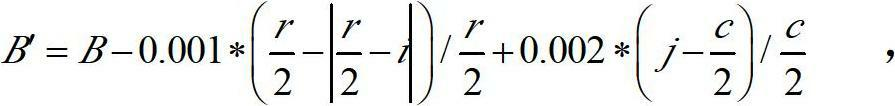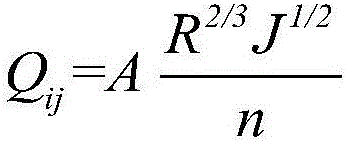Patents
Literature
303 results about "Elevation - value" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
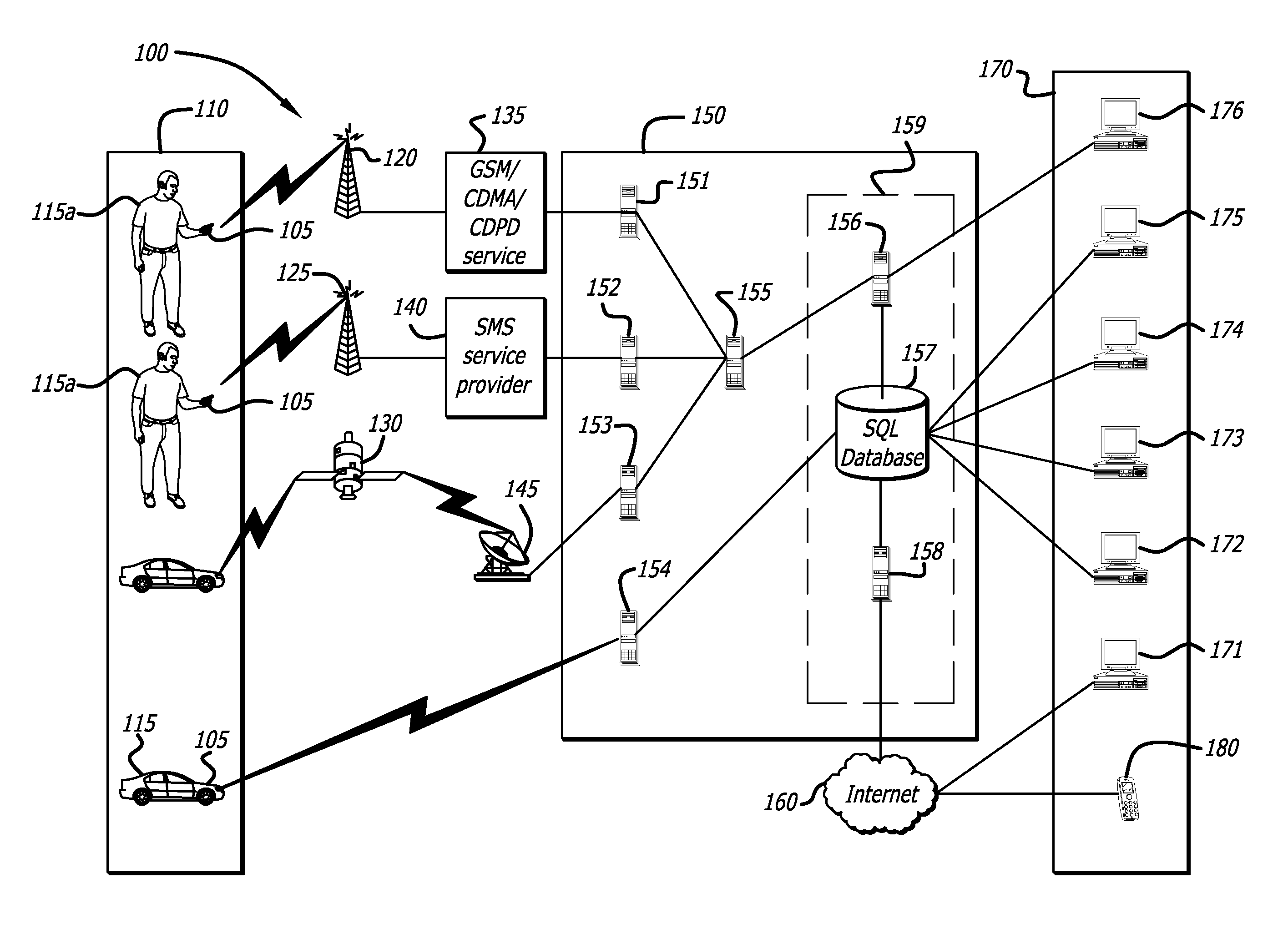
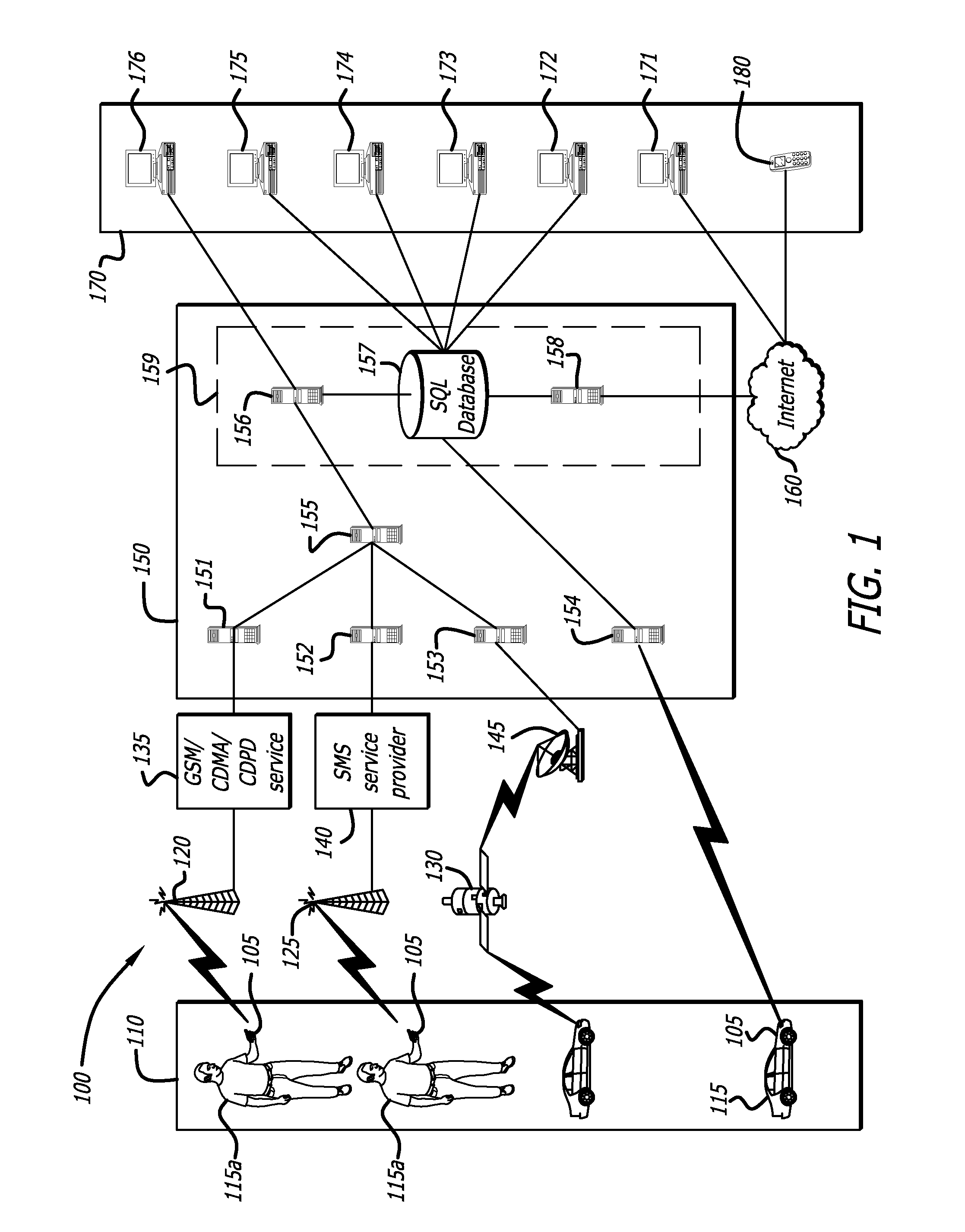
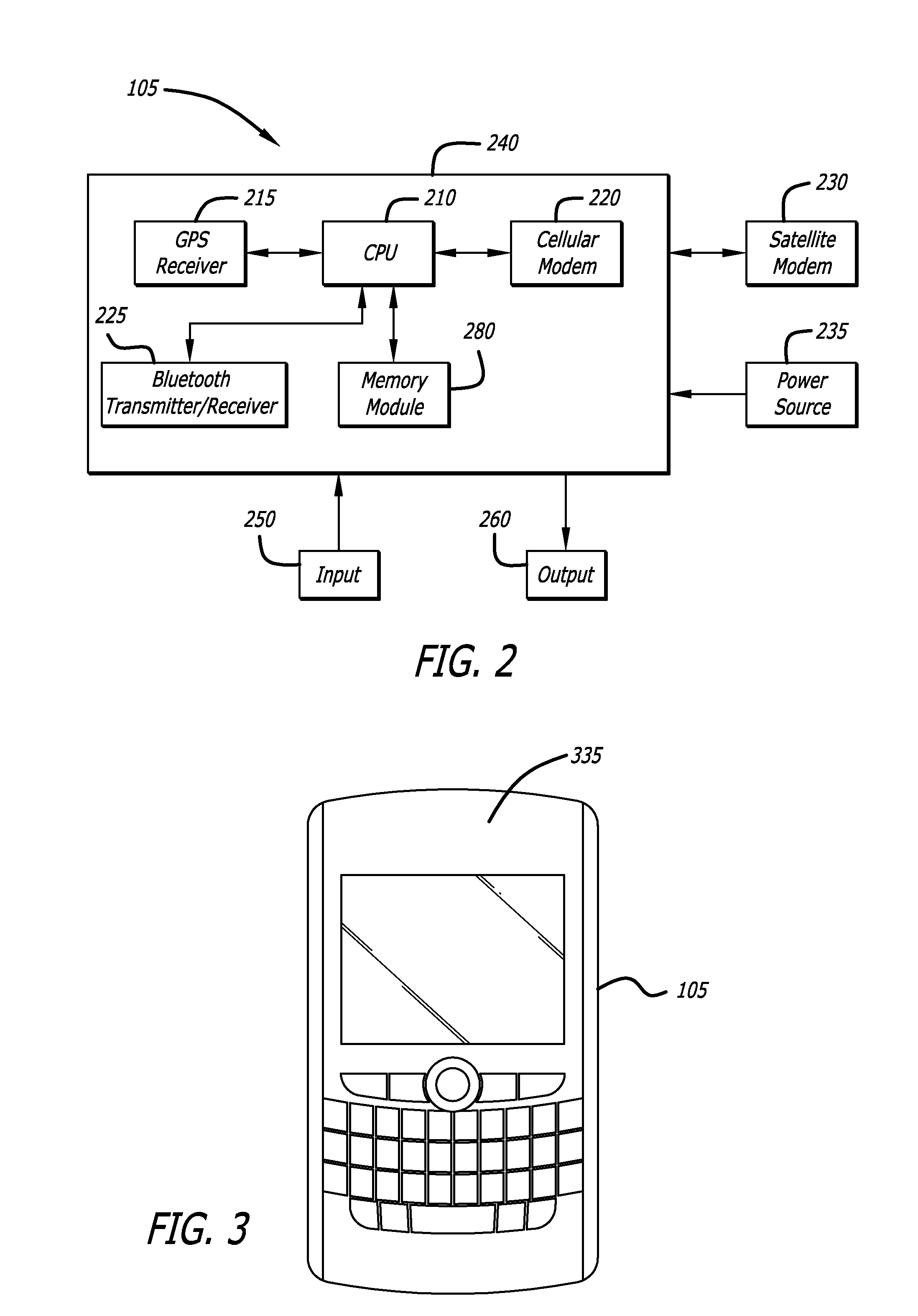
Configuring and using multi-dimensional zones
ActiveUS20090132163A1Locate very closeRoad vehicles traffic controlPosition fixationLongitudeGeographical zone
A method to define a three-dimensional geographical zone that is utilized with a movable entity having at least one attached transponder is disclosed. The method comprises allowing a user to enter at least one waypoint, and loading at least one waypoint on at least one transponder. In one or more embodiments, a waypoint is defined by a geographical coordinate and a radius. The geographical coordinate is represented by a latitude value, a longitude value, and an elevation value. And, the radius is represented by a distance magnitude. In some embodiments, the method further comprises regulating the movable entity by monitoring, controlling, and / or visualizing the movement, non-movement, or position of the movable entity. The transponder determines whether the transponder is located inside the three-dimensional geographical zone by obtaining global positioning coordinates, and calculating whether or not the global positioning coordinates are located inside at least one waypoint.
Owner:WIRELESSWERX IP LLC
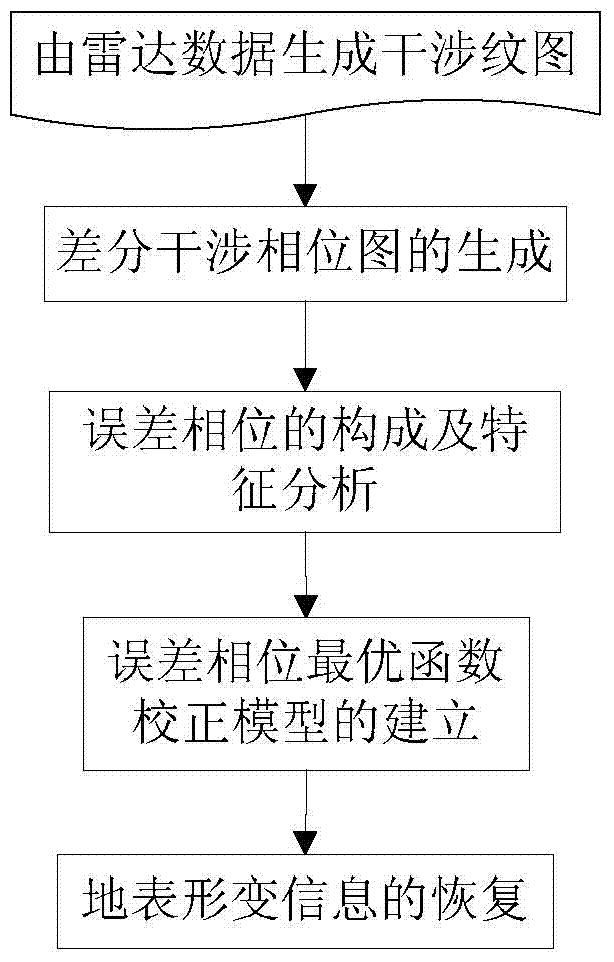
Method for improving earth surface shape change monitoring precision of InSAR (Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar) technology based on high-precision DEM (Digital Elevation Model)
InactiveCN103675790AError Phase CancellationHigh precisionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionShape changeInterferometric synthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses a method for improving earth surface shape change monitoring precision of an InSAR (Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar) technology based on a high-precision DEM (Digital Elevation Model). The method comprises five steps below: step 1, generating an interferogram by using radar data; step 2, generating a differential interference phase diagram; step 3, establishing error phases and performing feature analysis; step 4, establishing an error phase optimal function calibration model; step 5, recovering earth surface shape change information of a monitoring region based on results of steps 2 and 4. According to the invention, the error phases and elevation values or the error phases, the elevations and coordinate values along a distance / azimuth of different regions of a research region are extracted, the optimal function calibration models of the error phases of corresponding regions are established respectively based on a least square method, and a simulative error phase is finally removed from the differential interference phase diagram to further recover shape change information along a direction of a sight line of a radar in the monitoring region. The method for improving the earth surface shape change monitoring precision of the InSAR technology based on the high-precision DEM has practical value and wide application foreground in the application field of a satellite borne synthetic aperture radar monitoring technology for earth surface shape change.
Owner:CHINA AERO GEOPHYSICAL SURVEY & REMOTE SENSING CENT FOR LAND & RESOURCES
Digital map compression and display method
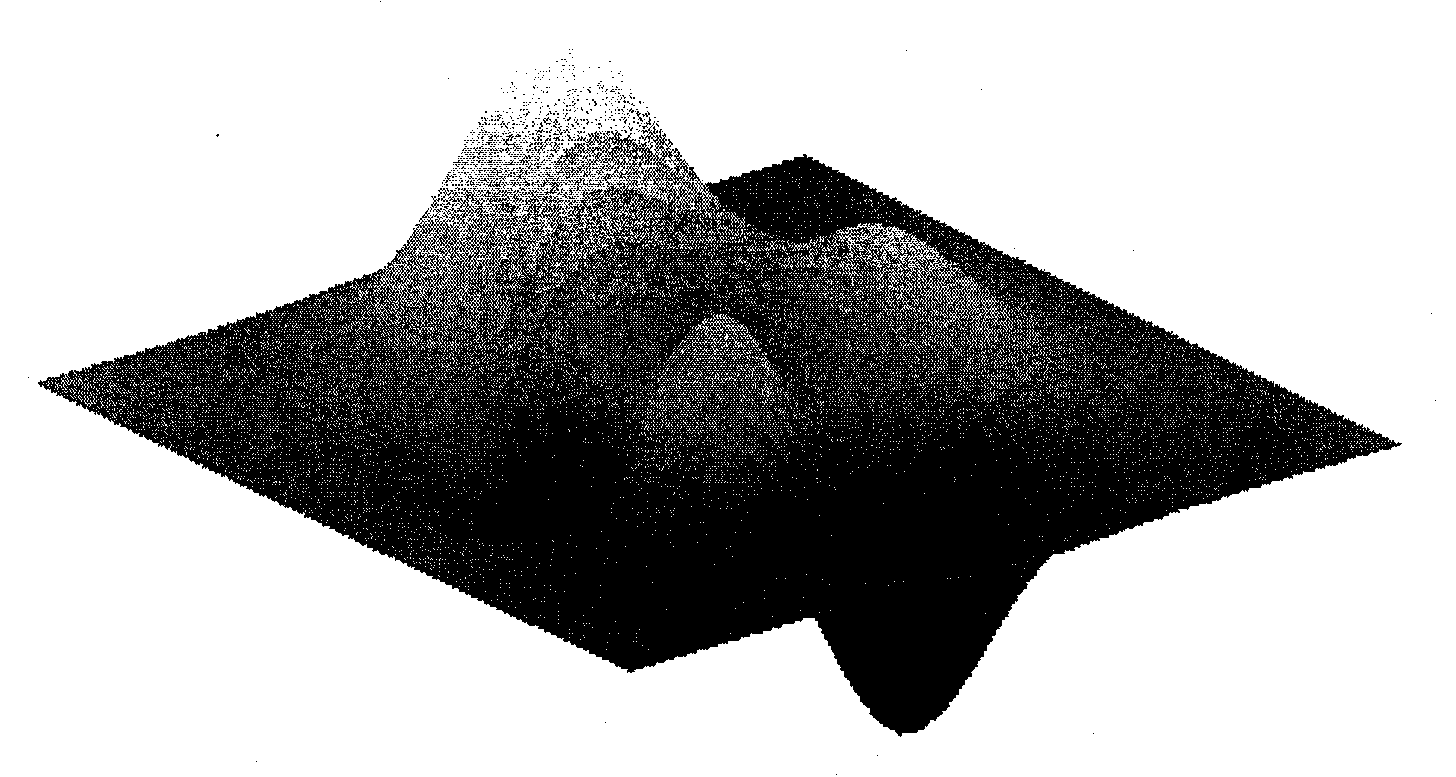
A digital elevation database is compressed to create a compressed digital map database which is used by a digital computer system for displaying three-dimensional terrain data in the form of polygons. The compressed digital map database is produced from a database of elevation points by selecting every mth row and every nth column, thereby resulting in a reduction of database storage requirements. During program run-time the intersection of rows and columns forms cells with four corners. The elevation value of a center elevation point for each cell is formed by various methods, thereby creating a cell made up of four three-dimensional triangles. One method for creating the elevation of the center elevation point uses the elevations of the four corners of the cell. Another method uses extrapolated elevation values from the cell's extended diagonals. The three-dimensional triangles formed from the center elevation point are then transformed and projected using standard computer graphics methods on a digital computer to produce a three-dimensional projected display.
Owner:RATEZE REMOTE MGMT LLC +1
Configuring and using multi-dimensional zones
A method to define a three-dimensional geographical zone that is utilized with a movable entity having at least one attached transponder is disclosed. The method comprises allowing a user to enter at least one waypoint, and loading at least one waypoint on at least one transponder. In one or more embodiments, a waypoint is defined by a geographical coordinate and a radius. The geographical coordinate is represented by a latitude value, a longitude value, and an elevation value. And, the radius is represented by a distance magnitude. In some embodiments, the method further comprises regulating the movable entity by monitoring, controlling, and / or visualizing the movement, non-movement, or position of the movable entity. The transponder determines whether the transponder is located inside the three-dimensional geographical zone by obtaining global positioning coordinates, and calculating whether or not the global positioning coordinates are located inside at least one waypoint.
Owner:WIRELESSWERX IP LLC
Construction method for digital elevation model for discrete expression of landform on earth surface
InactiveCN101900546AHigh precisionHeight/levelling measurementProfile tracingOriginal dataDiscretization
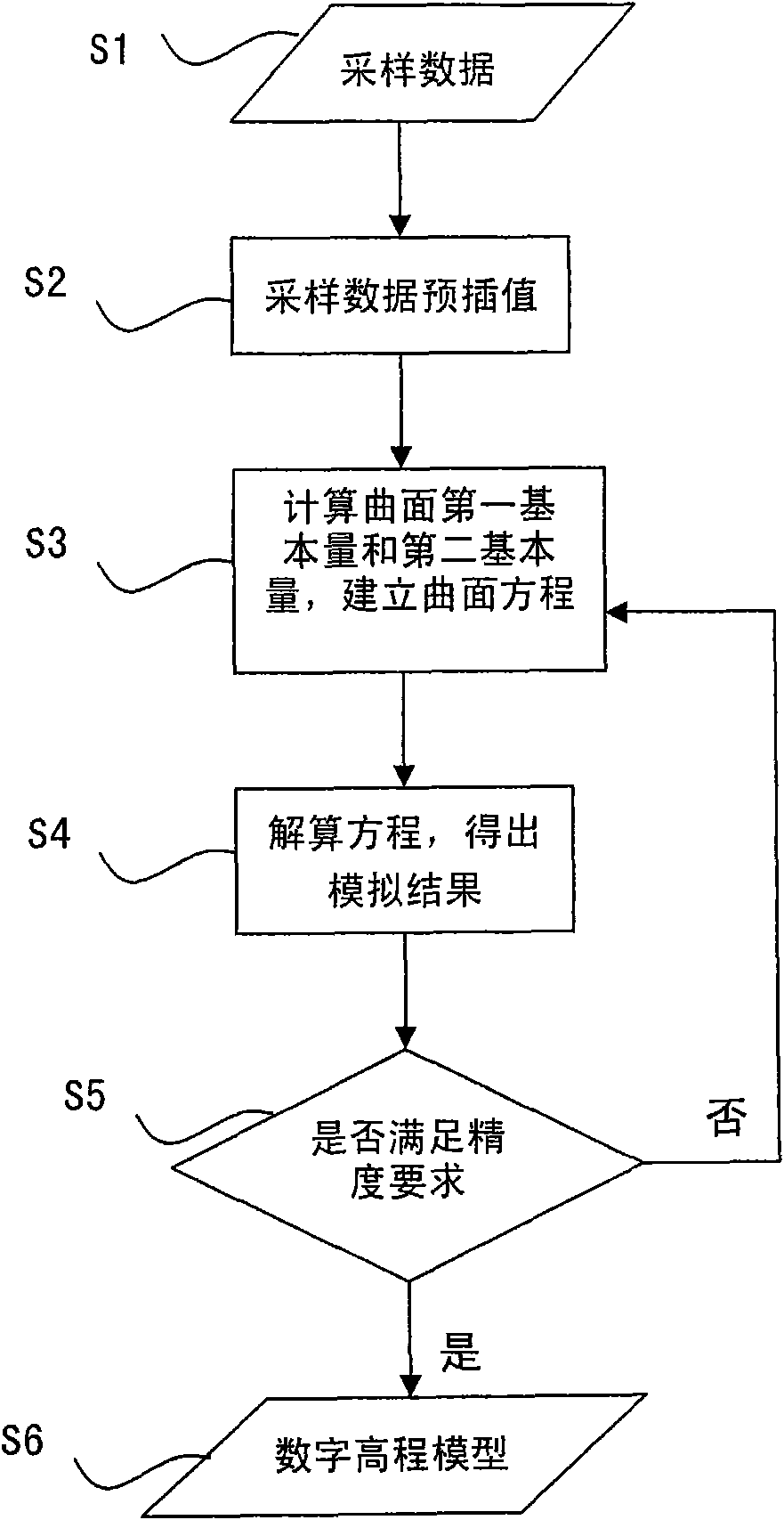
The invention discloses a construction method for a digital elevation model for discrete expression of landform on the earth surface. The construction method comprises the following steps of: extracting elevation values of sampling points from the original data of the earth surface and performing spatial discretization on the elevation values to generate a plurality of landform curved surface grid points of the known elevation values of the sampling points; solving the elevation values of the landform curved surface grid points of non-sampling points; calculating first fundamental quantity and second fundamental quantity of each landform curved surface grid point according to the elevation values of all landform curved surface grid points and establishing a landform curved surface equation set by using a Gauss equation and elevation sampling points; solving the landform curved surface equation set by using a Gauss-Seidel iterative algorithm, wherein a simulation result of the digital elevation model is obtained after each iteration is finished; judging whether the simulation result of the digital elevation model meets the accuracy requirement; if the simulation result meets the requirement, stopping the iterative computation and outputting a group of ordered values to express the digital elevation model of a ground elevation entity in an array form, wherein the digital elevation model is used for the discrete expression of the landform on the earth surface; and if the simulation result does not meet the requirement, repeating the iterative computation.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
Terrain modeling method and system fusing geometric characteristics and mechanical characteristics
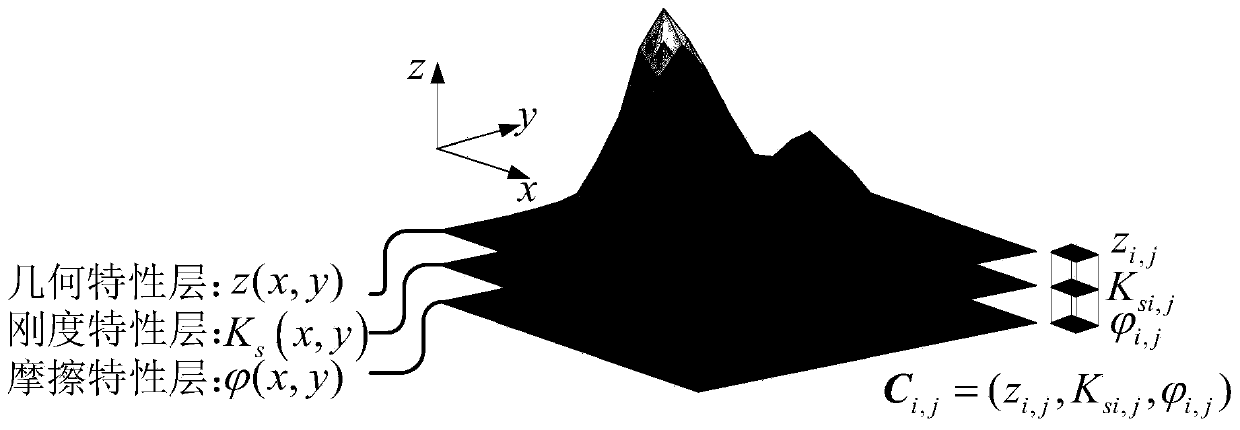
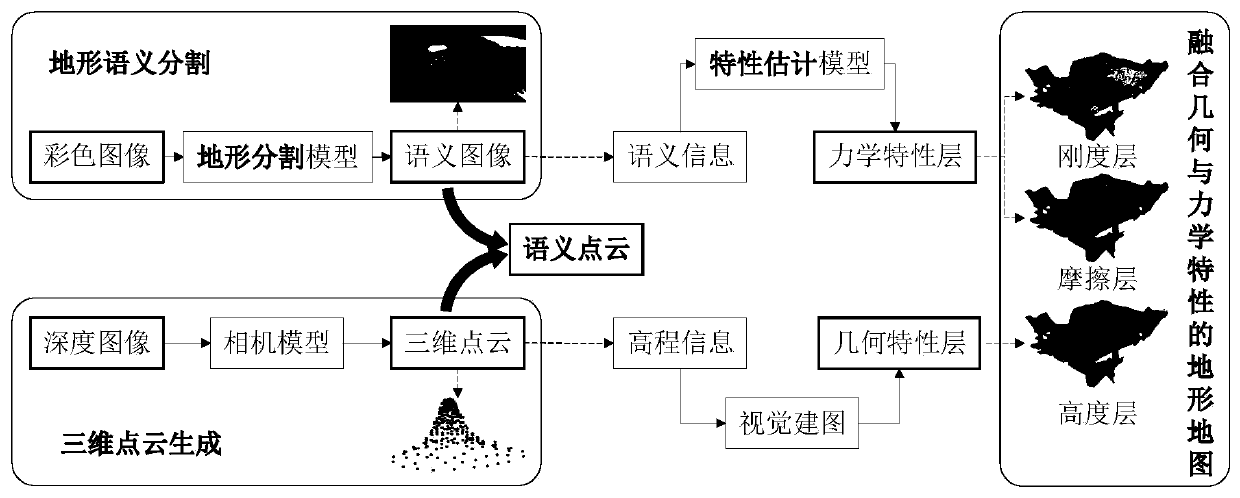
The invention provides a terrain modeling method and system integrating the geometric characteristics and the mechanical characteristics, and relates to the technical field of environment modeling. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining a color image and a depth image of a detection area, carrying out terrain semantic segmentation on the color image, and fusing a semantic segmentation result and the depth information contained in the depth image at the same moment to generate a semantic point cloud; mapping the semantic point cloud into a grid map under a map coordinate system to generate the corresponding grids, and updating the elevation values and the semantic information in the semantic point cloud to the corresponding grids; and performing ground mechanical property calculation according to the semantic information, updating a calculation result to the corresponding grid, and generating a terrain model. According to the method, the mechanical property parameters are added into topographic factors, and the topographic characterization is innovatively carried out from two dimensions of geometric properties and mechanical properties. The ground pressure-bearing characteristic and the shear characteristic of a non-contact area are deduced in advance in a visual perception mode, and the perception range is expanded.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for geocoding a perspective image
ActiveUS20070002040A1Without computational difficultySufficient speedPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer Aided DesignComputer graphics (images)
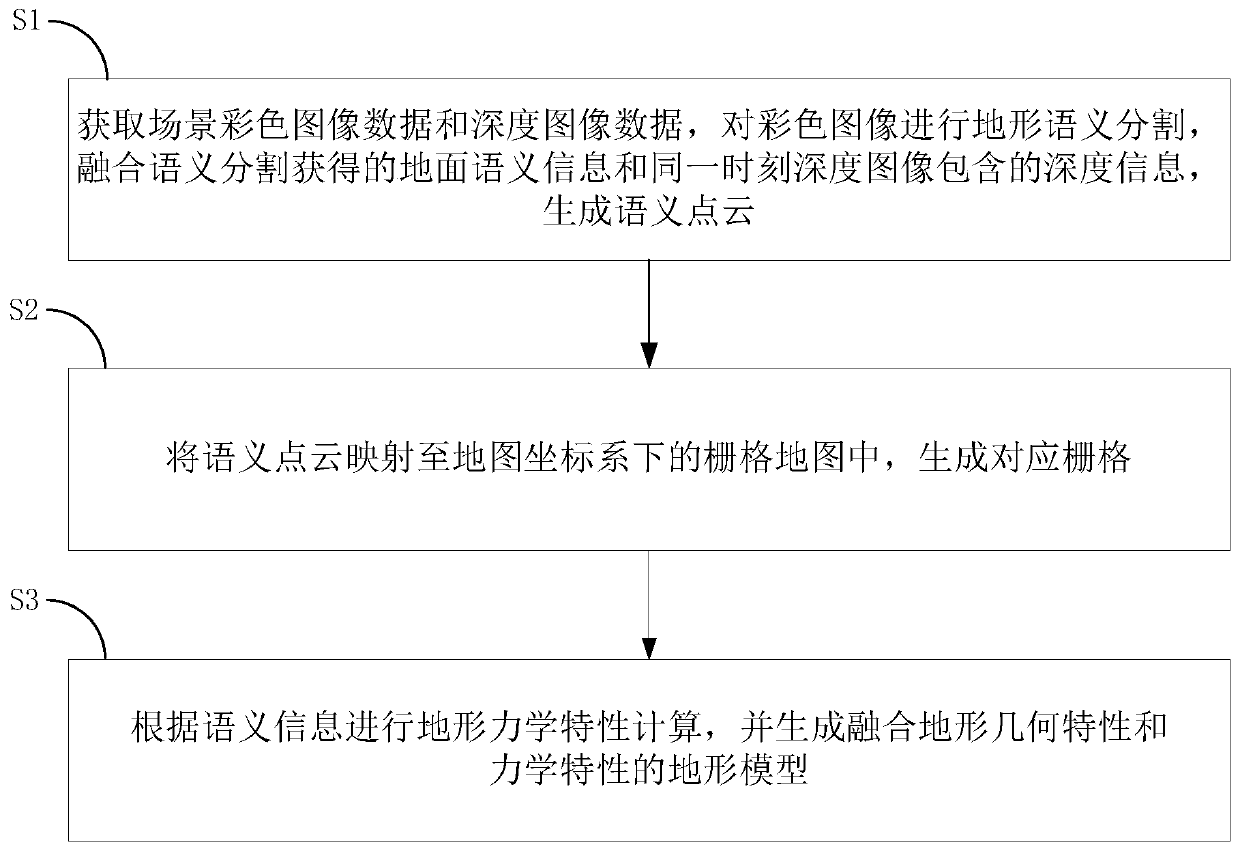
A method for geographically registering a perspective image of a location assigns elevation values to elements or pixels of a two dimensional array of image elements or pixels of the location. The elevation value for each image pixel is obtained using a corresponding database stored reference digital elevation model, or a three dimensional surface model of the location. The reference elevation model or surface model is composed of rows and columns of elevation values corresponding to two dimensions of location values at a sensed location shown in the image, or is composed of a three dimensional surface or volume model of the location, such as a computer-aided design model or any other means of describing the three dimensional characteristics of the sensed location.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
InSAR point cloud fusion and three-dimensional deformation monitoring method for high-resolution SAR image
ActiveCN110058237AGuaranteed accuracyUsing optical meansRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTerrainTime domain
The invention provides an InSAR point cloud fusion and three-dimensional deformation monitoring method for a high-resolution SAR image. The method comprises the following steps of selecting a proper time sequence DS-InSAR technology to respectively carry out interference pair combination and single-view interference processing on multi-time-domain data of each platform according to a space-time baseline, introducing external DEM data to weaken dense stripes caused by the regional terrain, and carrying out nonLocal filtering and coherence revaluation on an obtained differential interference pattern to obtain an optimal parameter estimation value; and correcting a coded elevation value of each distributed scatterer by utilizing a terrain residual estimated value, acquiring three-dimensionalgeodetic coordinates of all DSs, and accurately registering and fusing a plurality of platforms DS point clouds by utilizing an ICP technology. According to the method, the multi-source SAR data is accurately fused, the mistake matching rate of observation values in a parameter estimation process is reduced, the precision and accuracy of monitoring are improved, and three-dimensional enhanced information of a research area can be obtained in combination with a small amount of ground control points.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for orthocorrecting satellite-acquired image
InactiveUS6810153B2Improve accuracyImage enhancementGeometric image transformationImage segmentationEarth model
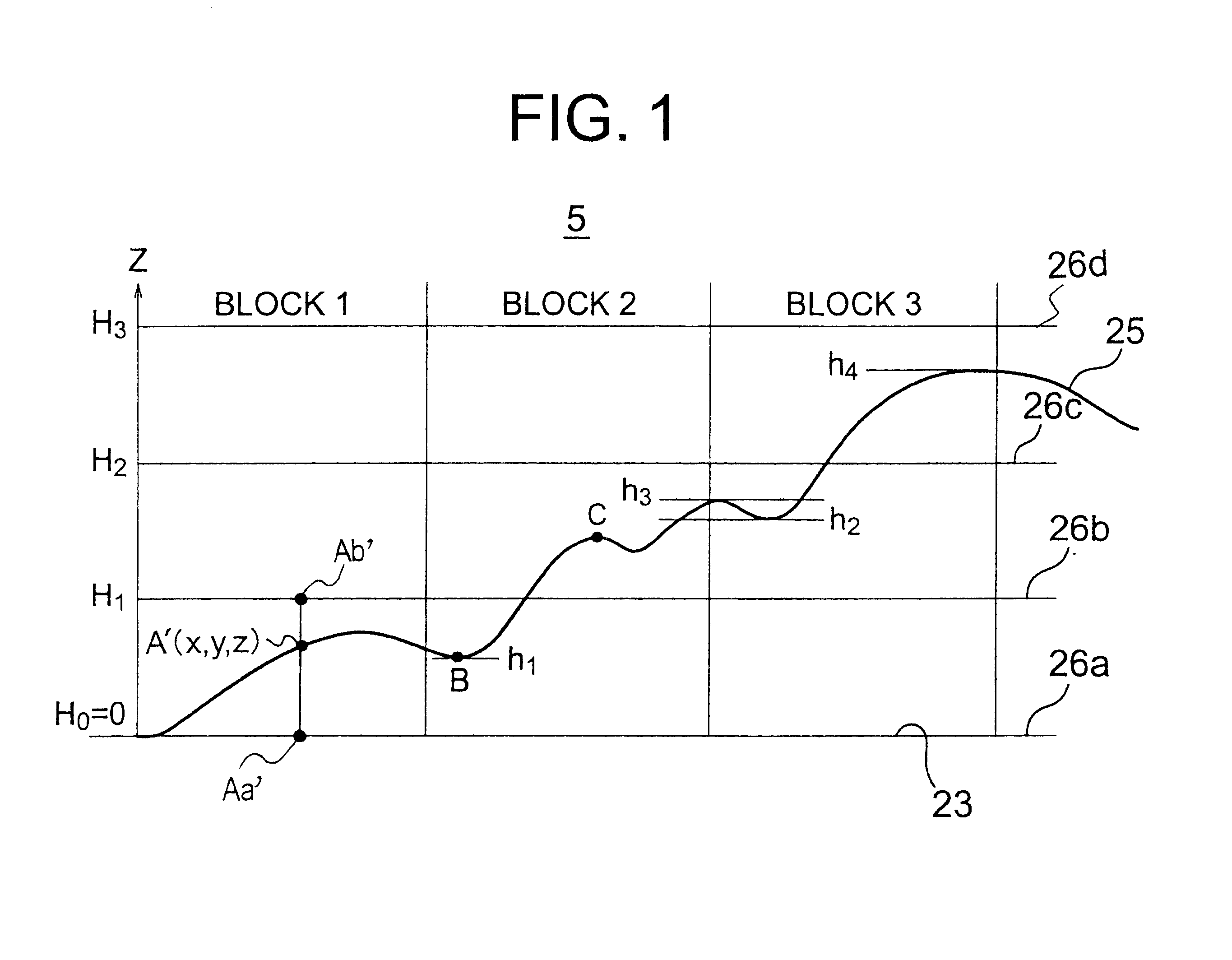
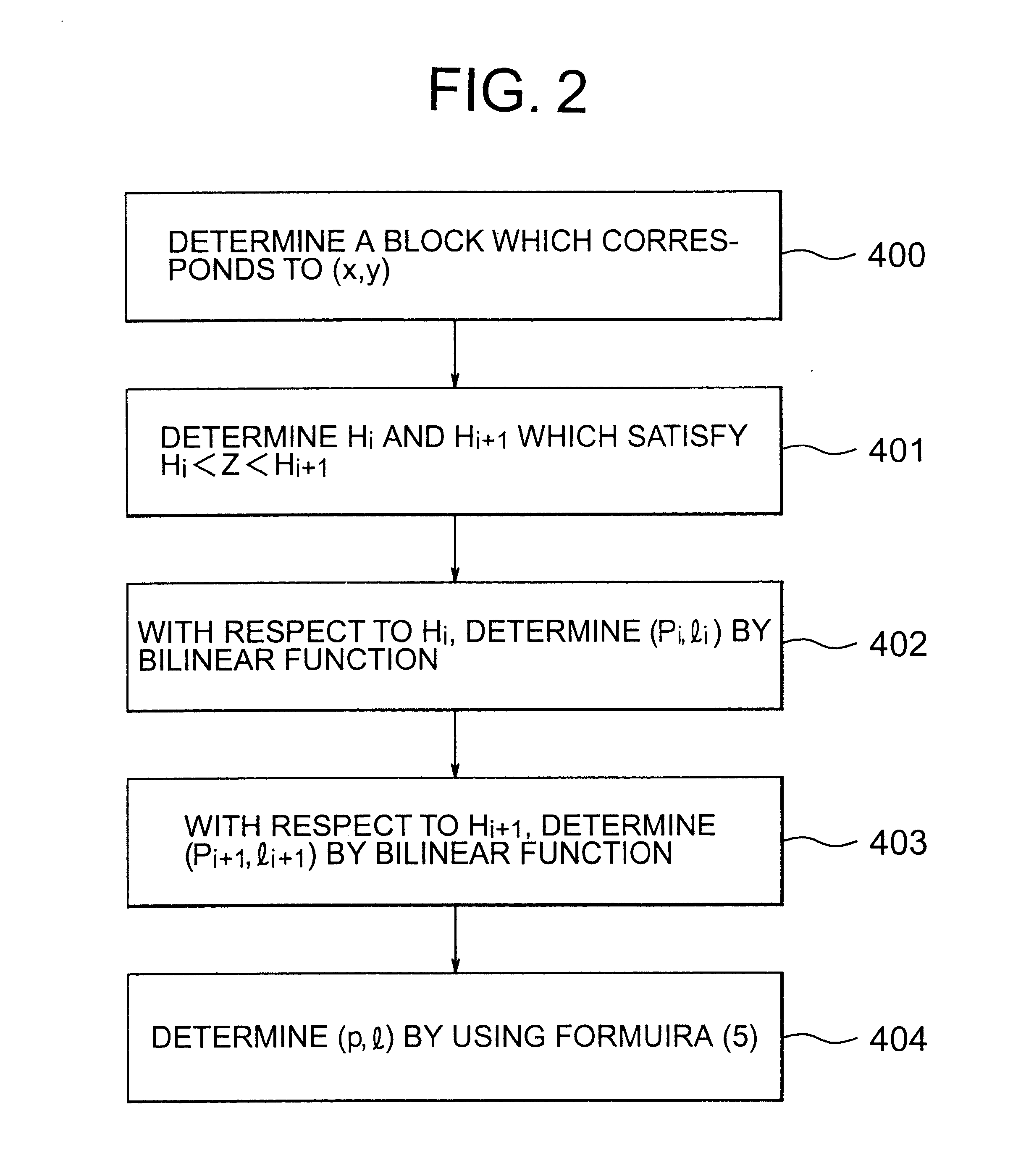
A method is provided for the orthocorrection of a satellite-acquired image. This method can be applied even if ground control points are not set. Without propagation of an error throughout the image and also without needing an excessively large amount of calculations, the method makes it possible to correct ground-relief-associated distortions caused by the relief of a ground surface. According to the method, a plurality of control planes of different elevations are set relative to a control plane of a zero elevation of a reference rotating ellipsoidal earth model. A corrected image is divided into blocks by lattices of equal intervals. With respect to each of these blocks, distortion model formulas in the form of bilinear functions are determined for the respective control planes. Concerning each pixel position in the corrected image, two pixel positions in an observed image, which correspond to the elevation value of the pixel position in the block, are calculated by using distortion model formulas for two control planes which directly sandwich the value of elevation above and below the value in the corresponding block. By the value of elevation, the two pixel positions are linearly interpolated to determine the desired pixel position in the observed image.
Owner:HITACHI SOFTWARE ENG
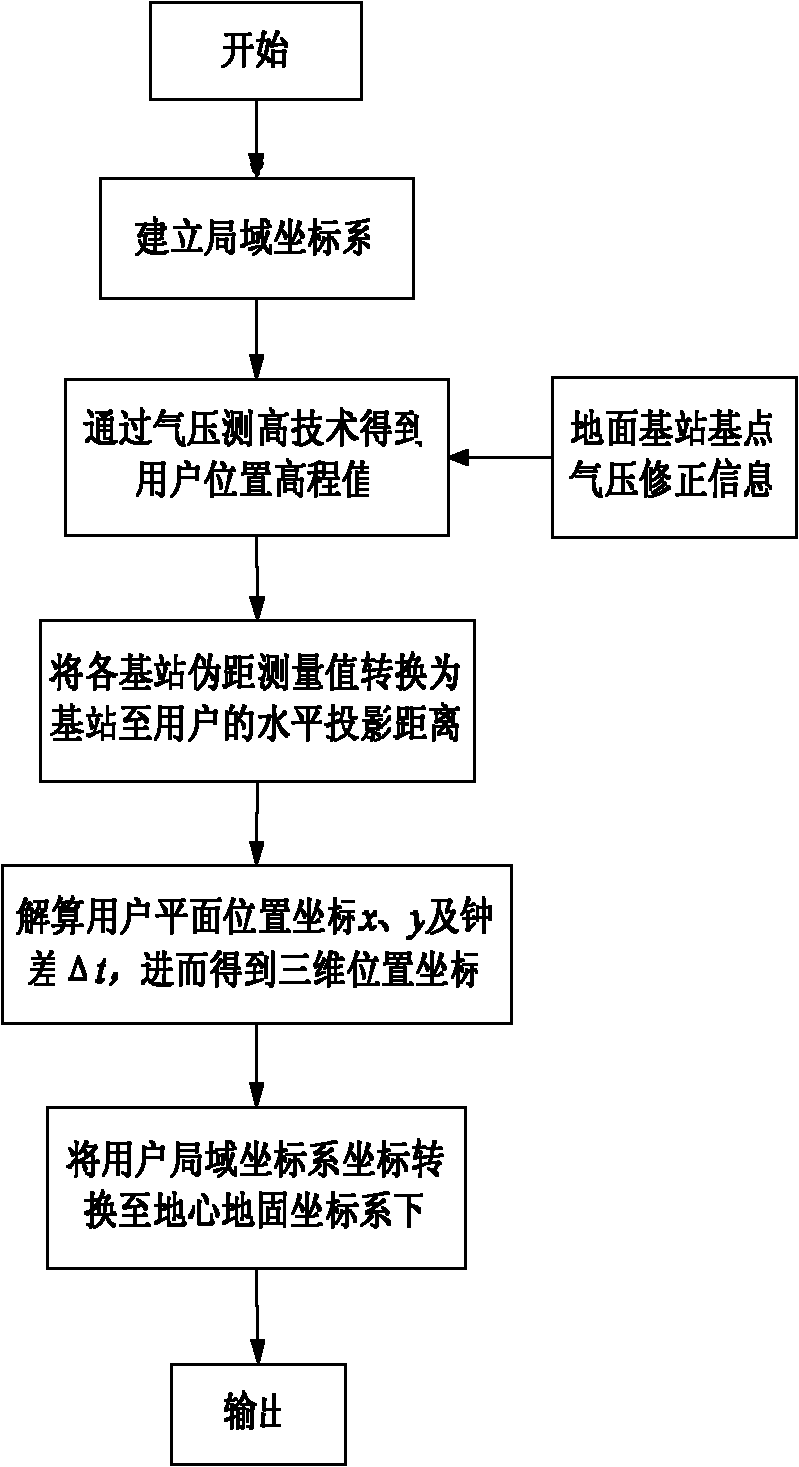
Base station based air pressure relative measurement method for calculating precise elevation
InactiveCN102735213AImprove calculation conversion precisionIncrease distribution densityHeight/levelling measurementTwo temperatureEngineering
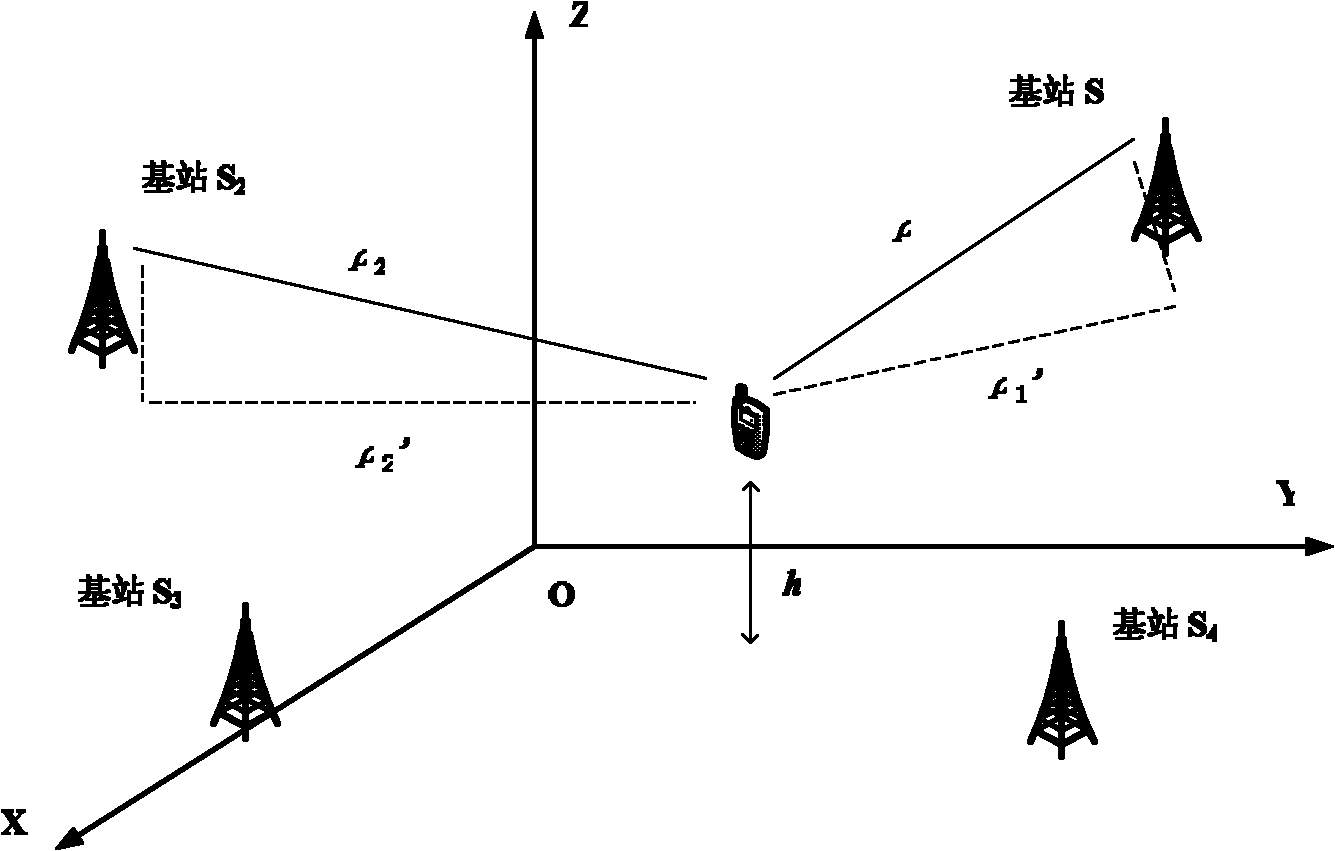
The invention discloses a base station based air pressure relative measurement method for calculating a precise elevation. The method uses a known elevation value and an air pressure measurement value of a wireless communication network base station and an air pressure measurement value of a point to be measured to calculate the elevation of the point to be measured. In particular, the base station of ground mobile communication network is installed with an air pressure measuring sensor as a relative measurement station. A base station transmission link is used to transfer the measured data to a user; the user terminal is provided with an air pressure sensor chip to measure air pressure value of the terminal, so as to facilitate calculation of a relative elevation of the terminal to an installation location of the base station air pressure sensor by utilizing the corresponding relationship between elevation and air pressure value. Similarly, if temperature values of the base station and the terminal are known, the two temperature measurement values can be used to correct the relationship between elevation and air pressure value to further improve conversion accuracy of elevation calculation. The elevation calculation value of the method of the invention can be substituted into various positioning measurement equations to further improve accuracy of three-dimensional positioning solution of the measurement equations.
Owner:NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORIES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
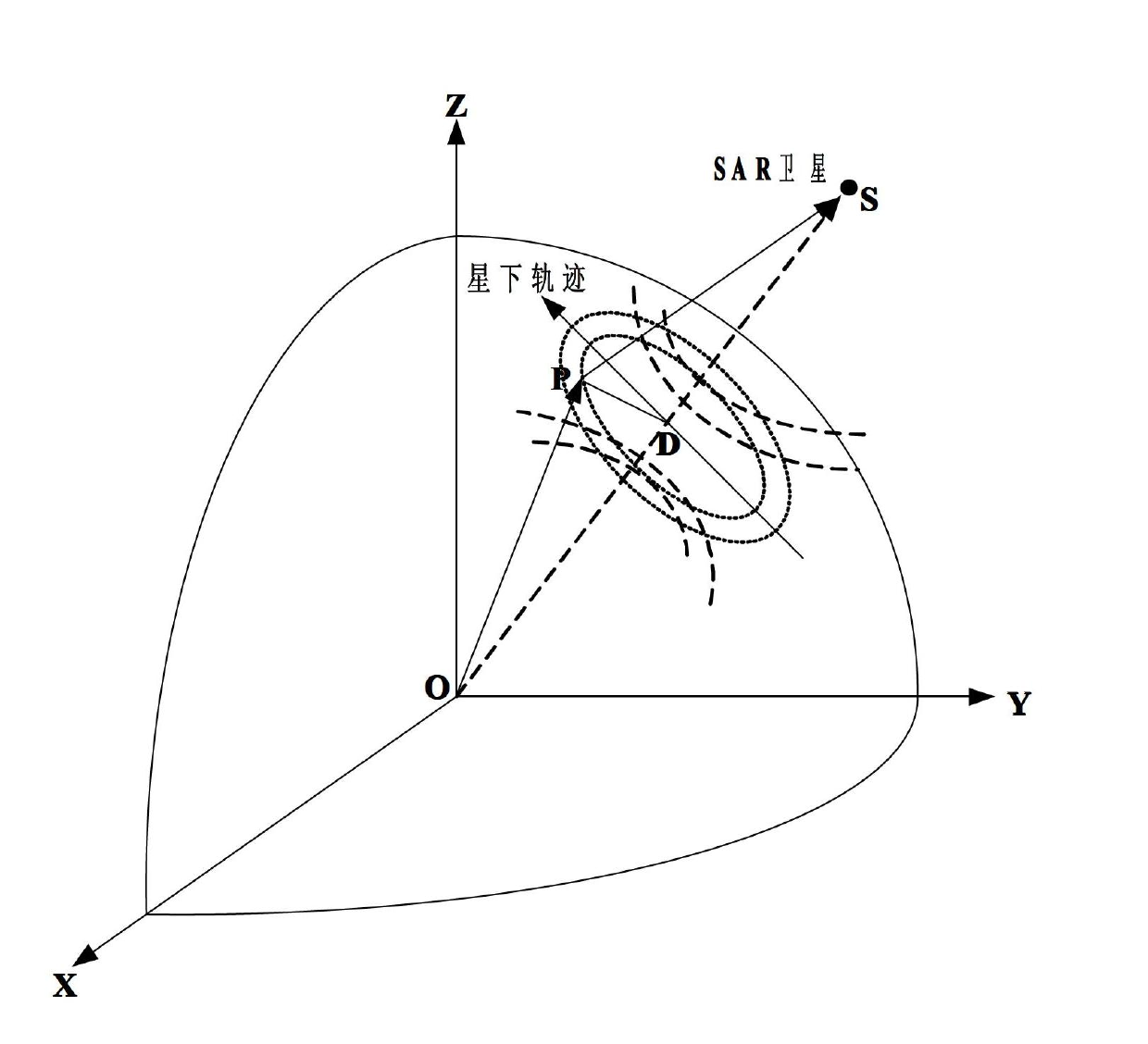
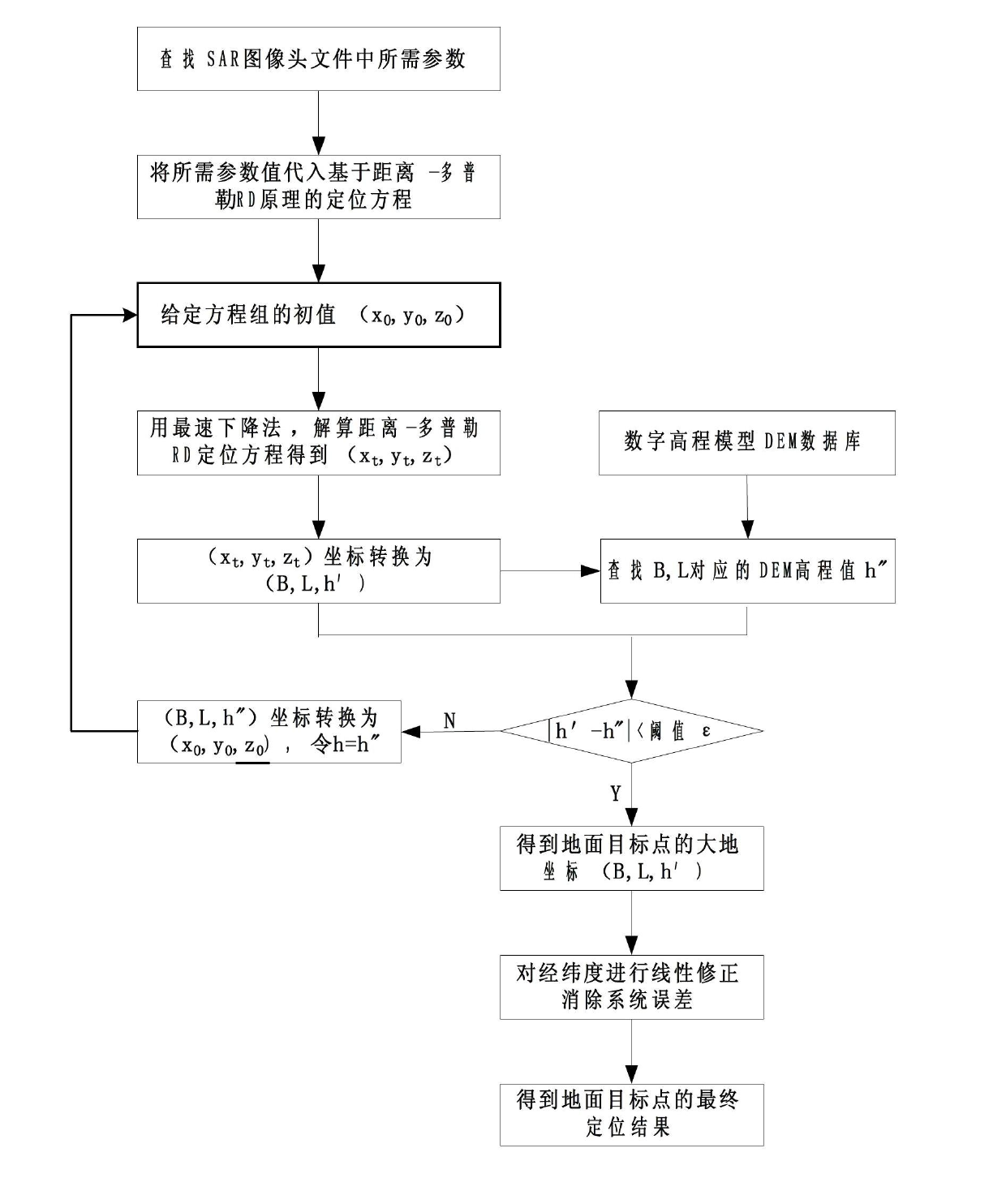
Image registration method based on synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image and digital elevation model (DEM) data
InactiveCN102654576AHigh precisionReduce computationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSteep descentSynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses an image registration method based on a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image and digital elevation model (DEM) data, wherein the problems that the positioning precision to ground target points in SAR image is not high and positioning is difficult to realize in actual projects in the prior art are mainly solved. The method comprises the following steps of: solving a longitude L, a latitude B and an elevation value h' of a ground target point in a spherical coordinate system by using a steepest descent method according to the Range-Doppler (RD) principle and the earth model equation, and transforming the values into a geodetic coordinate system; looking up the elevation value h' corresponding to B and L in a DEM database, and comparing the absolute value of h'- h' with a set threshold value epsilon, if the absolute value of h'- h' is greater than epsilon, enabling h to be equal to h' and returning to resolve the equation system again, and if the absolute value ofh'- h' is identical to or less than epsilon, stopping iteration, and taking h' as the elevation value of the ground target point, and the corresponding latitude B and longitude L as the latitude and longitude of the ground target point; linearly correcting the longitude and latitude to eliminate system errors, so that a final ground target point positioning result is obtained. The image registration method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of small operand and high positioning precision, and can be used for positioning ground target points in SAR images in actual projects.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Structure Model Creation from a Three Dimensional Surface
ActiveUS20150130797A1Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognition3d surfacesThree dimensional surface
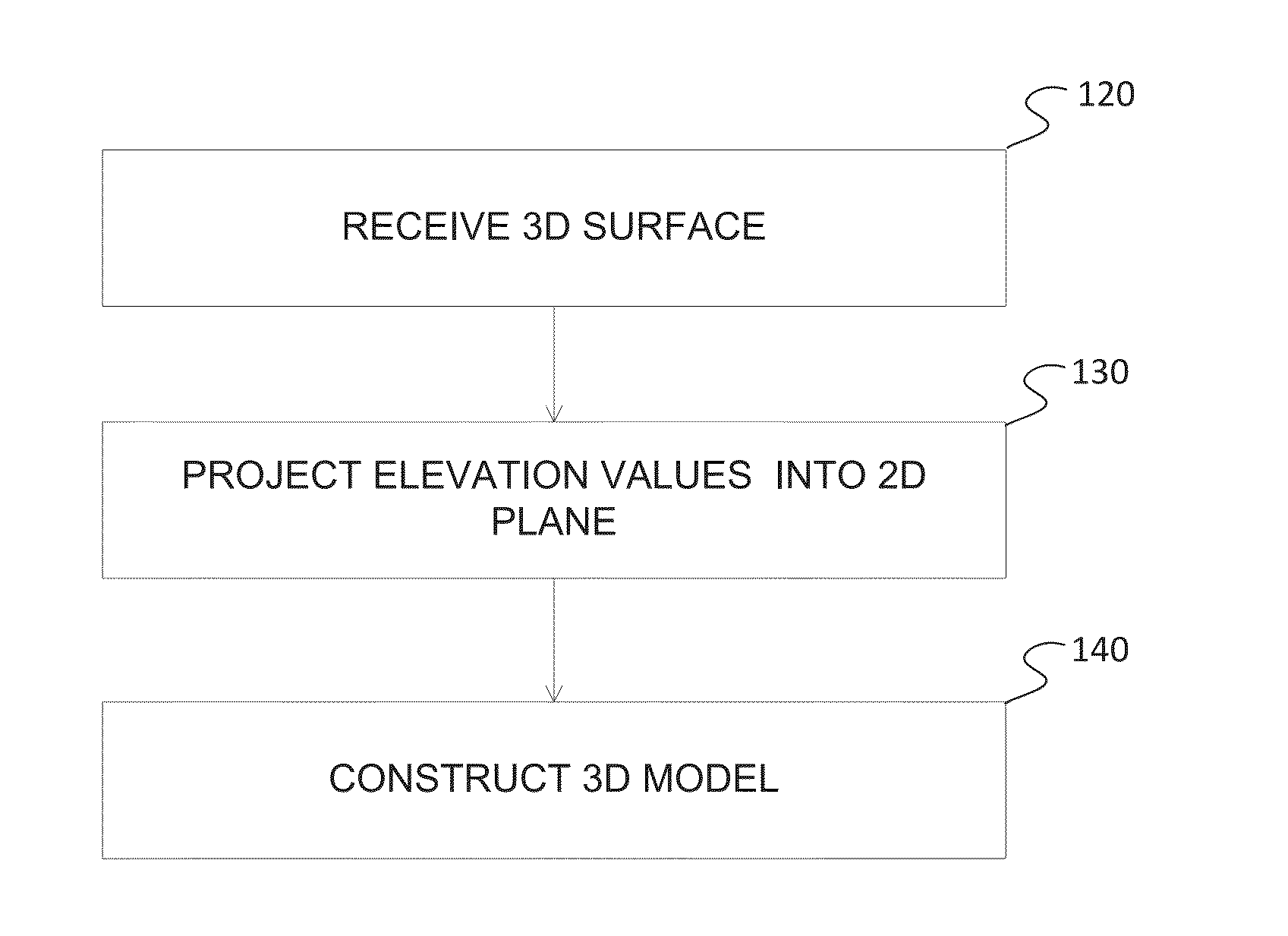
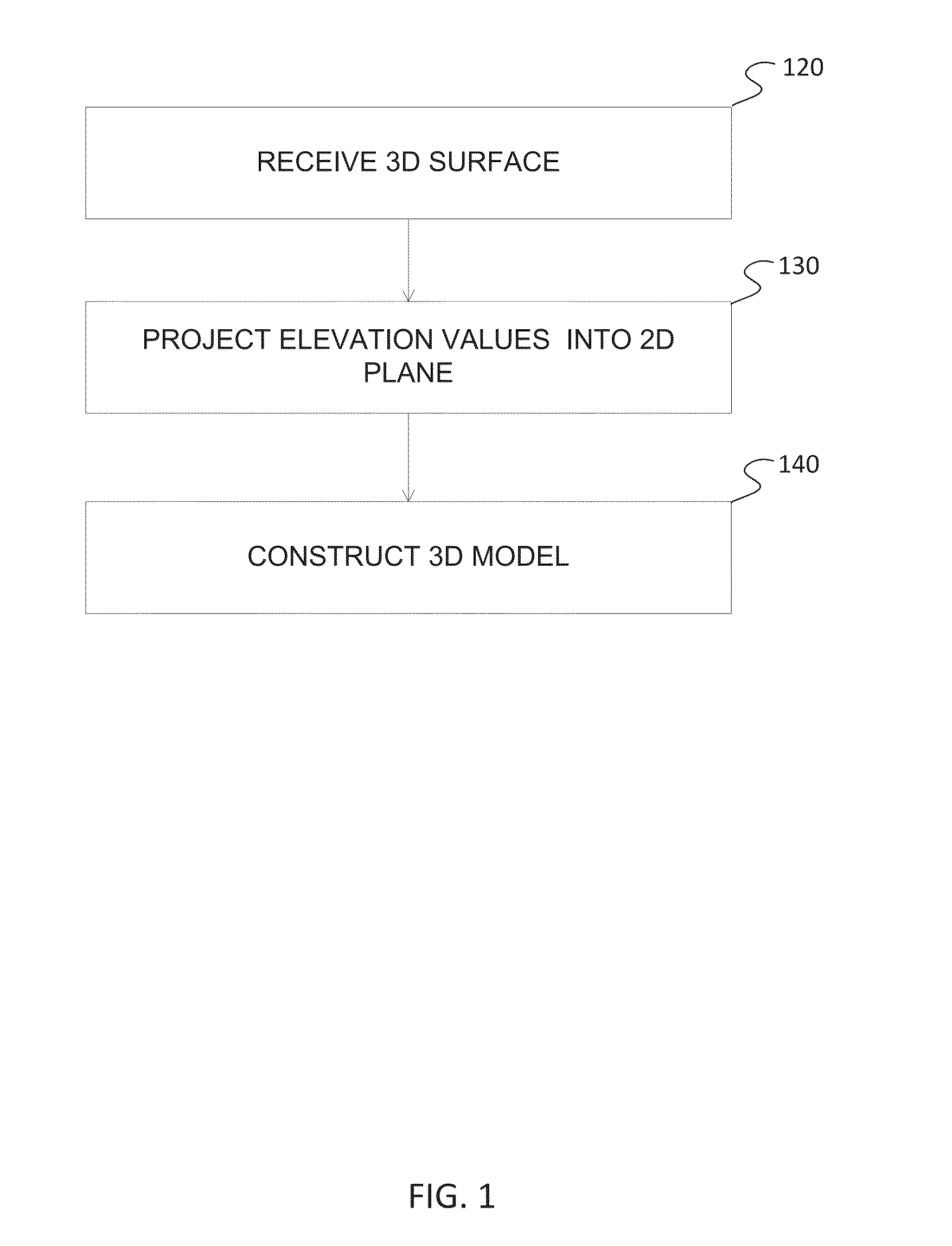
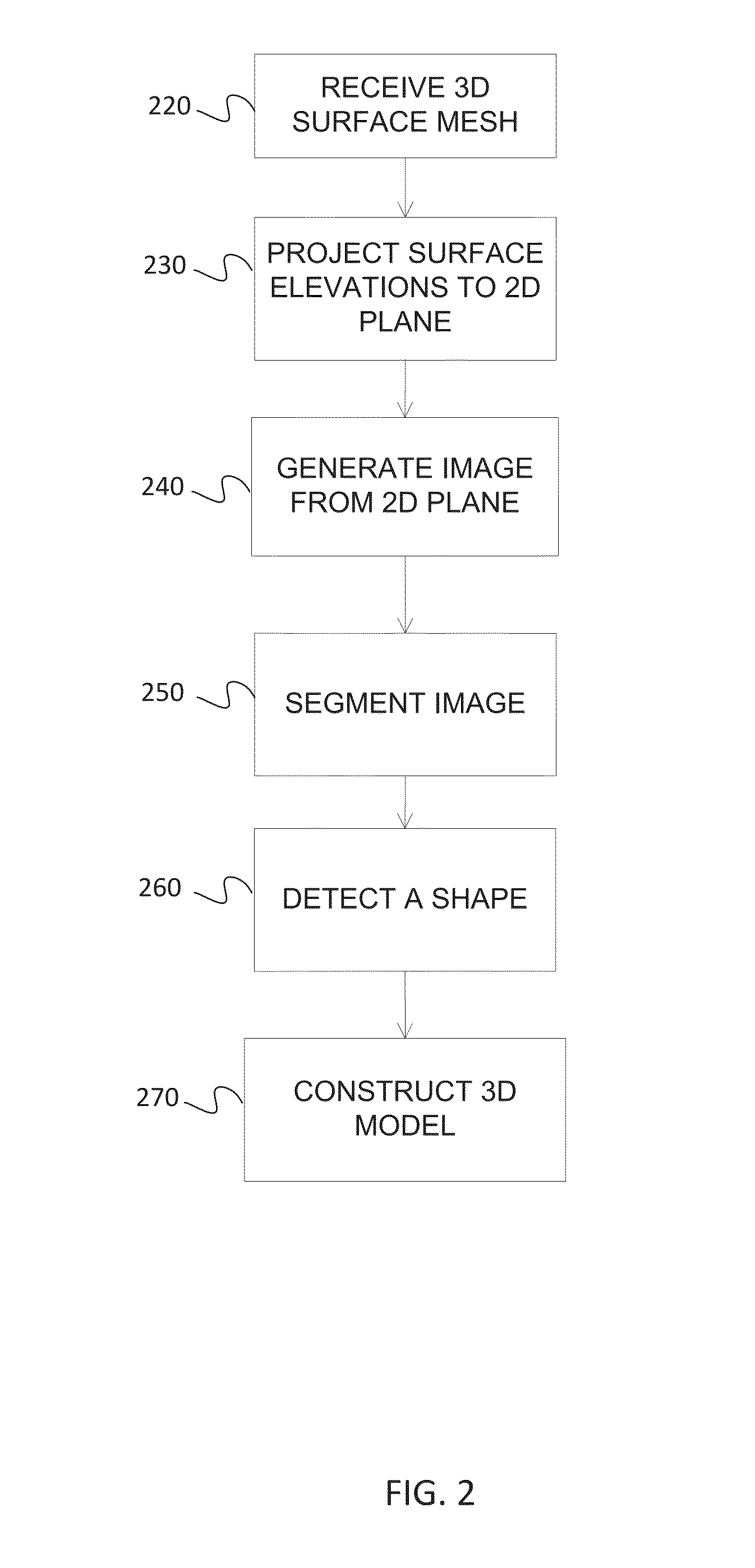
Constructing a three dimensional (3D) model of a structure may involve receiving a 3D surface representing a geographic area, the surface having elevation values associated with points of the surface and the geographic area comprises a structure having a geographic footprint smaller than the geographic area. Constructing a 3D model may also involve projecting the elevation values into a two dimensional (2D) plane. Further, a 3D model may be constructed of the structure by assigning model heights based on the elevation values projected into points of the 2D plane.
Owner:HERE GLOBAL BV
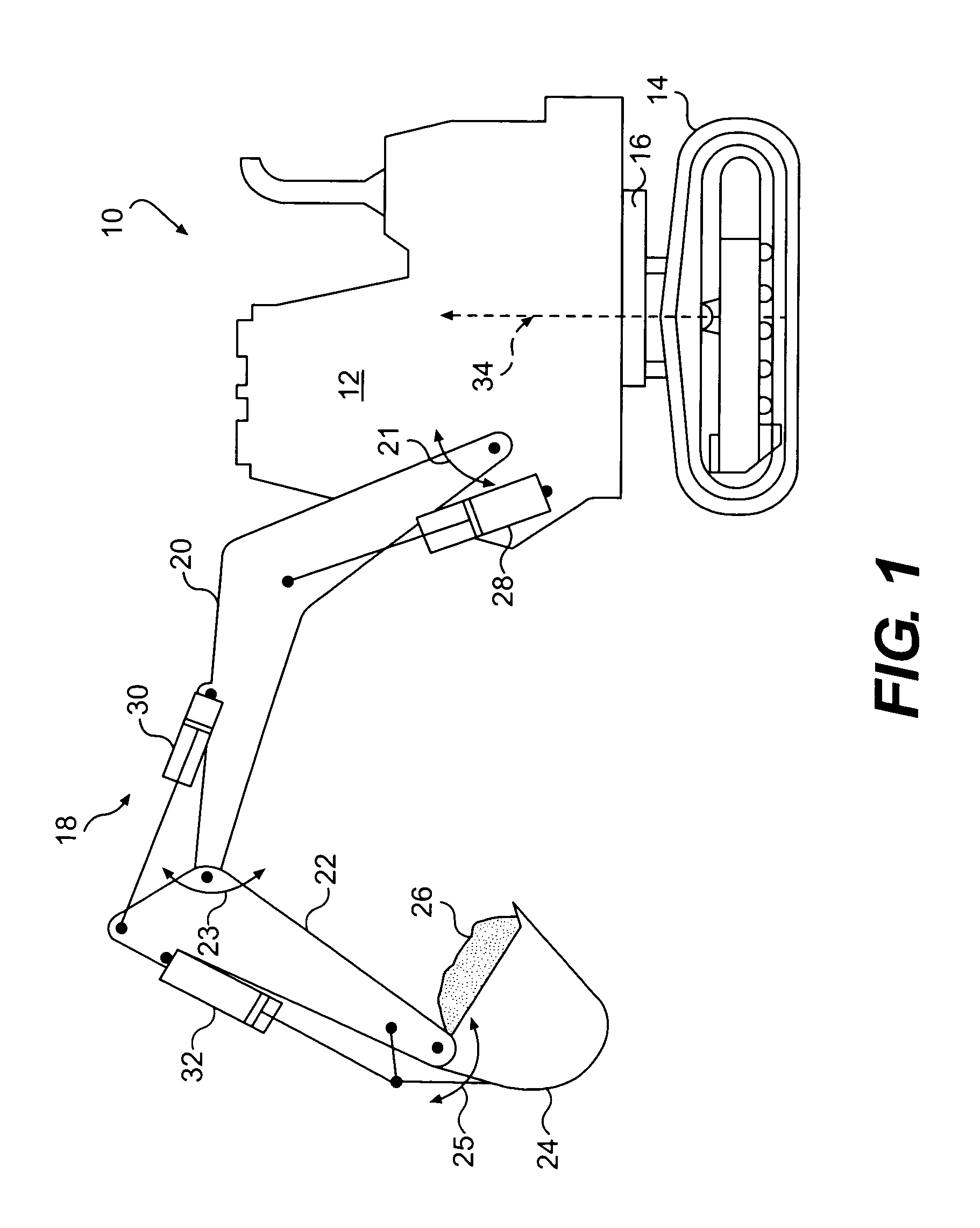
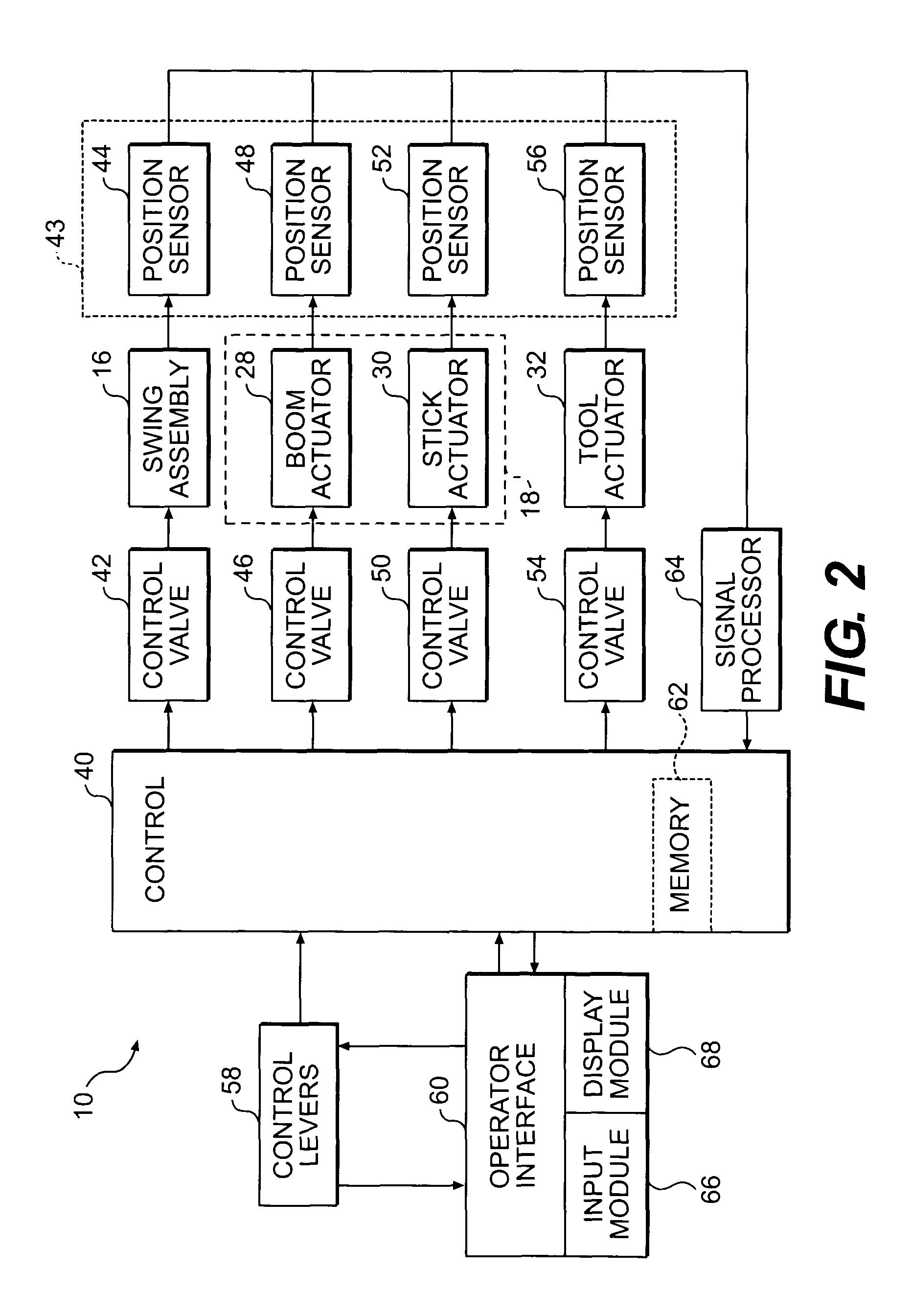
Work machine display system
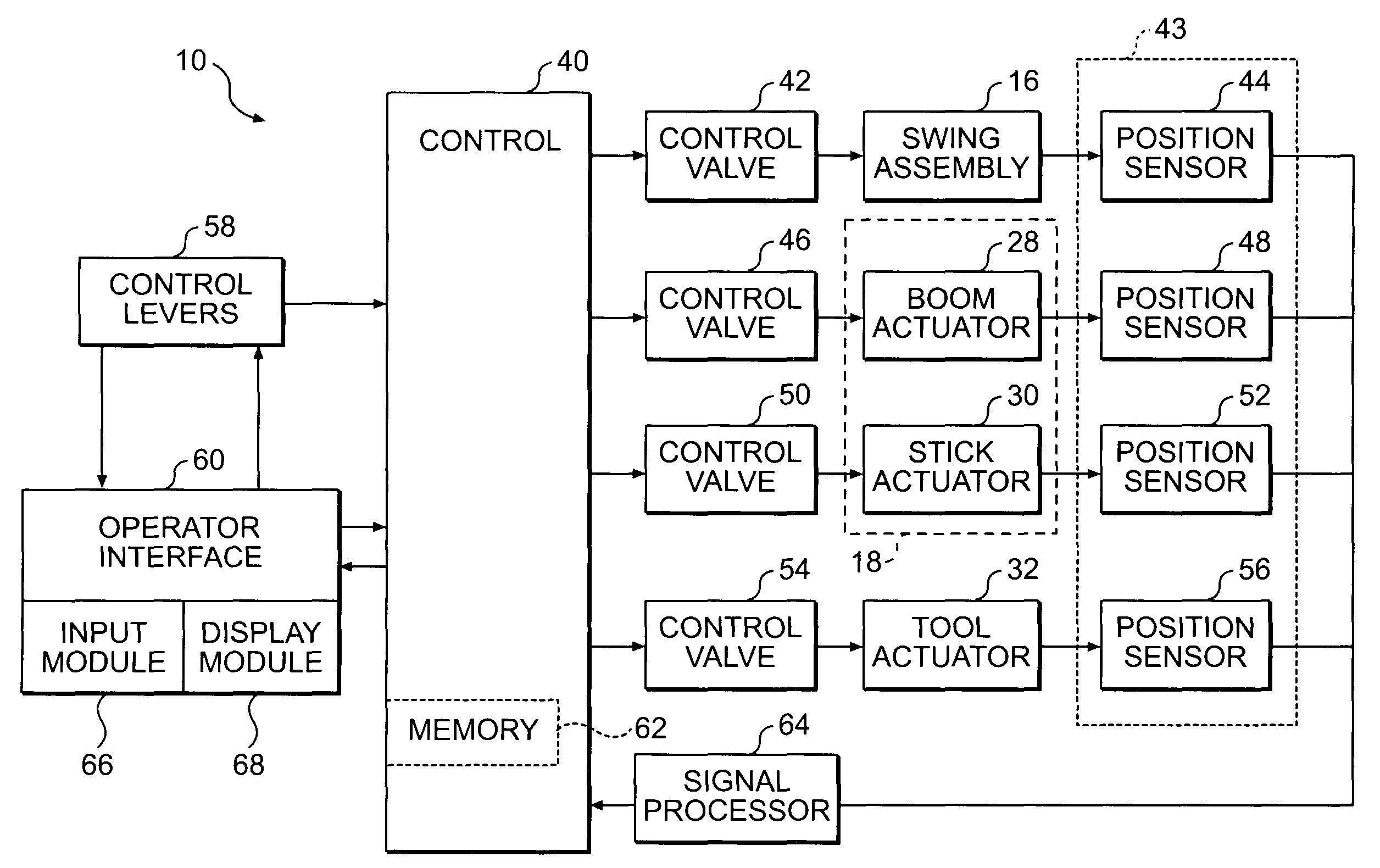
A display system and method for a work machine is provided. A terrain map indicative of a current surface configuration for a geographic location is displayed. The display of the terrain map includes a plurality of elevation segments. Each of the plurality of elevation segments has an actual surface elevation value for a discrete area of the geographic location. A position of a ground engaging tool operatively connected to the work machine is monitored. A current elevation of the ground engaging tool is identified. The display of the elevation segment corresponding to the location of the ground engaging tool is updated when the current elevation of the ground engaging tool indicates a change in the actual surface elevation value for the elevation segment corresponding to the location of the ground engaging tool.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
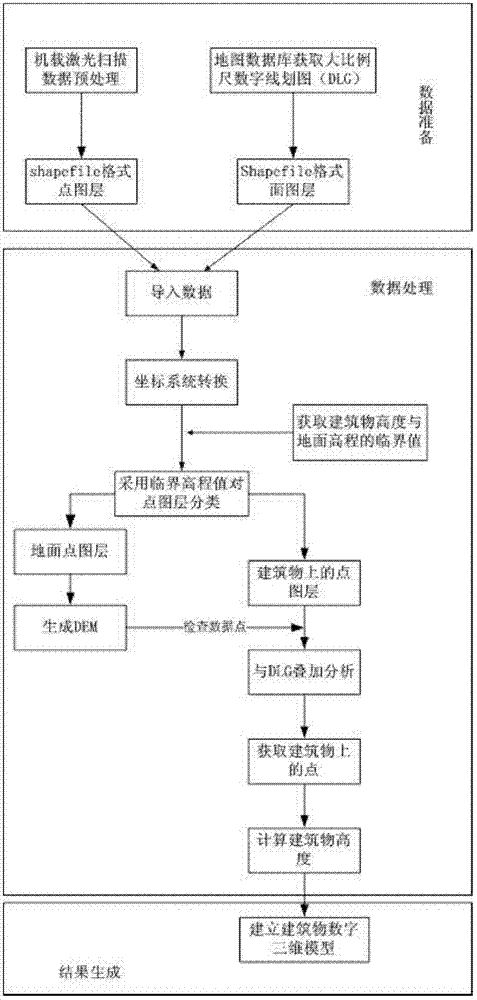
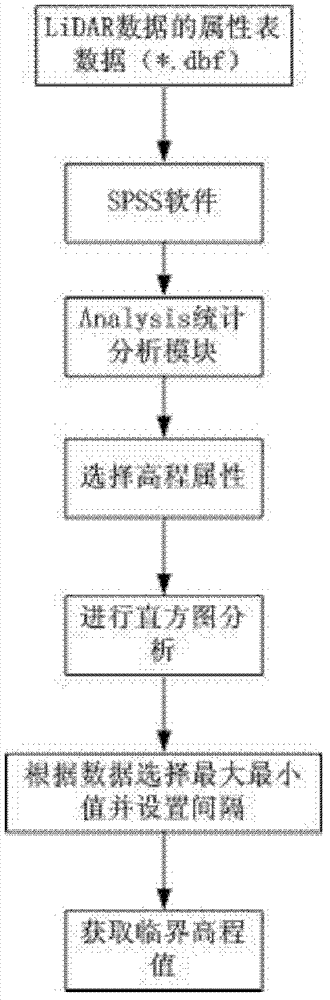
Method and system for acquiring three-dimensional building information rapidly
The invention discloses a method and system for acquiring the three-dimensional building information rapidly. The method comprises the following steps: preparing data, processing data and generating data. The method comprises the following specific steps: (1) preprocessing the original data; (2) acquiring the critical elevation value; (3) guiding the data into service processing software; (4) converting a coordinate system; (5) classifying the point layer data; (6) establishing a digital terrain model and acquiring a terrain continuously-varying interval; (7) checking and extracting points on buildings; (8) calculating the height of the buildings; and (9) establishing and displaying the digital three-dimensional models of the buildings. A method for constructing a digital city rapidly according to the buildings in a set area is designed by using the system integrating mode, and the three-dimensional models of the city buildings can be established and displayed rapidly. The method can be applied to the fields of land utilization condition survey, the digital city construction and the like. The method and the system can be used for acquiring the three-dimensional building information rapidly and effectively at low cost.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
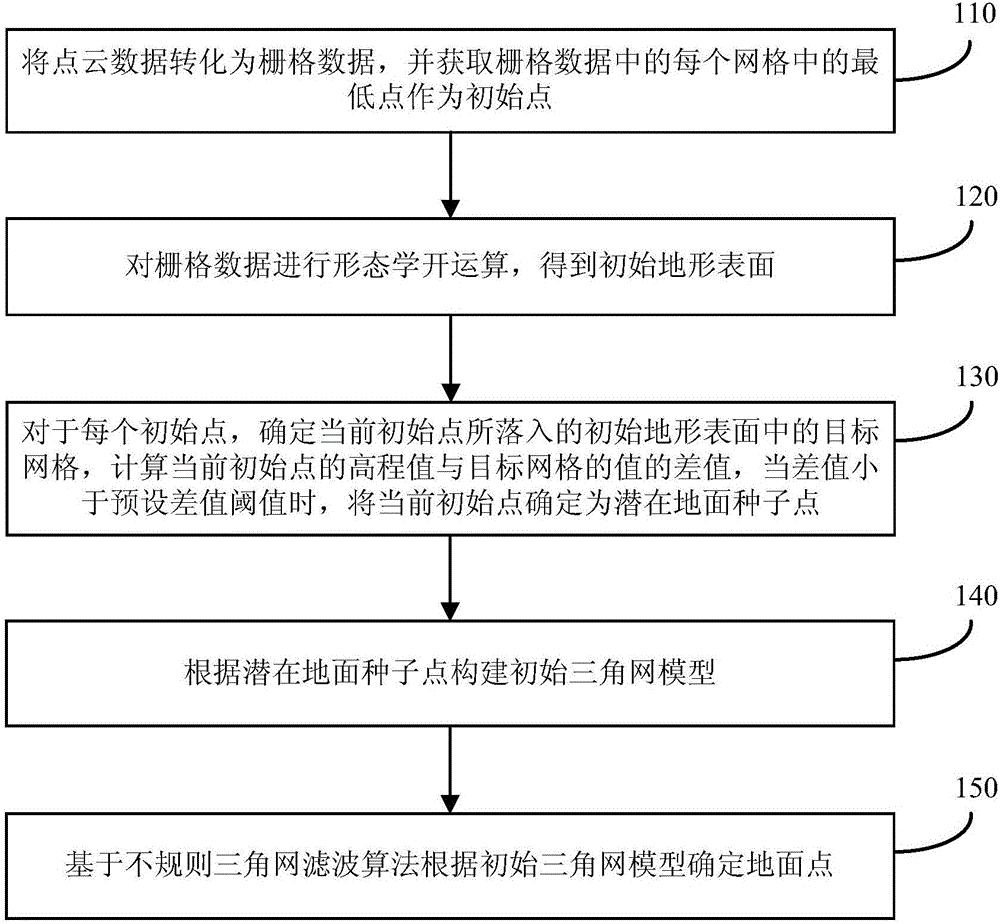
Filtering method and device for point cloud data
InactiveCN106408604APrecise screeningGuaranteed accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisTerrainPoint cloud
An embodiment of the invention discloses a filtering method and a filtering device for point cloud data. The filtering method comprises the steps of: converting the point cloud data into raster data, and acquiring the lowest point in each raster as the initial point; performing morphological opening operation on the raster data to obtain an initial terrain surface; for each initial point, determining the current initial point as a potential ground seed point if a difference value between an elevation value of the current initial point and a value of the target raster which the current initial point falls into; constructing an initial triangulation network model according to the potential ground seed point; and determining a ground point according to the initial triangulation network model based on an irregular triangulation network filtering algorithm. By adopting the filtering method and the filtering device, the ground seed point can be reasonably determined, and the filtering efficiency is improved while guaranteeing the accuracy and precision of the initial triangulation network model, thereby the ground point in the point cloud data can be screened quickly and accurately.
Owner:BEIJING GREEN VALLEY TECH CO LTD
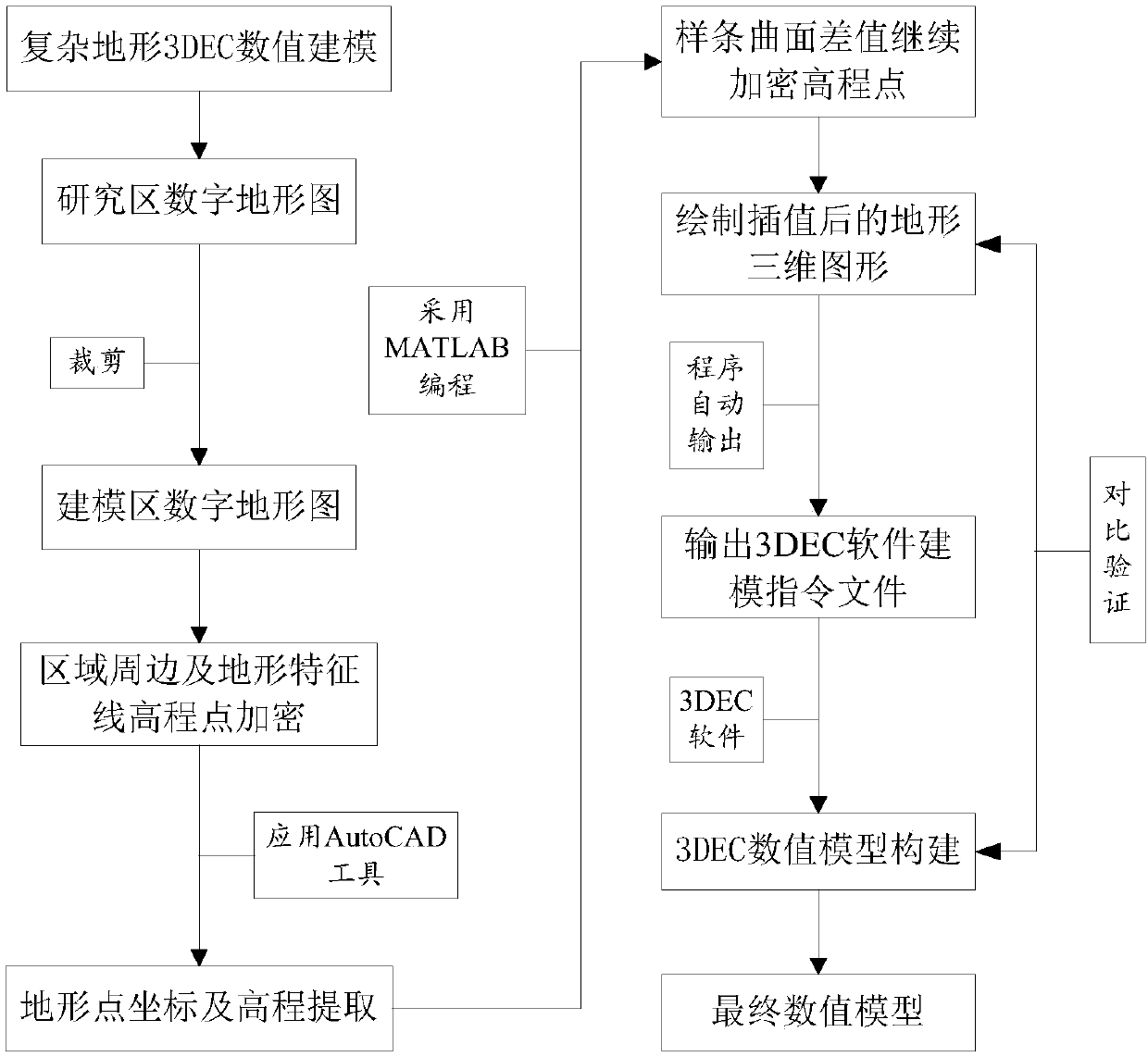
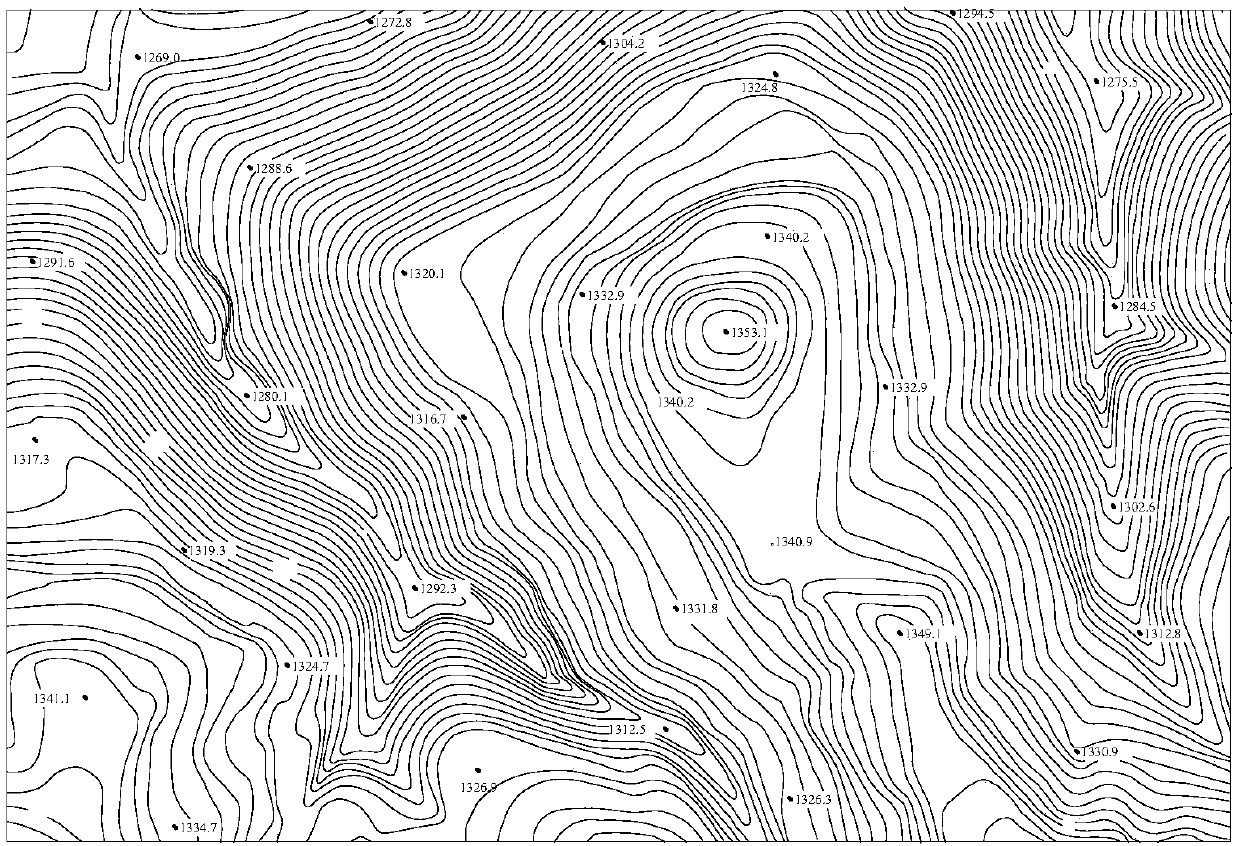
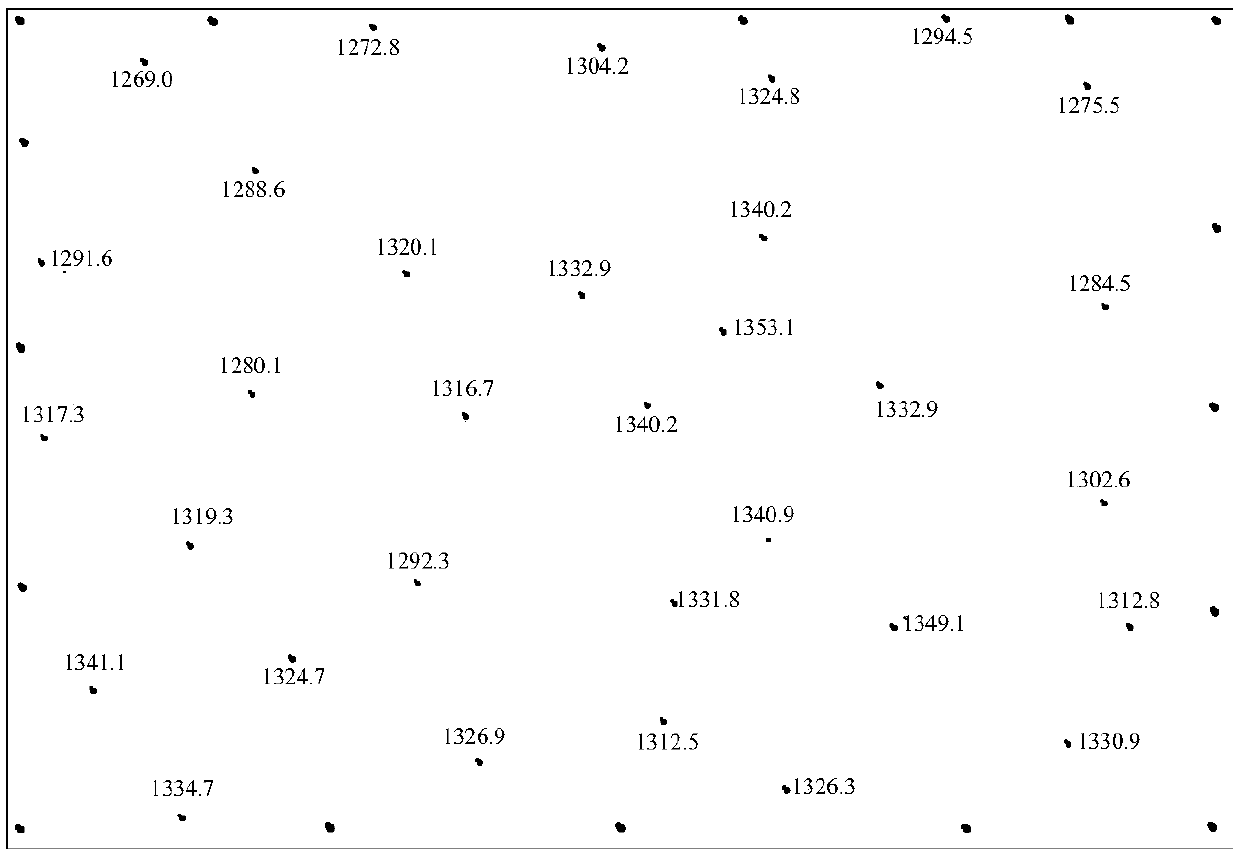
Modeling method for 3D discrete element method numerical model of complicated terrain based on contour line
ActiveCN107562833AHigh degree of intelligenceRealize automatic drawingSpecial data processing applications3D modellingTerrainData file
The present invention provides a modeling method for 3D discrete element method numerical model of complicated terrain based on contour line, and belongs to numerical simulation research fields in geological engineering and mining engineering fields. The method comprises: firstly, acquiring a digital topographic map of a modeling area, encrypting elevation points at a boundary of the area and an area with sparse elevation points and obtaining elevation values of each encrypted elevation point, and extracting 3D spatial information of each elevation point and saving the information; then performing surface spline interpolation on the digital topographic map, and drawing a modeling area surface 3D graphics; inputting the 3D spatial information of all the elevation points after surface splineinterpolation into a final terrain data file, and establishing a 3D numerical model by 3D discrete element method software; and by comparison and verification with the surface 3D graphics, obtaininga final 3D discrete element method numerical model of the modeling area. According to the method, high-precision numerical modeling can be performed on any complicated terrain area, and the established model surface has smaller deviation than the actual terrain surface, and the method has higher application value.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING) +1
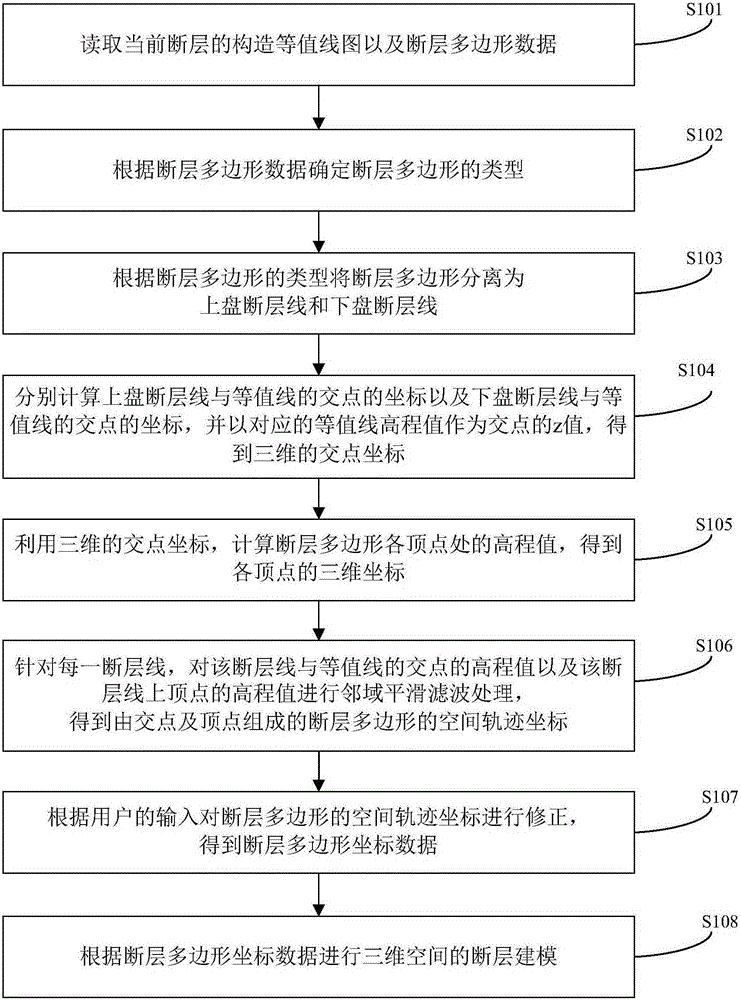
Method and apparatus for establishing fault model based on spatial fault polygon
ActiveCN105225273AAccurately establishedAccurately obtained3D modellingSimulationIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
The invention discloses a method and an apparatus for establishing a fault model based on a spatial fault polygon. The method comprises: reading a structural contour map and fault polygon data; determining the type of the fault polygon according to the fault polygon data; separating the fault polygon into a hanging wall fault line and a footwall fault line according to the type; calculating coordinates of an intersection point between the hanging wall fault line and a contour line and an intersection point between the footwall fault line and the contour line, and obtaining three-dimensional intersection point coordinates by taking a corresponding elevation value of the contour line as a z value of the intersection point; calculating an elevation value of each vertex of the fault polygon by utilizing the three-dimensional intersection point coordinates to obtain three-dimensional coordinates of each vertex; for each fault line, performing neighbor smoothing filtering on the evaluation values of the vertex and the intersection point on the fault line to obtain spatial trajectory coordinates of the fault polygon; correcting the spatial trajectory coordinates to obtain coordinate data; and performing fault modeling according to the coordinate data. The three-dimensional data of the fault polygon is obtained quickly and accurately, and an accurate model is established, so that the workload of later correction is reduced.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
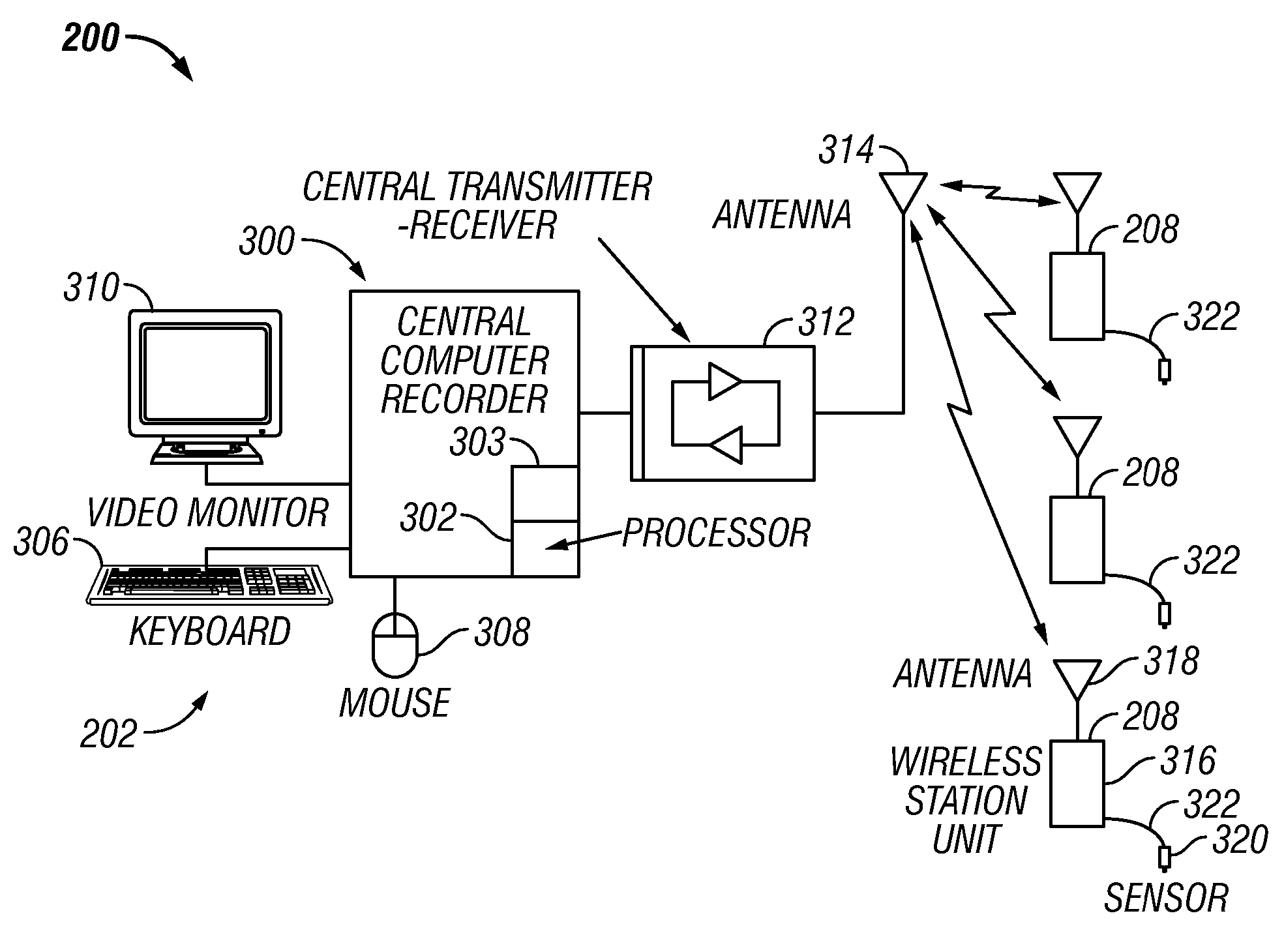
Digital Elevation Model for Use with Seismic Data Acquisition Systems
ActiveUS20070286023A1Improve accuracyEfficiently determinedSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal transmissionDigital elevation modelElevation - value
A seismic data acquisition system includes a controller, a plurality of sensor stations and a plurality of seismic sources. Each sensor station includes a sensor coupled to the earth for sensing seismic energy in the earth. The sensor provides a signal indicative of the sensed seismic energy and a recorder device co-located with the sensor unit that receives and stores the signals. A communication device is co-located with the sensor station and provides direct two-way wireless communication with the central controller. In one embodiment, in-field personnel determine elevation values, or Z values, for the sensor stations and seismic source by accessing a digital elevation model or a look-up table based on the digital elevation model. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:INOVA
Method for reconstructing LiDAR original point cloud building contour
ActiveCN106570468AContour speedImprove efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionPoint cloudThree-dimensional space
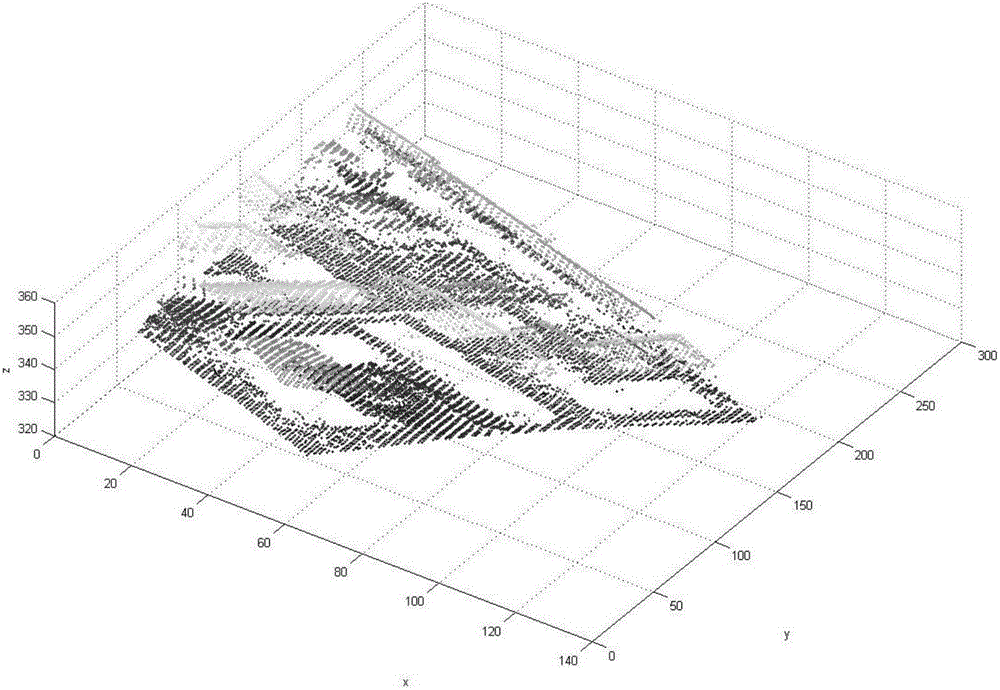
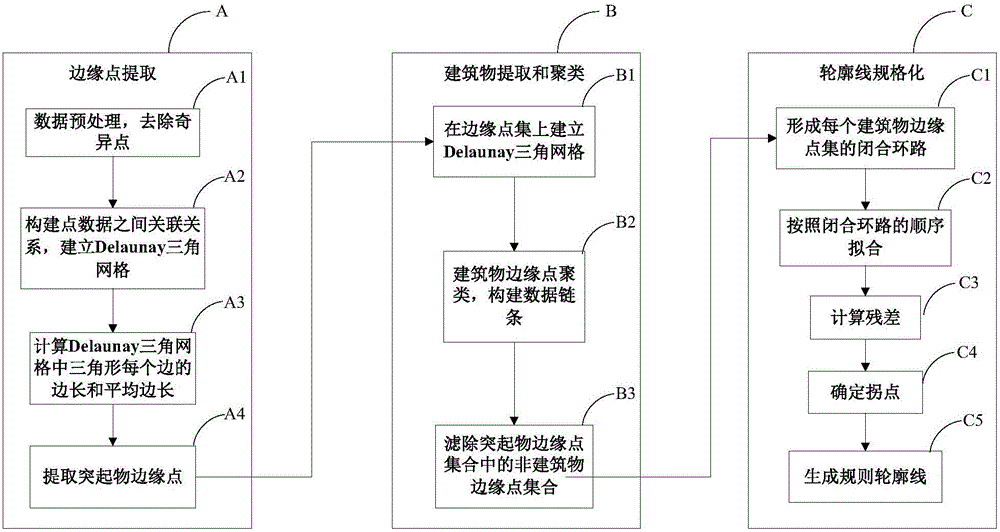
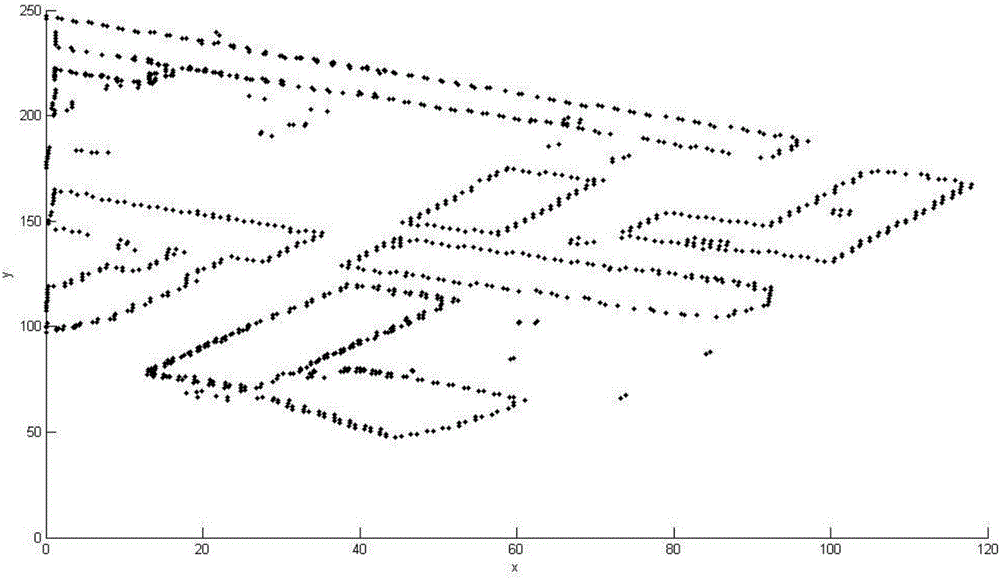
The invention provides a method for reconstructing a LiDAR original point cloud building contour. The method includes constructing a triangular mesh according to the Delaunay triangular mesh principle on the basis of LiDAR discrete point cloud; extracting the two points with the greater elevation value in a triangle with a long edge in the Delaunay triangular mesh in a three dimensional space and storing the two points in a pair; taking the point pair as a data chain node and connecting the data chain nodes to form a circular data chain to completing the clustering of the edge points of each protruding object; counting the points in a point set of each protruding object and screening the non-building edge point set; and successively adding the points into the fitting data to be re-fitted according to the connection sequence, and connecting the intersection points of the adjacent fitting edges to obtain the contour of a building by taking the distance from the new point to the fitting straight line in the previous step as the criteria. The method is high in speed, speed, and accuracy, and solves the problems of discreteness and non-characteristics of the LiDAR data and the regularity of contour reconstruction.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNIV PLA
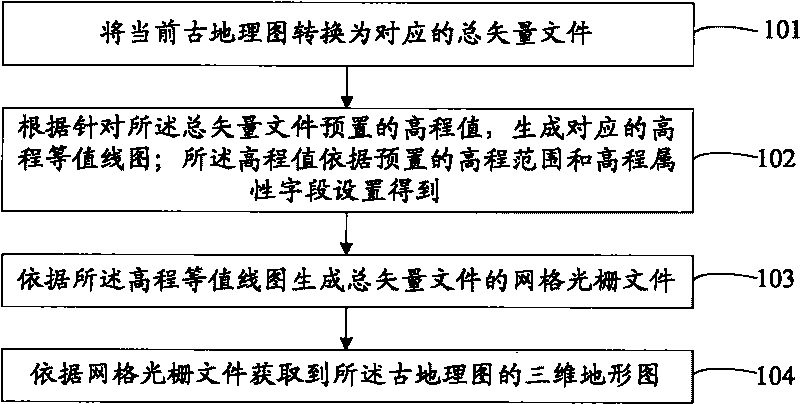
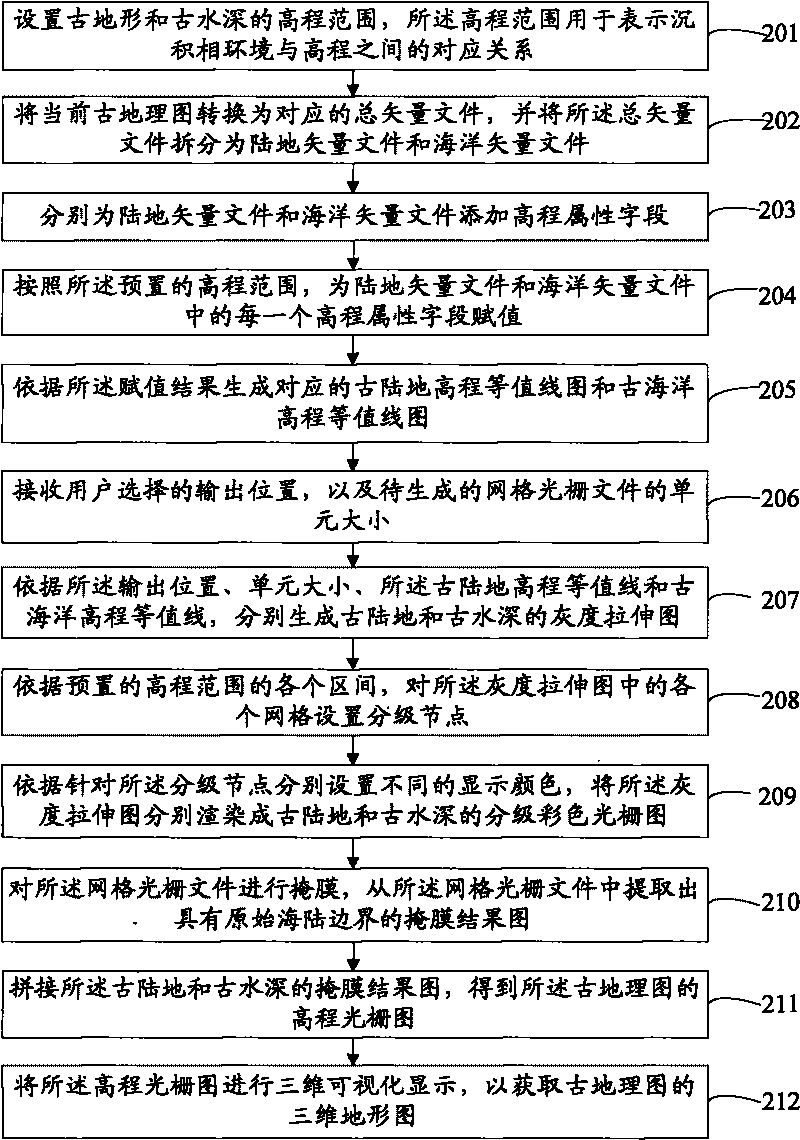
Method and device for acquiring three-dimensional paleotopographic map
The invention provides a method and a device for acquiring a three-dimensional paleotopographic map. The method comprises the following steps: converting the current three-dimensional paleotopographic map into a corresponding total vector file; generating a corresponding elevation contour map according to an elevation value preset for the total vector file, wherein the elevation value is obtained according to a preset elevation range and an elevation attribute field; generating a grid grating file of the total vector file according to an elevation contour line; and acquiring a three-dimensional topographic map of the paleotopographic map according to the grid grating file. The acquisition method in the embodiment of the invention does not need relatively professional parameters, so the method has very high operability and can adapt to different occasions in practical application.
Owner:陈建平 +7
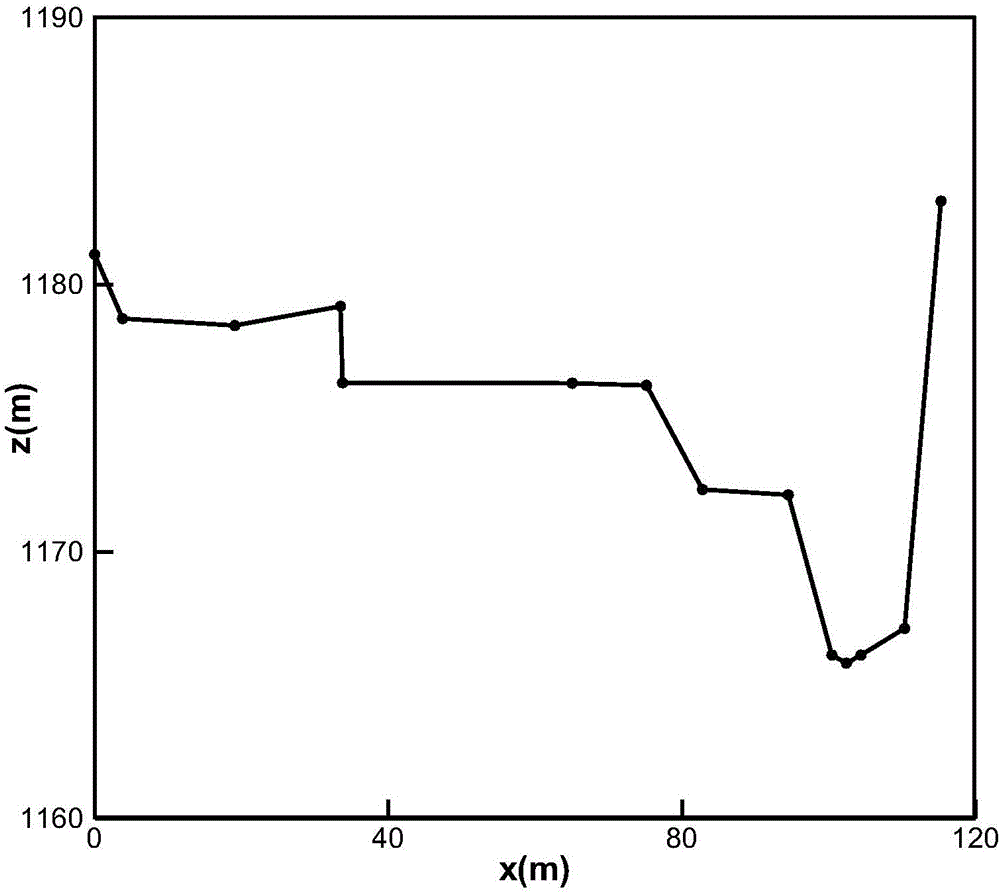
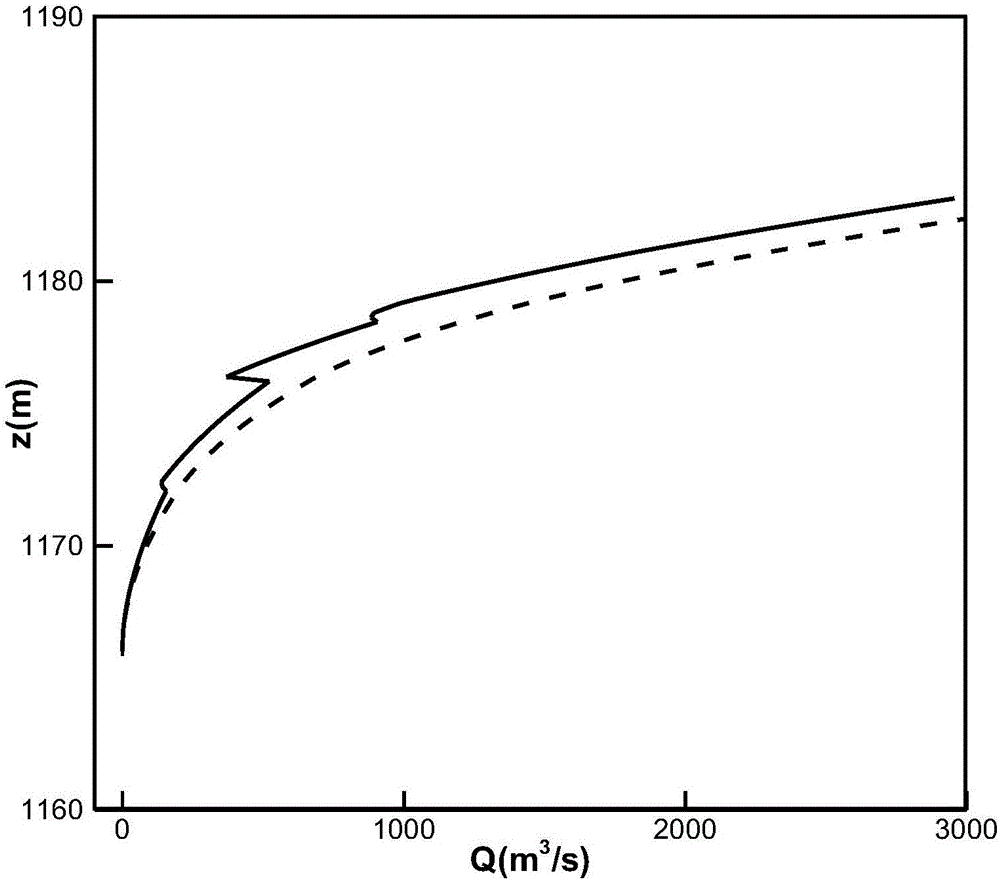
A natural river course cross section stage-discharge relation determining method
ActiveCN106021854AAvoid Double Value ProblemsInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsHigh elevationDouble Value
The invention provides a natural river course cross section stage-discharge relation determining method. The method comprises the steps of firstly, obtaining actually-measured cross section data (xi, zi) of a target cross section, forming M subsections between the cross section x1 and xN equally (xni, xni+1), and obtaining the elevation value corresponding to a node of each subsection; secondly, determining the Manning roughness coefficients n of the different cross sections; thirdly, forming Nz layers equally between the lowest elevation and the highest elevation of the cross sections, calculating the discharge value Qij of each subsection of each elevation equal division layer, and calculating the sum of the discharge values Qij of all the subsections to obtain the total cross section discharge value Qj corresponding to the layer; obtaining a stage-discharge relation according to the total cross section flow value Qj of each layer and the stage corresponding to the layer. The method is based on subsection calculation of stage-discharge relations, performs segmentation calculation of corresponding discharges on the river course cross sections according to the roughness and thus obtains the stage-discharge relation corresponding to a whole cross section; the method can avoid the double value problem in conventional stage-discharge relation determination.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Target low elevation estimation method based on real number field generalized multiple-signal sorting algorithm
InactiveCN103364772AReduce operational complexityHeavy computationWave based measurement systemsHat matrixSorting algorithm
The invention discloses a target low elevation estimation method based on a real number field generalized multiple-signal sorting algorithm. The target low elevation estimation method includes the implementation steps of (1) sampling radar received back waves, (2) using sample data to calculate a sampling covariance matrix, (3) carrying out spatial smoothing and unitary transformation on the sampling covariance matrix to obtain a real number field covariance matrix (4) carrying out eigenvalue decomposition on the real number field covariance matrix to obtain a noise projection matrix, (5) constructing a real number field guiding vector manifold, (6) using the noise projection matrix and the real number field guiding vector manifold to constructing a spatial spectrum, conducting two-dimensional angle searching on the spatial spectrum and obtaining an initial angle estimated value, (7) using the initial angle estimated value to estimate a multi-path attenuation coefficient, constructing a secondary spatial spectrum and obtaining an angle estimated value through the two-dimensional angle searching, and (8) comparing the two angles in the estimated values, and considering the maximum angle as the target elevation value. According to the target low elevation estimation method, the algorithm complexity is reduced, and the angle estimation performance of a radar under the low signal-to-noise ratio is improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
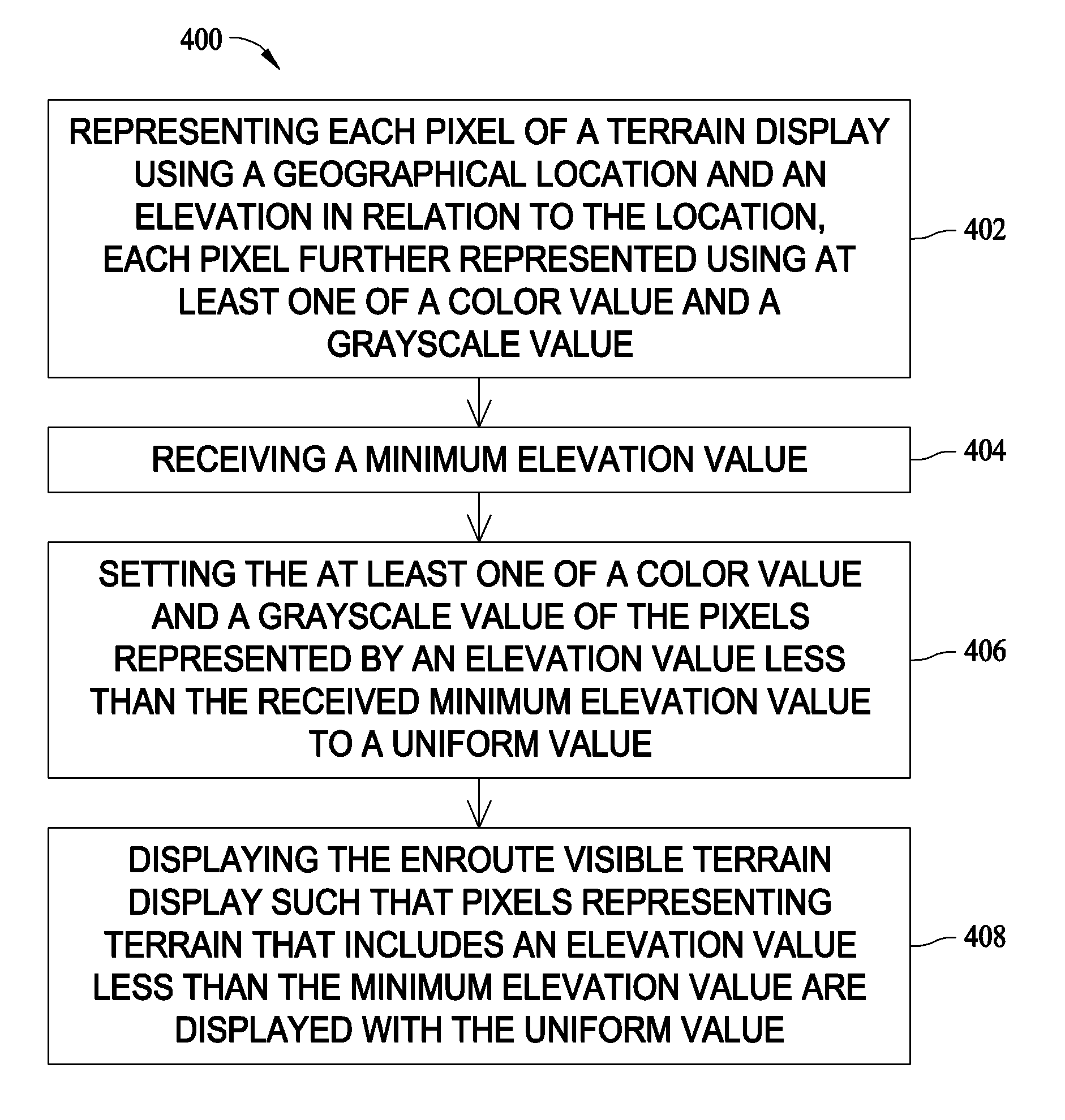
Methods and systems for generating en-route visible terrain displays
ActiveUS20070150125A1Easy to readAnalogue computers for vehiclesDigital data processing detailsTerrainComputer graphics (images)
Methods and systems for displaying an en-route visible terrain display for an aircraft are provided. The method includes representing each pixel of a terrain display using a geographical location and an elevation above the location, each pixel further represented using at least one of a color value and a grayscale value, receiving a minimum elevation value, setting the at least one of a color value and a grayscale value of the pixels represented by an elevation value less than the received minimum elevation value to a uniform value, and displaying the en-route visible terrain display such that pixels representing terrain that includes an elevation value less than the minimum elevation value are displayed with the uniform value such that non-terrain-impacted, primary-navigation areas of the display are more easily readable.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
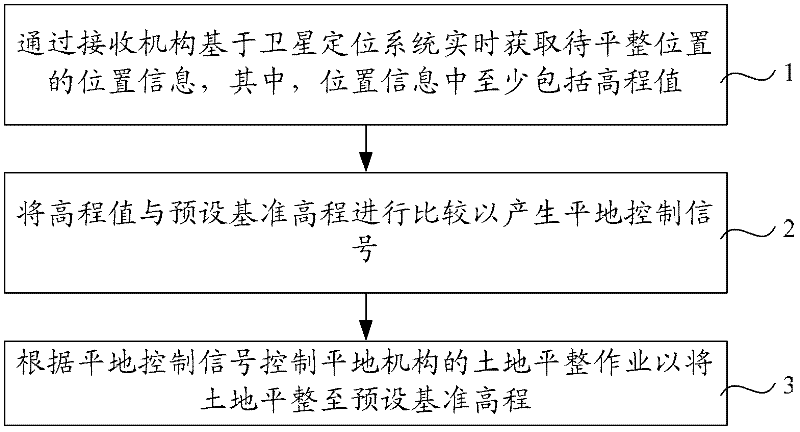
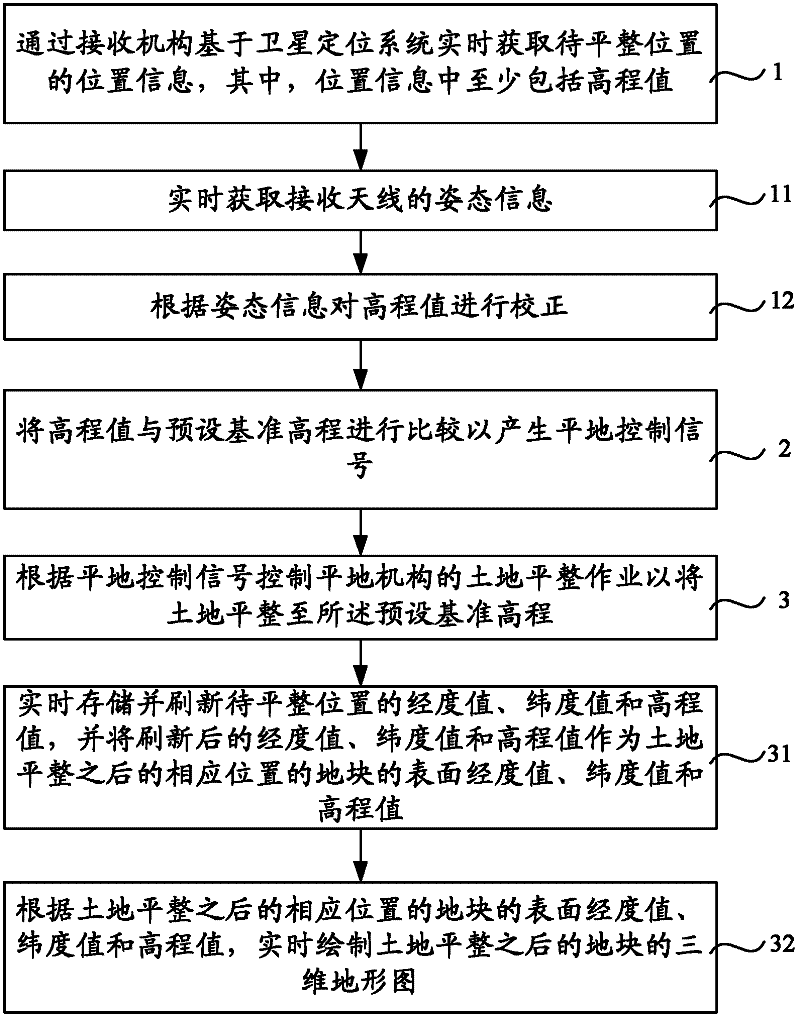
Land leveling method, land leveling control device and land leveling device
InactiveCN102282925AThe scope of work is not limitedAgricultural machinesProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersControl signalAgricultural engineering
The invention discloses a land leveling method, a land leveling control device and a land leveling device. The land leveling method comprises: obtaining the position information of the position to be leveled in real time through a receiving mechanism based on a satellite positioning system, wherein the position information includes at least an elevation value ;Comparing the elevation value with the preset reference elevation to generate a leveling control signal; controlling the land leveling operation of the leveling mechanism according to the leveling control signal, so as to level the land to the preset reference elevation. The land leveling method is based on the satellite positioning system to obtain the elevation value of the position to be leveled in real time and compare it with the preset reference elevation to generate a leveling control signal to control the leveling operation of the leveling mechanism. The operation range is not limited, and any area of the leveling ground can be used. blocks for land leveling.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Simplified creation of customized maps
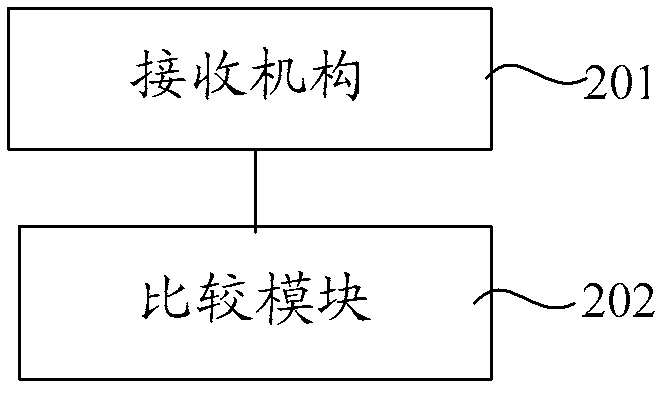
ActiveUS8902260B2Efficient and timely productionRoad vehicles traffic controlCathode-ray tube indicatorsReverse geocodingComputer science
Embodiments of the present invention relate to providing a method for creating customized labeled maps that include displaying a map using a presentation device based on a selectable elevation value, where the map contains geocoded information and the user selects at least one position on the displayed map. The method continues by automatically creating and displaying at least one label located in proximity to the selected position, where at least one label is based on reverse geocoded information associated with the selected position.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
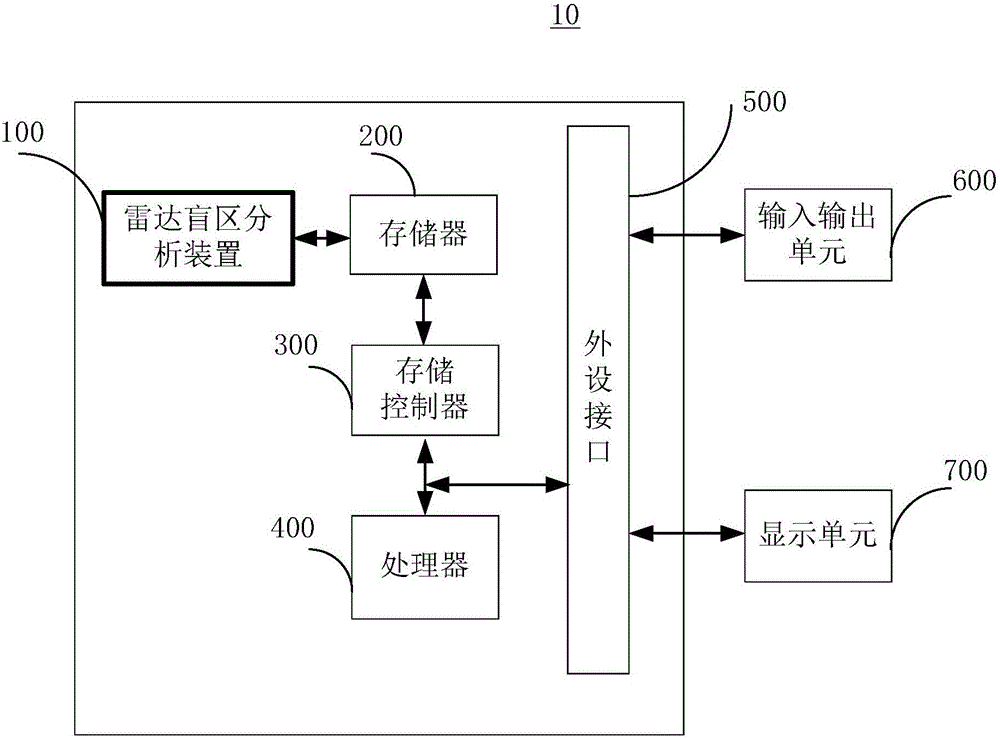
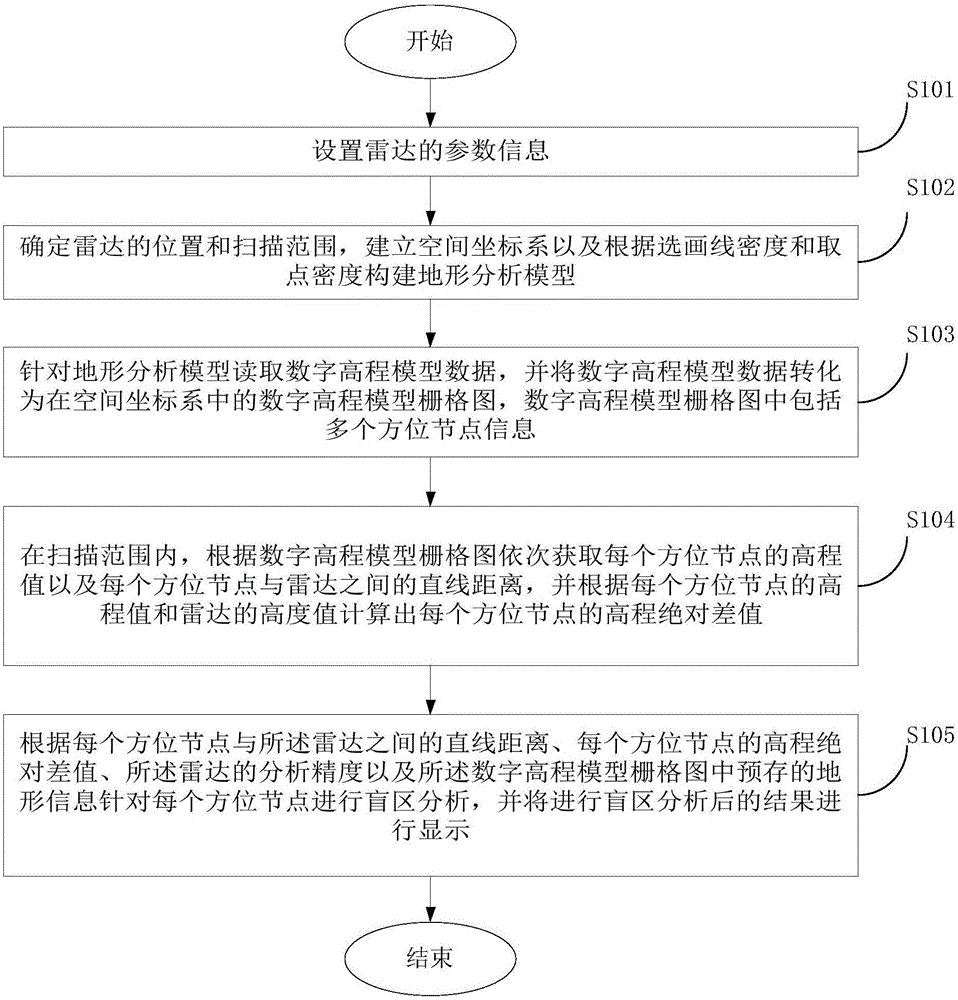
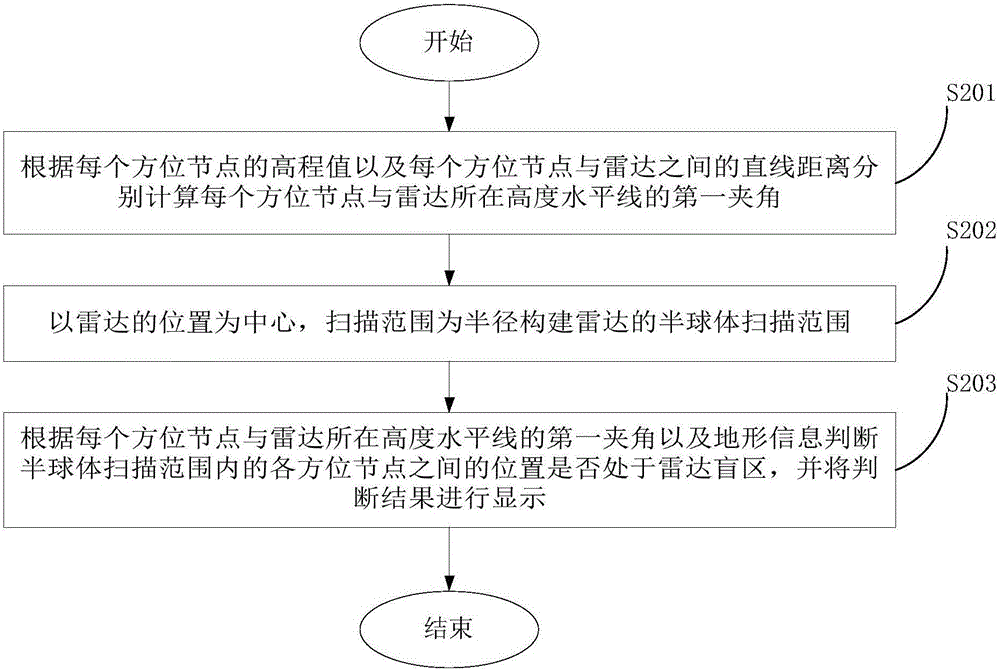
Radar blind area analysis method and device
ActiveCN105842676AReduce calculation stepsReduce the amount of calculationWave based measurement systemsRadarAbsolute difference
The embodiment of the invention provides a radar blind area analysis method and device, and belongs to the technical field of detection. The radar blind area analysis method comprises the steps that the location and the scanning range of radar are determined, and a terrain analysis model is constructed according to preset line selecting and drawing density and point taking density; digital elevation model data are converted into digital elevation model grid maps; the elevation value of each azimuth node and the straight-line distance between each azimuth node and the radar are acquired according to the digital elevation model grid maps, and the elevation absolute difference value of each azimuth node is calculated; and blind area analysis is performed according to the straight-line distance between each azimuth node and the radar, the elevation absolute difference value of each azimuth node, the analytical precision of the radar and the pre-stored terrain information of the digital elevation model grid maps, and the result of blind area analysis is displayed. The calculation steps, the calculation amount and calculation time consumption of calculation of radar blind areas can be effectively reduced.
Owner:CHENGDU ZHONGKE HEXUN TECH CO LTD
Method for analyzing geographic location and elevation data and geocoding an image with the data
ActiveUS7873240B2Without computational difficultySufficient speedPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer Aided DesignComputer vision
A method for geographically registering a perspective image of a location assigns elevation values to elements or pixels of a two dimensional array of image elements or pixels of the location. The elevation value for each image pixel is obtained using a corresponding database stored reference digital elevation model, or a three dimensional surface model of the location. The reference elevation model or surface model is composed of rows and columns of elevation values corresponding to two dimensions of location values at a sensed location shown in the image, or is composed of a three dimensional surface or volume model of the location, such as a computer-aided design model or any other means of describing the three dimensional characteristics of the sensed location.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
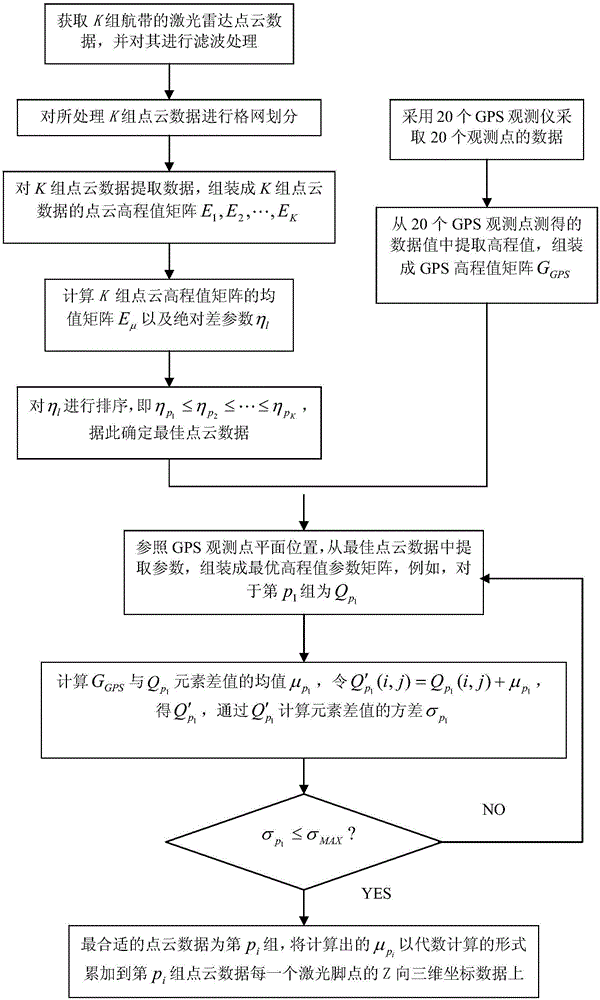
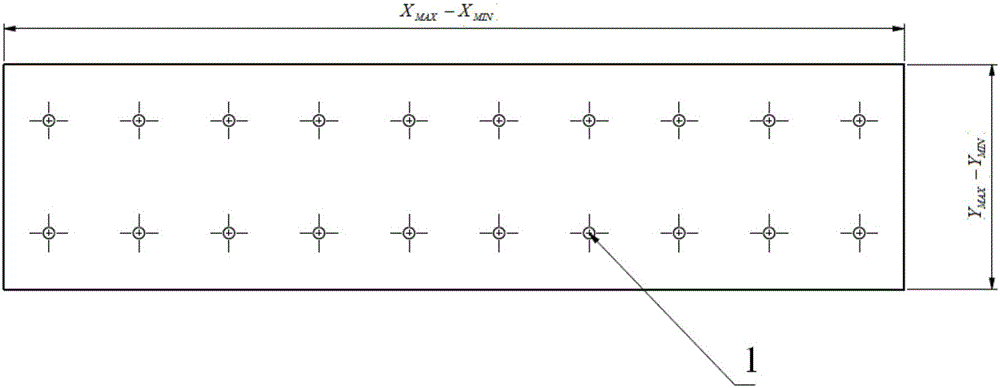
Ground-GPS-assisted method for correcting error of difference of elevation of LiDAR data
The invention provides a ground-GPS-assisted method for correcting the error of the difference of elevation of LiDAR data. The method comprises: an onboard LiDAR device performs repeated measurement on a measured geomorphic object for K times to obtain K groups of air strip point cloud data; the point cloud data is subjected to gross error elimination and regular grid; before the onboard LiDAR measurement, a certain number of ground GPS measurers have been arranged in an tested air strip to measure the absolute position of a ground point; an absolute difference parameter [eta]l is used for optimal ordering on the obtained K groups of point cloud data; an elevation value of the absolute position of the ground point measured by GPS is compared with an elevation value parameter corresponding to the optimal point cloud data to obtain the elevation error variance, and according to the variance, point cloud data that may be subjected to error correction is determined, and eventually accurate LiDAR data is obtained through correction.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
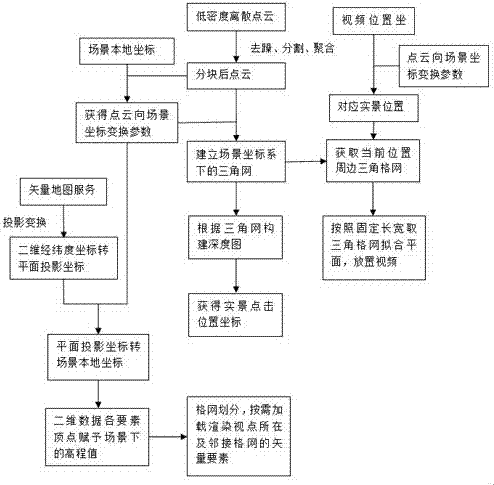
Dynamic measurable real scene map creation method
ActiveCN107993282AImplement direct loadingSolve dynamic update renderingImage enhancementImage analysisPoint cloudViewpoints
The invention discloses a dynamic measurable real scene map creation method. According to the method, low-density discrete point cloud data within a designated range in a viewpoint range is acquired;point cloud data noise removal is performed according to a point cloud data adjacent relation; a partitioning plane where the point cloud data is divided is calculated; the point cloud data is saved in blocks; a triangular network is established; a depth map is constructed; real scene click position coordinates are obtained; the position of video data in a measurable real scene is calculated; a triangular network within a preset range around the position of the video data is acquired; a plane with fixed length and width is fitted to server as a placement plane of the video data; elevation values of corresponding positions in a three-dimensional scene are given to all element coordinates of two-dimensional plane data; and an on-demand loading strategy is adopted during scene vector elementrendering. Through the method, the problem that a wrong position is prone to be acquired when the position coordinates are acquired through the depth map created based on point cloud is solved, and meanwhile the precision of the click acquisition position in the low-density point cloud is improved through plane structure characteristics.
Owner:江苏省测绘研究所
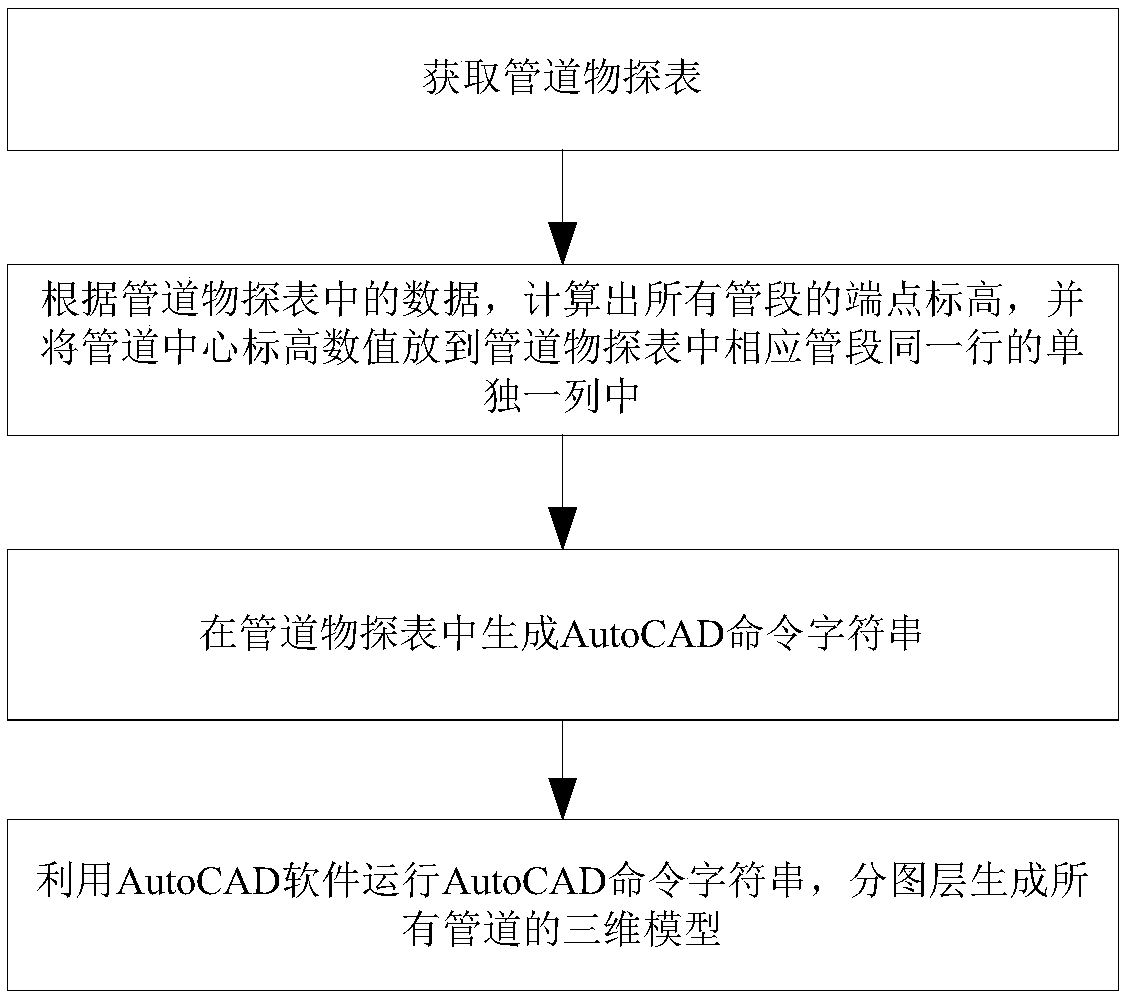
A pipeline three-dimensional modeling method and a pipeline design method
ActiveCN109359351AGenerate accuratelyImprove build efficiencyGeometric CADData processing applicationsDimensional modelingEngineering
The invention discloses a pipeline three-dimensional modeling method and a pipeline design method, wherein, the pipeline three-dimensional modeling method comprises the following steps: obtaining a pipeline geophysical prospecting table; according to the data in the pipeline geophysical prospecting table, the end point elevation of all pipe segments is calculated, and the pipe center elevation value is put into a single column in the same row of the corresponding pipe segments in the pipeline geophysical prospecting table; generating AutoCAD command string in pipeline geophysical exploration table; using AutoCAD software to run AutoCAD command strings, and generating the three-dimensional models of all pipelines in different layers. It greatly improves the efficiency of pipeline design, which is convenient for designers to carry out pipeline comprehensive design, and also visually facilitates the proofreading and auditing work.
Owner:JINAN MUNICIPAL ENG DESIGN & RES INSITITUTE GRP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com