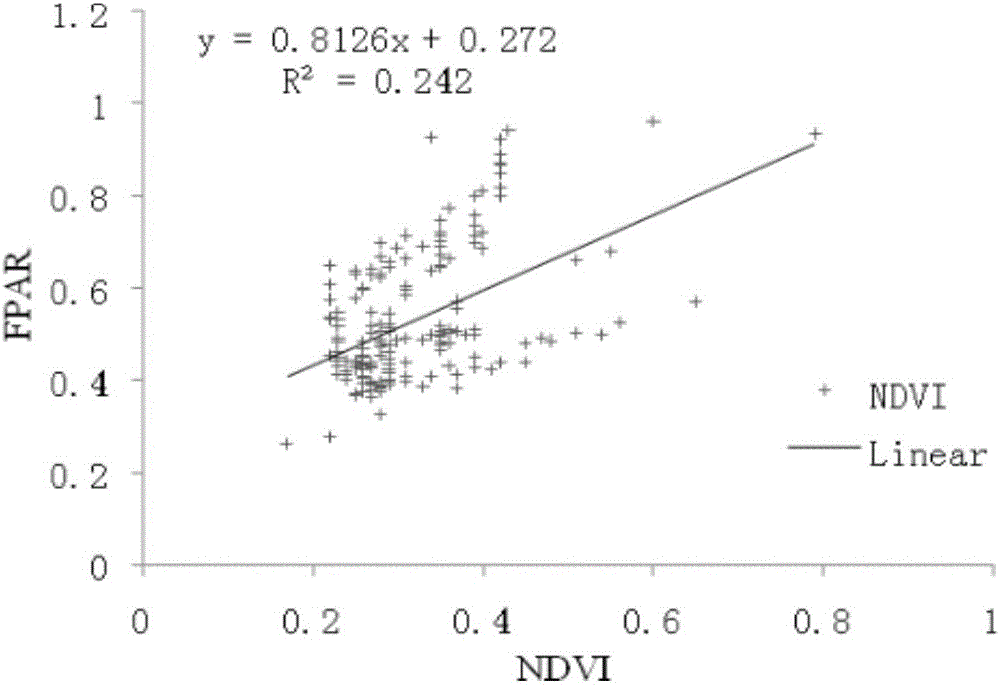
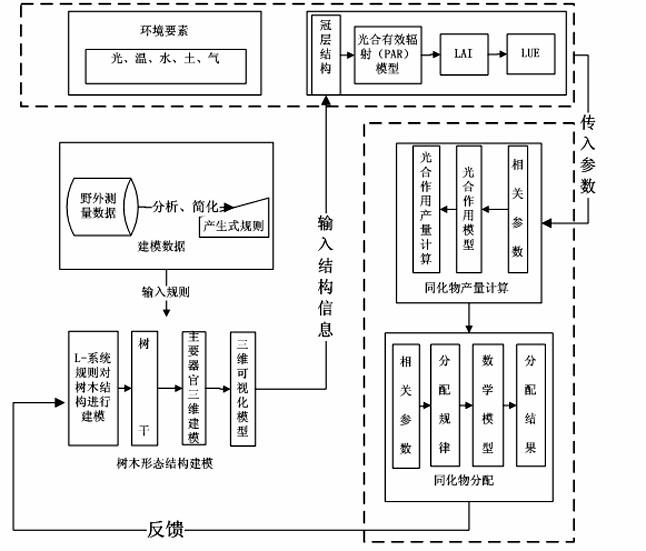
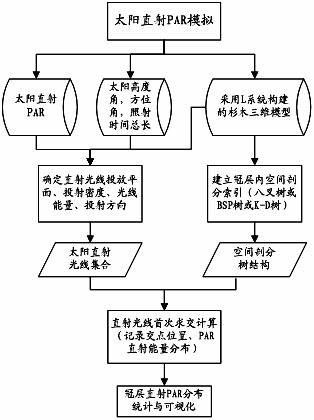
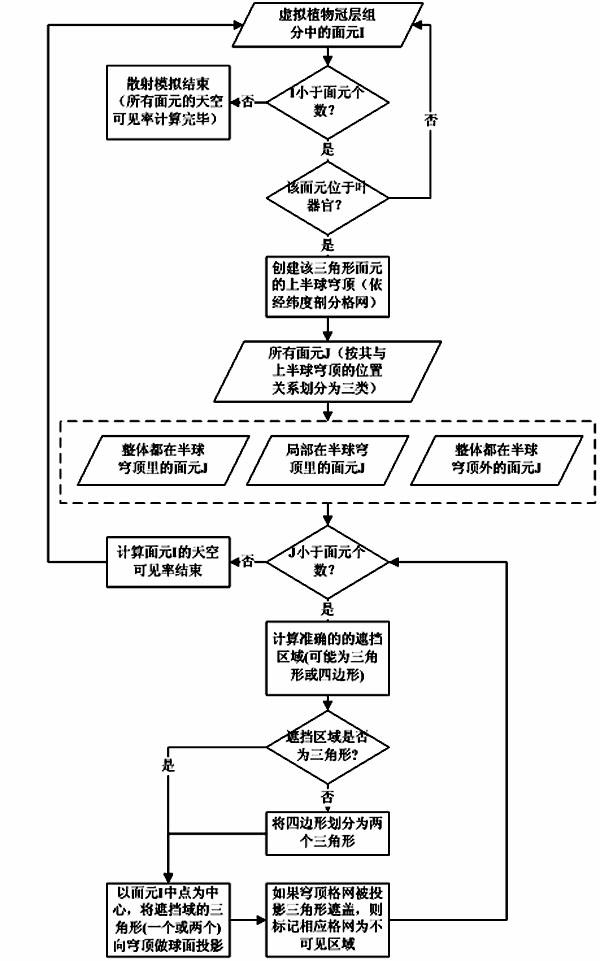
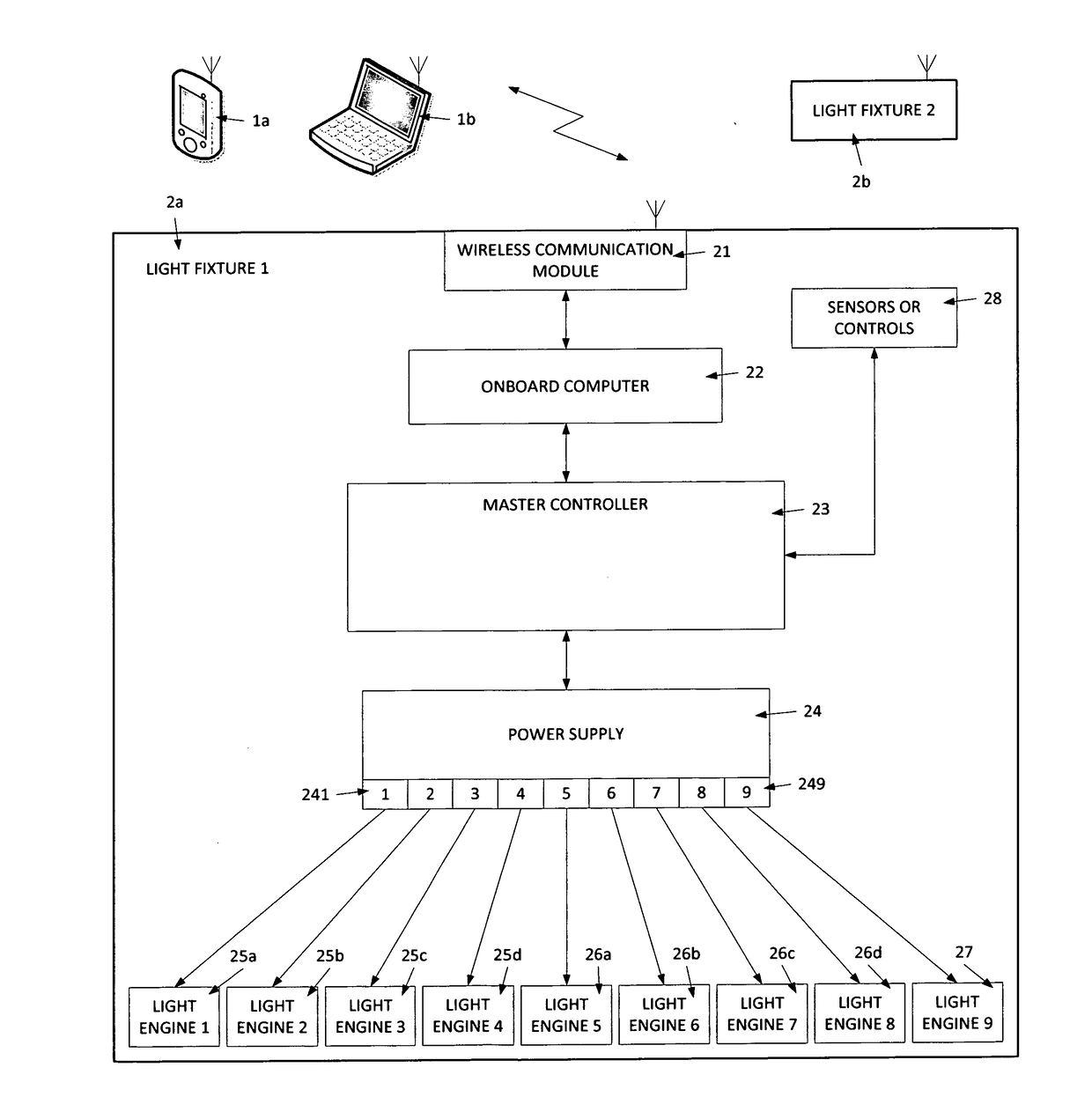
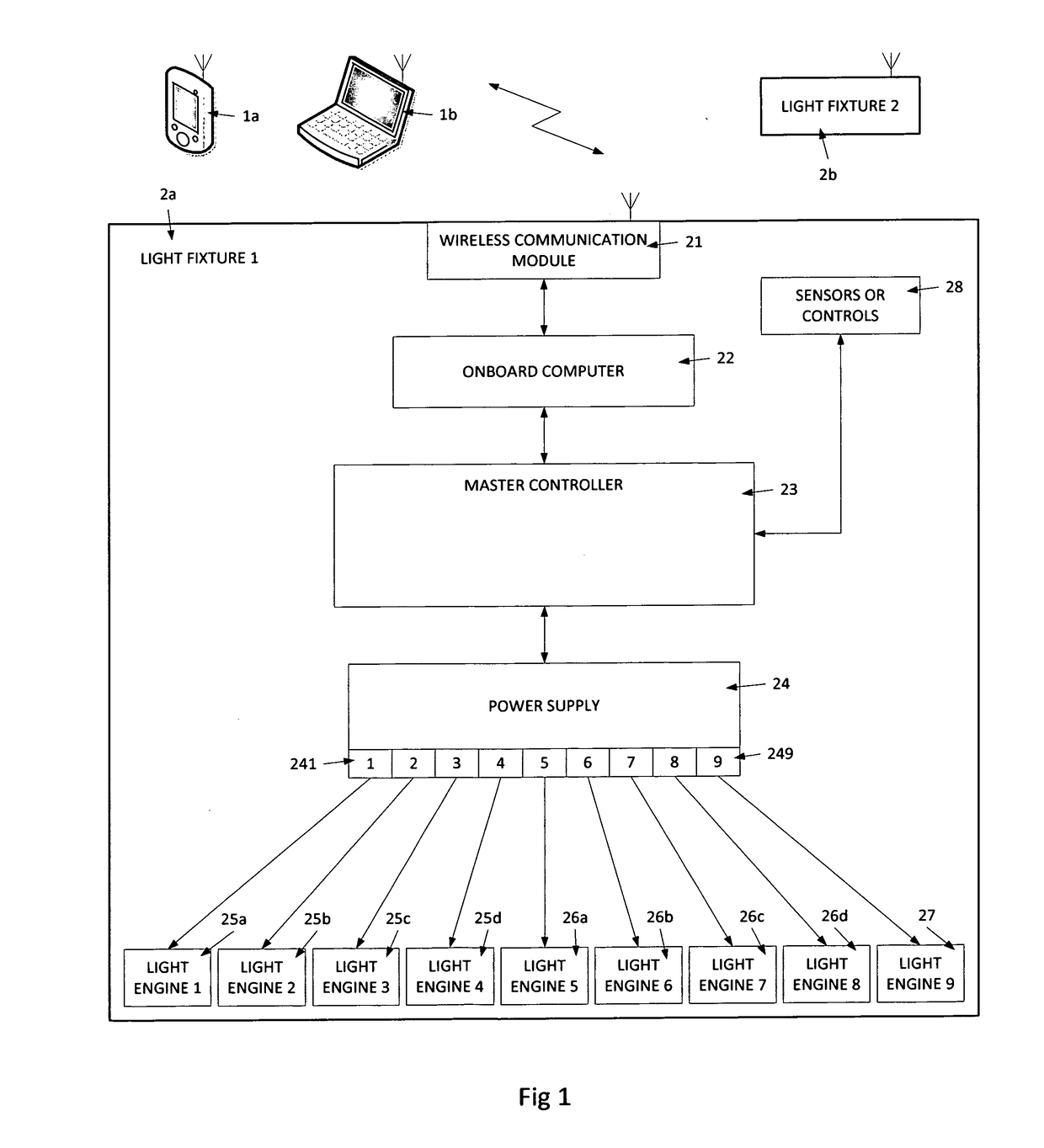
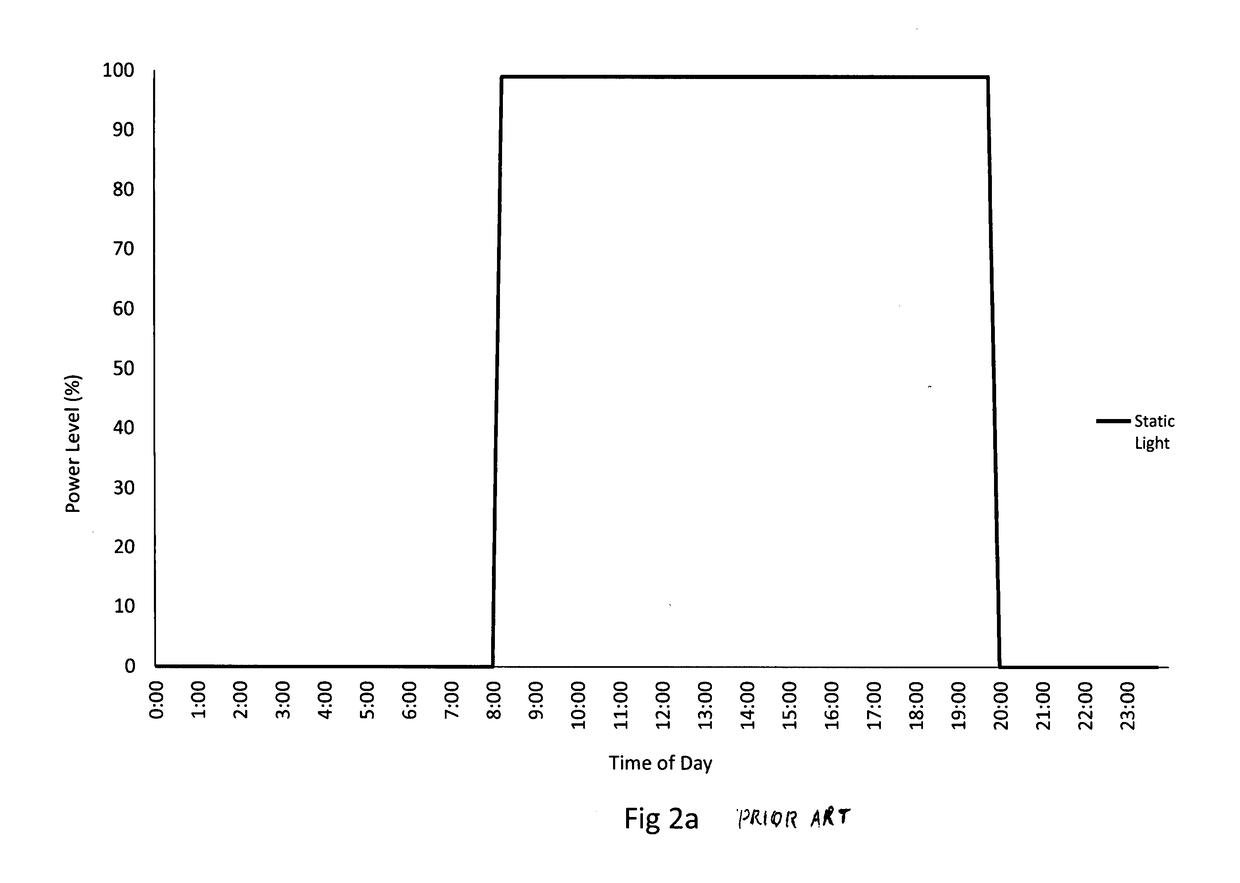
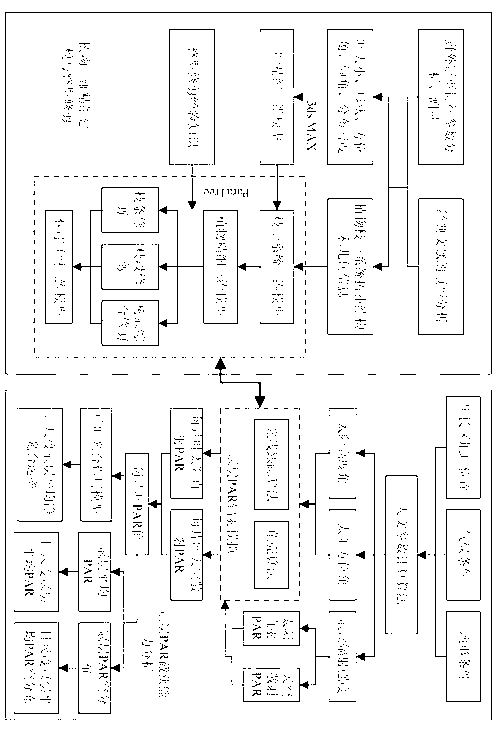
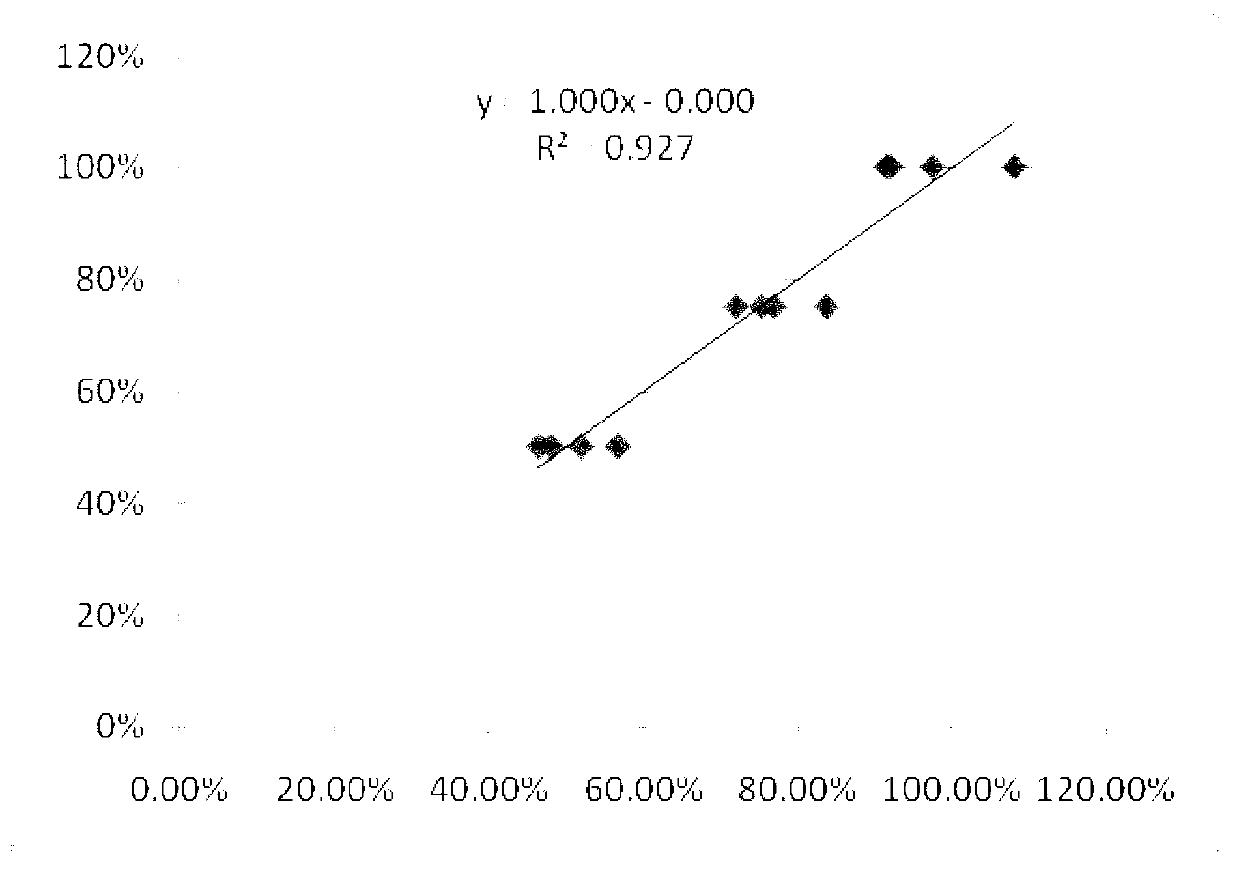
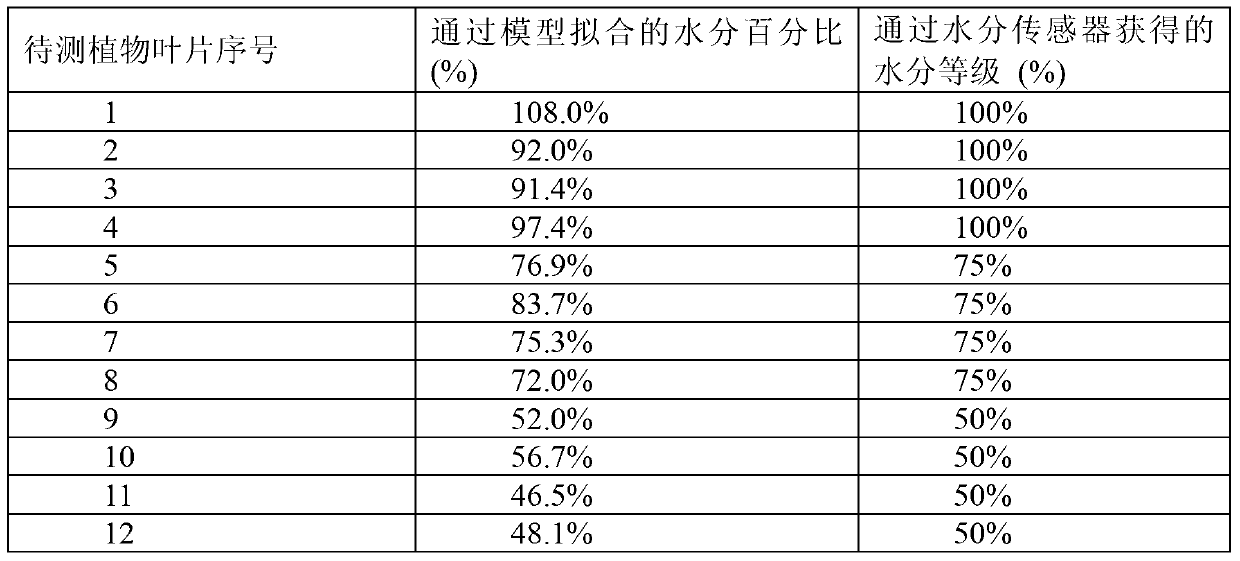
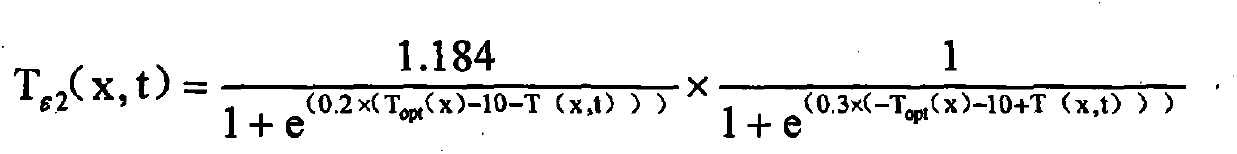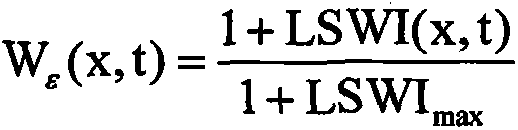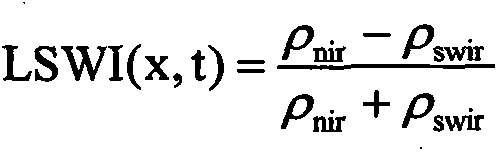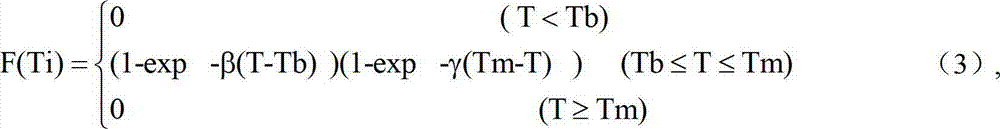Patents
Literature
134 results about "Photosynthetically active radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
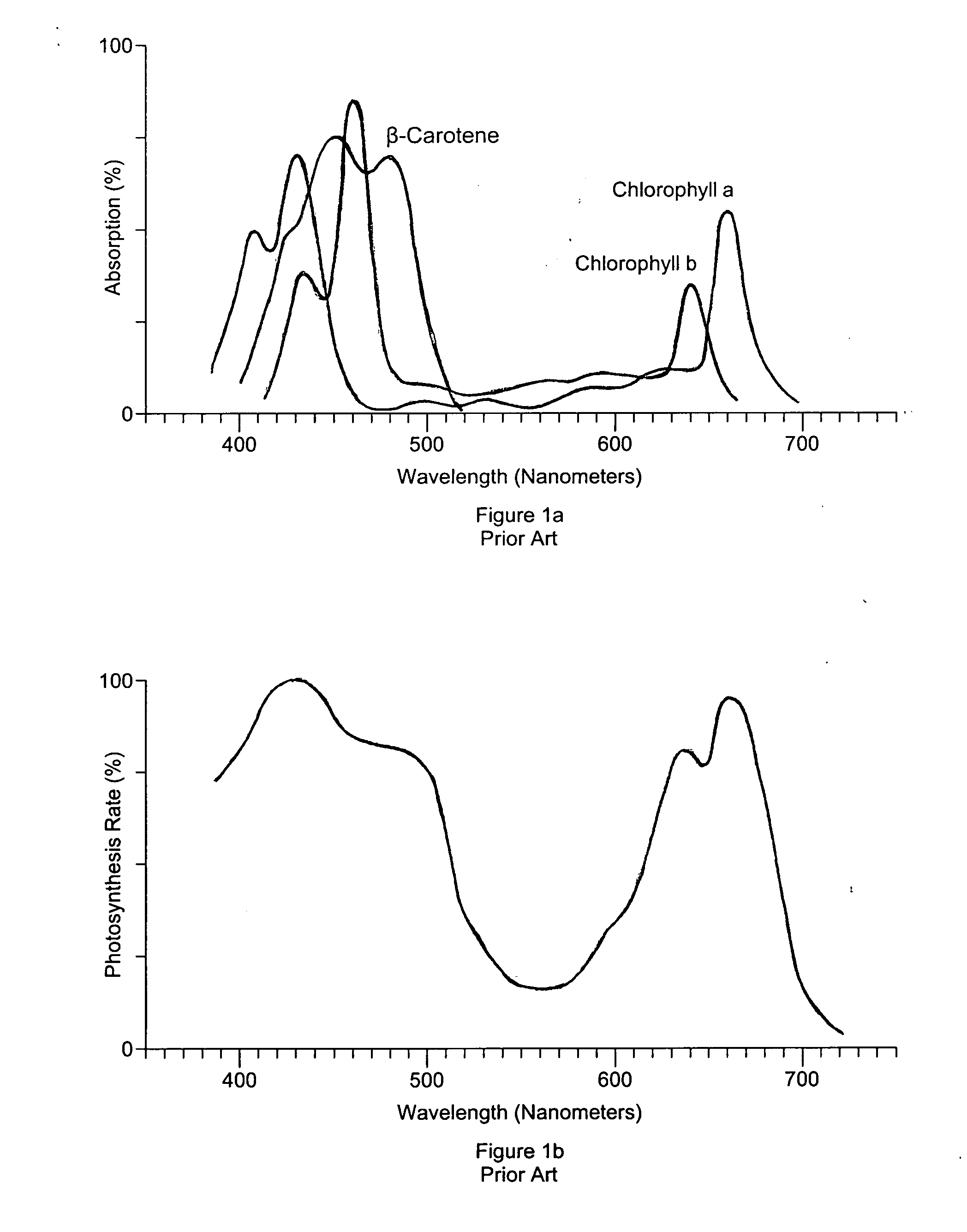
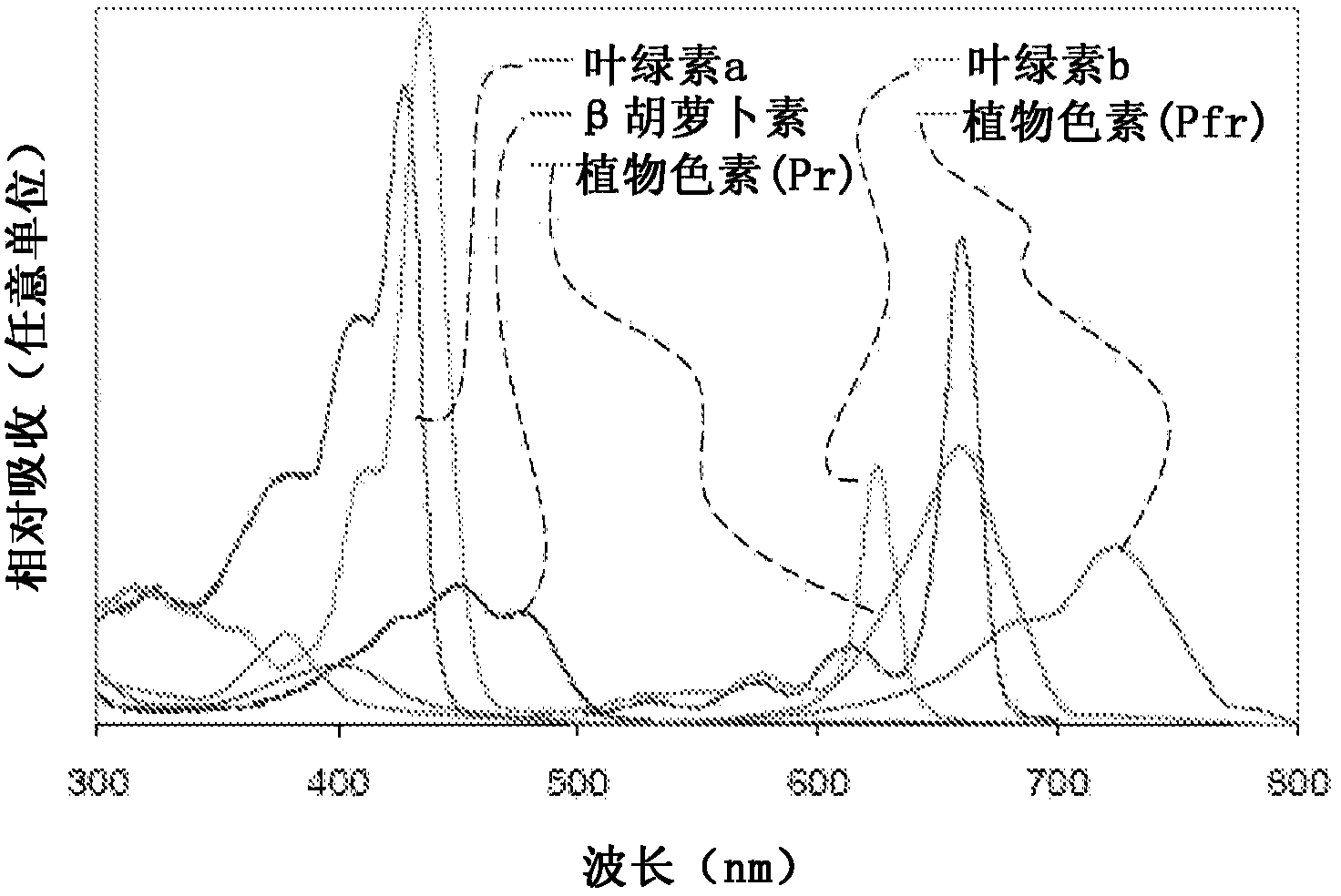
Photosynthetically active radiation, often abbreviated PAR, designates the spectral range (wave band) of solar radiation from 400 to 700 nanometers that photosynthetic organisms are able to use in the process of photosynthesis. This spectral region corresponds more or less with the range of light visible to the human eye. Photons at shorter wavelengths tend to be so energetic that they can be damaging to cells and tissues, but are mostly filtered out by the ozone layer in the stratosphere. Photons at longer wavelengths do not carry enough energy to allow photosynthesis to take place.
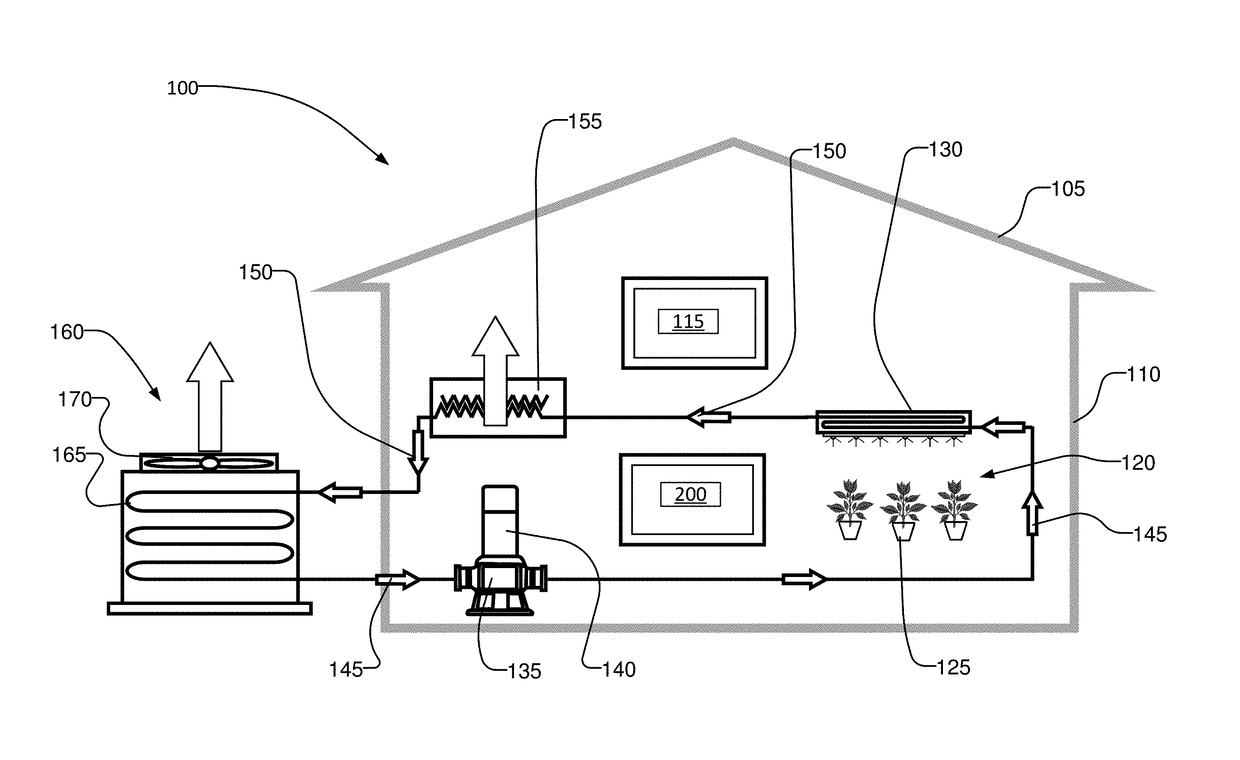
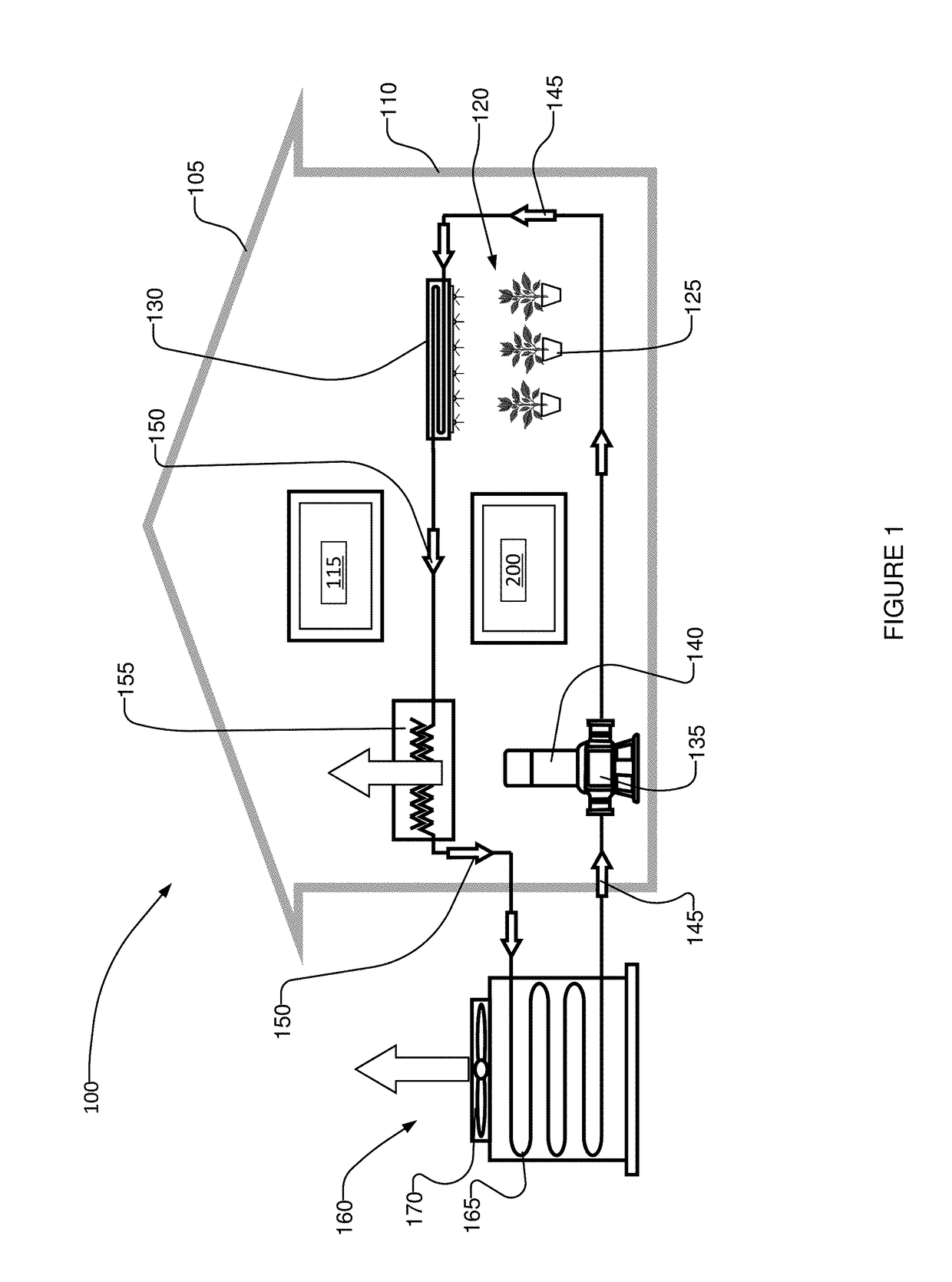
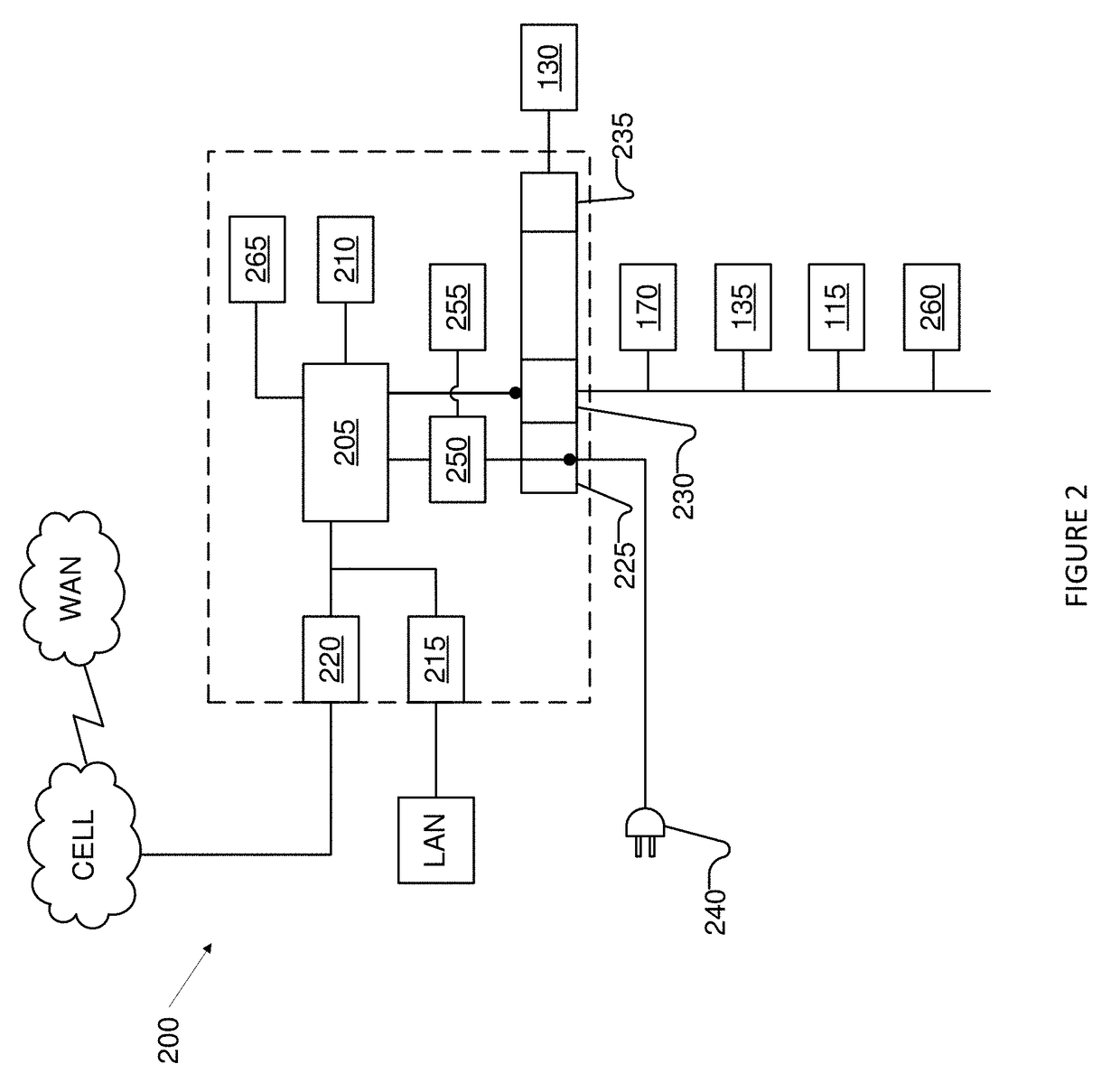
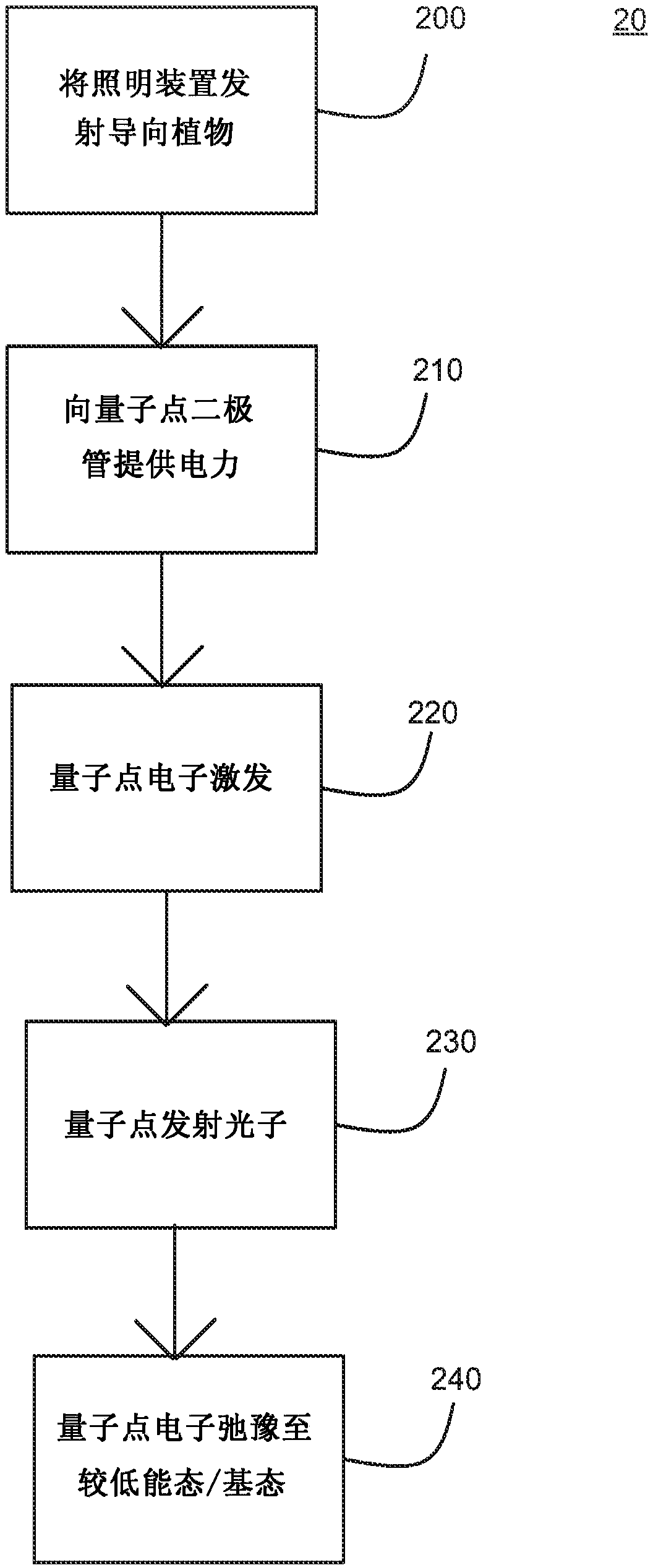
LED lighting system and opertaing method for irradiation of plants
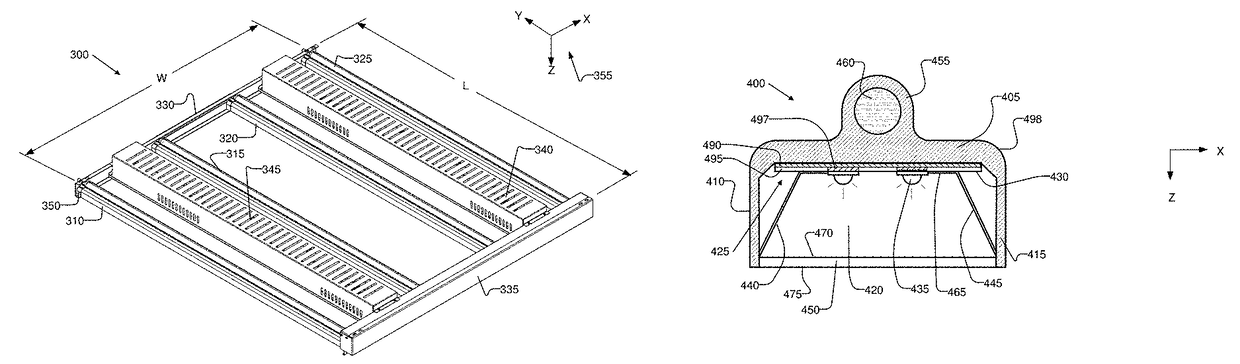
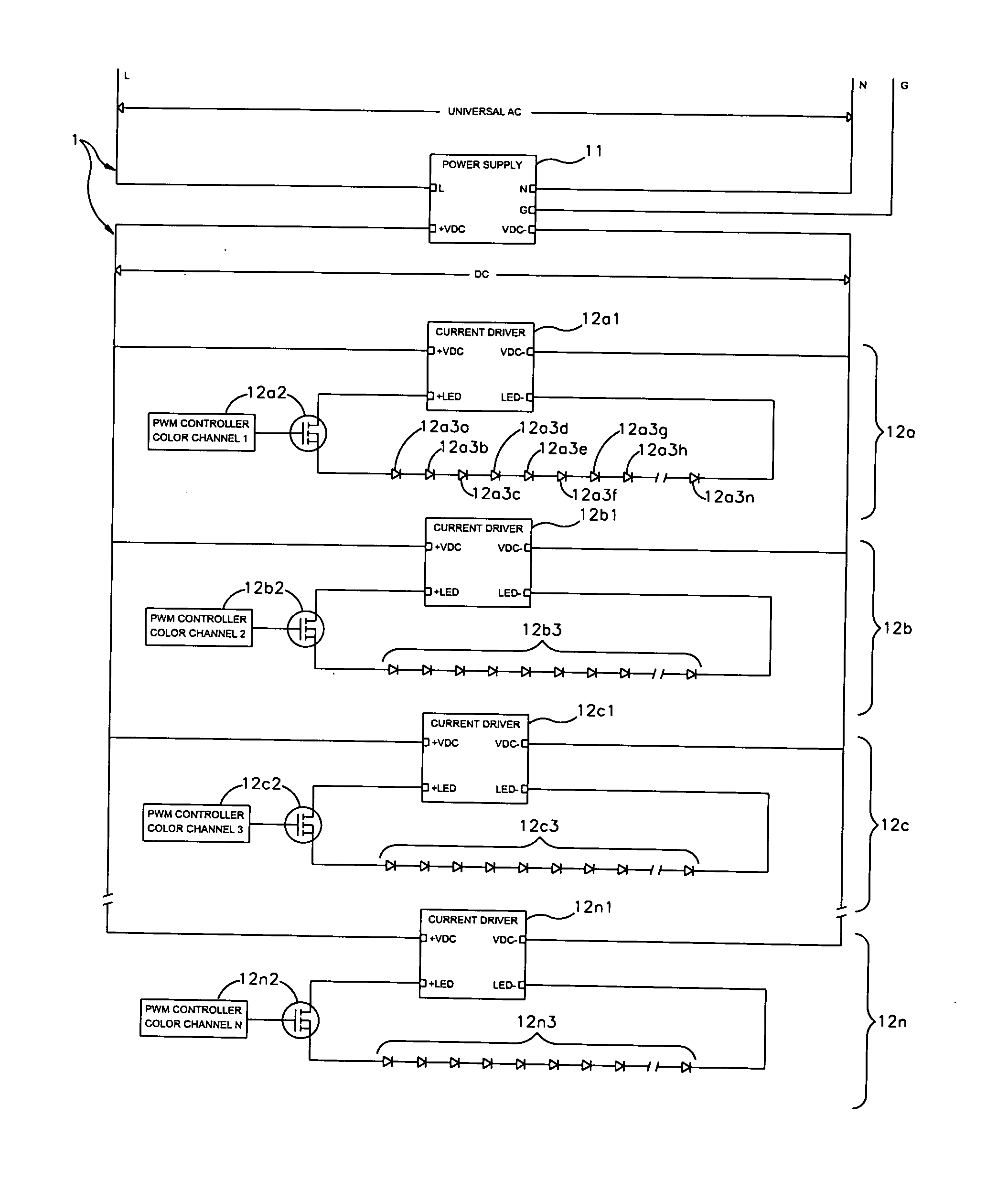
An LED illumination system is operable to irradiate plant materials with photosynthetically active radiation. A lighting assembly includes a plurality of different LED types. Each LED lamp has a different spectral power matched to an absorption peak of the plant materials. All of the LED lamps of each different lamp type are driven by a different dedicated power source. Each power source can be independently modulated to vary the collective spectral power output of the LED illumination system. The lighting assembly includes fluid conduits disposed proximate to the LED lamps and a cooling fluid is flowed through the fluid conduits to removed thermal energy from the LED lamps.
Owner:ADAPTIIV GROW TECH INC
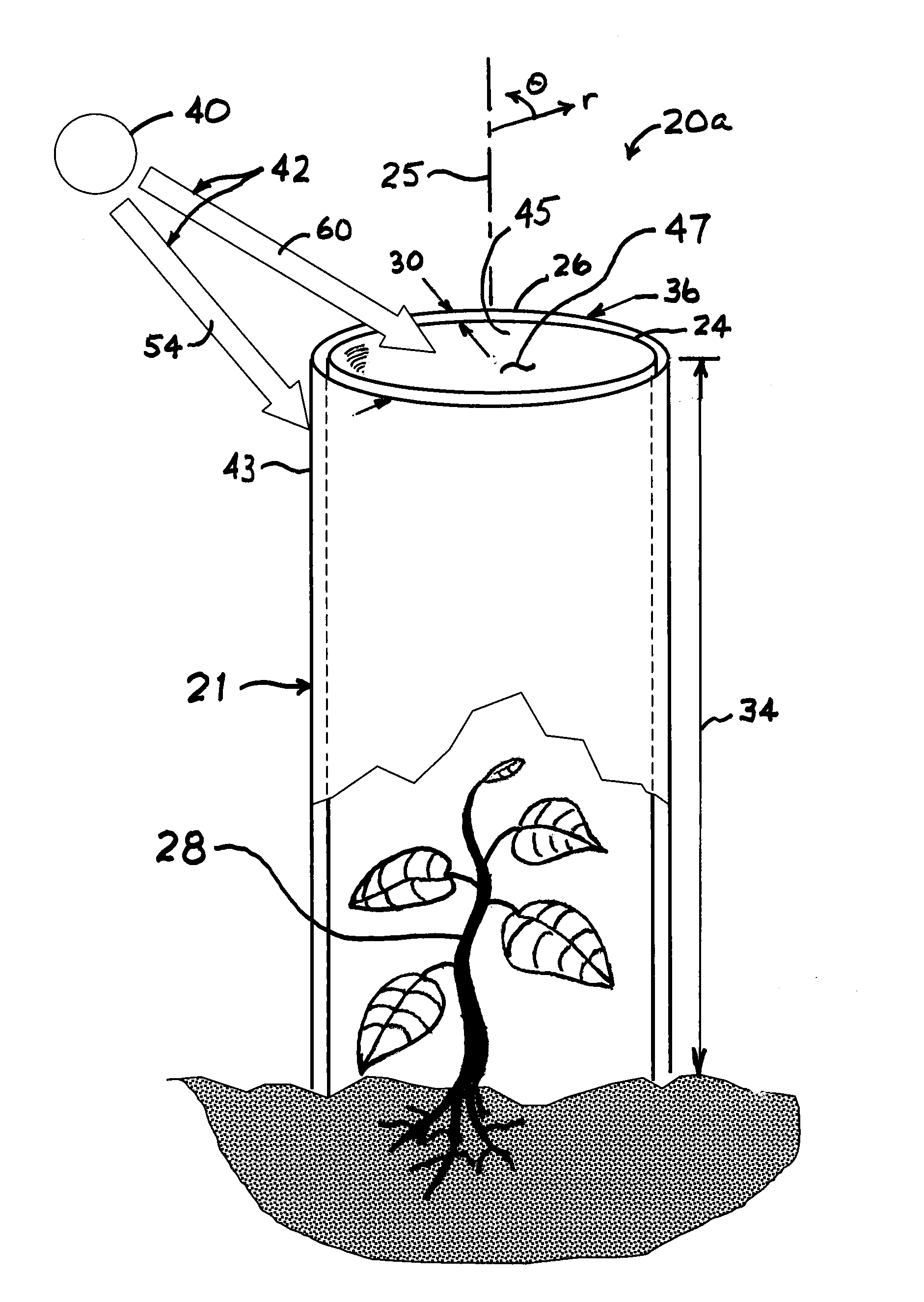
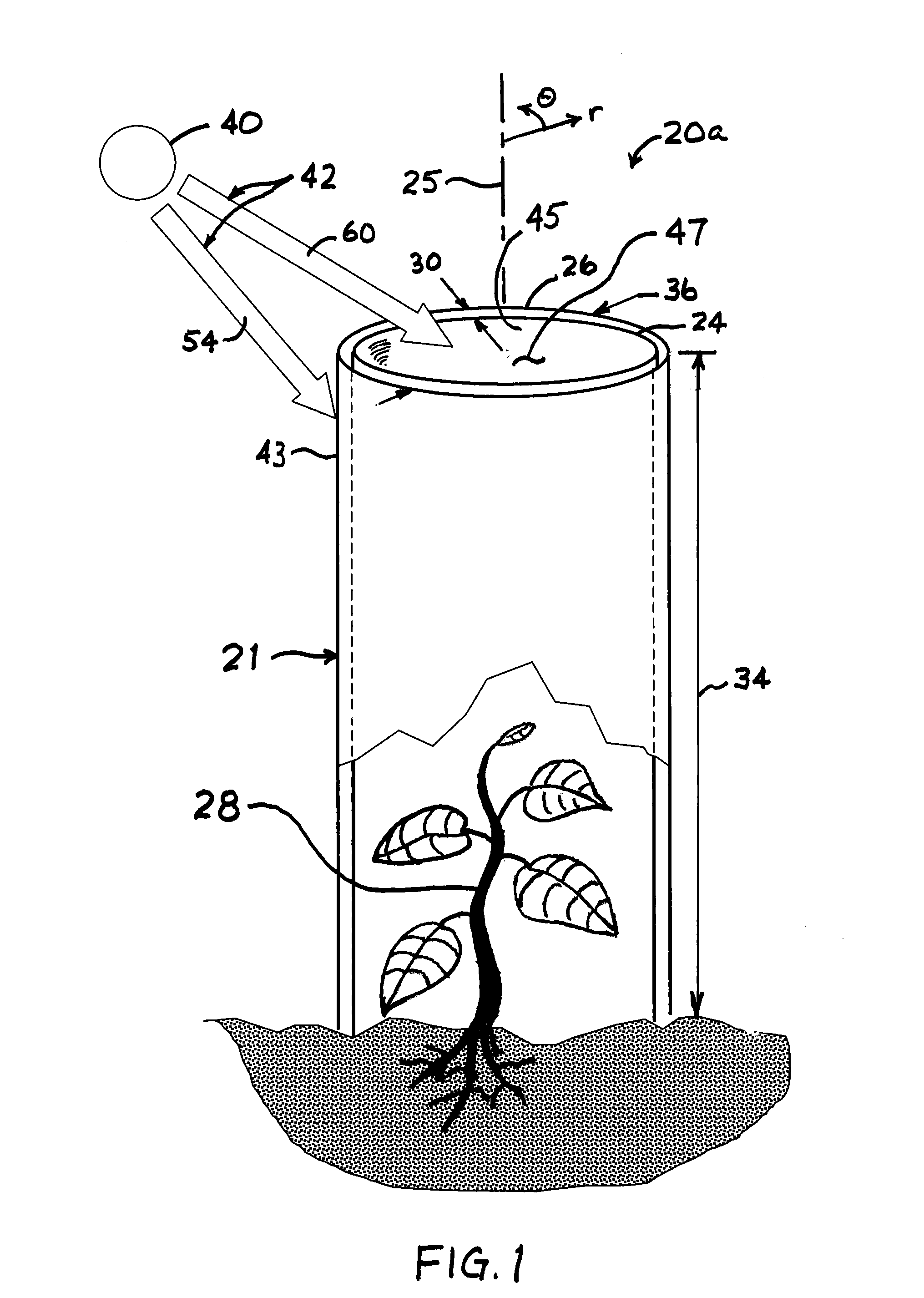
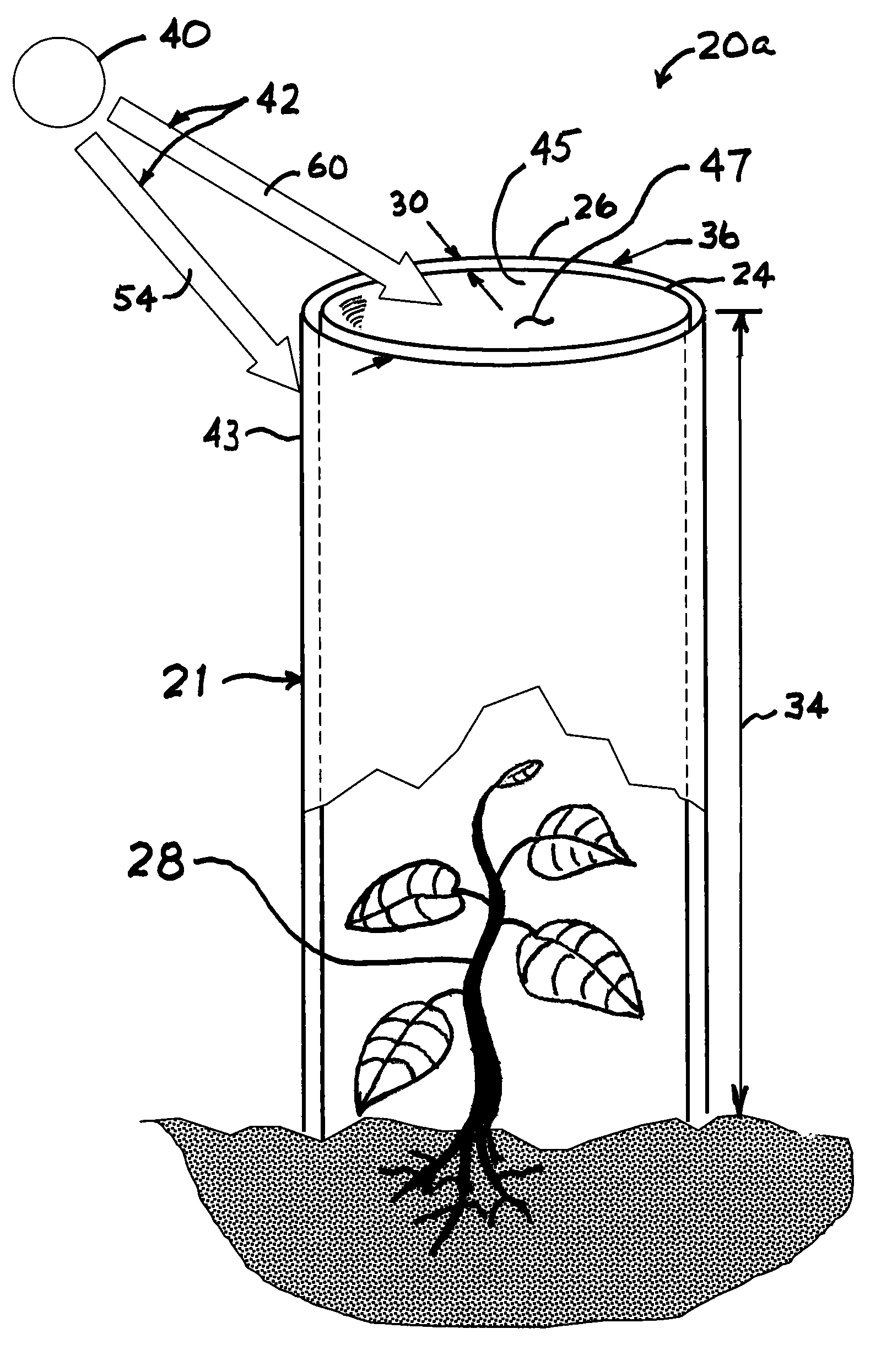
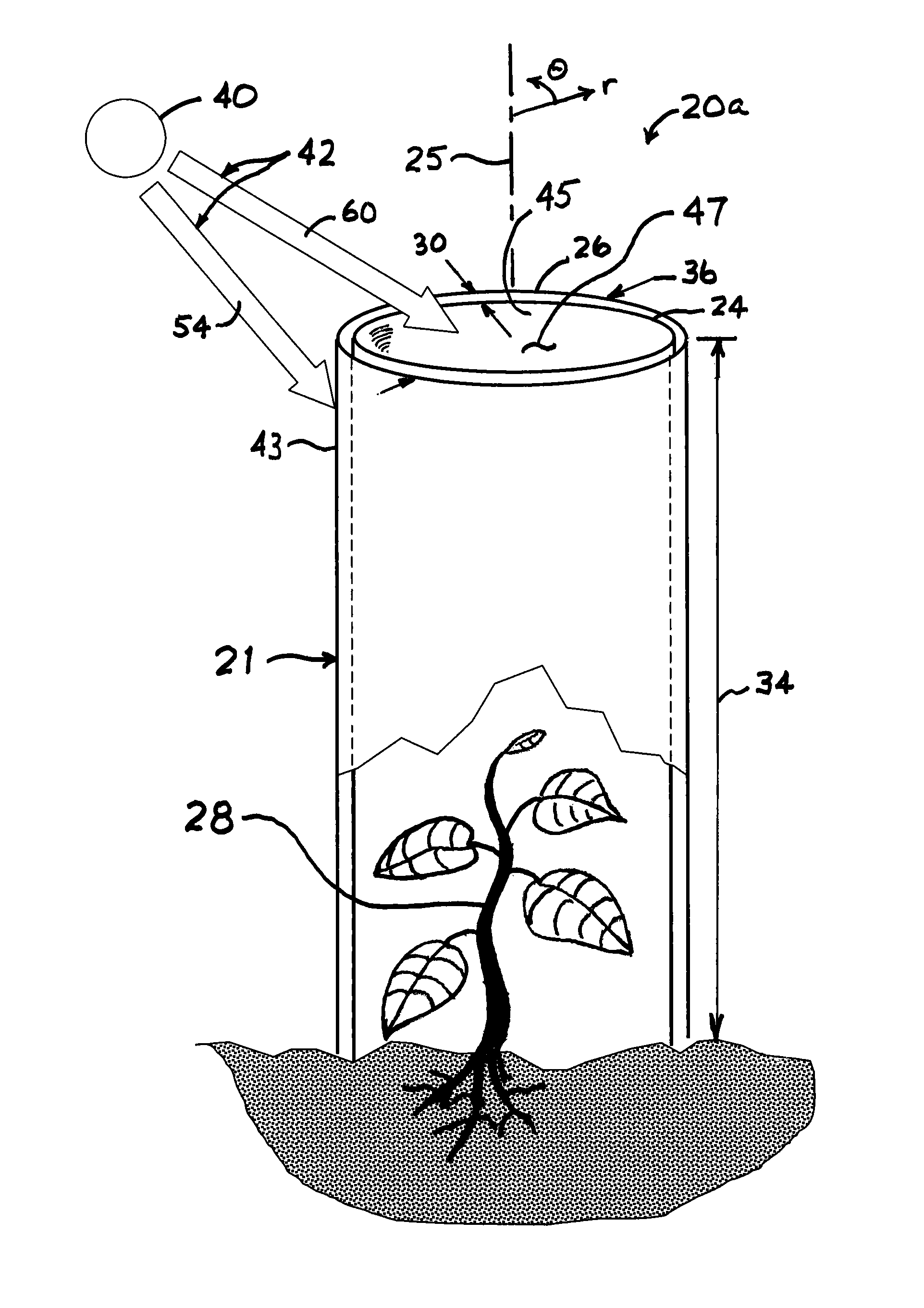
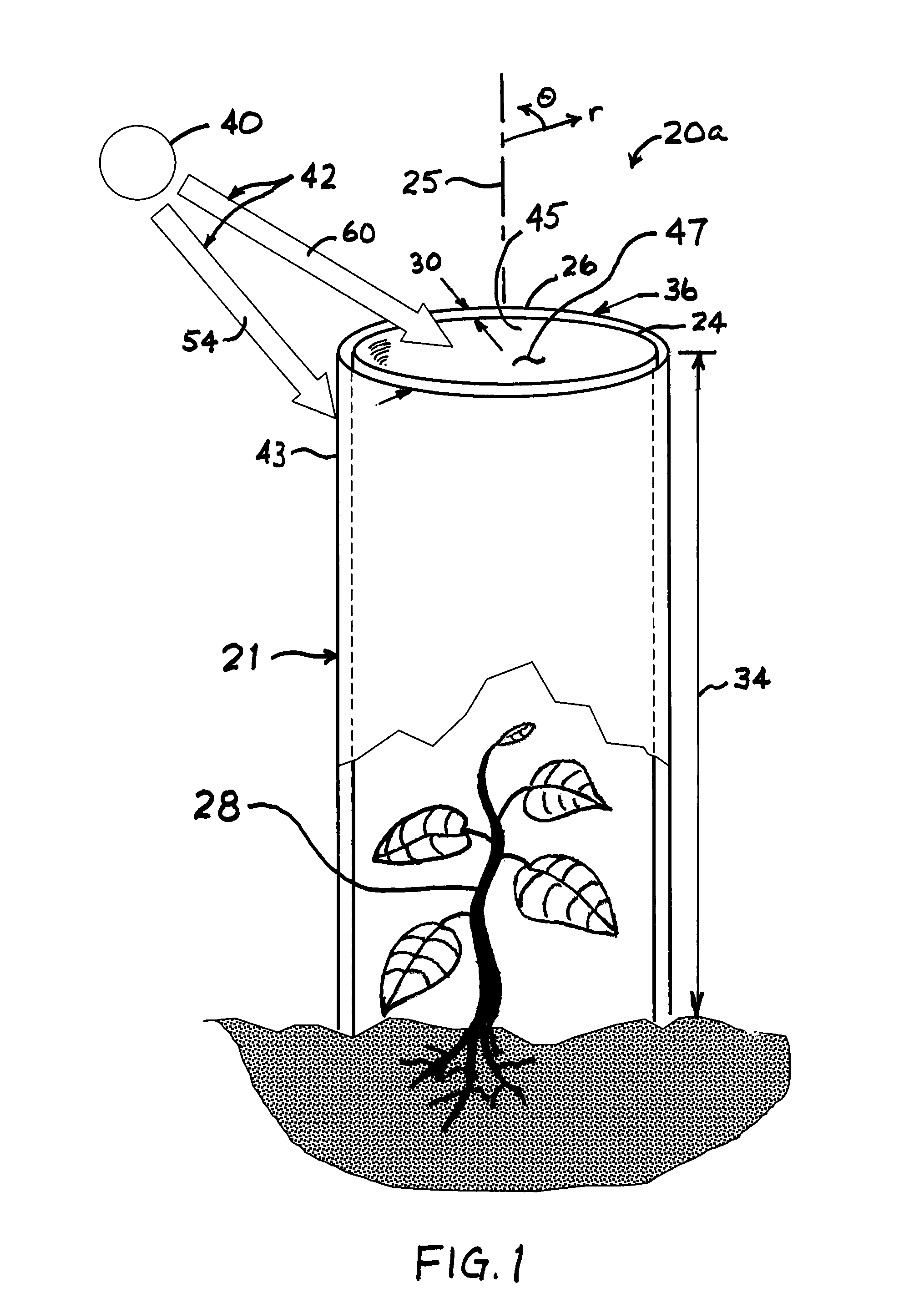
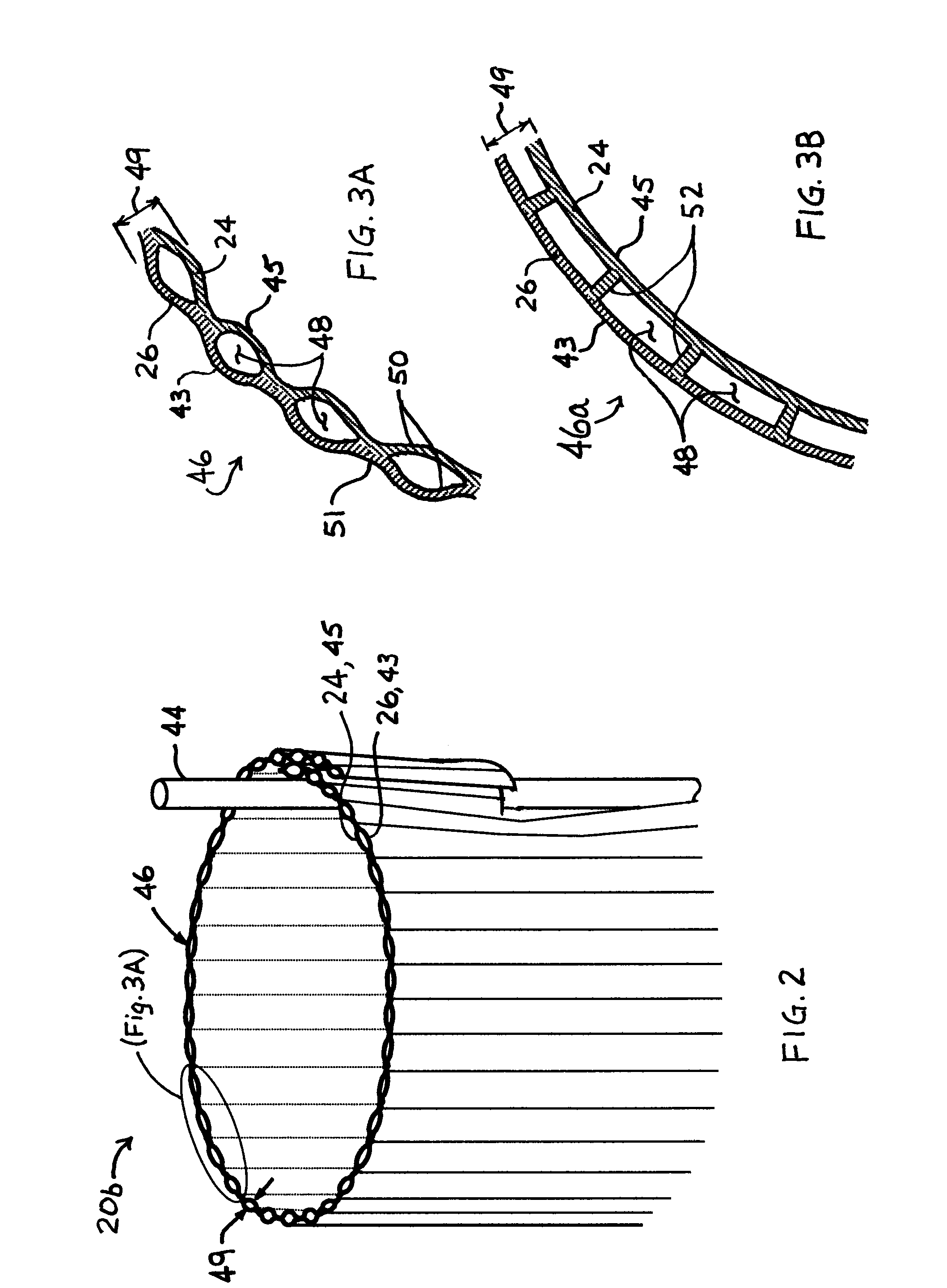
Spectrally selective grow tube
InactiveUS20100299993A1Improve scalabilityReduce escapeSeed and root treatmentPlant phenotype modificationOrganismBiology
A biodegradable spectrally selective grow tube or tree shelter that improves the establishment of woody plant forms by reduction and / or elimination of certain biotic and abiotic stress factors. The grow tube may provide an enhanced micro climate that is humid, CO2-replenished and promotes photosynthesis by selectively propagating photosynthetically active radiation. In addition to providing a physical barrier to wind and herbivores, certain embodiments of the grow tube can also provide protection from chemical sprays while permitting ventilation of the grow tube. Various embodiments of the spectrally selective grow tube may comprise separate interior and exterior members for enhancement of the interior and exterior surface functions and that may be constructed from a biodegradeable polymer or paper-based material. The interior member can be dyed or pigmented to selectively transmit wavelengths of the visible spectrum known to promote photosynthesis, such as red light and / or blue light.
Owner:PLANTRA
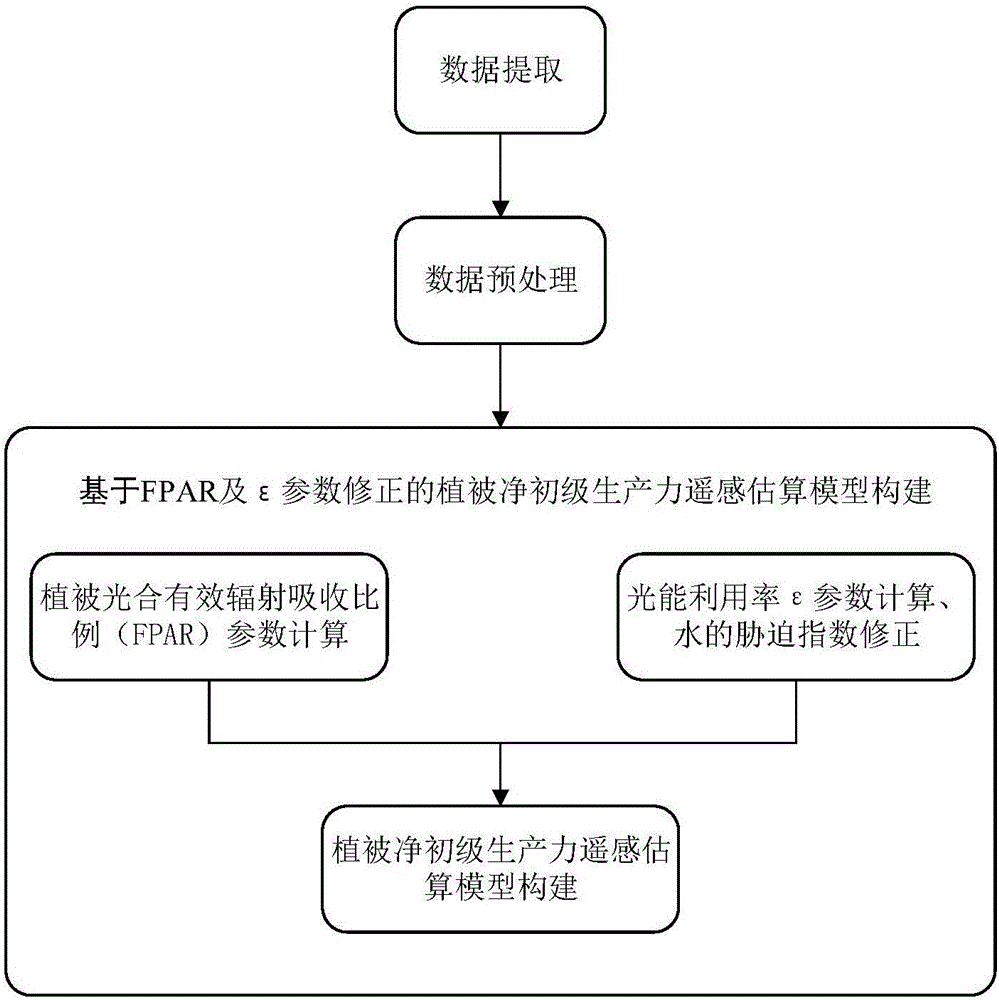
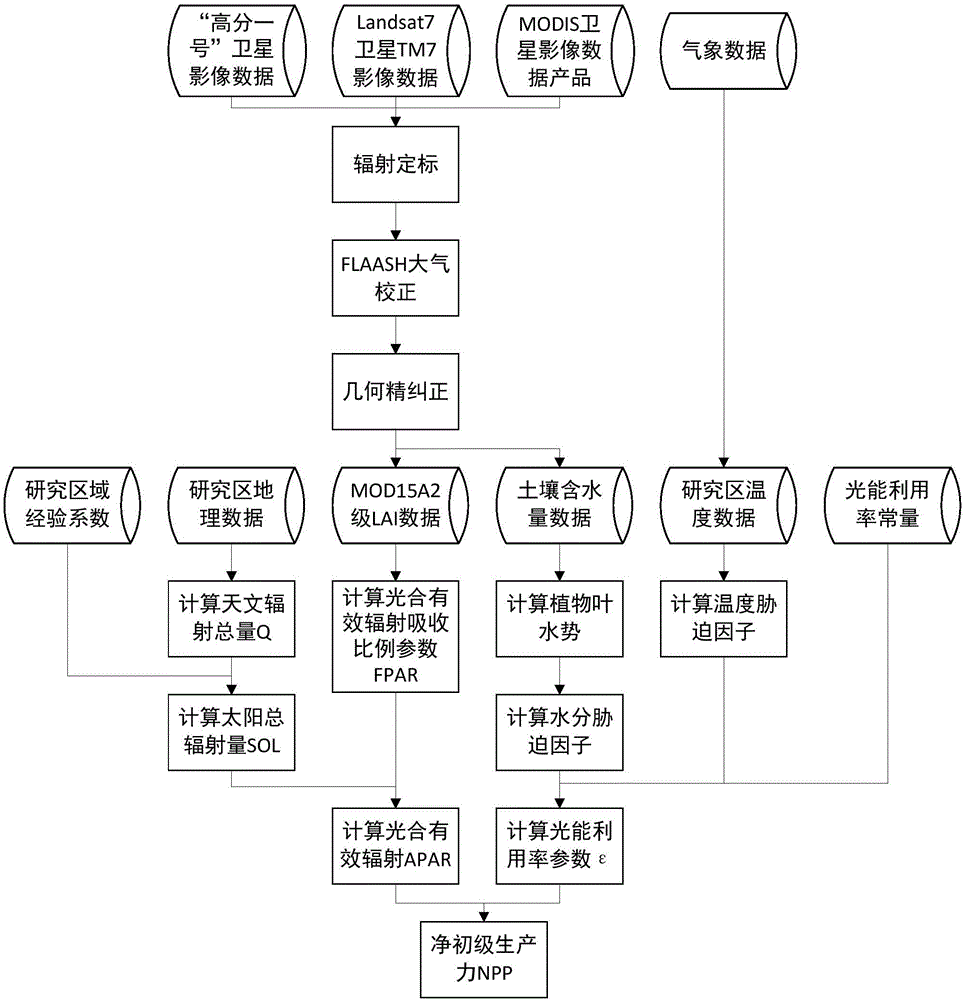
Method for remote sensing estimation of net primary productivity of plants
InactiveCN106446564AImprove estimation accuracyAvoid difficultiesImage enhancementImage analysisLongitudePrimary production
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for estimating plant growth biomass liveweight variation based on virtual plants
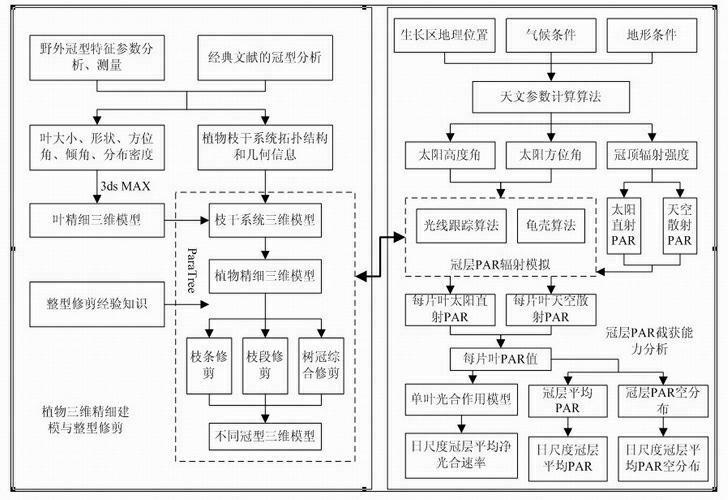
The invention discloses a method for estimating plant growth biomass liveweight variation based on virtual plants, aiming to the defect that a linkage relationship between a vegetation structure model and a mechanism model is ignored in the current method for estimating forest biomass liveweight variation. The method for estimating the plant growth biomass liveweight variation comprises the following steps of: firstly obtaining morphology parameters and textures of simulated plants, and establishing a plant geometric model based on a plant growth rule and a parameterization L-system; simulating photosynthetically active radiation in a virtual canopy by utilizing a ray tracing method based on the plant geometric model and applying to plant biomass liveweight accumulation, and establishing a plant structure-function feedback model; feeding parameter values obtained by calculation of the functional model back to the plant structure model, carrying out plant growth and development simulation at a certain growth cycle or a plurality of growth cycles; and simulating the photosynthetically active radiation in the virtual canopy on the grown and developed plant geometric structure model again, so repeatedly, dynamically developing the radiation simulation, and finally estimating the plant growth biomass liveweight in the simulated cycle(s).
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Multiple colors, and color palettes, of narrowband photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) time-staged over hours, days, and growing seasons yields superior plant growth
ActiveUS20180007838A1Lower energy requirementsImprove welfareElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesPeak valueGrowing season
Plants are optimally grown under artificial narrowband Photosynthetically Active Radiation (“PAR”) of multiple colors, and color palettes, applied in but partially time-overlapping cycles. As well as a long, growing season, cycle, the colored lights are cyclically applied on a short, diurnal, cycle that often roughly simulates a peak-season sunny day at the earth latitude native to the plant. Bluer lights are applied commencing before redder lights, and are likewise terminated before the redder lights. Infrared light in particular, is preferably first applied at a time corresponding to early afternoon, and is temporally extended past a time corresponding to sunset. The colored lights and light palettes preferably rise to, and fall from, different peak intensities over periods from 10 minutes to 2 hours, and relative peak intensities of even such different colors as are used at all vary up to times two (×2) in response to differing PAR requirements of different plants. Computer-controlled colored LED lights realize all.
Owner:SYMBIOTIC SYST INC
Method for analyzing intercept ability of canopy on photosynthetic active radiation based on virtual plant
InactiveCN102708254AReduce lossesPrecisely predict the effects of pruningSpecial data processing applicationsSkyVirtual plant
The invention relates to a method for analyzing intercept ability of a canopy on photosynthetic active radiation based on a virtual plant. The method comprises the following steps of: building a fine three-dimensional model of a plant in a natural growth form, shaping and trimming the plant, forming fine three-dimensional models of the plant in different crown types; obtaining crown radiation intensity by adopting an astronomical parameter calculation method; respectively simulating direct solar radiation PAR (peer assessment rating) space distribution of the canopy and sky radiation PAR space distribution by adopting a ray tracing algorithm and a turtle shell algorithm; calculating a PAR value of each leaf, obtaining PAR space distribution of the canopy and mean PAR values at different moments; calculating net photosynthetic rates of different canopies by combining a photosynthesis model; repeatedly shaping and trimming, and analyzing the intercept ability of the canopy on the PAR from mean PAR value, PAR space distribution and mean net photosynthetic rate of the canopy at day scale. The method benefits to quantitative analysis on scientific rationality of plant crown types so as to achieve the purpose of scientifically and rationally shaping and trimming the plant or designing the plant.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
LED lighting system and operating method for irradiation of plants
An LED illumination system is operable to irradiate plant materials with photosynthetically active radiation. A lighting assembly includes a plurality of different LED types. Each LED lamp has a different spectral power matched to an absorption peak of the plant materials. All of the LED lamps of each different lamp type are driven by a different dedicated power source. Each power source can be independently modulated to vary the collective spectral power output of the LED illumination system. The lighting assembly includes fluid conduits disposed proximate to the LED lamps and a cooling fluid is flowed through the fluid conduits to removed thermal energy from the LED lamps.
Owner:ADAPTIIV GROW TECH INC
Method for measuring ecological compensation quantity based on remote-sensing images
InactiveCN103345567ASimple and fast operationReliable measurement dataSpecial data processing applicationsVegetationSensing data
The invention discloses a method for measuring ecological compensation quantity based on remote-sensing images. The method includes the steps that (1), in a target region, in combination with obtained data of the remote-sensing images and obtained temperature data of meteorological stations, a photosynthetic active radiation index and an actual solar energy utilization efficiency index for the target region are respectively investigated and inspected; (2), a NPP parameter estimating module is input, and a CASA model is established for estimating net primary productivity; (3), through a data extracting module, NPP parameters in the NPP parameter estimating module are extracted, a region landscape value estimating module is input, estimation is performed according to a region landscape value estimating model, and values of the ecological compensation quantity of types of vegetation in the measured region are obtained. The method for measuring the ecological compensation quantity based on the remote-sensing images has the advantage that through the finite remote-sensing data, the ecological compensation quantity of the different types of vegetation can be roughly measured.
Owner:QINGHAI NORMAL UNIV
System and method suitable for measurement, control and calibration of carbon dioxide in greenhouse environment
ActiveCN102523954AChange the way of beingHigh measurement accuracyHorticulture methodsMaterial analysisWireless controlGreenhouse
The invention relates to the technical field of measurement, control and calibration of facility production carbon dioxide and discloses a system and a method suitable for measurement, control and calibration of carbon dioxide in a greenhouse environment. The system comprises a wireless carbon dioxide measuring device (16) and a wireless control device (18). The wireless carbon dioxide measuring device (16) is used for collecting fertilization concentration of carbon dioxide in a greenhouse, photosynthetically active radiation values, air temperature and humidity data and storing air fertilizer standard values of different crops at different growth periods so as to serve as a decision basis for carbon dioxide concentration fertilizing time and fertilizing amount. The wireless control device (18) is used for obtaining the data and the standard values from the wireless carbon dioxide measuring device (16) and controlling instructions to perform carbon dioxide fertilization control. The wireless carbon dioxide measuring device (16) adopts calibration methods including gas concentration change rate tracking, outdoor gas concentration, temperature and humidity compensation and the like to perform carbon dioxide calibration. The system and the method can achieve measurement, control and calibration of carbon dioxide in the greenhouse environment.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT OF INTELLIGENT EQUIP FOR AGRI
RGB LED package for optimized emissions of photosynthetically active radiation
InactiveUS20120099305A1Increase profitReduce colorSolid-state devicesSaving energy measuresLength waveLight-emitting diode
Disclosed is a device for providing photosynthetic photon flux to a plant by the simultaneous emission of red, green and blue light at photosynthetically active wavelengths. Light emitting diodes emitting red, green and butte at photosynthetically active wavelenghts are used.
Owner:BUCOVE JEFFERY
Tea withering device based on light-emitting diode (LED) light source, and withering method of tea withering device
InactiveCN104642574ADissipate quicklyPromotes clear floral and fruity aromaPre-extraction tea treatmentControl cellEngineering
The invention relates to a tea withering device based on a light-emitting diode (LED) light source, and a withering method of the tea withering device. The withering method comprises the steps of flatly laying fresh tea on a conveyor belt, wherein the spreading thickness of the fresh tea is controlled to be 5-50mm; blowing hot wind with temperature of 30 DEG C by a hot-blast device, and carrying out natural spreading treatment for 0.5h to remove the water on the surface of the tea; controlling the temperature of a light withering environment to be 25-30 DEG C and the relative humidity of the light withering environment to be 60-70%; setting the distance between an LED lamp band and the tea to be 100-400mm; starting a stepping motor, and conveying the tea to the parts just under withering devices based on the LED light sources having different characteristic spectrums by the conveyor belt; controlling a spectrum adjusting module by a control unit to enable photosynthetic active radiation to be equal to 100-600mu mol.m<-2>.s<-1>, and controlling the irradiation time to be 0.5-3.0 hours; opening a power module, and irradiating the tea by the withering devices based on the LED light sources; after illumination, continuously withering until the water loss rate of the tea reaches 68%, thereby finishing the withering process. Compared with the traditional hot wind withering technology under the conditions of same temperature and humidity, the withering method is capable of shortening the withering time of the fresh tea by 1.0-2.0 hours; compared with the natural withering, the method is capable of improving the quality of the tea by 1-2 grades.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
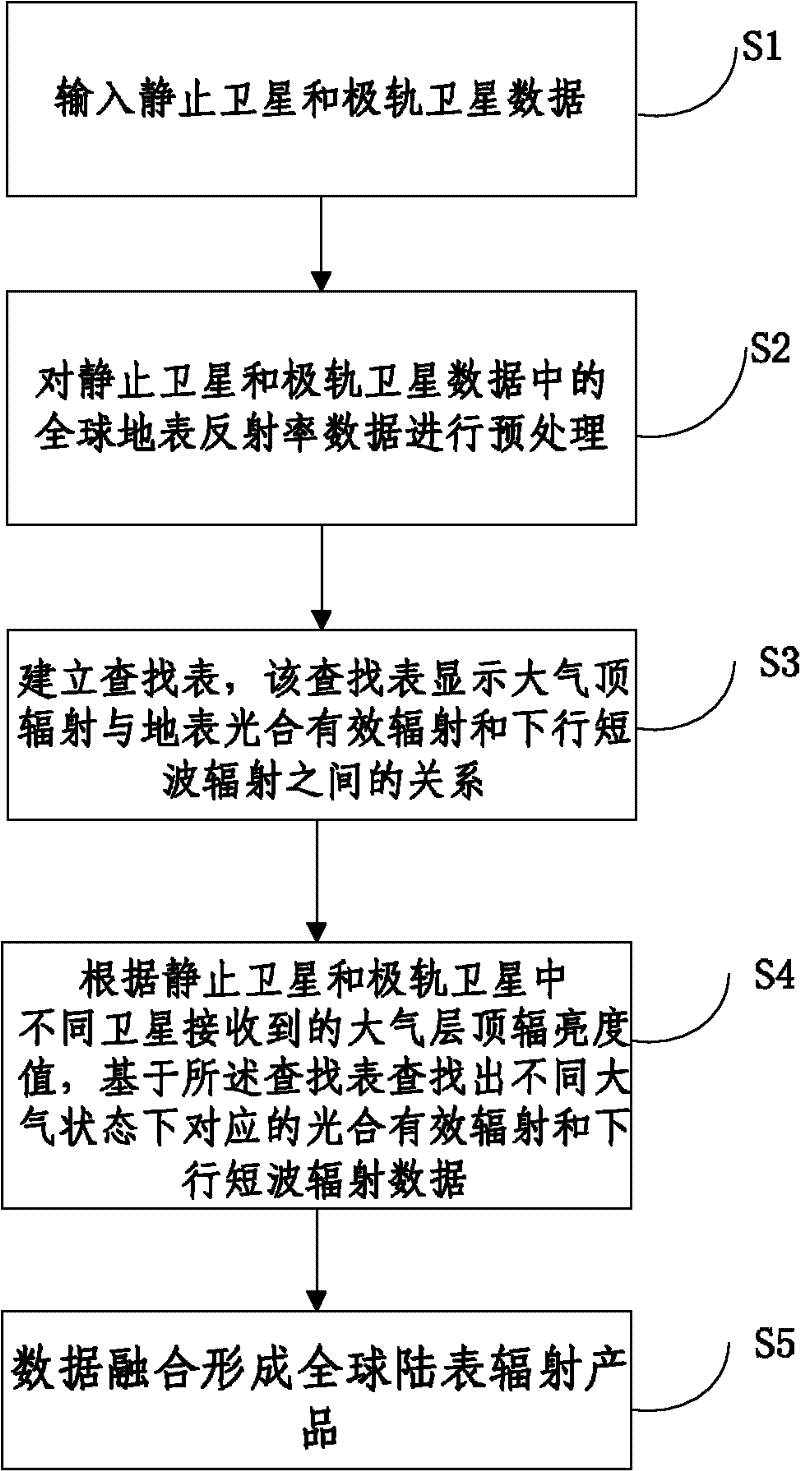
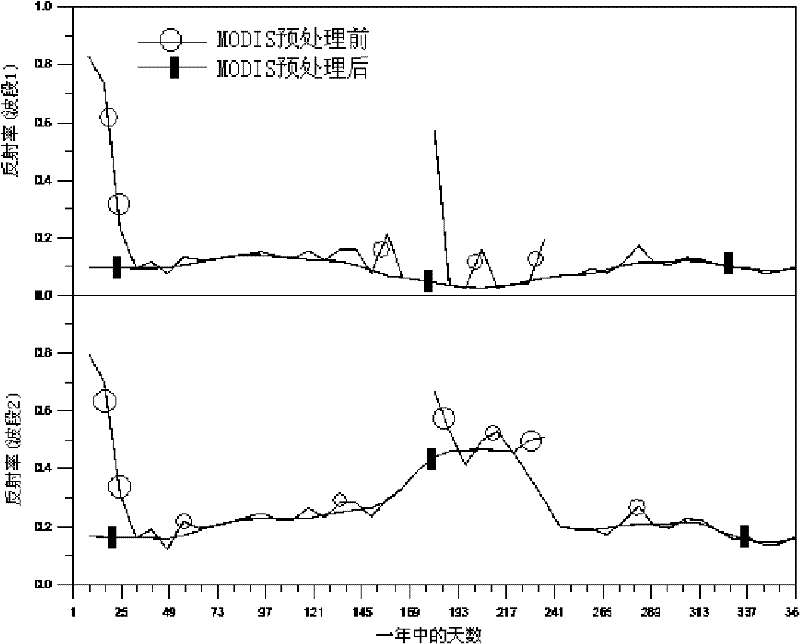
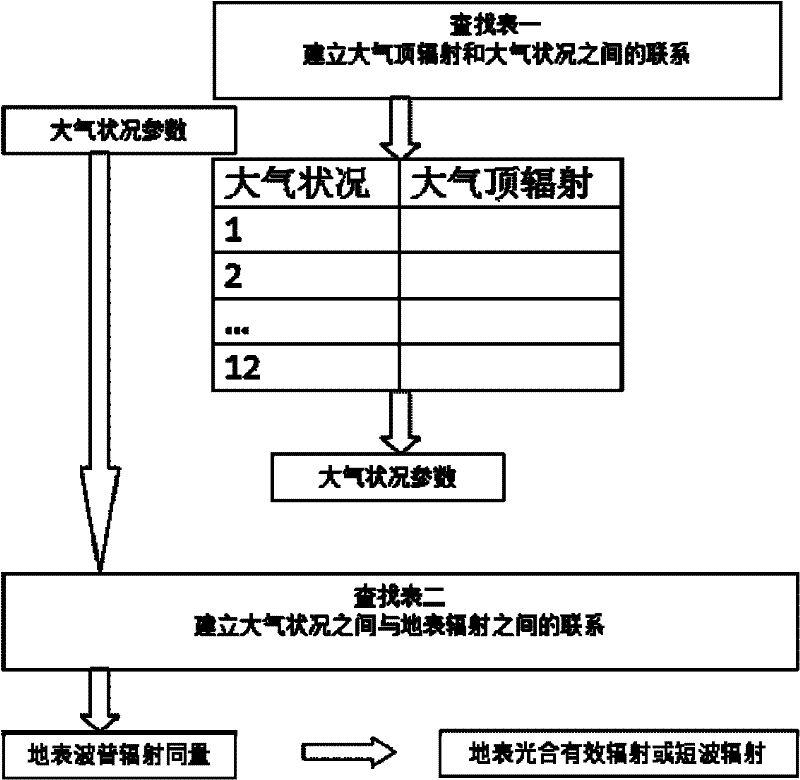
Inversion method and system of downlink shortwave radiation and photosynthetically active radiation data
InactiveCN102338869AImprove calculation accuracyHigh precisionWave based measurement systemsSpecial data processing applicationsSatellite dataAtmospheric sciences
The invention relates to the technical field of satellite remote sensing and application and discloses an inversion method and system of downlink shortwave radiation and photosynthetically active radiation data. The method comprises the following steps of: (S1) inputting stationary satellite and polar orbital satellite data; (S2)pre-processing global surface reflectance data in the stationary satellite and polar orbital satellite data so as to remove the influence of the cloud on the ground reflectance; (S3) establishing a lookup table, wherein the lookup table displays the relationship between the extraterrestrial radiation and the surface photosynthetically active radiation and downlink shortwave radiation; (S4) on the basis of extraterrestrial radiation brightness values received by different satellites in the stationary satellite and polar orbital satellite, figuring out corresponding photosynthetically active radiation and downlink shortwave radiation under different atmospheric conditions according to the lookup table; and (S5) forming a global epicontinental radiation product according to data fusion. According to the invention, the calculation accuracy of the downlink shortwave radiation and photosynthetically active radiation data inversion is improved.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Multi-sensor technology-based grape water stress diagnosis method and system therefor
ActiveCN103278503AGuaranteed accuracyEnhance explanatoryMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnosis methodsThermal infrared
The invention discloses a multi-sensor technology-based grape water stress diagnosis method and a system therefor. The multi-sensor technology-based grape water stress diagnosis method comprises the following steps of 1, acquiring a canopy coverage rate value, a canopy temperature characteristic value and a canopy photosynthetically active radiation value of a grape sample for modeling, 2, building a detection model by the canopy coverage rate value, the canopy temperature characteristic value and the canopy photosynthetically active radiation value as input variables, and a canopy water stress level as an output variable, and 3, by the step 1, acquiring a canopy coverage rate value, a canopy temperature characteristic value and a canopy photosynthetically active radiation value of a grape sample needing to be detected, and substituting the acquired canopy coverage rate value, the canopy temperature characteristic value and the canopy photosynthetically active radiation value into the detection model, and calculating a canopy water stress level of the detected grape sample. Through utilization of the multispectral imaging technology, the thermal infrared imaging technology and the multiple informative data fusion technology, the multi-sensor technology-based grape water stress diagnosis method realizes fast, early-stage and real-time detection of a grape water stress level and improves a detection precision.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Narrowband photosynthetically active radiation ('PAR") substantially only at each of multiple emission wavelengths yields good photosynthesis at reduced energy cost
ActiveUS20140123555A1Promote plant growthSave energySeed and root treatmentSaving energy measuresGrowth plantLength wave
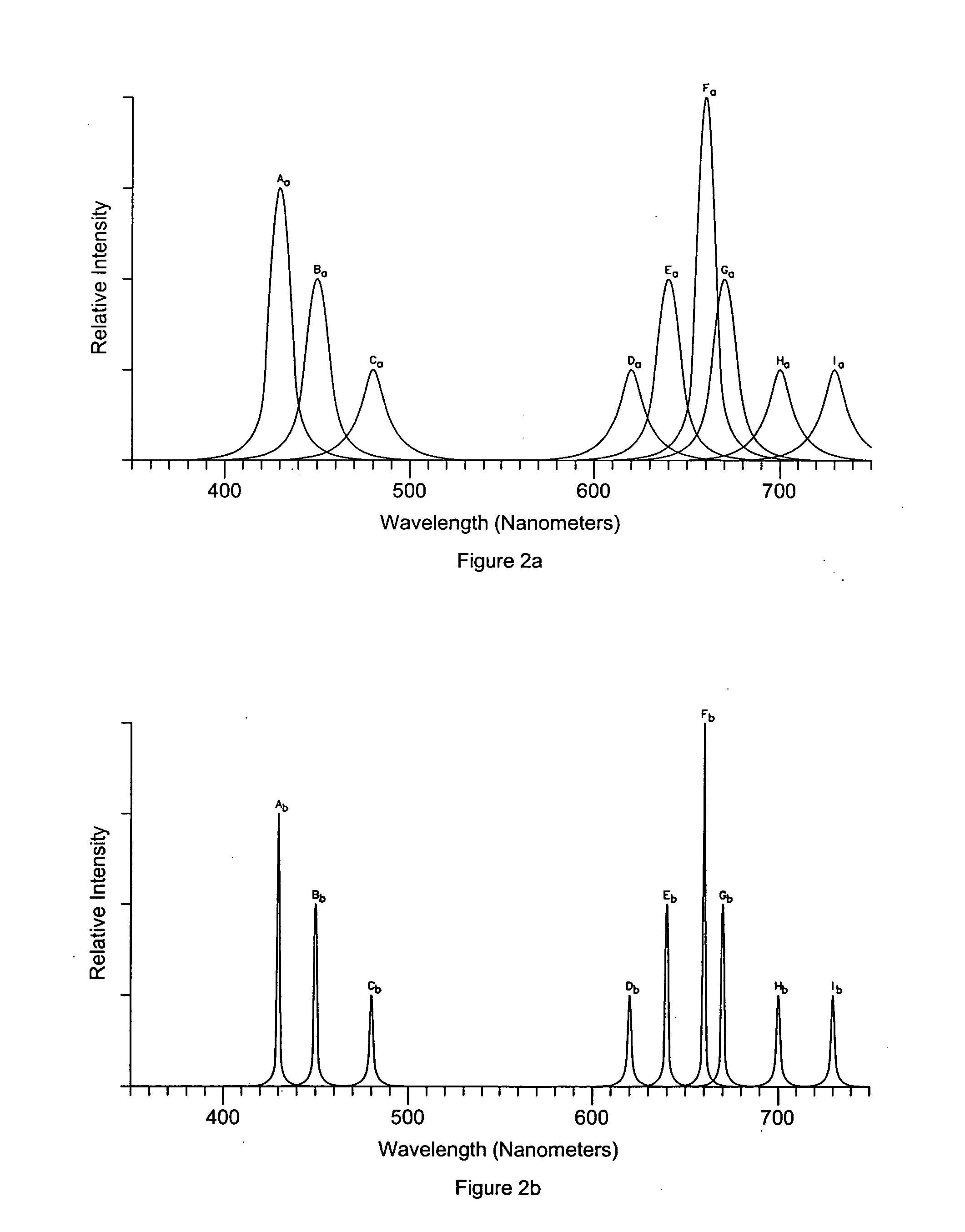
Produced PAR neither replicates the spectral ban—width of sunlight at the surface of the earth, nor the absorption spectrum of green plants, nor the absorption spectrum of photosynthetic processes, but—based on discovery that PAR at only a number of unique wavelengths is optimally energy-efficient to promote normal or better plant growth—instead desirably concentrates PAR emissions in a limited number, preferably about nine (9), narrow bands. Narrowband, even extremely narrowband, radiation is preferred at 430 and 662 nanometers wavelength; 453 and 642 nanometers wavelength and still other wavelengths. Preferably more than 50% of the total PAR flux is within a total bandwidth of less than 160 nanometers wavelength in the range between 360 and 760 nanometers wavelength, and more preferably 90% of the PAR flux is within a total bandwidth of less than 80 nanometers wavelength within this range.
Owner:SYMBIOTIC SYST INC
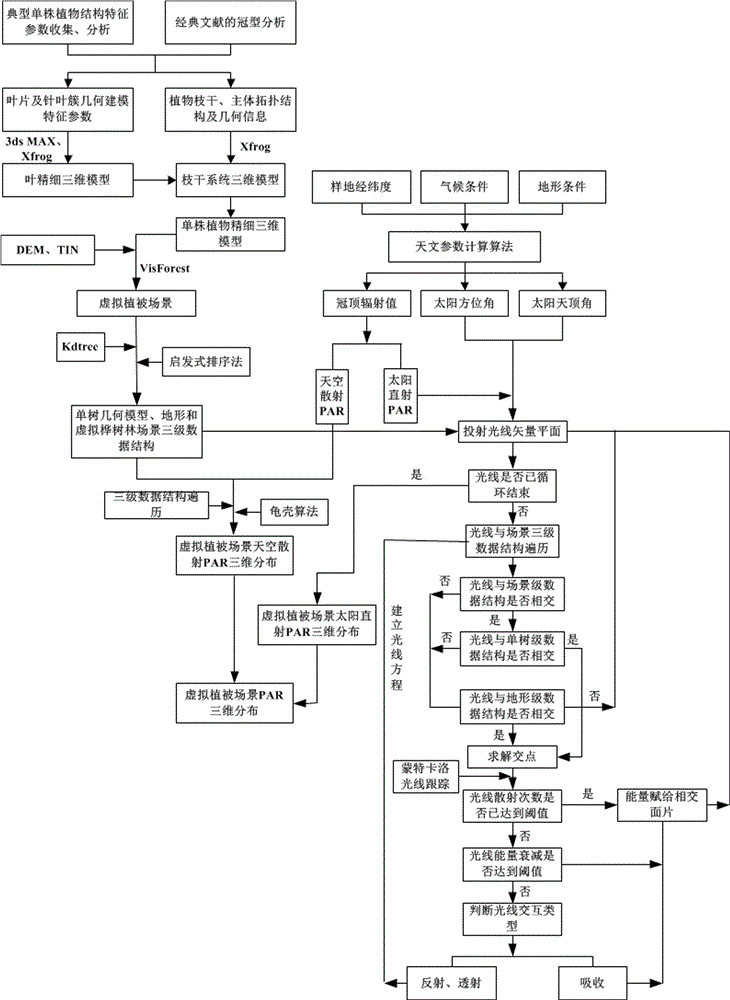
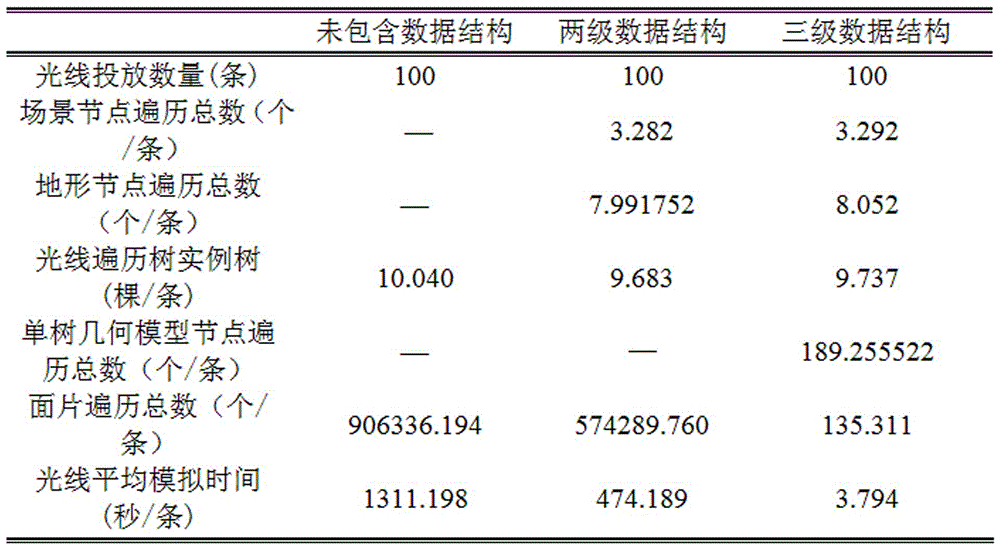
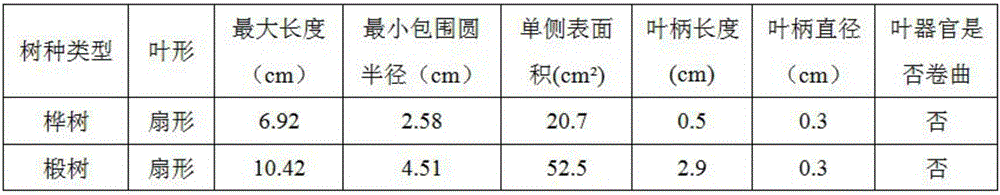
Virtual plant canopy photosynthesis effective radiation distribution simulating method of multi-layer data structure
ActiveCN105701313AImprove Simulation EfficiencyReduce demandGeographical information databasesSpecial data processing applicationsTerrainTrack algorithm
The invention relates to a virtual plant canopy photosynthesis effective radiation distribution simulating method of a multi-layer data structure. The method includes the following steps of establishing a virtual plant model and a virtual plane scene high in fidelity and complexity, collecting plant canopy photosynthesis effective radiation intensity values through a related astronomical parameter method or a field measurement method, sequentially establishing the three-layer data structure with a virtual plane scene single-tree geometrical model, a scene and a terrain through a data structure starting method, establishing a direct solar radiation and sky scattering PAR ray vector plane, sequentially tracing all ray vectors on the ray plane through a Monte Carlo ray tracing algorithm and a turtle shell algorithm, traversing the three-layer data structure with the scene, the single tree and the terrain, judging whether rays intersect with triangular patches or not, counting the sky visible rates of all the triangular patches, and calculating direct solar radiation PAR and sky scattering PAR of all the triangular patches to obtain a virtual plane canopy PAR three-dimensional space distribution simulating result.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method and system for improving calculation accuracy of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR)
InactiveCN102004848AImprove resolutionImprove calculation accuracySpecial data processing applicationsTerrainThermodynamics
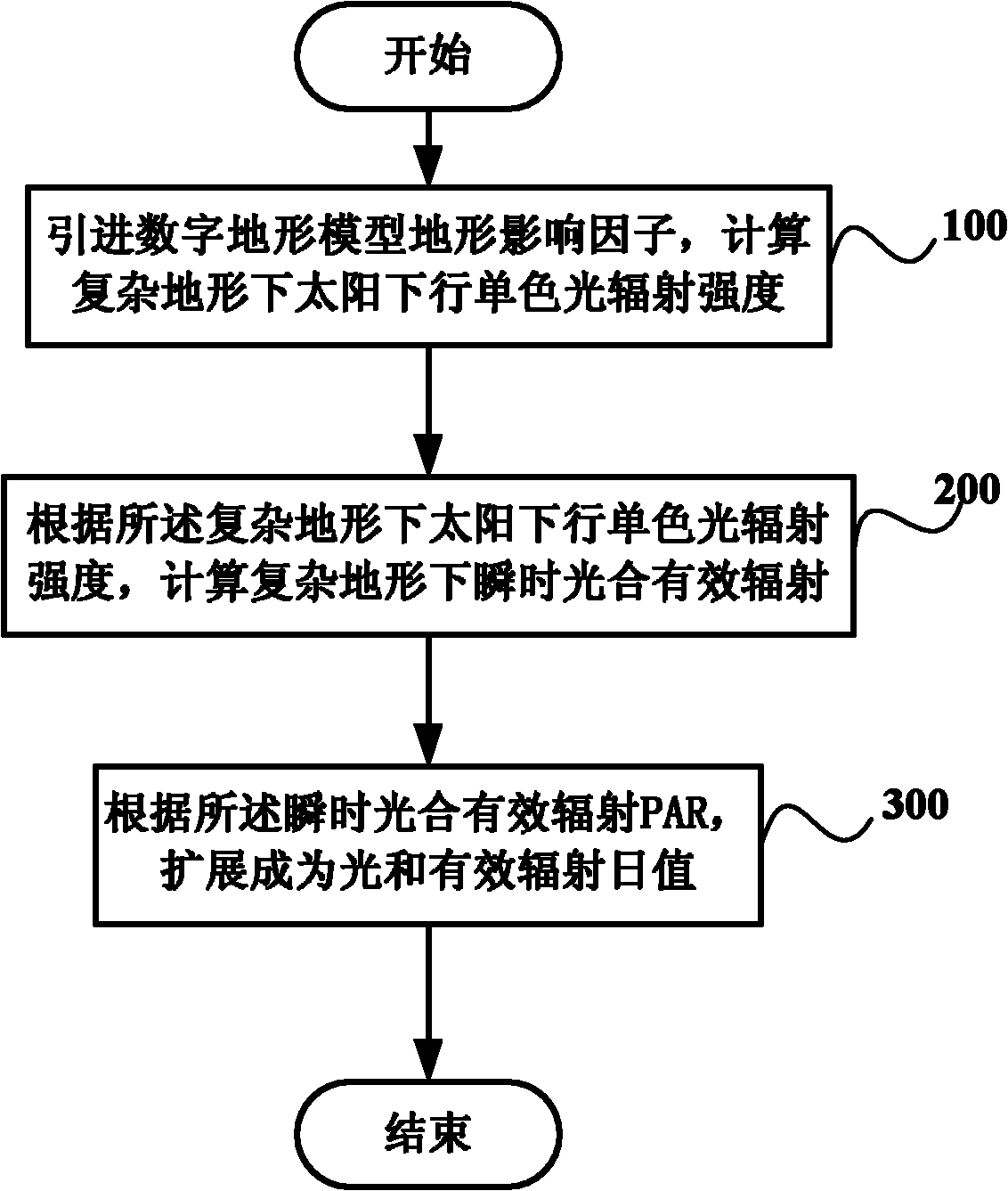
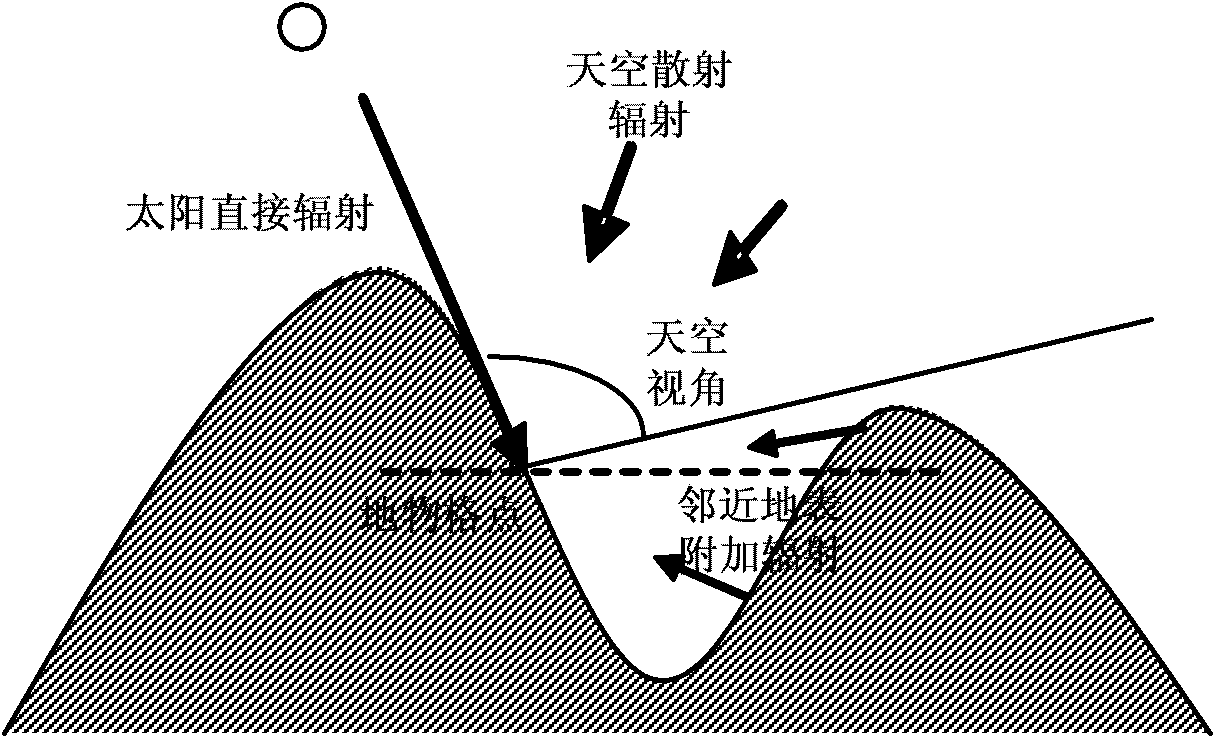
The invention discloses a method and a system for improving calculation accuracy of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR). The method comprises the following steps of: introducing a terrain influence factor of a digital terrain model, and calculating solar downlink monochromatic light radiation intensity under the condition of a complex terrain, namely I lambda=I dir+ I dif+ I adj, wherein lambda is the wavelength in vacuum; calculating instantaneous PAR under the condition of the complex terrain according to the solar downlink monochromatic light radiation intensity I lambda under the condition of the complex terrain; and expanding into a PAR day value PARd according to the instantaneous PAR.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
Index-linear equation-based facility crop dry matter production simulation method
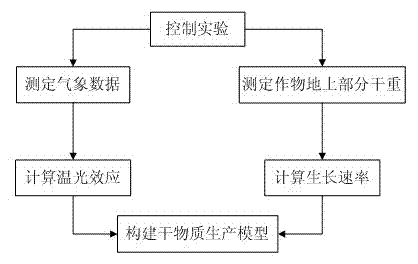
The invention discloses an index-linear equation-based facility crop dry matter production simulation method, and belongs to the technical field of agricultural information processing. The method comprises the following steps: measuring the dry weight of an overground part of a crop through a facility crop cultivation experiment; calculating daily temperature light effect of the crop according to environment meteorological data and crop growth and development three cardinal temperature acquired by consulting documents; calculating the maximum growth rate of the dry weight of the overground part of the crop in a linear growth stage and an index stage; and establishing an index-linear equation-based facility crop dry matter simulation model. The dry matter production module established by the method can predict the production of the dry matter of the overground part of the crop in any day after field planting, and has a few parameters. By measuring daily average temperature and photosynthetically active radiation, the production of the dry matter of the overground part of the facility crop can be predicted.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Plant illumination device and method
InactiveCN103563102AImprove qualityImprove consistencySaving energy measuresGreenhouse cultivationPlant growthLight emission
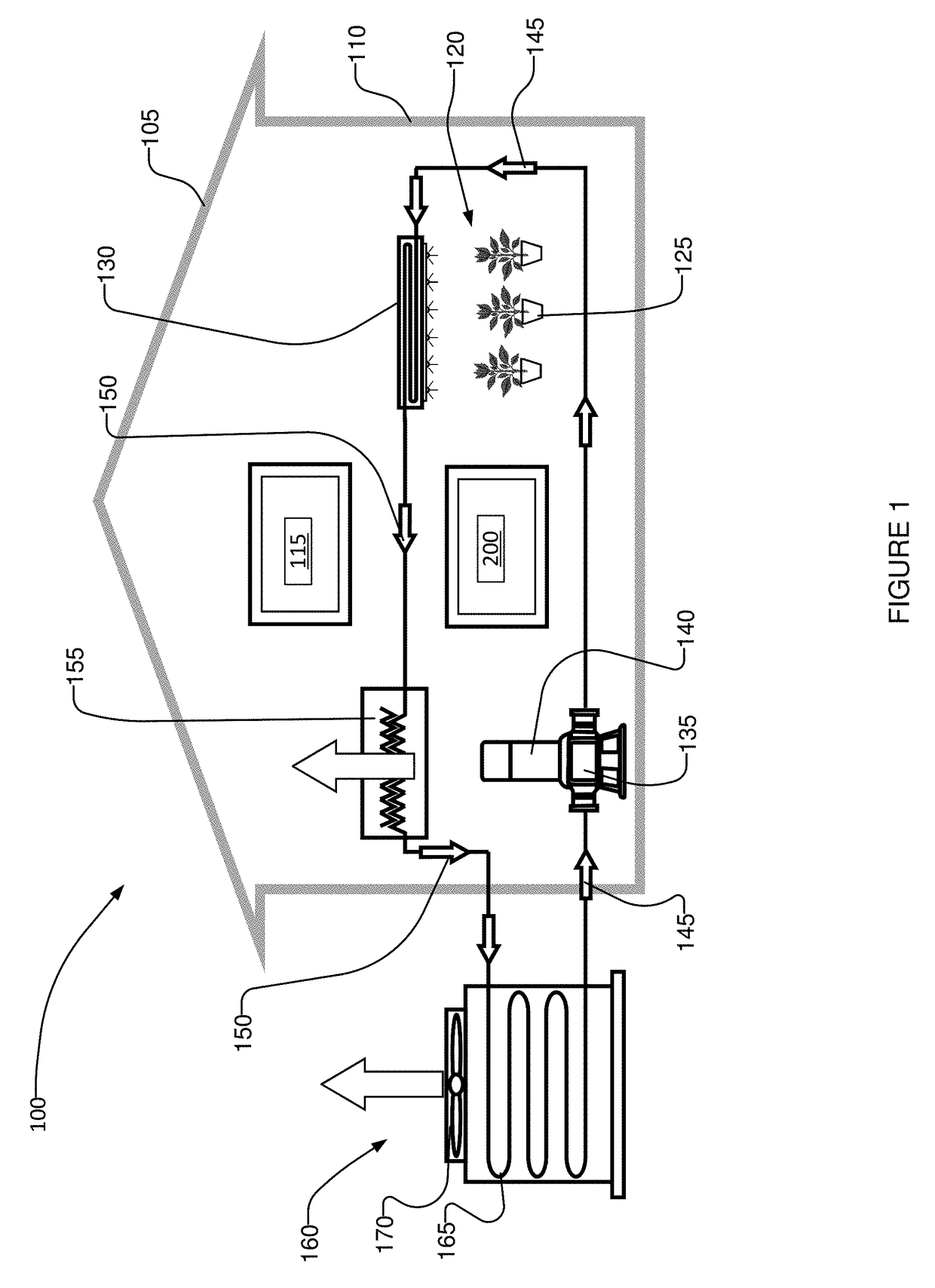
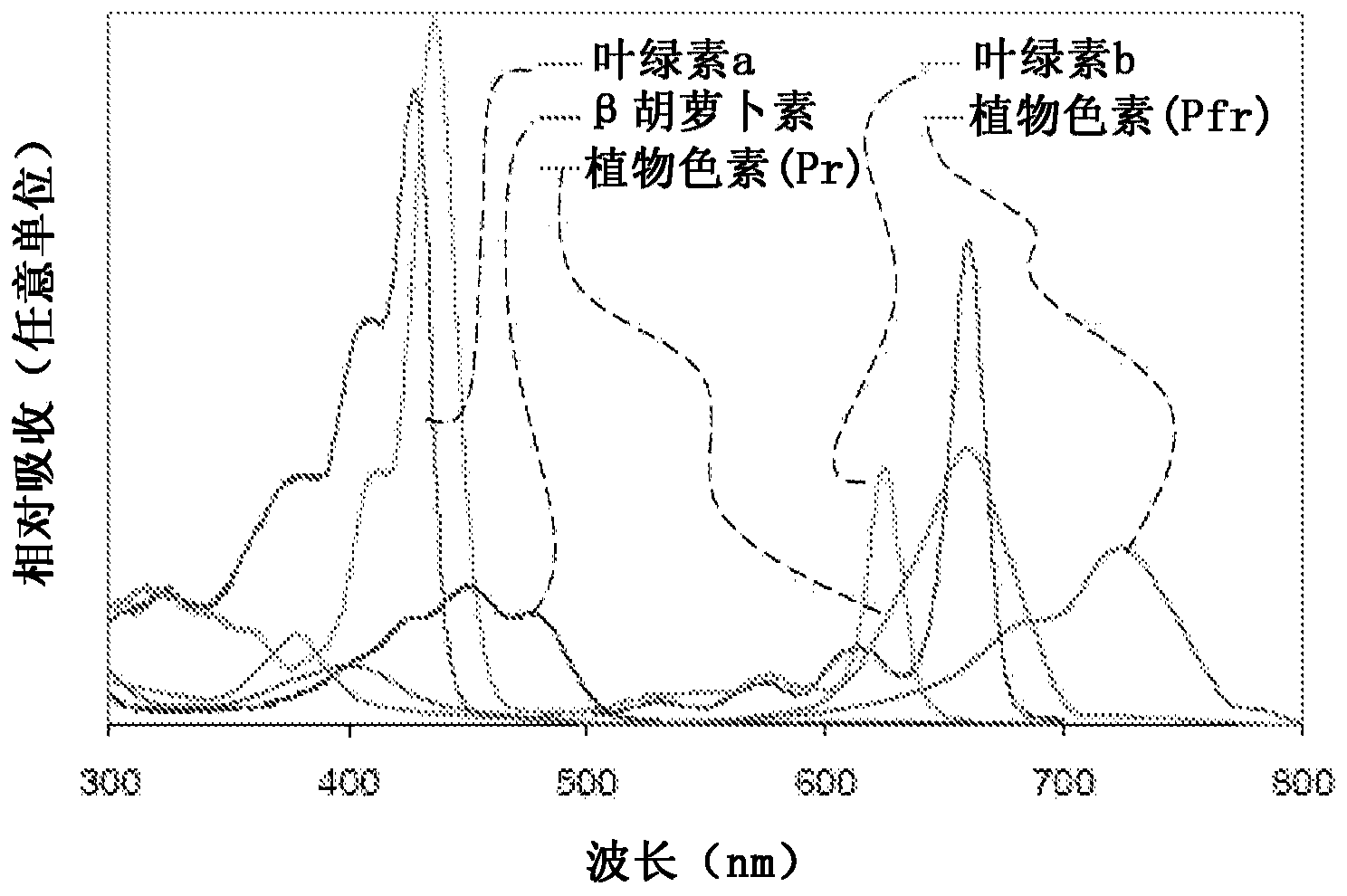
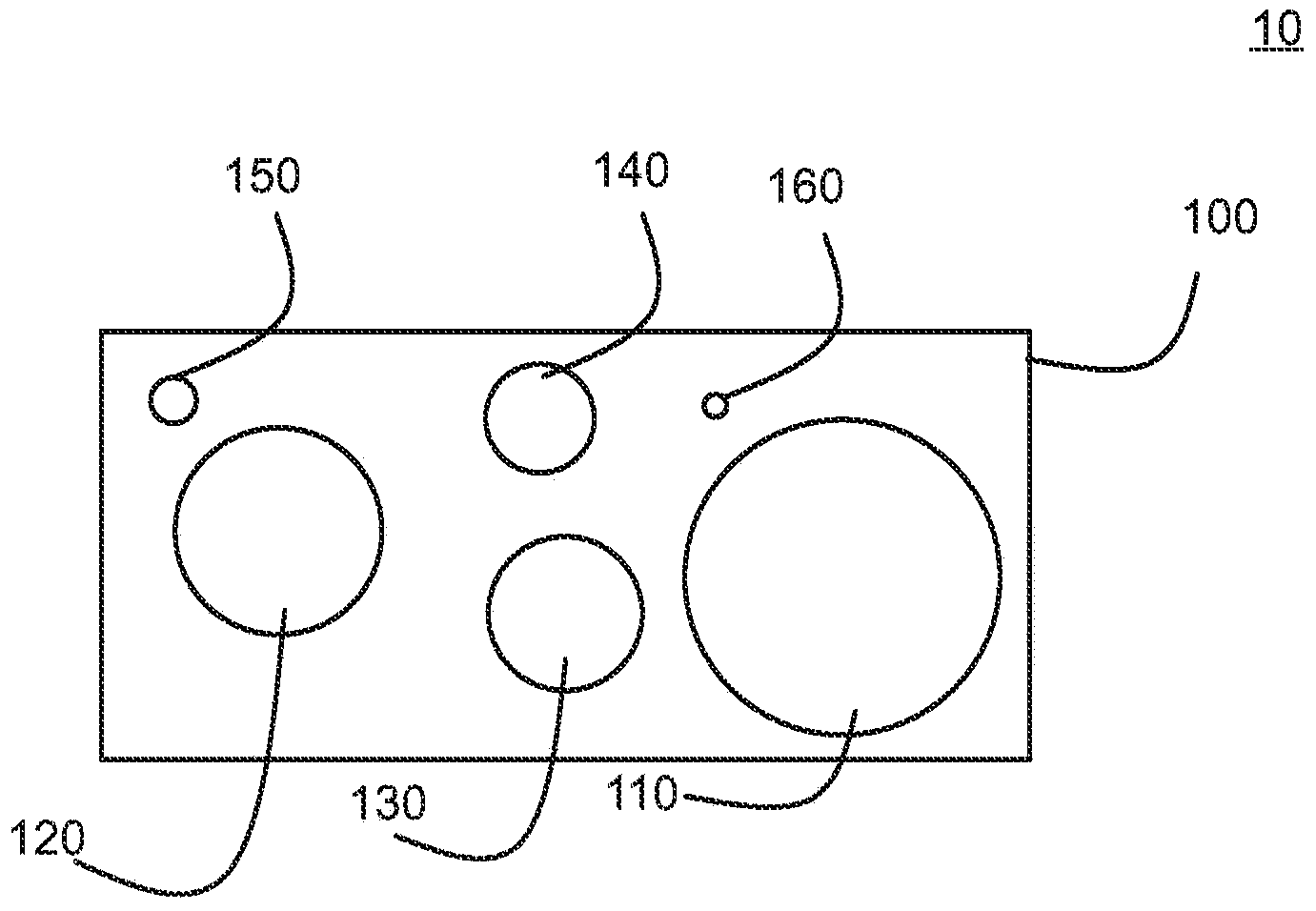
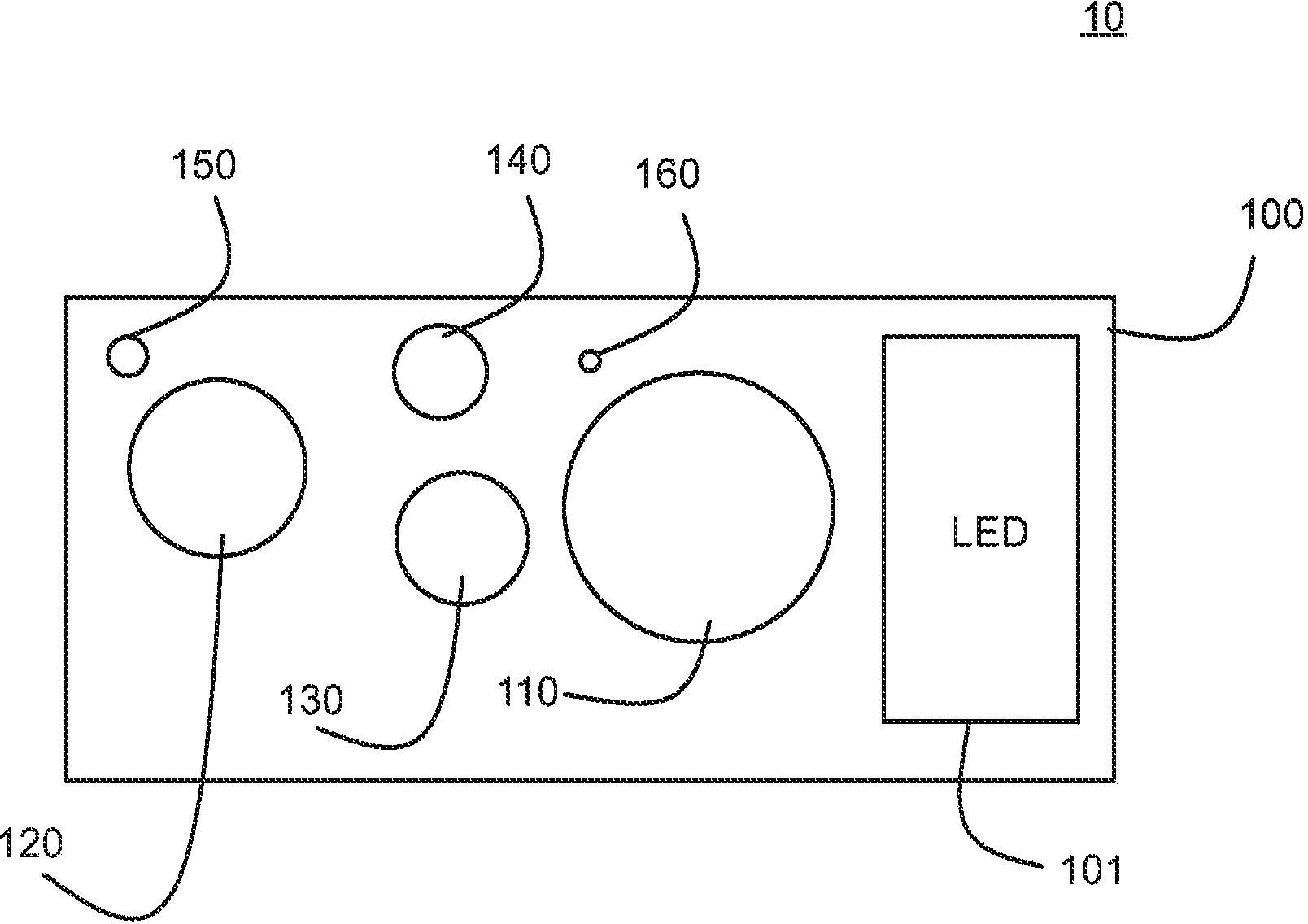
The invention relates to an improved method to produce artificial light for plant cultivation. In more particular, the invention relates to an illumination device with a semiconductor light emission solution and device suited for plant cultivation in a greenhouse environment. The best mode of the invention is considered to be a lighting device with binary alloy quantum dots (110, 120, 130, 140, 150, 160) made by colloidal methods to produce a size distribution of quantum dots that produces an emission spectrum similar to the photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) spectrum. The methods and arrangements of the invention allow more precise spectral tuning of the emission spectrum for lights used in plant (310, 311) cultivation. The invention therefore realises unexpected improvements in the photomorphogenetic control of plant growth, and further improvements in plant production.
Owner:VALOYA
Device for measuring light distribution in crop canopy
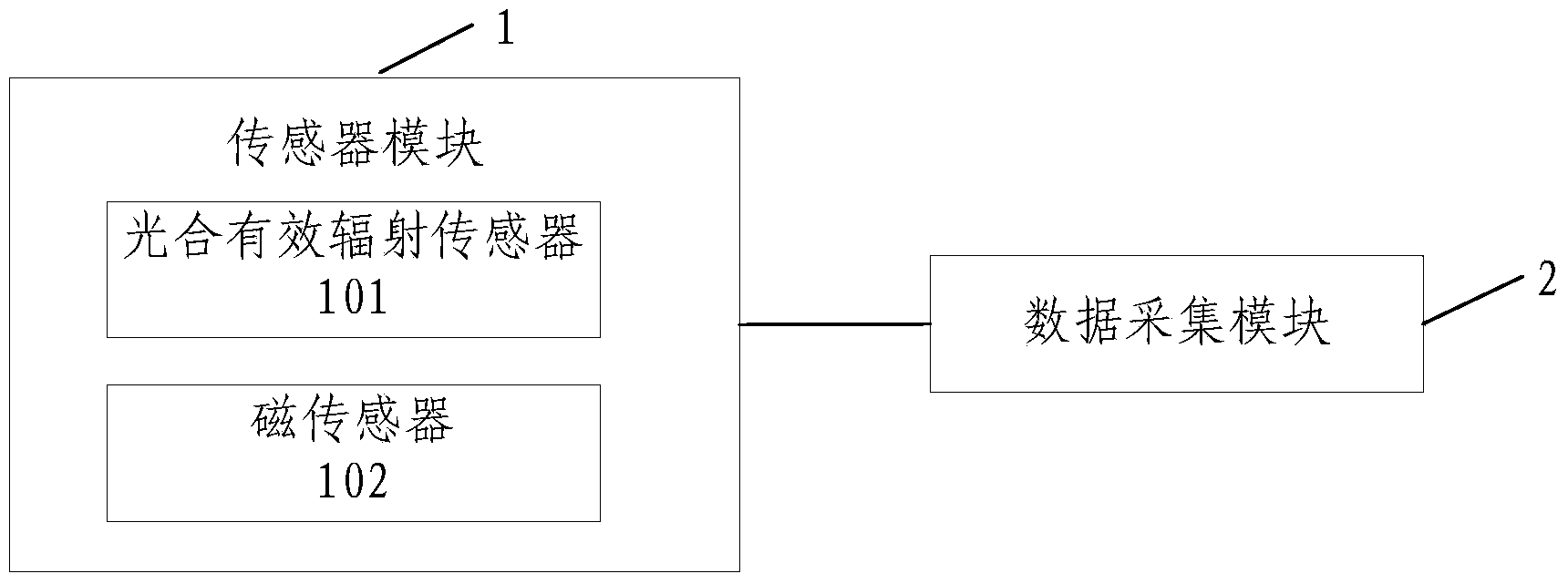
The invention provides a device for measuring light distribution in a crop canopy. The device comprises a sensor module and a data acquisition module. The sensor module comprises a photosynthetic active radiation sensor and a magnetic sensor, the photosynthetic active radiation sensor is used for measuring photosynthetic active radiation information of a point to be measured in the plant canopy, and the magnetic sensor is used for measuring position information of the point to be measured. The module acquisition module connected with the sensor module and is used for acquiring the photosynthetic active radiation information and the position information measured by the sensor module and storing the acquired photosynthetic active radiation information and position information. The device for measuring light distribution in the crop canopy can conduct synchronous measurement on the photosynthetic active radiation information and the position information of the point to be measured in the crop canopy and provide an effective method which enables people to have a more accurate understanding of light distribution in the crop canopy.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT FOR INFORMATION TECH & AGRI
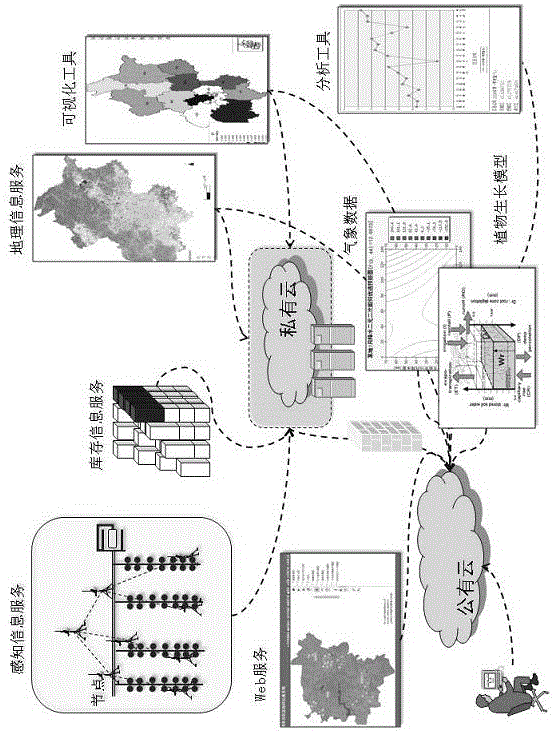
Cloud-based agricultural Internet of things production and management system
InactiveCN106305371ARealize local irrigationRealize analysisMeasurement devicesTransmission systemsGeneral Packet Radio ServiceCloud base
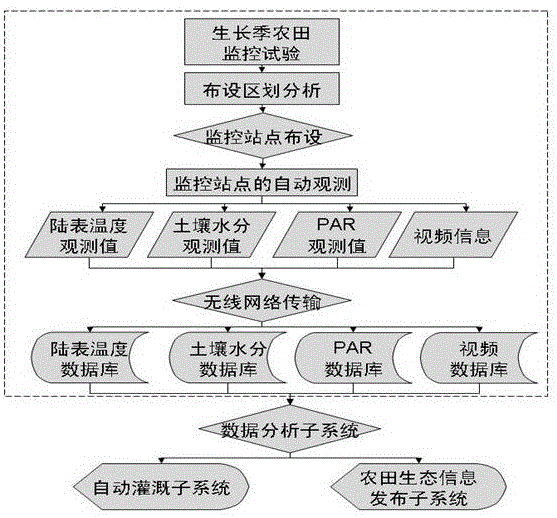
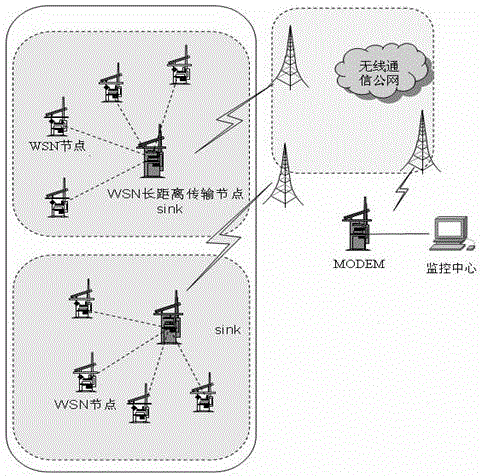
The invention discloses a cloud-based agricultural Internet of things production and management system. The cloud-based agricultural Internet of things production and management system comprises a farmland production environment monitoring subsystem, a data analysis expert subsystem, a farmland ecological information publishing subsystem and an irrigation control subsystem, wherein the data analysis expert subsystem and the farmland ecological information publishing subsystem are arranged on a public cloud; the irrigation control subsystem and the farmland production environment monitoring subsystem are arranged on a private cloud. By adopting the system, the land surface temperature, soil moisture, video information and PAR (photosynthetically active radiation) index of a multi-user agricultural production place can be monitored comprehensively; farmland information is transmitted through Zigbee and GPRS (General Packet Radio Service), so that data analysis and processing can be performed, analysis and publishing of agricultural condition information are realized, an irrigation instruction can be issued according to a crop demand, and local irrigation of a farmland is realized through an automatic irrigation subsystem according to the irrigation instruction.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Determining method of reasonable illuminating dose of facility vegetable
InactiveCN101642032ALow accumulation levelIncrease productionFluorescence/phosphorescenceHorticulture methodsGrowing seasonChlorophyll
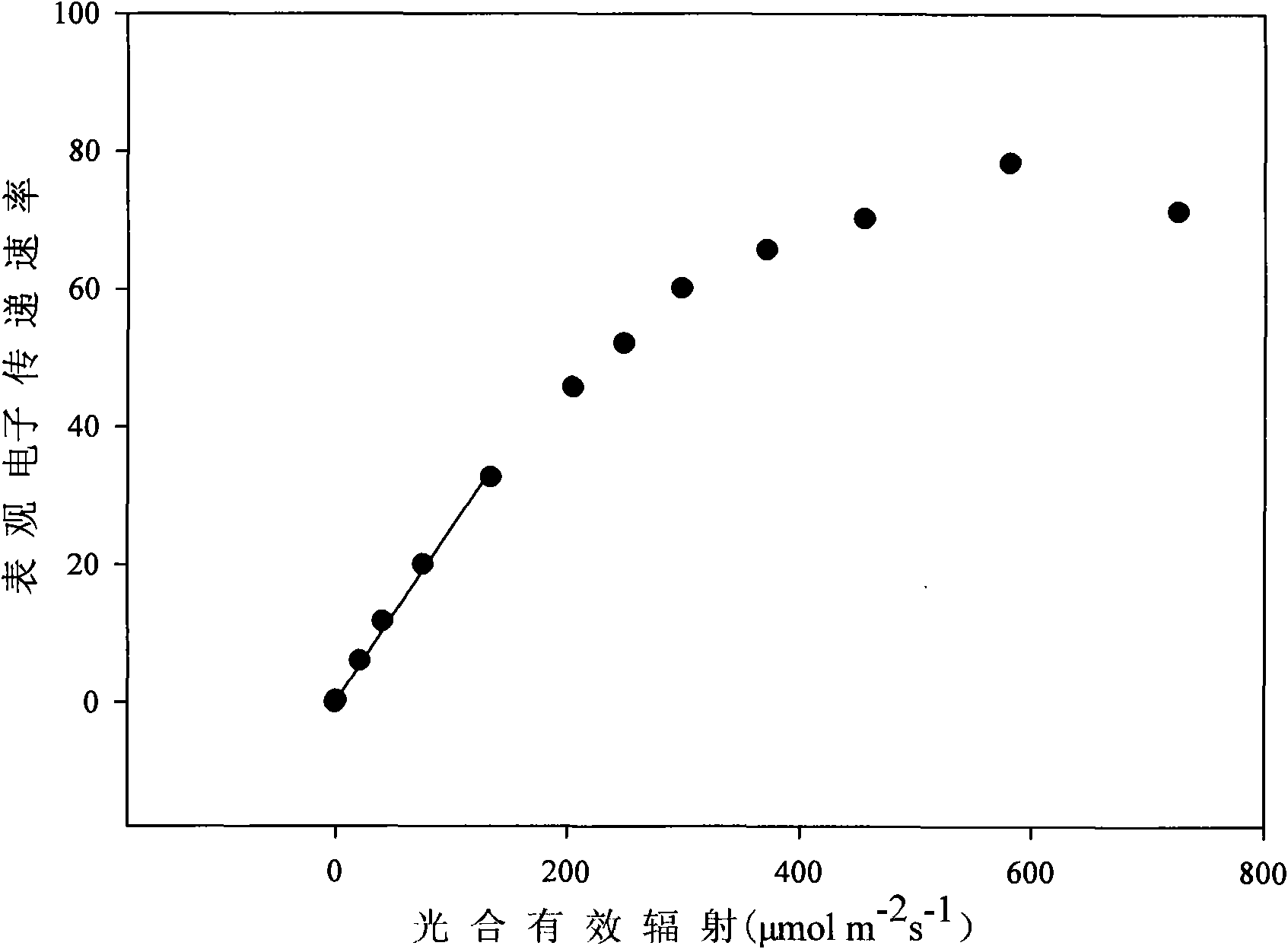
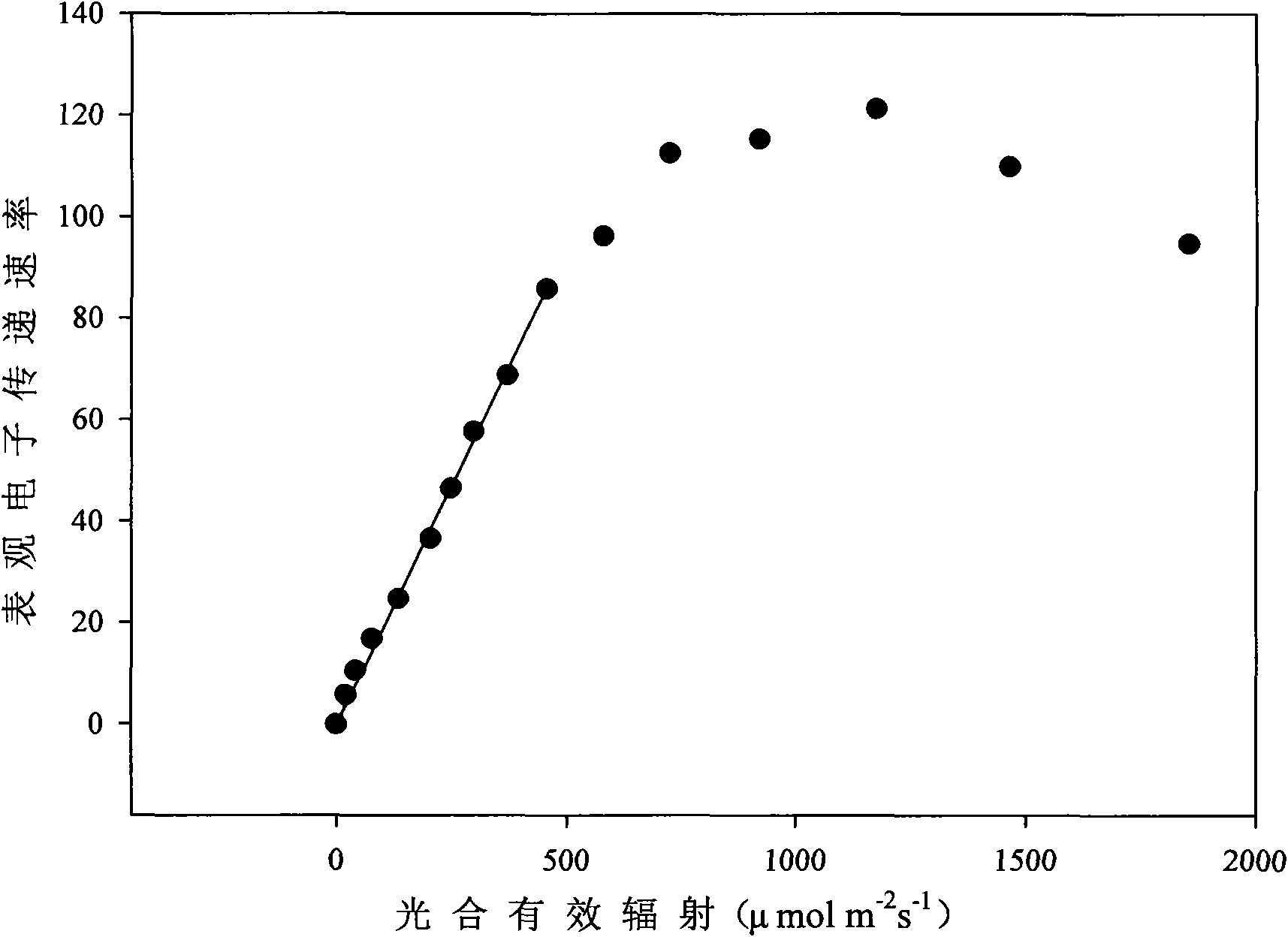
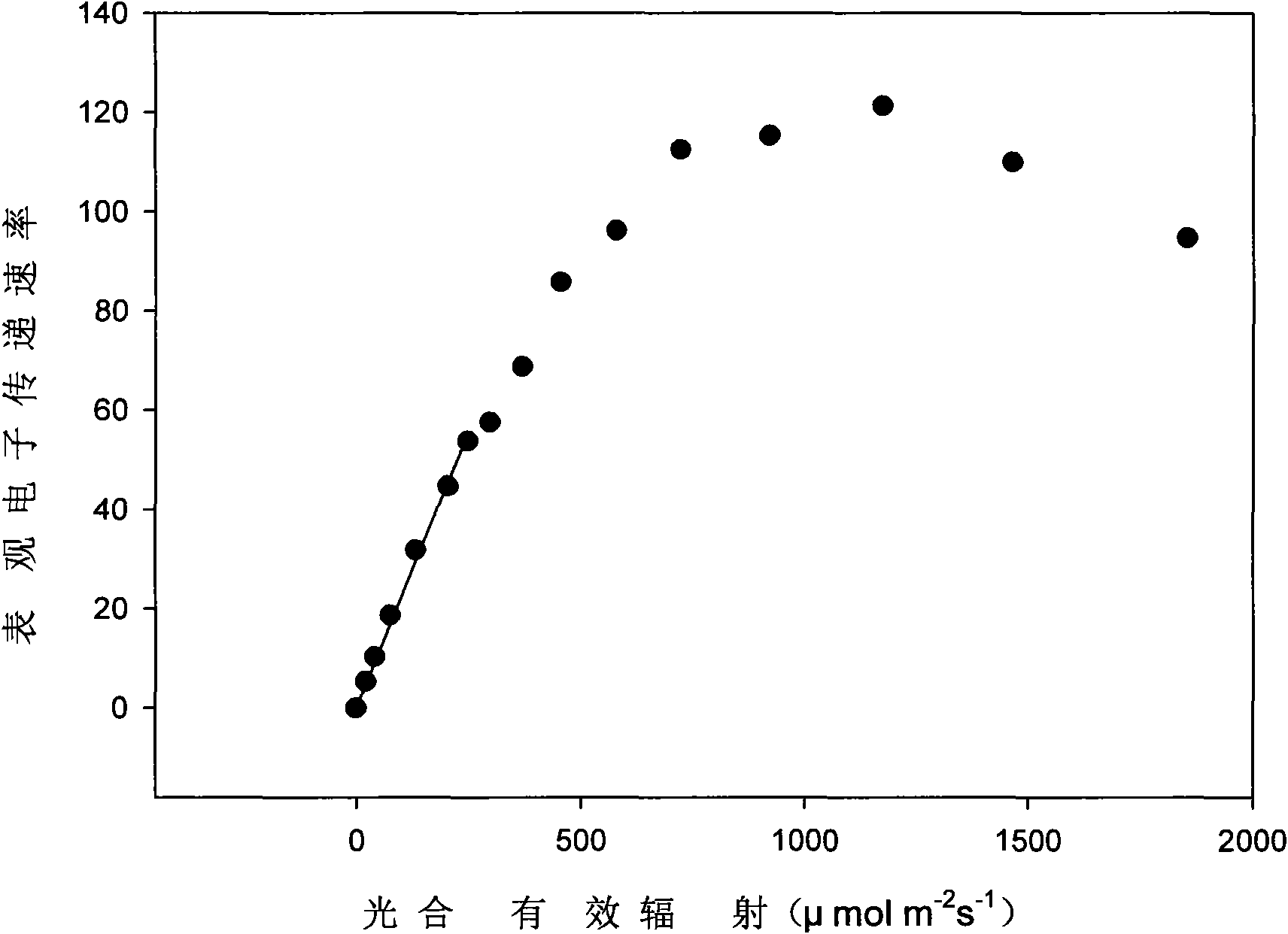
The invention discloses a determining method of reasonable illuminating dose of a facility vegetable, which belongs to the technical field of facility growth. The reasonable illuminating dose of the facility vegetable is determined according to the following steps: taking the facility vegetable in the peak of a growing season; measuring a quick light response curve of vegetable leaves by a chlorophyll luminoscope and determining the reasonable illuminating dose of the facility vegetable according to a response curve of the transmission rate of apparent electrons to photosynthetic effective radiation in the quick light response curve of the vegetable leaves. By using the reasonable illuminating dose of the facility vegetable determined by the method, higher yield and lower nitrate accumulation level are ensured and energy sources are saved to the maximum, thereby the unification of high yield, good quality and low consumption is realized. The method has the advantages of high efficiencyand speed, convenient operation and wide application range and can be used for facility growth vegetables and facility growth medicaments.
Owner:YUNNAN JIANGSHI TECH CO LTD
Plant illumination device and method for dark growth chambers
ActiveCN103563101AFine spectral tuningImprove qualityLight source combinationsProtective devices for lightingPlant growthLight emission
The invention relates to an improved method to produce artificial light for plant cultivation. In more particular, the invention relates to an illumination device with a semiconductor light emission solution and device suited for plant cultivation in a greenhouse and / or dark growth chamber environment. The best mode of the invention is considered to be a lighting device with LEDs that produces an emission spectrum similar to the photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) spectrum in a dark growth chamber. The methods and arrangements of the invention allow more precise spectral tuning of the emission spectrum for lights used in plant (310, 311) cultivation. The invention therefore realises unexpected improvements in the photomorphogenetic control of plant growth, and further improvements in plant production, especially in dark growth chambers, such as basements.
Owner:VALOYA
Spectrally selective grow tube
InactiveUS8171668B2Inhibition of colonizationReducing invitationFlower holdersPlant protective coveringsLighting spectrumBiology
A spectrally selective grow tube or tree shelter that improves the establishment of woody plant forms by reduction and / or elimination of certain biotic and abiotic stress factors. The grow tube may provide an enhanced micro climate that is humid and rich in CO2 and promotes photosynthesis by selectively propagating photosynthetically active radiation. In addition to providing a physical barrier to wind and herbivores, certain embodiments of the grow tube can also provide protection from chemical sprays while permitting ventilation of the grow tube. Various embodiments of the spectrally selective grow tube may comprise separate interior and exterior members for enhancement of the interior and exterior surface functions and that may be co-extruded. The interior member may be dyed or pigmented to selectively transmit wavelengths of the visible spectrum known to promote photosynthesis, such as red light and / or blue light. The exterior member may include a semi-reflective coating such as TiO2 or ZnS that reflects at least a portion of the visible light spectrum while enabling transmission of infrared wavelengths therethrough for radiative cooling.
Owner:PLANTRA
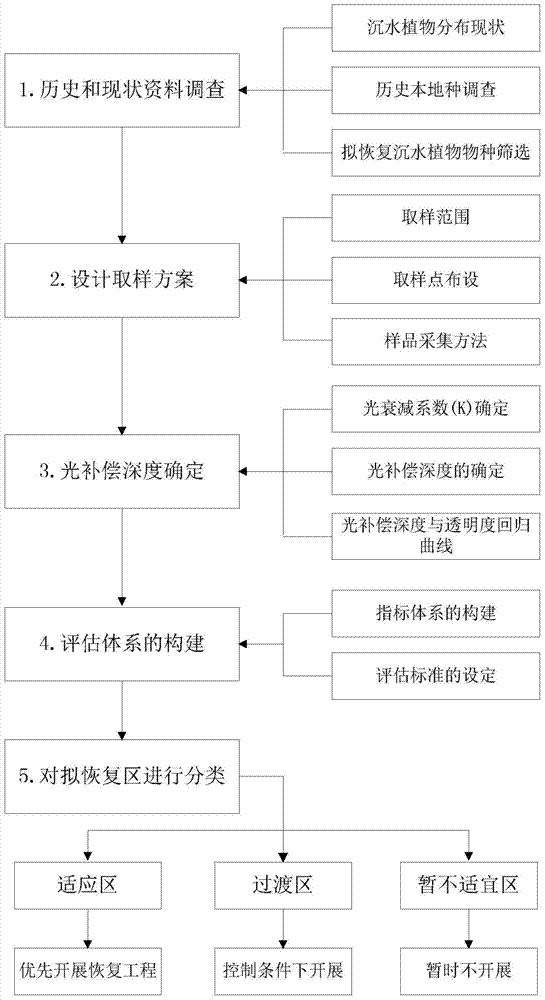
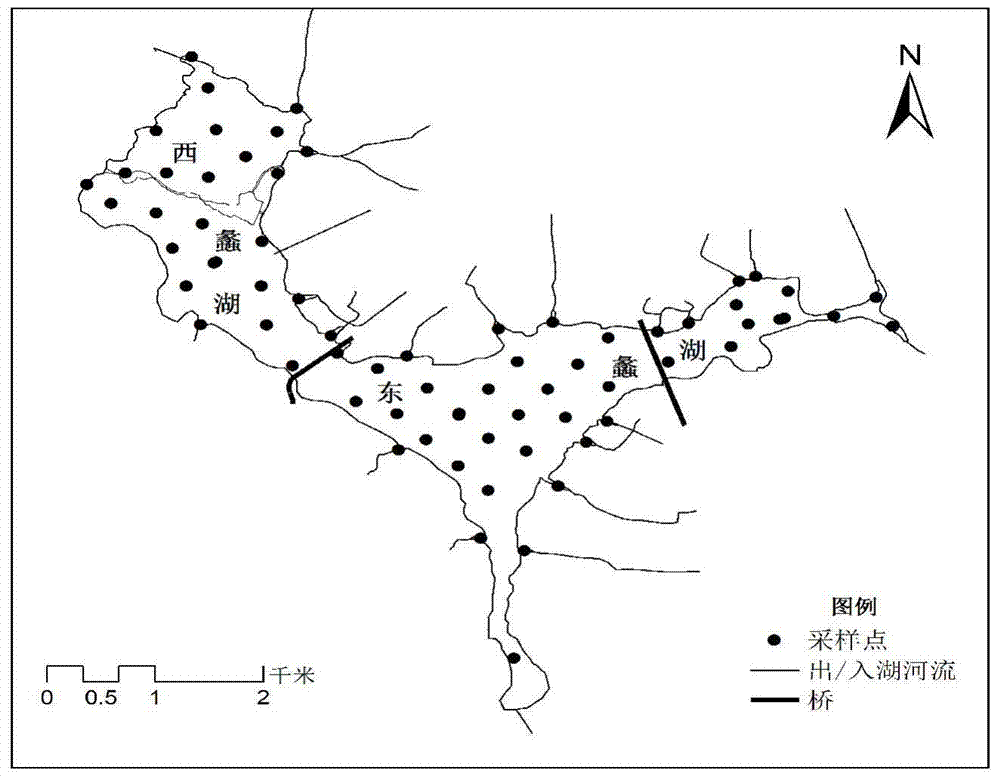
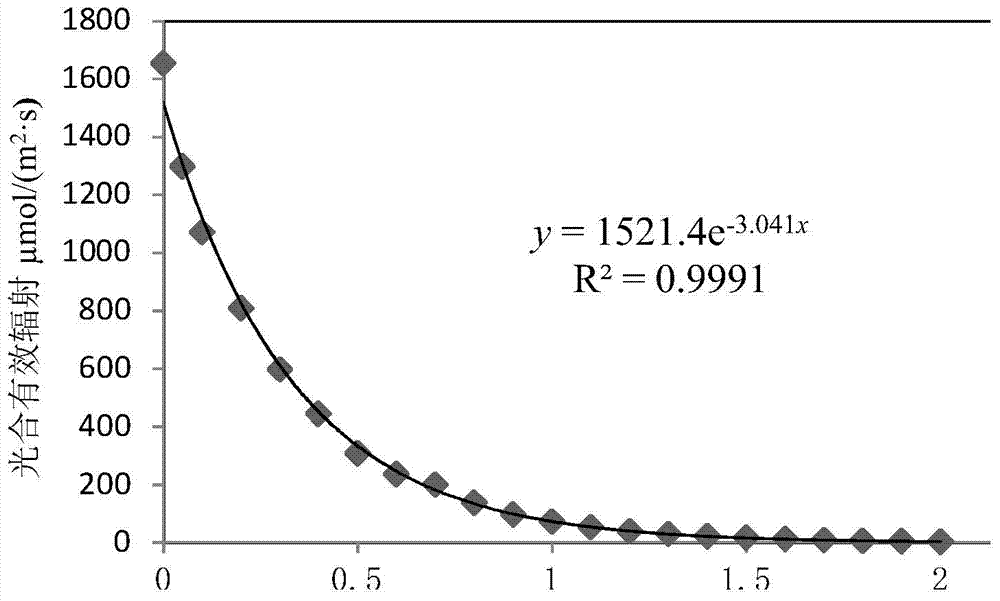
Method for determining target water area submerged plant recovery area
ActiveCN103778319ATargetedClear boundariesSpecial data processing applicationsOperabilitySpatial analysis
The invention discloses a method for determining a target water area submerged plant recovery area. The method includes the steps of (1) determining sampling points of a target water area, and measuring data including the water body depths, the ignition losses and the different-gradient water depth illumination intensities, (2) obtaining attenuation coefficients K of photosynthetic effective radiation of the sampling points, (3) calculating submerged plant population light compensation depths HC of the sampling points, (4) determining an assessment criteria of submerged plant recovery, wherein LOI serves as the ignition losses, and Qi serves as specific values of the submerged plant population light compensation depths to the water body depths; (5) making thematic maps of the LOI vectors and the Qi vectors, and (6) overlaying the thematic maps through a space analysis module of a geographic information system to obtain nine combinations. By means of the method, the submerged plant population recovery area has specific boundaries, and the operability is high; the recovery area has the step performance, a proper area can be preferentially recovered, and a transition area is then recovered after the conditions such as the transparency and bottom mud are met.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Fruit-cracking preventing method for jun jujube cultivated in drought desert oasis in dwarf compact planting mode
ActiveCN104737871AReduce fruit crackingEffectively regulate temperature and humidity changesCultivating equipmentsBlack spotCataphyll
A fruit-cracking preventing method for jun jujube cultivated in a drought desert oasis in a dwarf compact planting mode comprises the following steps of jujube garden mesh coverage, (2) jujube garden ground surface coverage, and (3) leaf surface fertilizer supplementation in the fruit developmental phase. By means of the fruit-cracking preventing method, the changes of the temperature and the humidity of a jujube garden are effectively controlled, dew formation on the surfaces of the jun jujube fruits is avoided, the photosynthetically active radiation of the jujube garden in the hottest month is properly lowered, the photosynthesis of leaves is enhanced, it is promoted that the jujube flesh tissue is compactly developed, the fruit cracking degree of the jun jujube is relieved through control over the two aspects of the internal cause and the external cause, so that the occurrence of black spots and rot of the jujube fruits is reduced, the purpose of increasing the high-quality fruit rate is achieved, and great significance is achieved on the healthy and sustainable development of the red jujube industrial in Sinkiang.
Owner:TARIM UNIV
Spectrally selective grow tube
A biodegradable spectrally selective grow tube or tree shelter that improves the establishment of woody plant forms by reduction and / or elimination of certain biotic and abiotic stress factors. The grow tube may provide an enhanced micro climate that is humid, CO2-replenished and promotes photosynthesis by selectively propagating photosynthetically active radiation. In addition to providing a physical barrier to wind and herbivores, certain embodiments of the grow tube can also provide protection from chemical sprays while permitting ventilation of the grow tube. Various embodiments of the spectrally selective grow tube may comprise separate interior and exterior members for enhancement of the interior and exterior surface functions and that may be constructed from a biodegradeable polymer or paper-based material. The interior member can be dyed or pigmented to selectively transmit wavelengths of the visible spectrum known to promote photosynthesis, such as red light and / or blue light.
Owner:PLANTRA
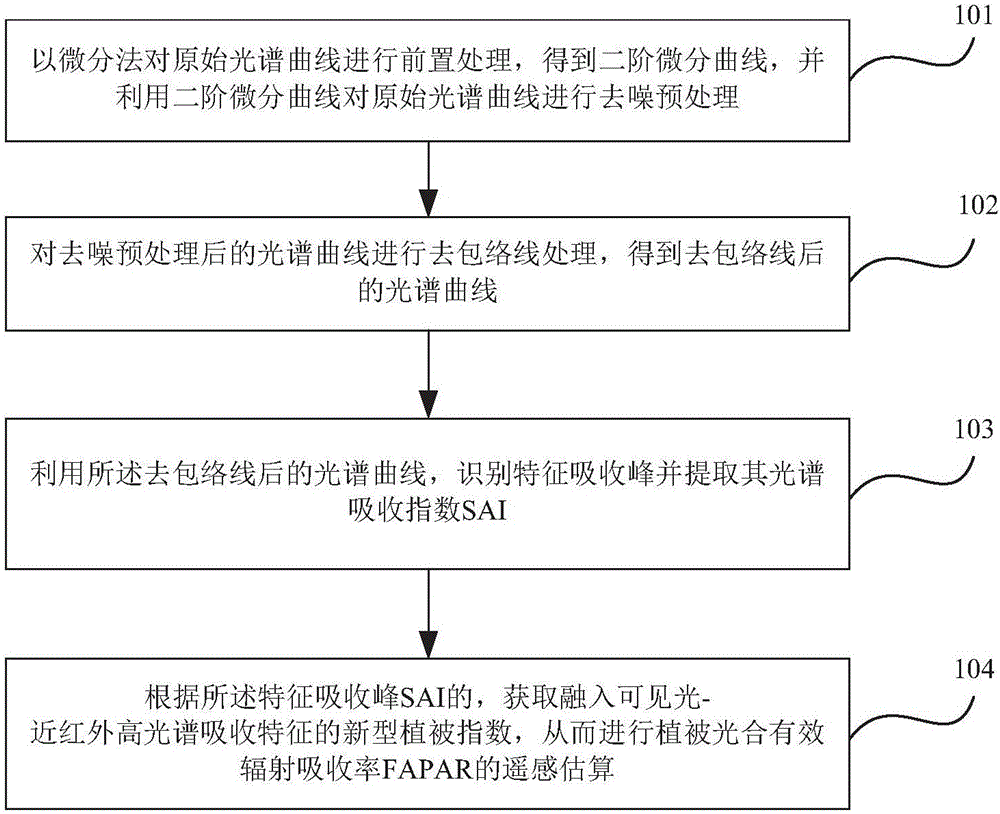
Method and device for remotely sensing and estimating fractions of absorbed photosynthetically active radiation of vegetation
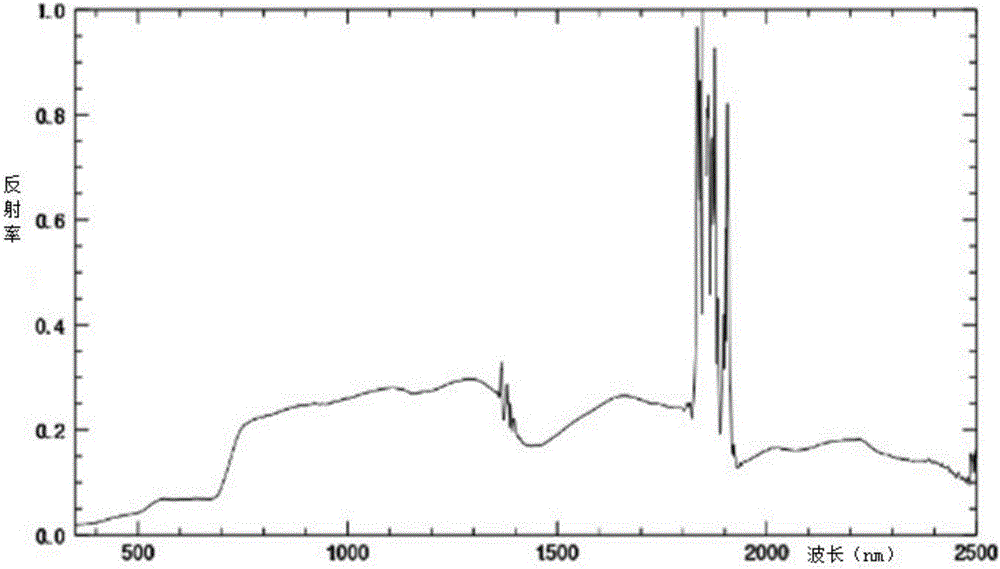
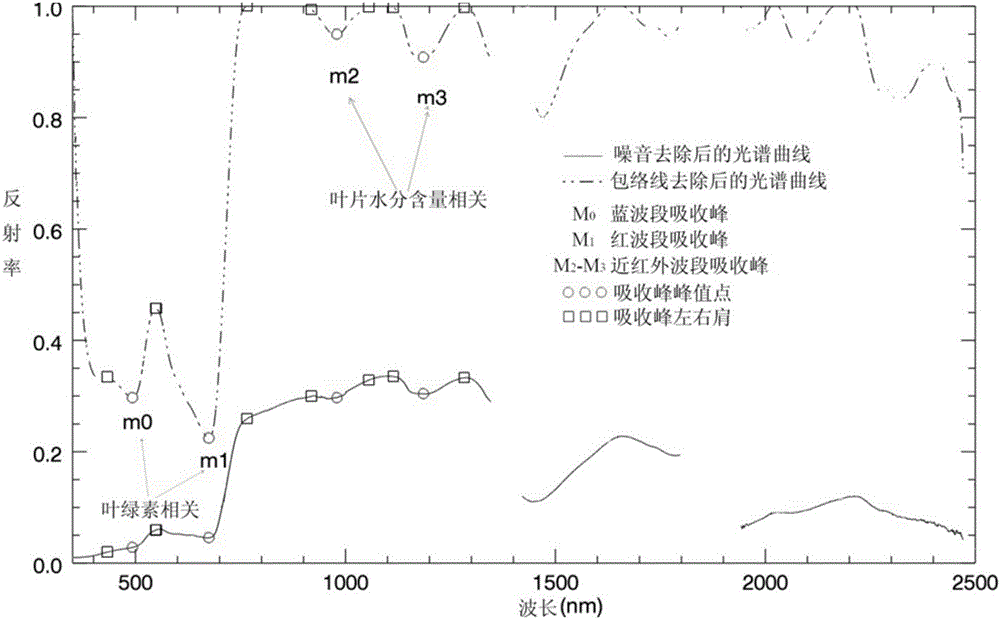
ActiveCN106198437AImprove estimation accuracyImproving the accuracy of remote sensing estimationMaterial analysis by optical meansAbsorption ratioSpectral curve
An embodiment of the invention provides a method and a device for remotely sensing and estimating fractions of absorbed photosynthetically active radiation of vegetation. The method includes carrying out front-end processing on original spectral curves by the aid of differential processes to obtain second-order differential curves and carrying out noise elimination preprocessing on the original spectral curves by the aid of the second-order differential curves; carrying out envelope curve removal processing on the spectral curves after noise elimination preprocessing is carried out on the spectral curves so as to obtain spectral curves without envelope curves; identifying characteristic absorption peaks by the aid of the spectral curves without the envelope curves and extracting spectral absorption indexes SAI of the characteristic absorption peaks; acquiring novel vegetation indexes integrated with visible light-near infrared hyper-spectral absorption characteristics according to the SAI of the characteristic absorption peaks so as to remotely sense and estimate the fractions of absorbed photosynthetically active radiation FAPAR of the vegetation. According to the technical scheme, the method and the device have the advantages that the novel vegetation indexes integrated with the visible light-near infrared hyper-spectral absorption characteristics are created, accordingly, the overall estimation accuracy of conventional visible light-near infrared vegetation indexes can be improved, and the remote sensing and estimation accuracy of the fractions of absorbed photosynthetically active radiation of the vegetation can be improved.
Owner:中国土地勘测规划院
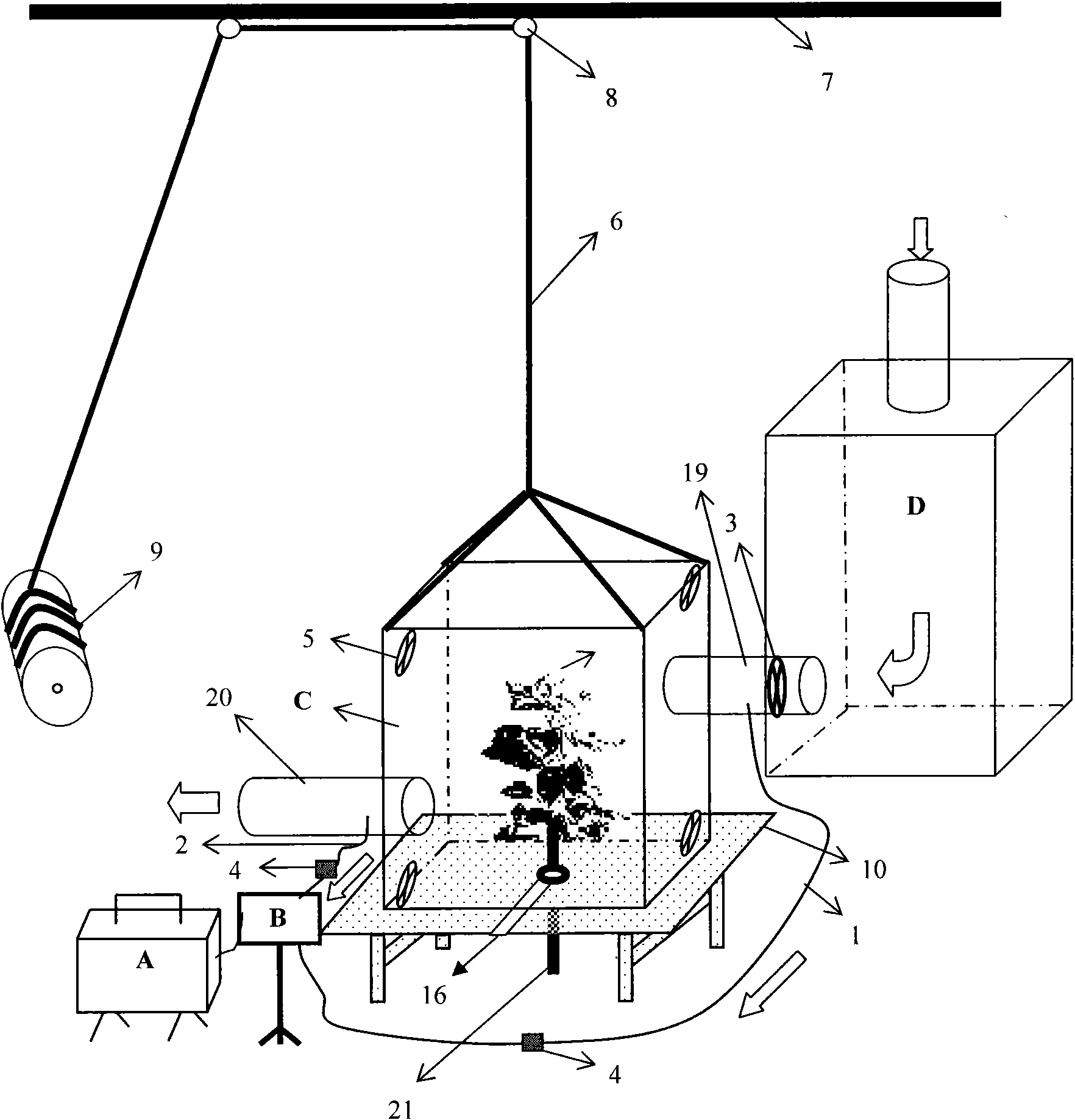
Open box system for determining whole tree gas exchange
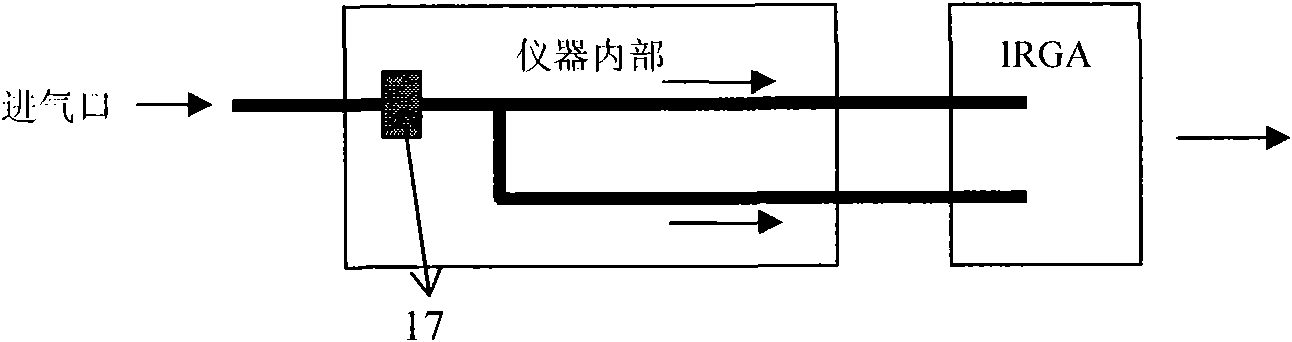
InactiveCN101622945AAvoid enteringAutomatic temperature monitoringHorticulture methodsEngineeringRelative air humidity
The invention relates to plant-atmosphere gas exchange determination technology, in particular to an open box system for determining whole tree gas exchange, which solves the problems that the prior art has no mature observation system with reliable use, simple and convenient operation and commercialization directly applied to single plant level gas exchange observation and the like. The system comprises lifting equipment, an air buffer box, a box body, a base, a piping system and a gas analyzer, wherein the box body used for closing determined tree is connected with the lifting equipment and arranged on the base; the air buffer box is communicated with the box body; and a sensor of the gas analyzer is communicated with the box body through the piping system. The system can realize simultaneous observation of gas concentration of CO2 and H2O of the whole tree, automatically acquire and store data, and automatically monitor air temperature of the box body, relative air humidity, photosynthetic active radiation, atmospheric pressure and other environment factors, and is favorable for research and application of tree gas exchange.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
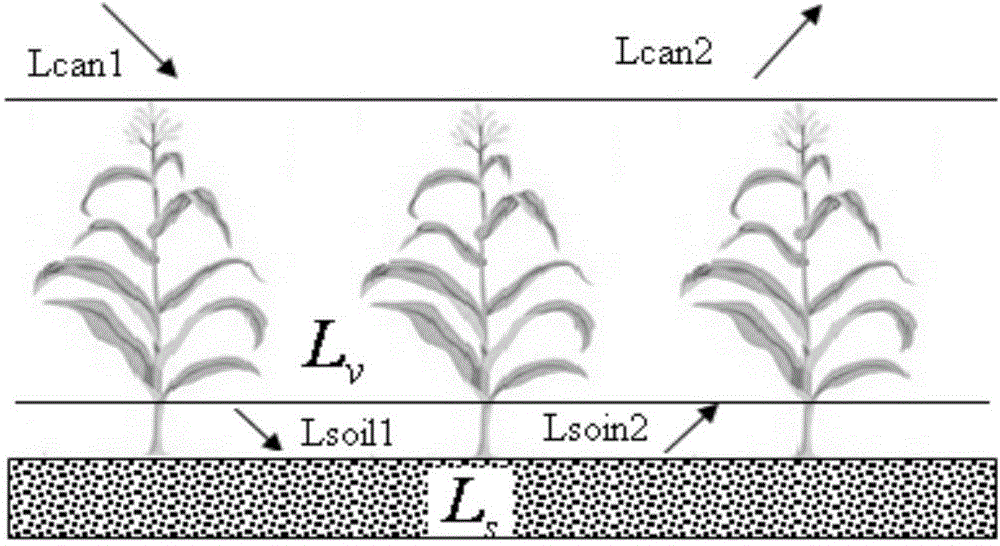
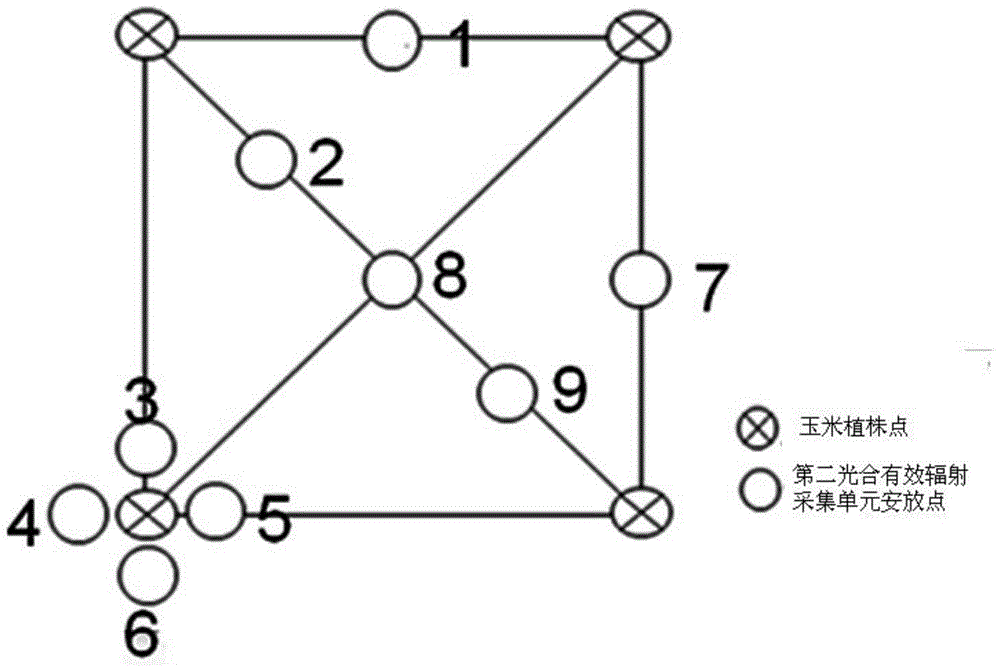
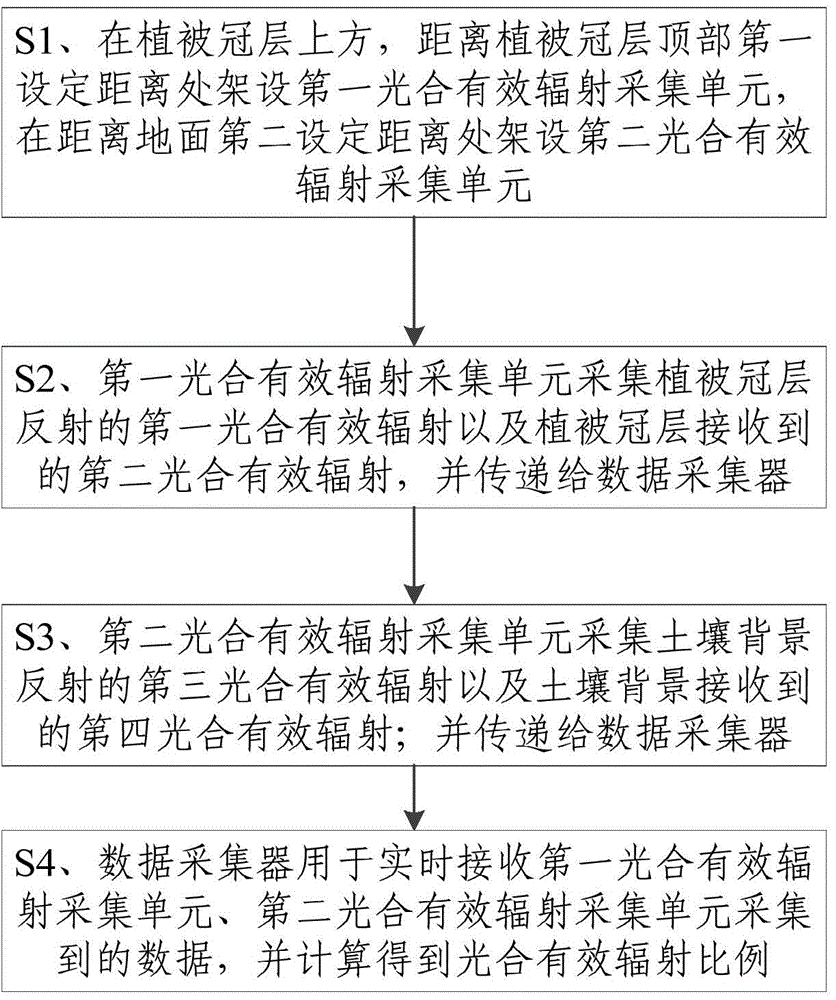
System and method for observing plant canopy photosynthetically active radiation absorptivity
ActiveCN104568145ARealize automatic observationAchieve recordPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsData acquisitionAtmospheric sciences
The invention discloses a system and method for observing plant canopy photosynthetically active radiation absorptivity. The system comprises a first photosynthetically active radiation acquisition unit which is a first set distance away from the top of the canopy of a plant and located above the canopy of the plant, a second photosynthetically active radiation acquisition unit which is a second set distance away from the ground, and a data acquirer receiving data acquired by the first photosynthetically active radiation acquision unit and the second photosynthetically active radiation acquision unit. By the adoption of the system and method, automatic observing and recording can be achieved, cost, errors and man-made interference of manual measurement are reduced, real-time and long-time-series data can be obtained, and real-time automatic continuous plant canopy photosynthetically active radiation absorptivity observation can be achieved on the premise that universality is high, using is convenient and precision is high.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Blade active and inactive chlorophyll fluorescence long-time-series cooperative observation system
InactiveCN104007094AIdea scienceSimple structureFluorescence/phosphorescenceArbitrary Fluorescence UnitEngineering
The invention discloses a blade active and inactive chlorophyll fluorescence long-time-series cooperative observation system. The system consists of a synchronous observation frame, a spectrum collecting device, an active fluorescence collecting device, a photosynthetically active radiation collecting device and a host machine, wherein the spectrum collecting device, the active fluorescence collecting device and the photosynthetically active radiation collecting device are installed on the synchronous observation frame; the spectrum collecting device, the active fluorescence collecting device, the photosynthetically active radiation collecting device and the synchronous observation frame are connected with the host machine by data lines, and through the host machine, spectra, fluorescence kinetic parameters and photosynthetically active radiation data are collected and a motor on the synchronous observation frame is controlled. The blade active and inactive chlorophyll fluorescence long-time-series cooperative observation system is scientific in concept, simple in structure, convenient to carry and high in stability, effectively guarantees the consistency of measurement objects and a measurement environment during active and inactive fluorescence measurement, and can develop cooperative observation of long time series.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com