Method and device for remotely sensing and estimating fractions of absorbed photosynthetically active radiation of vegetation
A technology of photosynthetically active radiation and absorptivity, which is applied in the field of remote sensing, can solve the problems of poor uniformity of vegetation coverage, weak FAPAR sensitivity, and large soil spectral interference, so as to improve the accuracy of remote sensing estimation and the overall estimation accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] The following will clearly and completely describe the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention with reference to the accompanying drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments are only some, not all, embodiments of the present invention. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without making creative efforts belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
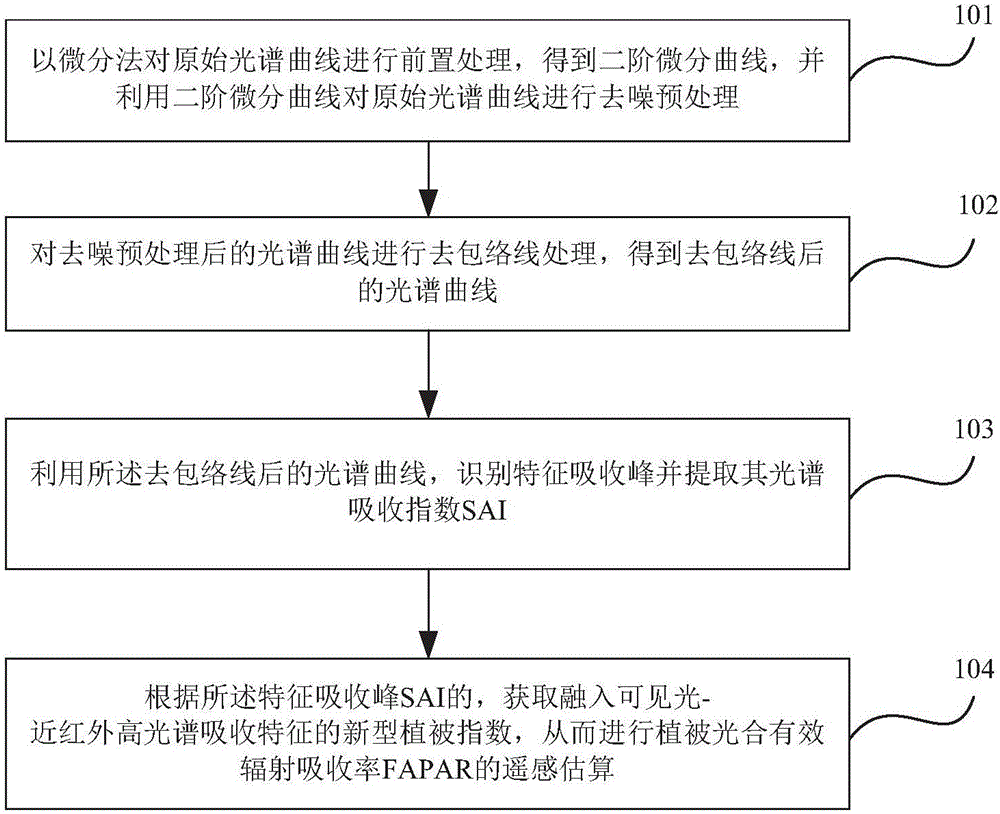
[0023] Such as figure 1 As shown, it is a flowchart of a remote sensing estimation method for plant photosynthetically active radiation absorptivity according to an embodiment of the present invention, and the method includes:
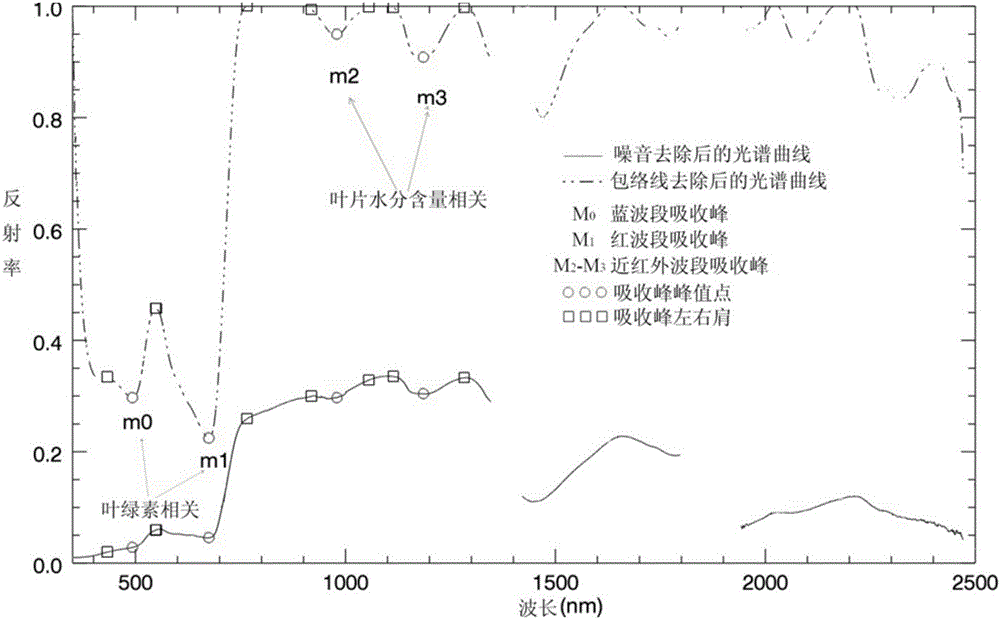
[0024] 101. Pre-process the original spectral curve by differential method, and use the formula for each sampling point on the band of the original spectral curve: Calculate its second-order differential component to obtain the secon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com