Patents
Literature
517 results about "Background process" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
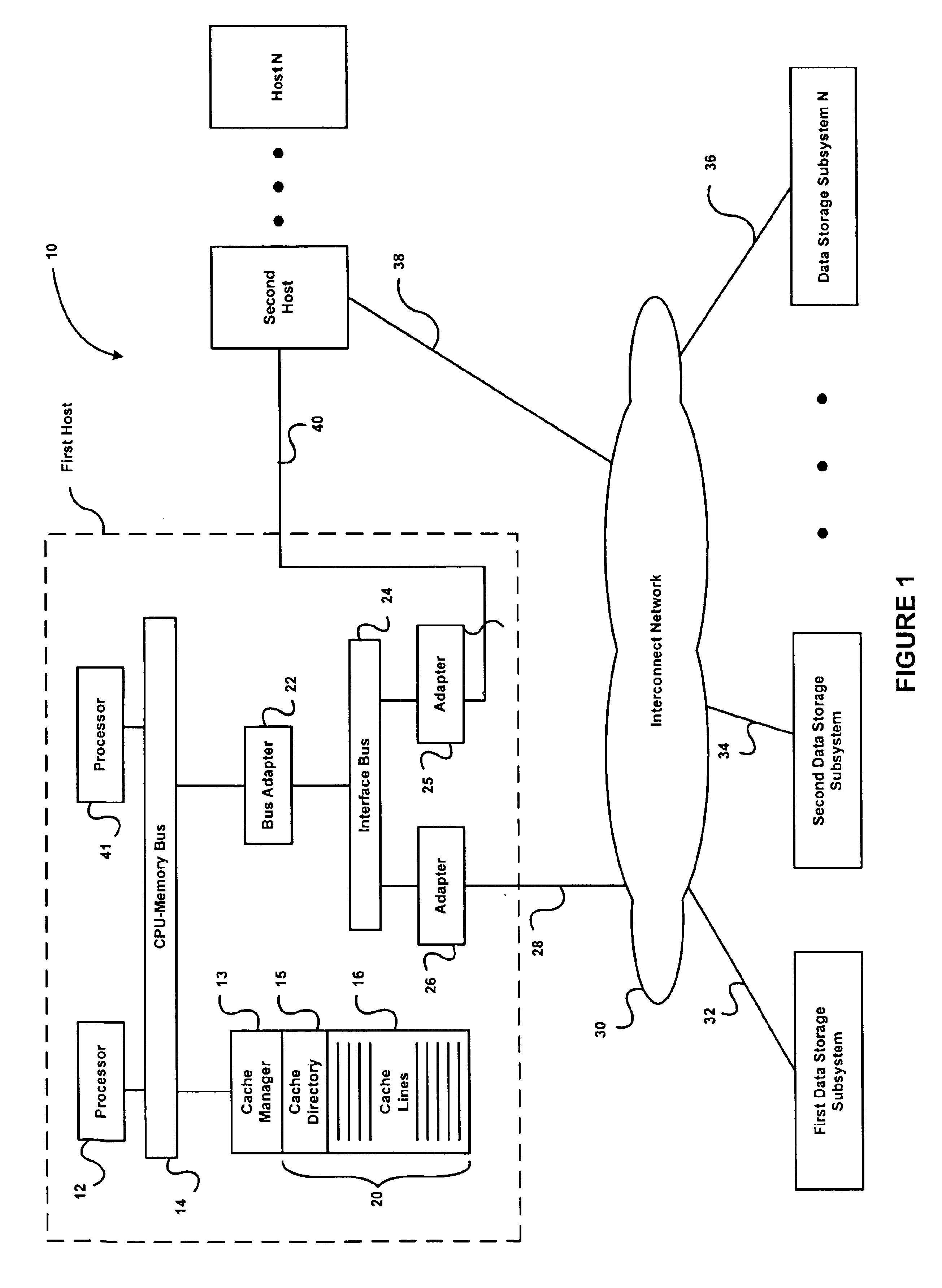
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A background process is a computer process that runs behind the scenes (i.e., in the background) and without user intervention. Typical tasks for these processes include logging, system monitoring, scheduling, and user notification. The background process usually is a child process created by a control process for processing computing task. After the creation, the child process will run on its own course for performing the task independent of the control process, therefore, the control process is free of performing other designated task.
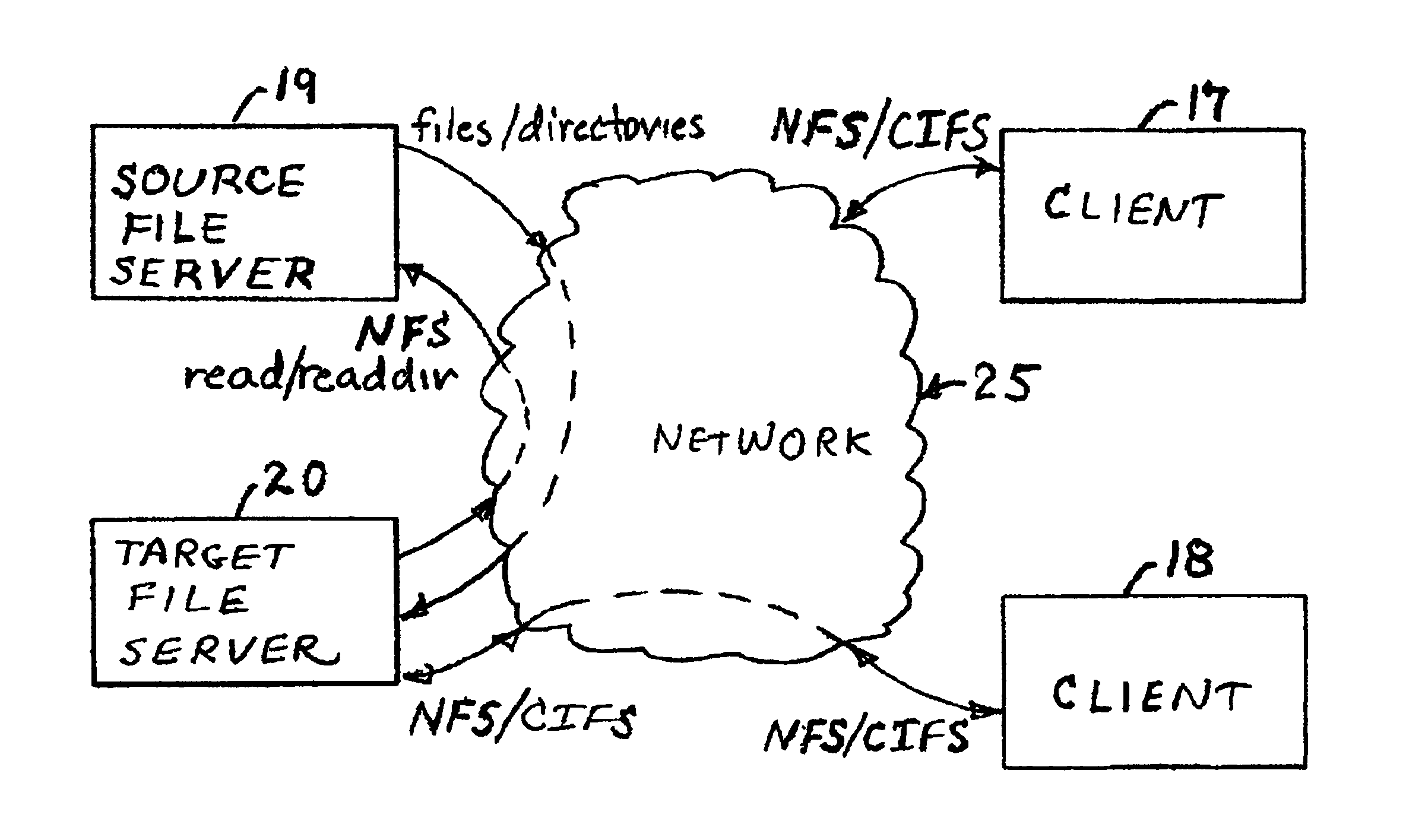
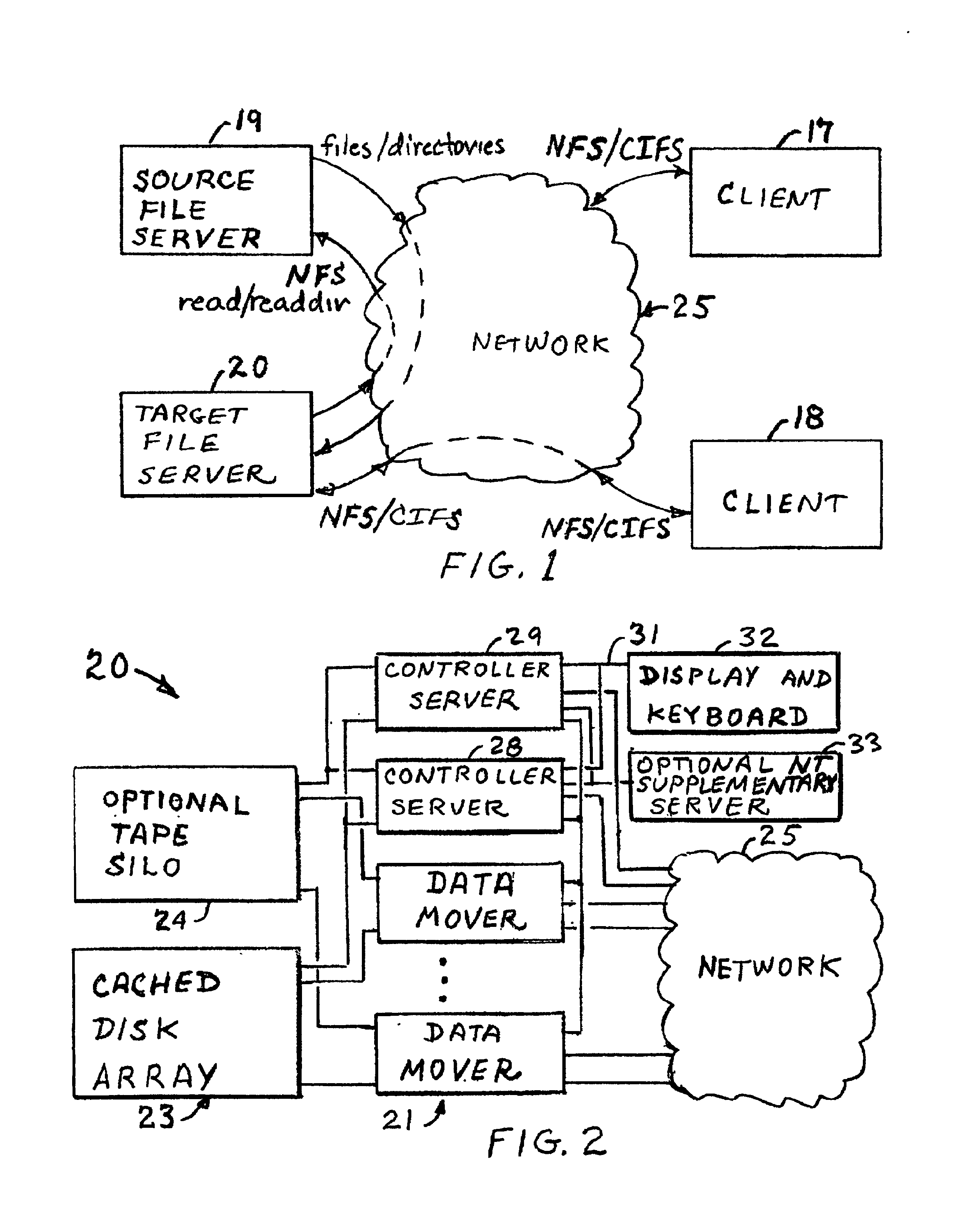
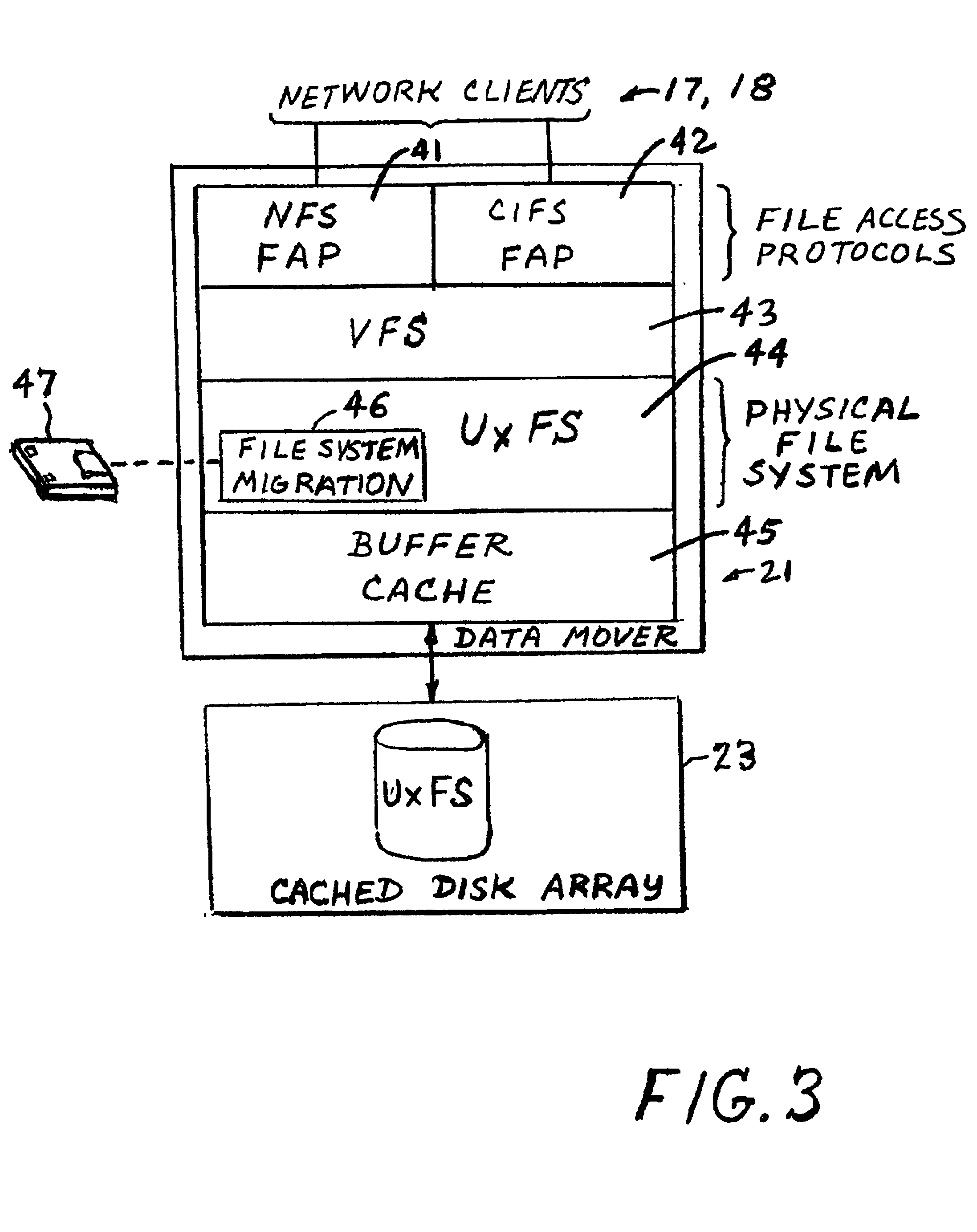
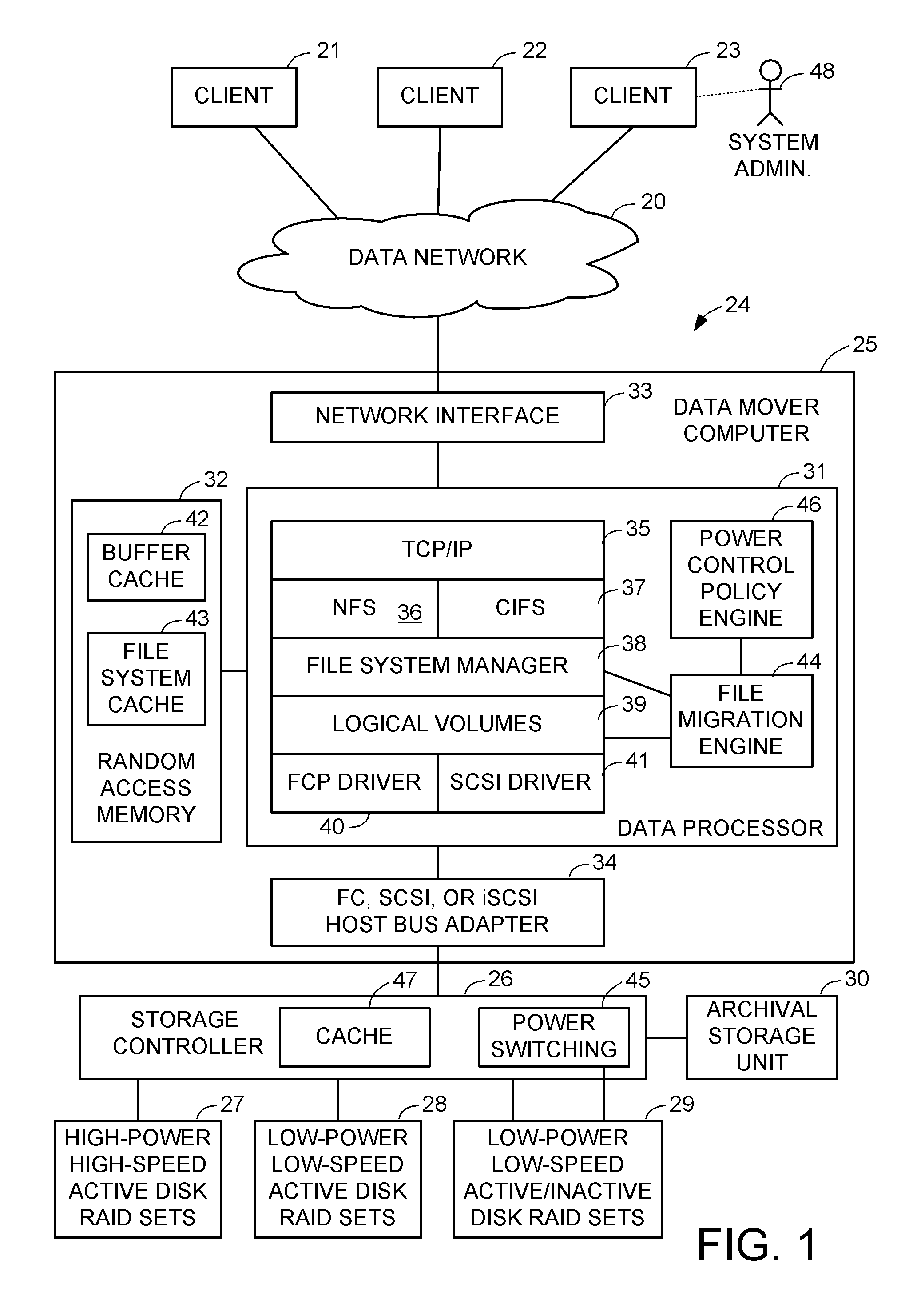
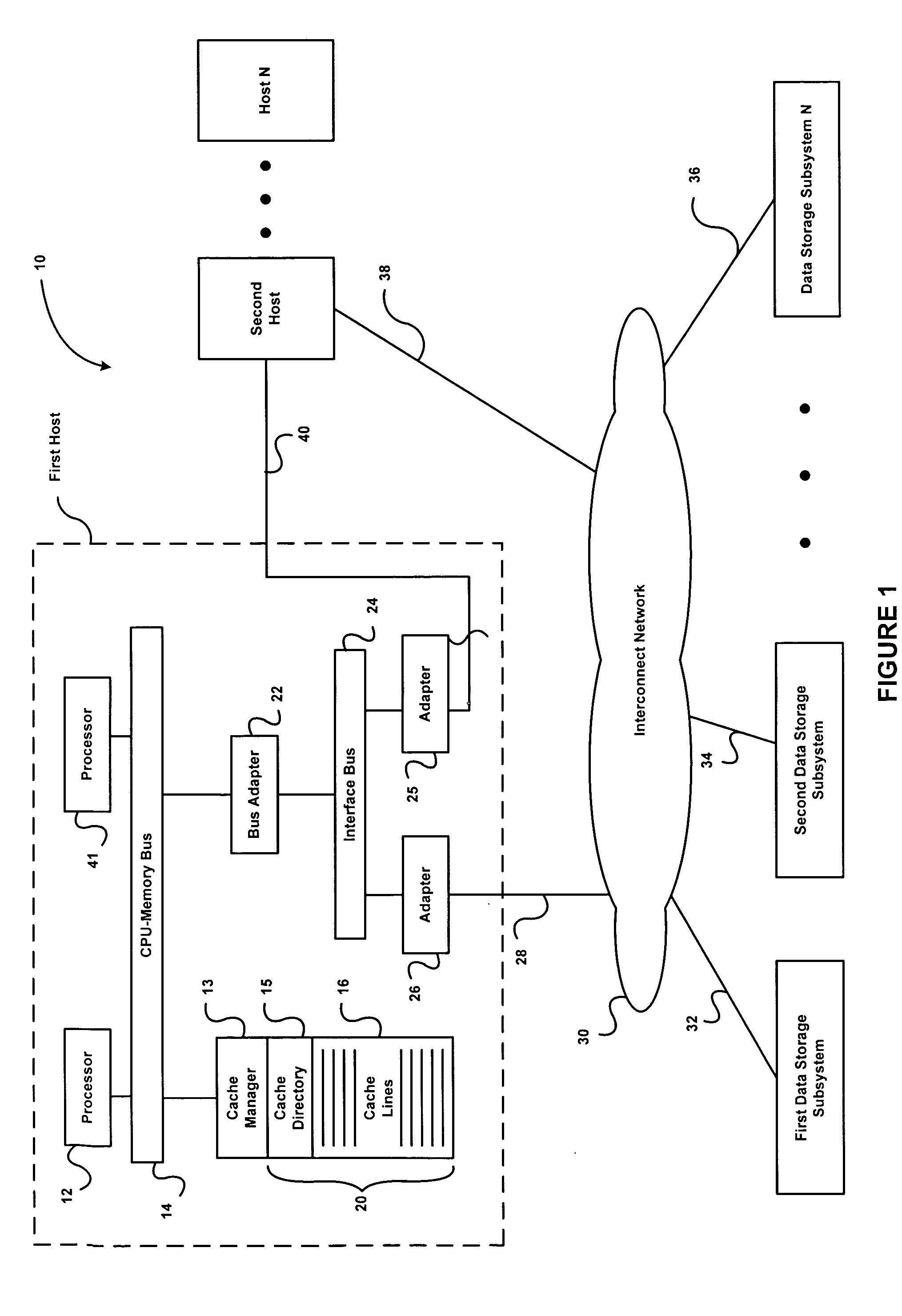
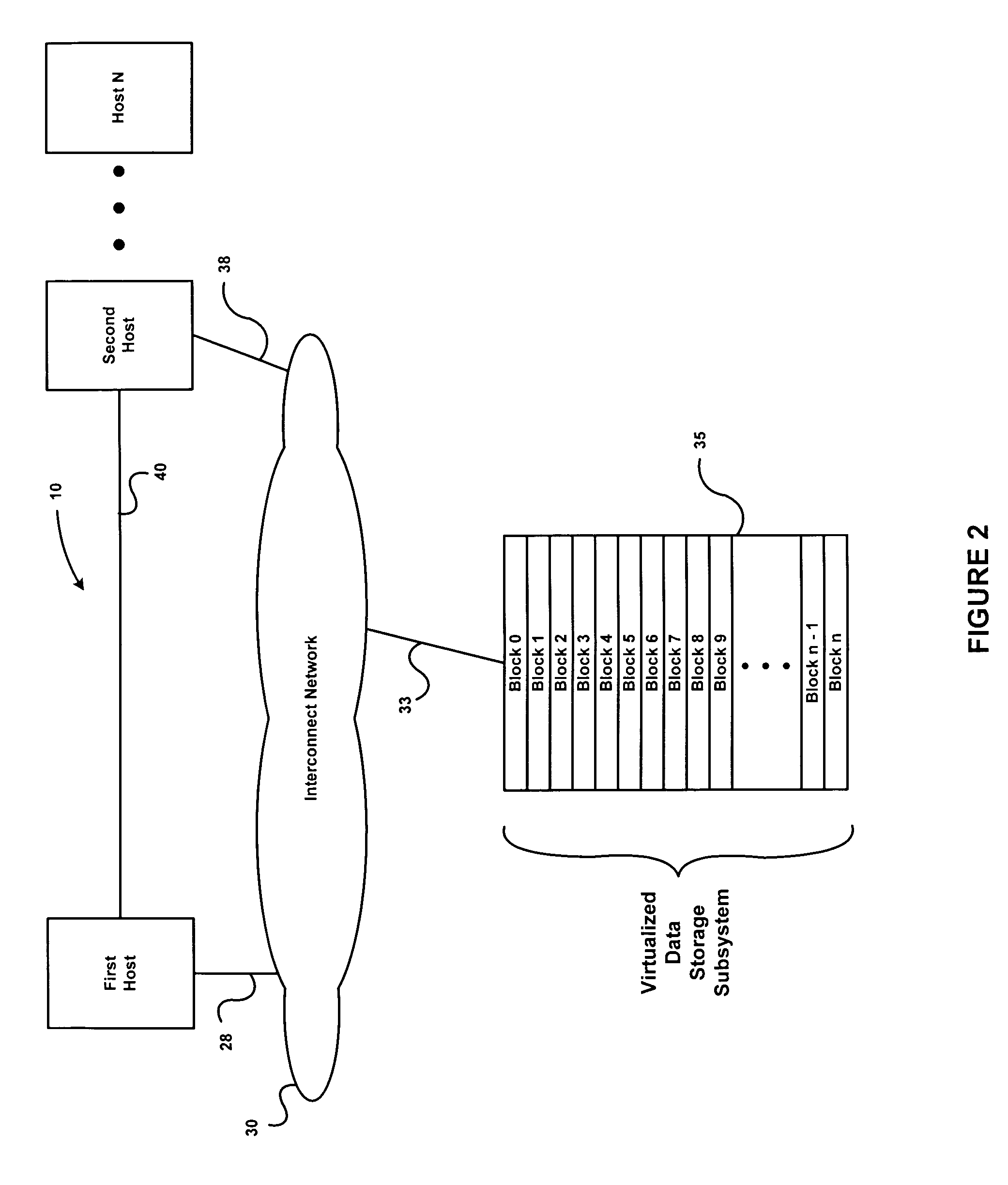
Concurrent file across at a target file server during migration of file systems between file servers using a network file system access protocol
InactiveUS6938039B1Digital data information retrievalData processing applicationsFile systemNetwork File System
A file system is migrated from a source file server to a target file server in a data network while permitting clients to have concurrent read / write access to the file system. The target file server issues directory read requests and file read requests to the source file server in accordance with a network file access protocol to transfer the file system from the source file server to the target file server. Concurrent with the transfer of the file system from the source file server to the target file server, the target file server responds to client read / write requests for access to the file system. In a preferred embodiment, the target file server maintains a hierarchy of on-line nodes off-line nodes. The online nodes represent file system objects that have been completely migrated, and the offline nodes representing file system objects that have not been completely migrated. The target file server executes a background process that walks through the hierarchy in order to migrate the objects of the offline nodes. When an object has been completely migrated, the target file server changes the offline node for the object to an online node for the object.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
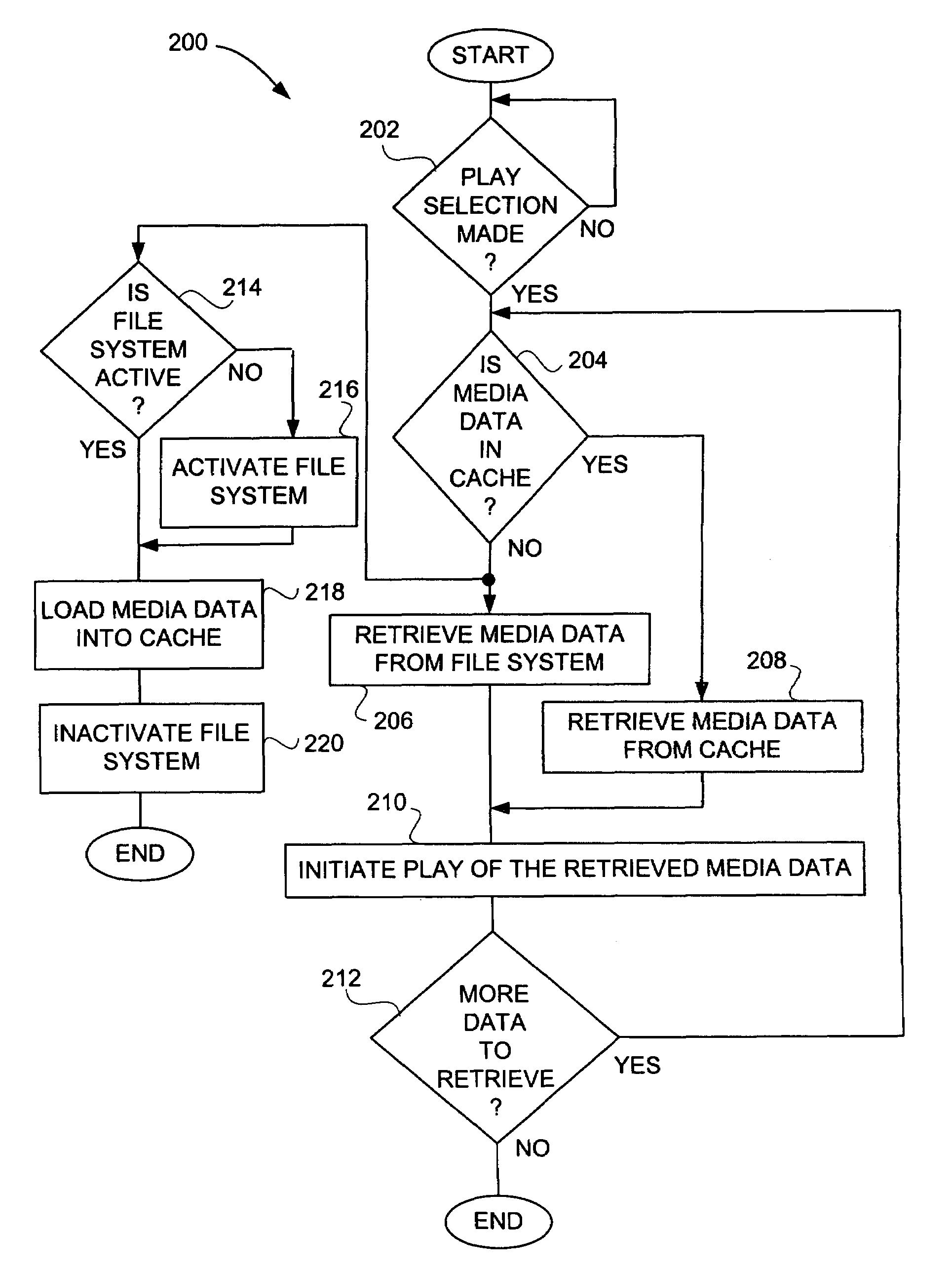
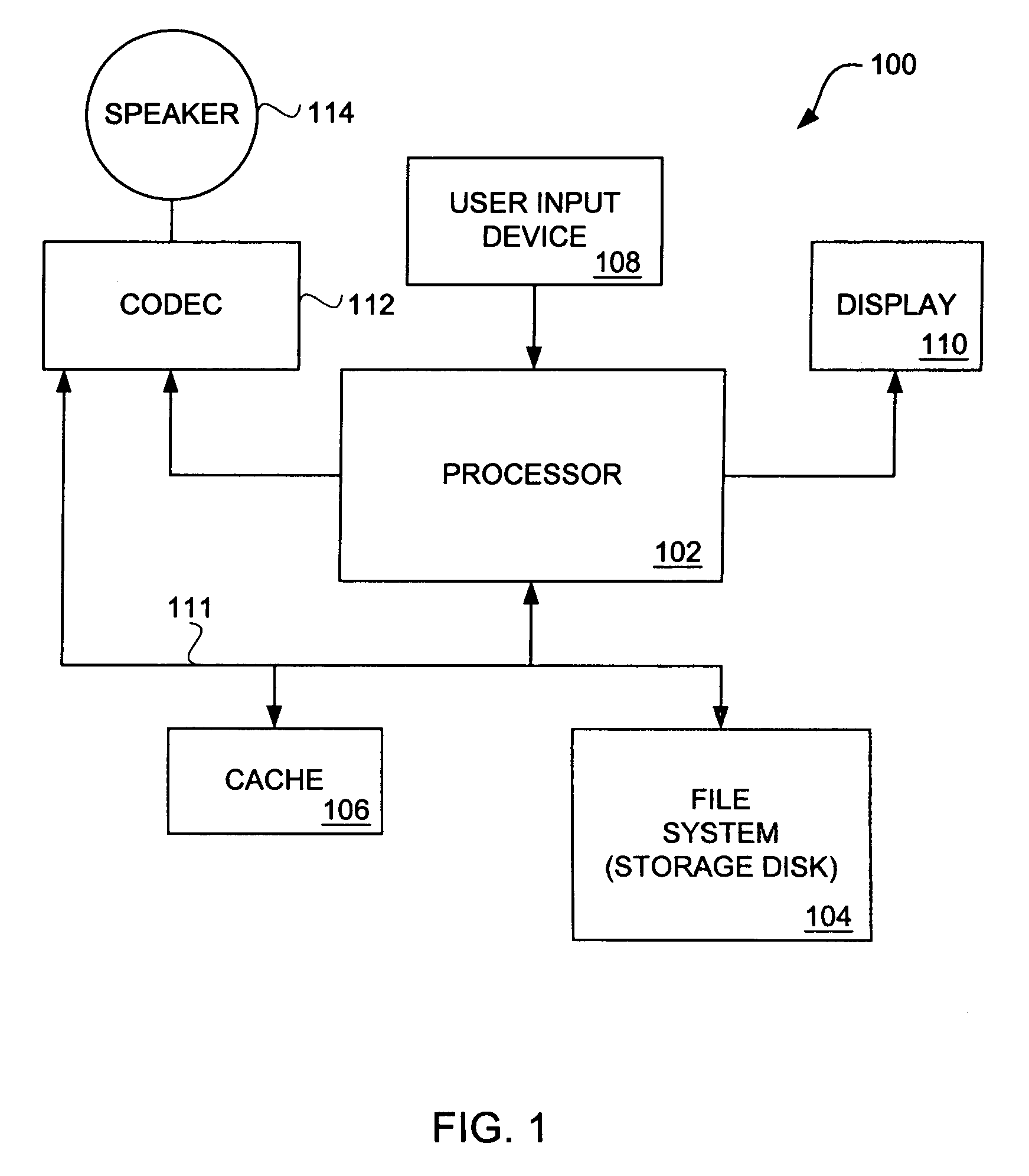
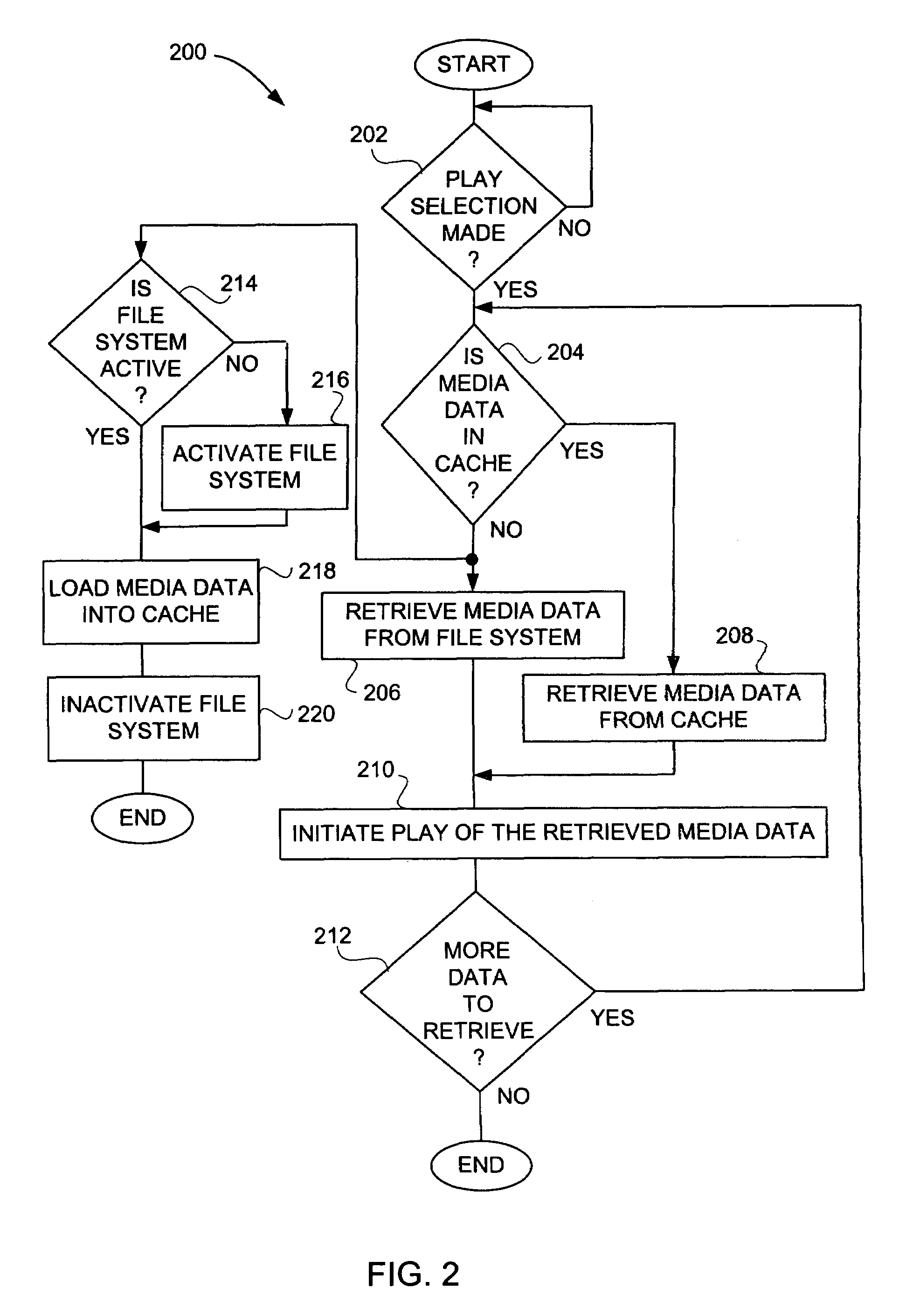
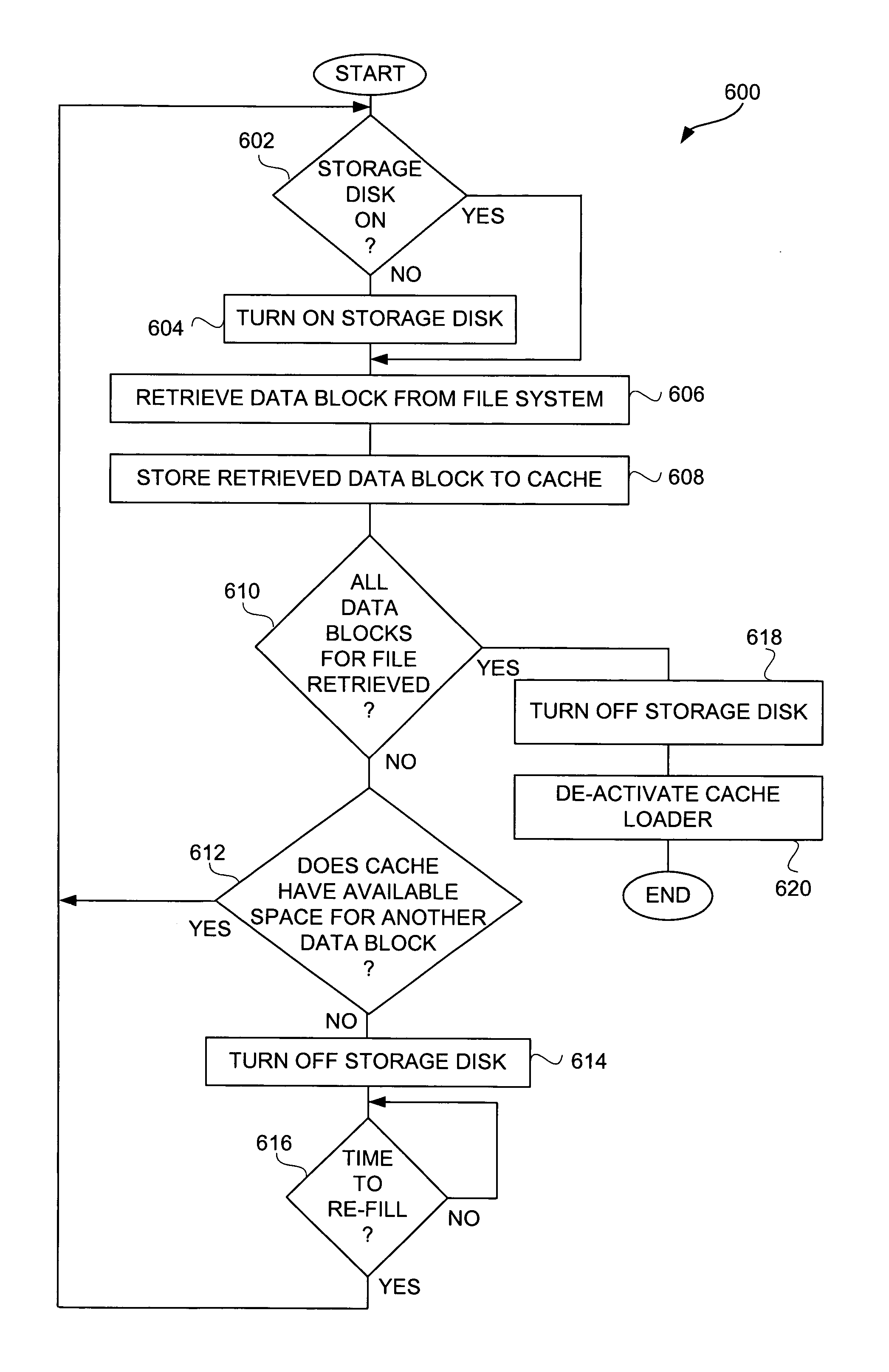
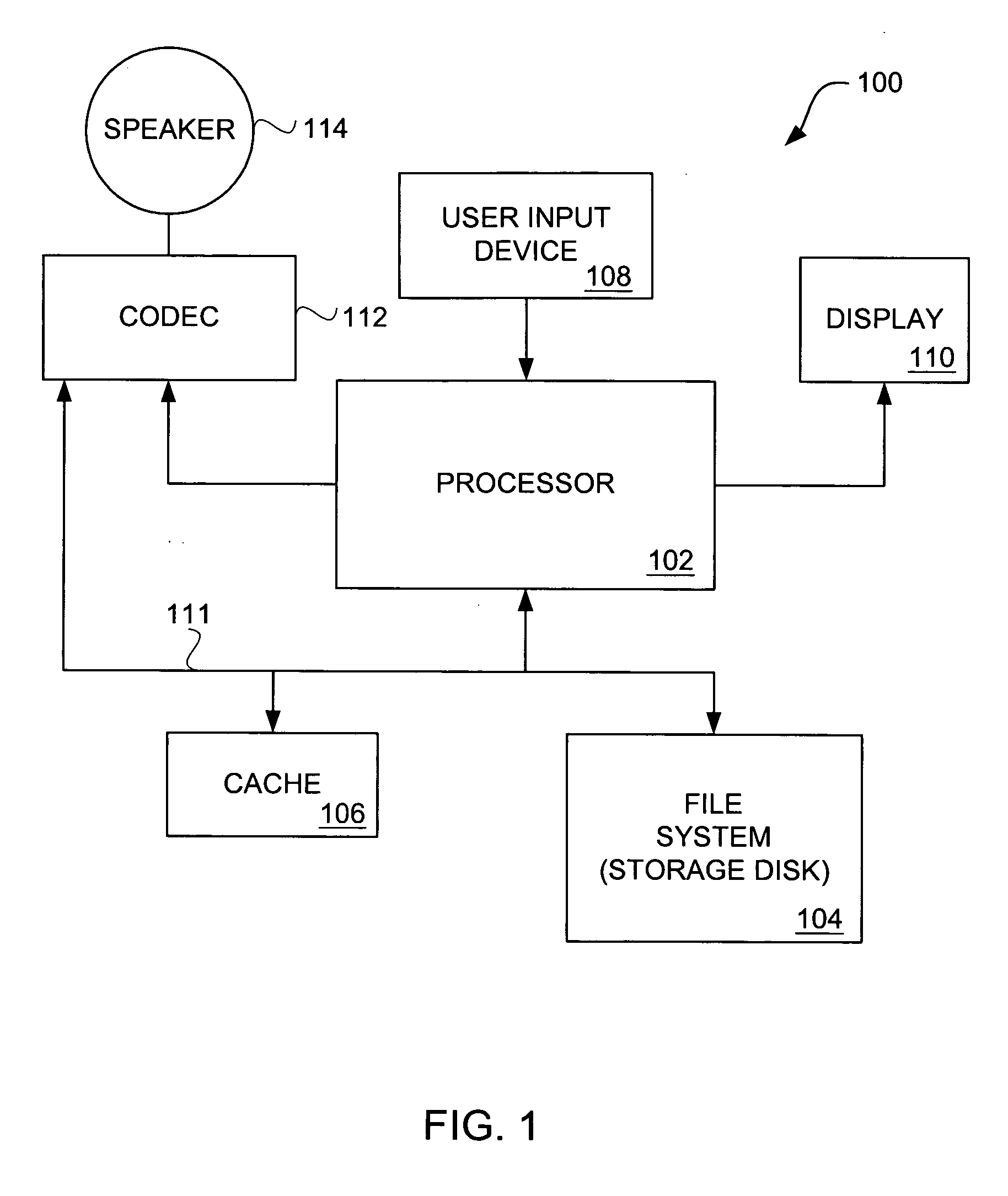
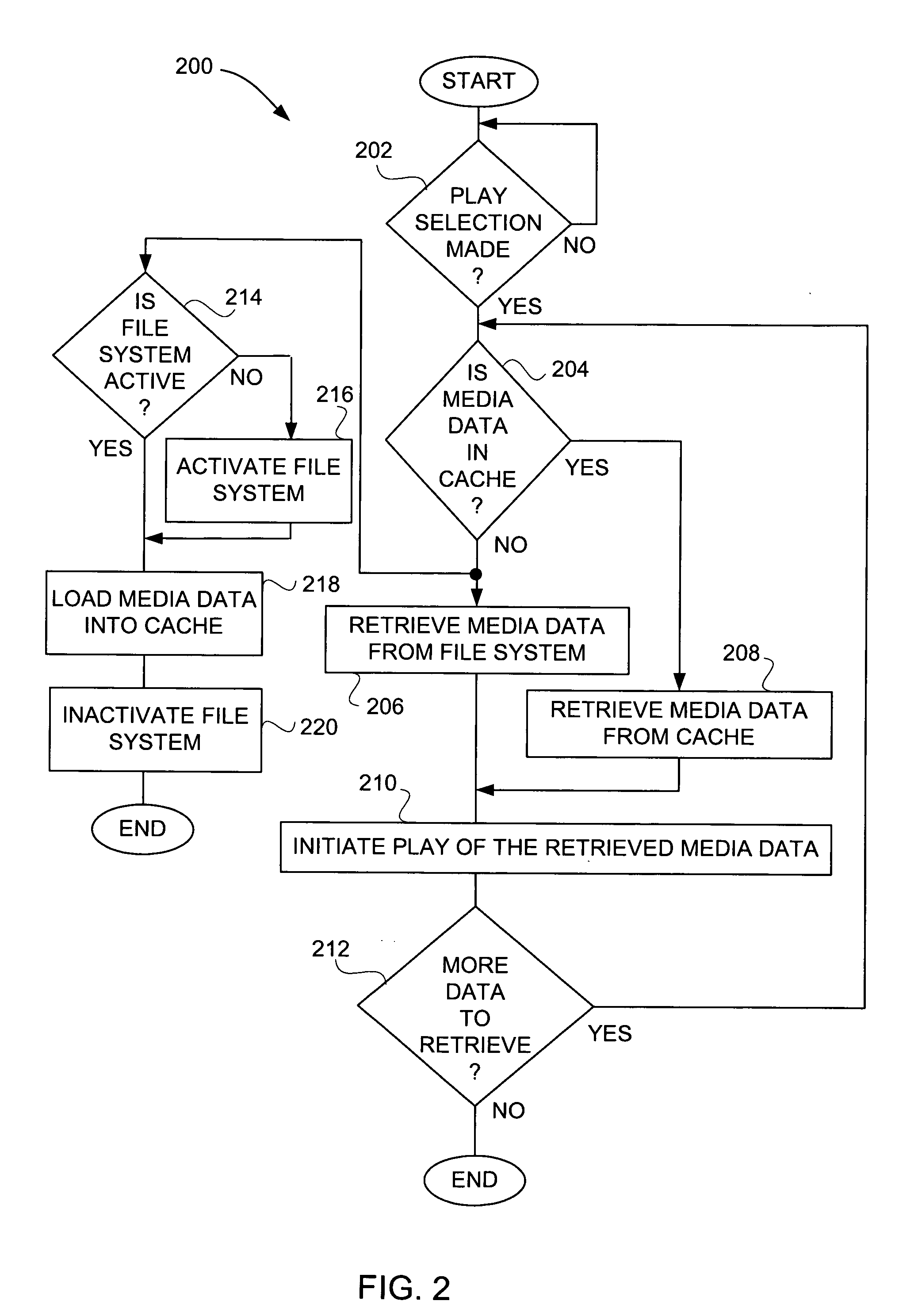
Media player with instant play capability
InactiveUS6934812B1Extend battery lifeAggressively “powered offEnergy efficient ICTTelevision system detailsElectrical batteryBackground process
A media player and a method for operating a media player are disclosed. A media program is able to substantially immediately begin playing after a media play selection has been made. Through intelligent operation, the media program is able to start playing even before the media program has been substantially or completely loaded from disk storage into semiconductor memory (i.e., cache memory). Additionally, the media program can be loaded into semiconductor memory through use of a background process without disturbing the playing of the media program. Further, if desired, the disk storage is able to be aggressively “powered off” when not being accessed, thereby enhancing battery life when being battery-powered.
Owner:APPLE INC
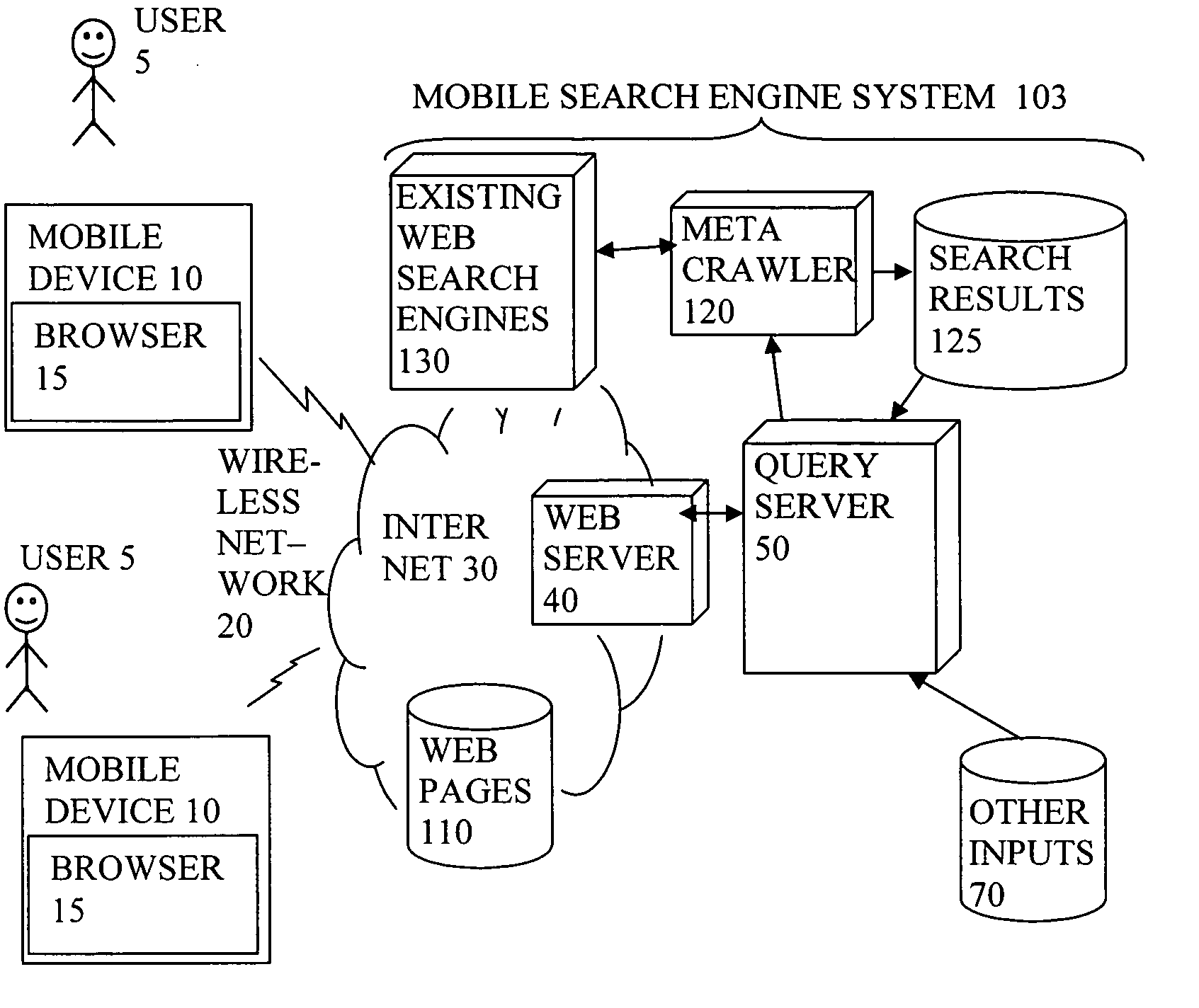
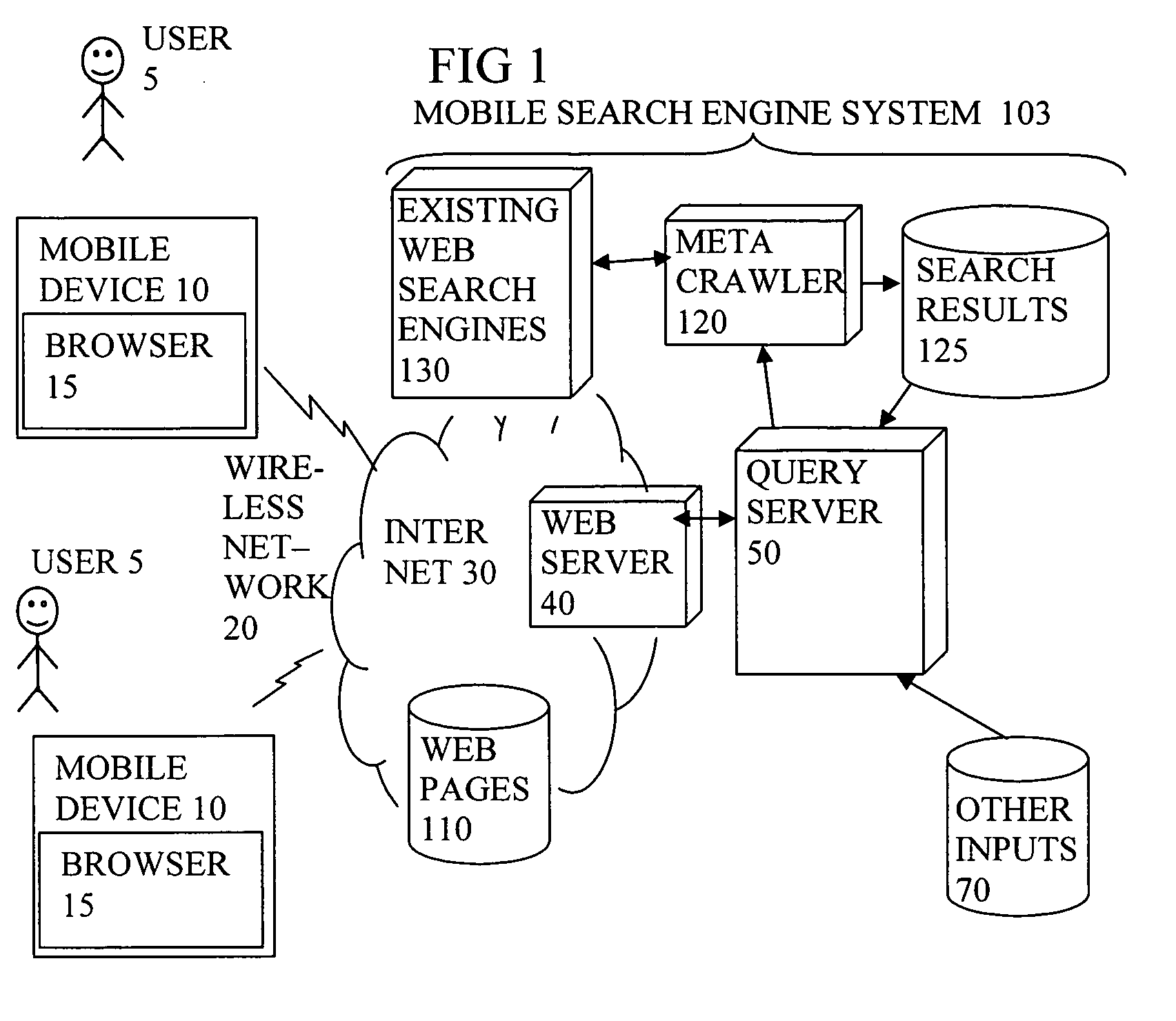
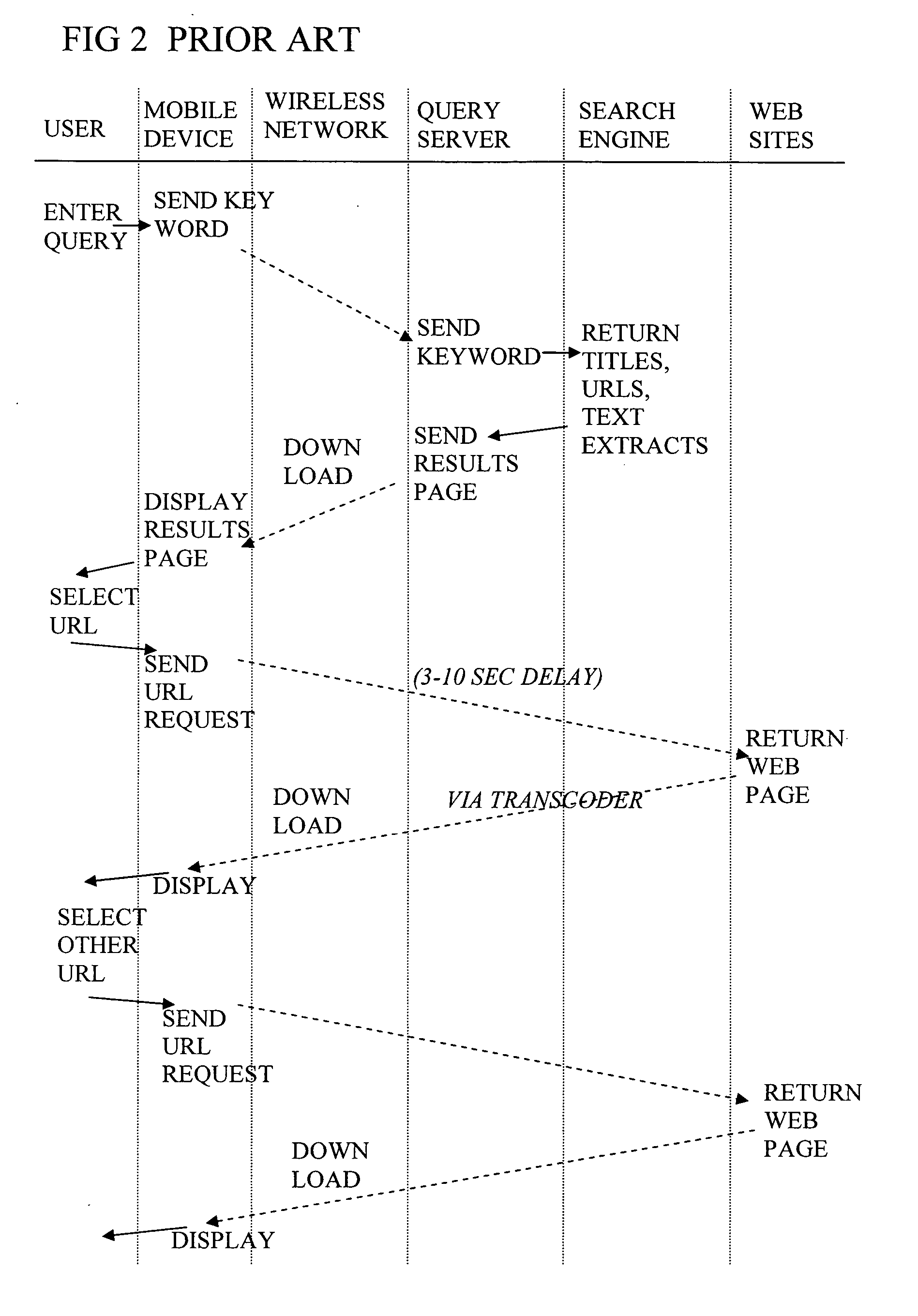
Display of search results on mobile device browser with background process
InactiveUS20070067305A1Improve user experienceFast downloadWeb data indexingMarketingScripting languageMobile search
A query server of a mobile search engine system for searching content items accessible online, is arranged to send at least a first screenview of search results (63) to a browser of a mobile device (10), and send instructions (69, 74) in a scripting language to the browser for a background process to fetch further search results to the mobile device for presentation later. The further search results can then be viewed as desired without the need for a further round trip delay across the wireless network. The user can be presented with a simpler navigation model. The first screenview can be sent in the form of a page formatting template, and results data. The formatting information can be reused for other results, to reduce formatting overhead in the downloads. The instructions can also be used for showing information while waiting for downloads, or downloading information during entry of search queries.
Owner:TAPTU LTD
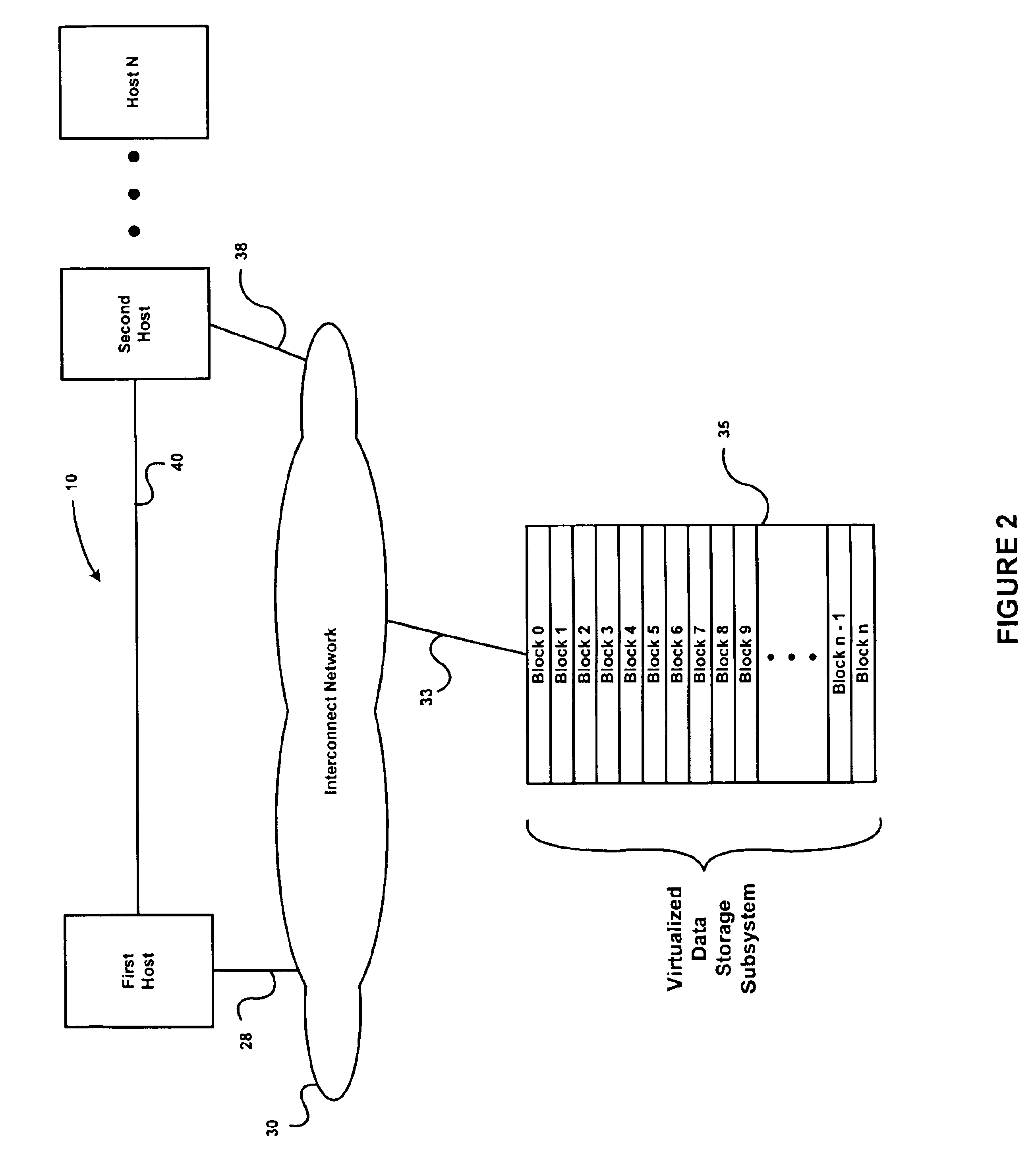
Media player with instant play capability
InactiveUS20050216674A1Aggressively “powered offExtend battery lifeEnergy efficient ICTTelevision system detailsElectrical batteryBackground process
A media player and a method for operating a media player are disclosed. A media program is able to substantially immediately begin playing after a media play selection has been made. Through intelligent operation, the media program is able to start playing even before the media program has been substantially or completely loaded from disk storage into semiconductor memory (i.e., cache memory). Additionally, the media program can be loaded into semiconductor memory through use of a background process without disturbing the playing of the media program. Further, if desired, the disk storage is able to be aggressively “powered off” when not being accessed, thereby enhancing battery life when being battery-powered.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method of planning a route to a destination
InactiveUS20070106465A1Cost of greatly dependTime of arrival at each destinationInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlPredictabilityBackground process
The present invention combines the geographical coverage possible with fixed, pre-defined route segment costs (e.g. the legal speed limit) with, wherever possible, richer time dependent costs. A user of, for example, a portable navigation device, can therefore continue route planning as before to virtually any destination in a country covered by the stored map database, but wherever possible, can also use traffic data with time-dependent costs, so that the effect of congestion with any time predictability can be accurately taken into account as an automatic, background process. It leaves the user to simply carry on driving, following the guidance offered by the navigation device, without needing to be concerned about congestion that exists now, and whether it will impact his journey.
Owner:TOMTOM INT BV
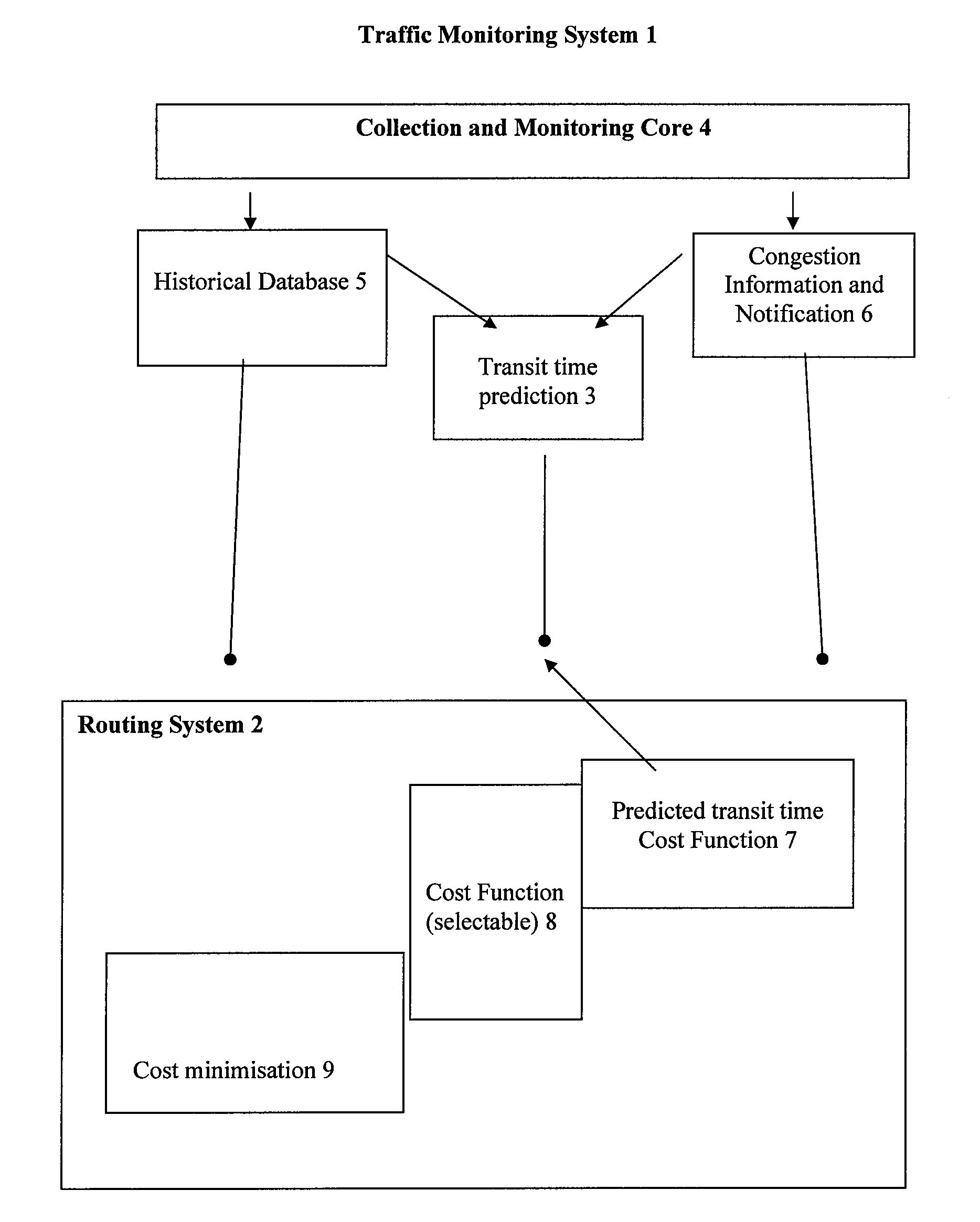
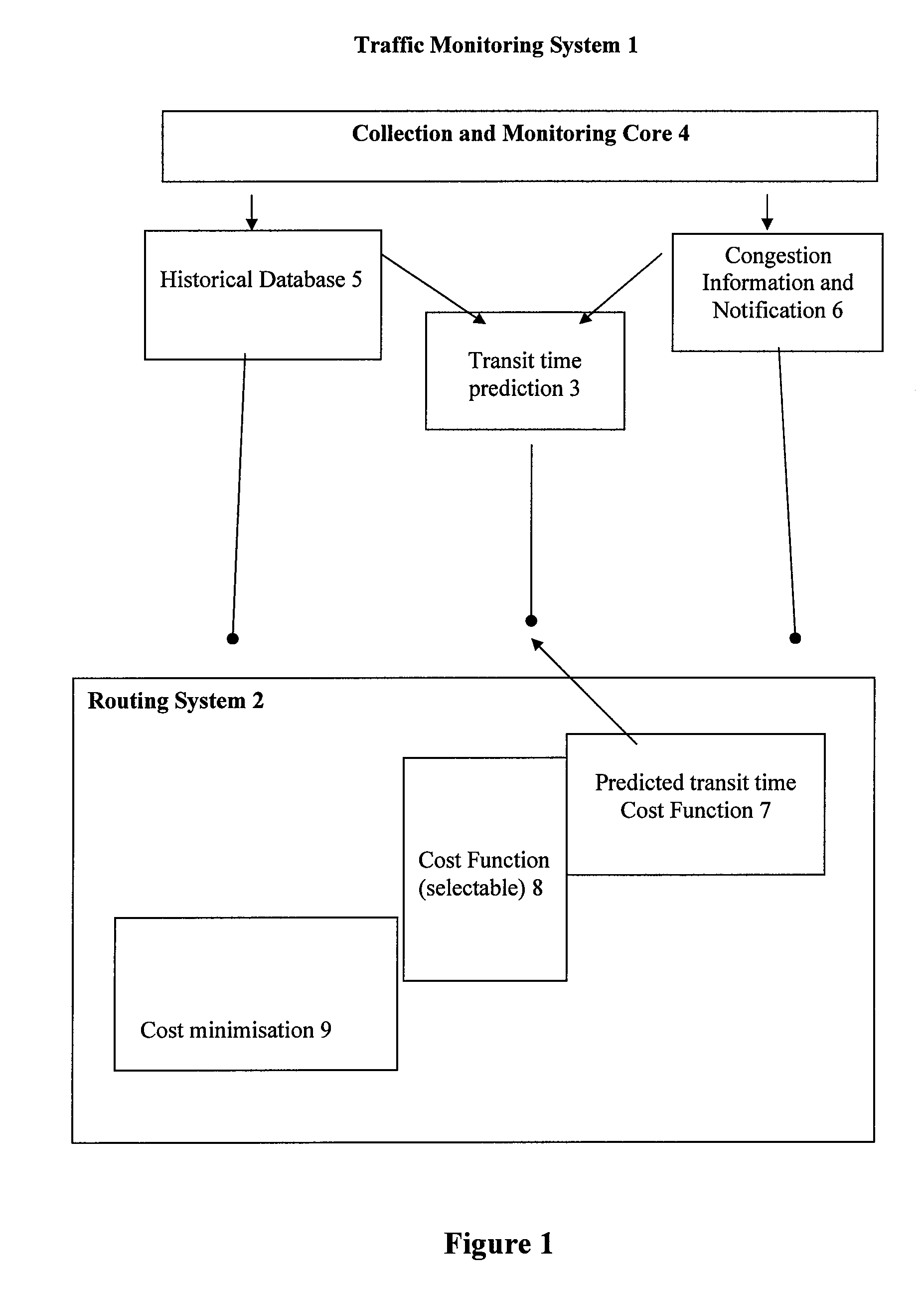
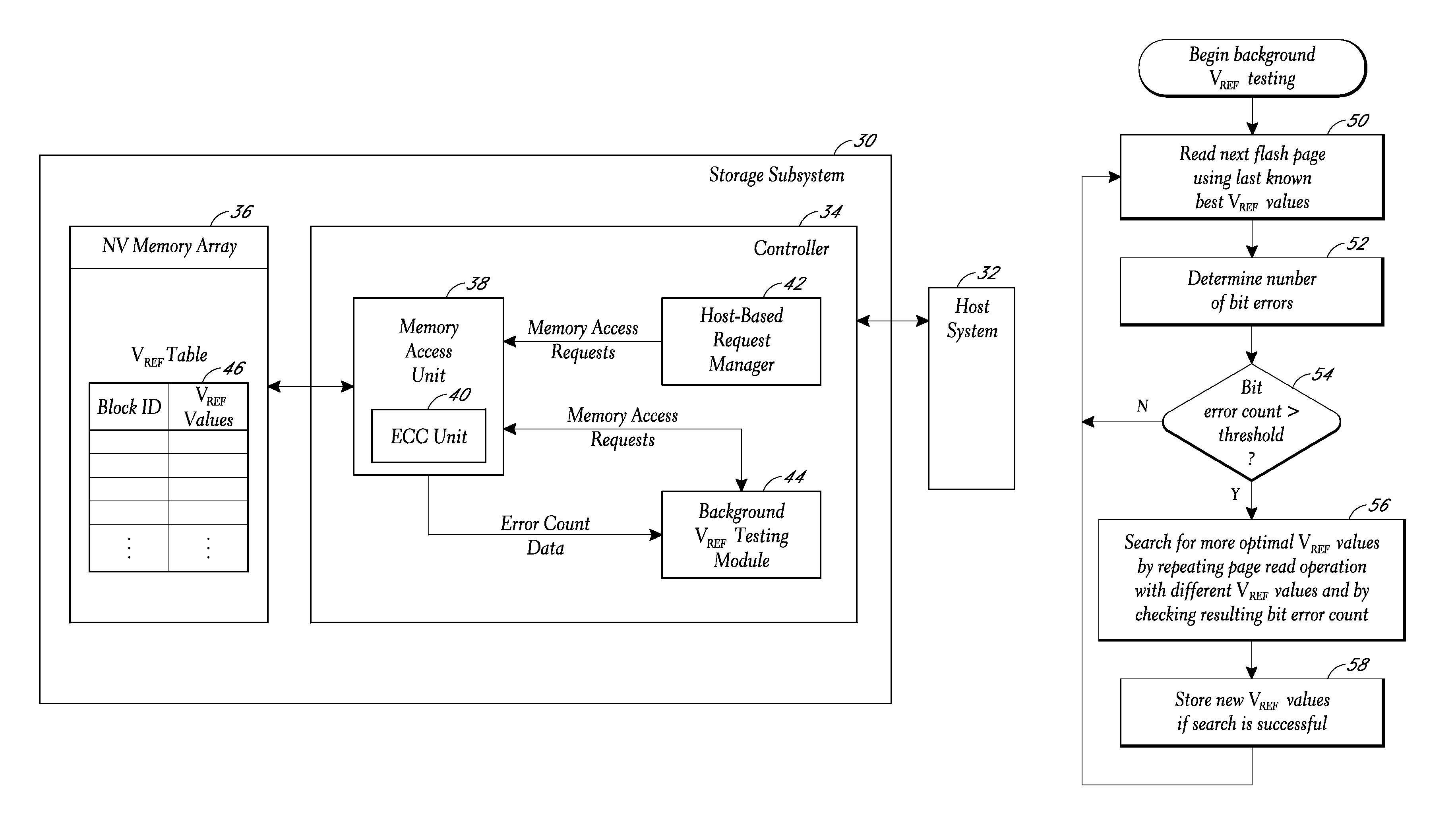
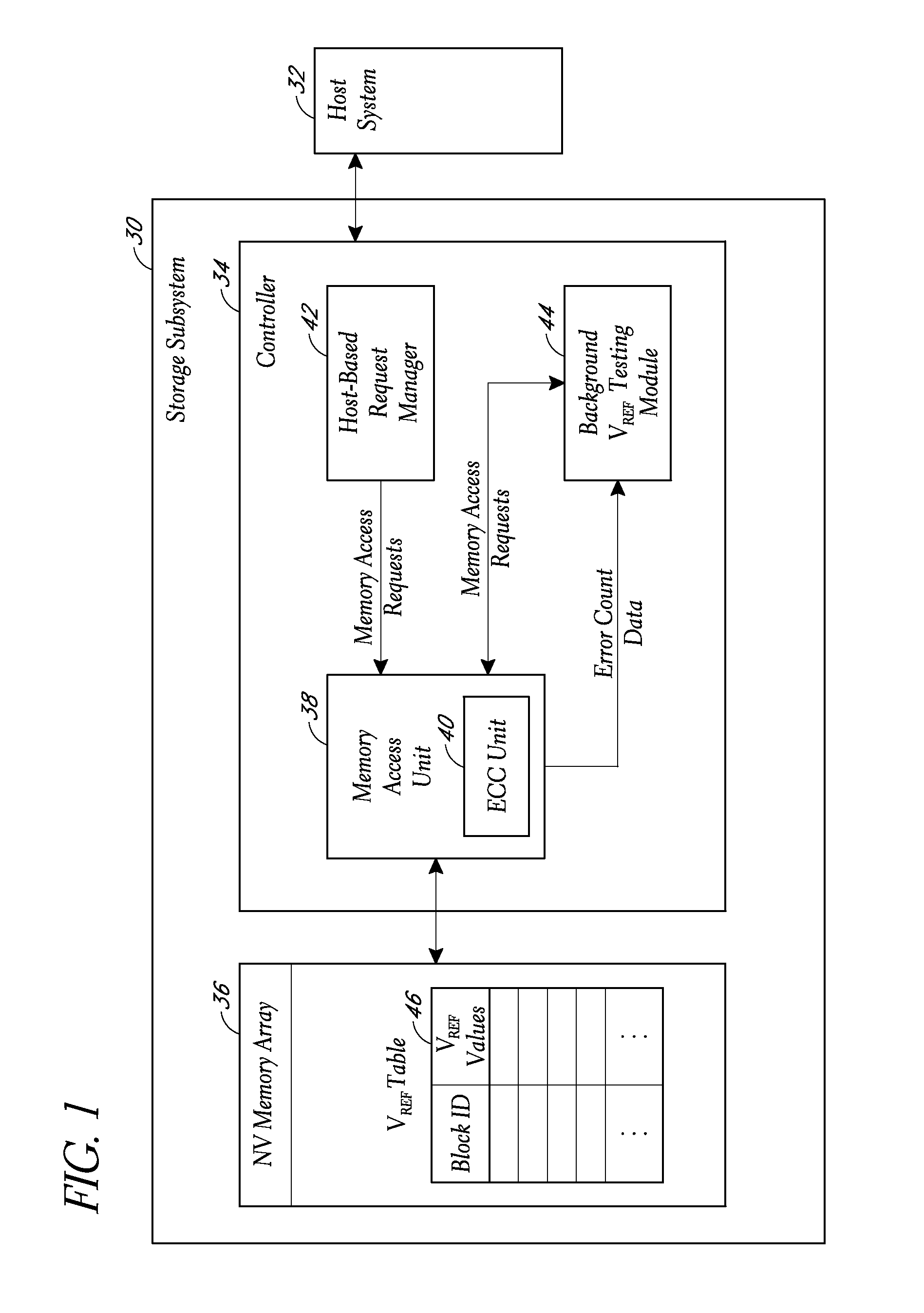
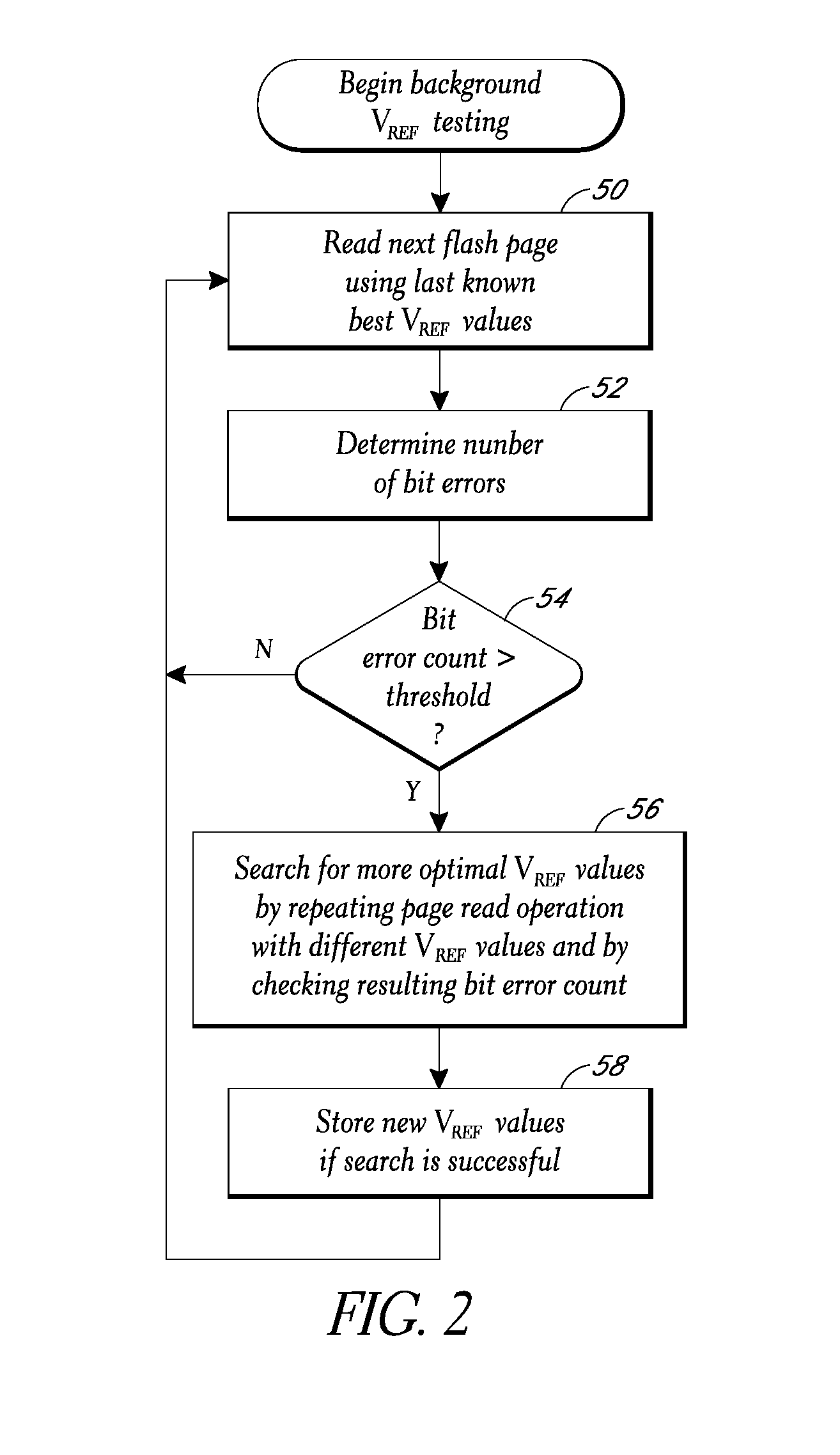
Background selection of voltage reference values for performing memory read operations
A storage subsystem implements a background process for selecting voltage reference values to use for reading data from a non-volatile memory array, such as an array of multi-level cell (MLC) flash memory. The process involves performing background read operations using specific sets of voltage reference values while monitoring the resulting bit error counts. The selected voltage reference values for specific pages or other blocks of the array are stored in a table. Read operations requested by a host system are executed using the corresponding voltage reference values specified by the table.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
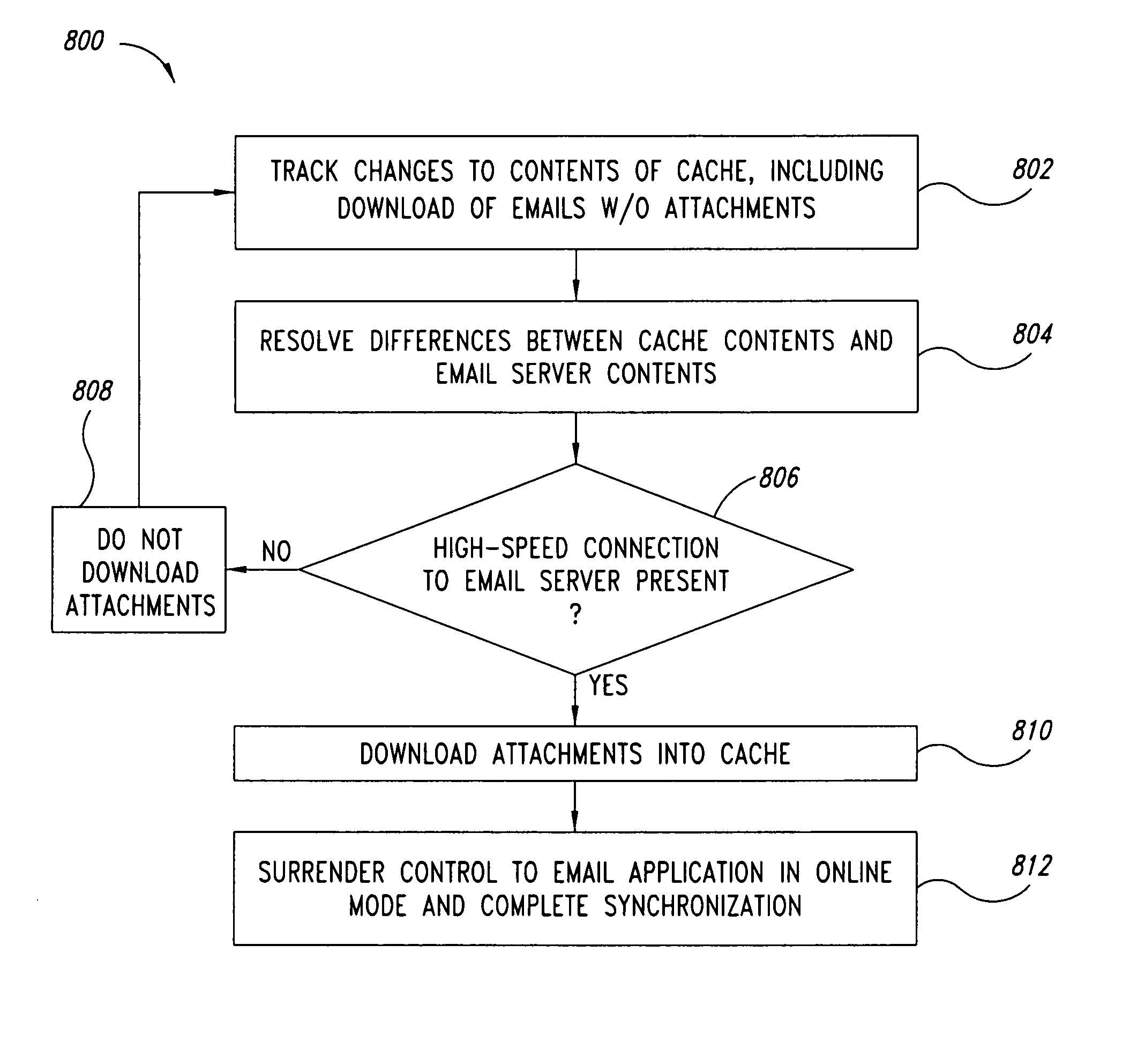
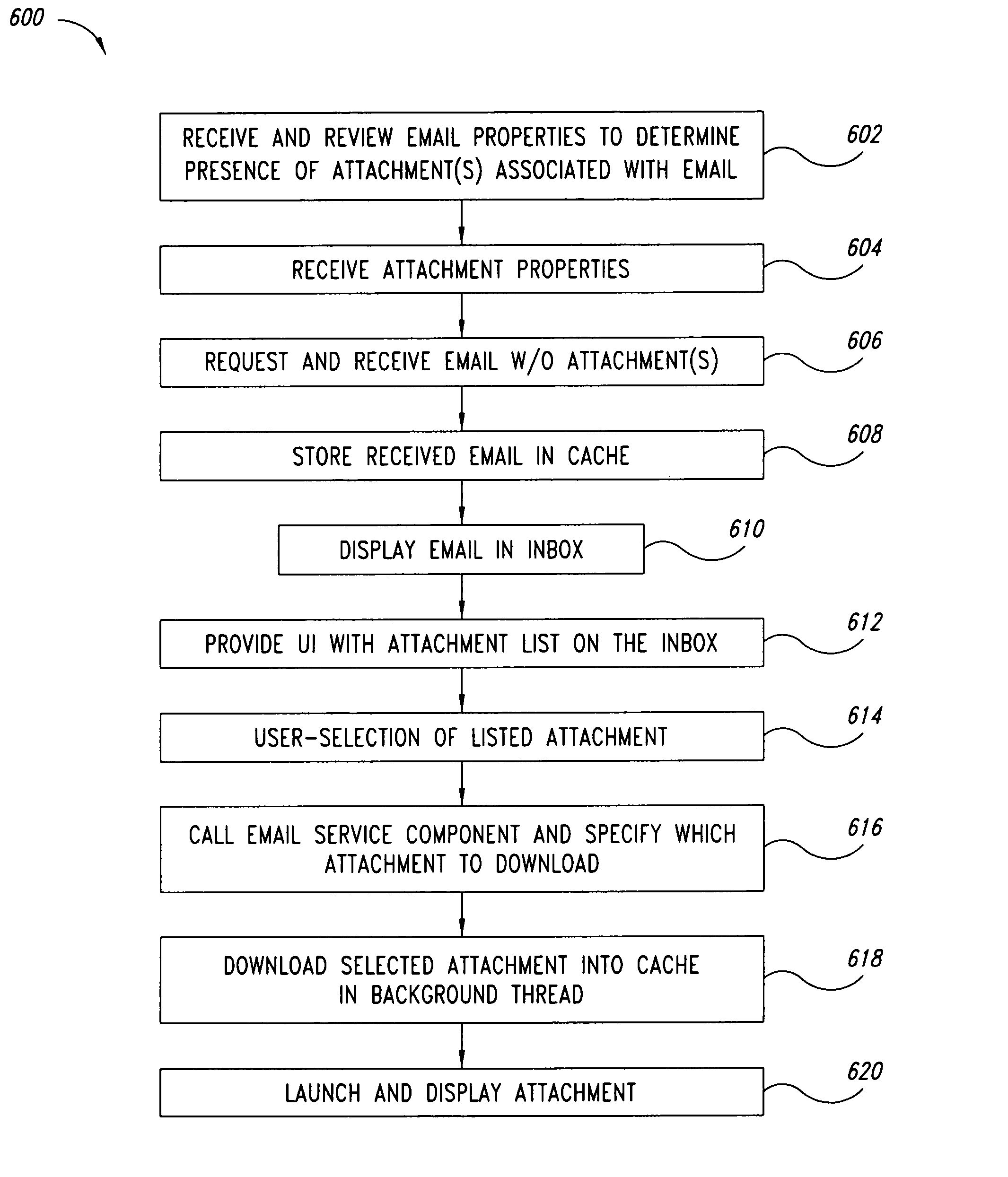
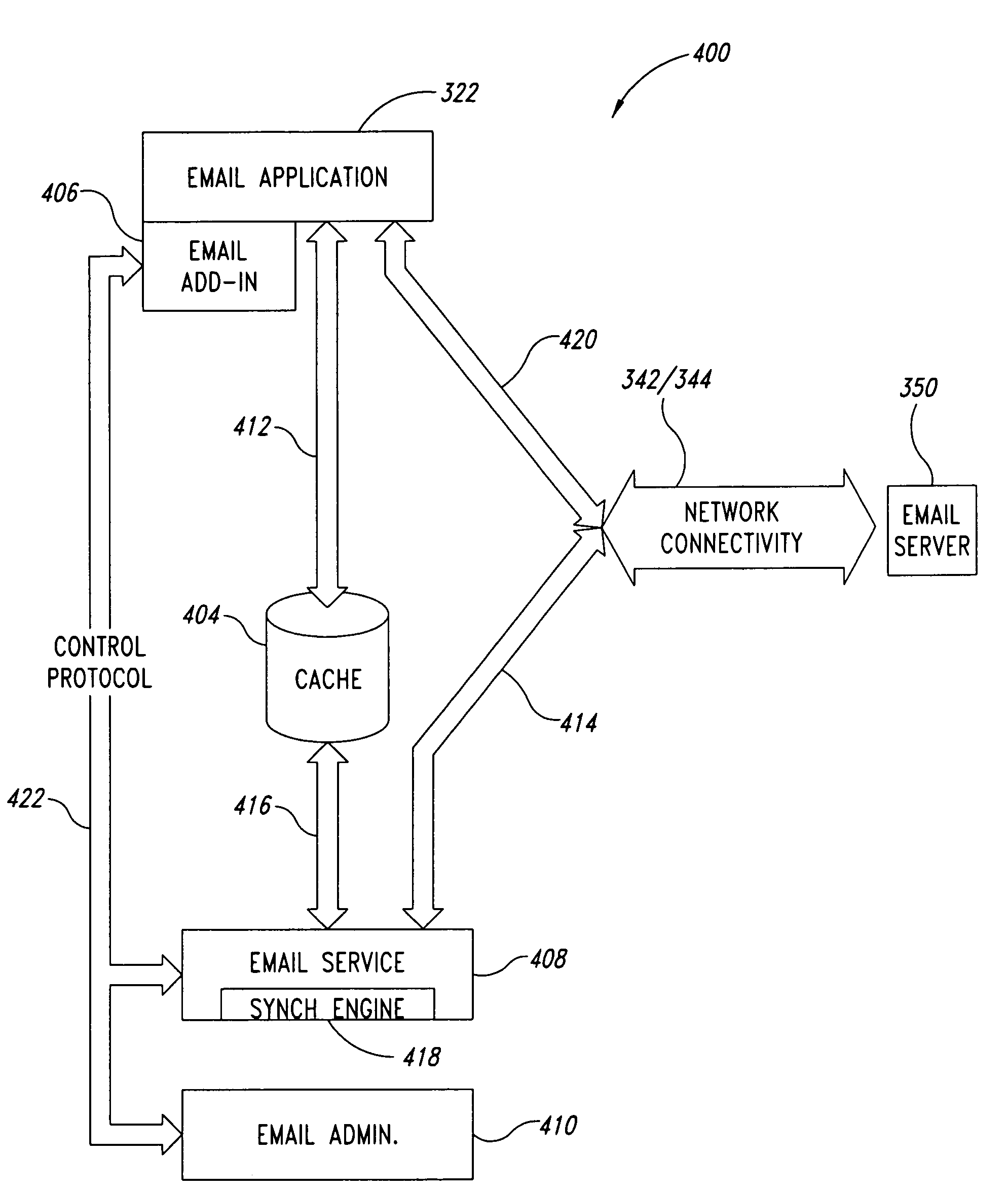
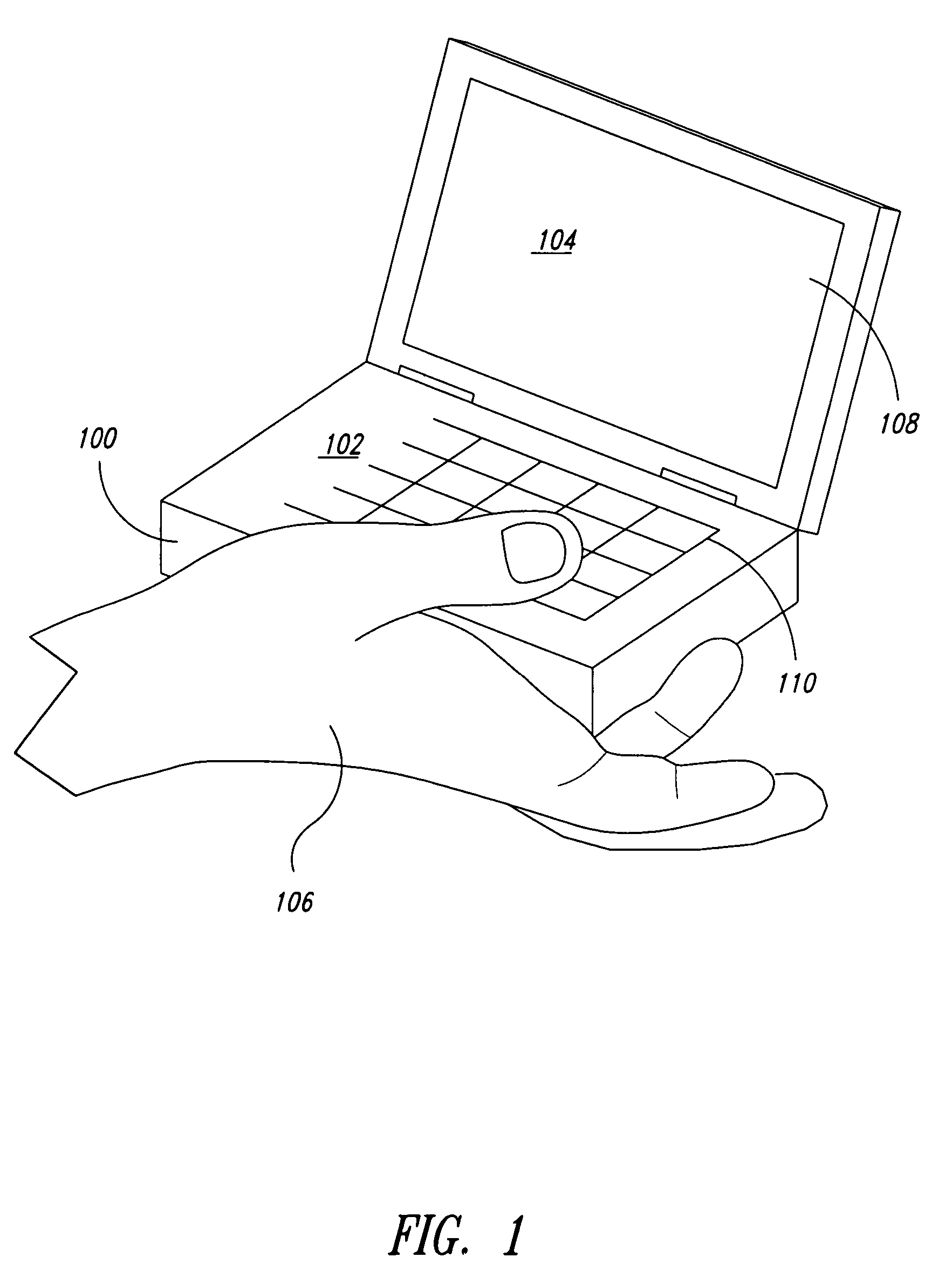
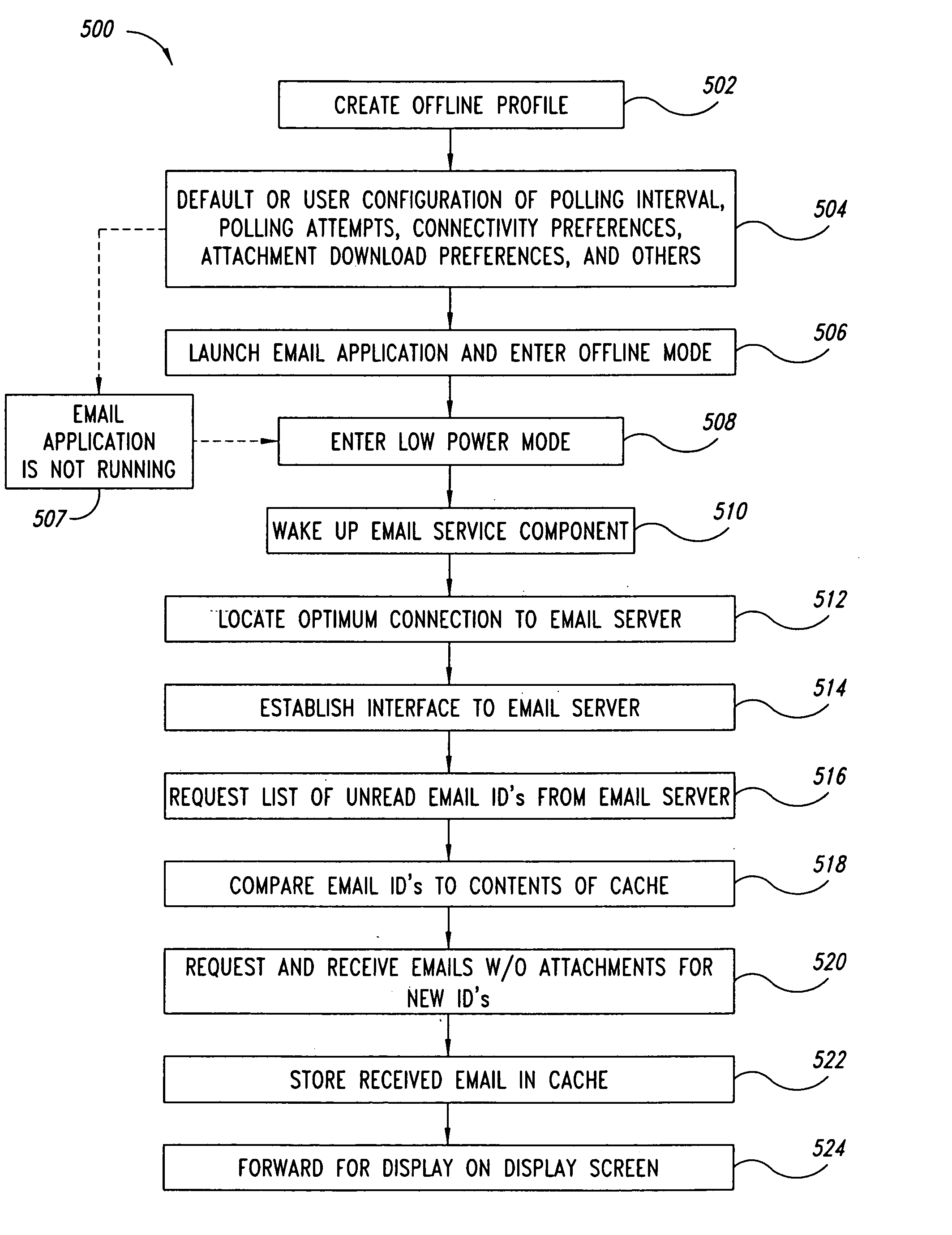
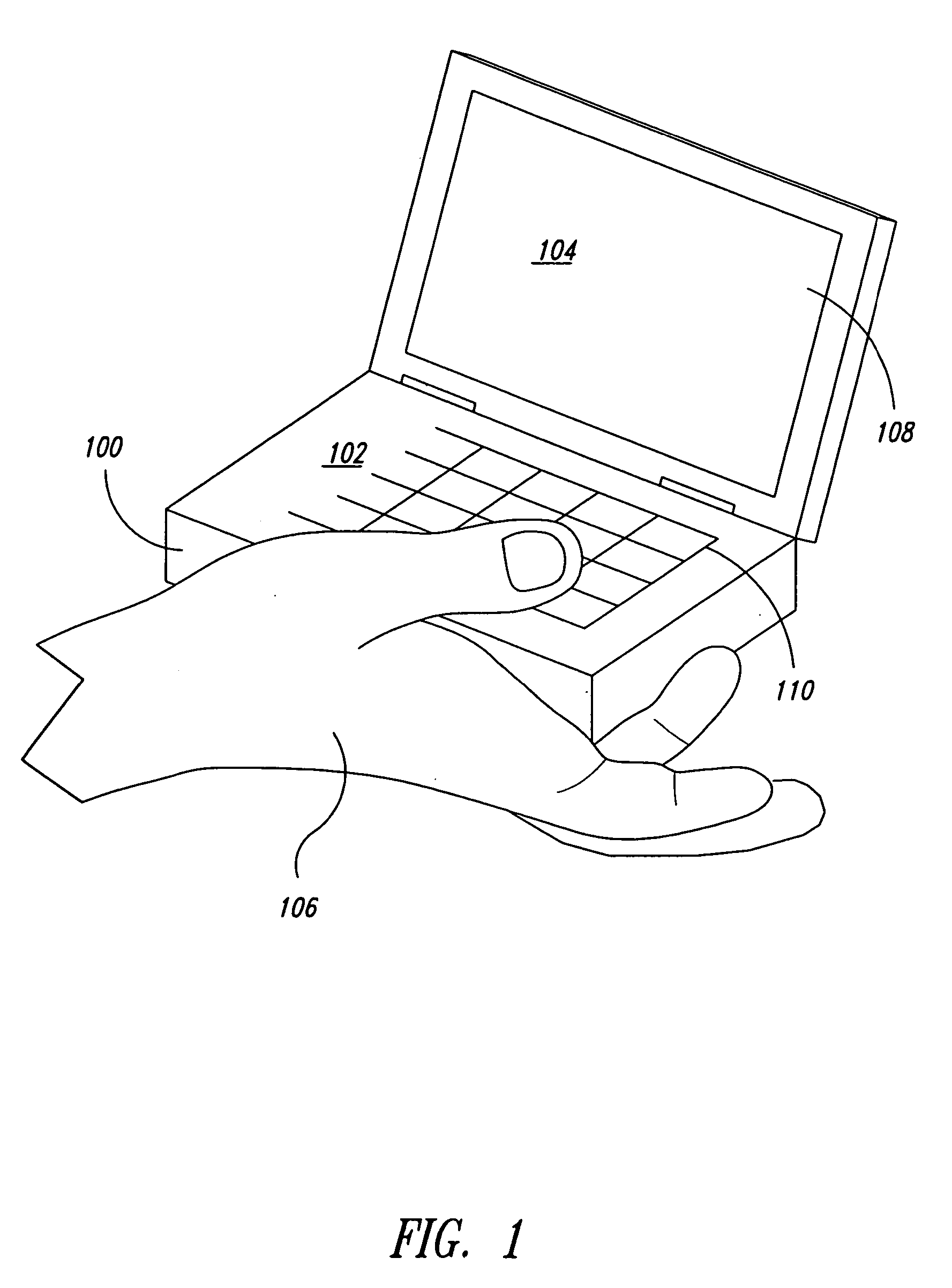
Method and system for email synchronization for an electronic device
An electronic device, such as a hand-held portable computer, is provided with client-side email capability that allows emails to be independently downloaded from a server, regardless of an operating mode of an email application and without using the standard email retrieval mechanism of the email application. The emails are periodically downloaded without attachments in response to a poll of the server and if a sufficient high-speed connection to the server is available, and then the downloaded email is locally stored in a local cache of the portable computer. Attachments associated with downloaded emails stored in the local cache can be selectively downloaded, via a background process, from the server independently of the operating mode of the email application and during any suitable power state of the electronic device. Synchronization of attachments to emails in the local cache is also independently performed, thereby bypassing synchronization that is normally performed by the email application while in the online mode.
Owner:VULCAN PORTALS
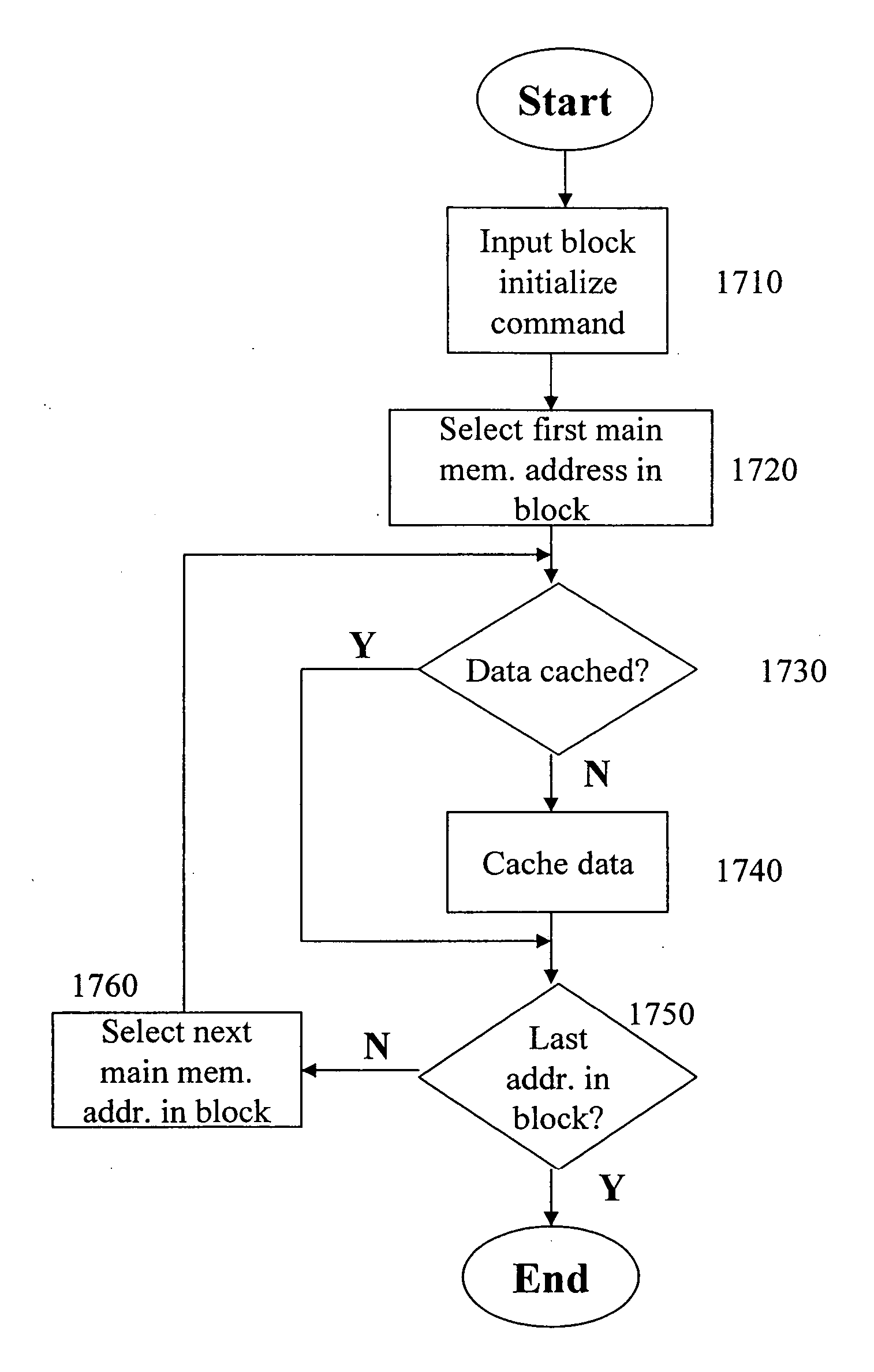
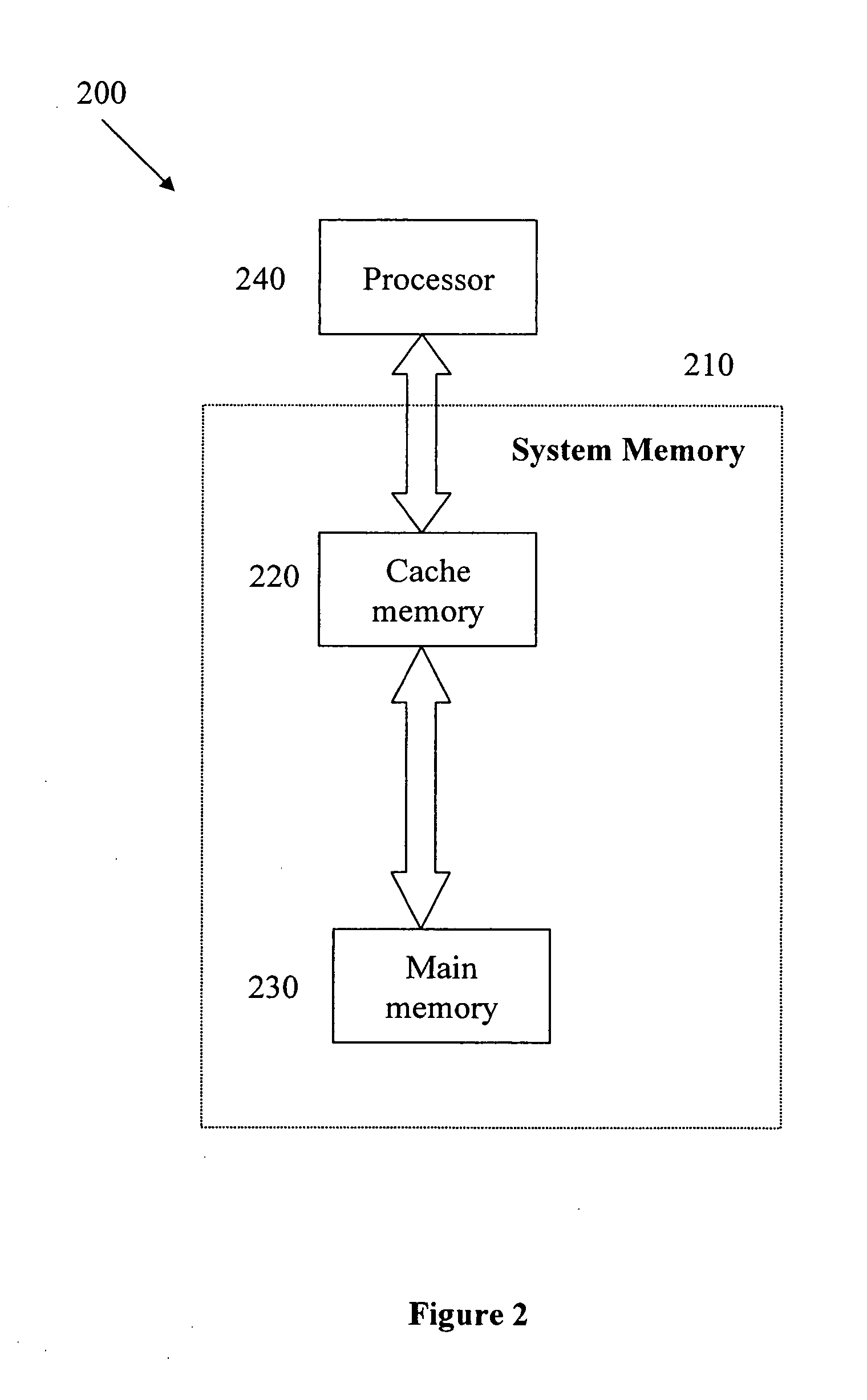
Cache memory background preprocessing
A cache memory preprocessor prepares a cache memory for use by a processor. The processor accesses a main memory via a cache memory, which serves a data cache for the main memory. The cache memory preprocessor consists of a command inputter, which receives a multiple-way cache memory processing command from the processor, and a command implementer. The command implementer performs background processing upon multiple ways of the cache memory in order to implement the cache memory processing command received by the command inputter.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Method and system for email synchronization for an electronic device
An electronic device, such as a hand-held portable computer, is provided with client-side email capability that allows emails to be independently downloaded from a server, regardless of an operating mode of an email application and without using the standard email retrieval mechanism of the email application. The emails are periodically downloaded without attachments in response to a poll of the server and if a sufficient high-speed connection to the server is available, and then the downloaded email is locally stored in a local cache of the portable computer. Attachments associated with downloaded emails stored in the local cache can be selectively downloaded, via a background process, from the server independently of the operating mode of the email application and during any suitable power state of the electronic device. Synchronization of attachments to emails in the local cache is also independently performed, thereby bypassing synchronization that is normally performed by the email application while in the online mode.
Owner:VULCAN PORTALS
Method and system for polling a server for new emails, downloading the new emails in a background process, and caching the downloaded emails for access by an email application of an electronic device, such as a portable computer
An electronic device, such as a hand-held portable computer, is provided with client-side email capability that allows emails to be independently downloaded from a server, regardless of an operating mode of an email application and without using the standard email retrieval mechanism of the email application. The emails are periodically downloaded without attachments in response to a poll of the server and if a sufficient high-speed connection to the server is available, and then the downloaded email is locally stored in a local cache of the portable computer. Attachments associated with downloaded emails stored in the local cache can be selectively downloaded, via a background process, from the server independently of the operating mode of the email application and during any suitable power state of the electronic device. Synchronization of attachments to emails in the local cache is also independently performed, thereby bypassing synchronization that is normally performed by the email application while in the online mode.
Owner:VULCAN PORTALS
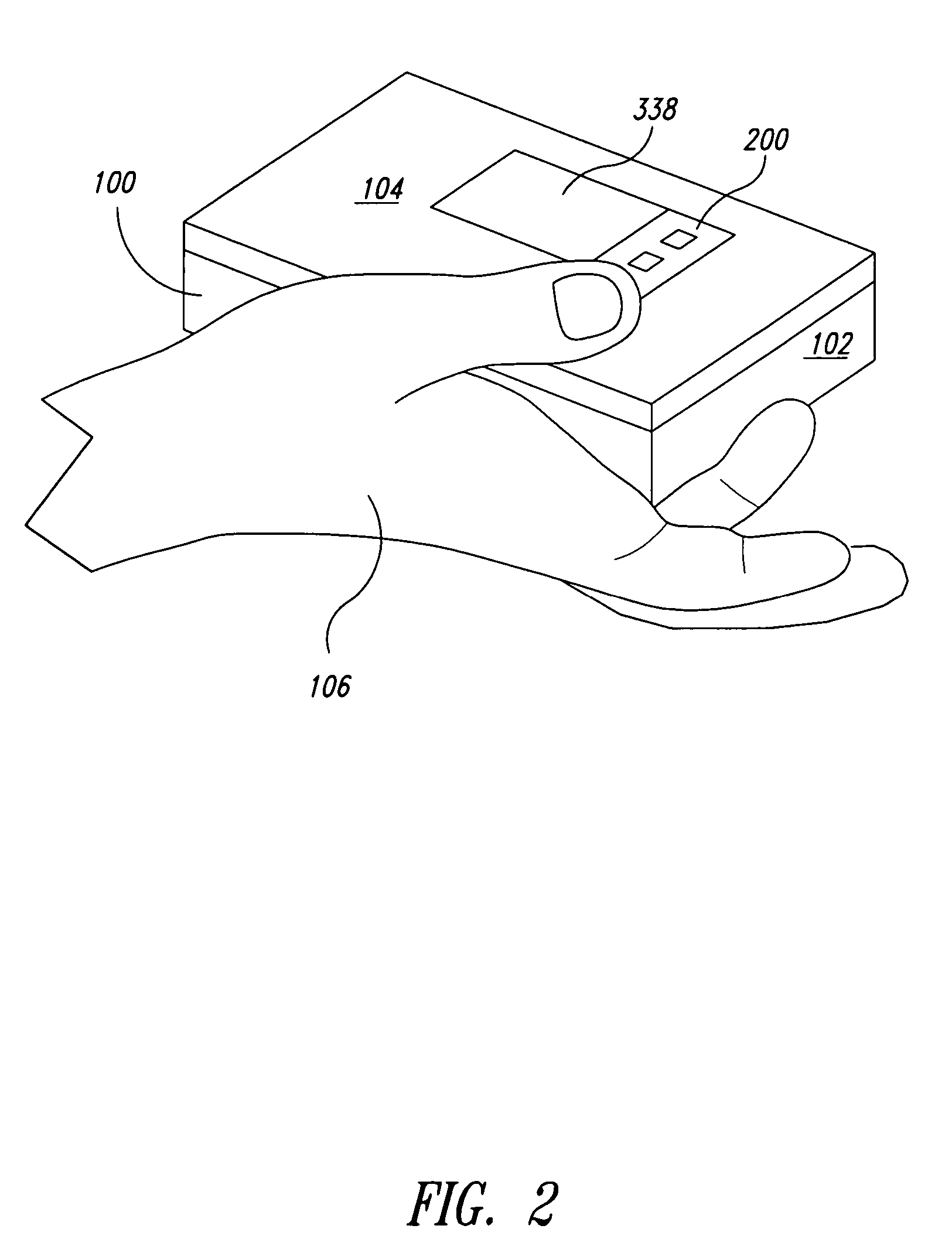
Method and system for managing email attachments for an electronic device
InactiveUS20050076085A1Multiple digital computer combinationsElectric digital data processingHand heldEmail attachment
An electronic device, such as a hand-held portable computer is provided with client-side email capability that allows emails to be independently downloaded from a server, regardless of an operating mode of an email application and without using the standard email retrieval mechanism of the email application. The emails are periodically downloaded without attachments in response to a poll of the server and if a sufficient high-speed connection to the server is available, and then the downloaded email is locally stored in a local cache of the portable computer. Attachments associated with downloaded emails stored in the local cache can be selectively downloaded, via a background process, from the server independently of the operating mode of the email application and during any suitable power state of the electronic device. Synchronization of attachments to emails in the local cache is also independently performed, thereby bypassing synchronization that is normally performed by the email application while in the online mode.
Owner:VULCAN PORTALS
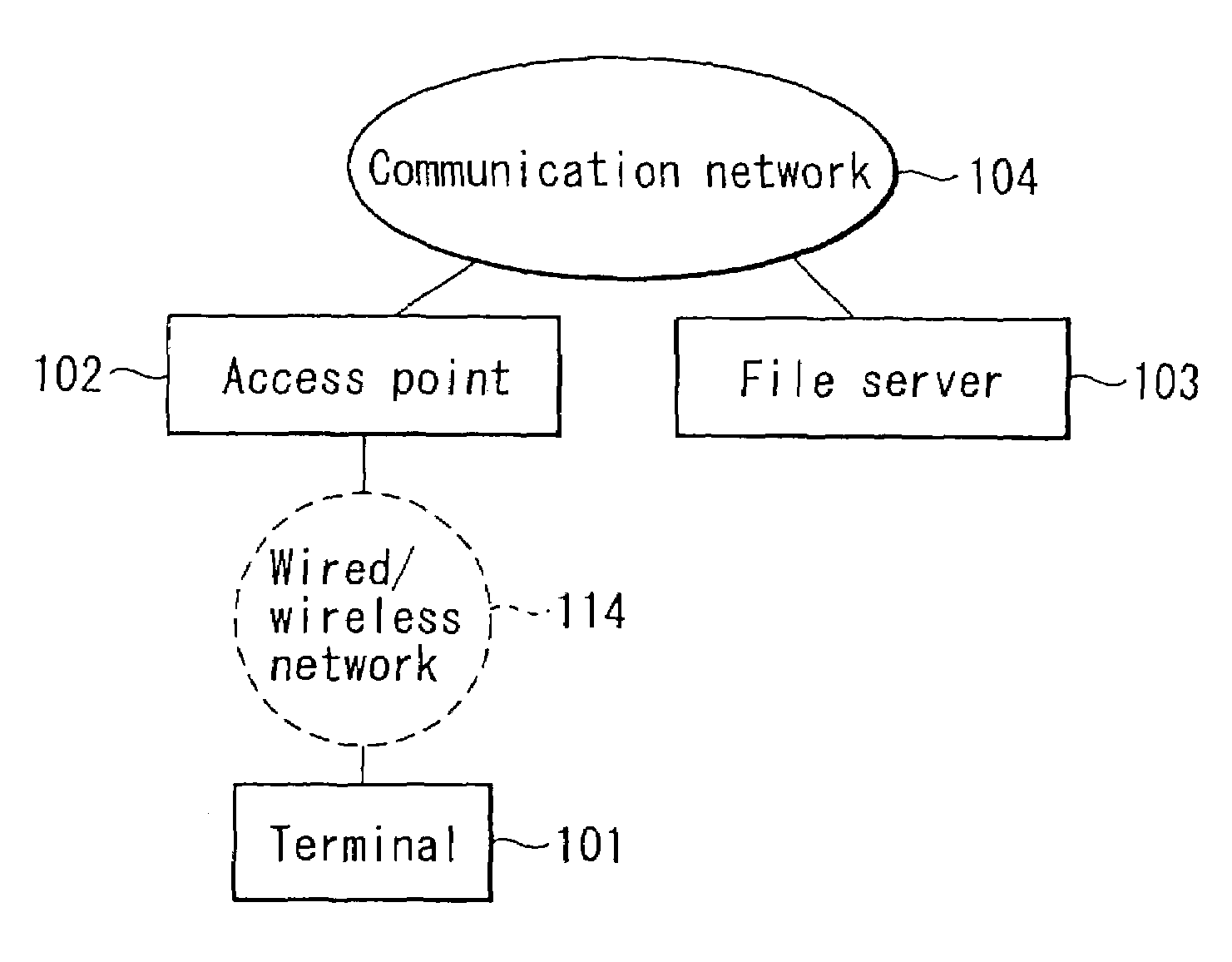
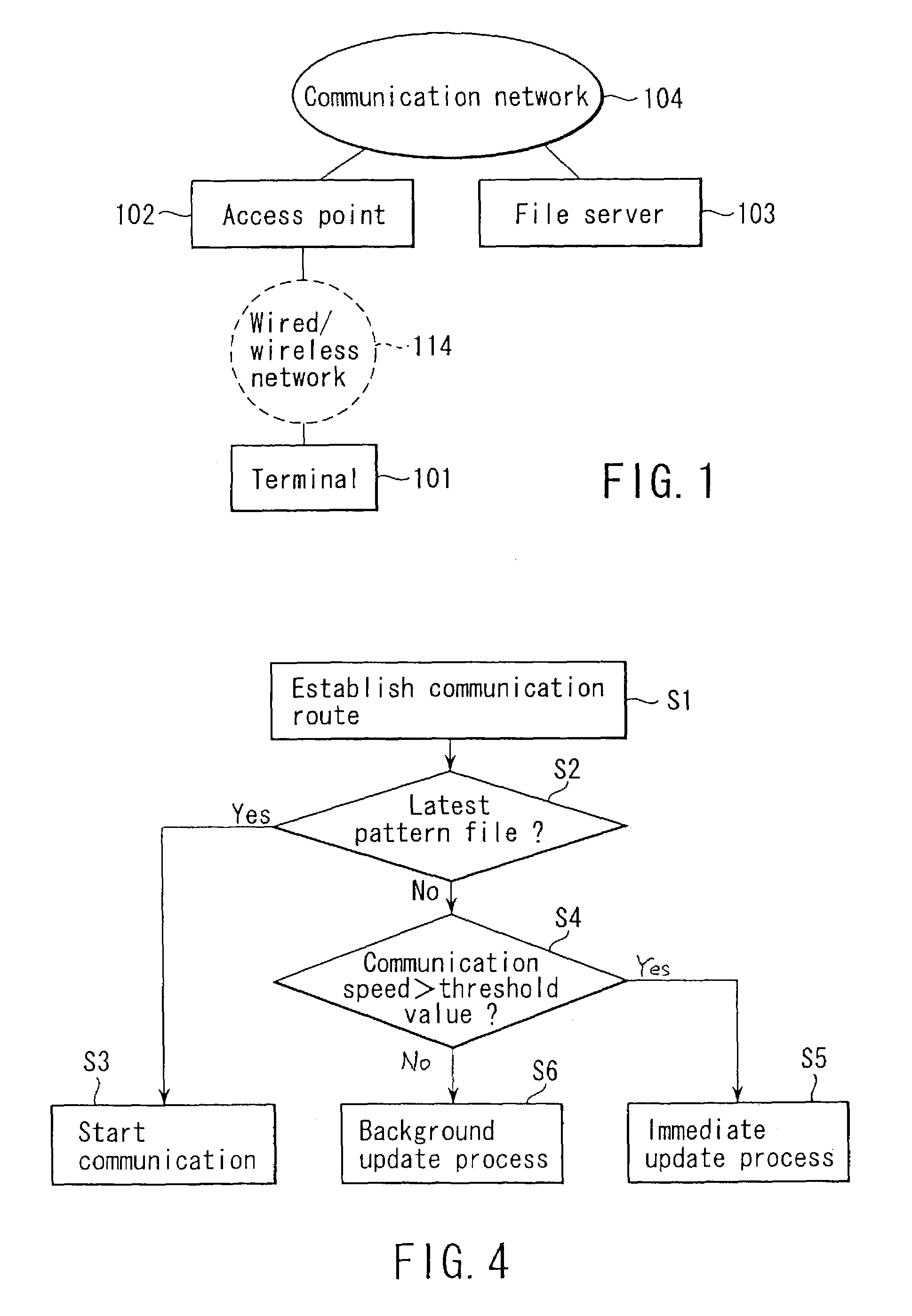
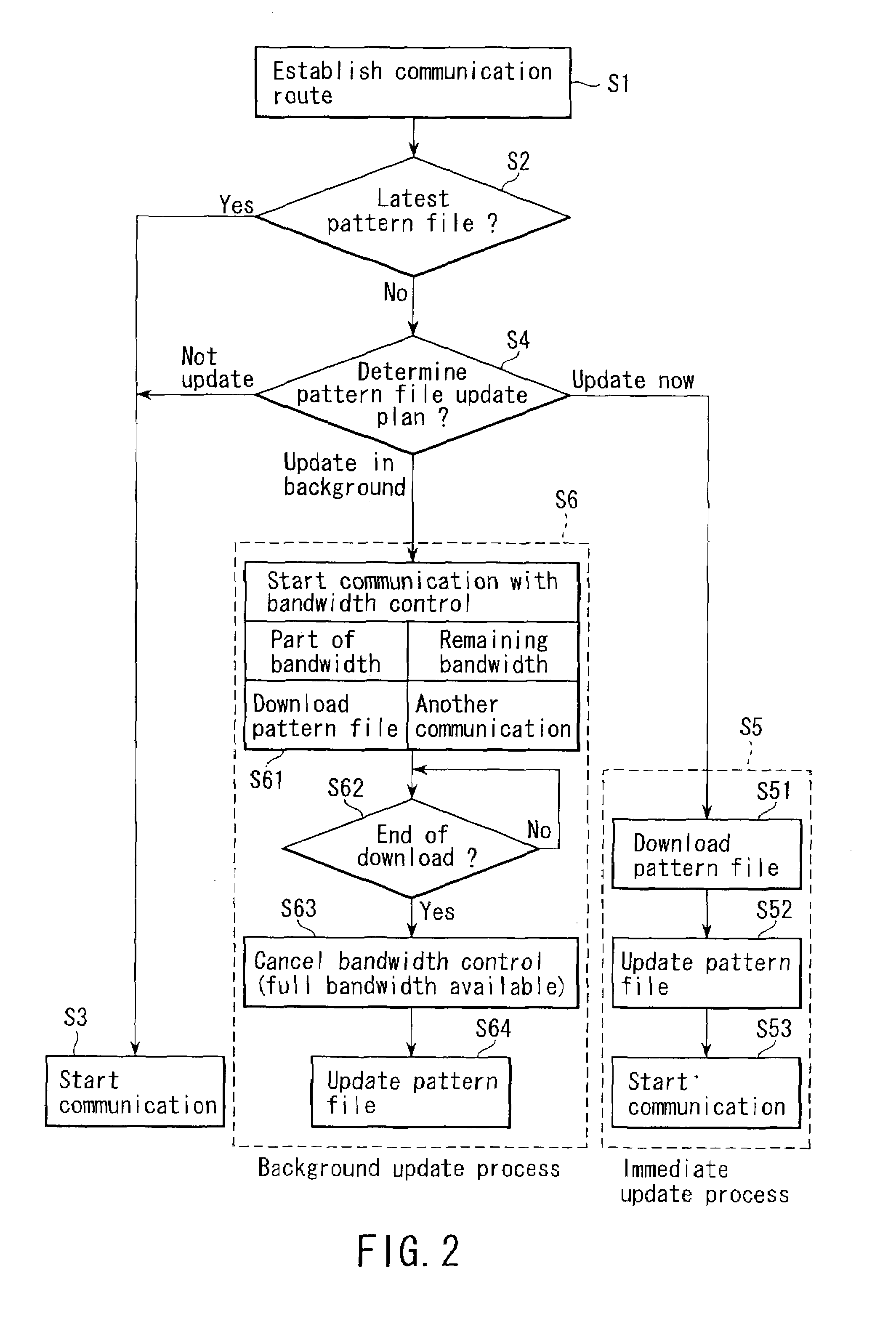
Communication system and communication method
InactiveUS7028077B2Without impairing user's convenienceDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationCommunications systemTelecommunications link
A communication system includes a first network on which a file server and an access point are connected via a first communication link and a second network on which the access point and a terminal are connected via a second communication link. The terminal establishes a connection with the access point to access the file server. The file server stores a file to be downloaded. The terminal accesses the file server through the access point to request the file. The terminal then selects a download process from one of a foreground process, background process and postponement process, and executes the download process to download the file from the file server.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
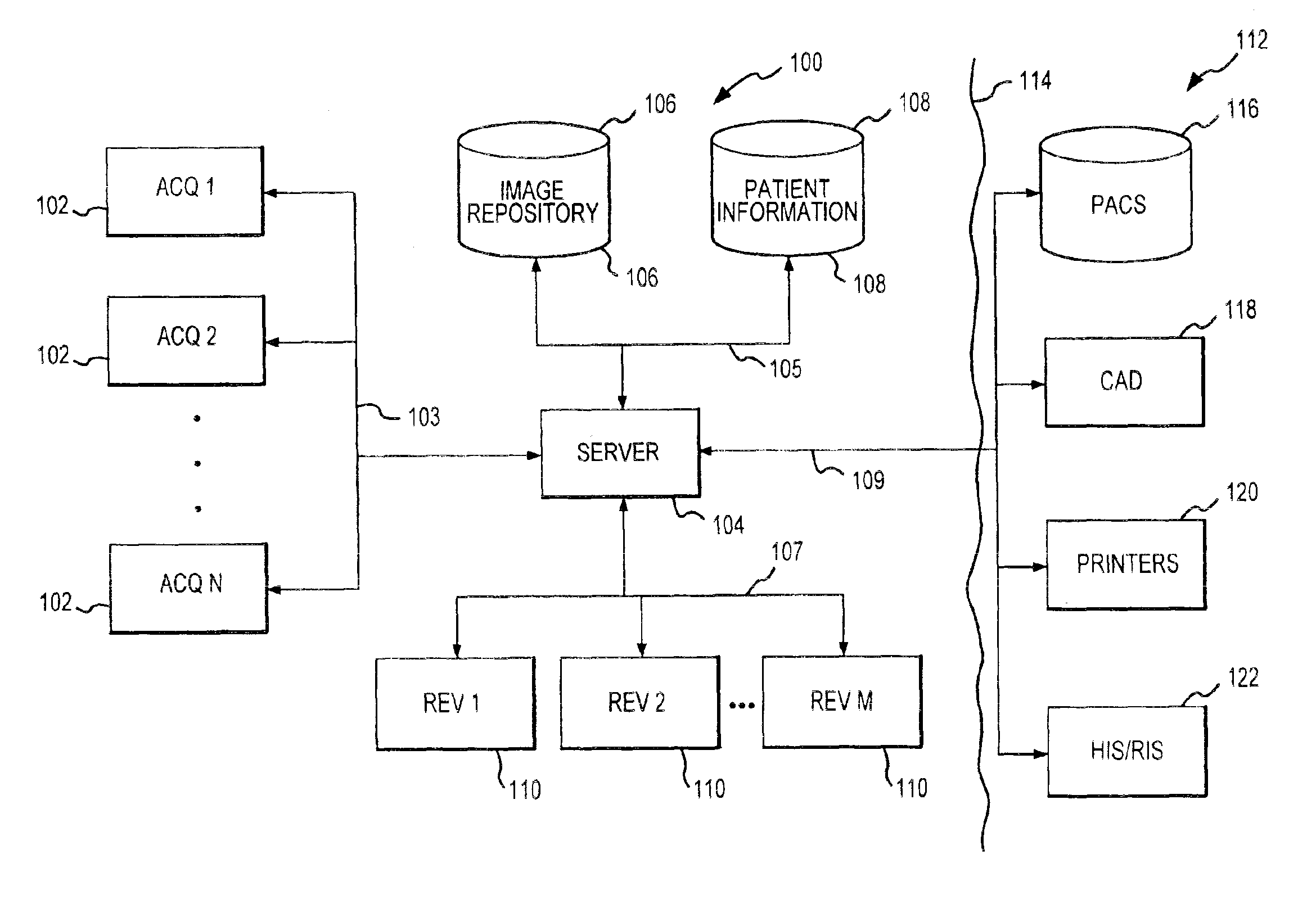
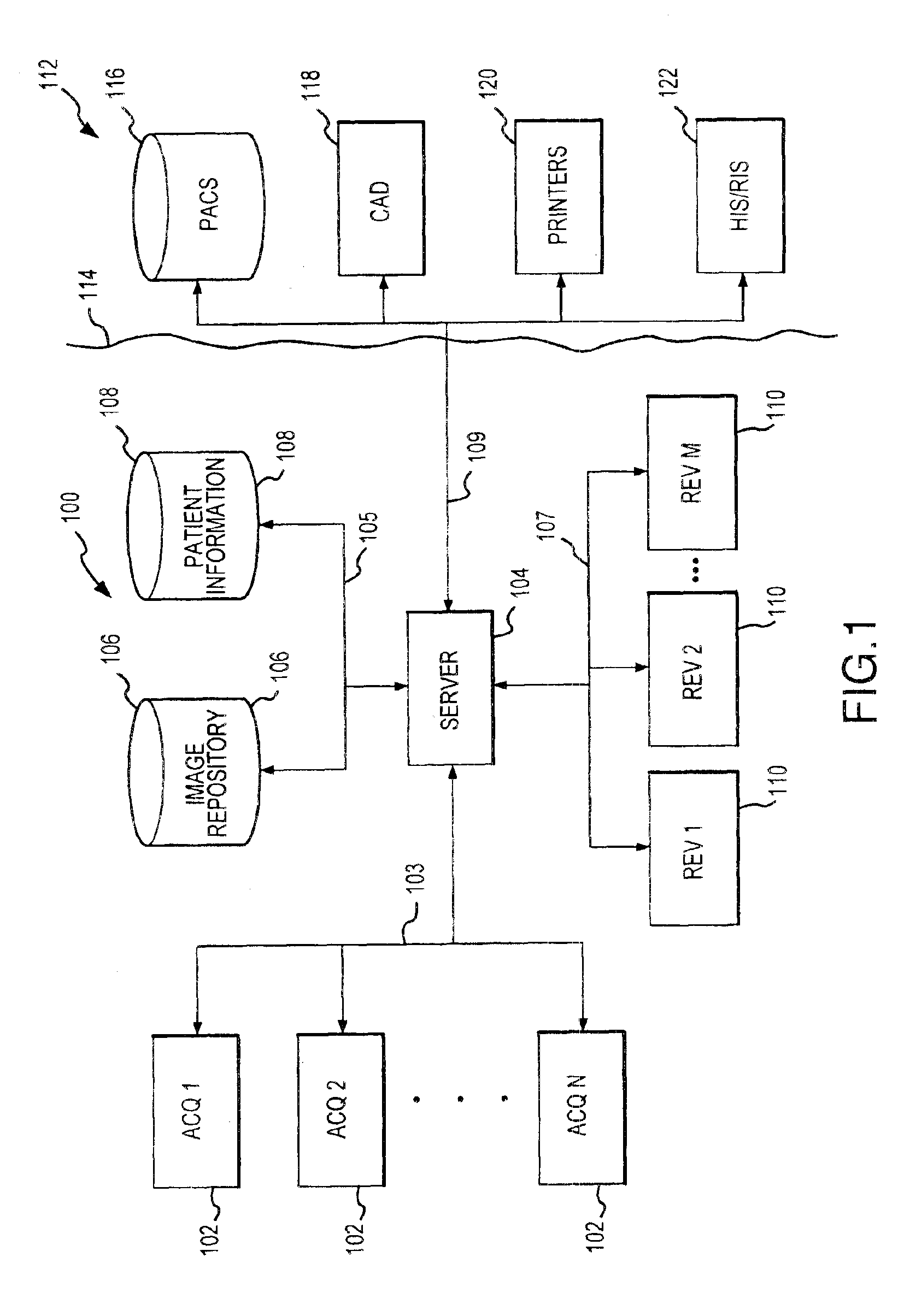
Automated background processing mammographic image data
InactiveUS6891920B1Improve efficiencyQuick displayPatient positioning for diagnosticsCharacter and pattern recognitionRapid accessDigital image
Disclosed is a mammographic imaging system and tools for processing mammographic images to enhance image acquisition and review workflow. The systems and tools enable rapid access to digital image information providing for improved workflow management and identification of images, upon initial review. The system and tools also allow for background processing of image information to reduce workflow delay. Specifically, digital images are processed in the background, i.e., they are automatically processed, free from specific task-orientated direction by a user, using resources that are not otherwise occupied addressing user-directed tasks. Background processing that may be supported includes preprocessing and interim processing. Preprocessing refers to processing of an image that occurs prior to initial review of that image by a physician. Interim processing refers to background processing that occurs during a review session, e.g., in a time period between initial review and a subsequent review of an image.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
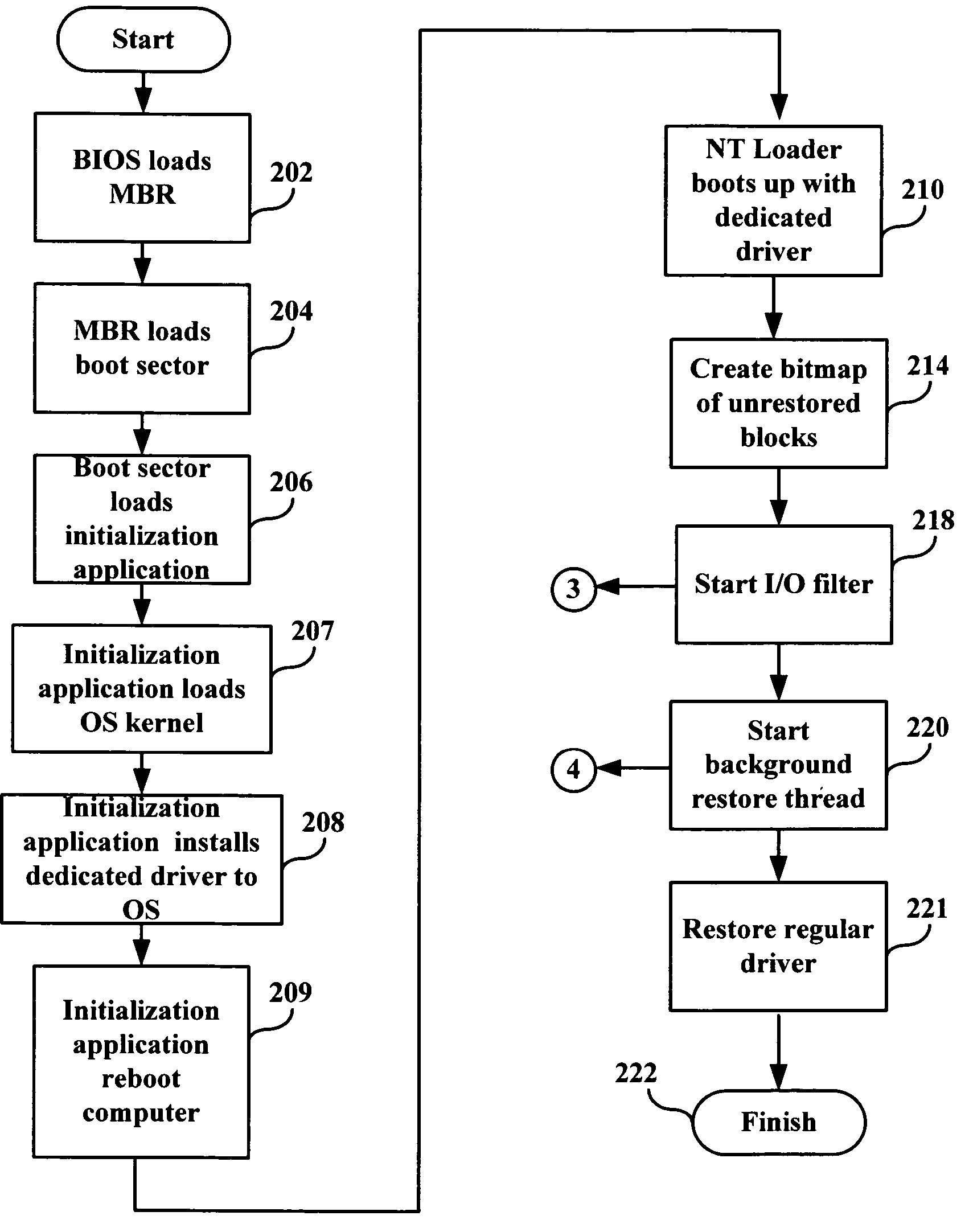
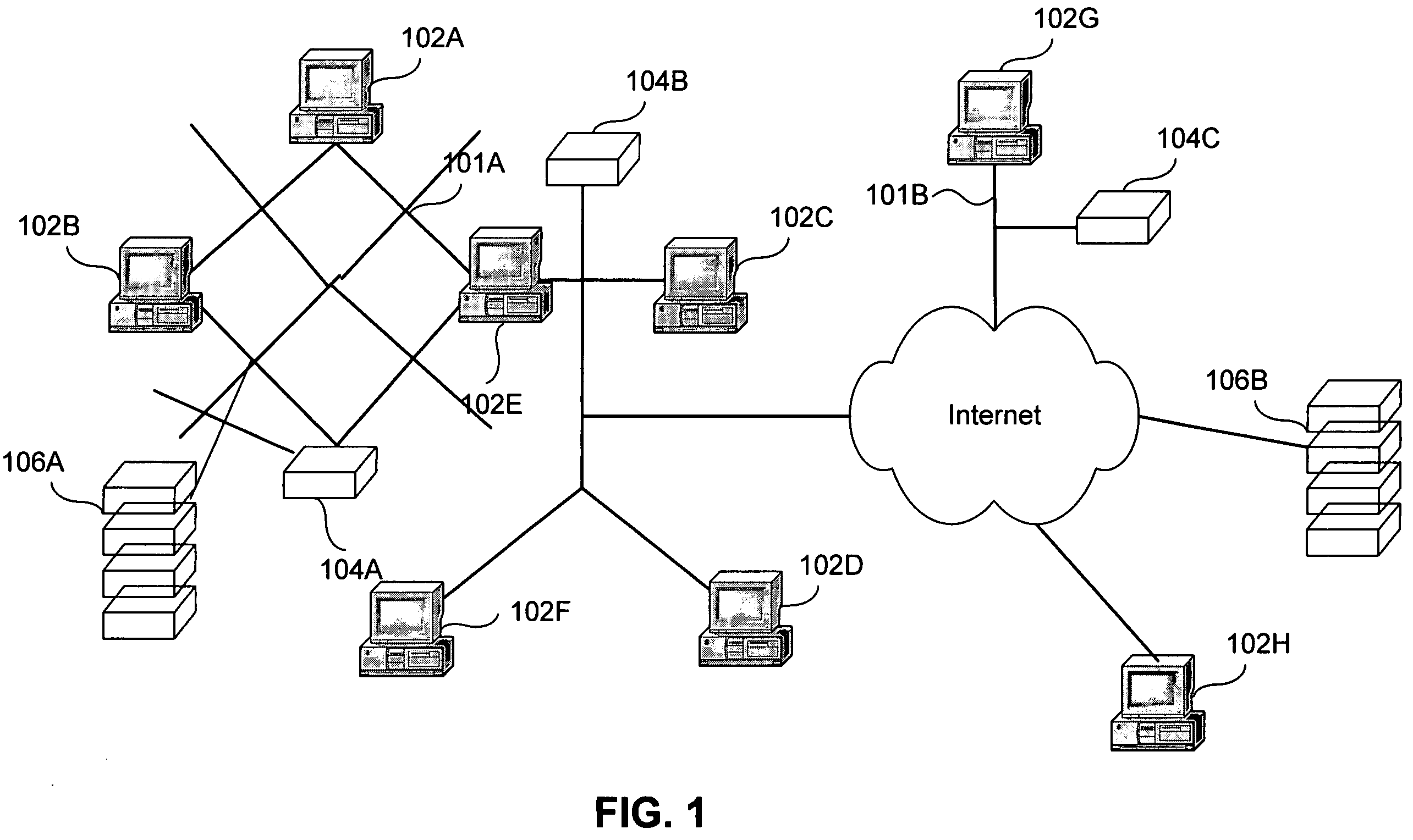
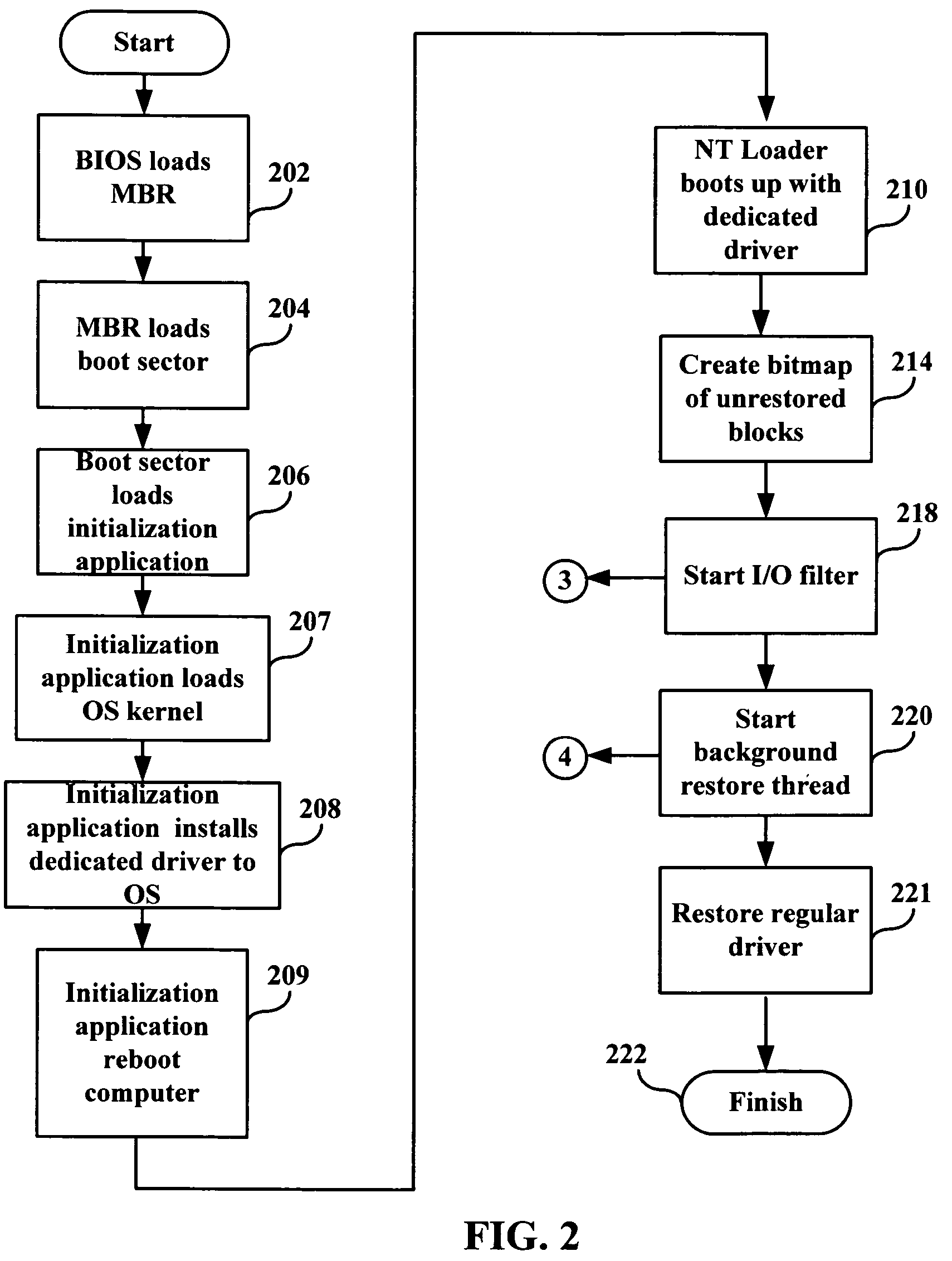
System and method for rapid restoration of server from back up
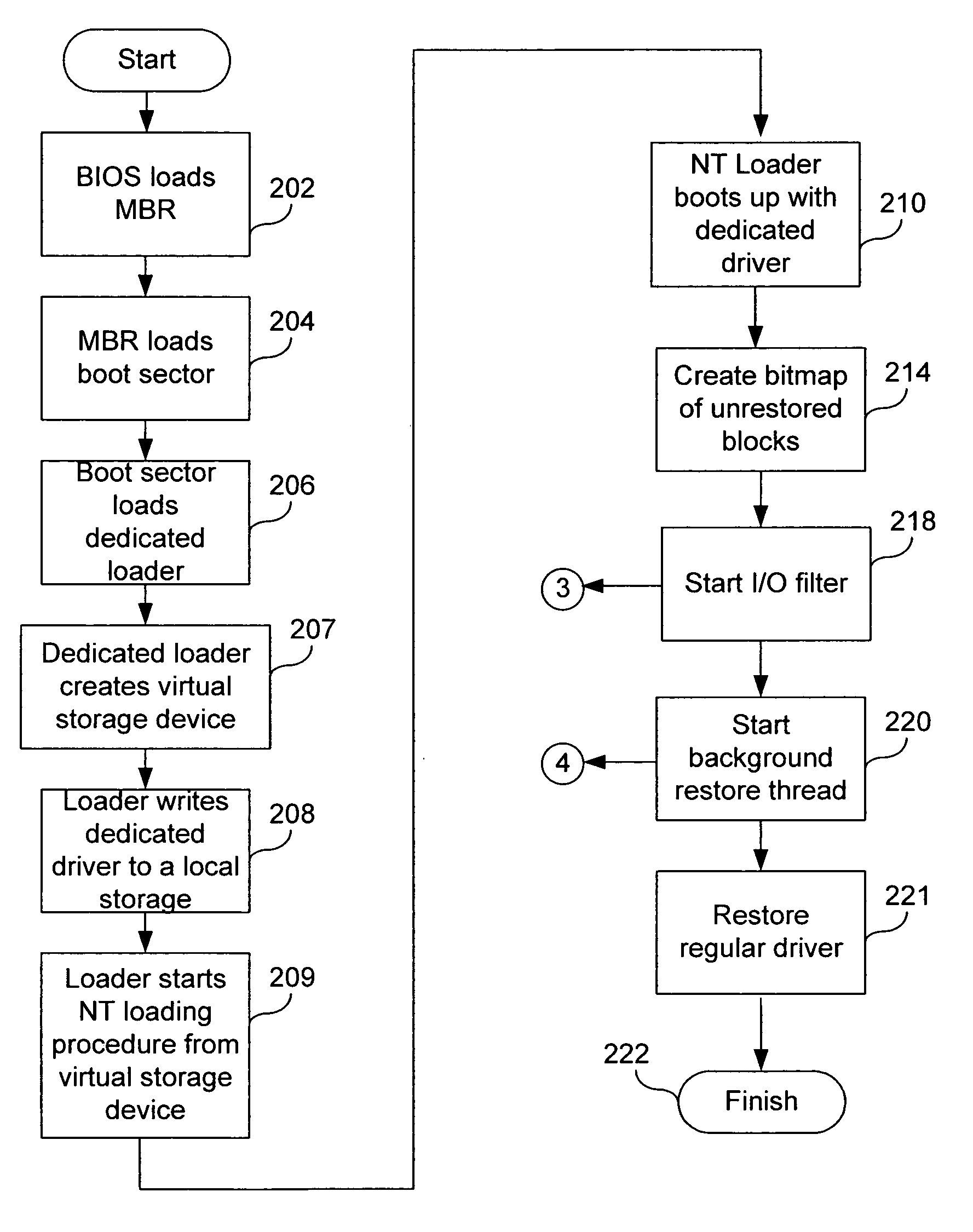
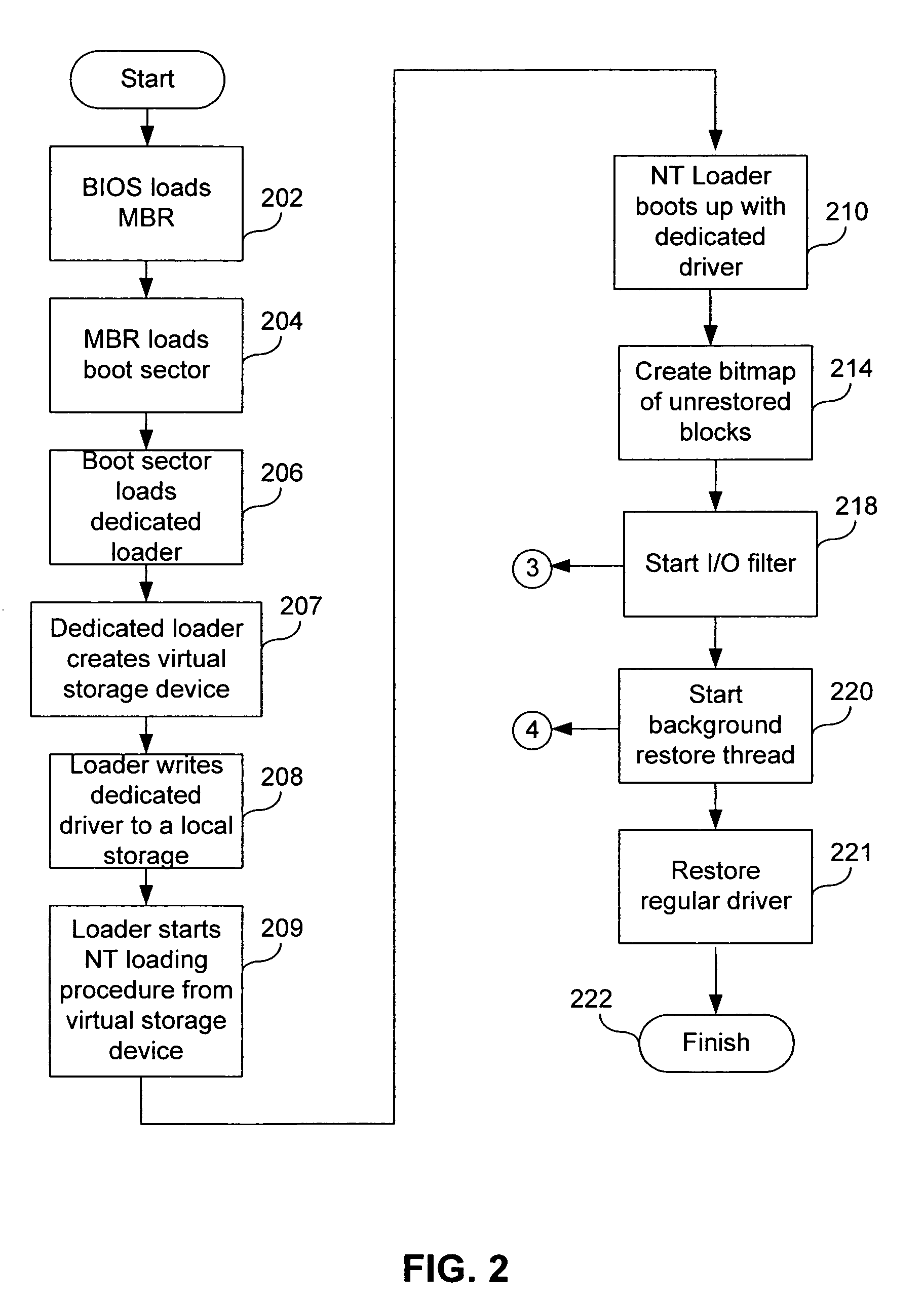
A method of restoring a storage device includes creating an image of the storage device of a computer system; during execution of a boot loader, starting an initialization application that at least partially restores to the storage device, operating system data from the image; modifying a disk driver of the operating system to form a driver that redirects unexecutable storage device read requests to the image; rebooting the computer system using the at least partially restored operating system data; and restoring unaltered portions of remaining data from the image as a background process.
Owner:MIDCAP FINANCIAL TRUST
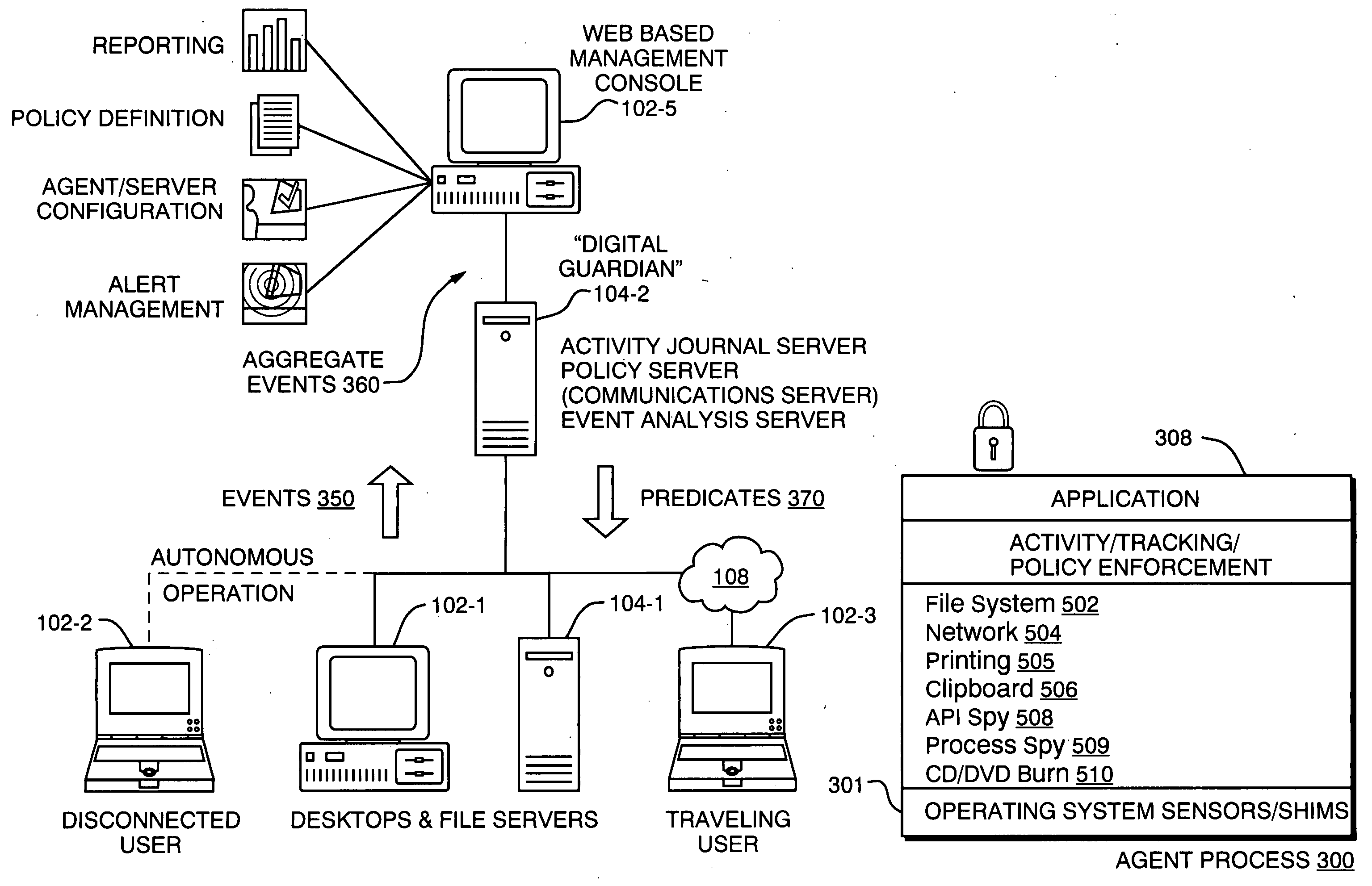
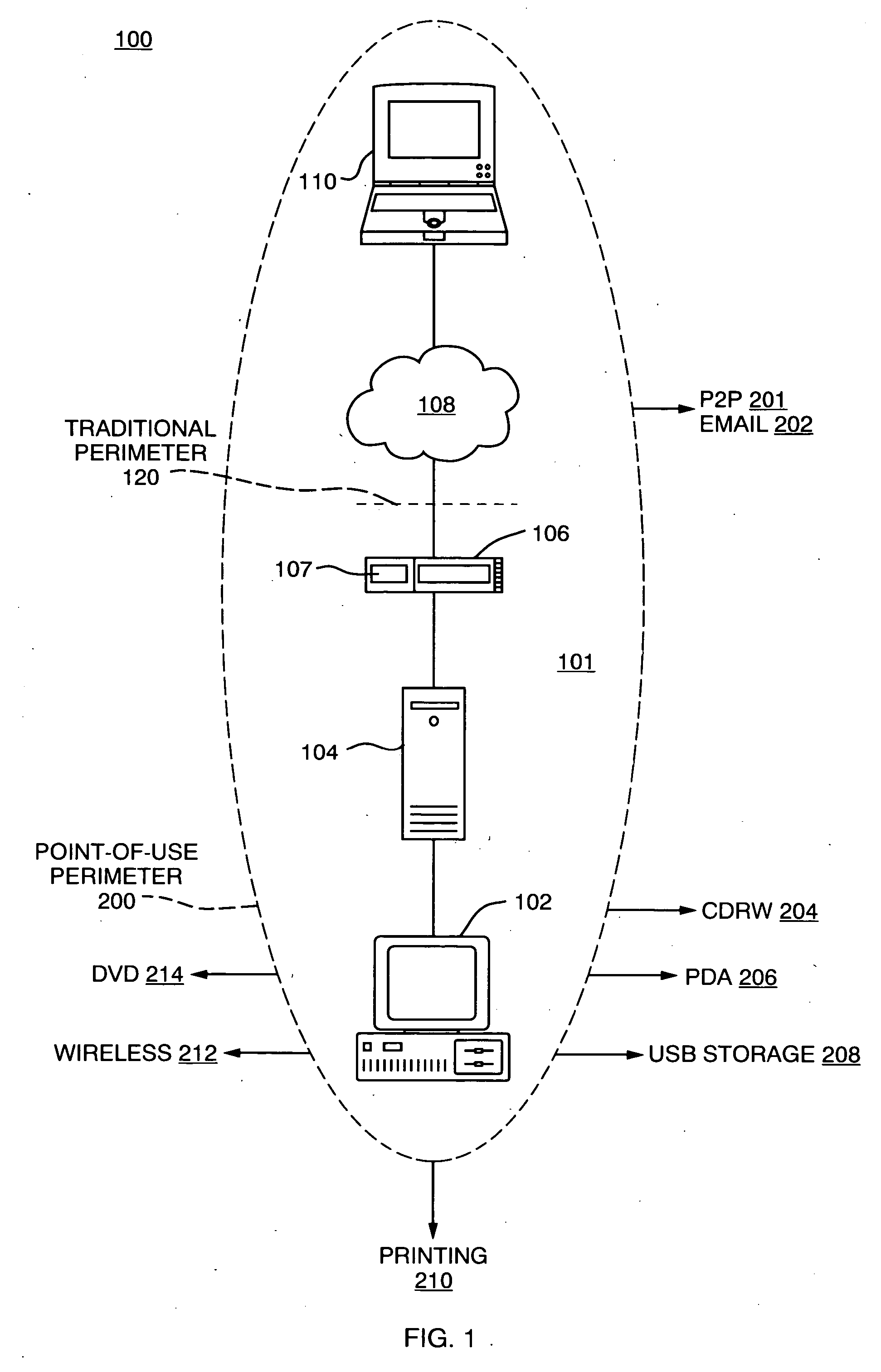
Managed distribution of digital assets
ActiveUS20050060537A1High acceptanceEasy to produceHardware monitoringComputer security arrangementsOperational systemNetwork connection
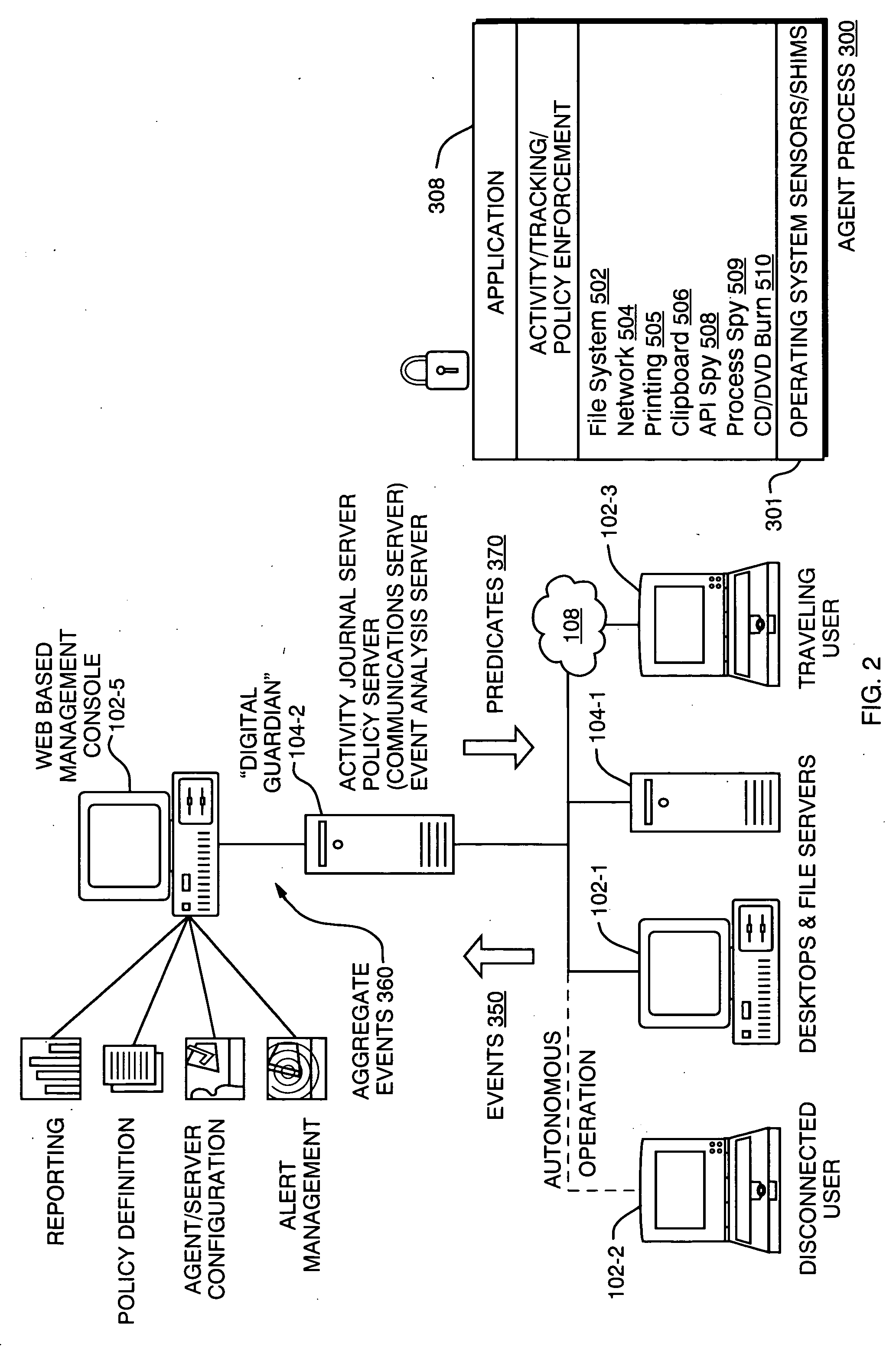
A technique for establishing usage control over digital assets such as computer files. The system model not only tracks authorized users' access to files, but monitors passage of such files to uncontrollable removable storage media or through network connections and the like which may indicate possible abuse of access rights. In accordance with a preferred embodiment, an autonomous independent agent process running at a point of use, such a background process in a client operating system kernel, interrupts requests for access to resources. The agent process senses low level system events, filters, and aggregates them. A policy engine analyzes sequences of aggregate events to determine when policy violations occur.
Owner:DIGITAL GUARDIAN LLC
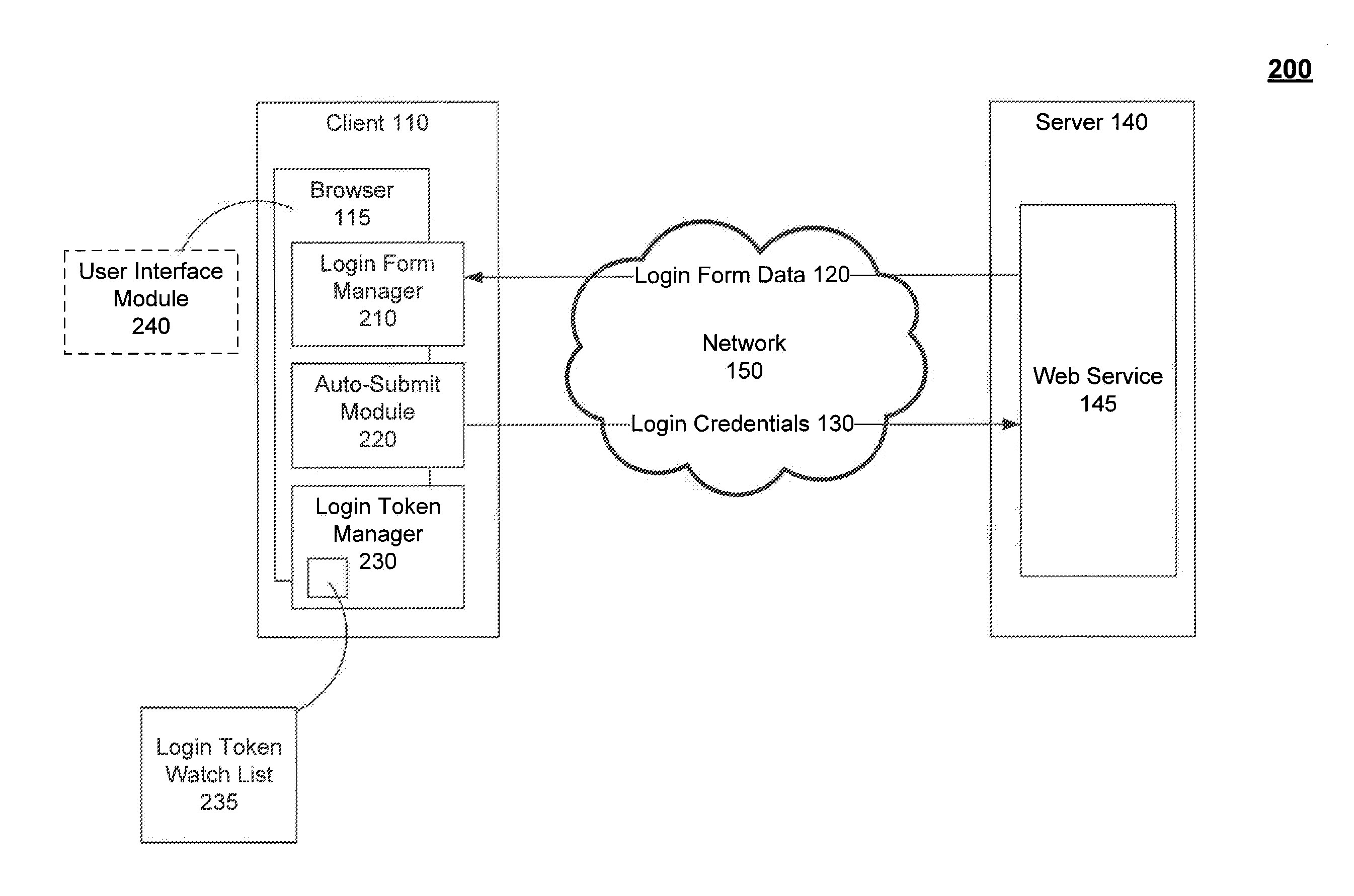
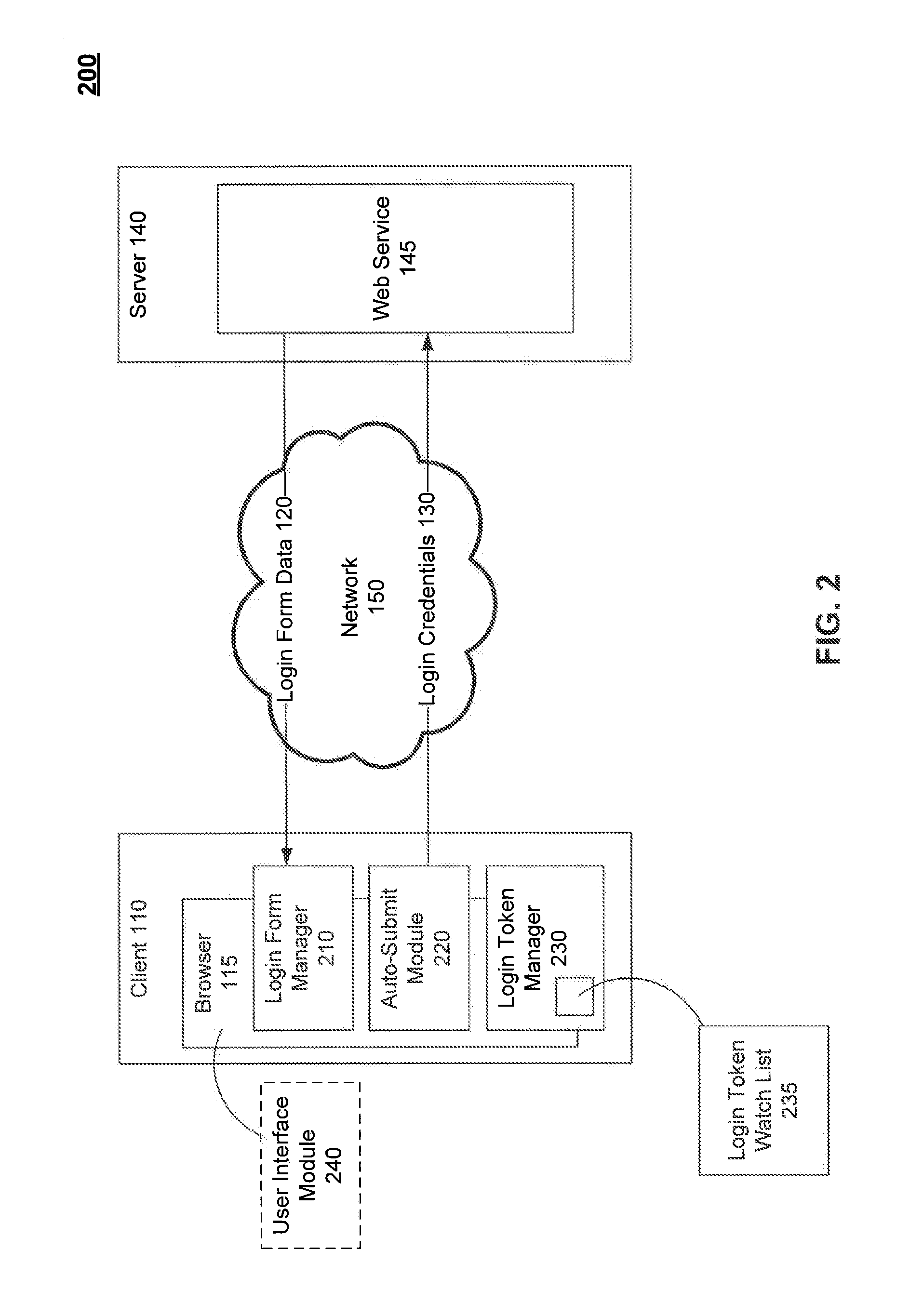
Background auto-submit of login credentials
A method and system for automatically submitting login credentials as a background process for a user of a web service are provided. Login information corresponding to a login form of the web service is stored, where the login information comprises a login endpoint of the web service and the login credentials are used to authenticate the user for a session of the web service. A login token, generated by the web service, and its expiration date are tracked. The login credentials are then automatically submitted, without user intervention, to the web service based on the login endpoint and the expiration date of the login token.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Element management system with dynamic database updates based on parsed snooping
InactiveUS7185075B1Easy accessSpecial service for subscribersDigital computer detailsElement management systemBackground process
A new approach to maintaining concurrency in a network element management database. A background process constantly monitors the channels which carry network element configuration commands, and automatically parses any messages which carry information about the status of network elements. The information derived from parsing these messages is then used for a dynamic update of the database of network element attributes. This means that the database is completely current on the very latest status changes, and operators do not have to cross-check log files to see if their data is current. Instead, a simple database query retrieves fully current information.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
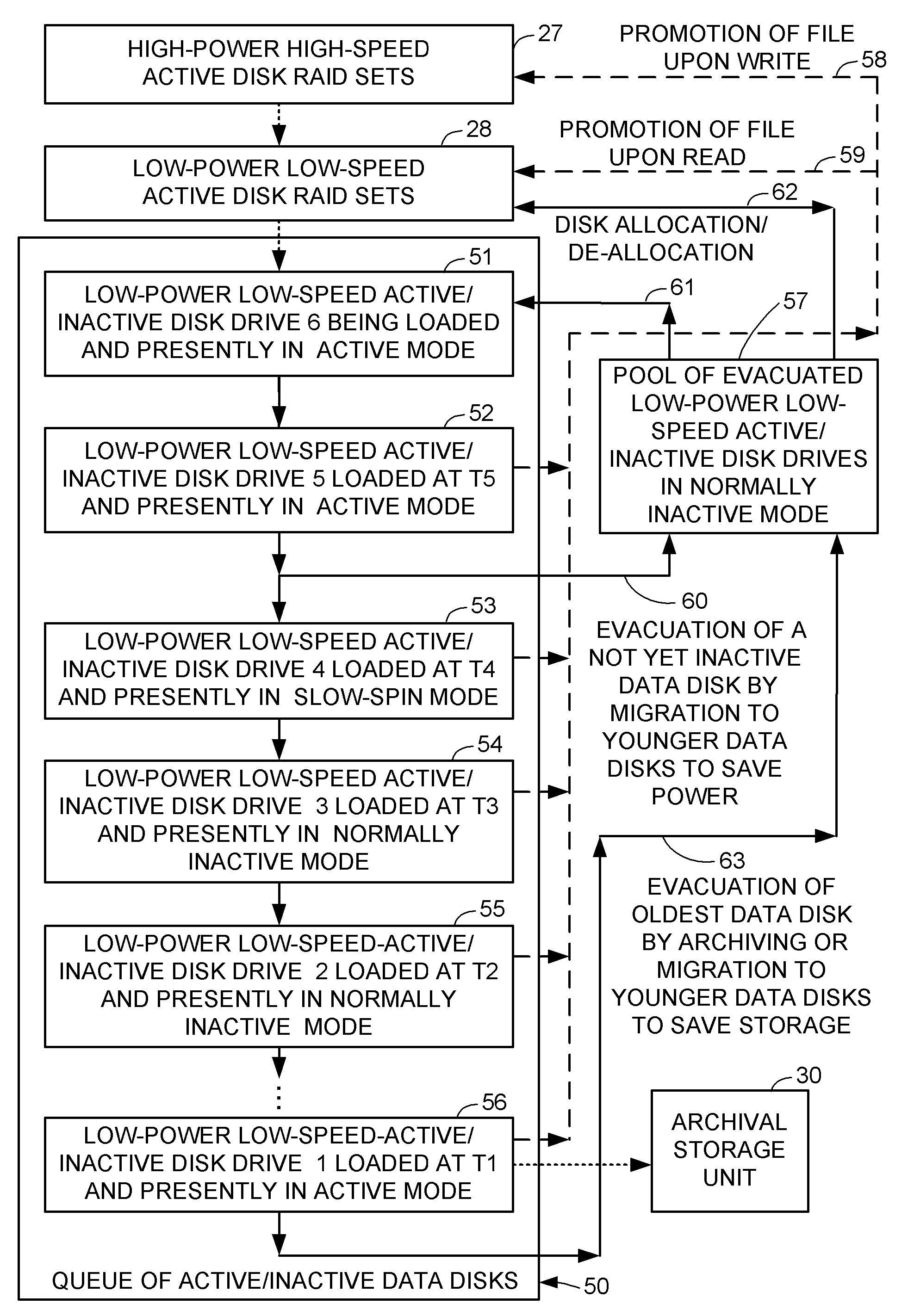
Intelligent file system based power management for shared storage that migrates groups of files based on inactivity threshold
A file server includes active storage containing frequently accessed files, and active / inactive disk drives for containing infrequently accessed files. Groups of the files having become inactive in the active storage are successively migrated to respective evacuated active / inactive disk drives so that each active / inactive disk drive is loaded with files having a similar probability of access when access to the active / inactive disk drive reaches an inactivity threshold for powering down the active / inactive disk drive. Storage of the active / inactive disk drives is reclaimed when an oldest group of the files is archived or when an active / inactive disk drive is evacuated by migrating files from the active / inactive disk drive to storage having been released in other disk drives by promotion of files for client access to the promoted files. Therefore, recovery of storage can be planned and scheduled in advance and performed efficiently in a background process.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
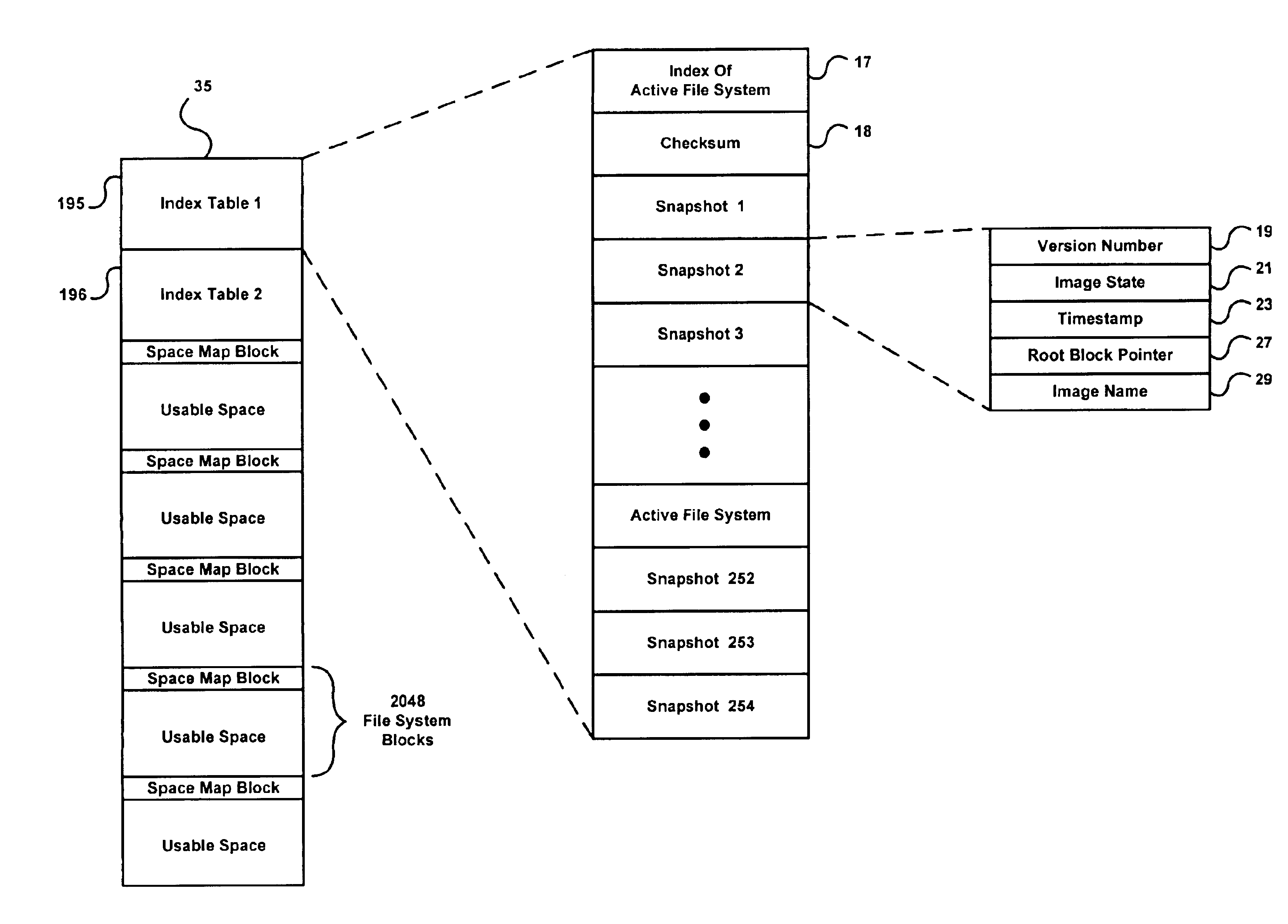
Management of file system snapshots
ActiveUS20060271604A1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalFile systemData space
The present invention relates to methods and systems of snapshot management of a file system in a data storage system. To represent the snapshots, the invention maintains pointers to the root block pointer of each snapshot. When the active file system is modified, this invention avoids overwriting any blocks used by previous snapshots by allocating new blocks for the modified blocks. When the invention needs to put an established block in a new location, it must update a parent block to point to the new location. The update to the parent block may then require allocating a new block for the new parent block and so forth. Parts of the file system not modified since a snapshot remain in place. The amount of space required to represent snapshots scales with the fraction of the file system that users modify. To maintain snapshot integrity, this invention keeps track of the first and last snapshots that use each block in space map blocks spread throughout the file system data space. When users delete snapshots, this invention may use a background process to find blocks no longer used by any snapshot and makes them available for future use.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
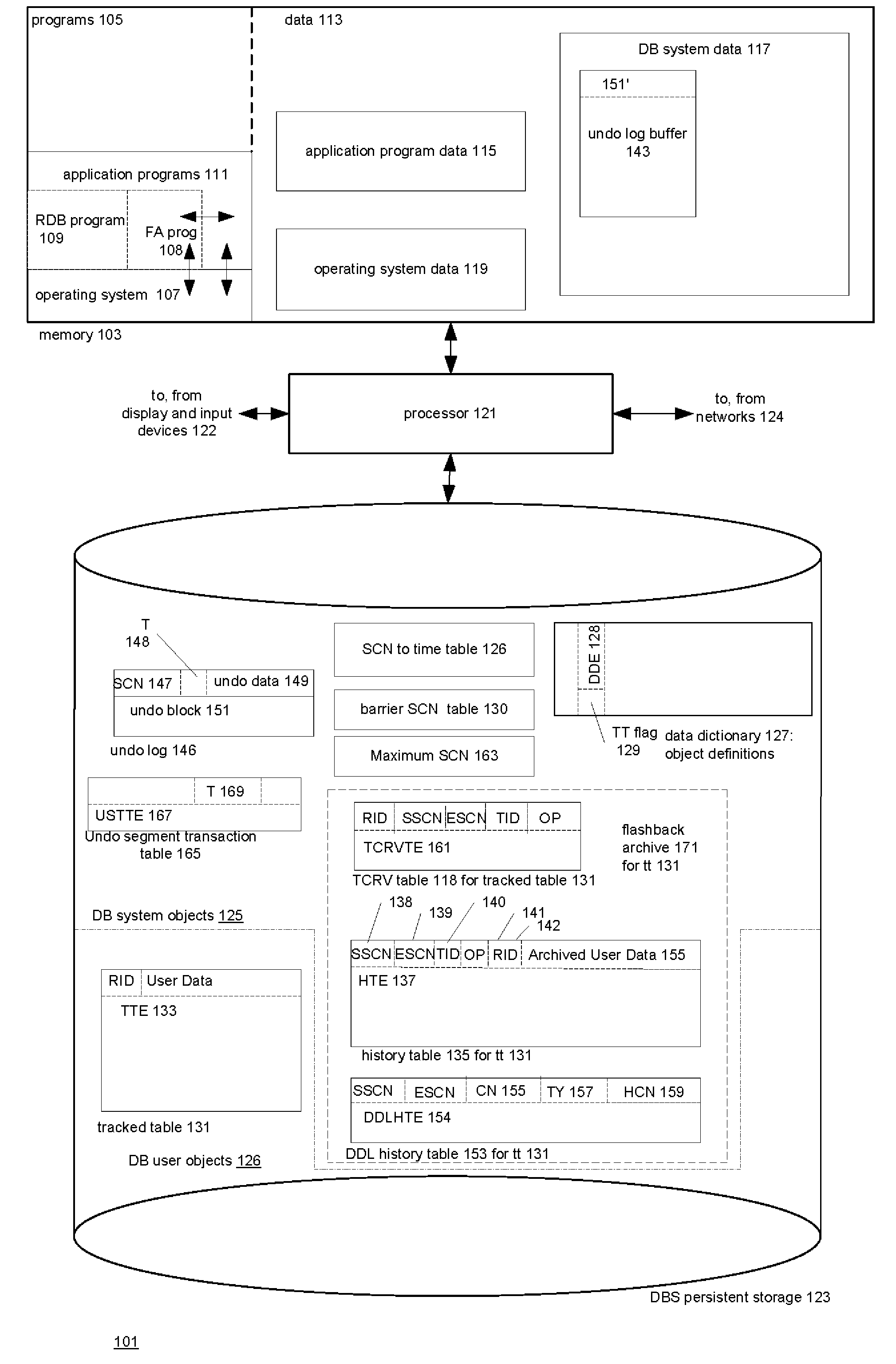
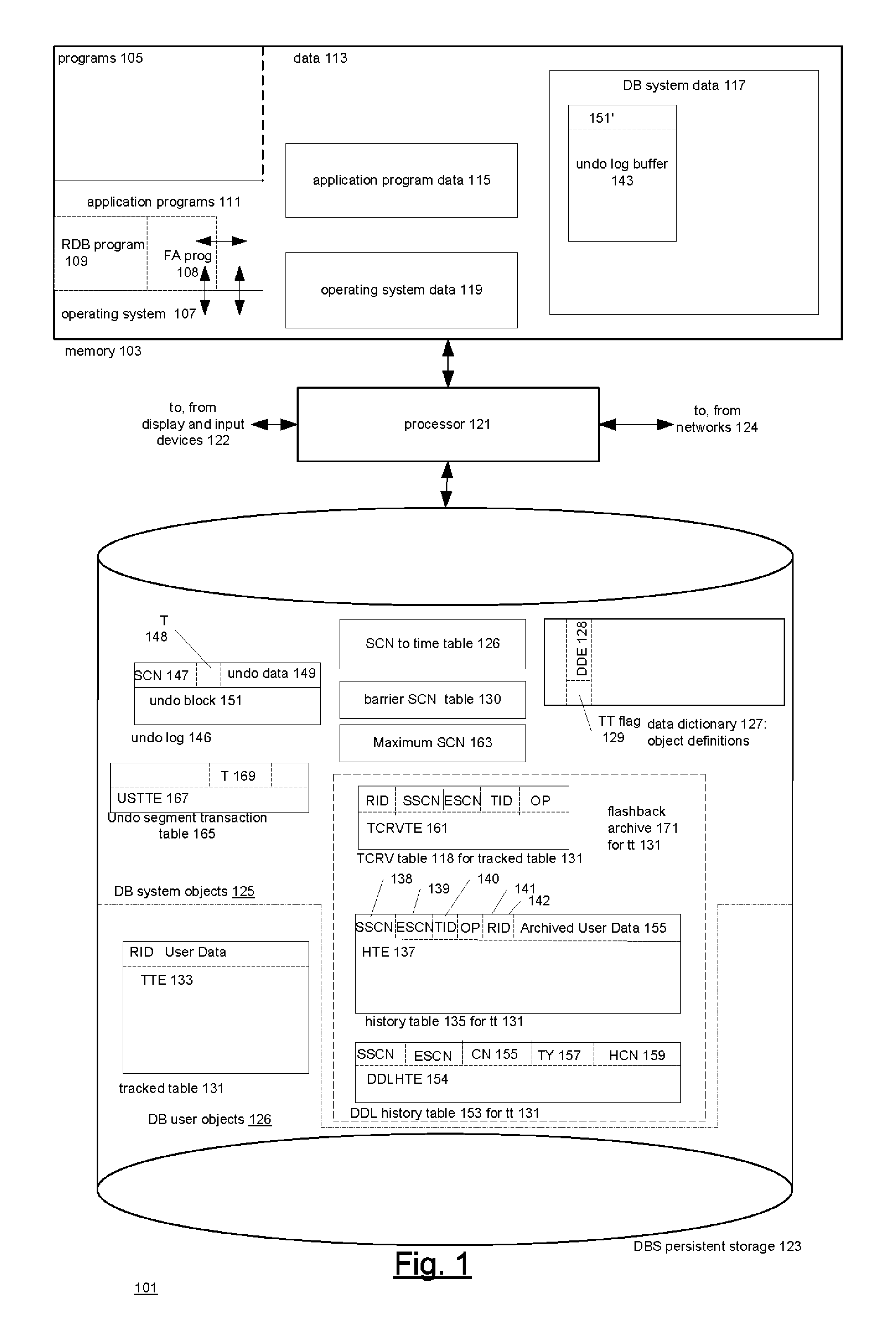
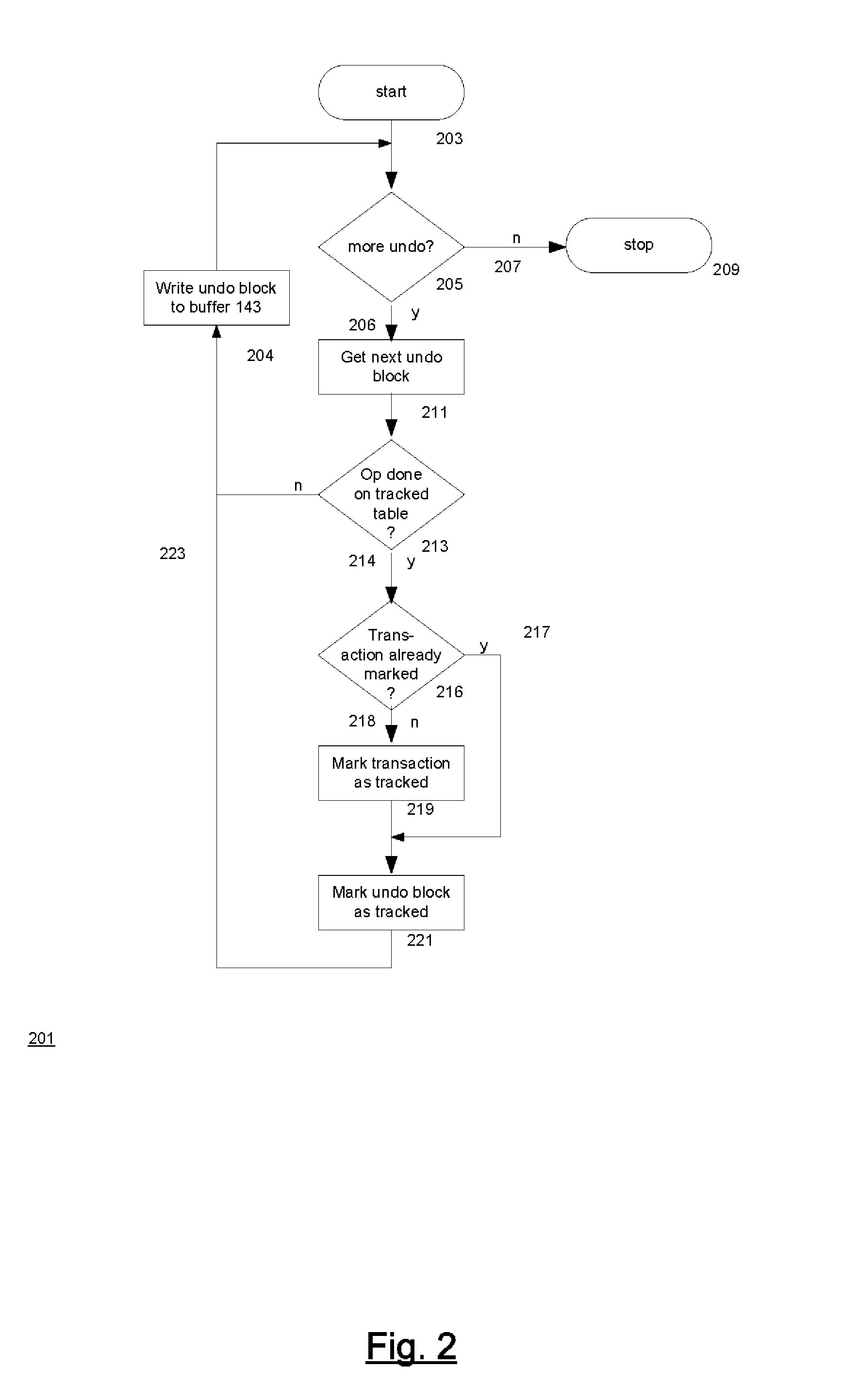
Techniques for automatically tracking and archiving transactional data changes
ActiveUS20080098045A1Error detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsBackground processManagement system
A technique for making versions of rows of a user-defined tracked table temporally queryable. The database management system of the technique permits temporal queries of user-defined tables. The queries return versions of rows in the user-defined table that are currently in an undo log maintained by the database system. Associated with the tracked table are a system history table which contains versions of the rows and temporal metadata indicating when the versions were in the tracked table and a system form history table which contains versions of the form of the tracked table and metadata indicating when the tracked table had the form. These tables are created and maintained by a background process in the database management system. A temporal query on the tracked table combines results from the undo log with results from the system history table. The results' form is determined by the system form history table.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System and method for rapid restoration of server from backup
ActiveUS7353355B1Promote recoveryDigital computer detailsSpecial data processing applicationsOperational systemBackground process
A server is restored by creating an image of a local drive of a server; replacing a driver in the boot up procedure of the server, the replacement driver redirecting disk drive access requests from the local drive to the image; on-demand copying portions of the operating system needed for start up from the image to memory of the server; and copying a remainder of the image from the image to the local drive as a background process. The data is copied on-demand from the image to the local drive. The copying is performed over a network. The image is created on a different server connected to a network. The copying of the remainder of the image, after critical start-up data has been copied, is done based on a priority of a sector of the image being copied. A bitmap is created corresponding to sectors of the image, and the server decides whether to access a particular sector on the local drive or on the image based on the bitmap.
Owner:MIDCAP FINANCIAL TRUST
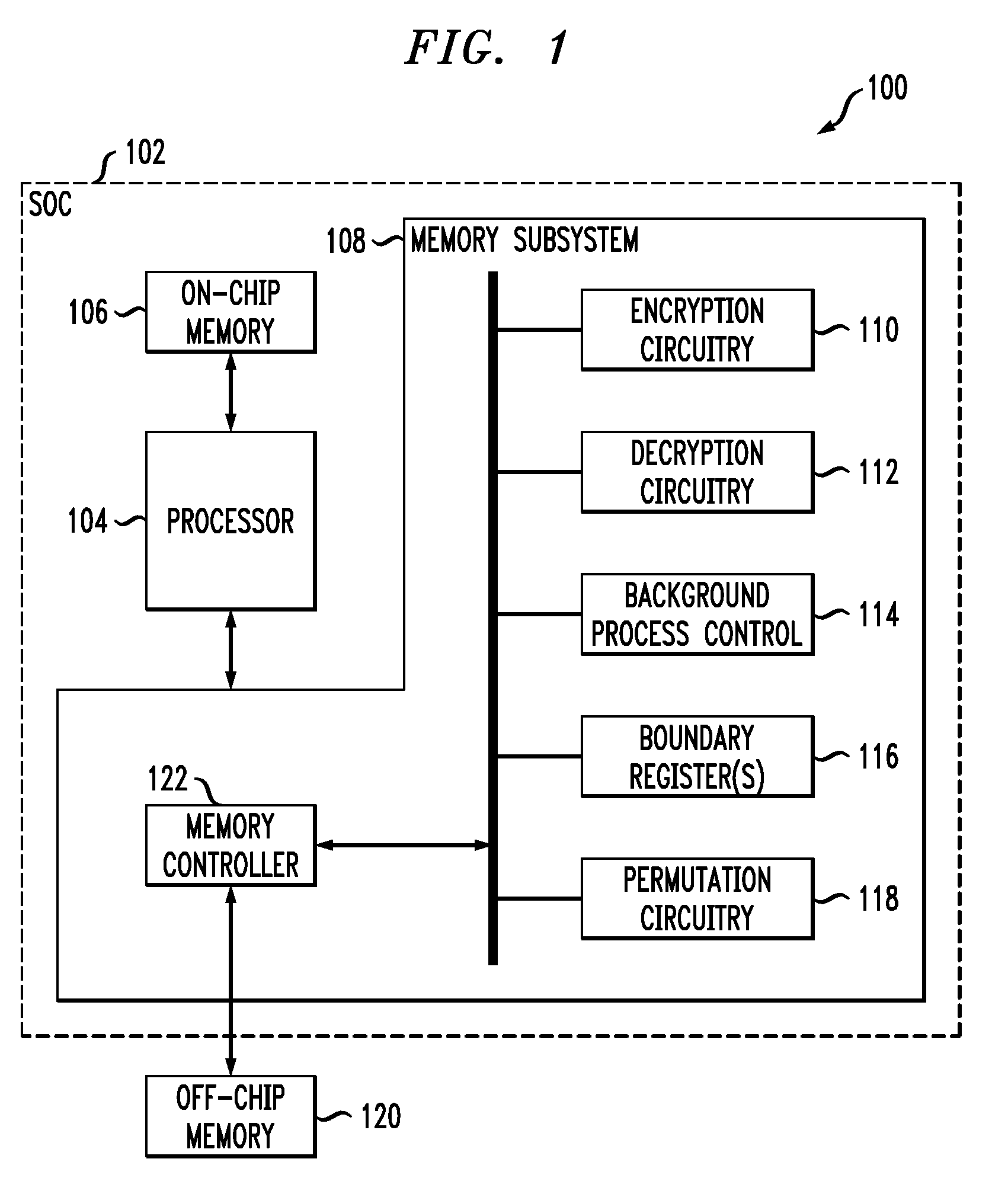
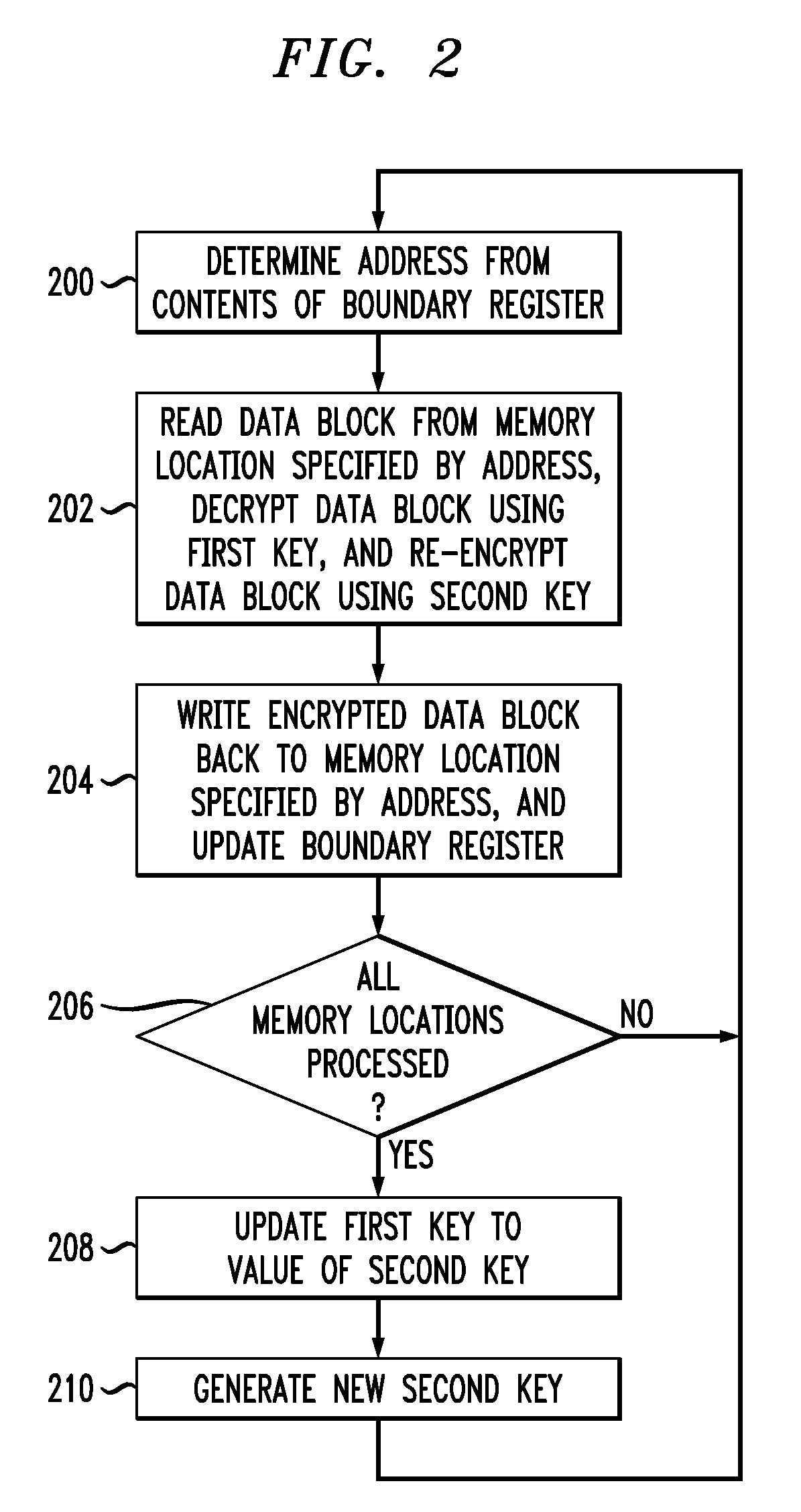
Secure data storage with key update to prevent replay attacks
InactiveUS20090187771A1Undermines effectivenessAvoid problemsEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUnauthorized memory use protectionProcessor registerComputer data storage
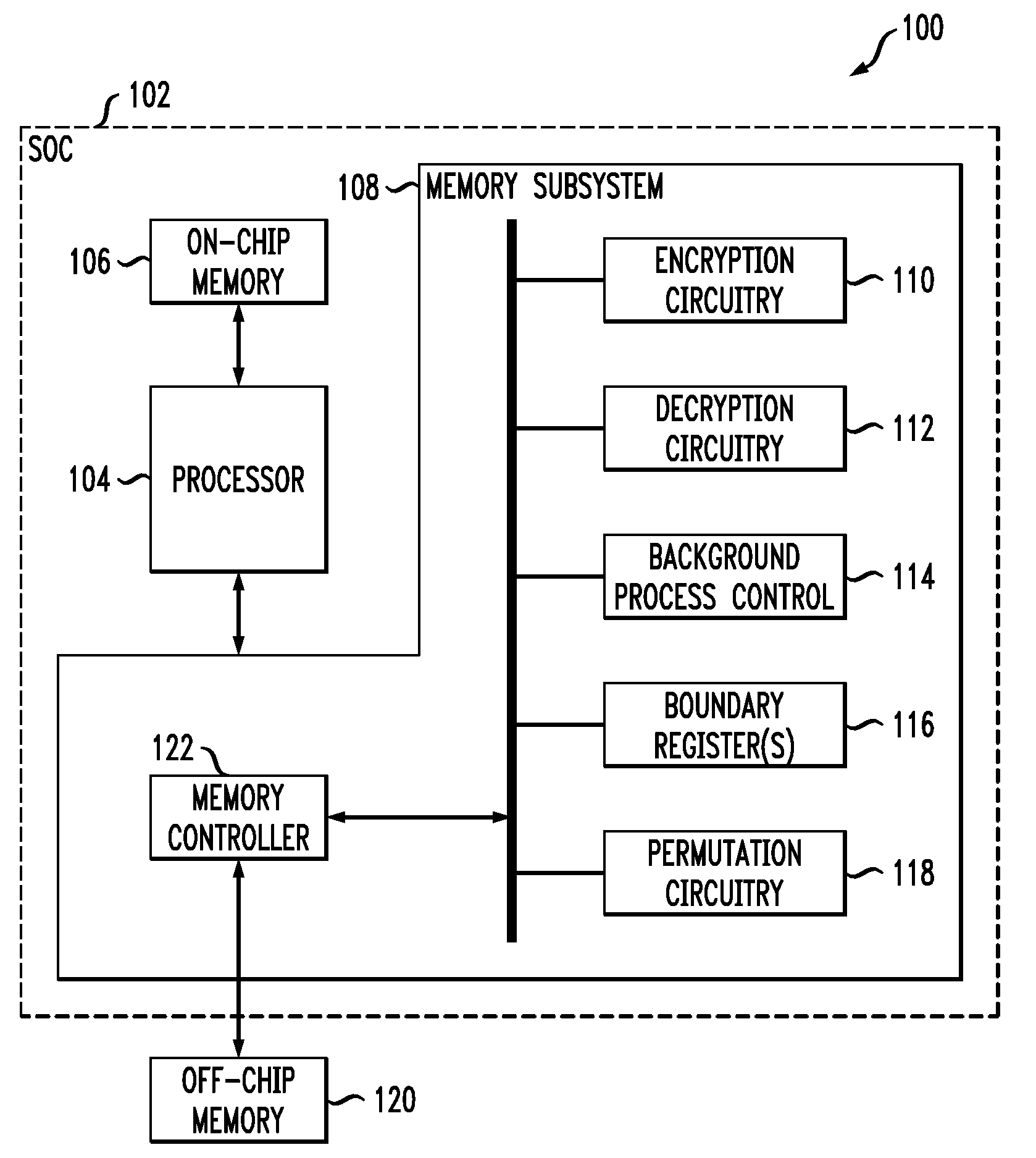
A key update process applied to encrypted memory in a processing system determines an address from contents of a boundary register, reads an encrypted data block from a memory location specified by the address, decrypts the encrypted data block using a first key, re-encrypts the decrypted data block using a second key, writes the re-encrypted data block back to the memory location specified by the address, and updates the boundary register. These operations are repeated for one or more additional addresses. The boundary register contents are also used to determine appropriate keys for use in other read and write transactions to the memory. The key update process can be run as a background process, separate from the other read and write transactions to the memory, so as to incur minimal processing overhead.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
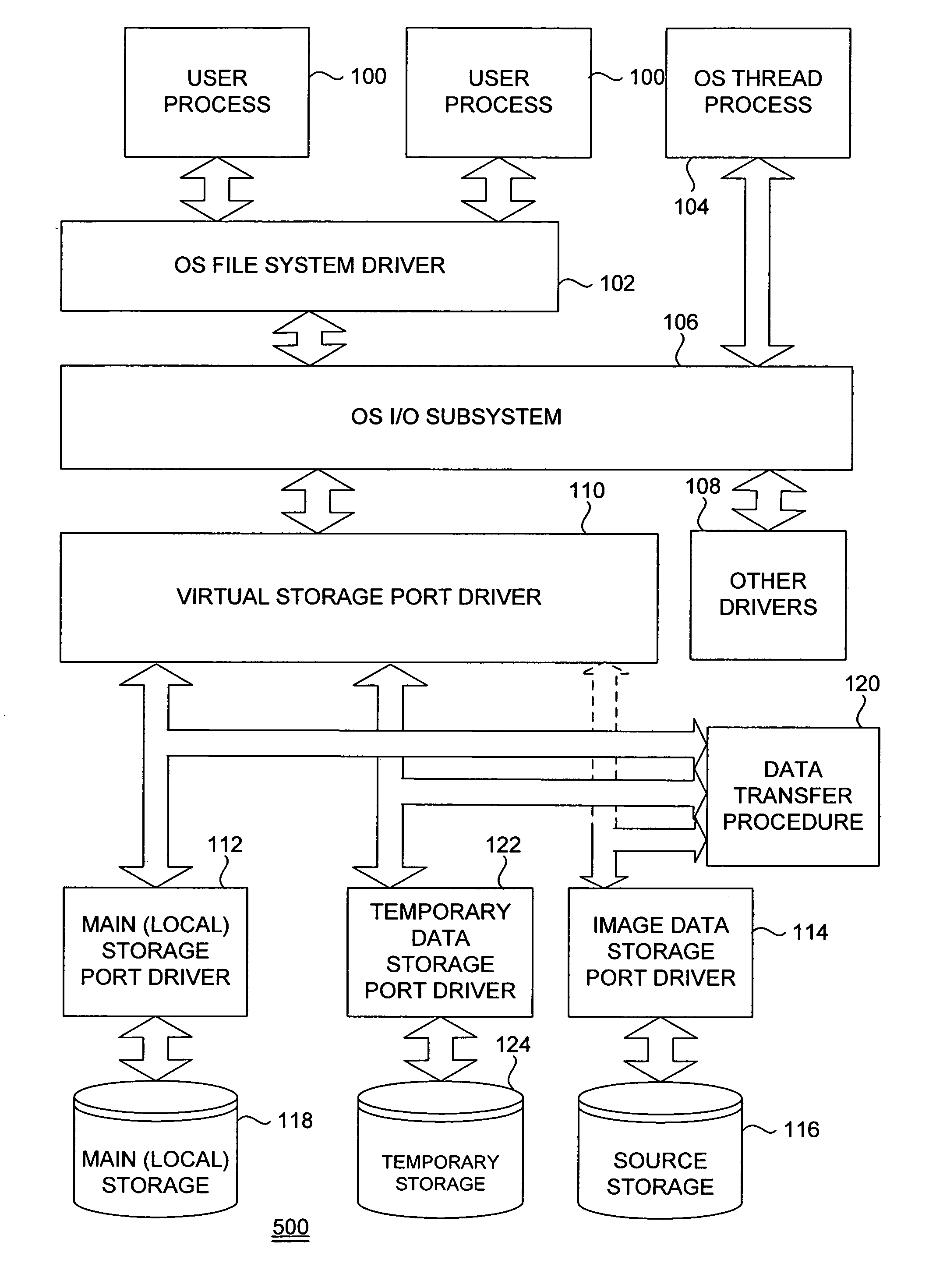
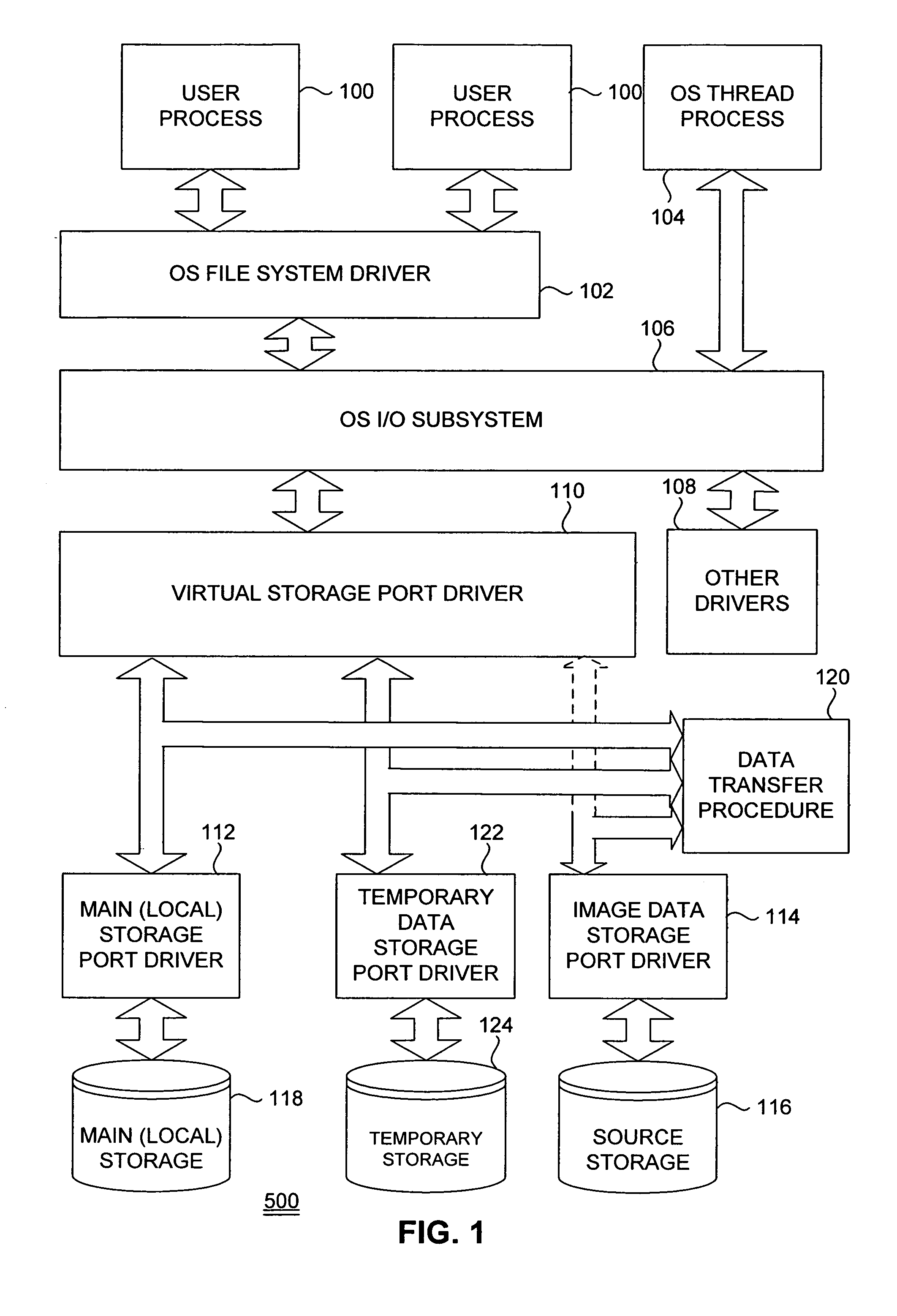
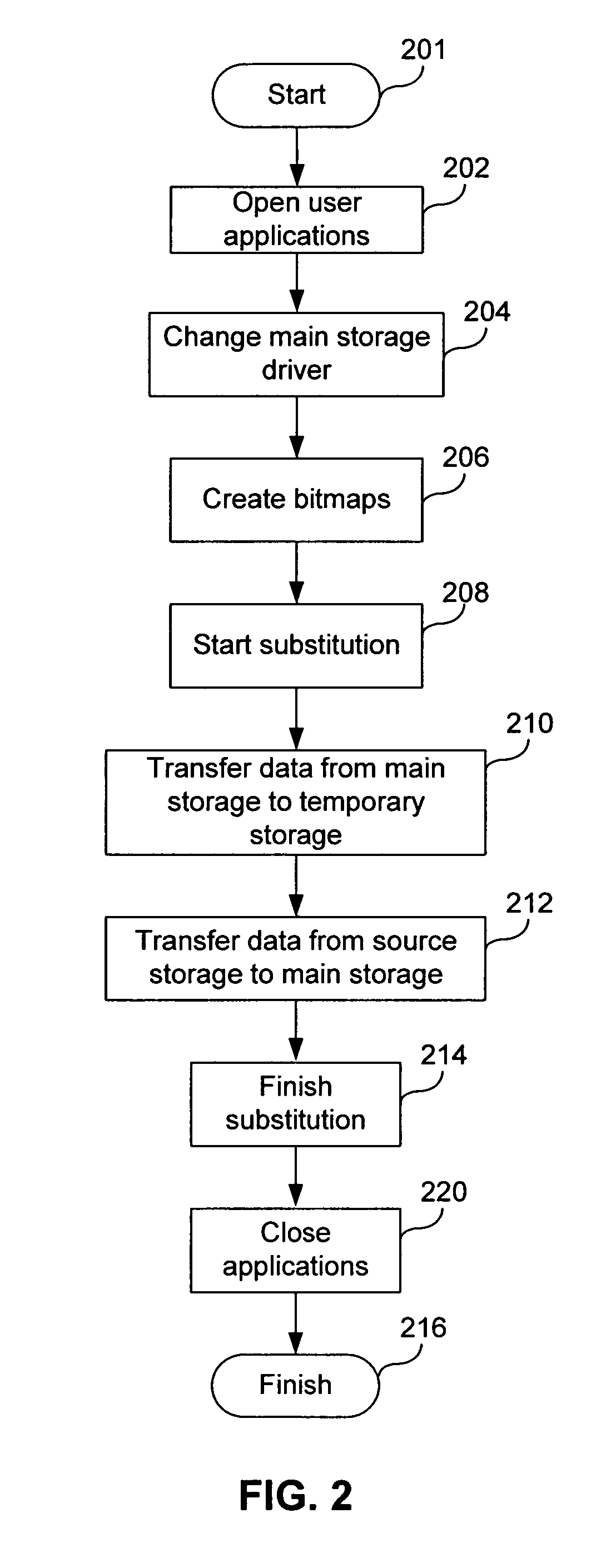
System and method for online data migration
ActiveUS7281104B1Eliminate disadvantagesError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsOperational systemBackground process
A method of changing storage drive contents includes changing, in an operating system, a main storage driver to create a virtual storage driver, wherein the virtual storage driver redirects access requests to a main storage either to one of the main storage and a temporary storage; copying, as a background process, blocks from the main storage to the temporary storage; restoring, to the temporary storage as a background process, blocks from a source storage into blocks of the main storage that have already been copied; and redirecting, to the temporary storage, operating system's requests for access to blocks of the main storage that have been copied to the temporary storage. The method can also include hiding the temporary storage from the operating system. The main storage and the temporary storage can share partitions of the same physical storage drive. Free blocks of the physical storage drive can be used as blocks of the temporary storage. Blocks can be assigned to the temporary storage in succession.
Owner:MIDCAP FINANCIAL TRUST
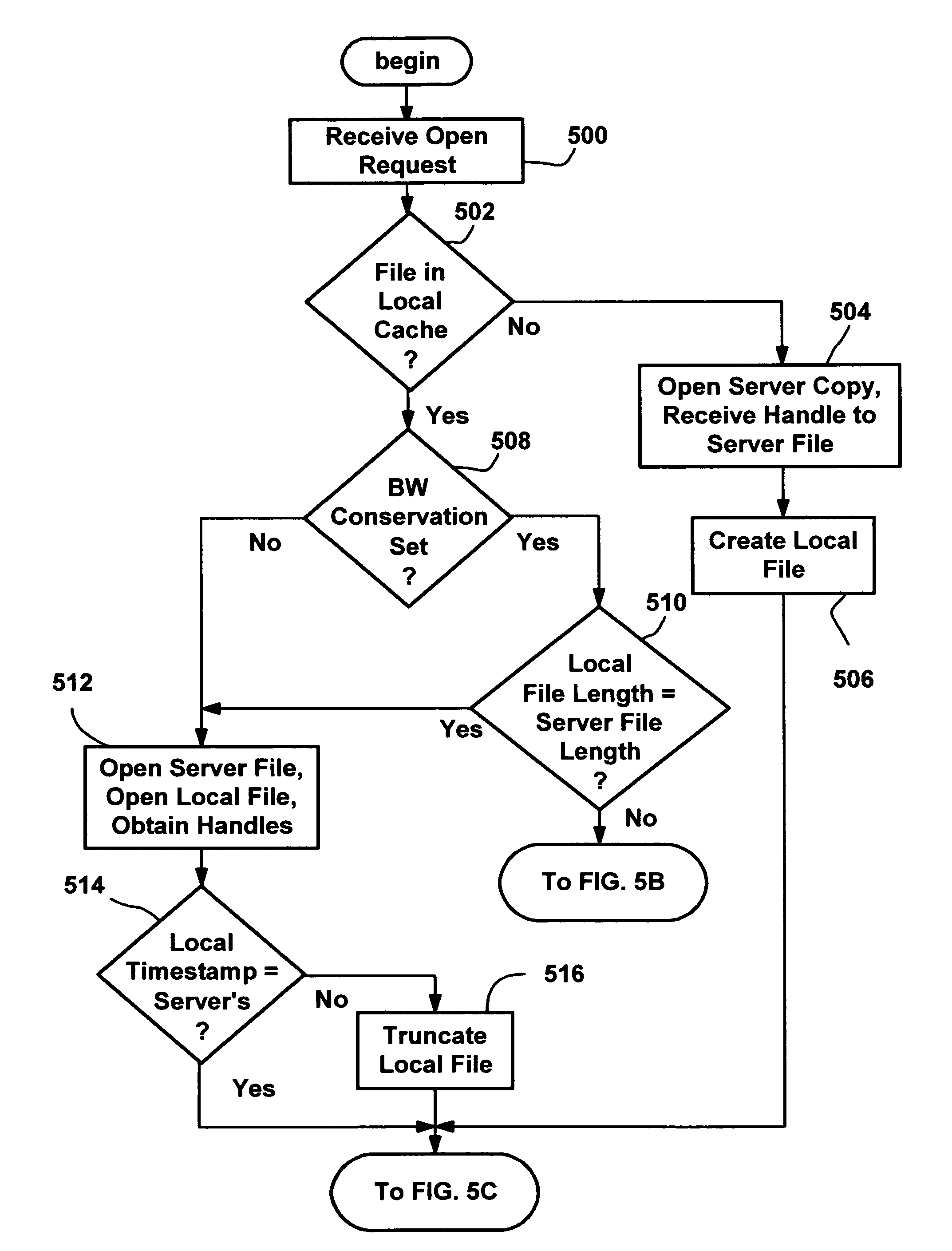
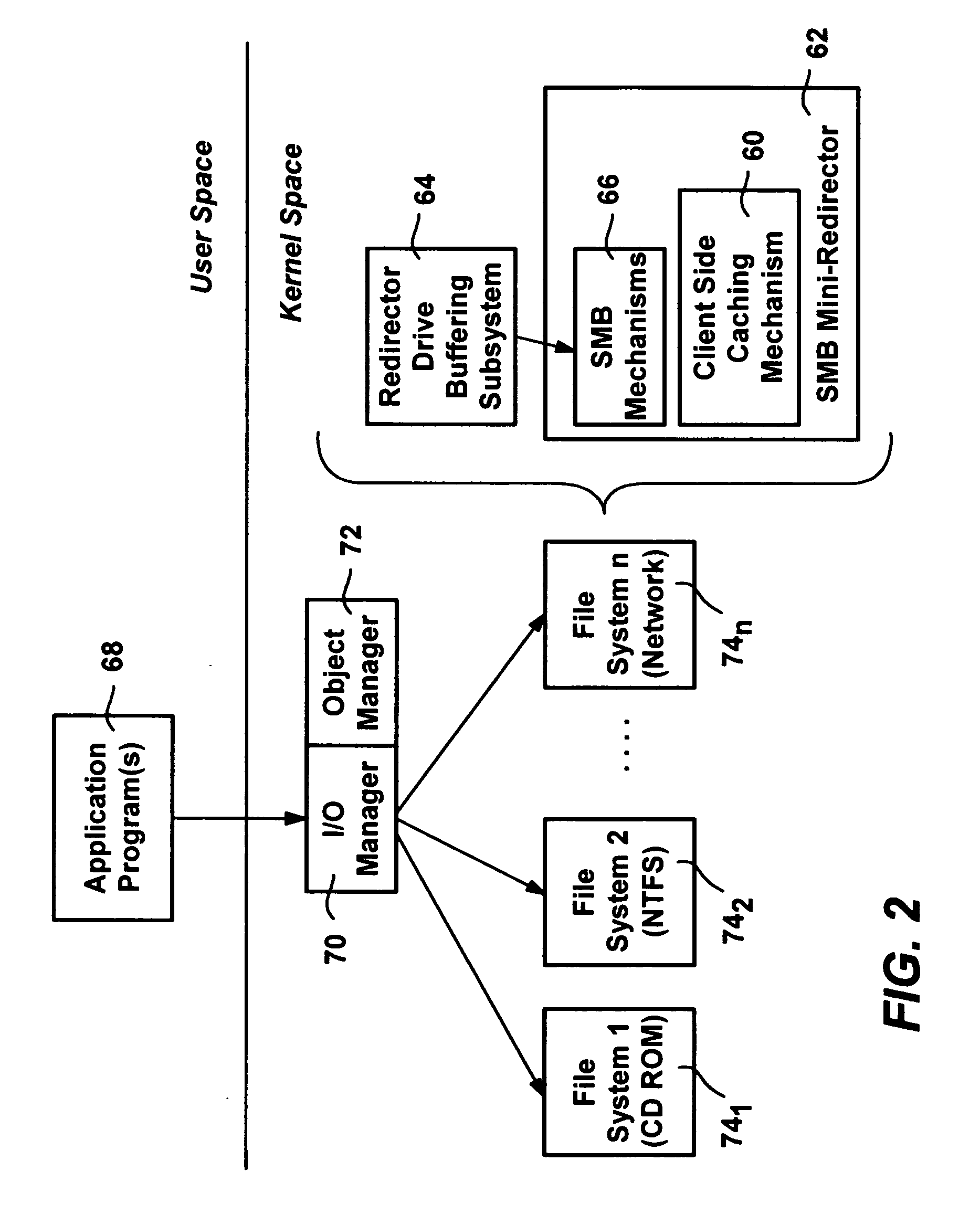
Method and system for client-side caching
InactiveUS20080028149A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsNetwork redirectorProbable Case
An improved method and system for client-side caching that transparently caches suitable network files for offline use. A cache mechanism in a network redirector transparently intercepts requests to access server files, and if the requested file is locally cached, satisfies the request from the cache when possible. Otherwise the cache mechanism creates a local cache file and satisfies the request from the server, and also fills in a sparse cached file as reads for data in ranges that are missing in the cached file are requested and received from the server. A background process also fills in local files that are sparse, using the existing handle of already open server files, or opening, reading from and closing other server files. Security is also provided by maintaining security information received from the server for files that are in the cache, and using that security information to determine access to the file when offline.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for restoring data on demand for instant volume restoration
ActiveUS20070124341A1Digital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsFile systemData access
A technique is disclosed for restoring data of sparse volumes, where one or more block pointers within the file system structure are marked as ABSENT, and fetching the appropriate data from an alternate location on demand. Client data access requests to the local storage system initiate a restoration of the data from a backing store as required. A demand generator can also be used to restore the data as a background process by walking through the sparse volume and restoring the data of absent blocks. A pump module is also disclosed to regulate the access of the demand generator. Once all the data has been restored, the volume contains all data locally, and is no longer a sparse volume.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Snapshots of file systems in data storage systems
ActiveUS20050021565A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsFile systemData space
The present invention relates to methods and systems of snapshot management of a file system in a data storage system. To represent the snapshots, the invention maintains pointers to the root block pointer of each snapshot. When the active file system is modified, this invention avoids overwriting any blocks used by previous snapshots by allocating new blocks for the modified blocks. When the invention needs to put an established block in a new location, it must update a parent block to point to the new location. The update to the parent block may then require allocating a new block for the new parent block and so forth. Parts of the file system not modified since a snapshot remain in place. The amount of space required to represent snapshots scales with the fraction of the file system that users modify. To maintain snapshot integrity, this invention keeps track of the first and last snapshots that use each block in space map blocks spread throughout the file system data space. When users delete snapshots, this invention may use a background process to find blocks no longer used by any snapshot and makes them available for future use.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
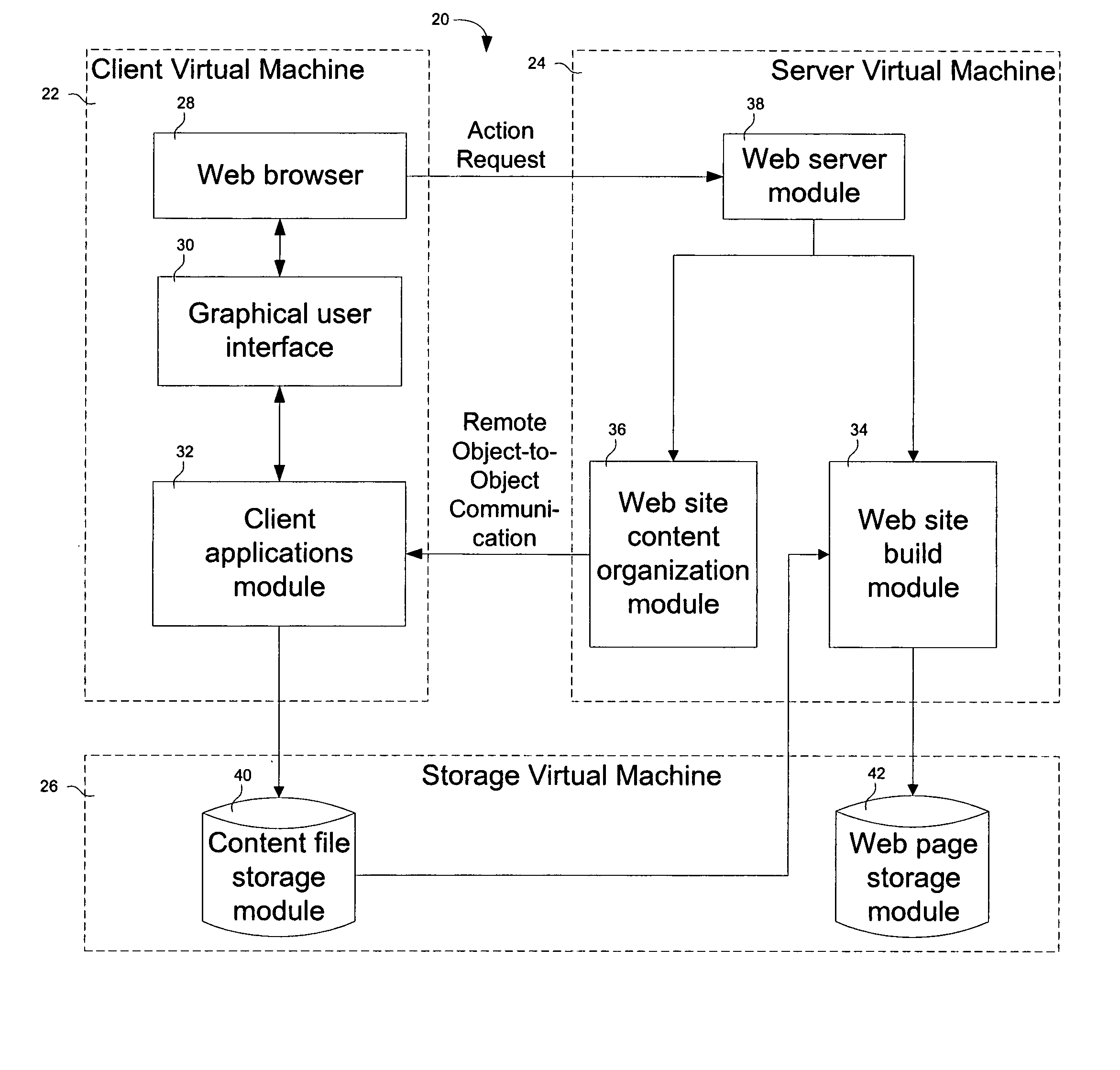
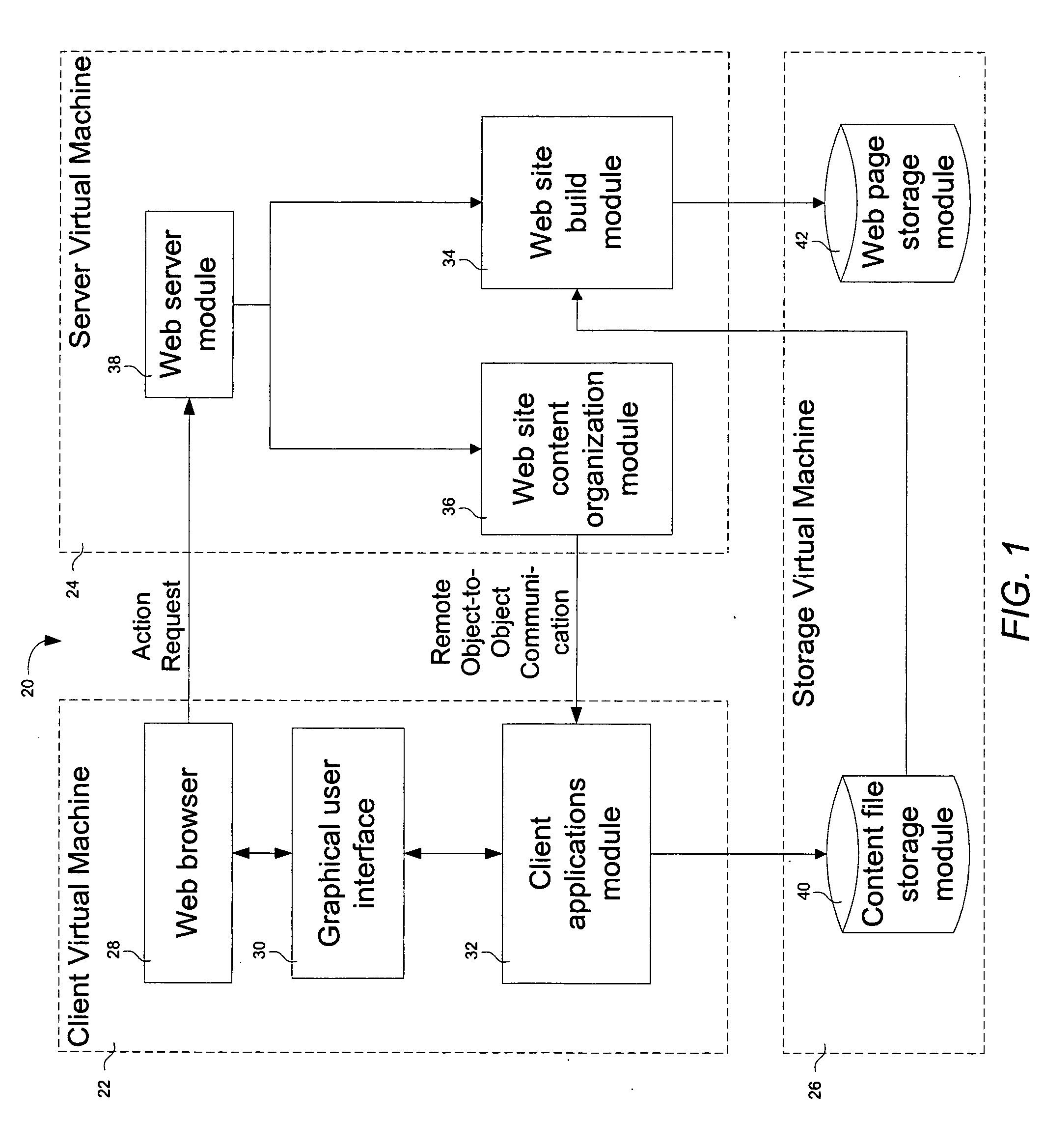
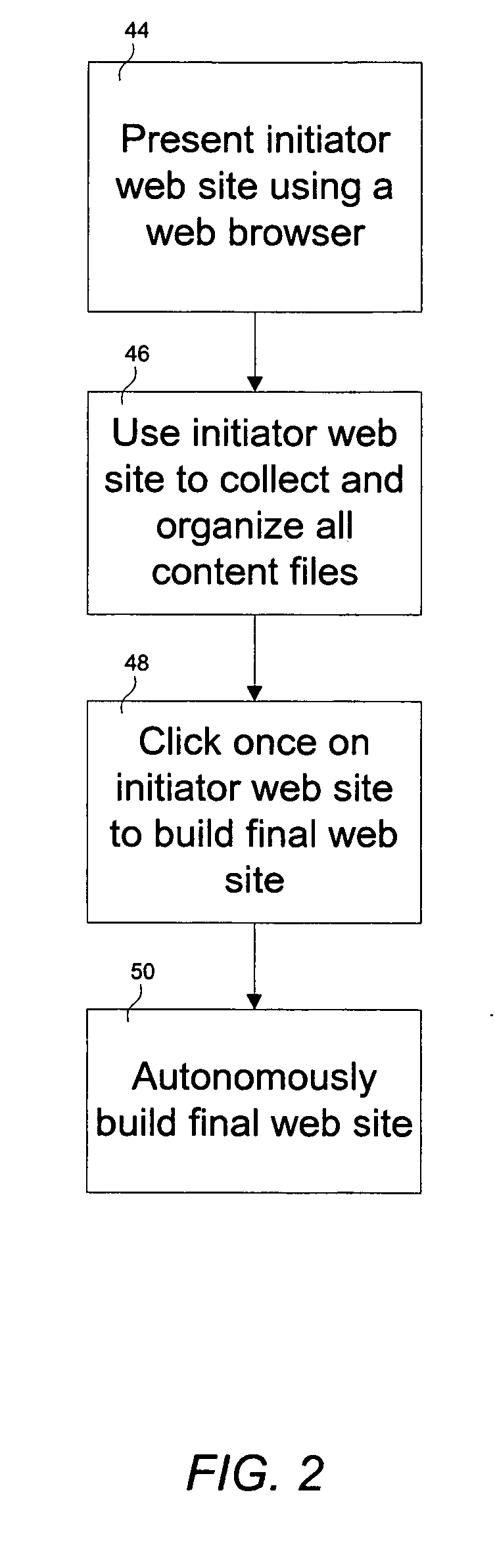
Browser-based web site generation system and method
InactiveUS20050188361A1Natural language data processingMultiple digital computer combinationsWeb siteWeb browser
A web site generation system includes a client virtual machine (VM), a server virtual machine (VM), and a storage virtual machine (VM). The client VM runs as a foreground process, interfaces with a user, and includes a web browser. The server VM runs as a background process, communicates remotely with the client VM in response to an action request from the web browser, and autonomously generates a web site upon a single web site build command from the user via the web browser. The storage virtual machine (VM) is operatively coupled between the client VM and the server VM and is used to store web site content files and web pages.
Owner:CAI HENRY +1
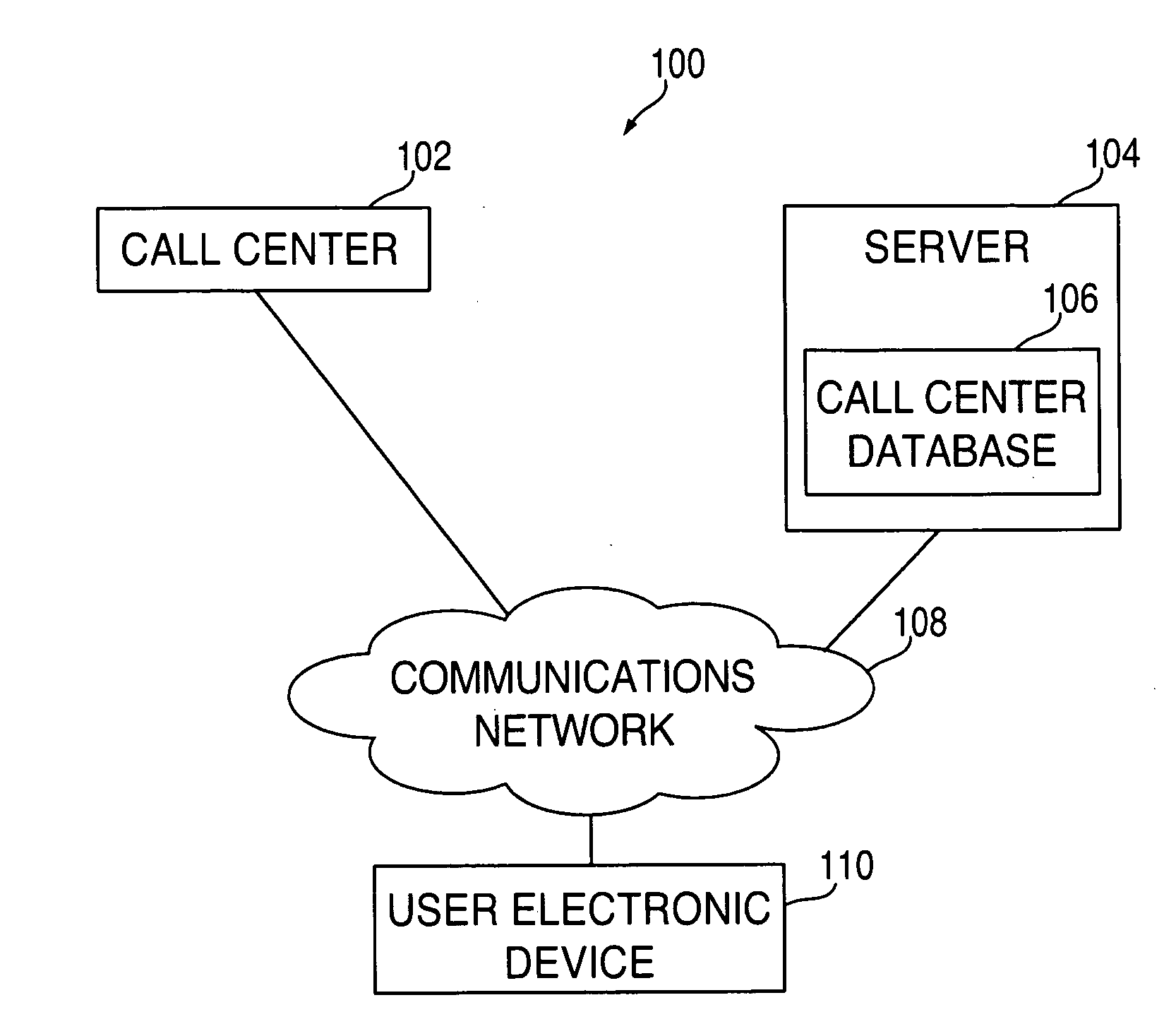
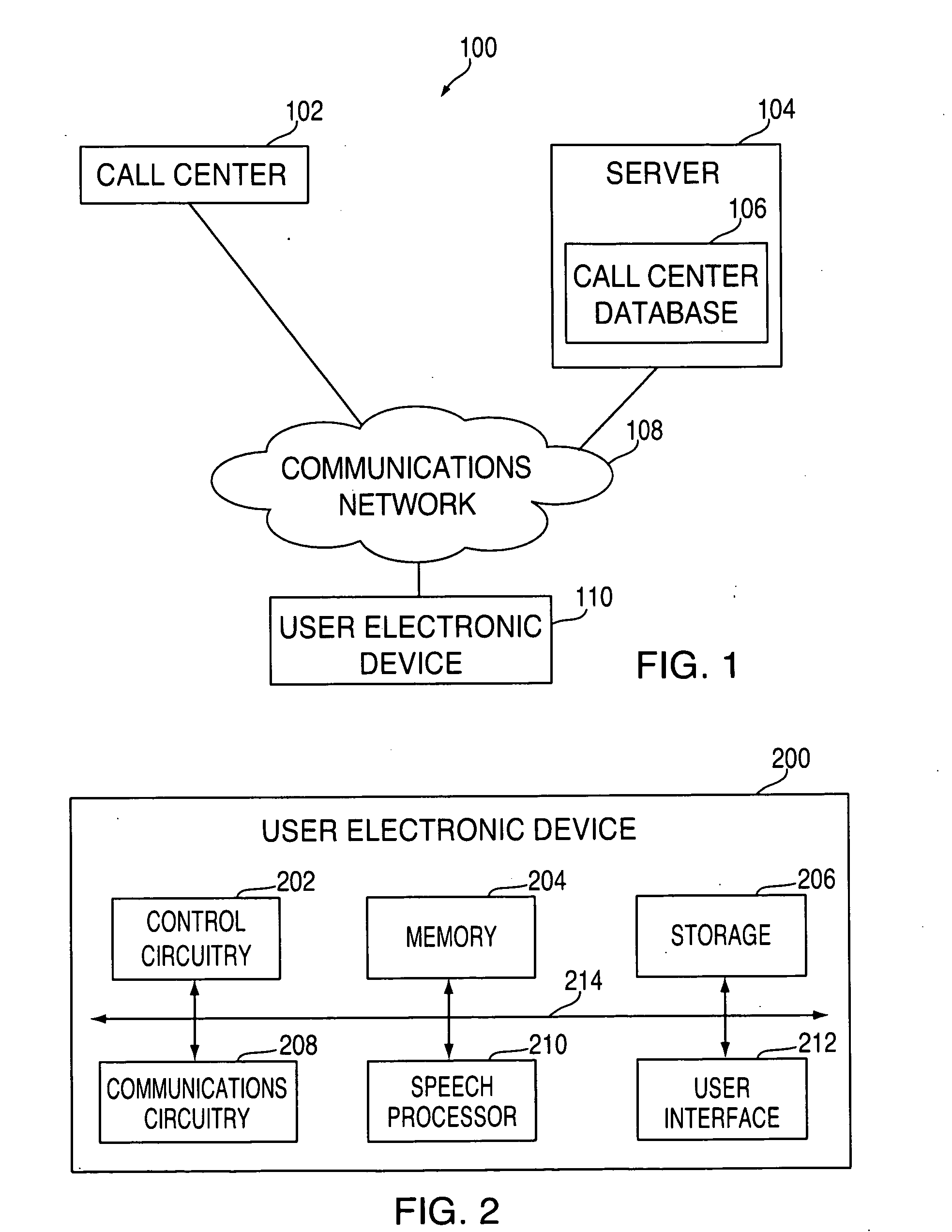
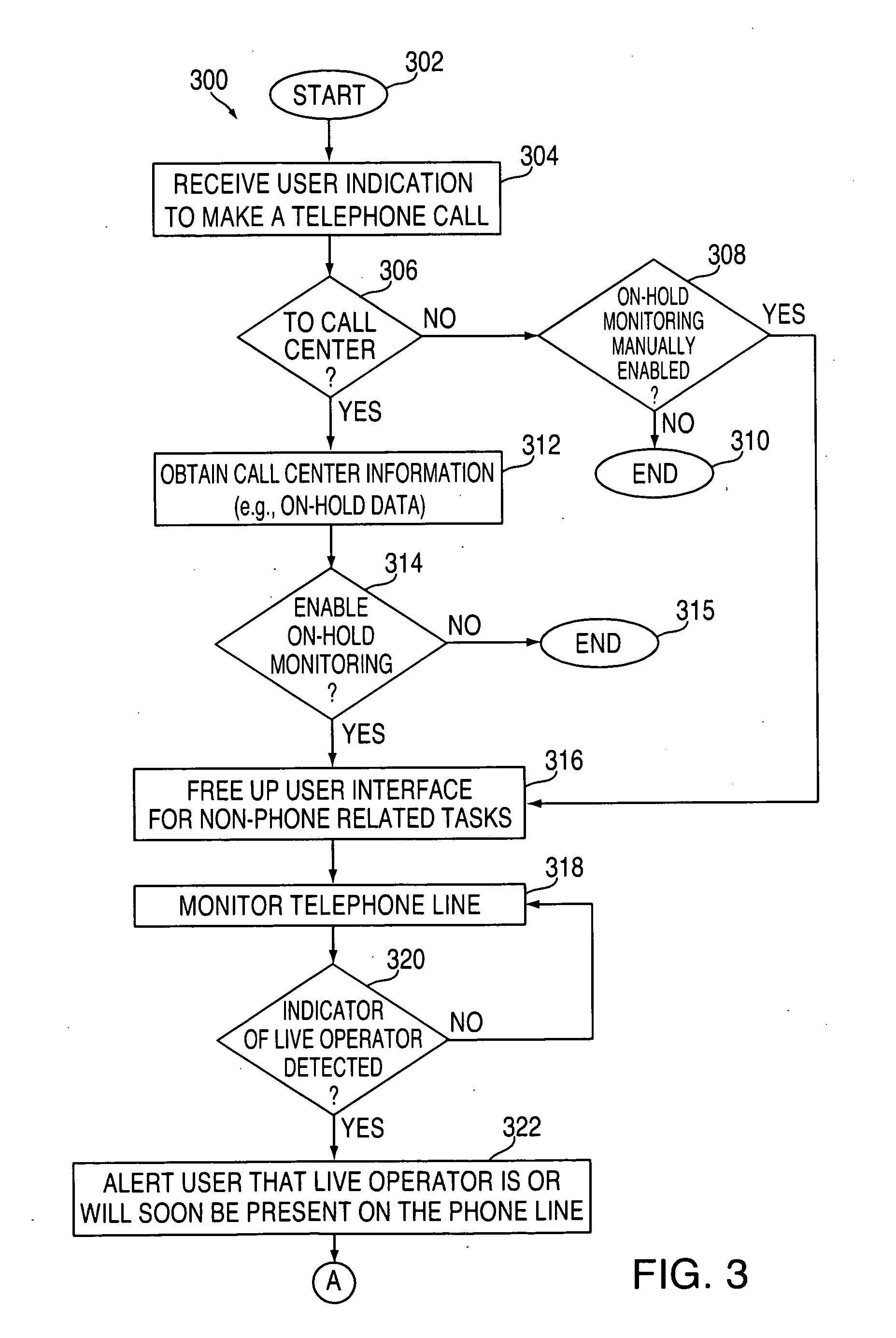
On-hold call monitoring systems and methods
Systems and methods are provided for monitoring telephone calls that are placed on hold. The telephone calls may be between user electronic devices and call centers, such as customer service departments. In some embodiments, the electronic device can monitor an on-hold telephone call using a background process, which may free up a user interface of the electronic device for one or more non-phone-related tasks. The electronic device can monitor the telephone call for an indicator that a live operator is or will soon be present on the telephone call. Responsive to detecting the indicator, the electronic device can alert the user and allow the user to take control of the telephone call. In some embodiments, the electronic device can obtain information about the call center, such as expected on-hold wait-times, to determine whether an on-hold call should be monitored.
Owner:APPLE INC
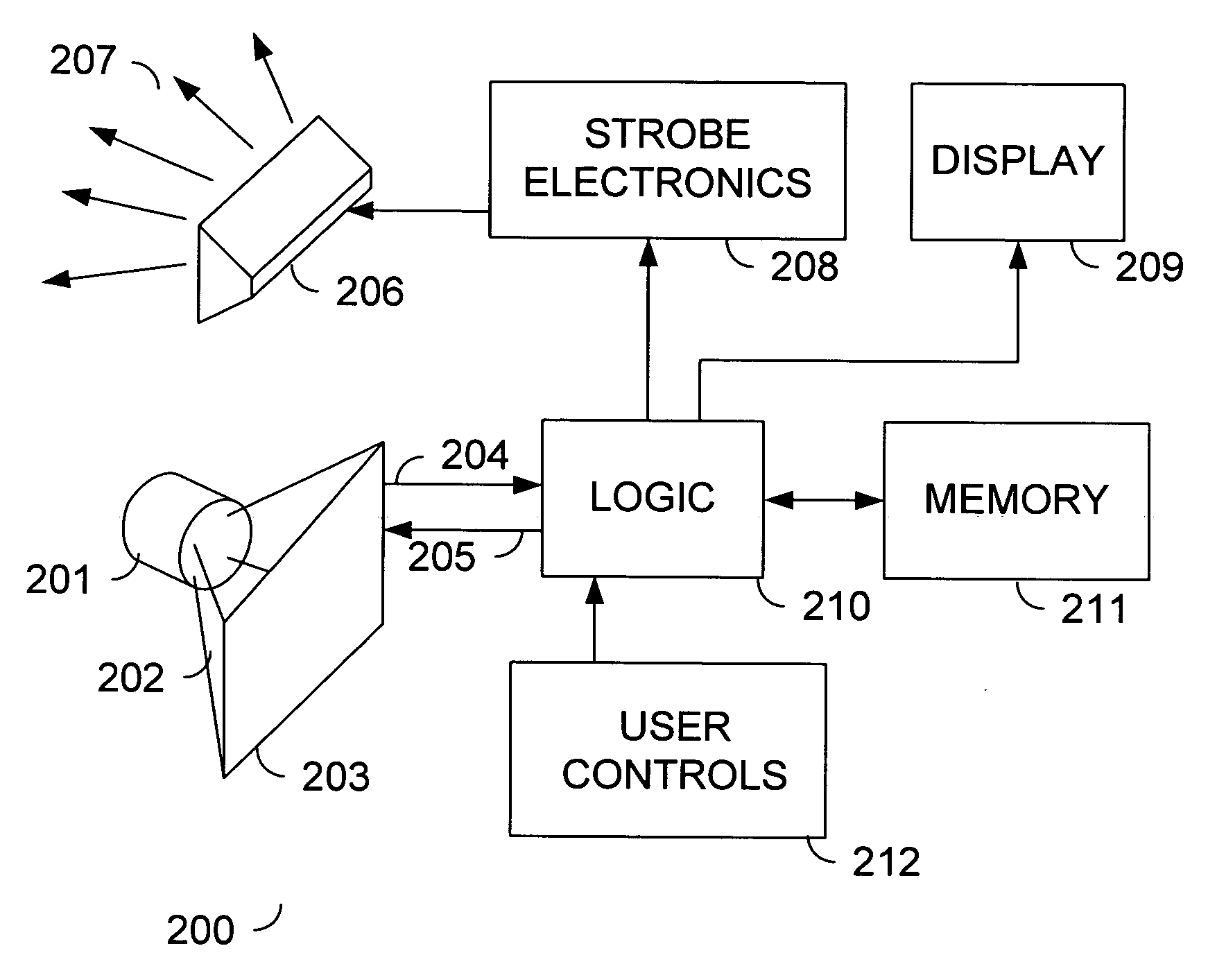
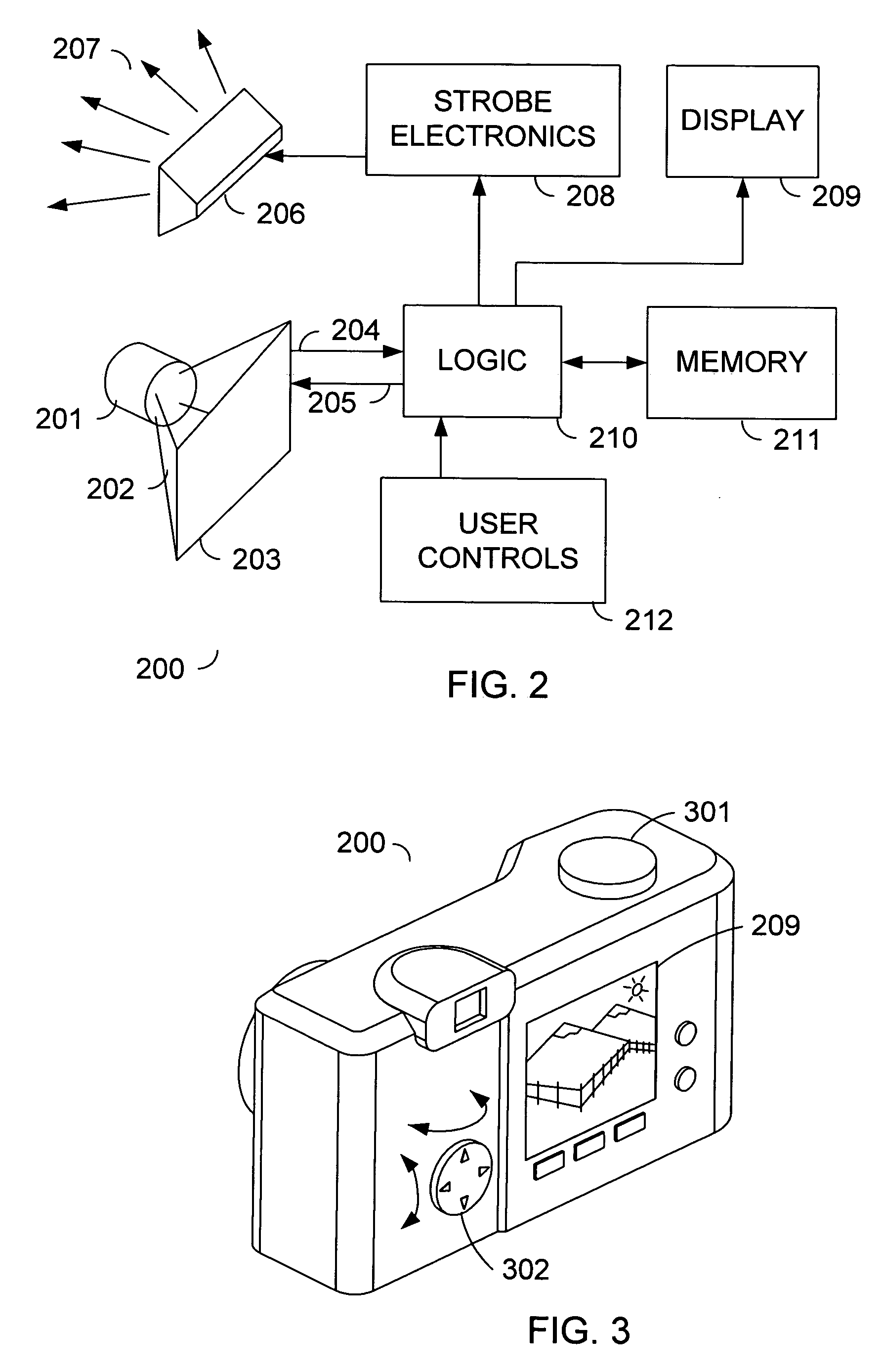
In-camera panorama stitching method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060268130A1Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Image resolution
A method and apparatus are disclosed for accomplishing in-camera stitching of a high-resolution panoramic photograph from a set of component photographs while providing a satisfactory user experience. A low-resolution panorama is stitched, and a user of the camera performs a review of the low-resolution panorama using a display comprised in the camera. During the review, a high-resolution panoramic photograph is stitched by the camera in a background process.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Snapshots of file systems in data storage systems
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com