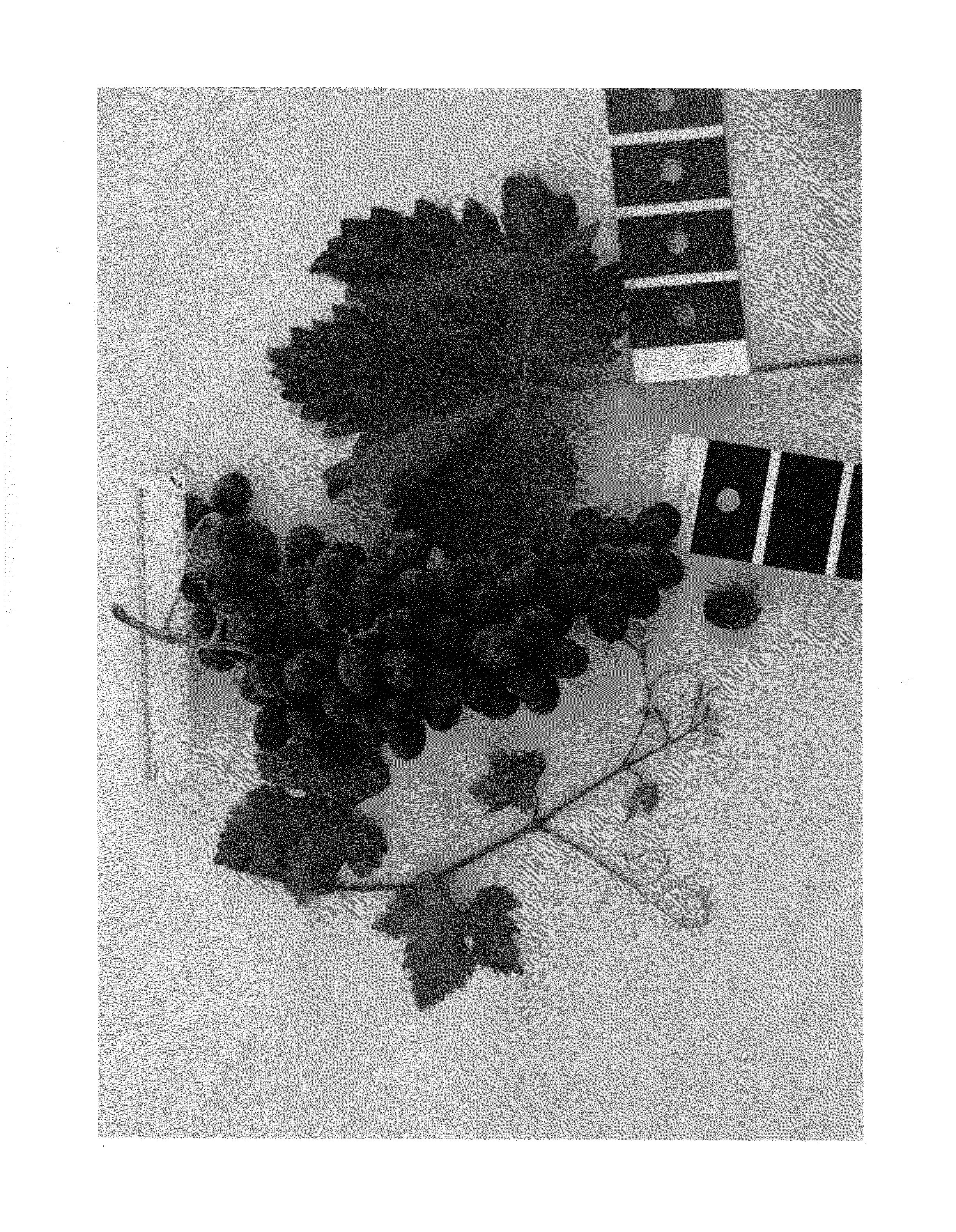Patents
Literature
33 results about "Late season" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Controlling plant pathogens with bacterial/fungal antagonist combinations
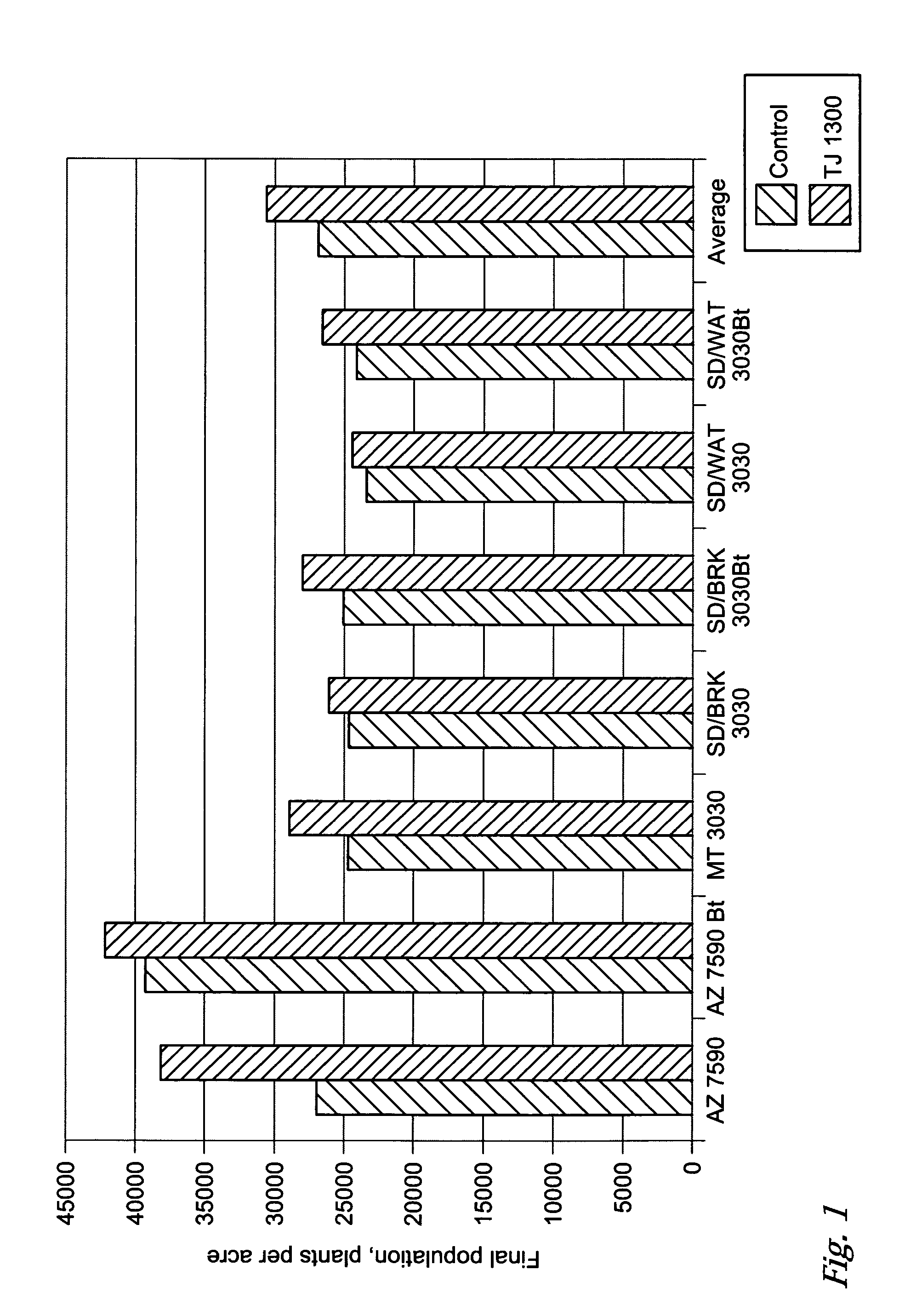
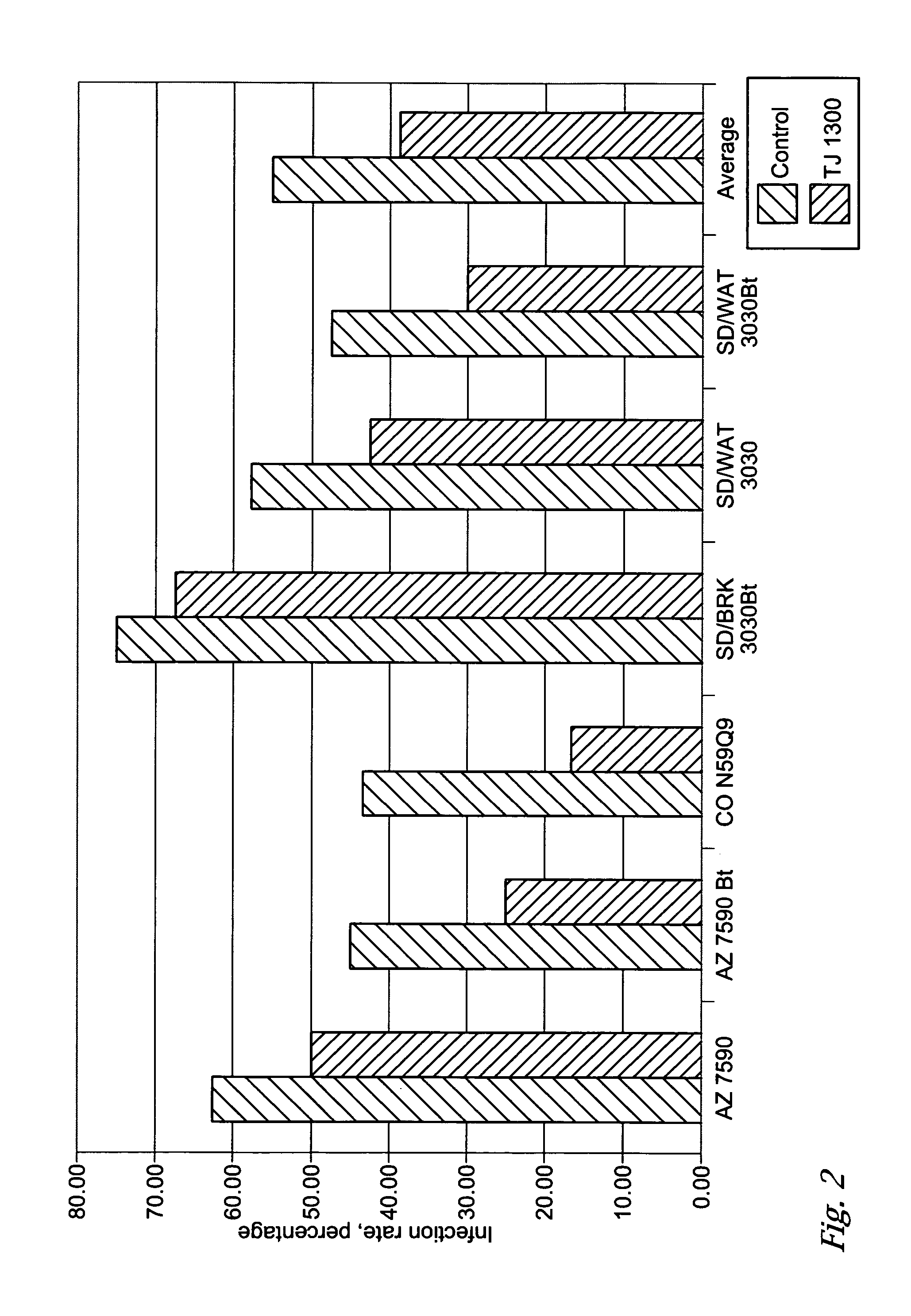
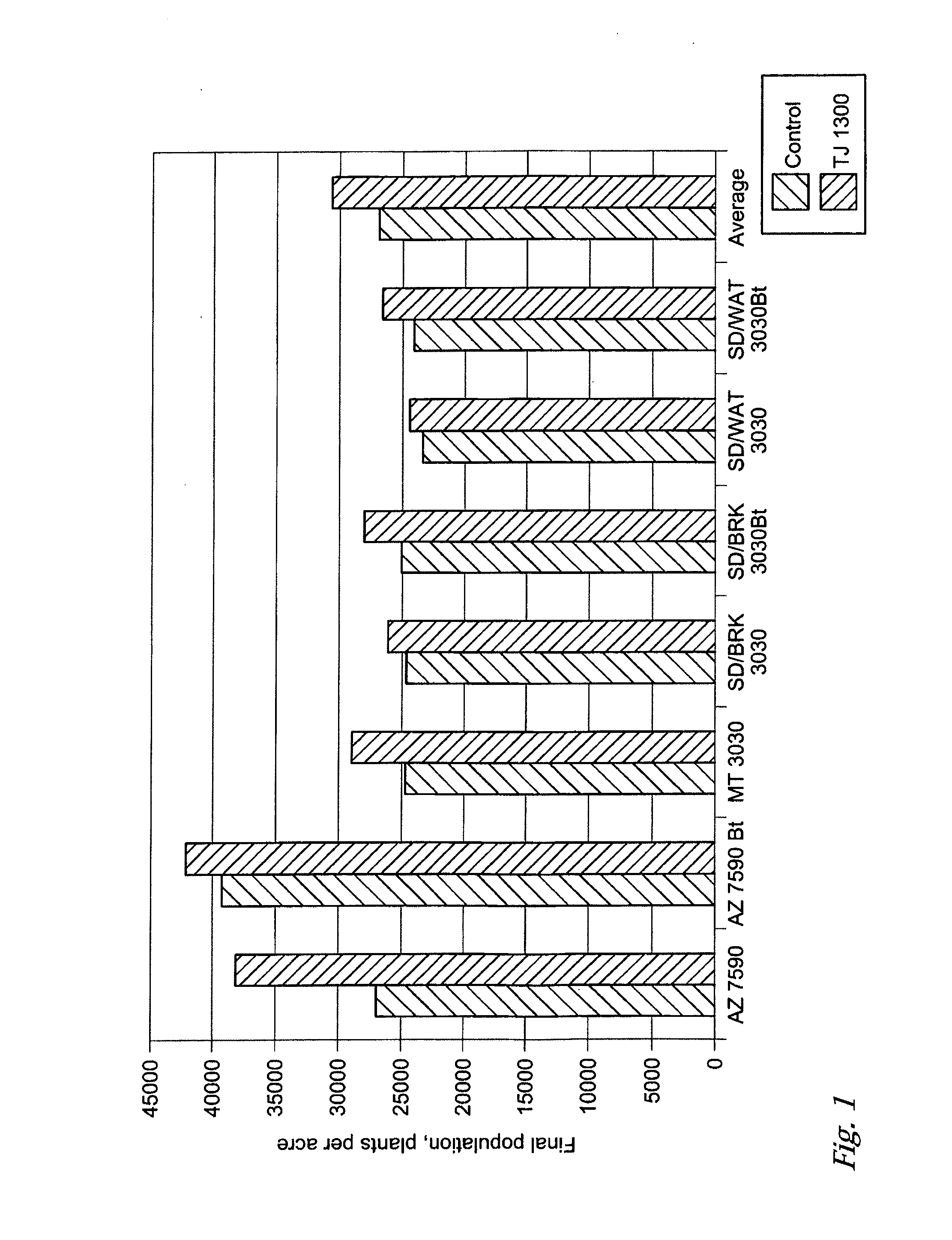
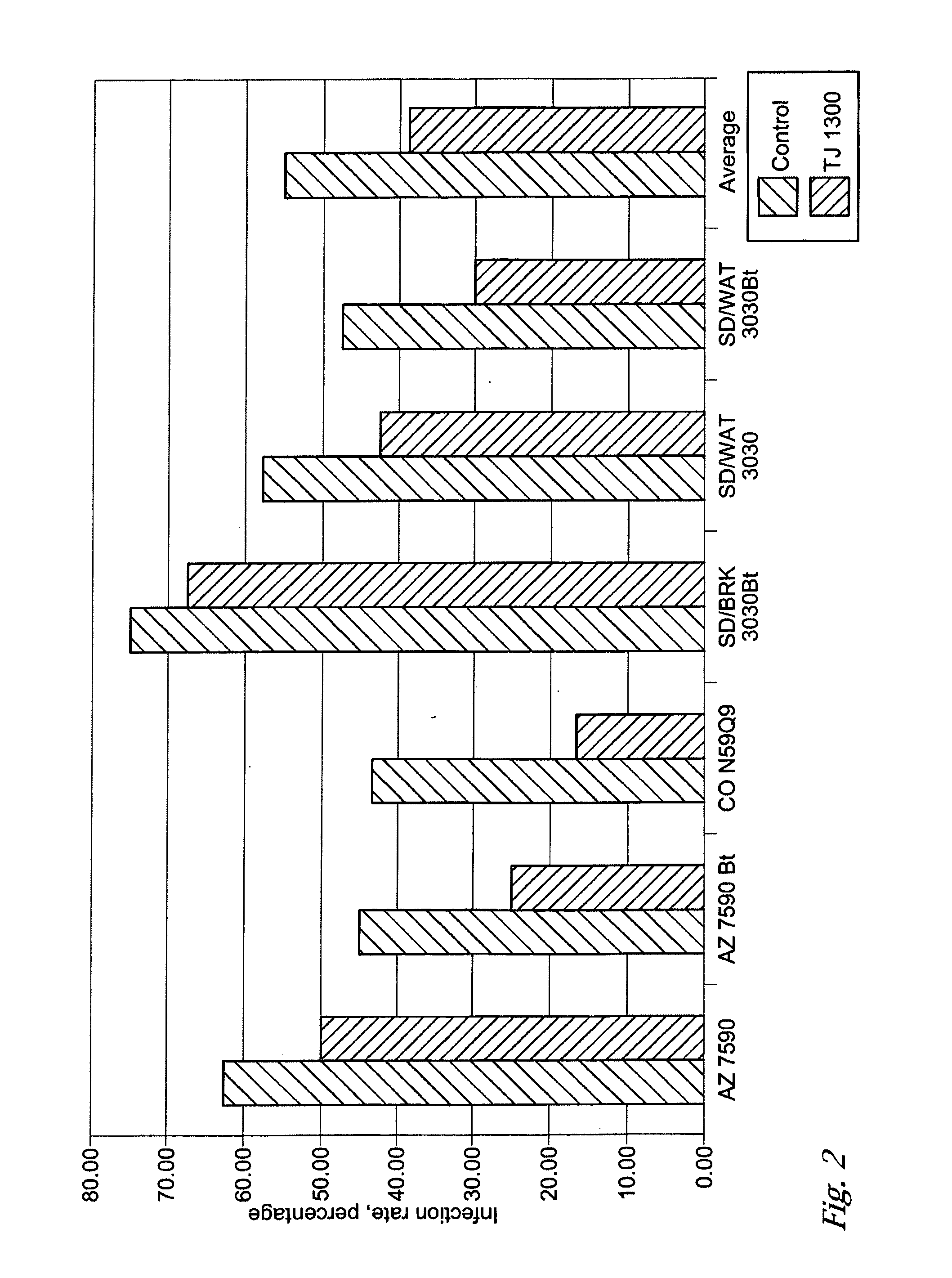
Fungal / bacterial antagonist combinations, a seed coated with one of the combinations and a plant protected from plant pathogens by one of the combinations. The invention is also a fungal / bacterial antagonist combination comprising a Trichoderma virens fungal antagonist and a Bacillus subtilis var. amyloliquefaciens (Bacillus amyloliquefaciens) bacterial antagonist and its use for controlling plant pathogens as a biocontrol agent, bio-pesticide or bio-fungicide. The invention also finds utility as a fungal / bacterial antagonist combination applied to the seed, stalk or leaf that results in an increase in plant yield. Control of early and late season stalk and root rot caused by fungi such as Fusarium, Phythium, Phytophthora and Penicillium in tomatoes, peppers, turf grass, soybeans, sunflower, wheat and corn is achieved.
Owner:NOVOZYMES BIOAG AS
Yield and stress tolerance in transgenic plants
ActiveUS20080010703A1Increase productionImprove adverse reactionsClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesIncreased toleranceLow nitrogen
Polynucleotides and polypeptides incorporated into expression vectors have been introduced into plants and were ectopically expressed. The polypeptides of the invention have been shown to confer at least one regulatory activity and confer increased yield, greater height, greater early season growth, greater canopy coverage, greater stem diameter, greater late season vigor, increased secondary rooting, more rapid germination, greater cold tolerance, greater tolerance to water deprivation, reduced stomatal conductance, altered C / N sensing, increased low nitrogen tolerance, increased low phosphorus tolerance, or increased tolerance to hyperosmotic stress as compared to the control plant as compared to a control plant.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY) +1
Controlling plant pathogens with bacterial/fungal antagonist combinations
InactiveUS20050096225A1Extended shelf lifeEffective controlBiocideClimate change adaptationPhytophthora sp.Trichoderma sp.
Fungal / bacterial antagonist combinations, a seed coated with one of the combinations and a plant protected from plant pathogens by one of the combinations. The invention is also a fungal / bacterial antagonist combination comprising a Trichoderma virens fungal antagonist and a Bacillus subtilis var. amyloliquefaciens (Bacillus amyloliquefaciens) bacterial antagonist and its use for controlling plant pathogens as a biocontrol agent, bio-pesticide or bio-fungicide. The invention also finds utility as a fungal / bacterial antagonist combination applied to the seed, stalk or leaf that results in an increase in plant yield. Control of early and late season stalk and root rot caused by fungi such as Fusarium, Phythium, Phytophthora and Penicillium in tomatoes, peppers, turf grass, soybeans, sunflower, wheat and corn is achieved.
Owner:NOVOZYMES BIOAG AS
Mandarin variety named 'Tango'
A new mandarin variety called ‘Tango’ is distinguished by production of fruit that combines mid to late season maturity, moderately large fruit size, very smooth rind texture with a deep orange color, and a rich, sweet flavor. It further distinguishes itself by being very low seeded and easy to peel.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Plant seed assemblies comprising bacterial/fungal antagonists
InactiveUS20080320615A1Extended shelf lifeEffective controlBiocideClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyBacteroides
A seed treated with a fungal / bacterial antagonist combination and a seed assembly comprising a seed and a fungal / bacterial antagonist combination. The fungal / bacterial antagonist combination comprises a Trichoderma virens fungal antagonist and a Bacillus amyloliquefaciens bacterial antagonist for controlling plant pathogens as a biocontrol agent, bio-pesticide or bio-fungicide. In preferred embodiments, the invention produces an increase in plant yield. Control of early and late season stalk and root rot caused by fungi such as Fusarium, Phythium, Phytophthora and Penicillium in tomatoes, peppers, turf grass, soybeans, sunflower, wheat and corn is achieved.
Owner:NOVOZYMES BIOAG AS
Plant seed assemblies comprising fungal/ bacterial antagonists
InactiveUS20120157304A1Extended shelf lifeEffective controlBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPhytophthora sp.Planting seed
A seed treated with a fungal / bacterial antagonist combination and a seed assembly comprising a seed and a fungal / bacterial antagonist combination. The fungal / bacterial antagonist combination comprises a Trichoderma virens fungal antagonist and a Bacillus amyloliquefaciens bacterial antagonist for controlling plant pathogens as a biocontrol agent, bio-pesticide or bio-fungicide. In preferred embodiments, the invention produces an increase in plant yield. Control of early and late season stalk and root rot caused by fungi such as Fusarium, Phythium, Phytophthora and Penicillium in tomatoes, peppers, turf grass, soybeans, sunflower, wheat and corn is achieved.
Owner:NOVOZYMES BIOAG AS
Yield and stress tolerance in transgenic plants iv
InactiveUS20100186106A1Increase productionAmeliorate adverse effect of waterClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesIncreased toleranceLow nitrogen
Polynucleotides and polypeptides incorporated into expression vectors have been introduced into plants and were ectopically expressed. The polypeptides of the invention have been shown to confer at least one regulatory activity and confer increased yield, greater height, greater early season growth, greater canopy coverage, greater stem diameter, greater late season vigor, increased secondary rooting, more rapid germination, greater cold tolerance, greater tolerance to water deprivation, reduced stomatal conductance, altered C / N sensing, increased low nitrogen tolerance, increased low phosphorus tolerance, or increased tolerance to hyperosmotic stress as compared to the control plant as compared to a control plant.
Owner:MONSANTO CO (MONSANTO CY) +1
High-yield cultivation method for direct seeding of early-season rice, direct seeding of late rice and clover seeds
InactiveCN106105645AHigh quality riceFully reflect the outputCultivating equipmentsRice cultivationGreen manurePaddy field
The invention discloses a high-yield cultivation method for direct seeding of early-season rice, direct seeding of late rice and clover seeds. The method comprises following steps: 1, direct-seeding of early-season rice around April.10th and harvest by utilization of a harvester before July.15th; 2, direct-seeding of late rice from July.15th to July.20th and full heading before September 20th and harvest by utilization of the harvester before Oct.25th; 3, direct-seeding of clover seeds in late-rice fields from the last ten days of September to the first ten days of October, retting early-season rice as green manure before direct seedling around 12 days. The method further comprises step 1, high-yield cultivation technology of direct seeding of early-season rice; step 2, high-yield cultivation technology of direct seeding of late-season rice; step 3, high-yield cultivation of clover seeds. The high-yield cultivation method for direct seeding of early-season rice has following features: a good mode of output, quality and efficiency can be fully represented; and labor is saved, rice seedling beds, fertilizers, medicine and water are saved; soil is improved; rice quality is good, output and income are increased.
Owner:XIANNING AGRI ACADEMY OF SCI
Juices incorporating mid-season orange cultivars
InactiveUS20070248735A1Improve sensory propertiesExcellent color attributeFood scienceFruit juiceBrix
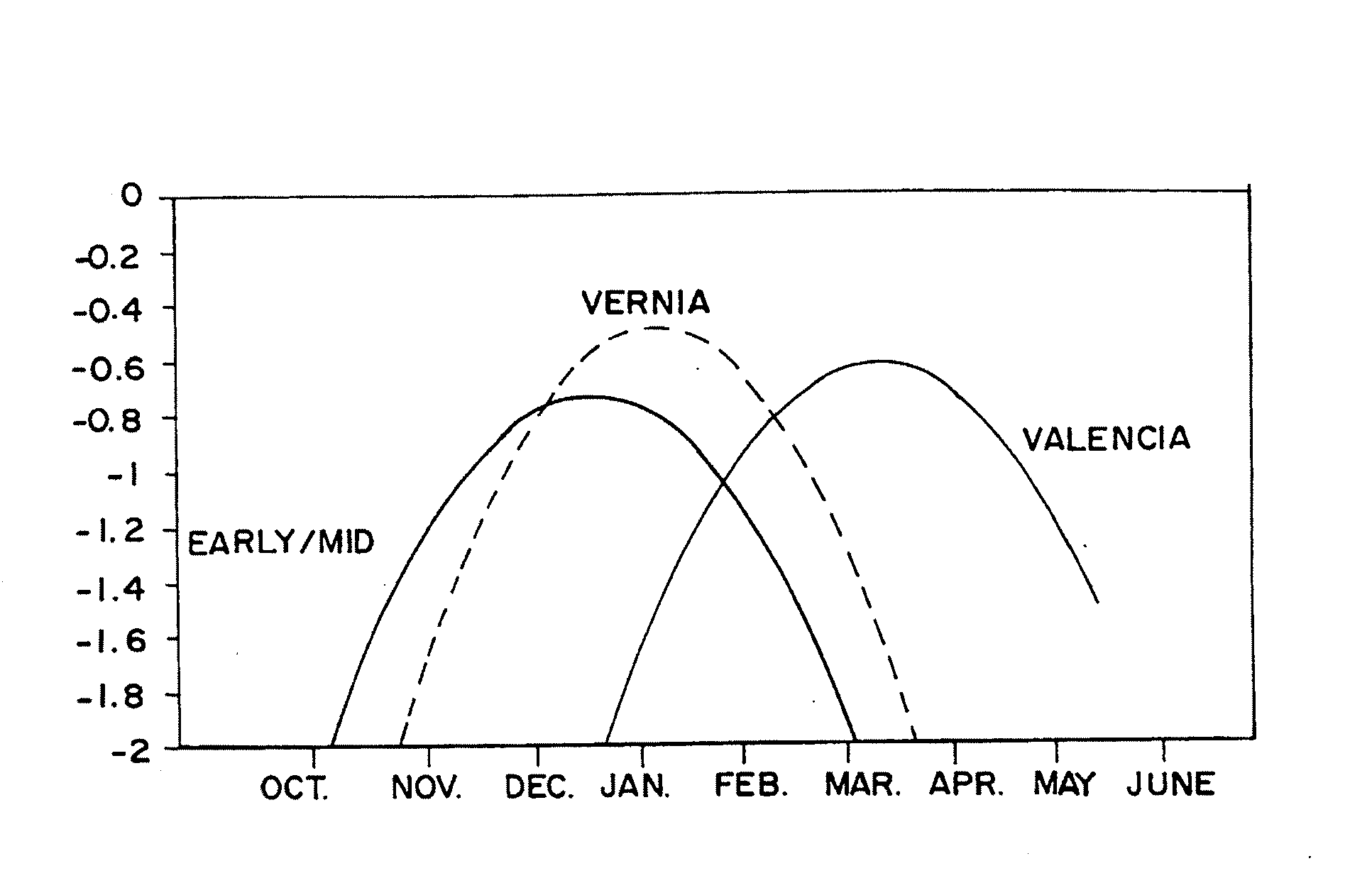
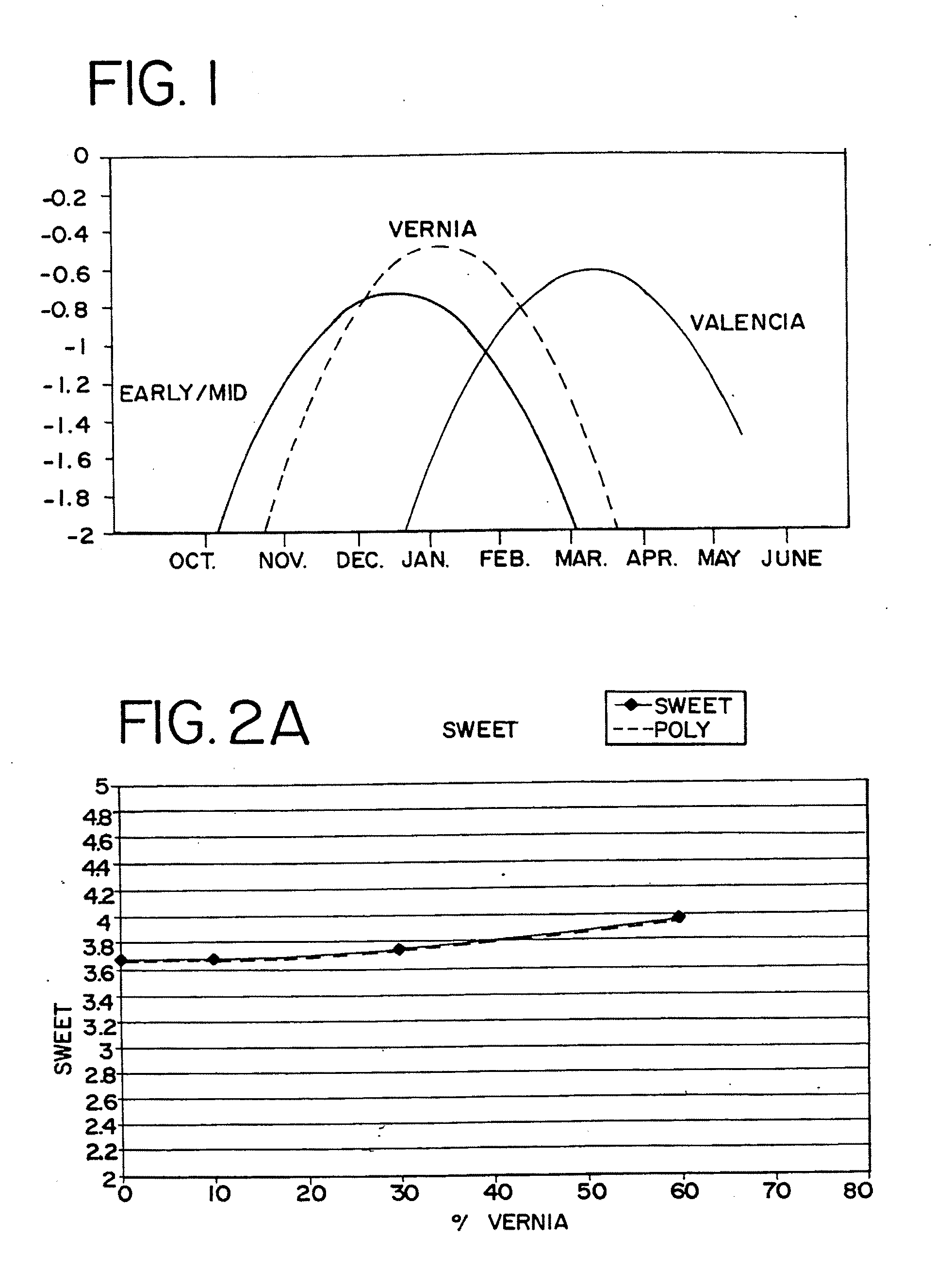
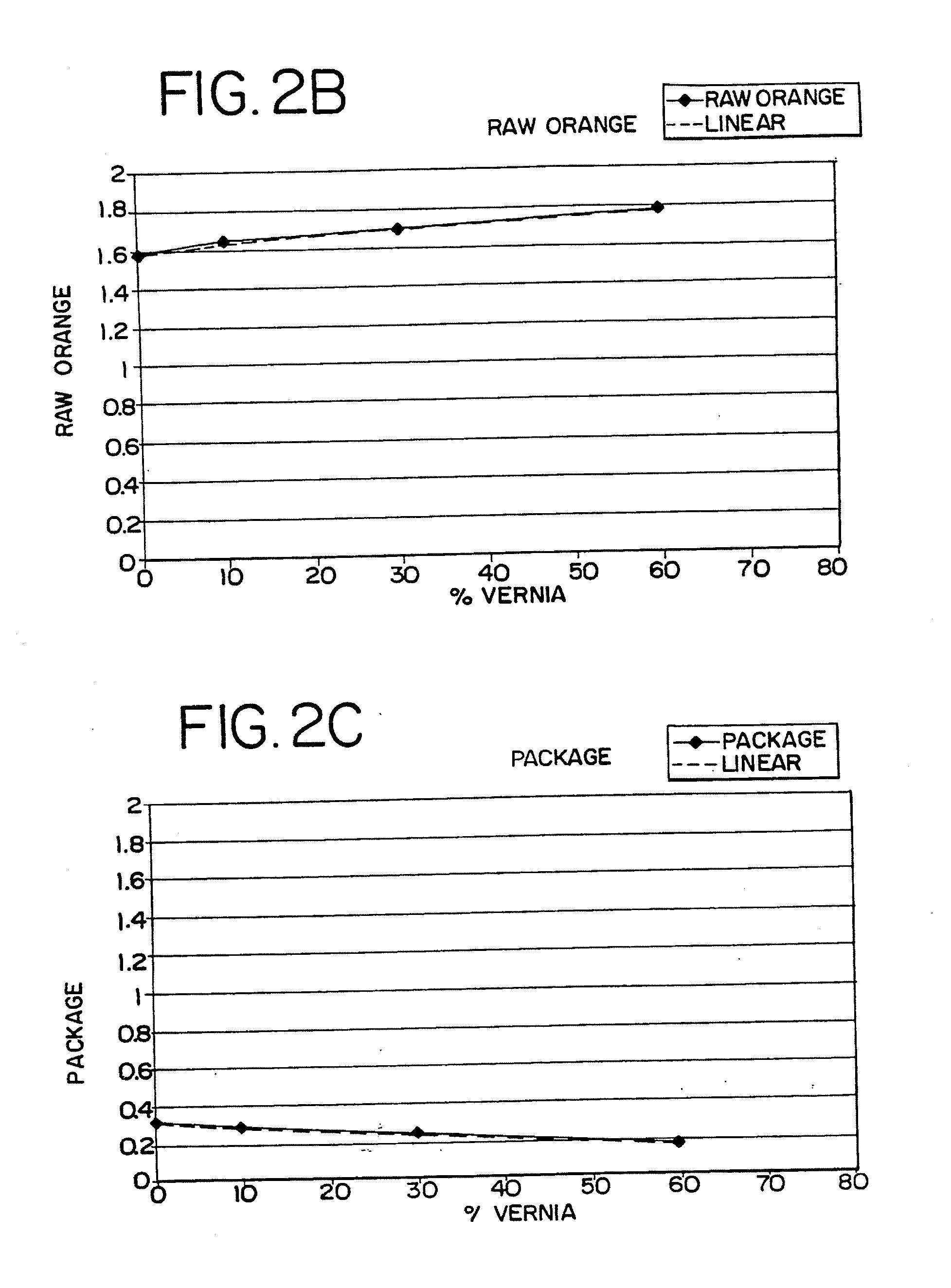
Orange juice products are provided which include as a component juice extracted from a mid-season round orange cultivar having a peak harvest season in December, January and February. The preferred mid-season round orange cultivar is the Vernia cultivar. The juice extracted from such mid-season cultivar has sensory attributes which are superior to those of traditional late season Valencia round orange cultivar juice. The mid-season juice has a Brix-to-acid ratio and a color intensity at least as high as juice provided by the traditional Valencia cultivars which are harvested at the same time as the mid-season cultivar.
Owner:TROPICANA PROD INC
Mixed planting method of sweet basil, oilseed rape and corn
InactiveCN105900651AGive full play to the effect of increasing productionConducive to continuous increase in productionSuperphosphatesExcrement fertilisersLate seasonGrowing season
Provided is a mixed planting method of sweet basil, oilseed rape and corn. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of land selection and preparation, oilseed rape planting, sweet basil planting, early-season corn planting, oilseed rape harvesting, late-season corn planting and daily management of the sweet basil, early-season corn and late-season corn. The mixed planting method of the sweet basil, oilseed rape and corn has the advantages that by means of land interplanting of the sweet basil, oilseed rape and corn, land can be fully utilized, crop groups can be reasonably arranged according to the planting and growing seasons, fertility of the land is sufficient, and high yield and high efficiency are achieved; the yield-increase effect of dominance in border row is fully exerted, the land is fertilized through the land, the yields of crops are increased, land fertility is improved, and the method is beneficial for sustainable yield increase.
Owner:马家庆
Mandarin tree named ‘Tango’
A new mandarin variety called ‘Tango’ is distinguished by production of fruit that combines mid to late season maturity, moderately large fruit size, very smooth rind texture with a deep orange color, and a rich, sweet flavor. It further distinguishes itself by being very low seeded and easy to peel.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
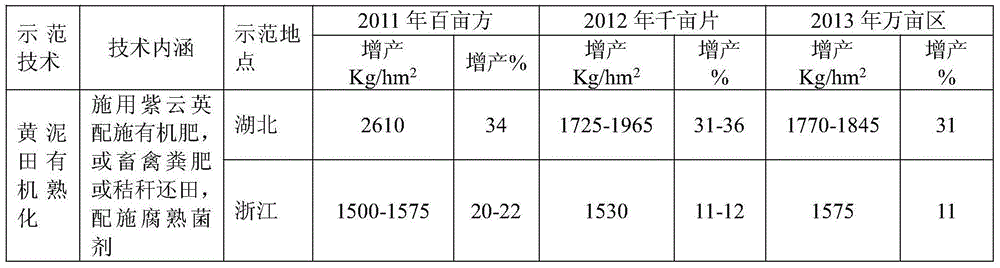
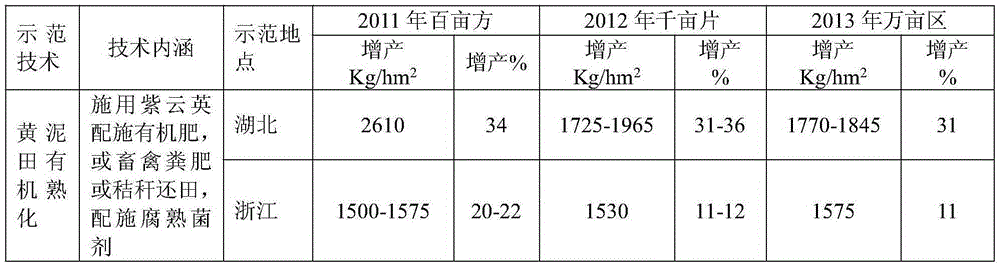
Improvement method for organic maturation of yellow mud fields
The invention discloses an improvement method for organic maturation of yellow mud fields. For an early season rice field, the improvement method includes the steps: 1), planting astragalus sinicus and applying inorganic fertilizer; 2), applying nitrogen fertilizer at a stage when astragalus sinicus sends forth a first true leaf, wherein scalar quantity of the nitrogen fertilizer is 6.9-10.35 kilograms per hectare; 3), reapplying the nitrogen fertilizer at a stage when astragalus sinicus grows vigorously, wherein scalar quantity of the nitrogen fertilizer is 17.25-34.5 kilograms per hectare; 4), taking astragalus sinicus as green manure to be returned to the field, and applying chemical fertilizer. For double cropping rice, the improvement method includes 1), directly returning straw of early season rice into field in situ, or applying livestock and poultry manure for soil maturation; 2), additionally applying nitrogen fertilizer, and adjusting C / N ratio of the straw; 3), applying rotten organic fertilizer or mushroom residue before seeding middle-season rice or late-season rice; 4), performing light dewatering and ventilating after transplanting of the middle-season rice or the late-season rice, and re-watering. By the improvement method, soil structure is improved, soil volume weight is lowered, soil cation exchange quantity is increased, community structure of soil microorganisms and soil enzyme activity are affected.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Yield and stress tolerance in transgenic plants iii
InactiveUS20100186105A1Increase productionAmeliorate adverse effect of waterClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesNucleotideLow nitrogen
Polynucleotides and polypeptides incorporated into expression vectors have been introduced into plants and were ectopically expressed. The polypeptides of the invention have been shown to confer at least one regulatory activity and confer increased yield, greater height, greater early season growth, greater canopy coverage, greater stem diameter, greater late season vigor, increased secondary rooting, more rapid germination, greater cold tolerance, greater tolerance to water deprivation, reduced stomatal conductance, altered C / N sensing, increased low nitrogen tolerance, increased low phosphorus tolerance, or increased tolerance to hyperosmotic stress as compared to the control plant as compared to a control plant.
Owner:MONSANTO CO +1
Method for producing aquatic vegetable and green manure during crop rotation of water mimosa and paddy rice
ActiveCN105993472AGuaranteed outputGuaranteed incomeCultivating equipmentsOrganic fertilisersGreen manureLate season
The invention discloses a method for producing aquatic vegetables and a green manure during crop rotation of water mimosa and paddy rice. With the method, paddy rice and water mimosa are planted according to a certain ratio during a double-cropping rice period. Water mimosa can grow together with paddy rice in a paddy environment. Rhizobium of the water mimosa on the part on the surface of the paddy can fix nitrogen, such that soil nitrogen content can be increased. After the harvesting of early-season rice, the edible parts of water mimosa are harvested, and all the non-edible parts are turned back to the field as green manure; after the harvesting of late-season rice, winter cropping of water mimosa is carried out; about 1 month before early-season rice planting in the next year, the edible parts of the winter-cropping water mimosa are harvested, and all the non-edible parts are turned back to the field as green manure. With the paddy rice and water mimosa crop rotation method, soil fertility can be maintained on a basis of increasing paddy rice yield. Also, the use of chemical fertilizer nitrogen can be reduced, such that non-point source pollution caused by paddy rice production can be retarded.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Apple tree named 'Swedes Fuji'
A new and distinct late season variety of apple tree, named `Swedes Fuji` originating from a mutation of the standard Fuji. This new cultivar displays a brilliant red blush uniform coloration which extends over the entire surface of the apple. The cultivar is generally similar to the parent with the exception of: 1) fruit color and 2) it is easier to harvest because it has a more uniform rate of coloration throughout the entire tree when the fruit is maturing in late fall.
Owner:PICKERING DENNIS K +1
Plant seed assemblies comprising fungal/bacterial antagonists
InactiveUS20130252810A1Extended shelf lifeEffective controlBiocideDead animal preservationBiotechnologyPhytophthora sp.
Owner:NOVOZYMES BIOAG AS
Asian pear tree named `Asio 6`
ActiveUSPP18876P3Sweet mild flavorComparable in crispnessAngiosperms/flowering plantsLenticelPear tree
Owner:SUBARASHII KUDAMONO
Grapevine 'IFG Twenty'
This invention is a new and distinct grapevine variety denominated ‘IFG Twenty’. The new grapevine is characterized by producing naturally large seedless blue-black berries having a narrow ellipsoidal to cylindrical shape with a strong fruity labrusca flavor. Fruits normally ripen mid to late season about early to mid-September near Delano Calif. Fruits are fairly low in acidity, with medium dense firm texture, occasionally noticeable seed trace. Vines are productive and can be spur pruned.
Owner:BLOOM FRESH INT LTD
Intelligent accurate temperature control method for wet curtain
ActiveCN113703494AControl the maximum temperatureGuarantee normal lifeAnimal housingTemperature control using electric meansTemperature controlCooling effect
Owner:BEIJING HUADU YUKOU POULTRY
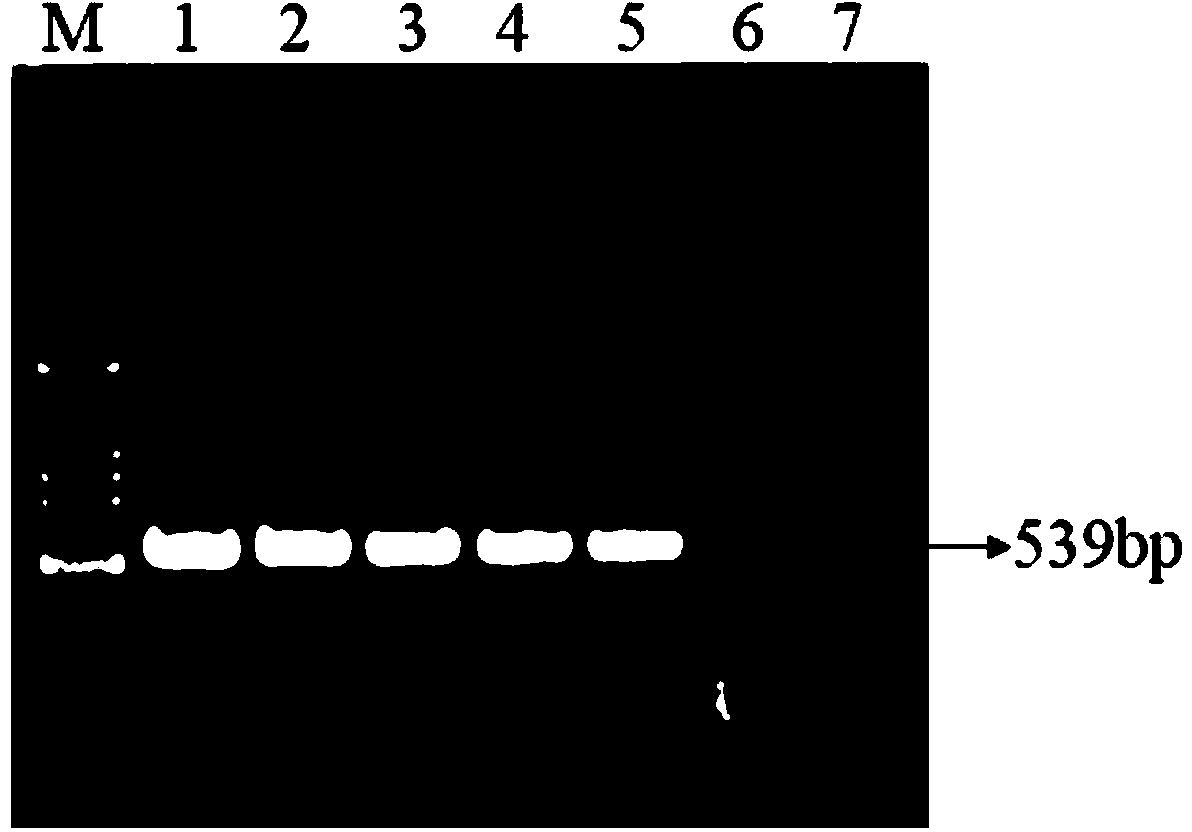
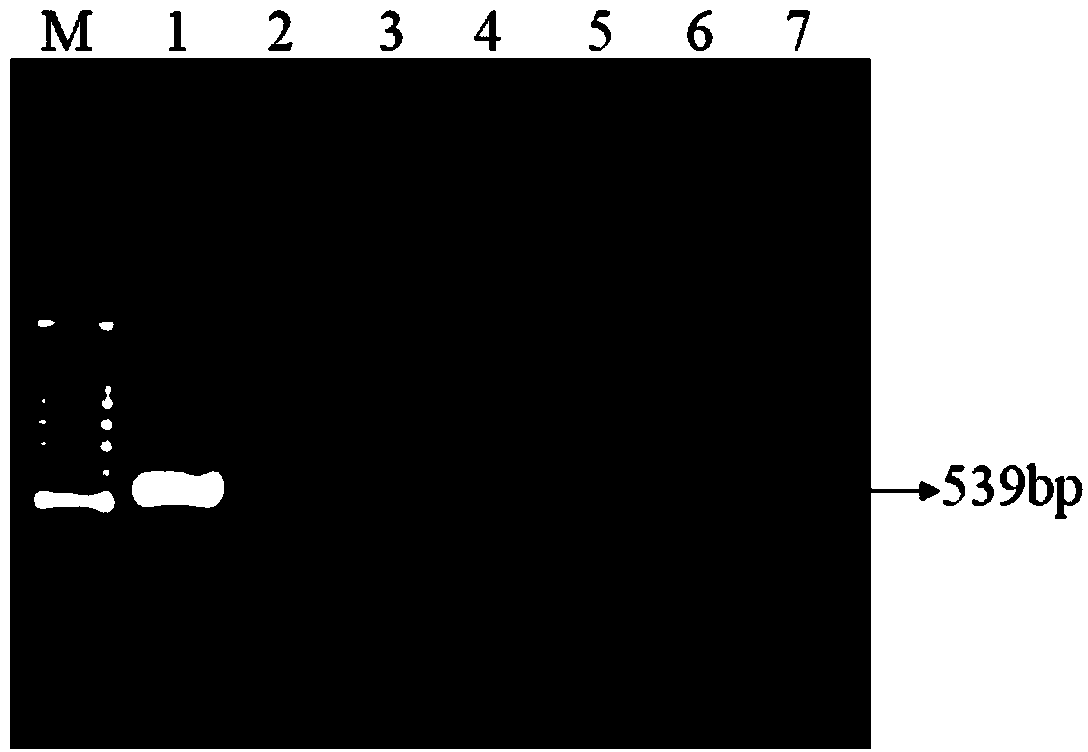
Narcissus late season yellows virus detection kit and method
ActiveCN103484567ARealize detectionStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementPositive controlReverse transcriptase
The invention relates to a narcissus late season yellows virus detection kit and method specific for narcissus late season yellows virus detection. The knit comprises an outside upstream primer, an outside downstream primer, an inside upstream primer, an inside downstream primer, an RTBuffer, an RNA enzyme inhibiting factor, reverse transcriptase, dNTPs, a PCR Buffer, MgCl2, TaqDNA polymeras, positive control, negative control and RNase-free ddH2O. Specific primers are designed according to narcissus late season yellows virus gene sequences, and a nested RT-PCR technology is utilized to detect narcissus late season yellows viruses. Firstly, inverse transcription is carried out with extracted RNA as the template to synthesize cDNA, first-round PCR amplification is carried out with the cDNA as the template, second-round PCR amplification is then carried out with first-round PCR products as the template, and agarose gel electrophoresis detection is conducted on amplification products: if a specificity target fragment of the size of 539bp appear, the judgment result indicates that a detected virus is a narcissus late season yellows virus. The narcissus late season yellows virus detection kit and method have the advantages of being strong in specificity, high in sensitivity, good in accuracy and short in detection time and are suitable for quickly detecting and monitoring narcissus late season yellows viruses in entry ports, exit ports and agricultural production.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT OF FUJIAN ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
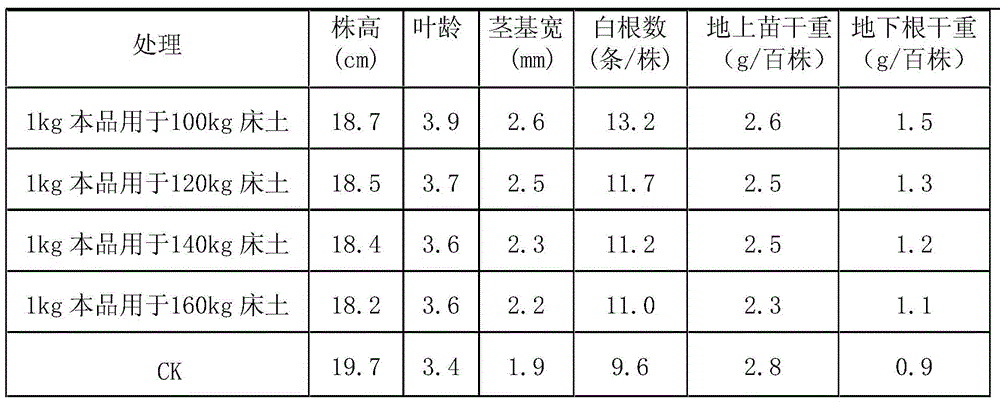
A kind of acid-regulating nutrient agent for paddy rice seedling bed soil
ActiveCN104211544BIncrease the degree of filtrationGood physical and chemical propertiesFertilizer mixturesPhosphoric acidLate season
The invention discloses an acidity-adjusting nutritional agent for dry rice seedling raising bed soil and relates to the rice seedling raising technique. The acidity-adjusting nutritional agent is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 60-70 parts of fermented rice husk, 4-6 parts of 60% dilute sulfuric acid, 12-17 parts of ammonium sulfate, 12-17 parts of calcium superphosphate, 1-2 parts of potassium chloride and 0.5-0.8 part of zinc sulfate; a preparation method of the acidity-adjusting nutritional agent comprises the steps of (1) preparing materials, (2) performing acid treatment and (3) mixing. The acidity-adjusting nutritional agent is capable of either adjusting the acidity or enhancing the fertility, and also capable of improving the physicochemical properties of the bed soil; besides, the preparation method of the acidity-adjusting nutritional agent has the characteristics of wide raw material source, simple process, low cost, suitability for production in south of China; the acidity-adjusting nutritional agent is applicable to dry-raising machine transplanted seedlings and hand transplanted seedlings of early season rice, middle-season rice and late-season rice all over the country.
Owner:湖南省湘晖农业技术开发有限公司
Method of improving lodging resistance of high-quality rice variety Xiangyaxiangzhan
PendingCN109169076AReasonable group structureSteady tiller growthData processing applicationsFertilising methodsPanicleTotal nitrogen
The invention discloses a method of improving the lodging resistance of a high-quality rice variety Xiangyaxiangzhan. The method comprises steps: (1) the target yield of Xiangyaxiangzhan is determined; (2) the land capacity yield is determined; (3) the reasonable total amount of nitrogen application is calculated, wherein the total nitrogen application amount calculation method is: the total nitrogen application amount (kg / mu)= [the target yield per mu (kg) - the land capacity yield per mu (kg)]*R / 100, R is a nitrogen application constant and refers to the nitrogen application amount for producing per 100 kg of rice on the basis of the land capacity yield, R has different values for early and late seasons, R=7 in an early season and R=8 in a late season; and (4) the nitrogen application ratio of a base fertilizer to a tillering fertilizer to a panicle fertilizer is reasonably distributed. According to climatic conditions, soil fertility and variety characteristics, the reasonable nitrogen application amounts during the full-growth period of rice and the planning and management ratio of the nitrogen fertilizer in early, middle and late stages of the rice growth are designed by the method, the number of stems and tillers during the rice growth process develops steadily, the population structure is reasonable, the plant height is shorter, the internode is shortened, and the lodging resistance of the variety is thus improved.
Owner:广东海纳农业研究院 +2
The method of building inner ridges under the co-cropping mode of shrimp and rice
InactiveCN104885975BGrowth impactEasy to manageClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaShrimpDragonet
The present invention discloses an inner-periphery ridge building method for a shrimp and rice joint culturing mode, wherein a ridge is built, in a rice field with an enclosed ditch, along the enclosed ditch; the ridge has a height of 20-40 cm and a bottom width of 30-50 cm; the ridge goes around the rice field and an outer edge of the ridge has a distance of 40-60 cm from an inner edge of the enclosed ditch; and the soil for building the ridge comes from the outer side of the ridge, and 15-25 cm thick surface soil is fetched on the outside surface of the field to build the ridge. When field sunning is needed in a rice growing season, a water outlet is arranged on the inner ridge and the water surface of the enclosed ditch is made to be lower than the field surface by using drainage and irrigation equipment; during rice fertilization, the water outlet on the inner ridge must be blocked to prevent fertilizers from flowing into the ditch; and after middle-season rice or late-season rice have been harvested, the field is irrigated to be filled with deep water, ensuring that the water surface is higher than the inner-periphery ridge, so that the entire field surface can culture small lobsters; in the following year and before transplanting of the next-season rice, the inner-periphery ridge should be reinforced to prevent leakage. The inner-periphery ridge building method of the present invention enables the water surface of the cultural ditch and the water surface of the rice field to be manually isolated and controlled, facilitating farming operation and water and fertilizer management of the rice field.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION & SOIL FERTILIZER HUBEI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +2
Grapevine named ‘IFG Twenty’
ActiveUSPP26799P3Reduce acidityMedium denseAngiosperms/flowering plantsVitis ripariaConus californicus
This invention is a new and distinct grapevine variety denominated ‘IFG Twenty’. The new grapevine is characterized by producing naturally large seedless blue-black berries having a narrow ellipsoidal to cylindrical shape with a strong fruity labrusca flavor. Fruits normally ripen mid to late season about early to mid-September near Delano Calif. Fruits are fairly low in acidity, with medium dense firm texture, occasionally noticeable seed trace. Vines are productive and can be spur pruned.
Owner:BLOOM FRESH INT LTD
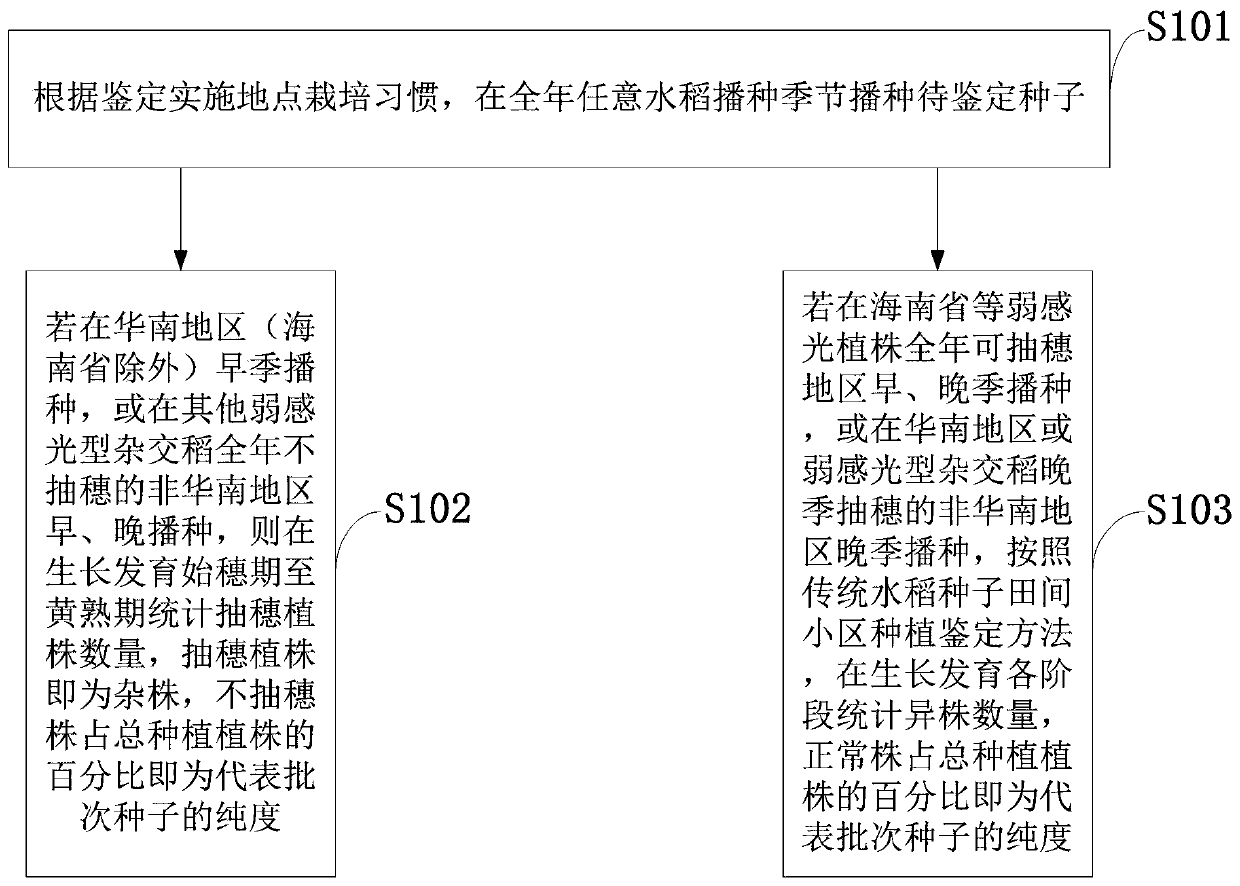
Purity identifying method of weak photosensitivity hybrid rice seeds
The invention belongs to the technical field of seed purity detection, and discloses a purity identifying method of weak photosensitivity hybrid rice seeds. The method comprises the steps of for the hybrid rice seeds of which restoring line and a sterile line are both a temperature-sensing type, and F1 is weak in photosensitivity, performing single-plant planting on the seeds in the early season or the late season under the condition that the same type of restoring lines, weak photosensitivity sterile lines and restoring lines do not exist in an isolation region and parents hybrid plant typesin the production process of the seeds, according to the earing condition of the weak photosensitivity rice plants at the planting region, counting the number of hybrid plants, and through combinationof the capacity of samples, calculating the seed purity. Based on a rice field small-region planting identifying method, the purity identifying period of the weak photosensitivity hybrid rice seeds produced under special condition is shortened to half a year from one year, the identification time of the field small-region planting purity identifying method of the weak photosensitivity hybrid riceseeds is prolonged to the early season and the later season from the later season, and the identifying location is extended to global regions where rice is suitable for growth from South China rice regions and corresponding appropriate regions.
Owner:广东华茂高科种业有限公司
A kind of paddy and dry crop rotation method of no-tillage and multiple cropping of spring corn and late rice
ActiveCN105724012BIncreased probability of safe ripe harvestNot susceptible to stainsCereal cultivationCultivating equipmentsField cropAgricultural science
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Mandarin tree named 'kinnowls'
ActiveUS20130097754P1Quality improvementEasy to produceAngiosperms/flowering plantsLate seasonBiology
‘KinnowLS’ is a mid- to late-season maturing (depending on climate) diploid mandarin that combines large-sized fruit of excellent quality and production with low seed content even in mixed plantings. It may be successful in the mid-to-late season marketing window that currently has few low-seeded, high quality cultivars.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Asian pear tree named 'Asio 6'
ActiveUS20070271639P1Sweet mild flavorComparable in crispnessAngiosperms/flowering plantsLenticelPear tree
A new and distinct cultivar of Asian Pear tree is provided. The new cultivar forms attractive excellent quality late-season large conical to round fruit having a mottled reddish-brown russet surface with prominent tan lenticels and a very sweet mild flavor. The tree is medium-sized and possesses a well-branched upright growth habit. The leaves are medium green in coloration and possess pinnate venation and an acuminate apex. The fruit of the new cultivar has been found to be capable of storage for a longer period of time than most Asian Pear cultivars.
Owner:SUBARASHII KUDAMONO
A method for simultaneously producing aquatic vegetables and green manure by intercropping intercropping between acacia and rice
ActiveCN105993472BGuaranteed outputGuaranteed incomeCultivating equipmentsOrganic fertilisersRoot noduleLate season
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
An improved method for organic ripening of yellow mud fields
The invention discloses an improvement method for organic maturation of yellow mud fields. For an early season rice field, the improvement method includes the steps: 1), planting astragalus sinicus and applying inorganic fertilizer; 2), applying nitrogen fertilizer at a stage when astragalus sinicus sends forth a first true leaf, wherein scalar quantity of the nitrogen fertilizer is 6.9-10.35 kilograms per hectare; 3), reapplying the nitrogen fertilizer at a stage when astragalus sinicus grows vigorously, wherein scalar quantity of the nitrogen fertilizer is 17.25-34.5 kilograms per hectare; 4), taking astragalus sinicus as green manure to be returned to the field, and applying chemical fertilizer. For double cropping rice, the improvement method includes 1), directly returning straw of early season rice into field in situ, or applying livestock and poultry manure for soil maturation; 2), additionally applying nitrogen fertilizer, and adjusting C / N ratio of the straw; 3), applying rotten organic fertilizer or mushroom residue before seeding middle-season rice or late-season rice; 4), performing light dewatering and ventilating after transplanting of the middle-season rice or the late-season rice, and re-watering. By the improvement method, soil structure is improved, soil volume weight is lowered, soil cation exchange quantity is increased, community structure of soil microorganisms and soil enzyme activity are affected.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com