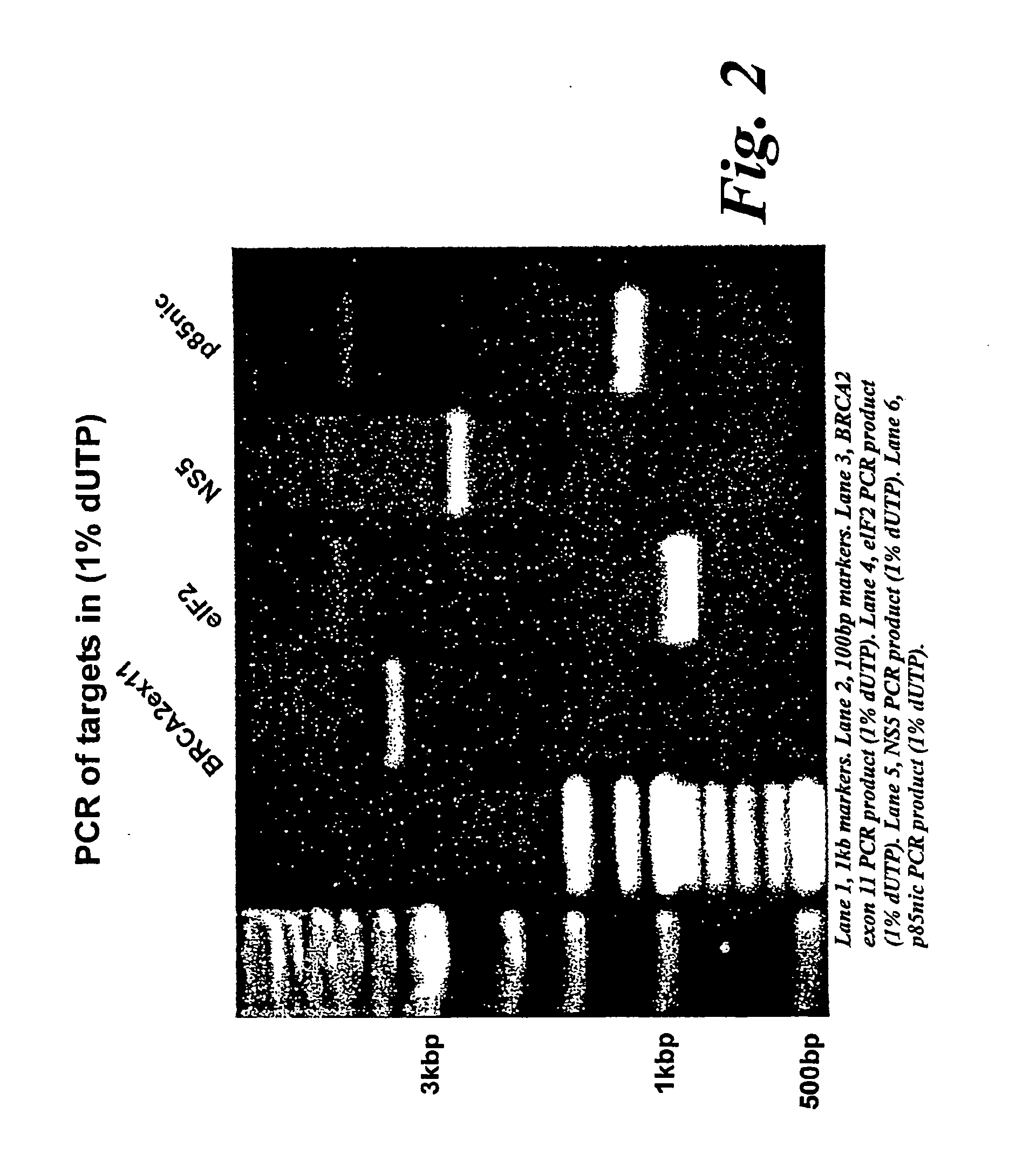
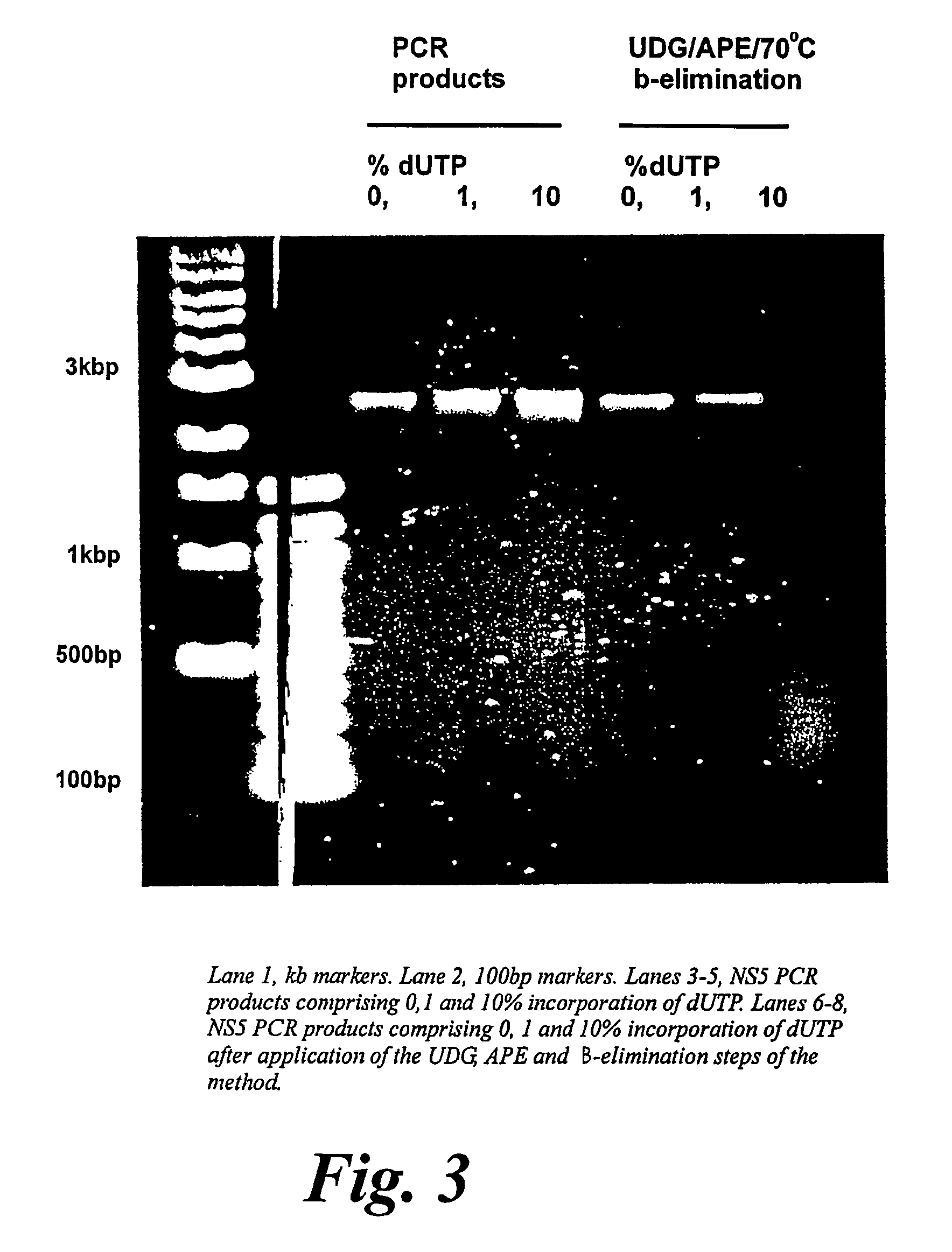
Patents
Literature
201 results about "Cloned genes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
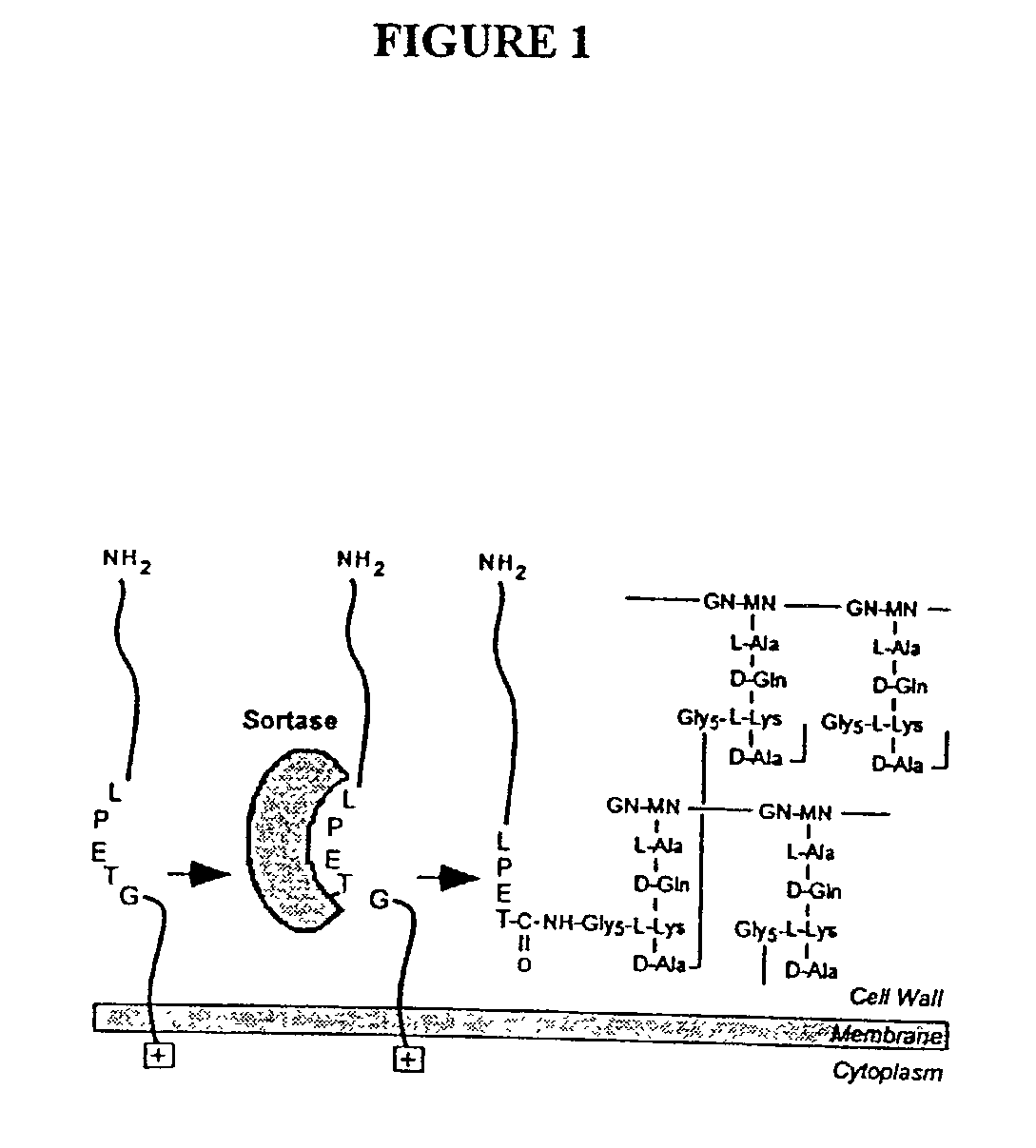
Identification of sortase gene
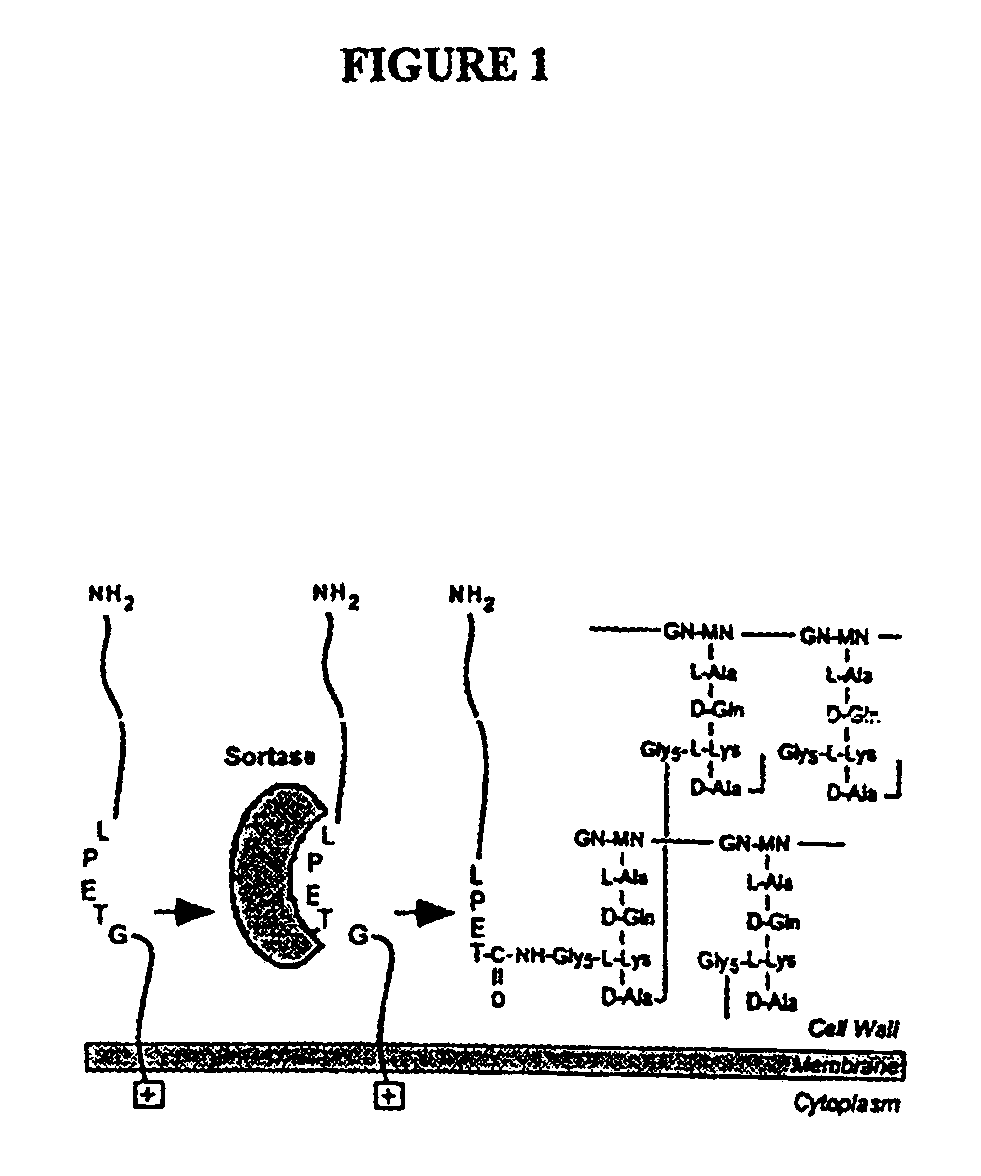
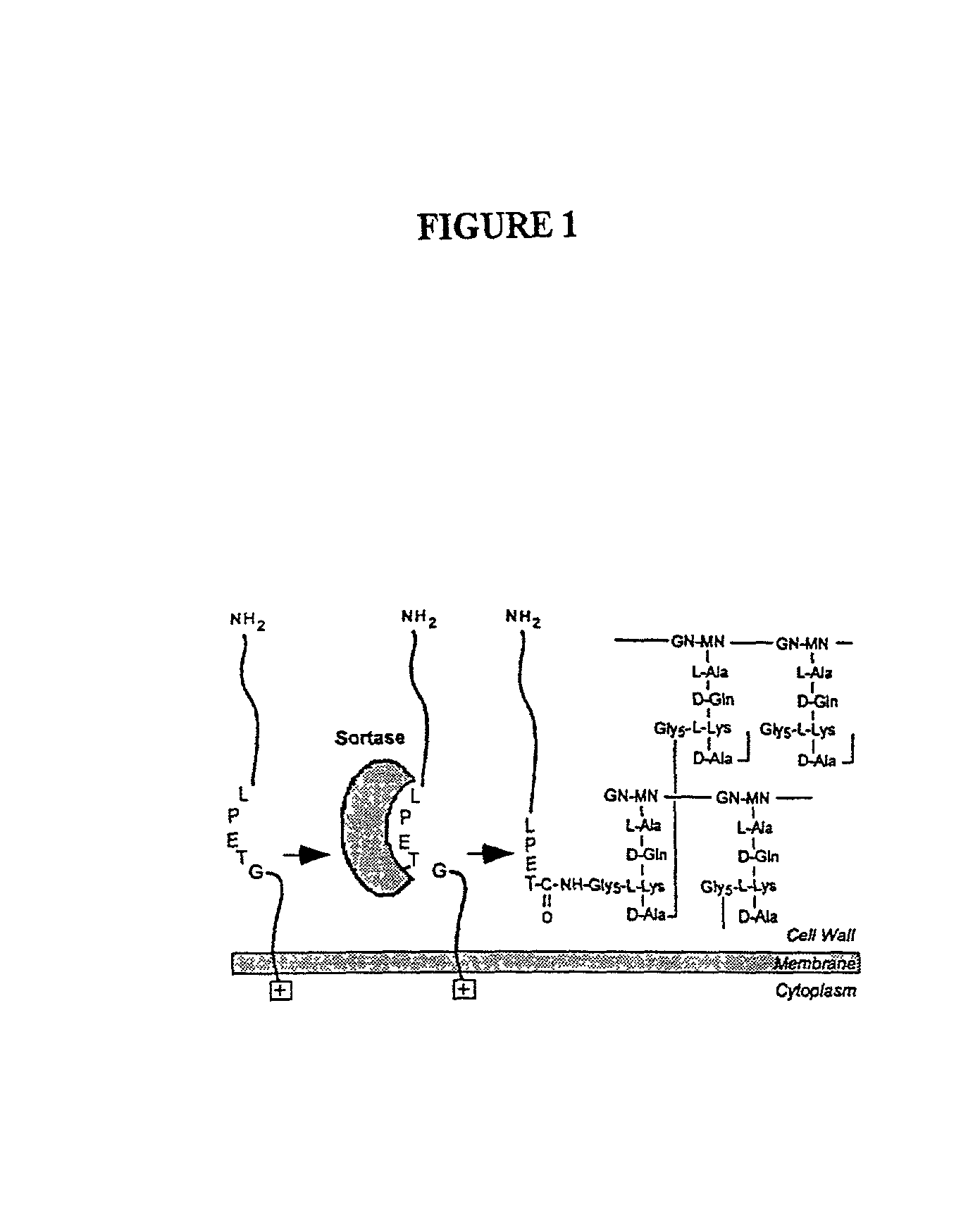
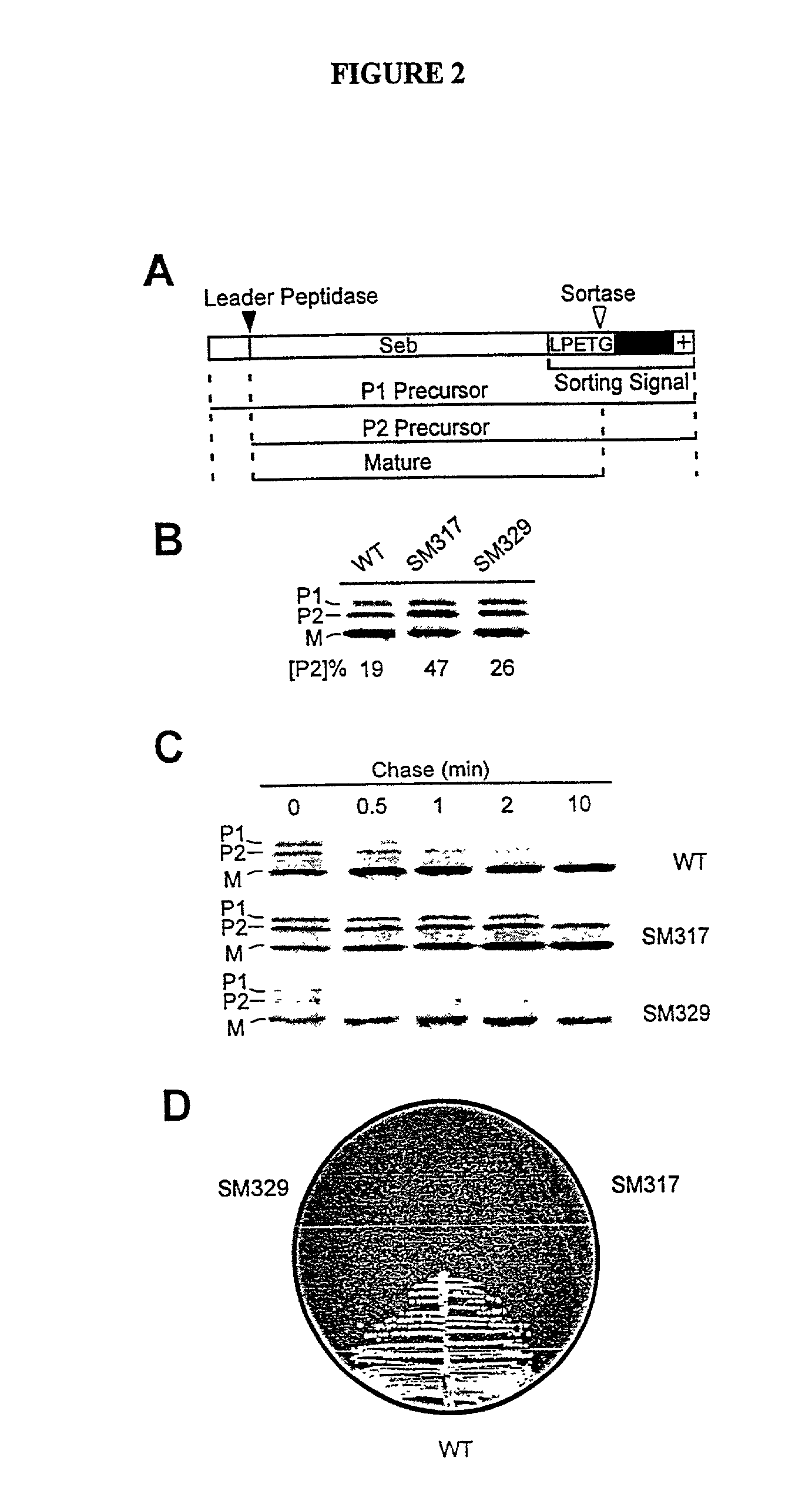
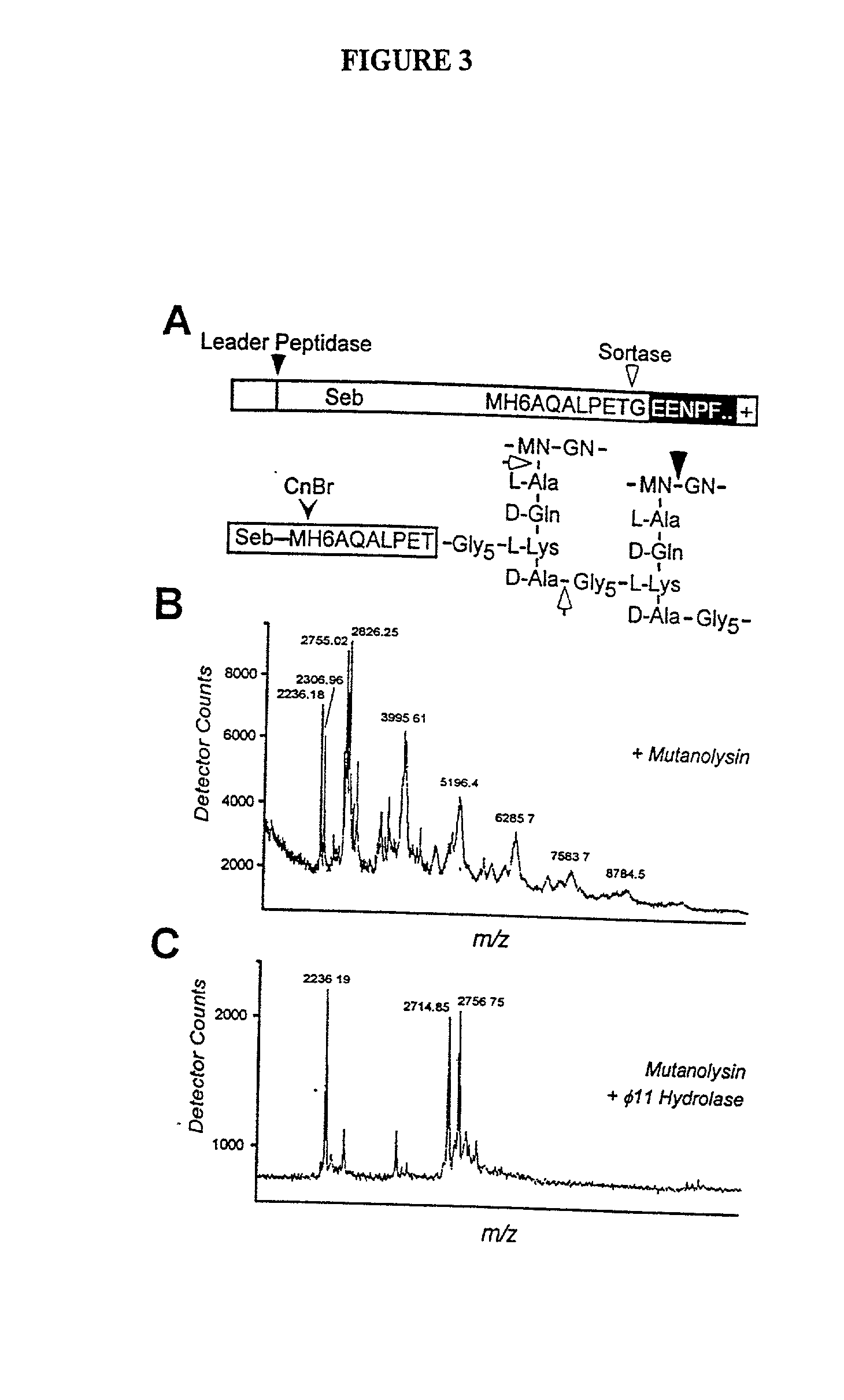
The present invention is a substantially purified sortase-transamidase enzyme from Gram-positive bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus. A specific sortase-transamidase enzyme disclosed has a molecular weight of about 29,076 daltons and catalyzes a reaction that covalently cross-links the carboxyl terminus of a protein having a sorting signal to the peptidoglycan of a Gram-positive bacterium, where the sorting signal has a a motif of NPQ / KTN / G therein. Variants of the enzyme, methods for cloning the gene encoding the enzyme and expressing the cloned gene, and methods of use of the enzyme, including for screening for antibiotics and for display of proteins or peptides on the surfaces of Gram-positive bacteria, are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Identification of sortase gene
InactiveUS20030022178A1Fluorescence enhancementIncreased cleavageAntibacterial agentsFungiEnzyme GeneCarboxyl radical
The present invention is a substantially purified sortase-transamidase enzyme from Gram-positive bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus. The enzyme having a molecular weight of about 23,539 or about 29,076 daltons and catalyzing a reaction that covalently cross-links the carboxyl terminus of a protein having a sorting signal to the peptidoglycan of a Gram-positive bacterium, the sorting signal having: (1) a motif of LPX3X4G therein; (2) a substantially hydrophobic domain of at least 31 amino acids carboxyl to the motif; and (3) a charged tail region with at least two positively charged residues carboxyl to the substantially hydrophobic domain, at least one of the two positively charged residues being arginine, the two positively charged residues being located at residues 31-33 from the motif, wherein X3 is any of the twenty naturally-occurring L-amino acids and X4 is selected from the group consisting of alanine, serine, and threonine, and wherein sorting occurs by cleavage between the fourth and fifth residues of the LPX3X4G motif. Variants of the enzyme, methods for cloning the gene encoding the enzyme and expressing the cloned gene, and methods of use of the enzyme, including for screening for antibiotics and for display of proteins or peptides on the surfaces of Gram-positive bacteria, are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
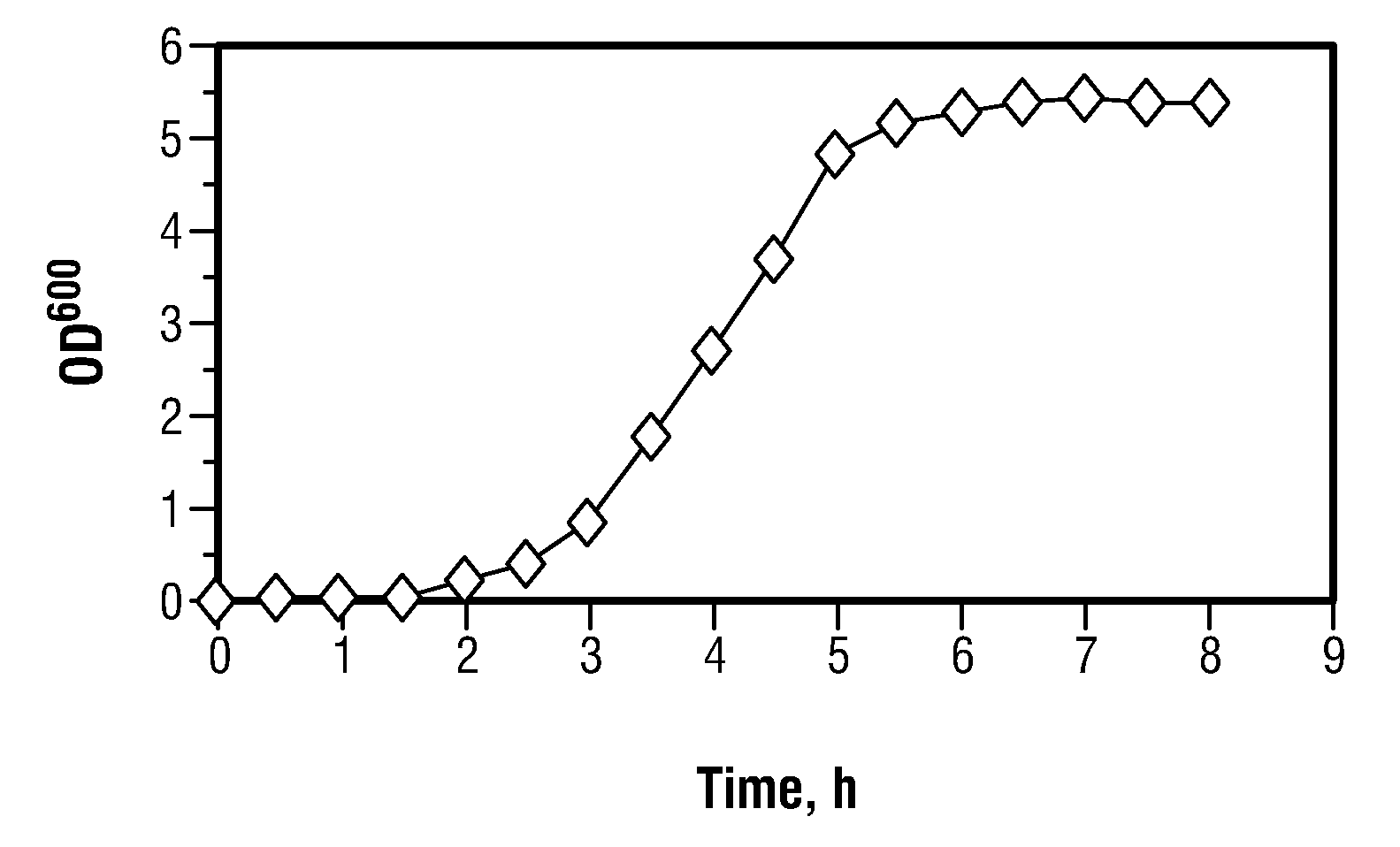
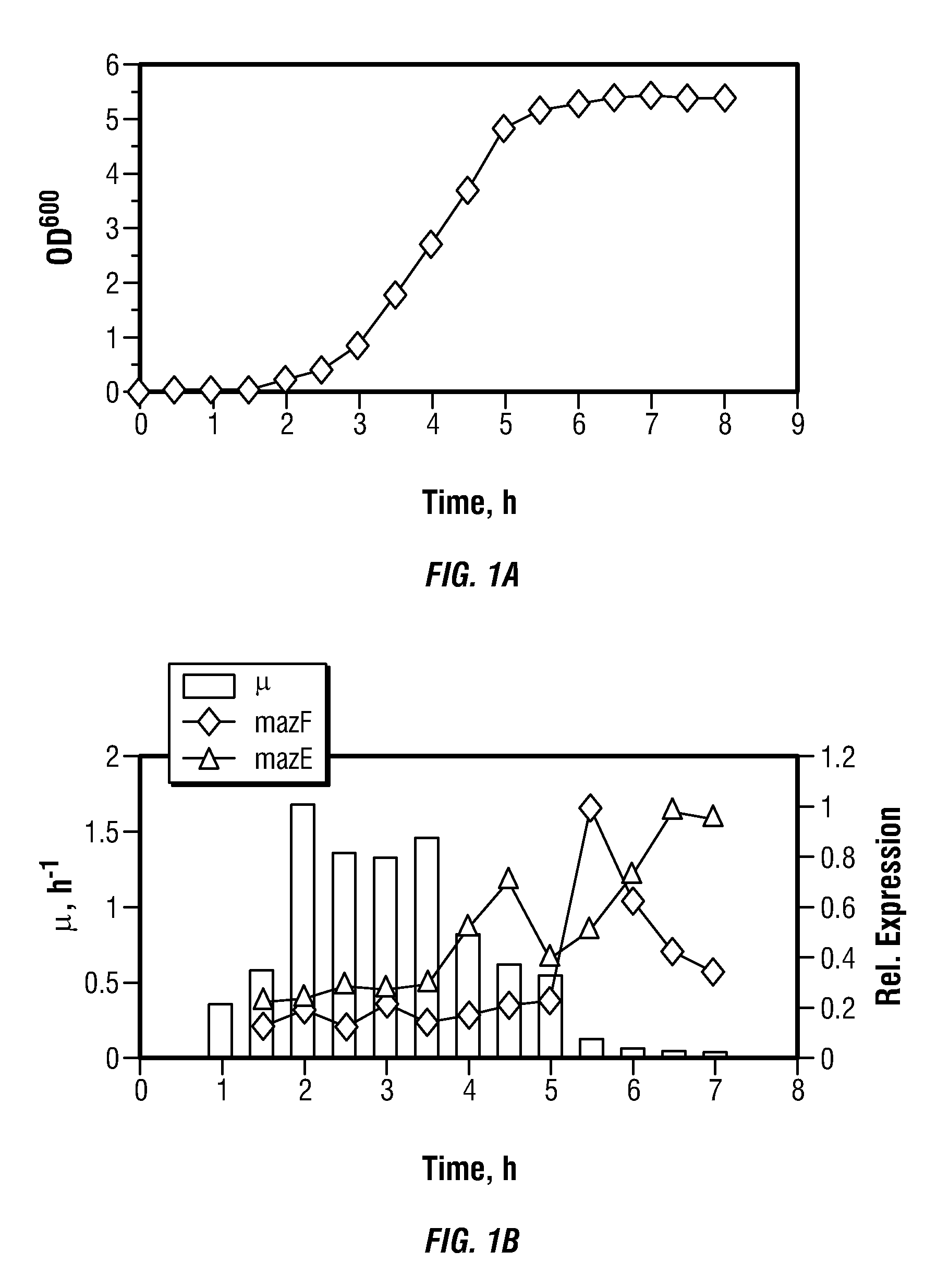
Toxin/antitoxin systems and methods for regulating cellular growth, metabolic engineering and production of recombinant proteins
The present invention provides compositions and method for regulating cellular growth and metabolism, intra- and extracellular enzymatic activities, and synthesis of endogenous and / or heterologous proteins, comprising the steps of cloning genes encoding an mRNA interferase (toxin) and its cognate antitoxin; expressing these proteins in a host cell from two separate constitutive or inducible promoters on one or more plasmid vectors or on a chromosome; and regulating the cellular growth and metabolism by controlling the ratio of toxin and antitoxin present in the host cell. Optionally, the method provides further steps of modifying an endogenous or heterologous gene of interest to substitute all mRNA recognition sequences with sequences that are not cleavable by the mRNA interferase being expressed without any change in the amino acid sequence of the protein encoded by the gene; and co-expressing the gene of interest in the same host cell.
Owner:MAZEF BIOSCI
Diphtheria toxin muton CRM197 and its preparation process
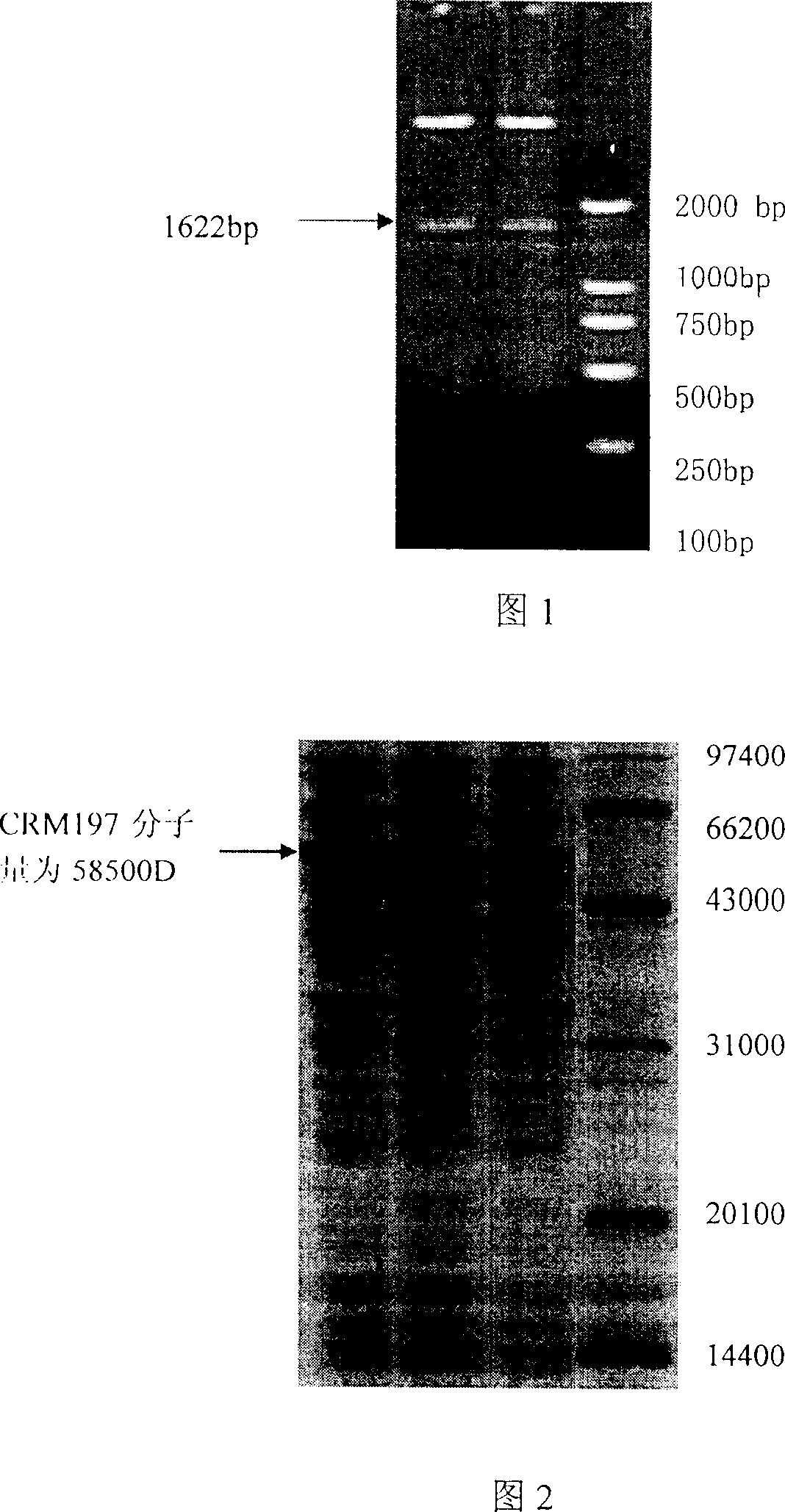
The present invention is diphtheria toxin mutant CRM197 and its preparation process, and belongs to the field of immune protein carrier technology. The diphtheria toxin mutant CRM197 is expressed in colibacillus in the form of inclusion body, and the target product has sequence length of 536 amino acids, the immunogenicity the same as that of diphtheria toxin and no toxicity similar to that of diphtheria toxin. The present invention clones gene coding CRM197, constructs recombinant expression plasmid expressing CRM197 and transforms to colibacillus host for expression in the form of inclusion body. The present invention has target protein accounting for over 24 % of total protein content, high CRM197 purity over 95 % and high target protein recovering rate. The preparation process is simple, low in cost and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:QILU PHARMA HAINAN
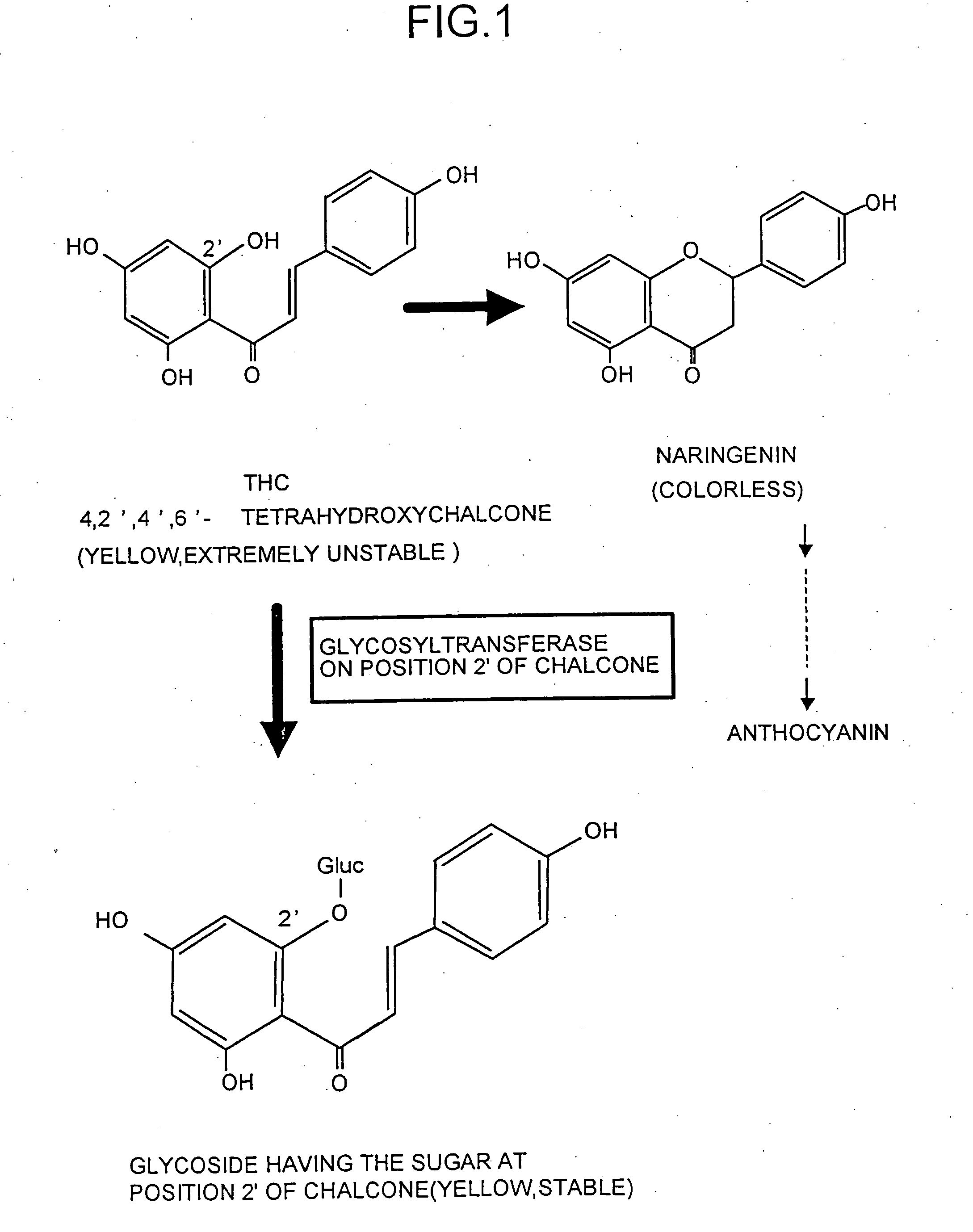
Glycosyltransferase gene
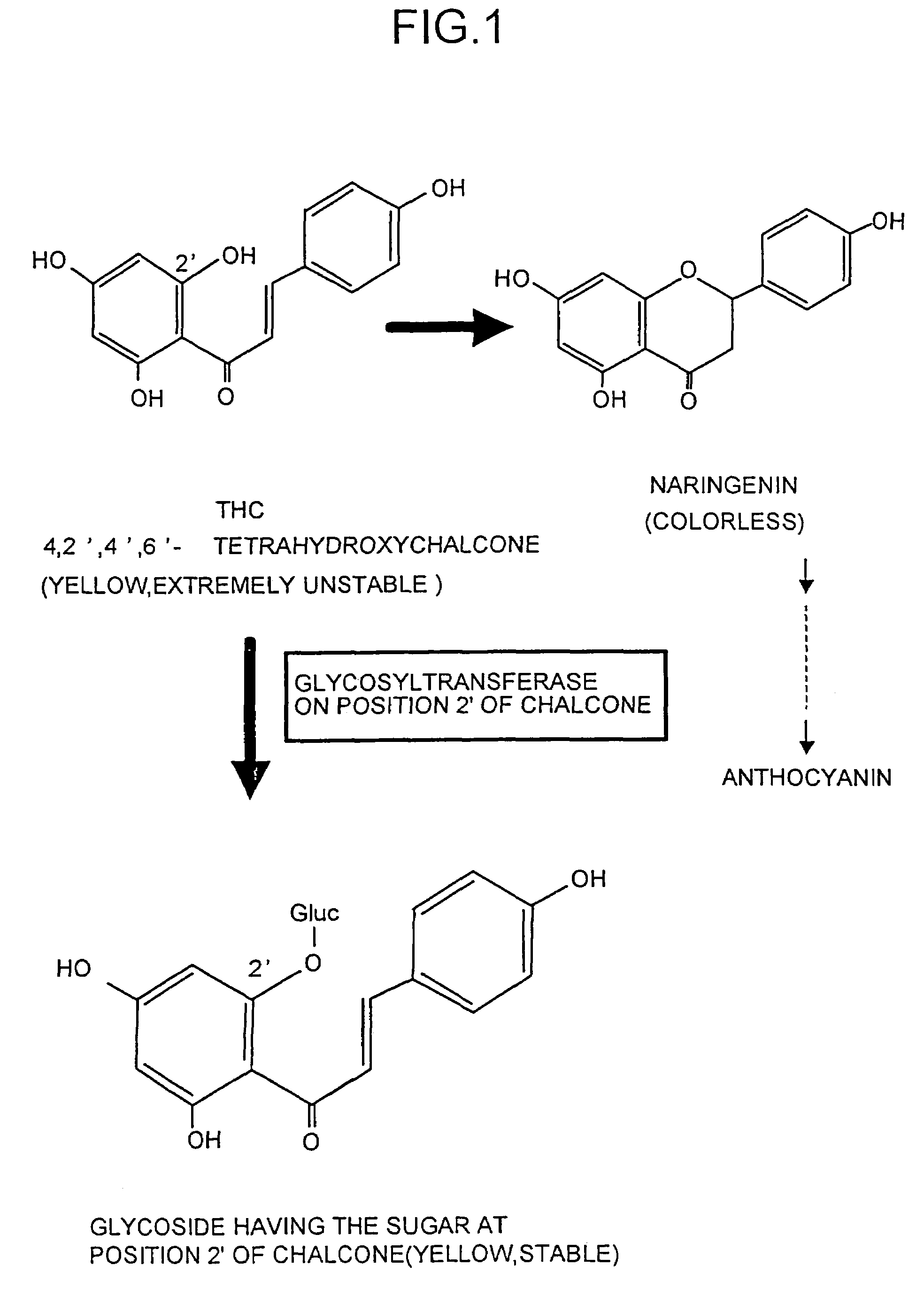
The present invention provides an enzyme which catalyzes a reaction to transfer sugar to a hydroxyl group at position 2′ of chalcones and a gene thereof, and preferably an enzyme which catalyzes a reaction to transfer glucose to a hydroxyl group at position 2′ of the chalcones. Furthermore, the invention provides a plant whose flower color has been changed using the glycosyltransferase. Using probes corresponding to conservative regions of the glycosyltransferase, some tens of glycosyltransferase genes having nucleotide sequences corresponding to the conservative regions were cloned from flower petal cDNA libraries of carnation and the like. Furthermore, each of the glycosyltransferase genes was expressed in Escherichia coli, activity to transfer glucose to position 2′ of the chalcone, i.e., the glycosyltransferase activity at position 2′ of chalcone was confirmed in an extract solution of the Escherichia coli, and it was confirmed that cloned genes encoded the glycosyltransferase at position 2′.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Method for preparing (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate by catalyzing with recombinant carbonyl reductase
InactiveCN102618590AAvoid inhibitionImprove conversion abilityMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliEthyl butyrate
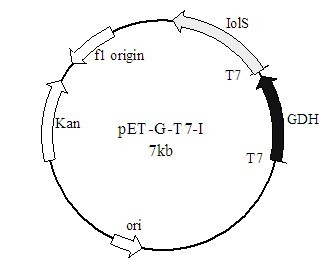
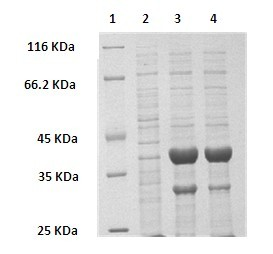
The invention discloses a method for preparing (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate by catalyzing recombinant carbonyl reductase, which belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: cloning gene segments of carbonyl reductase (IolS) and glucose dehydrogenase (GDH) from bacillus subtilis CGMCC NO.1.1508, expressing an IolS gene and a GDH gene in series by adopting a dual-starter method to construct a recombinant plasmid pET24a-G-T7-I, and introducing the plasmid into escherichia coli BL21(DE3); and under the condition of not adding or adding a small amount of NADP+cofactors, performing biotransformation by taking a cell-free extract of the escherichia coli recombinant plasmid as a catalyst, 2-oxo-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate as a substrate and glucose as a substrate to obtain (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate, wherein the enantiomeric excess value of the product is higher than 99.5 percent. In the method, IolS and GDH are co-expressed, so that efficient regeneration of an intra-cellular cofactor NADP(H) is realized, production cost is lowered, and a good industrial application prospect is achieved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Rapid immunoselection cloning method
InactiveUS7119183B2Large amount of proteinImprove efficiencyPeptide librariesPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenCDNA library
A simple and highly efficient method for cloning cDNAs including CD27 (SEQ ID NO:28) from mammalian expression libraries based on transient expression in mammalian host cells has been discovered. Novel expression vectors allowing highly efficient construction of mammalian cDNA libraries are disclosed. The cloning method of the invention which has been used to clone genes for cell surface antigens of human lymphocytes, has general application in gene cloning. Cell surface antigens cloned according to the present invention have been purified, and the nucleotide and amino acid sequences determined. These antigens have diagnostic and therapeutic utility in immune-mediated infections in mammals, including humans.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
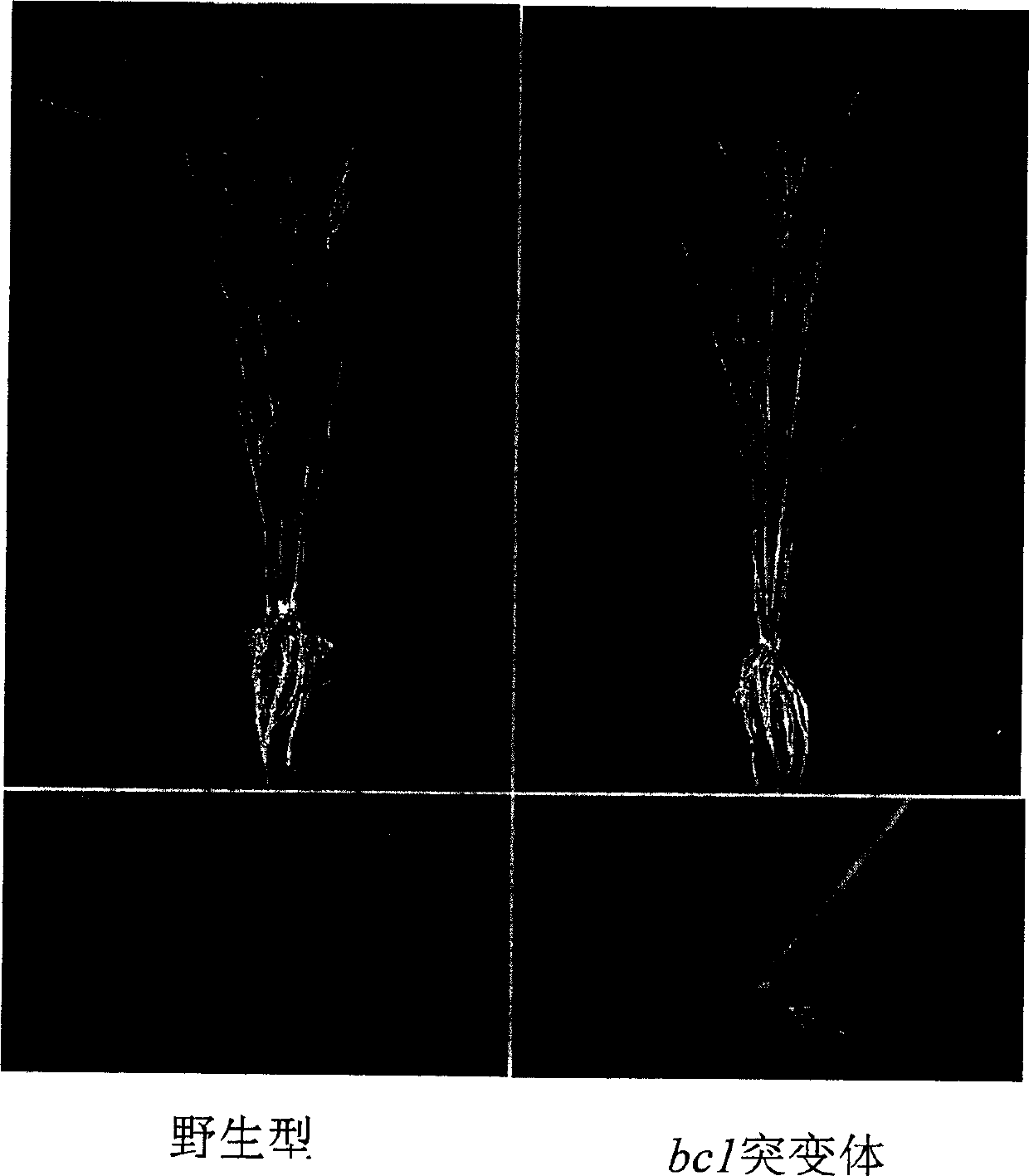
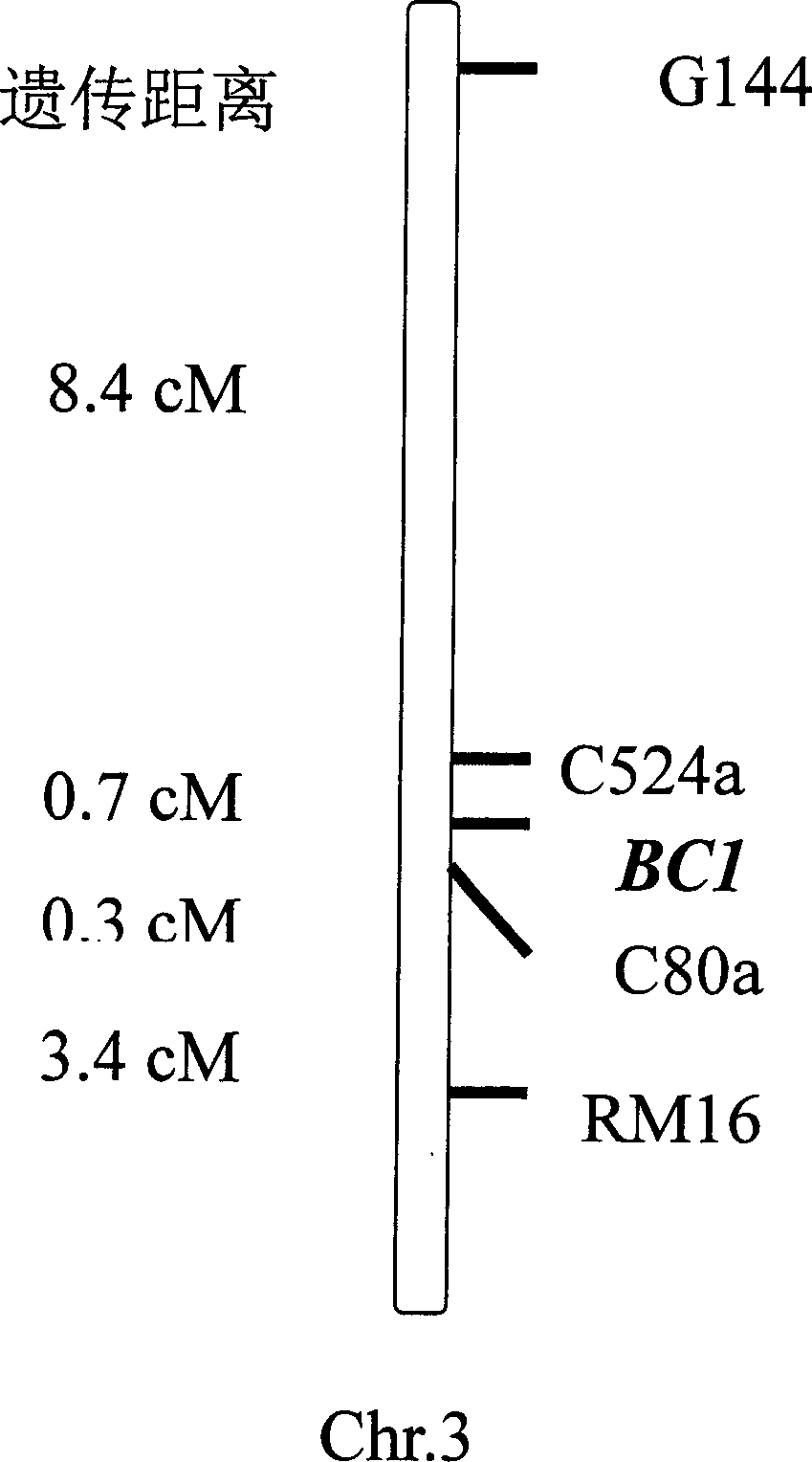
Paddy rice fragile straw controlling gene BC1 and use thereof
InactiveCN1488643AReduce pollutionImprove lodging resistanceClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesPlant cellFragility
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Rice leaf color control gene heme oxygenase2 (HO2) and application thereof
InactiveCN103114076AAppropriate leaf colorIncrease productionBacteriaOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyChloroplast
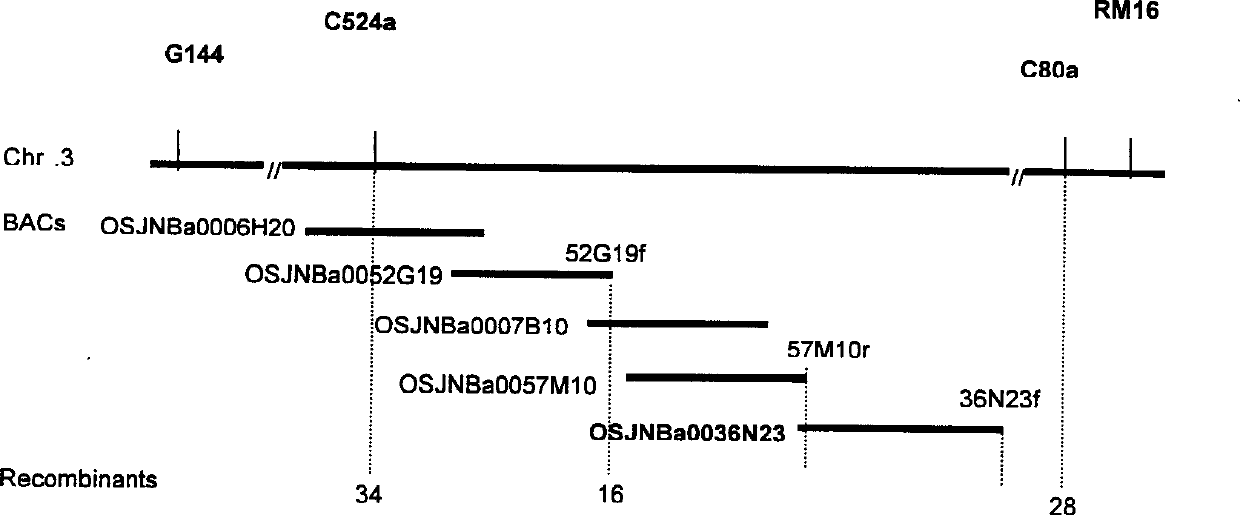
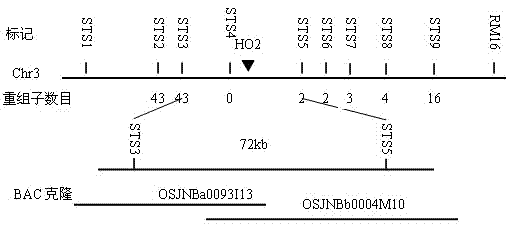
The invention discloses a rice leaf color control gene heme oxygenase2 (HO2) and an application thereof. A gene which is cloned from a rice leaf control mutant ho2 and is proved to have the effect of controlling the color of a rice leaf is named after HO2. A transgene functional complementation assay proves that the HO2 is the gene which controls the color of the rice leaf. Comparative analysis on amino acid sequences shows that HO2 protein belongs to a hemeoxygenase protein family. Phenotype observation and biophysical analysis prove that the cloned gene has the effects of regulating and controlling the development of chloroplasts and then controlling the color of the leaf. The invention also discloses an application of the rice leaf color control gene HO2 in fine seed breeding and cross breeding by taking a green yellow leaf character as a marker character by using genetic engineering. The rice leaf color control gene HO2 is obtained by using a map-based cloning technology, and the effects of the gene is tested through the transgene functional complementation test. Therefore, the rice leaf color control gene HO2 has the effect of ensuring rice to keep an appropriate leaf color, so that the photosynthetic efficiency of the rice is improved, and finally the rice yield can be improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
High viscosity diutan gums
ActiveUS20080319186A1Increased biosynthetic productionHigh viscosity propertySugar derivativesBacteriaBiotechnologyPhysical property
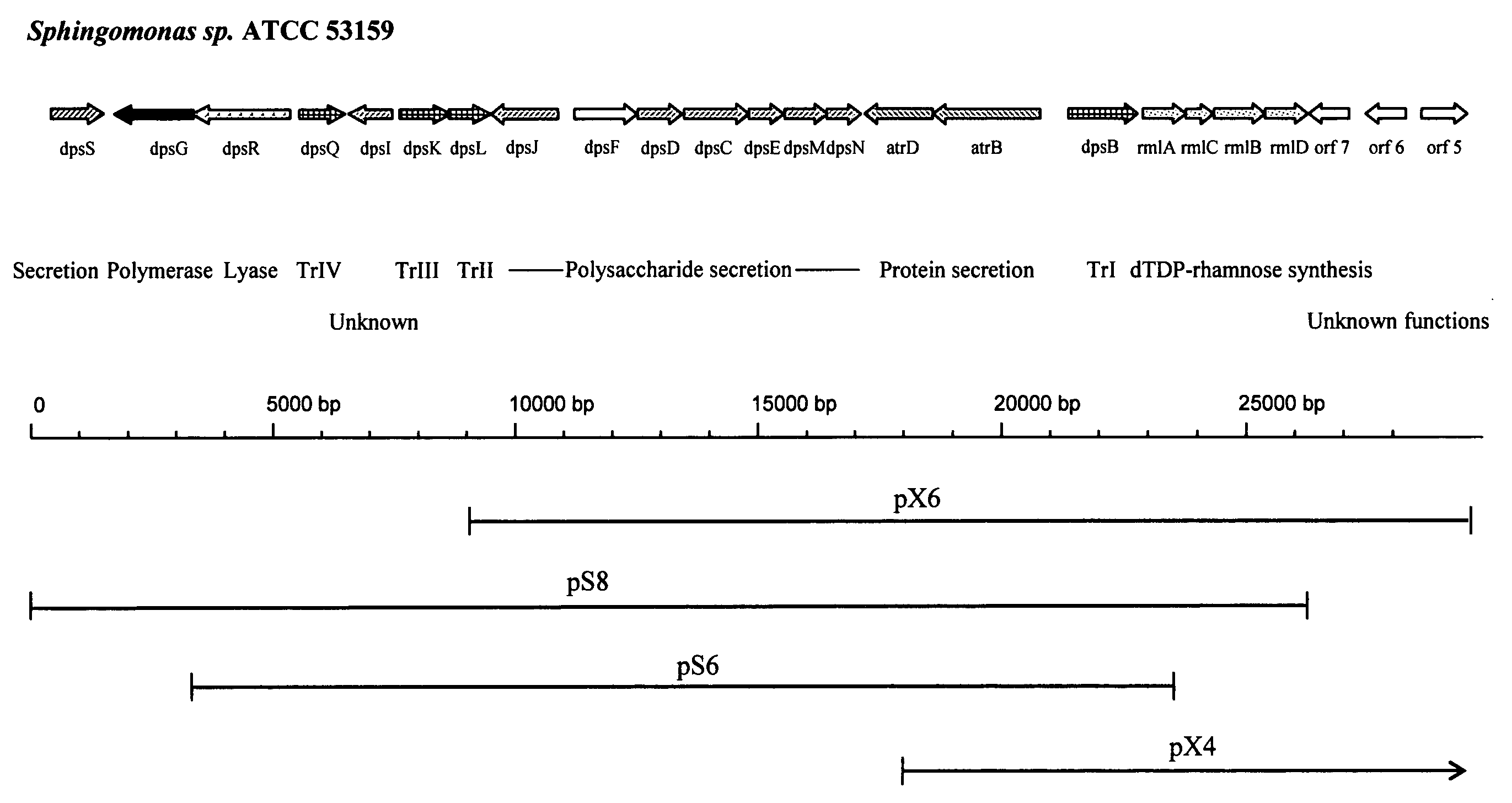
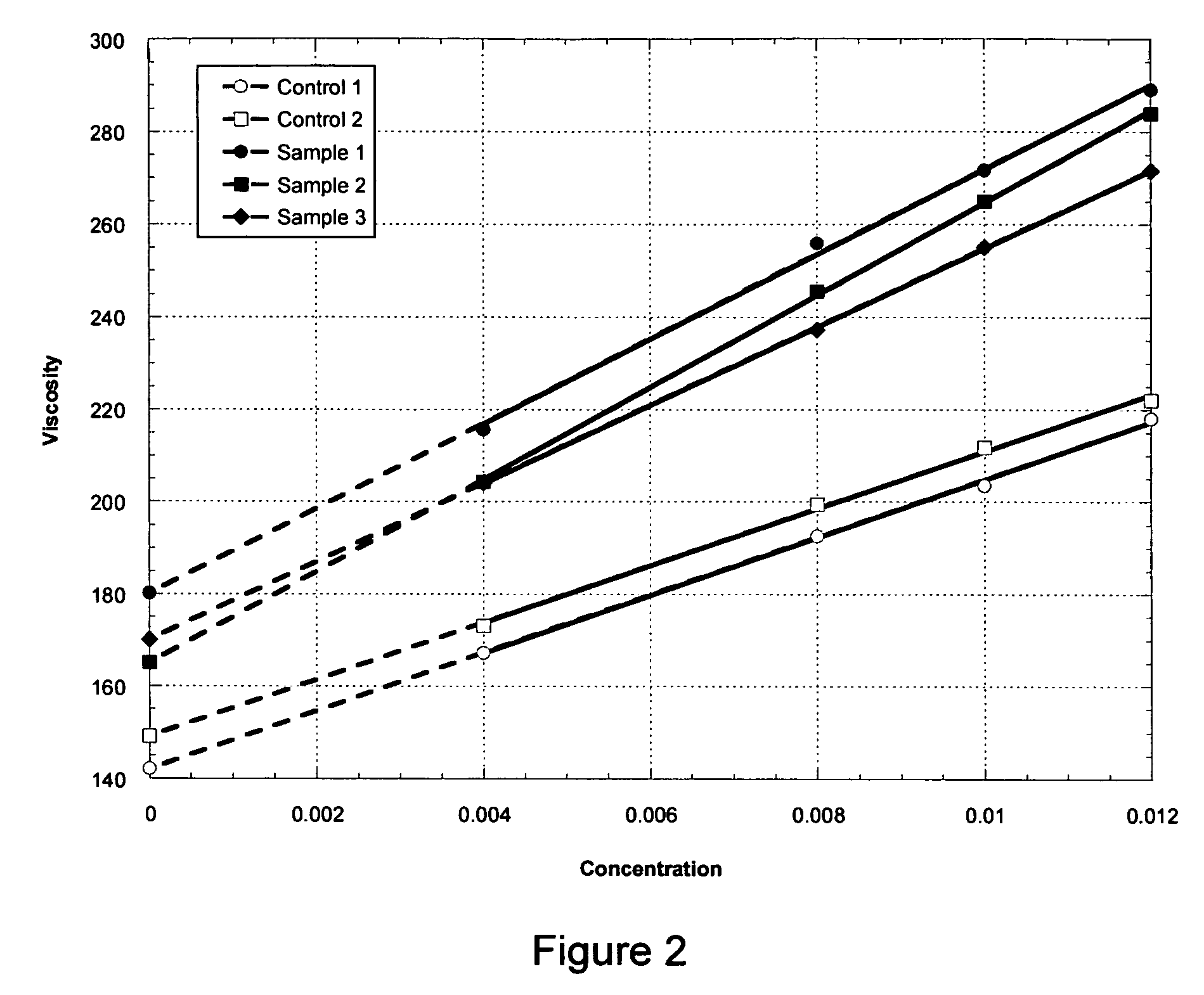
The production of a diutan polysaccharide exhibiting increased viscosity properties as compared with previously produced polysaccharide of the same type of repeating units. Such an improved diutan polysaccharide is produced through the generation of a derivative of Sphingomonas sp. ATCC 53159 that harbors a multicopy broad-host-range plasmid into which genes for biosynthesis of diutan polysaccharide have been cloned. The plasmid provides the capability within the host Sphingomonas strain to produce multiple copies of genes for such polysaccharide synthesis. In such a manner, a method of not just increased production of the target diutan polysaccharide, but also production of a diutan polysaccharide of improved physical properties (of the aforementioned higher viscosity) thereof is provided. Such a diutan polysaccharide has proven particularly useful as a possible viscosifier in oilfield applications and within cement materials. The inventive methods of production of such an improved diutan polysaccharide, as well as the novel cloned genes required to produce the improved diutan within such a method, are also encompassed within this invention. Additionally, the novel engineered Sphingomonas strain including the needed DNA sequence is encompassed within this invention.
Owner:CP KELCO U S INC
Identification of sortase gene
InactiveUS20030153020A1Fluorescence enhancementIncreased cleavageBacteriaHydrolasesCross-linkStaphylococcus aureus
The present invention is a substantially purified sortase-transamidase enzyme from Gram-positive bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus. A specific sortase-transamidase enzyme disclosed has a molecular weight of about 29,076 daltons and catalyzes a reaction that covalently cross-links the carboxyl terminus of a protein having a sorting signal to the peptidoglycan of a Gram-positive bacterium, where the sorting signal has a a motif of NPQ / KTN / G therein. Variants of the enzyme, methods for cloning the gene encoding the enzyme and expressing the cloned gene, and methods of use of the enzyme, including for screening for antibiotics and for display of proteins or peptides on the surfaces of Gram-positive bacteria, are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method of obtaining a purified, biologically active heterologous protein
ActiveUS8802816B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsHeterologousOrganism
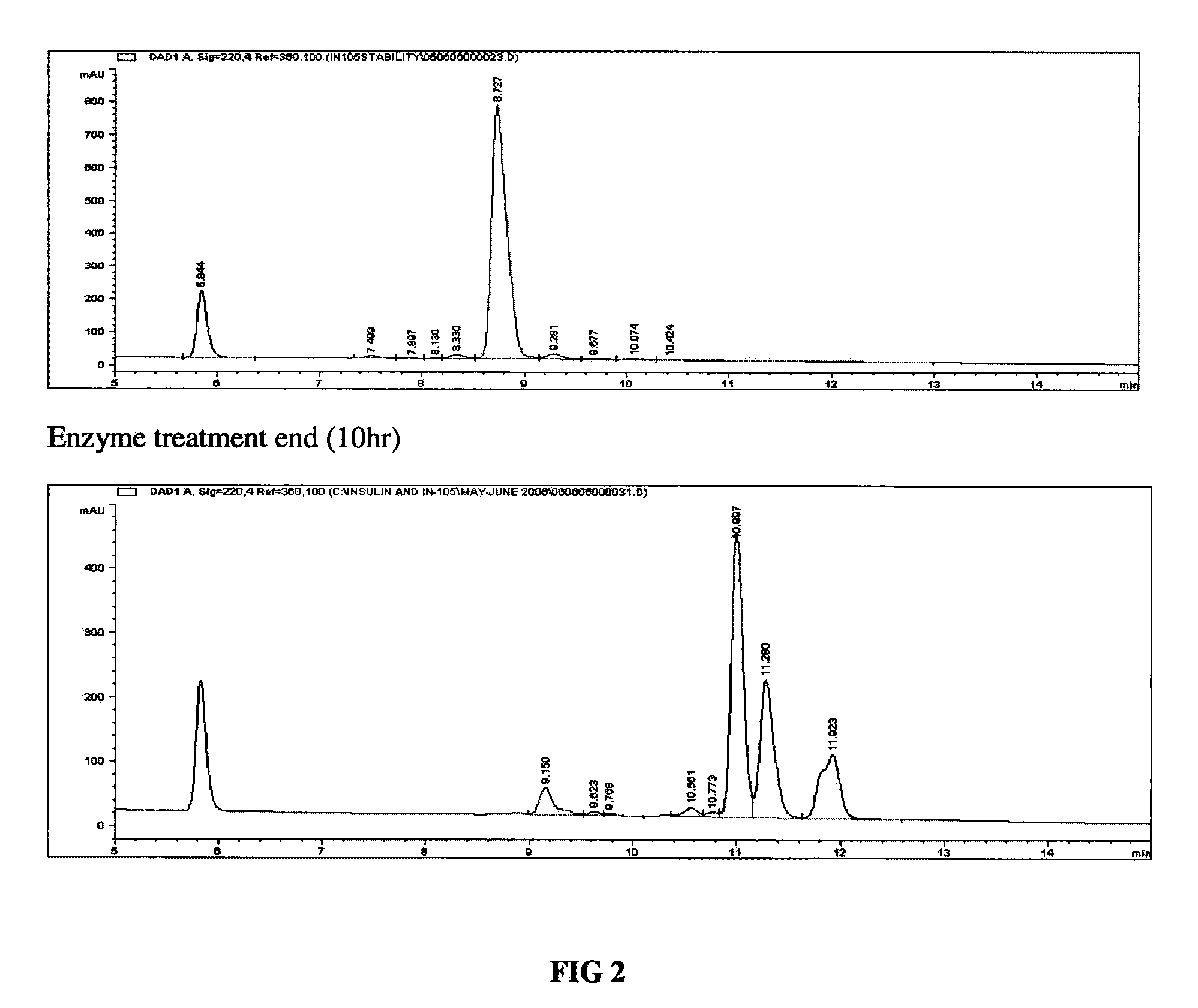
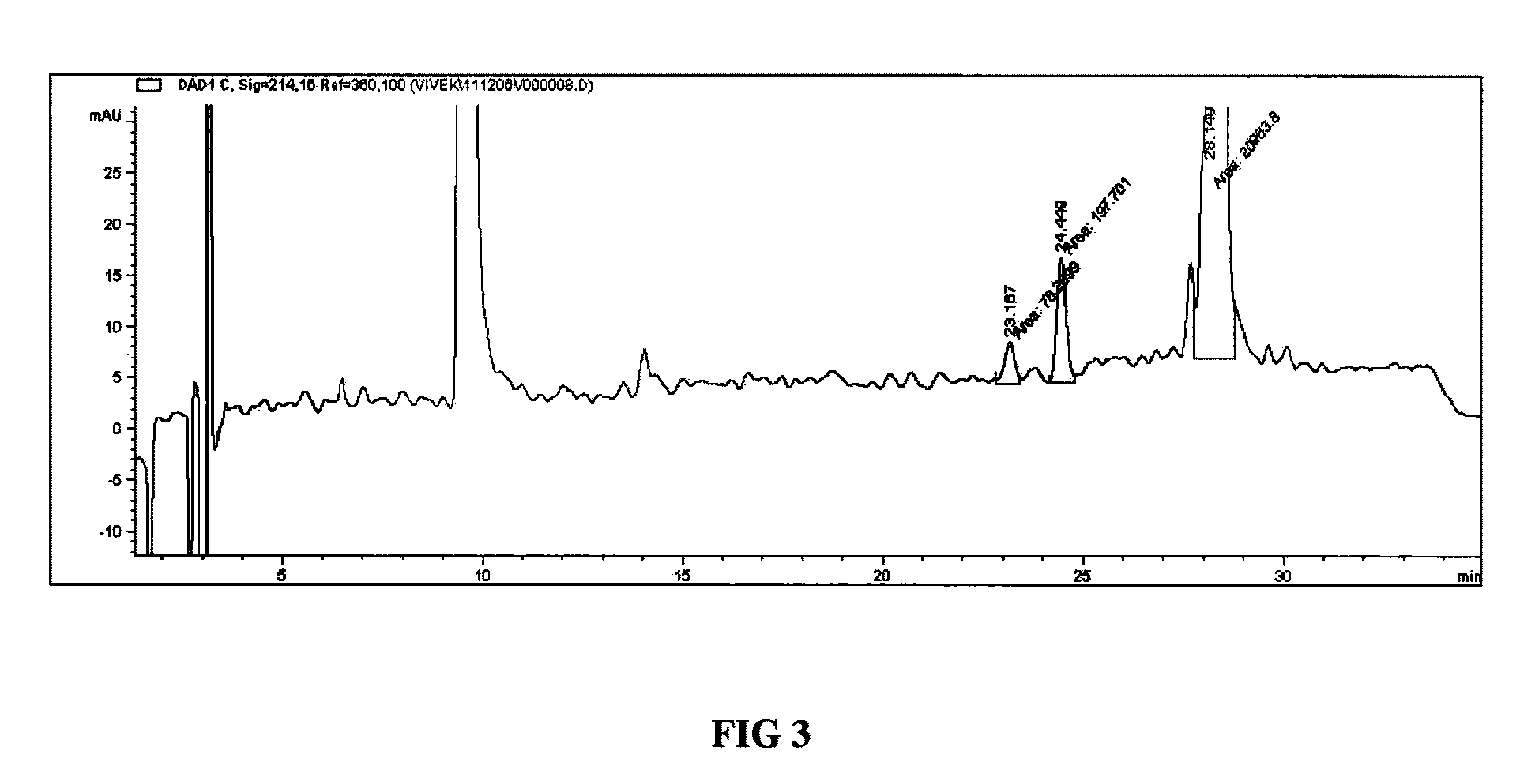
The invention relates to methods of separation and / or purification of impurities yielding a purified heterologous protein product devoid of related impurities or with substantially minimal quantities of such glycosylated impurities. More specifically, the invention relates to the identification of glycosylated forms of insulin analogues such as glargine impurities characterized post expression in yeast based systems such as Pichia pastoris. The invention also relates to methods used to clone gene encoding the protein insulin glargine; inserting the related gene in a suitable yeast host; producing culture of the recombinant strain, stimulating expression of the heterologous polypeptide, its secretion and purification post fermentation and related enzymatic conversions.
Owner:BIOCON LTD
Yunnan red pear PybMYB gene as well as prokaryotic expression vector and application thereof
InactiveCN103146710AStrong specificityPrecise positioningImmunoglobulins against plantsPlant peptidesEscherichia coliImmunoprecipitation
The invention discloses a Yunnan red pear PyMYB gene through pigment synthesis regulation and trichome development regulatory protein as well as a prokaryotic expression vector thereof and an application of the prokaryotic expression vector. The PyMYB gene is cloned from red fruit peel of Yunnan red pear NO.1 by using a RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) technology, and then the gene is expressed in escherichia coli Rosetta (DE3) by using the prokaryotic expression vector and is purified by a GST (Glutathione S-transferase) gel column purification method to obtain a Yunnan red pear PyMYB purified protein, wherein the Yunnan red pear PyMYB purified protein is used for the preparation of a PyMYB specific antibody and the application thereof in a PyMYB protein expression detection and immunoprecipitation, a chromatin co-immunoprecipitation and a fusion protein sedimentation experiment. The antibody prepared by the invention is strong in specificity, can accurately detect subcellular localization of the PyMYB protein, and is used for verifying protein interaction in the co-immunoprecipitation experiment, efficiently separating the protein and DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) segment combined by the PyMYB protein and detecting the expression of the antibody in a transgenic plant.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method of creating high-oil cotton material by using cotton GhPEPC gene
InactiveCN106755018AReduce expressionReduce synthesisMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationAgricultural scienceCloned genes
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant gene engineering, in particular to a method of creating a high-oil cotton material by using a cotton GhPPC gene. The invention relates in particular to the gene GhPPC cloned from upland cotton, and functional verification and an application of the gene. Part of a conservative cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence of the obtained encoding gene is as shown as SEQ ID NO: 1 (sequence identifier number 1) in a sequence table. The invention further discloses an application of the gene GhPPC in genetic modification of the upland cotton, and a cottonseed oil content of the upland cotton can be increased by regulating expression of the cloned gene.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
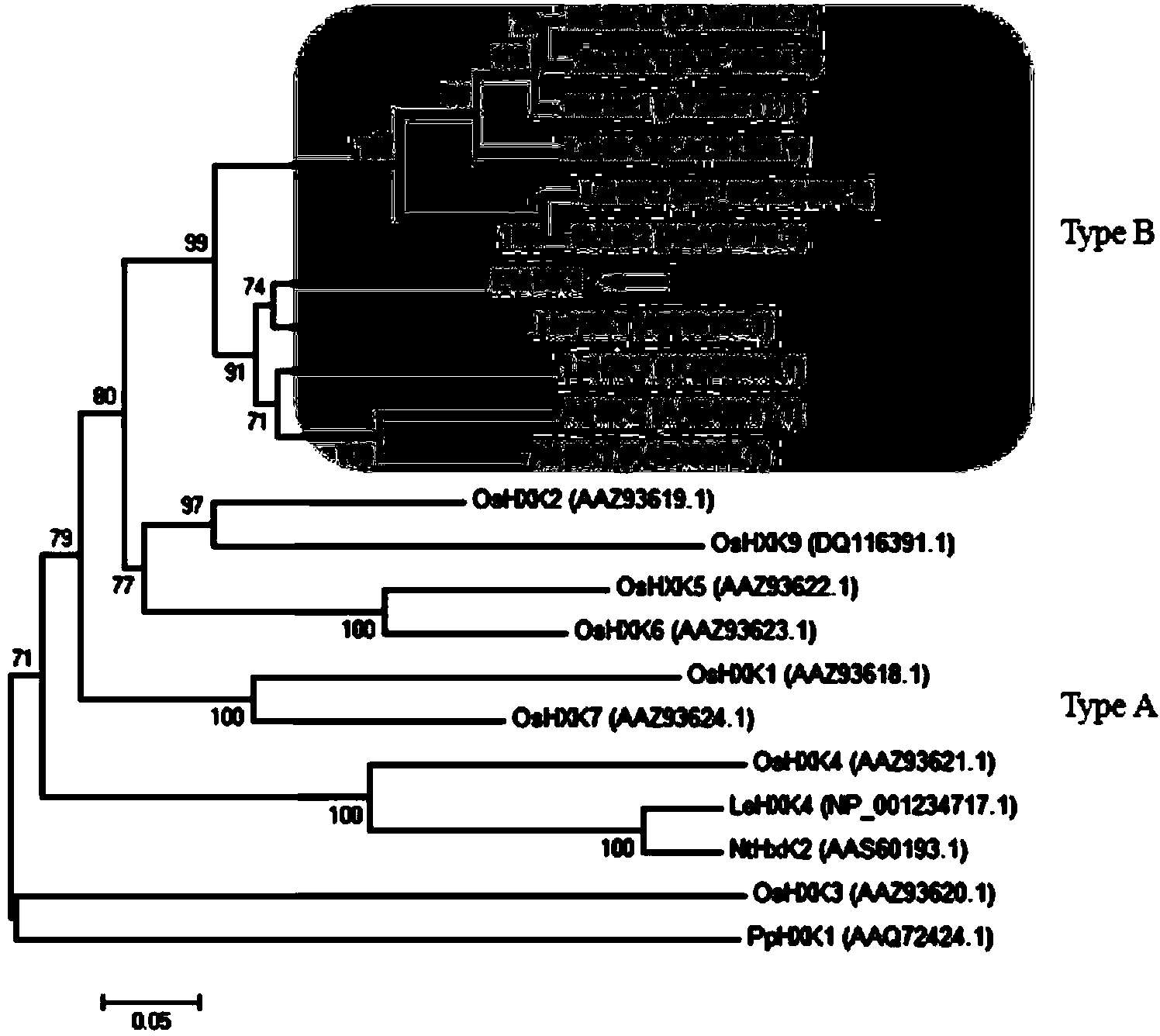
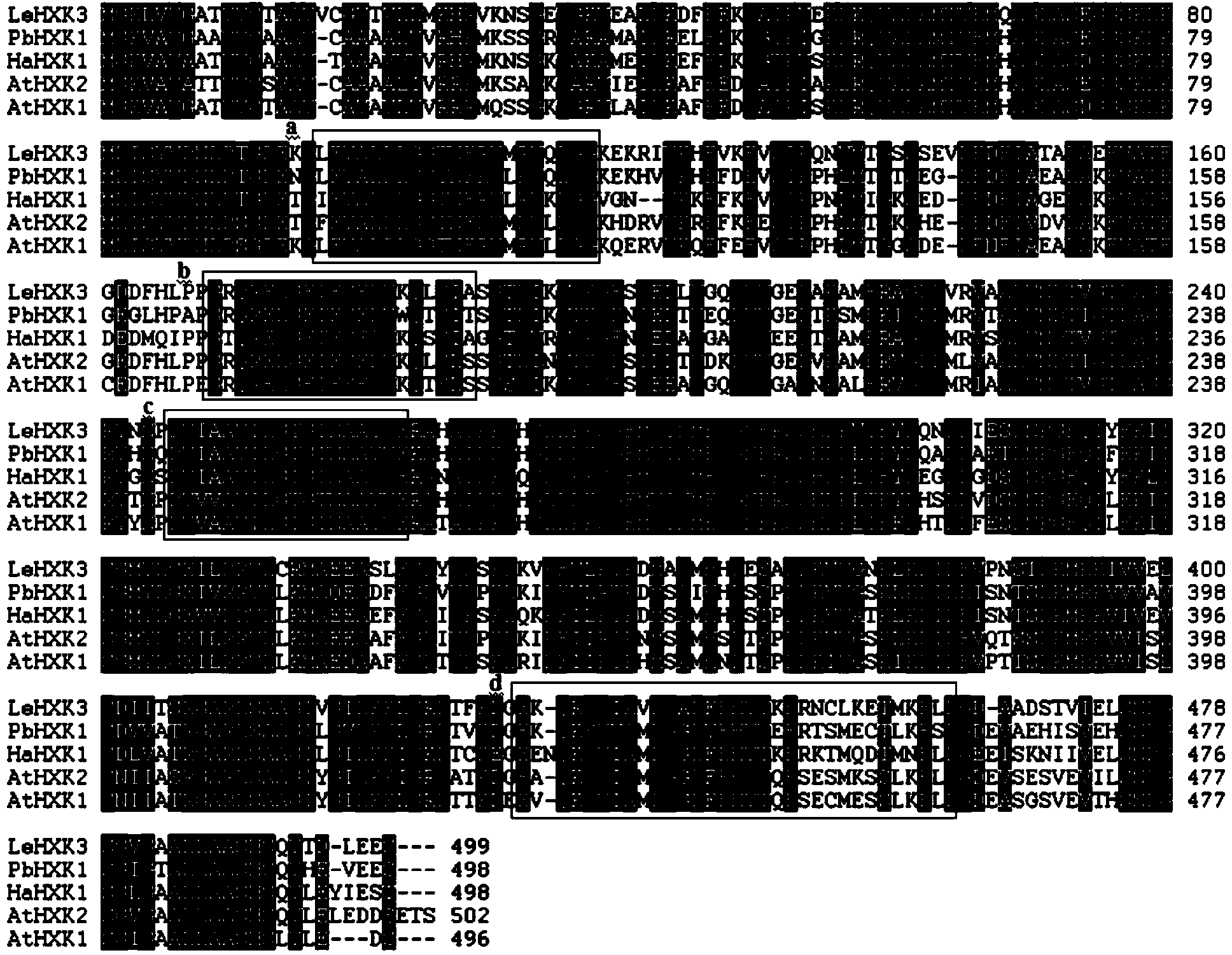
Pear hexokinase gene PbHXK1 and application thereof
The invention discloses a pear hexokinase gene PbHXK1 and an application thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as a sequence table SEQ ID No.1, wherein an amino acid sequence corresponding to the nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as a sequence table SEQ ID No.2. The gene PbHXK1 is inoculated into tomato to carry out functional verification; the expression quantity of the gene PbHXK1 and the activity of the hexokinase of a transgenosis tomato plant which is obtained by taking a wild tomato plant as a reference are obviously improved, the growth of the plant is obviously inhibited and the content of soluble sugar is obviously reduced so as to show that the cloned gene PbHXK1 is a functional structure gene for coding the hexokinase, has the function of phosphorylating hexose, plays a regulation role in the fruit sugar accumulation process and also takes part in regulation of the growth and the development of the plant.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Cultivated silkworm peptidoglycan identification protein gene
InactiveCN101139599AIncrease lethalityGrowth inhibitionFermentationGenetic engineeringBacteroidesCloned genes
The invention provides an identifying protein gene for a silkworm peptidoglycan. First of all, predicating PGRPs gene by using a silkworm gene database and EST database source, then extracting PGA-induced 5-instar silkworm epiploon, synthesizing CDNA, and cloning gene. PGRPs gene can obviously kill bacteria, and PGRPs pertain solution of low concentration can also suppress bacteria growth. The congenital immunity identifying receptor of silkworm activates the congenital immunity and adjusts the antibiotic peptide expression, and can be used for culturing antibiotic silkworms.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
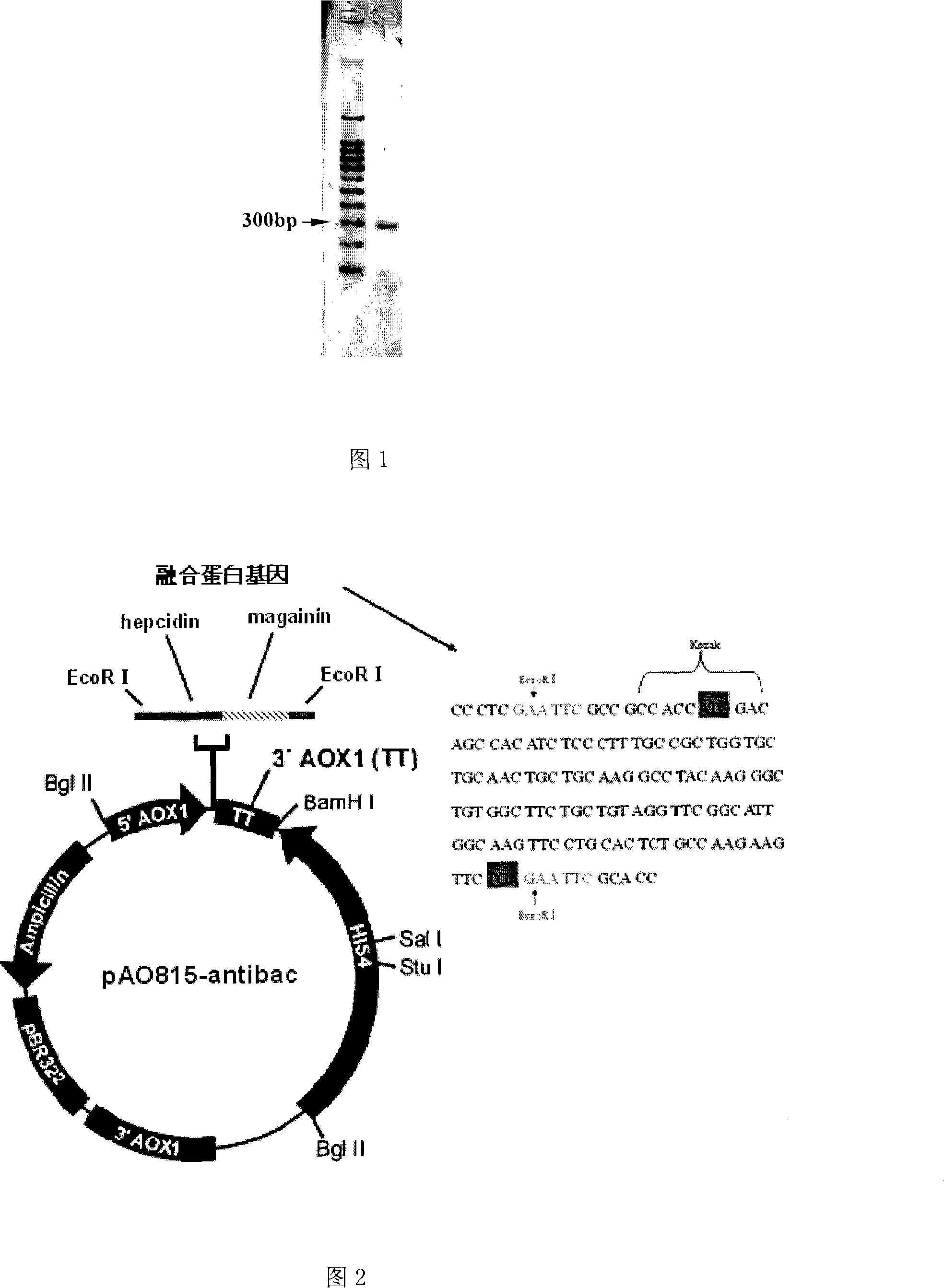
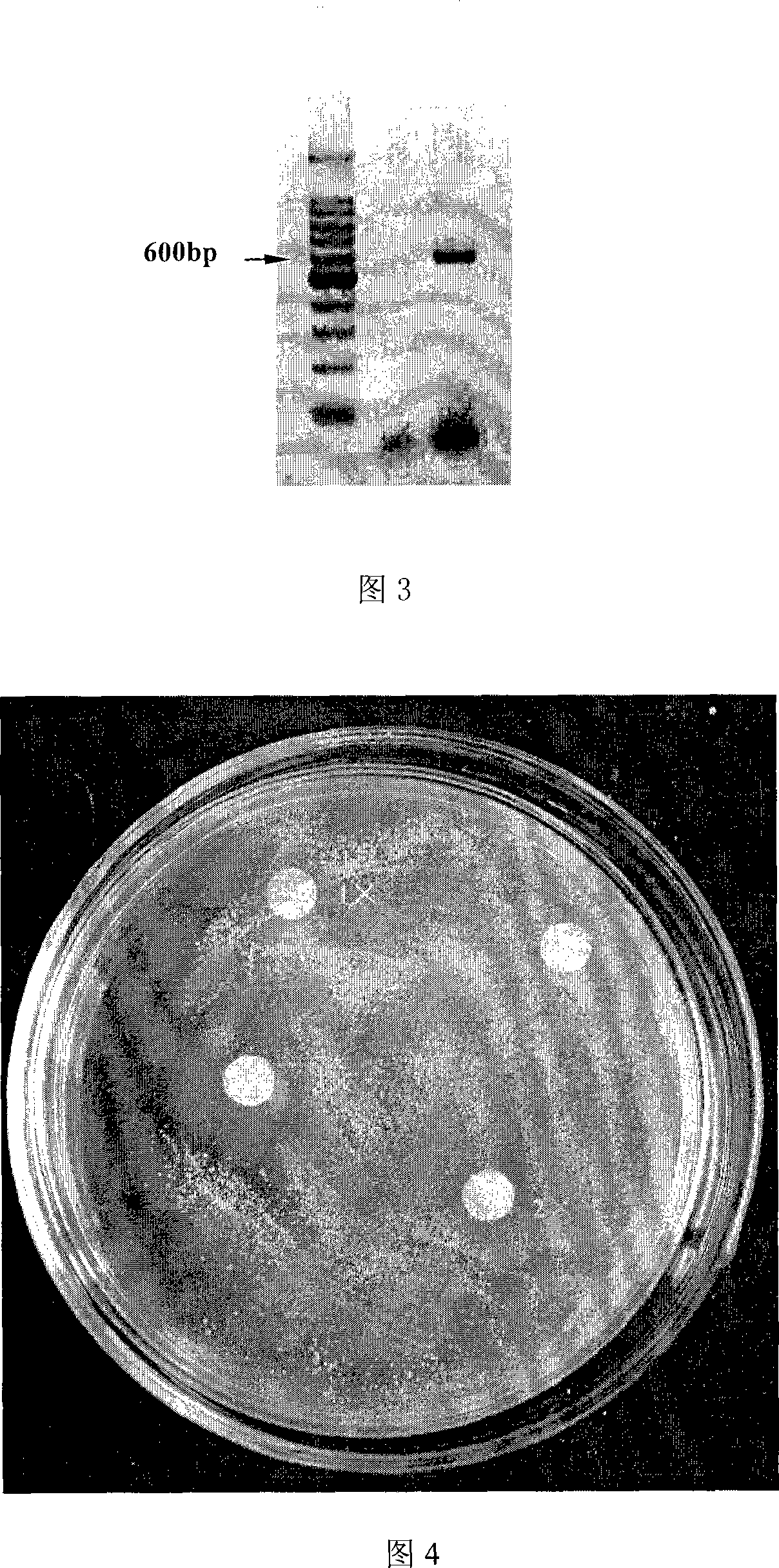
Fusion protein having antibiotic function and uses thereof
InactiveCN101182360AStrong antibacterial activitySolve the problem of cumulative excessAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseBacteroides
The invention discloses a fusion protein with antibacterial function and its application. The fusion protein gene sequence consists of a cloned hepcidinl precursor antimicrobial peptide gene and an artificially synthesized magainin antimicrobial peptide gene, which are composed of a novel fusion protein cDNA and integrated into the yeast genome by genetic engineering means, and induced The fusion protein cDNA is expressed in yeast, and then a large amount of fusion protein is obtained through yeast fermentation. The fusion protein of the present invention has obvious antibacterial activity after testing, and can be used for the prevention and treatment of bacterial diseases of aquatic organisms and farmed animals, or the purified fusion protein can be directly used as medicine to replace antibiotics for diseases caused by bacteria or even viruses Treatment.
Owner:THE FIRST INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY SOA
Gene modification based method for expressing exogenous drug through probiotic and application of method
InactiveCN108660148ATo achieve the purpose of treating tumor diseasesImprove securityTumor rejection antigen precursorsBacteriaEscherichia coliNutritional deficiency
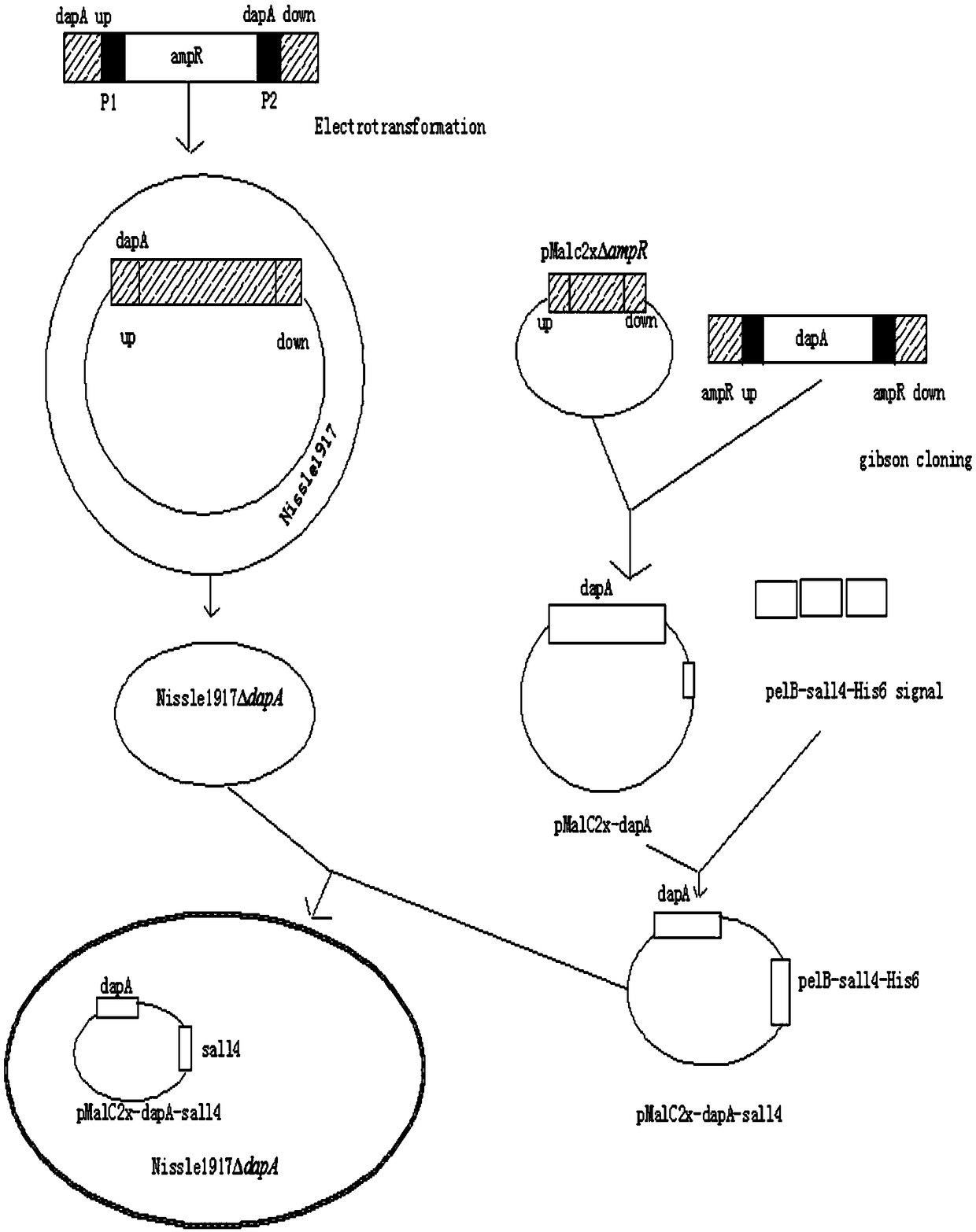
The invention discloses a gene modification based method for expressing an exogenous drug through a probiotic and an application of the method, the homologous recombination and the one-step seamless cloning are used to knock out an indispensable gene dapA of escherichia coli Nissle1917 to obtain an escherichia coli nutritional deficiency strain Nissle1917deltadapA, the dapA gene is cloned to construct a complementary plasmid pMalc2x-dapA of the nutritional deficiency strain, the complementary plasmid pMalc2x-dapA is electrically shocked to convert into the strain Nissle1917deltadapA, an amicillin resistance gene ampR of a pMalc2x carrier is substituted through the homologous recombination to obtain a plasmid balance system without an antibiotics resistance marker, 12 amino polypeptide sequence genes of an amino terminal sall4 are synthesized in vitro at a sall4 amino terminal, a pelB signal peptide gene sequence of an erwinia carotovora pectinase is fused at the N end, a gene sequenceof a His protein tag is added at the C end, the gene sequences are closed into the complementary plasmid pMalc2x-dapA together to obtain an exogenous drug expression plasmid pMalc2x-dapA-sall4, the plasmid is imported into the escherichia coli nutritional deficiency strain Nissle1917deltadapA, the obtained strain effectively expresses the sall4 polypeptide, and the method has an obvious effect ontreating the liver cancer.
Owner:奇元科技(武汉)有限公司
Novel glycosyltransferase gene
The present invention provides an enzyme which catalyzes a reaction to transfer sugar to a hydroxyl group at position 2′ of chalcones and a gene thereof, and preferably an enzyme which catalyzes a reaction to transfer glucose to a hydroxyl group at position 2′ of the chalcones. Furthermore, the invention provides a plant whose flower color has been changed using the glycosyltransferase. Using probes corresponding to conservative regions of the glycosyltransferase, some tens of glycosyltransferase genes having nucleotide sequences corresponding to the conservative regions were cloned from flower petal cDNA libraries of carnation and the like. Furthermore, each of the glycosyltransferase genes was expressed in Escherichia coli, activity to transfer glucose to position 2′ of the chalcone, i.e., the glycosyltransferase activity at position 2′ of chalcone was confirmed in an extract solution of the Escherichia coli, and it was confirmed that cloned genes encoded the glycosyltransferase at position 2′.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
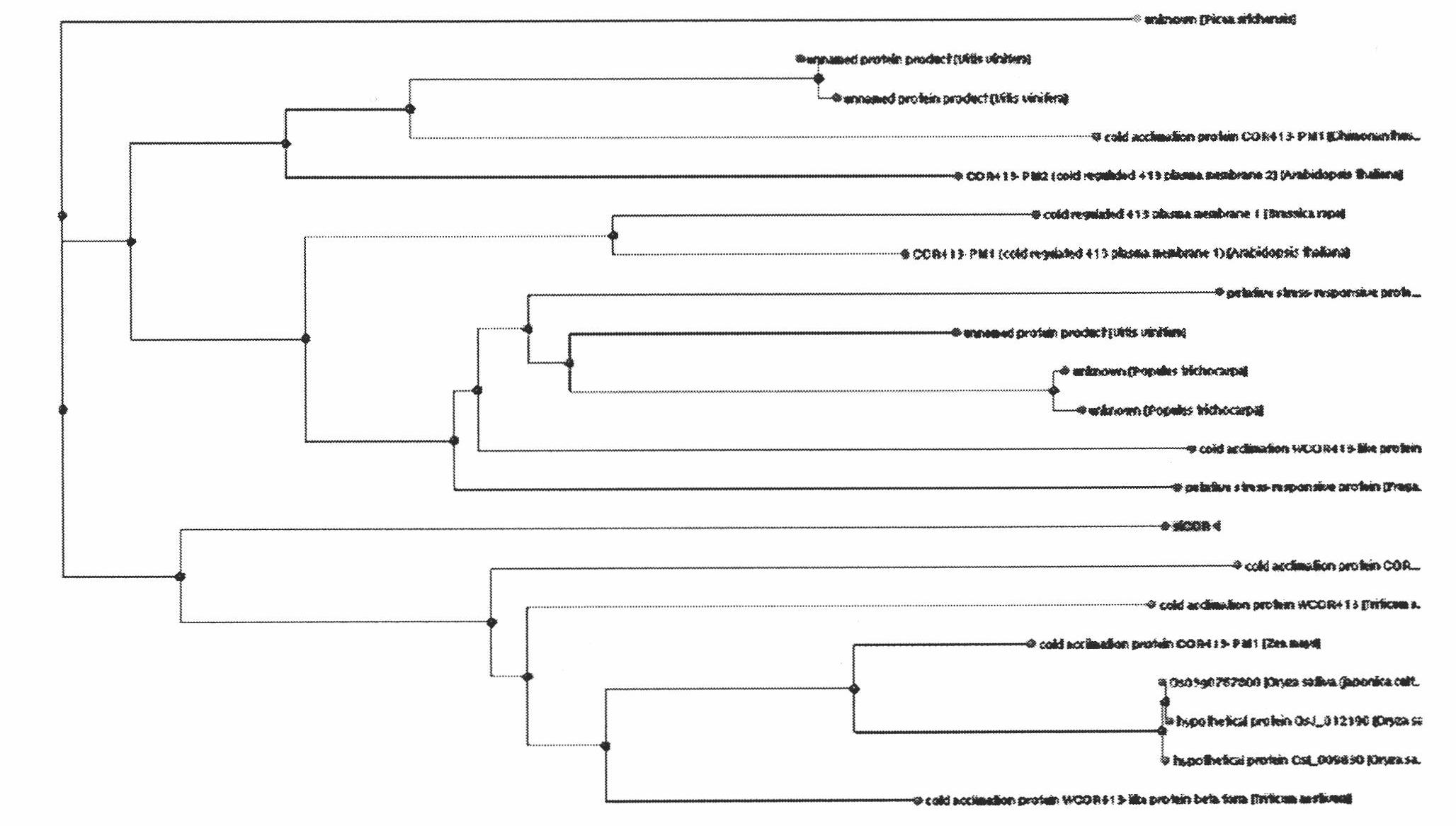
Application of herba saussureae involucratae sikCOR gene in cultivating cold resistant plant
ActiveCN101818156AImprove low temperature resistanceRich biological theoryFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionTemperature stressCloned genes
The invention relates to application of a herba saussureae involucratae sikCOR gene in cultivating a cold resistant plant. In the invention, a sikCOR gene is cloned from a herba saussureae involucratae, and a plant expression vector is constructed by utilizing the gene to obtain the cold resistant transgenic plant through genetic transformation. The sikCOR gene is cloned from the herba saussureae involucratae and then is expressed in the transgenic plant to improve the cold resistance of the transgenic plant, improve the low temperature stress resistance of the plant through excessive expression of the gene and finally obtain the plant with obviously enhanced low-temperature resistant capability. By screening and cloning genes directly related to cold resistance from the herba saussureae involucratae, the low-temperature adaptability mechanism of the saussureae involucratae is revealed. The herba saussureae involucratae sikCOR gene is used in breed improvement of crops, thus having great academic and economic value.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Yunnan red pear PybHLH gene as well as prokaryotic expression vector and application thereof
InactiveCN103146709AStrong specificityReduce non-specific bandsImmunoglobulins against plantsPlant peptidesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a Yunnan red pear PybHLH gene through anthocyanin biosynthesis, trichome development and a salt stress regulatory protein and a prokaryotic expression vector thereof. The PybHLH gene is cloned from red fruit peel of Yunnan red pear NO.1 by using a RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) technology, then the prokaryotic expression vector pGEX-4T-PybHLH is constructed, PybHLH protein is expressed in escherichia coli Rosetta (DE3) by pGEX-4T-PybHLH vector and then is purified, and Yunnan red pear PybHLH purified protein is obtained; the prokaryotic expression vector of the PybHLH gene is applied to preparing a pybHLH specific antibody, and the obtained pybHLH specific antibody is also used for researching the interaction of the protein and protein as well as the protein and DNA(deoxyribonucleic acid) and the detection to PybHLH transgenic plant. The obtained pybHLH specific antibody contains glutathione S transferase (GST) and is applied to researching the interaction of the protein through Far Western blotting and co-immunoprecipitation and accurately separating and obtaining the protein and DNA segment which are interacted with PybHLH.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
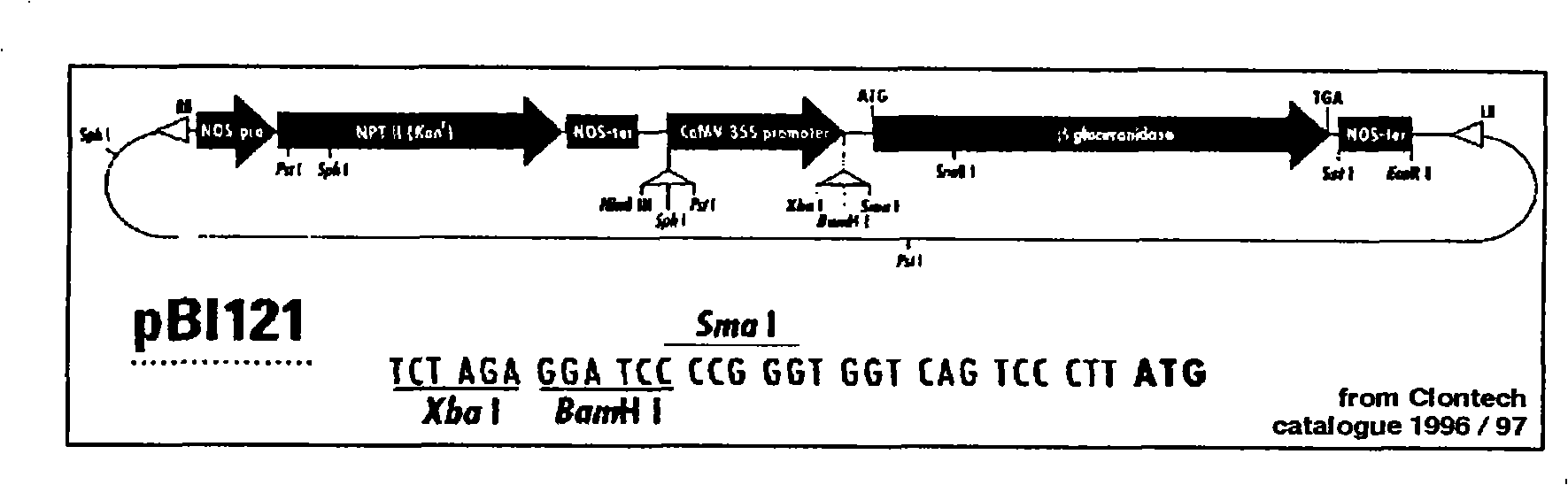
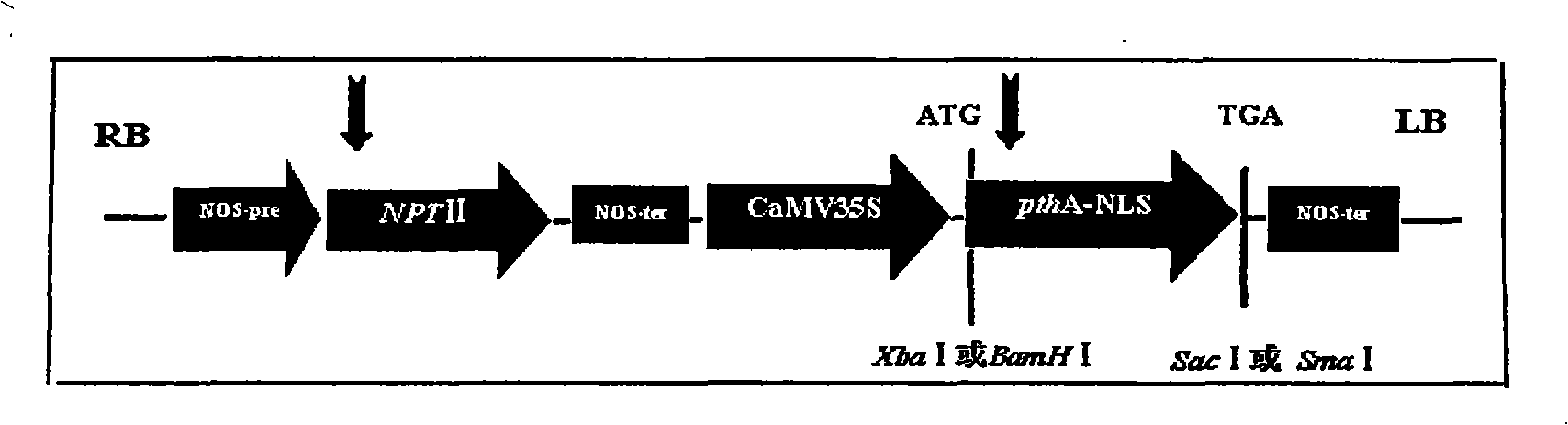
Orange canker resistant pthA-nls gene and its construction method and application
The invention provides an anti-citrus bacterial canker disease pthA-nls gene, a construction method and application thereof. The invention uses the pathogenic gene pthA-mediated broad-spectrum disease resistance theory of the citrus bacterial canker disease to construct a new anti-citrus bacterial canker disease gene (pthA-nls). The construction method comprises the following steps of: (1) primer design; (2) clone of NLS sequence; (3) recovery and enzyme digestion of PCR product; (4) double enzyme digestion of a plant expression vector; (5) connection between product of enzyme digestion of pBI121 and corresponding product of PCR enzyme digestion of the NLS sequence by T4 DNA ligase; (6) acquisition of positive cloned gene pthA-nls by converting ligation product into colon bacillus DH5alpha. The gene pthA-nls can further perform genetic transformation on susceptible varieties of orange so as to acquire new anti-citrus bacterial canker disease germ plasm. The anti-citrus bacterial canker disease pthA-nls gene provides an effective tool for breeding of anti-citrus bacterial canker disease.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Method for sequencing clone genes with recessive mixed pools
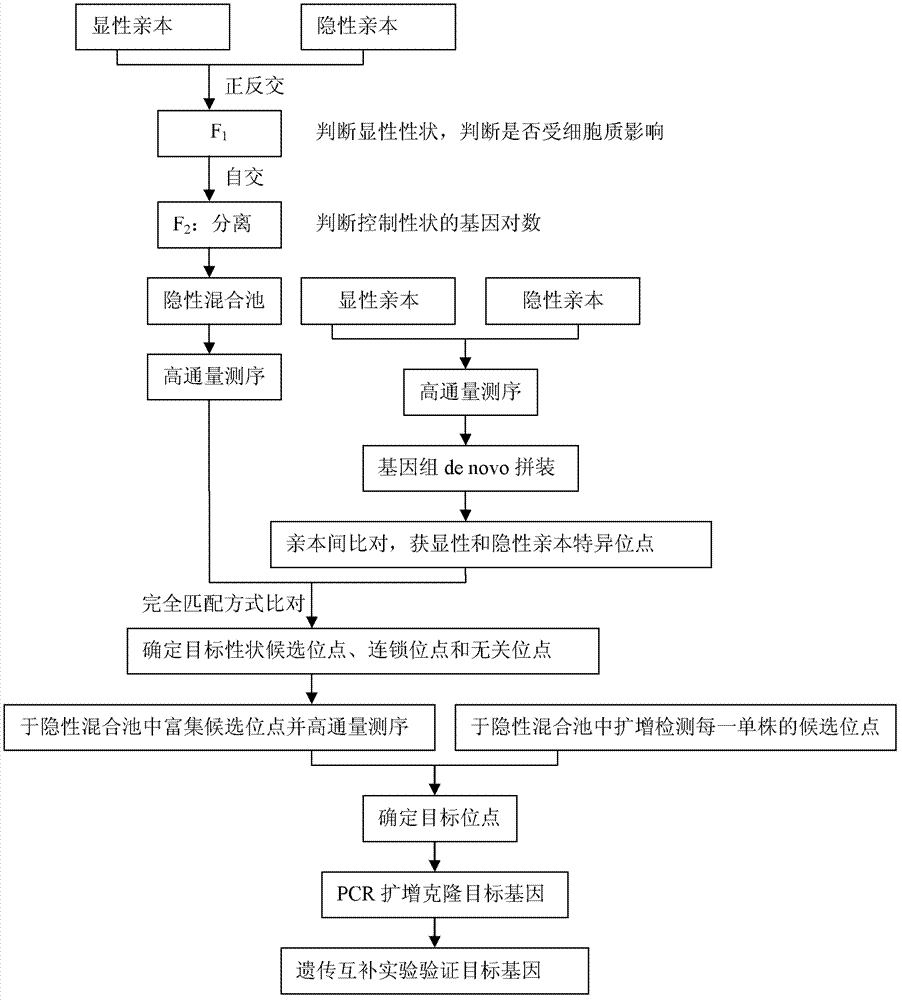
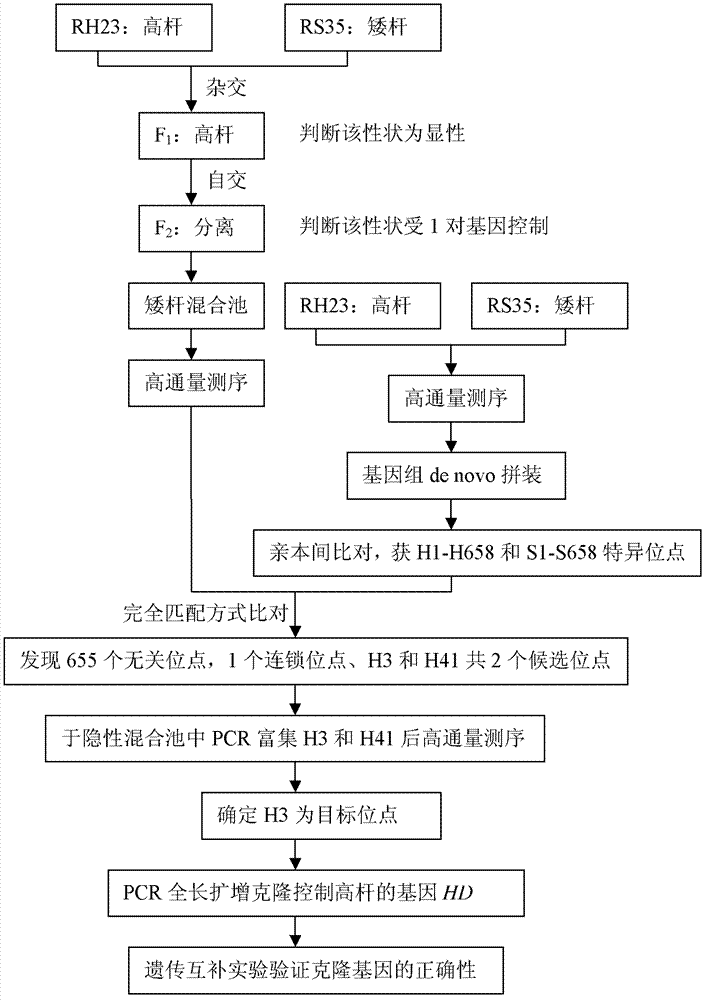
InactiveCN102899315AExpand the scope of useReduce workloadMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationRe sequencingCandidate Gene Association Study
The invention discloses a method for sequencing clone genes with recessive mixed pools. The method comprises the following steps of constructing segregation populations by hybridizing parents; allocating pools for the segregation populations according to individual target properties; obtaining dominant and the recessive specific loci of the parents through high-throughput sequencing; comparing with the sequencing results of the recessive mixed pools to obtain candidate genes; gathering the candidate genes in the recessive mixed pools and re-sequencing clone target genes; The method is on the basis of sequencing, can be used for any species, and directly clones genes themselves. With the method, workload is decreased greatly, speed is substantially accelerated; and risks are reduced.
Coding gene of haemaphysalis qinghaiensis aquaporin (AQP) and application of coding gene
The invention discloses a coding gene of haemaphysalis qinghaiensis aquaporins (AQPs) and an application of the coding gene. The coding gene of the AQPs can be used for preparing novel anti-tick medicines and anti-tick vaccines. A sequence of the coding gene of the AQPs is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The invention also provides specific primers cloned by the coding gene of the AQPs, wherein sequences ofthe specific primers are shown as SEQ ID NO:2 and SEQ ID NO:3; the invention also provides a method for cloning the coding gene of the AQPs, and the cloned gene product can be also applied to in-vitro recombinant protein expression and antibody preparation; and an obtained antibody can be used for preparing the novel anti-tick medicines and the anti-tick vaccines. The invention has important theoretical significance an potential application value on prevention and control of ticks. The coding gene of the haemaphysalis qinghaiensis aquaporins (AQPs) and the cloning method of the coding gene provided by the invention are applicable to systematic researches of subtype, varieties, expression distributin, protein structures, biological functions and the like of the AQPs.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
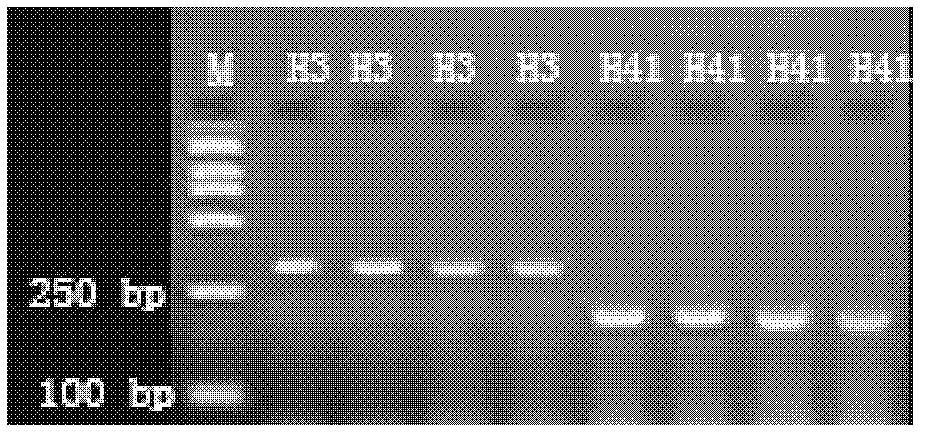
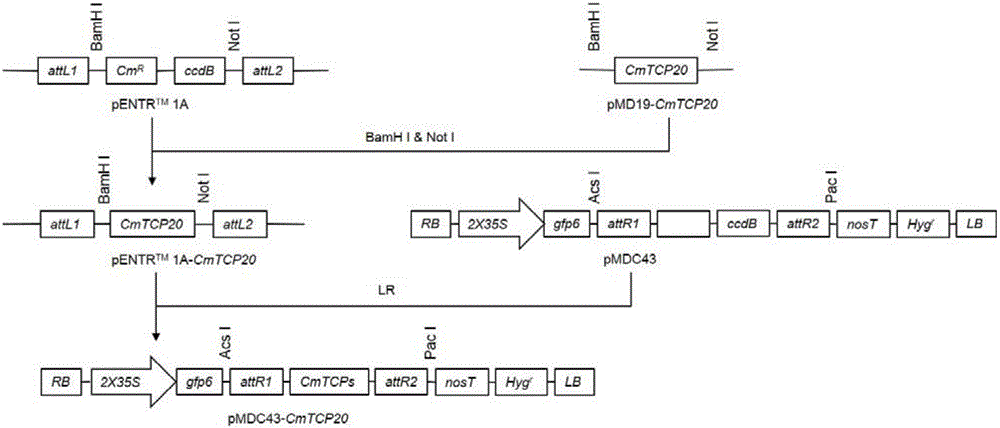
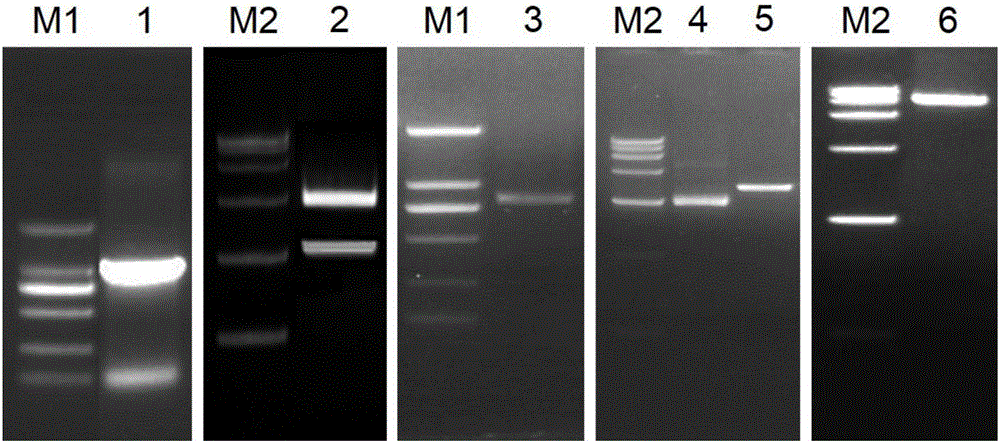
Method for regulating and controlling growth of chrysanthemum petals through conversion of CmTCP20 gene
ActiveCN105671056APromote growthMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesTranscriptional expressionPetal
The invention belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering and transgenic breeding and relates to a method for regulating and controlling growth of chrysanthemum petals through conversion of the CmTCP20 gene.The method includes the following steps that the CmTCP20 gene is cloned from florist's chrysanthemum 'ShenMa'; a plant expression vector of the CmTCP20 gene is constructed; the plant expression vector is transferred into chrysanthemum through an agrobacterium-mediated method, culturing is conducted, and a resistant plant is preliminarily obtained; the converted plant is subjected to PCR and quantitative RT-PCR detection to verify that the CmTCP20 endogenous gene is integrated to a genome DNA of the transgenic plant and subjected to transcription; the transgenic plant is subjected to phenotypic observation and statistic analysis, and it is found that compared with a plant not subjected to transgenosis, the petal growth amount of the transgenic plant is obviously increased.According to the method, the endogenous CmTCP20 transcription factors are converted and subjected to normal transcriptional expression, so that growth of the chrysanthemum petals is regulated and controlled, a novel and practical method is provided for improving ornamental quality of chrysanthemum through a genetic engineering technology, and the chrysanthemum biotechnology breeding process can be effectively promoted.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
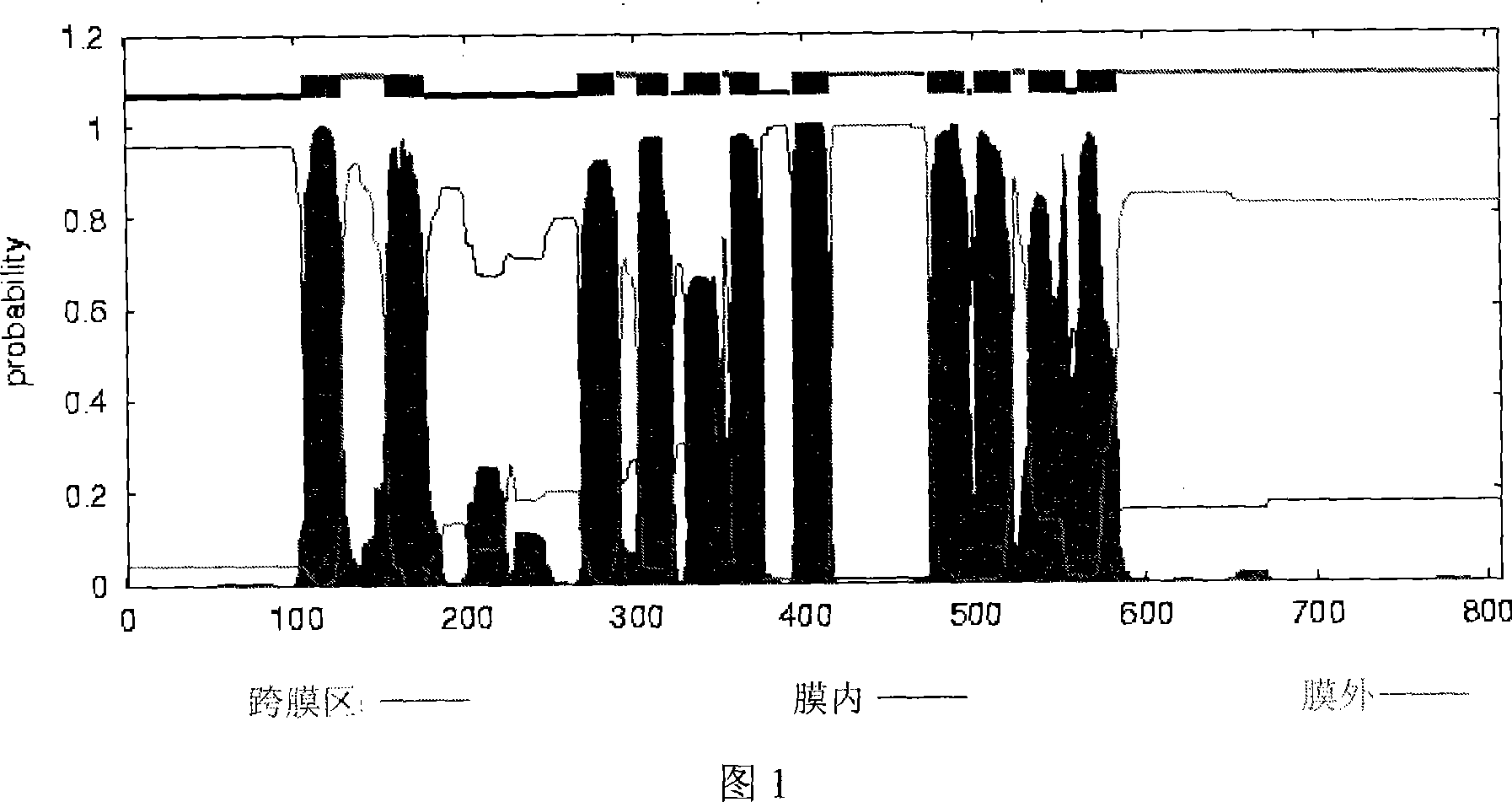
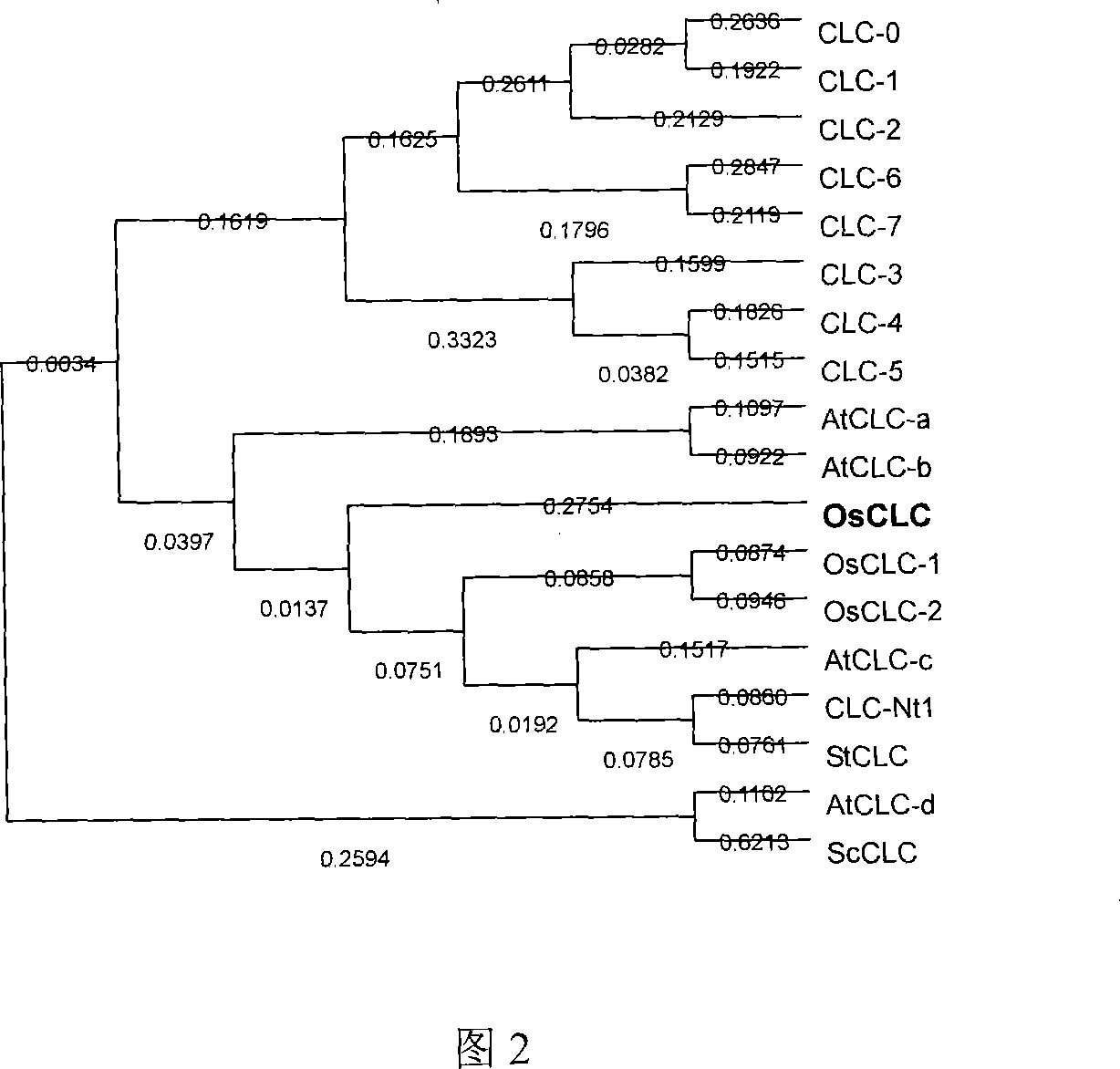
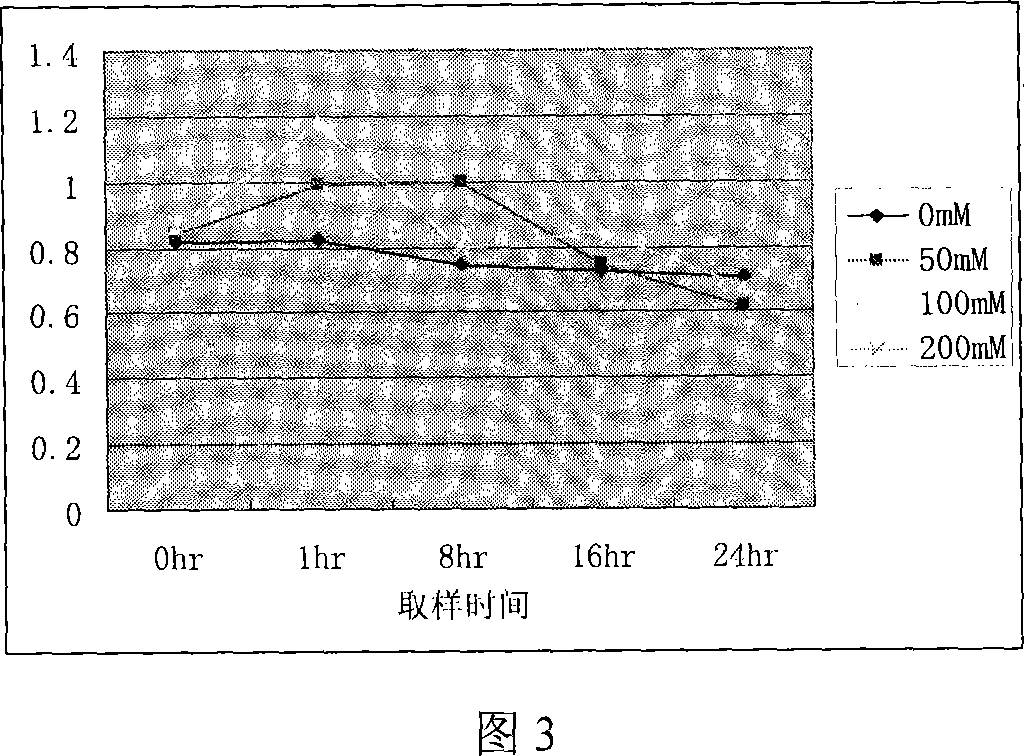
Rice chlorine ion passage gene OsCLC, coding protein and clone method thereof
InactiveCN101054586AInhibition sensitiveNo sensitivityPlant peptidesFermentationENCODEGene expression level
The present invention relates to rice chlorine ion passage gene OsCLC, its coded protein and clone method. The gene has sequence indicated by SEQ NO 3. The gene of 2429bp is cloned from differentiated rice callus. The opening reading frame of cloned gene encodes protein of 808 amino acid (molecular weight 88KD)which has 11 trans-membrane region indicated by trans-membrane region analysis. Cluster analysis indicates the OsCLC gene is new member of CLC family. The OsCLC gene expression level has positive correlation with salt concentration rise in a certain time range and respond to the salt stress and other environmental stress. The gene can be induced to produce partial complementary GEF1 function in yeast mutant and partially inhibit the sensitivity to NaCl and recover growth function. The gene is sensitive to pH value variety and not sensitive to different cation.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Heterologous intron within an immunoglobulin domain
ActiveUS20140234893A1Driving strong and stable gene expressionHigh expressionAnimal cellsVectorsHeterologousCloned genes
The invention concerns the field of recombinant gene engineering. It concerns novel introns and compositions comprising such introns as well as a method to improve expression of polypeptides from nucleic acids such as cloned genes with heterologous introns, especially genes encoding antibodies and antibody derived fragments, and the production of various polypeptides in eukaryotic host cells using said novel intron sequences as heterologous introns.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
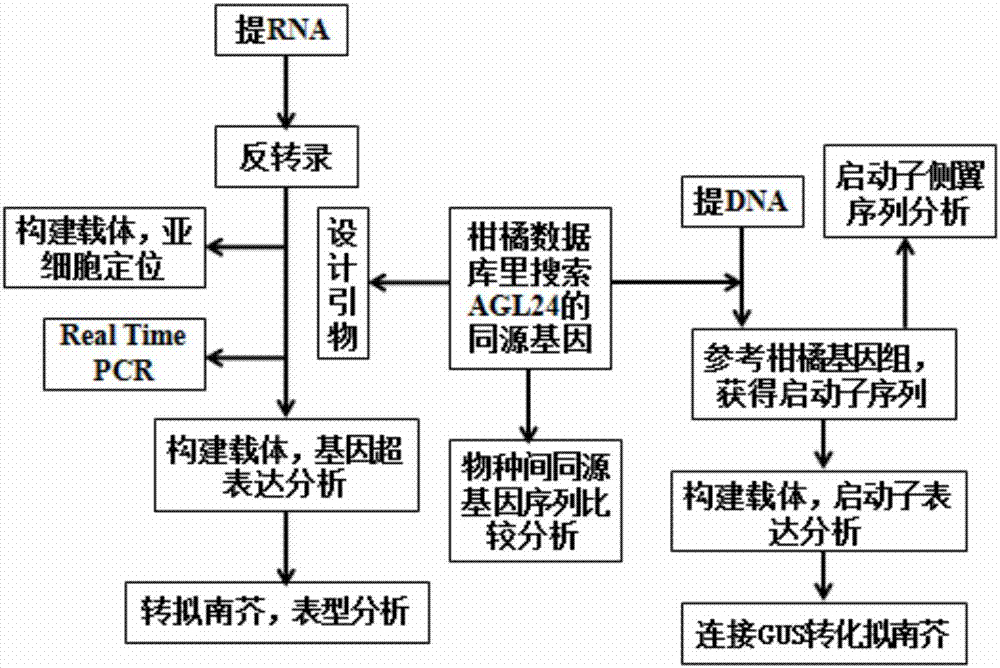
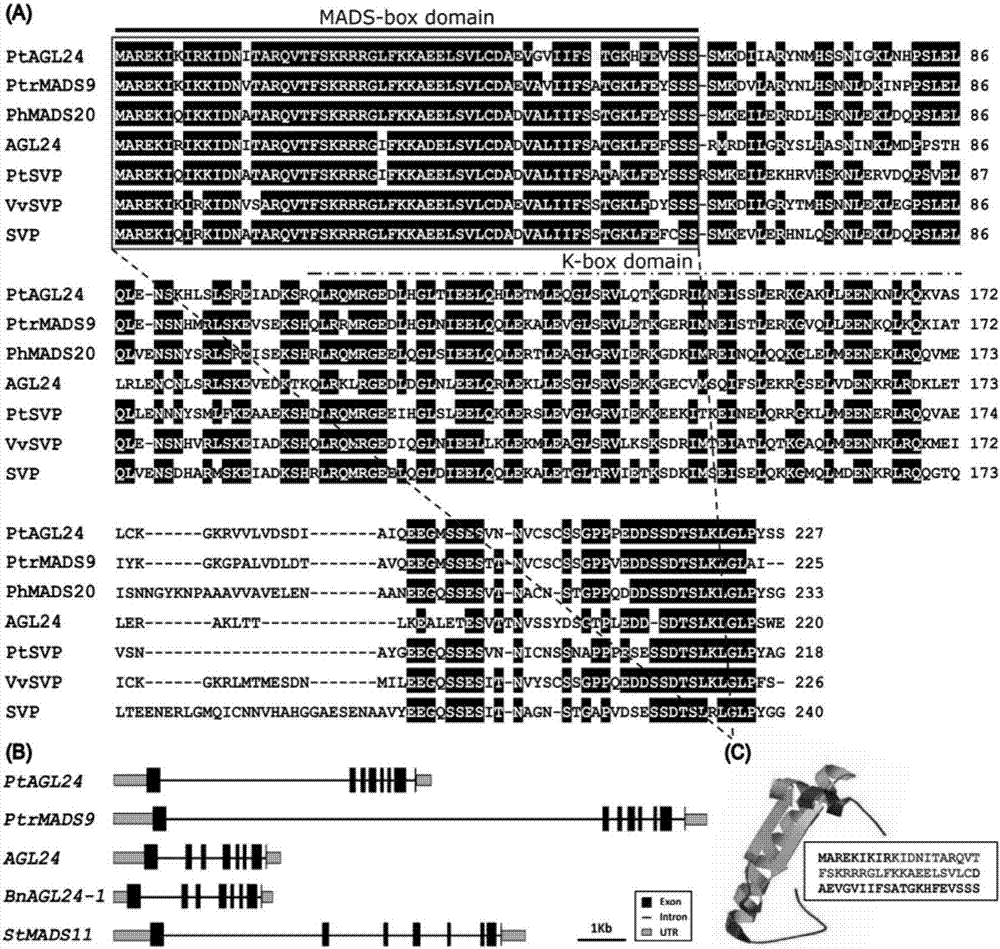
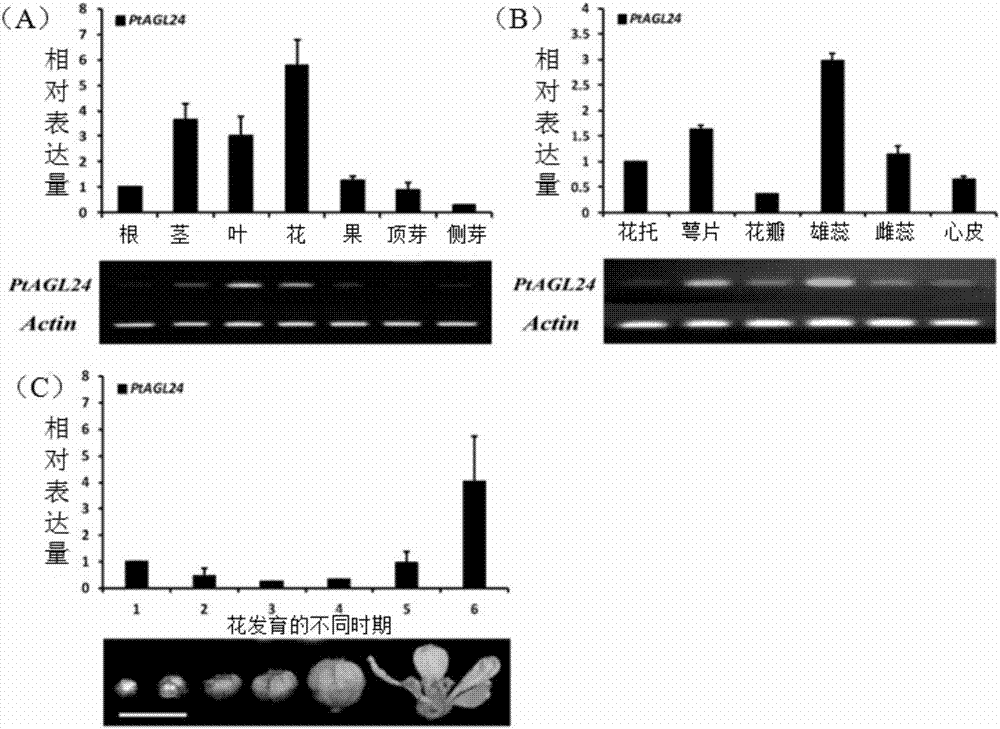
Precocious trifoliate orange PtAGL24 gene separation and application with effect of regulating and controlling plant early blossoming
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. Specifically, it relates to the separation and application of the PtAGL24 gene that can regulate the early flowering of plants. The nucleotide sequence of the PtAGL24 gene is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, the sequence of the protein encoded by the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO: 2; the nucleotide sequence of the promoter PtAGL24P is shown in SEQ ID NO: 3. The ectopic overexpression of the gene can significantly shorten the childhood period of the plant and promote the early flowering of the plant. The gene and promoter of the invention provide biological resources for the breeding of perennial woody fruit trees and the shortening of flowering process. The role of PtAGL24 in the whole development process of the plant is further revealed through the spatial expression of the promoter, which shows that the cloned gene of the present invention is also induced by the low temperature of the environment, and has a certain response to the external environmental stress. The gene and promoter of the present invention can be used in regulating plant flowering period and low temperature stress.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for producing and identifying soluble protein domains
InactiveUS20050019773A1Strong anti-tag signalEfficient purificationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCloned genesDNA
Methods for producing and identifying fragments of proteins, and more particularly to methods for generating and identifying soluble protein domains are disclosed based on a method for generating a library of nucleic acid fragments from nucleic acid encoding a desired polypeptide, and more especially a library of essentially, randomly sampled fragments of coding DNA sequence predominantly of defined size range and a method for selecting cloned gene fragments from the library that encode soluble protein domains.
Owner:DOMAINEX
Application of corn transcription factor ZmMYB42 gene to drought-resistant breeding of plants
The invention discloses an application of a corn transcription factor ZmMYB42 gene to drought-resistant breeding of plants. A gene ZmMYB42 is cloned from corn, the gene or a RNAi structure thereof isrecombined into a plant expression vector in a sense form, a fusion gene or a ZmMYB42RNAi structure is introduced into crops by using a transgenic technology, drought resistance determination is performed on transgenic plants, transgenic plants with obviously improved or reduced drought resistance and progenies thereof are screened out, and new plant germplasm with application value is created. The cDNA sequence of the corn transcription factor ZmMYB42 is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1, and the coded amino acid sequence of the corn transcription factor ZmMYB42 is as shown in SEQ ID No. 2. The plantsrefer to cultivated cereal crops. The application disclosed by the invention is of great significance for increasing the crop yield under drought stress.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com