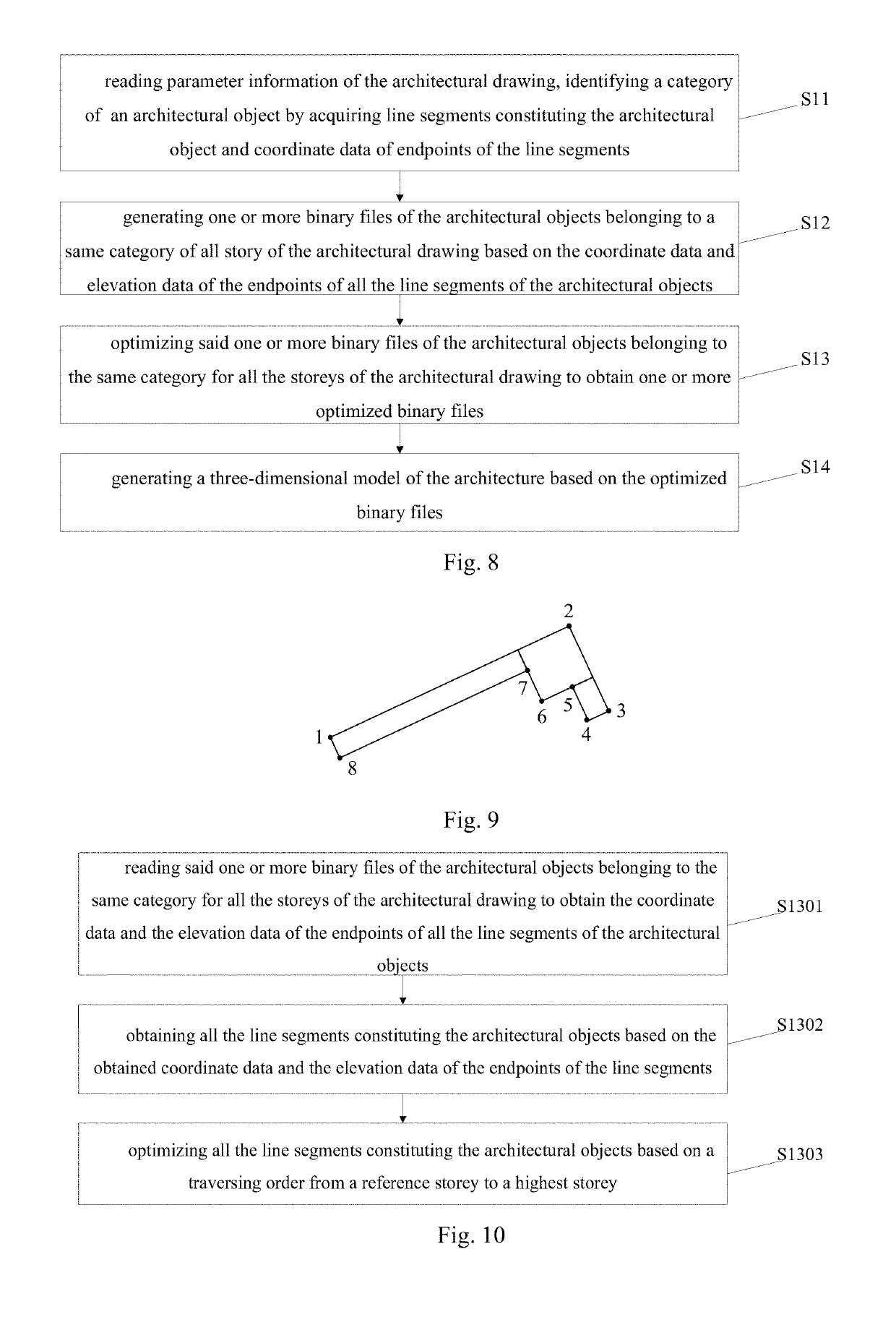
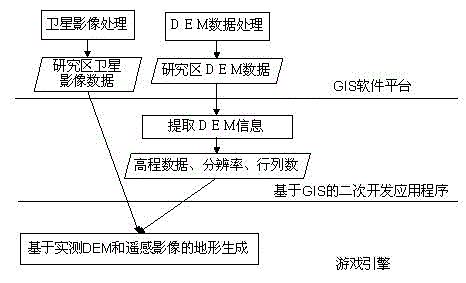
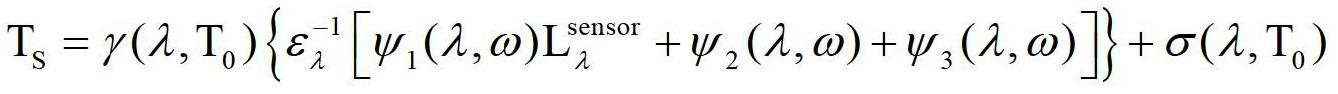Patents
Literature
863 results about "Elevation data" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
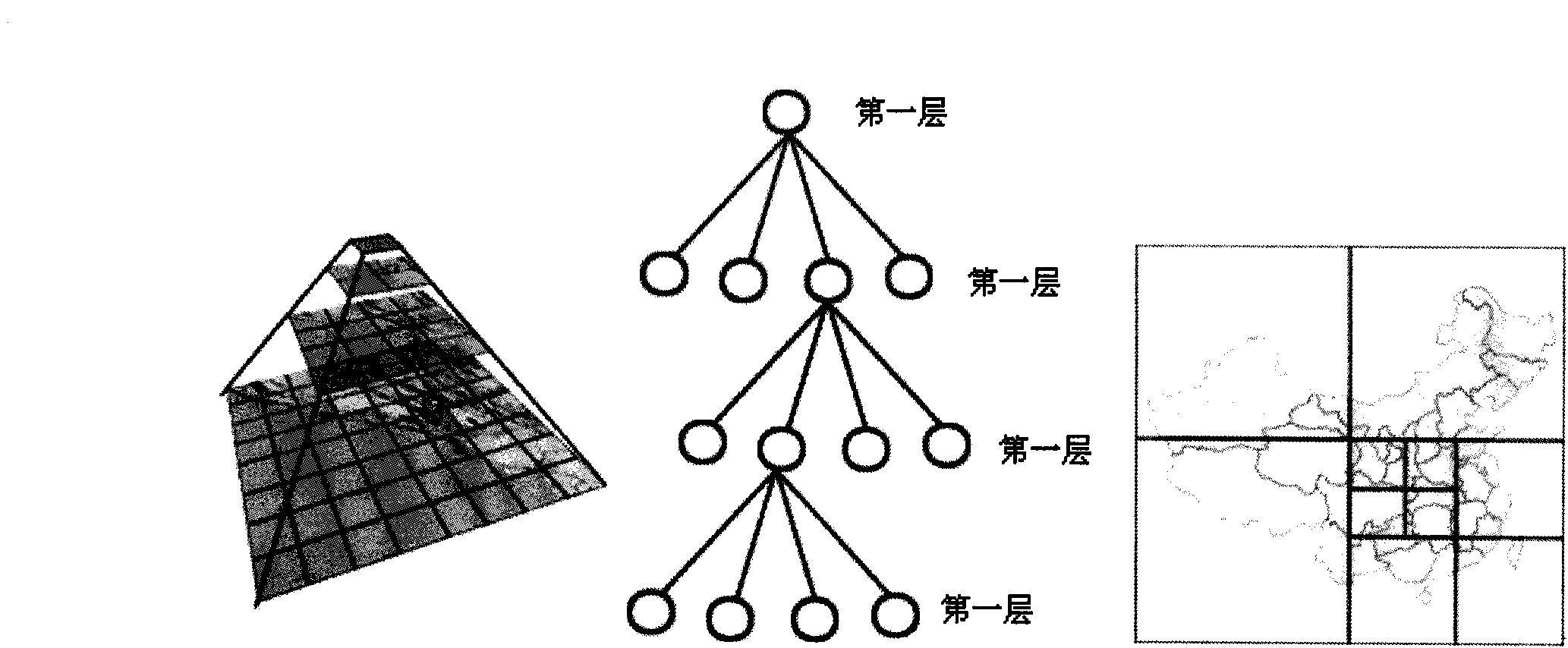
Three-dimensional digital earth-space data organizing and rendering method based on quad-tree index
InactiveCN101887595AShorten the timeImprove execution efficiency3D-image rendering3D modellingDigital EarthData format
The invention provides a three-dimensional digital earth-space data organizing and rendering method based on a quad-tree index, which belongs to the technical fields of cartography, geography information systems and virtual reality. The method comprises the following steps of: unifying common spatial data formats under multi-scale and multi-projection conversion, multispectral, multi-temporal and high-resolution remote sensing satellite images and aerial images as well as digital thematic maps with different scales into same coordinate system, carrying out operation on the attribute of each element and the parameter regulation of quad-tree tiles, outputting in the form of the quad-tree tiles, carrying out quad-tree cutting on three-dimensional landscape map data, leading spatial data into a relevant database, and carrying out unified management. By using the method, common vector data, raster data, altitude data and three-dimensional map data are organically integrated and issued into a three-dimensional digital earth prototype, thereby shortening the time of data preprocessing, improving the execution efficiency and providing a new integration method for three-dimensional digital earth fundamental geographic data dissemination.
Owner:WUHAN IMMERSION ENVIRONMENT
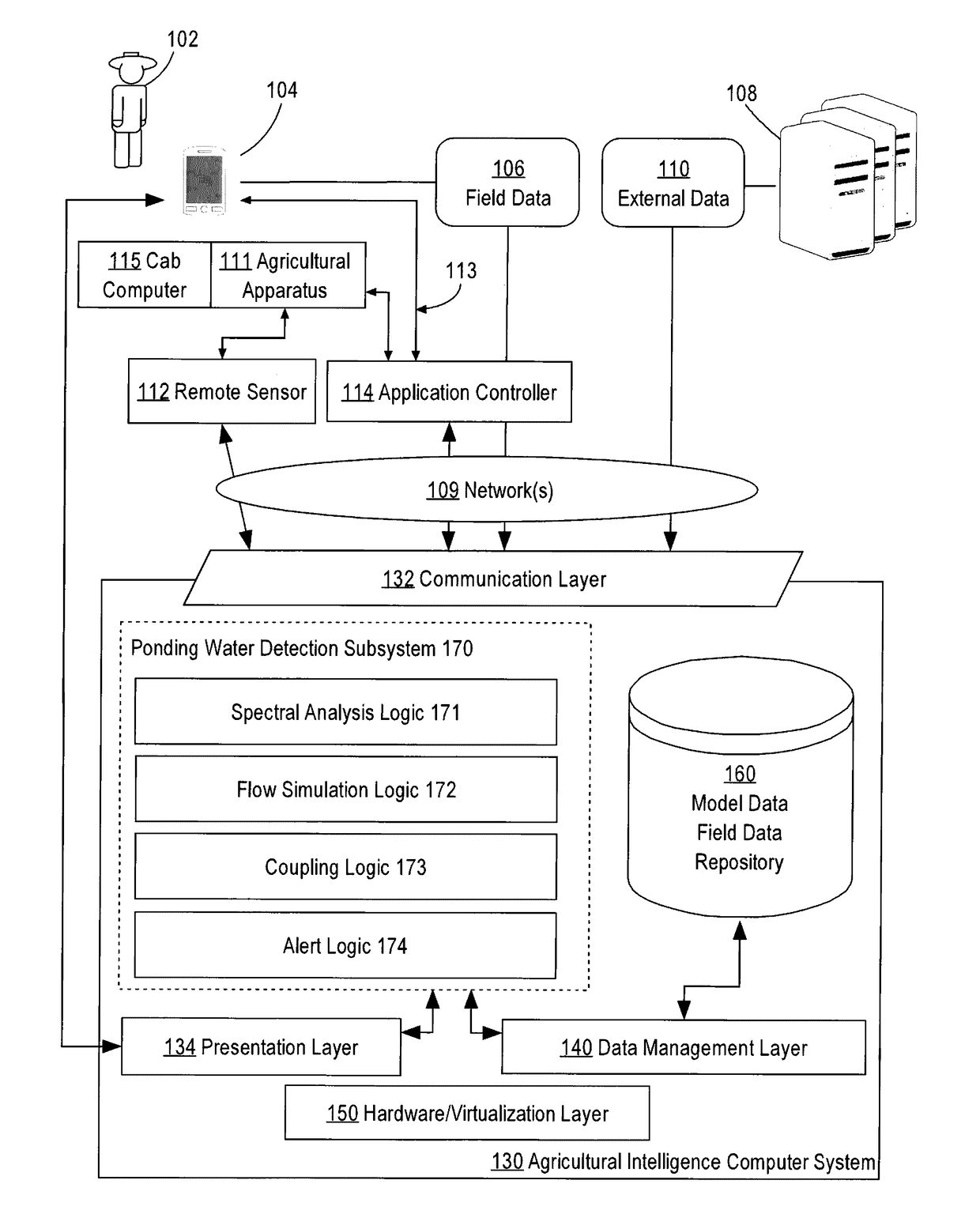
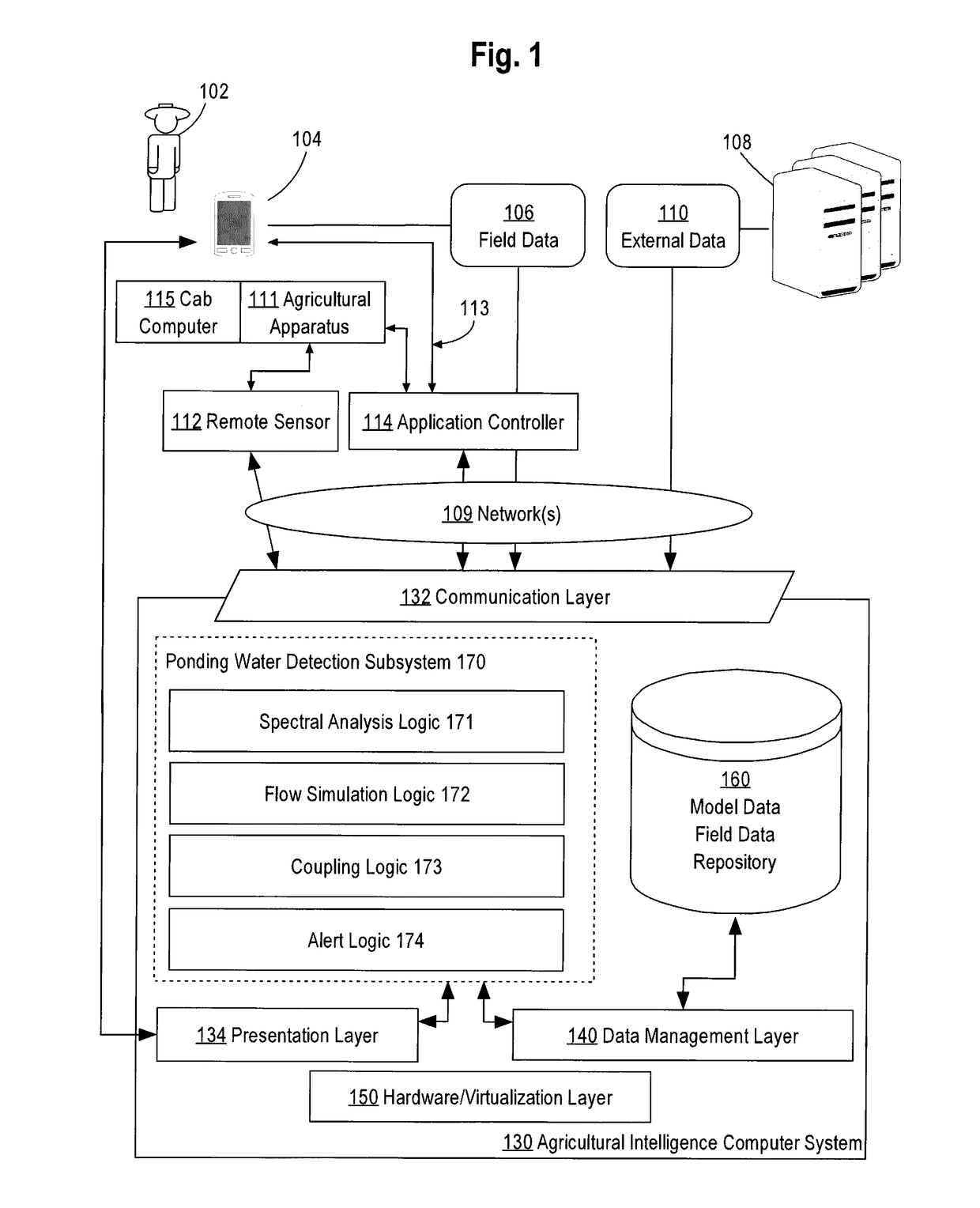
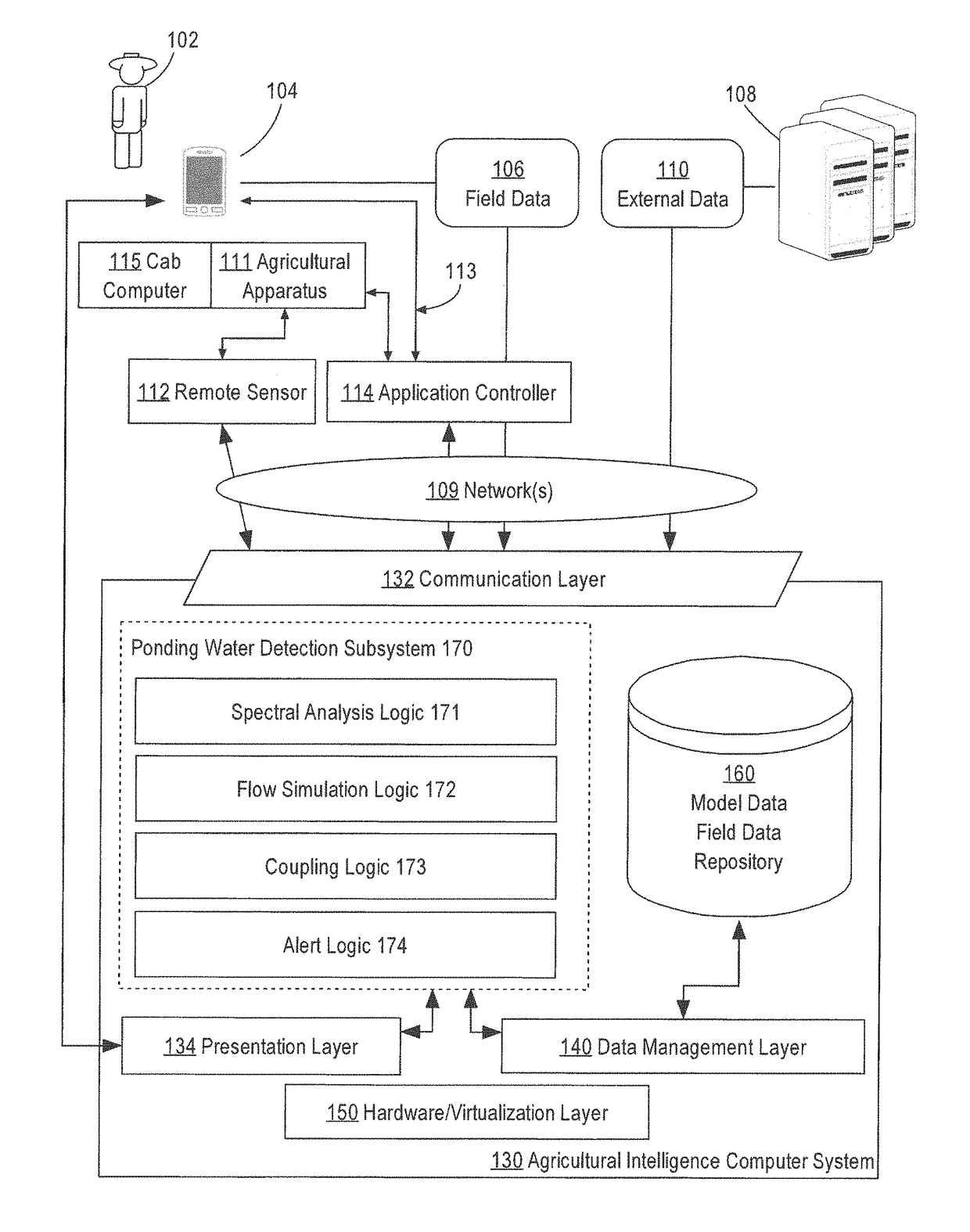
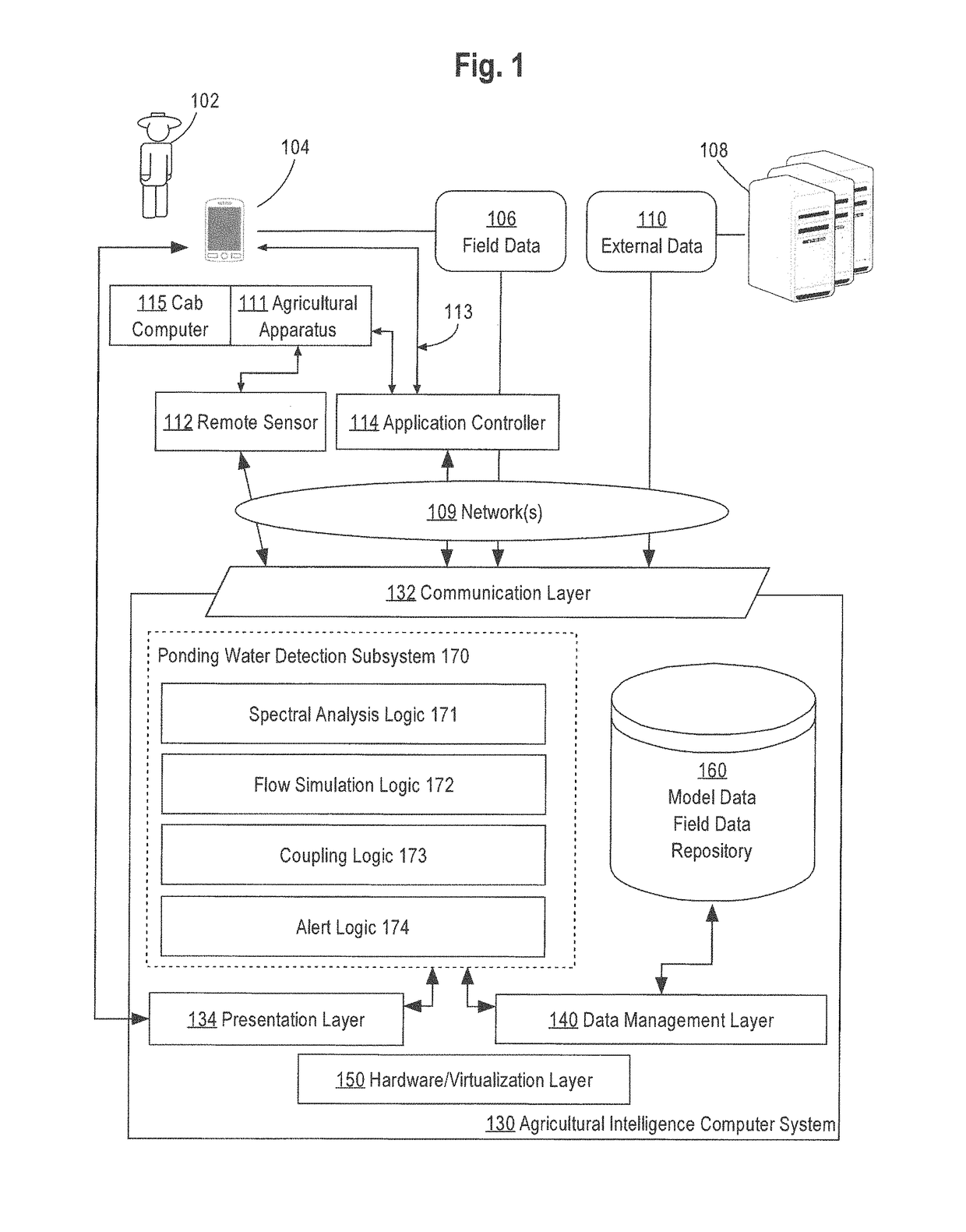
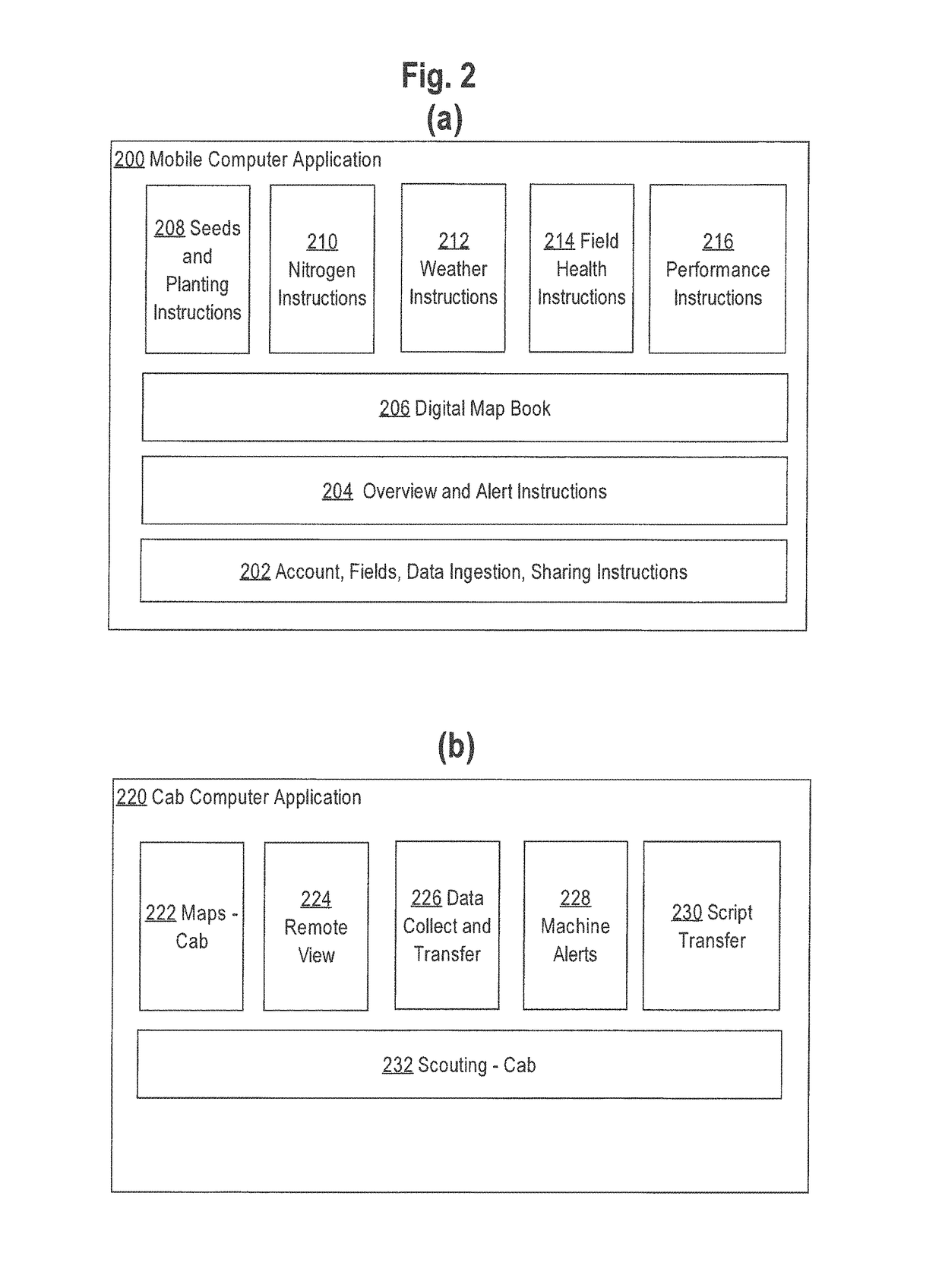
Ponding water detection on satellite imagery
A system for identifying ponding water located on a field from image data is described. In an approach, an image of an agricultural field is analyzed using a classifier that has been trained based on the spectral bands of labeled image pixels to identify a probability for each pixel within the image that the pixel corresponds to water. A flow simulation is performed to determine regions of the field that are likely to pool water after rainfall based on precipitation data, elevation data, and soil property data of the field. A graph of vertices representing the pixels and edges representing connections between neighboring pixels is generated. The probability of each pixel within the graph being ponding water is set based on the probability pixel being water, the likelihood that water will pool in the area represented by the pixel, the probability of neighboring pixels being ponding water, and a cropland mask that identifies which pixels correspond to cropland. A class for each pixel is then determined that maximizes the joint probability over the graph.
Owner:THE CLIMATE CORP
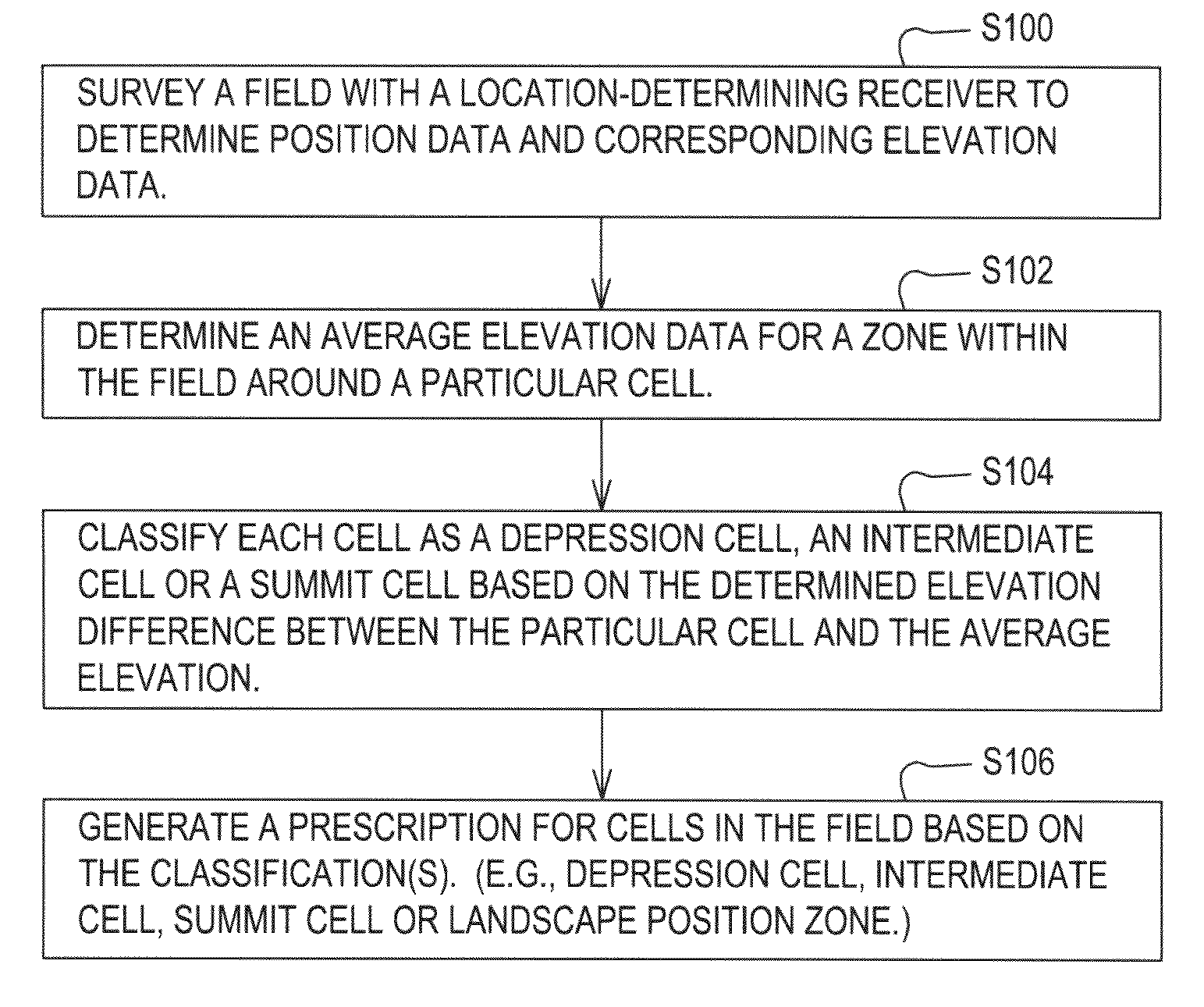
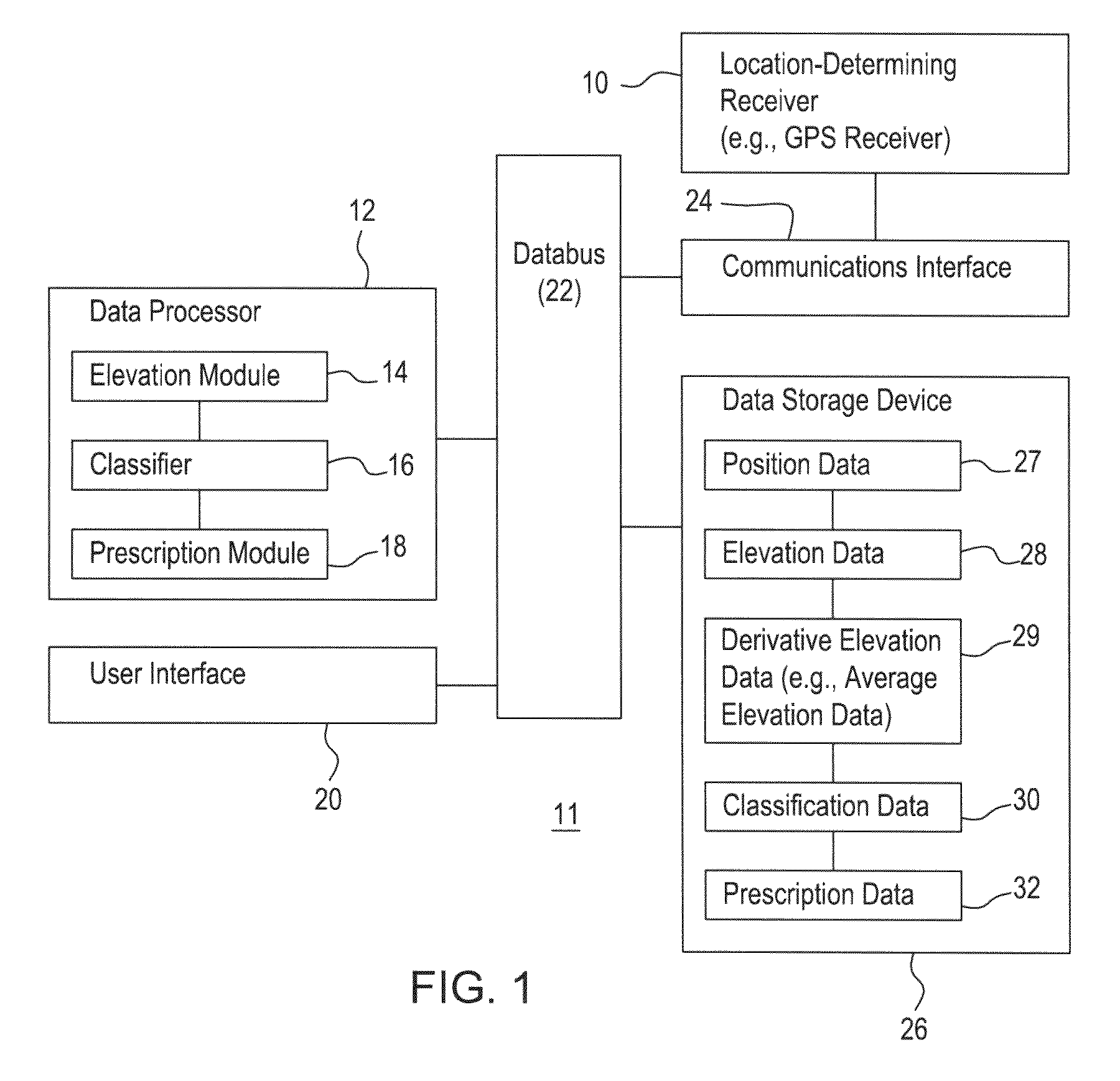
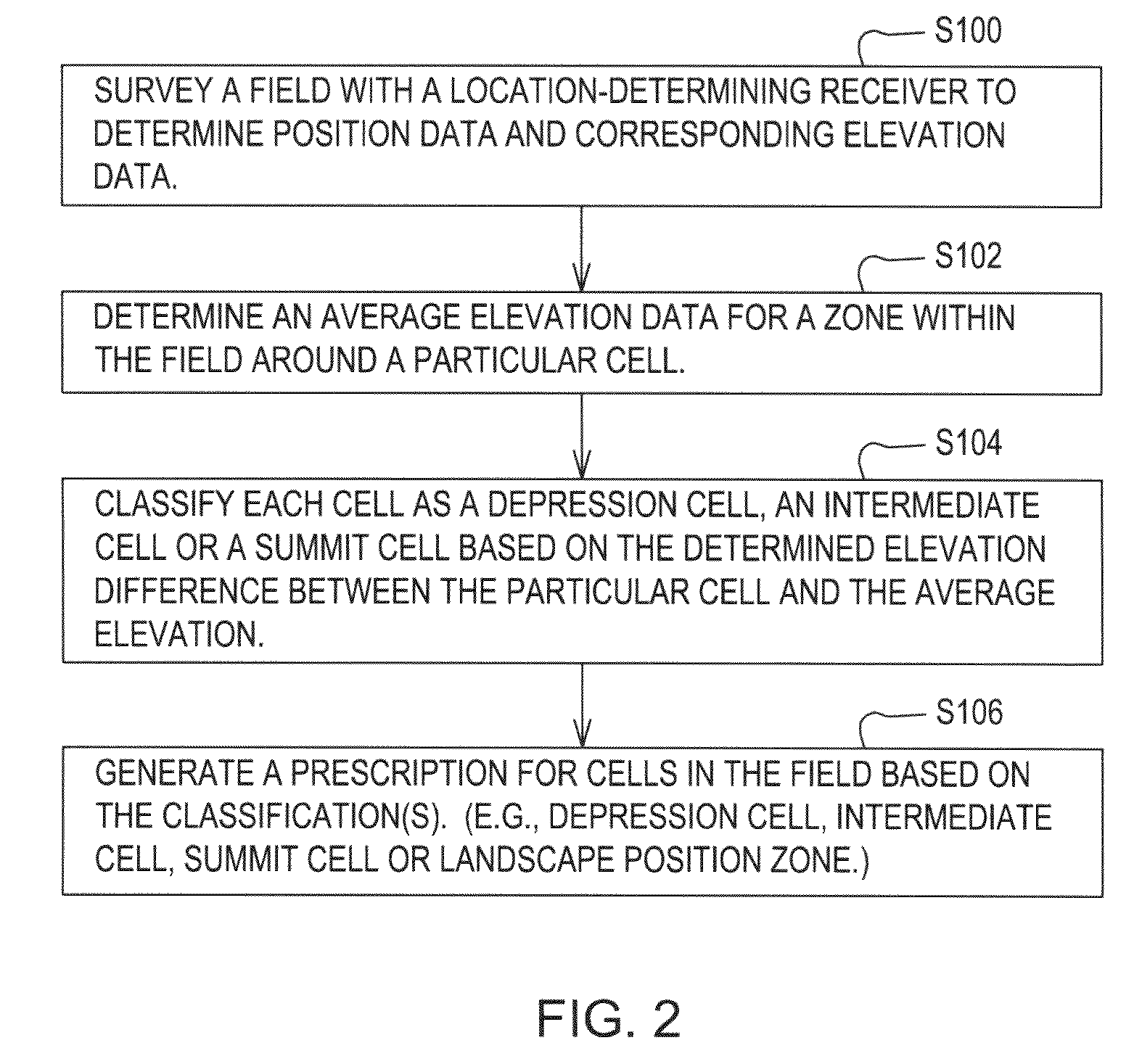
Method for making a land management decision based on processed elevational data
A method for making a land management decision comprises surveying a field with a location-determining receiver to determine position data and corresponding elevation data. A data processor or elevation module determines an average elevation data for a zone within the field around a particular cell. The data processor or classifier classifies each cell into classifications comprising a depression cell and a summit cell based on the determined elevation difference between the particular cell and the average elevation. The data processor and the prescription module generate a prescription for the cells in the field based on at least one of the classification and the determined elevation difference.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Three-dimensional terrain model real-time smooth drawing method with combination of GPU technology
InactiveCN105336003ATroubleshoot preprocessing issuesEliminate noise3D modellingVideo memoryEngineering
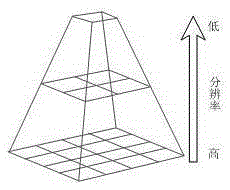
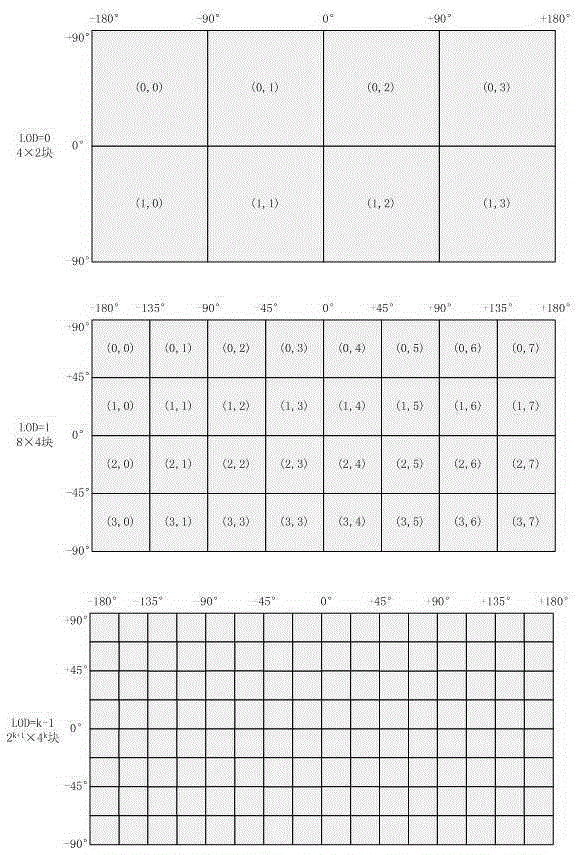
The invention provides a three-dimensional terrain model real-time smooth drawing method with combination of a GPU technology, and belongs to the technical field of image processing. The objective of the invention is to provide the three-dimensional terrain model real-time smooth drawing method with combination of the GPU technology so that cache reuse in multiple times of drawing can be realized based on the current popular programmable GPU technology with a global digital elevation model acting as a data source, and load of computation space is effectively reduced. The method comprises the steps of construction of a multi-resolution pyramid model, elimination of image noise points, filtering of images, partitioning of planar projection of the earth according to equal latitude and longitude, and construction of different hierarchical levels of pyramid layers according to a mode from the top to the bottom. Acceleration and enhancement of terrain rendering are realized based on the programmable GPU technology, i.e. all phases of a graphical drawing pipeline are controlled by using shader languages, two and textures are respectively generated by vertex information and index information of elevation data to be stored in video memory for scheduling of whole terrain drawing; and vertex interpolation and migration are performed in the geometric phase by utilizing a curved surface subdivision and fractal technology so that procedural details are generated and the phenomenon of edges and corners of the terrain mesh when resolution is insufficient can be compensated.
Owner:PLA AIR FORCE AVIATION UNIVERSITY
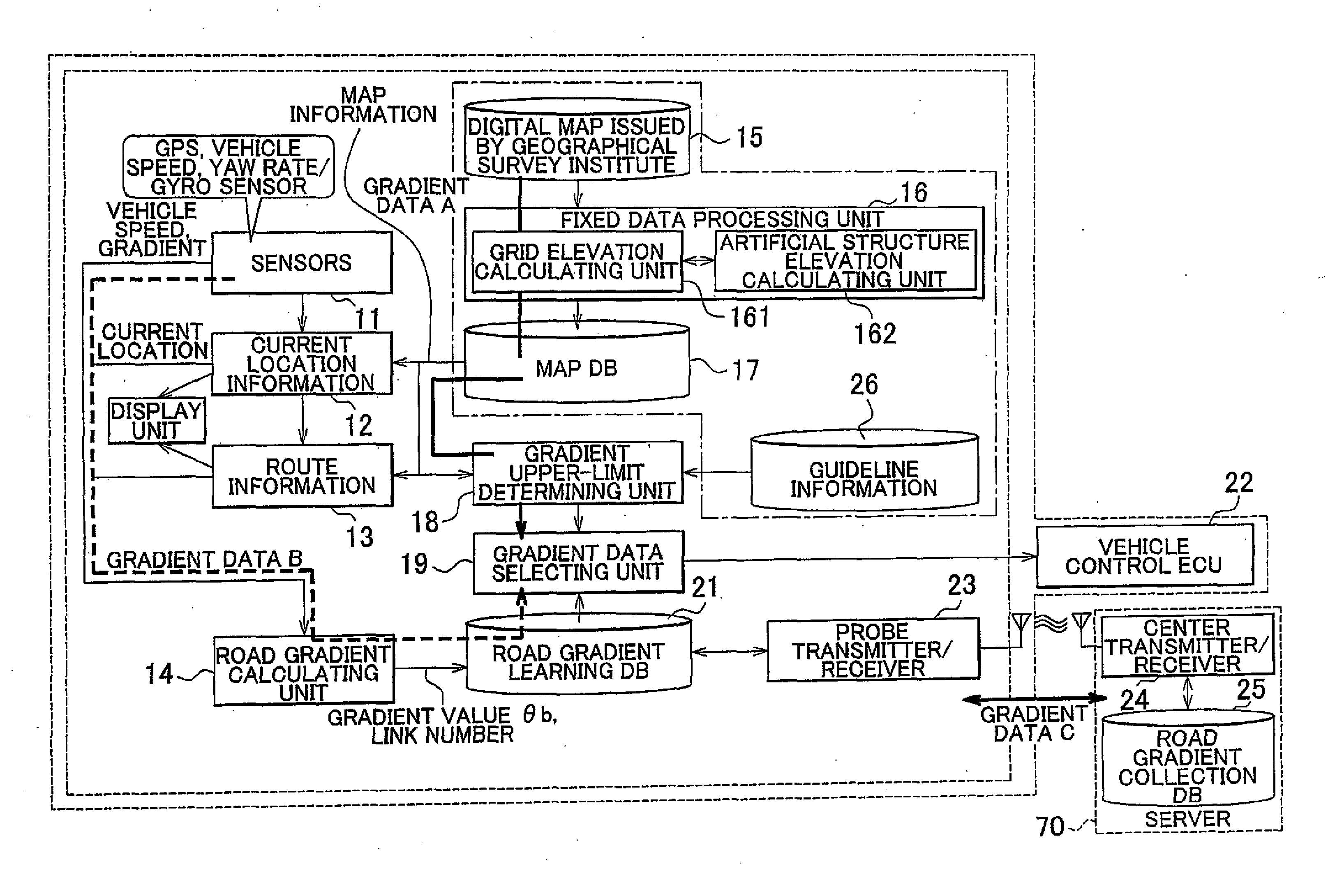
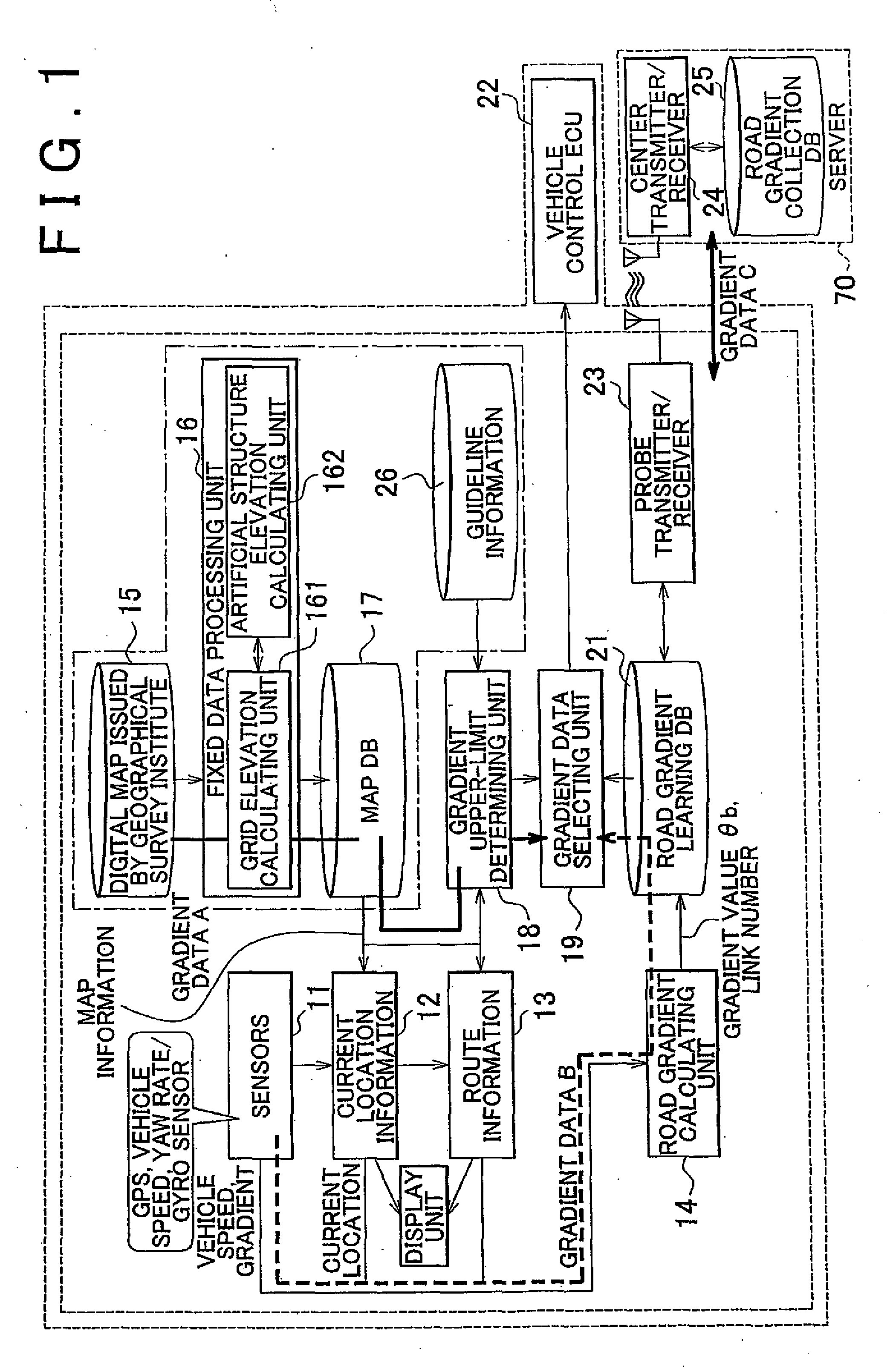
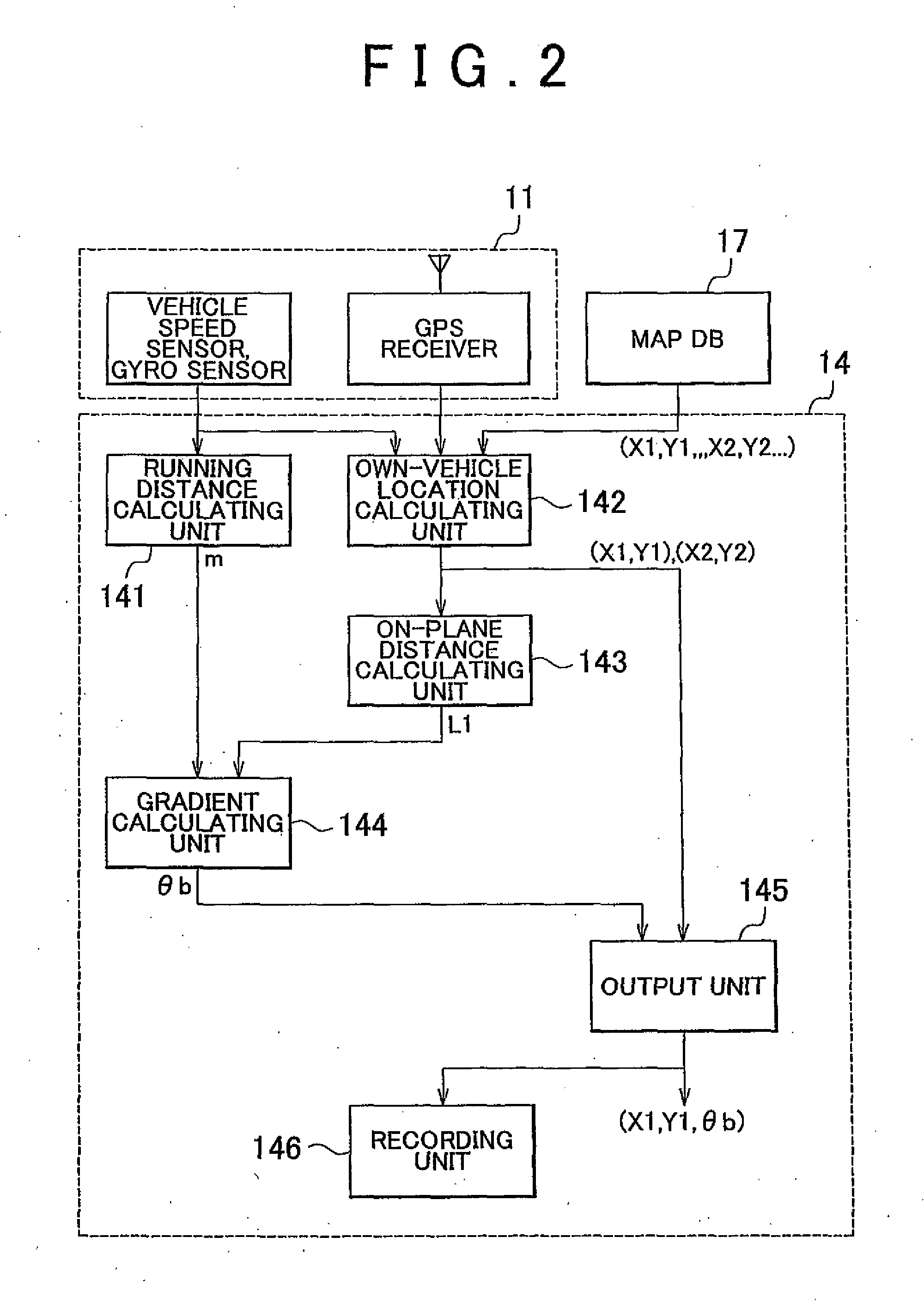
Gradient information calculating system, vehicle running control system, navigation system, and gradient information calculating method
ActiveUS20100324752A1High densityInstruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsControl systemData selection
A gradient information calculating system includes a first calculating unit (14) that detects three-dimensional location information through autonomous navigation, and calculates a first gradient value (θb, B), based on a distance (m) traveled, and an on-plane distance (L1) obtained by projecting the distance (m) traveled on a horizontal plane, a road map information storing unit (17) that stores road map information that represents each road by nodes of which the location information is known, and a link that connects the nodes, a second calculating unit (16) that estimates elevations of the nodes from previously measured elevation data, and calculates a second gradient value (A), based on a difference in elevation between the nodes and the length of the link, and a gradient data selecting unit (19) that selects one of the first and second gradient values to be adopted as a gradient value of the link, according to a difference between the first and the second gradient values.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
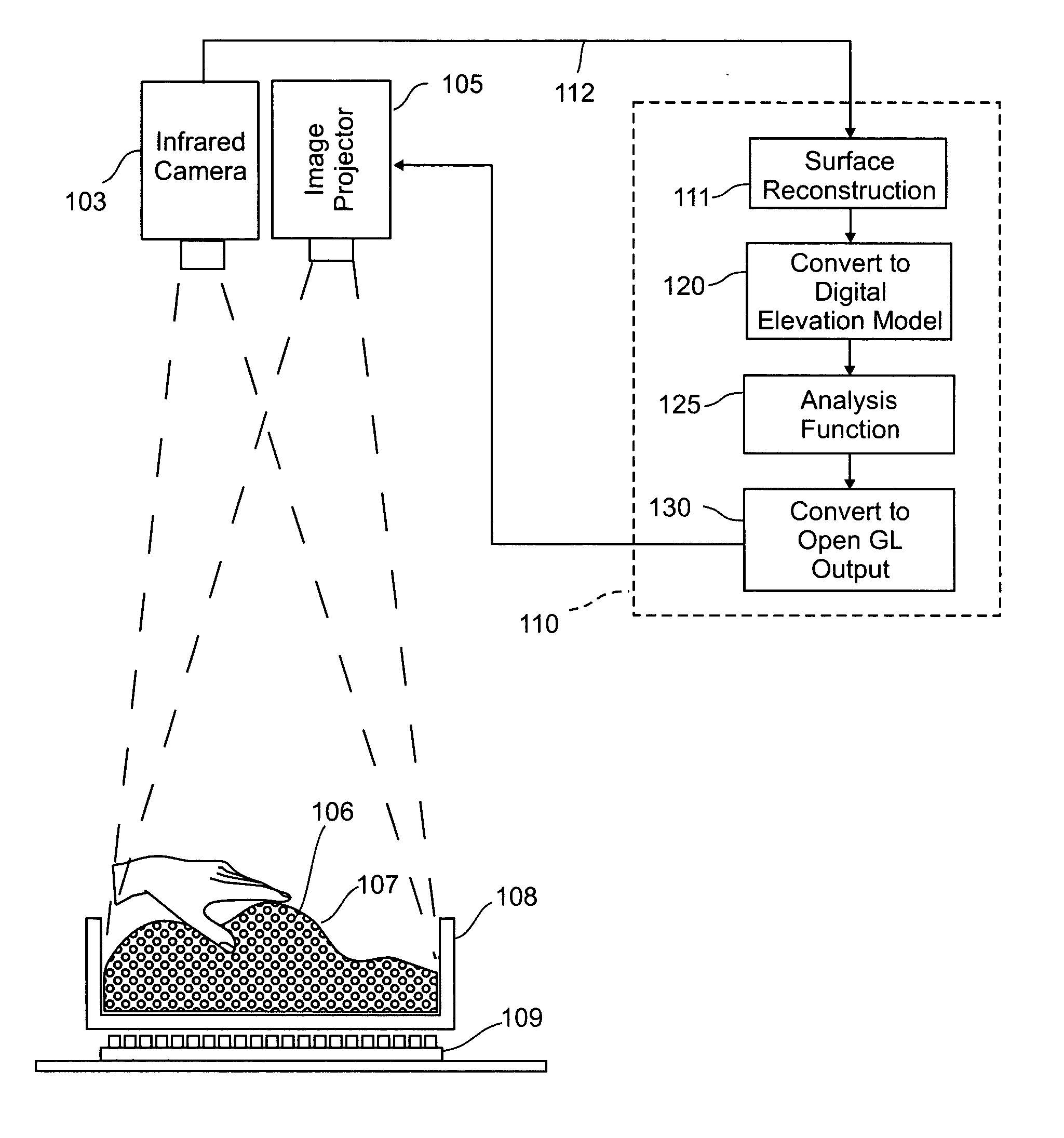
Three dimensional tangible interface for interacting with spatial-temporal data using infrared light sources and infrared detectors
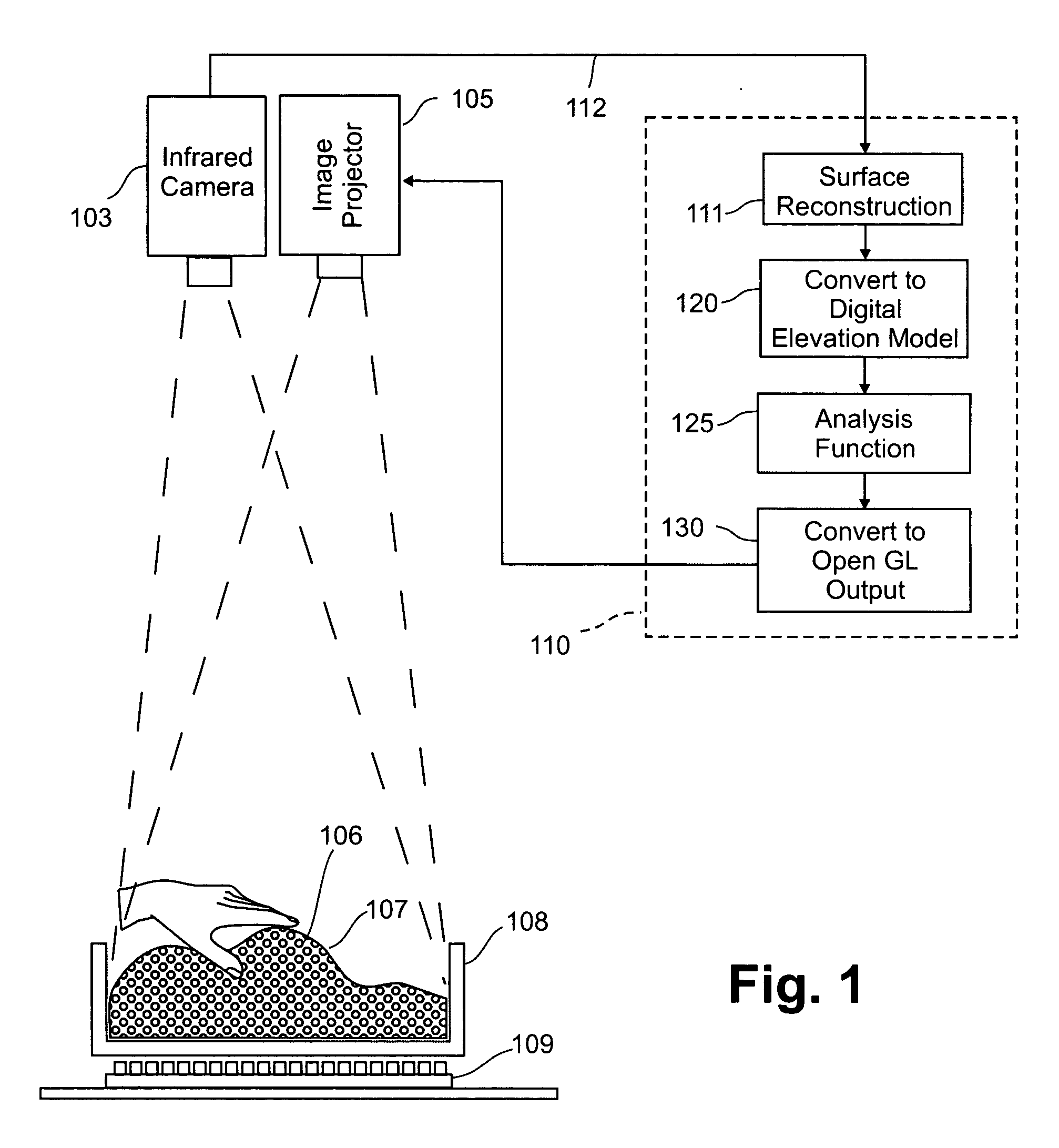
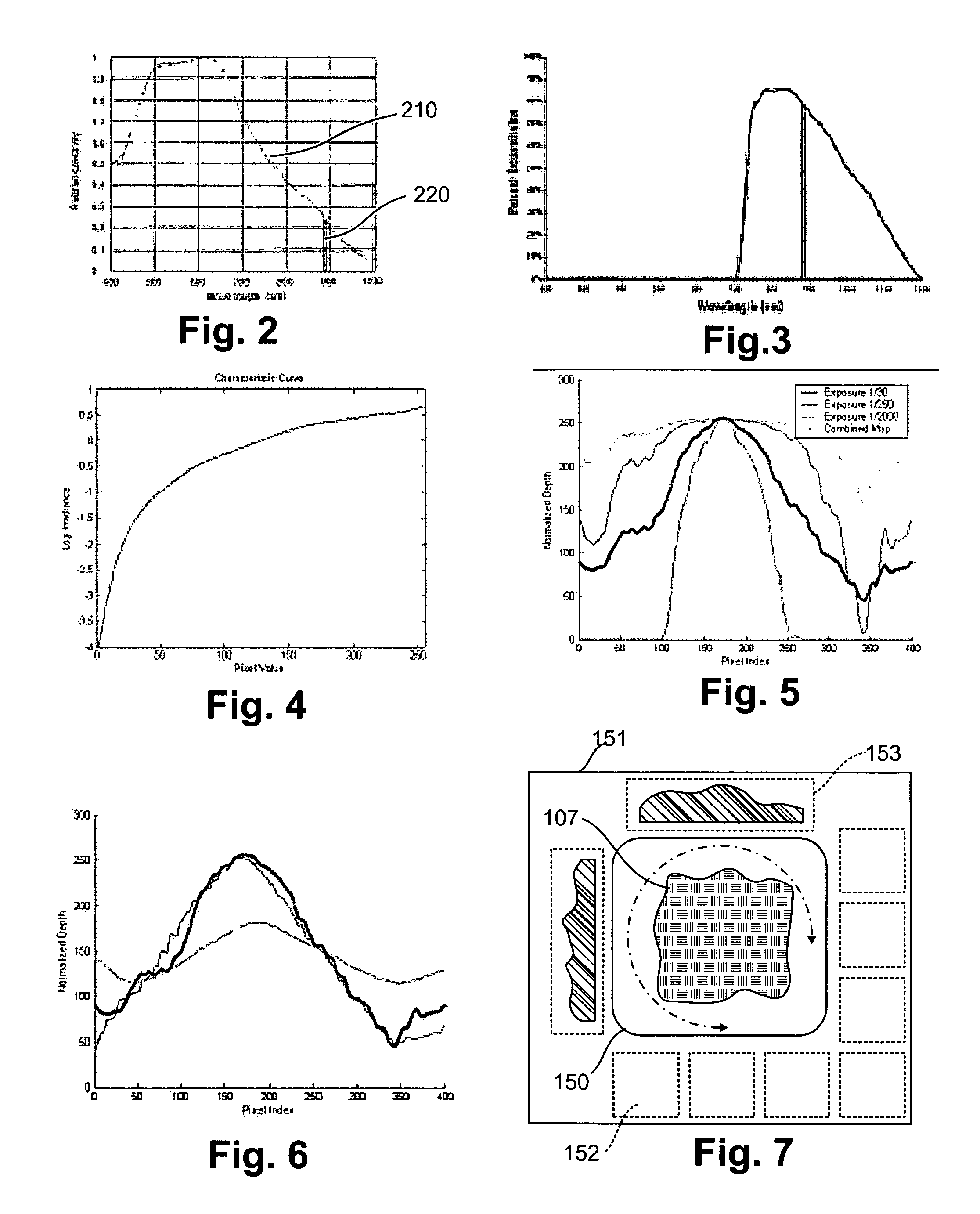
InactiveUS20050013477A1Easy to processEnhanced interactionImage analysisCathode-ray tube indicatorsPhysicsElevation data
An interface that allows a user to model and analyze the properties of three dimensional surface and the regions surrounding such surfaces. The user manipulates a deformable bed of translucent glass beads that defines the geometry of a surface. An array of light emitting diodes underneath the beads transmits infrared light upwardly through the beads such that the intensity of radiation from each position on the surface of the beads is related to the depth of the beads at that position. A digital camera captures radiation image data which is then processed to create elevation data specifying the geometry of the surface. A processor processes the elevation data using a selected analysis function to produce result data representing computed characteristics of the surface or its surrounding region. The result data is projected as an image onto the surface of the beads. The interface permits the user to modify a surface geometry and directly visualize the characteristics of the modified geometry in real time.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
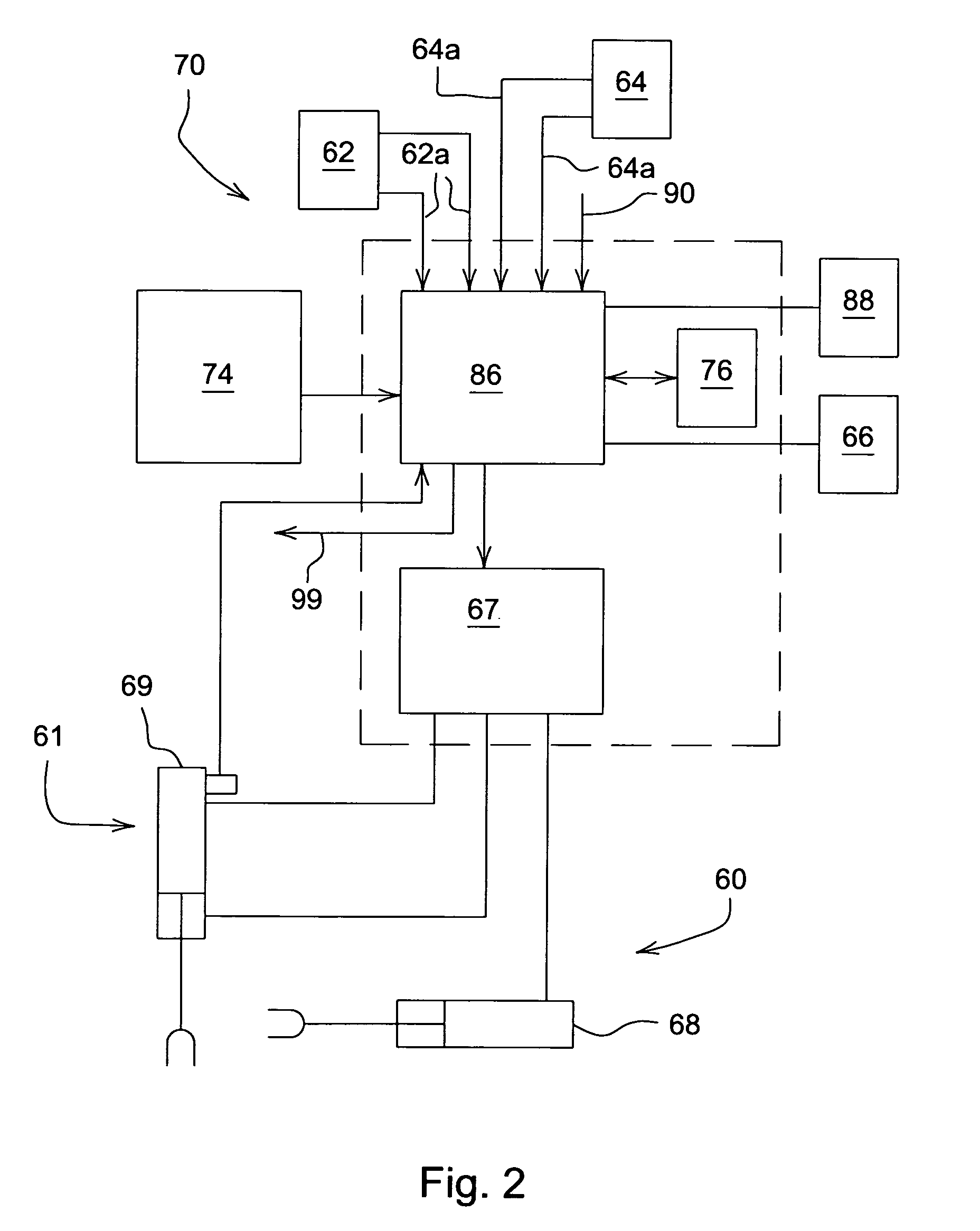
Controlling the position of an agricultural implement coupled to an agricultural vehicle based upon three-dimensional topography data
ActiveUS20080177449A1Achieve positioningShorten speedAnalogue computers for trafficMowersData controlControl signal
A system for controlling the position of an agricultural implement coupled to an agricultural vehicle comprises a control unit connected to a field topography database containing three-dimensional data of the topography of a field, a location signal generation arrangement providing location data of the position of the vehicle and / or the implement in the field, an implement position sensor arranged to sense the position of the implement with respect to the ground and to a positioning arrangement configured to move the implement in response to position control signals from the control unit. The control unit is operable to provide the control signals based upon a combination of actual position data received from the implement position sensor and expected required position change data that are derived from elevation data recalled from the field topography database based upon the location data.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Digital map compression and display method
A digital elevation database is compressed to create a compressed digital map database which is used by a digital computer system for displaying three-dimensional terrain data in the form of polygons. The compressed digital map database is produced from a database of elevation points by selecting every mth row and every nth column, thereby resulting in a reduction of database storage requirements. During program run-time the intersection of rows and columns forms cells with four corners. The elevation value of a center elevation point for each cell is formed by various methods, thereby creating a cell made up of four three-dimensional triangles. One method for creating the elevation of the center elevation point uses the elevations of the four corners of the cell. Another method uses extrapolated elevation values from the cell's extended diagonals. The three-dimensional triangles formed from the center elevation point are then transformed and projected using standard computer graphics methods on a digital computer to produce a three-dimensional projected display.
Owner:RATEZE REMOTE MGMT LLC +1
Systems and methods of creating and blending proxy data for mobile objects having no transmitting devices
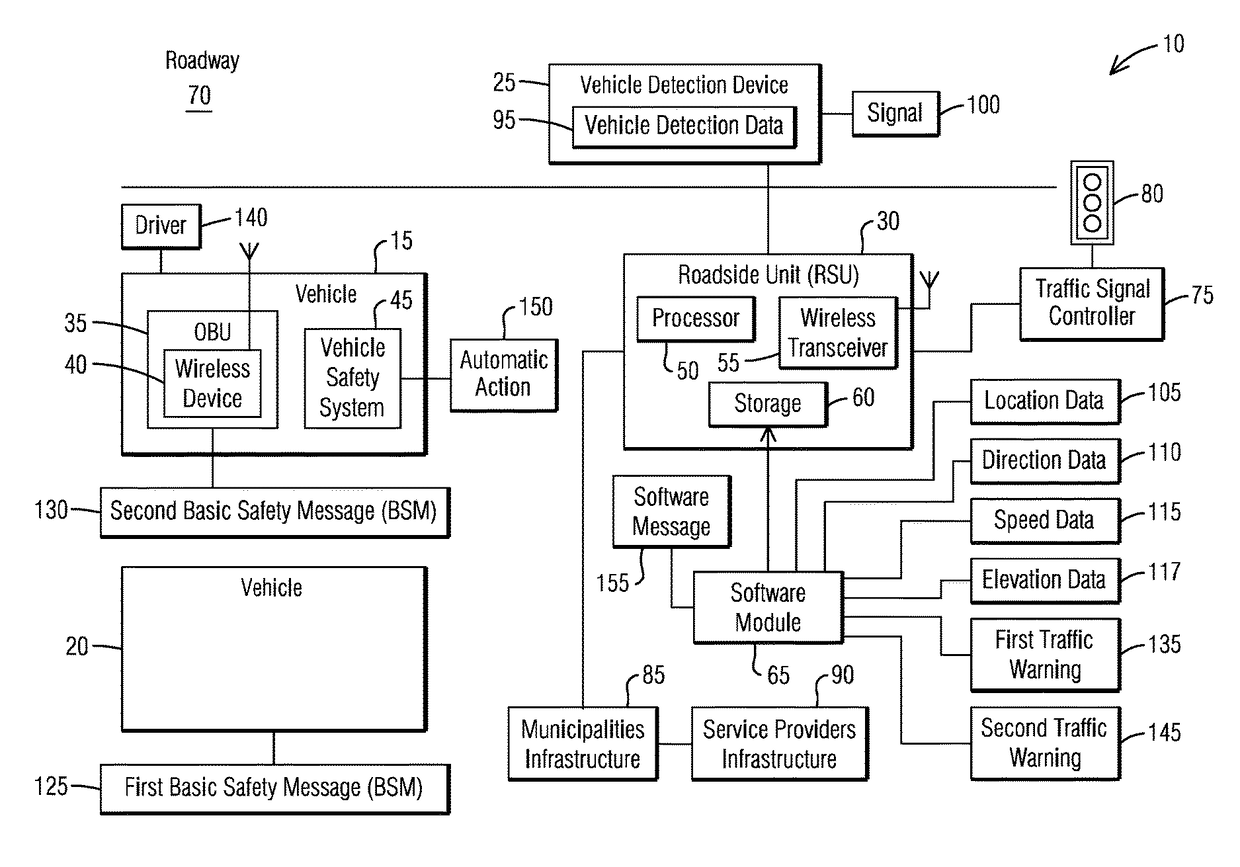
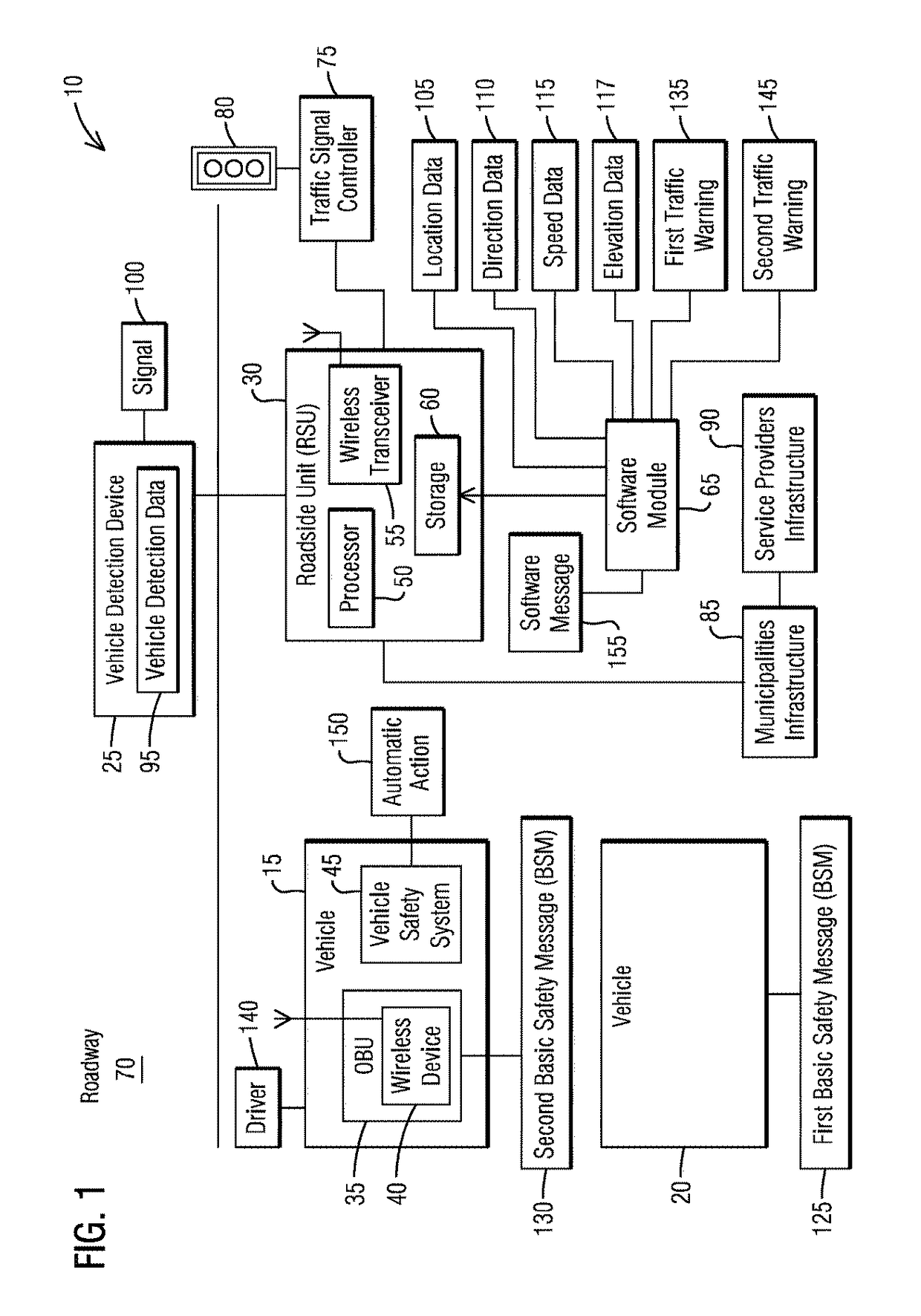
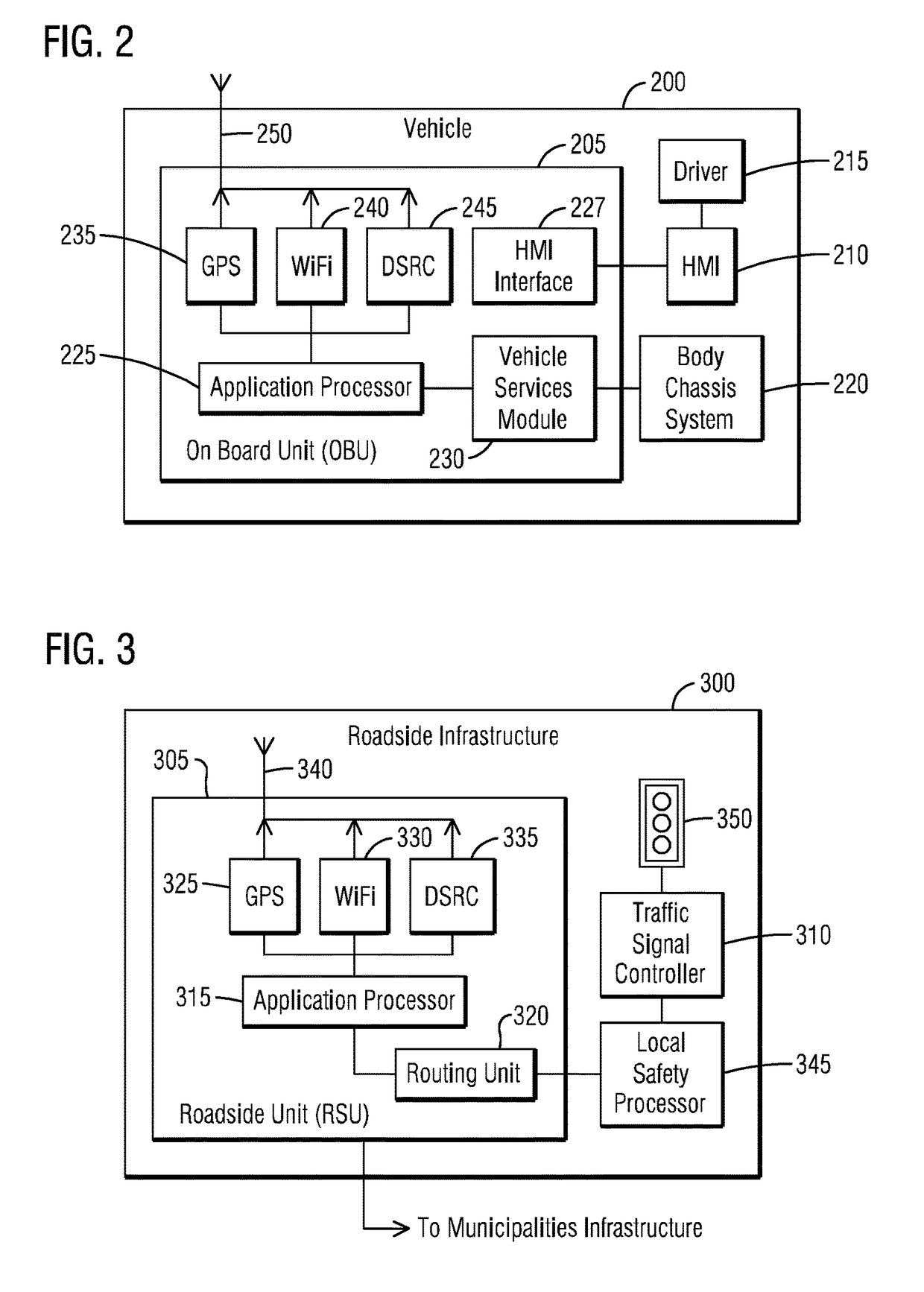
ActiveUS9646496B1No costAvoid traffic jamsControlling traffic signalsParticular environment based servicesBasic safety messageTraffic signal
A connected traffic safety system comprises at least one roadside unit and a vehicle detection device. The roadside unit is configured to transmit wireless signals and receive corresponding responses from a corresponding wireless device of an Onboard Unit (OBU)-equipped vehicle, and to send at least one of vehicle location data, direction heading data, elevation data and speed data from the OBU-equipped vehicle to a traffic signal controller. The vehicle detection device is configured to generate vehicle detection data of at least one non-Onboard Unit (OBU)-equipped vehicle. The roadside unit to receive the vehicle detection data for creating a proxy data wireless message for the non-Onboard Unit (OBU)-equipped vehicle. The roadside unit to mimic the proxy data wireless message as a first Basic Safety Message (BSM) for the non-Onboard Unit (OBU)-equipped vehicle that would have been available to the Onboard Unit (OBU)-equipped vehicle present nearby.
Owner:SIEMENS MOBILITY INC
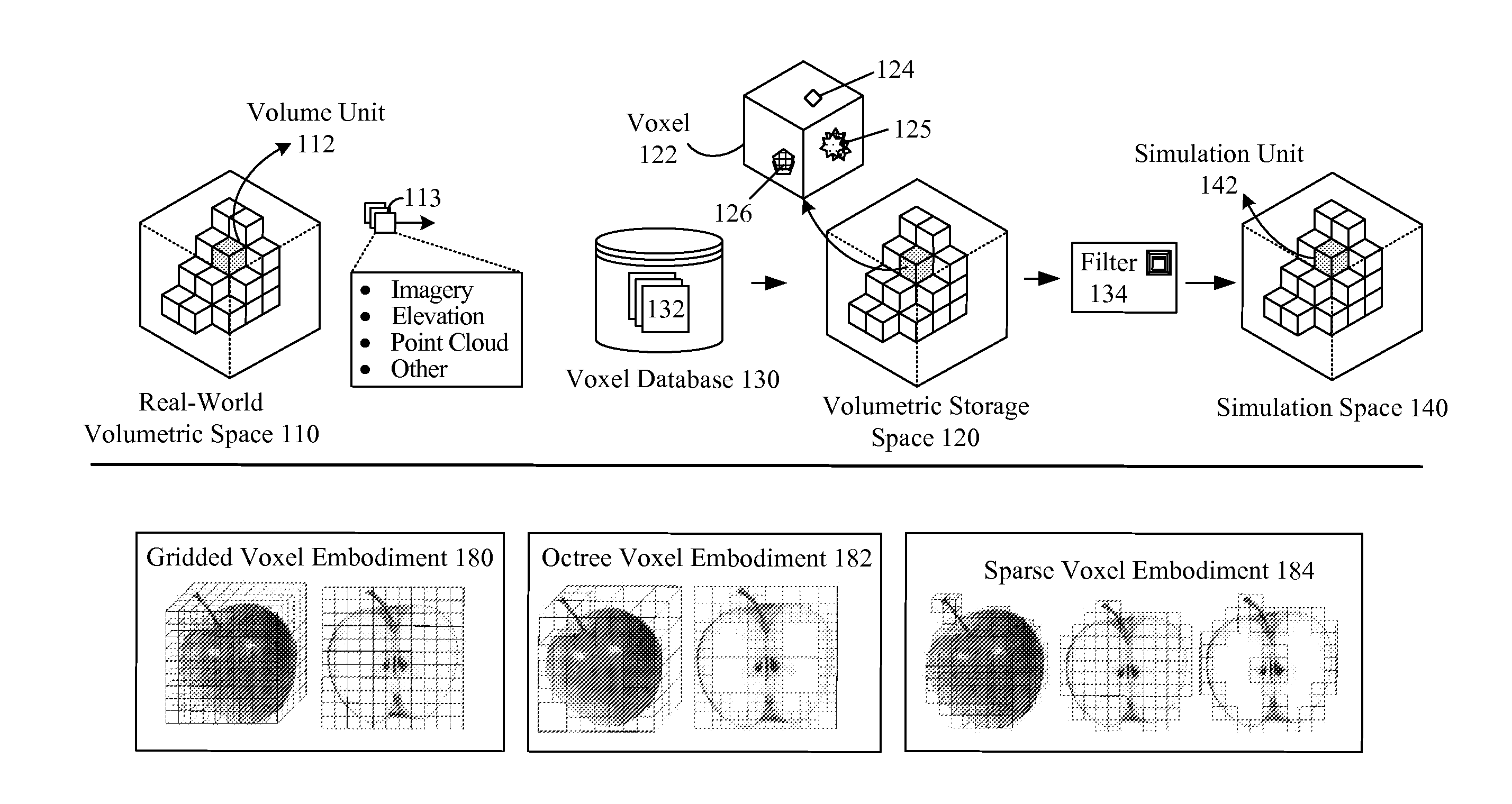
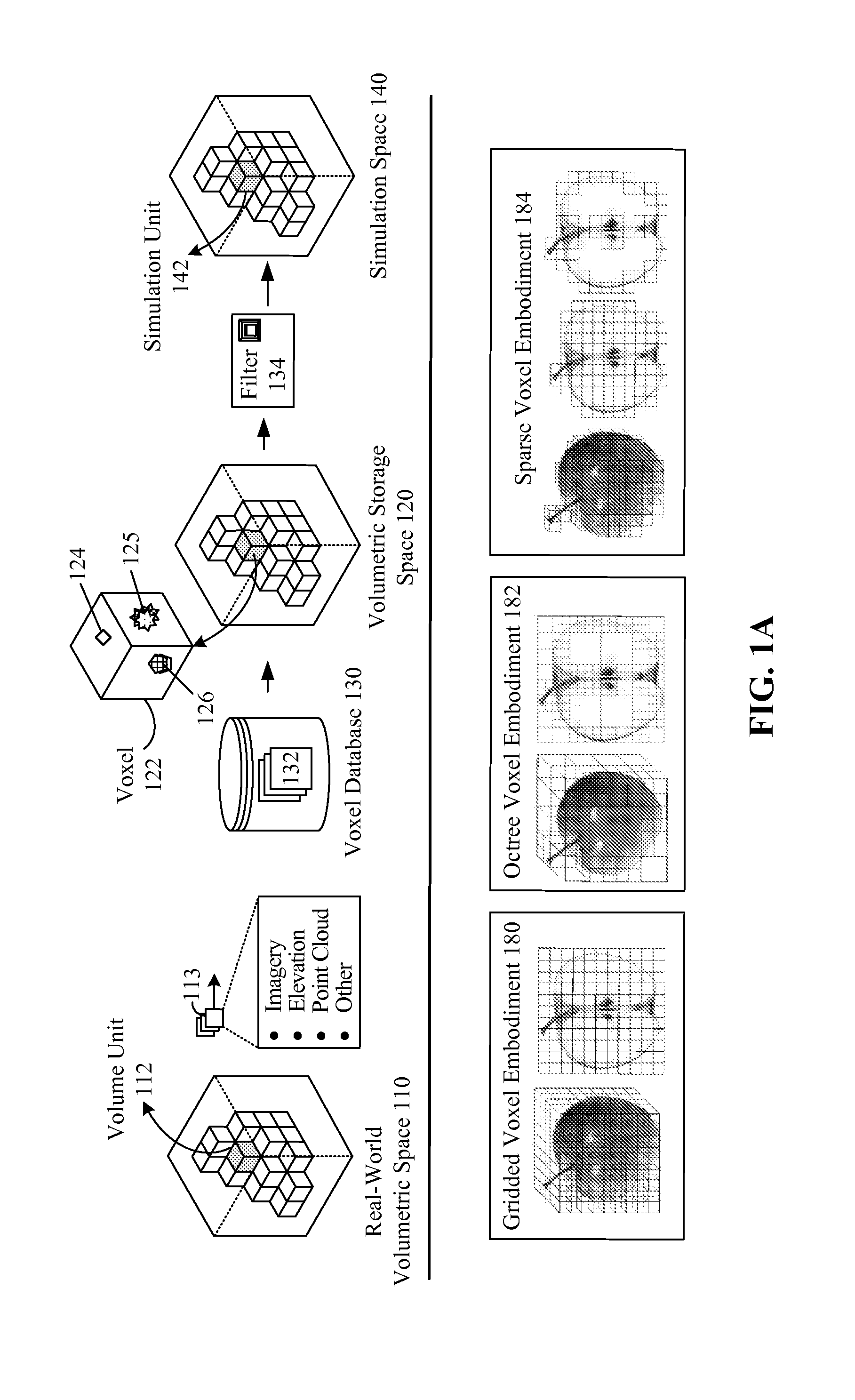
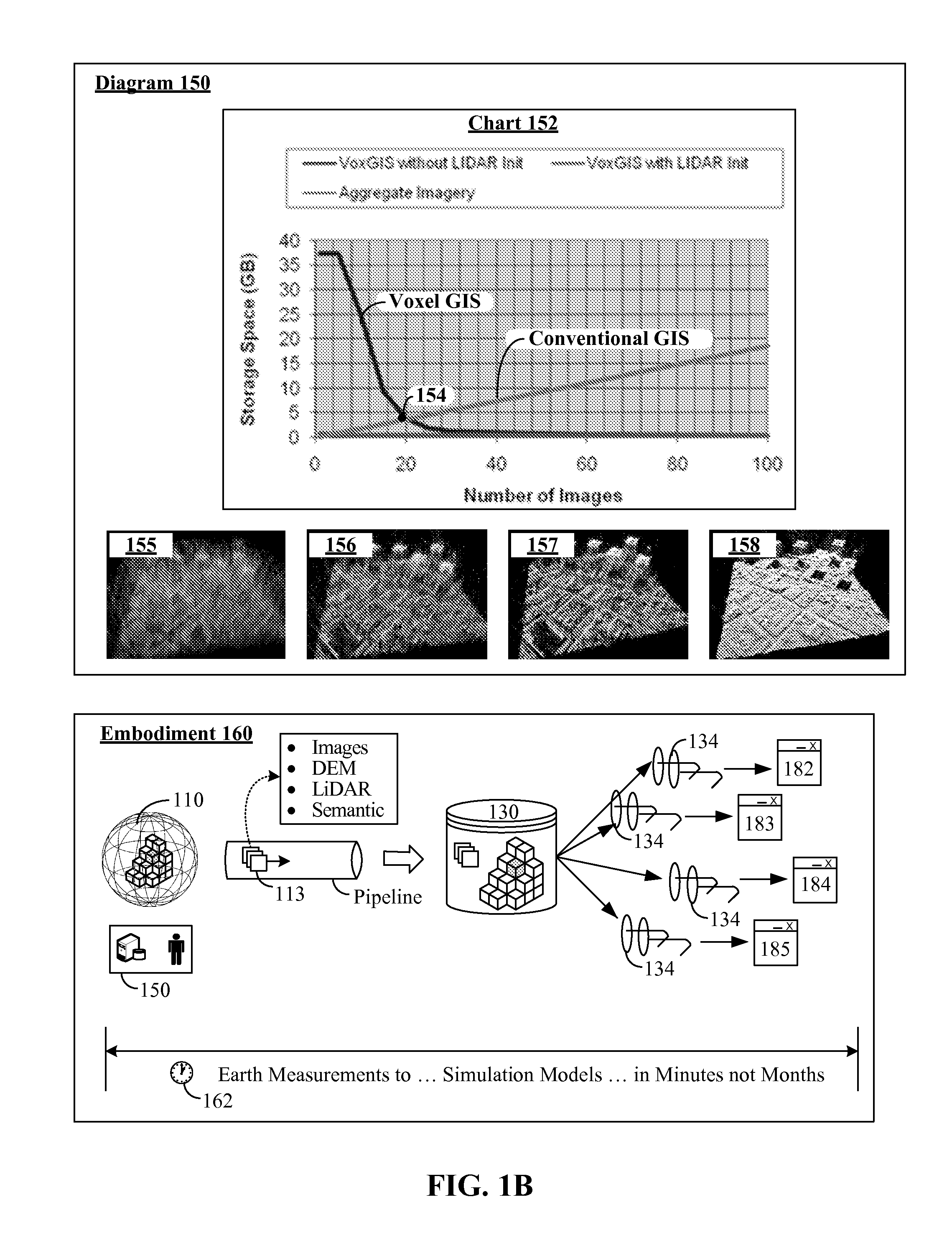
Voxel approach to terrain repositories for modeling and simulation
InactiveUS20110202538A1Increase spacingDigital data processing detailsGeographical information databasesTerrainVoxel
A set of sensors can capture raw data that geospatially corresponds to a real world volumetric space. The raw data can include point cloud data encoded in a light detecting and ranging (LiDAR) information format, imagery and video data, and elevation data encoded in a digital elevation model (DEM) or digital surface model (DSM) format. The real-world volumetric space can be segmented into a set of volumetric units, wherein datum of the raw data is indexed against the volumetric units. Each of the volumetric units of the real-world volumetric space can be mapped to a voxel in a storage volumetric space of a voxel database. The raw data can then be stored and fused in the voxel database such that each voxel in the voxel database represents a combination of volumetrically stored data for all source products that includes providing point cloud data, imagery data, and elevation data.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Displaying data
InactiveUS6748323B2Navigational calculation instrumentsPosition fixationComputer graphics (images)Display device
A technique for displaying topographical data, for example, on a screen of a portable hand-held device includes: optionally receiving GPS (Global Positioning System) signals and generating a digital output indicative of a position location of the display device in response to the received GPS signals or inputting location data manually to produce an image on a display screen of the device in response to the digital output; and storing true digital elevation data as compressed cells and decompressing on-the-fly only data needed to provide elevation data for an image area displayed on the display screen.
Owner:DIDI HK SCI & TECH LTD
Method and system for generating detail-in-context lens presentations for elevation data
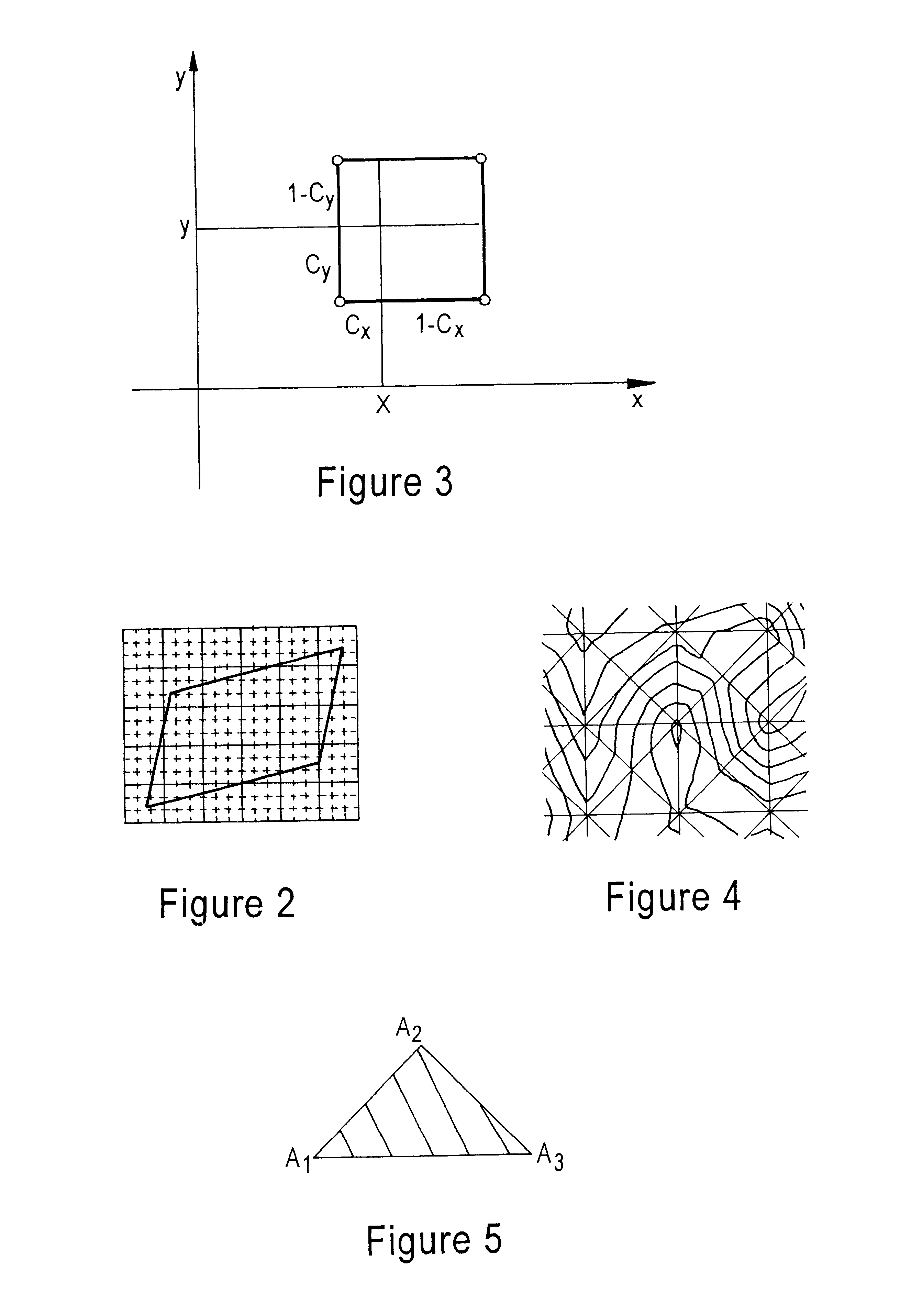
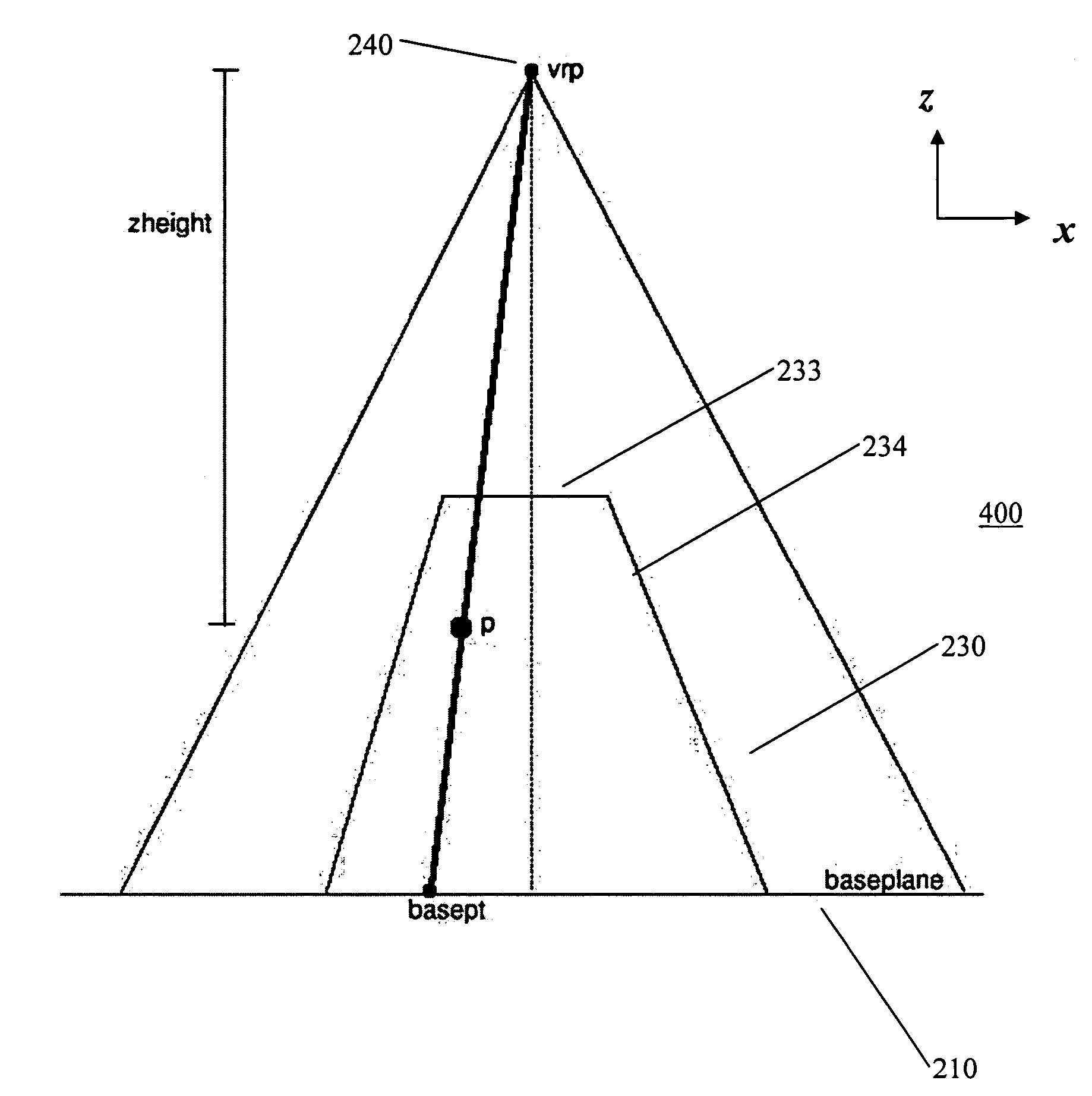
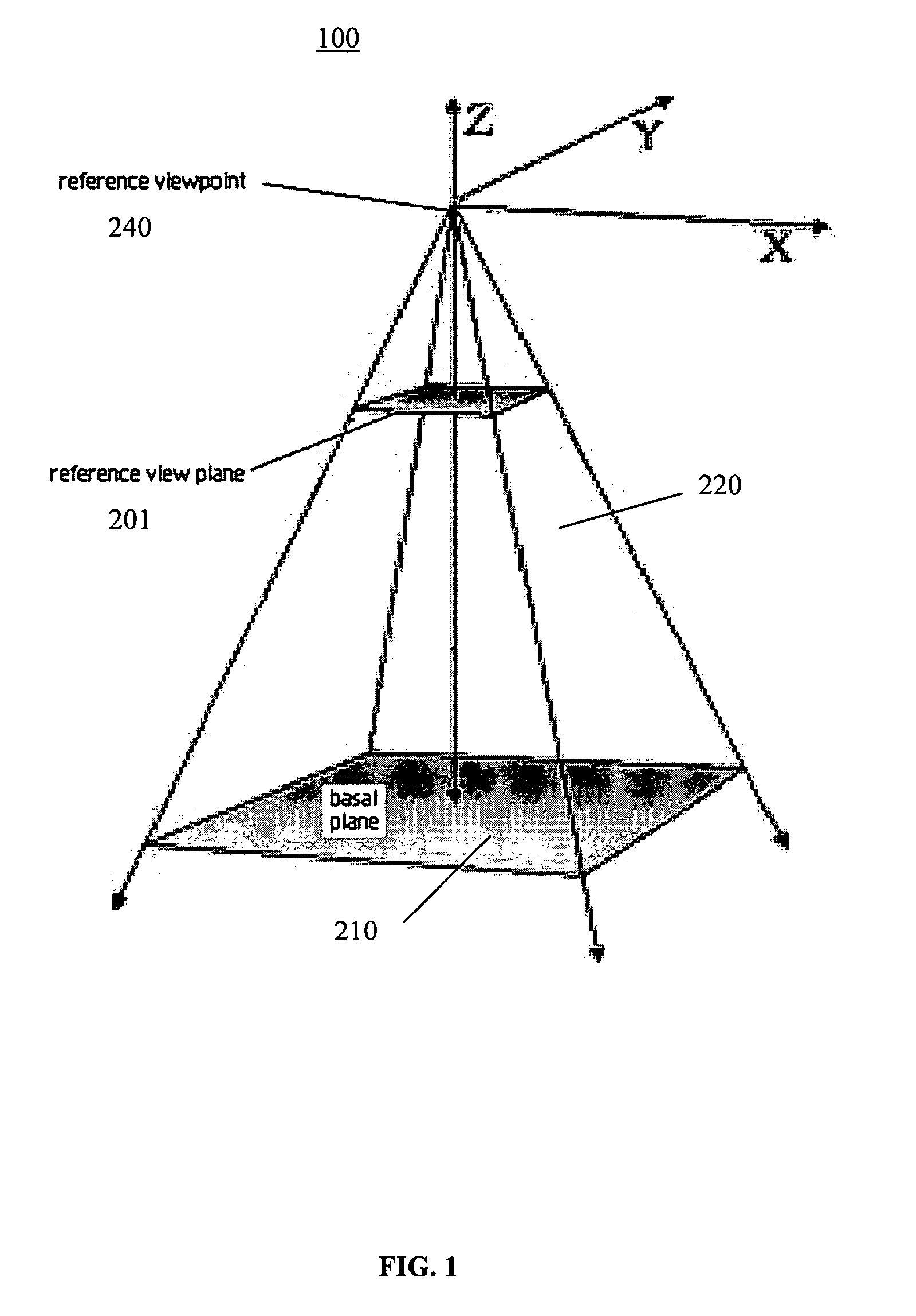
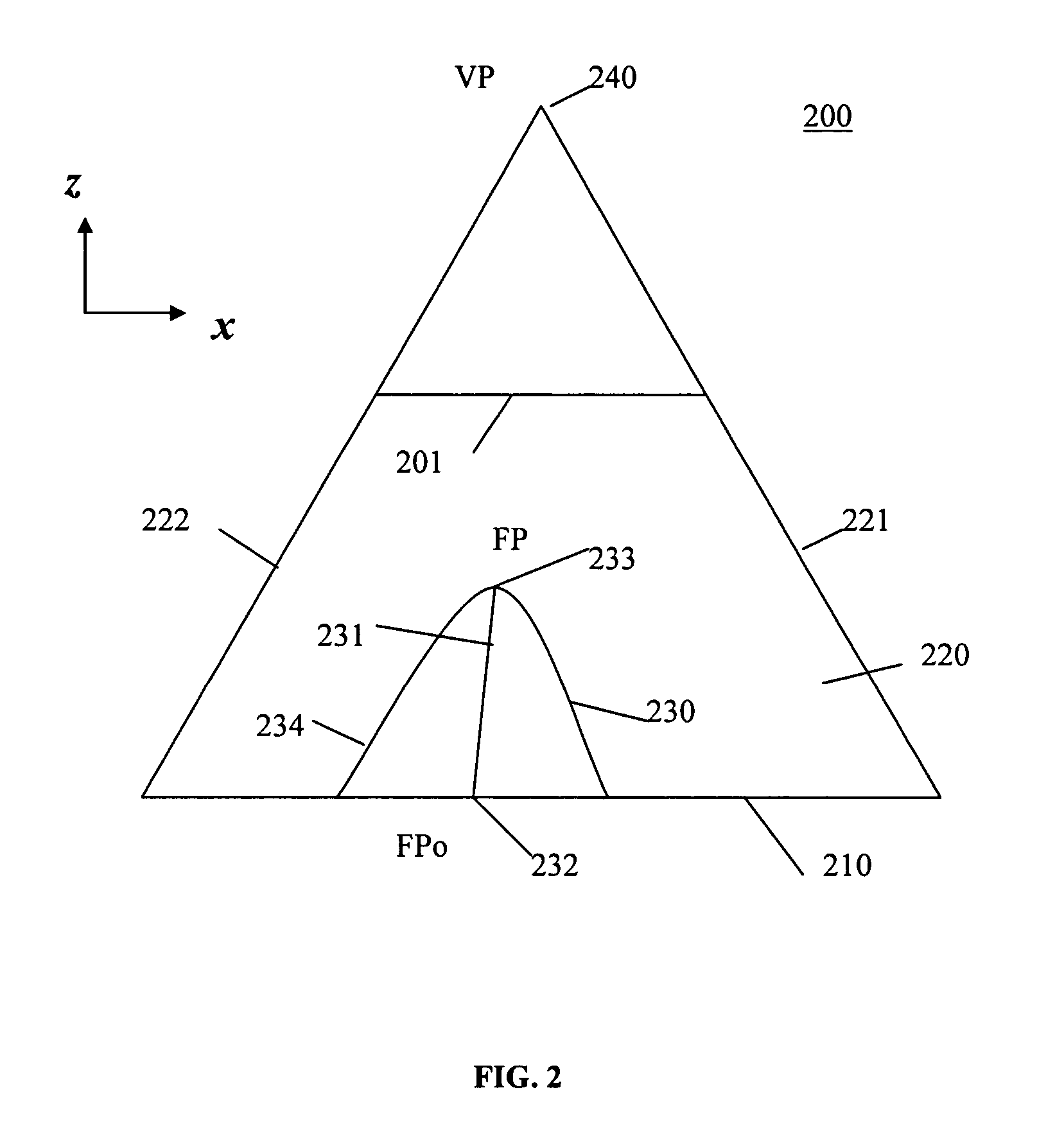
A method for generating a presentation of a region-of-interest in an elevation data representation for display on a display screen, comprising: calculating a displacement height for at least one point in the representation falling within a lens by inversely scaling a vertical height of the point from a viewpoint for the presentation by a magnification for the lens; if the point is within a shoulder region of the lens, scaling the displacement height by a value of the shoulder function evaluated at a value given by a distance between a projection point in the basal plane and a closest point on a perimeter of a focal region as projected onto the basal plane, the distance being scaled by a distance between the closest point and an intersection point on a perimeter of the shoulder region; and, displacing the point by the displacement height to generate the presentation.
Owner:NOREGIN ASSETAB N V L L C
Method for constructing three-dimensional terrain vector model based on multi-beam sonar submarine measurement data
ActiveCN102446367AResolve can only provide discrete terrain elevationSolve the shortcoming of only being able to query the terrain parameters of the survey point3D modellingOcean bottomSonar
The invention discloses a method for constructing a three-dimensional terrain vector model based on multi-beam sonar submarine measurement data, and relates to a method for constructing the three-dimensional vector terrain model with measurement data of multi-beam sonar, which solves the defect that a multi-beam ranging sensor can only provide discrete terrain elevation and can only query terrainparameters at a measurement point. The method is used for non-structural submarine terrain modeling and vector data retrieval. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a horizontal coordinate of a sampling point of the terrain of a submarine area and corresponding elevation data; defining a data structure of a terrain triangular net model according to characteristics of multi-beam sonar terrain measurement data; and finally, establishing a Delaunay triangular net vector model according to elevation data of each point of the multi-beam sonar terrain measurement and the data structure of a Delaunay triangular net.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
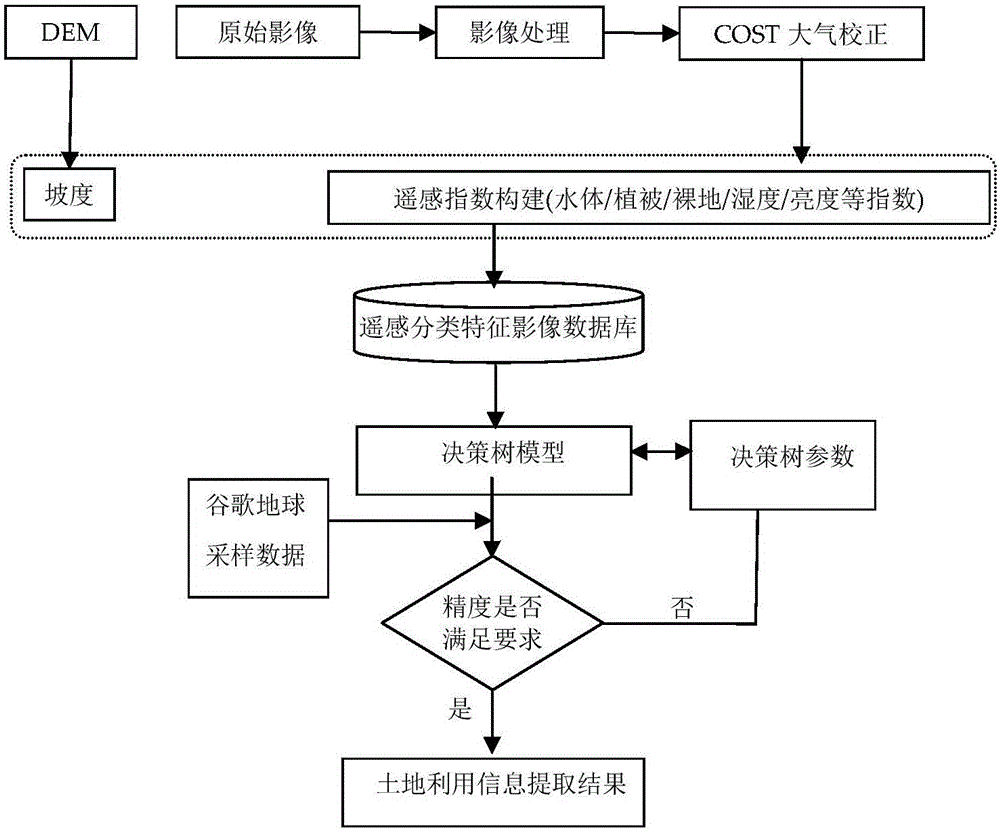
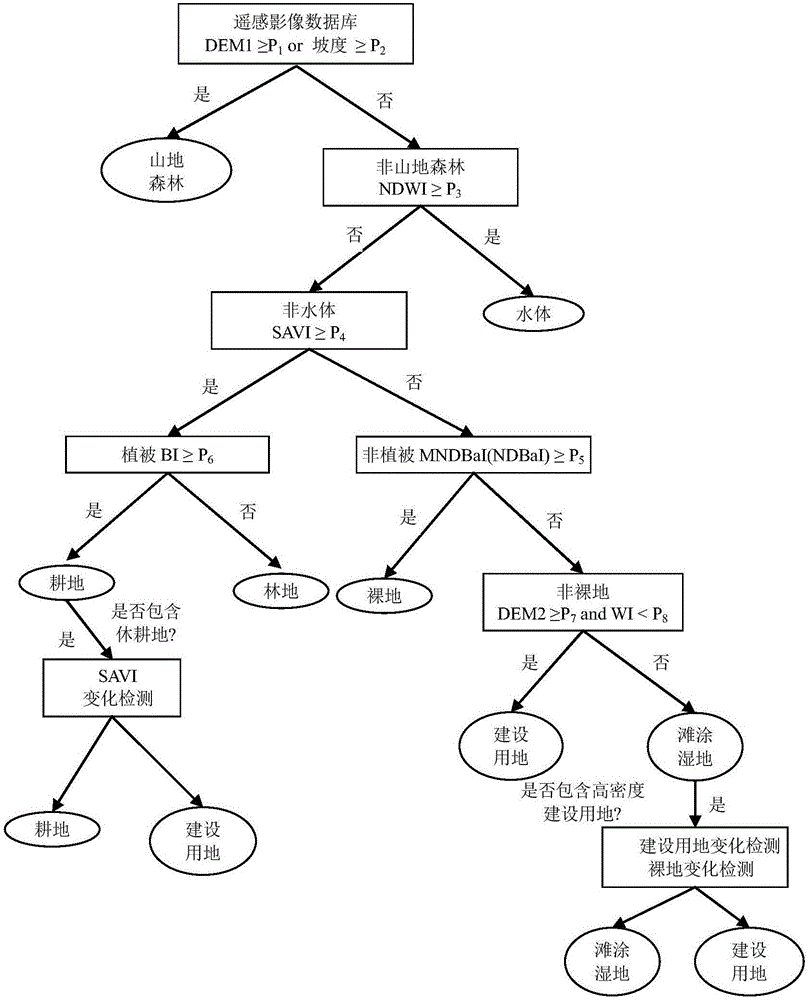
Coastal city time sequence land utilization information extracting method
ActiveCN106650689AImprove robustnessImprove universalityImage enhancementImage analysisAtmospheric correctionCritical question
The invention discloses a coastal city time sequence land utilization information extracting method. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a remote-sensing image Landsat, and preforming atmospheric correction on the same; constructing a remote-sensing classification feature index database by selecting a group of remote-sensing classification features; acquiring data elevation image DEM data to obtain elevation data and slope data; constructing a decision rule of single-classification feature index or multiple classification feature indexes according to different land utilization types of the coastal city based on a multi-feature decision tree model, classifying the coastal city land utilization step by step according to the rule, and finally determining various branches of the decision tree, detecting the time sequence remote-sensing image change, and distinguishing a mistaken classification land type and a missed classification land type, wherein the method further comprises the content of two parts: evaluating classification precision, and outputting the land utilizationclassification map extracted based on the decision tree model. By use of the extracting method disclosed by the invention, the coastal city land utilizationclassification precision can be greatly improved, and a key problem in the coastal city land utilizationclassification is solved.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV OF TECH
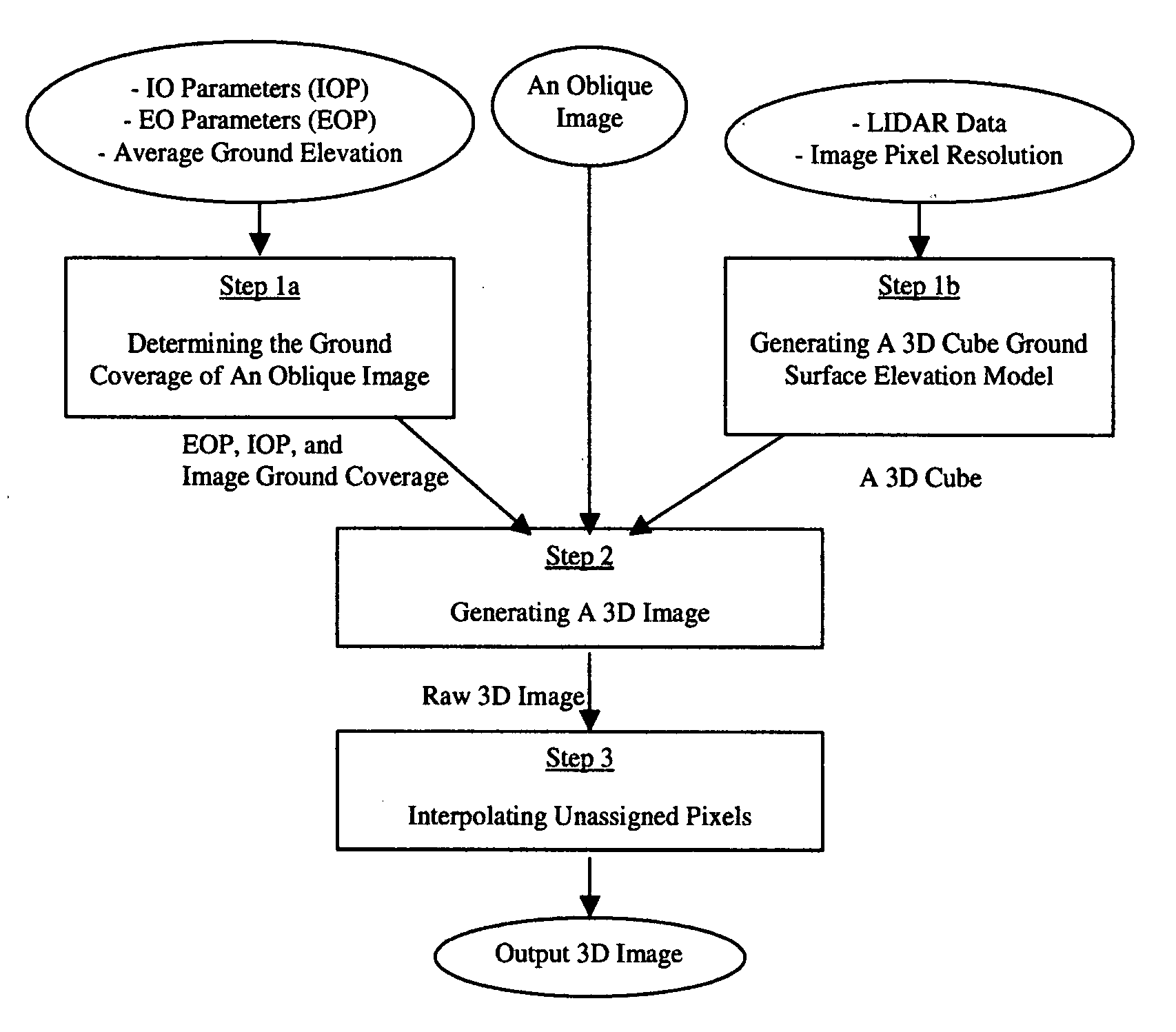
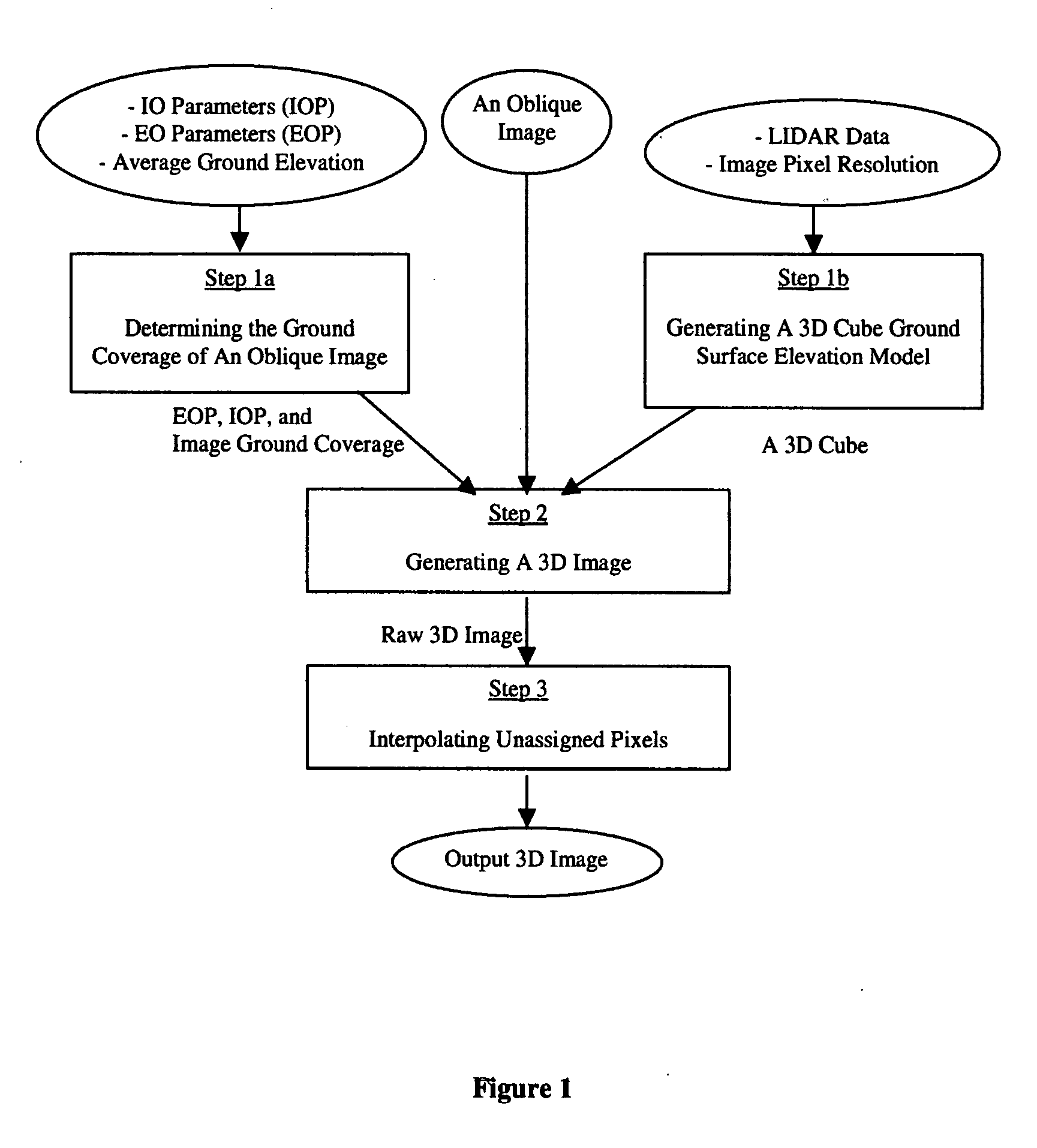
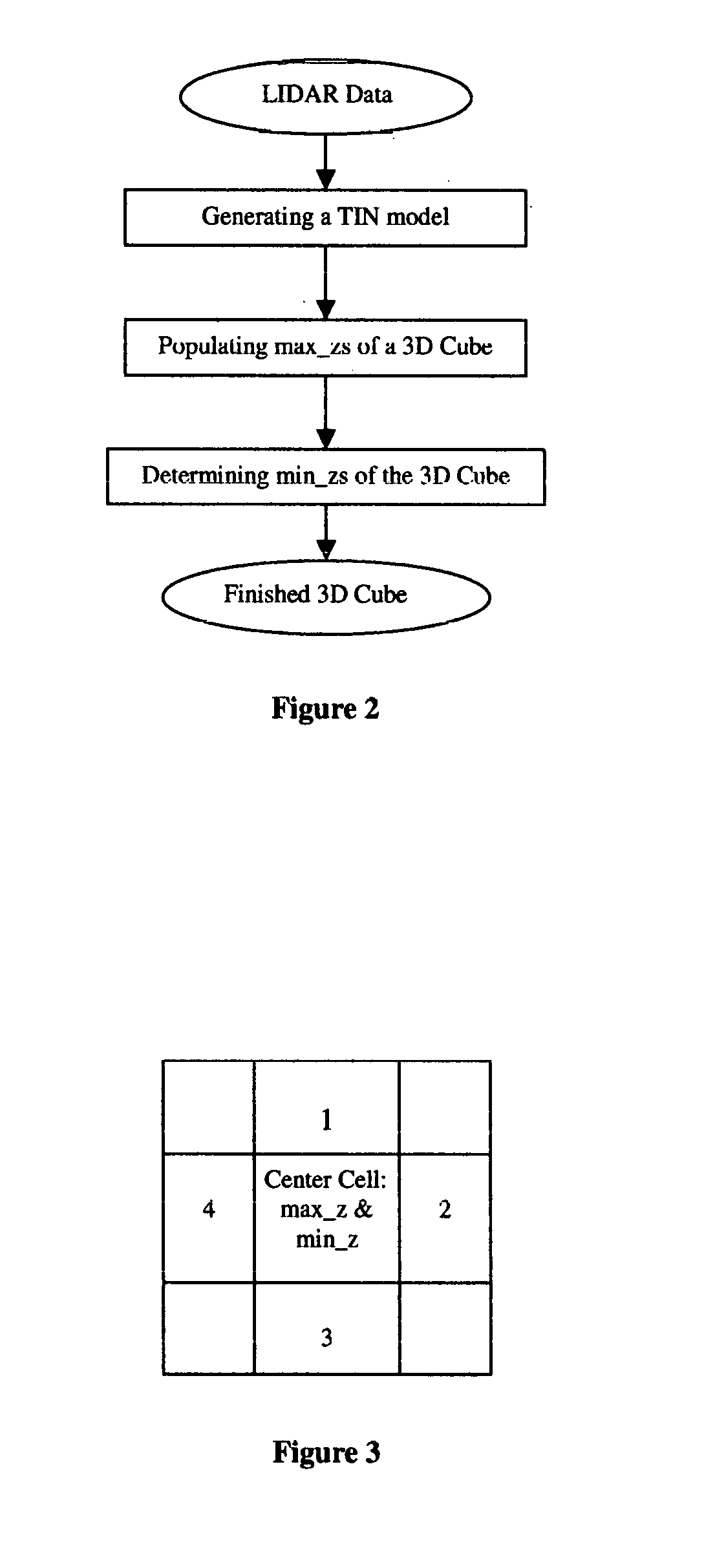
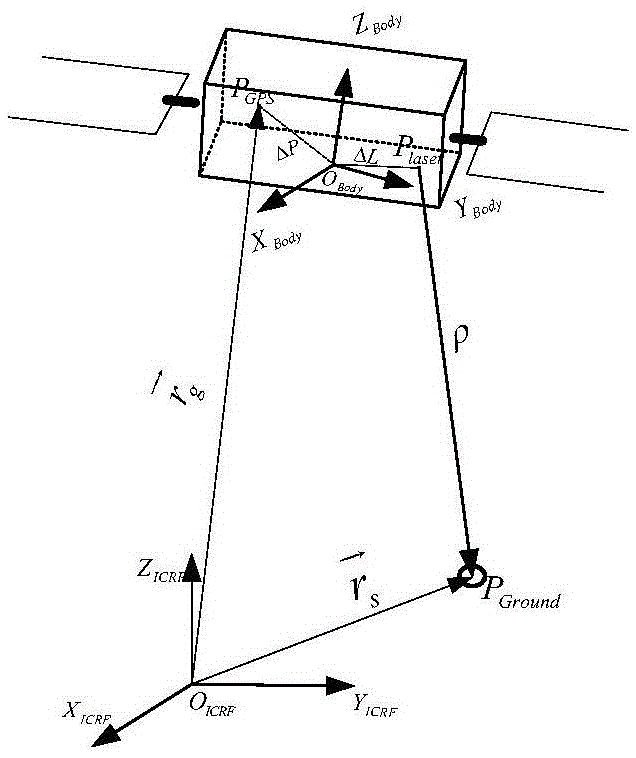
Method and System of Generating 3D Images with Airborne Oblique/Vertical Imagery, GPS/IMU Data, and LIDAR Elevation Data
This invention relates to a three-dimensional image of ground surface and the method and system that generates the three-dimensional image. Here, a three-dimensional image is an image that has three-dimensional XYZ coordinates in a ground coordinate system for every pixel of the image and the ground surface means the bare-earth surface plus all the objects on the bare-earth surface. The scene covered and represented by such a three-dimensional image is a three-dimensional real world scene where everything visible in the three-dimensional image has three-dimensional coordinates. The three-dimensional XYZ coordinates of all the pixels of a three-dimensional image are attributed by the method and system of this invention for generating three-dimensional images with airborne oblique / vertical imagery, GPS / IMU, and LIDAR ground surface elevation or range data. On such a three-dimensional image, one can make direct measurements of location, length, distance, height, area, and volume and indirect measurements including but not limited to profile and sight of view all in the real world three-dimensional coordinate system. Additionally, application systems that utilize three-dimensional images can make three-dimensional displays or perspective views of the ground surface with fly-through or walk-through, rotations and zoom in and out, and three-dimensional manipulation and simulation of ground surface.
Owner:HUAZHENG GEOSPACE
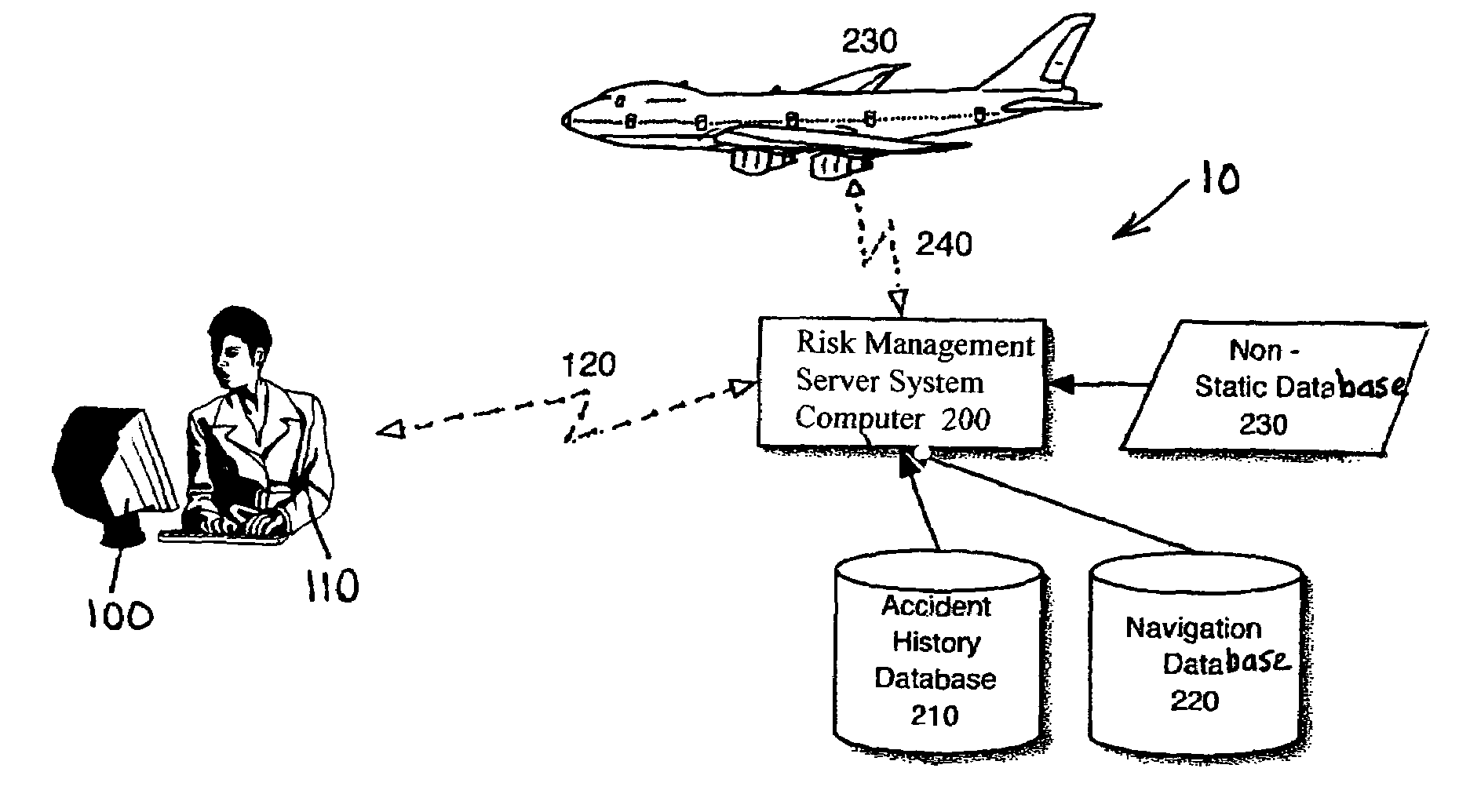
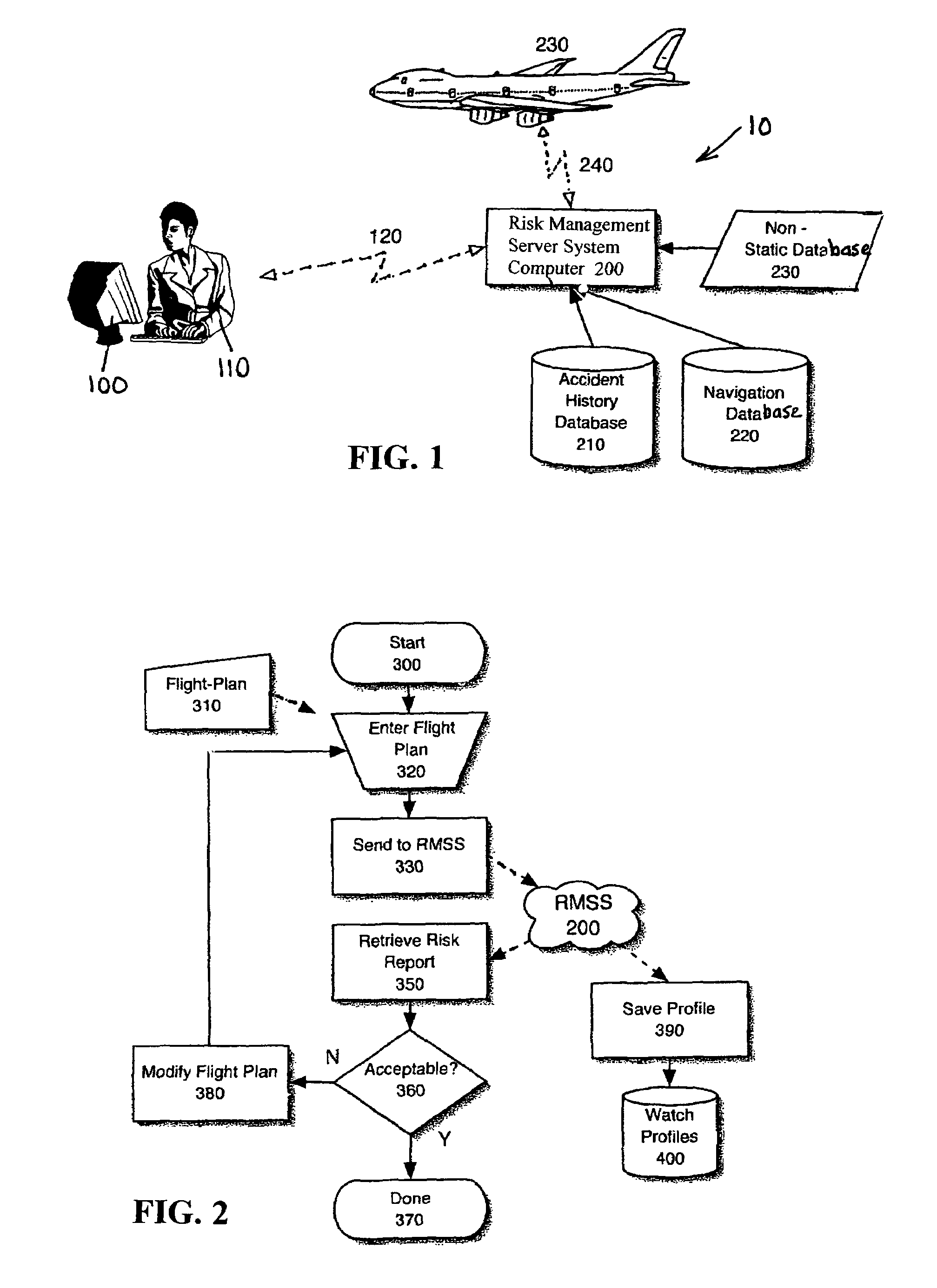
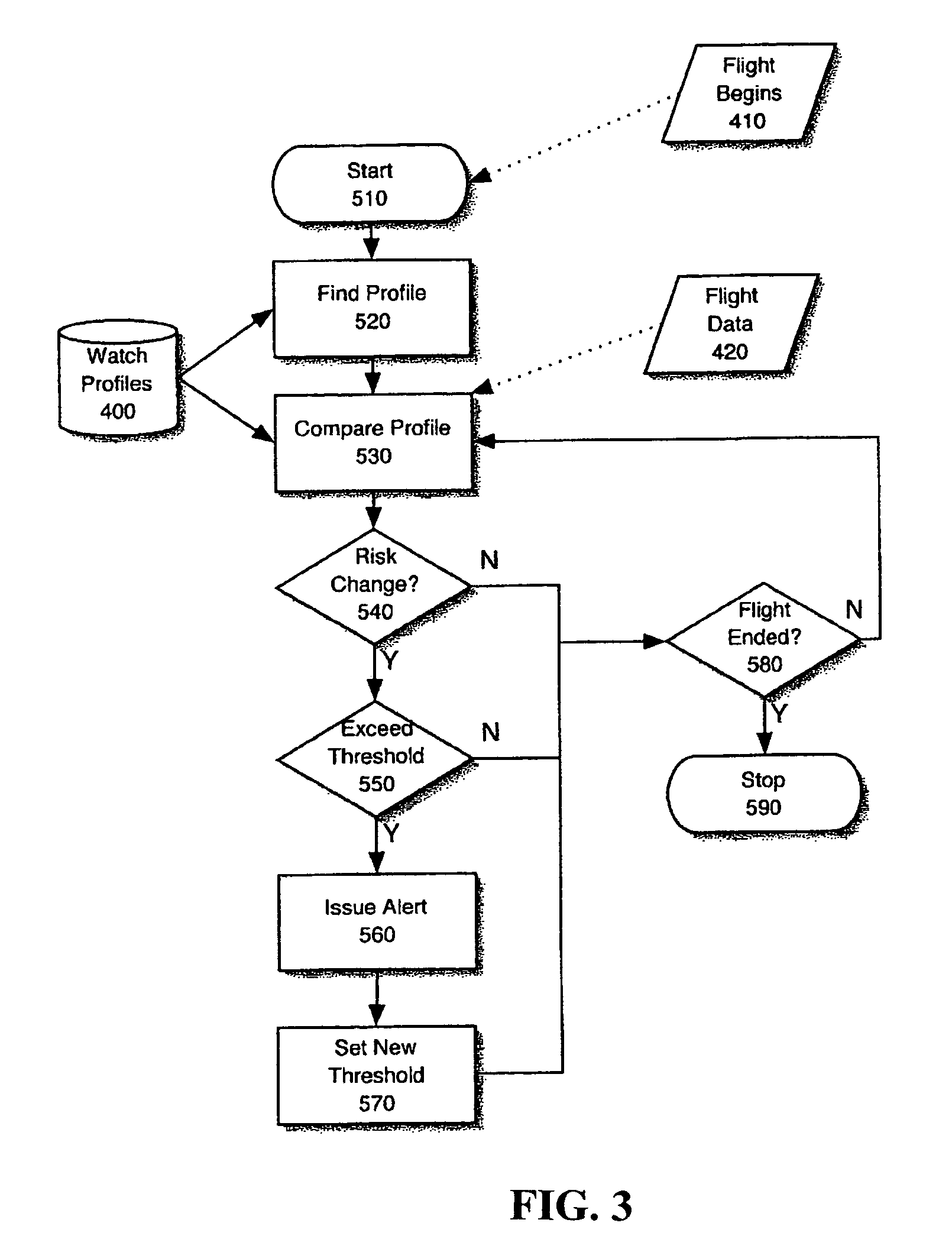
Aircraft flight risk measuring system and method of operation
ActiveUS6940426B1Improve flight safetyAnalogue computers for trafficComputations using stochastic pulse trainsOn boardAircraft flight mechanics
An aircraft flight risk measuring system for analyzing risks related to a flight of an aircraft. A user of the risk measuring system can be a flight dispatcher, an owner / operator, a pilot and other interested parties. The risk measuring system includes a risk management server system computer. The system computer has a two-way communication with a user computer operated by the user. An accident history database is connected to the system computer for providing accident reports related to the aircraft and other accident data. Also, a navigation database is connected to said system computer for providing airspace data, radio navigation aids, preferred routes, elevation data, geographic data and information related to a destination airport. Further, a non-static database is connected to the system computer for providing live information related to weather forecasts and data related to the aircraft's flight. As an option, a two-way communication between said system computer and an aircraft computer on board the aircraft can be included. The two-way communication used for receiving and transmitting encoded data from the aircraft when the flight is in progress.
Owner:AUCTNYC 3
System for sensing aircraft and other objects
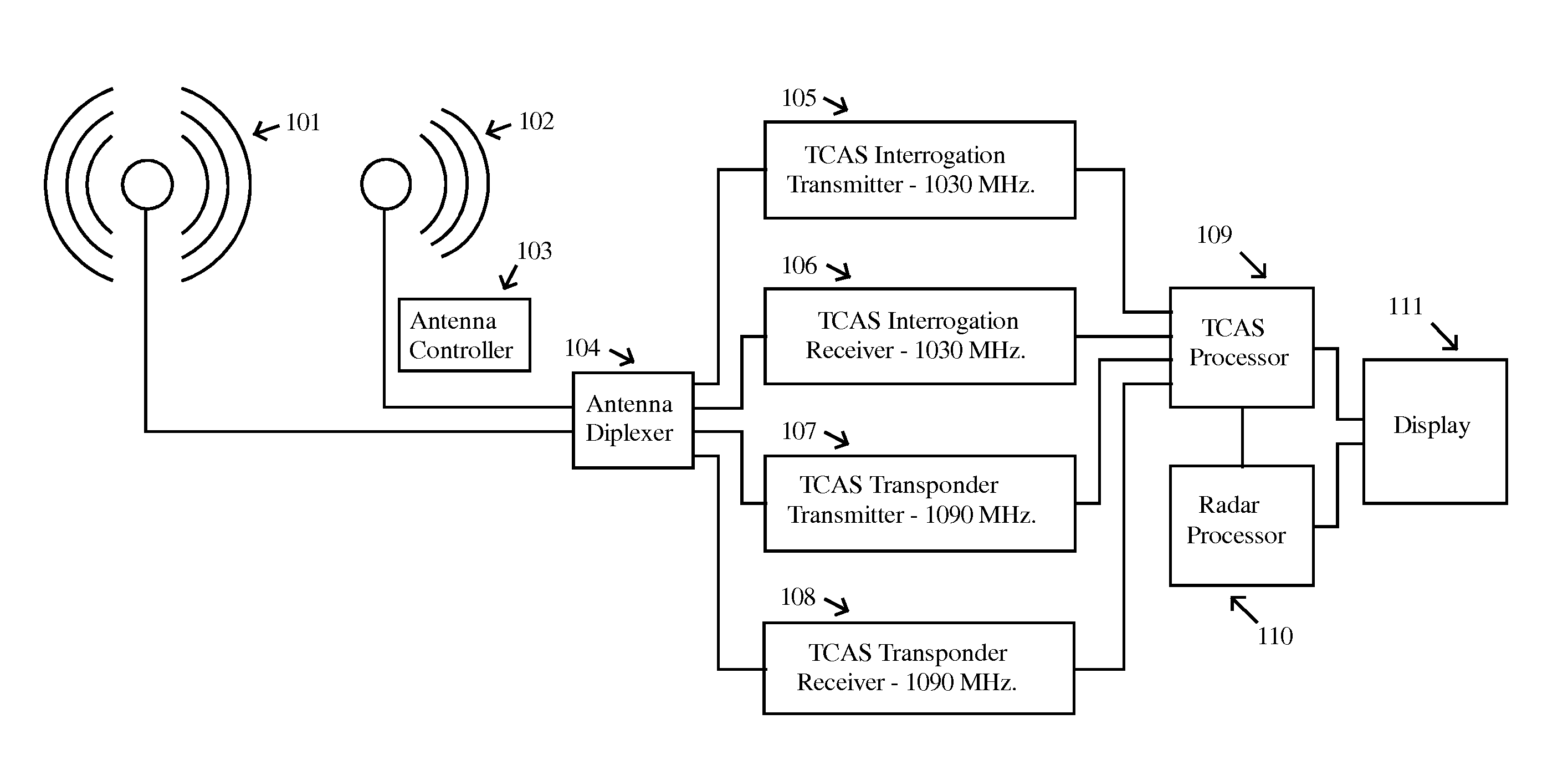
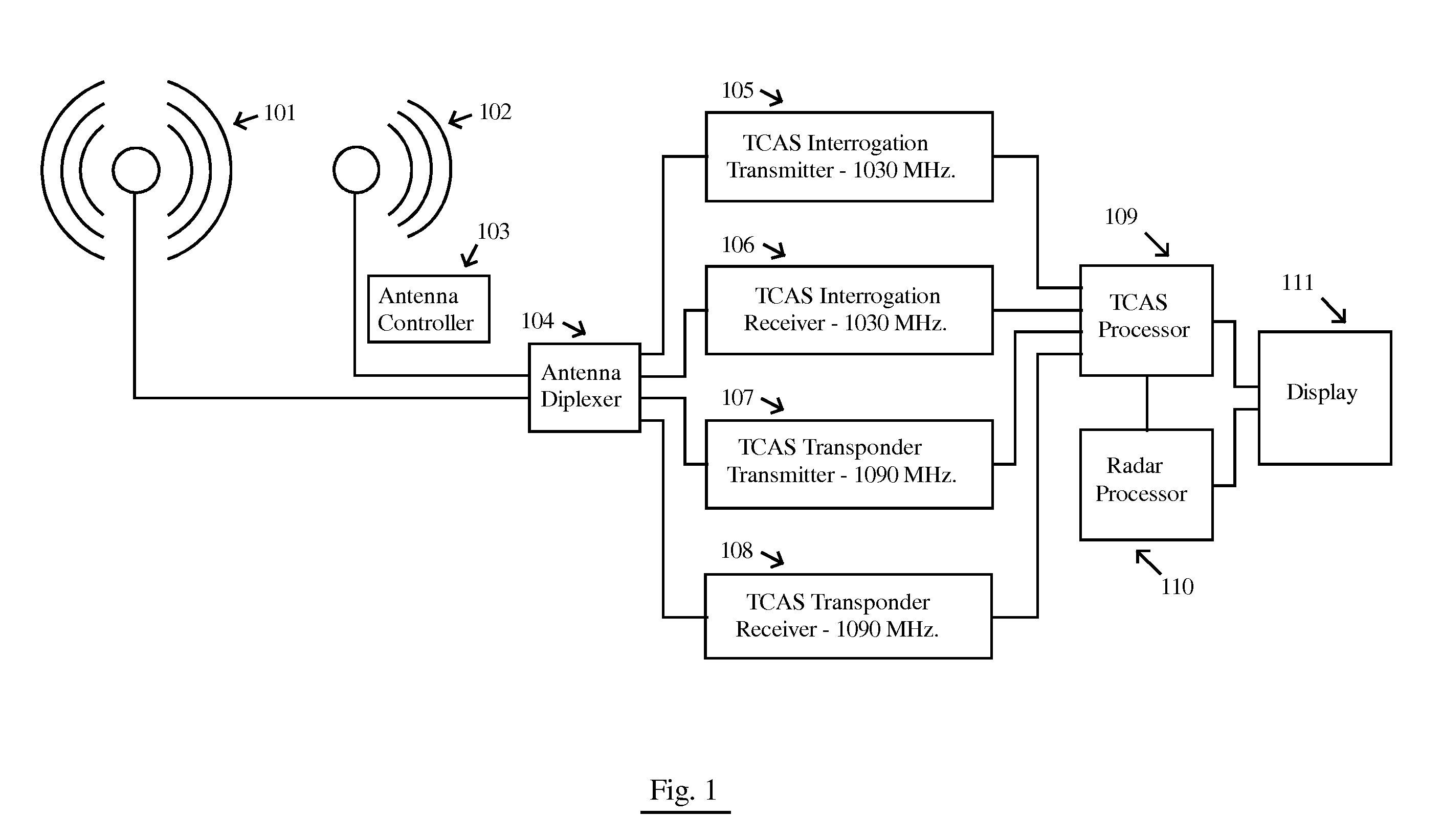
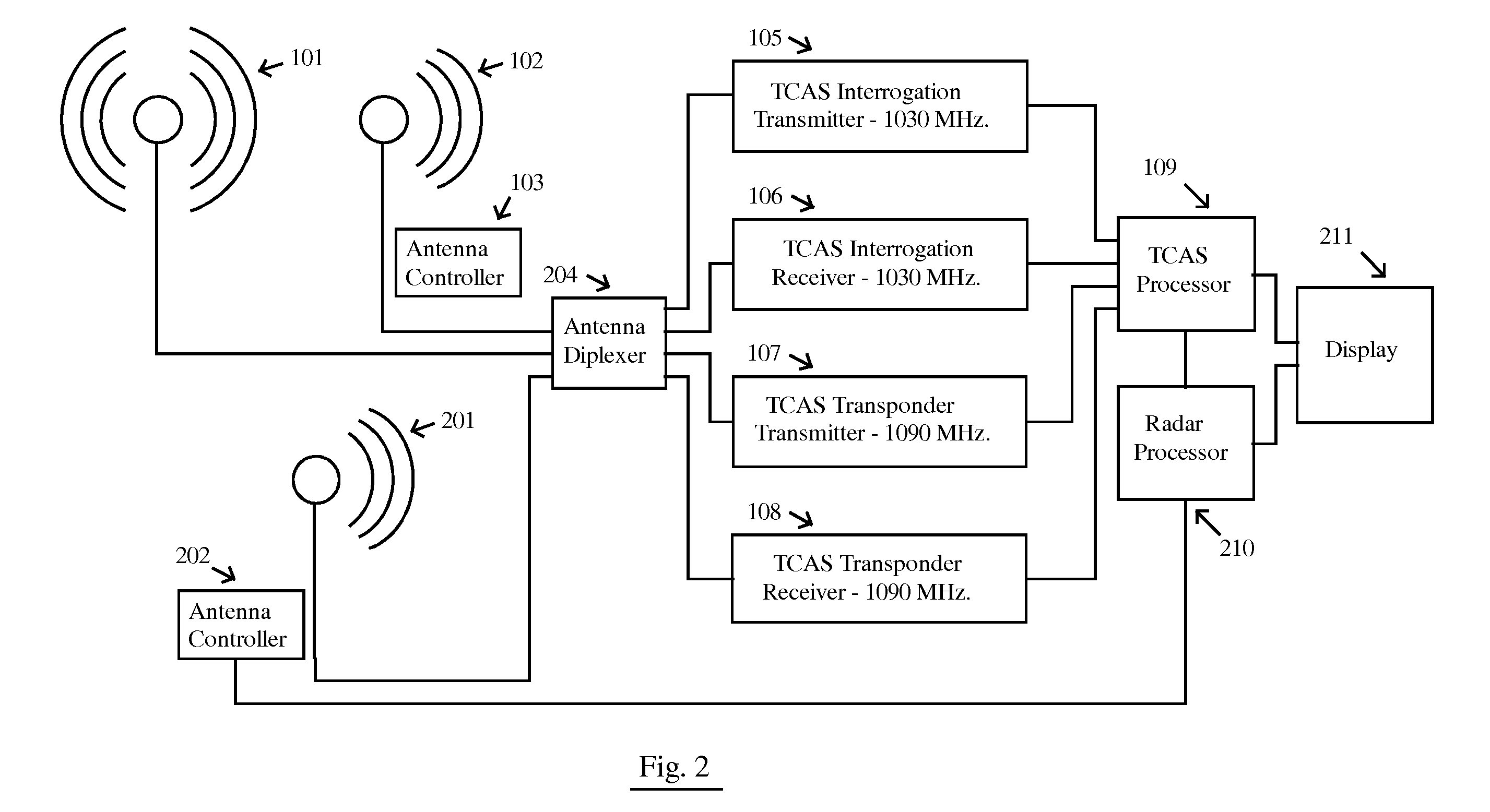
InactiveUS20110169684A1Reduce RF NoiseReduce noisePosition fixationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionCommunications systemFlight vehicle
A system for sensing aircraft and other objects uses bistatic radar with spread-spectrum signals transmitted from remotely located sources such as aircraft flying at very high altitudes or from a satellite constellation. A bistatic spread spectrum radar system using a satellite constellation can be integrated with a communications system and / or with a system using long baseline radar interferometry to validate the digital terrain elevation database. The reliability and safety of TCAS and ADS-B are improved by using the signals transmitted from a TCAS or ADS-B unit as a radar transmitter with a receiver used to receive reflections. Aircraft and other objects using spread spectrum radar are detected by using two separate receiving systems. Cross-Correlation between the outputs of the two receiving systems reveals whether a noise signal is produced by the receiving systems themselves or is coming from the outside.
Owner:MARGOLIN JED
Method and apparatus for developing a flight path
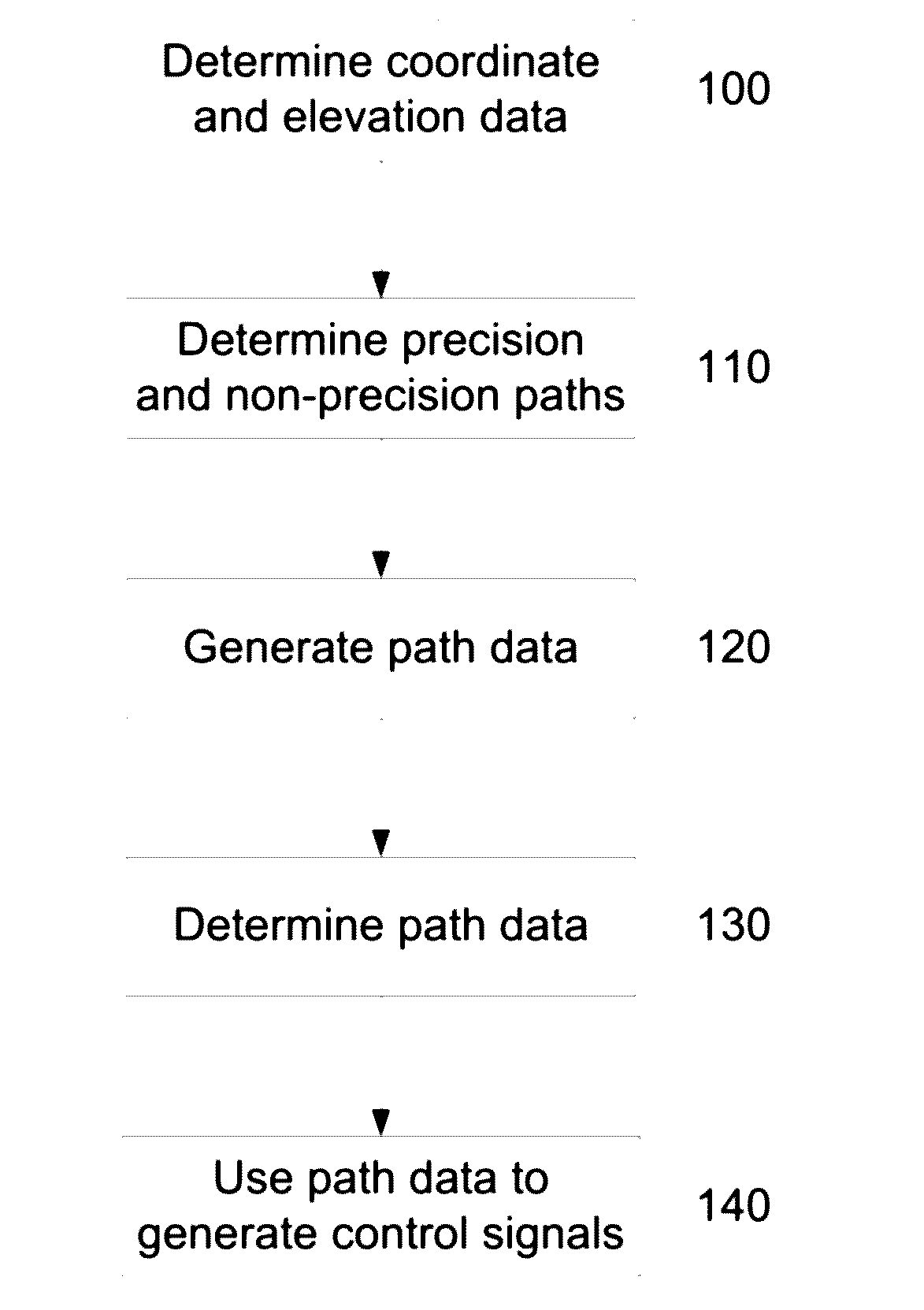
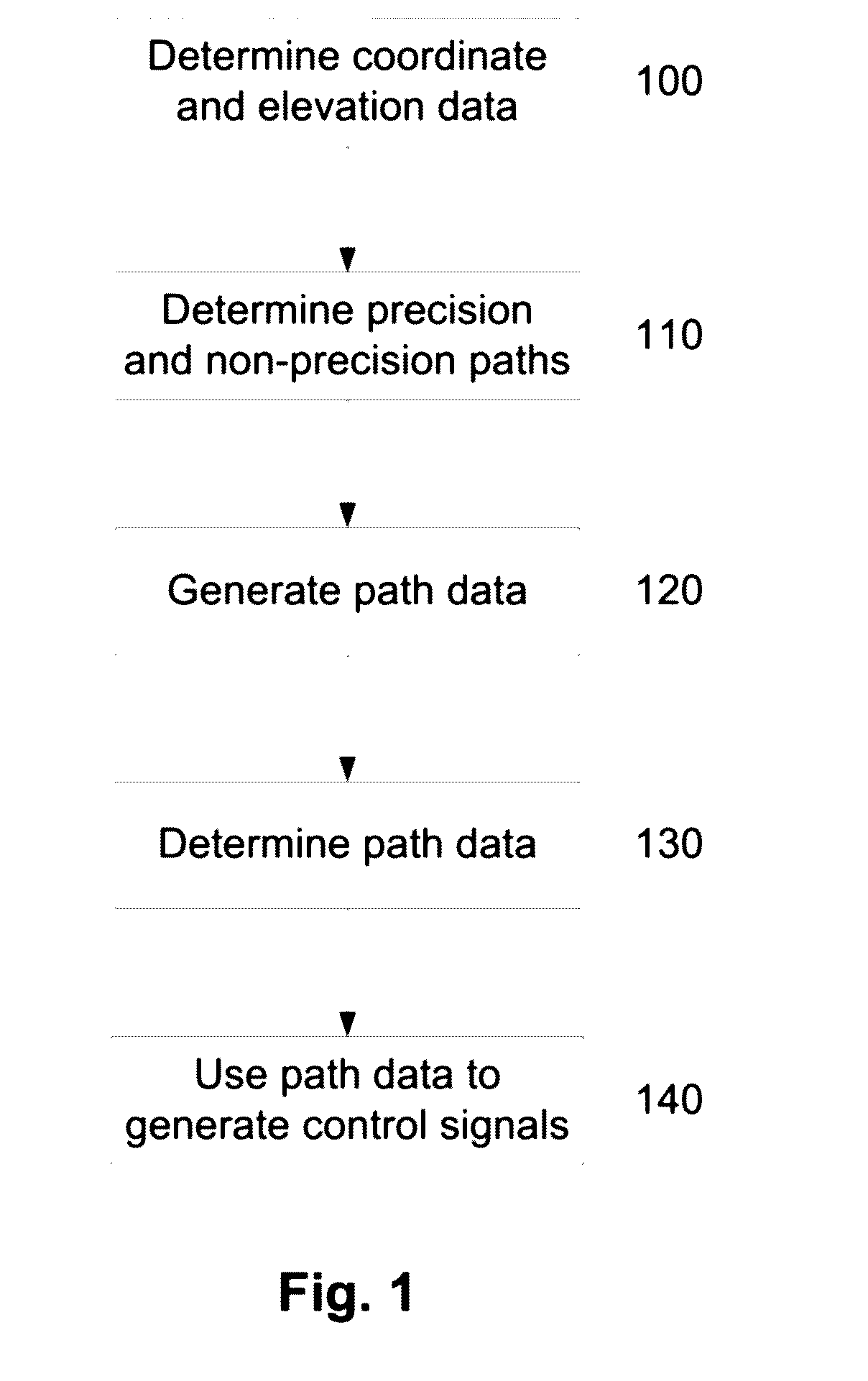
InactiveUS20160299506A1Overcome disadvantagesAircraft power plantsMeasuring points markingControl signalElevation data
A method of developing a flight path for precision flying over an area of interest, the method including, in an electronic processing device, determining coordinate and elevation data relating to an area of interest, using the coordinate and elevation data to determine a flight path including precision paths corresponding to precision flying trajectories and non-precision paths interconnecting at least some of the precision paths, and generating path data at least partially indicative of the flight path, the path data being useable in generating control signals for at least partially controlling operation of the aircraft, in use.
Owner:SPATIAL INFORMATION SYST RES
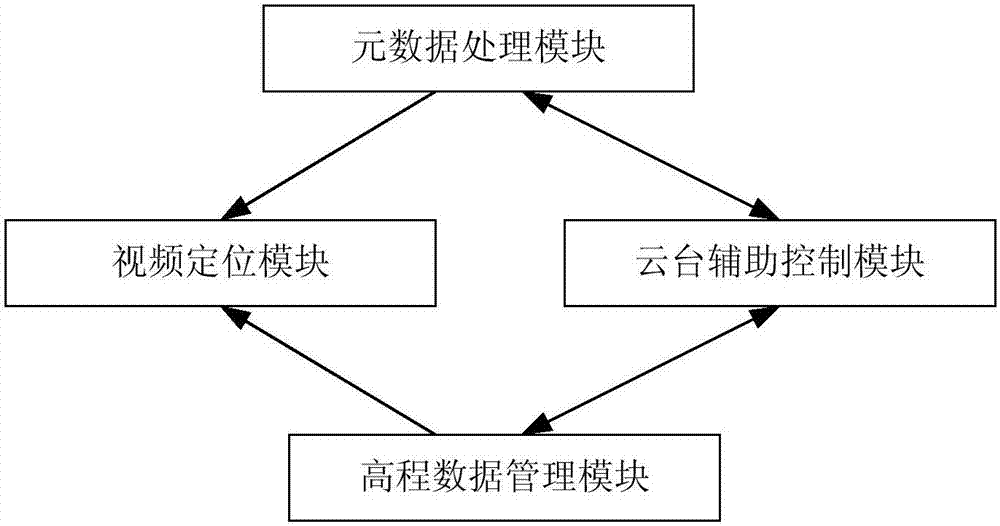
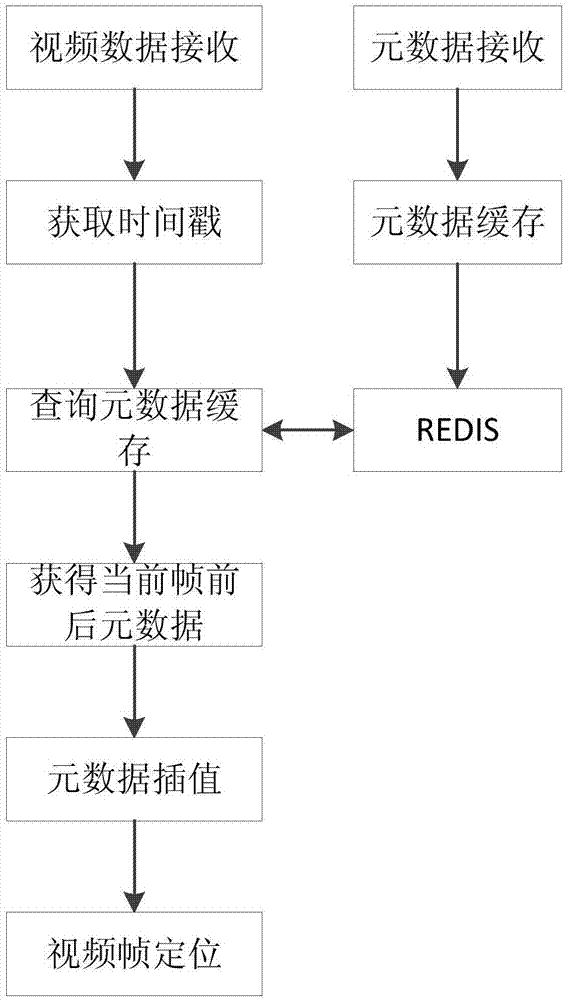
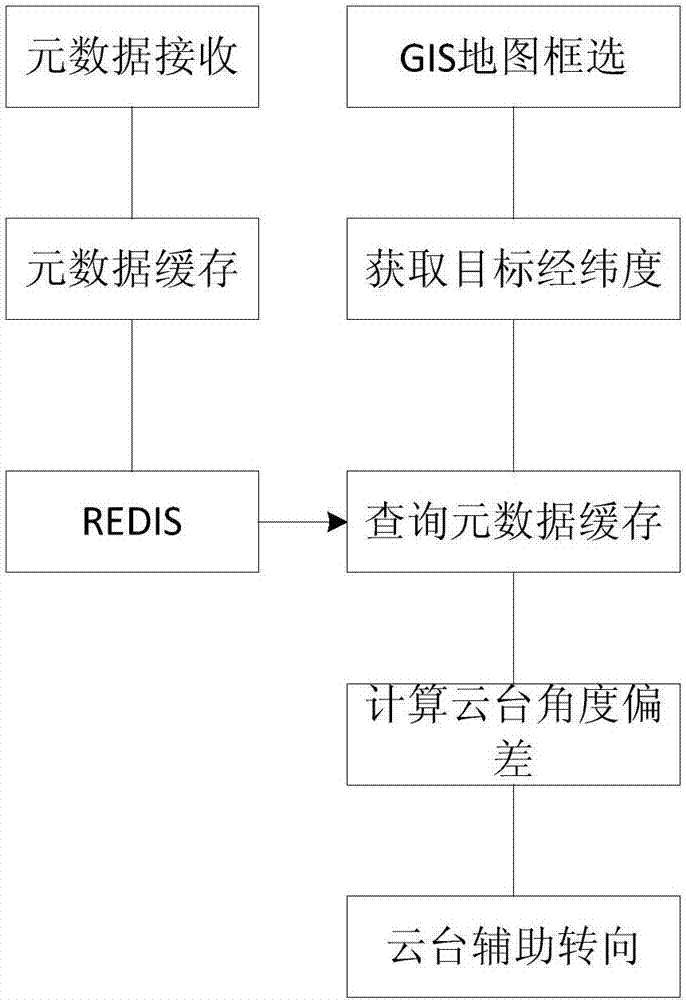
Unmanned plane video image target positioning system and method and holder control method
InactiveCN107247458ASimple control strategyImprove work efficiencyCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsSimulationElevation data
The invention discloses an unmanned plane video image target positioning system and method based on metadata and a holder control method and solves a problem that the position of a shot target of a video can not be acquired and displayed in the prior art. In combination with the target area position and the position and flight parameters of an unmanned plane, holder orientation and a pitch angle parameter are solved in real time, the target in the video is positioned, the target is assigned through frame selection of the video returned by the unmanned plane in an unmanned plane flight process, target positioning is supported, and the target area acquired through frame selection is displayed in a GIS map in real time. The method is advantaged in that a problem of inconvenience in manually adjusting a holder in the prior art is solved, point clicking on the GIS map to assign the target is supported, according to the unmanned plane, the target position, the flight parameter and the elevation data information, holder parameters are solved, the holder is controlled for rotation, and the target is made to be at a sensor vision axis center.
Owner:THE 28TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
Three-dimensional map data processing method based on multiple detailed layers
ActiveCN105427380AImprove clarityImprove real-time access performanceImage enhancementImage analysisAudio power amplifierLevel of detail
A three-dimensional map data processing method based on multiple detailed layers comprises three steps including digital orthographic image cutting, digital altitude data cutting, altitude data inlaying and edging. The highest three-dimensional map precision reaches 20 m at present. When a sight point is close with a surface texture, a single texture pixel will cover multiple pixel points under effects of a texture amplifier, so that an image becomes very vague. The three-dimensional map data processing method based on the multiple detailed layers provided by the invention increases definition of a three-dimensional map during display, wherein landform details are closer to real landform conditions; and real-time access performance of the three-dimensional map is enhanced by a database storage technology based on a three-dimensional model, pressure to a database server during access to the three-dimensional map is reduced, and concurrent access performance is also increased simultaneously.
Owner:KUNMING ENERSUN TECH
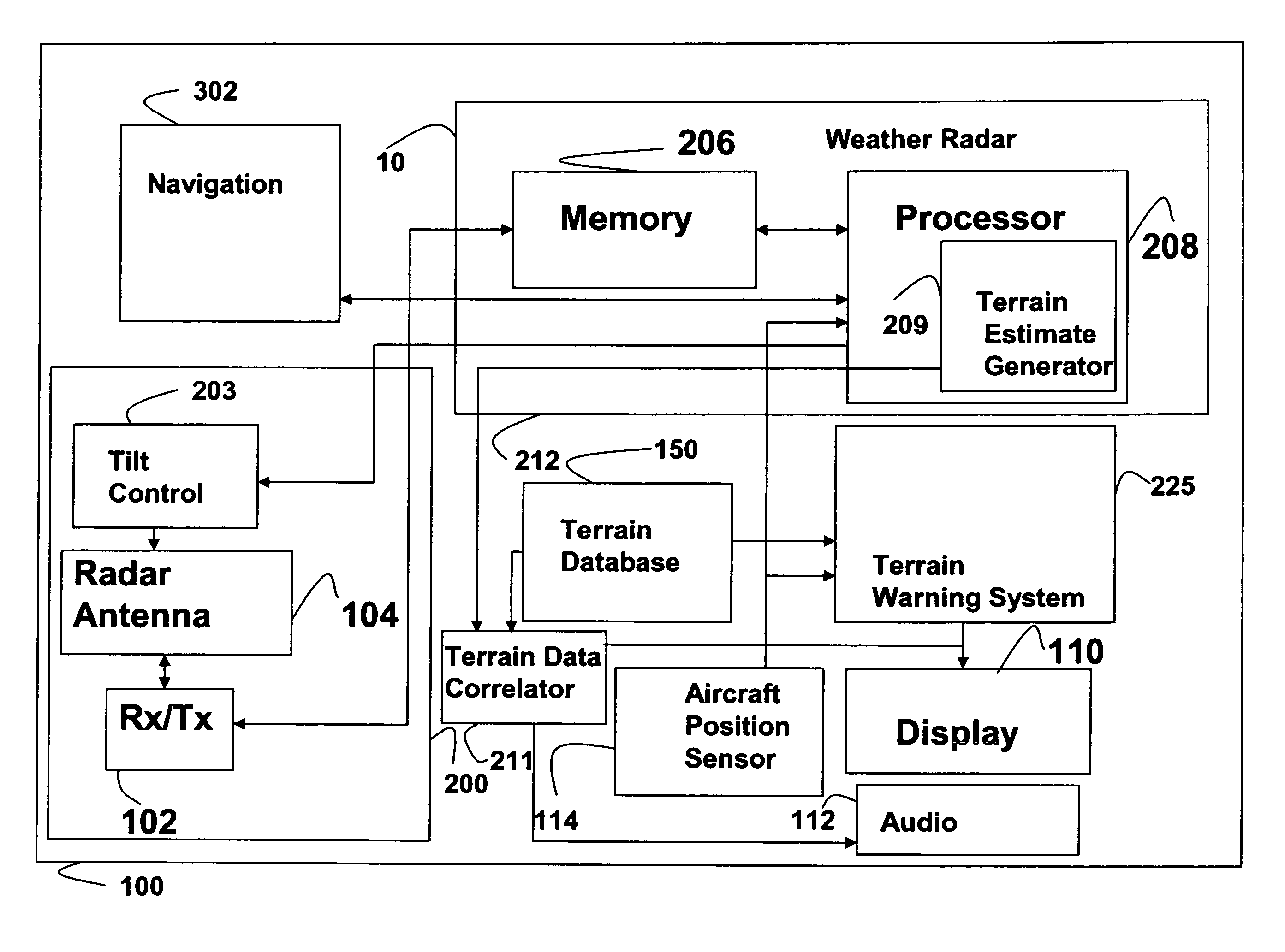
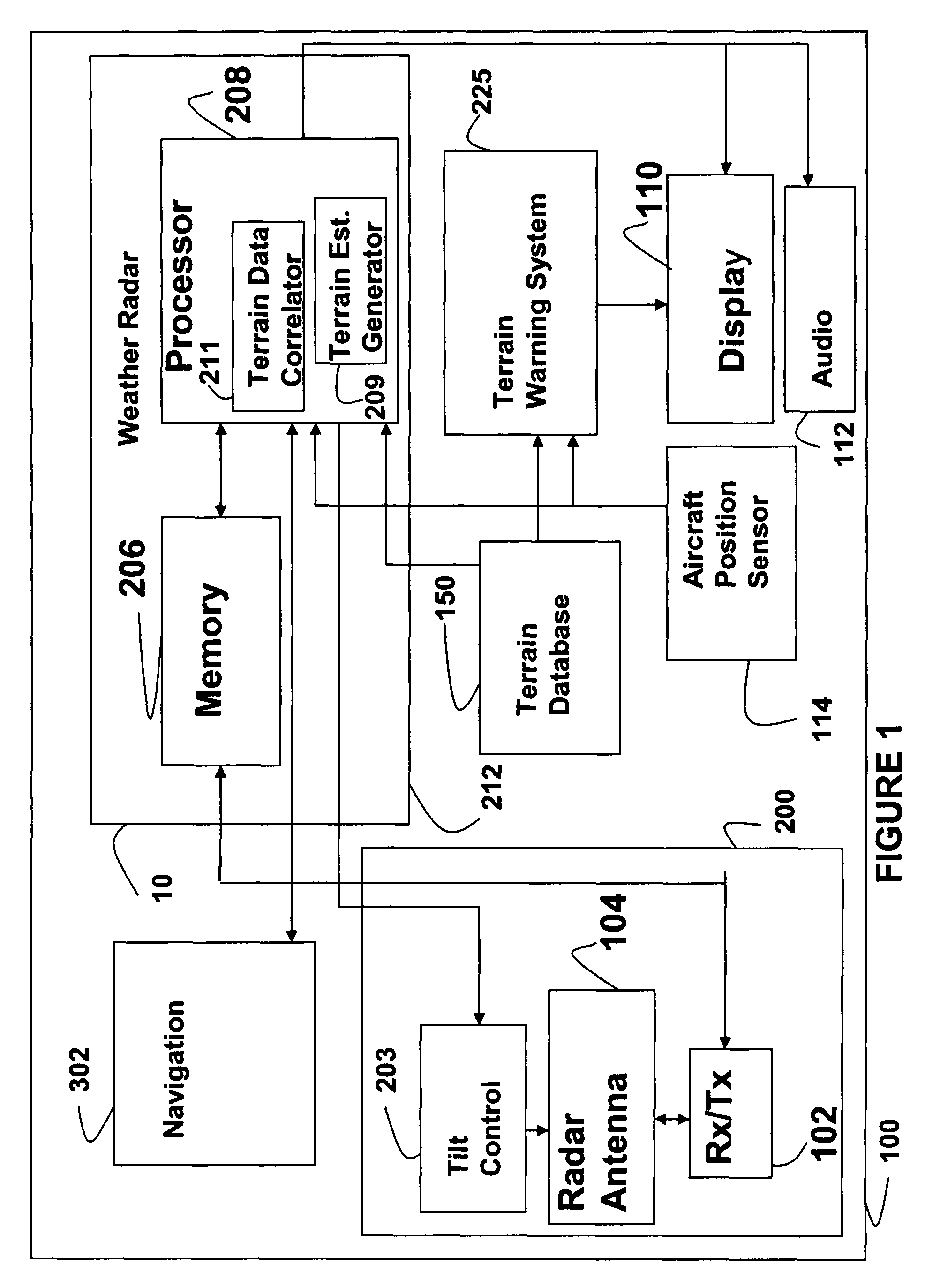
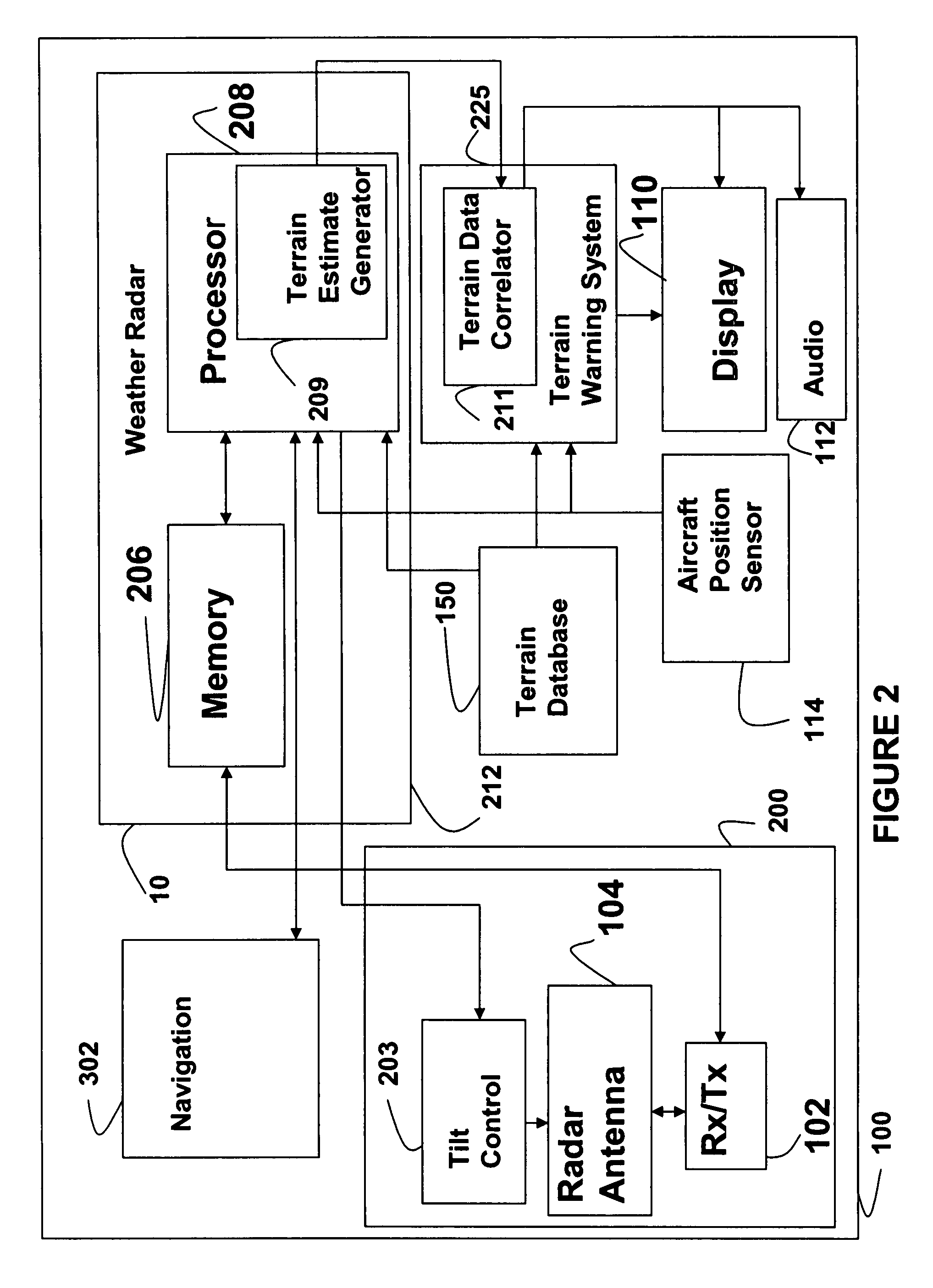
System and method for a terrain database and/or position validation
An aircraft weather radar system can be used with a terrain avoidance system. The aircraft weather radar system is coupled to an antenna. A processor receives radar returns received by the antenna. The processor determines terrain elevation estimates for use with the terrain avoidance system from the radar returns. The terrain elevation estimates are compared to stored terrain elevation data used with the terrain avoidance system to verify position or to check the integrity of the stored elevation data. The processor can be part of a terrain avoidance system, a weather radar system, a navigation system, or can be a standalone system.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
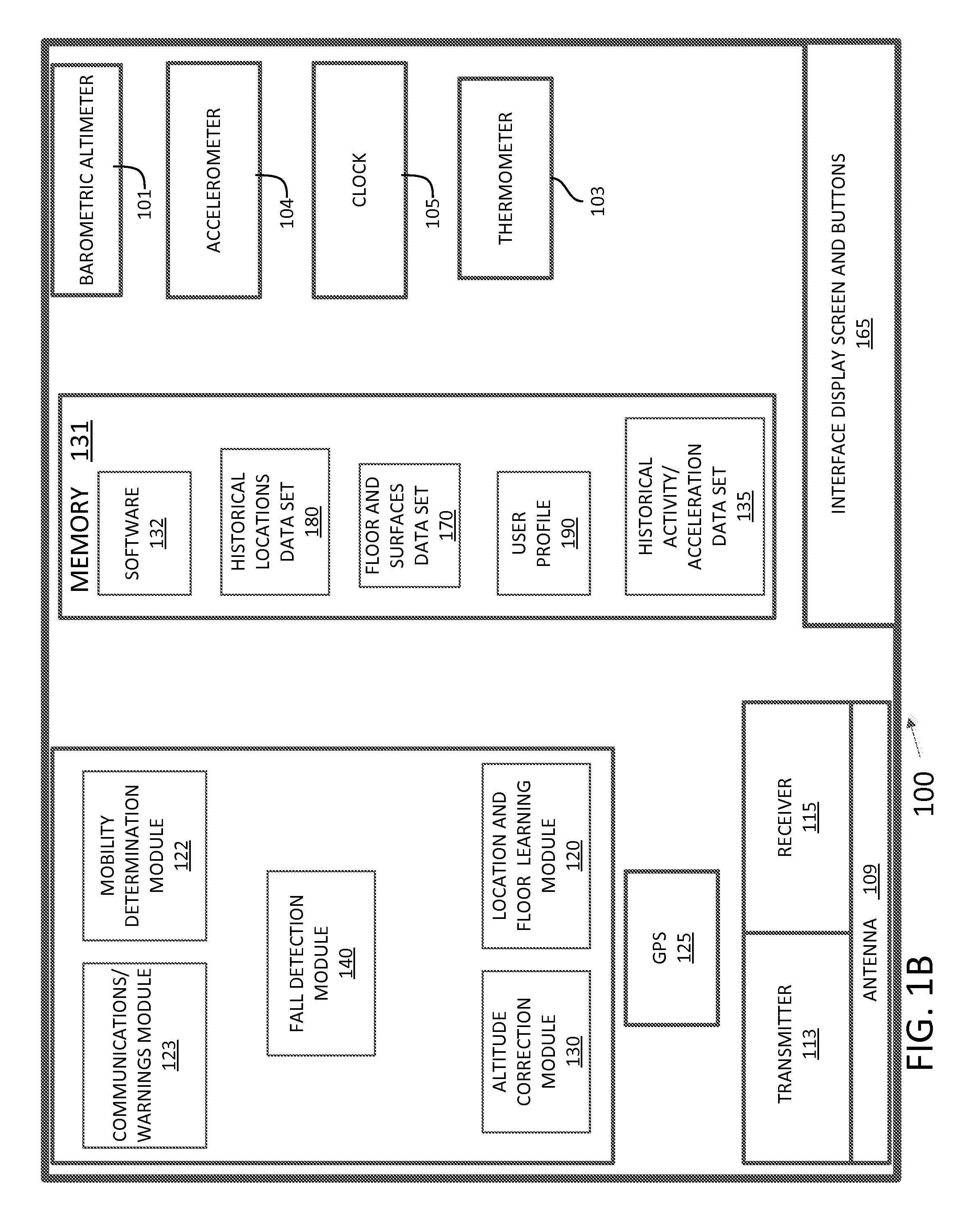
Fall detection apparatus with floor and surface elevation learning capabilites
This disclosure describes a wearable fall detection device configured to utilize several methods that facilitate monitoring a wearer of the device. The device comprises a first sensor configured to generate elevation data that represents an elevation of the device, and a second sensor configured to generate acceleration data that represents a magnitude of acceleration of the device. The device also includes a processor configured to determine, based on the elevation data, an elevation of a floor located underneath the wearer, and detect a fall affecting the wearer. Detecting a fall may be done by determining that the acceleration data satisfies a fall hypothesis condition, and determining, based on the elevation data, that the apparatus is vertically displaced from the floor by less than a threshold distance.
Owner:ZHANG JACK KE
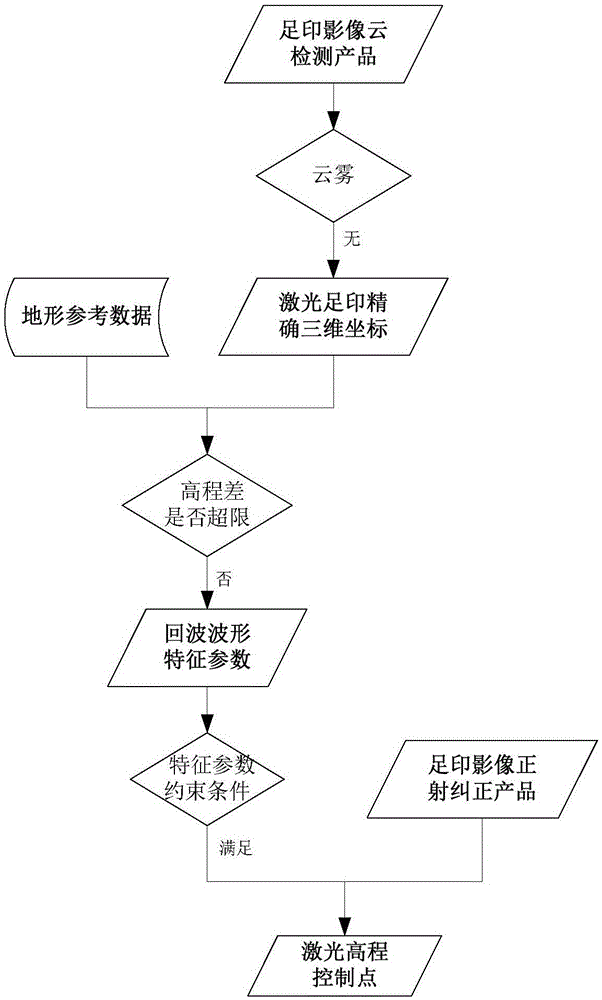
Automatic extraction method for Earth observation laser height measurement satellite elevation control points and data processing method
ActiveCN105550639AGuaranteed accuracyImprove accuracyPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryScene recognitionEarth observationPeak value
The invention relates to an automatic extraction method for Earth observation laser height measurement satellite elevation control points and a data processing method. The laser elevation control point extraction method comprises steps that an effective earth observation laser distance value measurement evaluation method is employed, determined cloudless footprint image blocks are kept, and laser elevation data of determined thin-cloud or thick-cloud footprint image blocks are removed; reflectivity Epsilon smaller than 1 of laser footprint points is taken as a screening parameter, laser footprint points of the kept footprint image blocks are screened, Epsilon=reception pulse energy / emission pulse energy, laser footprint points which have only one wave peak, have the peak value greater than the threshold, have the standard deviation sigma not greater than 3.2ns after waveform fitting are selected from an echo waveform, and parameters used for determining the threshold comprise the emission energy and a reception caliber of a laser device. Through the method, influence of clouds on laser distance measurement can be reduced, laser distance measurement precision can be guaranteed, and accuracy of the laser elevation reference data is effectively improved.
Owner:SATELLITE SURVEYING & MAPPING APPL CENTSASMAC NAT ADMINISTATION OF SURVEYING MAPPING & GEOINFORMATION OF CHINANASG
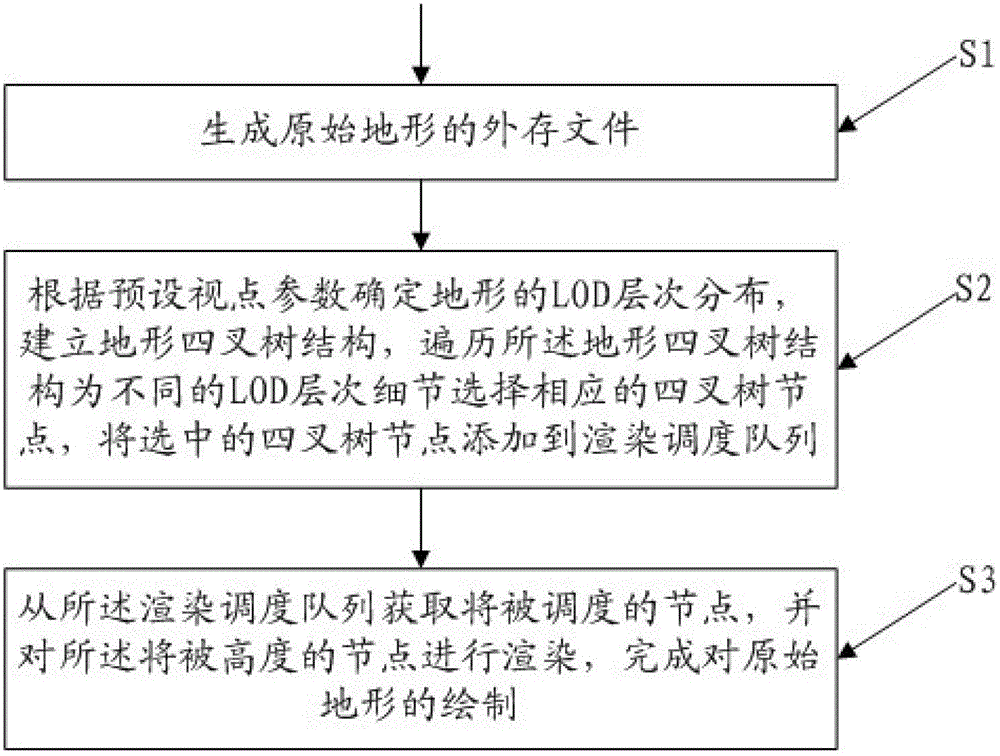
Graphics processing unit (GPU)-orientated large-scale terrain fast drawing method
InactiveCN102867331AImprove drawing efficiencyTake full advantage of programmability3D-image rendering3D modellingTerrainLevel of detail
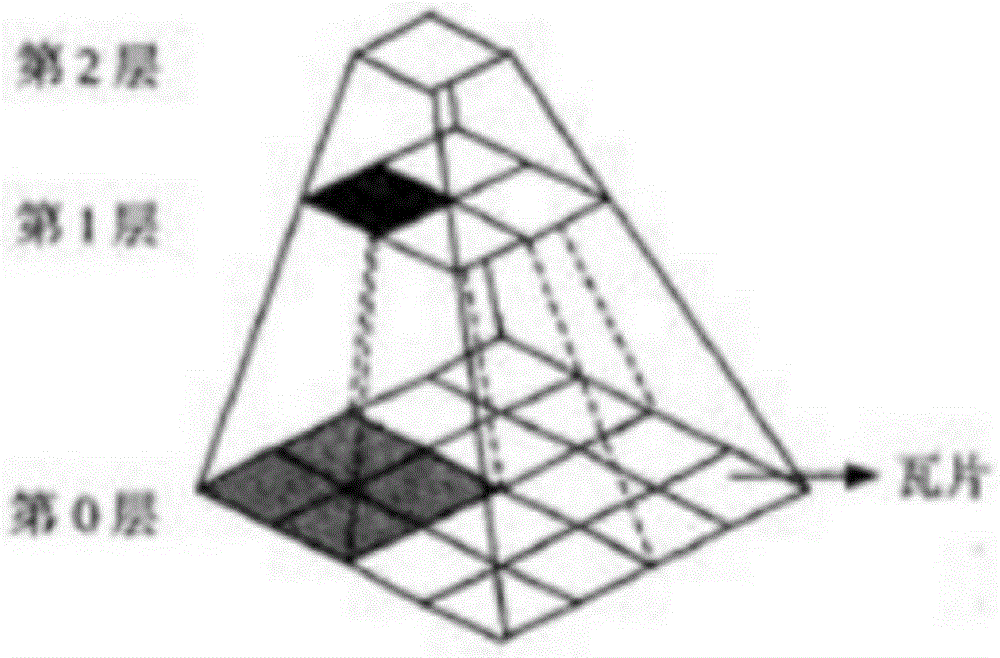
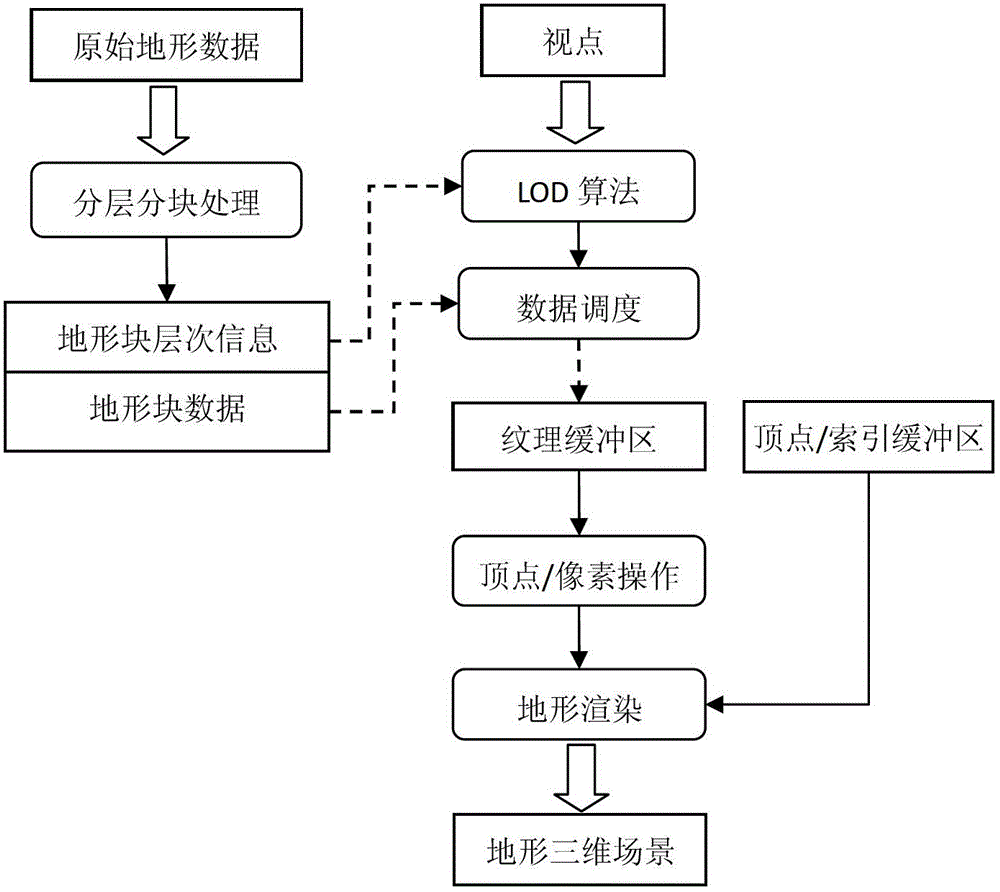
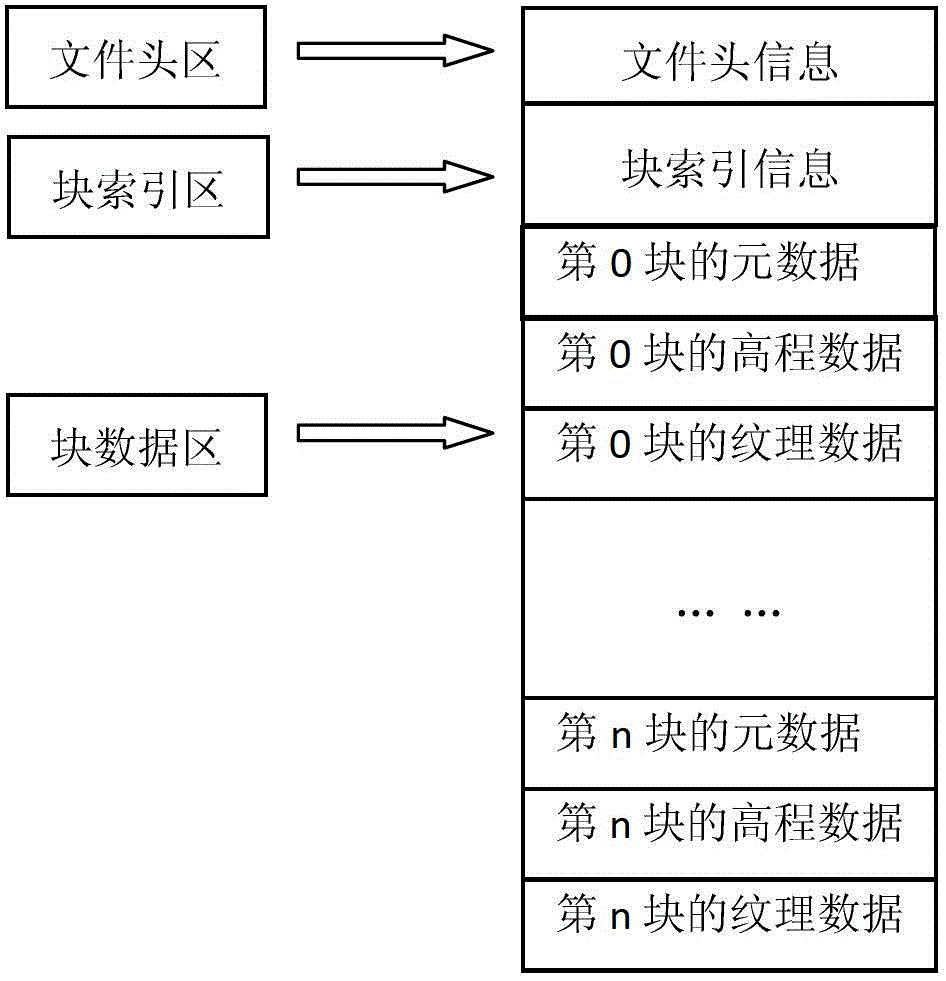
The invention provides a graphics processing unit (GPU)-orientated large-scale terrain fast drawing method. The method comprises the following steps of: generating an out-of-core file of original terrain, wherein the out-of-core file stores a plurality of terrain blocks containing original terrain data, an indexing serial number of each terrain block and compressed texture blocks corresponding to the terrain blocks, and the terrain data comprises texture data and altitude data; determining the level of detail (LOD) hierarchical distribution of the terrain according to a predetermined view point, establishing a terrain quadtree structure, traversing the terrain quadtree structure, selecting a corresponding quadtree node for different LODs, and adding the selected quadtree node to a rendering scheduling queue, wherein each node of the terrain quadtree structure corresponds to the corresponding compressed terrain block in the out-of-core file and is used for storing the LOD and the altitude data of the corresponding compressed terrain block; and acquiring the node to be scheduled from the rendering scheduling queue, and rendering the node to be scheduled to finish the drawing of the original terrain.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
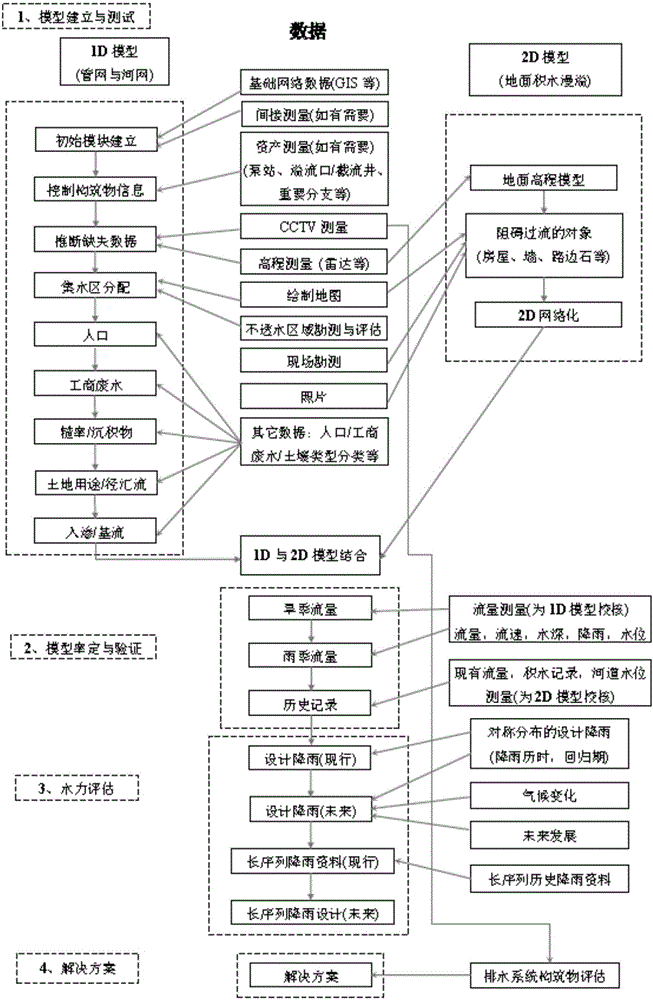
Municipal drainage pipe network diagnostic assessment method giving consideration to key node
The invention relates to a municipal drainage pipe network diagnostic assessment method giving consideration to a key node. The method includes the following steps that (1) the key node of a municipal drainage pipe network is obtained, a water level monitor and a flow monitor are additionally arranged at the position of the key node, actual running water level and flow data of the key node are obtained, and on-site pipe data at the position of the key node are obtained through CCTV measurement; (2) in cooperation with the actual running water level and flow data, topological data of the drainage pipe network, the on-site pipe data, boundary water level data, GIS data, ground elevation data and other data of the key node, a municipal drainage pipe network hydraulic model giving consideration to the key node is built; and (3) calibration is carried out on the municipal drainage pipe network hydraulic model, the municipal drainage pipe network hydraulic model obtained after calibration is adopted for simulating the running state of an actual municipal drainage pipe network system, and the running state of the system is assessed. Compared with the prior art, the municipal drainage pipe network diagnostic assessment method has the beneficial effects of giving consideration to the key node, being accurate in modeling, capable of achieving combined assessment, real and effective, improving efficiency and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL SEWERAGE CO LTD
Apparatus and method for topographical parameter measurements
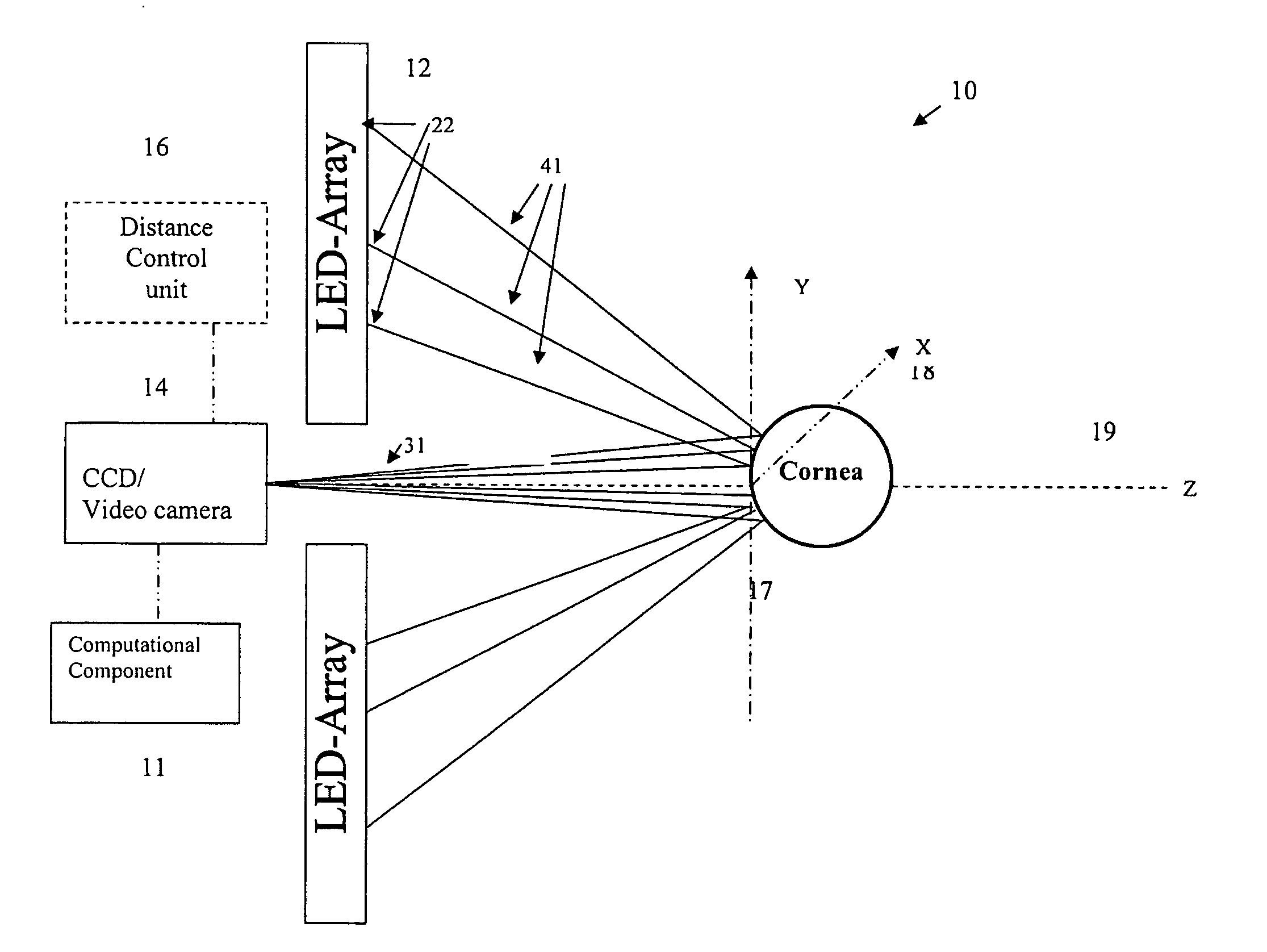
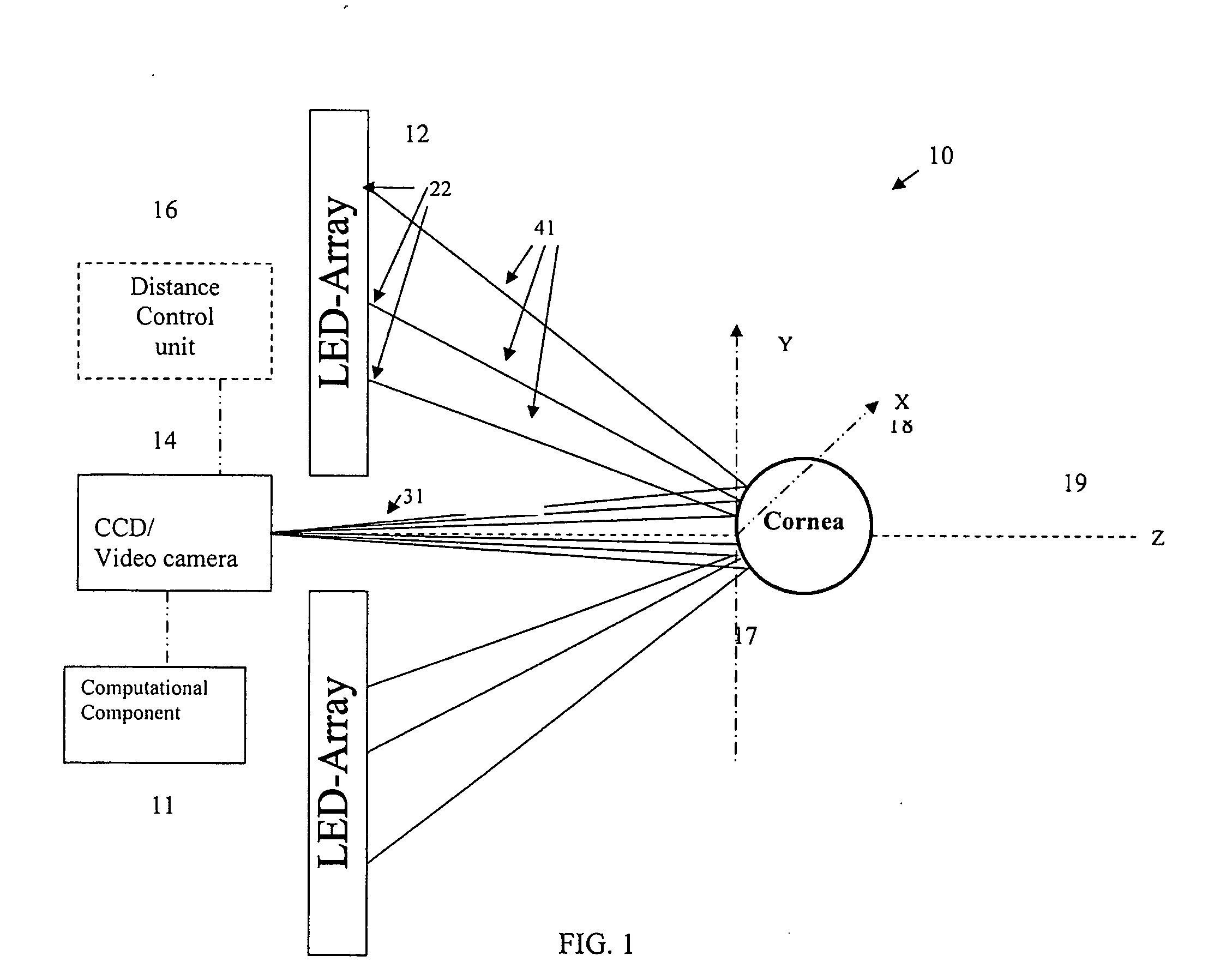
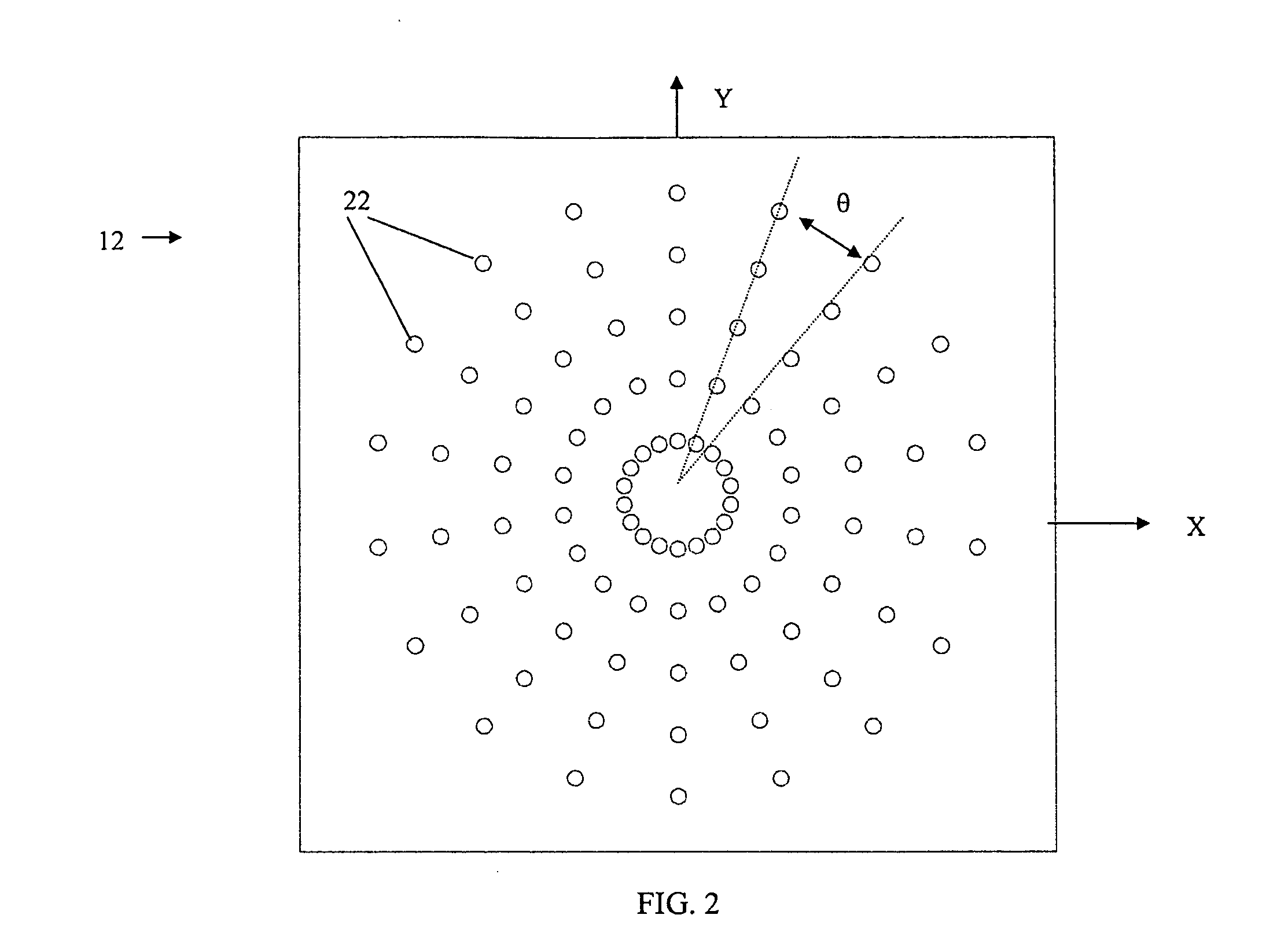
A topographical parameter measuring device and method utilizes a technique based on wave front reconstruction according to, e.g., Hartmann-Shack principles. The device includes a planar illuminator comprising a known array of illumination sources for projecting a light spot pattern onto a target surface. A CCD camera detects the positions of the reflected image spots in a manner similar to that in a Hartmann-Shack wave front sensor. The displacements of the light spots from reference coordinates are indicative of the slope of the surface at the plurality of sample points. A computational component is used to fit the slope data of a reference surface and the target surface to a polynomial, for example, a Zernike polynomial. The polynomial, properly weighted with the calculated coefficients, provides a continuous mapping of the elevation of the target surface. Based on the elevation data, all other topographical parameters including axial curvature, dioptric power, sphere, cylinder and others can be computed and displayed.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Method for Automatic Modeling of an Architecture Based on an Architectural Drawing
ActiveUS20190251209A1Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElevation dataComputer science
The present disclosure provides a method for automatic modeling of an architecture based on an architectural drawing, comprising steps of: reading parameter information of the architectural drawing, identifying a category to which any architectural object belongs by acquiring line segments constituting the architectural object and coordinate data of endpoints of the line segments; generating a binary file or a preset number of binary files based on the coordinate data and elevation data of the endpoints of all the line segments of architectural objects belonging to the same category for all storeys of the architectural drawing; optimizing the binary file or the binary files corresponding to the architectural objects belonging to the same category for all the storeys of the architectural drawing; and generating a three-dimensional model of the architecture. The modeling precision and modeling efficiency of the architecture can be improved by adopting the technical solution of the present disclosure.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Three-dimensional geographical scene simulation method for virtual emergency exercises
ActiveCN104318617AAvoid the problem of cutting into many blocksGuaranteed accuracy3D modellingTerrainElement model
The invention relates to a three-dimensional geographical scene simulation method for virtual emergency exercises. The method comprises the steps of: obtaining elevation data in DEM by using GIS software, and interpreting earth surface appendage information by using a registered high-resolution remote sensing image, or obtaining surface features and land utilization information by using an existing measured drawing; then, establishing topography and landforms by using the information with true geographic meanings in a game engine, wherein a key technical process is the conversion between a rectangular coordinate system in the game engine and a geographic coordinate system in the GIS software; at last, combining and reconstructing a three-dimensional terrain and geographic element model with true geographic meanings on a game engine platform, and achieving establishment of a realistic three-dimensional scene. The three-dimensional geographical scene simulation method virtual emergency exercises is convenient to operate and unnecessary to limit shape and size of the area, ensures elevation accuracy of DEM, and can automatically generate the three-dimensional science with the true geographic meanings.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Ponding water detection on satellite imagery
A system for identifying ponding water located on a field from image data is described. In an approach, an image of an agricultural field is analyzed using a classifier that has been trained based on the spectral bands of labeled image pixels to identify a probability for each pixel within the image that the pixel corresponds to water. A flow simulation is performed to determine regions of the field that are likely to pool water after rainfall based on precipitation data, elevation data, and soil property data of the field. A graph of vertices representing the pixels and edges representing connections between neighboring pixels is generated. The probability of each pixel within the graph being ponding water is set based on the probability pixel being water, the likelihood that water will pool in the area represented by the pixel, the probability of neighboring pixels being ponding water, and a cropland mask that identifies which pixels correspond to cropland. A class for each pixel is then determined that maximizes the joint probability over the graph.
Owner:THE CLIMATE CORP
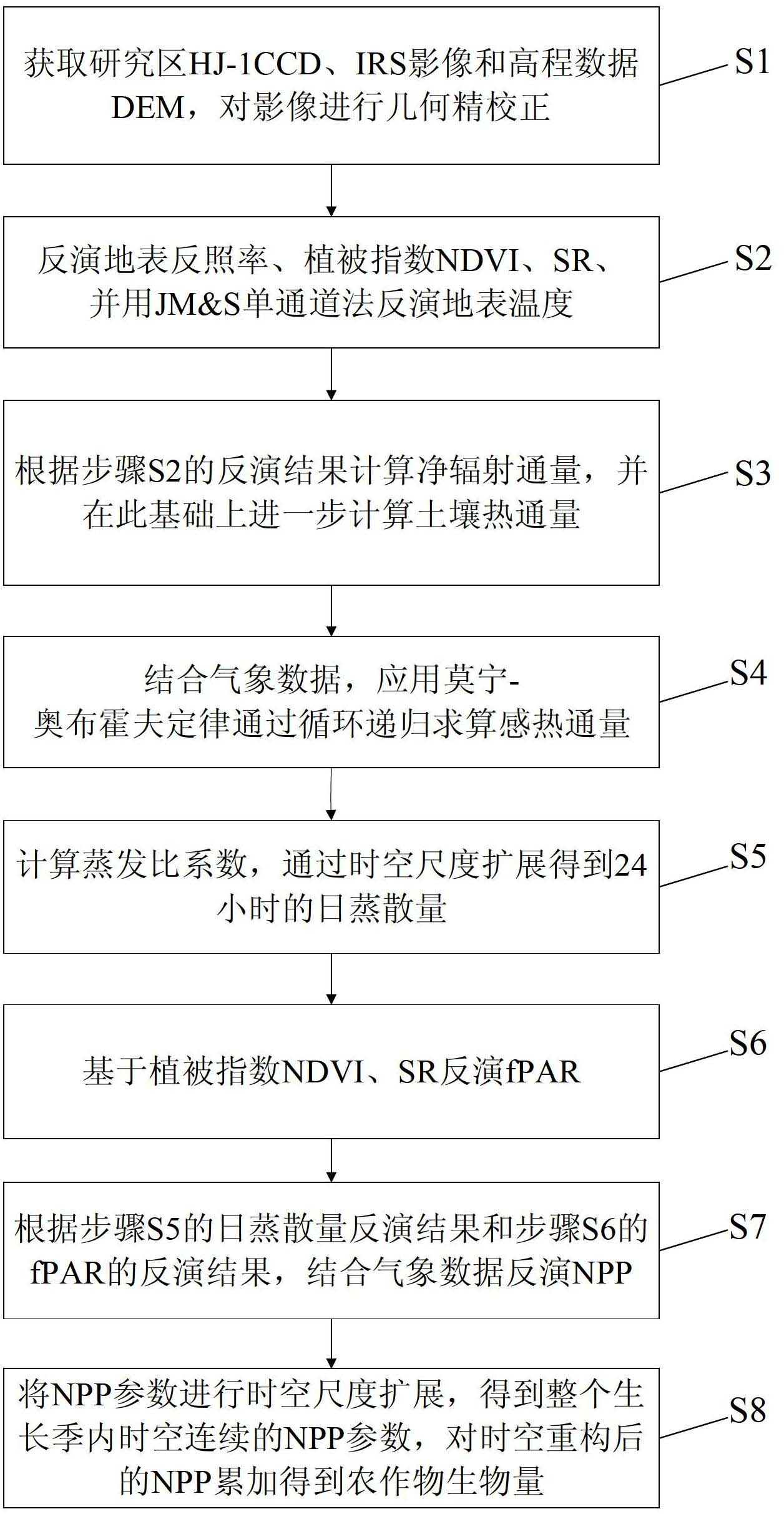
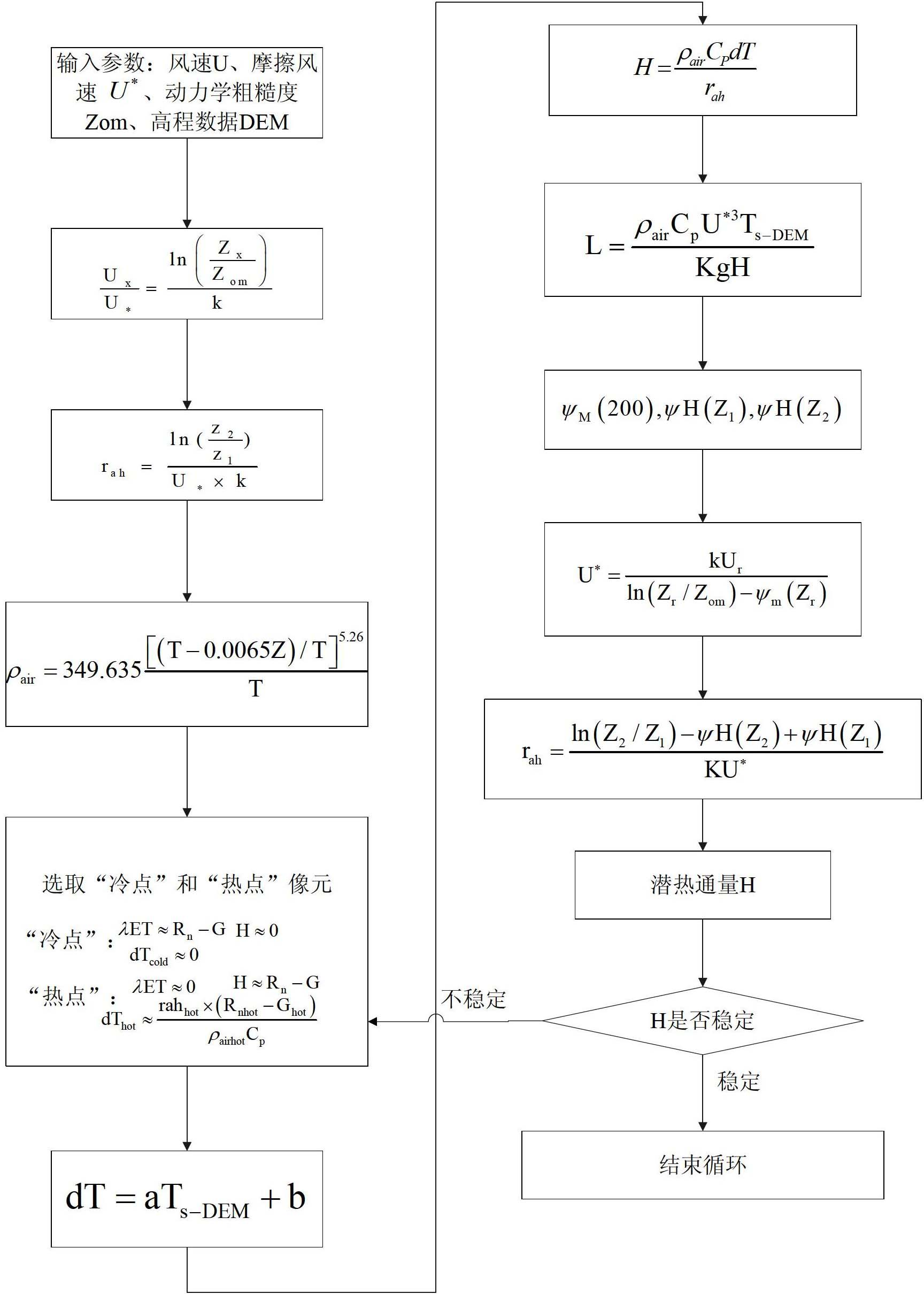
Crop biomass inversion method based on SEBAL-HJ model
ActiveCN102650587AImprove inversion accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansCyclic reductionEvaporation
The invention discloses a crop biomass inversion method based on a SEBAL-HJ model. The crop biomass inversion method is characterized by comprising the following steps: S1, acquiring HJ-1 CCD, IRS images and elevation data DEM in a research plot, and carrying out geometric fine revision to the images; S2, inversing a land surface albedo, NDVI, SR, land surface emissivity and inversing land surface temperature; S3, calculating net radiation flux according to inversion results in the S2, and further calculating soil heat flux on the basis; S4, calculating sensible heat flux through cyclic reduction; S5, calculating the coefficient of evaporation ratio and obtaining evapotranspiration per day through space-time dimension expansion; S6, inversing fPAR on the basis of vegetative cover indexes NDVI and SR; S7, inversing NPP according to the inversion results of evapotranspiration per day in the step S5 and the inversion results of fPAR in the step S6; and S8, obtaining crop biomass through the accumulation of NPP after space-time reconstruction. According to the invention, the high-precision inversion of crop biomass is achieved, and the amount of calculation is relatively smaller.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com