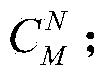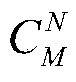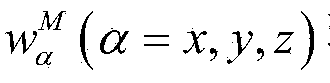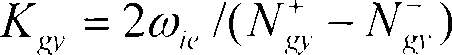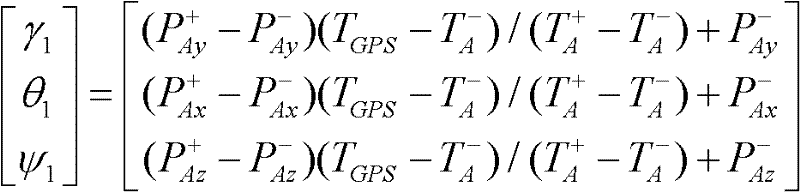Patents
Literature
563 results about "Geographic coordinate system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
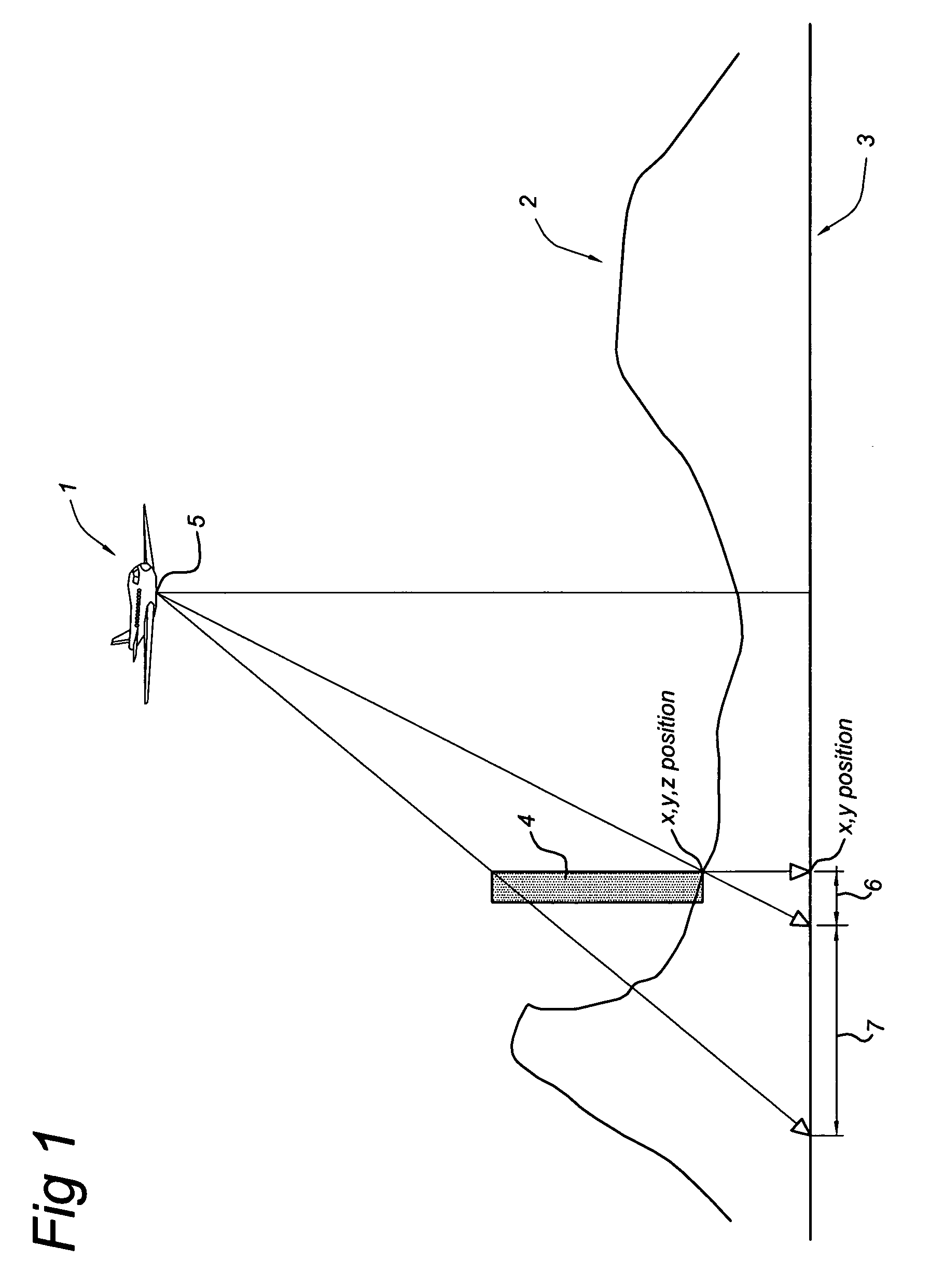
A geographic coordinate system is a coordinate system that enables every location on Earth to be specified by a set of numbers, letters or symbols. The coordinates are often chosen such that one of the numbers represents a vertical position and two or three of the numbers represent a horizontal position; alternatively, a geographic position may be expressed in a combined three-dimensional Cartesian vector. A common choice of coordinates is latitude, longitude and elevation. To specify a location on a plane requires a map projection.
Method of generating a Geodetic Reference Database Product
ActiveUS20110282578A1Precise definitionSuperior hardwareInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlTriangulationVehicle driving
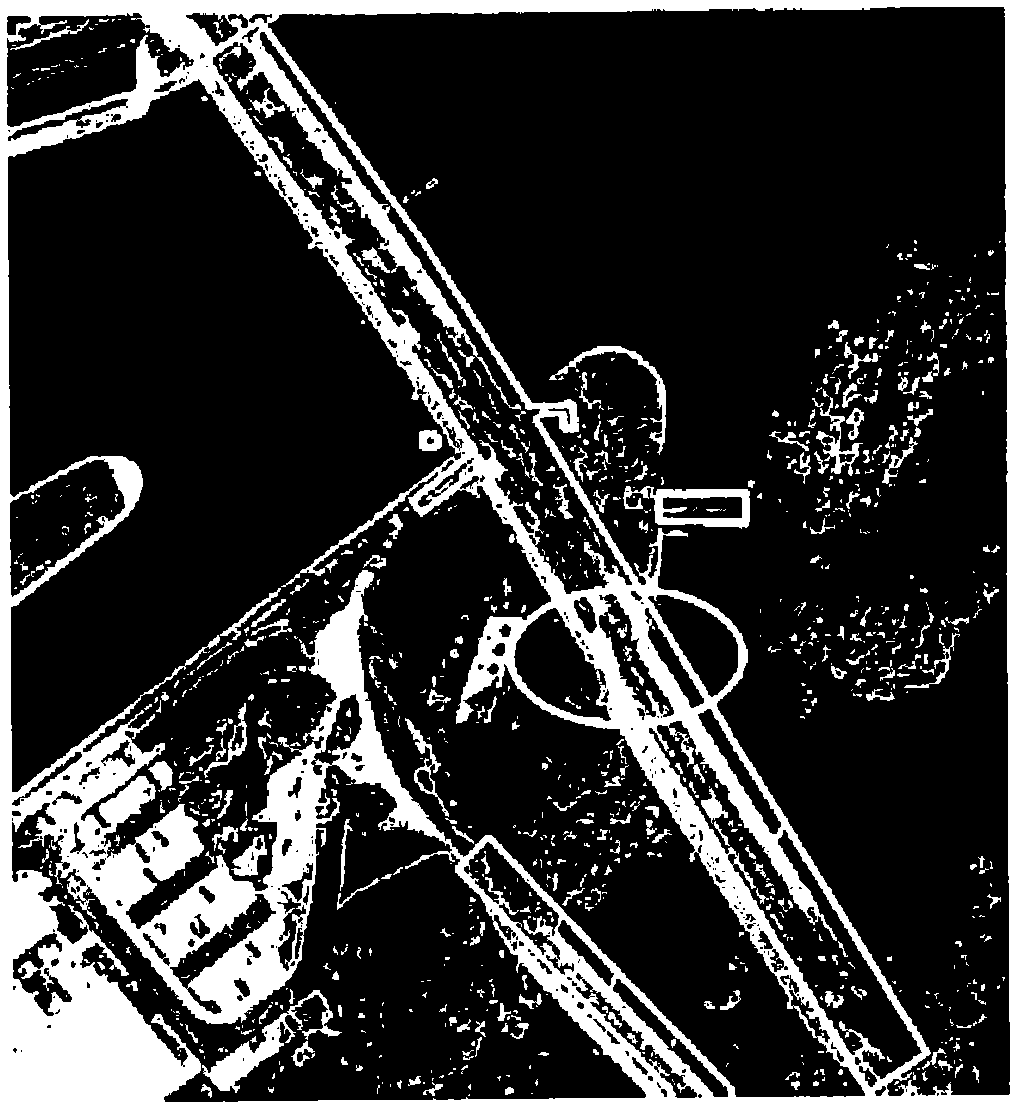
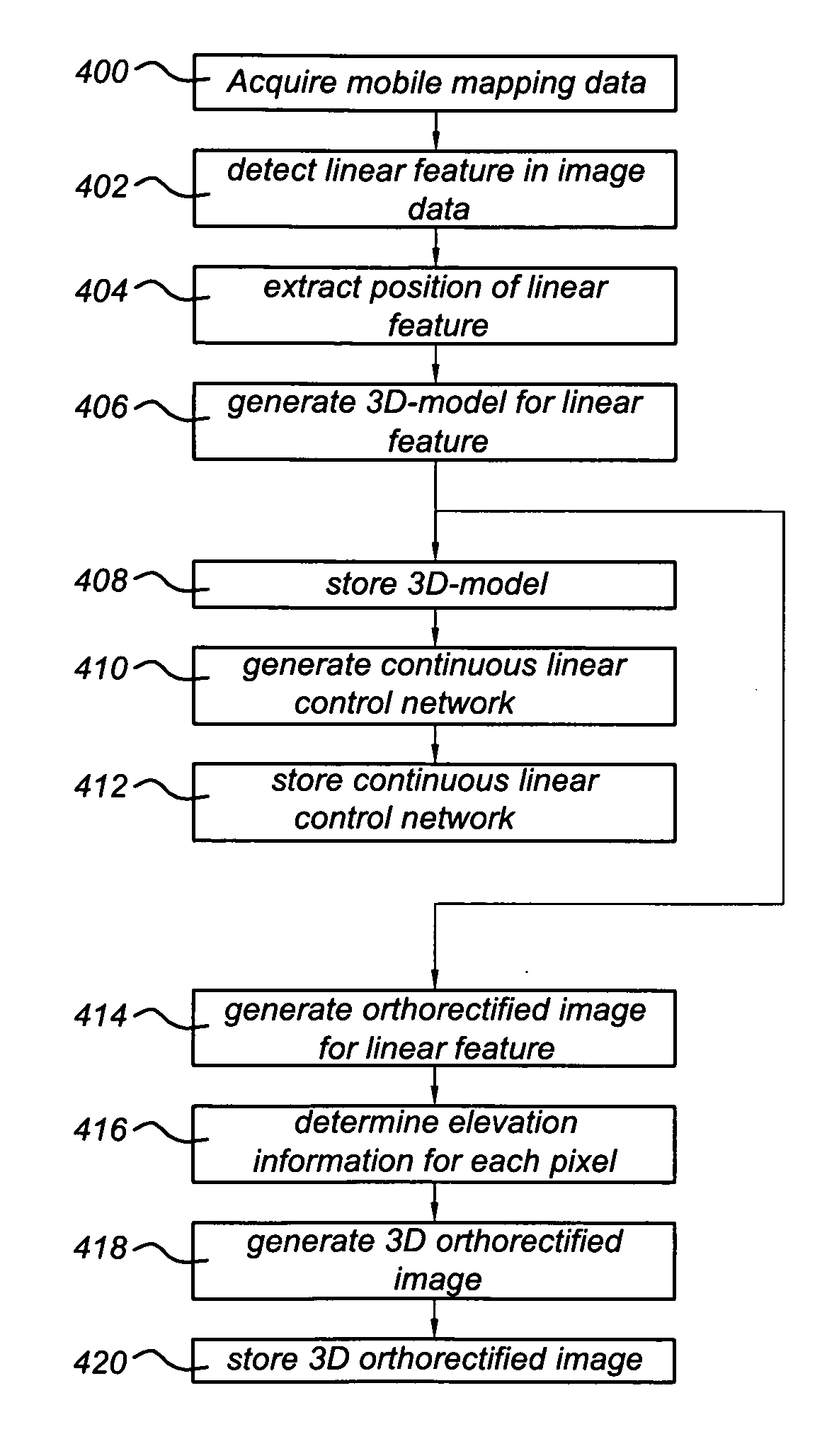
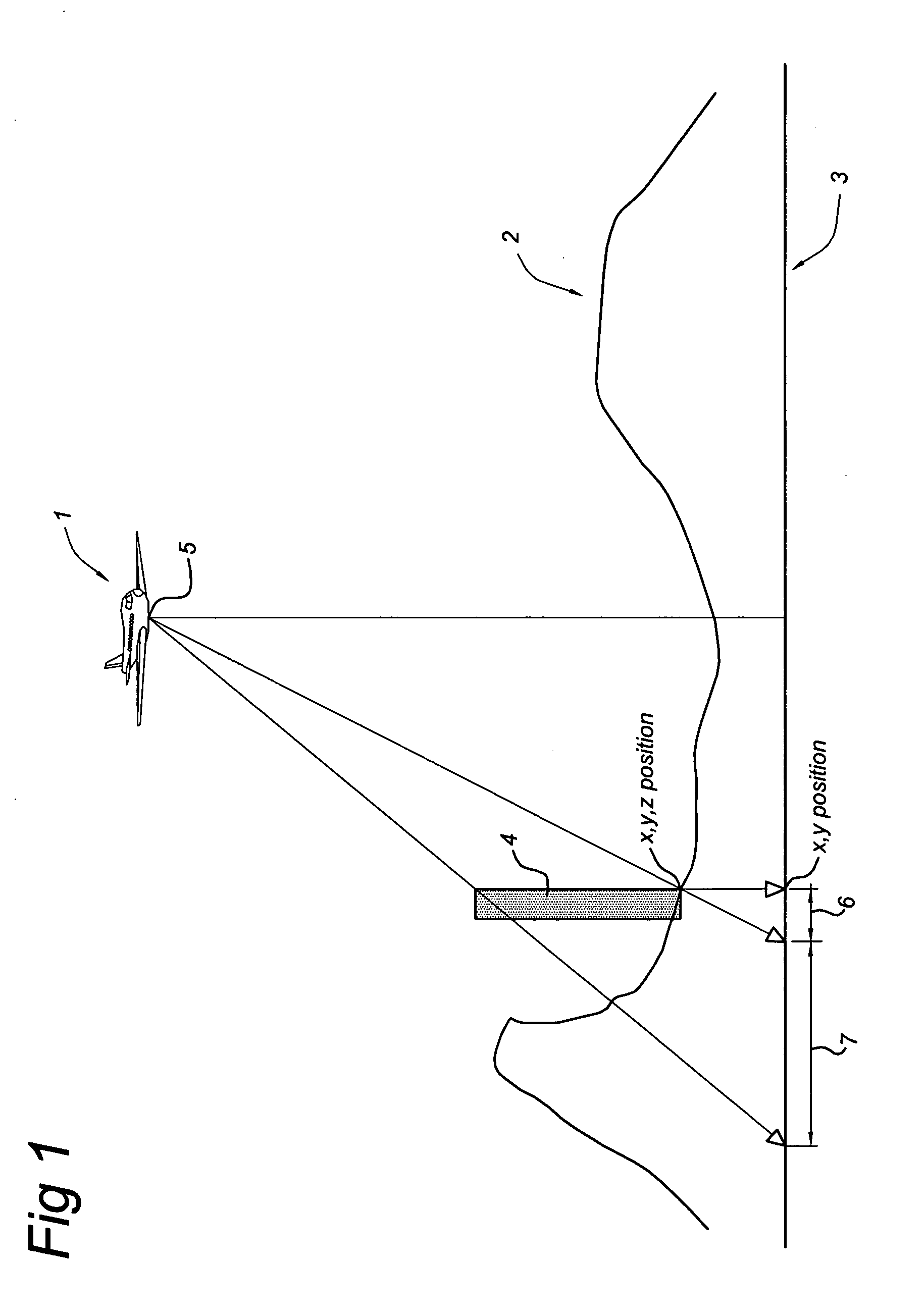
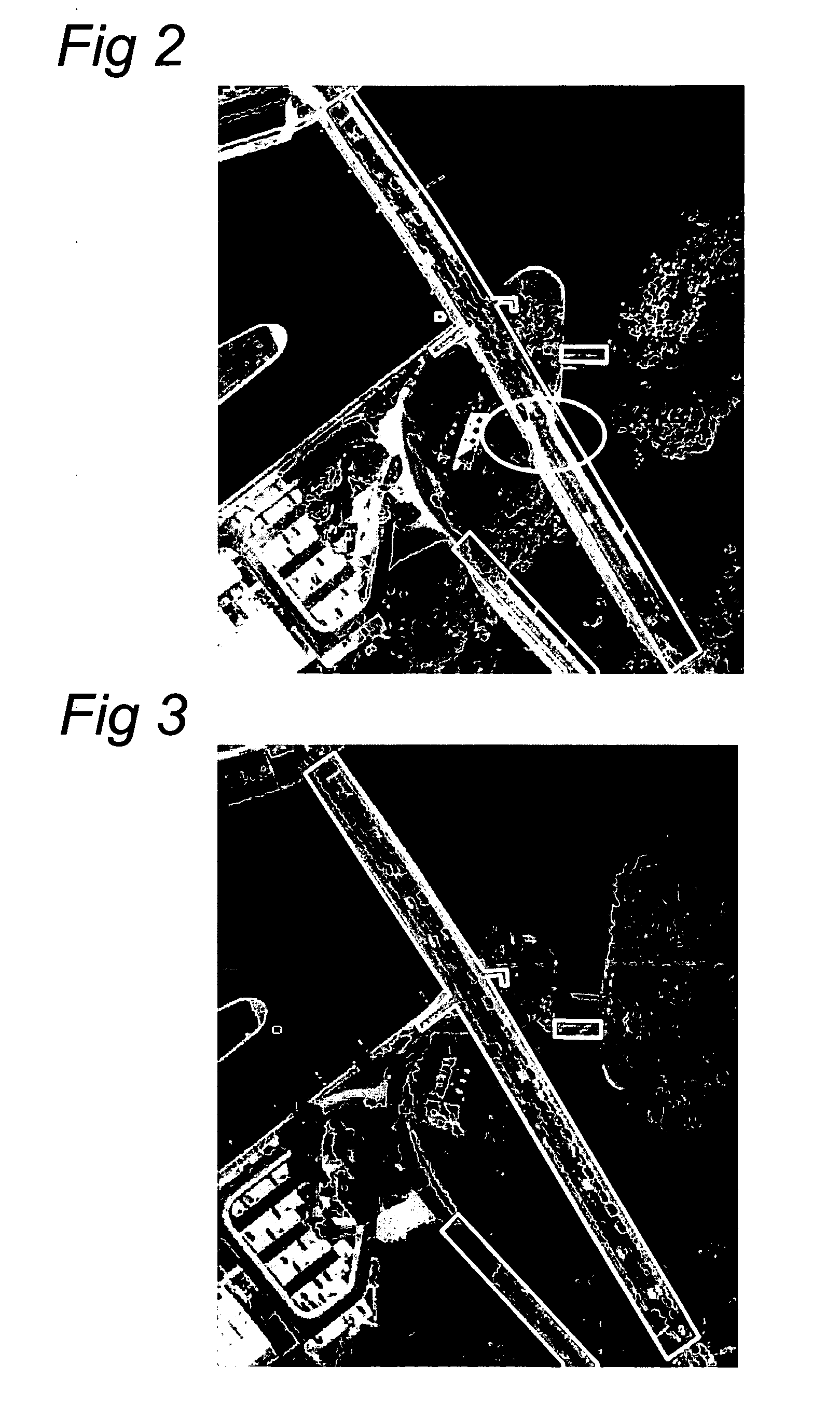
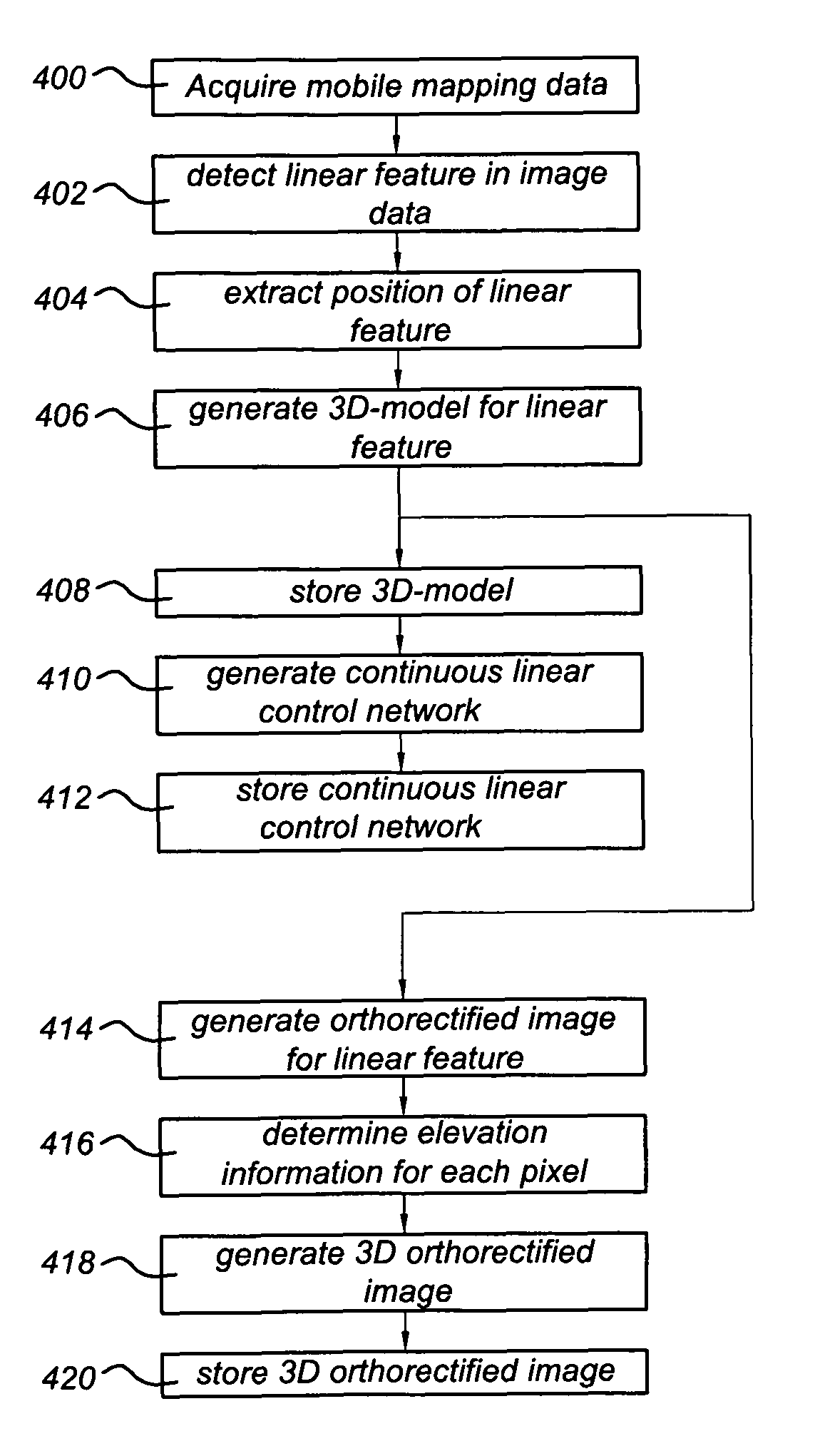
A method of generating a geodetic reference database product is disclosed The method comprises acquiring mobile mapping data captured by means of digital cameras, range sensors and position determination means including GPS and IMU mounted to a vehicle driving across the earth surface, the mobile mapping data comprising simultaneously captured image data, range data and associated position data in a geographic coordinate system. Linear stationary earth surface features are derived from the mobile mapping data by processing the image data, range data and associated position data. 3D-models are generated for the linear stationary earth surface features in the geographic coordinate system from the image data, range data and associated position data and stored in a database to obtain the geodetic reference database product. A 3D-model could include an image representing the colors of the surface of the 3D model or a set of smaller images representing photo-identifiable objects along the model. The 3D-models could be used to rectify aerial imagery, to correct digital elevation models and to improve the triangulation of digital elevation models.
Owner:TOMTOM GLOBAL CONTENT
Method of generating a geodetic reference database product
ActiveUS8958980B2Superior hardwareSpeed up the processInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlReference databaseMobile mapping
A method of generating a geodetic reference database product is disclosed The method comprises acquiring mobile mapping data captured by means of digital cameras, range sensors and position determination means including GPS and IMU mounted to a vehicle driving across the earth surface, the mobile mapping data comprising simultaneously captured image data, range data and associated position data in a geographic coordinate system. Linear stationary earth surface features are derived from the mobile mapping data by processing the image data, range data and associated position data. 3D-models are generated for the linear stationary earth surface features in the geographic coordinate system from the image data, range data and associated position data and stored in a database to obtain the geodetic reference database product. A 3D-model could include an image representing the colors of the surface of the 3D model or a set of smaller images representing photo-identifiable objects along the model. The 3D-models could be used to rectify aerial imagery, to correct digital elevation models and to improve the triangulation of digital elevation models.
Owner:TOMTOM GLOBAL CONTENT
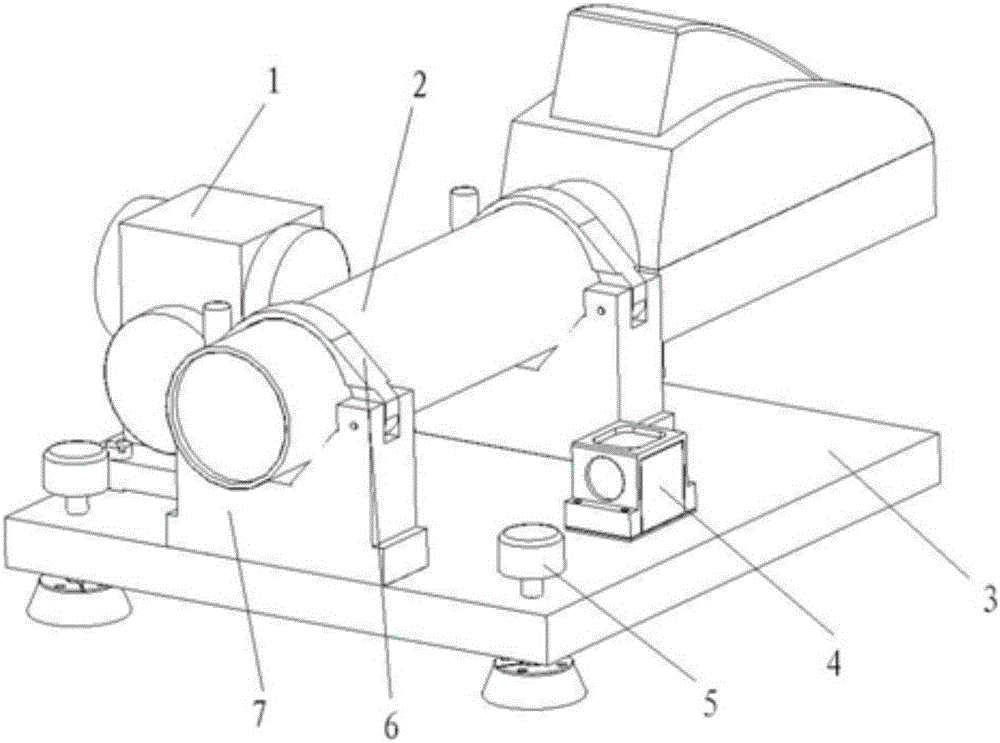
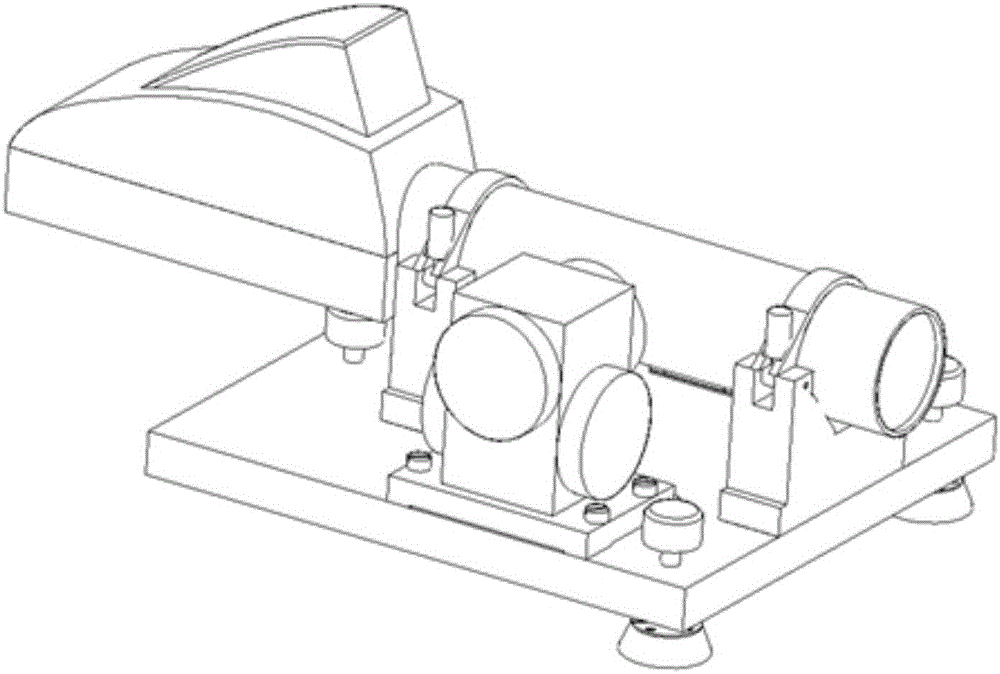
Attitude testing apparatus and method based on autocollimator
ActiveCN105021211AContinuous attitude measurementMeet measurement needsMeasurement devicesAttitude testingAutocollimation
The invention relates to an attitude testing apparatus and method based on an autocollimator. The apparatus mainly comprises the autocollimator, an optical hexahedron, a double-shaft electronic level meter and a pedestal with a leveling function. The method comprises the following steps: putting the attitude testing apparatus on a firm base, allowing the autocollimator to collimate a reflecting surface of an object, then collimating the optical hexahedron with an autocollimation gyro theodolite and measuring the included angle between the apparatus and a true north azimuth reference; starting the autocollimator for recording and retrieving of continuous data of the attitude of the reflecting surface of the object and starting the double-shaft electronic level meter for recording and retrieving of continuous data of horizontal attitude; and after completion of recording and retrieving of the data, processing the data of the autocollimator and the double-shaft electronic level meter by using a data processing method for the attitude testing apparatus so as to eventually obtain continuous changes of the attitude of the reflecting surface of the object in a geographic coordinate system, thereby meeting demands of continuous absolute measurement.
Owner:TIANJIN NAVIGATION INSTR RES INST
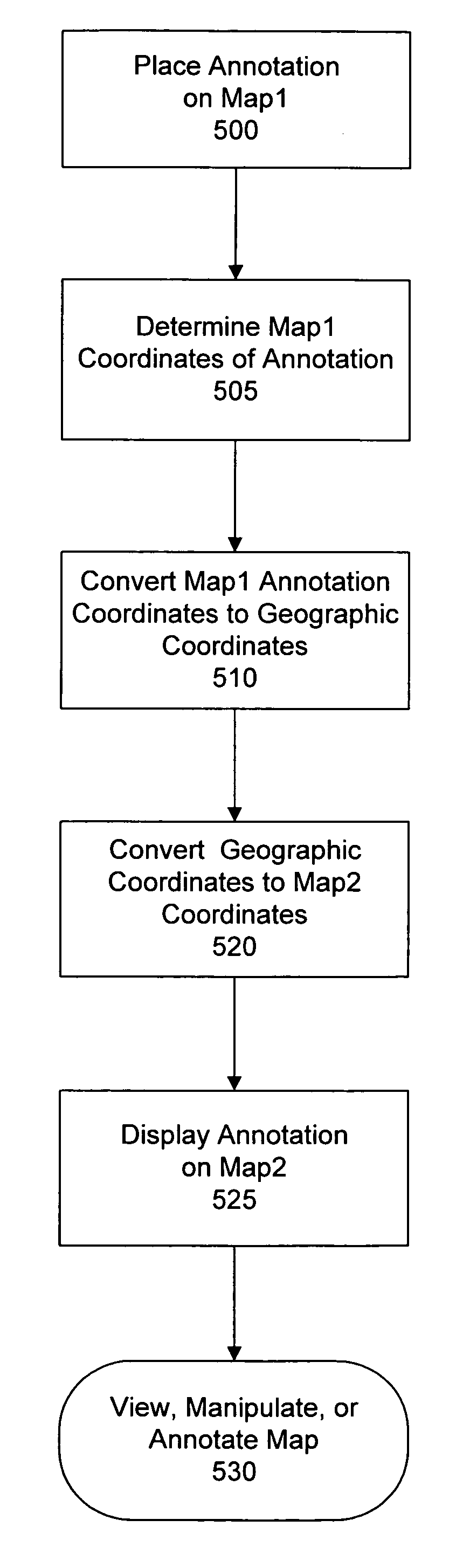
System and method for synchronizing raster and vector map images
InactiveUS7161604B2Enhance the imageEasy to operateCathode-ray tube indicatorsMaps/plans/chartsOperational transformationLongitude
A system and method for coordinated manipulation of multiple displayed maps, even when the maps use different internal coordinate systems. According to this embodiment, each map image to be displayed is first georeferenced, to provide a set of conversion functions between each map's internal coordinate system and a geographic coordinate system, which is latitude / longitude in the preferred embodiment. After this is done, any point on each map can be referenced using the geographic coordinate set. Since this is the case, the maps can now be manipulated, edited, and annotated in a synchronized manner, by defining the manipulations in terms of the geographic coordinate system, and using the georeferencing functions to translate the manipulation to each map's internal coordinate system.
Owner:SOURCEPROSE CORP
Celestial autonomous navigation method based on star sensors
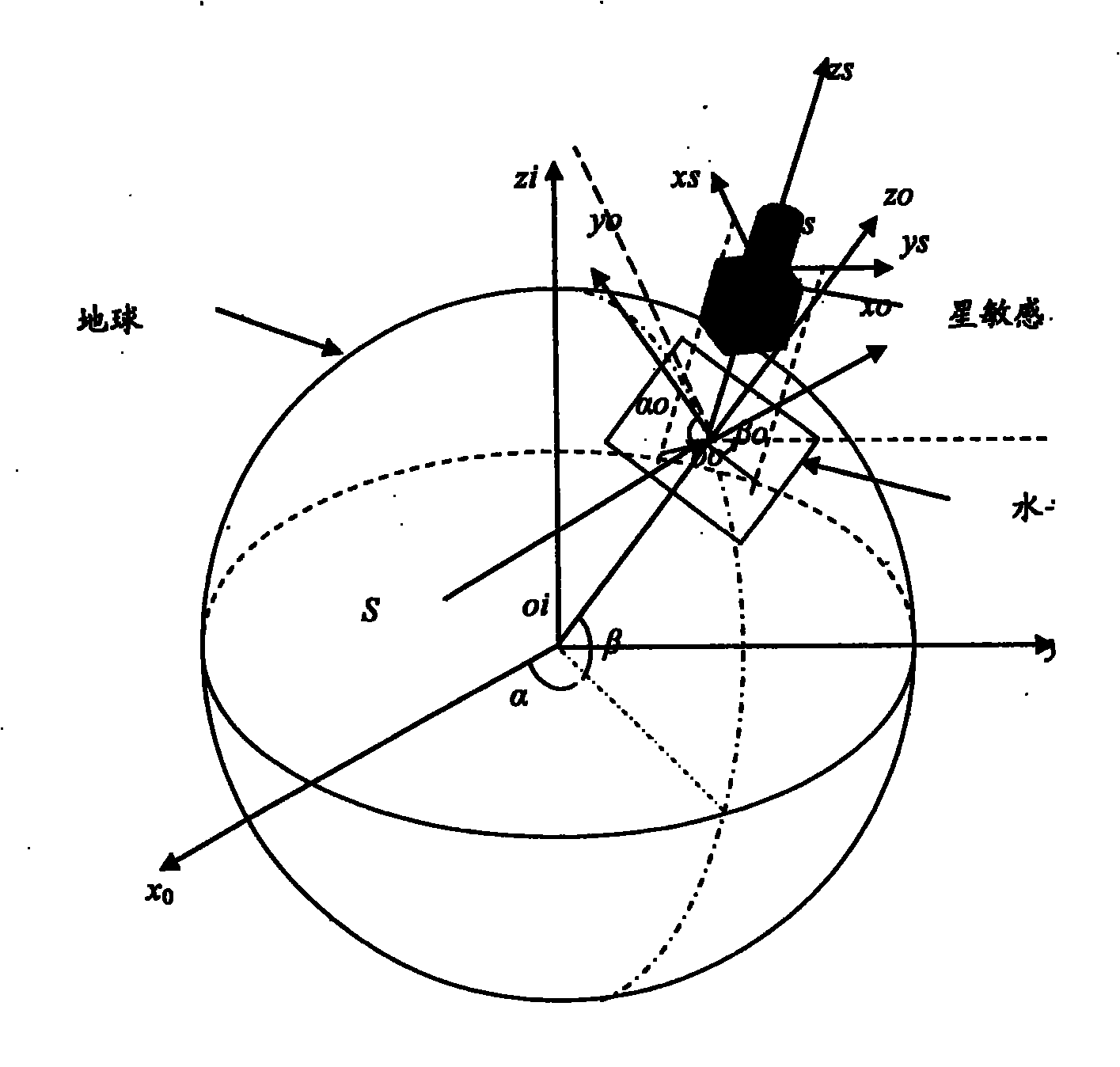
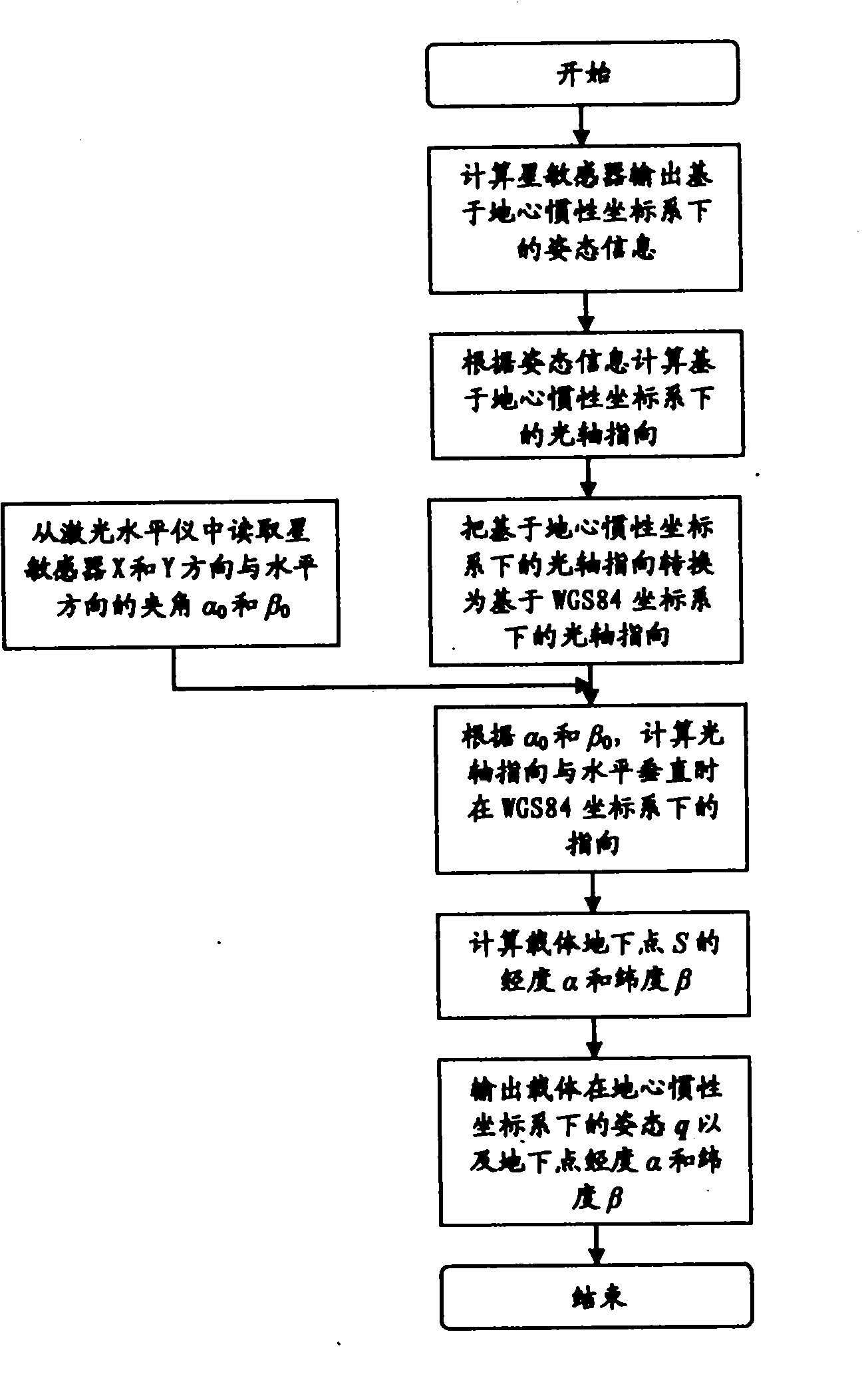
InactiveCN101893440ARealize autonomous navigationAvoid measurement errorsNavigation by astronomical meansOptical axisLongitude
The invention provides a celestial autonomous navigation method based on star sensors, which comprises the following steps: calculating attitude information based on a geocentric inertial coordinate system, which is output by a star sensor; calculating the optical axis direction based on the geocentric inertial coordinate system; converting the optical axis direction based on the geocentric inertial coordinate system into optical axis direction based on a WGS84 coordinate system; reading the included angles alpha 0 and beta 0 between the X and Y directions of the star sensor and the horizontal direction from a laser level meter; calculating the direction in the WGS84 coordinate system when the optical axis direction is perpendicular to the horizontal level; calculating the longitude alpha and latitude beta of the underground point S of the carrier; and outputting the attitude q and the longitude alpha and latitude beta of the underground point of the carrier in the geocentric inertial coordinate system. The invention avoids measurement and control errors caused by horizontal reference platforms, enhances the measuring accuracy, and simultaneously outputs the attitude of three axes and the longitude and latitude of the carrier in the geographic coordinate system in real time, thereby completely realizing celestial autonomous navigation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Course angle obtaining method based on inertial sensor
ActiveCN104121905AAccurate heading angleHigh precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsGyroscopeComputational physics
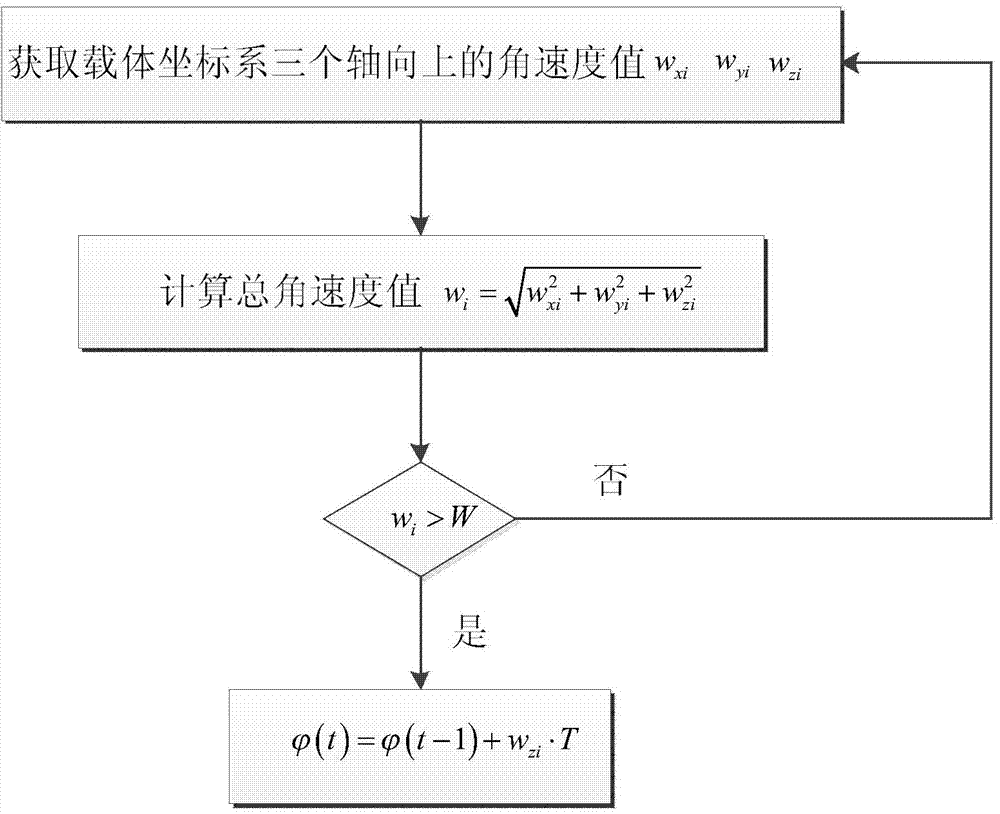
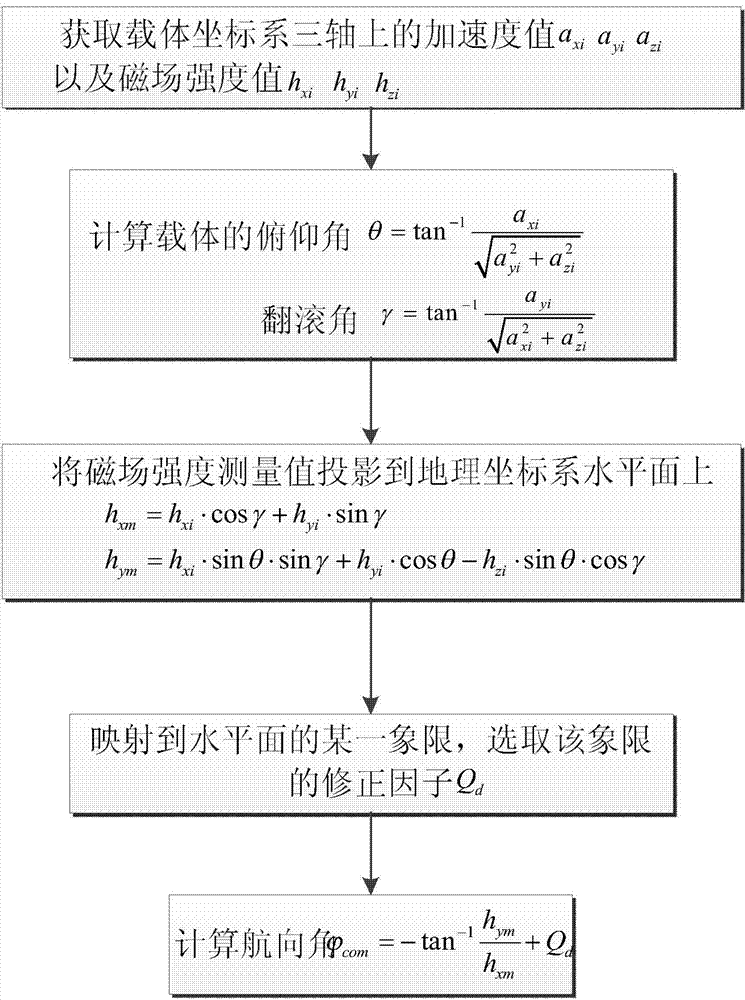
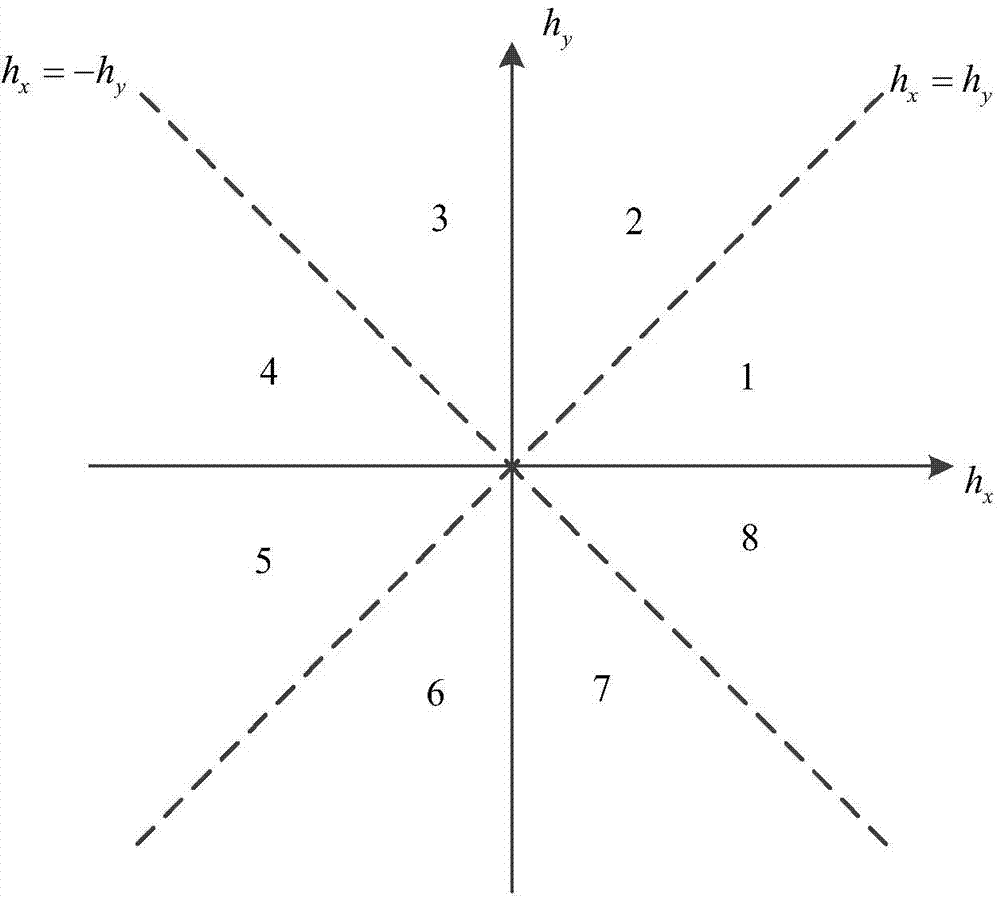
The invention discloses a course angle obtaining method based on an inertial sensor. The course angle obtaining method comprises the following steps: firstly, course angles are independently calculated by using measured values of a gyroscope and a magnetometer, and then weight fusion is carried out on two results. Specifically, when the course angle is calculated by using the gyroscope, integration is performed on a z-direction angular speed under a carrier coordinate system, which is measured by the gyroscope, wherein whether the integration is carried out or not is judged according to a size relation between a total angular speed at the current moment and a threshold value; when the course angle is calculated by using the magnetometer, a horizontal plane of a geographic coordinate system is divided into eight quadrants, magnetic field strength values measured by the magnetometer are projected to the horizontal plane and correspond to the specific quadrants according to a horizontal plane axis and magnetic field strength components in the axial direction, and in each quadrant, an existing course angle calculation formula is corrected by adopting different correction factors; finally, a weighting coefficient is set by using a variance yield of the angular speed and the course angles calculated by the two methods are fused. According to the course angle obtaining method, the accurate course angle value can be obtained so that the positioning precision is high.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Coordinate system transformation method for detection of vehicle motion acceleration
ActiveCN104198765ARealize information conversionAcceleration measurement using interia forcesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometerGyroscope
The invention relates to a coordinate system transformation method for detection of vehicle motion acceleration. The method includes the steps of establishing a correlative relationship between an MEMS (micro-electromechanical system) coordinate system and a geographic coordinate system through MEMS accelerometers and MEMS magnetometers; acquiring an attitude matrix according to outputs of the gyroscopes during navigation; according to the attitude matrix, acquiring a transformation matrix C<n><m> of the MEMS coordinate system and the geographic coordinate system; by the aid of the transformation matrix C<N><M>, transforming an acceleration output by the MEMS accelerometers into a geographic coordinate acceleration; according to a GPS (global positioning system) east velocity V<GPS><E> output by a GPS and a vehicle velocity V<R>, acquiring a relative course angle Psi<N><NB>; according to the related course angle, acquiring a transformation matrix C<N> from the geographic coordinate system to a vehicle body coordinate system; after a calculation method of the transformation matrix C<N> and the transformation matrix C<N><M> is acquired, acquiring a transformation matrix C<M> of the MEMS coordinate system and the vehicle body coordinate system by the Strassen algorithm; according to the transformation matrix C<M> of the MEMS coordinate system and the vehicle body coordinate system, transforming outputs of all of the MEMS gyroscopes and accelerometers to the vehicle body coordinate system.
Owner:DALIAN ROILAND SCI & TECH CO LTD
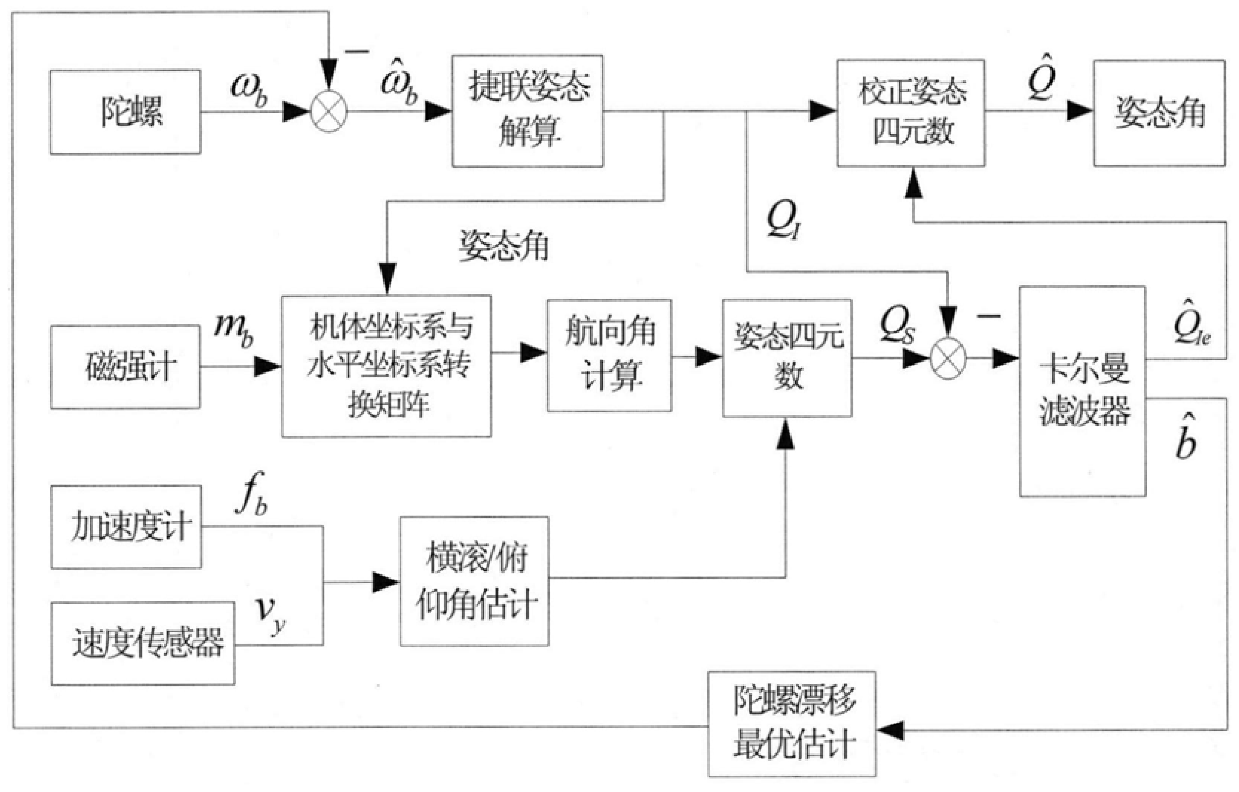
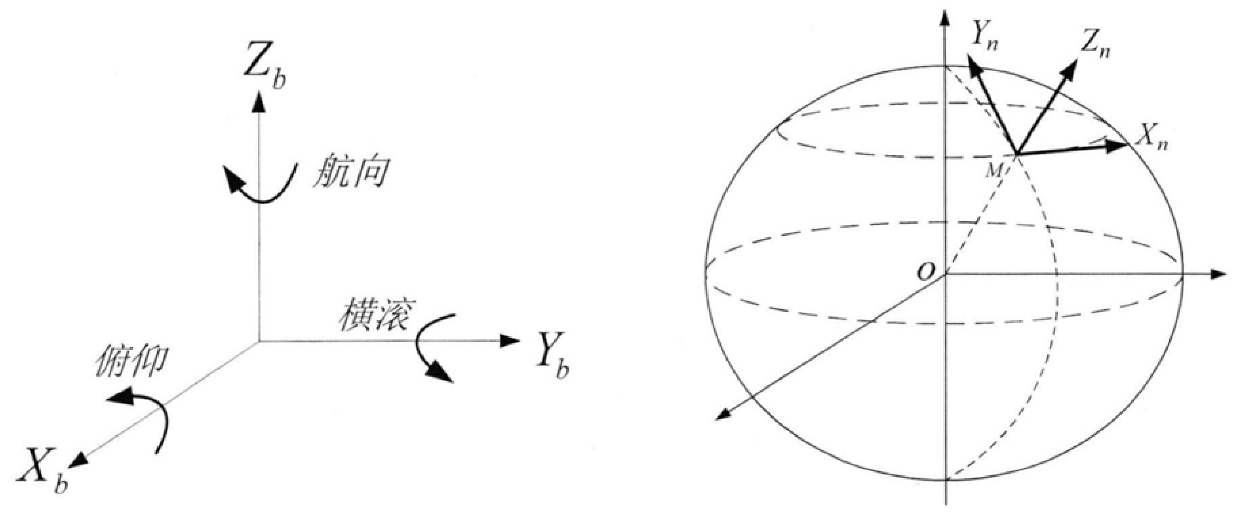
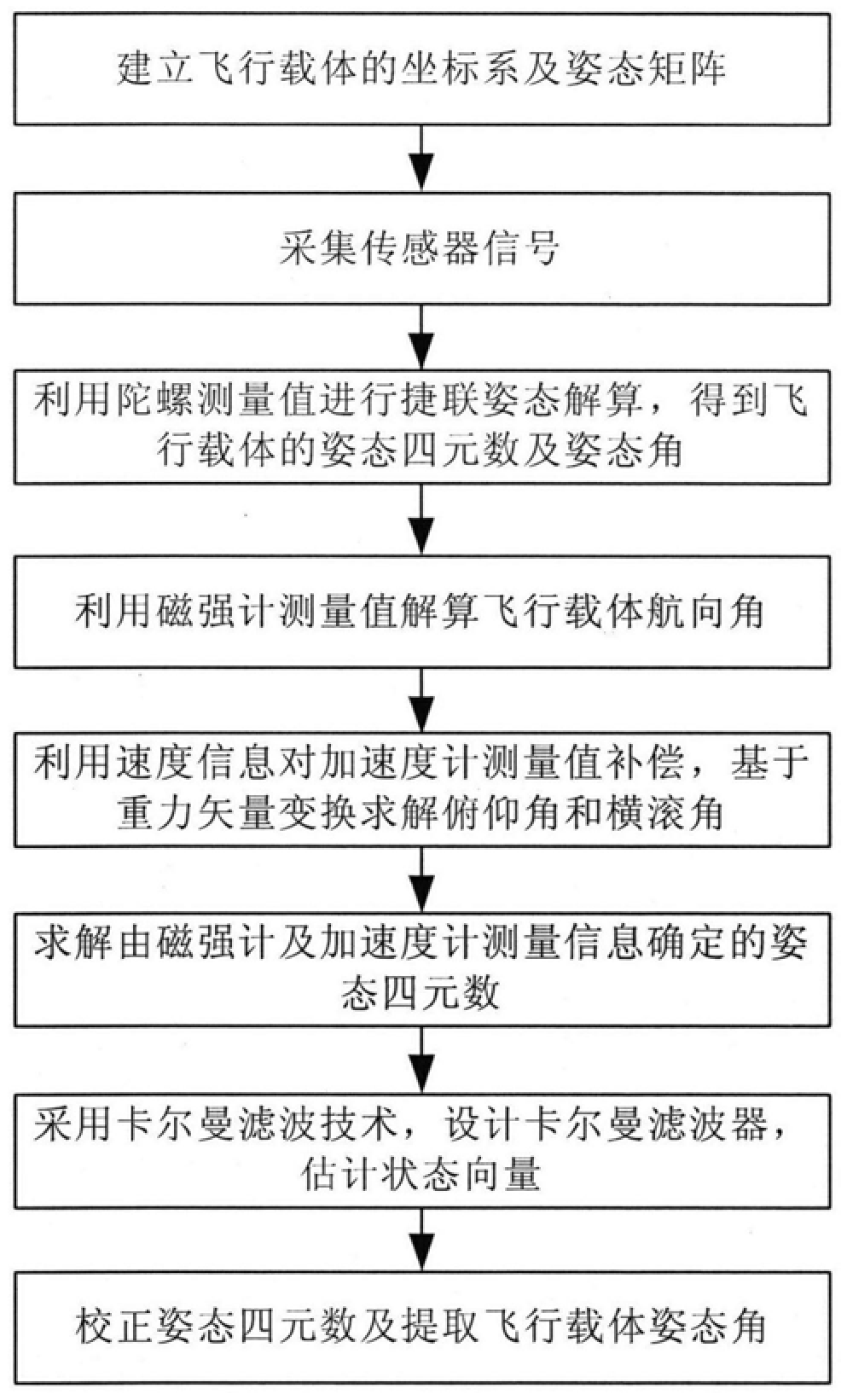
A Method for Determining the Attitude of a Flight Carrier
InactiveCN106342284BHigh measurement accuracyMeet the requirements of real-time attitude controlAttitude controlKaiman filterAccelerometer
The invention discloses a method for determining the attitude of a flight carrier, which belongs to the field of attitude measurement. The main steps include: establish the coordinate system and attitude matrix of the flight carrier; collect sensor signals; use the gyro measurements to carry out strapdown attitude calculations to obtain the attitude quaternions and attitude angles of the flight carrier; use the magnetometer measurements to calculate the flight Carrier heading angle; use speed information to compensate acceleration measurement value, solve pitch angle and roll angle; solve attitude quaternion determined by magnetometer and accelerometer information; design Kalman filter, estimate state vector; correct attitude four arity and extract attitude angle. This method combines gyroscopes, accelerometers, magnetometers, and speed sensors to meet the requirements of real-time attitude control of the flight carrier; introduces gyroscope drift into the system state vector, estimates and corrects it in real time, and uses the measured value of the magnetometer to directly Calculate the heading angle, avoid the calculation of the geomagnetic field vector in the geographic coordinate system, and improve the accuracy of attitude determination.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
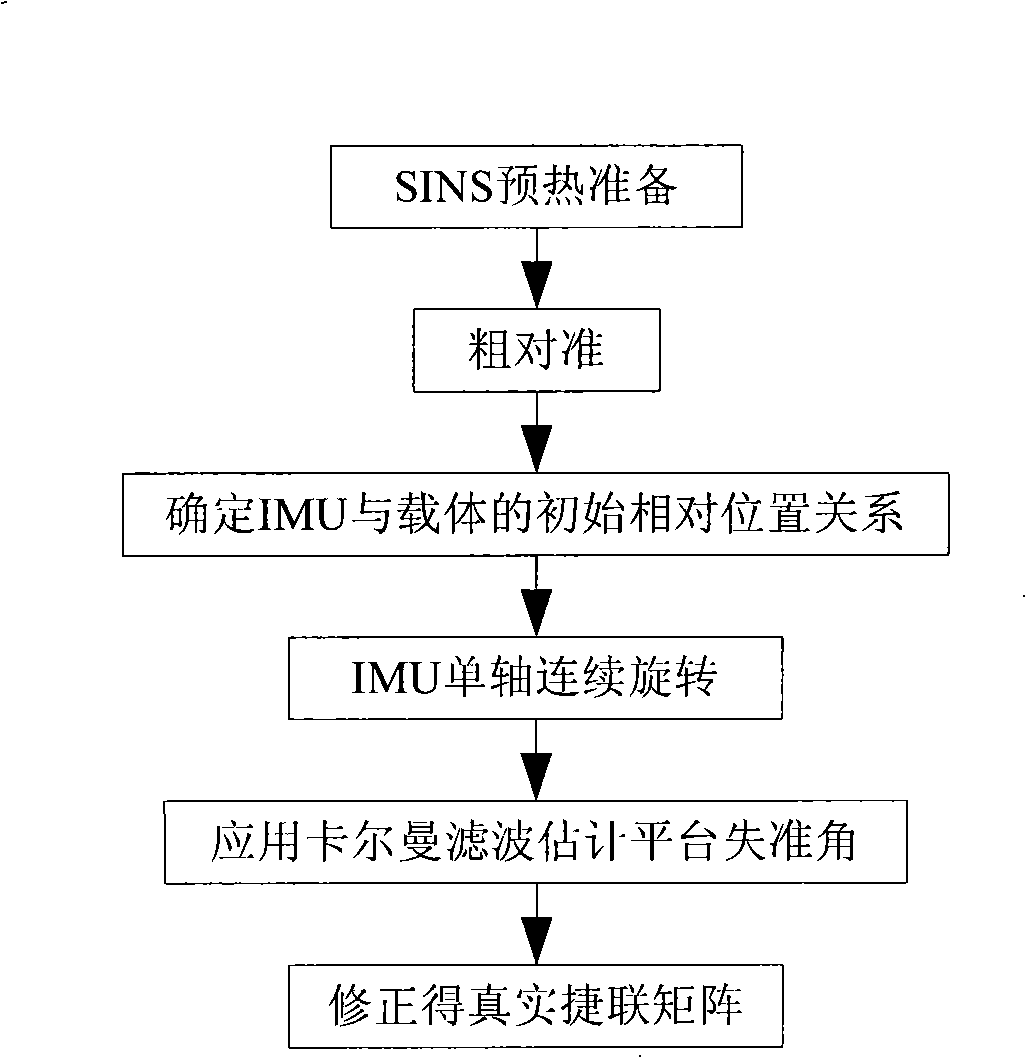
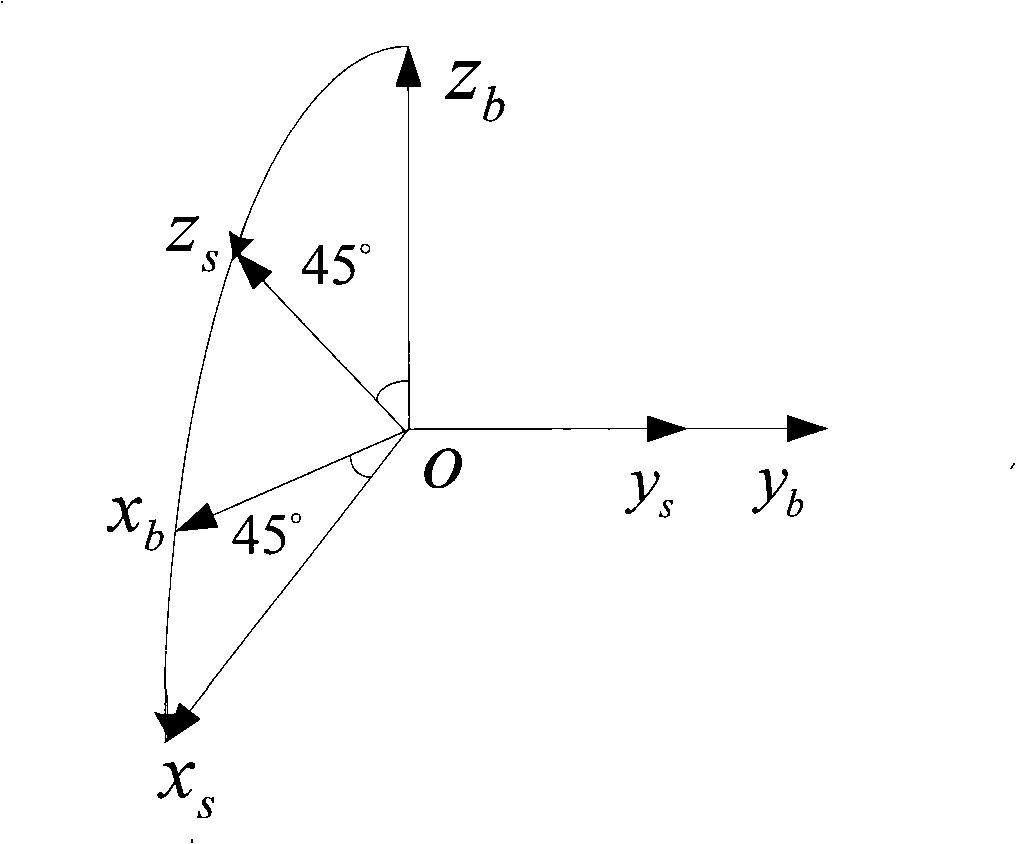
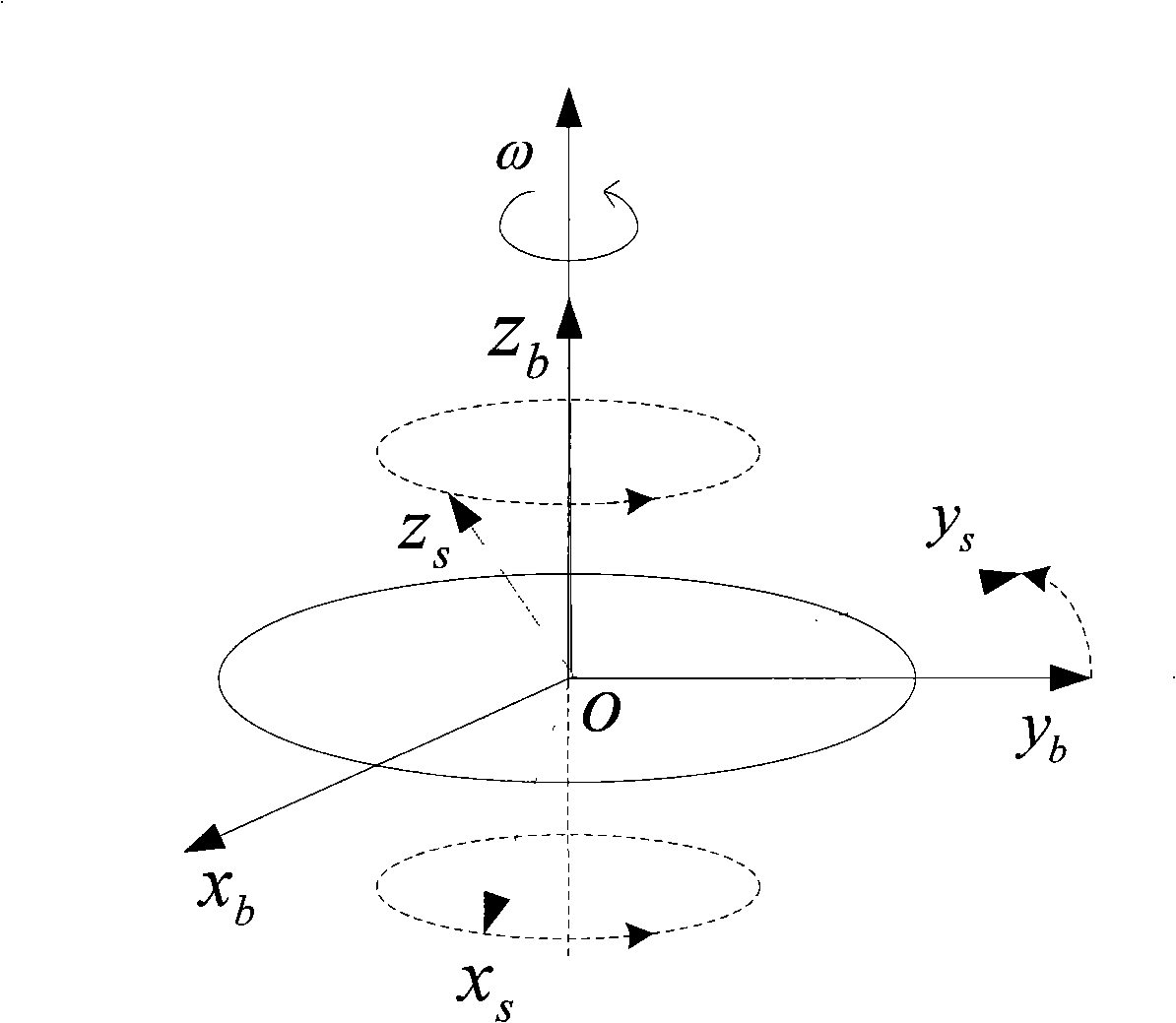
Method for initial alignment of a single-axis rotation strap-down inertial navigation system (SINS)
The invention provides a method for initial alignment of a single-axis rotation strap-down inertial navigation system (SINS). The method comprises the following steps: building a carrier coordinate system and computing a transfer matrix between geographic coordinate systems on the basis of coarse alignment completed by collecting the information output by gyroscopes and accelerometers in the SINS with the carrier being in a static state; establishing Kalman filtering state equations with speed errors as the state variables and measurement equations with the speed errors as the measurement variables; and estimating the misalignment angles of the carrier by the Kalman filtering technique and feeding back to the SINS to complete the initial alignment of the SINS. The invention can overcome the influence on the estimation precision of the azimuth misalignment angles caused by the equivalent gyroscope drift of the geographic coordinate systems and improve the alignment precision.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
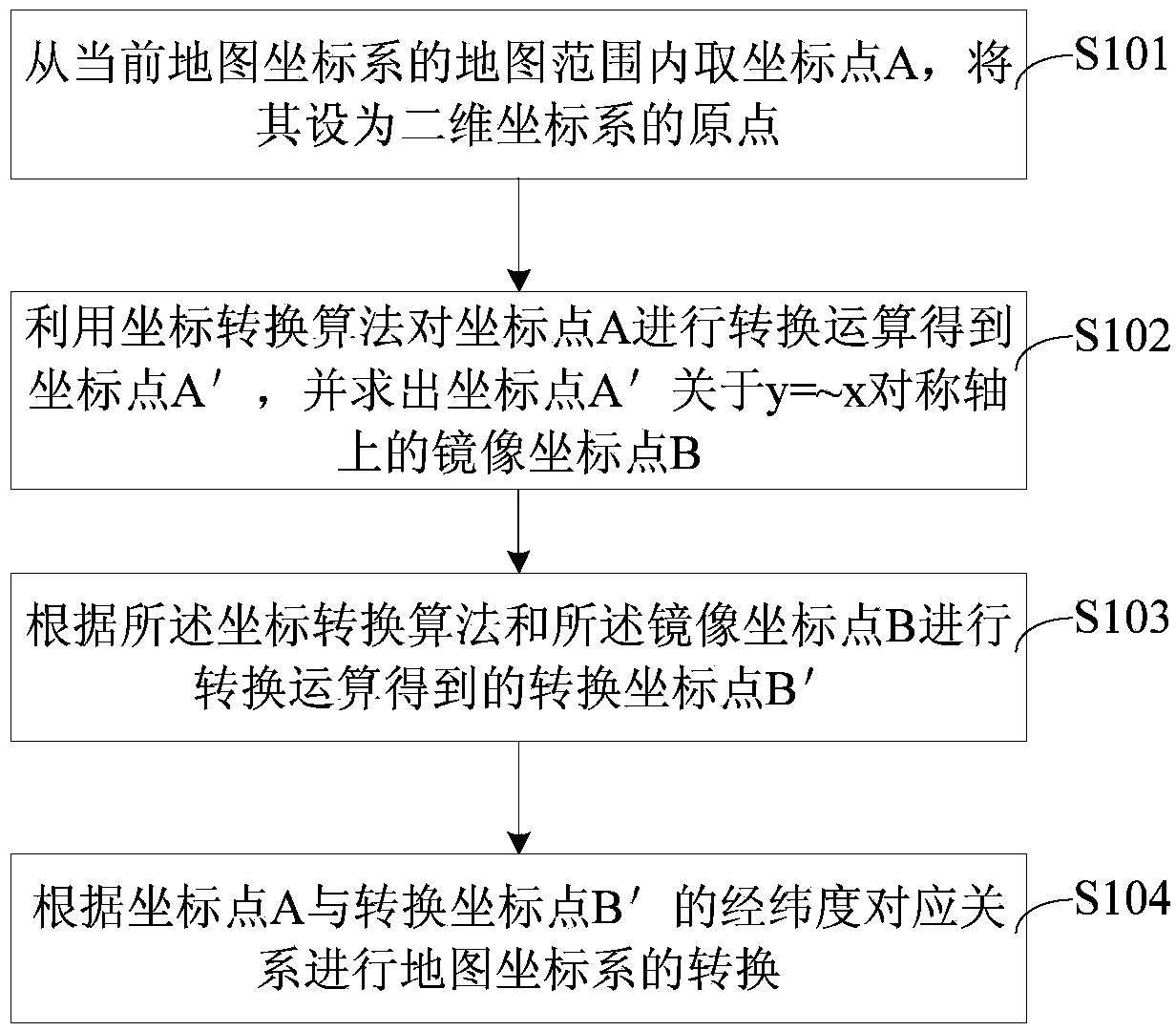
Method and system for transforming map coordinate system
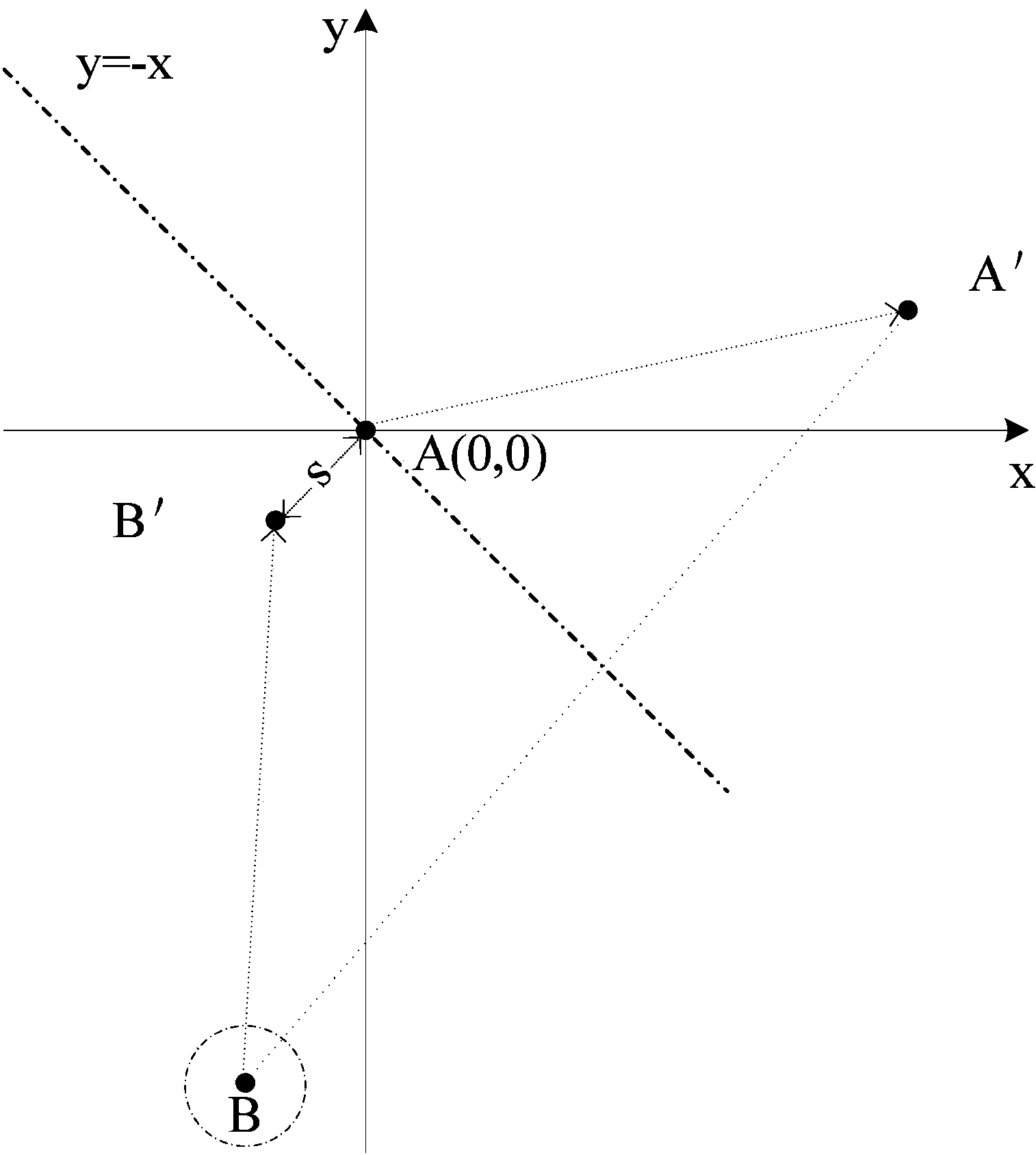
ActiveCN104048659ARealize mutual free conversionRealize free conversionNavigational calculation instrumentsTransverse axisTransformation algorithm
The invention provides a method and a system for transforming a map coordinate system. The method comprises the following steps: taking a coordinate point A in a map range of the current map coordinate system, and setting the coordinate point A as an original point of a two-dimensional coordinate system; transforming the coordinate point A to obtain a coordinate point A' by utilizing a coordinate transformation algorithm, and solving a mirror-image coordinate point B of the coordinate point A' about a symmetric axis of y=-x, wherein y is a longitudinal axis of the two-dimensional coordinate system, and x is a transverse axis of the two-dimensional coordinate system; transforming the mirror-image coordinate point B to obtain a transformed coordinate point B' according to the coordinate transformation algorithm; transforming the map coordinate system according to a longitude and latitude corresponding relation of the coordinate point A and the transformed coordinate point B'. By adopting the method and the system, the longitude and latitude among different geological coordinate systems can be mutually transformed freely, an effective and feasible corrective method can be provided for the coordinate encryption algorithm, the longitude and the latitude among different SDK (software development kit) of different maps can be corrected, and the precision and working efficiency for collecting the map information can be improved.
Owner:GCI SCI & TECH
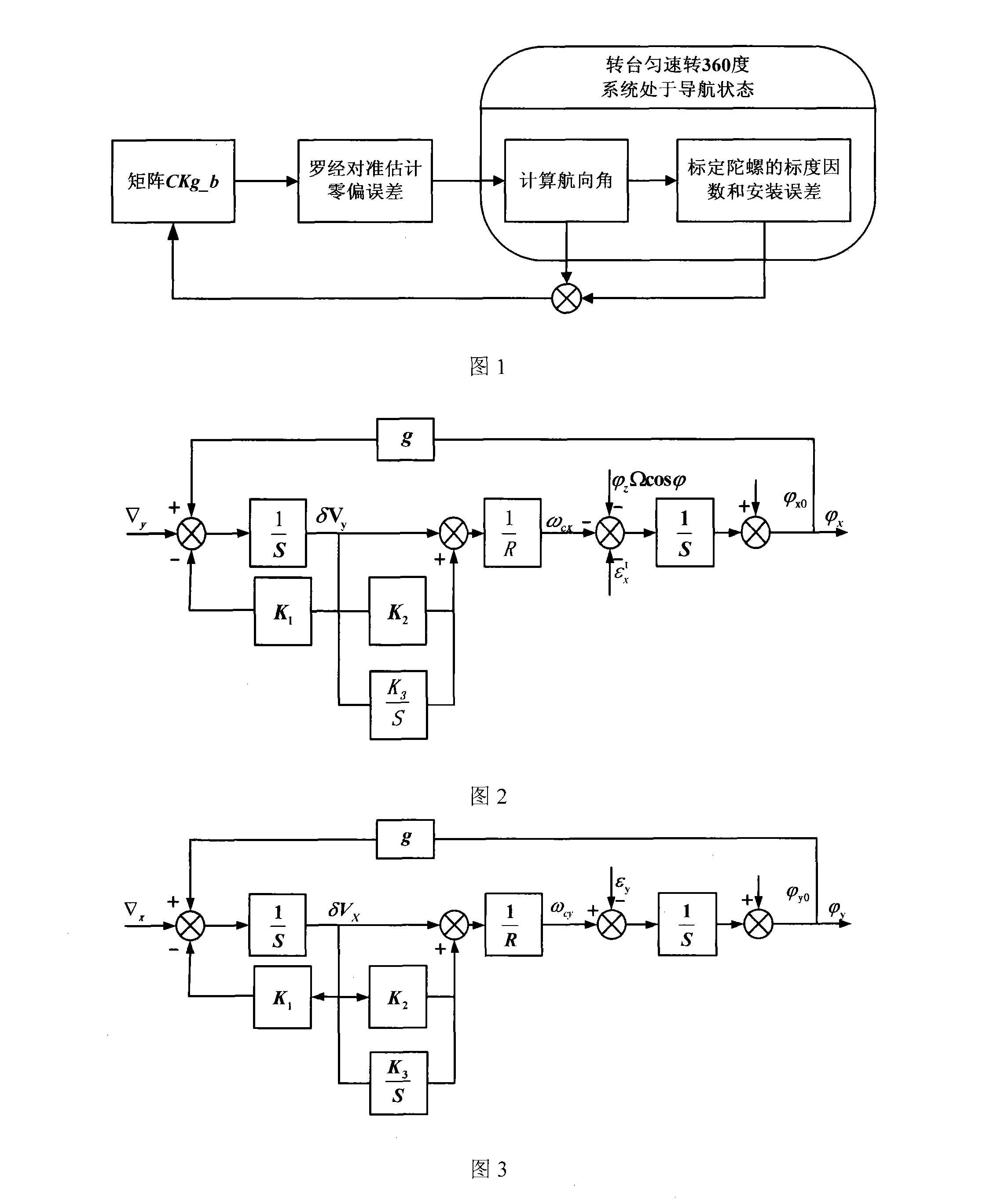
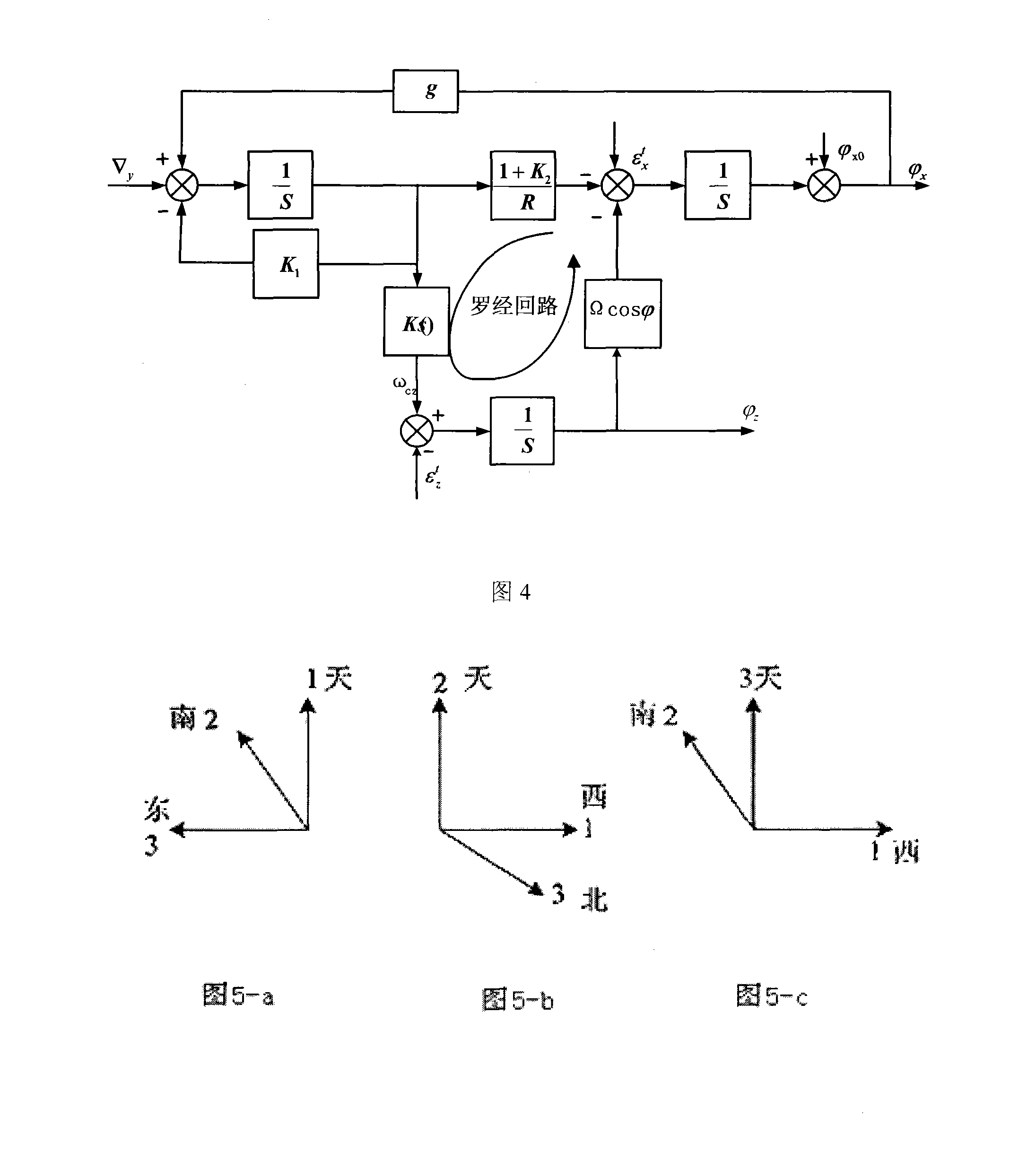
Closed-loop calibration method of micro-mechanical gyroscope inertial measuring component
The invention provides a closed-loop calibration method of a micro-mechanic gyro inertia measuring component, which comprises the following steps: data output by a gyro and an accelerometer is collected; a scale factor of the Y axis is roughly measured; a matrix CKg-b is constructed by using the roughly determined scale factor and an installation error; the alignment of a micro-mechanic strapdown inertial navigation system is implemented according to a compass loop method, and a course angle that is output by system navigation parameters and control angular velocities on each axis of a geographical coordinate system are read after the compass alignment is finished, thus measuring constant drift of the gyro; when the system enters a navigation phase, the scale factor and the installation error angle of the gyro are precisely calibrated; the updated matrix CKg-b and the course angle are written into a navigation computer, and a next round of calibration is implemented, when the difference between the course angles that are obtained from two calibrations is less than a given constant 0.0001 degree, the calibration is finished. By using the calibration method provided by the invention, the system lies in a closed-loop feedback state and can implement the feedback calibration of the calibration error, thus improving calibration precision.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
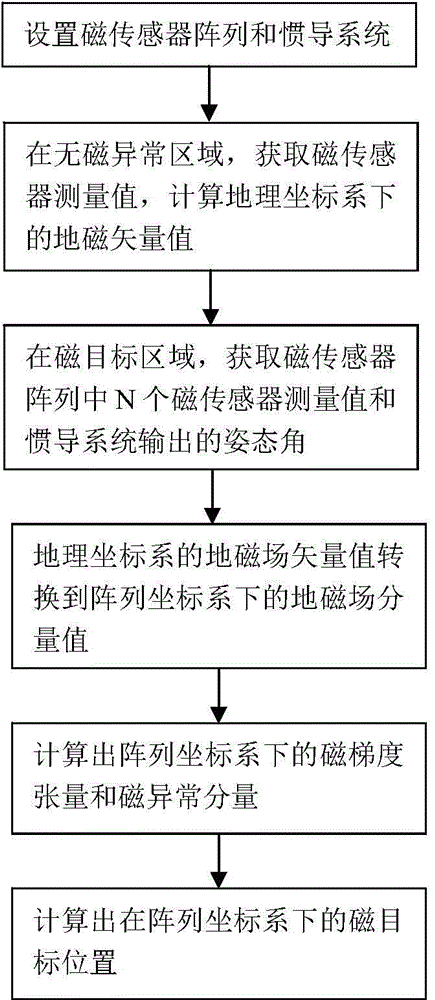
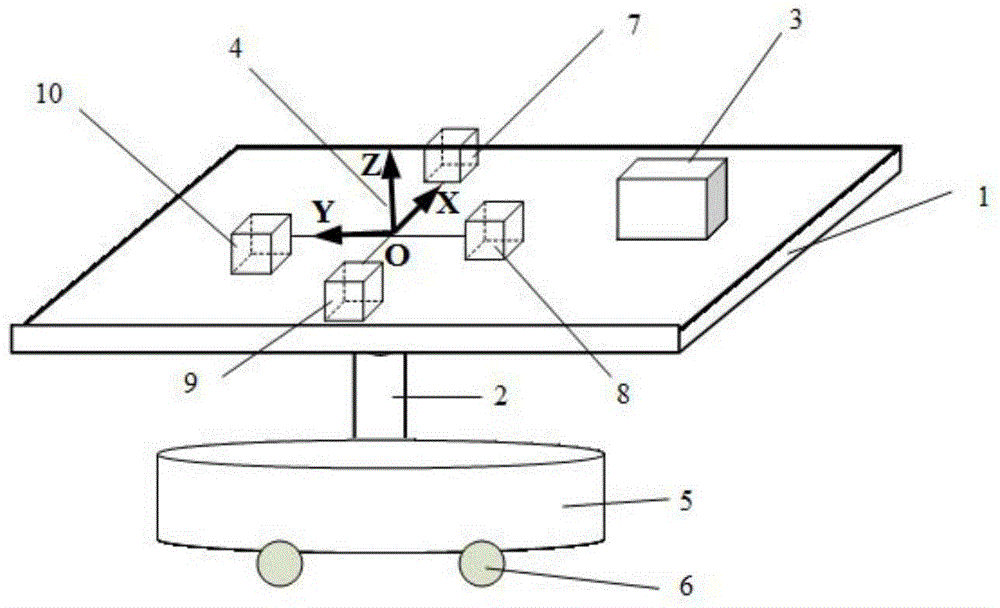
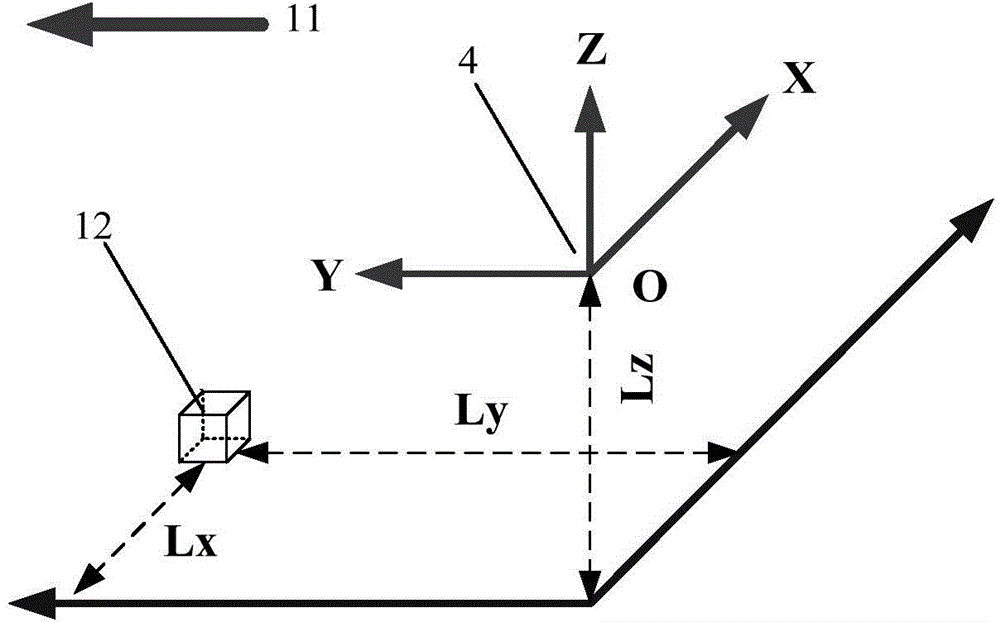
Movable type location method based on magnetic gradient tensor and geomagnetic vector measurement
ActiveCN104535062AOvercome component variation effectsAvoid geomagnetic vector inaccuracy problemsNavigation by terrestrial meansSensor arrayMagnetic gradient
The invention belongs to the technical field of magnetic measurement, and particularly relates to a movable type location method based on magnetic gradient tensor and geomagnetic vector measurement. The method comprises the following steps: (S1) setting a magnetic sensor array and an inertial navigation system; (S2) in a nonmagnetic abnormal area, acquiring a measured value of a magnetic sensor and calculating a geomagnetic vector value in a geographic coordinate system; (S3) allowing a nonmagnetic moving device to move in a magnetic target area to acquire the measured value of the magnetic sensor and an attitude angle output by the inertial navigation system; (S4) calculating a geomagnetic field component value in an array coordinate system; (S5) calculating the magnetic gradient tensor and a magnetic abnormal component in the array coordinate system; and (S6) calculating the position of a magnetic target in the array coordinate system according to the magnetic gradient tensor and the magnetic abnormal component in the array coordinate system. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for achieving movable type real-time location, overcoming the requirement for immobility of the array in static location and acquiring the projection of a magnetic field in a magnetic sensor coordinate system more accurately by attitude conversion.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
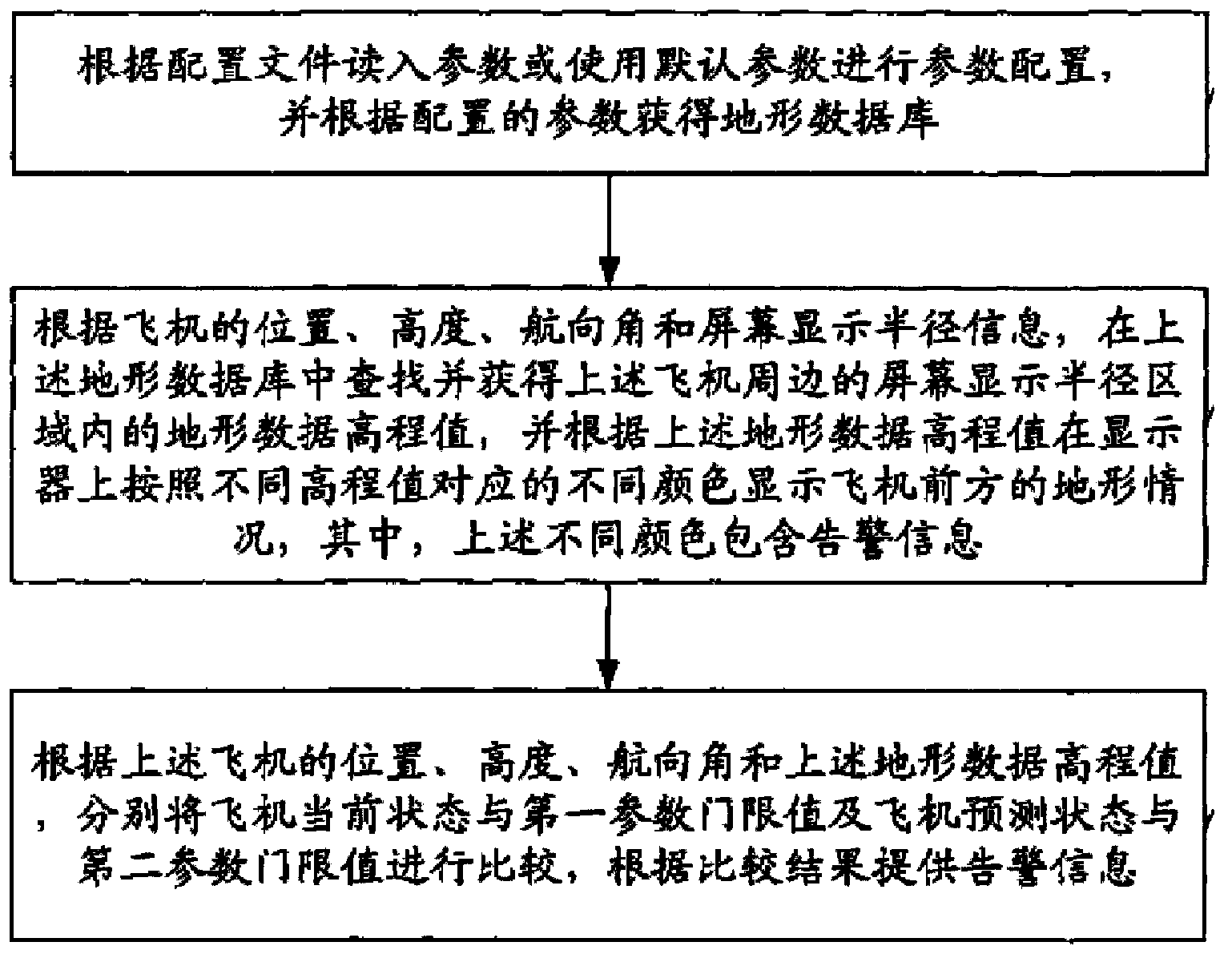
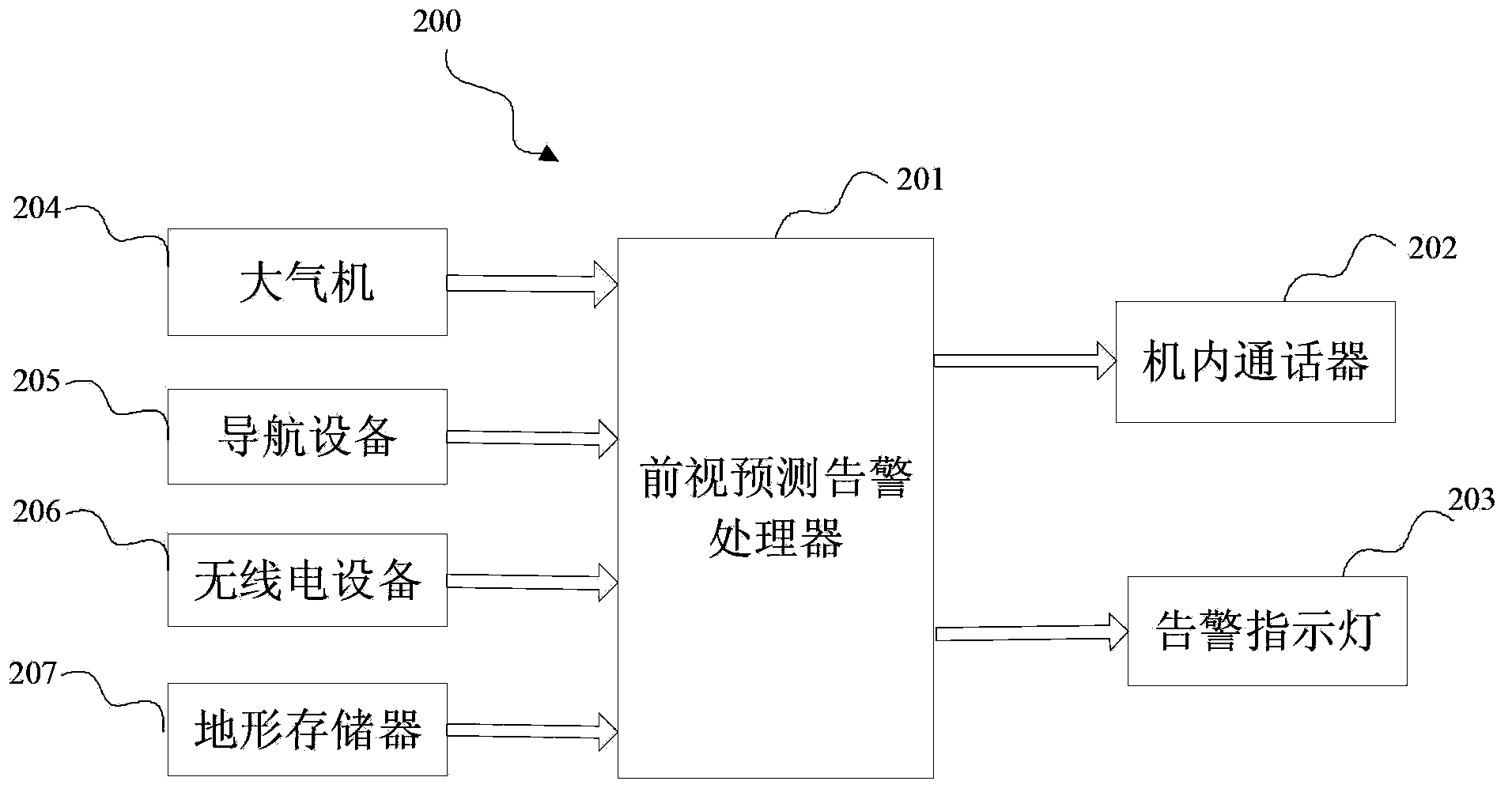
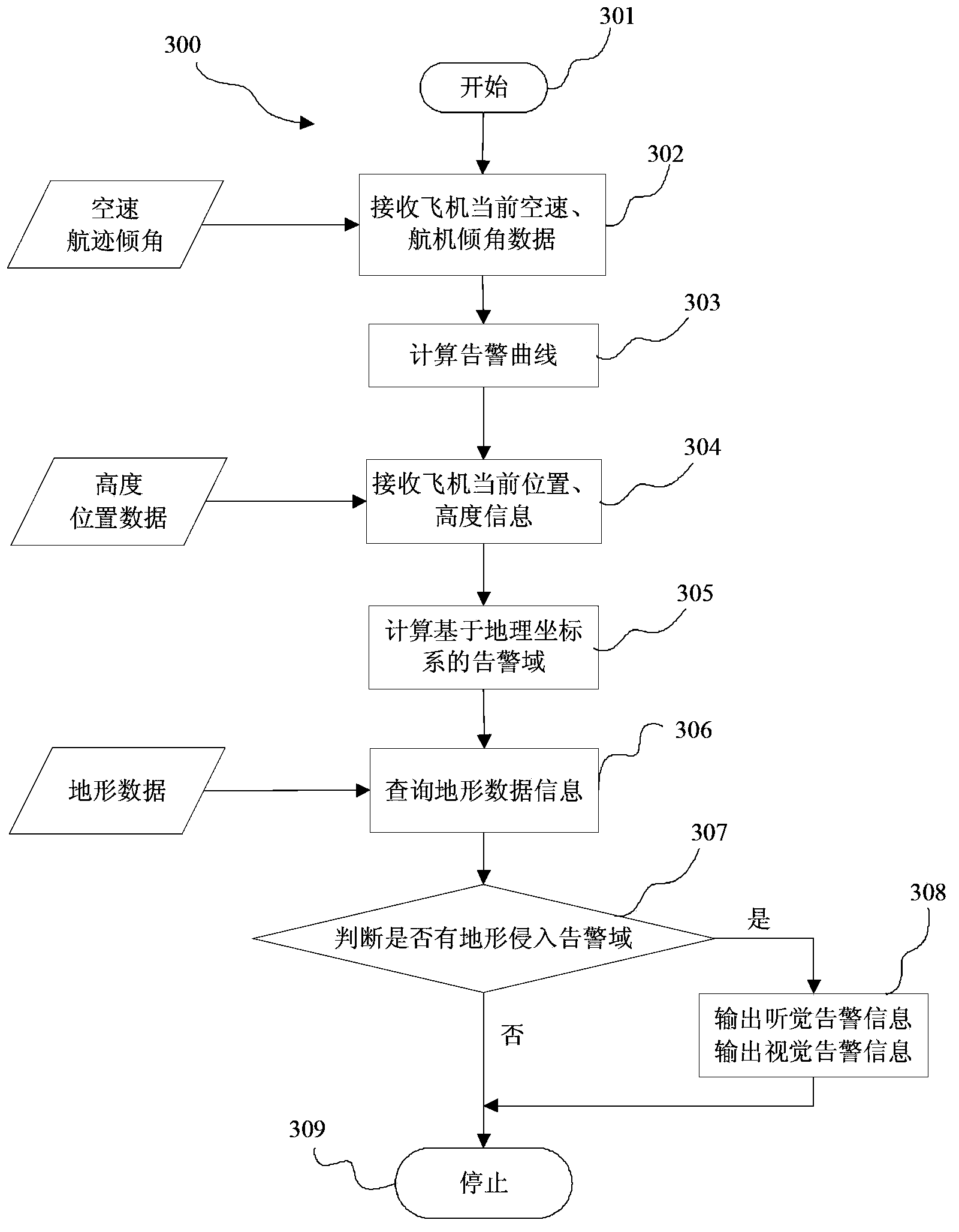
Forward-looking forecast warning system in ground proximity warning system and method
ActiveCN103903482AEnsure flight safetyFlight safety protectionAircraft traffic controlRadio equipmentNavigation system
The invention discloses a forward-looking forecast warning system in a ground proximity warning system and a method, which is characterized in that the forward-looking forecast warning system comprises a forward-looking forecast warning processor. The input end of the forward-looking forecast warning processor is connected with an air data computer, a navigation system, radio equipment, and a terrain memory, the aircraft speed and the flight path angle information are received, a warning domain based on the current aircraft position is calculated on the basis of built-in warning domain calculation method, a warning domain on the basis of the geographic coordinate system is calculated in combination with aircraft position information, query is carried out in a terrain database, warning is generated if a terrain invades the warning domain, and the warning information is outputted. The system and the method have the advantages of reducing false alarms and missing alarms to the maximal degree, improving warning performances and ensuring flying security.
Owner:SHANGHAI AVIATION ELECTRIC
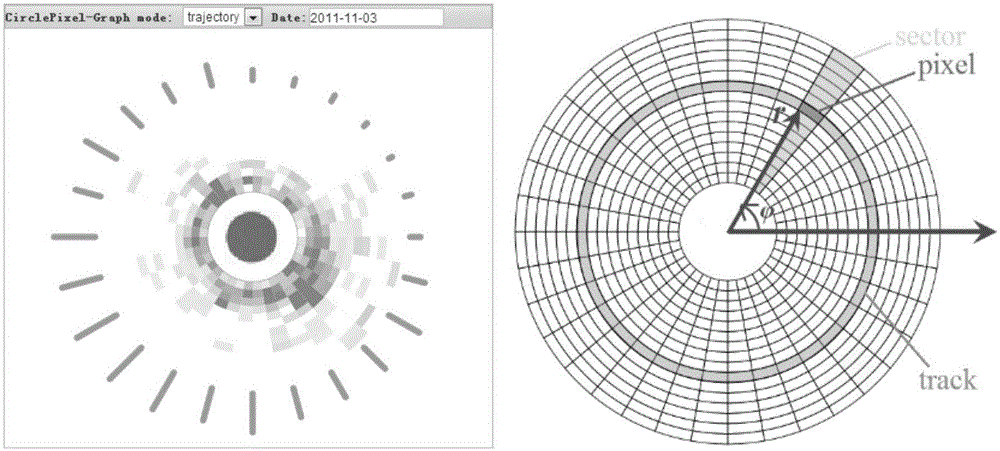
Large-scale taxi OD data visual analysis method
A large-scale taxi OD data visual analysis method comprises the following steps that noise in GPS original data is eliminated, and it is guaranteed that the longitude and latitude coordinates of a GPS point are consistent with a geographic coordinate system of an online map; the GPS point of a taxi track are matched to a corresponding road through an ST-matching algorithm to be calibrated; taxi taking passenger get-on and get-off information is extracted through a vehicle-mounted mark, and grid storage is carried out on track data based on a grid index technology; bin clustering is adopted, and after clustering is completed, a heat map and a clustering map are generated; an interested area or a distinctive area is selected through the heat map and the clustering map; after the interested area is selected, an O / D-mode spatio-temporal analysis view is shown through annular pixel maps and space-time stacking maps of visual assemblies; the space-time stacking maps are opened through distance projection or direction projection, and a pair of starting and ending areas is selected by highlighting one or more adjacent pixels of the annular pixel maps or layers in the space-time stacking maps.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
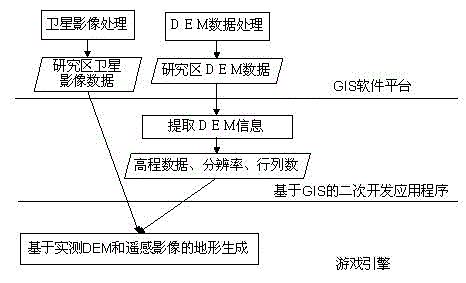
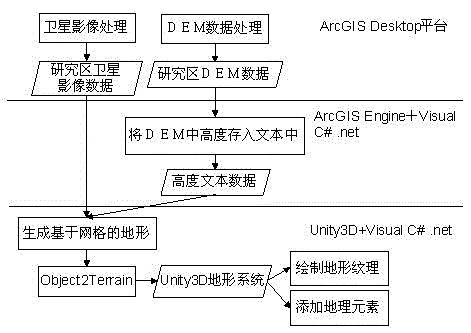
Three-dimensional geographical scene simulation method for virtual emergency exercises
ActiveCN104318617AAvoid the problem of cutting into many blocksGuaranteed accuracy3D modellingTerrainElement model
The invention relates to a three-dimensional geographical scene simulation method for virtual emergency exercises. The method comprises the steps of: obtaining elevation data in DEM by using GIS software, and interpreting earth surface appendage information by using a registered high-resolution remote sensing image, or obtaining surface features and land utilization information by using an existing measured drawing; then, establishing topography and landforms by using the information with true geographic meanings in a game engine, wherein a key technical process is the conversion between a rectangular coordinate system in the game engine and a geographic coordinate system in the GIS software; at last, combining and reconstructing a three-dimensional terrain and geographic element model with true geographic meanings on a game engine platform, and achieving establishment of a realistic three-dimensional scene. The three-dimensional geographical scene simulation method virtual emergency exercises is convenient to operate and unnecessary to limit shape and size of the area, ensures elevation accuracy of DEM, and can automatically generate the three-dimensional science with the true geographic meanings.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
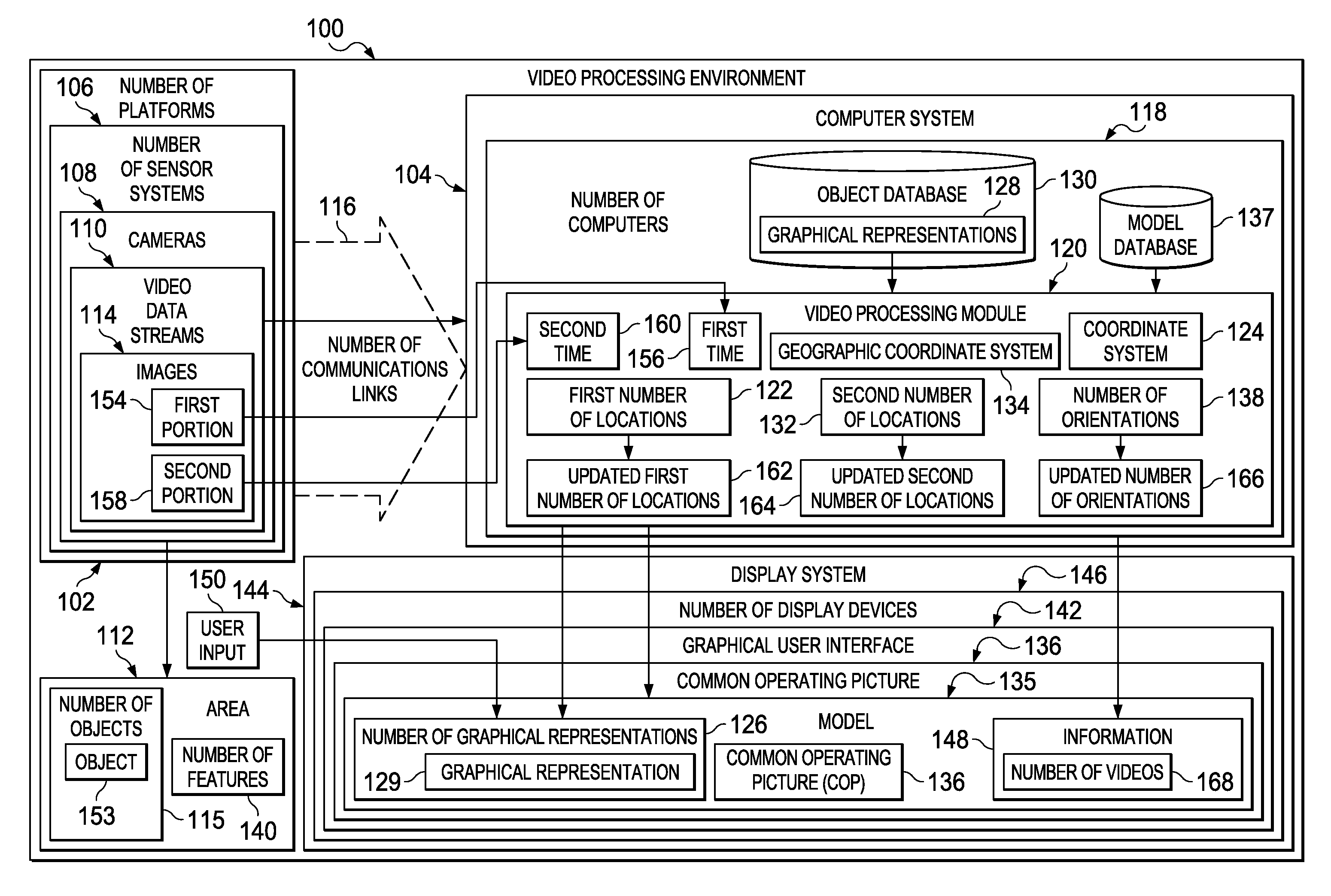
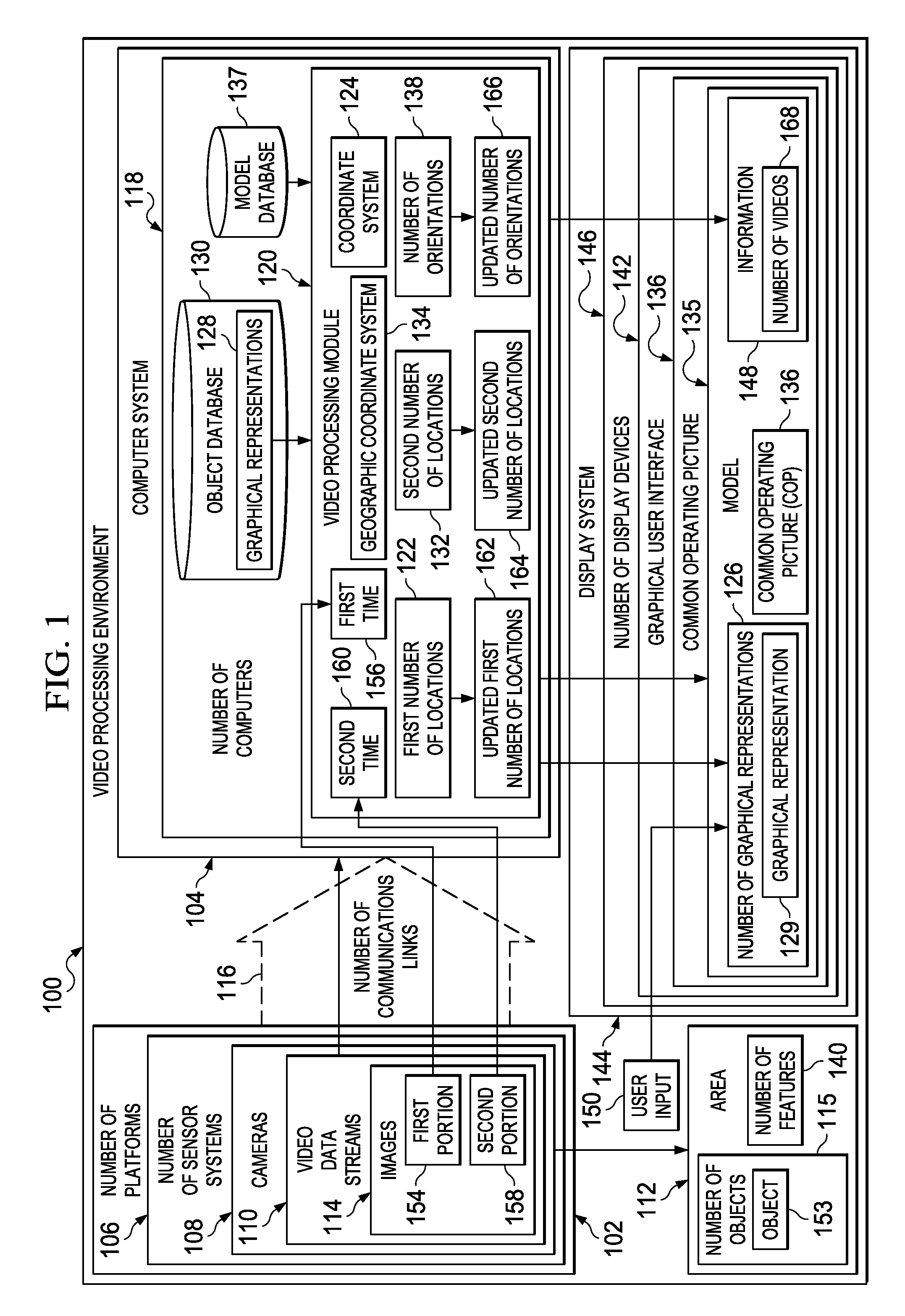
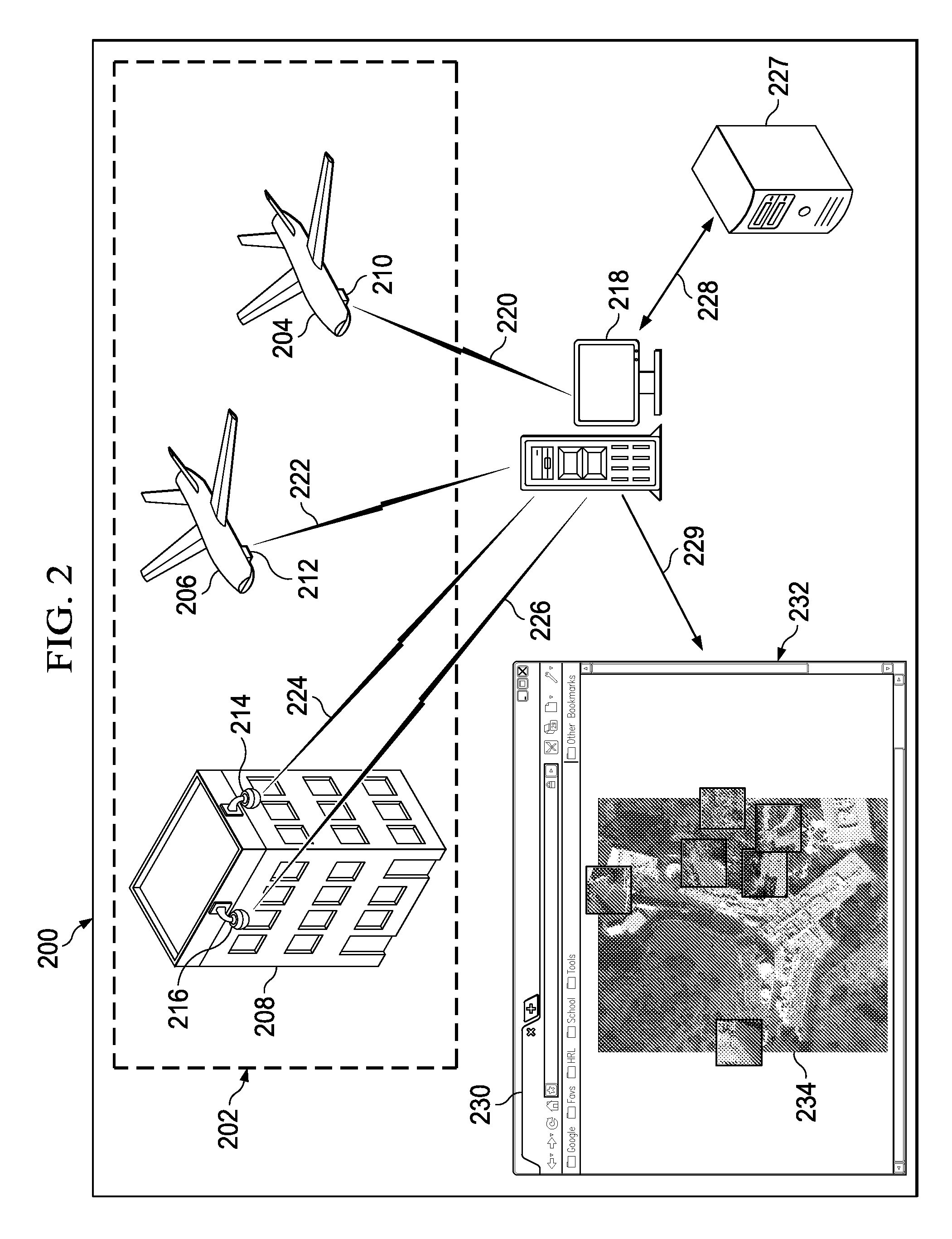
Multi-Sensor Surveillance System with a Common Operating Picture
A method and apparatus for processing video data streams for an area. Objects are identified in the area from images in the video data streams. The video data streams are generated by cameras. First locations are identified for the objects using the images. The first locations are defined using a coordinate system for the images. Graphical representations are formed for the objects using the images. The graphical representations are displayed for the objects in second locations in a model of the area on a display system with respect to features in the area that are represented in the model. The second locations are defined using a geographic coordinate system for the model. A first location in the first locations for an object in the objects corresponds to a second location in the second locations for a corresponding graphical representation in the graphical representations.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
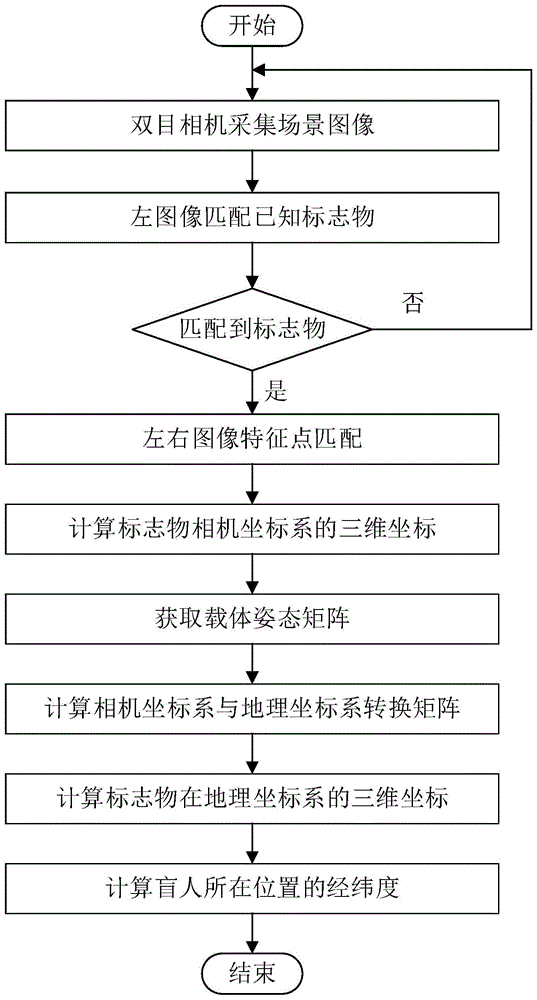
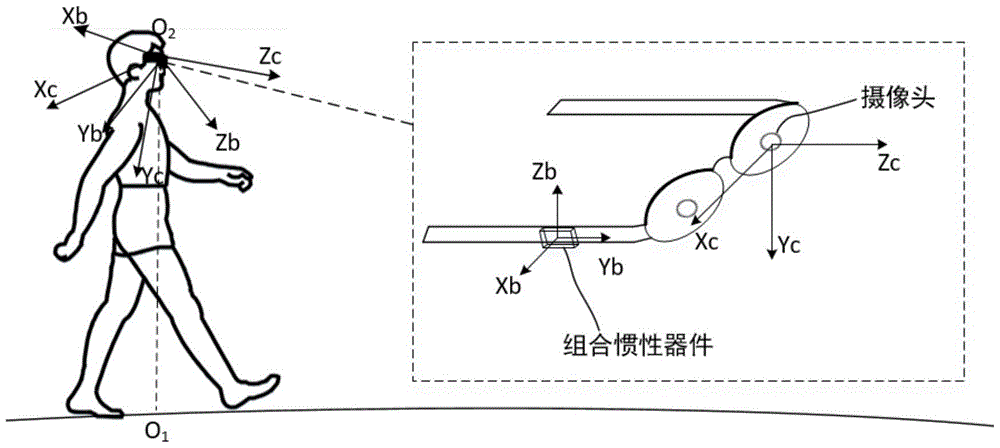
Blind person walking positioning method based on computer binocular vision and inertial measurement
ActiveCN105761242AImprove positioning reliabilityImage analysisWalking aidsComputer graphics (images)Longitude
The invention discloses a blind person walking positioning method based on computer binocular vision and inertial measurement. On one hand, a binocular camera worn on the head of a blind person is used for acquiring a scene image, a marker with longitude and latitude already known in the scene is searched in an image feature matching method, and a computer binocular stereo vision method is adopted to calculate three-dimensional coordinates of the marker in a camera coordinate system; on the other hand, a combined inertial device fixed on the camera is used for measuring the attitude angle of the camera, and a conversion matrix for the camera coordinate system in relative to a geographic coordinate system for the position where the blind person is is calculated; and the conversion matrix is used for converting the camera coordinate system for the marker into the geographic coordinate system for the position where the blind person is, and the longitude and the latitude of the marker are further used for calculating the longitude and the latitude of the position where the blind person walks. The method of the invention integrates the computer binocular vision algorithm and the inertial measurement technology, positioning of a blind person walking position is realized, the positioning is simple and easy to operate, the accuracy is high, and the method of the invention is particularly suitable for positioning for blind person walking guiding.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
System and method for synchronizing raster and vector map images
InactiveUS7148898B1Enhance the imageEasy to operateCathode-ray tube indicatorsMaps/plans/chartsOperational transformationGrating
A system and method for coordinated manipulation of multiple displayed maps, even when the maps use different internal coordinate systems. According to this embodiment, each map image to be displayed is first georeferenced, to provide a set of conversion functions between each map's internal coordinate system and a geographic coordinate system, which is latitude / longitude in the preferred embodiment. After this is done, any point on each map can be referenced using the geographic coordinate set. Since this is the case, the maps can now be manipulated, edited, and annotated in a synchronized manner, by defining the manipulations in terms of the geographic coordinate system, and using the georeferencing functions to translate the manipulation to each map's internal coordinate system.
Owner:SOURCEPROSE CORP
Subway subgrade structure monitoring method and device based on foundation InSAR
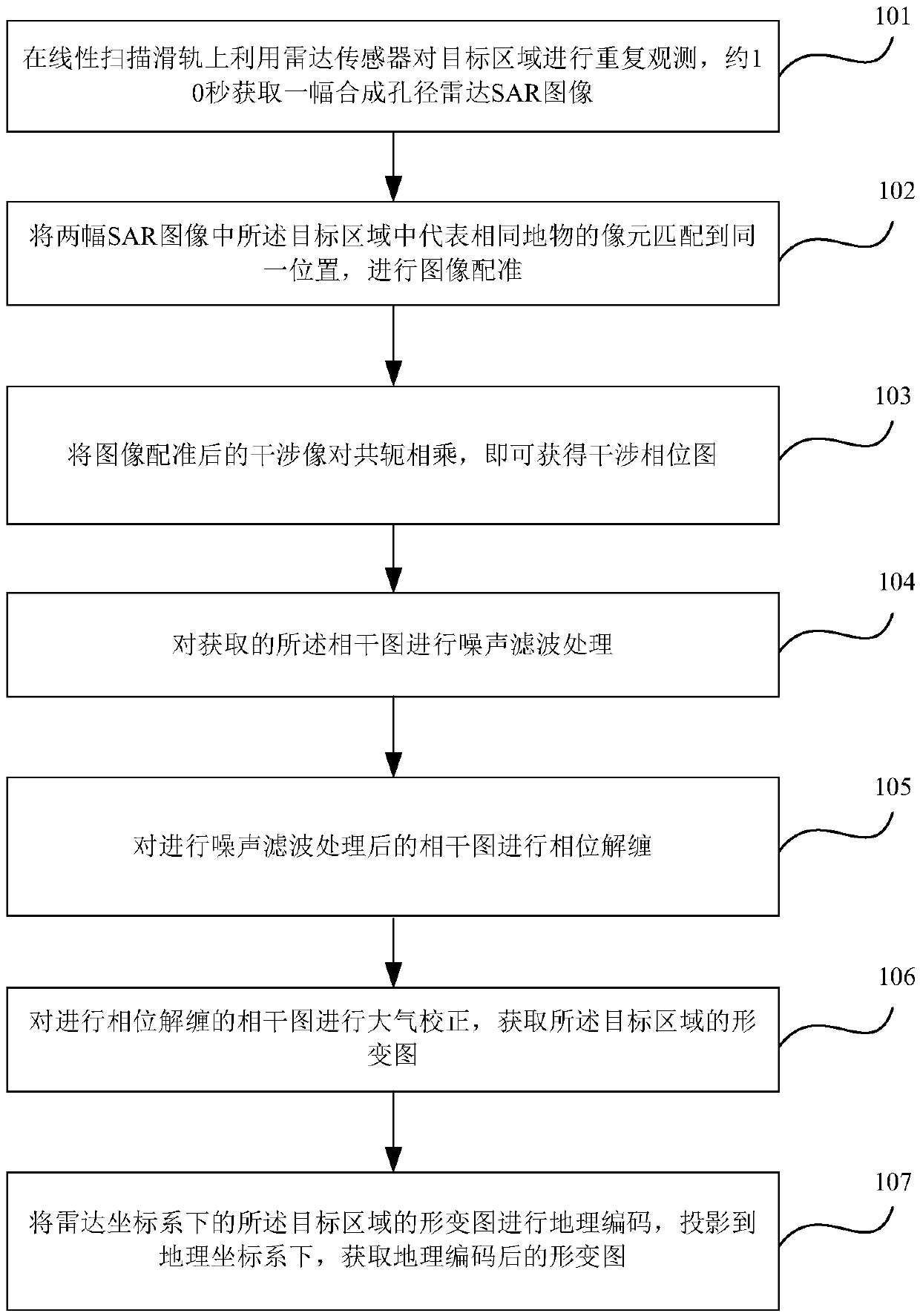
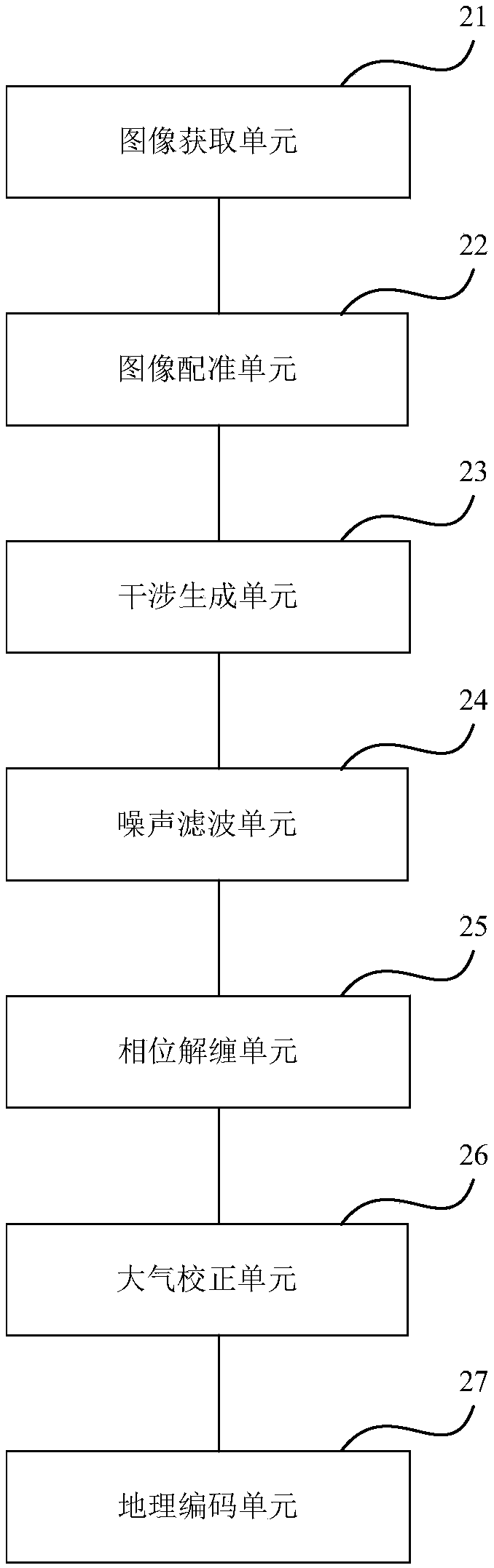
InactiveCN108627834ARealize non-contact remote monitoringOvercome workloadRadio wave reradiation/reflectionStructural monitoringExtreme weather
The embodiment of the invention provides a subway subgrade structure monitoring method and device based on foundation InSAR. The method comprises the steps of using a radar sensor for repeatedly observing a target area on a linear scanning slide rail, and obtaining a synthetic aperture radar SAR image in about 10 seconds; matching image elements representing the same object in the target region inthe two SAR images to the same position, carrying out image registration; subjecting an interference image pair after image registration to conjugate multiplication (as shown in the description) to obtain an interference phase graph; carrying out noise filtering processing on the obtained coherent graph gamma; carrying out phase unwrapping on the coherent graph gamma subjected to noise filteringprocessing; carrying out atmospheric correction on the coherent image gamma subjected to phase unwrapping to obtain a deformation graph of the target area; carrying out geocoding on the deformation graph of the target area under the radar coordinate system, projecting to the geographic coordinate system, and obtaining a geographic coded deformation graph. High-precision and continuous deformationmonitoring of the whole area of the subway elevated and roadbed structure can be implemented under the extreme weather conditions or long distances (4Km) range.
Owner:BEIJING URBAN CONSTR EXPLORATION & SURVEYING DESIGN RES INST
Combination measurement method for high precision position, azimuth angle and pitch angle, and device thereof
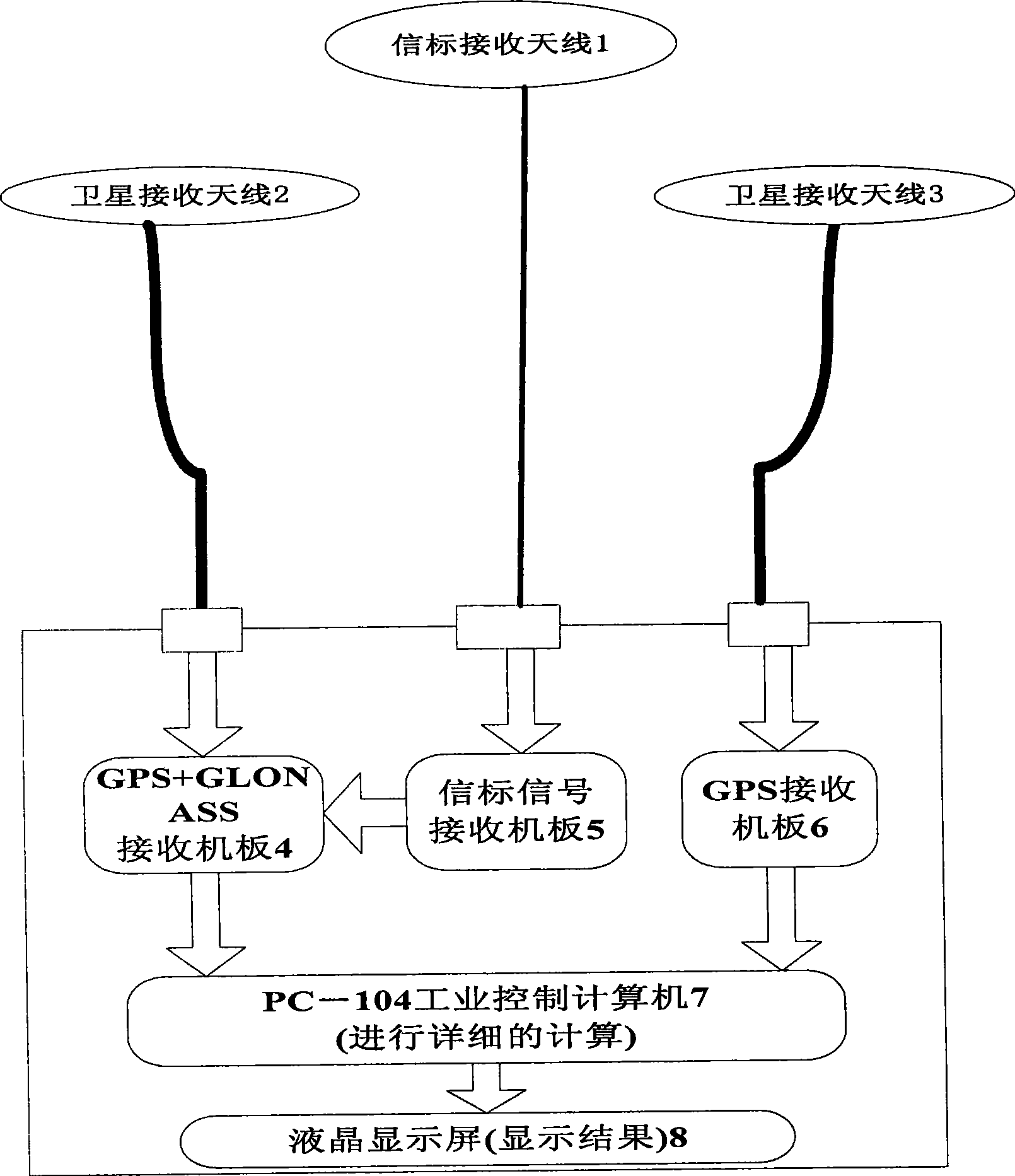
InactiveCN101446634AReal-time measurementAccurate measurementPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingLiquid-crystal displayGps receiver
The invention discloses a combination measurement method for high precision position, azimuth angle and pitch angle, and a device thereof; a measurement basic line consists of measurement marking points where two satellite receiving antennas are arranged; a dual-system satellite positioning receiver plate and a beacon receiver plate synchronously receive the signals of a first satellite antenna and a beacon antenna; the dual-system satellite positioning receiver plate synchronously receives the digital signals of the beacon receiver; a GPS receiver plate synchronously receives the signals of a second satellite antenna; the first and second satellite antenna signals and beacon signals are synchronously calculated so as to precisely measure the three-dimensional position where the satellite antenna is arranged and measure the azimuth angle and pitch angle of the antenna basic line under geographic coordinates. The method and the device integrate the dual-system satellite positioning, GPS, beacon receiver plate and computer; the device is provided with a liquid crystal display screen, two satellites and a beacon receiving antenna outside the box, ensures the positioning precision more than 8 meters, receives beacon differential signals at coastal areas, leads the precision to be more than 1 meter and has the directional precision more than 0.1DEG under the basic line of 3 meters.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
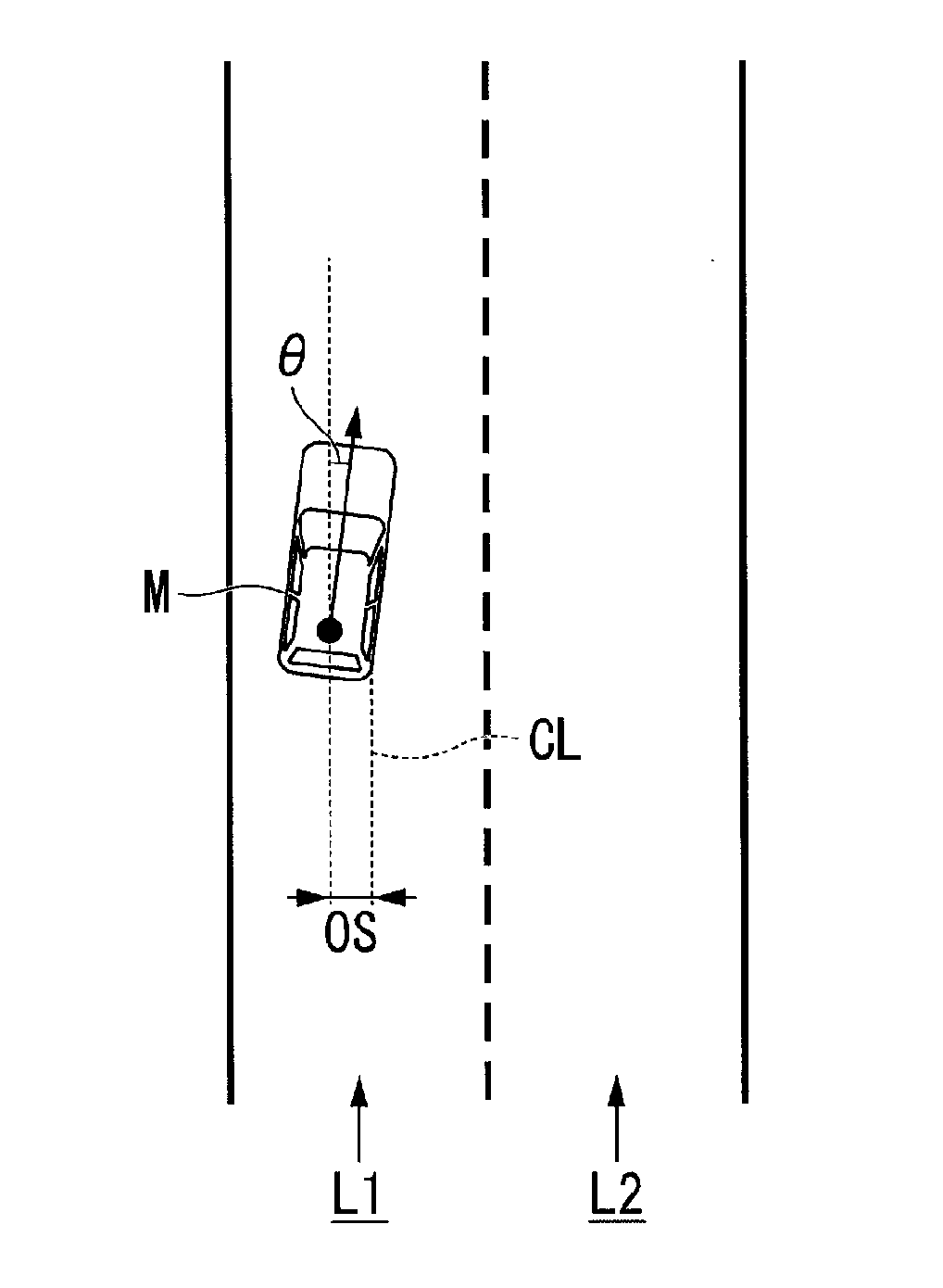
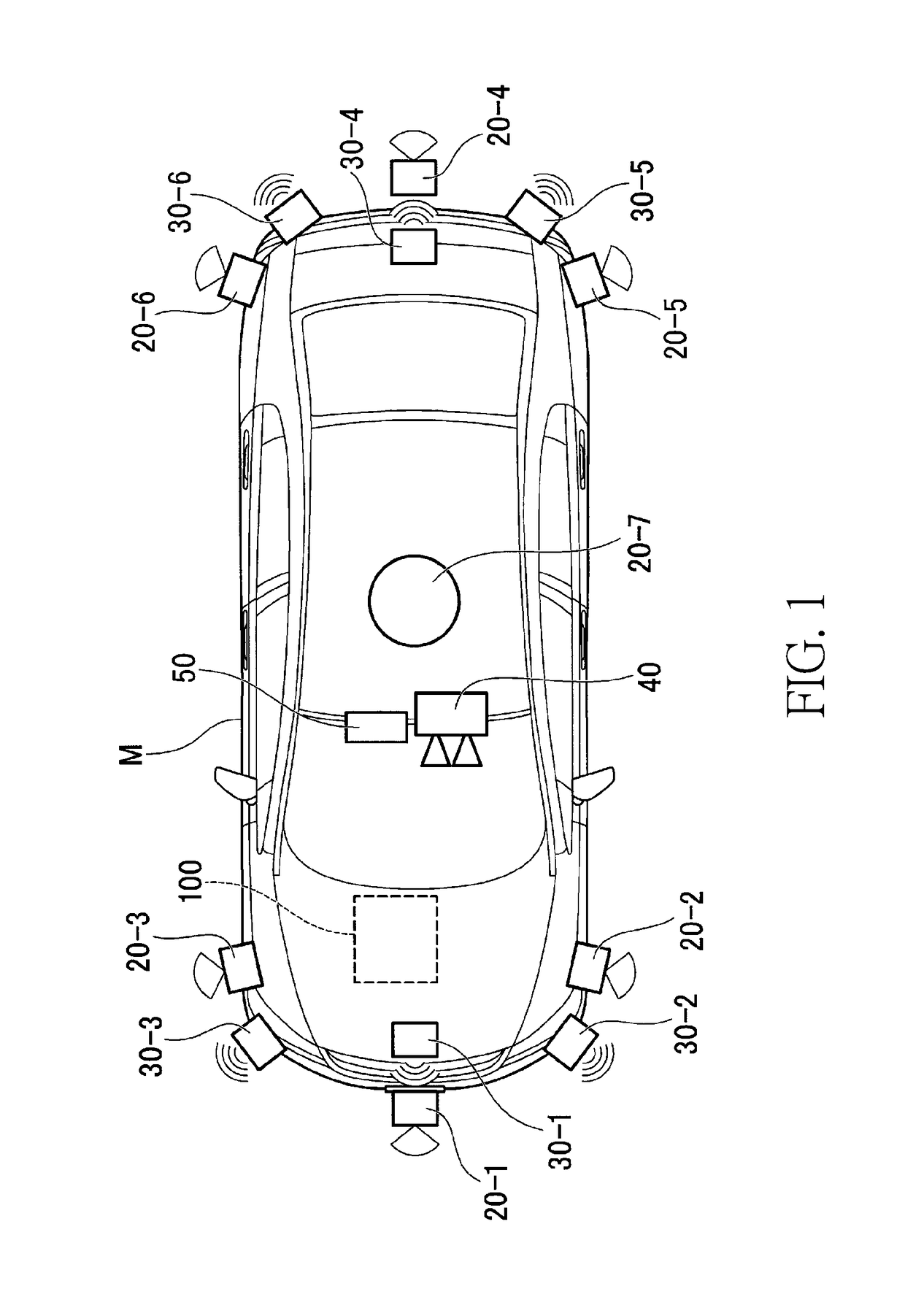
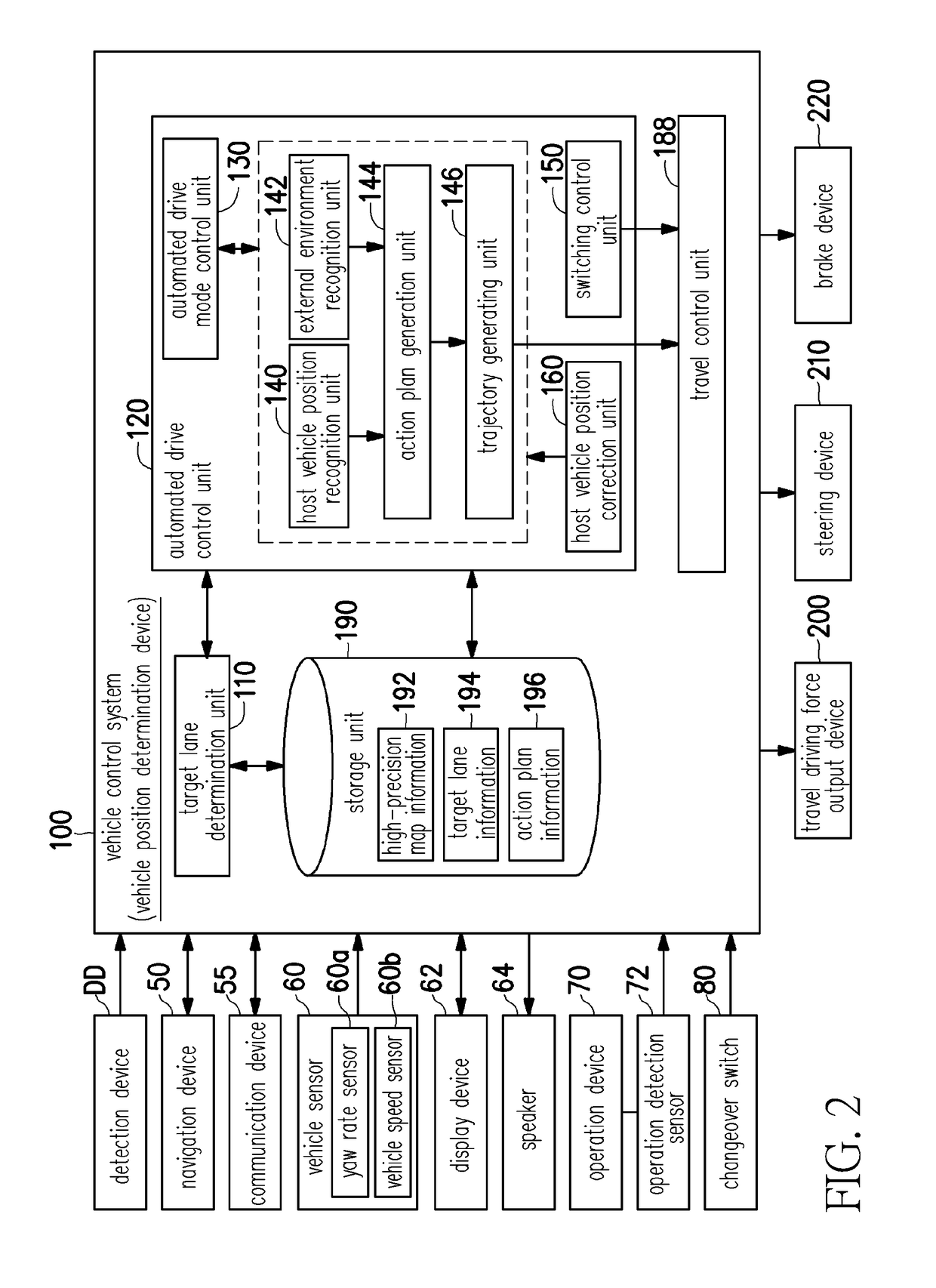
Vehicle position determination device, vehicle control system, vehicle position determination method, and vehicle position determination program product
ActiveUS20170336515A1Accurately determineInstruments for road network navigationCharacter and pattern recognitionControl systemEngineering
An object is to provide a vehicle position determination device, a vehicle control system, a vehicle position determination method, and a vehicle position determination program capable of determining a position of a vehicle with higher accuracy. A vehicle position determination device includes a coordinates acquisition unit that acquires a position of a vehicle in a geographic coordinate system, a recognition unit that acquires lane information of a road on which the vehicle travels and recognizes the position of the vehicle on the lane, and a control unit that corrects the position acquired by the coordinates acquisition unit on the basis of the position recognized by the recognition unit, and determines the position of the vehicle in the geographic coordinate system.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
System and method for synchronizing raster and vector map images
InactiveUS7142217B2Improved graphic image manipulationEnhance the imageCathode-ray tube indicatorsMaps/plans/chartsOperational transformationLongitude
A system and method for coordinated manipulation of multiple displayed maps, even when the maps use different internal coordinate systems. According to this embodiment, each map image to be displayed is first georeferenced, to provide a set of conversion functions between each map's internal coordinate system and a geographic coordinate system, which is latitude / longitude in the preferred embodiment. After this is done, any point on each map can be referenced using the geographic coordinate set. Since this is the case, the maps can now be manipulated, edited, and annotated in a synchronized manner, by defining the manipulations in terms of the geographic coordinate system, and using the georeferencing functions to translate the manipulation to each map's internal coordinate system.
Owner:SOURCEPROSE CORP
Method of generating a geodetic reference database product
InactiveCN102246159ADetailed descriptionBroad descriptionPicture interpretationGeographical information databasesMobile mappingReference database
A method of generating a geodetic reference database product is disclosed. The method comprises acquiring mobile mapping data captured by means of digital cameras, range sensors and position determination means including GPS and IMU mounted to a vehicle driving across the earth surface, the mobile mapping data comprising simultaneously captured image data, range data and associated position data in a geographic coordinate system. Linear stationary earth surface features are derived from the mobile mapping data by processing the image data, range data and associated position data. 3D-models are generated for the linear stationary earth surface features in the geographic coordinate system from the image data, range data and associated position data and stored in a database to obtain the geodetic reference database product. A 3D-model could include an image representing the colors of the surface of the 3D model or a set of smaller images representing photo-identifiable objects along the model. The 3D-models could be used to rectify aerial imagery, to correct digital elevation models and to improve the triangulation of digital elevation models.
Owner:TELE ATLAS NORTH AMERICA +1
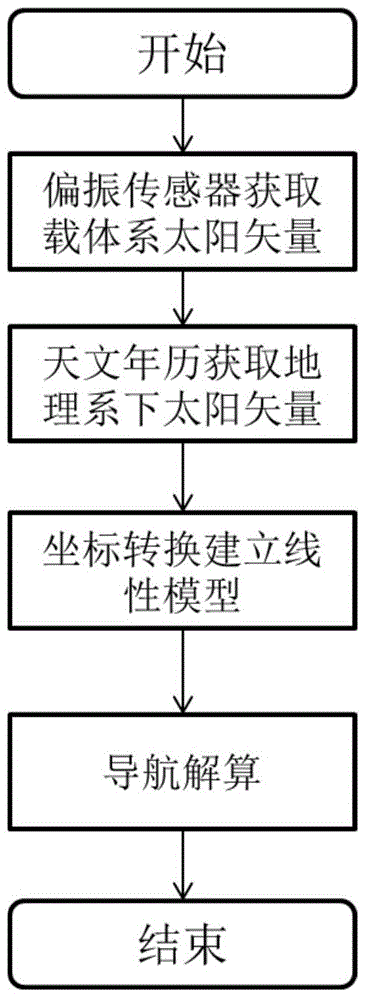
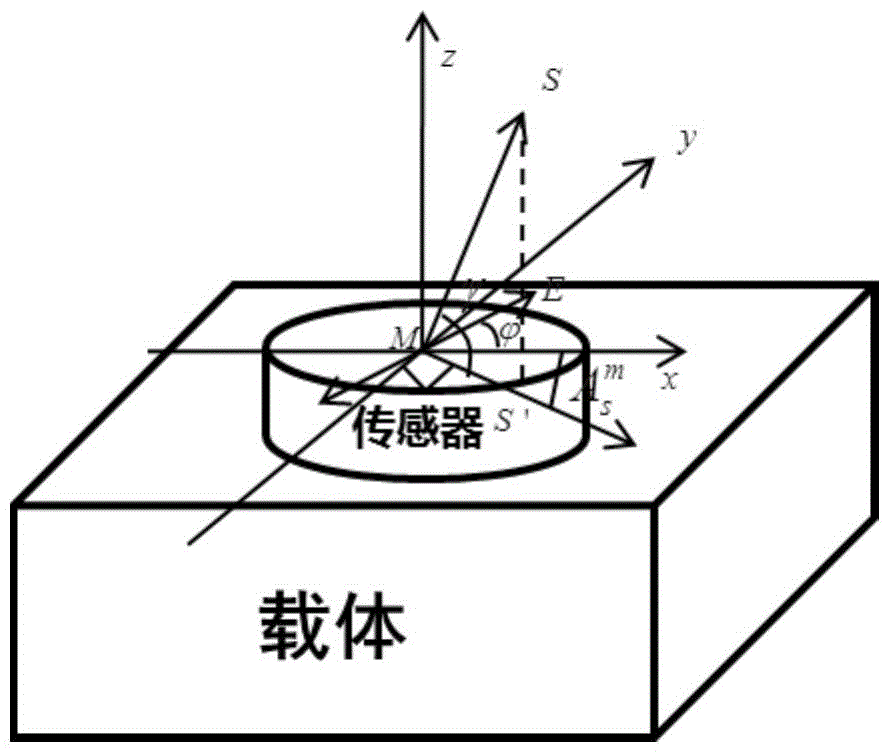
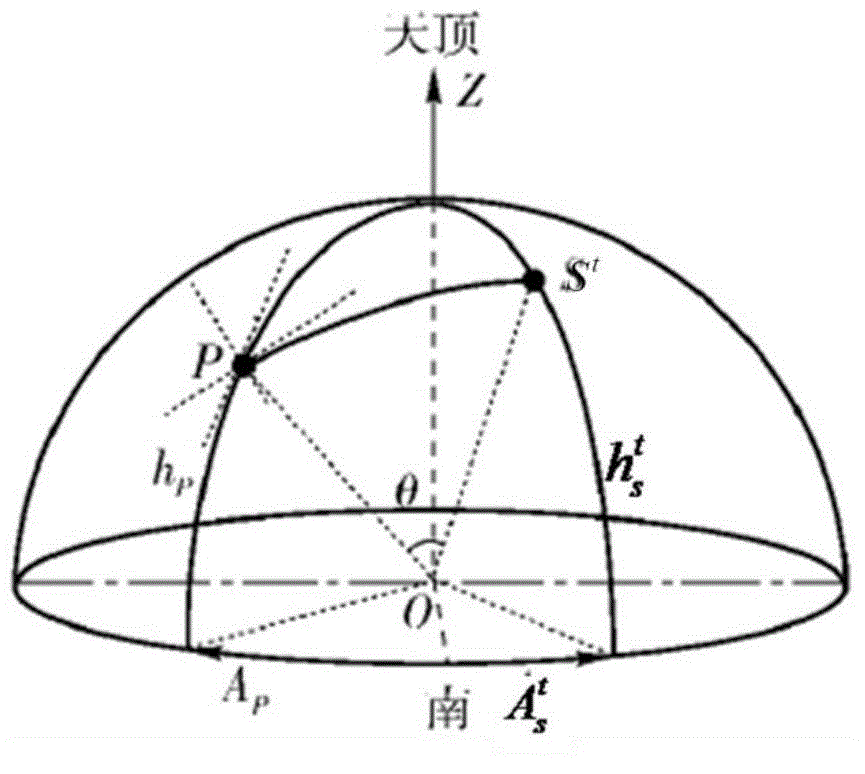
Polarization aided navigation method based on solar vectors
ActiveCN104880191AImplement fixesSuccessful navigation solutionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSensor arrayKaiman filter
The invention relates to a polarization aided navigation method based on solar vectors. The polarization aided navigation method based on the solar vectors comprises the following steps of firstly, obtaining a unit solar vector Sm under a module coordinate system by using a polarization sensor array carried by a carrier; secondly, calculating a unit solar vector St under a geographic coordinate system on the basis of the geographic position and the time information of the carrier according to an astronomical almanac value; and finally, establishing a polarization navigation linear model by using the unit solar vectors under the different coordinate systems and estimating navigation parameters by using a Kalman filter. By the method, the solar vectors are obtained by an atmosphere polarization mode to perform aided navigation, the precision is high, the polarization aided navigation method is not disturbed by other factors of the outside, and passive, non-radiative and full-autonomous navigation can be implemented.
Owner:青岛智融领航科技有限公司
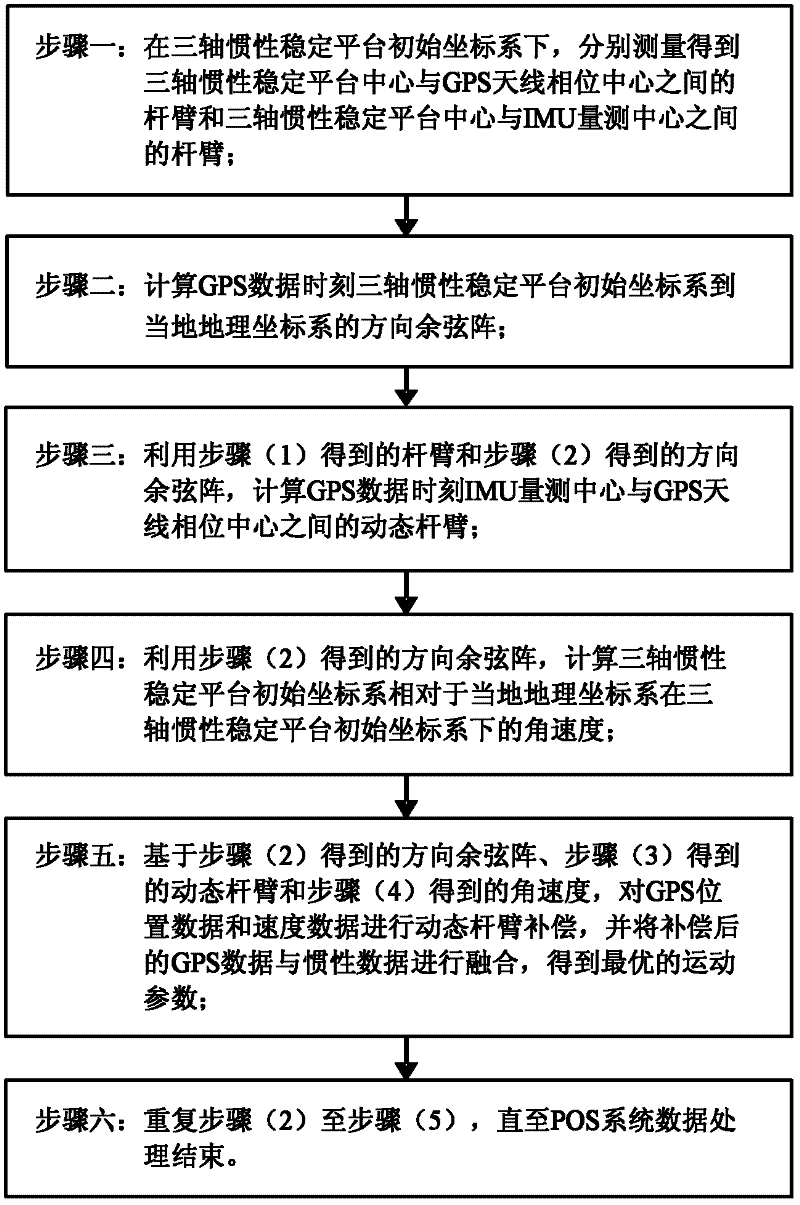
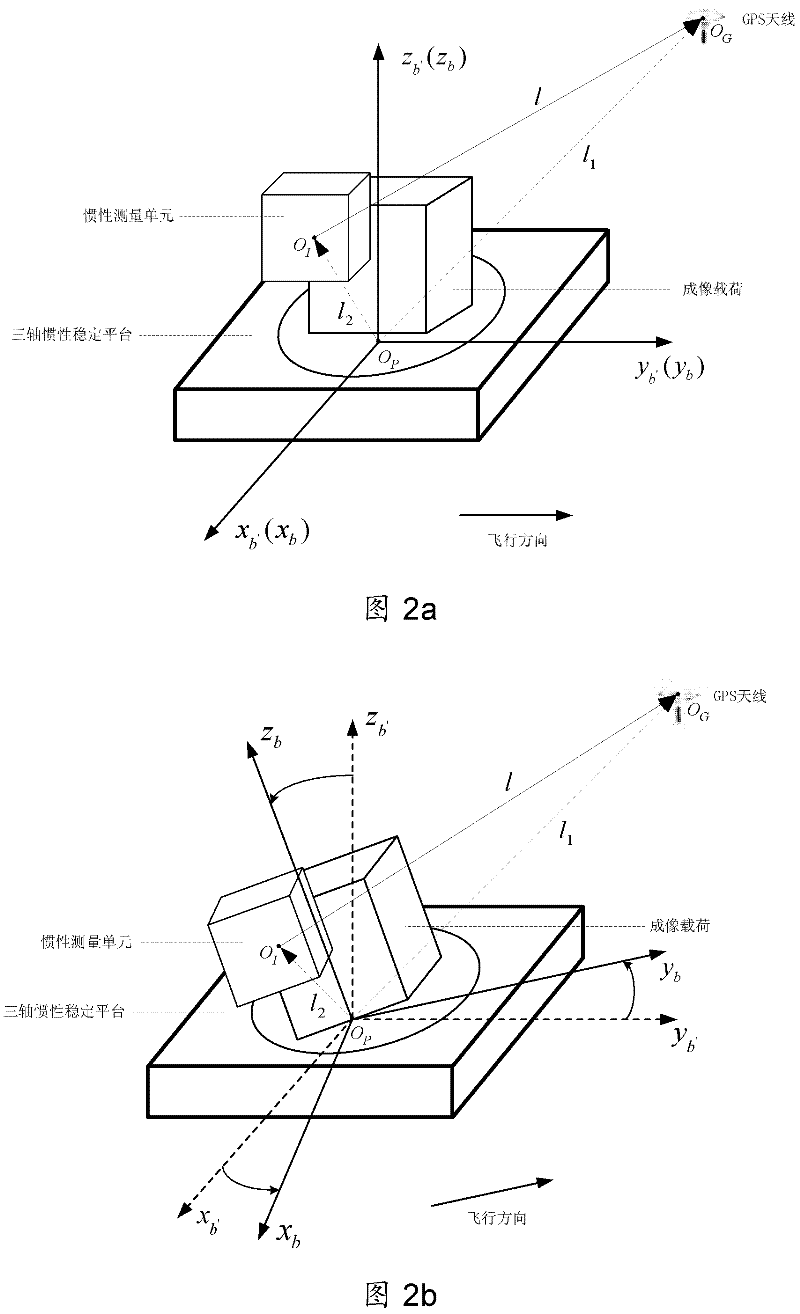
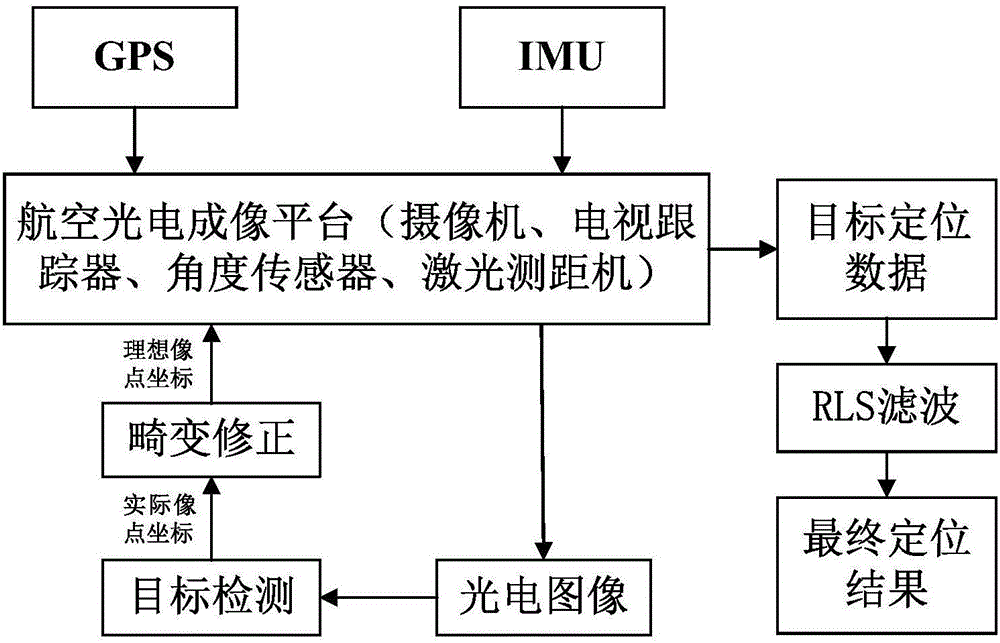
Dynamic lever arm compensating method of position and posture measuring system (POS) for aerial remote sensing
InactiveCN102393201AHigh precisionSolve problems that are difficult to compensate preciselyInstruments for comonautical navigationSatellite radio beaconingAviationAngular velocity
The invention provides a dynamic lever arm compensating method of a position and posture measuring system (POS) for aerial remote sensing. The method comprises the following steps of: to solve the problem of real-time variation of the lever arm between a measuring center of an inertia measuring unit (IMU) and phase center of a GPS (Global Positioning System) antenna due to rotation of a three-axis inertia stabilizing platform frame, obtaining an actual lever arm between the IMU measuring center and the phase center of the GPS antenna through calculating a dynamic lever arm between the center of the three-axis inertia stabilizing platform and the IMU measuring center in real time; and figuring out angular velocity of an initial coordinate system of the three-axis inertia stabilizing platform under the initial coordinate system of the three-axis inertia stabilizing platform relative to a local geographic coordinate system so as to compensate the dynamic lever arm. The dynamic lever arm compensating method provided by the invention has the characteristics of high accuracy, simplicity in operation and easiness for realization; the problem that the POS lever arm is hard to be accurately compensated while the three-axis inertia stabilizing platform is adopted for aerial remote sensing is solved; and the accuracies of POS and aerial remote sensing imaging load are improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Device and method for obtaining relevant parameters of aviation superconductive full-tensor magnetic gradient measuring system
InactiveCN104345348AReduce computational difficultyImprove computing efficiencyElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationAviationMagnetic gradient
The invention relates to an aviation geophysic magnetic type exploration data processing method. The method is characterized in that the baseline direction unit vectors and sensor plane normal vectors, corresponding to an inertia navigation coordinate system, and the sensor plane normal vectors, corresponding to a three-component magnetic instrument coordinate system, of five plane superconductive magnetic gradient sensors can be accurately obtained, and then the premise is provided for accurately obtaining five independent components of a full-tensor magnetic gradient corresponding to a geographic coordinate system; the five independent components of the full-tensor magnetic gradient are calculated by a coordinate system conversion method, the middle process of calculating the attitude angles, corresponding to the coordinate system, of the five plane superconductive magnetic gradient sensors is not needed, the inertial navigation coordinate system is used as the coordinate system of the measurement system, and the attitude data measured by inertial navigation are converted by the one-time coordinate system, so as to obtain the five independent components of the full-tensor magnetic gradient corresponding to the geographic coordinate system. The method has the advantages that the calculation difficulty is decreased, the calculation efficiency is improved, and the method is more suitable for measuring the attitude time varying of measuring platforms, such as aviation magnetic measuring.
Owner:JILIN UNIV +1
Simplified unmanned aerial vehicle multi-target location method
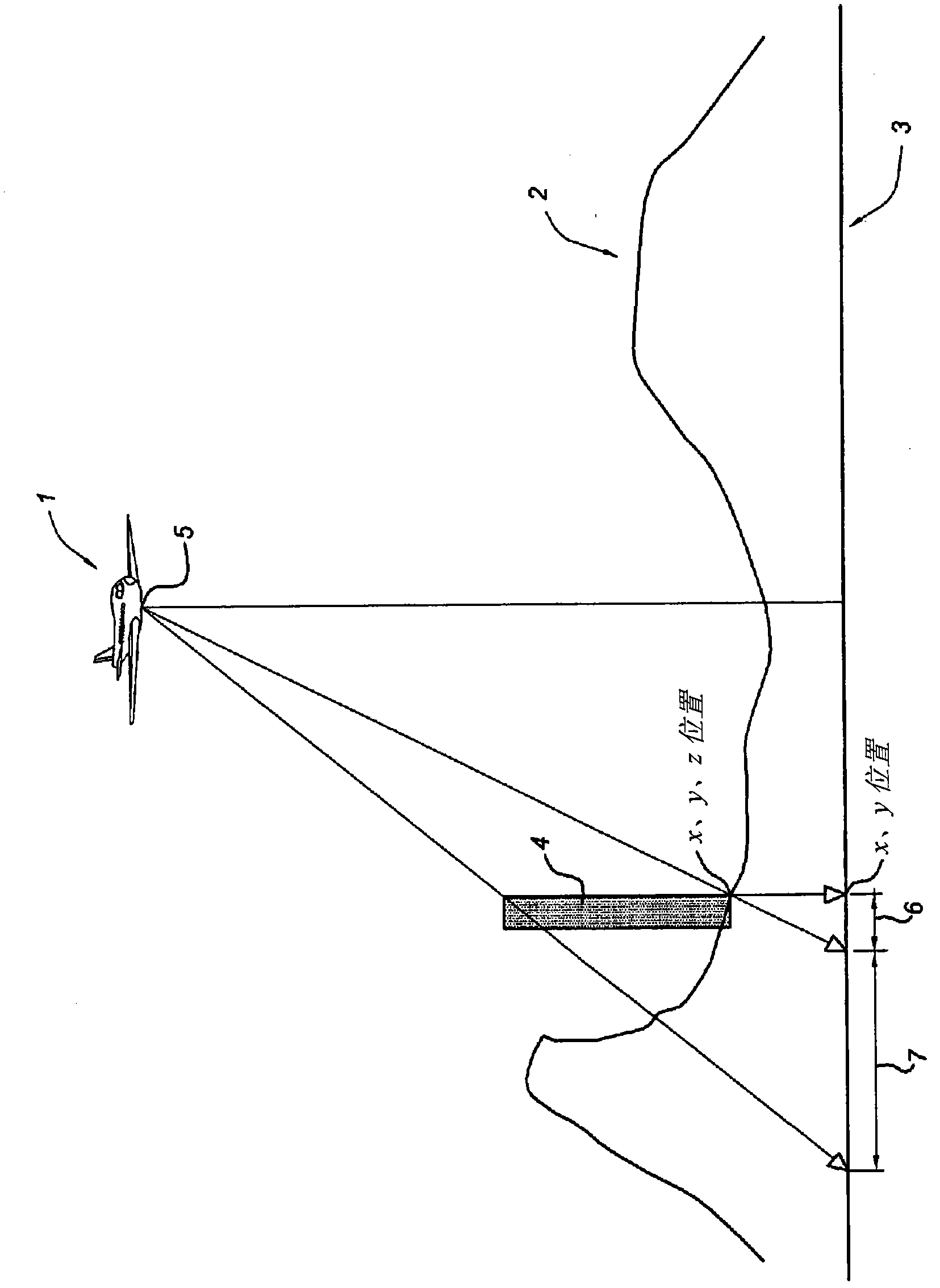
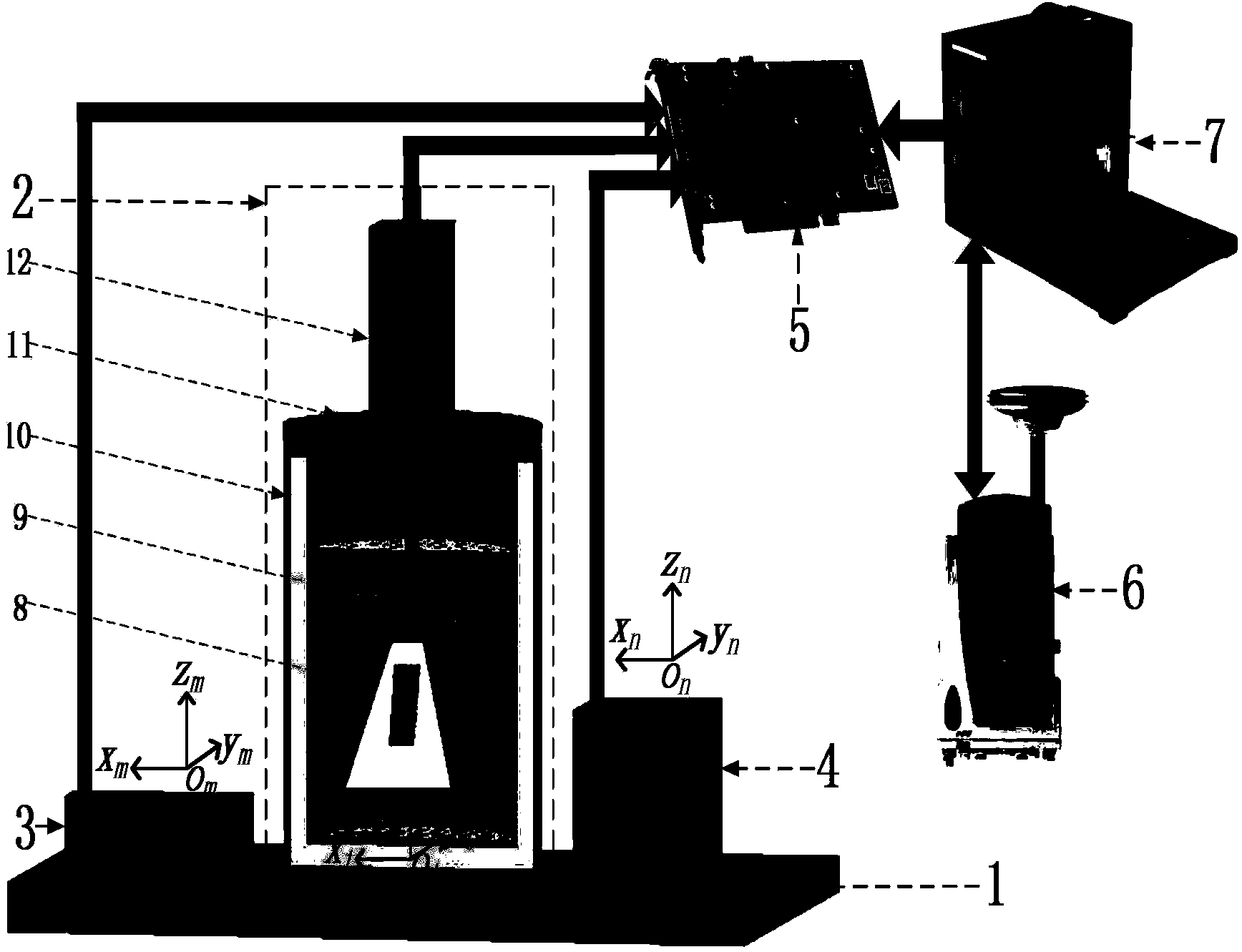
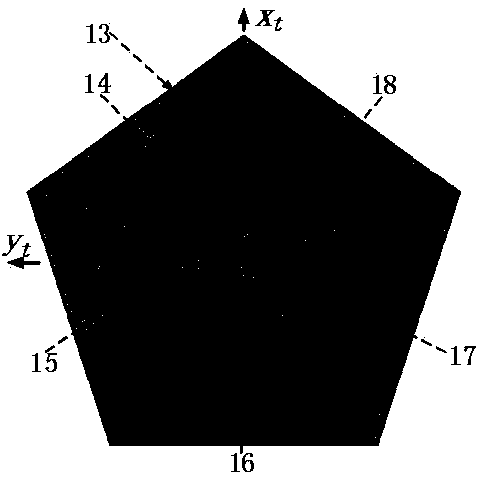
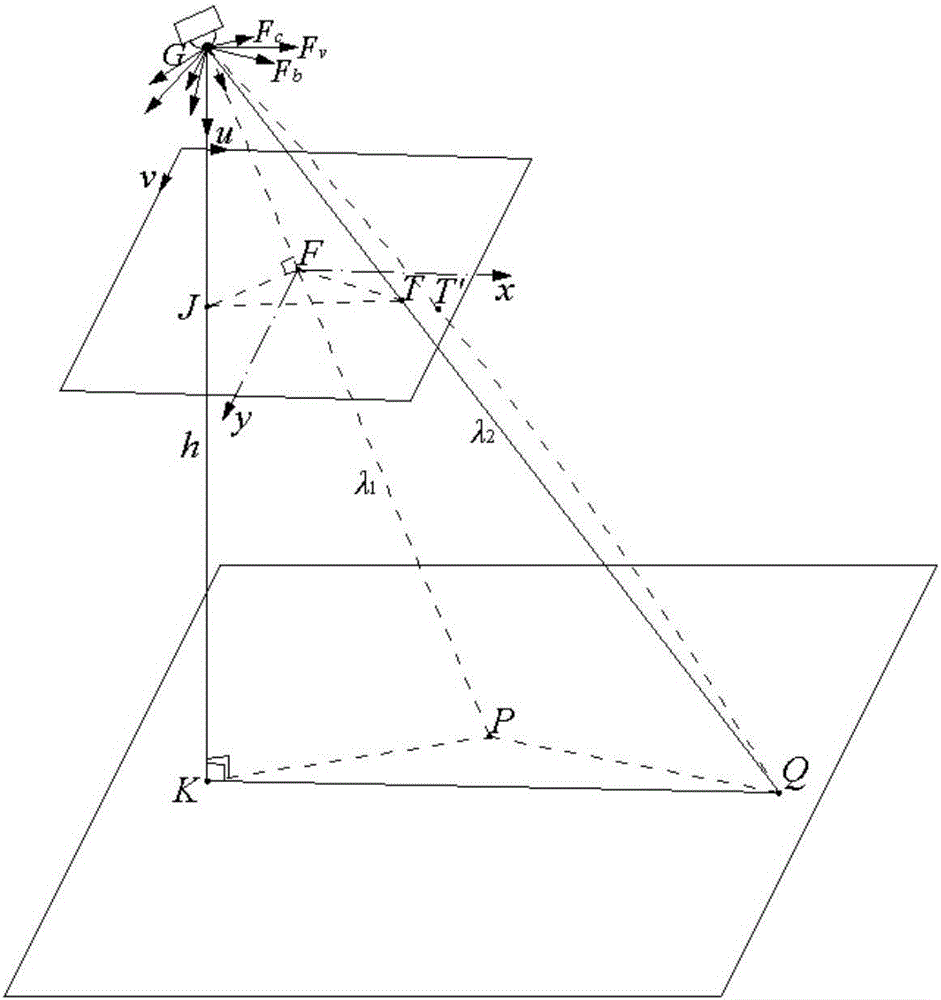
InactiveCN106373159APrecise positioningImprove efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisGeographic coordinate systemCcd camera
The present invention discloses a simplified unmanned aerial vehicle multi-target location method. The simplified unmanned aerial vehicle multi-target location method can perform location in real time while realizing multiple targets, and is simple in hardware device. An area array CCD camera is employed to perform grounding imaging, and obtaining the pixel coordinates of each target; performing distortion correction, and obtaining the ideal imaging points of each target; constructing the sight vectors of a main target, a sub target and a lower machine point in the camera coordinate systems; employing the coordinate transformation to obtain the sight vectors of the main target, the sub target and the lower machine point in the aerial carrier geographic coordinate system; calculating the coordinates of each target in the aerial carrier geographic coordinate system according to the distance from the main target and the sub target to a photoelectricity platform and the sight vectors of the main target and the sub target in the aerial carrier geographic coordinate system; and finally, obtaining the geodetic coordinates through the coordinate transformation, namely locating the result.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Scaler and satellite pointing alignment determination method
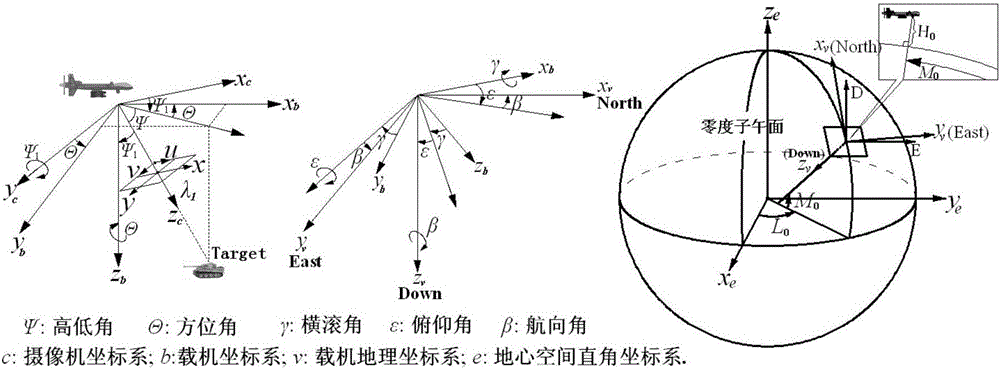
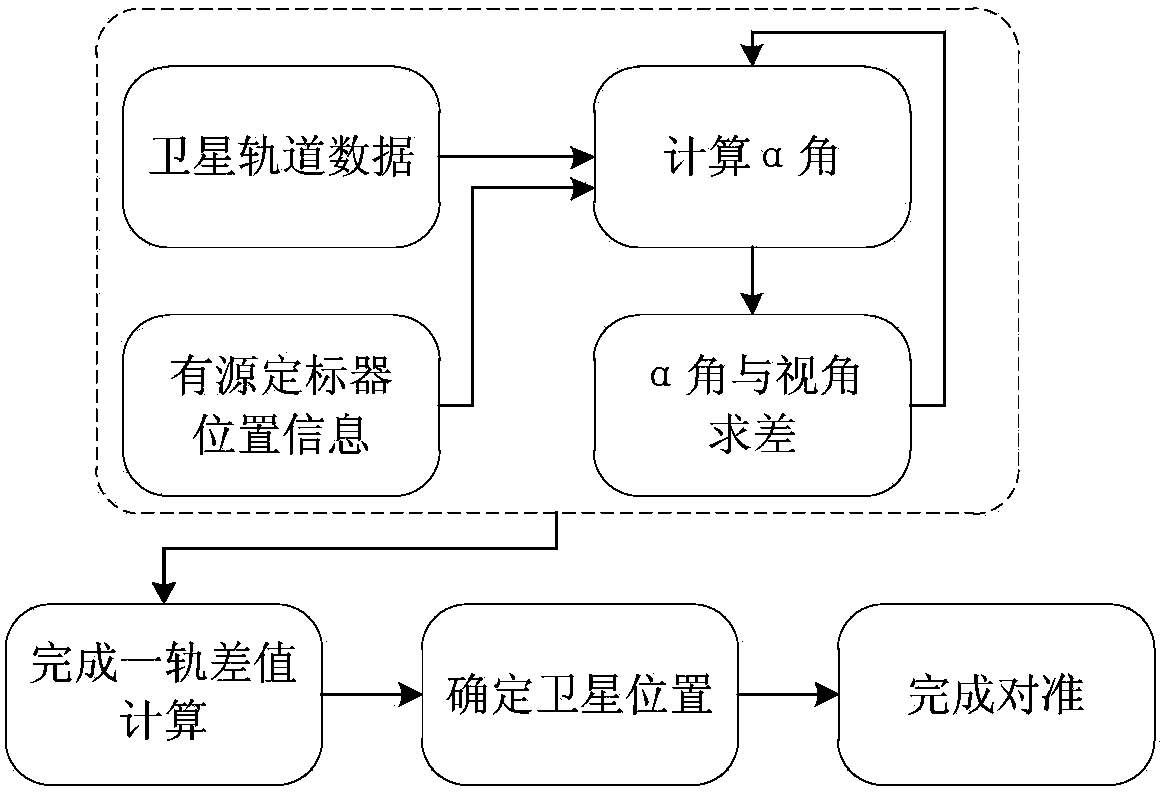
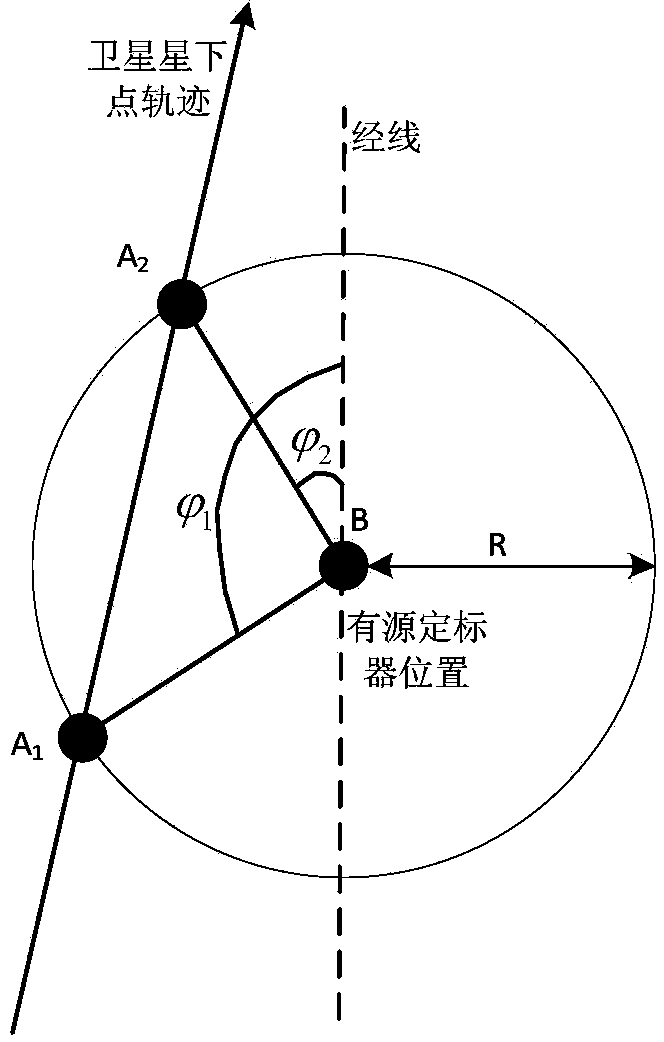
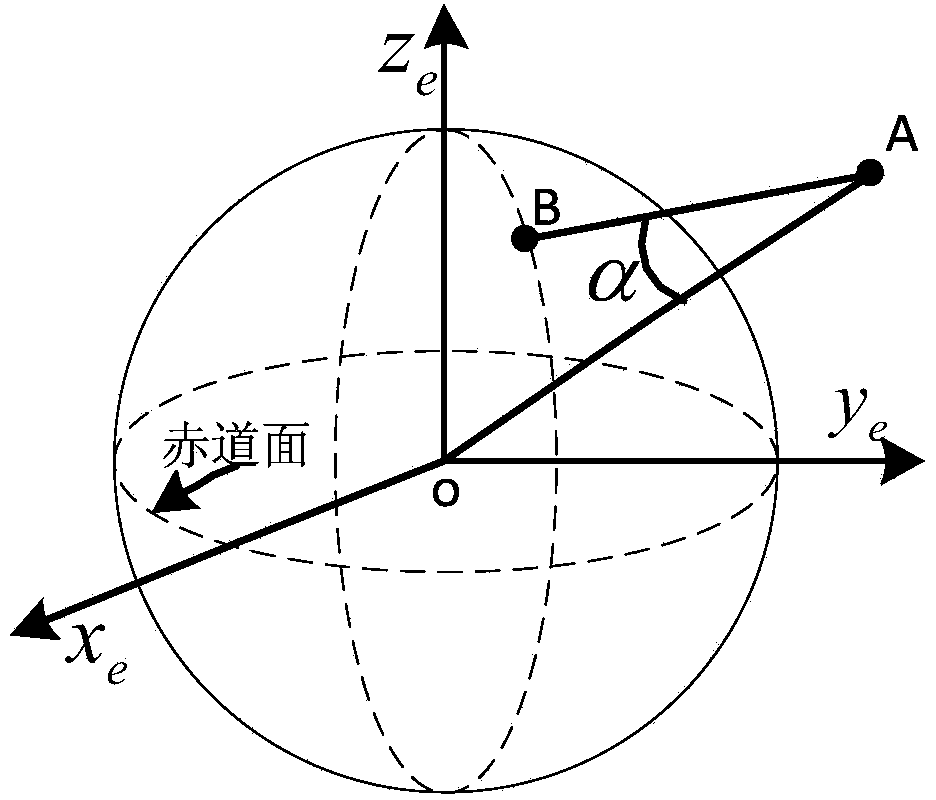
ActiveCN103675773AClear processEasy to implementWave based measurement systemsGeographic coordinate systemSatellite orbit
Disclosed is a scaler and satellite pointing alignment determination method. The invention provides a novel design idea: when an included angle between a satellite-center of earth line and a satellite-active scaler line, and view angle difference of a satellite are the minimum, an intersection of the beam center of a satellite antenna with the earth is closest to an active scaler. The specific steps include: 1, establishing an earth coordinate system, a geographic coordinate system and a carrier coordinate system; 2, acquiring satellite orbit predicted data and active scaler positional information; 3, calculating a vector of the satellite-scaler line and the included angle alpha of the earth's center-satellite line; 4, locating the satellite; 5, converting the vector to the carrier coordinate system; 6, calculating azimuth psi and pitch angle theta of a scaler antenna relative to the scaler (carrier coordinate system); 7, controlling the antenna to rotate according to the two angles through a servo control system so as to align the scaler with the satellite. According to the coordinate transformation theory, the method has no approximate error and high alignment precision.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Spatial synchronization method of bistatic synthetic aperture radar (SAR)
ActiveCN102967851AGuaranteed accuracyPrecise alignmentWave based measurement systemsInterferometric synthetic aperture radarRectangular coordinates
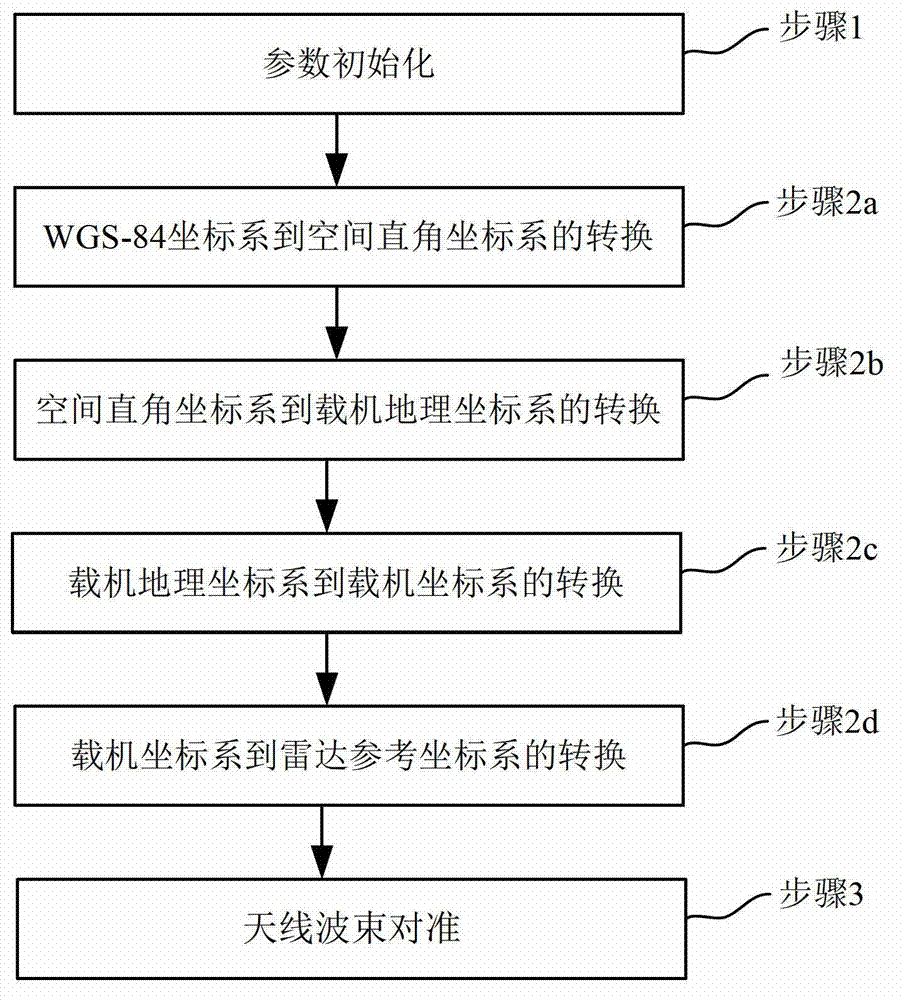
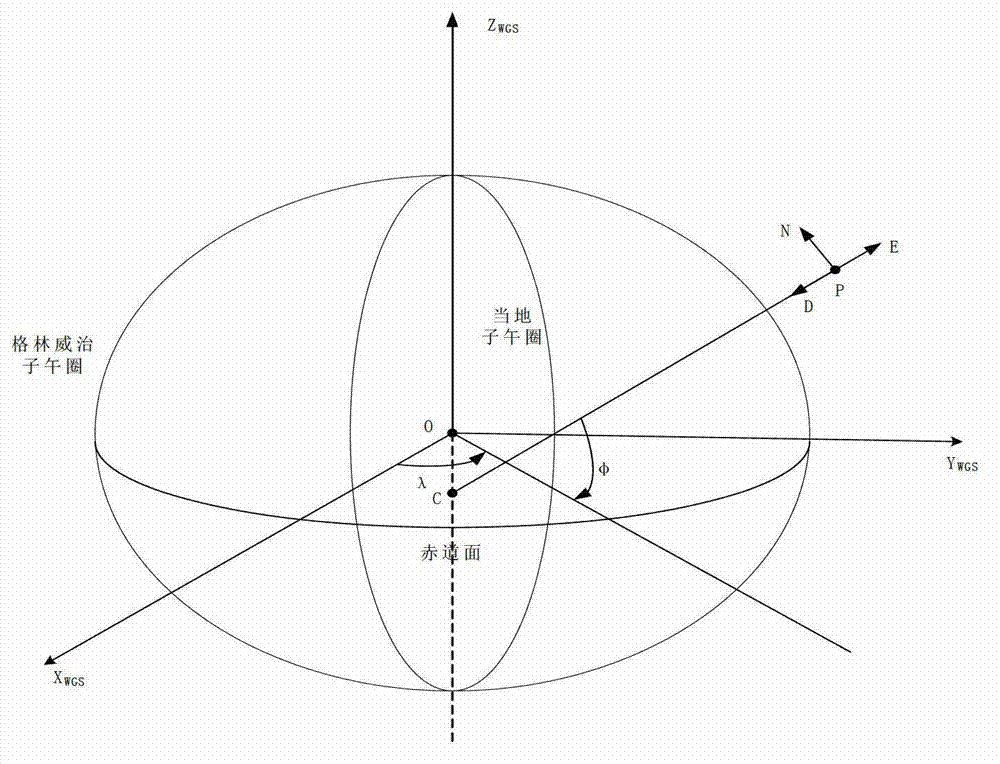
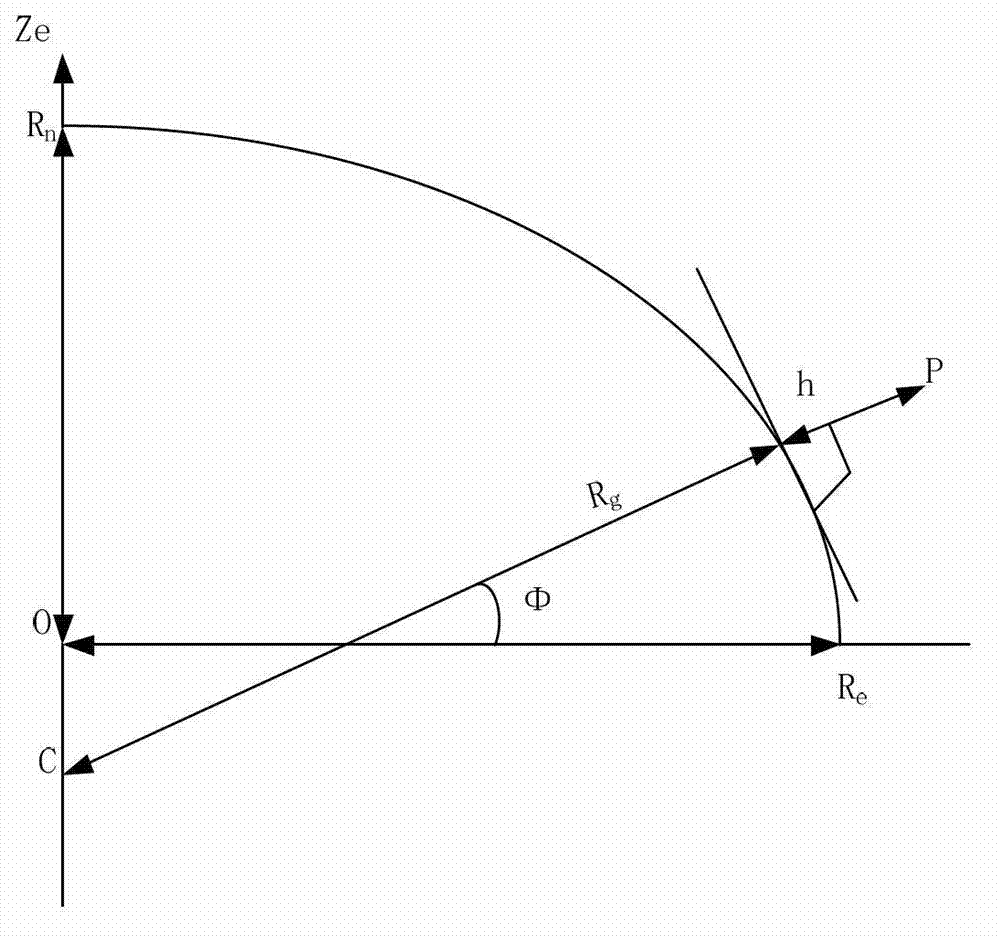
The invention discloses a spatial synchronization method of bistatic synthetic aperture radar (SAR). The method comprises steps of initializing parameters and converting a World Geodetic System (WGS)-84 coordinate system to a spatial rectangular coordinate system; converting the spatial rectangular coordinate system to an aerial carrier geographic coordinate system; converting the aerial carrier geographic coordinate system to an aerial carrier coordinate system; converting the aerial carrier coordinate system to a radar reference coordinate system; and aligning antenna beams. Global positioning system (GPS) special coordinate information and attitude information of an aerial carrier platform are used, the coordinate conversion is conducted in accordance with the sequence of the WGS-84 coordinate system, the spatial rectangular coordinate system, the aerial carrier geographic coordinate system, the aerial carrier coordinate system and the radar reference coordinate system, the accuracy of antenna pointing control parameters which are obtained finally can be guaranteed, the GPS special coordinate information and the attitude information of the aerial carrier platform are used, airborne bistatic SAR antenna pointing control parameters can be exported through the conversion of multi-coordinate systems, and the antenna beam pointing for receiving and transmitting the aerial carrier can be aligned through antenna pointing control parameters.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
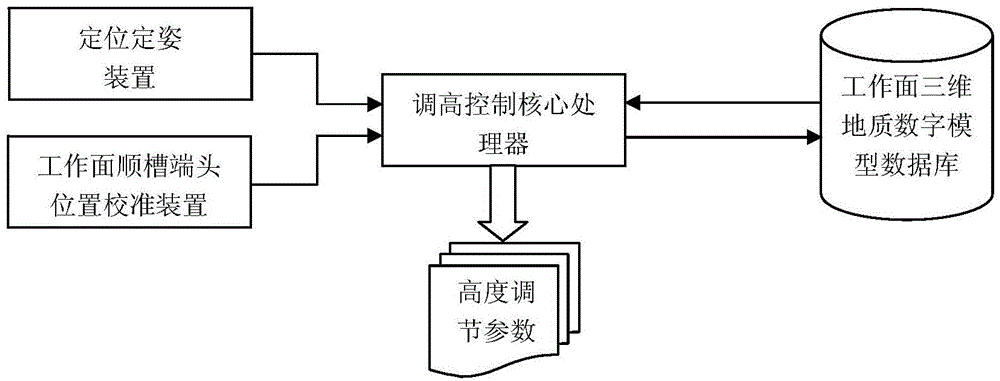
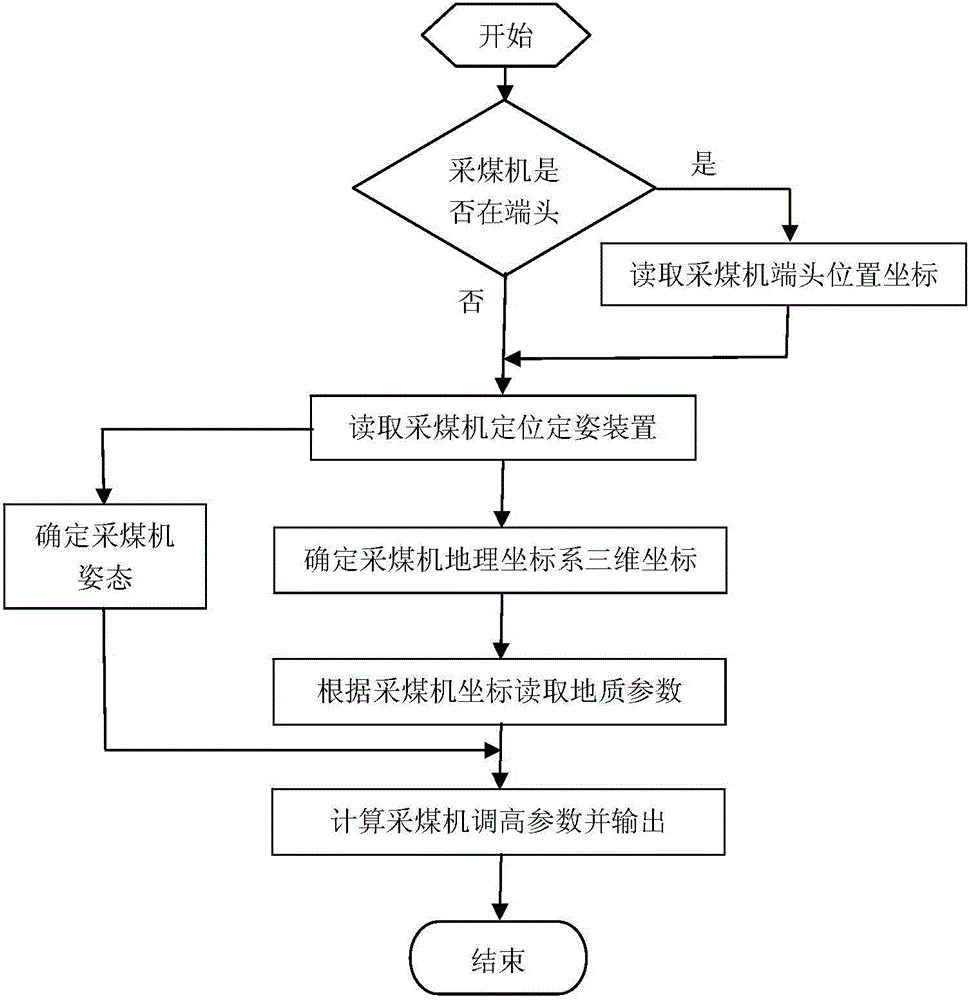
Coal-cutter roller automatic height-adjusting system
ActiveCN104481534ARealize automatic height adjustmentRealize intelligenceSlitting machinesCutting machinesThree-dimensional spaceEngineering
A disclosed coal-cutter roller automatic height-adjusting system determines the position and the attitude of a coal cutter under a working-face geographic coordinate system through a positioning attitude-determining device and a working-face crossheading end position calibrating device, and a height-adjusting control core processor fuses measure data into a working-face three-dimension geological digital model according to the coal-cutter coordinates, performs three-dimension space analysis in the working-face three-dimension geological digital model according to the position of the coal cutter, obtains the cut coal layer thickness and cut coal layer variation at the position of the coal cutter, and real-timely dynamically adjusts the cutting height of the coal cutter by combining address environment parameters including coal layer dirt band. The provided coal-cutter roller automatic height-adjusting system is capable of realizing automatic height adjusting of a coal-cutter roller.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com