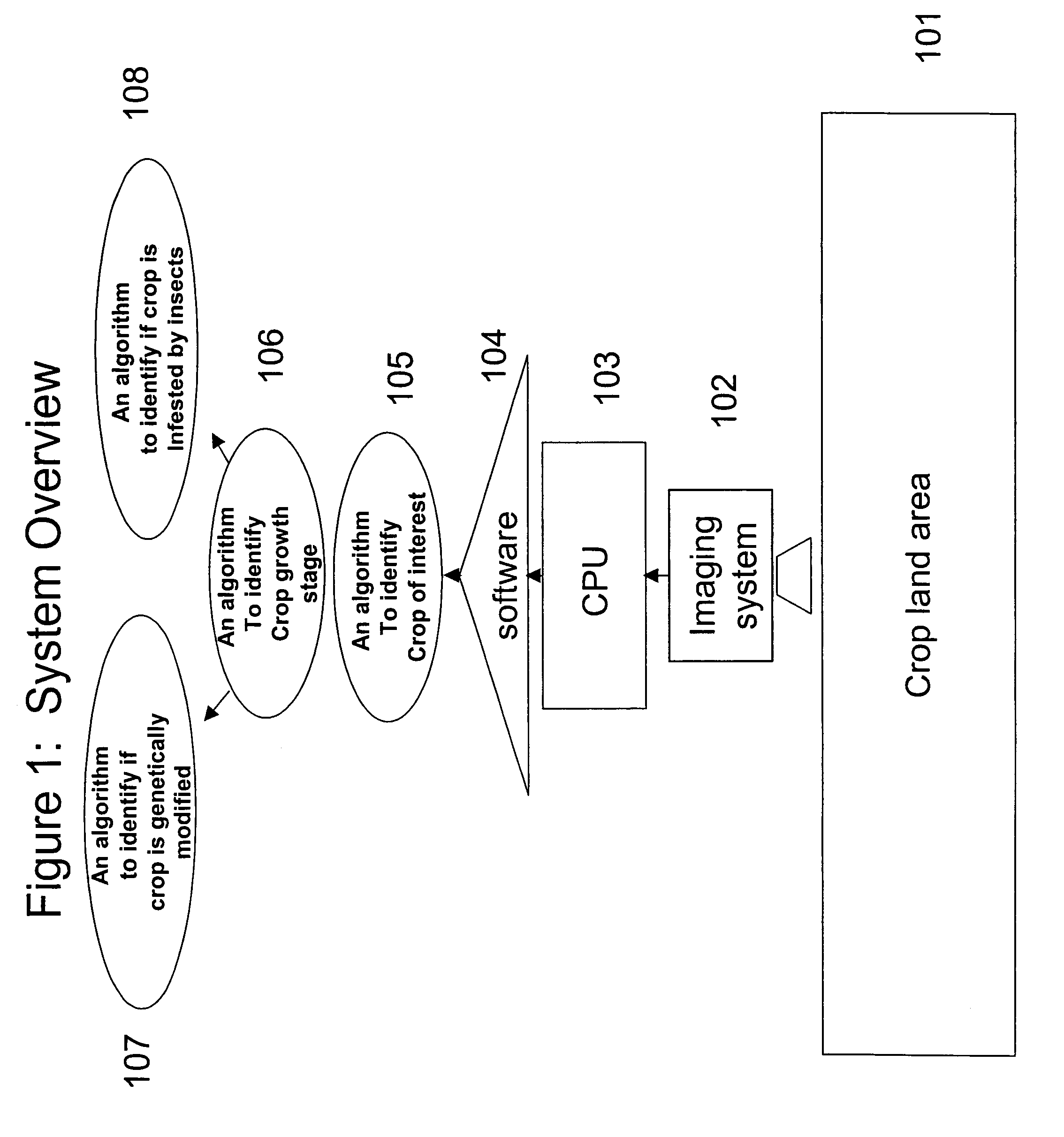
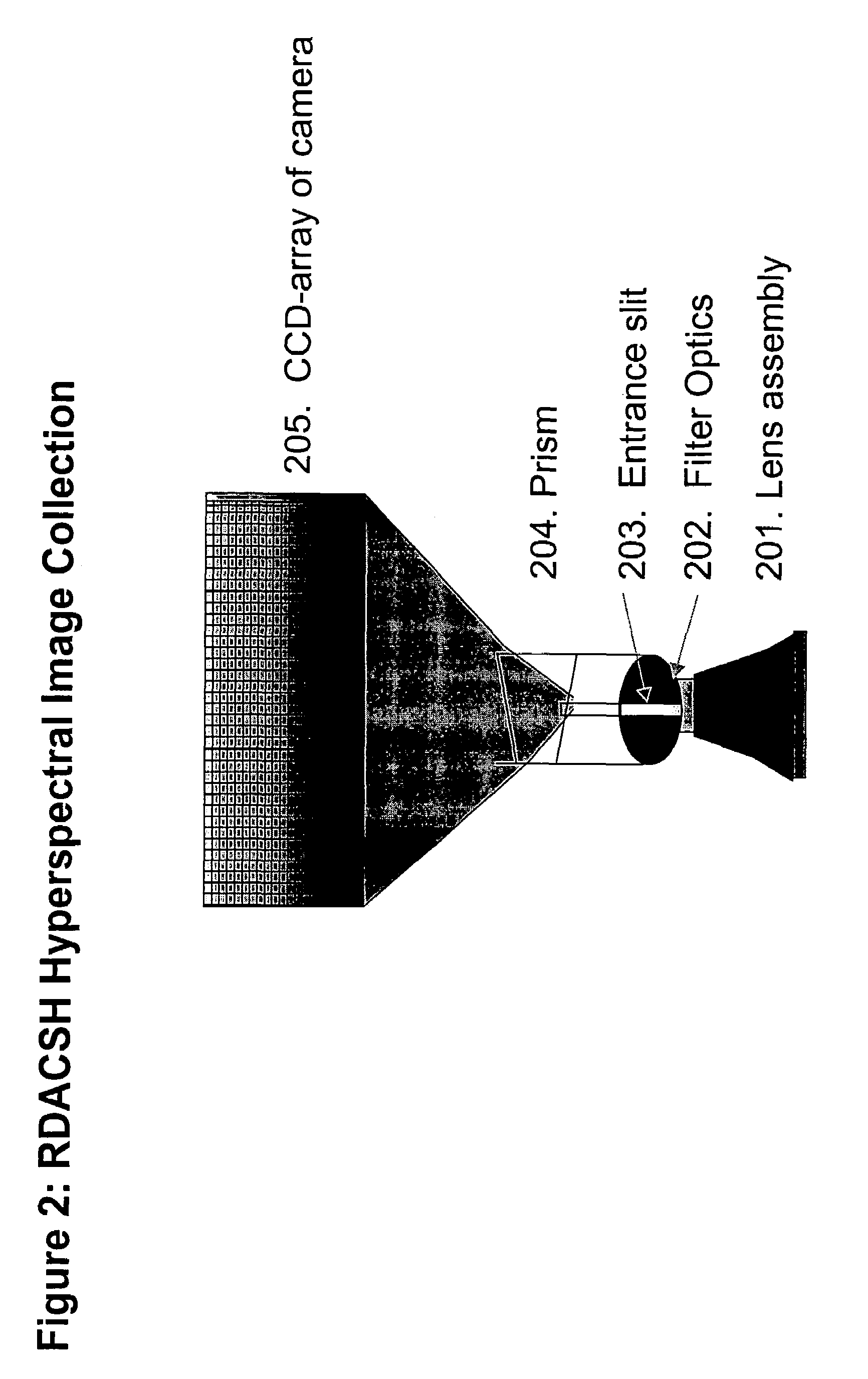
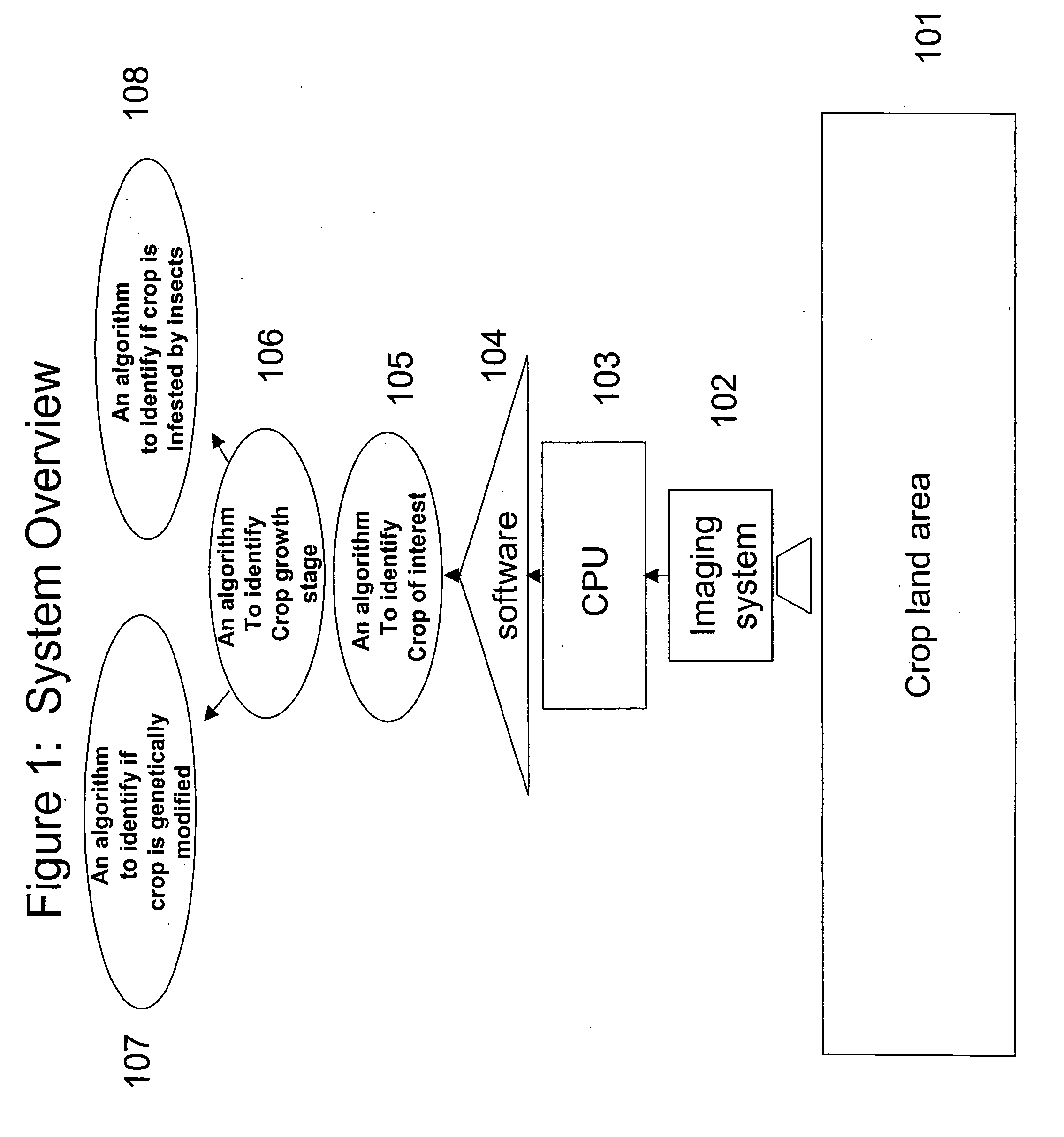
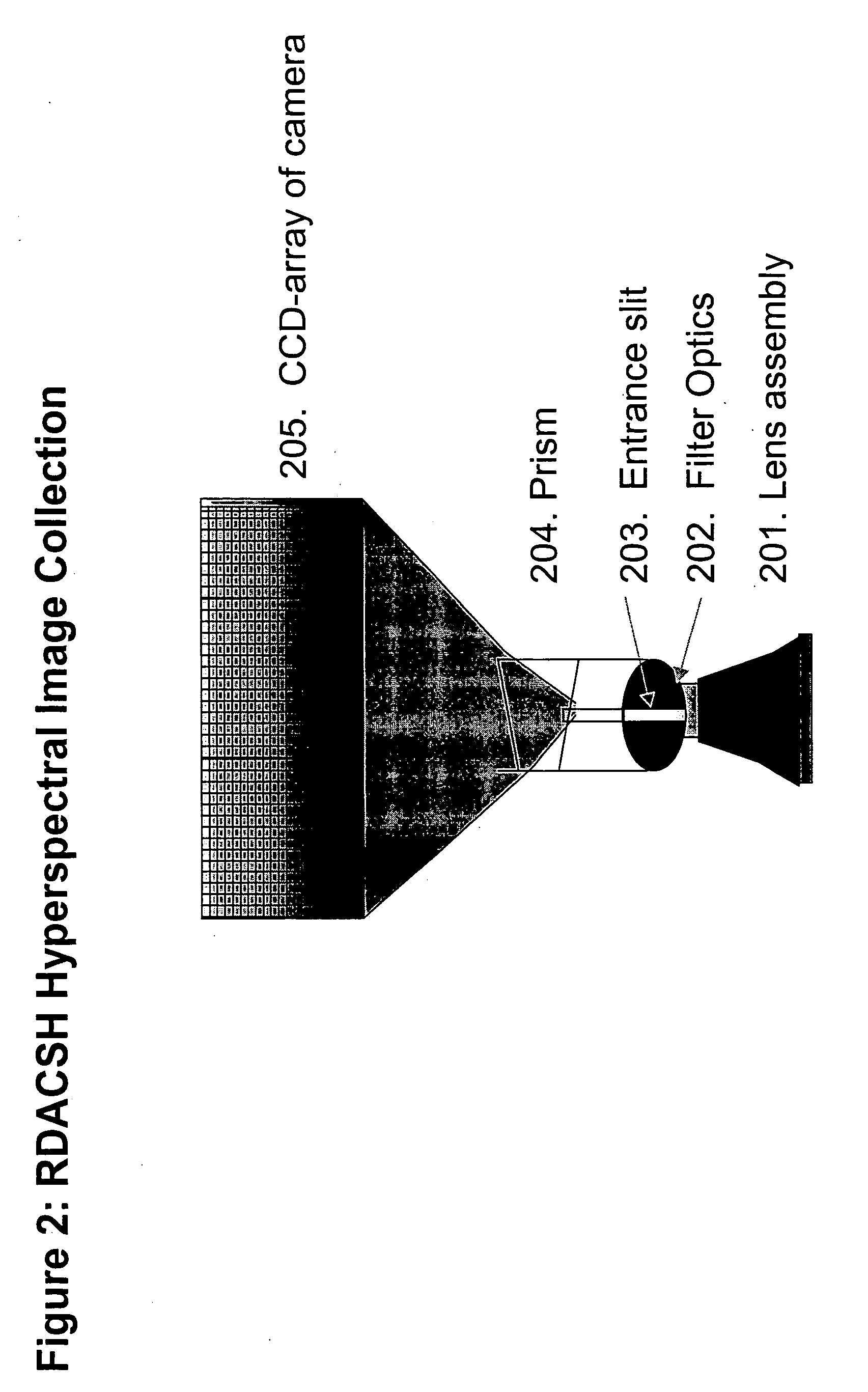
Patents
Literature
1160results about "Investigation of vegetal material" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
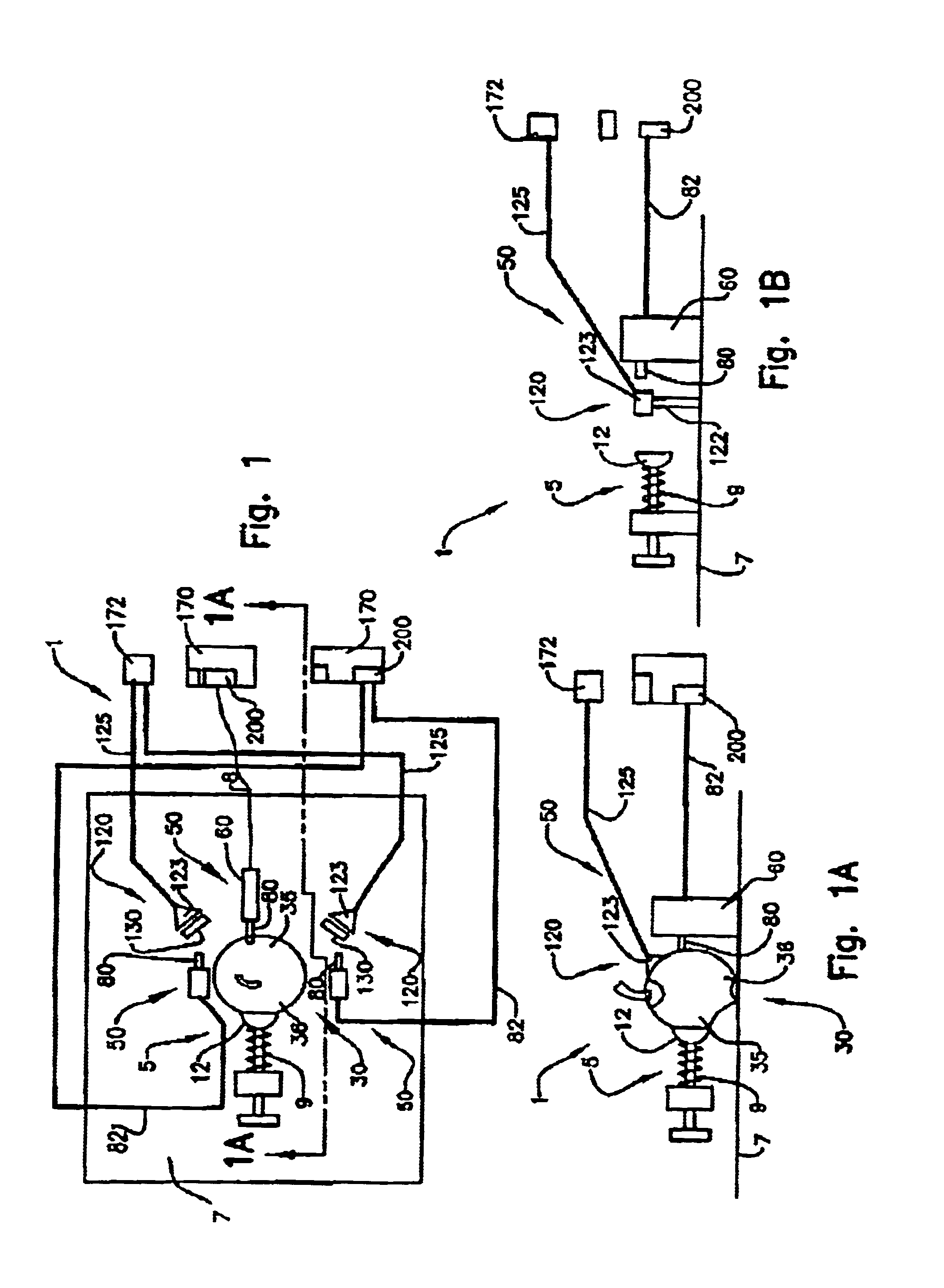
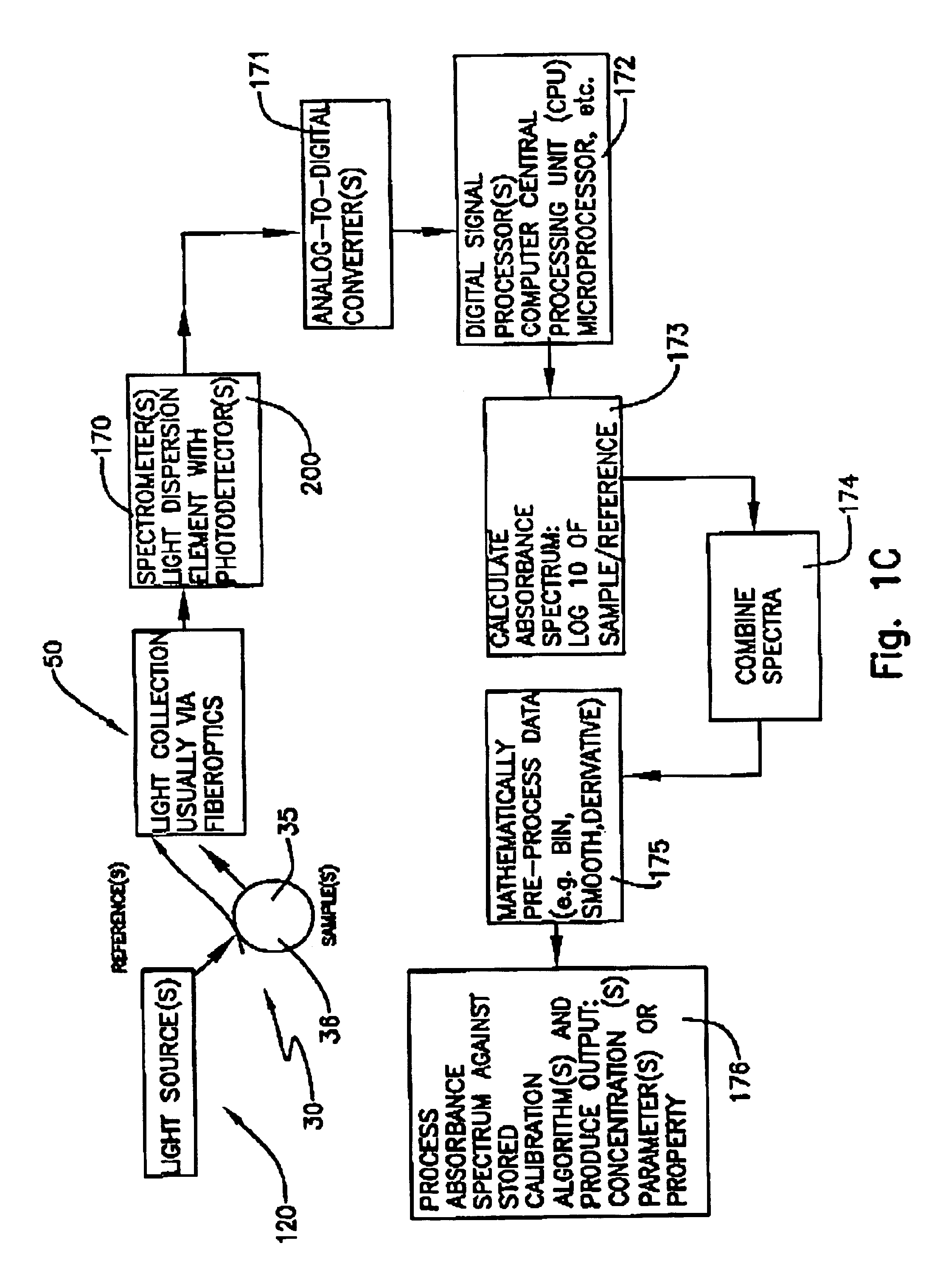
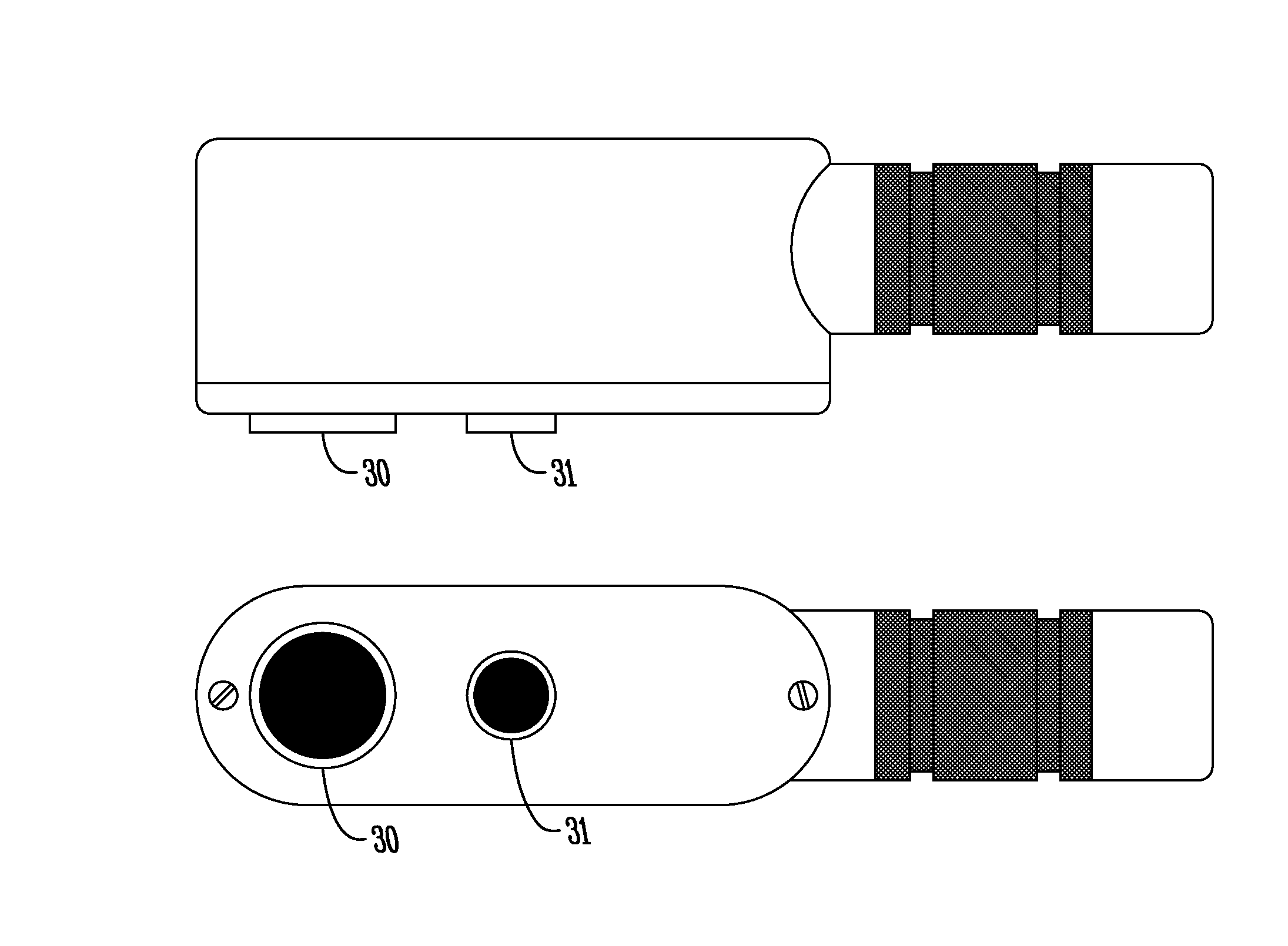
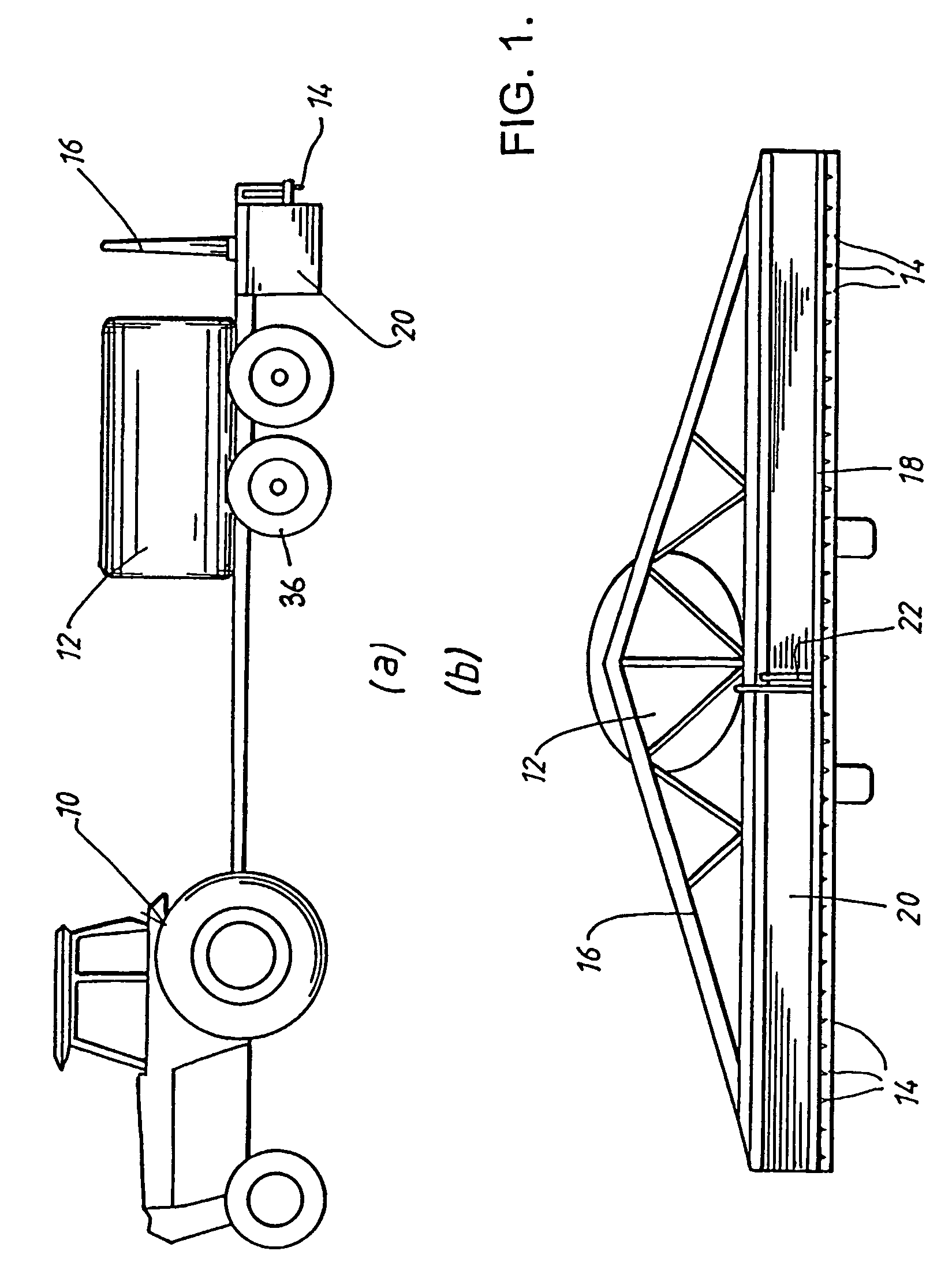
Light sensor with modulated radiant polychromatic source
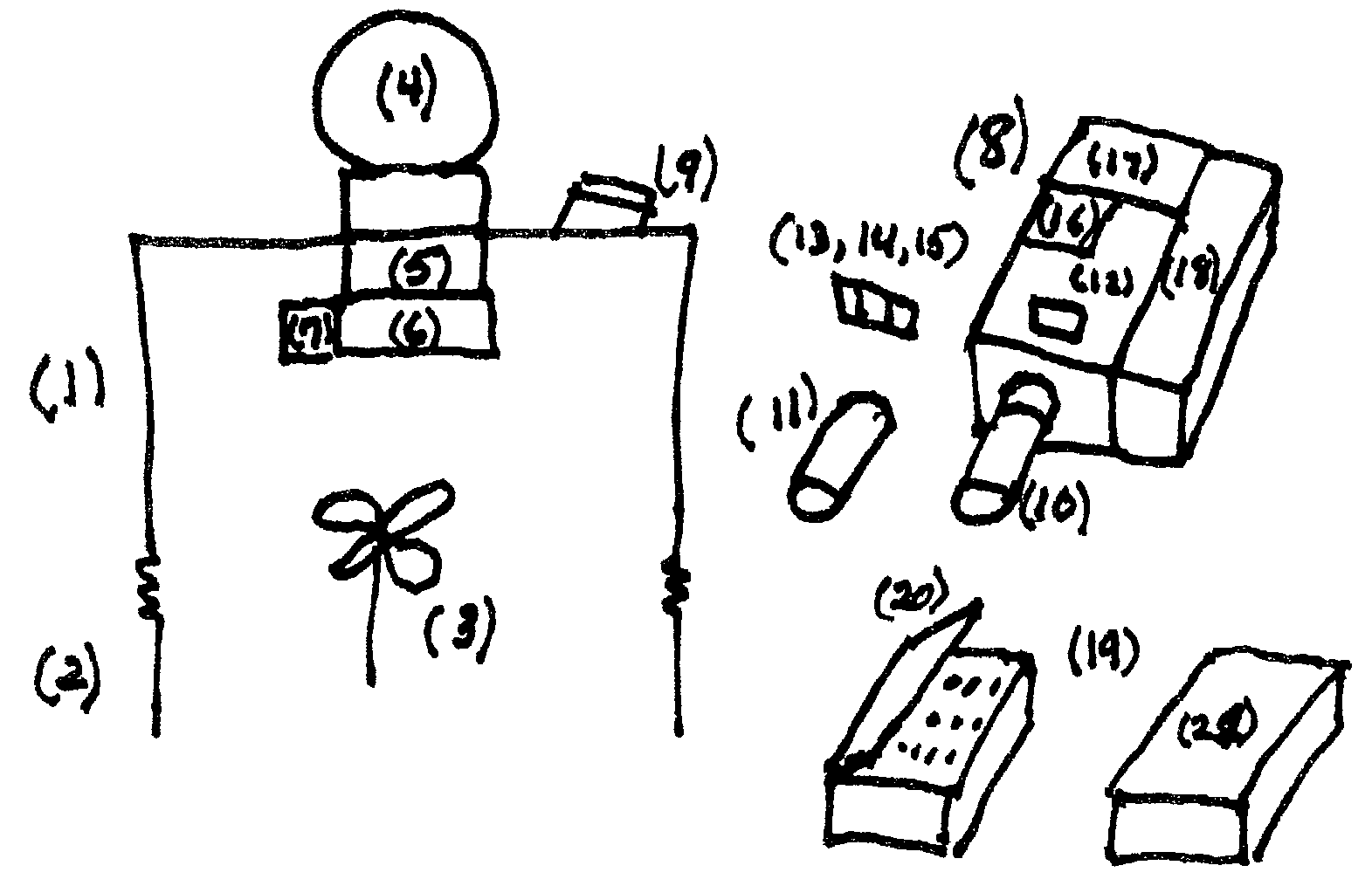
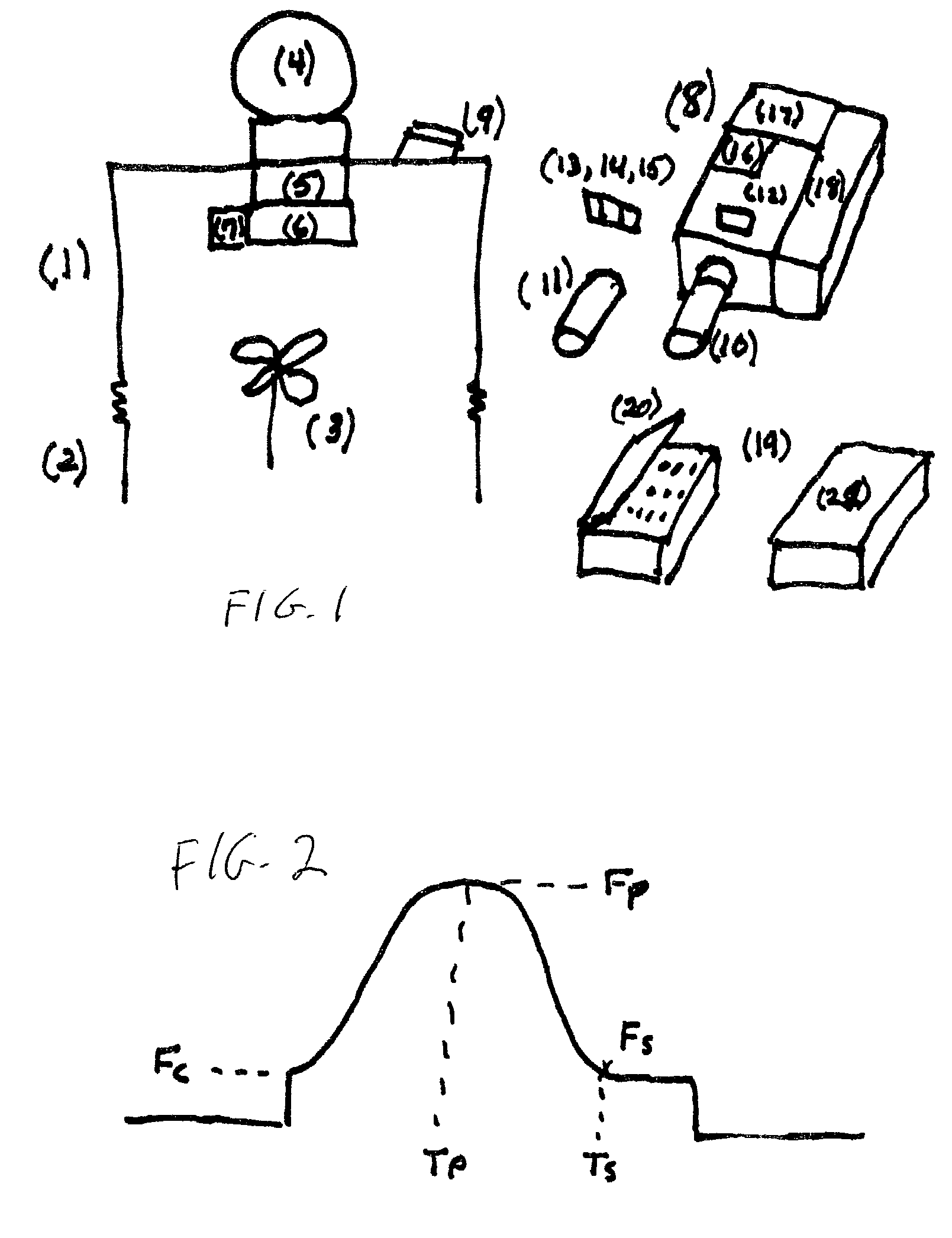
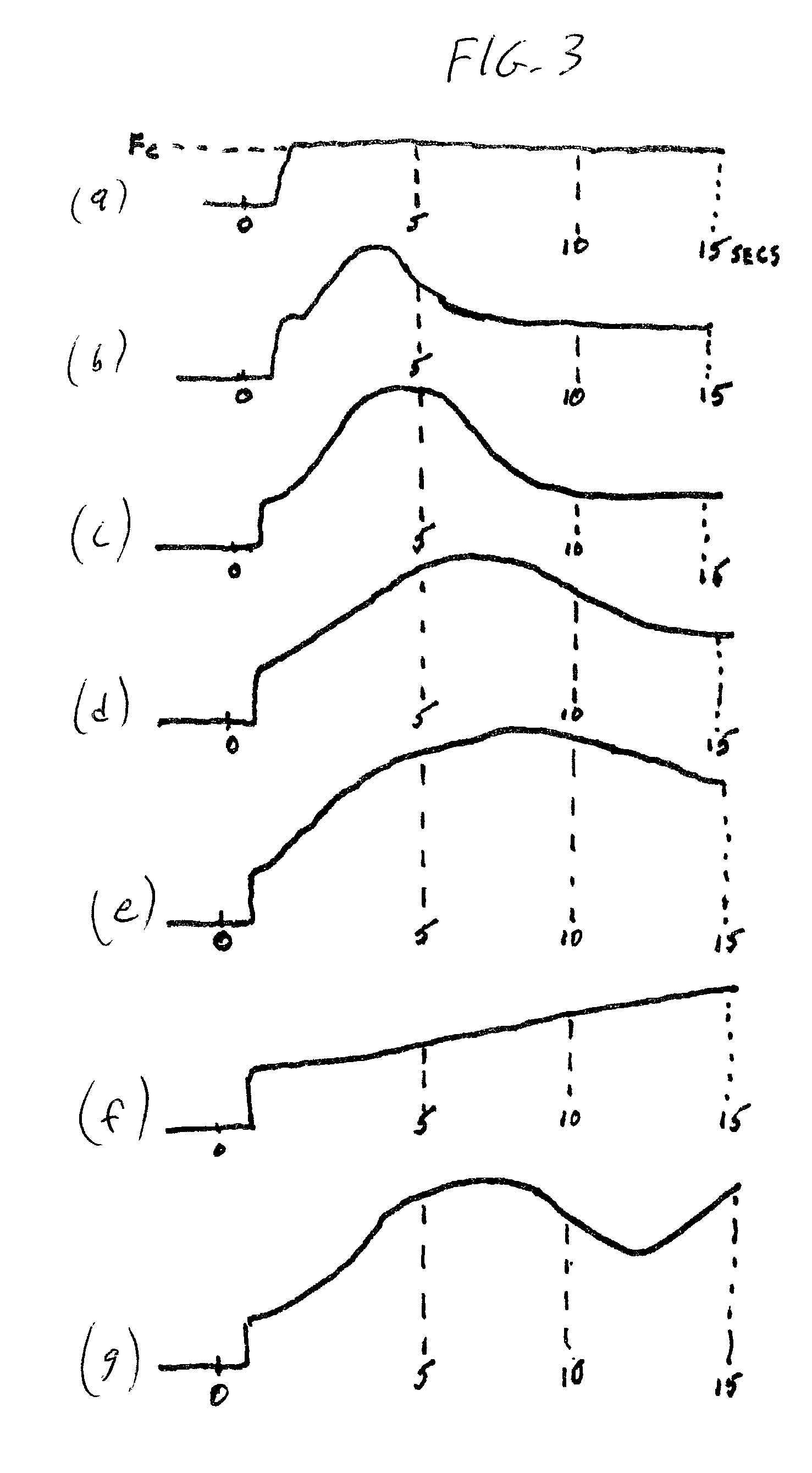
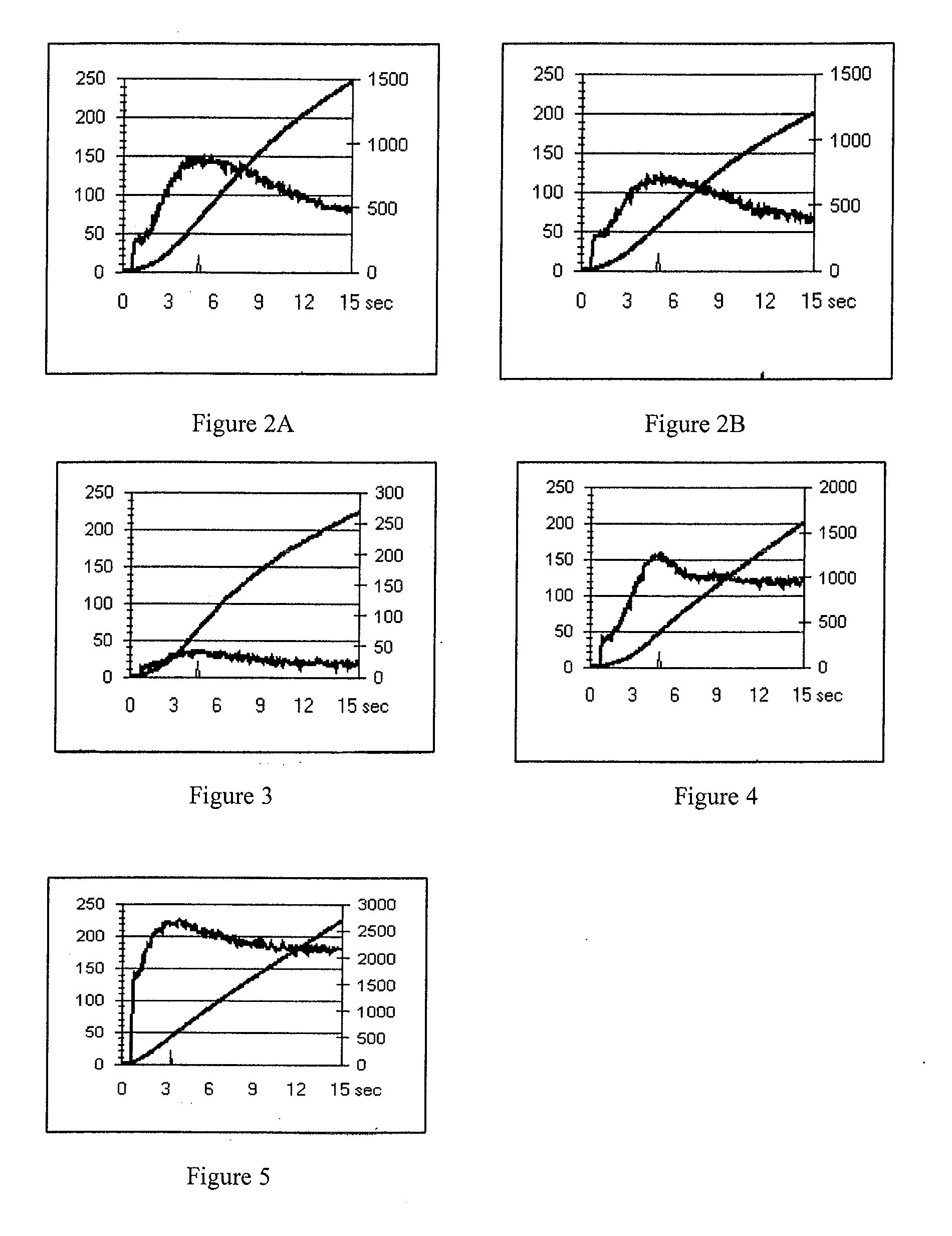
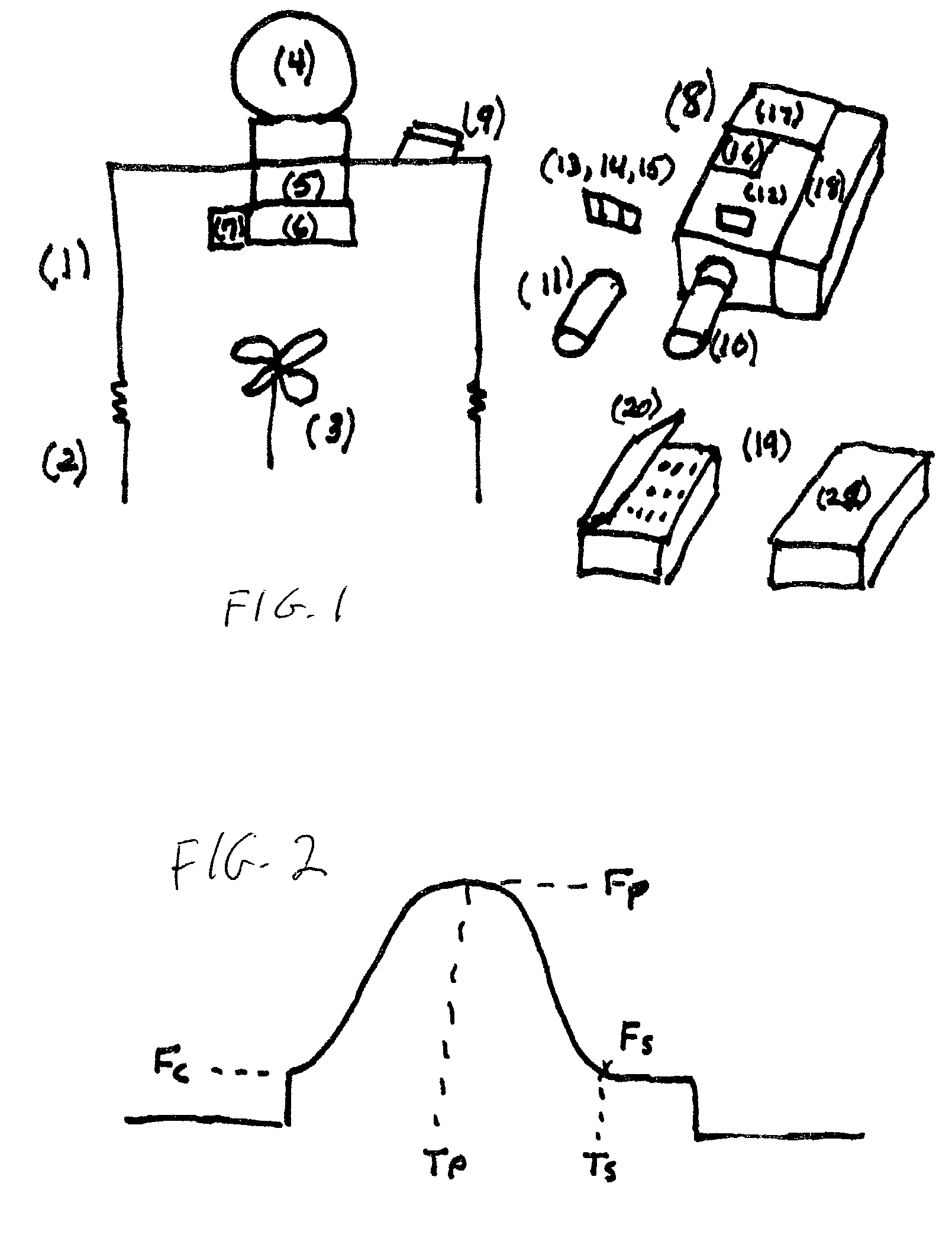
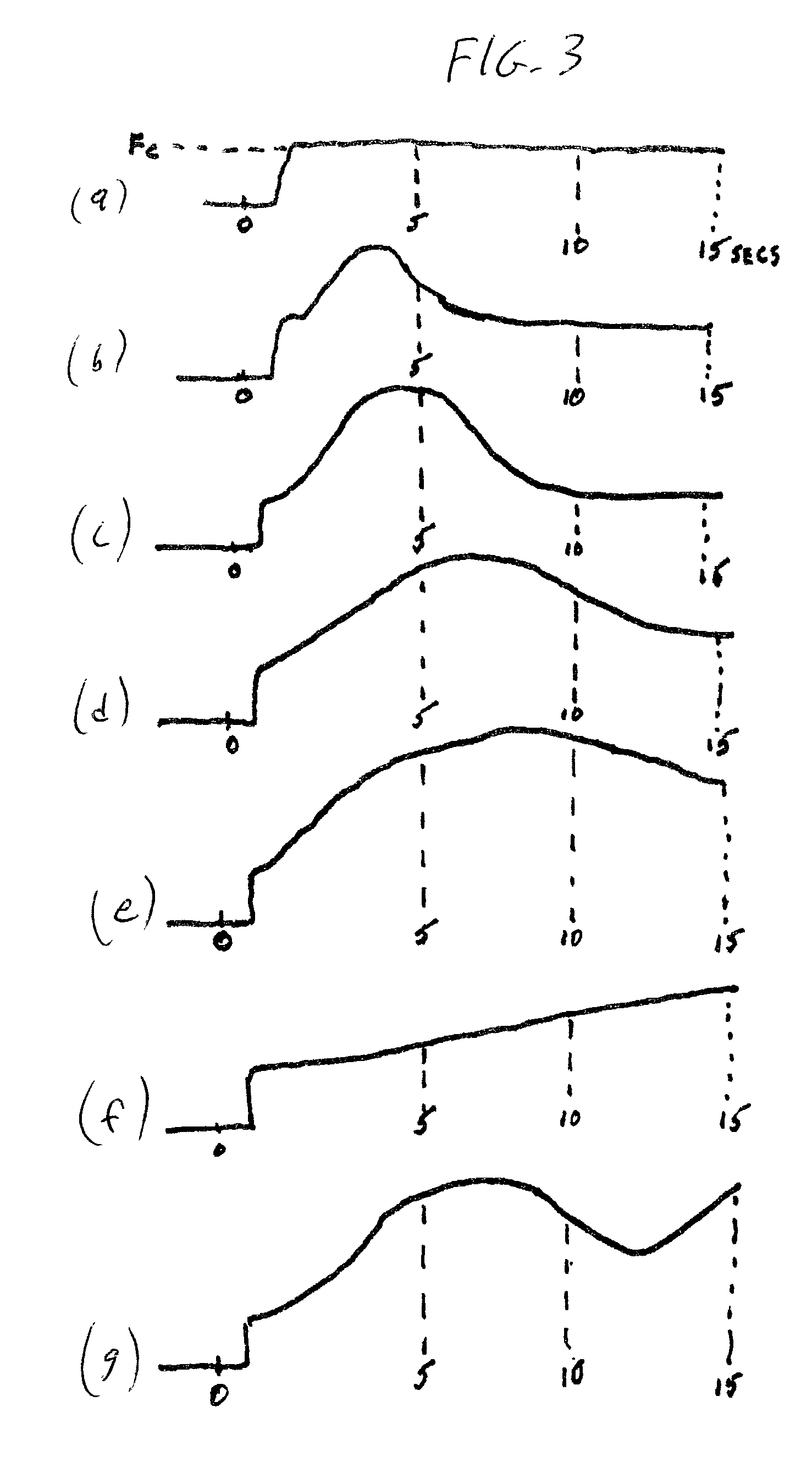
ActiveUS20050098713A1Increase costImprove performancePhotometry using reference valueRadiation pyrometryDetector arrayAnalytical control
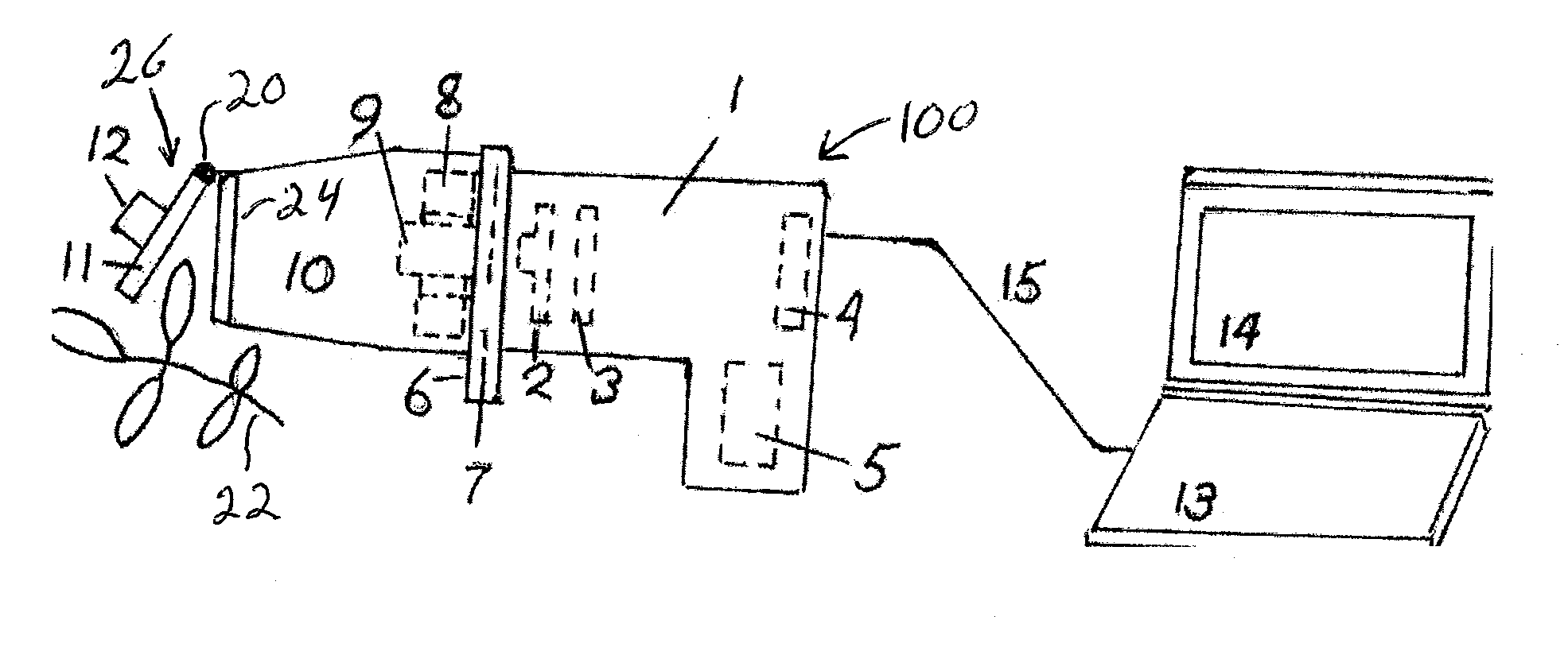
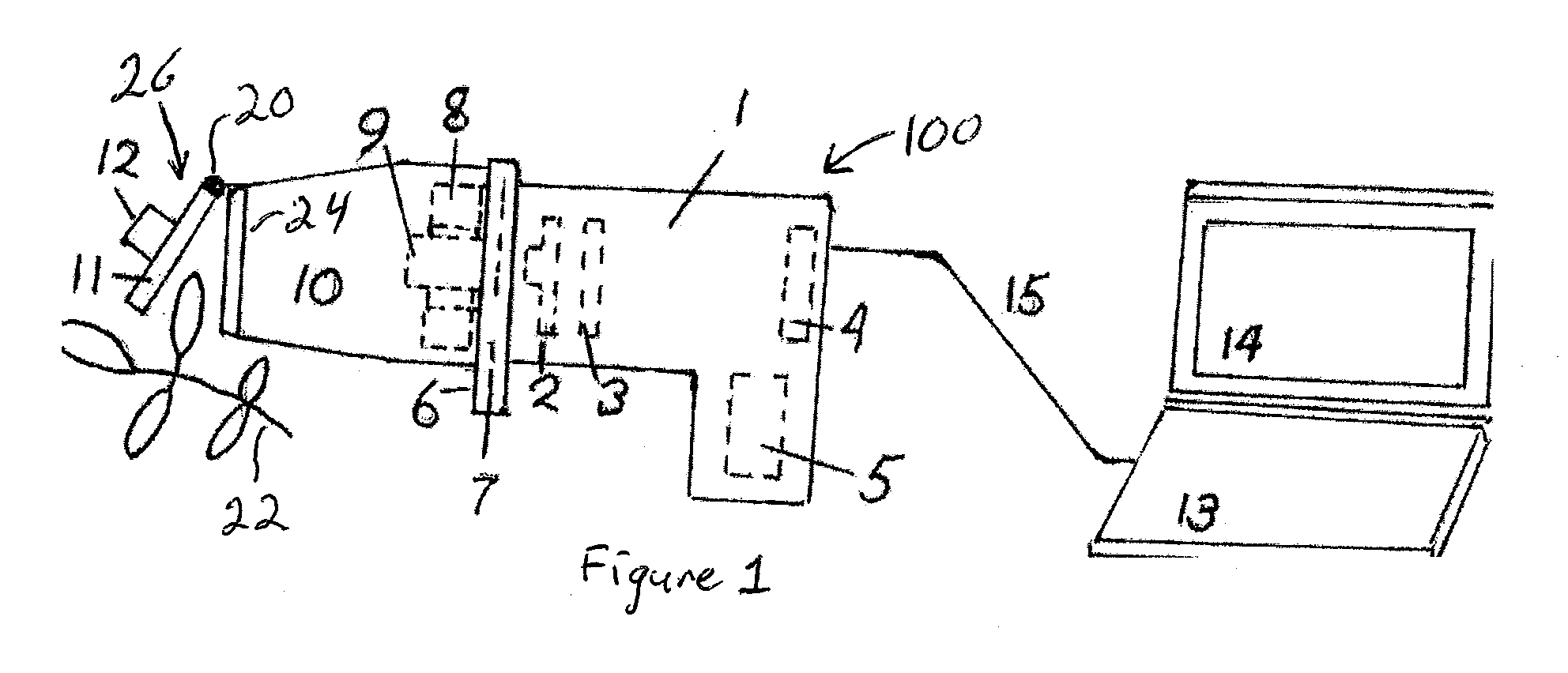
An apparatus is described for assessing plant status using biophysical and biochemical properties of the plant remotely sensed by the invention thereby allowing selective monitoring, elimination or treatment of individual plants. In a preferred embodiment, a single polychromatic emitter provides coincident light beams; one beam substantially in the visible portion of the spectrum (400 nm to 700 nm) and the other in the near infrared (NIR) portion of the spectrum (700 nm to 1100 nm). This light beam illuminates a small surface area on the ground, which may be bare ground, desired plants or undesired weeds. The beam of light may be focused, collimated or non-focused. A detector array, usually composed of a visible detector and a NIR detector, detects portions of this polychromatic light beam reflected by the surface area and provides a signal indicative of whether the detected light was reflected by a plant or by some non-plant object such as soil. A controller analyzes this signal and, assuming a plant is detected, responds by activating a device to take some action with respect to the plant or stores the analyzed signal with corresponding DGPS position in the controller's memory for later analysis. A number of actions may be taken by the controller. For instance, if the plant is a weed, the desired action might be to spray herbicide on the weed. Or, if the plant is a crop that is determined to be lacking in nutrient, the desired action may be to apply fertilizer. Additionally, if the plant under test is a turf landscape, such as found on golf courses and sporting fields, plant biomass may be mapped and geo-located using GPS for later, comparative analysis.
Owner:KYLE H HOLLAND TRUSTEE OF THE MARANATHA TRUST DATED JULY 30 2013
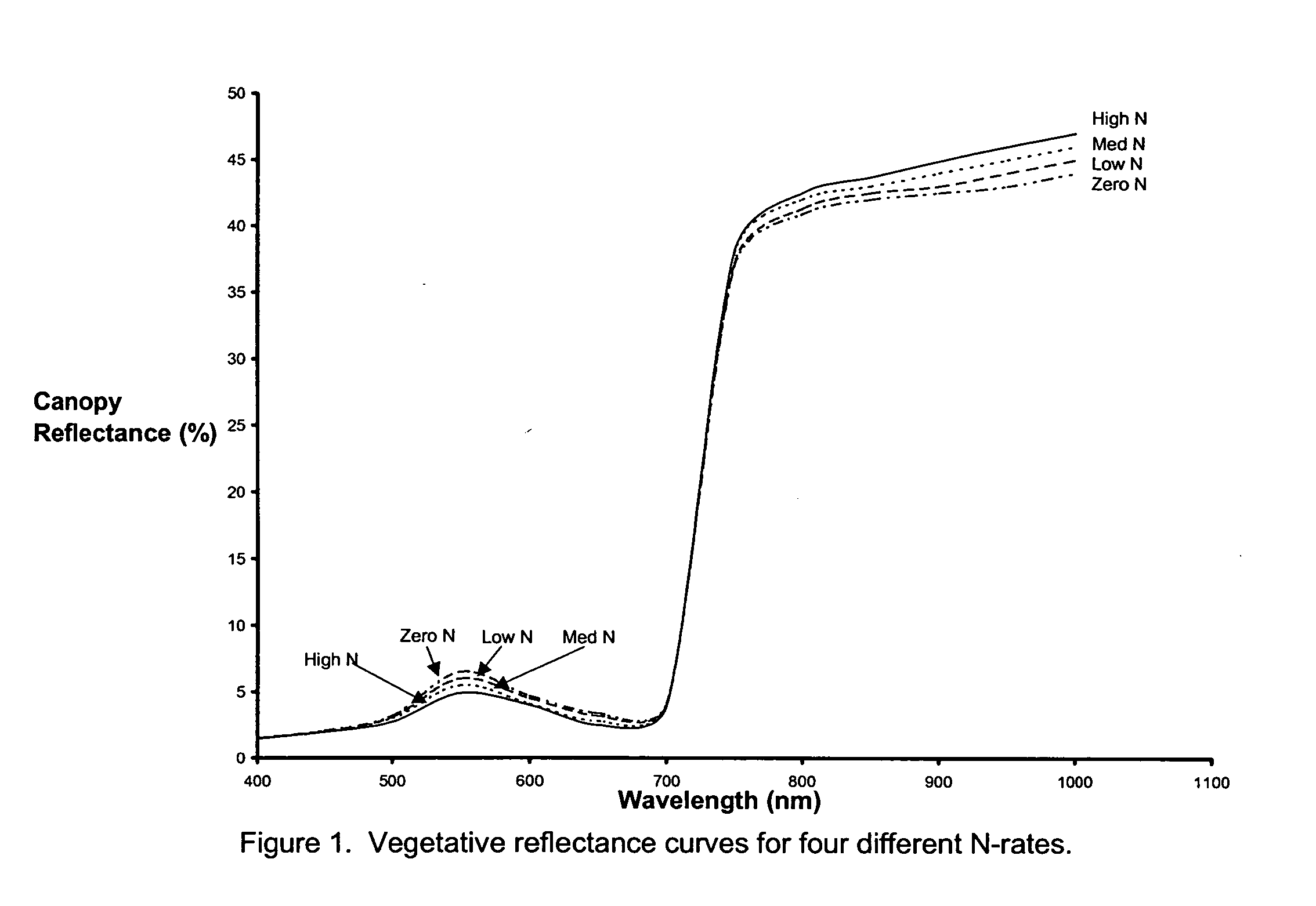
Apparatus and method and techniques for measuring and correlating characteristics of fruit with visible/near infra-red spectrum
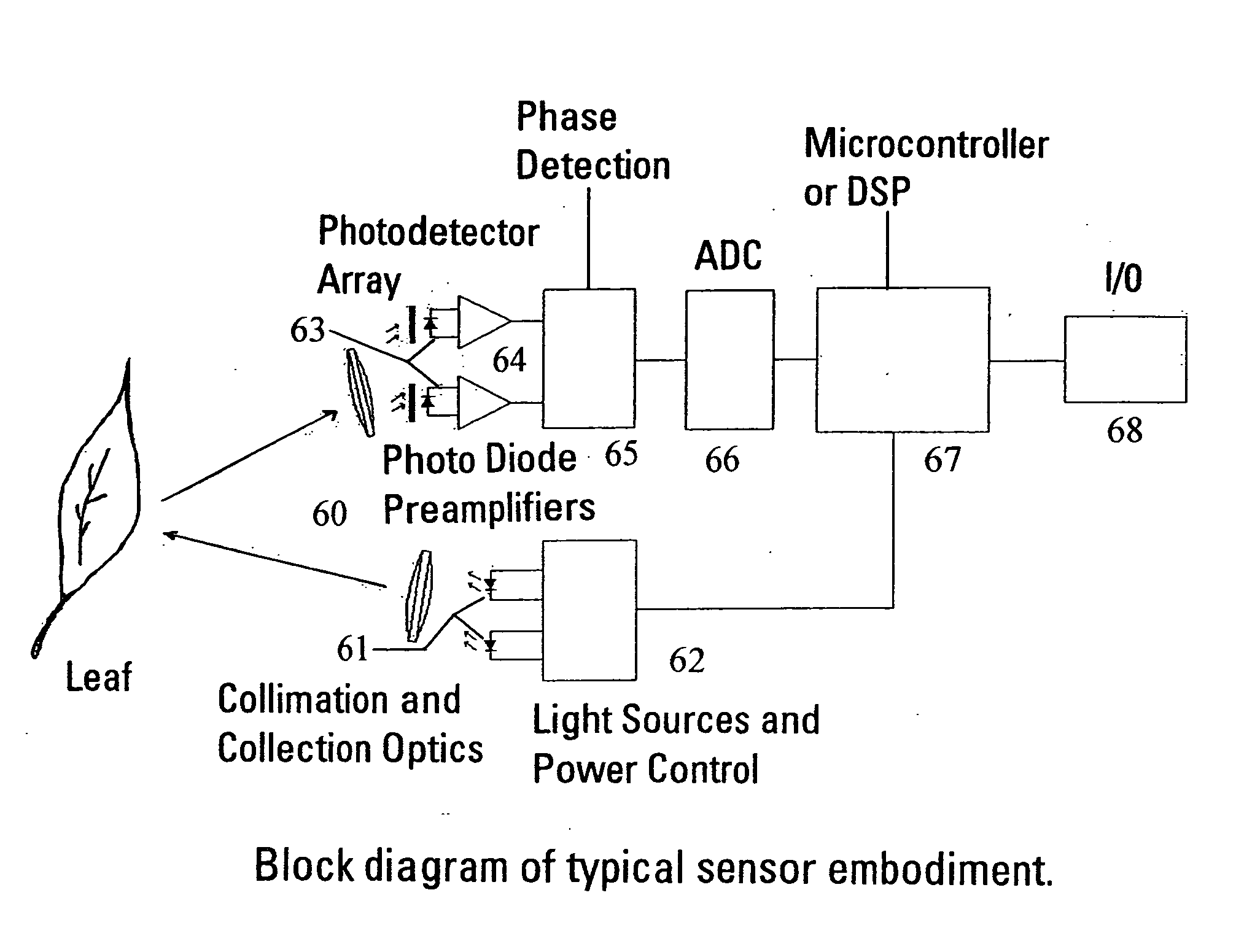
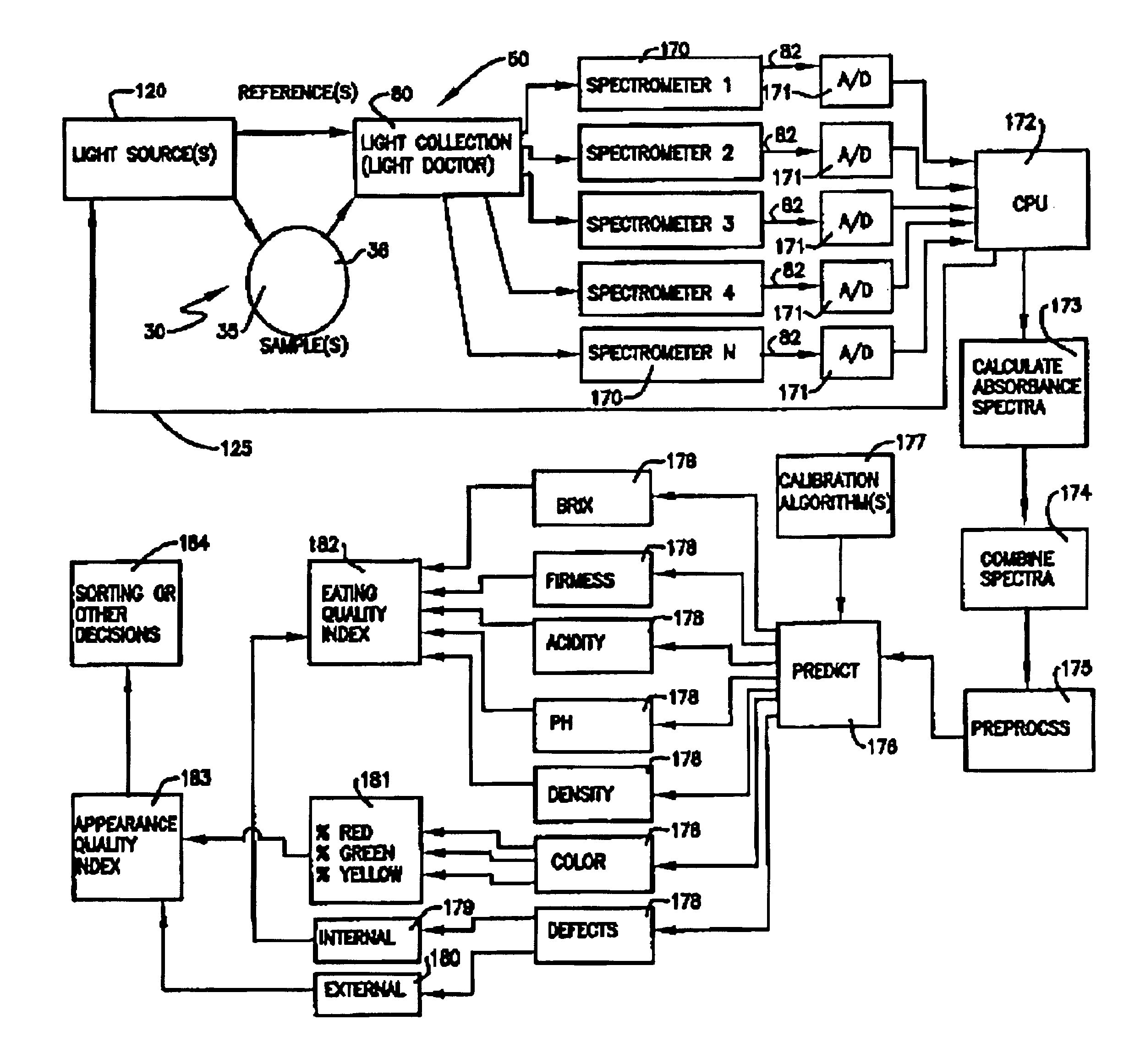
InactiveUS6847447B2Better signal to noise ratioImproves Brix prediction accuracyRadiation pyrometryInvestigation of vegetal materialBrixPeak value
This disclosure is of 1) the utilization of the spectrum from 250 nm to 1150 nm for measurement of prediction of one or more parameters, e.g., brix, firmness, acidity, density, pH, color and external and internal defects and disorders including, for example, surface and subsurface braises, scarring, sun scald, punctures, in N—H, C—H and O—H samples including fruit; 2) an apparatus and method of detecting emitted light from samples exposed to the above spectrum in at least one spectrum range and, in the preferred embodiment, in at least two spectrum ranges of 250 to 499 nm and 500 nm; 3) the use of the chlorophyl band, peaking at 690 nm, in combination with the spectrum from 700 nm and above to predict one or more of the above parameters; 4) the use of the visible pigment region, including xanthophyll, from approximately 250 nm to 499 nm and anthocyanin from approximately 500 to 550 nm, in combination with the chlorophyl band and the spectrum from 700 nm and above to predict the all of the above parameters.
Owner:FPS FOOD PROCESSING SYST BV
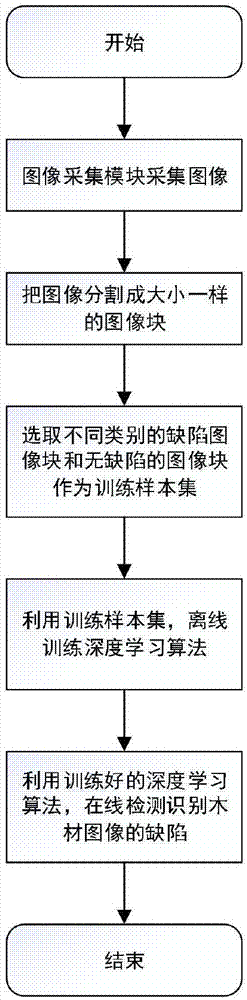
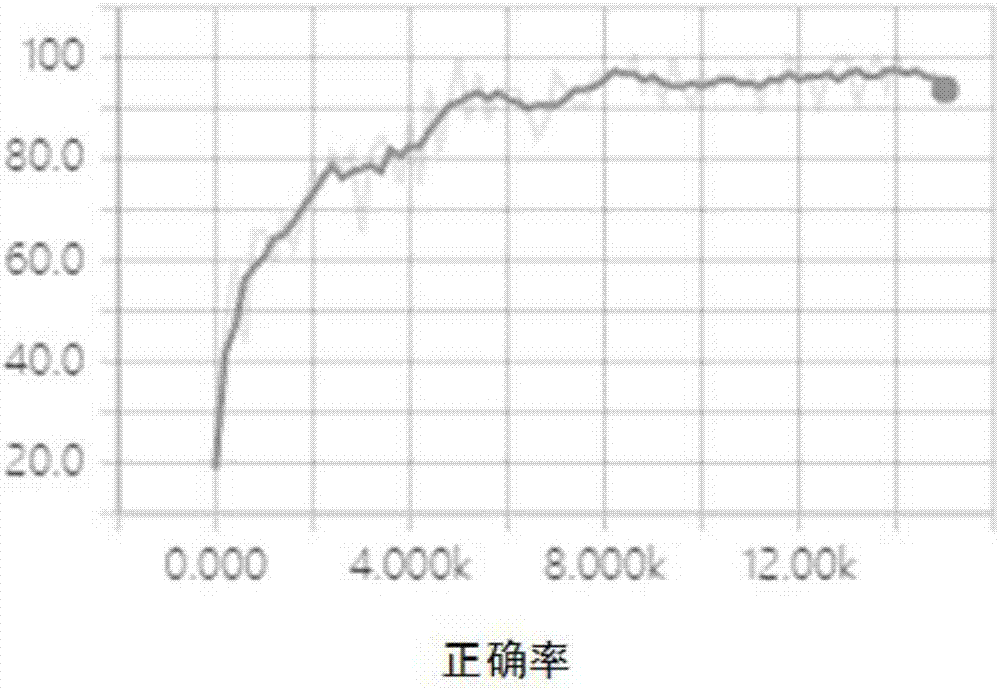
Wood defect detection method based on deep learning and system thereof
ActiveCN107392896ASolve the problem of not being able to detect and identify complex texture defectsMeet real-time requirementsImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
The invention provides a wood defect detection method based on deep learning. The method comprises the following steps of collecting images; segmenting the images into image blocks with a same size; selecting defect image blocks with different types and non-defective image blocks as a training sample set; using the training sample set to train a deep learning algorithm in an off-line mode; and using a trained deep learning algorithm to detect and identify defects of a wood image in an online mode and the like. In the invention, through the powerful deep learning algorithm, defects on different complex texture wood surfaces are detected and identified in high precision and online modes and a problem that a traditional image processing algorithm can not solve is solved. The invention also provides a wood defect detection system based on deep learning. Through cooperation among an image acquisition module, a deep learning algorithm processing module and a control execution module, a detection speed can be effectively accelerated and practicality is increased.
Owner:FOSHAN NANHAI GUANGDONG TECH UNIV CNC EQUIP COOP INNOVATION INST +1
Systems and methods for monitoring agricultural products
ActiveUS20130325346A1Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyInvestigation of vegetal materialUsing optical meansGrowth plantAgricultural science
Owner:AGERPOINT
Hyperspectral polarization profiler for remote sensing
InactiveUS6052187AMinimize healthMinimize problemsRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyFluorescenceLarge range
A device to provide hyperspectral reflection spectrum, hyperspectral depolarization, and hyperspectral fluorescence spectrum data in a portable, remote sensing instrument. The device can provide a large range of remotely-sensed optical property data, presently only obtainable in laboratories, in a low-cost field instrument. Among its many uses, the present invention can be used by farmers as a tool for determining the nitrogen content of crops to optimize fertilizer laydown.
Owner:CONTAINERLESS RES
Bio-imaging and information system for scanning, detecting, diagnosing and optimizing plant health
InactiveUS20050072935A1Accurate measurementImprove efficiencyInvestigation of vegetal materialPhotometryArbitrary Fluorescence UnitBiology
A portable Chlorophyll Fluorescence Imaging Time (CFIT) system for use in determining plant health. The system includes an enclosure for placement around a plant to be imaged in-situ. There is a controlled light source that controllably provides to the plant light of a desired wavelength range, to controllably irradiate the plant within the enclosure. The chlorophyll fluorescence emitted from the plant both spatially and temporally is captured, and the captured fluorescence information is analyzed to provide plant health information.
Owner:LUSSIER ROBERT
Systems and methods for monitoring agricultural products
ActiveUS20180259496A1Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyInvestigation of vegetal materialColor/spectral properties measurementsGrowth plantPoint cloud
The present invention relates to systems and methods for monitoring agricultural products. In particular, the present invention relates to monitoring fruit production, plant growth, and plant vitality. According to embodiments of the invention, a plant analysis system is configured determine a spectral signature of a plant based on spectral data, and plant color based on photographic data. The spectral signatures and plant color are associated with assembled point cloud data. Morphological data of the plant can be generated based on the assembled point cloud data. A record of the plant can be created that associates the plant with the spectral signature, plant color, spectral data, assembled point cloud data, and morphological data, and stored in a library.
Owner:AGERPOINT
Plant treatment based on a water invariant chlorophyll index
ActiveUS20110047867A1Overcome limitationsImprove performanceRadiation pyrometryInvestigation of vegetal materialGrowth plantOptical property
A method and system of treating plants is provided. The method includes measuring optical properties of a plant using a plurality of spectral bands. The method further includes calculating in a computational device at least two vegetative indexes using the optical properties, each of the at least two vegetative indexes correlating to one or more plant growth parameters. The method further includes calculating in the computational device a water invariant chlorophyll index from at least two vegetative indexes using the plurality of spectral bands. The also provides for treating one or more of the plants based on the water invariant chlorophyll index.
Owner:KYLE H HOLLAND TRUSTEE OF THE MARANATHA TRUST DATED JULY 30 2013
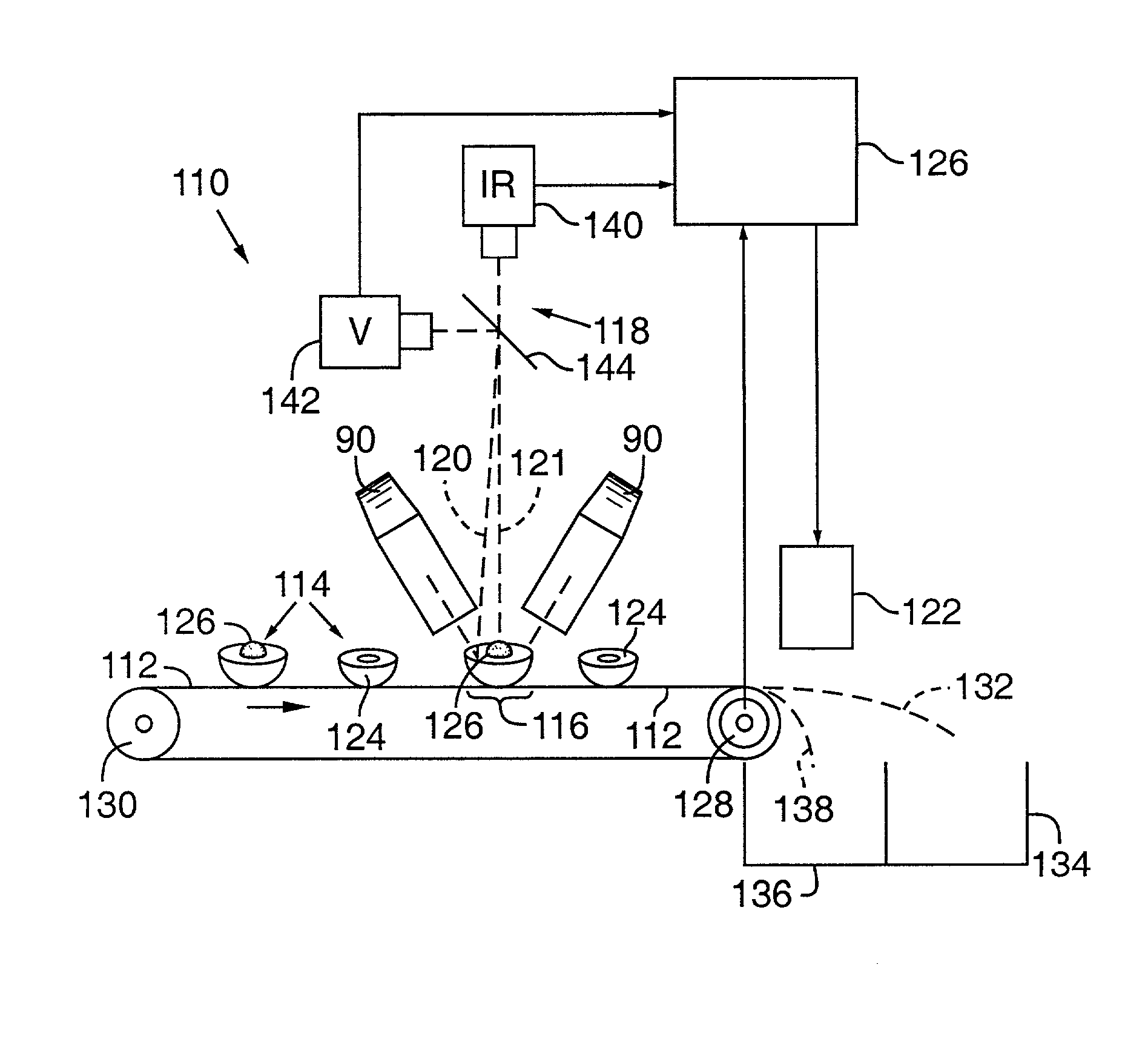
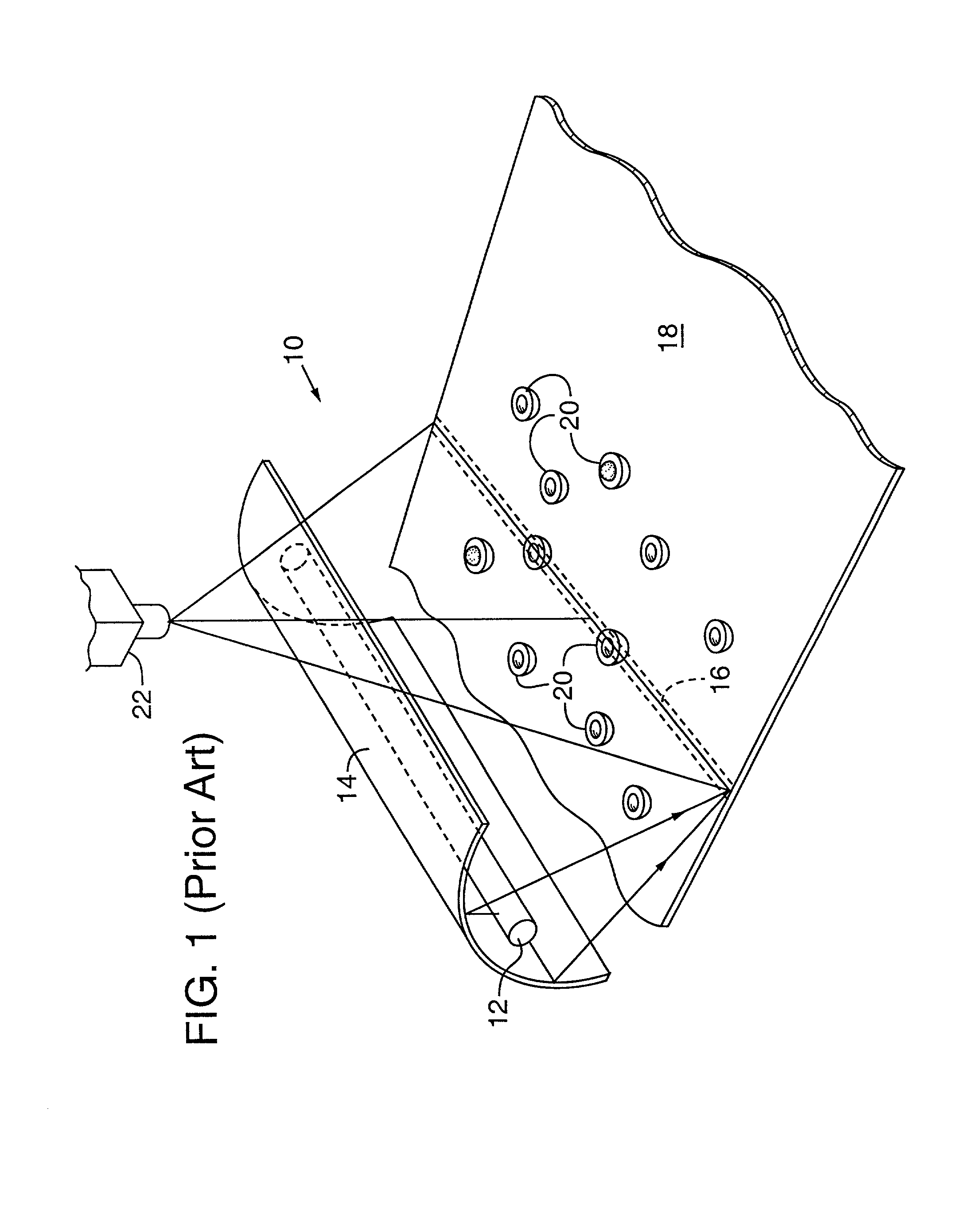
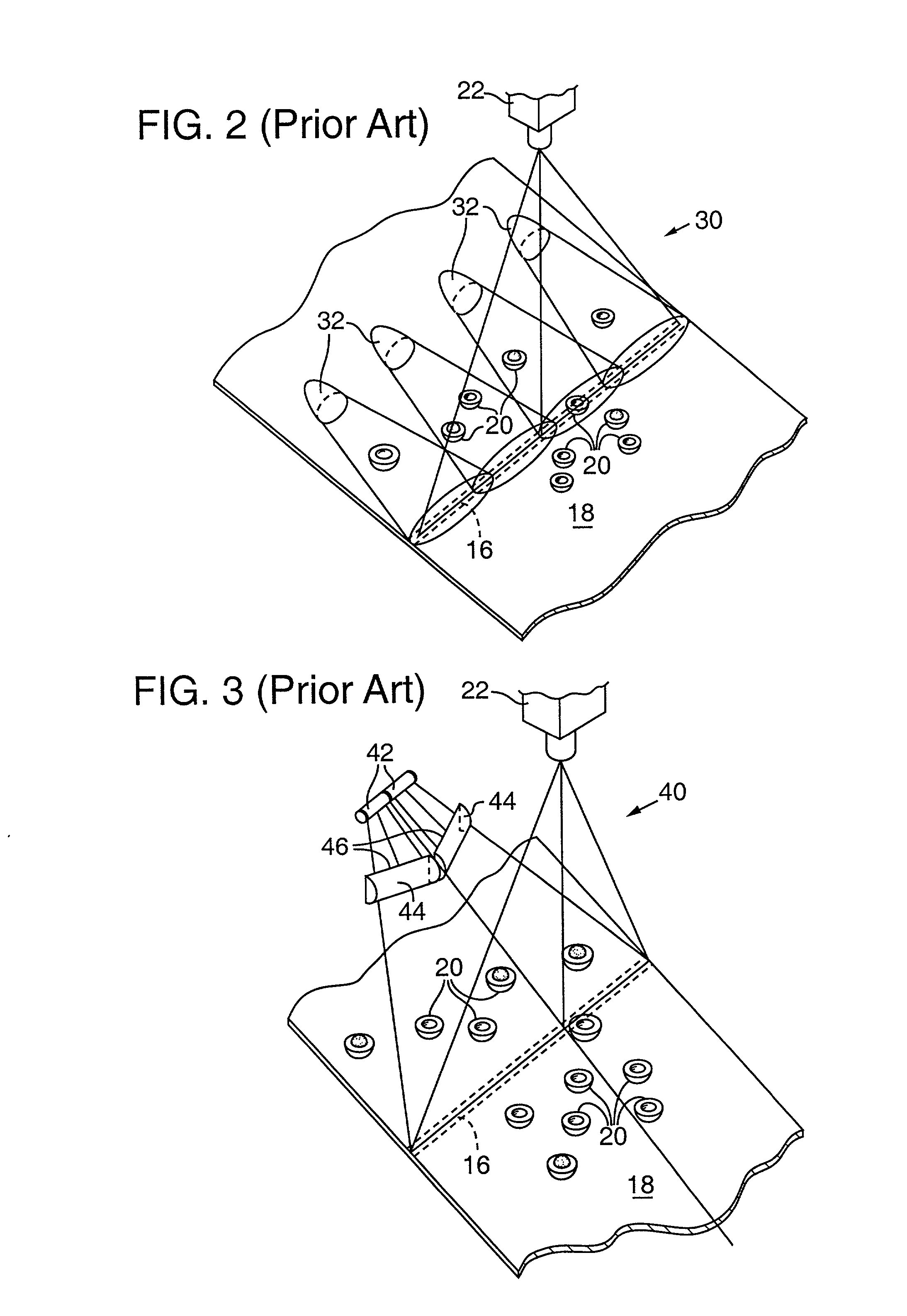
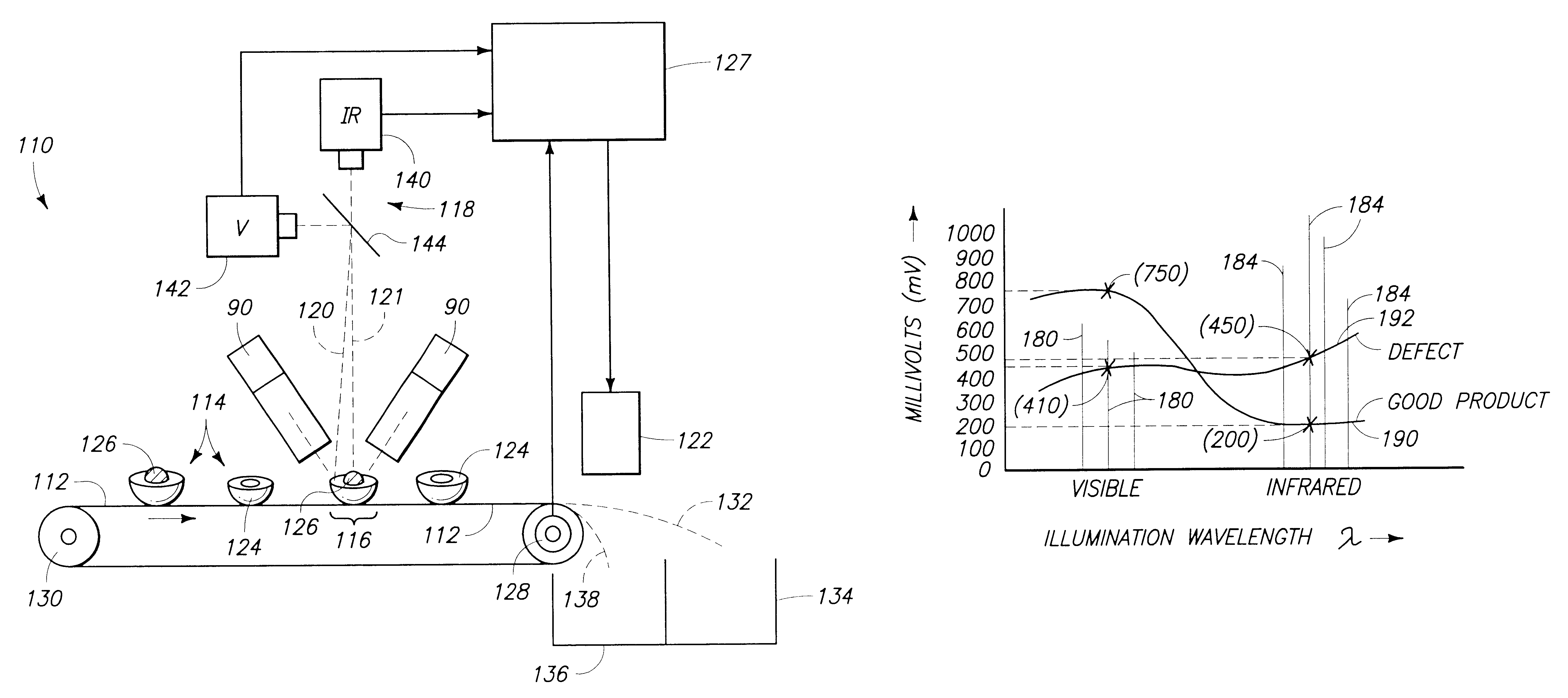
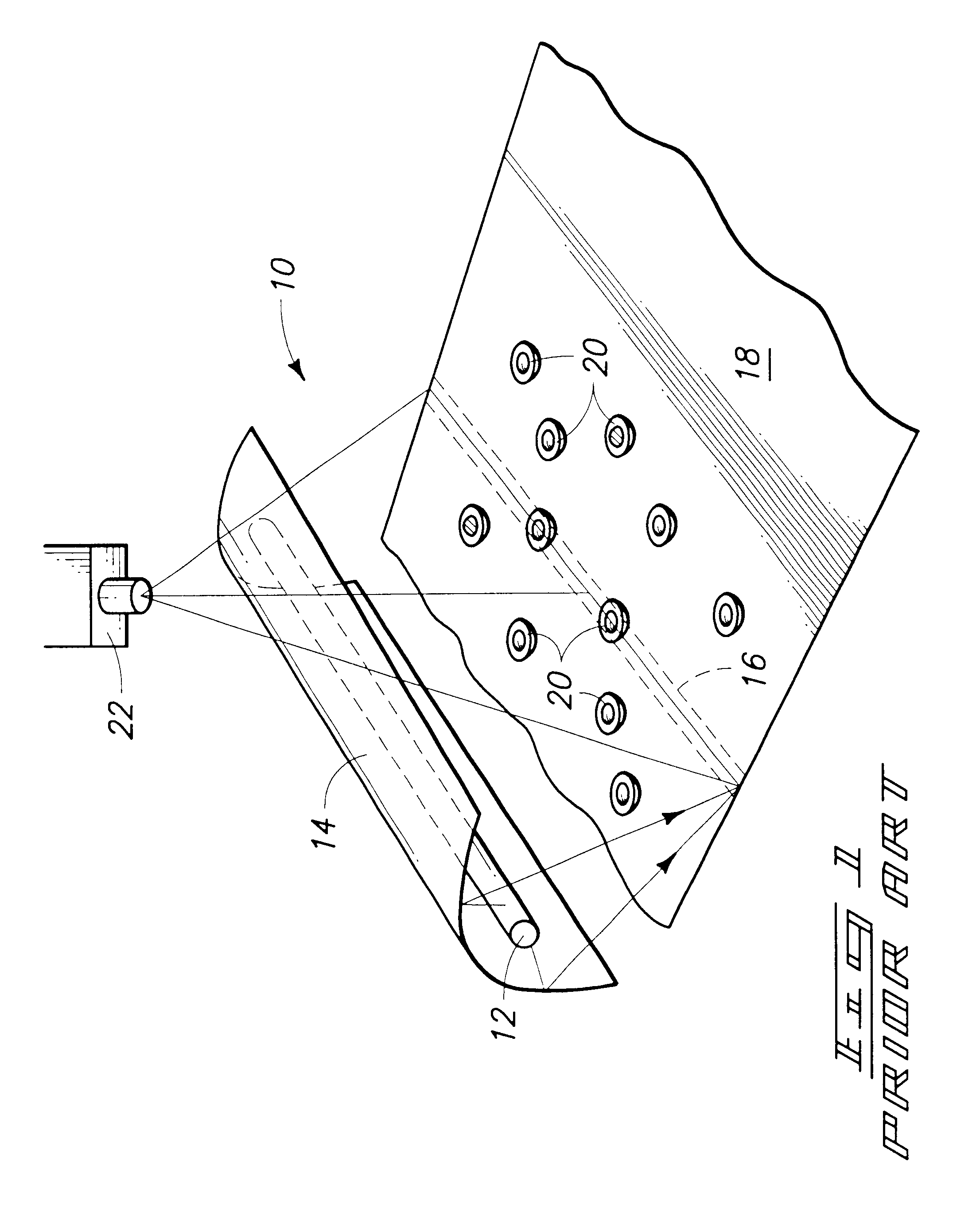
Agricultural article inspection apparatus and method employing spectral manipulation to enhance detection contrast ratio
InactiveUS20020008055A1Diminishes chlorophyll effect reflectanceImprove image contrastInvestigation of vegetal materialInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsIodideImage contrast
A sorting system (110) conveys articles, such as peaches (114) on a conveyor belt (112) past an inspection zone (126) that is lighted by an illumination source (90) radiating a number of emission peaks over visible and infrared portions of the spectrum. The illumination source generates the radiation from an Indium Iodide lamp (92) that is reflected off a parabolic reflector (94) and through a "soda straw" collimator (100) to illuminated the peaches. A detector system (118) employs line scanning visible and infrared cameras (142, 140) to sense visible and IR wavelength reflectance values for the peach meat (124) and peach pit or pit fragments (126). Various image processing and analysis methologies, such as subtraction, ratio, logarithmic, regression, combination, angle, distance, and shape may be employed to enhance the image contrast and classify the resulting data for sorting the peaches. Employing subtraction also cancels "glint" caused by specular reflections of the illumination source off the peaches and into the cameras.
Owner:KII TEKU INC
Agricultural article inspection apparatus and method employing spectral manipulation to enhance detection contrast ratio
InactiveUS6410872B2Improve image contrastCancels "glInvestigation of vegetal materialInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsIodideConveyor belt
A sorting system (110) conveys articles, such as peaches (114) on a conveyor belt (112) past an inspection zone (126) that is lighted by an illumination source (90) radiating a number of emission peaks over visible and infrared portions of the spectrum. The illumination source generates the radiation from an Indium Iodide lamp (92) that is reflected off a parabolic reflector (94) and through a "soda straw" collimator (100) to illuminated the peaches. A detector system (118) employs line scanning visible and infrared cameras (142, 140) to sense visible and IR wavelength reflectance values for the peach meat (124) and peach pit or pit fragments (126). Various image processing and analysis methologies, such as subtraction, ratio, logarithmic, regression, combination, angle, distance, and shape may be employed to enhance the image contrast and classify the resulting data for sorting the peaches. Employing subtraction also cancels "glint" caused by specular reflections of the illumination source off the peaches and into the cameras.
Owner:KII TEKU INC
Crop Automated Relative Maturity System
InactiveUS20110047636A1Investigation of vegetal materialPicture taking arrangementsMap LocationSet-aside
An automated relative maturity system for measuring the relative maturity of a large number of plots of diverse varieties of plants growing in a field or fields. A field to be evaluated is laid out in multiple plots with a specific variety assigned to a preselected plot or plots and with areas set aside throughout the field for planting of check varieties of known relative maturity. High-precision GPS is used with a planter to record the location of each plot within the field on a map. When leaf senescence is under way throughout the field, a radiometric crop sensor mounted on a vehicle also equipped with high-precision GPS is used to scan the plants in the plots to record readings of the plants synchronized to the GPS map locations, including the check plants of known relative maturity. Software is used to calculate the relative maturity of each variety.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Optical system for plant characterization
InactiveUS7715013B2Investigation of vegetal materialMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseLight energy
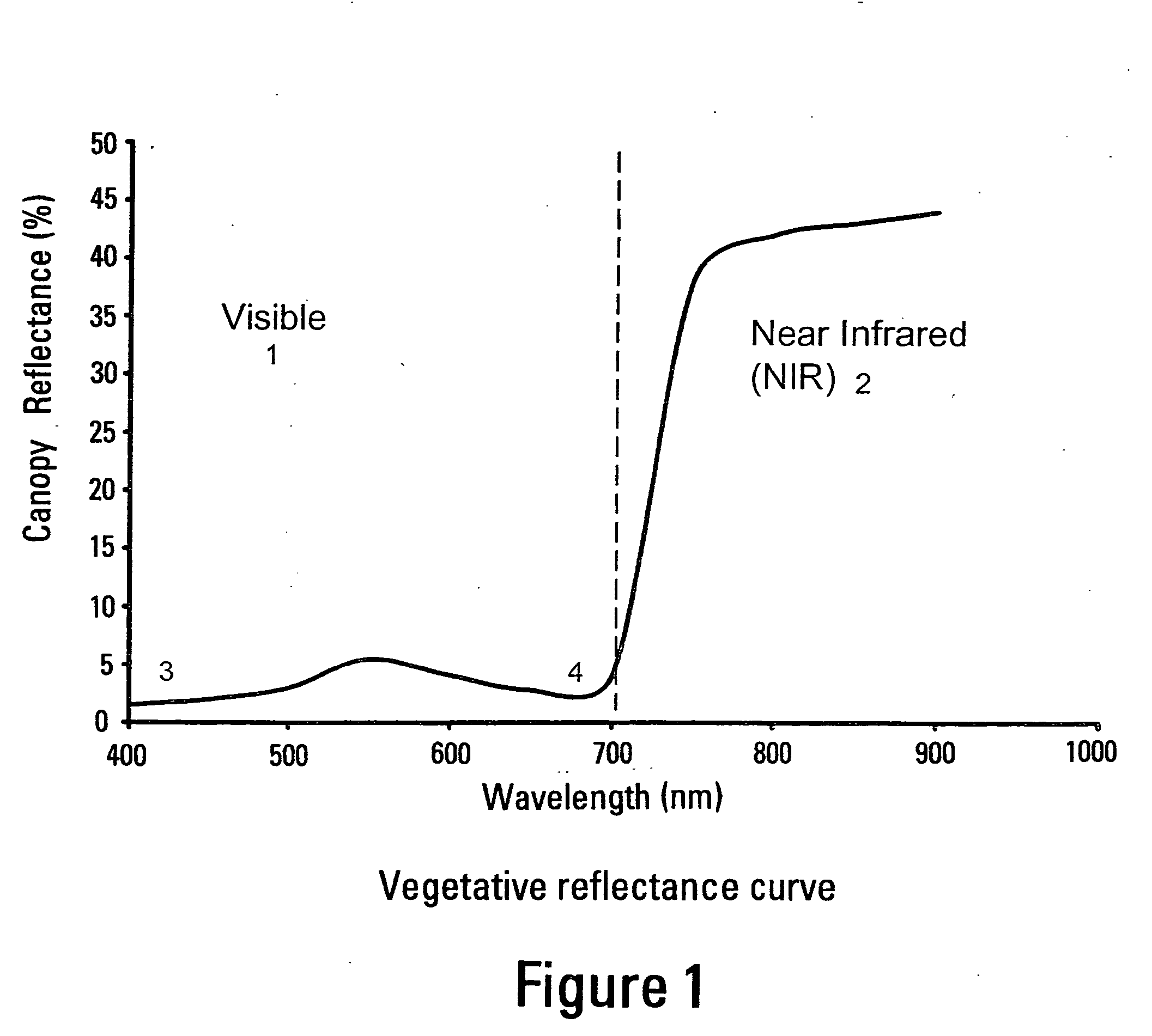
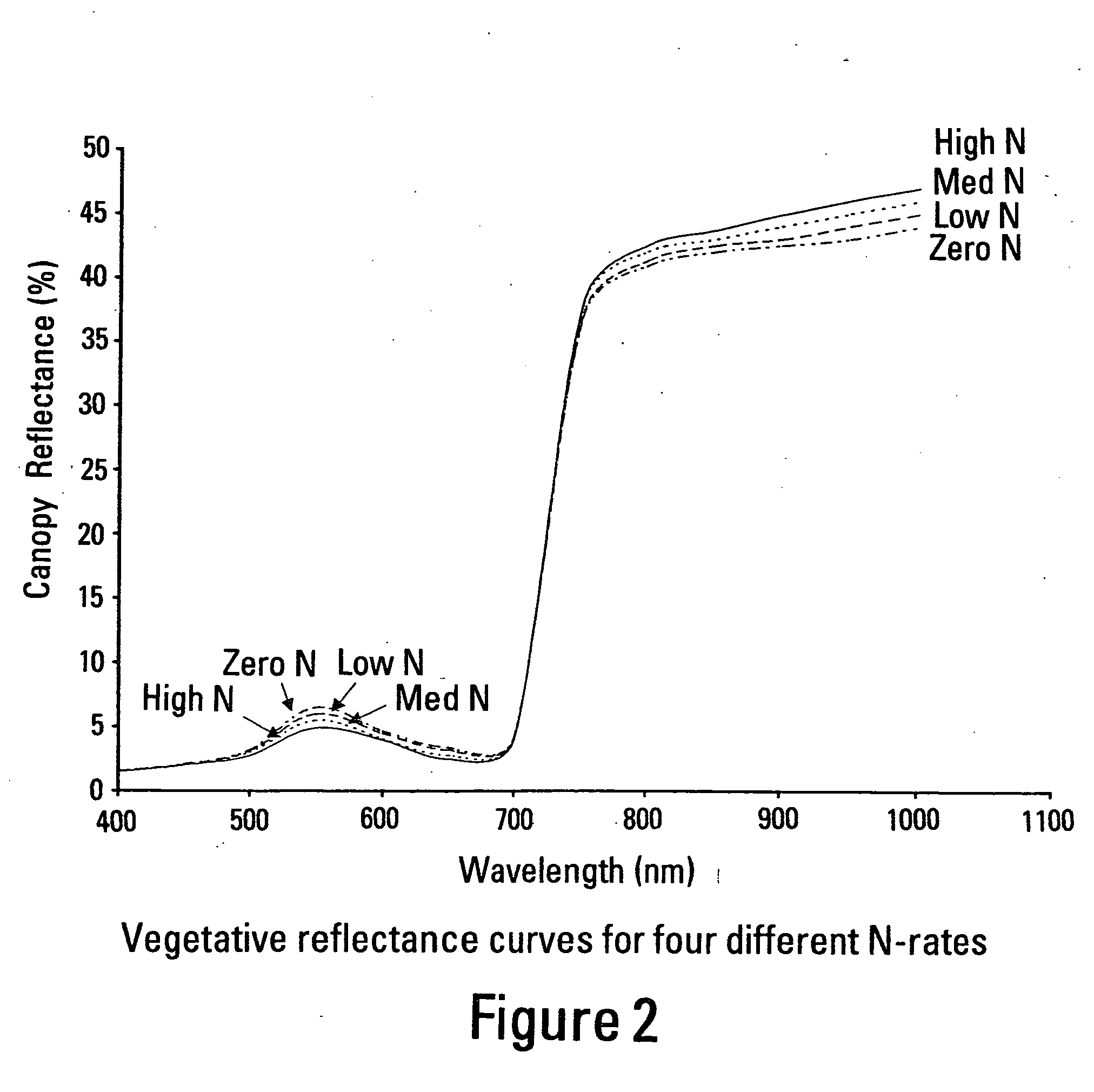
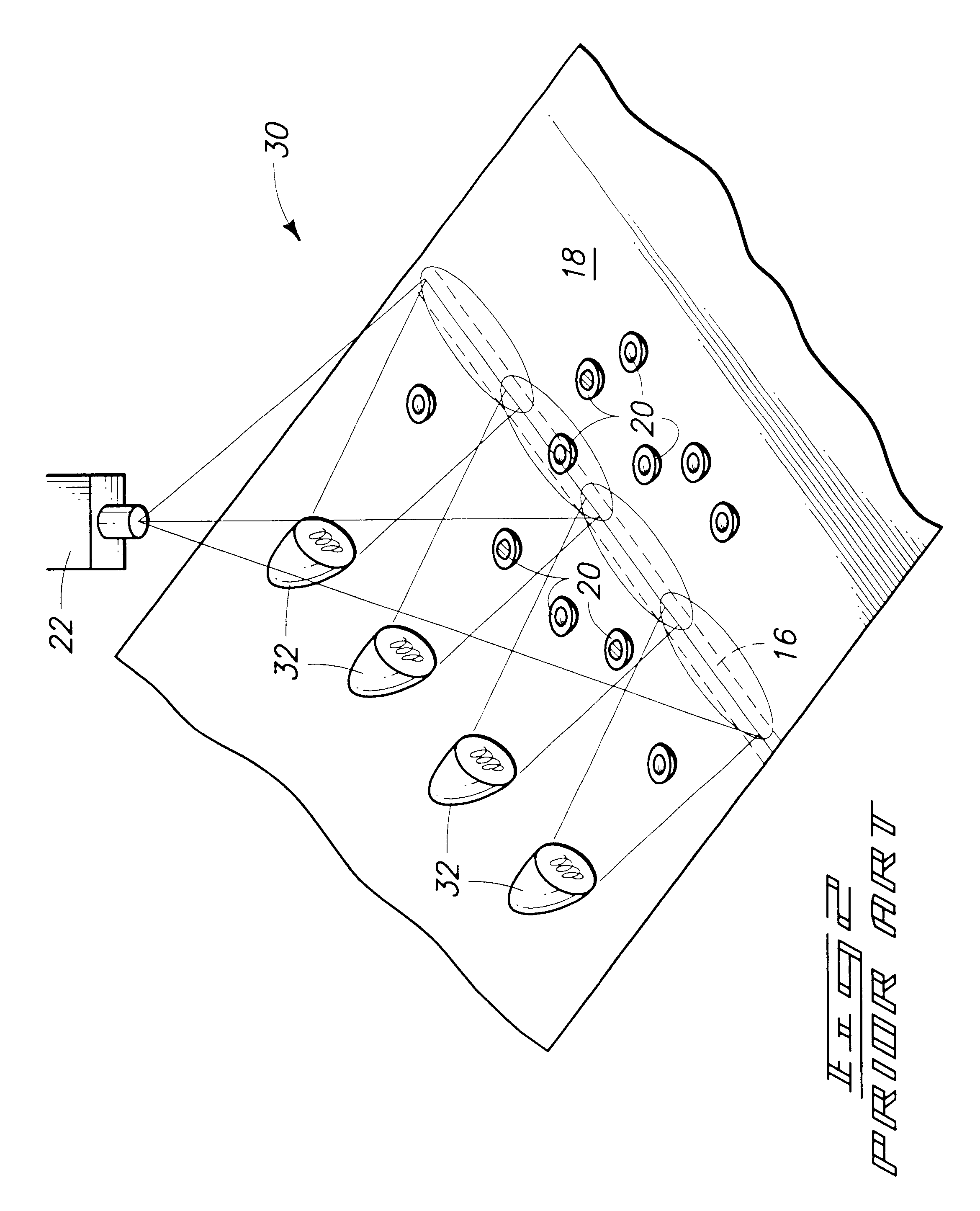
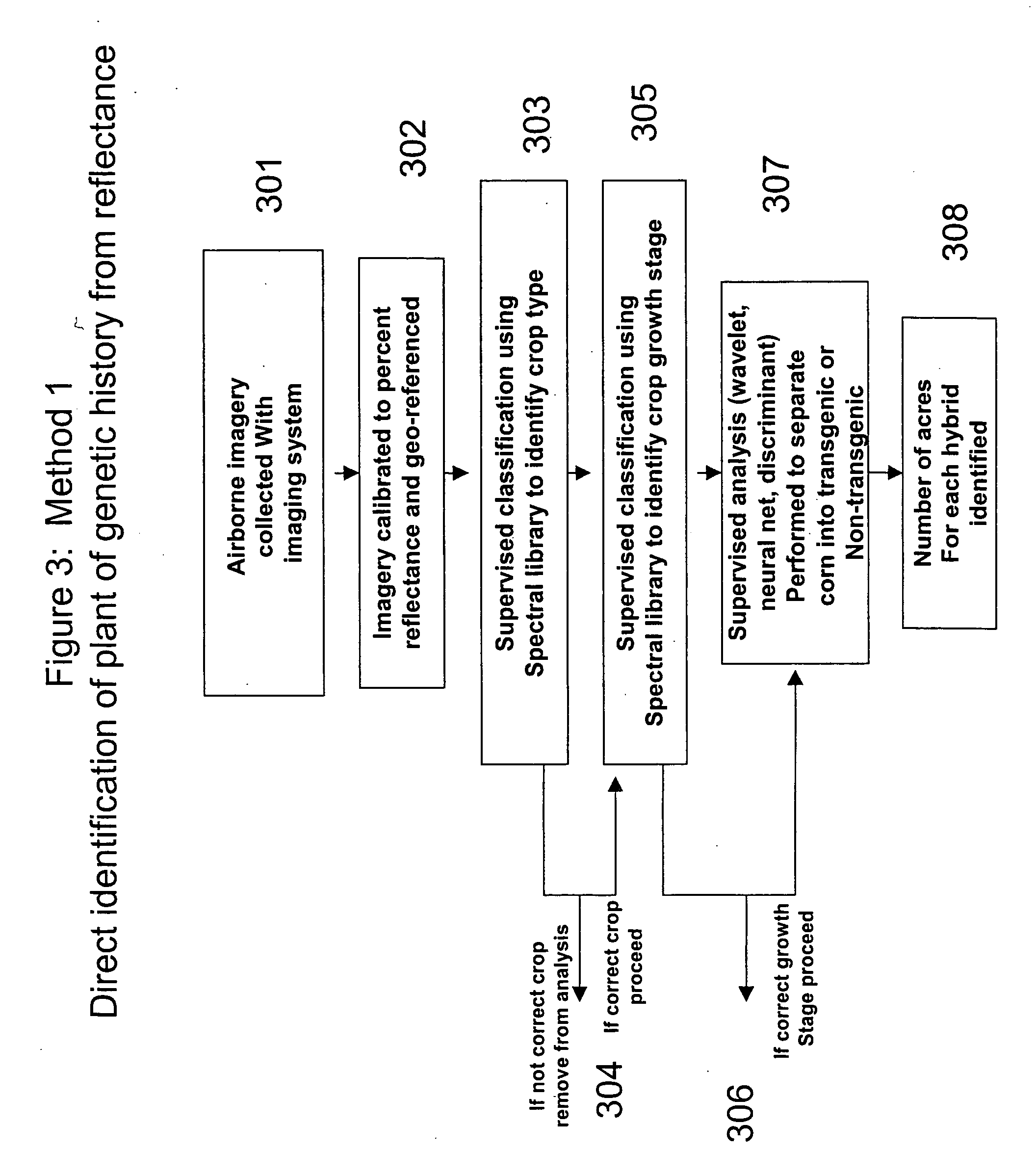
A system is provided to monitor targeted pest populations, disease, presence of transgenic and non-transgenic plants, or targeted pest population in a transgenic crop using remote imagery to discern differences in crops along with pest infestation in all crop varieties. The system relies on the fact that plant leaves are known to change color based on stress, herbivory, and other environmental factors. The system provides a special camera that can see reflected light energy across the visible and near infrared (about 400-1000 nm) to identify these effects.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY US
Optical system for plant characterization
InactiveUS20070065857A1Investigation of vegetal materialMicrobiological testing/measurementGMO PlantsPopulation
A system is provided to monitor targeted pest populations, disease, presence of transgenic and non-transgenic plants, or targeted pest population in a transgenic crop using remote imagery to discern differences in crops along with pest infestation in all crop varieties. The system relies on the fact that plant leaves are known to change color based on stress, herbivory, and other environmental factors. The system provides a special camera that can see reflected light energy across the visible and near infrared (about 400-1000 nm) to identify these effects.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY US
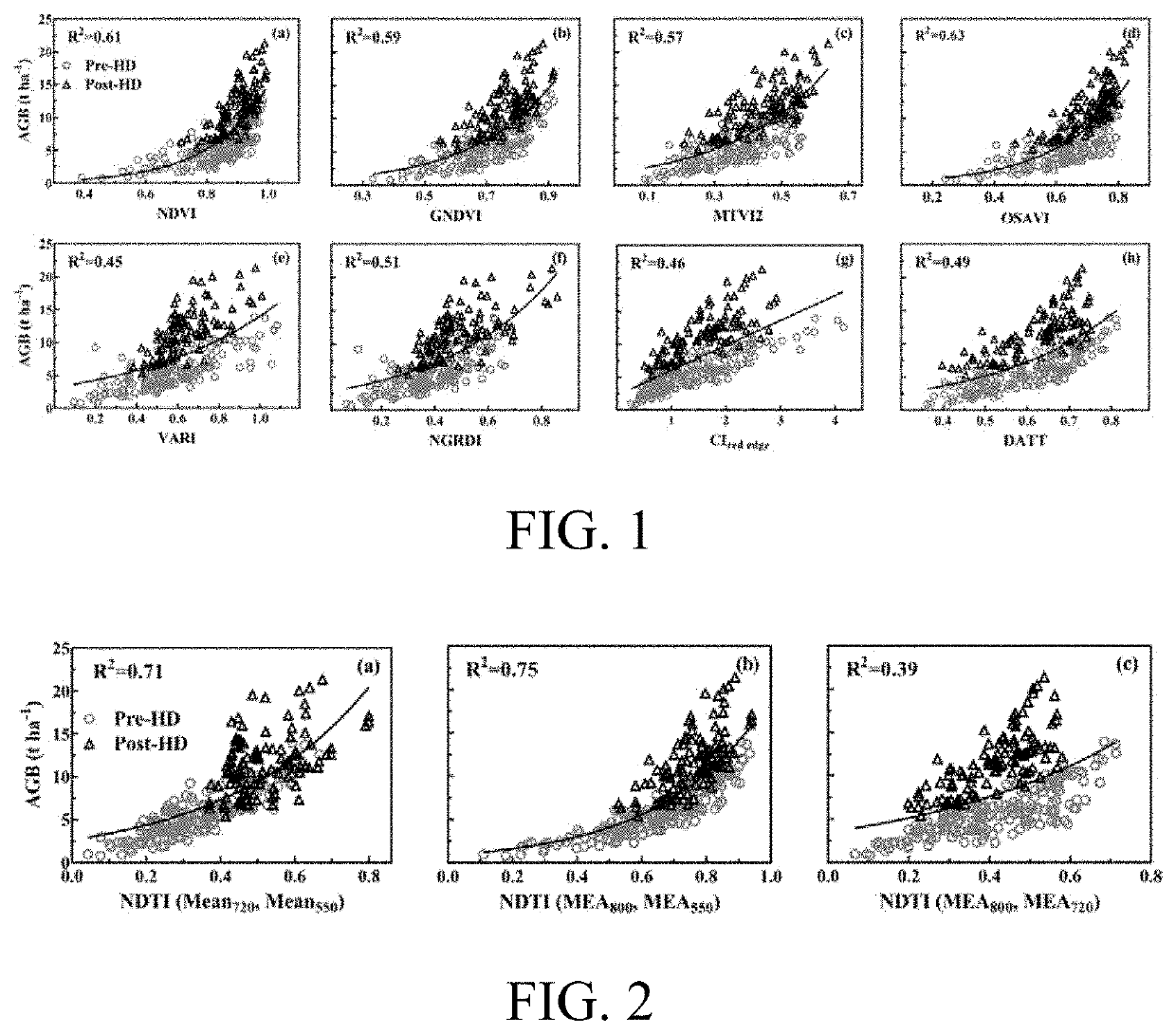
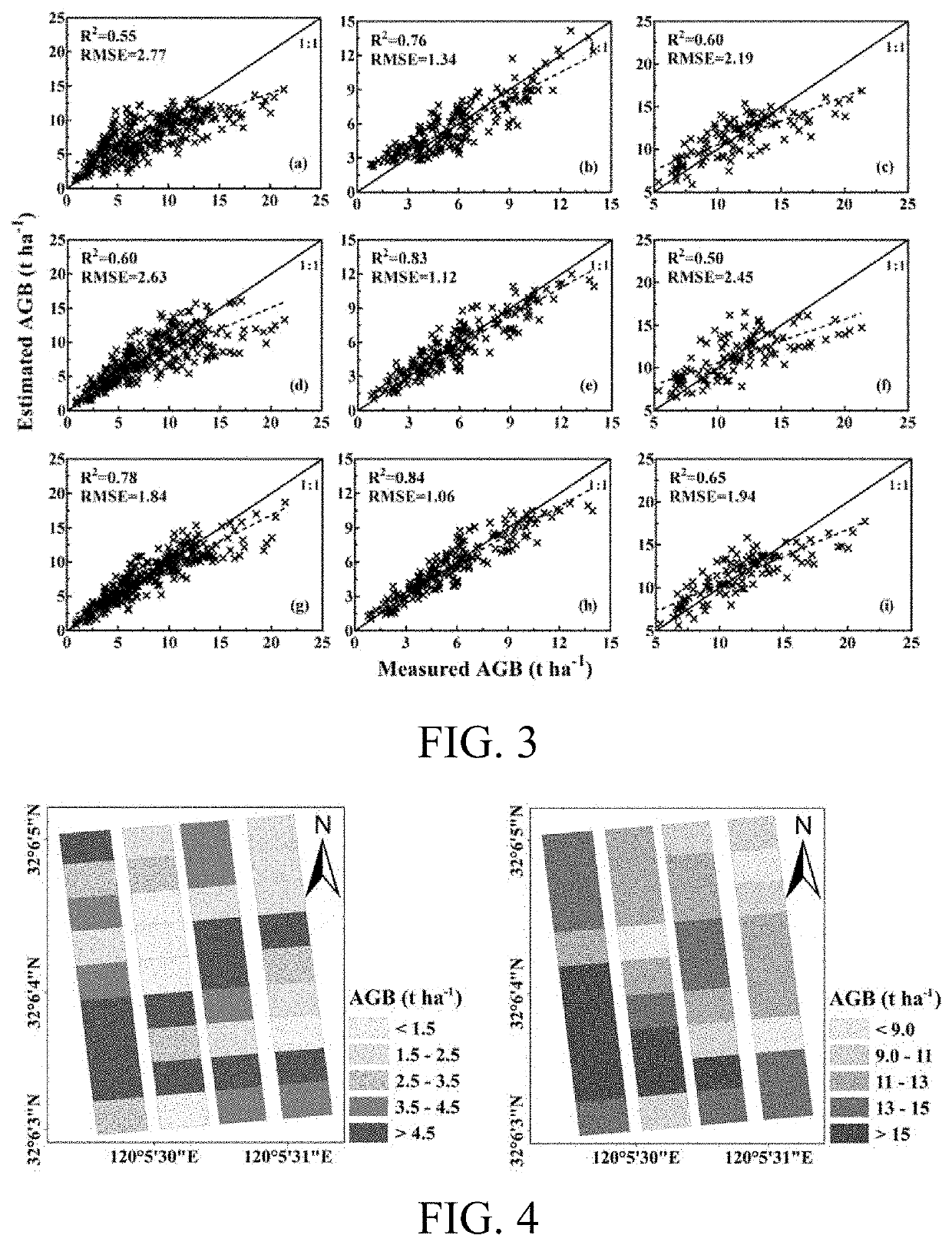
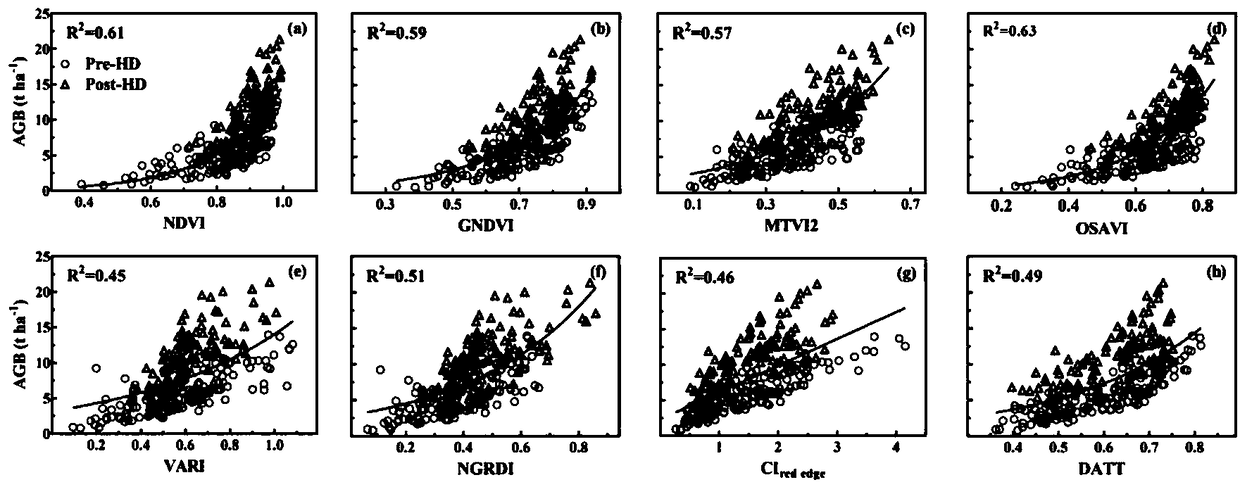
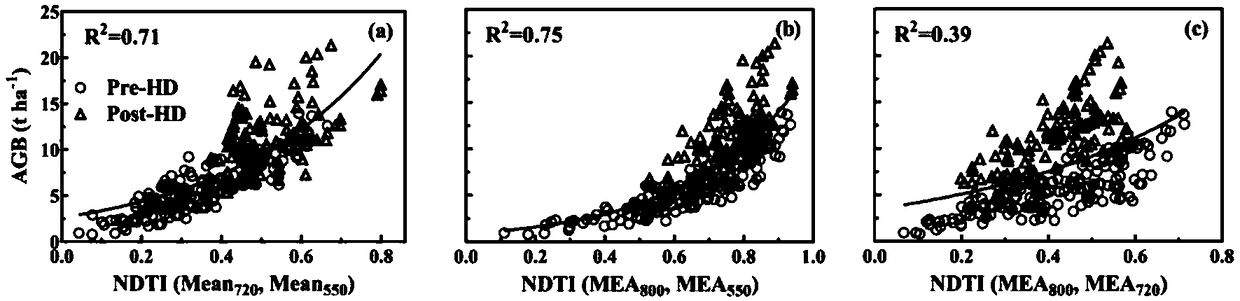
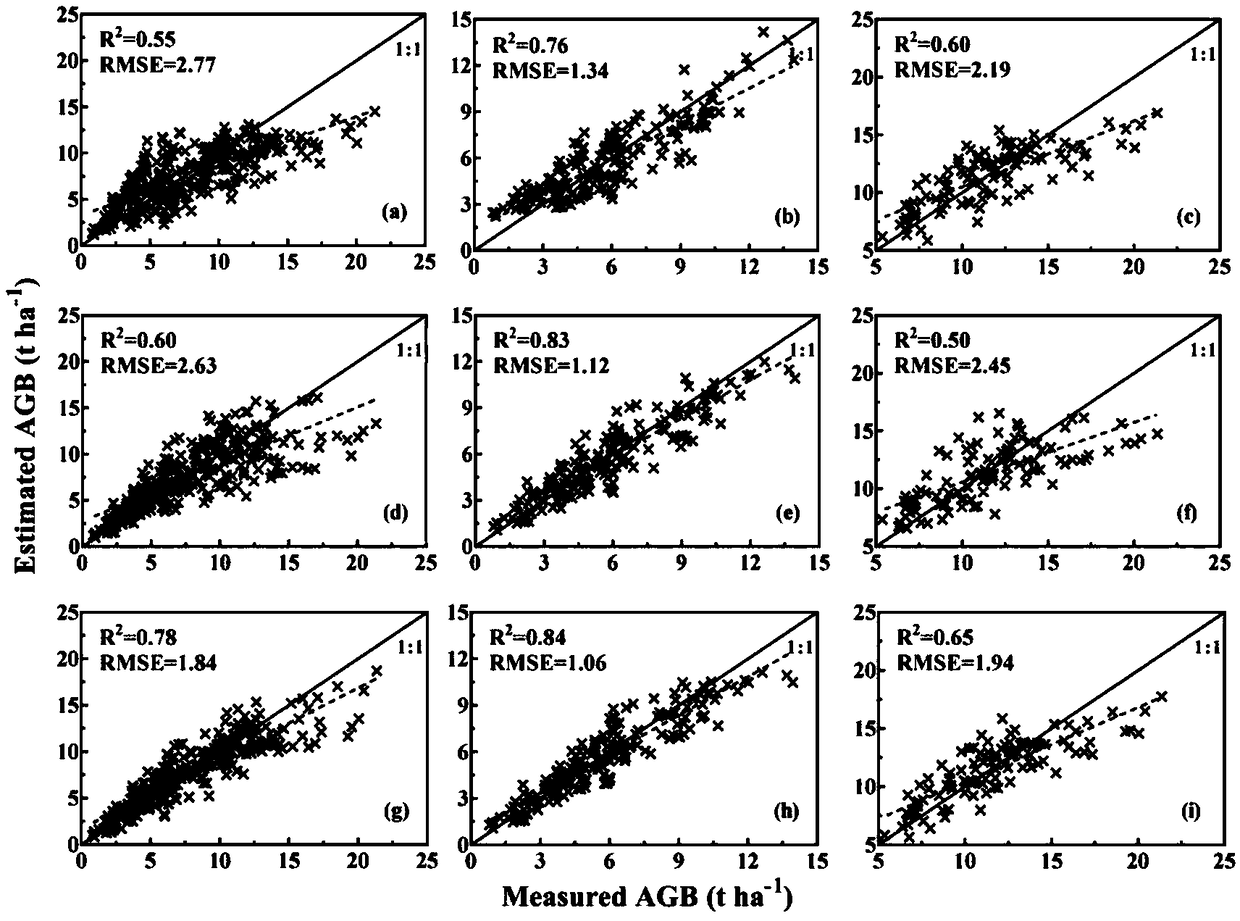
Method for estimating aboveground biomass of rice based on multi-spectral images of unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveUS20200141877A1Low input data requirementImprove estimation accuracyImage enhancementInvestigation of vegetal materialMultivariate linear modelVegetation Index
A method for estimating the aboveground biomass of rice based on multi-spectral images of an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), including: normatively collecting UAV multi-spectral image data of rice canopy and ground measured biomass data; after collection, preprocessing images, extracting reflectivity and texture feature parameters, calculating a vegetation index, and constructing a new texture index; and by stepwise multiple regression analysis, integrating the vegetation index and the texture index to estimate rice biomass, and establishing a multivariate linear model for estimating biomass. A new estimation model is verified for accuracy by a cross-validation method. The method has high estimation accuracy and less requirements on input data, and is suitable for the whole growth period of rice. Estimating rice biomass by integrating UAV spectrum and texture information is proposed for the first time, and can be widely used for monitoring crop growth by UAV remote sensing.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
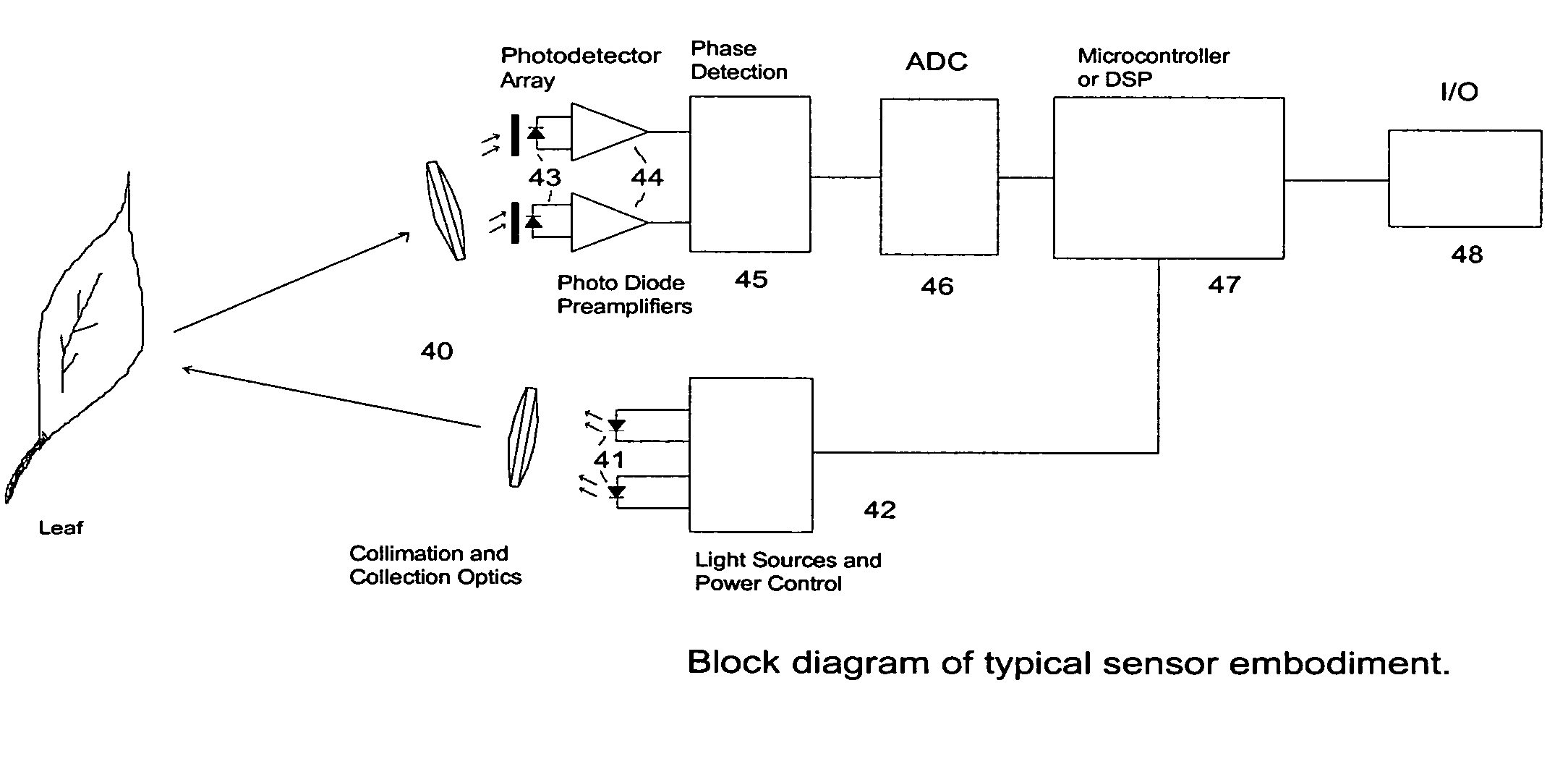
Active Light Sensor
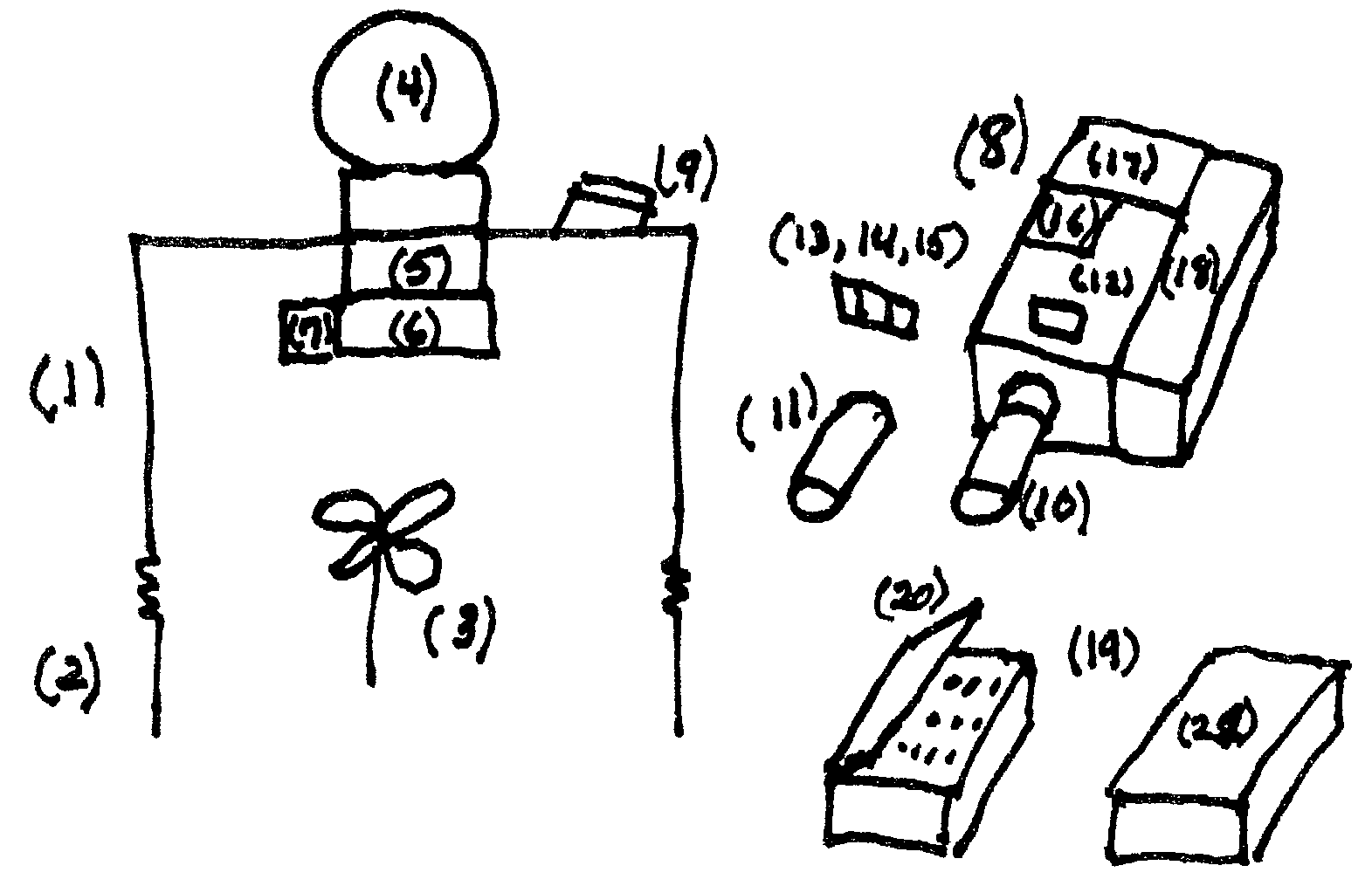
InactiveUS20080291455A1Improve performanceGuaranteed lighting lifeInvestigation of vegetal materialSpectrum investigationOpto electronicInstrumentation
An apparatus is described for assessing plant status remotely sensed by the invention thereby allowing selective monitoring or treatment of individual plants. Additionally, the apparatus may be utilized for measuring the reflectance characteristics of soil or of objects in general. The apparatus utilizes a solid state light source to illuminate a plant canopy or object under investigation. An array of spectrally sensitive photosensors are incorporated into the apparatus to detect light reflected from a plant or object resulting from the integral light source. The instrument may be mounted to a vehicle, mounted to a tripod or held in the hand of an operator for use. A controller can be used in conjunction with the invention to analyze measured reflectance signals and can respond by activating a device to take some action with respect to the plant and / or object or store the analyzed signals with corresponding DGPS position in the controller's memory for later analysis.
Owner:KYLE H HOLLAND TRUSTEE OF THE MARANATHA TRUST DATED JULY 30 2013
Portable Intelligent Fluorescence and Transmittance Imaging Spectroscopy System
A portable fluorescence and transmittance imaging spectroscopy system for use in diagnosing plant health. The system has a primary LED light source array with spectral wavelengths in the 400-600 nm range, a focus cone that collects the LED light source output and focuses it, a controller that controls the primary LED array to turn it on and off, or certain of the spectral wavelengths on and off such that the primary LED array controllably emits light of a desired wavelength in the range, the light irradiating the plant through the focus cone, a digital imaging device that both spatially and temporally captures a fluorescence image comprising chlorophyll fluorescence emitted by the plant due to the emitted light from the LED array, a leaf holder located proximate to the output of the focus cone to maintain a consistent position and distance between the digital imaging device, the LED light source and the leaf and providing for fixed position and non-destructive leaf imaging and testing, a secondary light source for providing broad-band transmissive light through the leaf, a lens for focusing onto the imaging device the light emitted from the secondary light source, and one or more memory devices that store the fluorescence image and the transmitted light data received by the digital imaging device and store a library of plant fluorescence-intensity data indicative of both healthy plants and stressed or diseased plants, and plant light transmittance data indicative of certain plant conditions.
Owner:LUSSIER ROBERT
System and method of determining nitrogen levels from a digital image
ActiveUS8391565B2Minimize shadowsImage analysisInvestigation of vegetal materialFully developedInternal standard
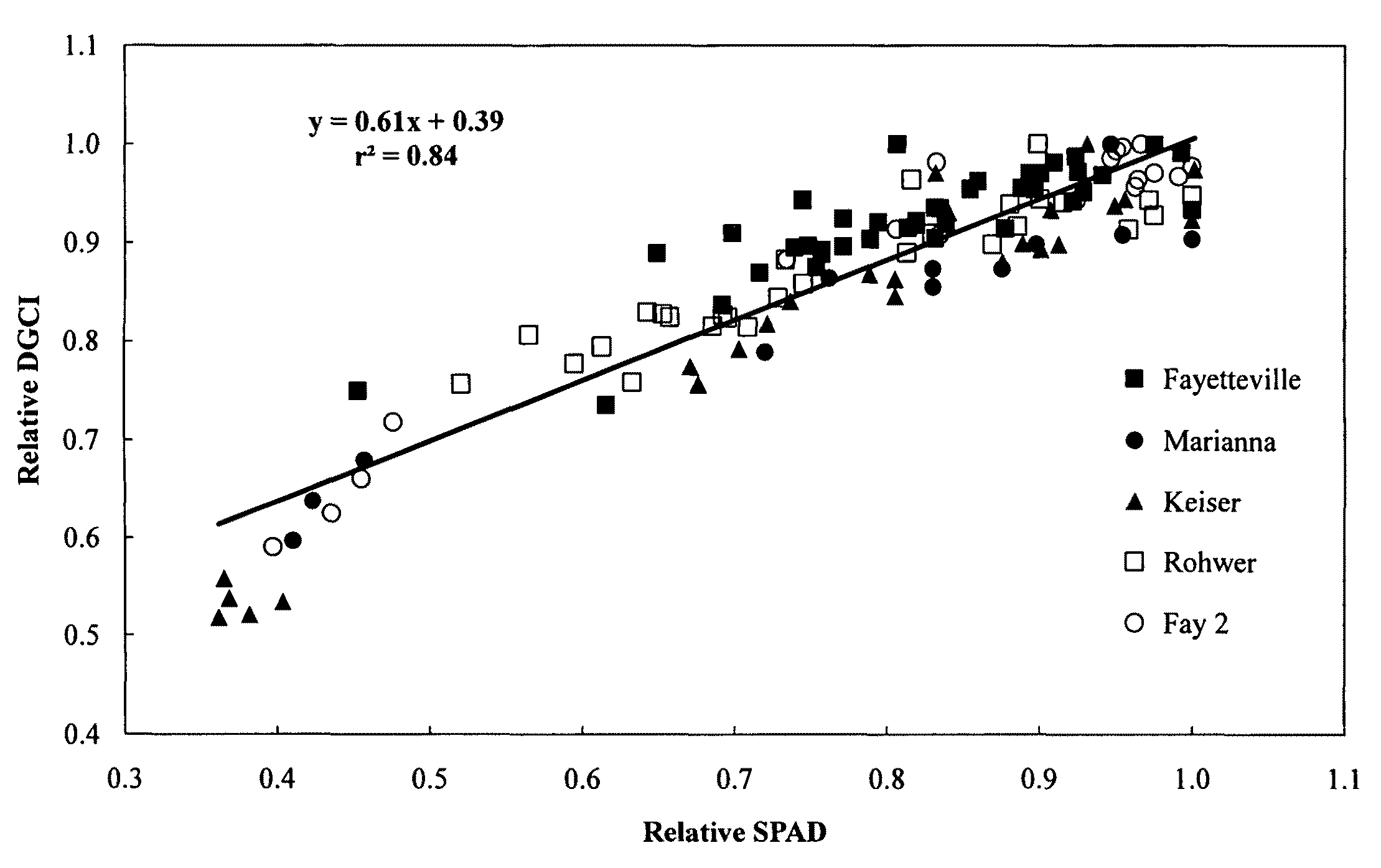
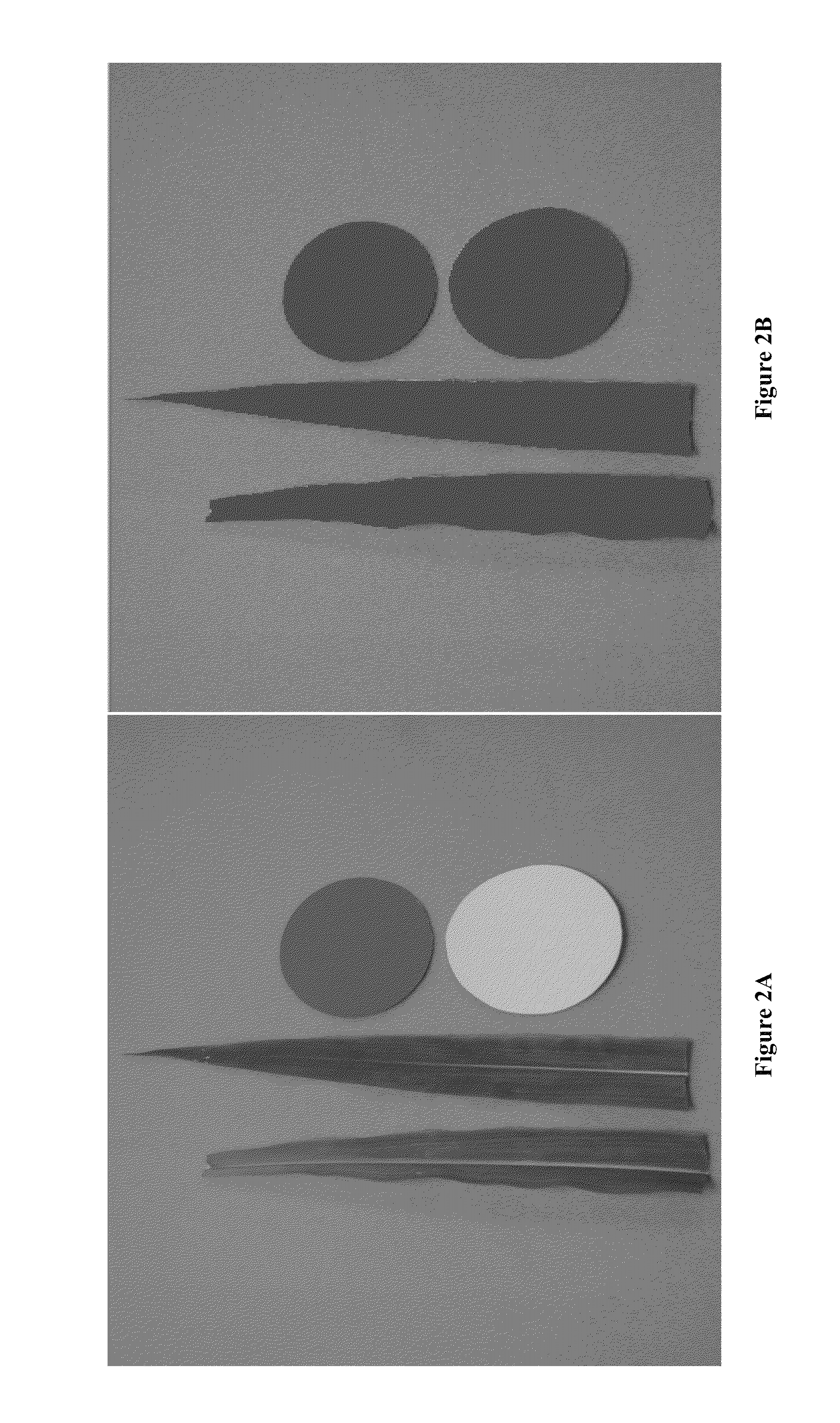
A system and method of determining nitrogen levels from a digital image. In particular, a method of determining leaf nitrogen concentration and yield from a digital photograph of a fully developed leaf (collared leaf) of a crop of nonlegumes, such as corn, rice, wheat, cotton, potatoes or sugarcane. The digital image is processed to determine a dark green color index (“DGCI”), which is closely related to leaf nitrogen concentration and yield. Standardized color disks having known DGCI values are included in the digital photograph and serve as an internal standard. The internal standard allows correction of DGCI of samples when using different cameras and / or when lighting conditions change.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Bio-imaging and information system for scanning, detecting, diagnosing and optimizing plant health
InactiveUS7112806B2Accurate measurementImprove efficiencyInvestigation of vegetal materialPhotometryArbitrary Fluorescence UnitBiology
A portable Chlorophyll Fluorescence Imaging Time (CFIT) system for use in determining plant health. The system includes an enclosure for placement around a plant to be imaged in-situ. There is a controlled light source that controllably provides to the plant light of a desired wavelength range, to controllably irradiate the plant within the enclosure. The chlorophyll fluorescence emitted from the plant both spatially and temporally is captured, and the captured fluorescence information is analyzed to provide plant health information.
Owner:LUSSIER ROBERT
Miniaturized unmanned aerial vehicle crop information obtaining and fertilization irrigation guiding apparatus
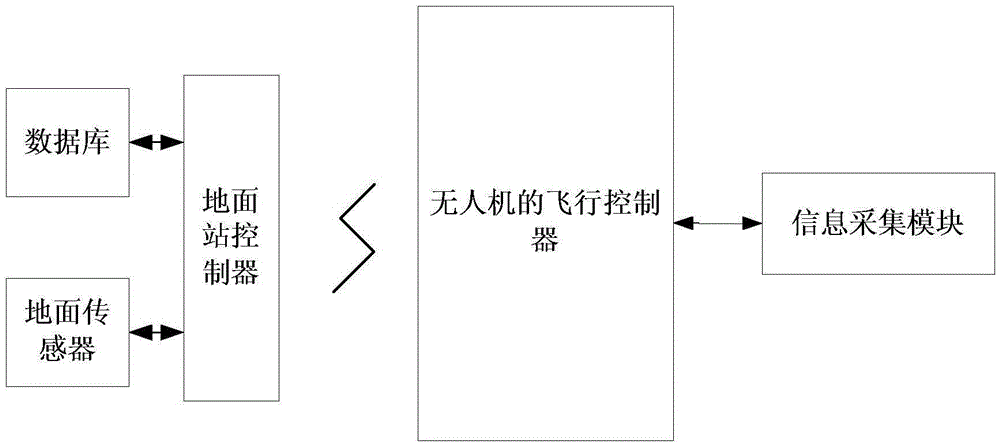
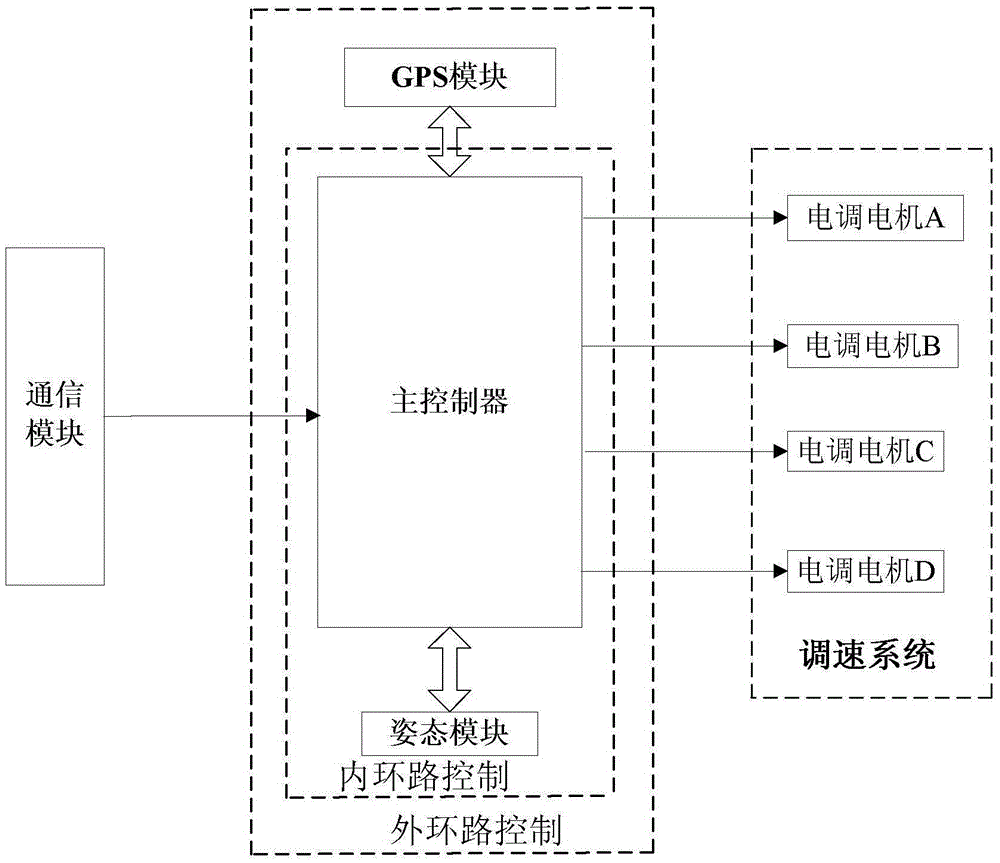
InactiveCN105547366ALow costSimple structureInvestigation of vegetal materialPosition/course control in three dimensionsUncrewed vehicleEngineering
The invention discloses a miniaturized unmanned aerial vehicle crop information obtaining and fertilization irrigation guiding apparatus and belongs to the technical field of crop monitoring, for solving the problems high cost and poor reliability existing in conventional crop monitoring. The apparatus comprises an information acquisition module, a ground sensor, a database, a ground station and an unmanned aerial vehicle, wherein the ground station carries out course planning and information acquisition point setting on a crop area to be detected; a flight controller of the unmanned aerial vehicle, according to a planned course, controlling flight of the unmanned aerial vehicle, and when the unmanned aerial vehicle arrives at information acquisition points, the information acquisition module acquires air indexes of the information acquisition points, and at the same time, performs hyperspectal shooting on crops at the information acquisition points so as to obtain growth information of the crops; the database stores data corresponding to the year with previous optimal output; the ground sensor is arranged at the crop area to be detected for measuring soil indexes; and the ground station, according to the air indexes acquired at the corresponding information acquisition points, the crop growth information and the soil indexes, makes a comparison with corresponding data in the database so as to obtain fertilization and irrigation instructions.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for controlling a growth cycle for growing plants using state oriented control
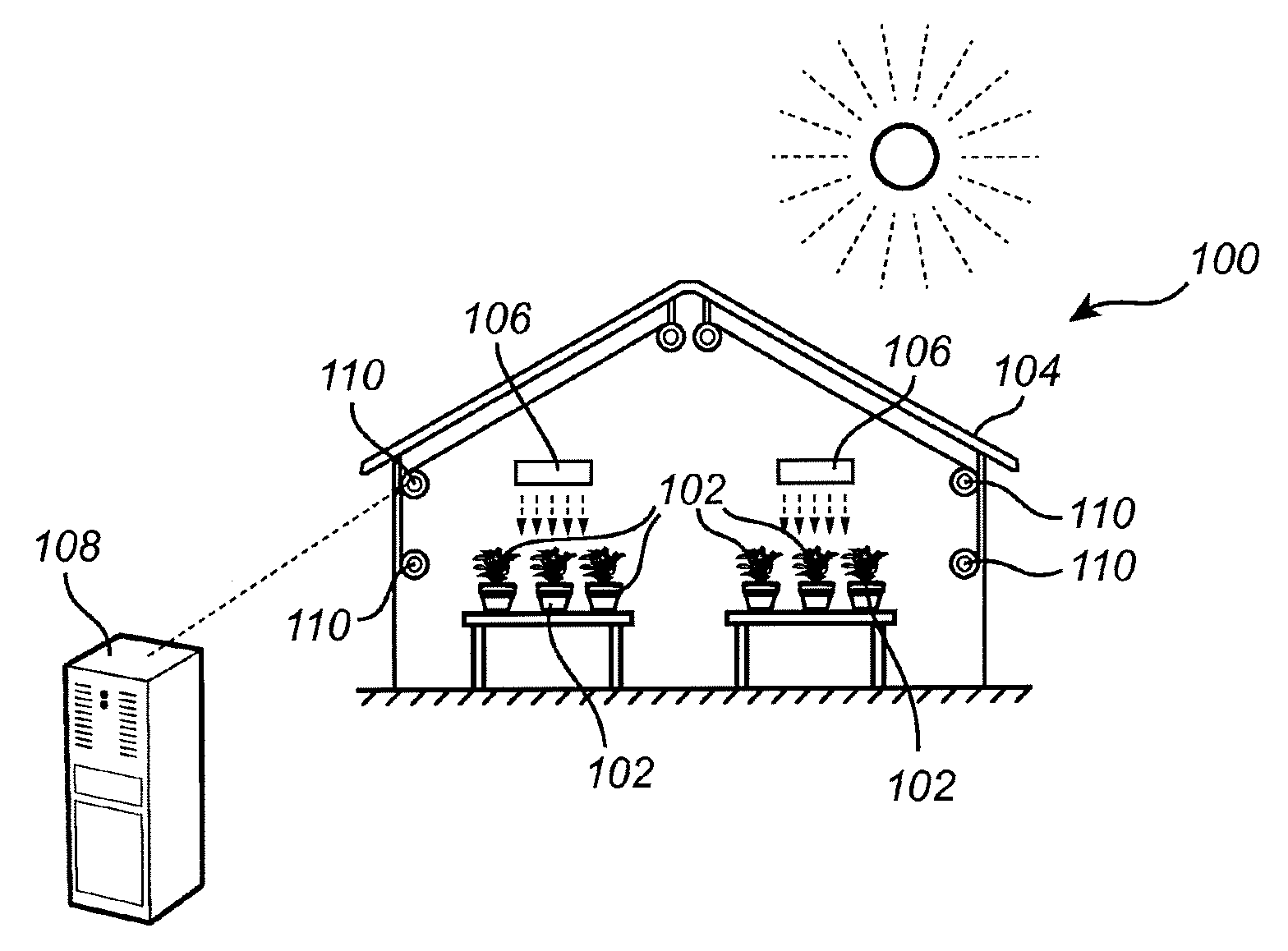
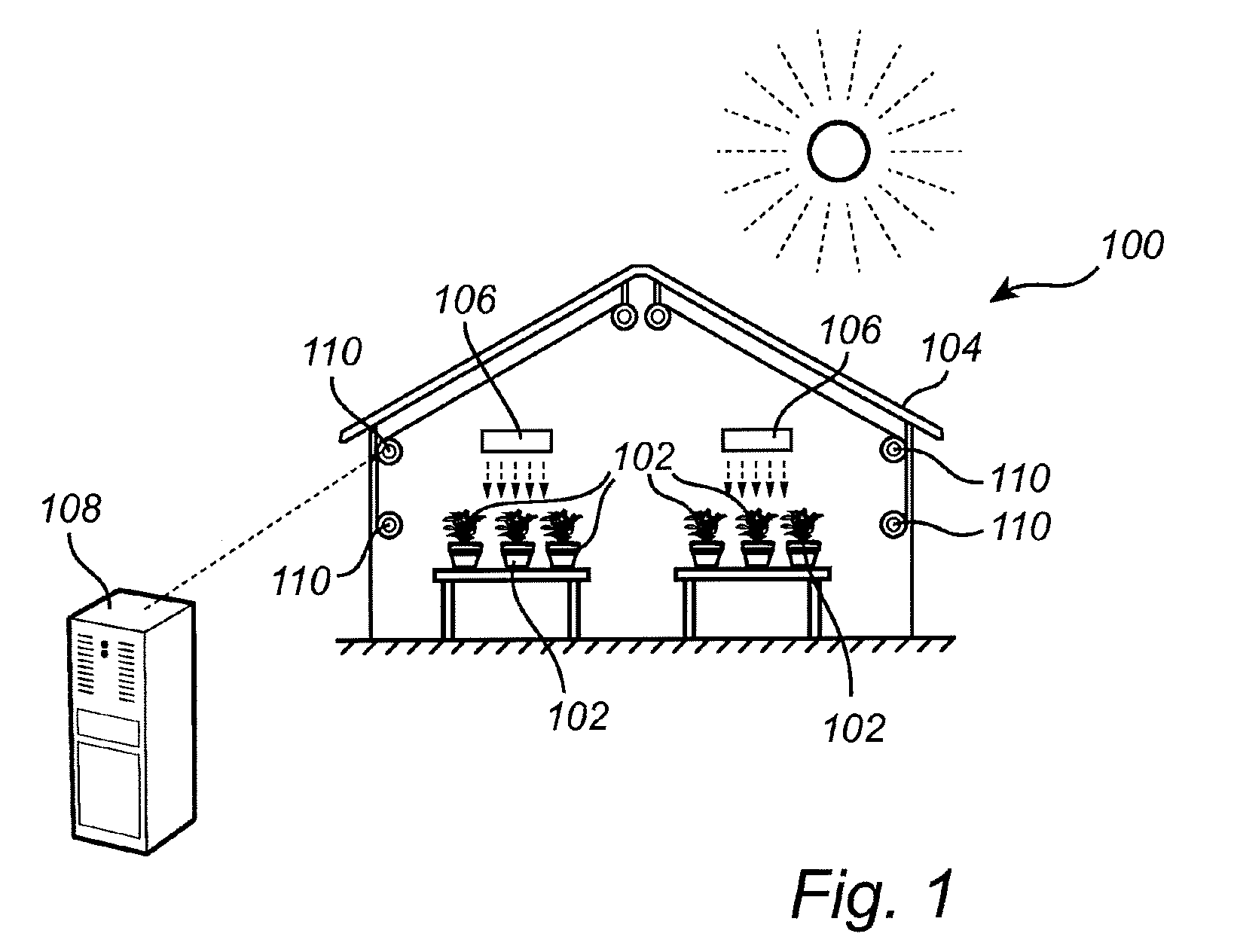
ActiveUS20160278300A1Optimizing growth controlEasy to controlInvestigation of vegetal materialGreenhouse cultivationGrowth plantGrowth cycle
The present invention relates to a method for controlling of a growth cycle for a plant being arranged in a controlled environment and subject to light emitted by at least one artificial lighting arrangement. The invention also relates to a corresponding system device and to a computer program product.
Owner:HELIOSPECTRA
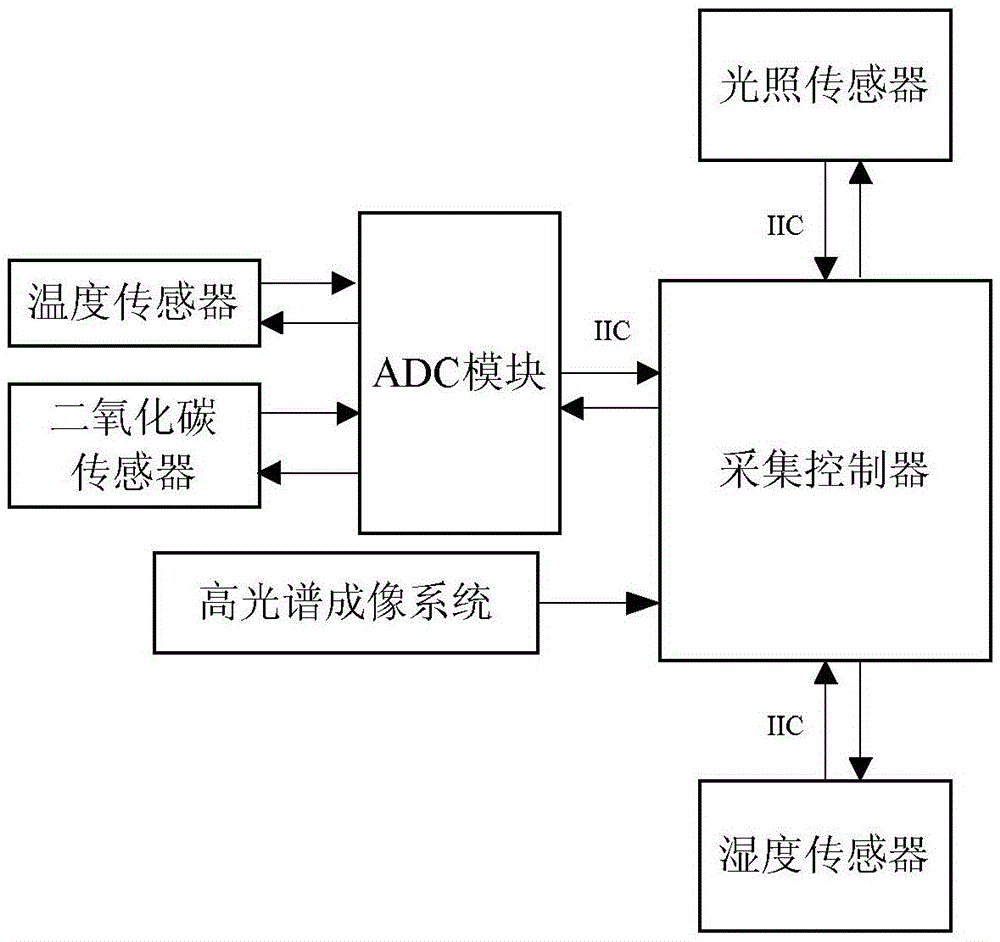
Non-destructive detecting method and detecting instrument for portable plant nitrogen and water content
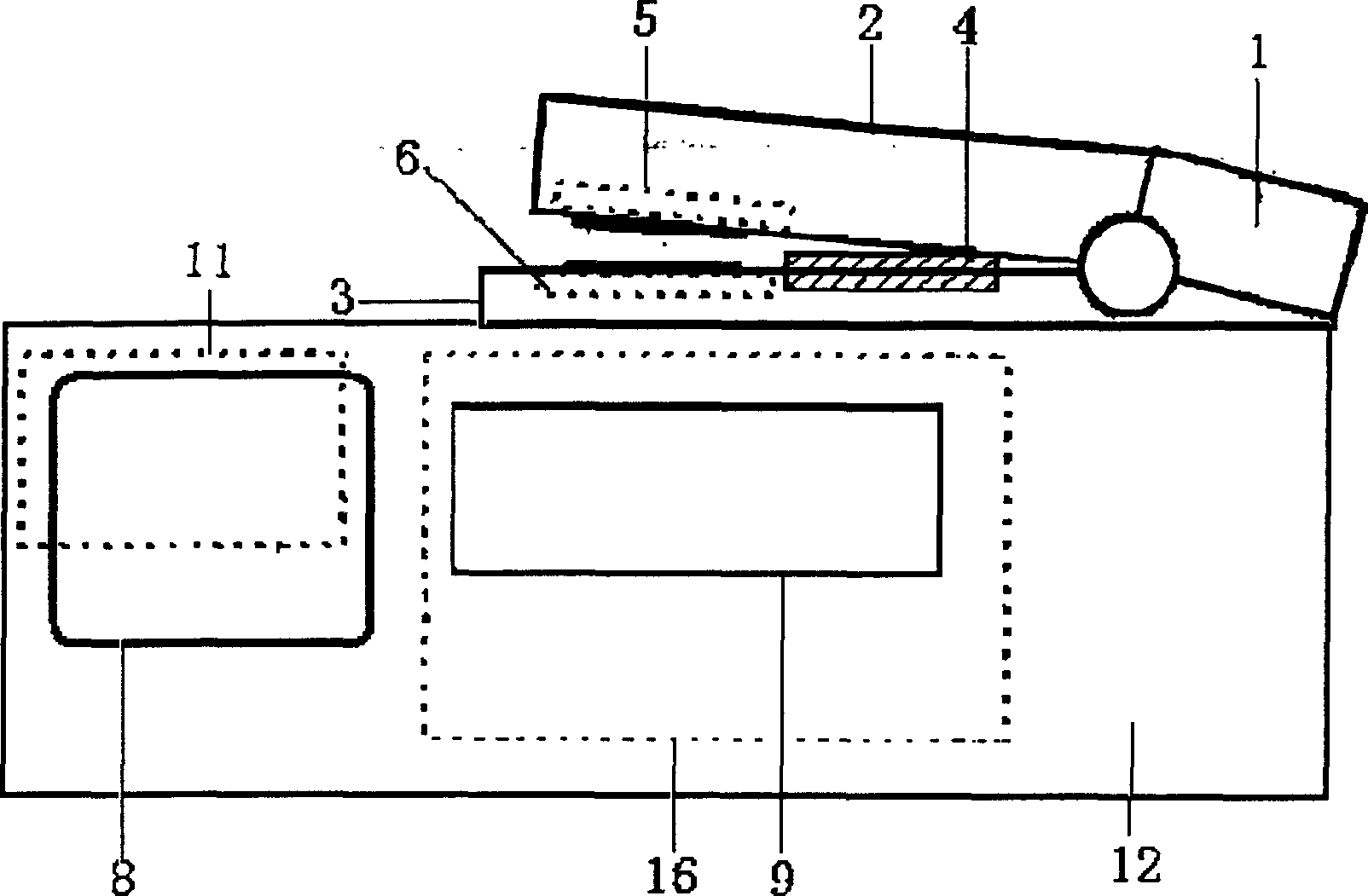
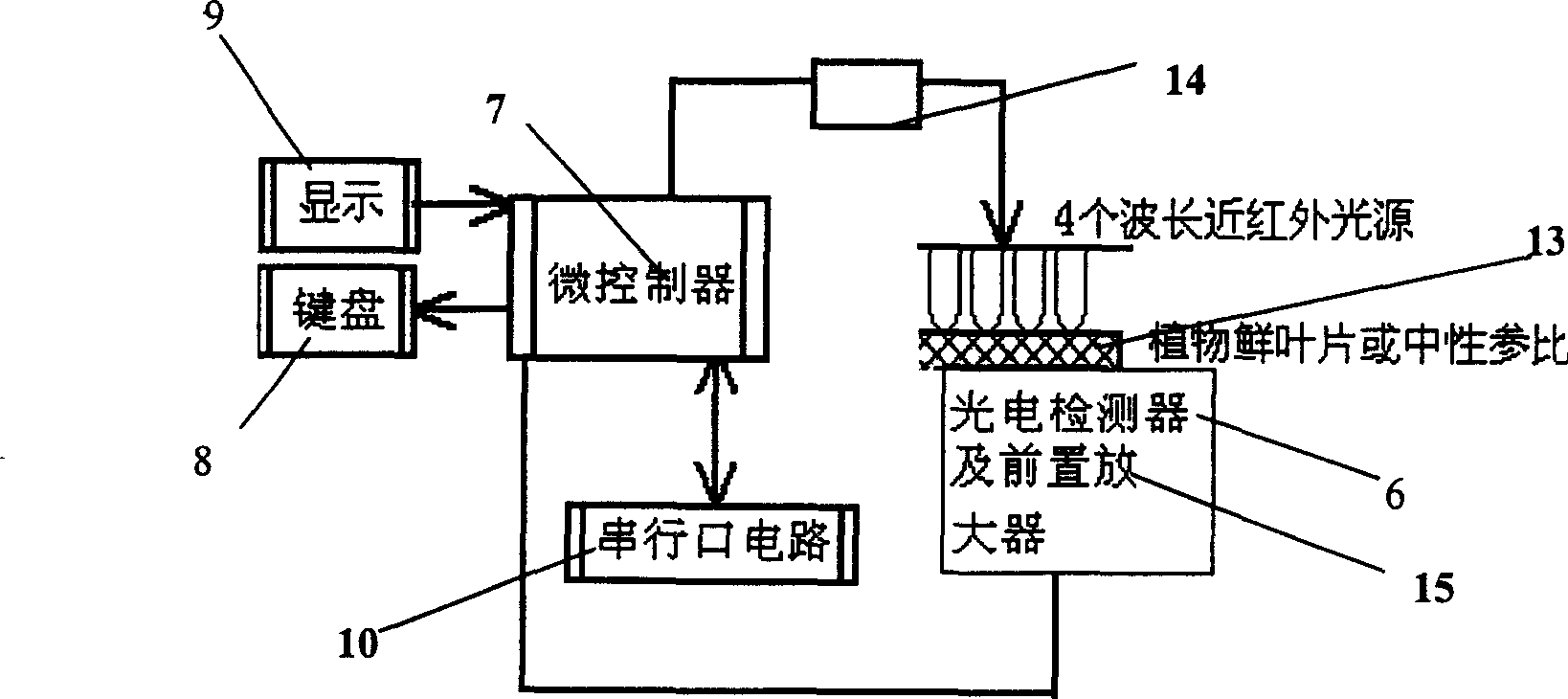
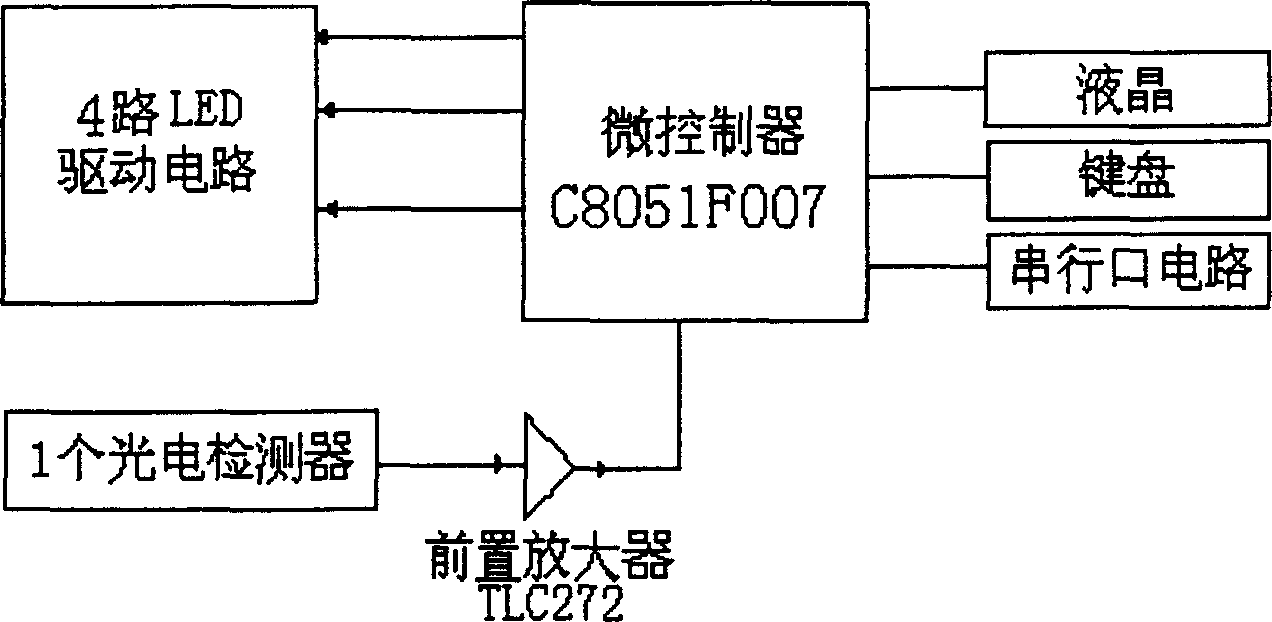
InactiveCN1715880AImprove efficiencyNo pollution in the processInvestigation of vegetal materialTransmissivity measurementsReference sampleMeasurement device
The portable non-destructive plant nitrogen and water content detection system includes four wavelength spectral measurement device with oppositely set light source and detector, neutralized reference sample or leaf to be measured, micro controller connected to the light source and the detector, serial port circuit connected electrically to the micro controller, and display and keyboard connected electrically to the micro controller too. The detection method includes detecting data I0 and I, calculating the fresh leaf transmission T= I / I0 of different wavelengths, and calculating the plant chlorophyll, water content and relative content NI reflecting the nitrogen level in the leaf in chemical metering algorithm. Compared with traditional measurement method, the present invention has decades times raised efficiency and no production of environment harming matter, and may be used in great area fast field measurement.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT FOR INFORMATION TECH & AGRI
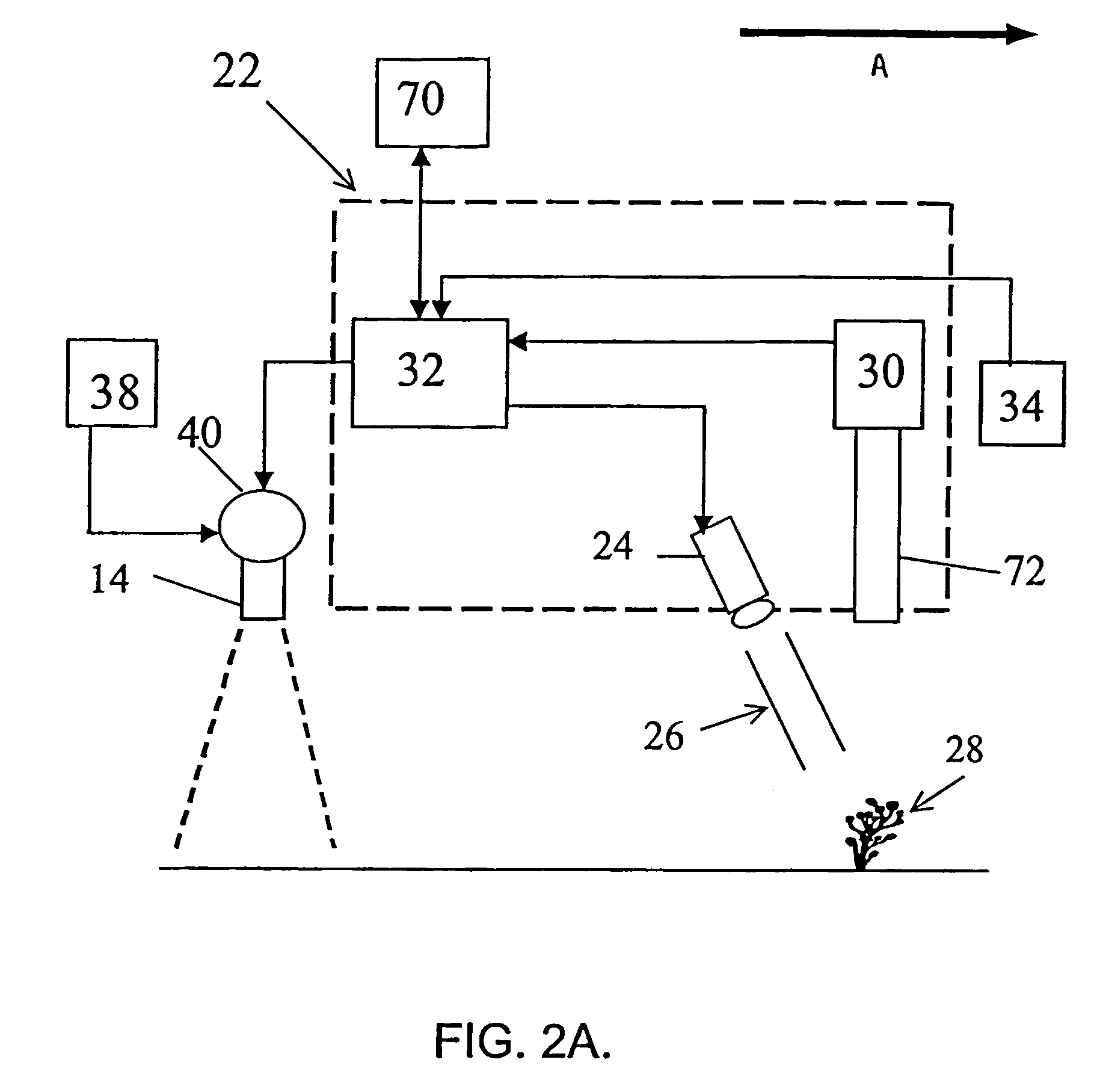
Selective weed discrimination
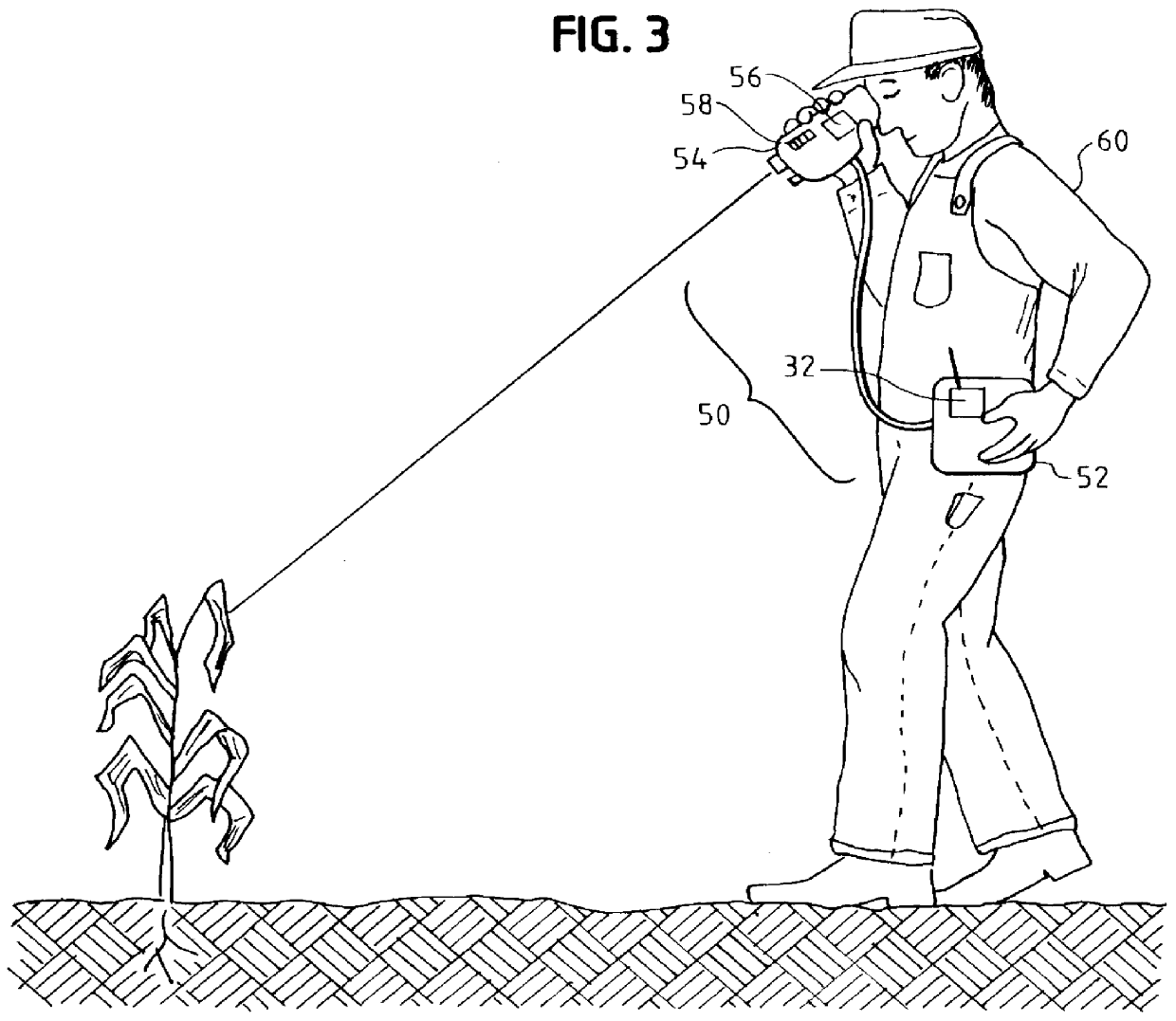
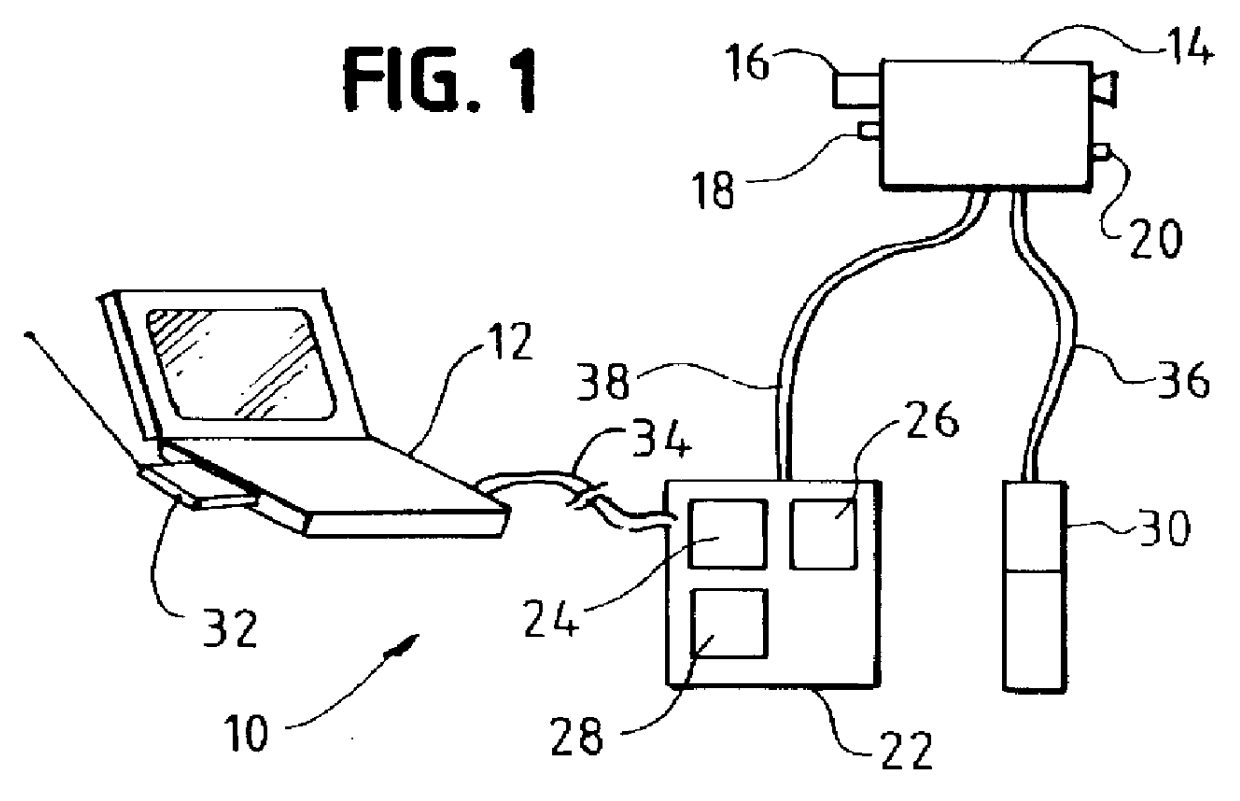
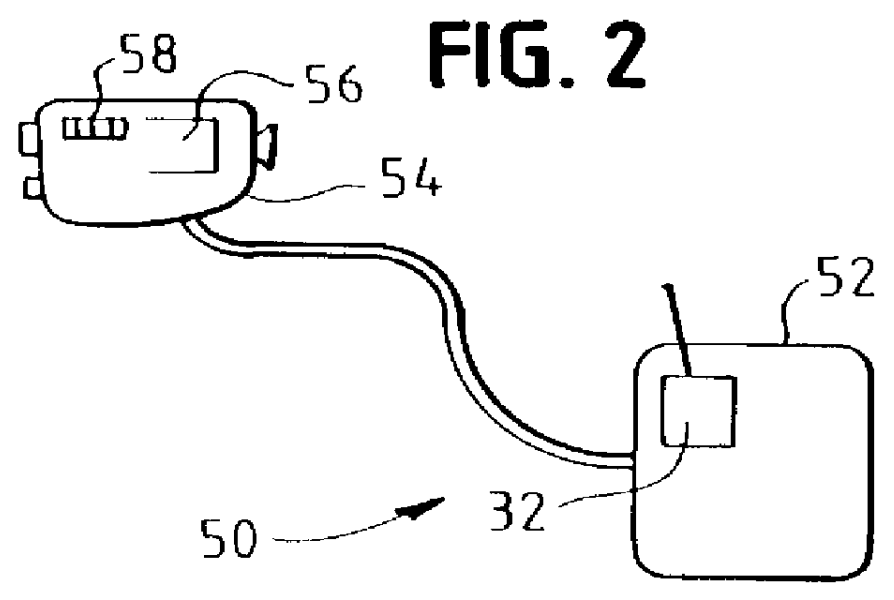
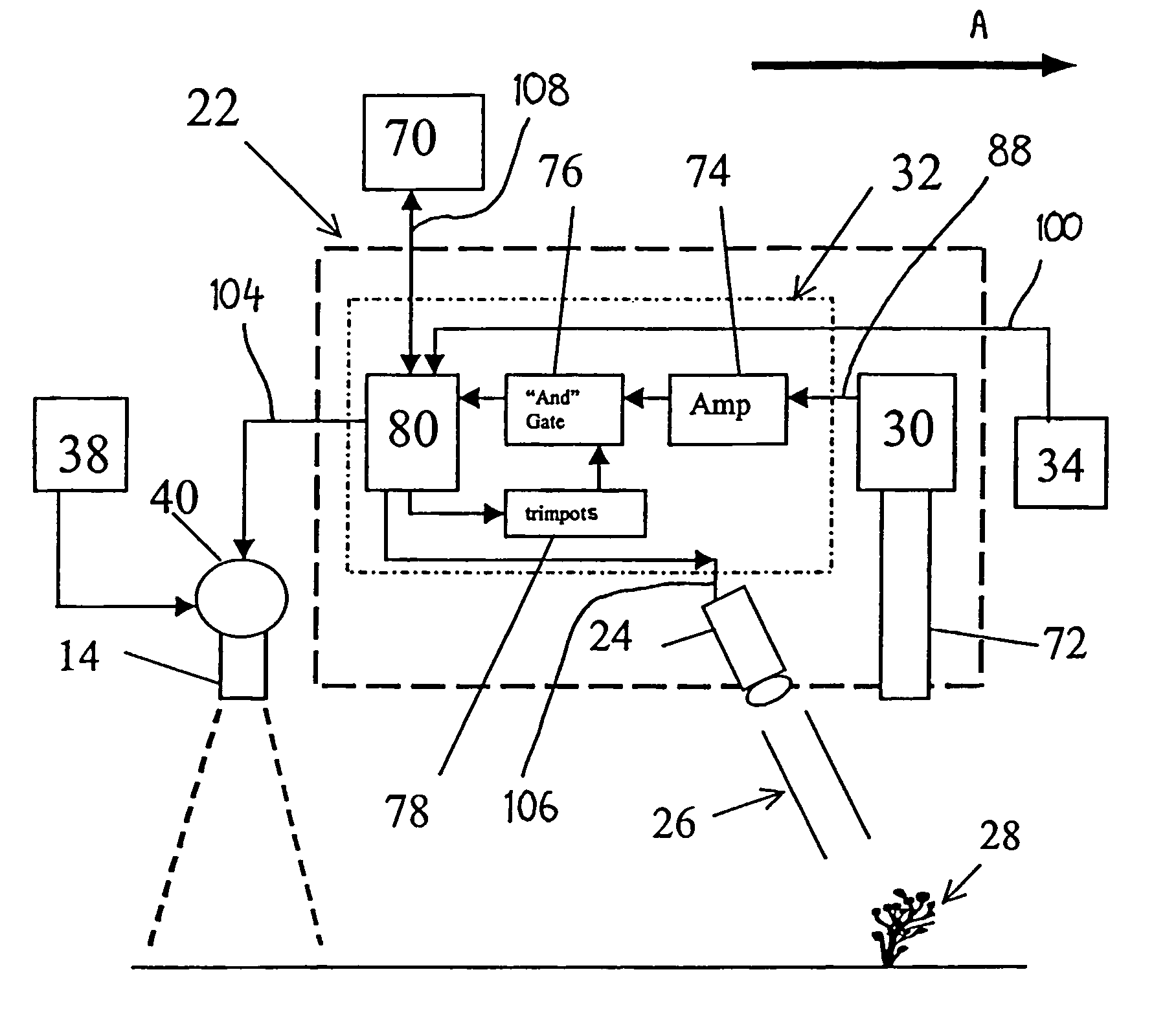
InactiveUS7081611B2Reduce morbidityInvestigation of vegetal materialSelf-acting watering devicesVegetationLight sensing
An apparatus (22) for selectively discriminating vegetation or plant matter (28) comprises a light emitting means (24), a light sensing means (30) and a distance sensing means (34). The light emitting means generates a beam of light (26) that can be directed onto plants or plant matter moving relative to the apparatus. The light sensing means senses light transmitted from said light emitting means and reflected from the plants or plant matter, and generates a reflection signal in response to the sensing of the reflected light. The distance sensing means senses the relative distance moved and generates a distance signal. A processing means (32) is operatively connected to the light sensing means and the distance sensing means to combine the reflection signal and distance signal to discriminate different types of plants or plant matter.
Owner:WEED CONTROL AUSTRALIA
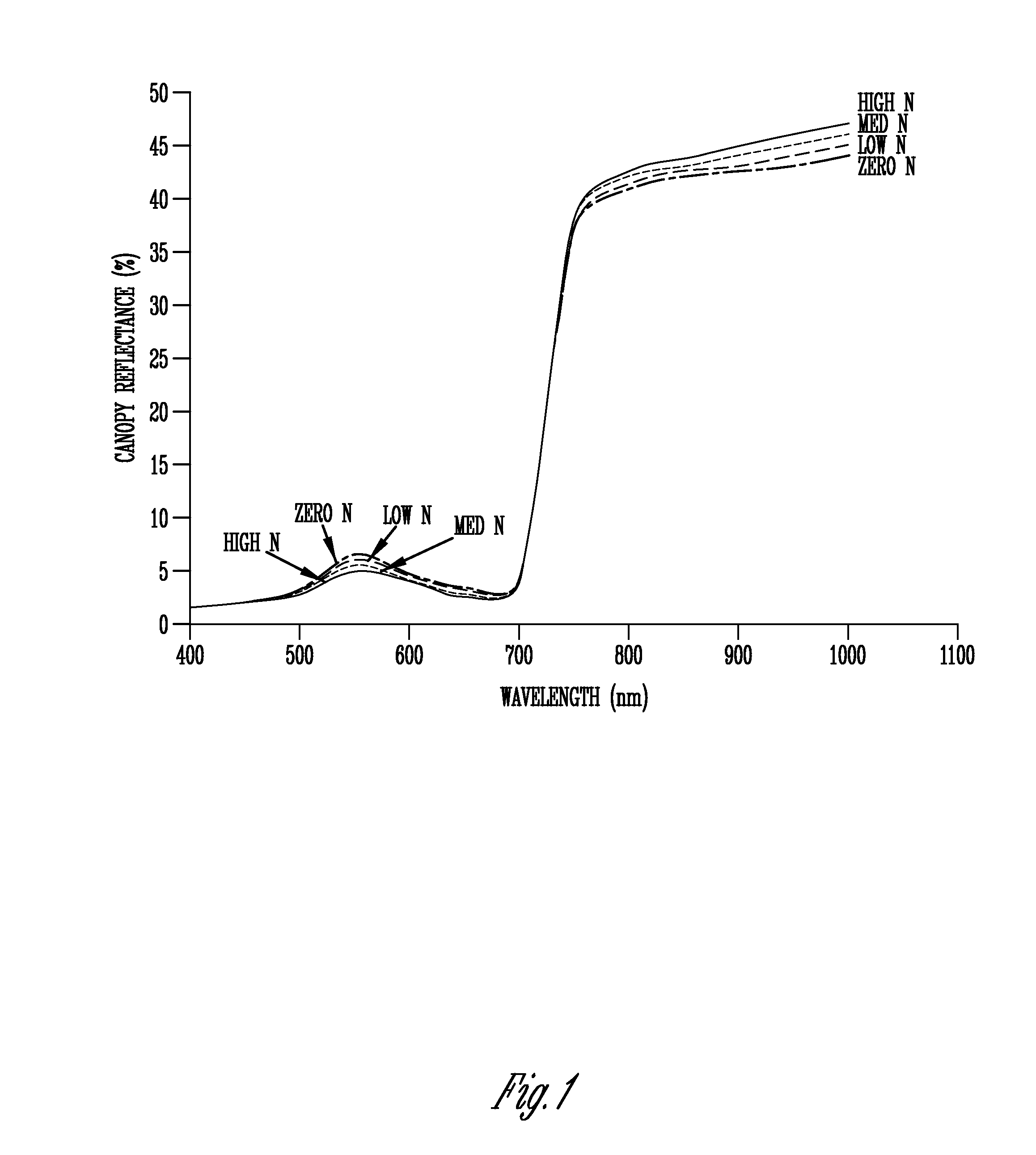
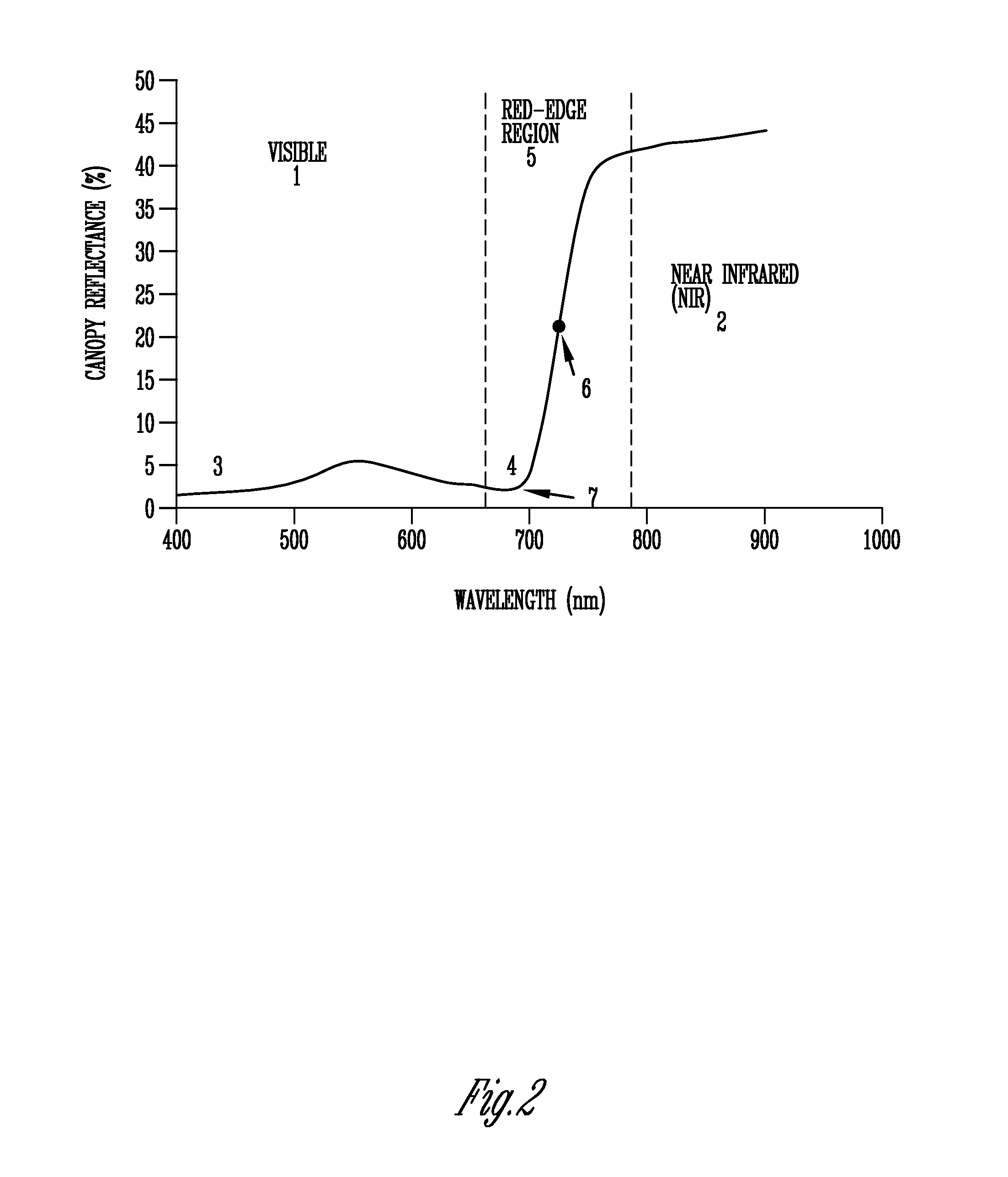
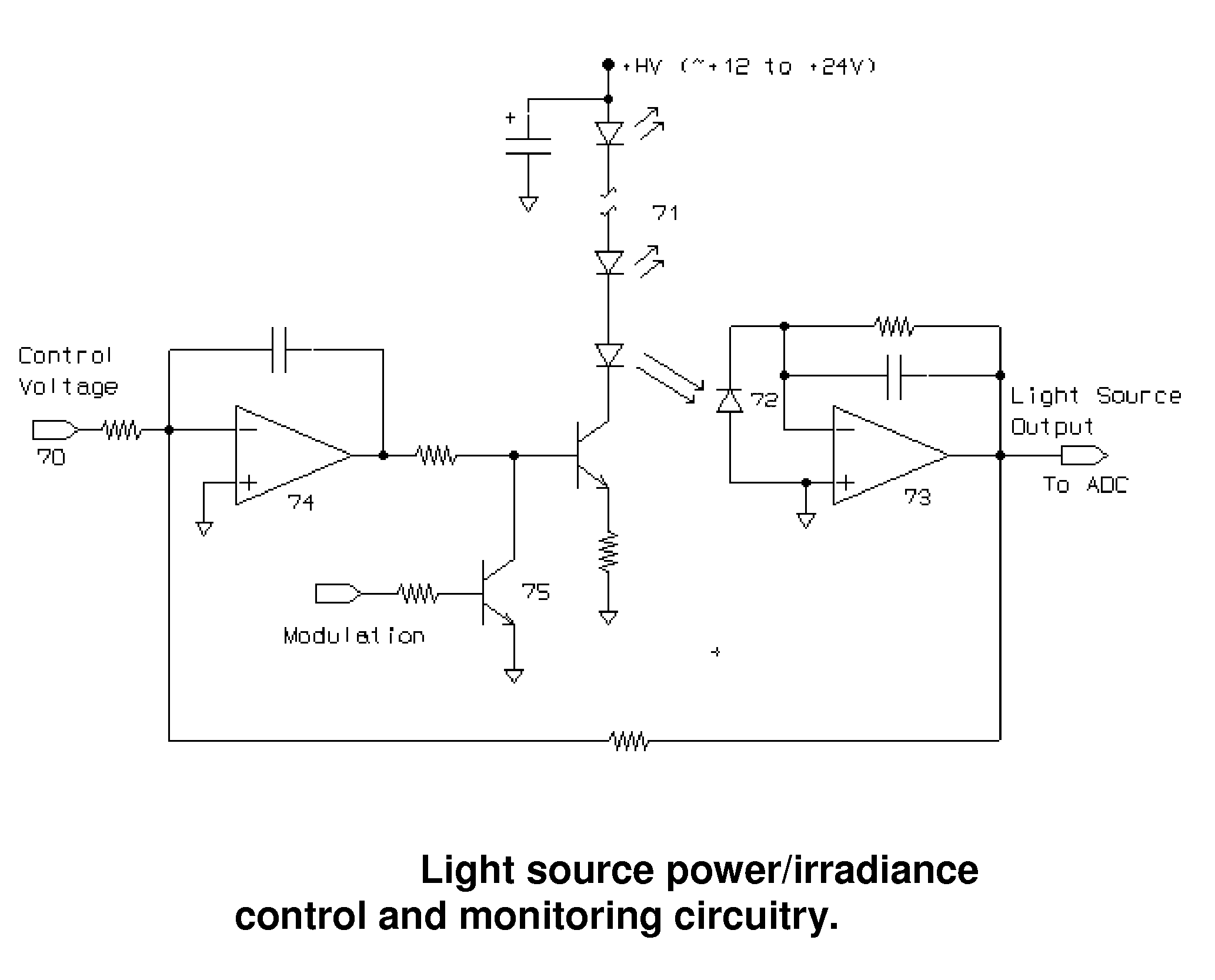
Light sensor with modulated radiant polychromatic source
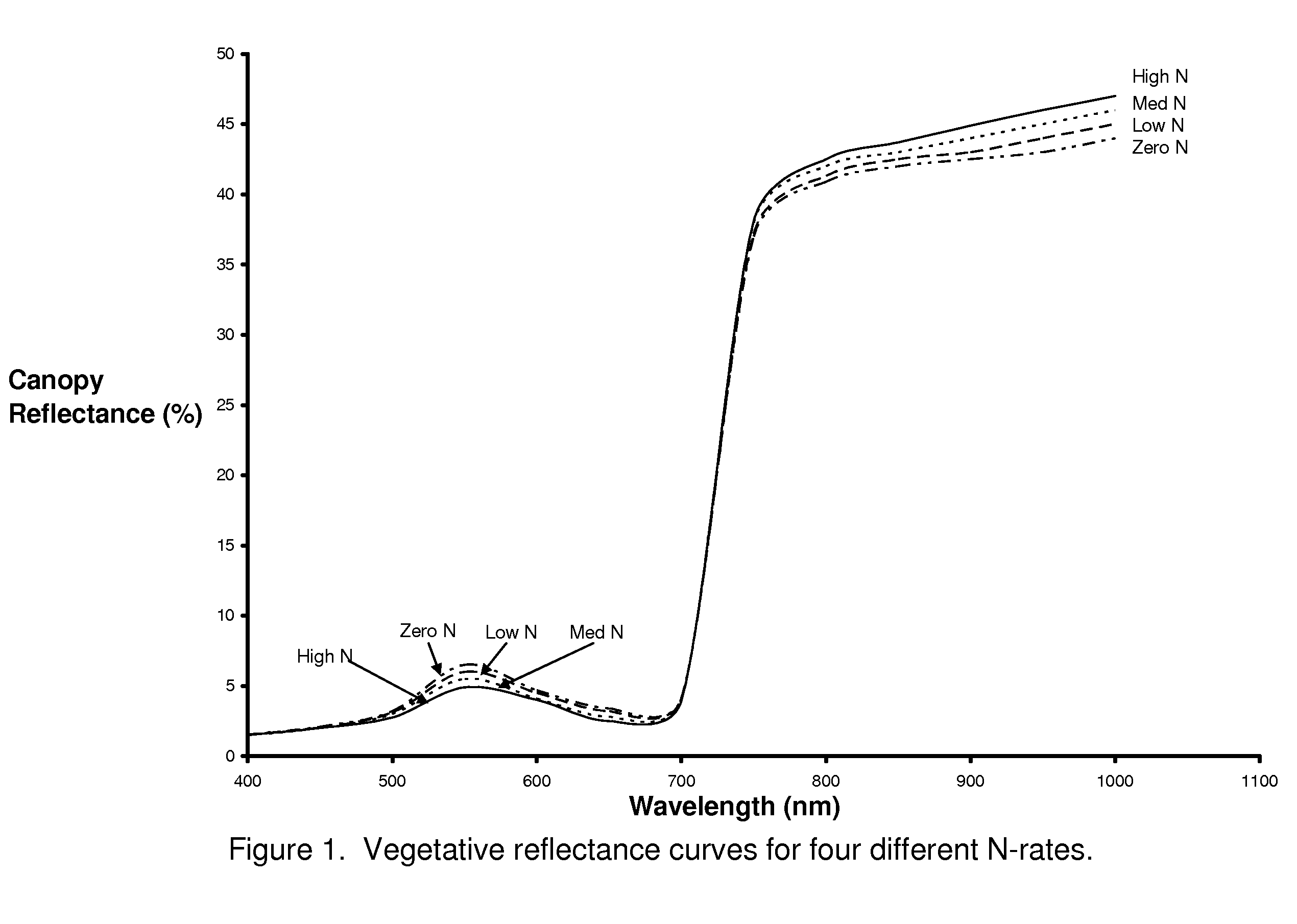
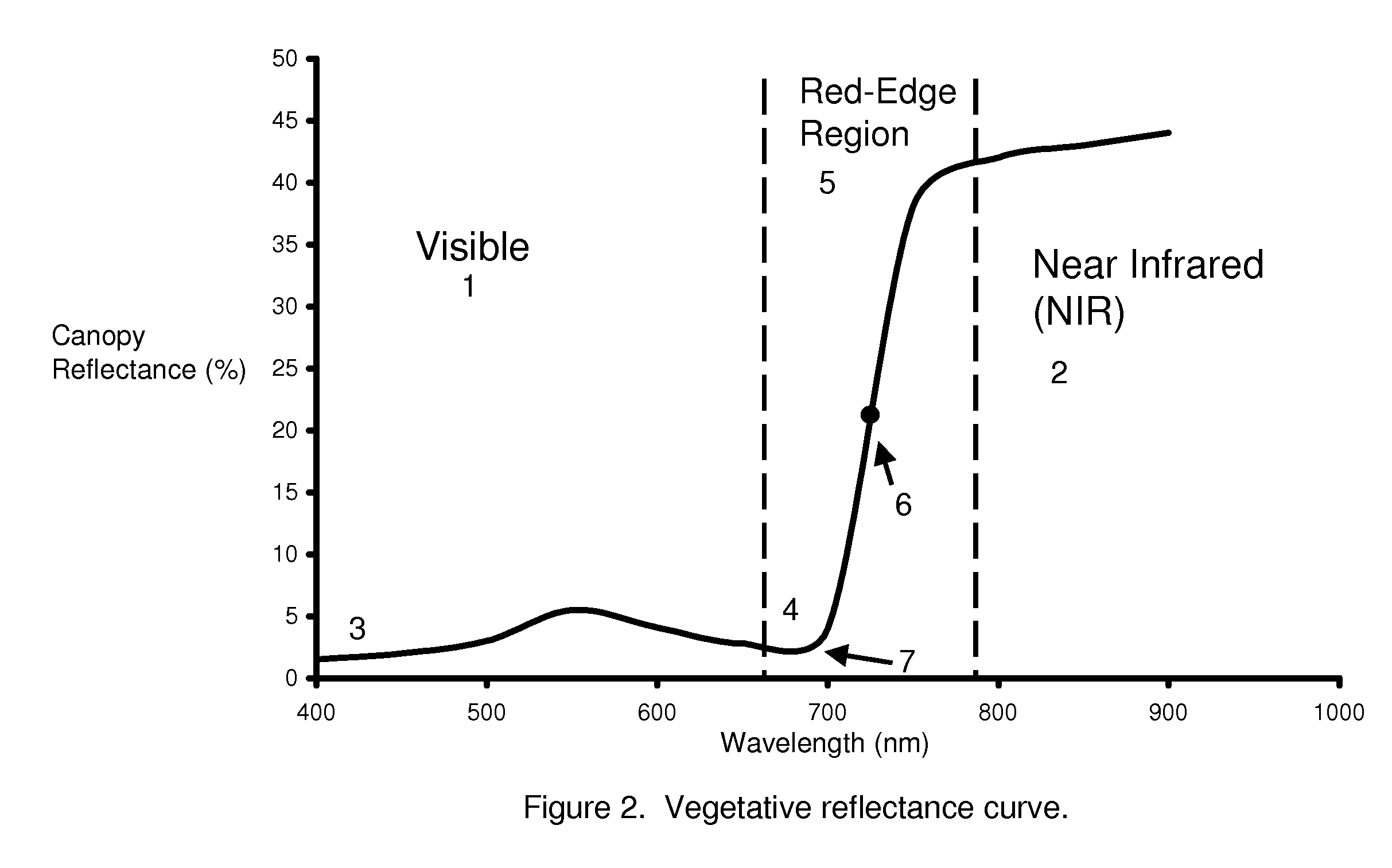
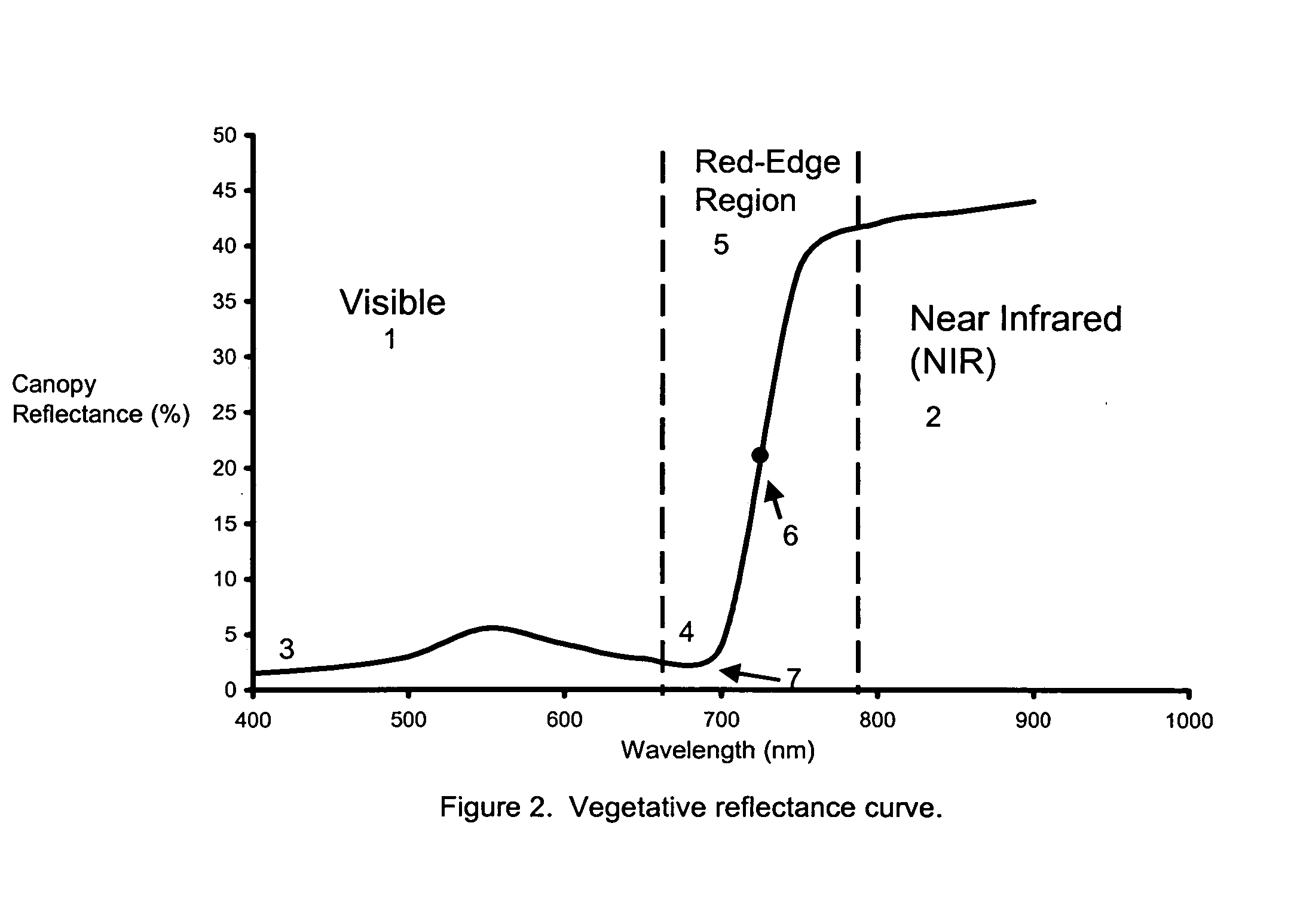
InactiveUS20060208171A1Improve performanceOvercome limitationsRadiation pyrometryInvestigation of vegetal materialRed edgePhotovoltaic detectors
An apparatus is described for assessing plant chlorophyll content remotely sensed by the invention thereby allowing selective monitoring or treatment of individual plants. In one preferred embodiment, a polychromatic emitter provides light beams substantially in the red edge portion of a plant's reflectance spectrum. This light beam illuminates a surface area on the plant, which may be bare ground or plants. The beam of light may be focused, collimated or non-focused. A detector array, usually composed of an array of spectrally sensitive detectors, detects portions of this polychromatic light beam reflected by the surface area and provides a signal indicative of the change in chlorophyll status by determining the wavelength of the red edge inflection point REIP. In another preferred embodiment of the invention, an array of sequentially pulsed monochromatic emitters provides light beams having wavelengths substantially along the red edge portion of a plant's reflectance spectrum. These light beams illuminate a surface area on the plant, which may be bare ground or plants. The beams of light may be focused, collimated or non-focused. A photodetector detects the light reflected by the surface area and provides a signal indicative of the change in chlorophyll status by determining the wavelength of the red edge inflection point REIP. In both embodiments, a controller analyzes the resulting REIP wavelength and responds by activating a device to take some action with respect to the plant or stores the analyzed signal with corresponding DGPS position in the controller's memory for later analysis.
Owner:HOLLAND KYLE
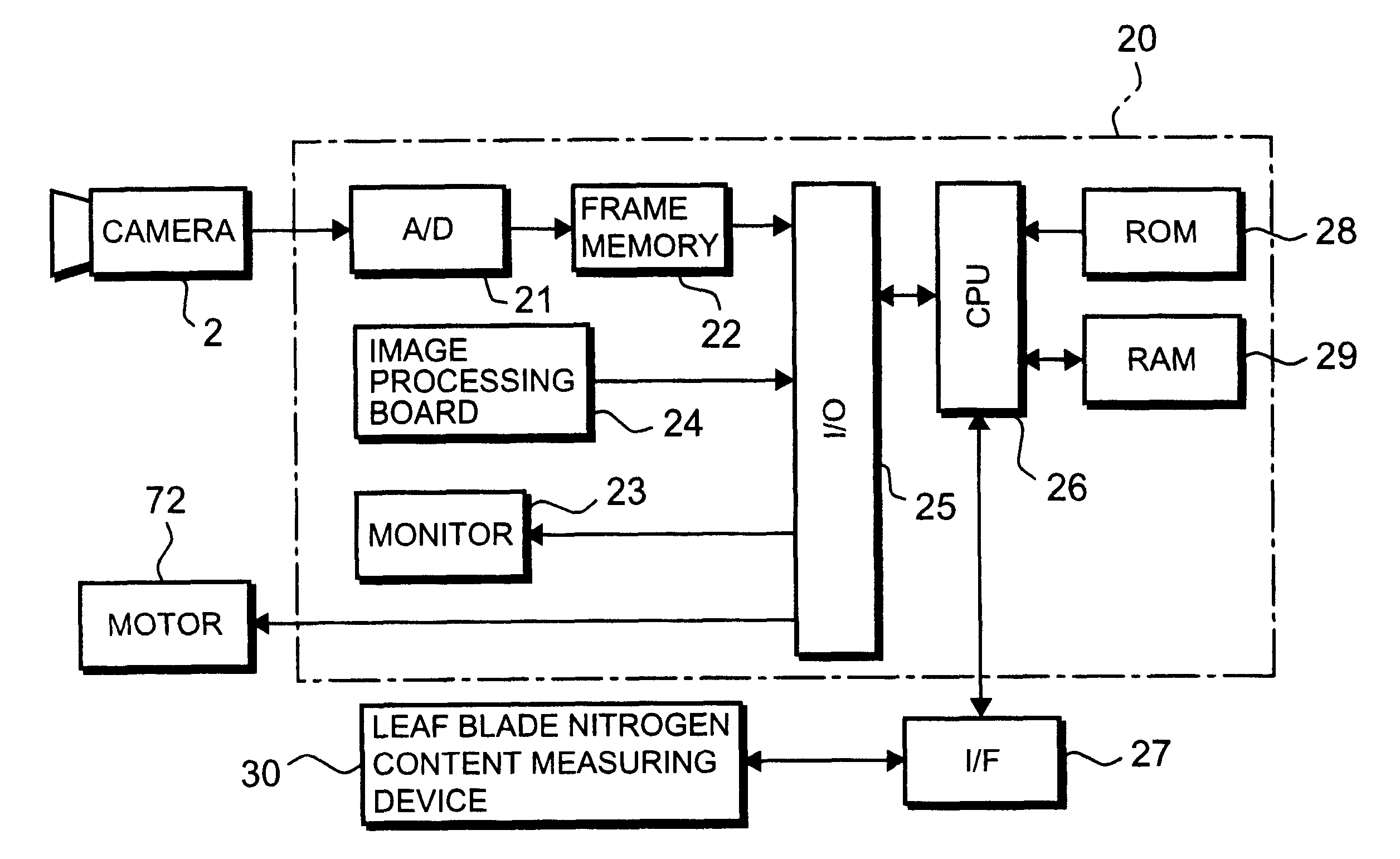
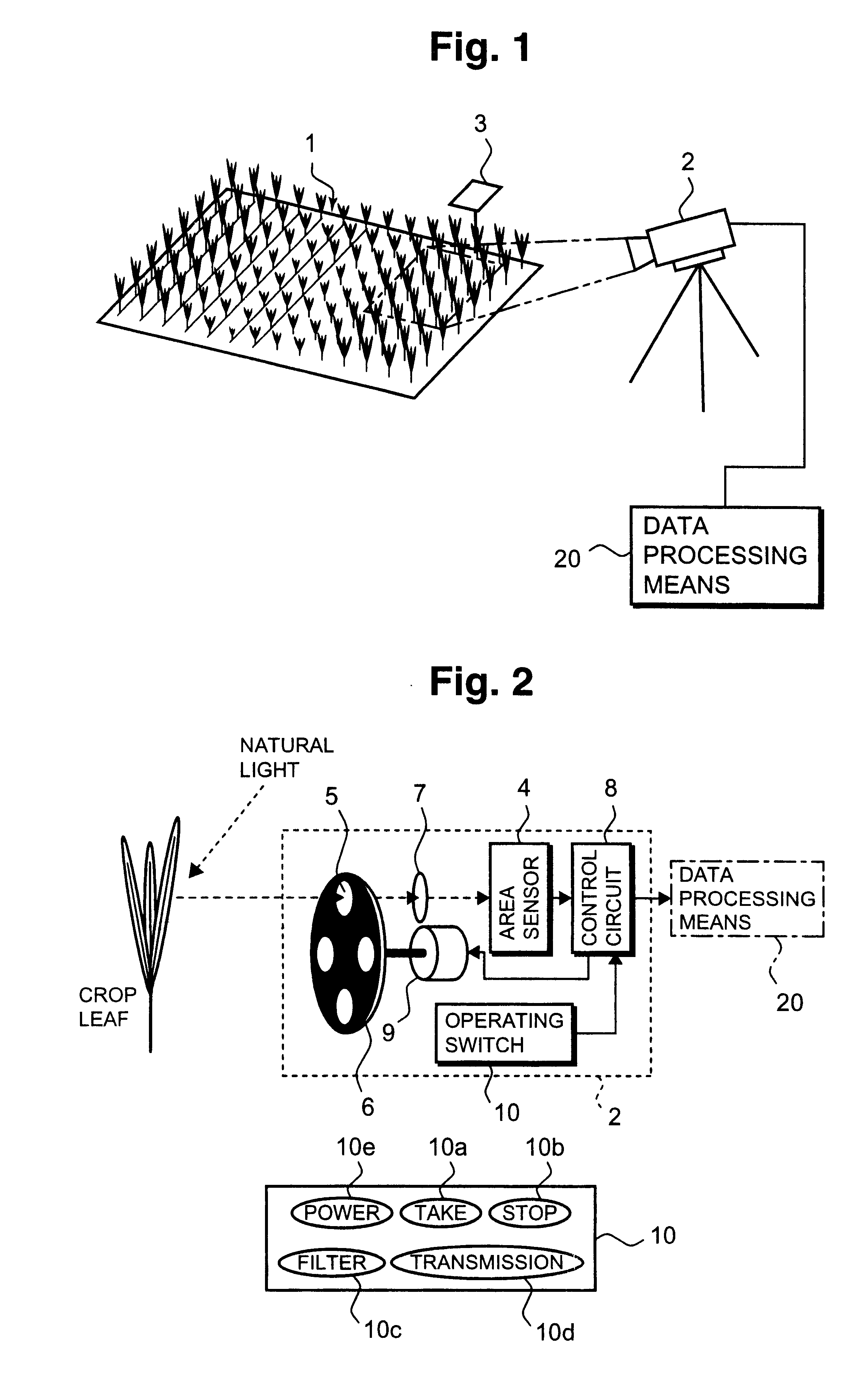
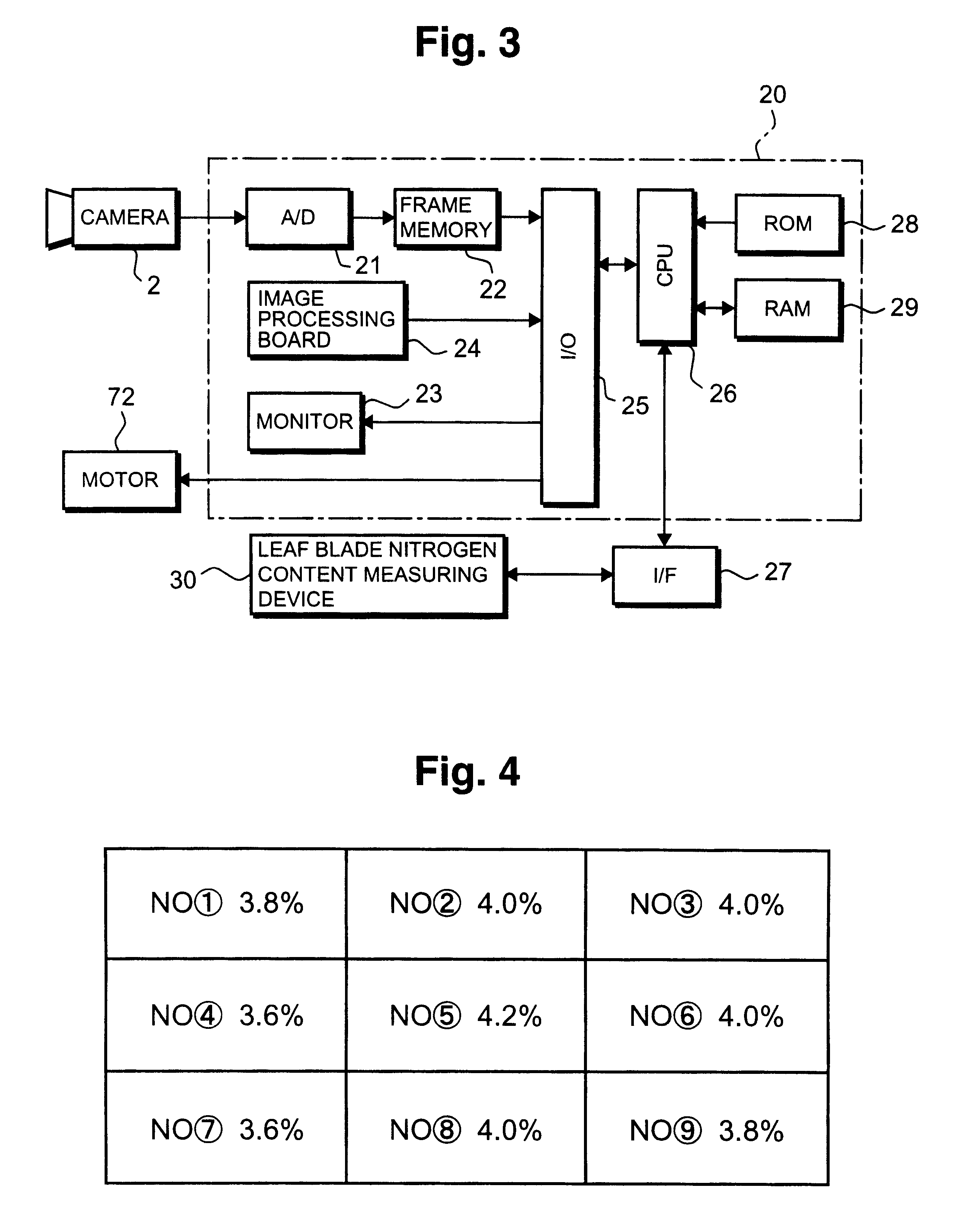
Method of diagnosing nutritious condition of crop in plant field
From the crop of a predetermined area in a plant field under exposure to natural light, a reflectivity of the light having relation to crop information such as nitrogen content rate is measured by a camera; the crop information as first crop information is obtained from the first crop related formula established in advance for obtaining the crop information from the reflectivity; light is irradiated on crop leaf blades in the same area as the predetermined area and an amount of the light is measured; the crop information as second crop information is obtained from the second crop related formula established in advance for obtaining the crop information from the amount of the light; differences are calculated from the first crop information and the second crop information; the first crop information is obtained from the unknown crop in the predetermined area within the crop field of the same area; the first crop information is corrected based on the differences; and the nutritious diagnosis of the crop in the field is conducted by the corrected first crop information. In conducting diagnosis of crop by measuring the reflection light amount from the crop, since compensation or correction is performed, no great errors occur caused by differences in the measurement locations and the planting densities, and the diagnosis of the crop is simple and easy and, more over, the precision in the measuring is enhanced.
Owner:SATAKE CORP
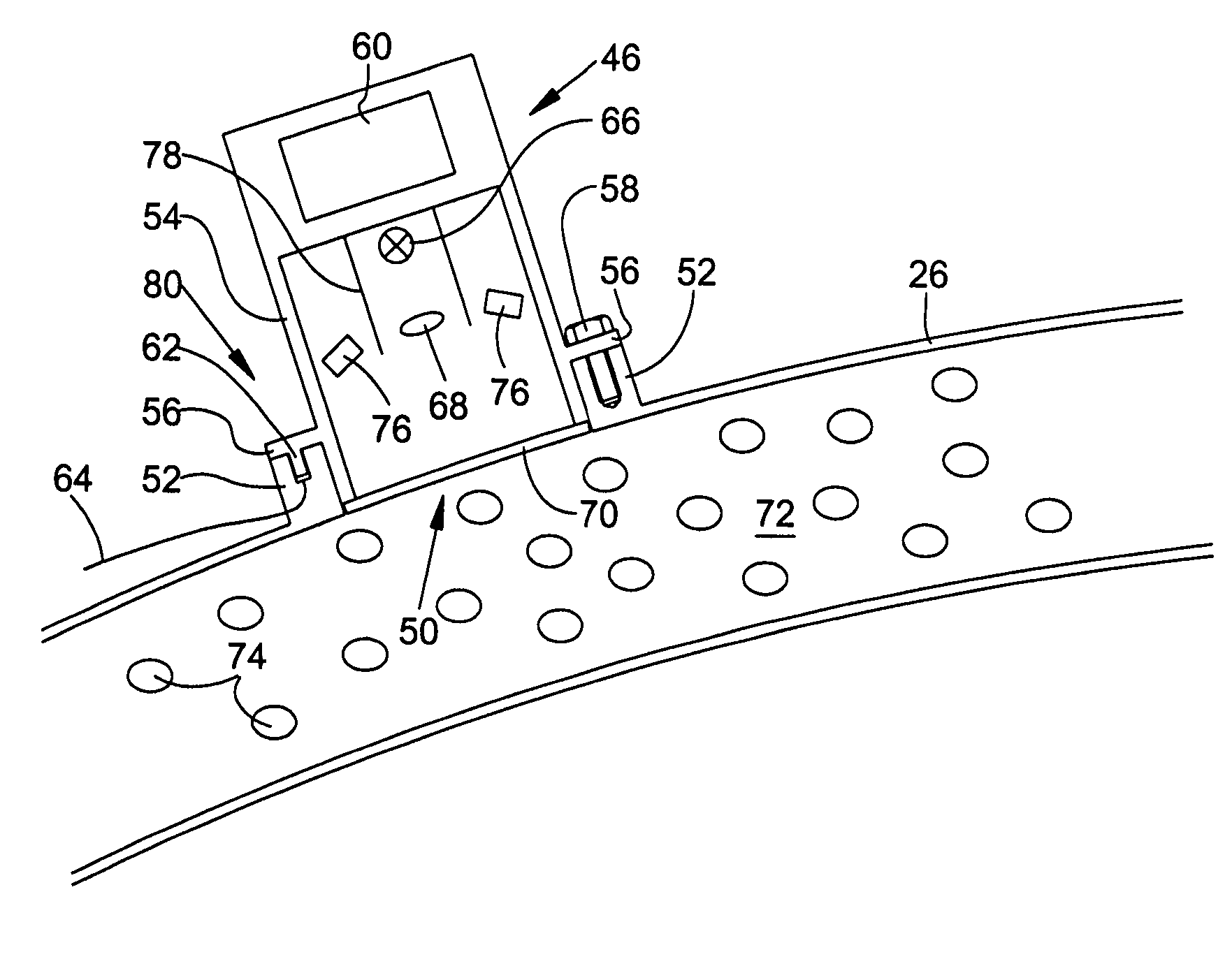
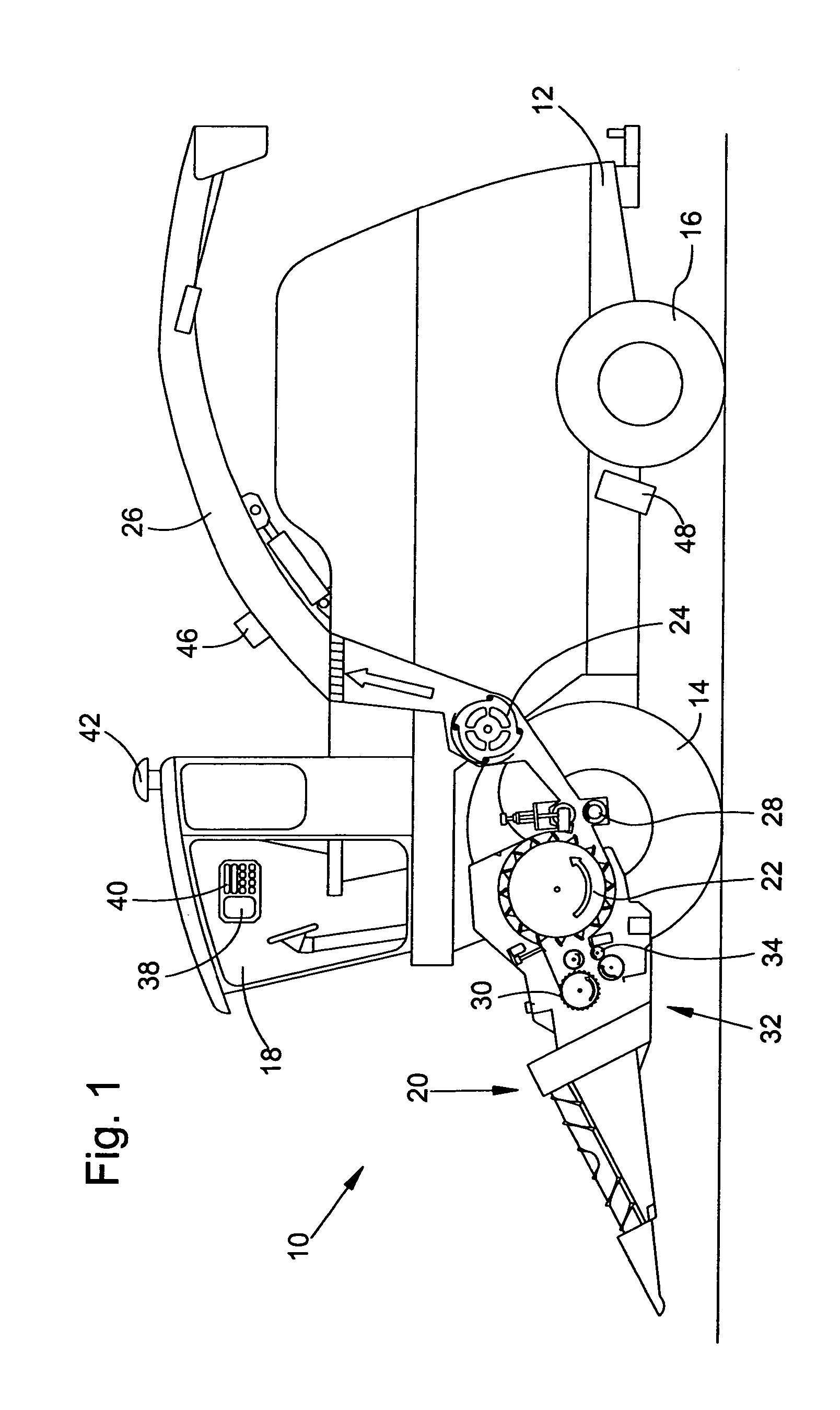
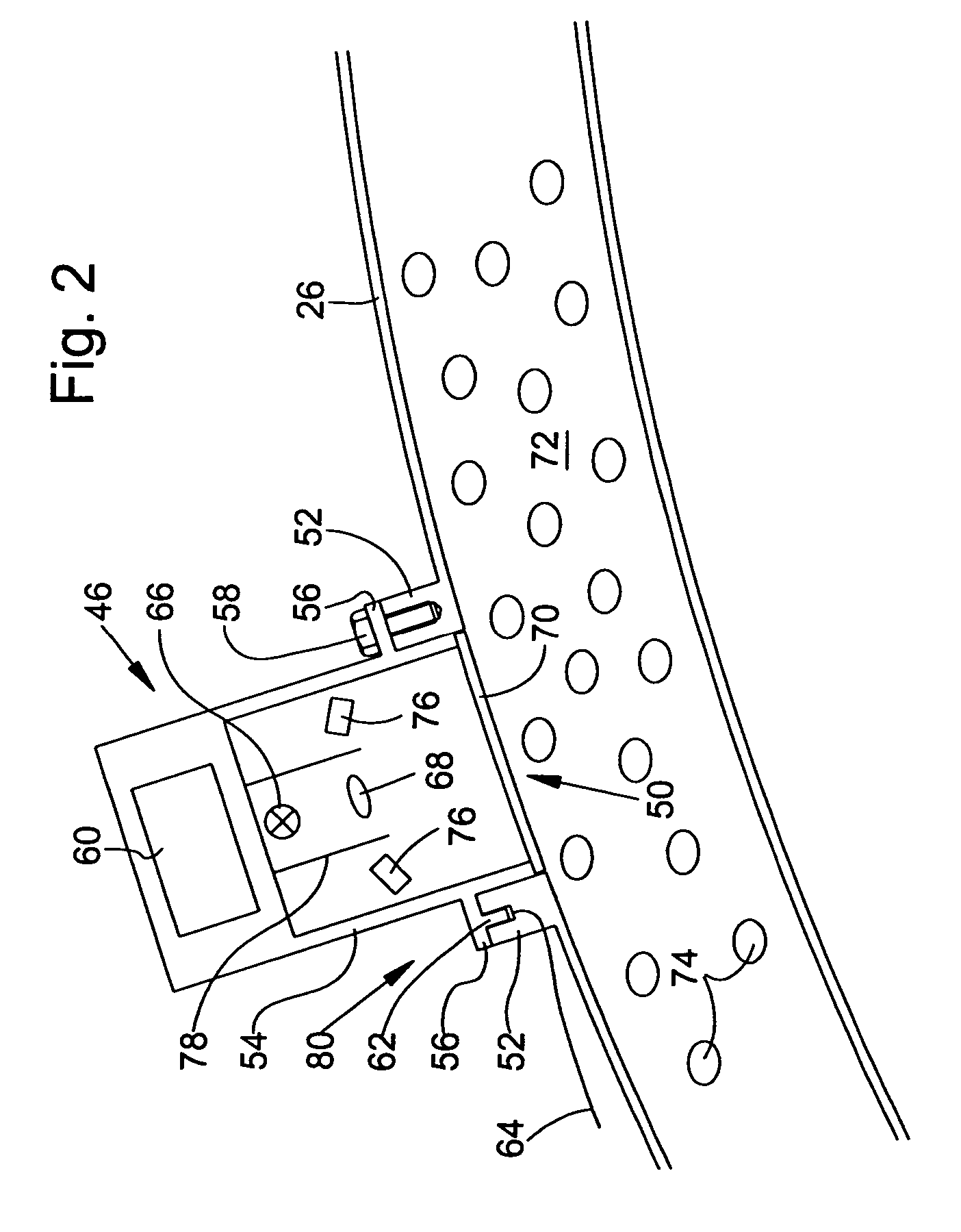
Crop measuring arrangement
A crop measuring arrangement is arranged on a harvesting vehicle to interact with a material that is to be investigated in order to detect at least one component of the material, and that can be fastened to a vehicle by means of a retaining arrangement, so that the measuring arrangement can be operated in the condition in which it is fastened to the retaining arrangement in order to analyze material handled and / or processed by means of the vehicle. The retaining arrangement for securing the measuring arrangement to the vehicle is constructed so that the measuring arrangement can be easily separated from the retaining arrangement and used to investigate material in a stationary application.
Owner:DEERE & CO
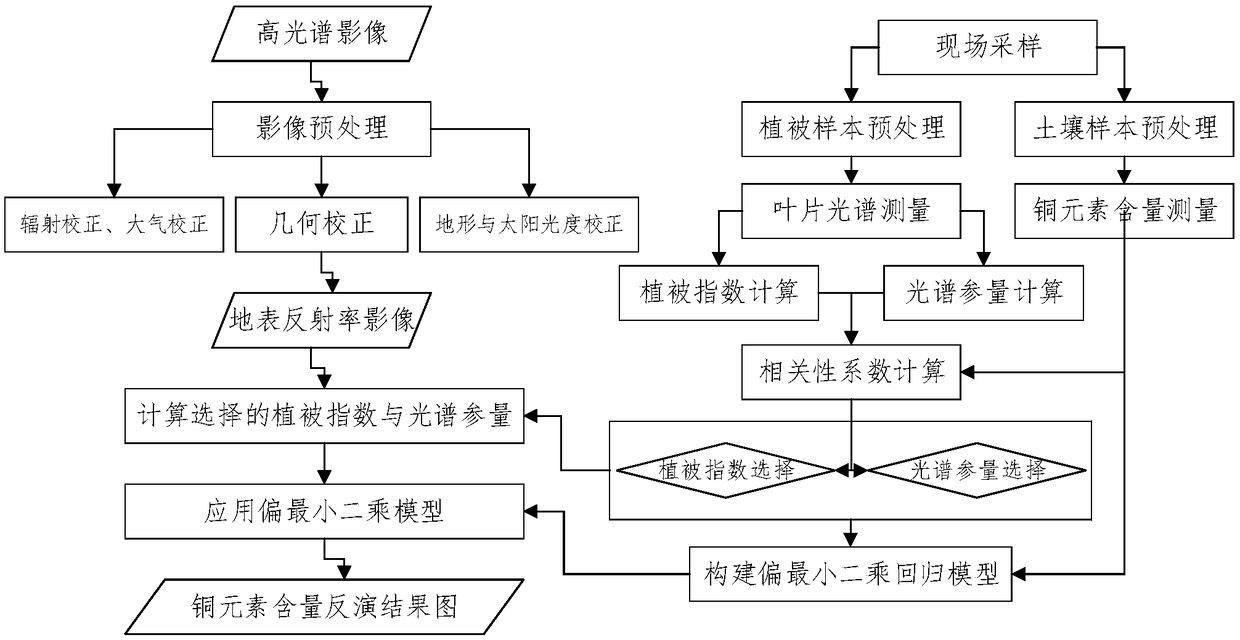
Inversion method for copper elements in soil in vegetation-covered areas on basis of measured spectra of leaves
ActiveCN108663330ALarge detectable rangeHigh speedInvestigation of vegetal materialWithdrawing sample devicesSoil heavy metalsVegetation cover
The invention relates to an inversion method for copper elements in soil in vegetation-covered areas on the basis of measured spectra of leaves. The inversion method includes steps of firstly, acquiring and preprocessing images; secondly, carrying out in-situ sampling; thirdly, processing samples; fourthly, measuring and preprocessing the spectra of the leaves; fifthly, measuring the contents of the copper elements in the soil samples; sixthly, computing vegetation indexes and spectral parameters; seventhly, analyzing correlations and selecting parameters; eighthly, building models; ninthly, carrying out large-area inversion on the content of the copper elements in the soil. The inversion method has the advantages that images of the content of the copper elements in the large-area soil inthe vegetation-covered areas can be obtained, accordingly, indication information and mineral exploration clues can be provided to mineral resource investigation, and scientific bases can be providedto land quality evaluation and soil comprehensive treatment; heavy metal pollution diffusion conditions of the soil and control effect evaluation can be obtained on the basis by means of multi-temporal analysis; the inversion method is wide in detectable range and high in speed, monitoring can be carried out in real time, and the like.
Owner:中国自然资源航空物探遥感中心
Method And System For Growth Status Determination Of A Plant
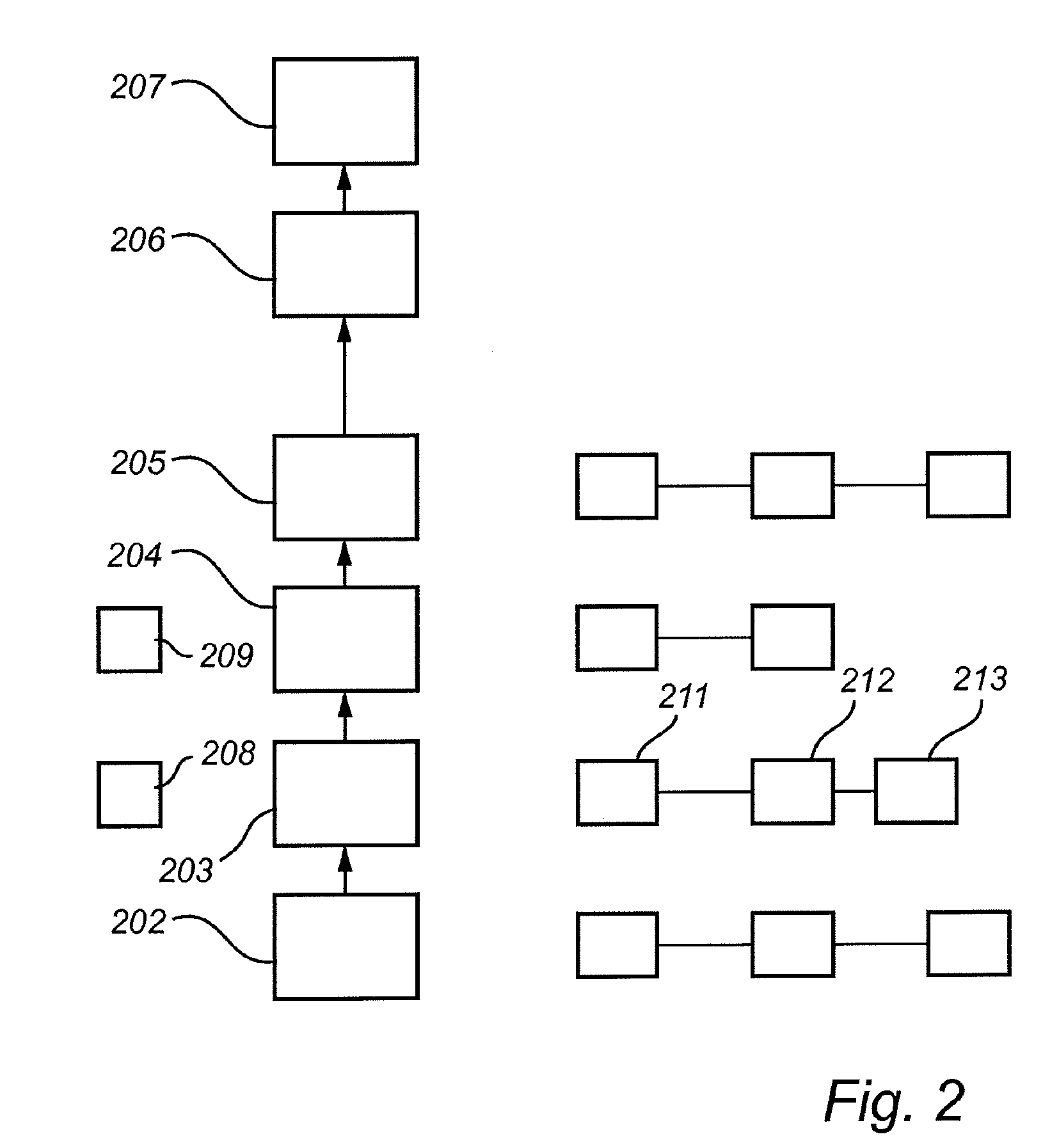
ActiveUS20170339839A1Improve accuracyReduce the impactInvestigation of vegetal materialElectrical apparatusChlorophyllUltimate tensile strength
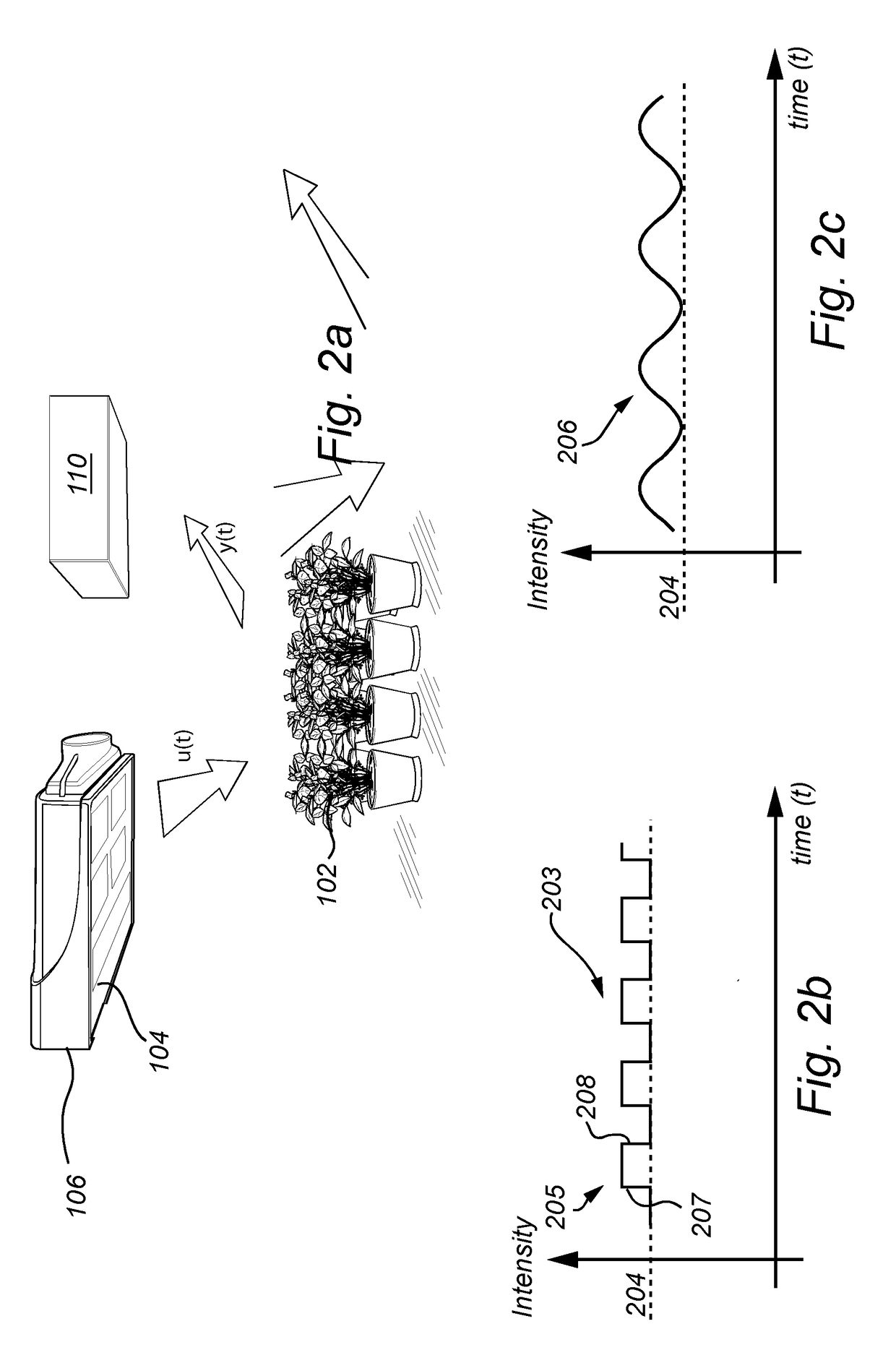
The present invention relates to a method for determining a growth status of a plant comprising chlorophyll, the method comprising the steps of: illuminating the plant (102) with input light including a light intensity modulation component (205, 206, 207, 208); detecting light emitted from the plant; determining (S702) an offset light intensity (204) surrounding the plant, the offset light intensity being a static component of the input light; determining (S718) a phase and a gain between the input light and the detected light, determining (S720) a growth status of the plant based on a predetermined relationship between input light and detected light, and on the phase and the gain. The invention also relates to a corresponding system and to a computer program product.
Owner:HELIOSPECTRA
System and method of in-season nitrogen measurement and fertilization of non-leguminous crops from digital image analysis
ActiveUS20130044919A1Minimize shadowsImage enhancementInvestigation of vegetal materialAnimal ForagingFully developed
Systems and methods of determining nitrogen levels from a digital image and in-season nitrogen measurement and fertilization of non-leguminous crops from digital image analysis are disclosed herein. In particular, a method of determining leaf nitrogen concentration and yield from a digital photograph of a fully developed leaf (collared leaf) of a crop of non-legumes, such as corn, wheat, rice, cotton, potatoes sugarcane, turfgrass or forage grass species. The digital image is processed to determine a dark green color index (“DGCI”), which is closely related to leaf nitrogen concentration and yield. Standardized color disks having known DGCI values are included in the digital photograph and serve as an comparative standard. The comparative standard allows correction of DGCI of samples when using different cameras and / or when lighting conditions change. The DGCI values can then be used to determine the amount of nitrogen fertilizer that should be applied to recover crop yield potential.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
High-throughput plant phenotype analysis device and method based on optical imaging technique
ActiveCN105717115AAccurate analysisRealize high-throughput analysisInvestigation of vegetal materialArbitrary Fluorescence UnitAnalysis method
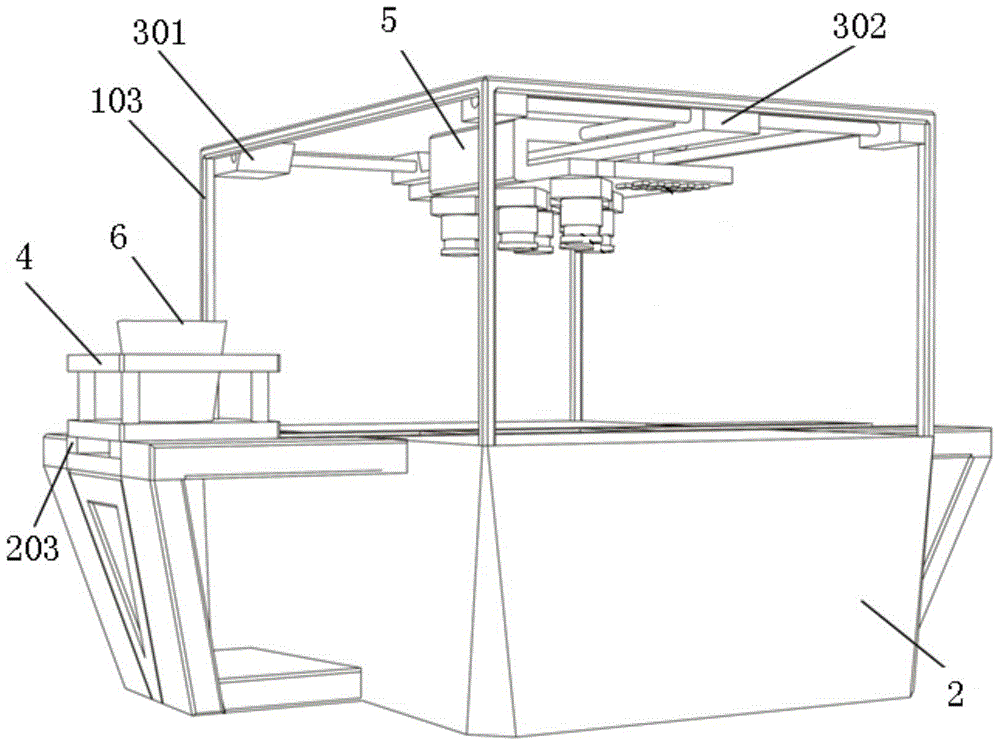
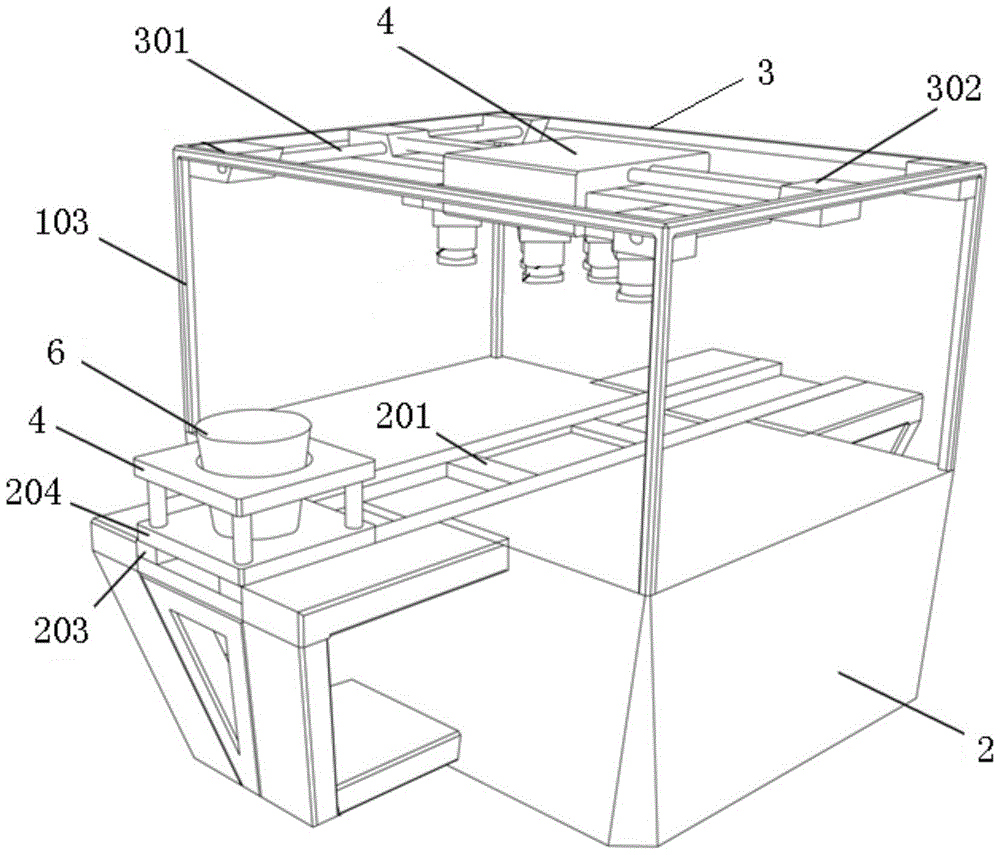
The invention discloses a high-throughput plant phenotype analysis device based on an optical imaging technique.The device comprises a light shading cover, a base, a top frame, a material carrying table, a sensor panel, a chlorophyll fluorescence imager, a near-infrared multi-spectral facial form imager, an infrared thermal imager, a three-dimensional reconstruction imager and a light source set; the base is installed in the light shading cover, and a working position is arranged in the middle of the base; the top frame is installed in the light shading cover and fixed over the base; the material carrying table is installed on the working position of the base; the sensor panel is installed on the top frame through a translation mechanism; the chlorophyll fluorescence imager, the near-infrared multi-spectral facial form imager, the infrared thermal imager and the three-dimensional reconstruction imager are installed on the sensor panel; the light source set is installed on the sensor panel and supplies exciting light and illuminating light to the imagers.The invention further discloses a high-throughput plant phenotype analysis method based on the optical imaging technique.According to the device and method, use is convenient, complete plant phenotype data can be acquired, and the test result is accurate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Rice overground portion biomass estimation method based on multispectral images of unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveCN109459392ALow input data requirementsImprove estimation accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisVegetationRegression analysis
The invention a rice overground portion biomass estimation method based on multispectral images of an unmanned aerial vehicle. The rice overground portion biomass estimation method based on the multispectral images of the unmanned aerial vehicle comprises the following steps: standardly acquiring rice canopy unmanned aerial vehicle multispectral image data and ground actually measured biomass data; after the data are acquired, preprocessing images, extracting reflectivity and texture feature parameters, calculating vegetation indexes, and constructing new texture indexes; and integrating the vegetation indexes and the texture indexes to estimate rice biomass by using a step-by-step multivariate regression analysis method, and establishing a multivariate linear model for estimating the biomass on that basis. The precision of a new estimation model is verified by a cross validation method. By the method, the estimation precision is high, the requirements for input data are low, the riceoverground portion biomass estimation method based on the multispectral images of the unmanned aerial vehicle is suitable for rice in the whole growth period, meanwhile, the method for establishing the biomass of rice by integrating unmanned aerial vehicle spectra and texture information is proposed for the first time at present, and thus, the rice overground portion biomass estimation method based on the multispectral images of the unmanned aerial vehicle can be widely used for monitoring crop growth in a remote sensing manner by the unmanned aerial vehicle.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com