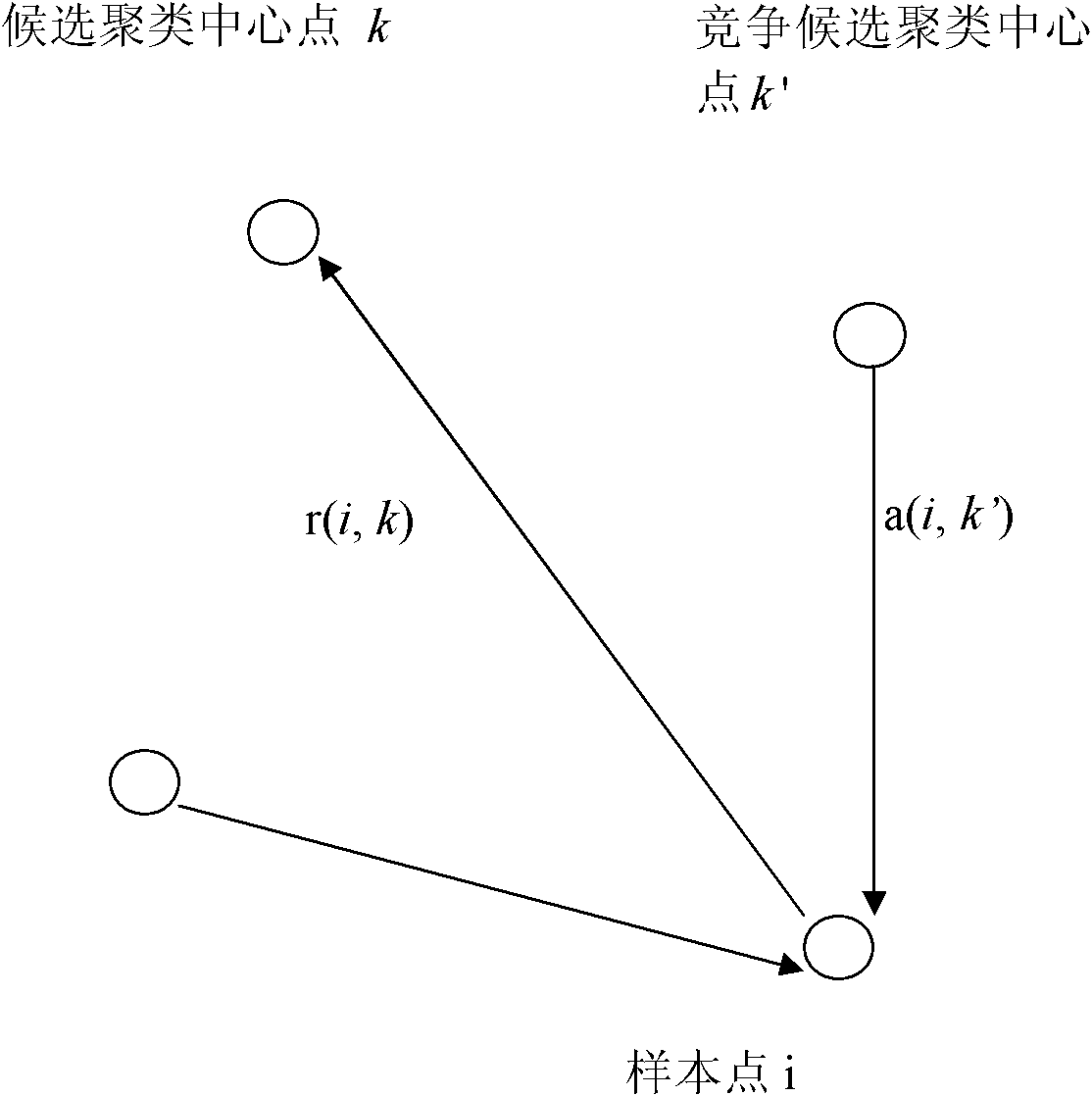
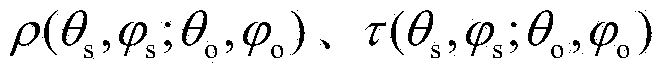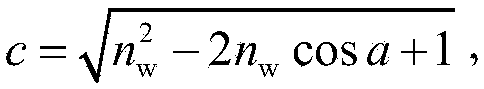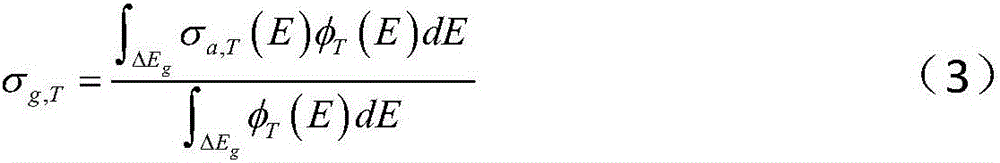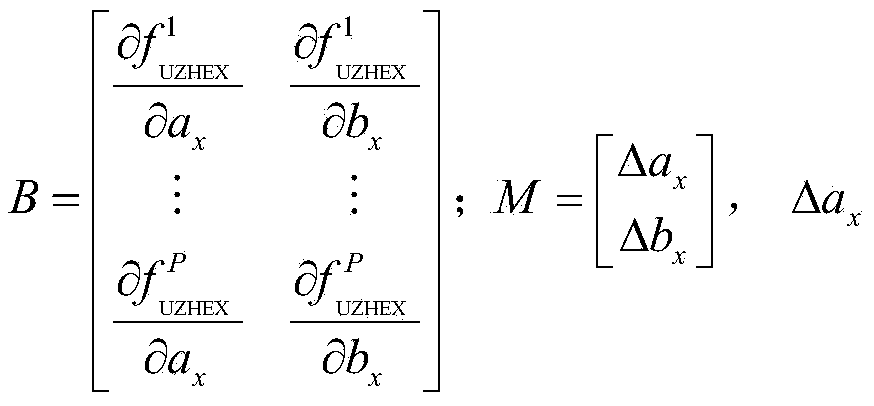Patents
Literature
80 results about "S-matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
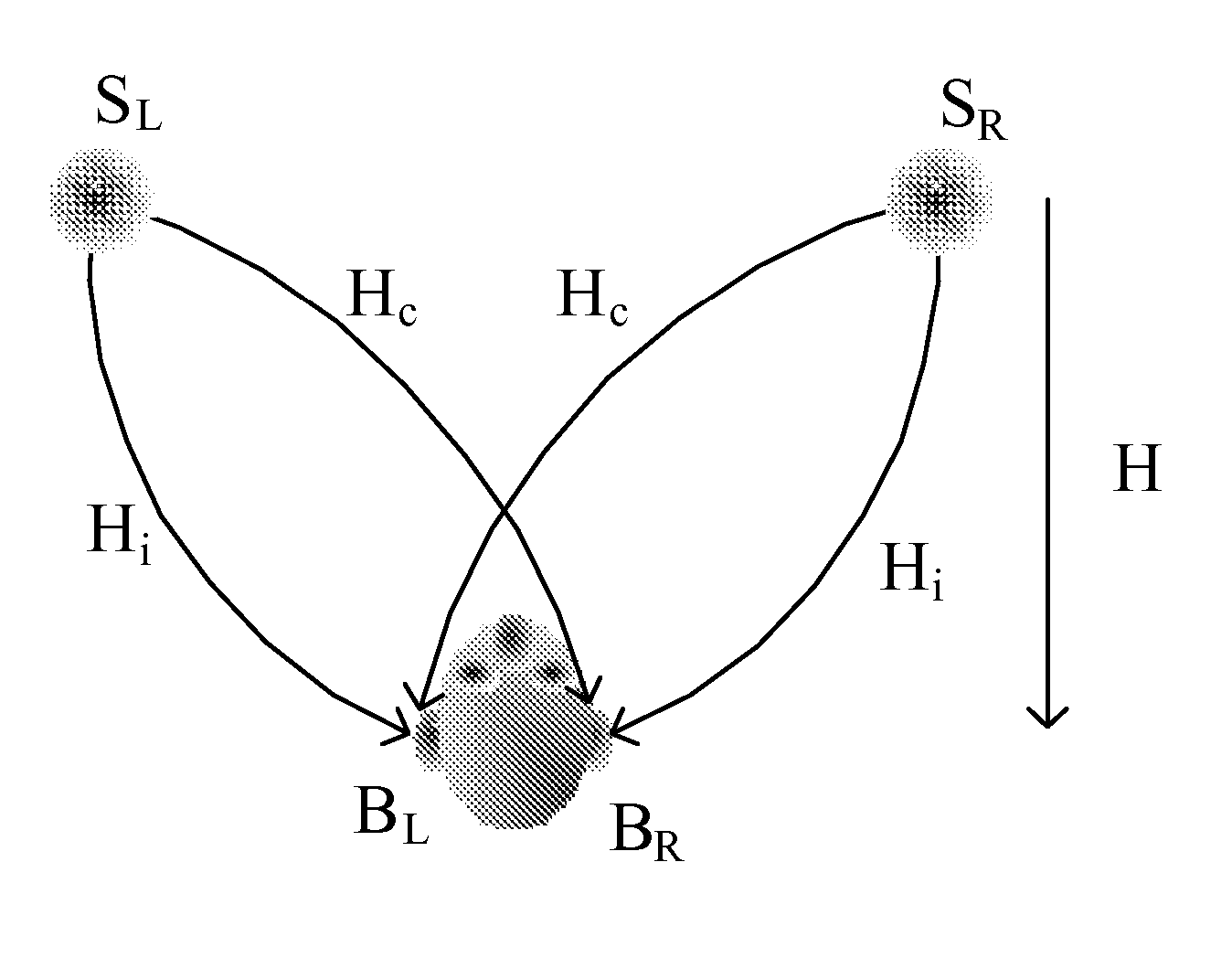
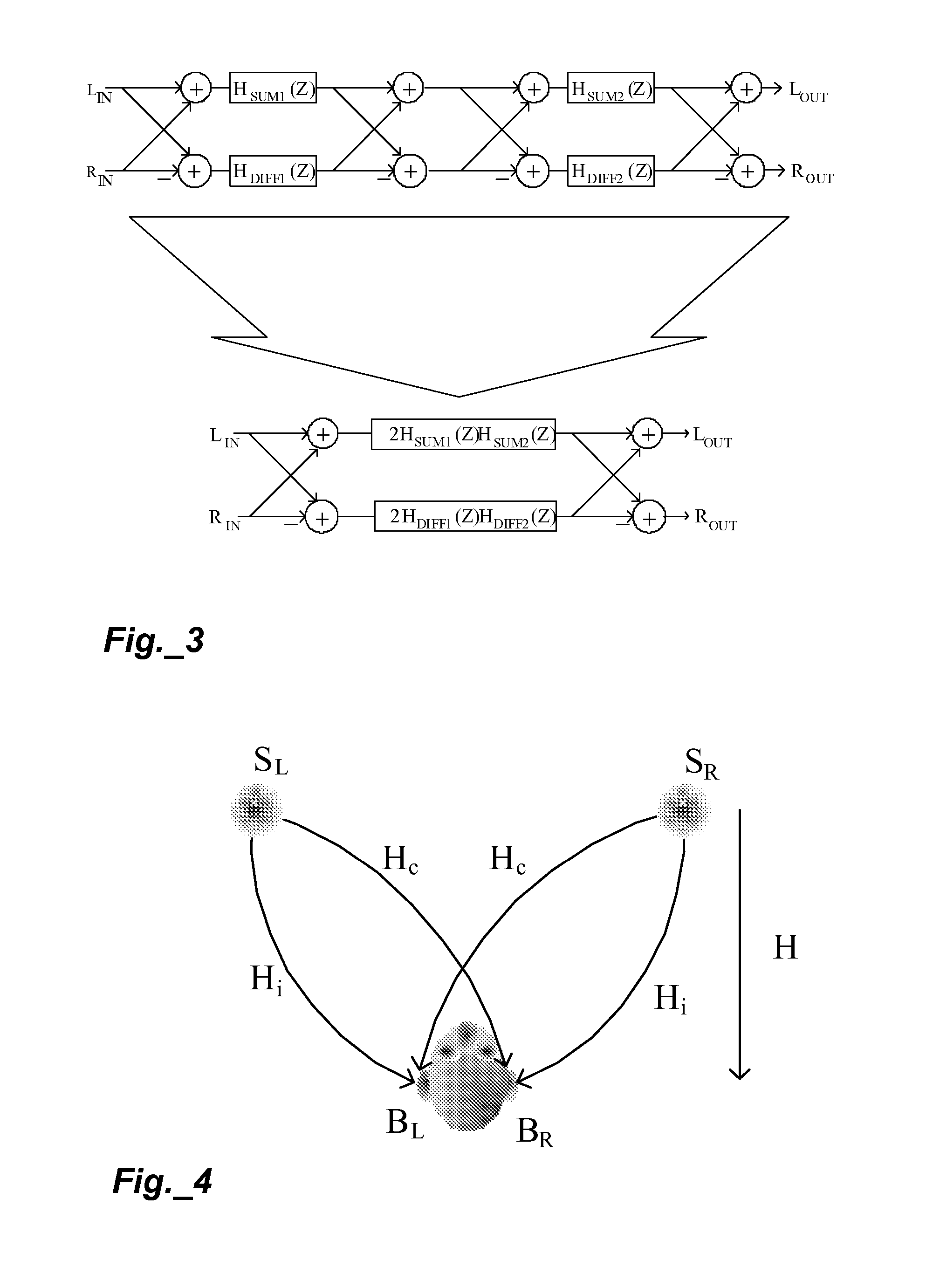
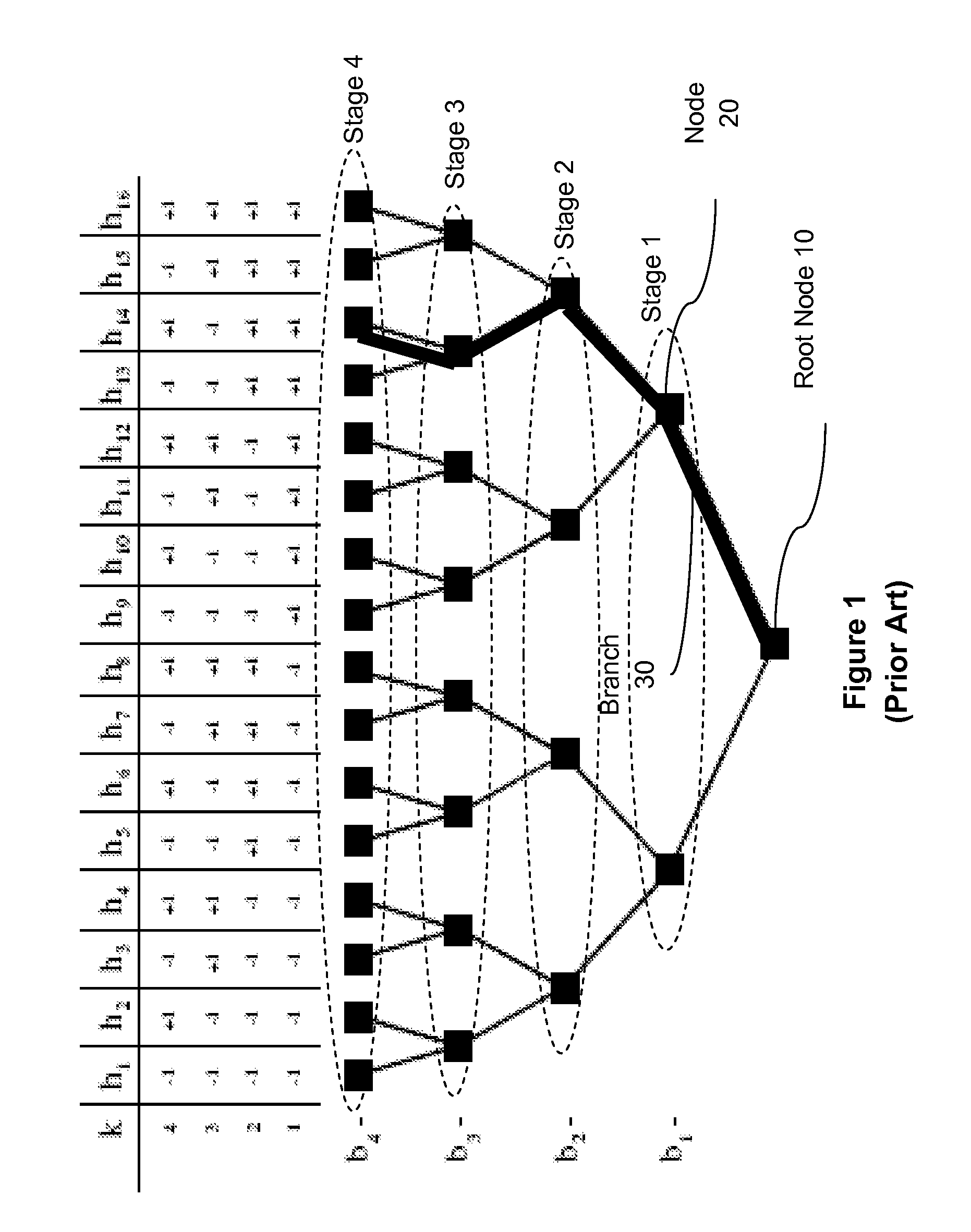
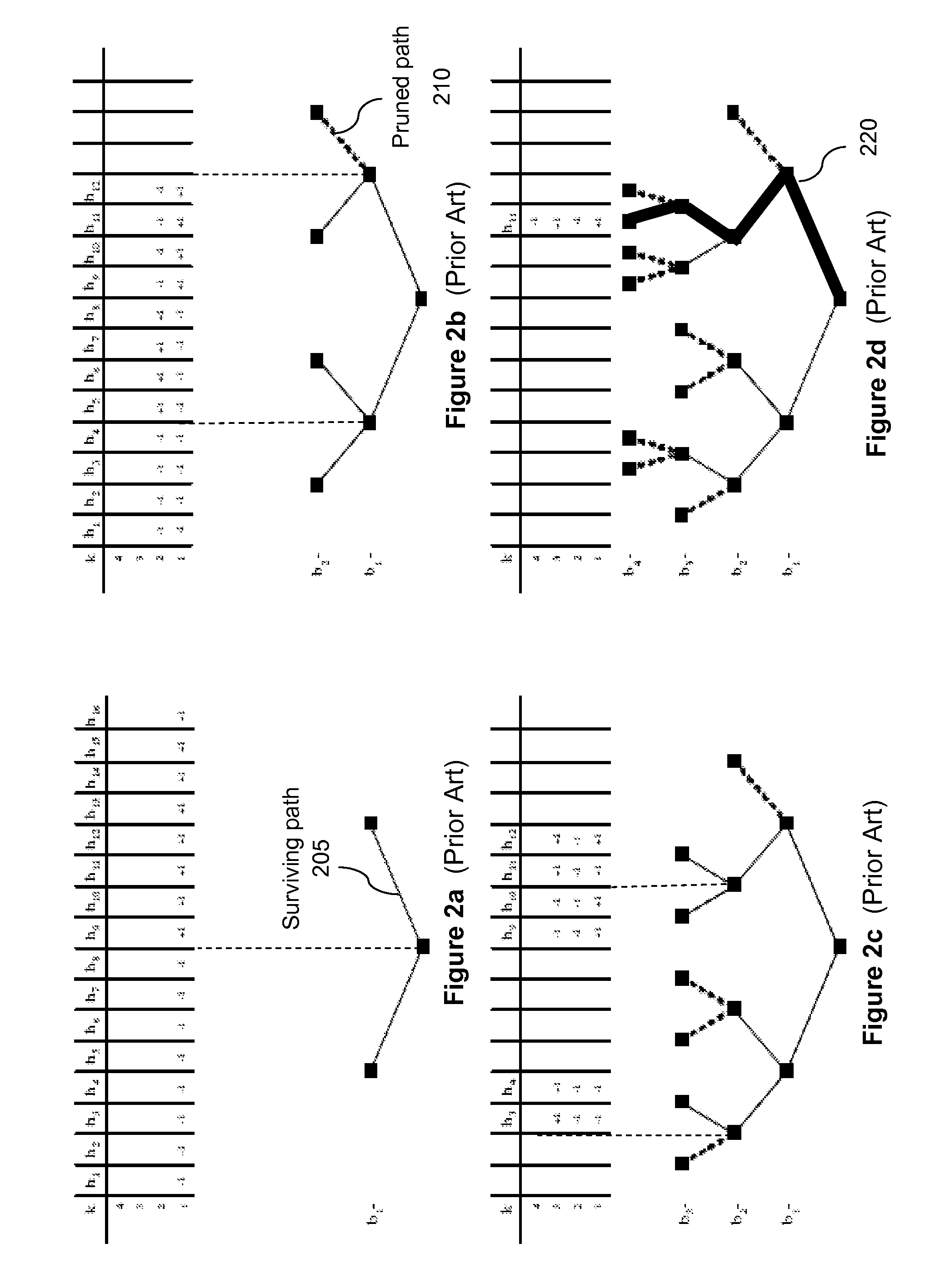
In physics, the S-matrix or scattering matrix relates the initial state and the final state of a physical system undergoing a scattering process. It is used in quantum mechanics, scattering theory and quantum field theory (QFT).
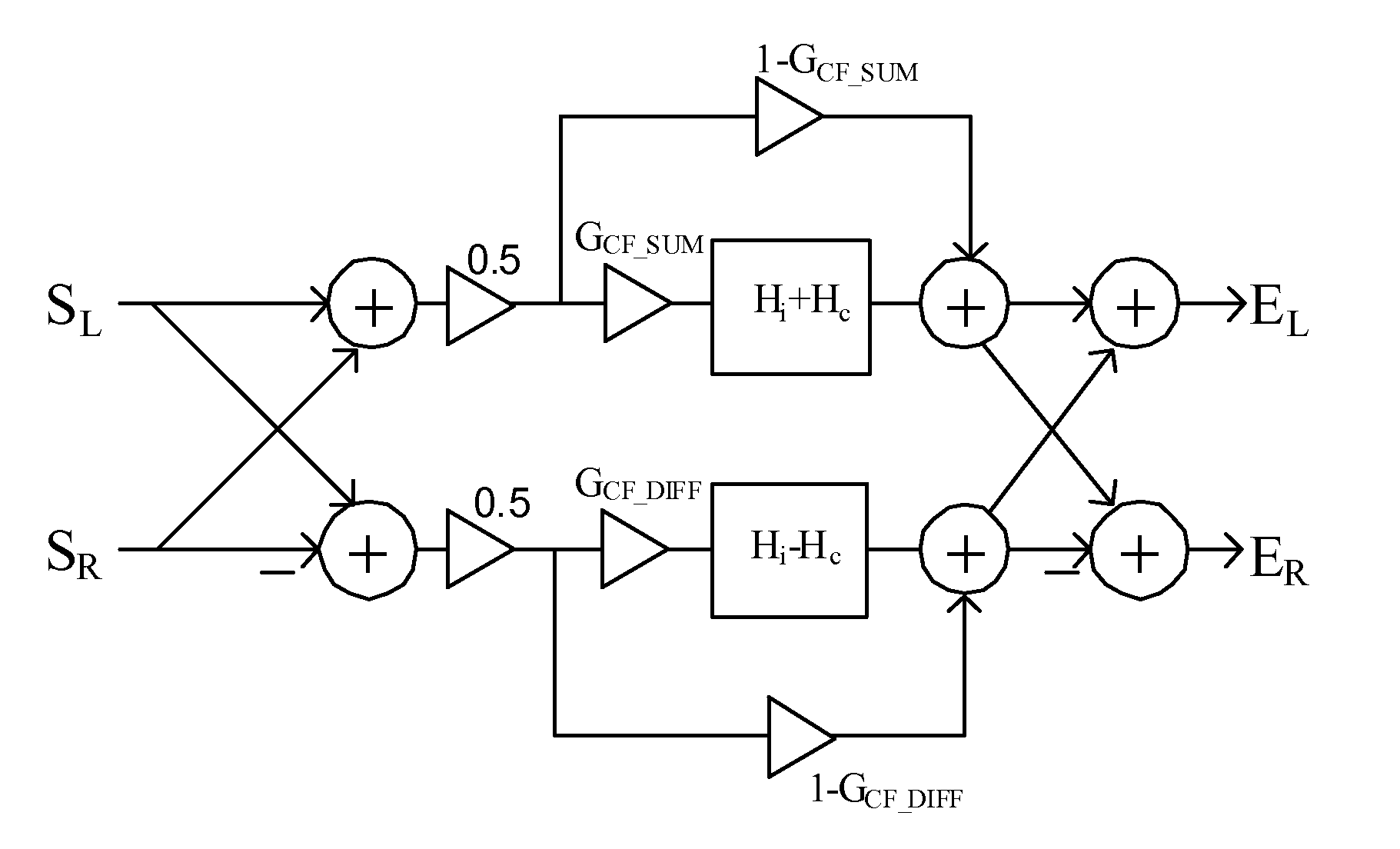
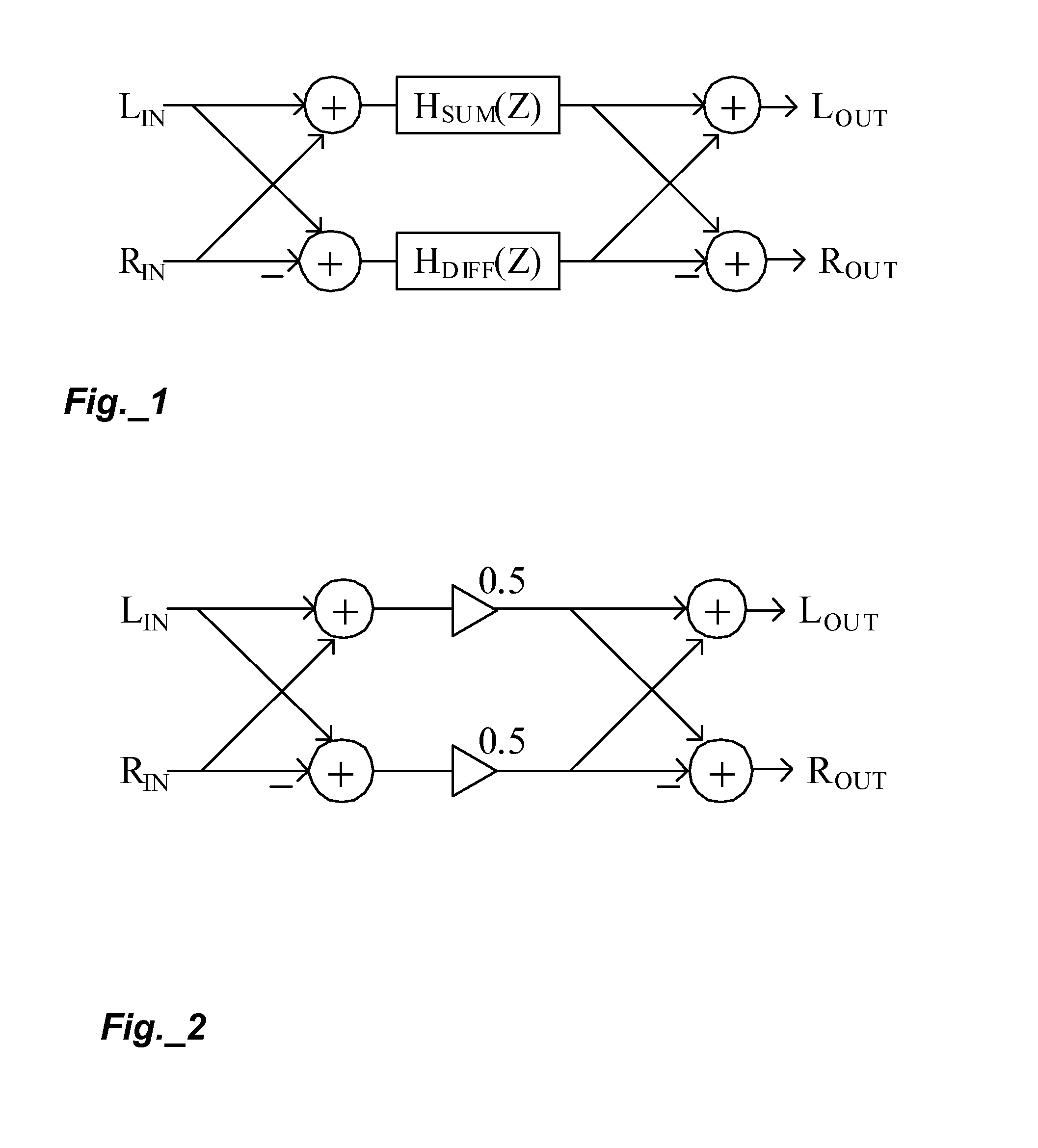
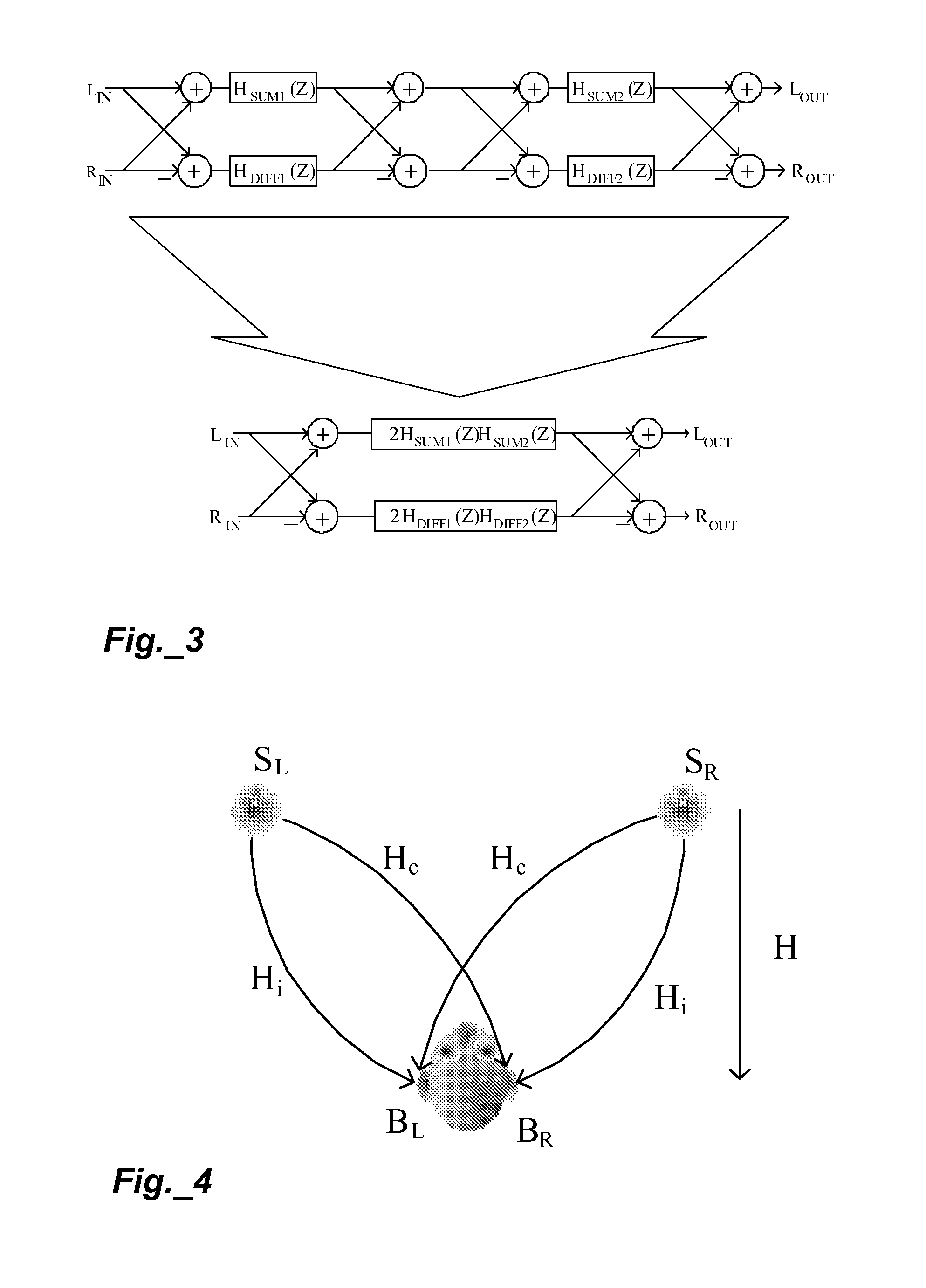
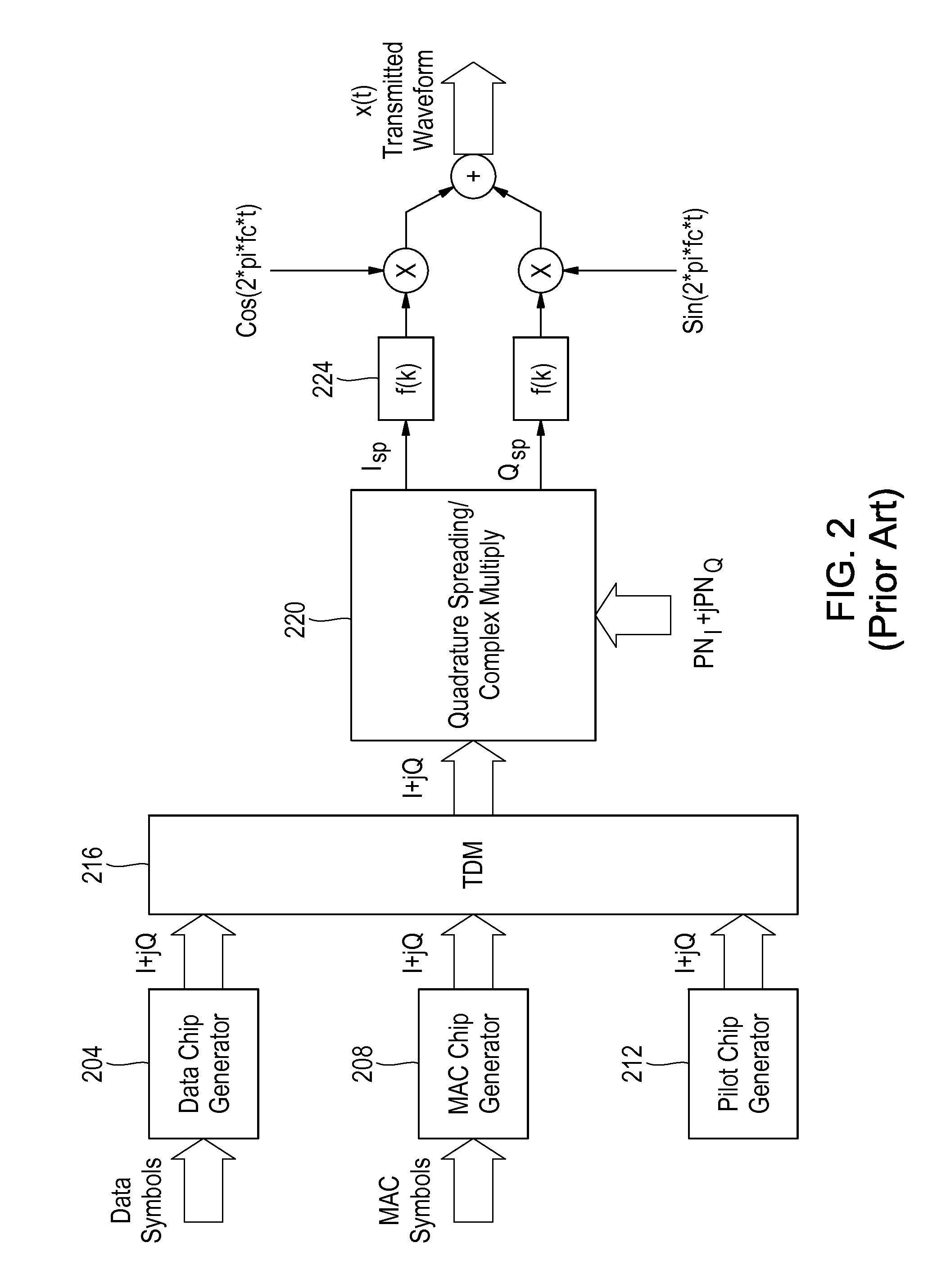
Spatial audio enhancement processing method and apparatus
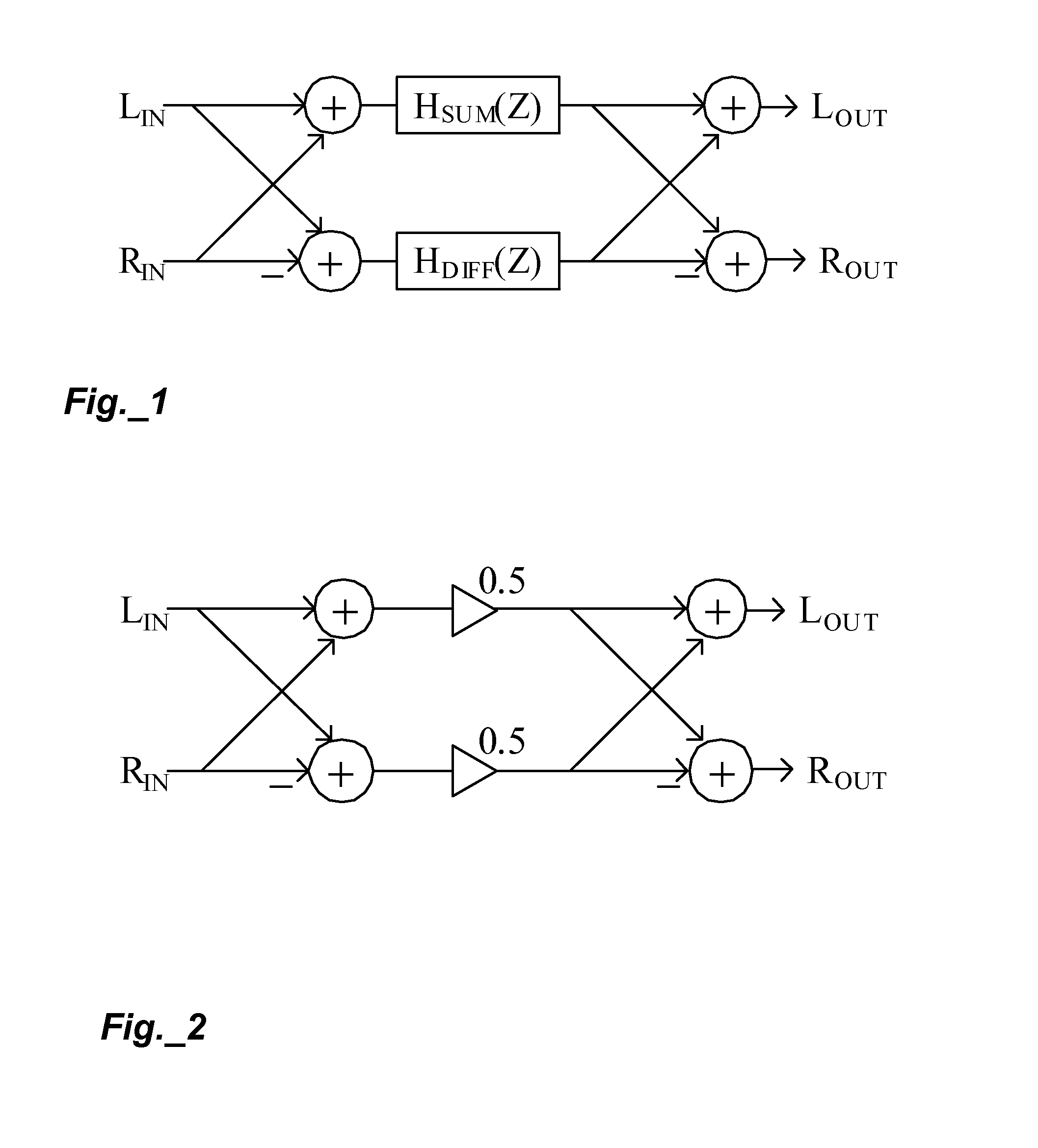
The present invention describes techniques that can be used to provide novel methods of spatial audio rendering using adapted M-S matrix shuffler topologies. Such techniques include headphone and loudspeaker-based binaural signal simulation and rendering, stereo expansion, multichannel upmix and pseudo multichannel surround rendering.
Owner:CREATIVE TECH CORP
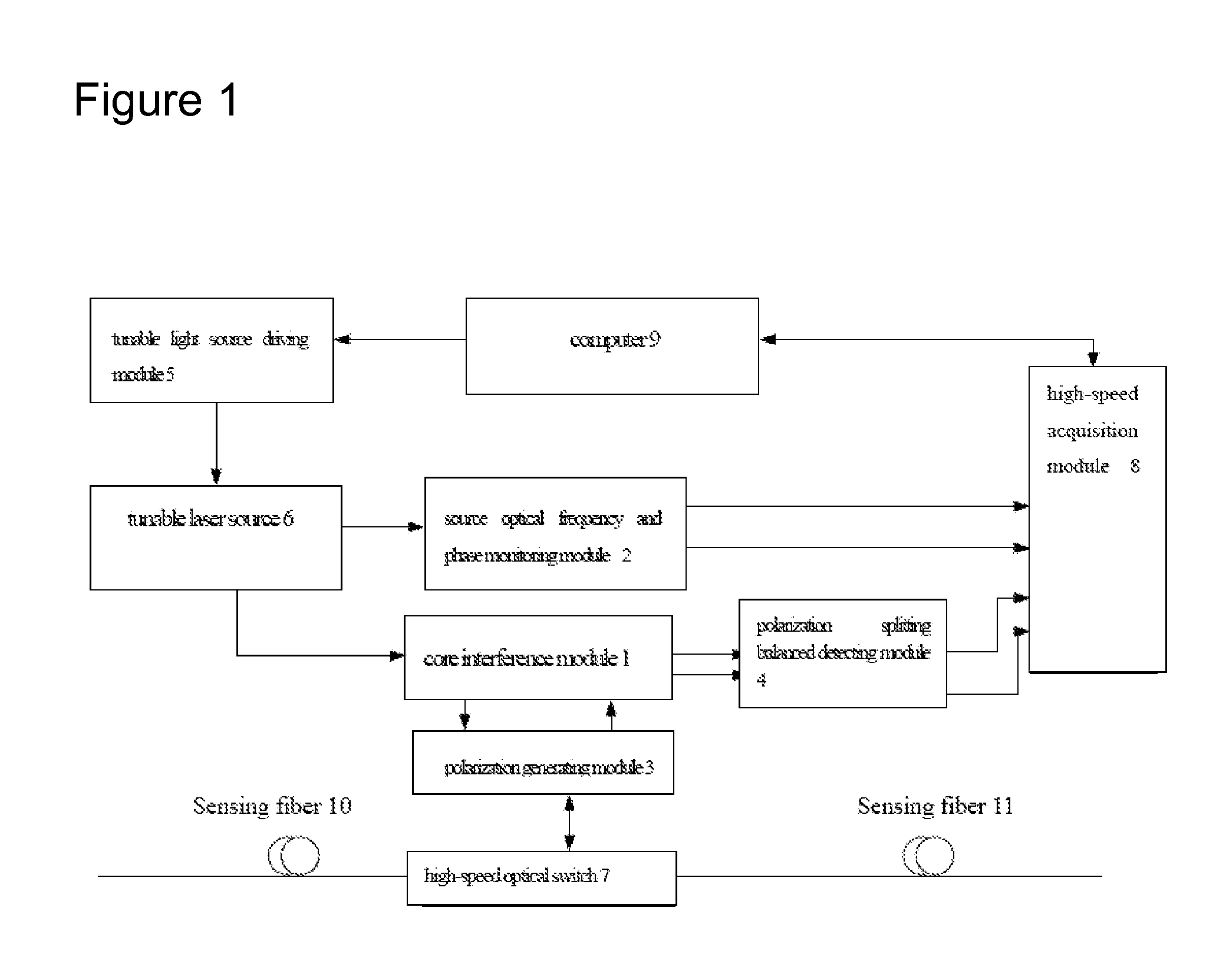
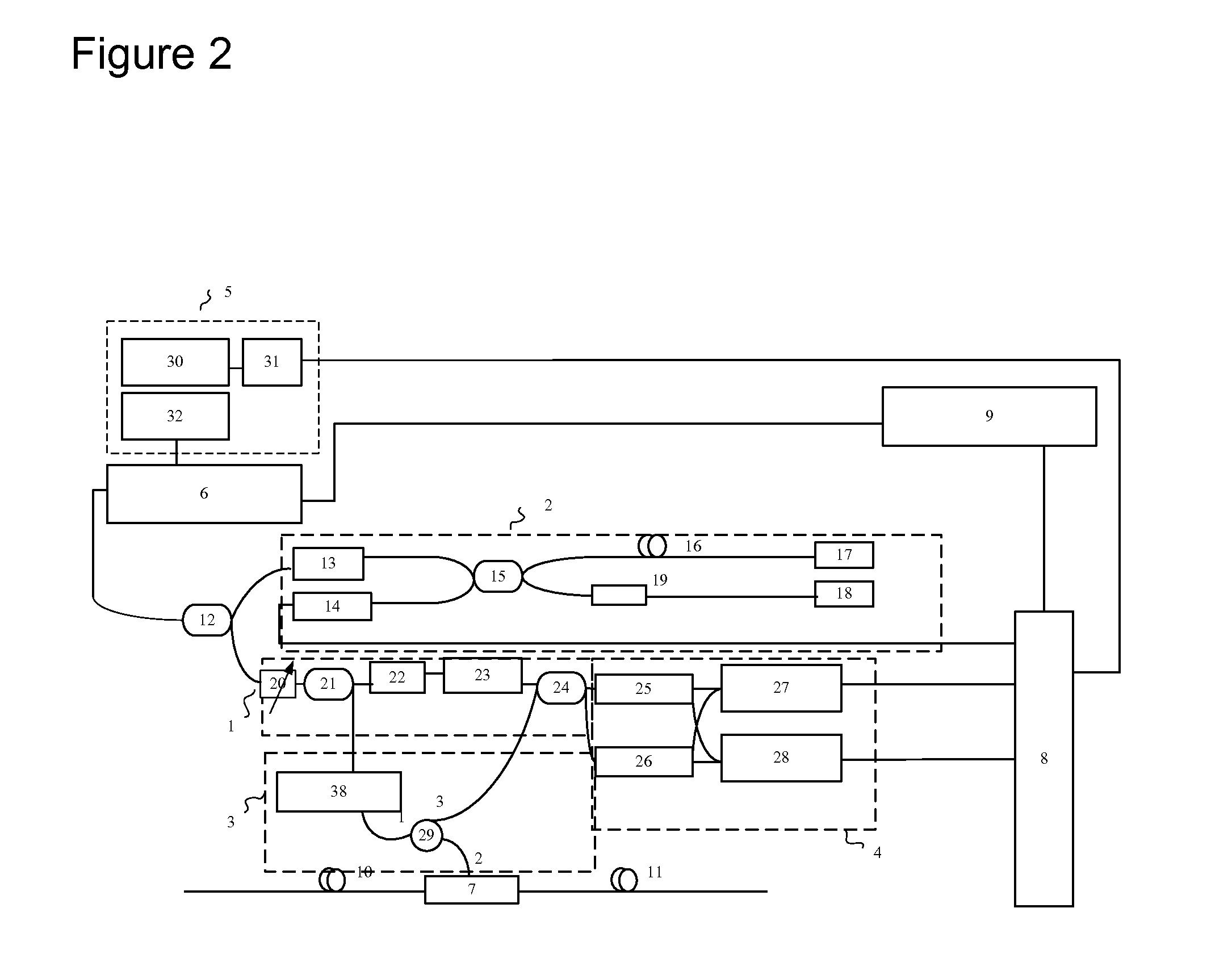
Distributed disturbance sensing device and the related demodulation method based on polarization sensitive optical frequency domain reflectometry
ActiveUS20140176937A1Long test distanceImprove spatial resolutionReflectometers dealing with polarizationSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementInformation analysisS-matrix
This invention relates to a distributed disturbance sensing device based on polarization sensitive optical frequency domain reflectometry (OFDR) and the related demodulation thereof. The device, adopting OFDR, polarization controlling and analysis techniques, consists of a ultra-narrow linewidth tunable laser source module, polarization generating and polarization splitting balanced detecting module, laser source optical frequency and phase monitoring module, high-speed optical switch and so on to establish a large-scale and long-distance optical sensing network. The demodulation method consists of analysis the polarization information from sensing optical fiber, the method of suppressing and compensating of the non-linear optical frequency and the laser phase noise, super-resolution analyzing, advanced denoising method and the polarization information analysis method based on Jones and Mueller's matrices using distributed wave plate model of optical fiber.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
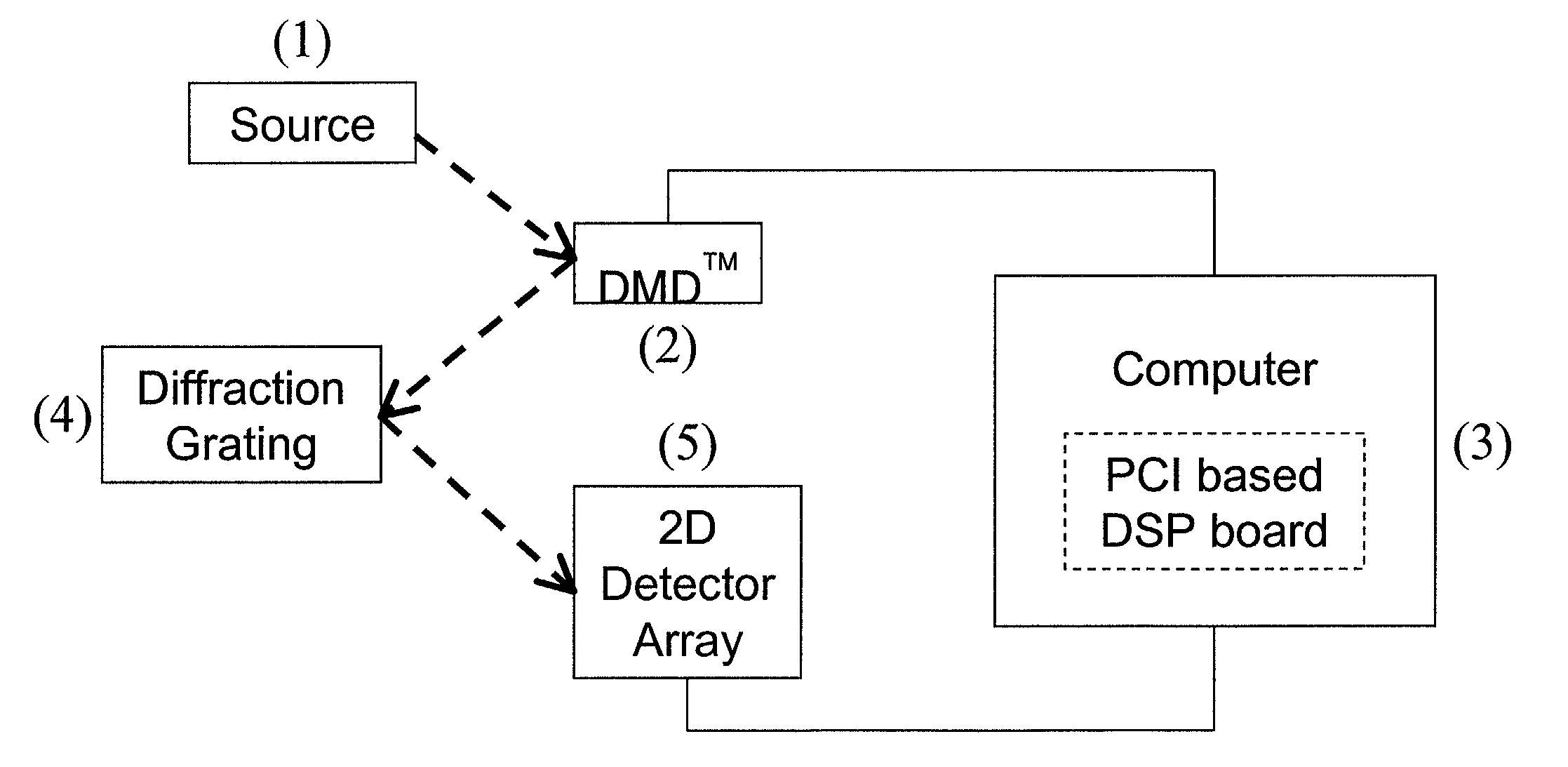
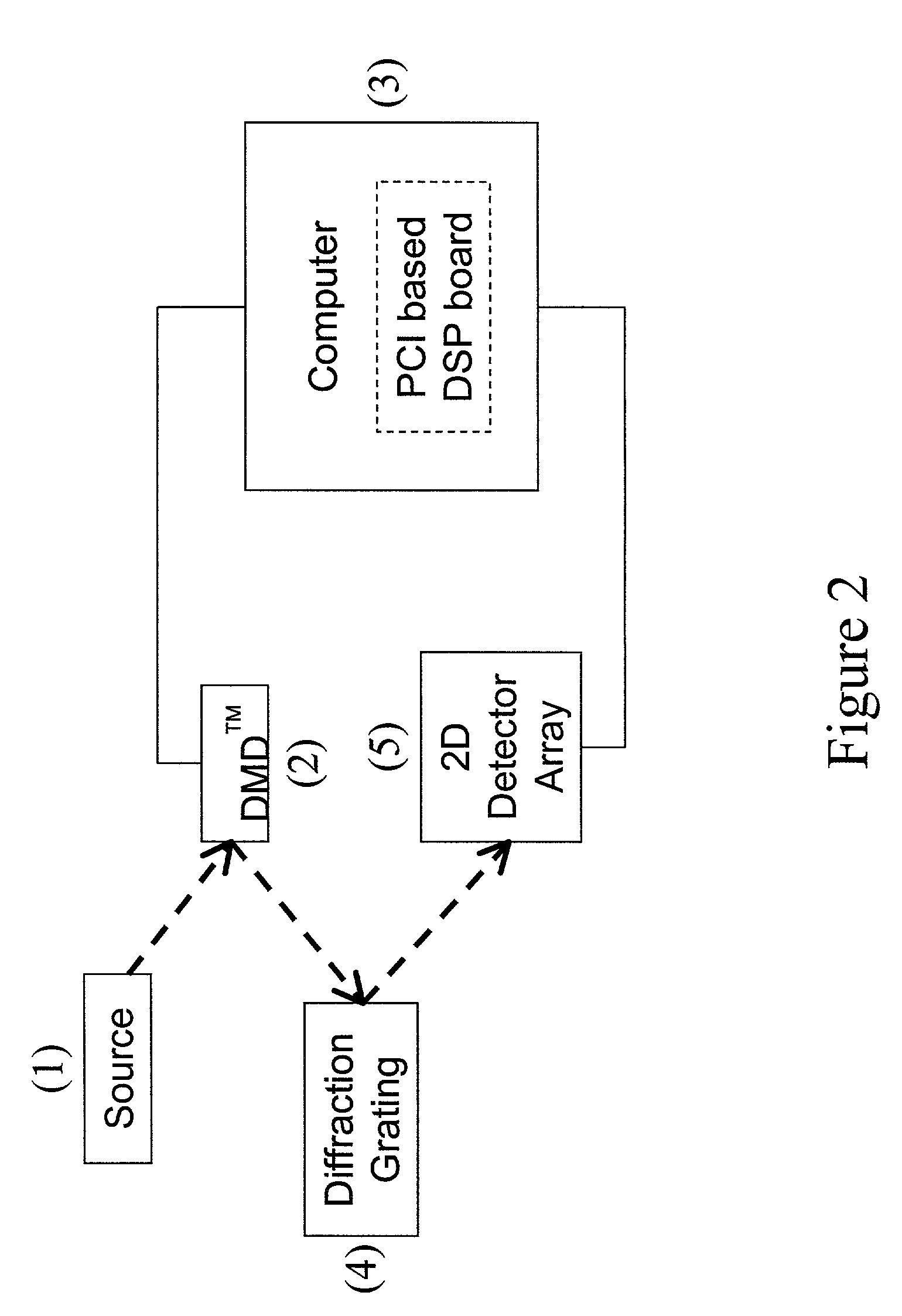
Staring 2-D hadamard transform spectral imager
ActiveUS6996292B1Maintain integrityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationHadamard transformFrequency spectrum
A staring imaging system inputs a 2D spatial image containing multi-frequency spectral information. This image is encoded in one dimension of the image with a cyclic Hadamarid S-matrix. The resulting image is detecting with a spatial 2D detector; and a computer applies a Hadamard transform to recover the encoded image.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
Spatial audio enhancement processing method and apparatus
The present invention describes techniques that can be used to provide novel methods of spatial audio rendering using adapted M-S matrix shuffler topologies. Such techniques include headphone and loudspeaker-based binaural signal simulation and rendering, stereo expansion, multichannel upmix and pseudo multichannel surround rendering.
Owner:CREATIVE TECH CORP
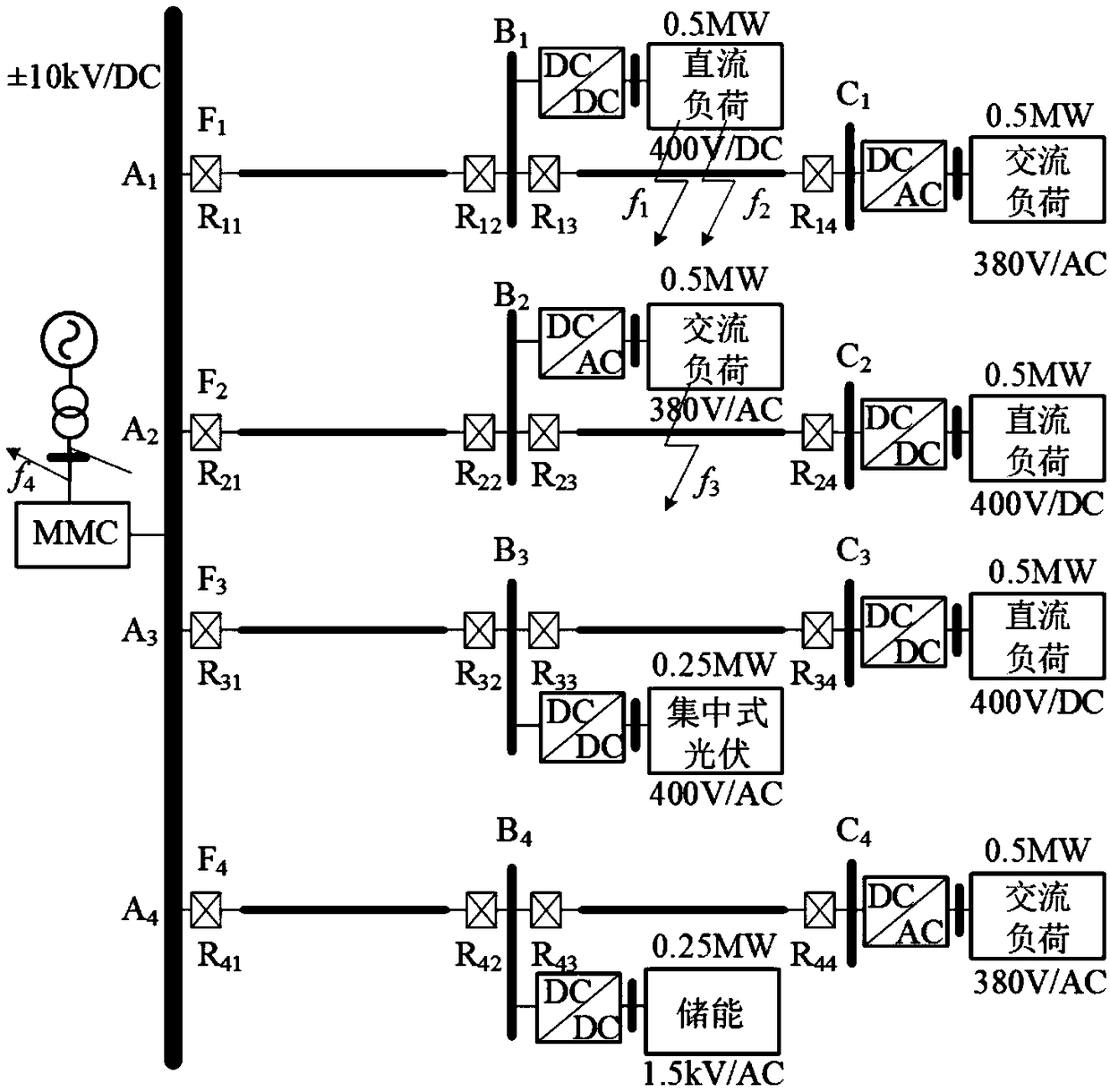
Flexible direct-current power distribution network monopole fault line selection and section positioning method and system
ActiveCN108663602AAdaptableReliable identificationFault location by conductor typesInformation technology support systemEngineeringSelection criterion
The invention discloses a flexible direct-current power distribution network monopole fault line selection and section positioning method and system. The method comprises the steps that positive and negative currents of each feeder line of a direct-current power distribution line are collected and filtered; current sudden change data in a data window is extracted, S-transform is carried out on thedata to obtain a complex time-frequency S matrix of current signals; a characteristic frequency band is calculated according to line parameters; STCFB and W are calculated according to the complex time-frequency S matrix; a monopole fault line selection criterion and a section positioning criterion of the direct-current power distribution feeder lines are established, and fault feeder line identification is carried out on the basis of current sudden change Pearson correlation coefficients according to the line selection criterion; if the line is a faulty feeder line, the transient energy sumsof positive current and negative current sudden change characteristic frequency bands are compared for fault pole judgment; if the line is a faulty polar line, fault feeder line identification is carried out by using current sudden change correlation between the left side and the right side of each feeder line section. The method is not affected by factors such as transition resistance, data asynchronization and fault positions, and is rapid, sensitive and reliable.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +2
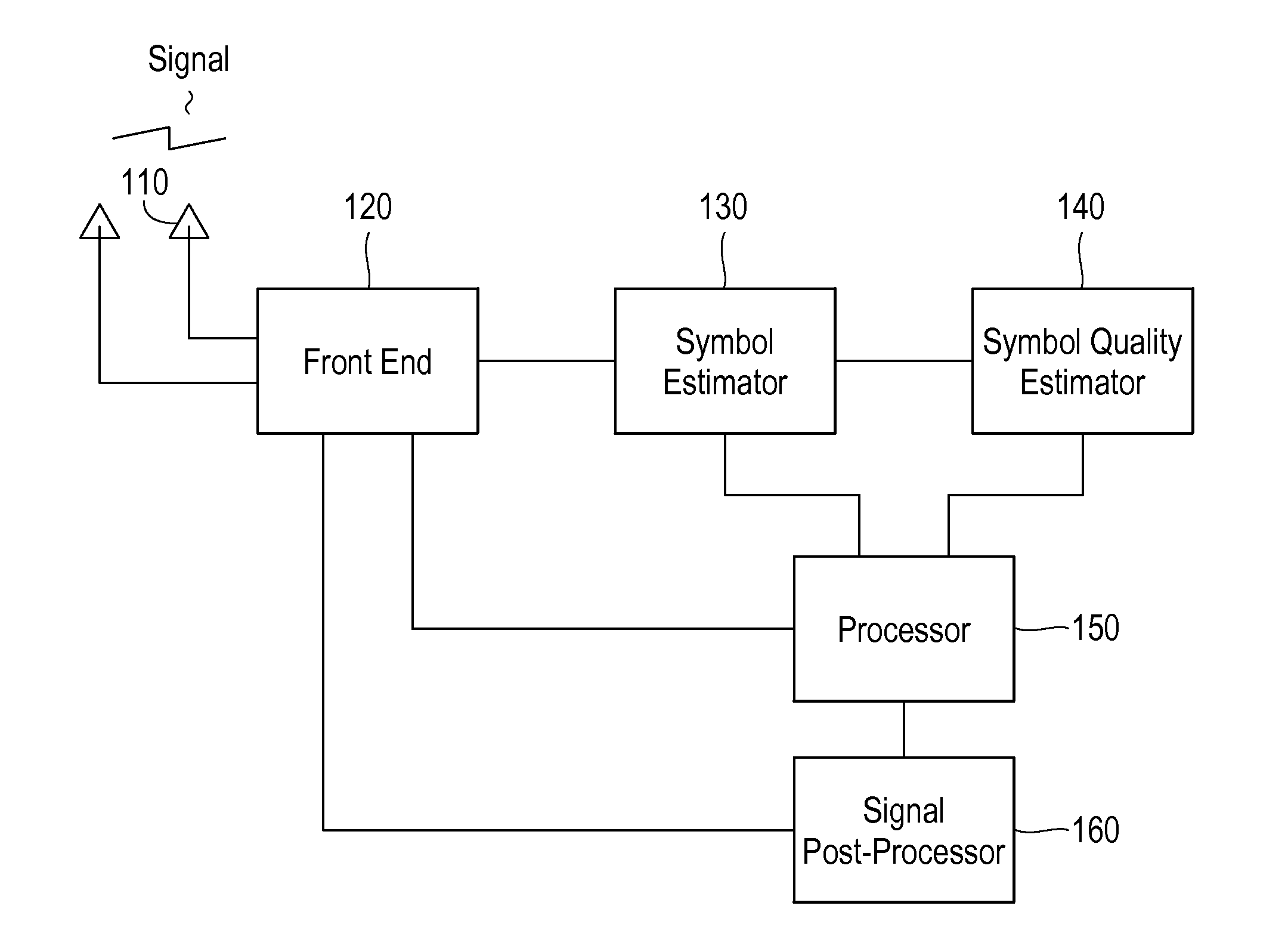
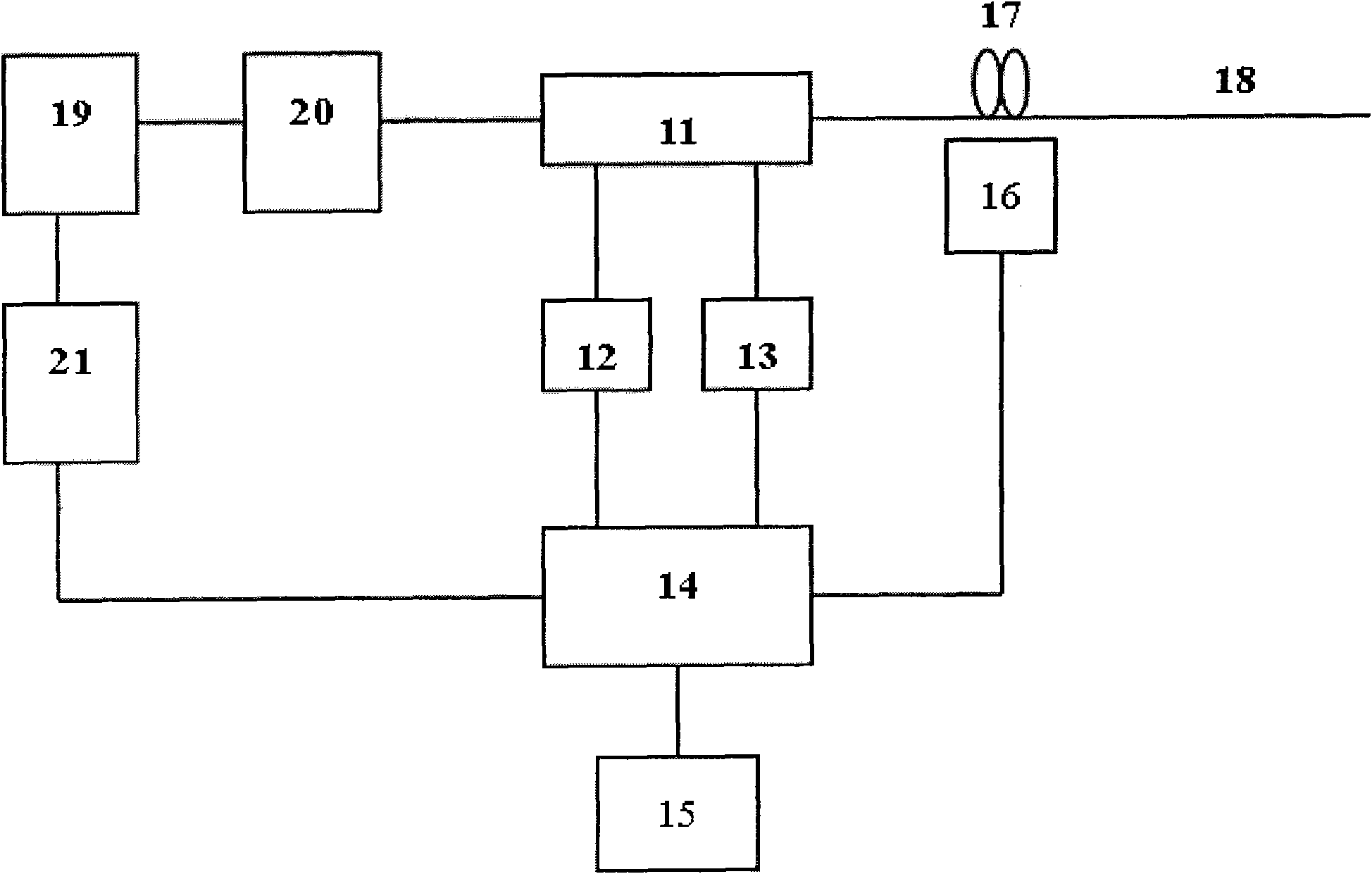
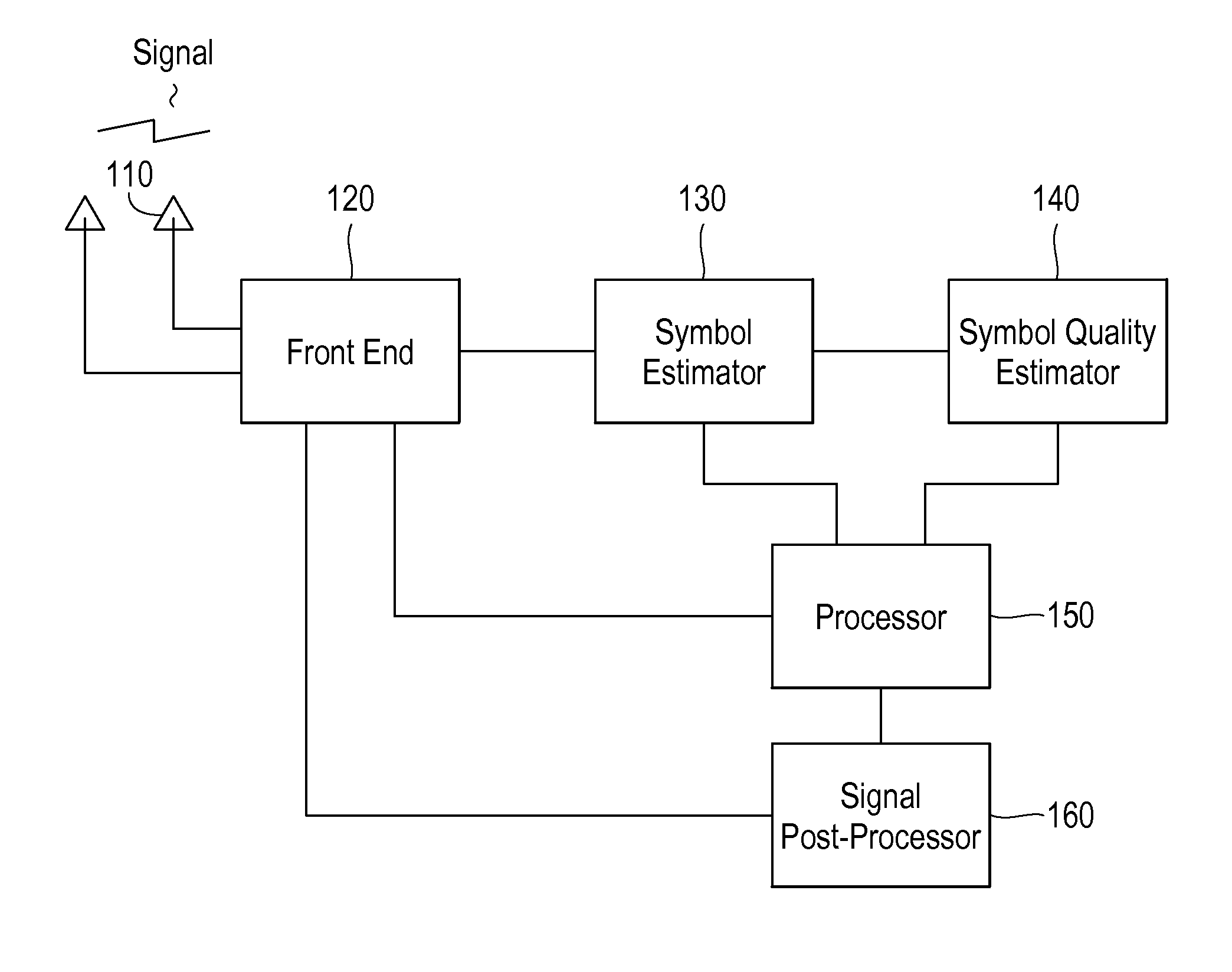
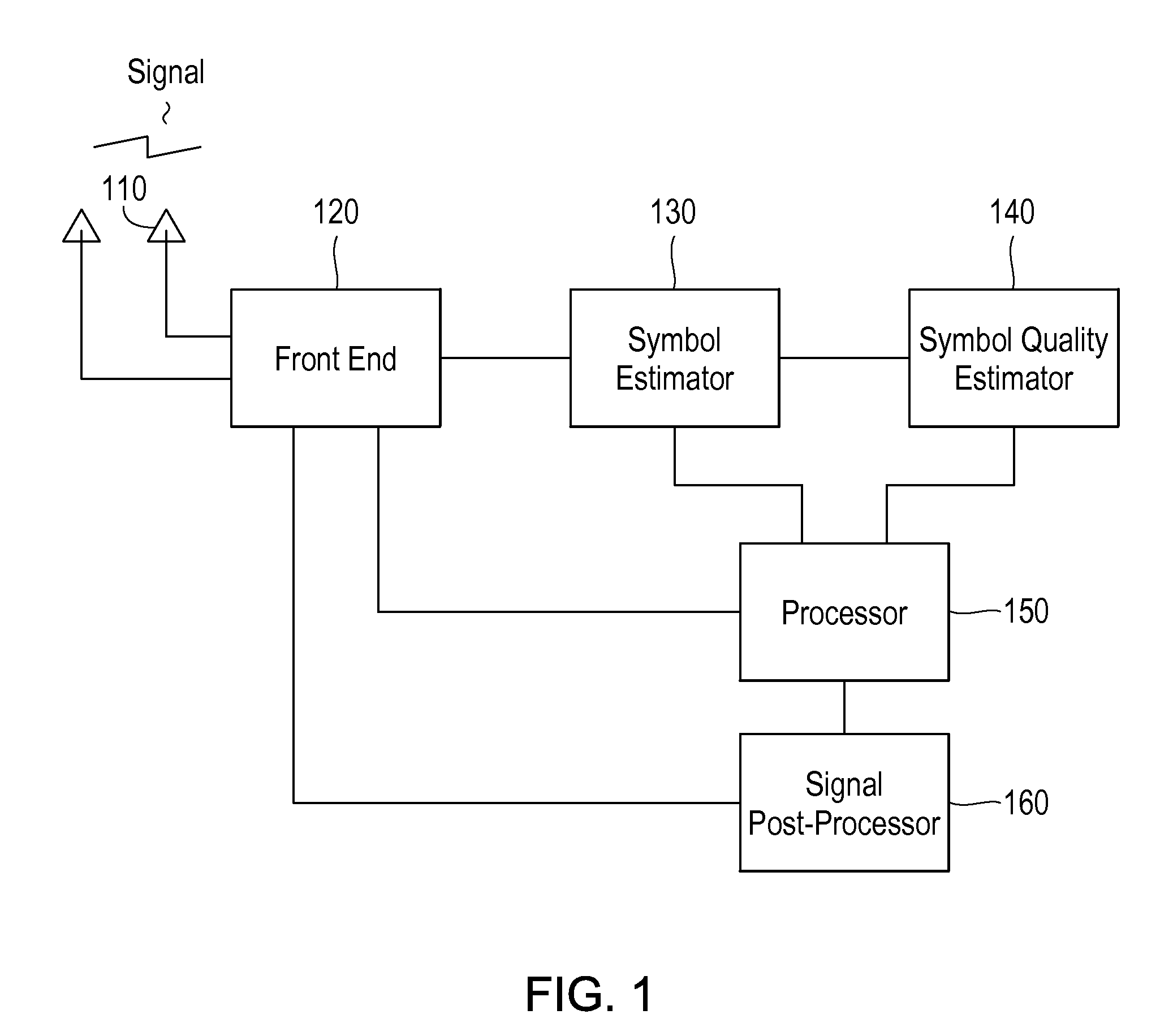
Method and Apparatus for Interference Suppression with Efficient Matrix Inversion in a DS-CDMA System
InactiveUS20110069742A1Improving symbol estimationImprove power efficiencyPolarisation/directional diversityLine-faulsts/interference reductionInterference cancellerComputer module
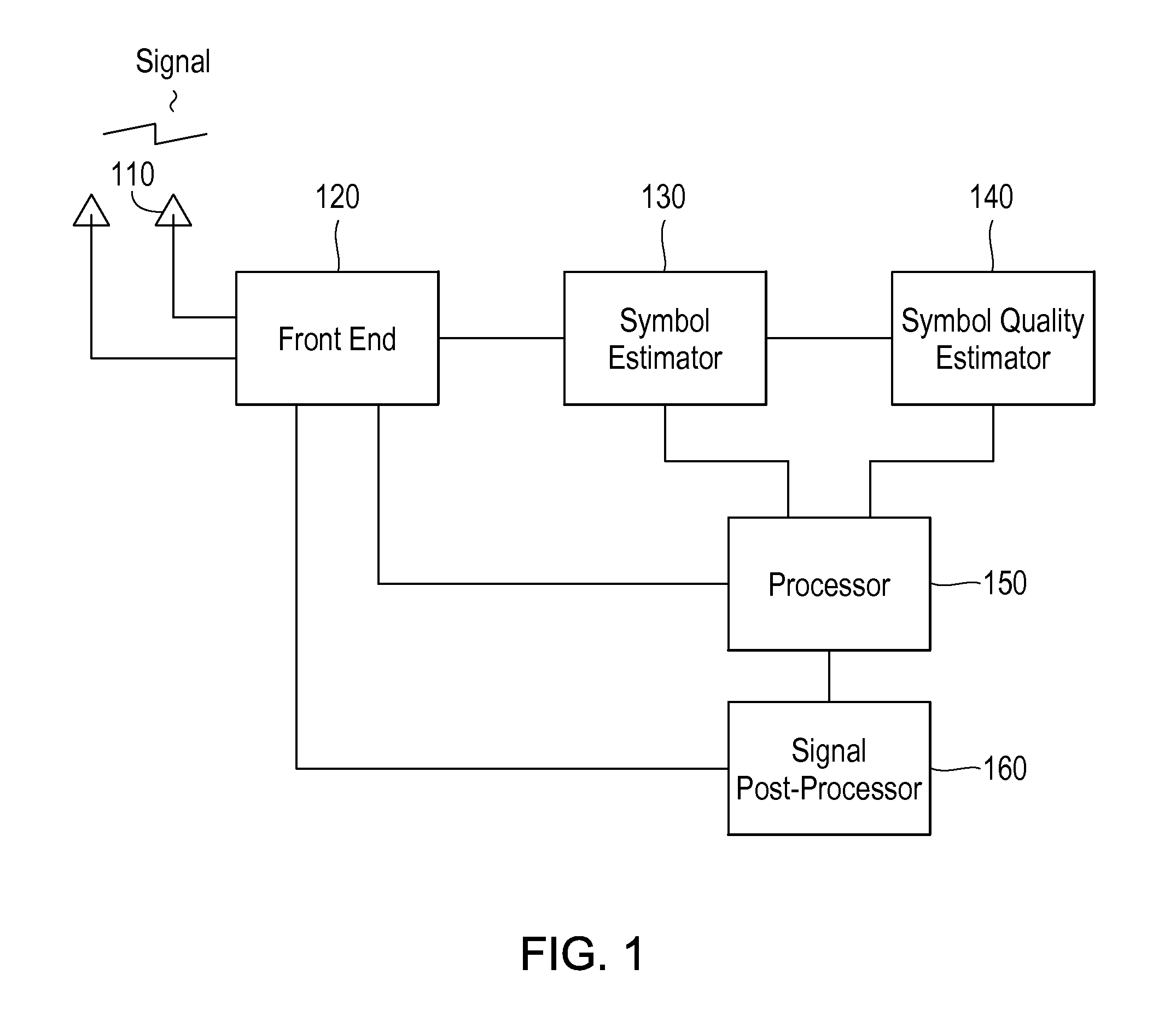
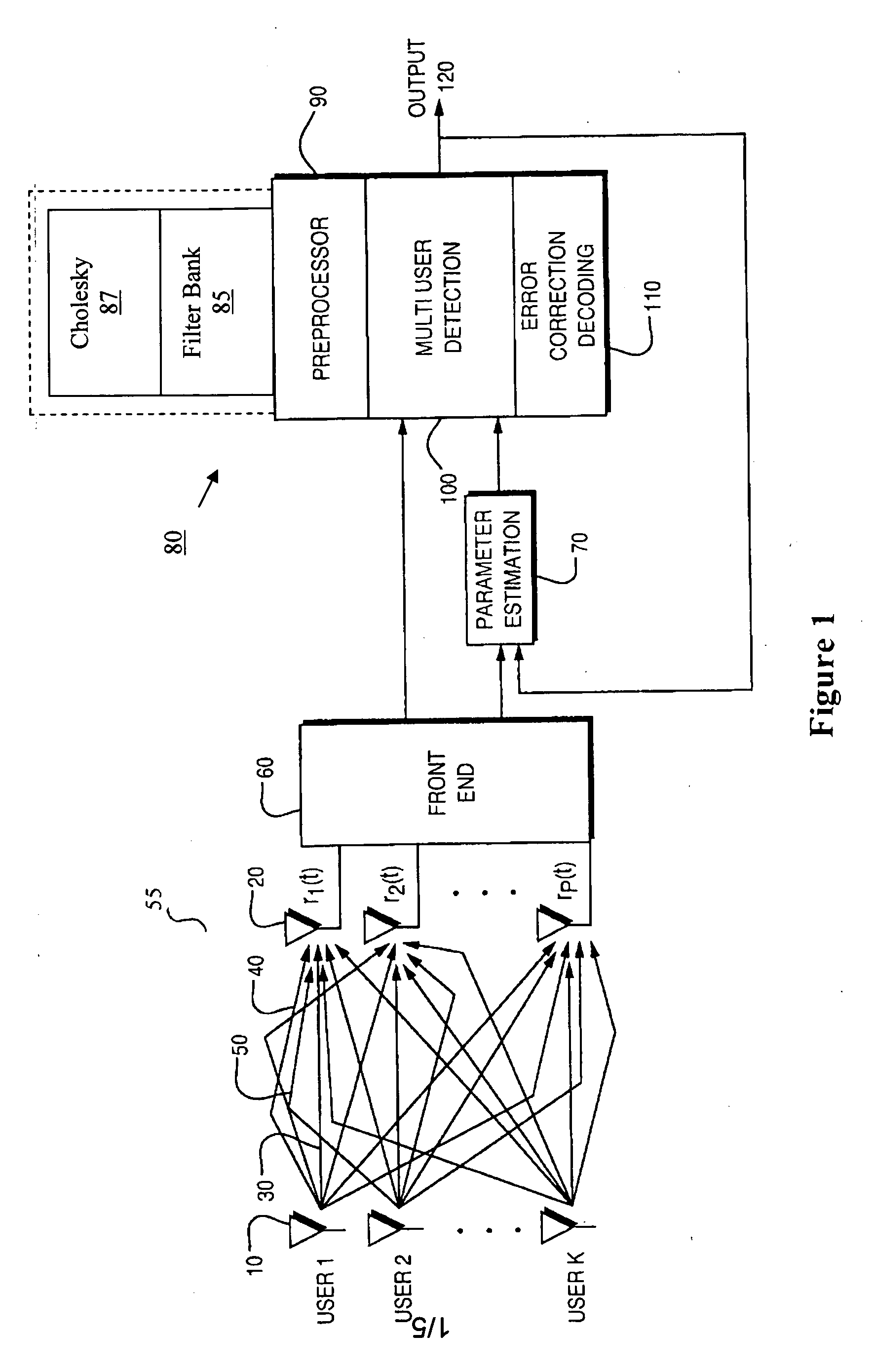
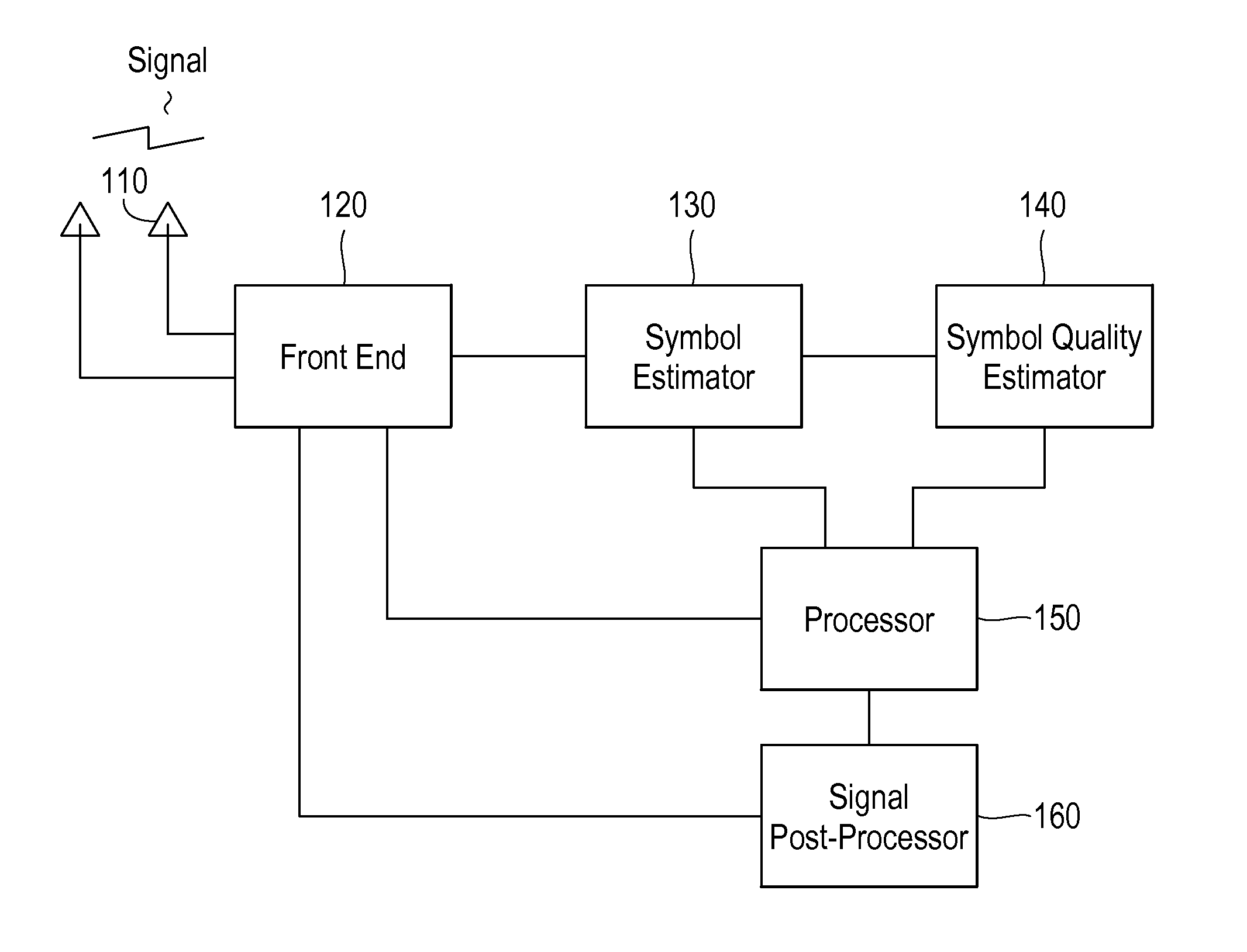
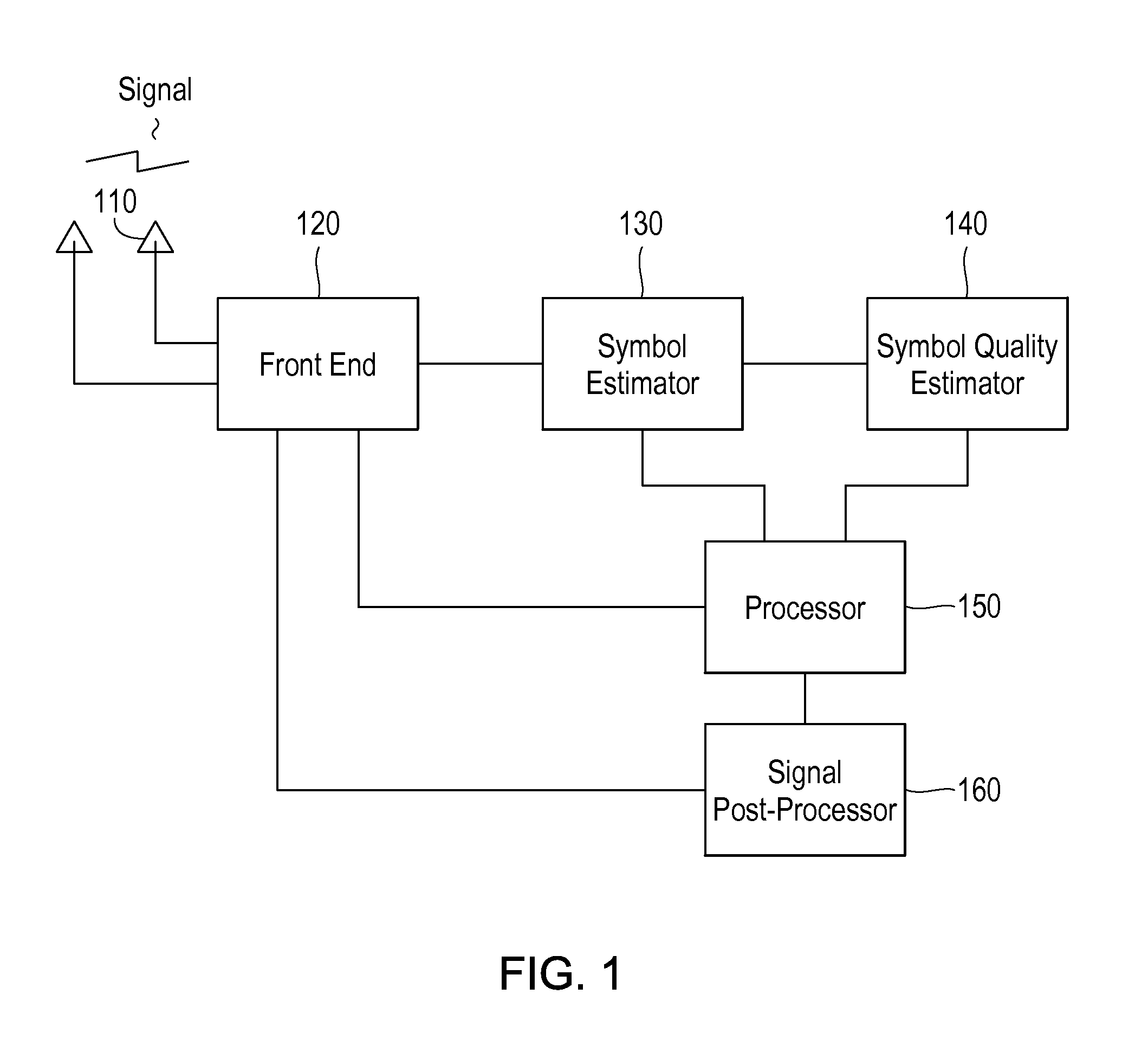
A receiver in a CDMA system comprises a front end processor that generates a combined signal per source. A symbol estimator processes the combined signal to produce symbol estimates. An S-Matrix Generation module refines these symbol estimates based on the sub channel symbol estimates. An interference canceller is configured for cancelling interference from at least one of the plurality of received signals for producing at least one interference-cancelled signal.
Owner:III HLDG 1
Distributed optical fiber Raman temperature sensor coding and decoding by adopting sequential pulse
InactiveCN101819073AAvoid nonlinear effectsHigh strengthThermometers using physical/chemical changesSignal onPeak value
The invention discloses a distributed optical fiber Raman temperature sensor coding and decoding by adopting sequential pulses, which is a distributed optical fiber temperature measuring system coding and decoding a signal on the basis of S-matrix transformation and carrying out optical fiber on-line positioning temperature measurement by utilizing the effect of optical fiber Raman light intensity modulated by temperature and an optical time domain reflection principle. The distributed optical fiber Raman temperature sensor can obtain better signal-to-noise radio under the condition of spending same measuring time by using a sequential multidigit laser pulse coding and decoding technology, increase the number of emitted photons, enhance the space resolution by narrowing the thicknesses of laser pulses and also effectively prevent the nonlinear effect of optical fibers by lowering the requirements on the peak value power of a single laser pulse; and in addition, the invention effectively solves the contradiction of space resolution enhancement-signal-to-noise radio reduction and signal-to-noise radio enhancement-space resolution reduction or measuring time increase of the traditional optical fiber distribution temperature sensor, enhances the temperature measuring precision, can be used for a distributed optical fiber temperature sensor which has ultra long range and high space resolution.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Systems and Methods for Serial Cancellation
InactiveUS20110064172A1Improving symbol estimationImprove power efficiencyError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionInterference cancellerEngineering
A receiver in a CDMA system comprises a front end processor that generates a combined signal per source. A symbol estimator processes the combined signal to produce symbol estimates. An S-Matrix Generation module refines these symbol estimates based on the sub channel symbol estimates. An interference canceller is configured for cancelling interference from at least one of the plurality of received signals for producing at least one interference-cancelled signal.
Owner:III HLDG 1
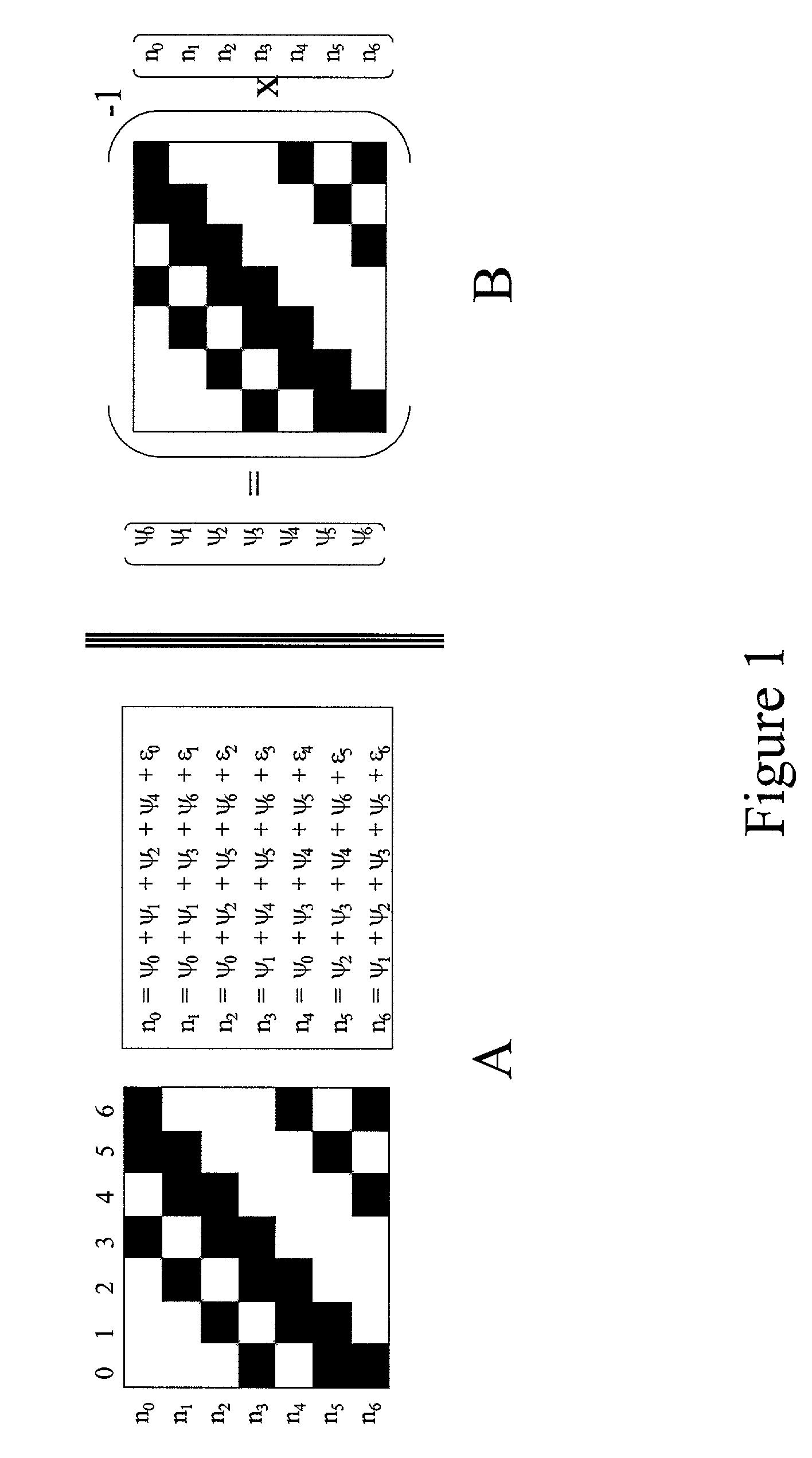
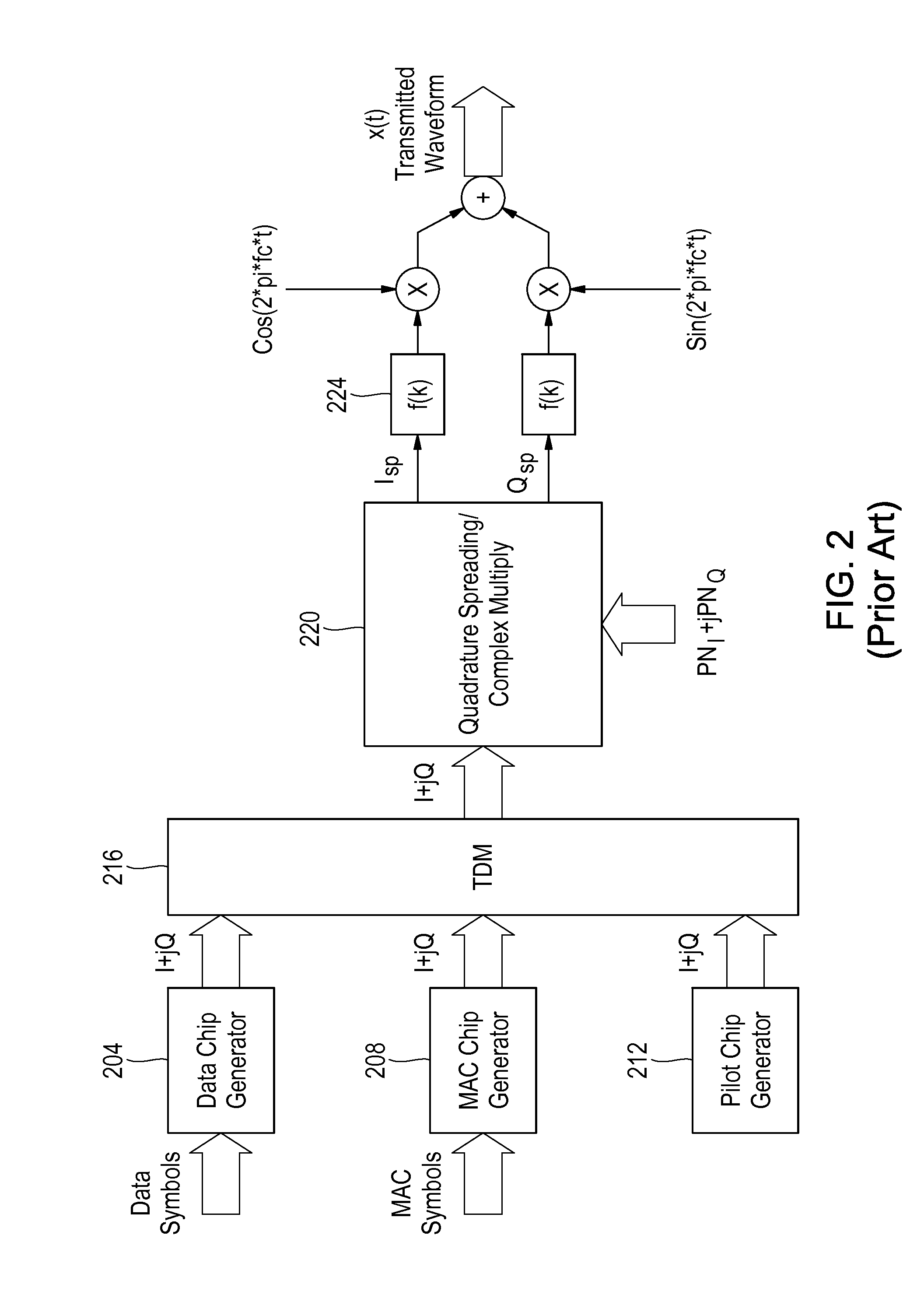
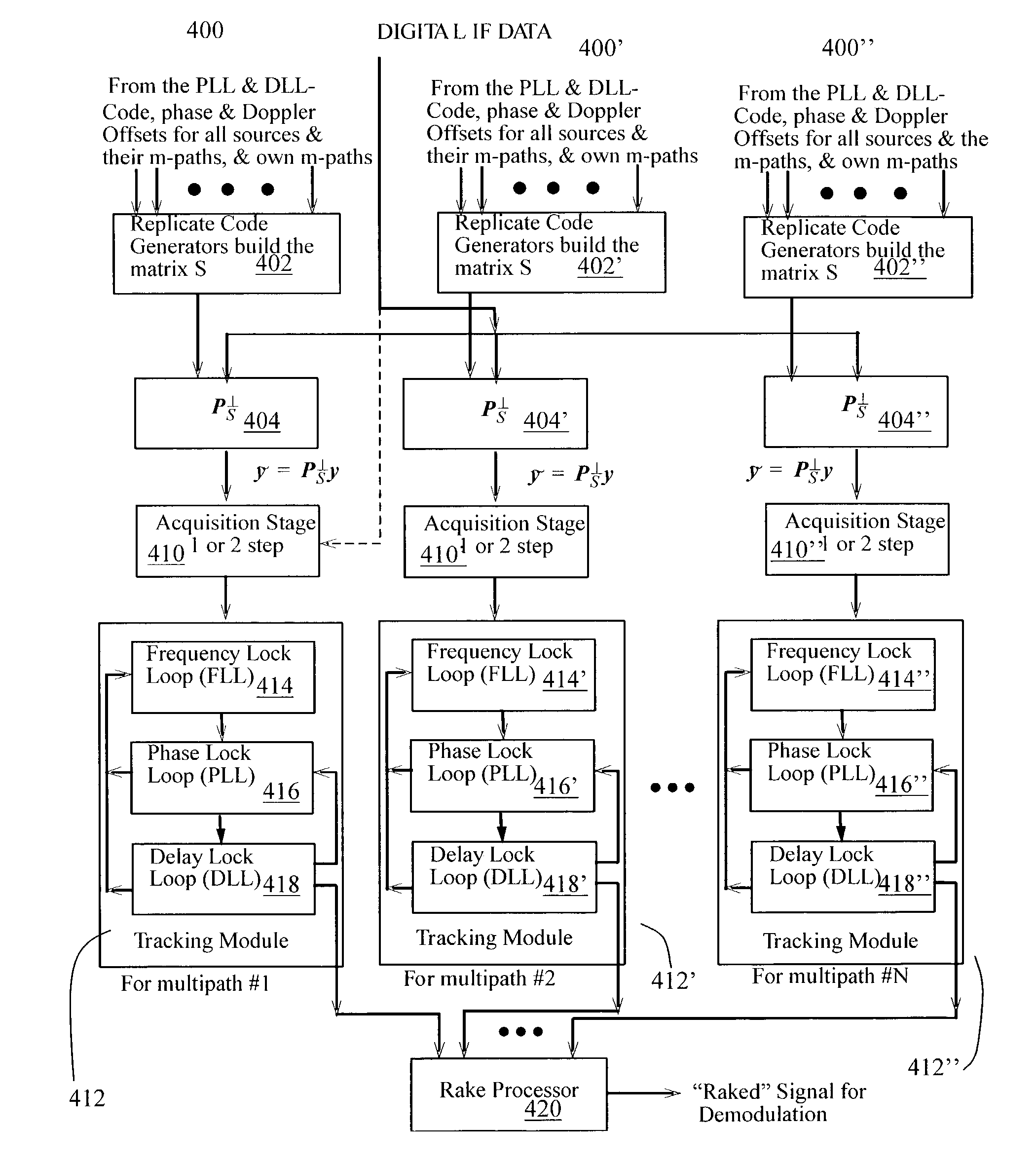
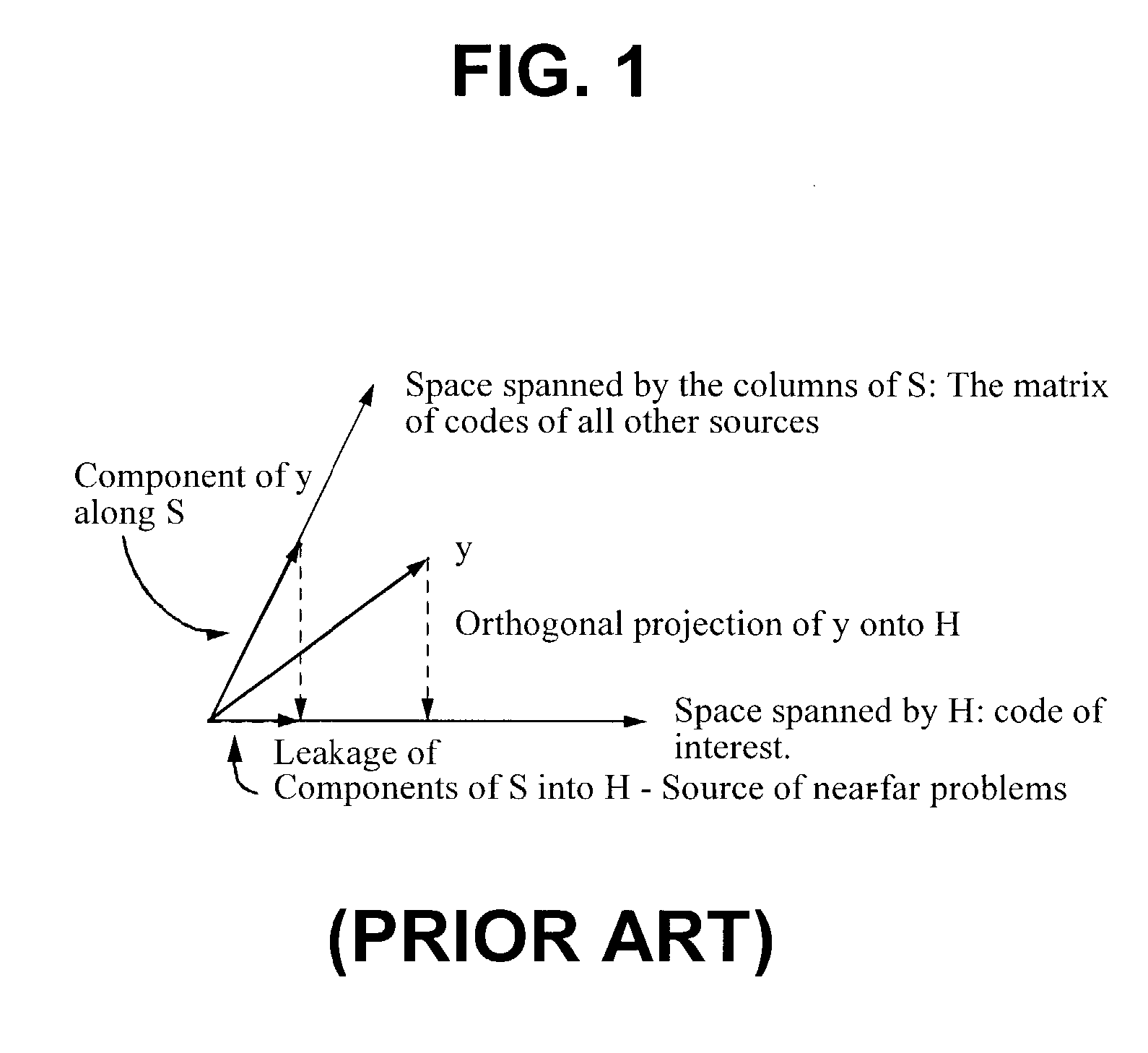
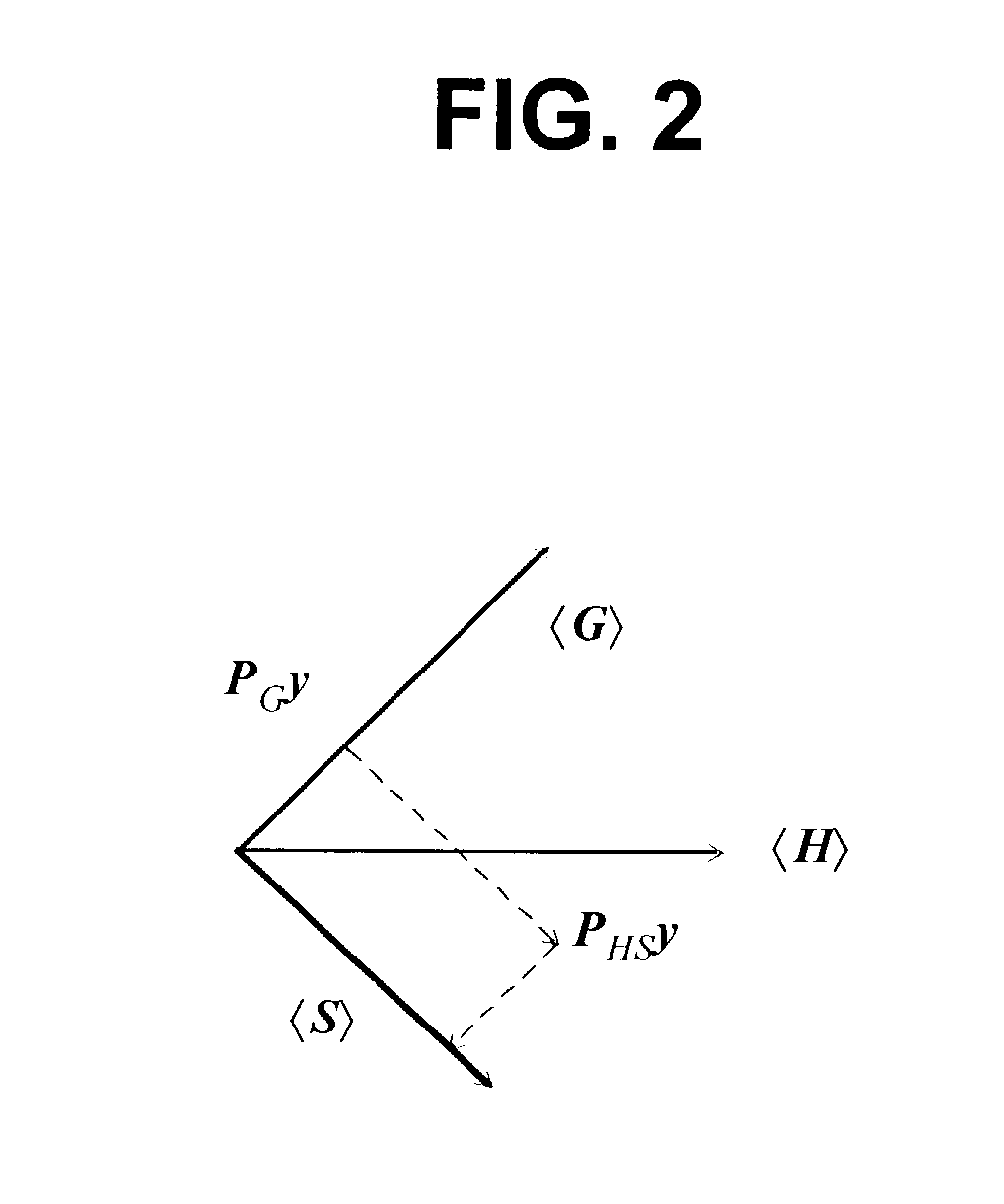
Construction of an interference matrix for a coded signal processing engine
ActiveUS7200183B2Facilitate acquisition and tracking and demodulationGood acquisition and tracking and demodulationRadio transmission for post communicationTransmission noise suppressionEngineeringS-matrix
A novel method for generating an interference matrix S is disclosed. The method comprises the following steps: A) Determining the number of active channels N in a transmitter; B) Selecting the transmitter to be canceled and assigning the transmitters sequentially to the variable t; C) Selecting the channel to be cancelled and assigning the channels sequentially to the variable n, where n is less than or equal to N; D) Determining if a multipath signal should be canceled and assigning the multipaths of interest to the respective variable M; E) Generating a sequence of column vectors V; F) Repeating steps B, C, D, E, F and G for each column vector of interest; and G) Defining the S matrix as S=[V1 V2 . . . Vc] wherein the index denotes the column index c. In addition, an apparatus for generating the interference matrix is also disclosed.
Owner:III HLDG 1
Universal aquatic vegetation radiation transmission model
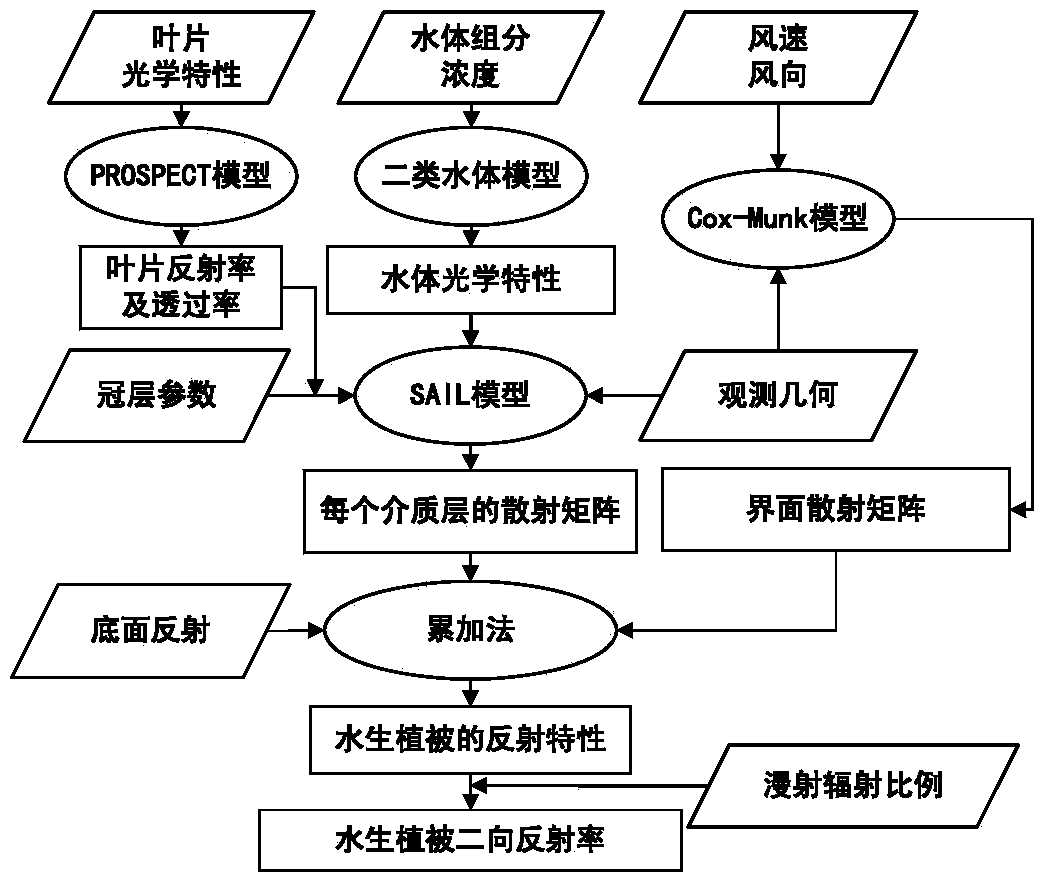
InactiveCN103632040AInnovativePhysical concepts are clearScattering properties measurementsSpecial data processing applicationsExtinctionReflectance spectroscopy
The invention relates to a universal aquatic vegetation radiation transmission model. Building of the model includes the following steps that a whole aquatic vegetation system is divided into a plurality of dielectric layers which are evenly mixed and consistent in horizontal optical properties; vegetation canopy structure parameters, observation geometry and other conditions, and reflectivity and transmittance of a single leaf are input into an SAIL model for calculation extinction and scattering coefficients of a vegetation canopy to radiation, wherein the reflectivity and the transmittance of the single leaf are obtained through calculation of an SPECT model; the water body component concentration is given, absorption and back scattering coefficients of a water body are calculated on the basis of a case 2 water body optical model, and extinction and scattering coefficients of the water body and the vegetation mixed dielectric layers are calculated; according to a Cox-Munk model, scattering matrixes of a wave surface to direct radiation and diffusion radiation are calculated; bidirectional reflectivity of the aquatic vegetation system is calculated according to an adding method. The universal aquatic vegetation radiation transmission model achieves precise description of a reflectance spectrum and directional reflection features of aquatic vegetation, and is the premise and basis of radiation and aquatic vegetation interaction mechanism researches and precise remote sensing inversion of water environment parameters.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
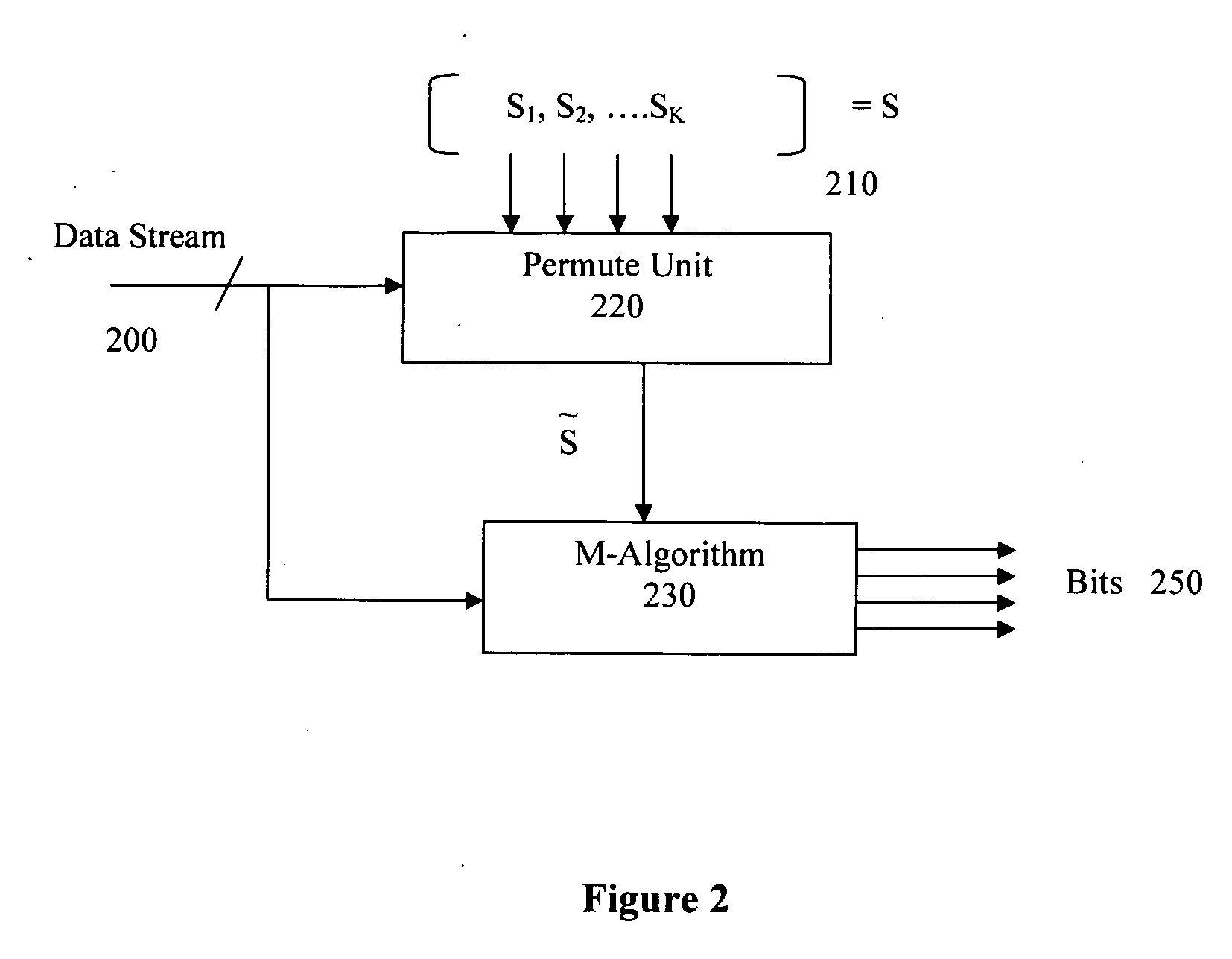
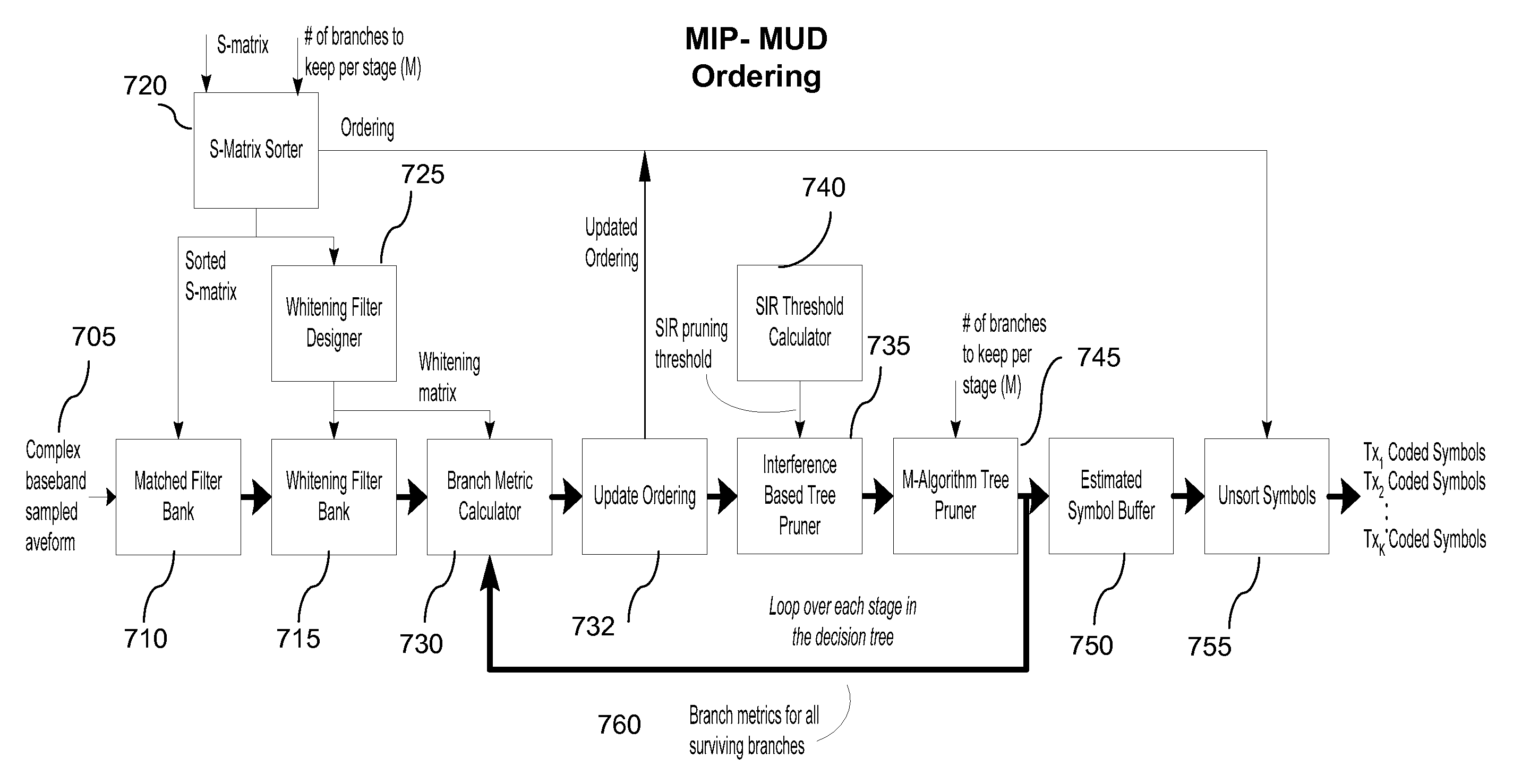
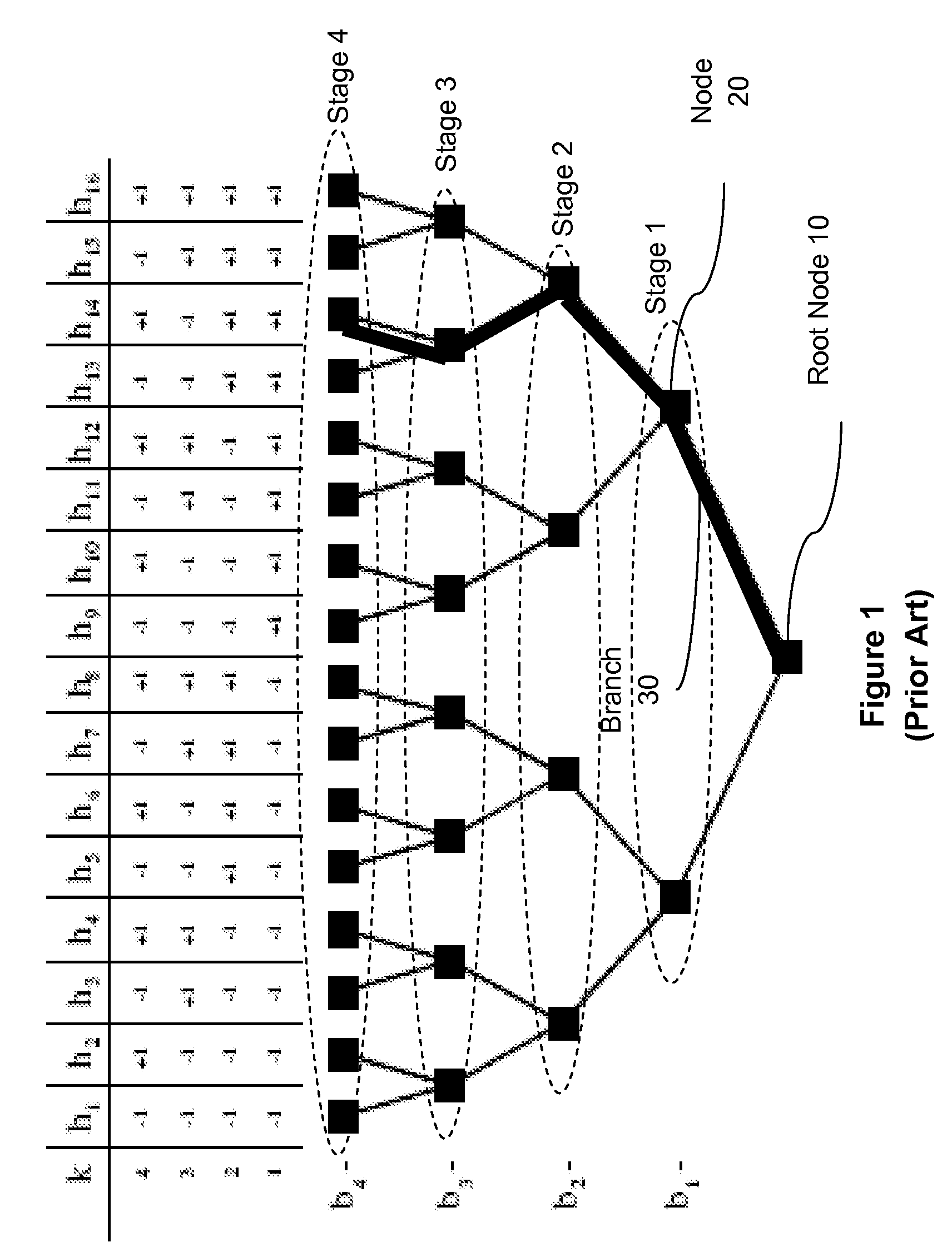
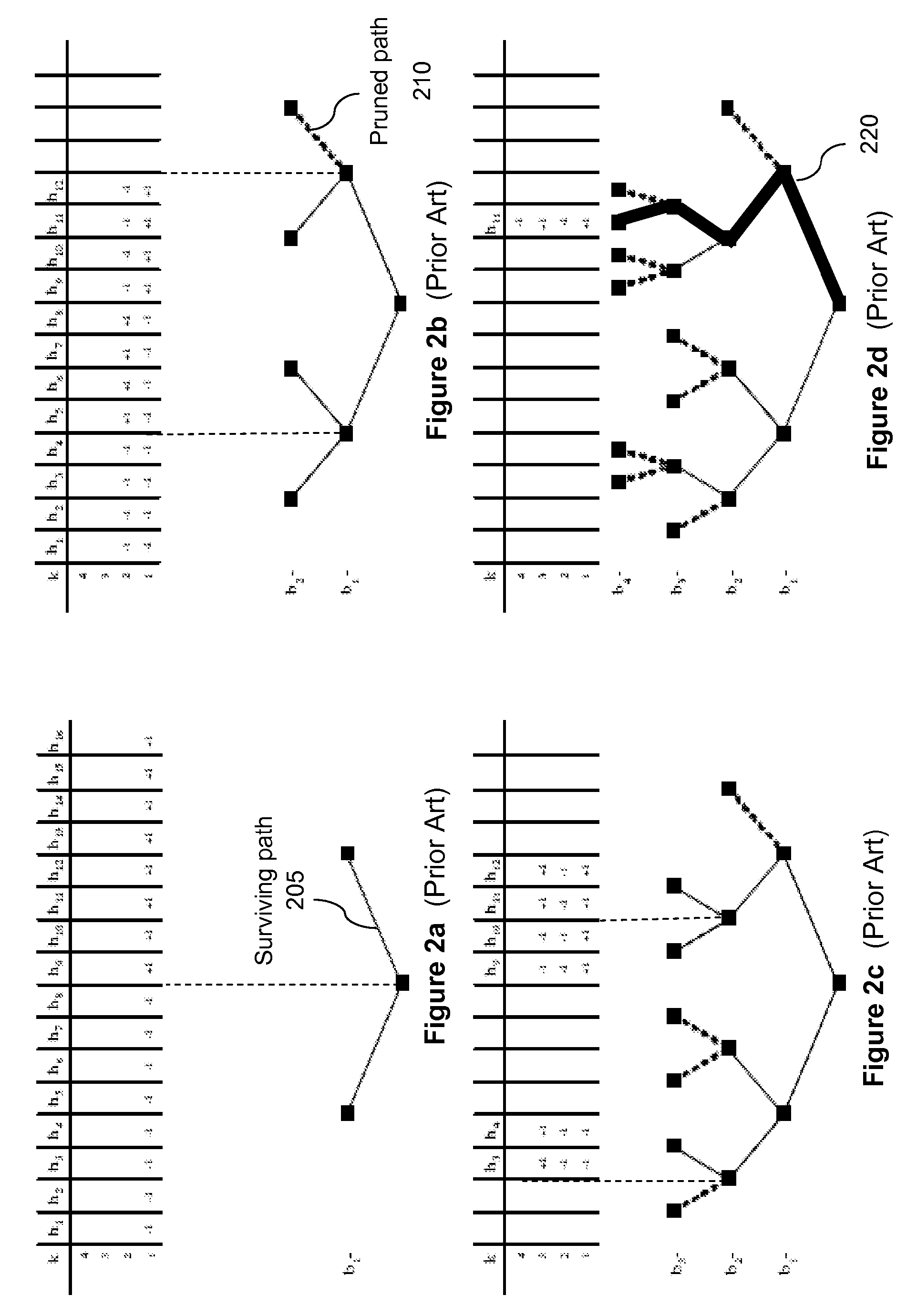
M-algorithm with prioritized user ordering
InactiveUS20060115026A1Improve MUD computationReduce in quantityTime-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsS-matrixMultiuser detector
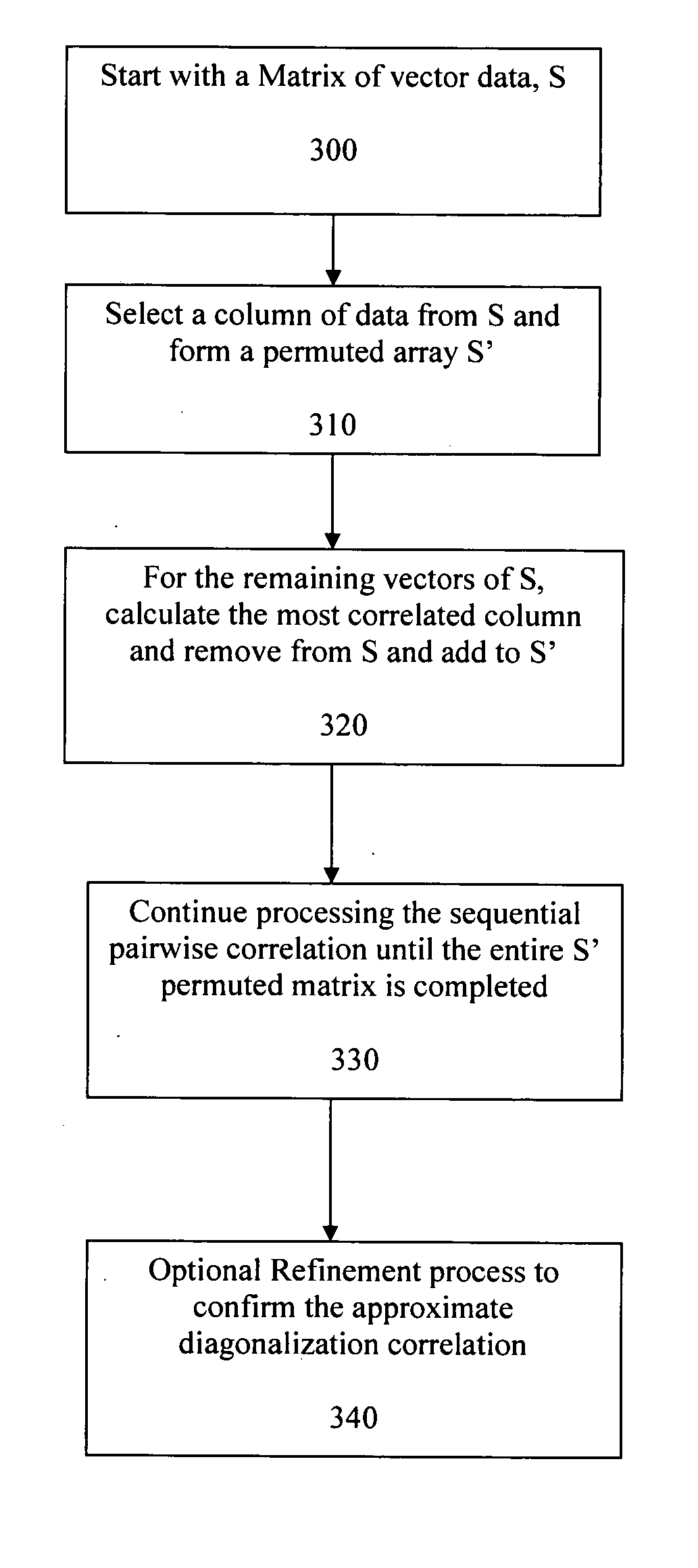
Performing approximate diagonalization of a correlation metric by user permutation to improve Multiuser Detector (MUD) processing. The system reorders the entries in the S-Matrix in order to move the bit decisions closer together in the decision tree. In one embodiment the reordering is a sequential pairwise correlation.
Owner:COLLISION COMM
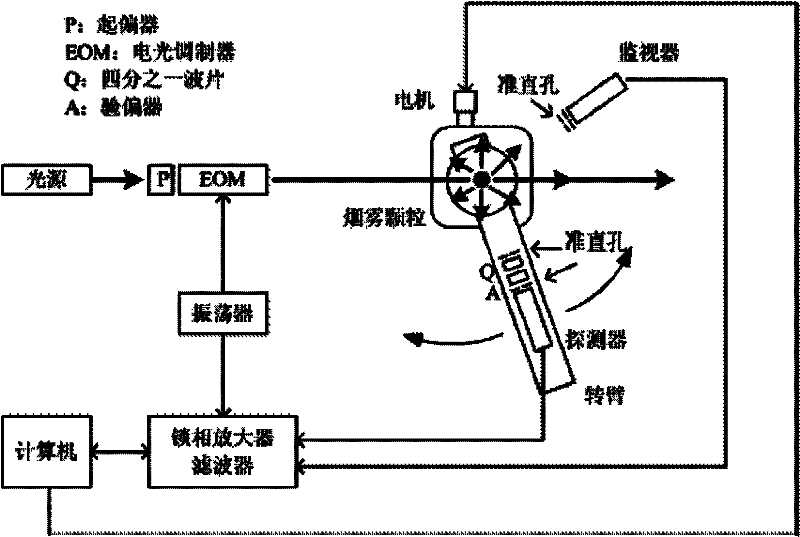
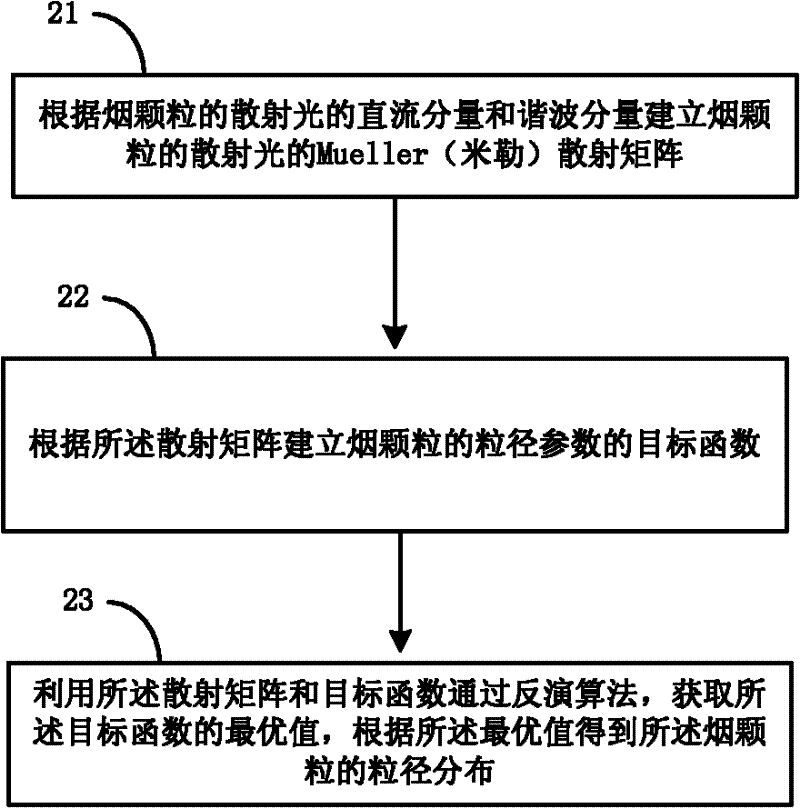
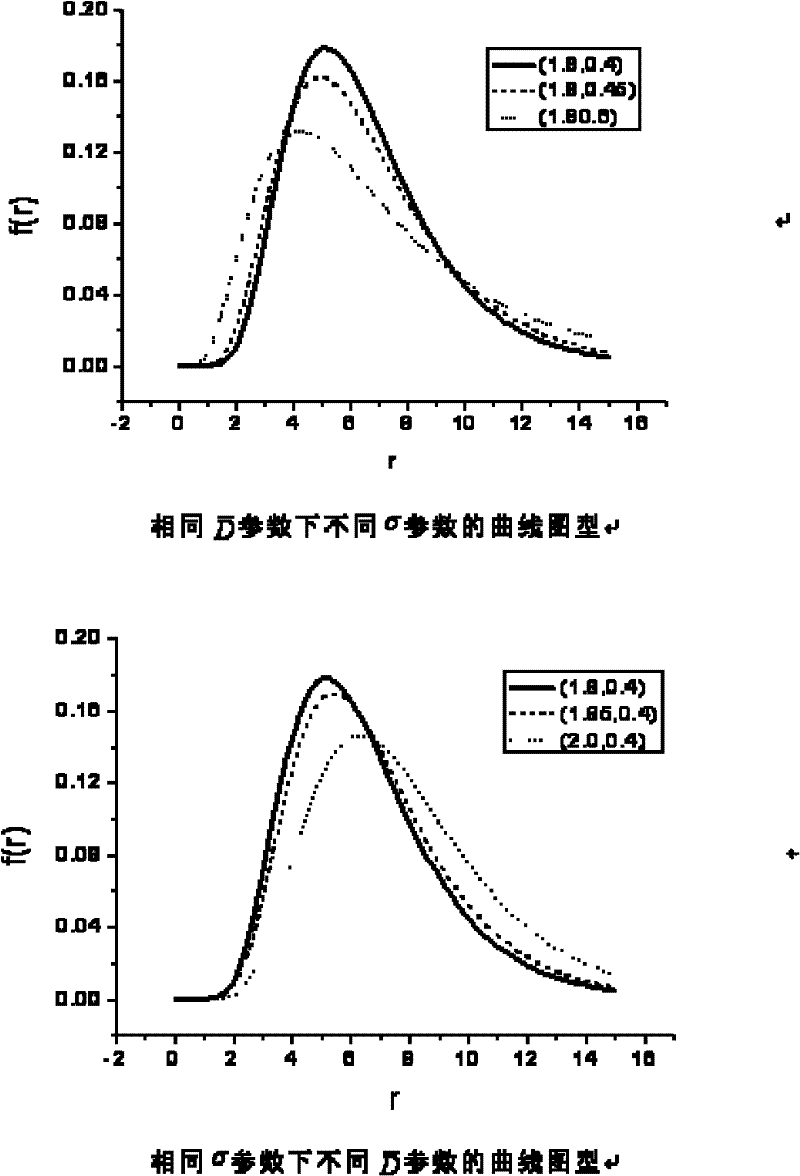
Method and device for measuring particle size of soot particle
InactiveCN102507399AEfficiently measure particle size distributionMeasuring Particle Size DistributionParticle size analysisParticle physicsS-matrix
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and a device for measuring the particle size of soot particles. The method mainly comprises: building a scattering matrix of the scattered light of the soot particles according to the direct current component and harmonic wave component of the scattered light of the soot particle; and constructing a target function of the particle size parameter of the soot particles according to the scattering matrix, working out the optimal value of the target function by using the scattering matrix and the target function and by an inversion algorithm, and obtaining the particle size distribution of the soot particles according to the optimal value. According to the embodiment of the invention, the particle size inversion under a spherical model of the light scattering of soot particles in a fire disaster and the like by starting from a Mueller matrix which completely reflects the light scattering character of the particles, and thus, the particle size distribution of soot particles in a dire disaster and the like can be measured effectively.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
M-Algorithm multiuser detector with correlation based pruning
ActiveUS7613228B2Line-faulsts/interference reductionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsHypothesisRound complexity
A multiuser detector system with correlation based pruning including a parameter estimation module adapted to receive complex signals, and to produce estimated signature waveforms for each of K co-channel interfering signals. Pre-processing the estimated signature waveforms using an S-matrix module and producing a more valid set of hypotheses, wherein the S-matrix module uses apriori knowledge of an unnormalized cross correlation matrix, and processing the more valid set of hypotheses for pruning with an M-algorithm in a multiuser detector module. An improvement to the M-algorithm in which the interference structure based on the signal correlation matrix used during the optimization process aids in selecting a better subset of hypotheses to test. This approach has the benefit of reducing computational complexity and improving performance over the existing M-algorithm.
Owner:COLLISION COMM INC
Methods for Estimation and Interference Cancellation for signal processing
ActiveUS20110064066A1Improving symbol estimationImprove power efficiencyCode division multiplexRadio transmissionInterference cancelationInterference canceller
A receiver in a CDMA system comprises a front end processor that generates a combined signal per source. A symbol estimator processes the combined signal to produce symbol estimates. An S-Matrix Generation module refines these symbol estimates based on the sub channel symbol estimates. An interference canceller is configured for cancelling interference from at least one of the plurality of received signals for producing at least one interference-cancelled signal.
Owner:III HLDG 1
M-algorithm multiuser detector with correlation based pruning
ActiveUS20070036250A1Line-faulsts/interference reductionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsRound complexityHypothesis
A multiuser detector system with correlation based pruning including a parameter estimation module adapted to receive complex signals, and to produce estimated signature waveforms for each of K co-channel interfering signals. Pre-processing the estimated signature waveforms using an S-matrix module and producing a more valid set of hypotheses, wherein the S-matrix module uses apriori knowledge of an unnormalized cross correlation matrix, and processing the more valid set of hypotheses for pruning with an M-algorithm a multiuser detector module. An improvement to the M-algorithm in which the interference structure based on the signal correlation matrix used during the optimization process aids in selecting a better subset of hypotheses to test. This approach has the benefit of reducing computational complexity and improving performance over the existing M-algorithm
Owner:COLLISION COMM
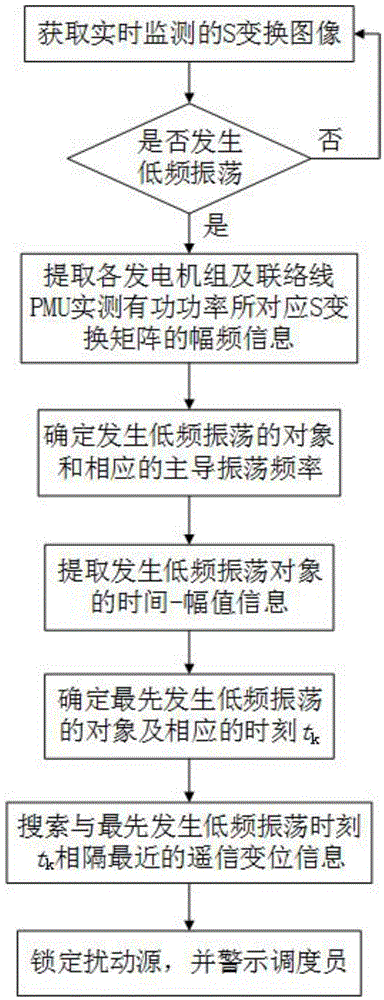
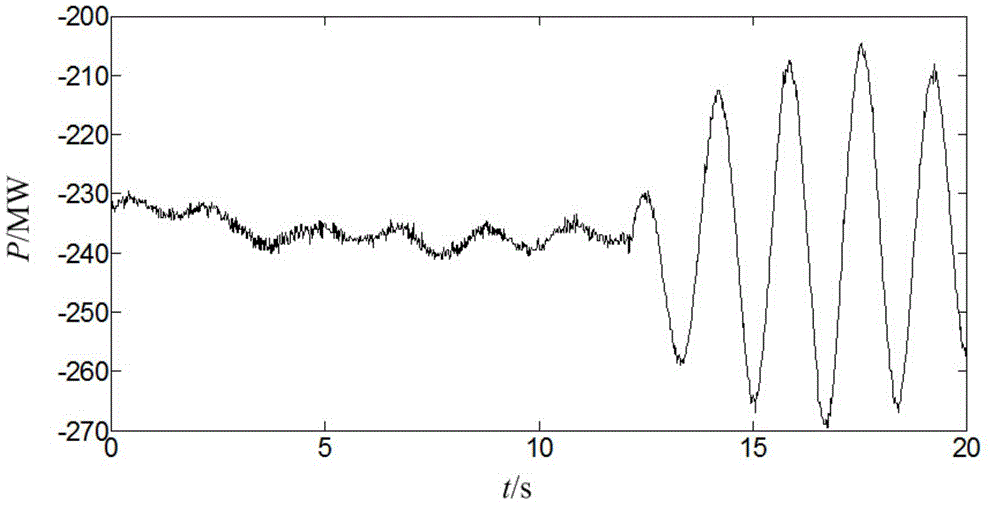
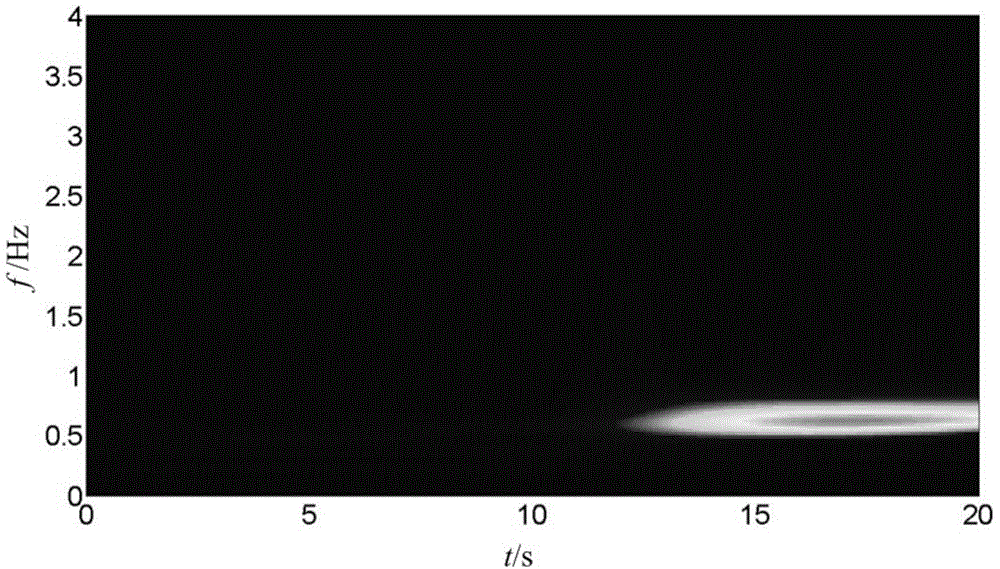
Method for positioning low-frequency oscillation disturbance source of electric power system
The invention discloses a method for positioning a low-frequency oscillation disturbance source of an electric power system, which comprises the following steps: 1) determining whether a low-frequency oscillation occurs in a power grid according to an S transformation image; 2) extracting amplitude frequency information in an S transformation matrix which corresponds with an active power signal that is actually measured by each power generator set and each tie line phasor measurement unit (PMU), determining an object with the low-frequency oscillation and a corresponding dominant oscillation frequency; 3) extracting time and amplitude information which correspond with the dominant oscillation frequency in each S matrix, determining the object in which the low-frequency oscillation firstly occurs and a corresponding time point tk; and 4) determining the disturbance source of the low-frequency oscillation based on a disturbance time correlation analyzing method. The method of the invention has functions of quickly locking the disturbance source, helping a dispatcher to quickly and accurately analyze the reason of oscillation, taking effective control measures in time for quickly stopping oscillation, and preventing further enlargement of the fault.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for obtaining intermediate resonance factor in reactor multigroup nuclear database
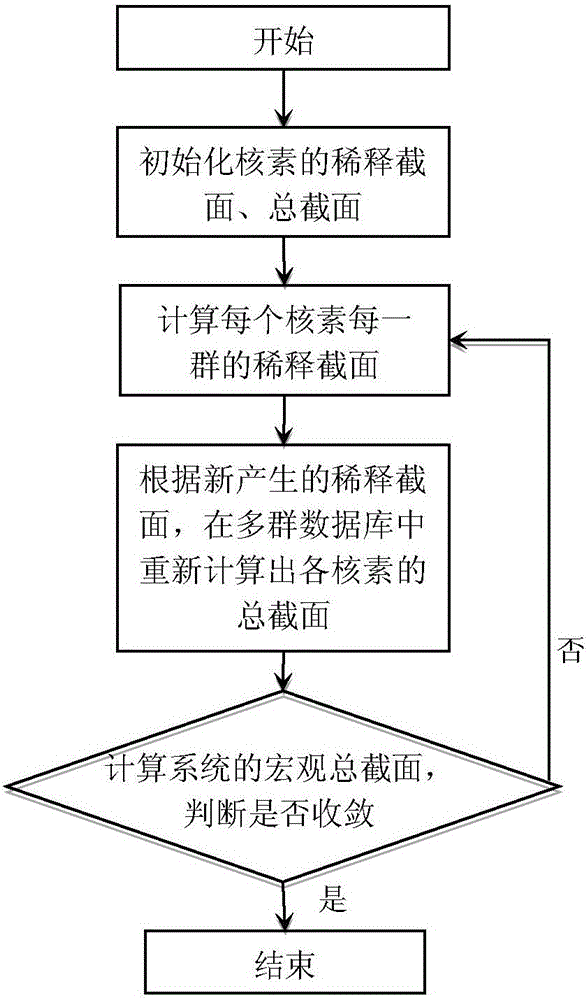
ActiveCN106202868AAccurate multi-group absorption cross sectionAccurate Intermediate Resonance FactorInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsResonanceMatrix expression
The invention relates to a method for obtaining an intermediate resonance factor in a reactor multigroup nuclear database. On the basis of a free gas model, a continuum energy neutron scattering matrix expression Sigma<r, s, T> (E->E') of the resonance absorption nuclide relevant to the temperature TK is obtained through formula derivation; a neutron slowing down equation is solved on the basis of the continuum energy neutron scattering matrix at the temperature TK to obtain the neutron-flux density at the temperature TK; the multigroup adsorption cross section of the resonance absorption nuclide at the temperature TK is further worked out through group merging calculation; the intermediate resonance factor is finally obtained through the intermediate resonance factor calculation; and an intermediate resonance factor multinomial coefficient using the temperature and the background cross section as independent variables is obtained by a least squares fitting method. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the intermediate resonance factor after the intermediate resonance factor calculation is more accurate; the calculation precision and the calculation efficiency of the intermediate resonance factor are improved; and finally, in the reactor physical calculation, the resonance calculation precision is improved, and the resonance calculation speed is accelerated.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
High-accuracy fast neutron reactor assembly few-group cross section obtaining method
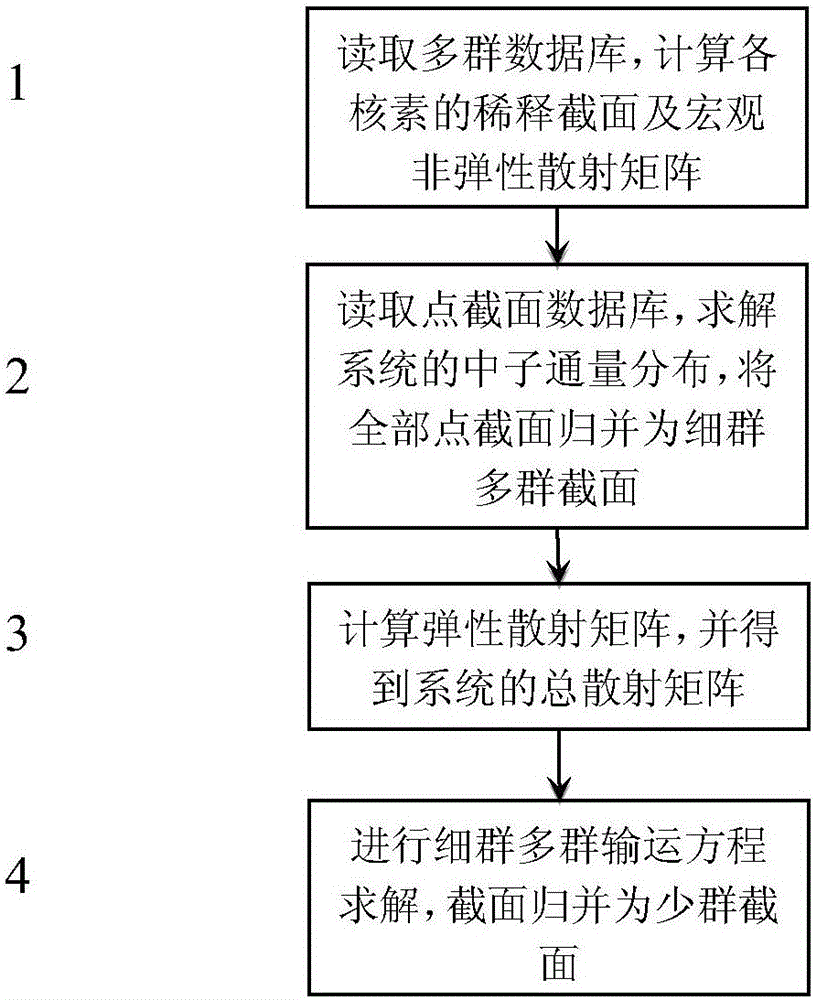
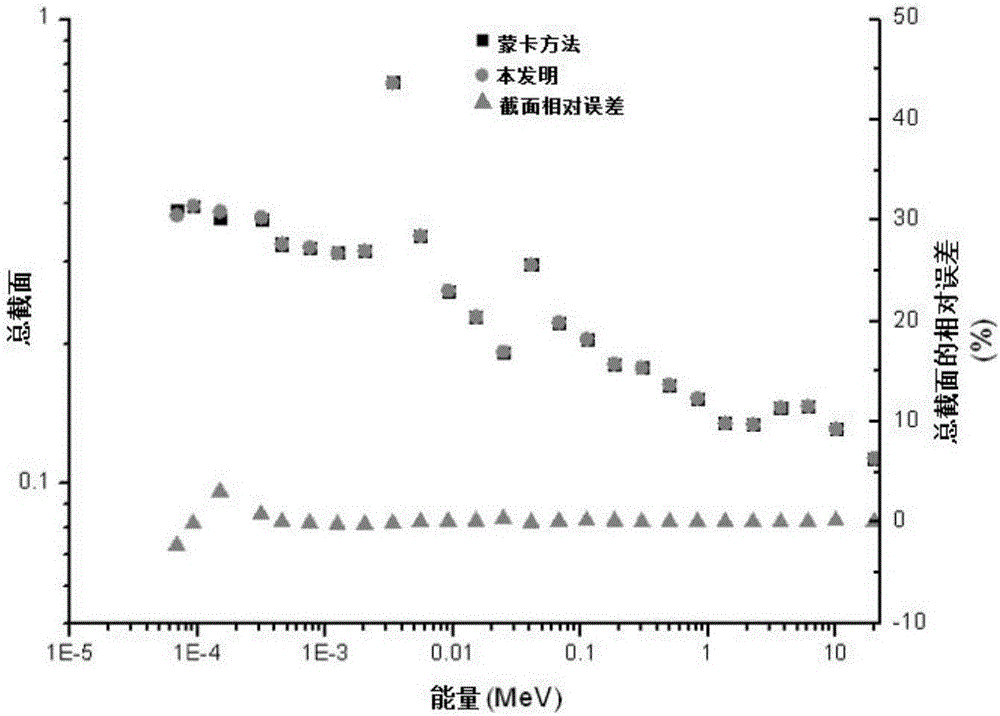
InactiveCN106128518AFine-grained consideration of elastic scattering resonance effectsCareful consideration of resonance interference effectsNuclear energy generationFast fission reactorsReal systemsNeutron transport
Provided is a high-accuracy fast neutron reactor assembly few-group cross section obtaining method. The fine-group cross section of a fast neutron reactor assembly is calculated in the mode that point cross section data and multi-group data are combined, online calculation of an elastic scattering matrix is performed, a neutron transport equation is solved by using the fine-group cross section to obtain fine-group neutron-flux density, energy groups are merged on the basis, and accordingly few-group parameters of the fast reactor assembly are obtained. Due to the fact that the method directly uses the point cross section data, the elastic scattering resonance effect of a medium mass nuclide and the resonance interference effects of all nuclides are accurately considered. The neutron-flux density of a real system is adopted in the energy group merging process, and merging results are more accurate. The overall errors of fast reactor assembly few-group parameters calculated by adopting the method are within 1% compared with a reference value, and the method has higher accuracy.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
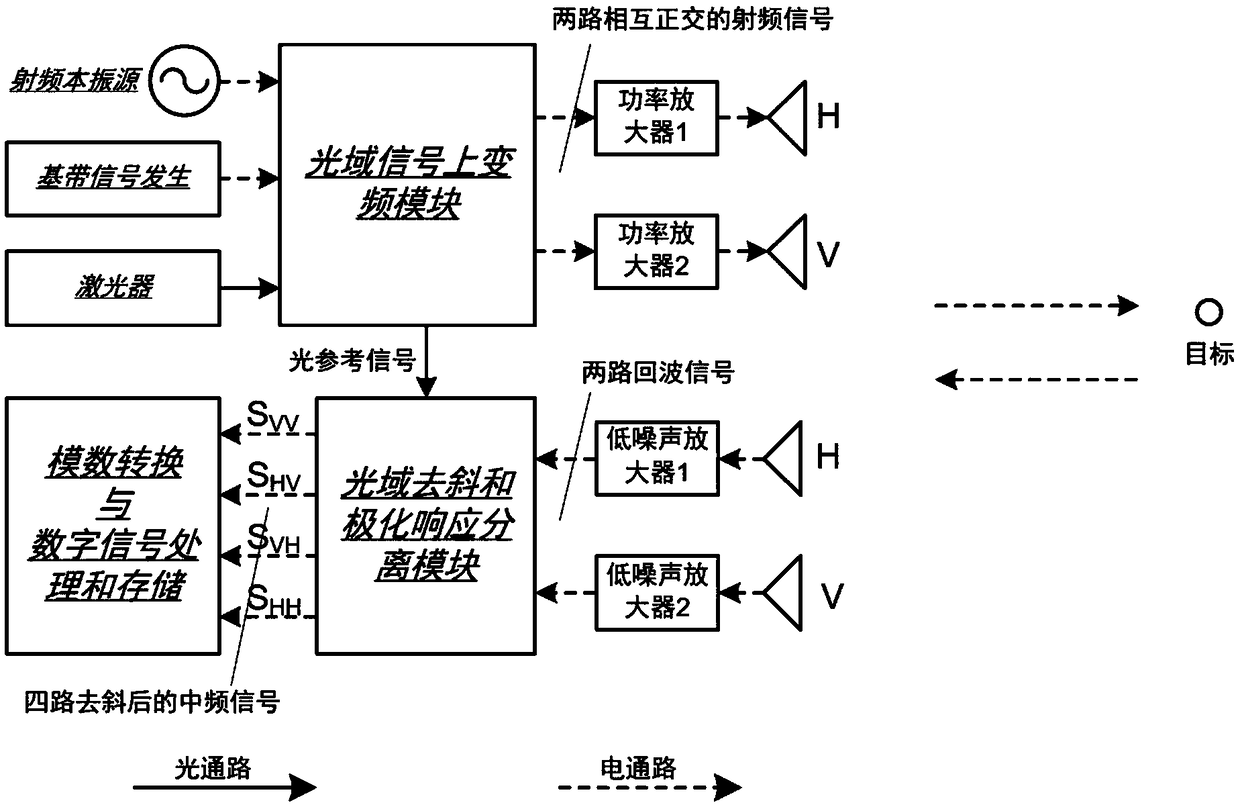
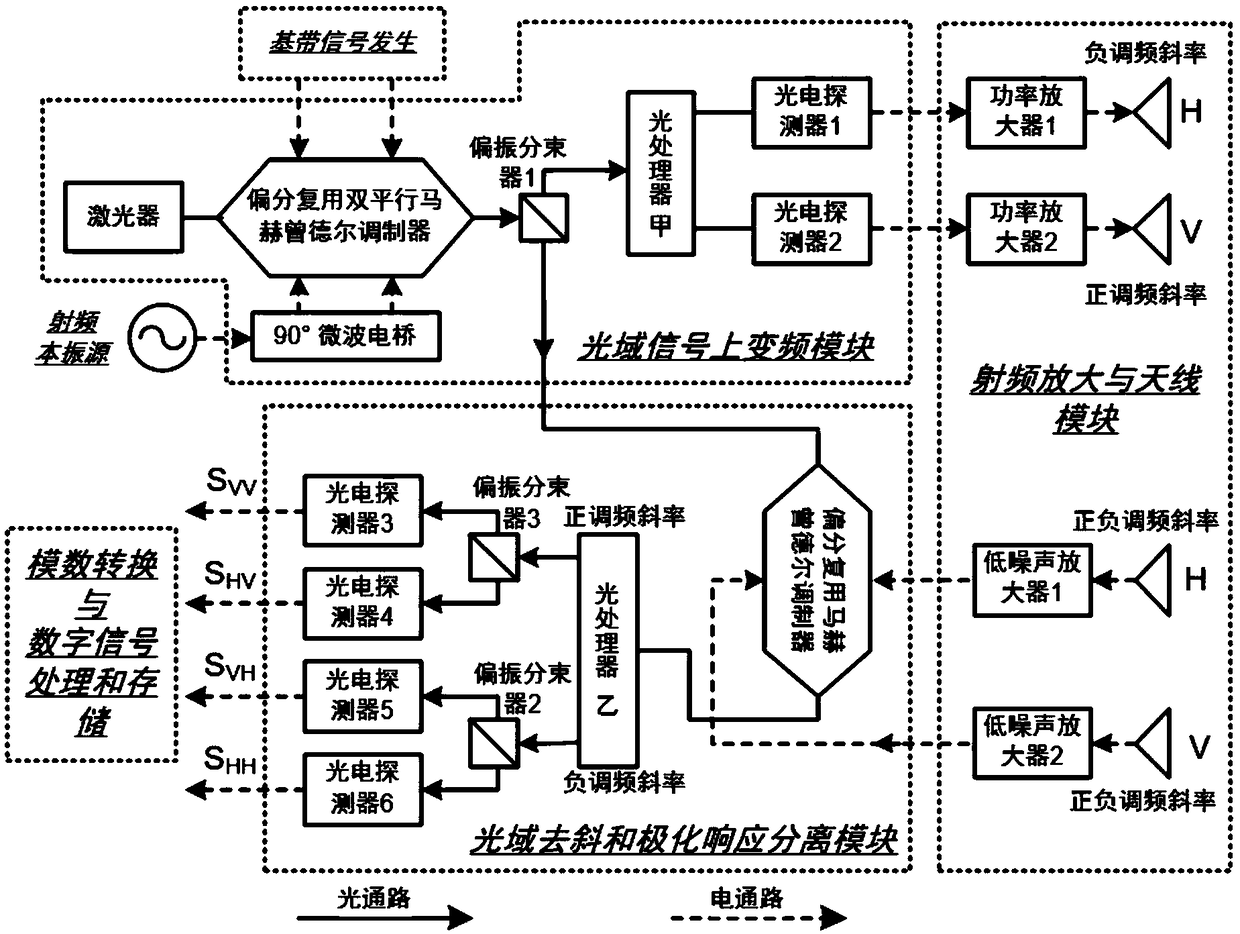
Microwave photonic radar fully polarimetric radar detection method and microwave photonic fully polarimetric radar
ActiveCN108761437ALarge instantaneous bandwidthRanging highElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionIntermediate frequencyS-matrix
The invention discloses a microwave photonic radar fully polarimetric radar detection method. The method includes the following steps that: 1, up-conversion processing is performed on optical carriers, complex baseband signals and radio frequency local oscillation signals in an optical domain, so that two orthogonal paths of radio frequency signals, and one path of optical reference signals are generated; 2, the two orthogonal paths of radio frequency signals are respectively sent to a horizontal polarization antenna and a vertical polarization antenna, and the horizontal polarization antennaand the vertical polarization antenna radiate two orthogonal paths of polarized electromagnetic waves, so that the polarized electromagnetic waves irradiate a target, and the horizontal polarization antenna and the vertical polarization antenna receive the echoes of the target, so that two paths of echo signals are obtained; and 3, the two paths of echo signals and the optical reference signals are subjected to deramp and polarization response separation processing in the optical domain, so that four paths of intermediate-frequency analog electrical signals corresponding to four elements in atarget polarization scattering matrix are obtained; and 4, the four paths of intermediate-frequency analog electrical signals are processed, so that target detection information can be obtained. The invention also discloses a microwave photonic radar fully polarimetric radar. With the microwave photonic radar fully polarimetric radar detection method and the microwave photonic fully polarimetric radar of the invention adopted, a problem that the bandwidth of a fully polarimetric radar is limited, the problem of the structural complexity of the fully polarimetric radar and a problem that it isdifficult for the fully polarimetric radar to realize instantaneous measurement can be solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Near-field microscope of optical wave band
InactiveCN1710402ANo drynessIncreased ability to interact with electromagnetic fieldsSurface/boundary effectScanning probe microscopyFeature setBeam splitting
A near field microscope of optical band consists of near field viewfinder, near field coding plat , light wave guide for switching over , beam splitting system and photoelectric probe . It features setting near field coding plate as sub wavelength microhole array circulated as per S matrix distribution with microhole diameter being less than r value in Rayleigh criterion, picking up light coming from viewfinder and extracting it in microhole and converting it to be conduction wave for being sent to the following device.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Distribution-type optical-fiber Raman temperature sensor adopting circulating pulse coding and decoding and Rayleigh demodulation
InactiveCN102706475AHigh peak powerReduce transmission lossThermometers using physical/chemical changesSignal onOpto electronic
The invention discloses a distribution-type optical-fiber Raman temperature sensor adopting circulating pulse coding and decoding and Rayleigh demodulation, and the sensor comprises a pulse optical-fiber laser, an acoustic-optic demodulator, an integrated optical-fiber wavelength division multiplexer with four ports, two photoelectric receiving amplification modules, a coding-decoding demodulation digital signal processor, an optical-fiber temperature sampling ring, an intrinsic temperature measuring optical fiber, a digital temperature detector and a personal computer (PC). The sensor codes and decodes a signal on the basis of the circulating S matrix conversion, and the online location temperature measurement of the optical fiber is realized by utilizing an effect that the optical-fiber Raman optical strength is demodulated by the temperature and utilizing an optical time domain reflection principle. The circulating laser pulse coding and decoding is realized, and a Rayleigh channel is used as a temperature demodulation reference channel, so that the signal-to-noise ratio of the system is greatly improved, and the measuring precision and the measuring distance of the system are improved.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Construction method for special structure protograph QC-LDPC code based on Pascal's triangle
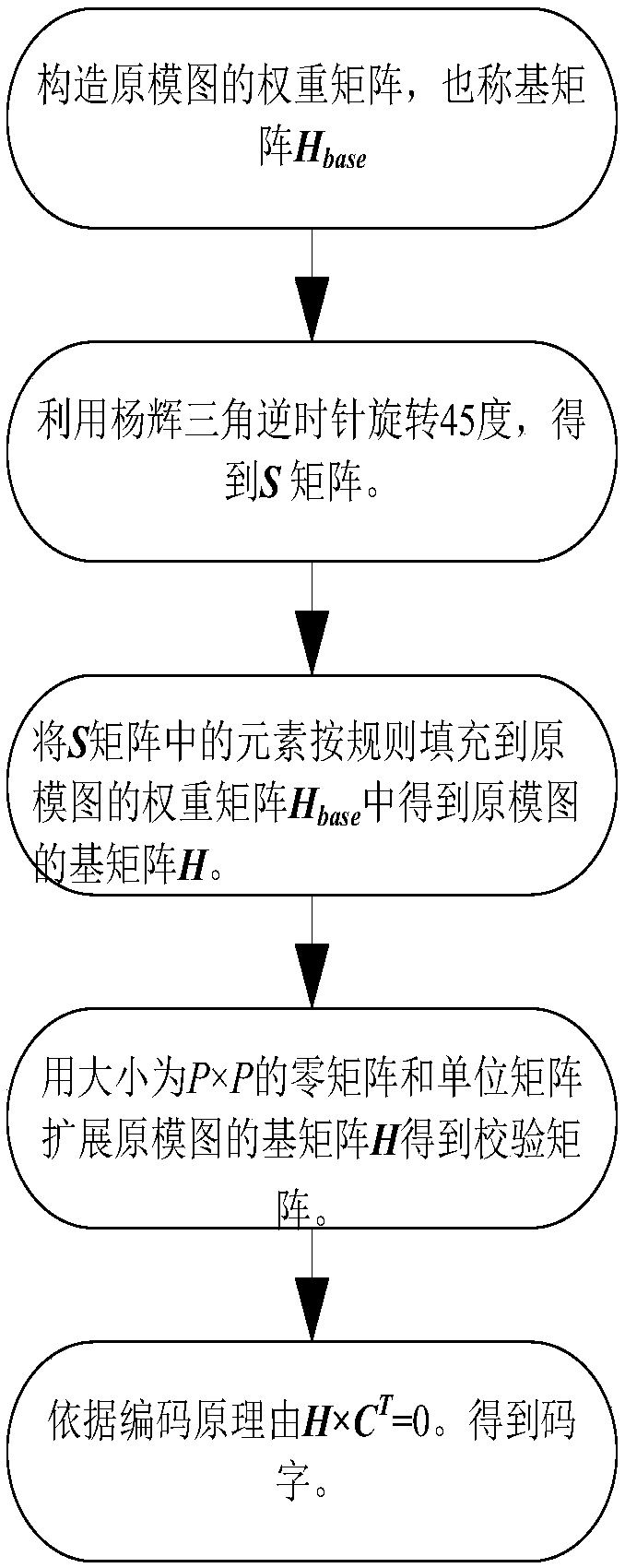
InactiveCN108134610AOvercome the problem of low code weightQuick codingError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionSignificant errorZero matrix
The invention relates to a construction method for a special structure protograph QC-LDPC code based on a Pascal's triangle, and belongs to the technical field of channel coding research. The method utilizes the Pascal's triangle to construct a matrix, and specifically comprises the following steps of constructing a weight matrix of the protograph, namely a base matrix Hbase; performing anticlockwise rotation by using the Pascal's triangle structure to acquire an S matrix; filling elements in the S matrix into the weight matrix Hbase of the protograph according to a rule to acquire a base matrix H of the protograph; extending the protograph base matrix H via a zero matrix and a unit matrix to acquire a check matrix, and providing a fast iterative coding algorithm of the codon according tothe structure of H. The base matrix has a quasi bidiagonal structure, avoids four rings and can achieve fast coding, is reduced in coding complexity, and has better iterative decoding performance without significant error floors.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Actuator based on sensor actuator network and method of actuating the same
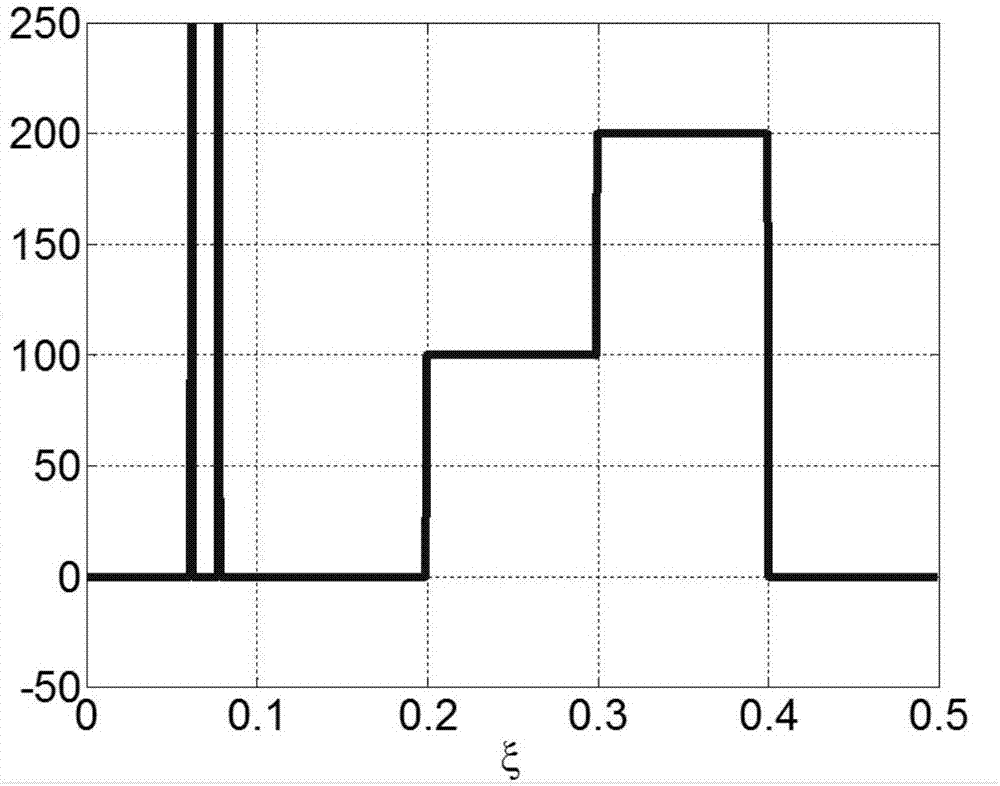
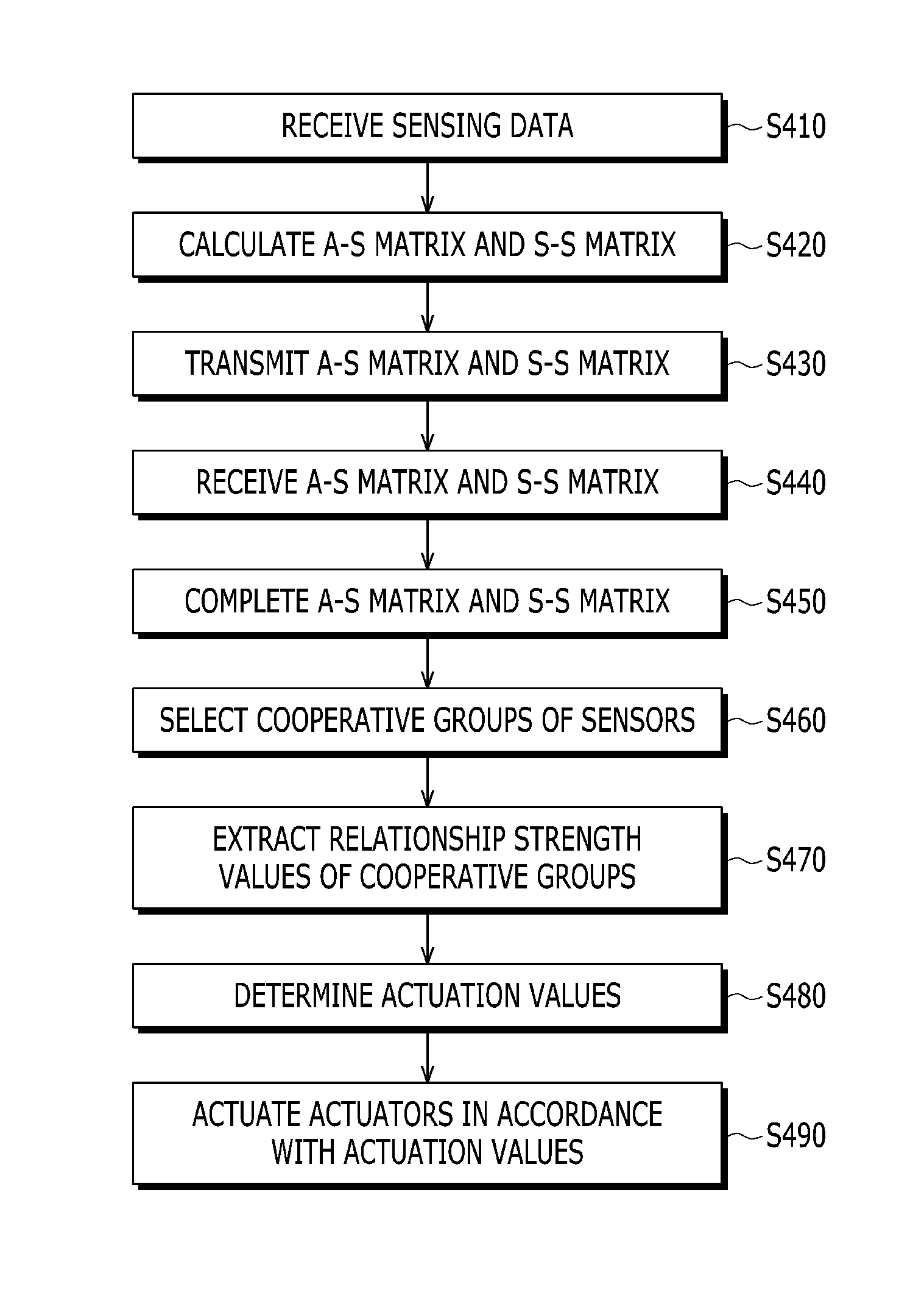
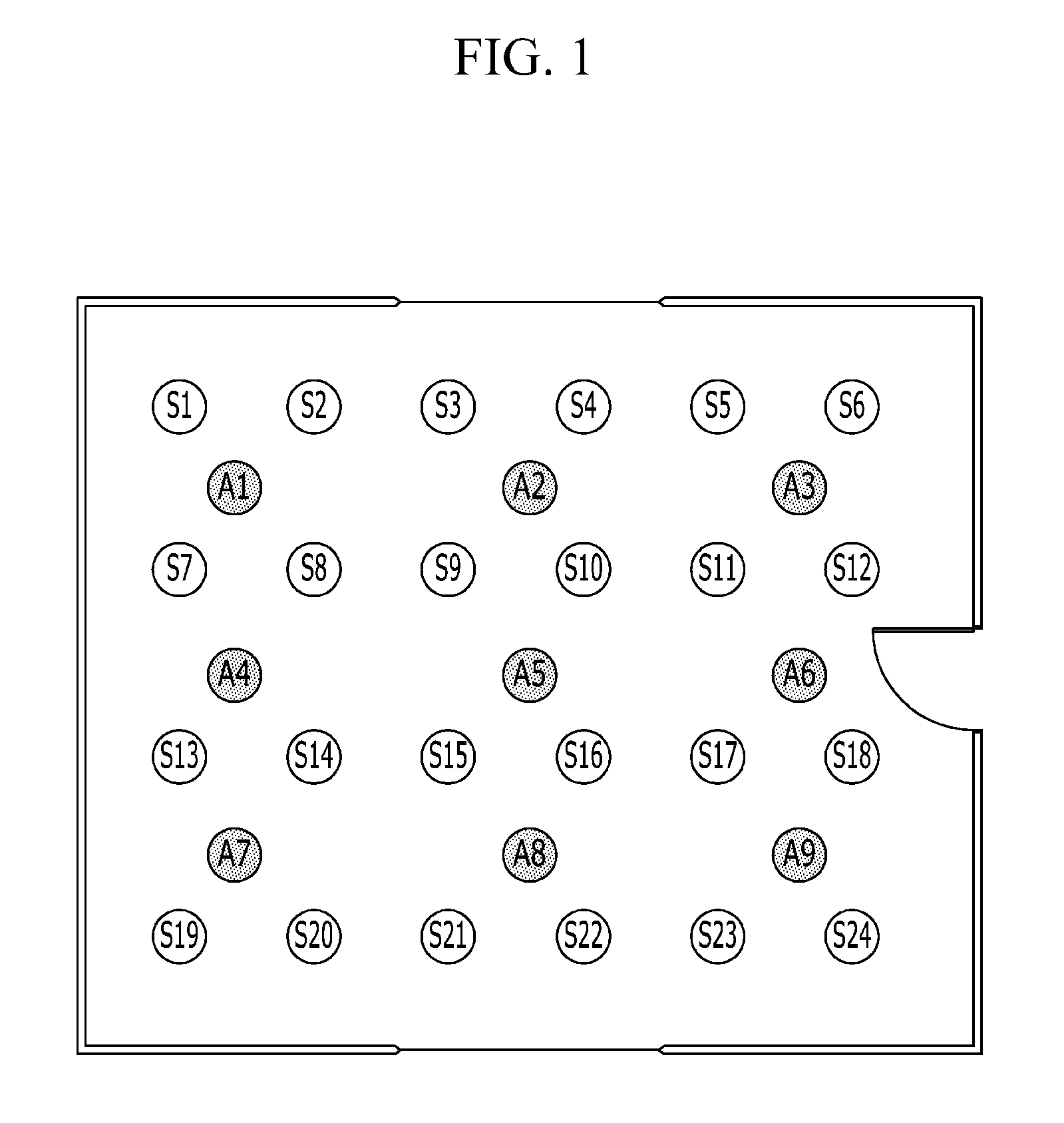
ActiveUS20150022374A1Easy to operateReduce energy wasteSpecial service provision for substationProgramme controlSensing dataSensor actuator
In a wireless sensor actuator network system, actuators to be actuated to correspond to a plurality of sensors are selected using an A-S matrix that represents relationship strength between a plurality of actuators and the plurality of sensors based on sensing data of the plurality of sensors, and only the selected actuators determine actuation values based on values of the A-S matrix.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
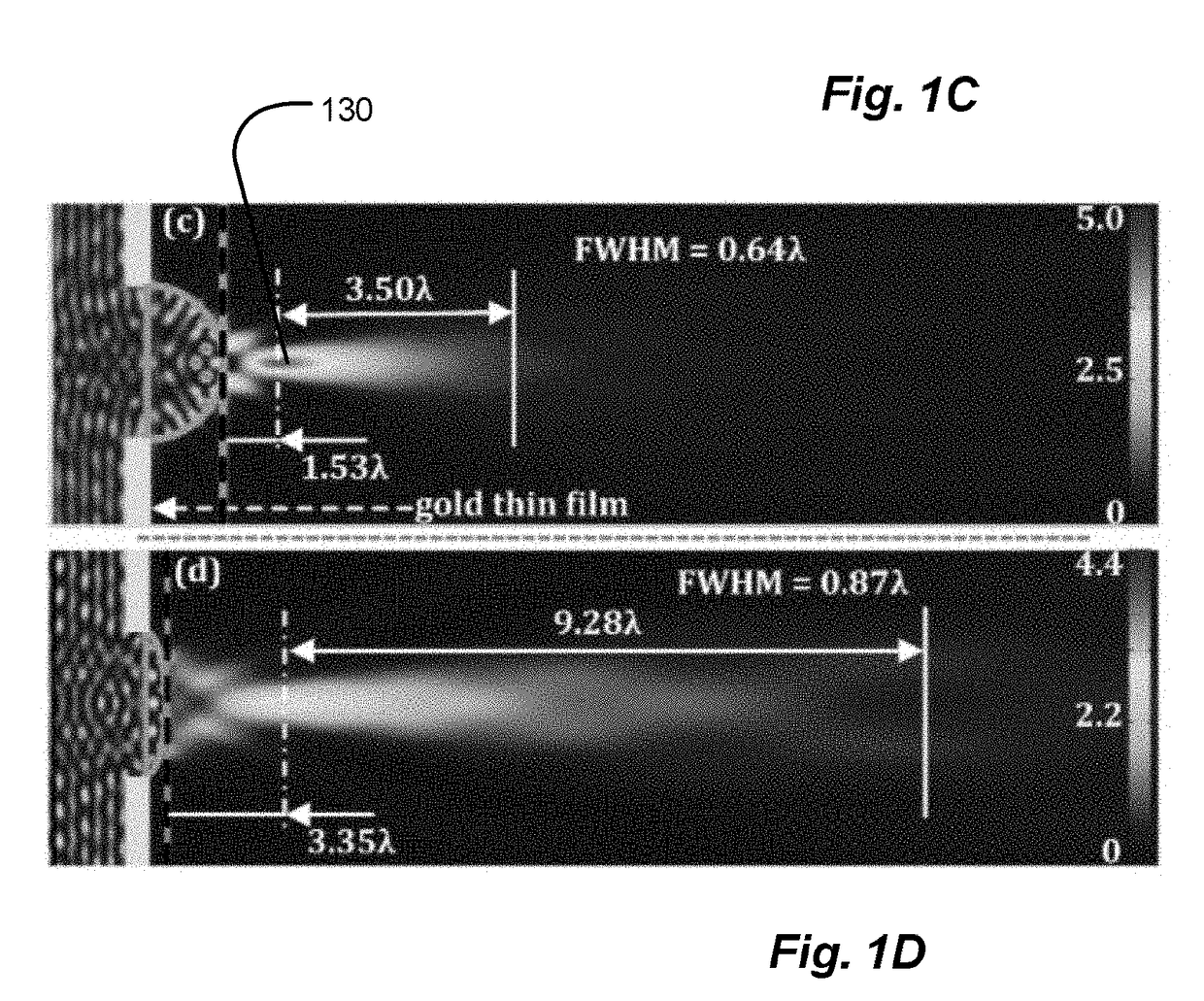
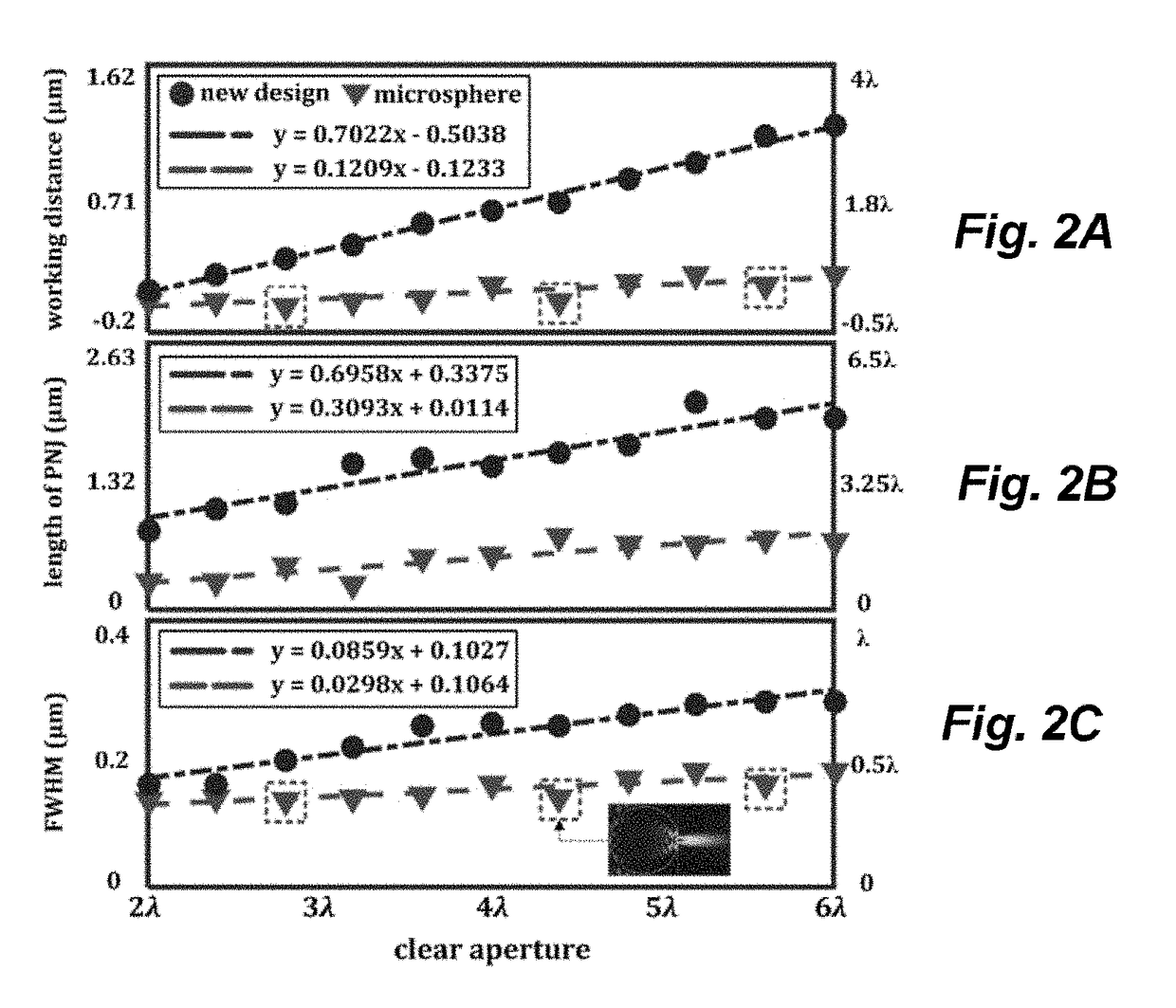
Spatial Control of the Optical Focusing Properties of Photonic Nanojets
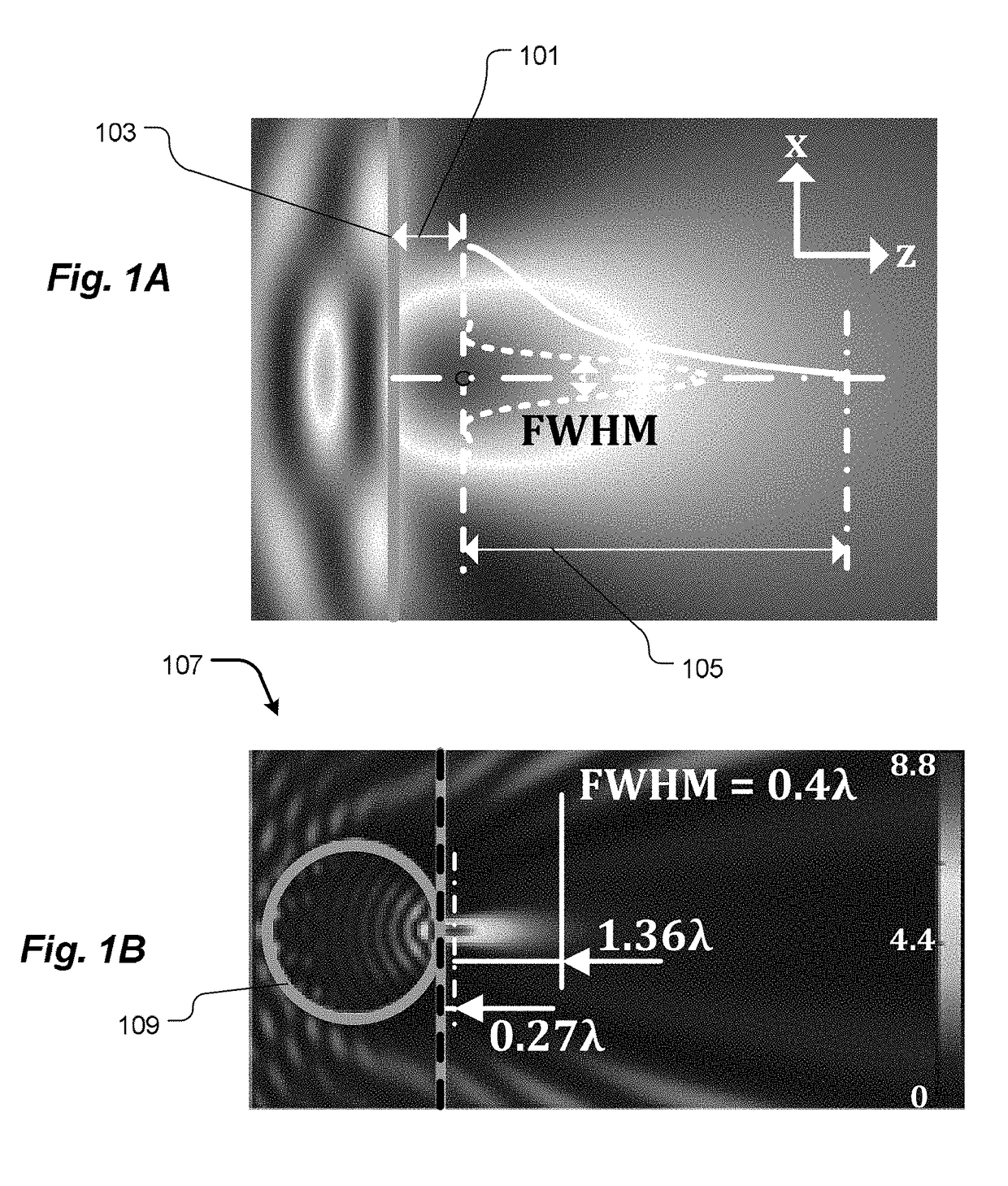
Methods and apparatus for concentrating light into a specified focal volume and for collecting light from a specified volume. Incident light is coupled through a plurality of successive transmissive asymmetric microstructure elements. The succession of transmissive asymmetric microstructure elements may be designed by representing an electromagnetic field as a linear combination of eigenmodes of one of the succession of transmissive asymmetric microstructure elements. The asymmetric microstructure elements are represented as a plurality of mesh lattice units and eigenmode solutions to Maxwell's equations are obtained for each mesh lattice unit subject to consistent boundary conditions. S-matrix formalism is employed to calculate a field output and weighting coefficients for the eigenmodes are selected to achieve a specified set of field output characteristics.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
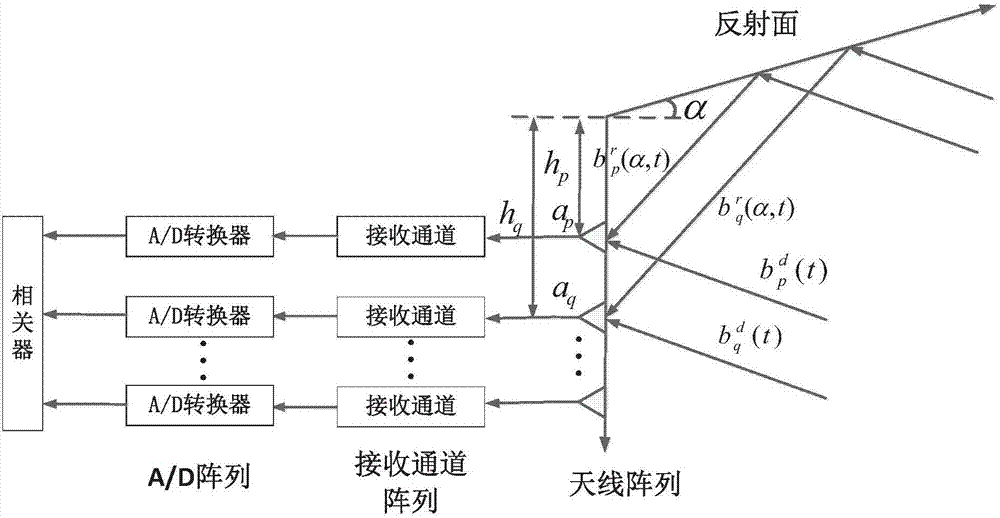
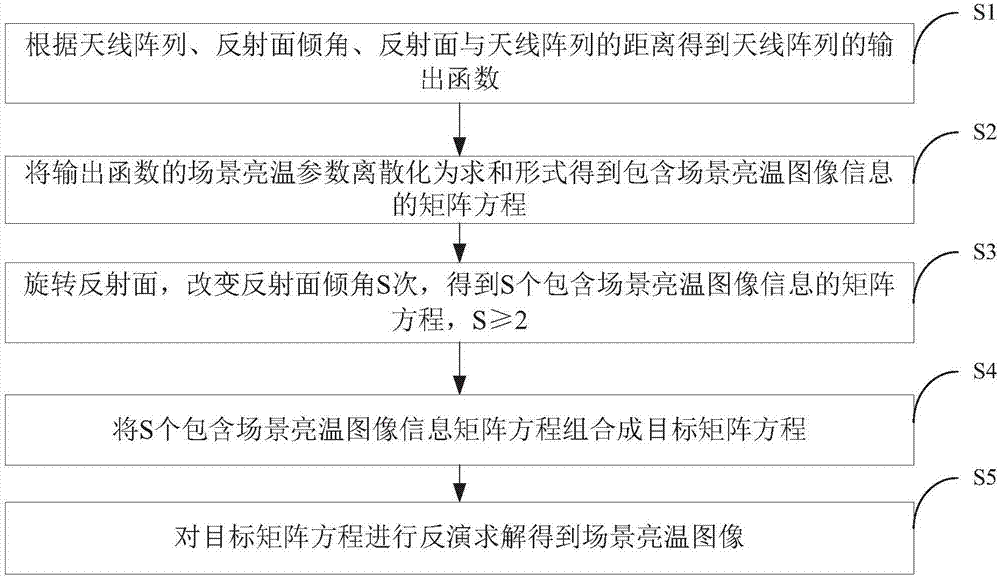
Rotating-reflection-surface-based imaging method and system of mirroring synthetic aperture radiometer
ActiveCN106932774AHigh-resolutionReduce volumeDirection finders using radio wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarImaging quality
The invention discloses a rotating-reflection-surface-based imaging method and system of a mirroring synthetic aperture radiometer. The method comprises: according to an antenna array, a reflection surface angle, and a distance between the reflection surface and the antenna array, an output function of the antenna array is obtained; a scene brightness temperature of the output function is discretized into a summation form to obtain a matrix equation containing scene brightness temperature image information; the reflection surface is rotated and the inclination angle of the reflection surface is changed by S times to obtain S matrix equations containing the scene brightness temperature image information, wherein the S is larger than or equal to 2; the S matrix equations containing the scene brightness temperature image information are combined into a target matrix equation; and the target matrix equation is inversed to obtain a scene brightness temperature image. The larger the frequency of rotation of the reflection surface, the smaller the angle of the rotation each time; and the larger the combined target matrix equation, the higher the scene brightness temperature image quality.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Actuator based on sensor actuator network and method of actuating the same
ActiveUS9445216B2Easy to operateReduce energy wasteSpecial service provision for substationEnergy efficient ICTLine sensorSensing data
In a wireless sensor actuator network system, actuators to be actuated to correspond to a plurality of sensors are selected using an A-S matrix that represents relationship strength between a plurality of actuators and the plurality of sensors based on sensing data of the plurality of sensors, and only the selected actuators determine actuation values based on values of the A-S matrix.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Cell sorting method for affine propagation clustering
ActiveCN101853507AEffective classificationImprove real-time performanceImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmDiagonal
The invention relates to a cell sorting method for an affine propagation clustering, which comprises the following steps: (1) selecting a circularity parameter C and a rectangularity parameter R of a cell image, designing a sample coordinate X sample=lambda C+(1-lambda) R, selecting an area parameter Area of the cell image as another sample coordinate Y sample and selecting a nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio parameter prop of the cell image as another sample coordinate Z sample, wherein lambda represents a prior input value; (2) using euclidean distance of the three-dimensional sample coordinates as sample distance, wherein a diagonal value of an S matrix of the affine propagation clustering is an average value of distances among the samples; (3) under the initial condition, setting an membership grade matrix A(i, k)=0, updating a matrix R and updating a matrix A; and (4) stopping after the number of iteration times is set and obtaining different types of cells from a sorting result. The invention provides the cell sorting method for the affine propagation clustering, which is suitable to process mass data, has excellent real-time property and can effectively carry out cell sorting.
Owner:山东兰香食品有限公司第一分公司
High-precision insect body axis orientation extracting method based on polarization scattering matrix estimation
The invention discloses a high-precision insert bdy axis orientation extracting method based on polarization scattering matrix estimation. The high-precision insert axis orientation extracting method can be used for extracting an insect body axis orientation by means of a rotation-polarized insect radar with a vertical beam. According to the high-precision insert body axis orientation extracting method, an insect echo signal model of orientation directions which are acquired by the rotation-polarized insect radar is established; furthermore a method of extracting the polarization scattering matrix from an insect echo signal through a two-order polynomial approximate iteration method is presented; and then a method of extracting the insect body axis orientation from the polarization scattering matrix is introduced; and effectiveness and accuracy of a body axis orientation extraction algorithm are verified through insect data which are actually measured by an S-waveband radar.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
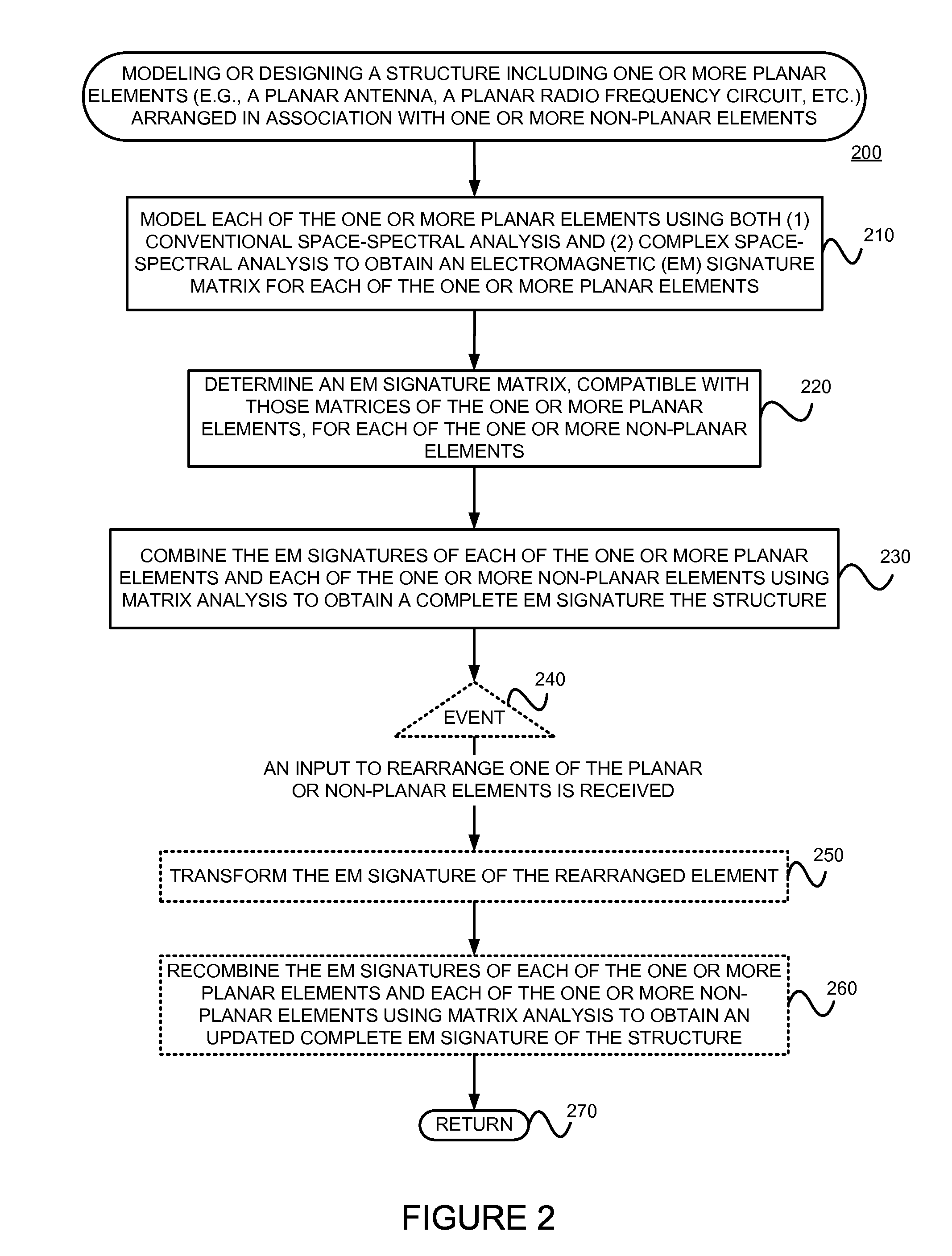
Modular modeling and design of antennas and radio frequency circuits that are arranged in a class of composite structural configurations
InactiveUS20130116980A1Computationally efficientComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsBrute forceModularity
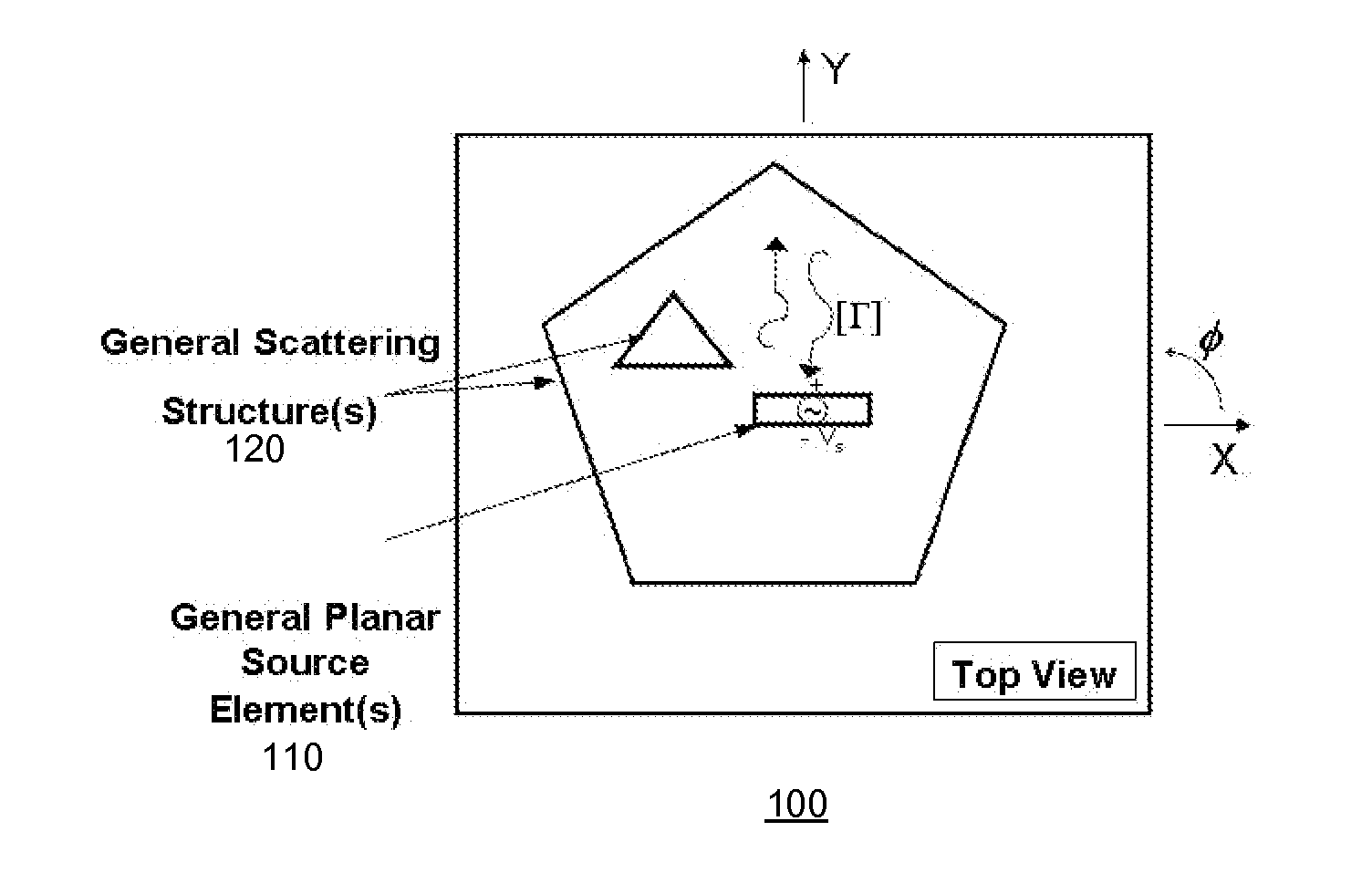
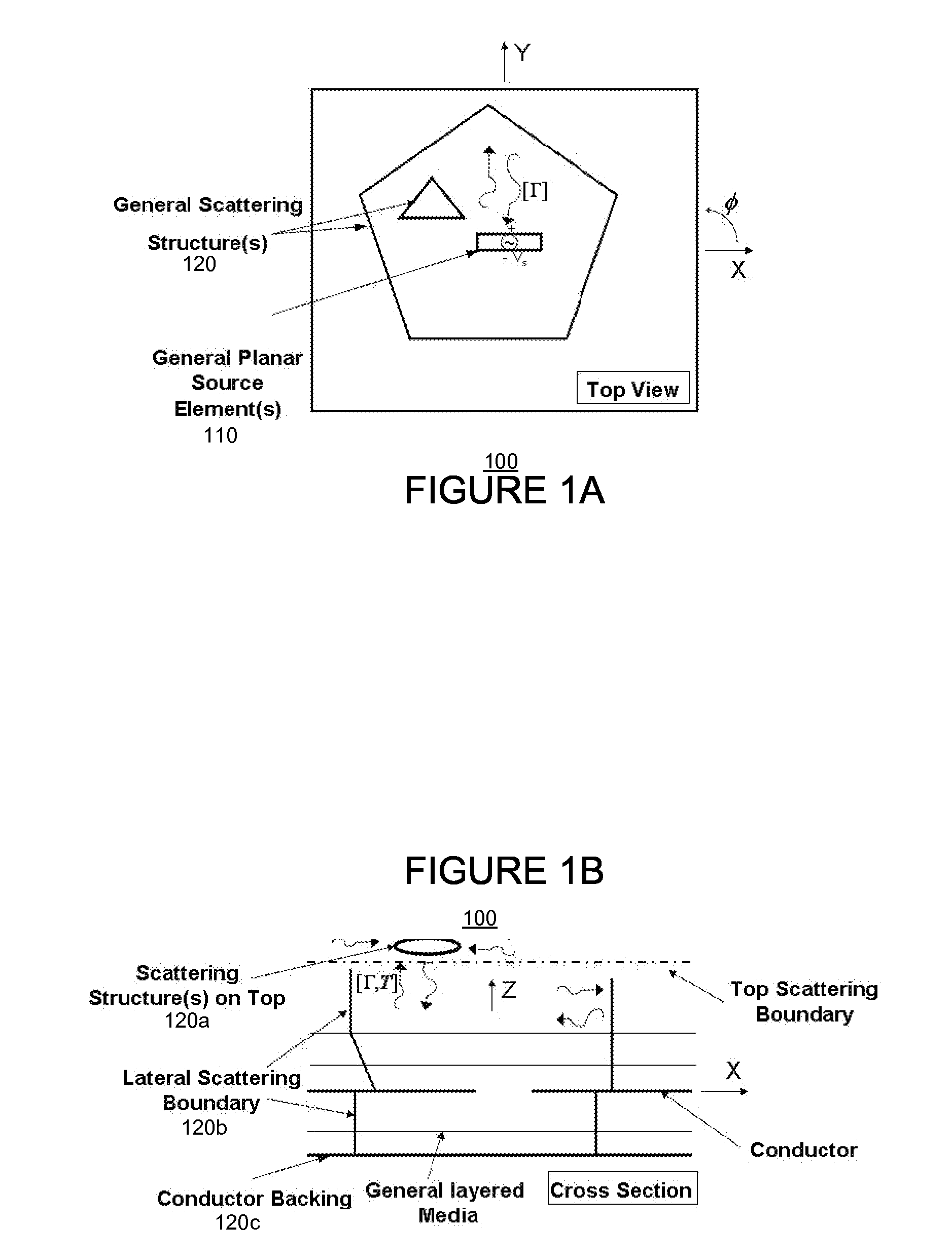
The problem of modeling and designing a structure including a planar element(s) (e.g., antenna, RF circuit, etc.) arranged in association with a non-planar element(s) (e.g., non-planar packaging, a non-planar scattering element, a complex meta material, a periodic array element, etc.), in a computationally efficient and rigorous manner is solved by (1) modeling each of the planar elements using both conventional space-spectral analysis and complex space-spectral analysis to obtain an electro-magnetic (EM) signature matrix for each planar element, (2) determining (e.g., using a brute force modeling based on Maxwell's equations, by measuring experimentally, or by reading one from a stored library) an EM signature matrix (e.g., reflection and scattering matrices) compatible with those of the planar elements, for each of the non-planar elements, and (3) combining the EM signatures of the elements using matrix analysis to obtain a complete EM signature the structure.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Polarization synthetic aperture radar calibration method based on natural bare soil
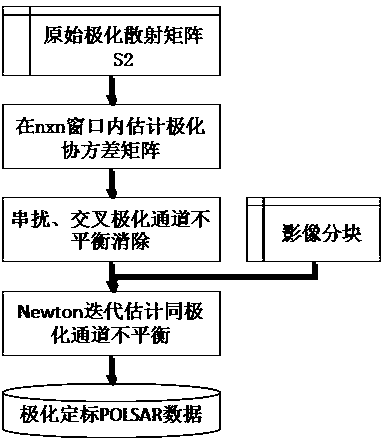
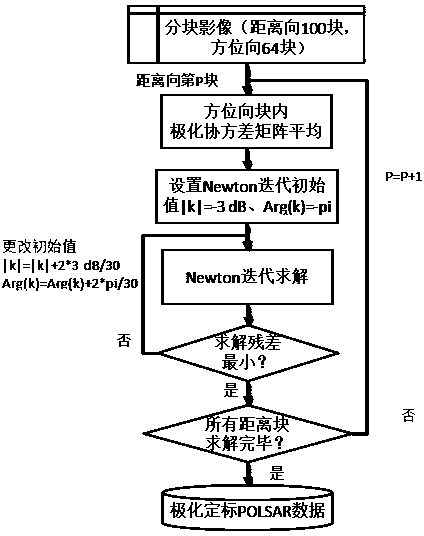
InactiveCN103869299AUnbalanced Stability EstimationImproving Imaging AccuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsNatural disaster
The invention discloses a polarization synthetic aperture radar calibration method based on natural bare soil. The method comprises the steps that the crosstalk and cross polarization channel imbalance parameters of a POLSAR radar image are estimated and removed at first; then, the POLSAR radar image is parted in the distance direction and the azimuth direction; finally, an optimization function is built with the low spirochete ingredient of real soil as an optimization object, and imbalance of a same polarization channel is solved through the characteristic that blocks in the same distance direction have the identical unknown numbers. The weak scattering characteristic of the spirochete of the natural bare soil is utilized, calibration is carried out on emission and receiving distortion matrixes existing in a POLSAR radar system, biased observed values are re-calibrated to be a real scattering matrix, and powerful guarantees can be provided for a radar in the application aspects of territorial resources surveys, natural disaster emergency responses and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com