Method for building high-spatial resolution NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index) time series data
A high-spatial-resolution, time-series technology, applied in the field of building high-spatial-resolution NDVI time-series data, can solve the problems of continuous monitoring difficulty, time blind spots, and inability to obtain vegetation changes, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
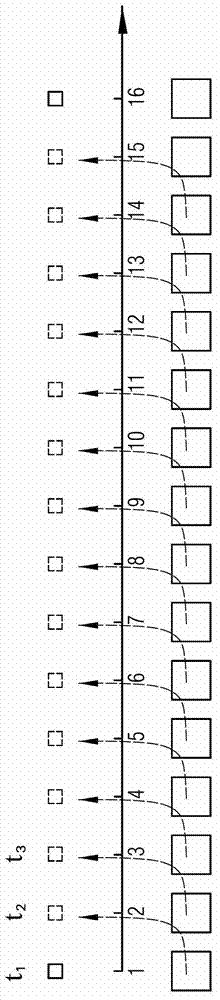
[0039] refer to figure 2 , which is shown in the figure 1 Based on the schematic diagram of predicting the corresponding TM NDVI data based on the MODIS NDVI data, the dotted line shows the predicted TM NDVI data.
[0040] Since the satellites that acquire TM NDVI data and MODIS NDVI data have similar orbital parameters and satellite transit time intervals of less than 30 minutes, it can be assumed theoretically that, in terms of time series, TM NDVI data and MODIS NDVI data are in a short period of time. can be assumed to vary linearly.
[0041] That is to say, figure 2 In the TM NDVI data above the time axis, the NDVI value of the TM pixel of the adjacent "picture" is assumed to change linearly with time, because the MODIS NDVI data below the time axis and the TM NDVI data are from satellite orbit to transit time Therefore, it can also be inferred that in the MODIS NDVI data below the time axis, the NDVI values of the MODIS pixels of adjacent "pictures" also change ...
Embodiment 2
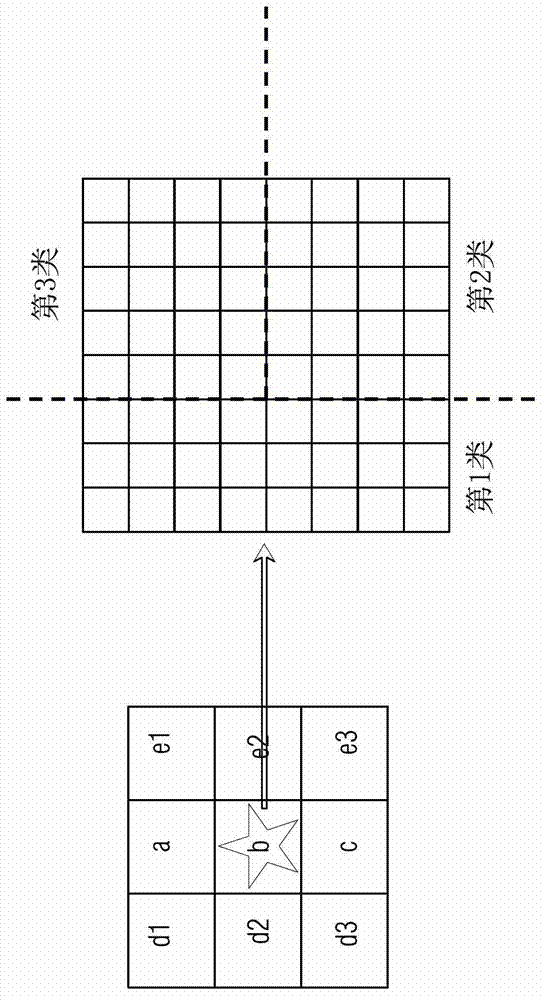
[0070] The method for constructing high spatial resolution NDVI time series data according to the present invention will be further described below with a specific example. Such as image 3 As shown in , it shows a schematic diagram of the corresponding relationship between MODIS pixels and TM pixels.
[0071] see image 3 , where the left side of the figure represents a 3*3 MODIS pixel, each small square represents a MODIS pixel, and there are 9 MODIS pixels in total. The right side of the figure shows the enlarged image of the MODIS pixel (target MODIS pixel) marked with a star on the left, which is filled according to the TM pixel scale, that is, each small square on the right represents the corresponding A TM pixel. It should be noted that since the spatial resolution of MODIS pixels is 250m*250m, and the spatial resolution of TM pixels is 30m*30m, in order to facilitate later calculations, MODIS pixels are resampled to 240m*240m, so each MODIS pixel is equal to 8 *8=6...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com