Patents
Literature
117 results about "Geographical zone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
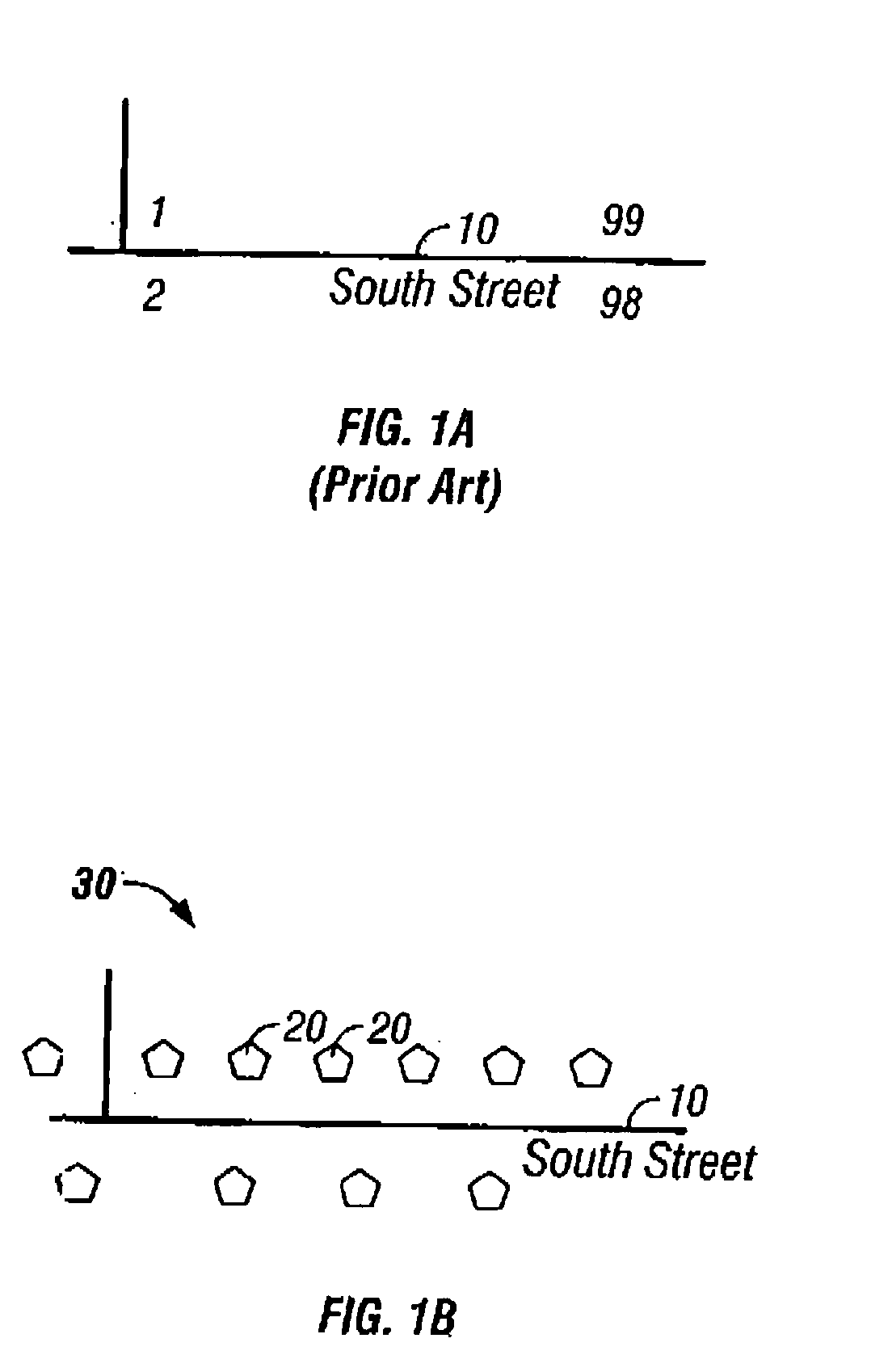
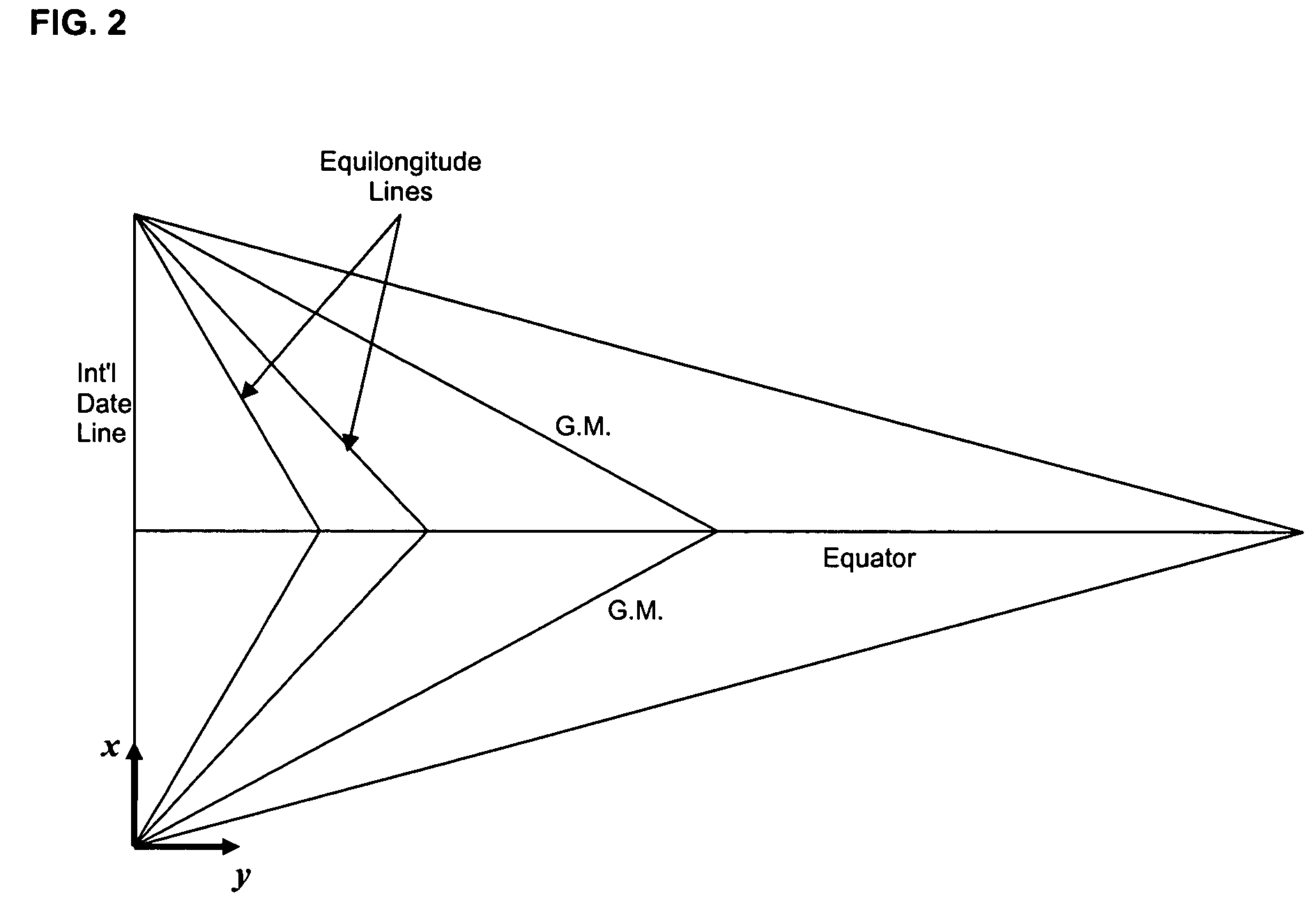
The five main latitude regions of the Earth's surface comprise geographical zones, divided by the major circles of latitude. The differences between them relate to climate. On the basis of latitudinal extent, the globe is divided into three broad heat zones.
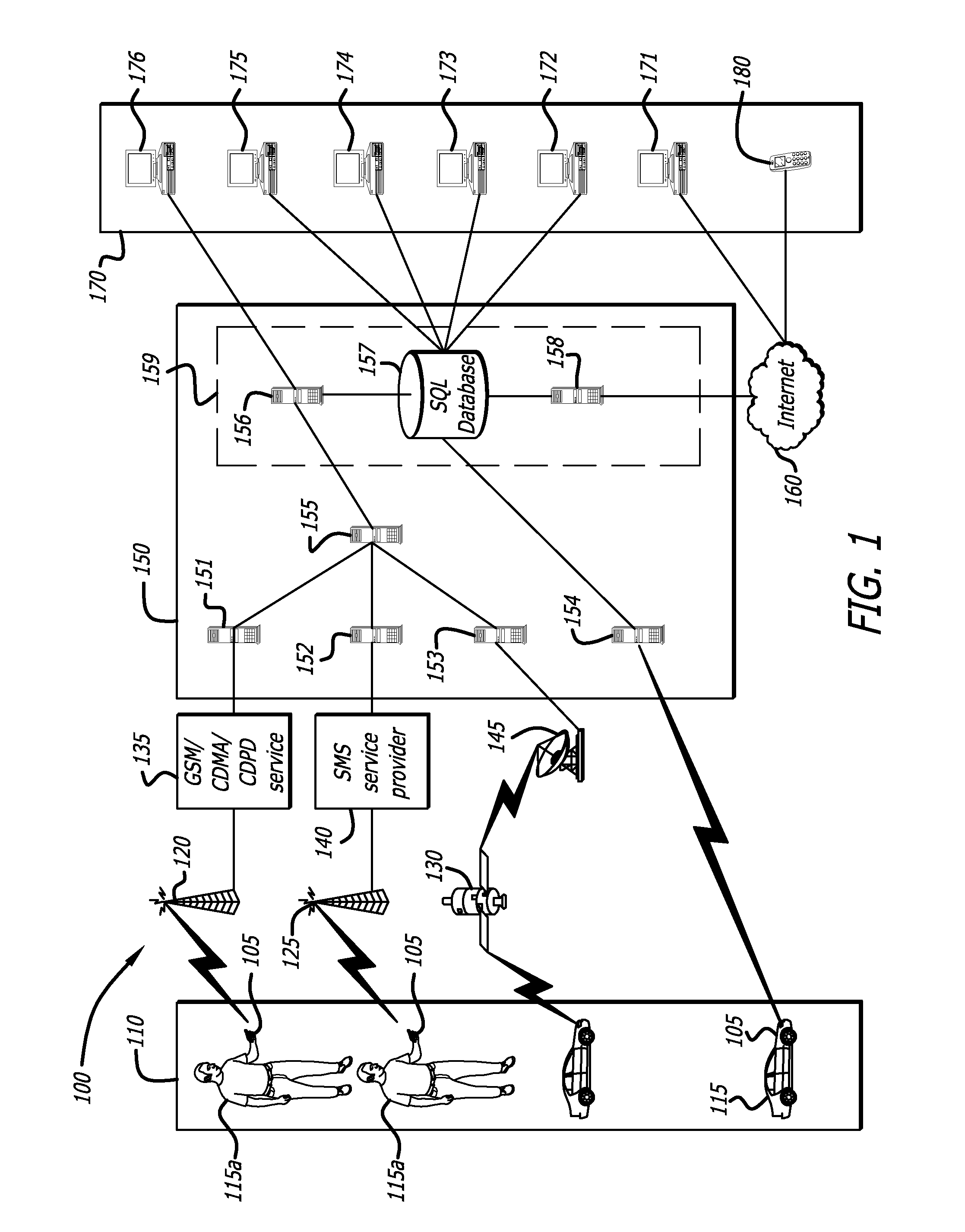
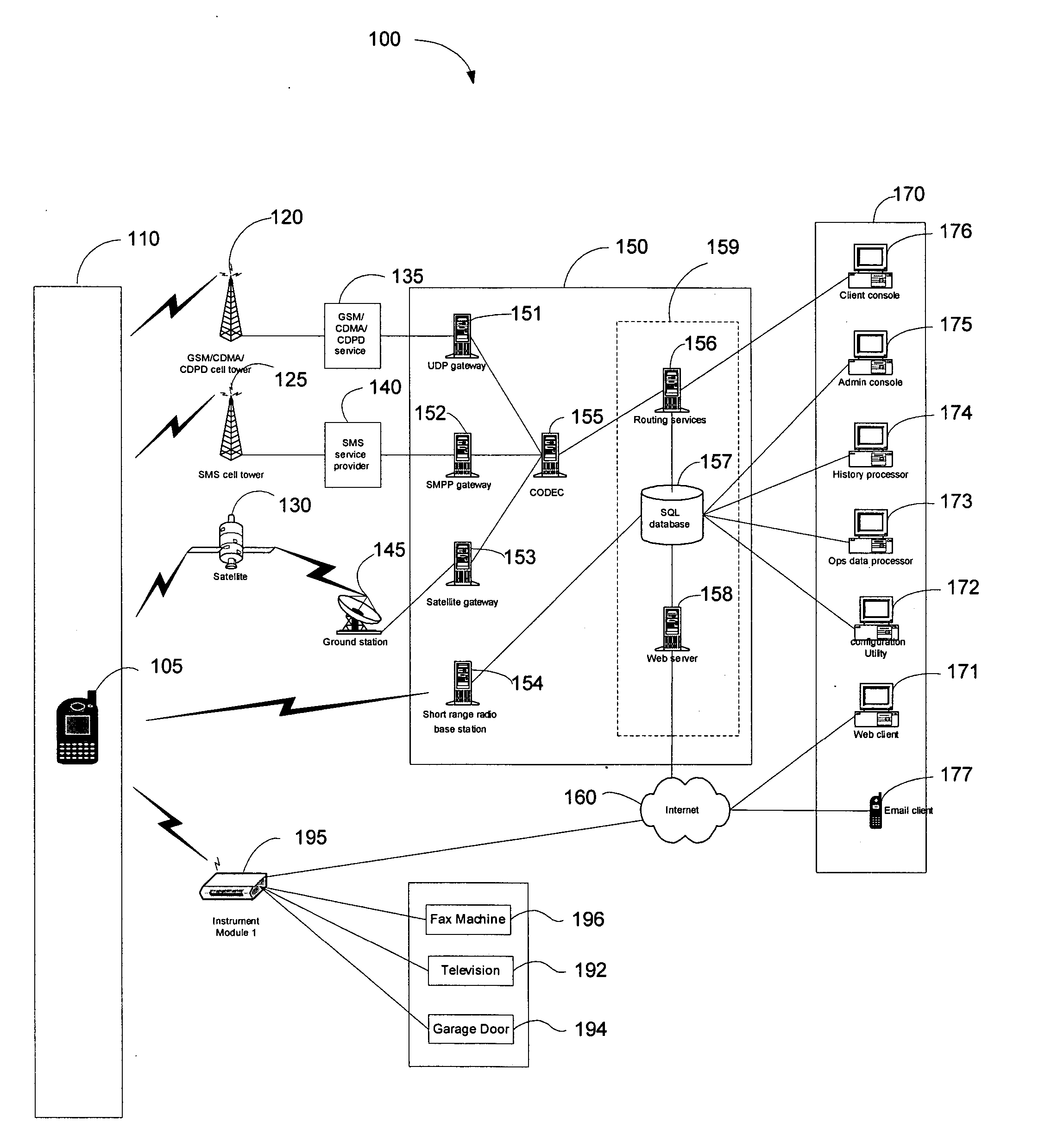
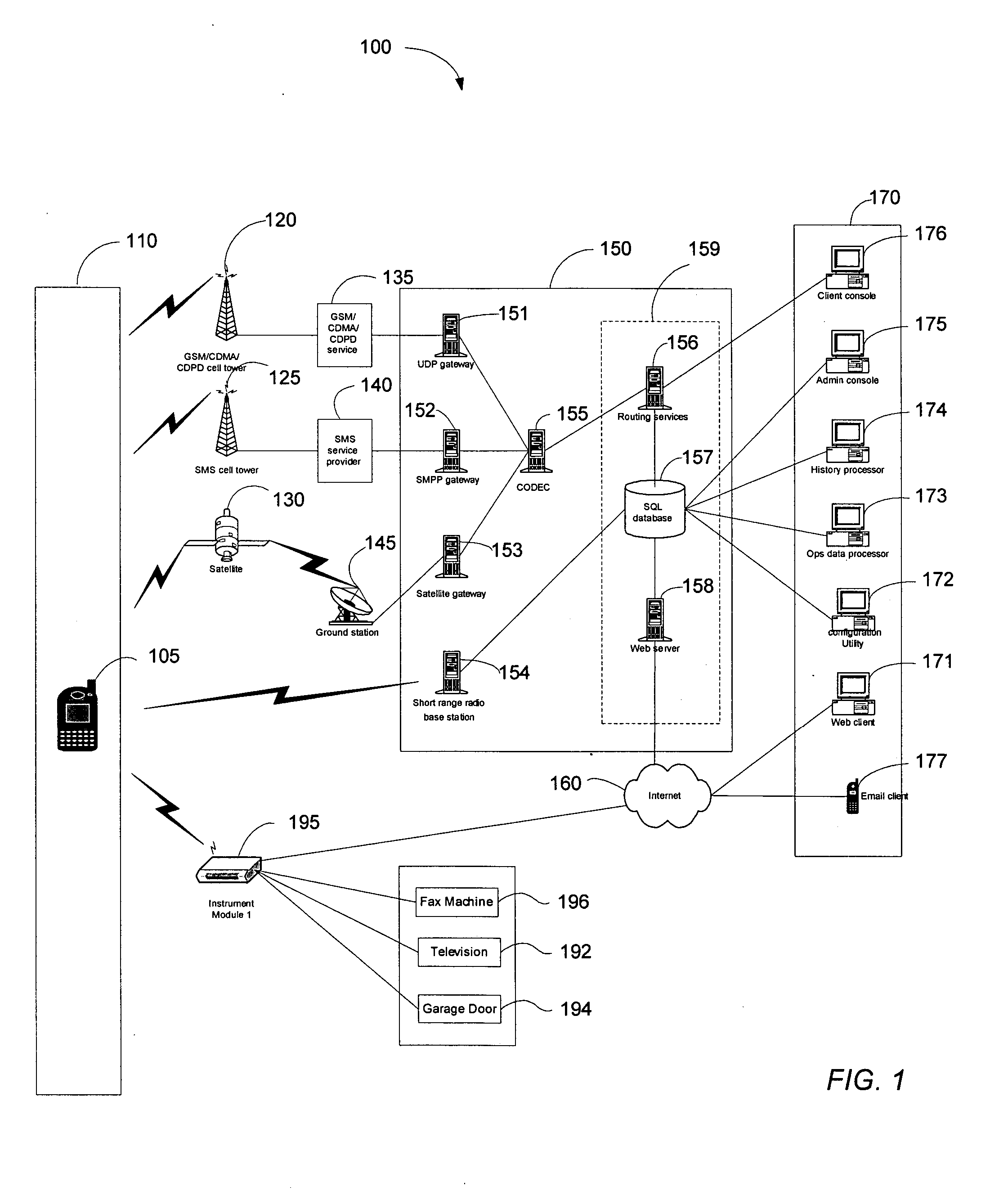
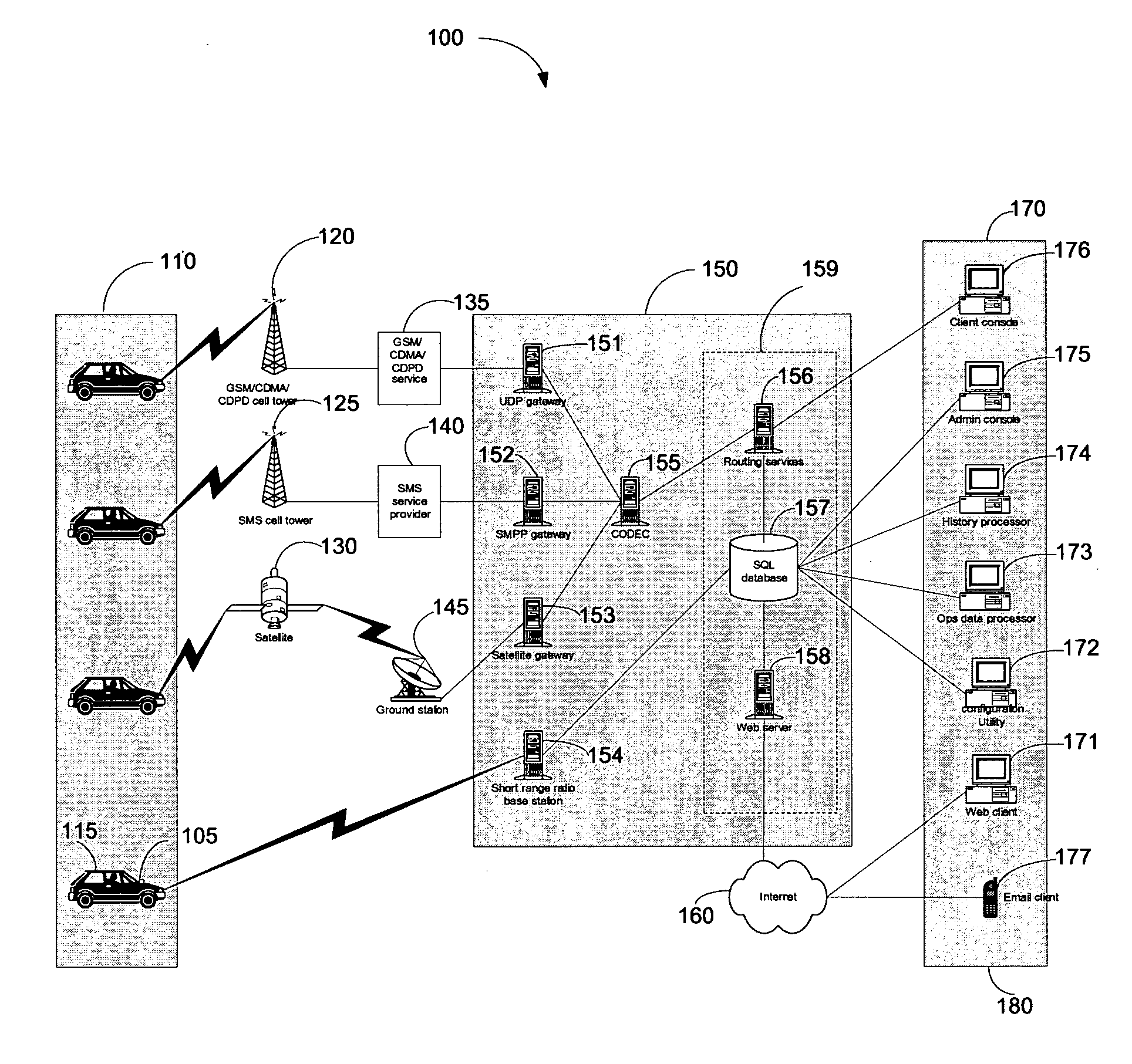
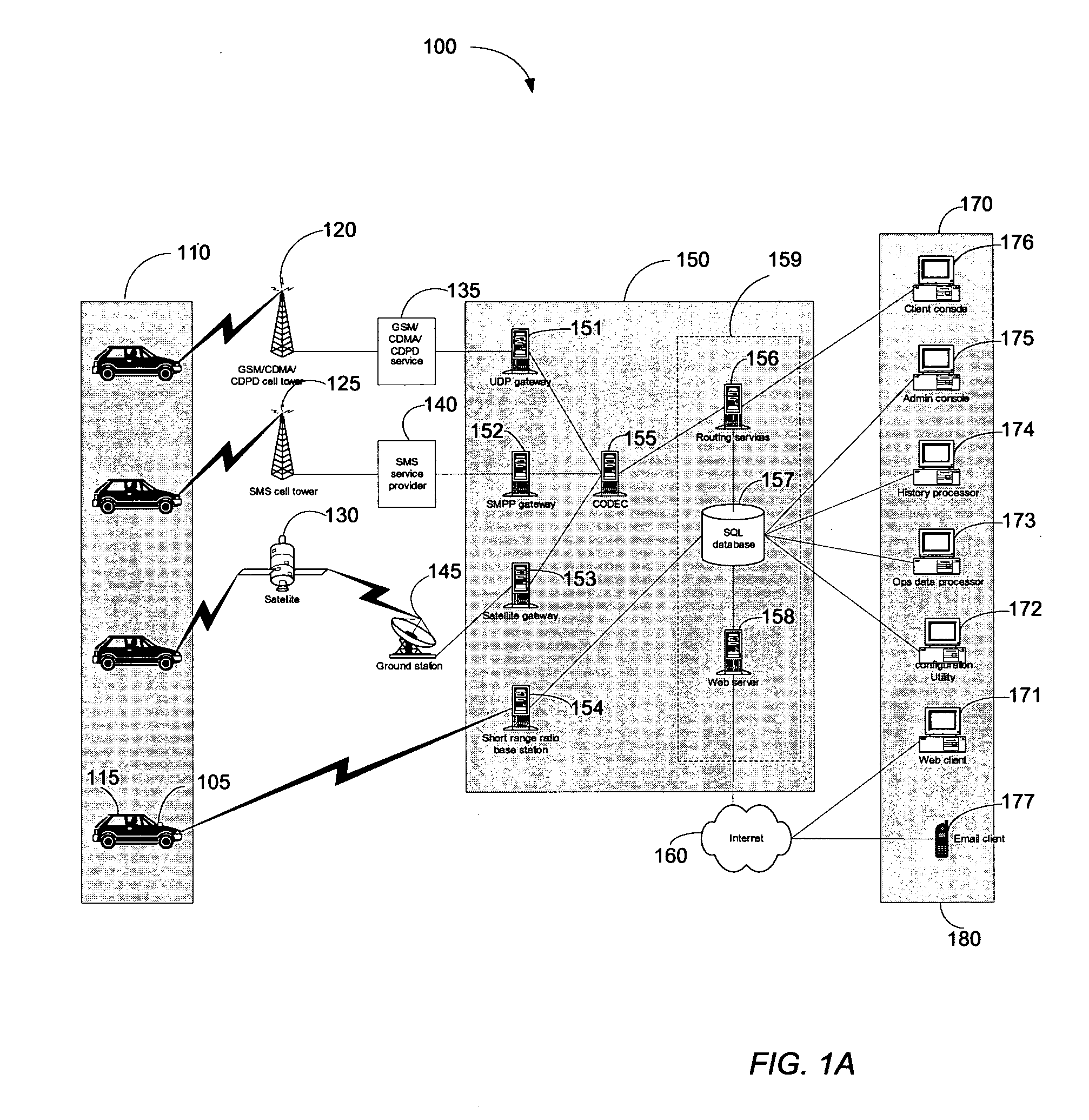
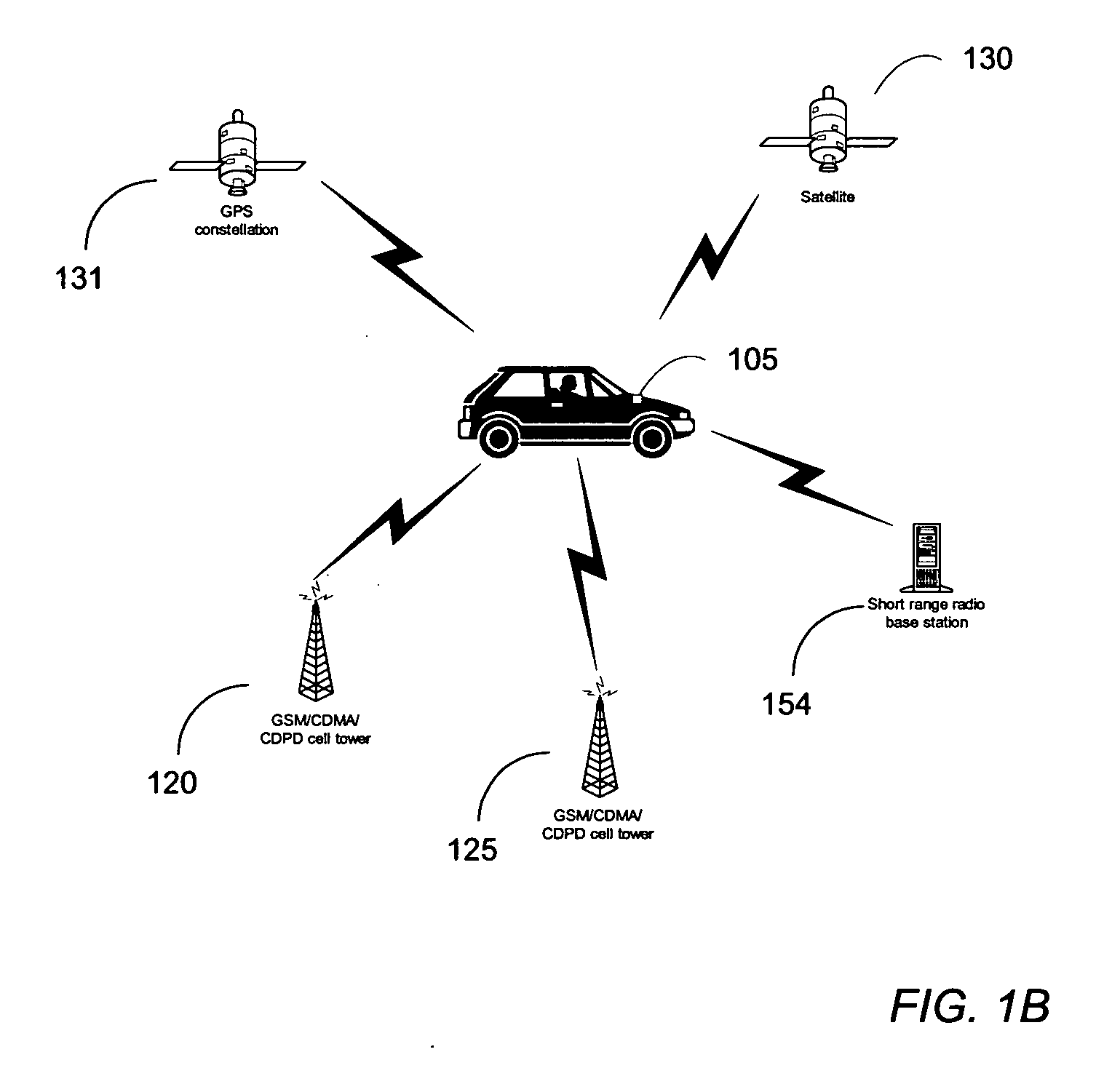
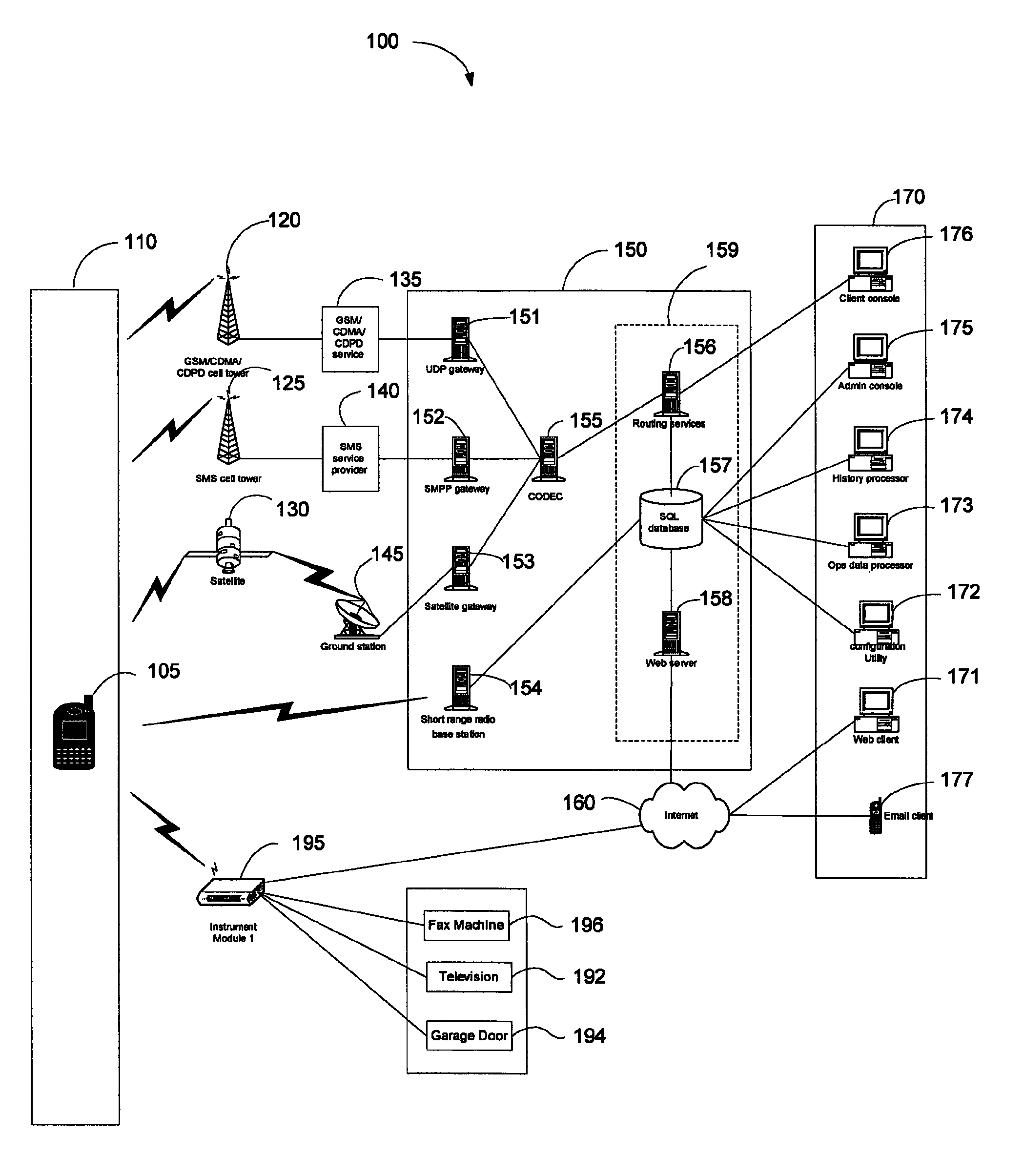
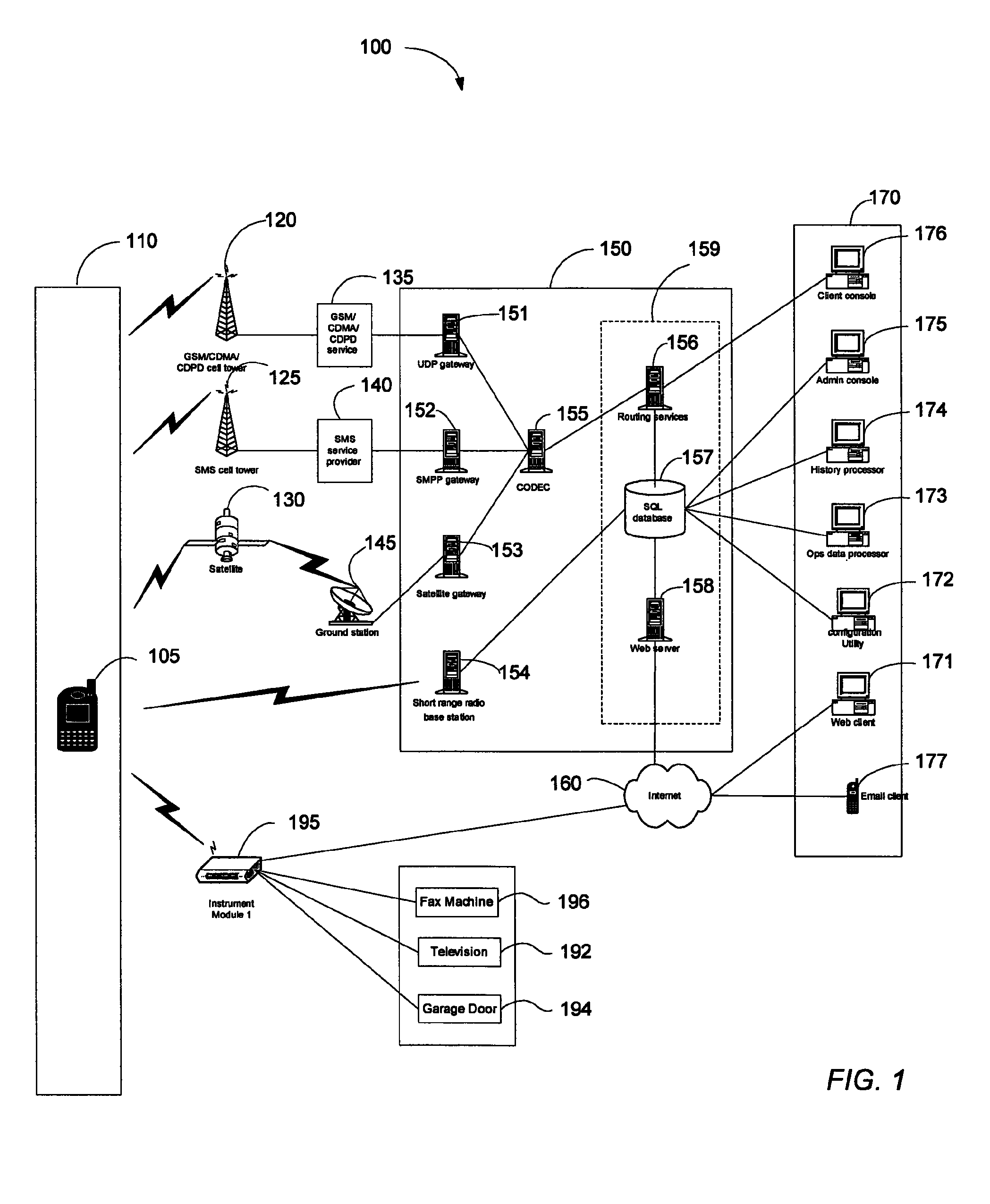
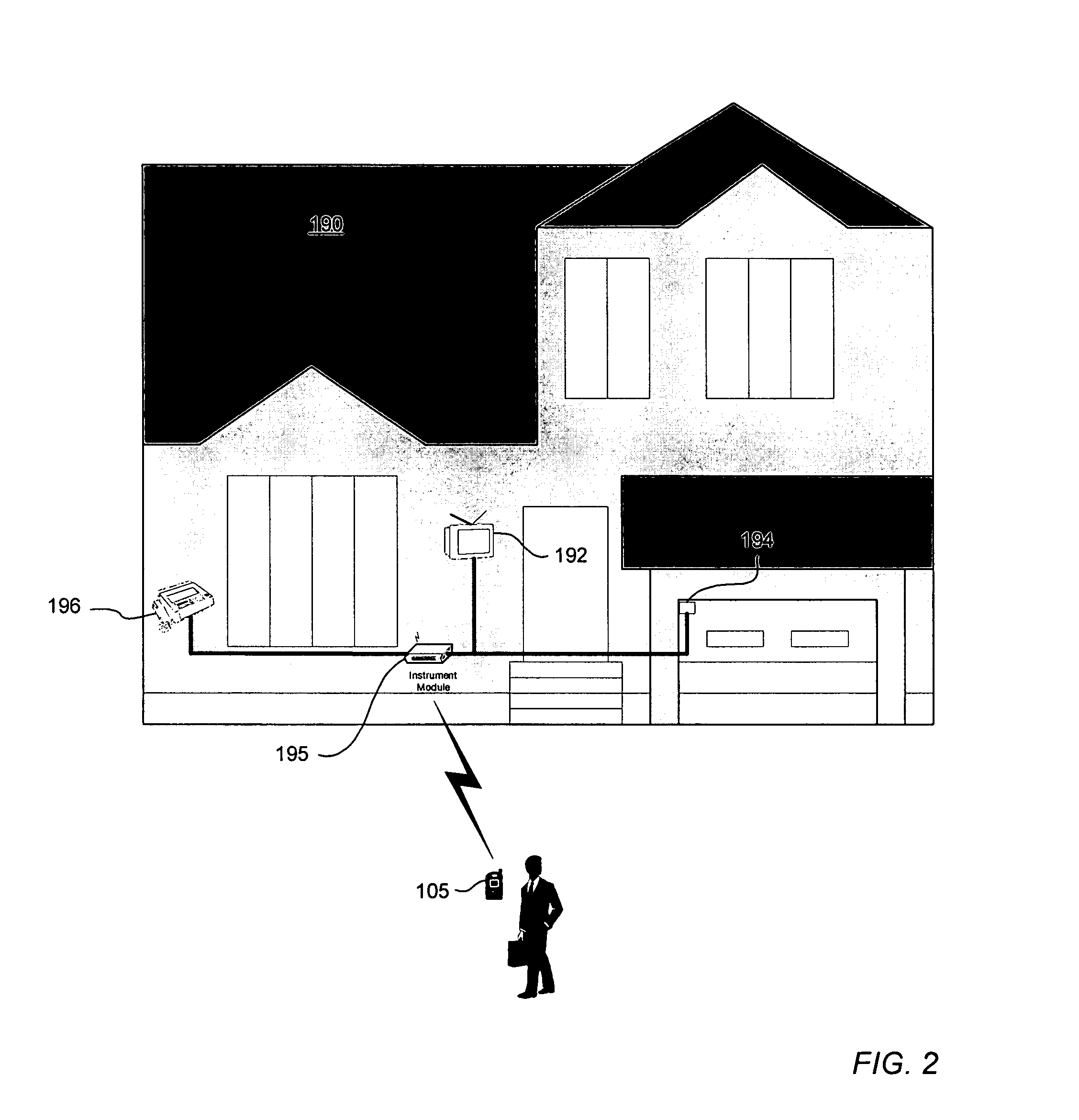
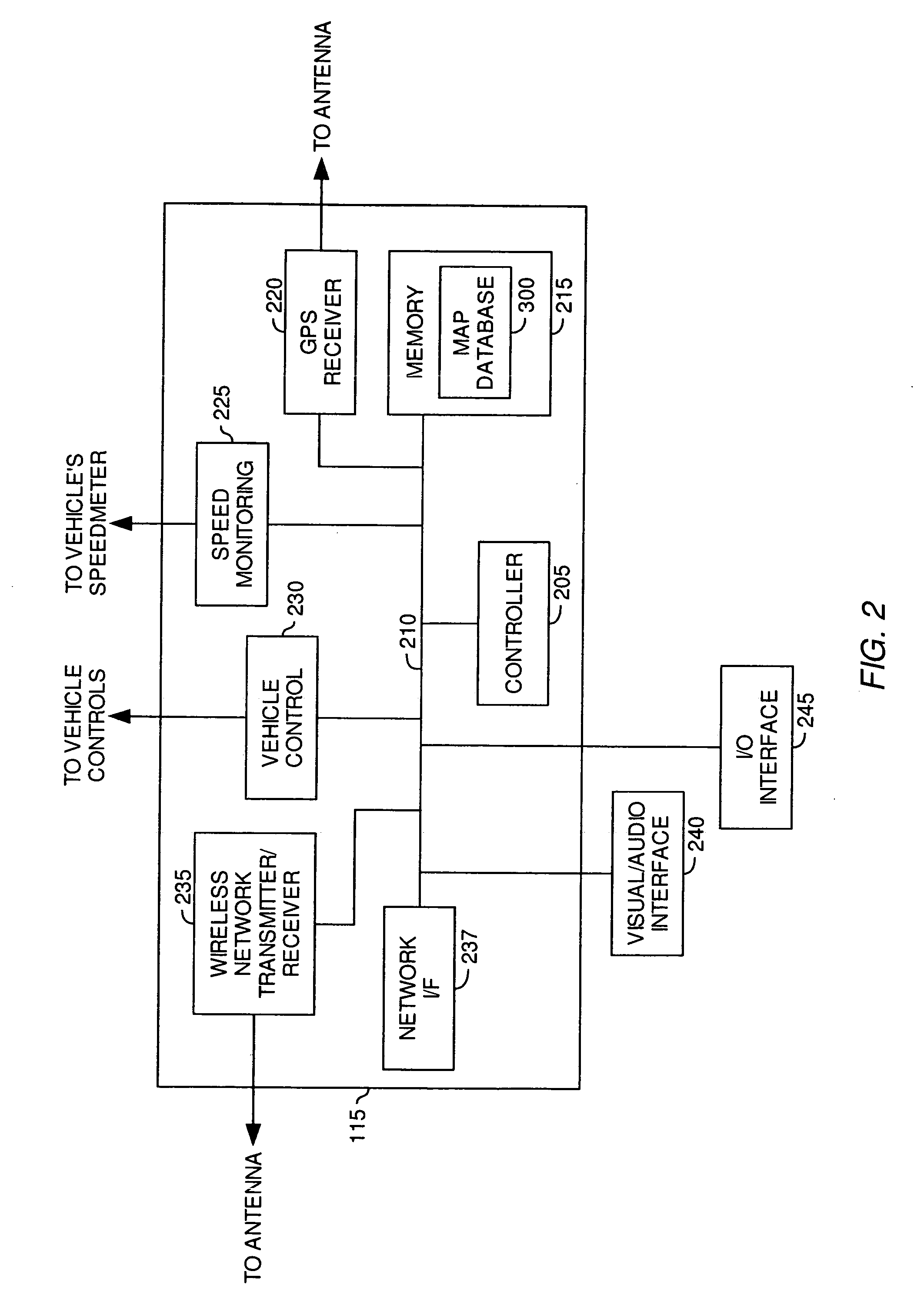
Map-based interfaces for storing and locating information about geographical areas
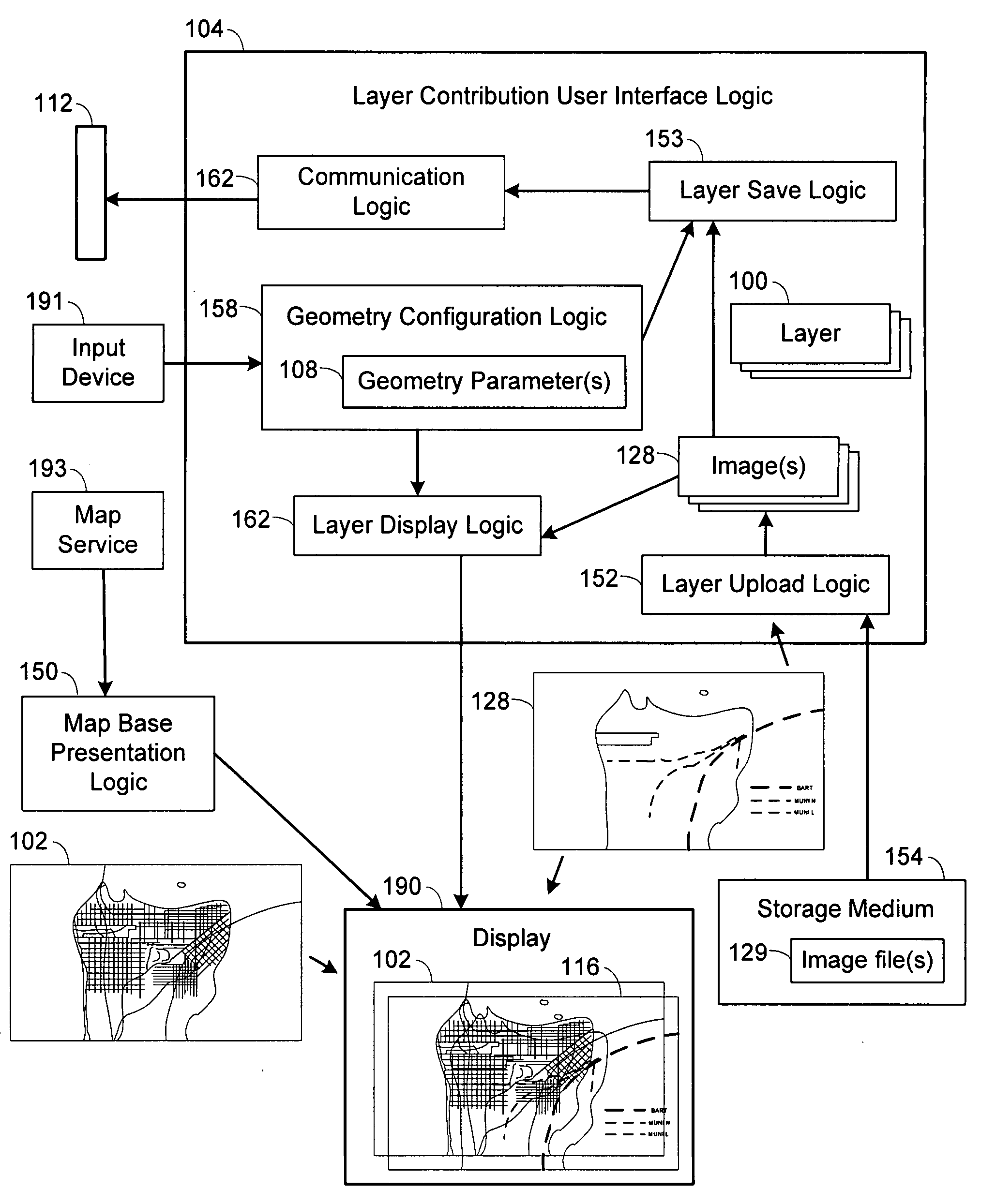
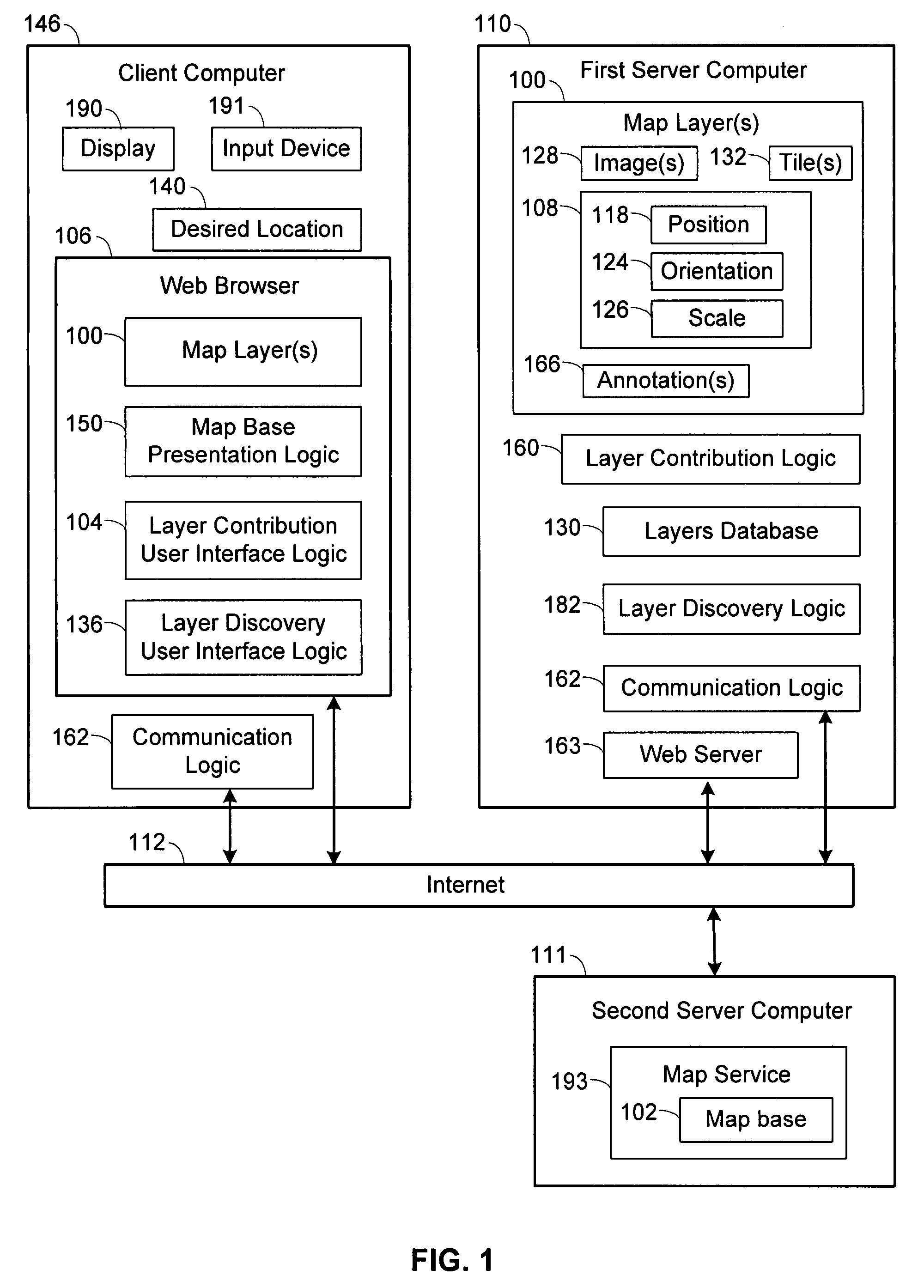
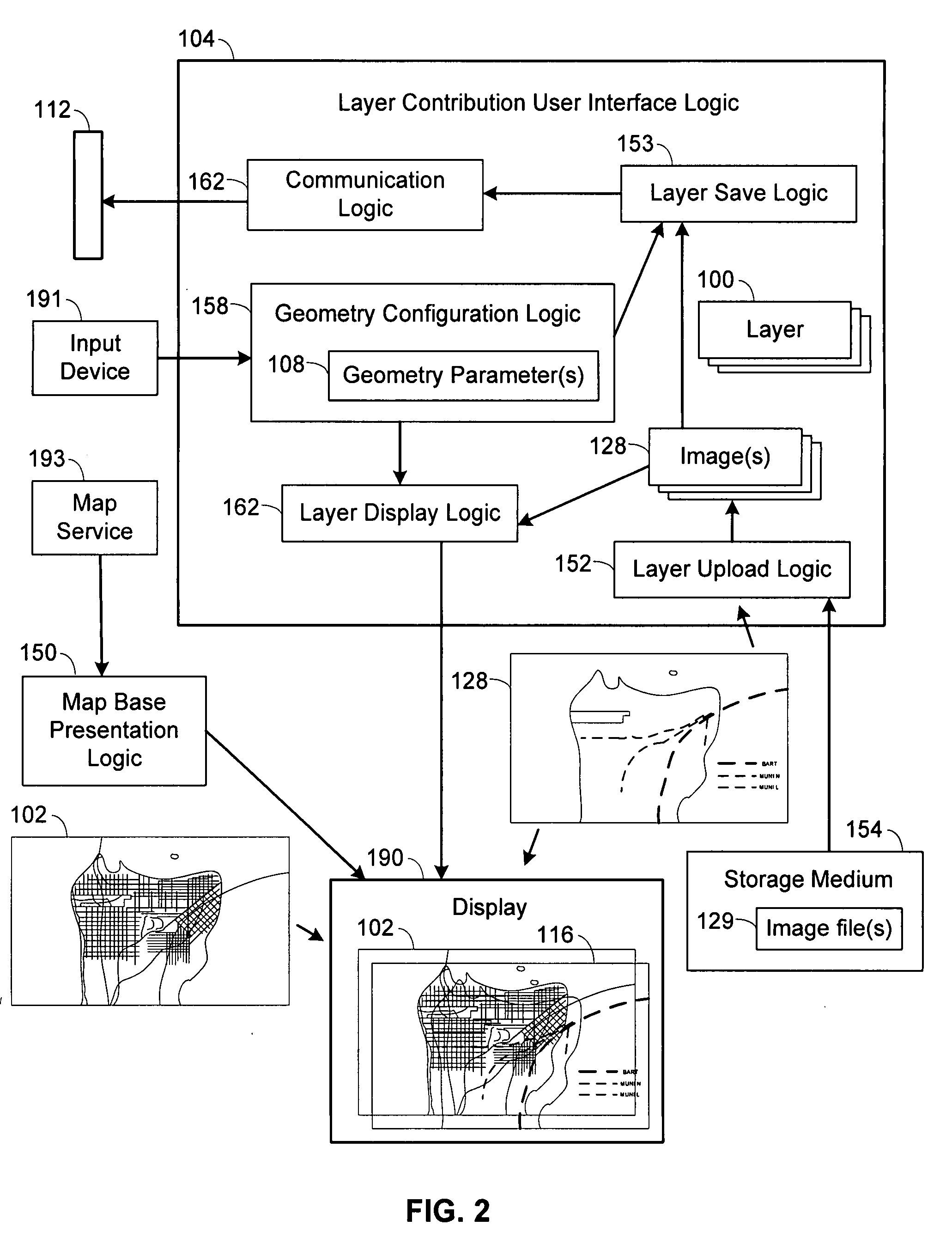
User interfaces and computer enabled methods for defining, discovering, and viewing map layers are provided. The map layers annotate an existing map by providing additional information that is not present in the existing map. A contribution user interface receives and configures the map layer on a web browser. The contribution user interface allows the map layer to be positioned over a desired location and displayed as a semi-transparent image overlay superimposed over the existing map. The map layer may be enlarged, reduced, and rotated to match the features of the existing map. The map layer is stored for use by other users. The layer may be retrieved by users who search for the desired location or for related or nearby locations. The layer may be displayed as a search result, and may be displayed for viewing by users as a partially-transparent image overlay over the existing map.
Owner:OATH INC
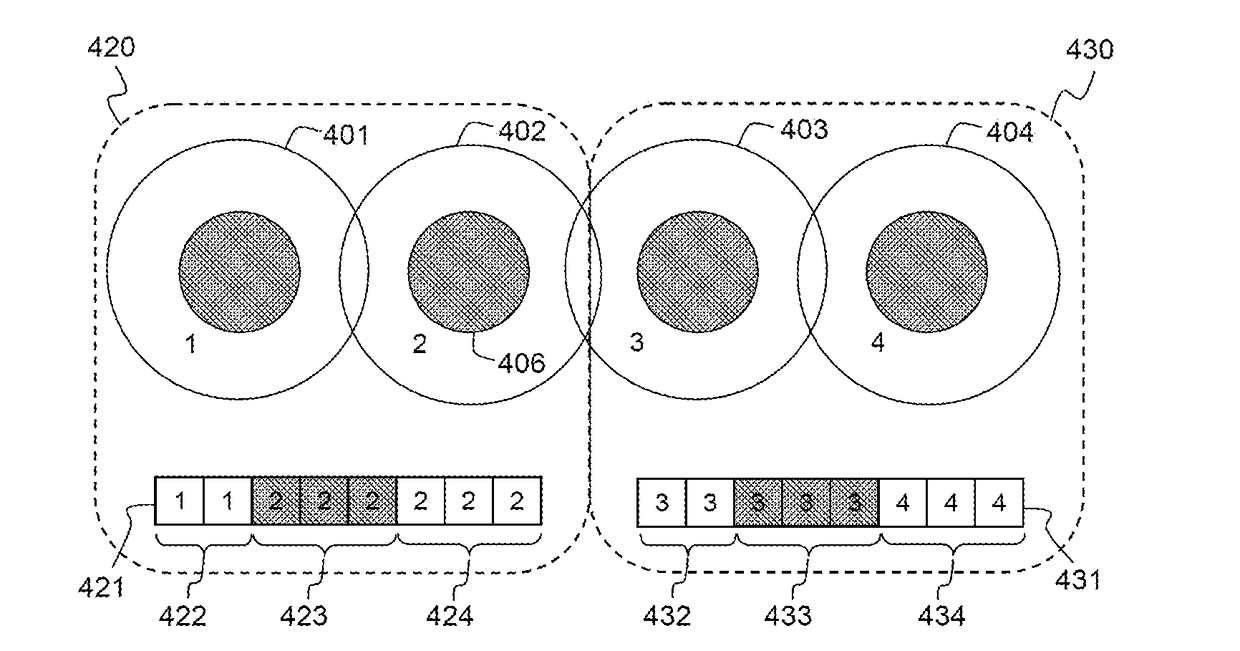
Configuring and using multi-dimensional zones
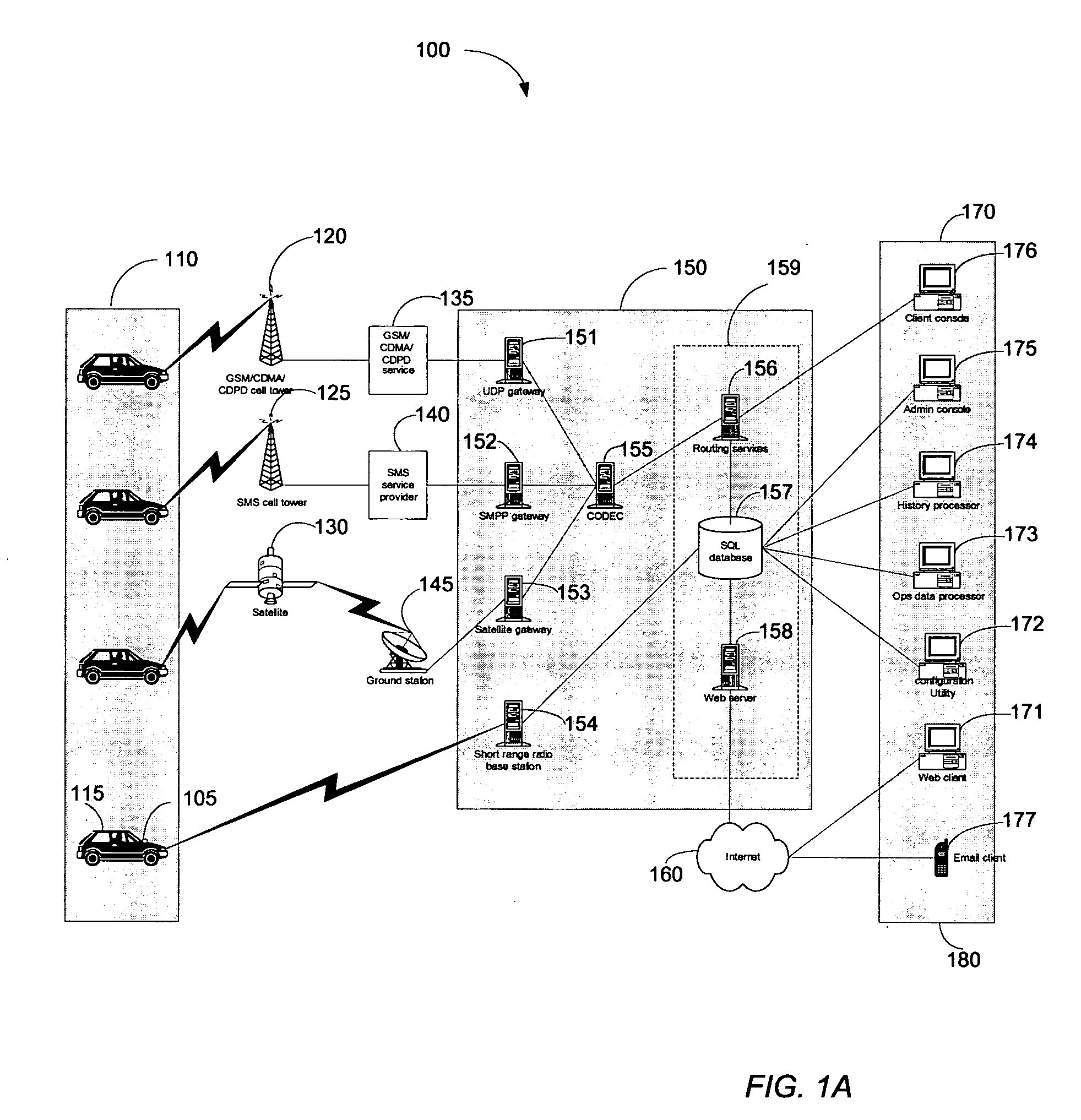
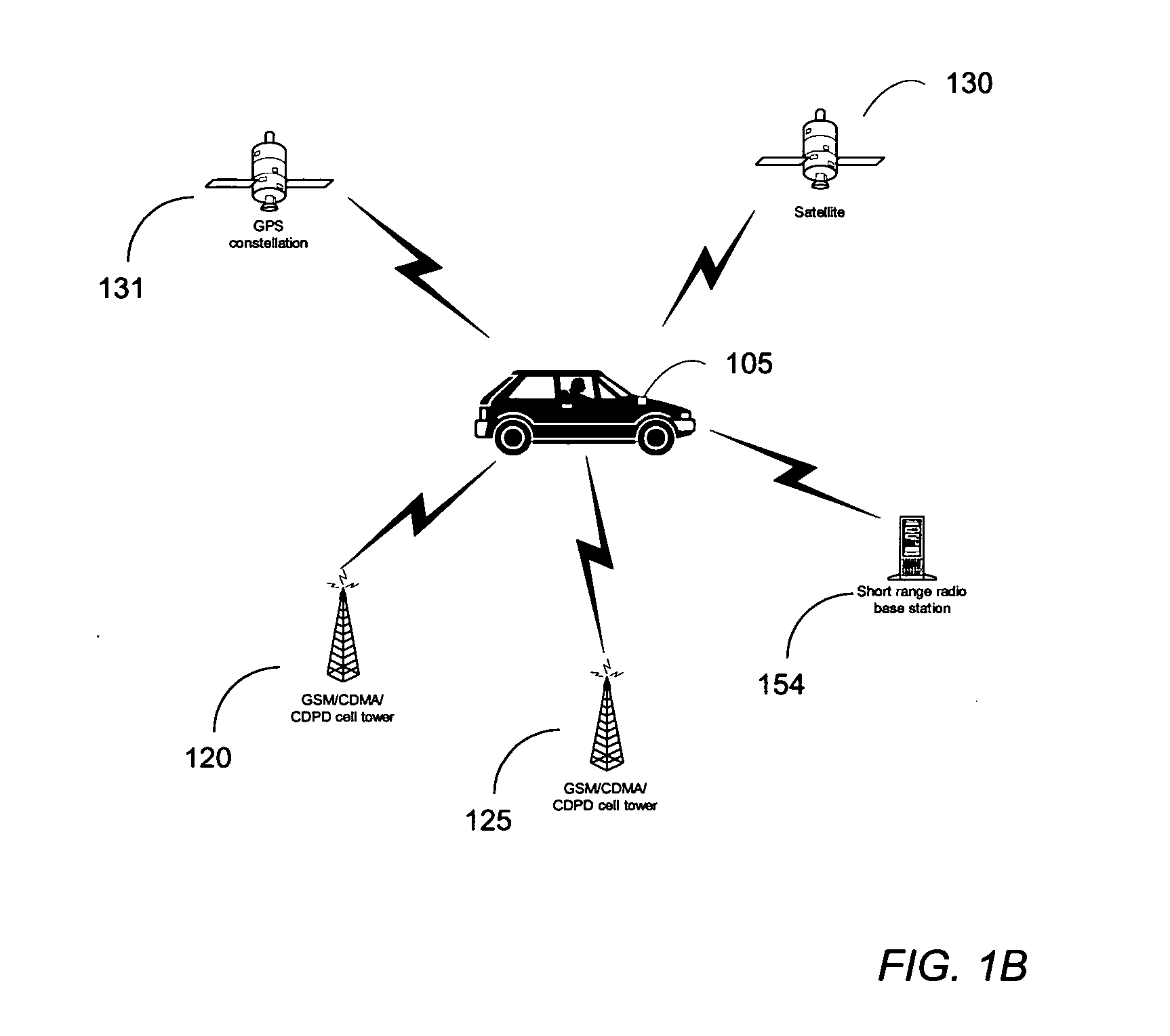
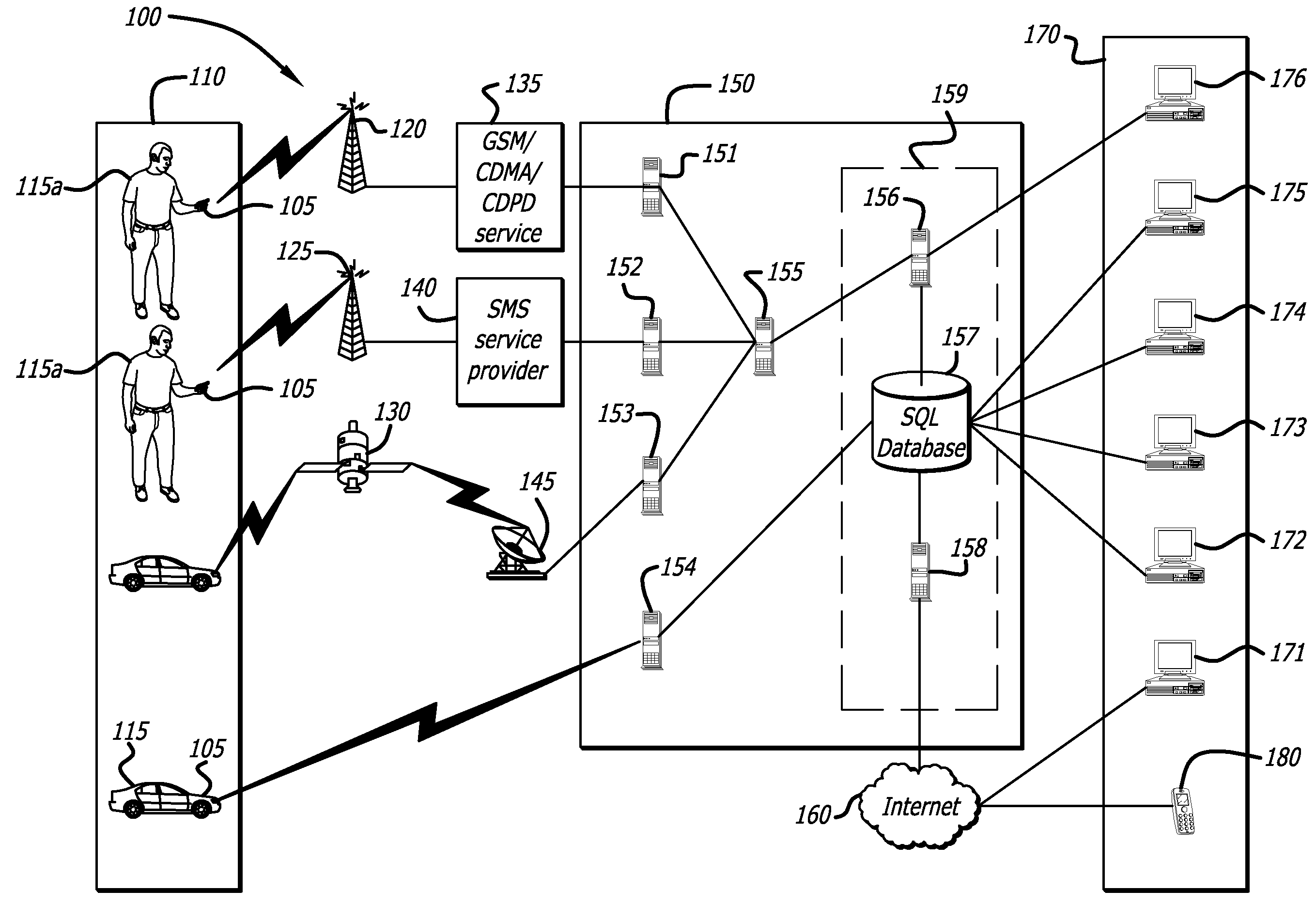
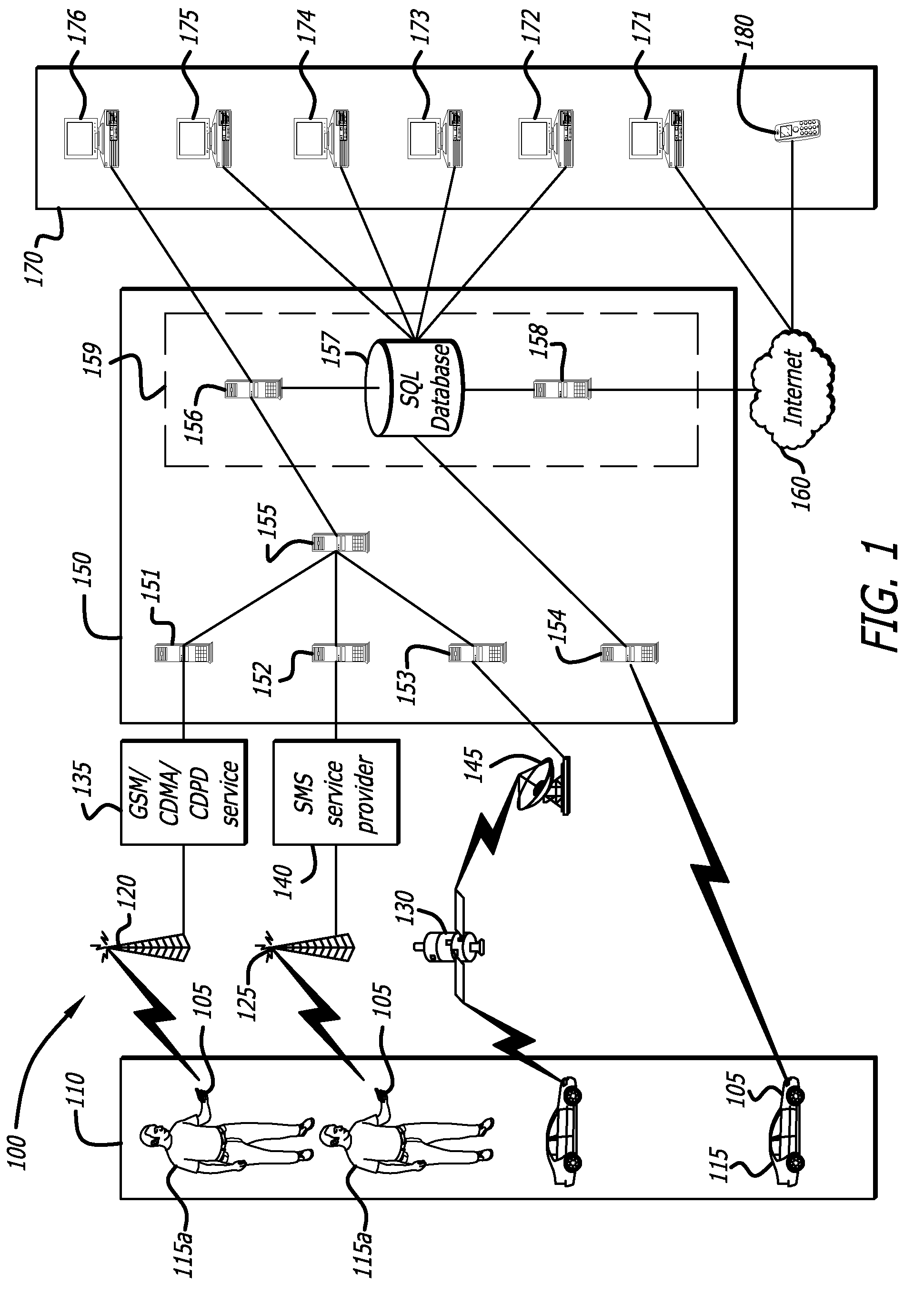
ActiveUS20090132163A1Locate very closeRoad vehicles traffic controlPosition fixationLongitudeGeographical zone
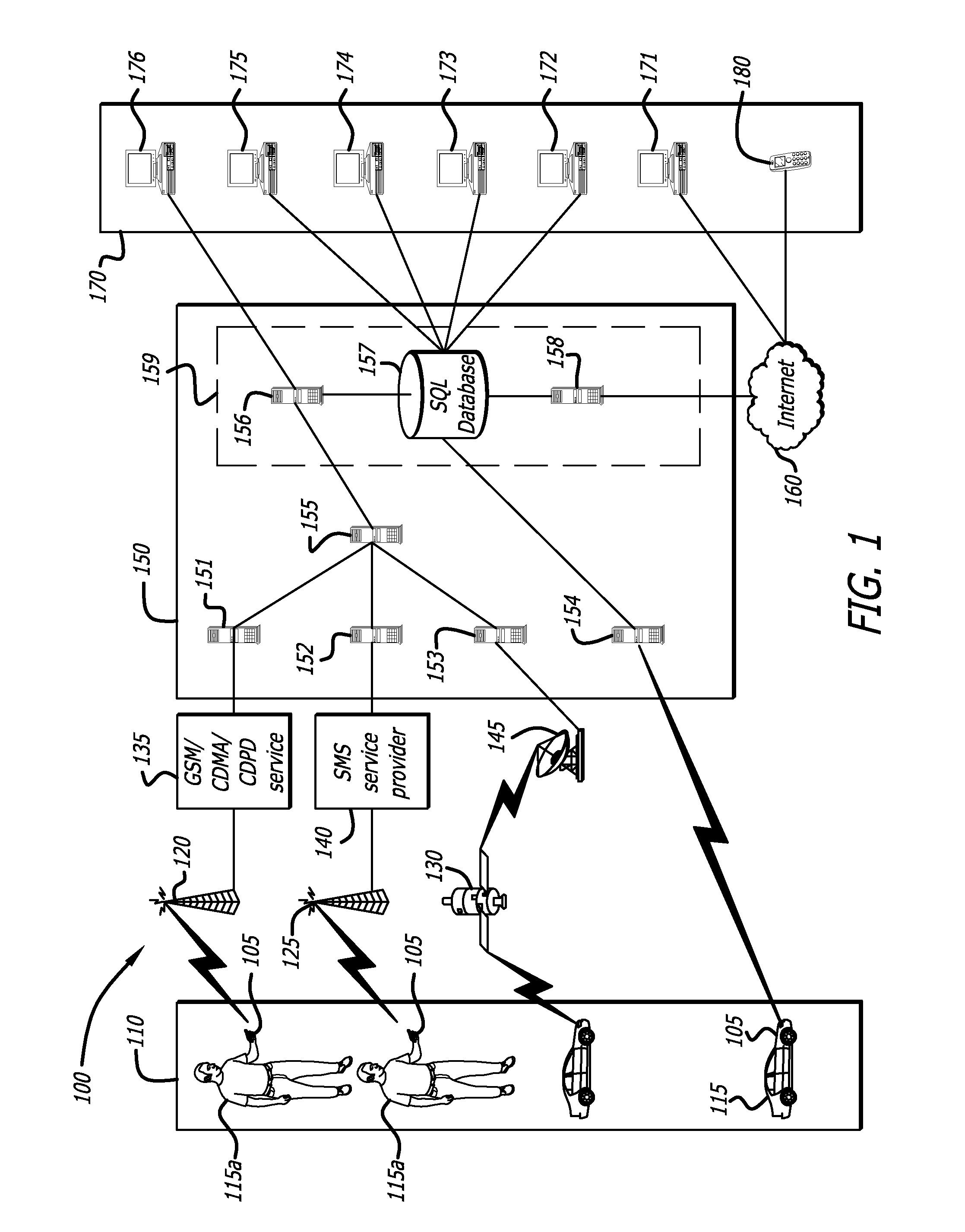
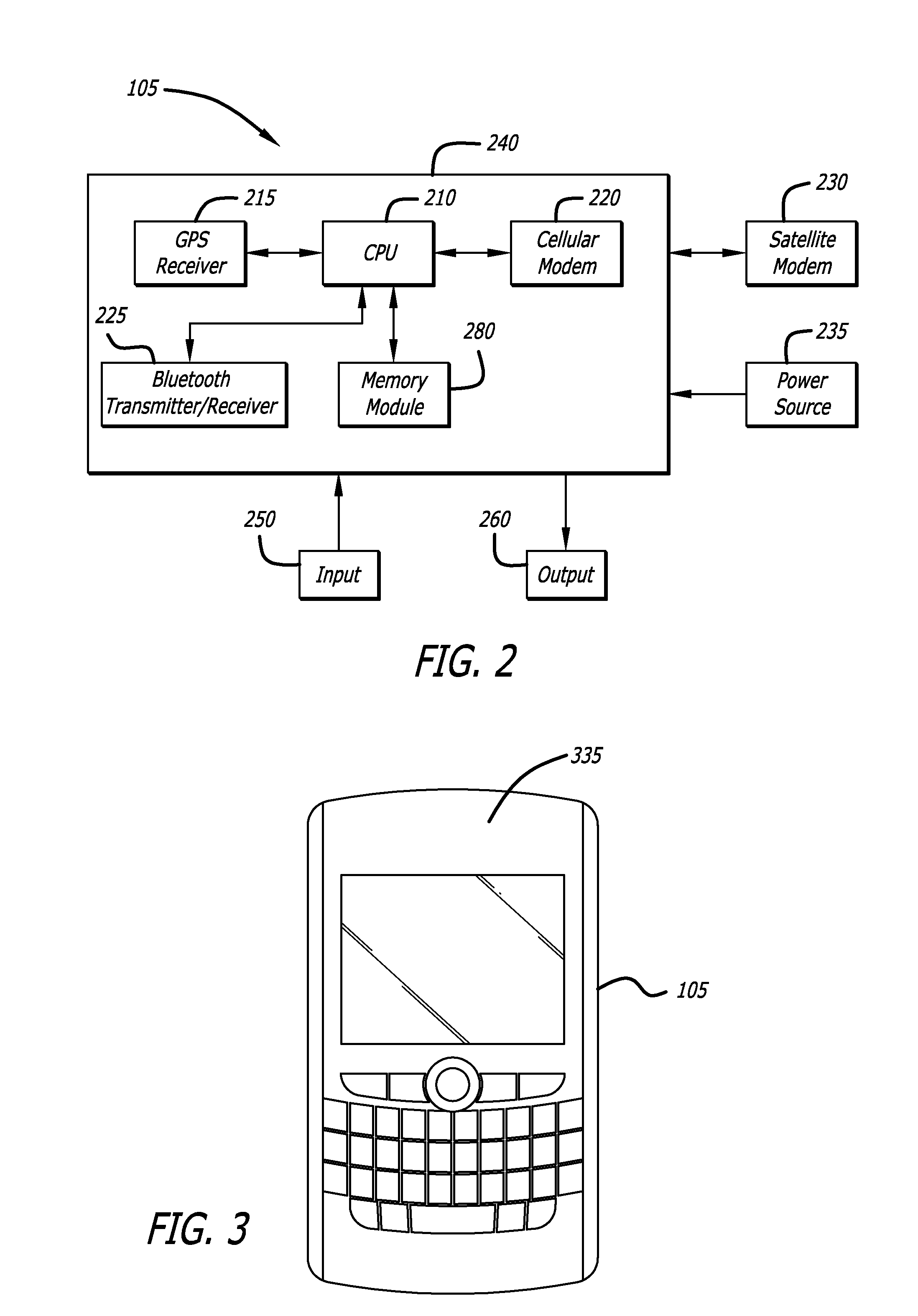
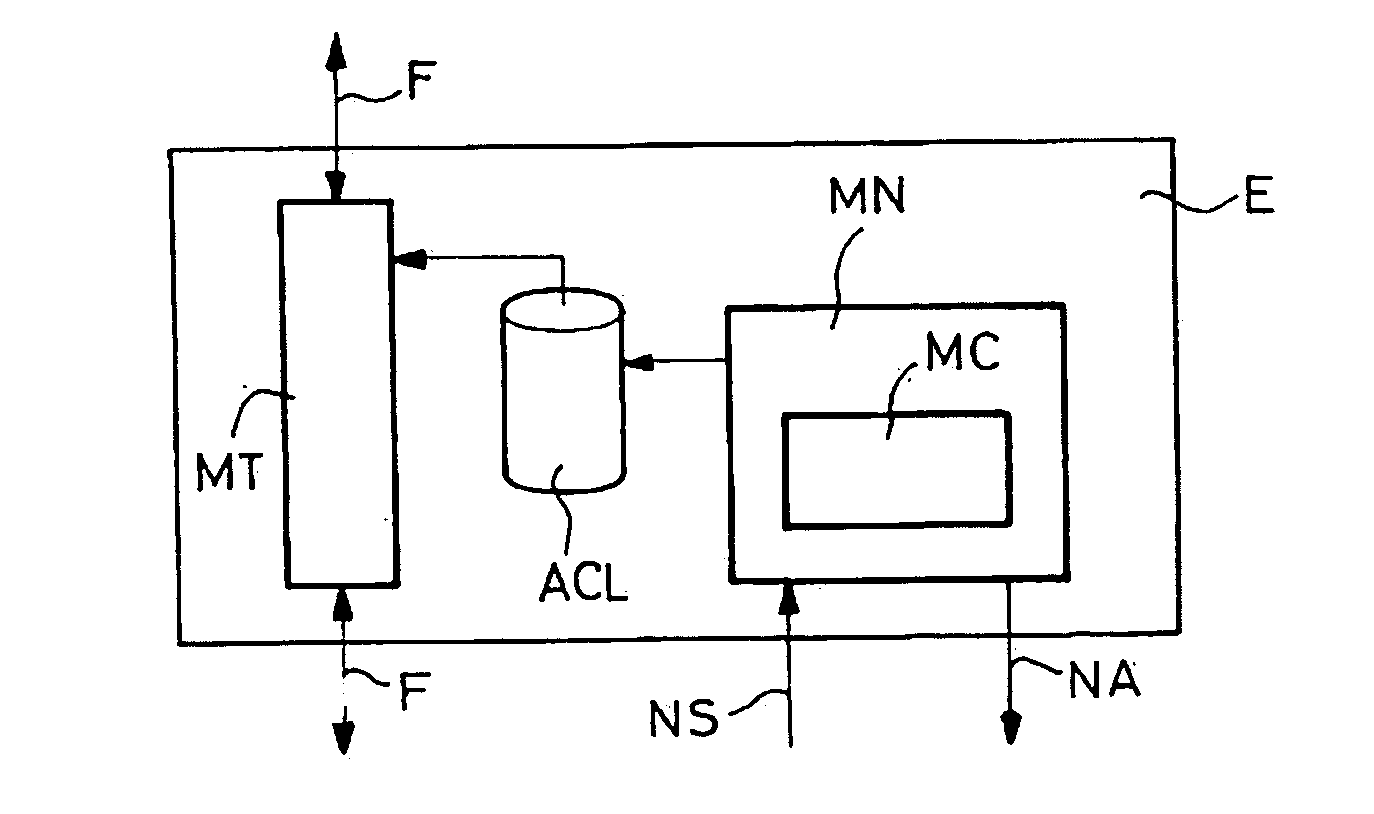
A method to define a three-dimensional geographical zone that is utilized with a movable entity having at least one attached transponder is disclosed. The method comprises allowing a user to enter at least one waypoint, and loading at least one waypoint on at least one transponder. In one or more embodiments, a waypoint is defined by a geographical coordinate and a radius. The geographical coordinate is represented by a latitude value, a longitude value, and an elevation value. And, the radius is represented by a distance magnitude. In some embodiments, the method further comprises regulating the movable entity by monitoring, controlling, and / or visualizing the movement, non-movement, or position of the movable entity. The transponder determines whether the transponder is located inside the three-dimensional geographical zone by obtaining global positioning coordinates, and calculating whether or not the global positioning coordinates are located inside at least one waypoint.
Owner:WIRELESSWERX IP LLC
Method and system to monitor and control devices utilizing wireless media
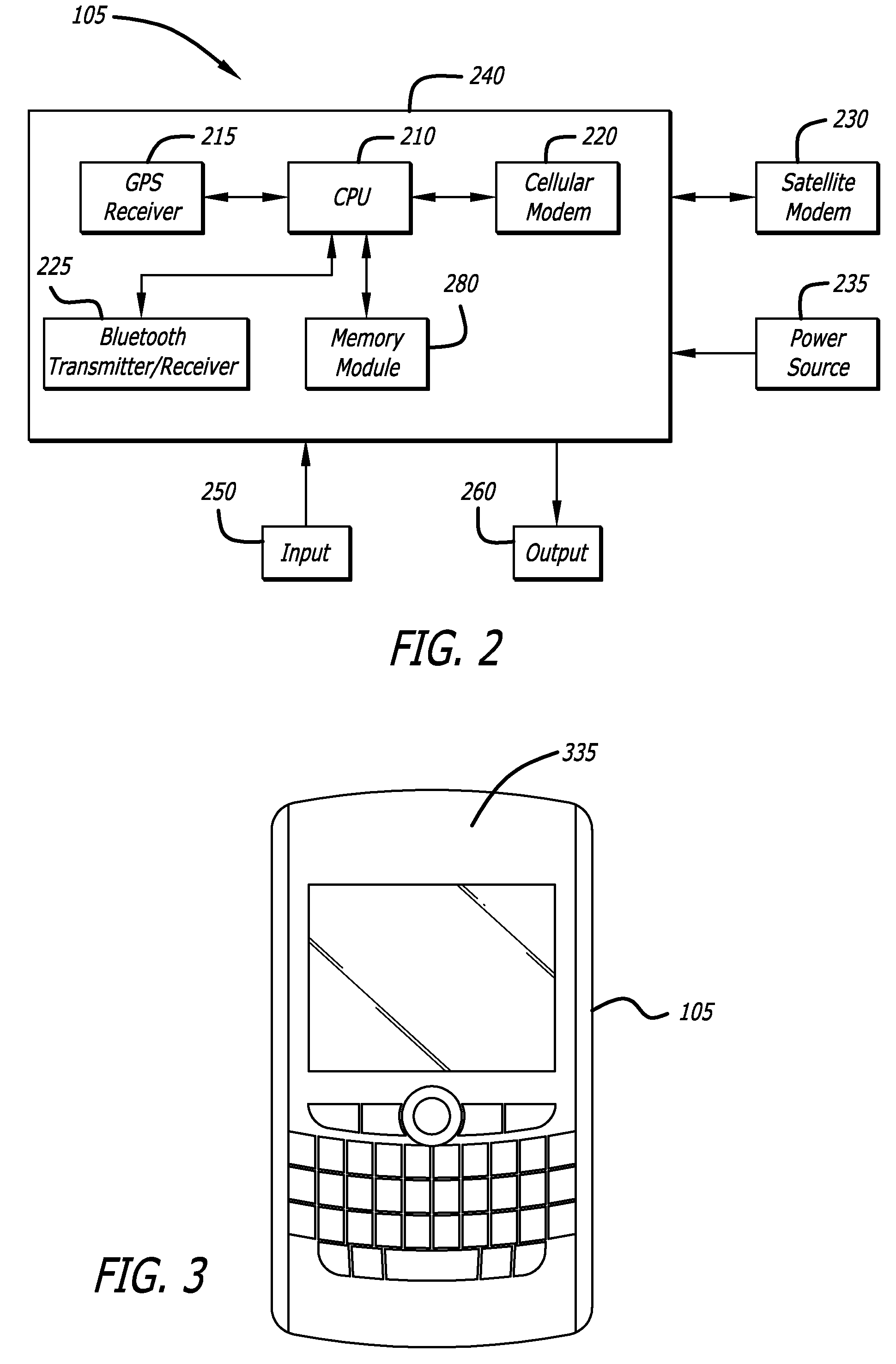
ActiveUS20060099971A1High enough resolutionSolve the lack of resolutionTransmission systemsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsLongitudeEngineering
A method and system of selectively communicating with one or more devices within pre-defined geographical zones is disclosed. A plurality of geographical zones is defined, each zone being defined by latitude and longitude attributes. A plurality of devices is associated with each geographical zone with which a portable device can communicate, the portable device having data representative of the plurality of geographical zones. The portable device also has a ground positioning unit receiver to obtain geographical coordinates of the portable device. If the portable device determines that its location is within one of the plurality of geographical zones, the portable device communicates with the devices in associated with the geographical zone.
Owner:WIRELESSWERX IP LLC
Weather prediction method for forecasting selected events
InactiveUS7069258B1Accurate predictionWeather condition predictionDigital computer detailsData setPrincipal component analysis
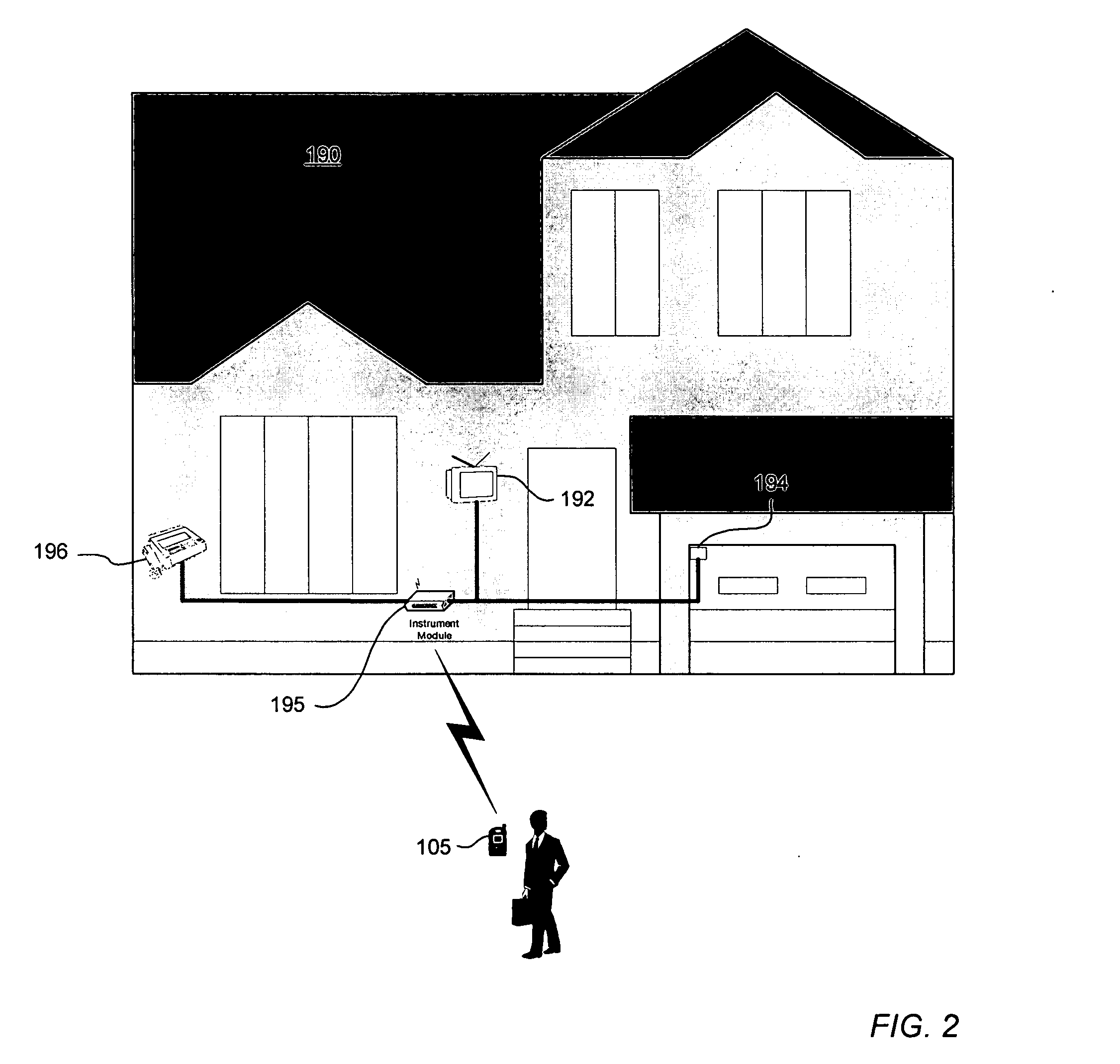
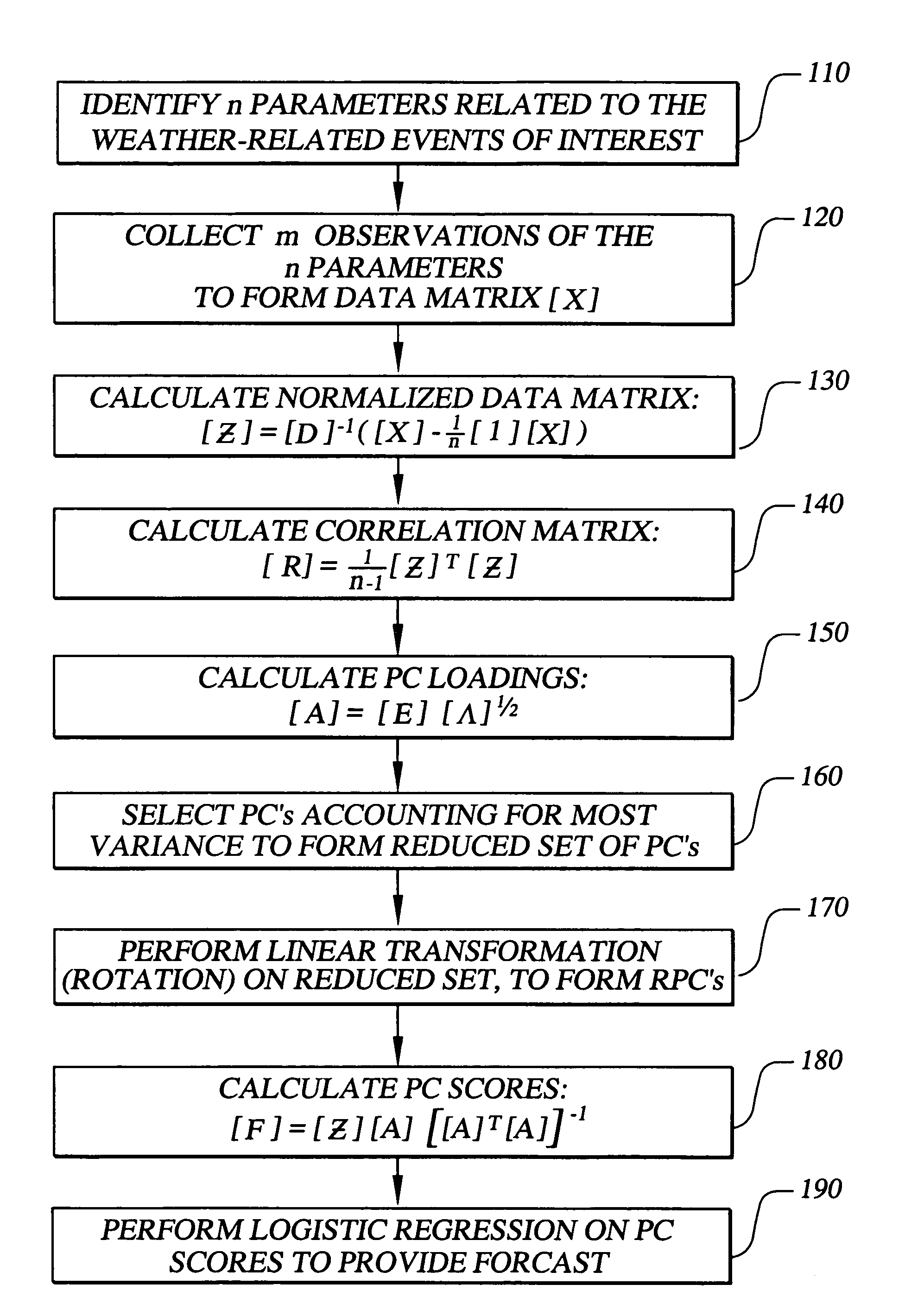
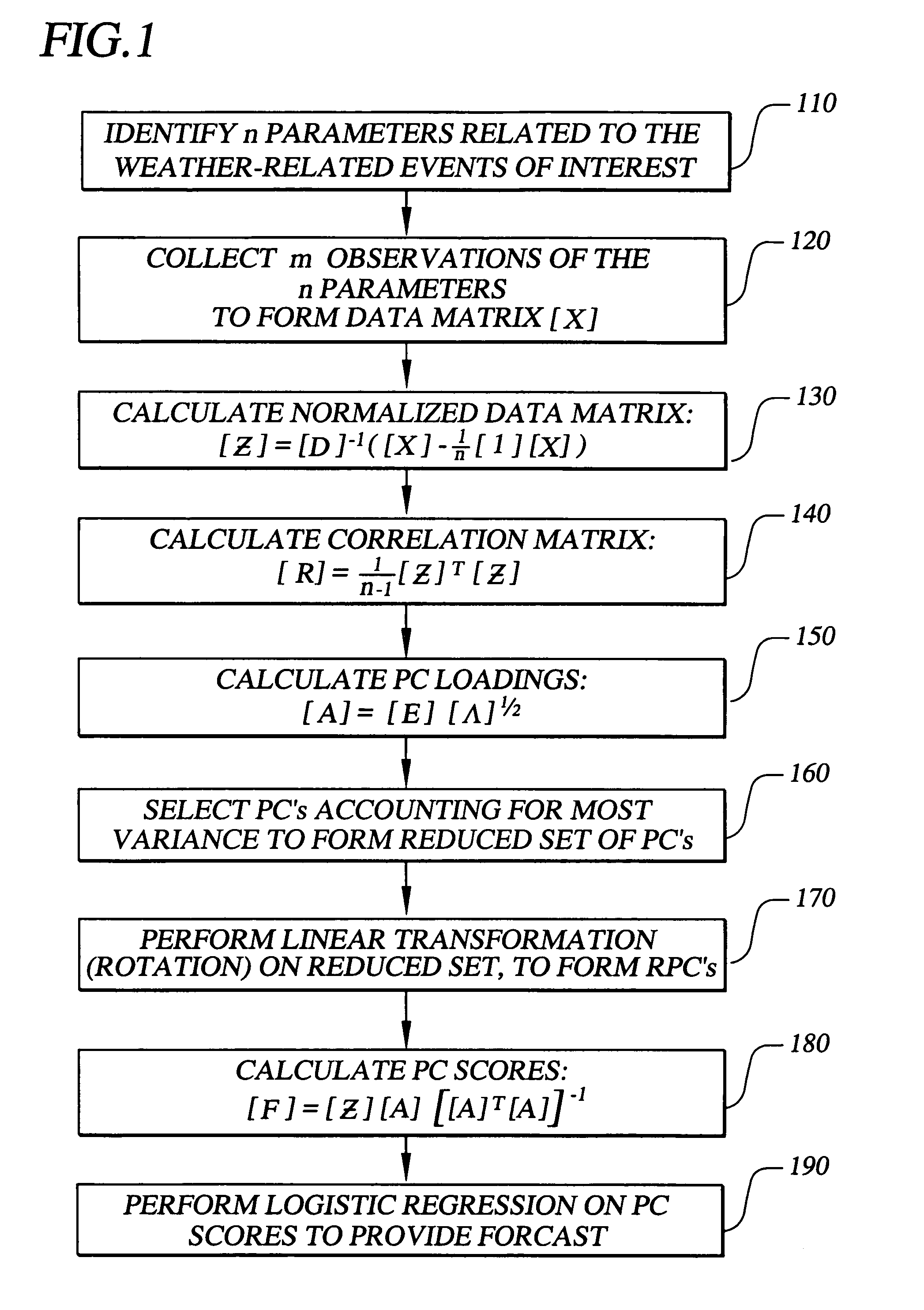
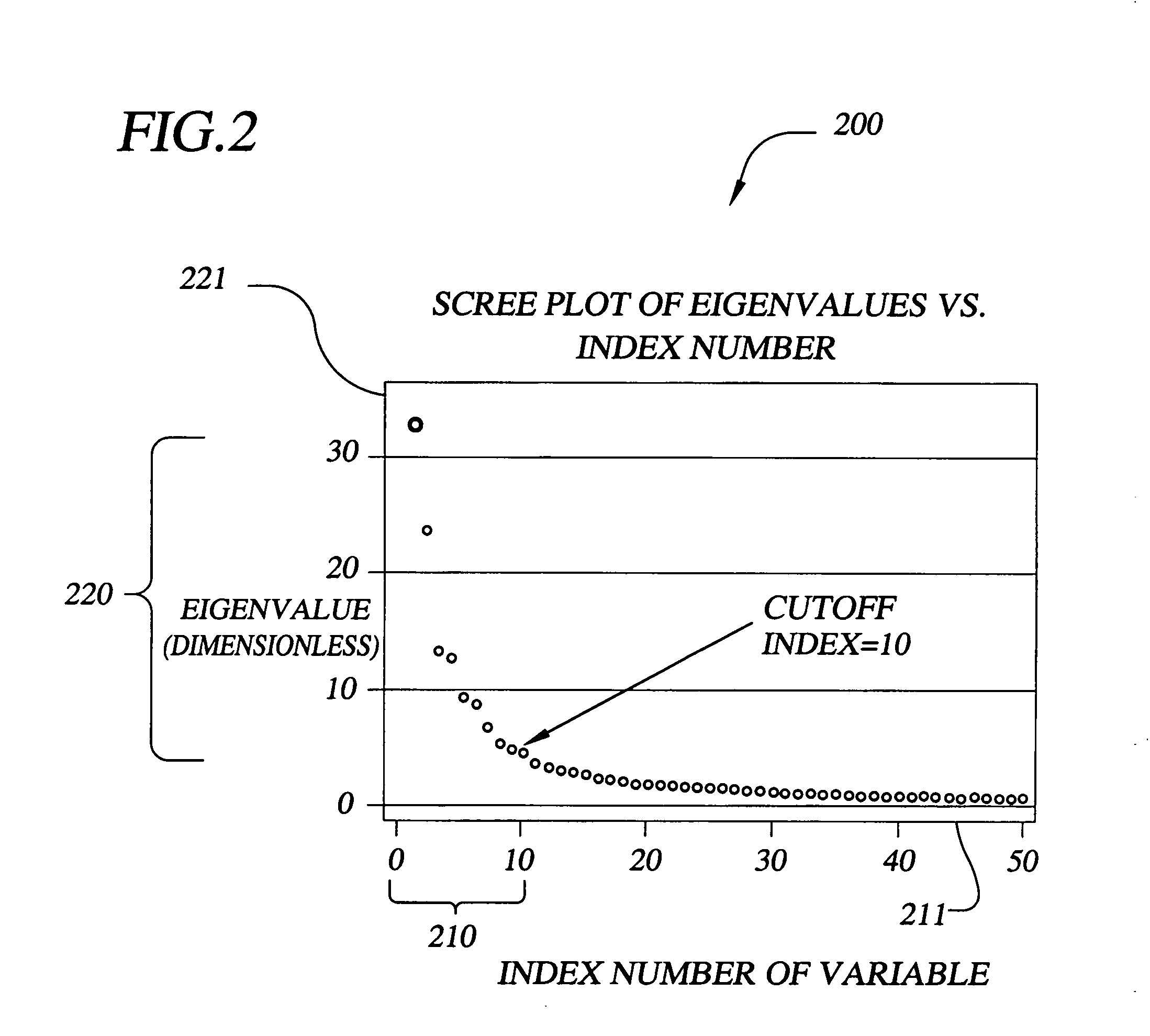
The invention provides methods, systems, and computer program products for short term probability forecasting of selected weather-related events. These embodiments are adaptable for any geographical region that can be identified and for which a reasonable number of data points exist. The inventive method uses a data set of n observations of m parameters, where the parameters may be statistically correlated. A Principal Component Analysis may be performed, with the data set as input, to provide a reduced set of principal components that are uncorrelated and account for most of the variance in the input data set. An orthogonal transformation may be performed on the reduced set of principal components to provide a rotated set of principal components that are aligned with the corresponding parameters in the input data set. Finally a logistic regression may be performed on the rotated set of principal components to derive an S-shaped predictive equation for the probability of a binary weather-related event of interest. An illustrative embodiment of the invention is given for forecasting the probability for the number of lightning flashes exceeding a selected value, for the western United States climatological area.
Owner:BOTHWELL PHILLIP D
System and method of geospatially mapping topological regions and displaying their attributes
InactiveUS20050209781A1Digital computer detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsTopological orderLongitude
A geographical information system and a method are disclosed for geospatially mapping a least one parcel polygon within a geographical region and for displaying at least one specific attribute of each parcel polygon, i.e. a topological area within the given geographical region, as an attached attribute of latitude and longitude coordinates. The centroid or center point of each of the parcel polygons is determined and stored into conventional computer storage means. The latitude and longitude point feature at the centroid of each parcel polygon is established and similarly stored. A unique tax identification number, e.g. the Assessor Parcel Number (APN) or Parcel Identifier Number (PIN), is assigned to each of the point features. A correlation is then made between the unique tax identification number of the point feature to a text list of at least one attribute, e.g., the physical address of the parcel polygon, of each of the point features. This attribute becomes attached to each point feature. The resulting parcel polygon map and point features with one or more of the attached attributes can then be displayed within a GIS or CAD system to provide the user, for example, accurate locations of street addresses for use in environments that require pinpoint accuracy, such as emergency response.
Owner:GIS DATA RESOURCES
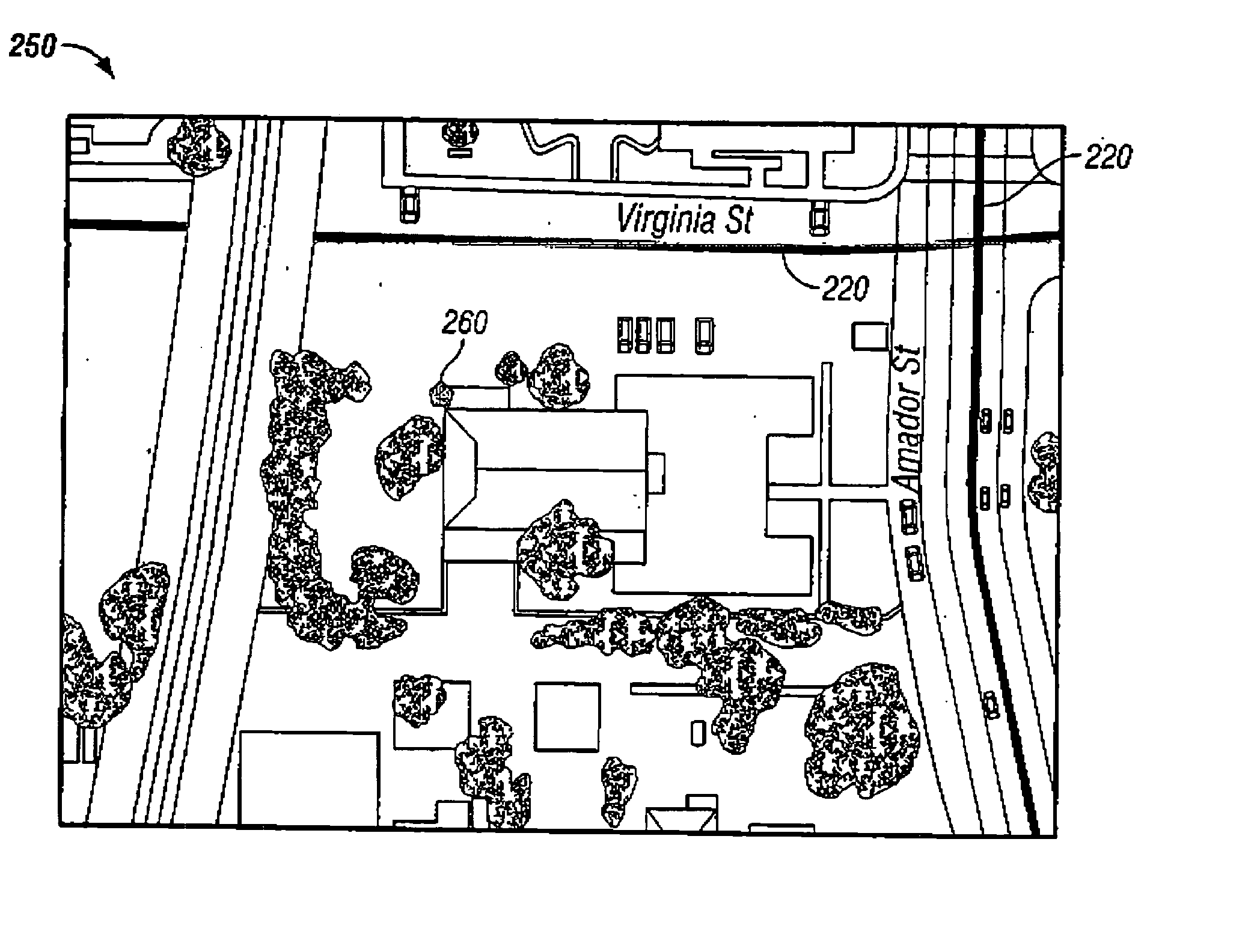
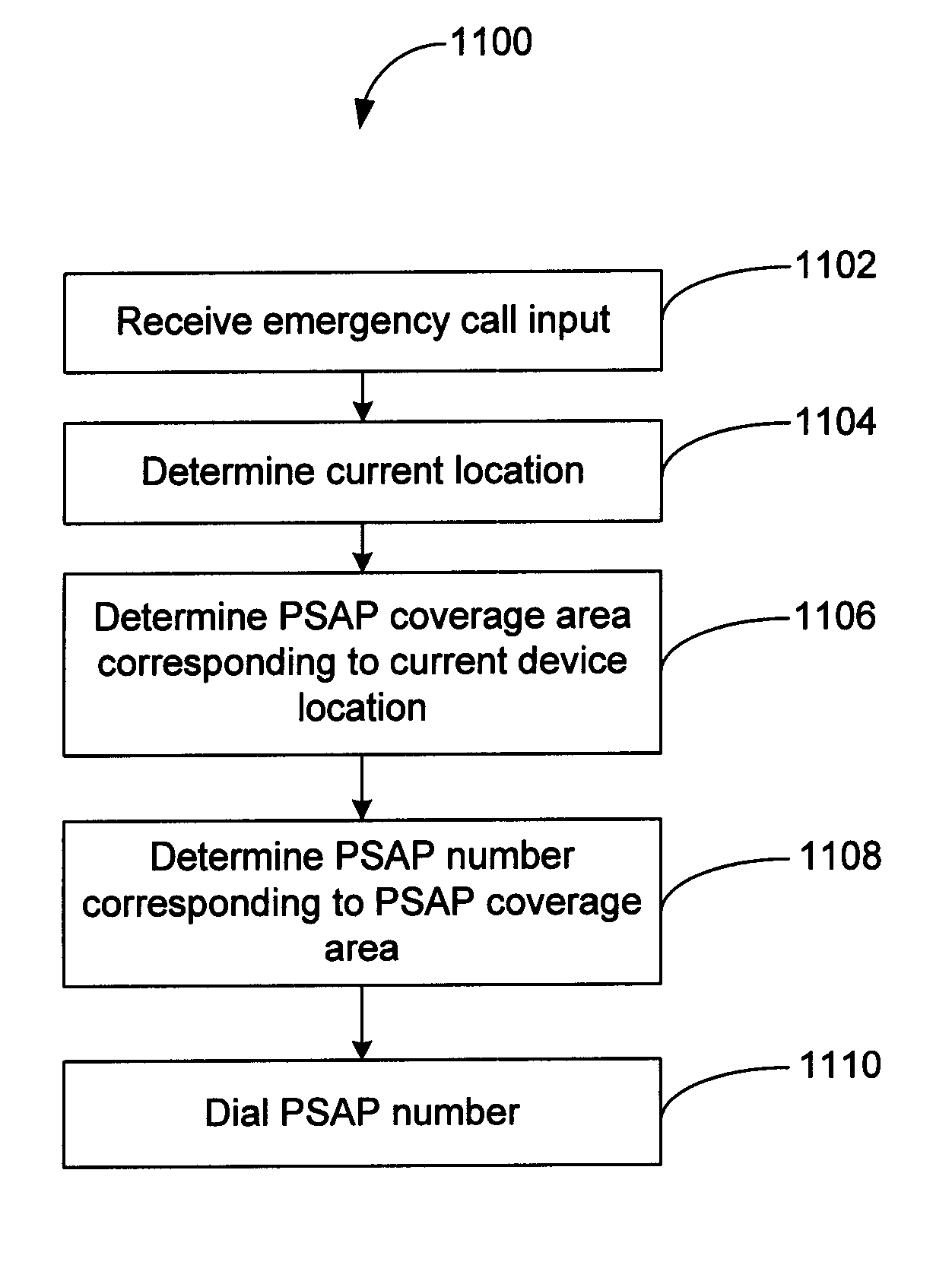
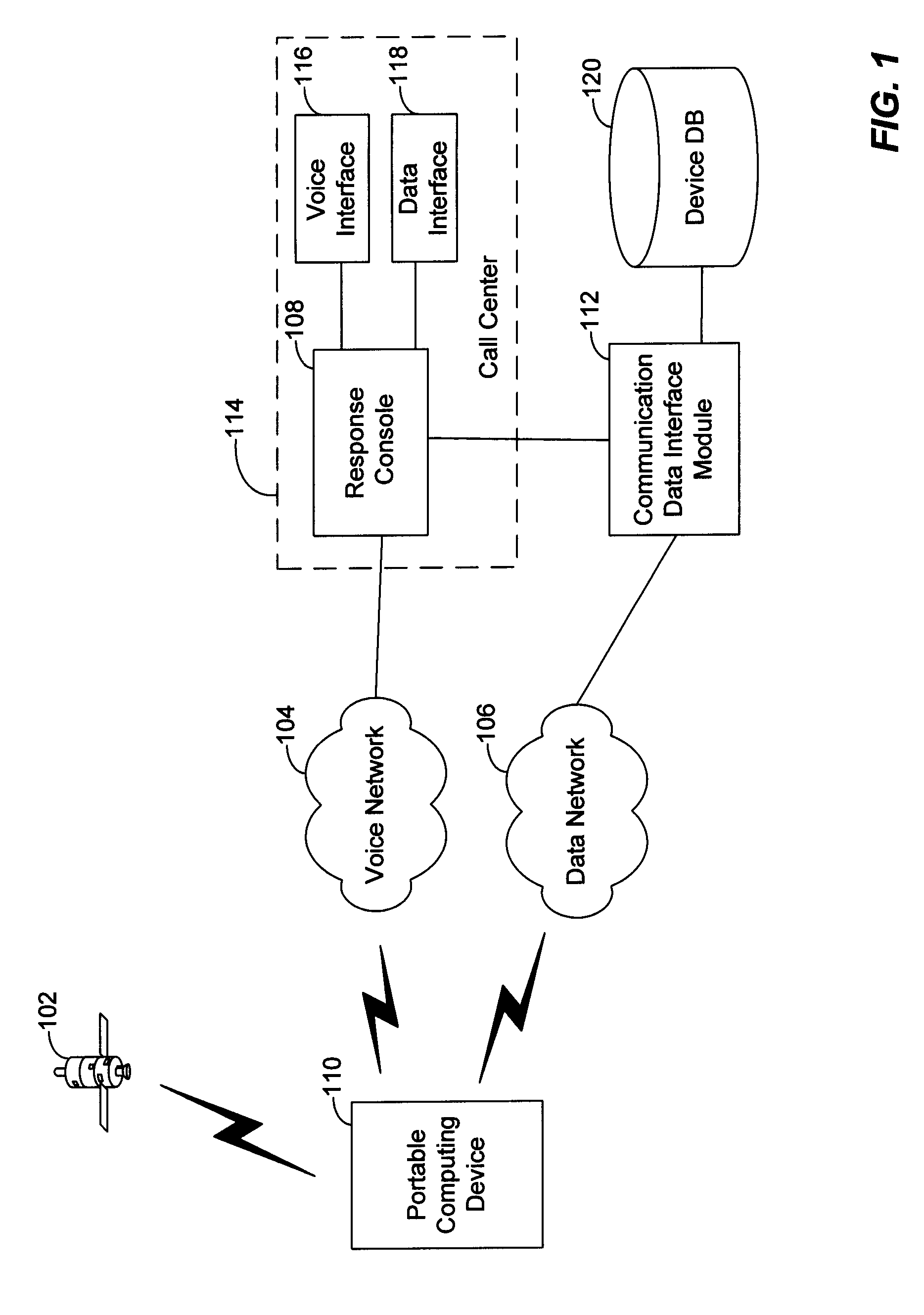
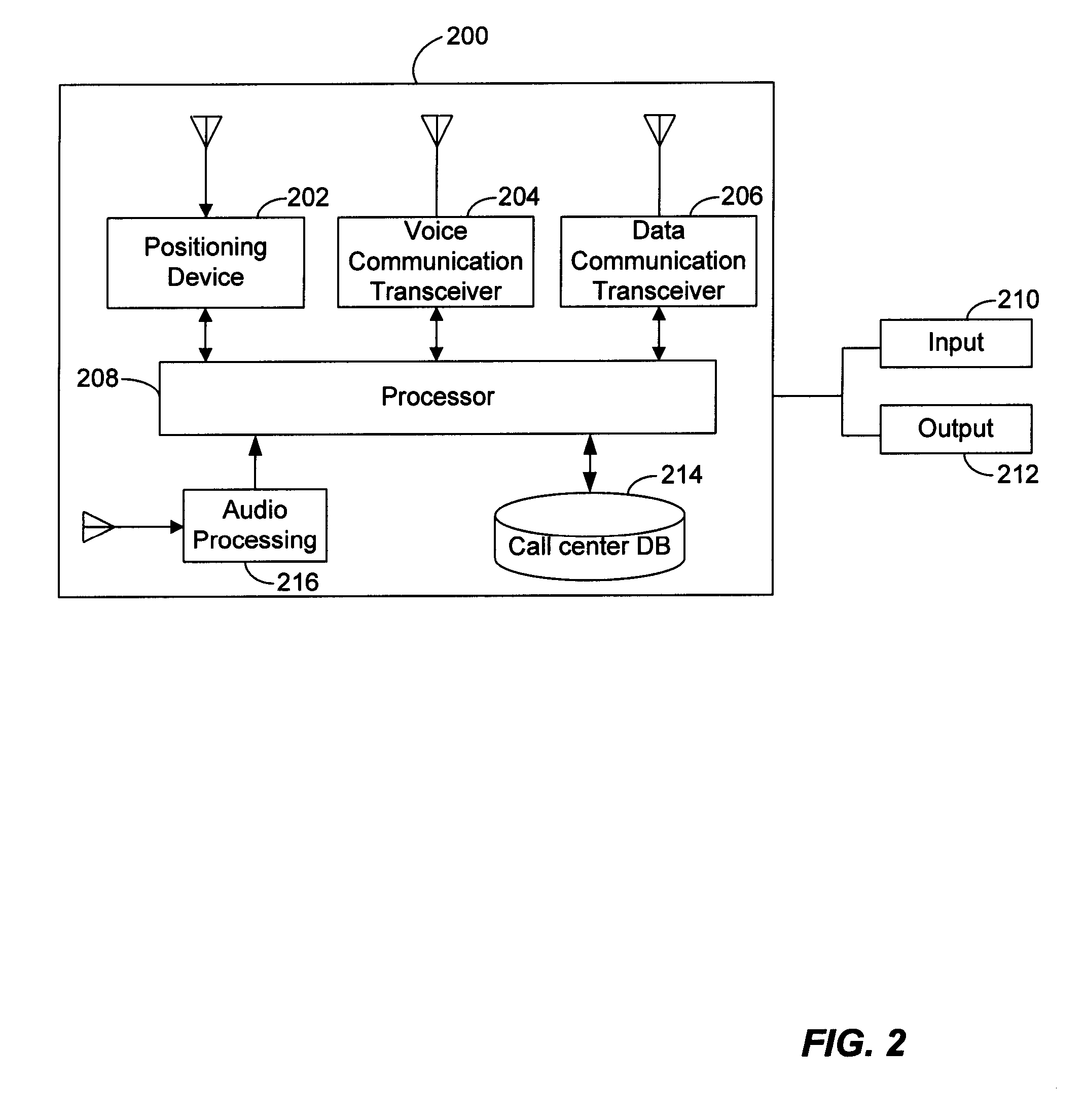
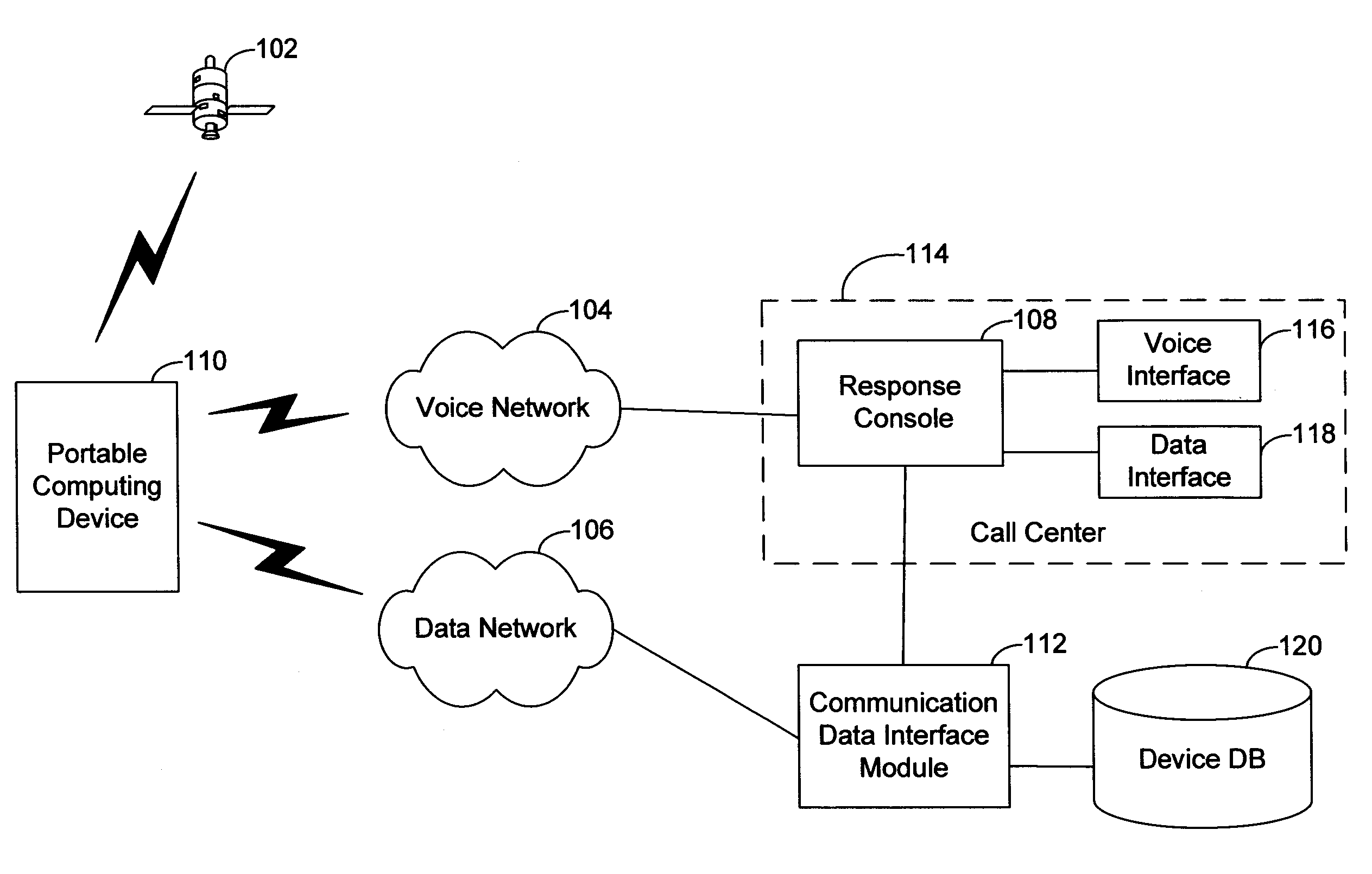
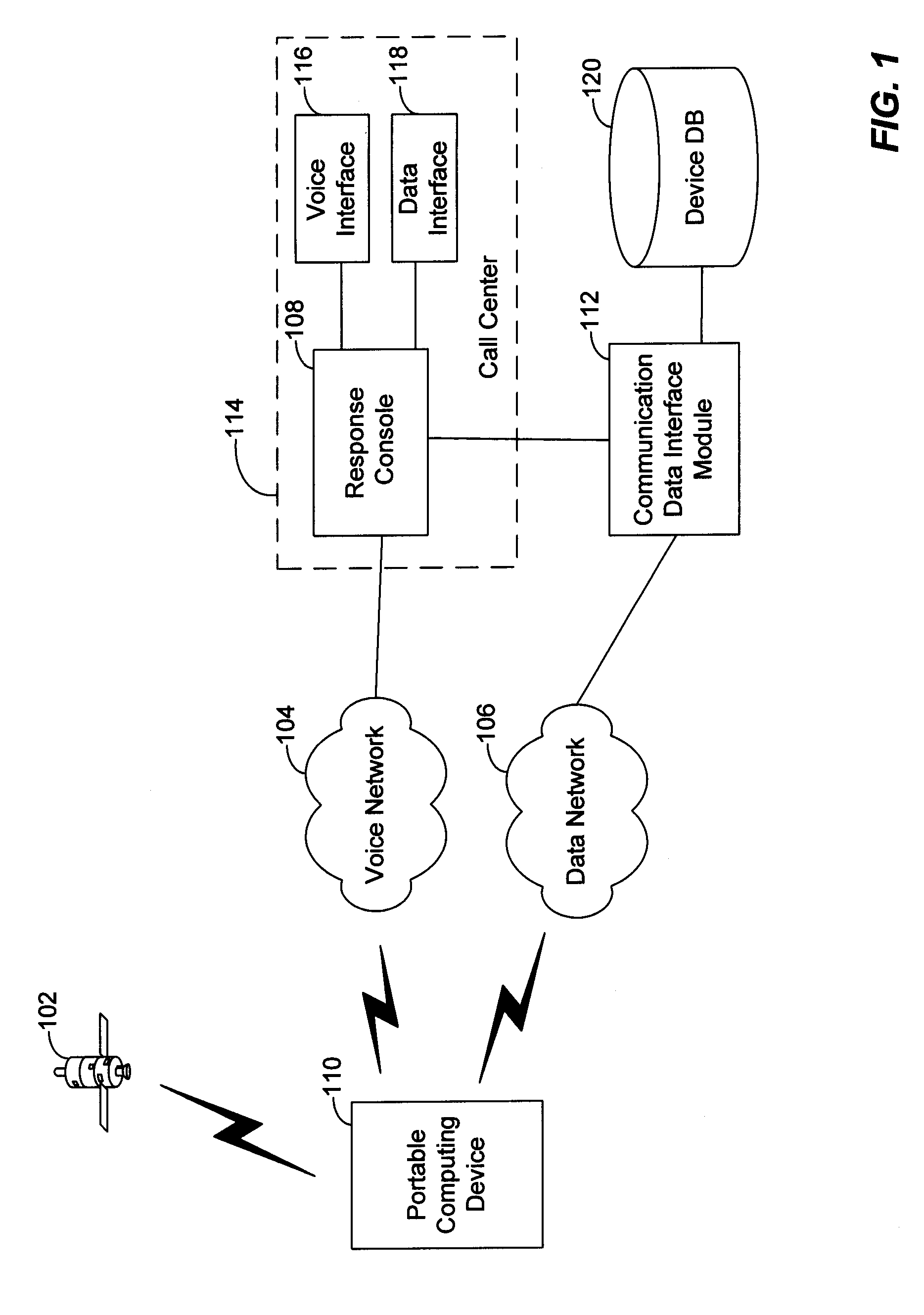
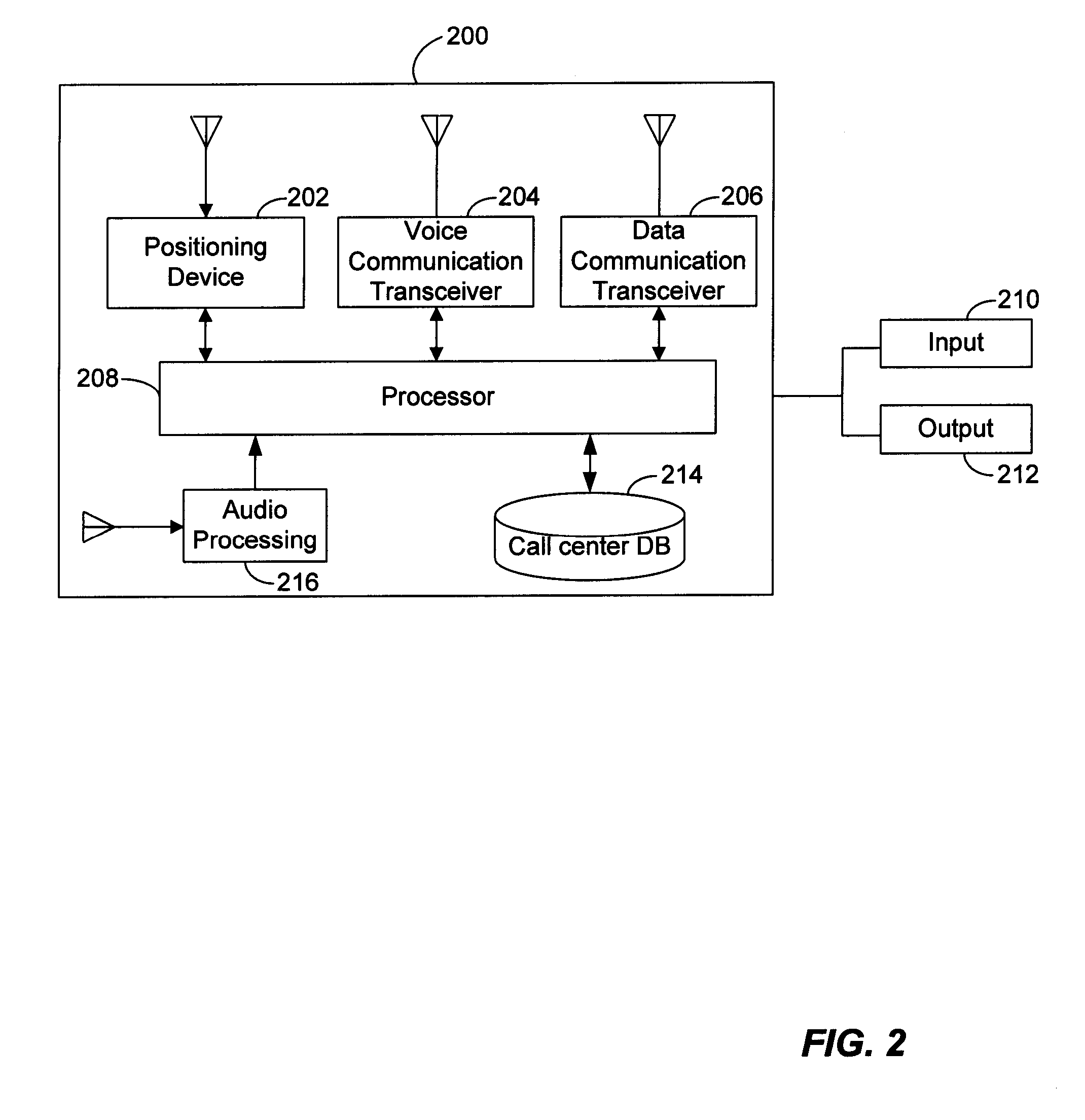
Method and system for initiating and handling an emergency call utilizing geographical zones
A method and system of making an emergency voice call is disclosed. Location data is received from a positioning device. A location area identifier is determined. The location area identifier corresponds to a geographical area encompassing a geographical location being represented by the location data. A voice call destination number is identified. The voice call destination number is associated with the location area identifier. The voice call destination number is utilized in order to communicate with a public safety answering point.
Owner:WIRELESSWERX IP LLC
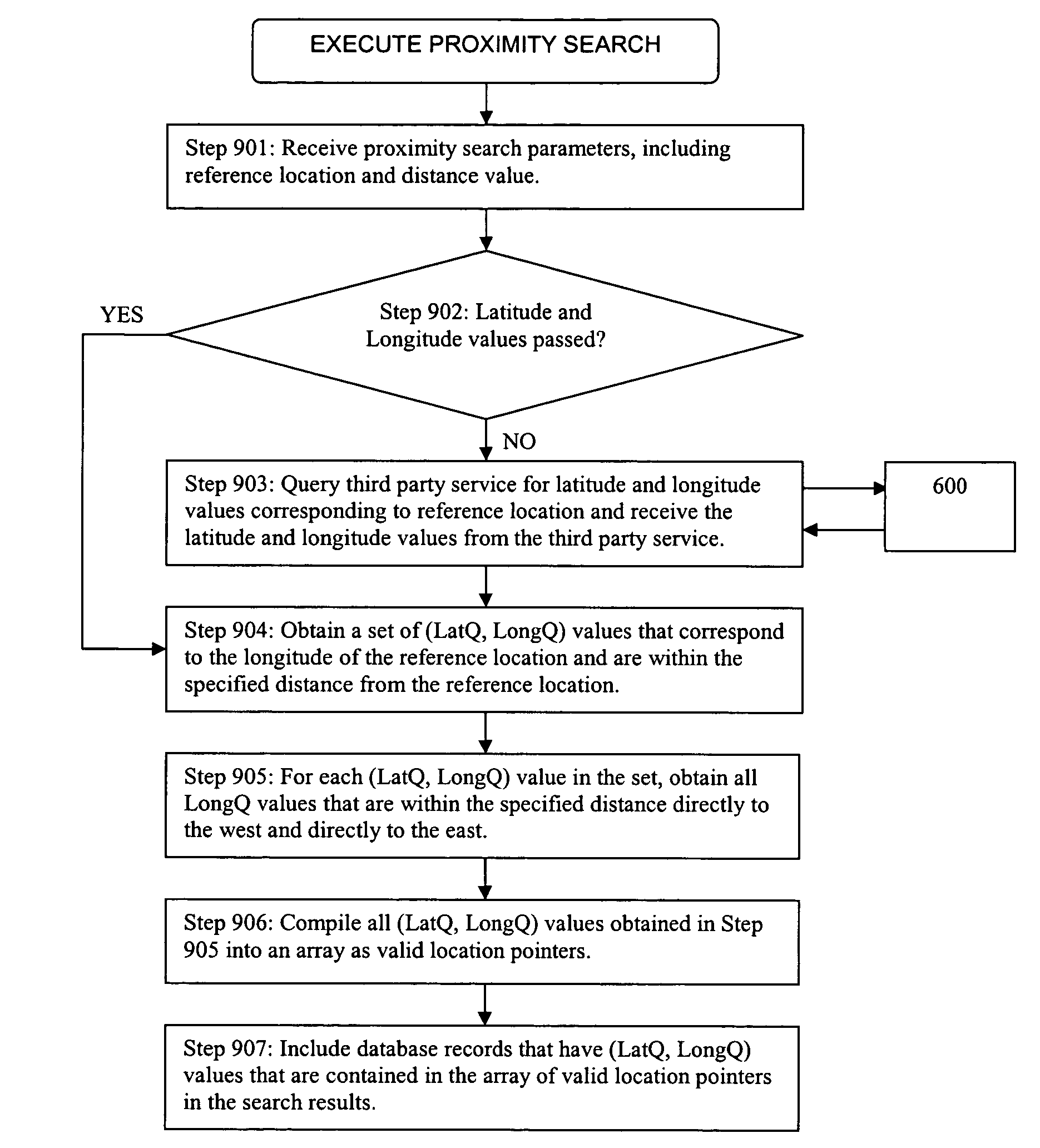
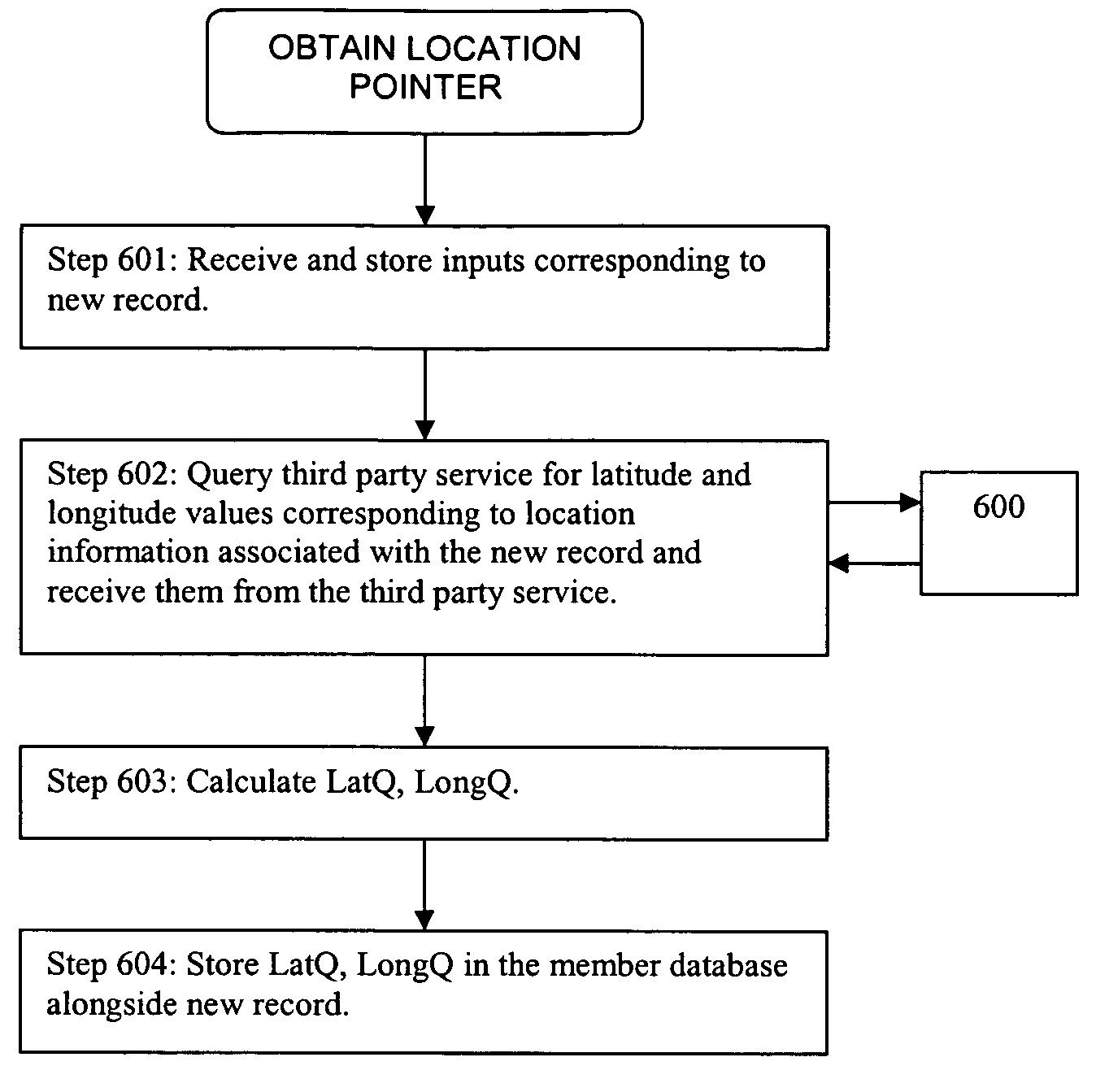
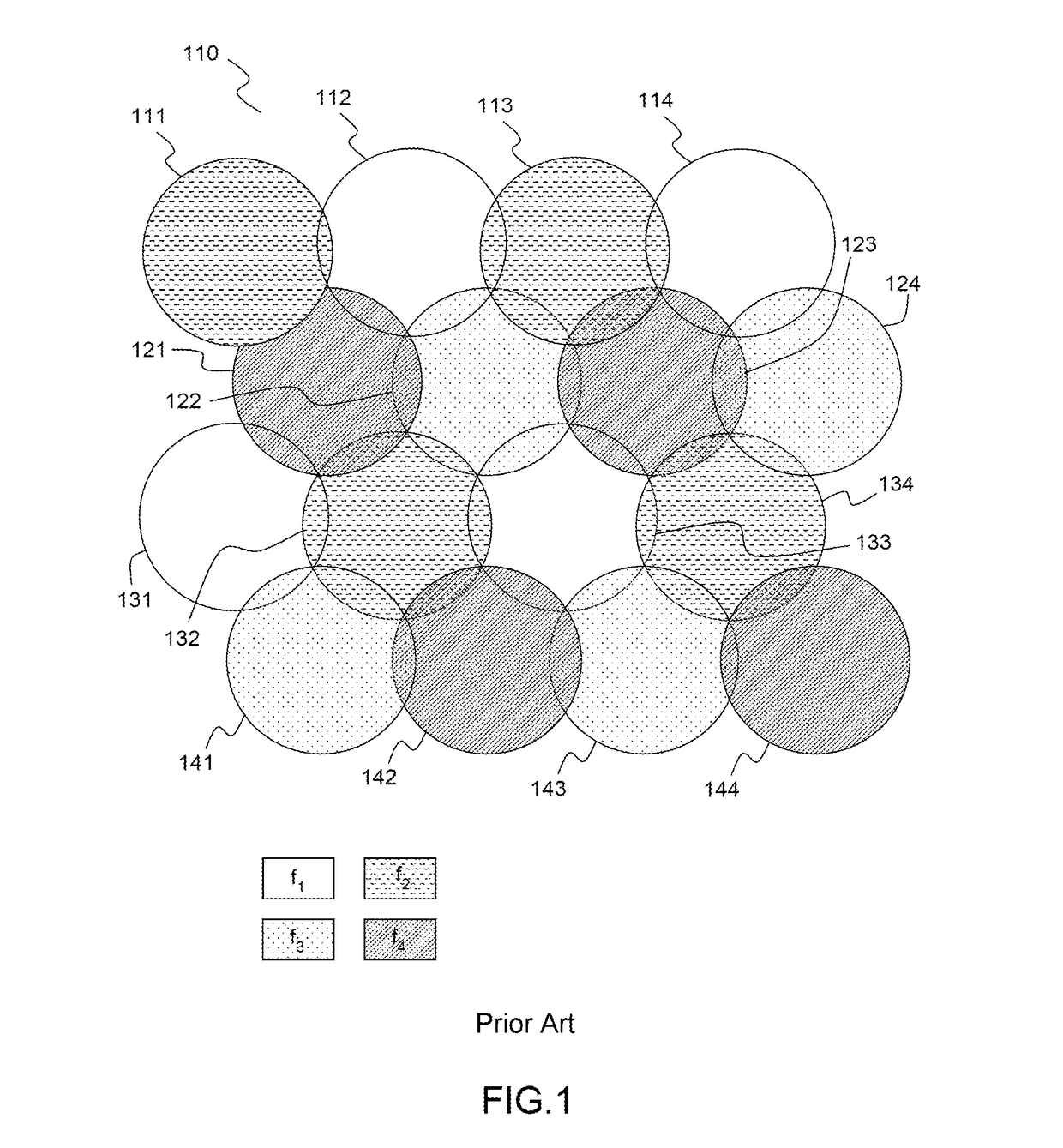
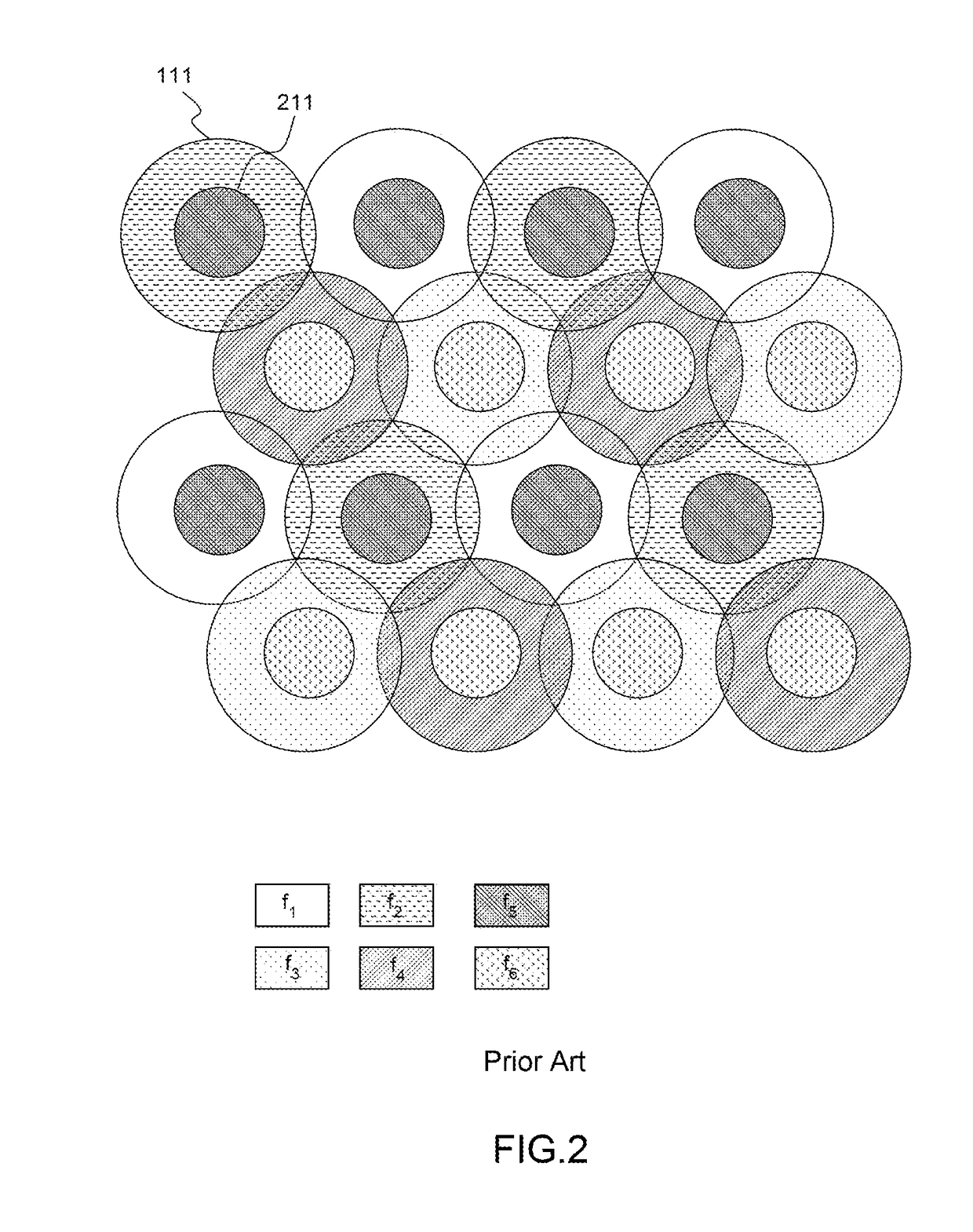
Proximity search methods using tiles to represent geographical zones
ActiveUS7606687B2Reduce in quantityImprove execution speedRoad vehicles traffic controlNavigation instrumentsGeographical zoneComputer science
A proximity search engine for carrying out a proximity search with respect to a reference location uses as a reference frame the earth divided into tiles, which are predefined geographic regions of substantially equal areas. Records that are searched based on proximity to a reference location include location pointers, each of which identifies a particular tile that encompasses the physical location indicated by the corresponding record. When the proximity search is carried out, the tiles that are within a specified distance from the reference location are obtained and records having location pointers corresponding to such tiles are selected for inclusion in the search results.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
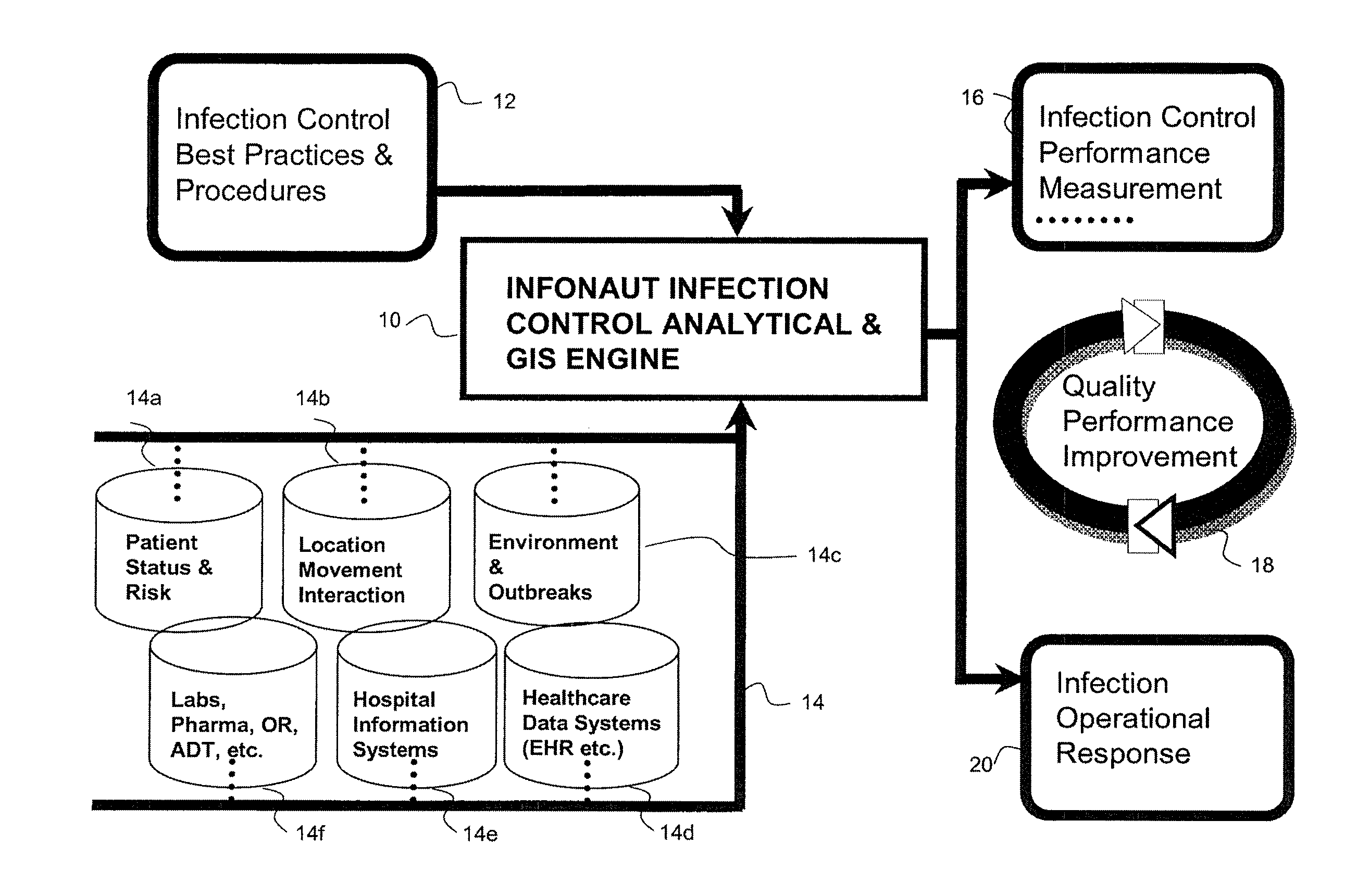
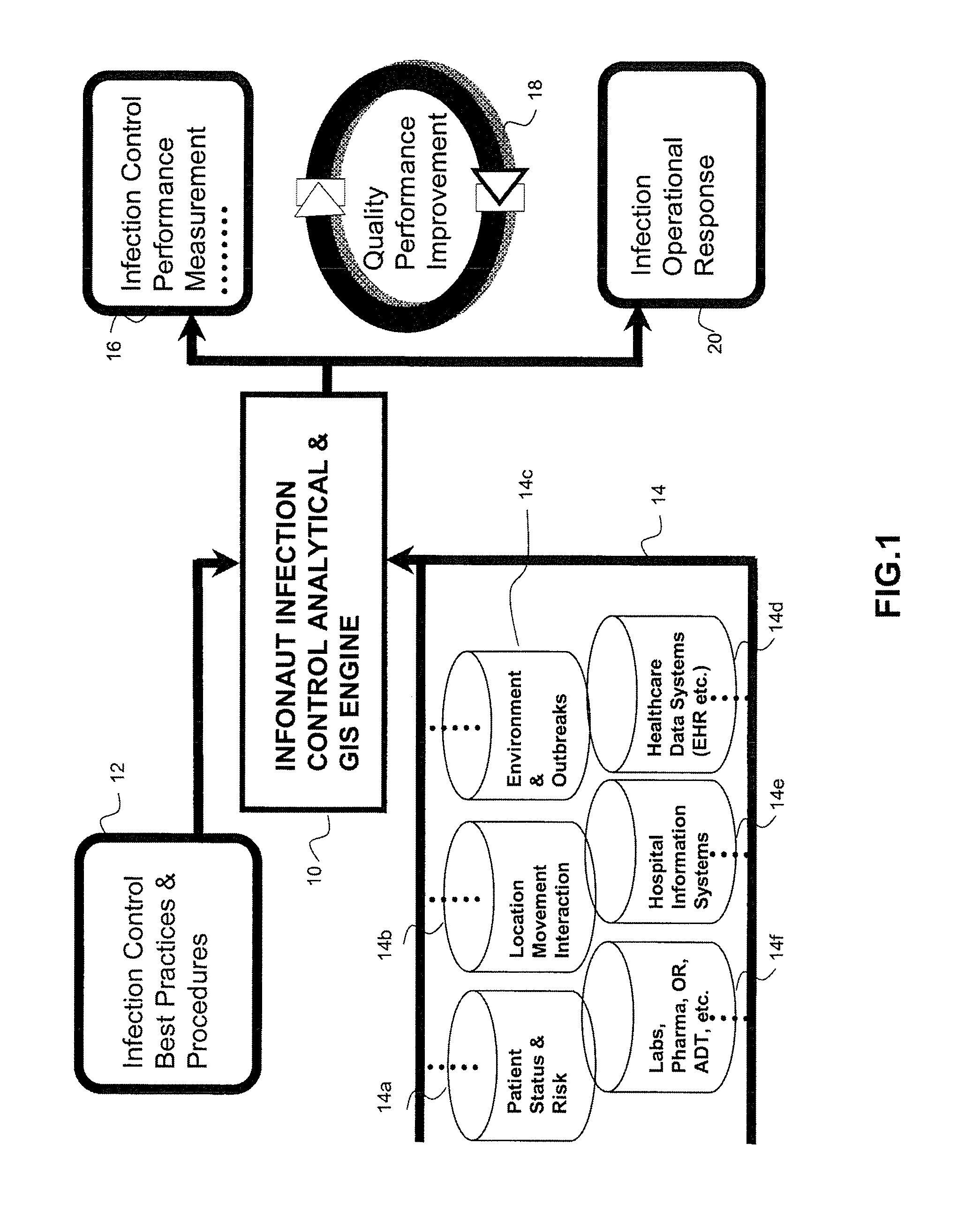
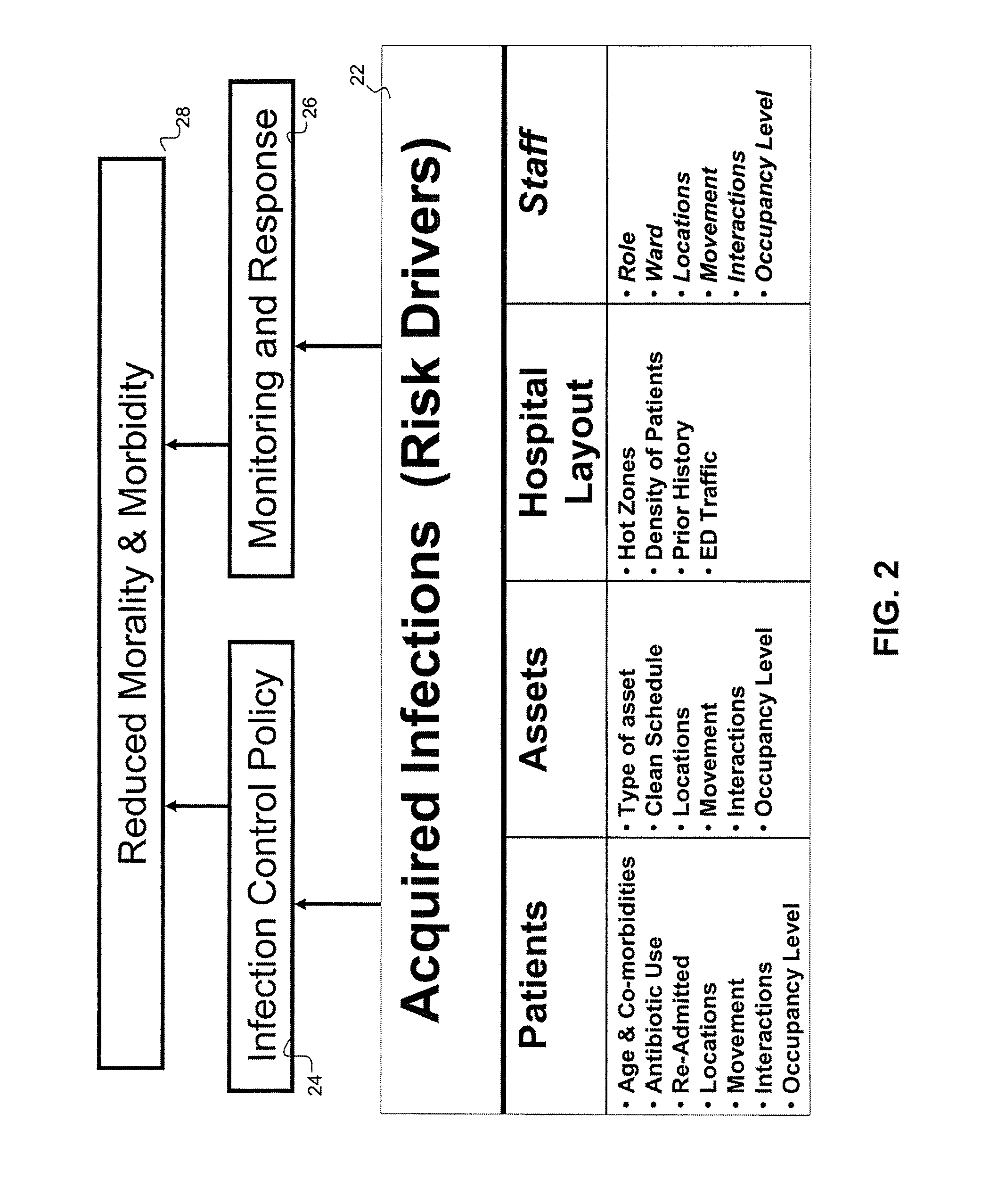
Disease Mapping and Infection Control System and Method
Owner:INFONAUT
Proximity search methods using tiles to represent geographical zones
ActiveUS20060058958A1Reduce in quantityImprove execution speedInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlGeographical zoneComputer science
A proximity search engine for carrying out a proximity search with respect to a reference location uses as a reference frame the earth divided into tiles, which are predefined geographic regions of substantially equal areas. Records that are searched based on proximity to a reference location include location pointers, each of which identifies a particular tile that encompasses the physical location indicated by the corresponding record. When the proximity search is carried out, the tiles that are within a specified distance from the reference location are obtained and records having location pointers corresponding to such tiles are selected for inclusion in the search results.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
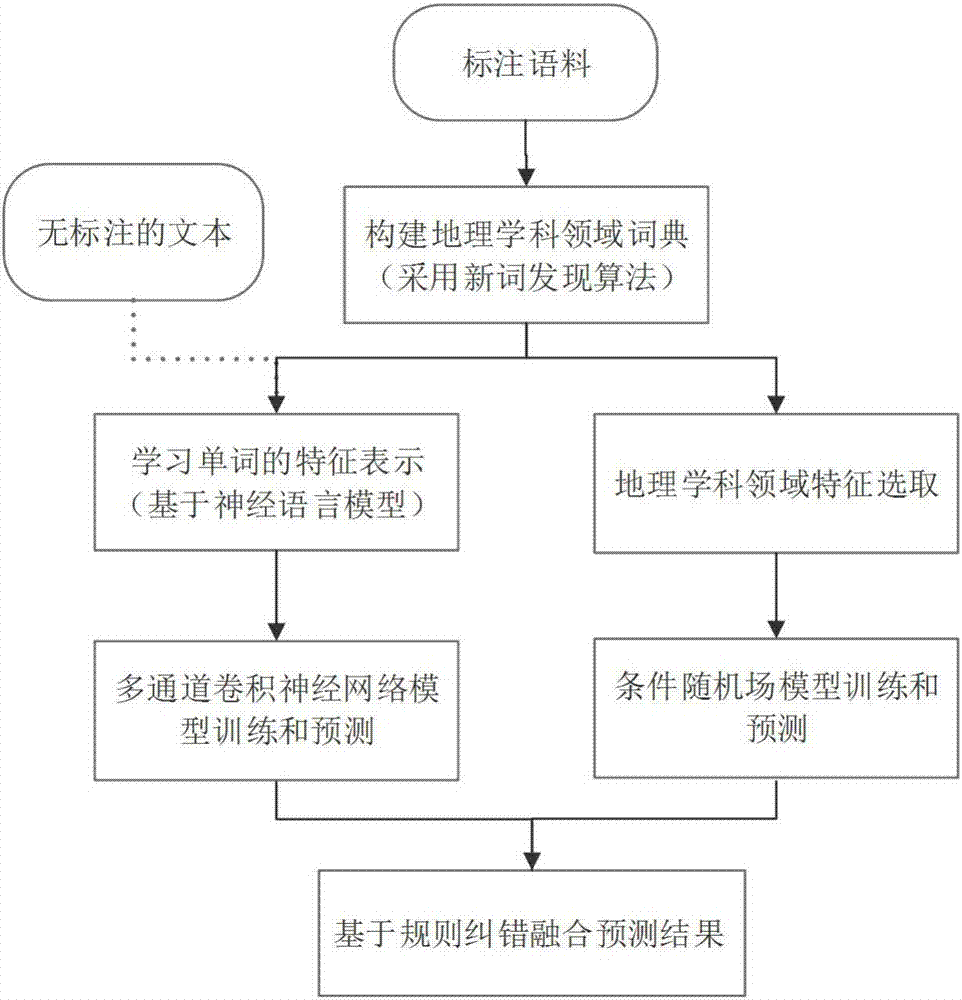
Geographical science domain named entity recognition method
ActiveCN107133220AEntity recognition implementationCorrect mislabeling issueSemantic analysisSpecial data processing applicationsDomain nameConditional random field
The invention discloses a geographical science domain named entity recognition method, which is used for recognizing geographical science core term entities and geographical location entities. The method mainly comprises three steps of (1) establishing a geographical science domain dictionary, and using a new word discovery algorithm to identify new words in the geographical science domain in an unsupervised way; (2) training and testing based on a conditional random field (CRF) model and a multichannel convolutional neural network (MCCNN) model; (3) carrying out error correcting and fusion on entities recognized by the models by using a rule-based method. According to the geographical science domain named entity recognition method, the new words of the domain are identified as the dictionary in an unsupervised way by using the new word discovery algorithm, so that the work distinguishing effect is improved. The semantic vectors of the words are learnt from large-scale unmarked data in an unsupervised way, and basic characteristics of the words are synthesized and are taken as the input characteristics of the MCCNN model, so that manual selection and construction of the characteristics are avoided. The predicting results of the two models are fused by means of a custom rule, so that the problem of error marking in a recognition process can be corrected.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
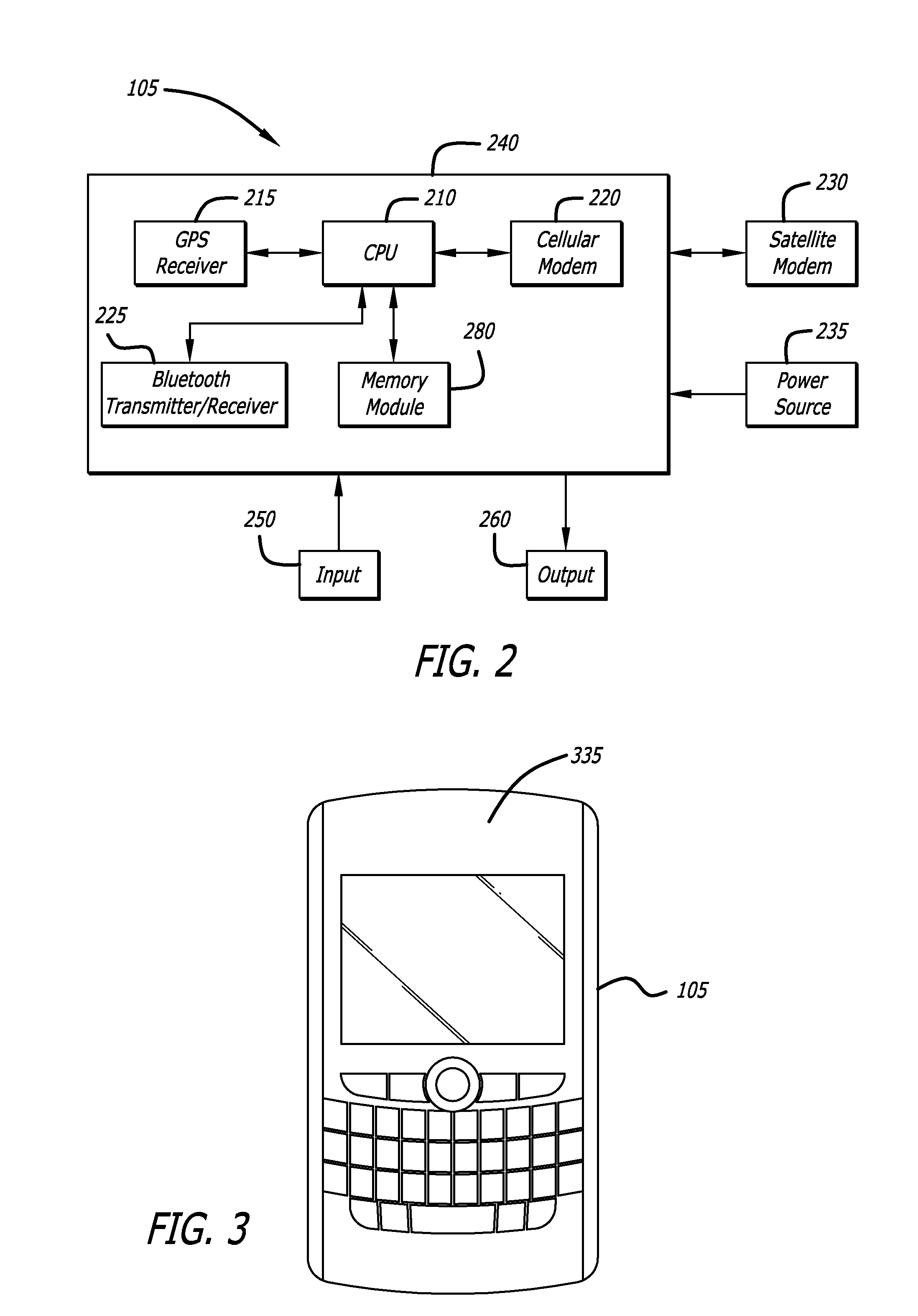
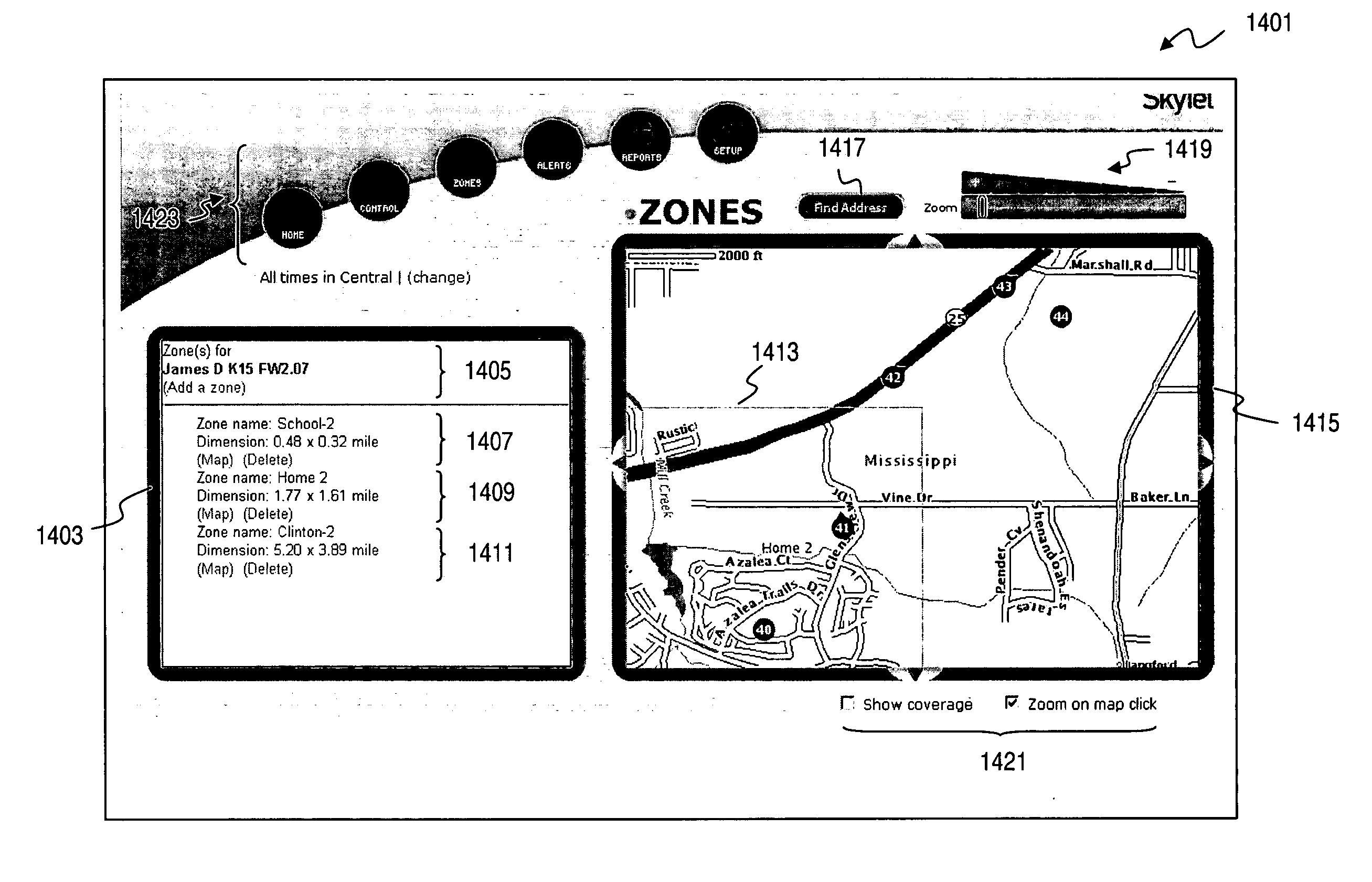
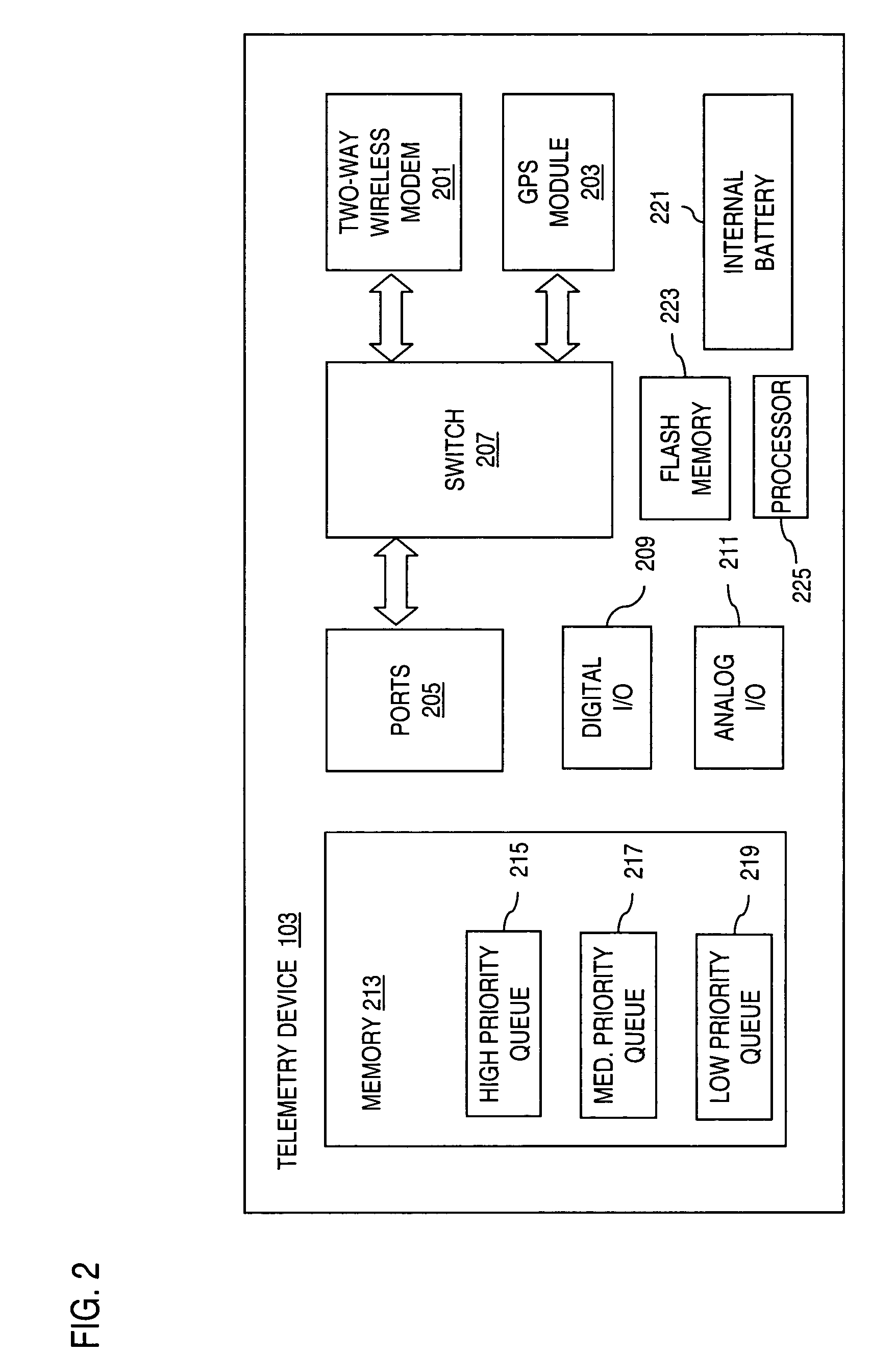
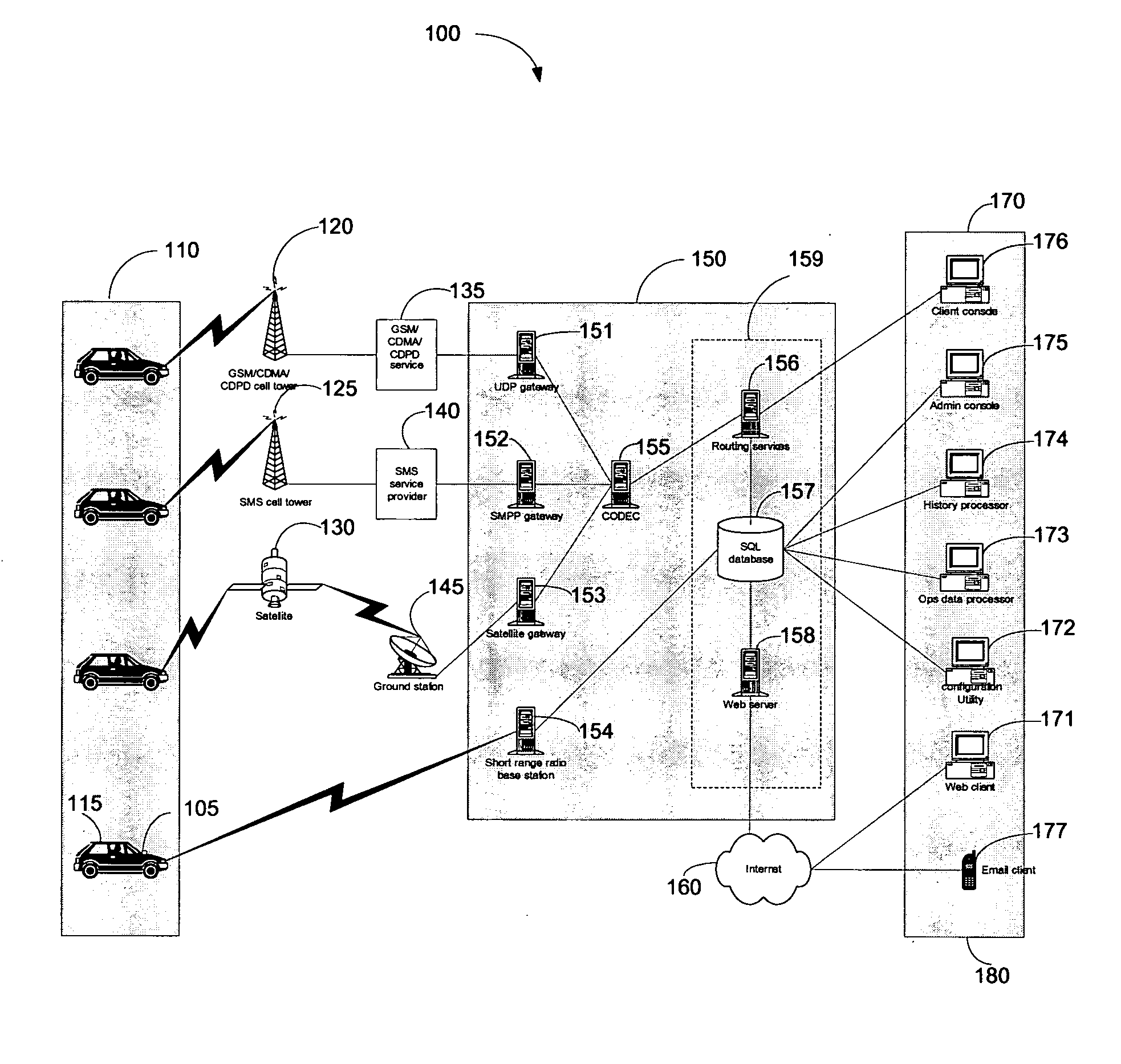
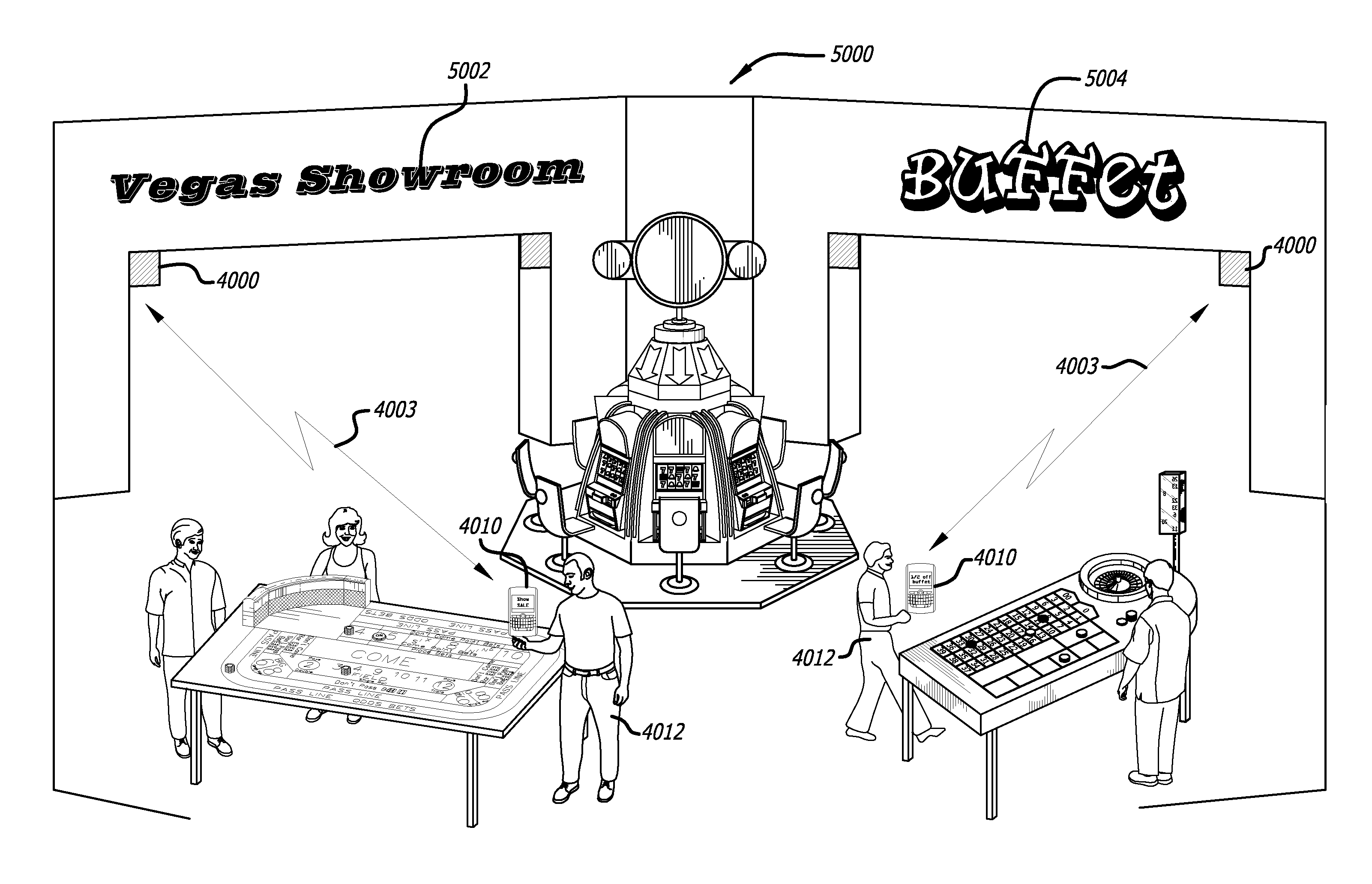
User interface for defining geographic zones for tracking mobile telemetry devices
InactiveUS20050168353A1Control with pedestrian guidance indicatorAnti-theft devicesGraphicsGraphical user interface
An approach is provided for tracking a vehicle via a web interface. A graphical user interface (GUI) screen includes a map showing an icon representing position of the vehicle. A zoom area is established over the map according to a rubber-band mechanism utilized by a user.
Owner:SKYGUARD
Method and system to control movable entities
ActiveUS20060109107A1High speedDecreasing speedInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlState dependentMobile entity
Owner:WIRELESSWERX IP LLC
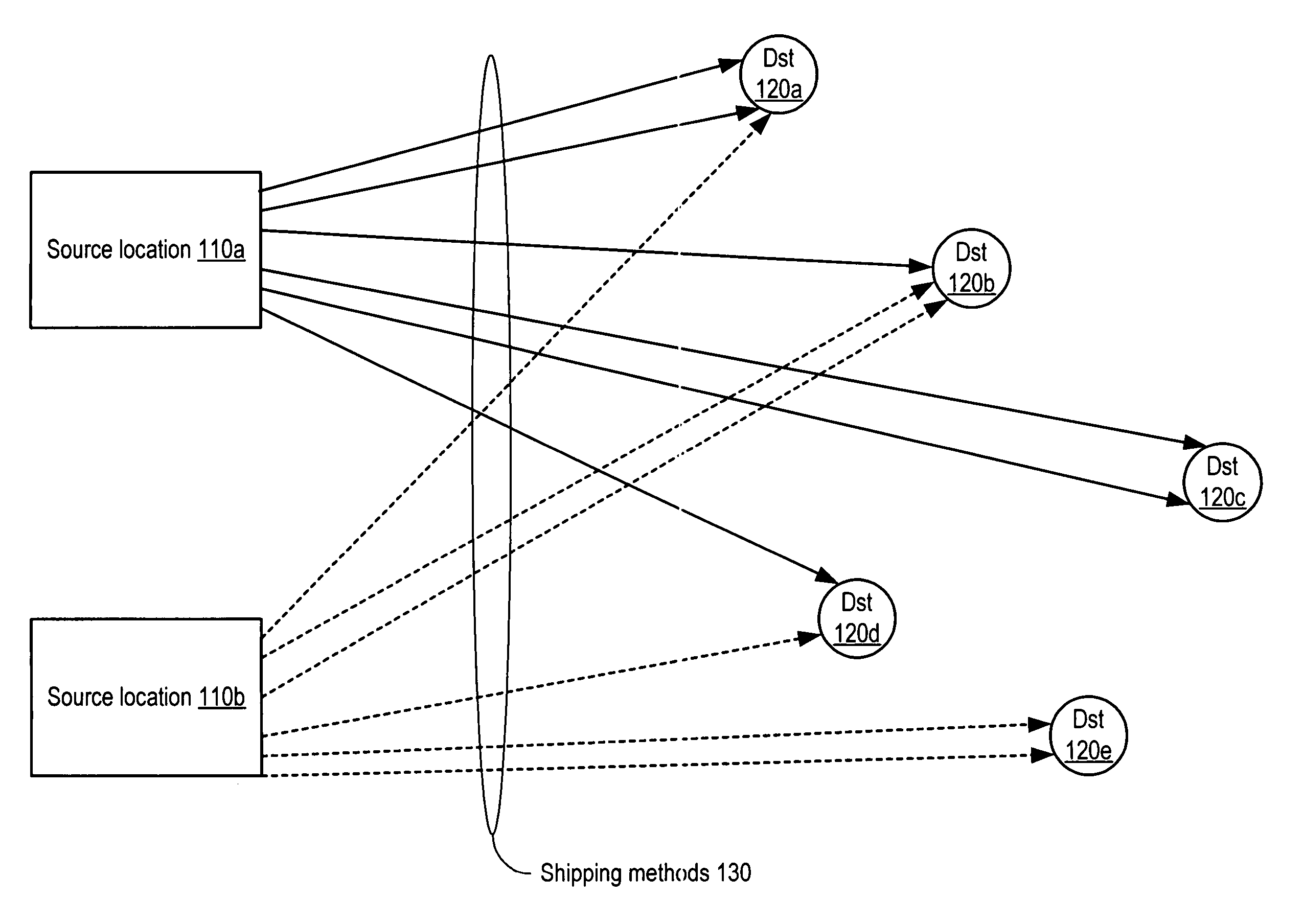
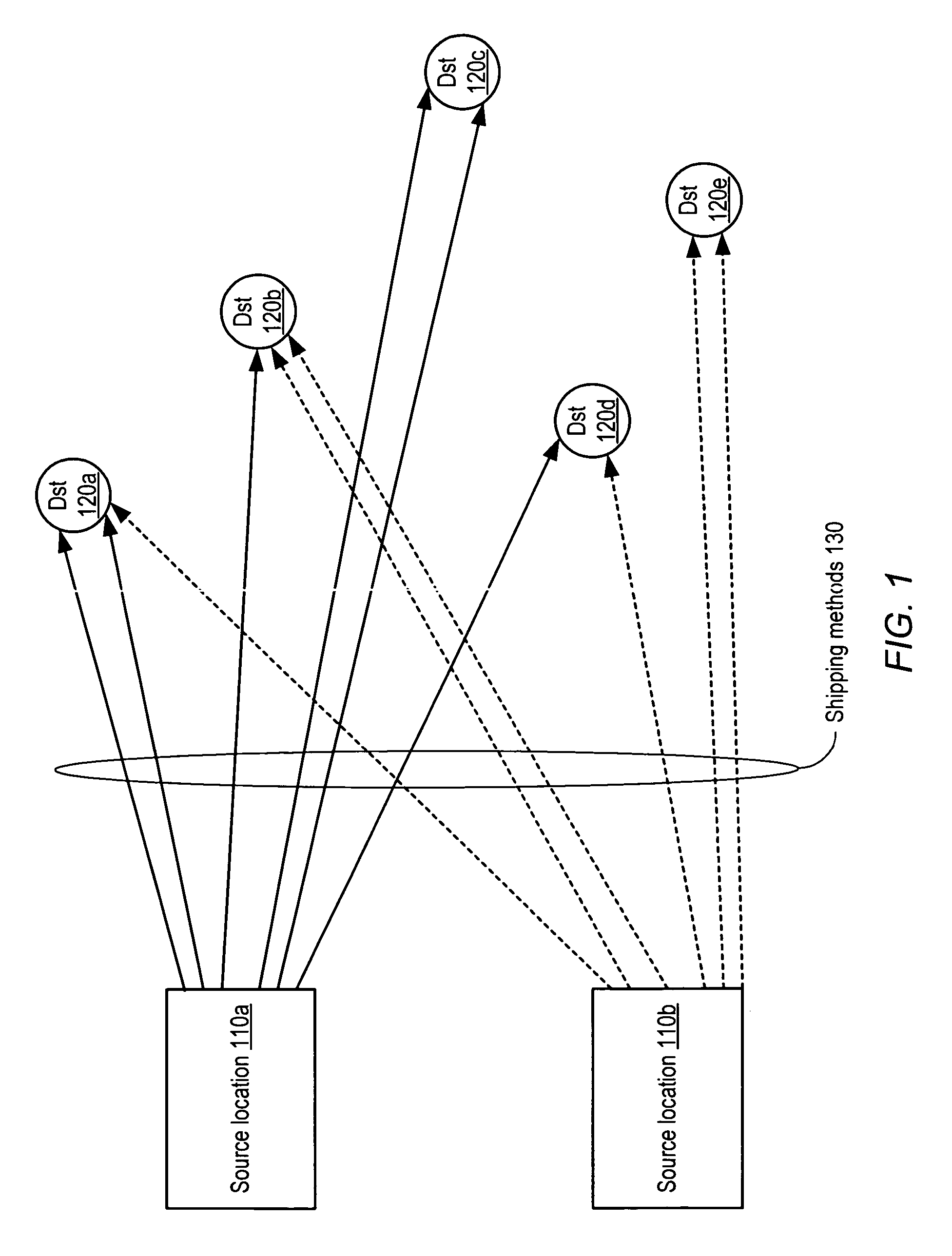
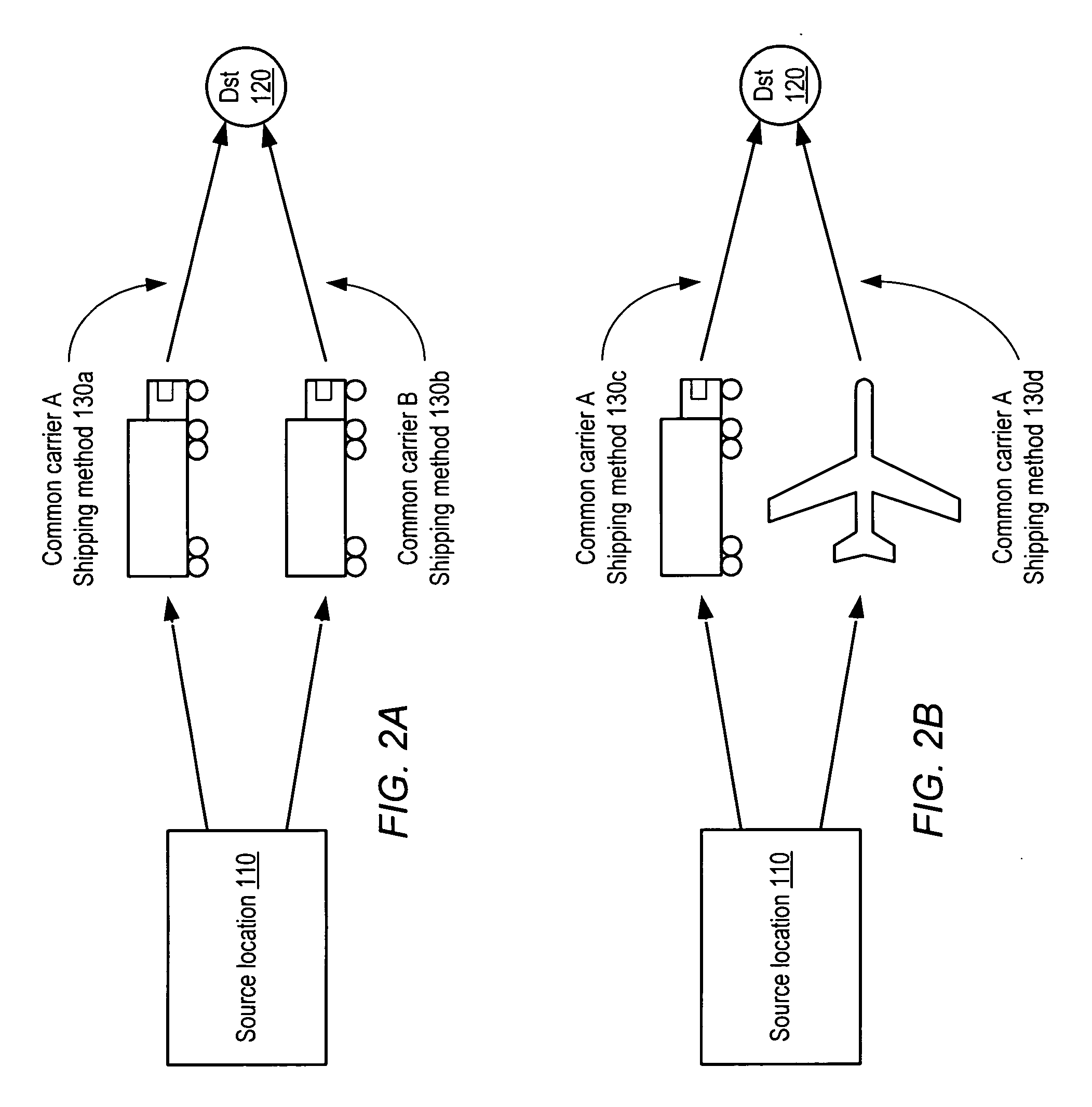
Method and system for transit characteristic prediction
A method and system for transit characteristic prediction. In one embodiment, a method may include determining respective transit latencies from a source location to a number of destination locations, and grouping the destination locations according to a similarity criterion into a number of subsets corresponding to respective geographical regions, where transit characteristics of locations grouped into a geographical region may each satisfy the similarity criterion. The method may further include determining a respective distribution associated with each of the geographical regions, where a given respective distribution correlates a given transit characteristic from the source location to a given geographical region with a respective surety factor, where the respective surety factor includes a cumulative probability that the given transit characteristic will be achieved. The method may also include dynamically updating the respective transit characteristic, the grouping of destination locations into geographical regions and the respective distributions dependent upon collecting empirical transit data.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
Method and system to configure and utilize geographical zones
ActiveUS20060100777A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlGeographical zoneComputer science
A method to define a geographical zone is disclosed. The geographical zone can be utilized to regulate a movable entity and the actions within the geographical zone. The geographical zone can be defined by allowing a user to define and load to a transponder a plurality of waypoints, each waypoint defined by a geographical coordinate and a radius originating from the geographical coordinate. The geographical zone can also be defined by selecting a plurality of coordinates that are loaded to a transponder and mapped on a pixilated image.
Owner:WIRELESSWERX IP LLC
Adapting a vehicle control strategy based on historical data related to a geographical zone
ActiveUS20180170349A1Mitigate such drawbackAccurate predictionHybrid vehiclesRoad vehicles traffic controlEngineeringGeographical zone
A method and system are provided for adapting a vehicle control strategy of an on-road vehicle following a reoccurring fixed route to a predetermined destination, which fixed route extends through at least one geographical zone associated with at least one environmental restriction. When it is determined that the vehicle is approaching the geographical zone, historical data collected from previous passages of one or several vehicles through the zone is accessed, and the vehicle control strategy inside the geographical zone is adapted based on the historical data and the environmental restriction.
Owner:VOLVO BUS
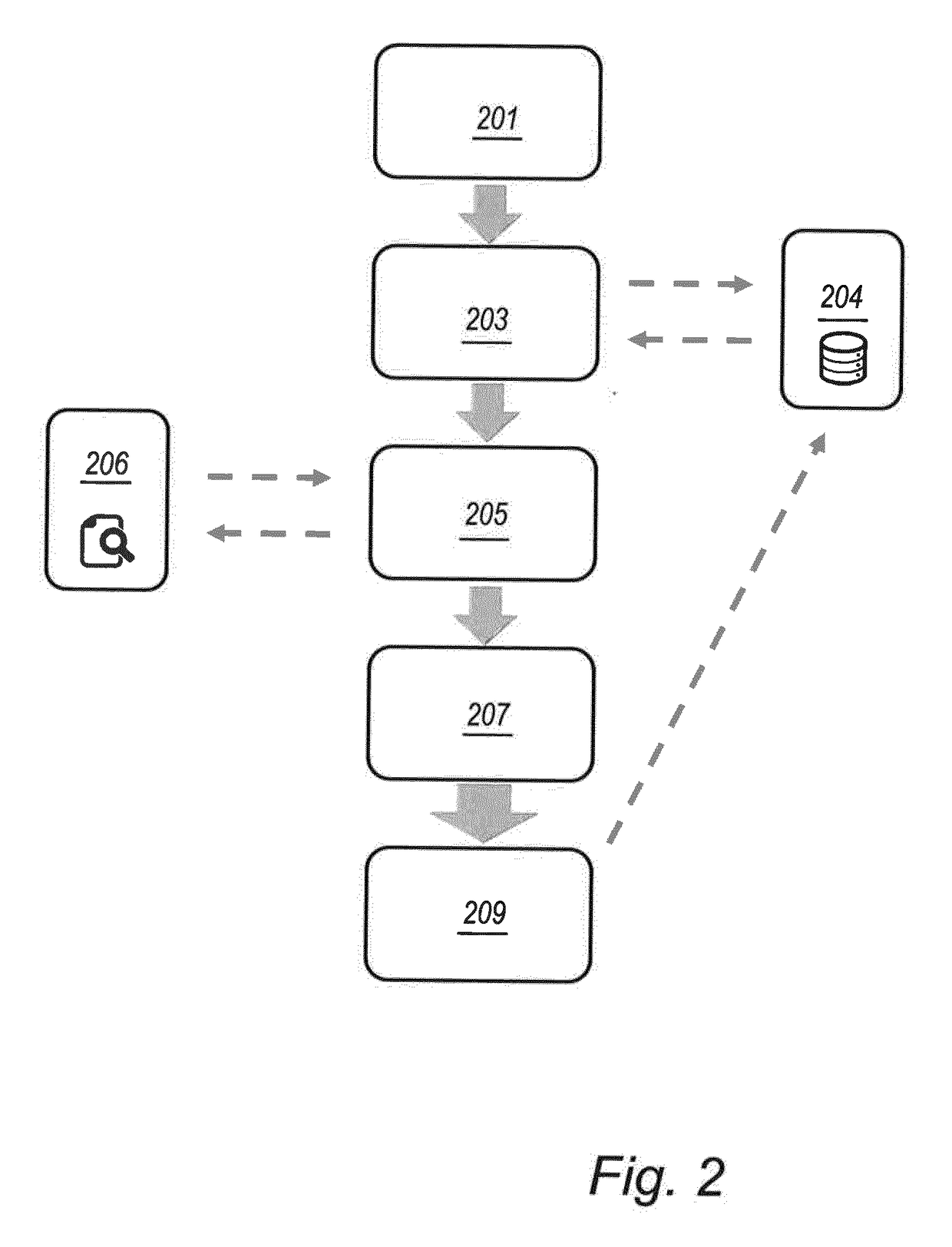
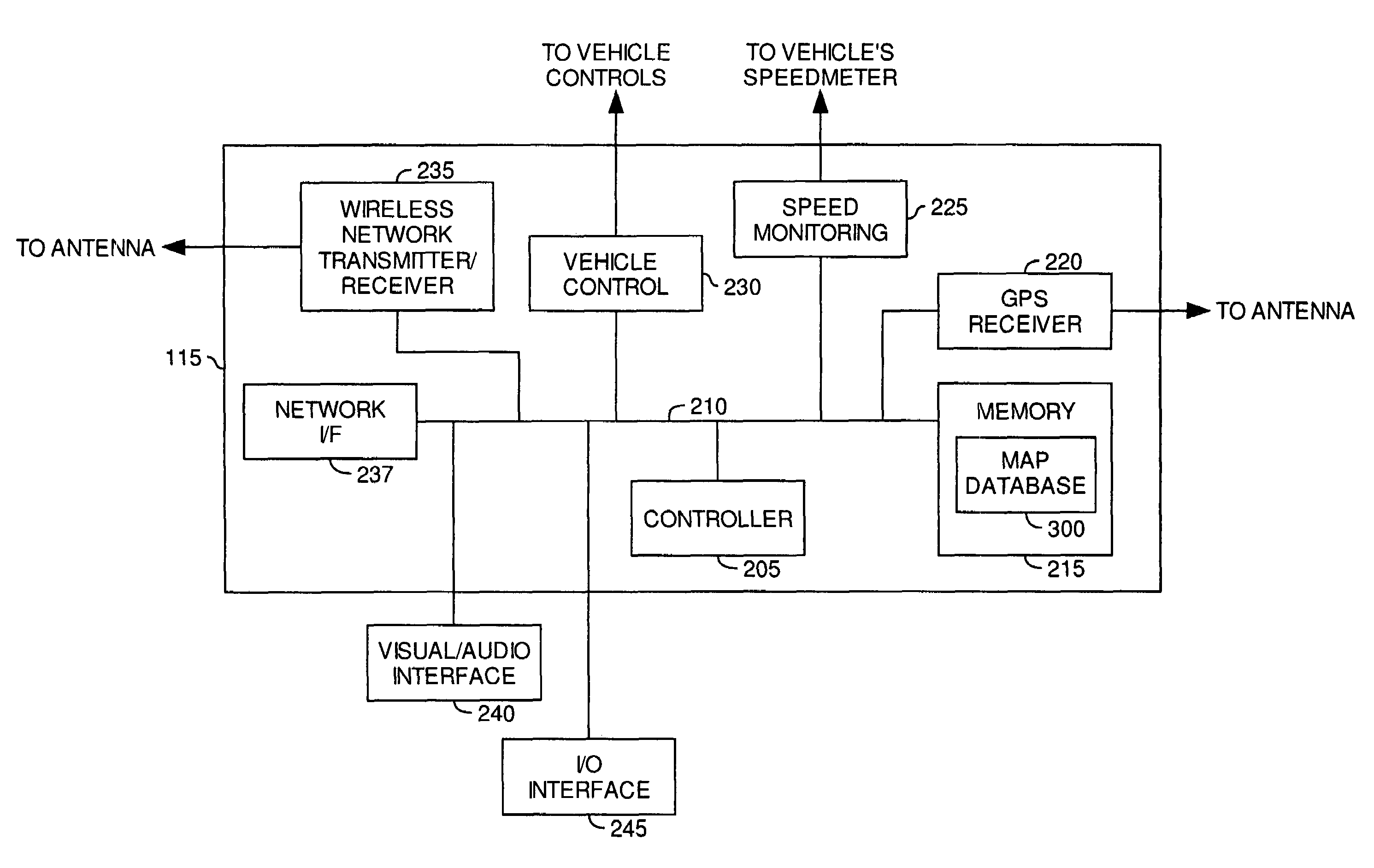
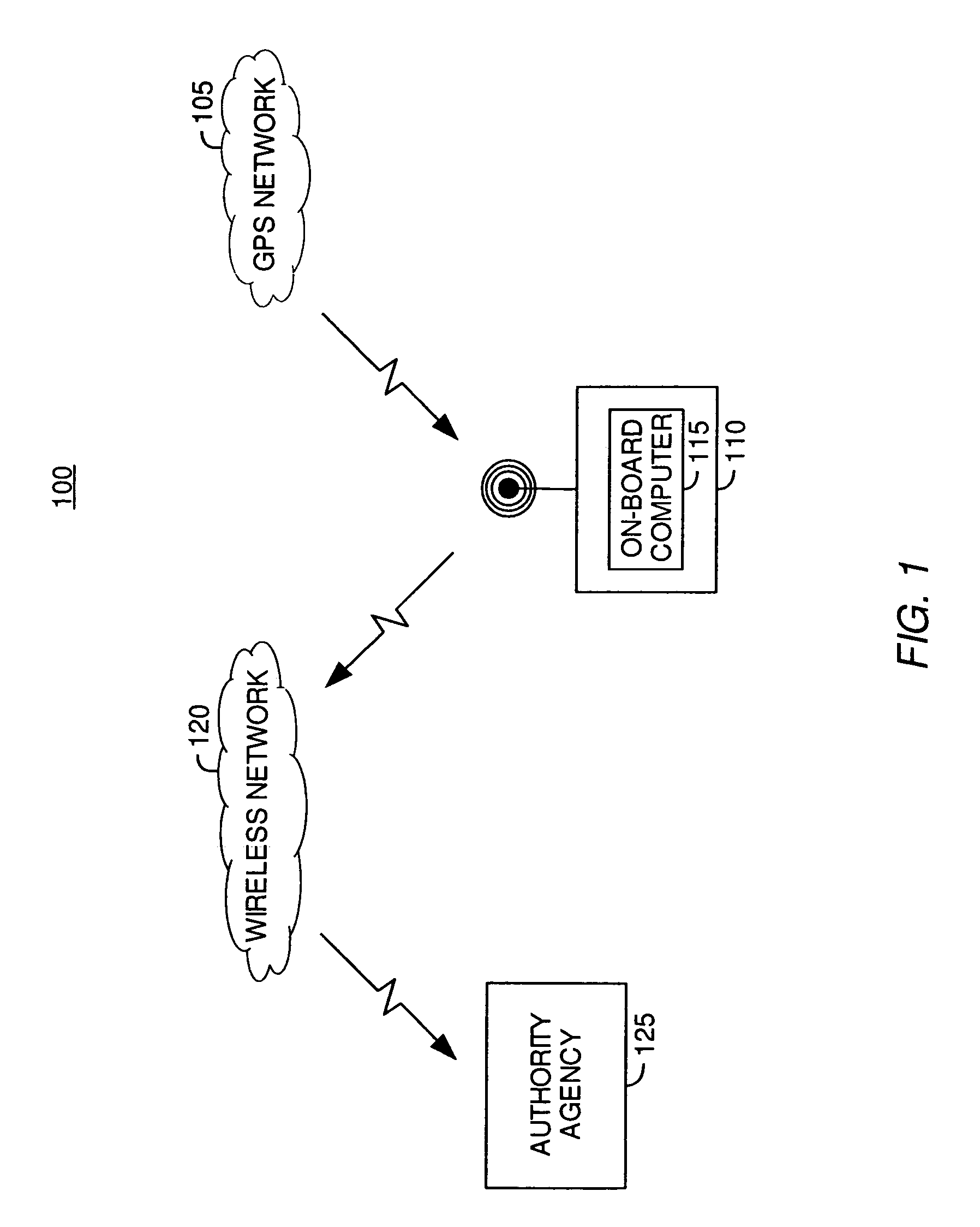
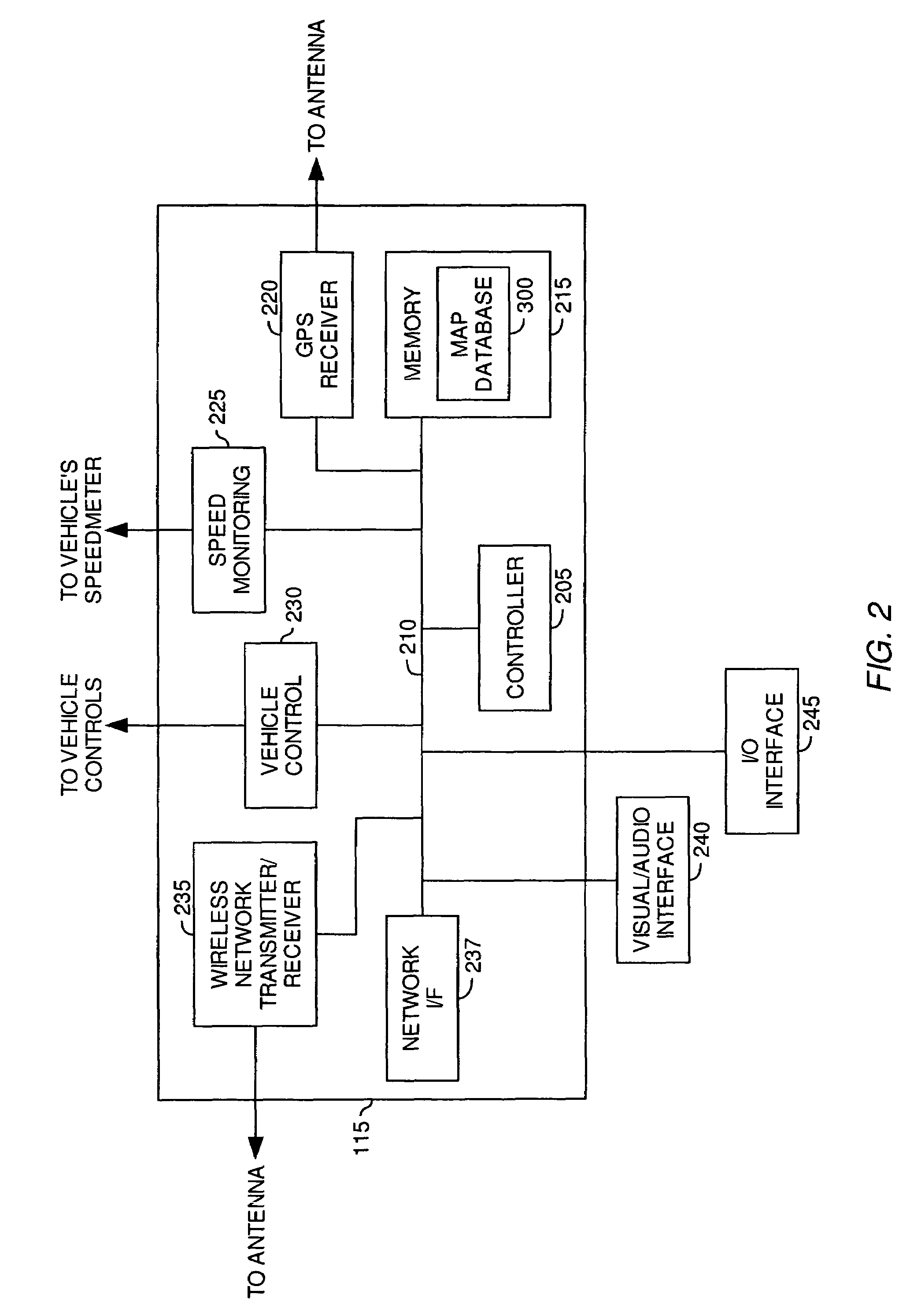
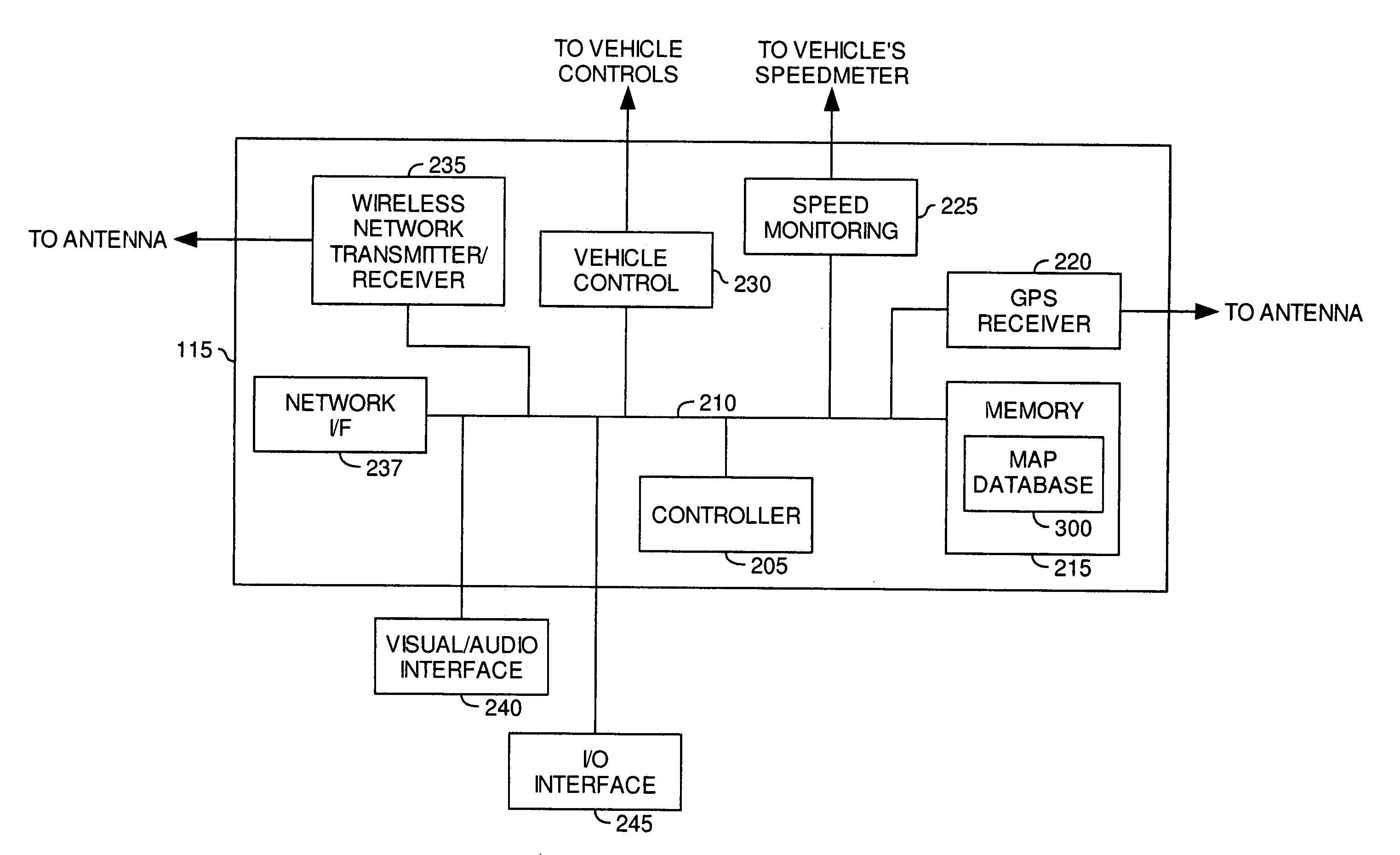
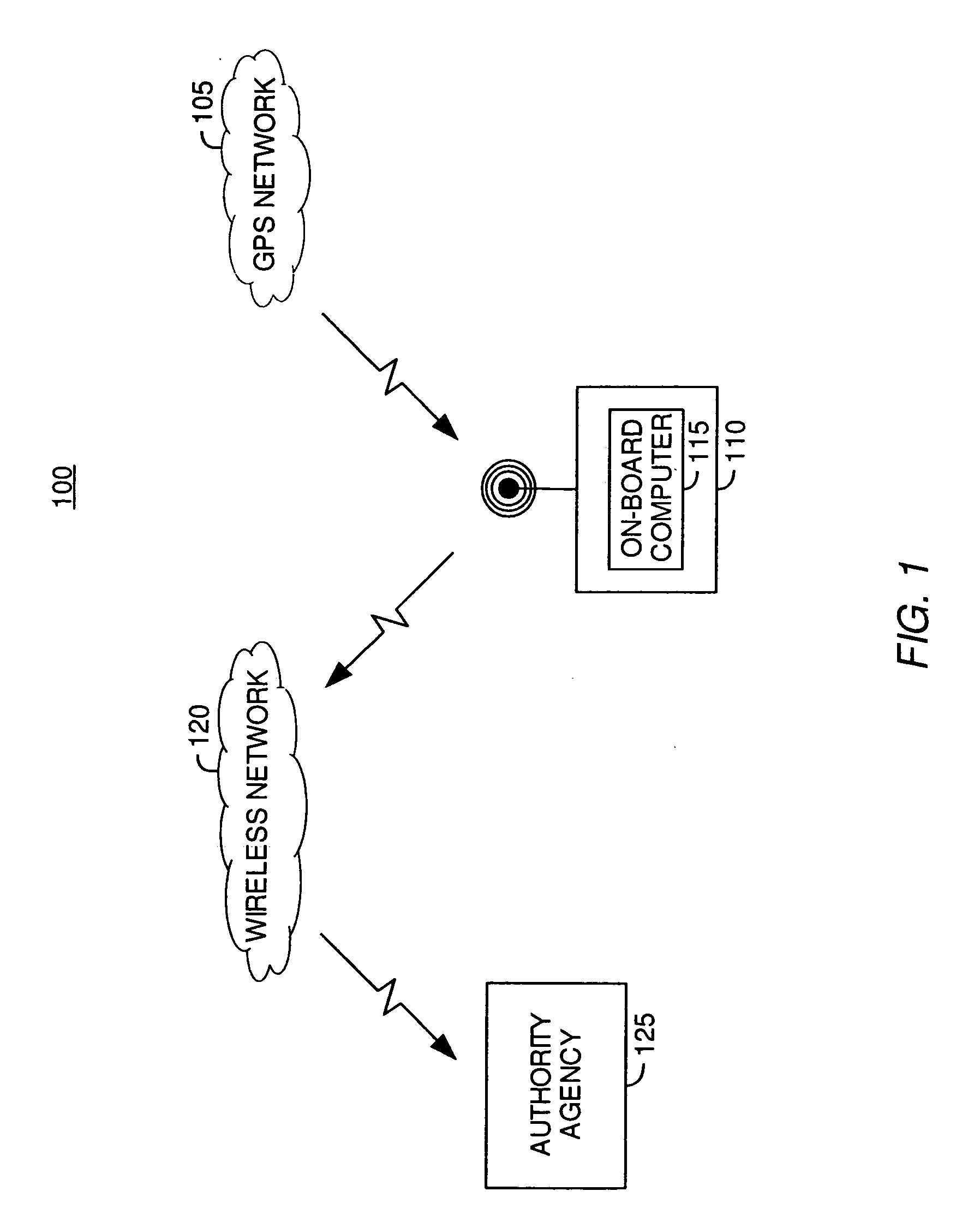
Telematic parametric speed metering system
InactiveUS7375624B2Reduce the possibilityAnalogue computers for vehiclesArrangements for variable traffic instructionsInternal memoryDriver/operator
Embodiments of the present invention provide systems, articles of manufacture and methods for a telematic parametric speed metering system. In one embodiment, a system may determine a vehicle's location and speed. Once the location has been determined, corresponding geographical zone based speed limits and / or other information may be acquired via internal memory or data transmission. The speed of the vehicle may then be compared against the speed limits for the zone. If the vehicle's speed exceeds those speed limits, one or more of a plurality of actions may be performed including (but not limited to) warning the driver via a visual or audio signal, informing an authority agency via data transmission, logging the excessive speeding condition (e.g., time, date, speed, location, driver name, etc).
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Configuring and using multi-dimensional zones
A method to define a three-dimensional geographical zone that is utilized with a movable entity having at least one attached transponder is disclosed. The method comprises allowing a user to enter at least one waypoint, and loading at least one waypoint on at least one transponder. In one or more embodiments, a waypoint is defined by a geographical coordinate and a radius. The geographical coordinate is represented by a latitude value, a longitude value, and an elevation value. And, the radius is represented by a distance magnitude. In some embodiments, the method further comprises regulating the movable entity by monitoring, controlling, and / or visualizing the movement, non-movement, or position of the movable entity. The transponder determines whether the transponder is located inside the three-dimensional geographical zone by obtaining global positioning coordinates, and calculating whether or not the global positioning coordinates are located inside at least one waypoint.
Owner:WIRELESSWERX IP LLC
Laundry Article
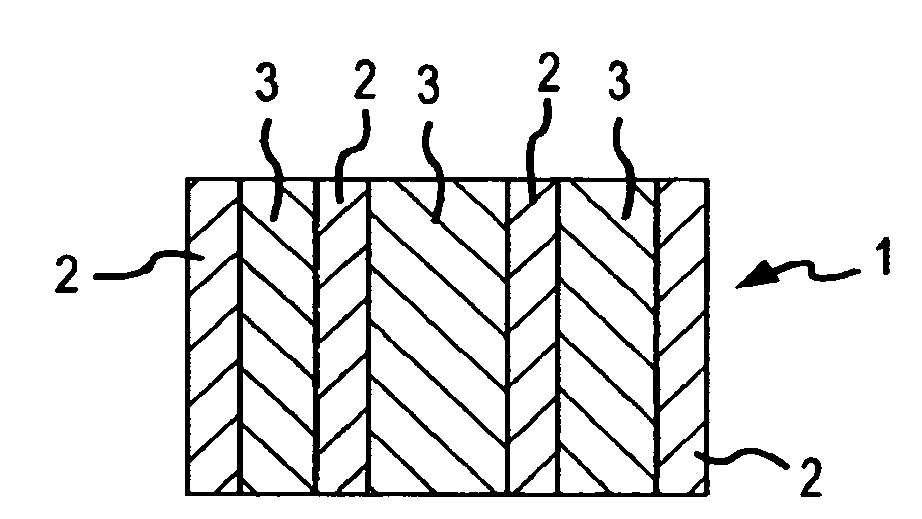
InactiveUS20090144913A1Unique benefit and flexibility in handlingEasy to cleanSoftening compositionsDetergent materialsFiberEngineering
A laundry article of manufacture is described that may be used to both wash and condition fabrics when used sequentially first in the washer and then carried along with the wet fabrics into the dryer. The laundry article preferably comprises at least one detergent and at least one softener composition each solidified into geographical zones onto a nonwoven substrate. The optimized article comprises a nonwoven substrate with sidedness, and although the softener composition is solidified within the fibers of the lofted side of the substrate, the softener is unexpectedly found to subsequently express out from the flat side of the substrate while in the heated clothes dryer.
Owner:DIAL CORPORATION
Positioning system
ActiveUS20140365488A1Good delayGood estimateDigital data processing detailsPosition fixationGeographical zoneComputer science
There is disclosed a method of managing a database of positioning data, the positioning data including electromagnetic signal source data for use by a positioning system, and the method comprising: receiving signal data relating to signals received from a plurality of electromagnetic signal sources; associating an appropriate one of a plurality of zone identifiers with each of the electromagnetic signal sources, each zone identifier being associated with a respective geographical zone; selecting a subset of the plurality of electromagnetic signal sources in dependence on their associated zone identifiers; processing the signal data relating to the subset of the plurality of electromagnetic signal sources to compute position estimates of the electromagnetic signal sources; and updating the database of electromagnetic signal source data in dependence on the computed position estimates.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Emergency control in a multi-dimensional space
ActiveUS20090131012A1Control with pedestrian guidance indicatorTelephonic communicationMobile deviceGeographical zone
A geographical zone, which can be multi-dimensional, such as in three dimensions, can be utilized to regulate the location of a movable user within the geographical zone. A mobile device associated with a user located in a specific area of a geographical zone is in communication at least one node, which is, in turn, in communication with at least one control center. Detailed local information from the location nodes is downloaded. The nodes communicate with each other wirelessly via radio frequency (RF) using Bluetooth™ protocol. Mobile devices interact with location nodes that are in communication range. A messaging system is used to send emergency and security communications to users associated with mobile devices in particular locations.
Owner:WIRELESSWERX IP LLC
Method and System for Initiating and Handling an Emergency Call Utilizing Geographical Zones
A method and system of making an emergency voice call is disclosed. Location data is received from a positioning device. A location area identifier is determined. The location area identifier corresponds to a geographical area encompassing a geographical location being represented by the location data. A voice call destination number is identified. The voice call destination number is associated with the location area identifier. The voice call destination number is utilized in order to communicate with a public safety answering point.
Owner:WIRELESSWERX IP LLC
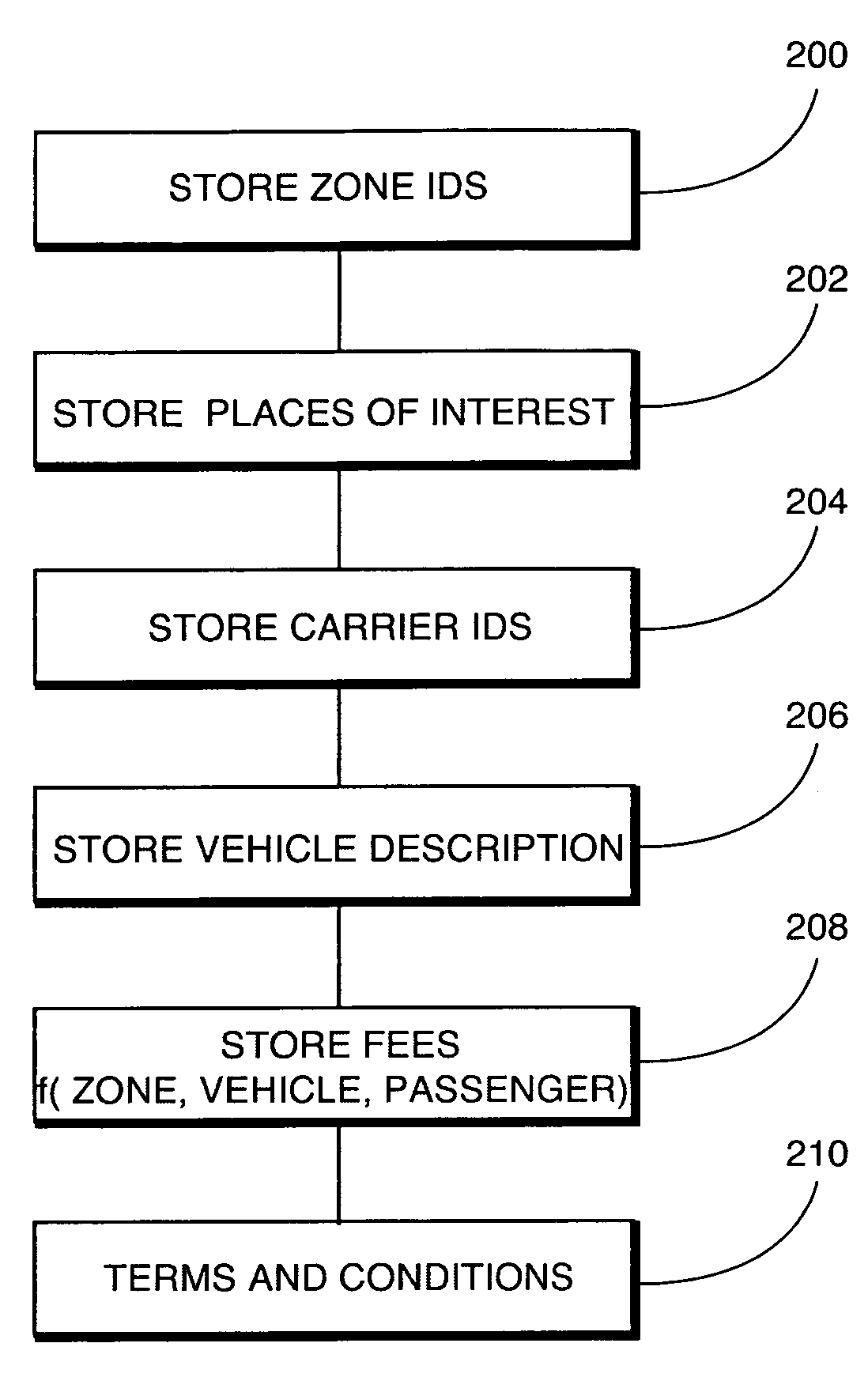
System and method for reserving ground transportation
An inventory of ground transportation vehicles is stored at a server. The inventory includes information about each ground transportation vehicle including fees for travel in a respective ground transportation vehicle as a function of geographical zones to be traveled. A request is made by an end user from a remote computer in communication with the server for ground transportation vehicle. The request includes an origination geographical zone and destination geographical zone. The server compares the request to the inventory and determines those ground transportation vehicles that travel from the origination geographical zone to the destination geographical zone and forwards those ground transportation vehicles and associated fees for traveling between the origination geographical zone and destination geographical zone to the remote computer for display.
Owner:TRAVELTRANZ
Method of modified facies proportions upon history matching of a geological model
A method of modifying a geological model representative of an underground reservoir is disclosed which respects average proportions of the lithologic facies imposed by a production data calibration process which has application to petroleum reservoir development. A geographical zone Z is defined within the geological model and an average proportion in zone Z allowing the production data to be calibrated is determined for k facies, with an optimization process. The proportions of these facies are modified using a block indicator cokriging method constrained by the average proportions to be respected. A new geological model constrained by the modified facies proportions is simulated and the development of the underground medium is optimized by the simulated model.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Method and system to monitor and control devices utilizing wireless media
ActiveUS7881733B2Solve the lack of resolutionTransmission systemsAutomatic exchangesLongitudeEngineering
A method and system of selectively communicating with one or more devices within pre-defined geographical zones is disclosed. A plurality of geographical zones is defined, each zone being defined by latitude and longitude attributes. A plurality of devices is associated with each geographical zone with which a portable device can communicate, the portable device having data representative of the plurality of geographical zones. The portable device also has a ground positioning unit receiver to obtain geographical coordinates of the portable device. If the portable device determines that its location is within one of the plurality of geographical zones, the portable device communicates with the devices in associated with the geographical zone.
Owner:WIRELESSWERX IP LLC
Method of satellite communication with flexible capacity distribution based on beam hopping and on a fractional reuse scheme
ActiveUS20170181160A1Increase capacityNetwork topologiesRadio transmissionBeam hoppingGeographical zone
A method, and associated equipment, for dynamically allocating resources in a satellite network comprising at least one satellite configured to form a plurality of satellite beams and terminals, comprises the steps of: clustering the beams into groups of beams, allocating frequency resources to each of the groups of beams, determining geographical zones in which these frequency resources can be used simultaneously, determining a hop frame comprising first timeslots, in which the frequency resources are allocated to the whole set of terminals of one of the beams of the group, and second timeslots, in which the frequency resources are allocated to a subset of terminals of at least one beam of the group, identifying the subset of terminals and allocating to the terminals of the frequency resources, and uploading of information relating to the overall loading of each of the beams.
Owner:THALES SA
Telematic parametric speed metering system
InactiveUS20070236342A1Reduce the possibilityAnalogue computers for vehiclesArrangements for variable traffic instructionsInternal memoryDriver/operator
Embodiments of the present invention provide systems, articles of manufacture and methods for a telematic parametric speed metering system. In one embodiment, a system may determine a vehicle's location and speed. Once the location has been determined, corresponding geographical zone based speed limits and / or other information may be acquired via internal memory or data transmission. The speed of the vehicle may then be compared against the speed limits for the zone. If the vehicle's speed exceeds those speed limits, one or more of a plurality of actions may be performed including (but not limited to) warning the driver via a visual or audio signal, informing an authority agency via data transmission, logging the excessive speeding condition (e.g., time, date, speed, location, driver name, etc).
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method and system for providing a home data index model
InactiveUS20130103459A1Market predictionsProduct appraisalModeling perspectiveSignificant difference
The present invention builds Home Data Index (HDI) models. One driving force behind this HDI initiative is that no one model or measure can truly capture the widely dynamic movement of home prices. Even within a small geographical area, such as a ZIP code, there is significant variation in property sale types, sale frequencies and sale values. To better describe these variations, the present invention presents a suite of paired sales and price per square foot index models built around an array of property transaction characteristics. These HDI models expand on the usage and understanding of traditional home price indices (HPIs) by implementing a multidimensional index comprised of four main dimensions: geography; time frames; value range; and property sales type. Several layers exist within each dimension, allowing for more than 300 different index model perspectives for a given property address. For each permutation among the layers of the four main dimensions, a model is constructed with an associated confidence score that reflects the statistical relevance of each estimate.
Owner:CLEARCAPITAL COM INC
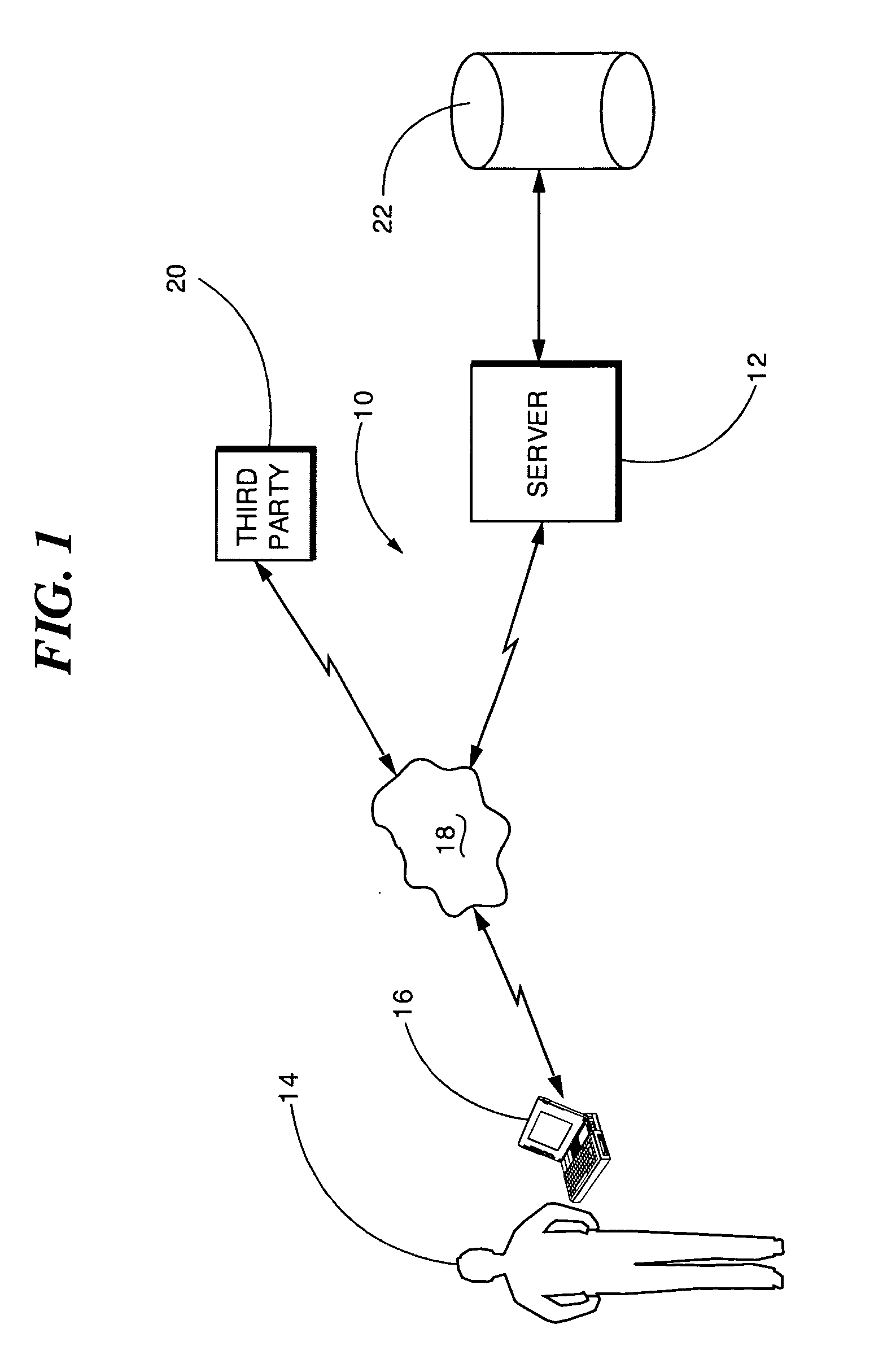
Methods For Advertising
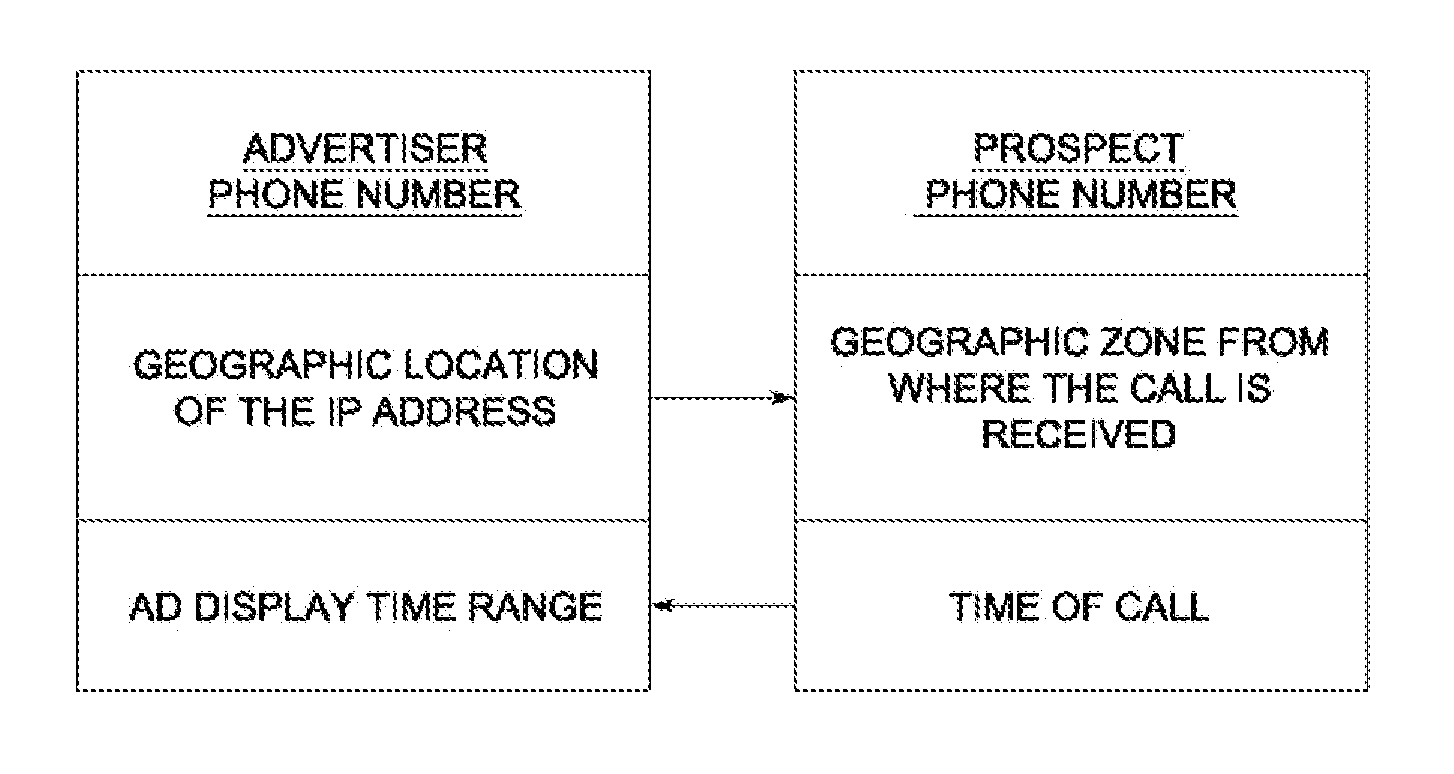
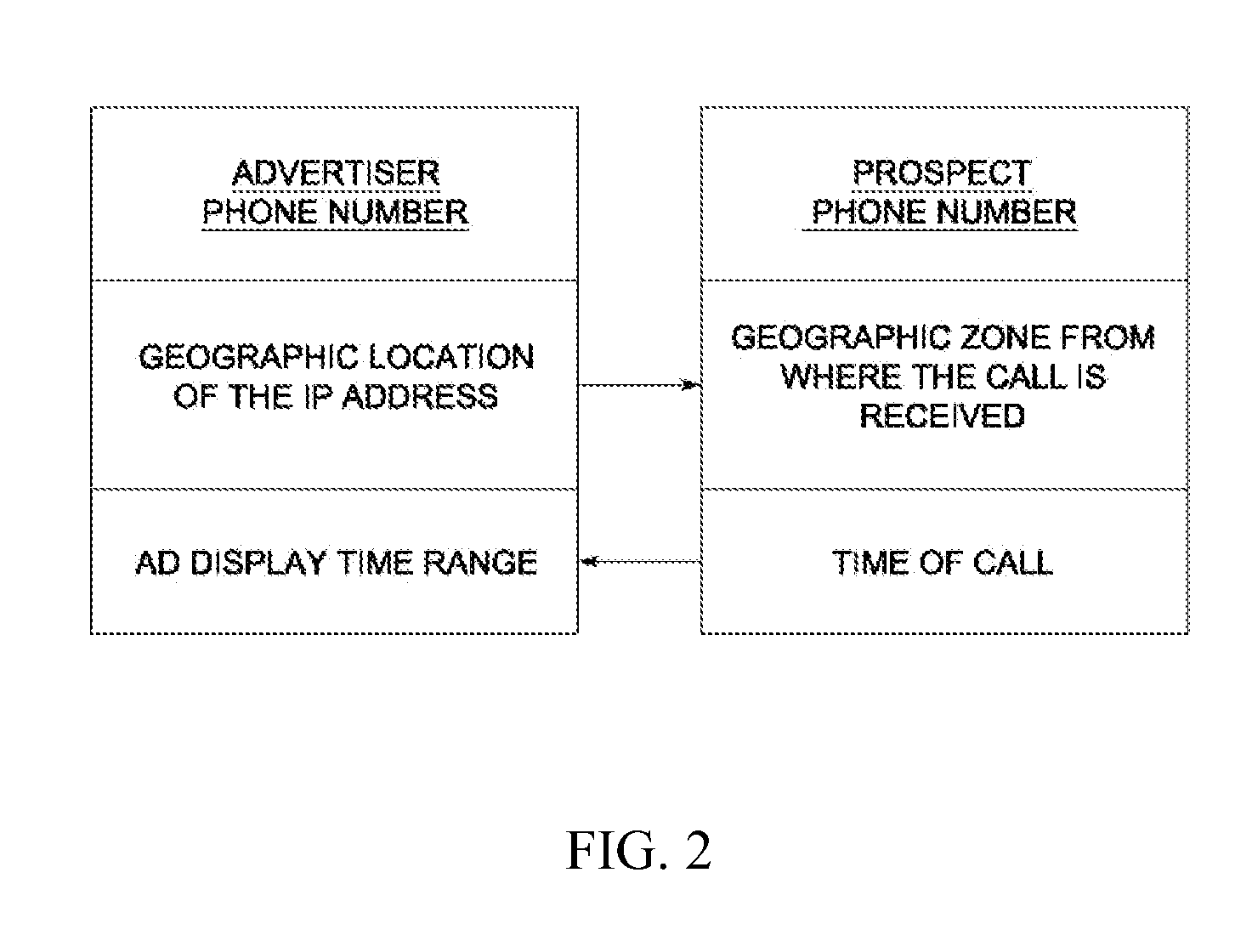
A web conversion method based on phone calls is disclosed. Some embodiments comprise distributing a multiplicity of ads across a multiplicity of online media channels, displaying a unique advertiser phone number on each ad for a limited time every time a prospect visits a webpage hosting the ad, determining that the prospect called the advertiser phone number within the limited time, determining that the geographical zone of the prospect at the time of the call encompasses the geographical location of the IP address at where the unique phone number is displayed, and charging an advertiser for the ad that displayed the advertiser phone number.
Owner:BIONIC CLICK
Access control of mobile equipment to an IP communication network with dynamic modification of the access policies
InactiveUS20070036110A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesCommunication interfaceGeographical zone
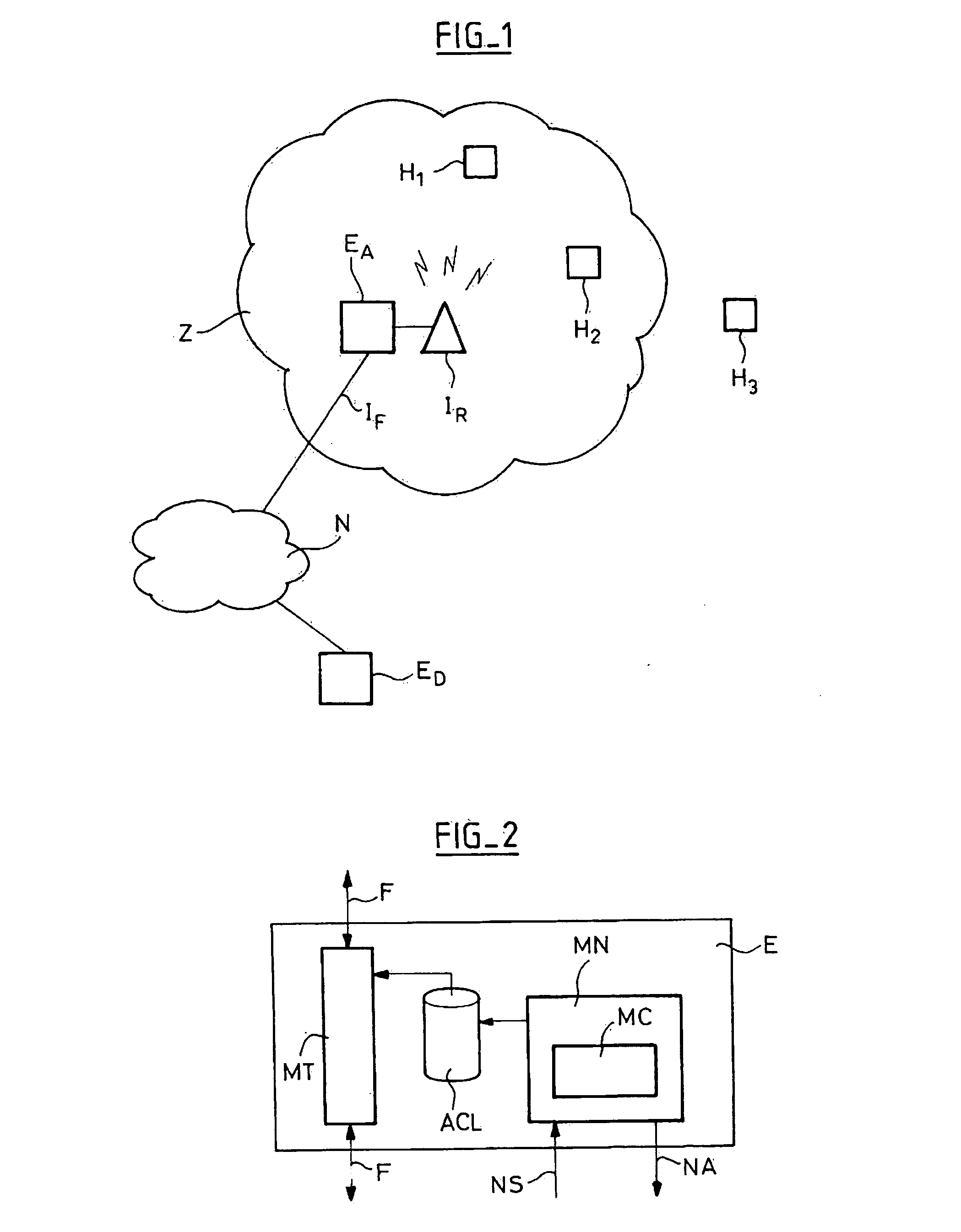
Access equipment (EA) to a communication network (N), equipped with a radio-communication interface (IR) capable of transmitting packets to mobile hosts (H1, H2, H3) located in a geographical zone (Z) linked to the interface, negotiation means intended to set up an exchange of data packets with a host of this zone, requesting access to the network, and transmission means to allow a data flow between one or multiple remote equipments (ED) situated in the communication network and the hosts recorded on the list of authorized mobile hosts, wherein the transmission means do not transmit any data packets to or from hosts not recorded on the list. This equipment is characterized by the fact that the negotiation means comprise control means intended to authenticate the host on the basis of the exchange of data packets and to modify the list in function of this authentication.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
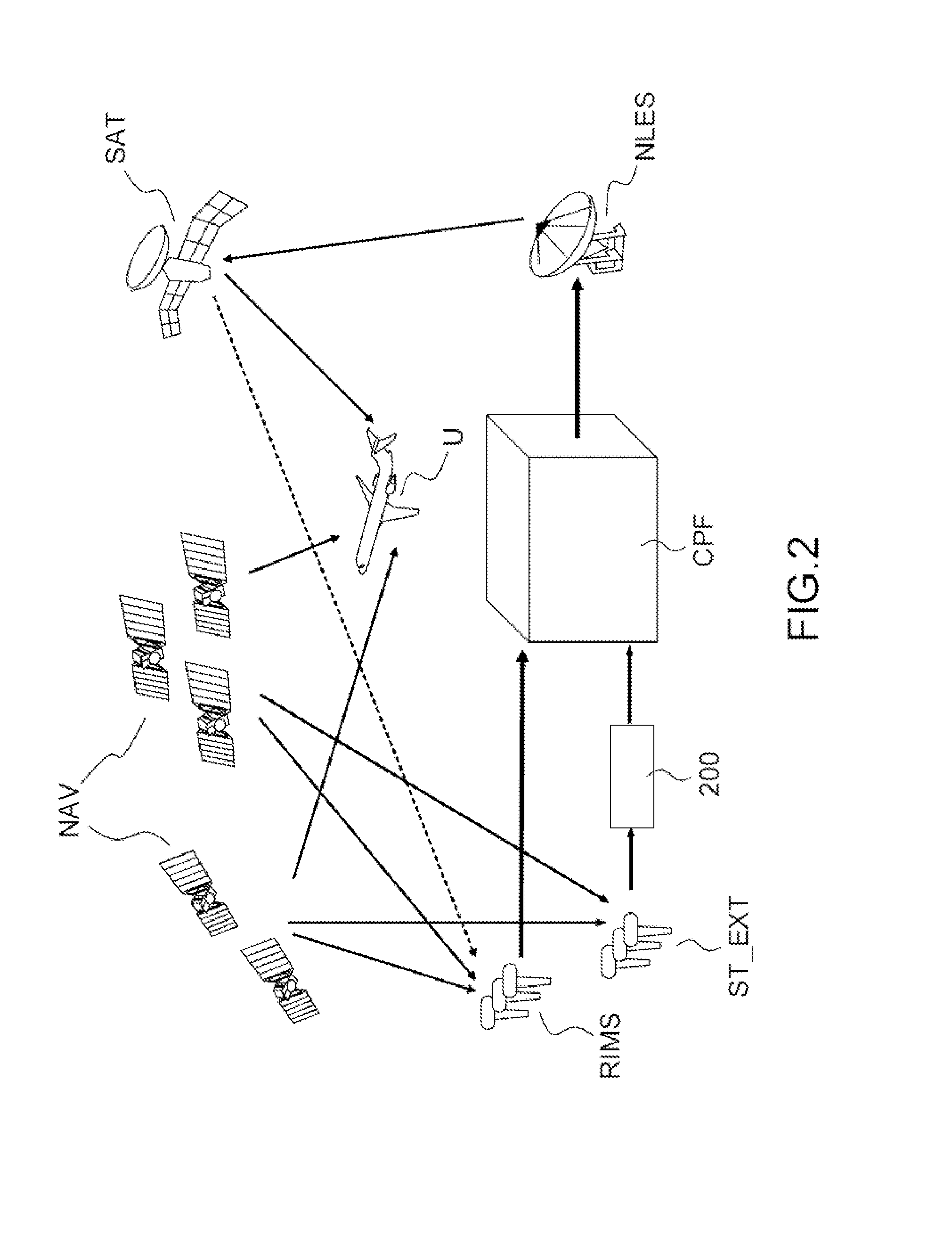
Method of monitoring the integrity of radio-navigation stations in a satellite based augmentation system
ActiveUS20140035778A1Minimizes probabilityImprove usabilitySatellite radio beaconingVisibilityRadio navigation
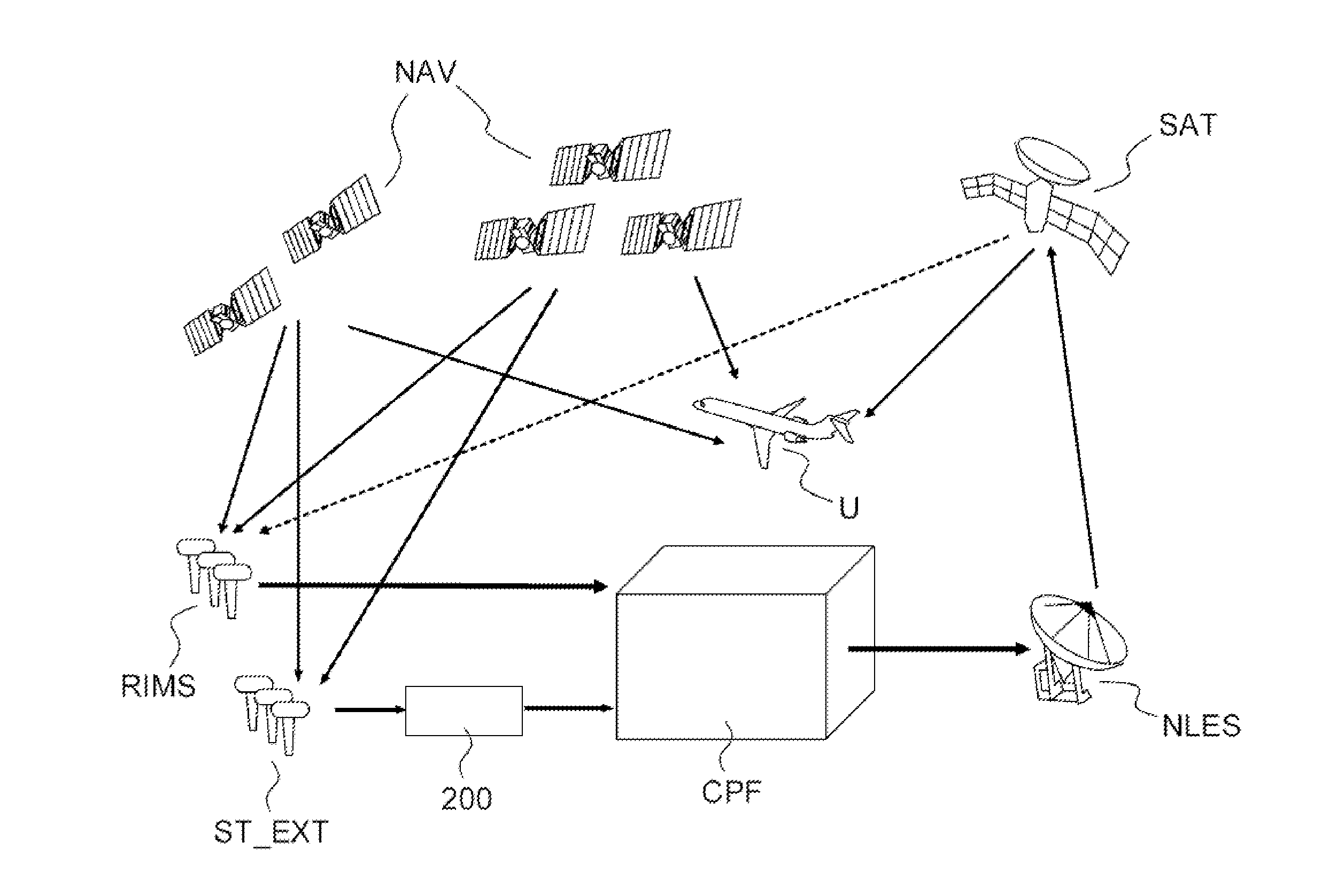
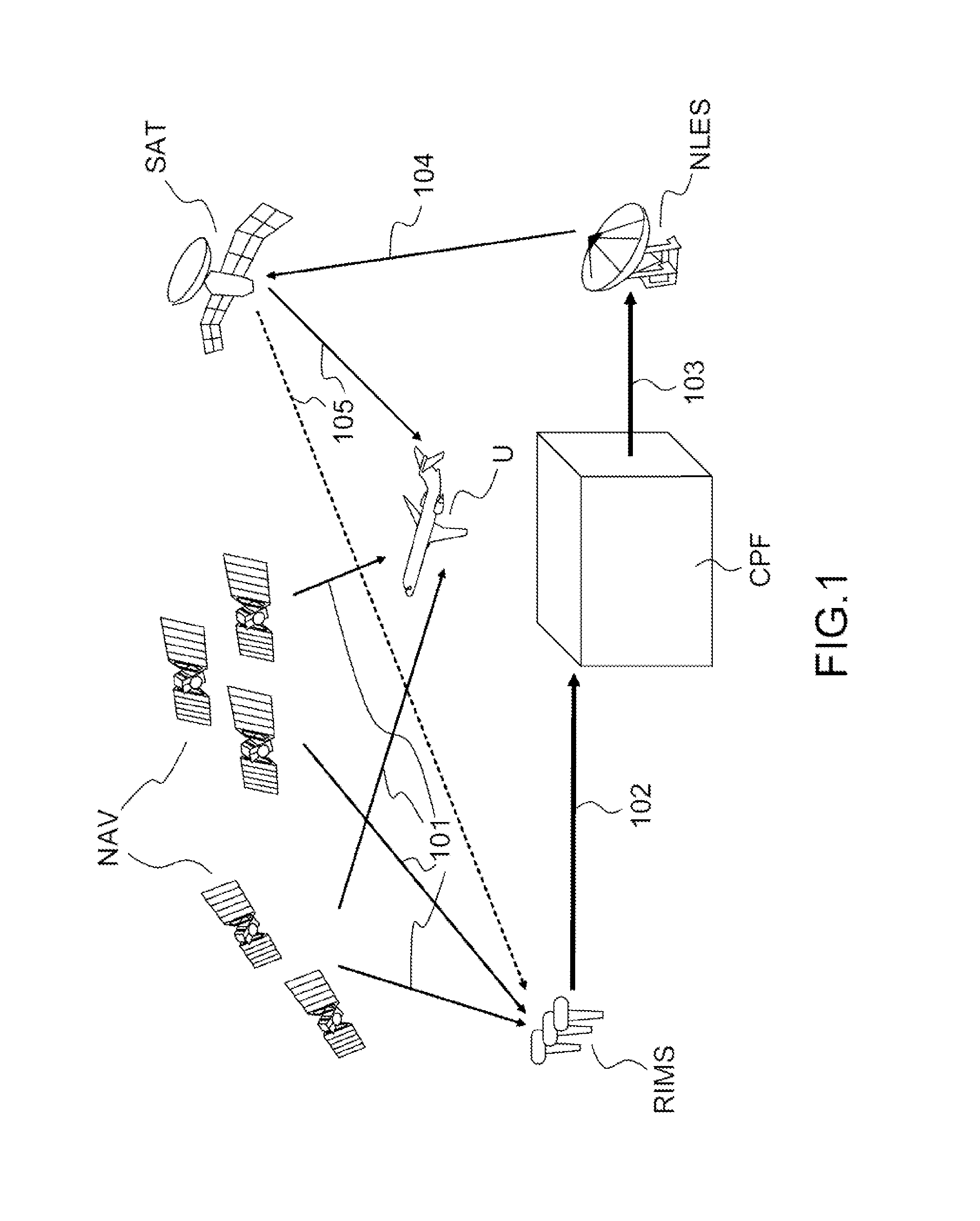
A method of monitoring the integrity of stations for observing radio-navigation signals in a satellite based augmentation system SBAS comprises: defining a geographical zone comprising a plurality of observation stations, calculating, for each observation station of the said zone and for each line of sight between the said station and a satellite, the discrepancy between the theoretical pseudo-distance D and the measured pseudo-distance D′, calculating the average m of the said discrepancies D-D′ over the said zone for at least one satellite in visibility of the said zone, validating the integrity of at least one observation station of the said zone if the said discrepancy, for the said station and for at least one line of sight between the said station and a satellite, is less than or equal to the said average that is multiplied by a predetermined exclusion threshold, and excluding this observation station in the converse case.
Owner:THALES SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com