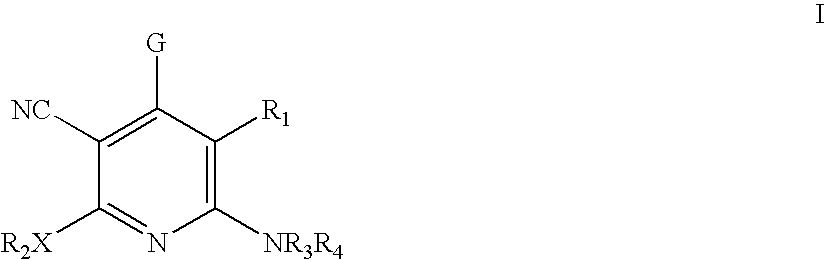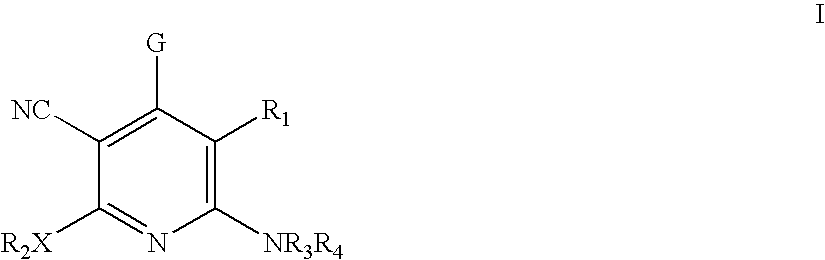Patents
Literature
276 results about "Probable Case" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The term “probable cause” refers to the right that a police officer has to make an arrest, search a person or his property, or obtain a warrant. Probable cause requires that facts and evidence presented in a case are of the type that would lead any reasonable person to believe that the suspect had committed a crime.
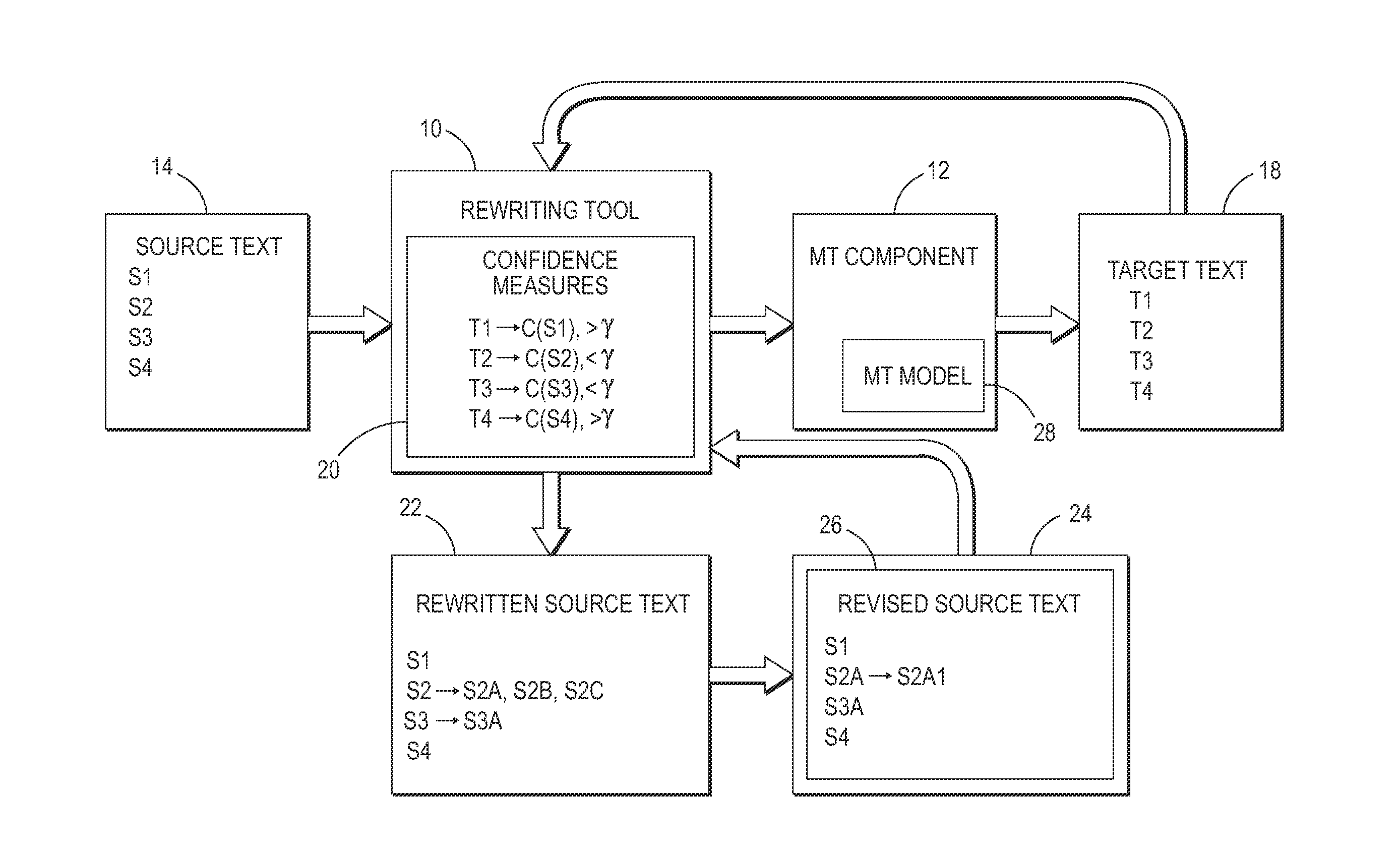
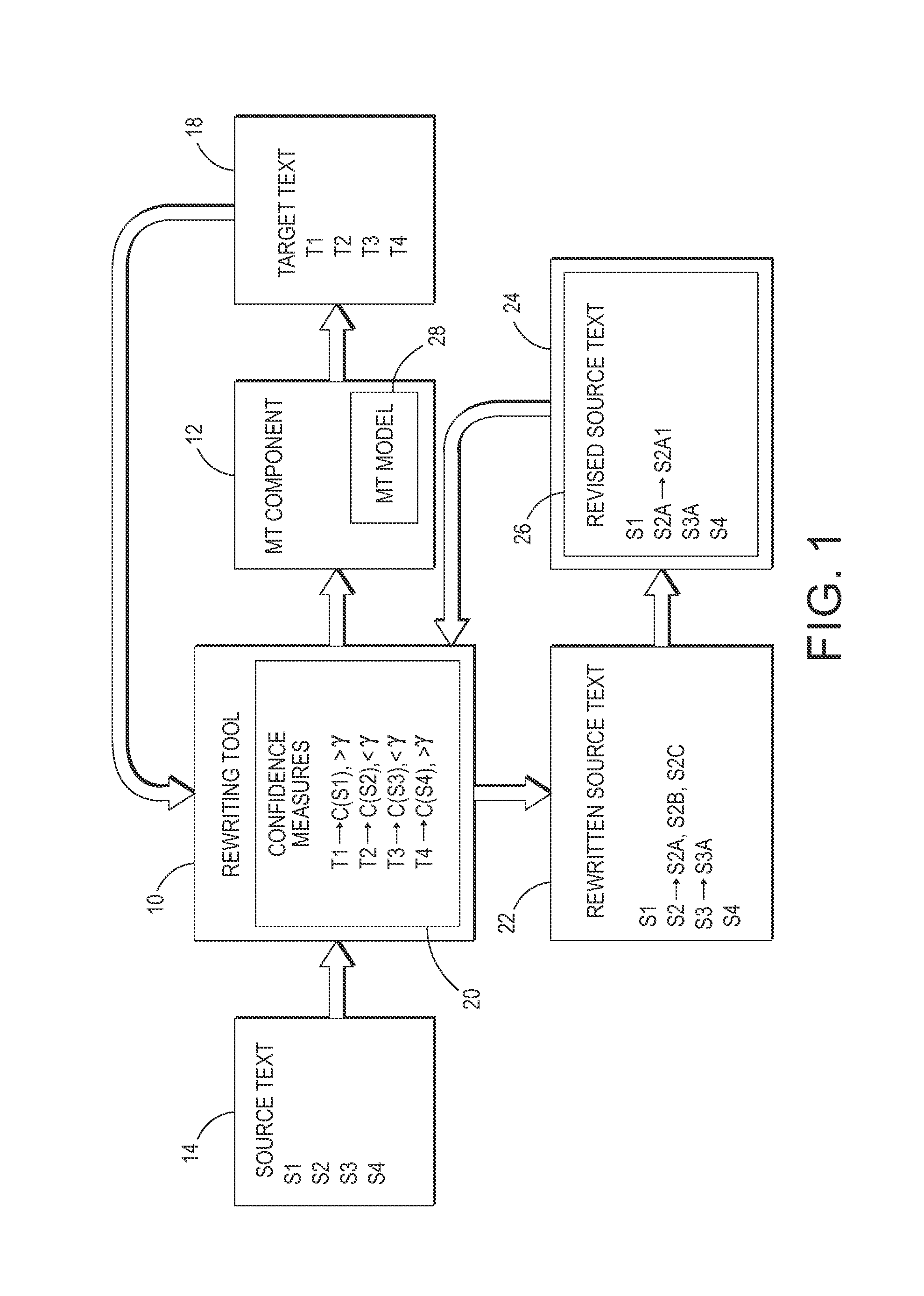
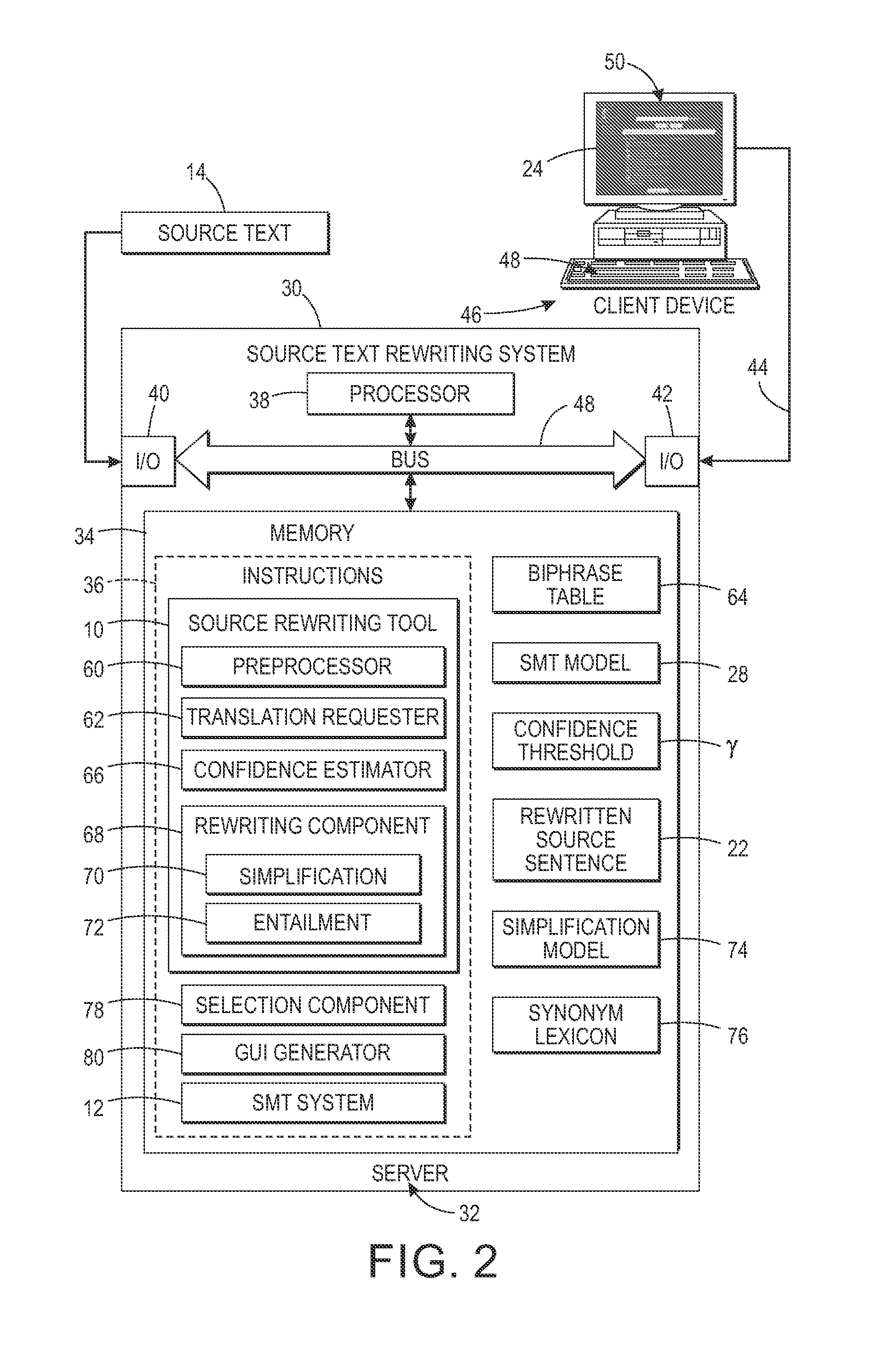
Confidence-driven rewriting of source texts for improved translation
InactiveUS20140358519A1Natural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsGraphical user interface
A method for rewriting source text includes receiving source text including a source text string in a first natural language. The source text string is translated with a machine translation system to generate a first target text string in a second natural language. A translation confidence for the source text string is computed, based on the first target text string. At least one alternative text string is generated, where possible, in the first natural language by automatically rewriting the source string. Each alternative string is translated to generate a second target text string in the second natural language. A translation confidence is computed for the alternative text string based on the second target string. Based on the computed translation confidences, one of the alternative text strings may be selected as a candidate replacement for the source text string and may be proposed to a user on a graphical user interface.
Owner:XEROX CORP
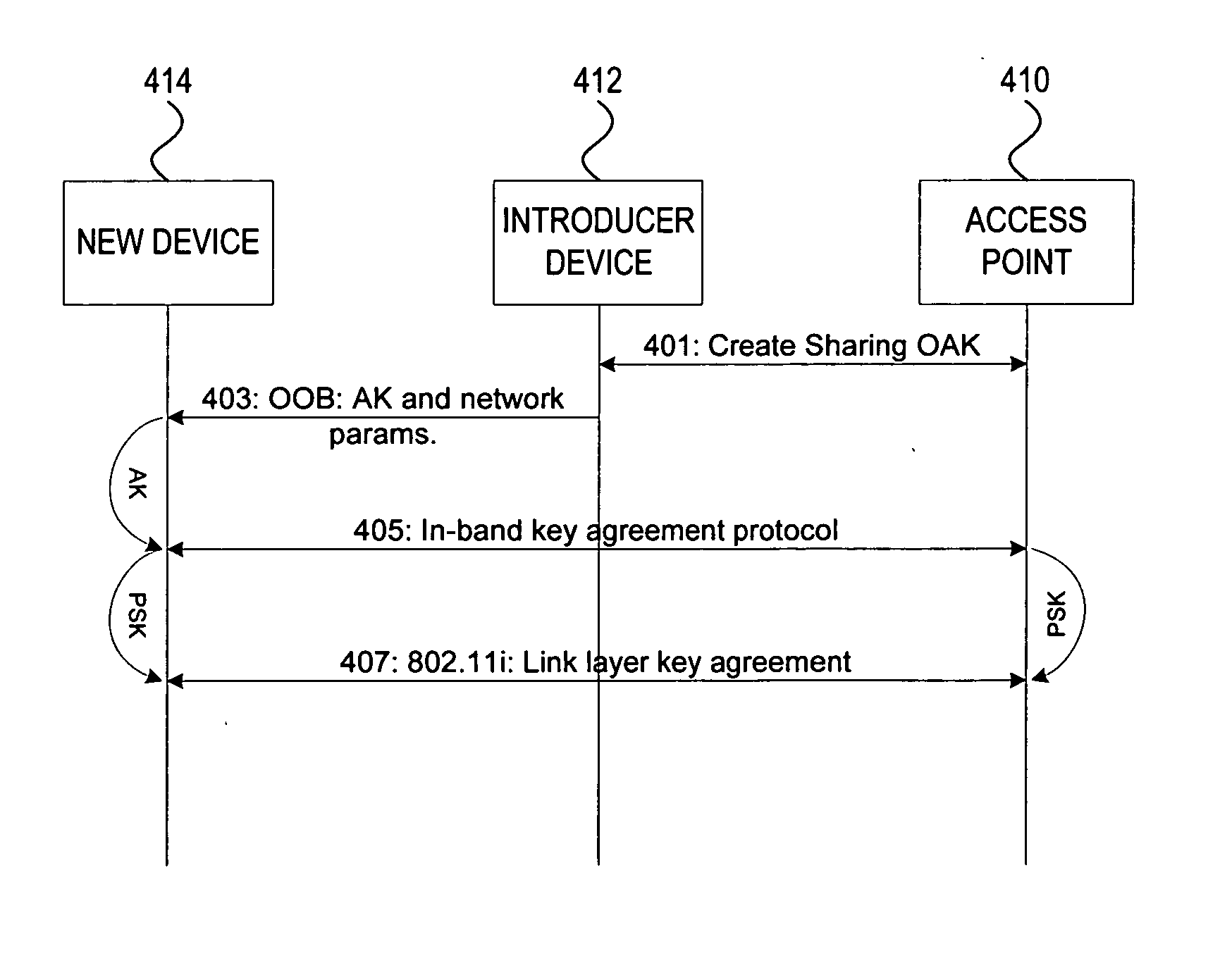
Administration of wireless local area networks
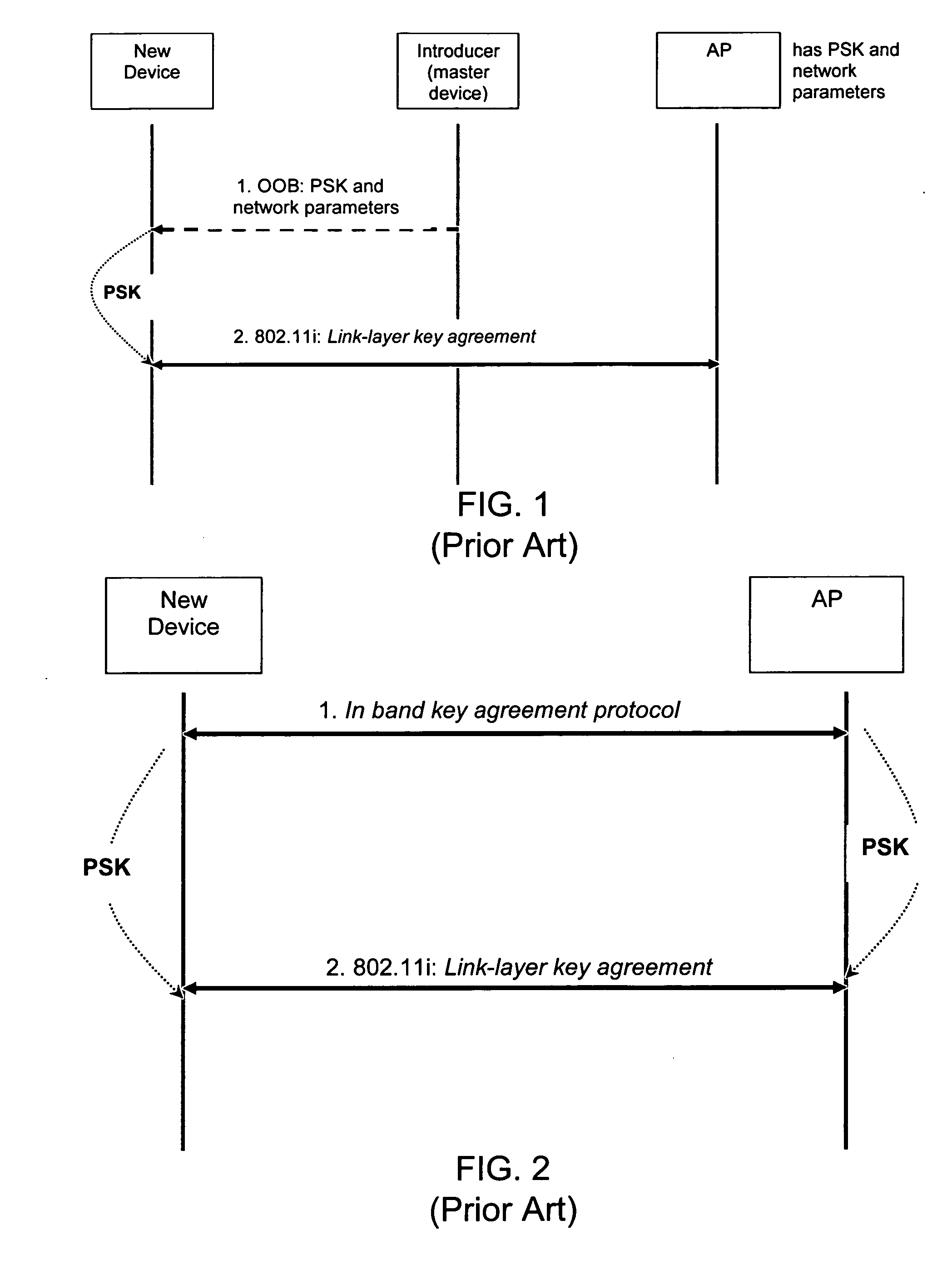
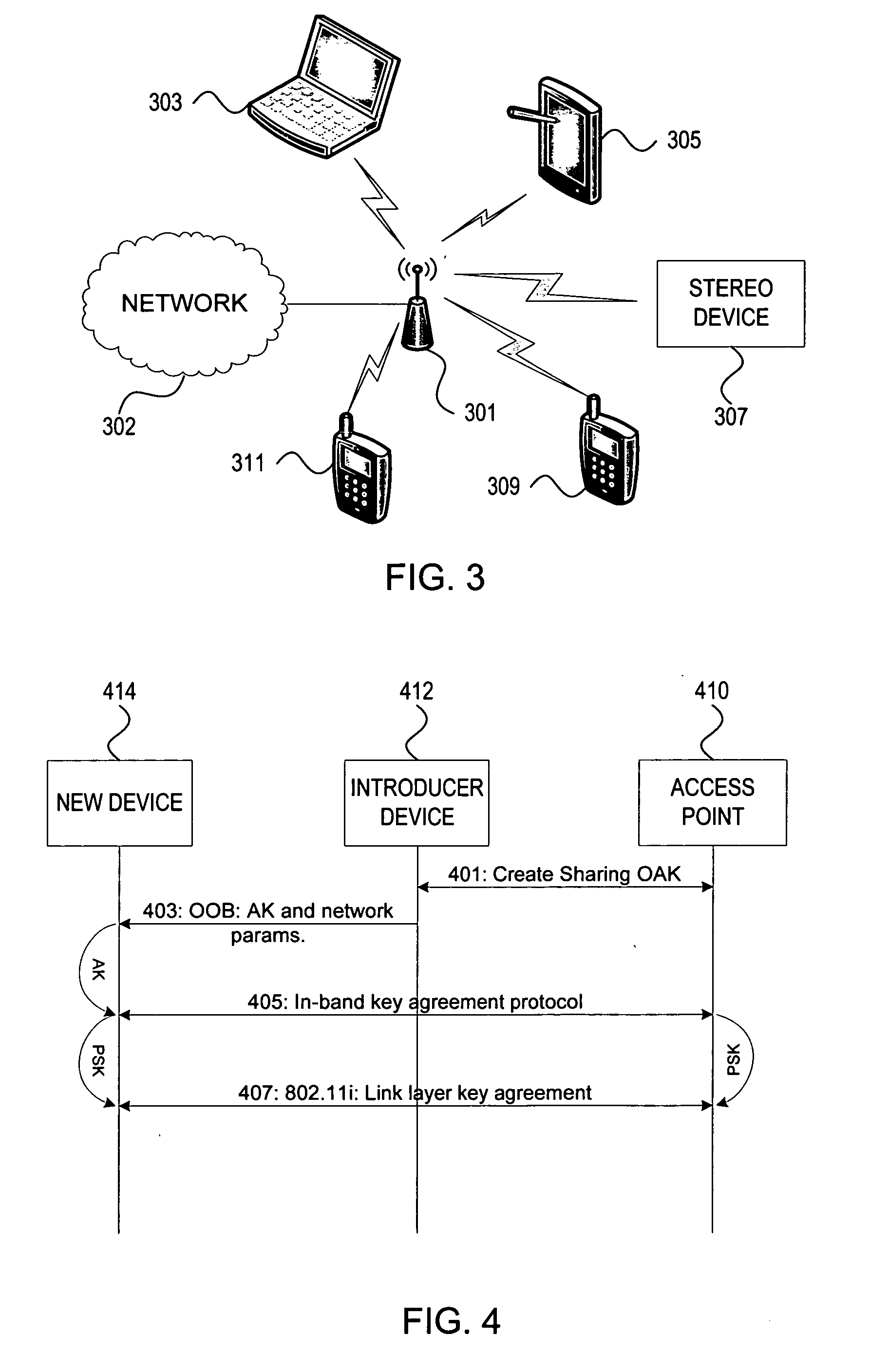
ActiveUS20060251256A1Improve securityImprove usabilityKey distribution for secure communicationAssess restrictionProbable CaseNetwork addressing
Methods and systems for managing access to a wireless local area network are provided. A wireless access point (AP) may use a unified approach that utilizes an out-of-band channel to communicate authentication key and network address information to a guest device, and utilizes an in-band channel to establish communications with the guest device, and also provides support for in-band setup on all devices. The ability to use out-of-band where possible provides for an increase to security and usability, and the possibility of delegating access from one device to another. The unified approach thereby also provides easy management of guest access to the WLAN.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
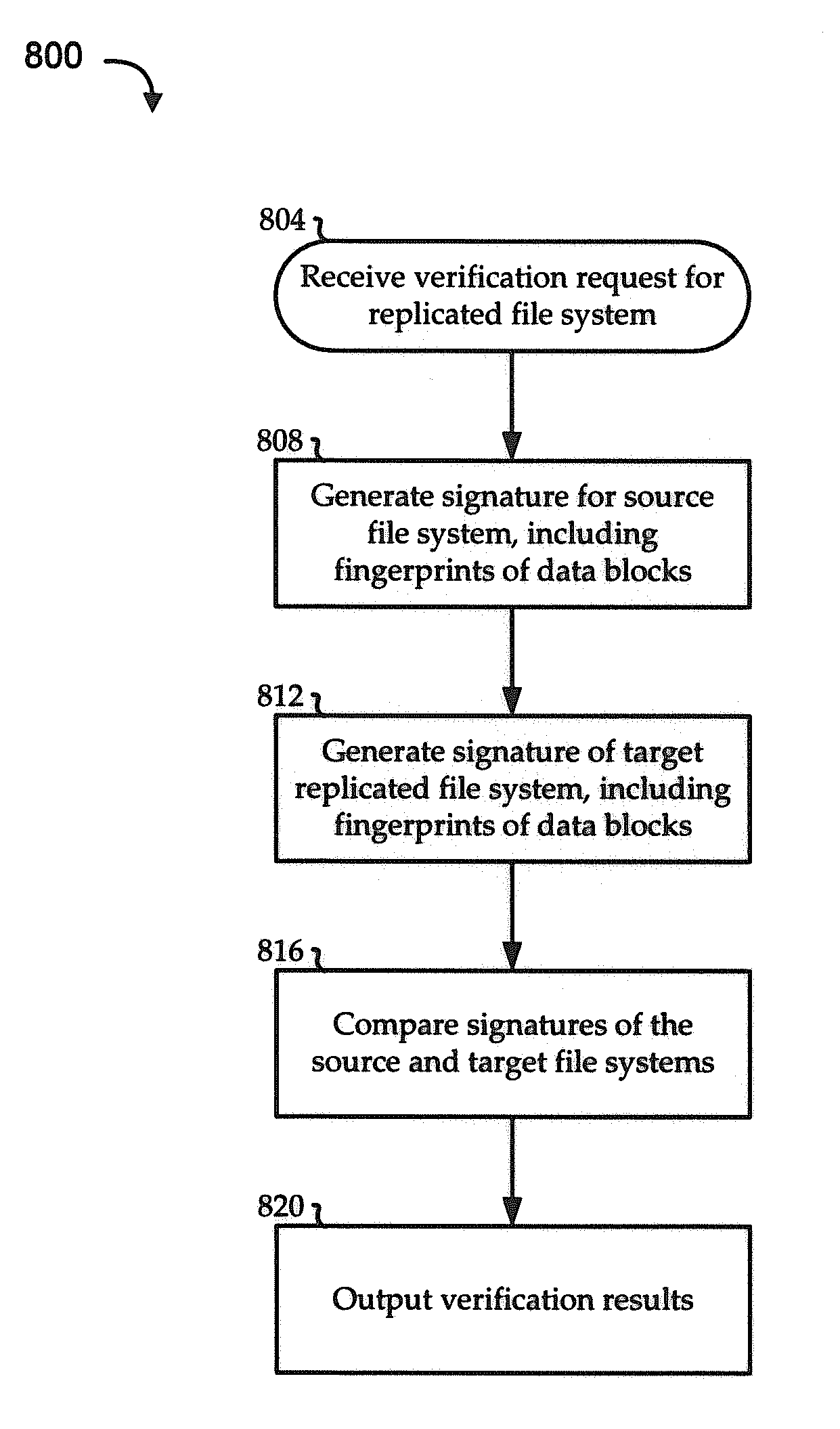
Offline verification of replicated file system
Embodiments of the invention include systems and methods for providing block-level verification of replicated file systems. Embodiments operate in context of data storage environments, which may typically have multiple file systems, snapshots of file systems, and replicas of file systems. In one illustrative scenario, a replica is created of a file system having multiple associated snapshots, and a user desires to verify the accuracy of the replica. A signature is created for each of the source active file system and the target replica file system, so that each signature includes records of both block-level signatures and block-level allocations. The signatures are compared to discover any differences. The differences may then be reconciled, where possible, to determine whether the differences indicate a corrupt or otherwise invalid replica.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
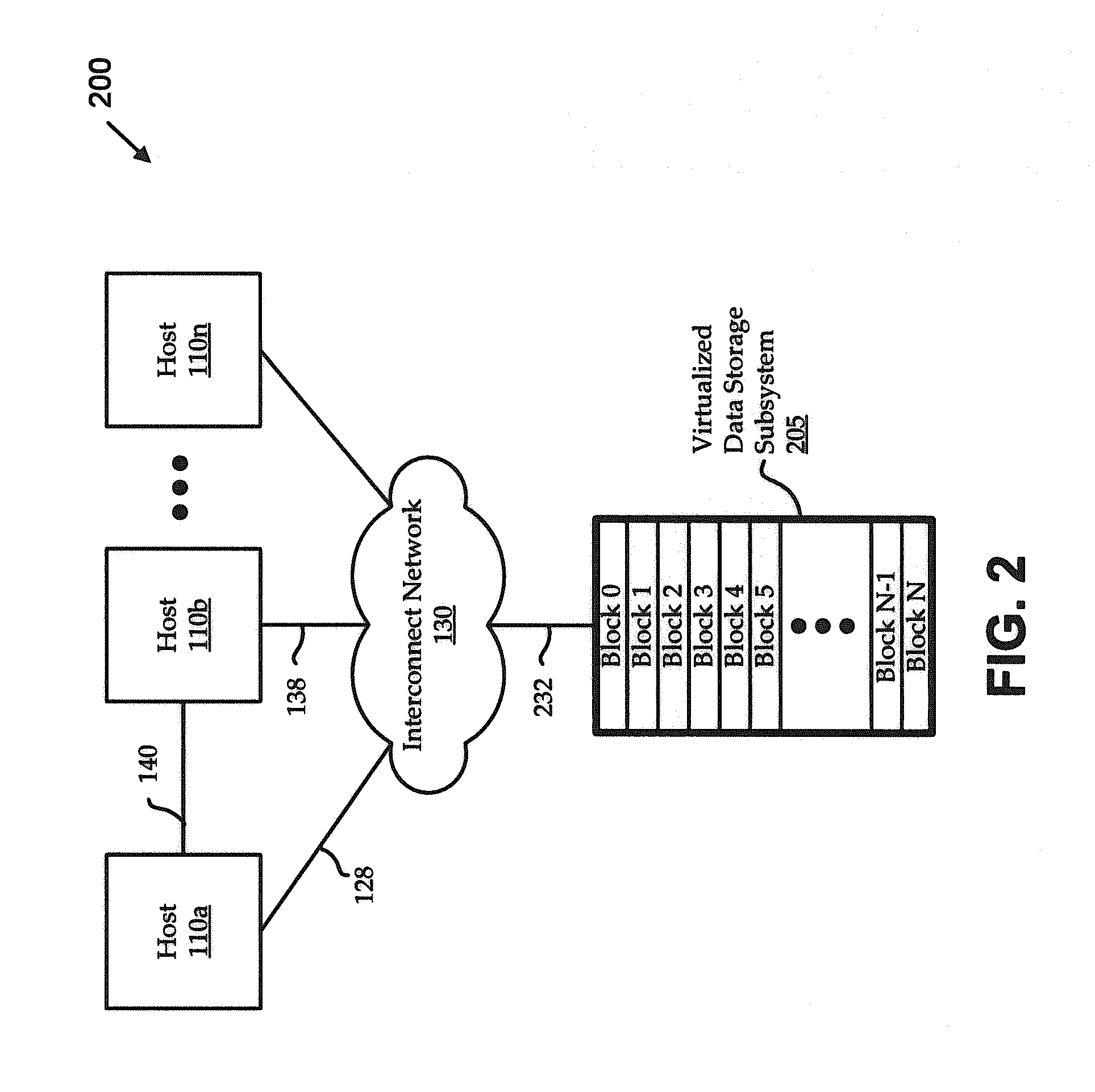
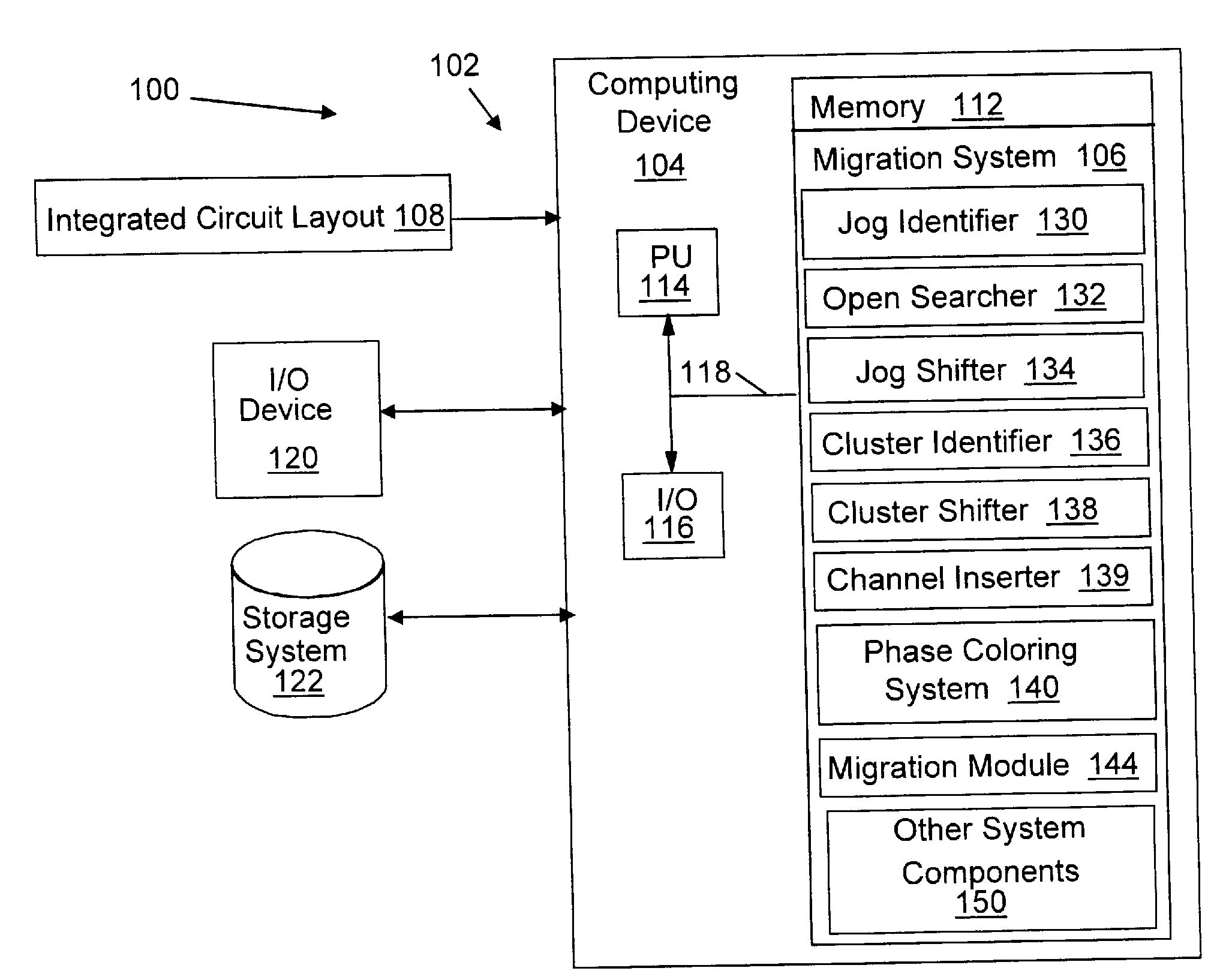
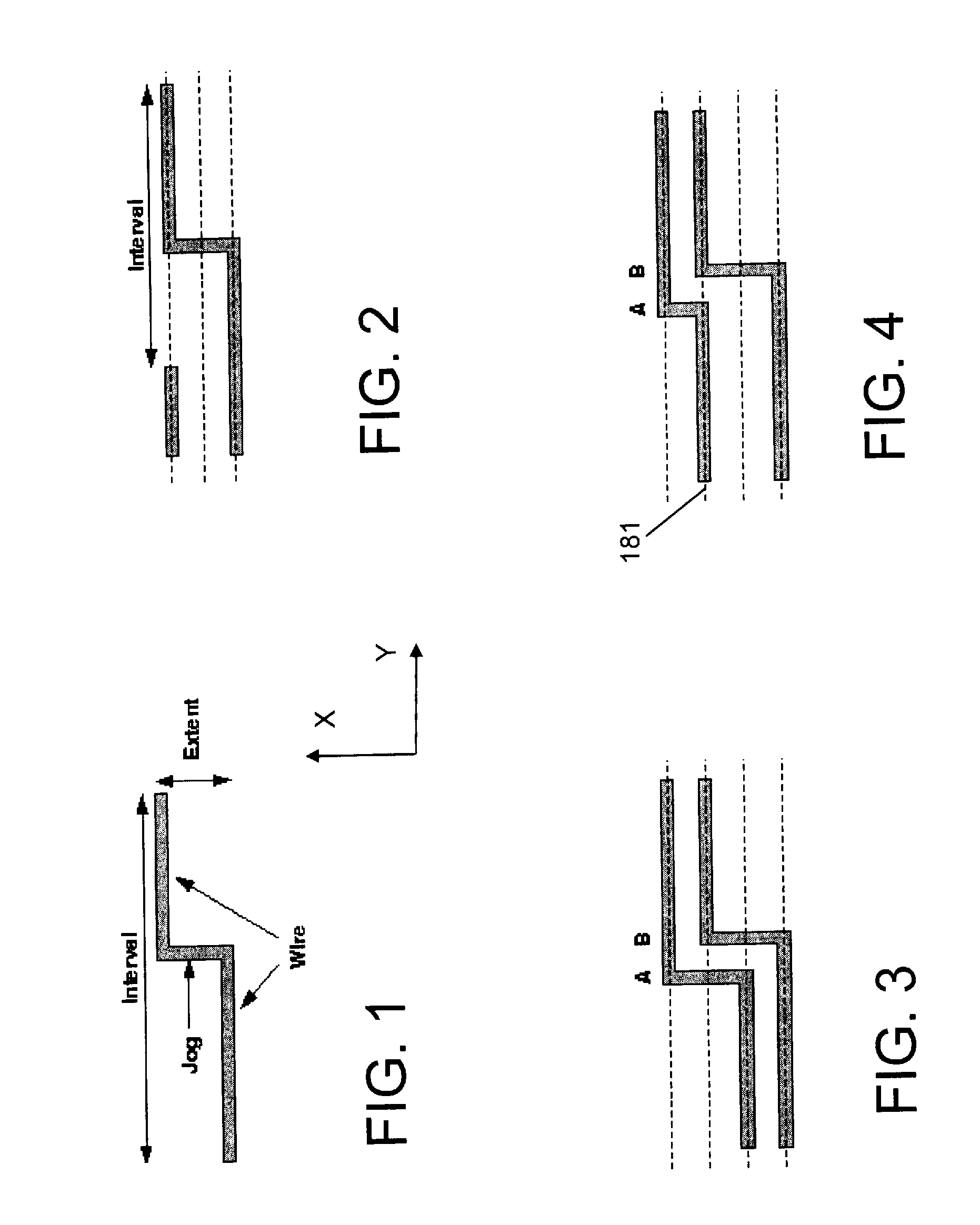
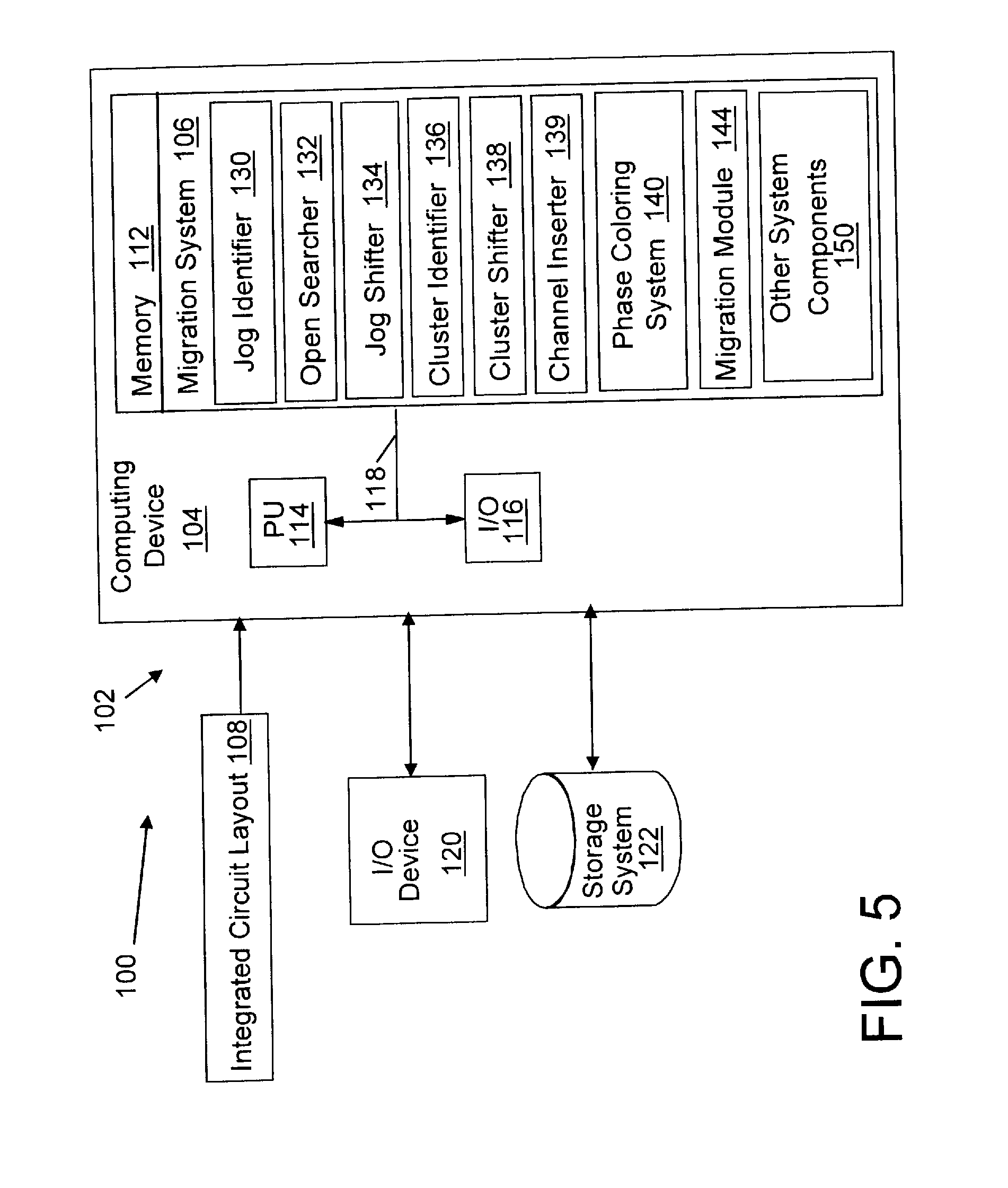
Migration of integrated circuit layout for alternating phase shift masks
InactiveUS20080244494A1Space is requiredCAD circuit designOriginals for photomechanical treatmentPhase shiftedProbable Case
Method, system and program product for migrating an integrated circuit (IC) layout for, for example, alternating aperture phase shift masks (AltPSM), are disclosed. In order to migrate a layout to phase compliance, jogs are identified on a first (AltPSM) layer and shifted to another second layer. Isolated or clustered jogs are shifted into an open channel portions on the second layer where possible. Remaining clustered jogs are shifted into as few new channels as possible on the second layer. The jog removal process leaves unidirectional wires that can be trivially phase colored. Standard technology migration techniques are then used to legalize the results on the layers.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method of using 3-cyano-4-arylpyridine derivatives as modulators of androgen receptor function
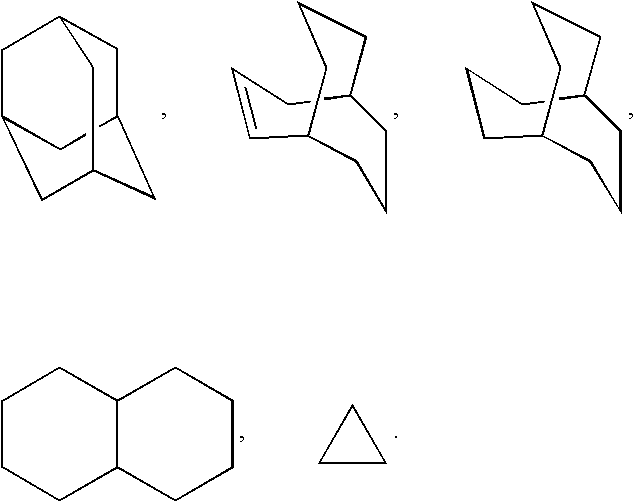
A method is provided for treating androgen receptor-associated conditions such as age-related diseases, for example sarcopenia, employing a compound of the structure wherein R1 is CN or H; X is O or S;R2 is alkyl or substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl or substituted cycloalkyl, arylalkyl or substituted arylalkyl, aryl or substituted aryl, or heteroaryl or substituted heteroaryl; R3 and R4 are the same or different and are independently selected from H, C(O)R2a, alkyl or substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl or substituted cycloalkyl, arylalkyl or substituted arylalkyl, aryl or substituted aryl, or heteroaryl or substituted heteroaryl; R2a is alkyl or substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl or substituted cycloalkyl, arylalkyl or substituted arylalkyl, aryl or substituted aryl, or heteroaryl or substituted heteroaryl; G is aryl or heteroaryl, or aryl or heteroaryl substituted with one, two, three, four or five, where possible, of the substituents selected from the group consisting of hydrogen (H), halo, NO2, CN, OR2b, OH, CF3, NR3aR4a; wherein R3a and R4a, and R2b are the same or different and are independently selected from alkyl or substituted alkyl, cycloalkyl or substituted cycloalkyl, arylalkyl or substituted arylalkyl, aryl or substituted aryl, or heteroaryl and substituted heteroaryl; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and a prodrug ester thereof.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
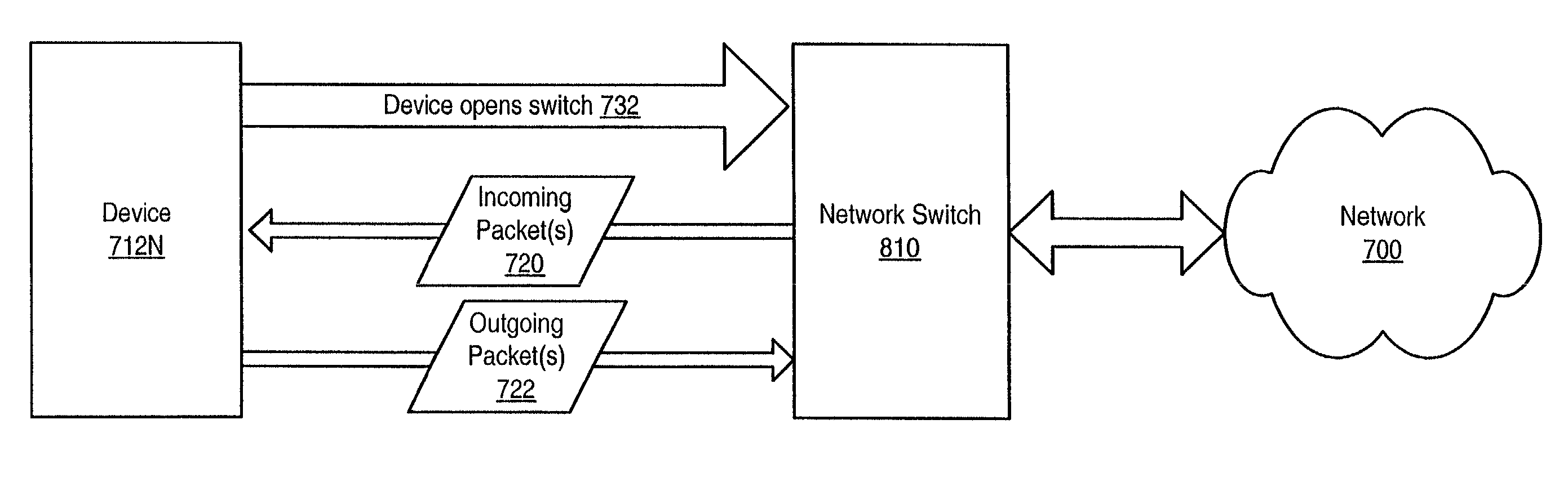
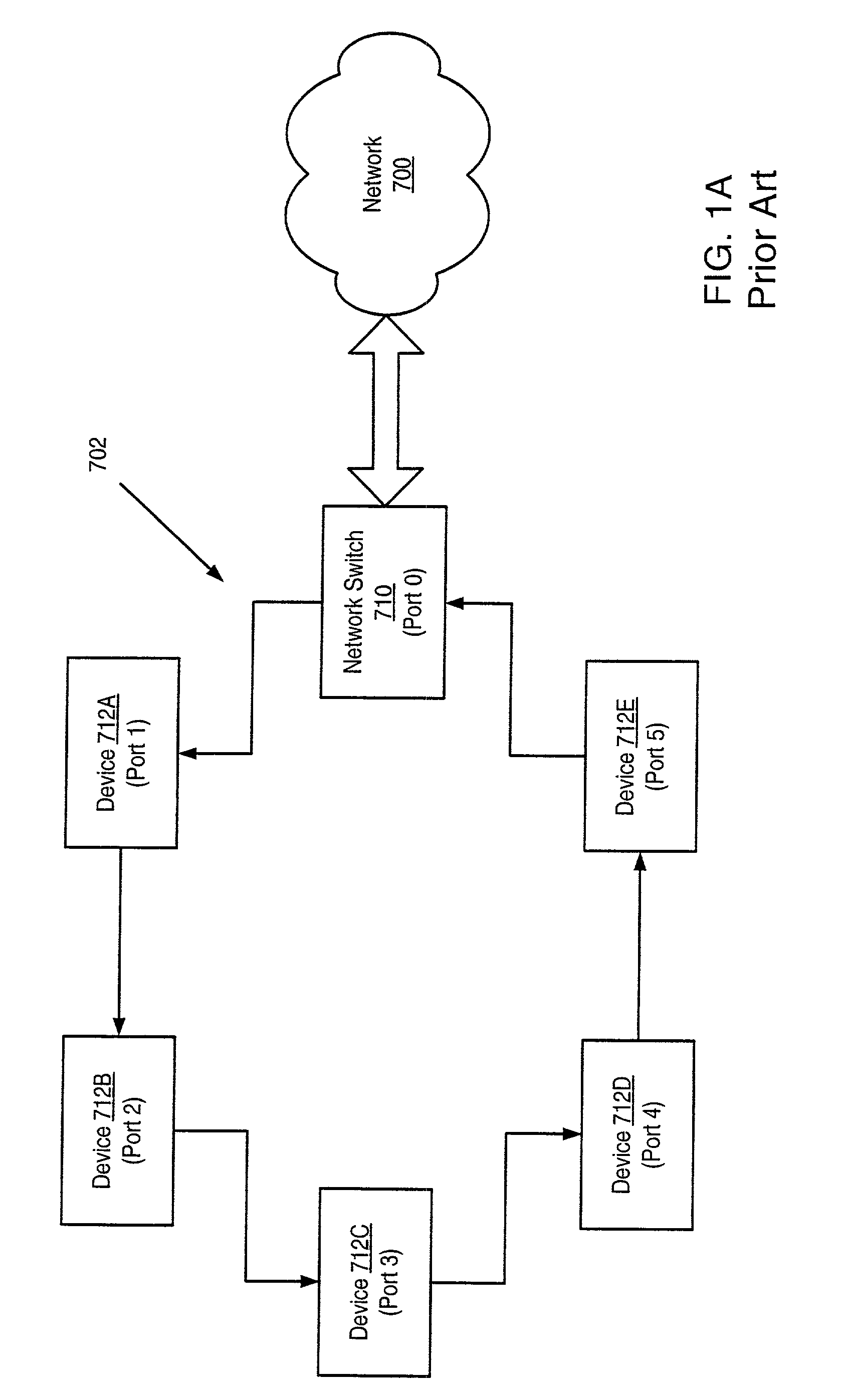
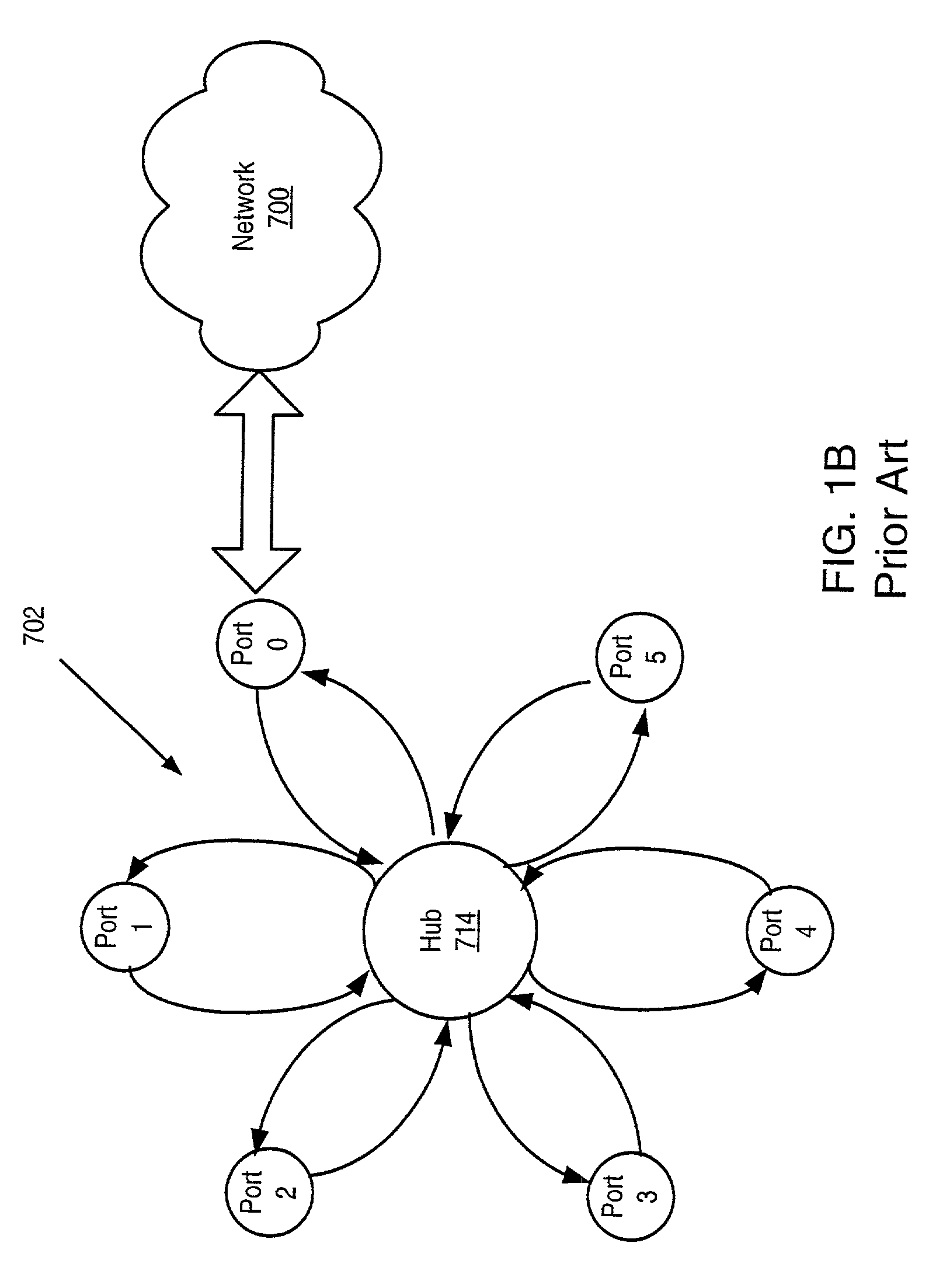
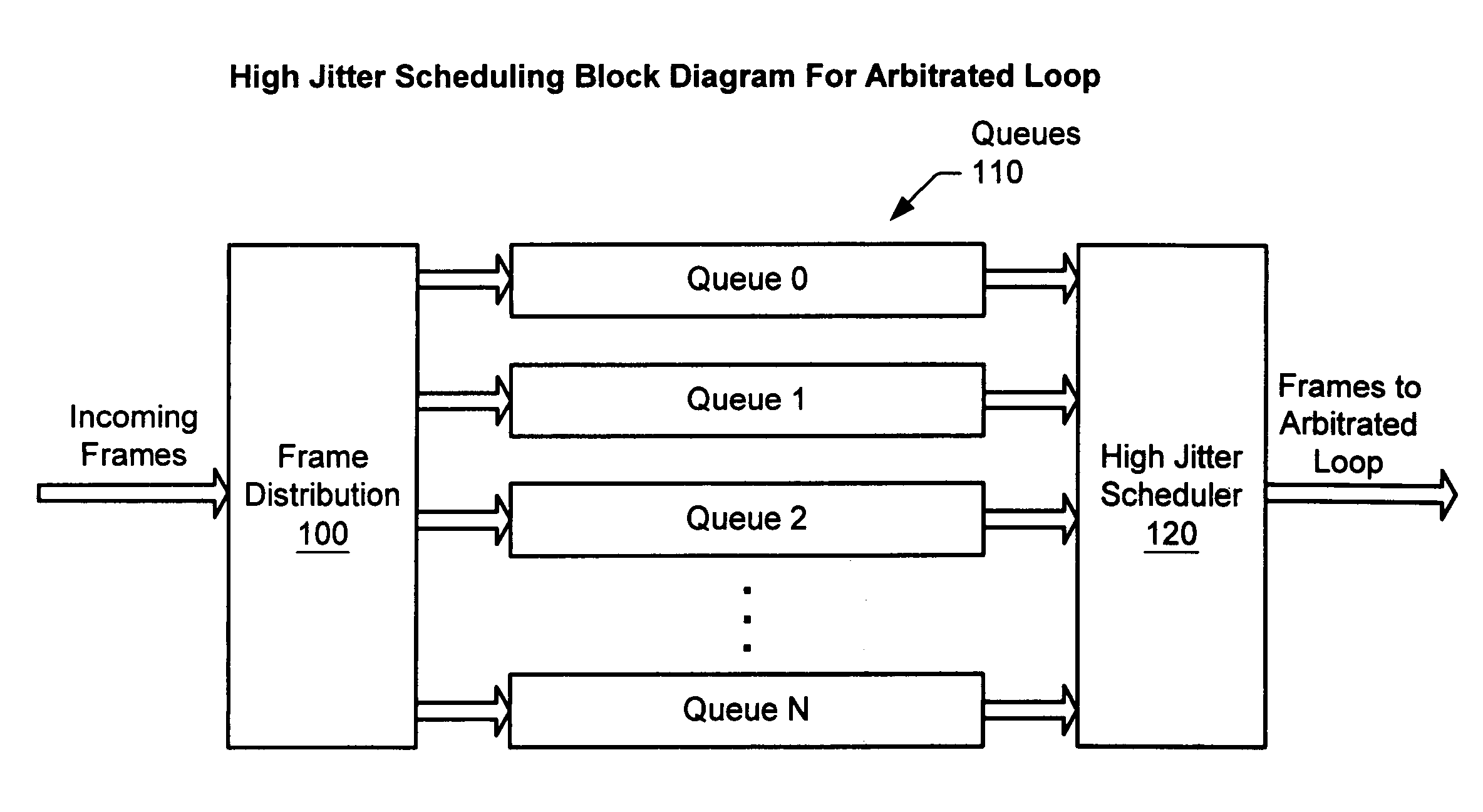
Method and apparatus for scheduling packet flow on a fibre channel arbitrated loop
A system and method for enabling a network switch to transmit queued packets to a device when opened by the device, and thus to utilize the Fibre Channel Arbitrated Loop (FC-AL) in full-duplex mode when possible. The switch may include a plurality of queues each associated with a device on the FC-AL for queuing incoming packets for the device. The switch may determine a next non-empty queue, open the device associated with the queue, and send packets to the device. The device may send packets to the switch concurrently with receiving packets from the switch, thus utilizing the FC-AL in full-duplex mode. When a device opens the switch to transmit packets to the switch, the switch may determine if there are packets for the device in the queue and, if so, send packets to the device concurrently with receiving packets from the device, thus utilizing the FC-AL in full-duplex mode.
Owner:BROCADE COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS
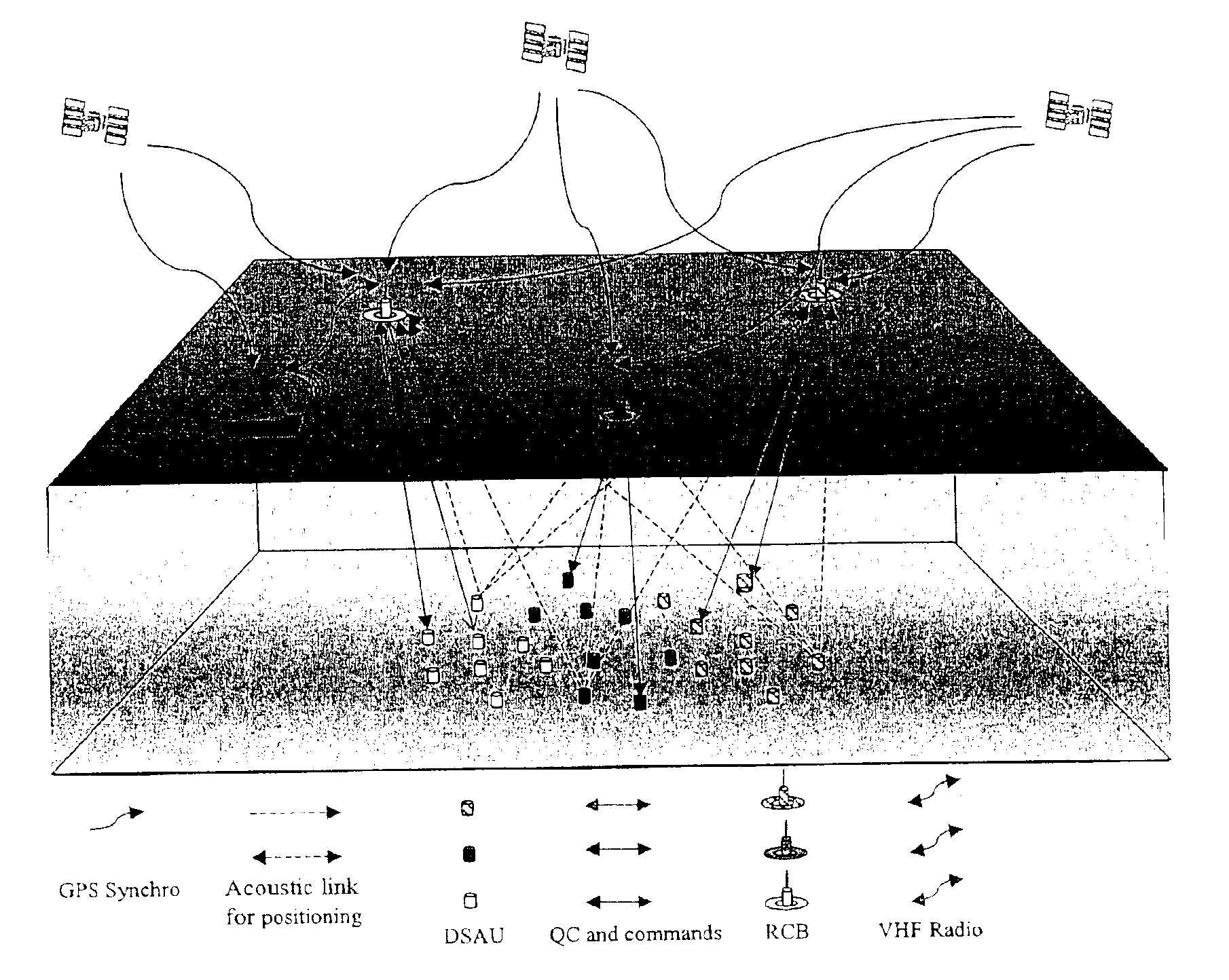
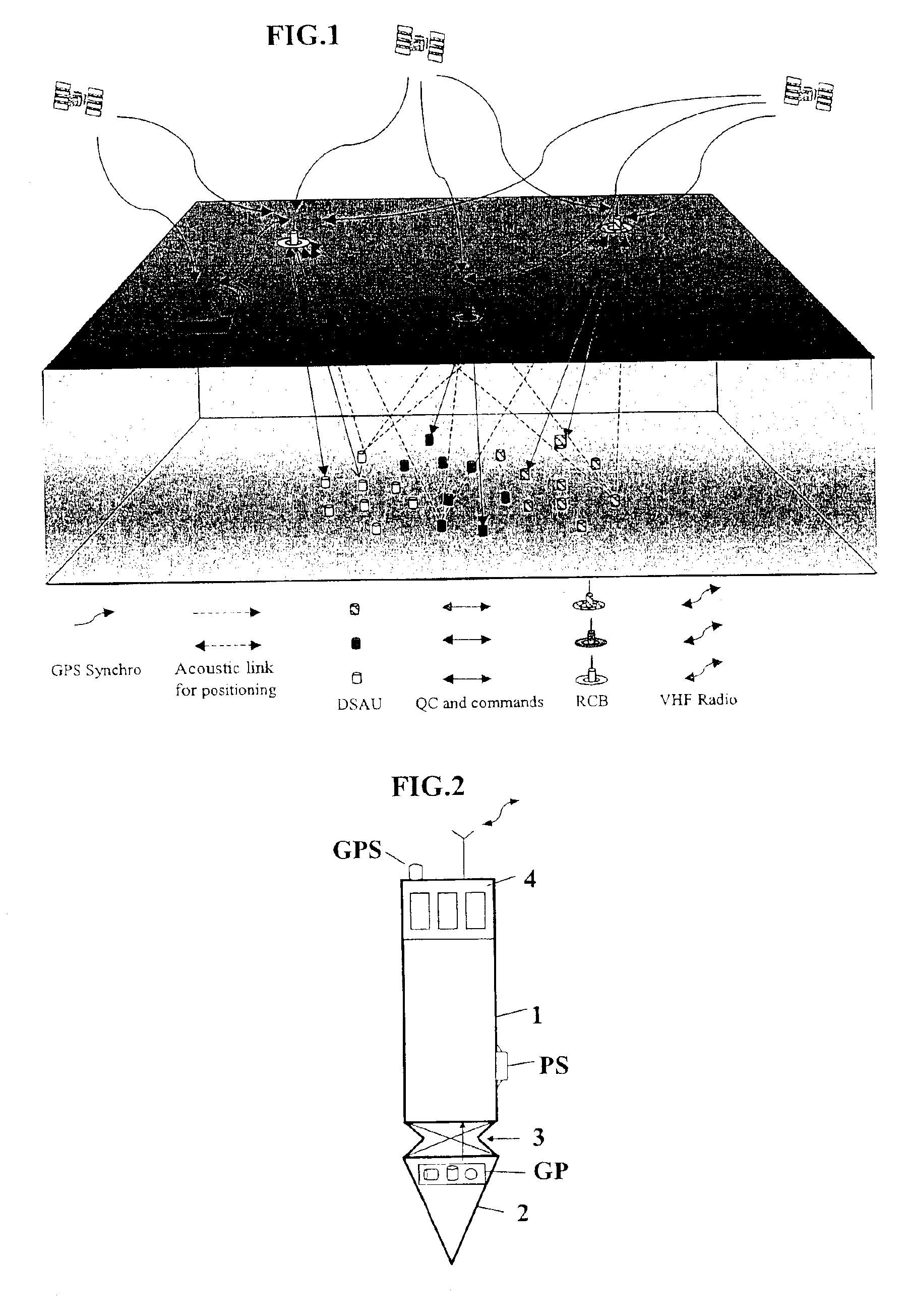
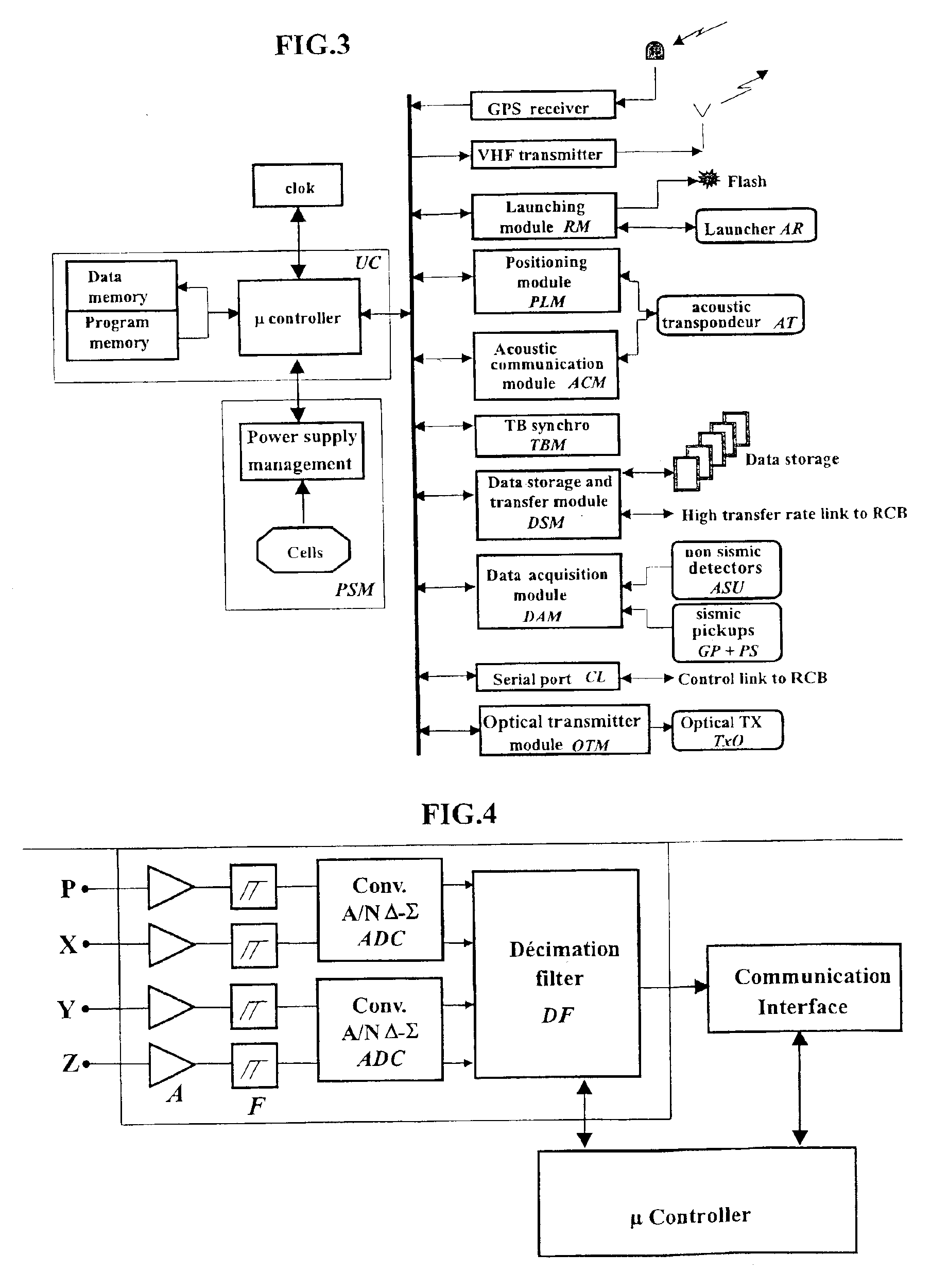
Seismic data acquisition system using acquisition stations set on the sea bottom
InactiveUS7016260B2Good synchronizationTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsTransmission systemsSystems designData acquisition
The invention is a system designed for acquisition of seismic data by means of acquisition stations set on water bottom of a water body. The system comprises acquisition stations (DSAU) combining a streamlined boom suited to penetrate the bottom and thus couple seismic receivers with the underlying formation, a sealed body for electronic data acquisition and communication modules. These acquisition stations (DSAU) are placed in the water and drop to the bottom under the effect of gravity. Relay buoys (RCB) are positioned at the surface, each with a GPS positioning module, a radio link with a central station (CCRU), on a ship for example, and modules providing acoustic communication with bottom acquisition stations (DSAU), which are used to determine the position of the stations in relation to the relay buoys and to exchange control data and seismic data (good running order data or possibly seismic traces acquired if the conditions lend themselves thereto) to provide seismic prospecting or monitoring of an underground formation.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Method of scanning, analyzing and identifying electro magnetic field sources
InactiveUS20100125438A1Easy to identifyAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDosimetersProbable CaseElectromagnetic field
A method for determining the energy level of an electromagnetic field (EMF) received from an EMF source (EMFS) and for identifying the EMFS is provided, the method comprising: receiving an EMF signal, separating the EMF signal into EMF sub-signals; determining, when possible, the energy level of EMF sub-signals; identify, when possible, the EMFS corresponding to the EMF sub-signals; and recording EMF related data. An apparatus, a system and a user graphical interface is also provided herein. Further, a network of EMFDD adapted to share EMF data therebetween is also provided herein.
Owner:MAUTECH
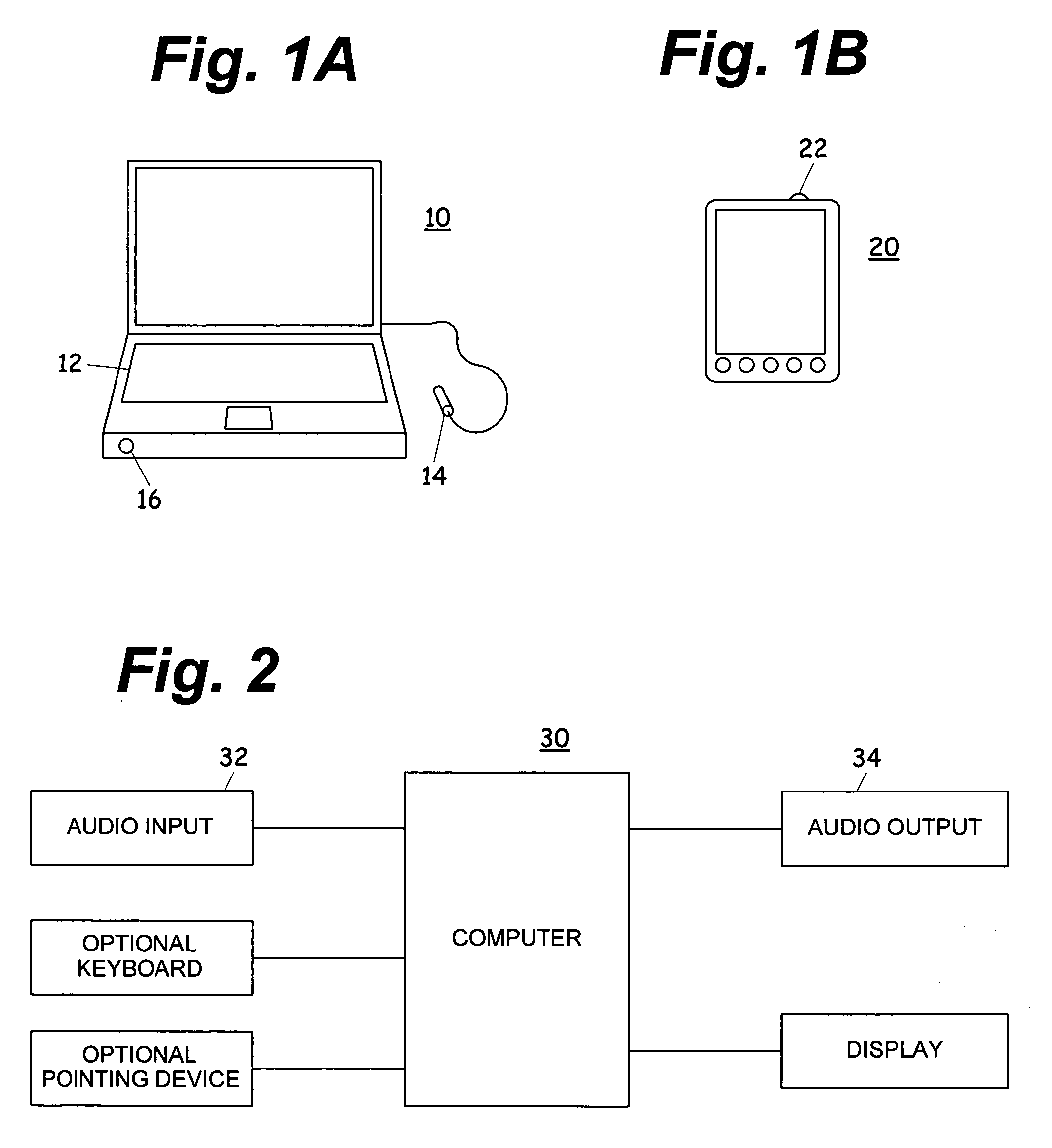
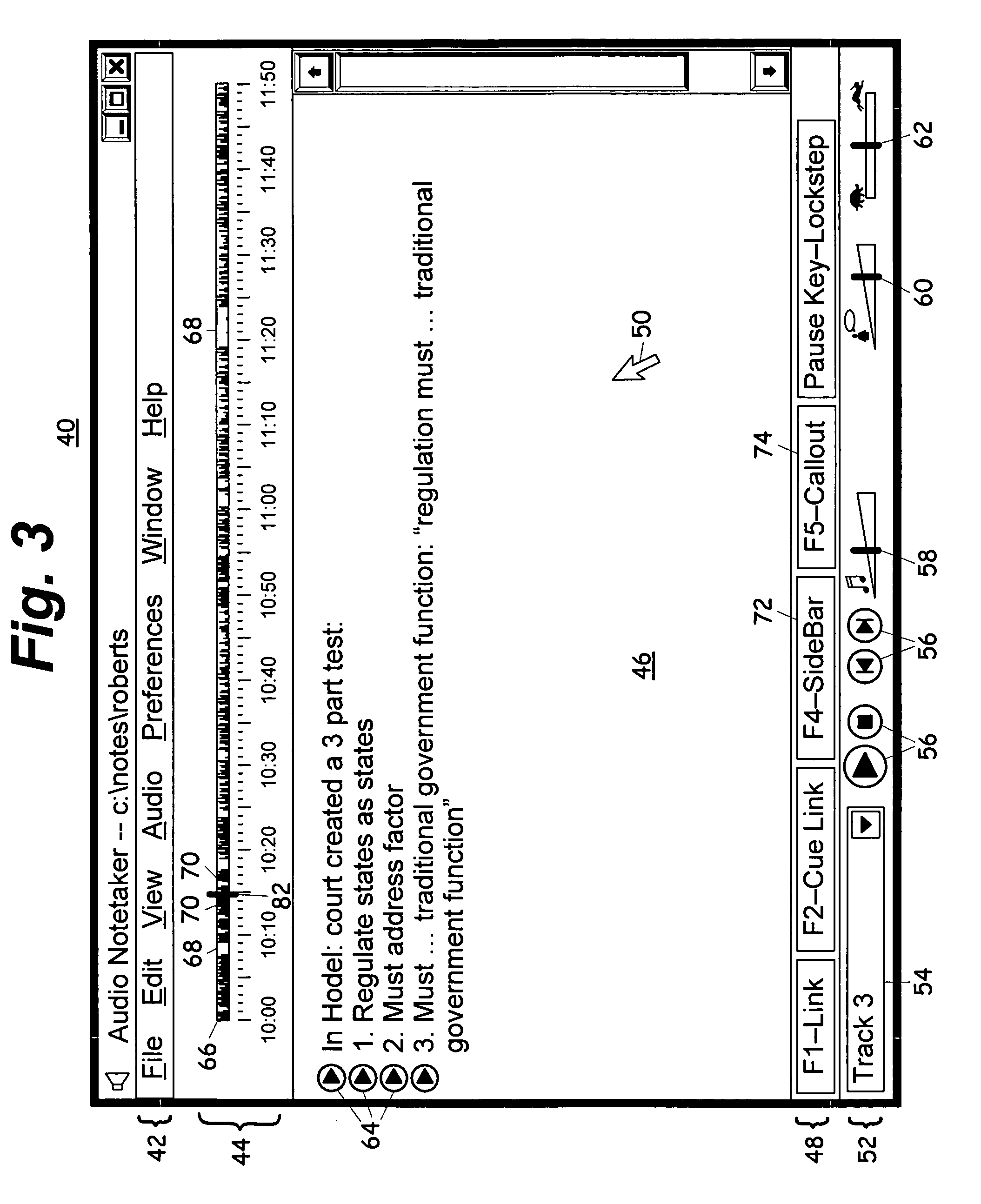
Computerized notetaking system and method
InactiveUS20060075347A1Improve experienceImprove user experienceSound input/outputSpeech recognitionTimestampProbable Case
A computerized notetaking system that records audio and links notes to the audio and has enhancements such as: Always-on audio recording and external timestamp button that work even when the system is turned off. A “next-topic” command that prepares and timestamps a new paragraph while allowing the user to complete the current paragraph. Commands for creating callouts and sidebar boxes in the user notes. A choice of audio filters. Speech recognition for searching through and navigating an audio recording. Speech recognition accuracy enhancement based upon typed notes. Playback, including lockstep playback, that prefers starting and stopping at word boundaries without overlap when possible. A self-adjusting preplay parameter. A “repeat slower” command that replays a few seconds of audio and then resumes at normal speed. Integrated background audio that plays music or white noise when notes-related audio is not being played. Several other enhancements are disclosed.
Owner:REHM PETER H
Error recovery for data processing systems transferring message packets through communications adapters
InactiveUS20050081080A1Rapid meanImprove speed and efficiency and reliabilityError detection/correctionTransmissionInternal memoryData processing system
A method and system are provided for error recovery in the process of message packet transfer using communications adapters connected between data processing nodes and a switched network. The communications adapter are provided with internal storage that is capable of storing specific information concerning the failure of one or more message packet transfers. This storage may be queried from nodes external to the adapter to more precisely determine the error and to take corrective actions, where possible.
Owner:IBM CORP
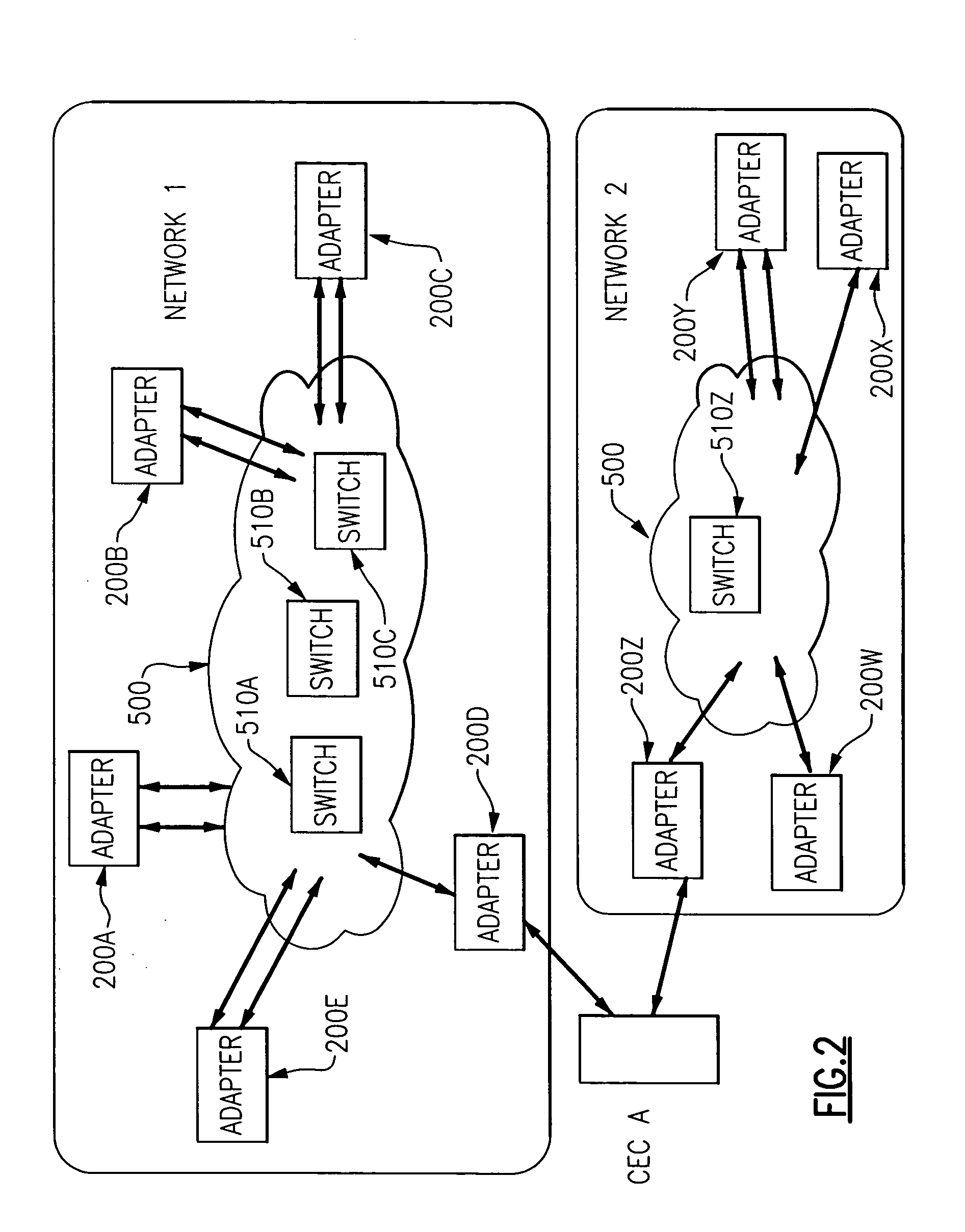
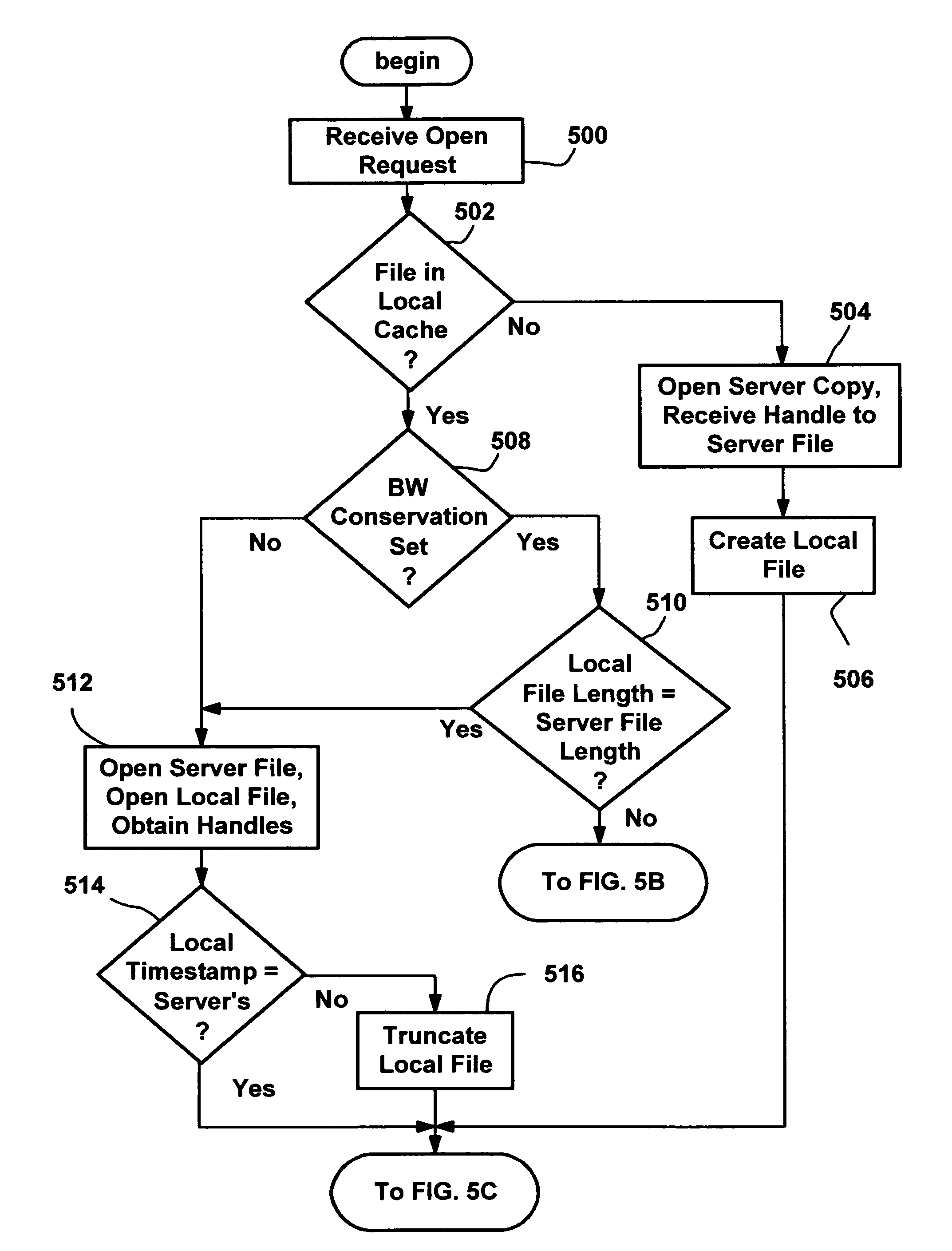
Method and system for client-side caching
InactiveUS20080028149A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsNetwork redirectorProbable Case
An improved method and system for client-side caching that transparently caches suitable network files for offline use. A cache mechanism in a network redirector transparently intercepts requests to access server files, and if the requested file is locally cached, satisfies the request from the cache when possible. Otherwise the cache mechanism creates a local cache file and satisfies the request from the server, and also fills in a sparse cached file as reads for data in ranges that are missing in the cached file are requested and received from the server. A background process also fills in local files that are sparse, using the existing handle of already open server files, or opening, reading from and closing other server files. Security is also provided by maintaining security information received from the server for files that are in the cache, and using that security information to determine access to the file when offline.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for scheduling packet flow on a fibre channel arbitrated loop
InactiveUS7215680B2Efficient use ofRaise priorityData switching by path configurationDuplex signal operationFiberPacket loss
A system and method for enabling a network switch to transmit queued packets to a device when opened by the device, and thus to utilize the Fibre Channel Arbitrated Loop (FC-AL) in full-duplex mode when possible. The switch may include a plurality of queues each associated with a device on the FC-AL for queuing incoming packets for the device. The switch may determine a next non-empty queue, open the device associated with the queue, and send packets to the device. The device may send packets to the switch concurrently with receiving packets from the switch, thus utilizing the FC-AL in full-duplex mode. When a device opens the switch to transmit packets to the switch, the switch may determine if there are packets for the device in the queue and, if so, send packets to the device concurrently with receiving packets from the device, thus utilizing the FC-AL in full-duplex mode.
Owner:BROCADE COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS
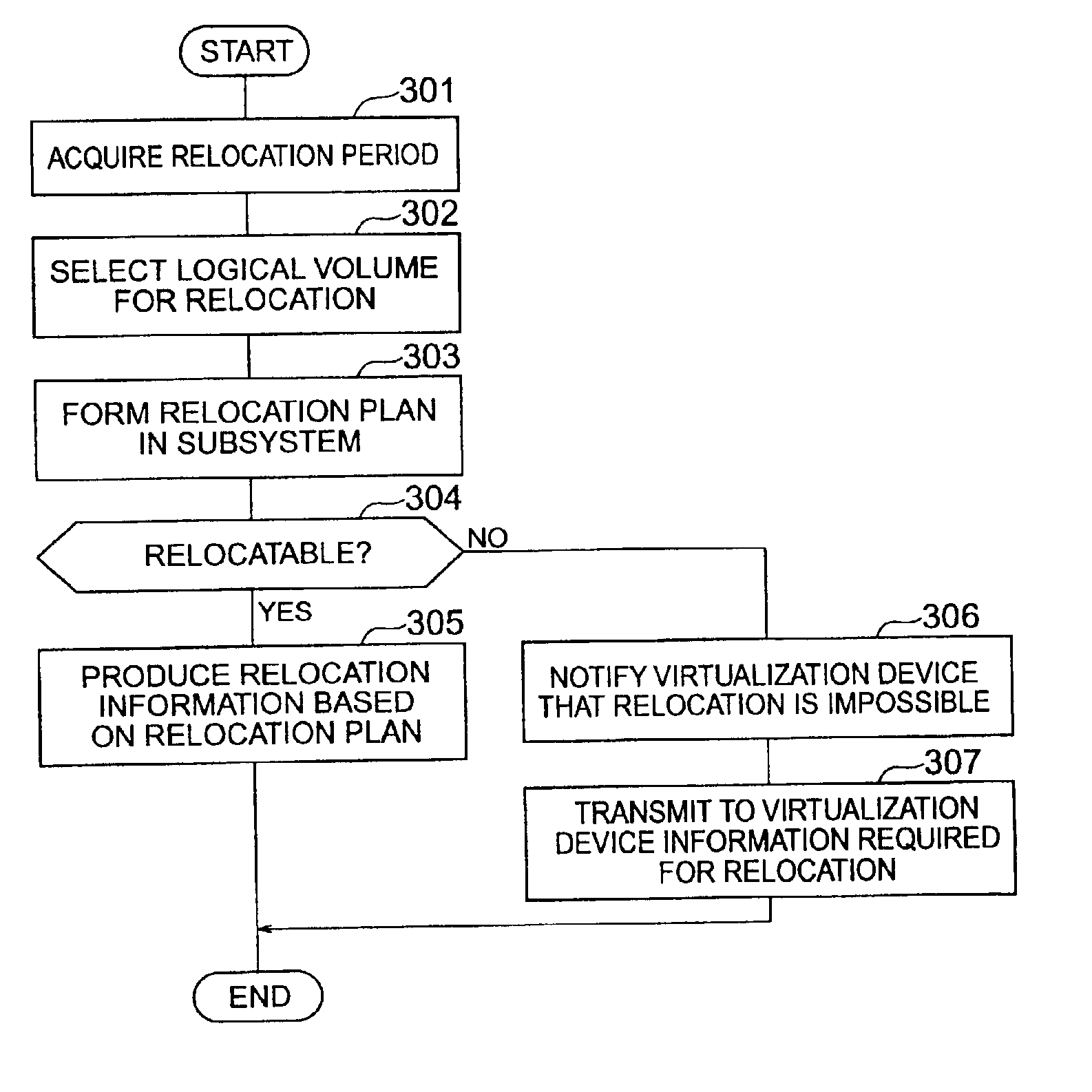
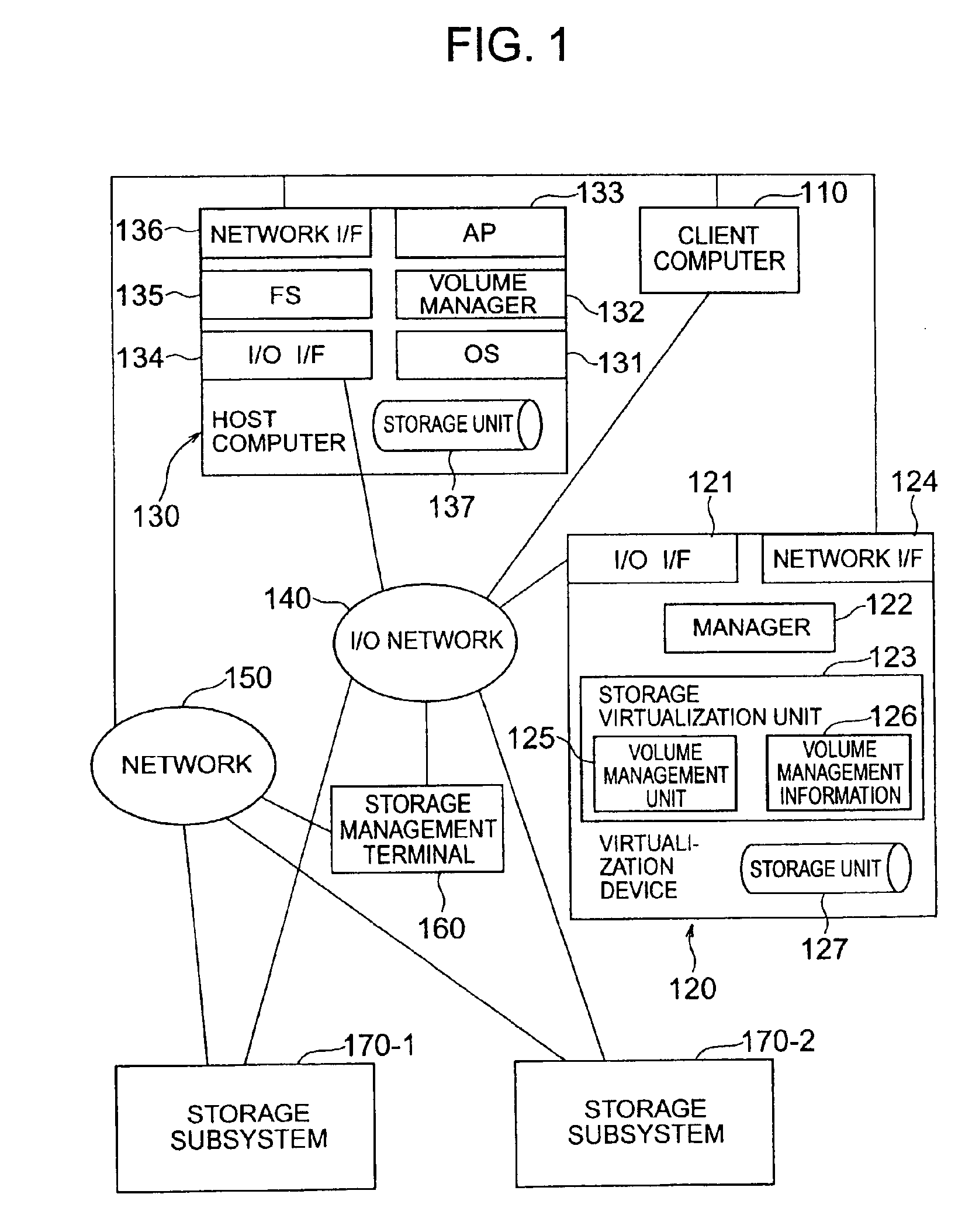
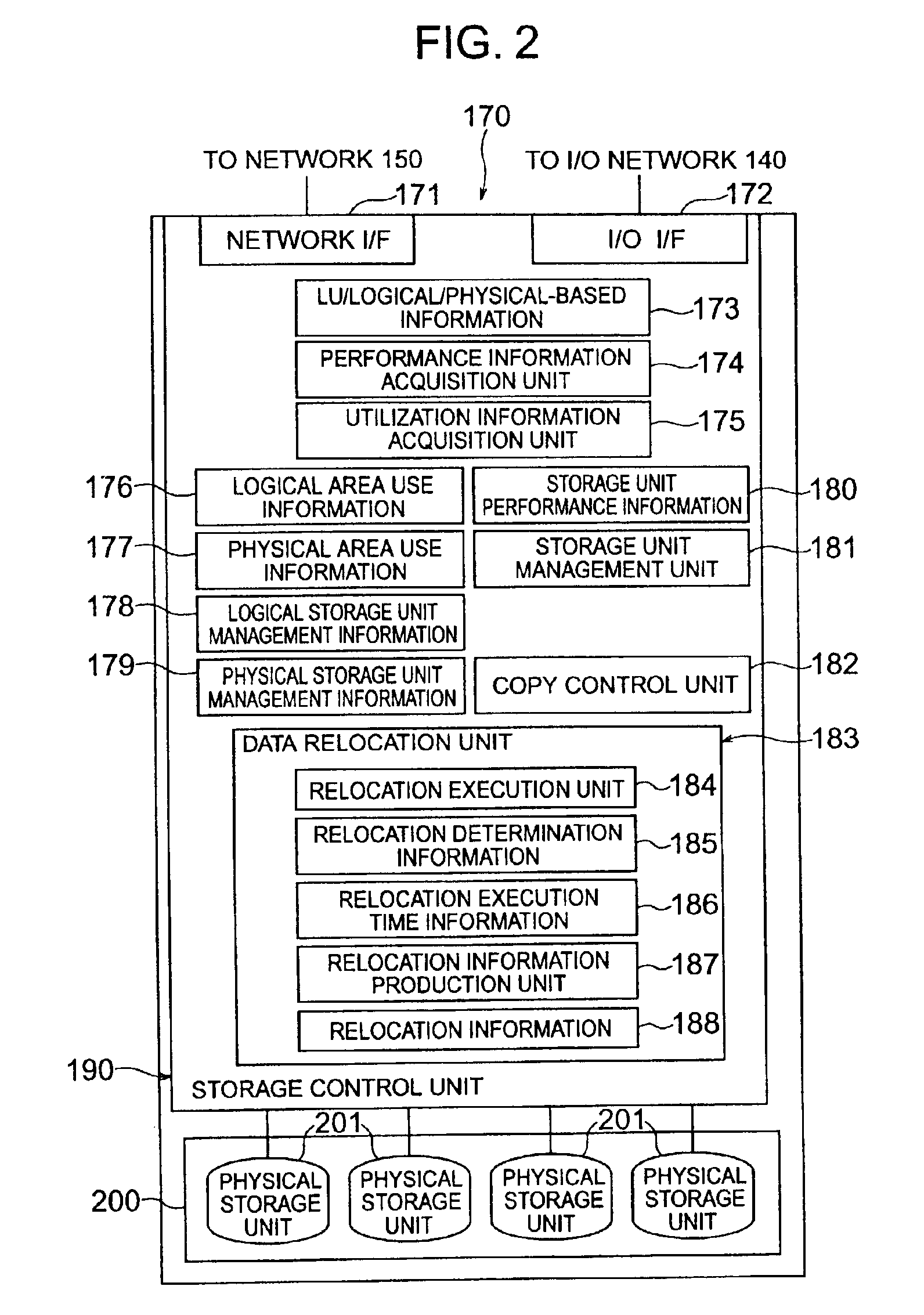
Method and apparatus for data relocation between storage subsystems
InactiveUS6895483B2Input/output to record carriersMemory loss protectionVirtualizationComputer hardware
A storage subsystem that has detected the necessity of the data relocation determines whether the data relocation is possible or not from one storage unit to another within the particular storage subsystem. A virtualization device is notified in the case where the data relocation in the particular subsystem is impossible. The manager of the virtualization device gives an inquiry to the storage subsystems as to whether any one of them can become a relocation destination or not. A storage subsystem determines, based on the related information, whether the data relocation requested is possible or not within the particular storage subsystem. In the case where such a relocation is possible, the copying process is carried out for data relocation from one storage subsystem to another in compliance with an instruction from the virtualization device.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
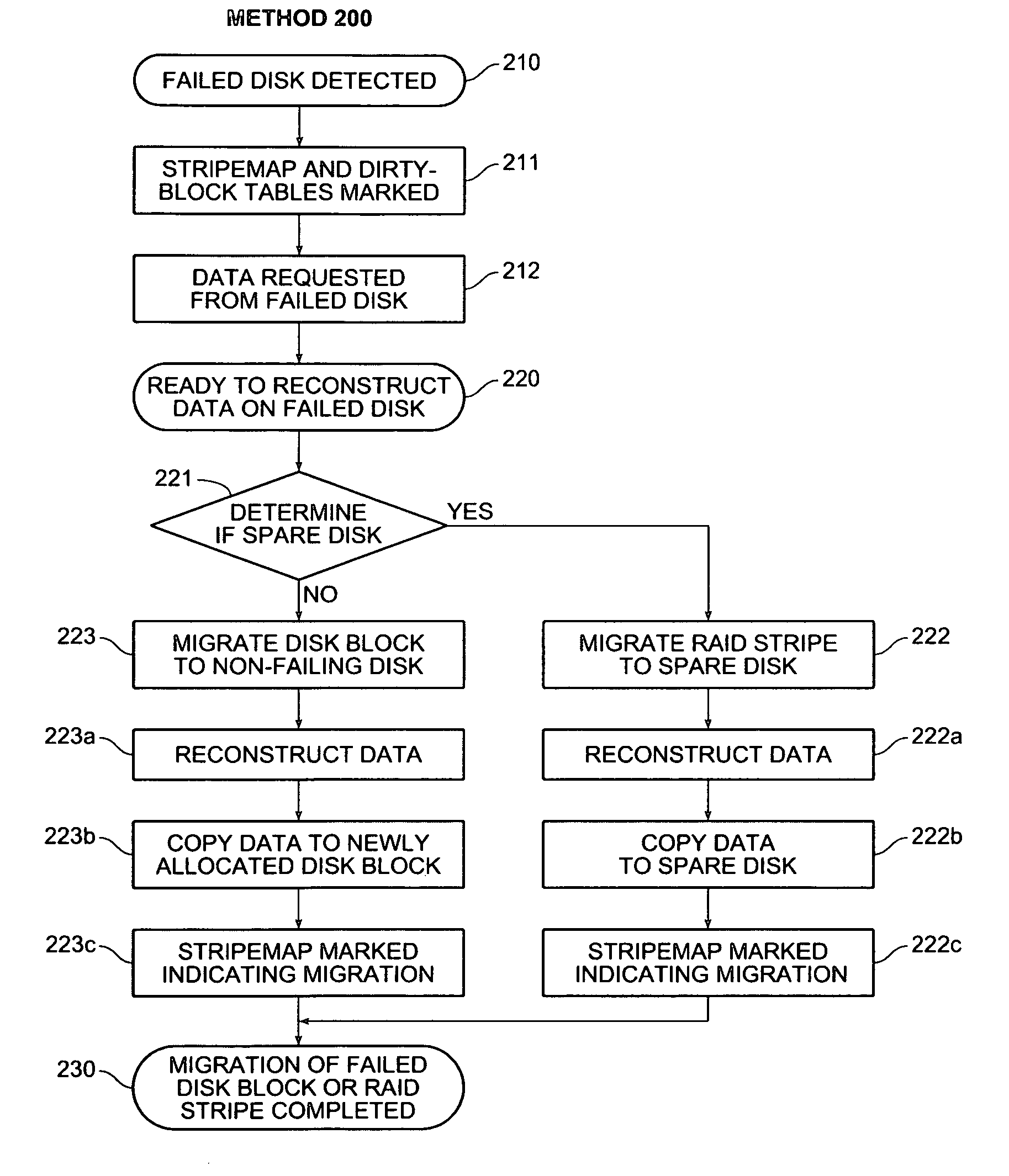
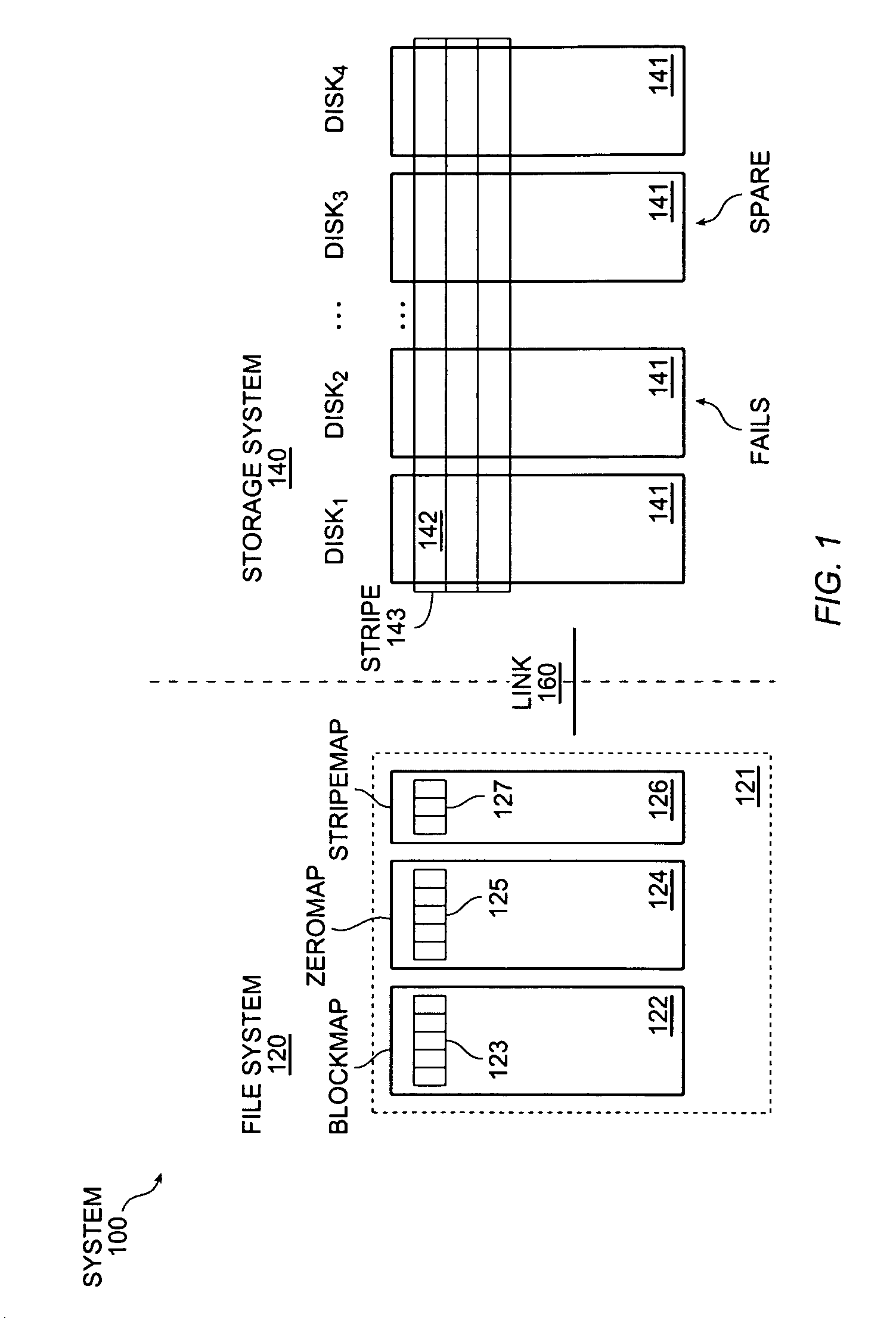
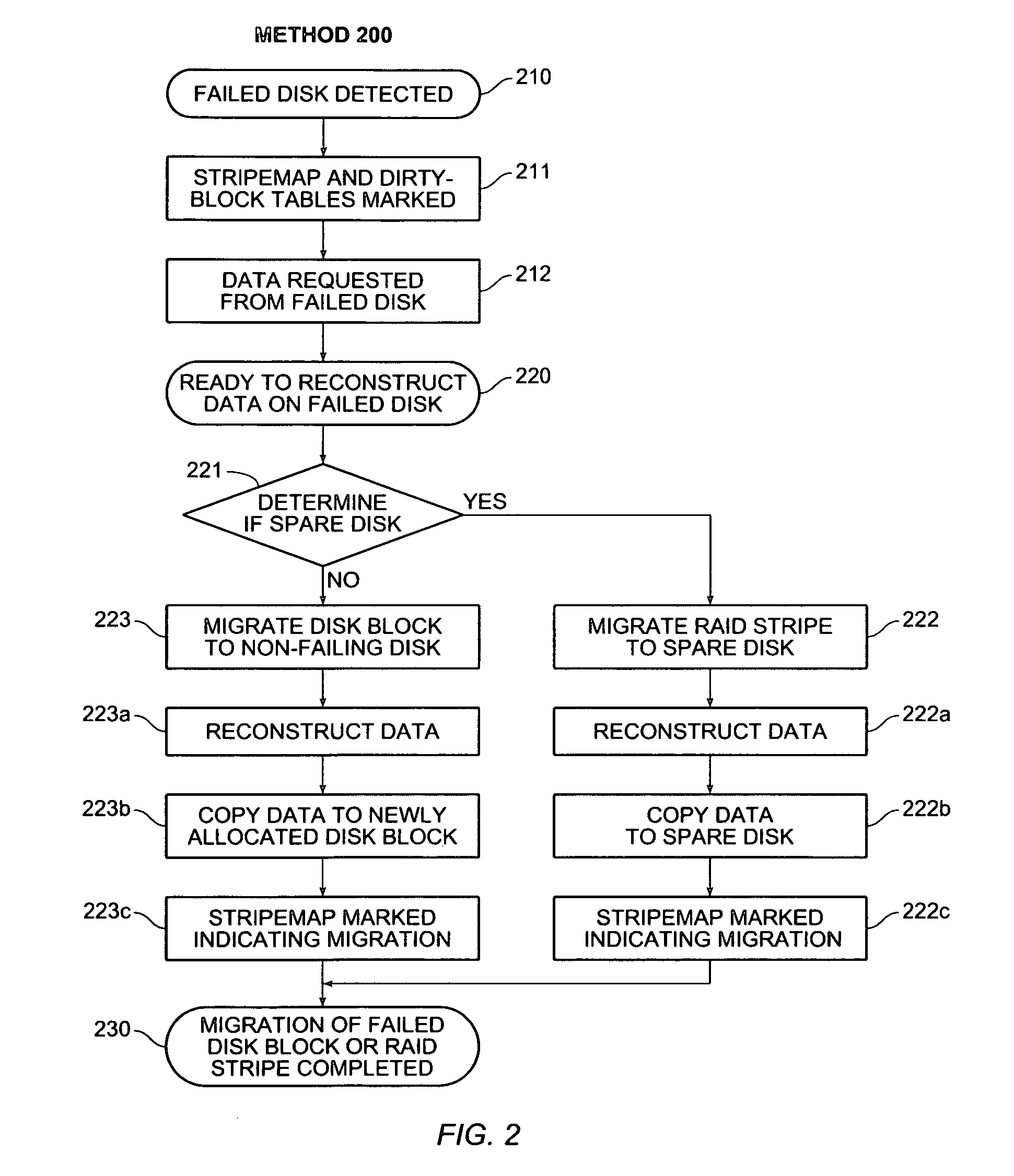
Using file system information in raid data reconstruction and migration
InactiveUS7024586B2Quantity minimizationMaintaining data reliabilityInput/output to record carriersEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionRAIDFile system
On disk failure, the storage system migrates only those disk blocks that included allocated data, and treats unallocated disk blocks as being logically zero when possible. When there is no spare disk, the source data block is logically set to zero and parity is recalculated for the RAID stripe associated with the source data block. When there is a spare, unallocated blocks on the spare are logically or physically set to zero upon migration. Write operations for the failed disk are redirected to other non-failing disks, and a record of which in-use disk blocks have been thus “migrated” to those other non-failing disks in maintained. Unused disk blocks are proactively set to zero. A target mirror copy is created using information regarding allocated disk blocks, by copying those blocks including allocated data or parity, and by clearing at the mirror those blocks not including any allocated data or parity.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
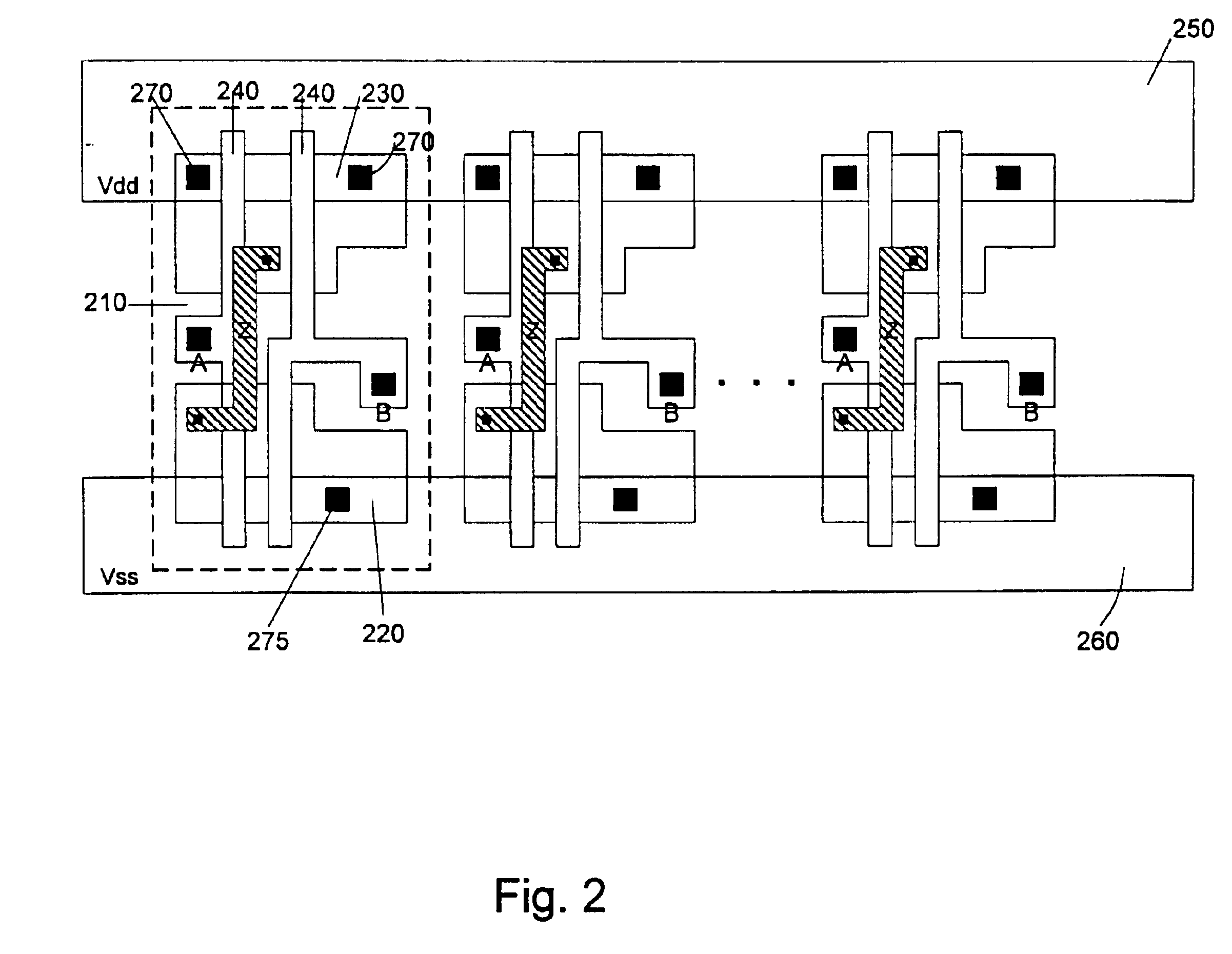
Dual-height cell with variable width power rail architecture
InactiveUS6838713B1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHigh densityElectrical conductor
A standard cell architecture with a basic cell that spans multiple rows of the standard cell. This multi-row basic cell may be a dual-height cell that spans two rows, or it may span more than two rows. The multi-row basic cell may be intermixed in a standard cell design with smaller, single-height cells for high-density applications. The single-height cells may be used where possible and higher-drive dual-height basic cells where larger transistors are desired. Other multiple height cells may also be included if even more current is desirable. The power rail may include conductors of varying width.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
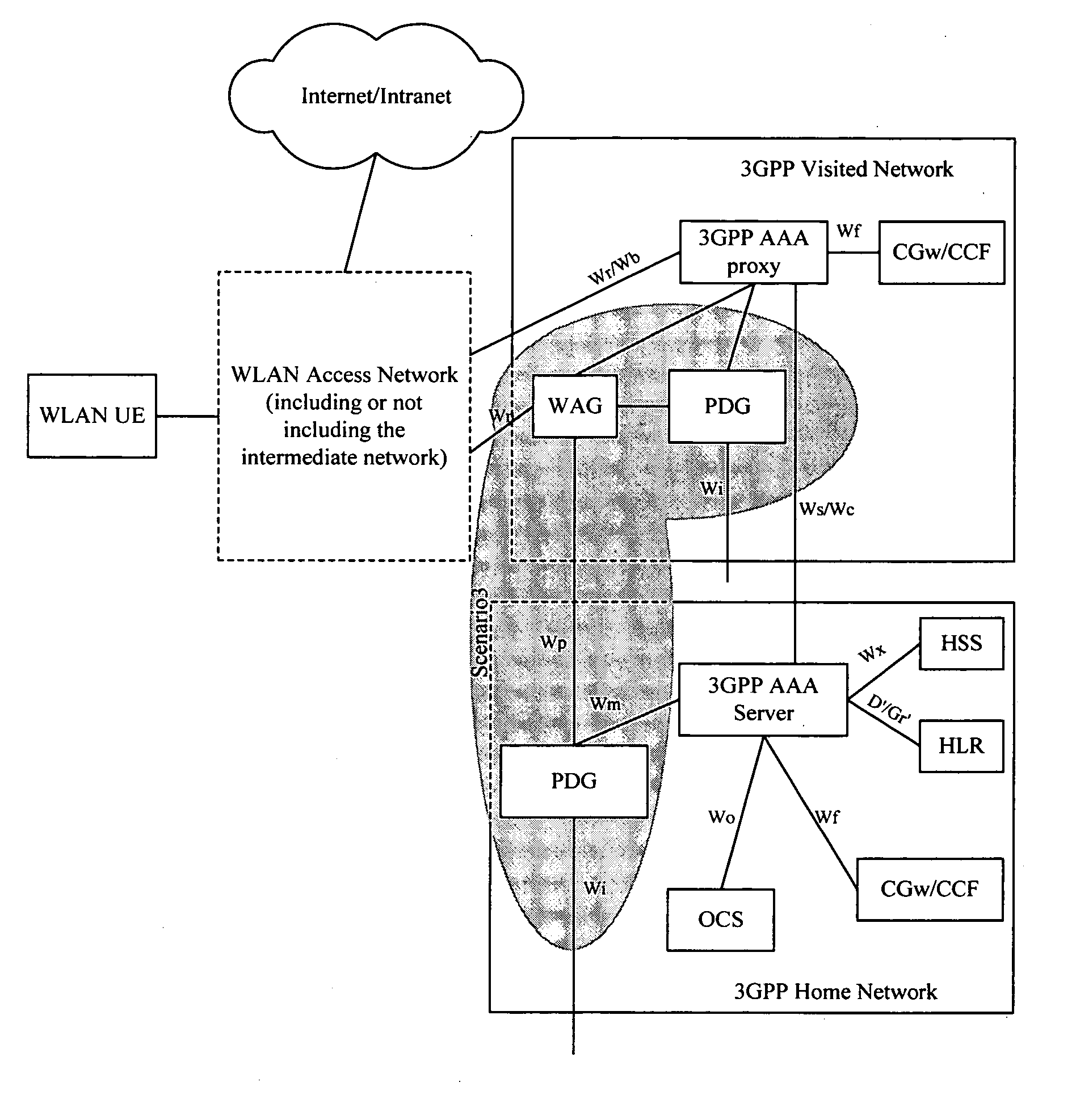
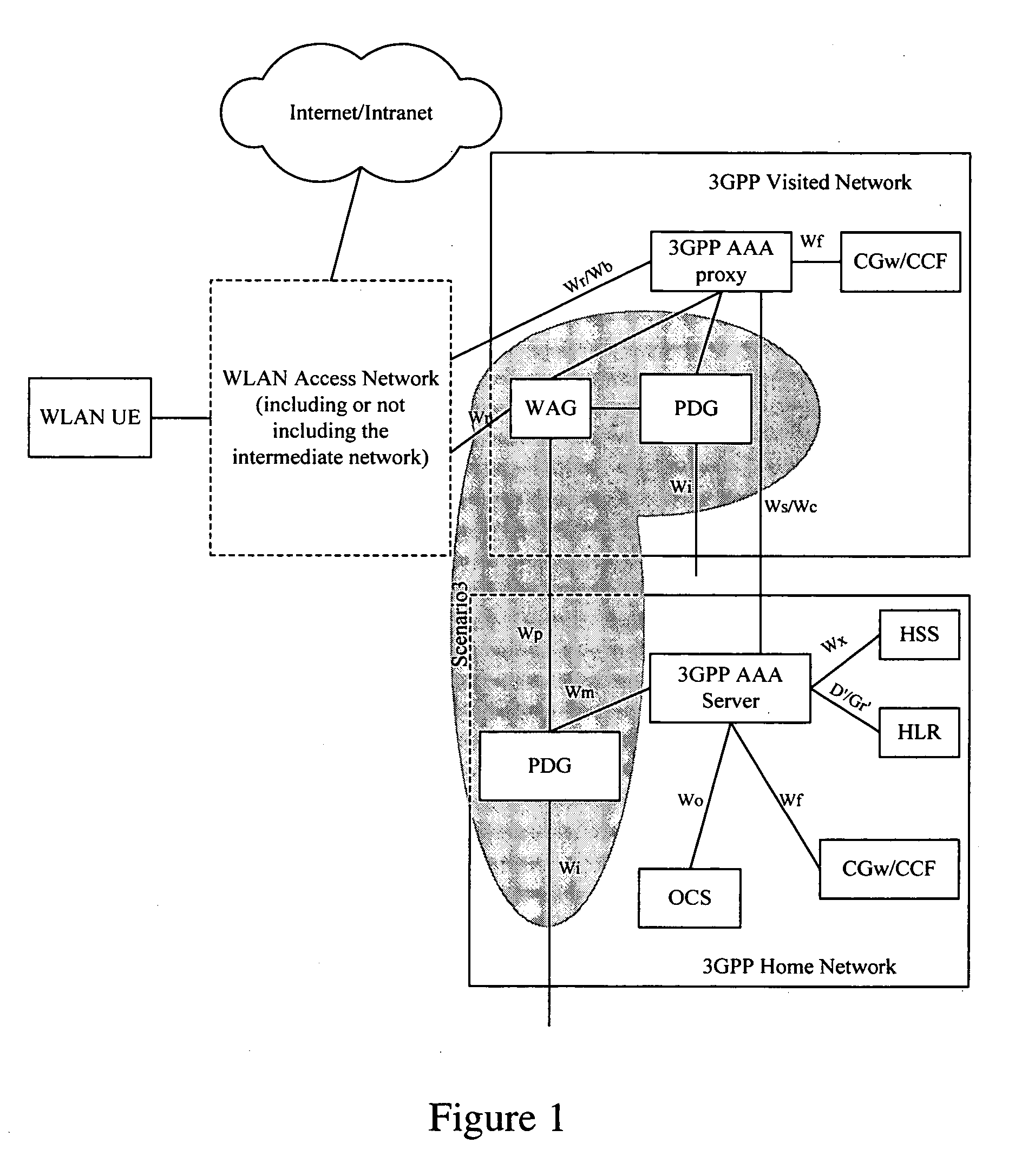
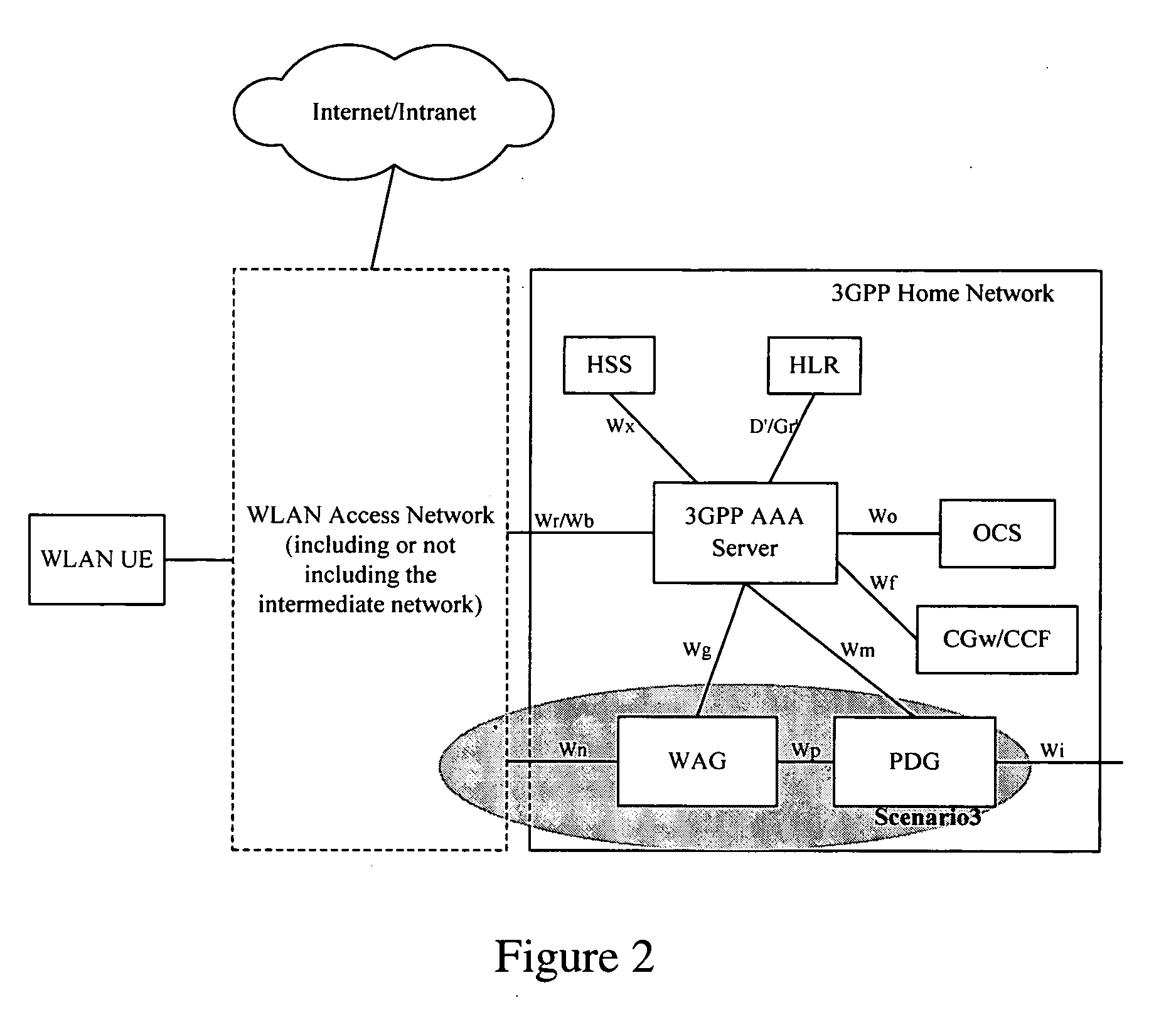
Method for user equipment selection of a packet data gateway in a wireless local network
InactiveUS20060126584A1Avoid unnecessary signalingSave network resourcesNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionTelecommunicationsIp address
Disclosed herein is a method for Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) User Equipment (UE) selection of a Packet Data Gateway (PDG). When the WLAN UE fails to access, the PDG returns a message containing the failure cause value to the WLAN UE that has sent the request such that the WLAN UE could perform different operations according to the specific failure cause value in the message to select a PDG. For example, the WLAN UE may request DNS again to obtain the IP address of the PDG in a home network by parsing in connection with a requested service, or the WLAN UE may first subscribe to the service before re-performing the operation of selecting a PDG, or the WLAN UE may re-select a PDG with another parsed IP address and send a connection request thereto. As a result, the process of WLAN UE asking DNS to re-direct to the home network to select PDG is left out when possible, unnecessary signaling is avoided, and the network resources are saved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
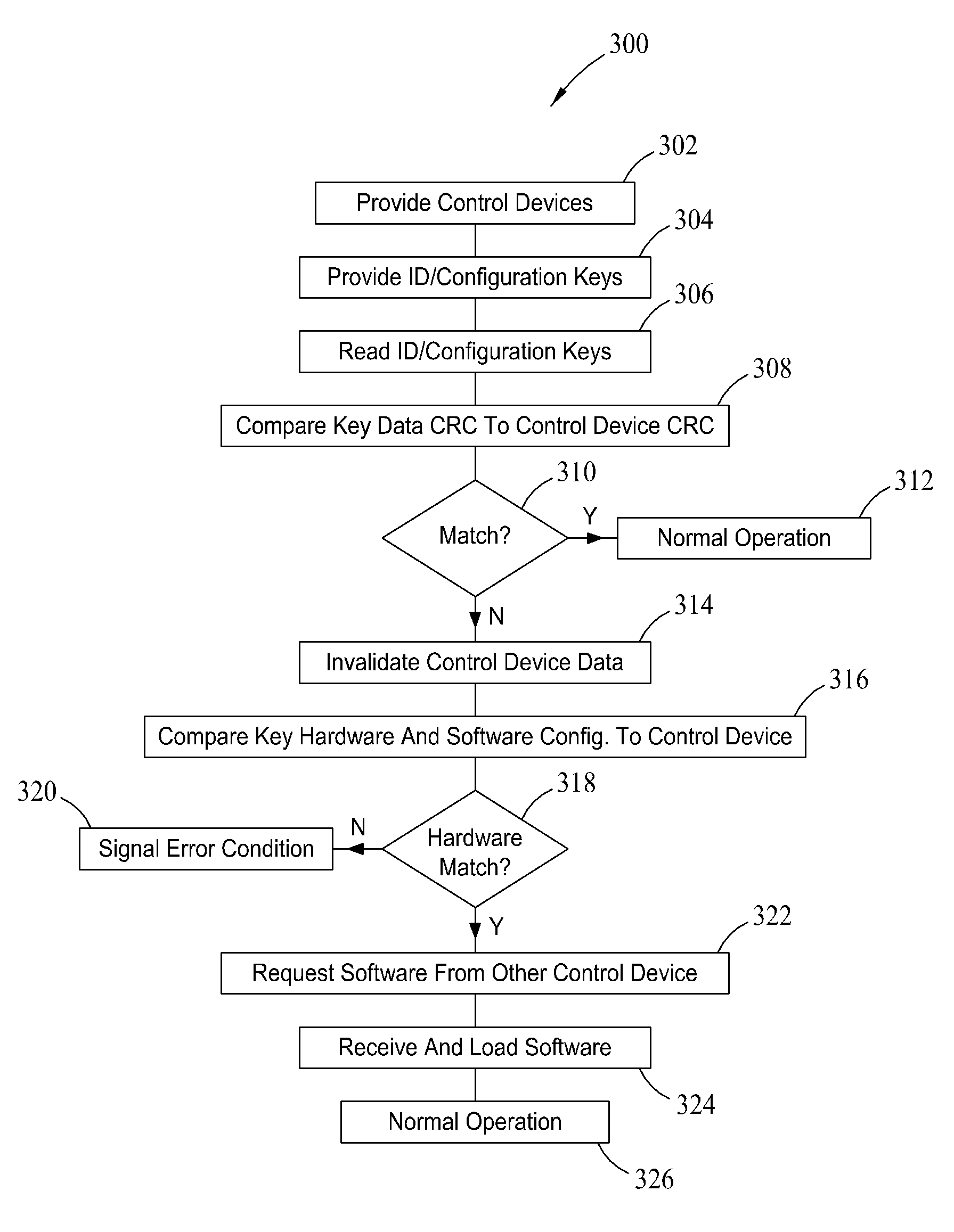
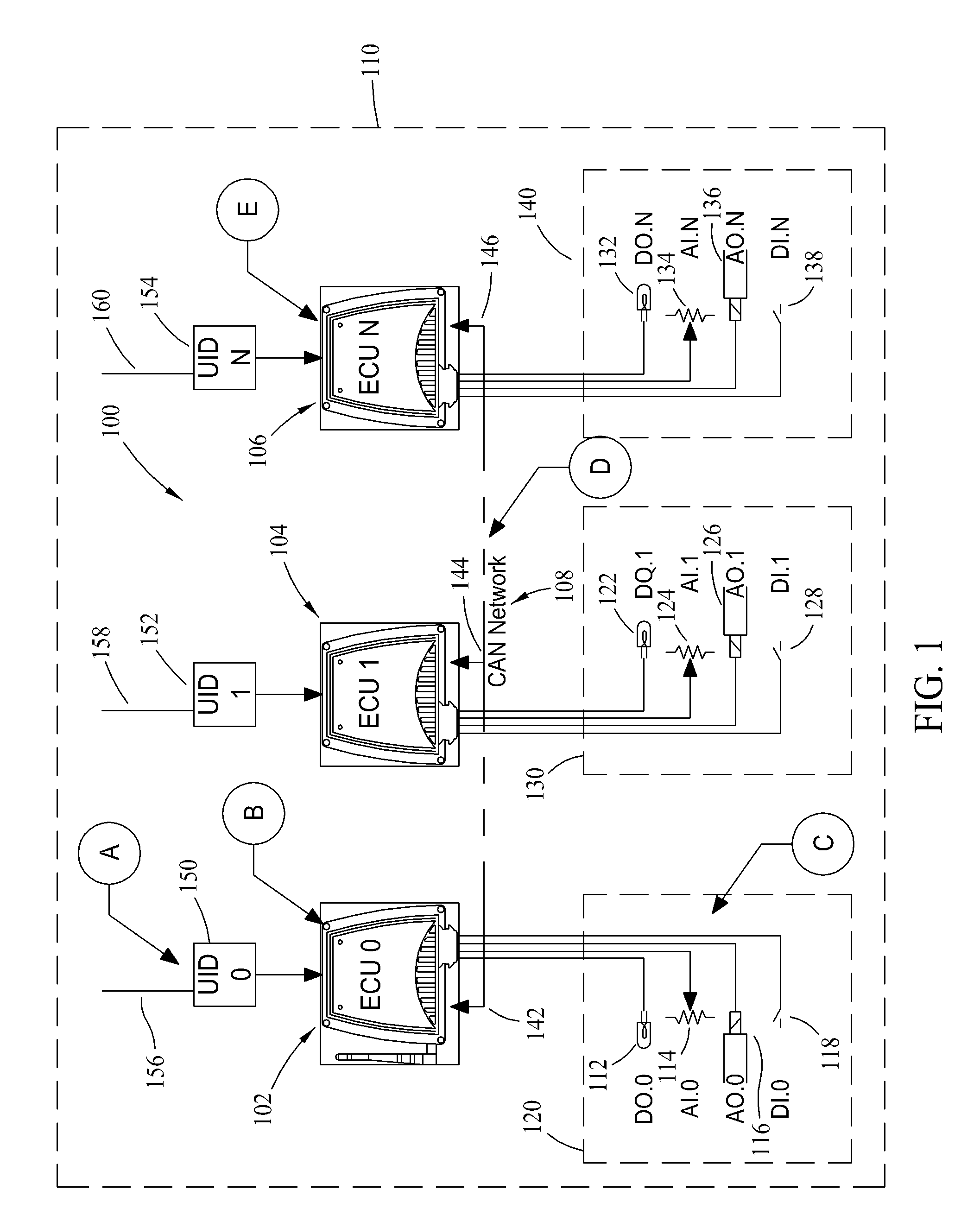
Methods and systems for identifying and configuring networked devices
Auto-detection and configuring systems and methods for interconnected, position dependent control devices are disclosed. Embedded identification and configuration keys are associated with each of the control devices in a network, such that specific connection nodes for each controller may be determined by electronically reading the identification as the control devices are installed. Hardware and software compatibility issues may be detected and resolved, including self configuring of the control devices with the proper software where possible. Otherwise, error conditions are signaled.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
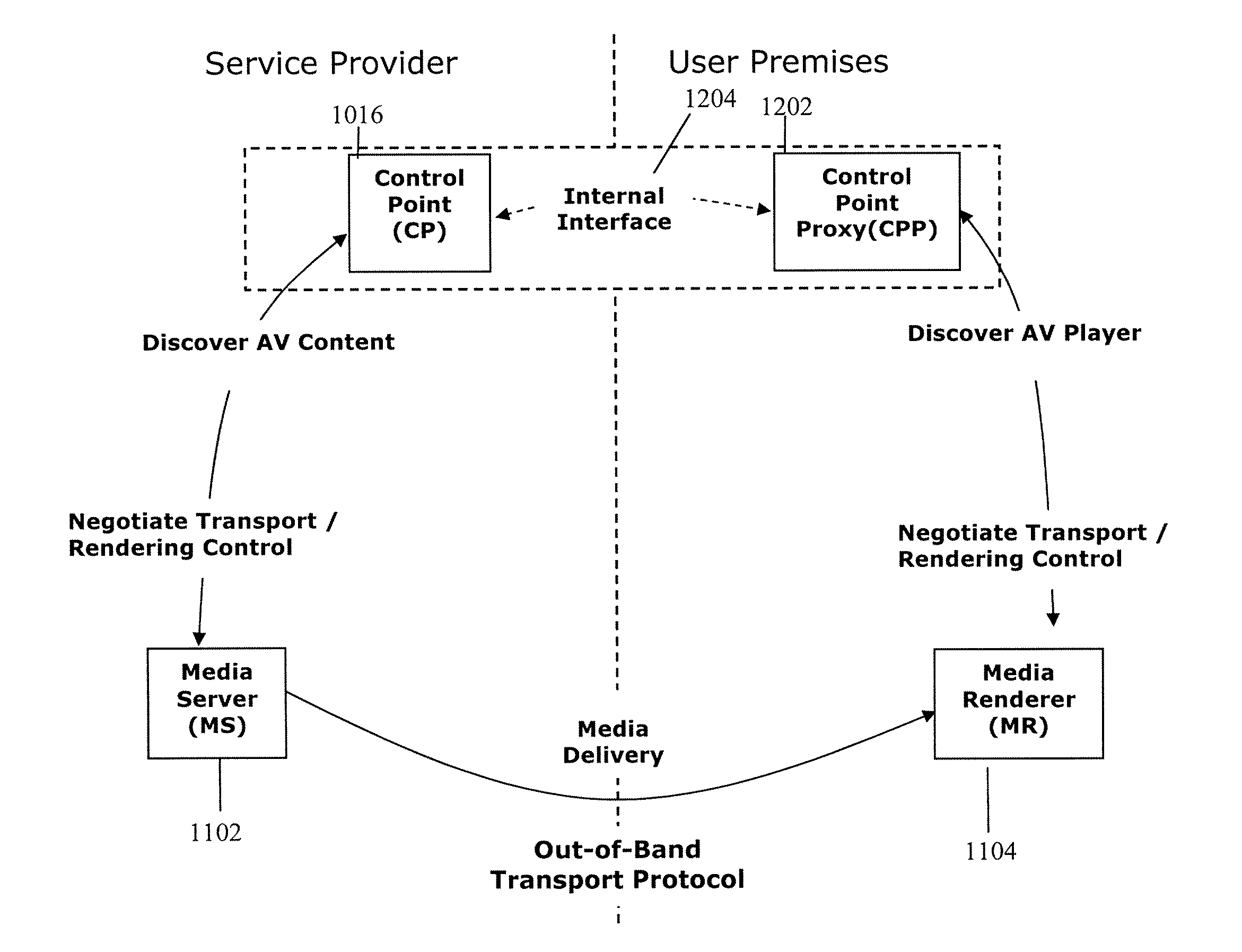
Digital home networks having a control point located on a wide area network
A method of controlling and delivering media content from a media server (MS) to a media renderer (MR) utilizing a wide area IMS network for control. The method involves: provisioning a serving node in the IMS network with control point (CP) logic that includes logic to negotiate media content delivery with a least one of an MS and an MR; provisioning a user endpoint (UE) device of the IMS network with control point proxy (CPP) logic that includes logic to negotiate media content delivery and VCR controls to control media presentation; in response to a media content delivery request, invoking the CPP logic and the CP logic to cooperatively negotiate media content delivery between an MS and an MR that uses local wireless or land line connections when possible in order to minimize wide area bandwidth usage.
Owner:AYLUS NETWORKS
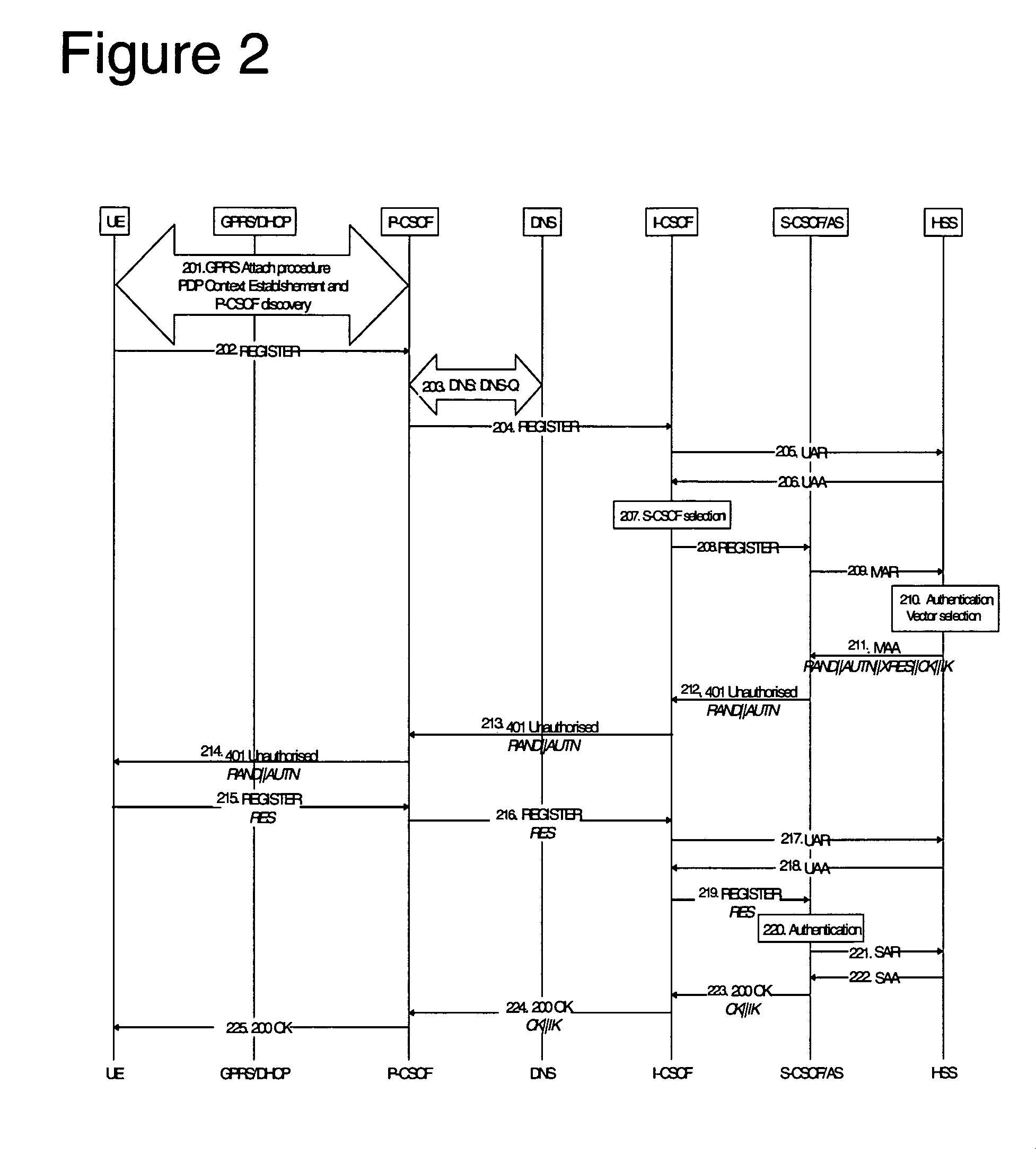
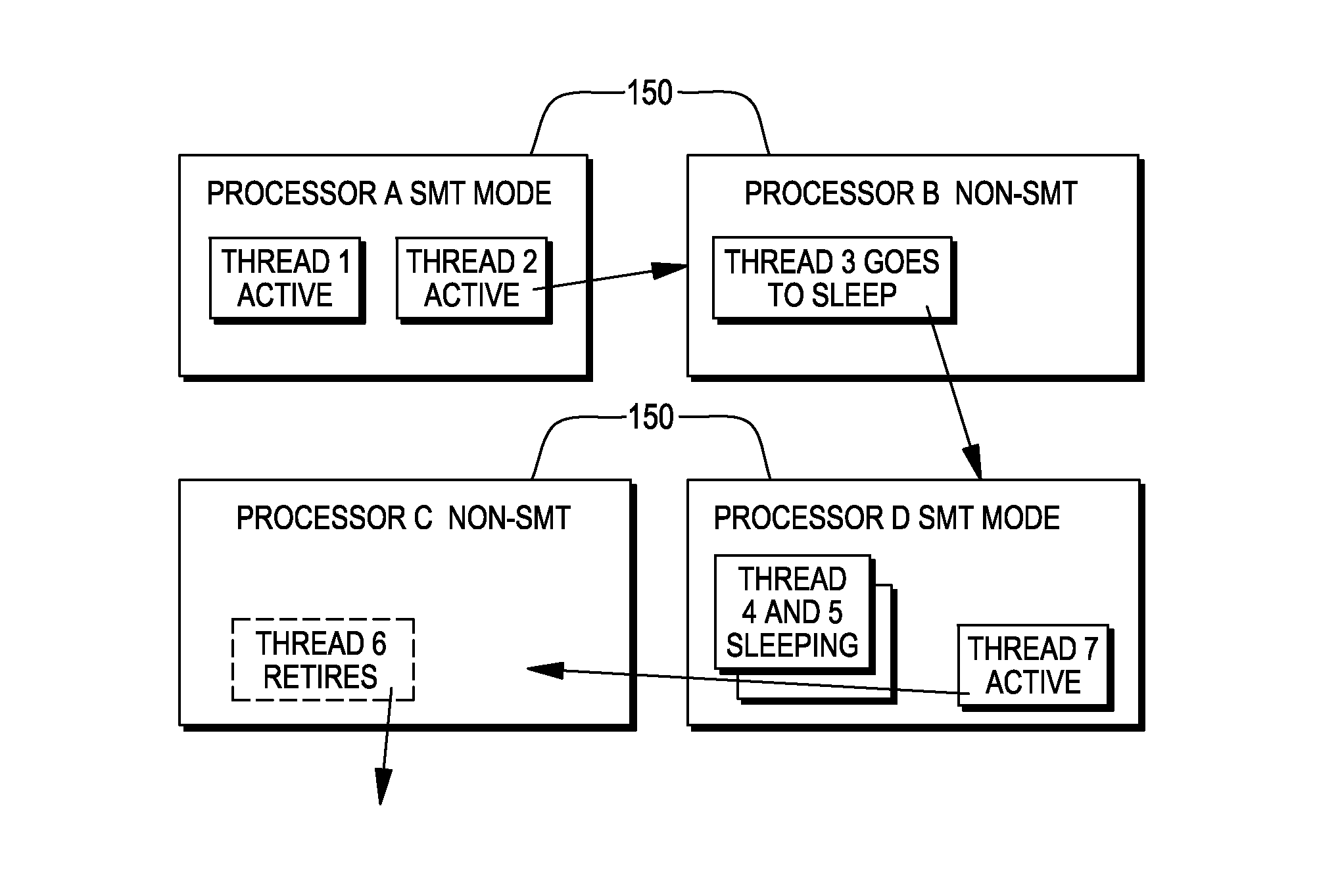
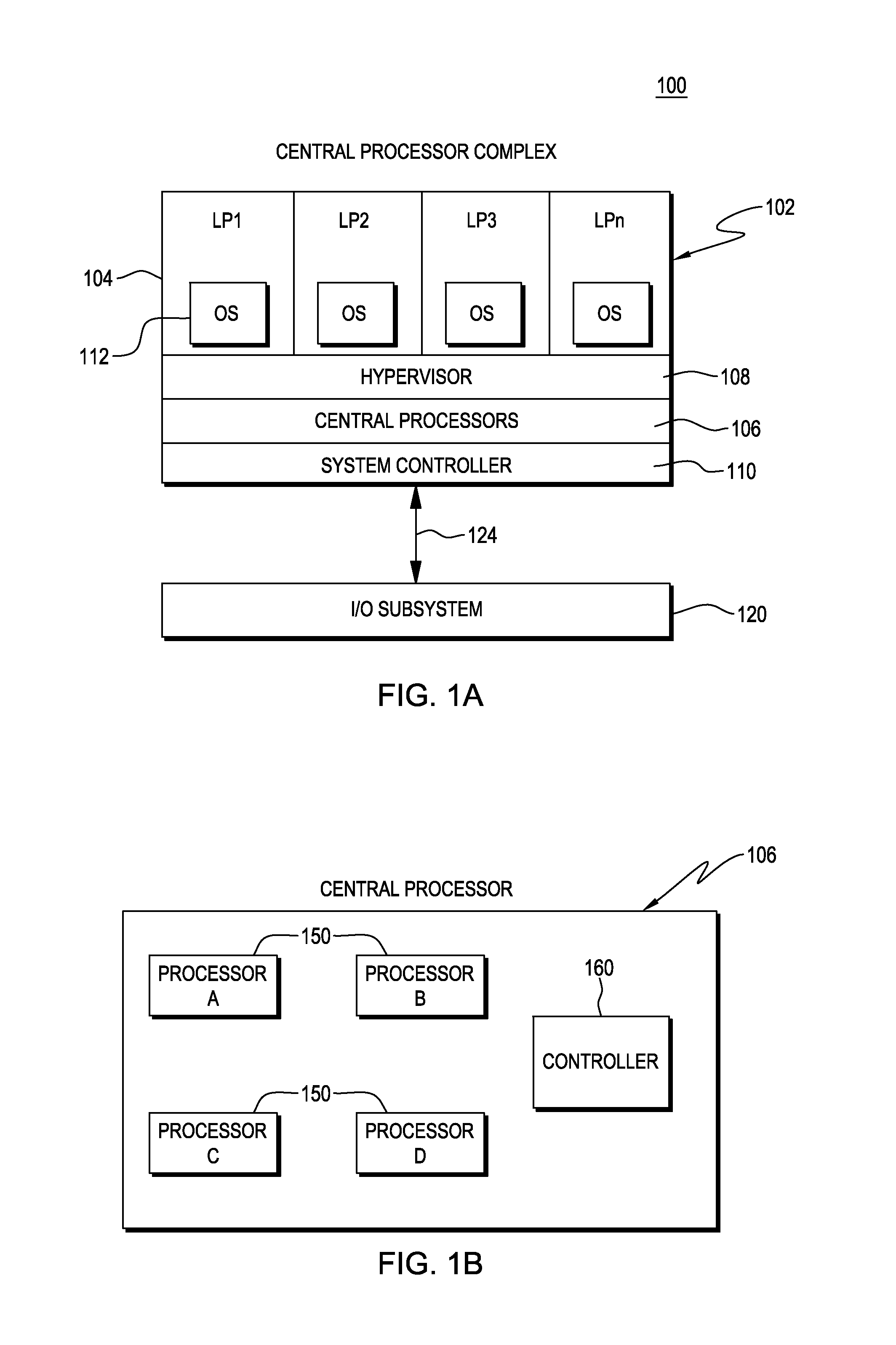
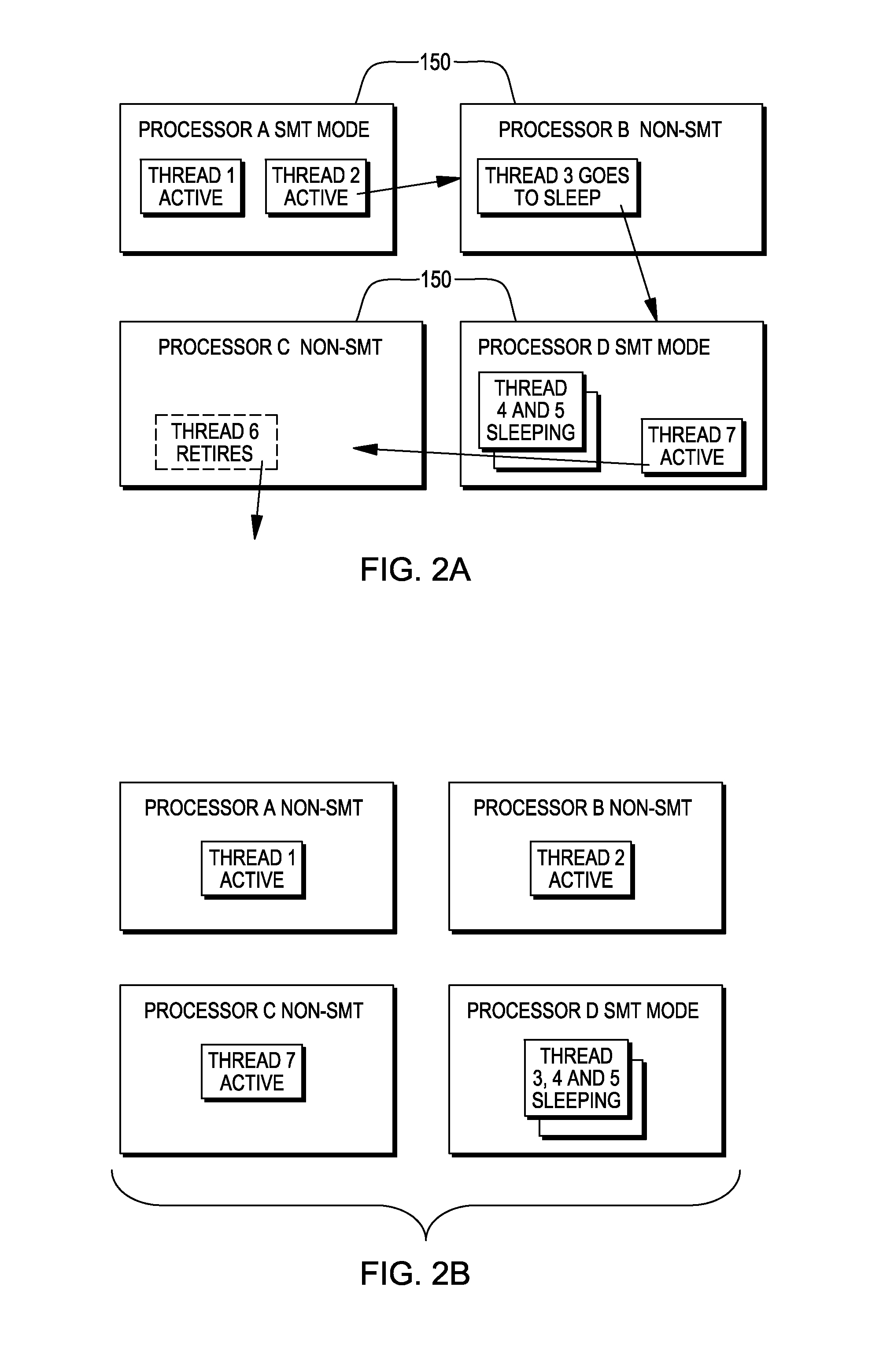
Management of threads within a computing environment
ActiveUS20130191832A1Easy to manageEnhanced advantageMultiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsProbable CaseParallel computing
Threads of a computing environment are managed to improve system performance. Threads are migrated between processors to take advantage of single thread processing mode, when possible. As an example, inactive threads are migrated from one or more processors, potentially freeing-up one or more processors to execute an active thread. Active threads are migrated from one processor to another to transform multiple threading mode processors to single thread mode processors.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus for and method of forming seals in fuel cells and fuel cell stacks
InactiveUS6852439B2Good chemical resistanceImprove robustnessCellsEngine sealsFuel cellsProbable Case
A sealing technique is provided for forming complex and multiple seal configurations for fuel cells and other electrochemical cells. To provide a seal, for sealing chambers for oxidant, fuel and / or coolant, a groove network is provided extending through the various elements of the fuel cell assembly. A source of seal material is then connected to an external filling port and injected into the groove network, and the seal material is then cured to form the seal. There is thus formed a “seal in place”, that is robust and can accommodate variations in tolerances and dimensions, and that can be bonded, where possible, to individual elements of the fuel cell assembly. This avoids the difficulty, labor intensive cost and complexity of manually assembling many individual gaskets into complex groove shapes and the like. The seal material can be selected to be comparable with a wide variety of gases, liquid coolants and the like.
Owner:HYDROGENICS CORP
Consolidation of product data models
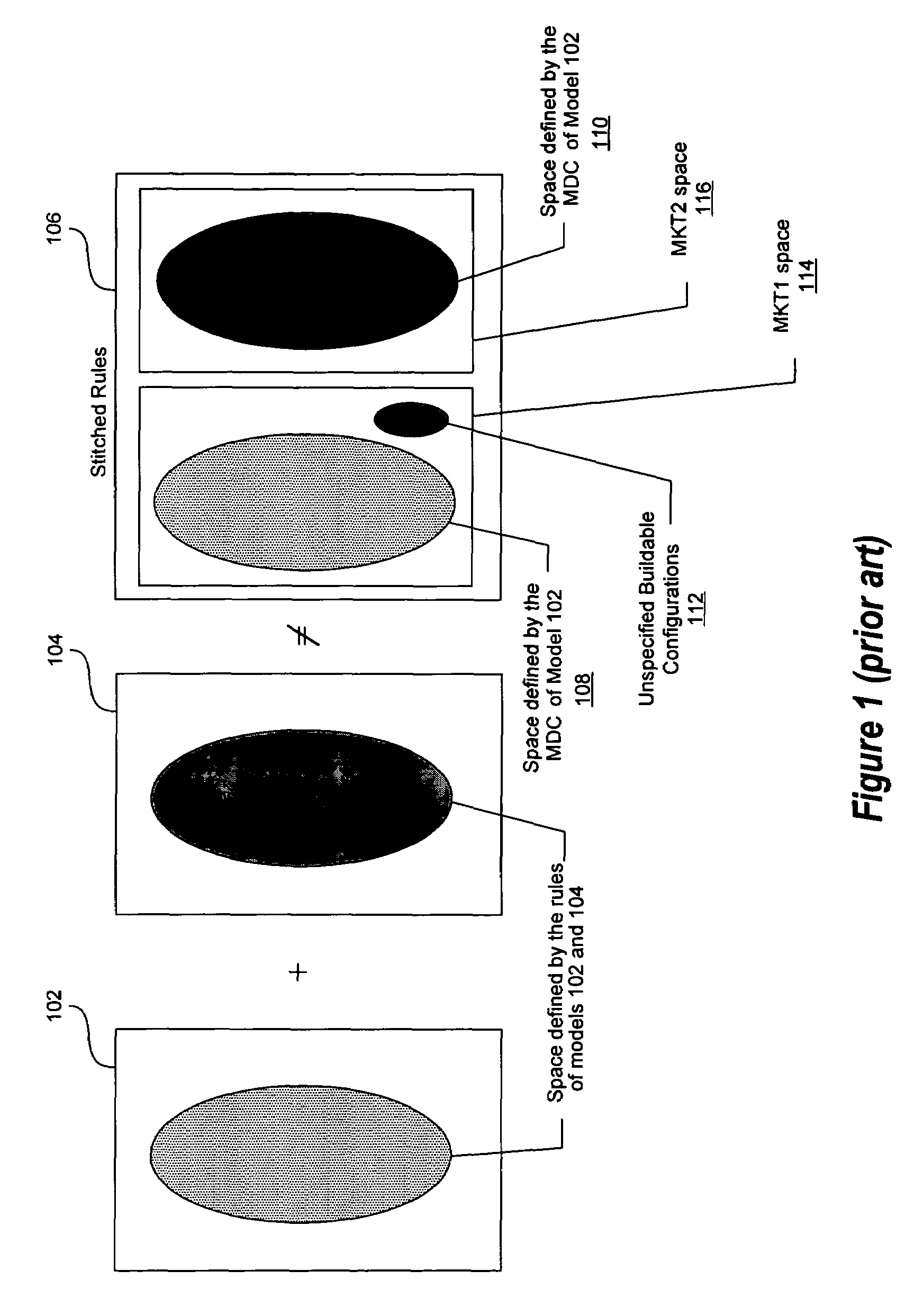
ActiveUS7739080B1Computation using non-denominational number representationConstraint-based CADProbable CaseComputer compatibility
A model consolidation process combines multiple configuration models into a single unified configuration model that contains the union of the allowable combinations (i.e. combinations that are buildable) from each of the original models. An aspect of at least one embodiment of the model consolidation process is that it allows models to be combined in such a way that any incompatibilities or contradictions between models are detected and automatically resolved where possible. If an incompatibility is detected that cannot be automatically resolved, then the configuration models should not be combined. Instead if this incompatibility case occurs, at least one embodiment of the model consolidation process produces a description of the problem encountered and report the problem along with the necessary information required for a human to resolve it.
Owner:VERSATA DEV GROUP
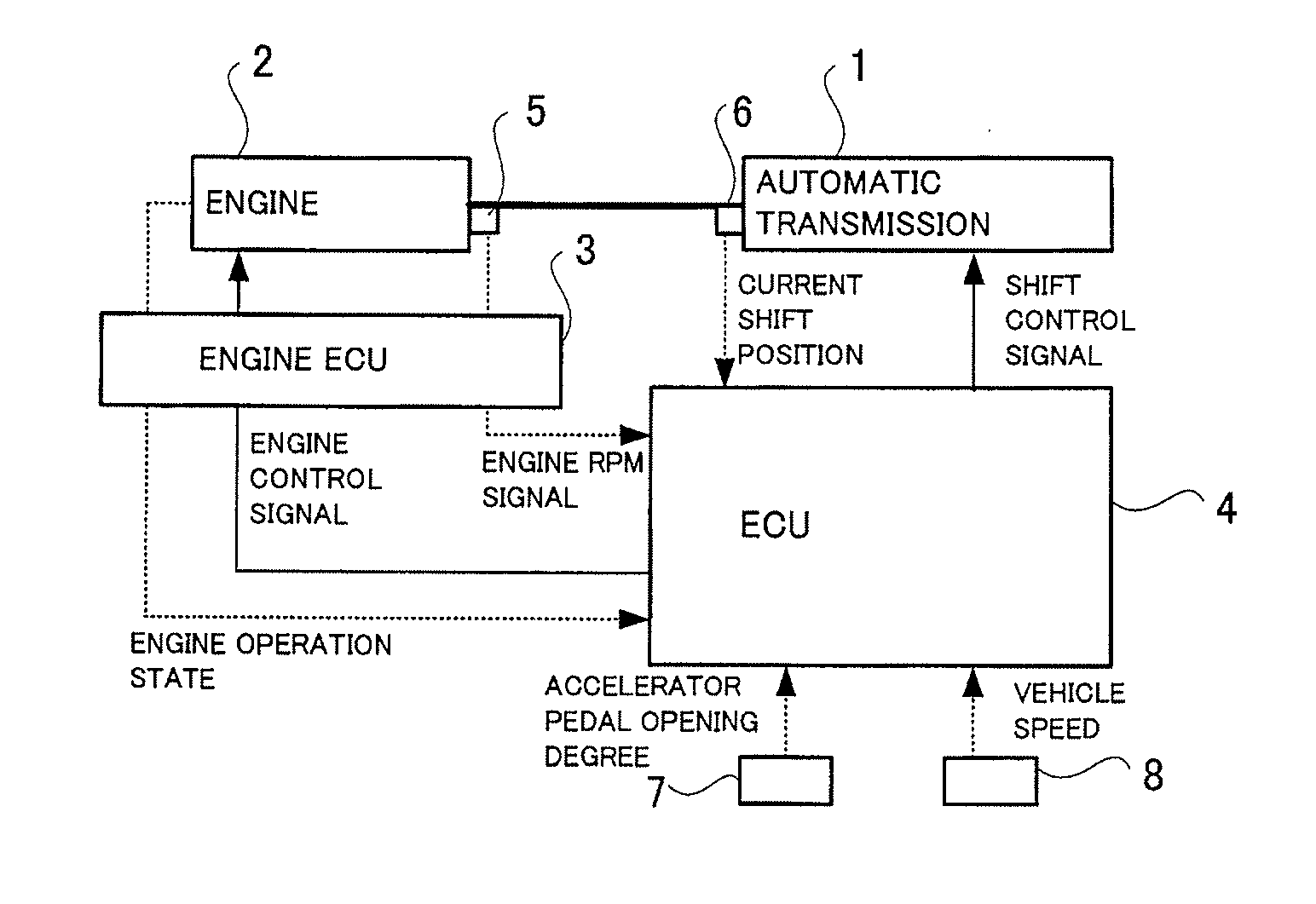
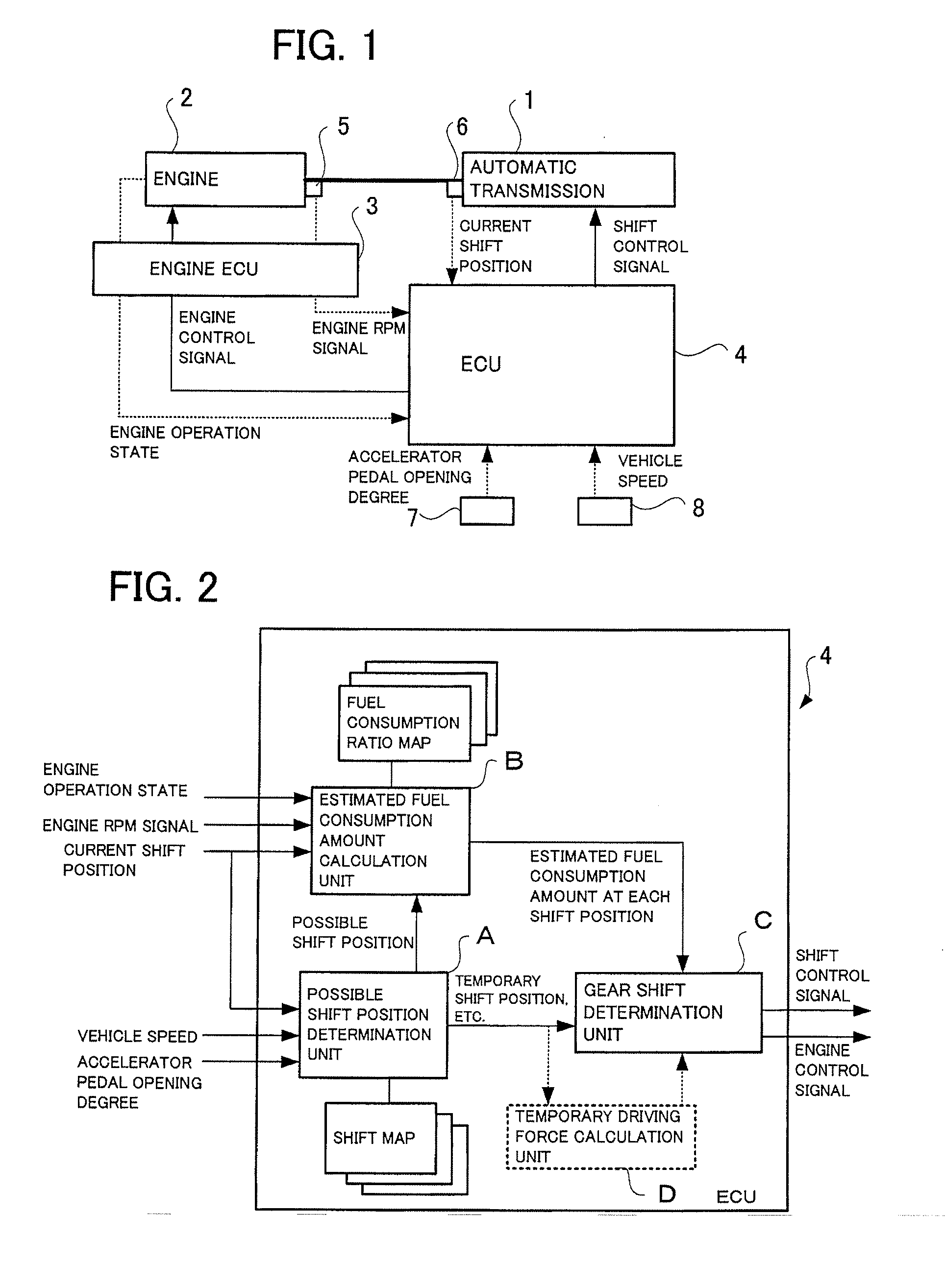
Control device for automatic transmission
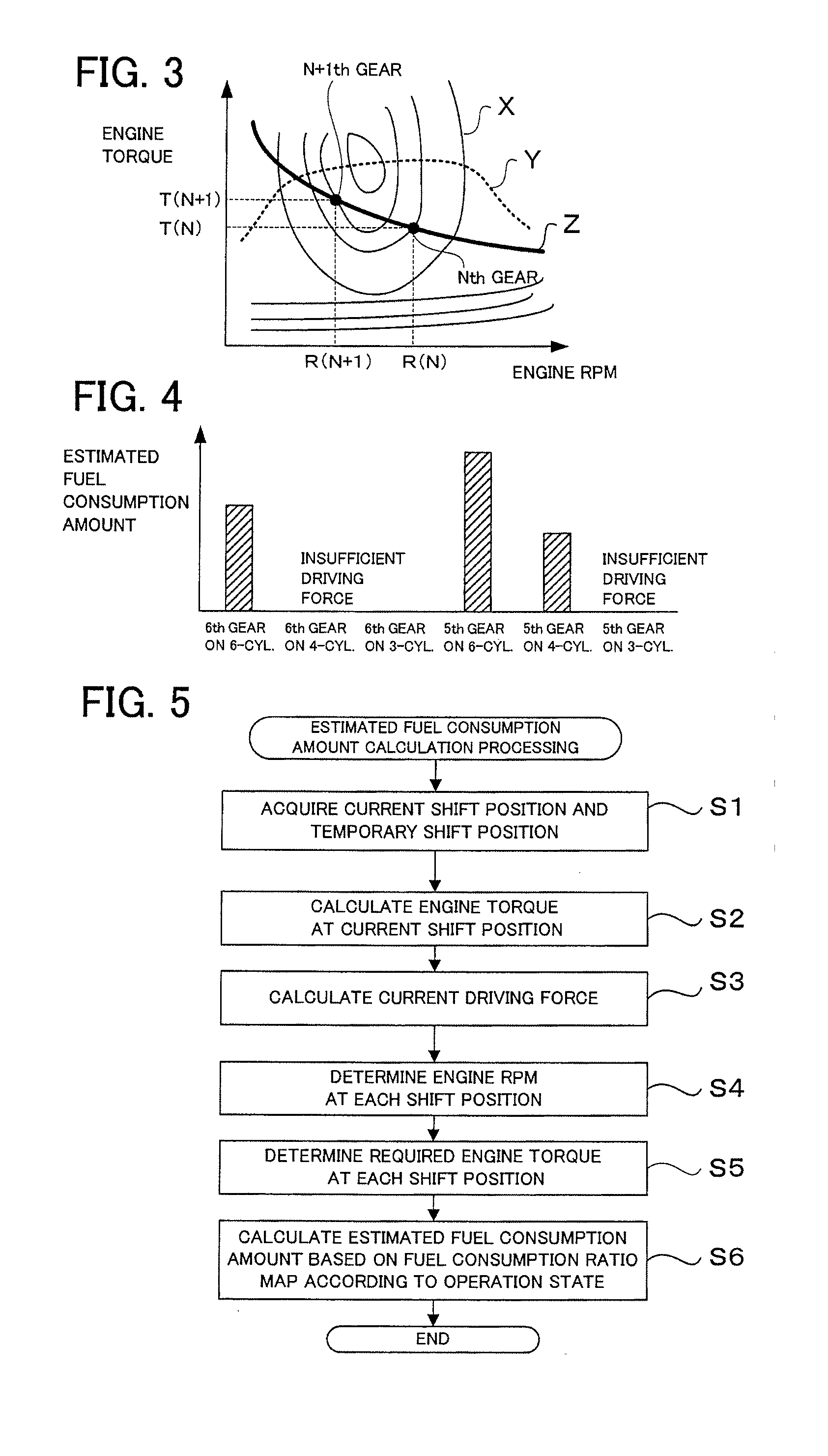
ActiveUS20130184949A1Reduce fuel consumptionSmall fuel consumption amountDigital data processing detailsRoad transportAutomatic train controlAutomatic control
For each engine operation state to which a variable cylinder engine can be switched, a fuel consumption amount to be consumed to generate a driving force required to maintain a current traveling state of a vehicle for each of a current gear and a new gear after a possible shift-up is calculated. An automatic shift control of shifting up to the new gear is performed in a condition that a calculated fuel consumption amount of the new gear after the possible shift-up is smaller than a calculated fuel consumption amount of the current gear. In this way, the fuel consumption amount can be optimally reduced and the shift control can be performed without degrading the traveling performance, even in the vehicle equipped with the variable cylinder engine.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
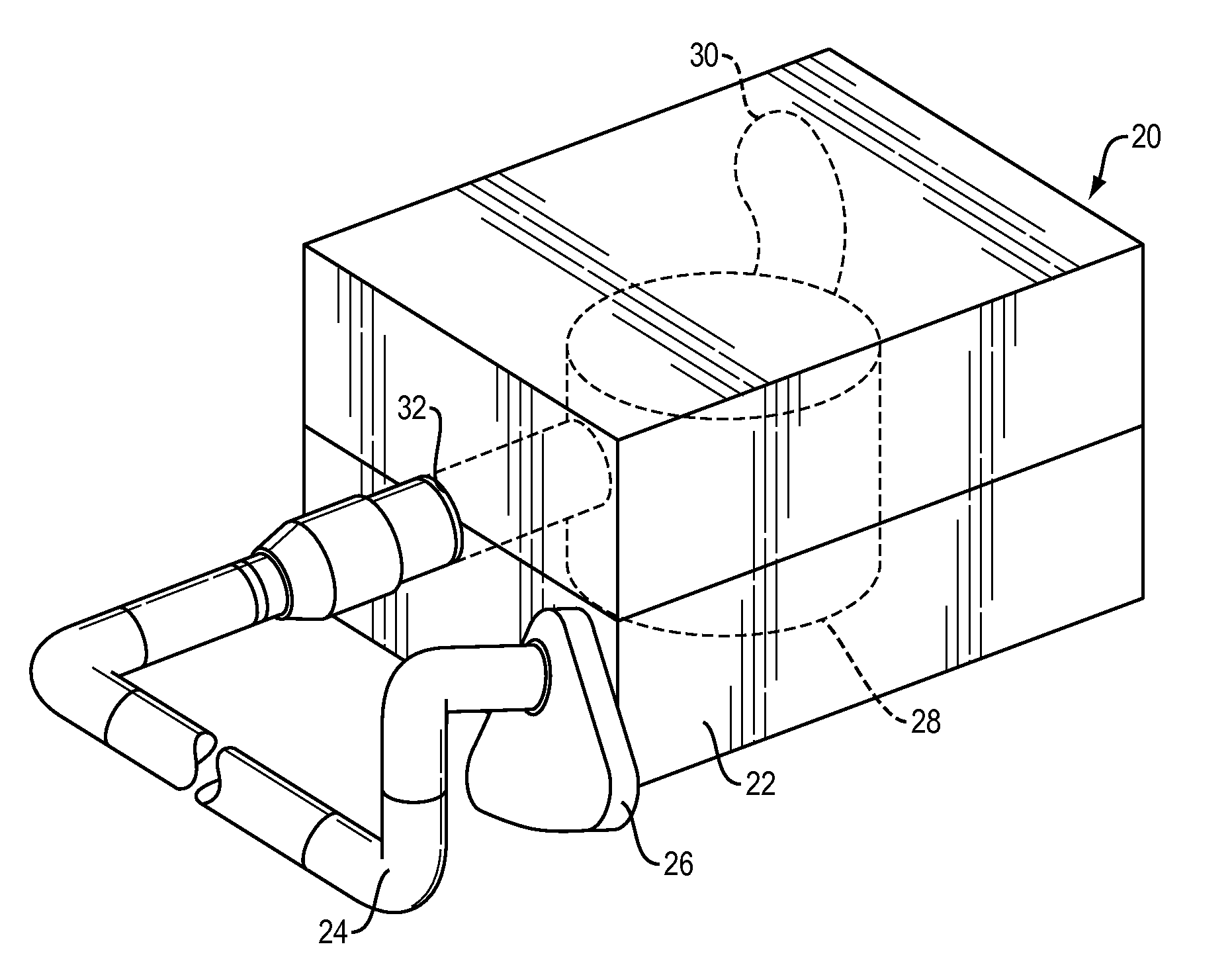
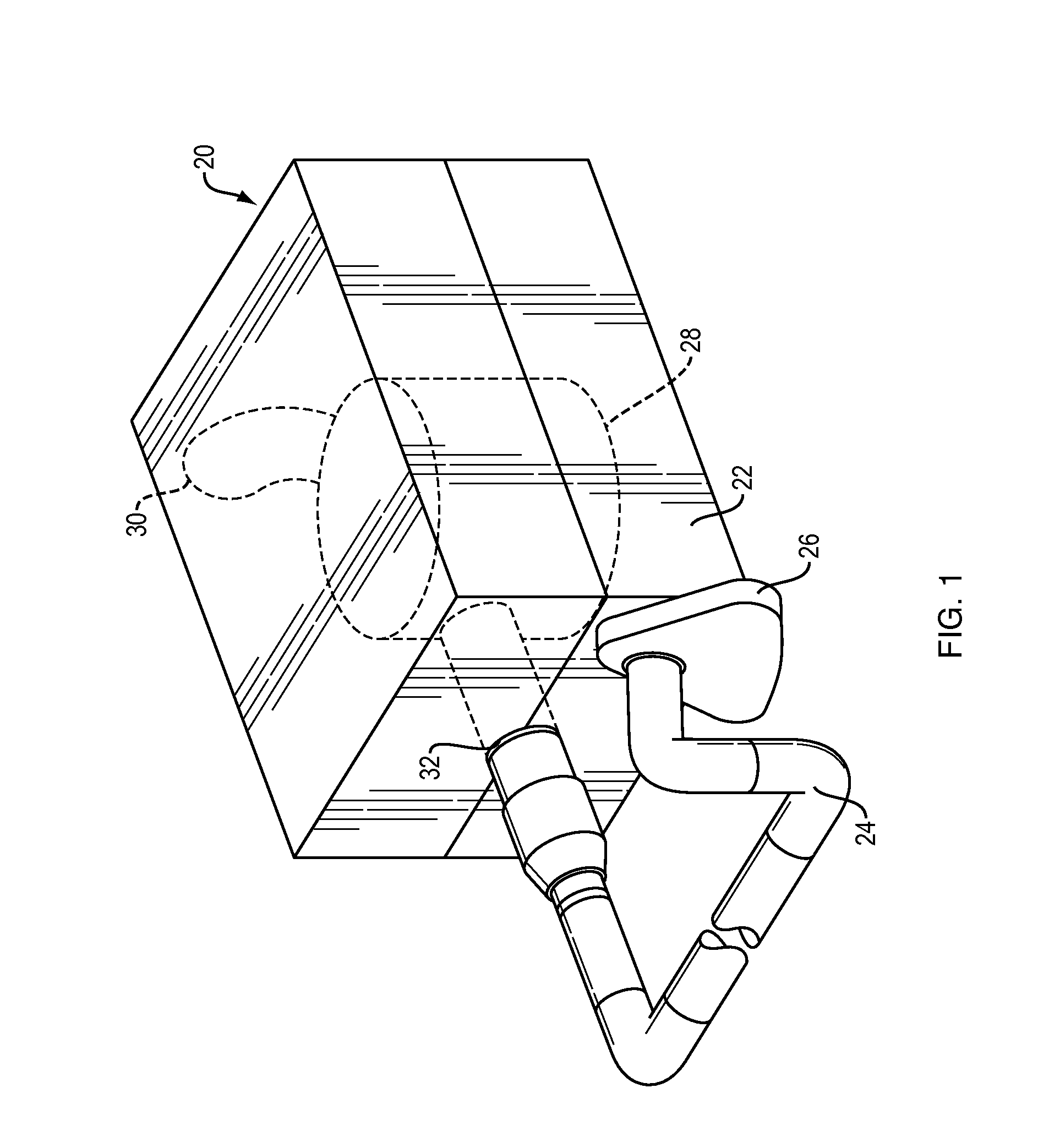
Drain cover for generally open flat drainage areas with debris blockage and open drainage portions
InactiveUS8557109B1High strengthLarge apertureFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesSewerage structuresProbable CaseEngineering
A drain cover having a main drainage surface with relatively larger apertures or openings therein, comprising generally 50 percent of the surface, so that larger debris is accepted into a related drain pipe when a depending skirt portion of the drain cover, having smaller perforations, becomes clogged. In this way a two-layer drainage system for a generally flat surface is provided that allows draining of water and small particulates alone when possible, but upon the clogging of the smaller openings the generally flat surface can be protected from flooding by allowing larger particulates to drain into the main drainage surface. The main drainage surface is held above the flat surface by the depending skirt, at a level of ⅜ to 1 inch above the flat surface. When the depending skirt openings are clogged the water and debris will rise until allowed to drain into the larger openings of the main drainage surface.
Owner:SUTHERLAND MARK
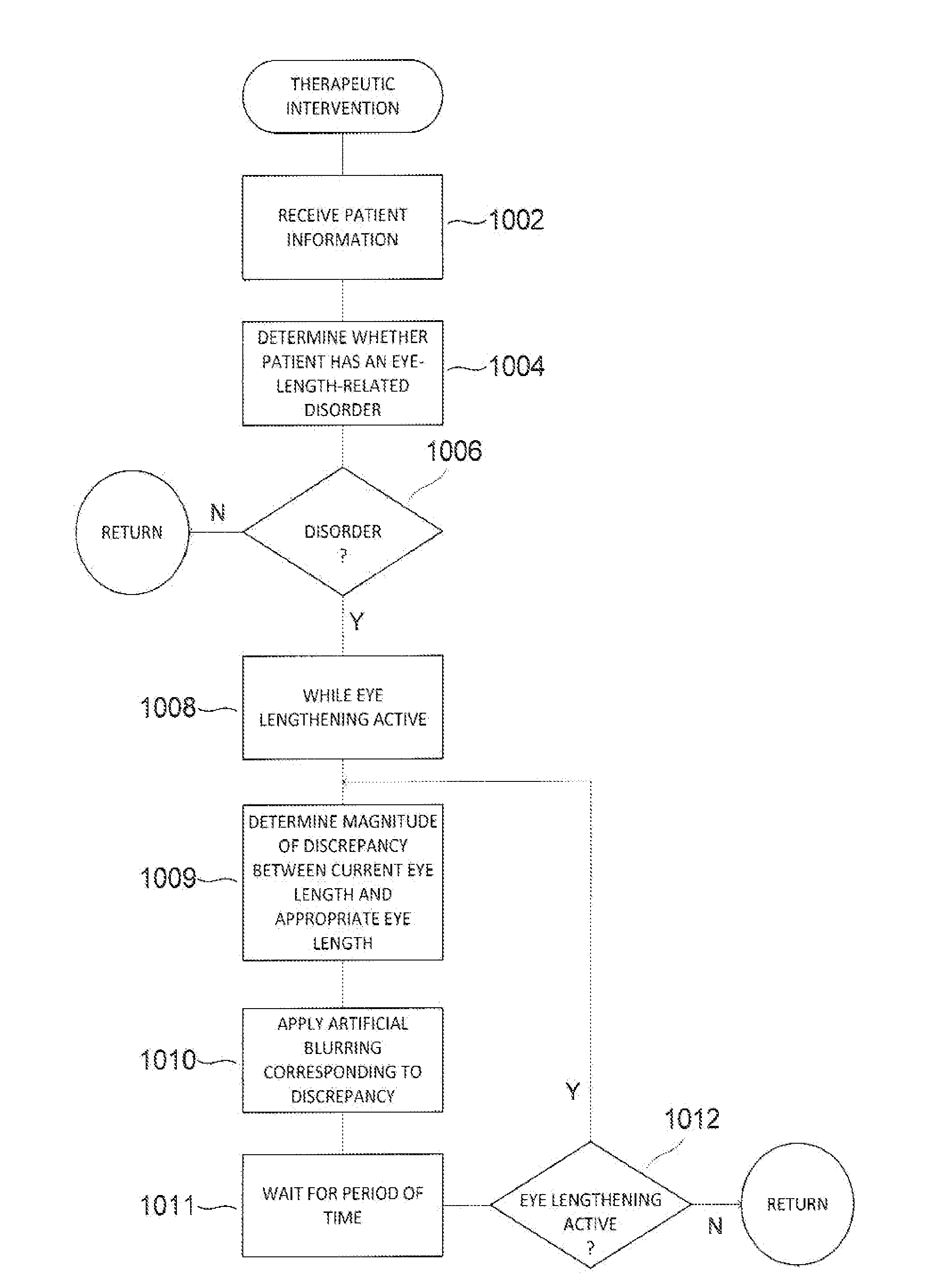
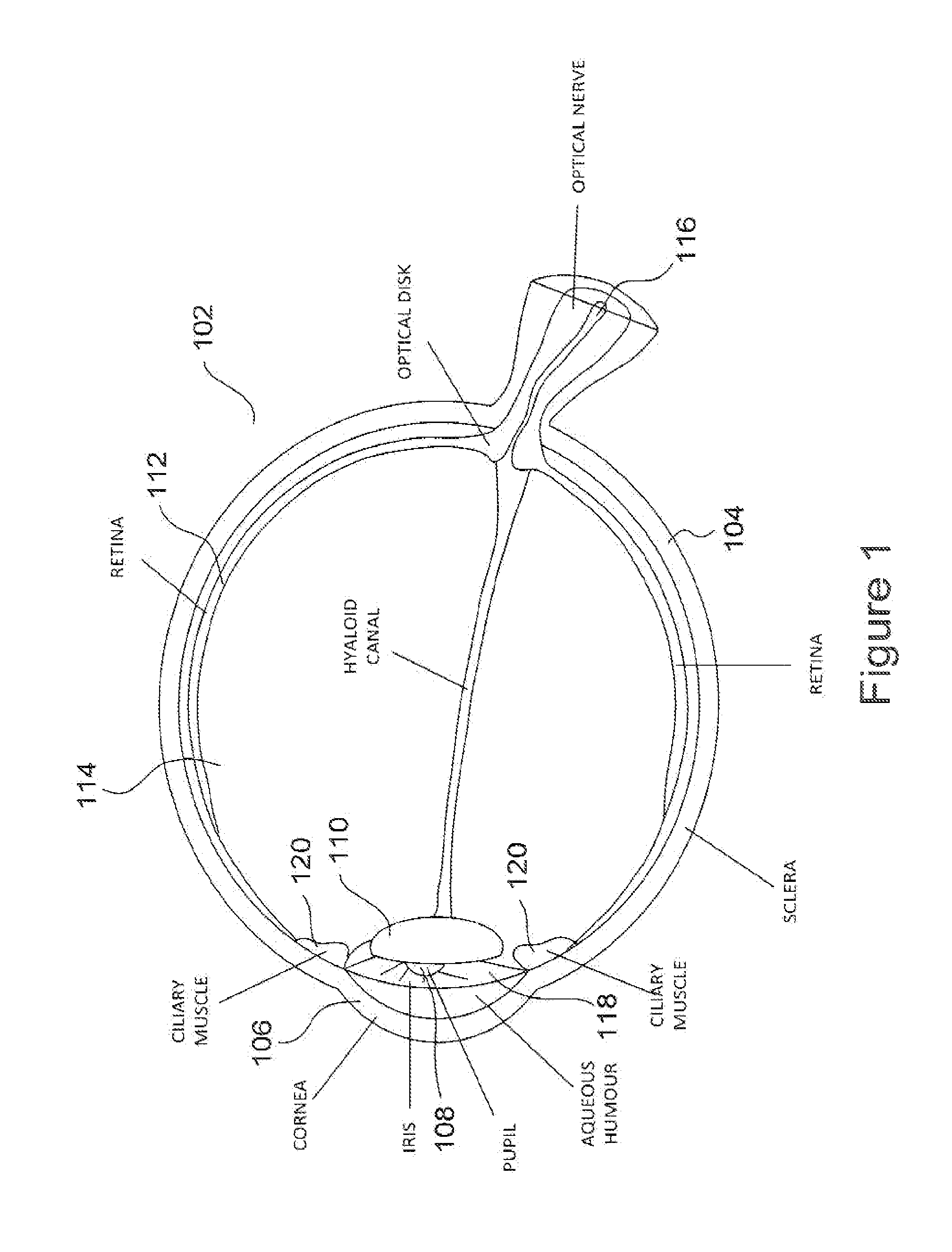
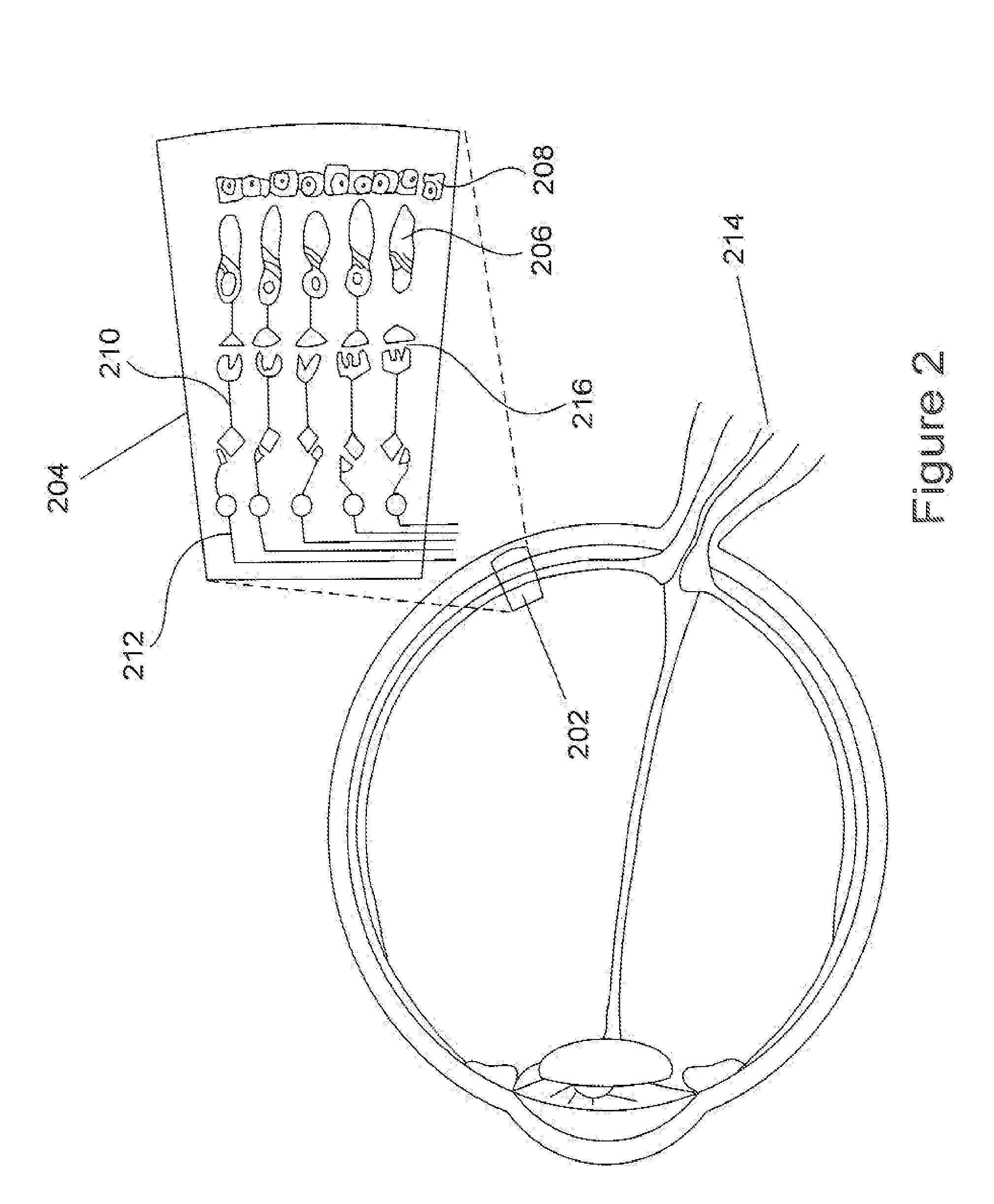
Method and apparatus for limiting growth of eye length
ActiveUS20110313058A1Prevent and ameliorate and reverse effectInhibiting further degradation of visionBiocideSenses disorderProbable CaseLeg length
Owner:THE MEDICAL COLLEGE OF WISCONSIN
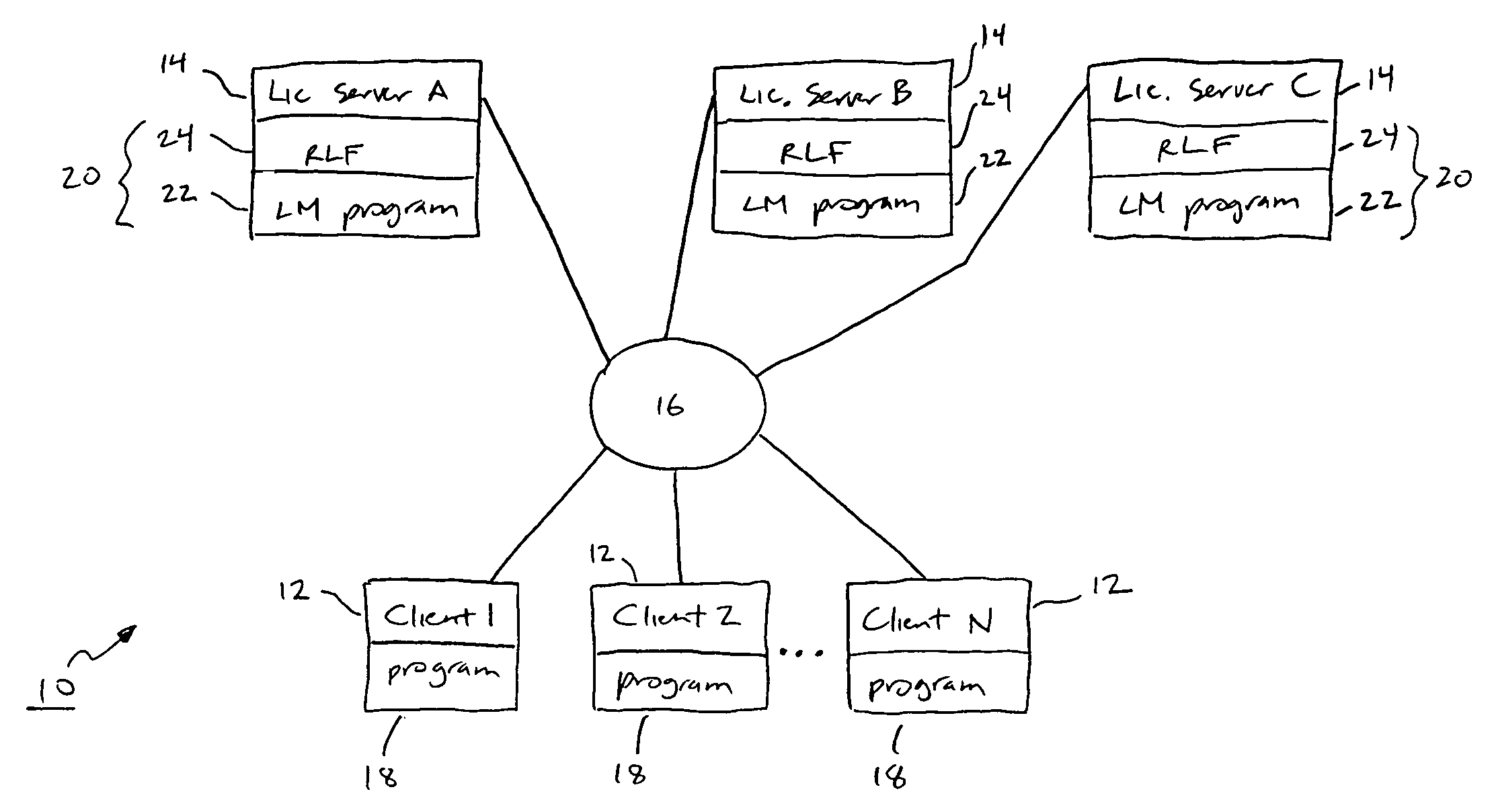
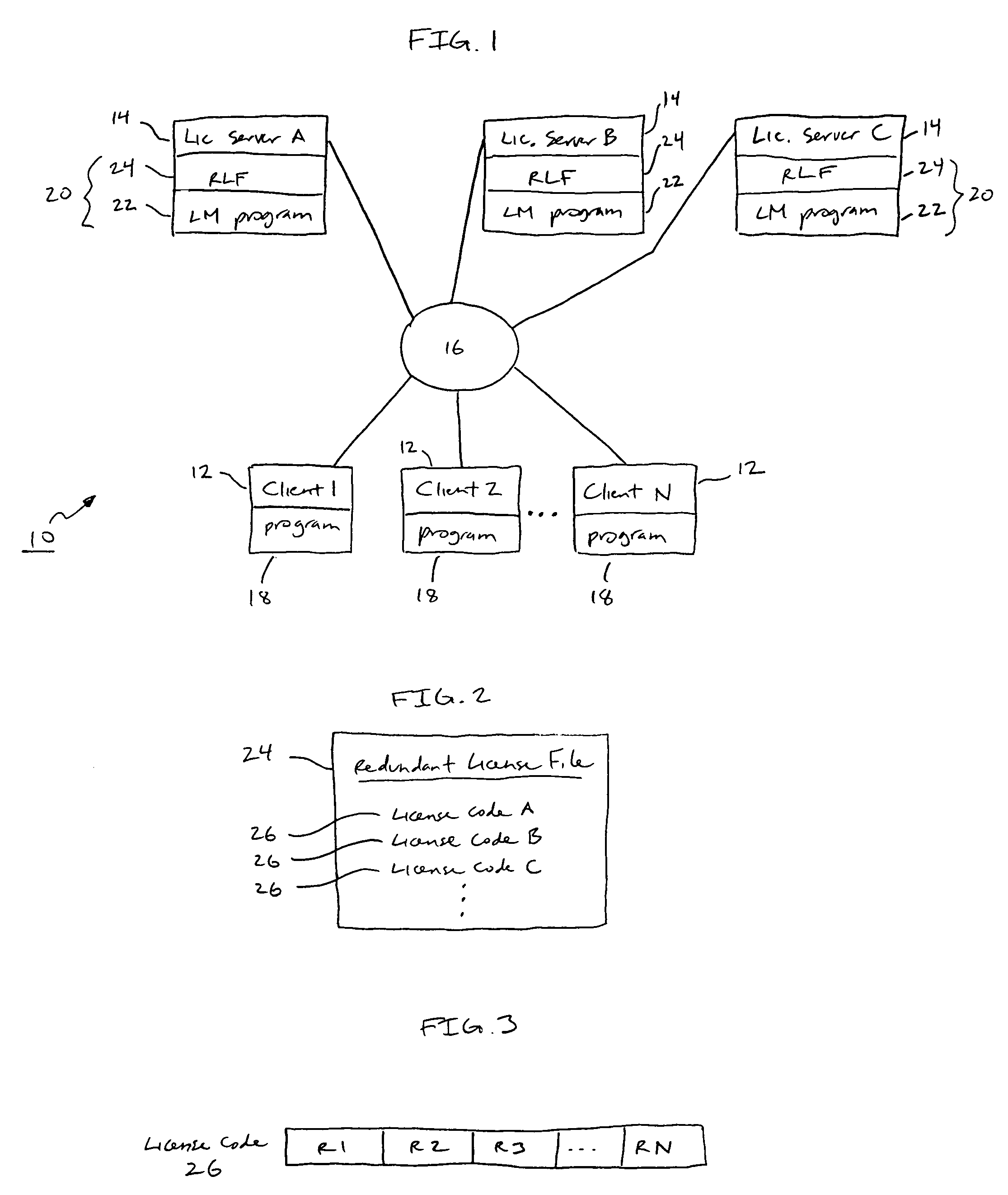
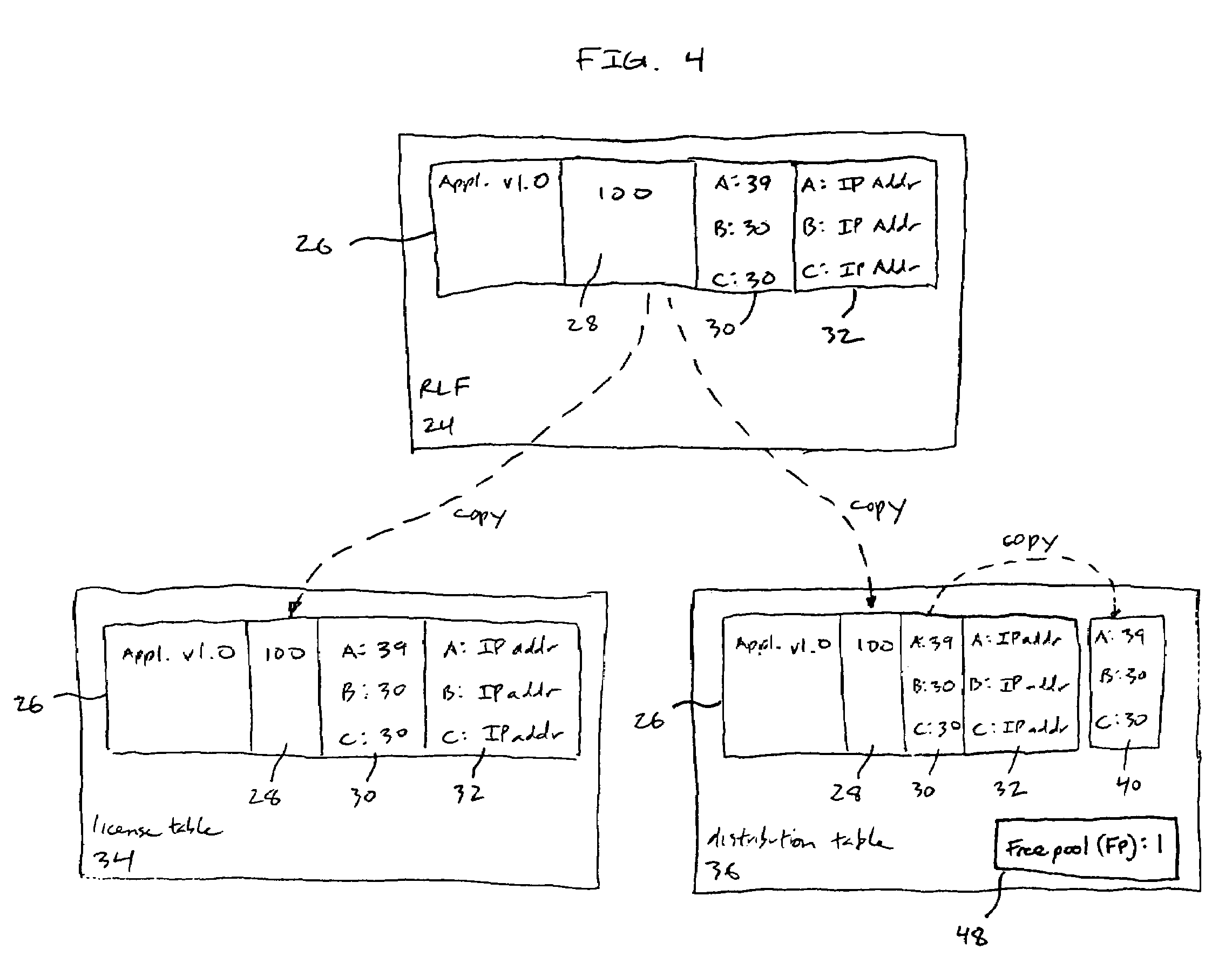
License management system and method with license balancing
ActiveUS7716348B1Improve balanceMultiple digital computer combinationsOffice automationProbable CaseClient-side
A system for balancing a distribution of allocations for protected software over a communication network is disclosed. The system is comprised of at least one client computer and a pool of license servers coupled to the communication network. The client computers request authorizations to use the protected software, while a distribution of allocations is managed among the pool of servers for tracking and managing available allocations for using the protected software. One license server in the pool is designated as the current leader server. When a particular license server does not have a selectable minimum amount of available allocations, the current leader server re-assigns, where possible, the allocations within the pool by updating memory containing the distribution tables of license servers in the pool, to give at least one additional allocation to the particular license server.
Owner:THALES DIS CPL USA INC
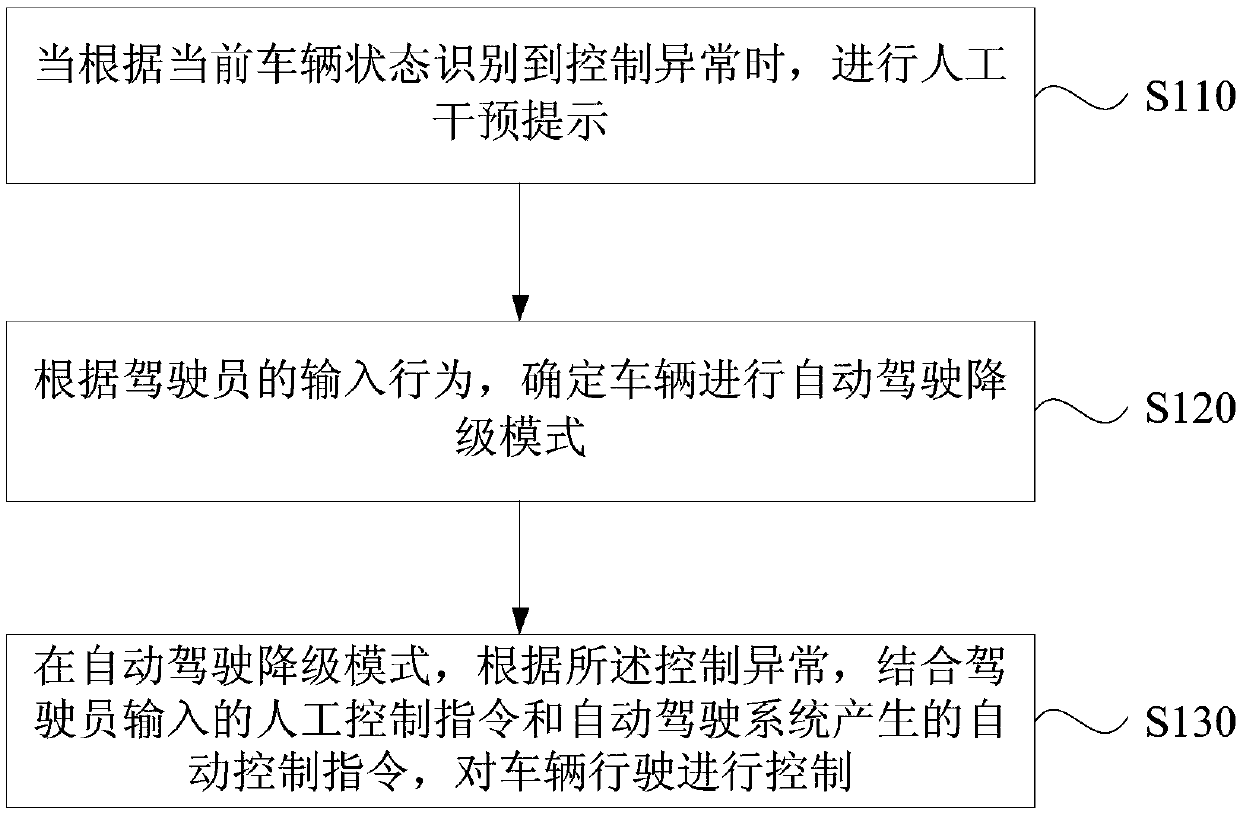
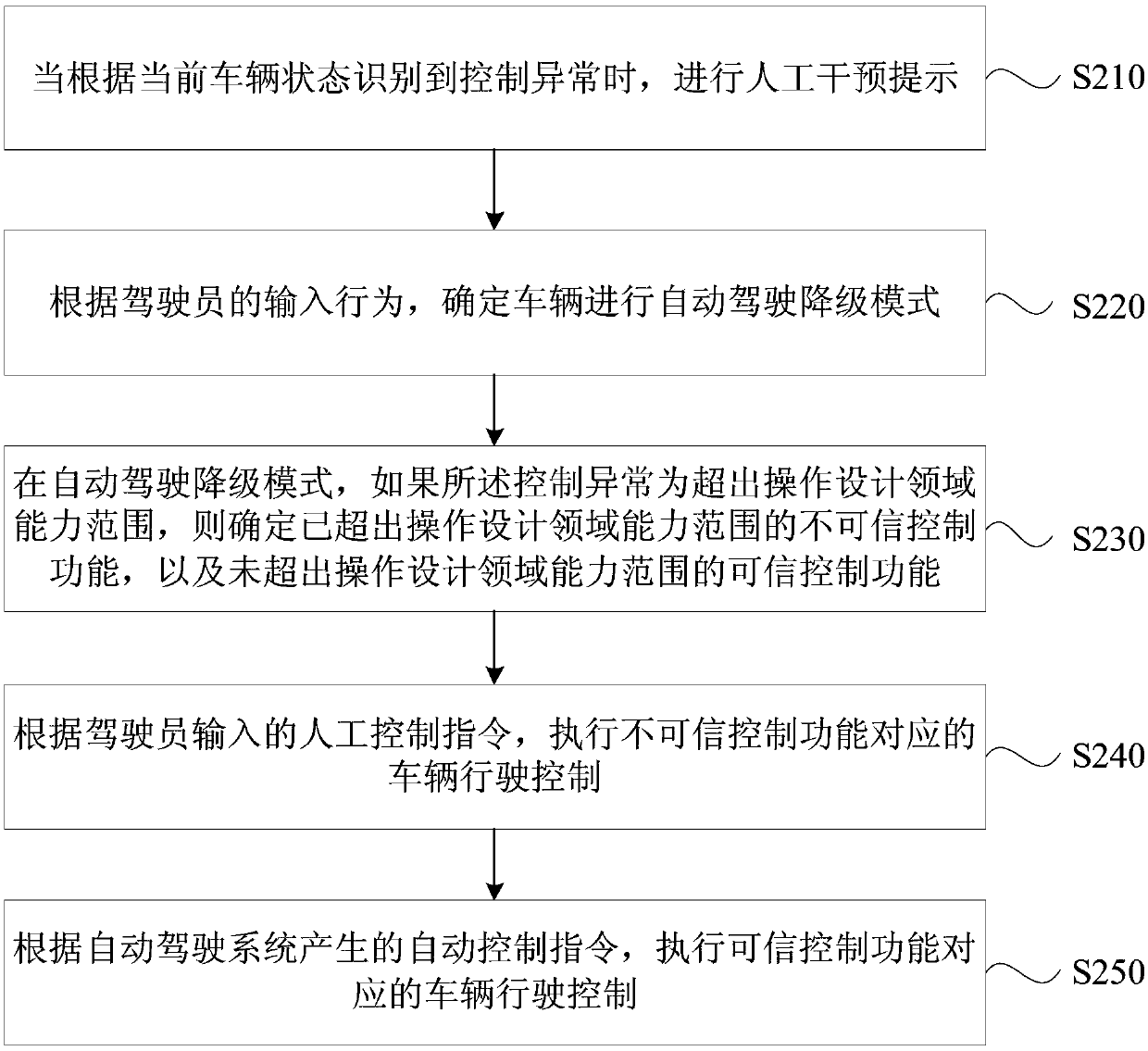
Vehicle control method and device based on automatic driving, equipment and medium
ActiveCN109606385AReduce the burden onEnsure safetyVehicle position/course/altitude controlPosition/direction controlAutomatic controlIn vehicle
Embodiments of the invention disclose a vehicle control method and device based on automatic driving, equipment and a medium. The method includes the following steps: when control abnormality is recognized according to a current vehicle state, a manual intervention prompt is performed; it is determined that a vehicle performs an automatic driving degradation mode according to an input behavior ofa driver; and in the automatic driving degradation mode, according to the control abnormality, and combining a manual control instruction input by the driver and an automatic control instruction generated by an automatic driving system, driving of the vehicle is controlled. The technical scheme of the embodiments solves the problem that when a self-driving vehicle exits automatic driving, the vehicle directly stops running, the driver lacks of intermediate transition from completely not participating in vehicle control to safely controlling the vehicle, achieves that when a driving level of adriverless vehicle needs to be rolled back, if conditions are possible, rollback of moderate degradation is performed to reduce the burden of the driver, and is beneficial to maintain the safety effect.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
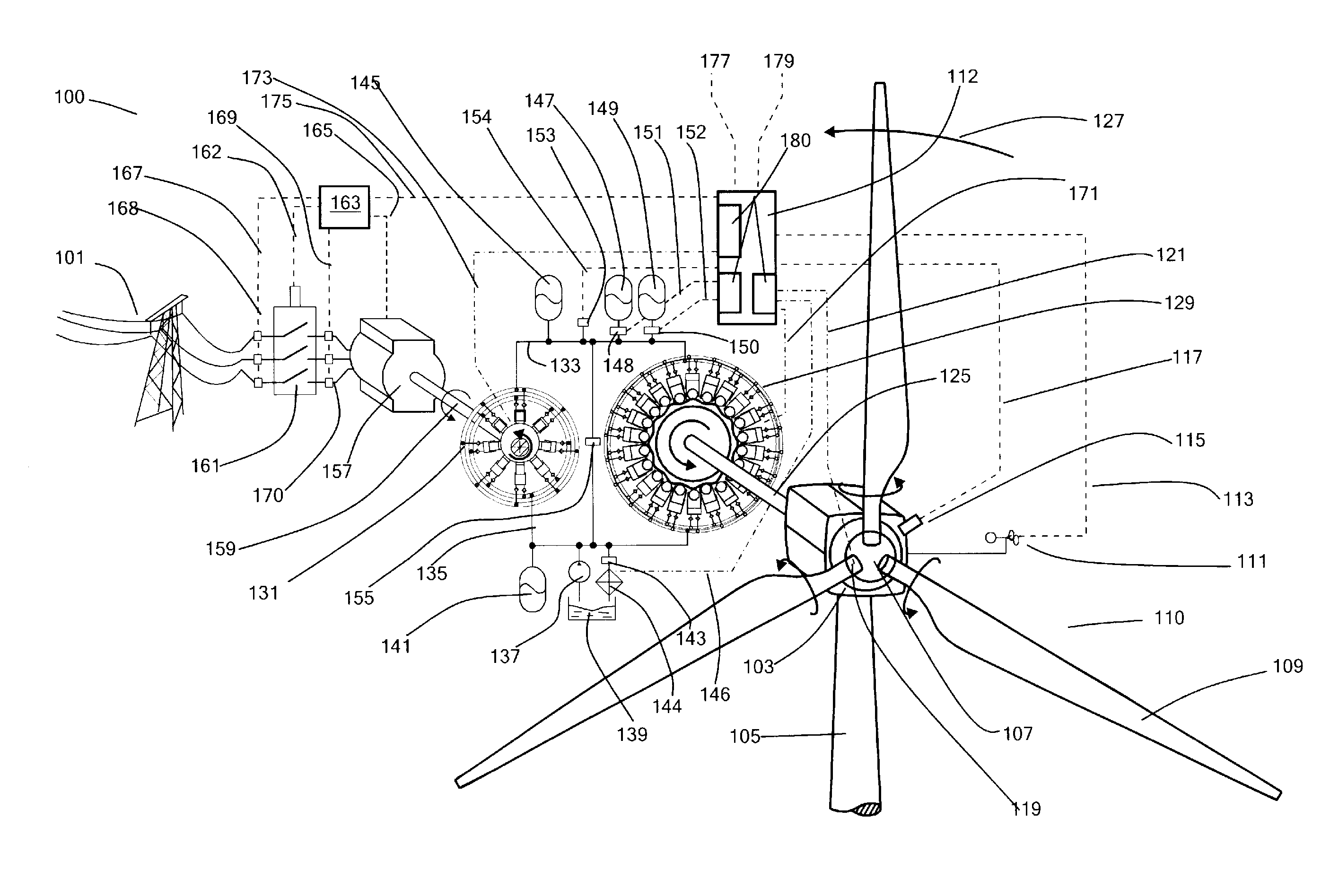
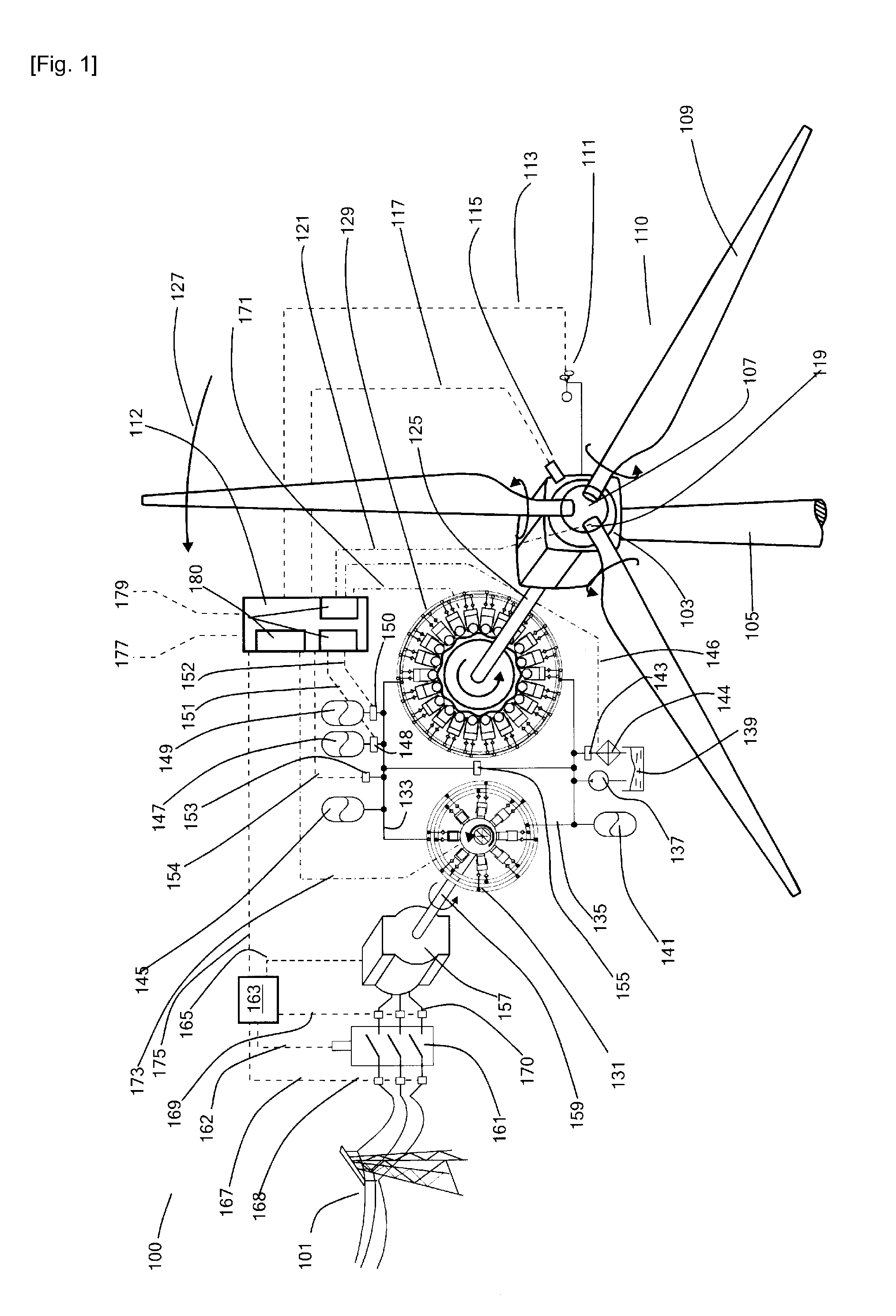
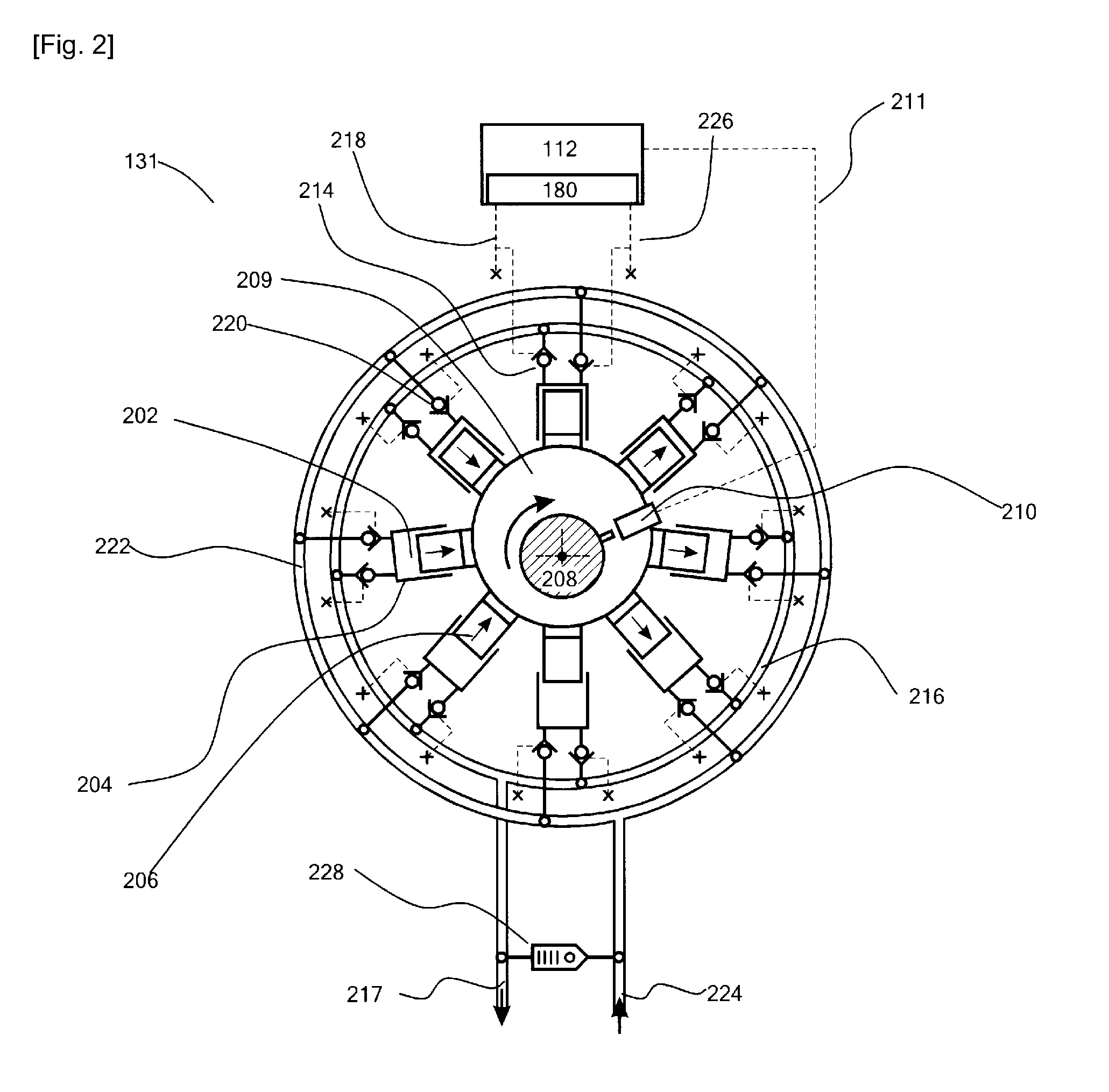
Energy extraction device, group of energy extraction devices and operating methods
InactiveUS20130221676A1Reduce the amount requiredEngine fuctionsWind energy generationWorking fluidControl signal
A wind turbine generator (100), or other energy extraction device, has a hydraulic circuit comprising a hydraulic pump (129) driven by a rotating shaft (125) and a hydraulic motor (131) driving an electricity generator (157), or other load. A high pressure manifold (133) extending between the pump and motor is in communication with an accumulator (145, 147, 149). A controller receives a control signal and regulates the displacement of working fluid by the hydraulic pump and the hydraulic motor relative to each other. Thus, power input through the rotating shaft and output to the load can be decoupled for at least a period of time and the energy output of energy extraction device can be varied, for example to smooth the total power output to an electricity grid (101), without compromising power input. A group of energy extraction devices can be controlled in concert to maximise power input while providing smooth power output. Individual electricity generators in different energy extraction devices can be switched on and off in concert to provide smooth power output while benefiting from the reduced energy losses that can be obtained by switching off electricity generators where possible.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
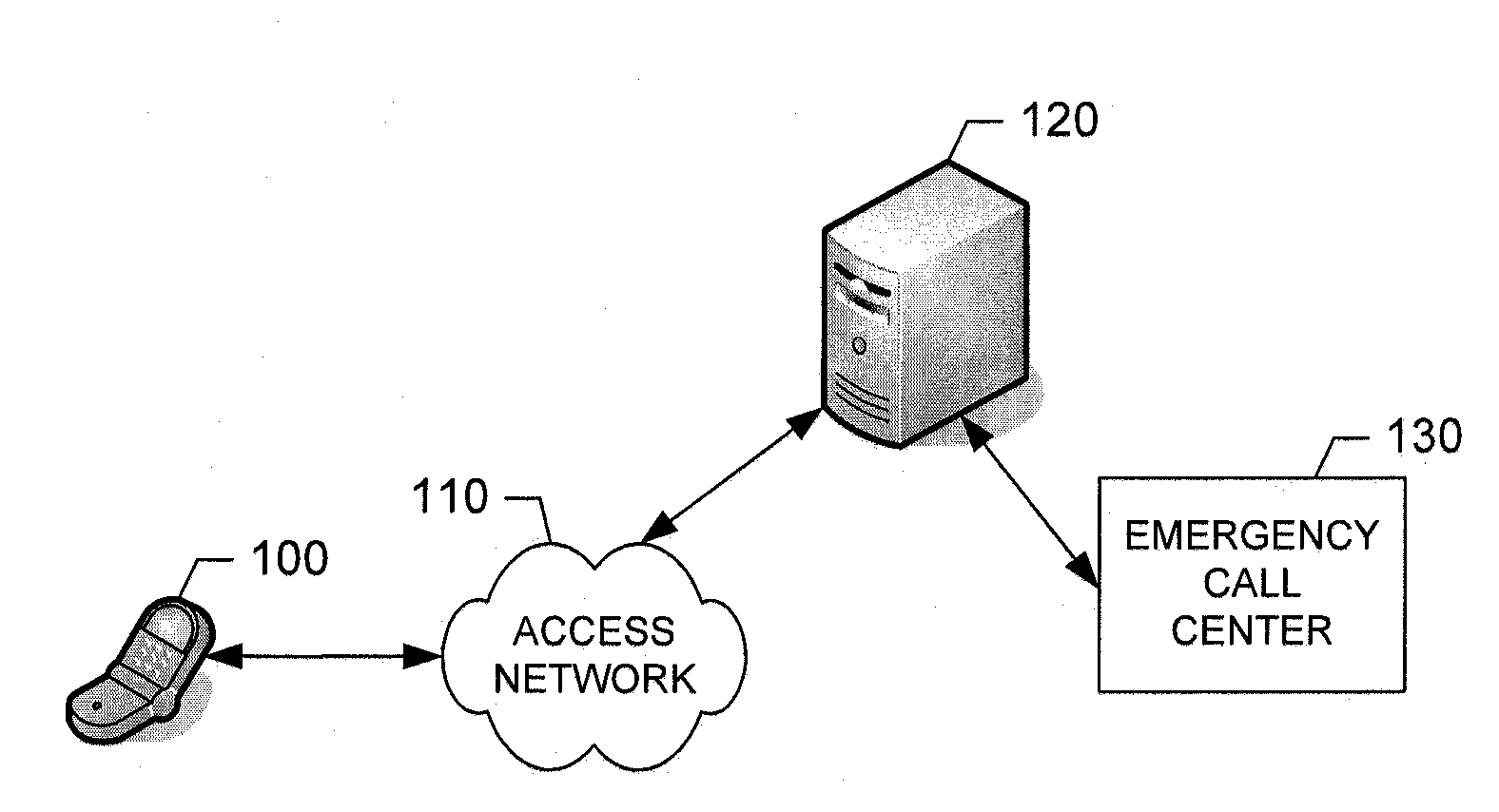
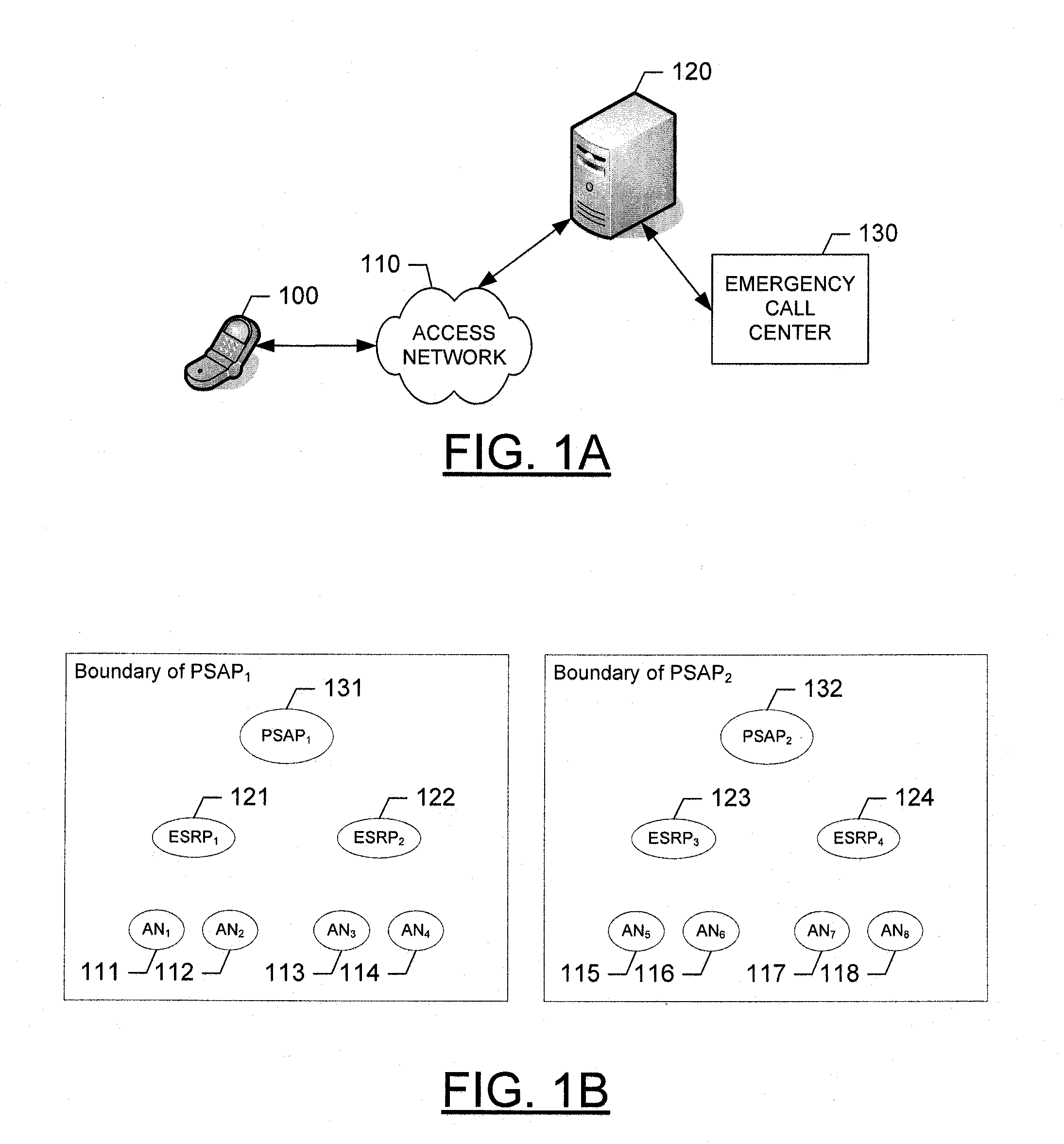
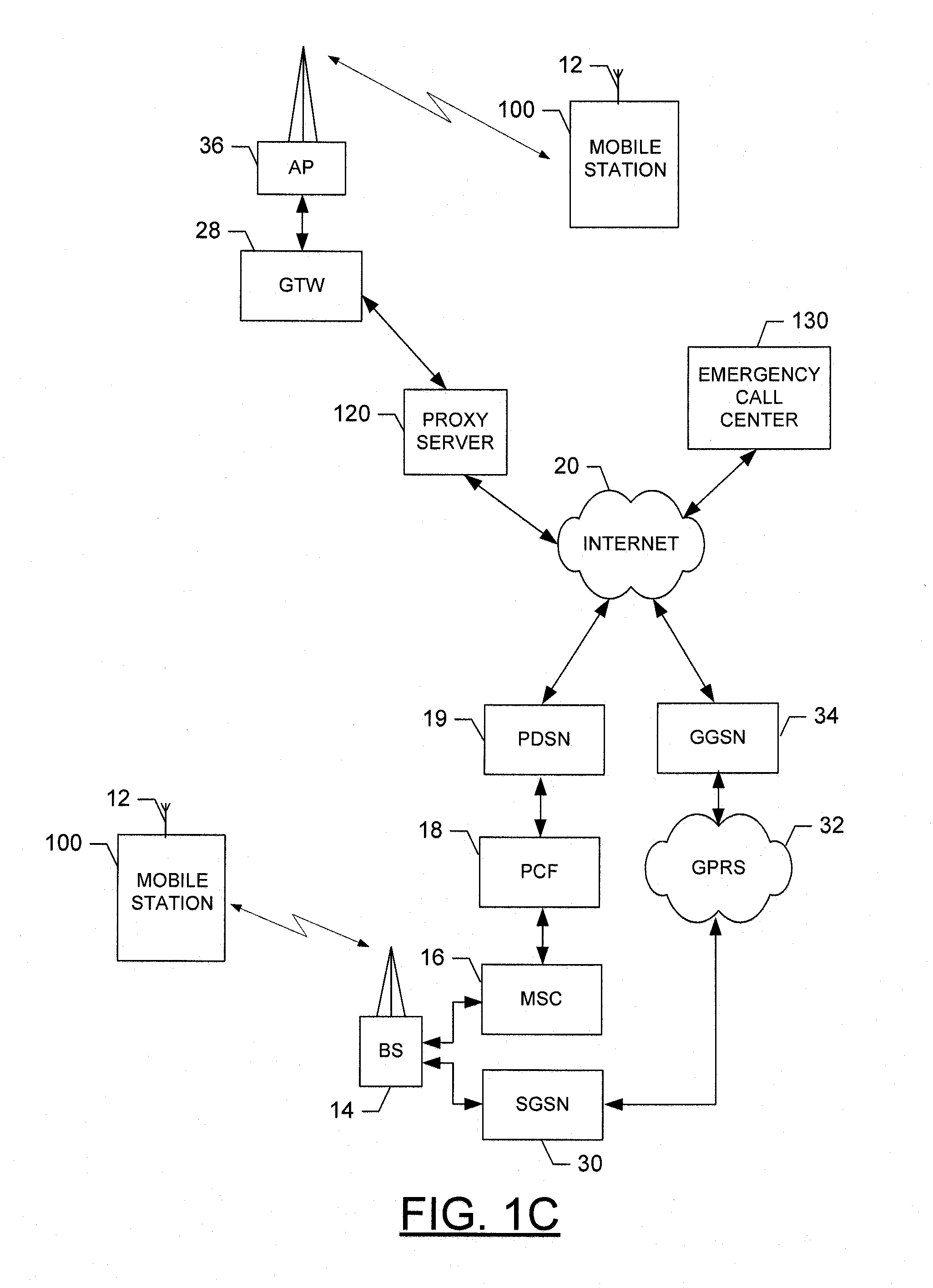
Apparatus, method and computer program product for maintaining emergency calls during mobile device movement
InactiveUS20090176474A1Keep in touchEmergency connection handlingTelephonic communicationProbable CaseGeolocation
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
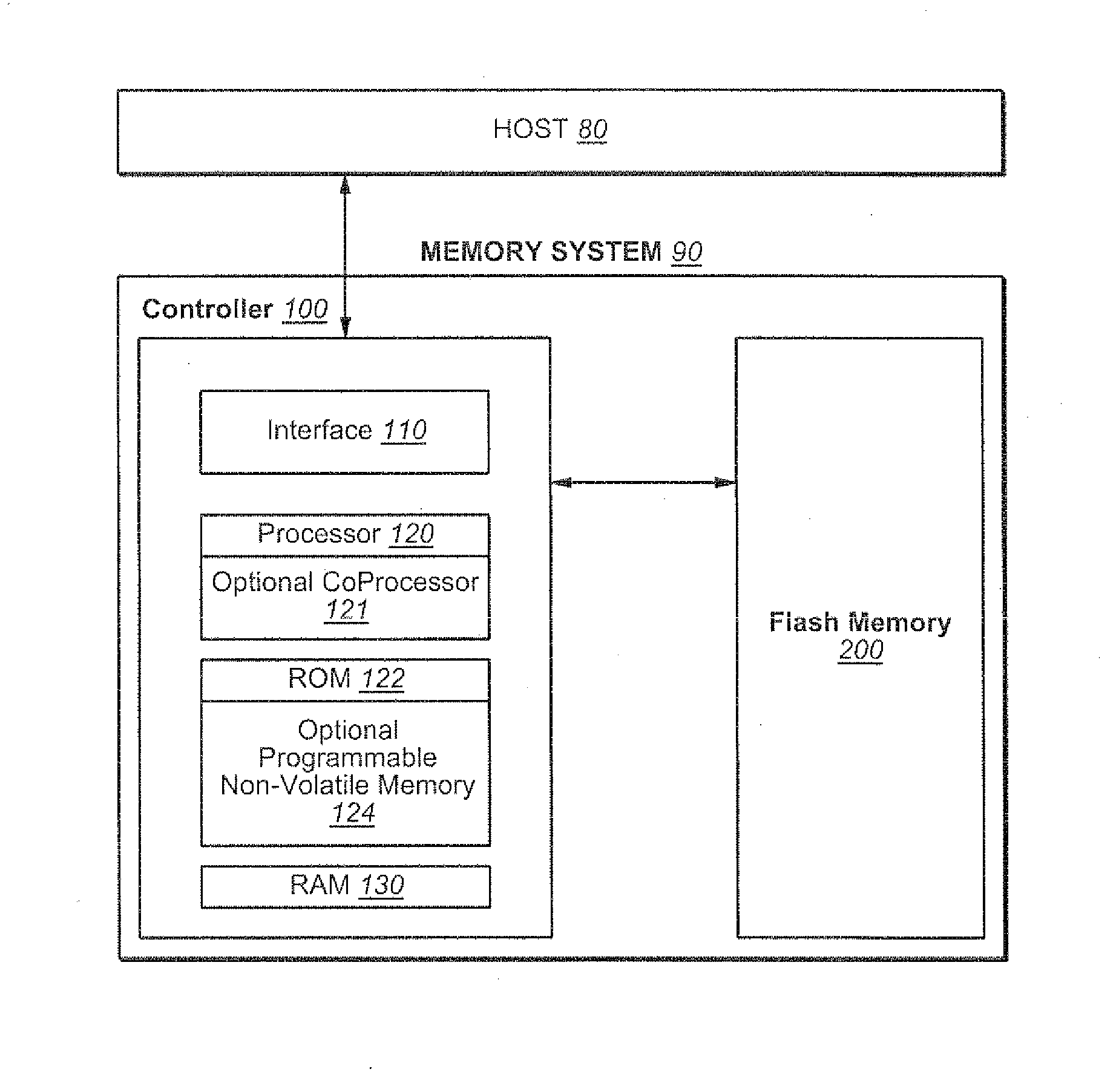
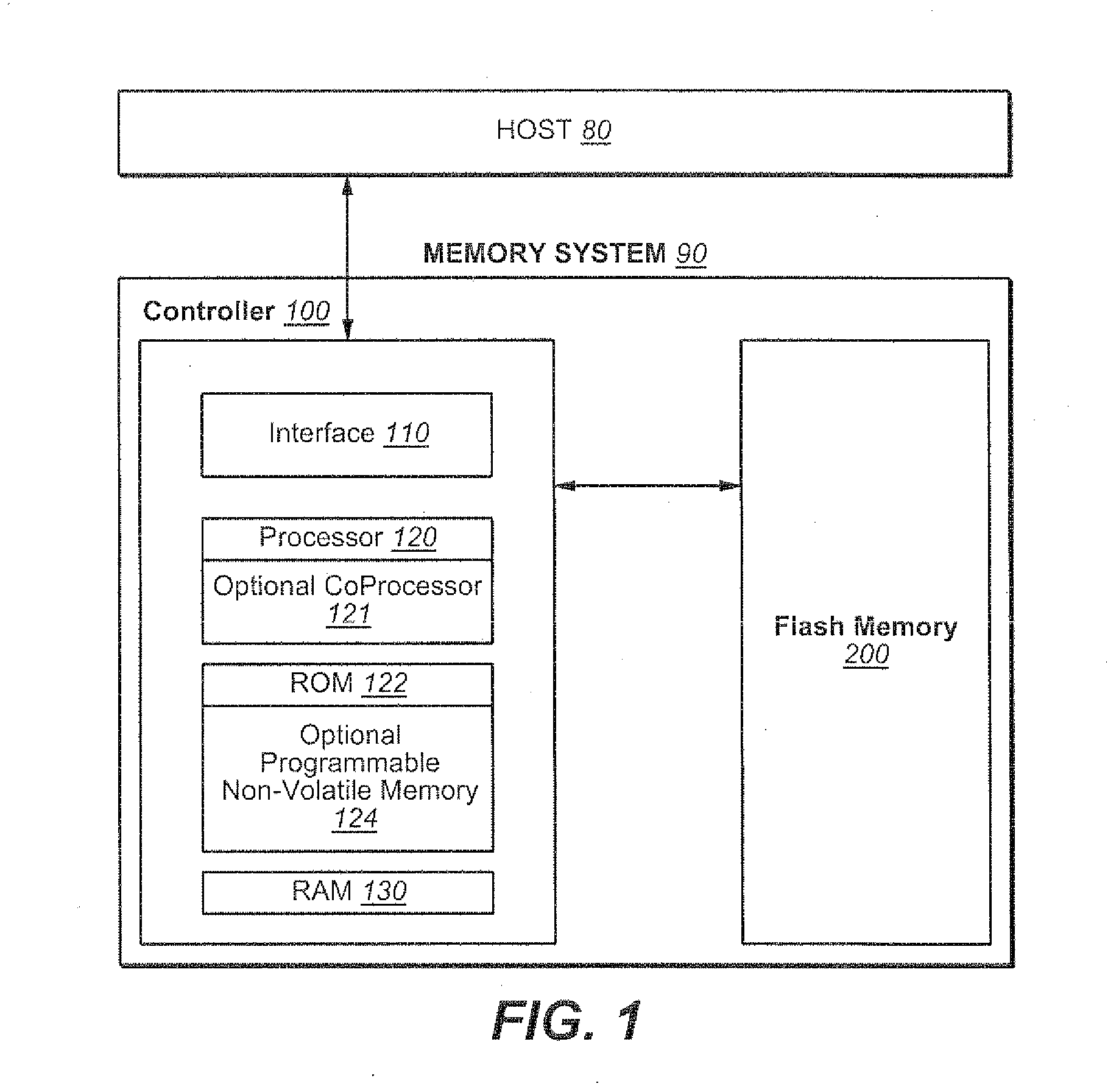
Dynamic Optimization of Back-End Memory System Interface
Techniques are presented for dynamically optimizing the performance of the controller-memory (or “back-end”) interface of a non-volatile memory system. Memory systems are usually designed to have a certain amount of error tolerance for error that can then be corrected by ECC. In may circumstances, such as when a device is new, the ECC capabilities of the system exceed what is needed to correct data storage errors. In these circumstances the memory system internally allots a non-zero portion of this error correction capacity to the back-end interface. This allows for the interface to operate at, for example, higher speed or lower power, even though this will likely lead to transmission path error. The system can also calibrate the back-end interface to determine that amount of error that result from various operating conditions, allowing the operating parameters of the back-end interface to be set according to amount of error that is allotted to the transfer process.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
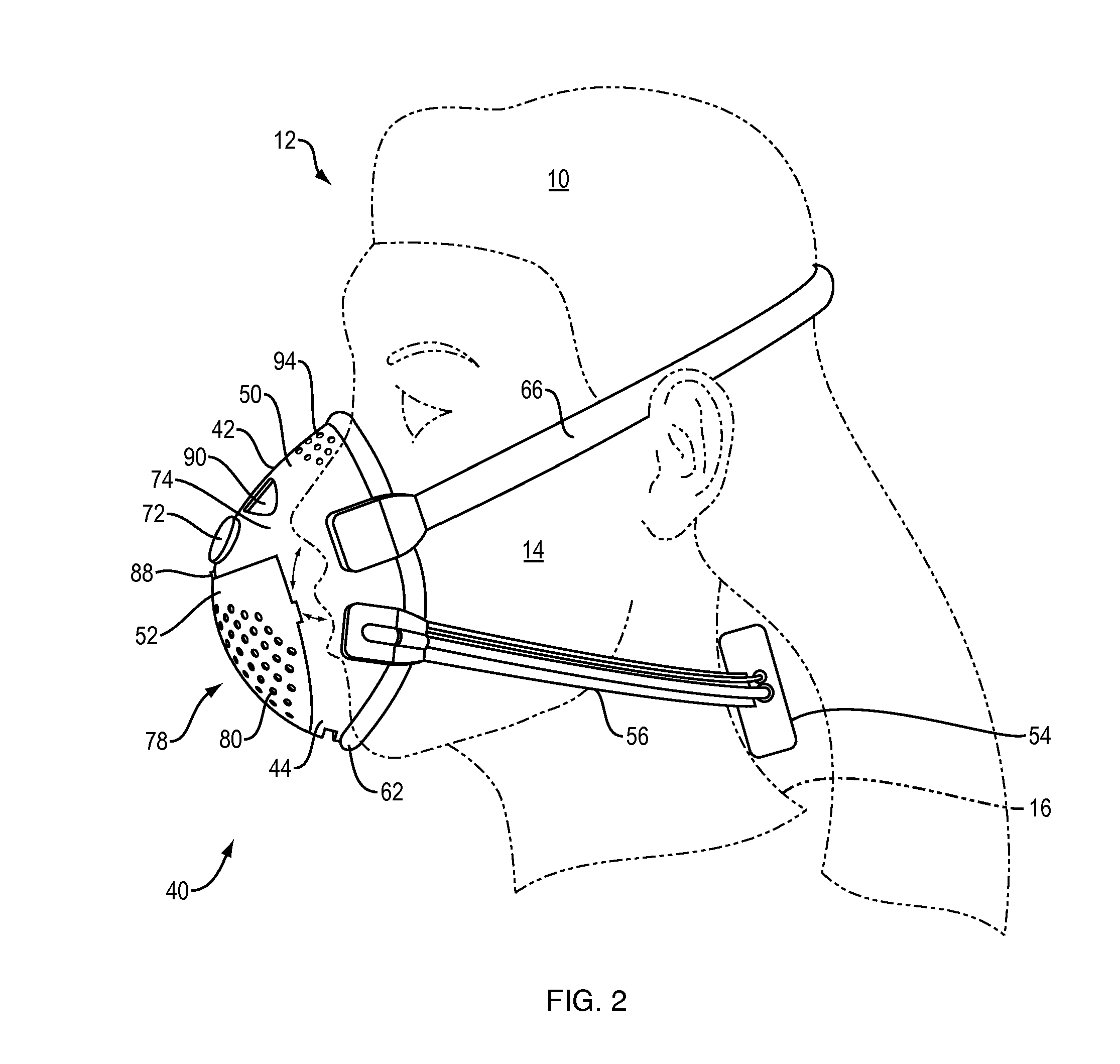
Cpap system with heat moisture exchange (HME) and multiple channel hose
ActiveUS20120304985A1Breathe freelyRespiratory masksBreathing masksPositive airway pressureHEAT/MOISTURE EXCHANGE
A continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) system provides positive airway pressure therapy. It has been recognized that users generally prefer to breathe freely rather than to fight the pressurized air when possible. A continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) system provides positive airway pressure therapy when required, but allows the user to breathe freely with the mask on when positive airway pressure is not required. The system has a valve that moves between two positions to open and close the unassisted breathing vent and the outlet from the flow generator.
Owner:HUMAN DESIGN MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com