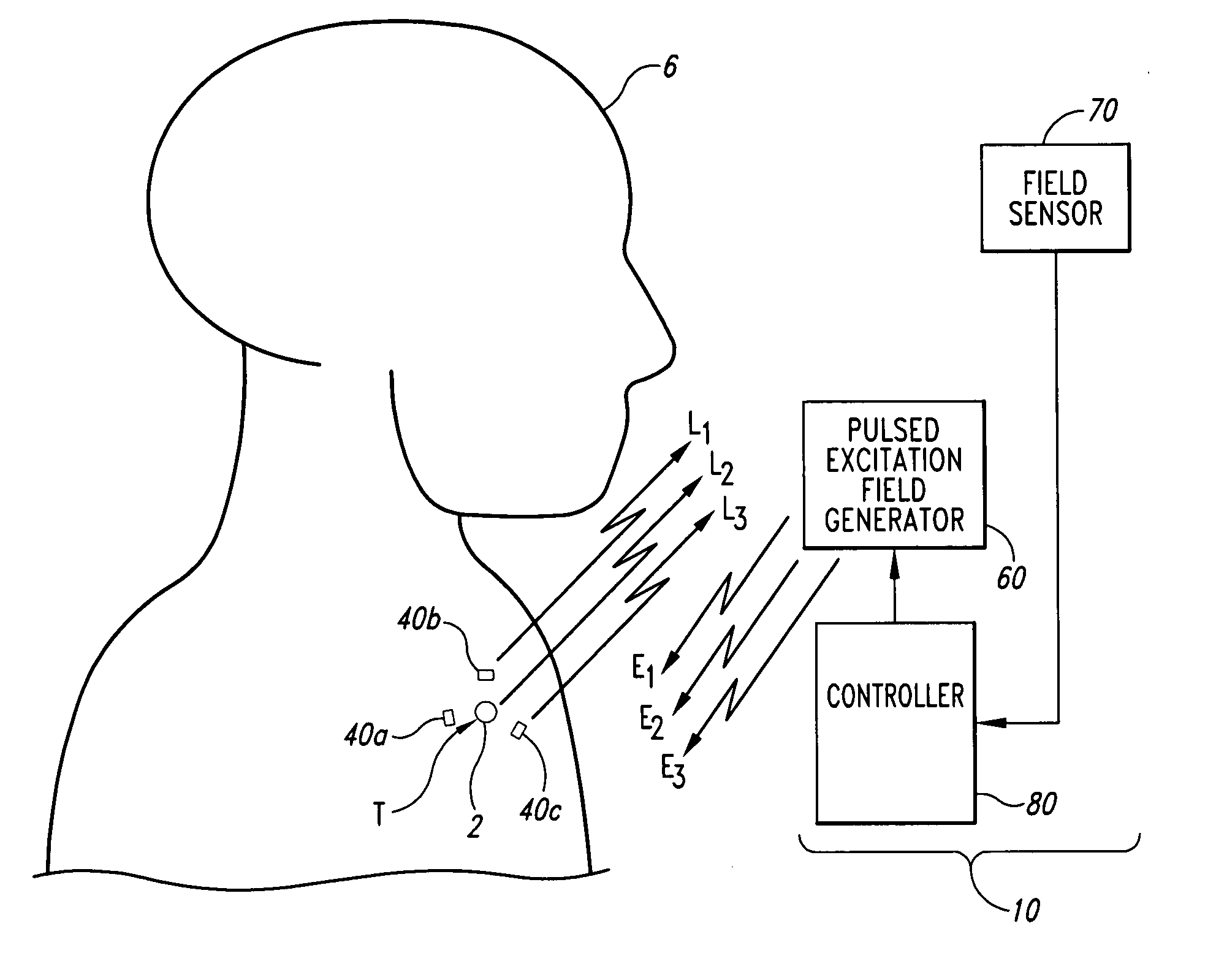
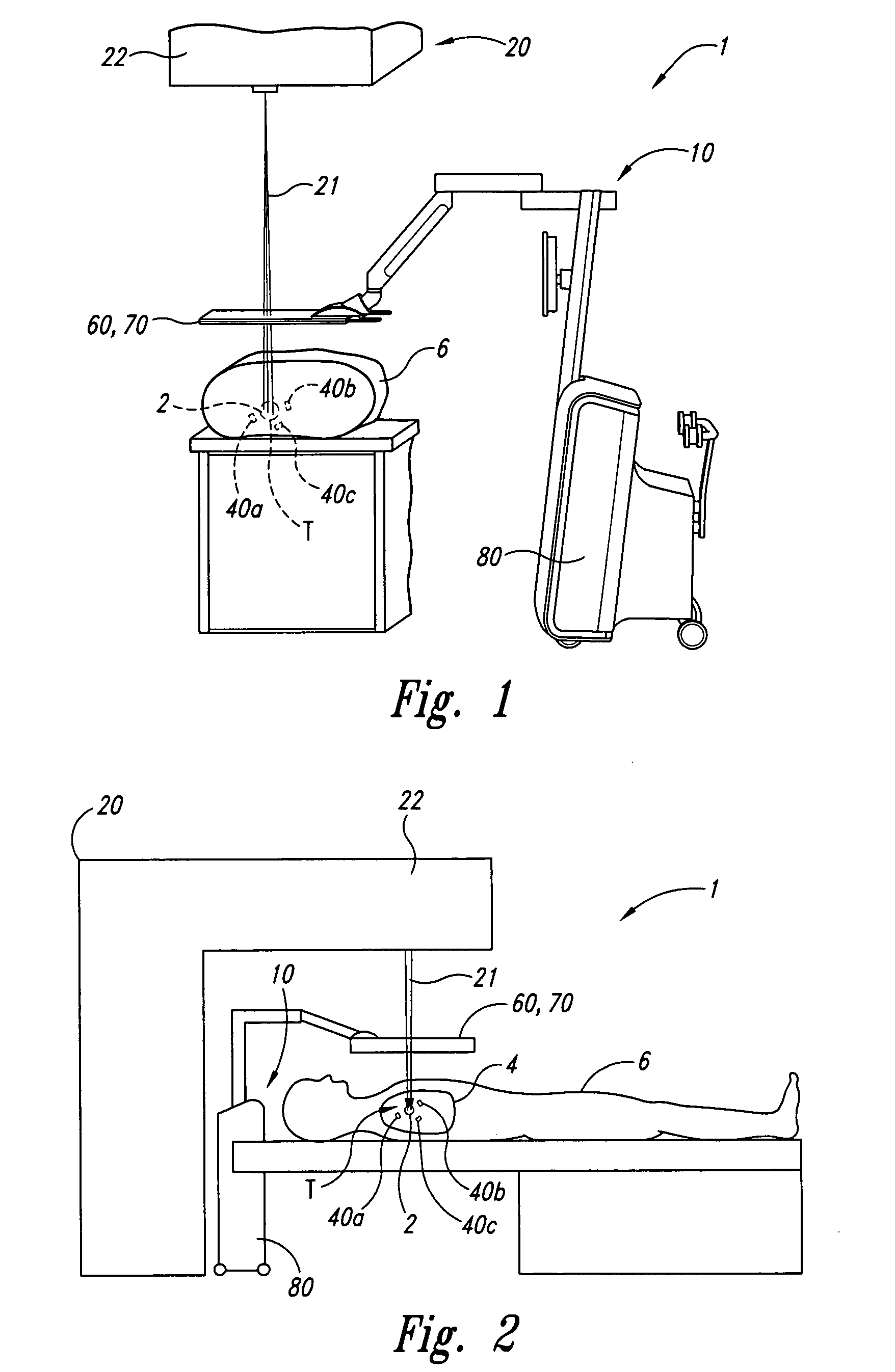
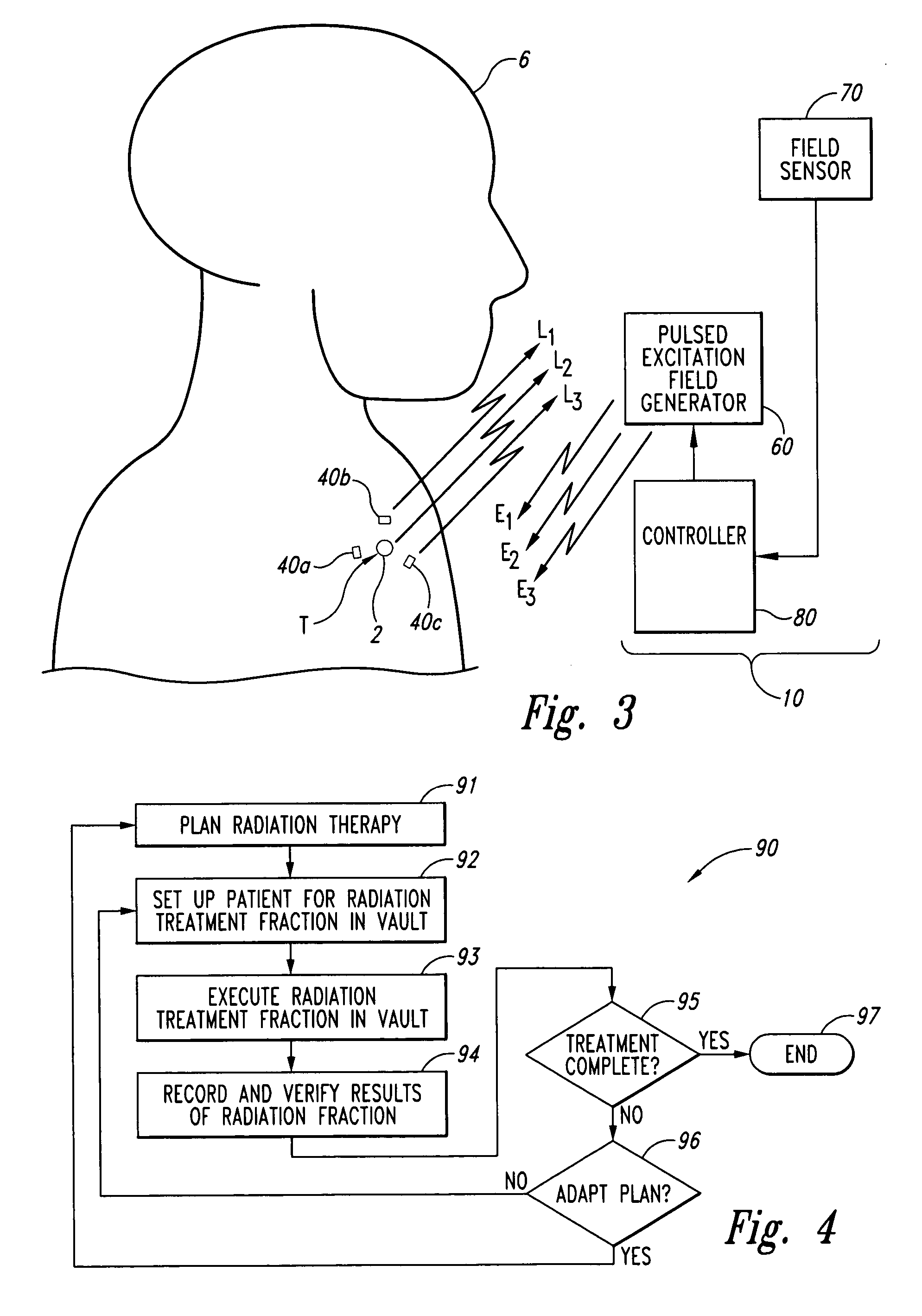
Systems and methods for real time tracking of targets in radiation therapy and other medical applications
a technology of radiation therapy and target tracking, applied in the field of radiation therapy systems, can solve the problems of increasing the potential for complications of healthy tissues, moving the target often within the patient, and not being a desirable solution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
Overview
[0138] An experimental phantom based study was conducted to determine effectiveness of this system for real-time tracking. In this experiment, a custom 4D stage was constructed to allow arbitrary motion in three axes for speeds up to 10 cm / sec in each dimension, with accuracy to 0.3 mm. Position accuracy was measured by a 3D digitizing arm attached to the stage system. As shown in FIG. 21, two ellipses were created with peak to peak motion of 2 cm, 4 cm and 2 cm; and 1 cm by 2 cm and 1 cm in the x, y and z direction respectively. Three periods were used to correspond to 15, 17 and 20 breaths per minute. A single transponder was used with an integration time of 33 ms, 67 ms and 100 ms and two transponders were used with integration times of 67 ms and 100 ms. The transponders were placed in a custom phantom mounted to the 4D stage. The experiment was performed with the isocenter placed 14 cm from the AC magnetic array to simulate the position of an average lung cancer patien...
experiment summary
[0139] As shown in FIG. 22, the root mean square (RMS) error was less than 1 mm for each ellipse, period and transponder integration time. The system was able to track points throughout the path of the ellipse, for example, in a trajectory of a large ellipse moving at 17 breaths per minute. FIG. 23 is a histogram of localization errors illustrating that the range of error was low for each point measured. As shown in FIG. 24, the RMS error was higher in areas of increased velocity in most trajectories. With respect to this experiment, a single transponder system performed slightly better than dual transponder systems, with the best system being a single transponder with a 67 ms integration time.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com