Determining method of reasonable illuminating dose of facility vegetable
A technology for determining methods and vegetables, applied in botany equipment and methods, horticultural methods, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient light, unfavorable human health, etc., and achieve the effects of wide application range, high yield, and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
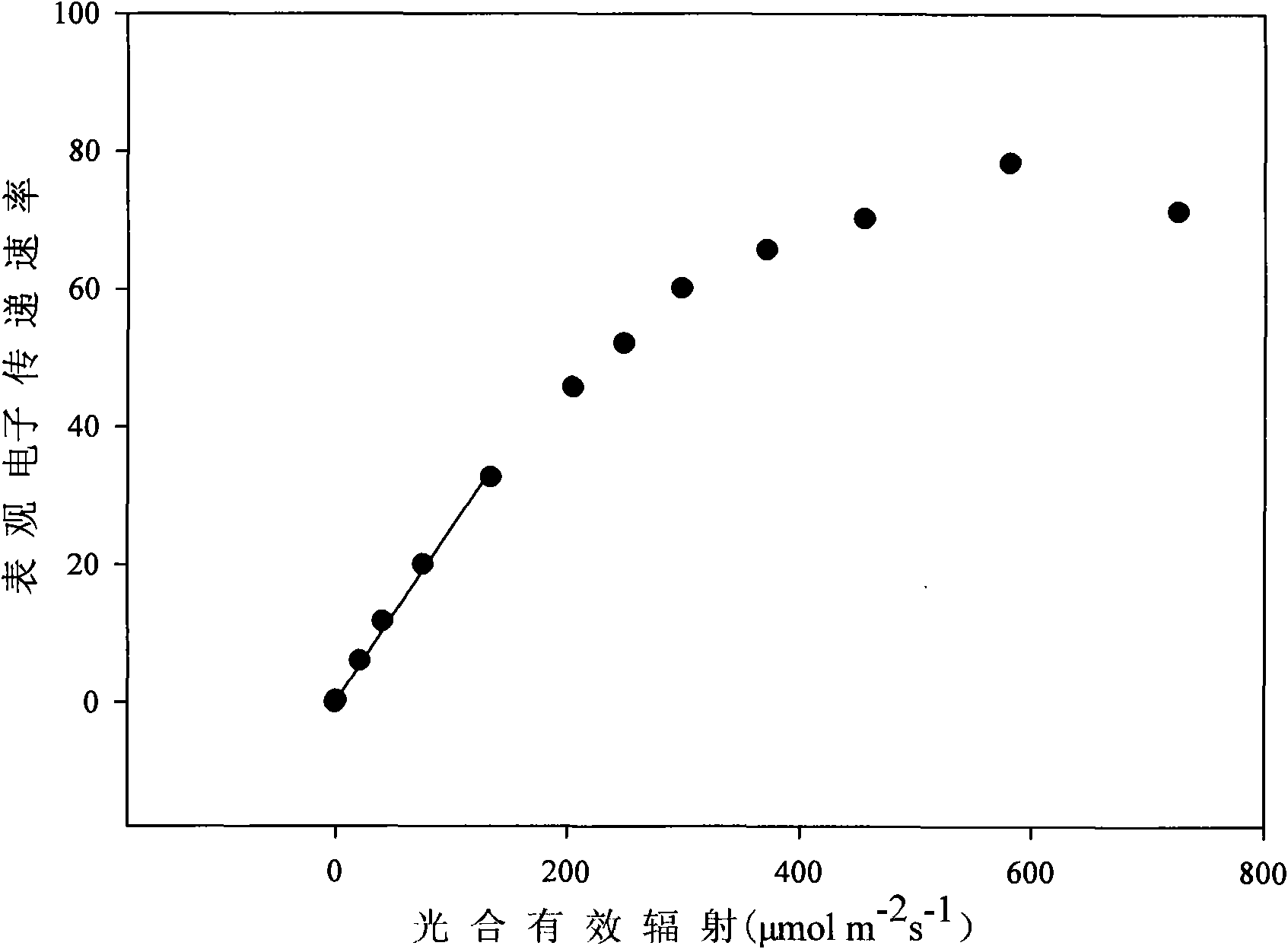
[0019] Greenhouse lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) (variety: Italian bolting-resistant lettuce) 30 days after the seedlings were taken out. The rapid light response curve of lettuce leaves was measured with PAM-2000 modulated chlorophyll fluorescence instrument. According to the response curve of apparent electron transfer rate to photosynthetically active radiation ( figure 1 ) Follow the steps below to determine a reasonable light dose.
[0020] Step 1 calculates the actual photosynthetic electron transfer rate. Find out under low photosynthetically active radiation, the linear part in the curve of apparent electron transfer rate and photosynthetically active radiation, utilize statistical software to obtain the linear equation Y=aX of this part (a is a constant, represents apparent electron transfer rate and photosynthetic active radiation initial slope of the effective radiation curve). The equation is:
[0021] Y=0.252X(R 2 =0.997, n=6, P-2 the s -1 ) (1)
[0022] Y is...
Embodiment 2
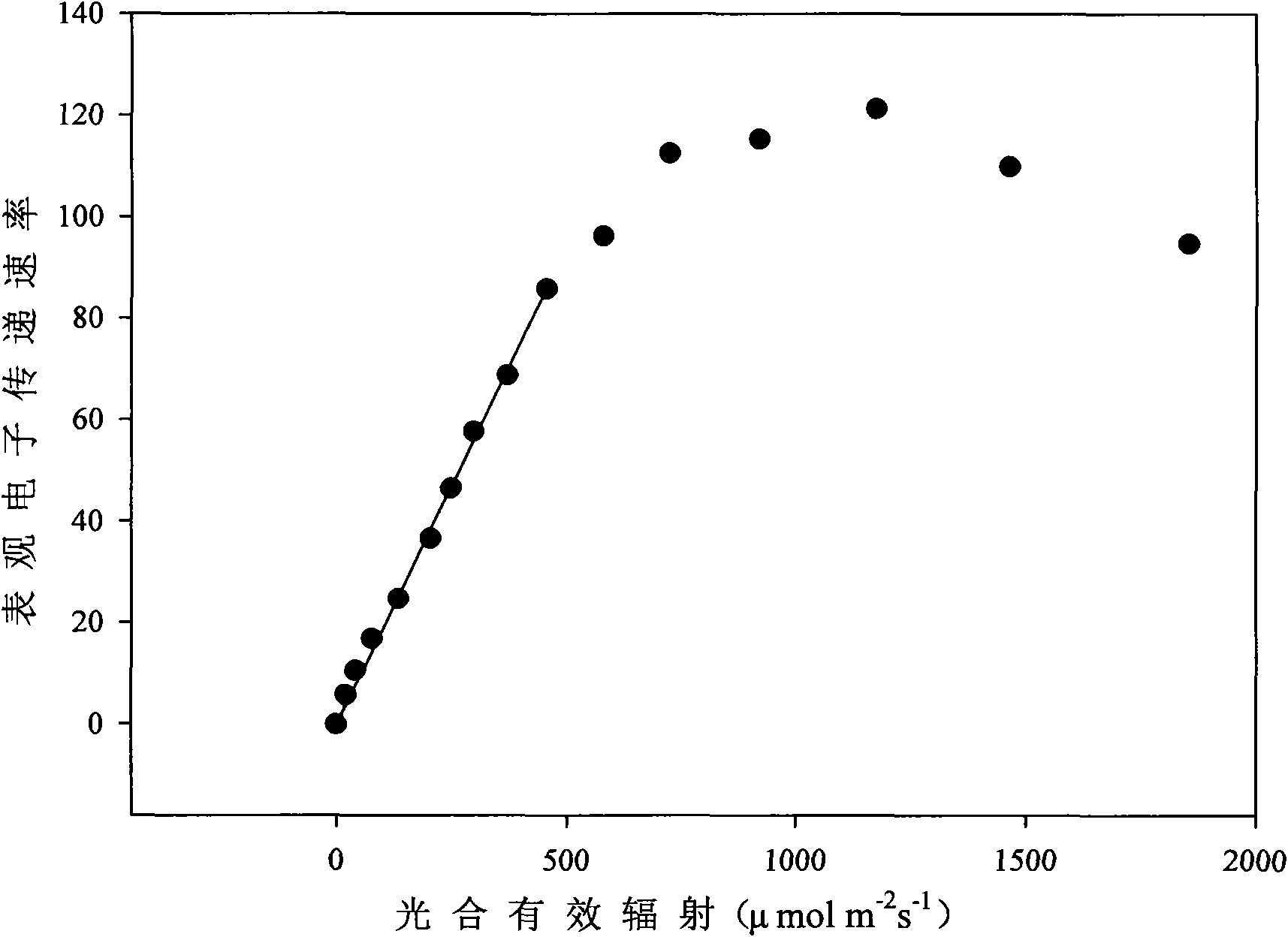
[0030] Greenhouse Zhuge dish (Orychophragmus violaceus L.) 45 days after seedling was taken out. The fast photoresponse curve of Zhuge kale was measured with PAM-2000 modulated chlorophyll fluorescence instrument. According to the response curve of apparent electron transfer rate to photosynthetically active radiation ( figure 2 ), follow the steps below to determine a reasonable light dose.
[0031] Step 1 calculates the actual photosynthetic electron transfer rate. Find out under low photosynthetically active radiation, the linear part in the curve of apparent electron transfer rate and photosynthetically active radiation, utilize statistical software to obtain the linear equation Y=aX of this part (a is a constant, represents apparent electron transfer rate and photosynthetic active radiation initial slope of the effective radiation curve). The equation is:
[0032] Y=0.189X(R 2 =0.998, n=10, P-2 the s -1 ) (2)
[0033] Y is the apparent electron transfer rate, X i...
Embodiment 3
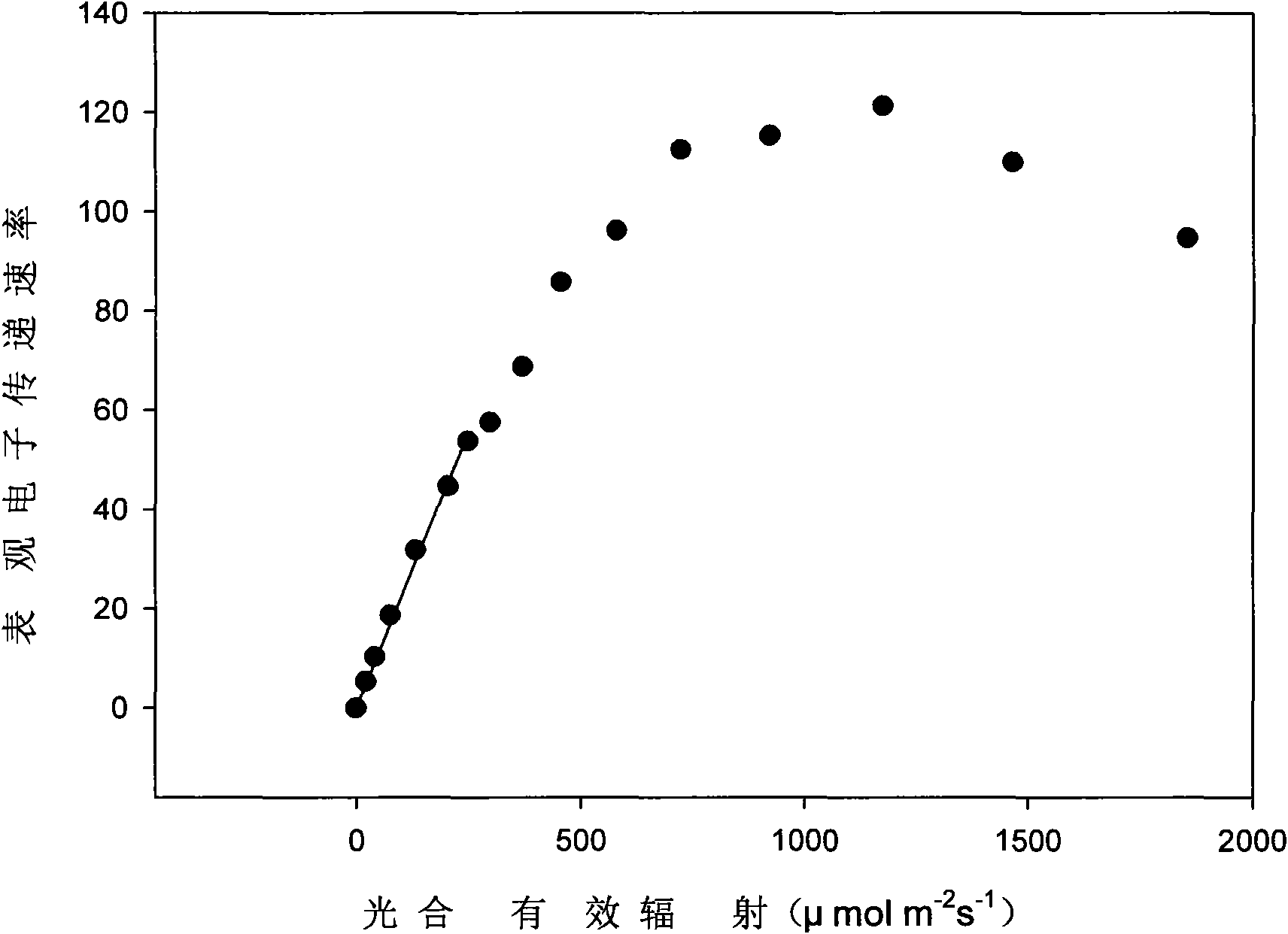
[0041]Greenhouse heading cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis) 45 days after seedling was taken out. The rapid light response curve of head cabbage was measured with PAM-2000 modulated chlorophyll fluorescence instrument. According to the response curve of apparent electron transfer rate to photosynthetically active radiation ( image 3 ) Follow the steps below to determine a reasonable light dose.
[0042] Step 1 calculates the actual photosynthetic electron transfer rate. Find out under low photosynthetically active radiation, the linear part in the curve of apparent electron transfer rate and photosynthetically active radiation, utilize statistical software to obtain the linear equation Y=aX of this part (a is a constant, represents apparent electron transfer rate and photosynthetic active radiation initial slope of the effective radiation curve). The equation is:
[0043] Y=0.223X(R 2 =0.997, n=7, P-2 the s -1 ) (3)
[0044] Y is the apparent electron transfer ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com