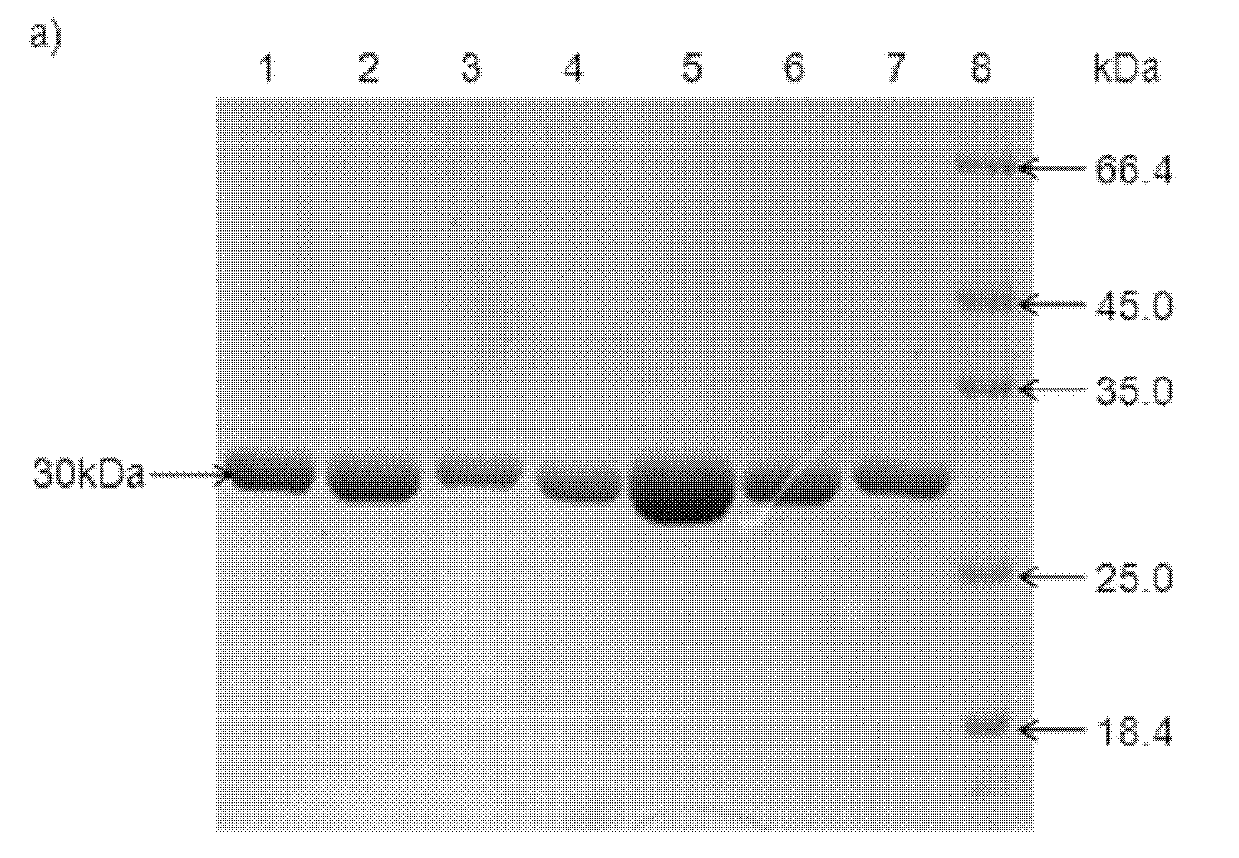
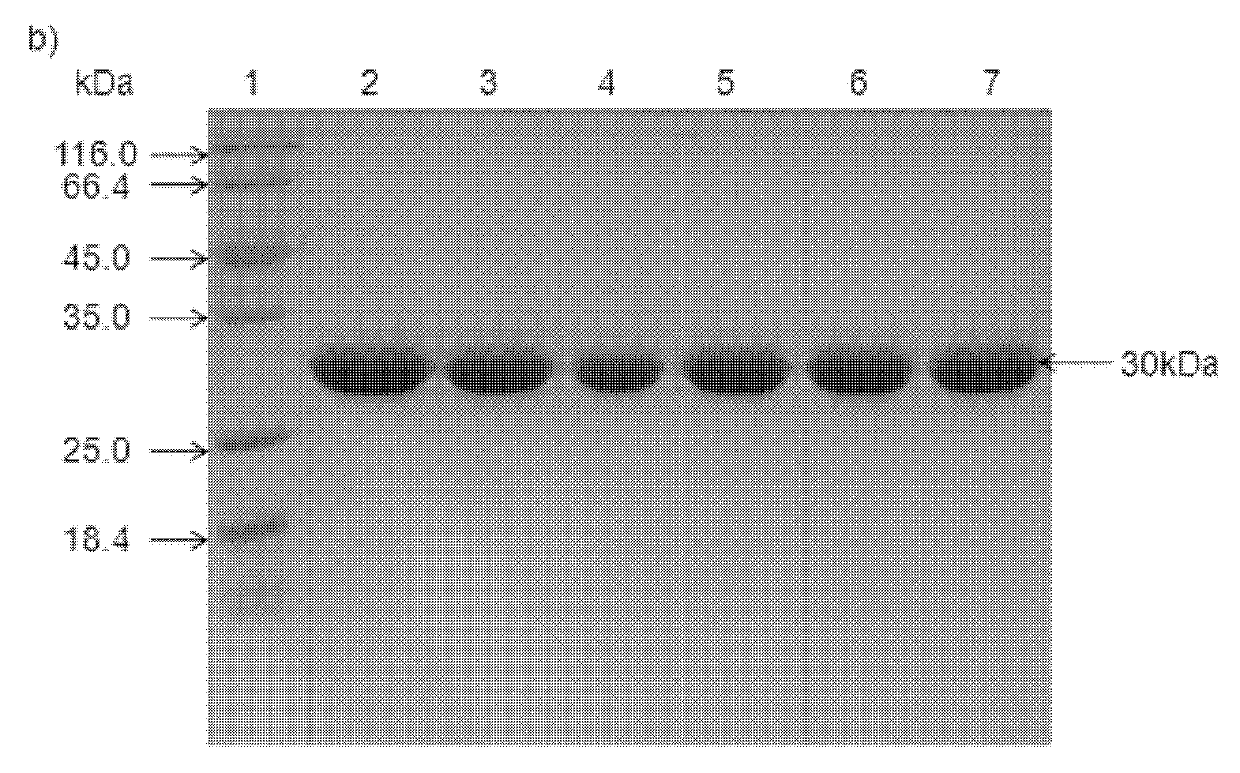
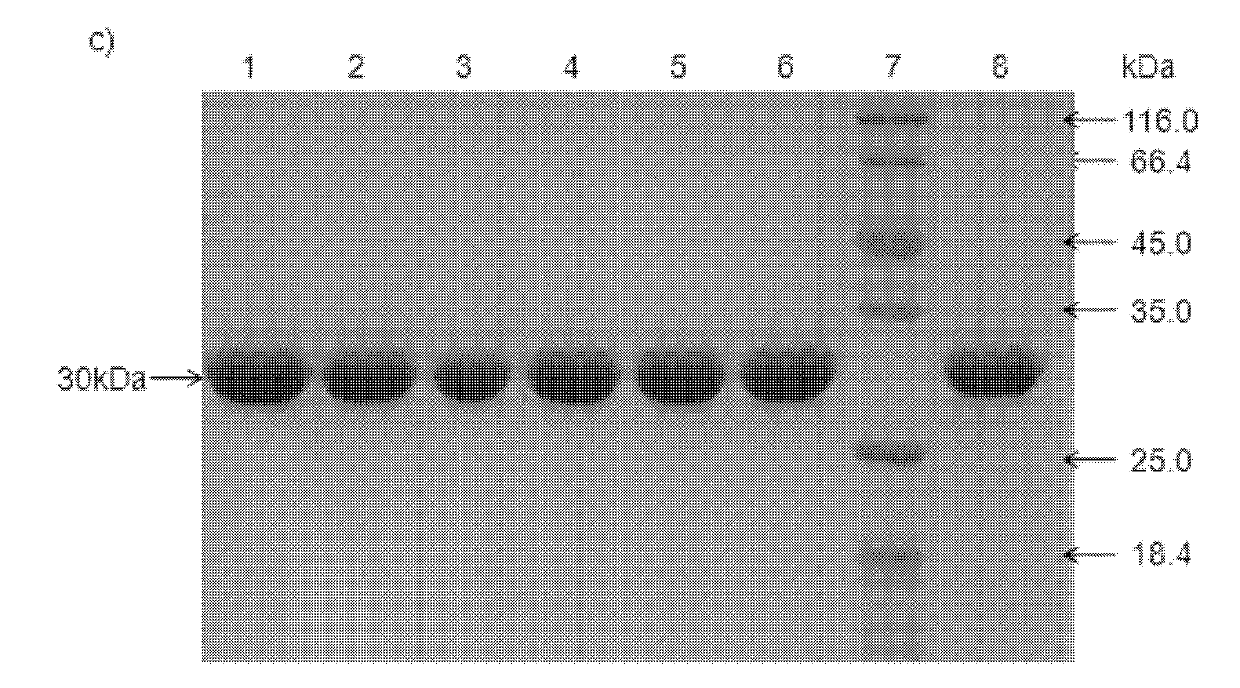
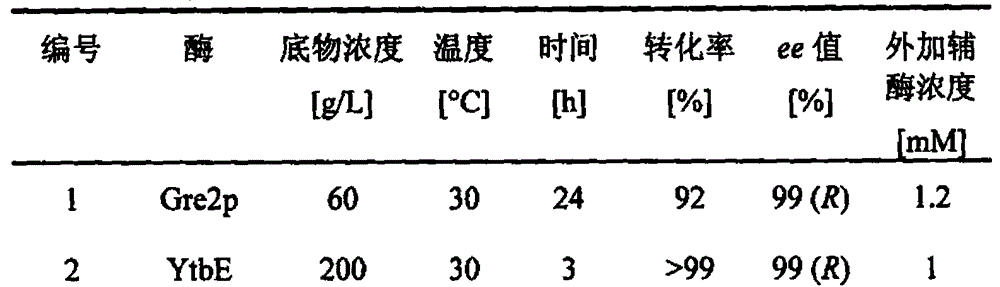
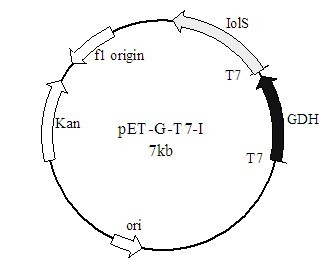
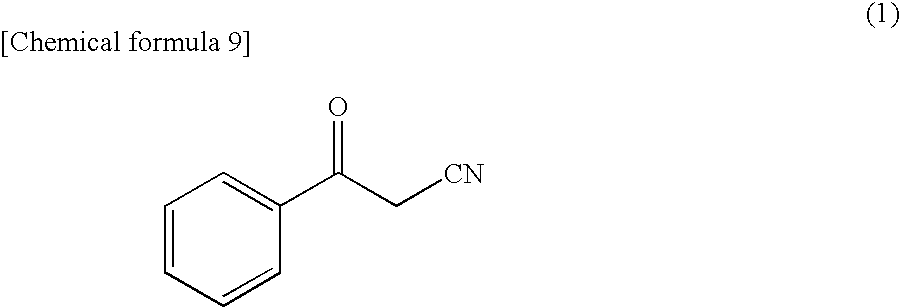
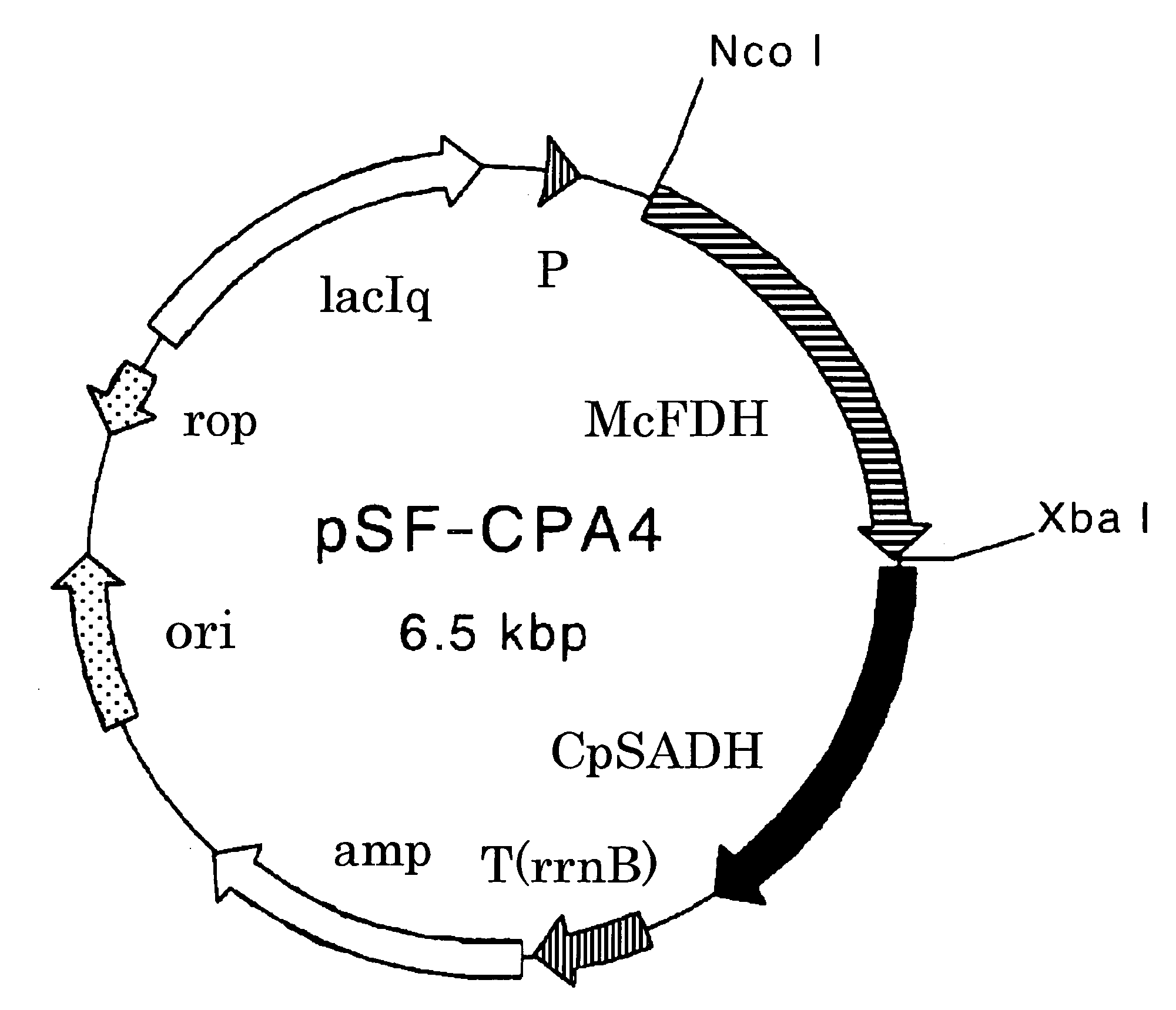
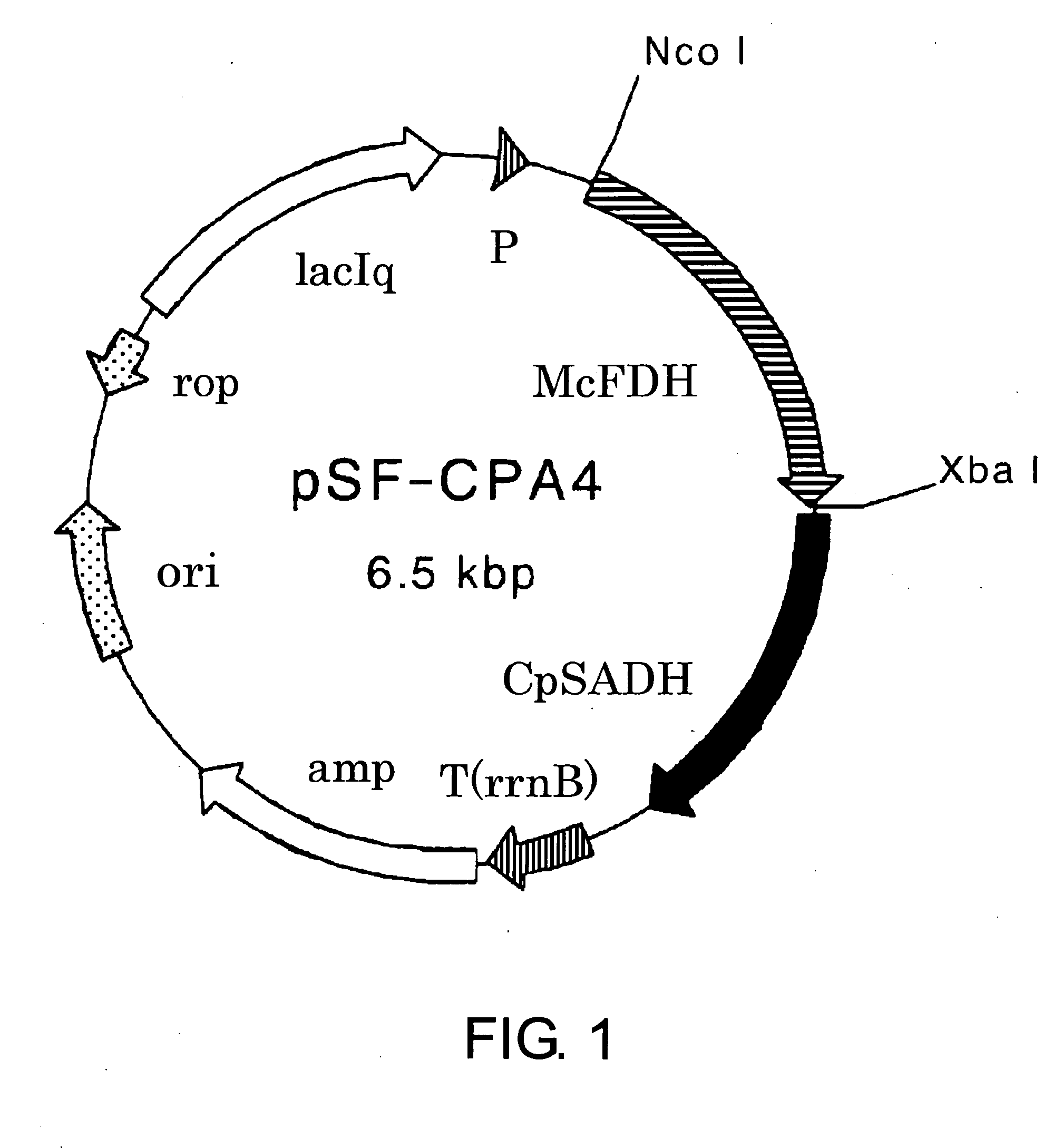
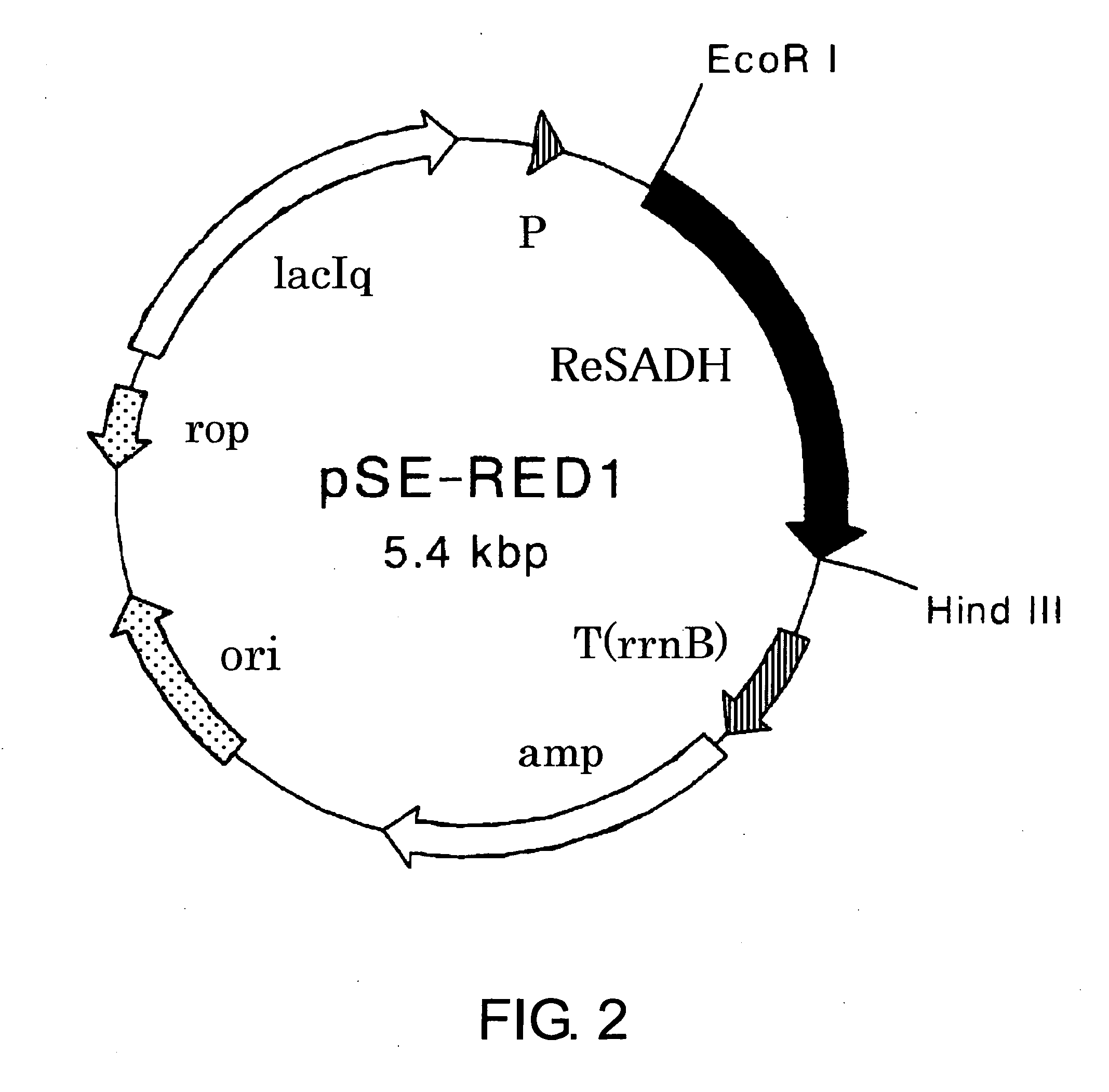
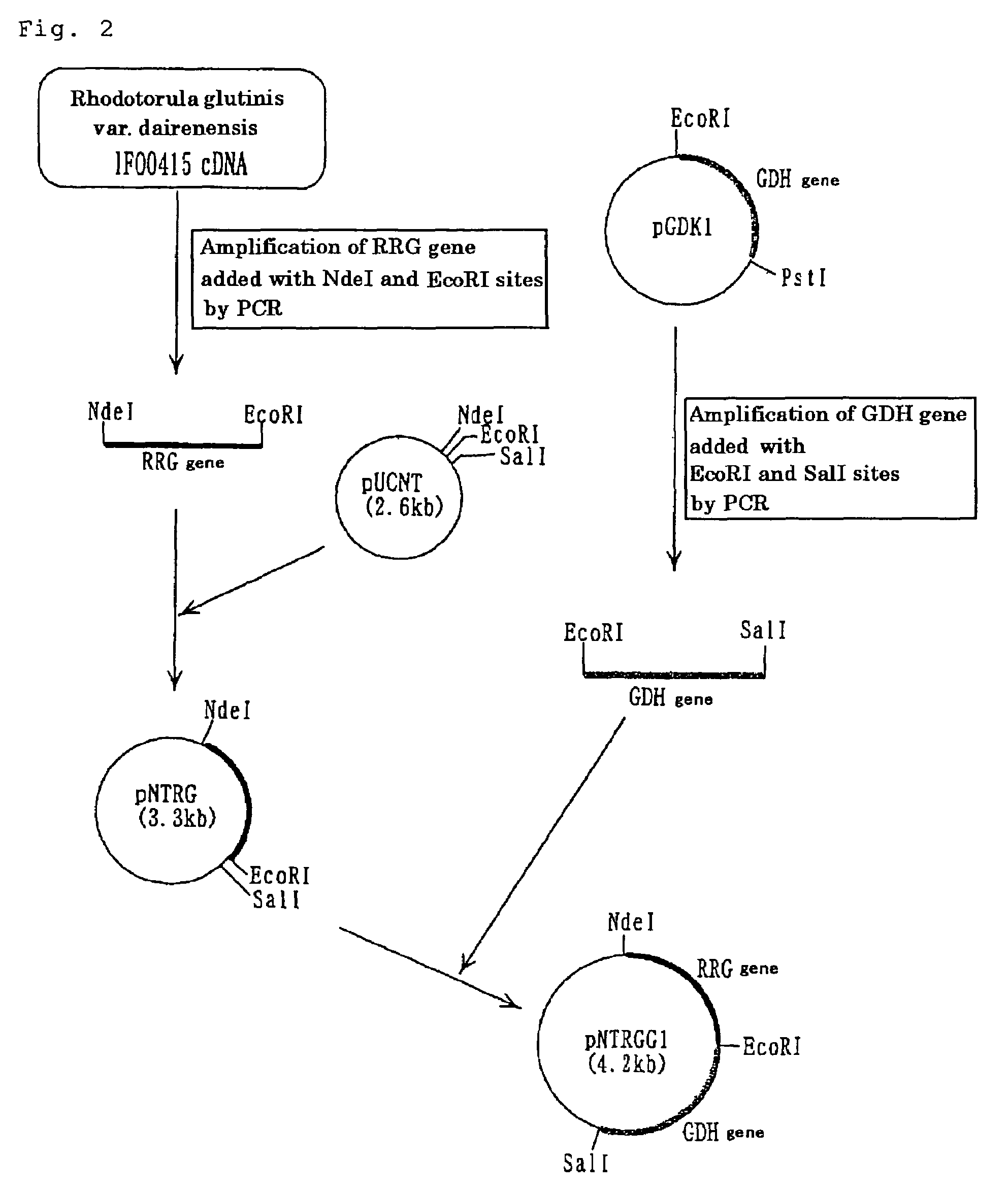
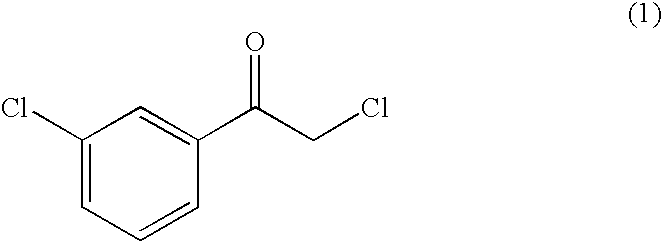
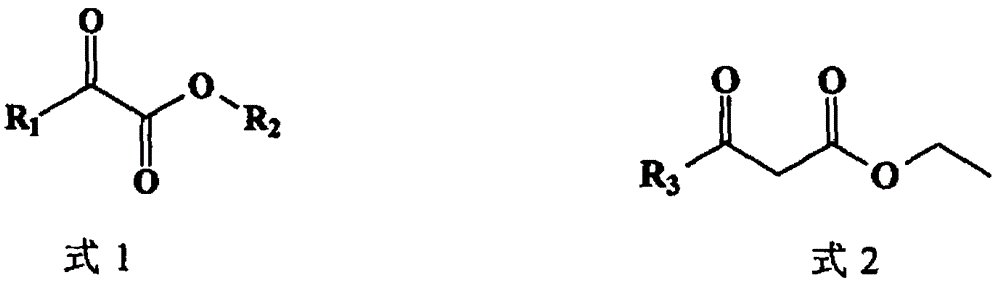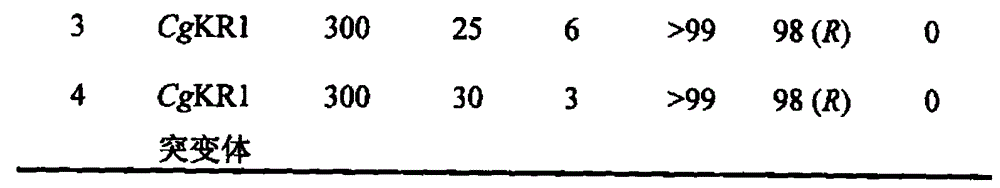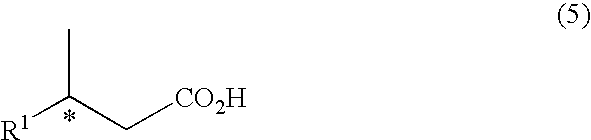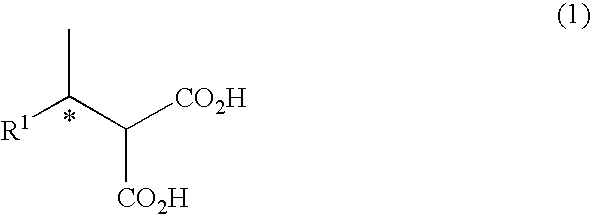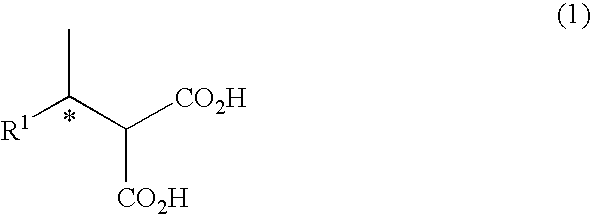Patents
Literature
188 results about "Carbonyl Reductase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In enzymology, a carbonyl reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.1.1.184) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction R-CO-R' + NADPH + H⁺ ⇌ :R-CHOH-R' + NADP⁺ Thus, the two products of this enzyme are R-CHOH-R' and NADP⁺, whereas its 3 substrates are R-CO-R', NADPH, and H⁺. This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on the CH-OH group of donor with NAD⁺ or NADP⁺ as acceptor.
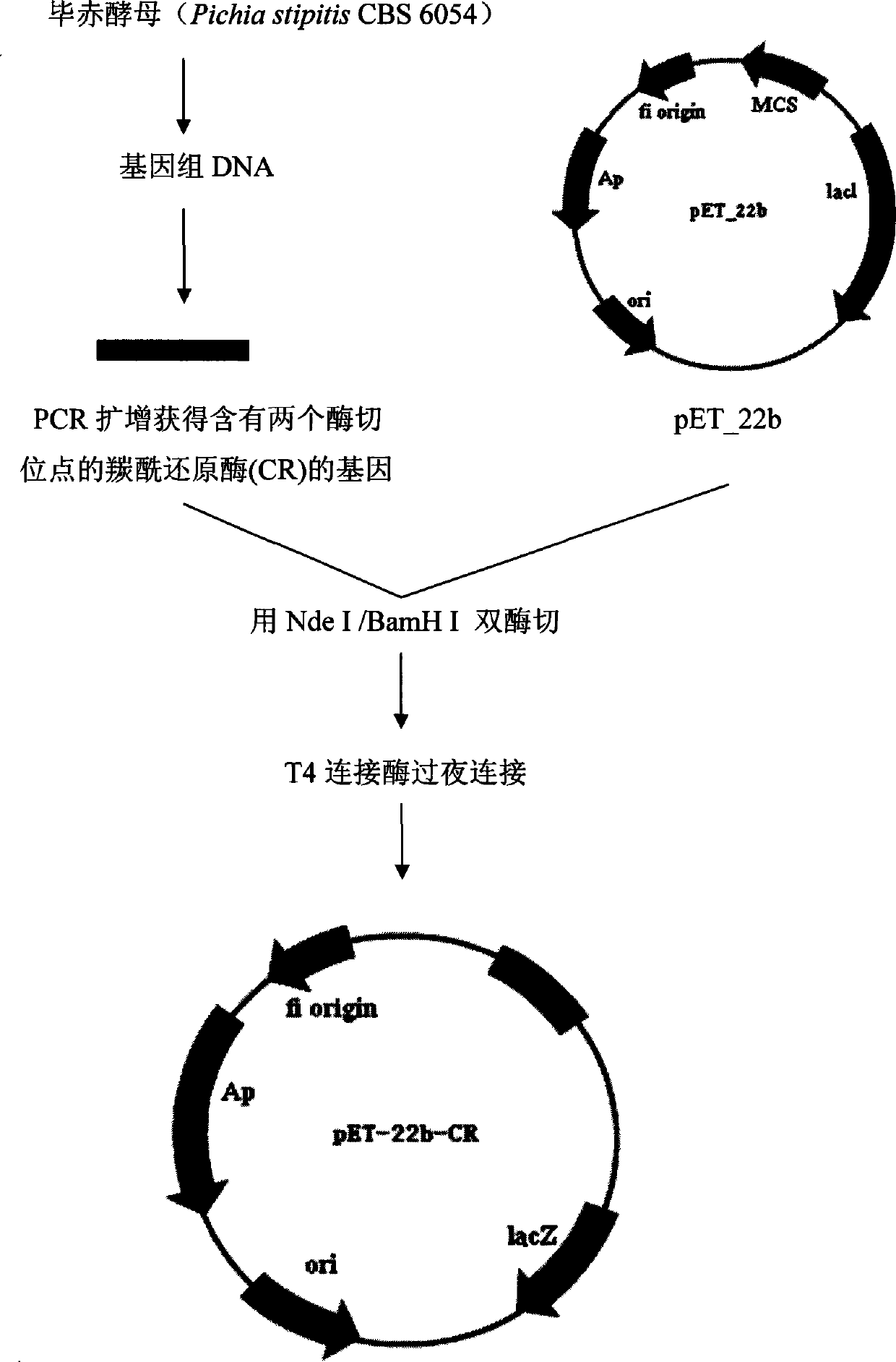
Double carbonyl reductase mutant and its application
InactiveCN102277338AEffective catalytic reduction reactionImprove conversion efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCarbonyl ReductaseTransformation efficiency
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and in particular relates to a mutant of diketoreductase (DKR) that can be used as a catalyst for chiral alcohol synthesis; the invention discloses a mutant of diketoreductase, the diketoreductase The amino acid sequence of the mutant has more than 80% homology with any amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1-SEQ ID NO.20. Compared with the wild-type double carbonyl reductase, the double carbonyl reductase mutant of the present invention has higher transformation efficiency and higher stereoselectivity.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Carbonyl reductase mutant as well as gene and application thereof
InactiveCN104099305AImprove thermal stabilityIncreased reductase activityBacteriaOxidoreductasesMethyl o-chloromandelateMandelic acid
The invention relates to a carbonyl reductase CgKR1 mutant, a coding gene of the mutant, a recombinant expression vector containing the gene of the carbonyl reductase mutant, a recombinant expression transformant, a recombinase, a preparation method of the recombinase, and an application of the carbonyl reductase mutant to asymmetric reduction of ketonic ester for preparation of optically pure chiral hydroxyl ester, such as catalysis of o-cyano methyl phenylglyoxylate for asymmetric reduction to prepare (R)-o-chloro mandelic acid methyl ester. Compared with wild enzymes, the carbonyl reductase mutant has the advantages that the thermal stability is substantially improved, and the catalytic activity of part of the mutant to the o-chlorobenzoic acid formyl methyl ester is also obviously improved. The multiple mutants can be applied to catalysis of the ketonic ester for asymmetric reduction to prepare the optical purely-chiral hydroxyl ester, such as catalysis of the o-cyano methyl phenylglyoxylate for asymmetric reduction to prepare the optically pure (R)-o-chloro mandelic acid methyl ester. The carbonyl reductase mutants have the very good industrial application prospect.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate by catalyzing with recombinant carbonyl reductase
InactiveCN102618590AAvoid inhibitionImprove conversion abilityMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliEthyl butyrate
The invention discloses a method for preparing (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate by catalyzing recombinant carbonyl reductase, which belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: cloning gene segments of carbonyl reductase (IolS) and glucose dehydrogenase (GDH) from bacillus subtilis CGMCC NO.1.1508, expressing an IolS gene and a GDH gene in series by adopting a dual-starter method to construct a recombinant plasmid pET24a-G-T7-I, and introducing the plasmid into escherichia coli BL21(DE3); and under the condition of not adding or adding a small amount of NADP+cofactors, performing biotransformation by taking a cell-free extract of the escherichia coli recombinant plasmid as a catalyst, 2-oxo-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate as a substrate and glucose as a substrate to obtain (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate, wherein the enantiomeric excess value of the product is higher than 99.5 percent. In the method, IolS and GDH are co-expressed, so that efficient regeneration of an intra-cellular cofactor NADP(H) is realized, production cost is lowered, and a good industrial application prospect is achieved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
6- cyano-(3r, 5r)-dyhydroxyl hexanoic acid tert-butyl ester prepared by biological catalysis, and bacterial strain thereof
ActiveCN102643757AHigh stereoselectivityMild reaction conditionsFungiMicroorganism based processesCarbonyl ReductaseBacterial strain
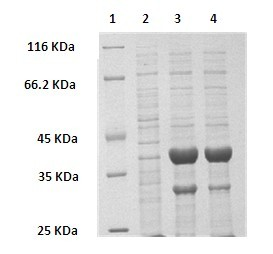
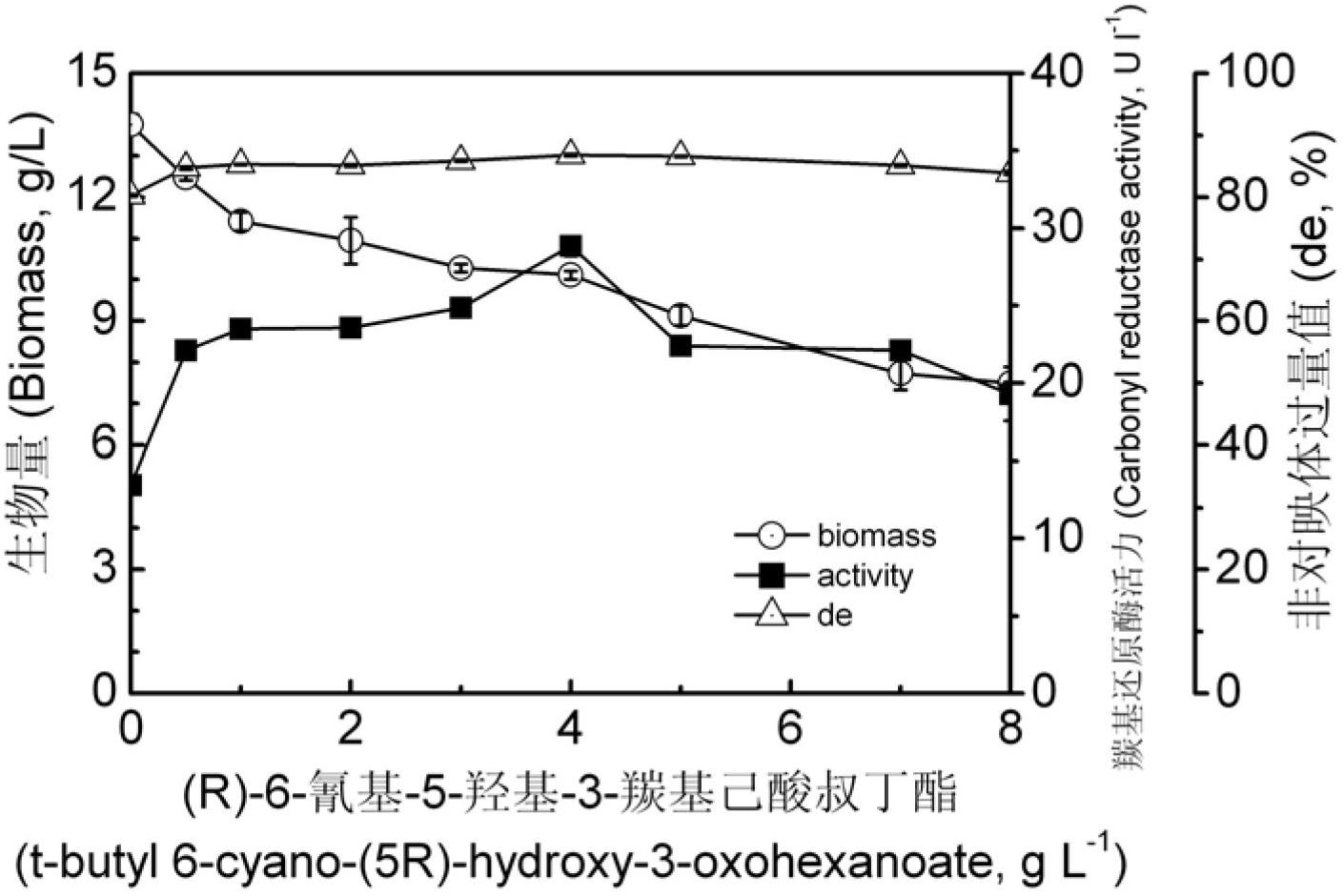
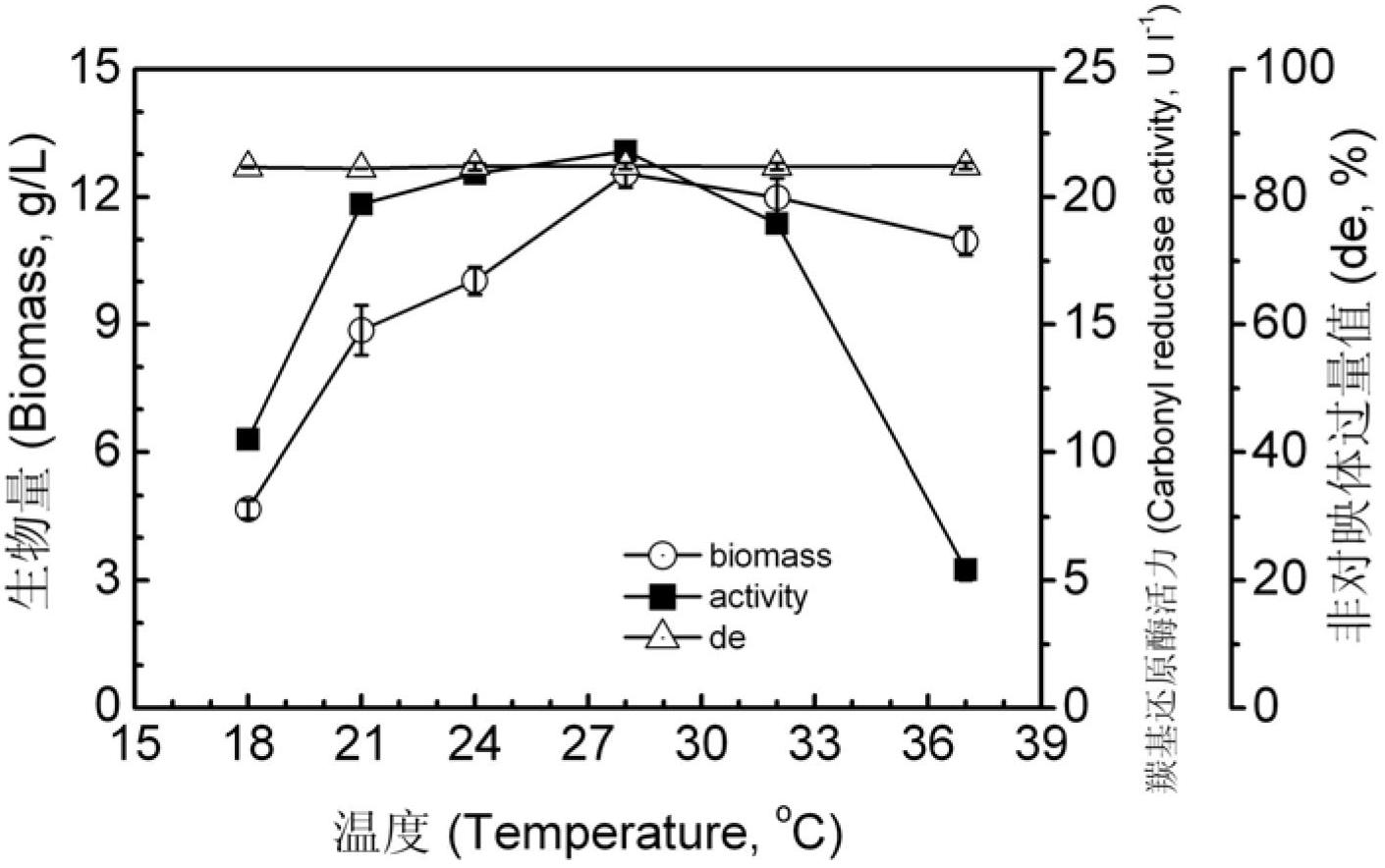
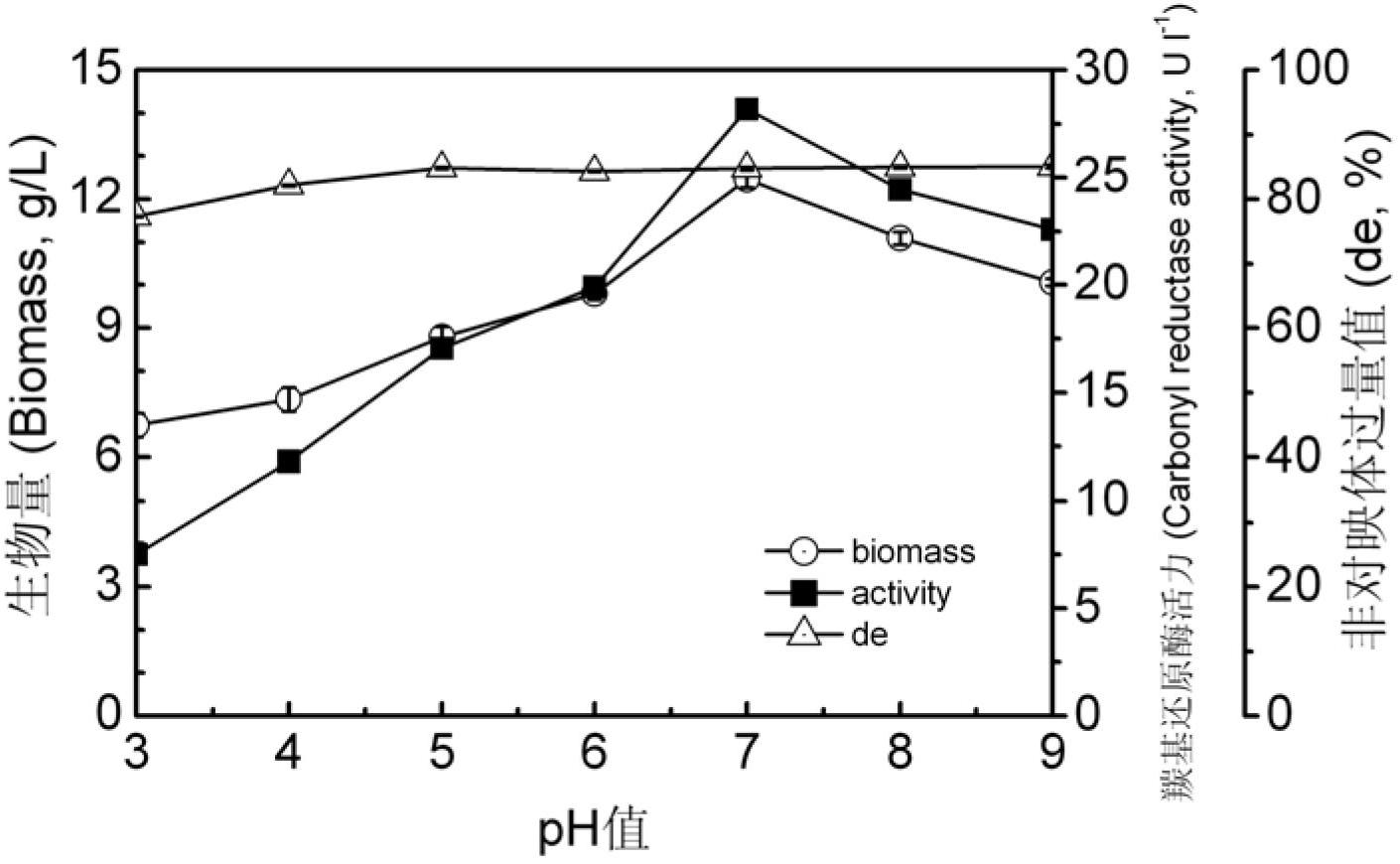
The invention provides a Pichia guilliermondii X25 which is enriched and screened from soil, has high diastereoselectivity and is a carbonyl reductase active microbial new strain, and application of the Pichia guilliermondii X25 in preparation of 6-cyano-(3R, 5R)-dyhydroxyl hexanoic acid tert-butyl ester by biological asymmetric reduction (R)-6-cyano-5-hydroxyl-3-carbonyl hexanoic acid tert-butylester. The strain is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), the address is Wuhan university, Wuhan, China, the post code is 430072, the CCTCC No. is M 2011386, and the preservation date is November11th,2011. The optical pure 6-cyano-(3R, 5R)-dyhydroxyl hexanoic acid tert-butyl ester prepared by using carbonyl reductase generated by the Pichia guilliermondii X25 to convert (R)-6-cyano-5-hydroxyl-3-carbonyl hexanoic acid tert-butyl ester is high in stereoselectivity, mild in reaction condition and environment-friendly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Use of carbonyl reductase in (S)-4-chloro-3 hydroxy butyric ether production
The invention discloses an application of carbonyl reductase with the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:2 to prepare (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutanoic ethyl ester by asymmetric reduction of 4-chloracetyl ethyl acetate. The carbonyl reductase with the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:2 is taken as a catalyst, the ethyl 4-chloracetyl ethyl acetate is taken as a substrate, and NADPH is taken as a cofactor, and the (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutanoic ethyl ester is prepared by the asymmetric reduction. The carbonyl reductase with the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:2 is applied to preparing the (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutanoic ethyl ester by the asymmertric reduction of the 4-chloroacetyl ethyl acetate for the first time, which produces good effect; the yield of the substrate is up to 95%, and the enantiomer excess value of the product is 100%, the yield is high, and the production cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Application of Chryseobacterium sp. and carbonyl reductase thereof in production of aprepitant chiral intermediate
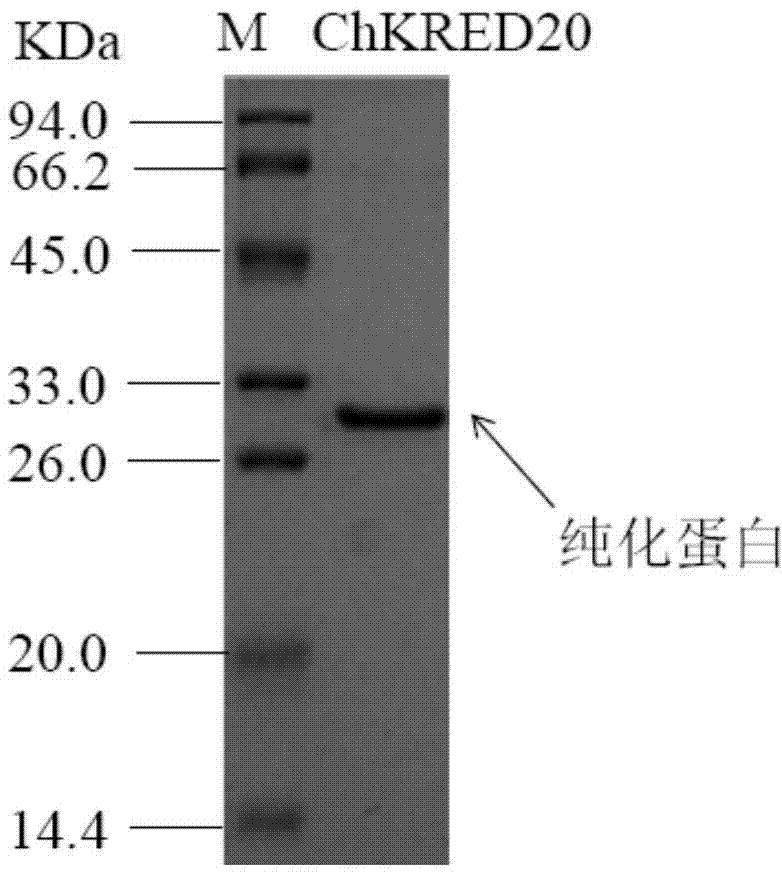
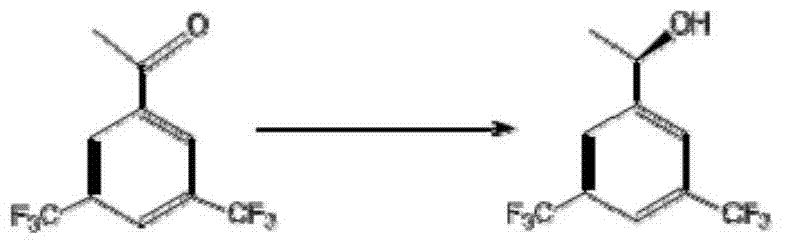
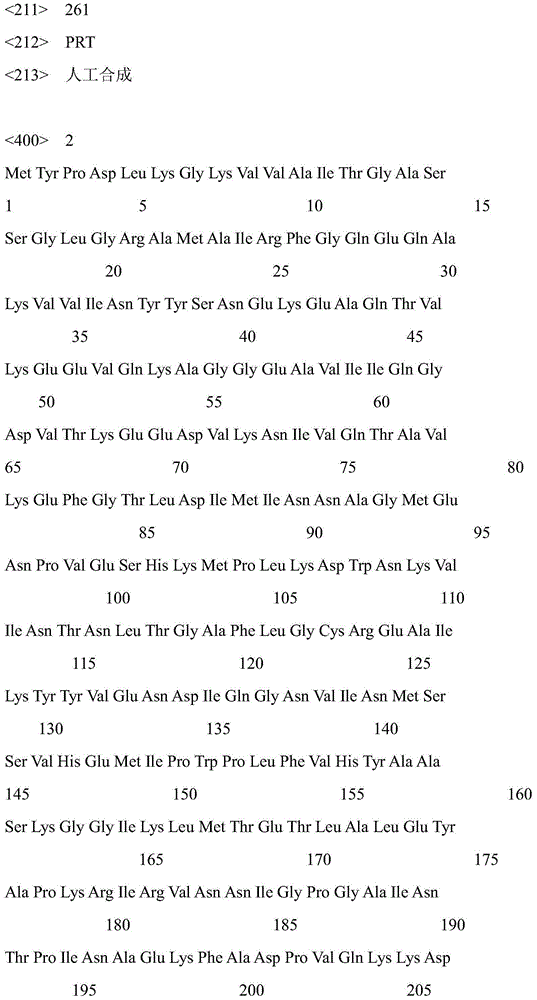
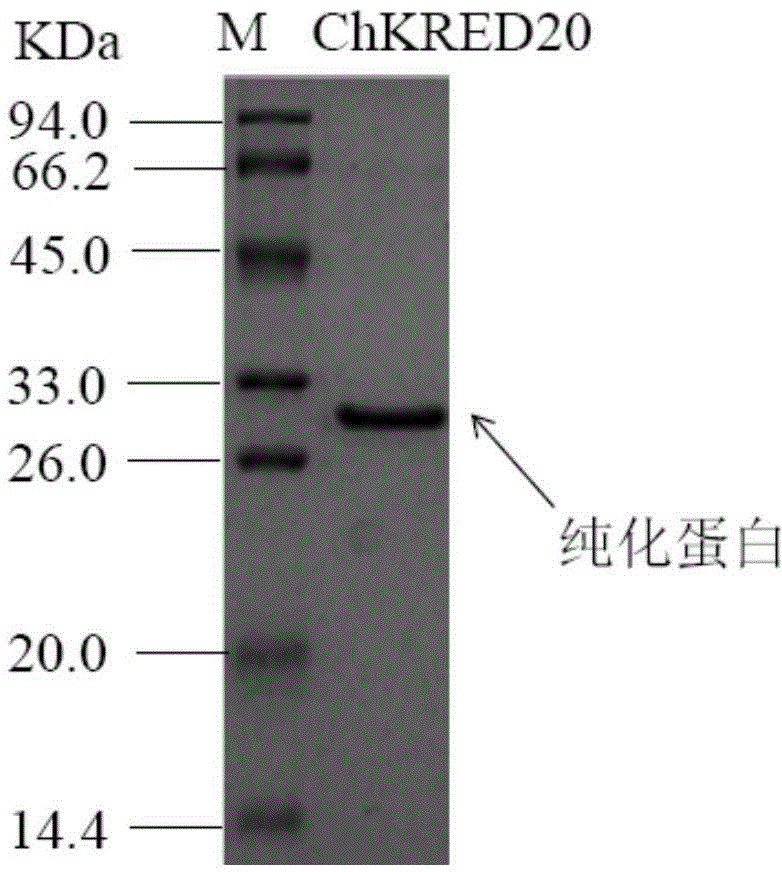
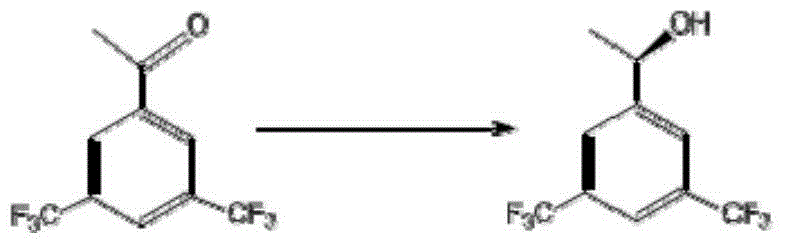
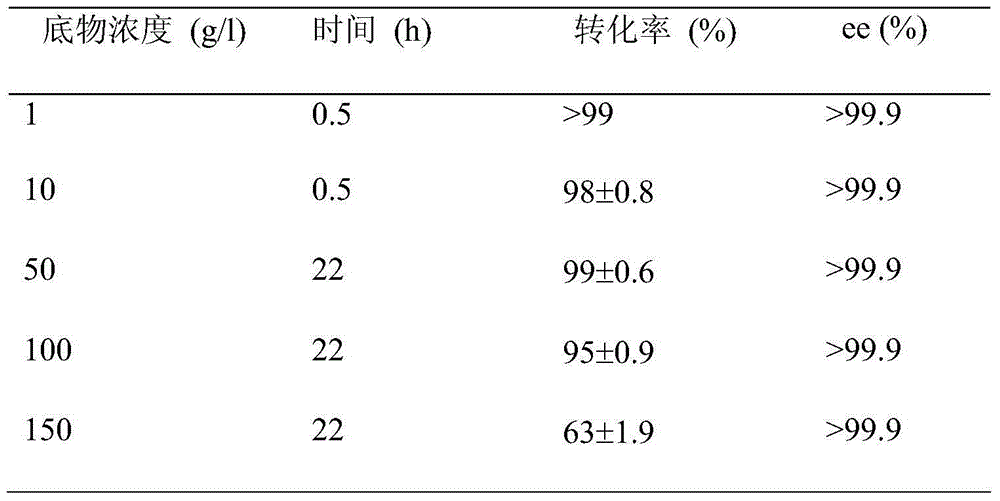
The invention discloses a strain of Chryseobacterium sp. CA49 (with an accession number of CCTCC M2012484), carbonyl reductase ChKRED20 coded by the genome of the strain and preparation of an aprepitant chiral intermediate (R)-1-[3,5-di(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanol by using the original strain of Chryseobacterium sp. or the carbonyl reductase as a biocatalyst. The enantiomeric excess value of the produced intermediate is greater than 99.9%. Crude ChKRED20 enzyme powder can catalyze up to 200 g / L of a substrate and enables a conversion rate of more than 99% to be obtained in 24 h; a coenzyme circulating system is simple and cheap, the produced intermediate is easy to separate and purify, and a high recovery rate and good industrial application prospects are obtained.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Enzyme immobilization method and application
InactiveCN105969757AEasy to getGood repeatabilityChemical industryOxidoreductasesAlcoholPolyhistidine-tag
The invention discloses a simple and convenient method for recombinase immobilization. According to the method, the characteristic that a histidine label of recombinant protein and metal ion affinity chromatography resin are combined specifically is utilized, and therefore recombinase is immobilized on the resin, and the immobilized recombinase is prepared. Immobilized carbonyl reductase is used for continuous production of chiral alcohol, and the space time yield is greatly increased.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Carbonyl reductase expressed recombination engineering bacterium and application thereof
The invention discloses a carbonyl reductase expressed recombination engineering bacterium and application thereof. The engineering bacterium comprises a host cell and a recombinant vector transferred into the host cell, wherein the recombinant vector consists of an original vector and a target gene connected into the original vector, the host cell is Escherichiacoli Rosetta (DE3), the target gene is a carbonyl reductase gene, and the base sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. According to the recombination engineering bacterium, the expression level of a carbonyl reductase is high, bacterial cells which are prepared through induced culture are used for converting N,N-dimethyl-3-oxy-3-(2-thienyl)-l-propylamine hydrochloride into (S)-N,N-dimethyl-3-hydroxy-3-(2-thienyl)-l-propylamine or converting 4-chloroethyl acetoacetate into (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxyethyl butyrate, and the two products are higher in both optical purity and conversion rate.
Owner:NINGBO MENOVO PHARMA +1
Recombinant carbonyl reductase mutant, gene, vector, engineering bacterium and application of recombinant carbonyl reductase mutant
ActiveCN107058251AHigh activityIncreased substrate toleranceBacteriaOxidoreductasesWild type enzymeEnzyme
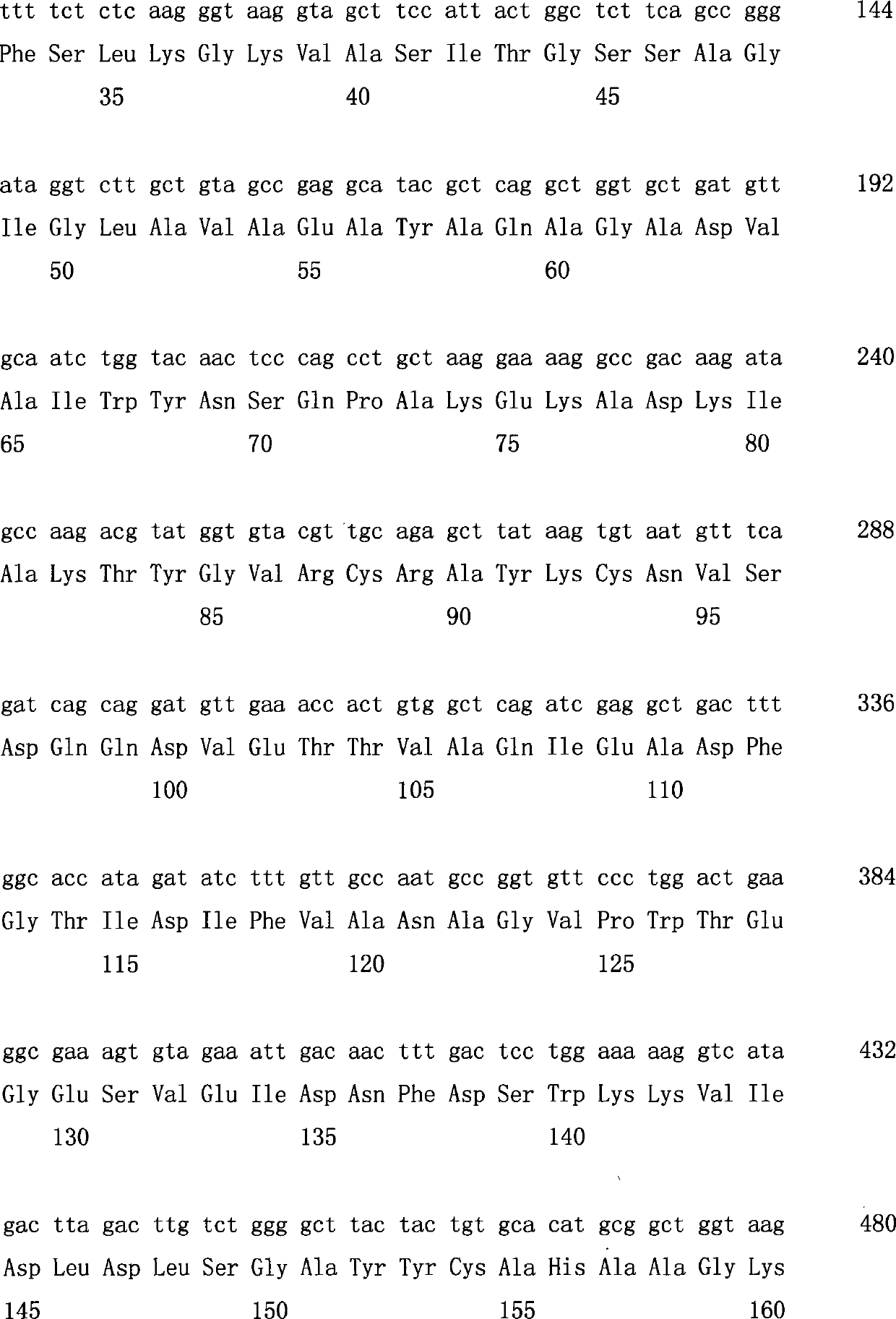
The invention discloses a recombinant carbonyl reductase mutant, a gene, a vector, an engineering bacterium and application of the recombinant carbonyl reductase mutant. The mutant is obtained by performing single-point mutation on the 95th locus, the 144th locus or the 156th locus of an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The recombinant carbonyl reductase mutant has reduced (S)-6-chloro-5-hydroxy-3-oxohexanoate, and compared with a wild type enzyme, has the advantages that the catalytic activity and the substrate tolerance are greatly improved when such reaction is converted, and the time consumption of a reaction process is obviously reduced. Compared with a chemical method for preparing (3R,5S)-6-chloro-3,5-dihydroxyhexanoate, such a technology has the advantages that an obtained product is high in stereoselectivity, a tedious chemical catalysis step is simplified, the reaction condition is milder, the requirement on equipment is low, the reaction cost is reduced, and the technology is environment-friendly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing pro-xylane from biological enzyme by one-pot method
PendingCN111876452AThe method is simple, reliable and directLow costOxidoreductasesFermentationNiacinamideNucleotide
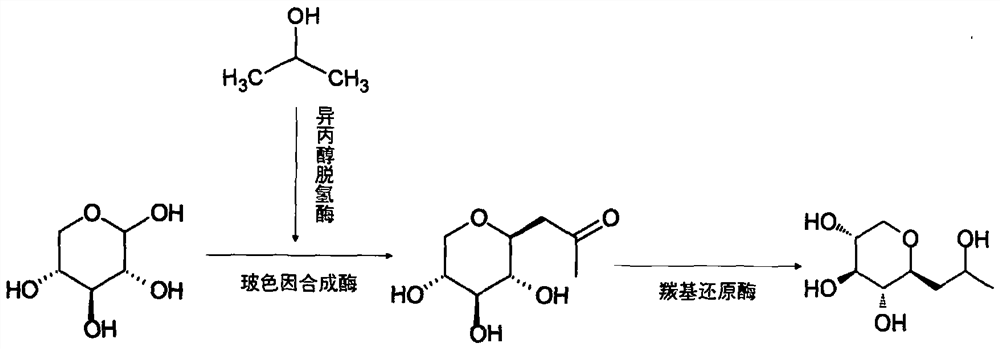
The invention discloses a method for preparing pro-xylane from a biological enzyme by a one-pot method. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of taking xylose and isopropanol as substrates, generating the pro-xylane under the catalytic action of isopropanol dehydrogenase, pro-xylane synzyme, carbonyl reductase and coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. The method is simple in process, free of chemical reagents, low in cost, high in yield and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:江苏瑞蓓丽生物科技有限公司
Carbonyl reductase AcCR and encoding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN105349503ACan be catalyzed to generateAchieve in situ regenerationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAlcoholEnantiomer
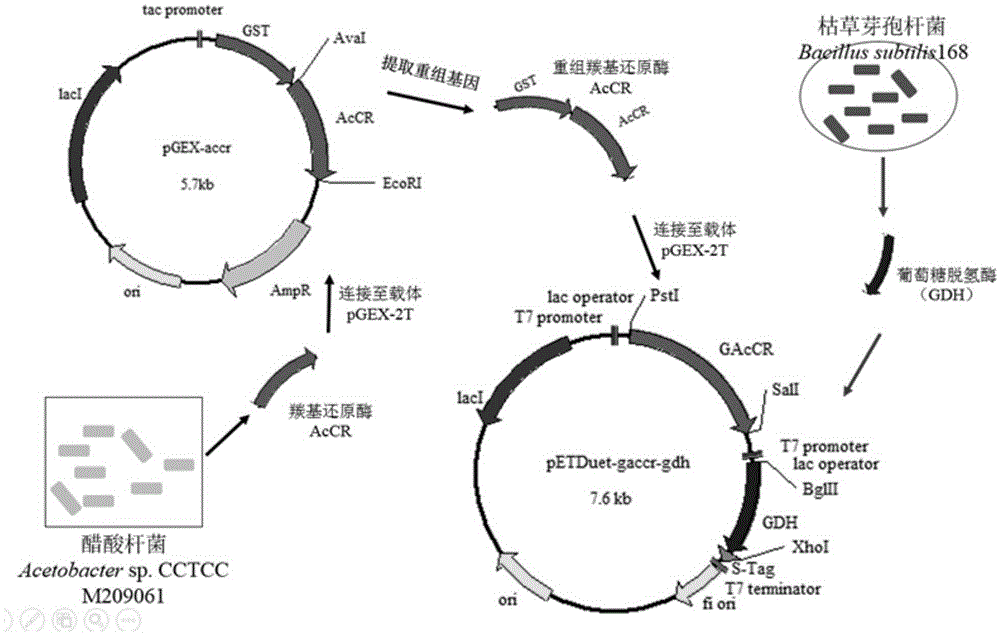
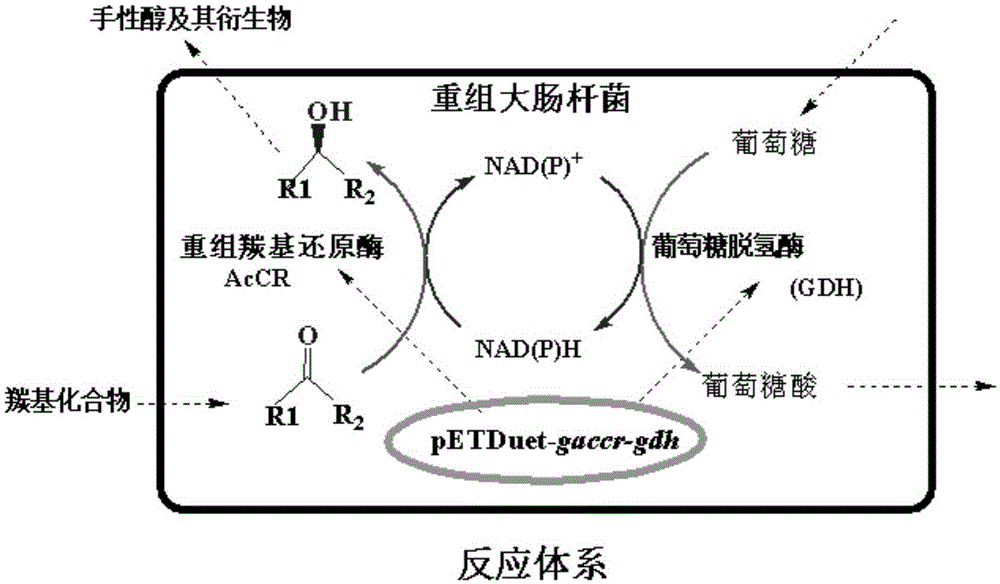
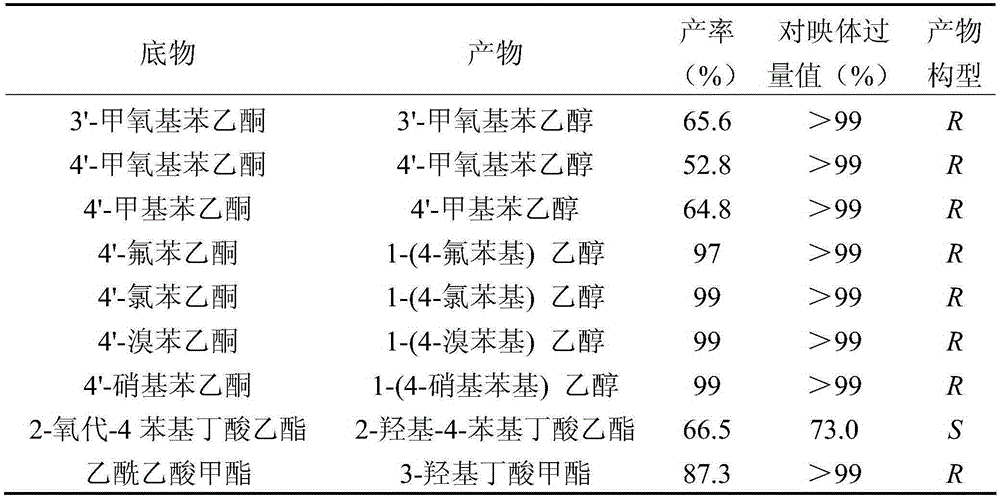
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering and particularly relates to carbonyl reductase AcCR and an encoding gene and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the carbonyl reductase AcCR is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The nucleotide sequence of the gene for encoding the carbonyl reductase AcCR is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The carbonyl reductase AcCR comes from bacillus aceticus XZY003 and can catalyze 13 carbonyl compounds to generate corresponding chiral alcohol of single enantiomers. The carbonyl reductase AcCR and glucose dehydrogenase GDH are co-expressed in a prokaryotic expression system or a eukaryotic expression system, the biological reaction process of biological catalytic conversion is conducted through the carbonyl reductase, in-situ regeneration of coenzyme is achieved, production cost is greatly reduced, the optical purity of an obtained product is high, the reaction process is efficient, and conditions are moderate.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for biological catalysis of unsymmetrical reduction carbon based compound in water/ion liquid diphasic system
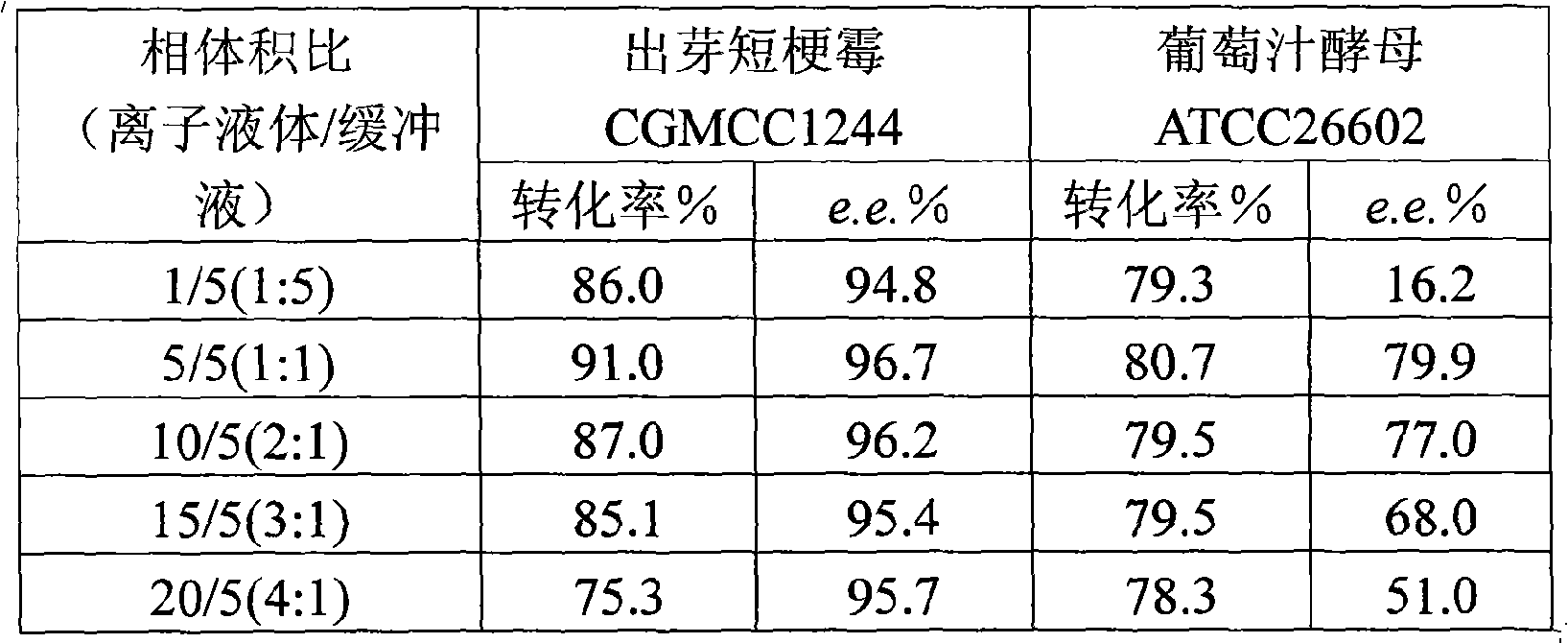
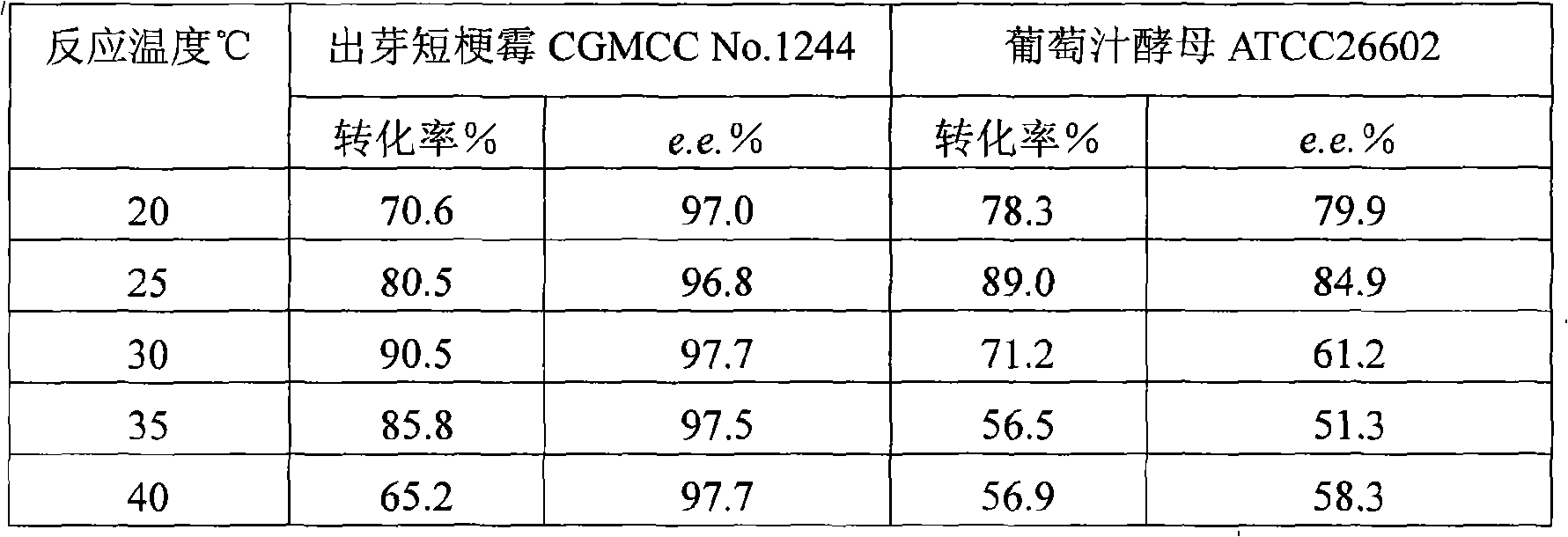
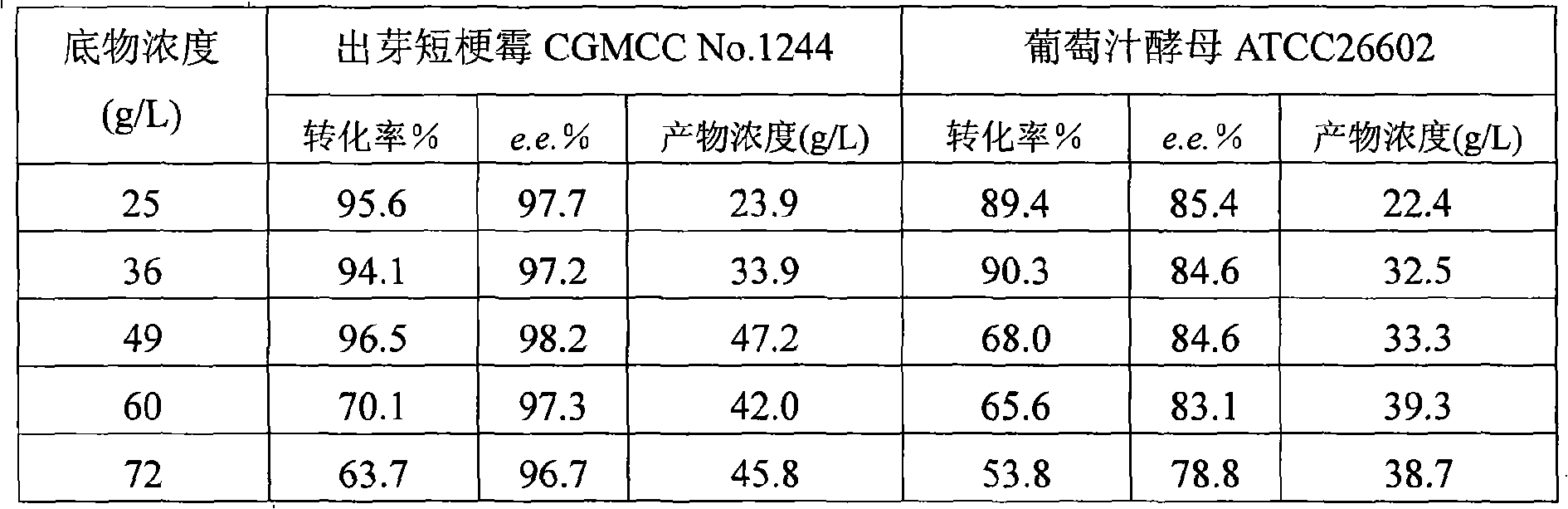
InactiveCN101319236AEasy to separateEasy to recycleMicroorganism based processesFermentationHydroxybutyric acidBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a method for asymmetrically reducing a carbonyl compound by biocatalysis in a water / ion liquid biphasic system, which belongs to the biochemical engineering technical field. The method takes a selective strain producing carbonyl reductase as a starting strain, and prochiral ketone as a substrate to perform reducing preparation of corresponding chiral alcohol in the water / ion liquid biphasic system; the method comprises the following steps that: Aureobasidium pullulans CGMCC No.1244 is used to catalyze 4-chloro-acetoacetic acid ethyl ester to perform the asymmetrical reduction preparation of (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyric acid ethyl ester, and Saccharoinyces uvarum ATCC 26602 is used to catalyze 4,4,4-trifluoroacetoacetate to perform the asymmetrical reduction preparation of (R)-4, 4, 4-trilfluoro-3-hydroxybutyrate. The method shows the advantages of no toxicity, no smell, difficult volatilization, good biocompatibility, no environmental pollution, simple product separation, easy recovery, repeated use and so on, of ion liquid. At the same time, the method improves the transformation rate, the concentration and an enantiomeric excess value of a reaction product, and quickens the process of the reaction.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Carbonyl reductase mutant, vector, engineering bacterium and application thereof
ActiveCN107586763AGood catalytic activityGood prospects for application developmentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesXyloseKetone
The invention provides a carbonyl reductase mutant, a recombinant expression vector, a genetically engineered bacterium, a method for preparing the mutant, and the application of the mutant in preparing an optically pure chiral alcohol by asymmetric reduction of a series of prochiral ketones. A catalyst is easy to prepare, reaction conditions are mild, substrate adaptability is wide, environmentalfriendliness is high, recombinant cells can efficiently catalyze the asymmetric reduction of the high-concentration prochiral ketones in a reaction system containing dimethyl sulfoxide and xylose without addition of any coenzymes, and the produced chiral alcohol with high optical purity (ee larger than or equal to 99%) has good industrial application prospects.
Owner:杭州馨海生物科技有限公司
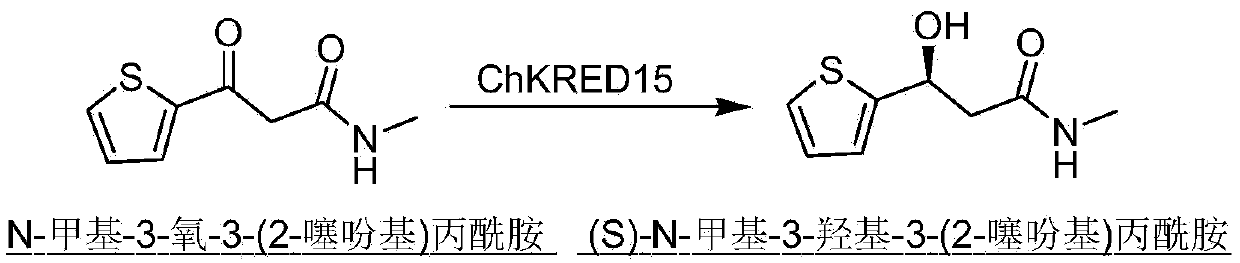
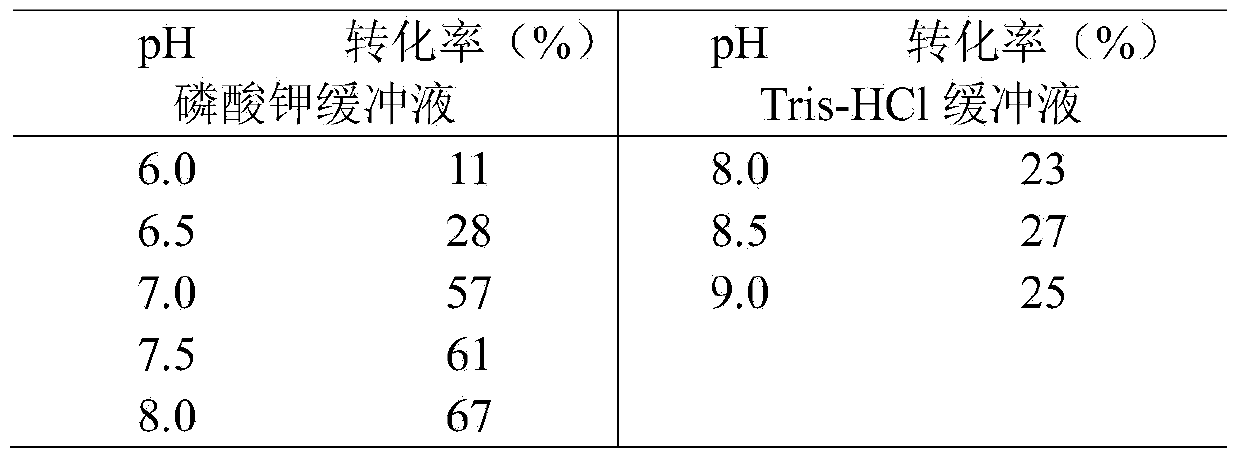
Carbonyl reductase, gene thereof, and application thereof in preparing Duloxetine chiral intermediates
The invention discloses a carbonyl reductase (i)Ch ( / i) KRED15 derived from Chryseobacterium ((i) Chryseobacterium ( / i) (i) ( / i) sp. CA49), and a coding gene thereof; the invention also discloses application of the carbonyl reductase as a biocatalyst in preparing a Duloxetine chiral intermediate ((i) S ( / i))-N-methyl-3-hydroxy-3-(2-thienyl) propanamide. The enantiomer excess of products is greater than 99.9%. 20 g / L of substrate can be catalyzed by Ch( / i) KRED15 crude enzyme (2U / mL), and the conversion rate of over 99% can be obtained in 2 hours; a coenzyme circulation system is simple, and has large industrial application prospect.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Carbonyl reductase mutant as well as coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN108624605AHigh catalytic efficiencyHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAlcoholPhenylbutyrate
The invention discloses a carbonyl reductase mutant as well as a coding gene and application thereof. A carbonyl reductase mutant gene has a sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 1; an amino acid sequence of acarbonyl reductase mutant coded by the carbonyl reductase mutant gene is shown as SEQ ID NO. 2. A genetically engineered bacterium for producing carbonyl reductase contains the carbonyl reductase gene provided by the invention. A preparation method of the carbonyl reductase comprises the following step: culturing the genetically engineered bacterium for producing the carbonyl reductase to obtainthe carbonyl reductase through recombinant expression. The carbonyl reductase prepared by the recombinant expression is used as catalyst, and optical active chiral alcohol is prepared through an asymmetric reducing carbonyl compound; preparation of the recombinant carbonyl reductase is realized, and the recombinant carbonyl reductase is used for asymmetrically synthesizing and catalyzing (R)-2-hydroxyl-4-ethyl phenylbutyrate. The substrate conversion rate reaches 96.8 percent and the ee of a reduction product is greater than 99 percent.
Owner:宿迁阿尔法科技有限公司
Method For Producing Alcohol and Carboxylic Acid Having Optical Activity
InactiveUS20080233621A1High optical purityProduced inexpensively and efficientlyOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsCarboxylic acidMethyl group
It is an object of the present invention to provide an inexpensive and efficient industrial method for obtaining (S)-2-pentanol, (S)-2-hexanol, 1-methylalkyl malonic acid and 3-methyl carboxylic acid at a high optical purity. The present invention provides a method of producing (S)-2-pentanol or (S)-2-hexanol which comprises allowing certain types of microorganisms or transformed cells, a product obtained by treating said microorganisms or cells, a culture solution of said microorganisms or cells, and / or a crude purified product or purified product of a carbonyl reductase fraction obtained from said microorganisms or cells, to act on 2-pentanone or 2-hexanone.
Owner:API CORP (JP)
Method for improving transformation efficiency of (S)-phenyl glycol by coupling glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and (S)-carbonyl reductase
The invention relates to a method for improving the transformation efficiency of (S)-phenyl glycol by coupling glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and (S)-carbonyl reductase, belonging to the technical field of biological catalytic asymmetric transformation. The invention provides the method for preparing the (S)-phenyl glycol by recombinant Pichia pastoris with CGMCCNo.4198 and 2-hydroxyacetophenone catalyzed by the recombinant Pichia pastoris with CGMCCNo.4198 in multiple batches. In the invention, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene and the Candida parapsilosis (S)-carbonyl reductase gene are simultaneously integrated into the Pichia pastoris genome, under the participation of 5% (w / v) glucose, the whole cells are reused for 10 batches, and the optical purity and yield of the (S)-phenyl glycol prepared by asymmetric transformation are maintained at 100% and higher than 85% all the time. The recombinant strain improves the batch stability of full cell transformation of the (S)-phenyl glycol by polygene coexpression, which well relieves the limit of coenzyme regenerative cycle in a biological transformation reaction; and simultaneously an efficient approach for preparing the (S)-phenyl glycol industrially in multiple batches at low cost is provided.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
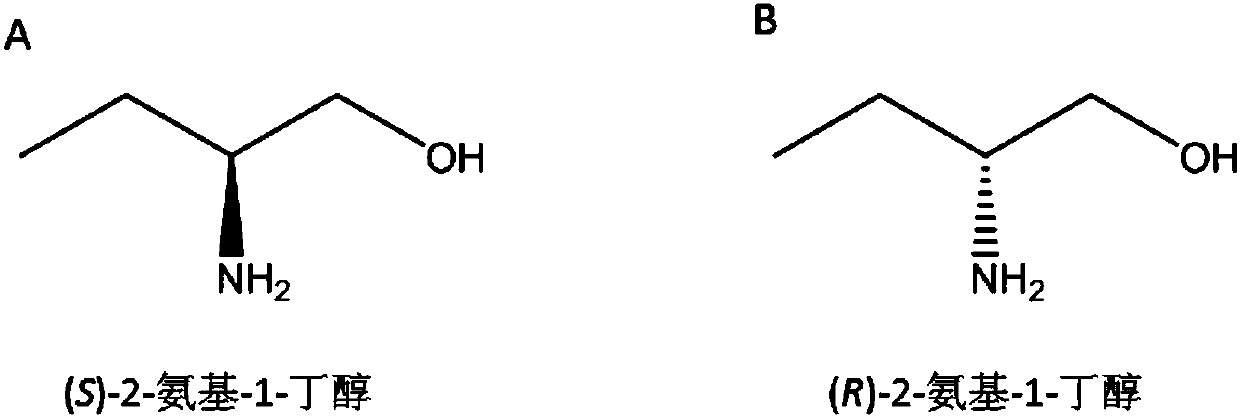
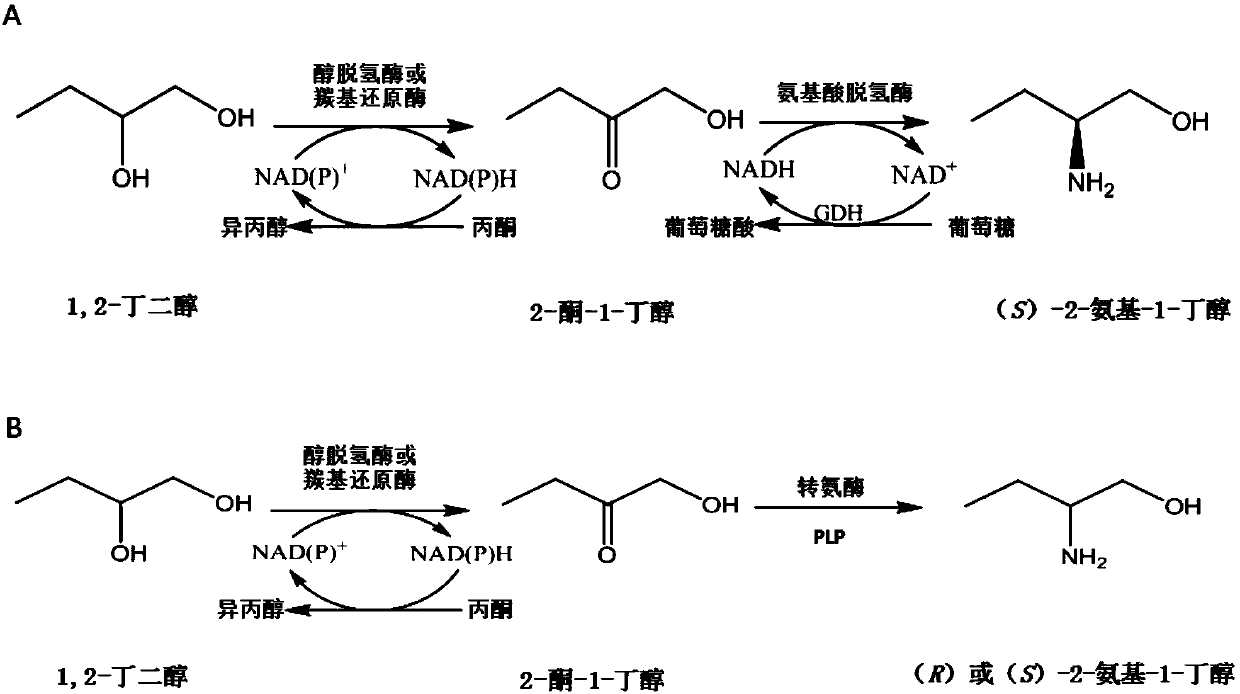
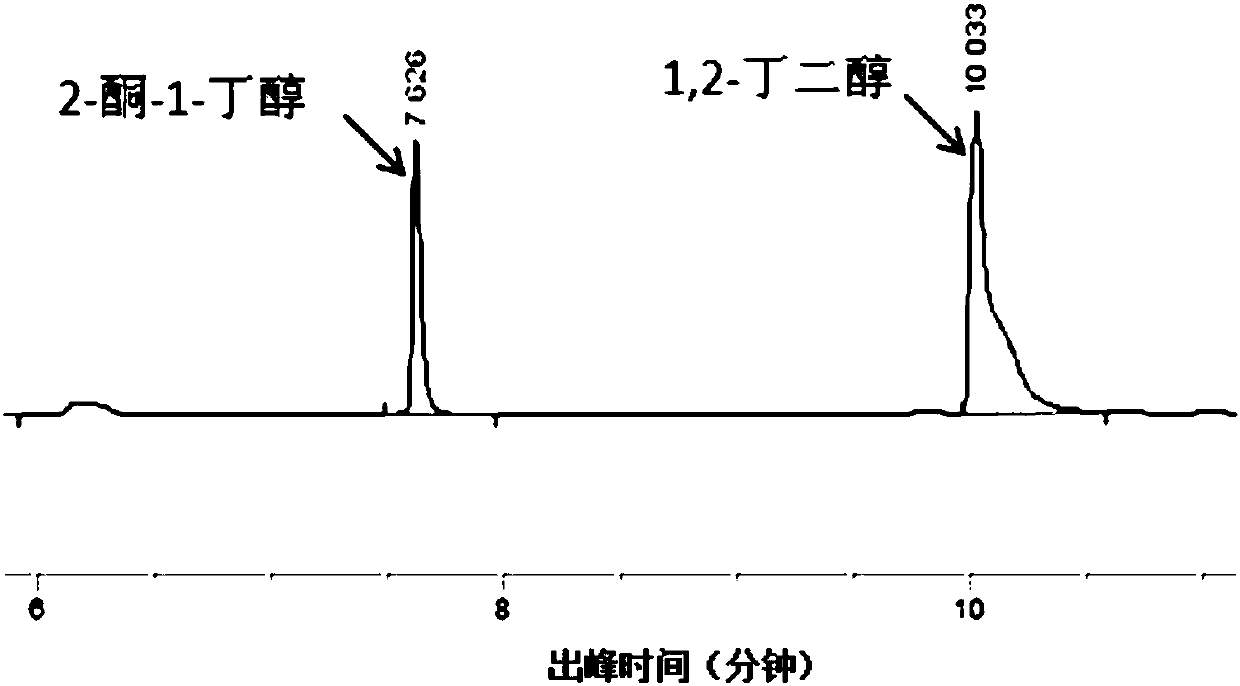
Method for synthesizing chiral 2-amino-1-butanol
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing chiral 2-amino-1-butanol. The method comprises the following steps: 1,2-butanediol is used as a substrate and is catalyzed by enzyme A and coenzyme thereof to generate 2-ketone-1-butanol; the 2-ketone-1-butanol serves as a substrate, and the 2-amino-1-butanol is generated through catalytic reaction of enzyme B and coenzyme thereof. The enzyme A isselected from alcohol dehydrogenase, carbonyl reductase or mutants of the two enzymes; the enzyme B is selected from amino acid dehydrogenases, transaminases or mutants of the two enzymes. The invention provides a brand-new green biosynthesis route. The cheap 1,2-butanediol is used as a raw material, and the chiral 2-amino-1-butanol is synthesized through multi-enzyme co-expression or cascade or step-by-step catalysis, namely (S)-2-amino-1-butanol and (R)-2-amino-1-butanol.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for preparing (R)-phenylglycol from SD-AS sequence coupled (R)-carbonyl reductase and glucose dehydrogenase
InactiveCN104830744AHigh optical purityHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRecombinant escherichia coli
The invention discloses a method for preparing (R)-phenylglycol from SD-AS sequence coupled (R)-carbonyl reductase and glucose dehydrogenase and belongs to the technical field of biological catalytic asymmetric transformation. The invention provides recombinant escherichia coli E. coli RIL / pET-R-SD-AS-G. The recombinant escherichia coli E. coli RIL / pET-R-SD-AS-G is preserved in the China center for type culture collection (CCTCC) and has a preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2015170. R-carbonyl reductase and glucose dehydrogenase are coupled by a coexpression way, and the coupled enzyme, a cultured recombinant strain and 2-hydroxyacetophenone as a substrate undergo a catalytic asymmetric transformation reaction under optimized biotransformation reaction conditions to produce (R)-phenylglycol with optical purity of 100% and a yield of 99.9%. The method utilizes a SD-AS sequence high efficiency coupling double-enzyme technology, solves the problem of limitation of chiral catalytic reaction coenzyme regeneration cycle and provides an effective approach for high efficiency bio-preparation of the (R)-phenylglycol.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Novel Carbonyl Reductase, Gene Therefor and Use Thereof
The present invention is to provide a process for efficiently producing an optically active alcohol including (R)-3-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanenitrile. One of the features of the present invention is a polypeptide having an activity of asymmetrically reducing 3-oxo-3-phenylpropanenitrile isolated from a microorganism belonging to the genus Candida to produce (R)-3-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanenitrile, DNA encoding the polypeptide and a transformant of producing the polypeptide. Another feature of the present invention is a process for producing an optically active alcohol such as (R)-3-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanenitrile by reducing a carbonyl compound such as 3-oxo-3-phenylpropanenitrile by use of the polypeptide or the transformant.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Recombinant carbonyl reductase ReCR, encoding gene, vector, engineering bacterium and application thereof
InactiveCN105671014AStereoselective specificityHigh optical purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAmino acidHigh concentration
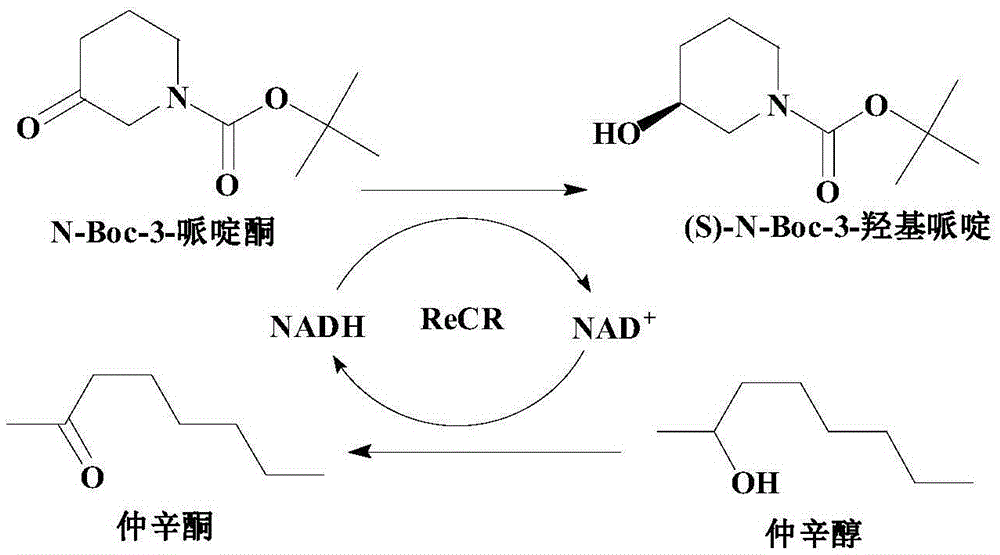
The invention discloses a recombinant carbonyl reductase ReCR, a coding gene, a carrier, an engineering bacterium and its application in the biological enzymatic preparation of (S)-N-Boc-3-piperidinol. The recombinant carbonyl reductase ReCR The amino acid sequence of the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2; the method of the present invention uses the recombinant carbonyl reductase ReCR of high activity, stereoselective specificity, and irreversible reduction of N-Boc-3-piperidone as a biocatalyst, so that The reaction balance is beneficial to the formation of (S)-N-Boc-3-piperidinol, and the product has high optical purity; using 2-octanol as the cosubstrate, the efficient cycle of coenzyme is realized; using 2-octanol as the organic phase to construct two The phase catalysis system, combined with the whole cell catalysis method, greatly reduces the inhibition of enzyme activity by high-concentration substrates, by-substrates and products. The applicable substrate concentration is as high as 200g / L, and the reaction time is <12h. The product (S)-N The yield of -Boc-3-piperidinol was 94.17%, and the e.e. value of the product was >99%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Process for Production of Optically Active Alcohol
The present invention provides methods for producing (S)-1,1,1-trifluoro-2-propanol, which include the step of reacting an enzyme of any one of alcohol dehydrogenase CpSADH, alcohol dehydrogenase ReSADH, carbonyl reductase ScoPAR, (2S,3S)-butanediol dehydrogenase ZraSBDH, carbonyl reductase ScGCY1, tropinone reductase HnTR1, tropinone reductase DsTR1, or alcohol dehydrogenase BstADHT, a microorganism or a transformant strain that functionally expresses the enzyme, or a processed material thereof, with 1,1,1-trifluoroacetone. The present invention also provides methods for producing (R)-1,1,1-trifluoro-2-propanol, which include the step of reacting alcohol dehydrogenase PfODH, a microorganism or a transformant strain that functionally expresses the enzyme, or a processed material thereof, with 1,1,1-trifluoroacetone.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Carbonyl reductase, gene thereof and use of the same
The present invention provides a novel polypeptide forming (R)-2-chloro-1-(3′-chlorophenyl)ethanol, a polynucleotide coding for said polypeptide, and use of the same.The present invention relates to a polypeptide having the following physical and chemical properties (1) to (4):(1) activity: acting on 2-chloro-1-(3′-chlorophenyl)ethanone with NADPH or NADH as a coenzyme, to form (R)-2-chloro-1-(31-chlorophenyl)ethanol;(2) optimum pH for activity: 5.0 to 6.0;(3) optimum temperature for activity: 40° C. to 50° C.;(4) molecular weight: about 40,000 as determined by gel filtration analysis, about 30,000 as determined by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis. The present invention also relates to a polypeptide comprising the amino acid sequence shown under SEQ ID NO:1 in the sequence listing, a polynucleotide coding for said polypeptide, and a transformant producing said polypeptide at high levels.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Modified carbonyl reducing enzyme and gene
An object of the present invention is to modify a wild-type enzyme that is less reactive in the presence of an organic solvent to provide altered carbonyl reductases having better reactivity in the presence of the organic solvent than the wild-type enzyme, and / or to provide transformants producing such reductases. The present inventors have found altered carbonyl reductases having better reactivity in the presence of an organic solvent than the wild-type enzyme, from among a mutant enzyme library prepared by randomly mutating the wild-type enzyme gene, thereby arriving at completion of the present invention.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
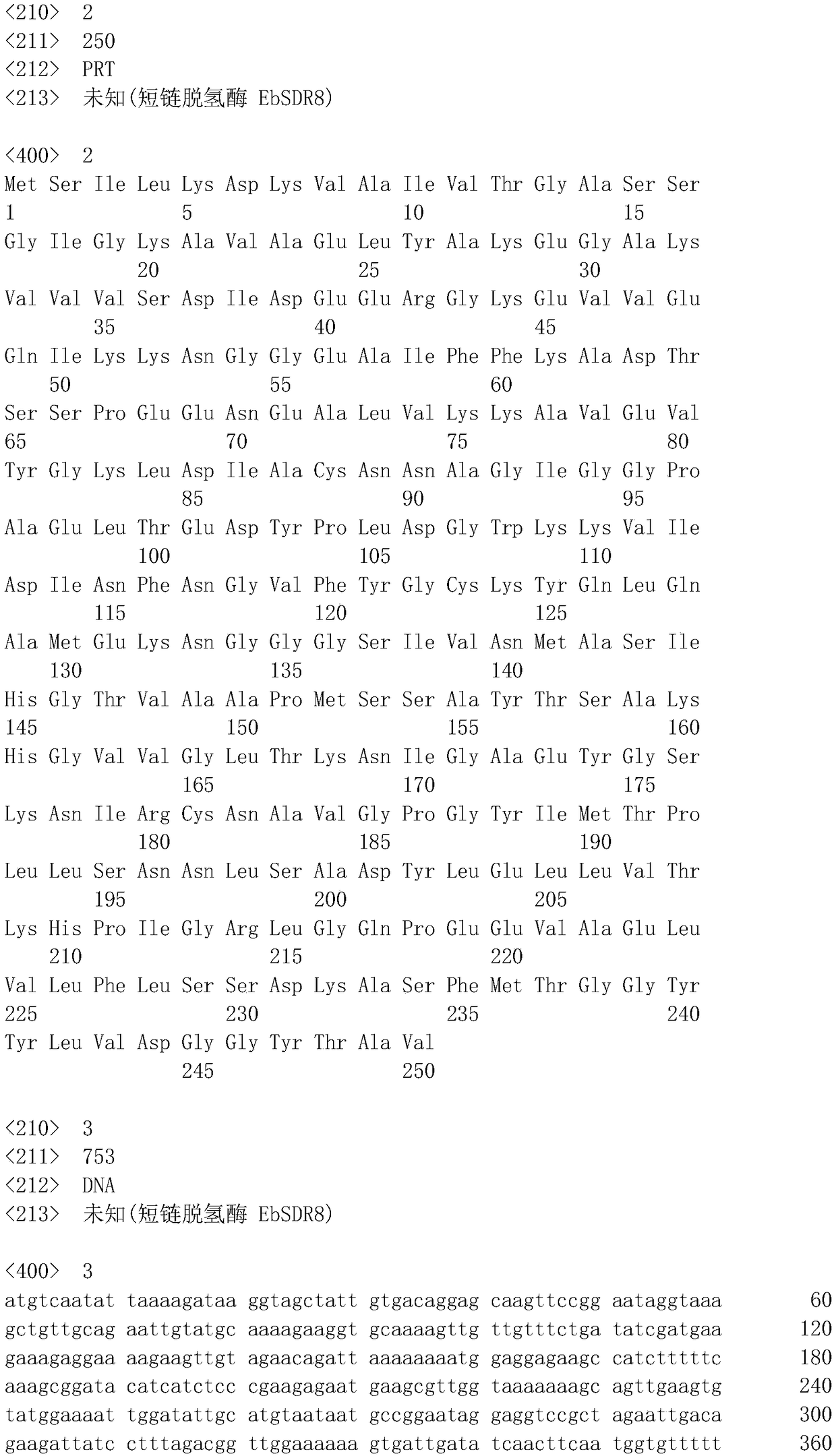
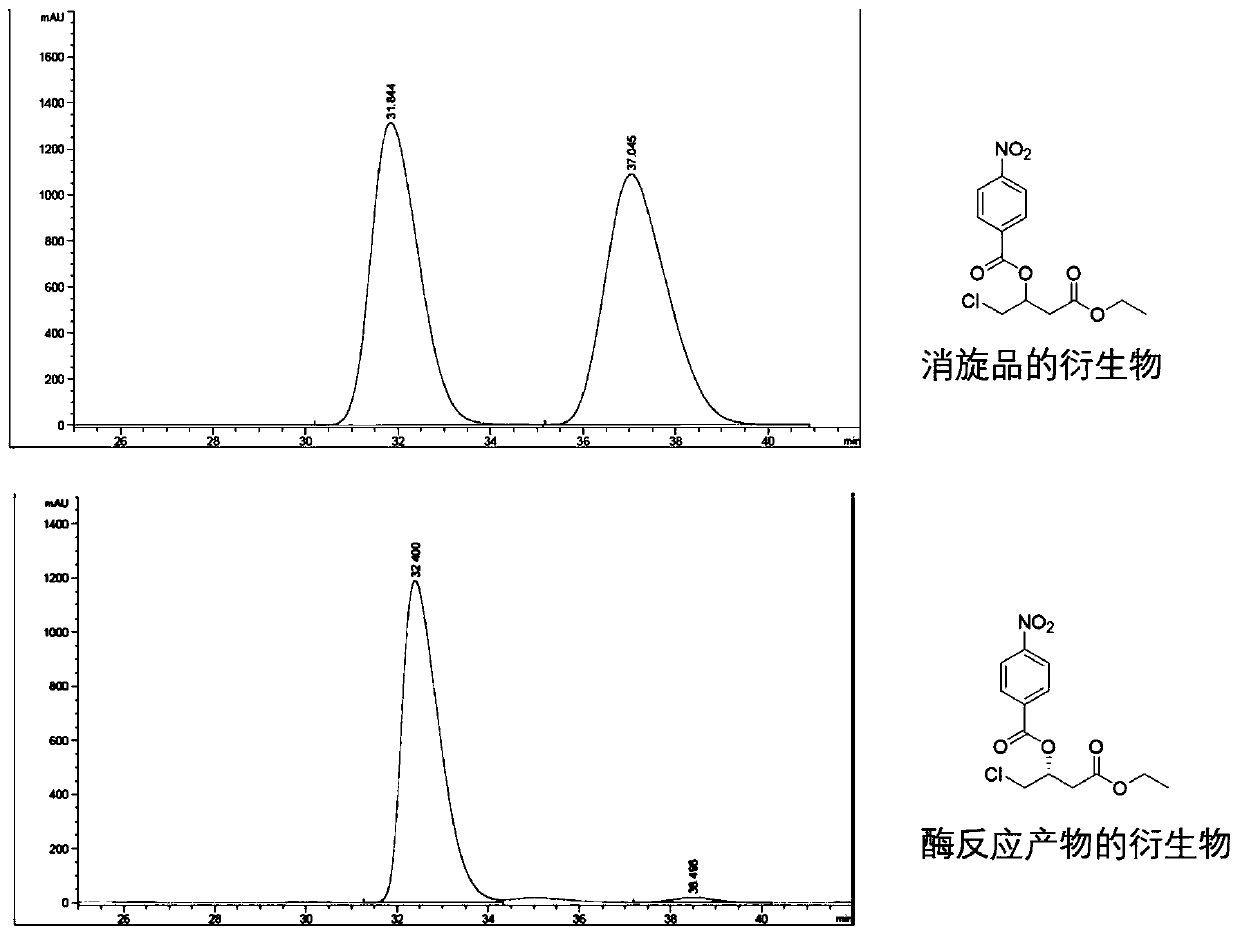
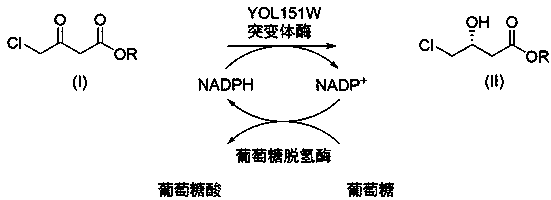
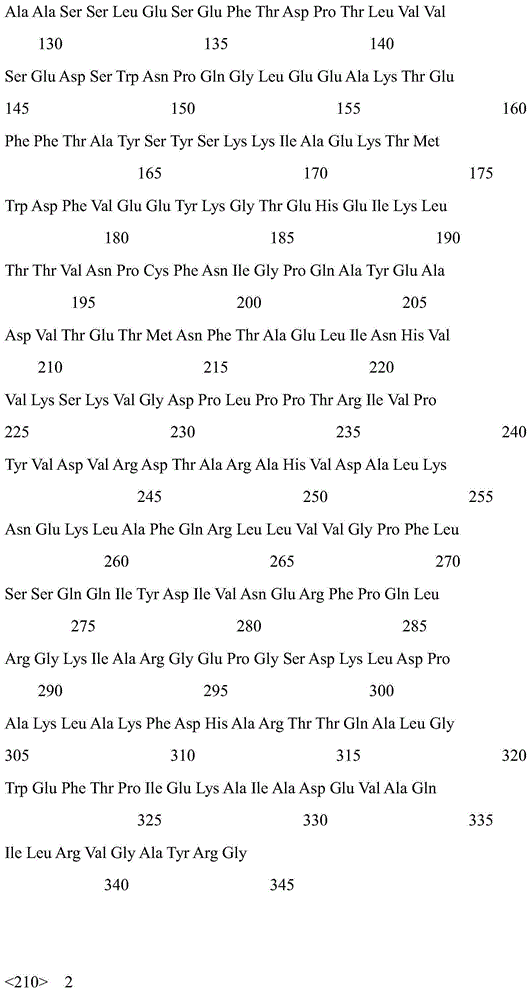
Carbonyl reductase EbSDR8 mutant as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN109468291AHigh catalytic activityHigh activityMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesTert-leucineGlutamic acid
The invention discloses a carbonyl reductase EbSDR8 mutant as well as a construction method and application thereof, wherein the amino acid sequence of carbonyl reductase EbSDR8, as shown in SEQ ID NO.2, has single-point mutation or two-point combination mutation in 97th-site alanine or 160th-site lysine, wherein the 97th-site alanine is mutated to leucine and the amino acid sequence of the leucine is as shown in SEQ ID NO.4; the 160th-site lysine is mutated to glutamic acid and the amino acid sequence of the glutamic acid is as shown in SEQ ID NO.6. The invention aims at providing the carbonyl reductase EbSDR8 mutant as well as the construction method and application thereof, and the catalytic activity of the carbonyl reductase EbSDR8 is improved.
Owner:杭州馨海生物科技有限公司
Carbonyl reductase mutant and application thereof in preparation of (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy-butyrate
ActiveCN111172124AHigh substrate concentrationHigh stereoselectivityBacteriaOxidoreductasesCarbonyl ReductaseBio engineering
The invention belongs to the technical fields of biological pharmacy and biological engineering, and particularly relates to a carbonyl reductase mutant and application thereof in preparation of (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy-butyrate. The carbonyl reductase mutant disclosed by the invention is obtained by replacing phenylalanine at the 85th site of a sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2 with methionine, or is obtained by replacing one or more sites except the 85th site with amino acid residues on the basis that phenylalanine at the 85th site of the sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2 is replaced with methionine.The invention also relates to a recombinant expression vector containing the carbonyl reductase mutant gene, an engineering bacterium containing the carbonyl reductase mutant gene and a glucose dehydrogenase gene, and application of the genetic engineering bacterium in preparation of (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy-butyrate by asymmetric reduction of chloroacetoacetate. Compared with a wild enzyme, the carbonyl reductase mutant disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the reducing capability on chloroacetoacetate is obviously improved and the carbonyl reductase mutant has good industrial application prospect.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Fusion protein CR2-Linker-GDH and application thereof
InactiveCN104450637AHigh yieldHigh Complete ConversionsBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDrug biotransformationGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a fusion protein CR2-Linker-GDH and the application of the fusion protein CR2-Linker-GDH, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and biological catalysis. Fusion expression is carried out on carbonyl reductase and glucose dehydrogenase to achieve coupling between the two enzymes, and a separated and purified fusion protein in a successfully constructed recombinant bacteria package is utilized to carry out biotransformation COBE to obtain S-CHBE. By optimizing reaction conditions, a substrate of the fusion protein can be totally converted, the optical purity of a product is above 99%, and the TTN reaches up to 1200. The final concentration of the substrate is 305 mmol / L through a substrate batch replenishing strategy, the yield of the product reaches up to 53%, the product of 162 mmol / L is obtained, and the e.e. value remains above 99%. The fusion protein CR2-Linker-GDH and the application of the fusion protein CR2-Linker-GDH provide a novel research thought for coupling a coenzyme regeneration cycle approach into a biotransformation approach of the S-CHBE and have great significance for simplifying the a chiral transformed way.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Application of Chryseobacterium sp. and carbonyl reductase thereof in production of aprepitant chiral intermediate
ActiveCN103497911BHigh recovery rateEasy to separate and purifyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGenomeEthanol
The invention discloses a strain of Chryseobacterium sp. CA49 (with an accession number of CCTCC M2012484), carbonyl reductase ChKRED20 coded by the genome of the strain and preparation of an aprepitant chiral intermediate (R)-1-[3,5-di(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanol by using the original strain of Chryseobacterium sp. or the carbonyl reductase as a biocatalyst. The enantiomeric excess value of the produced intermediate is greater than 99.9%. Crude ChKRED20 enzyme powder can catalyze up to 200 g / L of a substrate and enables a conversion rate of more than 99% to be obtained in 24 h; a coenzyme circulating system is simple and cheap, the produced intermediate is easy to separate and purify, and a high recovery rate and good industrial application prospects are obtained.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Carbonyl reductase gene, codase, vector, strain and application of gene
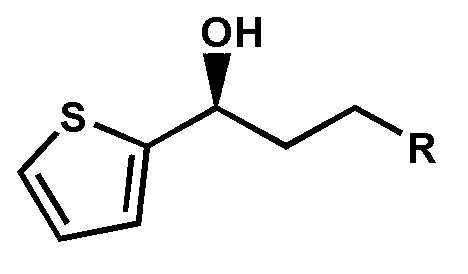
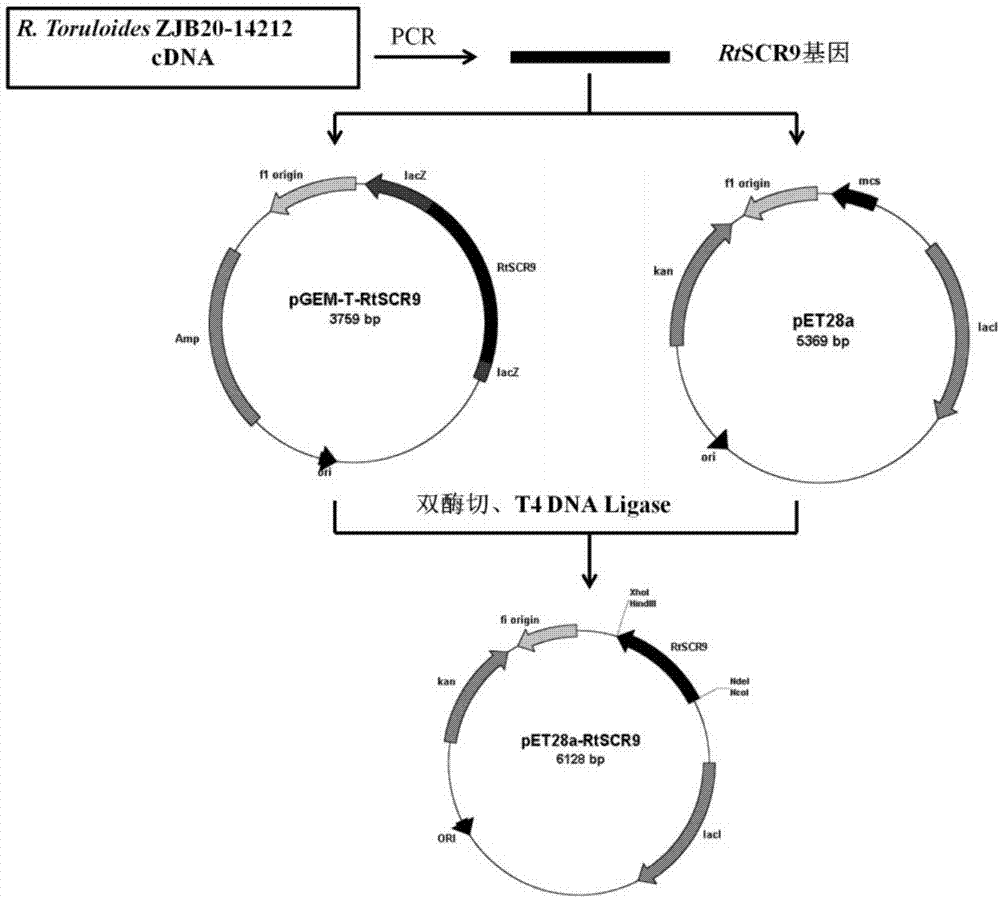
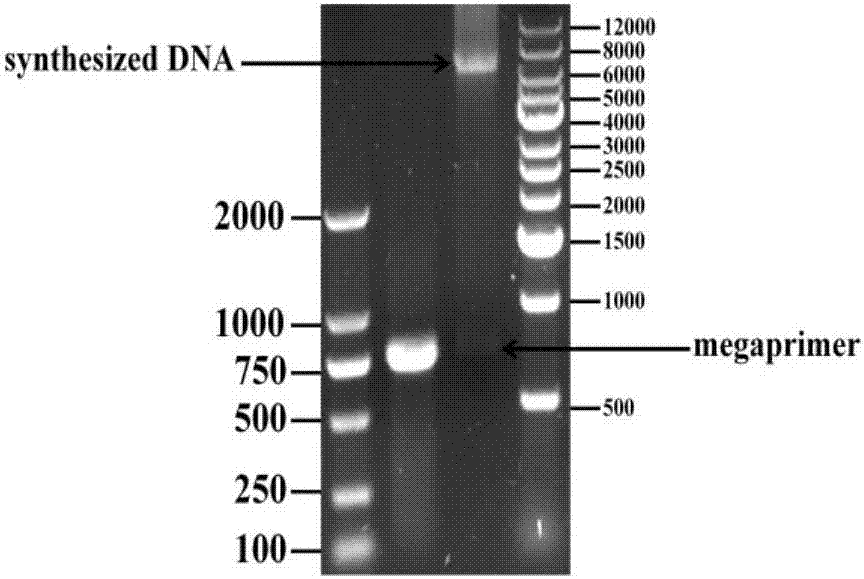
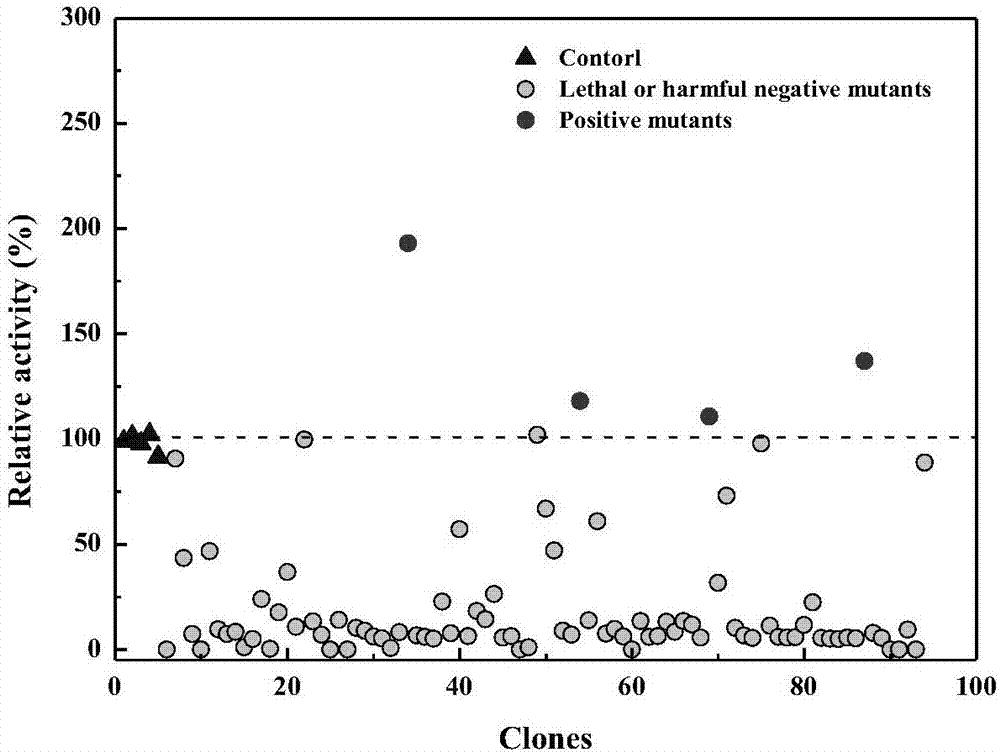
The invention discloses a carbonyl reductase derived from Rhodosporidium toruloides ZJB14212, a gene, a vector, a strain and an application of the carbonyl reductase in the preparation of chiral drug intermediates. The above carbonyl reductase can biologically catalyze preparation of highly optically pure (S)-N,N-dimethyl-3-hydroxy-3-(2-thienyl)propionamide, (S)-N-methyl-3-hydroxy-3-(2-thienyl)propionamide, (R)-3-chloro-1-(2-thienyl)1-propanol, ethyl (S)-3-hydroxy-3-(2-thienyl)propanoate, (S)-3-hydroxy-3-(2-thienyl)propionitrile, tert-butyl 6-chloro-(3R,5S)-dihydroxyhexanoate, (4S)-3-[(5S)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-hydroxyvaleryl]-4-phenyl-1,3-oxazolidine-2-one and methyl [S-(E)]-2-[3-[3-[2-(7-chloro-2-quinolyl)vinyl]phenyl]-3-hydroxypropyl]benzoate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Biscarbonyl reductase, and coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN103937759AThe synthesis steps are simpleReduce production pollutionFungiBacteriaHalogenAmino acid
The invention discloses a biscarbonyl reductase, and a coding gene and application thereof. The biscarbonyl reductase has one of the following amino acid sequences: 1) amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ NO.1; or 2) SEQ NO.1-derived amino acid sequence subjected to substitution, and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acids with the function of stereoselectively reducing the formula disclosed in the specification into the formula disclosed in the specification, wherein the SEQ NO.1-derived amino acid sequence has more than 80% of homology with SEQ NO.1.R1 is selected from aryl group, alkyl group, cycloalkyl group, alkyl-substituted aryl group, halogen-substituted aryl group, aryl alkyl heterocyclic group, and cycloheteroalkyl or cyclohetero alkylated alkyl group; and R2 is selected from alkyl group, cycloalkyl group, and haloalkyl group or halocycloalkyl group. The biscarbonyl reductase can reduce a diketone substrate in one step to obtain 3R,5S-dihydroxy compounds with single optical purity.
Owner:ASYMCHEM LAB TIANJIN +5
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com