Method for sequencing clone genes with recessive mixed pools
A cloning method and mixed pool technology, applied in the field of genetics, can solve the problems of difficult polymorphism marking, increased workload, partial separation of traits, etc., and achieve the effects of broadening the scope of utilization, eliminating sequencing errors, and reducing workload.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
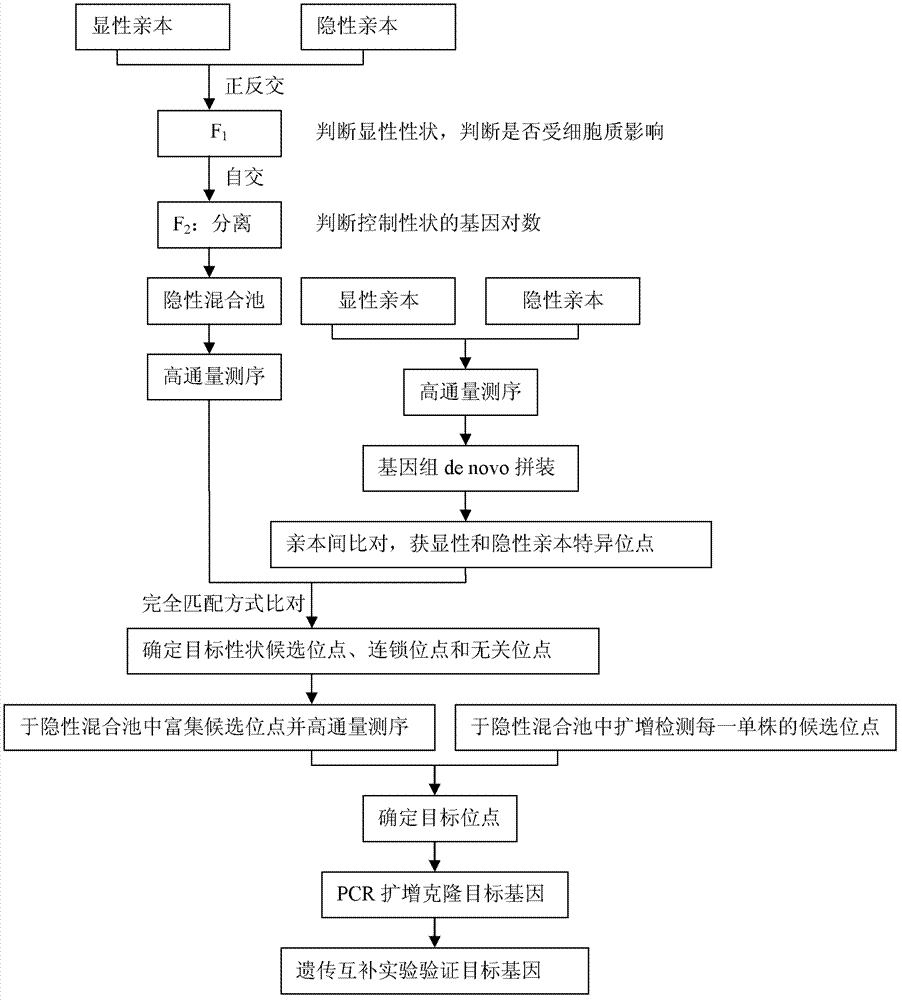
[0032] A recessive hybrid pool sequencing gene cloning method (see figure 1 )
[0033] (1) Construct segregation groups
[0034] Select two parents with relative target traits for reciprocal crossing (except for target traits, the smaller the difference in other traits, the better, and such parents can be created by means of mutant strains / wild strains or backcross breeding to generate sister lines). According to F 1 Judging whether the gene locus controlling the trait is dominant or recessive according to the performance of the reciprocal cross; whether there is a difference in the traits of the reciprocal cross, it is judged whether there is a cytoplasmic effect, if there is no difference, it indicates that it is not affected by the cytoplasmic gene, otherwise the trait is related to the cytoplasmic gene; f 1 F 2 group. According to relative traits in F 2 The proportion of plants in the population was used to determine the logarithm of the genes controlling the target ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The present invention will be further described below by a specific embodiment:
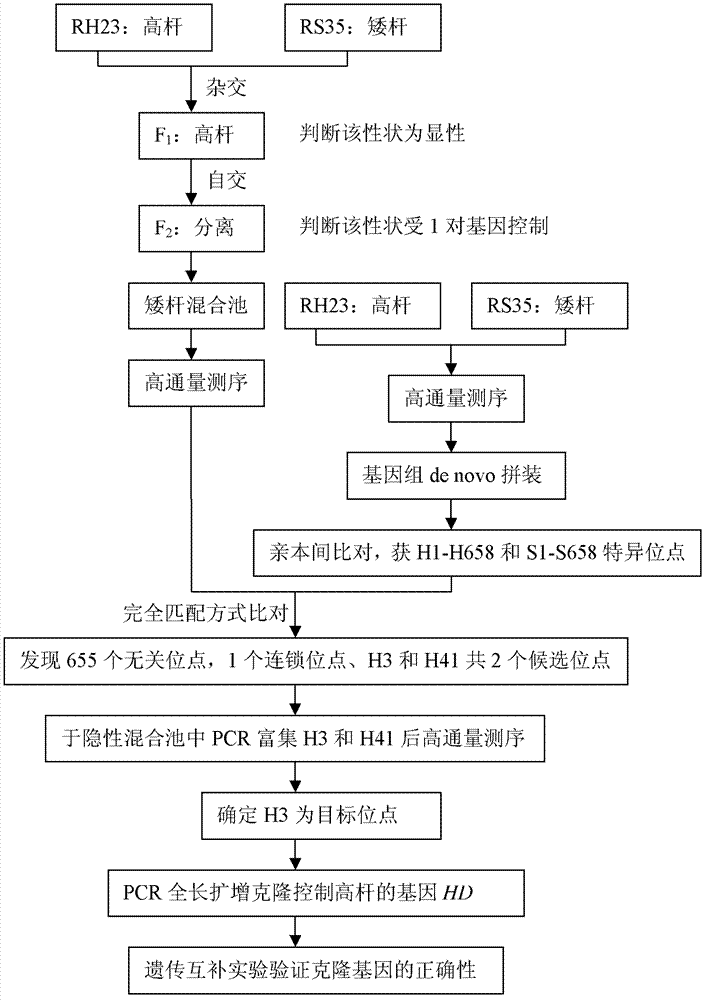
[0047] Rice tall stem gene cloning method (see figure 2 ):
[0048] (1) Group construction
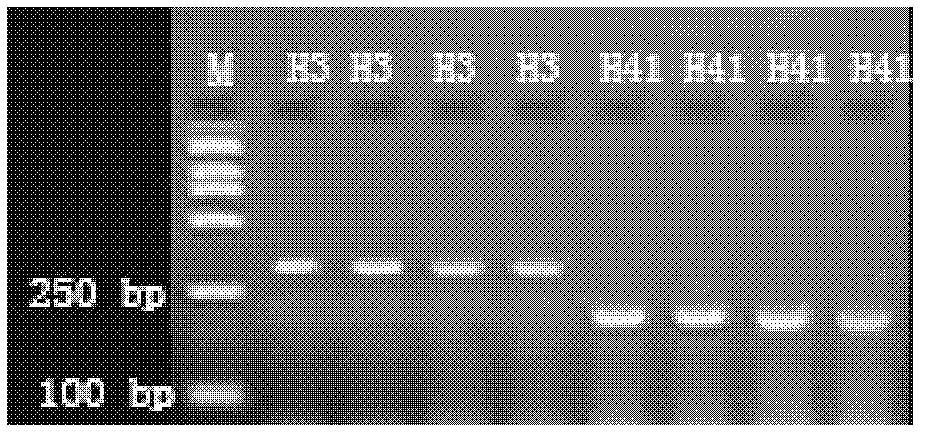
[0049] RH23 and RS35 are two rice parents selected for breeding. Among them, the average plant height of RH23 is 134.56 cm, and the average plant height of RS35 is 87.89 cm. The two are sister lines, except for the traits of plant height, other traits are basically the same. F 1 , F 1 It showed tall stems (average plant height 134.49cm), indicating that tall stems were dominant and short stems were recessive, and there was no significant difference in plant height between reciprocal crosses, indicating that plant height was not controlled by cytoplasmic genes. Plant F 2 A total of 20,000 plants were divided into high-stem and short-stem populations according to plant height >135cm and <90cm, among which 13,783 were high-stalks and 4,637 were short-stalks. The chi-square test met the requireme...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com