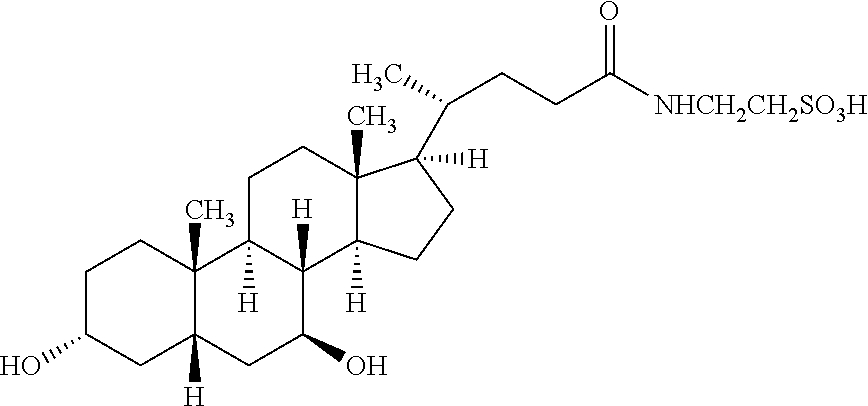
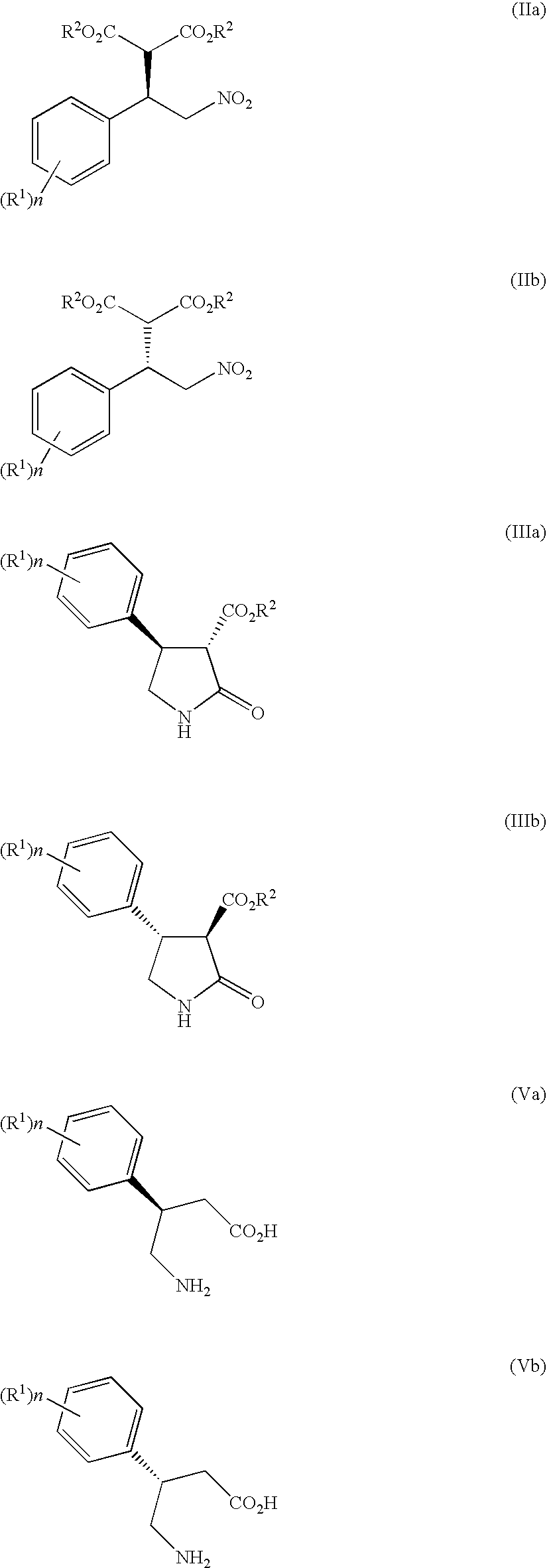
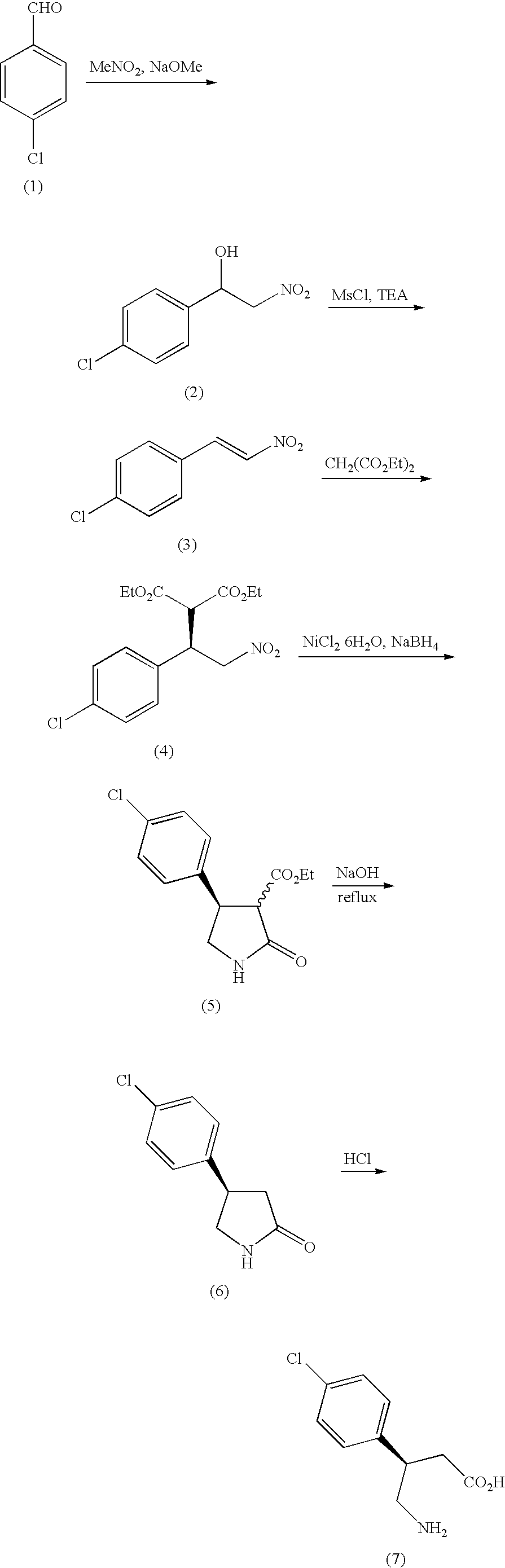
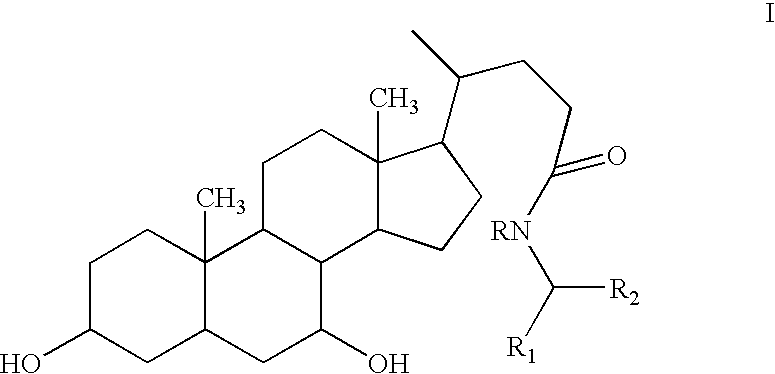
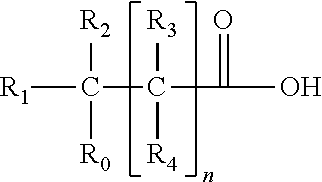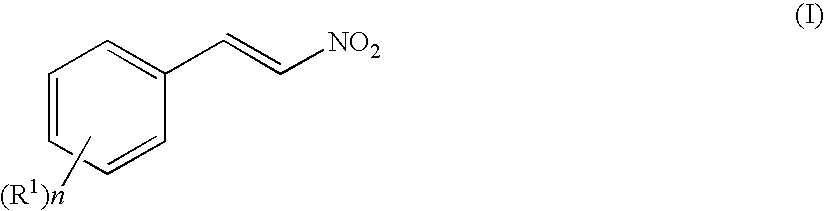Patents
Literature
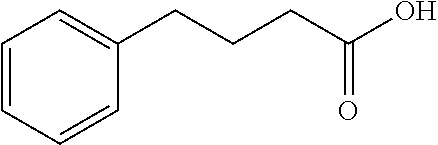
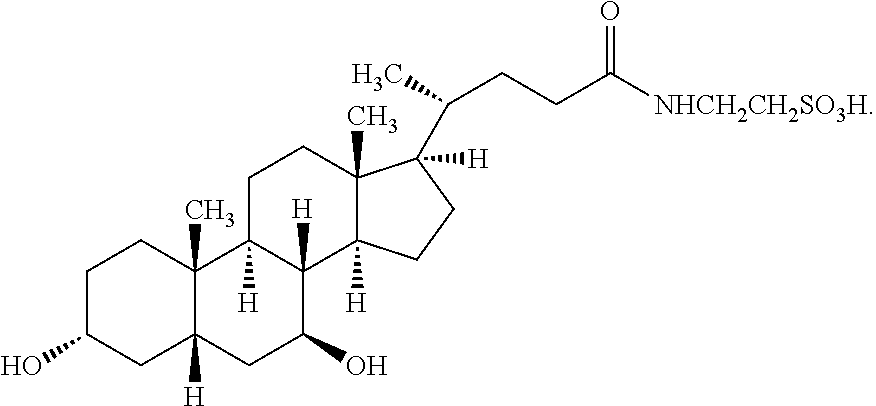
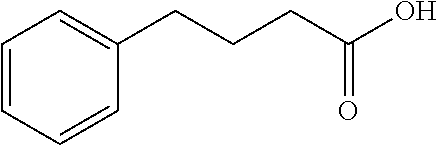
153 results about "Phenylbutyrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An orally active derivative of the short-chain fatty acid butyrate with potential antineoplastic activity. 4-Phenylbutyrate inhibits histone deacetylase, resulting in cell cycle gene expression modulation, reduced cell proliferation, increased cell differentiation, and apoptosis. This agent also initiates fragmentation of genomic DNA, resulting in decreased DNA synthesis and the inhibition of tumor cell migration and invasion. Check for http://www.cancer.gov/Search/ClinicalTrialsLink.aspx?id=41827&idtype=1 active clinical trials or http://www.cancer.gov/Search/ClinicalTrialsLink.aspx?id=41827&idtype=1&closed=1 closed clinical trials using this agent. (http://nciterms.nci.nih.gov:80/NCIBrowser/ConceptReport.jsp?dictionary=NCI_Thesaurus&code=C1440 NCI Thesaurus)
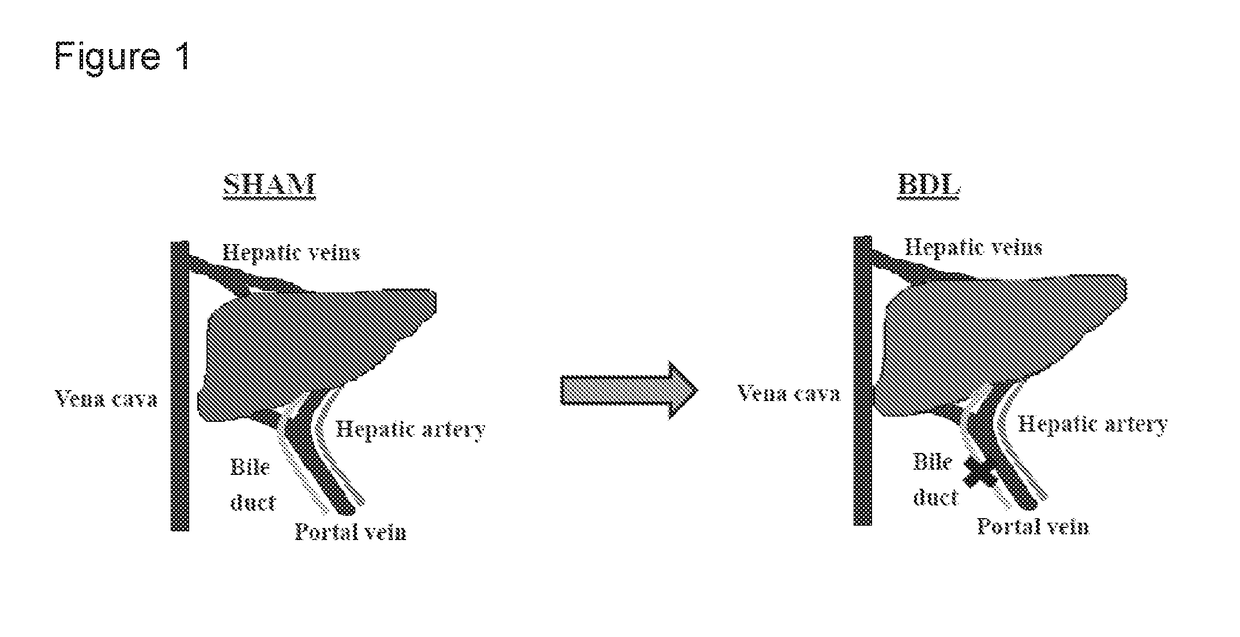
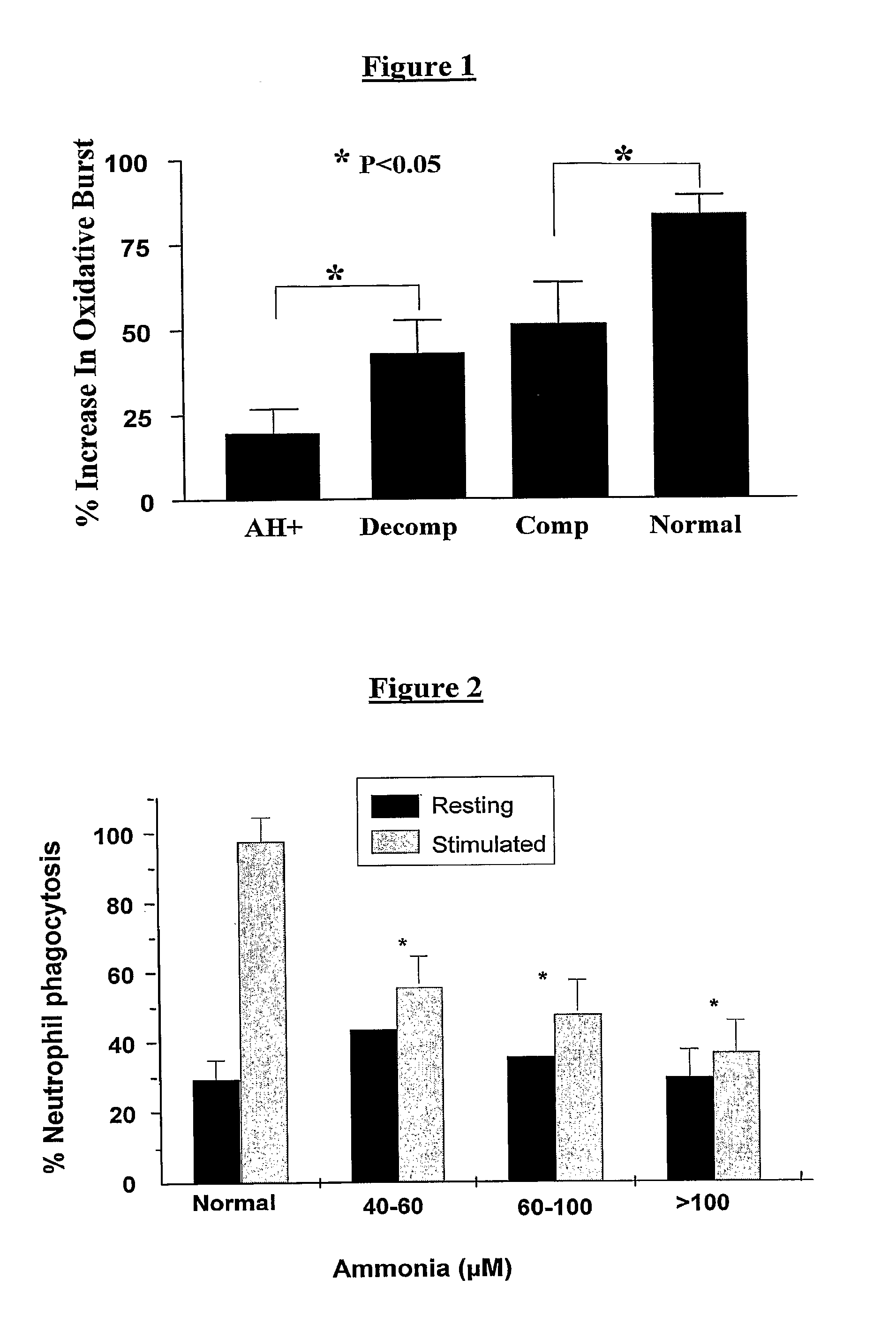
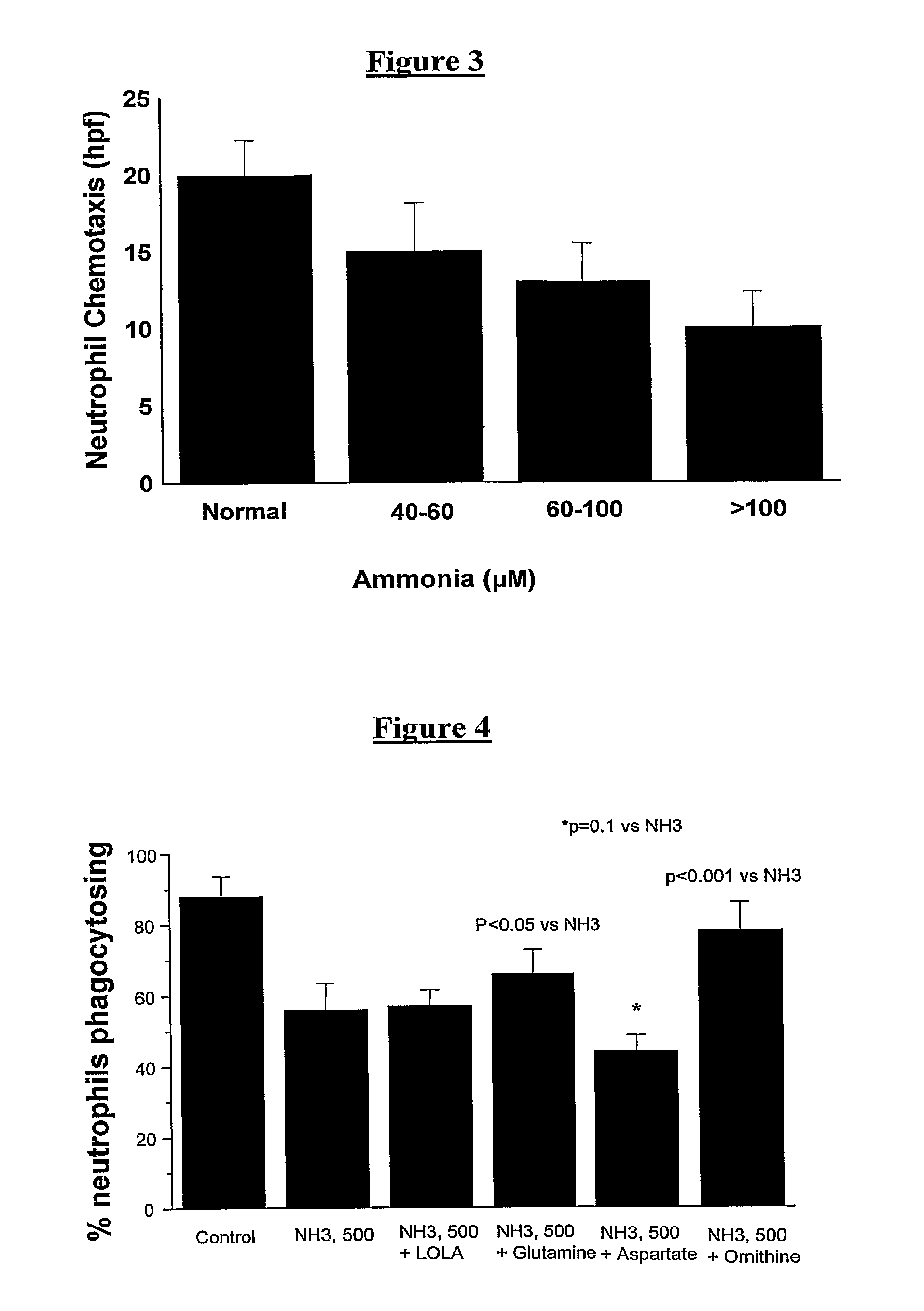
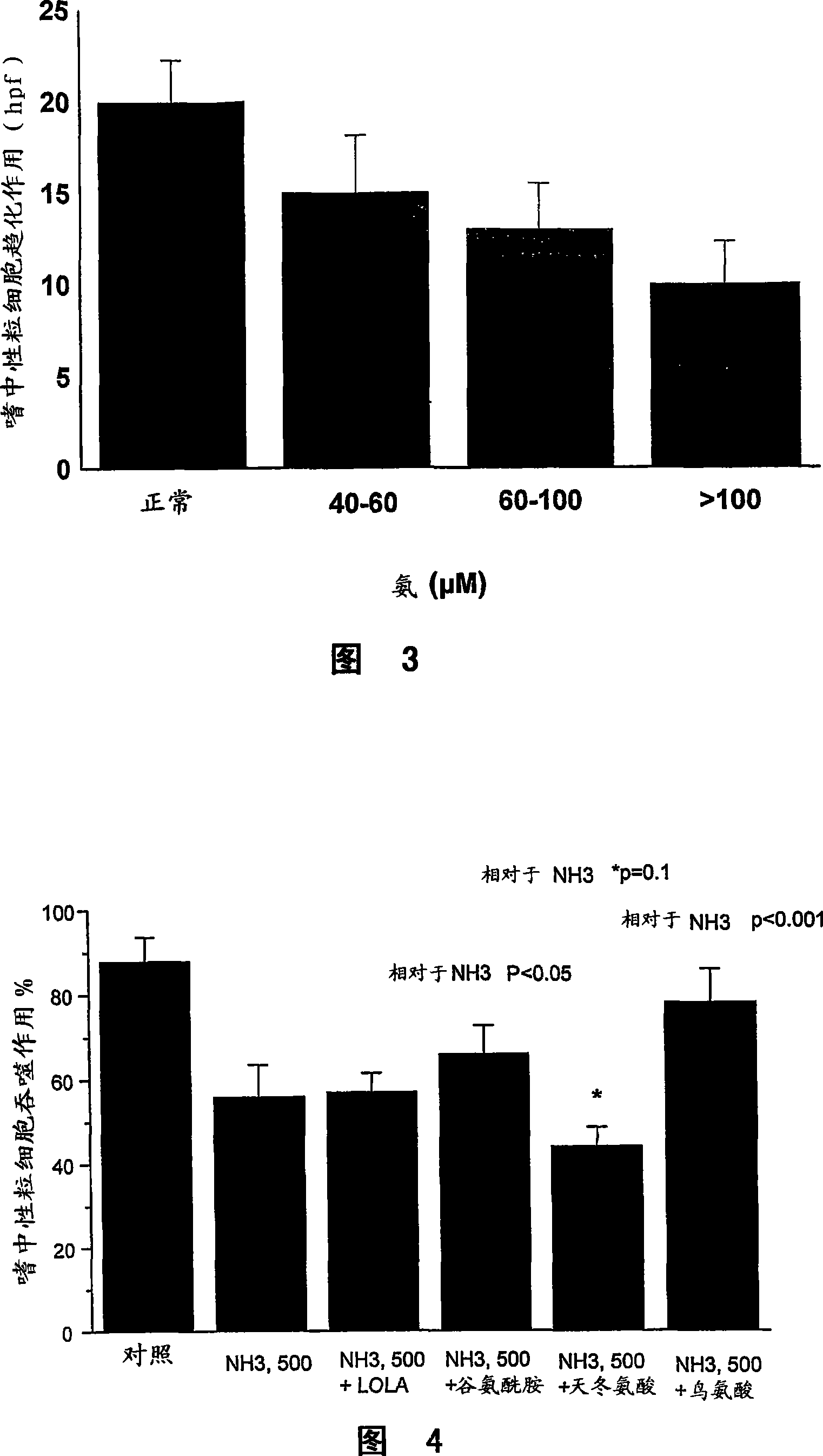
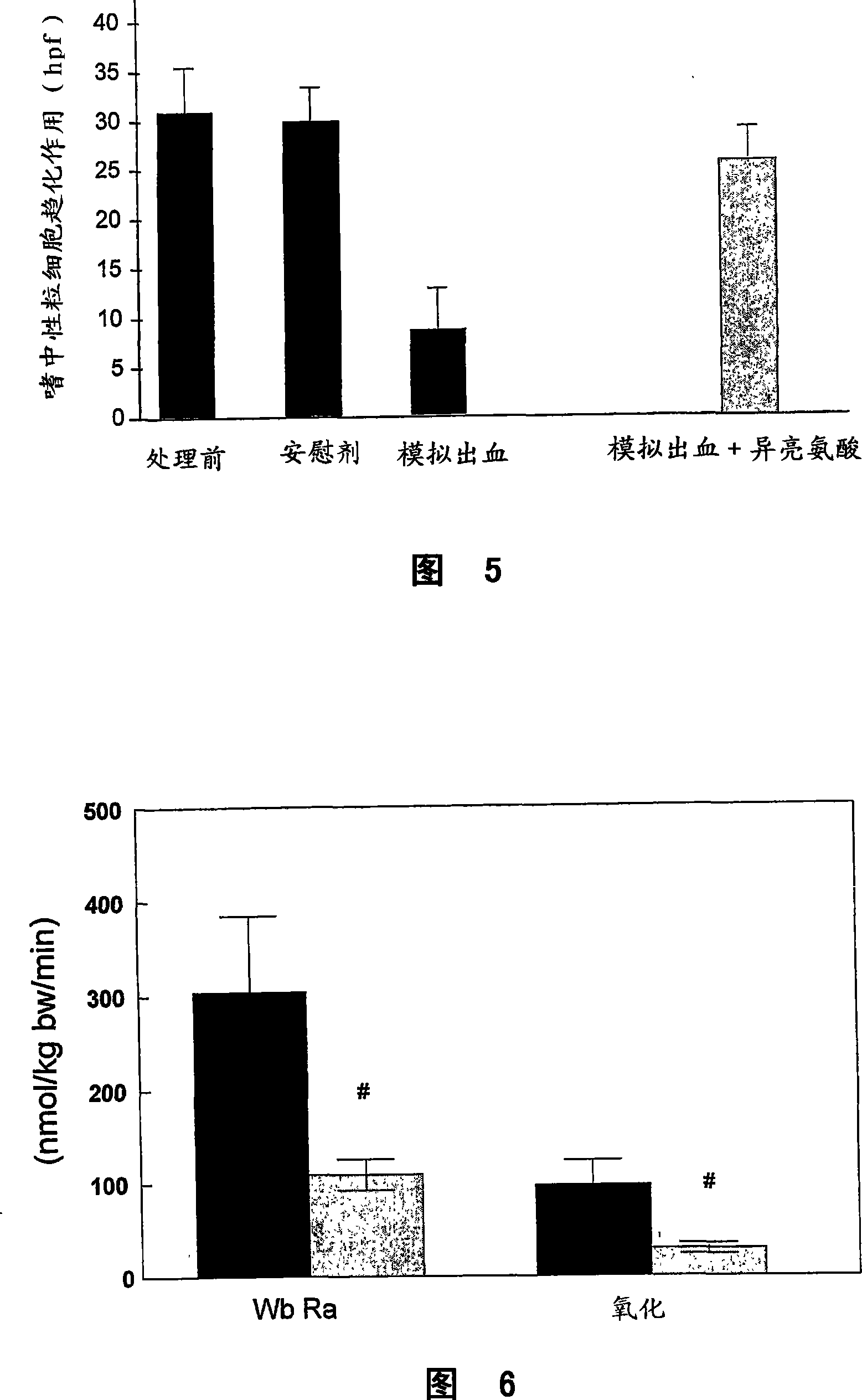
Compositions Comprising Ornithine And Phenylacetate Or Phenylbutyrate For Treating Hepatic Encephalopathy
ActiveUS20080119554A1Avoid treatmentAntibacterial agentsBiocideOrnithine aspartateLiver decompensation
The present invention relates to use of ornithine in the manufacture of a medicament for use in combination with at least one of phenylacetate and phenylbutyrate for preventing or treating liver decompensation or hepatic encephalopathy. The invention also relates to use of at least one of phenylacetate and phenylbutyrate in the manufacture of a medicament for use in combination with ornithine for preventing or treating liver decompensation or hepatic encephalopathy.
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
4-phenylbutyric acid controlled-release formulations for therapeutic use
InactiveUS20060045912A1Low costReduce the amount requiredBiocideNervous disorderHalf-lifeNeuro-degenerative disease
Controlled-release formulations and dosage forms containing 4-phenylbutyric acid sodium salt, or other pharmaceutically acceptable salts, esters or prodrugs, and a controlled release material for use in the treatment of diseases and disorders including neoplastic disorders and neurodegenerative diseases The formulations provide extended release and extended half-life.
Owner:LUNAMED
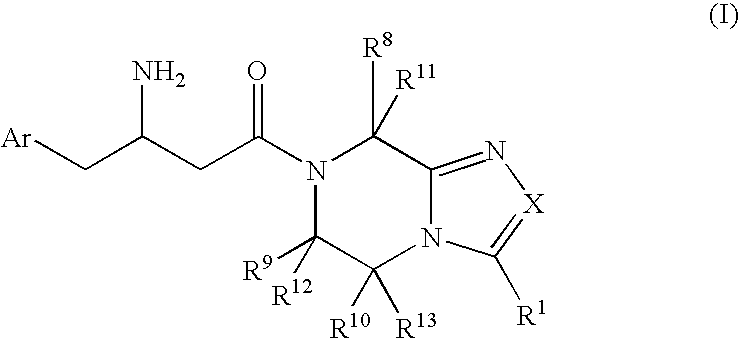
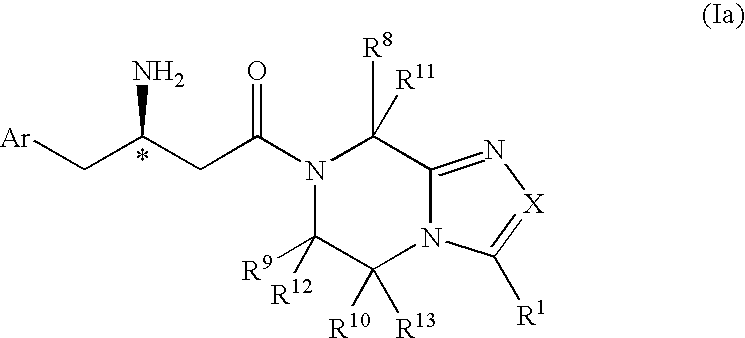
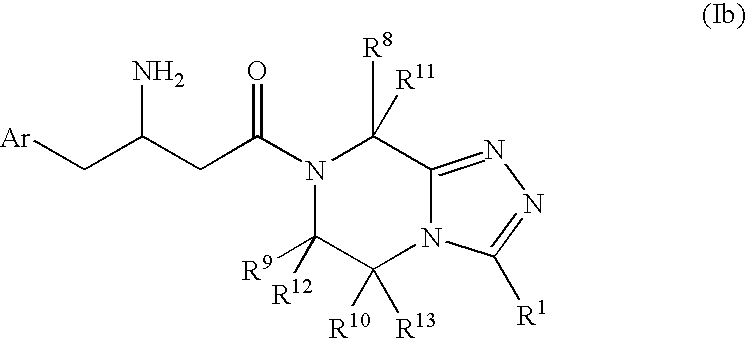
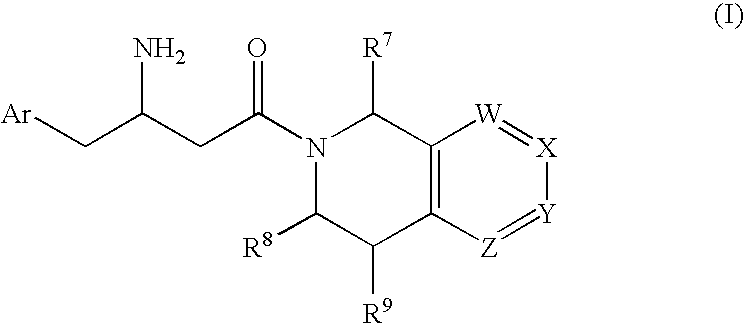
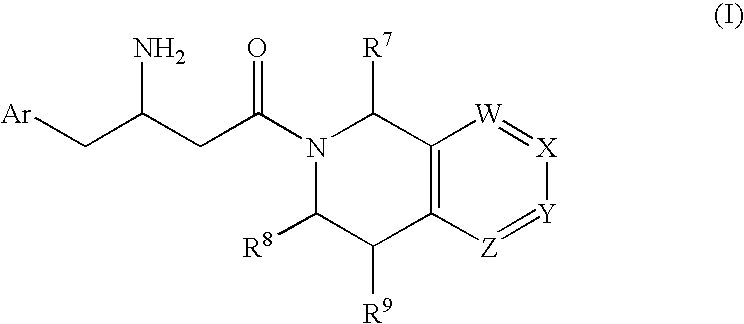
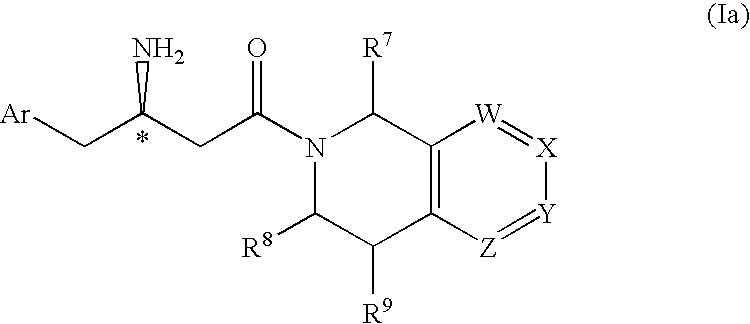
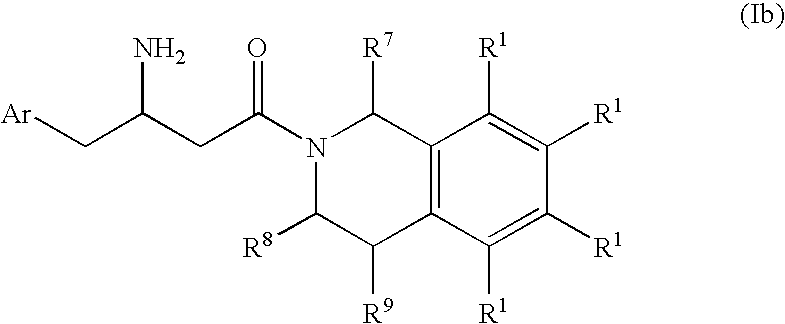
3-Amino-4-phenylbutanoic acid derivatives as dipeptidyl peptidase inhibitors for the treatment or prevention of diabetes
The present invention is directed to 3-amino-4-phenylbutanoic acid derivatives which are inhibitors of the dipeptidyl peptidase-IV enzyme (“DP-IV inhibitors”) and which are useful in the treatment or prevention of diseases in which the dipeptidyl peptidase-IV enzyme is involved, such as diabetes and particularly type 2 diabetes. The invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising these compounds and the use of these compounds and compositions in the prevention or treatment of such diseases in which the dipeptidyl peptidase-IV enzyme is involved.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
3-Amino-4-phenylbutanoic acid derivatives as dipeptidyl peptidase inhibitors for the treatment or prevention of diabetes
The present invention is directed to 3-amino-4-phenylbutanoic acid derivatives which are inhibitors of the dipeptidyl peptidase-IV enzyme (“DP-IV inhibitors”) and which are useful in the treatment or prevention of diseases in which the dipeptidyl peptidase-IV enzyme is involved, such as diabetes and particularly type 2 diabetes. The invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising these compounds and the use of these compounds and compositions in the prevention or treatment of such diseases in which the dipeptidyl peptidase-IV enzyme is involved.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
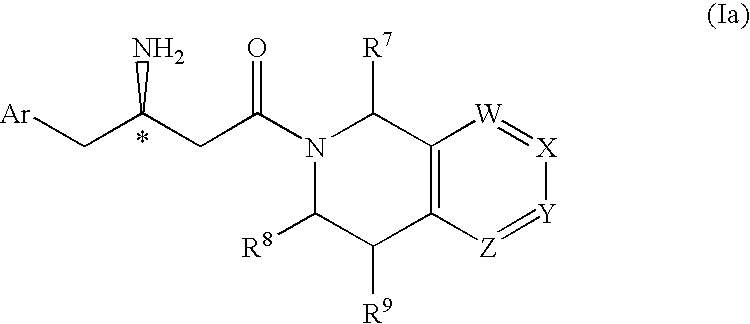
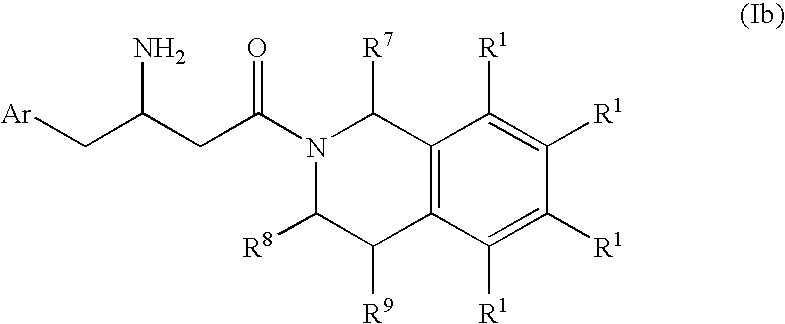
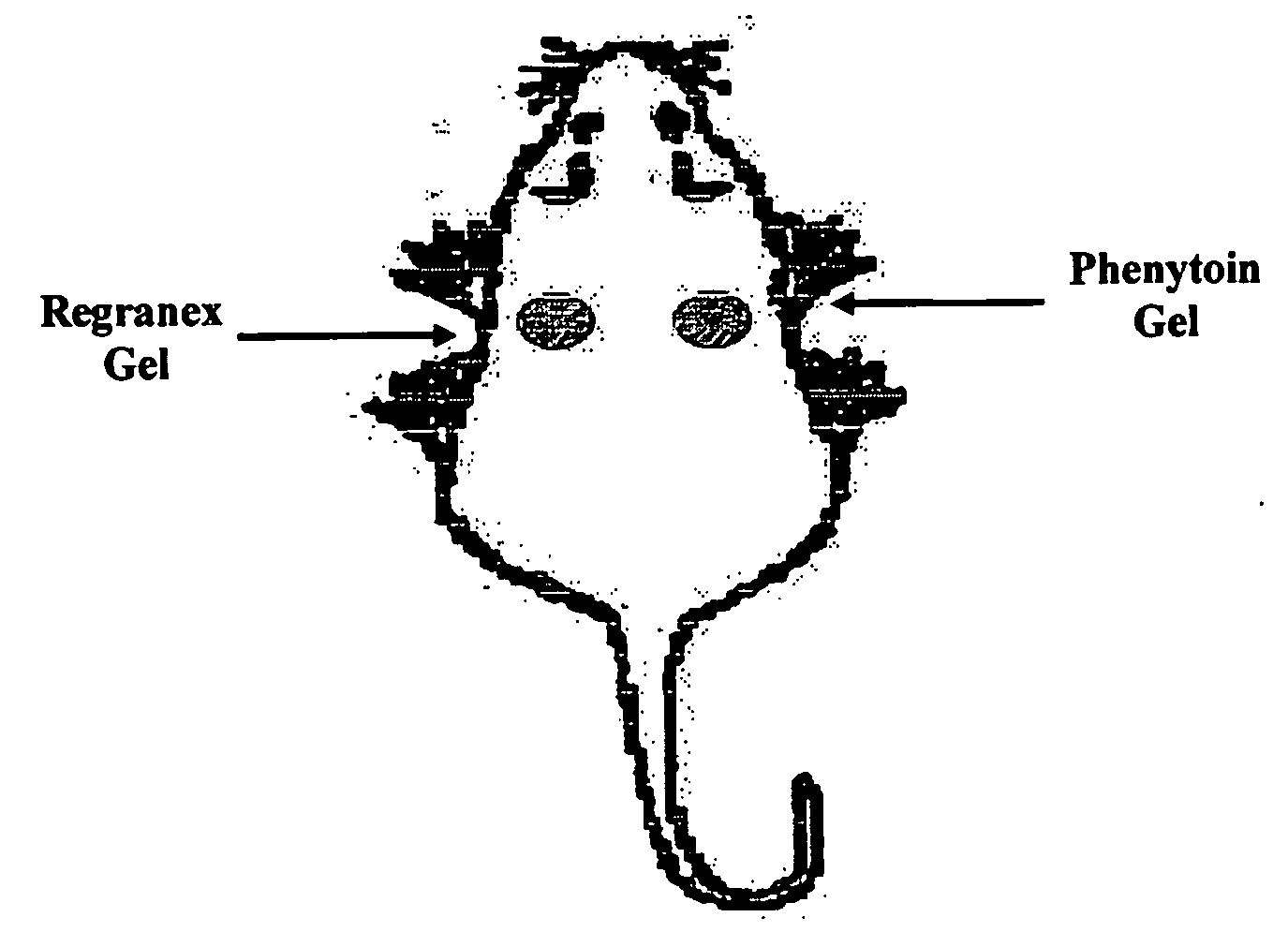
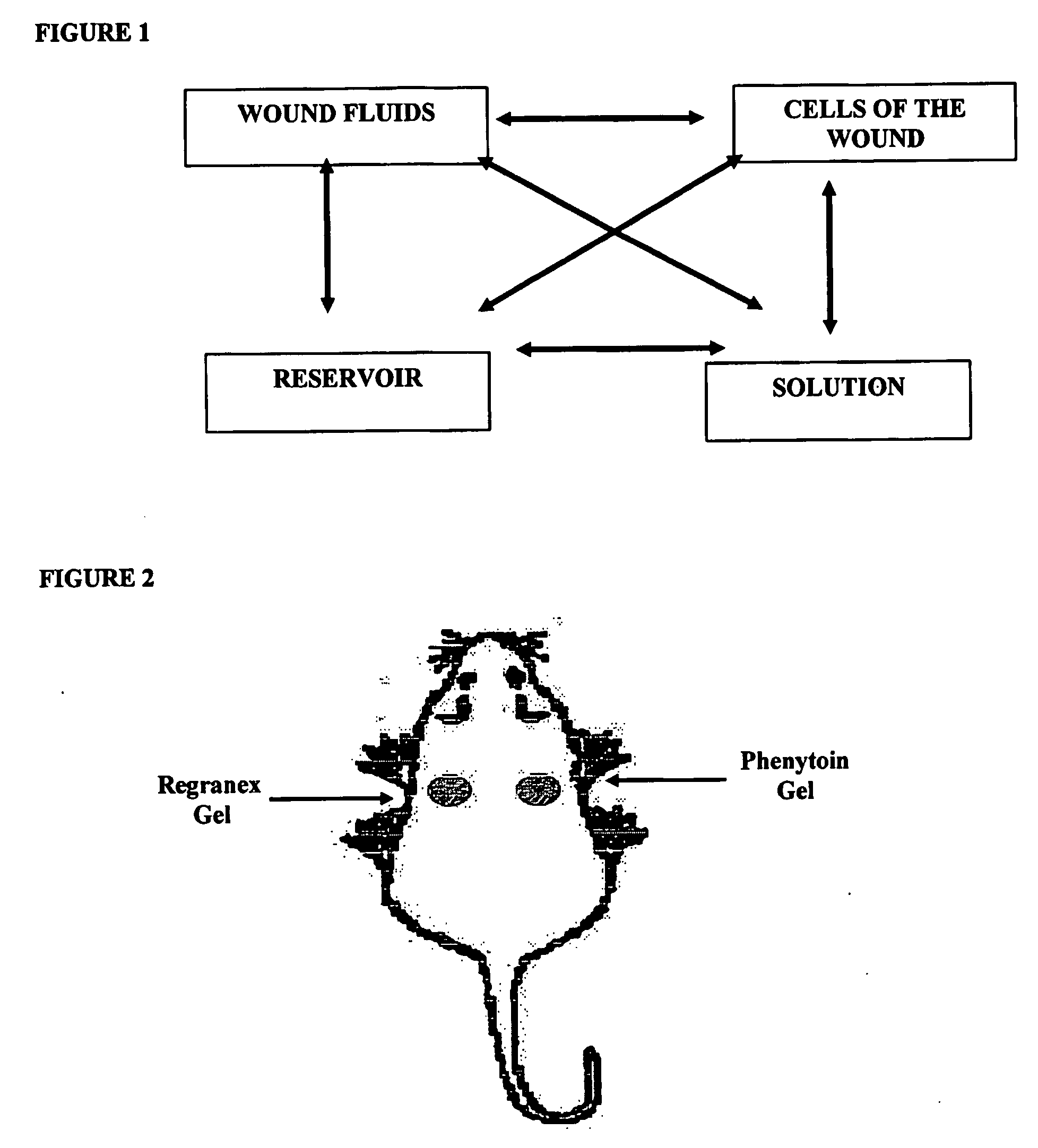
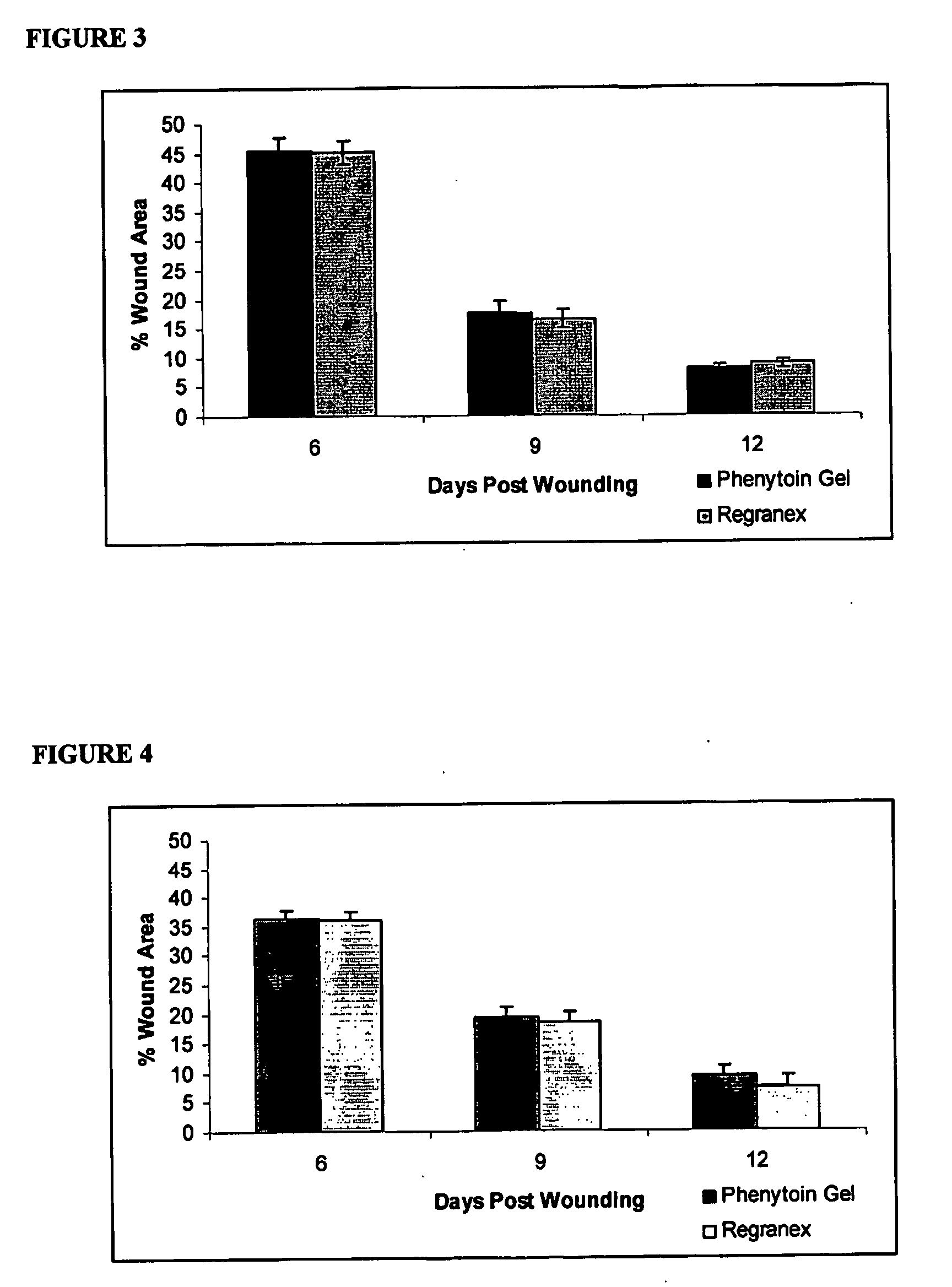
Phenytoin Formulations, and Uses Thereof in Wound Healing
InactiveUS20090022779A1Promote wound healingCut woundOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryWound healingPhenylbutyrate
A formulation of phenyloin suitable for topical application to a wound comprises a reservoir of phenyloin entrapped within a stabilising matrix, and an amount of dissolved phenyloin, wherein the dissolved phenyloin is in chemical equilibrium with the phenyloin entrapped within the stabilised matrix. The stabilised matrix may comprise a gel matrix, especially a gel matrix in which the polymer of the gel forms ion-pairs with the phenyloin. Also described are methods of treating a wound in diabetic and non-diabetic patients using a formulation according to the invention.
Owner:ROYAL COLLEGE OF SURGEONS & IRELAND
Method for ameliorating pruritus
Owner:SUNNY PHARMTECH +1
Carbonyl reductase, gene and mutant and application thereof to asymmetrical reduced carbonyl compound
ActiveCN102618513AHigh optical purityMild reaction conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationMethyl o-chloromandelate
The invention discloses a novel carbonyl reductase, a gene, a mutant thereof, a recombinant expression vector containing the gene and the mutant, a recombinant expression transformant, a recombinase preparation method, and applications of the carbonyl reductase and recombinase to preparation of active chiral alcohols with a chiral carbonyl compound before asymmetrical reduction. The carbonyl reductase is derived from candida glabrata, is applied to preparation of a plurality of optically-active chiral alcohols such as (R)-chloromandelic acid methyl ester, (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate, (R)-4-chlorin-3-phenyl ethyl butyrate and the like. Compared with other preparation methods, a product prepared through the method has high concentration, does not require additionally or slightly adding any expensive coenzyme, has high optical purity, and has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, easiness and convenience for operating, easiness for amplifying and the like, and has a good industrial application prospect in the production of clopidogrel, L-carnitine and perindopril antihypertensive medicinal intermediates.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
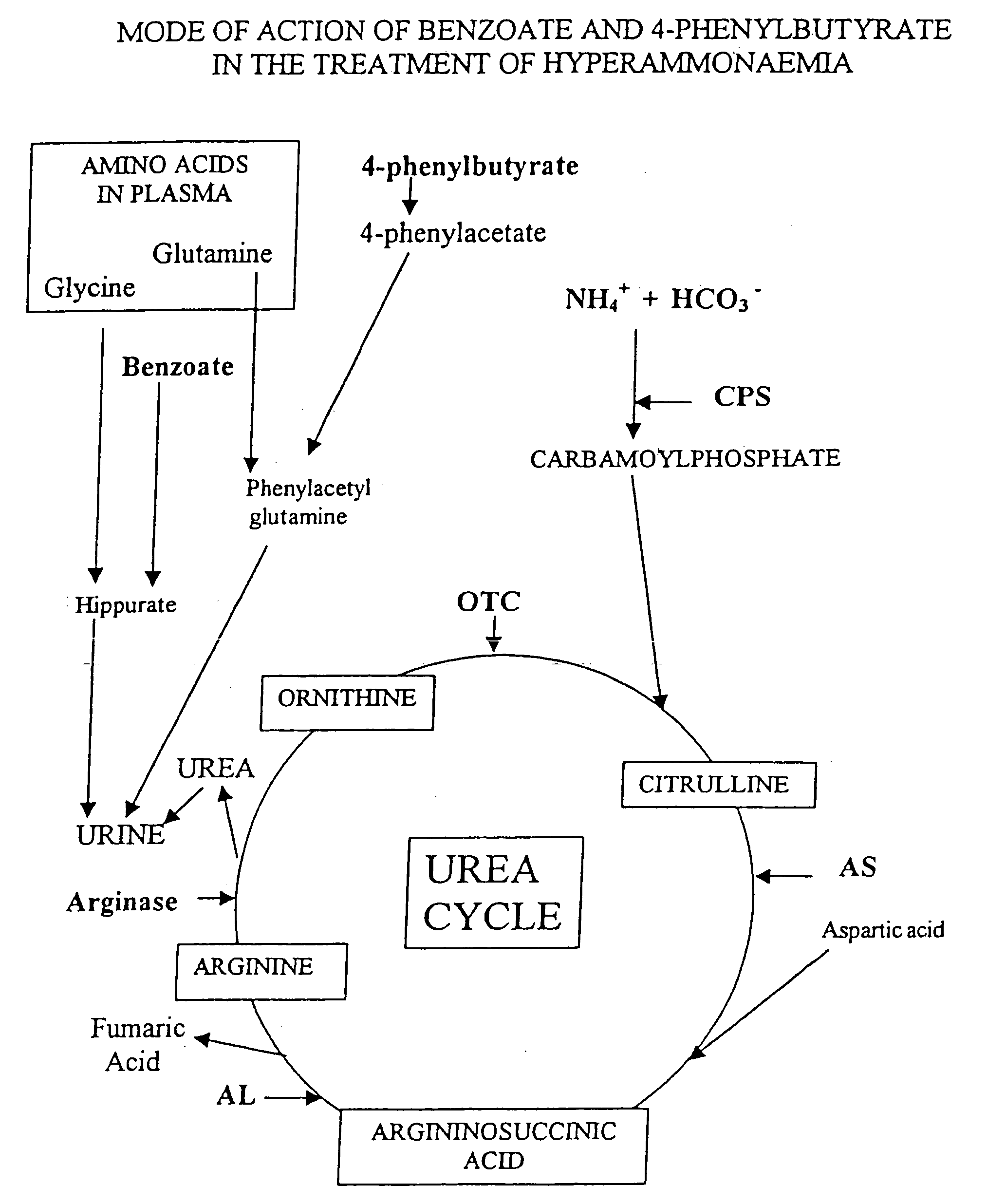
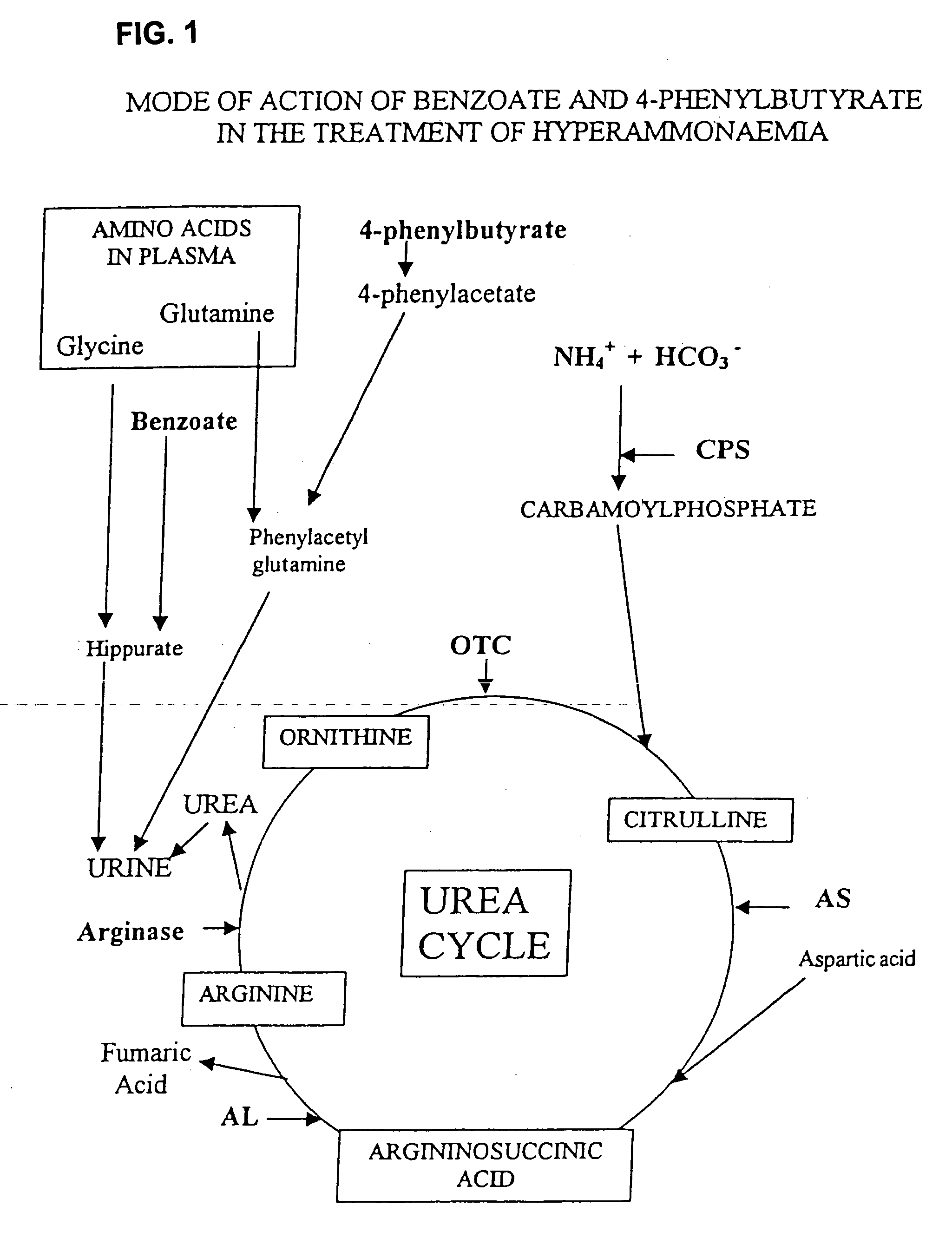
Pharmaceutical composition and method for treatment of a urea cycle deficiency or sickle-cell anaemia
A pharmaceutical composition is disclosed comprising sodium 4-phenylbutyrate, an effective amount of at least one aromatic flavoring agent, and an effective amount of at least one synthetic sweetening agent. Also disclosed is a method of treatment of a urea cycle deficiency or sickle-cell anaemia.
Owner:SPECIAL PRODS
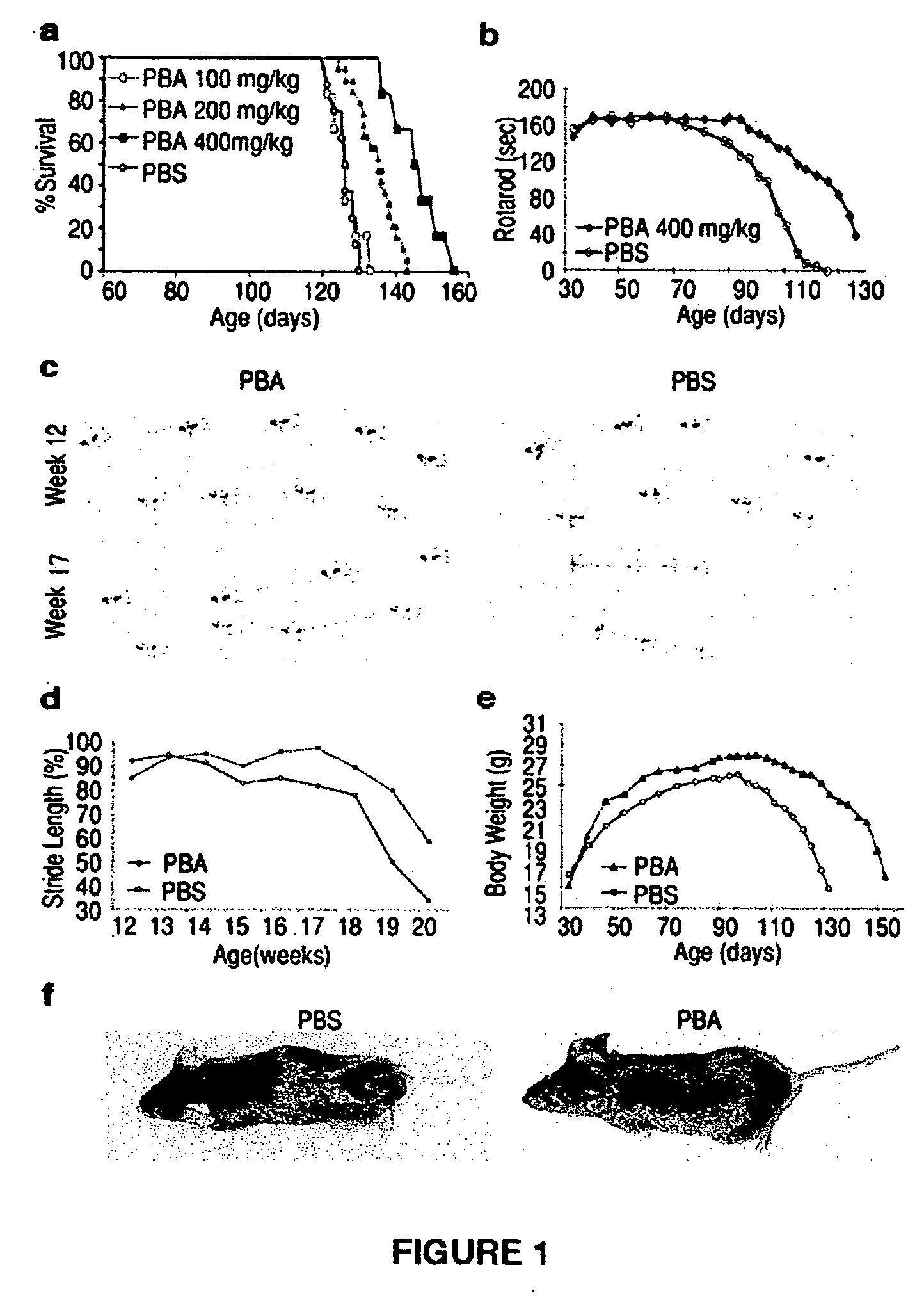
Method of ameliorating or abrogating the effects of a neurodegenerative disorder, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), by using a HDAC inhibiting agent
InactiveUS20060135612A1Improve survivalAmeliorated histone hypoacetylationBiocideAnimal repellantsAmyotrophic lateral sclerosisNeuro-degenerative disease
A method of ameliorating or abrogating the effects of a neurodegenerative disorder, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), includes administering a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor in a subject in need thereof. The HDAC inhibitor includes sodium butyrate or sodium phenylbutyrate.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
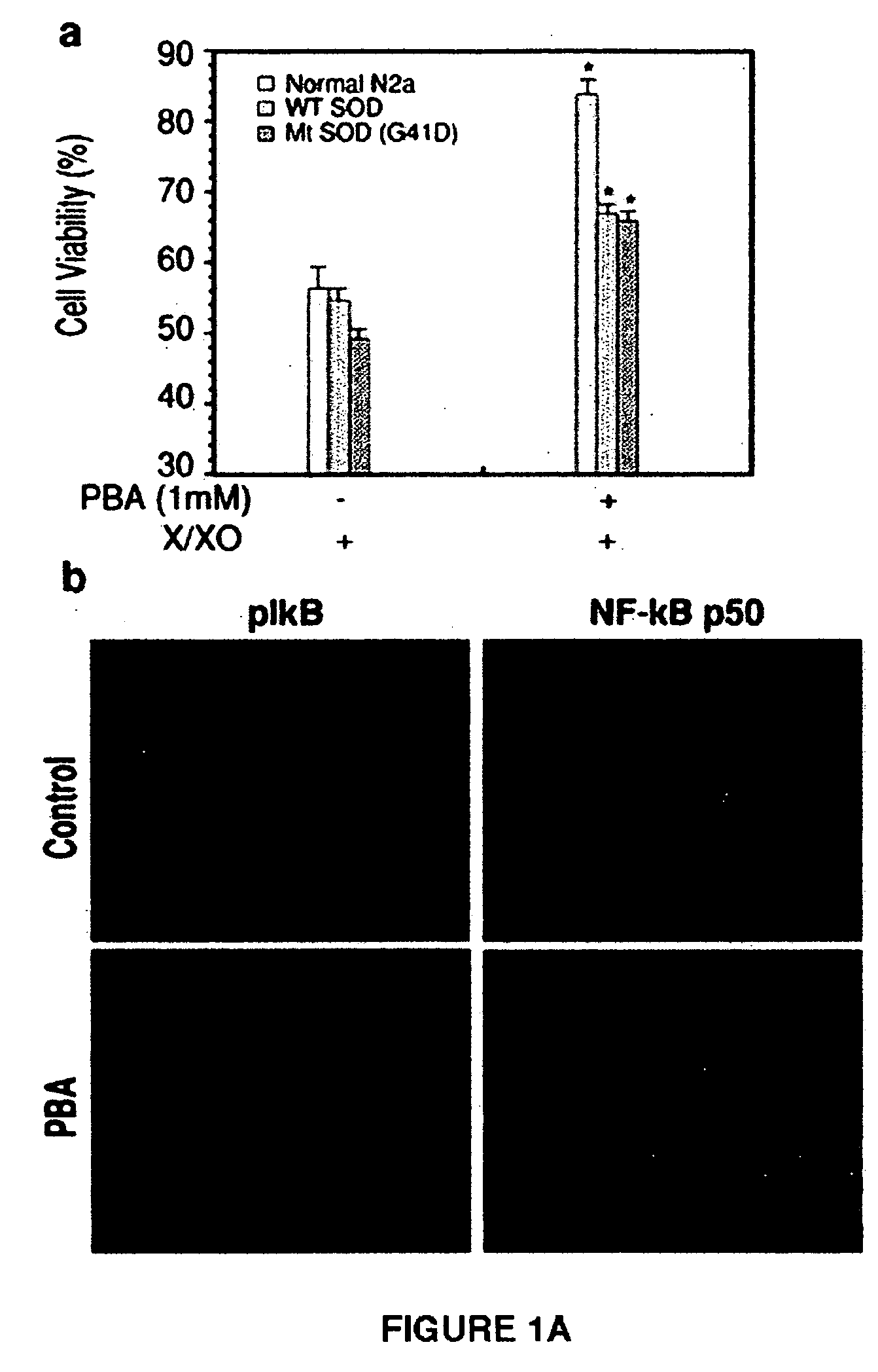
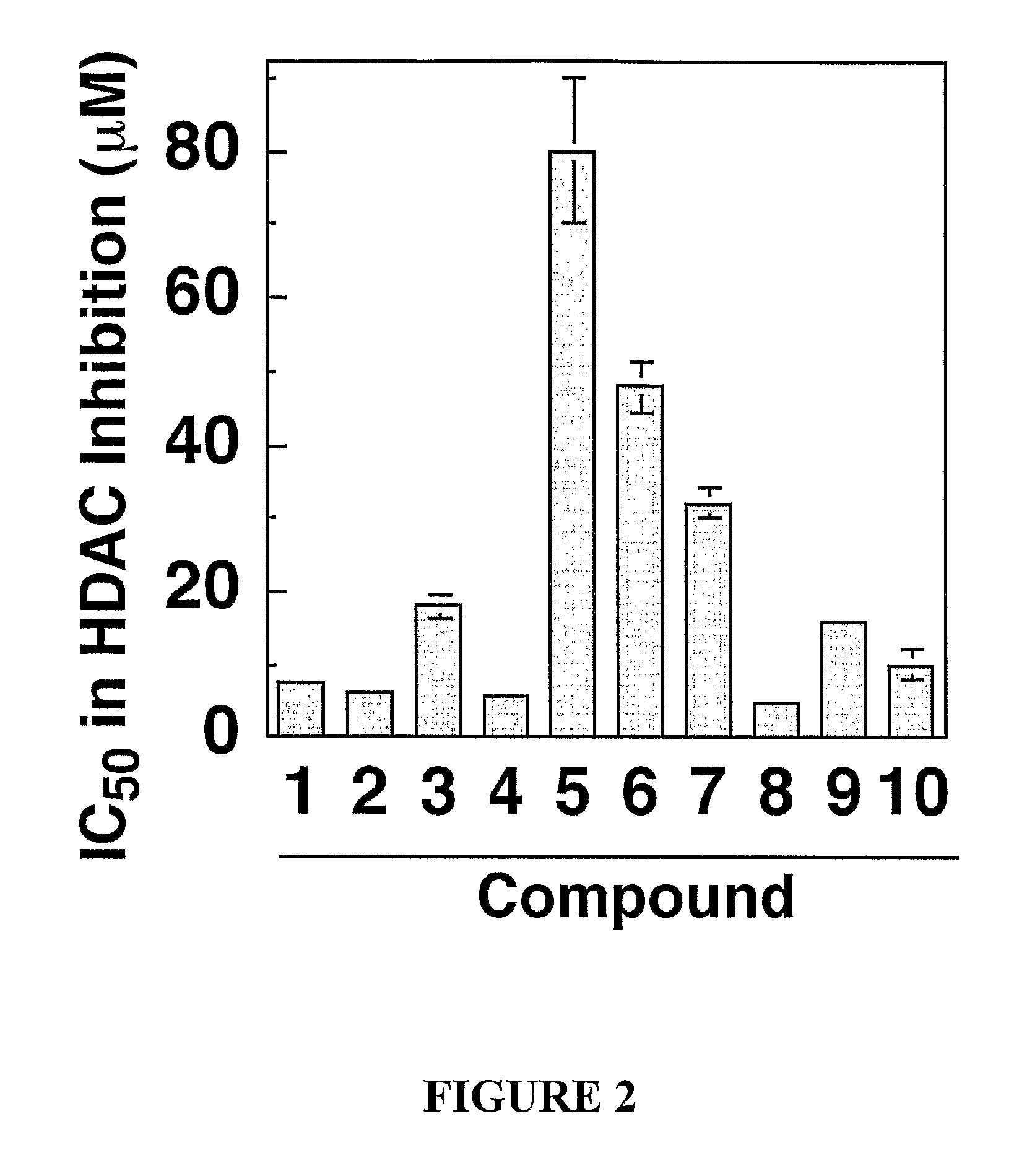
Zn2Motif-Tethered Short-Chain Fatty Acids as a Novel Class of Histone Deacetylase
Zn2+-chelating motif-tethered fatty acids as histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors. One hydroxamate-tethered phenylbutyrate compound, N-hydroxy-4-(4-phenylbutyrylamino)-benzamide (HTPB), displayed nM potency in inhibiting HDAC activity. Exposure of several cancer cell lines to HTPB at sub-μM concentrations showed reduced cell proliferation accompanied by histone hyperacetylation and elevated p21WAF / CIP1 expression, hallmark features associated with intracellular HDAC inhibition.
Owner:OHIO STATE INNOVATION FOUND
Methods and compositions for treating symptomes of diseases related to imbalance of essential fatty acids
The invention as disclosed herein provides pharmaneutical compositions and methods for treating, ameliorating, or preventing the symptoms of fatty acids imbalance and cell membrane dysfunction. The pharmaneutical compositions of the invention contain in an effective amount a first and a second composition, the first composition comprises an effective amount of one or more phosphatidylcholine formulations and the second composition comprises an effective amount of one or more constituents comprising essential fatty acid supplements, trace minerals, phenylbutyrate, electrolytes, methylating agents, reduced glutathione, or a combination thereof, in a suitable carrier.
Owner:BODYBIO INC
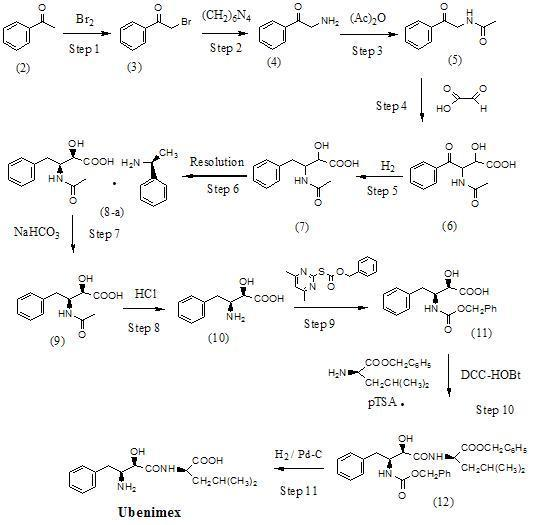
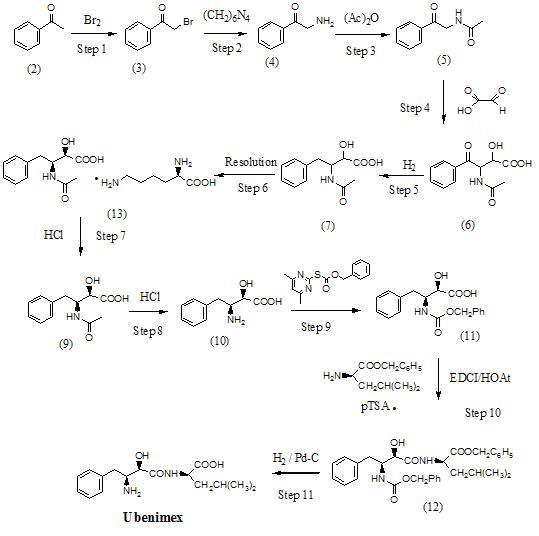
Preparation method for ubenimex
ActiveCN101891647AOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides optical isomer preparationArginine3-amino-2-hydroxy-4-phenylbutyric acid
The invention belongs to the field of antineoplastic agent preparation and provides a preparation method for ubenimex. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: preparing high-purity key intermediate (2S,3R)-3-amino-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl butyric acid by taking L-lysine, L-arginine or L-histidine as a resolving reagent; and preserving the chirality of C-5 in forming a peptide chain by taking EDCI / HOAt as a condensing agent. Due to the adoption of the method, the problem that the (2S,3R)-3-amino-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl butyric acid and the (2S,3R)-3-acetamino-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl butyric acid cannot be completely separated by the conventional resolving agent and the racemization problem in the condensation of amide are effectively solved; and the purity of the ubenimex prepared by the method can reach over 99.5 percent.
Owner:ZHEJIANG APELOA KANGYU PHARMA +1
Methods of modulation of branched chain acids and uses thereof
ActiveUS20120220661A1Decrease in blood plasma levelImprove enzymatic activityBiocideMetabolism disorderScavengerBlood plasma
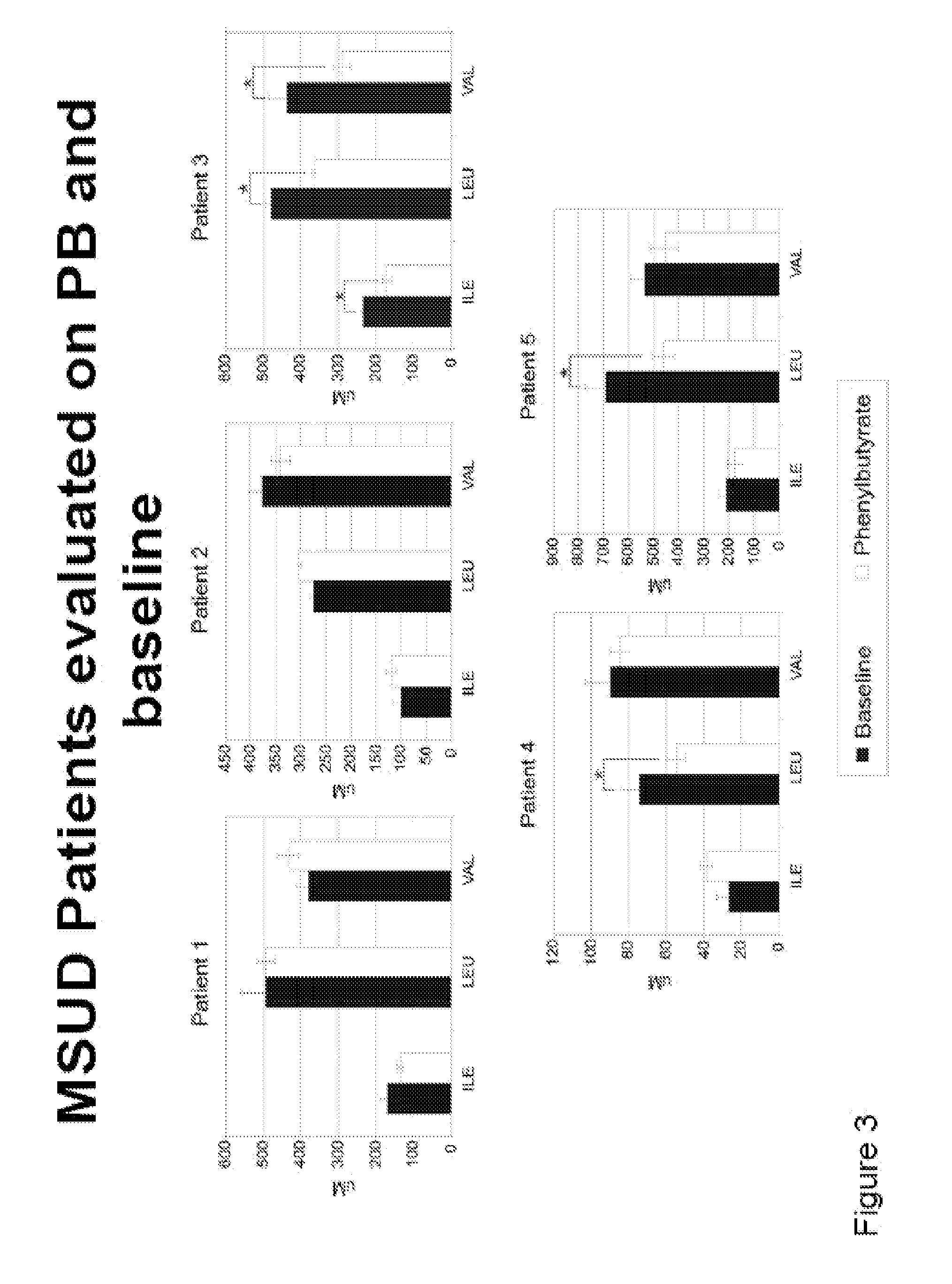
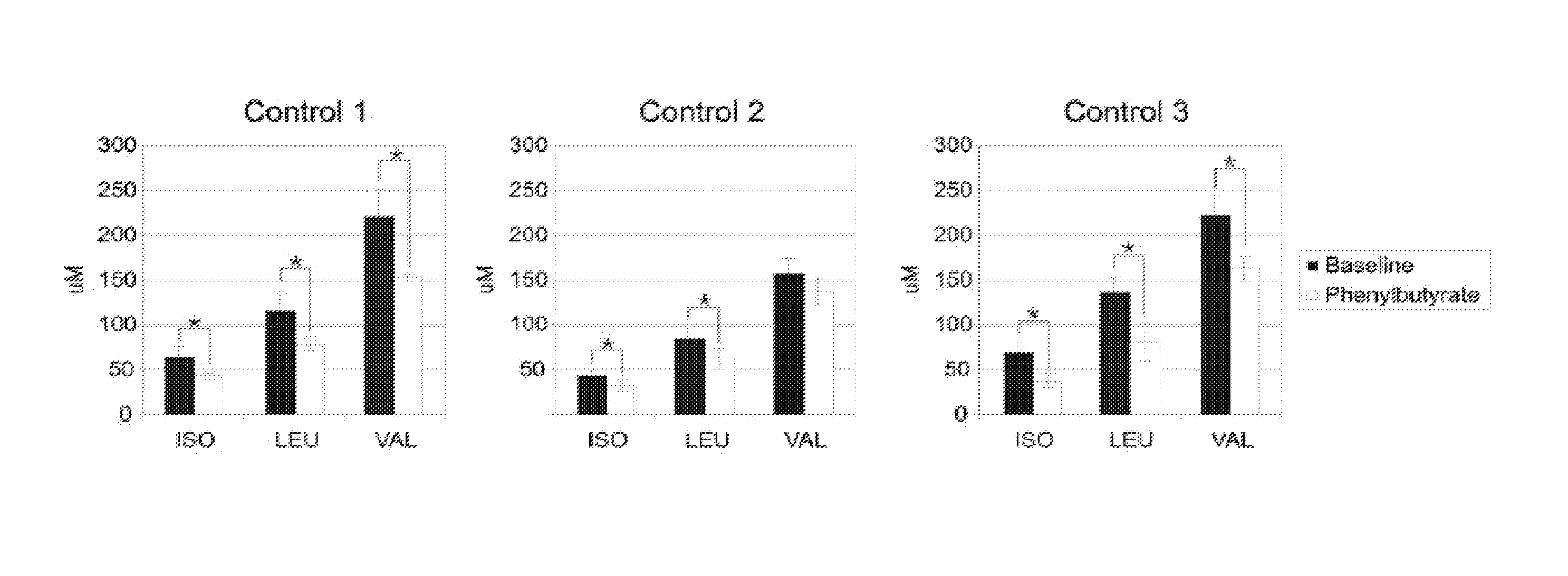
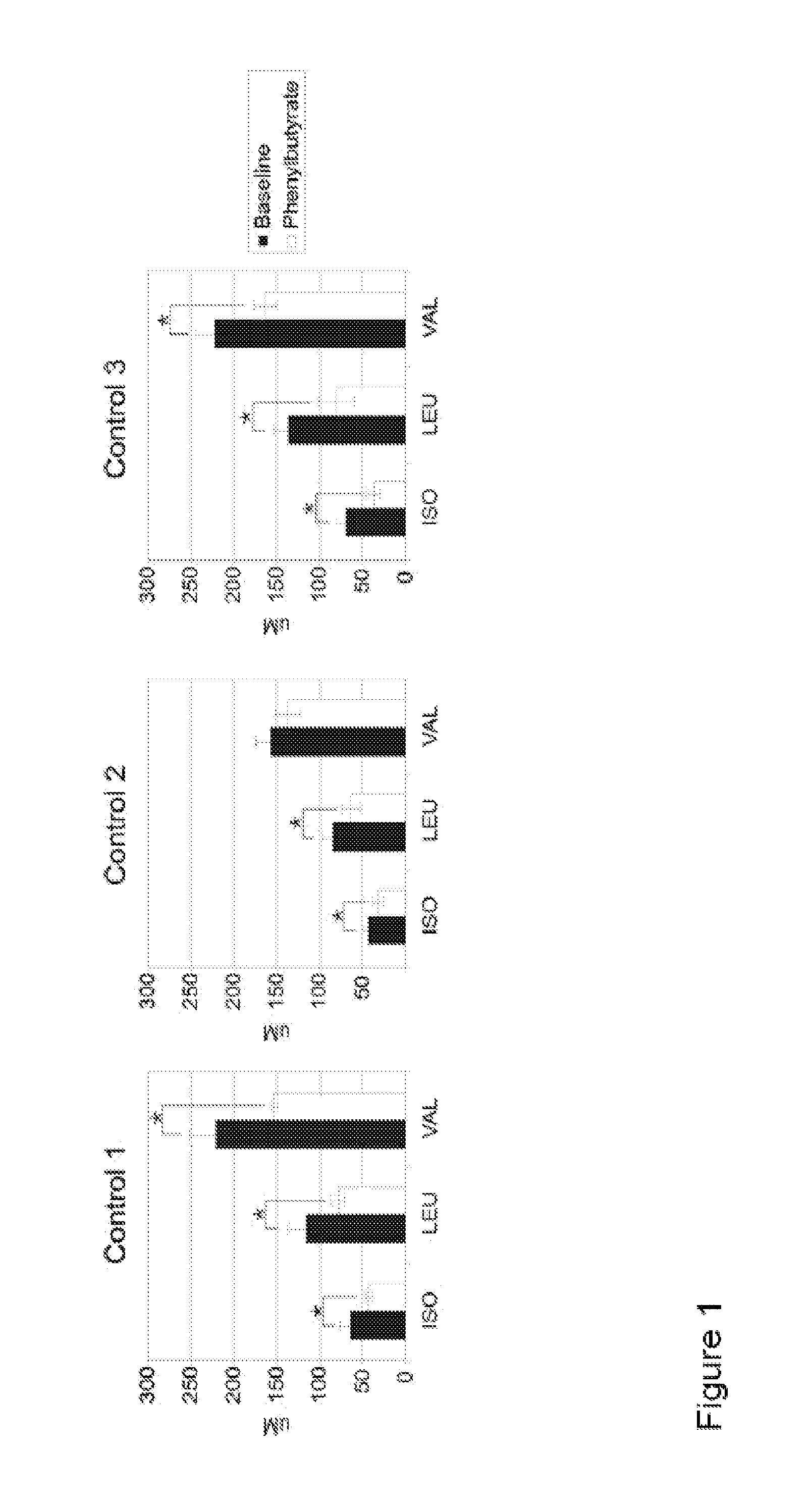
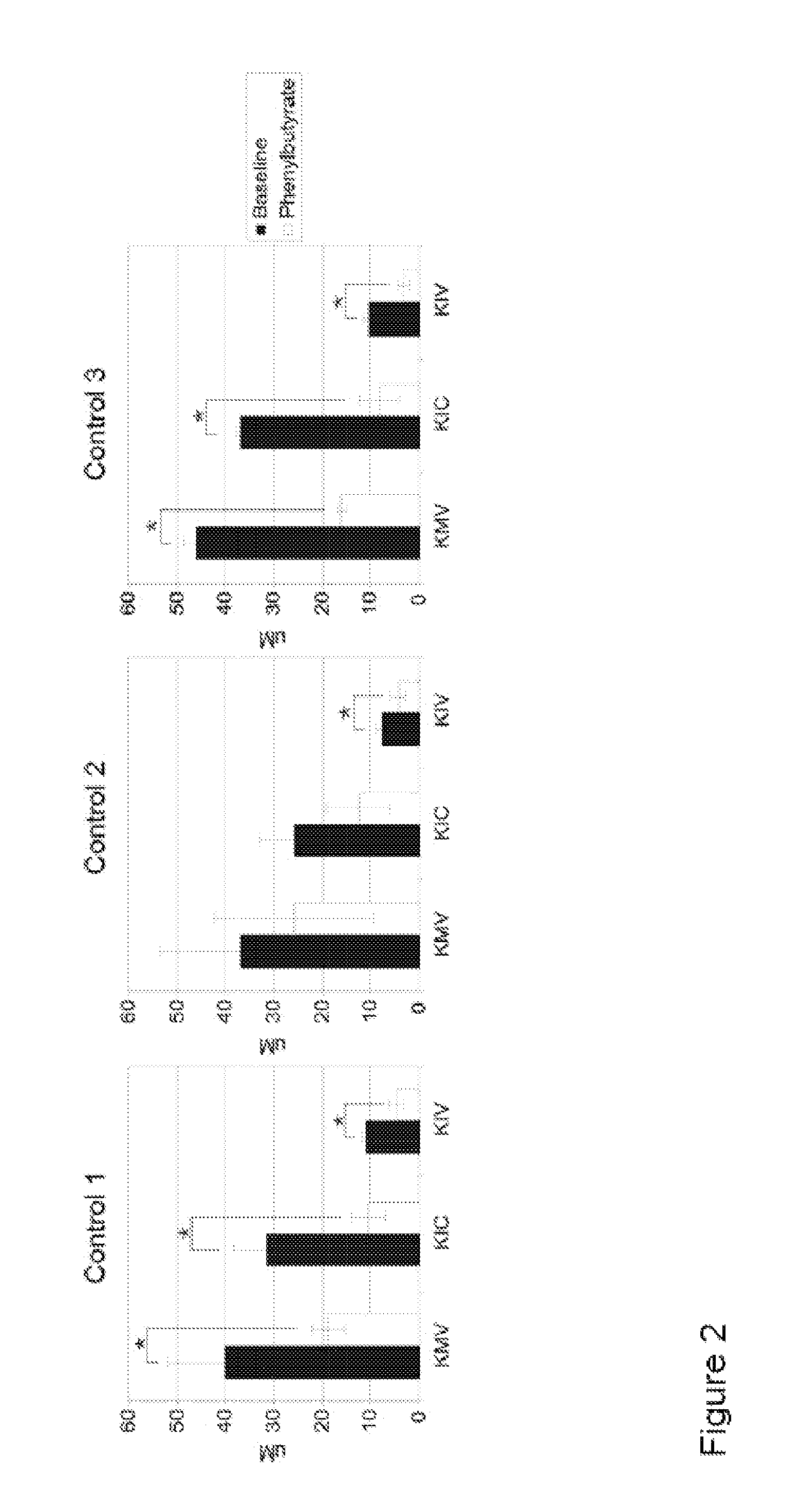
A method of modulating plasma levels of branched chain amino acids and branched chain alpha-keto acids is disclosed, wherein an ammonia scavenger compound or a salt thereof, for example phenylbutyrate or an even numbered congener thereof or a salt thereof, is administered to an individual in need thereof. In various methods, a decrease in plasma levels of branched chain amino acids and branched chain alpha-keto acids is effected to treat individuals suffering from an inborn error in metabolism of amino acids, such as Maple Syrup Urine Disease, for example.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Methods of modulation of branched chain acids and uses thereof
ActiveUS9078865B2Reduce phosphorylationEffective amountMetabolism disorderAnhydride/acid/halide active ingredientsScavengerBlood plasma
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Modulating endoplasmic reticulum stress in the treatment of tuberous sclerosis
InactiveUS20100022495A1Promote apoptosisReduce and prevent ER stressOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseHAMARTOMATOUS DISEASES
Endoplasmic reticulum stress has been found to be associated with the genetic disease tuberous sclerosis. Tuberous sclerosis is cause by defects in the two genes, TSC1 and TSC2. Agents that modulate ER stress may be used to treat tuberous sclerosis and other hamartomatous diseases. In particular, 4-phenyl butyric acid (PBA) has been shown to reduce ER stress is TSC-deficient cells. Other compounds useful in reducing ER stress are chemical chaperones such as trimethylamine N-oxide arid glycerol may also be useful in treating tuberous sclerosis. The present invention provides methods of treating a subject suffering from tuberous sclerosis using ER stress reducers such as PBA, TUDCA, UDCA, and TMAO. Methods of screening for ER stress reducers by identifying agents that reduce levels of ER stress markers in TSC-deficient cells are also provided. These agents may find use in methods and pharmaceutical compositions for treating tuberous sclerosis.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Modulating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in the Treatment of Tuberous Sclerosis
InactiveUS20140011761A1Promote apoptosisReduce and prevent ER stressBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsHAMARTOMATOUS DISEASESReticulum cell
Endoplasmic reticulum stress has been found to be associated with the genetic disease tuberous sclerosis. Tuberous sclerosis is cause by defects in the two genes, TSC1 and TSC2. Agents that modulate ER stress may be used to treat tuberous sclerosis and other hamartomatous diseases. In particular, 4-phenyl butyric acid (PBA) has been shown to reduce ER stress is TSC-deficient cells. Other compounds useful in reducing ER stress are chemical chaperones such as trimethylamine N-oxide arid glycerol may also be useful in treating tuberous sclerosis. The present invention provides methods of treating a subject suffering from tuberous sclerosis using ER stress reducers such as PBA, TUDCA, UDCA, and TMAO. Methods of screening for ER stress reducers by identifying agents that reduce levels of ER stress markers in TSC-deficient cells are also provided. These agents may find use in methods and pharmaceutical compositions for treating tuberous sclerosis.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method of producing optically active 4-amino-3-substituted phenylbutanoic acid
ActiveUS8293926B2Safe and efficient and advantageous scaleAsymmetric synthesesButyrateCombinatorial chemistry
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
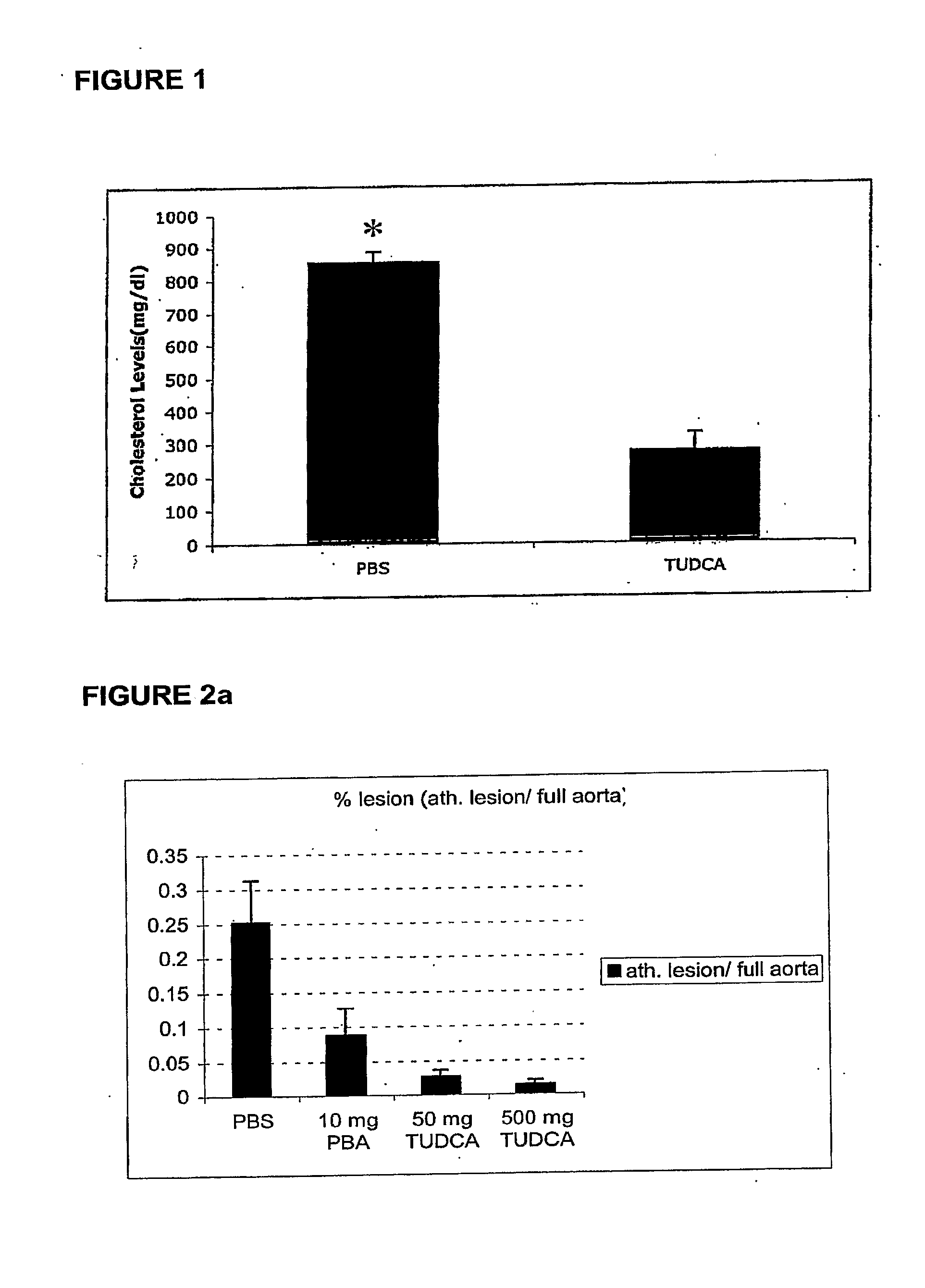
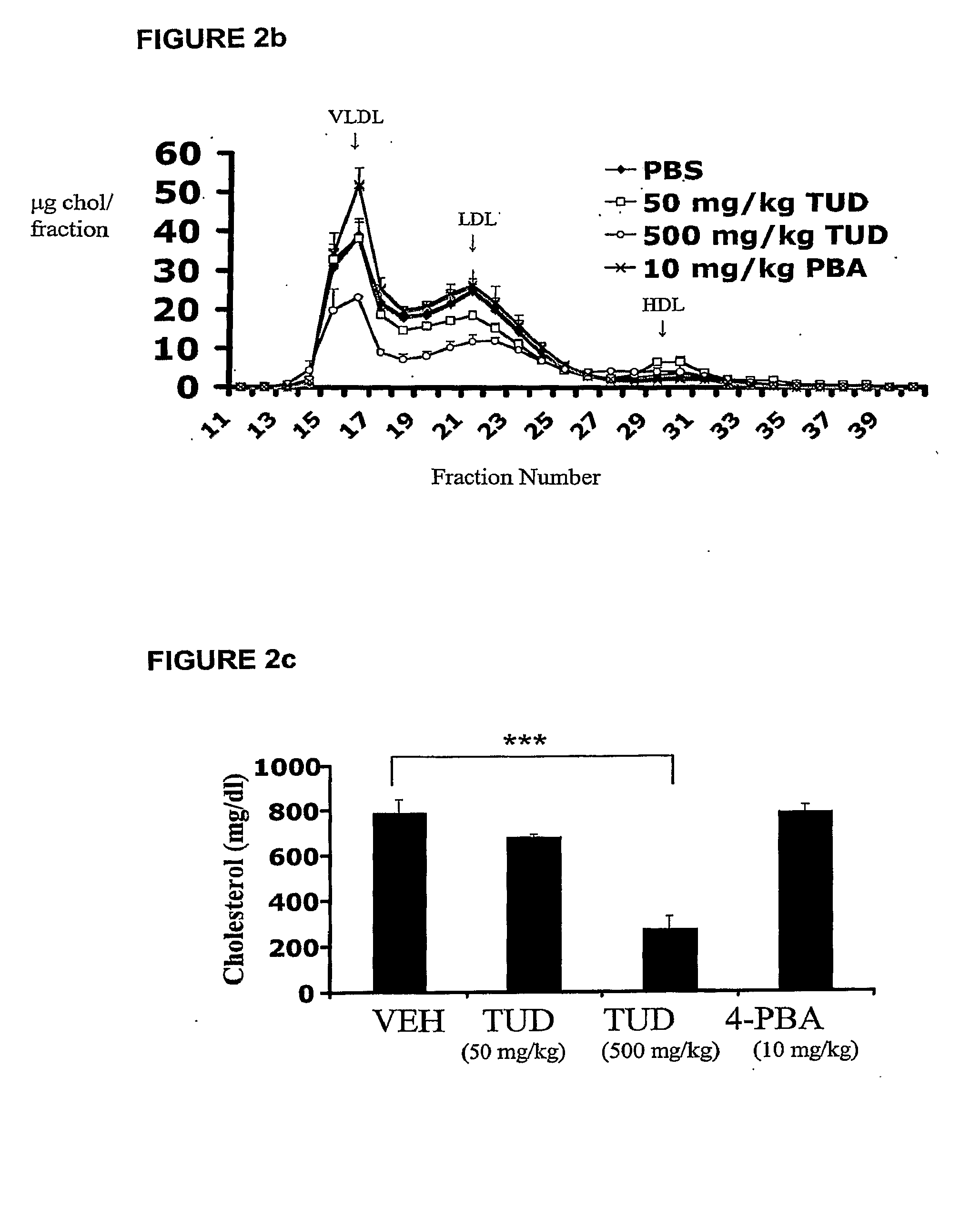
Methods for treating hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis
InactiveUS20090312297A1Restore glucose homeostasisIncrease insulin sensitivityBiocideMetabolism disorderDyslipidemiaCholesterol blood
The invention provides compounds and pharmaceutical compositions that can be used to treat or prevent atherosclerosis, stroke, and other ischemic vascular diseases, dyslipidemia and hypercholestcrolemia and prevent complications of these conditions. Agents in accordance with the invention include; tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA), and analogs and derivatives thereof; 4-phenyl butyric acid (PBA), and analogs and derivatives thereof; and trimethyl N-oxide (TMAO), and analogs and derivatives thereof.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method for preparing (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate by catalyzing with recombinant carbonyl reductase
InactiveCN102618590AAvoid inhibitionImprove conversion abilityMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliEthyl butyrate
The invention discloses a method for preparing (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate by catalyzing recombinant carbonyl reductase, which belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: cloning gene segments of carbonyl reductase (IolS) and glucose dehydrogenase (GDH) from bacillus subtilis CGMCC NO.1.1508, expressing an IolS gene and a GDH gene in series by adopting a dual-starter method to construct a recombinant plasmid pET24a-G-T7-I, and introducing the plasmid into escherichia coli BL21(DE3); and under the condition of not adding or adding a small amount of NADP+cofactors, performing biotransformation by taking a cell-free extract of the escherichia coli recombinant plasmid as a catalyst, 2-oxo-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate as a substrate and glucose as a substrate to obtain (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate, wherein the enantiomeric excess value of the product is higher than 99.5 percent. In the method, IolS and GDH are co-expressed, so that efficient regeneration of an intra-cellular cofactor NADP(H) is realized, production cost is lowered, and a good industrial application prospect is achieved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
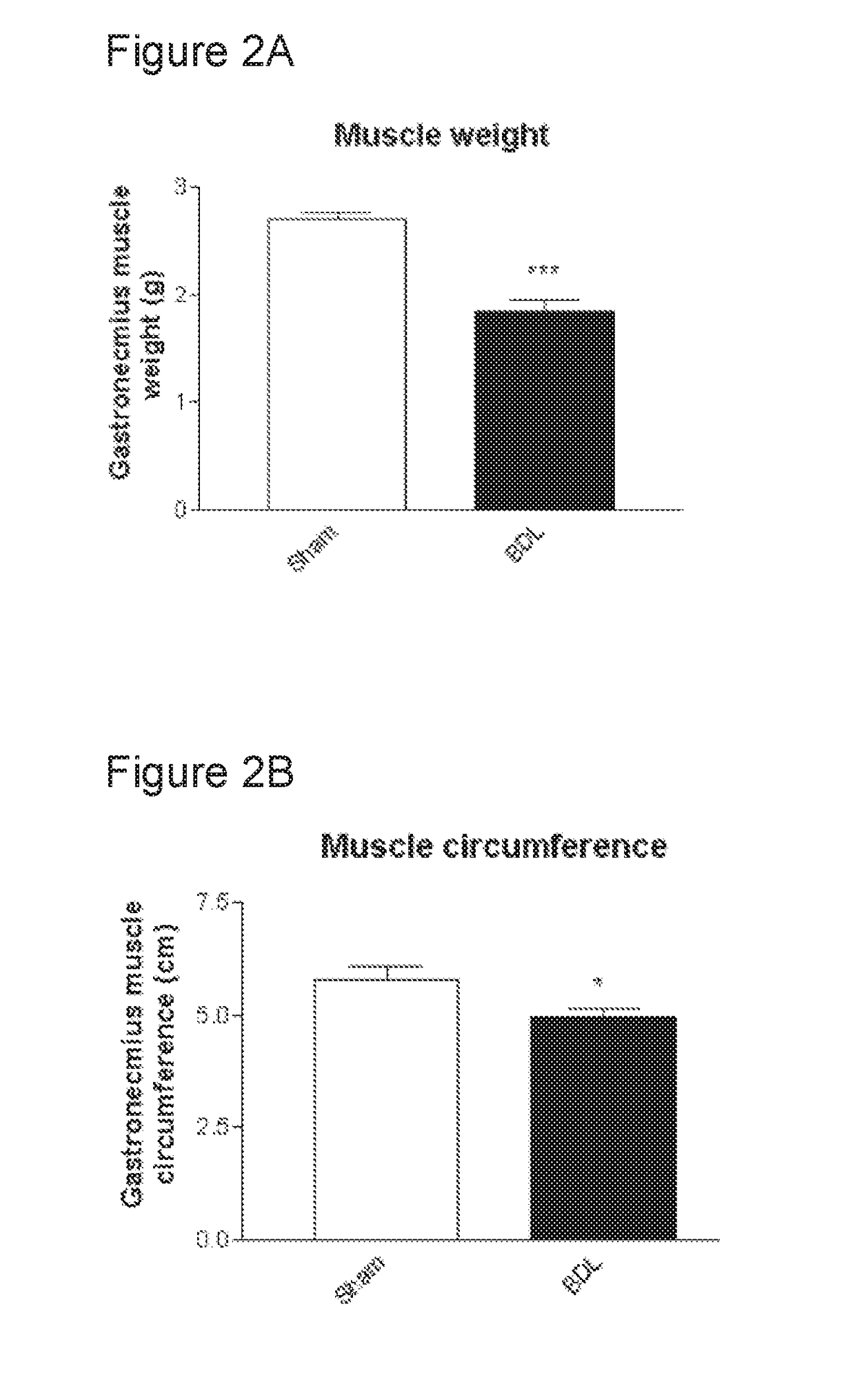
Treatment and prevention of muscle loss using l-ornithine in combination with at least one of phenylacetate and phenylbutyrate
ActiveUS20180221320A1Reducing blood ammoniaImproving muscle metabolismOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMuscle lossOrnithine synthesis
Disclosed herein are methods of treating and preventing muscle loss using ornithine in combination with at least one of phenyl acetate and phenylbutyrate.
Owner:OCERA THERAPEUTICS INC
Compositions comprising ornithine and phenylacetate or phenylbutyrate for treating hepatic encephalopathy
ActiveUS20120259016A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHepatic encephalopathyLiver decompensation
The present invention relates to use of ornithine in the manufacture of a medicament for use in combination with at least one of phenylacetate and phenylbutyrate for preventing or treating liver decompensation or hepatic encephalopathy. The invention also relates to use of at least one of phenylacetate and phenylbutyrate in the manufacture of a medicament for use in combination with ornithine for preventing or treating liver decompensation or hepatic encephalopathy.
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
Therapeutical use
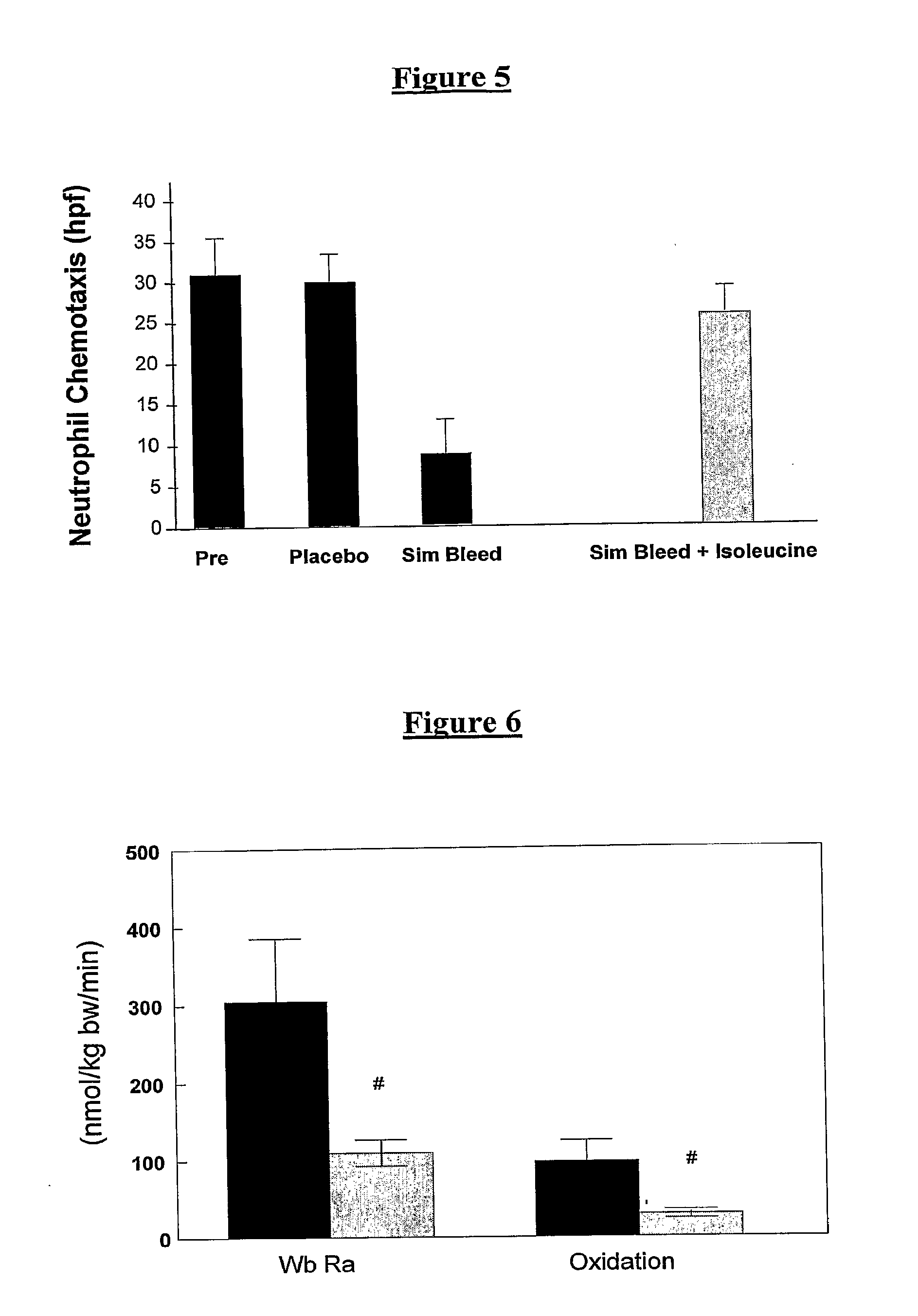
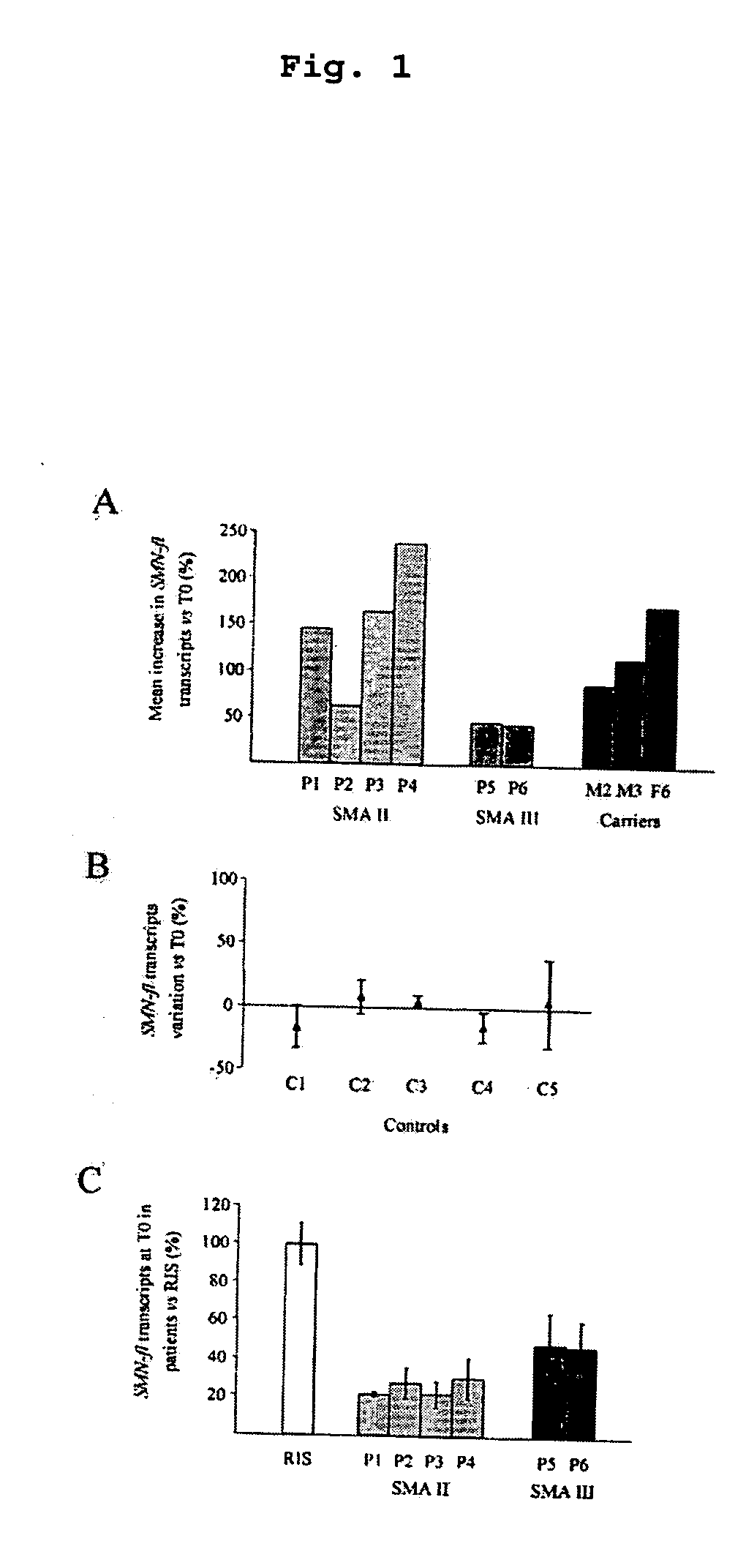
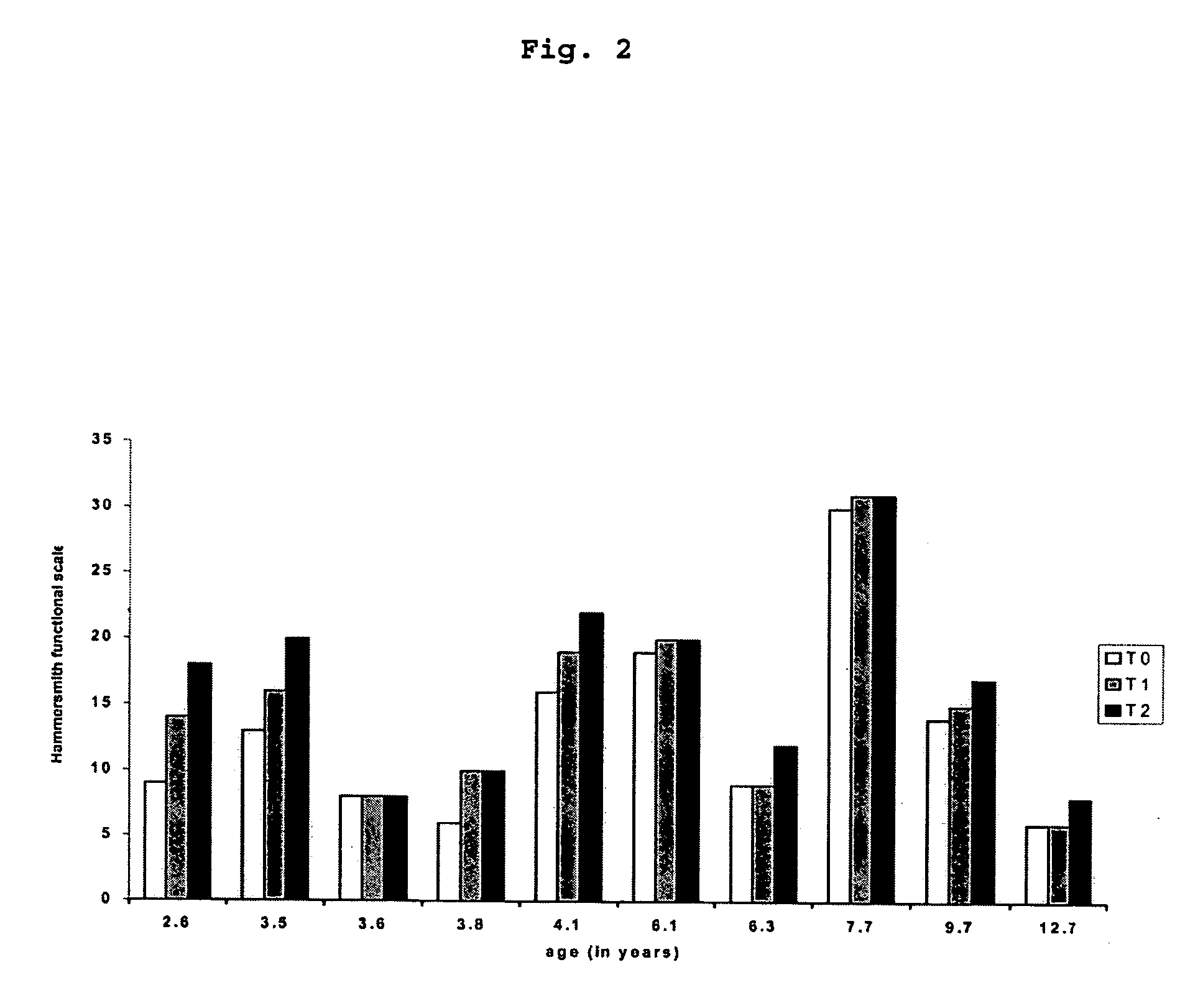
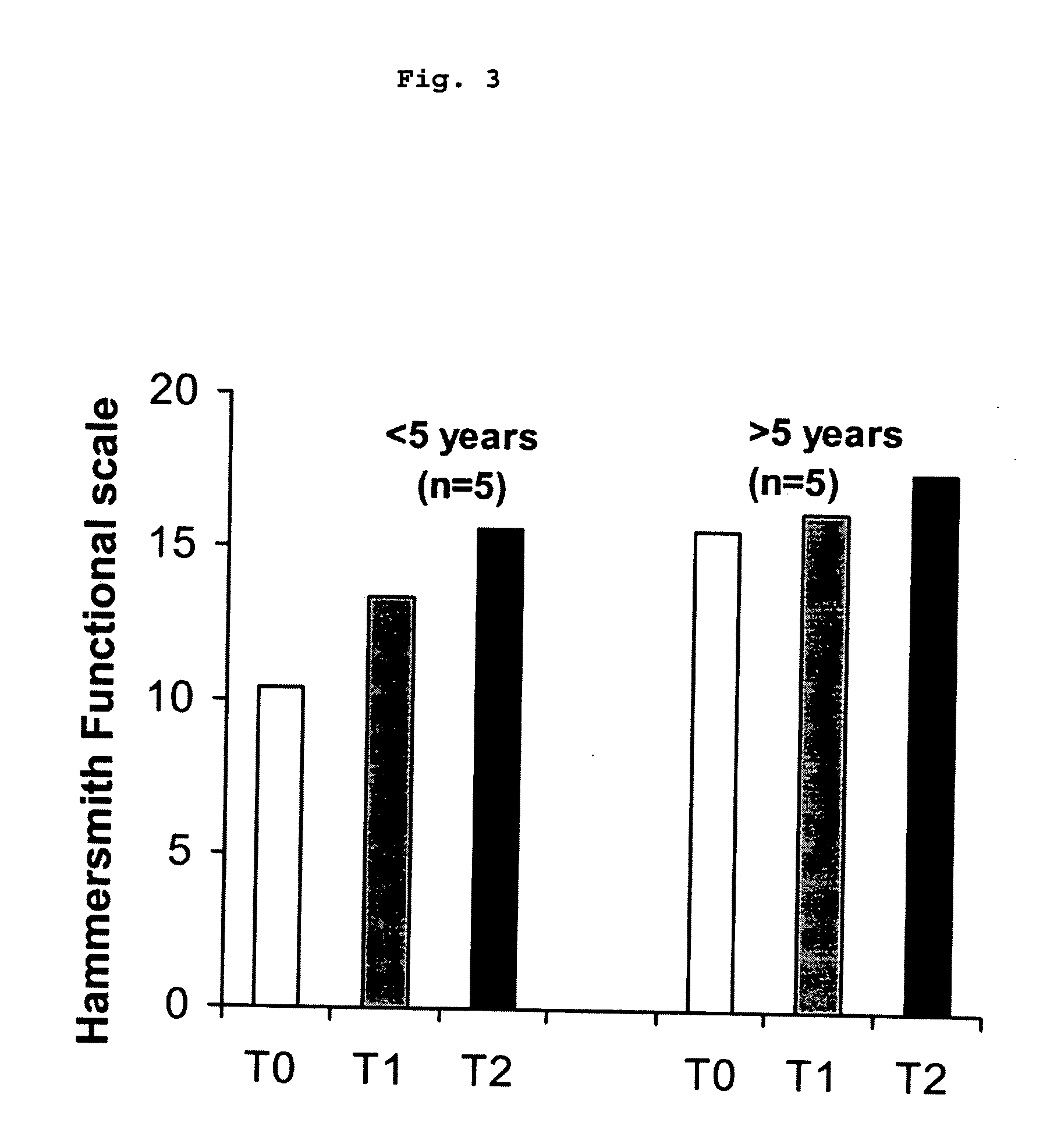
The invention relates to a method for the treatment of spinal muscular atrophy comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a therapeutically acceptable salt of phenylbutyrate to a subject in need of treatment of spinal muscular atrophy.
Owner:FYRKLOVERN SCANDINAVIA
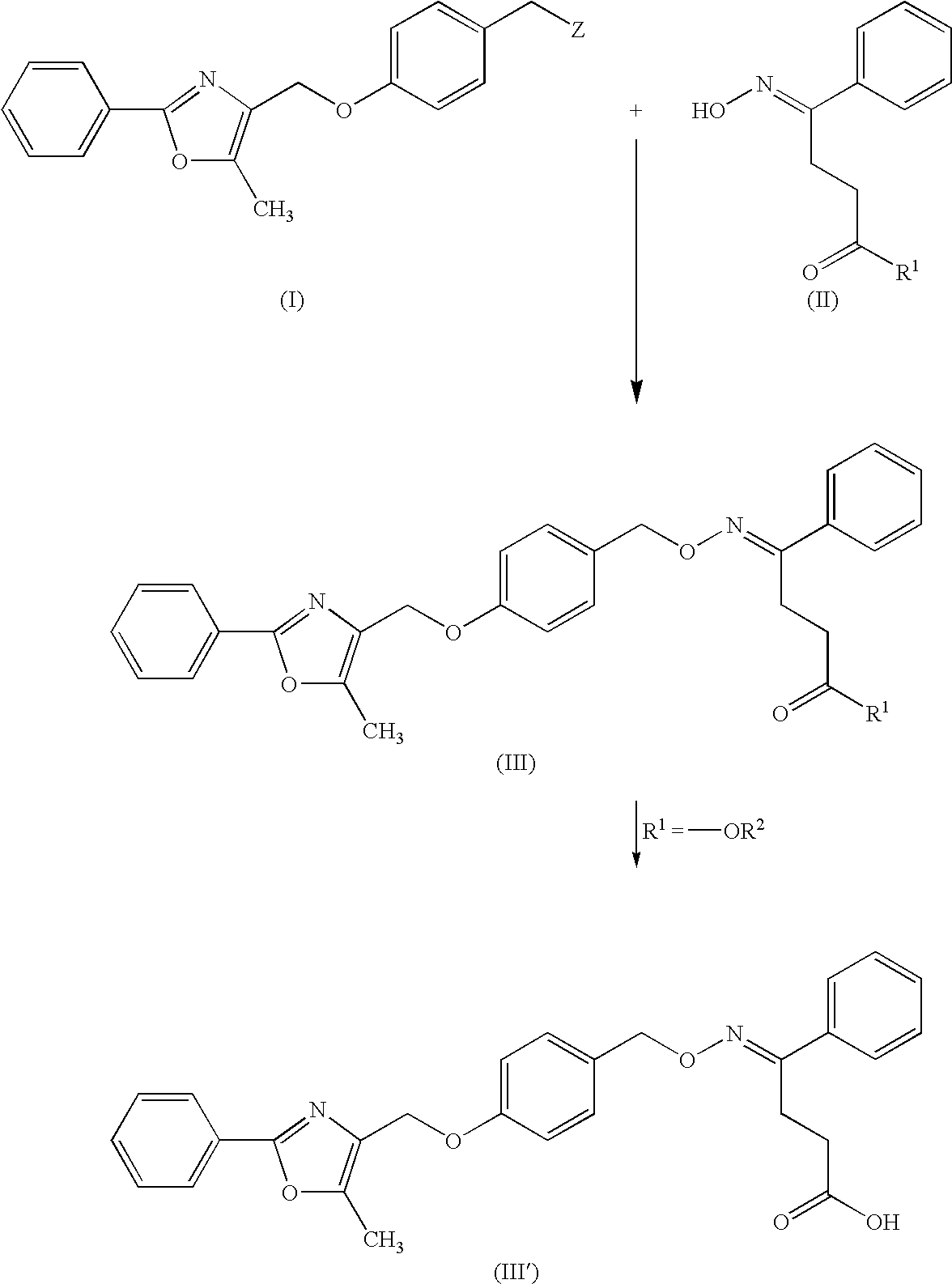
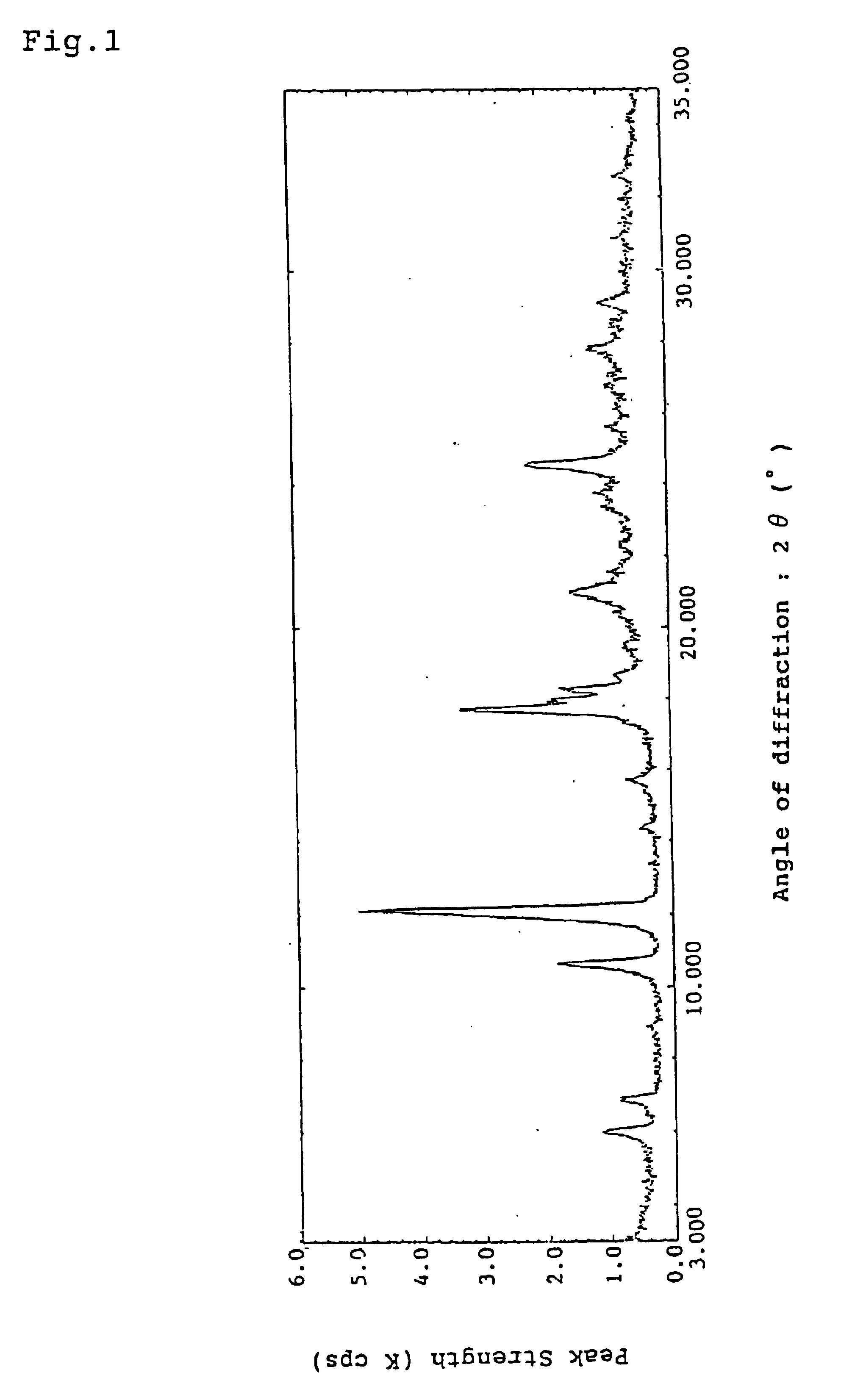
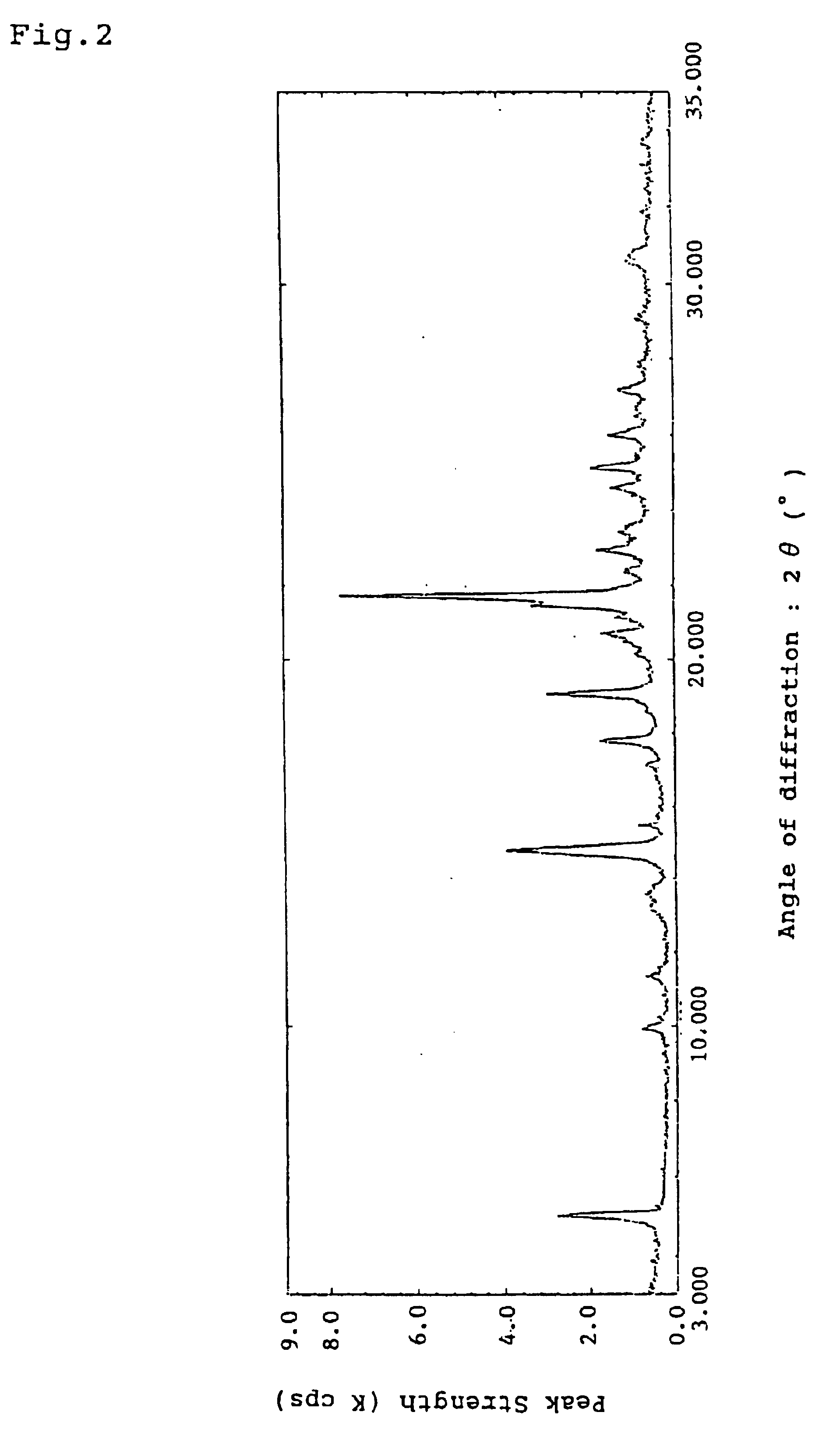
Crystals of an oxyiminoalkanoic acid derivative and their use as antidiabetics
Crystals of (E)-4-[4-(5-methyl-2-phenyl-4-oxazolylmethoxy)benzyloxyimino]-4-phenylbutyric acid (provided that crystals having a melting point of 126° C. to 127° C. are excluded), which have an excellent anti-diabetic action.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Compositions comprising ornithine and phenylacetate or phenylbutyrate for treating hepatic encephalopathy
The present invention relates to use of ornithine in the manufacture of a medicament for use in combination with at least one of phenylacetate and phenylbutyrate for preventing or treating liver decompensation or hepatic encephalopathy. The invention also relates to use of at least one of phenylacetate and phenylbutyrate in the manufacture of a medicament for use in combination with ornithine for preventing or treating liver decompensation or hepatic encephalopathy.
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
3-amino-4-phenylbutanoic acid derivatives as dipeptidyl peptidase inhibitors for the treatment or prevention of diabetes
The present invention is directed to 3-amino-4-phenylbutanoic acid derivatives which are inhibitors of the dipeptidyl peptidase-IV enzyme (“DP-IV inhibitors”) and which are useful in the treatment or prevention of diseases in which the dipeptidyl peptidase-IV enzyme is involved, such as diabetes and particularly type 2 diabetes. The invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising these compounds and the use of these compounds and compositions in the prevention or treatment of such diseases in which the dipeptidyl peptidase-IV enzyme is involved.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
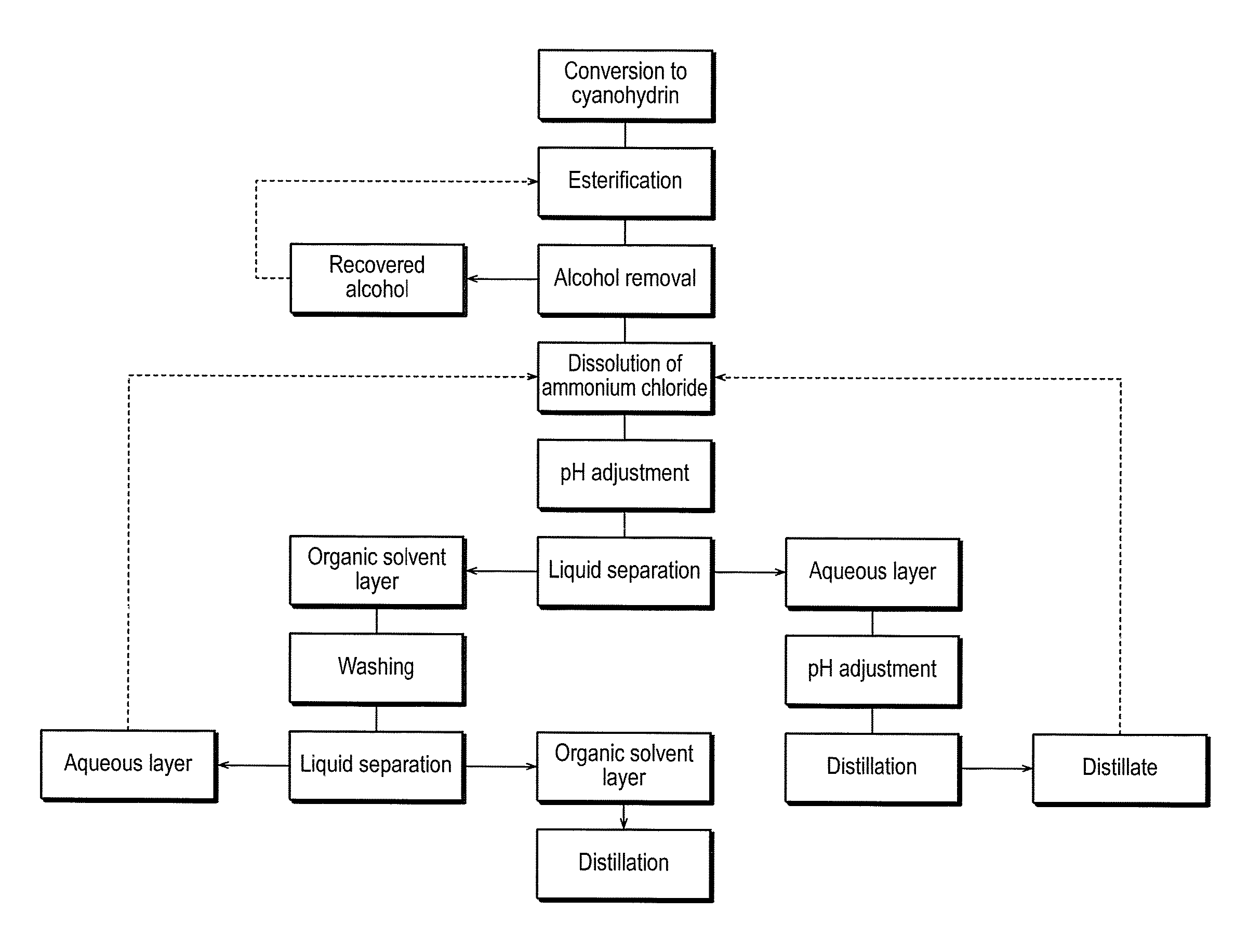
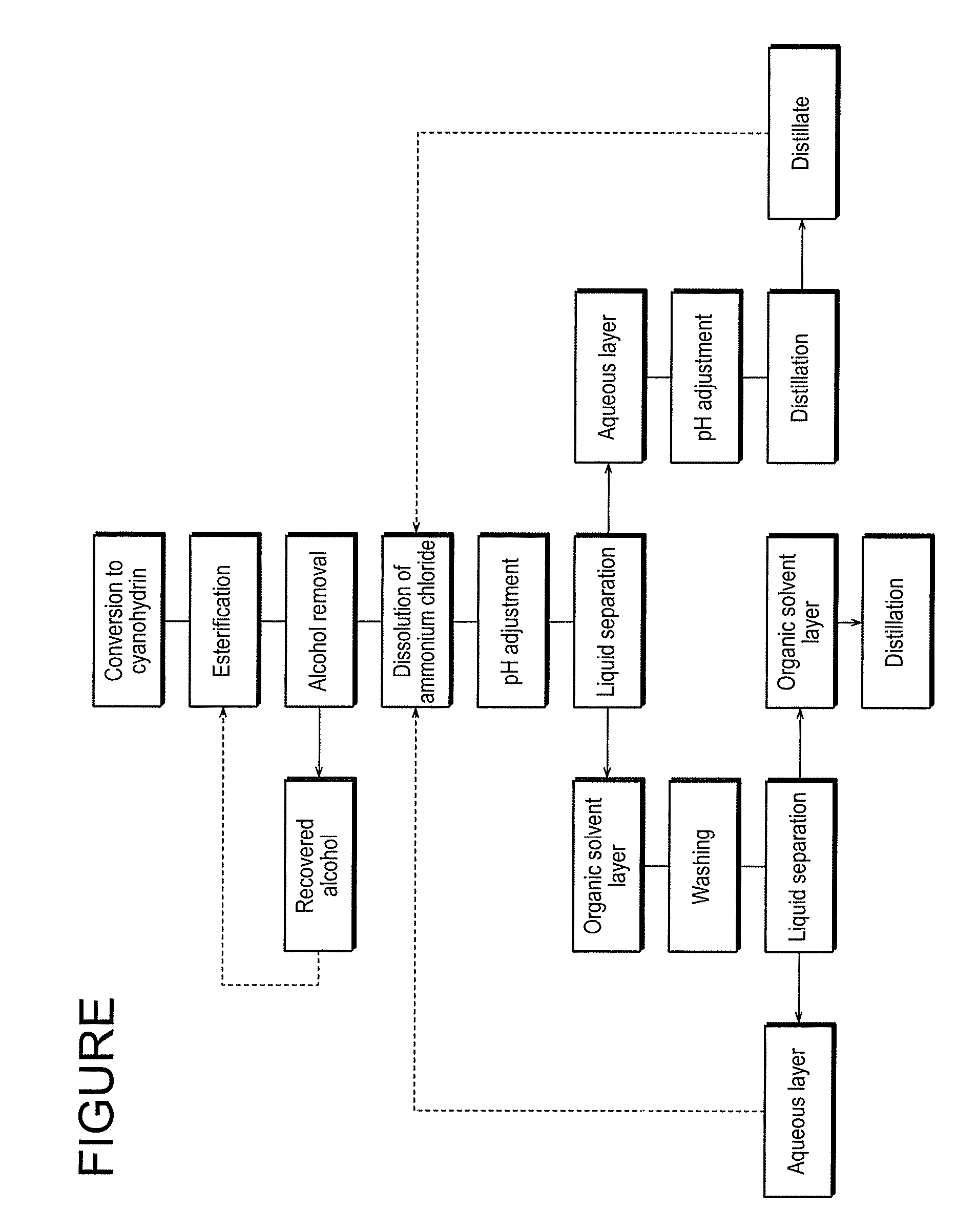
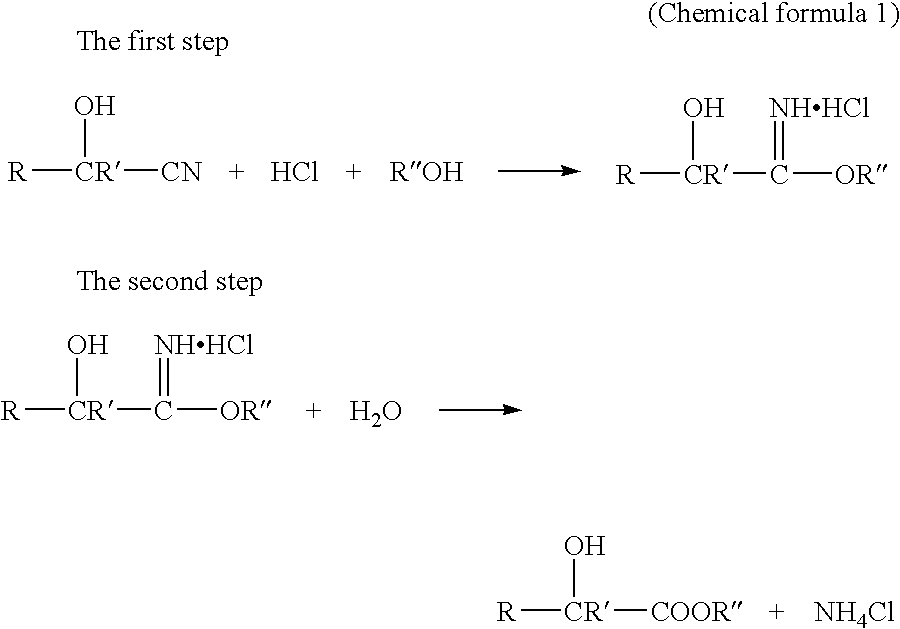
Method for producing 2-hydroxyester compound
InactiveUS7737296B2High yieldWaste solution treatment can be carried out extremely efficientlyOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationAlicyclic Hydrocarbons2-hydroxy-4-phenylbutyrate
A simple and easy-to-use method for producing a 2-hydroxyester compound using a cyanohydrin compound, as a raw material, is provided. A method for producing a 2-hydroxyester compound represented by the general formula (1) (provided that ethyl 2-hydroxy-4-phenylbutyrate is excluded), wherein an acid is introduced into a mixture of a cyanohydrin compound represented by the general formula (2), an alcohol, an organic solvent and water:(Chemical Formula 1)R1—CH(OH)—COOR2 (1)R1—CH(OH)(CN) (2)wherein, R1 is a hydrogen atom, a substituted or unsubstituted aliphatic hydrocarbon group having 1 to 12 carbon atoms, which may contain an oxygen atom, a sulfur atom or a nitrogen atom, a substituted or unsubstituted alicyclic hydrocarbon group having 3 to 12 carbon atoms, which may contain an oxygen atom, a sulfur atom or a nitrogen atom, and a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group or aralkyl group having 3 to 14 carbon atoms, which may contain an oxygen atom, a sulfur atom or a nitrogen atom; and R2 is an alkyl group having 1 to 12 carbon atoms, which may contain an oxygen atom, a sulfur atom or a nitrogen atom.
Owner:NIPPON CHEMICALS CO LTD
Method for biological catalysis preparation of (R)-2-hydroxyl-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate
InactiveCN101314784AIncrease concentrationHigh reaction molar conversionMicroorganism based processesFermentationEthyl butyrateGlucose polymers
The invention relates to a method for preparing (R)-2-hydroxyl-4- phenylbutyric ethyl butyrate by adopting biological catalysis, which belongs to the technology field of the biocatalytic anisomerous reducing preparation medical chiral intermediate. The method comprises the following steps: utilizing produced bacteria Candida boidinii of high antimer selective carbonyl reductase screened etc.; fermenting and producing enzyme under the optimizing condition; taking 2-hydroxyl-4-phenylbutyric ethyl butyrate as a substrate in a single water phase system, a water / organic two-phase system or a water / resin two-phase system; adding grape sugar to wet thalli; and preparing (R)-2- hydroxyl-4- phenylbutyric ethyl butyrate. When the concentration of the substrate of 2-hydroxyl-4-phenylbutyric ethyl butyrate is 1 to 50g / L, (R)-2- hydroxyl-4- phenylbutyric ethyl butyrate is subjected to transformation for 1h to 48h, so as to ensure that the enantiomeric excess of the (R)-2- hydroxyl-4- phenylbutyric ethyl butyrate reaches 84.9 to 98.88 percent, the transformation rate of Moore reaches 72.0 to 84.6 percent, and coenzyme is not needed during the whole reaction process.
Owner:重庆博腾精细化工有限公司
Carbonyl reductase and gene thereof as well as application of carbonyl reductase in asymmetrical reductive carbonyl compound
ActiveCN102492668AHigh optical purityMild reaction conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAngiotensin-converting enzymeAlcohol
The invention discloses a new carbonyl reductase and gene thereof, a recombinant expression vector containing the gene and a recombinant expression transformant containing the gene, a recombinase of the carbonyl reductase and a preparation method of the recombinase as well as an application of the recombinase serving as a catalyst in preparation of chiral alcohol from prochiral carbonyl compoundssuch as asymmetrical reductive 2-carbonyl-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate. The carbonyl reductase gene disclosed by the invention is derived from candida glabrata, can be used as a catalyst to be applied to preparation of multiple chiral alcohols with optical activities, such as (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate. Compared with the other methods for preparing (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl ethyl butyrate, a product obtained by catalysis with the method disclosed by the invention is high in concentration without additional expensive coenzyme; the product is high in optical purity, reaction condition is mild, operation is convenient and easy to amplify. Thus, the carbonyl reductase has a good industrial application prospect in production of an ACEI (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor) medicament intermediate.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing lisinopril intermediate
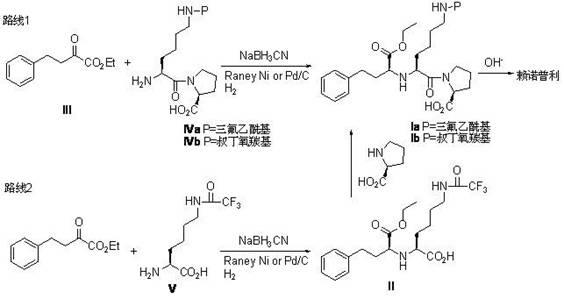
InactiveCN102617704AAvoid it happening againIncrease contentOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationSolventLisinopril
The invention relates to a method for preparing a lisinopril intermediate. The method comprises the following steps of: mixing and stirring N-protecting group-L-lysine or N-protecting group-L-lysine-L-proline, sodium triacetoxyborohydride, glacial acetic acid and a reaction solvent uniformly; cooling, dripping a mixed solution of alpha-oxo-phenylbutyrate and the reaction solvent, and continuing to react; reacting at room temperature for 2 to 6 hours; and adding water, extracting, recrystallizing, filtering and drying to obtain the lisinopril intermediate, wherein the sequence of dripping raw materials and the sequence of reaction can be adjusted. According to the method, NaBH3CN is replaced by NaBH(OAc), so that the generation of toxic side products is avoided; and the method is environment-friendly, and the reaction is performed under normal pressure, so that the efficiency and safety are improved, the content of an S isomer in the obtained product is improved, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:JIANGXI DIRUI SYNTHETIC CHEM
Carbonyl reductase mutant as well as coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN108624605AHigh catalytic efficiencyHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAlcoholPhenylbutyrate
The invention discloses a carbonyl reductase mutant as well as a coding gene and application thereof. A carbonyl reductase mutant gene has a sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 1; an amino acid sequence of acarbonyl reductase mutant coded by the carbonyl reductase mutant gene is shown as SEQ ID NO. 2. A genetically engineered bacterium for producing carbonyl reductase contains the carbonyl reductase gene provided by the invention. A preparation method of the carbonyl reductase comprises the following step: culturing the genetically engineered bacterium for producing the carbonyl reductase to obtainthe carbonyl reductase through recombinant expression. The carbonyl reductase prepared by the recombinant expression is used as catalyst, and optical active chiral alcohol is prepared through an asymmetric reducing carbonyl compound; preparation of the recombinant carbonyl reductase is realized, and the recombinant carbonyl reductase is used for asymmetrically synthesizing and catalyzing (R)-2-hydroxyl-4-ethyl phenylbutyrate. The substrate conversion rate reaches 96.8 percent and the ee of a reduction product is greater than 99 percent.
Owner:宿迁阿尔法科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com