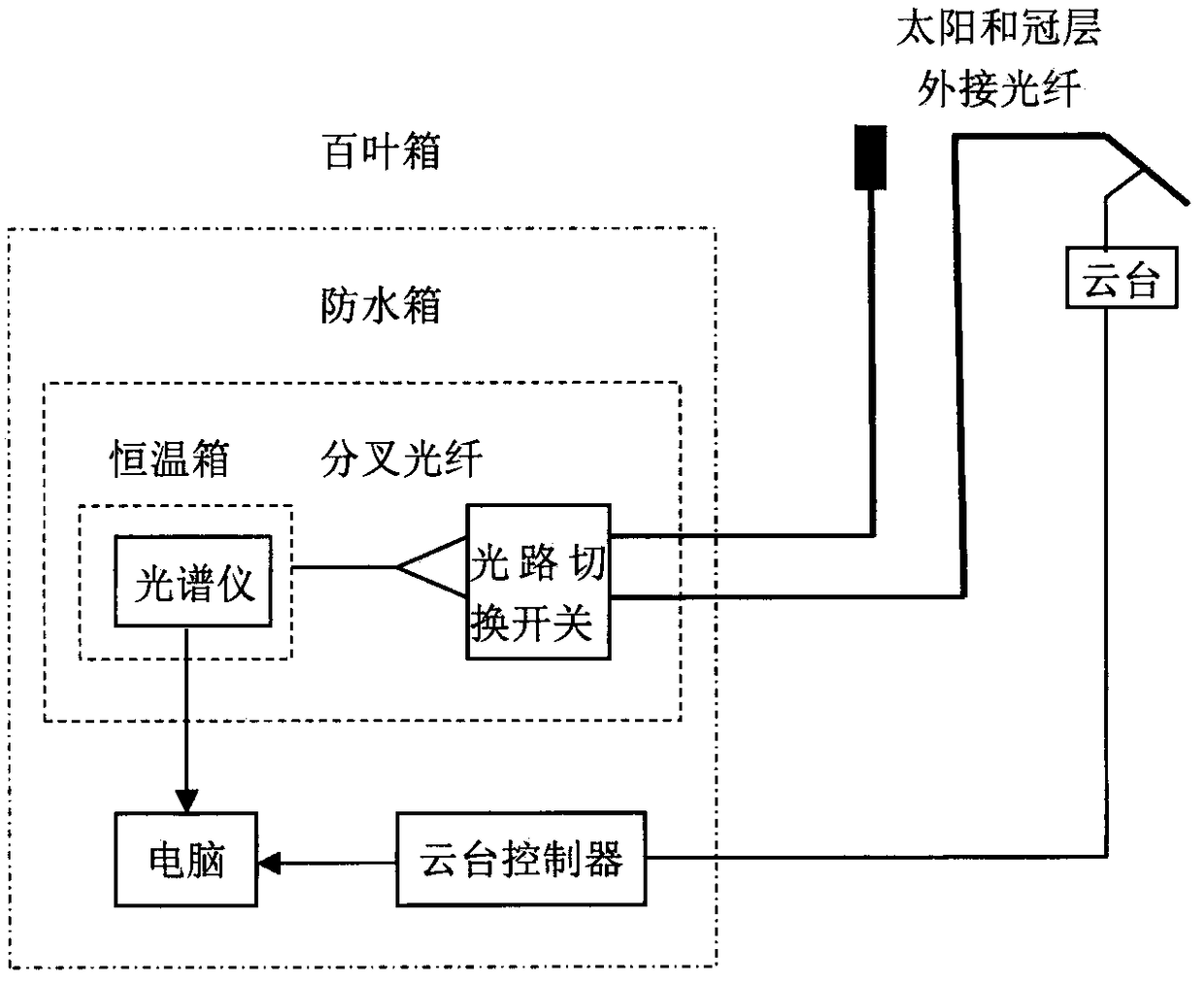
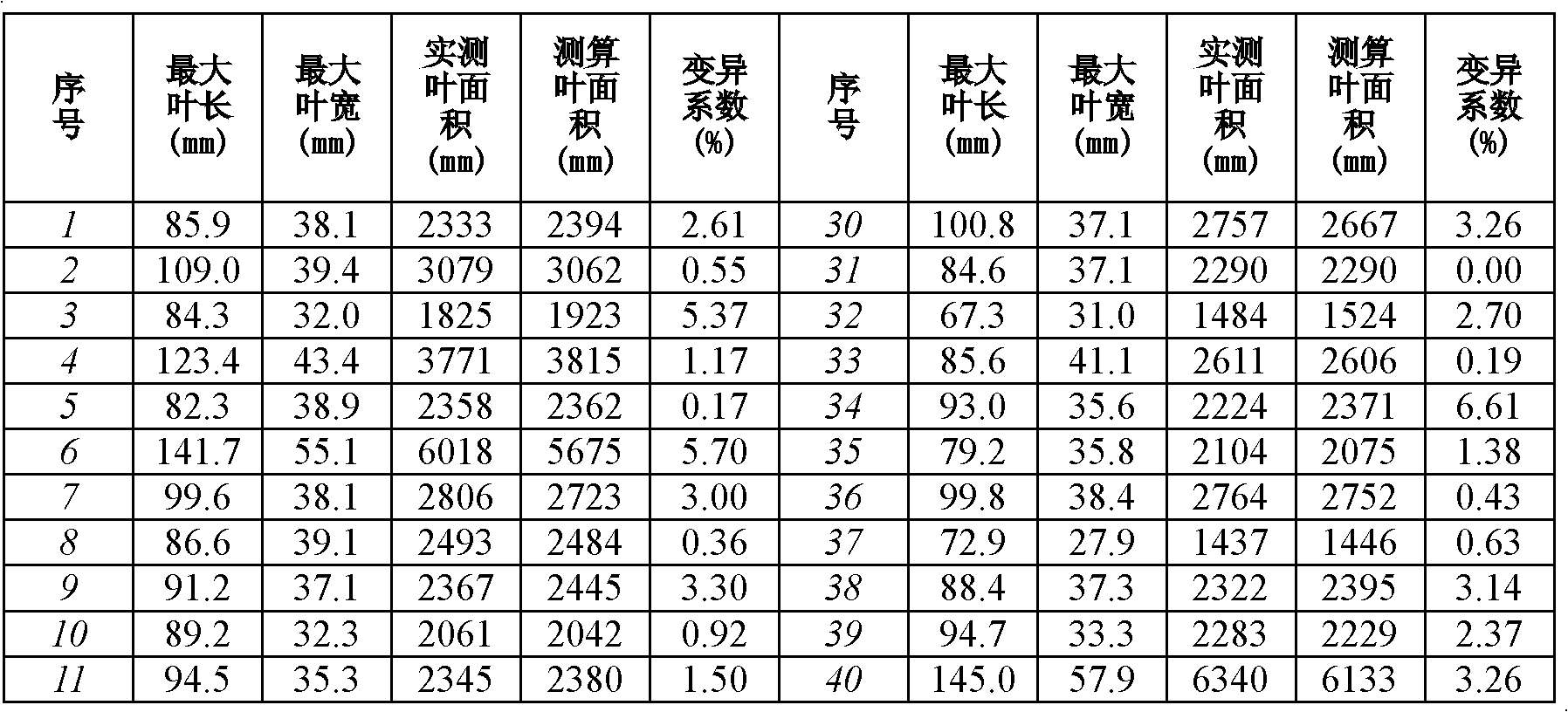
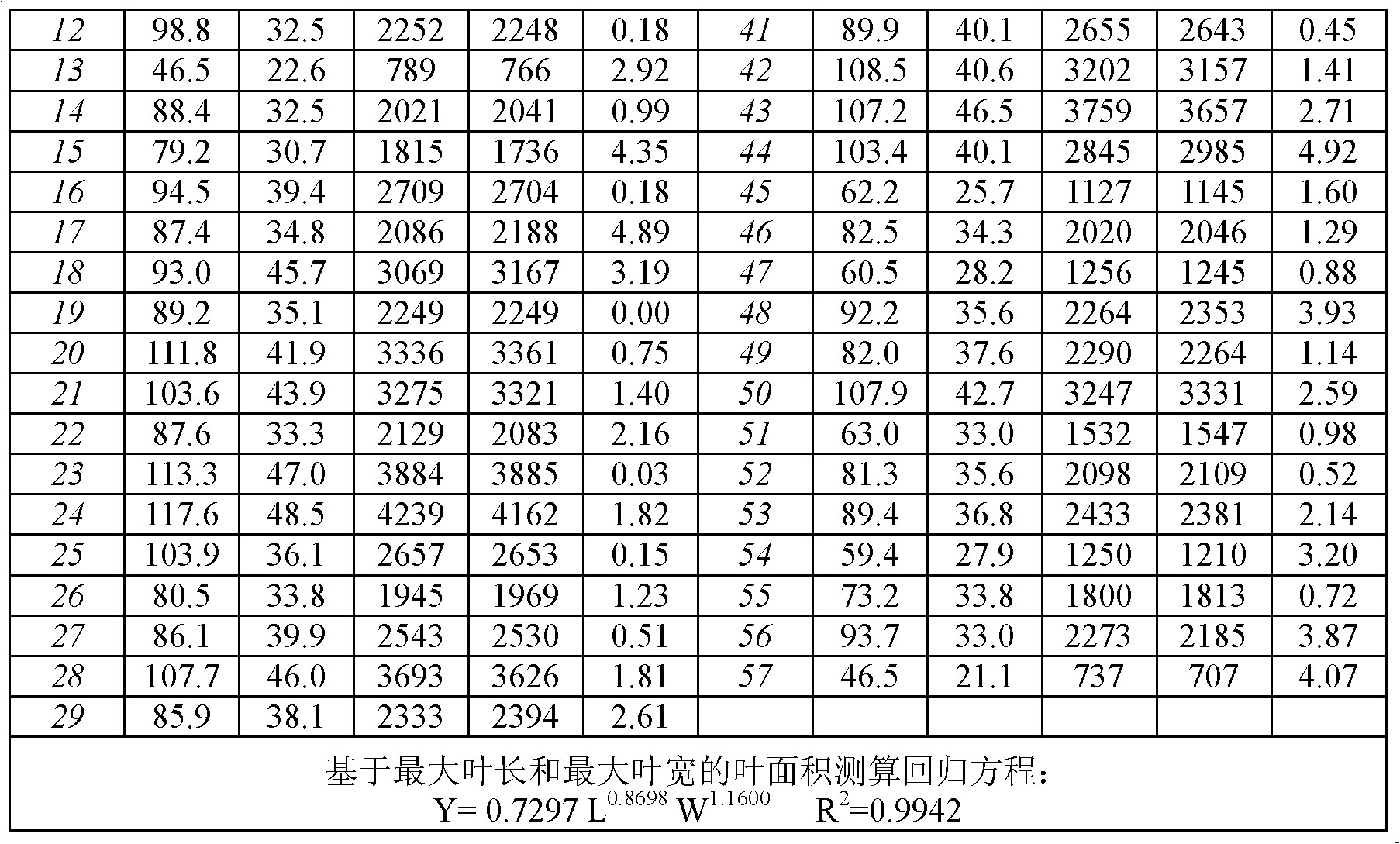
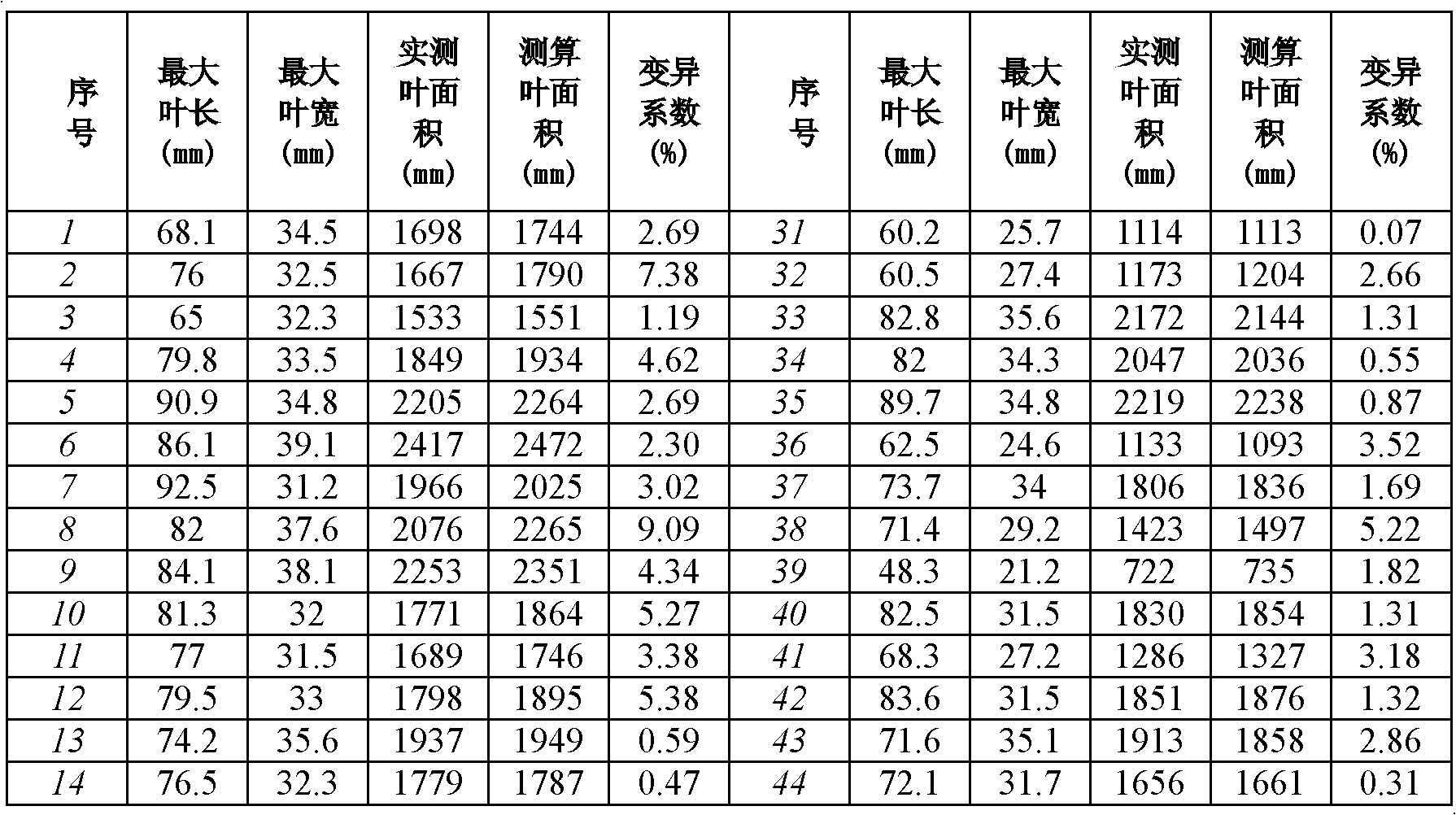
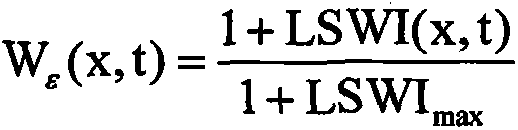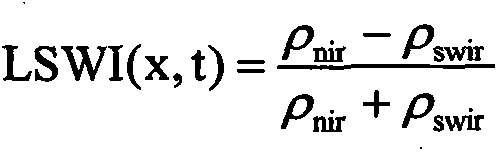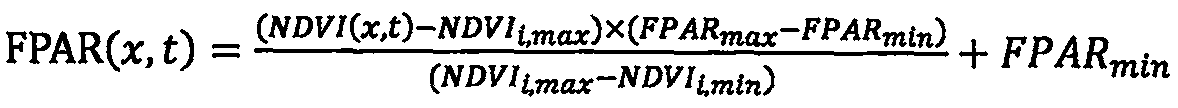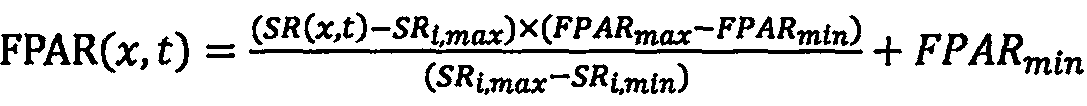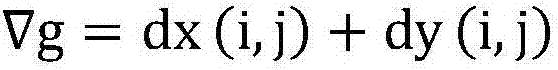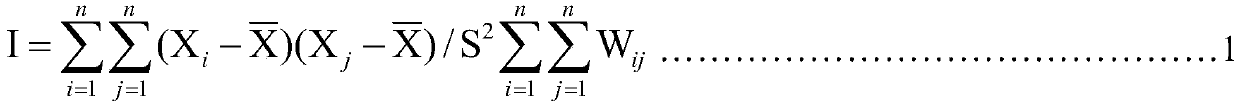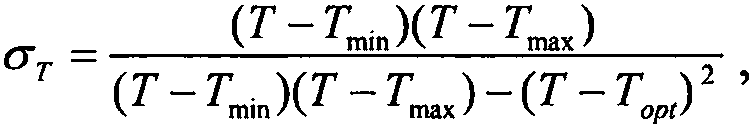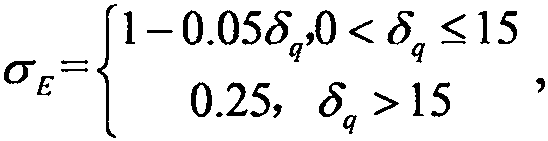Patents
Literature
105 results about "Primary productivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
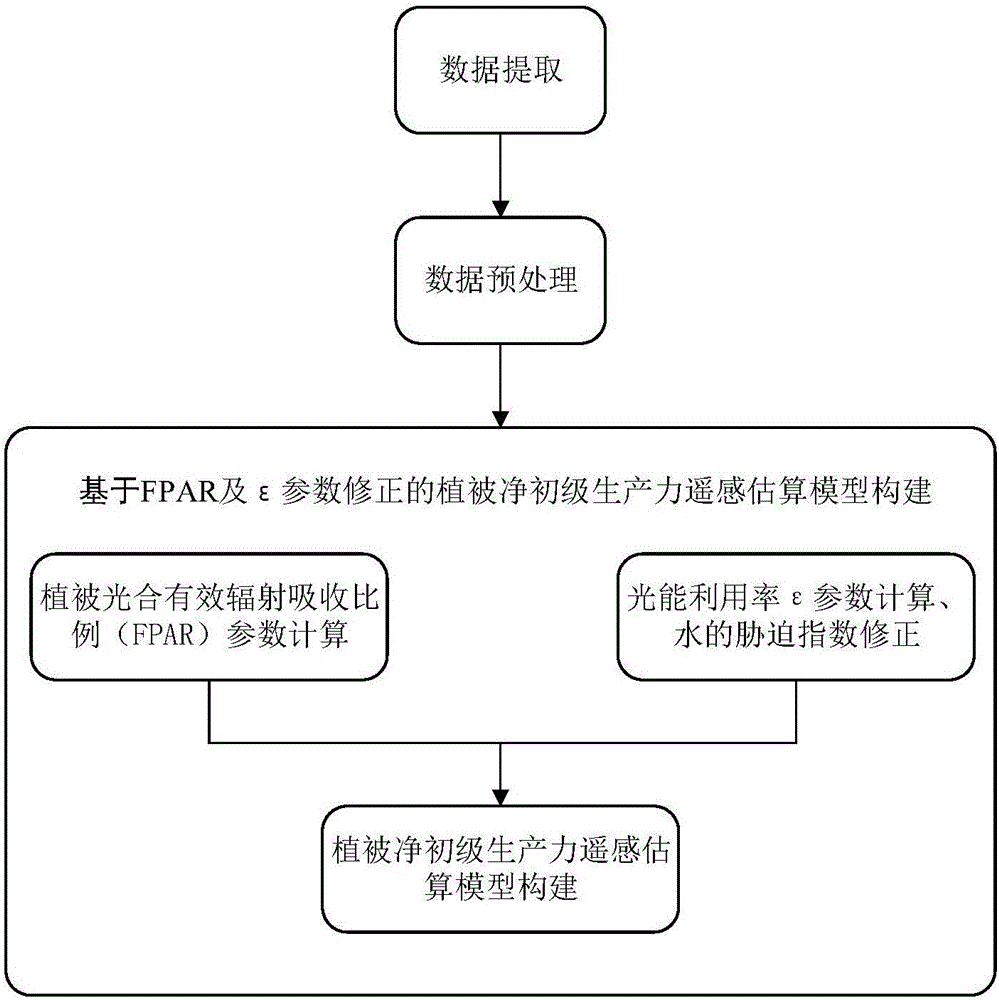
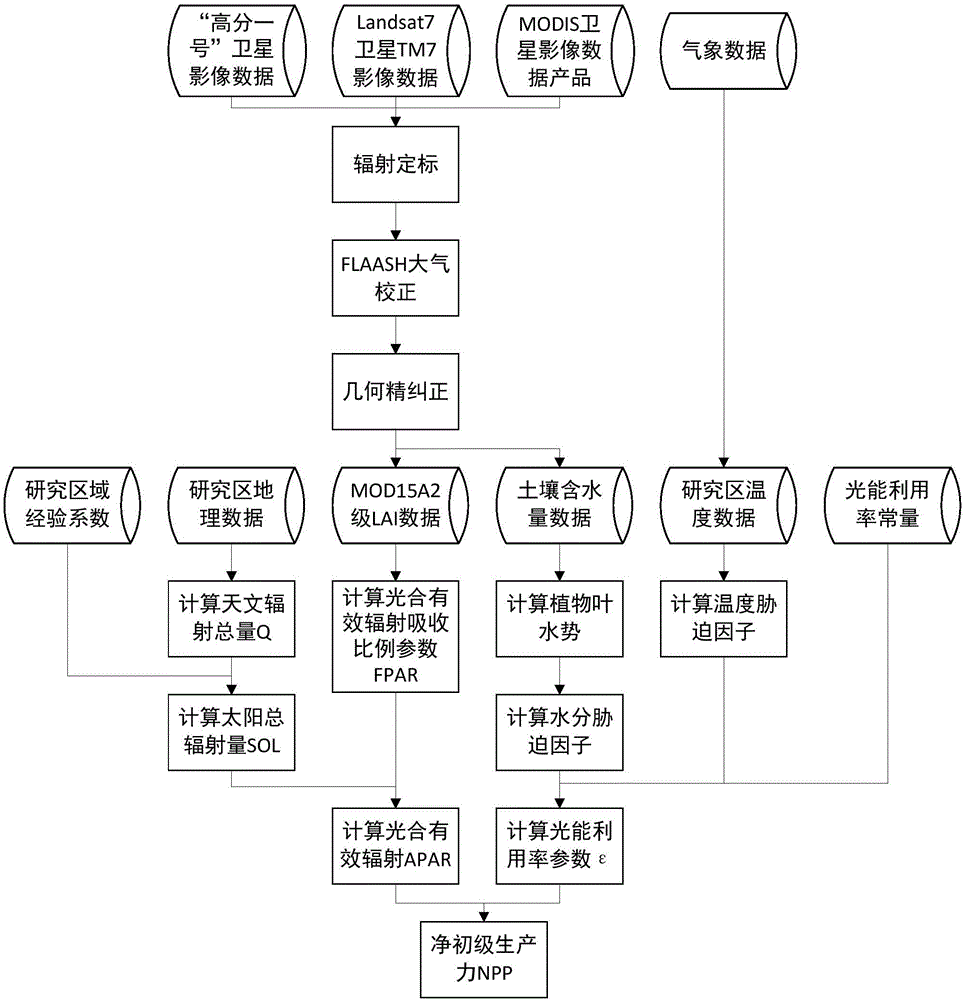
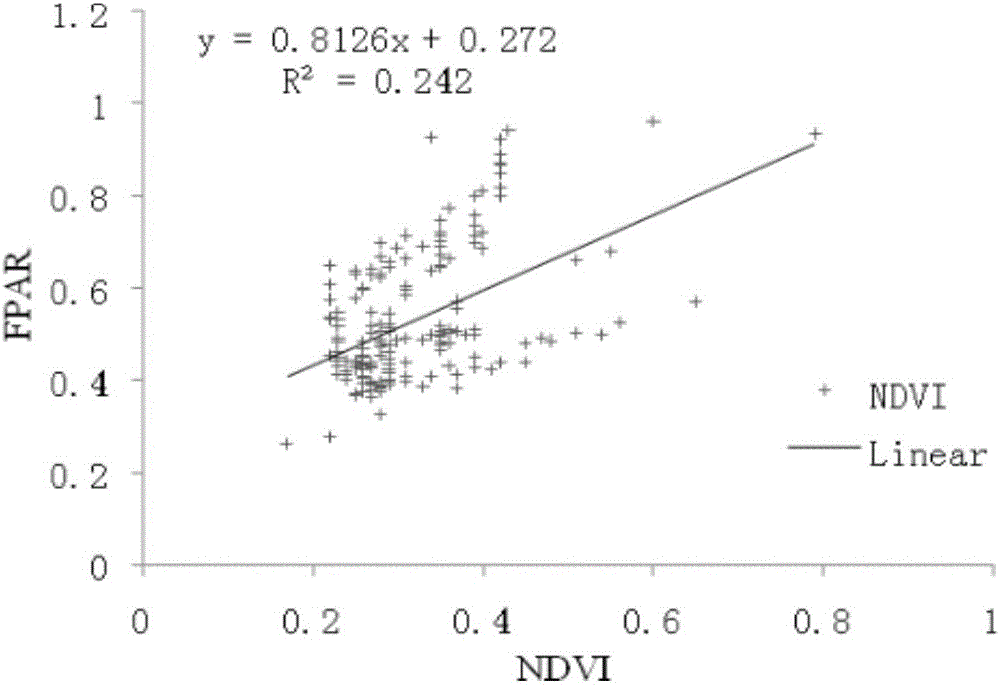
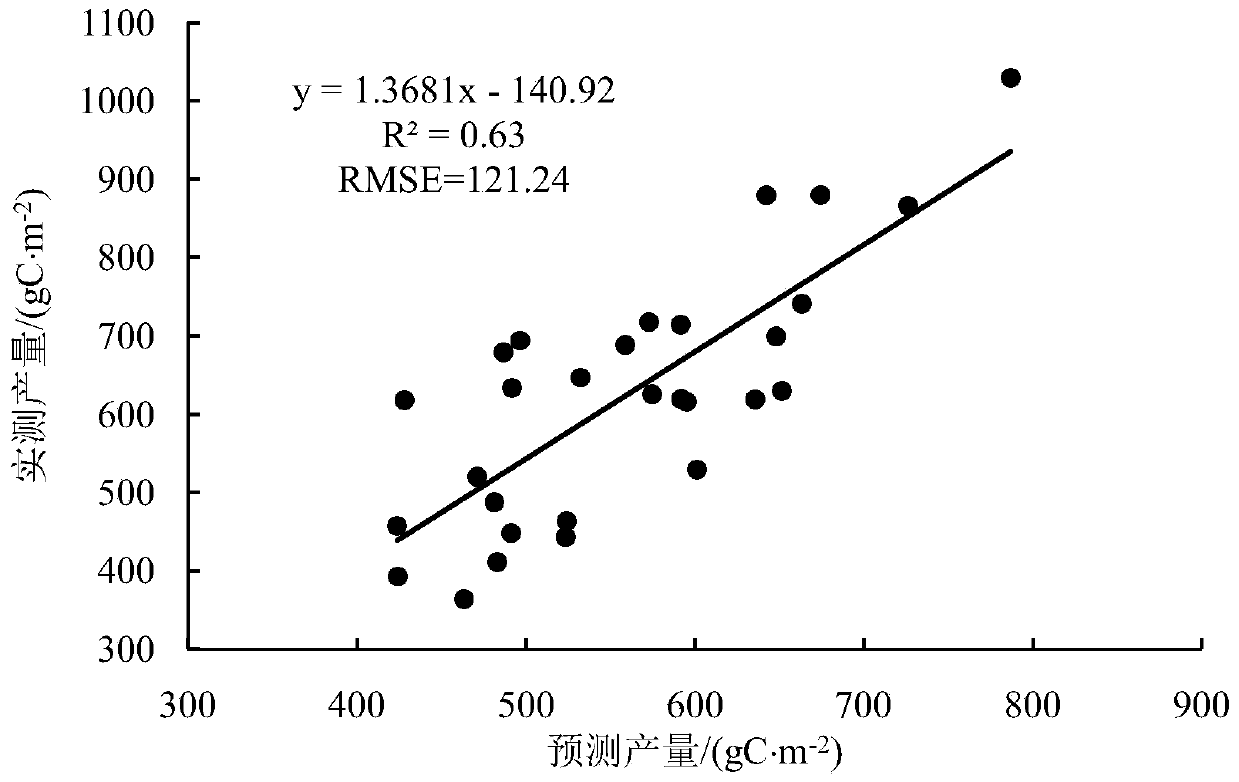
Method for remote sensing estimation of net primary productivity of plants
InactiveCN106446564AImprove estimation accuracyAvoid difficultiesImage enhancementImage analysisLongitudePrimary production
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
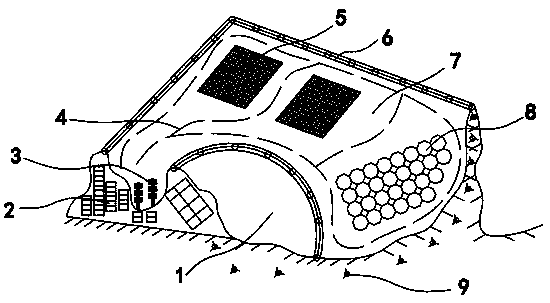
Multifunctional artificial fish reef
ActiveCN104304102AImprove the primary productivity of the sea areaThe effect of gathering fish is goodClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPrimary productivityNutrients substances
The invention discloses a multifunctional artificial fish reef, and aims to provide an artificial reef which is beneficial to formation of different flow field environments with upwelling, can raise nutrient substances deposited at the seabed, can improve the primary sea field productivity near the artificial reef and can provide sufficient feed to fishes. The multifunctional artificial fish reef comprises a reef body, an inner reef cavity and a plurality of inlets and outlets, wherein the inner reef cavity is arranged inside the reef body; the plurality of inlets and outlets are formed in the side surface of the reef body and are communicated with the inner reef cavity; the outer side surface of the reef body extends downwards from top to bottom towards the outer side of the reef body in an inclined manner; a partitioning plate which extends upwards and downwards is arranged inside the inner reef cavity.
Owner:MARINE FISHERIES RES INST OF ZHEJIANG
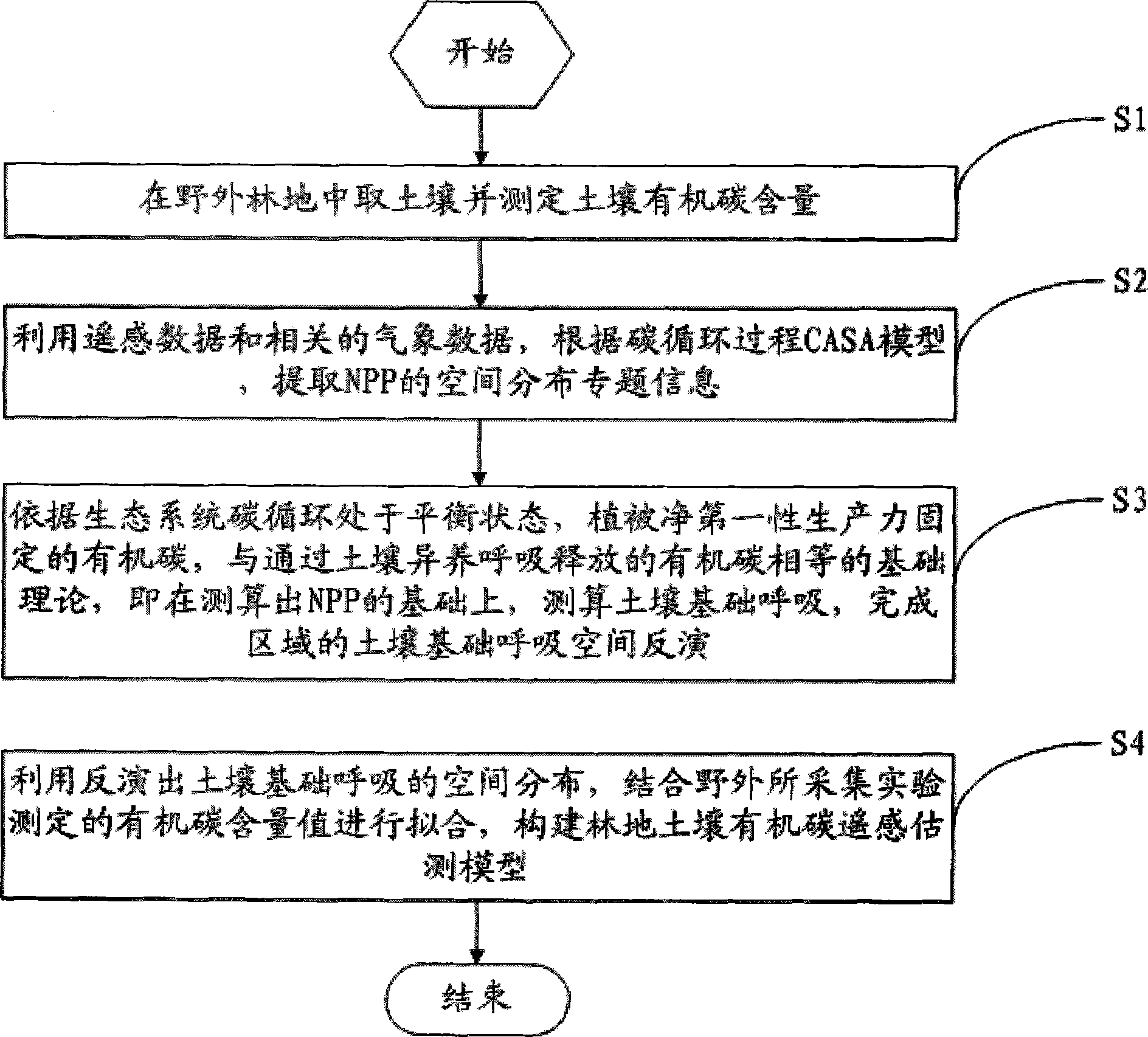
Method for remote sensing and estimating woodland soil organic carbon
InactiveCN104166782ARealization of Remote Sensing Estimation ResearchSpecial data processing applicationsCarbon storageModel parameters
The invention provides a method for remote sensing and estimating woodland soil organic carbon. As image elements of a remote sensing image of a woodland vegetation-covered area are manifested to be the spectral signature of vegetation, and a remote sensing image vegetation index NDVI is the vegetation index which is applied most widely at present, is most applicable, and can be widely applied to the estimation study of the primary productivity of the vegetation. For this, according to the method, by means of a CASA ecological process model, when the NDVI remote sensing data utilizing the high-resolution remote sensing image for reflecting regional difference are applied to a traditional soil organic carbon estimating model, model parameters with the spatial heterogeneity are simplified into constants, the defect of lowering the estimation precision is overcome, a relation model of the soil organic carbon storage amount and soil foundation breathing is set up according to the soil foundation breathing coefficient having the close relation with the soil organic carbon storage amount, and the remote sensing and estimating study of the woodland soil organic carbon can be achieved.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Forage grass planting method for rocky desert area and use method thereof
ActiveCN105027940ARaise and maintain primary productivityIncrease incomeHops/wine cultivationClimate change adaptationPrimary productivityEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a forage grass planting method for a rocky desert area. According to characteristics of the rocky desert area, through land rocky desertification grade classification, forage grass selection, land preparation, forage grass seed selection, seed processing, sowing time selection, sowing amount selection, sowing mode selection, post-sowing compression and a field management technology, scientific forage grass planting is achieved, high-yield forage grass planting is obtained, economic benefits are remarkable, the environment is greatly improved, the water and soil are preserved, the rock desertification environment is improved, the primary productivity of land can be maintained and effectively improved, the yields of forestry and animal husbandry are increased, and the income of farmers is increased; meanwhile, soil carbon sink can be effectively increased, and the environment quality is improved.
Owner:GUIZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Artificial upflow floating type aquatic organism resource breeding reef and fabrication method thereof
InactiveCN101946686APromote prosperitySimple structureClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaSurface layerPrimary productivity
The invention provides an artificial upflow floating type aquatic organism resource breeding reef, comprising a floater (1), a check valve (2), an upflow pipe (3) and a counter weight (4). The artificial upflow floating type aquatic organism resource breeding reef is characterized in that the floater (1) is arranged above the upflow pipe (3), the check valve (2) is arranged in the upflow pipe (3), the counter weight (4) is arranged below the upflow pipe (3), and the floater (1) is connected with a fixing anchor (6) through an anchor-tied mooring rope (5). The fabrication method of the invention comprises the following steps of: manufacturing molds of all parts, carrying out casting forming or other processing forming, and assembling. The invention has the advantages of simple structure, scientific design, low cost, higher practicability and convenience, economy, and suitability to wide popularization, and the artificial upflow floating type aquatic organism resource breeding reef can effectively utilize wave energy to form an artificial upflow field so as to suck deep nutritive salt in a placed water area to water body on a surface layer, thereby improving primary productivity and blooming aquatic organisms.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method for measuring ecological compensation quantity based on remote-sensing images
InactiveCN103345567ASimple and fast operationReliable measurement dataSpecial data processing applicationsVegetationSensing data
The invention discloses a method for measuring ecological compensation quantity based on remote-sensing images. The method includes the steps that (1), in a target region, in combination with obtained data of the remote-sensing images and obtained temperature data of meteorological stations, a photosynthetic active radiation index and an actual solar energy utilization efficiency index for the target region are respectively investigated and inspected; (2), a NPP parameter estimating module is input, and a CASA model is established for estimating net primary productivity; (3), through a data extracting module, NPP parameters in the NPP parameter estimating module are extracted, a region landscape value estimating module is input, estimation is performed according to a region landscape value estimating model, and values of the ecological compensation quantity of types of vegetation in the measured region are obtained. The method for measuring the ecological compensation quantity based on the remote-sensing images has the advantage that through the finite remote-sensing data, the ecological compensation quantity of the different types of vegetation can be roughly measured.
Owner:QINGHAI NORMAL UNIV
Multifunctional artificial fish reef
InactiveCN105684975AExtended service lifeAvoid cloggingClimate change adaptationAgricultural fishingBuoyOxygen
A multifunctional artificial fish reef is composed of a fish reef body, a buoy, a cable, a wire and a gas-guide tube, wherein the cable, the wire and the gas-guide tube are connected with the fish reef body and the buoy.The multifunctional artificial fish reef not only can provide a reproduction and forage place for fishes, but also can introduce air above the sea surface into the seabed by utilizing wave energy, water and gas exchange in the fish reef sea area is promoted, needed oxygen is provided for shellfishes and sea cucumbers and the like, and the blocking in the fish reef using process can be effectively avoided.Ocean current drives impellers to rotate, the distribution of a flow field in the sea area can be changed, bottom layer nutrient substances are driven to perform exchange with the upper layer water body, nutrient is provided for reproduction and growth of planktons and the like in the upper layer water body, a good marine organism habitat is created, and primary productivity in the surrounding water area is greatly improved.A solar panel on the buoy can convert solar energy into electric energy to supply power to LEDs on the reef body, and thus the goal of attracting phototactic fishes is achieved.Staggered separating tables in the reef body increase the adhering area of the artificial fish reef, and the number of organisms in the sea area is increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
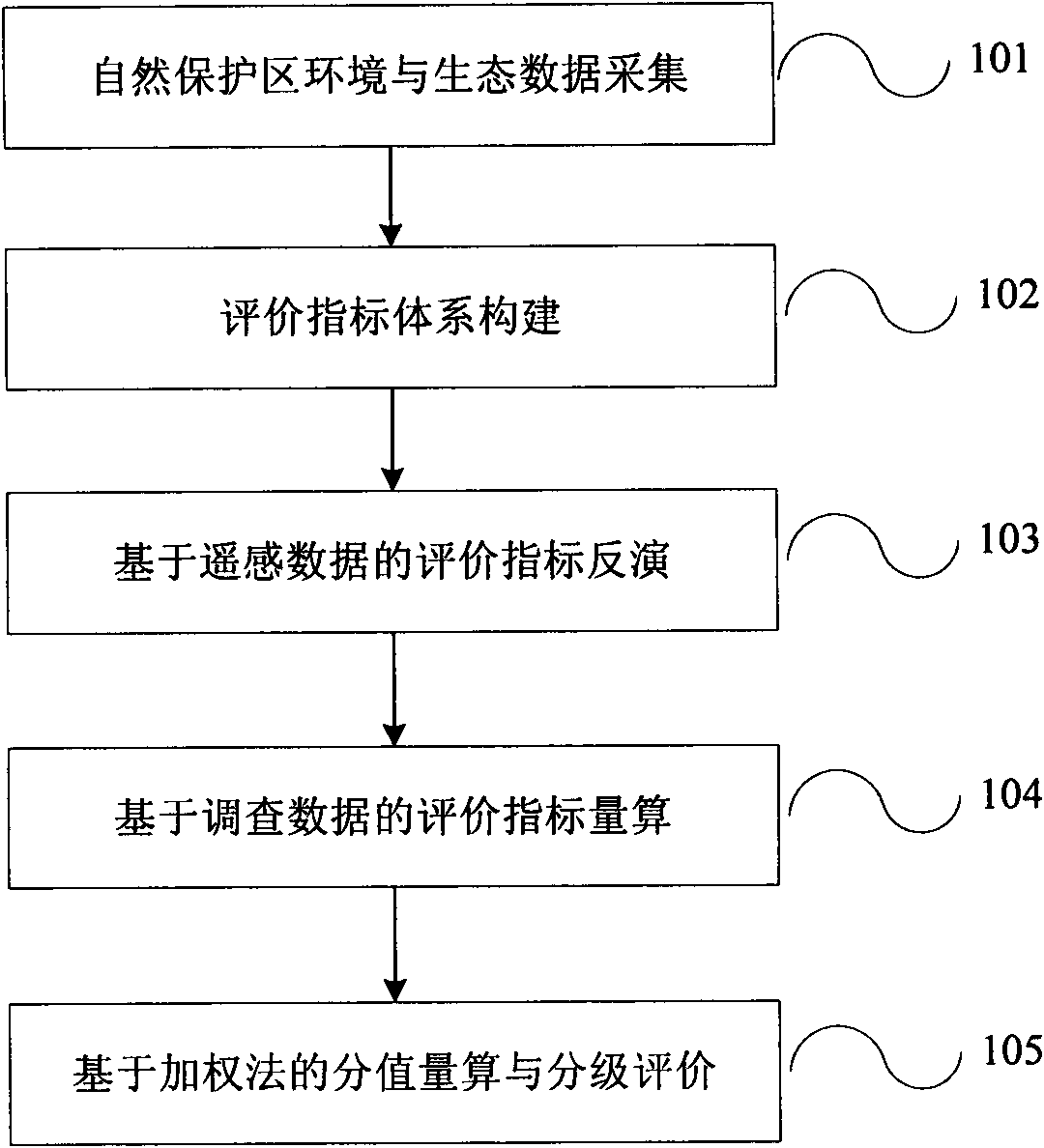
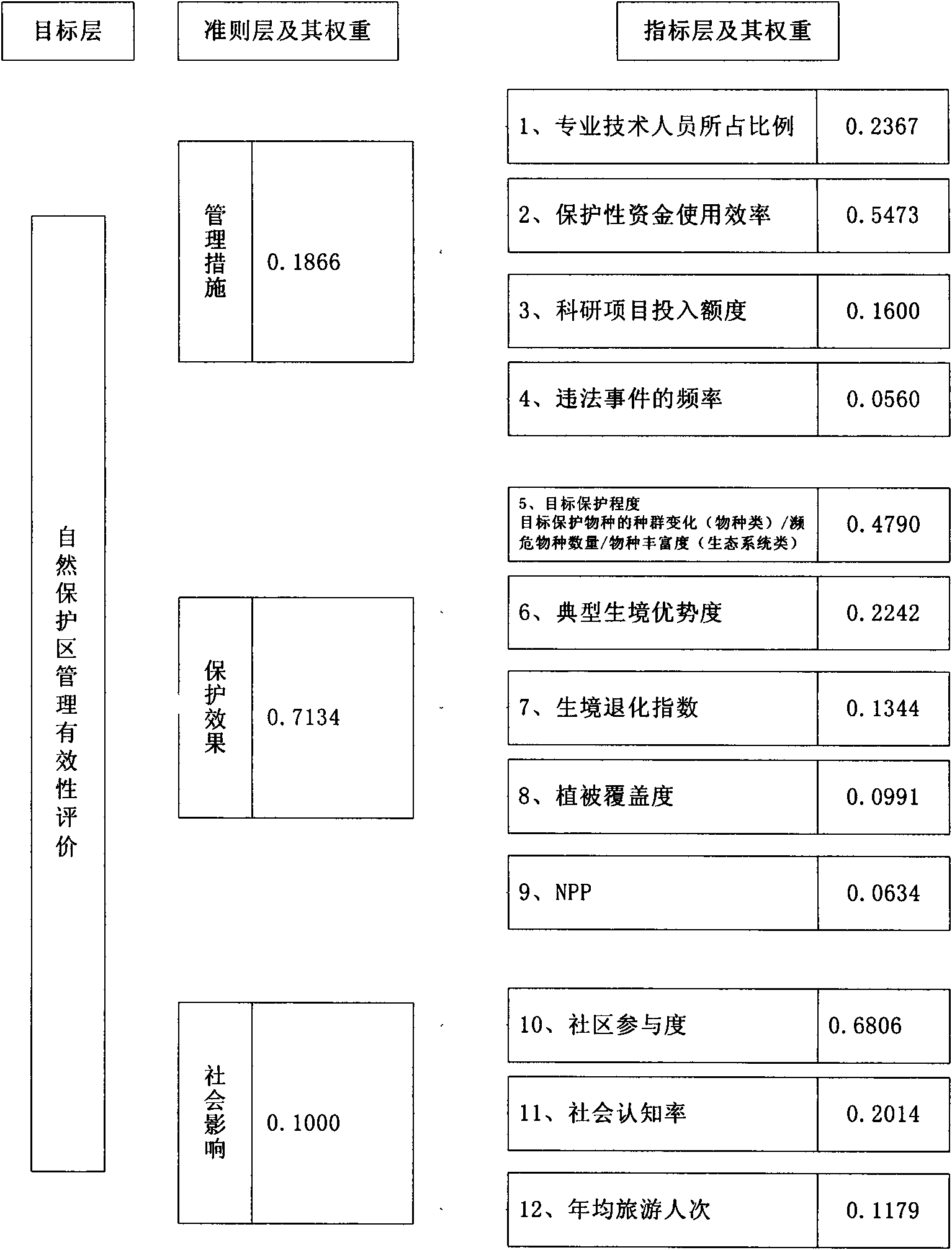
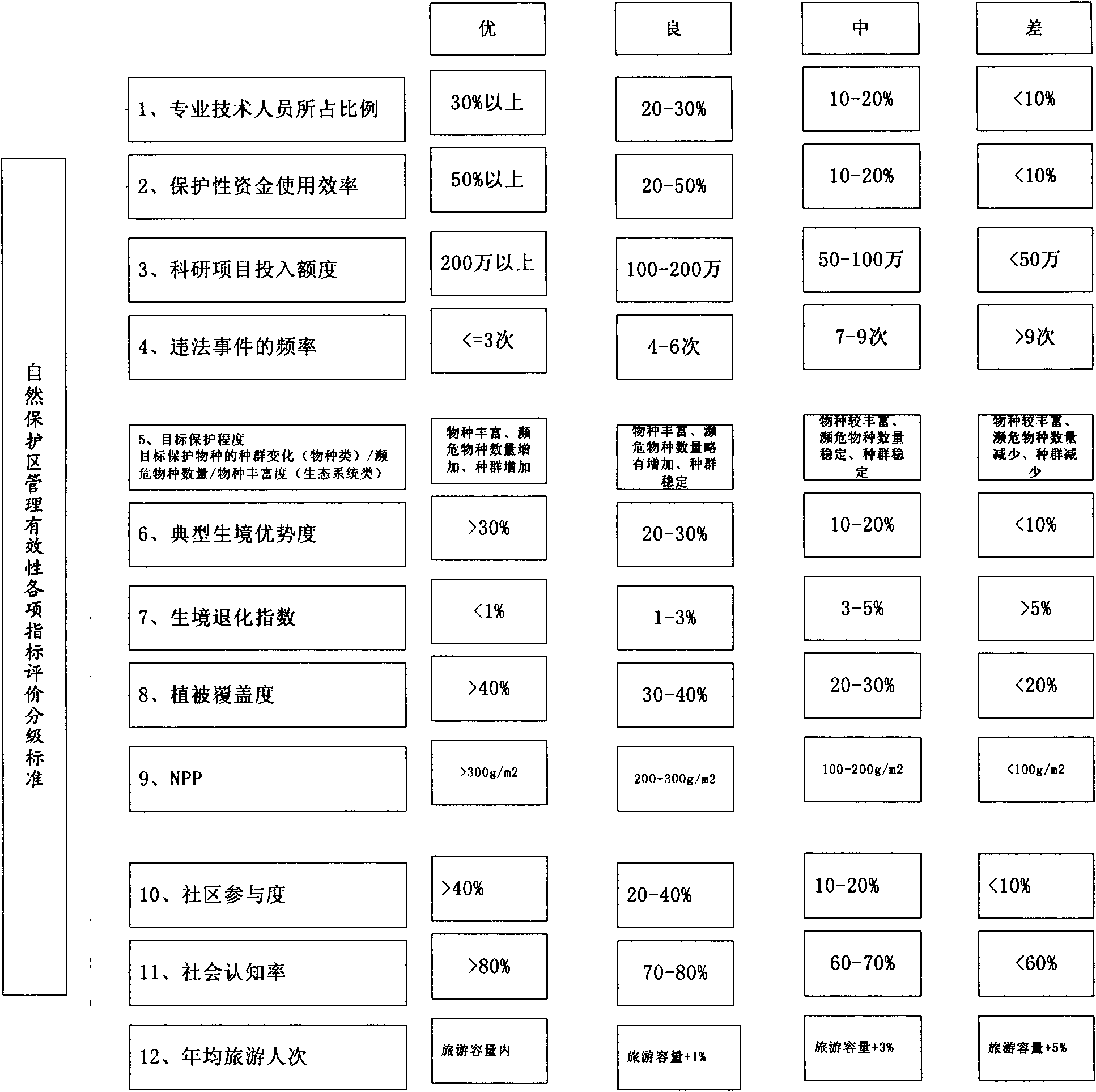
Natural preservation area management effectiveness quantitative evaluation method and system
InactiveCN102136103ARealization of Quantitative Evaluation of EffectivenessInstrumentsIndex systemDegradation index
The invention discloses a method and a system for quantitatively evaluating natural preservation area management effectiveness. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining environmental and ecological data of a natural preservation area by measures such as a remote sensing satellite and field survey and the like, determining a natural preservation area management effectiveness quantitative evaluation indexes system by utilizing an analytic hierarchy process and an expert scoring method, determining index intension and a quantitative measuring method of the index intension so as to be convenient for quantitative evaluation of the future preservation area; conducting inversion to index values of NPP (net primary productivity), vegetation coverage, a typical habitat dominance and habitat degradation indexes and the like by utilizing the remote sensing data; measuring management measures and social impact rule layer correlation indexes by utilizing ground investigation data; determining all index permissions by utilizing the analytic hierarchy process, and conducting weighting summation to measure all natural preservation area evaluation values; and determining an evaluation criterion, and conducting evaluation grading to the natural preservation area based on the standard. In the invention, the natural preservation area evaluation quantitative performance and representativeness are realized, so as to be beneficial to realization of on-line evaluation to the natural preservation area subsequently according to the category of the natural preservation areas.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
Machine learning-based vegetation net primary production remote sensing estimation method
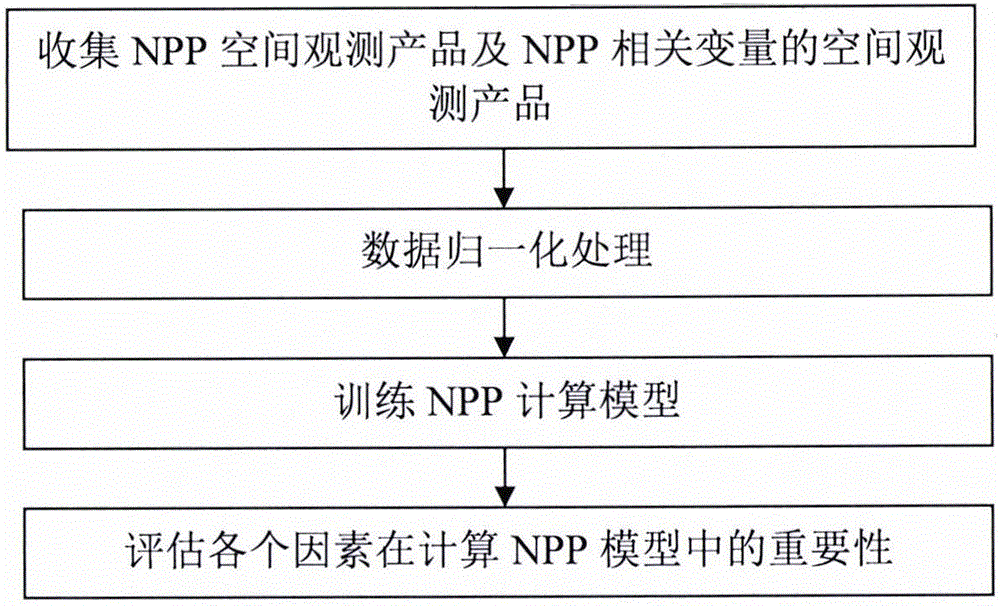
The invention discloses a method for building a vegetation net primary production (NPP) estimation model through machine learning based on a multi-source remote sensing product. According to the method, for analysis characteristics of massive data products, it is proposed that a global vegetation NPP estimation model is simulated and built by adopting the machine learning method, and the importance of related characteristic products in vegetation NPP estimation is calculated based on the model. The method mainly comprises four steps of (1) collecting NPP spatial observation products and spatial observation products of NPP related variables; (2) performing data normalization processing; (3) training the NPP estimation model; and (4) assessing the importance of each factor in the NPP estimation model. The method provides a new idea for performing vegetation NPP estimation by utilizing multi-spatial observation data.
Owner:三亚中科遥感研究所
Remote sensing estimation method and system of crop gross primary productivity
ActiveCN103886213AHigh precisionImprove relevanceSpecial data processing applicationsThermal energyModel system
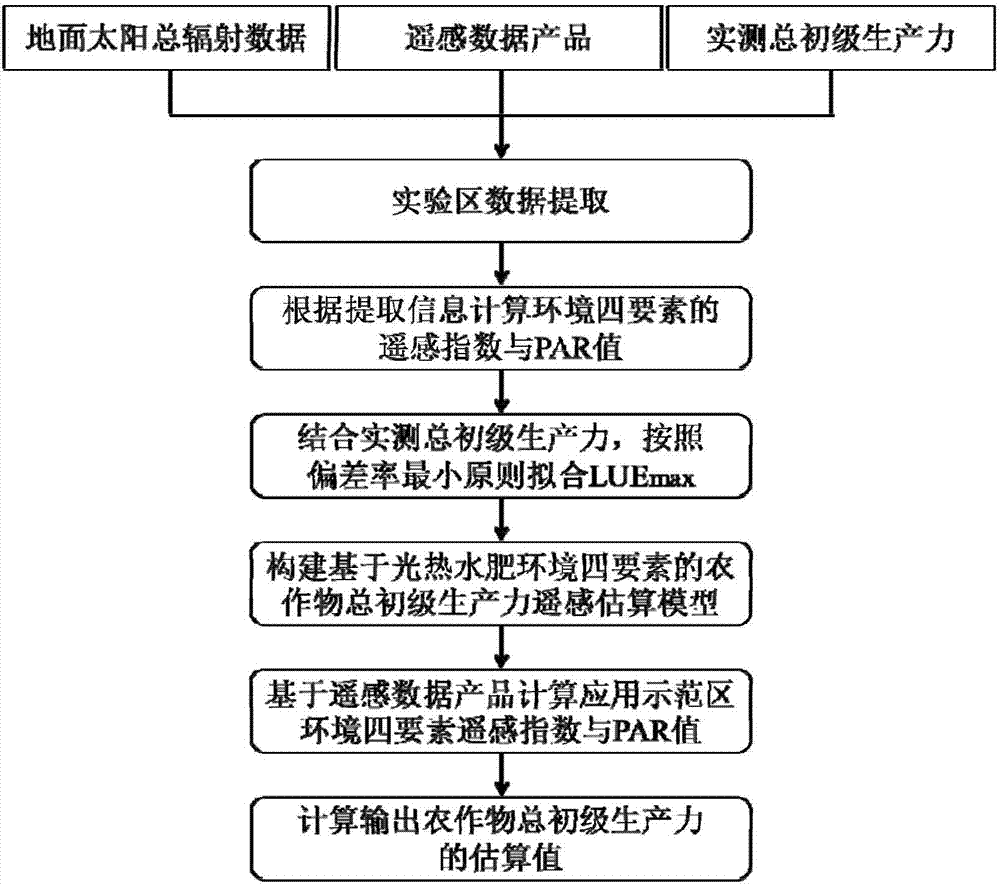
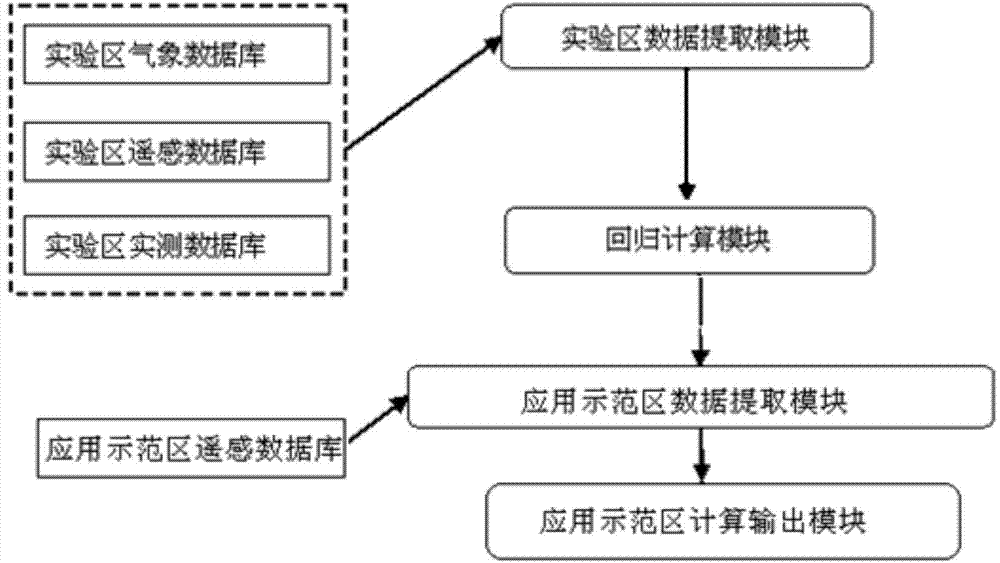
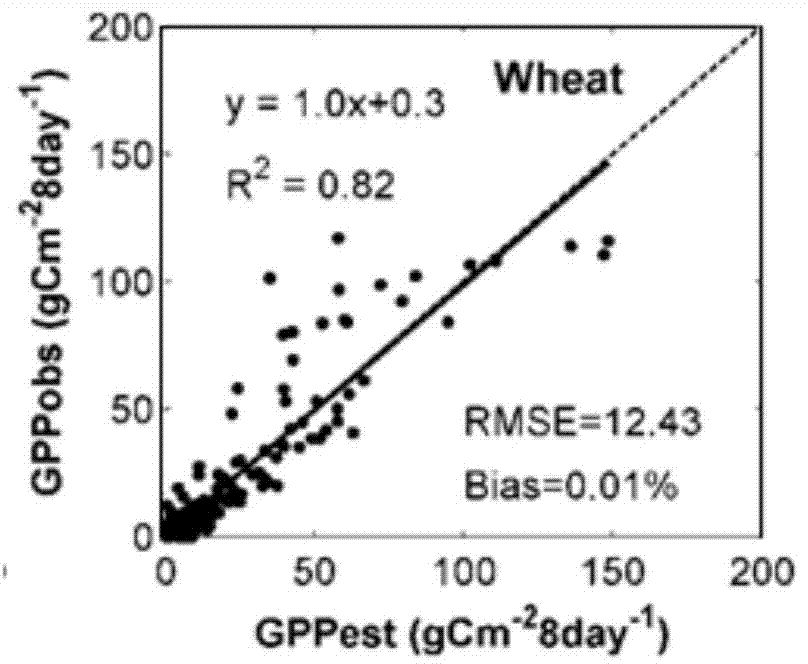
The invention discloses a remote sensing estimation method and system of crop gross primary productivity. The remote sensing estimation method of the crop gross primary productivity is mainly used for wheat and corns, compared with an existing method, through theoretical analysis and experimental measurement and application, multi-source remote sensing data are fully utilized, depending on a solar energy utilization efficiency model, the environmental elements of solar energy, thermal energy, water and nutrients on crop growth are fully considered, a maximum solar energy utilization efficiency coefficient is introduced, and a crop gross primary productivity remote sensing model based on the four environmental elements of solar energy, thermal energy, water and fertilizer is established. Compared with a traditional solar energy utilization efficiency model, the influence of multiple environmental elements on the crop gross primary productivity is comprehensively considered, the remote sensing data are applied to the largest extent, model estimation results are high in precision, and meanwhile the crop gross primary productivity aiming at one application demonstration area can be estimated by an estimation model system.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
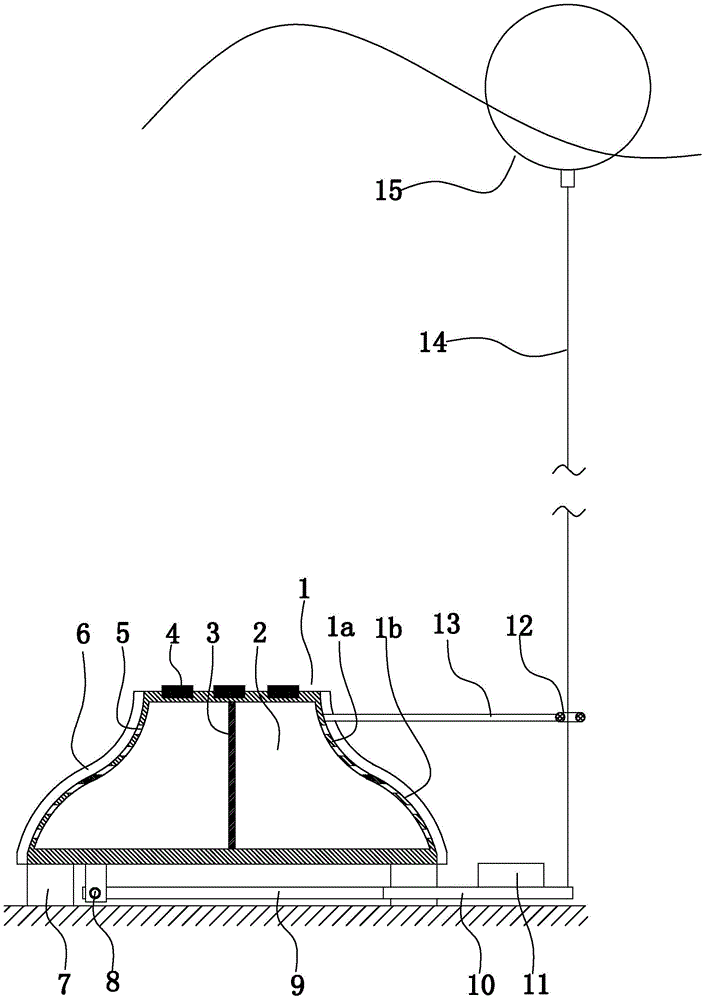
Test system for determining primary productivity of river benthic algae
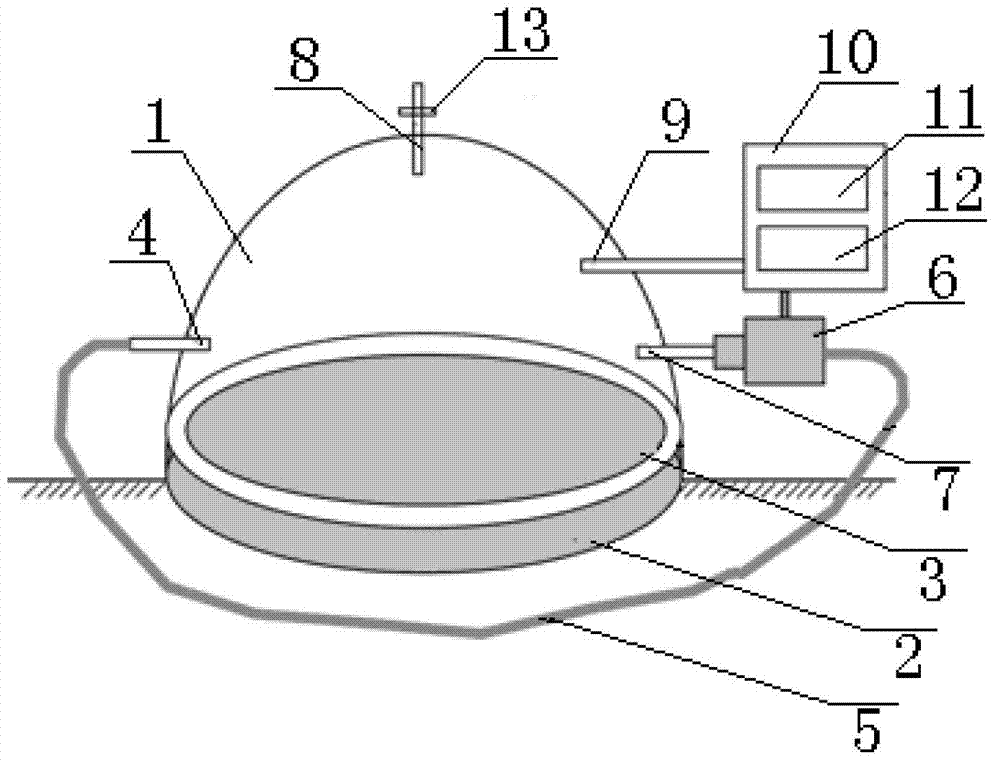
The invention provides a test system for determining the primary productivity of river benthic algae. The test system at least comprises a sample unit, a measure unit and a control unit, wherein the sample unit is a photobioreactor, and comprises a glass cover, a rotatable pedestal, a benthic alga growth matrix, a water circulation device and a gas discharge tube; the glass cover and the rotatable pedestal are manufactured through processing organic glass, the glass cover is a semi-spherical housing with a downward opening, the lower end of the glass cover is in rotary seal connection with the rotatable pedestal through screw threads, the benthic alga growth matrix is arranged between the glass cover and the rotatable pedestal, and a water sample is arranged between the glass cover and the benthic alga growth matrix; the measure unit is a dissolved oxygen sensor, the probe of the dissolved oxygen sensor is arranged in the water sample in the glass cover; and the control unit comprises a control panel, and a one-chip microcomputer and a power supply arranged in the control panel, and the one-chip microcomputer is connected with the dissolved oxygen sensor. Compared with traditional systems, the system of the invention has the advantages of high automation degree and working efficiency improvement.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Grassland above-ground biomass retrievalinversion method based on high-time resolution and high-spatial resolution multispectral remote sensing data
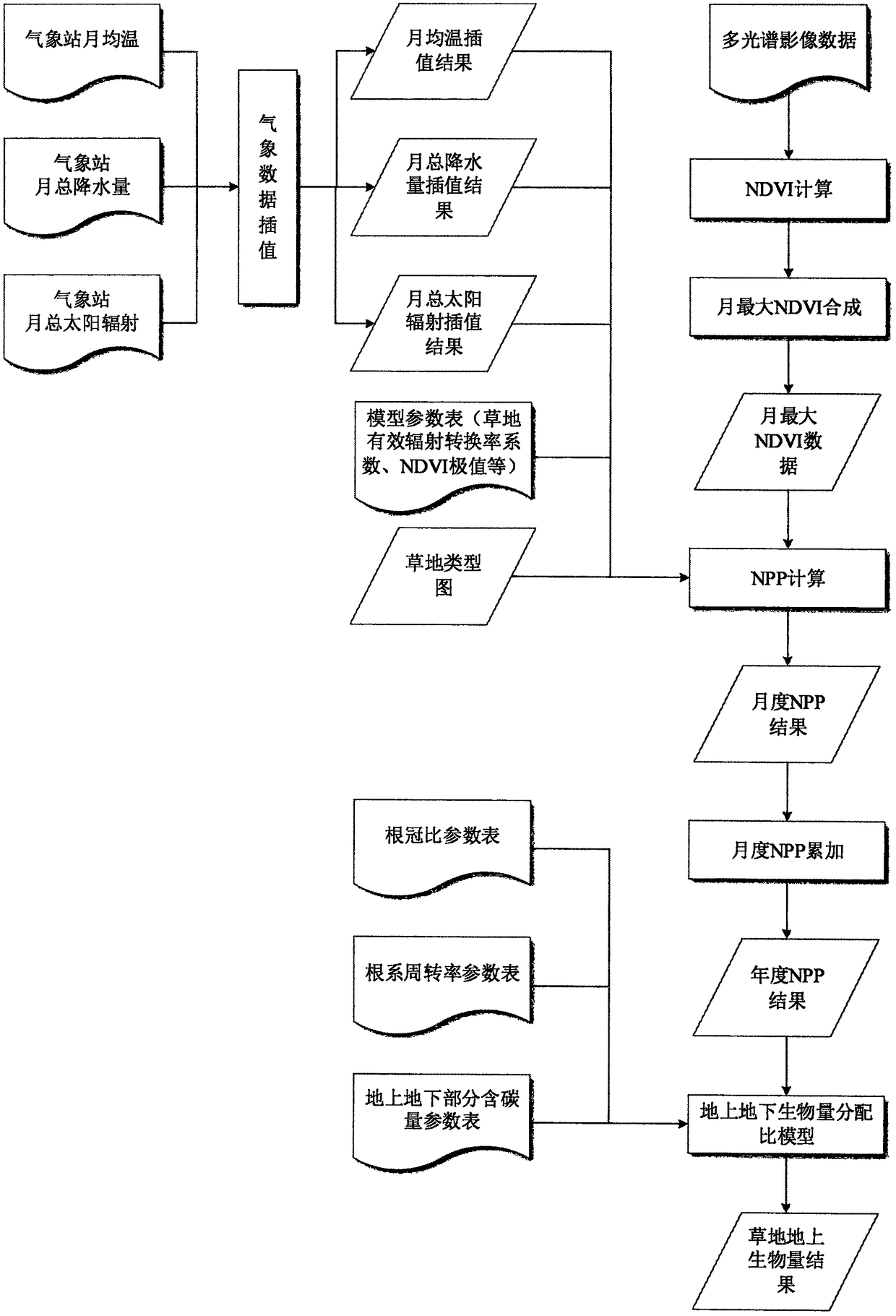
The invention discloses a grassland above-ground biomass retrievalinversion method based on high-time resolution and high-spatial resolution multispectral remote sensing data. The method comprises thefollowing specific steps: 1) selecting multispectral remote sensing data covering the a grassland growing season, calculating thean NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index), and synthesizing toobtain the monthly maximum NDVI covering the a research area; 2) interpolating according to the monthly mean temperature, the monthly total precipitation and the monthly total solar radiation data ofa meteorological station, to generate the monthly mean temperature, the monthly total precipitation and the monthly total solar radiation data covering the research area; 3) calculating the NPP (Net Primary Productivity) of the grassland by using a CASA (Carnegie-Ames-Stanford Approach) model based on the LUE (Light Use Efficiency) theory; 4) calculating the above-ground biomass of the grassland according to the NPP and the ratio of the above-ground biomass to the underground biomass.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS +1
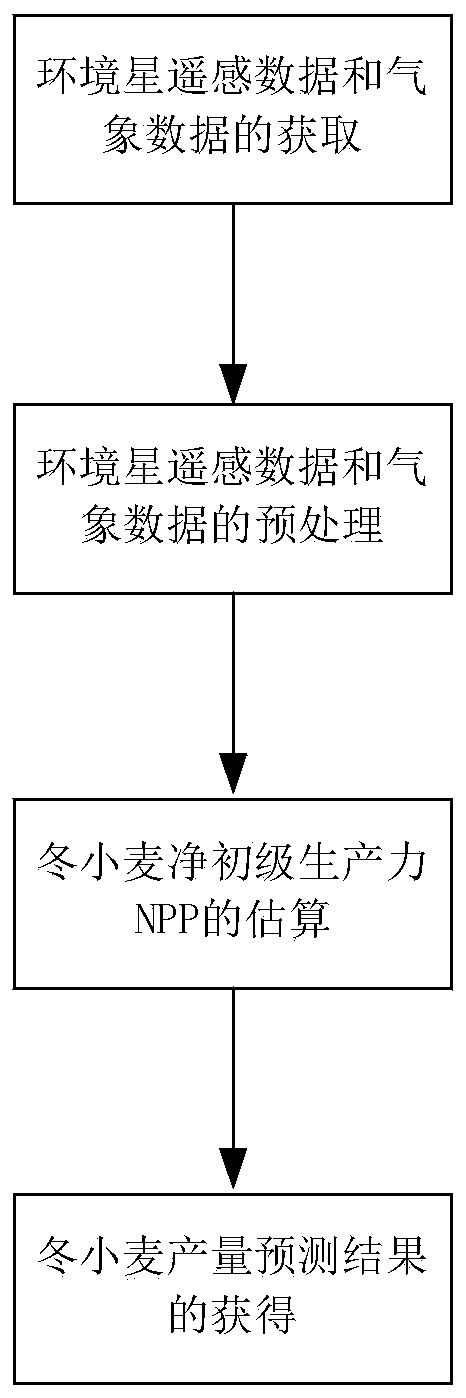
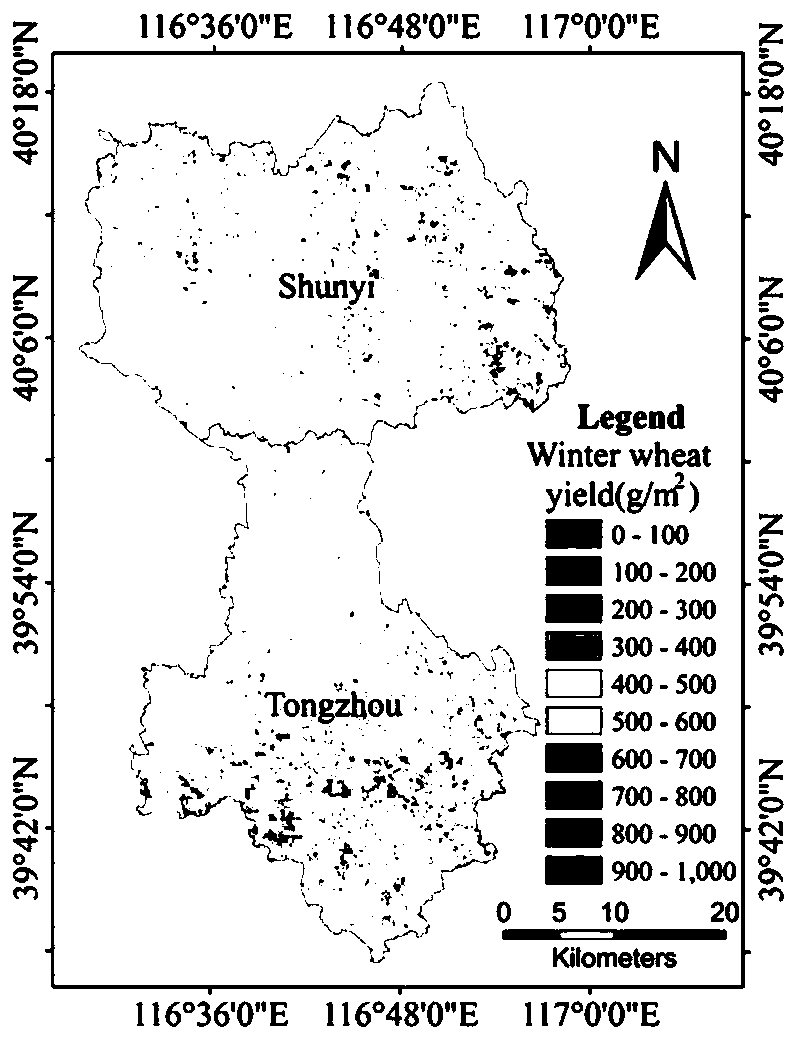
Winter wheat yield estimation method based on short-period remote sensing area data
PendingCN109919395AYield Estimation AchievedMeet the precision requirementsForecastingSensing dataEstimation methods
The invention relates to a winter wheat yield estimation method based on short-period remote sensing area data. Compared with the prior art, the winter wheat yield estimation method overcomes the defect that winter wheat yield prediction based on high temporal and spatial resolution NPP data does not exist. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining environmental satellite remote sensingdata and meteorological data; preprocessing the environmental satellite remote sensing data and the meteorological data; estimatingthe net primary productivity NPP of the winter wheat; and obtaining awinter wheat yield prediction result. By utilizing an improved CASA model, high-temporal-spatial-resolution winter wheat NPP spatial distribution information with 5 days as intervals is estimated, and an NPP-yield transformation model is combined so that remote sensing estimation of winter wheat yield is achieved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Establishment and application of desertization dynamic simulation model
InactiveCN108053072AMeet the dynamic simulation of regional desertificationMeet needsForecastingResourcesVegetationPrimary productivity
The invention discloses establishment and application of a desertization dynamic simulation model. The method includes the steps of selecting weather, soil moisture, population, economy, animal husbandry and land utilization as driving factors of simulating dynamic evolution of region desertization, using vegetation net primary productivity (NPP) as a generality index of measuring desertization change and different driving force action; collecting data of each driving factor and performing rasterization on data of each driving factor; quantifying influence of weather and soil moisture on vegetation NPP, quantifying influence of economy and population on vegetation NPP, quantifying influence of grazing on vegetation NPP, and quantifying influence of land utilization on vegetation NPP; and summarizing data after the influence of the driving factors on vegetation NPP is quantified, calculating the value of actual NPP of the same year, and classifying desertization grades in the region according to NPP ranges corresponding to different desertization grades. Action characteristics of various driving force in different scenes in the future can be reflected, and the requirements for regional desertization dynamic simulation and policy regulation are met.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
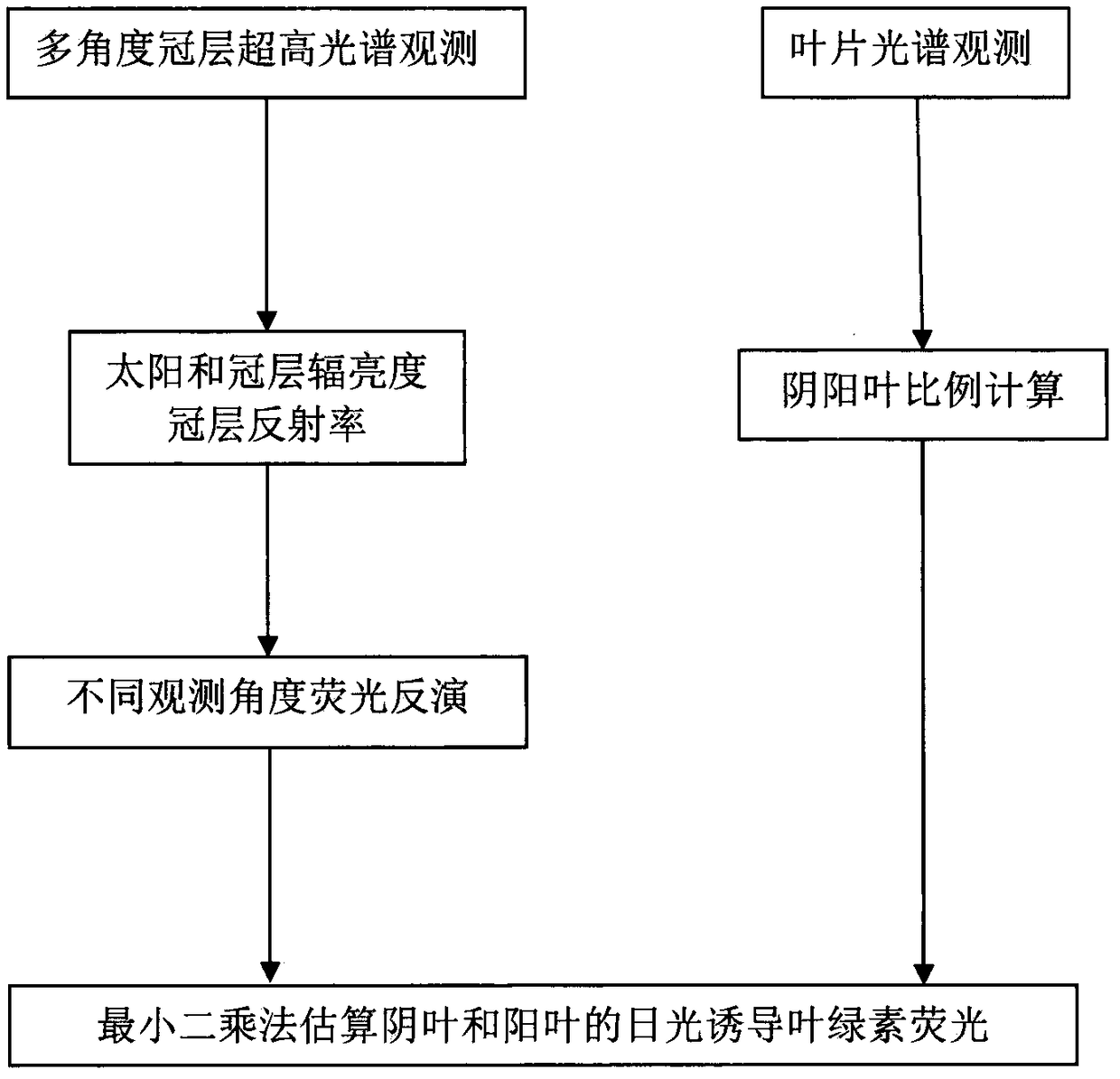
Method for multi-angle observing and precisely inverting sunlight induced chlorophyll fluorescence of shade/sun leaf of vegetation
The invention provides a method of utilizing a multi-angle observation system to obtain the vegetation canopy spectroscopic data to precisely inverting sunlight induced chlorophyll fluorescence of shade / sun leaves of a canopy, and belongs to the research field of vegetation remote sensing inversion parameter obtaining methods. The method comprises following steps: establishing a multi-angle super-hyperspectral observing system; obtaining multi-angle super-hyperspectral data; calculating the solar incident angle and canopy reflection brightness; calculating the reflection rate and inverted chlorophyll fluorescence; using a leaf clamp to observe the leaf reflection rate; utilizing the ratio of canopy reflection rate to leaf reflection rate, under the assistance of a geometrical optical model, calculating the ratio of shade / sun leaves from different observation angles, and obtaining the fluorescence of the sun leaves and shade leaves through fitting of least square method. The provided method can obtain continuous multi-angle vegetation canopy super-hyperspectral data, is used to invert chlorophyll fluorescence, can simply and effectively calculate the ratio of sun leaves and shade leaves of a canopy from different observation angles and solar incident angles based on the leaf reflection rate and a geometrical optical model, calculates the fluorescence of the sun leaves and shadeleaves, and improves the precision of monitoring the primary productivity of a land.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for measuring and calculating area of mangrove plant kandelia candel leaf
InactiveCN102628685ACalculations are easy and accurateMeasurement devicesKandelia candelRegression analysis
The invention relates to a method for measuring and calculating an area of a mangrove plant kandelia candel leaf, which belongs to the technical field of coastal mangrove forest wetland ecosystem protection and primary productivity evaluation. The method comprises the steps of: firstly picking kandelia candel leaves with a given quantity, the same size and normal shapes as well as statistical significance, and measuring data of each leaf such as an area, a maximal length and a maximal width by utilizing a leaf area scanner; implementing the regression analysis through a nonlinear equation of Y=aX1b1X2ba, and determining the regression coefficients a, b1 and b2; obtaining an equation capable of measuring the area of the kandelia candel leaf: A=aLb1Wb2; and measuring the maximal length and the maximal width of a kandelia candel leaf on site, and respectively putting the measured maximal length and maximal width into the equation to obtain the area of the kandelia candel leaf to be measured and calculated. The invention provides a simple, easy and precise method for measuring and calculating the kandelia candel leaf, so that a more convenient technology and a method for supporting the evaluation on the primary productivity of the mangrove forest ecosystem are provided.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Remote-sensing inversion method and system for primary productivity of Shenzhen marine sites
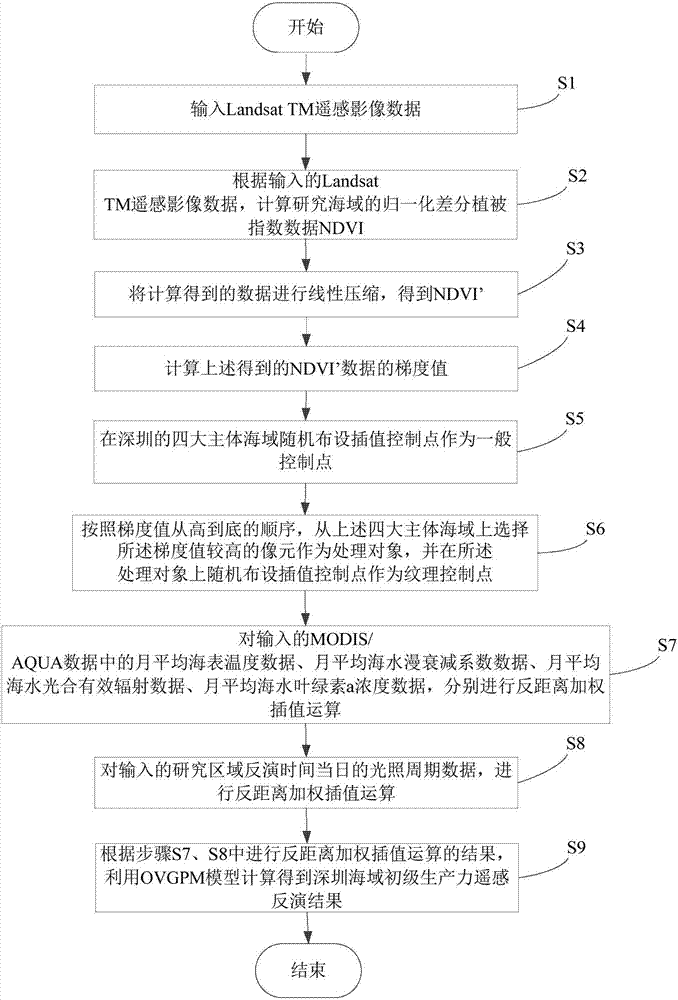
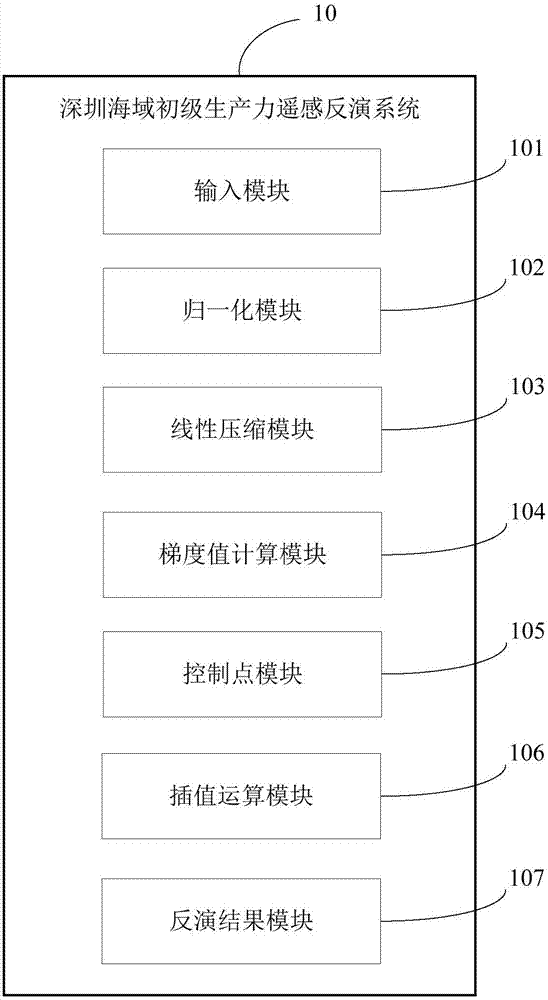
The invention relates to a remote-sensing inversion method for primary productivity of Shenzhen marine sites. The method comprises that Landsat TM remote-sensing image data is input; normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) data of the Shenzhen marine sites is calculated; the NDVI data is compressed linearly to obtain NDVI'; a gradient value nablag of the obtained NDVI' data is calculated; interpolation control points are laid in the four main Shenzhen marine sites randomly and serve as common control points; a pixel of a higher nablag value is selected from the four main Shenzhen marine sites and serves as a processing object deltap, and interpolation control points are laid in the deltap randomly and serve as texture control points; inverse-distance weighted interpolation operation is carried out on data in MODIS / AQUA; photoperiod data of the Shenzhen sites in the present day is inversed, and inverse-distance weighted interpolation operation is carried out; and an OVGPM model is used to obtain a remote-sensing inversion result of the primary productivity of the Shenzhen oscean sites by calculation. The invention also relates to a remote-sensing inversion system for the primary productivity of the Shenzhen marine sites. Thus, the primary productivity of the Shenzhen marine sites can be inversed in a more accurate, simpler and rapider way.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Device and application for simultaneously measuring primary productivity of phytoplankton and epiphytic algae in rivers
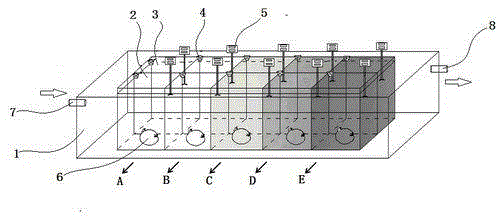
ActiveCN103954747AMake up for the shortcomings of primary productivityImprove work efficiencyBiological testingOxygen sensorPrimary productivity
The invention discloses a device and application for simultaneously measuring primary productivity of phytoplankton and epiphytic algae in rivers. The device comprises a sample photoreaction unit, an environmental simulation unit and a measurement control unit, wherein the sample photoreaction unit refers to multiple groups of algae photoreaction reactors; each group of algae photoreaction reactors comprises at least one phytoplankton photoreactor and at least one epiphytic algae photoreactor; the environmental simulation unit performs environmental simulation on illumination, water temperature and water flow; the illumination environment is that different shading degrees are adopted by different groups of algae photoreactors in the same light source environment; the water temperature and water flow environmental simulation adopts a water flow tank arranged outside the sample photoreaction unit; the water flow tank is provided with a water inlet and a water outlet; the measurement control unit comprises a dissolved oxygen sensor and a control panel; and a dissolved oxygen sensor probe stretches into the algae photoreactor water sample. The device is applied to measuring the primary productivity of the algae in rivers, the operation is simple, the primary productivity and photosynthesis parameters of the phytoplankton and epiphytic algae can be simultaneously obtained, and the experimental efficiency is improved.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Upwelling artificial fish reef
PendingCN106719222AEfficient use ofReduce lossesClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPlanktonPrimary productivity
The invention relates to an upwelling artificial fish reef. The upwelling artificial fish reef includes an upper fish reef body, a lower fish reef body, support columns and a base. The upwelling artificial fish reef can provide a necessary safe habitat for gathering, feeding, reproduction, growth and enemy avoiding of aquatic organisms such as fishes, can generate upward flow, can change distribution of an internal flow field in the sea area, can drive exchange between bottom nutriment salt materials and upper water, can provide nutriments for reproduction and growth of plankton in the upper water, can establish a good marine organism habitat environment, can enhance the reproduction ability of the plankton, can form an excellent bait field, can attract migration fish to gather and stop, and can achieve a better fish gathering effect. The Upwelling artificial fish reef can effectively prevent blocking of the fish reef in use; sea current flows through the lower fish reef body to generate the upward flow to drive sea water in a cavity of the upper fish reef body to flow so as to remove sand in the cavity of the upper fish reef body, the survival reproduction space of aquatic organism such as fishes can be ensured, and the primary productivity of a near sea area can be greatly improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
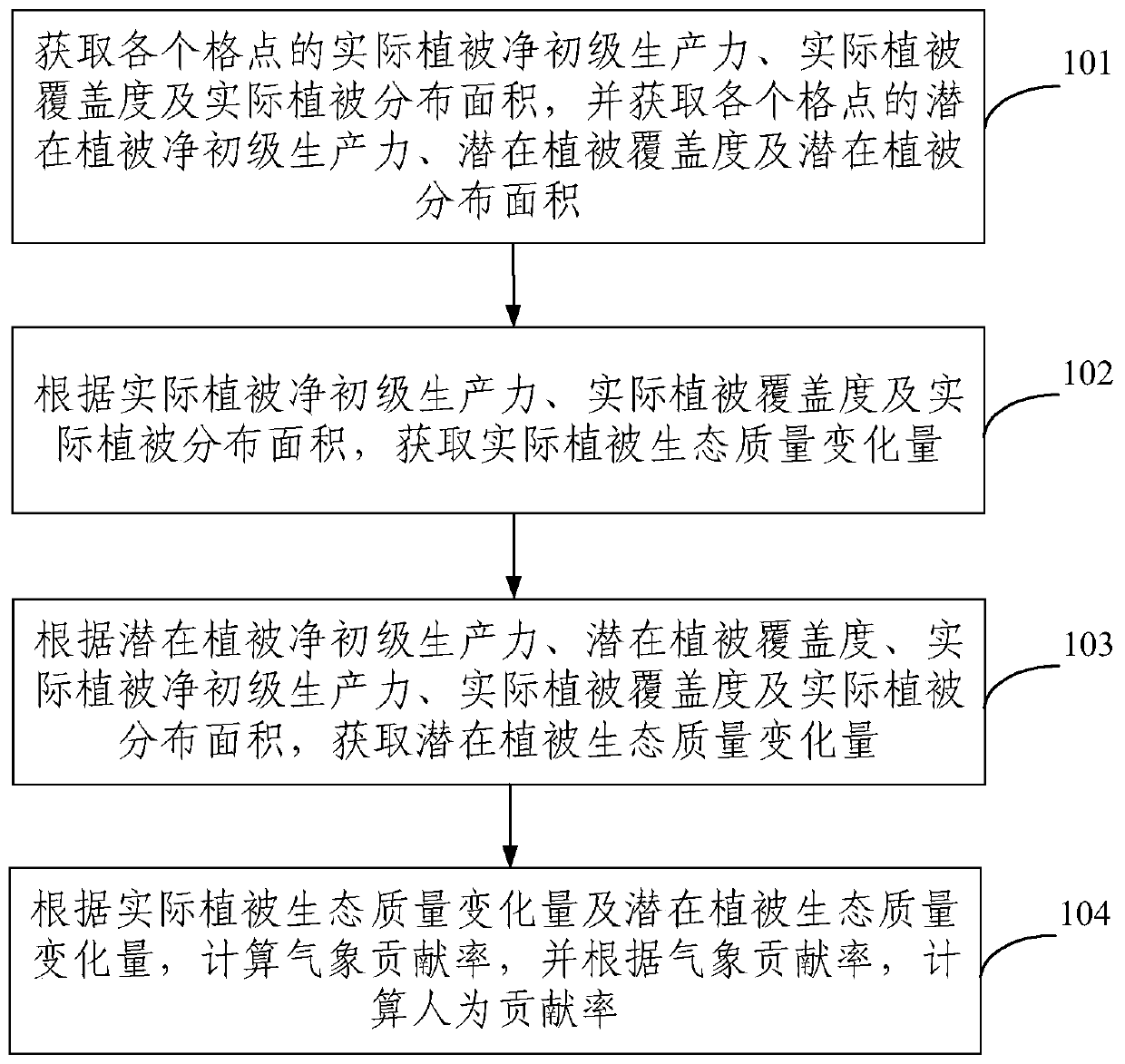
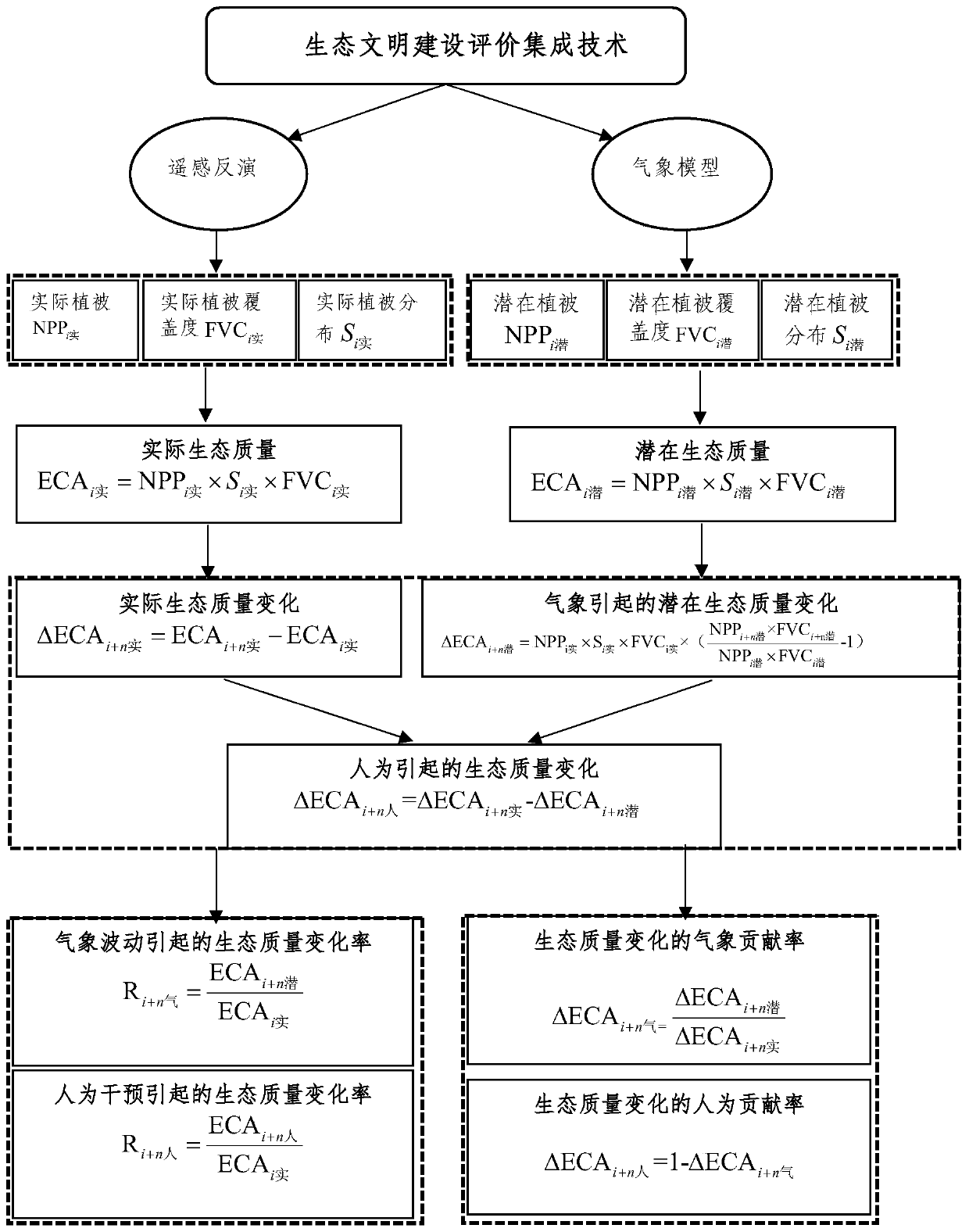
Ecological environment quality evaluation method and device
ActiveCN109919515AOvercome the disadvantages of being difficult to accurately quantify the relationship between the twoResolve separabilityResourcesVegetationEcological environment
The embodiment of the invention provides an ecological environment quality evaluation method and device, and belongs to the technical field of ecological environments. The method comprises the following steps: calculating vegetation net primary productivity, vegetation coverage and geographic distribution based on remote sensing information; calculating potential vegetation net primary productivity, potential vegetation coverage and potential geographic distribution based on meteorological conditions;calculating actual and potential vegetation ecological quality of vegetation net primary productivity, vegetation coverage and geographic distribution based on remote sensing information and meteorological conditions; calculating the actual vegetation ecological quality variation based on theremote sensing information and the potential vegetation ecological quality variation only considering the meteorological condition change influence; and calculating a meteorological contribution rateand a human factor contribution rate of the vegetation ecological quality change. According to the embodiment, the ecological civilization construction performance of nationwide scale, provincial scale, county scale and any evaluation area in different time periods can be evaluated, and meteorological condition contribution rate evaluation and thematic map manufacturing of the ecological civilization construction performance can be carried out.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF METEOROLOGICAL SCI
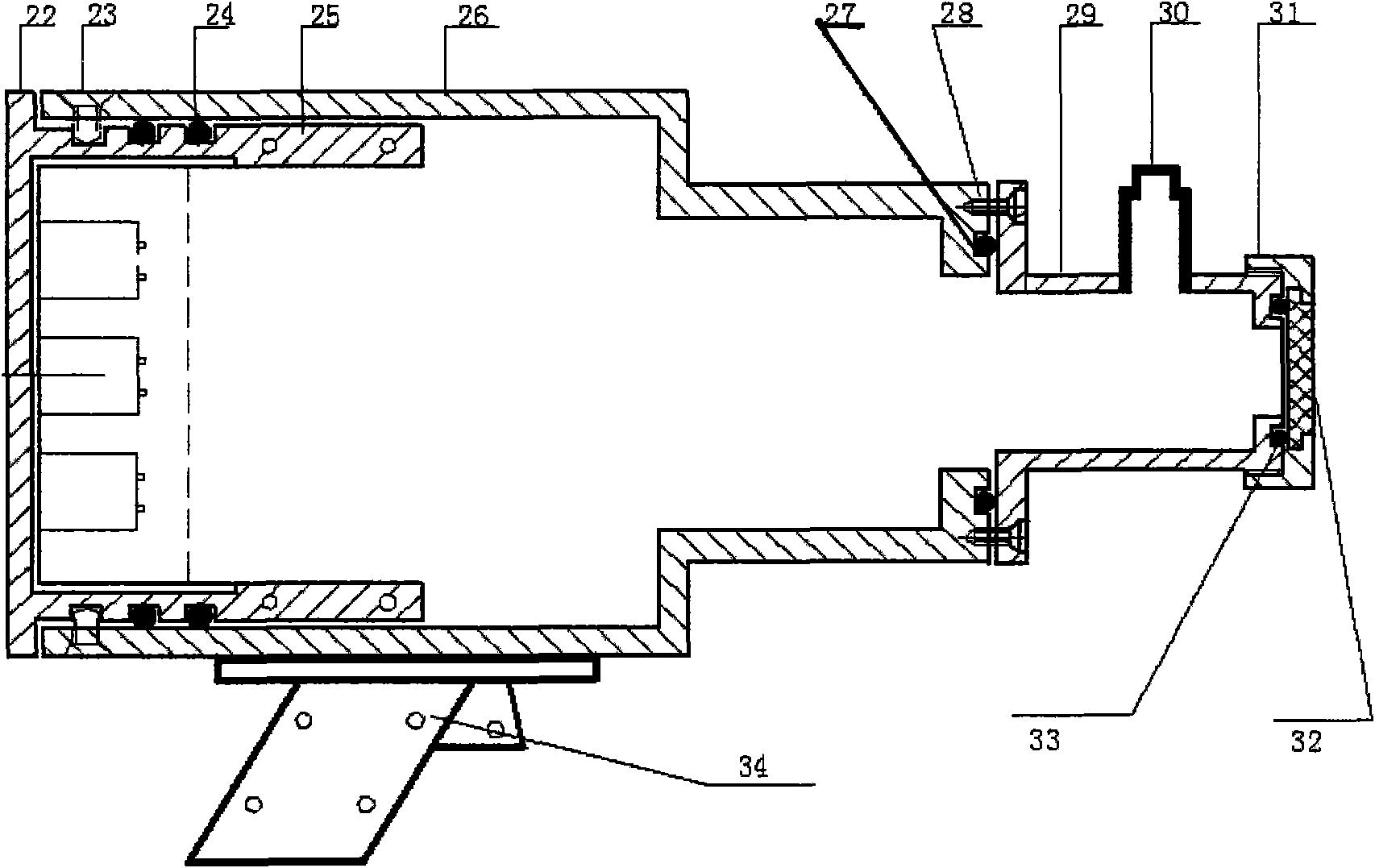
Primary productivity fluorescence detecting system of seat-base type coral reef
InactiveCN101539520AEasy detectionQuick detectionFluorescence/phosphorescenceTotal factory controlControl systemFluorescence
The invention discloses a primary productivity fluorescence detecting system of a seat-base type coral reef. The system sends out a pulse laser source to the coral reef, receives fluorescence generated by the coral reef and calculates the primary productivity of the coral reef according to the strength of the laser source and the fluorescence signal data. The system comprises a detector and a labcontrol system, wherein the detector comprises a fluorescence excitation device, a fluorescence collecting device and a maritime control device; the fluorescence excitation device sends out the pulselaser source to the coral reef for excitation and fluorescence generation; the fluorescence collecting device collects fluorescence signals generated by the coral reef in real time; and the maritime control device controls the switching and the fluorescence excitation frequency of the fluorescence excitation device and the switching and the fluorescence collecting frequency of the fluorescence collecting device and transmits the collected fluorescence signal data to the lab control system which collects, corrects, calculates and manages the fluorescence data. The invention can effectively improve the detection efficiency and is convenient and rapid to detect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
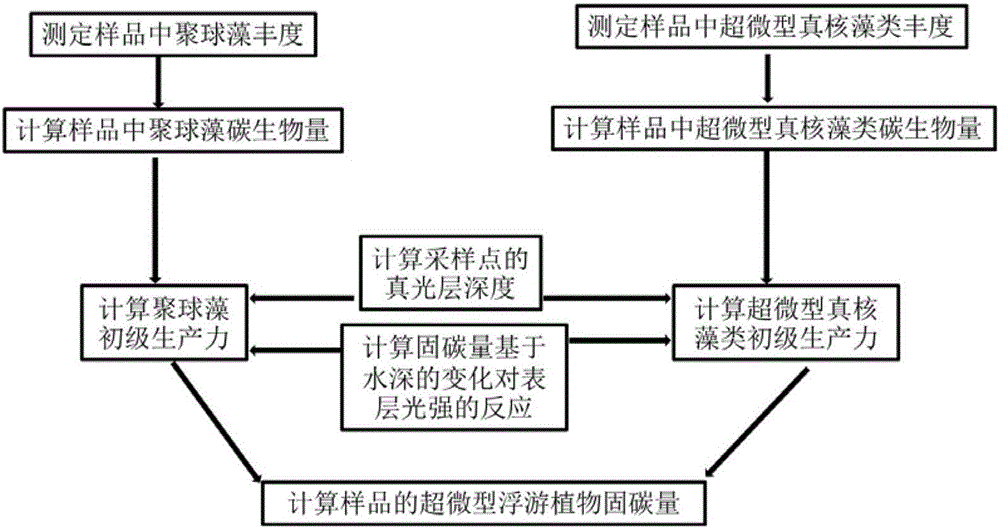
Method for estimating fixed carbon content of ocean ultra-miniature phytoplankton
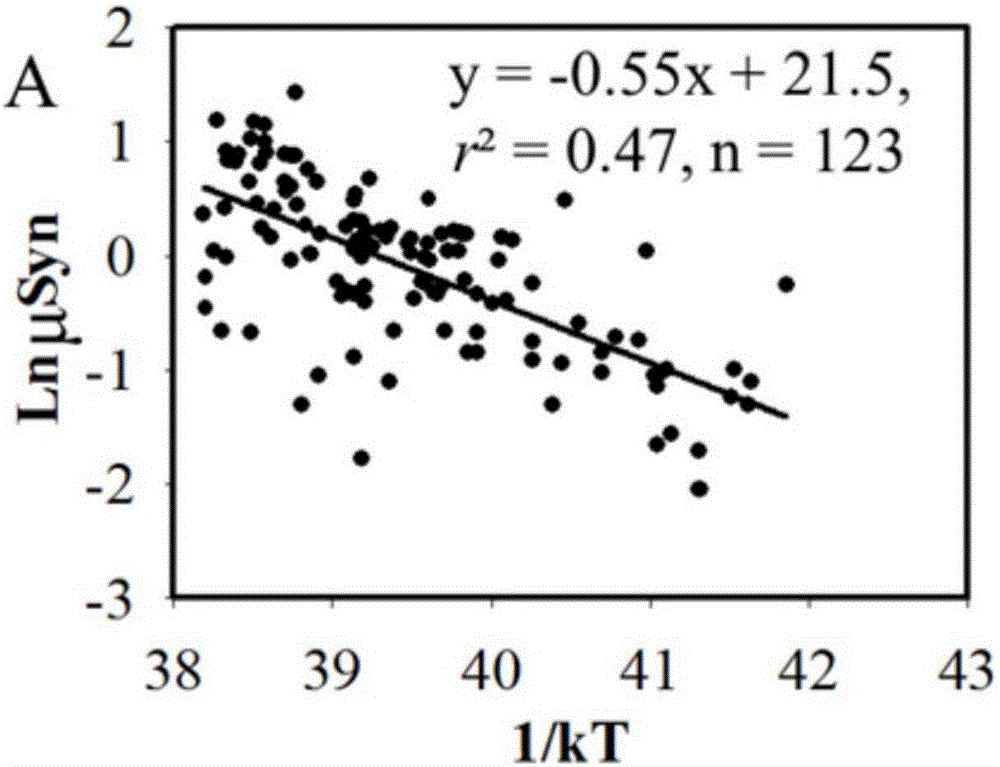
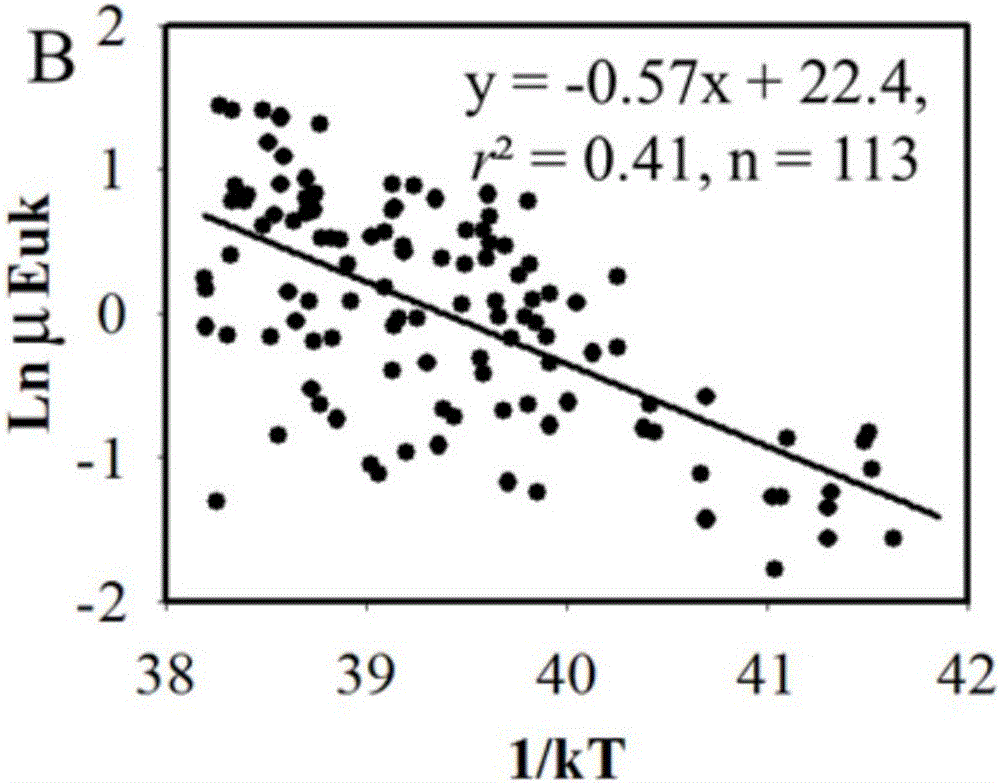
InactiveCN105760683AGood linear relationshipEstimated reliability is strongSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsSynechococcusLinear relationship
The invention relates to a model method for calculating the fixed carbon content of ocean ultra-miniature phytoplankton. The method comprises the following steps: respectively testing abundance of synechococcus and ultra-miniature eukaryotic algae in an acquired sample; respectively calculating the carbon biomass and growth velocity of the synechococcus and the ultra-miniature eukaryotic algae so as to obtain the euphotic layer depth of sampling points of the synechococcus and the ultra-miniature eukaryotic algae; respectively calculating responses of the synechococcus and the ultra-miniature eukaryotic algae to surface light intensity on the basis of water depth variation; respectively calculating primary productivity of the synechococcus and the ultra-miniature eukaryotic algae so as to obtain primary productivity of ultra-miniature phytoplankton at the sampling points. By adopting the method, the fixed carbon content of ultra-miniature phytoplankton in offshore, shelf sea and high-latitude open ocean (the latitude of which is greater than 40 degrees) can be calculated, compared with a method for determining the primary productivity of ultra-miniature phytoplankton on the basis of 14C in situ, the method saves time and labor, and can be used for estimating the primary conductivity of ultra-miniature phytoplankton in a relatively large research area. Tests show that the primary conductivity calculated by using the method has relatively good linear relationship with that of ultra-miniature phytoplankton tested on the basis of 14C, good estimation reliability is achieved, and a theoretic basis is provided for later practical study.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
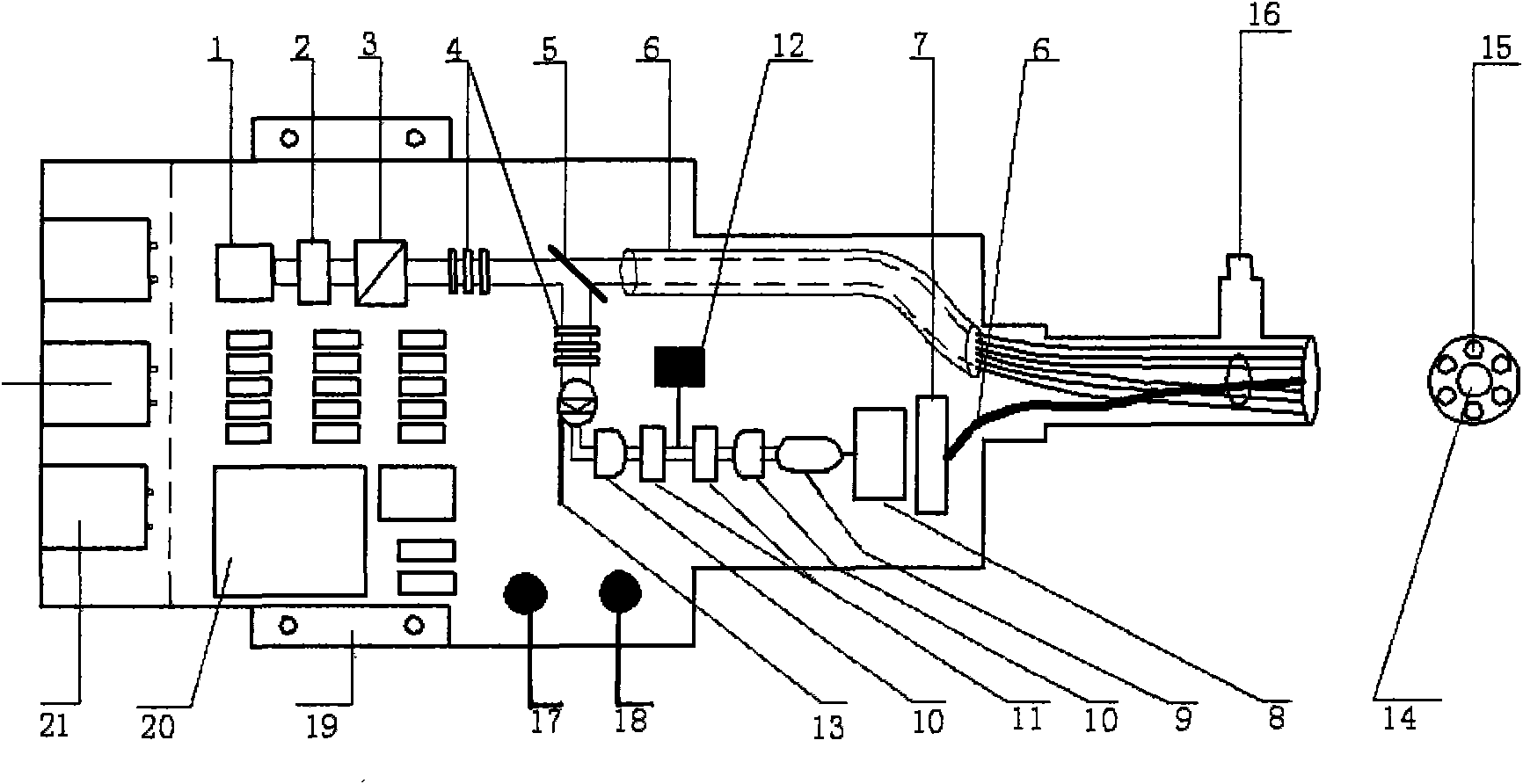
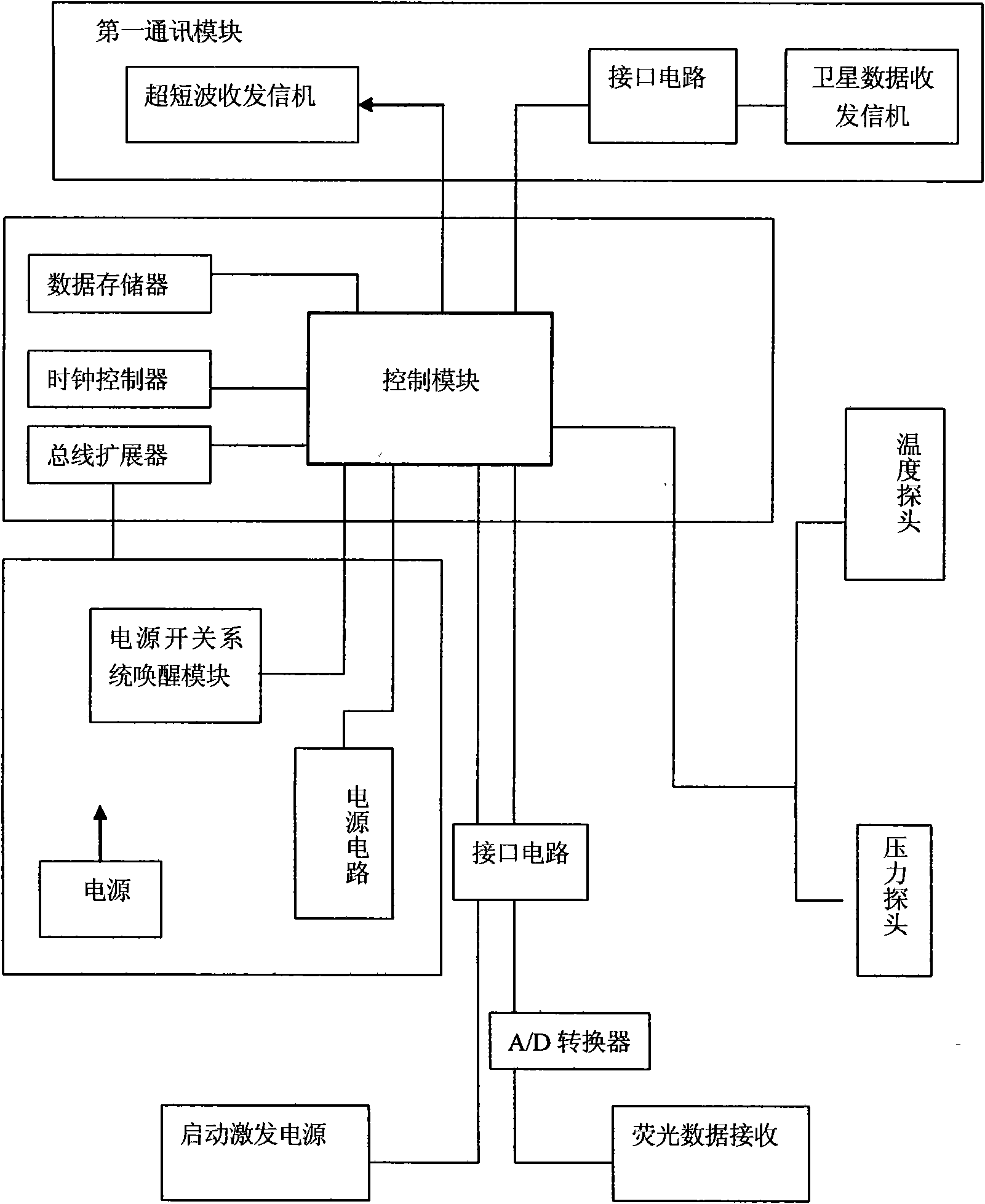
Measuring device and measuring method for in-situ quick determination of primary productivity of lakes
ActiveCN105954240AShort exposure timeHigh measurement accuracyAnalysis by material excitationOxygen sensorPrimary productivity
The invention discloses a measuring device and a measuring method for in-situ quick determination of primary productivity of lakes. The measuring device comprises a transmitting bottle, a shading bottle, a first bottle cap, a second bottle cap, a first dissolved oxygen sensor and a second dissolved oxygen sensor. The transmitting bottle is provided with a first opening, and the shading bottle is provided with a second opening. The first bottle cap is movably arranged on the transmitting bottle between a first opening position and a first closing position; the second bottle cap is movably arranged on the shading bottle between a second opening position and a second closing position. The first dissolved oxygen sensor is arranged on the transmitting bottle, and the second dissolved oxygen sensor is arranged on the shading bottle. The measuring device for in-situ quick determination of the primary productivity of the lakes has the advantages of short exposure time, high measuring accuracy, short measuring period, capability of achieving in-situ real-time observation and the like.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
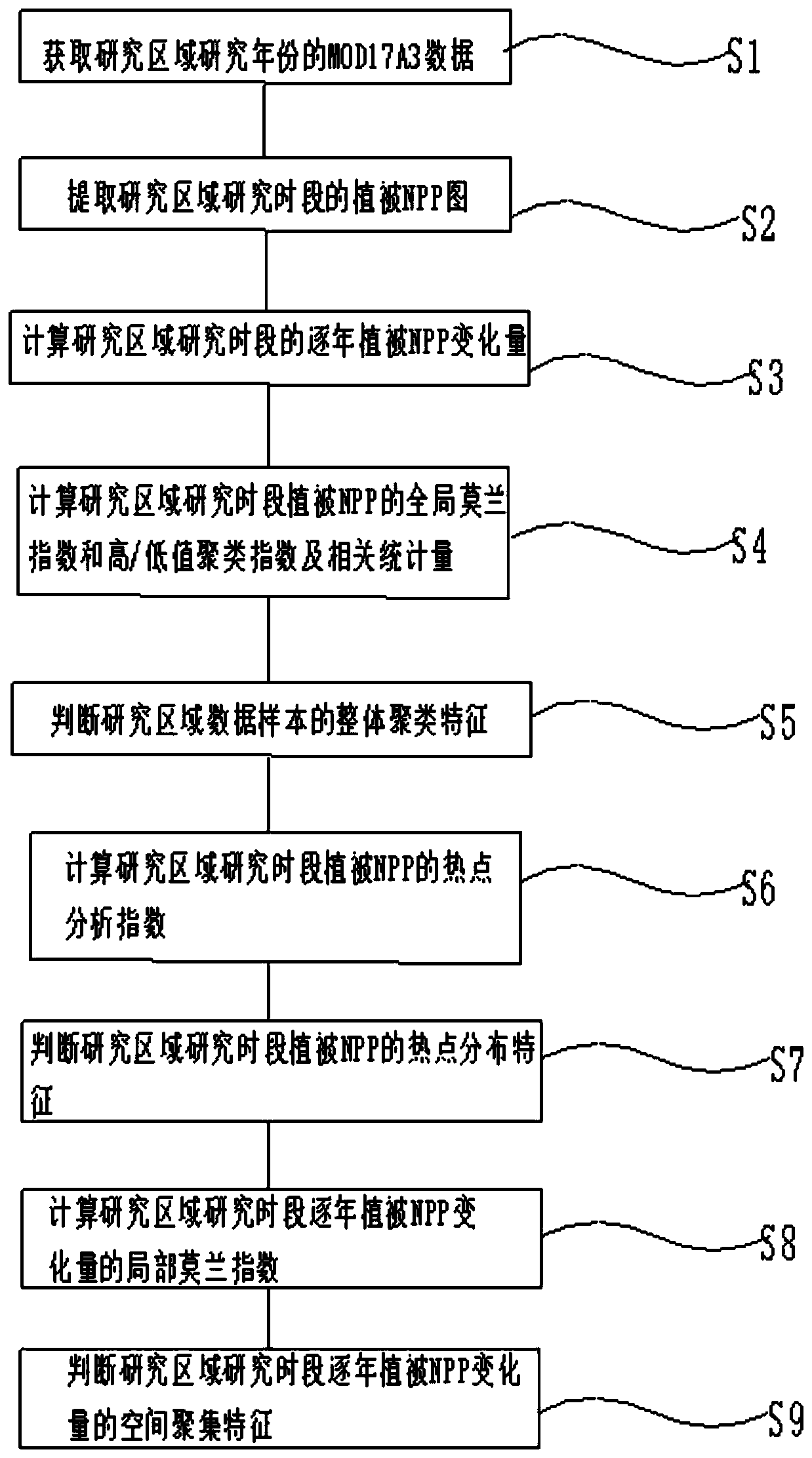
Spatial autocorrelation region-based spatial-temporal difference detection method for vegetation net primary productivity
ActiveCN110135368AAccurate detectionAccurate expressionCharacter and pattern recognitionVegetationPrimary productivity
The invention discloses a spatial autocorrelation region-based spatial-temporal difference detection method for vegetation net primary productivity. . The method comprises the following steps: S1, obtaining MOD17A3 data of research years of a research area; S2, extracting a vegetation NPP graph of a research time period of the research area; S3, calculating the vegetation NPP variable quantity inthe research time period of the research area; S4, calculating a global Moran index, a high / low value clustering index and related statistics of the vegetation NPP in the research period of the research area; S5, judging the overall clustering characteristics of the research area data samples; S6, calculating a hot spot analysis index of the vegetation NPP in the research time period of the research area; S7, judging hot spot distribution characteristics of the vegetation NPP in the research time period of the research area; S8, calculating a local Moran index of annual vegetation NPP variation in the research period of the research area; S9, judging spatial aggregation characteristics of annual vegetation NPP variations in the research period of the research area. The overall clustering characteristics of the vegetation NPP can be accurately expressed, and the local spatial characteristics can be detected.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
A method and system for evaluating the sustainable development of a nature reserve
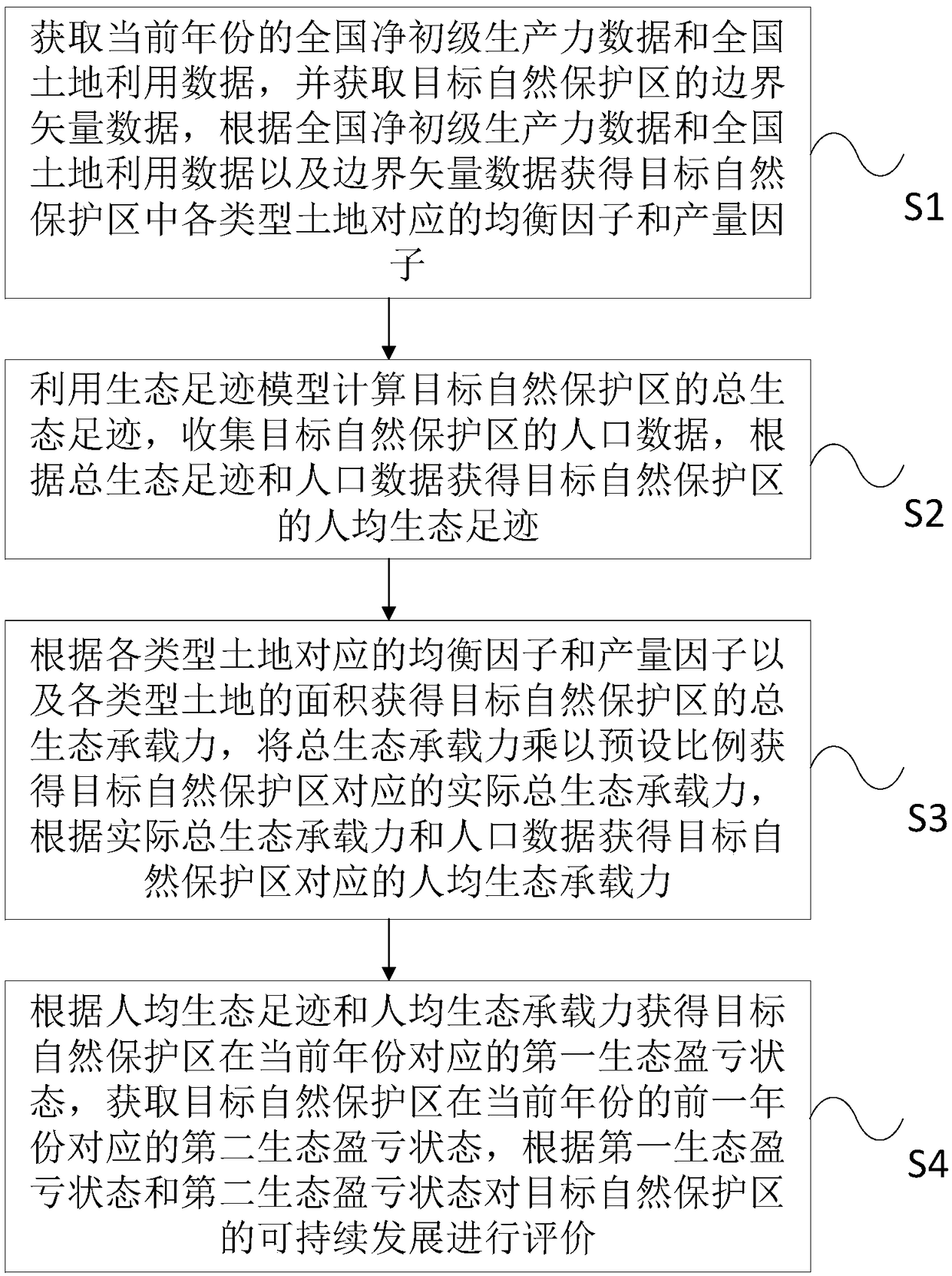
InactiveCN109086989AReflect the differenceOvercoming the problem of insufficient parameter elasticityResourcesBiologyEcological footprint
The invention provides a method and a system for evaluating the sustainable development of a nature reserve. Based on the Net Primary Productivity (NPP) data of each type of land in the target naturereserve, the equilibrium factors and yield factors of each type of land are determined respectively, which fully reflects the differences among different types of land and overcomes the problem of parameter elasticity insufficiency in the existing ecological footprint method. At the same time, the per capita ecological footprint and per capita ecological carrying capacity of the target nature reserve are calculated based on the improved equilibrium factor and yield factor, according to the per capita ecological footprint and per capita ecological carrying capacity, the method and system can accurately and quantitatively evaluate the sustainable development status of the target nature reserves, help to determine whether the intensity of human activities in nature reserves exceeds the ecological carrying capacity, provide scientific basis for the management and decision-making of nature reserves, and provide guidance for promoting the construction of ecological civilization.
Owner:SATELLITE ENVIRONMENT CENT MINIST OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
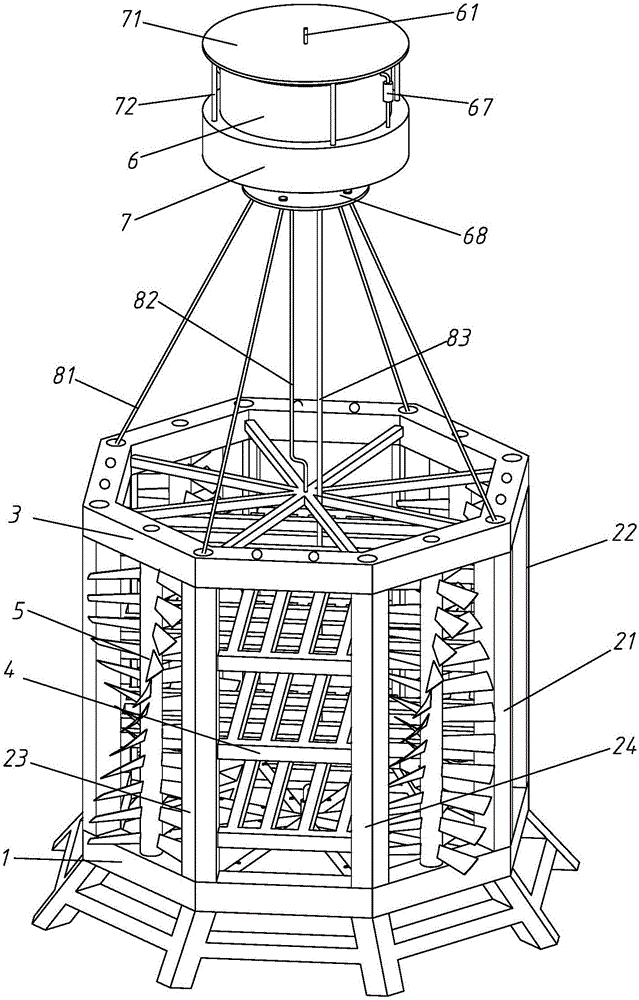
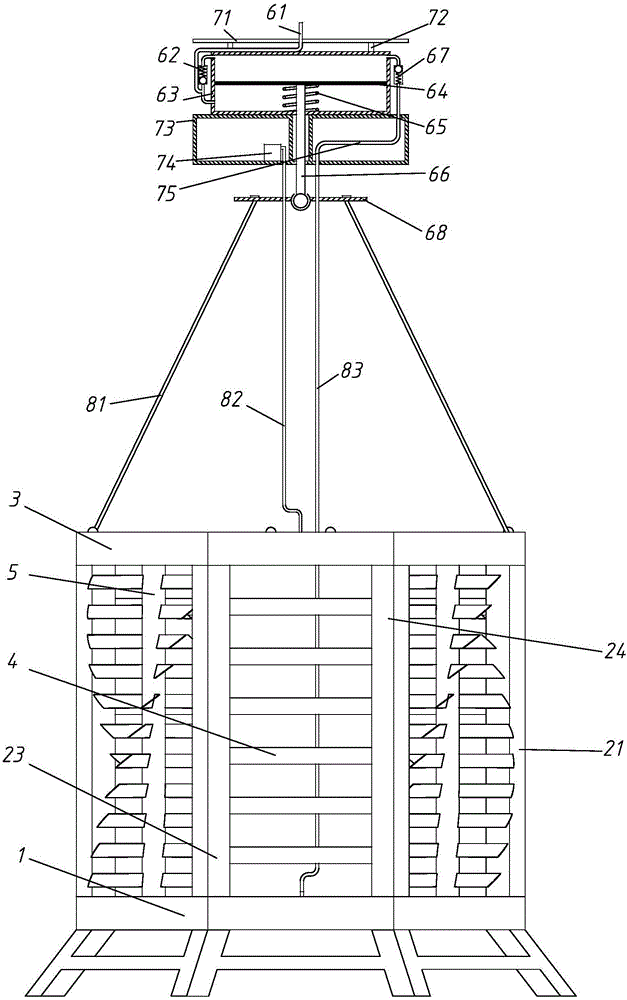
Artificial fish reef with impeller shafts
InactiveCN105850817AEasy to transportEasy to manufactureClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaImpellerEcological environment
The invention relates to an artificial fish reef with impeller shafts. The artificial fish reef with the impeller shafts is formed by a base, the impeller shafts, side plates and a top cover, can provide a place for breeding, growing and feeding fishes, meanwhile can effectively produce an upwelling, drives substances such as bottom nutritive salt to exchange with an upper water body, improves the ecological environment in a fish reef sea area, and provides sufficient baits for growing and breeding the fishes. At the same time, the rotation of the impeller shaft can also drive ventilation in the fish reef, and can effectively prevents the blockage of the fish reef during the application process; deflectors arranged on the side plates of the fish reef can also effectively guide an ocean current to flow upwards after passing through the fish reef so as to produce the upwelling, so that the primary productivity in adjacent sea areas of the fish reef is greatly improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
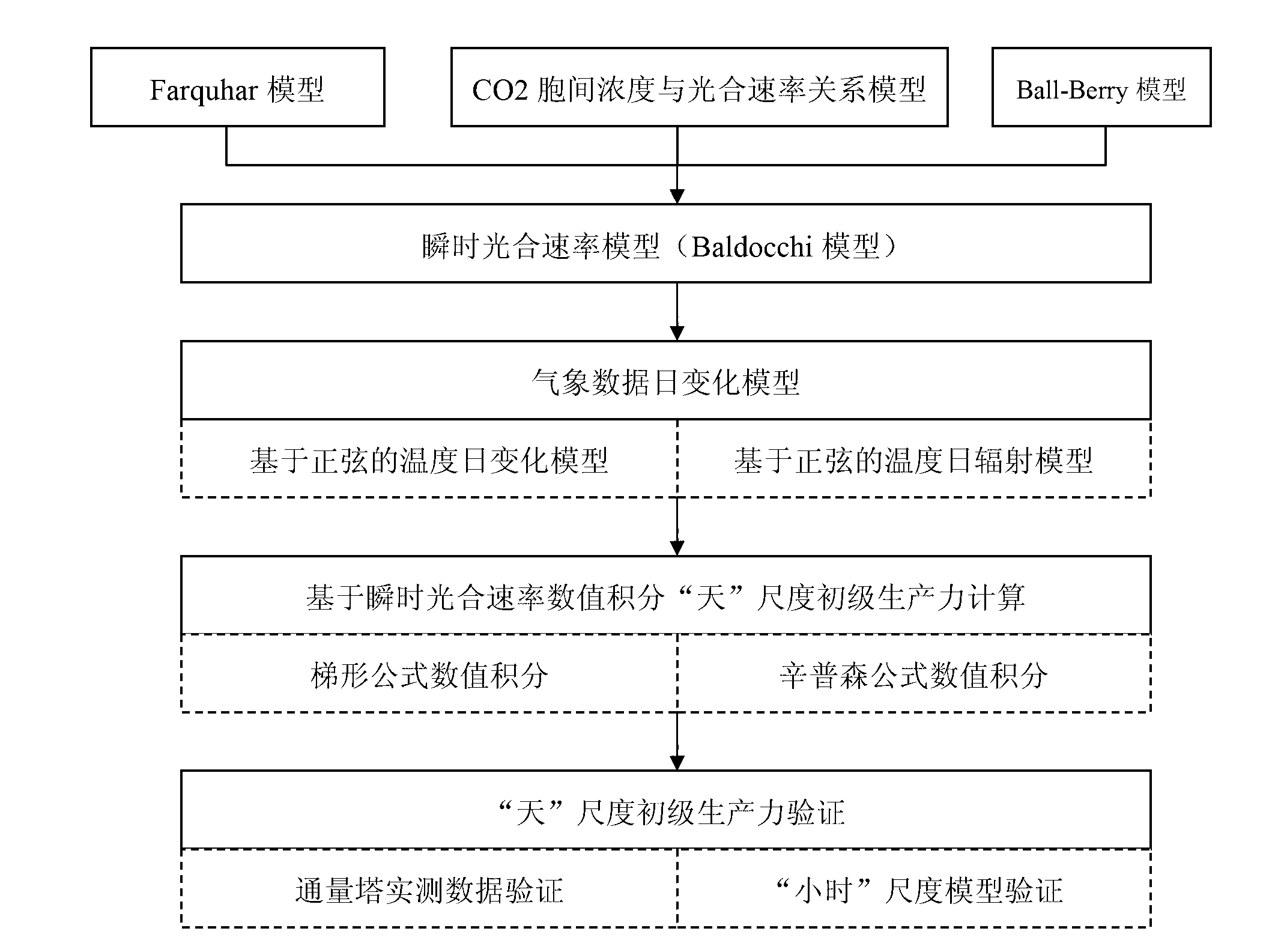
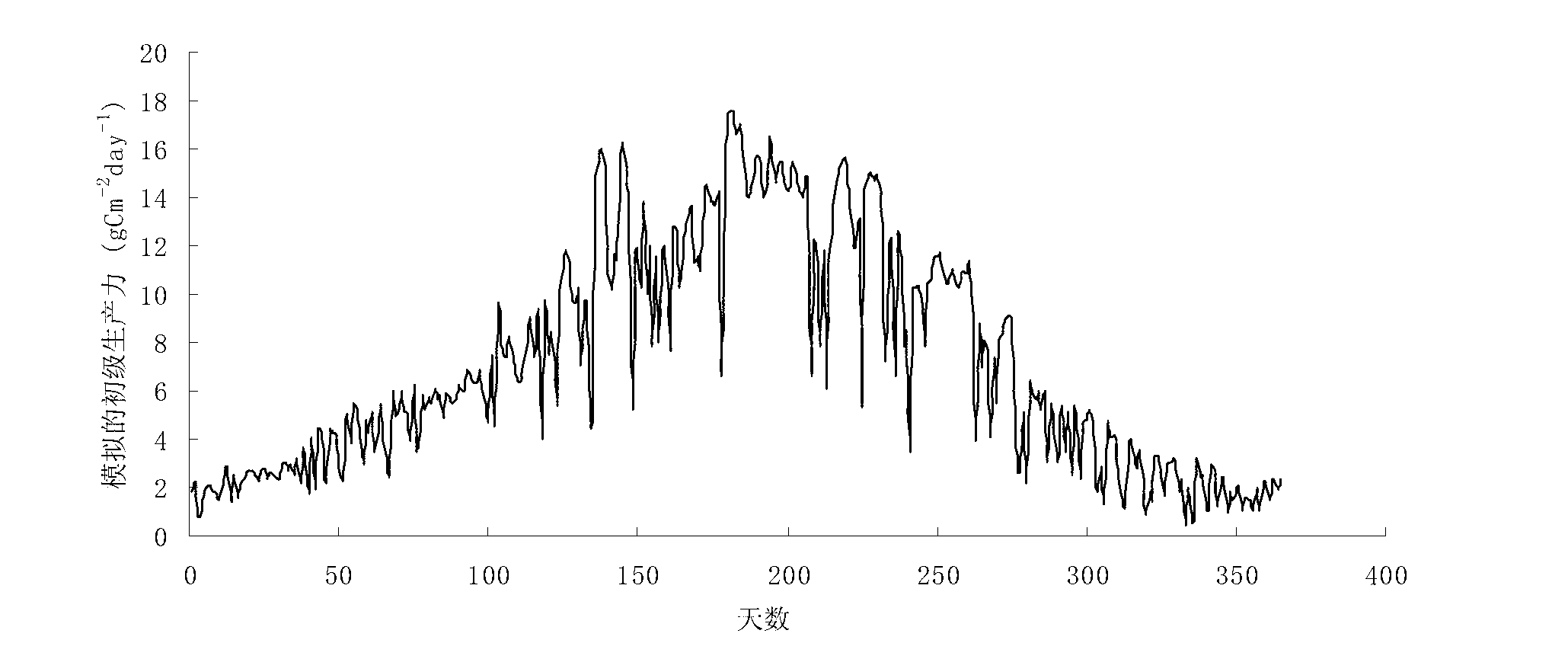
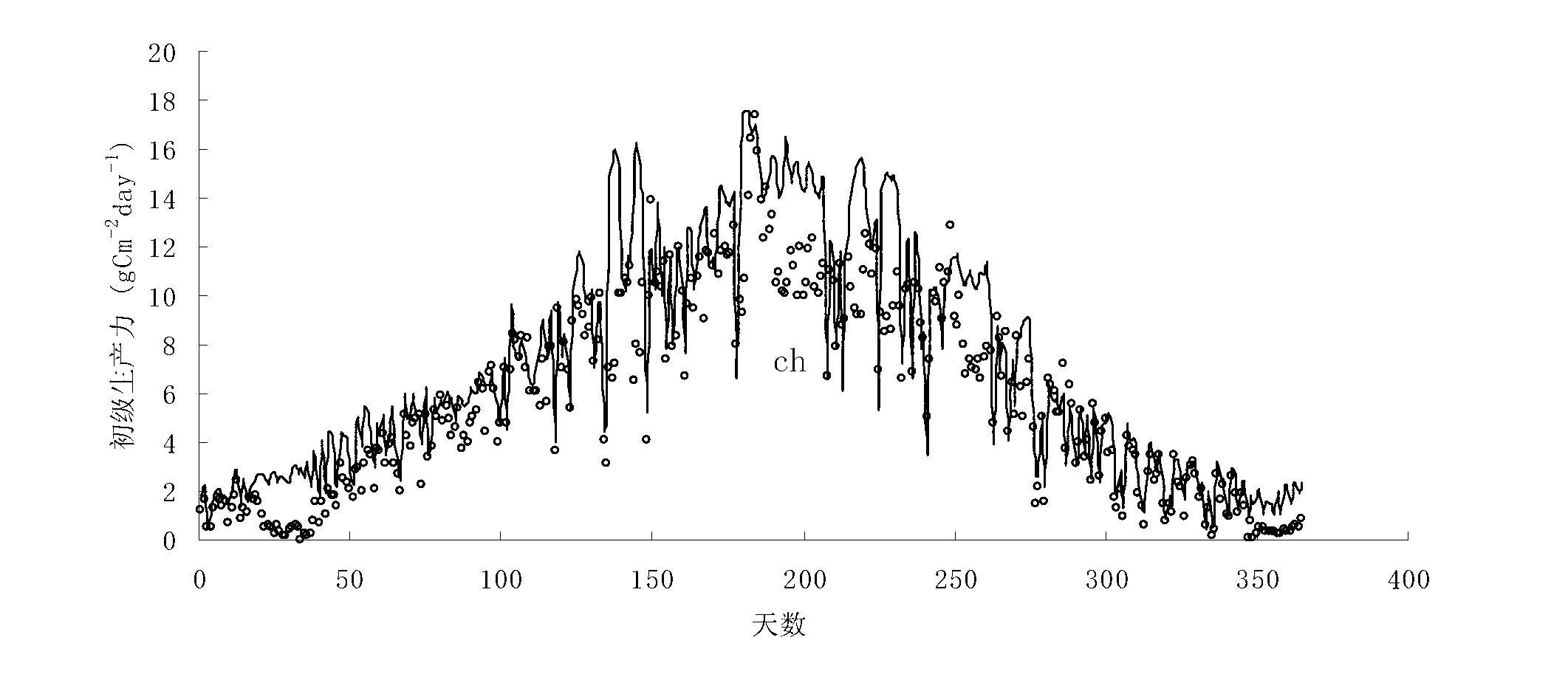
Day-scale primary productivity estimation method based on instantaneous photosynthetic rate integration
InactiveCN103020444AOptimization mechanismIncreased calculated clear heightSpecial data processing applicationsEstimation methodsPrimary productivity
The invention relates to a day-scale primary productivity estimation method based on instantaneous photosynthetic rate integration, and the method comprises the following steps of (1) calculation of instantaneous photosynthetic rate: establishing a cubic equation through a relationship formula among the coupled instantaneous photosynthetic rate, intercellular carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration and stomatal conductance, and calculating the instantaneous photosynthetic rate; (2) simulation of instantaneous weather data: simulating the instantaneous weather by utilizing a sinusoidal function through the characteristic that the temperature and radiation diurnal variation follows the sinusoidal variation principle; and (3) calculation of day-scale primary productivity integration: substituting the instantaneous photosynthetic rate solved in the step (1) in the simulated weather data to form a function adopting the time as a variable, utilizing a trapezoid or simpson formula to integrate the time, and acquiring the day-scale primary productivity. By utilizing the diurnal variation principle characteristics of the weather data and combining the instantaneous photosynthetic rate calculation formula, the measurement precision is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
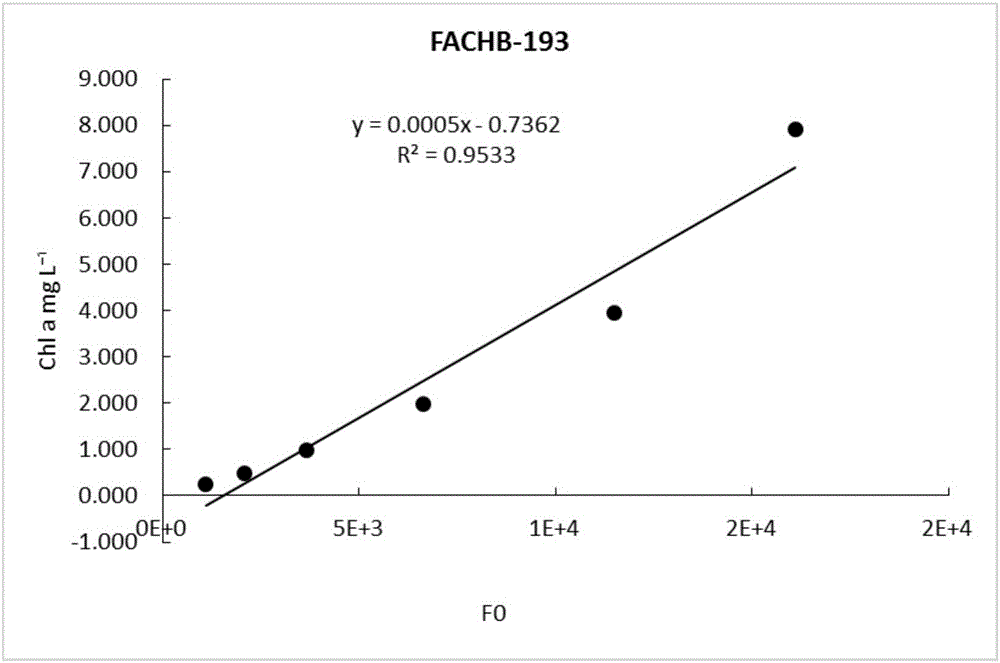
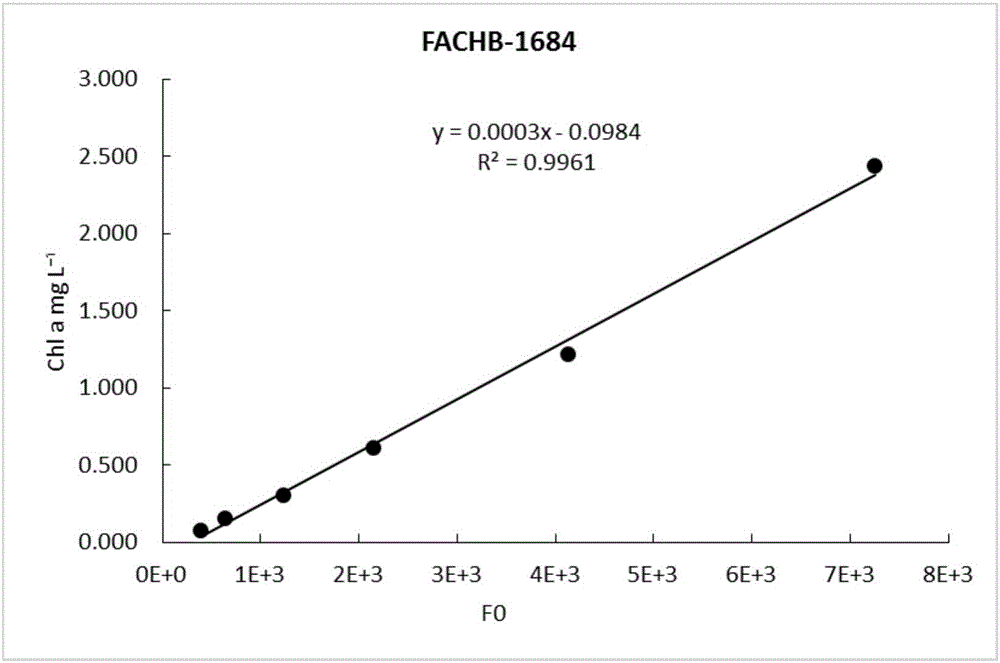
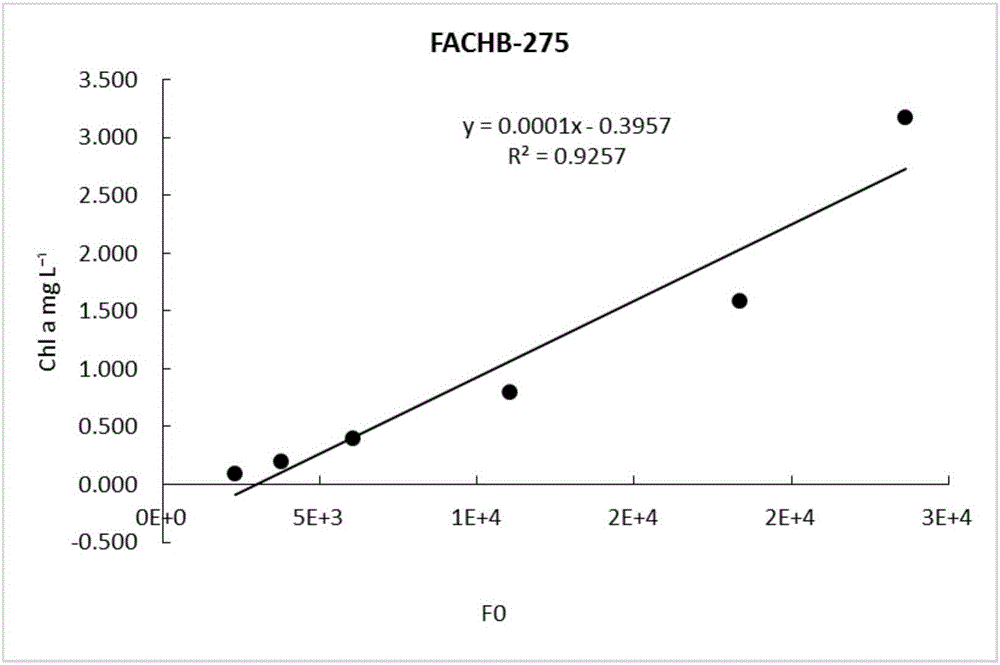
Method for measuring Fo so as to estimate primary productivity of water body
InactiveCN105759003ASimple and quick determinationAccurate calculation of primary productivityTesting waterChlorophyll aPrimary productivity
The invention provides a method for measuring Fo to represent chlorophyll a content. The method comprises the following steps: establishing an Fo-chlorophyll a content coherency equation; measuring the Fo of a sample; substituting the Fo into the obtained equation, and calculating the chlorophyll a content. The invention further provides a method for estimating primary productivity of a water body, and the method comprises the step of substituting the chlorophyll a content obtained in the previous method into an equation of P=K.r.c (Chla).DH so as to obtain the primary productivity of the water body. The method further provides a method for measuring algae cell density, and the method comprises the following steps: establishing an Fo-algae cell density coherency equation; measuring the Fo of a sample; substituting the Fo into the obtained equation, and calculating the algae cell density. By adopting all the methods, chlorophyll content and algae cell density in a photosynthetic microalgae culture solution, an aquaculture water body or a natural water body can be easily measured, the primary productivity in the aquaculture water body or the natural water body can be easily estimated, the health level of the water body is assessed, and further a necessary basis is provided for aquaculture, environment monitoring and the like.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
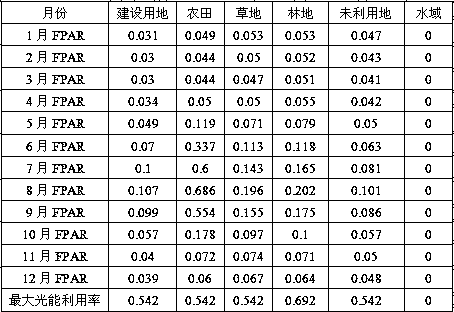
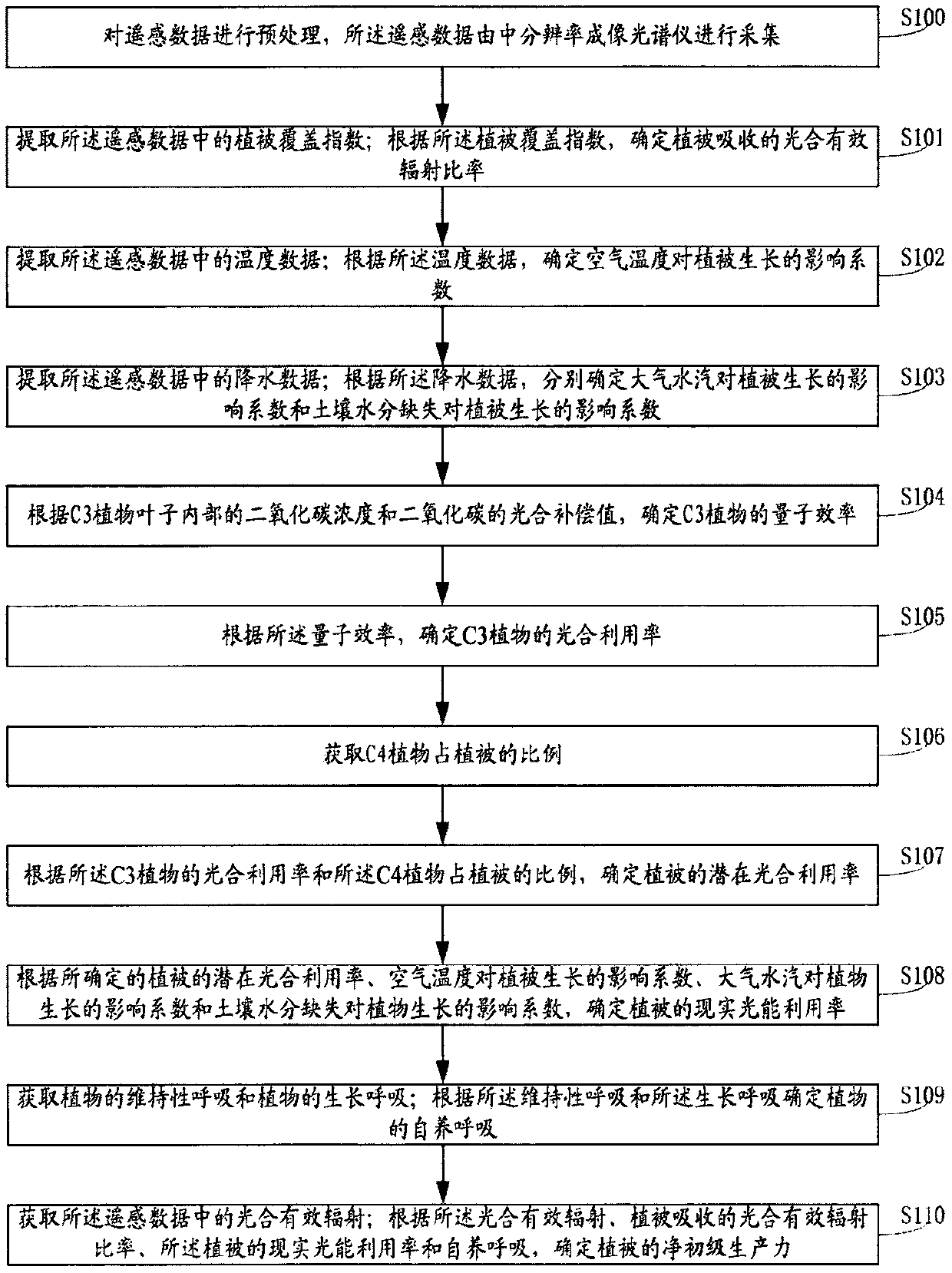
Remote sensing estimation method for net primary productivity of vegetation
ActiveCN110443504AImprove estimation accuracyImprove efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionColor/spectral properties measurementsLight energyPlant growth
The invention discloses a remote sensing estimation method for net primary productivity of vegetation. The method comprises the steps of determining a photosynthetically active radiation ratio absorbed by vegetation according to a vegetation coverage index in remote sensing data; according to temperature data, rainfall and other data in the remote sensing data, determining the potential photosynthetic utilization rate of vegetation, the influence coefficient of air temperature on vegetation growth, the influence coefficient of atmospheric water vapor on plant growth and the influence coefficient of soil moisture loss on plant growth, and then determining the actual light energy utilization rate of the vegetation; then, after the maintenance respiration of the plant and the growth respiration of the plant are obtained, determining the autotrophic respiration of the plant; then, after photosynthetically active radiation in the remote sensing data is obtained, the net primary productivityof the vegetation can be determined and obtained in combination with the photosynthetically active radiation ratio absorbed by the vegetation, the actual light energy utilization rate of the vegetation and autotrophic respiration. The remote sensing estimation method for net primary productivity of vegetation has the characteristics of high estimation precision and high estimation efficiency.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Marine ranch developing pattern
ActiveCN109349165AImprove fertilityIncrease production capacityPV power plantsClimate change adaptationElectric power systemPrimary productivity
The invention discloses a marine ranch developing pattern, and belongs to the technical field of facility culturing engineering. A fine culturing region is included, a photovoltaic generator unit anda wind power generator unit are arranged on shores of the two sides of the fine culturing region, a pile-type enclosing net is arranged in the outer circumference of the fine culturing region, a raft-type culturing group is arranged on the left side of the fine culturing region, and an artificial fish reef group is arranged on the right side of the fine culturing region. According to the pattern,a complete power system, culturing system and management system are constructed, a marine ranch is divided into two regions, a stocking pattern on land is achieved, and the arranged fish reef group can provide a sheltering place for fish to help to improve water body fertility and primary productivity level.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com