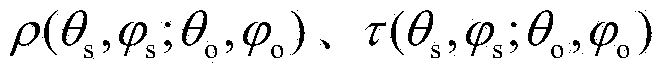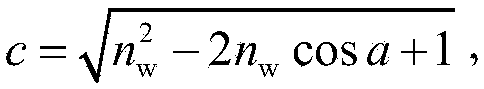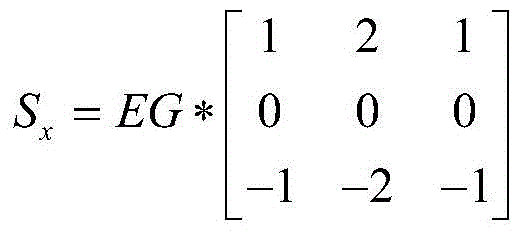Patents
Literature
116 results about "Vegetation canopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
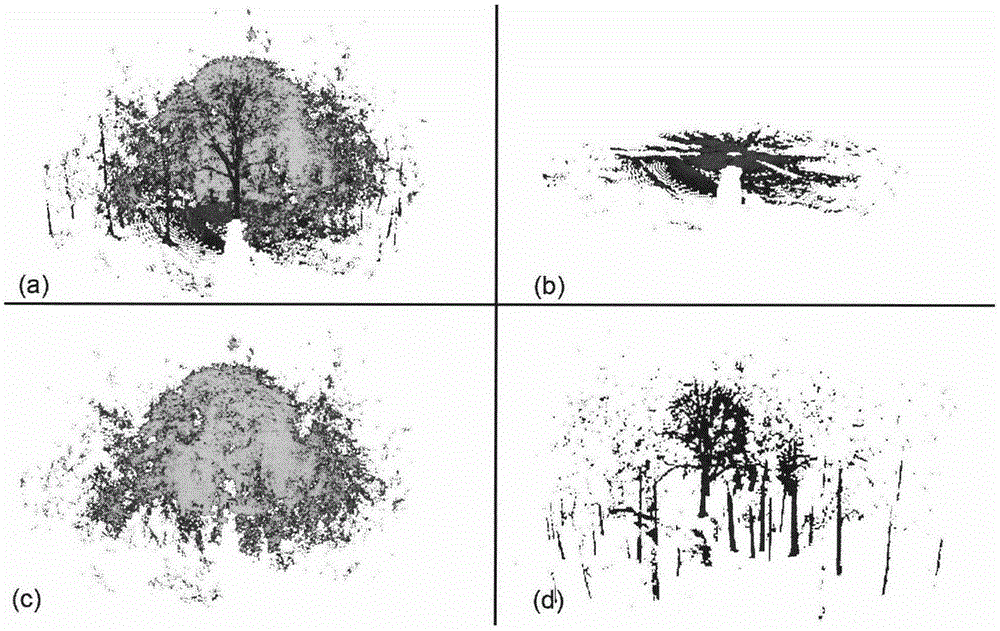
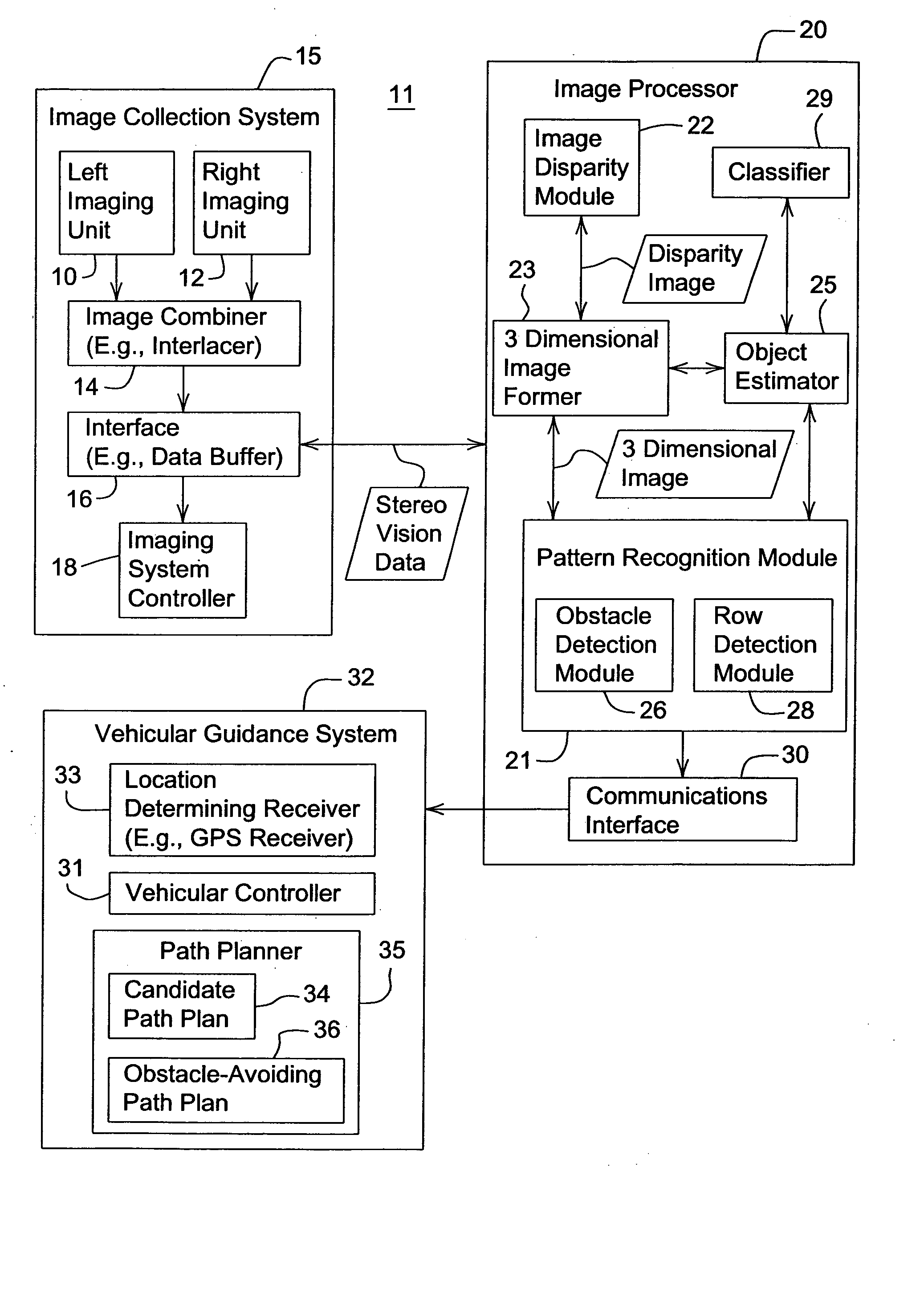
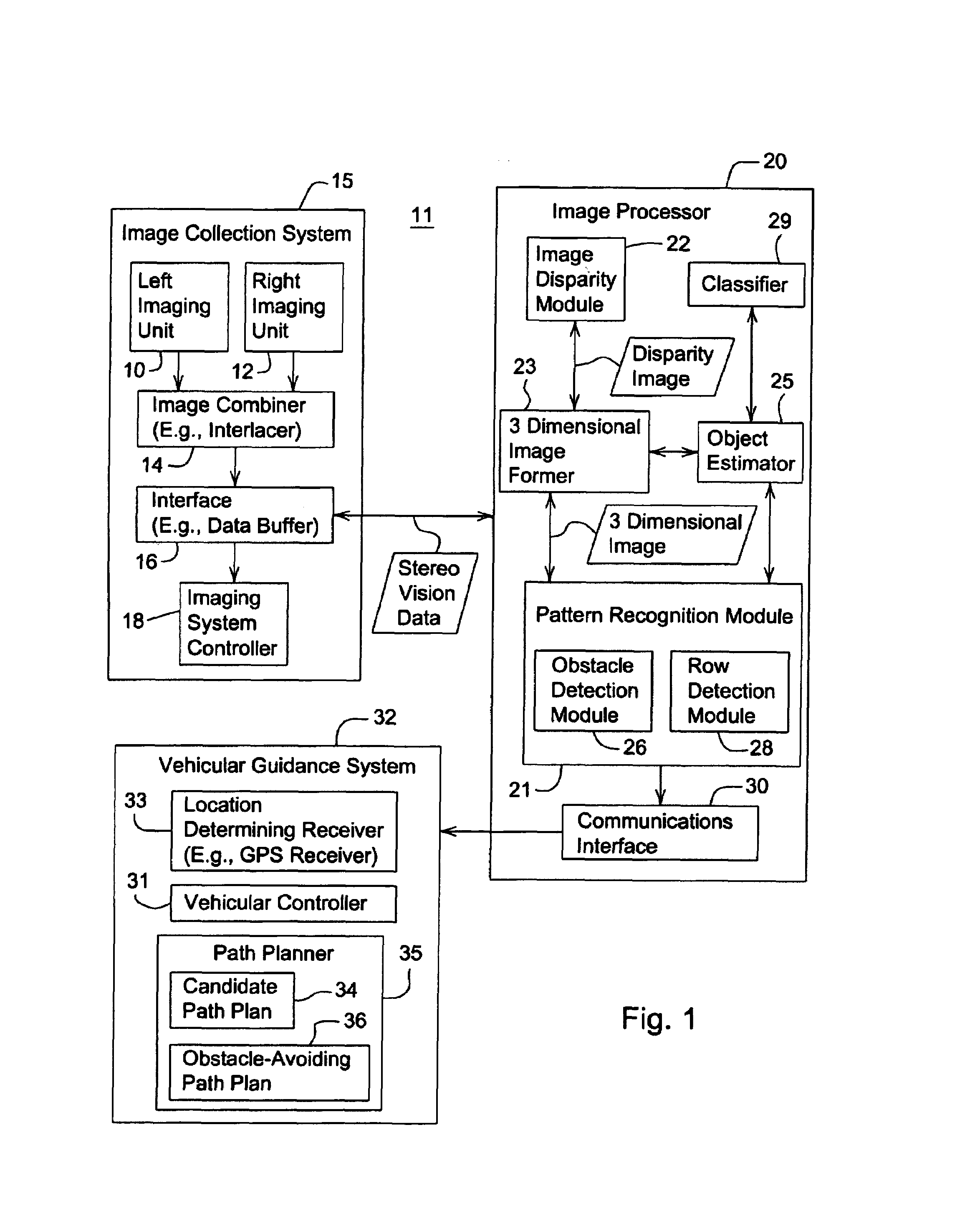
Obstacle detection using stereo vision
ActiveUS20060095207A1Analogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficVegetation heightObstacle avoidance
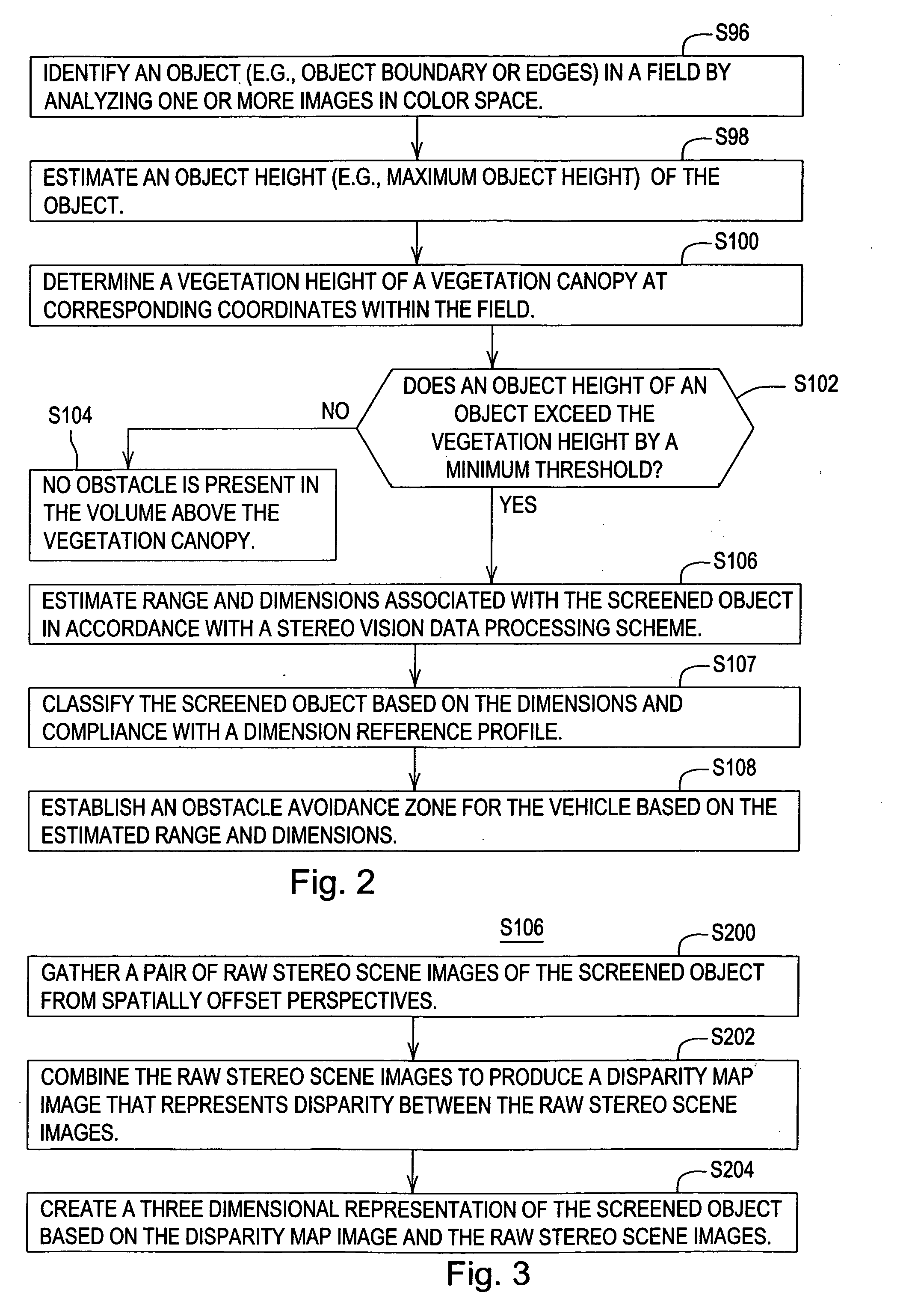
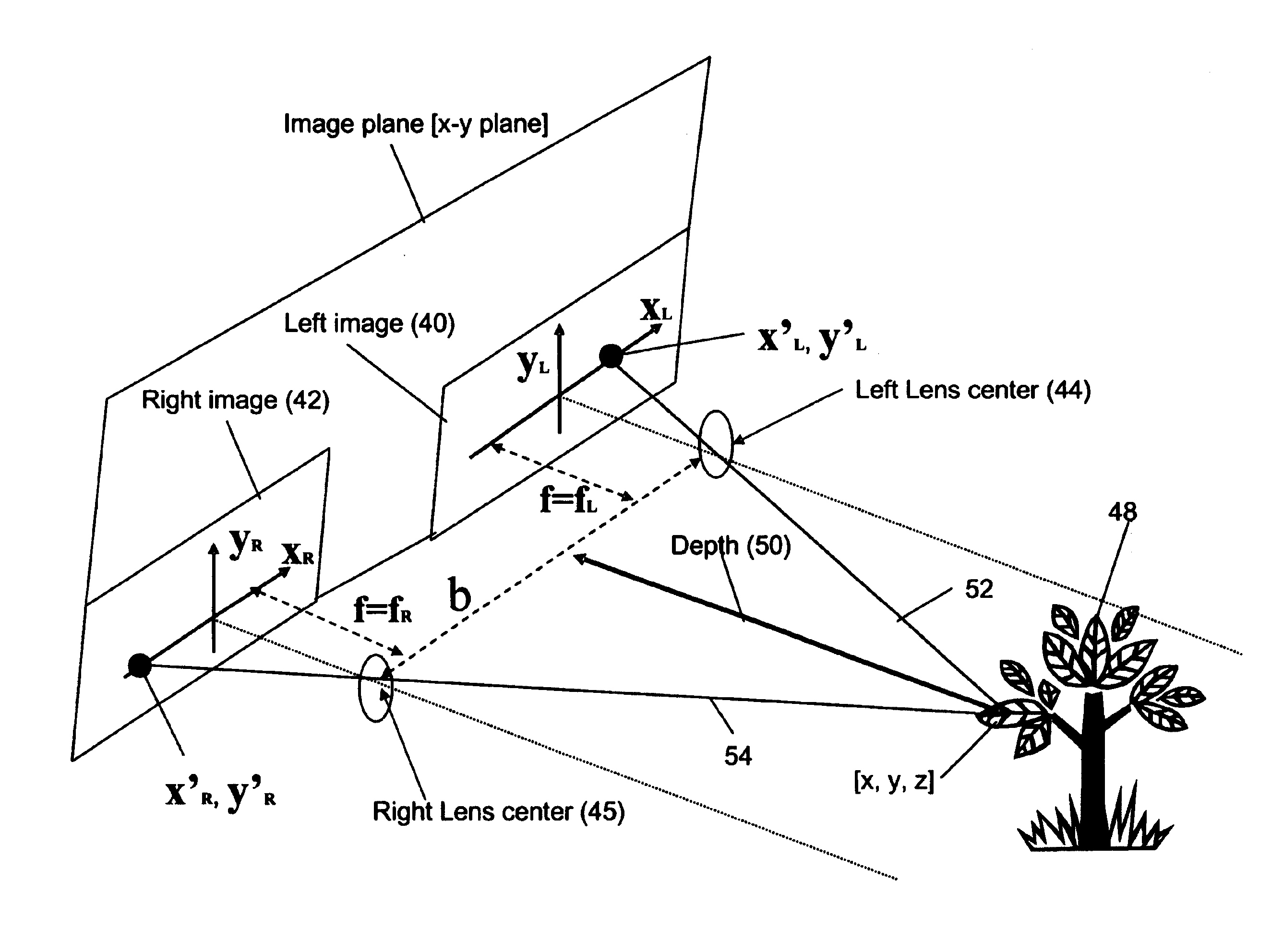
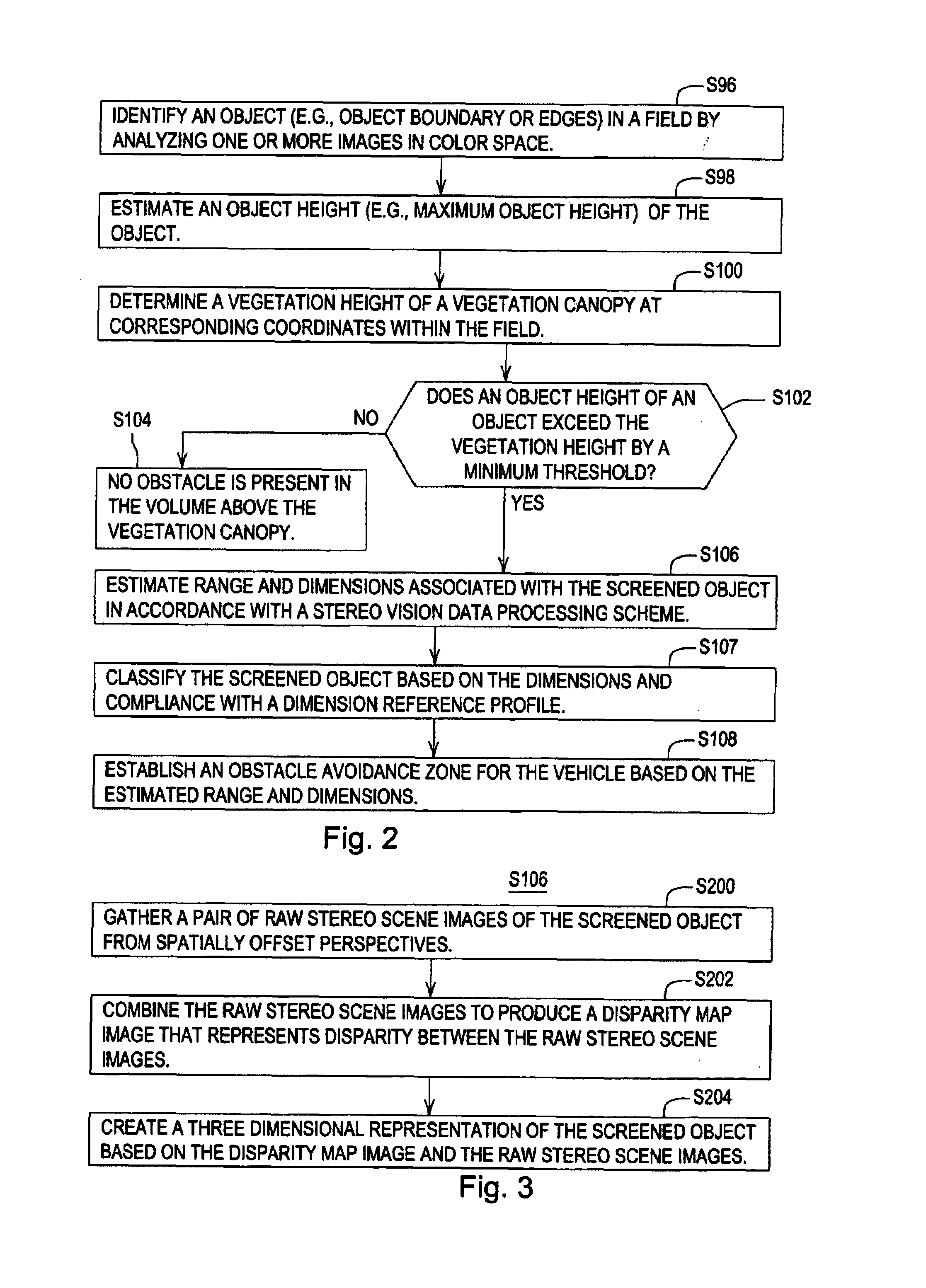
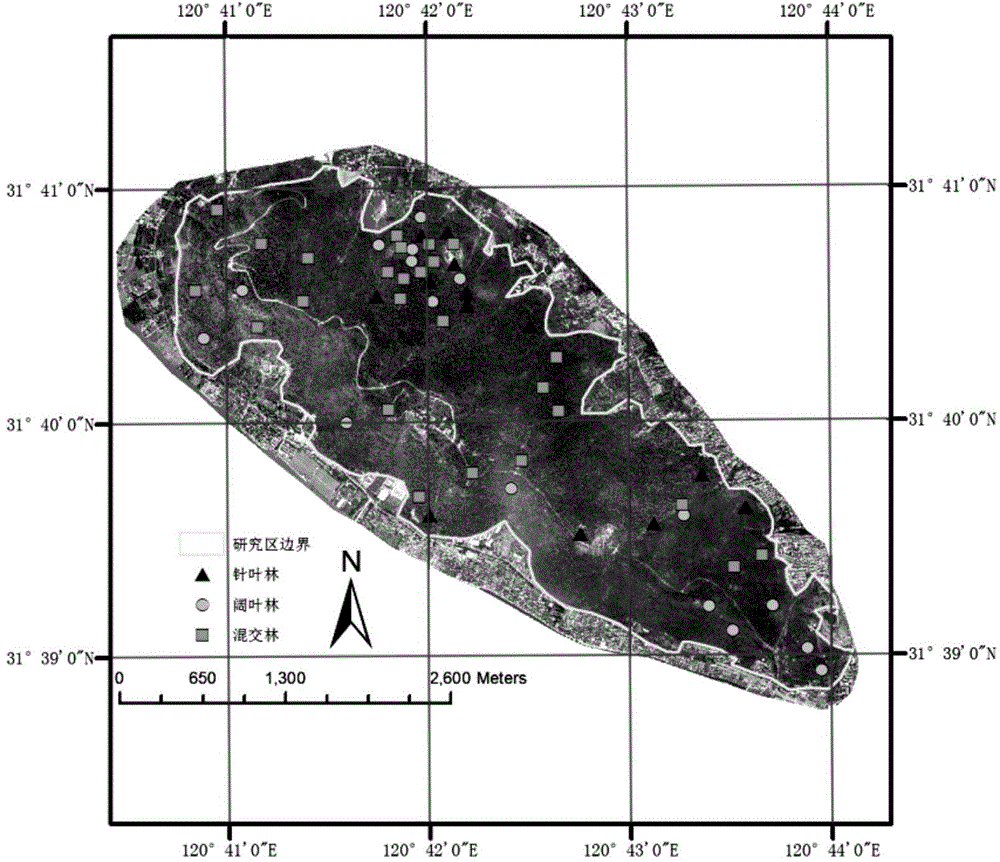
A system and method for detecting an obstacle comprises determining a vegetation height of a vegetation canopy at corresponding coordinates within a field. An object height is detected, where the object height of a object exceeds the vegetation height. A range of the object is estimated. The range of the object may be references to a vehicle location, a reference location, or absolute coordinates. Dimensions associated with the object are estimated. An obstacle avoidance zone is established for the vehicle based on the estimated range and dimensions.
Owner:DEERE & CO
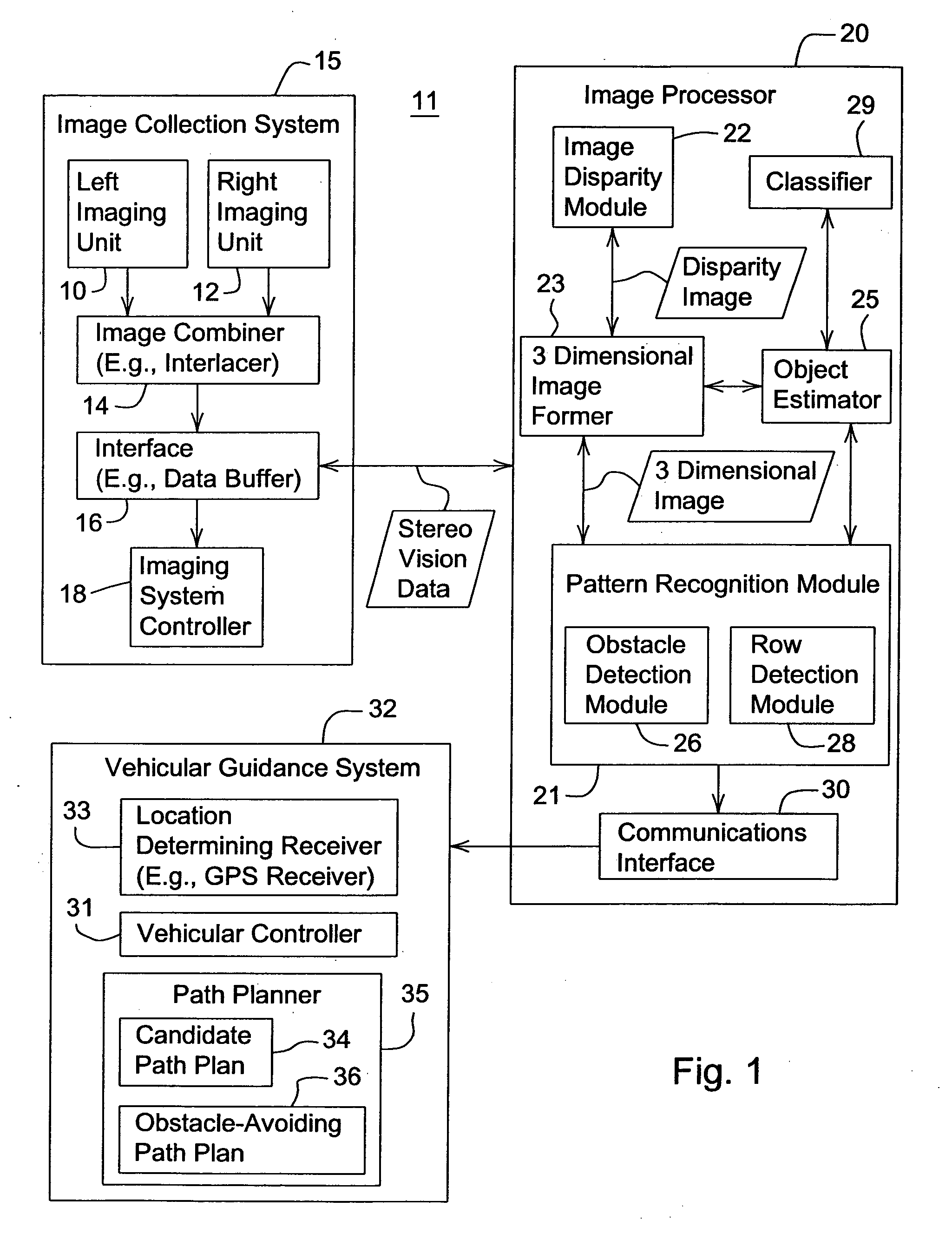
Obstacle detection using stereo vision
ActiveUS7248968B2Analogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficVegetation heightObstacle avoidance
Owner:DEERE & CO
Method for inverting remote sensing forest biomass
ActiveCN104656098AGood for mechanism explanationFacilitate method portabilityElectromagnetic wave reradiationSustainable managementCorrelation analysis
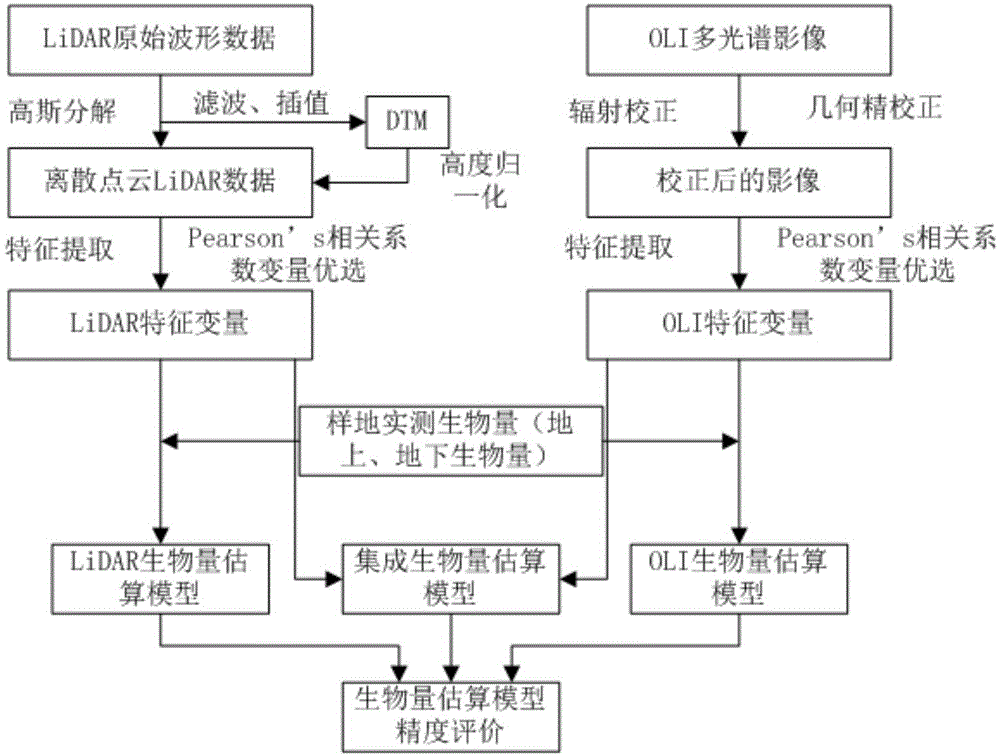
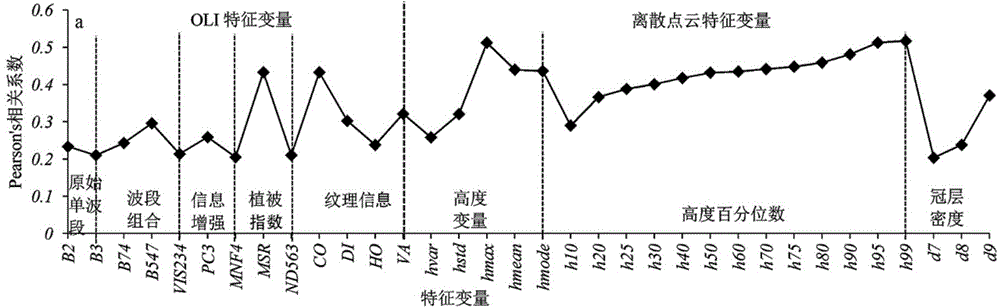
The invention discloses a method for inverting remote sensing forest biomass. The method comprises the following steps: on the basis of remote sensing data pretreatment, extracting characteristic variables of a vegetation canopy from a LiDAR point cloud (comprising canopy three-dimensional space information) and multispectrum (comprising spectrum information on the upper surface of the canopy) data respectively; screening the characteristic variables of the LiDAR point cloud and the multispectrum through correlation analysis, and inverting overground and underground biomass by combining the ground actually measured biomass information through a stepwise regression model. Through the adoption of the optimized inverting model of northern subtropical forest biomass, constructed by method, the 'determination coefficient' R<2> of the model can be increase by 3-24%; the forest biomass can be estimated in high precision, and the 'relative root-mean-square error' (rRMSE) can be reduced by 2-10%. The method can be applied to the fields of forestry investigation, forest resource monitoring, forest carbon reserve evaluation, forest ecosystem research and the like, and provides quantitative data support for forest sustainable management and forest resource comprehensive utilization.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Hyperspectral remote sensing data vegetation information extraction method
ActiveCN105352895ADoes not affect vegetation growthColor/spectral properties measurementsSensing dataEstimation methods
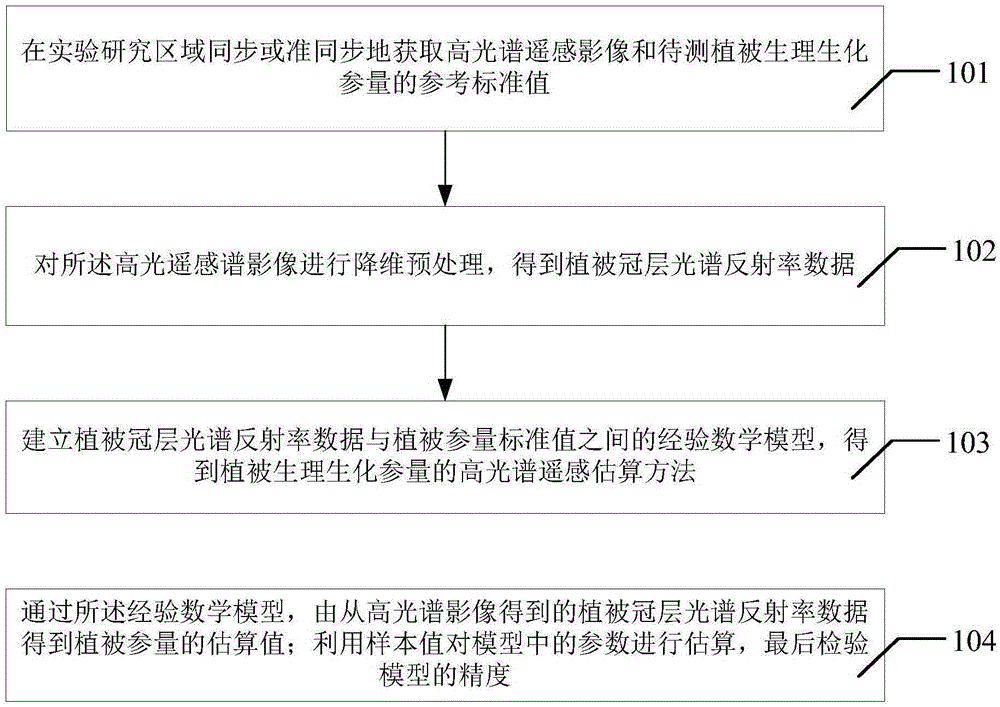
The invention discloses a hyperspectral remote sensing data vegetation information extraction method. The method comprises in an experiment research zone, synchronously or quasi-synchronously acquiring a hyperspectral remote sensing image and reference standard values of physiological and biochemical parameters of vegetation to be detected, carrying out dimensionality reduction pre-treatment on the hyperspectral remote sensing image to obtain vegetation canopy spectral reflectance data, building an empirical mathematic model of the vegetation canopy spectral reflectance data and the vegetation parameter standard values to obtain a hyperspectral remote sensing estimation method of the vegetation physiological and biochemical parameters, through the empirical mathematic model, acquiring a vegetation parameter estimated value by the vegetation canopy spectral reflectance data obtained by the hyperspectral remote sensing image, carrying out estimation on the parameters of the model by the sample value and carrying out examination on a model precision. Through the hyperspectral remote sensing data, vegetation physiological and biochemical parameter estimation is realized so that the method is convenient and fast, does not influence vegetation growth, is suitable for large-area popularization and has a measurement area of the whole earth range.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Universal aquatic vegetation radiation transmission model
InactiveCN103632040AInnovativePhysical concepts are clearScattering properties measurementsSpecial data processing applicationsExtinctionReflectance spectroscopy
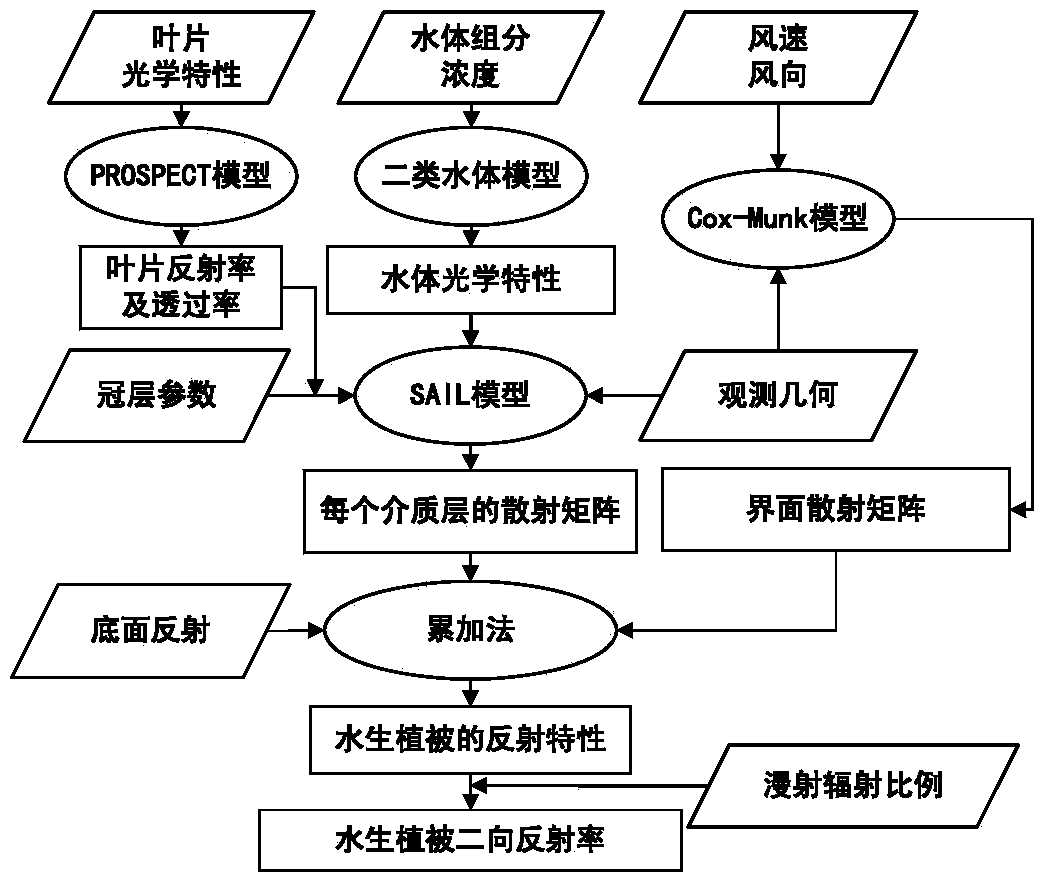
The invention relates to a universal aquatic vegetation radiation transmission model. Building of the model includes the following steps that a whole aquatic vegetation system is divided into a plurality of dielectric layers which are evenly mixed and consistent in horizontal optical properties; vegetation canopy structure parameters, observation geometry and other conditions, and reflectivity and transmittance of a single leaf are input into an SAIL model for calculation extinction and scattering coefficients of a vegetation canopy to radiation, wherein the reflectivity and the transmittance of the single leaf are obtained through calculation of an SPECT model; the water body component concentration is given, absorption and back scattering coefficients of a water body are calculated on the basis of a case 2 water body optical model, and extinction and scattering coefficients of the water body and the vegetation mixed dielectric layers are calculated; according to a Cox-Munk model, scattering matrixes of a wave surface to direct radiation and diffusion radiation are calculated; bidirectional reflectivity of the aquatic vegetation system is calculated according to an adding method. The universal aquatic vegetation radiation transmission model achieves precise description of a reflectance spectrum and directional reflection features of aquatic vegetation, and is the premise and basis of radiation and aquatic vegetation interaction mechanism researches and precise remote sensing inversion of water environment parameters.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for monitoring nitrogen concentration of vegetation canopies in wetland based on hyperspectral vegetation index
InactiveCN103868860AImprove estimation accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsVegetation IndexWetland vegetation
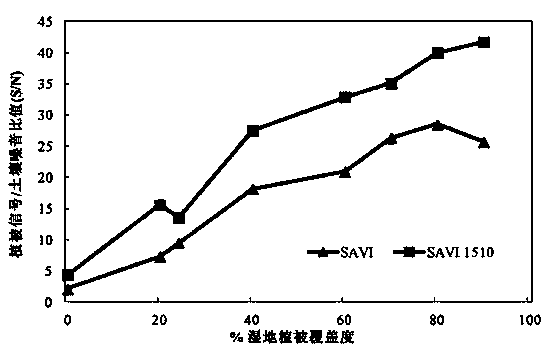
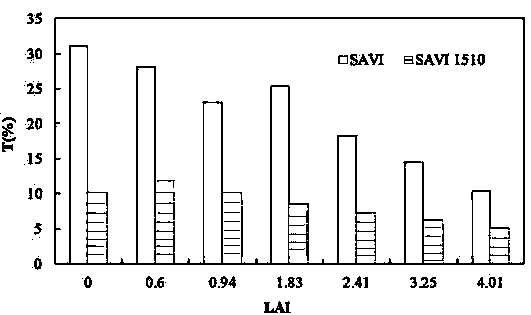
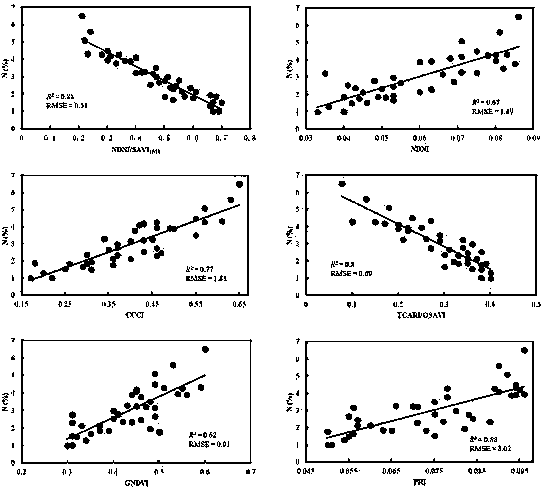
The invention discloses a method for monitoring the nitrogen concentration of vegetation canopies in a wetland based on a hyperspectral vegetation index. The method comprises the steps of measuring the spectrum, the leaf area index (LAI) and the nitrogen concentration of the vegetation canopies in the wetland; preprocessing a Hyperion hyperspectral remotely sensed image; improving an SAVI (soil adjusted vegetation index) to obtain an SAVI1510; constructing a hyperspectral vegetarian index NDNI / SAVI1510 applied to monitoring on the nitrogen concentration of vegetation canopies in the wetland, wherein the hyperspectral vegetarian index NDNI / SAVI1510 is applied to estimation on the performance of monitoring the nitrogen concentration of vegetation canopies in the wetland; and constructing a model for monitoring the nitrogen concentration of vegetation canopies in the wetland based on the hyperspectral vegetarian index NDNI / SAVI1510. The method for monitoring the nitrogen concentration of vegetation canopies in the wetland based on the hyperspectral vegetation index comprises the beneficial effects that the influence, caused by multiple scattering signals from a complicated background from vegetations in the wetland, on the wetland vegetation canopy nitrogen concentration estimation precision is weakened, and the nitrogen concentration of the vegetation canopies in the wetland can be estimated with high precision.
Owner:LIAONING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
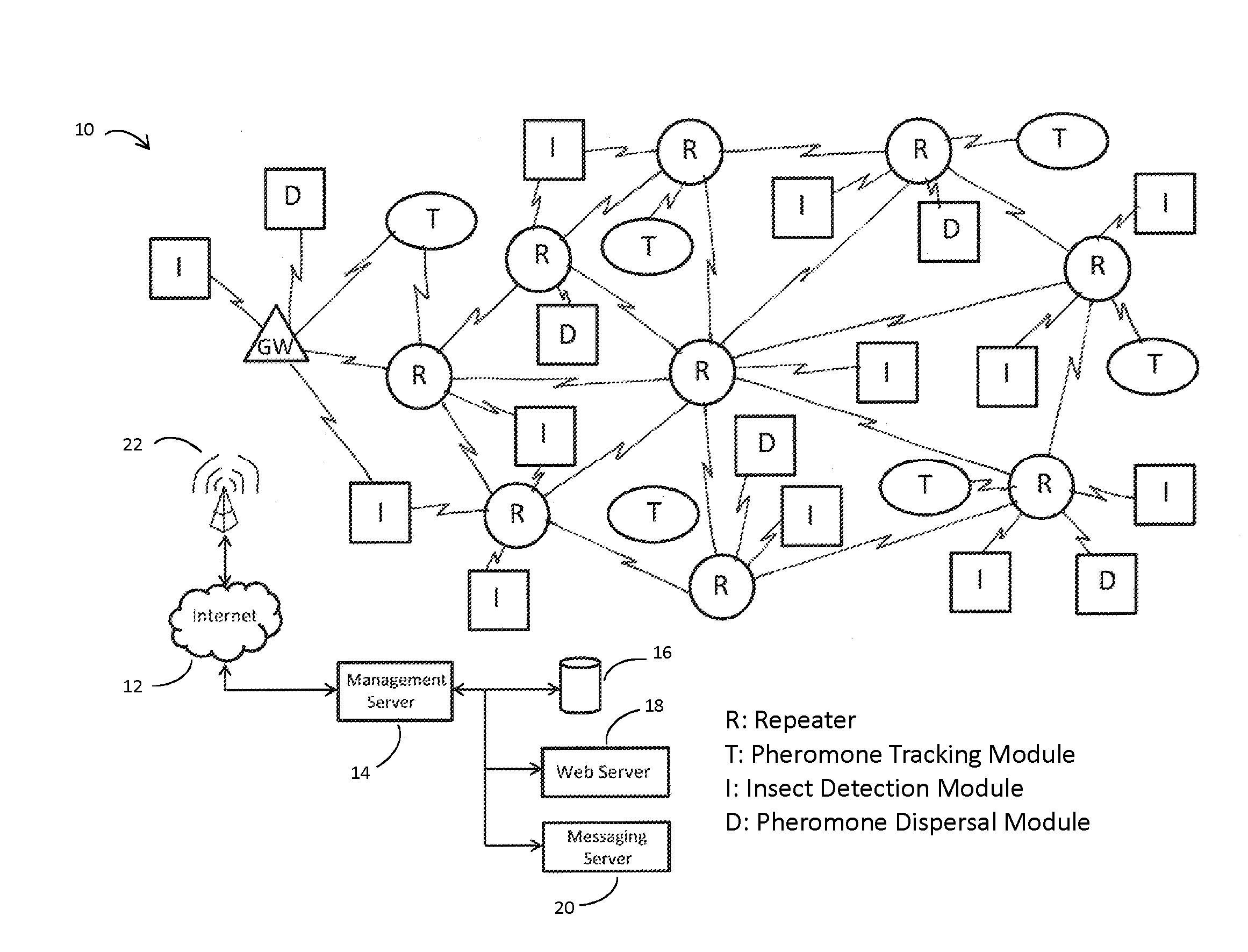
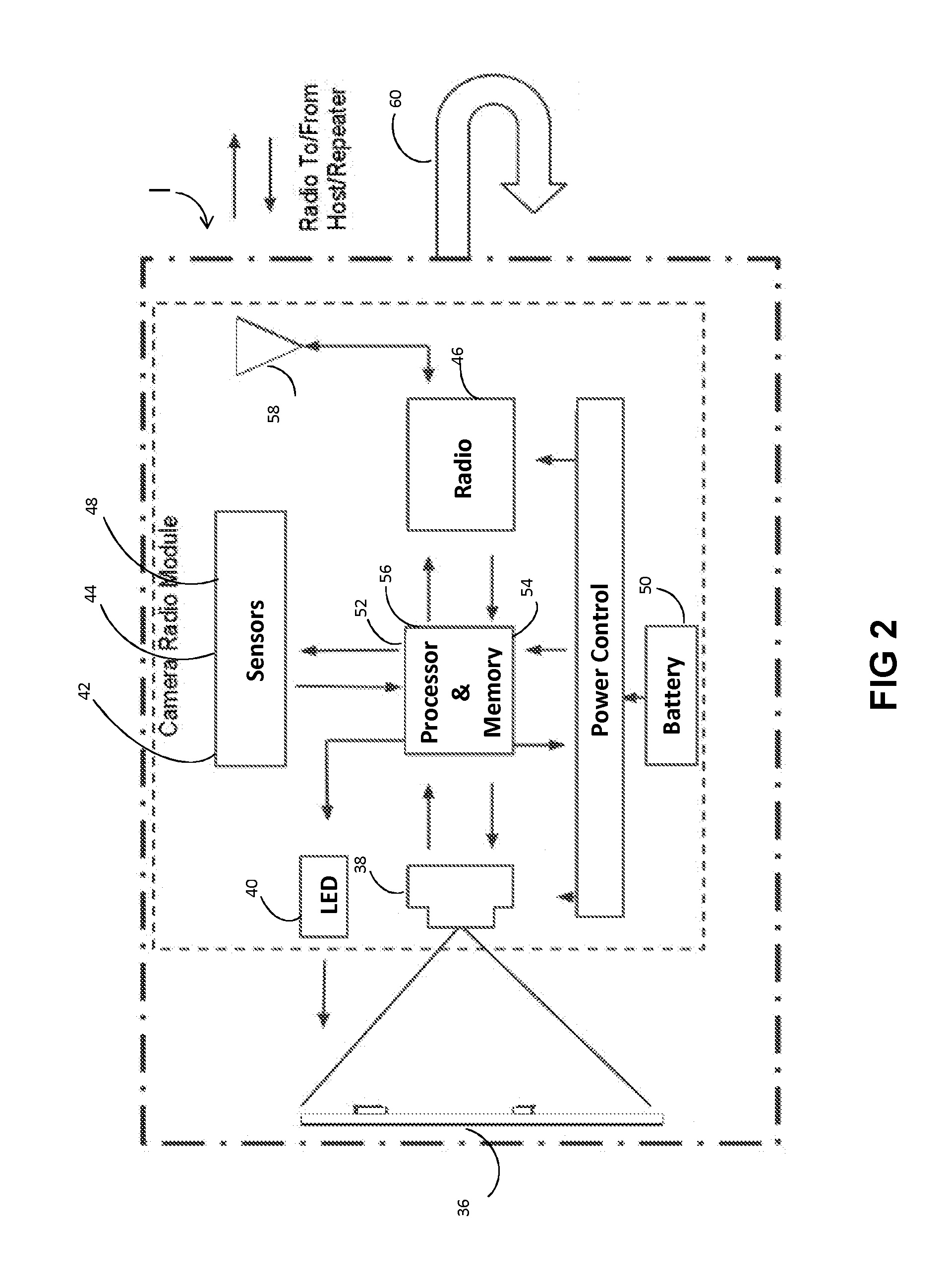
Monitoring and Control Systems for the Agricultural Industry
A mesh-based wireless network 10 of sensor / actuator devices I, D, T for an agricultural production area involves battery-powered sensors and actuators deployed under or within the foliage for broadcast communication with at least one repeater R according to broadcast time slots. The repeaters R are mounted above the vegetation canopy so as to be powered by solar panels. The repeaters R form a mesh network for routing data and commands to and from the sensors and actuators and at least one gateway GW. The gateway communicates over a cellular network with a remote agricultural management server 14 and database 16.
Owner:SEMIOSBIO TECH
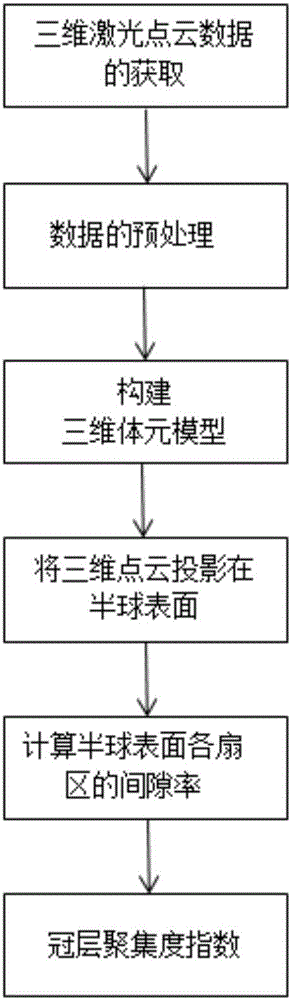
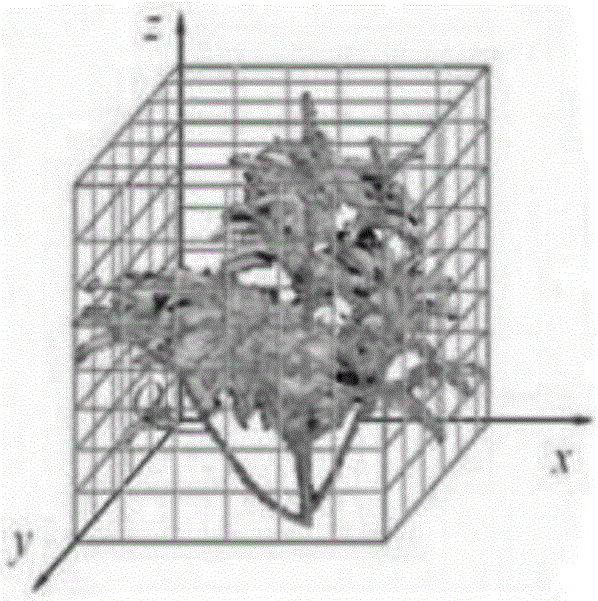
Method for extracting vegetation canopy aggregation degree index based on three-dimensional laser point cloud
ActiveCN106248003AQuick extractionAccurate extractionUsing optical meansMechanical measuring arrangementsClearance rateData acquisition
The invention belongs to the technical field of the laser radar remote sensing technology and particularly provides a method for extracting a vegetation canopy aggregation degree index based on the three-dimensional laser point cloud. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the remote sensing technology is adopted to obtain the three-dimensional point cloud data of a vegetation quadrat canopy. Through the processes of constructing a three-dimensional volume element model, converting a coordinate system, calculating a canopy clearance rate and the like, a method for extracting the vegetation canopy aggregation degree index based on ground high-resolution laser point cloud data is established. Based on the method, the vegetation canopy aggregation degree index can be quickly and accurately extracted, and the data acquisition is simple and convenient. Meanwhile, the process is not influenced by the lighting condition during observation. During the study, the pixel scale factor of satellite remote sensing data or products is not taken into consideration. Moreover, no adverse effect on vegetation structure and radiation characteristics exists. At the same time, the three-dimensional structural features of a vegetation sample can be permanently recorded. The method is simple, convenient and efficient, and does not have side effects on vegetation. The calculated amount is greatly reduced compared with the prior art.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
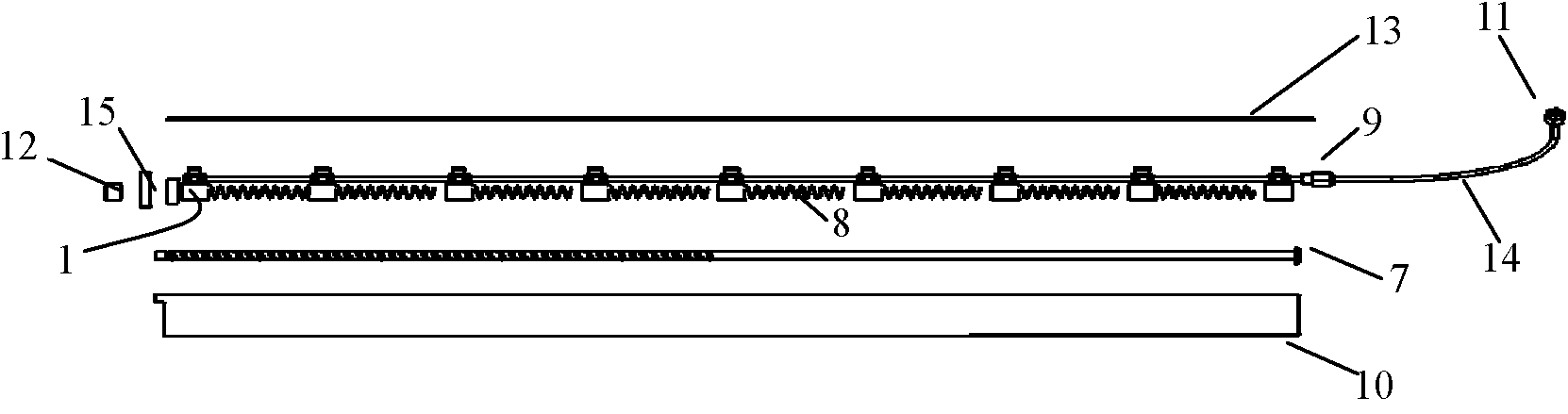
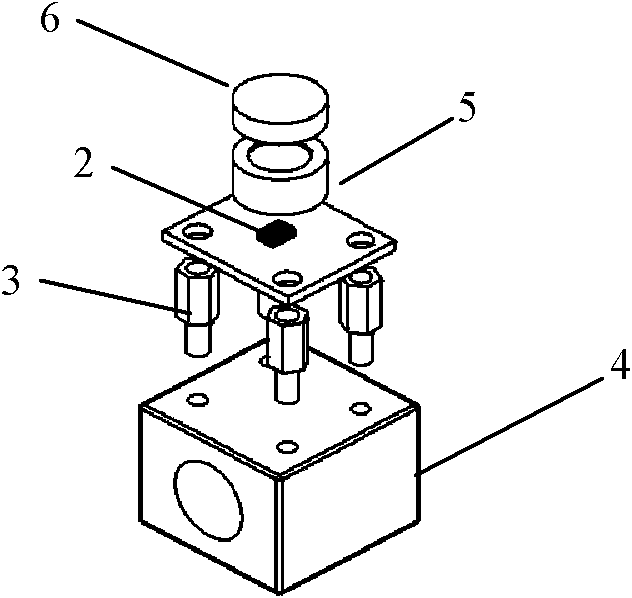
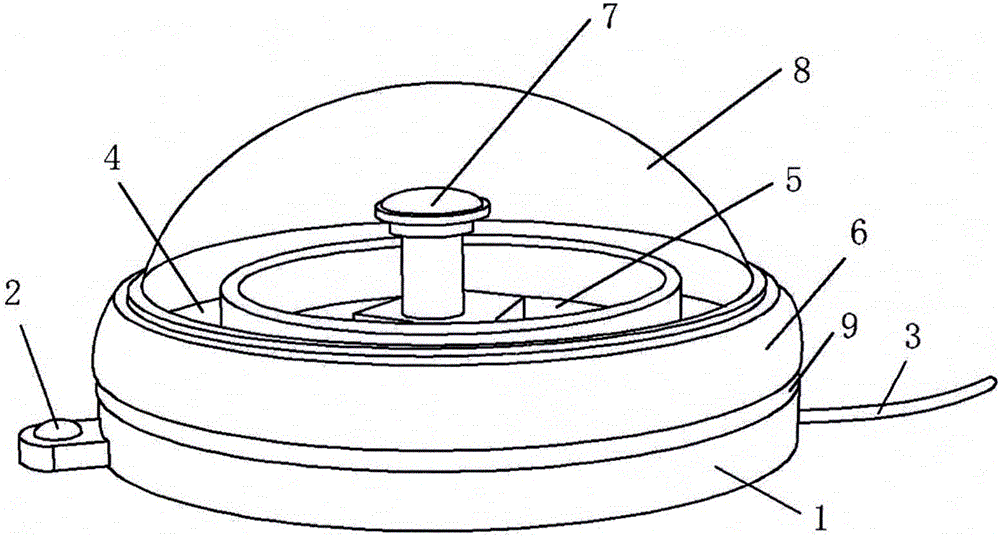
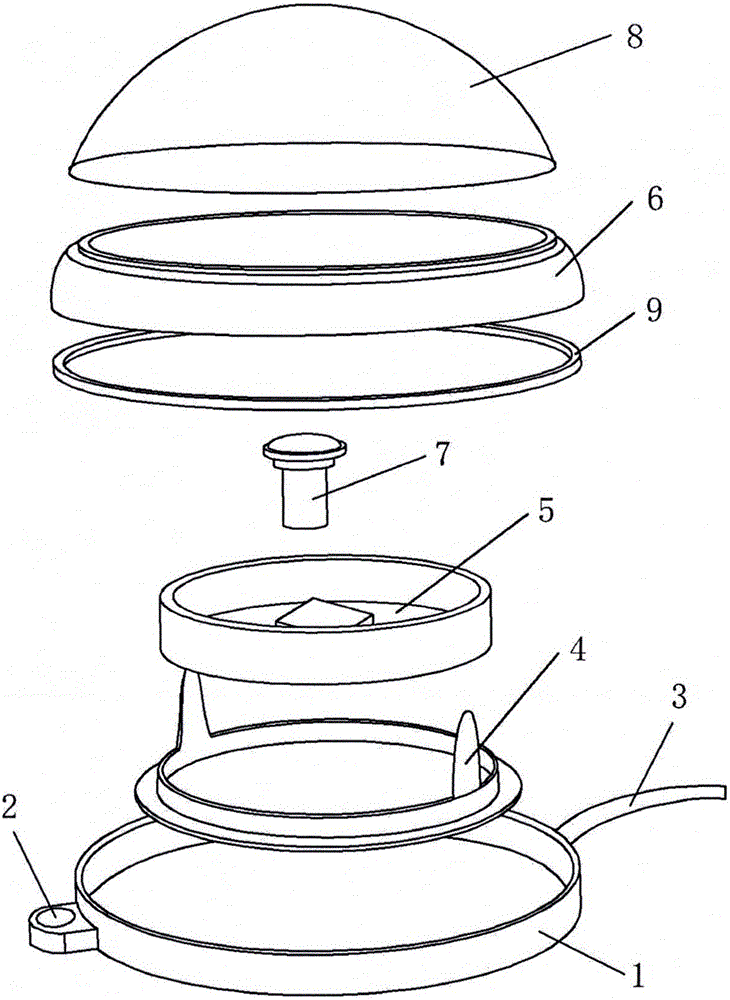
Automatic measuring device for acquiring vegetation canopy structure parameters
InactiveCN104089590ARealize continuous automatic measurementReduce complexityTransmission systemsUsing optical meansMeasurement deviceDigital imaging
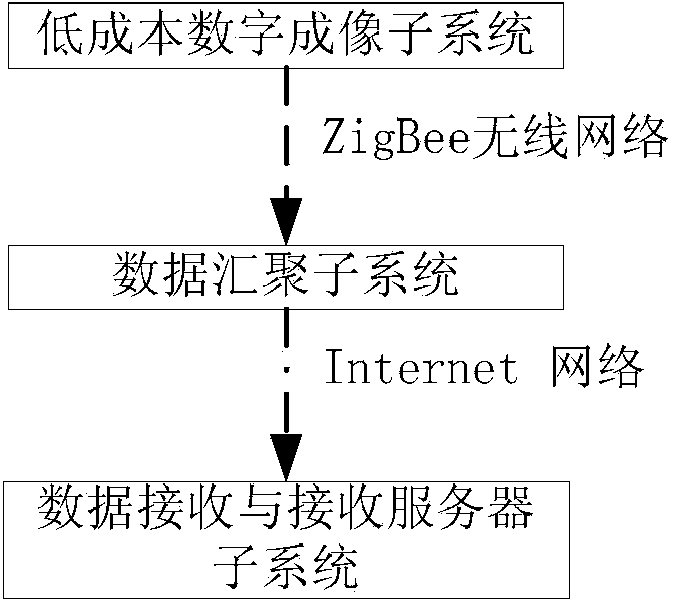
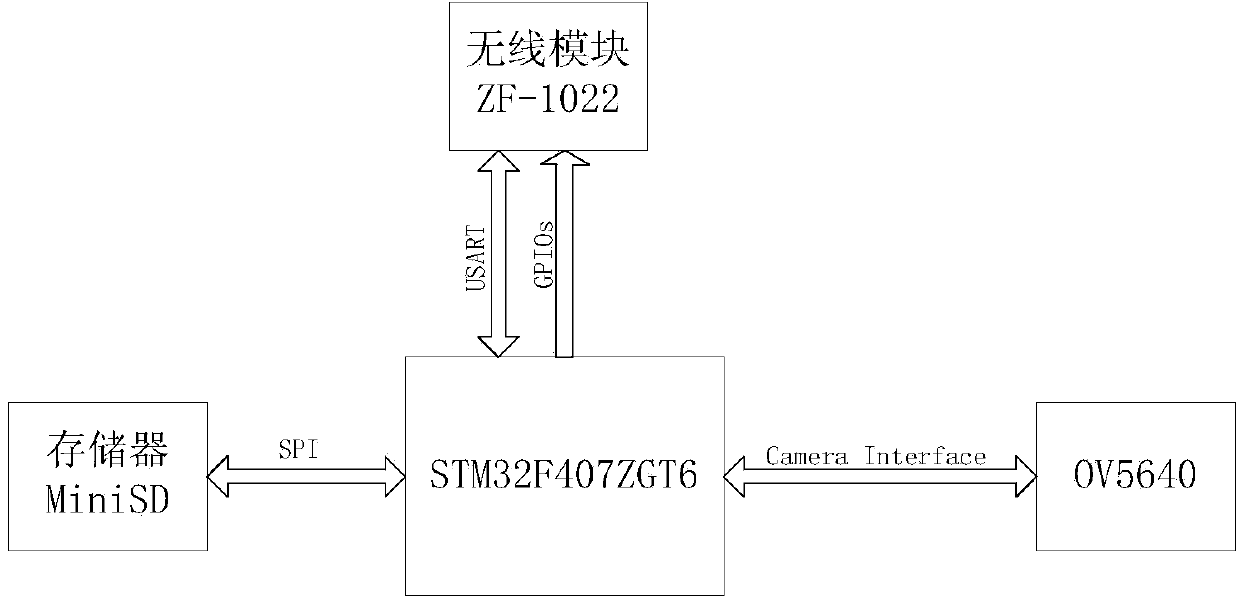
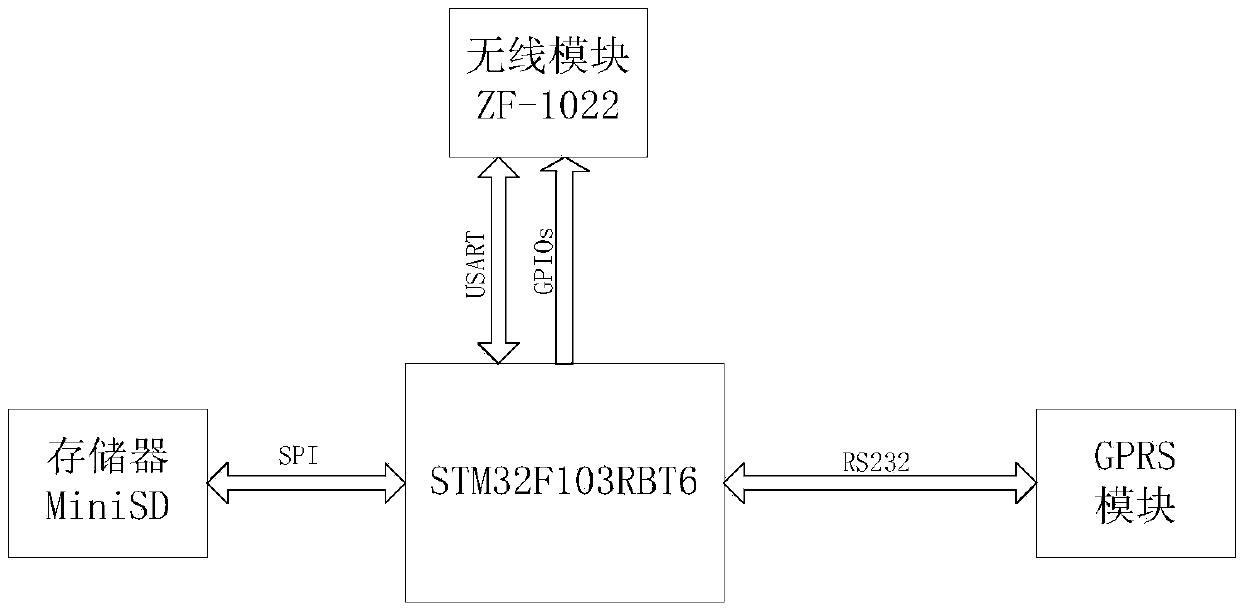
An automatic measuring device for acquiring vegetation canopy structure parameters is composed of three parts, namely, a low-cost digital imaging subsystem, a data aggregation subsystem and a data receiving and receiving server subsystem. The low-cost digital imaging subsystem is connected in a communication mode with the data aggregation subsystem through a ZigBee wireless network. The data aggregation subsystem is connected in a communication mode with the data receiving and receiving server subsystem through an Internet network. According to the invention, an automatic structure parameter measuring system is implemented by combining a traditional crop canopy structure parameter measuring principle and a data acquisition and data transmission technology based on a wireless network. The automatic measuring system enables continuous automatic measurement of leaf area index and canopy mean leaf angle of long-time-series and large-space vegetations to be realized, and has wide application prospects in the technical field of agriculture and ecology.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
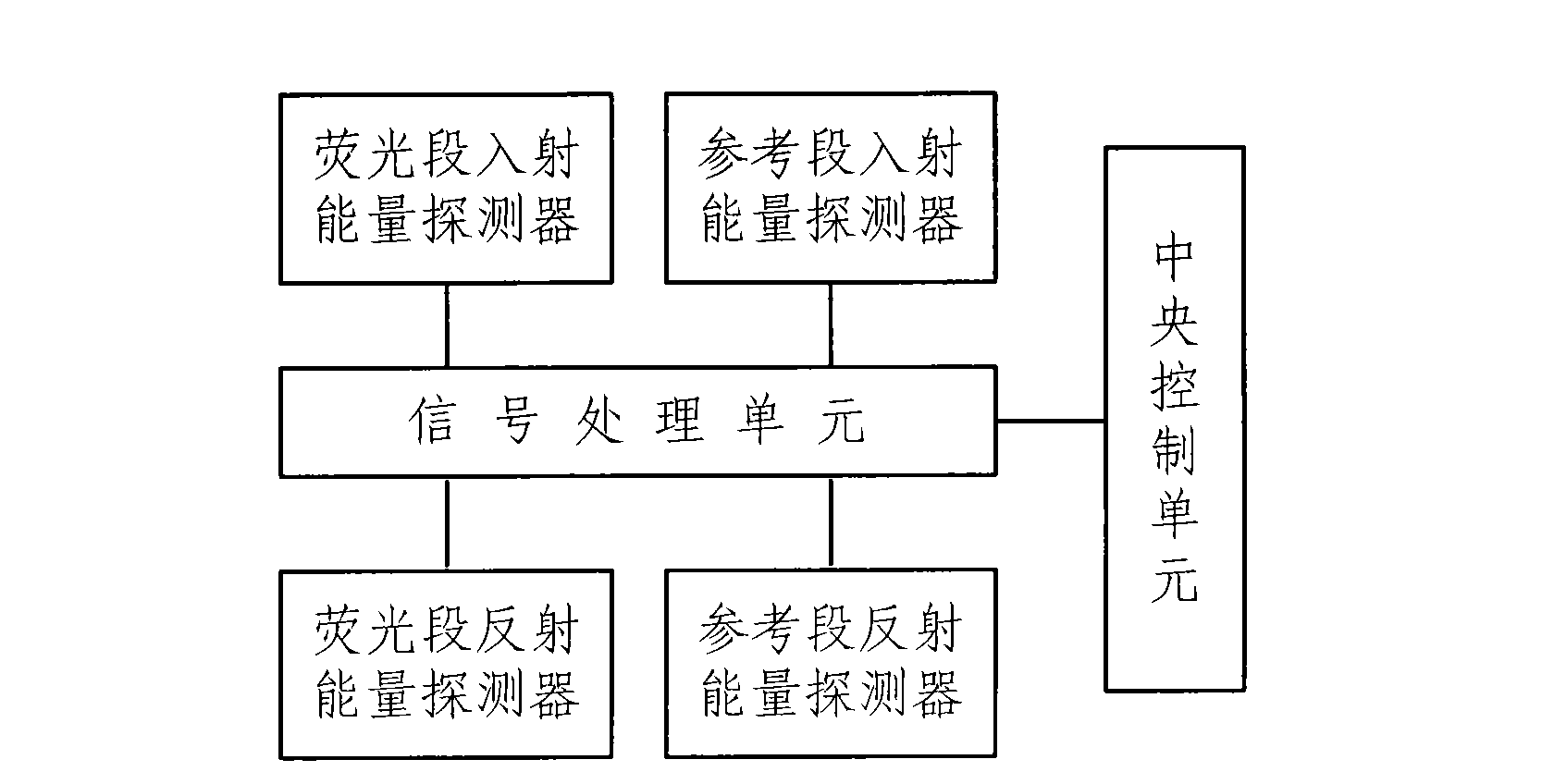
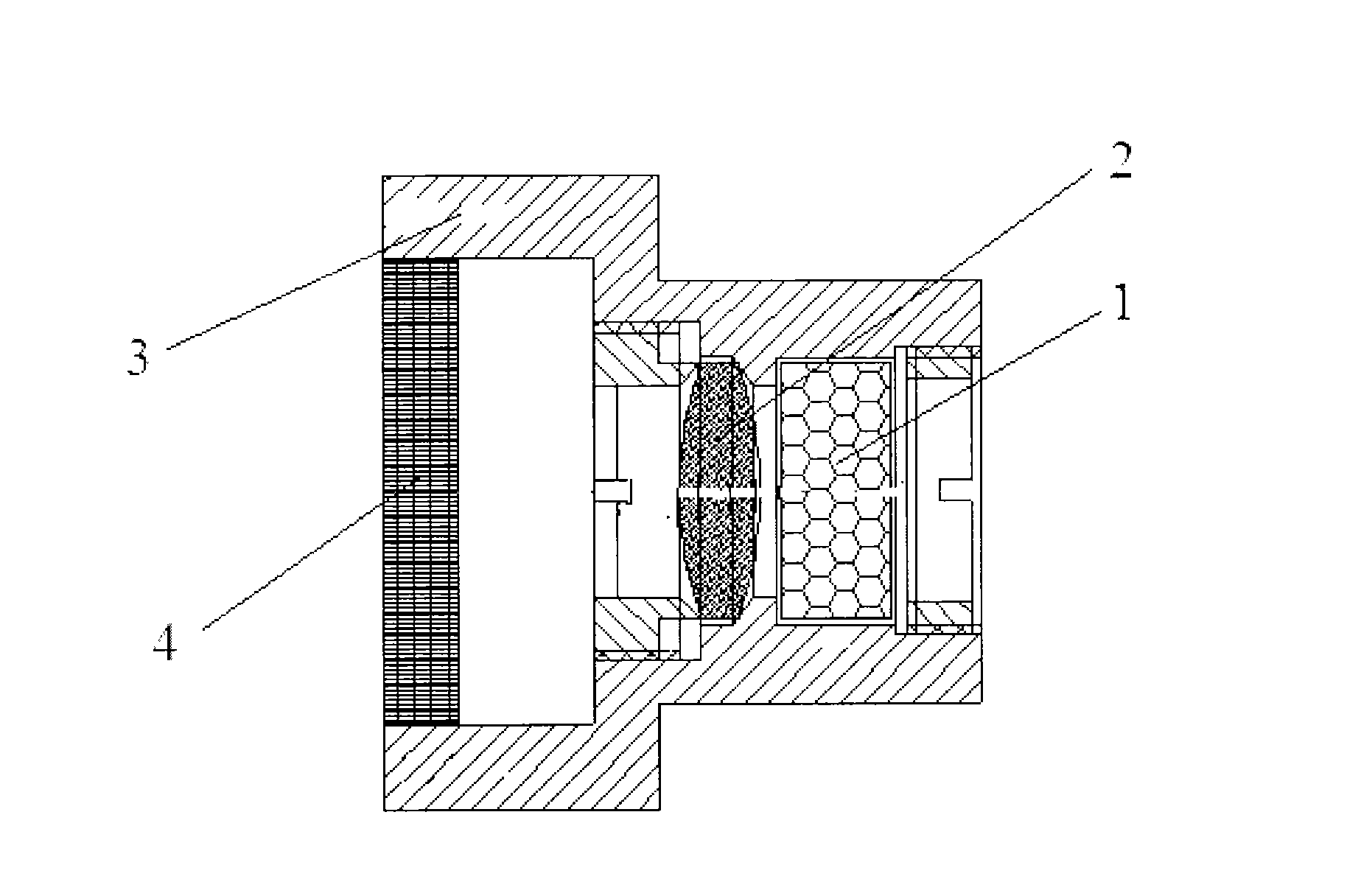
Vegetation fluorescent detection method and a device
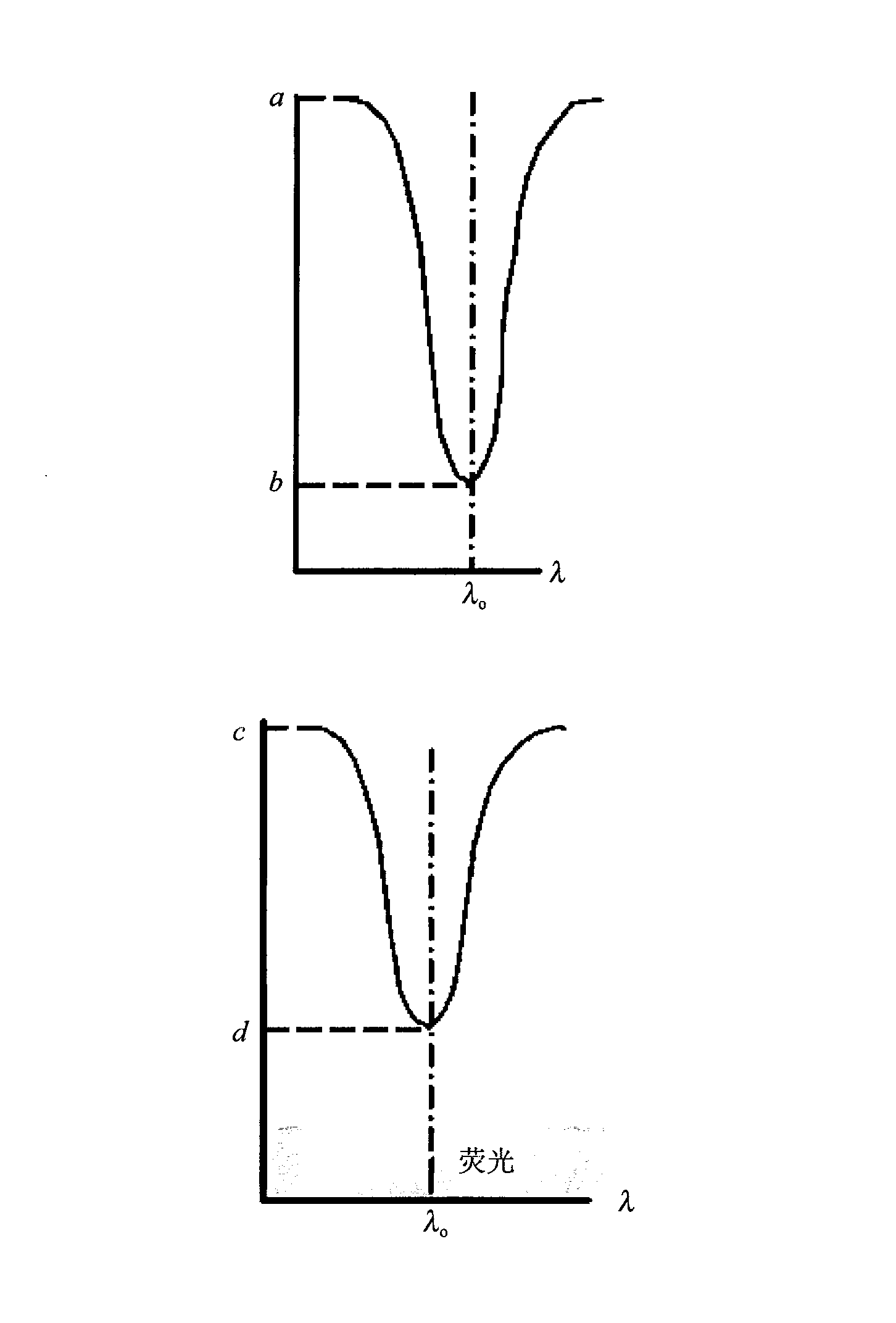
The invention discloses a vegetation fluorescent detection method under natural lighting and a device. The detection method comprises the following steps: under natural lighting, measuring incident energy of a fluorescent waveband and a reference waveband and reflection energy of the vegetation on the fluorescent waveband to be measured and the vegetation on the reference waveband; obtaining absolute fluorescence intensity of vegetation canopy according to the measured energy value. The method can more intuitively reflect the fluorescence information of photosynthesis under natural lighting and detect the fluorescence of the vegetation canopy. Owing to the characteristics of convenience, fastness, trueness and reliability, the device can be more easily used for aviation or satellite platforms and realize technical leap of the fluorescence detection from contact point measurement to large scale aviation or satellite remote sensing monitoring.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
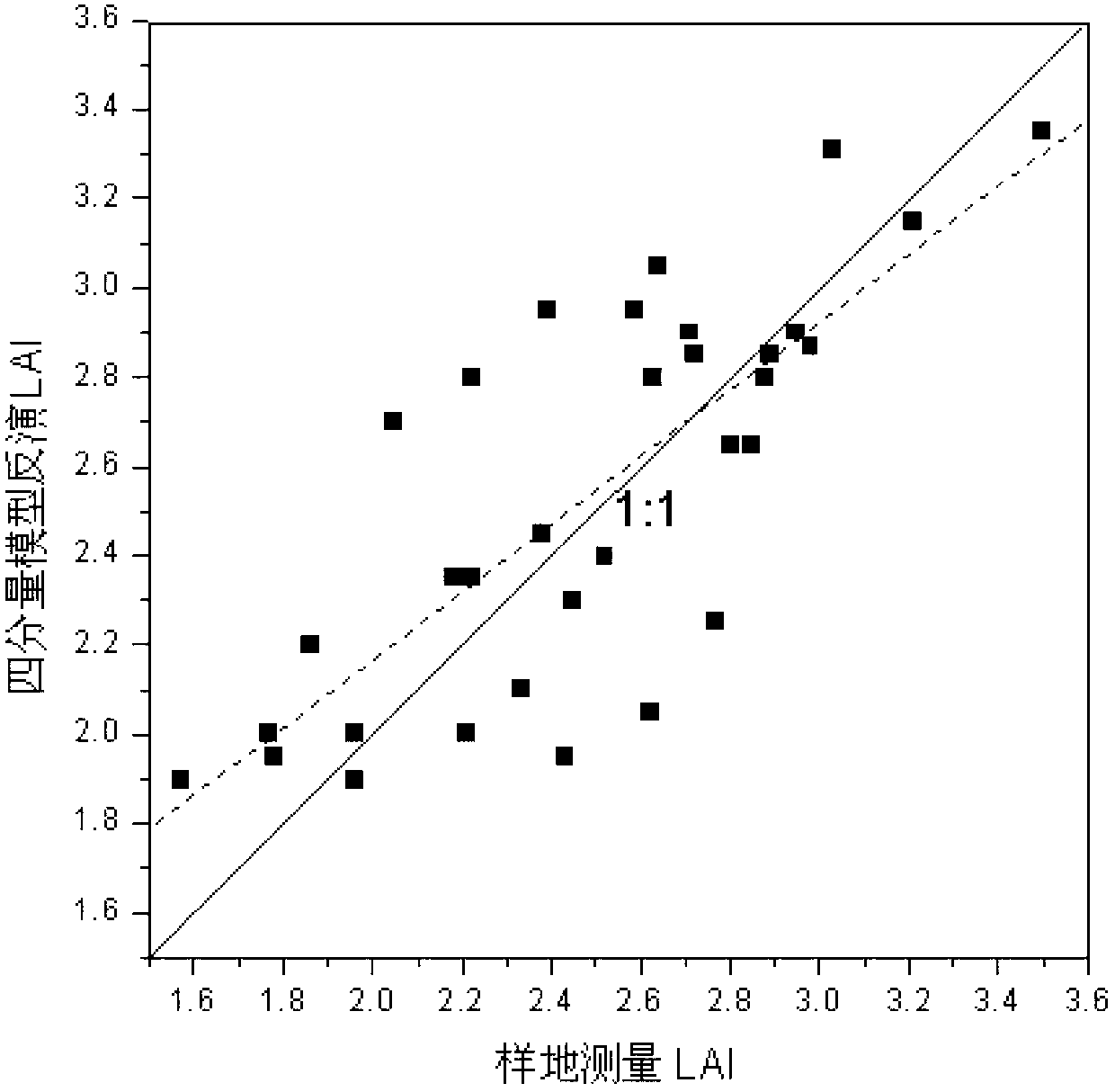
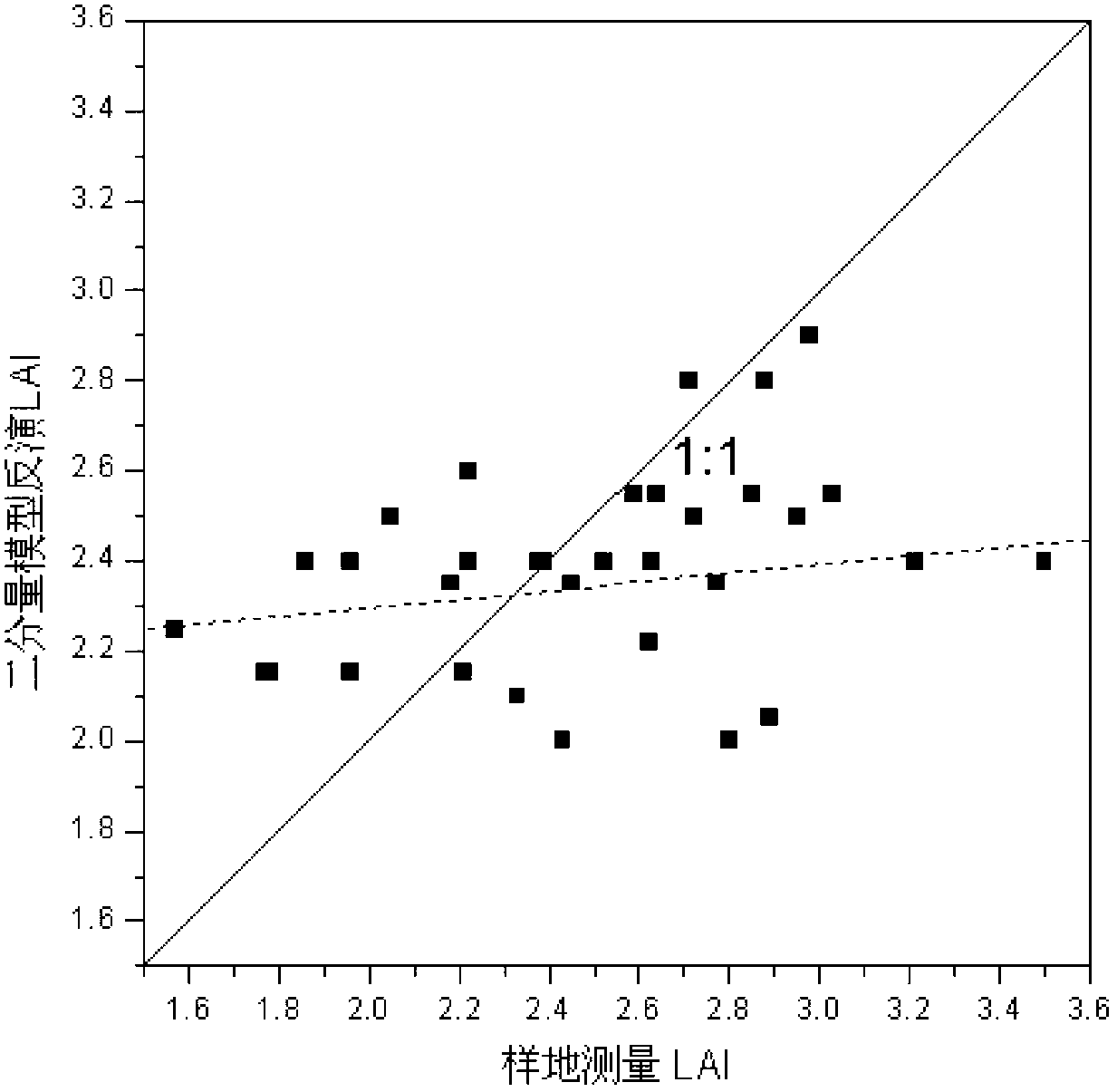
Four-component optical physical model based inversion method of leaf area index
ActiveCN102706293AFewer input parametersImprove inversion accuracyUsing optical meansImaging conditionMean square
The invention relates to a four-component optical physical model based inversion method of leaf area indexes, relating to the inversion method of the leaf area indexes and aiming at solving the problem that a simulated result of a physical model is inaccurate because the traditional two-component physical model can not accurately describe the real composition of a vegetation coverage pixel of a remote sensing image. The inversion method particularly comprises the following steps of: 1, determining the input parameters of the four-component optical physical model through the imaging conditions of the remote sensing image and the characteristics of a forest type; 2, setting an L value to be gradually increased according to 0.1 step length, and establishing a lookup table according to the L value and R4 corresponding to the L value so as to establish the one-to-one corresponding relationship of the leaf area indexes and the reflectivity data of a vegetation canopy; 3, traveling the lookup table by adopting a mean square root error optimization technology to ensure that the leaf area index corresponding to minimum mean square root error is an optimal leaf area index, and taking the optimal leaf area index as an inversion result, wherein the four-component optical physical model is shown as a formula. The invention is suitable for accurately describing the vegetation coverage of the remote sensing image.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG INST OF TECH
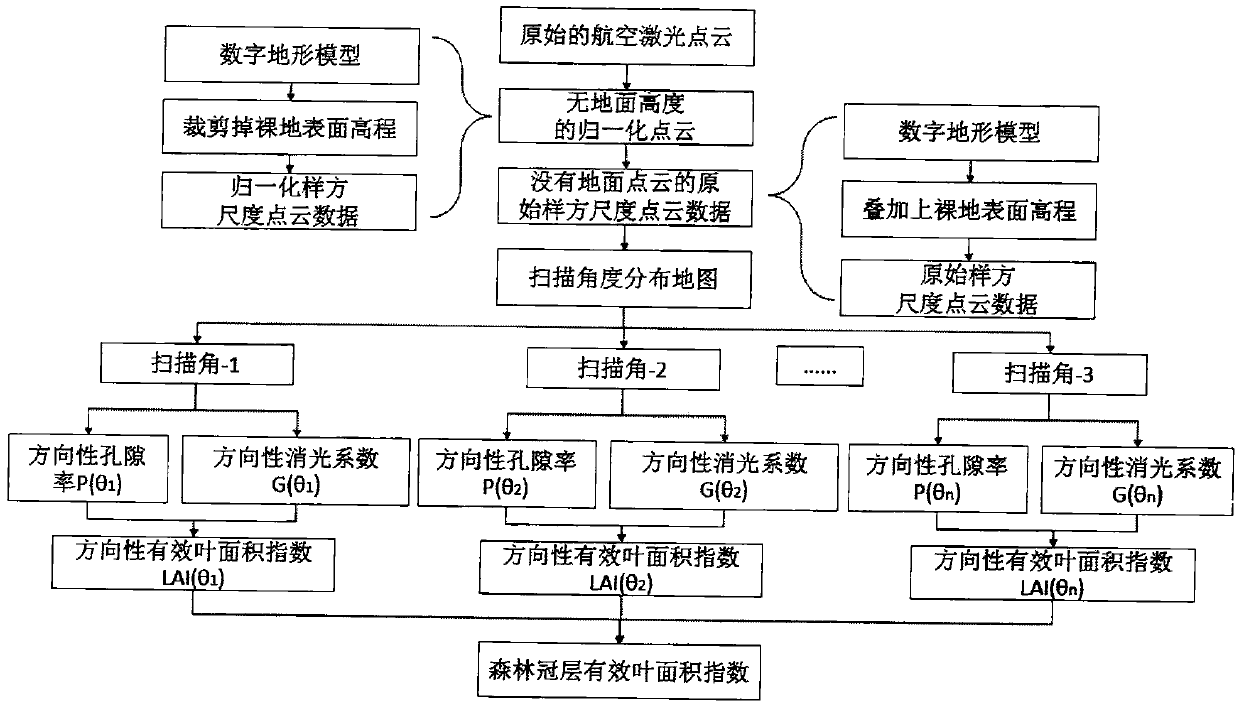
Method for utilizing aviation laser point cloud to calculate effective leaf area index
ActiveCN105371789AImprove estimation accuracyImprove estimation efficiencyUsing optical meansPorosityAviation
The invention provides a method for utilizing an aviation laser point cloud to calculate an effective leaf area index, and belongs to the research field of a forest canopy structure parameter obtaining method. The method comprises the steps of: obtaining and preprocessing three-dimensional laser point cloud data of a vegetation canopy; obtaining quadrat scale point cloud data having no ground point cloud data but having a ground height by means of a digital landform model; carrying out three-dimensional meshing on the point cloud data; under different scanning angles, respectively obtaining directional porosities directional extinction coefficients and directional effective leaf area indexes; and according to the effective leaf area index obtained under each scanning angle and the weight of the angle, obtaining the forest canopy effective leaf area index. Compared with other leaf area index calculating methods, the influences of scanning angle information on the directional porosities, the extinction coefficients and the effective leaf area indexes are fully considered; the canopy structure and the radiation characteristics are not destroyed, and the method is objective, effective and precise; in addition, the method for extracting a three-dimensional structure and biophysical diversity information from laser radar data is further developed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Sensor for measuring direct solar radiation transmittance under different vegetation canopies
InactiveCN102175653AAdjust relative distanceAdjustableTransmissivity measurementsWireless sensor networkingTransmittance
The invention relates to a sensor for measuring the direct solar radiation transmittance under different vegetation canopies, and the sensor provided by the invention comprises an upper canopy sensor and a lower canopy sensor, wherein the upper canopy sensor and the lower canopy sensor are connected through wireless communication; the upper canopy sensor is arranged at the upper parts or outsides of the vegetation canopies; the lower canopy sensor is arranged at the lower parts of the vegetation canopies; the shape of the upper canopy sensor is a rectangle and three light intensity sensor units are additionally arranged on the common wireless sensor network measuring nodes in a vegetation structure parameter measuring device based on a wireless sensor network; the shape of the lower canopy sensor is a long rod-shaped box; and the lower canopy sensor comprises a light intensity sensor unit, a threaded rod, a spring, a waterproof bayonet, a lower canopy sensor box body, a cable signal connector, a knob, a lower canopy sensor box cover, an eight-core cable and a front-end box cover, and the relative position of the 9 components is adjustable. The sensor provided by the invention has the advantages of low manufacturing cost, low energy consumption, wide application range and wide application prospects in the technical fields of agriculture and ecology.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
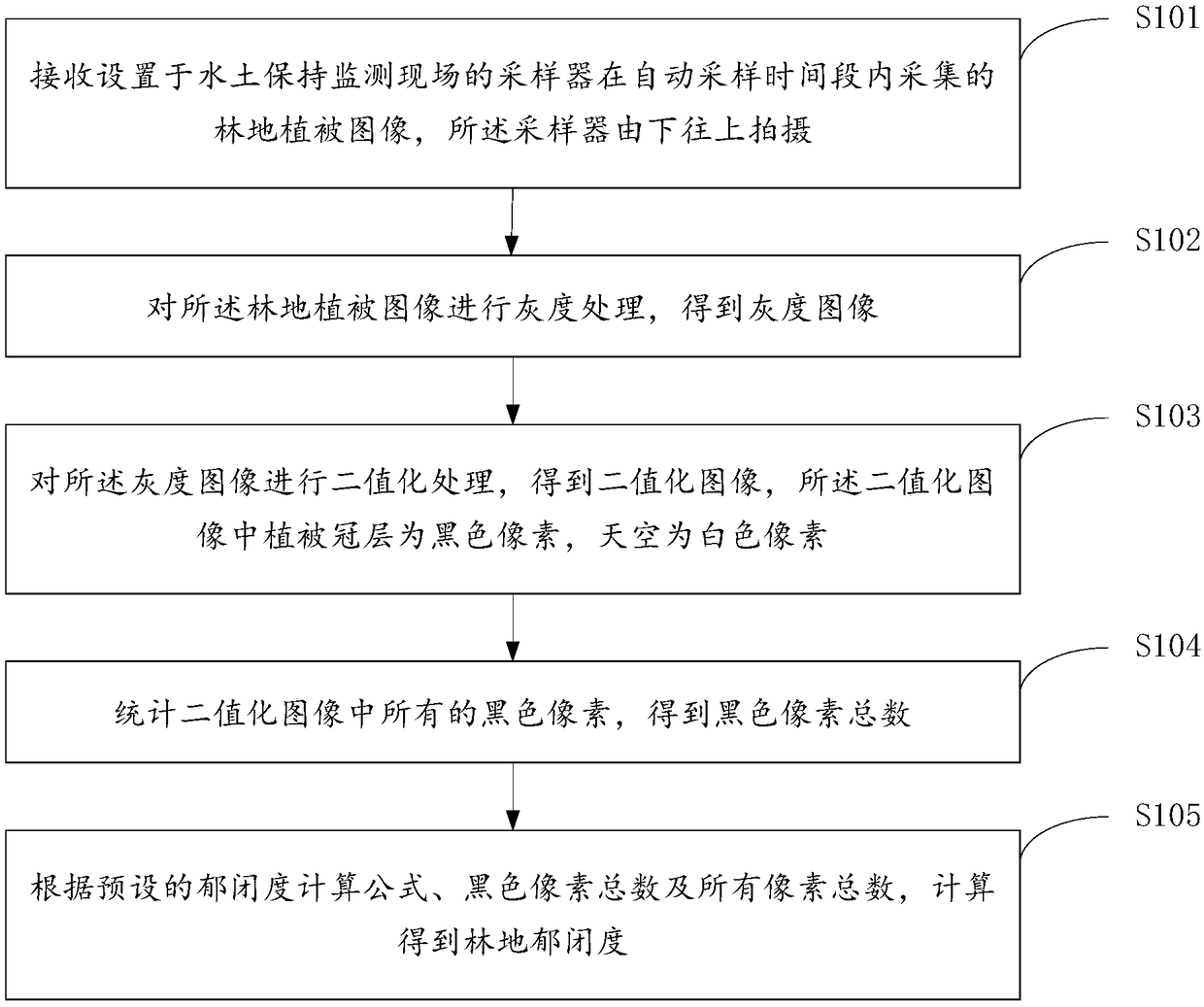
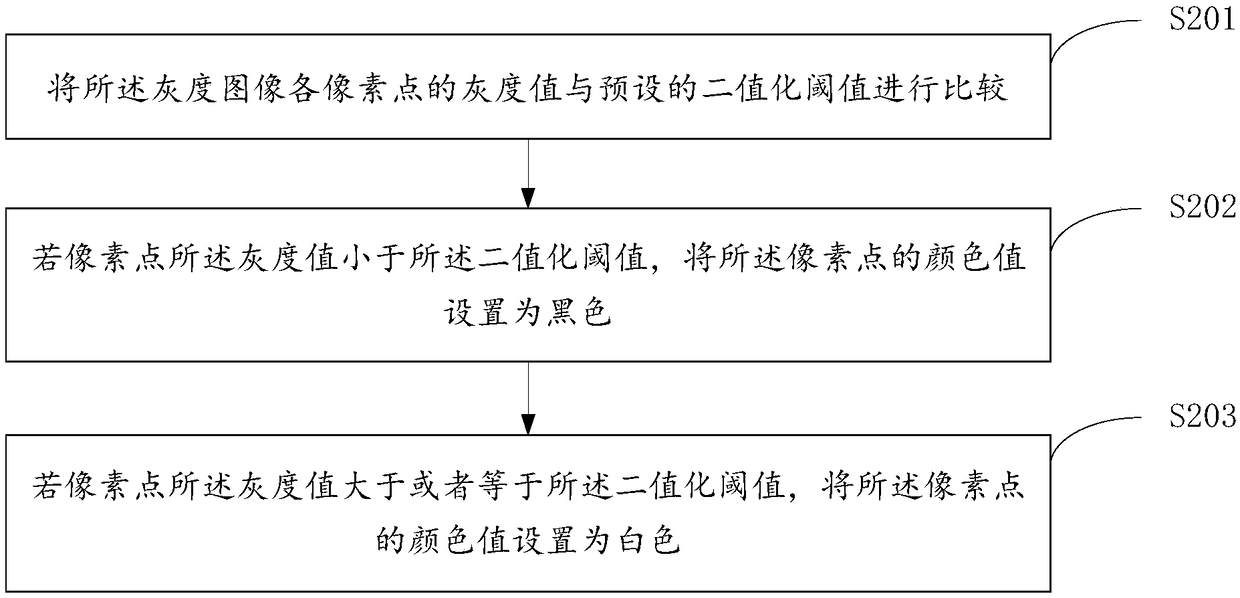
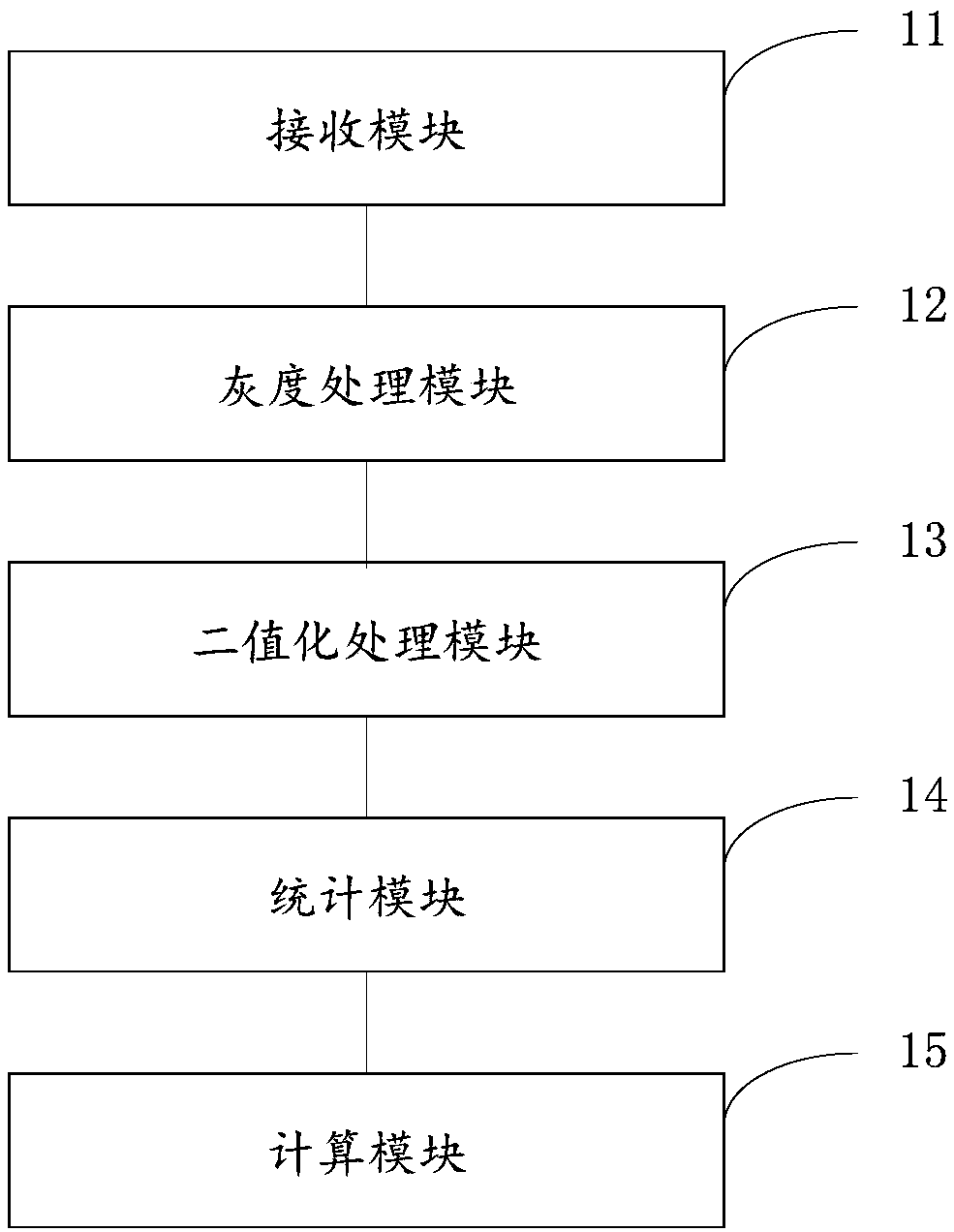
Method, device and system for determining canopy density of forest land
The invention provides a method, a device and a system for determining canopy density of a forest land, which relate to the technical field of soil and water conservation monitoring. The method comprises the following steps: receiving forest land vegetation images collected in an automatic sampling period by a sampler arranged at a soil and water conservation monitoring site; photographing the forest land vegetation images by the sampler from the bottom to the top; processing the grey scale image of woodland vegetation to obtain grey scale image; obtaining the binary image by binarizing the gray image, wherein the vegetation canopy is black pixel and the sky is white pixel in the binarized image; obtaining the total number of black pixels by counting all the black pixels in the binary image; according to the preset canopy density formula, the total number of black pixels and the total number of all pixels, performing calculation to obtain the canopy density of a forest land. The invention solves the technical problem that the canopy of vegetation can not be effectively distinguished from the deciduous leaves on the surface and the associated shrub leaves on the surface due to the very close color, and the measured value is similar to the canopy density of a forest land, and achieves the technical effect of obtaining the accurate canopy density data of a forest land.
Owner:POWERCHINA HUADONG ENG COPORATION LTD
Forest three-layer scattering model determination and analysis method suitable for PolInSAR inversion
ActiveCN110569624AWell describedHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSurface layerStructure function
The invention discloses a forest three-layer scattering model determination and analysis method suitable for PolInSAR inversion, and belongs to the technical field of remote sensing image processing.The objective of the invention is to solve the problem that an error still exists in a scattering process of an existing vegetation coherent scattering model compared with a real scattering process, and the inversion precision is affected. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, analyzing scattering characteristics of a ground surface layer and determining a vertical structure function form of the ground surface layer; step 2, analyzing scattering characteristics of a trunk layer and determining a vertical structure function form of the trunk layer; step 3, scattering characteristicsof the vegetation canopy are analyzed, and determining a vertical structure function form of the vegetation canopy; and step 4, deriving a vegetation general three-layer scattering model by combiningvertical structure functions of a ground surface layer, a trunk layer and a vegetation canopy on the vegetation vertical structure, determining an expression of an interference coherence coefficient,and analyzing the influence of height parameters on coherence. The method can be applied to the field of remote sensing image processing, and high-precision polarization interference SAR image vegetation parameter inversion is realized.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for estimating forest leaf-area index based on point cloud hemisphere slice
ActiveCN105389538AImprove simulation accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisVegetation canopyLeaf area index
The invention provides a method which can estimate the forest leaf-area index by means of ground laser point cloud data based on a point cloud hemisphere slice and belongs to the research field of a forest canopy structure parameter acquisition method. The method includes the following steps of: acquiring three-dimensional laser point cloud data of a vegetation canopy, and performing pretreatment on the three-dimensional laser point cloud data; automatically dividing the point cloud data into three types including the point cloud data of a photosynthesis canopy part (e.g. leaves and flowers), the point cloud data of a non-photosynthesis canopy part (e.g. trunks and branches) and the point cloud data of a bare land, based on a local set feature method; researching spatial distribution forms of the point cloud data of the photosynthesis canopy part and the point cloud data of the non-photosynthesis canopy part in a three-dimensional space according to a radial hemisphere point cloud slice algorithm, and calculating the angle porosity; calculating the extinction coefficient; extracting the effective leaf-area index; and evaluating a contribution value of a xylem part to calculation of the forest angle porosity and the forest effective leaf-area index according to a laser point cloud point-to-point classification result. The result show that: according to the ground laser point cloud data, the contribution rate of the xylem part to the effective leaf-area index is 19% to 54% in forests with different densities; and the correlation between the effective leaf-area index calculated by the method and the effective leaf-area index calculated through a fish-eye camera, reaches 74.27%. The method for estimating forest leaf-area index based on the point cloud hemisphere slice enriches the application that the ground laser point cloud data is used to extract a forest canopy three-dimensional structure and bio-physical parameters.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
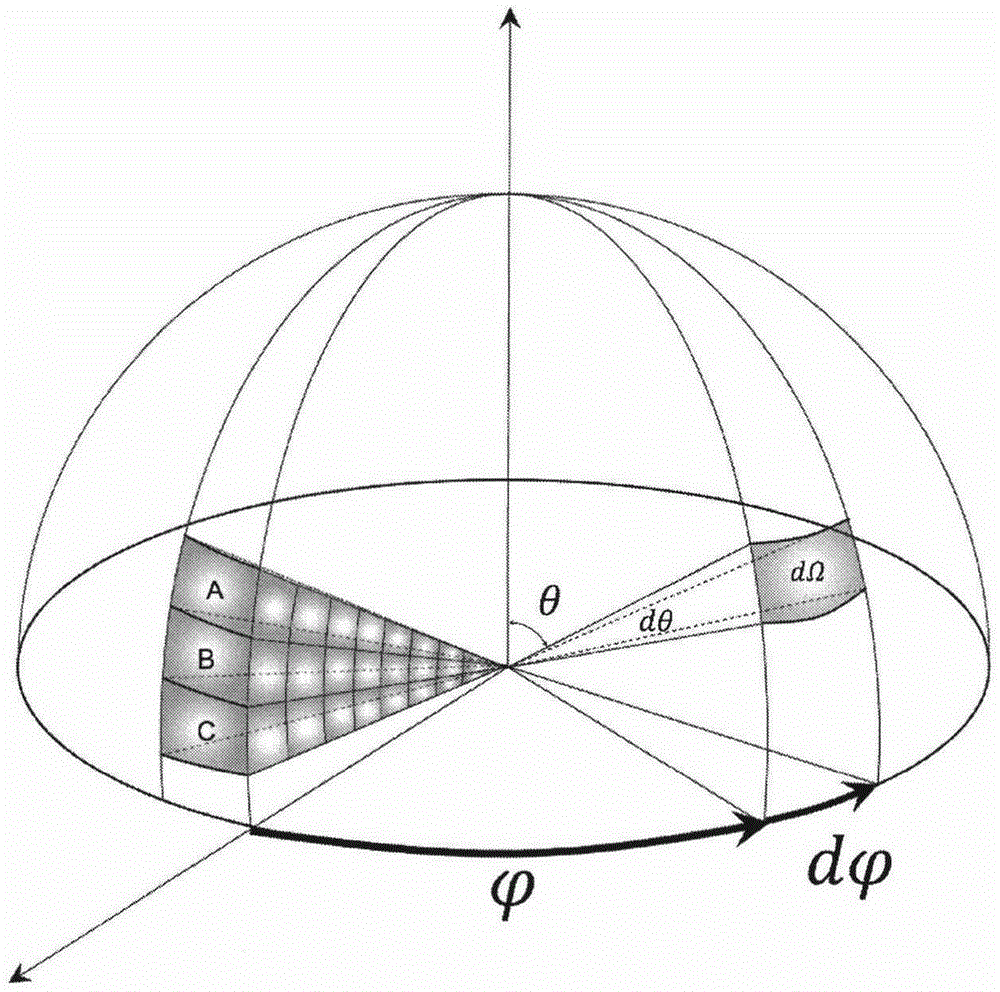
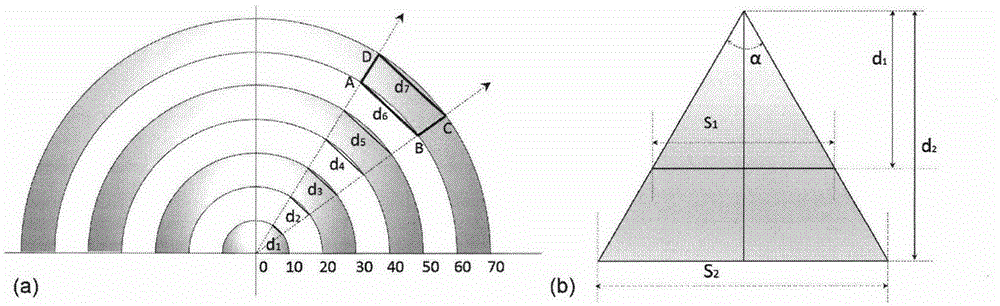
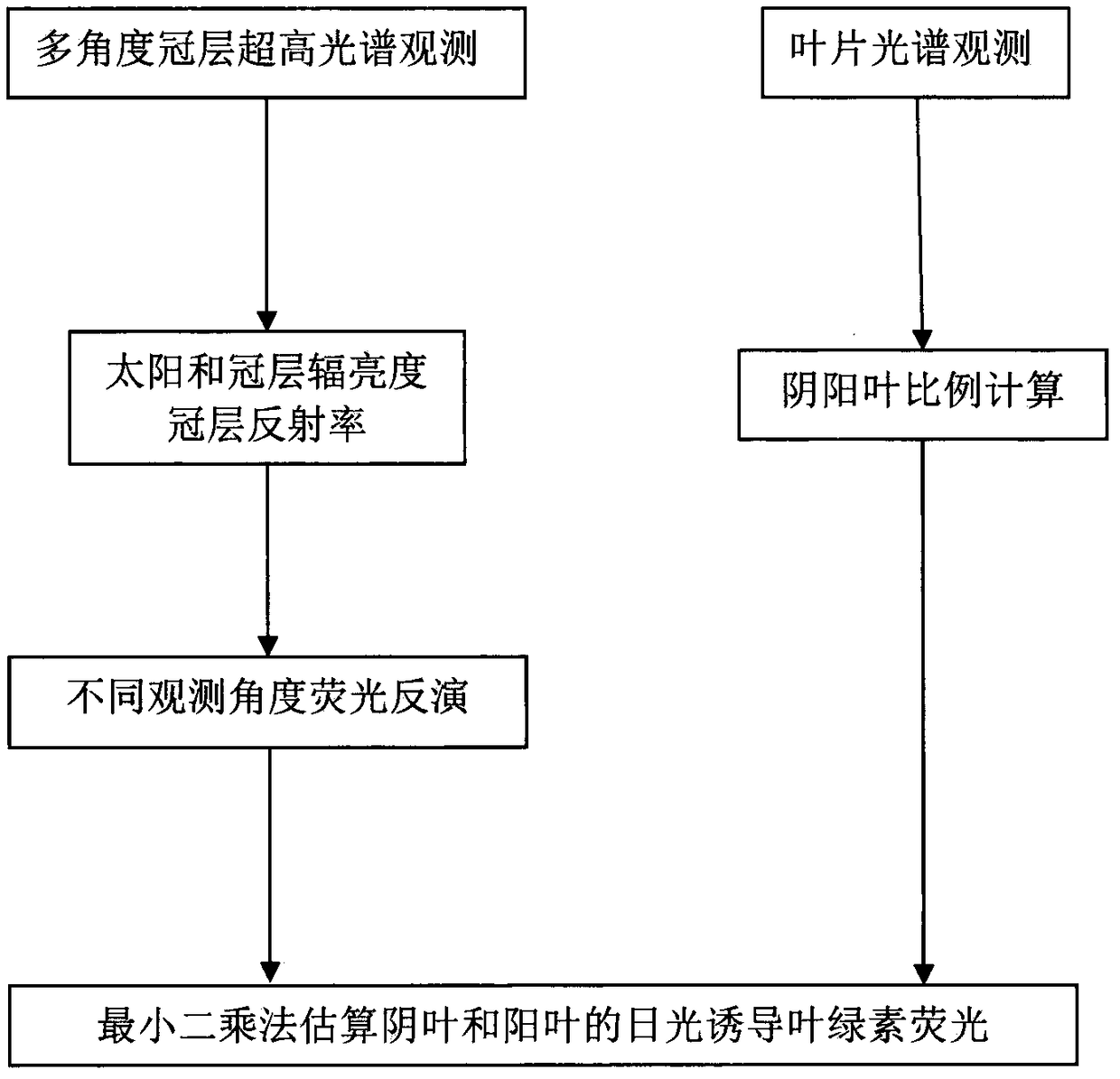
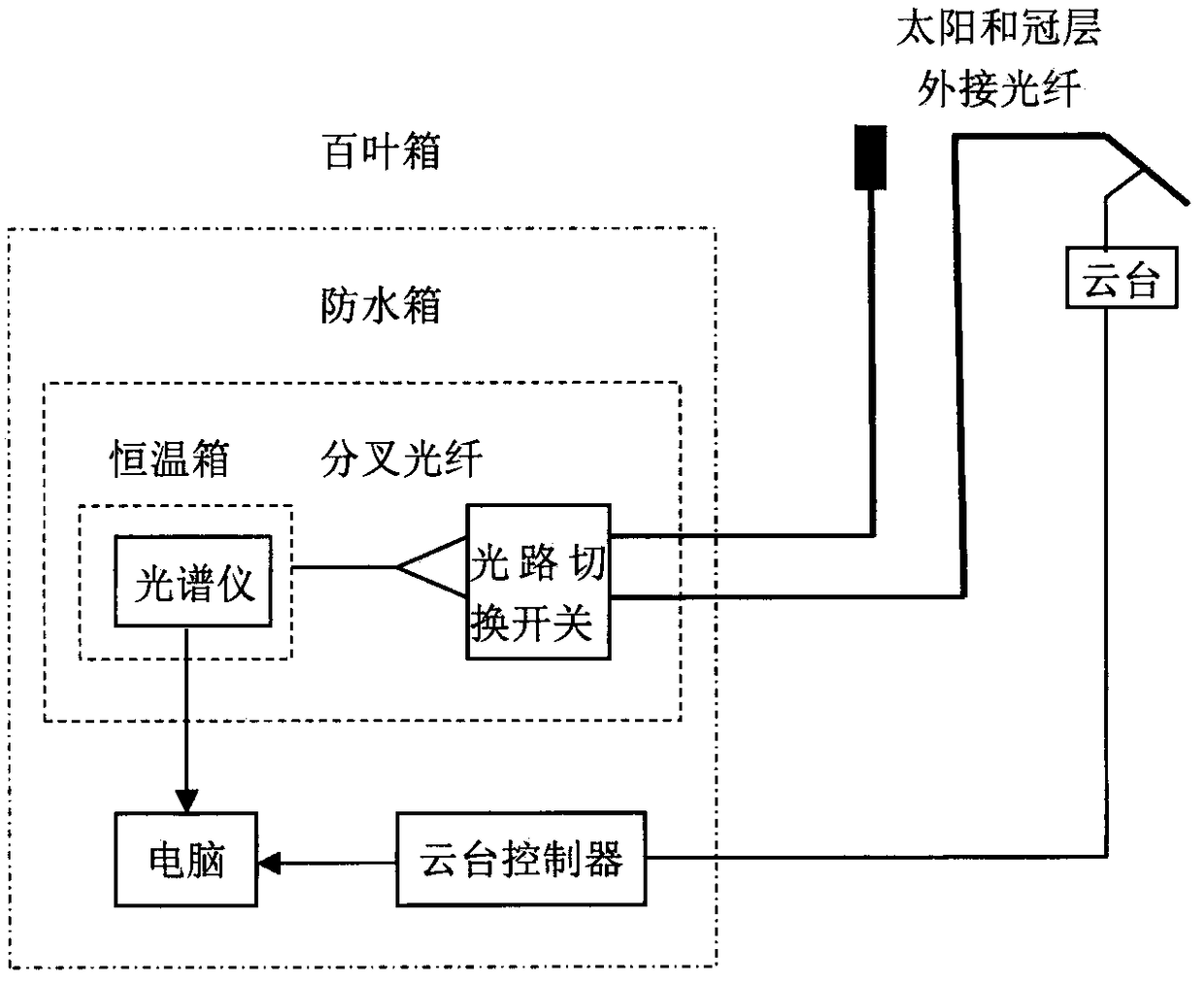
Method for multi-angle observing and precisely inverting sunlight induced chlorophyll fluorescence of shade/sun leaf of vegetation
The invention provides a method of utilizing a multi-angle observation system to obtain the vegetation canopy spectroscopic data to precisely inverting sunlight induced chlorophyll fluorescence of shade / sun leaves of a canopy, and belongs to the research field of vegetation remote sensing inversion parameter obtaining methods. The method comprises following steps: establishing a multi-angle super-hyperspectral observing system; obtaining multi-angle super-hyperspectral data; calculating the solar incident angle and canopy reflection brightness; calculating the reflection rate and inverted chlorophyll fluorescence; using a leaf clamp to observe the leaf reflection rate; utilizing the ratio of canopy reflection rate to leaf reflection rate, under the assistance of a geometrical optical model, calculating the ratio of shade / sun leaves from different observation angles, and obtaining the fluorescence of the sun leaves and shade leaves through fitting of least square method. The provided method can obtain continuous multi-angle vegetation canopy super-hyperspectral data, is used to invert chlorophyll fluorescence, can simply and effectively calculate the ratio of sun leaves and shade leaves of a canopy from different observation angles and solar incident angles based on the leaf reflection rate and a geometrical optical model, calculates the fluorescence of the sun leaves and shadeleaves, and improves the precision of monitoring the primary productivity of a land.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
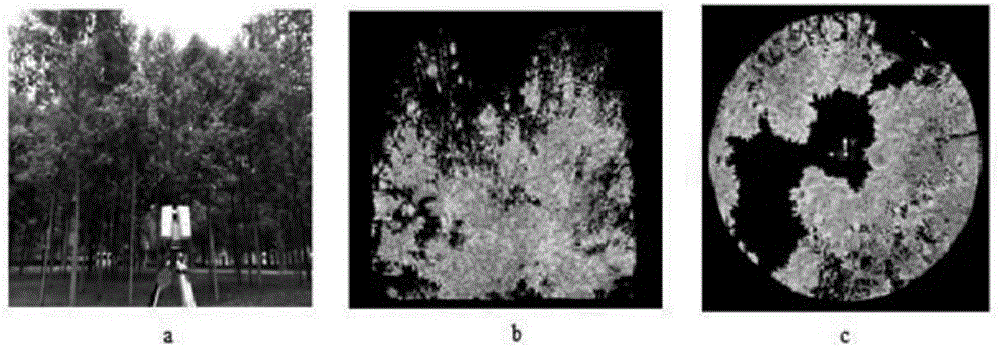
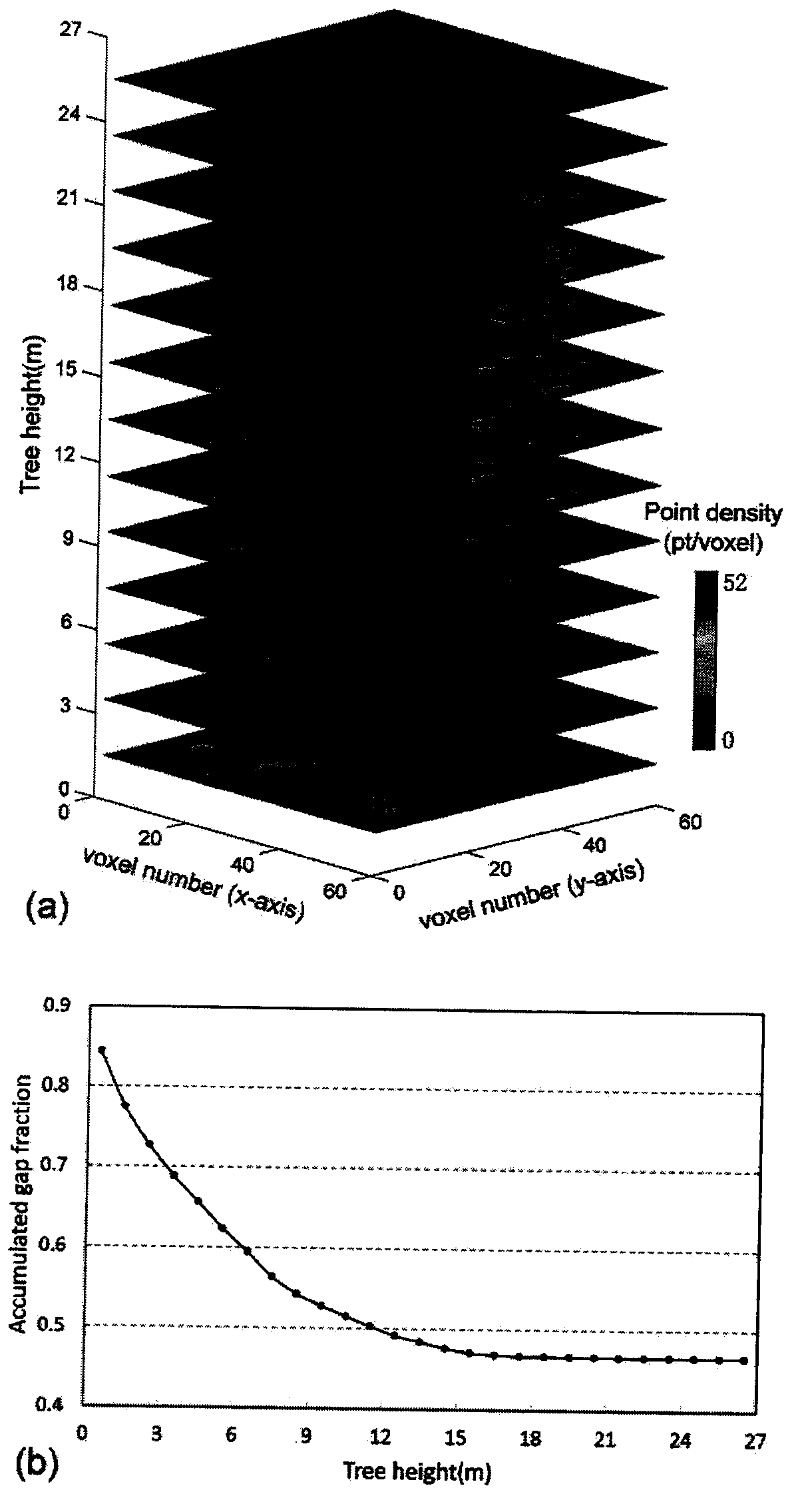
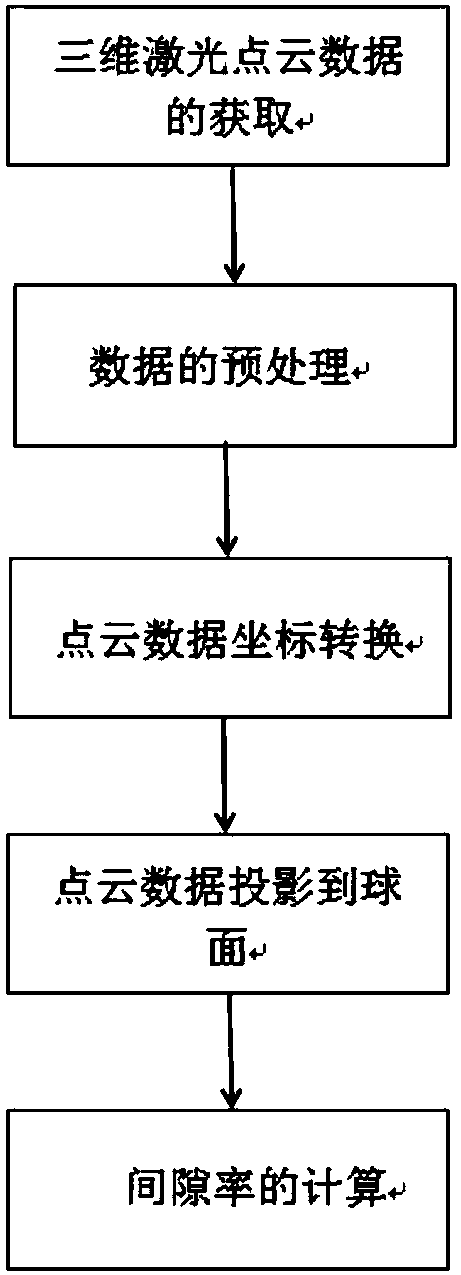
Method for extracting gap fraction of vegetation canopy by three-dimensional laser point cloud
ActiveCN108195736AQuick extractionAccurate extractionPermeability/surface area analysisVoxelRadar remote sensing
The invention belongs to the technical field of laser radar remote sensing, and specifically relates to a method for extracting a gap fraction of a vegetation canopy by a three-dimensional laser pointcloud. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: acquiring three-dimensional point cloud data of a vegetation-like square canopy by a ground three-dimensional laser radar scanning system without influence of illumination conditions, a camera and manually set thresholds during observation; then, projecting the cloud data to a sphere and a hemisphere for region division bya point cloud data conversion coordinate system; and finally, calculating the gap fraction of the canopy. The method provided by the invention projects the point cloud data to a sphere surface for solving the gap fraction and guaranteeing correlation of results, avoids problems of distortion, the large amount of calculation and time-consuming algorithm when using a voxel model to represent a canopy structure, and can rapidly and accurately extract the gap fraction of the vegetation canopy.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
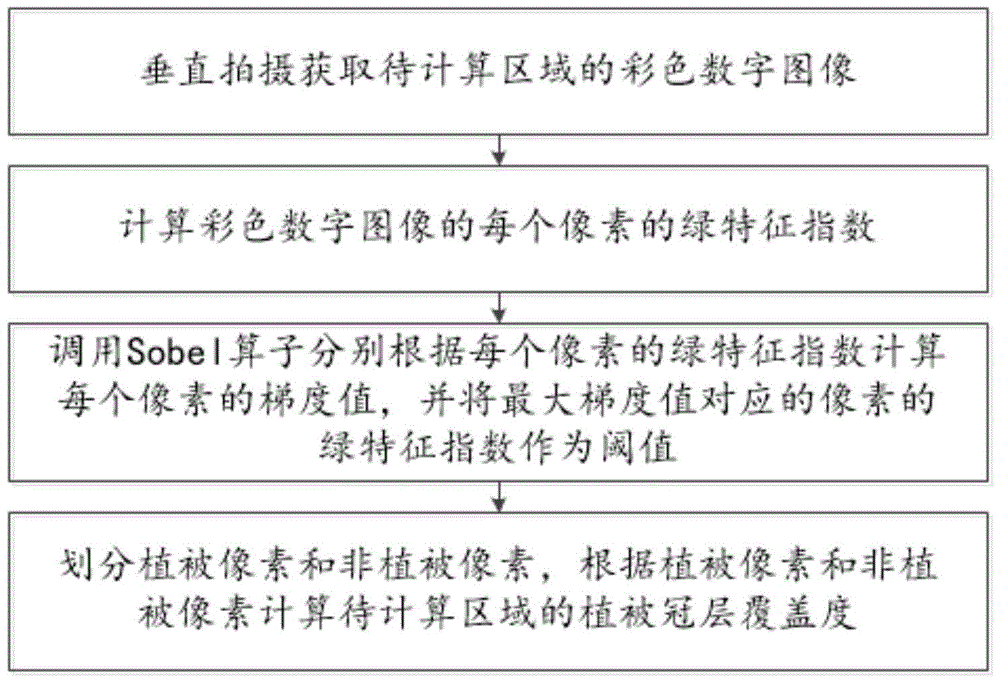
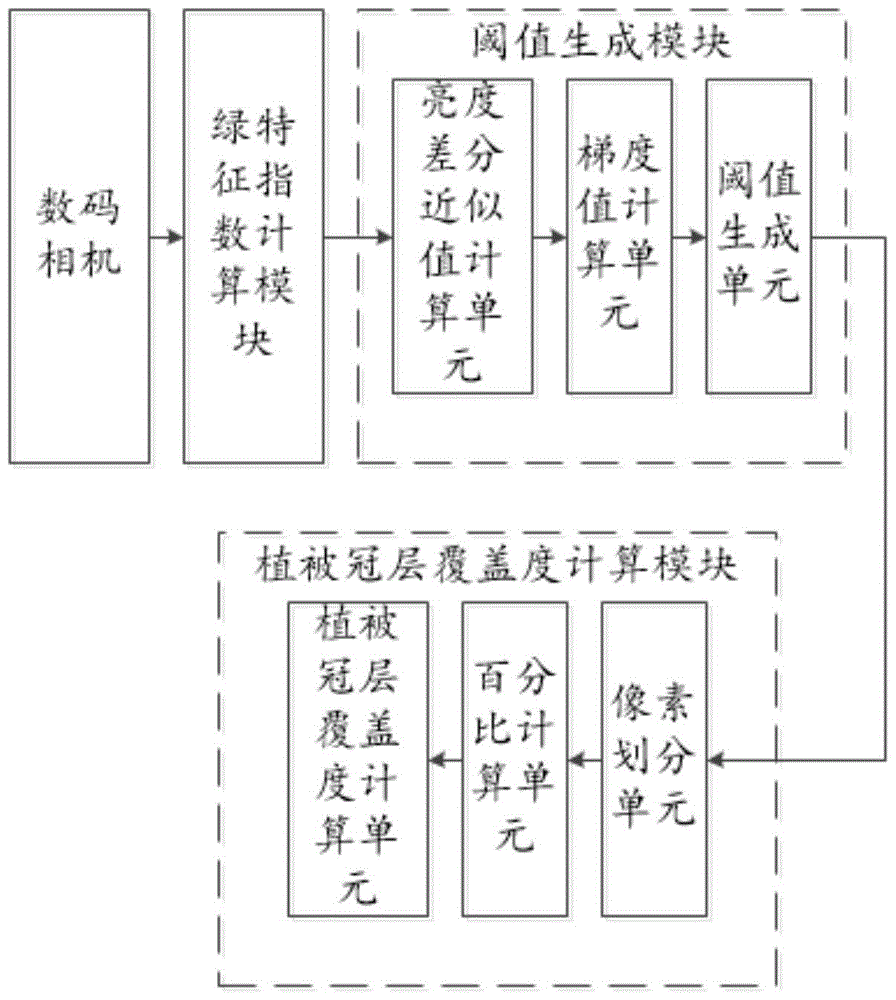
Vegetation canopy coverage calculation method and system based on colorful digital image
ActiveCN105719320AEasy to operateStrong applicability in the fieldImage enhancementImage analysisDigital imageComputer vision
The invention relates to a vegetation canopy coverage calculation method and system based on a colorful digital image. The method comprises that the colorful digital image of an area to be calculated is shot vertically; the green characteristic index of each pixel of the colorful digital image is calculated; a Sobel operation is called to calculate a gradient value of each pixel according to the green characteristic index of the pixel, and the green characteristic index of the pixel corresponding to the maximal gradient value serves as a threshold; and the green characteristic index of each pixel is compared with the threshold, the pixels whose green characteristic index is greater than or equivalent to the threshold are attributed to vegetation pixels, the pixels whose green characteristic index lower than the threshold are attributed to non-vegetation pixels, and the vegetation canopy coverage of the area to be calculated is calculated according to the vegetation pixels and the non-vegetation pixels. According to the invention, the vegetation canopy coverage is calculated in high precision, labor force is saved, and the self-adaptability is high.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
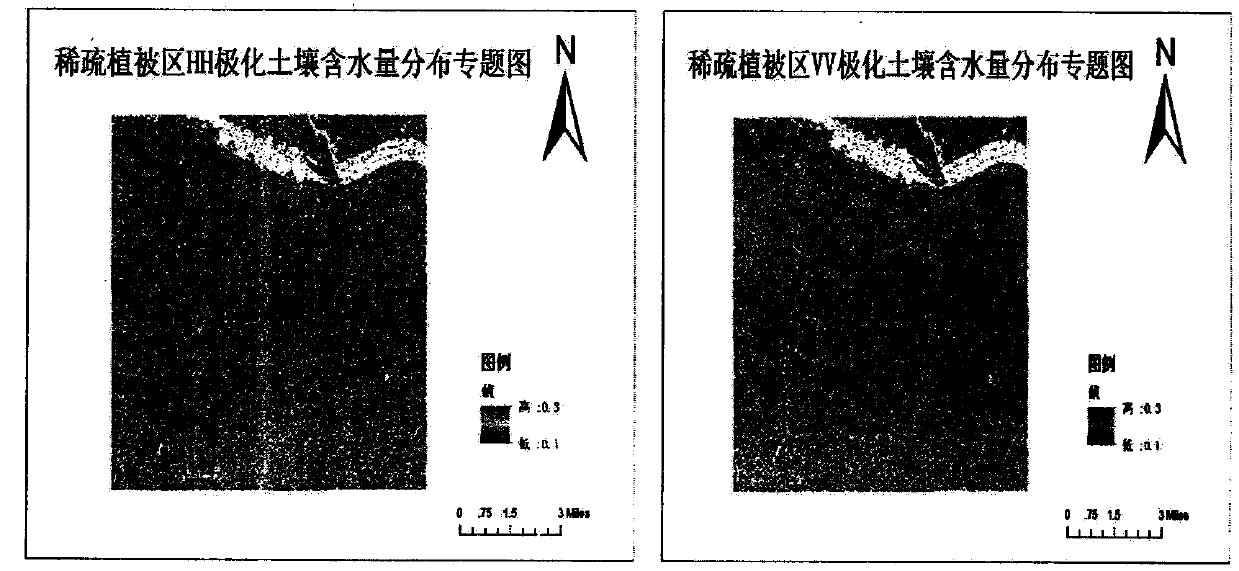
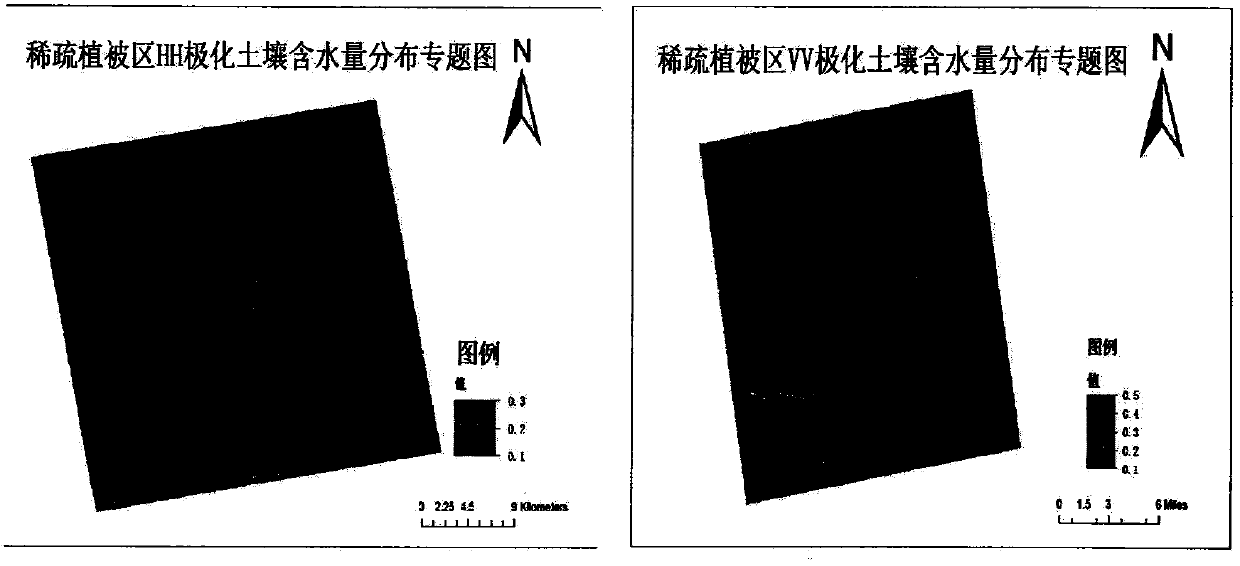
Inversion method for soil water content of vegetation coverage land surface based on multi-polarization RADARSAT-2 and Landsat8 data
The invention discloses an inversion method for the soil water content of a vegetation coverage land surface based on multi-polarization RADARSAT-2 and Landsat8 data. The method comprises the following steps that 1) a relation model among the backward scattering coefficient co-polarization difference, the backward scattering coefficient co-polarization sum, the land surface roughness and the soil water content is established based on an IEM model; 2) a relation model between backward scattering coefficient co-polarization data and the soil water content of a bare earth area is established based on a Dubois model and the step 1); 3) based on a PROSAIL radiation transfer model, a relation model between NDVI, NDWI1, NDWI2 and MSI and the vegetation canopy in the whole growth period (including the initial stage, the mid stage and the last stage) of corns and the initial stage of winter wheat is established, and a striograph of the vegetation water content is drawn; and 4) the inversion method for the soil water content of the vegetation coverage land surface is established by combining a soil water content semi-empirical model of the bare earth area with the vegetation water content model. The method can be used to further improve the inversion precision of the soil water content via multi-source data cooperation, multi-model fusion and multi-area test.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Remote sensing quantitative reversion method and system of crop physical and chemical parameters
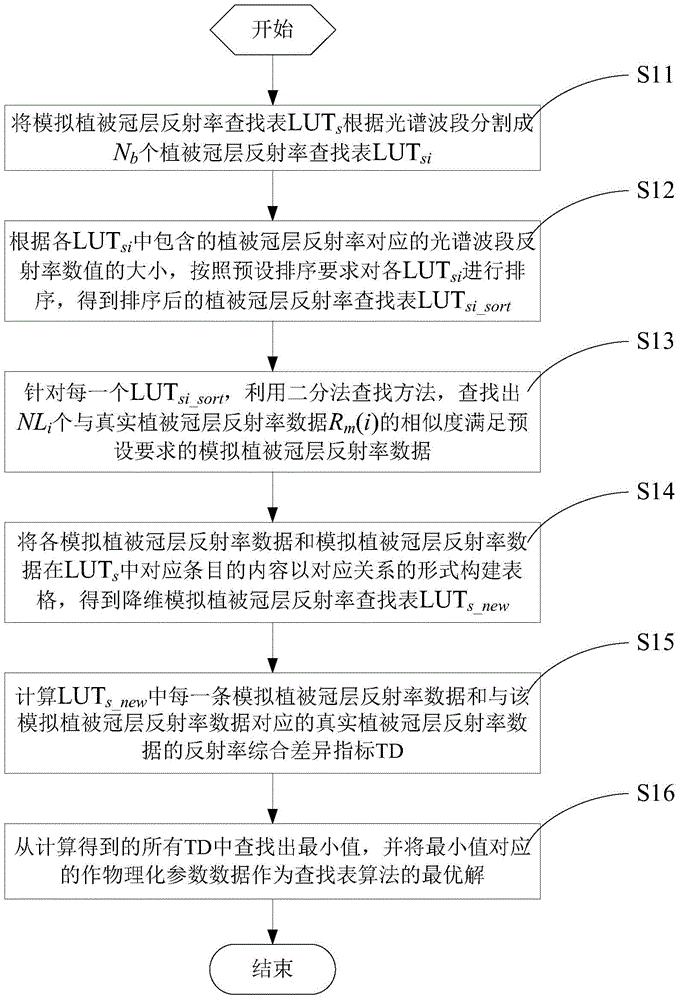
ActiveCN105738293AAccuracy meetsImprove numerical accuracy of inversionColor/spectral properties measurementsComputation complexitySpectral bands
The invention discloses a remote sensing quantitative reversion method and system of crop physical and chemical parameters.According to the method, LUTs is segmented into LUTsi of the same number according to the spectral band number, all the LUTsi are ranked to obtain LUTsi_sort, for each LUTsi_sort, a bisection method searching method is utilized for searching for simulating vegetation canopy reflectivity data with similarity to real vegetation canopy reflectivity data meeting the preset requirement, all the simulating vegetation canopy reflectivity data and content of corresponding items of the data in the LUTs are used for constructing a form in a corresponding relation form to obtain LUTs_new, each simulating vegetation canopy reflectivity data and TD of the real vegetation canopy reflectivity data corresponding to the simulating vegetation canopy reflectivity data in the LUTs_new are calculated, and crop physical and chemical parameter data corresponding to the minimum value in the TD serves as the optimal solution of the lookup table algorithm.According to the method and the system, the size and the direction character of the vegetation canopy reflectivity data are considered comprehensively, and the calculation complexity is reduced while the crop physical and chemical parameter inversion numerical precision is improved.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Vegetation canopy transpiration inversion algorithm considering phenological information
ActiveCN112182882AImprove estimation accuracyGood linear relationshipCharacter and pattern recognitionDesign optimisation/simulationStomaNonlinear model
The invention discloses a vegetation canopy transpiration inversion algorithm considering phenological information, belongs to the technical field of water circulation key parameter quantitative inversion. According to the invention, seasonal leaf area change and phenological rhythm information of a vegetation canopy by utilizing satellite remote sensing vegetation index data. The invention provides a dynamic parameterization method for a stomatal conductance slope parameter in a photosynthetic conductance model. The remote sensing leaf area index (LAI) refers to the growth activity of the vegetation canopy leaf, which indicates that the LAI and the stomatal conductance slope parameter have a good linear relationship in the annual period. The vegetation growth season is divided into a growth period and a fading period by utilizing the LAI time sequence change, and the relationship between the LAI and the stomatal conductance slope parameter is respectively established for different phenological periods, so that the asymmetric response of the stomatal conductance slope parameter to the LAI change can be clearly identified, and the important influence of the phenology on the leaf function is reflected; the result shows that the estimation precision of the nonlinear model on the stomatal conductance slope parameter is higher, and the seasonal error of canopy stomatal conductance and transpiration can be effectively reduced.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Leaf area index inversion method and device
ActiveCN109975250AHigh precisionReduce precisionScattering properties measurementsNeural architecturesNetwork modelComputer science
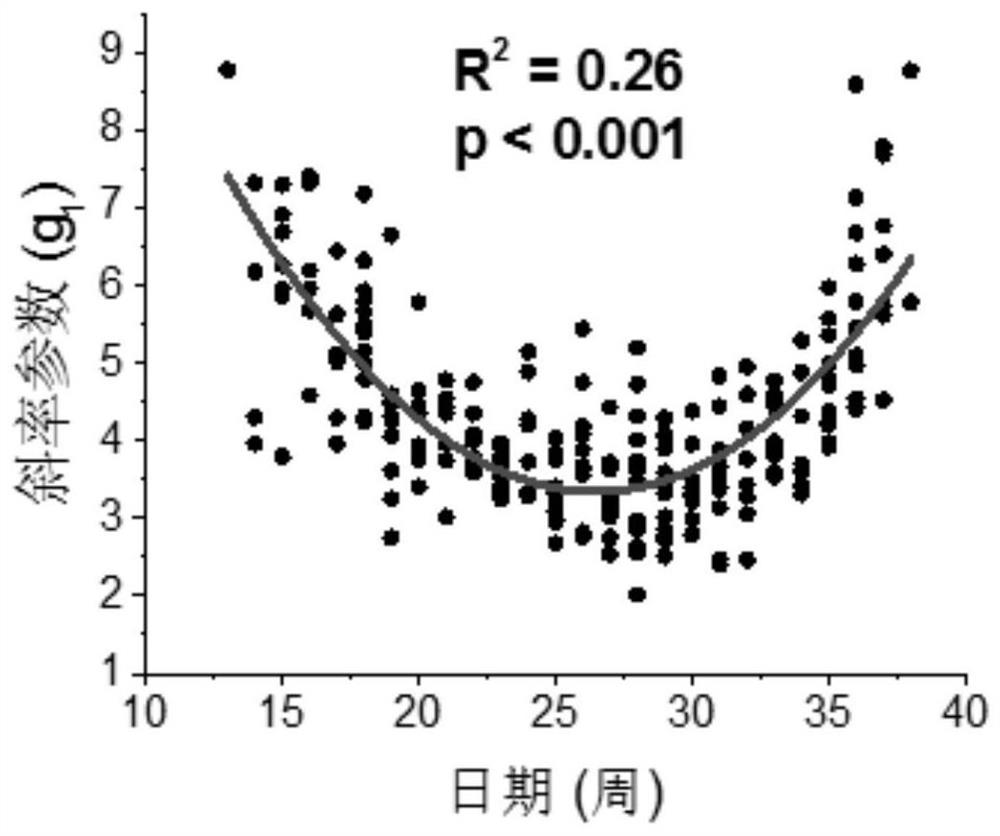
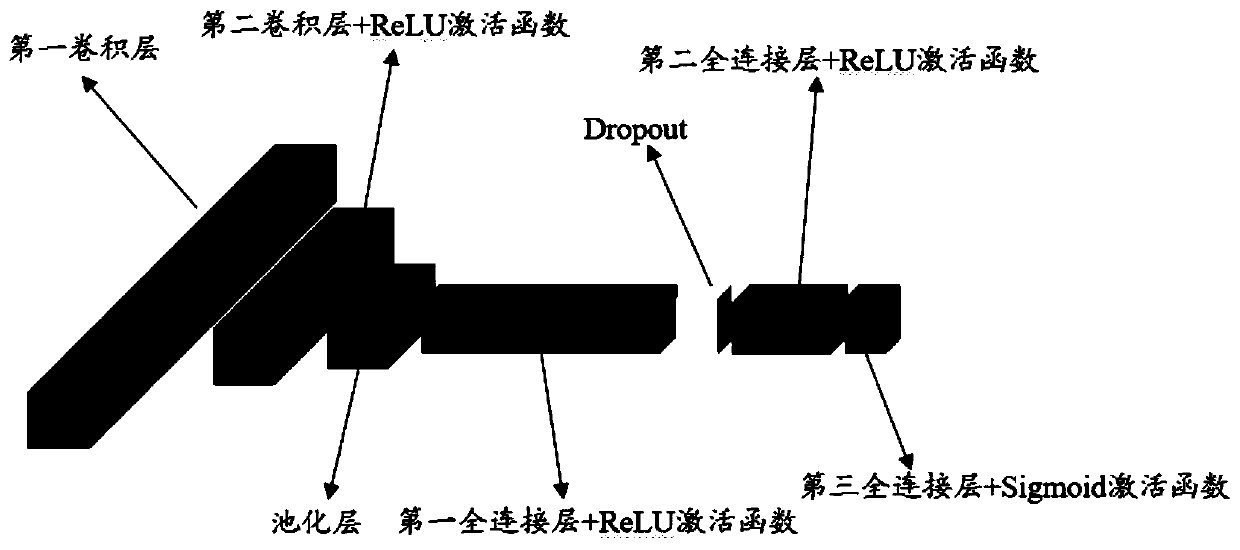
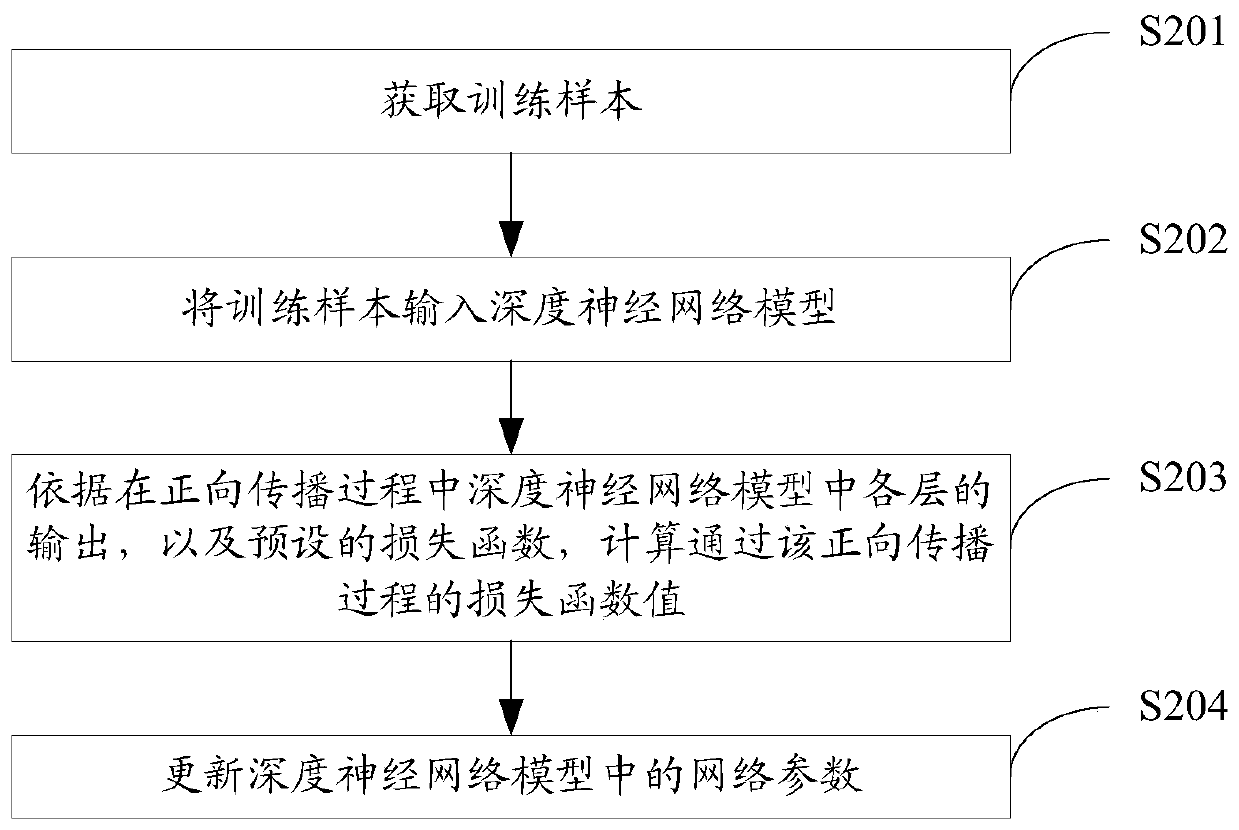
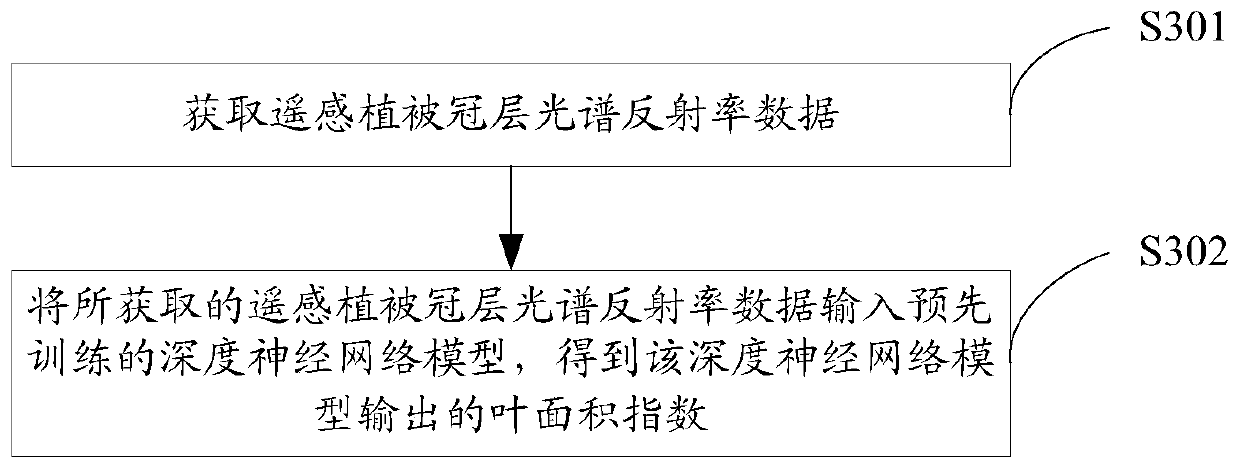
The invention discloses a leaf area index inversion method and device, wherein the method comprises the following steps of obtaining remote sensing vegetation canopy spectral reflectance data, and inputting the remote sensing vegetation canopy spectral reflectance data into a pre-trained deep neural network model to obtain a leaf area index output by the depth neural network model, wherein the deep neural network model comprises at least a convolutional layer, and the sampling stride of the convolutional layer is greater than 1 and takes no more than the maximum value of the scale value of thefilter used by the convolutional layer. Through this application, the leaf area index with high precision can be reversed.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Double channel automatic observation method of plant chlorophyll fluorescence
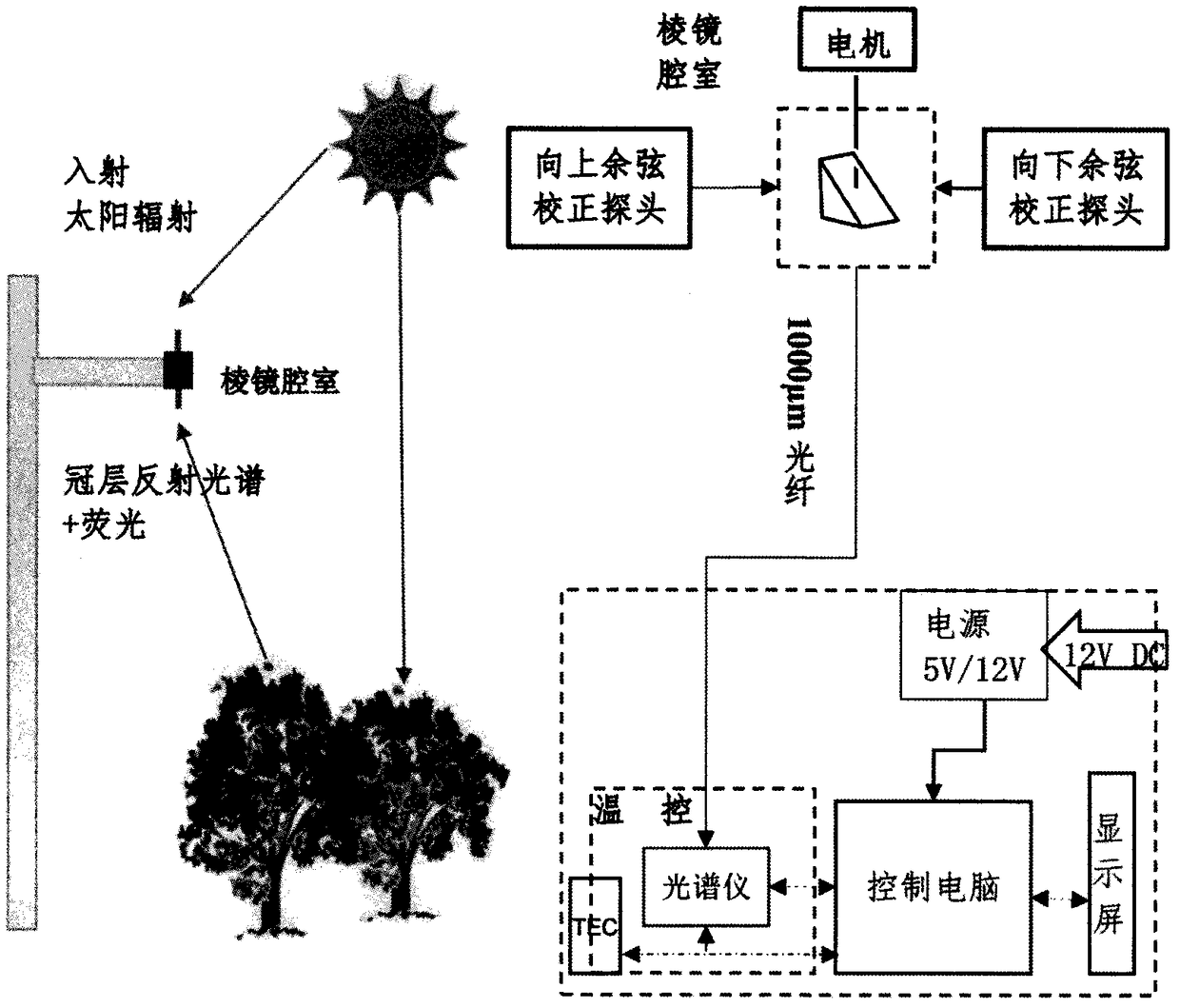
ActiveCN108593611AAvoid attenuationAvoid Spectral ShiftFluorescence/phosphorescenceOptical pathObservation method
The invention provides a method for accurately inverting canopy sunlight induction of chlorophyll fluorescence through plant canopy spectral data obtained by a spectral observation system based on a prism splitting optical path and belongs to the research field of plant remote sensing inversion parameter acquisition methods. The method comprises building a hyperspectral observation system using prisms to split and switch optical paths, automatically and continuously acquiring hyperspectral data, calculating solar incidence and canopy reflection radiance, calculating canopy reflectivity and inverting chlorophyll fluorescence. Through rotation of the prisms, the solar incident spectrum and the canopy reflection spectrum are alternately acquired so that the uniqueness of the optical path entering the spectrometer is guaranteed, the attenuation of the double optical paths or the multiple optical paths to lights and the offset between the spectral ends are avoided, the noise interference ofthe fluorescence inversion is reduced, the continuous and high quality plant canopy fluorescence data products are obtained and the accuracy of land primary productivity monitoring is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for detecting vegetation canopy sun leaves and shade leaves based on fluorescence remote sensing
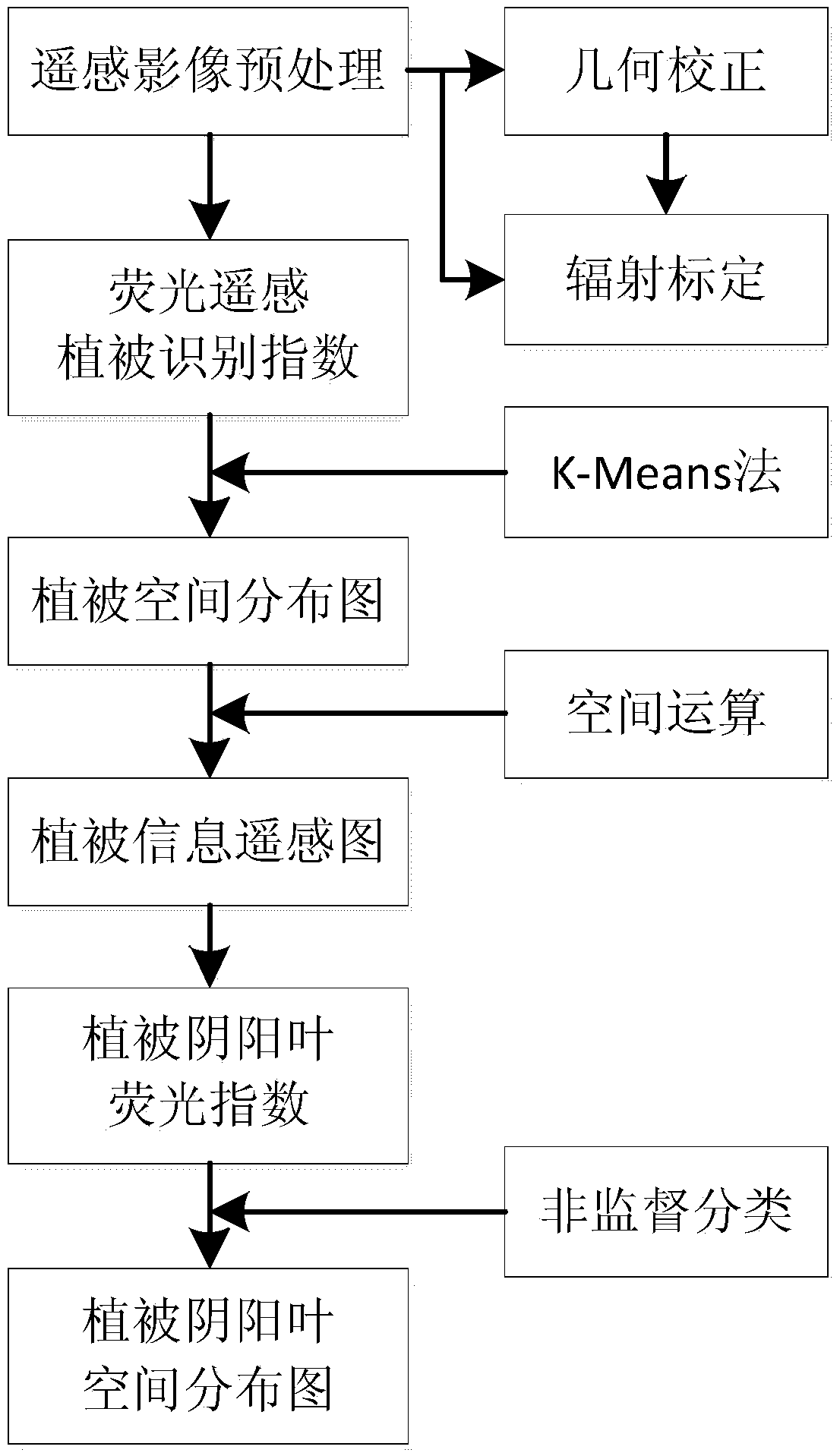
ActiveCN108399393AEliminate the effects ofImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionFluorescenceClassification methods
The invention discloses a method for detecting vegetation canopy sun leaves and shade leaves based on fluorescence remote sensing. The method comprises the steps that precise geometric correction andradiation calibration are conducted on a target remote sensing image; a fluorescence remote sensing vegetation identification index is established ad calculated; a vegetation spatial distribution mapis obtained by calculation through a K-means method; a remote sensing image map only containing vegetation information is obtained by adopting a spatial operation method; a vegetation sun-shade leaf fluorescence index is established ad calculated; and vegetation canopy sun-shade leaf information is extracted by adopting a remote sensing unsupervised classification method to obtain a vegetation sun-shade leaf spatial distribution map. The method for detecting vegetation canopy sun leaves and shade leaves based on the fluorescence remote sensing has the advantages that the influence of non-vegetation background information on a vegetation canopy sun-shade leaf detection result is eliminated furthest, and the accuracy and reliability of sun-shade leaf detection are improved; the problem of vegetation canopy sun leaves and shade leaves distinction is effectively solved, the detection precision is high, the operation processes are simple and flexible, the vegetation types are not limited, the manual interference is little, the automation degree is high, the universality is higher, and the promotion and application are easy.
Owner:河北省科学院地理科学研究所
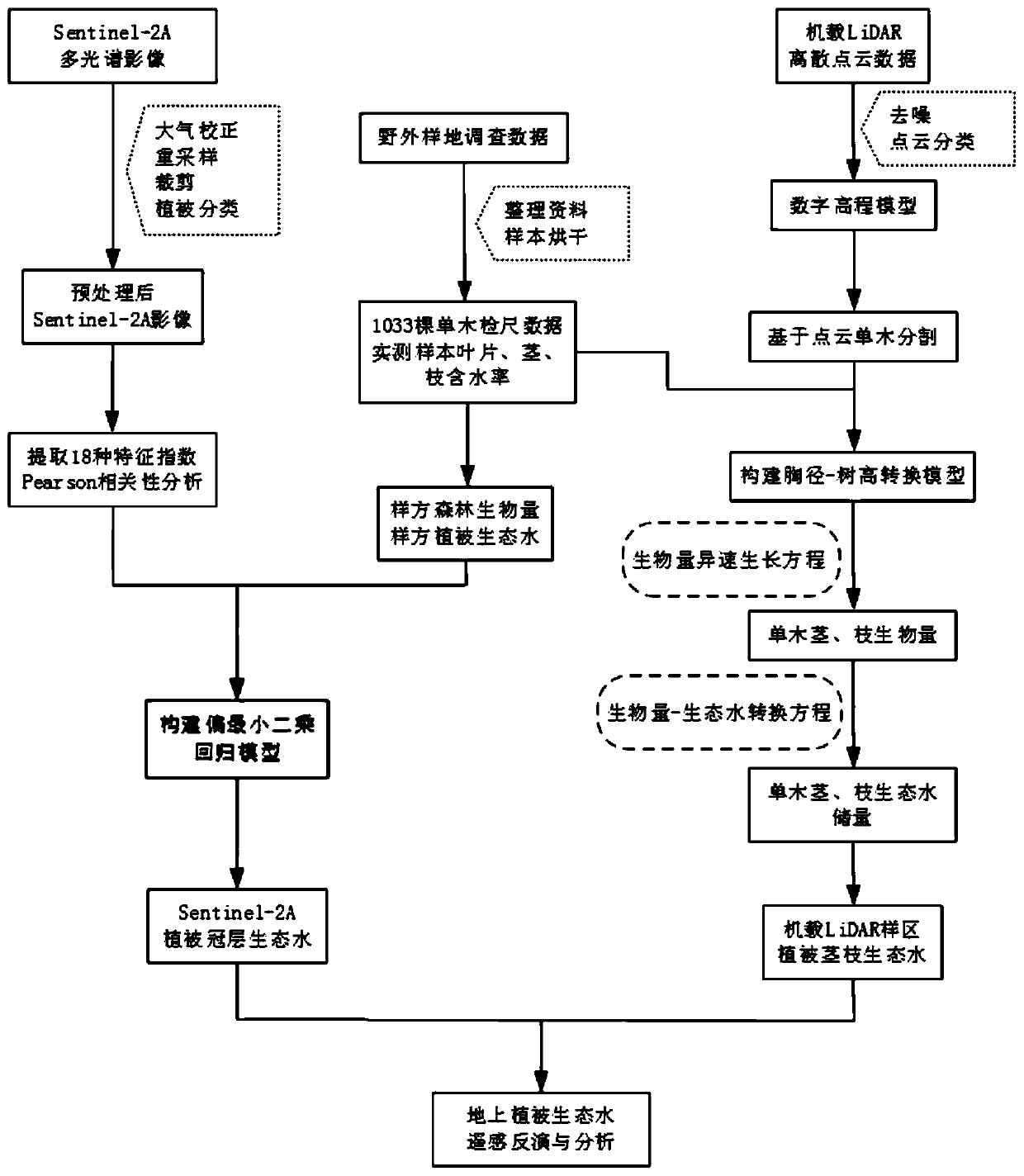
Aboveground vegetation ecological water estimation method based on airborne LiDAR (Light Detection And Ranging) and Sentinel-2A data
ActiveCN110378926AEliminate the effects ofKeep more feature informationImage enhancementImage analysisEnvironmental resource managementAbove ground
The invention relates to an aboveground vegetation ecological water estimation method based on airborne LiDAR and Sentinel-2A data, solves the hydrological effect problem of vegetation from a macroscopic level, undoubtedly is beneficial exploration and attempt, and comprises the following steps: step S10, selecting a research area, and collecting field sample plot survey data; s20, 18 characteristic indexes are extracted from Sentinel-2A remote sensing data, and a vegetation canopy ecological water model is constructed; s30, according to the field survey data, a nonlinear model is adopted to construct a coniferous tree and broad-leaved tree breast height-tree height conversion model; step S40, acquiring single-tree vertical structure information through airborne LiDAR data; s50, constructing an airborne LiDAR vegetation stem and branch ecological water inversion model; and step S60, combining the Sentinel-2A vegetation canopy ecological water with airborne LiDAR vegetation stem and branch ecological water to obtain an above-ground vegetation ecological water reserve result. Compared with a single passive remote sensing source, the above-ground vegetation ecological water reserve result has the advantage that the accuracy of the above-ground vegetation canopy, stem and branch ecological water estimation technology is greatly improved.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Multi-angle observing system of aquatic vegetation canopy spectra
Provided is a multi-angle observing system of aquatic vegetation canopy spectra. A servo motor is installed on a horizontal cross beam of a support frame, wherein an output shaft of the servo motor is arranged along the vertical direction, the output shaft of the servo motor is connected with a rigid semicircular track with an downward opening through an azimuth shaft and a track frame, and the track frame is connected with the midpoint of the track in a hinged mode; an observing hole which penetrates axially is formed in the track, a rack is installed on the outer wall of the track, and a fiber-optics probe trolley and a balance trolley are symmetrically distributed at two sides of the central line of the track to keep balance of the track; when the fiber-optics probe trolley operates to the position where a fiber-optics probe is aligned to the observing hole, and signals of aquatic plants are obtained; and the servo motor, the fiber-optics probe trolley, the balance trolley, a hall locating sensor, and a sensing piece are all connected with a central controller.
Owner:杭州瓦屋科技有限公司
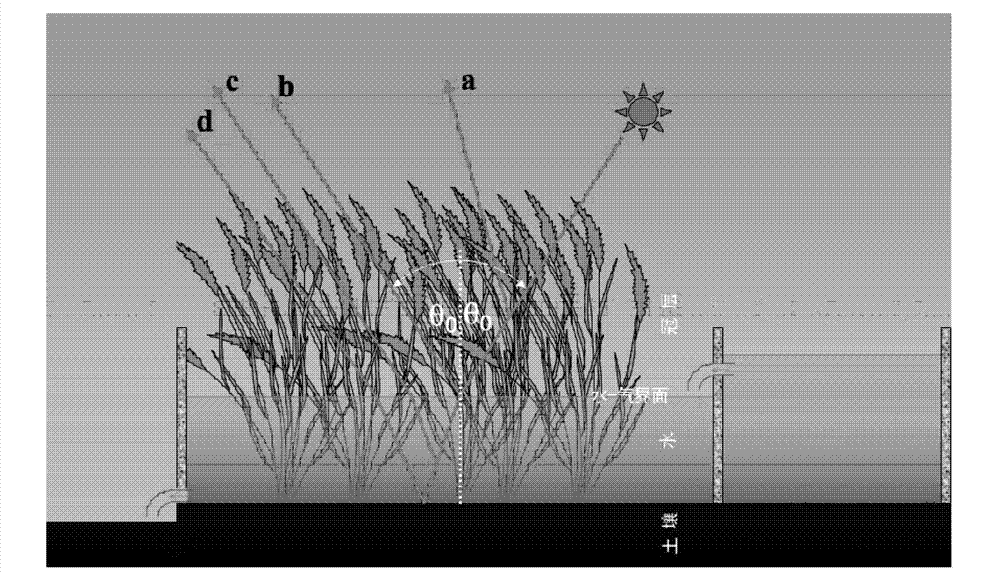
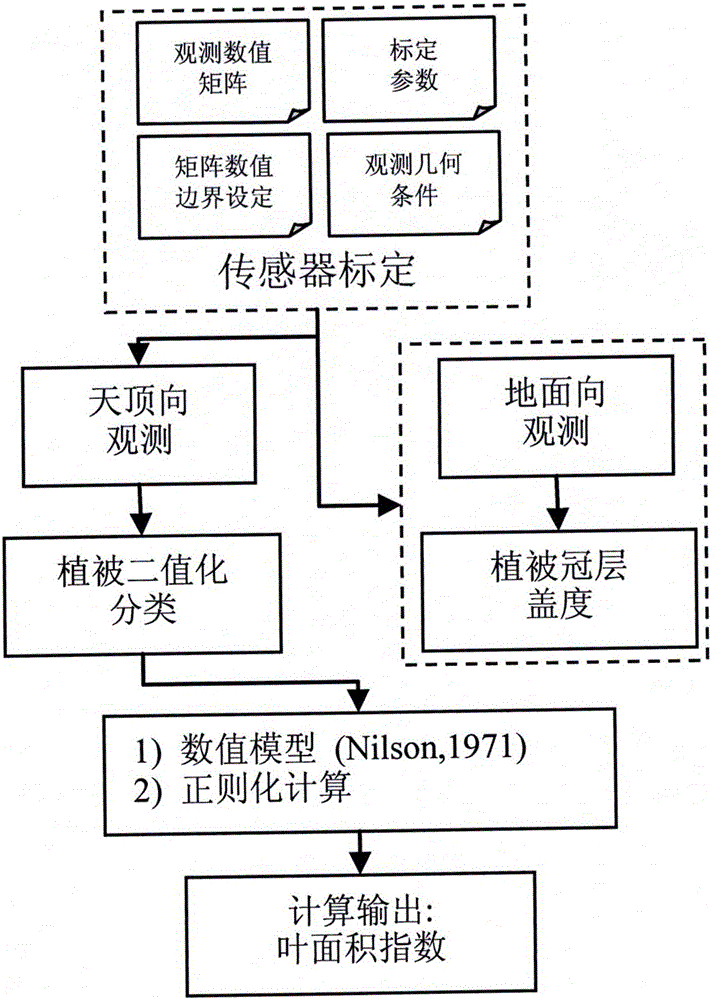
Multi-angle grassland vegetation leaf area index observation method and instrument
InactiveCN106482673AImprove the data collection processOptimize collection processUsing optical meansSoil scienceObservation data
The invention discloses a multi-angle grassland vegetation leaf area index observation method and an instrument. Firstly, a vegetation canopy multi-angle observation sensor used for research is calibrated, and each sampling pixel for multi-angle observation has calibrated multi-angle information; then, a lens after calibration is used for vegetation canopy radiation information multi-angle observation and conventional vegetation canopy vertical observation; the canopy multi-angle observation data are used for binary classification on vegetation and non vegetation, and the classification data are used for realizing calculation on a canopy gap rate and an aggregation index; and finally, a leaf area index estimation model built based on a regularization method is used for acquiring the numerical value of the vegetation leaf area and outputting the value. The sensor lens is used for observing the multi-angle radiation information of the grassland vegetation canopy and input data are provided for a numerical value algorithm; and the regularization numerical value calculation process is adopted, and the leaf area index numerical value result calculation algorithm can be realized based on the theoretical process.
Owner:GRASSLAND RES INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method and model for calculating canopy reflectivity of broad-leaved vegetation
ActiveCN106909750AImprove operational capabilitiesHigh precisionDesign optimisation/simulationColor/spectral properties measurementsExtinctionAlgorithm
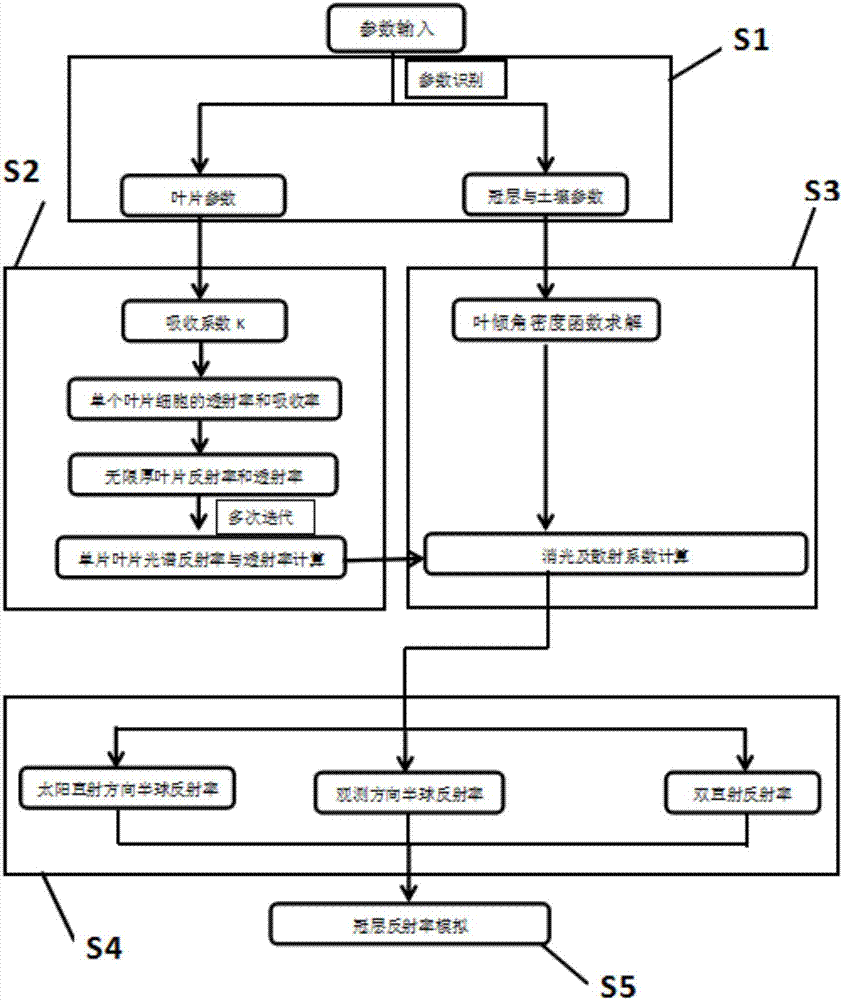
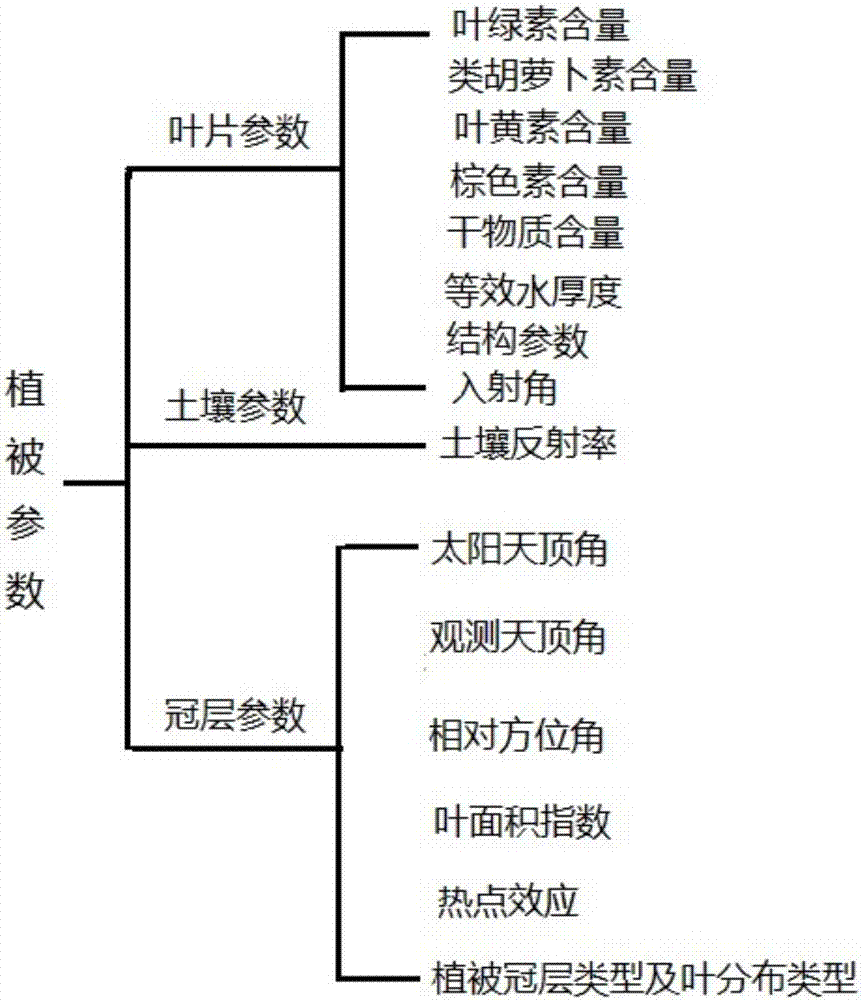
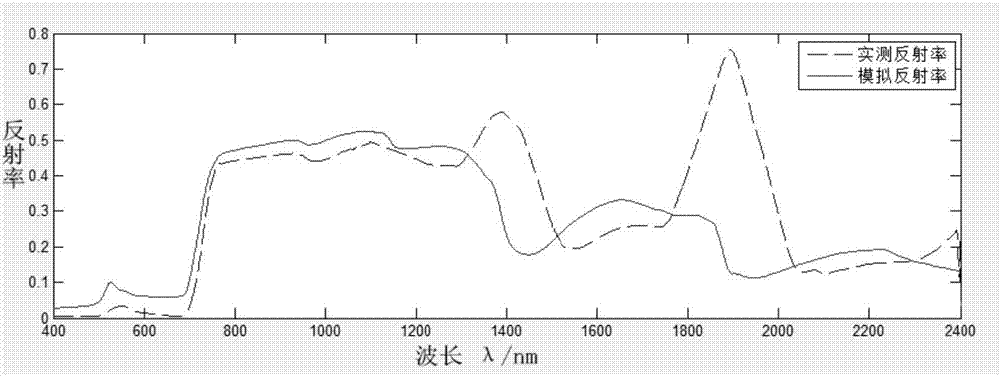
The invention discloses a method and model for calculating canopy reflectivity of broad-leaved vegetation. The method comprises the following steps: S1: inputting parameters, identifying the input parameters, and classifying the input parameters into leaf parameters, canopy parameters and soil parameters; S2: calculating reflectivity and transmissivity of each single leaf according to the leaf parameters; S3: calculating an extinction coefficient and a scattering coefficient of canopies according to the canopy parameters and the leaf parameters in the step S2; S4: calculating related reflection factor and reflectivity of the canopies according to the obtained canopy extinction and scattering parameters; S5: calculating the canopy reflectivity according to the related reflection factor and reflectivity of the canopies. According to the method and the model, a PROSPECT model and an SAIL model are coupled, and a leaf reflectivity and transmissivity input process in a vegetation canopy reflectivity simulation process is canceled under the condition of making full use of available parameters; a parameter acquisition problem in a vegetation canopy spectral information simulation process is effectively simplified, an algorithm is optimized, a calculating process is accelerated, and meanwhile, the coupled model facilitates parametric inversion of the vegetation.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Roof vegetation evapotranspiration measuring method based on thermal imaging technology
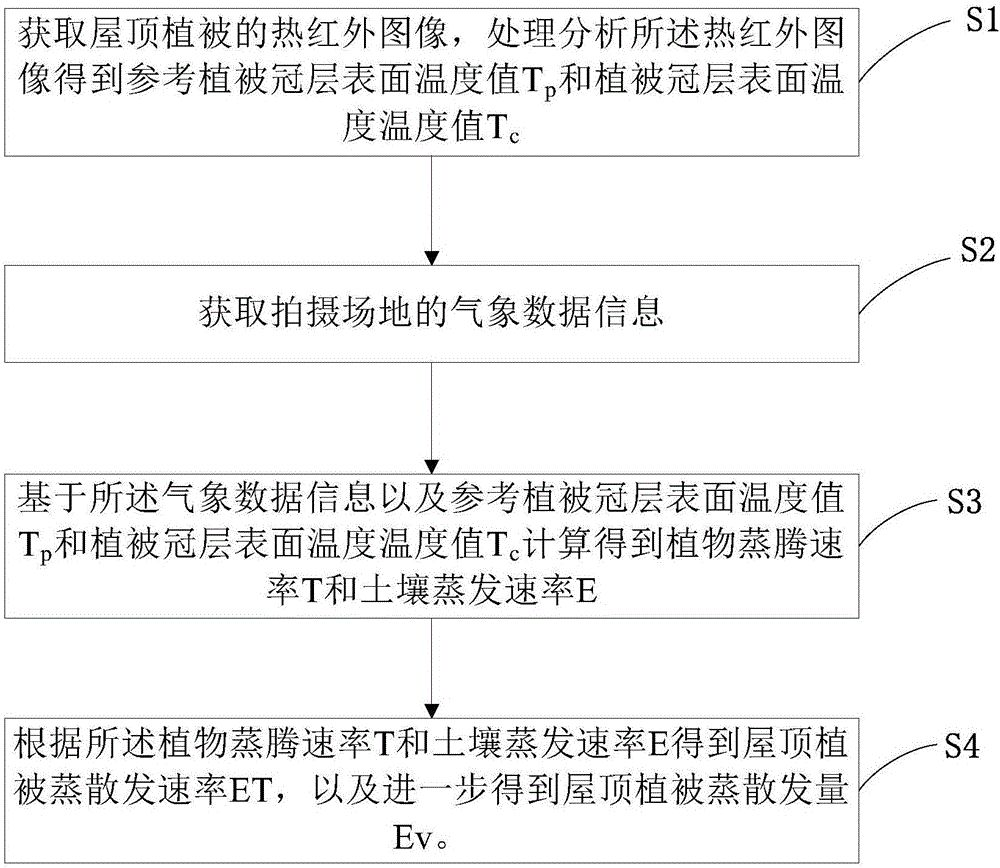
The invention provides a roof vegetation evapotranspiration measuring method based on the thermal imaging technology; the method comprises the following steps: obtaining a roof vegetation thermal infrared image, and processing the thermal infrared image so as to obtain a reference vegetation canopy surface temperature value Tp and a vegetation canopy surface temperature value Tc; obtaining meteorology data information of shooting place; calculating the meteorology data information, the reference vegetation canopy surface temperature value Tp and the vegetation canopy surface temperature value Tc so as to obtain a plant transpiration rate T and a soil evaporation rate E; using the plant transpiration rate T and the soil evaporation rate E to obtain a roof vegetation evapotranspiration rate ET, and further obtaining the roof vegetation evapotranspiration Ev. The roof vegetation evapotranspiration measuring method based on the thermal imaging technology can observe irregularly distributed vegetation without being affected by convection and without contacting the vegetation, thus accurately measuring city green roof evapotranspiration.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com