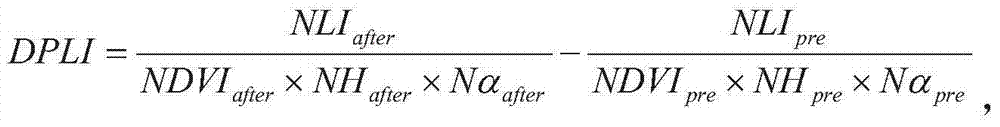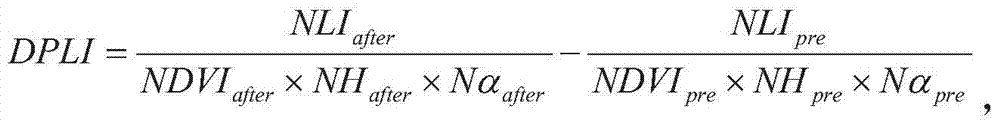Patents
Literature
31 results about "Thematic Mapper" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A Thematic Mapper (TM) is one of the Earth observing sensors introduced in the Landsat program. The first was placed aboard Landsat 4 (decommissioned in 2001), and another was operational aboard Landsat 5 up to 2012. TM sensors feature seven bands of image data (three in visible wavelengths, four in infrared) most of which have 30 metre spatial resolution. TM is a whisk broom scanner which takes multi-spectral images across its ground track. It does not directly produce a thematic map.
Method for classifying remote sensing images blended with high-space high-temporal-resolution data by object oriented technology
InactiveCN102609726AOvercome indistinguishable difficultiesSolve finelyPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryCharacter and pattern recognitionLand coverVegetation Index
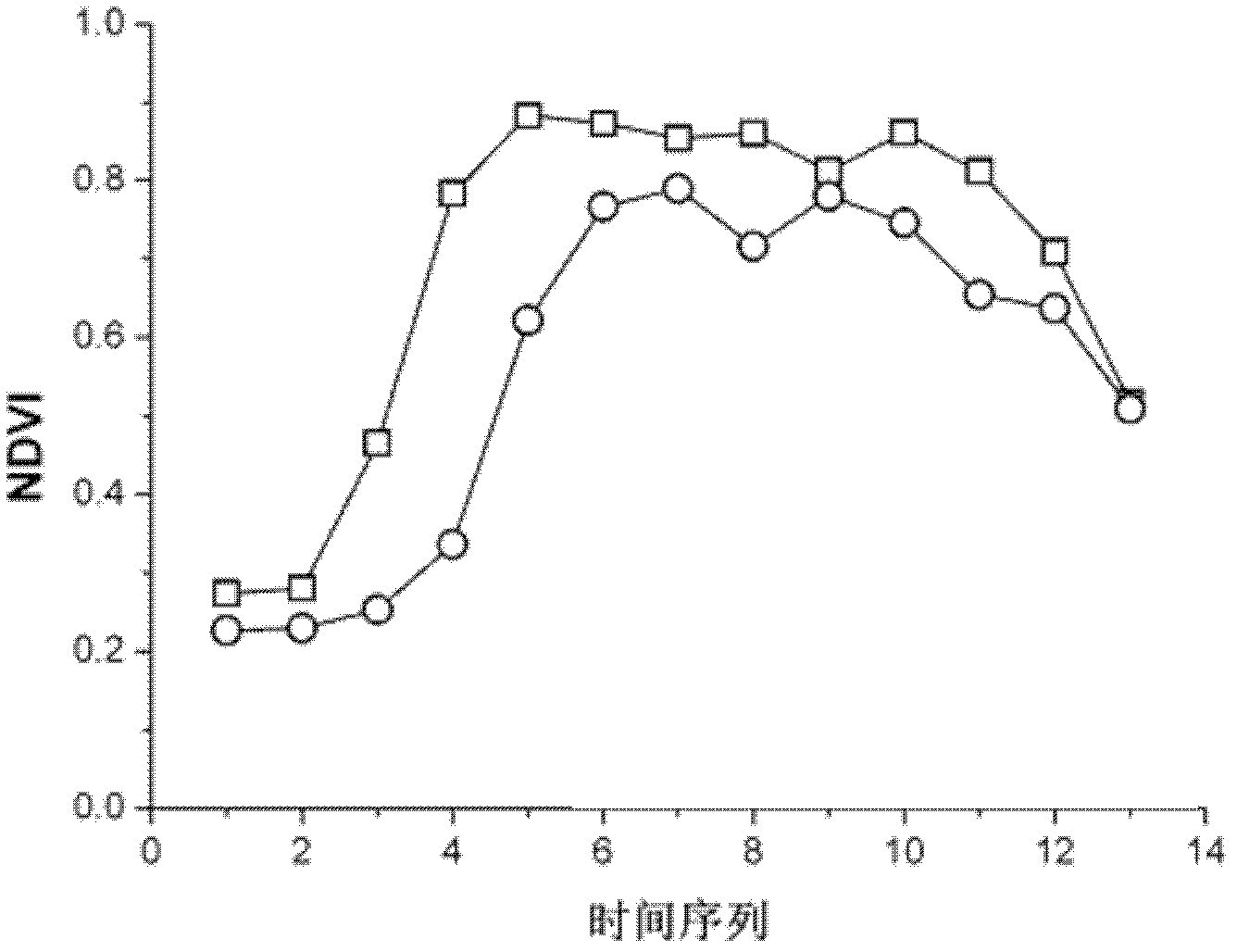
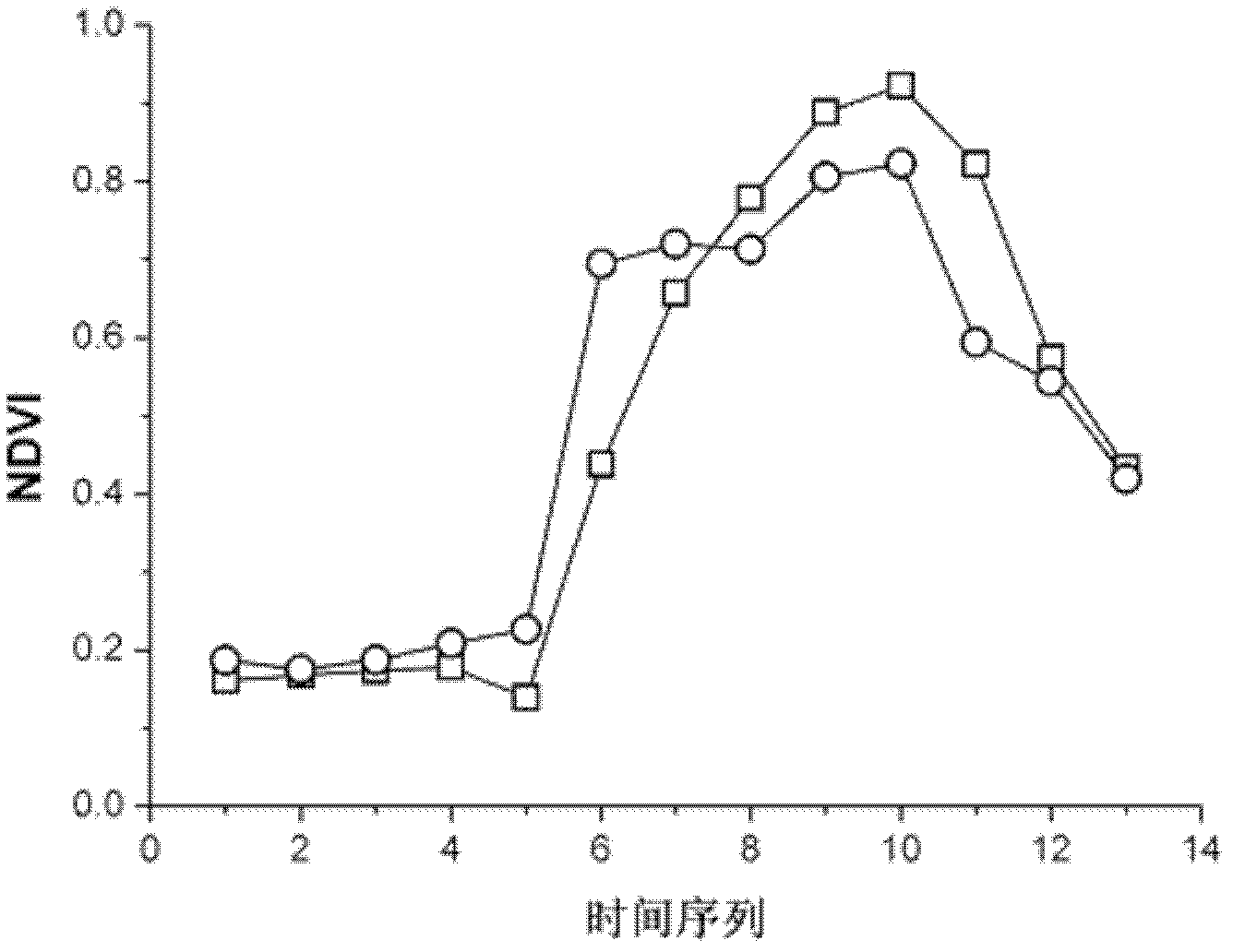
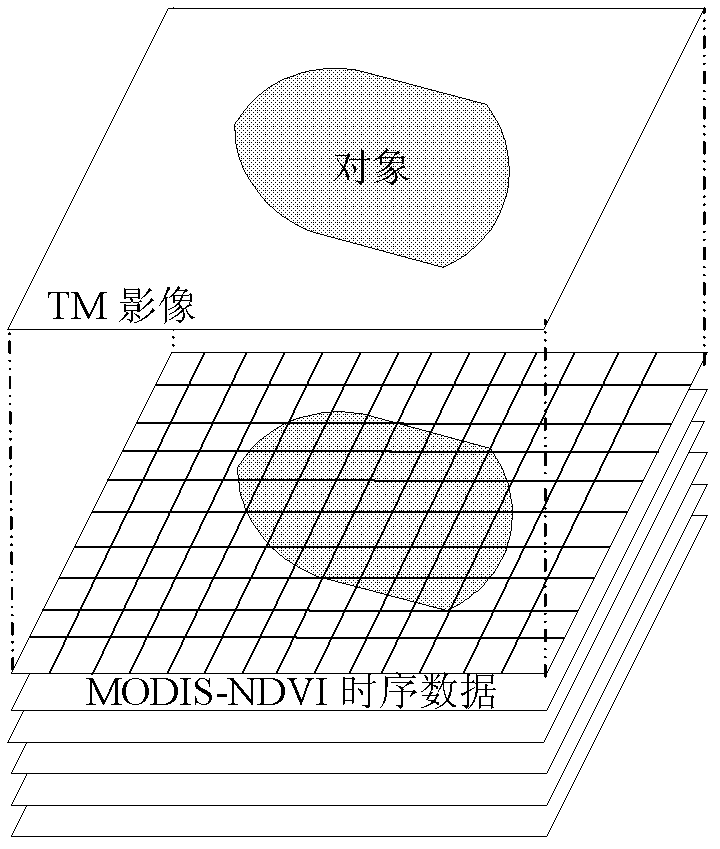
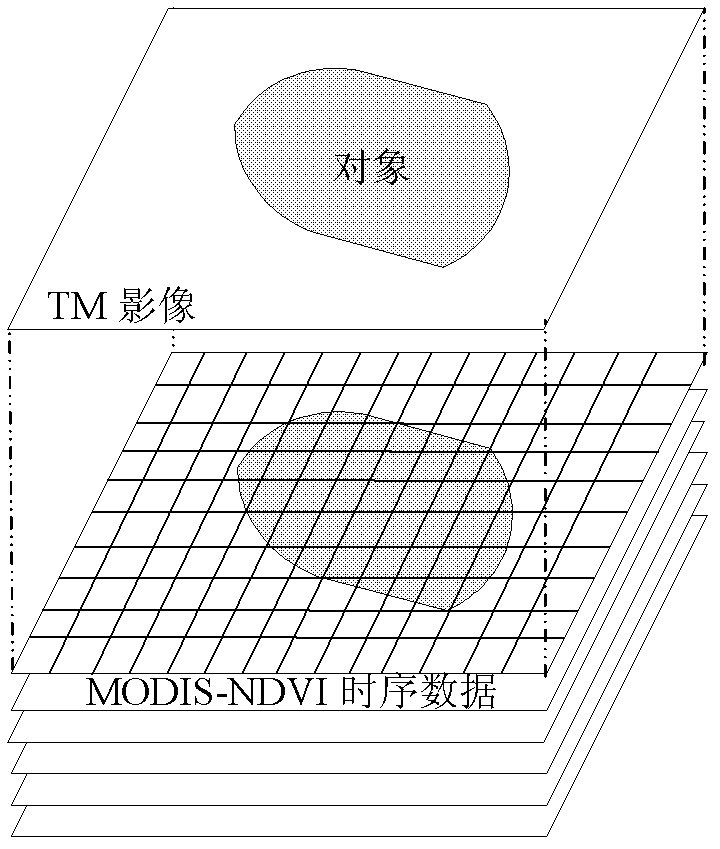
The invention discloses a method for classifying remote sensing images blended with high-space high-time resolution data by an object oriented technology, and relates to a method for classifying remote sensing images of an oriented object, which can be used for solving the problem that the previous method for classifying remote sensing images can not be used for distinguishing land cover types of 'foreign bodies with the same spectrum', and is not suitable for being applied to the remote sensing images with low-medium resolution ratio. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: carrying out filter processing by applying an SG (screen grid) filter; determining a time sequence curve of typical vegetational MODIS-NDVI (moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer-normalized difference vegetation index) in the remote sensing image to be classified; segmenting a TM (thematic mapper) image, wherein each segmentation unit is used as an object; extracting the characteristic information of each object; extracting all non-vegetation objects; removing the non-vegetation objects, and taking the obtained vegetational objects as planar vectors to segment MODIS-NDVI time sequence data, so as to obtain corresponding biotemperature information acquired by each vegetational object; and determining the vegetational type, to which each object belongs; and completing the land cover classification. The method provided by the invention can be used for distinguishing the land cover types.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
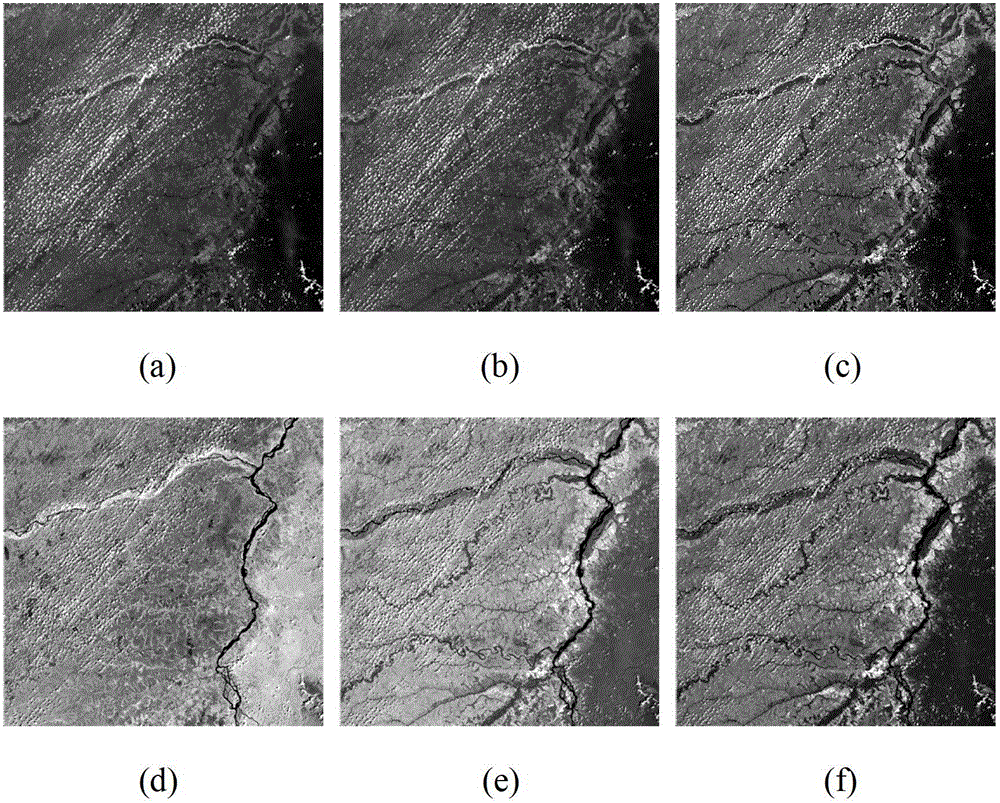
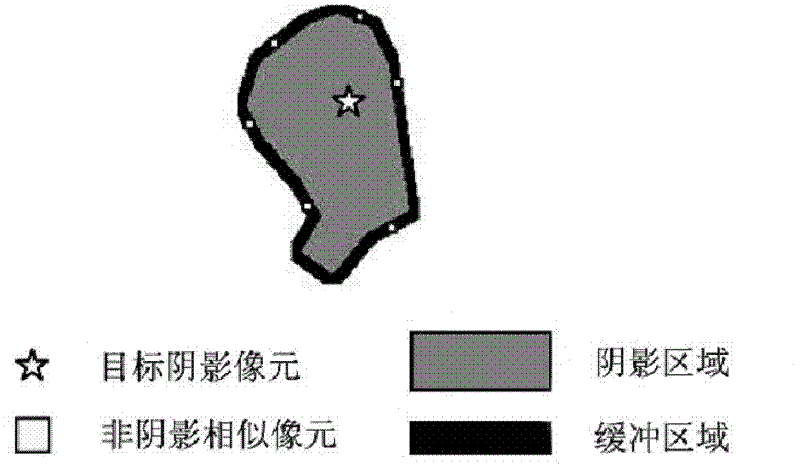
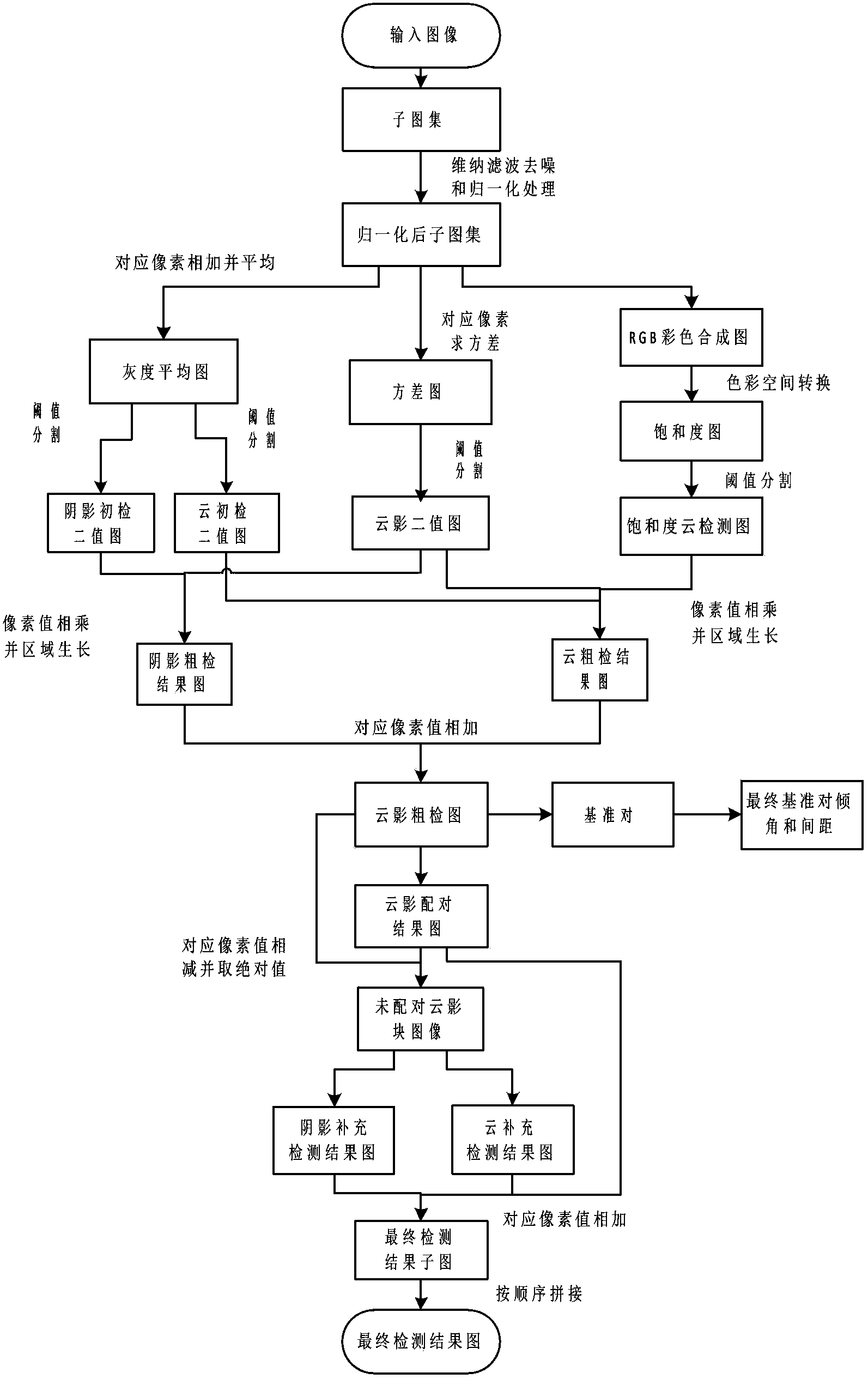
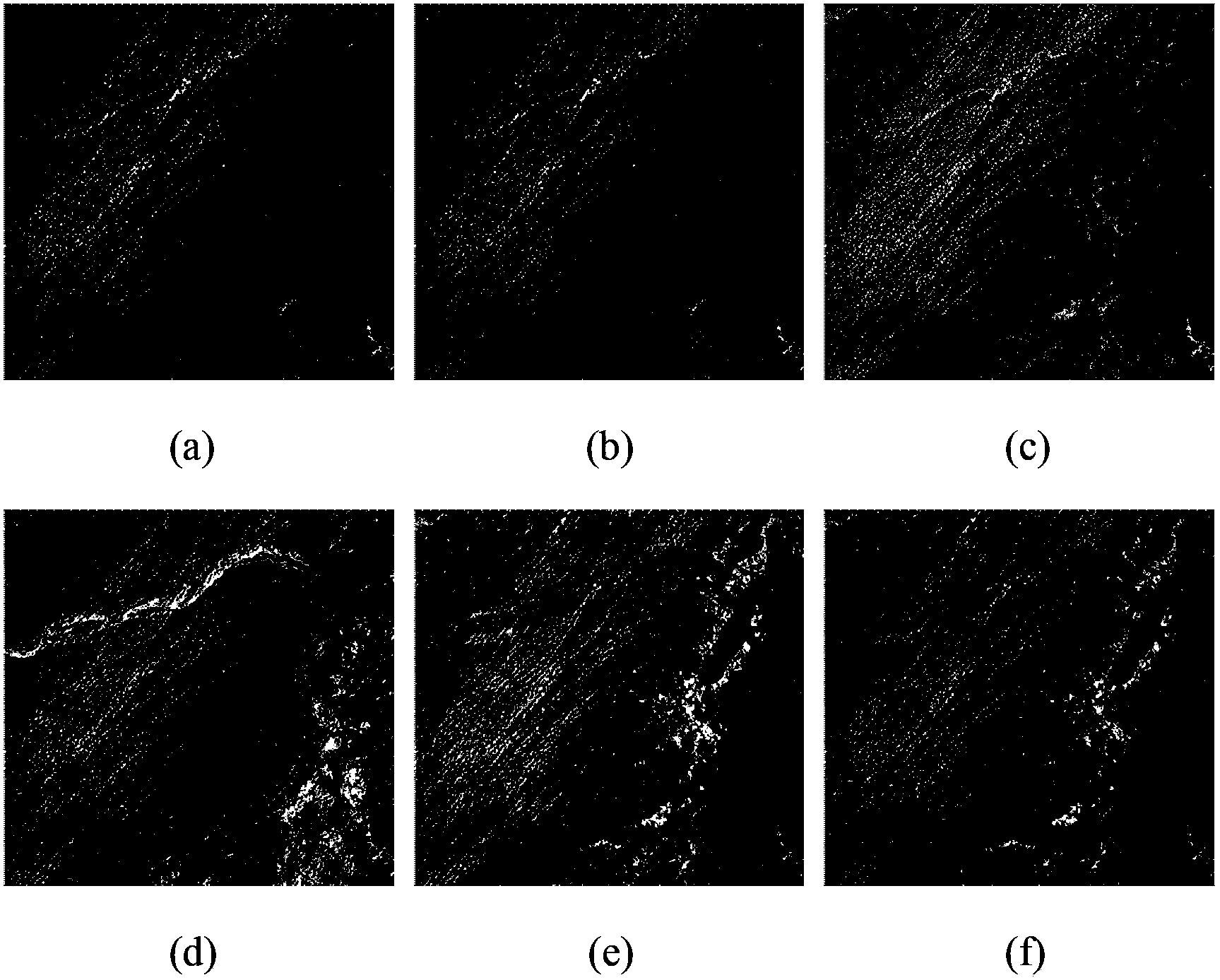
Method for detecting spissatus and spissatus shadow based on Landsat thematic mapper (TM) images and Landsat enhanced thematic mapper (ETM) images
InactiveCN102750701AHigh degree of automationReduce missed detectionImage analysisPattern recognitionThematic map
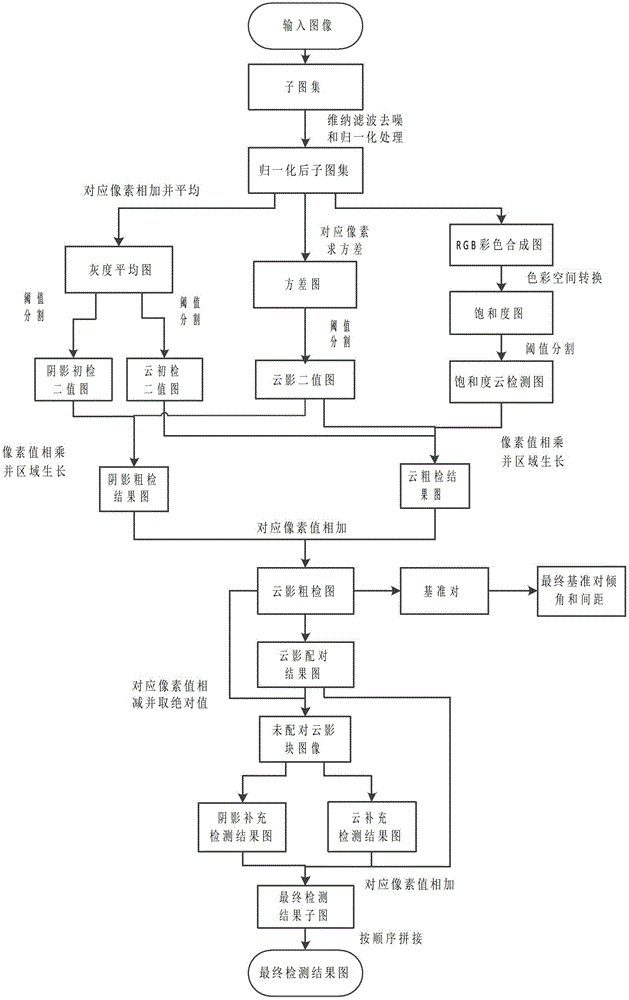
The invention discloses a method for detecting spissatus and spissatus shadow Landsat thematic mapper (TM) images and Landsat enhanced thematic mapper (ETM) images. The method comprises steps of dividing an input image into 16 sub-atlases and performing wiener filtering denoising and normalization for the 16 sub-atlases; performing rough detection for the spissatus and the shadow in the 16 sub-atlases and selecting reference pairs from a rough detection result; solving a mass center connection inclined angle and a space of a final reference pair in accordance with all reference pairs; matching the spissatus and the shadow in the 16 sub-atlases in accordance with the mass center connection inclined angle and the space of the final reference pair and performing supplementary detection for unmatched spissatus and unmatched shadow; adding a matching result of the spissatus and the shadow and a supplementary detection result and obtaining final detection result sub-images of all sub-atlases; and sequentially splicing final detection result sub-images of all sub-atlases and obtaining a final detection result image. Auxiliary information and manual intervention are not required, the detection precision is high and the method can be used in detection and classification of remote sensing image variation and pre-processing of image segmentation.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
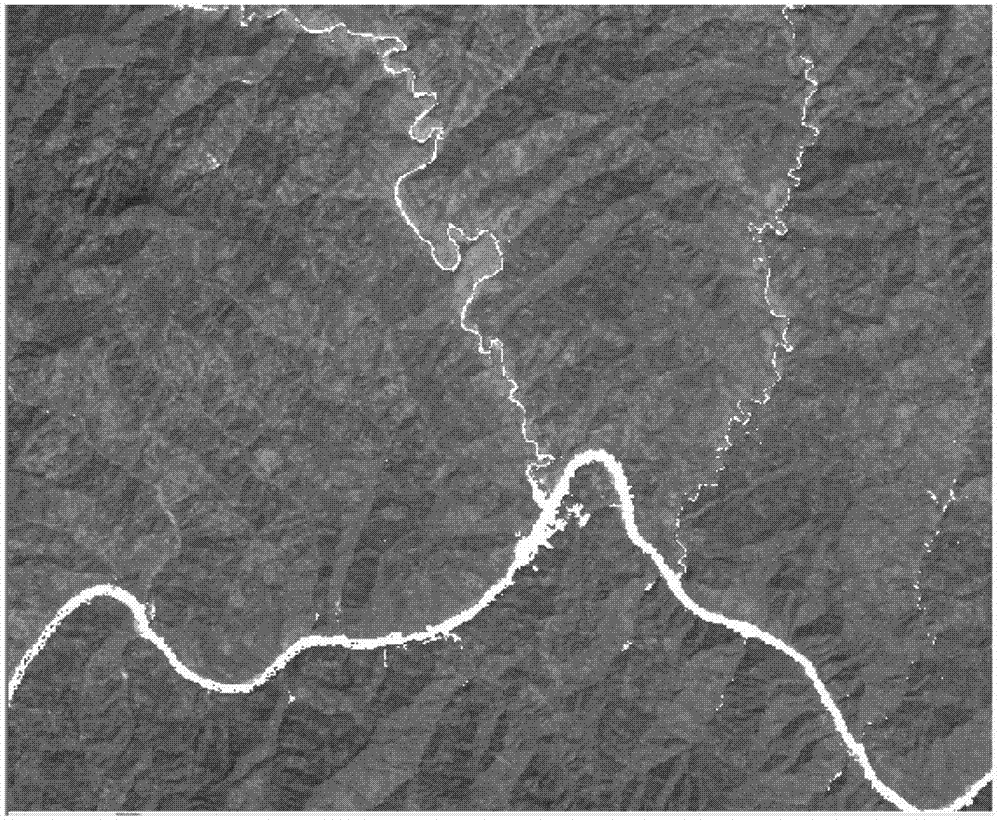
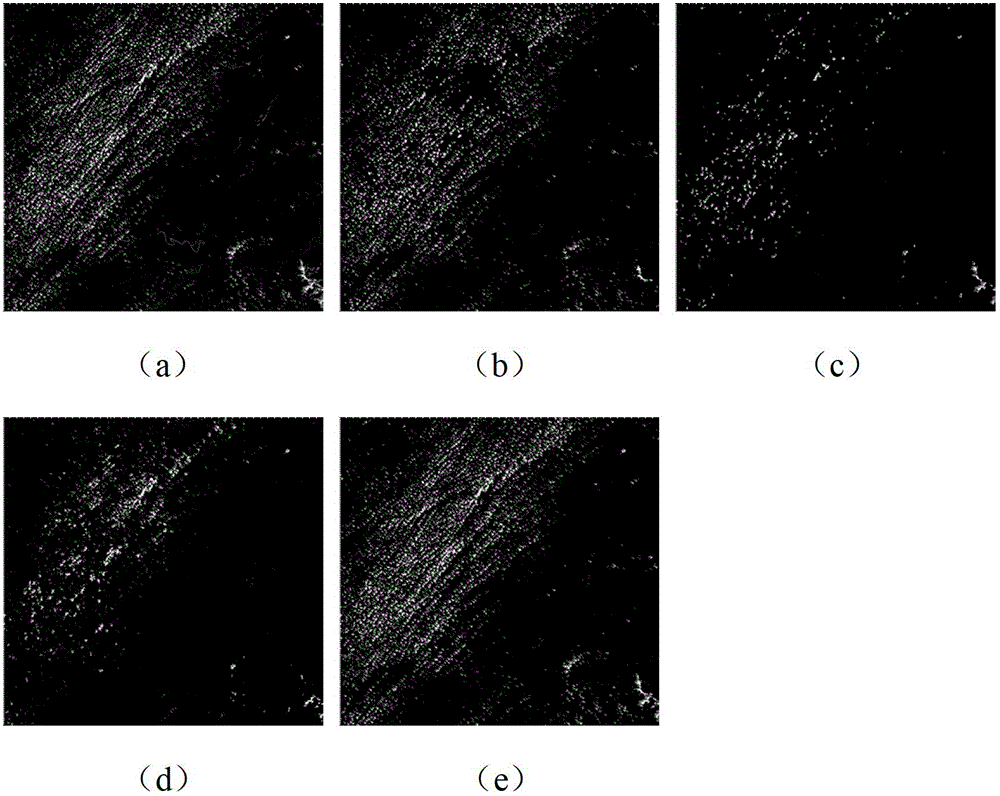
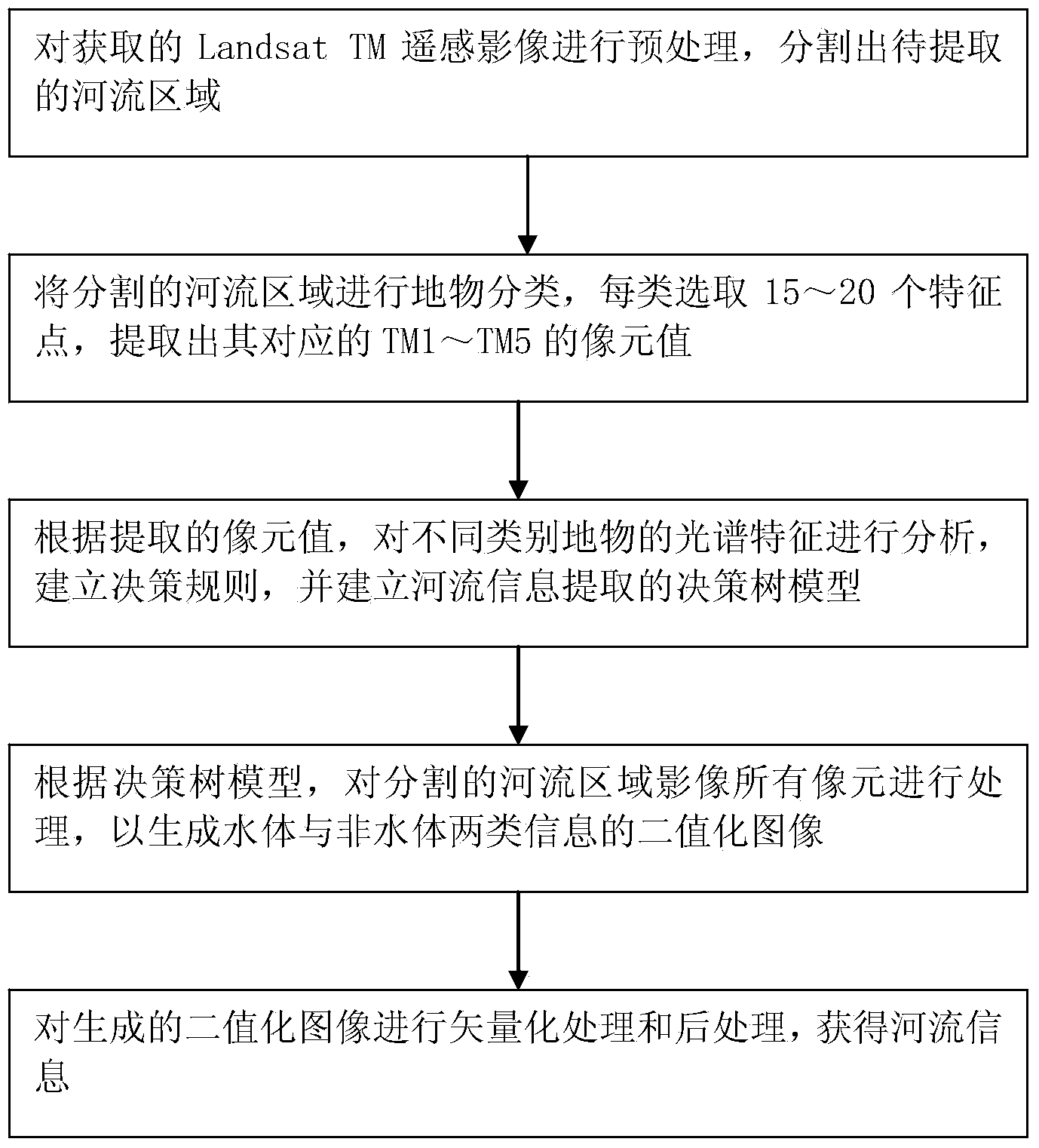
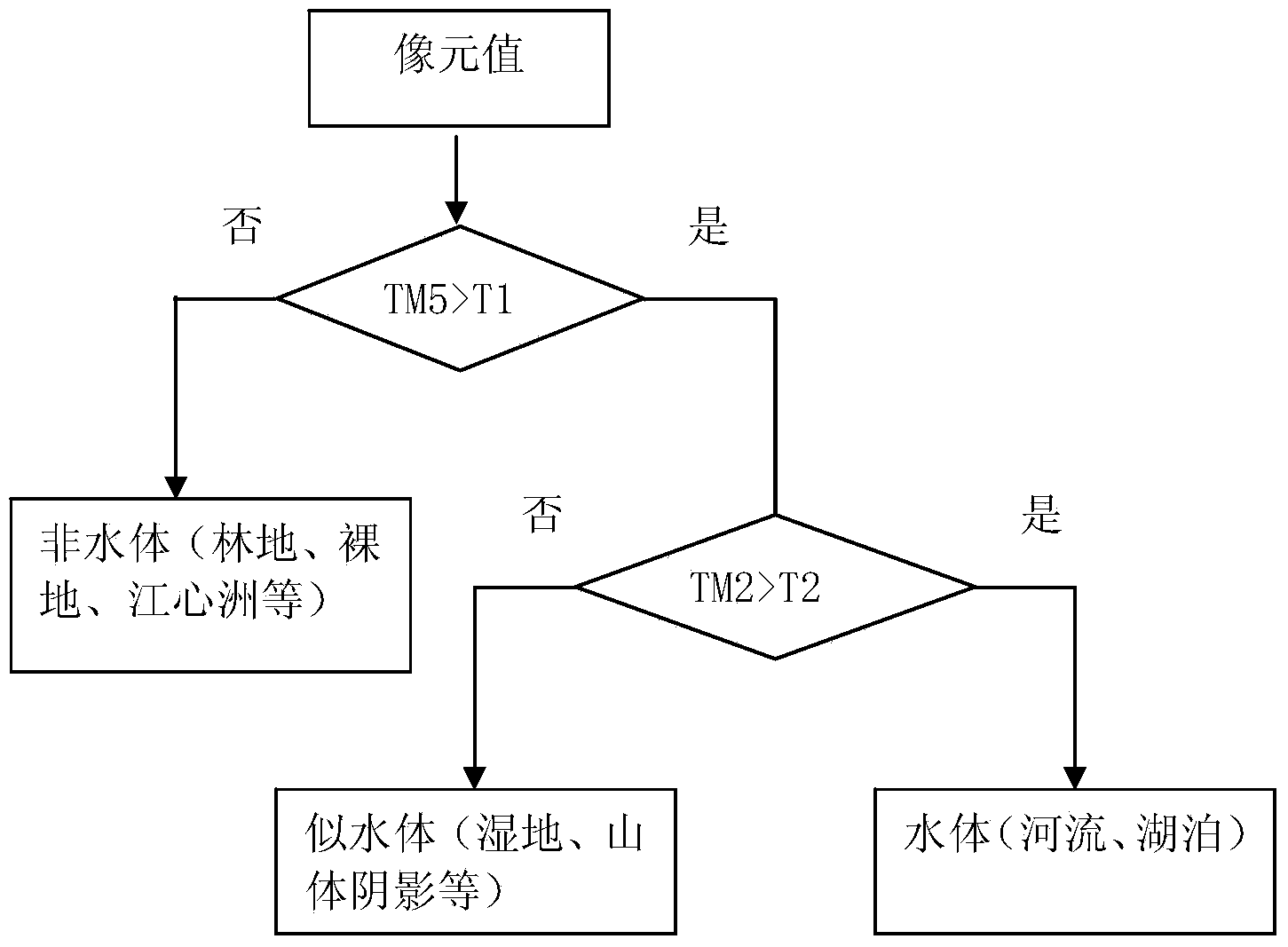
Decision tree model based multispectral remote sensing image river information extraction method
InactiveCN103646246AImprove extraction accuracyQuick extractionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionDecision takingThematic map
The invention discloses a decision tree model based multispectral remote sensing image river information extraction method. The decision tree model based multispectral remote sensing image river information extraction method comprises step 1, preprocessing an obtained Landsat TM (Thematic Mapper) remote sensing image and segmenting out a river area to be extracted; step 2, performing ground object classification on the segmented river area, selecting 15 to 20 feature points from every type and extracting out corresponding picture element values from TM1 to TM5; step 3, analyzing spectrum characteristics of the different types of ground objects according to the extracted picture element values, establishing a decision rule and establishing a decision tree model of river information extraction; step 4, processing picture elements of a segmented river area image according to the decision tree model so as to generate a binaryzation image of water body information and non-water-body information; step 5, performing vectorization processing and post-processing on the generated binaryzation image to obtain river information. According to the decision tree model based multispectral remote sensing image river information extraction method, rapid retraction of the river information can be achieved and the decision tree model based multispectral remote sensing image river information extraction method can be applied to the thematic map production directly.
Owner:TIANJIN RES INST FOR WATER TRANSPORT ENG M O T +2
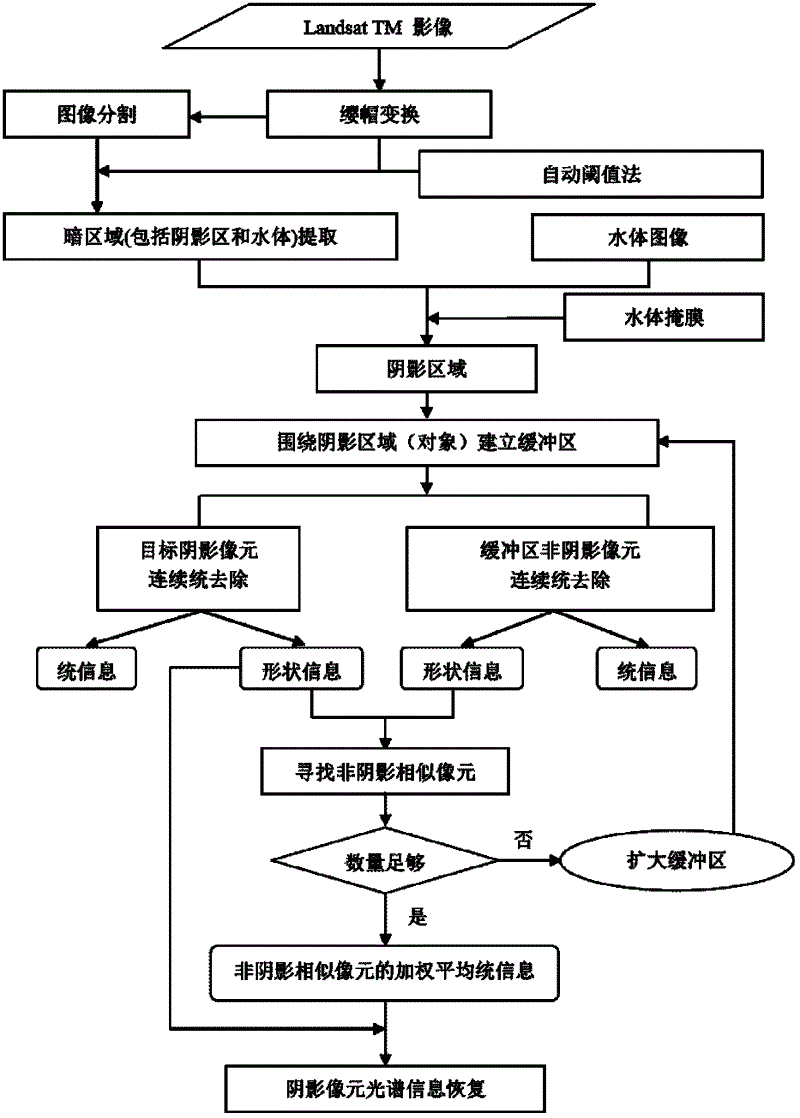
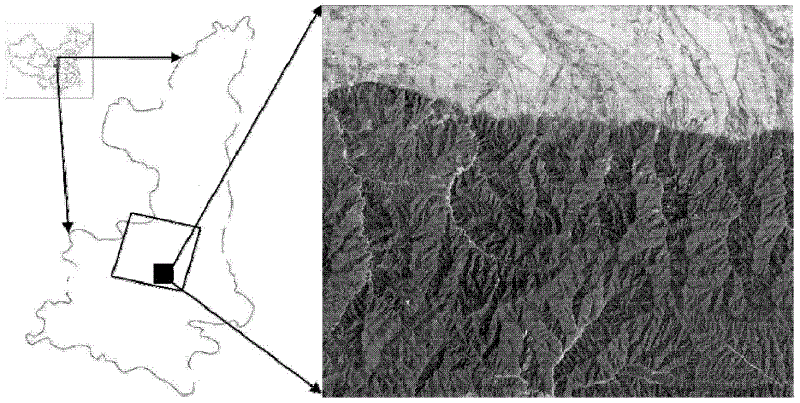
Method for recovering spectral information of hill shade area of Landsat thematic mapper/enhanced thematic mapper plus (TM/ETM+) image
The invention provides a method for recovering spectral information of a hill shade area of a Landsat thematic mapper / enhanced thematic mapper plus (TM / ETM+) image. The method comprises the following steps of: identifying and extracting the shade area, searching unshaded similar image elements and recovering the spectral information of the shade area. The method for recovering the spectral information of the hill shade area of the Landsat TM / ETM+ image is used for recovering the spectral information of the shade area of a remote sensing image. According to the method provided by the invention, by fully combining the proper weak spectral information of shade image elements with the spectral information of similar image elements near the shade image elements, the dependence of a traditional topographic correction algorithm on digital elevation model (DEM) data is rid of. When the resolution and the accuracy of the DEM data cannot meet the requirement of the topographic correction algorithm, the algorithm is capable of providing an effective shade processing method.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Thematic map based route optimization
According to an example aspect of the present invention, there is provided an apparatus comprising at least one processing core, at least one memory including computer program code, the at least one memory and the computer program code being configured to, with the at least one processing core, cause the apparatus at least to determine a route based at least partly on a thematic map database and a current location of the apparatus, present the determined route as a suggested route to a first user, and responsive to the first user approving the suggested route, initiate an activity session based on the suggested route.
Owner:SUUNTO OY
Method for building high-spatial resolution NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index) time series data
InactiveCN102831310AHigh resolutionGood precisionSpecial data processing applicationsImage resolutionHigh spatial resolution
The invention discloses a method for building high-spatial resolution NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index) time series data. The high-spatial resolution NDVI time series data is predicted and built according to low-spatial resolution MODIS (moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer) pixels in known MODIS NDVI data and high-spatial resolution TM (thematic mapper) pixels in TMNDVI (thematic mapper normalized difference vegetation index) data. TM data is combined with MODIS data, and accordingly high-spatial resolution NDVI time series data with quite fine precision can be obtained effectively.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
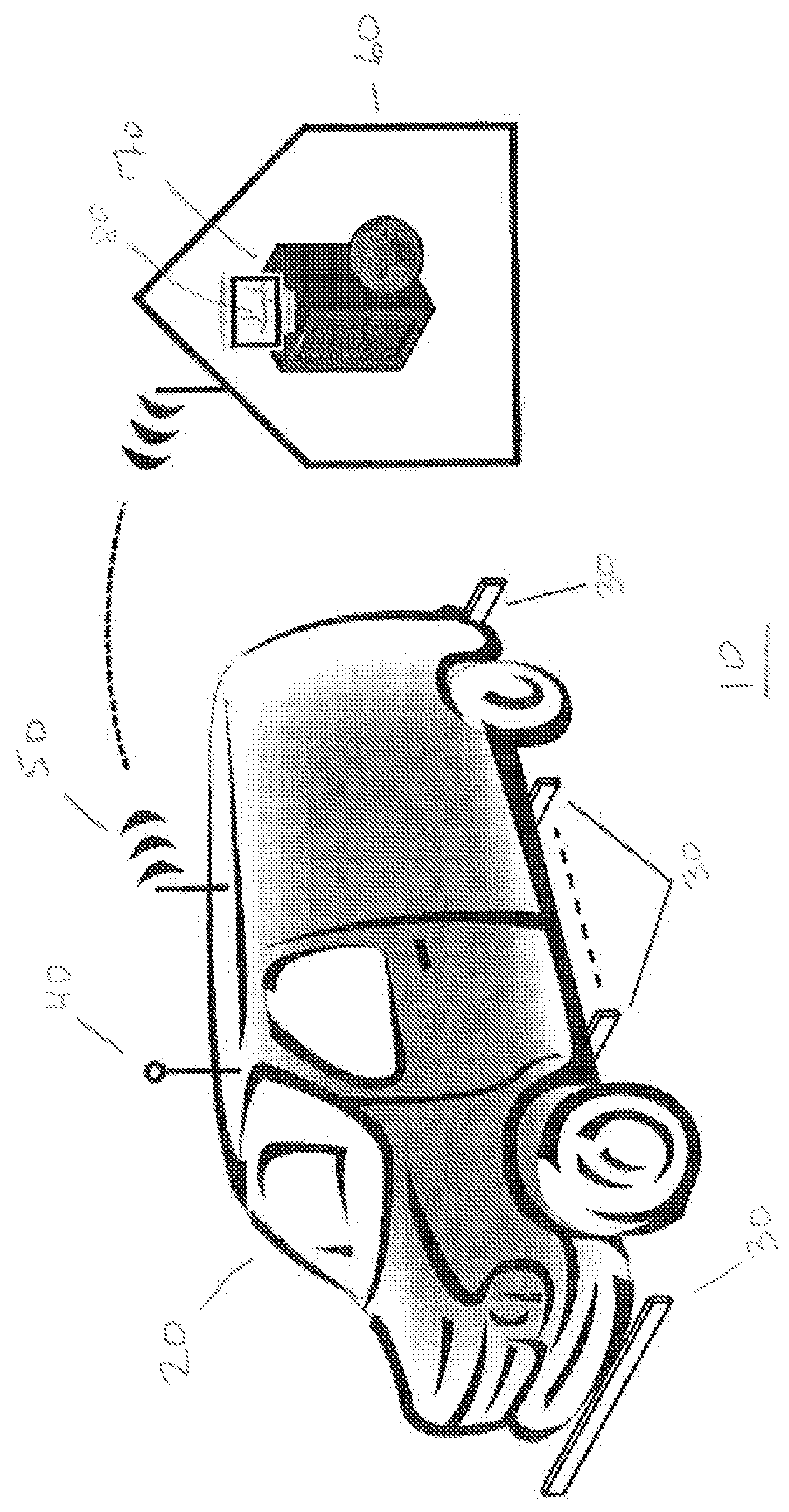
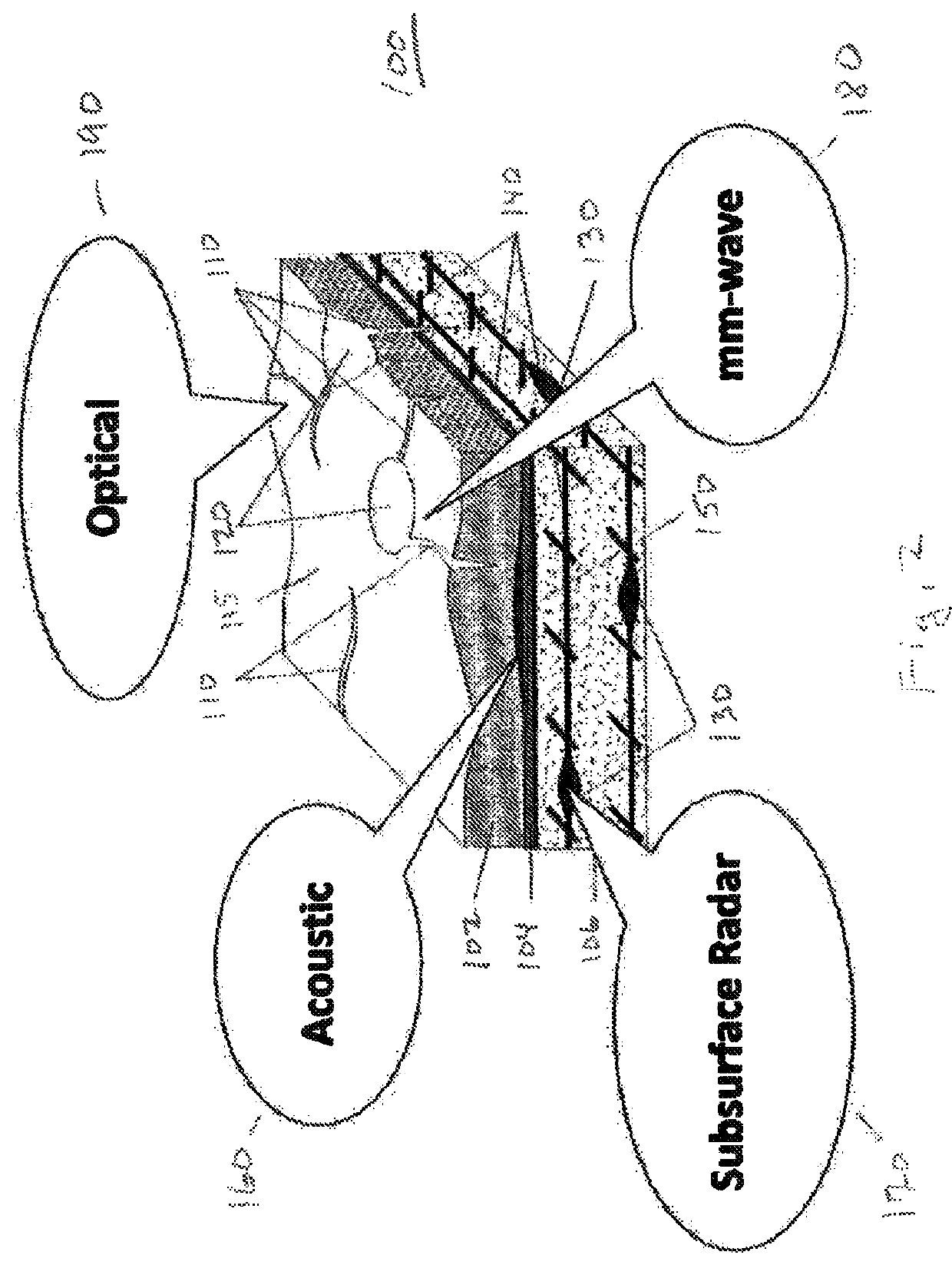
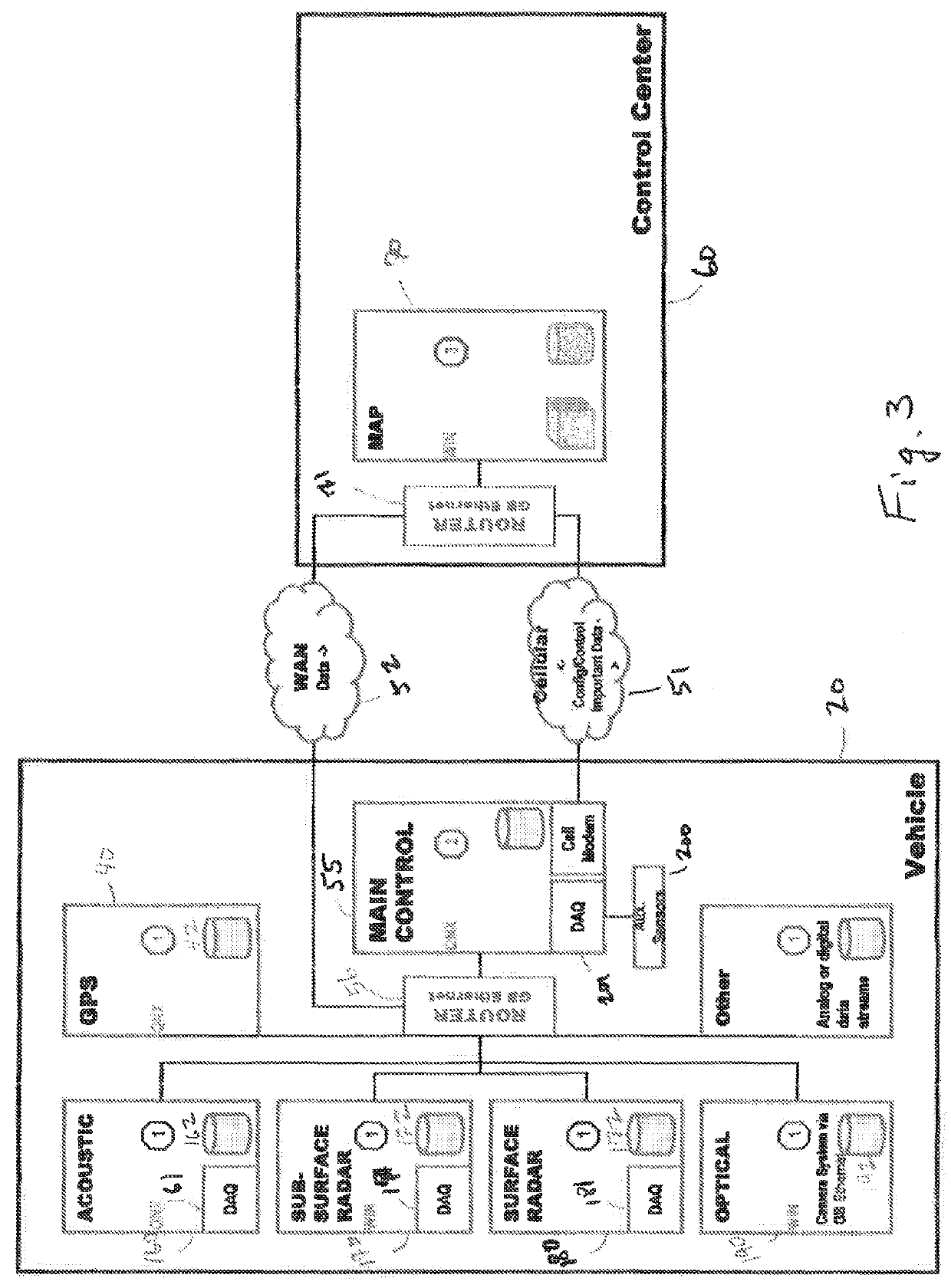
Roaming mobile sensor platform for collecting geo-referenced data and creating thematic maps
ActiveUS9377528B2Improve securityEliminate needRoad vehicles traffic controlNavigation instrumentsRebar corrosionBridge deck
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
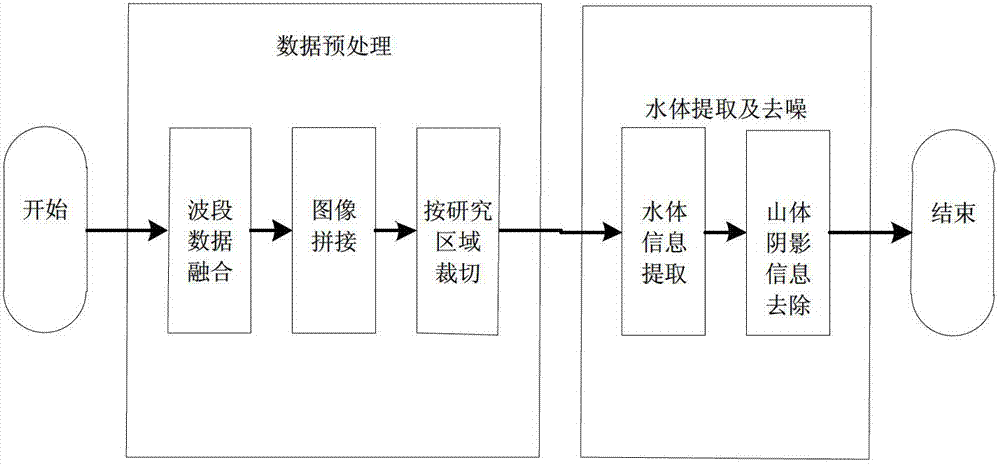
Water body information extraction method based on TM (Thematic Mapper) image
The invention discloses a water body information extraction method based on a TM (Thematic Mapper) image. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out data fusion on files of seven wave bands, and then setting a proper edge processing method to carry out splicing of image data; then utilizing a boundary of a rasterized target area to cut the spliced image data; establishing a water body information extraction model aiming at wave spectrum information of the TM image; and establishing a noise removal model aiming at mountain shadow noise in the extracted water body information. According to the water body information extraction method, the water body information can be accurately extracted as far as possible by utilizing a Landsat TM satellite image, and basic hydrology information is provided for subsequent research.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
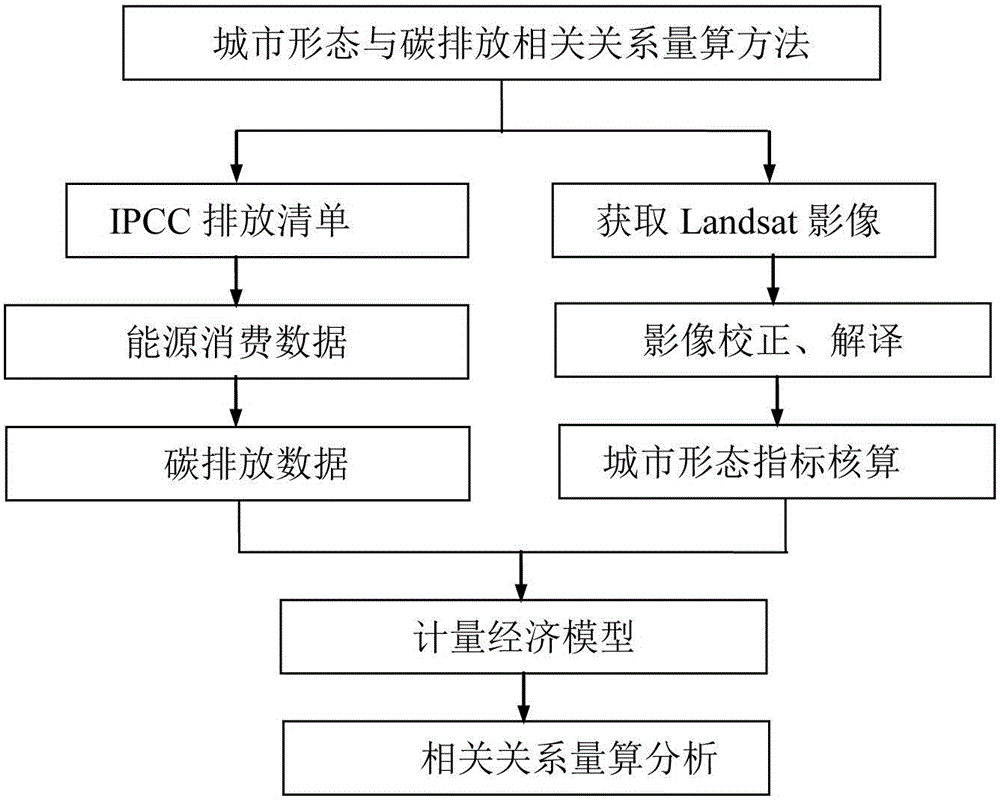
Method for measurement and calculation of correlation between urban form and carbon emission based on Landsat TM (Thematic Mapper) and ETM (Enhanced Thematic Mapper) images
InactiveCN106446314AEasy accessEasy to understandSpecial data processing applicationsEmission inventoryEnergy statistics
The invention provides a technical method for quantitatively evaluating measurement and calculation of a correlation between an urban form and carbon emission based on Landsat TM (Thematic Mapper) and ETM (Enhanced Thematic Mapper) images. The method comprises the main steps of: 1, calculating urban energy consumption carbon emission based on an IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) greenhouse gas emission inventory compilation method and various types of energy statistic data; 2, based on the Landsat TM and ETM images, quantitatively calculating urban form indexes by use of ENVI (Environment for Visualizing Images) / IDL (Interactive Data Language) 5.1 software and ArcGIS (Geographic Information System) 10.1 (ERSI) software; and 3, quantitatively calculating the correlation between the urban form-related indexes and carbon emission by use of an econometric model. The technical method is systematic, comprehensive and operable, and can provide an overall, objective and scientific optimized decision and regulation-control basis for urban spatial structure optimization.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
Method and system for manufacturing thematic map by fusing images based on MapGISK9
InactiveCN103955909AWith colorHigh resolutionImage enhancementGeometric image transformationGraphicsGoal recognition
The invention discloses a method and system for manufacturing a thematic map by fusing images based on the MapGISK9. The method for manufacturing the thematic map by fusing the images includes the following steps that firstly, a database is built in the MapGISK9, multispectral images and full-color images in the same area are led in; secondly, the geographical location information of the multispectral images and the full-color images which are led in is obtained; thirdly, the multispectral and images are calibrated with a MapGISK9 remote-sensing image platform; fourthly, the calibrated multispectral images and the full-color images are fused; fifthly, vectorization processing is performed on the fused images. According to the method and system for manufacturing the thematic map by fusing the images based on the MapGISK9, the multispectral images and the full-color images are fused, so that remote-sensing images have colors, the high resolution and projection information, and a series of processing of terrain classification and target identification is fully ensured.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
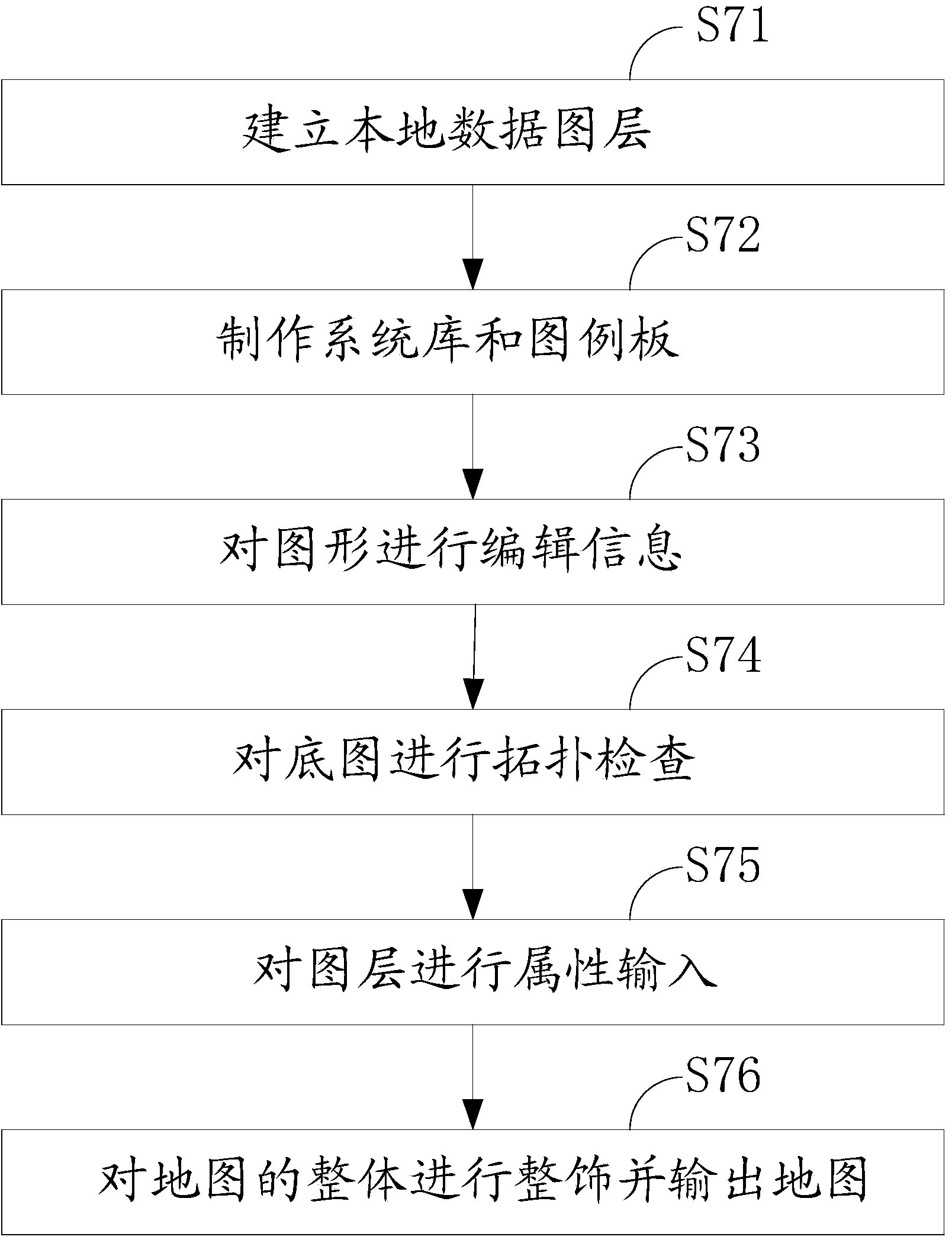
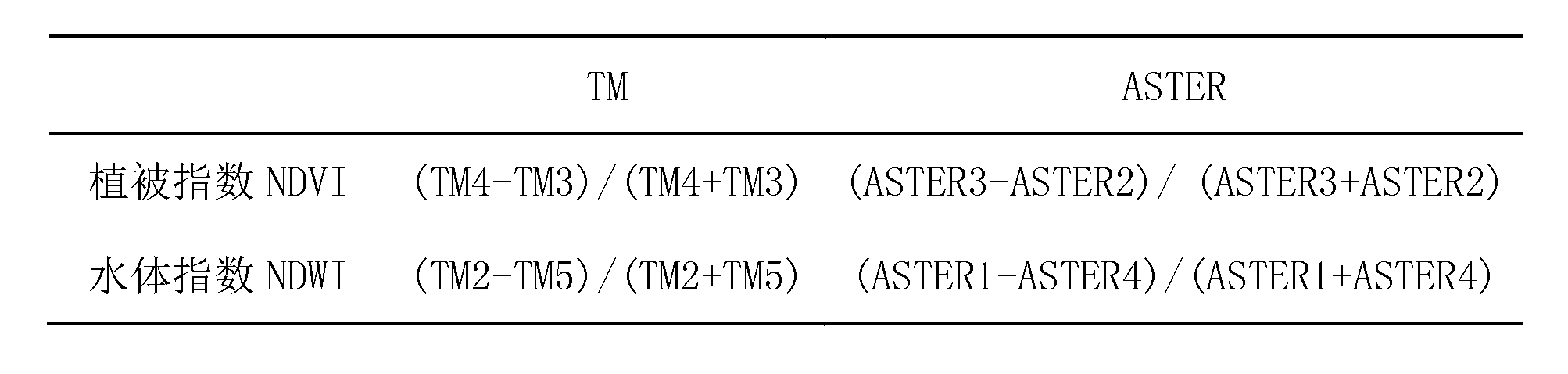
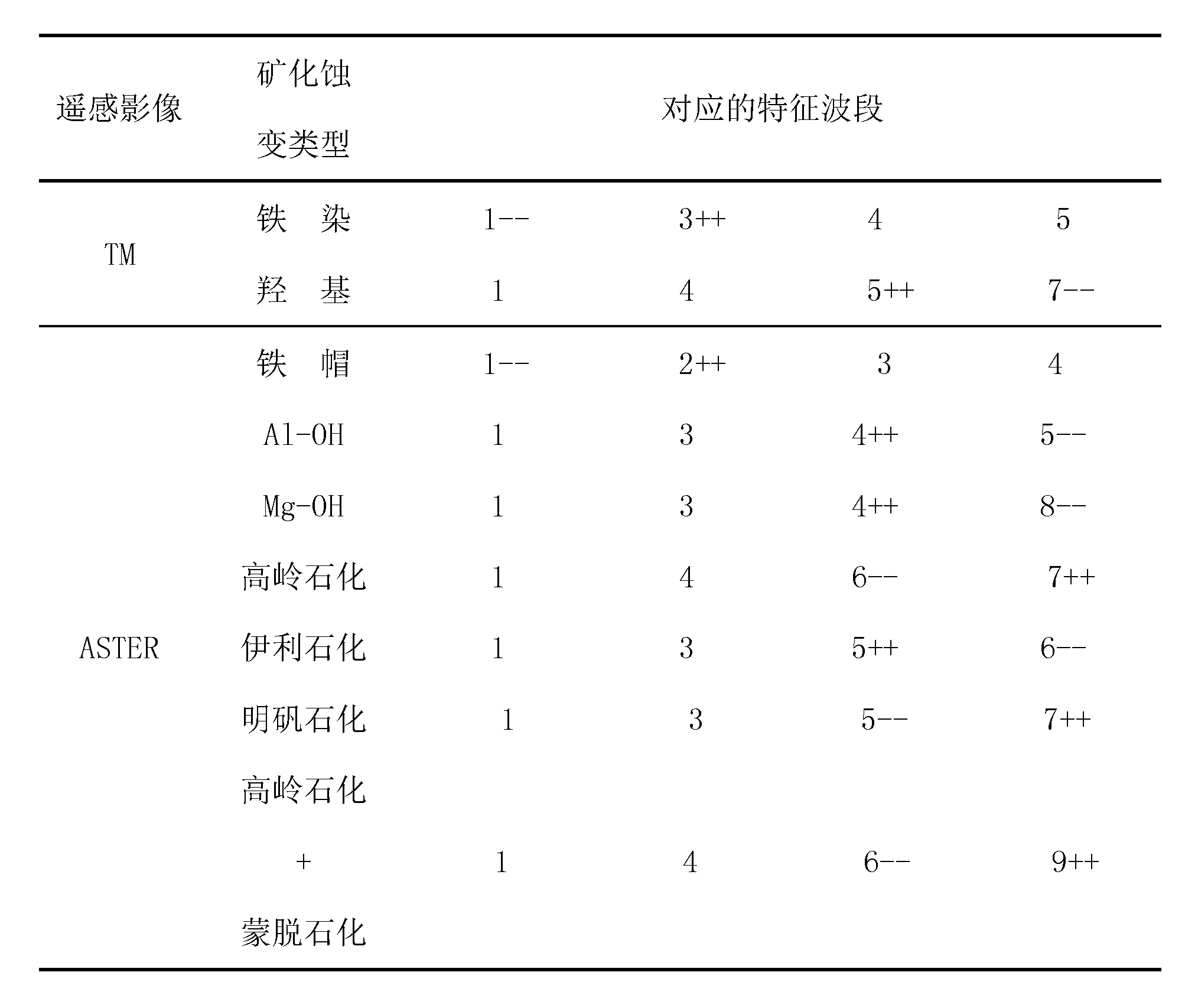
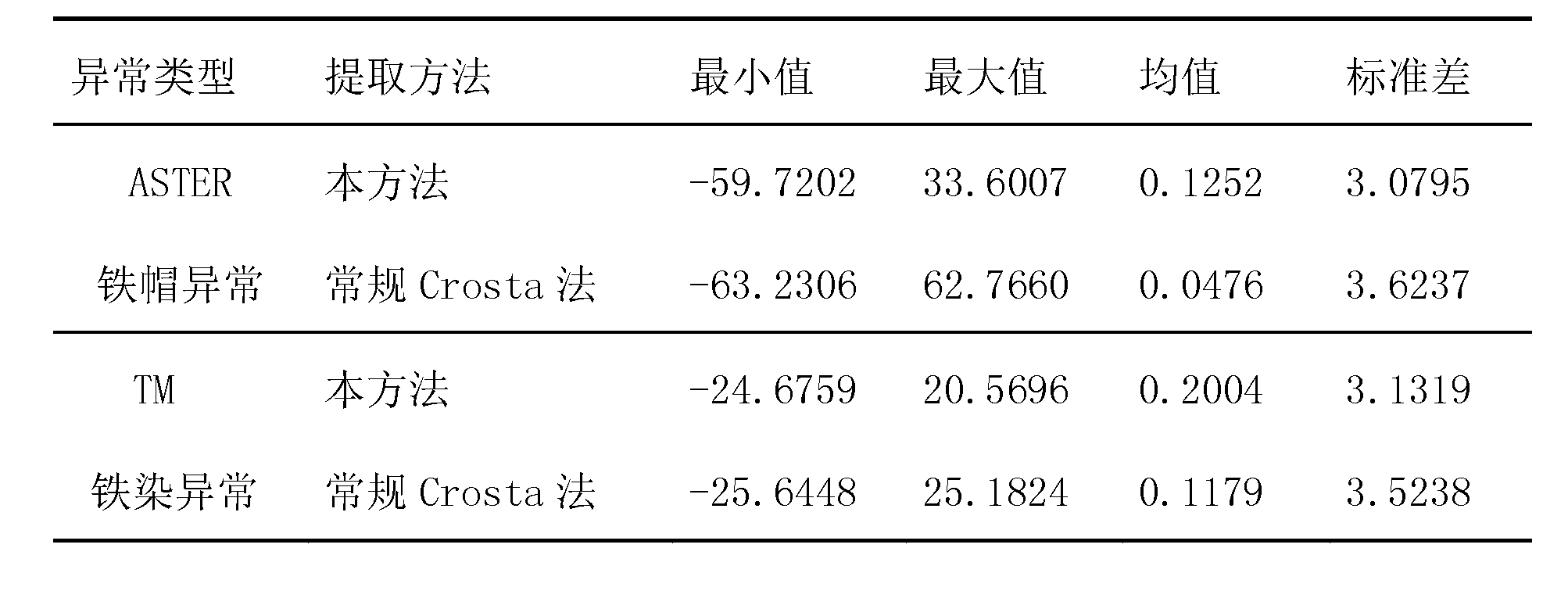
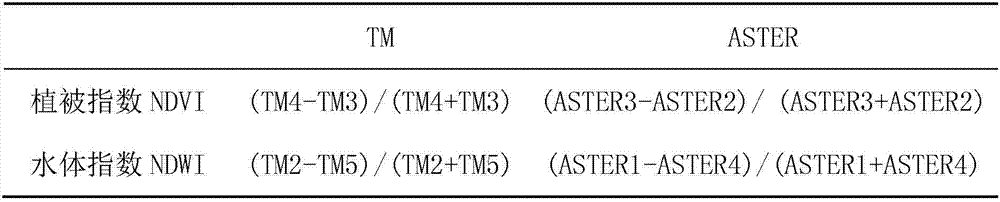
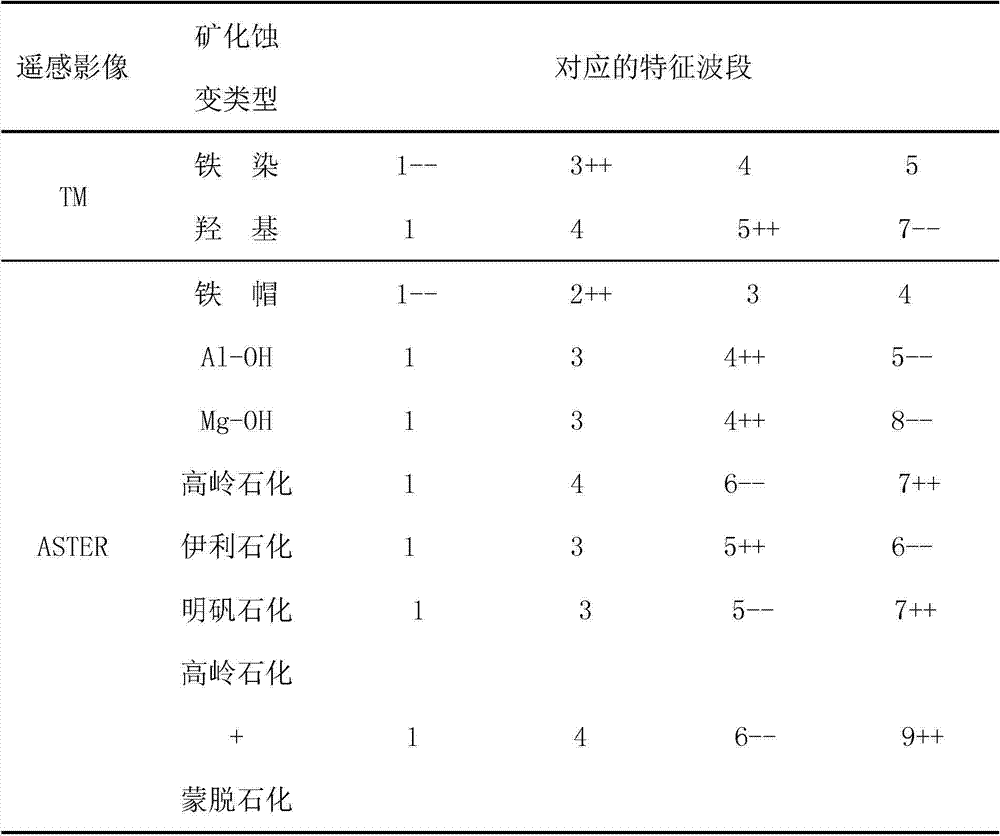
Method for extracting mineralization-alteration information
InactiveCN103207415AStrong filtering functionReduce noiseOptical prospectingLocal variablePrincipal component analysis
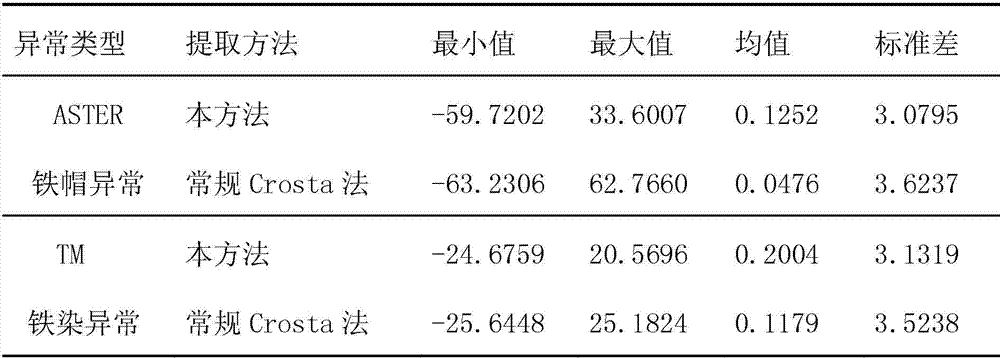
The invention discloses a method for extracting mineralization-alteration information. The method comprises the steps of effective background pixel identifications, selection of local variable windows, in-window main component analysis, construction of abnormal variables, abnormal recognition and assignment and alteration abnormal output. Interference information such as water, cloud, ice and snow is eliminated through identifications and statistics of effective background pixels; and statistics variables are limited within the windows rather than the whole image range during main component analysis through local variable windows, therefore further reduction of interference of ambient environment noise is facilitated, and the extraction capacity of alteration information is improved. By means of the method, the potential of mineralization-alteration charting of thematic mapper (TM) and advanced spaceborne thermal emission and reflection radiometer (ASTER) remotely-sensed can be further mined, and the indication capacity in geological exploration can be improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
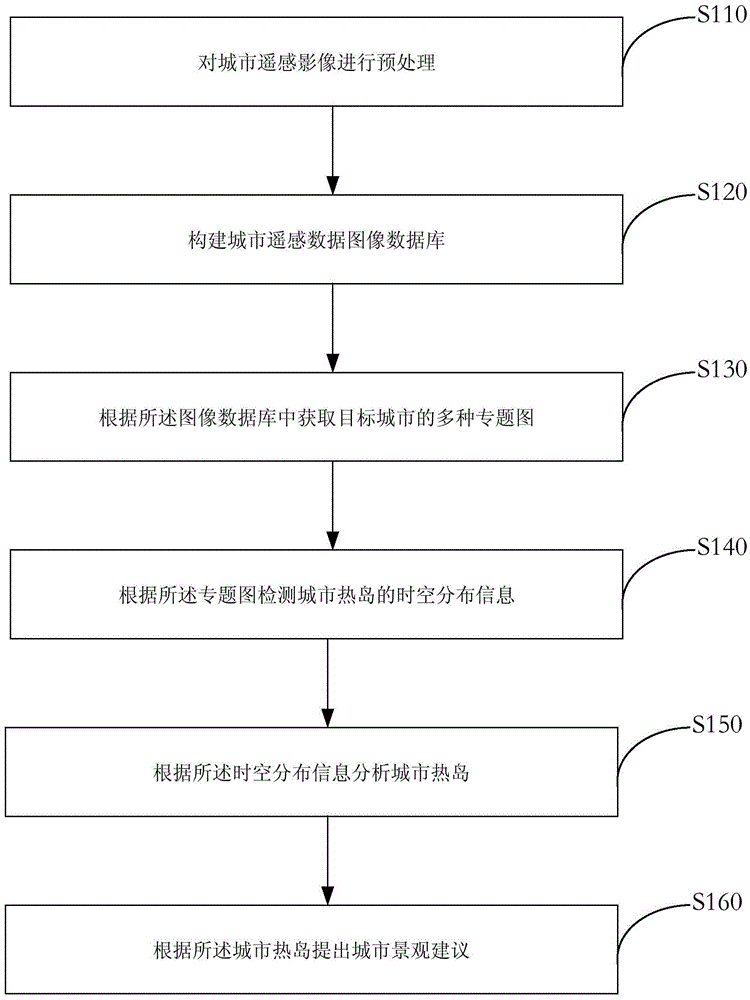
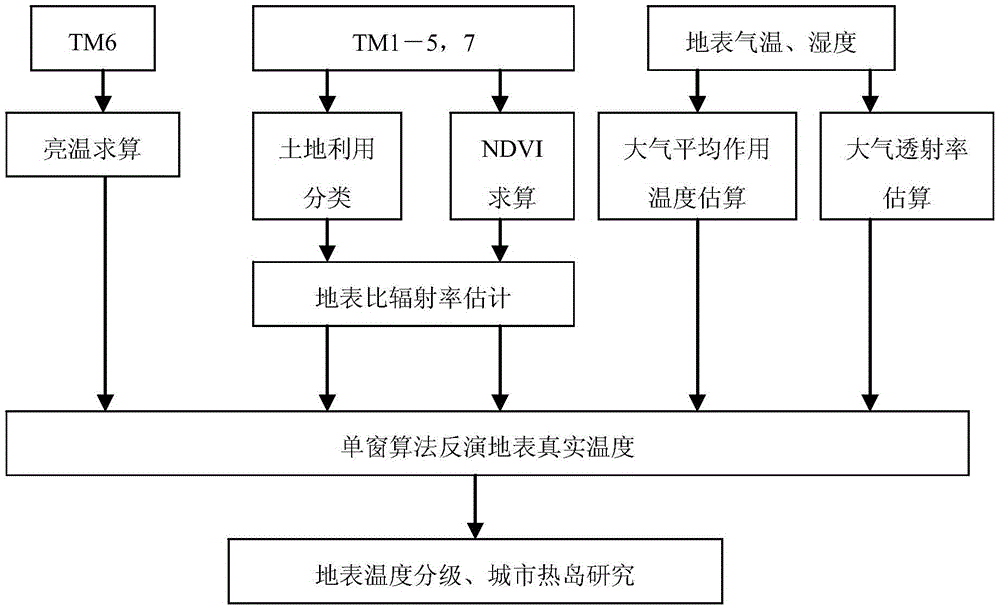
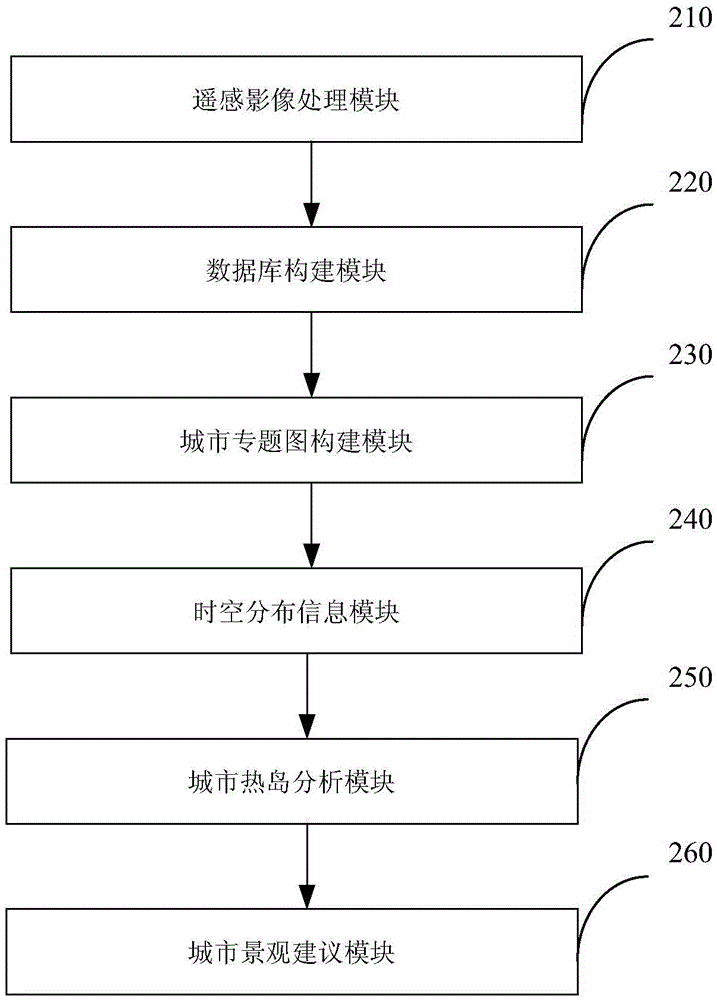
Urban heat island effect space variation detection method and system
InactiveCN105678225AOvercome the problem of spatial superposition algorithmImprove accuracyScene recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsSensing dataThematic map
The invention provides an urban heat island effect space variation detection method and system. The urban heat island effect space variation detection method comprises the steps: constructing an urban remote sensing data image database for the processed urban remote sensing images; according to the image database, acquiring a plurality of thematic images of a target city; and according to the thematic images, detecting the space-time distribution information of urban heat islands, and analyzing the urban heat islands; according to the urban heat islands, offering a proposal for urban landscape. Therefore, the urban heat island effect space variation detection method and system can overcome the spatial overlay algorithm problem between the heat island effect spatial distribution and other feature layers of the city, and can improve the accuracy for urban heat island effect space variation detection.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
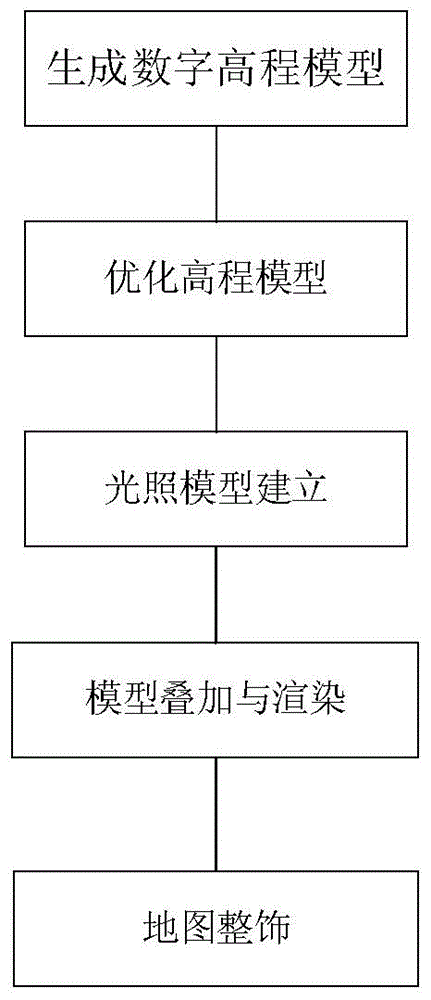
Acquisition method for watercourse underwater terrain thematic map
InactiveCN104537717AReflect the changing trendAdmirable3D-image rendering3D modellingUnderwaterThematic map
The invention discloses an acquisition method for a watercourse underwater terrain thematic map. The method comprises the following steps that first, a digital elevation model is created according to TIN data generated by elevation points and contour line data; second, optimizing process is carried out on the digital elevation model obtained in the first step; third, an illumination model is created, and the illumination model is utilized to carry out illumination model process on the digital elevation model optimized in the second step; fourth, model superposition and rendering are carried out, and then displaying is carried out. According to the acquisition method for the watercourse underwater terrain thematic map, the more vivid and intuitive watercourse thematic map with third dimension can be acquired; the variation trend of the watercourse terrain can be intuitively reflected, the availability in actual production is strong, and the appreciation is provided; meanwhile, the drawing efficiency is high, the production cost is low, and batch drawing can be accomplished by a procedure according to thematic map parameters.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Method for building high-spatial resolution NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index) time series data
InactiveCN102831310BHigh resolutionGood precisionSpecial data processing applicationsHigh spatial resolutionAlgorithm
The invention discloses a method for building high-spatial resolution NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index) time series data. The high-spatial resolution NDVI time series data is predicted and built according to low-spatial resolution MODIS (moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer) pixels in known MODIS NDVI data and high-spatial resolution TM (thematic mapper) pixels in TMNDVI (thematic mapper normalized difference vegetation index) data. TM data is combined with MODIS data, and accordingly high-spatial resolution NDVI time series data with quite fine precision can be obtained effectively.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Apparatus and method for web page access
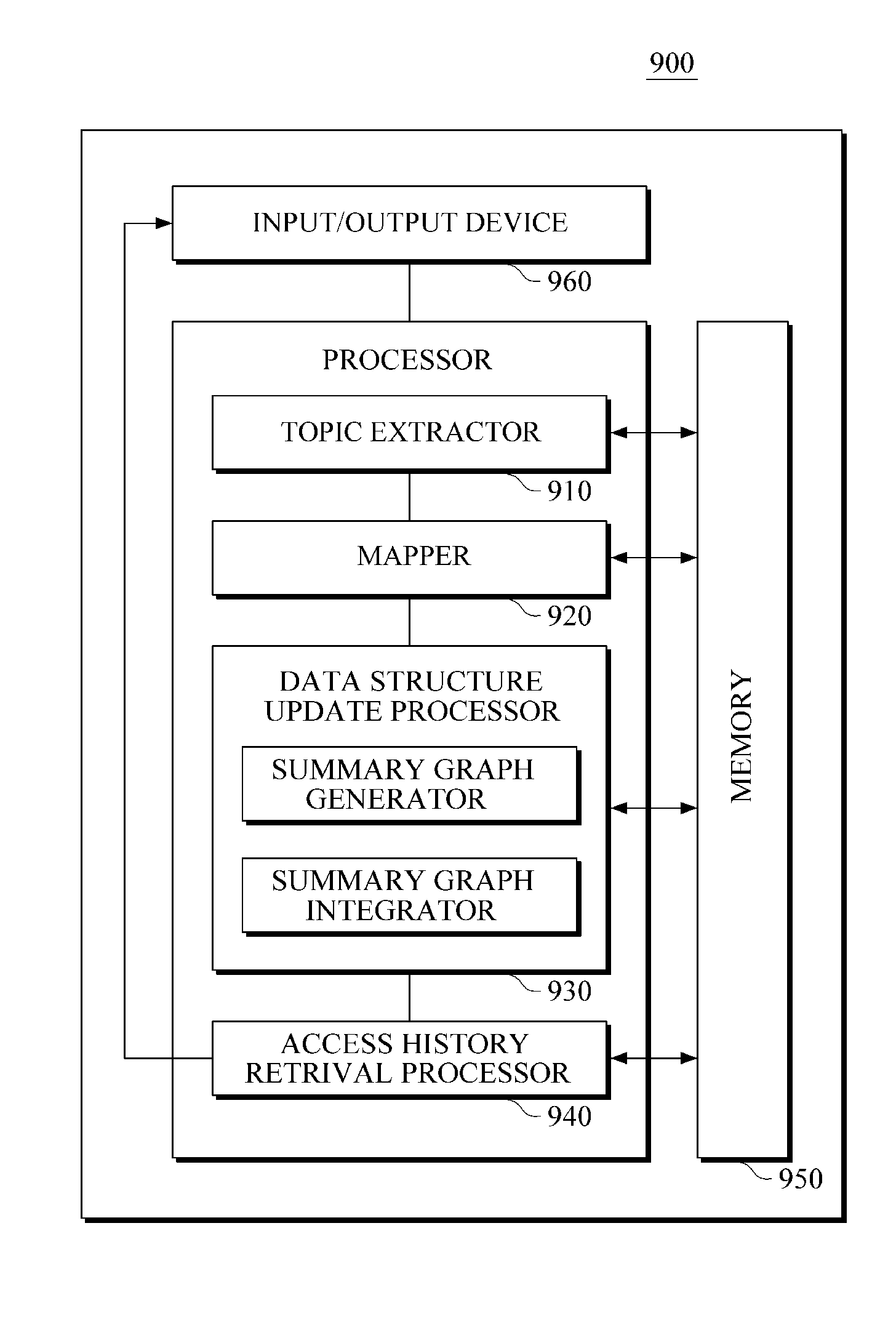
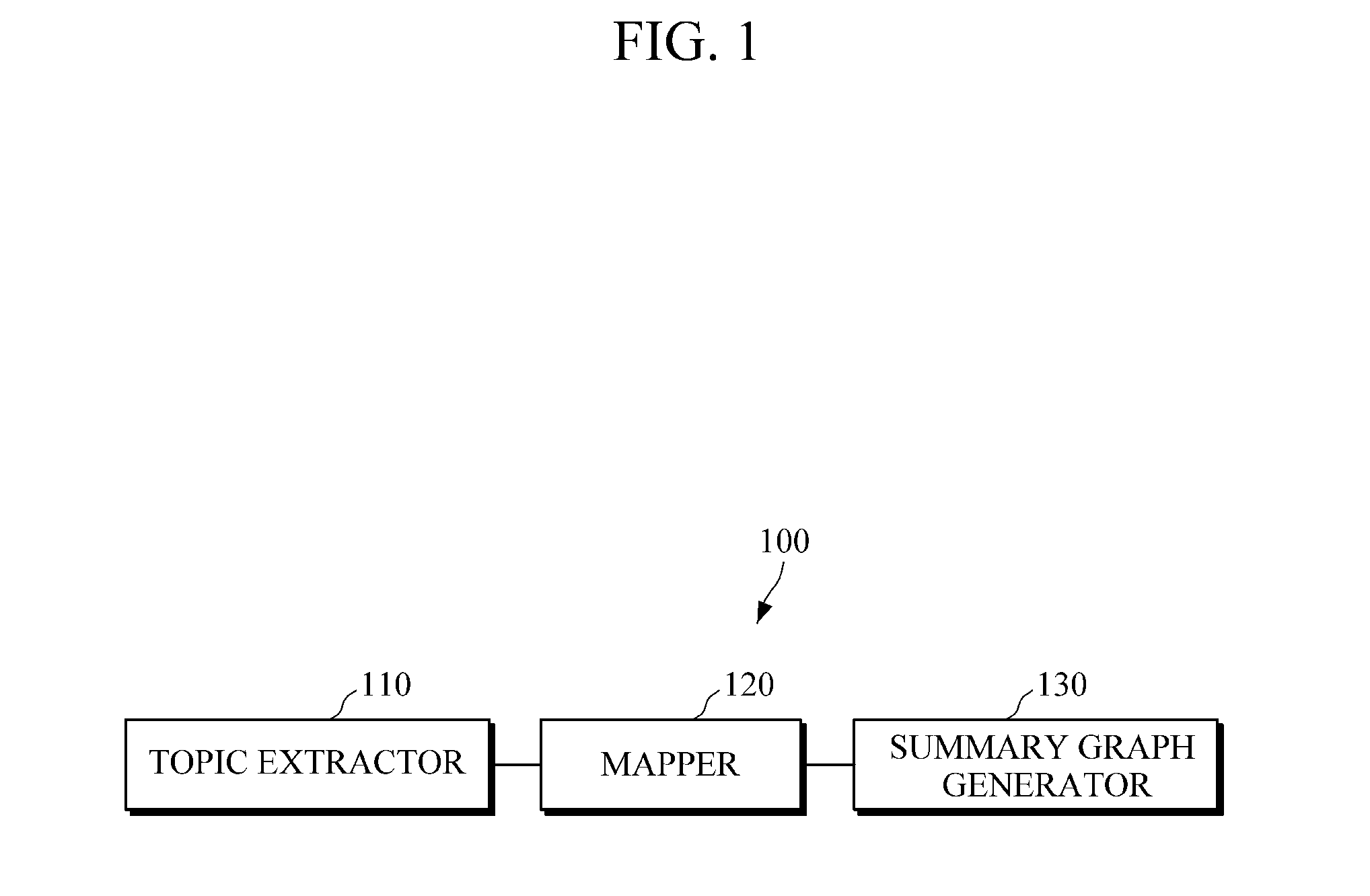
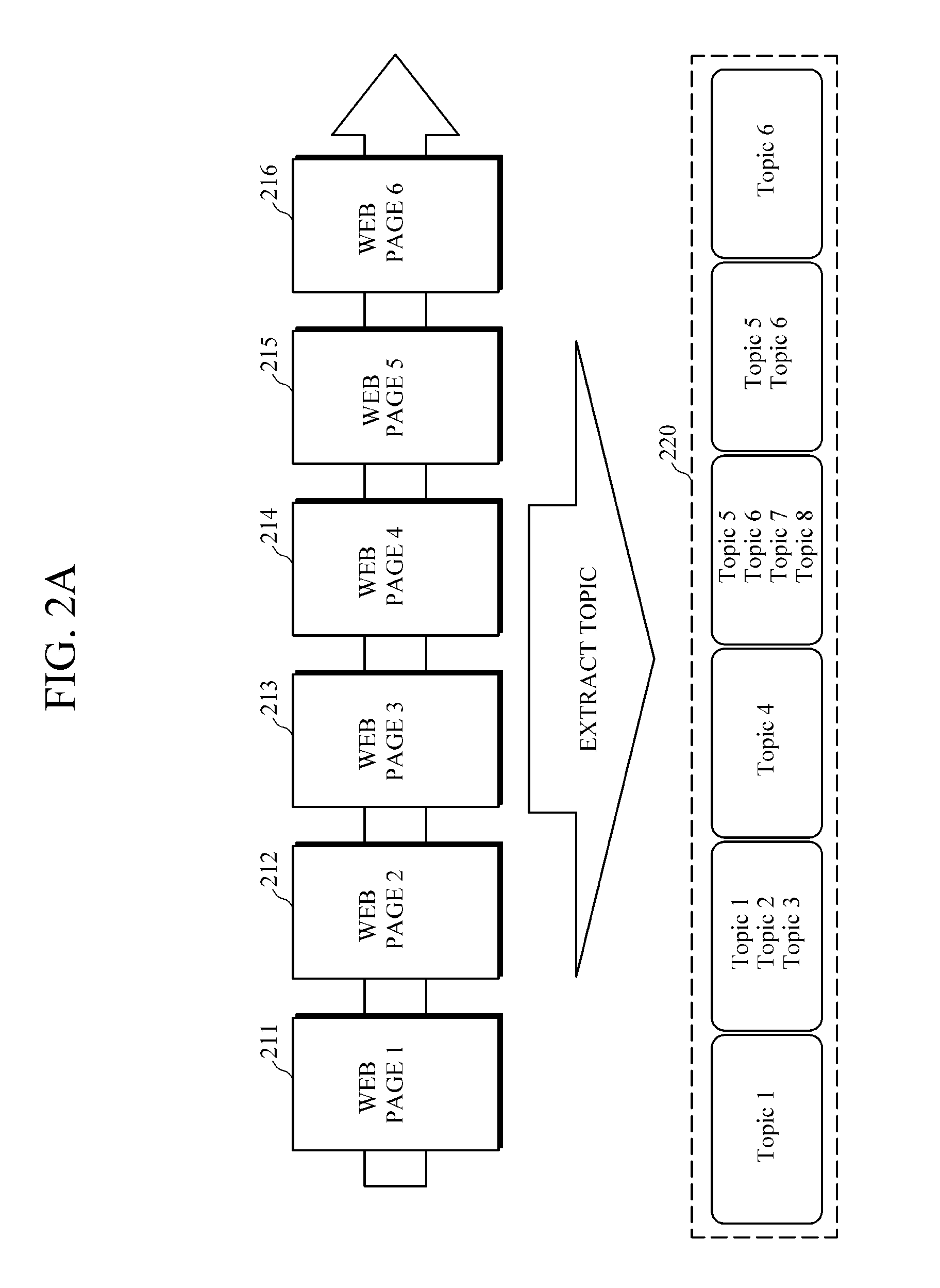
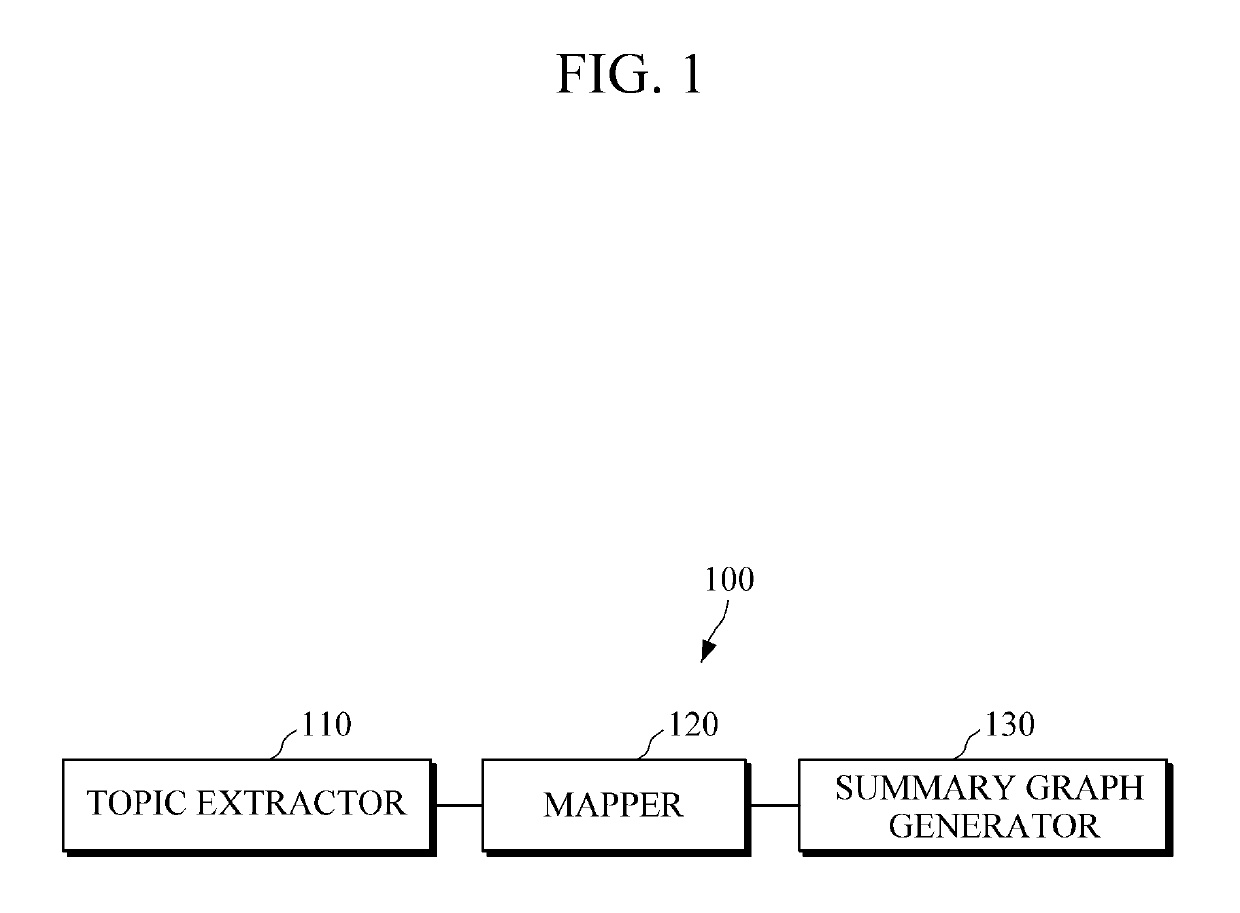
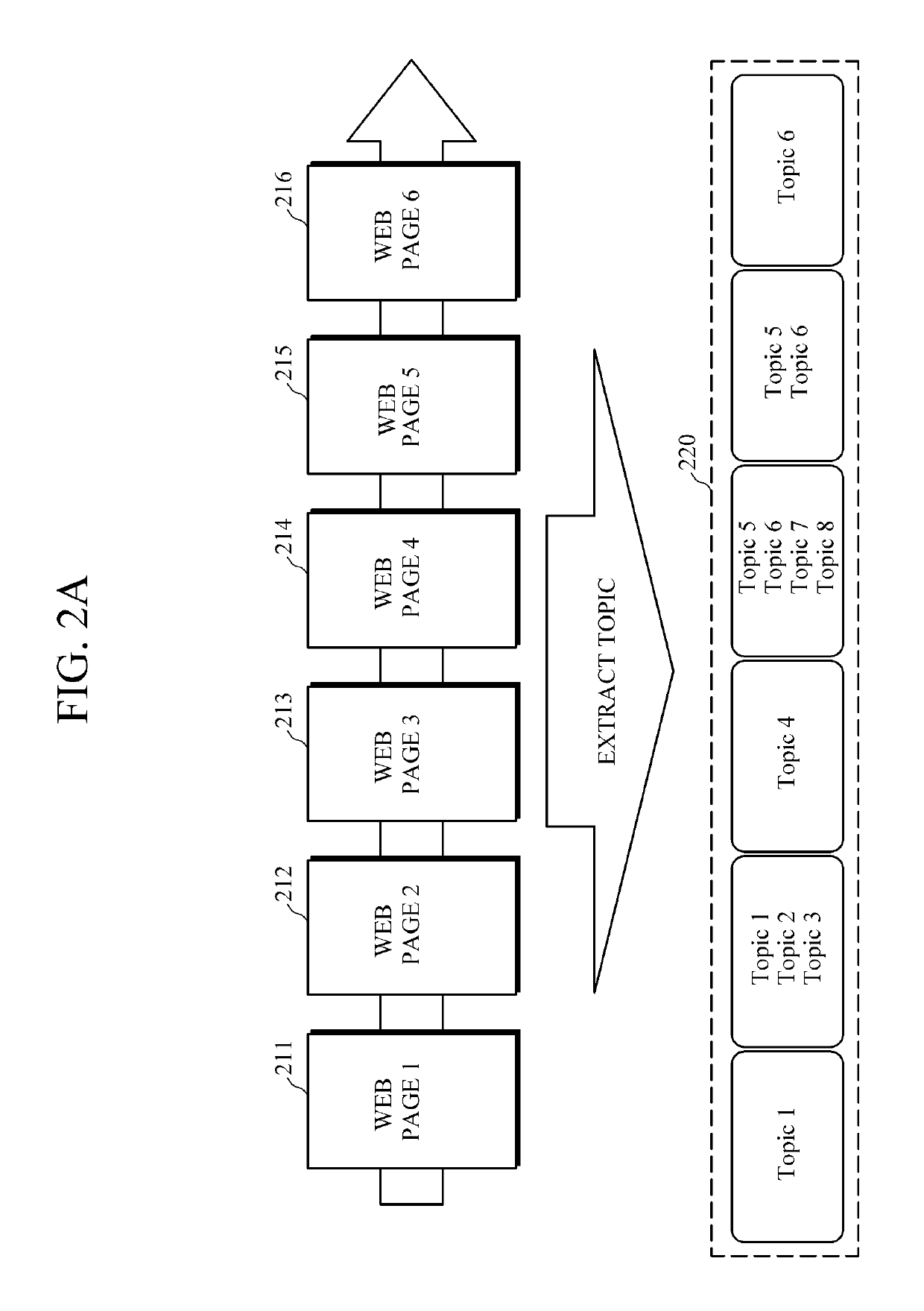
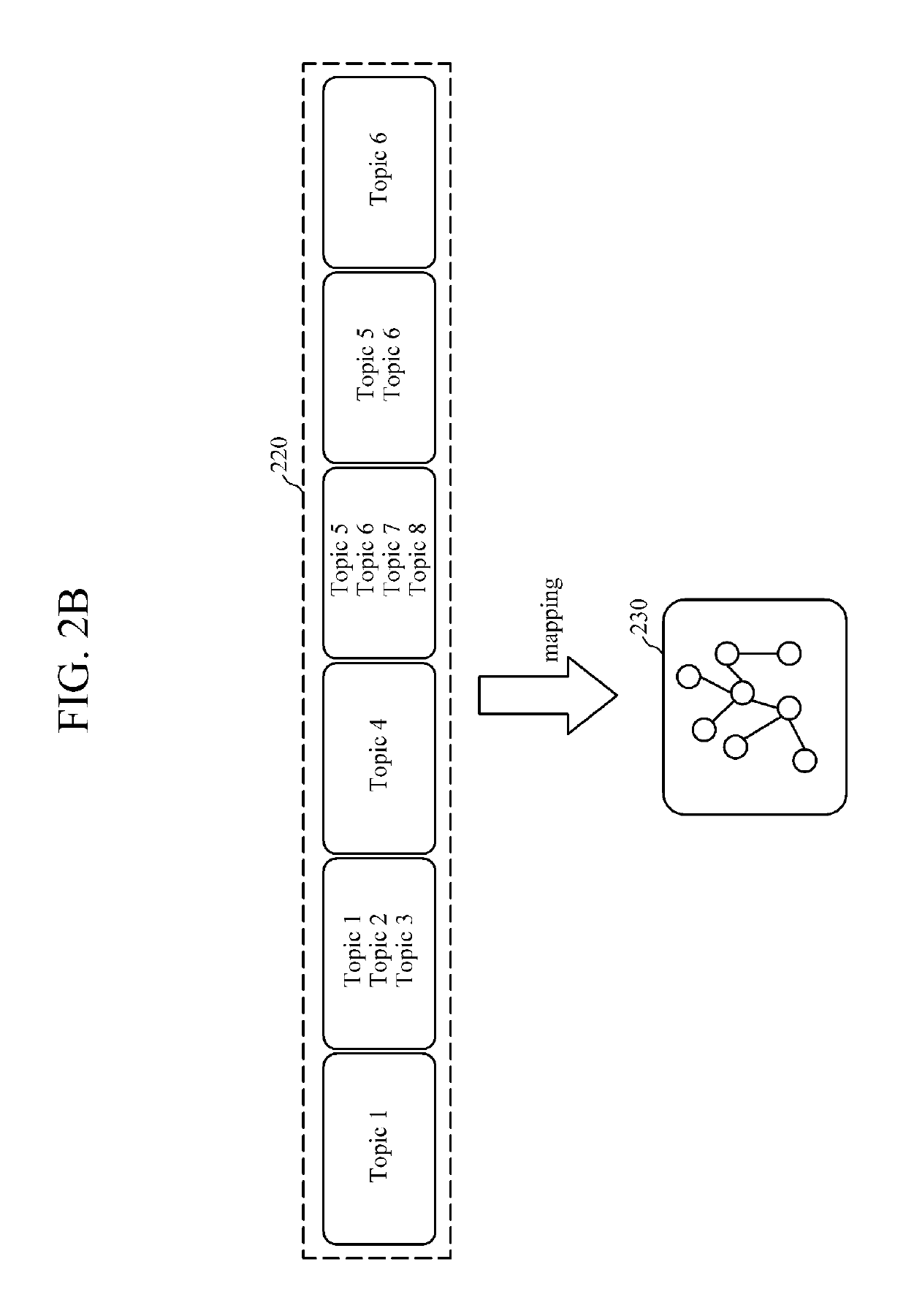
ActiveUS20150317408A1Well formedSemantic analysisDigital data processing detailsAccess historyWeb page
An apparatus and method for web page access and an apparatus and method for structuring a web page access history are provided. The apparatus for structuring a web page access history includes a topic extractor configured to analyze a web page accessed by a user to extract at least one topic related to the page, a mapper configured to map the at least one extracted topic onto a node of an ontology-based data structure, and a summary graph generator configured to extract a sub graph including the mapped node from the data structure, and to generate a summary graph based on the extracted sub graph.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
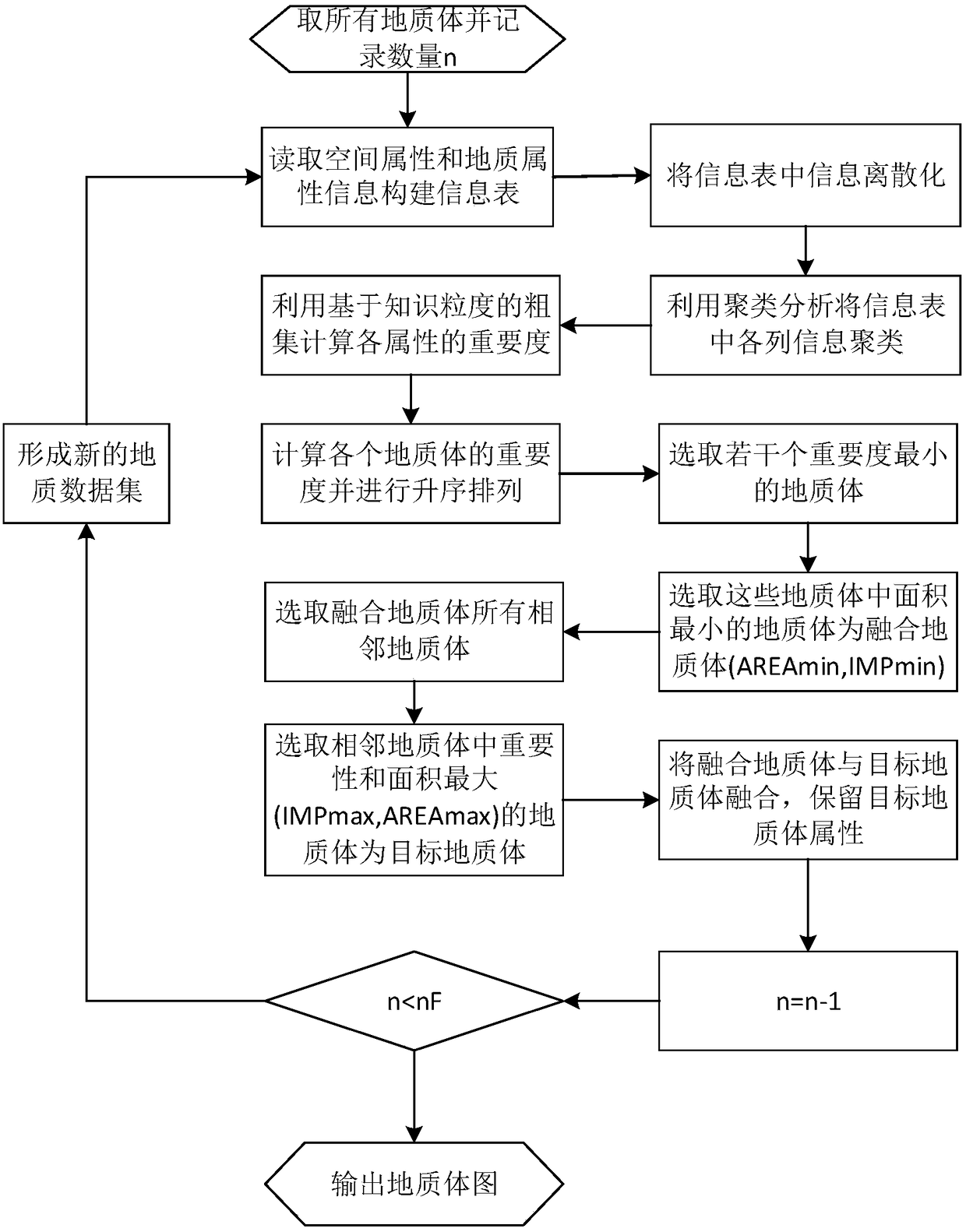
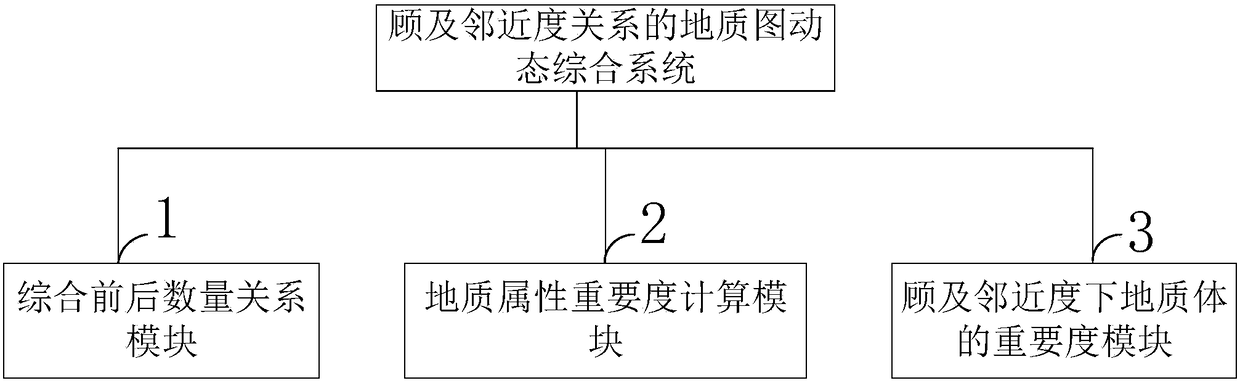
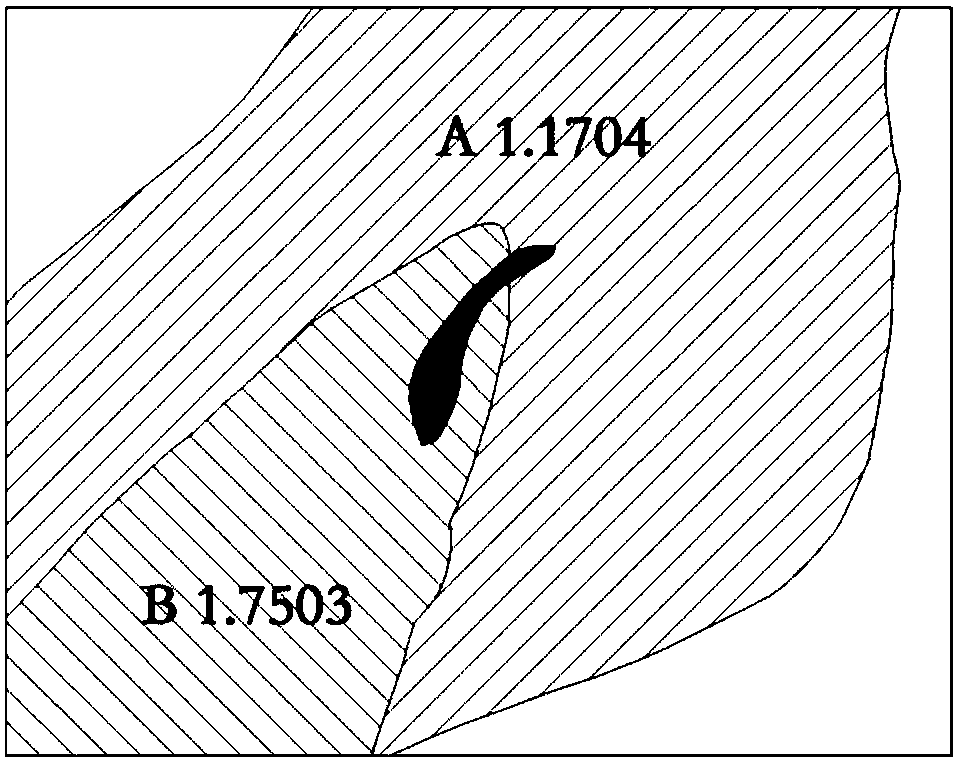
Geological map dynamic synthesis method and system considering proximity relationship
ActiveCN108491482AThe experimental results are accurateGood effectDrawing from basic elementsSpecial data processing applicationsMineral SourcesSynthesis methods
The present invention belongs to the technical field of geological detection data processing, discloses a geological map dynamic synthesis method and system considering a proximity relationship, and proposes a dynamic geological map synthesis method for the situation of over-reliance on labor existing in the current geological map synthesis. The method can be used to comprehensively process the Jiaguan town map. By using the dynamic geological map synthesis method disclosed by the present invention, the process of over-reliance on manual participation in the traditional geological map synthesis process is overcome, and the method is more efficient; the weight of the geological body spatial information and attribute information is analyzed, and the experimental result is more accurate; clustering analysis and rough set calculation are used, and better effects are achieved; and the method can be promoted to other cartographic fields such as mineral resource maps, planning and utilizationmaps and other thematic maps.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
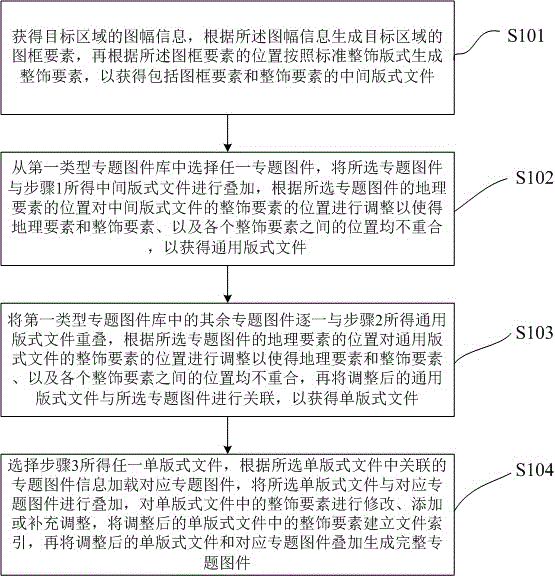
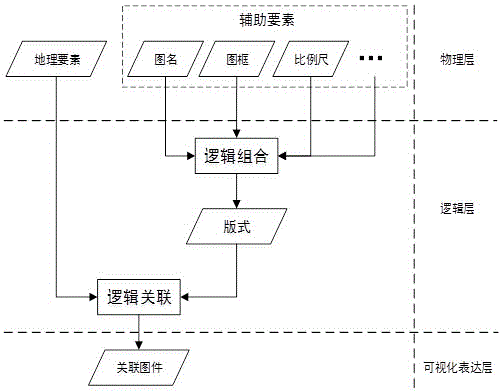
Manufacture method and system for thematic maps based on format relevancy model
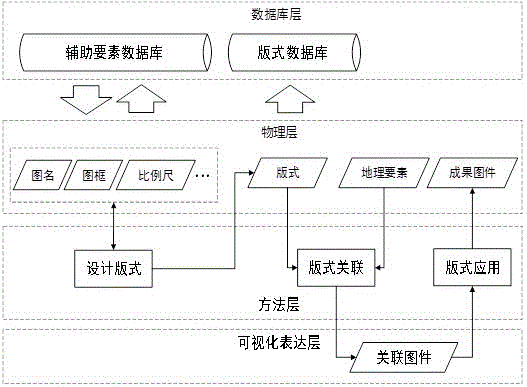
ActiveCN106126696AAvoid damageHigh degree of automationGeographical information databasesSpecial data processing applicationsThematic mapComputer science
The invention relates to the technical field of map manufacture, in particular to a manufacture method and system for thematic maps based on a format relevancy model. The method has following beneficial effects: as for manufacture of heterogeneous isomorphism thematic maps, a format concept is introduced; a same auxiliary element framework of heterogeneous isomorphism thematic maps can be physically saved; as for manufacture of multiple heterogeneous isomorphism maps with same auxiliary elements and different map elements, formats can be reused fully so that drawing efficiency is increased.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Automatic processing method for essential factors of remote-sensing image railway thematic map
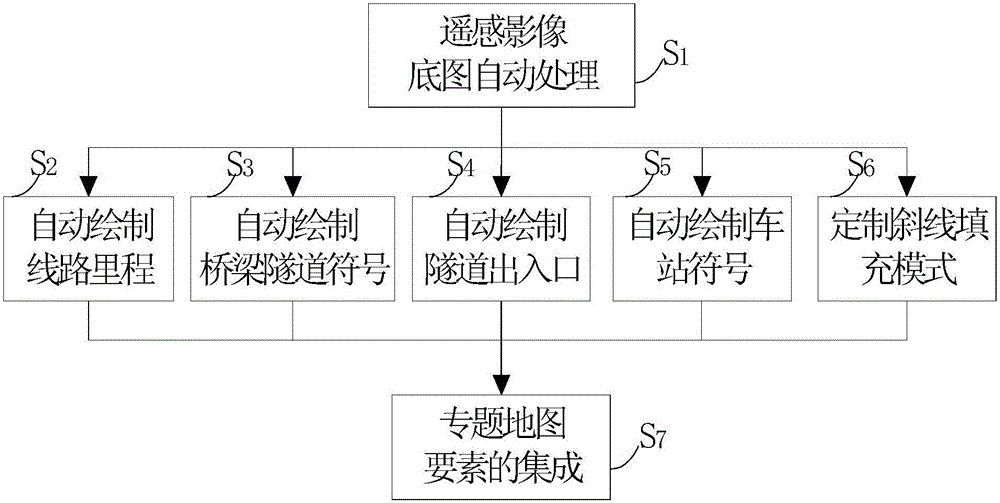
ActiveCN106409128ALess editing effortImprove drawing efficiencyMaps/plans/chartsThematic mapColour difference
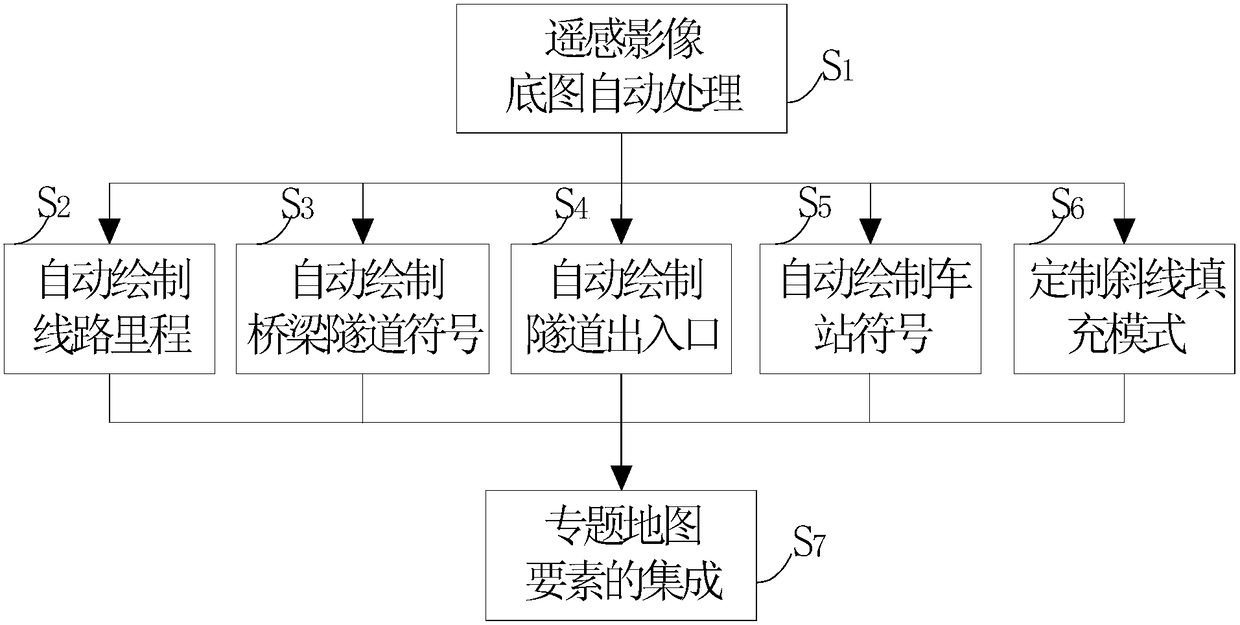
The invention discloses an automatic processing method for essential factors of a remote-sensing image railway thematic map. The method comprises technical steps that a base map of a remote sensing image is processed automatically, and aberration and color cast of batch of remote sensing image data are processed automatically; a route mileage is drafted automatically, and mileage marks and characters are drafted automatically by being perpendicular to a path; bridge and tunnel symbols are drafted automatically according to a foreground color; entrances and exits of the tunnels are drafted automatically; a station symbol is drafted automatically, and the length of a station mark and orientations of platforms are determined according to positions specified by a user; an inclined line filling mode is customized according to specific modes and angles; and the essential factors of the thematic map are integrated by adjusting the data topological relation of the essential factors of the thematic maps according to a map integration principle and integrating the data according to a file management mode.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY DESIGN GRP CO LTD
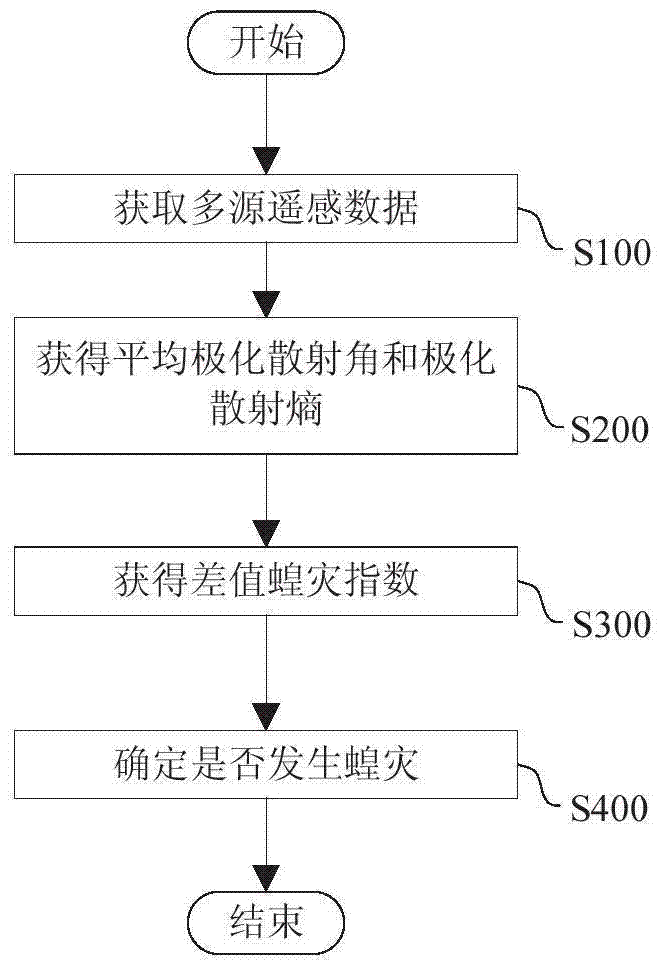
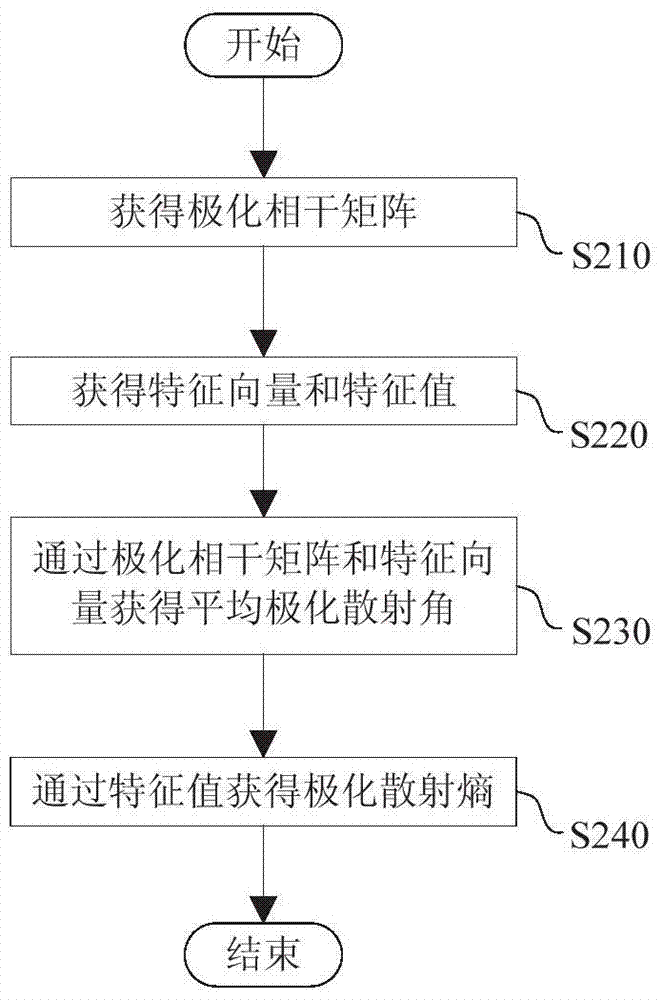
Locust plague detection method
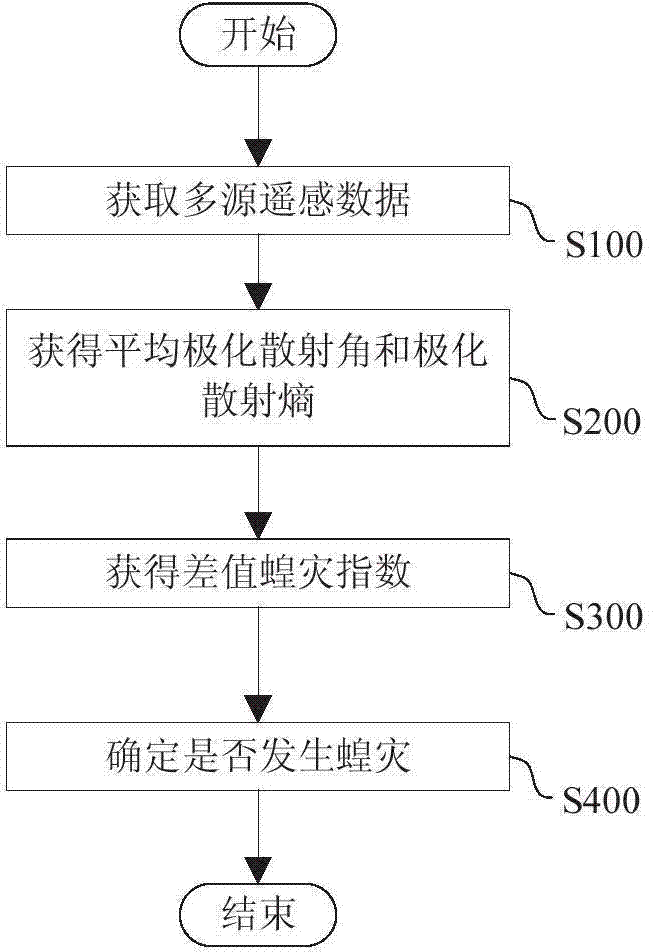
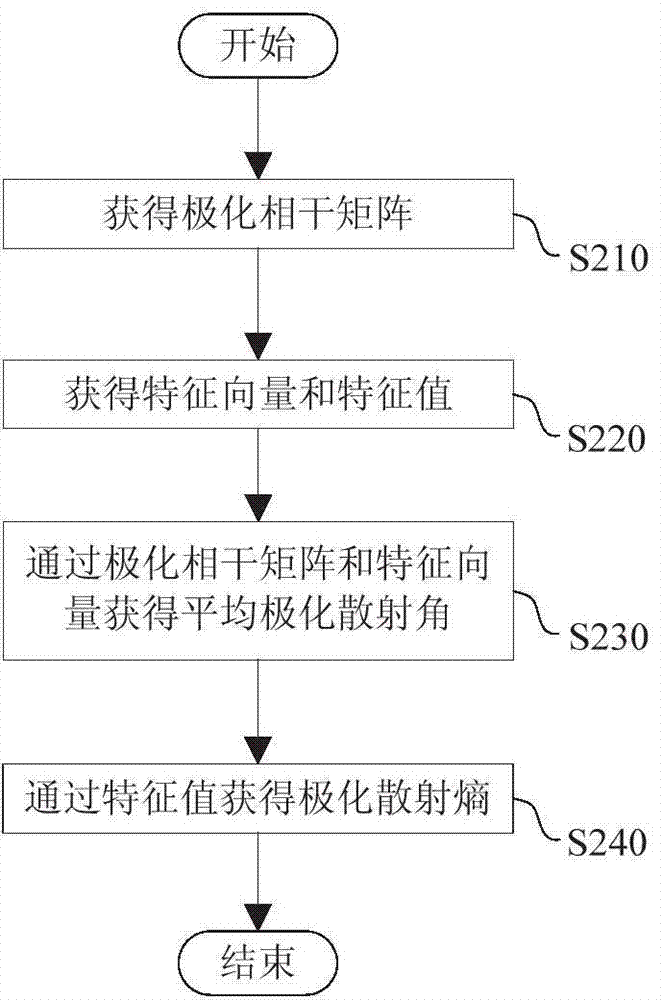
ActiveCN104504279AAccurate detectionHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsSensing dataModerate resolution image spectroradiometer
The invention provides a locust plague detection method. The method comprises the steps of (A) acquiring multi-source remote sensing data of a detected area, wherein the multi-source remote sensing data include polarimetric synthetic aperture radar data, temperature of a moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer and vegetation indexes of a thematic mapper; (B) acquiring an average polarimetric scattering angle and a polarimetric scattering entropy according to the polarimetric synthetic aperture radar data; (C) acquiring differential locust plague indexes according to the average polarimetric scattering angle, the polarimetric scattering entropy, the temperature of the moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer and the vegetation indexes of the thematic mapper; (D) determining whether locust plague occurs in the detection area according to the differential locust plague indexes.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
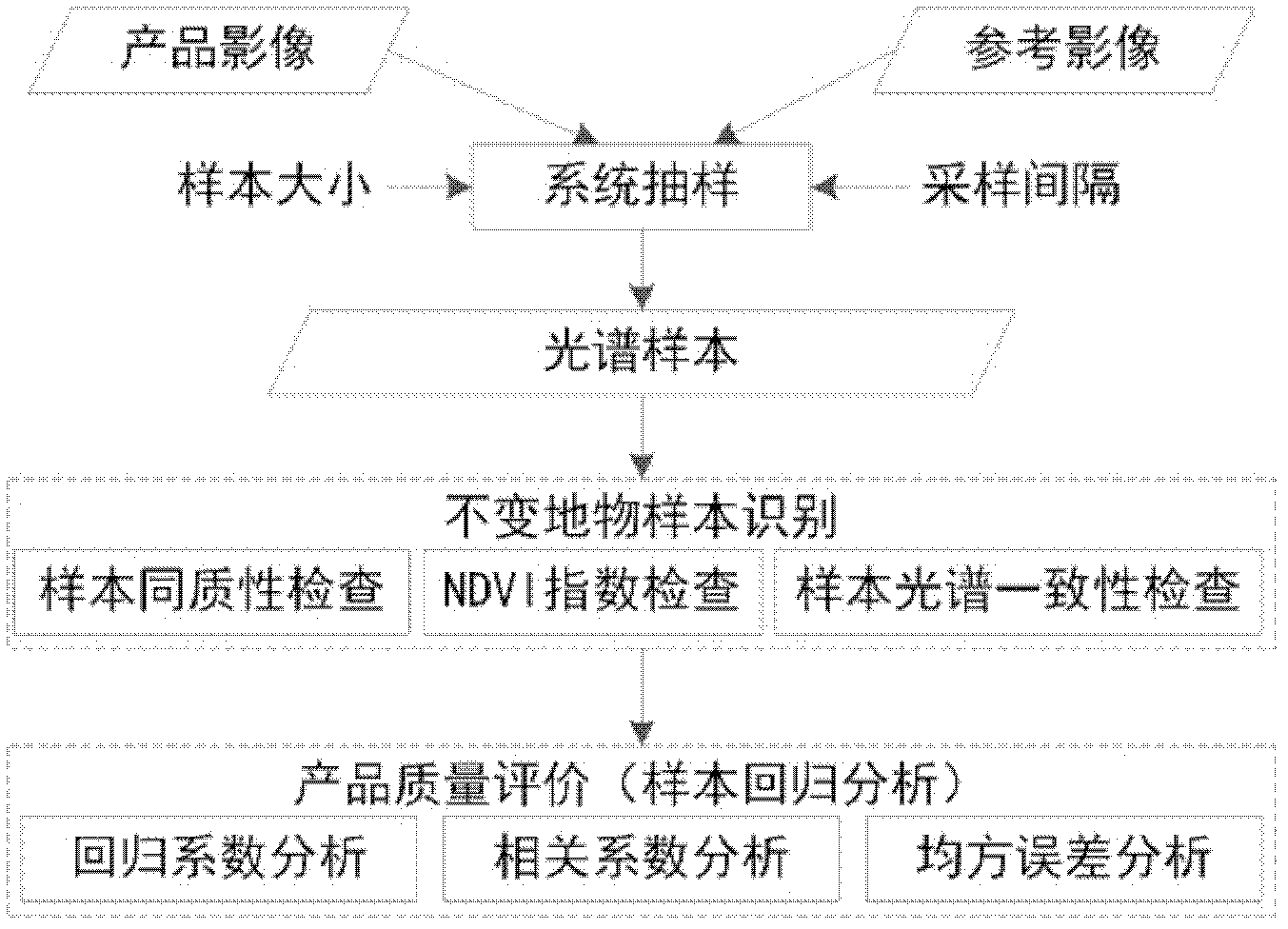
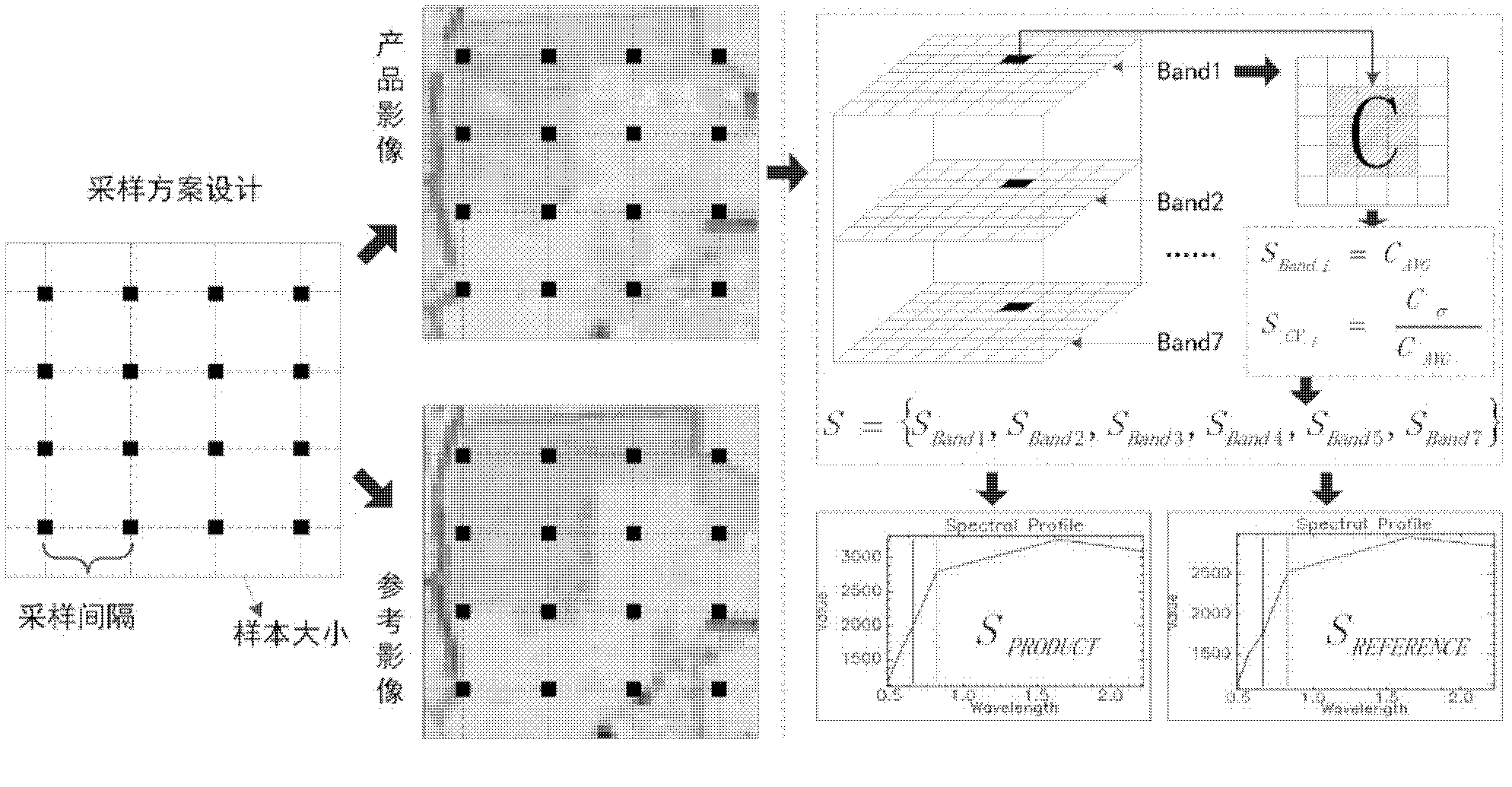
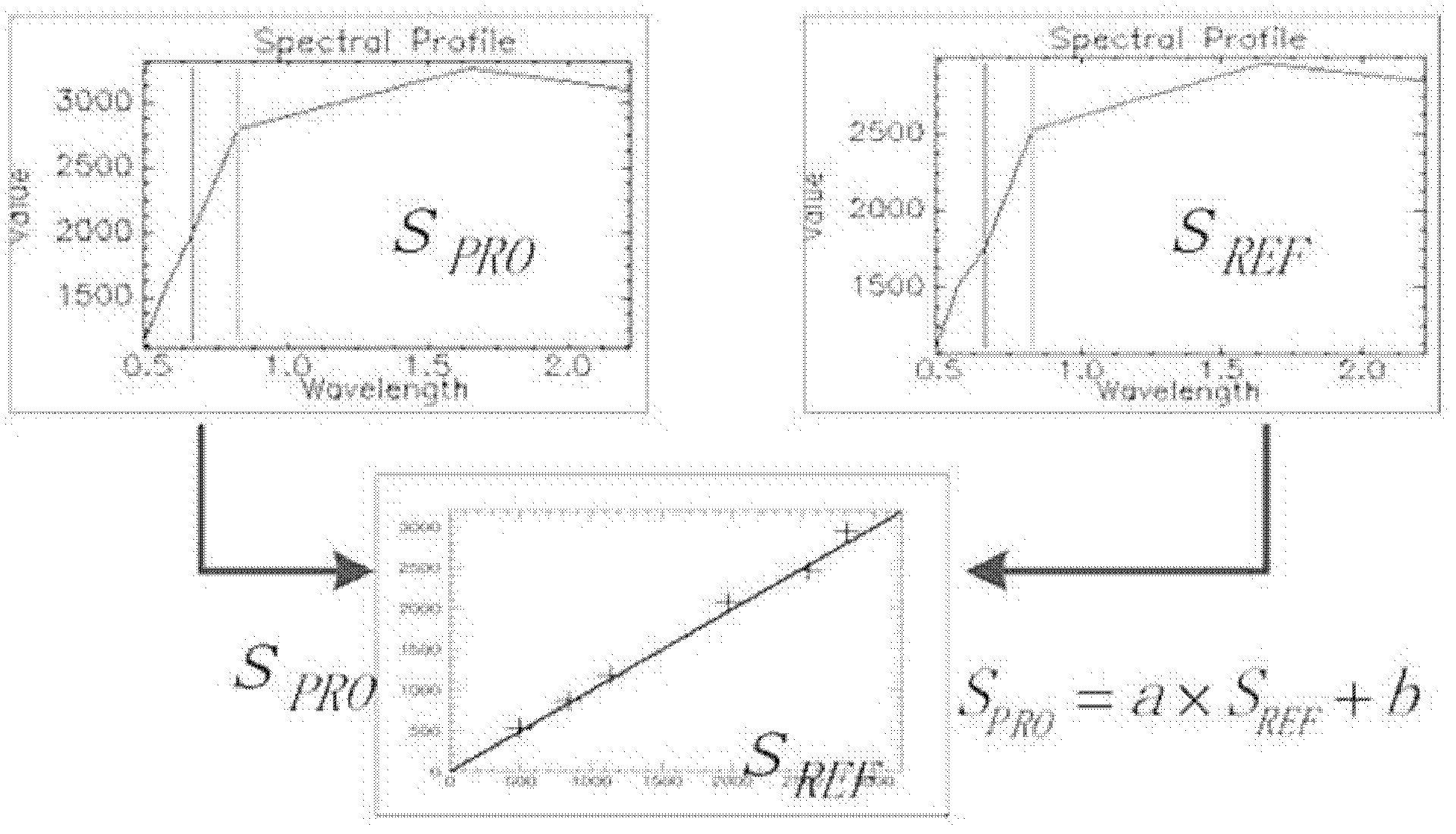
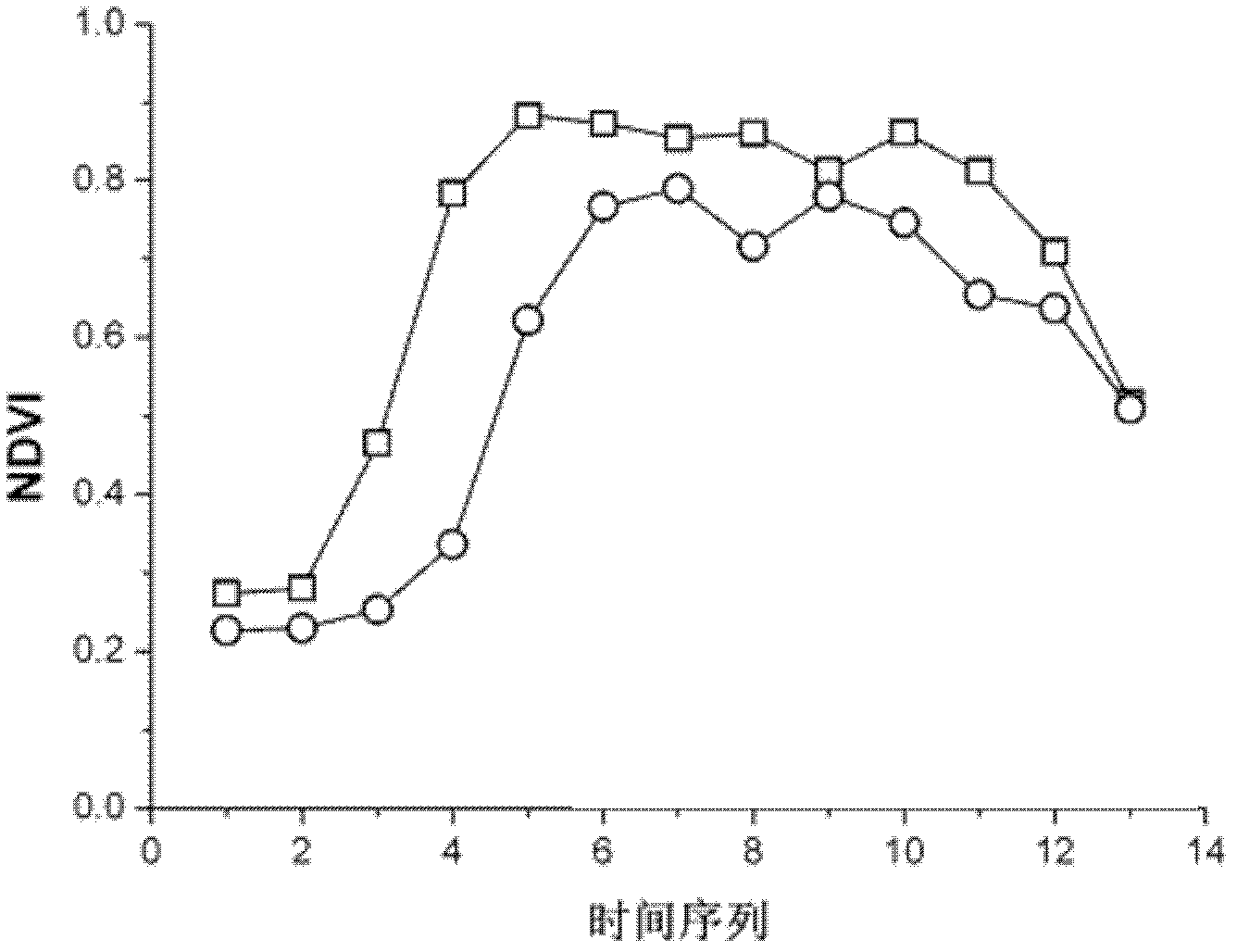
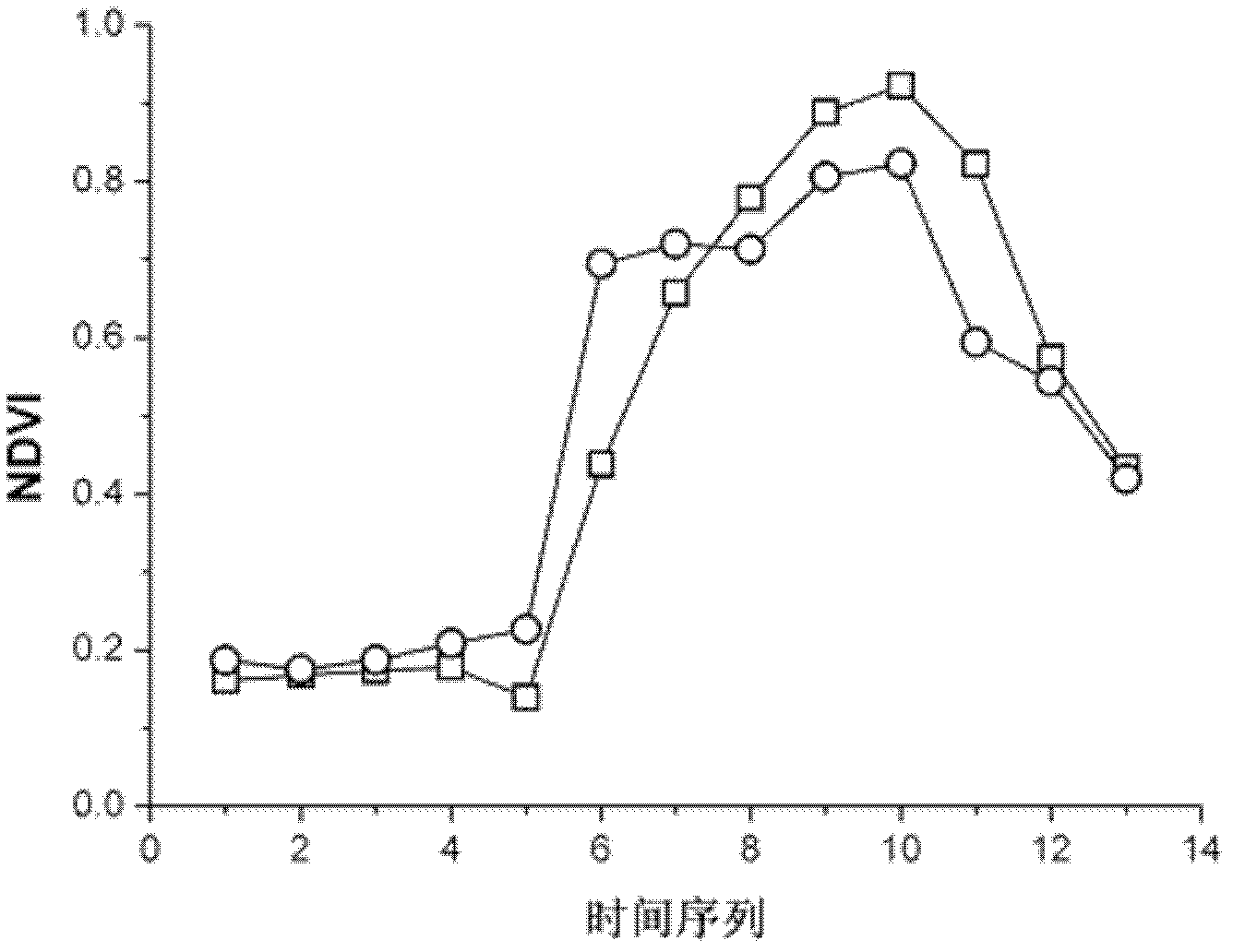
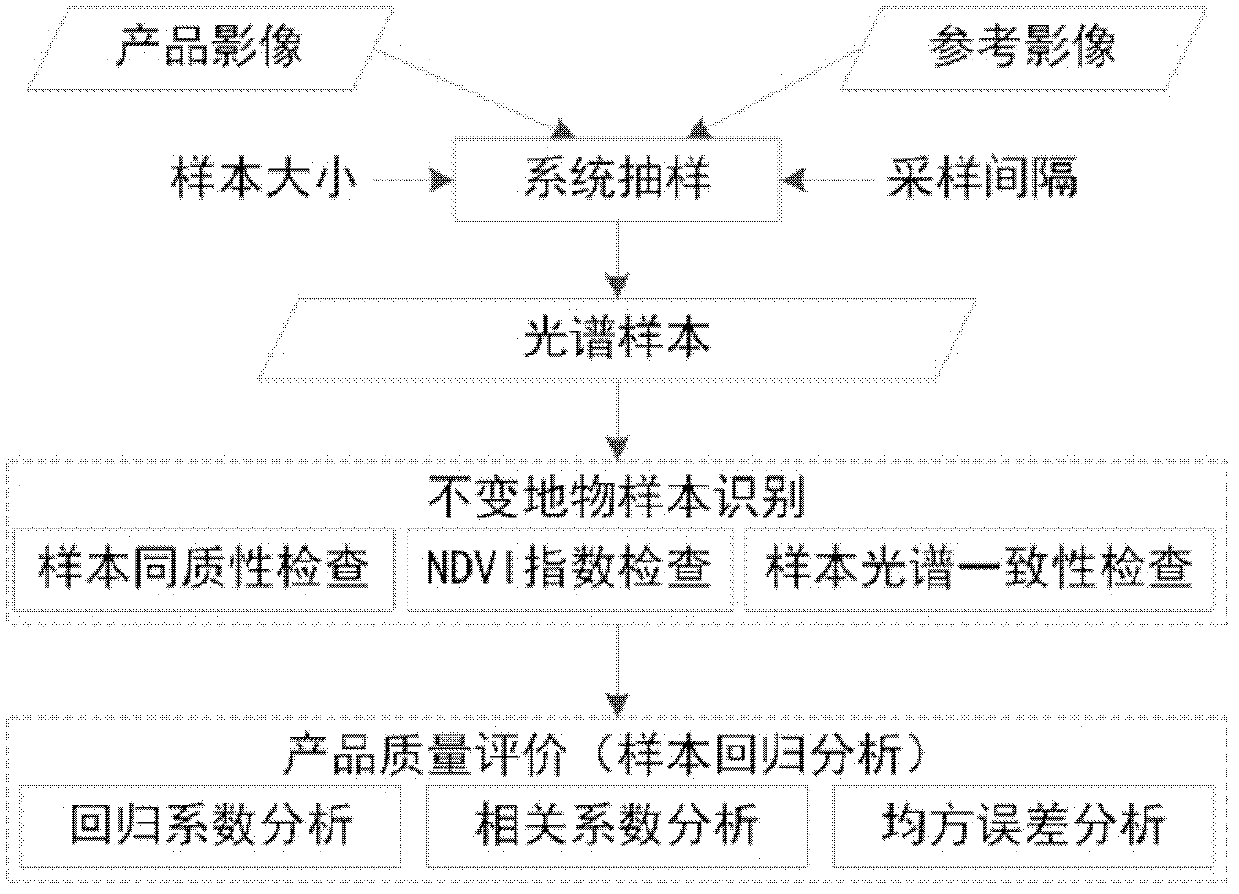
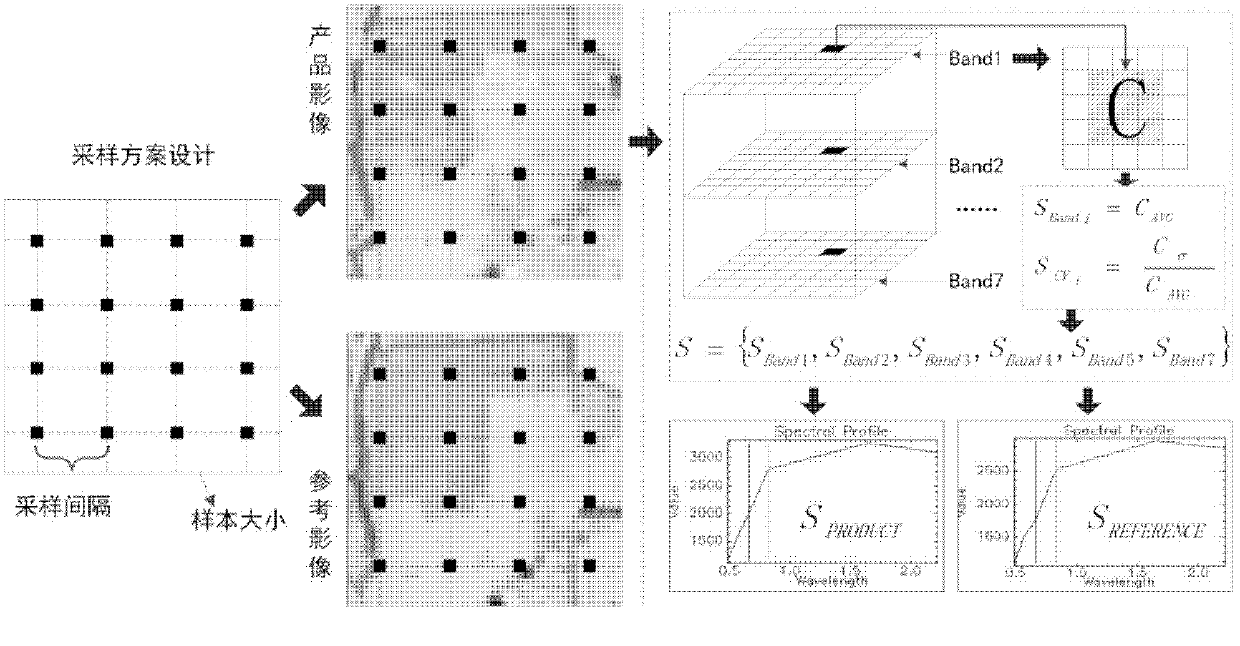
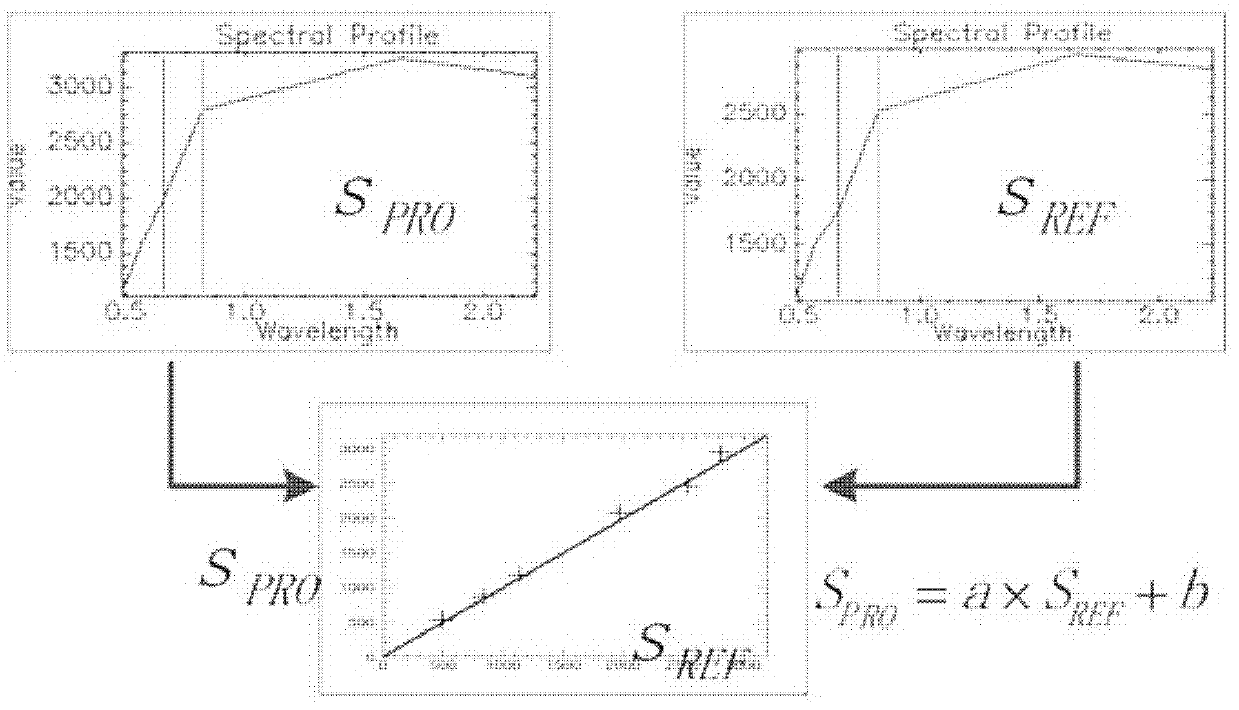
Evaluation method of TM/ETM (thematic mapper/enhanced thematic mapper) and image-based atmospheric correction product quality
ActiveCN102495405AGuaranteed accuracyAccurate identificationWave based measurement systemsAlgorithmImaging quality
The invention relates to an evaluation method of quality of a TM / ETM (thematic mapper / enhanced thematic mapper) and image-based atmospheric correction product. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, acquiring a product image, and randomly selecting a reference image; 2, matching a geographic coordinate system between the product image and the reference image in the step 1; 3,selecting a plurality of samples from the product image and the reference image by adopting a systematic sampling method, and respectively calculating spectral values of corresponding samples of the product image and reference image on the reference image and the product image; 4, respectively identifying constant land feature samples of the product image and the reference image in the step 2, and saving an effective constant land feature sample; and 5, analyzing the atmospheric correction quality of the product image according to the effective constant land feature sample in the step 4. The method has the advantages that: important basic image quality information can be provided to regional or global earth surface change researches, and PIFs (physical interfaces) samples can be accurately identified on the TM / ETM and image with different time phases / season phases.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for classifying remote sensing images blended with high-space high-temporal-resolution data by object oriented technology
InactiveCN102609726BOvercome indistinguishable difficultiesClear geographical meaningPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryCharacter and pattern recognitionLand coverImage resolution
The invention discloses a method for classifying remote sensing images blended with high-space high-time resolution data by an object oriented technology, and relates to a method for classifying remote sensing images of an oriented object, which can be used for solving the problem that the previous method for classifying remote sensing images can not be used for distinguishing land cover types of 'foreign bodies with the same spectrum', and is not suitable for being applied to the remote sensing images with low-medium resolution ratio. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: carrying out filter processing by applying an SG (screen grid) filter; determining a time sequence curve of typical vegetational MODIS-NDVI (moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer-normalized difference vegetation index) in the remote sensing image to be classified; segmenting a TM (thematic mapper) image, wherein each segmentation unit is used as an object; extracting the characteristic information of each object; extracting all non-vegetation objects; removing the non-vegetation objects, and taking the obtained vegetational objects as planar vectors to segment MODIS-NDVI time sequence data, so as to obtain corresponding biotemperature information acquired by each vegetational object; and determining the vegetational type, to which each object belongs; and completing the land cover classification. The method provided by the invention can be used for distinguishing the land cover types.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Evaluation method of TM/ETM (thematic mapper/enhanced thematic mapper) and image-based atmospheric correction product quality
ActiveCN102495405BGuaranteed accuracyAccurate identificationWave based measurement systemsAlgorithmImaging quality
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
A Method for Extracting Mineral Alteration Information
InactiveCN103207415BStrong filtering functionReduce noiseOptical prospectingLocal variablePrincipal component analysis
The invention discloses a method for extracting mineralization-alteration information. The method comprises the steps of effective background pixel identifications, selection of local variable windows, in-window main component analysis, construction of abnormal variables, abnormal recognition and assignment and alteration abnormal output. Interference information such as water, cloud, ice and snow is eliminated through identifications and statistics of effective background pixels; and statistics variables are limited within the windows rather than the whole image range during main component analysis through local variable windows, therefore further reduction of interference of ambient environment noise is facilitated, and the extraction capacity of alteration information is improved. By means of the method, the potential of mineralization-alteration charting of thematic mapper (TM) and advanced spaceborne thermal emission and reflection radiometer (ASTER) remotely-sensed can be further mined, and the indication capacity in geological exploration can be improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
A method for automatic processing of railway thematic map elements in remote sensing images
ActiveCN106409128BLess editing effortImprove drawing efficiencyMaps/plans/chartsSpecial data processing applicationsThematic mapComputer vision
The invention discloses an automatic processing method for essential factors of a remote-sensing image railway thematic map. The method comprises technical steps that a base map of a remote sensing image is processed automatically, and aberration and color cast of batch of remote sensing image data are processed automatically; a route mileage is drafted automatically, and mileage marks and characters are drafted automatically by being perpendicular to a path; bridge and tunnel symbols are drafted automatically according to a foreground color; entrances and exits of the tunnels are drafted automatically; a station symbol is drafted automatically, and the length of a station mark and orientations of platforms are determined according to positions specified by a user; an inclined line filling mode is customized according to specific modes and angles; and the essential factors of the thematic map are integrated by adjusting the data topological relation of the essential factors of the thematic maps according to a map integration principle and integrating the data according to a file management mode.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY DESIGN GRP CO LTD
Method and device for grading and coloring thematic map
InactiveCN101739888BAchieve classificationReduce the influence of human factorsMaps/plans/chartsThematic mapComputer science
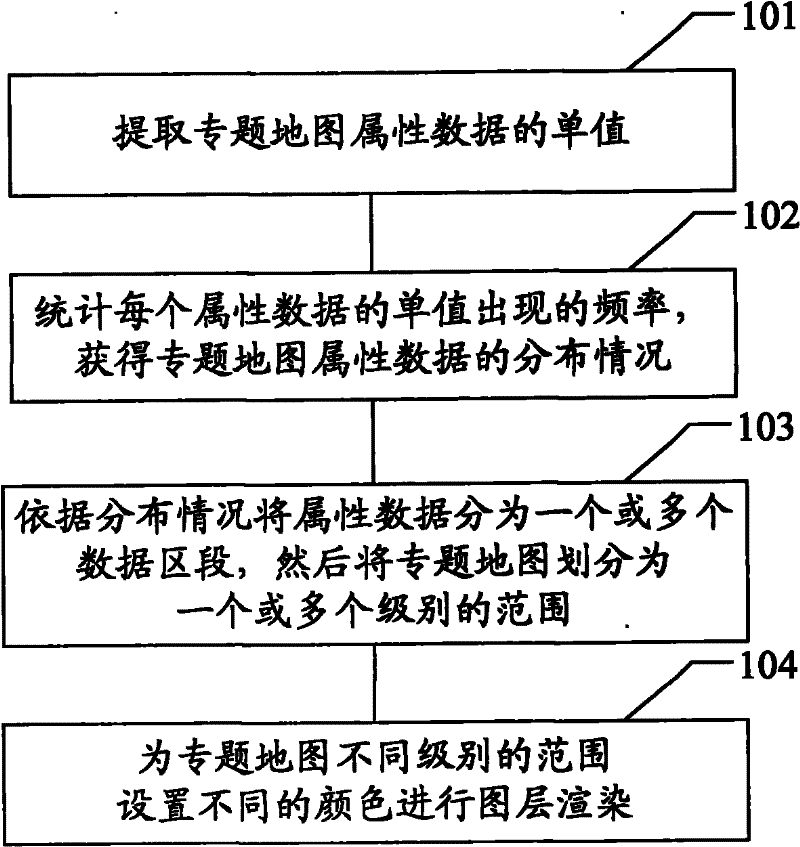
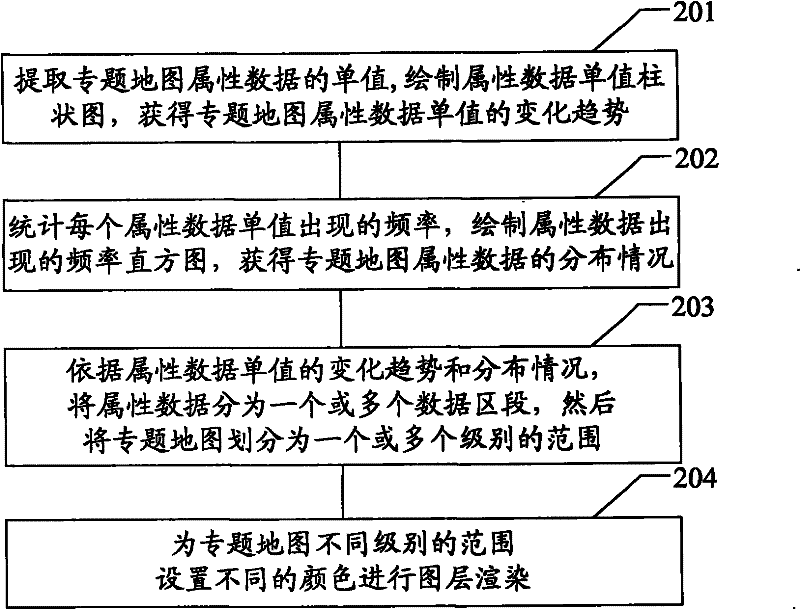
The invention provides a method and a device for grading and coloring a thematic map. The method comprises the following steps: extracting a single value of the attribute data of the thematic map; counting the frequency of occurring each single value of the attribute data to acquire the distribution condition of the attribute data of the thematic map; dividing the attribute data into one or more data sections according to the distribution condition and diving the thematic map into a range with one or more levels according to the data sections; and setting different colors for the range with different levels of the thematic map to perform layer render. According to the distributing rules of the attribute data in a characteristic analysis region of the thematic map, adjacent parts are merged to form a plurality of data sections, the grading of the map data is further realized, and the influence of personal factors in the grading and coloring process can be reduced to a greater degree. Therefore, the generated thematic map can make the characteristics and the distributing rules of the attribute data more prominent.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Apparatus and method for web page access
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
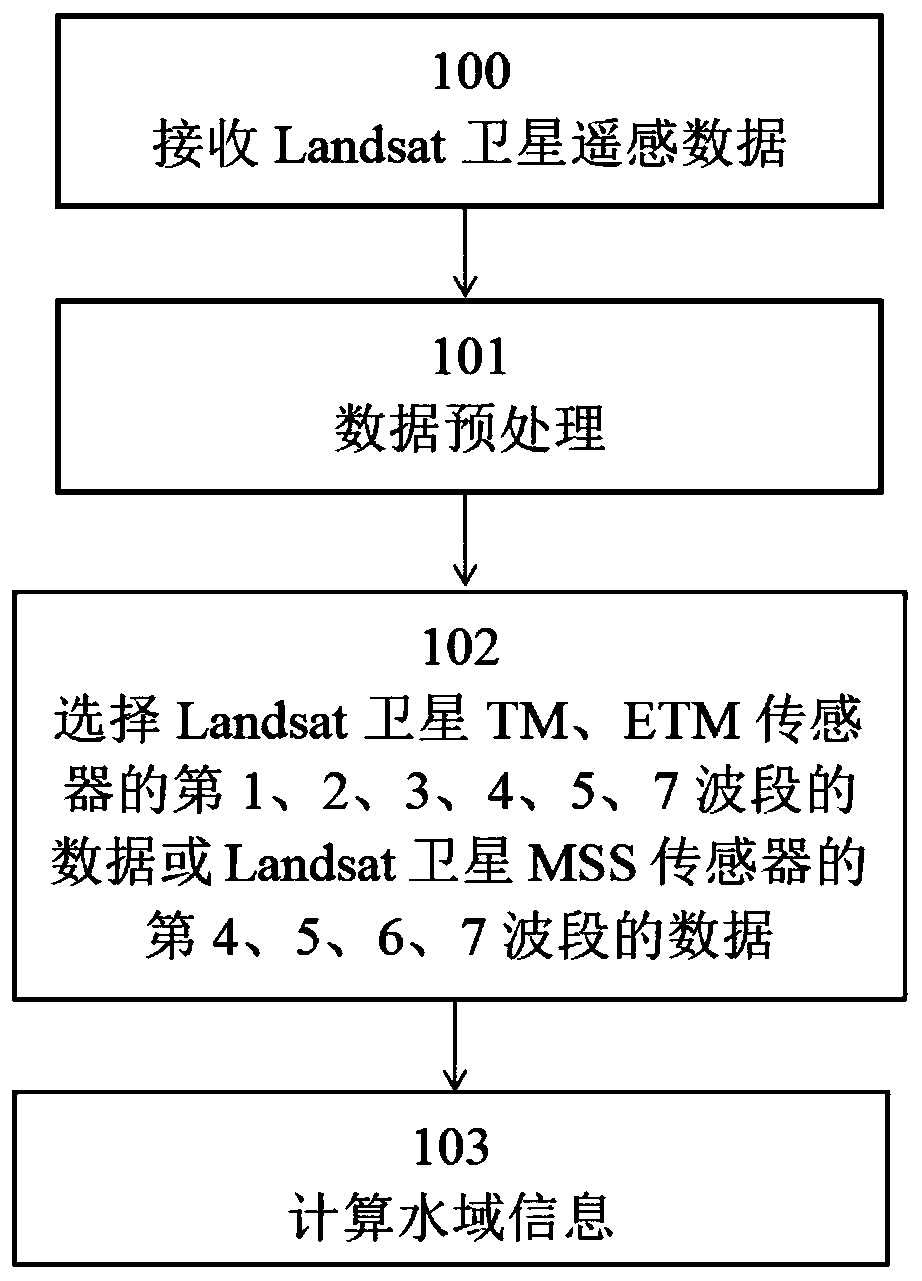
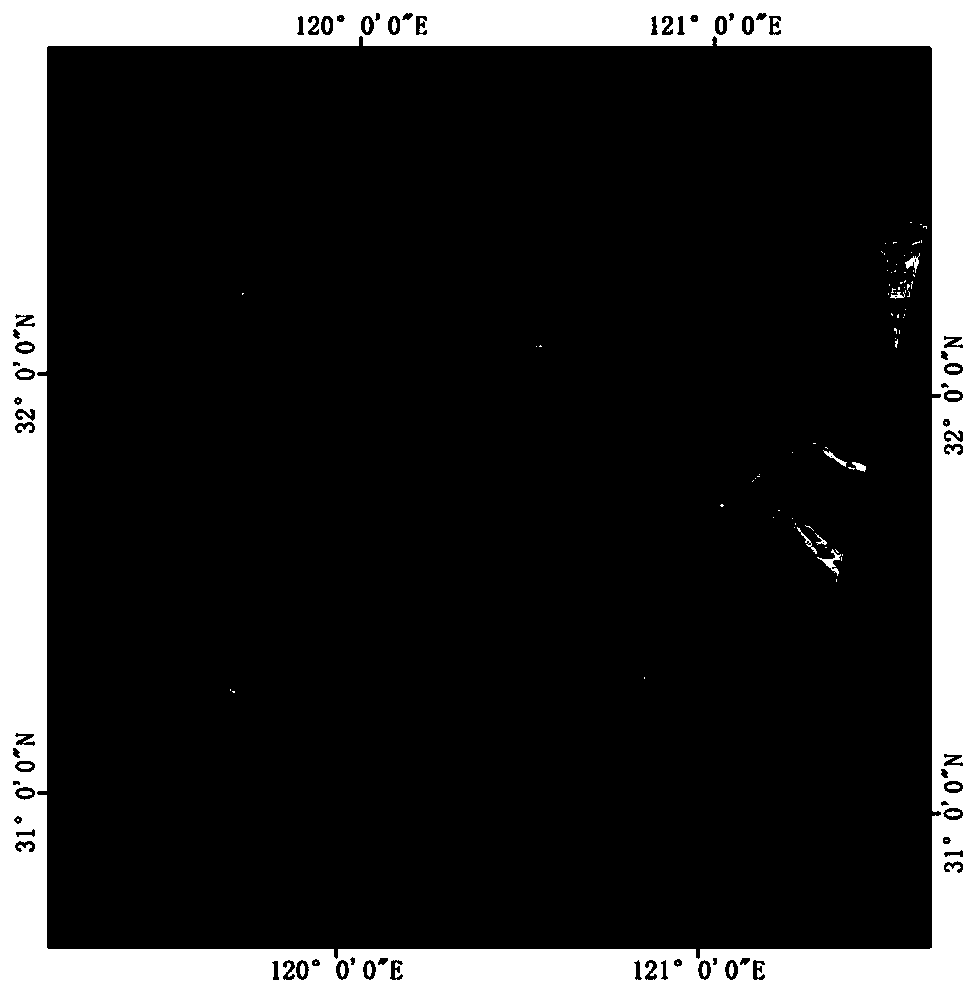
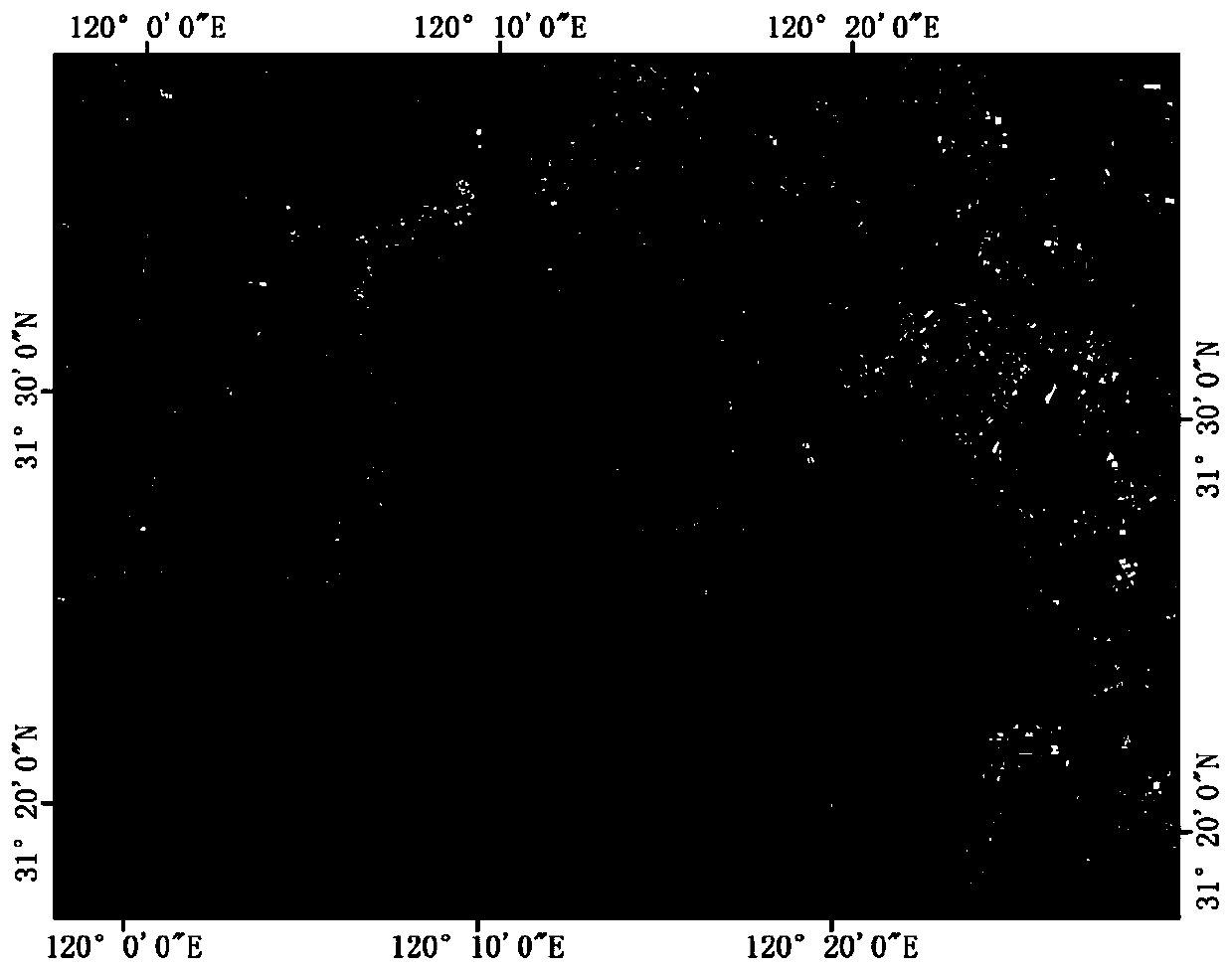
Calculation method of water area remote sensing information of Landsat satellite sensors
InactiveCN110686654AImprove extraction accuracyCalculate fitMaterial analysis by optical meansOpen water surveySensing dataEngineering
The invention discloses a calculation method of water area remote sensing information of Landsat satellite sensors. The calculation method comprises the following steps: step 100, receiving Landsat satellite remote sensing data; step 101, performing data preprocessing; and step 102, selecting data of the first, second, third, fourth, fifth and seventh wave bands of Landsat satellite Thematic Mapper (TM) sensor and Enhanced Thematic Mapper (ETM) sensor or data of the fourth, fifth, sixth and seventh wave bands of Landsat satellite Multi-Spectral Scanner (MSS) sensor. The calculation method of the water area remote sensing information of the Landsat satellite sensor is a method for obtaining water area information by judging remote sensing data through multiple conditions, so that extractionprecision of the water area information is improved. The calculation method of the water area information in the invention is more suitable for calculating the water area information by utilizing theLandsat satellite sensors, and is faster, automatic and less manual compared with actual measurement. Furthermore, the method has long time series, so that past precious historical data of the earthare kept, which is extremely important for calculating the water area information.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Thematic map based route optimization
According to an example aspect of the present invention, there is provided an apparatus comprising at least one processing core, at least one memory including computer program code, the at least one memory and the computer program code being configured to, with the at least one processing core, cause the apparatus at least to determine a route based at least partly on a thematic map database and a current location of the apparatus, present the determined route as a suggested route to a first user, and responsive to the first user approving the suggested route, initiate an activity session based on the suggested route.
Owner:SUUNTO OY
Methods of detecting locust infestations
ActiveCN104504279BAccurate detectionHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsSensing dataImage resolution
The invention provides a method for detecting locust disasters. The method includes: (A) acquiring multi-source remote sensing data of the detected area, wherein the multi-source remote sensing data includes: full polarization synthetic aperture radar data, medium resolution imaging spectrometer temperature and thematic mapping instrument vegetation index; ( B) Obtaining the average polarization scattering angle and polarization scattering entropy from the full polarization SAR data; (C) Obtaining the average polarization scattering angle, polarization scattering entropy, medium resolution imaging spectrometer temperature and thematic mapper vegetation index Difference locust plague index; (D) determine whether locust plague occurs in the detected area according to the difference locust plague index.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for detecting spissatus and spissatus shadow based on Landsat thematic mapper (TM) images and Landsat enhanced thematic mapper (ETM) images
InactiveCN102750701BHigh degree of automationReduce missed detectionImage analysisPattern recognitionThematic map
The invention discloses a method for detecting spissatus and spissatus shadow Landsat thematic mapper (TM) images and Landsat enhanced thematic mapper (ETM) images. The method comprises steps of dividing an input image into 16 sub-atlases and performing wiener filtering denoising and normalization for the 16 sub-atlases; performing rough detection for the spissatus and the shadow in the 16 sub-atlases and selecting reference pairs from a rough detection result; solving a mass center connection inclined angle and a space of a final reference pair in accordance with all reference pairs; matching the spissatus and the shadow in the 16 sub-atlases in accordance with the mass center connection inclined angle and the space of the final reference pair and performing supplementary detection for unmatched spissatus and unmatched shadow; adding a matching result of the spissatus and the shadow and a supplementary detection result and obtaining final detection result sub-images of all sub-atlases; and sequentially splicing final detection result sub-images of all sub-atlases and obtaining a final detection result image. Auxiliary information and manual intervention are not required, the detection precision is high and the method can be used in detection and classification of remote sensing image variation and pre-processing of image segmentation.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com