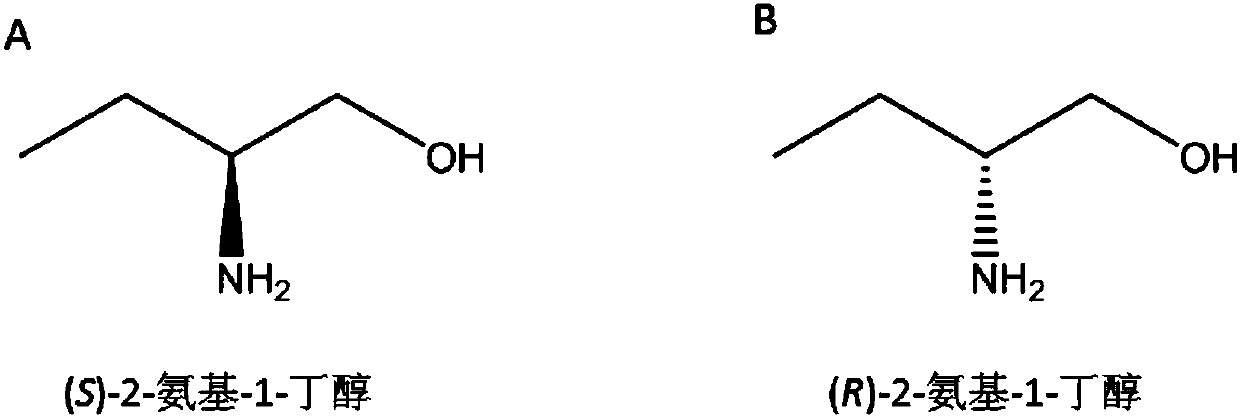
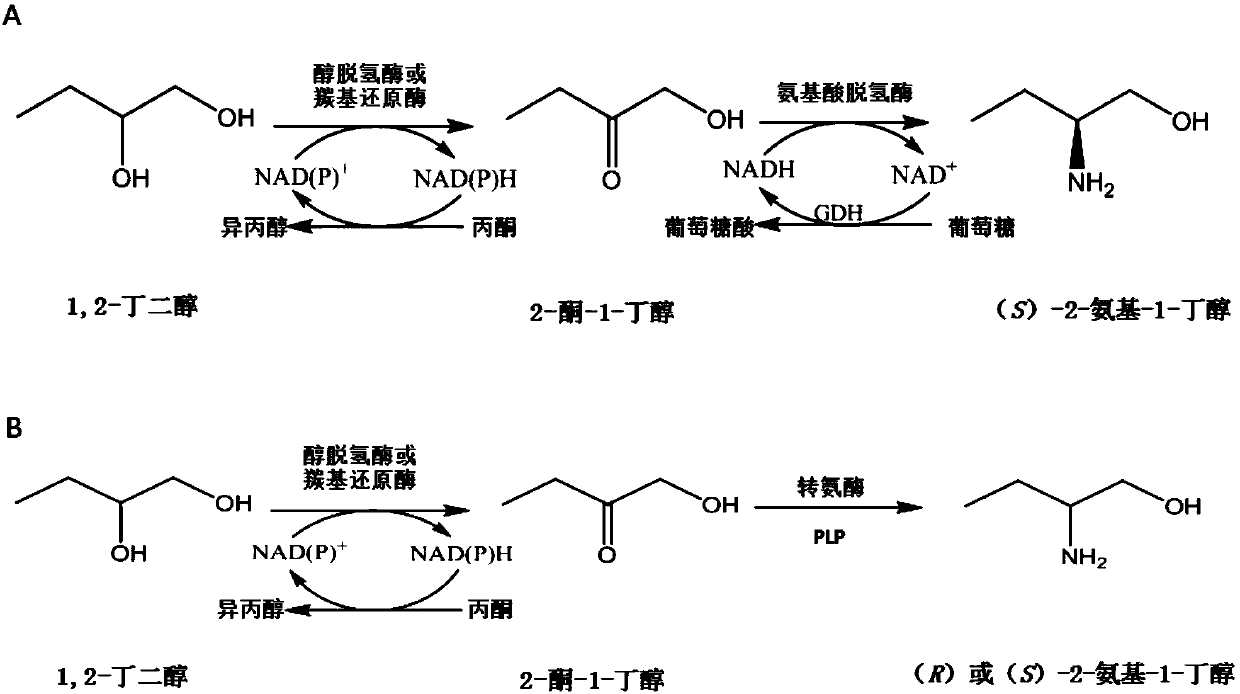
Method for synthesizing chiral 2-amino-1-butanol
A synthetic method, amino technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, enzymes, redox enzymes, etc., can solve the problems of large pollution, low safety factor, low yield, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0111] Example 1. Preparation of (S)-2-amino-1-butanol by coupling alcohol dehydrogenase or carbonyl reductase to leucine dehydrogenase or its mutant of Geobacillus stearothermophilus
[0112] 1. Preparation of engineering bacteria of recombinant alcohol dehydrogenase or its mutant, amino acid dehydrogenase or its mutant
[0113] The genes encoding the relevant enzymes are synthesized separately (codon optimization is performed with Escherichia coli as the host if necessary), and the synthesized genes are connected to various expression vectors to construct. The expression vectors are various conventional vectors in the art. The vector of the present invention is specifically pET22b(+), after inserting the coding gene of the relevant enzyme after the whole gene synthesis into the restriction site NdeI and XhoI of pET22b(+), and after the sequence verification is correct, the recombinant vector is obtained . The related gene mutants were obtained by site-directed mutagenesis....
Embodiment 2
[0137] Example 2, Preparation of (S)-2-amino-1-butanol by alcohol dehydrogenase or carbonyl reductase coupled transaminase
[0138] One, the preparation of engineering bacteria of recombinant alcohol dehydrogenase or carbonyl reductase, transaminase
[0139] Carry out with reference to Step 1 of Example 1.
[0140] See Table 4 for details of the enzymes and their mutants involved in this example.
[0141] Enzymes involved in table 4 embodiment 2 and mutants thereof
[0142]
[0143]
[0144] Note: The meanings of W1-W8 are the same as those in Table 1. W10 represents ATA-117 transaminase from Codexis; W11 represents transaminase derived from Aspergillus terreus; W12 represents transaminase derived from Aspergillus fumigatus; W13 represents Neosartorya fischeri derived from W14 means transaminase derived from Gibberella zeae; W15 means transaminase derived from Mycobacterium vanbaalenii. Wn-Mn represents a mutant of Wn (n is a natural number). The numbering and speci...
Embodiment 3
[0157] Example 3, Preparation of (R)-2-amino-1-butanol by coupling transaminase with alcohol dehydrogenase or carbonyl reductase
[0158] 1. Preparation of engineering bacteria for recombinant alcohol dehydrogenase and transaminase
[0159] Carry out with reference to Step 1 of Example 1.
[0160] See Table 6 for details of the enzymes and their mutants involved in this example.
[0161] Enzymes involved in table 6 embodiment 3 and mutants thereof
[0162]
[0163]
[0164] Note: The meanings of W1-W8 are the same as those in Table 1. W16 indicates transaminase derived from Bacillus megaterium; W17 indicates transaminase derived from Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa). Wn-Mn represents a mutant of Wn (n is a natural number). The numbering and specific nomenclature of protein and gene substitutions are the same as in Table 1.
[0165] 2. Expression of recombinant alcohol dehydrogenase and transaminase and preparation of crude enzyme
[0166] Carry out with refer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com