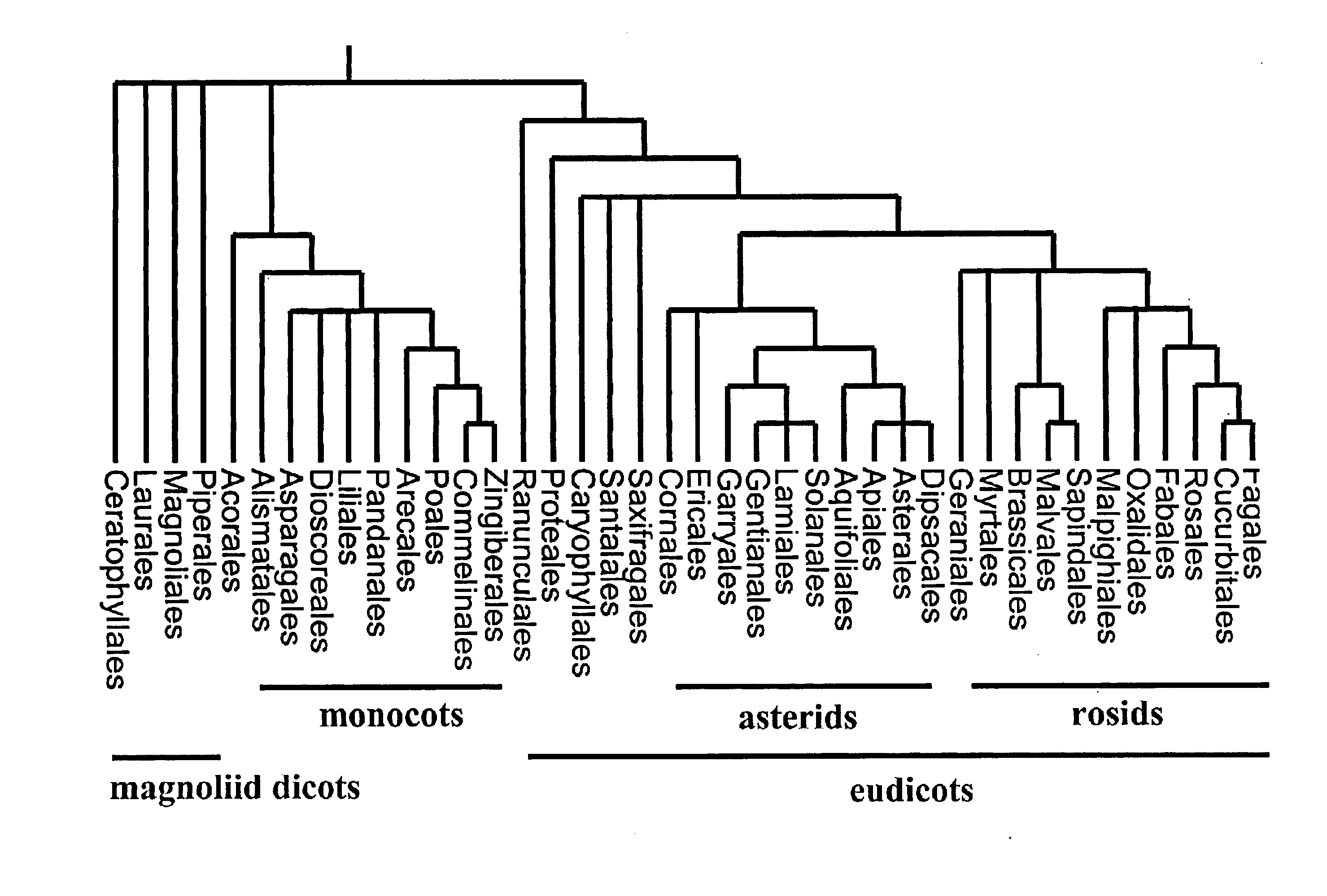
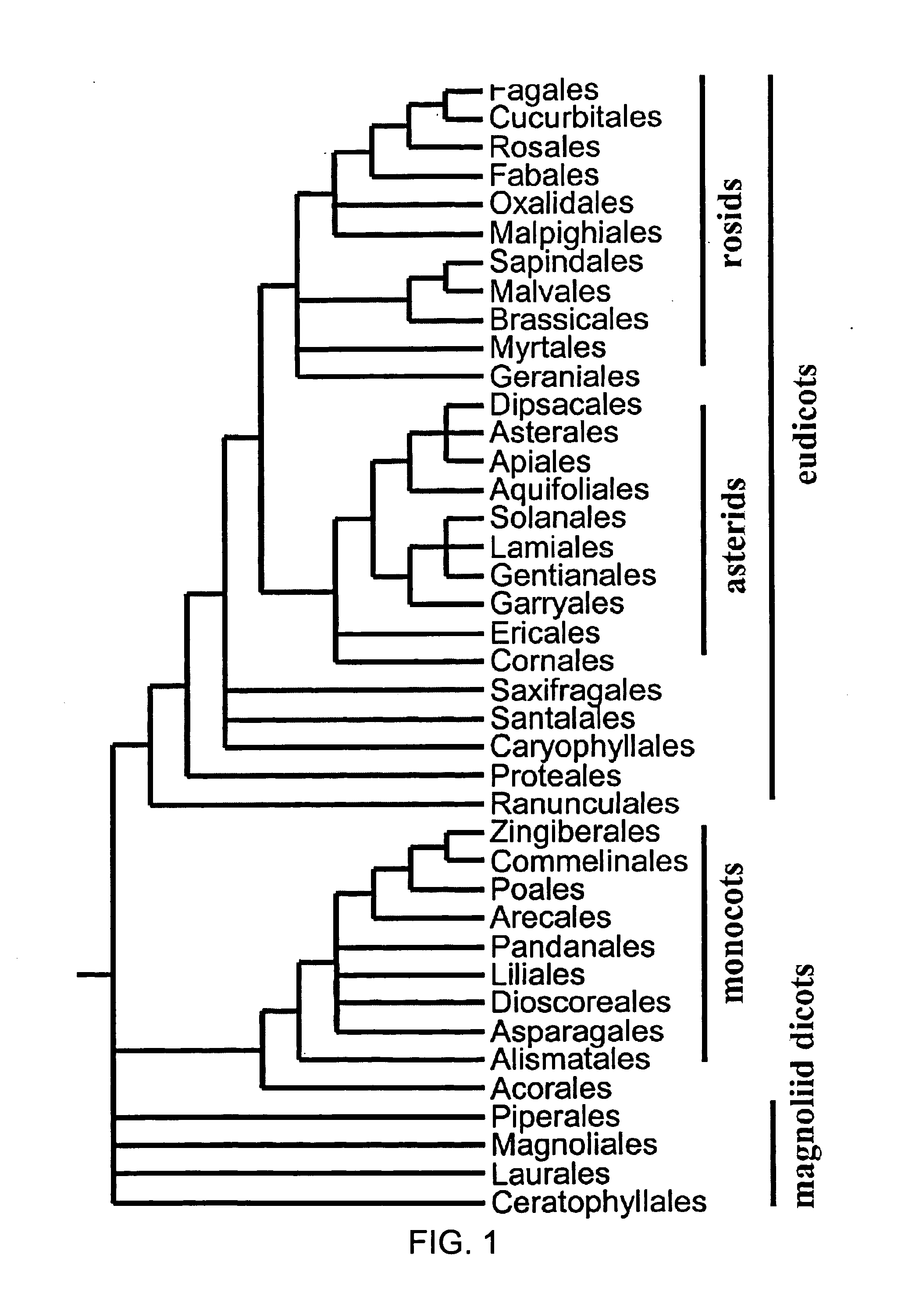
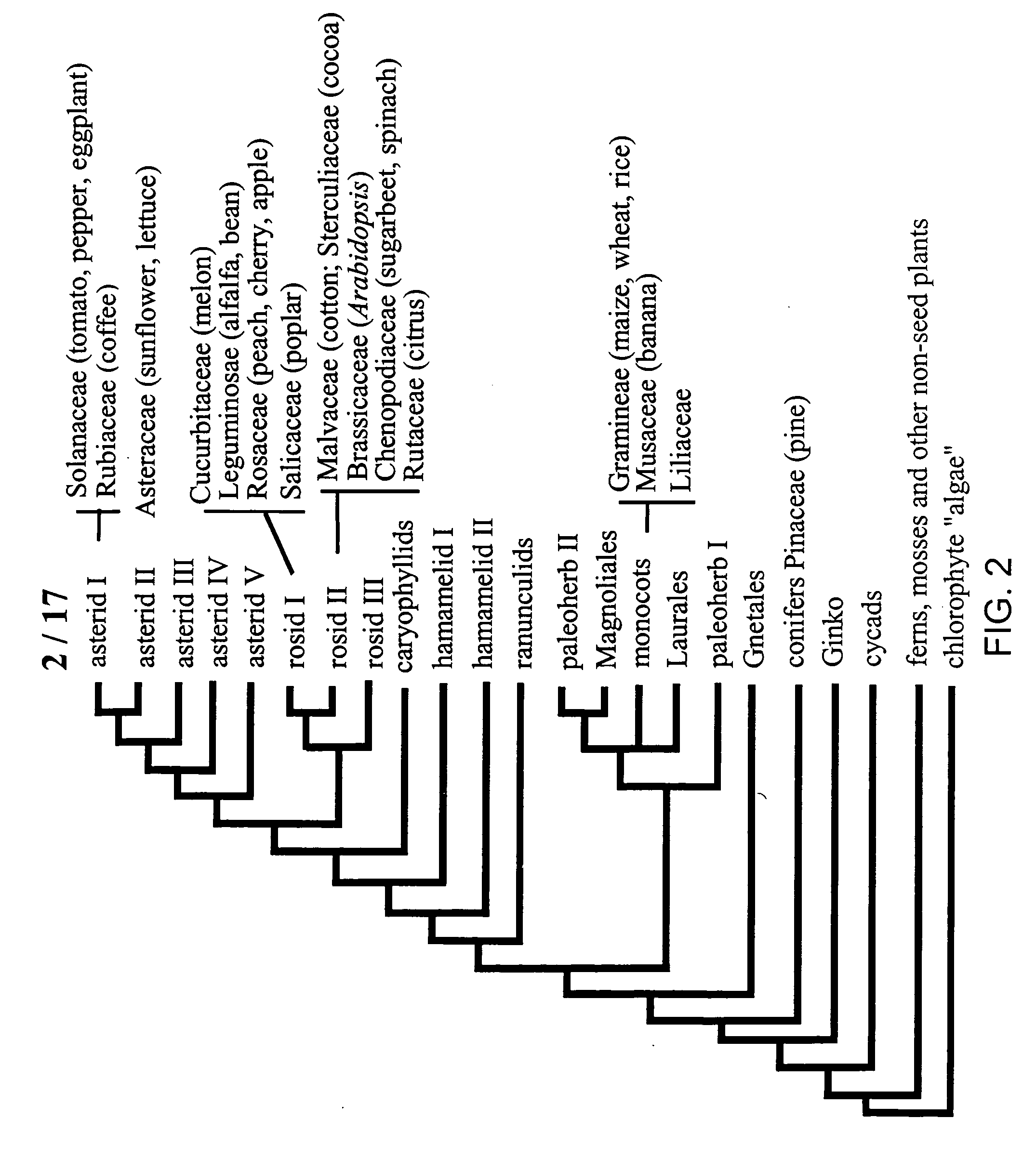
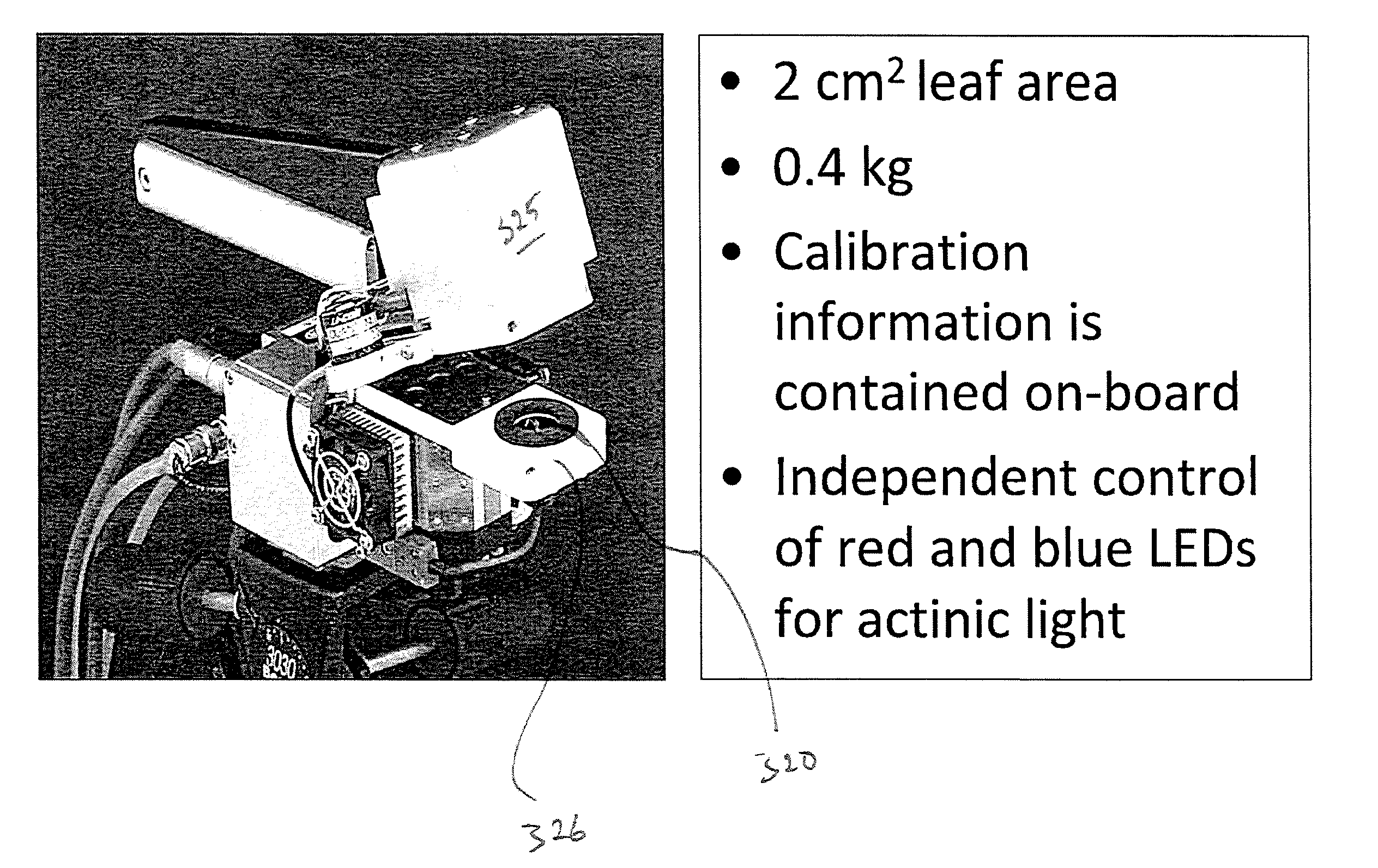
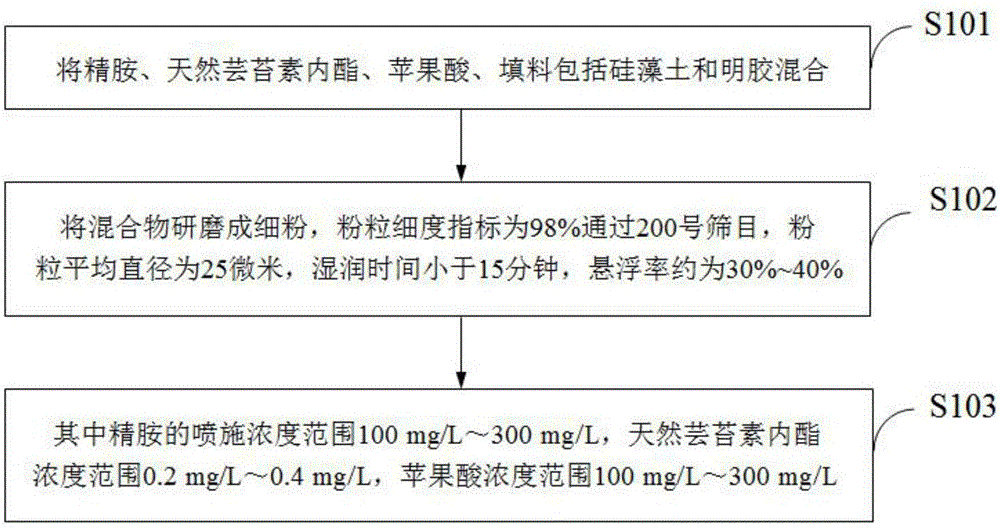
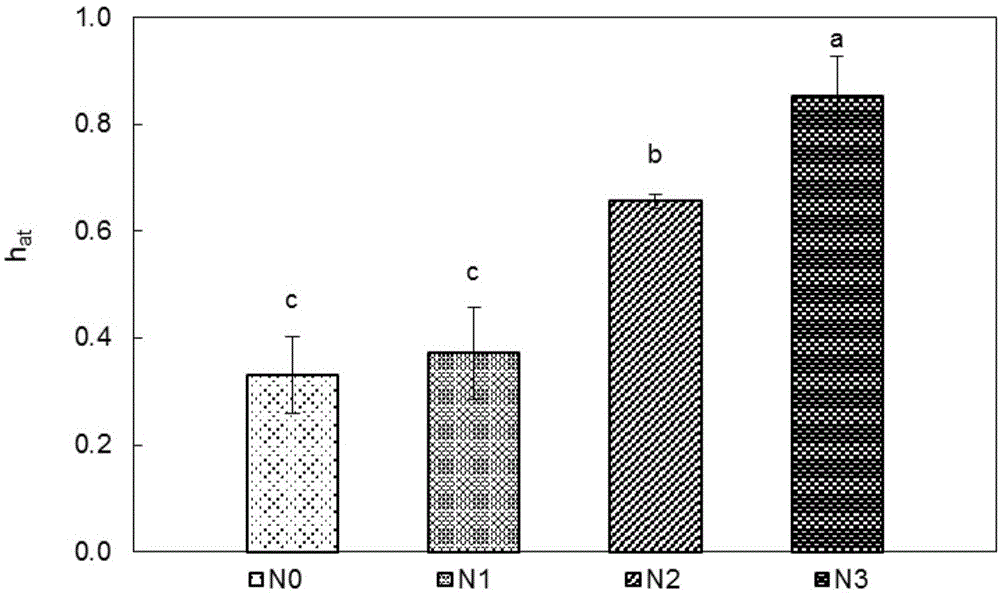
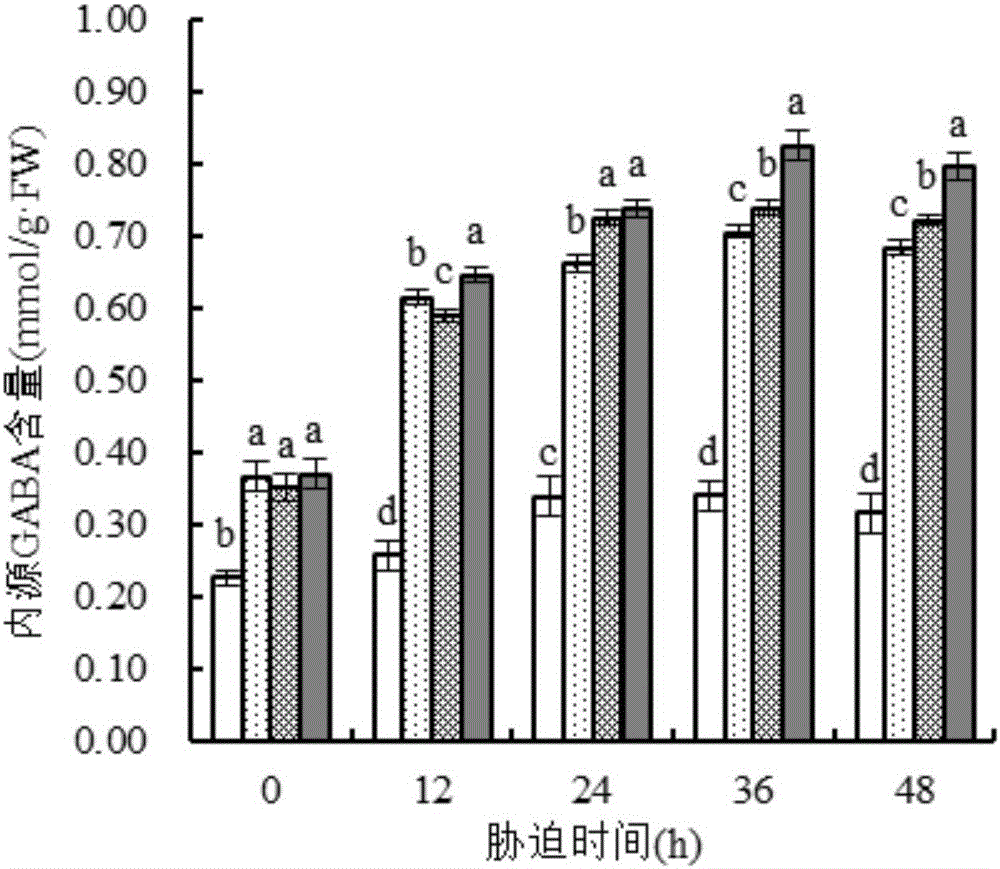
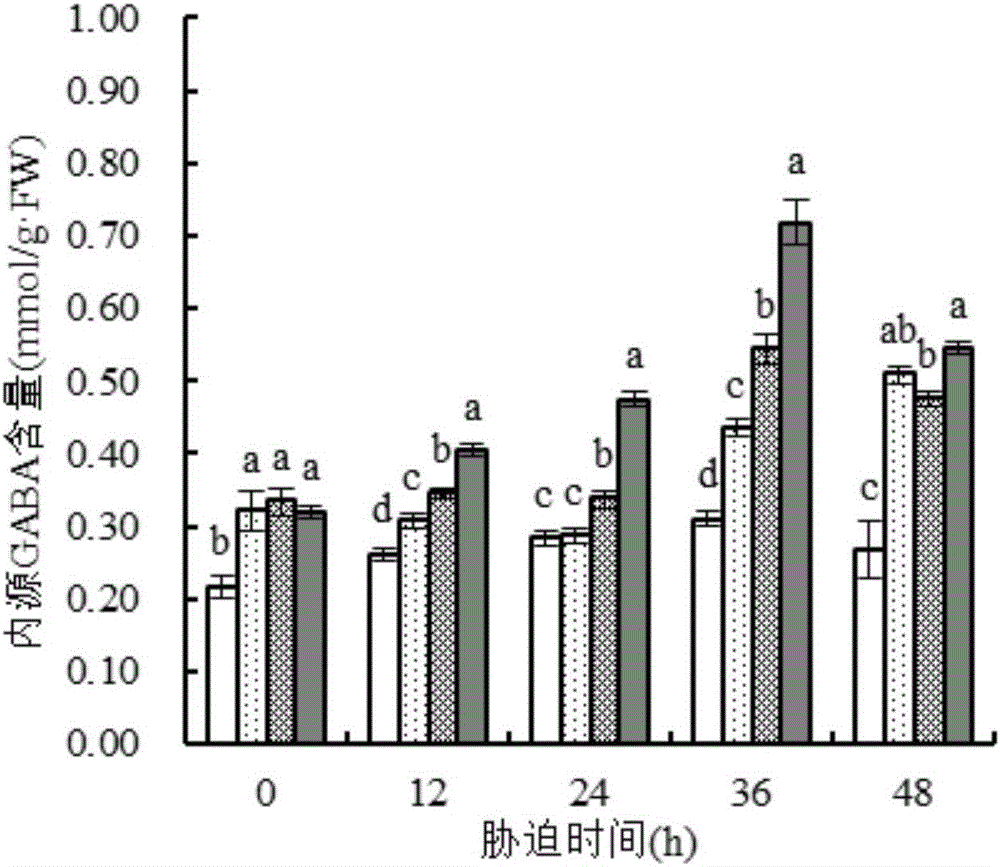
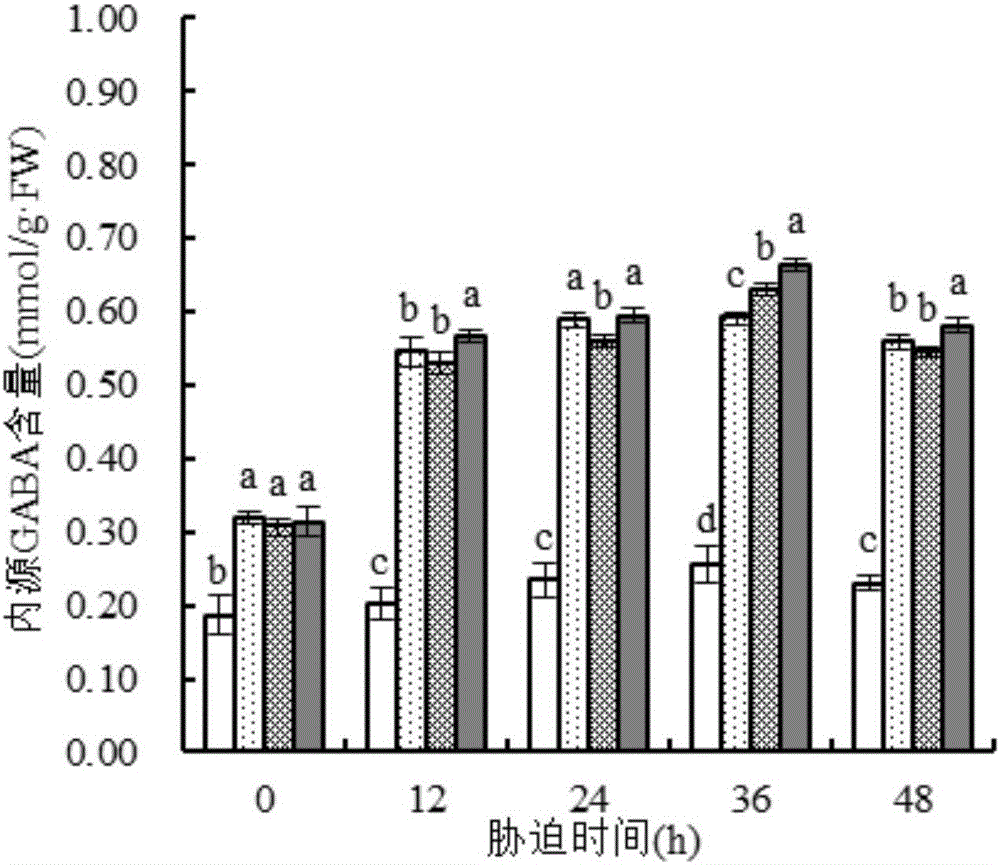
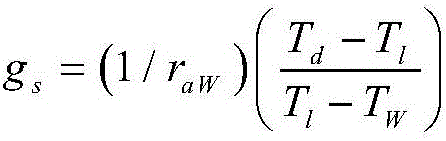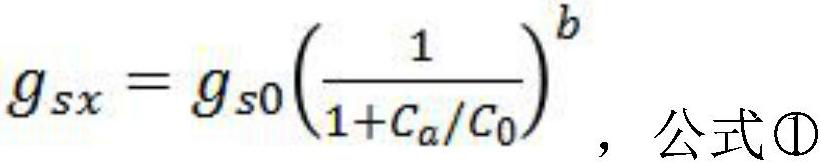Patents
Literature
97 results about "Stomatal conductance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
By definition, stomatal conductance, usually measured in mmol m⁻² s⁻¹, is the measure of the rate of passage of carbon dioxide (CO₂) entering, or water vapor exiting through the stomata of a leaf. Stomata are small pores on the top and or bottom of a leaf that are responsible for taking in CO₂ and expelling water vapour. The rate of stomatal conductance, or its inverse, stomatal resistance, is directly related to the boundary layer resistance of the leaf and the absolute concentration gradient of water vapor from the leaf to the atmosphere. It is under direct biological control of the leaf through the use of guard cells, which surround the stomatal pore (Taiz/Zeiger 1991). The turgor pressure and osmotic potential of guard cells is directly related to the stomatal conductance. Stomatal conductance is a function of stomatal density, stomatal aperture, and stomatal size. Stomatal conductance is integral to leaf level calculations of transpiration (E). Multiple studies have shown a direct correlation between the use of herbicides and changes in physiological and biochemical growth processes in plants, particularly non-target plants, resulting in a reduction in stomatal conductance and turgor pressure in leaves.
Yield and stress tolerance in transgenic plants
ActiveUS20080010703A1Increase productionImprove adverse reactionsClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesIncreased toleranceLow nitrogen
Polynucleotides and polypeptides incorporated into expression vectors have been introduced into plants and were ectopically expressed. The polypeptides of the invention have been shown to confer at least one regulatory activity and confer increased yield, greater height, greater early season growth, greater canopy coverage, greater stem diameter, greater late season vigor, increased secondary rooting, more rapid germination, greater cold tolerance, greater tolerance to water deprivation, reduced stomatal conductance, altered C / N sensing, increased low nitrogen tolerance, increased low phosphorus tolerance, or increased tolerance to hyperosmotic stress as compared to the control plant as compared to a control plant.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY) +1
Systems and methods for estimating photosynthetic carbon assimlation
InactiveUS20120310540A1High conductanceOptimal water usageInvestigation of vegetal materialPhotometryCarbon assimilationPhotovoltaic detectors
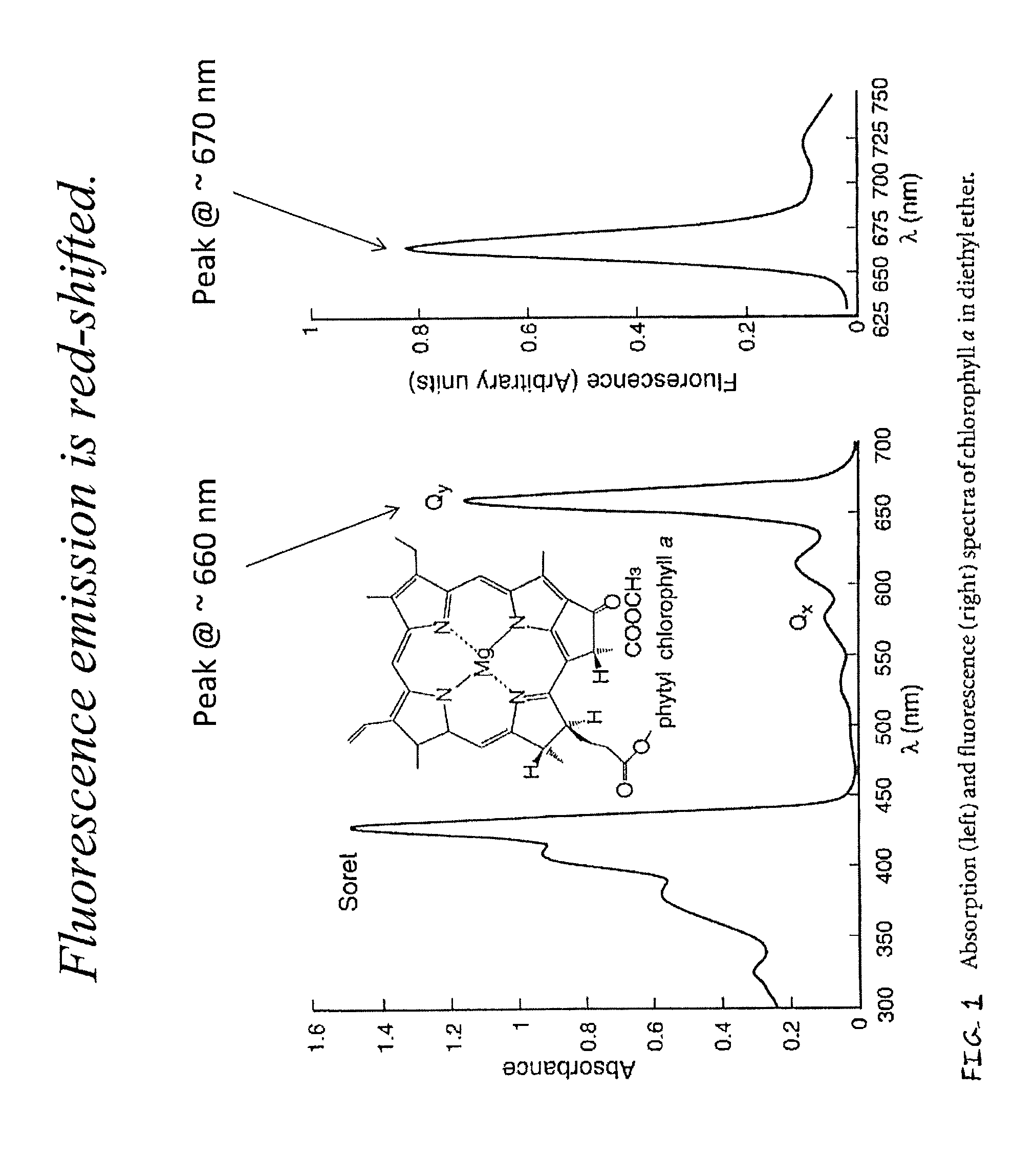
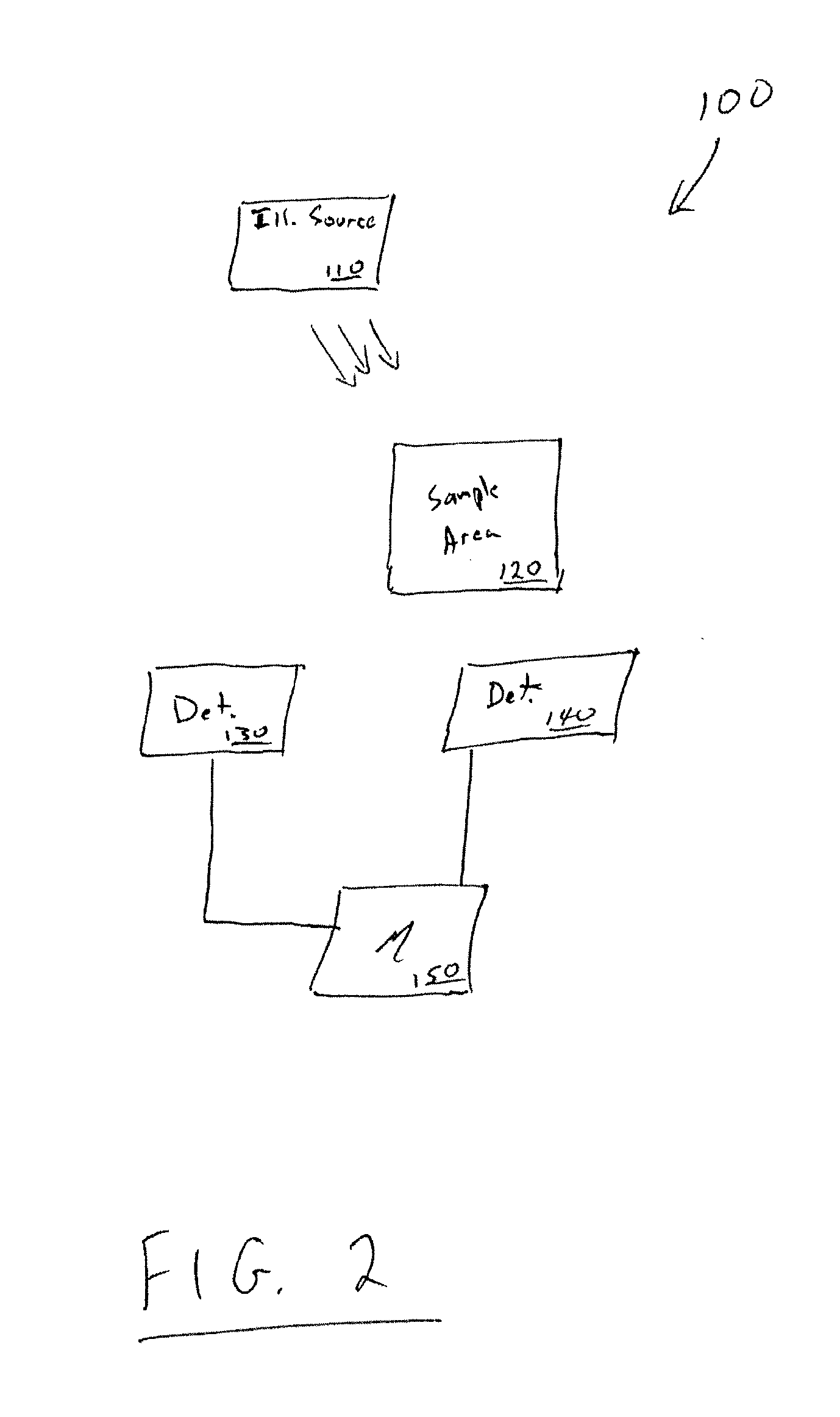
Methods, devices, and systems for measuring carbon assimilation based on simultaneous or near-simultaneous measurements of chlorophyll fluorescence and stomatal conductance of plant. A sample containing chlorophyll, such as a plant leaf, is illuminated with light, e.g., in the form of a single saturating pulse or multiple pulses, and chlorophyll fluorescence and stomatal conductance of the chlorophyll sample are measured. A porometer or infra-red gas analyzer is used to measure stomatal conductance and a photodetector is used to measure fluorescence. A carbon assimilation value for the chlorophyll sample is determined using the measured chlorophyll fluorescence and the measured stomatal conductance.
Owner:LI COR
Method for improving crop stress resistance by using hydrogen sulfide donor sodium hydrosulfide
InactiveCN108402078AWide variety of sourcesAvoid harmBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPlant rootsSodium hydrosulfide
The invention provides a method for improving crop stress resistance by using hydrogen sulfide donor sodium hydrosulfide. The method for improving the crop stress resistance by using the hydrogen sulfide donor the sodium hydrosulfide includes the steps of: soaking seeds in a sodium hydrosulfide solution with the concentration to be 0.01-1.6 millimole per litre for 6-24 hours and at the temperatureof 25-30 DEG C before sowing; or conducting plant root irrigation with the sodium hydrosulfide solution of the concentration of 0.01-1.6 millimole per litre in a seedling stage and replacing the treatment solution every 6 to 24 hours and replacing continuously for 2 to 5 times; or spraying on the foliage at different stages of stress with the sodium hydrosulfide solution of the concentration of0.01-1.6 millimole per litre during plant maturity. With different application methods and a certain concentration of sodium hydrosulfide solution according to different plants at different growth stages and different periods of stress, the method for improving the crop stress resistance by using the hydrogen sulfide donor the sodium hydrosulfide has the advantages of improving seed germination rate, increasing plant biomass, adjusting the chlorophyll content required for plant photosynthesis, alleviating the problems, caused by the stress, of plant water loss, photosynthetic rate, stomatal conductance, and intercellular carbon dioxide concentration and transpiration rate changes, and improving crops' ability to resist stress.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Alfalfa drought tolerance identification method
InactiveCN105393814AEasy to operateExclude the impact of drought tolerance identification resultsHorticulture methodsBound waterDry weight
The invention discloses an alfalfa drought tolerance identification method, comprising the following steps: after sterilization on seeds, carrying out a conventional sprouting experiment, after a seedling has 3-4 main leaves, performing thinning and final singling, reserving materials whose plant size and height are roughly consistent, and carrying out a water controlling experiment in a greenhouse; in the 8th-11th day, taking the plants out to count the number of roots of each plant of alfalfa, including the number of main roots, lateral roots, and fibrils on the lateral roots; after processing for 20 d, respectively measuring seedling height, fresh weight of root systems, dry weight of root systems, leaf chlorophyll contents, stomatal conductance, leaf free water content, leaf surface bound water content, proline content and root volume of each processing group; performing data reduction, calculating average values, and calculating a drought tolerance coefficients and a comprehensive drought tolerance value of each variety; and determining salt tolerance of the varieties according to the comprehensive drought tolerance value. The method performs multivariate statistical analysis on agronomical characters and indexes of an alfalfa seedling stage, so as to perform comprehensive judgement and evaluation on the drought tolerance of alfalfa.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG BAYI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Improved yield and stress tolerance in transgenic plants
Polynucleotides and polypeptides incorporated into expression vectors have been introduced into plants and were ectopically expressed. The polypeptides of the invention have been shown to confer at least one regulatory activity and confer increased yield, greater height, increased secondary rooting, more rapid germination, greater cold tolerance, greater tolerance to water deprivation, reduced stomatal conductance, altered C / N sensing, increased low N tolerance, increased low phosphorus tolerance, or increased tolerance to hyperosmotic stress as compared to the control plant as compared to a control plant.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC +1
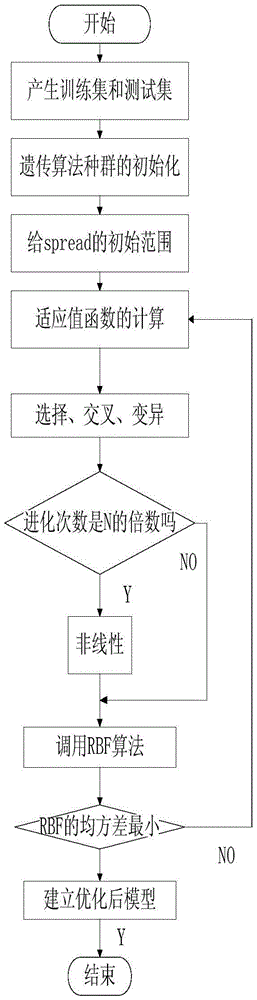
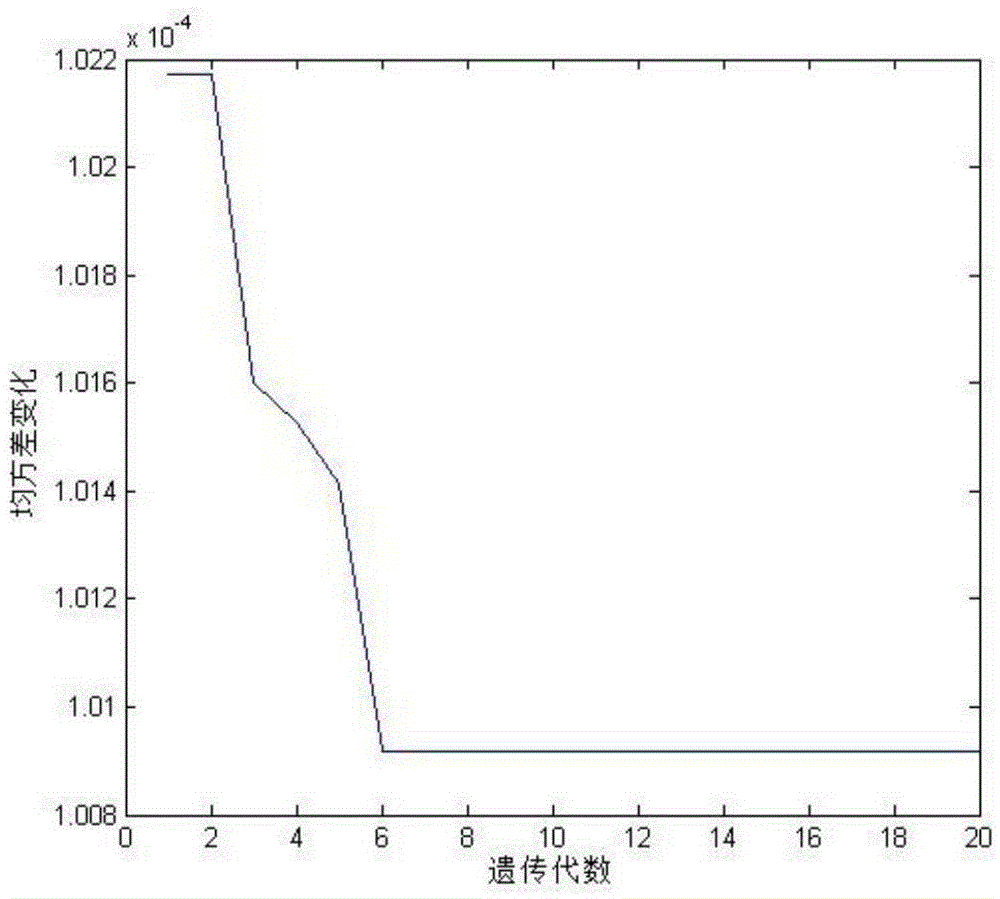
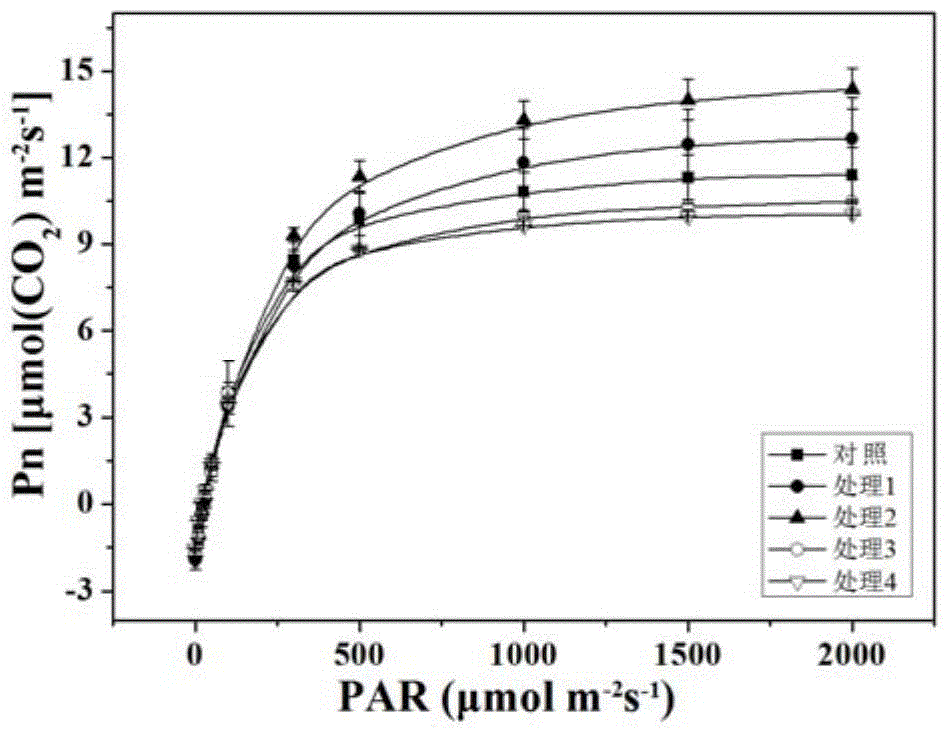
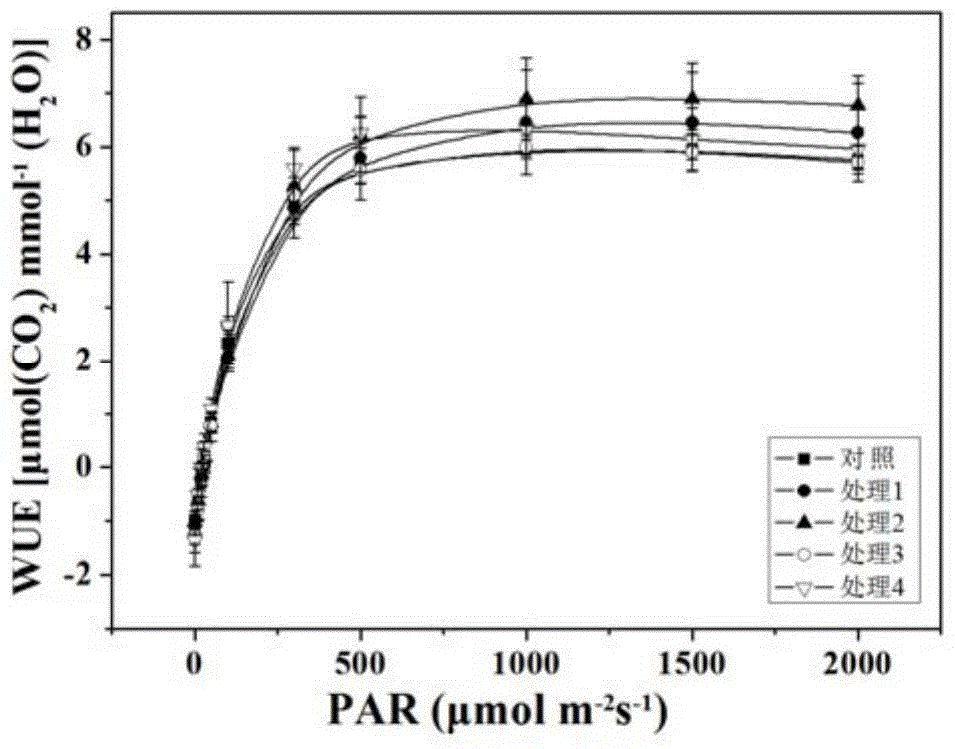
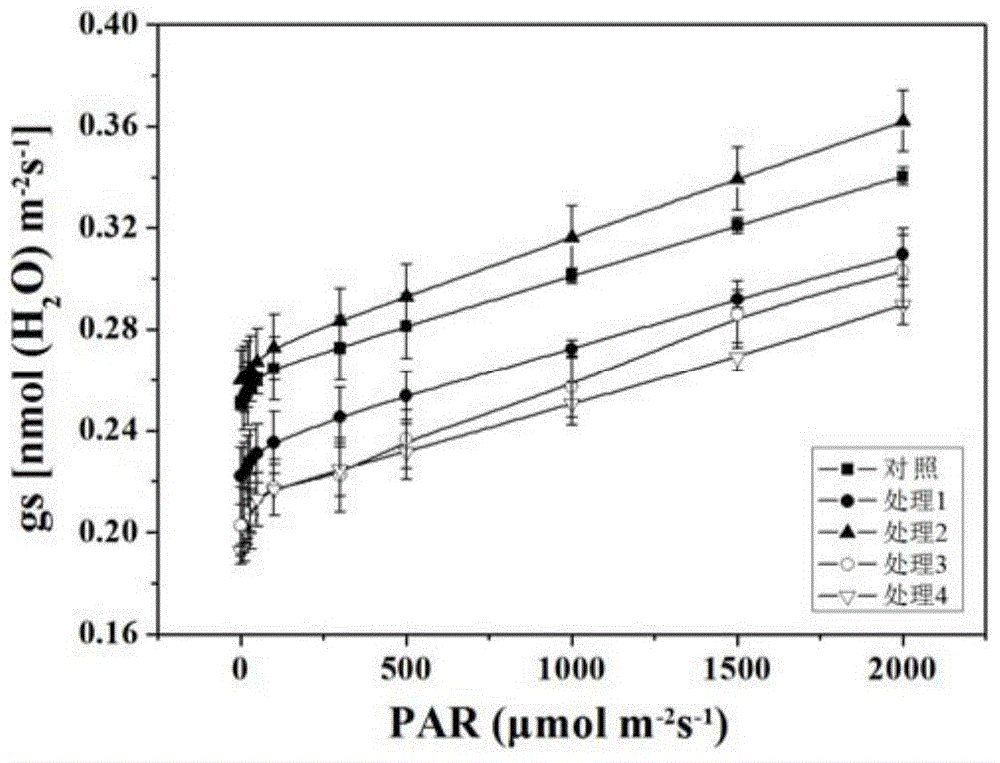
Modeling method for cucumber GA-RBF photosynthetic rate prediction model integrated with stomatal conductance
ActiveCN105678405AAvoid disadvantagesPromote photosynthesisForecastingNeural learning methodsModel methodAlgorithm
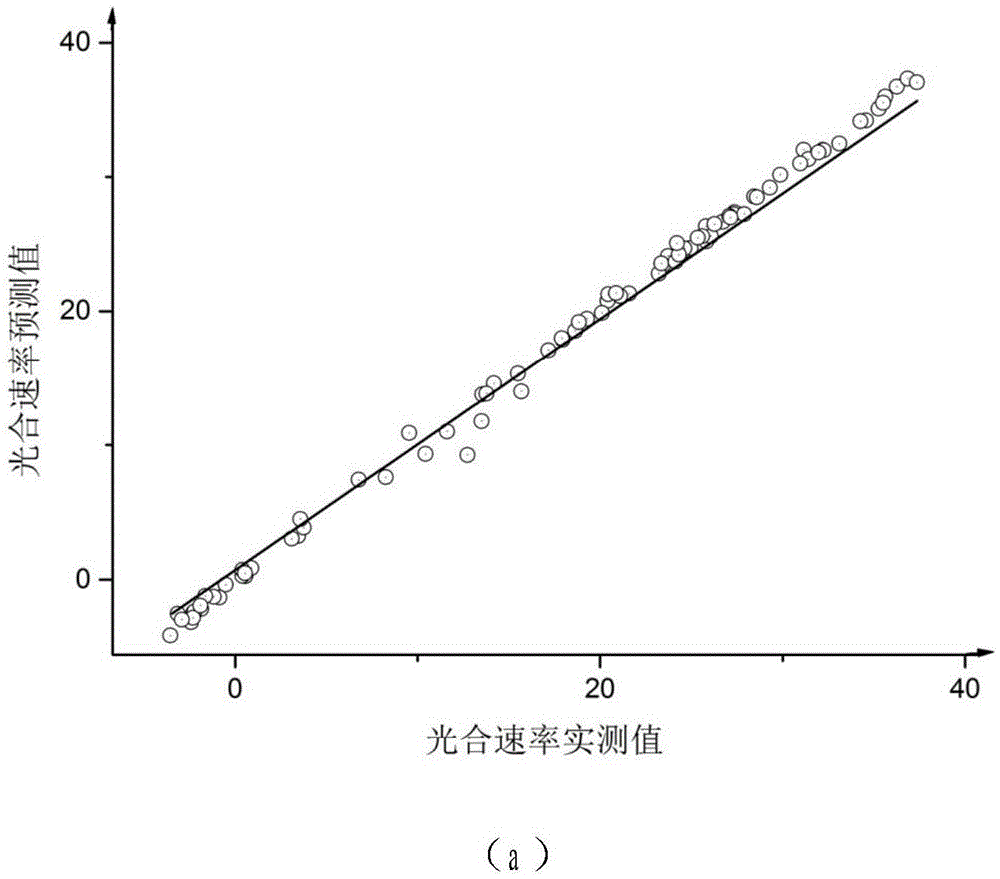
The invention provides a modeling method for a cucumber GA-RBF photosynthetic rate prediction model integrated with stomatal conductance. The method comprises the steps: utilizing a multi-factor nested test to obtain the experimental data taking the stomatal conductance, the temperature, the CO2 concentration, the illumination intensity and the relative humidity as input and taking the apparent photosynthesis rate as output; utilizing a genetic algorithm to perform initialization of population; according to the given initial range of the spread parameters, calculating a fitness function; and through selection, intersection and variation, finding out the optimal spread parameter in an RBF neural network, and constructing a cucumber GA-RBF photosynthetic rate prediction model integrated with stomatal conductance. The test result shows that the predicted value and actual measurement value determination coefficient is 0.99878; the linear gradient is 0.99781; the error is less than 6%; compared with the photosynthetic rate prediction model which does not use the genetic algorithm to optimize the RBF algorithm and does not integrated with stomatal conductance and the cucumber GA-RBF photosynthetic rate prediction model which is not integrated with stomatal conductance, the training result has better prediction effect.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Application of RAF49 protein and coding gene thereof in regulating and controlling drought resistance of plants
ActiveCN110904071AImprove drought resistanceAids in water retentionTransferasesFermentationBiotechnologyGene targets
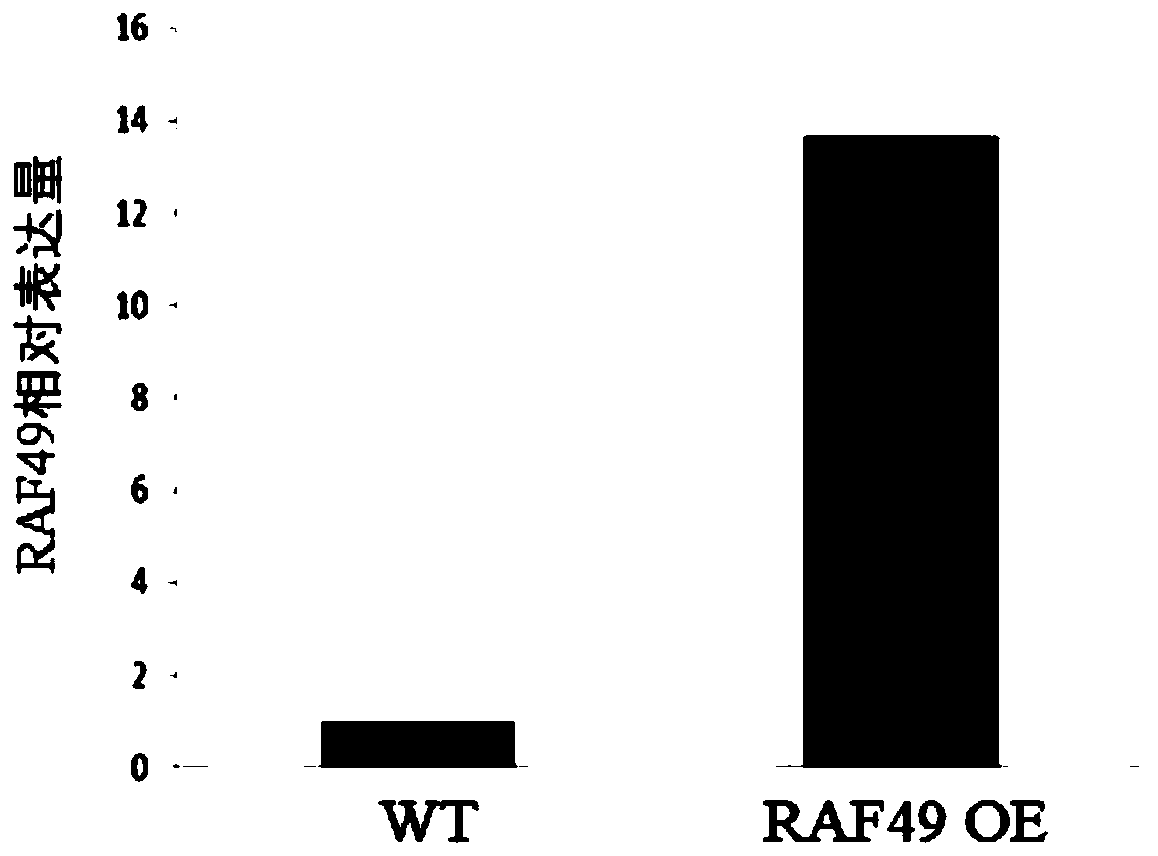
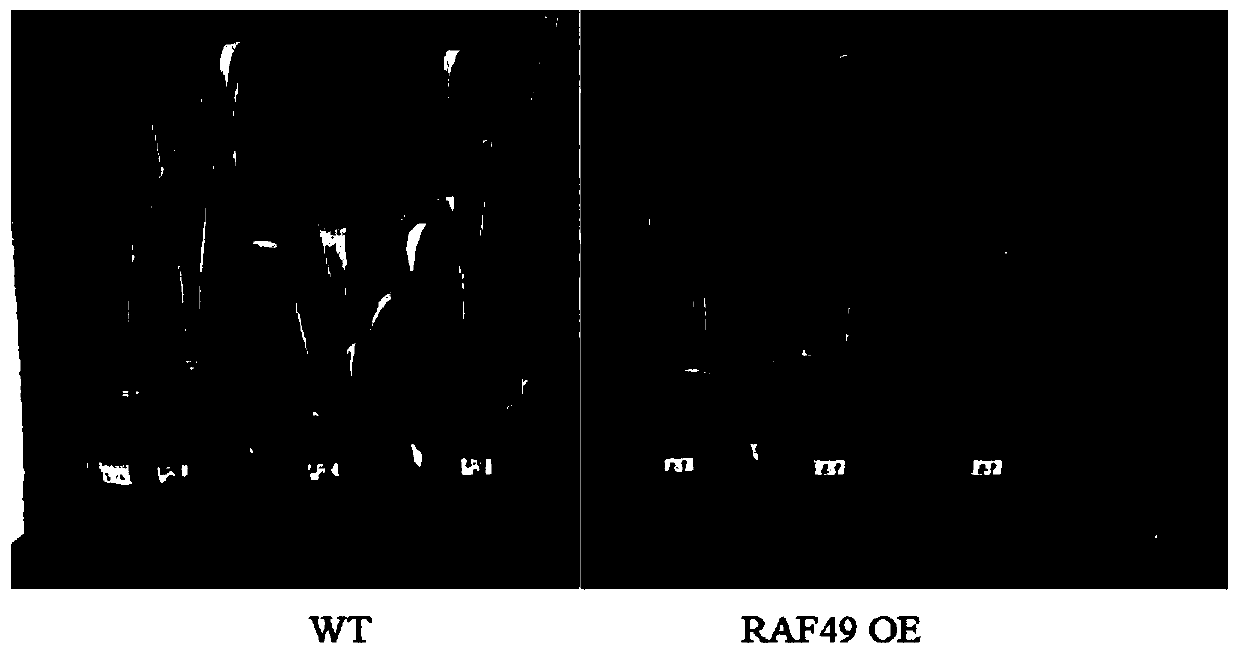
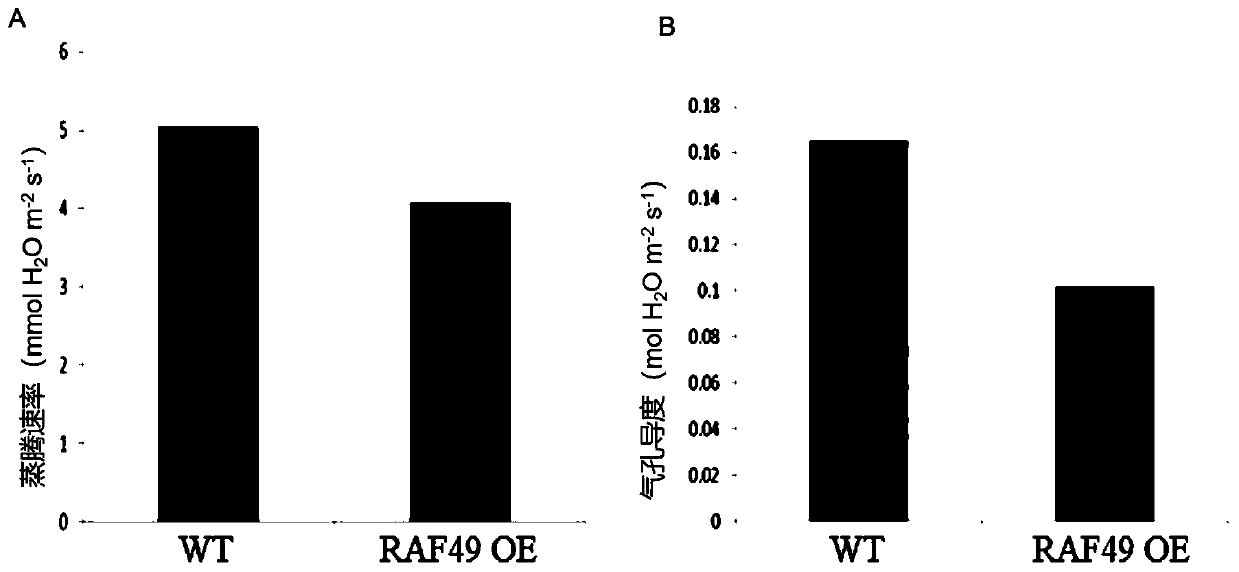
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, in particular to an application of RAF49 protein and an encoding gene of the RAF49 protein to regulation and control of drought resistance of plants. According to the invention, the corn RAF49 gene is found to positively regulate the drought resistance of the plant, and the drought resistance of the plant can be effectivelyimproved by increasing the expression quantity of the RAF49 gene. The RAF49 overexpression transgenic corn plant is constructed, the growth condition of the plant under the drought condition is obviously superior to that of a wild type corn plant, the leaf wilting degree is obviously reduced, the transpiration rate and the stomatal conductance are obviously lower than those of the wild type cornplant, the water loss of the plant is effectively reduced, and the drought resistance is obviously improved. The discovery of the drought-resistant function of RAF49 provides a new gene target and resources for cultivating new varieties of drought-resistant plants, and provides a theoretical basis for illustrating the molecular mechanism of plant drought stress signal response.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
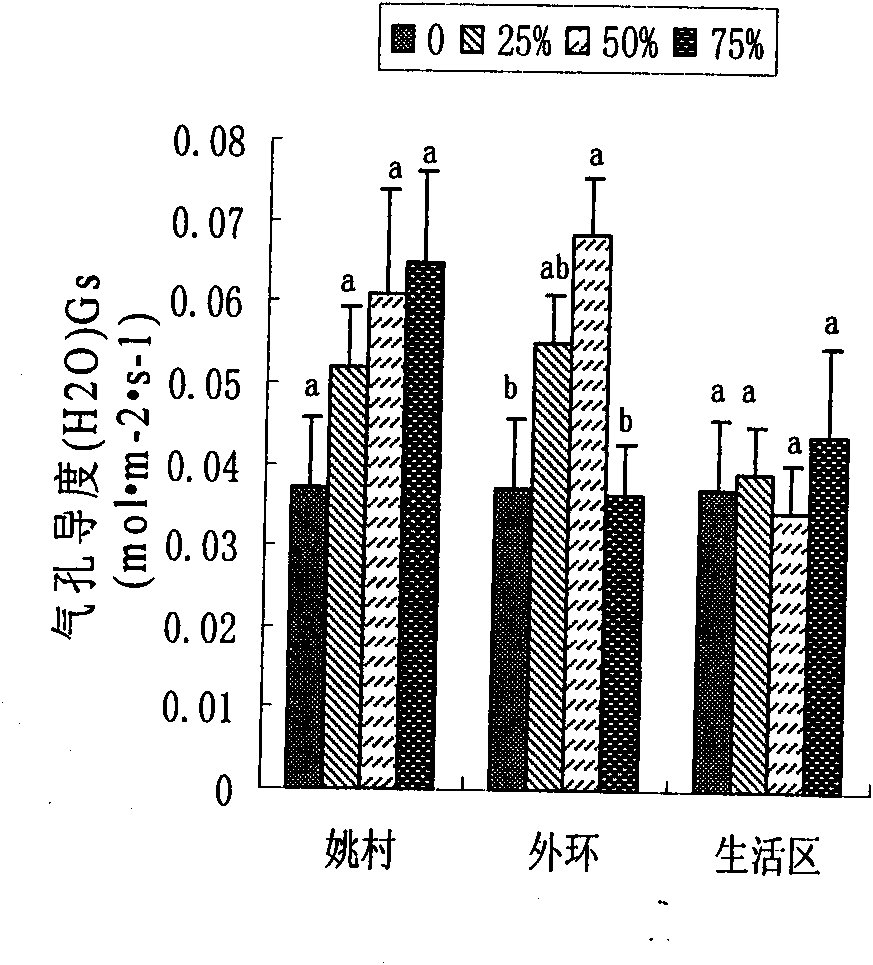
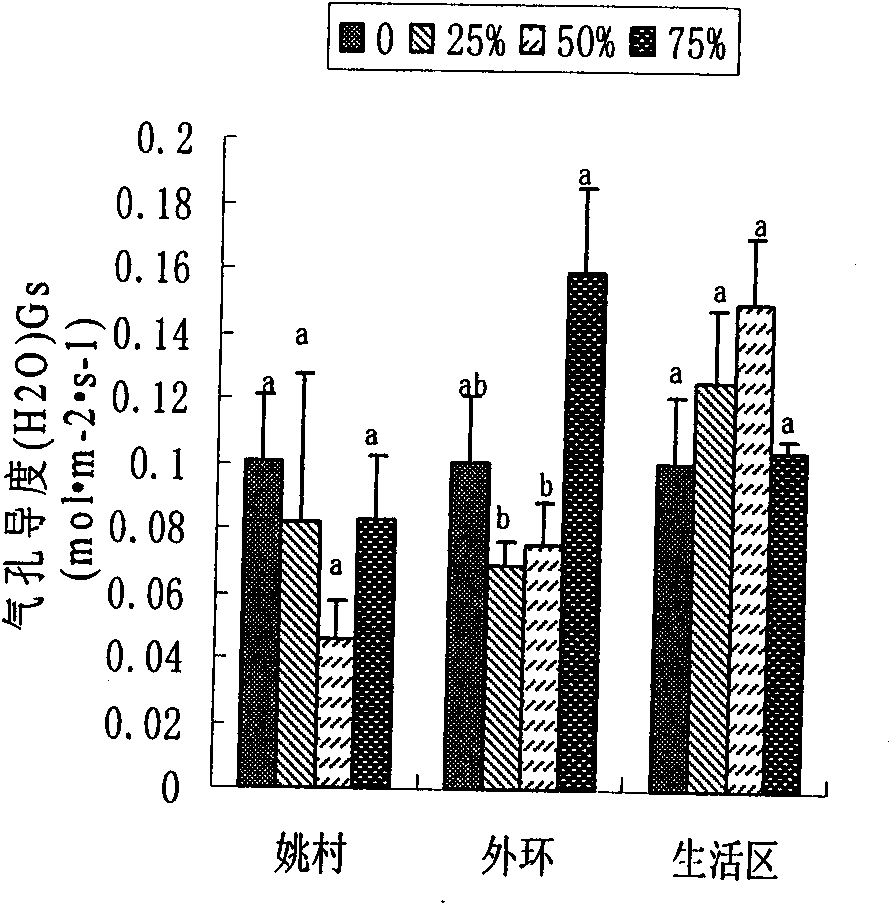
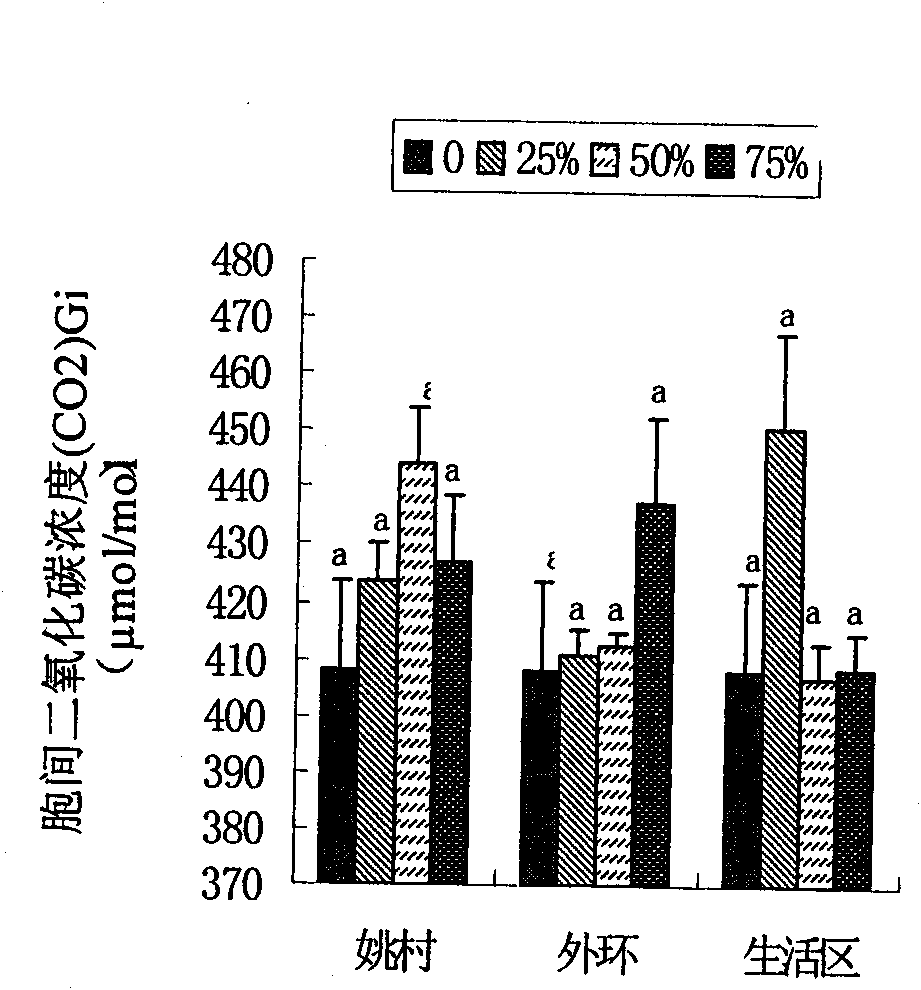
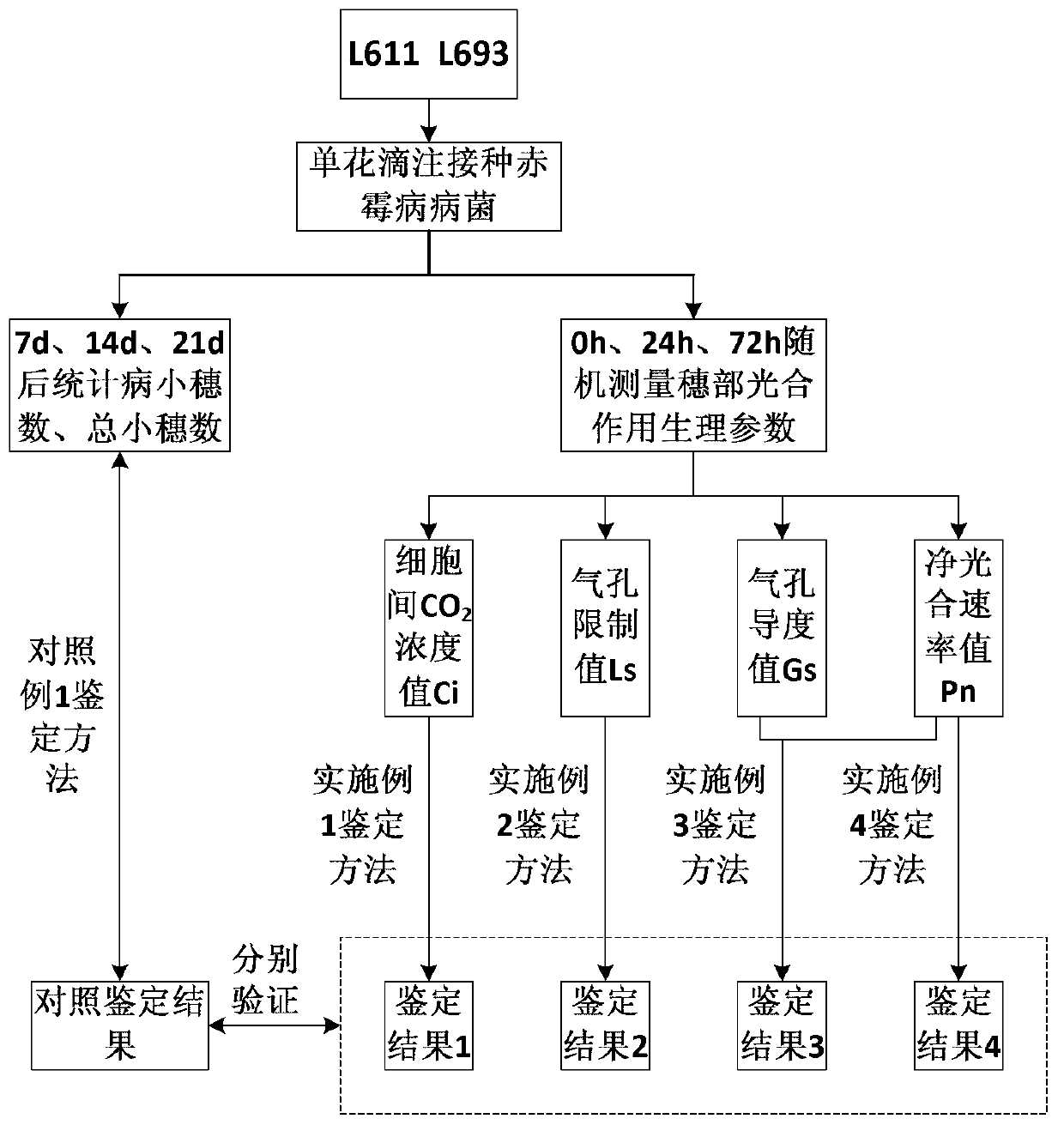
Physiological parameter-based fast identification method of resistance of wheat scab
InactiveCN102175611AAvoid human errorRapid identificationMaterial analysis by optical meansSporeAgricultural science
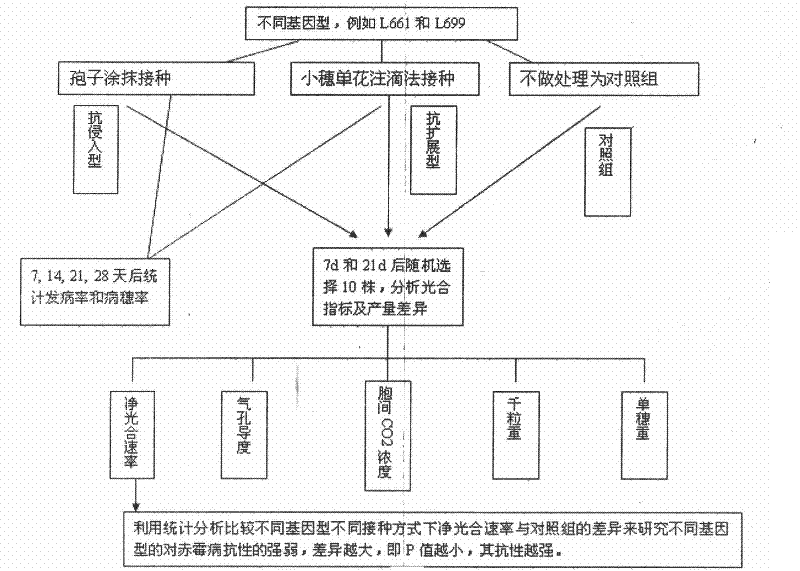
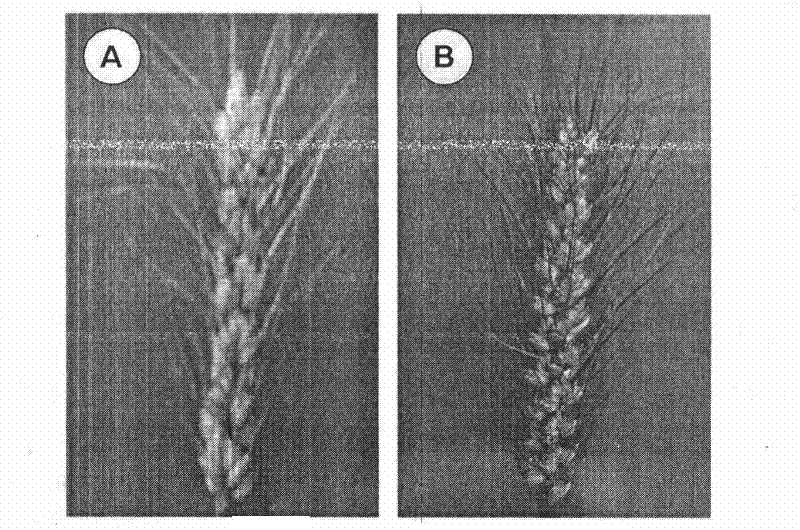
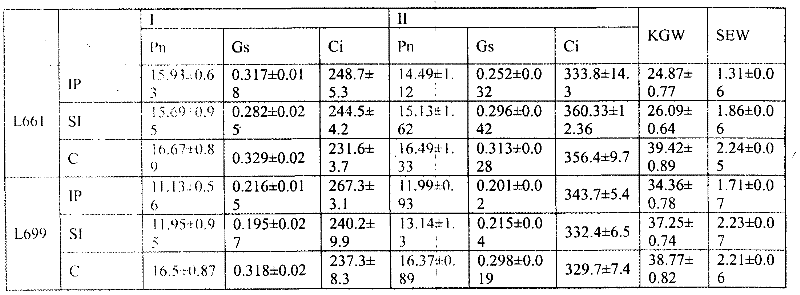
The invention discloses a physiological parameter based fast identification method of the resistance of wheat scab, comprising the following steps of: (1) planting materials with different genotypes; (2) carrying out wheat scab inoculation by adopting a spore coating or single flower instillation method; (3) recording illness states: respectively surveying a pathogenic spikelet number and a total spikelet number at seven, fourteen, twenty-one and twenty-eight days after the wheat scab inoculation, and calculating pathogenic spikelet rate; measuring Net photosynthesis rate (Pn), stomatic conductance (Gs) and intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci) by utilizing an Li-6400 photosynthetic measurement system at seven and twenty-one days after the wheat scab inoculation, wherein temperature is 21-24 DEG C, saturated vapour pressure difference is 0.55-0.65 kPa, illumination intensity is 1000 mmol m<-2> s<-1>, and measuring time is 30 seconds at a time; and (4) carrying out statistic analysis to obtain an identification conclusion: carrying out the statistic analysis to obtain the identification conclusion by utilizing SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Science) software.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Yield and stress tolerance in transgenic plants iv
InactiveUS20100186106A1Increase productionAmeliorate adverse effect of waterClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesIncreased toleranceLow nitrogen
Polynucleotides and polypeptides incorporated into expression vectors have been introduced into plants and were ectopically expressed. The polypeptides of the invention have been shown to confer at least one regulatory activity and confer increased yield, greater height, greater early season growth, greater canopy coverage, greater stem diameter, greater late season vigor, increased secondary rooting, more rapid germination, greater cold tolerance, greater tolerance to water deprivation, reduced stomatal conductance, altered C / N sensing, increased low nitrogen tolerance, increased low phosphorus tolerance, or increased tolerance to hyperosmotic stress as compared to the control plant as compared to a control plant.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY) +1
Vegetation canopy transpiration inversion algorithm considering phenological information
ActiveCN112182882AImprove estimation accuracyGood linear relationshipCharacter and pattern recognitionDesign optimisation/simulationStomaNonlinear model
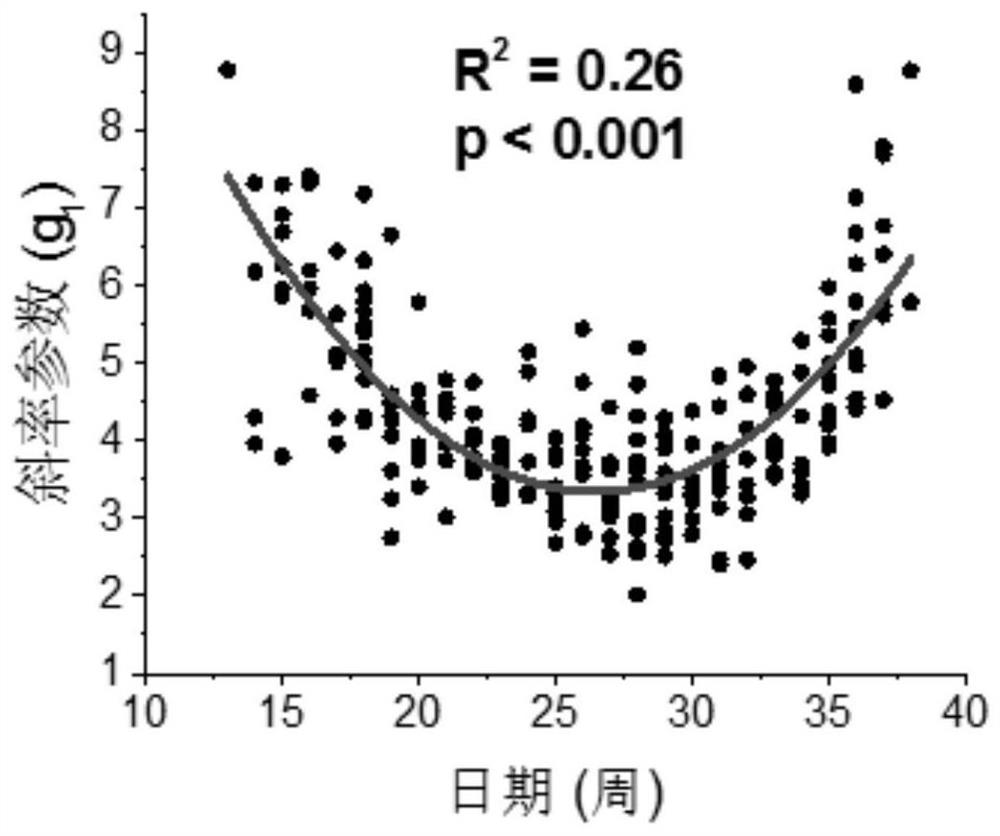
The invention discloses a vegetation canopy transpiration inversion algorithm considering phenological information, belongs to the technical field of water circulation key parameter quantitative inversion. According to the invention, seasonal leaf area change and phenological rhythm information of a vegetation canopy by utilizing satellite remote sensing vegetation index data. The invention provides a dynamic parameterization method for a stomatal conductance slope parameter in a photosynthetic conductance model. The remote sensing leaf area index (LAI) refers to the growth activity of the vegetation canopy leaf, which indicates that the LAI and the stomatal conductance slope parameter have a good linear relationship in the annual period. The vegetation growth season is divided into a growth period and a fading period by utilizing the LAI time sequence change, and the relationship between the LAI and the stomatal conductance slope parameter is respectively established for different phenological periods, so that the asymmetric response of the stomatal conductance slope parameter to the LAI change can be clearly identified, and the important influence of the phenology on the leaf function is reflected; the result shows that the estimation precision of the nonlinear model on the stomatal conductance slope parameter is higher, and the seasonal error of canopy stomatal conductance and transpiration can be effectively reduced.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Plant's water shortage status diagnosis method based on infrared imaging
InactiveCN106556569AAccurate monitoringImprove the efficiency of moisture monitoringMaterial analysis by optical meansScreening methodComputer science
The invention discloses a plant's water shortage status diagnosis method based on infrared imaging. The method comprises the following steps: firstly reading a document containing plant-leaf temperature data at the noon, obtaining plant-leaf temperature data Tl by a data screening method, obtaining temperature Td of reference dry leaf and temperature Tw of reference wet leaf according to infrared image temperature data of the reference dry leaf and reference wet leaf, calculating plant's stomatal conductance value gs by combining instantaneous wind speed Mu and leaf average length d, and comparing the calculated value with the maximum stomatal conductance gsmax of each plant at corresponding moment to obtain plant's water shortage status index v so as to further judge plant's water shortage status grade V. In comparison with the prior art, the method of the invention is adopted to evaluate plant's water shortage status by calculating plant's stomatal conductance through an infrared imaging technology, is simple to operate, and is time-saving and labor-saving.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method and system for diagnosing plant water stress based on high-flux stomatal conductance
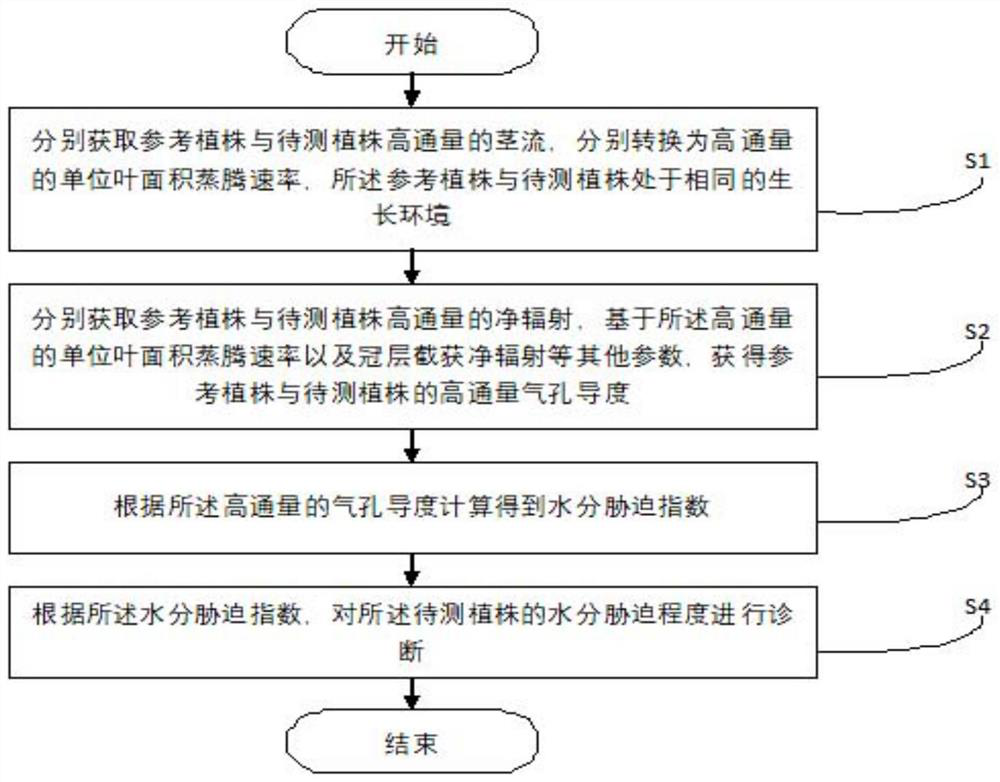
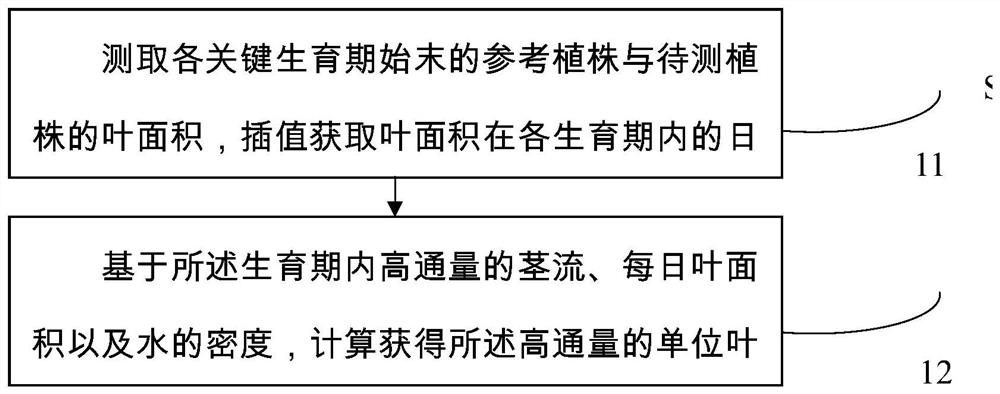
PendingCN113049750AWater stress is convenient and quickOvercome operational complexityTesting plants/treesStomaPlant Stomata
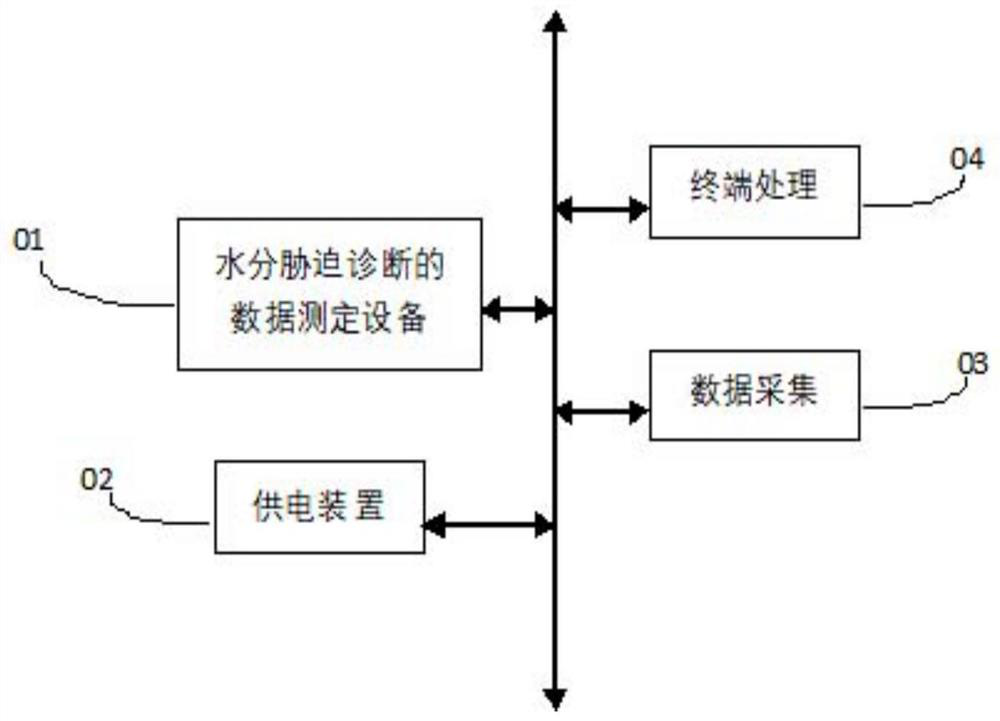
The invention discloses a method and system for diagnosing plant water stress based on high-flux stomatal conductance, and belongs to the technical field of agricultural irrigation. A plant water stress diagnosis system consisting of high-flux stem flow, meteorological data, net radiation measurement equipment and plant height leaf area parameter auxiliary measurement is combined with a P-M formula to continuously output high-flux stomatal conductance, so that a water stress index is calculated by utilizing the stomatal conductance; and the long-time, accurate, high-pass and continuous monitoring, quantification and diagnosis of plant water stress are realized; a reference plant growing under the condition of no water stress is placed in the same growth climate environment as a plant to be detected, and according to the characteristic that the stomatal conductance of the plant is very sensitive to the water stress, the invention provides an index for diagnosing the water stress of the plant. The index can be obtained by calculating the stem flow, net radiation and meteorological data of the to-be-measured plant and the reference plant which are automatically measured in a high-flux manner, so that the high-flux quantification and diagnosis of the water stress degree of the to-be-measured plant are realized. The method comprehensively considers plant physiological response and environmental influence, and has the characteristics of physiological basis, reliable data, long-time accuracy and high-pass continuity in the application of diagnosing plant water stress.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Nutrient liquid capable of improving resistance of cucumbers as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109678583AIncrease productionIncrease contentMagnesium fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserCalcium nitrate tetrahydrateVitamin C
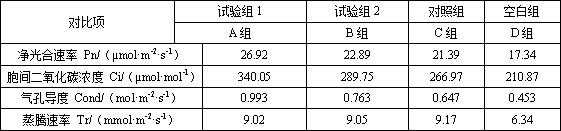
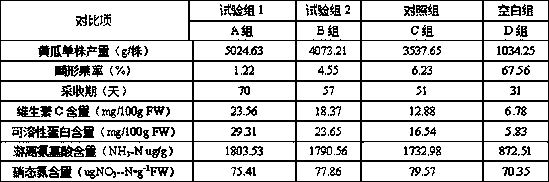
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant nutrient liquid and particularly discloses nutrient liquid capable of improving resistance of cucumbers as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The nutrient liquid comprises gamma-aminobutyric acid, potassium nitrate, calcium nitrate tetrahydrate, monopotassium phosphate, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, trace elements and the like, and comprises macroelements such as N, P, K, Ca, Mg and S. When the nutrient liquid is applied to the fruiting period of the cucumbers, the picking period of the cucumbers can be significantly prolonged, the malformation rate can be reduced, the fruit yield of single plant of cucumber can be increased, and the content of vitamin C, soluble protein and free amino acid of the cucumbers can be significantly increased; in addition, when the nutrient liquid is applied to the fruiting period of the cucumbers, the nitrate content of the cucumbers can be reduced, the net photosynthetic rate of the cucumbers is increased, intercellular carbon dioxide concentration and the stomatal conductance are increased, element deficiency symptoms in the middle and later fruiting period of the cucumbers are avoided, and the high-temperature resistance and the extreme environment resistance of the cucumbers are significantly enhanced.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Application of eutrophic water to improvement of photosynthetic capacity of lawn plants
InactiveCN101575225APromote photosynthesisReduce reprocessingClimate change adaptationSewage/sludge fertilisersTranspirationBiology
The invention discloses an application method of eutrophic water irrigation in the improvement of photosynthetic capacity of lawn plants, wherein the eutrophic water is the eutrophic water with 25 percent-75 percent of the original concentration thereof; and the eutrophic water has TN of 9.7mg / L-13.1mg / L, TP of 0.6mg / L-0.9mg / L and pH value of 8.12-8.99. Results show that the photosynthetic performances of the stomatal conductance, the intercellular carbon dioxide concentration, the net photosynthetic rate, the transpiration rate, the water content utilization efficiency and the like are improved if the diluted 25 percent-75 percent eutrophic water is used in the irrigation, thereby achieving the purpose of improving the lawn quality characters and protecting environment.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for rapidly identifying scab resistance of wheat
InactiveCN103276047AFast, efficient and accurate identificationShort response timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyLimit value
The invention discloses a method for rapidly identifying scab resistance of a wheat. The invention provides an identification method for identifying the resistance characteristic of the detected wheat against gibberellic disease by utilizing change of physiological parameters of wheat photosynthesis organs related to photosynthesis before or after the wheat is infected with bacteria aiming at the defects of the identification method in the prior art that the identification process is time-consuming and the identification result is affected by artificial subjective factors. The concrete physiological parameters include an intercellular CO2 concentration value Ci, a limiting value Ls of stomata, relative difference degree of a stomatal conductance value Gs and a net photosynthetic rate value Pn, variation amplitude of the net photosynthetic rate value Pn, and the like. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, one or more parameters are used for indentifying resistance characteristic of the gibberellic disease of wheat plants individually or all together. The invention also provides a preferable method in which wheatear parts are used as photosynthesis organs. The method is high in identification result accuracy, high in repeated reproducibility level, fast and efficient, and can be suitable for living plant identification.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
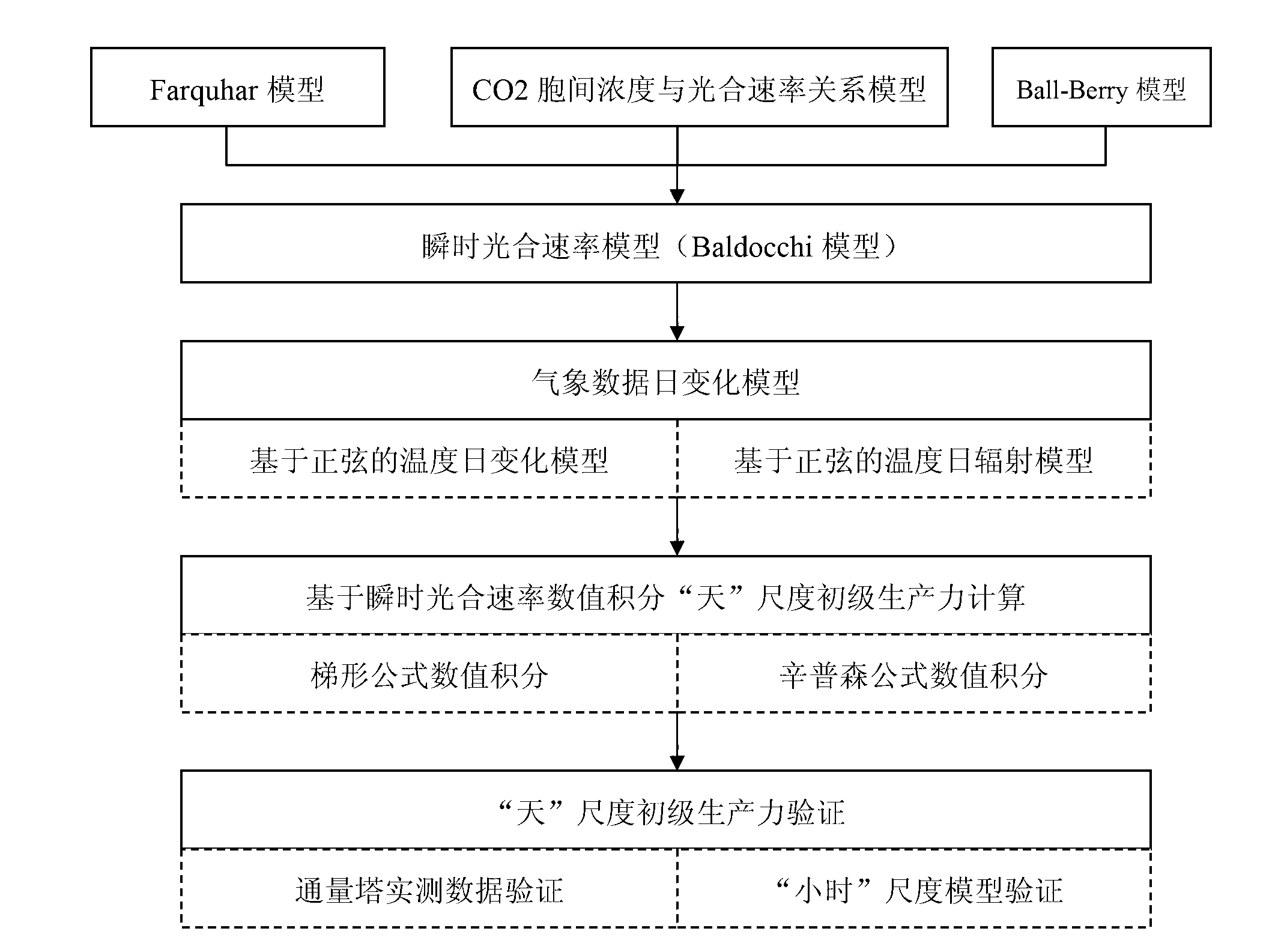
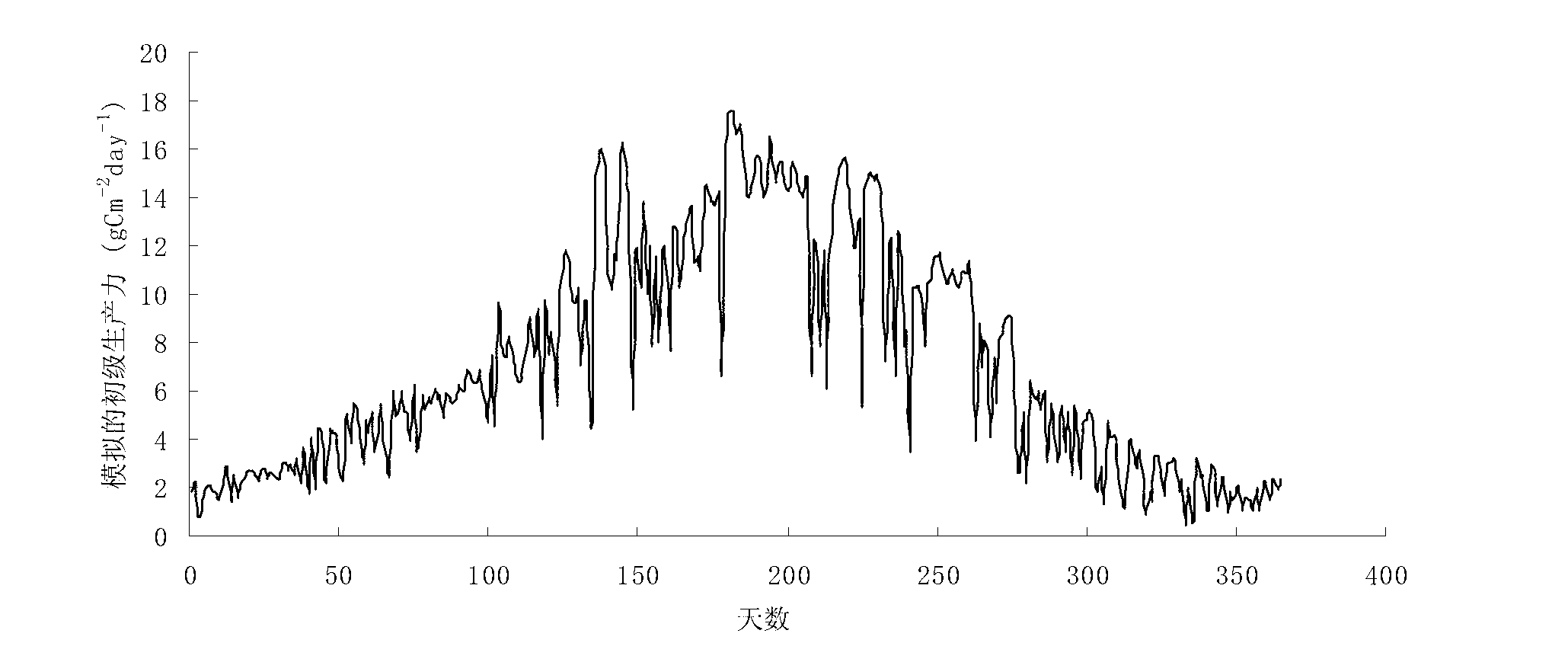
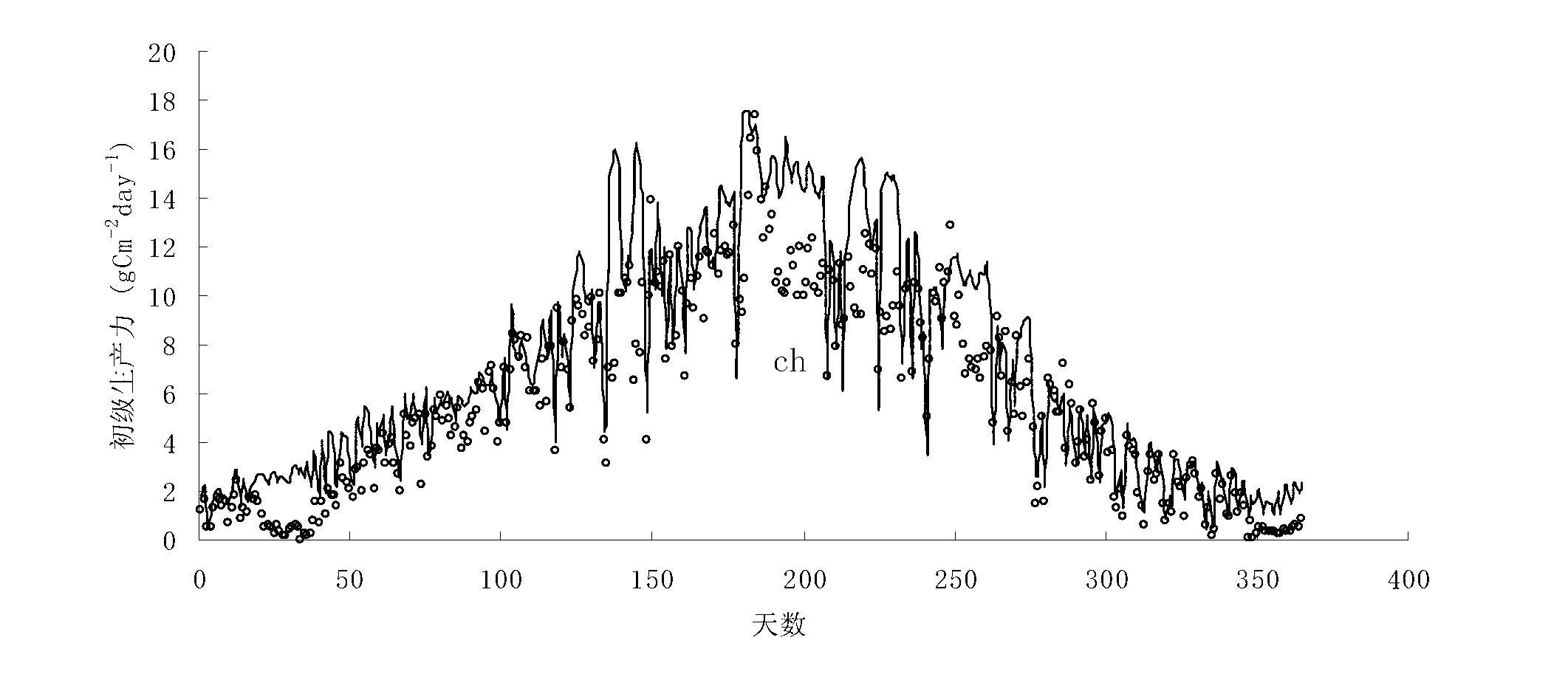
Day-scale primary productivity estimation method based on instantaneous photosynthetic rate integration
InactiveCN103020444AOptimization mechanismIncreased calculated clear heightSpecial data processing applicationsEstimation methodsPrimary productivity
The invention relates to a day-scale primary productivity estimation method based on instantaneous photosynthetic rate integration, and the method comprises the following steps of (1) calculation of instantaneous photosynthetic rate: establishing a cubic equation through a relationship formula among the coupled instantaneous photosynthetic rate, intercellular carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration and stomatal conductance, and calculating the instantaneous photosynthetic rate; (2) simulation of instantaneous weather data: simulating the instantaneous weather by utilizing a sinusoidal function through the characteristic that the temperature and radiation diurnal variation follows the sinusoidal variation principle; and (3) calculation of day-scale primary productivity integration: substituting the instantaneous photosynthetic rate solved in the step (1) in the simulated weather data to form a function adopting the time as a variable, utilizing a trapezoid or simpson formula to integrate the time, and acquiring the day-scale primary productivity. By utilizing the diurnal variation principle characteristics of the weather data and combining the instantaneous photosynthetic rate calculation formula, the measurement precision is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Research method of flower and fruit retaining effects of ilex verticillata by different growth regulators
ActiveCN105699348AIncrease photosynthetic rateIncrease the number of fruit per plantFluorescence/phosphorescenceTesting plants/treesMicrostomumStudy methods
The invention discloses a research method of flower and fruit retaining effects of ilex verticillata by different growth regulators. A flower and fruit retaining test is carried out on the ilex verticillata by adopting the different growth regulators to treat through setting treatment, determination and data analysis, and a conclusion that the net photosynthetic rate of the ilex verticillata is different along the treatment of the different growth regulators is obtained; 0.5% KH2PO3 and 0.1% urea are sprayed on the ilex verticillata at a bud stage, 25mg / l GA3 and 0.3% borax or 20-50mg / l 6-BA are sprayed at a full-bloom stage, and 25mg / l GA3 and / or 2mg / L CPUU are / is sprayed at a fruit mature period, so that a single-plant fruiting number of the ilex verticillata can be remarkably improved; the ilex verticillata is treated by GA3 and 6-BA or CPPU combined spraying, gas exchange parameters including the photosynthetic rate, the stomatal conductance, the moisture utilization rate and the like of the ilex verticillata, and chlorophyll fluorescence characters including PSII effective photochemical quantum yield, photochemical quenching, PSII actual photochemical quantum yield, electron transfer rate and the like can be improved; and the fruit retaining rate of the ilex verticillata is effectively improved, and theoretical evidences are provided for researching the growth regulators of the ilex verticillata.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Plant growth regulator for enhancing drought resistance of rice and preparation method and application thereof
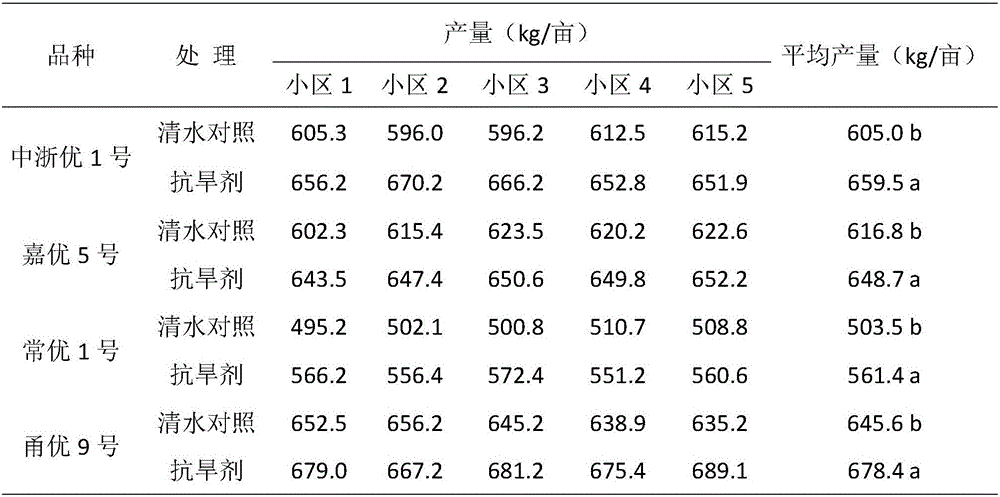
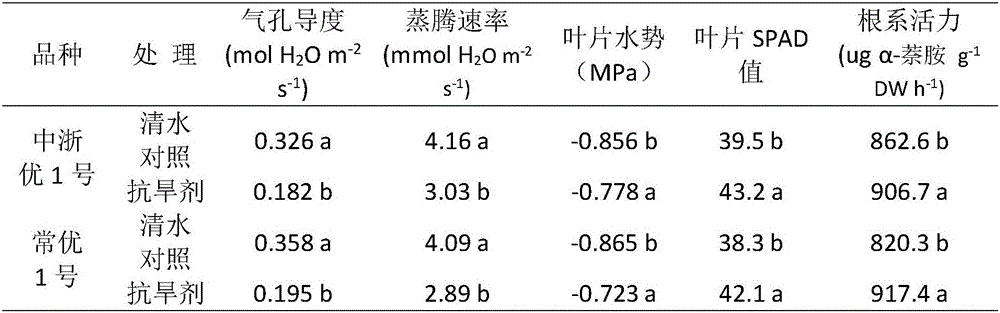
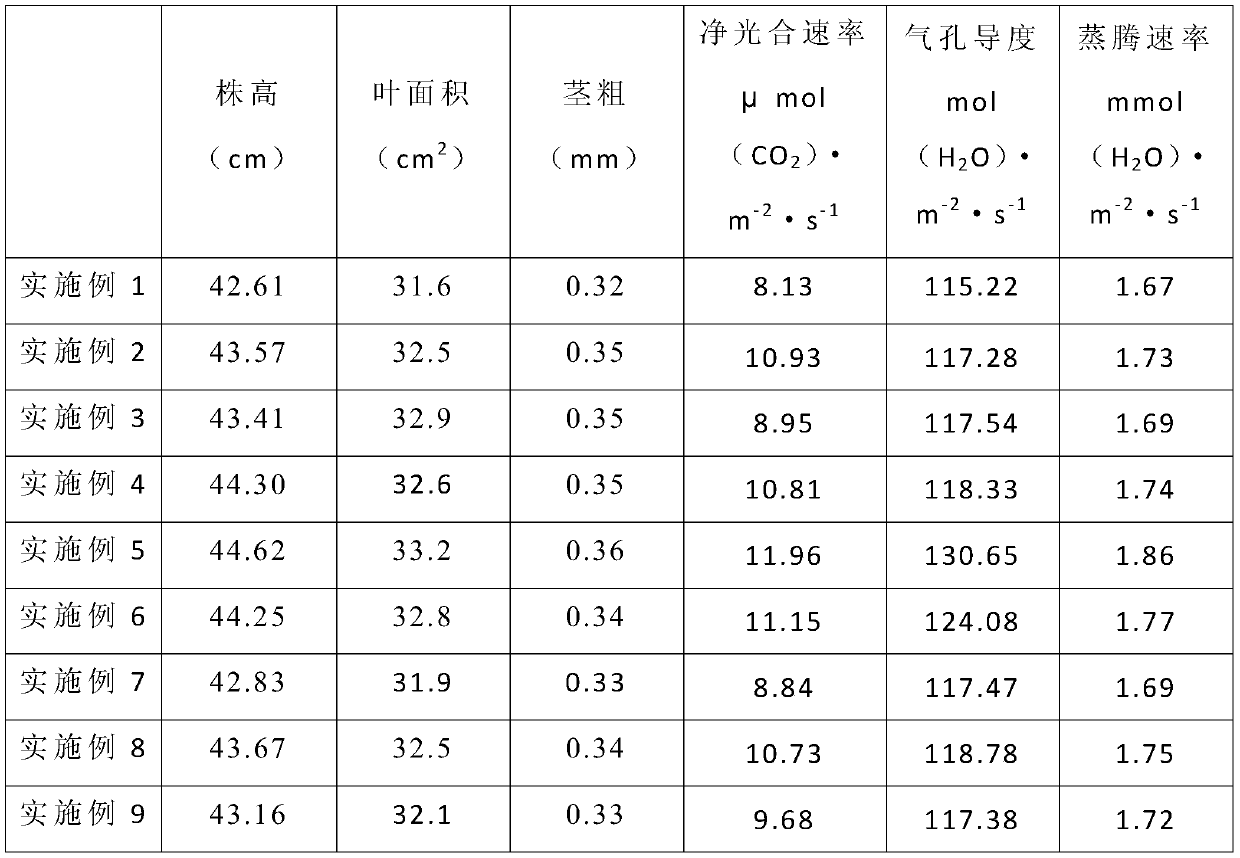
ActiveCN105875612ADecreased stomatal conductanceIncrease chlorophyll contentBiocidePlant growth regulatorsAbsorption capacityPlant growth
The invention discloses a plant growth regulator for enhancing drought resistance of rice and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of mixing a pesticide active compound spermine, natural brassinolide and malic acid according to a certain proportion, and a certain amount of auxiliary filler is added. The concentration of spermine ranges from 100 mg / L to 300 mg / L, the concentration of natural brassinolide ranges from 0.2 mg / L to 0.4 mg / L, and the concentration of malic acid ranges from 100 mg / L to 300 mg / L. The plant growth regulator is used for resisting to drought damage caused by the high temperature or water shortage, after the plant growth regulator is sprayed, stomatal conductance of leaves is reduced, and water consumption due to transpiration is lowered; the chlorophyll content is increased, and photosynthesis assimilation substance accumulation is increased; root activity is enhanced, water absorption capacity and water retention capacity of plants are enhanced, the effects of stabilizing the yield and increasing the yield are achieved, and the plant growth regulator and the preparation method and application thereof provide a new rice plantation technology for alleviating damage of rice regions which are prone to drought damage in China.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
Comprehensive control method for pepper scab
InactiveCN110214608AStrong anaerobic environmentImprove metabolic activityFertilising methodsOrganic fertilisersTranspirationAgricultural management
The invention belongs to the technical field of vegetable cultivation, and particularly relates to a comprehensive control method for pepper scab. The comprehensive control method for the pepper scabcomprises the following steps: (1) soil planting pretreatment; (2) seed treatment; (3) applying a base fertilizer for soil preparation; (4) applying the base fertilizer for soil preparation; and (5) spraying pesticide. According to the cultivation method, the plant height, the leaf area, the stem diameter, the net photosynthetic rate, the stomatal conductance and the transpiration rate of the peppers can be obviously improved by soaking seeds with a pesticide, applying a large amount of organic materials and covering the peppers with films before transplanting the peppers, and applying a pyrroloquinoline quinone solution at different periods of the growth of the peppers after transplanting, in combination with certain fertilization and agricultural management operations, so that the morbidity and the disease index of the pepper scab are effectively reduced, the plant characteristics of the peppers are improved, and growth and development of peppers are promoted.
Owner:HUNAN VEGETABLE RES INST
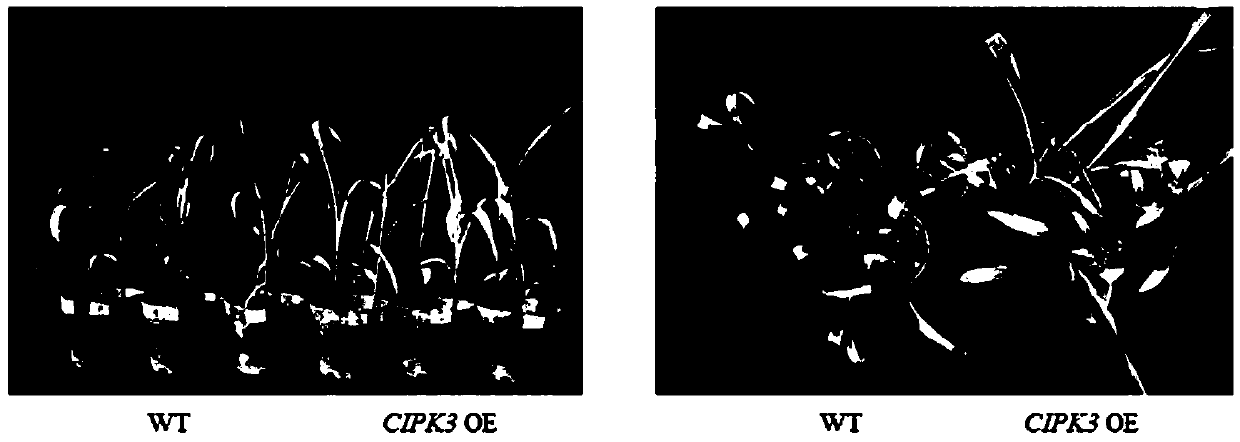
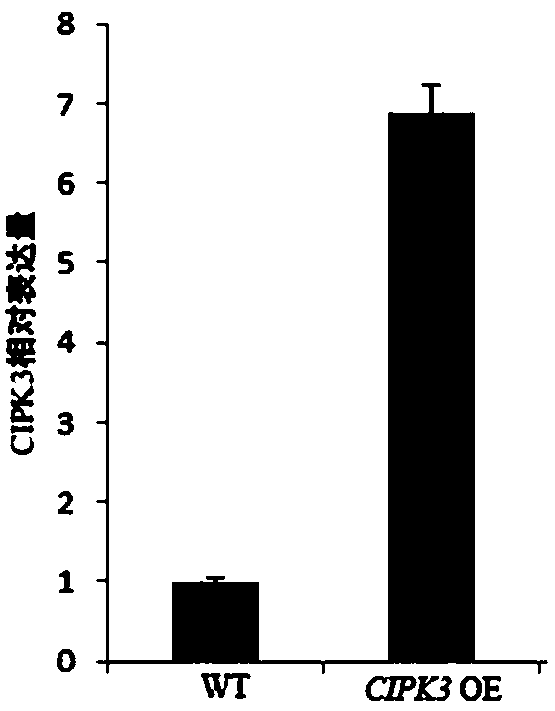
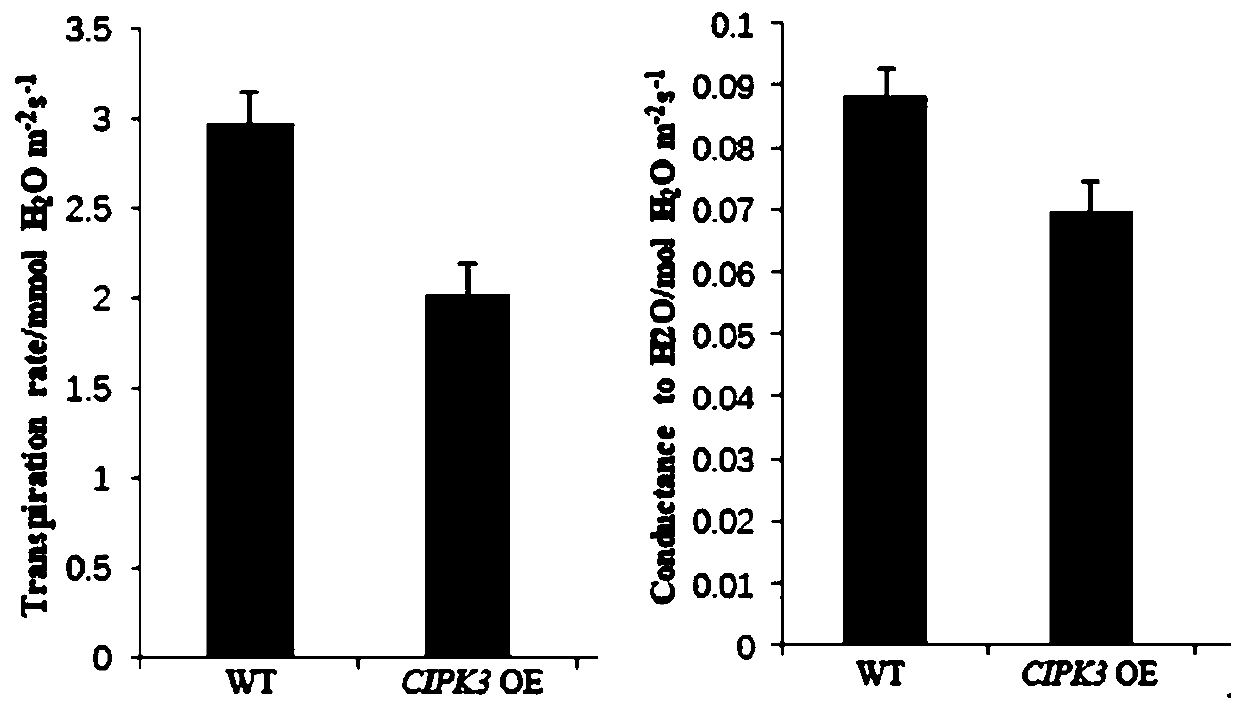
Application of CBL-interacting protein kinases (CIPK)3 protein and encoding genes thereof to plant drought resistance
InactiveCN110643627AReduce rateReduced stomatal conductanceTransferasesFermentationBiotechnologyCloned genes
The invention relates to application of a CBL-interacting protein kinases (CIPK)3 protein and encoding genes thereof to plant drought resistance. The CIPK3 protein has the amino acid sequence shown asSEQ ID NO.1. The CIPK3 genes are cloned, transgenic plants for overexpressing the CIPK3 genes are constructed to analyze characters of the obtained transgenic plants, thus it is found that by increasing the expression quantity of the CIPK3 protein in the plants, the transpiration rate of the plants can be significantly decreased, stomatal conductance of the plants can be significantly reduced, the water utilization rate of the plants is increased, and the growth conditions of the plants under the drought condition are improved. Therefore, the CIPK3 protein and the encoding genes thereof can be used for enhancing the drought resistance ability of the plants in production practice, the yield of the plants under the drought conditions is increased, and water resources are saved.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
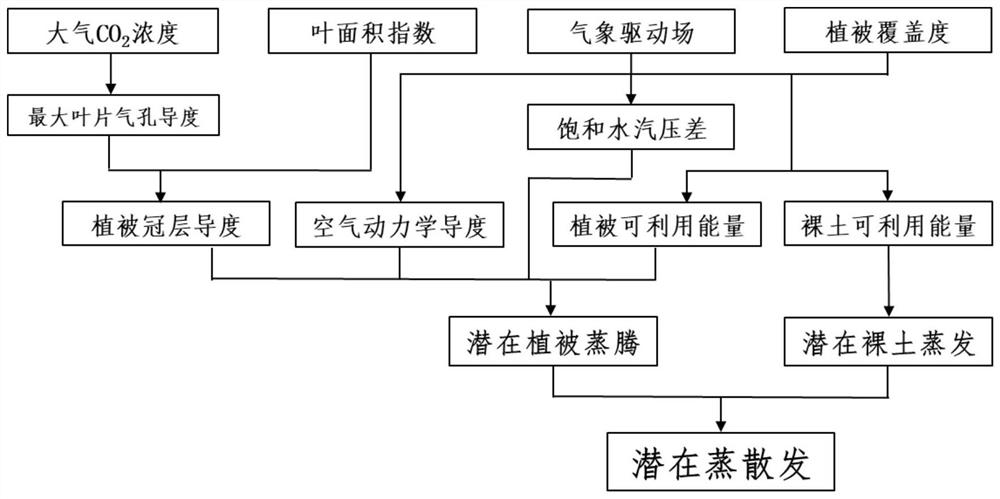
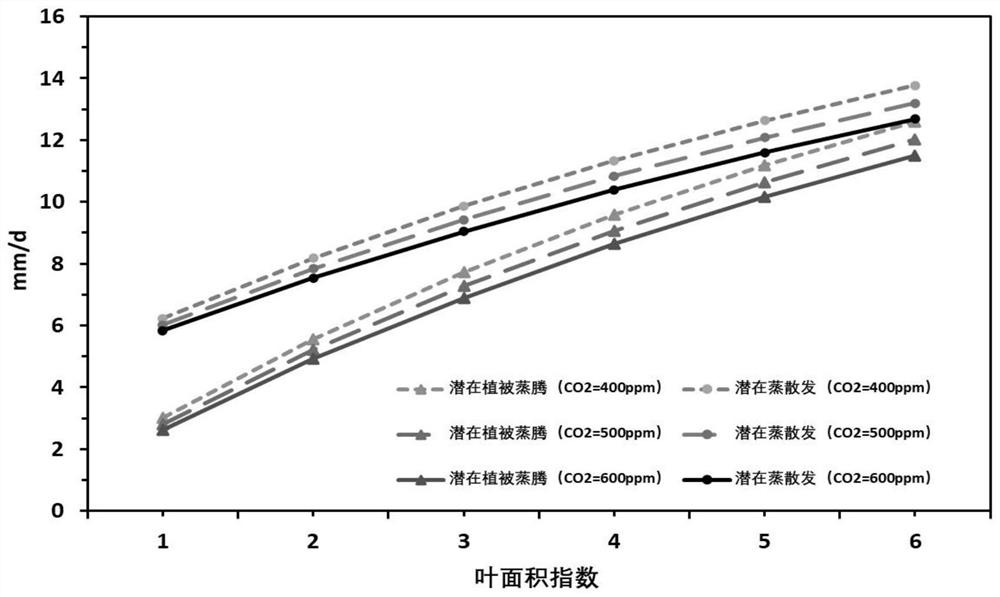
Potential evapotranspiration estimation method considering underlying surface condition change
The invention discloses a potential evapotranspiration estimation method considering underlying surface condition change. The method comprises the following steps: collecting pixel scale data of a research site or region; calculating the maximum blade stomatal conductance through the atmospheric CO2 concentration; combining the maximum leaf stomatal conductance with the leaf area index to calculate vegetation canopy conductance; calculating aerodynamic conductivity according to the near-surface wind speed and the canopy height; calculating vegetation available energy and bare soil available energy according to the available energy; and adding the vegetation potential transpiration amount and the bare soil potential transpiration amount to calculate the surface evapotranspiration amount. The method gets rid of hypothesis constraints of underlying surface conditions and vegetation canopy stomatal conductance invariance, and overcomes the applicability problem that an existing potential evapotranspiration algorithm is only suitable for limited surface coverage vegetation types; thus, a mathematical relation between the leaf maximum pore conductance and the atmospheric CO2 concentration under different ground cover vegetation types are established, and the process that the dynamic change of the atmospheric CO2 concentration affects the canopy pore conductance and potential evapotranspiration can be described reasonably.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
Improved transgenic plant yield and stress tolerance
The present invention relates to a polynucleotide with an inserted expression vector, the introduction of a polypeptide into a plant and the ectopic expression thereof. Embodiments of the invention show that, the polypeptide has at least one regulatory activity and is higher in yield, larger in height and better in secondary rooting effect compared with a control plant. Meanwhile, the plant is faster in germination speed, stronger in cold tolerance, better in resistance to water deprivation, lower in stomatal conductance, changed in C / N sensitivity, higher in low-nitrogen tolerance, increased in low-phosphorus tolerance or increased in hypertonic stress tolerance.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC +1
Method for improving drought resistance of citruses
InactiveCN107242080AImprove drought resistanceImprove drought tolerancePlant growth regulatorsBiocideEnvironmental resistanceAdditive ingredient
The invention provides a method for improving the drought resistance of citruses. The method comprises the step of applying a drought-resistant agent to the root circumference of citrus plants, wherein active ingredients of the drought-resistant agent include glomalin. The invention further provides ingredients and specific preparation steps of the drought-resistant agent. Through the adoption of the method for improving the drought resistance of the citruses, the effect of improving the drought resistance of the citruses is significant, the vegetative growth of the citrus plants is promoted, and the biomass is increased; the development of root configuration is promoted, and the length of main roots and the number of lateral roots at all levels are increased; the photosynthetic rate, transpiration rate, stomatal conductance and intercellular CO2 concentration of leaves are increased, and the temperature of the leaves is reduced; the relative water content of the leaves is increased, and the water potential of the leaves is reduced; the content of water stable aggregates in rhizosphere soil is increased, and the stability of the water stable aggregates is improved; the activity of antioxidant enzymes in plant leaves and roots is improved; the contents of abscisic acid, methyl jasmonate and auxin in the leaves and roots are increased. The method for improving the drought resistance of the citruses has the advantages that raw materials are easy to obtain, the production cost is low, the method is low in toxicity, efficienct, environmentally friendly, low in consumption and the like.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Application of progesterone as drought-resistant agent for crops and method for improving drought resistance of crops
ActiveCN109673654AImprove drought resistanceIncrease useBiocidePlant growth regulatorsField experimentFluorescence
The invention provides an application of progesterone as a drought-resistant agent for crops and a method for improving drought resistance of the crops. Research of a laboratory experiment, a pot experiment and a field experiment of the crops with three different volumes and in different environments shows that progesterone can affect wheat phenotype, malondialdehyde content in wheat, hydrogen peroxide content and activity of superoxide dismutase, catalase and peroxidase under the drought condition, can also affect net photosynthetic rate, stomatal conductance and fluorescence parameters of the wheat and can affect level of abscisic acid and cytokinin in the wheat and a root-shoot ratio of the wheat, thereby affecting the yield of the wheat finally. The application range of progesterone iswidened, and progesterone is not limited to medication of a human body and is applied to drought resistance and yield increase of the crops.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
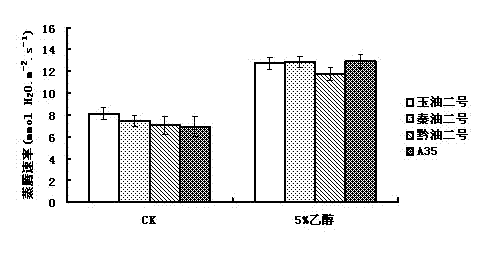
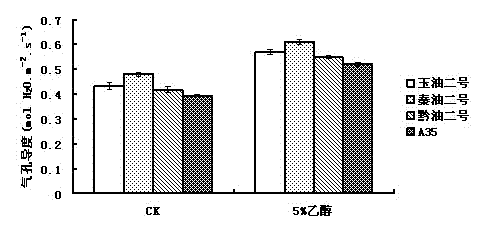
Application of ethanol in promoting plant growth
The invention discloses a new application of ethanol, namely, an application of ethanol as a treating agent in promoting plant growth, wherein when used, 2-8% of volume percent of ethanol solution is used for spraying leaves of plant seedlings growing for 2-3 weeks twice a week; continuously treating for 4-8 weeks, and observing the growth index of the plant; it is shown by experimental result that the photosynthesis ability of the plant seedlings after being treated by ethanol is strengthened, and the chlorophyll content, the net photosynthetic rate, the transpiration rate, the stomatal conductance and the intercellular CO2 concentration are increased notably; the ethanol treating agent can promote plant growth, and increase accumulation of the plant biomass (dry weight of overground part and dry weight of underground part).
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
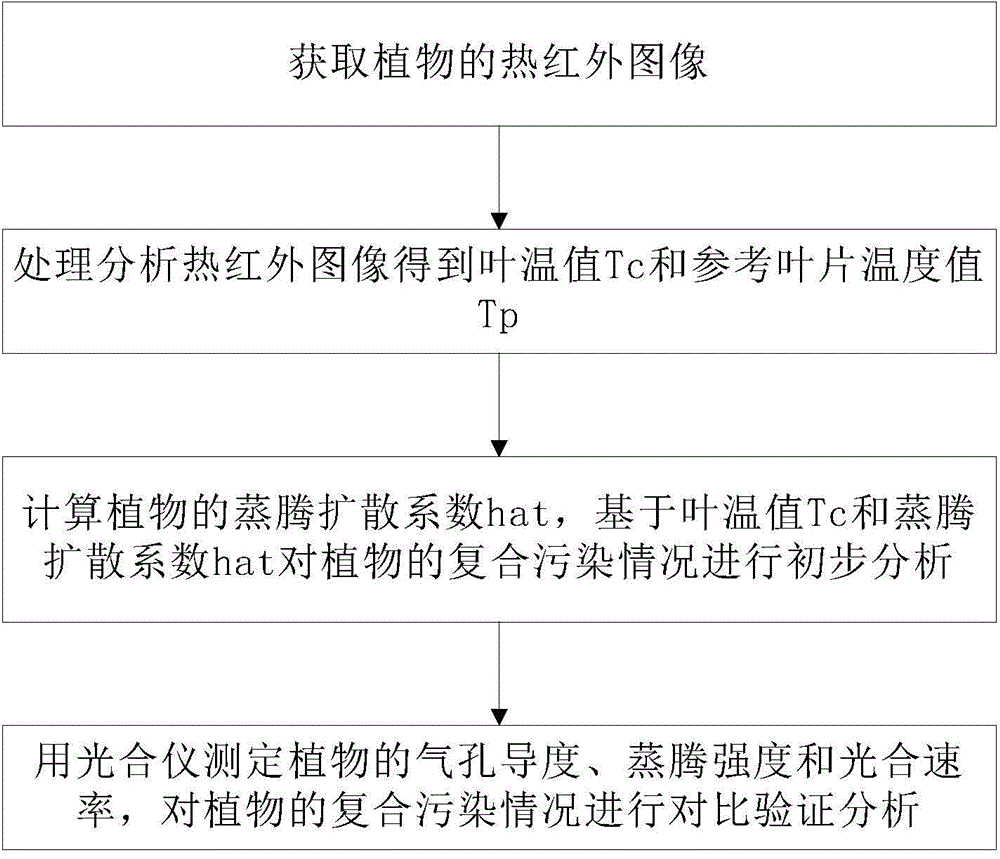
Nondestructive testing method for plant response combined pollution
The invention provides a nondestructive testing method for plant response combined pollution. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a thermal infrared image of plants, processing and analyzing the thermal infrared image, thereby obtaining a leaf temperature value and a reference leaf temperature value; calculating the transpiration diffusion coefficient of the plants, and performing preliminary analysis on the combined pollution condition of the plants based on the leaf temperature value and the transpiration diffusion coefficient; and measuring the stomatal conductance, transpiration intensity and photosynthetic rate of the plants by using a photosynthesis system, and performing comparison validation analysis on the combined pollution condition of the plants. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the response information of the plants on the combined pollution can be rapidly, nondestructively and accurately detected.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Application of Gamma-aminobutyric acid in enhancing salt-stressed maize photosynthesis and regulating endogenous hormone
InactiveCN106212459AHigh activityNo toxicityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsAbscisic acidGamma-Aminobutyric acid
The invention relates to application of Gamma-aminobutyric acid in enhancing salt-stressed maize photosynthesis and regulating endogenous hormone and relates to application of Gamma-aminobutyric acid in maize growth and development. The invention is intended to provide novel application of Gamma-aminobutyric acid. The Gamma-aminobutyric acid can regulate salt-stressed endogenous hormone in maize seedlings. The content of endogenous GABA in salt-stressed maize leaves and roots is increased. The decrease in the content of endogenous hormone in salt-stressed maize roots is relieved. The content of gibberellin in salt-stressed leaves and roots is increased. The decrease in the content of zeatin riboside in salt-stressed maize leaves and roots is relieved. The content of abscisic acid in salt-stressed leaves and roots is decreased. The Gamma-aminobutyric acid can regulate salt-stressed maize leave photosynthetic system, thereby increasing SPAD (soil and plant analyzer development) value, photosynthetic rate, transpiration rate and stomatal conductance for maize leaves. The application is used in the field of maize cultivation.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Urban green land species shade tolerance evaluation method and urban green land species selection method
PendingCN112529049APromote growthFunction increaseData processing applicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionShade toleranceEcology
The invention relates to an urban green land species shade tolerance evaluation method and an urban green land species selection method, and the method comprises the steps: respectively measuring 11 related parameters of species shade tolerance: the apparent quantum efficiency, the dark respiration rate, a light saturation point, a light compensation point, the net photosynthetic rate, the stomatal conductance, the intercellular carbon dioxide concentration, the transpiration rate, stomatal restriction, a chlorophyll content relative value of the leaves and the specific leaf area of the leaves; performing principal component analysis on the parameters, and calculating a principal component score, a membership function value and a comprehensive index weight to obtain a comprehensive shade tolerance evaluation index D value; and calculating shade tolerance comprehensive evaluation indexes of any two or more species, the shade tolerance of the species with a high comprehensive shade tolerance evaluation index D value being higher than that of the species with a low comprehensive shade tolerance evaluation index D. According to the method, the shade tolerance of common green land species is comprehensively evaluated, and a technical method is provided for screening of urban green land species.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Yield and stress tolerance in transgenic plants iii
InactiveUS20100186105A1Increase productionAmeliorate adverse effect of waterClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesNucleotideLow nitrogen
Polynucleotides and polypeptides incorporated into expression vectors have been introduced into plants and were ectopically expressed. The polypeptides of the invention have been shown to confer at least one regulatory activity and confer increased yield, greater height, greater early season growth, greater canopy coverage, greater stem diameter, greater late season vigor, increased secondary rooting, more rapid germination, greater cold tolerance, greater tolerance to water deprivation, reduced stomatal conductance, altered C / N sensing, increased low nitrogen tolerance, increased low phosphorus tolerance, or increased tolerance to hyperosmotic stress as compared to the control plant as compared to a control plant.
Owner:MONSANTO CO +1
Screening method for spring-rape high-photosynthetic-efficiency germplasm
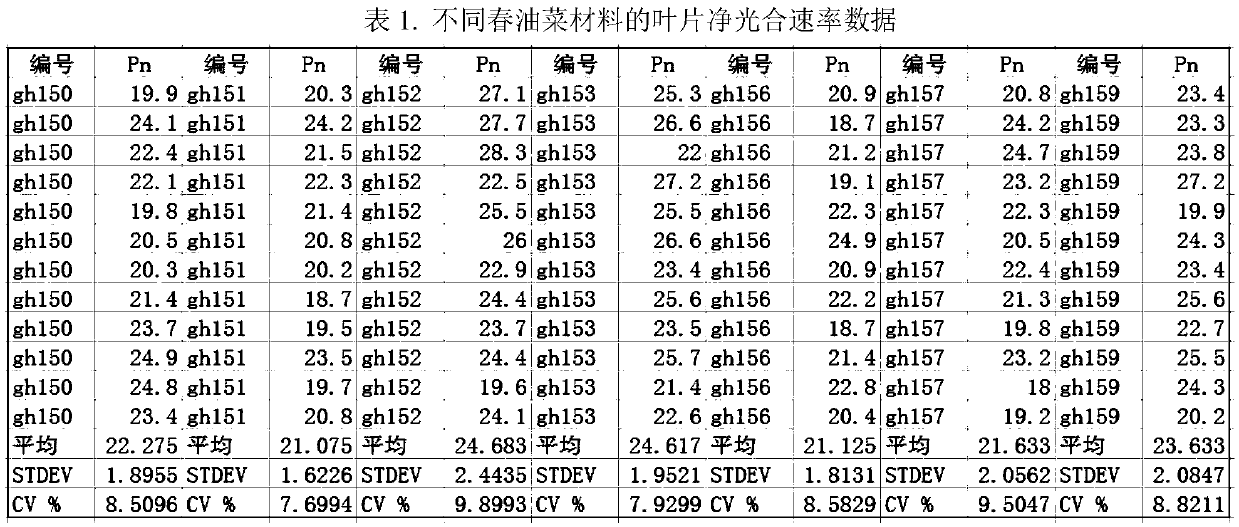
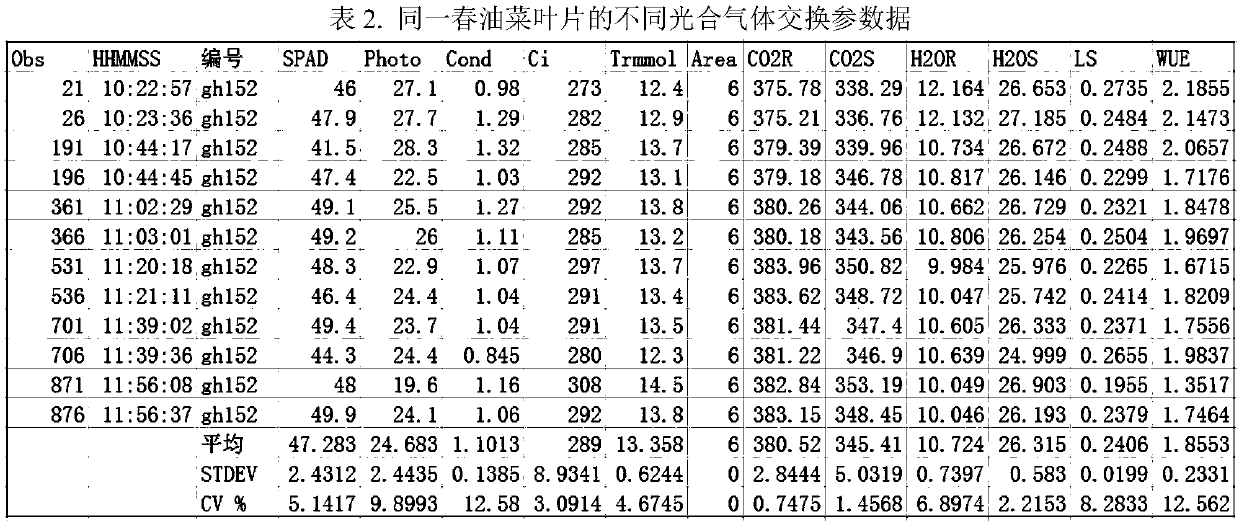
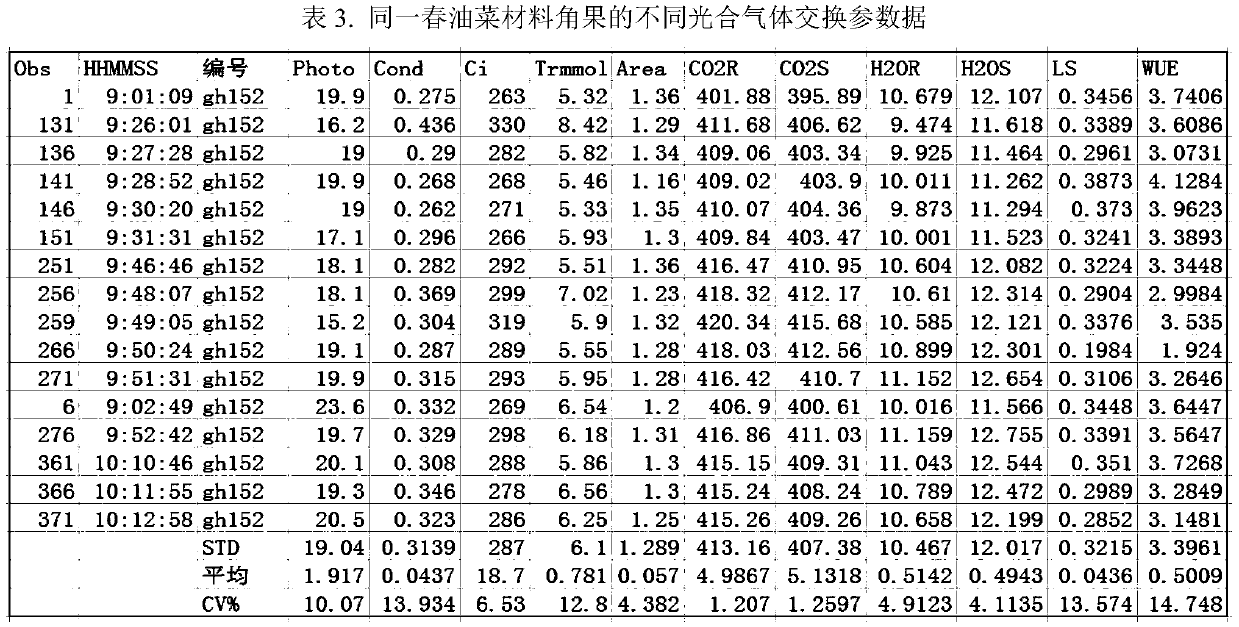
ActiveCN109618833AComprehensive assessment of photosynthetic propertiesClimate change adaptationLeaf crop cultivationScreening methodGermplasm
The invention discloses a screening method for spring-rape high-photosynthetic-efficiency germplasm. The screening method includes the steps that the net photosynthetic rate, the stomatal conductance,the intercellular CO2 concentration, the transpiration rate, the stomata limiting value and the water use efficiency of leaves and pods are measured; photosynthetic areas of spring-rape green pod skins are measured; the photoresponse curve and the CO2 response curve are measured; 1) long petiole leaves, short petiole leaves, sessile leaves and the pod net photosynthetic rate of a to-be-selected material at the seedling stage, the bolting stage, the flowering stage and the pod stage are compared with long petiole leaves, short petiole leaves, sessile leaves and the pod net photosynthetic rateof the comparison variety 'Qing hybridization 7' at the seedling stage, the bolting stage, the flowering stage and the pod stage, then an average value is solved, and a material higher than 5% of thecomparison group is a primary high-photosynthetic-efficiency material; 2) the photoresponse curve and the CO2 response curve of the short petiole leaves at the seedling stage and the bolting stage aremeasured; light saturation points, light compensation points and the light quantum efficiency are computed through the light response curve, and the carboxylation efficiency, CO2 compensation pointsand CO2 saturation points are computed through the CO2 curve; germplasm at least having a highlight saturation point or low CO2 compensation point serves as a final high-photosynthetic-efficiency material.
Owner:陕西省杂交油菜研究中心
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com