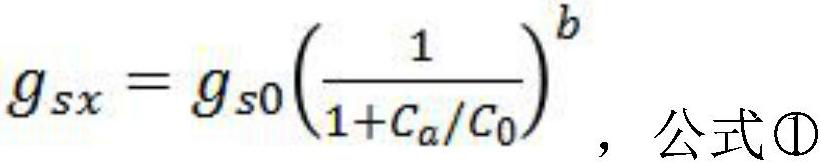Potential evapotranspiration estimation method considering underlying surface condition change
A potential technology for evapotranspiration, applied in the field of satellite remote sensing applications, which can solve problems such as inability to meet applicability requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0048]The present invention will be described in further detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
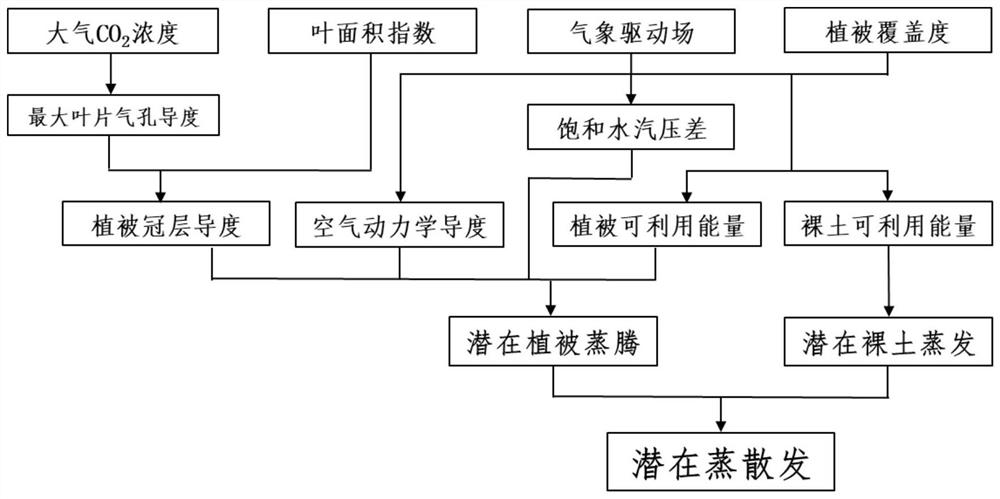
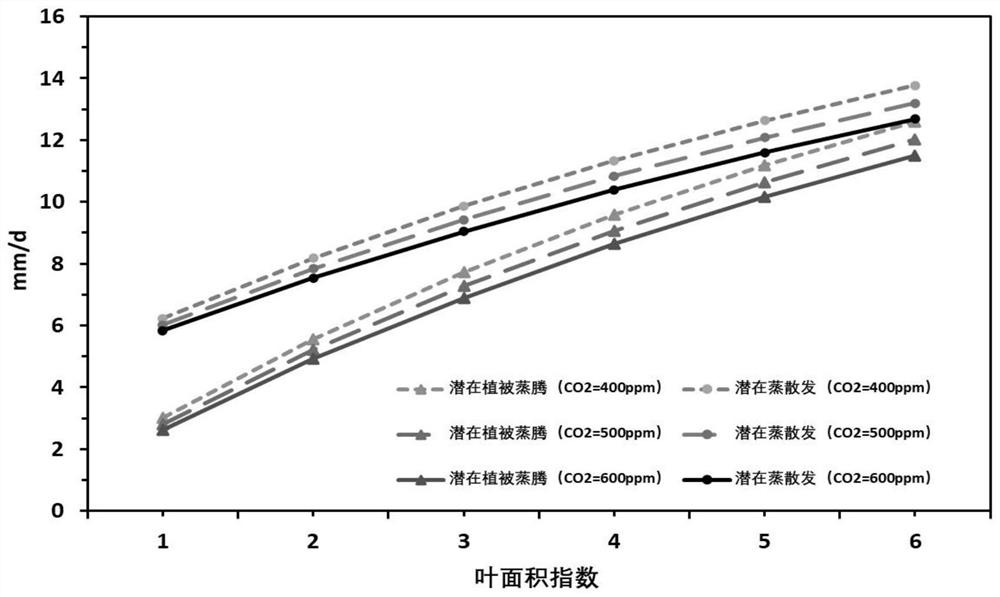
[0049]Such asfigure 1 The potential evapoatization estimation method shown in consideration of the underwent surface condition changes, in the terrestrial table or the pixel (down-pad type can be forest, grass, farmland, wetlands, shrubs and naked soil, etc.) atmosphere Co2The concentration, leaf area index, vegetation coverage, and meteorological drive are input, and the potential evapogenation is finally estimated by estimating potential vents and potential naked soil evaporation, respectively.
[0050]The specific calculation process is as follows:
[0051]Step 1, data collection: collect the atmosphere CO on the research site or area image dimension2Concentration (Ca), Leaf area index (LAI), vegetation coverage (Fc) Time series of meteorological drive field data; meteorological drive data includes temperature, air pressure, relative humidity, downl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com