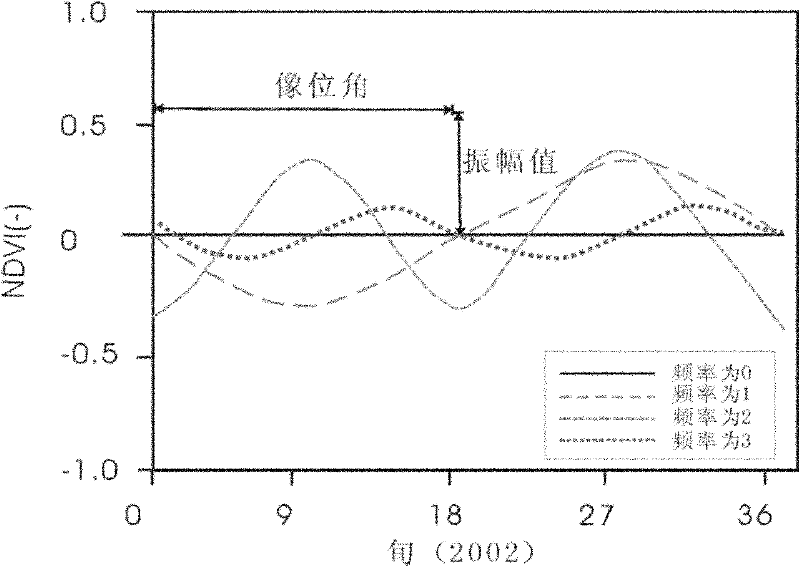
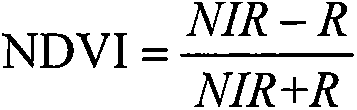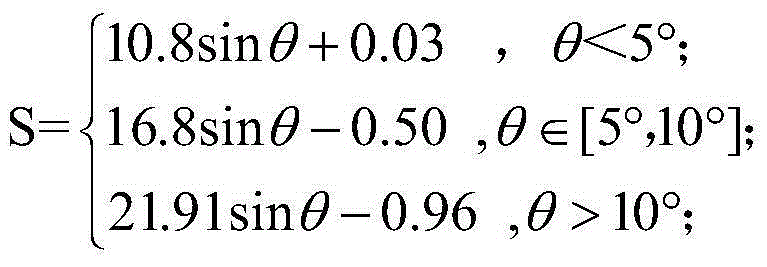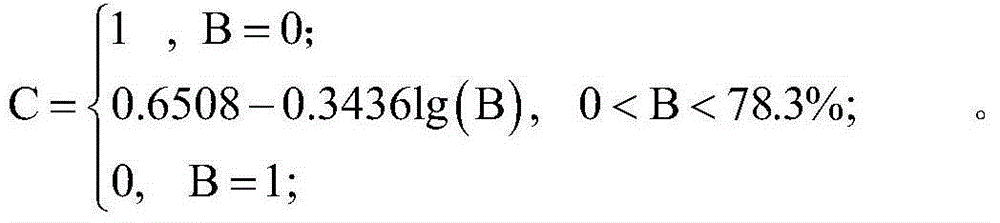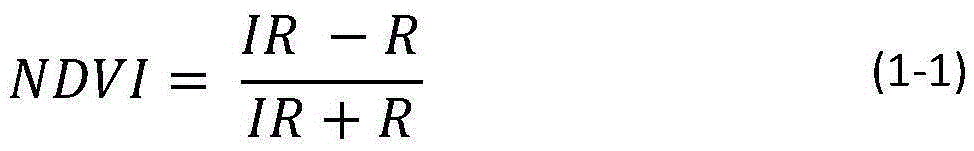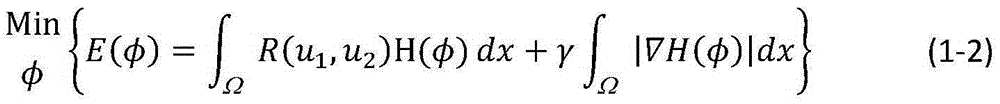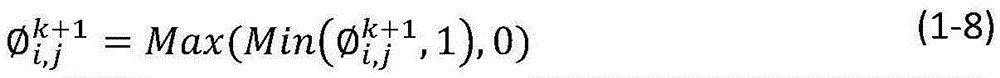Patents
Literature
83 results about "Normalized Difference Vegetation Index" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) is a simple graphical indicator that can be used to analyze remote sensing measurements, typically, but not necessarily, from a space platform, and assess whether the target being observed contains live green vegetation or not.
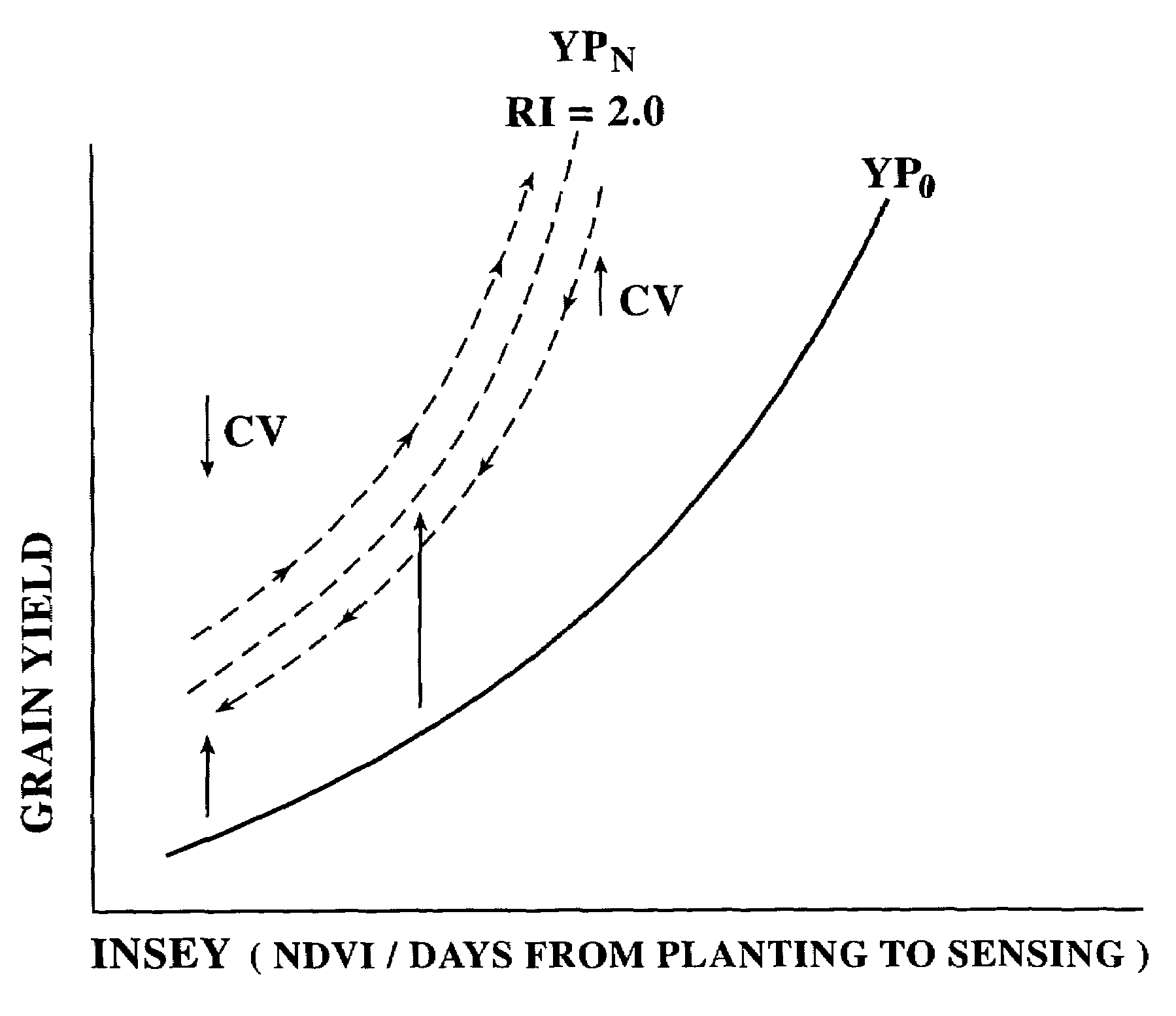
Use of within-field-element-size CV for improved nutrient fertilization in crop production
InactiveUS7188450B2Production be limitedPoor conditioningAnalogue computers for trafficFertilising methodsVegetation IndexMacro and micronutrients
A method for in-season macro and micronutrient application based on predicted yield potential, coefficient of variation, and a nutrient response index. The inventive method includes the steps of: determining a nutrient response index for a field; determining the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) of an area to fertilize; determining the coefficient of variation of NDVI over a plot; determining a predicted crop yield for the area without additional nutrient; determining an attainable crop yield for the area with additional nutrient; determining the nutrient requirement for the area as the difference between the nutrient removal at the attainable yield minus the nutrient removal at the predicted yield, adjusted by the efficiency of nutrient utilization in the particular crop as indicated by the coefficient of variation.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY
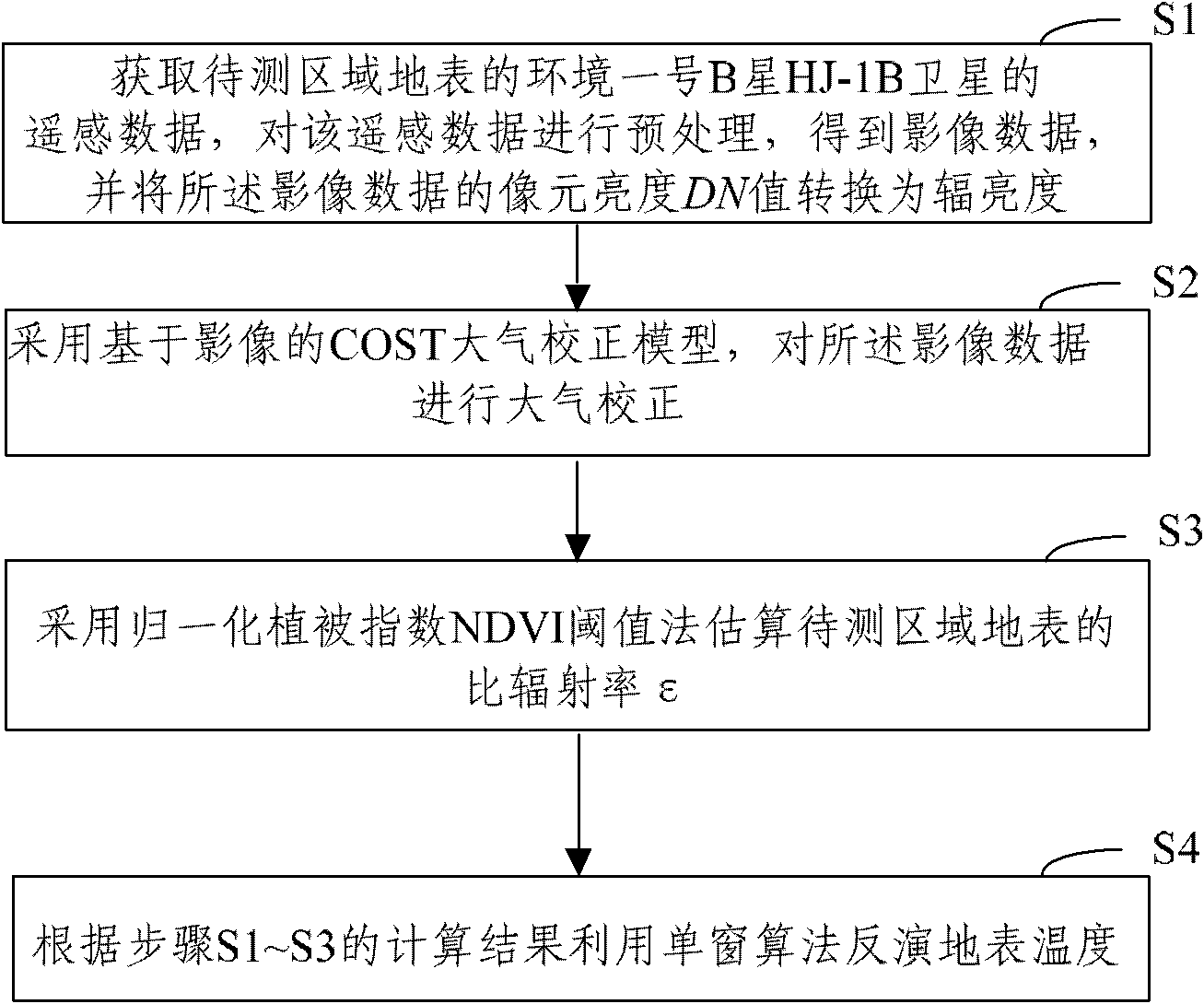
Environmental satellite 1-based surface temperature single-window inversion method
InactiveCN102103203AAchieve inversionWave based measurement systemsPyrometry using electric radation detectorsPixel brightnessAtmospheric correction
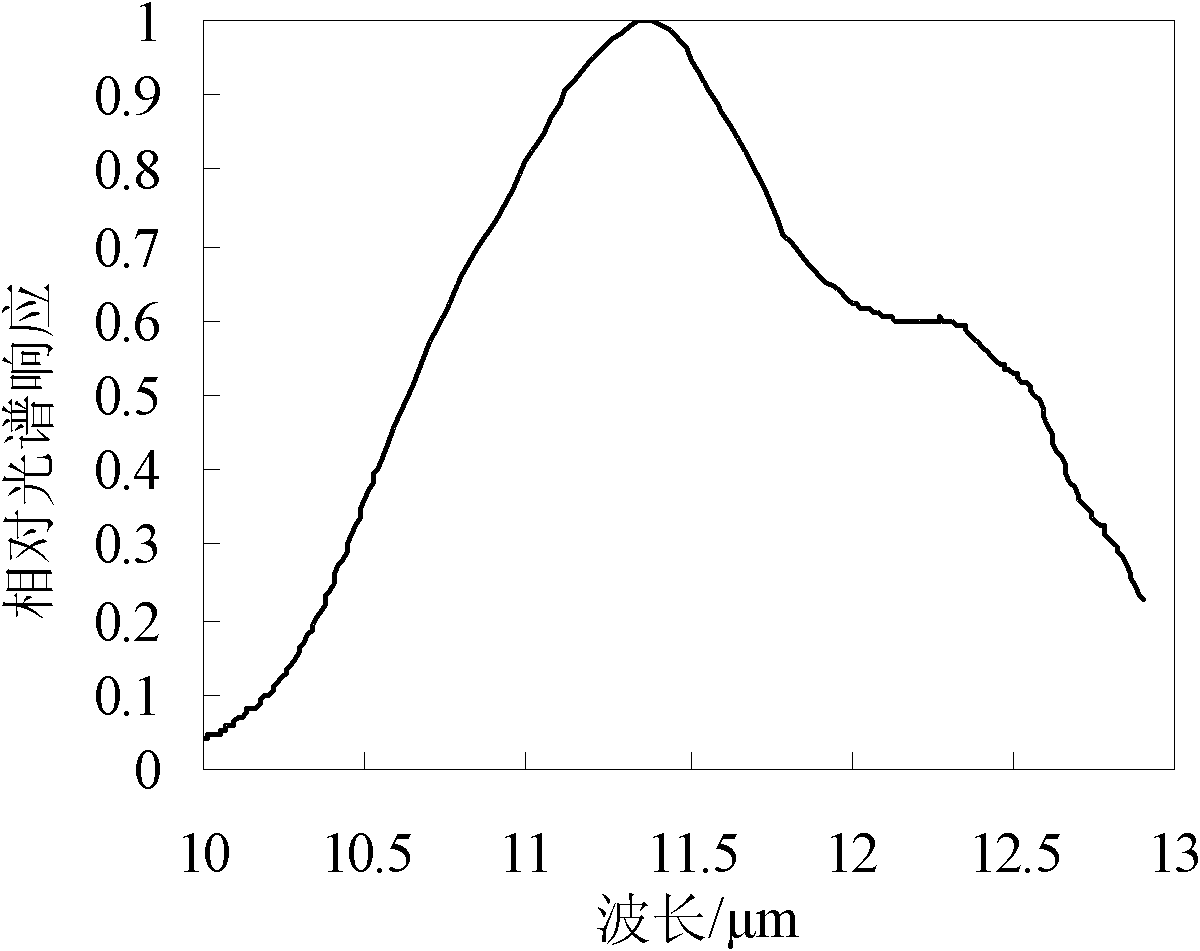
The invention discloses an environmental satellite 1-based surface temperature single-window inversion method. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, acquiring remote sensing data of an environmental satellite 1B, namely an HJ-1B satellite, of the surface of a region to be tested, preprocessing the remote sensing data to acquire image data and converting a pixel brightness digital number (DN) value of the image data into radiance; 2, performing atmospheric correction on the image data by using an image-based continental offshore stratigraphic test (COST) atmospheric correction model; 3, estimating emissivity epsilon of the surface of the region to be tested by a normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) threshold method; and 4, inverting the surface temperature by a single-window algorithm according to calculation results obtained in the steps 1 to 3. In the method, the image-based COST model atmospheric correction method and the surface temperature single-window algorithm with no need of an atmospheric water vapor content parameter are applied to the HJ-1B satellite remote sensing data, so that the inversion of the surface temperature is realized.
Owner:SATELLITE ENVIRONMENT CENT MINIST OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Land surface soil moisture downscaling method based on multisource remote sensing satellite merged data
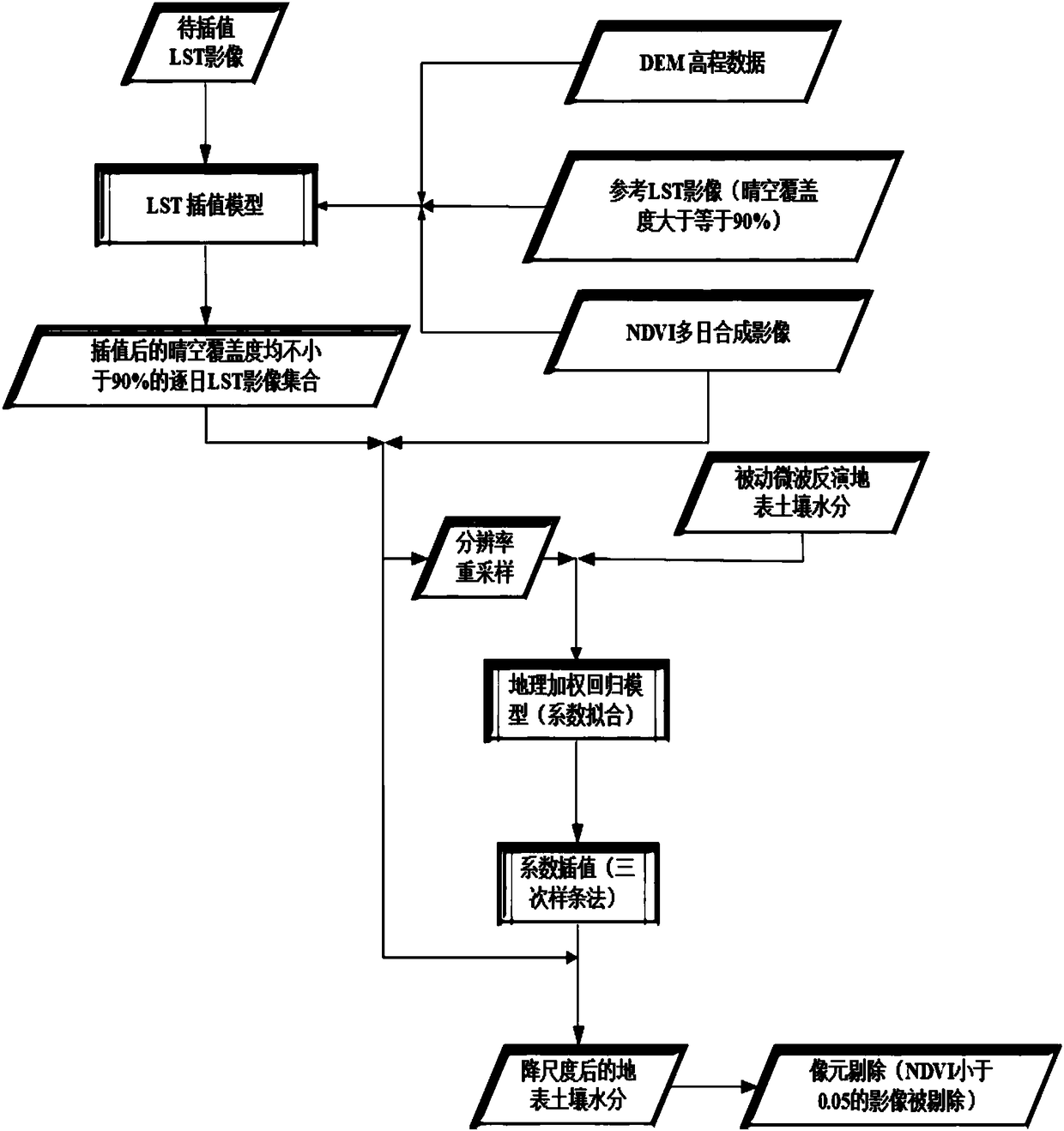
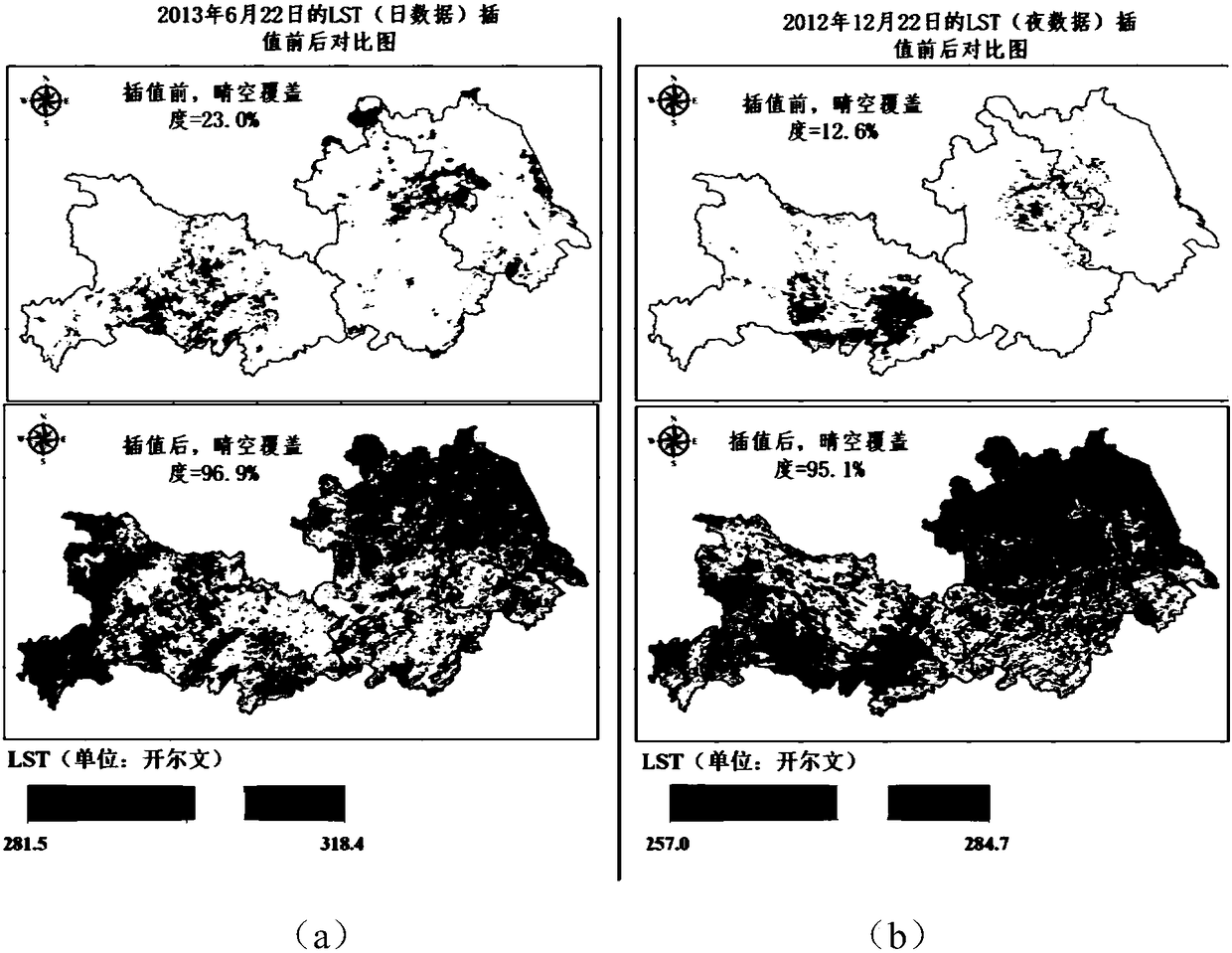
The invention discloses a land surface soil moisture downscaling method based on multisource remote sensing satellite merged data and is particularly applicable to cloudy and rainy areas. The method comprises the following steps: collecting and arranging a passive microwave soil moisture data set, an LST (land surface temperature) and NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index) data set and DEM(digital elevation model) data; performing spatial interpolation on LST images with serious pixel deletion affected by cloud and rain by adopting an NDVI and DEM data set as auxiliary data to obtain aday-by-day LST data set almost totally covering a research area; constructing a mathematic relation model for microwave soil moisture with optical remote sensing LST and NDVI by a geographical weighted regression model, and obtaining a land surface soil moisture data set with high spatial resolution with the mathematic relation model. Through the adoption of the method, reliability of a descalingresult and universality of descaling in the wide-range research area are improved effectively, and precision and efficiency of wide-range space mapping and monitoring for soil moisture content in thecloudy and rainy areas are improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
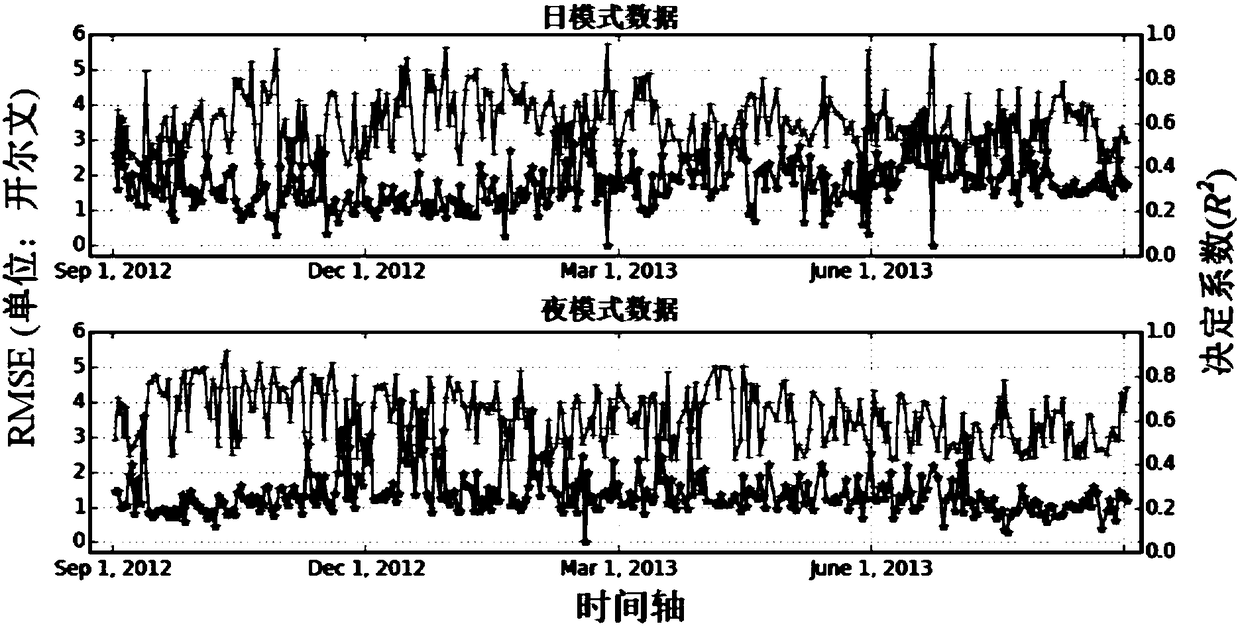
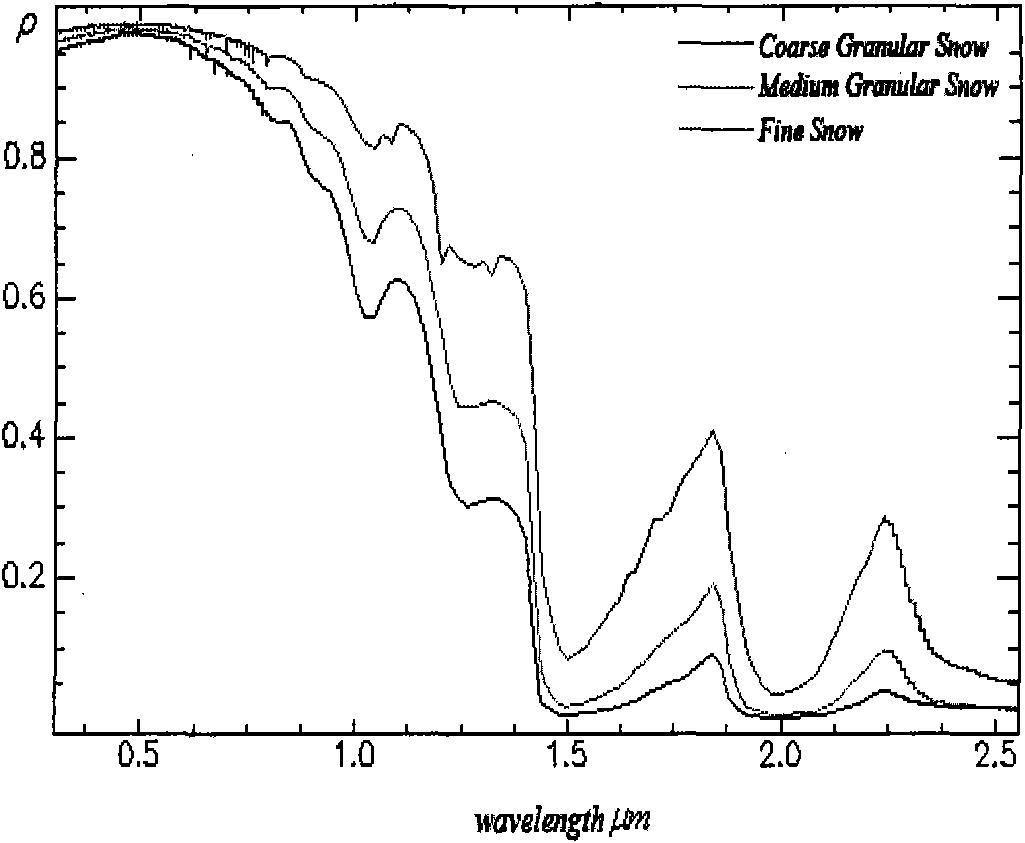
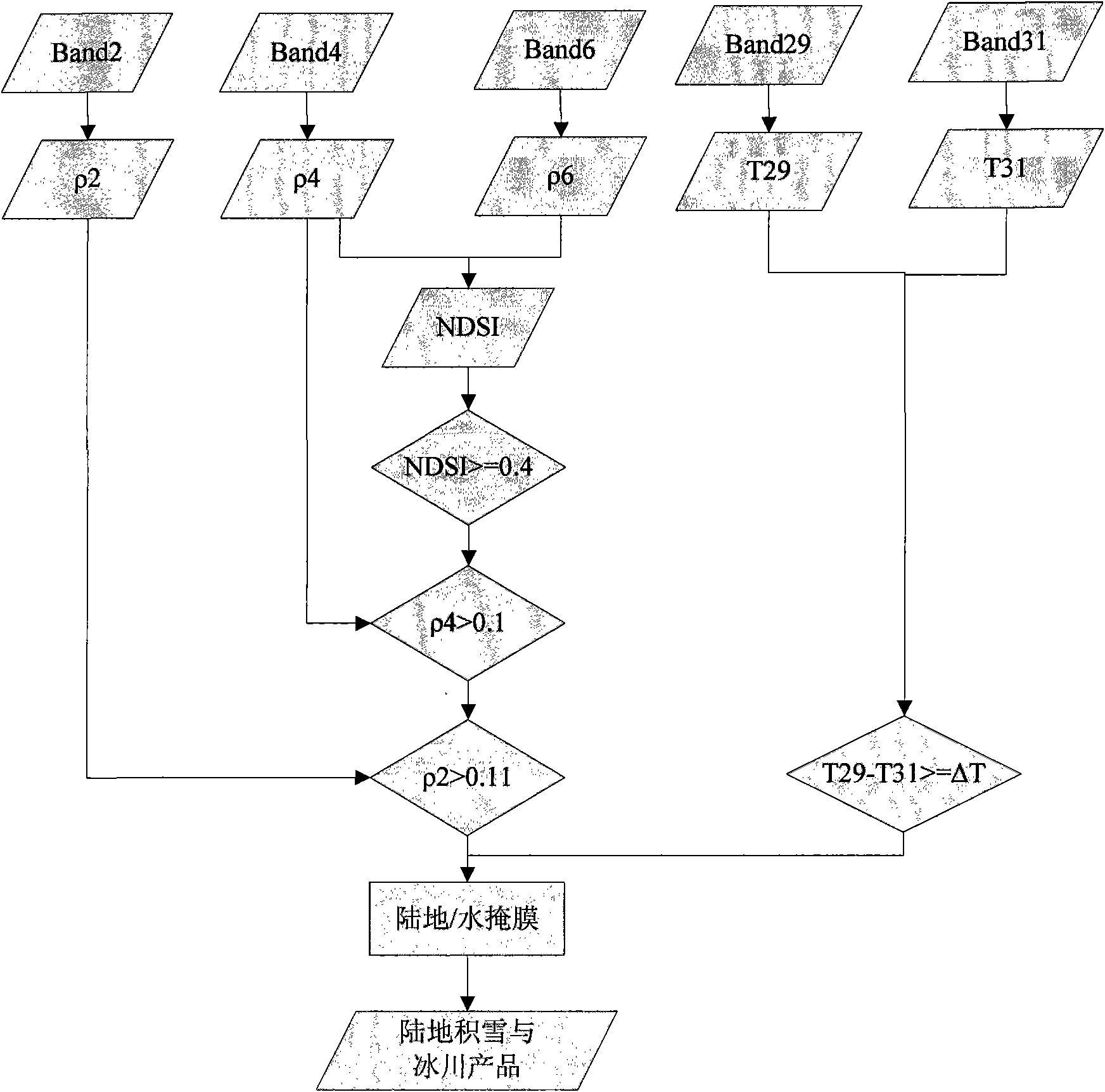
Snow disaster remote sensing monitoring simulation evaluation method based on disaster reduction small satellite
InactiveCN101799561AHigh resolutionImprove dynamic monitoring capabilitiesElectromagnetic wave reradiationSnowpackStatistical database
Owner:MIN OF CIVIL AFFAIRS NAT DISASTER REDUCTION CENT
Grassland dry matter mass remote sensing estimating method
ActiveCN102393238APromote healthy and sustainable developmentMaintain ecological balanceWeighing apparatusData acquisitionRemote sensing application
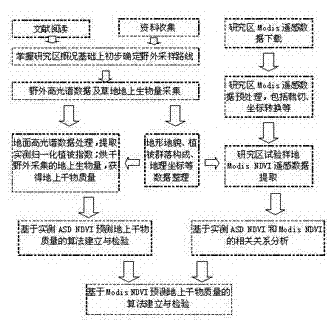
The invention discloses a grassland dry matter mass remote sensing estimating method, which belongs to the field of remote sensing application. The method comprises the following steps of: collecting and processing field test data; downloading and processing Modis (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) satellite data; analyzing and modeling the data and detecting the accuracy and the like. The method for establishing a ground spectrum model for predicating ground dry matter mass and correcting a Modis spectrum model through ground hyperspectral experiments is different from the method for directly predicating biomass liveweight by using NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) data of the Modis remote sensing satellite in other like researches so that the grassland dry matter mass remote sensing estimating method is helpful for improving the predicating accuracy, is beneficial for scientific management and reasonable utilization of the grassland resources and has important practical significance in correct evaluation of the real productivity of the grassland and the sustainable use of the grass resources.
Owner:高吉喜
Calculation method for large spatial scale vegetation coverage by combining with unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) image
ActiveCN107389036AImprove universalitySolid theoretical foundationPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryDecompositionAtmospheric correction
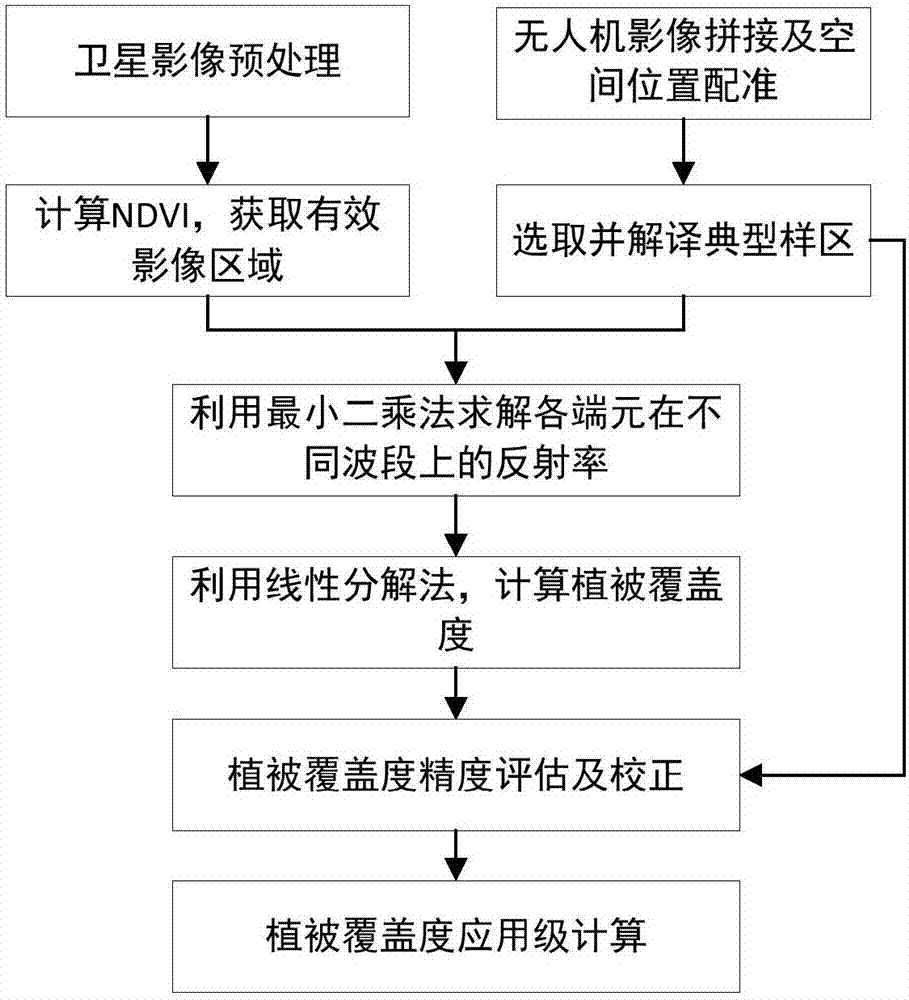
The invention discloses a calculation method for large spatial scale vegetation coverage by combining with an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) image. The calculation method comprises the following steps: carrying out atmospheric correction and geometrical correction on a remote sensing image, calculating NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) and obtaining an effective region according to a predetermined threshold value; splicing UAV pictures and obtaining an orthoimage, registering satellite data subjected to geometrical correction with the spatial position, selecting a typical sample area from the UAV image, and interpreting proportions of all ground objects in the typical sample area by using unsupervised classification; randomly selecting one part of the sample area, and solving the reflectivity of all ground object end elements by using the proportions of all the ground objects in the sample area and the corresponding satellite remote sensing band reflectivity and combining with a least square method; solving the vegetation coverage of all pixels in the effective image area by using a spectral decomposition model and the reflectivity of all the ground object end element; correcting calculation results of the vegetation coverage by using data of a residual sample area. The core of the calculation method disclosed by the invention is based on a method of acquiring the end-element reflectivity of the UAV and a vegetation coverage correction model, and the calculation accuracy of the large spatial scale vegetation coverage can be effectively improved.
Owner:PEARL RIVER HYDRAULIC RES INST OF PEARL RIVER WATER RESOURCES COMMISSION
Hyperspectral estimation method for chlorophyll contents at different rice growth periods
InactiveCN107024439AEasy to predictScattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsModel inversionEstimation methods
The invention discloses a hyperspectral estimation method for chlorophyll contents at different rice growth periods. The method belongs to the field of agricultural technology, and comprises the following steps of determining canopy spectrums, determining chlorophyll contents and processing data. According to the method, aiming at a rice elongation stage, a heading period, a milk-ripe stage and a dough stage in northwest region, through analyzing the correlation of canopy reflectance and chlorophyll content at each growth period, a rice chlorophyll content inversion model based on a sensitive band and NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) is built, the model inversion accuracy is compared, the correlation of canopy reflectance and chlorophyll contents at different growth periods of the rice is analyzed, and a theoretical basis is provided for utilizing a hyperspectral remote sensing technology for nondestructively, quickly and efficiently estimating rice canopy chlorophyll content research.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Point location data and remote sensing image data-based regional farmland quality monitoring method
InactiveCN102073869AFully reflect the grade distributionImprove discriminationCharacter and pattern recognitionPrincipal component analysisCorrelation analysis
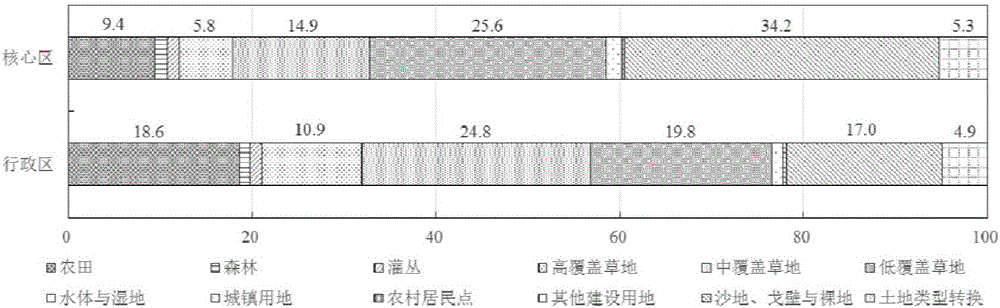
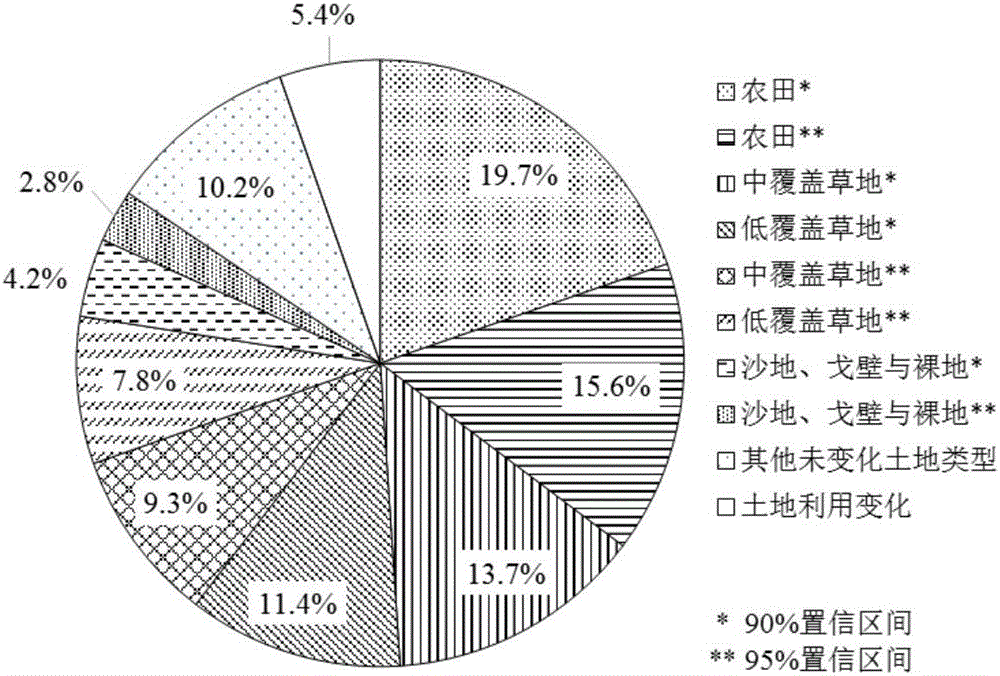
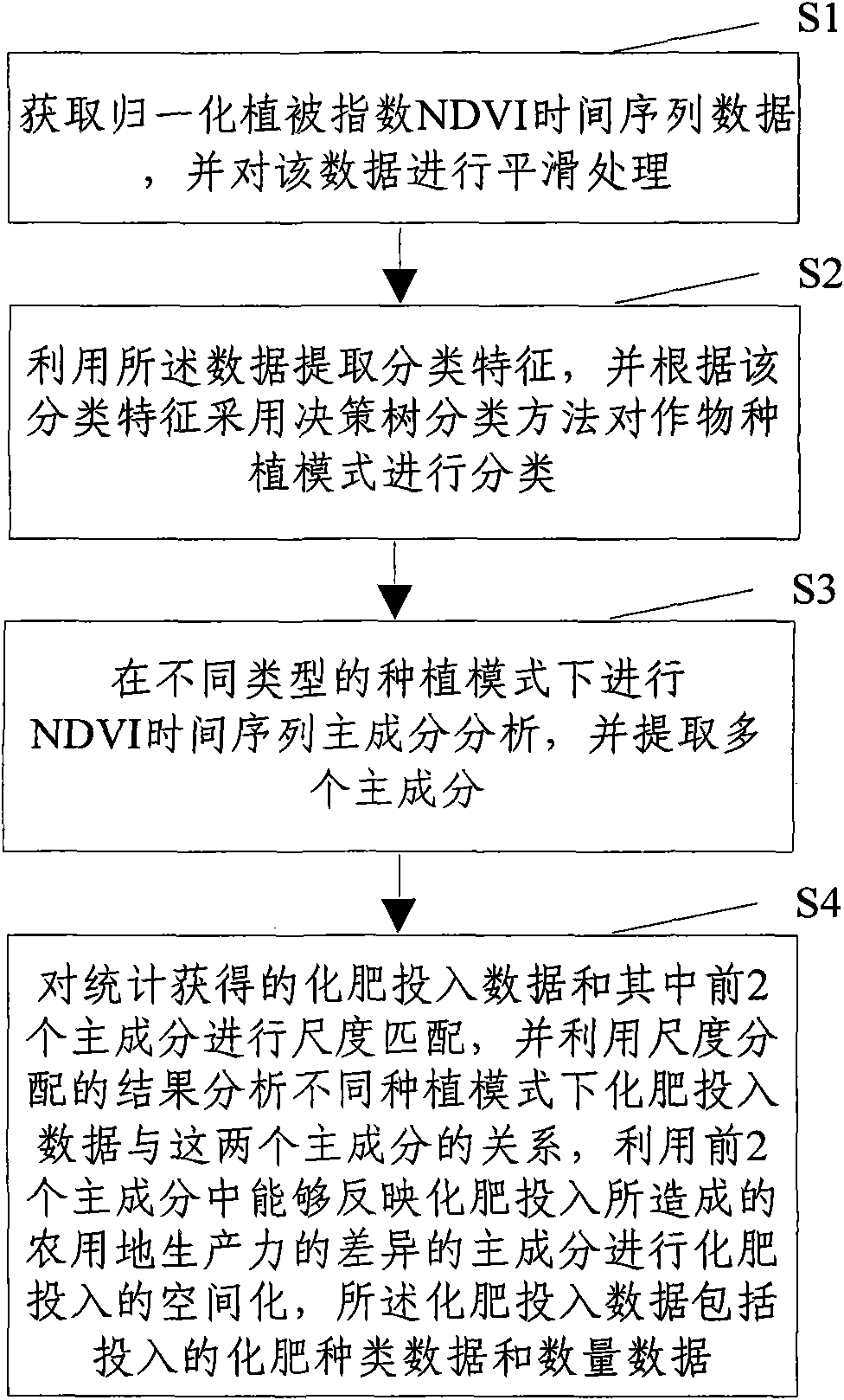
The invention discloses a point location data and remote sensing image data-based regional farmland quality monitoring method. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, acquiring a normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) time sequence data, and performing smoothing processing; S2, extracting classification characteristics and classifying crop planting modes according to the classification characteristics; S3, performing principal component analysis on an NDVI time sequence in different planting modes, and extracting a plurality of principle components; S4, performing the principal component analysis on indexes which reflect farmland quality by utilizing point location data, extracting the principle components, calculating farmland quality index numbers, and performing quantitative evaluation on the farmland quality of a monitoring point; S5, respectively performing correlation analysis on the farmland quality index numbers and the principal components of the NDVI time sequence in different planting modes by utilizing the point location data; and S6, establishing a regression model by utilizing the point location data according to the farmland quality index numbers and a first principal component in different planting modes to obtain a farmland quality grade distribution graph. The method can completely reflect farmland quality grade distribution essentially and can acquire good differentiation.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
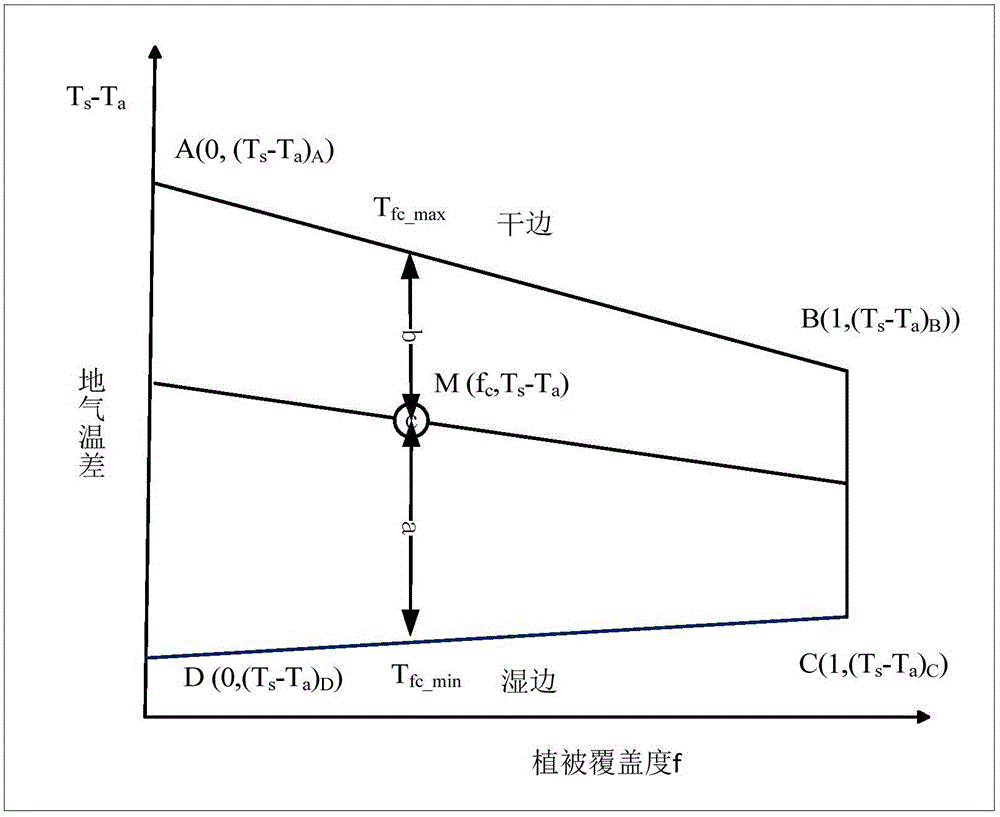
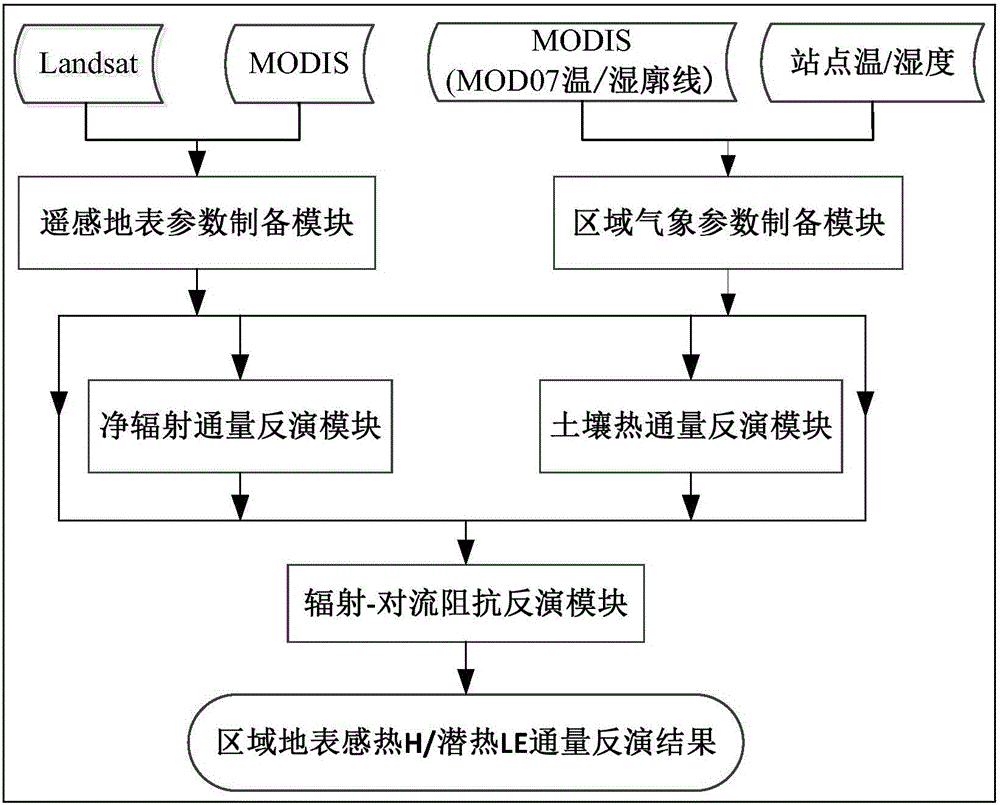
Regional earth surface sensible heat/latent heat flux inversion method and system based on remote sensing data
InactiveCN106169014AInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsEarth surfaceNormalized Difference Vegetation Index
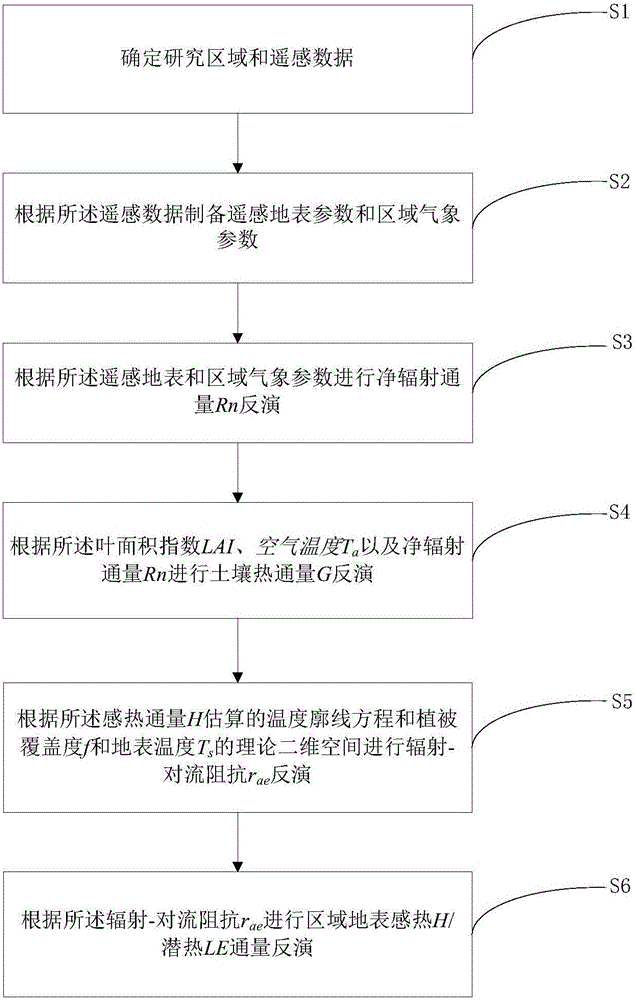
The invention discloses a regional earth surface sensible heat / latent heat flux inversion method based on remote sensing data. The method comprises the following steps that a research area and the remote sensing data are determined; remote sensing earth surface and regional meteorological parameters are prepared according to the remote sensing data, wherein the remote sensing earth surface parameters comprise a normalized difference vegetation index NDVI, vegetation coverage f, albedo, earth surface emissivity Emiss, earth surface temperature Ts and a leaf area index LAI, and the regional meteorological parameters comprise air temperature Ta and relative humidity RH; net radiation flux Rn inversion is conducted according to the remote sensing earth surface and regional meteorological parameters; soil heat flux G inversion is conducted according to the leaf area index LAI, the air temperature Ta and net radiation flux Rn; radiation-convection impedance rae inversion is conducted according to theoretical two-dimensional space of the net radiation flux Rn, soil heat flux G, the vegetation coverage f and the earth surface temperature Ts and a temperature profile equation estimated through sensible heat flux; regional earth surface sensible heat H / latent heat LE flux inversion is achieved according to radiation-convection impedance rae.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
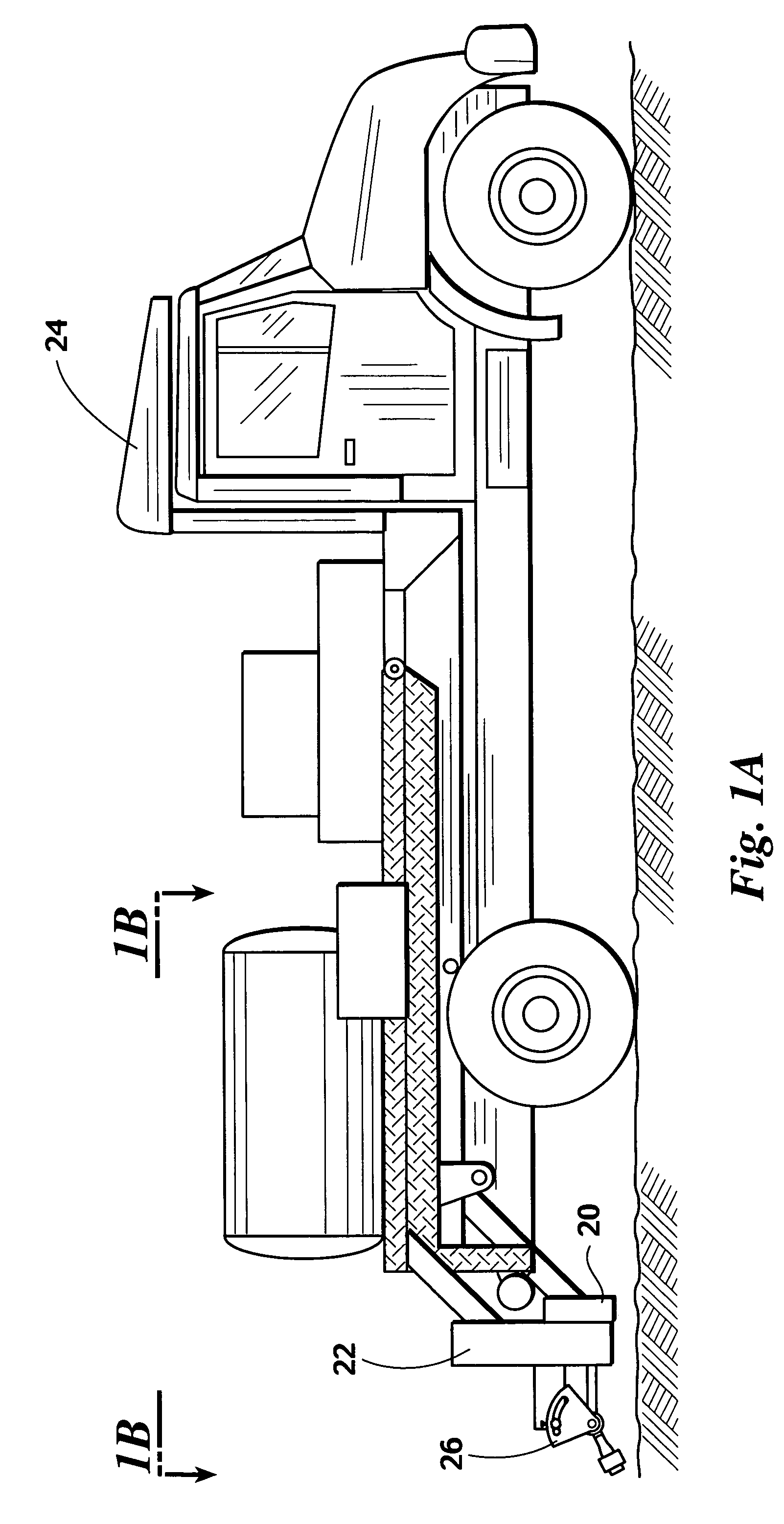
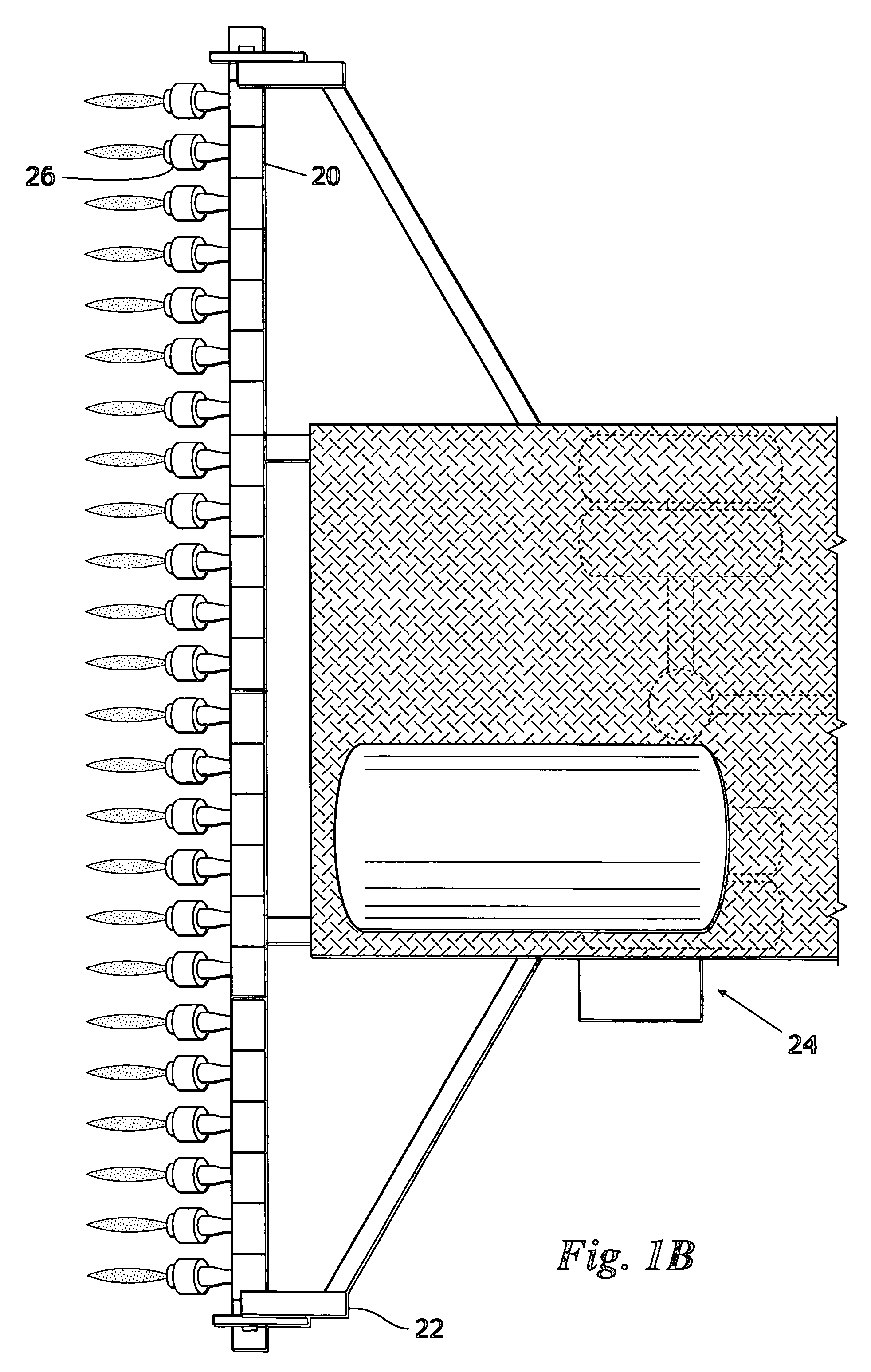
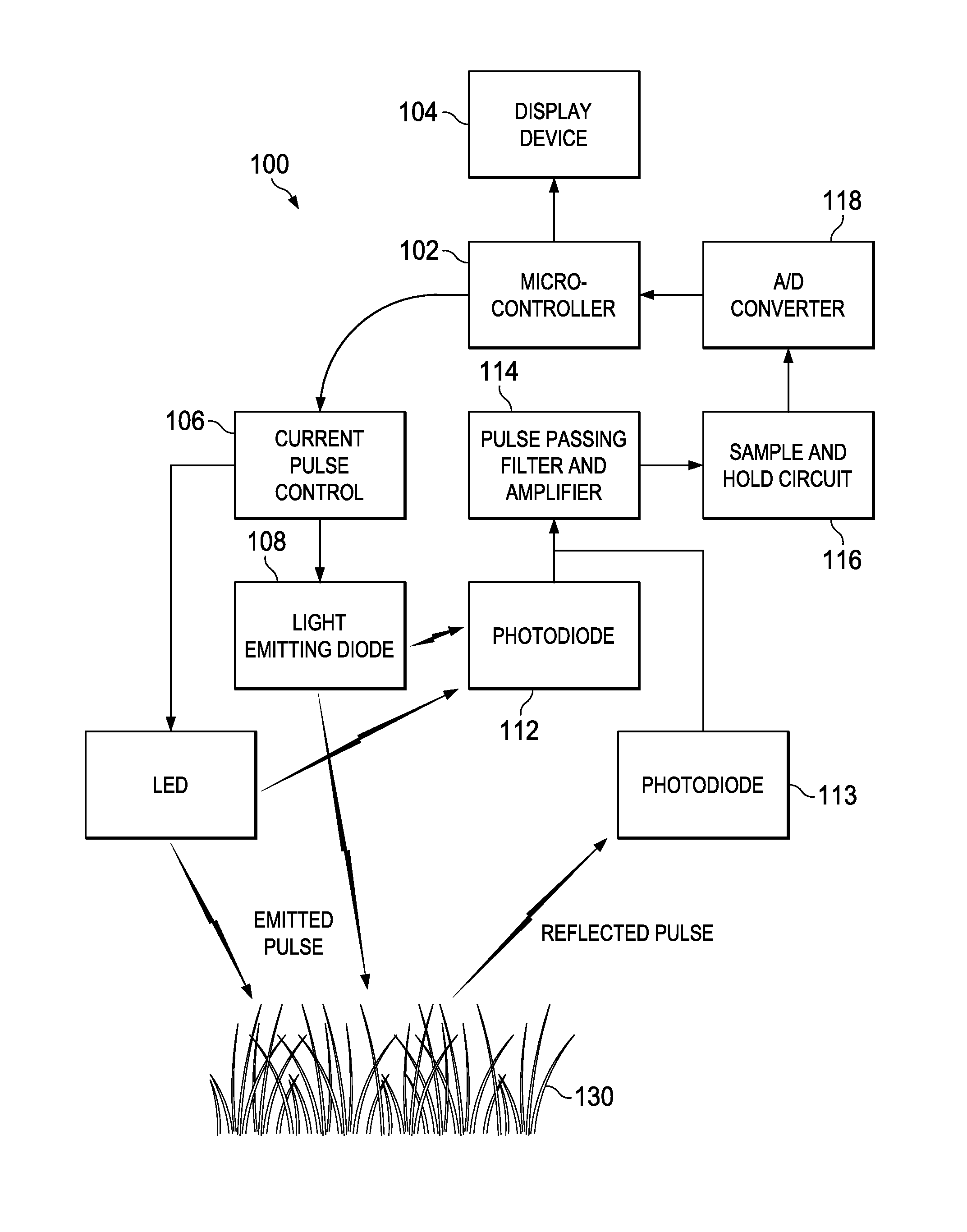
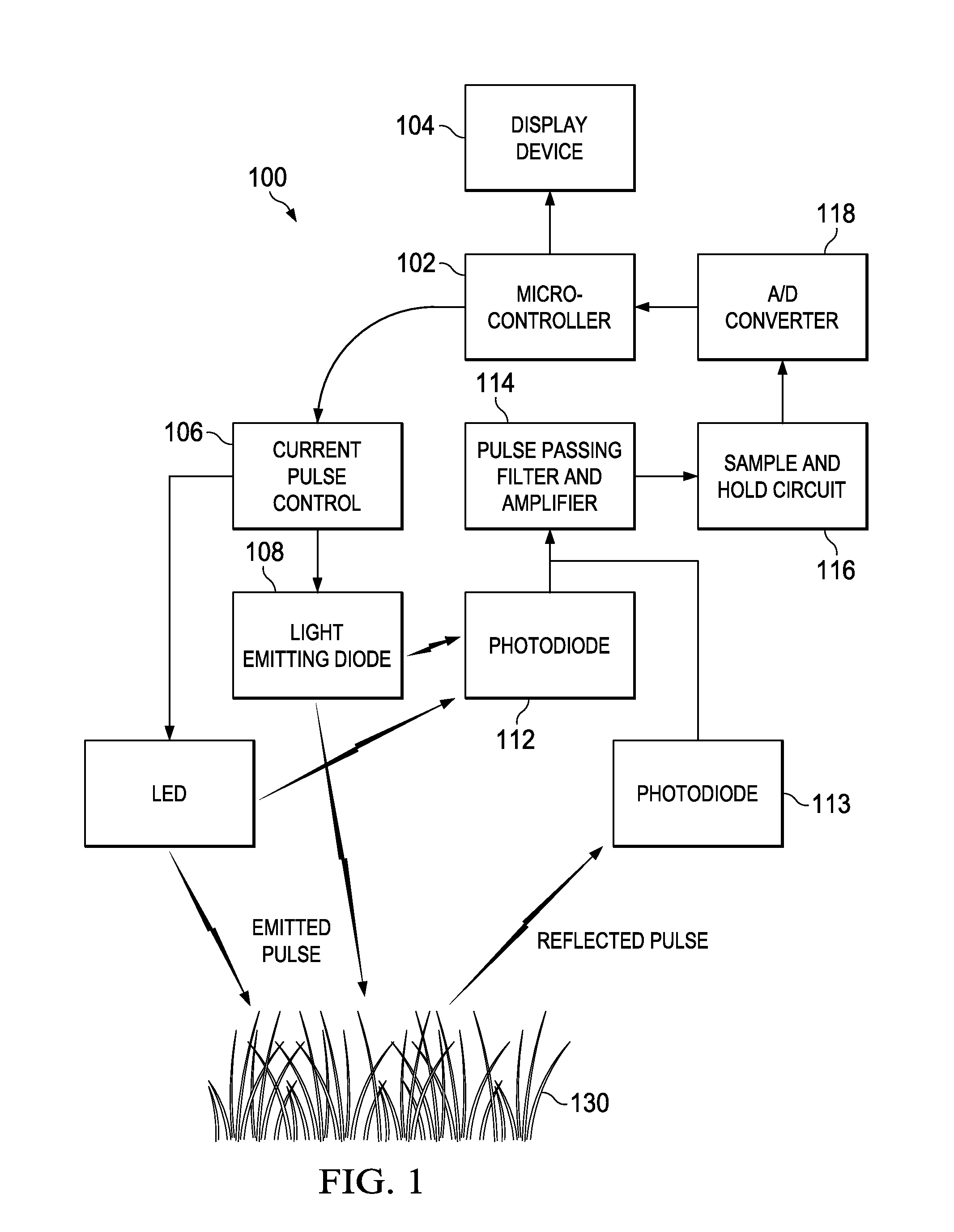
Handheld optical sensor for measuring the normalized difference vegetative index in plants
InactiveUS20100324830A1Radiation pyrometryScattering properties measurementsMicrocontrollerHand held
A handheld sensor is disclosed. The sensor has a microcontroller, a current pulse control unit coupled to a light emitting diode (LED), and a photodiode. The microcontroller controls the current pulse control unit to provide a pulsed illumination of a target plant and the photodiode reads the magnitude of the reflectance from the target plant. The microcontroller accepts the reading from the photodiode and computes a normalized difference vegetative index (NDVI) based at least on the reading.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY
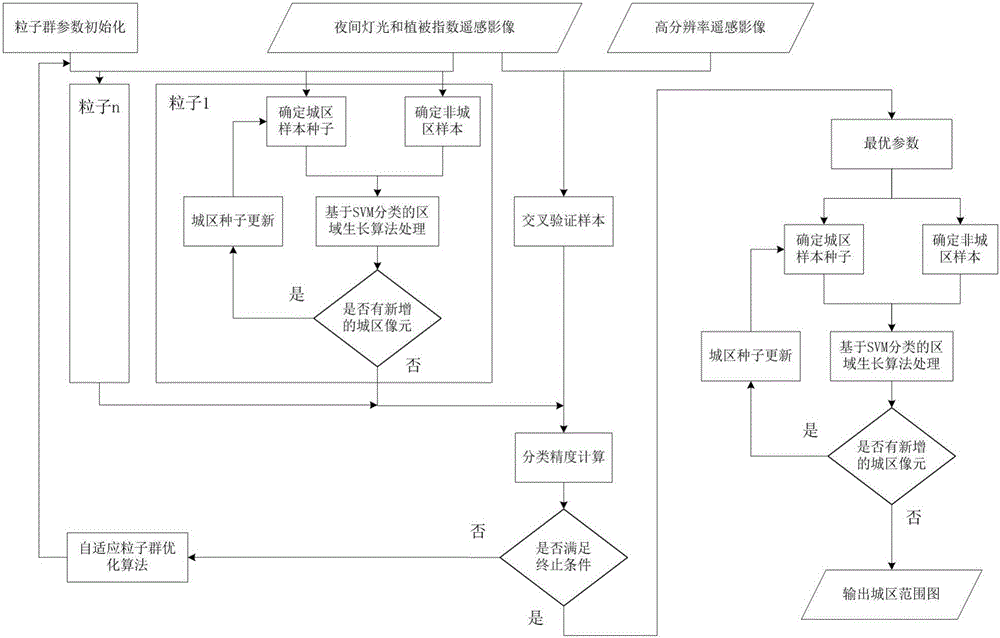
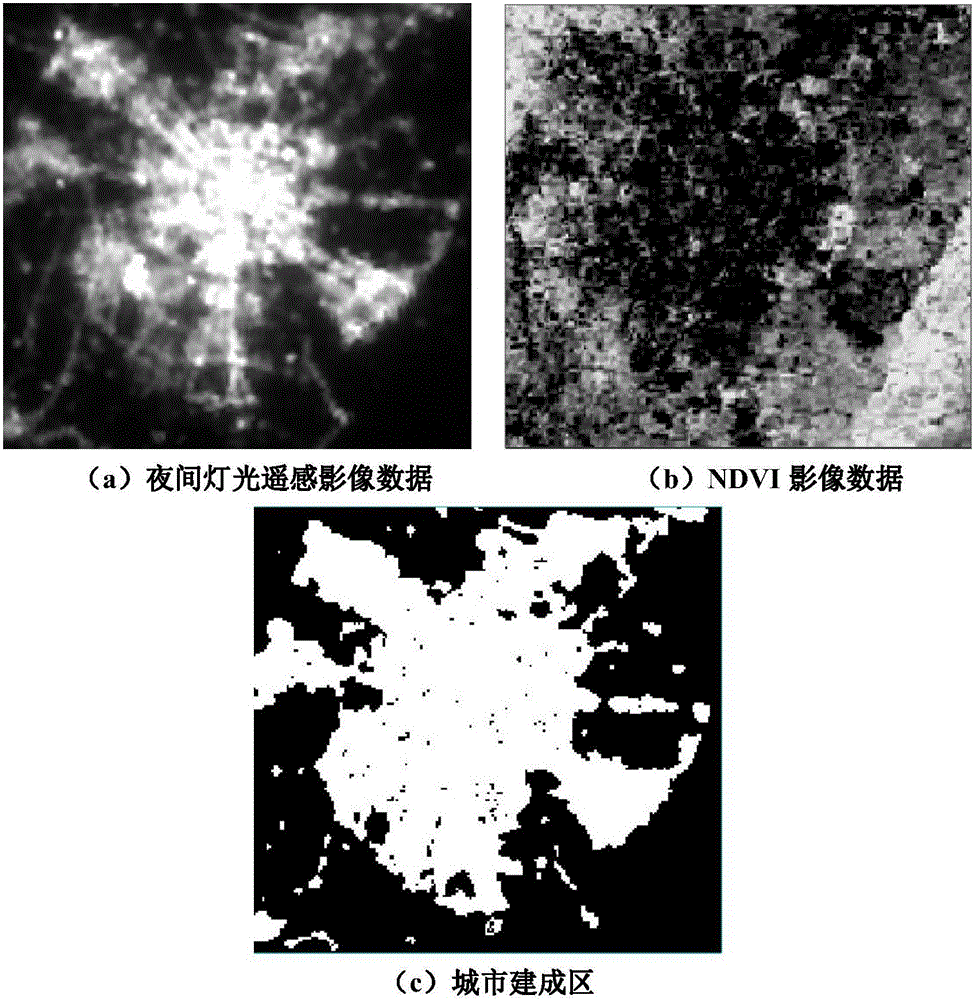
Intelligent extraction method of build-up area on the basis of nighttime light data
InactiveCN106127121AGood effectImprove processing efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionSupport vector machineAdaptive optimization
The invention relates to an intelligent extraction method of a build-up area on the basis of nighttime light data. The intelligent extraction method comprises the following steps: adopting an adaptive particle swarm optimization algorithm to realize the optimal selection of the selection parameters of a VIIRS (Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite) nighttime light image sample and a MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) normalized difference vegetation index image sample; adopting a region growing algorithm based on SVM (Support Vector Machine) classification to finish SVM model training, and adopting a cross validation method to carry out precision validation on the model; and according to an optimized parameter, determining a city sample and a non-city sample, and adopting the region growing algorithm based on the SVM to extract a city built-area range. By use of the intelligent extraction method, from a sample selection source, the adaptive optimization of a sample selection parameter is carried out, and the SVM and the region growing algorithm are adopted to improve processing efficiency and precision for the nighttime light data to extract the nighttime light data.
Owner:四川省遥感信息测绘院
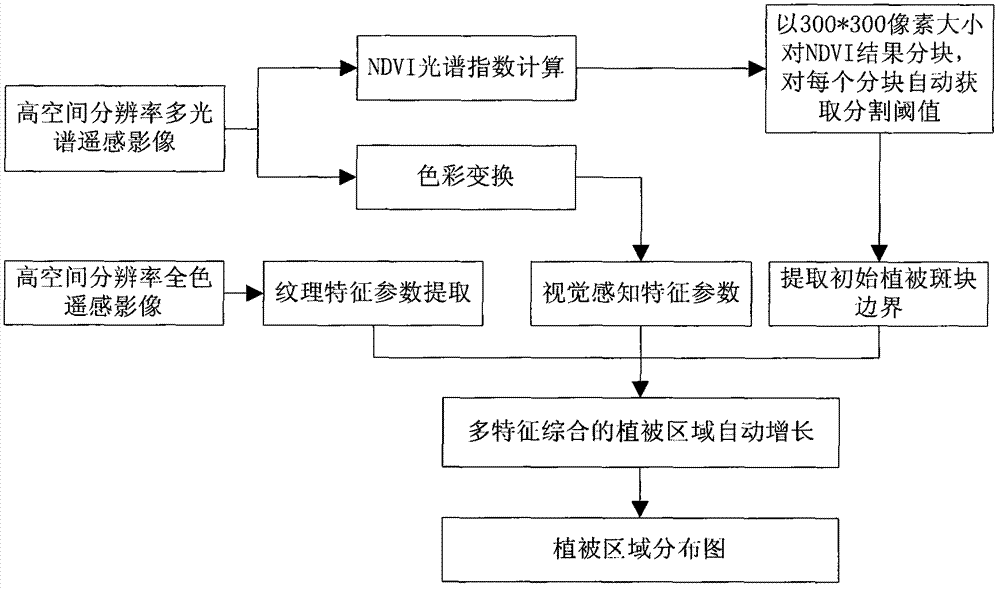
Urban vegetation automatic extraction method of multiple-spatial resolution remote sensing image
InactiveCN104851113AImprove adaptabilityAvoid feature differencesImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionNormalized Difference Vegetation IndexVisual perception
The present invention discloses an urban vegetation automatic extraction method of multiple-spatial resolution remote sensing images. The method comprises the steps of extracting vegetation initial plaques based on high-spatial resolution multispectral images, calculating visual perception parameters for the high-spatial resolution multispectral images, calculating textural feature parameters for high-spatial resolution panchromatic Images, automatic growing of multi-feature comprehensive vegetation regions, and obtaining a vegetation region distribution map. With adoption of image sectional division treatment, the image processing speed is accelerated. According to normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) features, automatic selection of maximal mathematical expectation algorithm adaptive dynamic thresholds is adopted. Panchromatic wave bands and multi-spectrum wave bands of the remote sensing images are fully utilized, the NDVI features, visual features and textural features of the panchromatic wave bands and multi-spectrum wave bands are synthesized, vegetation region judgment is performed on the vegetation, and the accuracy is raised.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV +1
Method for automatically extracting paddy rice growing region based on MODIS
InactiveCN106599844AAchieving change trend assessmentRapid preparation of large-scale rice mappingCharacter and pattern recognitionSurface waterNormalized Difference Vegetation Index
The invention discloses a method for automatically extracting a paddy rice growing region based on a MODIS. The method is characterized by subjecting MODIS data to preprocessing such as index calculation, cloud mask, time series synthesis and the filtering; eliminating different types of typical ground features by using a threshold value method based on a normalized difference vegetation index; detecting a normalized difference vegetation index curve of a pixel element by using an extremum detection method to find out pixel elements likely to be the paddy rice, and performing paddy rice heading stage inversion; and finally extracting the paddy rice pixel elements by using a relationship between a land surface water index and the normalized difference vegetation index during a paddy rice transplanting period. The method can extract the paddy rice pixel elements accurately, has strong applicability in different regions, and can distinguish single-cropping rice and multi-cropping rice, and can provide fast and accurate paddy rice spatial distribution for land, mapping, and agriculture departments, and provides support for the scientific decision of different departments.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
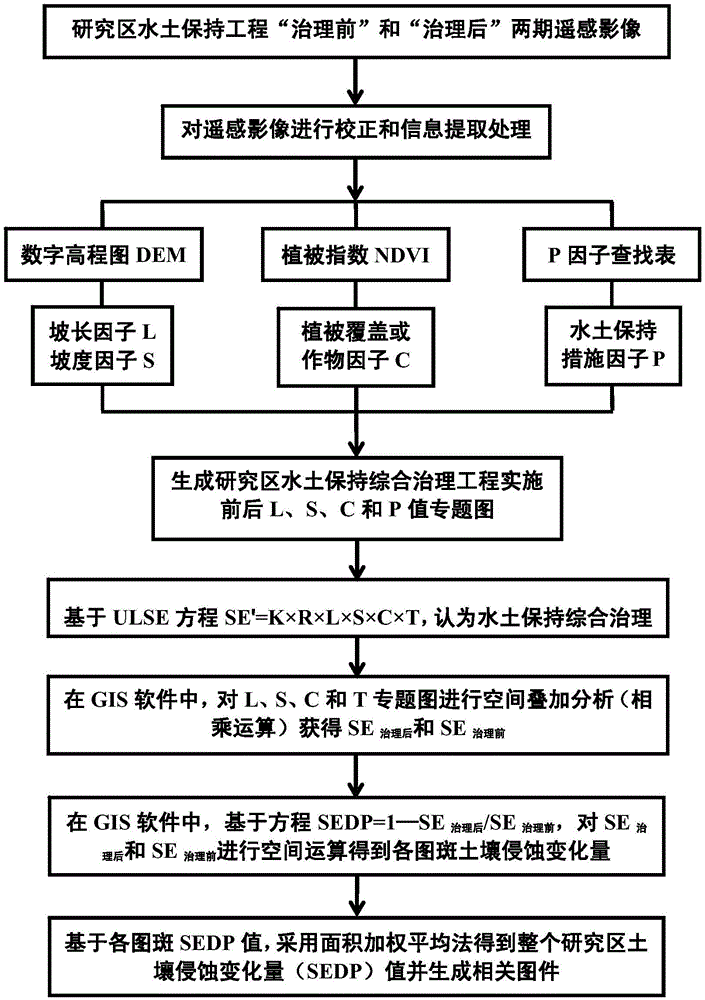
Method for quantitatively monitoring soil erosion change amount in real time for water and soil conservation comprehensive treatment
ActiveCN105004725ALow input costQuantitatively obtain the change of erosion amount in real timeMaterial analysis by optical meansCrop factorAfter treatment
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively monitoring the soil erosion change amount in real time for water and soil conservation comprehensive treatment. The method includes the steps that remote sensing images generated before and after water and soil conservation comprehensive treatment on a research area are acquired; a digital elevation model (DEM) and water and soil conservation measure remote sensing image pattern spots are extracted; the image pattern spots serve as a unit, and slope length factors L and gradient factors S of the pattern spots are calculated; vegetation coverage degrees B of the pattern spots are calculated through the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), and vegetation coverage or crop factors C of the pattern spots are estimated according to the vegetation coverage degrees B; water and soil conservation measure factors P of the pattern spots are assigned according to existing research results; the soil erosion amount reduction proportion SEDP is calculated according to the formula that SEDP=1-SE<after-treatment> / SE<before-treatment>, wherein the SE<before-treatment> and the SE<after-treatment> express the soil erosion amount obtained before water and soil conservation comprehensive treatment of the research area and the soil erosion amount obtained after water and soil conservation comprehensive treatment of the research area respectively. The soil erosion amount change can be acquired only through extraction of remote sensing image information, invested cost is relatively low, and the method is convenient and quick.
Owner:PEARL RIVER HYDRAULIC RES INST OF PEARL RIVER WATER RESOURCES COMMISSION
Method for predicting nitrogen content of cucumber leaf based on spectral image analysis
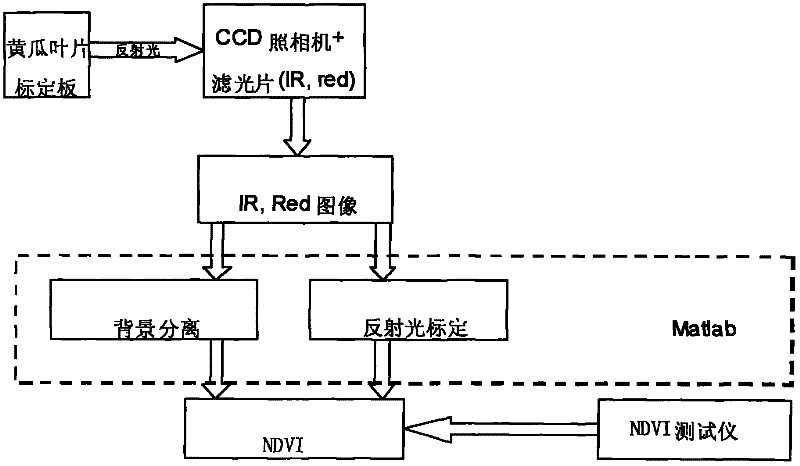
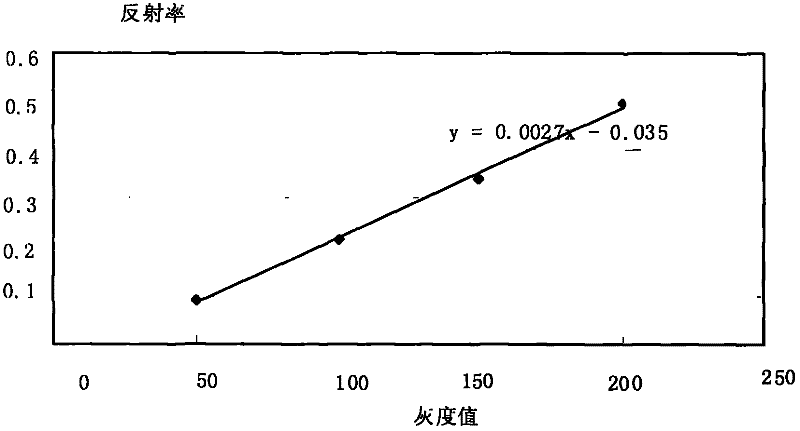
InactiveCN102175626AEasy to operateLow costColor/spectral properties measurementsWavelengthNormalized Difference Vegetation Index
The invention discloses a method for predicting nitrogen content of cucumber leaf based on spectral image analysis. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: adding an infrared and red light filter with a characteristic wave length in front of the lens of a CCD (charge coupled device) camera, and firstly collecting a near-infrared and red light image of the cucumber leaf to obtain the gray value of the cucumber leaf; measuring the vegetation reflection range RIR at the characteristic wave length of the infrared light and the reflection rate RR of the cucumber leaf at the infrared characteristic wave length through an empirical formula; obtaining a normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) according to the reflection rate values RIR and RR of the cucumber leaf at the infrared characteristic wave length and a red light wave segment; and judging the nitrogen content level of the cucumber leaf according to the NDVI so as to realize the prediction on the nitrogen content of the cucumber leaf. By the method, the nutrient state of crops can be obtained visually and effectively, and the nitrogen content of cucumber leaf can be predicted quickly and visually.
Owner:BEIJING KINGPENG INT HI TECH CORP
Portable crop growth information monitor based on active light source
ActiveCN103149162AWide working hoursReduce the effects of background distractionsColor/spectral properties measurementsNitrogen accumulationDry weight
Provided is a portable crop growth information monitor based on an active light source. The monitor is characterized by comprising a light source system, a spectrum signal acquisition system and a main unit system. The front end of the light source system is connected with the main unit system, the rear end of the light source system is connected with the spectrum signal acquisition system, the rear end of the spectrum signal acquisition system is connected with the main unit system, and the rear end of the main unit system is connected with the light source system. The monitor can simultaneously and comprehensively monitor and diagnose various physiology and zoology information including chlorophyll content of crops, a normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), a leaf area index, leaf dry weight, nitrogen content, nitrogen accumulation amount, a net photosynthetic rate, a transpiration rate, leaf temperatures and the like, and has functions of data acquisition, analysis, display, storage, checking and display. By means of application of built-in electronic information techniques, the system structure is simplified, and the monitor has the advantages of being convenient to carry and low in power consumption and the like.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
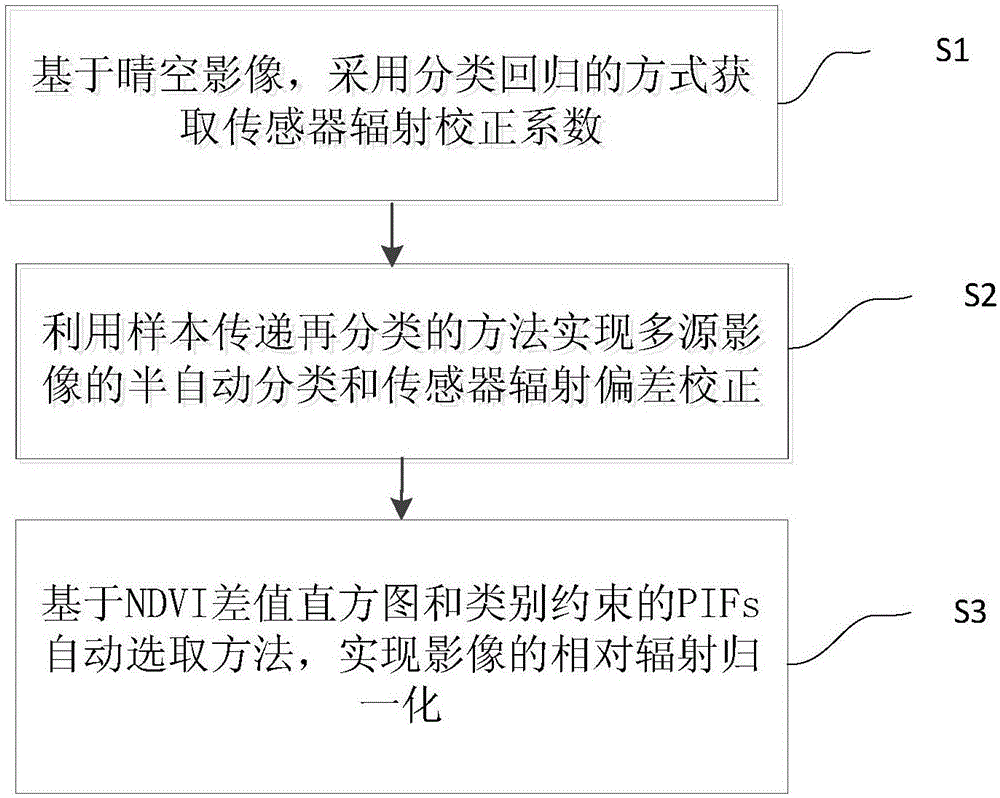
Multi-source remote sensing image radiometric normalization method
InactiveCN106295696AImplement semi-automatic classificationAchieving Radiation Bias CorrectionCharacter and pattern recognitionSkySemi automatic
The invention discloses a multi-source remote sensing image radiometric normalization method. The method is characterized in that relative radiometric normalization of a multi-source remote sensing image is divided into a sensor radiation correction process and a radiometric normalization process specific to external factors such as illumination. The method comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring a sensor radiation correction coefficient in a categorical regression way based on a clear sky image; S2, implementing semi-automatic classification and sensor radiation deviation correction of the multi-source image by a sample transmitting and reclassifying method; and S3, implementing relative radiometric normalization of the image through a PIFs (Pseudo Invariant Features) automatic selection method based on an NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) histogram of differences and a category constraint. Through adoption of the multi-source remote sensing image radiometric normalization method, radiation deviations among sensors are effectively corrected, and higher radiometric normalization accuracy is achieved as a whole than a conventional method. Meanwhile, radiation feature fluctuation among time-sequence images can be eliminated effectively through the method, so that aspect change information of land such as vegetative can be expressed more accurately, and a reference method is provided for cooperative utilization of the multi-source time-sequence images.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for building high-spatial resolution NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index) time series data
InactiveCN102831310AHigh resolutionGood precisionSpecial data processing applicationsImage resolutionHigh spatial resolution
The invention discloses a method for building high-spatial resolution NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index) time series data. The high-spatial resolution NDVI time series data is predicted and built according to low-spatial resolution MODIS (moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer) pixels in known MODIS NDVI data and high-spatial resolution TM (thematic mapper) pixels in TMNDVI (thematic mapper normalized difference vegetation index) data. TM data is combined with MODIS data, and accordingly high-spatial resolution NDVI time series data with quite fine precision can be obtained effectively.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
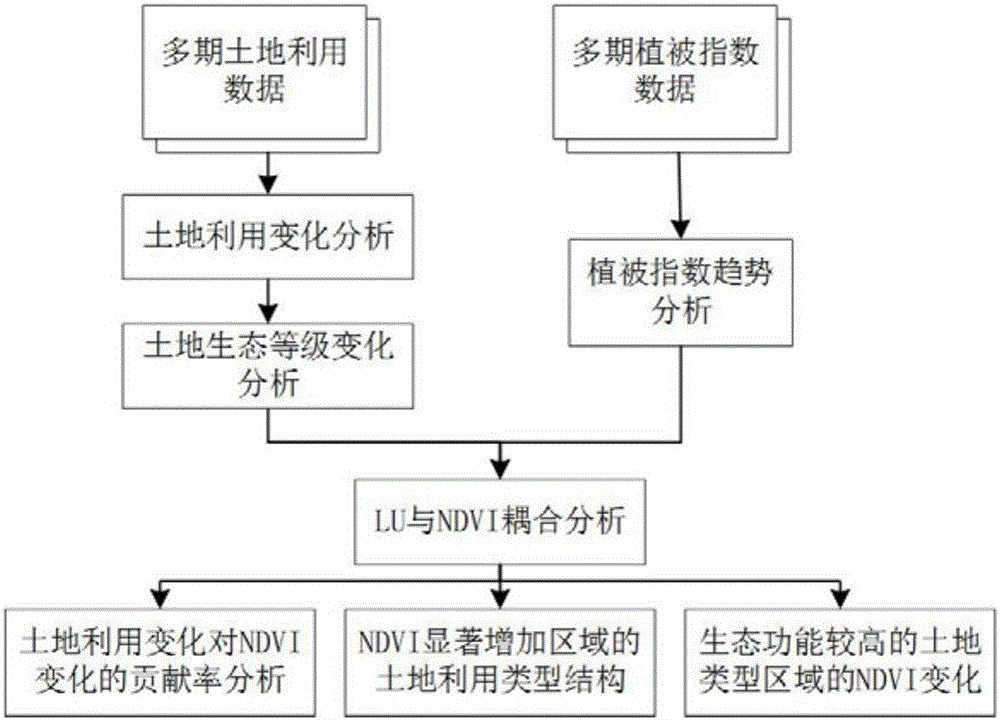
Ecological construction data processing method based on LU data and NDVI data
ActiveCN106548017ASpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsNormalized Difference Vegetation IndexLand use
The present invention discloses an ecological construction data processing method based on Land Use (LU) data and Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) data. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) collecting the LU data at the beginning and the end of the evaluation period of a target evaluation area; (2) forming raster data of NDVI series in the target evaluation area; (3) analyzing land use change scale and space distribution situation; (4) analyzing tendency characteristics and space distribution situation of NDVI change in the target evaluation area; and (5) resampling the land use data, and calculating a contribution rate of land use change to NDVI change, ratios of land use types in a region with significant NDVI change, and change rates of NVDI of land types with important ecological functions. Data obtained by applying the ecological construction data processing method can reflect "quality" change of the land use types, also reflect "quantity" change of vegetation cover, and can synthetically reflect implementation effect of ecological construction project.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
Statistical data and remote sensing image data based regional fertilizer application spatialization method
InactiveCN102156886AImprove discriminationCharacter and pattern recognitionKernel principal component analysisPrincipal component analysis
The invention discloses a statistical data and remote sensing image data based regional fertilizer application spatialization method. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, acquiring normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) time sequence data and performing smooth processing; 2, extracting classification characteristic by using the data and classifying a planting mode by using a decision tree classification method; 3, performing principal component analysis of the NDVI time sequence in different planting modes and extracting a plurality of principal components; 4, performing size matching on fertilizer application data and two principal components, analyzing relation between the fertilizer application data and the two principal components in different planting modes by using a size matching result, and selecting the principal components which can reflect productivity difference caused by fertilizer application for spatialization of the fertilizer application. By adopting the method, spatial distribution of the fertilizer application is substantially and completely reflected, and high discrimination can be achieved.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
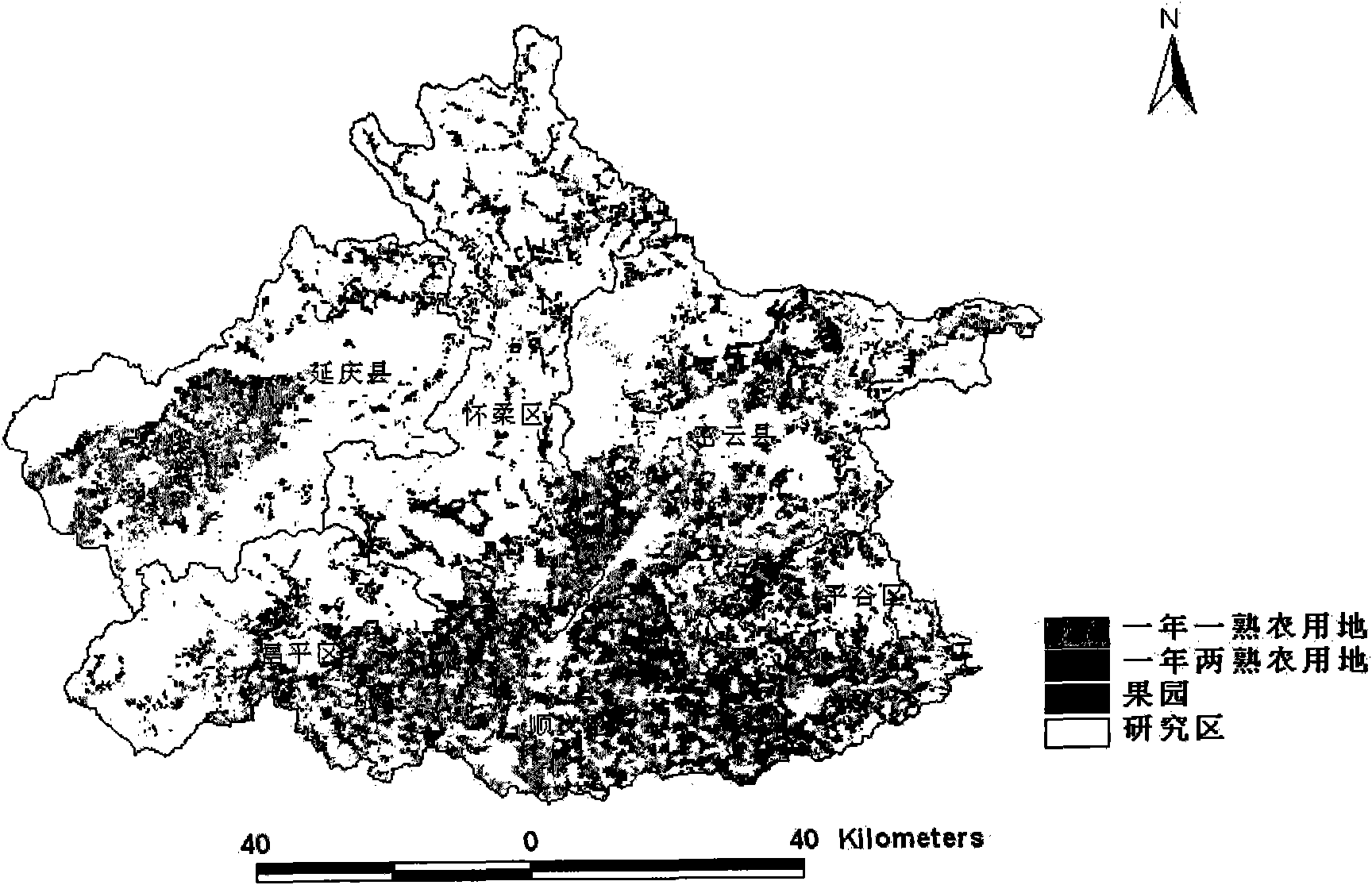
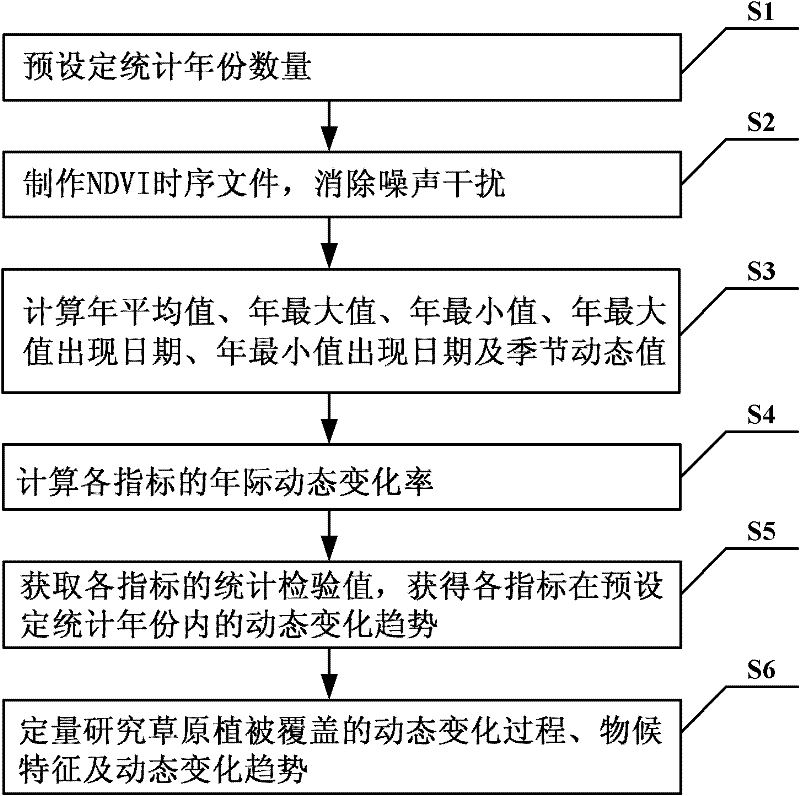
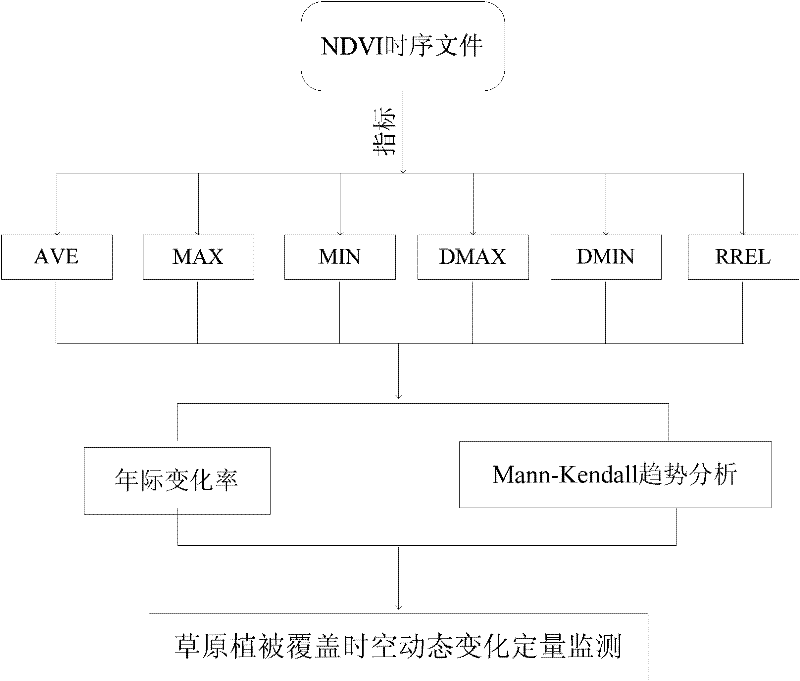
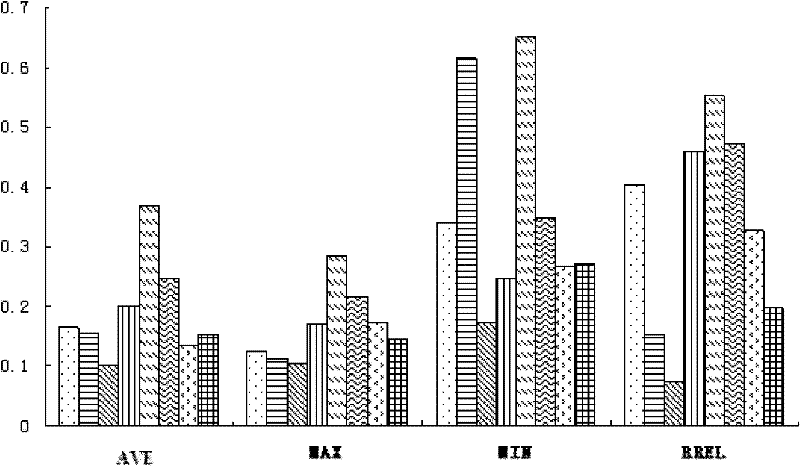
Method for remotely sensing and quantitatively monitoring steppe vegetation coverage space-time dynamic change
InactiveCN102184162AQuantitative Research ImplementationComplex mathematical operationsNormalized Difference Vegetation IndexSpacetime
The invention relates to a method for remotely sensing and quantitatively monitoring steppe vegetation coverage space-time dynamic change based on normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) data, and belongs to the technical field of vegetation coverage dynamic remote sensing and monitoring. In order to solve the problem that the quantitative research on remote sensing and monitoring of steppe vegetation coverage dynamic change is rare, the quantitative monitoring method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: calculating to obtain six NDVI indexes, such as an NDVI yearly value, a yearly maximum value, a yearly minimum value, a yearly maximum value appearance date, a yearly minimum value appearance date and a season dynamic, which represent a steppe vegetation coverage situation, by using an NDVI time sequence file; and quantitatively monitoring a space-time dynamic change process, a phenological characteristic and a dynamic change tendency of steppe vegetation coverage by calculating a yearly dynamic change rate of the NDVI indexes within a certain time period and performing trend analysis by a Mann-Kendall method. The method is applicable to all vegetation NDVI data.
Owner:SATELLITE ENVIRONMENT CENT MINIST OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
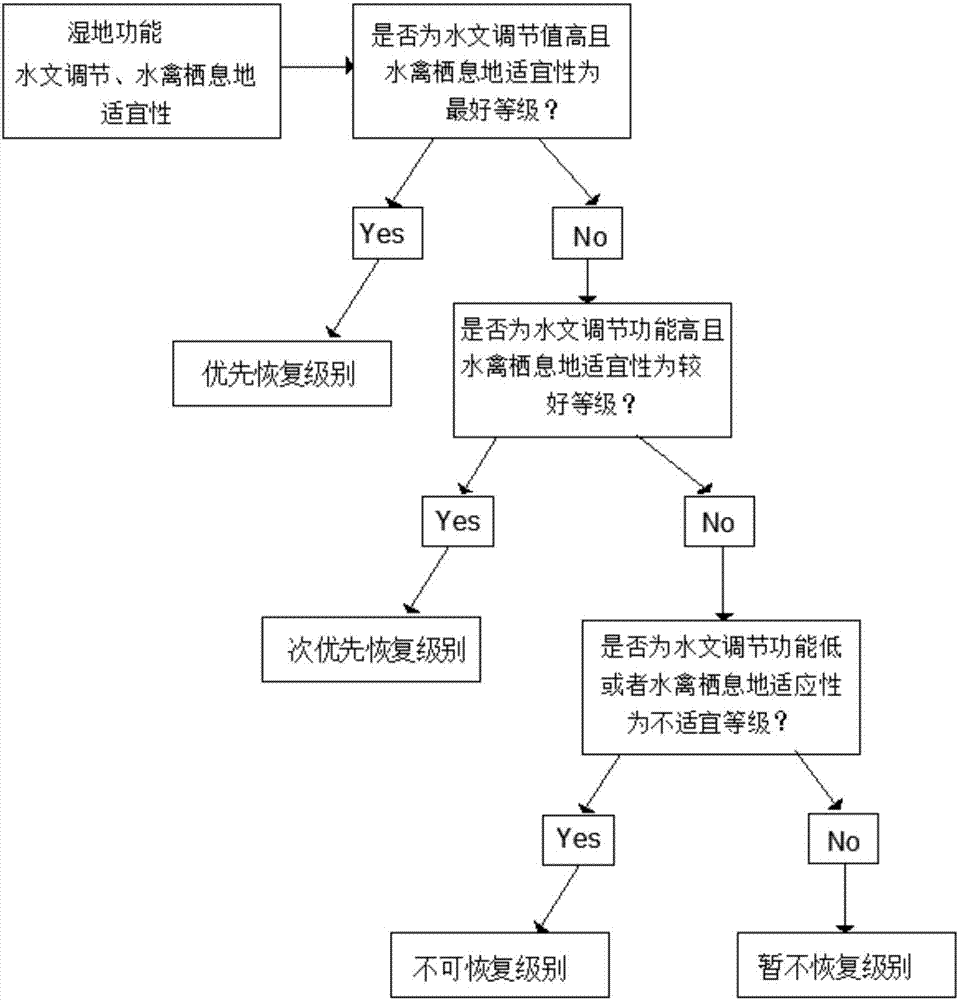
Spatial restoration analysis method for marsh wetland in river basin
InactiveCN107194160AImprove the ecological environmentEasy to implementClimate change adaptationScene recognitionMarshEcological environment
The invention discloses a spatial restoration analysis method for marsh wetland in a river basin. The method comprises the steps of firstly performing data collection: collecting TM remote sensing image data of the river basin, meteorological data, utilization data of land in the river basin, DEM (digital elevation model) data, NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index) data, LAI (leaf area index) data, and river and road vector data; secondly selecting a hydrology adjustment function and an aquatic bird habitat function of the marsh wetland in the river basin as marsh wetland restoration evaluation indexes; and finally performing marsh wetland restoration analysis. According to the method, function characteristics of the marsh wetland are fully considered, so that the functions of the marsh wetland can be brought into full play while the ecological environment of the marsh wetland is improved; and in addition, marsh wetland restoration of a large-range region can be realized, and a marsh wetland restoration region can be accurately determined, so that the convenience is brought for marsh wetland restoration project implementation.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
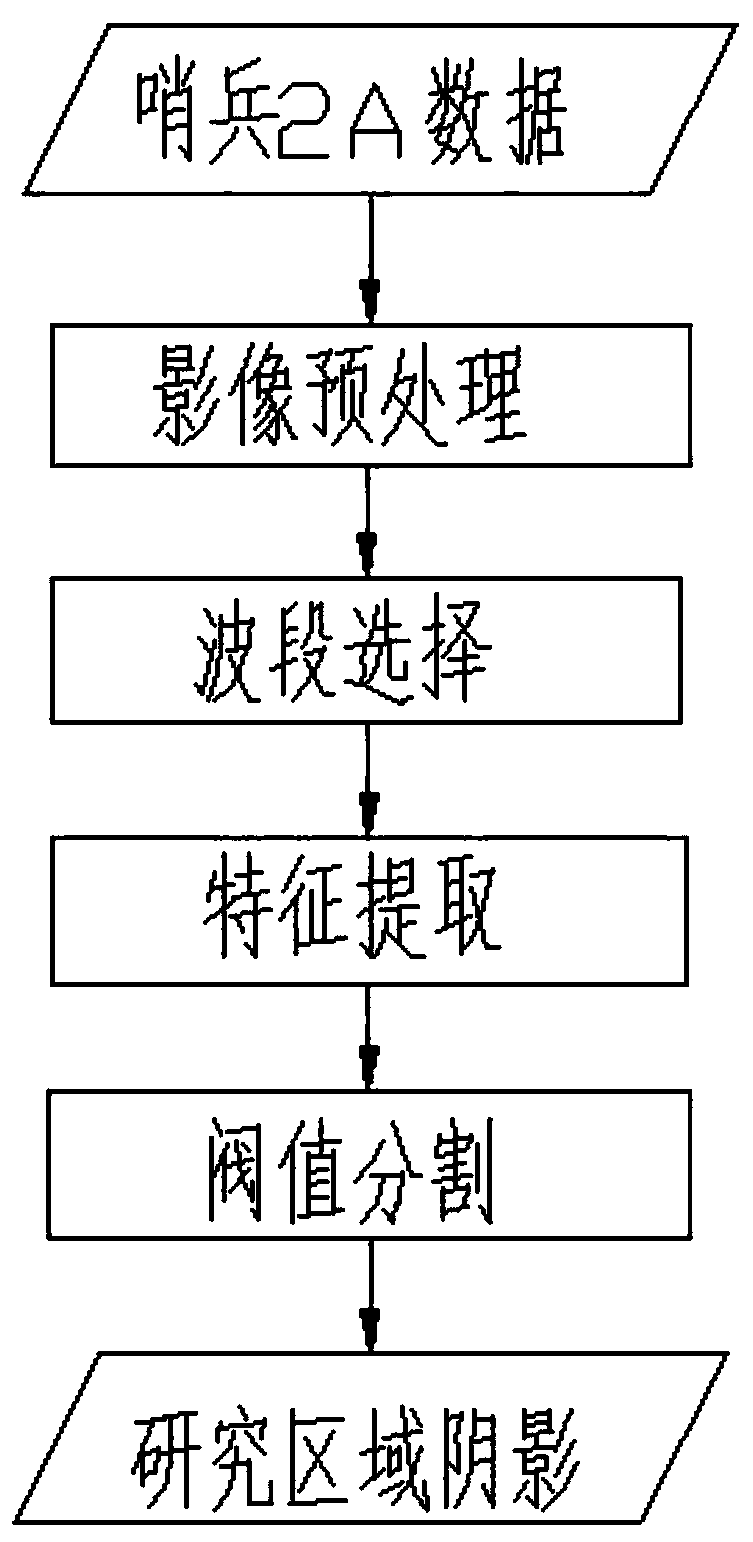
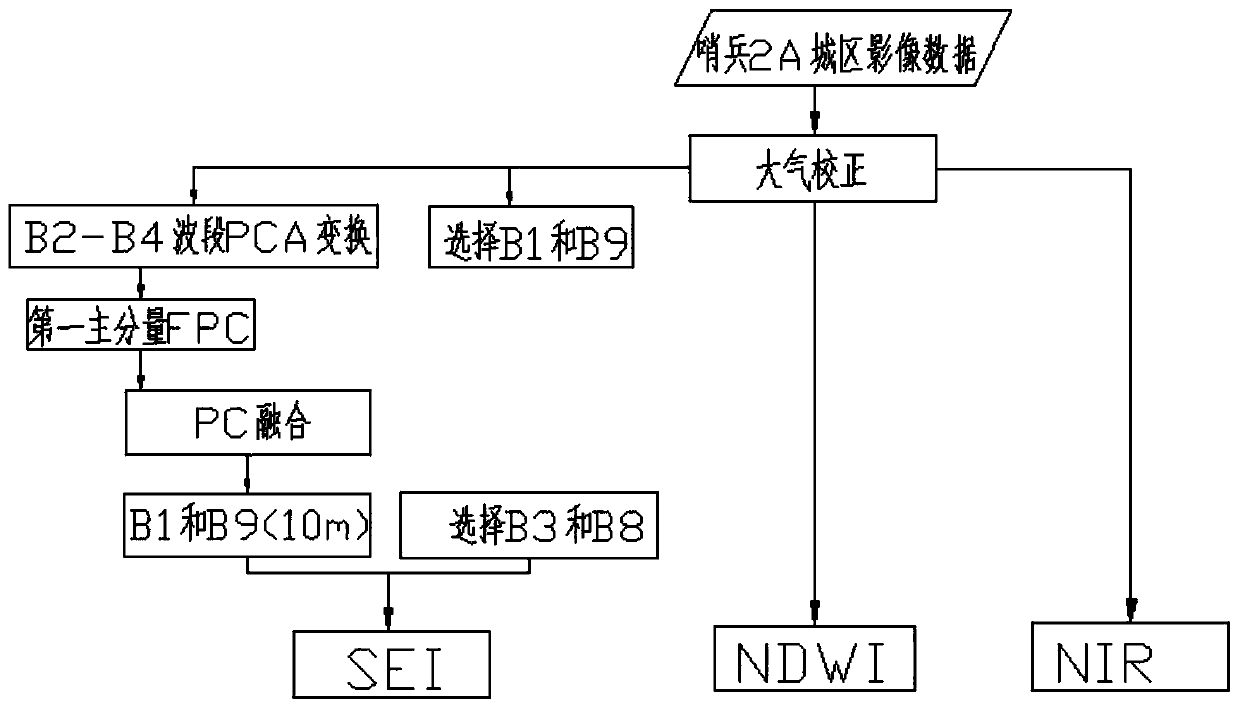
A building shadow extraction processing method for a sentinel 2A image
PendingCN109815894AEnhanced Building ShadowsIncrease the differenceCharacter and pattern recognitionSpectral bandsUrban area
The invention discloses a building shadow extraction processing method for a sentinel 2A image, and the method comprises the steps of S1, extracting the main ground feature component of an urban area,designing a shadow enhancement index based on a sentinel 2A original spectrum to enhance a building shadow; calculating a normalized difference water body index to enhance the water body; extractingan original spectral band Band 8 of the sentinel 2A to enhance other dark reflectivity ground objects; S2, based on the three extracted characteristic components, constructing a combined shadow indexto highlight a building shadow; and selecting an optimal threshold value by using an OTSU method to obtain a final urban building shadow distribution map. By the adoption of the technical scheme, thedifference between the shadow and other ground objects can be remarkably increased, the phenomenon that urban building shadow, water and dark reflectivity ground objects are mixed is effectively avoided, and the extraction precision of the urban building shadow is improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
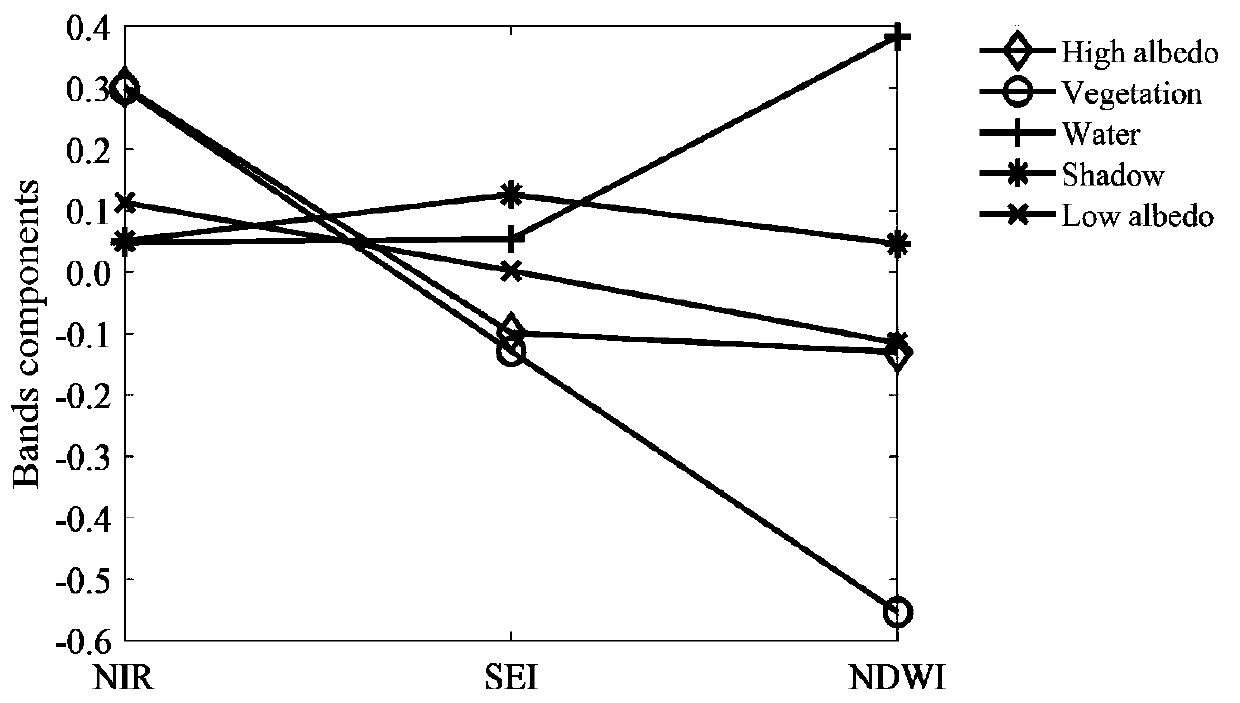
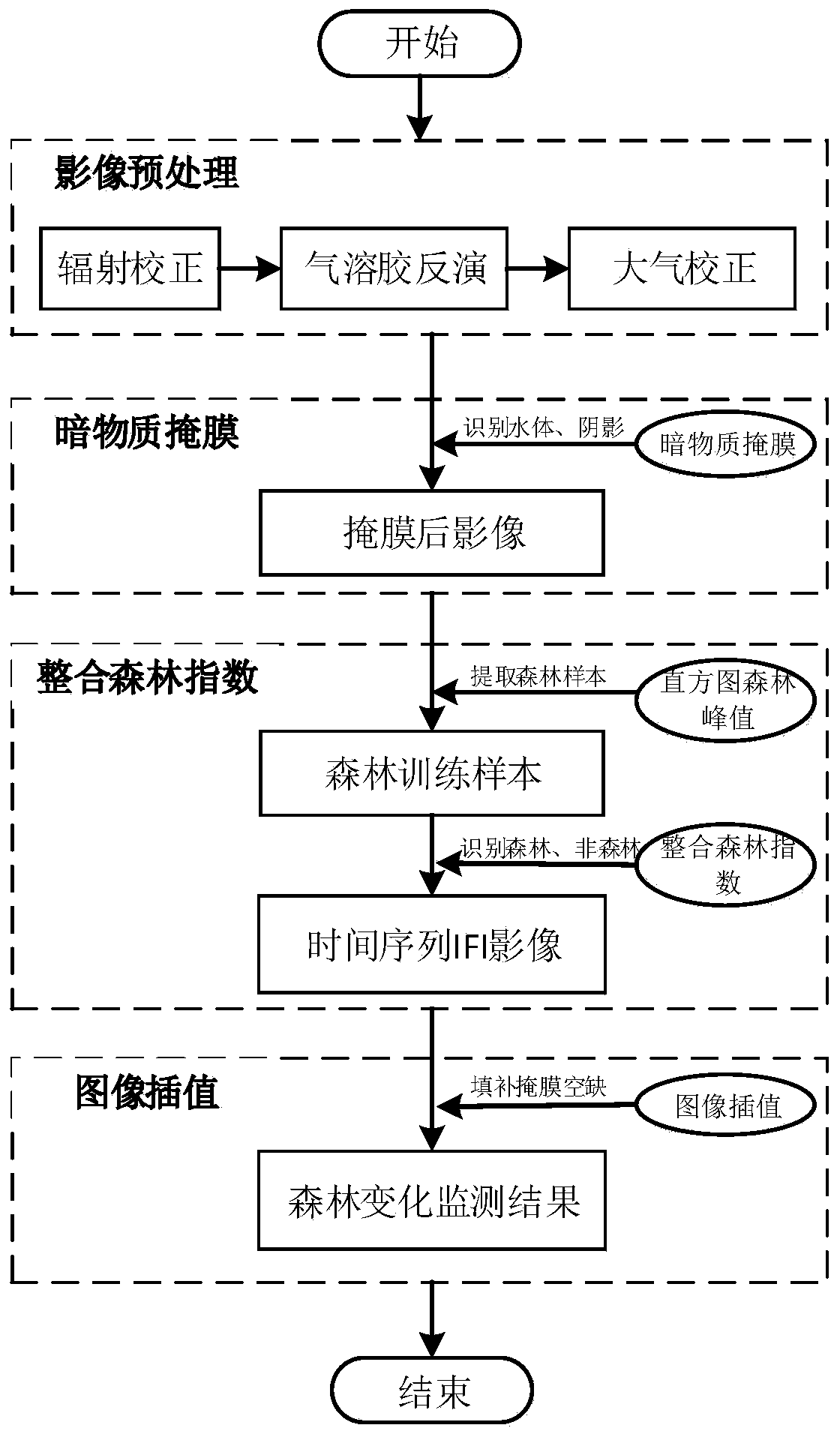
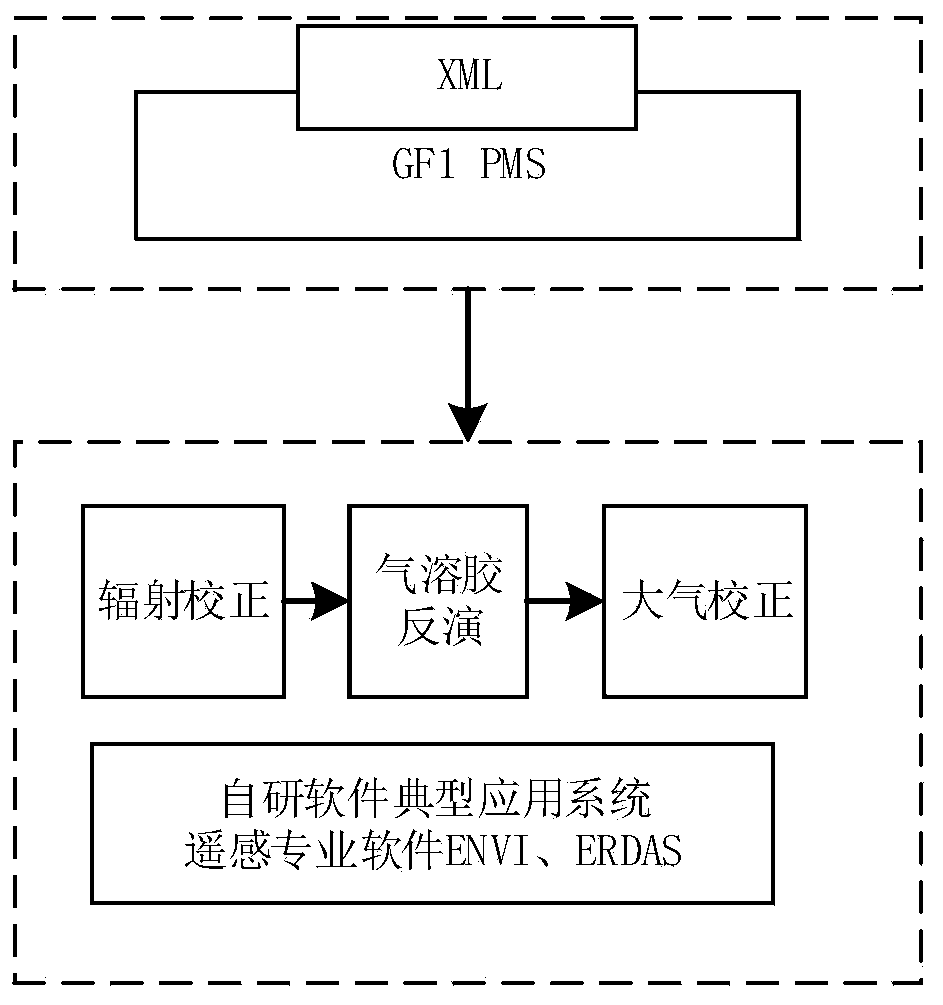
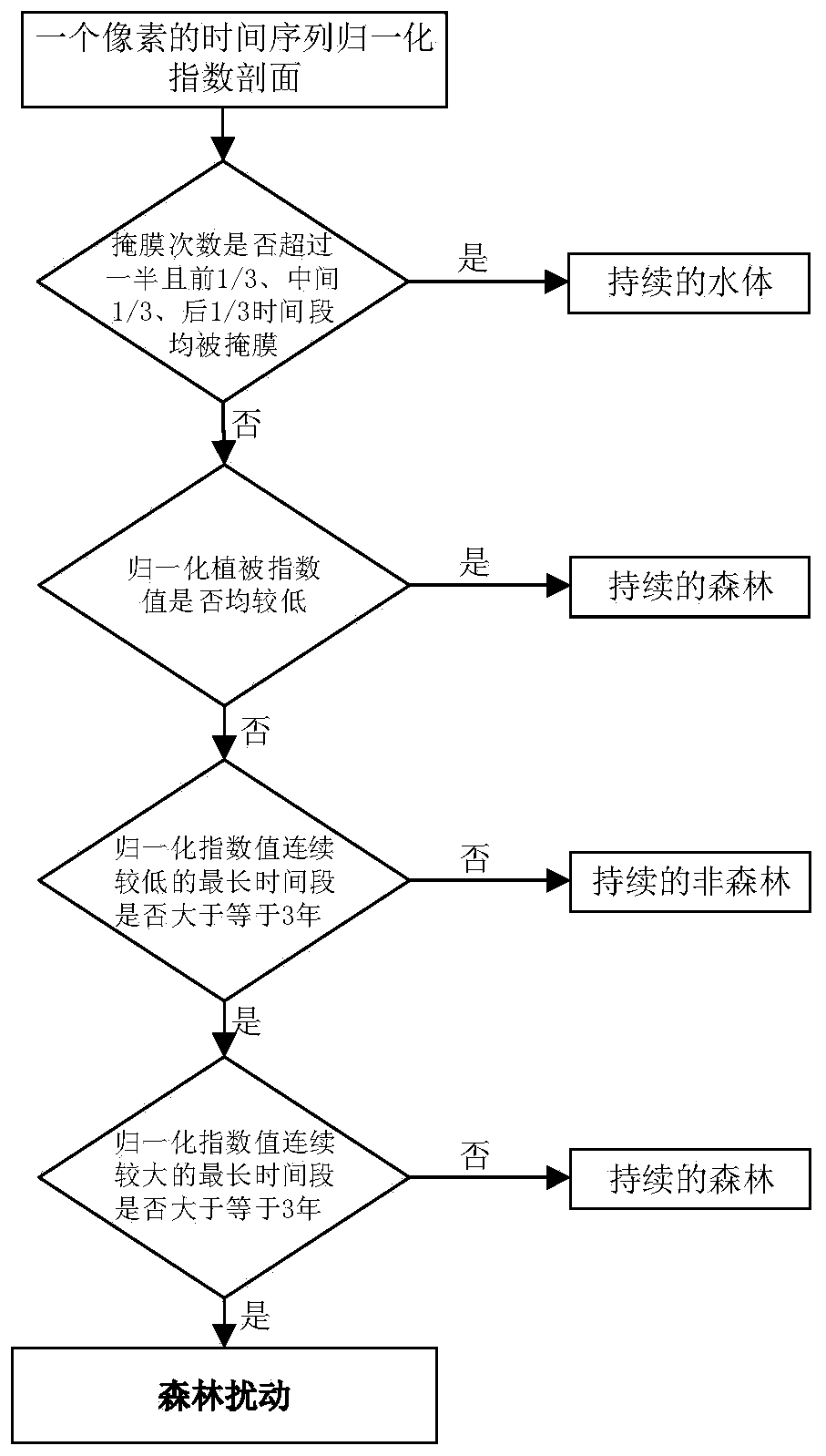
Time sequence forest change monitoring method based on IFI
InactiveCN110135322ARealize automatic identificationImprove change detectionCharacter and pattern recognitionNormalized Difference Vegetation IndexComputer science
The invention discloses a time sequence forest change monitoring method based on IFI. The method comprises the following steps: preprocessing a remote sensing image; establishing a normalized difference vegetation index NDVI by using reflectivity of near infrared band and red light band, then performing water body and shadow dark substance masking, and identifying the water body and shadow in themasked remote sensing image; using a window with a fixed size in a red light wave band to perform image segmentation processing, and executing automatic extraction operation on the remote sensing image to obtain a forest training sample; performing whole-scene remote sensing image forest and non-forest pixel identification according to the remote sensing image in the forest training sample and anintegrated forest index operation rule to obtain a time sequence IFI image; and complementing the information of the image of the masked part by using an image interpolation method, and carrying out forest change monitoring time sequence analysis to obtain a forest disturbance recovery information graph. According to the invention, full-automatic identification of forest change information is realized, errors are reduced, and the accuracy of forest change monitoring and the timeliness of a monitoring result are improved.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
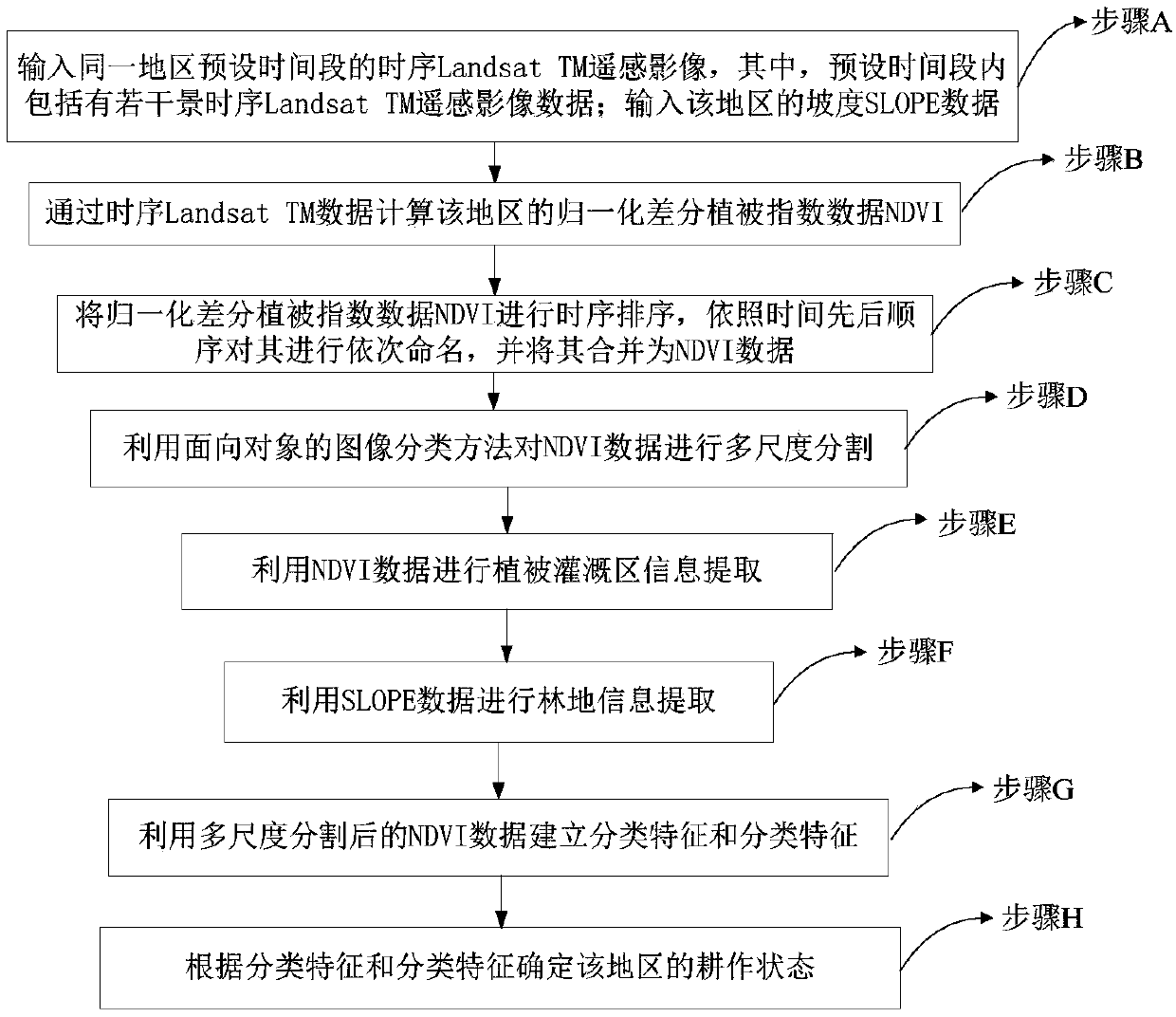
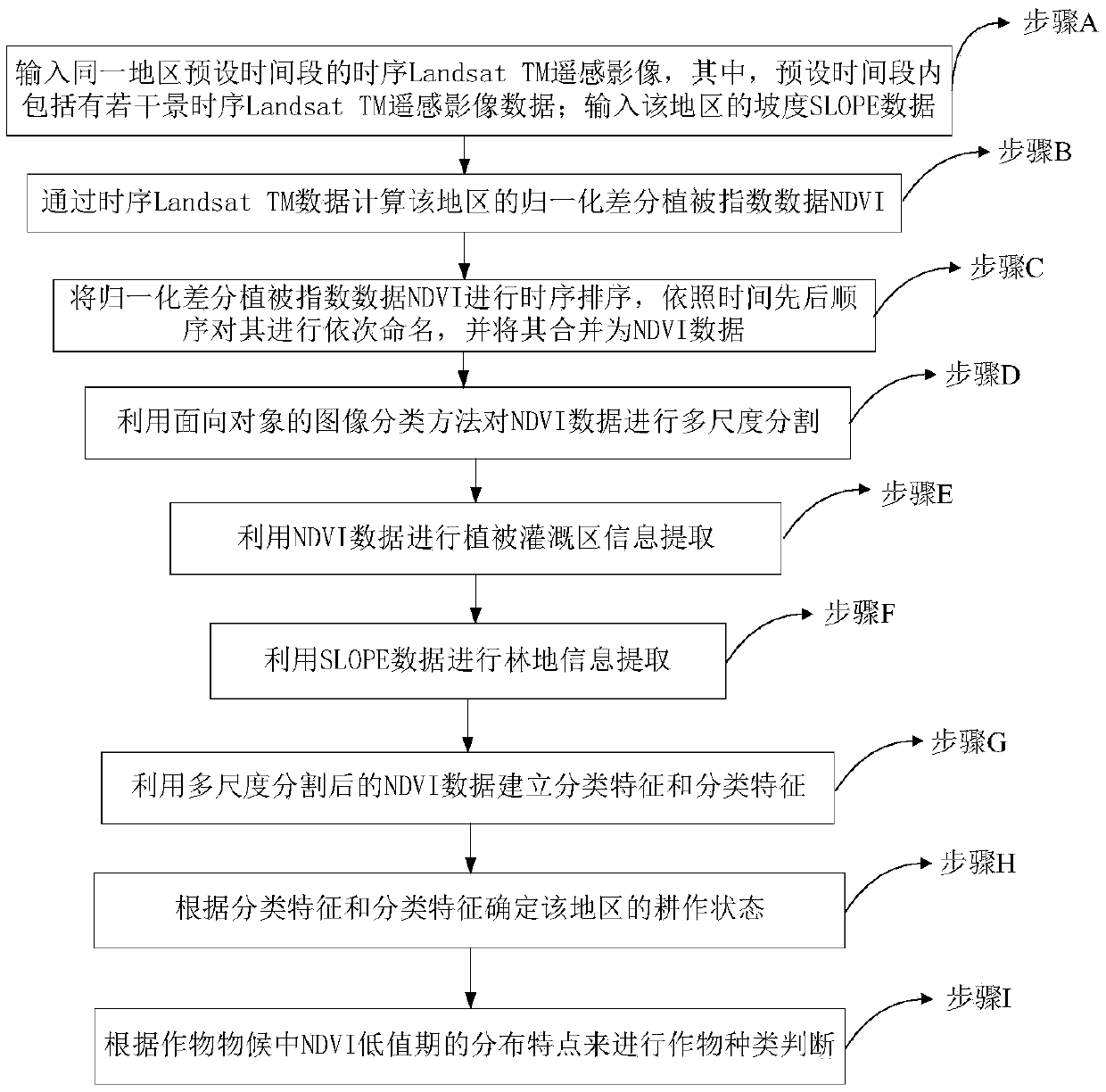
Method and device for identifying effective cultivated land, storage medium and processor
ActiveCN109635731AEasy accessReduce data volumeCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing dataData source
The invention relates to the field of cultivated land identification, and specifically relates to a method and a device for identifying effective cultivated land. According to the method and the device, Landsat TM remote sensing data of a long time sequence are used as a data source; Slope SLOPE data are used as auxiliary data. A normalized difference vegetation index NDVI is adopted as a classification feature. The phenological difference of crops on the agricultural cultivated land is taken as a basis; difference between crop interspecific planting periods is obtained; Characteristic differences such as spectral differences are reflected on a distribution change rule of time sequence NDVI data. An object-oriented decision classification rule combining a normalized difference vegetation index NDVI with other classification characteristics is designed. Spatial distribution information of part of crops on the agricultural cultivated land, especially the agricultural cultivated land in the western region, can be extracted. According to the method, the cultivation condition can be known, the influence of different crops in the complex planting period does not need to be considered, data sources needed by the method are easy to obtain, the data size needed to be processed is small, the classification rule is simple, the working efficiency is high, and the method is also suitable for regions with crushed cultivated land distribution.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
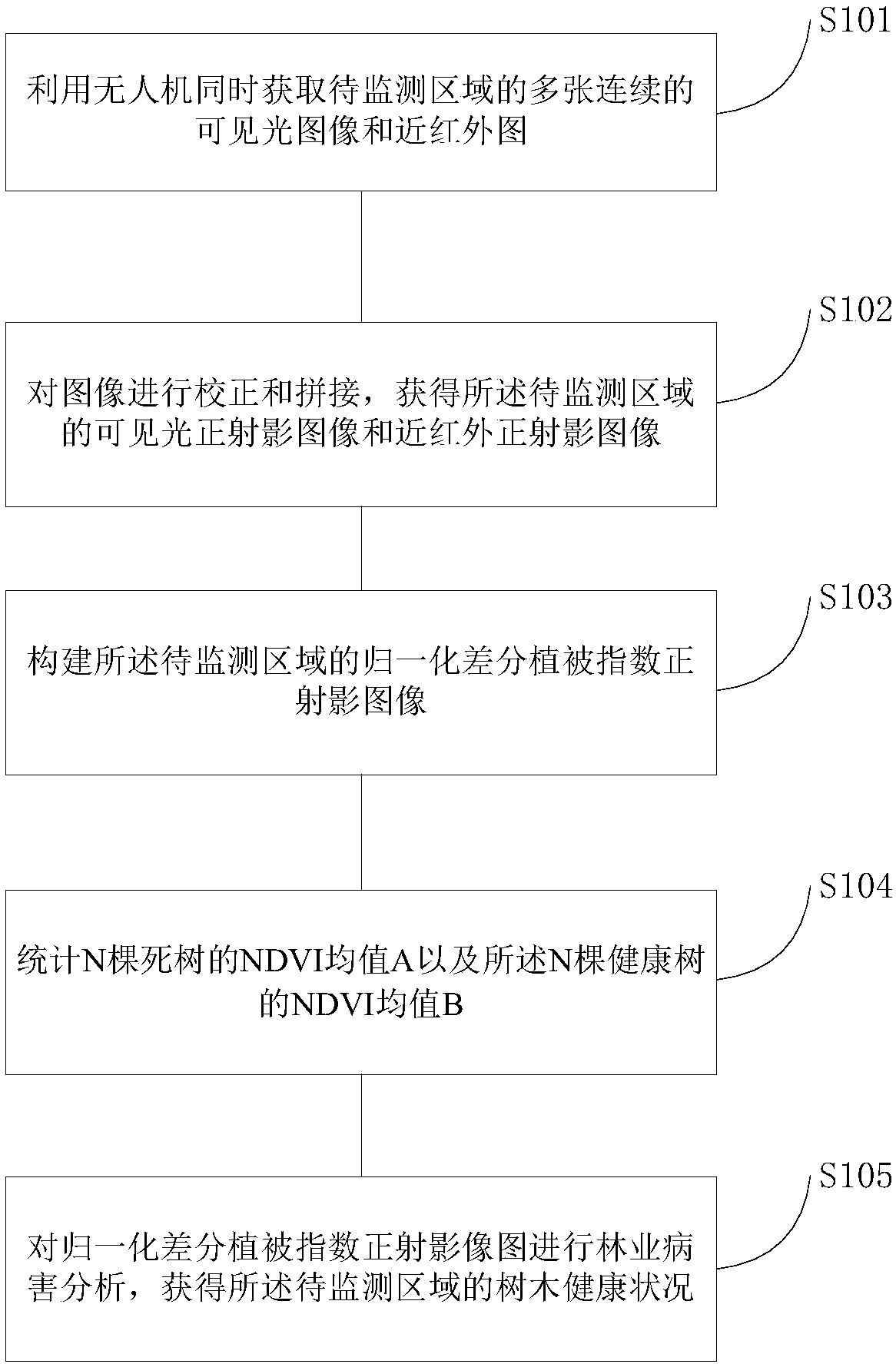
Forestry disease monitoring method and device based on unmanned aerial vehicle
InactiveCN108334110AEfficient and accurate determinationPosition/course control in three dimensionsDisease monitoringAerial photography
The invention discloses a forestry disease monitoring method and device based on an unmanned aerial vehicle. By loading a dual-light camera integrated by a visible light camera and an infrared cameraon the unmanned aerial vehicle, aerial photography monitoring is carried out on a forest in a to-be-monitored area; by analyzing aerial photography data and fully combining with image information of visible light and orthophoto images of normalized difference vegetation indexes, obviously healthy or dead trees are screened out on the basis of the image information of the visible light; then, by combining with NDVI indexes for further judgment, information about the dead trees and ill trees in the to-be-monitored area is thus determined quickly, accurately and efficiently. The current situations that the judgment efficiency is not high and the accuracy is low since identification on forestry diseases only relies on utilization of visible light images or the NDVI indexes are overcome, and therefore the problem that when the forestry diseases and forestry pest disasters happen in the prior art, the ill trees and the dead trees cannot be quickly and accurately found out is solved.
Owner:首欣(北京)科技有限公司
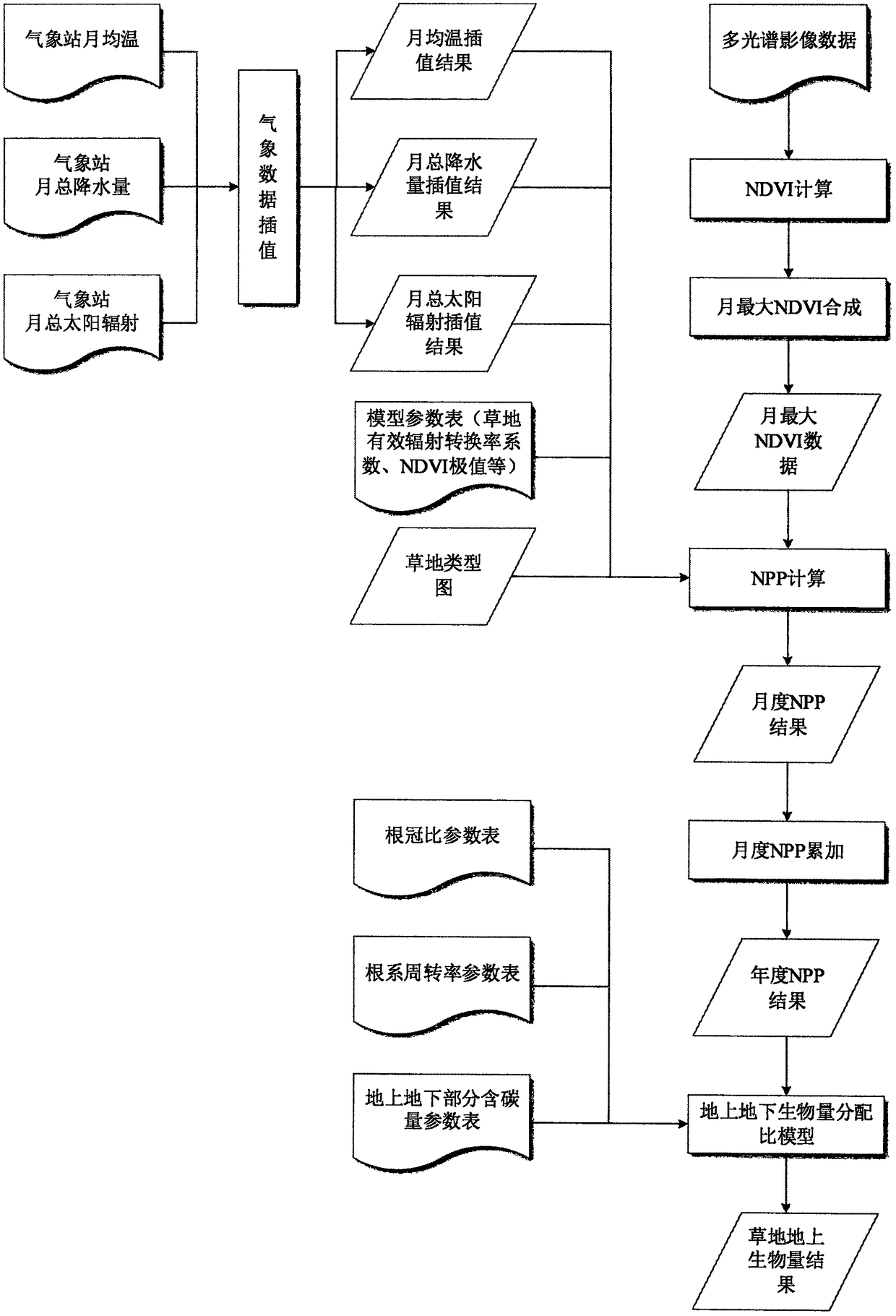
Grassland above-ground biomass retrievalinversion method based on high-time resolution and high-spatial resolution multispectral remote sensing data
The invention discloses a grassland above-ground biomass retrievalinversion method based on high-time resolution and high-spatial resolution multispectral remote sensing data. The method comprises thefollowing specific steps: 1) selecting multispectral remote sensing data covering the a grassland growing season, calculating thean NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index), and synthesizing toobtain the monthly maximum NDVI covering the a research area; 2) interpolating according to the monthly mean temperature, the monthly total precipitation and the monthly total solar radiation data ofa meteorological station, to generate the monthly mean temperature, the monthly total precipitation and the monthly total solar radiation data covering the research area; 3) calculating the NPP (Net Primary Productivity) of the grassland by using a CASA (Carnegie-Ames-Stanford Approach) model based on the LUE (Light Use Efficiency) theory; 4) calculating the above-ground biomass of the grassland according to the NPP and the ratio of the above-ground biomass to the underground biomass.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS +1
Green tide information extraction method
ActiveCN105427305ARealize business applicationThe principle is scientific and reasonableImage enhancementImage analysisOperabilityImage segmentation
The invention belongs to the technical field of remote sensing image processing, and relates to a green tide information extraction method. The method comprises: obtaining a sea area satellite remote sensing image with a conventional method, screening images of green tide regions, and performing preprocessing operations of geometric correction and image mosaicking; calculating and determining a green tide range by adopting a normalized difference vegetation index; cutting a region of interest in any shape to generate an irregular image file containing the green tide regions; extracting green tide information by adopting a split Bregman fast projection algorithm of a variational level set two-phase image segmentation based Chen-Wees model; and finally, quantitatively calculating the green tide regions by adopting a quantitative formula. The image segmentation based variational model accurately extracts and quantifies the green tide information on the satellite remote sensing image, so that a conventional manual threshold method can be completely replaced and operational application can be realized; and method is scientific and reasonable in principle, low in human factor quantity, high in calculation speed, accurate and stable in result, high in operability, friendly in application environment, high in practicality and easy to popularize.
Owner:国家海洋局北海预报中心
Method for removing cloud noise effects in normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) time sequence image
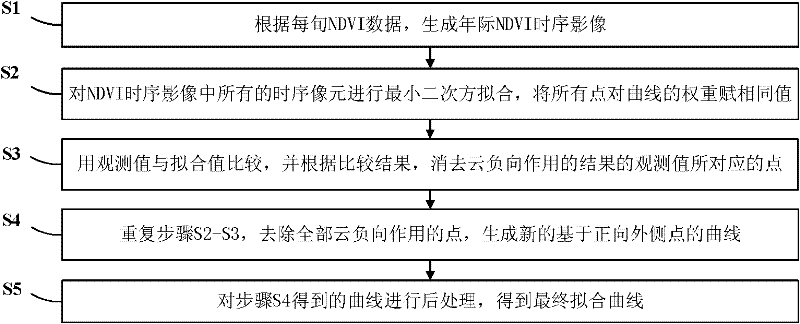
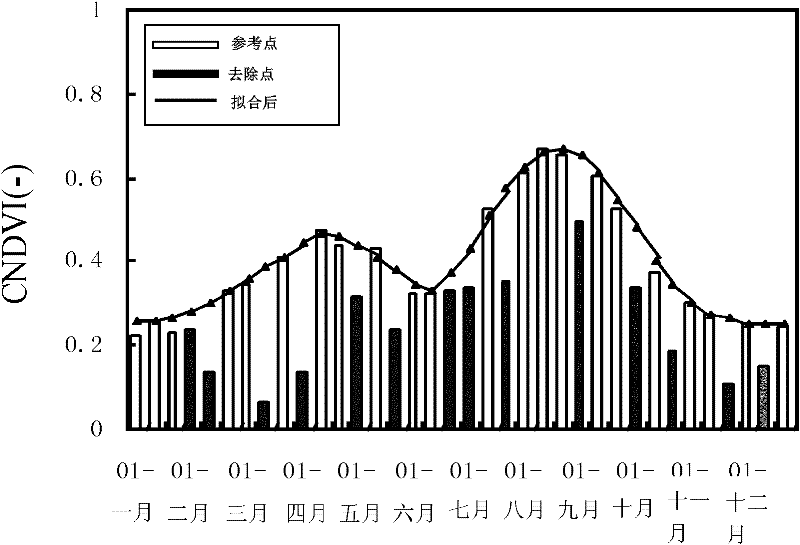
InactiveCN102176242AEfficiently remove shadowsEffectively removes atmospheric effectsImage enhancementData acquisitionComputer vision
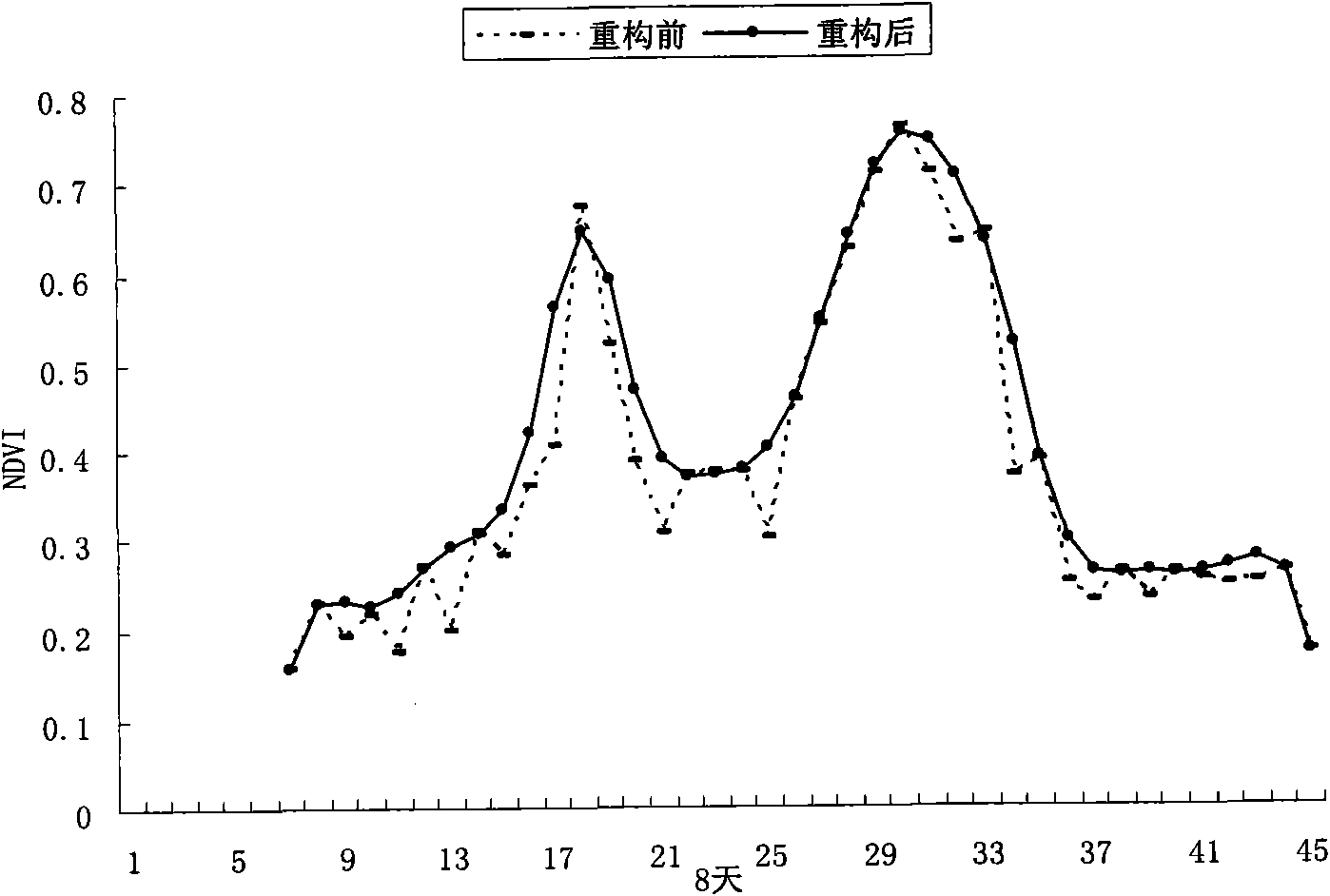
The invention discloses a method for removing cloud noise effects in a normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) time sequence image. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, generating an annual NDVI time sequence image according to NDVI data of every ten days; S2, carrying out least square fitting on all time sequence pixels in the NDVI time sequence image, and assigning same values to weights of all points relative to a curve; S3, comparing an observed value with a fitted value, and eliminating points under negative cloud action; S4, repeating the steps S2 and S3, eliminating all the points under the negative cloud action, and generating a new curve; and S5, post-processing the curve obtained in the S4 to obtain a finally fitted curve. In the method disclosed by the invention, by utilizing an NDVI time sequence file and a harmonic function analysis method based on the least square fitting, cloud shielding and atmospheric effects on a sensor in a data acquisition process are effectively removed, the time sequence image with cloud contamination removed can be generated, the obtained curve has the advantages of obvious trend, strong relative property among years and high precision, and the method has a wide applicable range.
Owner:SATELLITE ENVIRONMENT CENT MINIST OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
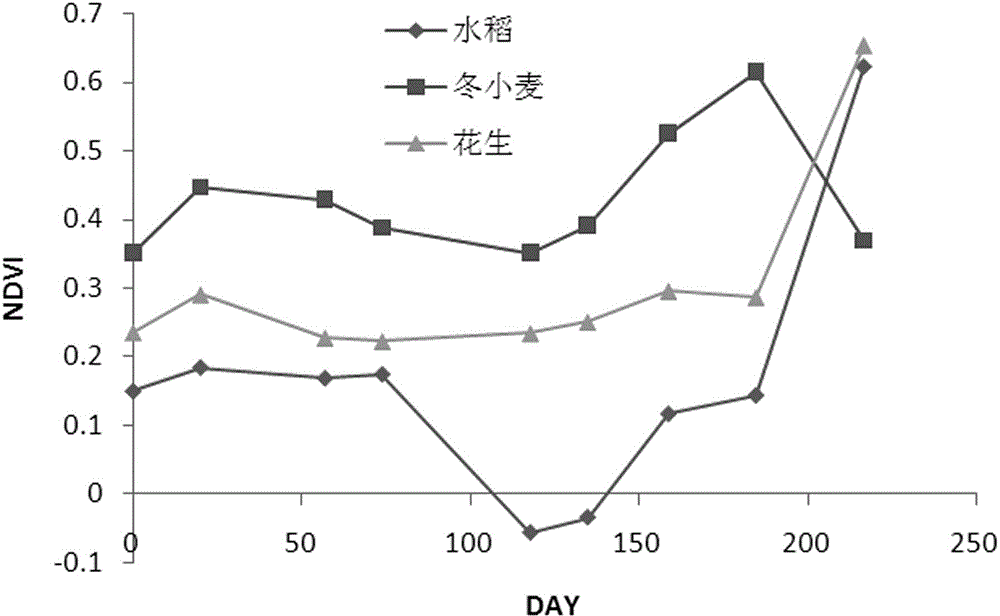
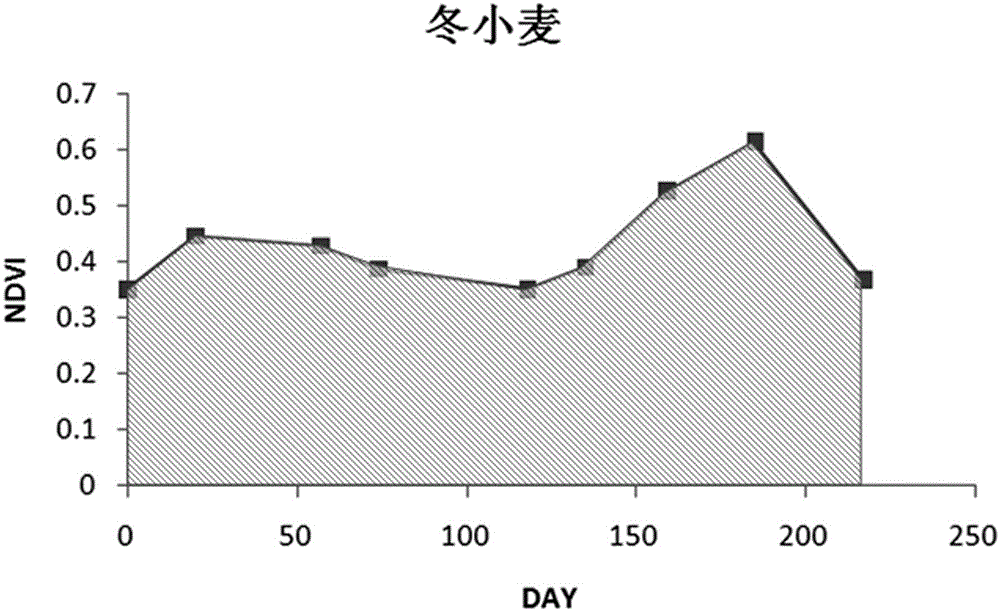
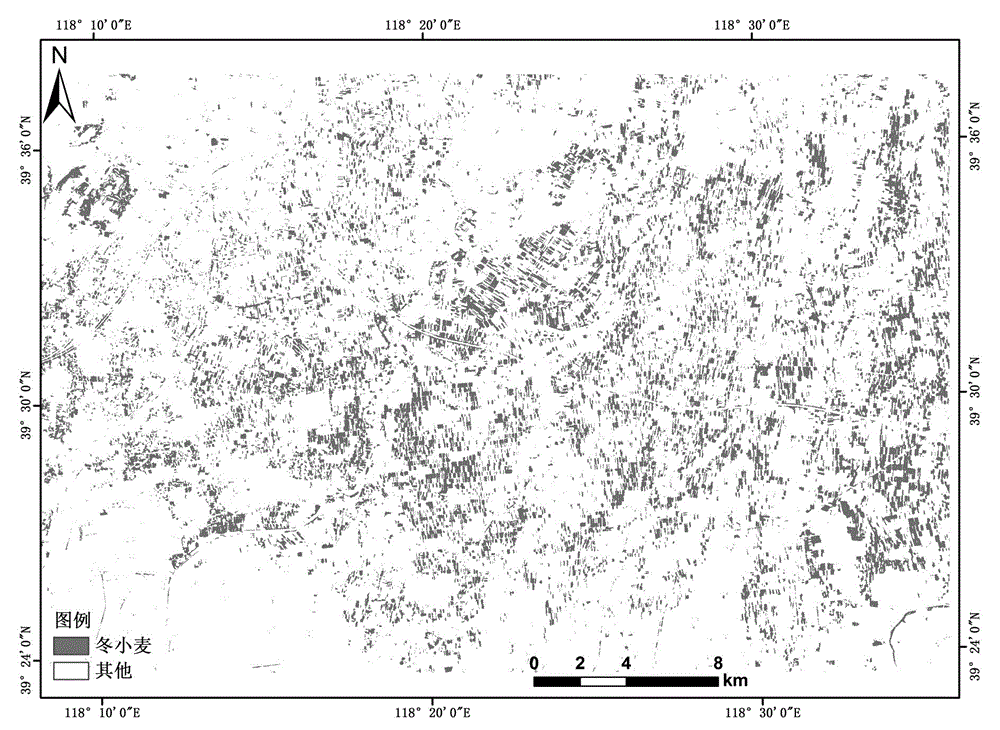
Winter wheat extraction method based on NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index) time series curve integral
ActiveCN104951772AImprove extraction accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionSoil scienceWide field
The invention discloses a winter wheat extraction method based on NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index) time series curve integral. The method is based on a WFV (wide field of view) camera carried by a GF-1 satellite, an NDVI time series covering the winter wheat growth cycle is adopted, the characteristic that an NDVI curve in the winter wheat growth cycle is higher, that is, the integral value of an NDVI curve chart of winter wheat along with time is higher than those of other crops, is fully used, automatic and high-precision identification of the winter wheat is realized on the basis of a curve integral method, the operation process is simple, and the effect is significant.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com