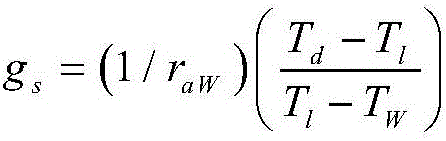Plant's water shortage status diagnosis method based on infrared imaging
A diagnostic method and infrared imaging technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, material analysis through optical means, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming and labor-consuming measurement, large errors, and can only be used for scientific research, so as to improve efficiency, Simple operation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
[0010] The method for diagnosing the water shortage condition of plants based on infrared imaging of the present invention, its preferred embodiment is:
[0011] Using the average temperature T of the leaves of the target plant l , reference dry leaf temperature T d and reference wet leaf temperature T w , combined with the blade shape parameter d and the instantaneous wind speed μ at the corresponding measurement time, and the maximum stomatal conductance value g at the current moment smax , to calculate the average stomatal conductance g of the plant leaf s and Water Scarcity Level V.
[0012] The average temperature T of the leaves of the target plant l , dry leaf temperature T d and wet leaf temperature T w Obtained by:
[0013] Use the infrared thermal imaging device to collect images of the target plants, export the temperature data corresponding to the images and remove redundant data, screen the temperature data sets of the plant leaves, and calculate the averag...
specific Embodiment
[0025] Using the leaf temperature T of the target plant l (°C), reference dry leaf temperature T d (°C) and reference wet leaf temperature T w (°C), combined with the blade shape parameters, namely the blade length d (m) and the instantaneous wind speed μ (m / s) at the corresponding measurement time, and the maximum stomatal conductance value g at the current moment smax (mmol m -2 the s -1 ), calculate the average stomatal conductance g of the plant leaf s (mmol m -2 the s -1 ) and water scarcity level V.
[0026]
[0027] Among them, r aW is the evaporation heat diffusion resistance of the boundary layer.
[0028] For ordinary blades, r aW =1 / (6.62(μ / d) 0.5 )
[0029] If it is a cylindrical blade, then r aW =1 / (4.03(μ 0.6 / d 0.4 ))
[0030] If it is a spherical blade, then r aW =1 / (5.77(μ 0.6 / d 0.4 ))
[0031] According to the calculated g s And the maximum stomatal conductance value, judge the plant water shortage status index v, and classify it into ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com