Patents
Literature
1710 results about "Location area" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
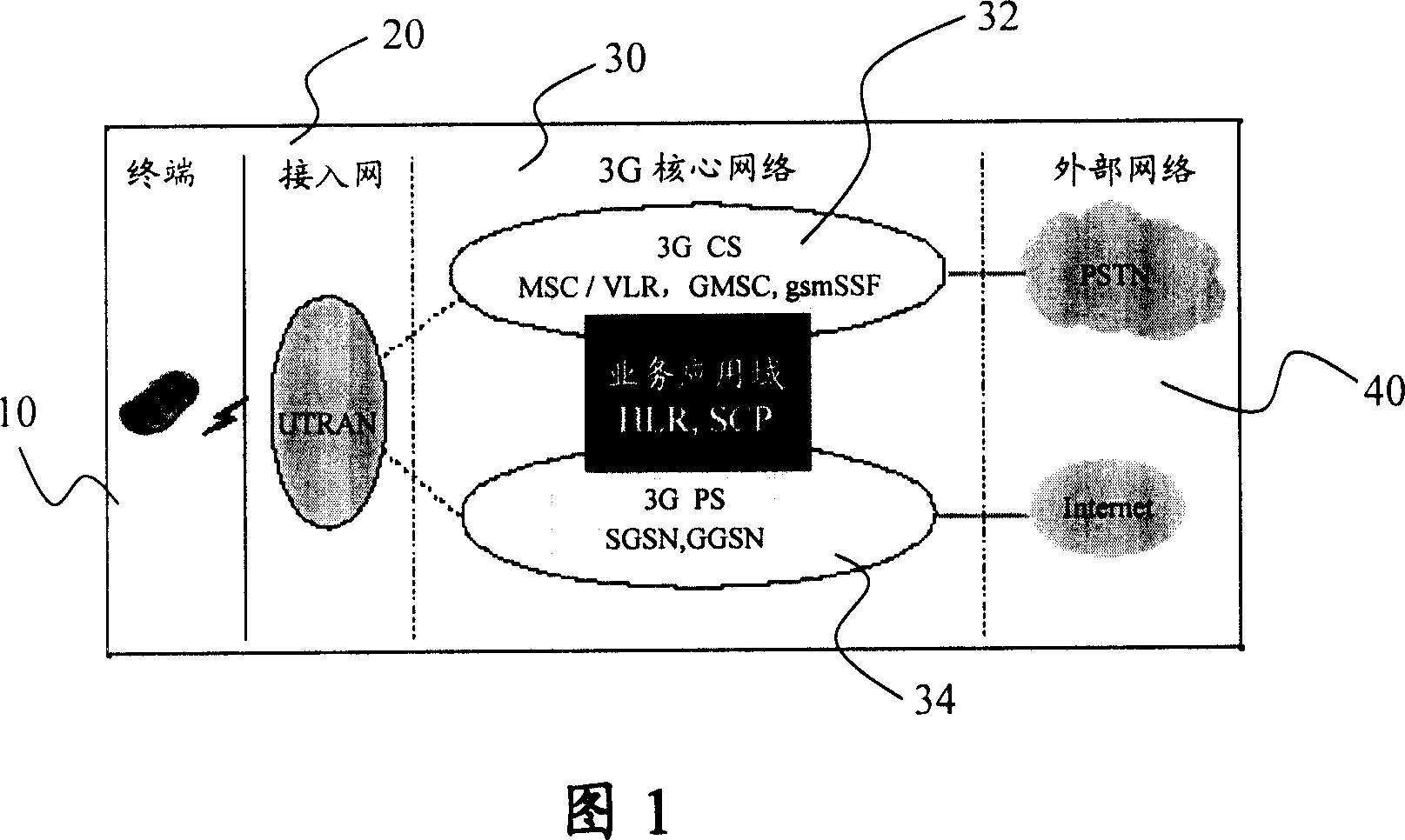
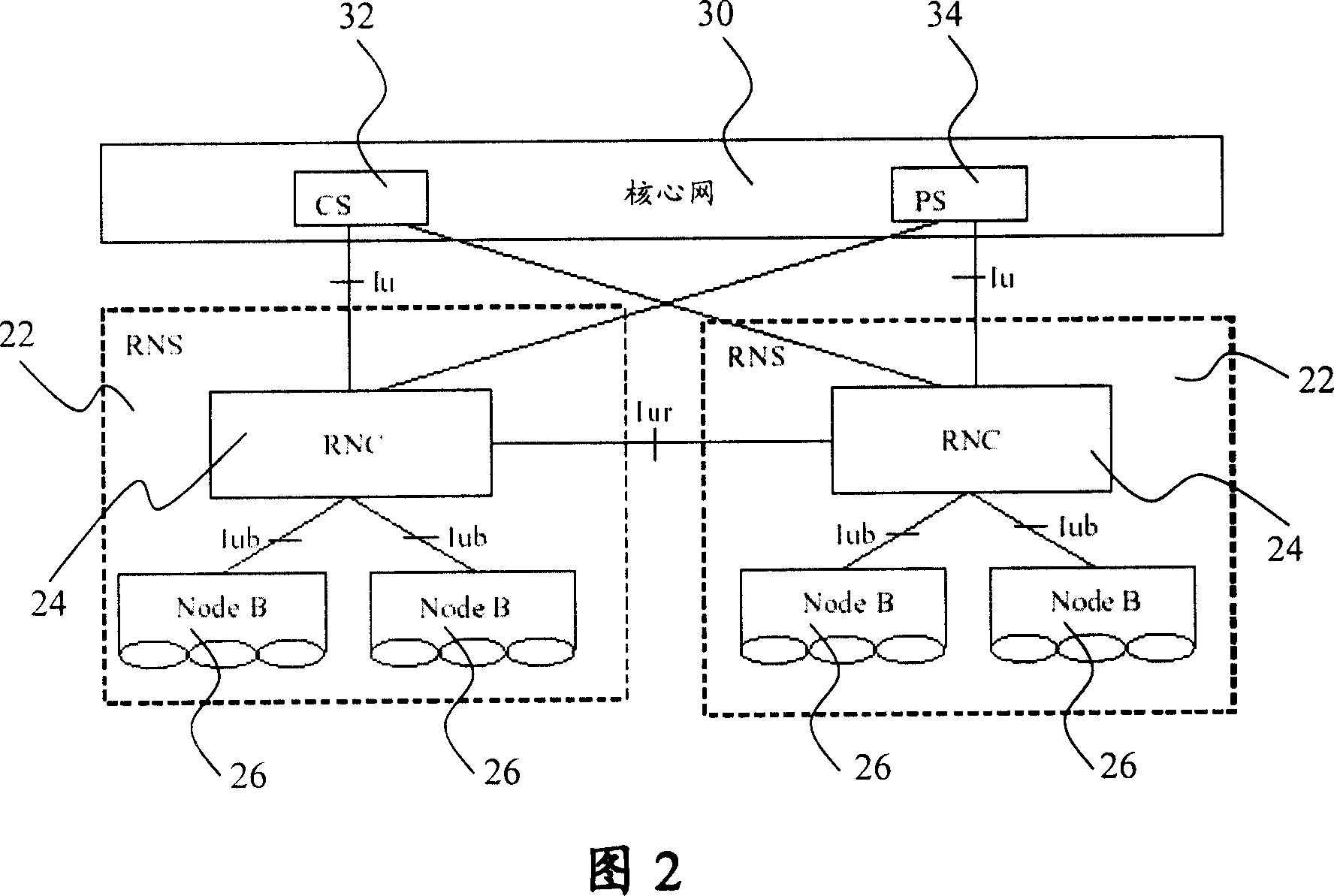
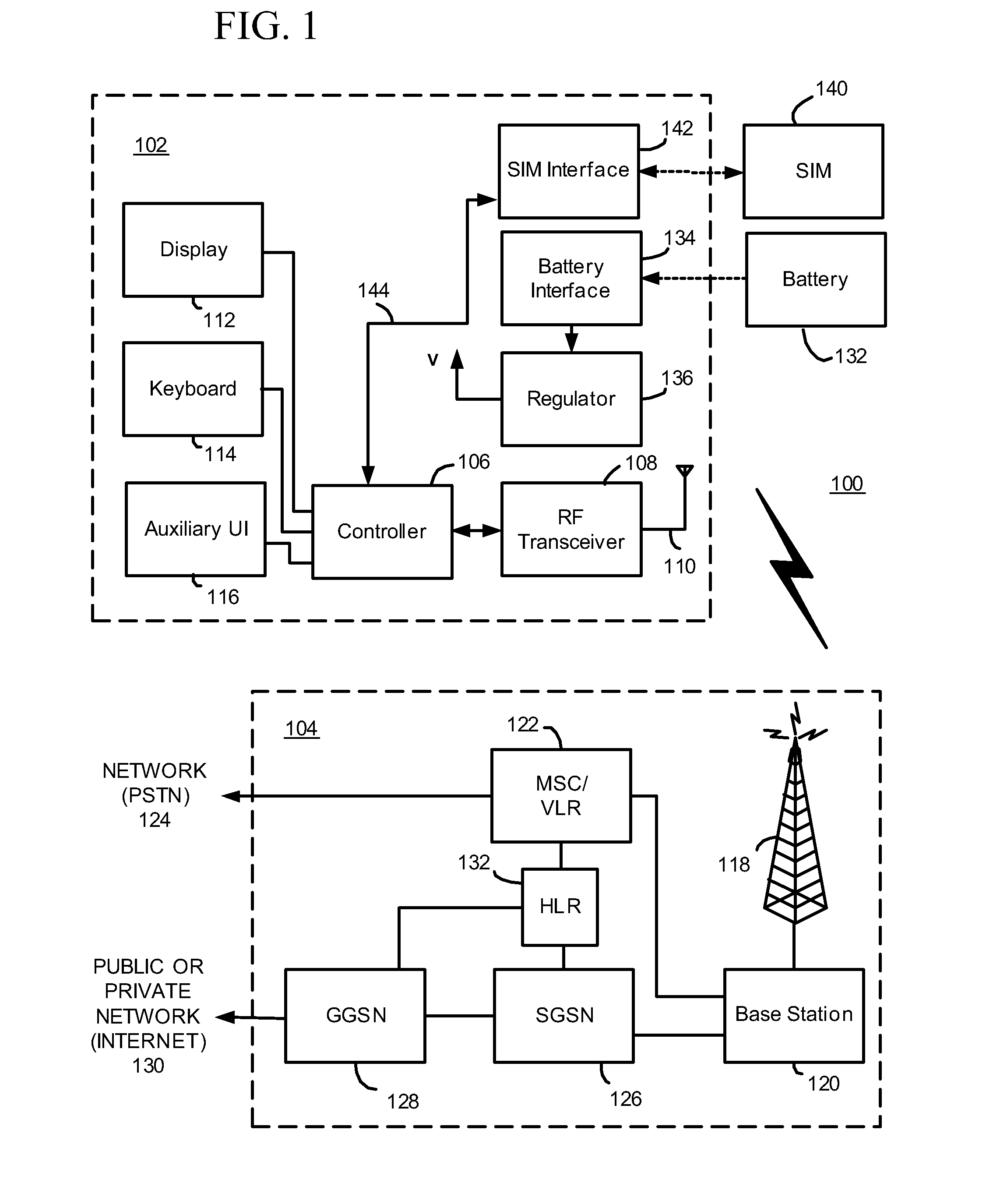
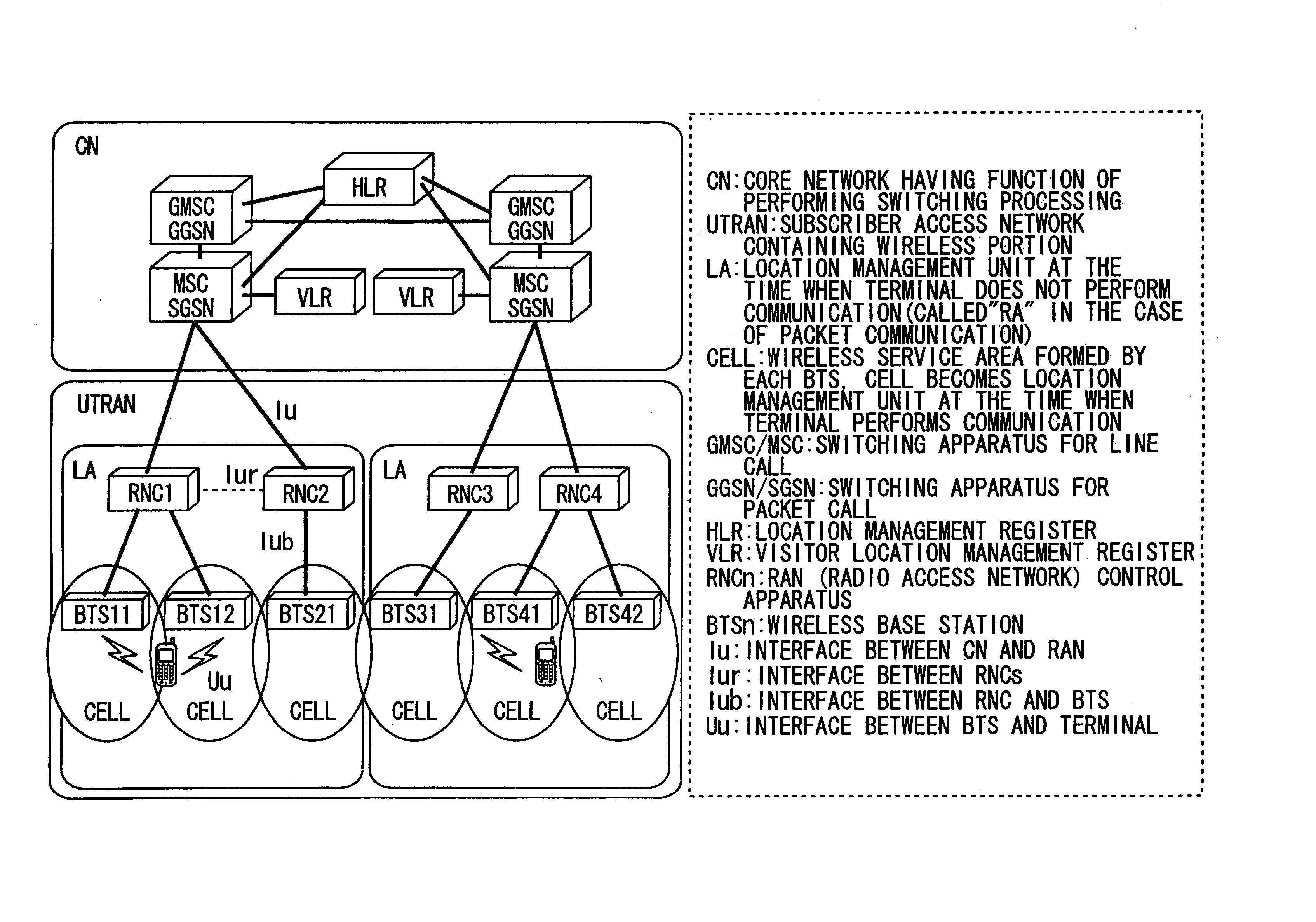
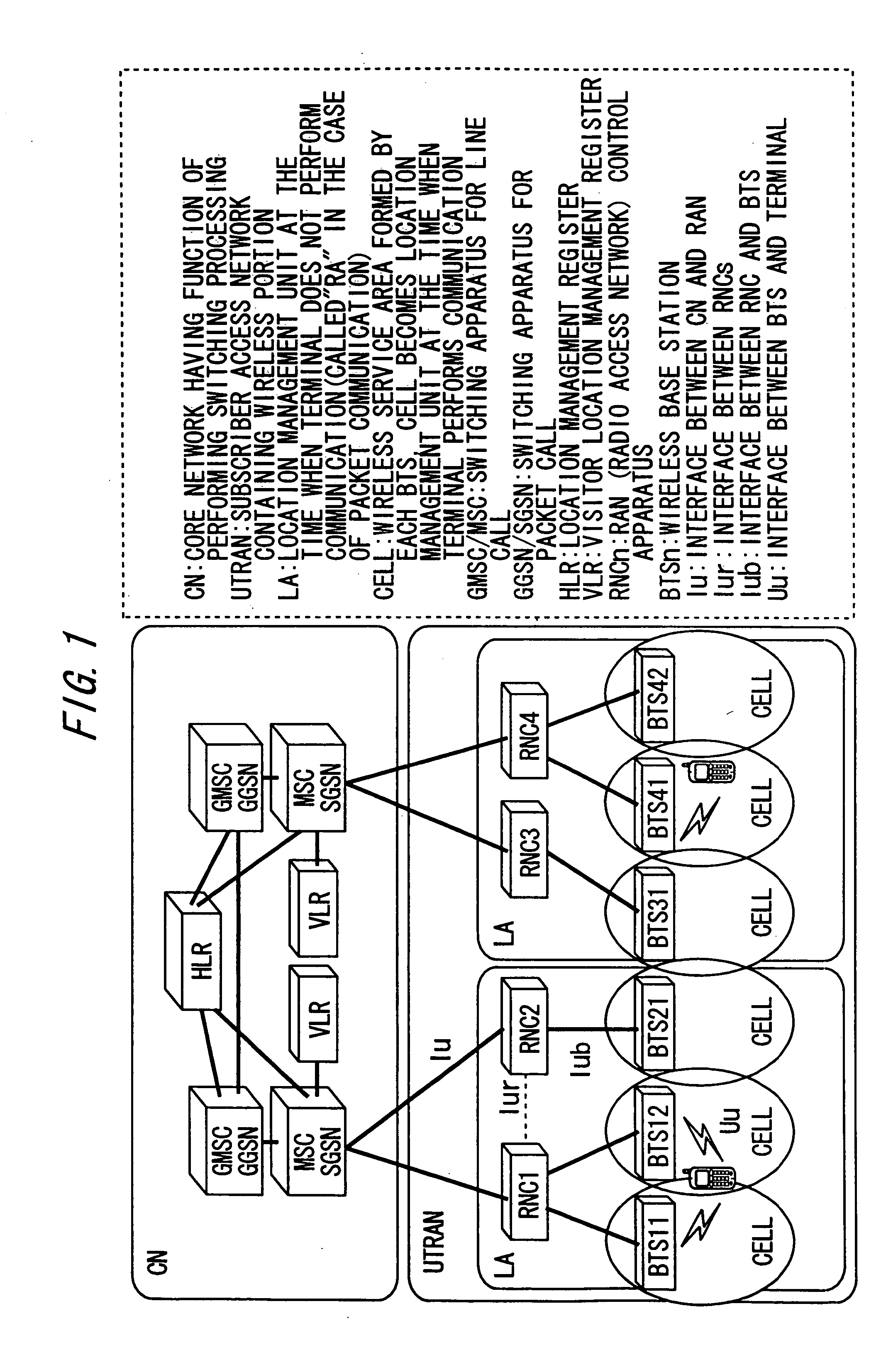
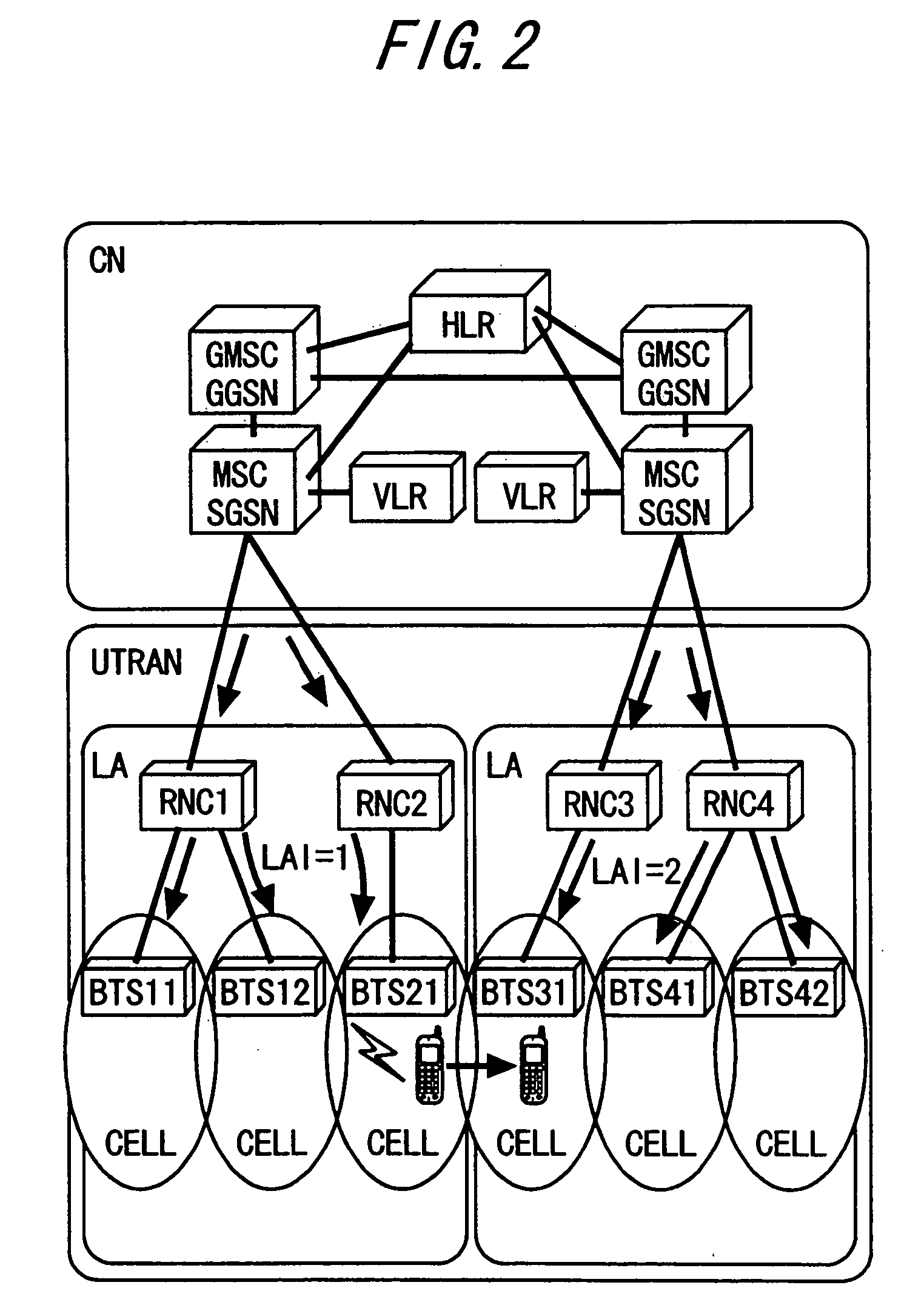
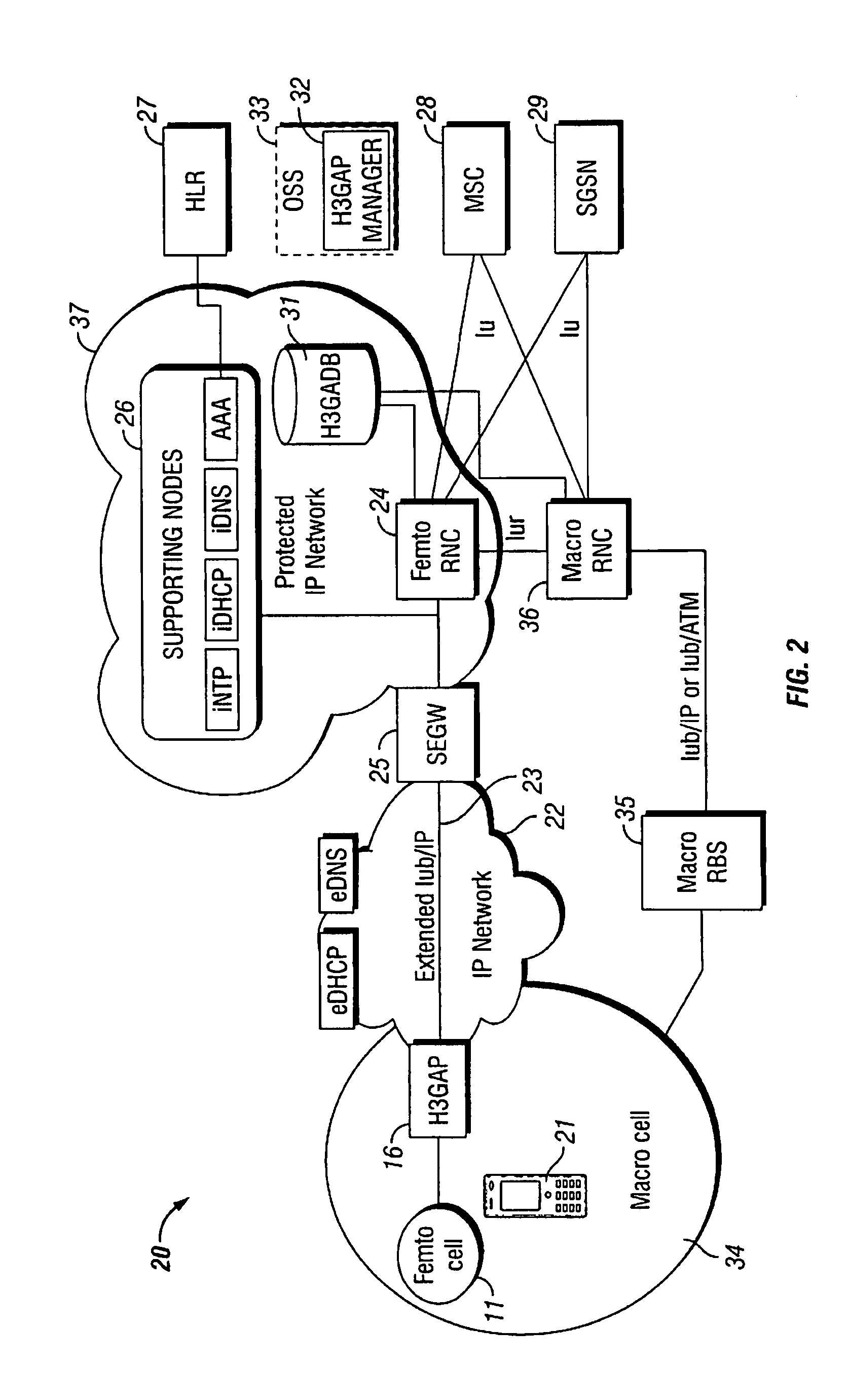
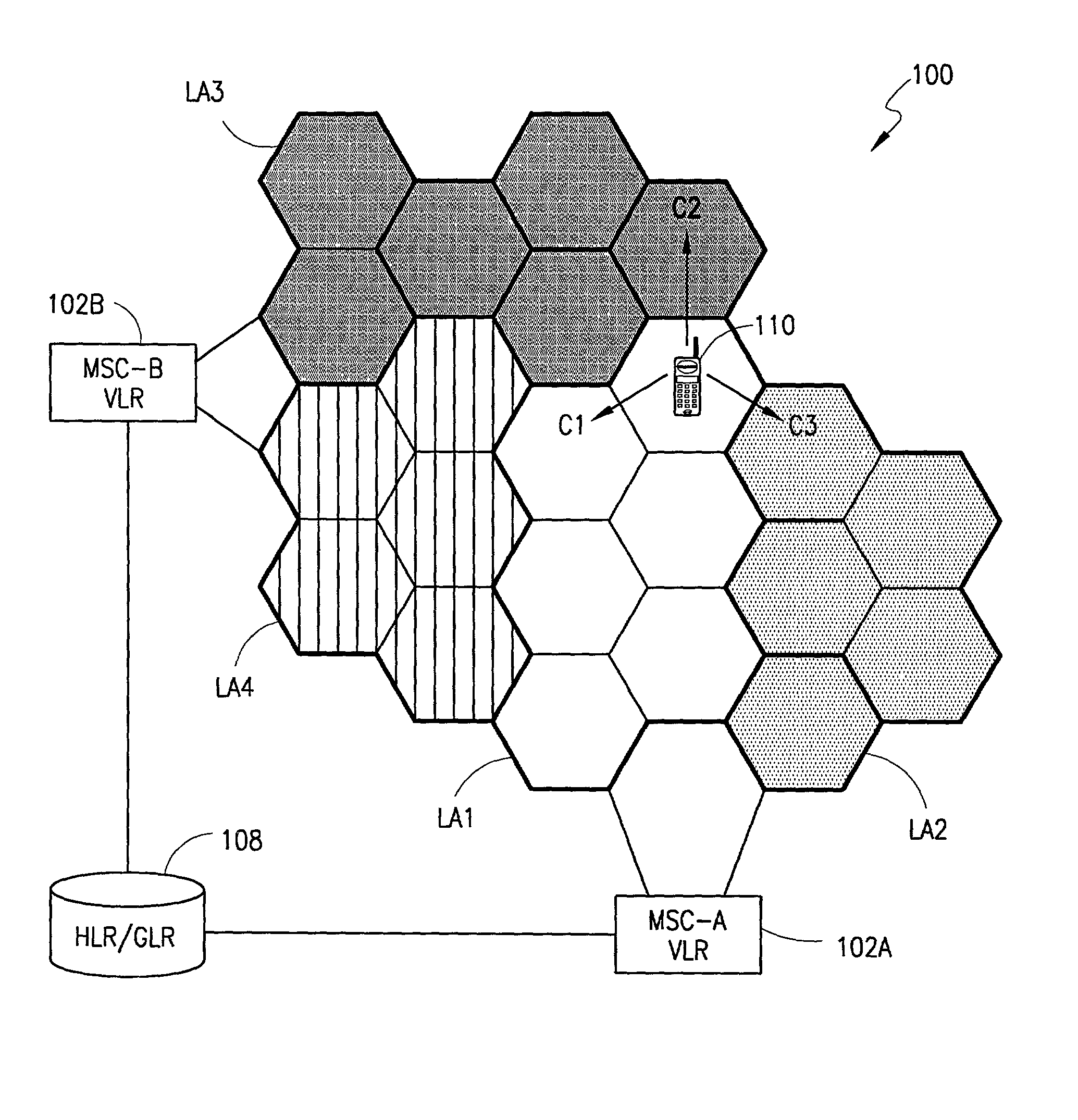
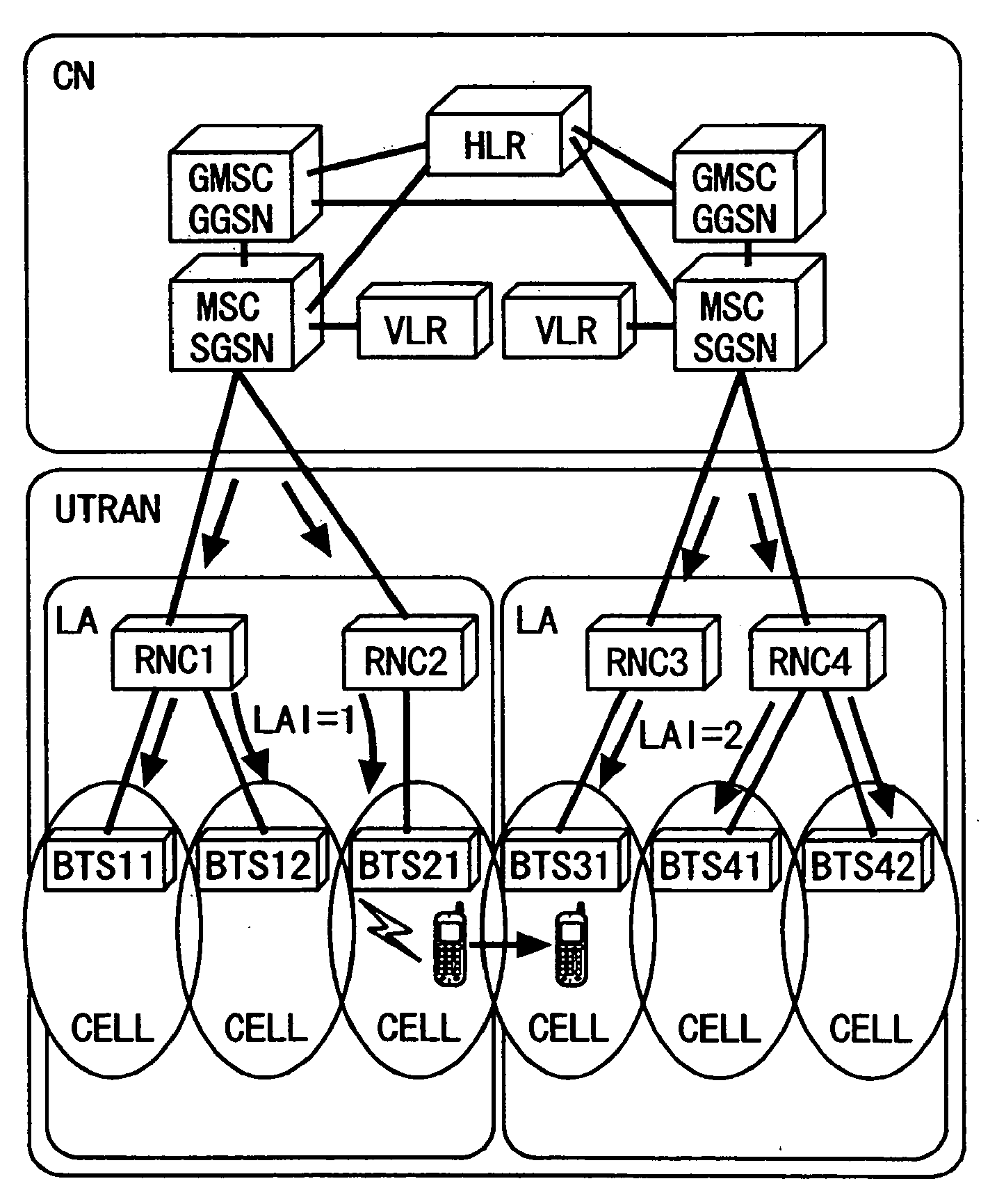
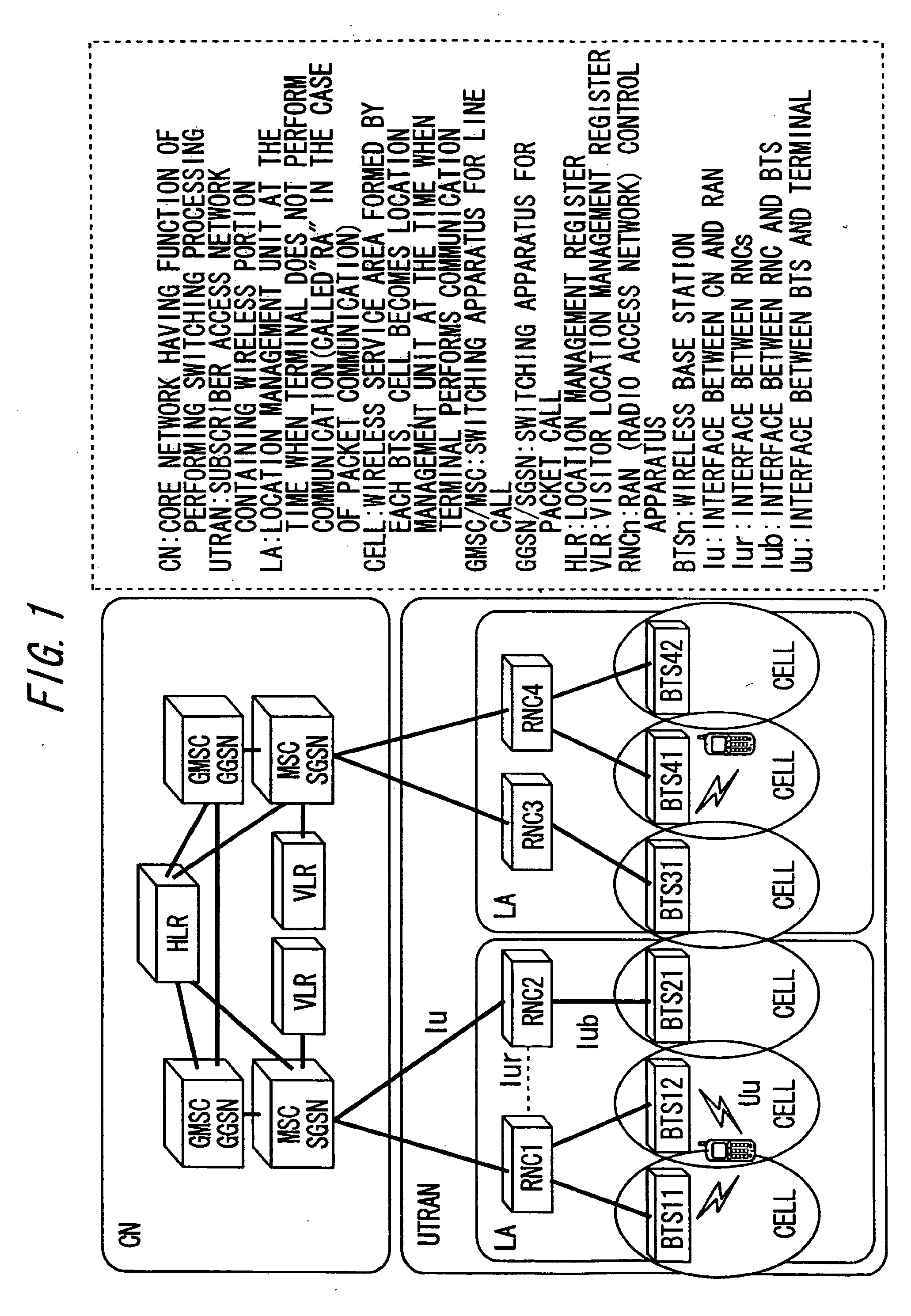
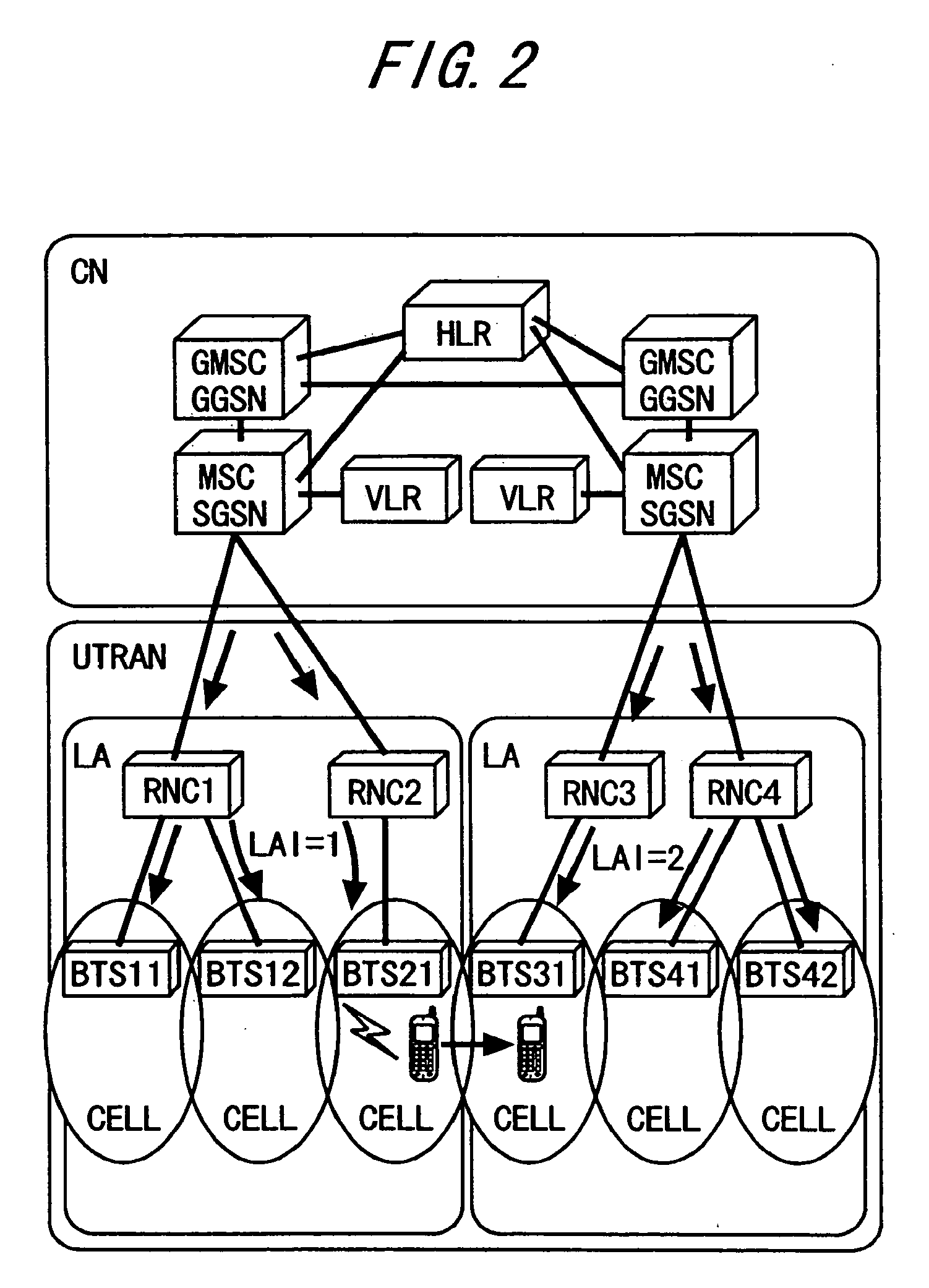
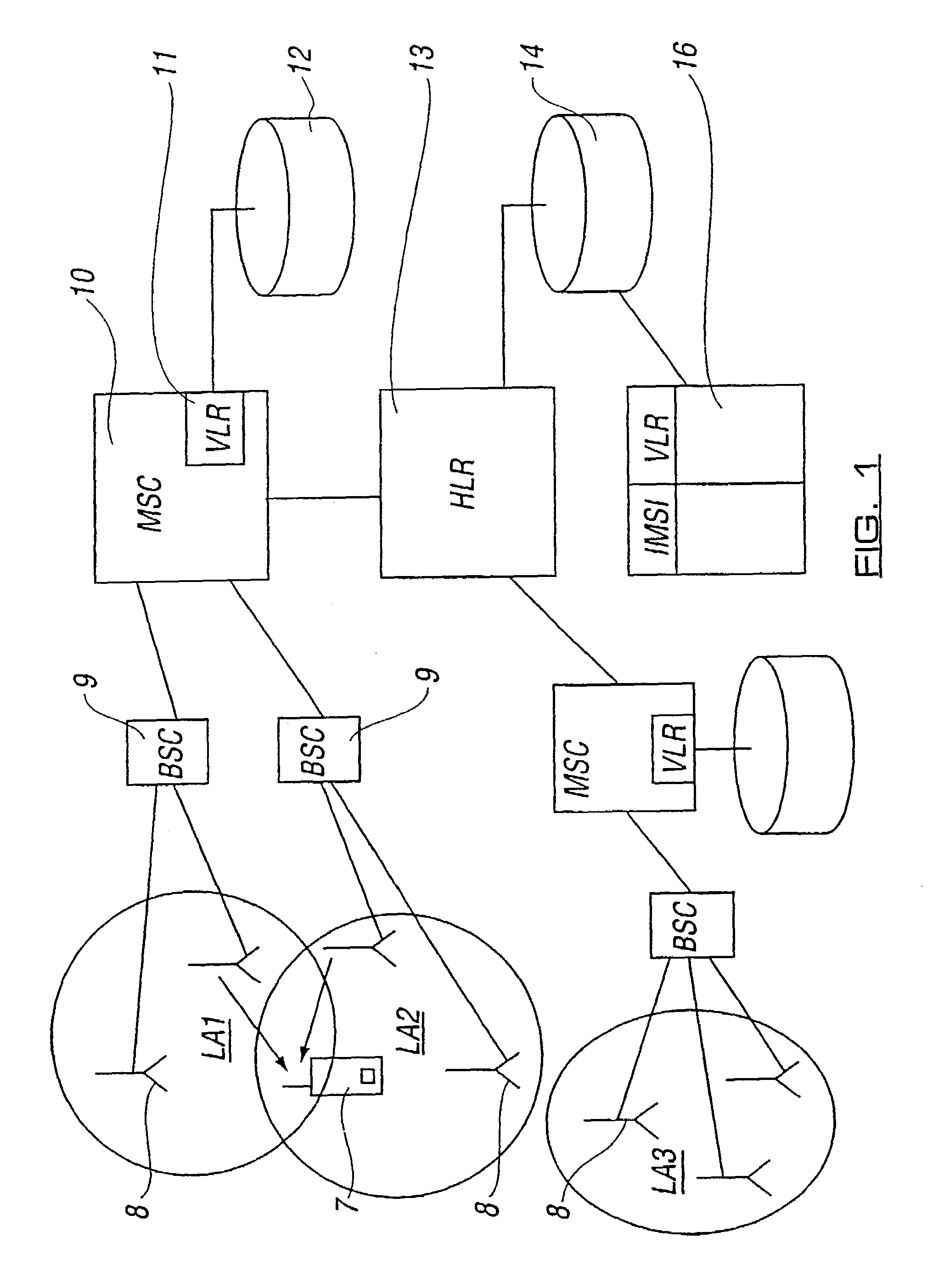
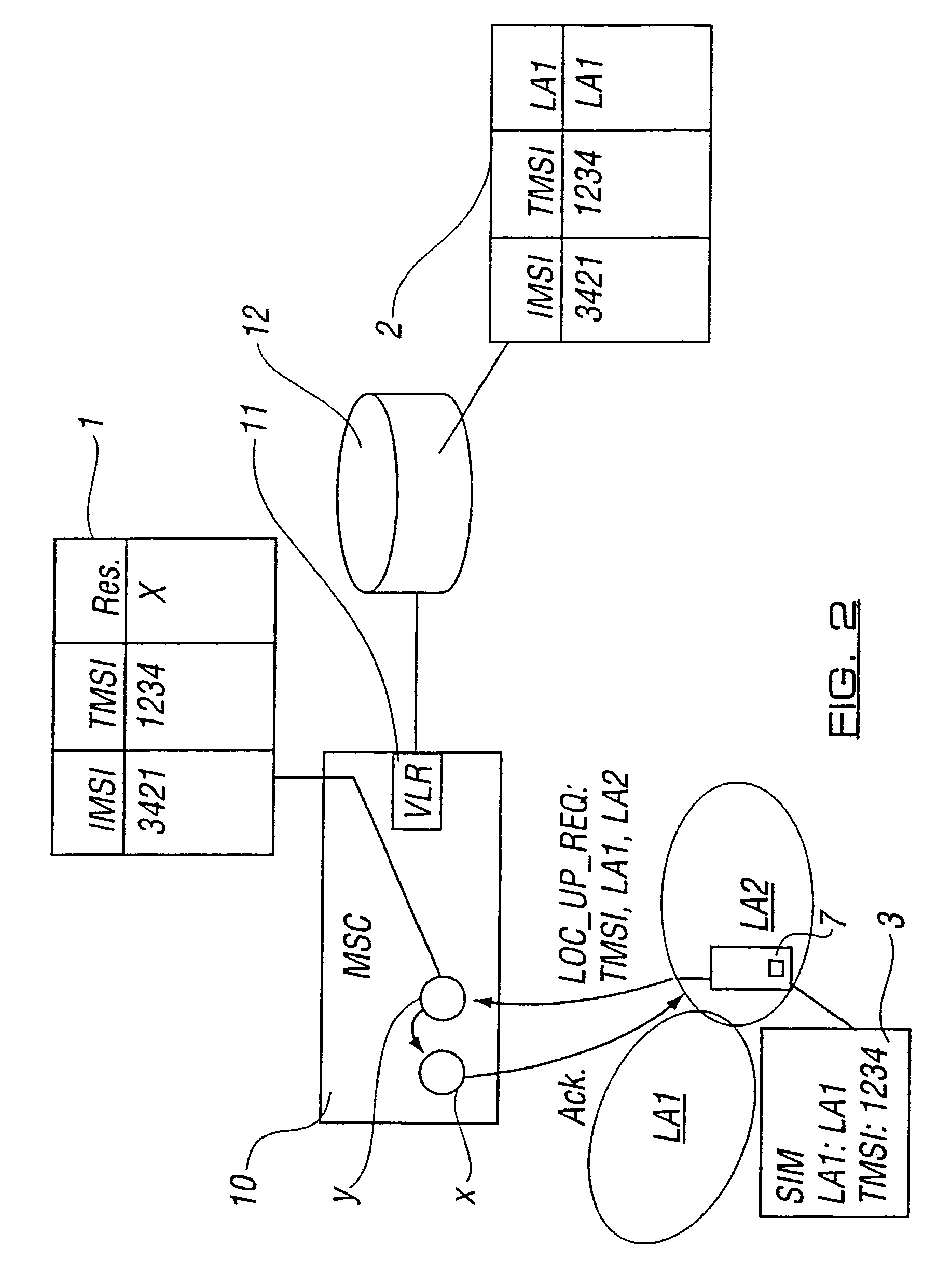
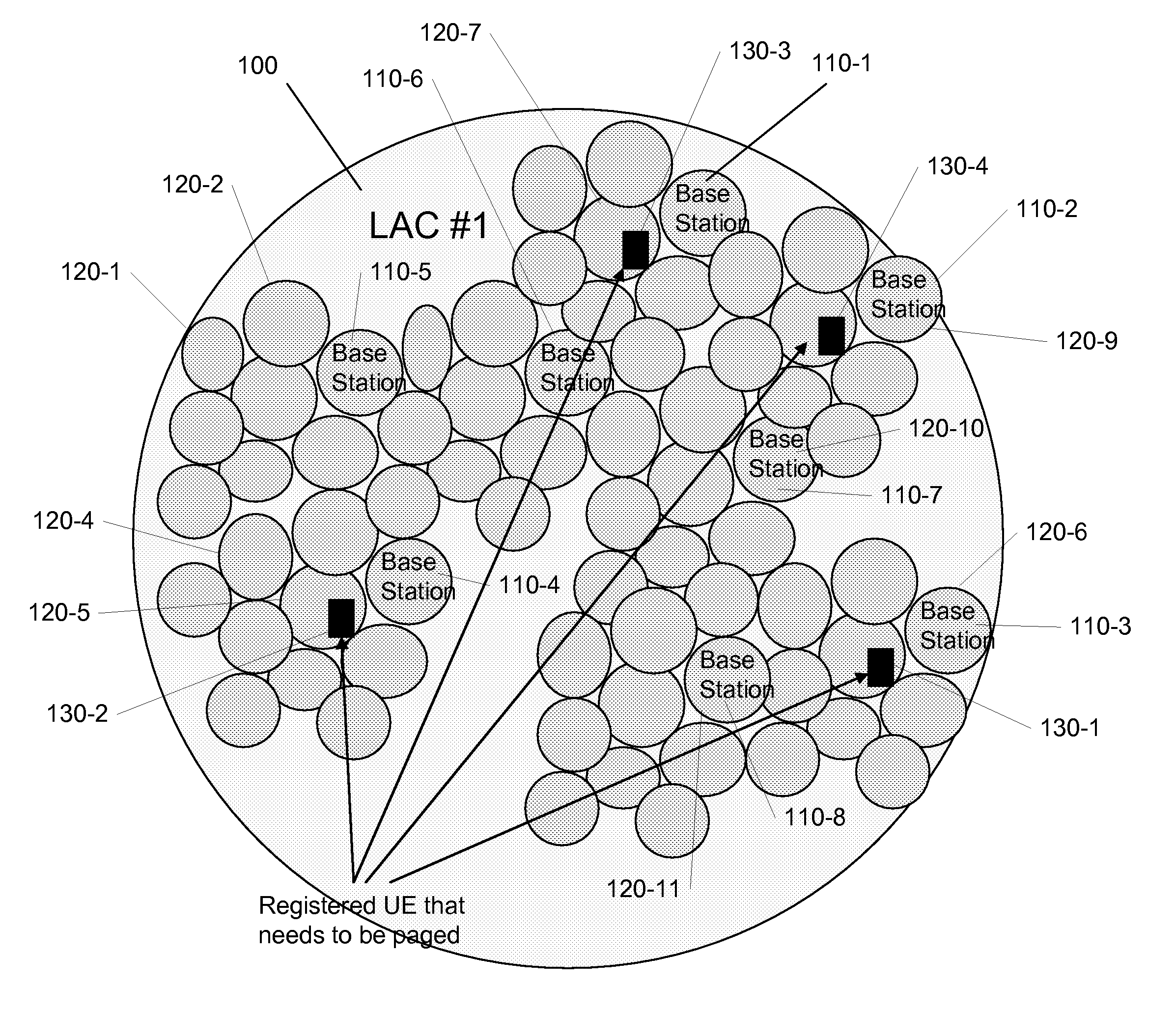
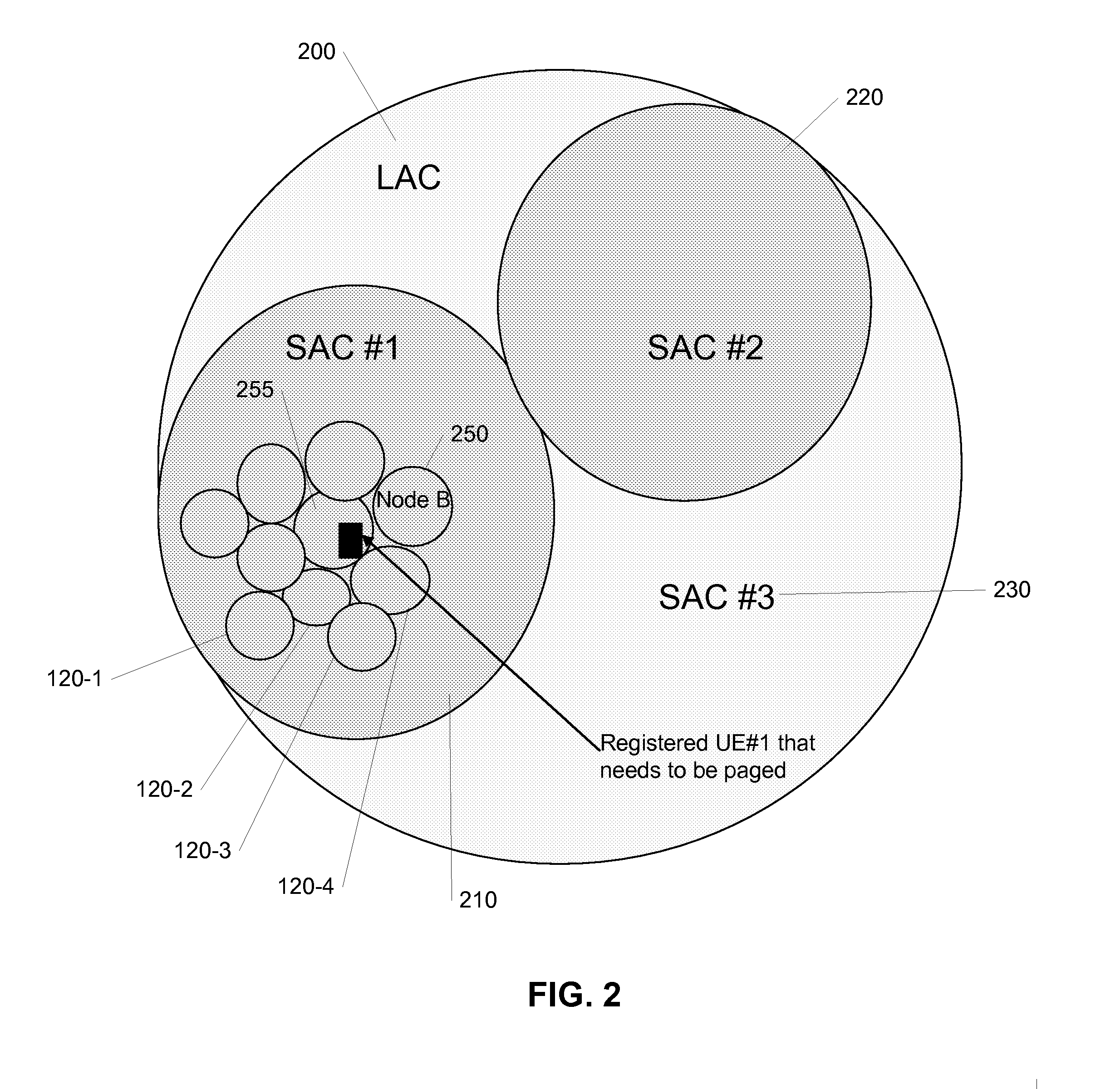
Location areas are comprised of one or several radio cells. Each location area is given an unique number within the network, the Location Area Code (LAC). This code is used as a unique reference for the location of a mobile subscriber.
Radio communication system and mobility management method
InactiveCN101035308AEnsure consistencyStay physically resident on the networkAssess restrictionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemMobility management
The invention discloses a wireless communication system and a mobile management method. And the wireless communication system comprises first wireless network and second wireless network, where the location area marks broadcasted by the first and second wireless networks are the same, and received by mobile terminal so as to make the mobile terminal in idle mode not initiate any location updating flow when roaming between the first and second wireless networks; and the configuration information of at least one support node of the core networks of the first and second wireless networks is set with information of expressing preferred network.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
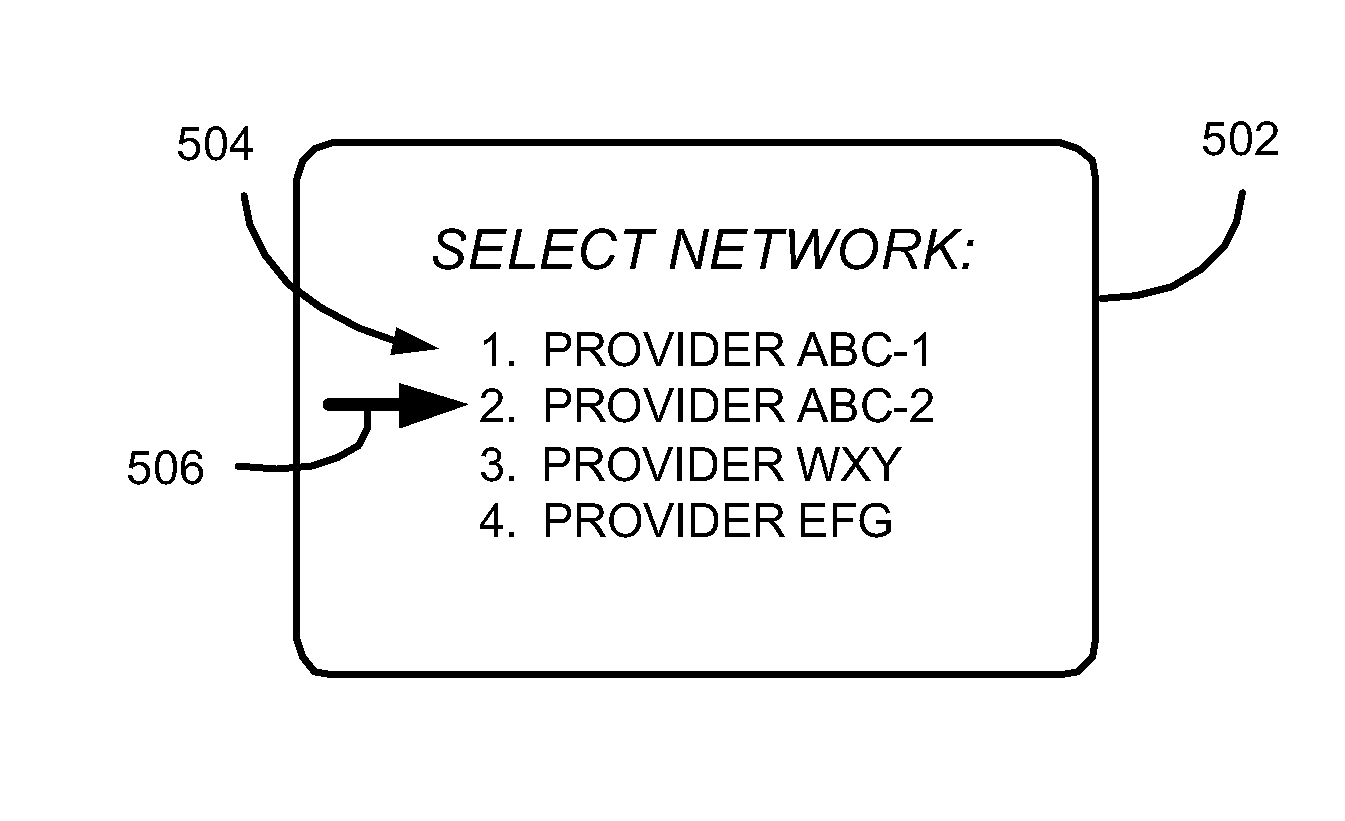
Methods And Apparatus For Providing Manual Selection Of A Communication Network For A Mobile Station
ActiveUS20080096559A1Assess restrictionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMobile network codeTelecommunications
Methods and apparatus for providing manual selection of a communication network for a mobile station are described. A plurality of communication networks are identified by scanning a coverage area within which the mobile station is operating. A plurality of network identifiers corresponding to the plurality of communication networks are then retrieved from memory of a Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) in accordance with an Enhanced Operator Name String (EONS) protocol. Preferably, each network identifier is retrieved based on a Mobile Country Code (MCC), a Mobile Network Code (MNC), and a Location Area Code (LAC). The plurality of network identifiers are visually displayed for user selection, and at least two of the network identifiers may be substantially the same. The user selected communication network is registered with and the network identifier associated with this network is visually displayed.
Owner:LEPATENT (BEIJING) CONSULTING CORP LTD
Terminal state control system
InactiveUS20050070283A1More communicationEasy to distinguishUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsControl systemLocation area
When a terminal enters a cell of a personal-use base station (NBTS) arranged in a certain location area, the terminal receives a location area identifier having a number that is different from an identifier of the location area, and transmits a location updating request with the reception of the location area identifier as a trigger. On receiving the location updating request, a VLR or an NRNC having a registration table, in which the ID of the personal-use base station and the ID of a terminal allowed to use the personal-use base station are registered, judges whether the terminal issued the location updating request is the terminal allowed to use the personal-use base station by referring to the registration table. If the terminal issued the location updating request corresponds to the terminal allowed to use the personal-use base station, the terminal is placed under a status where it is capable of performing communication in the cell, and if not, the terminal is placed under a status where it is incapable of performing communication in the cell.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Location system and method for client terminals which provide location-based service to mobile terminals
ActiveUS7277711B2Consume resourcesUseless trafficSpecial service for subscribersServices signallingClient-sideLocation area
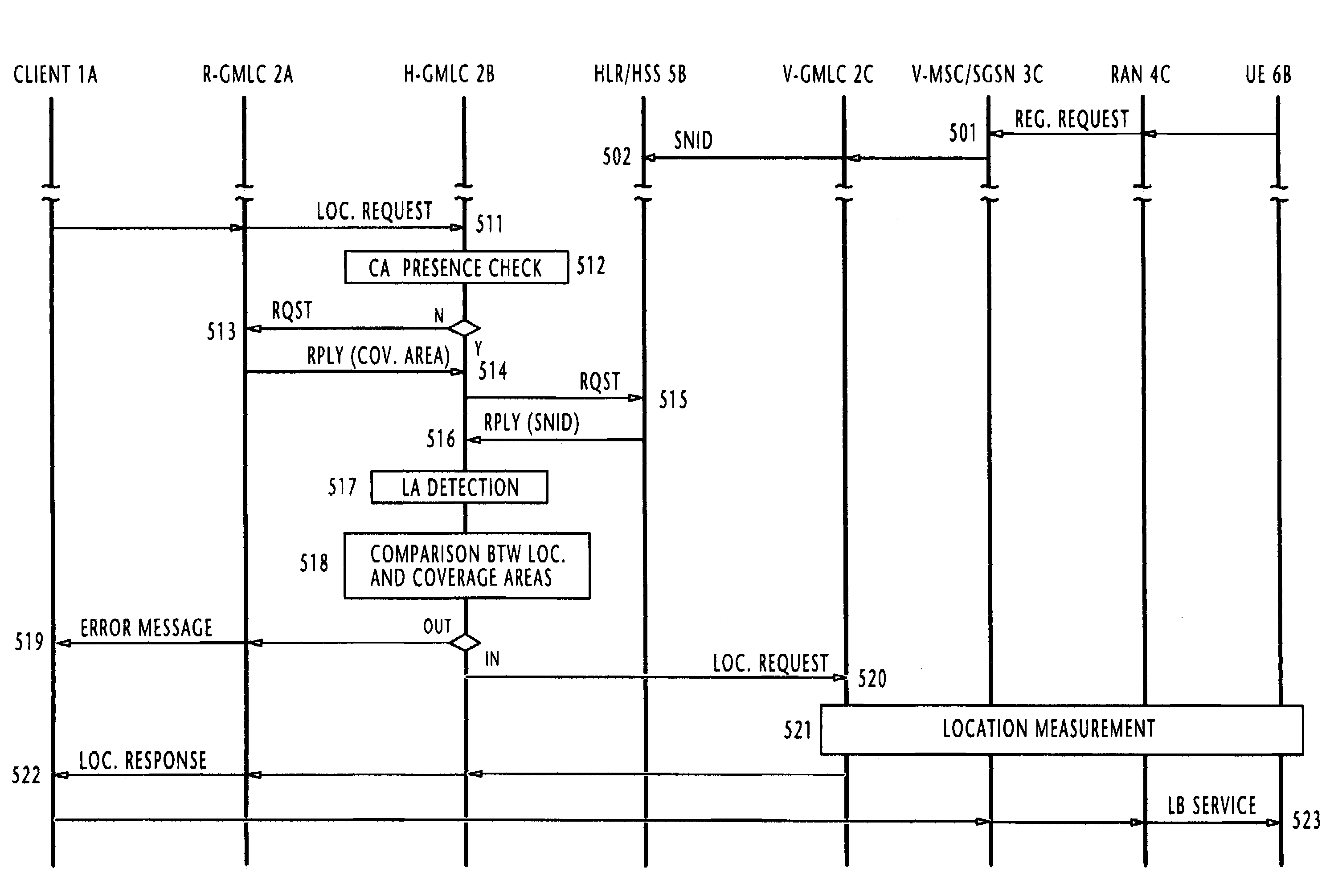
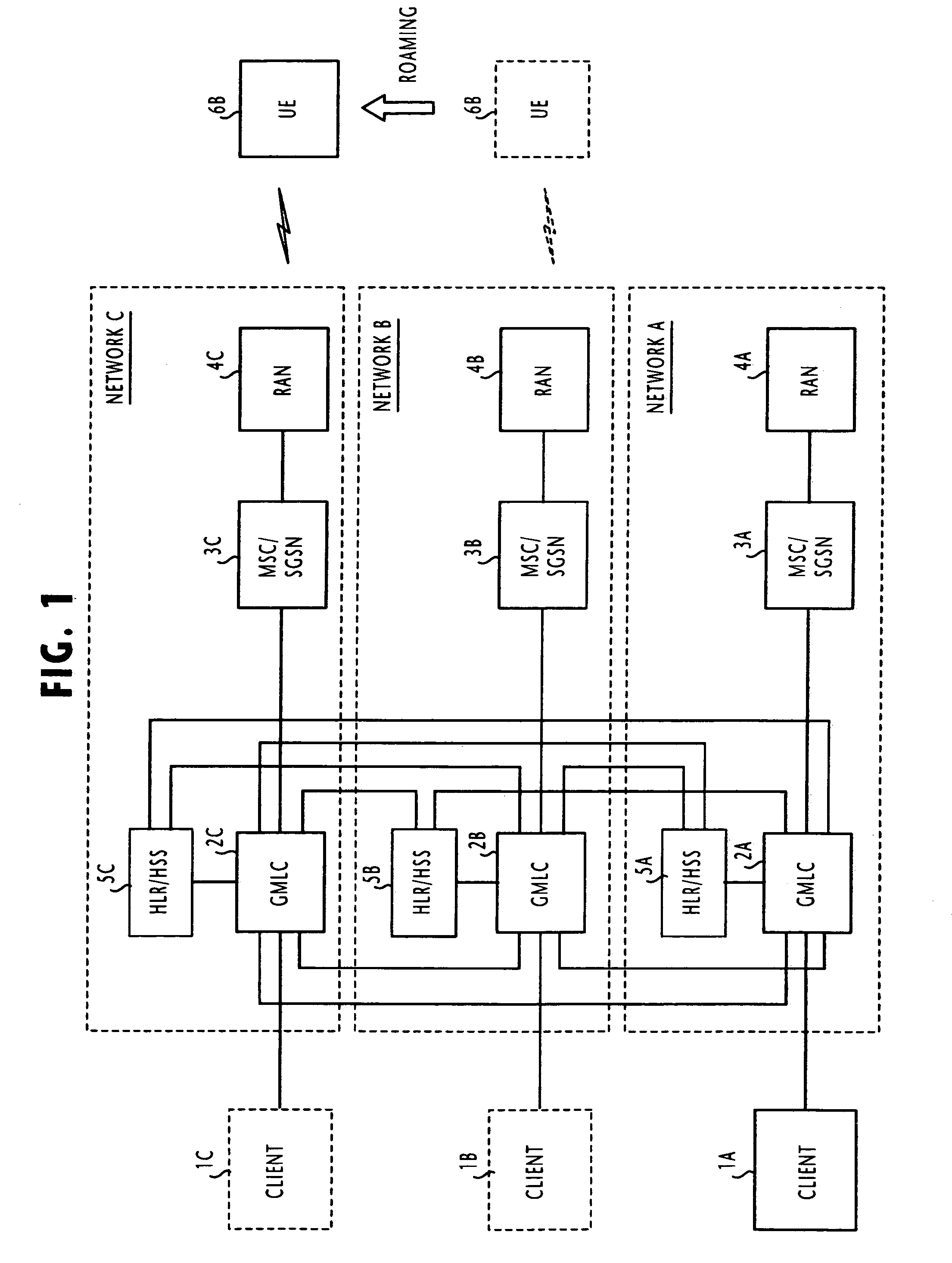
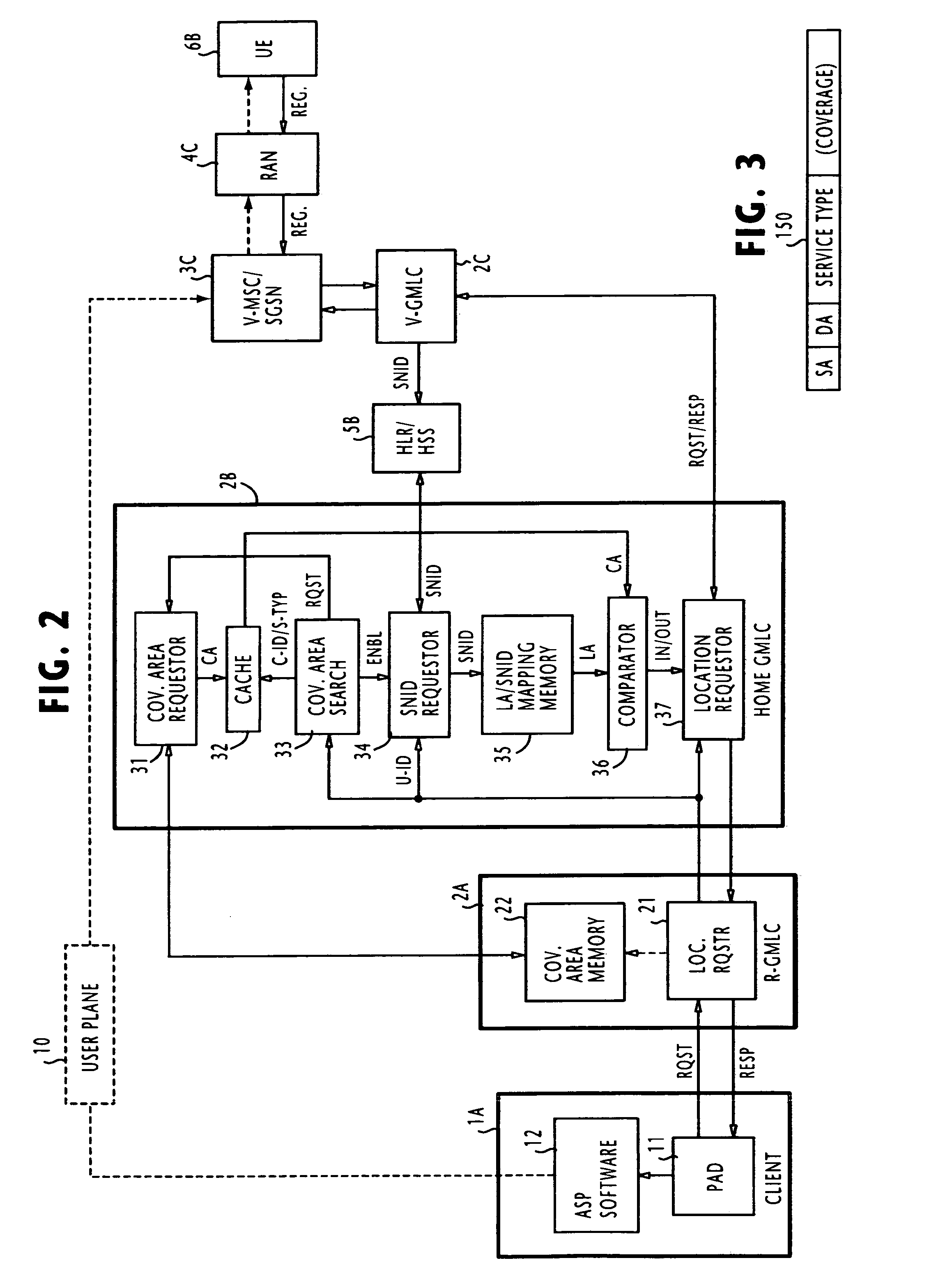
In one of multiple mobile communication networks, a serving node responsible for locating mobile terminals is responsive to a registration request from a mobile terminal for storing the serving node identity in a home location database to which the mobile terminal is subscribed. In response to a location request message from a client terminal requesting the location of a target mobile terminal, a serving node identity is retrieved from the home location database of the target mobile terminal. The serving node identity represents the current location of the target mobile terminal. If the current location area is within the coverage area of location-based service provided by the client terminal, the location request message is forwarded to a serving node identified by the retrieved serving node identity. Otherwise, an error message is transmitted to the client terminal to indicate that the target mobile terminal is roaming outside of the coverage area.
Owner:NEC CORP
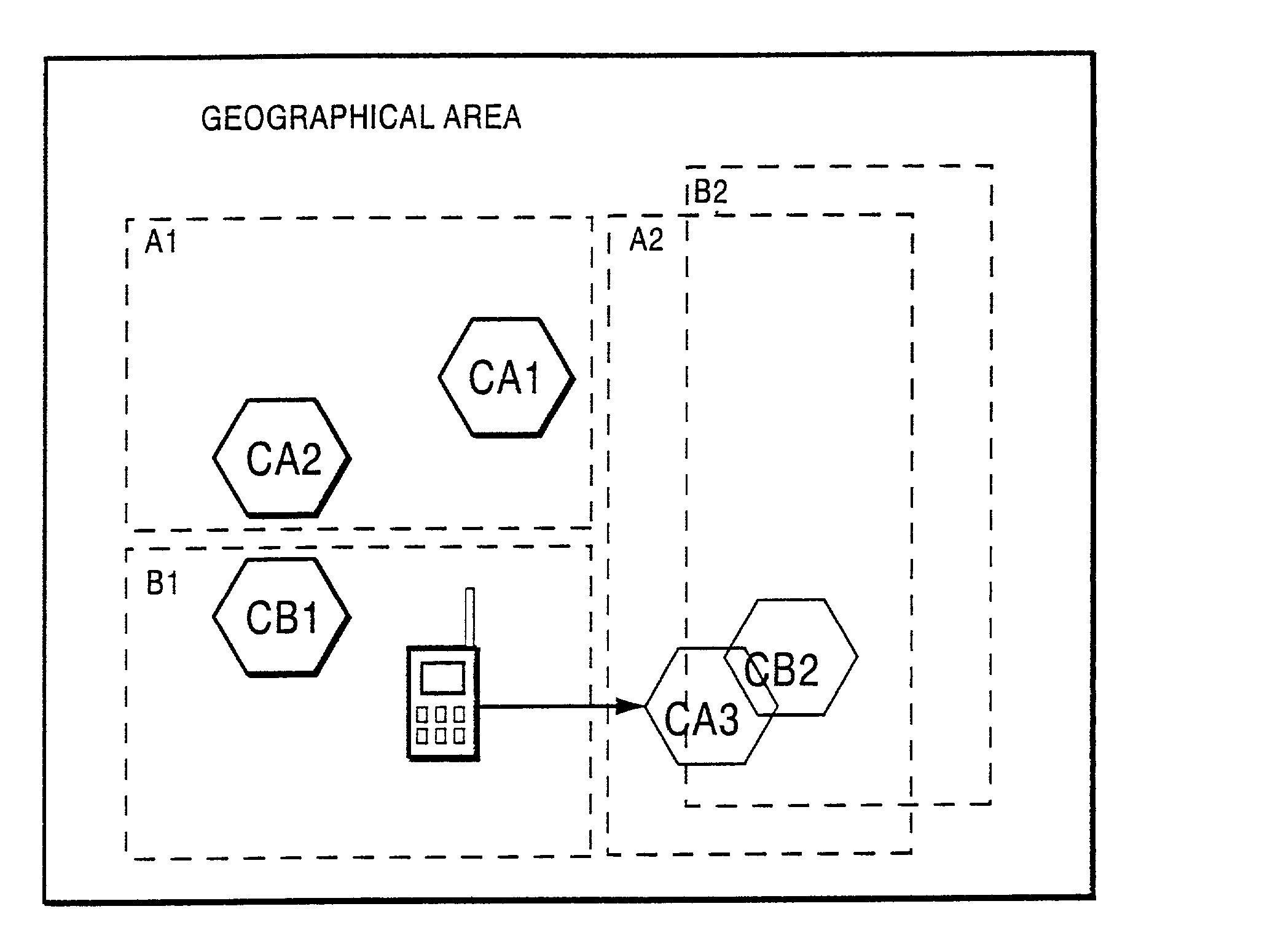
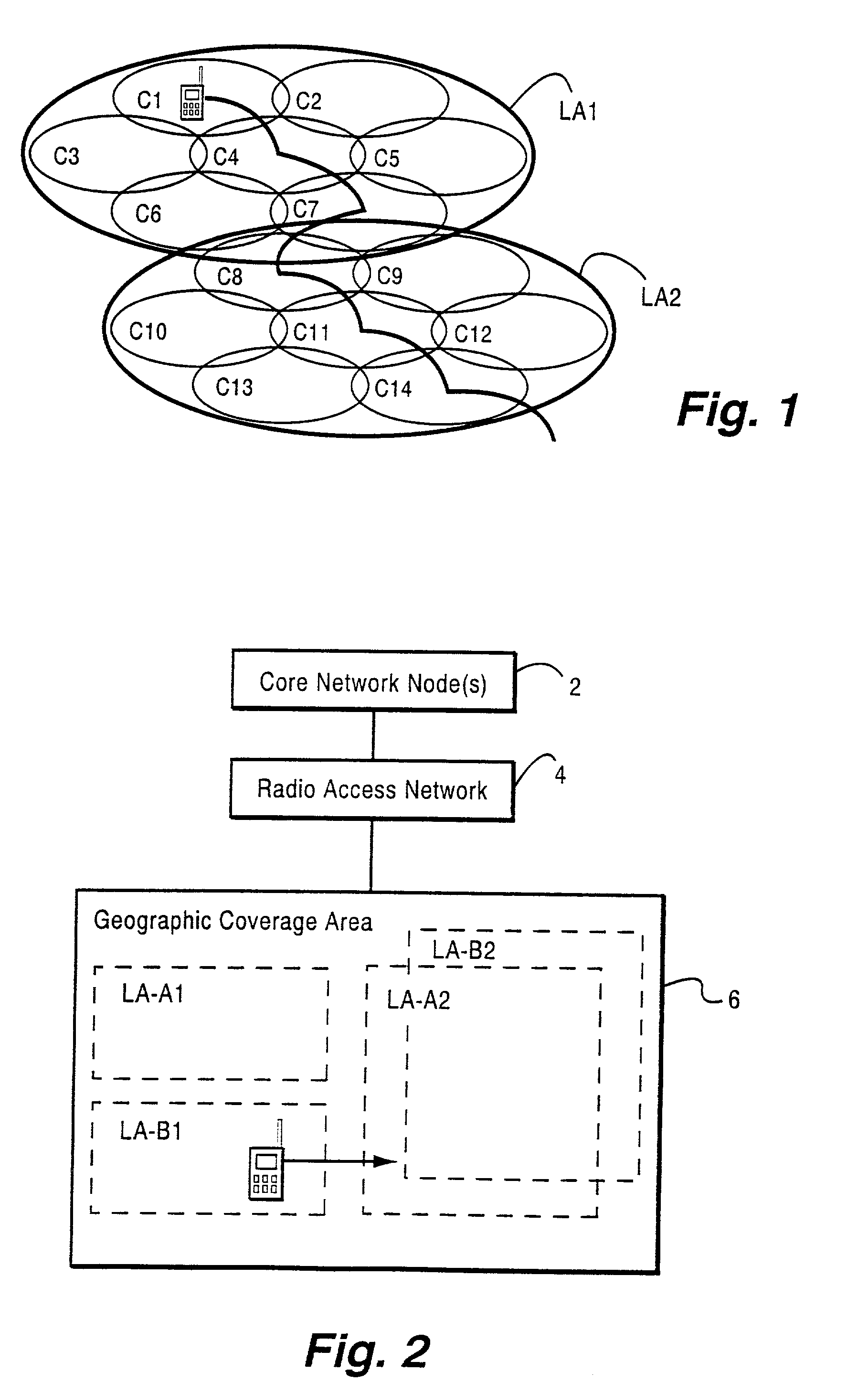
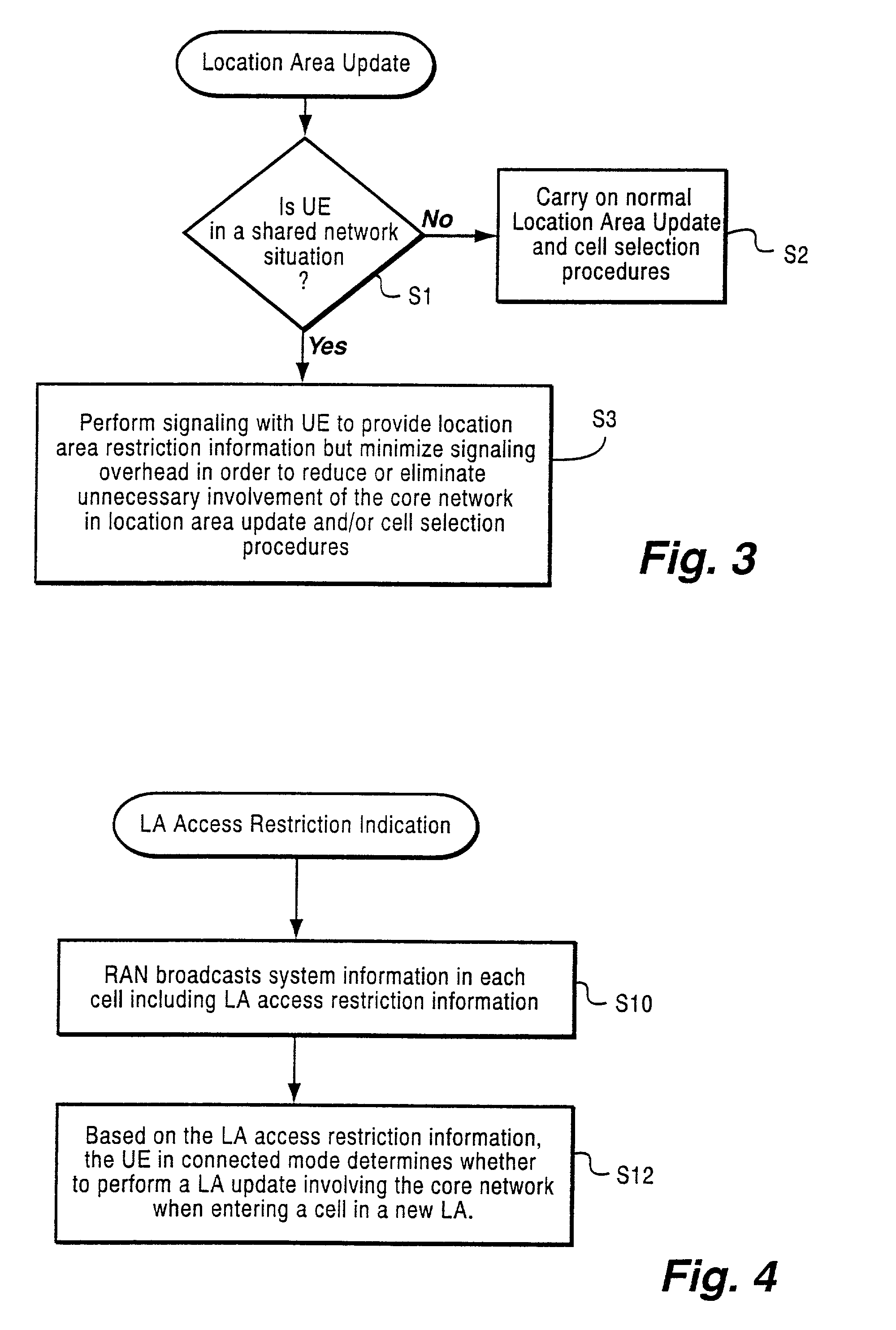
Method and apparatus for location area updating in cellular communications
InactiveUS20030040314A1No disruption to callIncrease speedAssess restrictionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio access networkMobile radio
A connection is established between a mobile radio terminal and a radio access network serving plural geographic coverage areas. The radio access network transmits information associated with one of the geographic coverage areas indicating whether the one geographic coverage area requires a geographic coverage area update procedure. During the connection, when the mobile radio terminal considers selecting the one geographic coverage area, it determines whether to perform a geographic coverage area update procedure depending on the transmitted information associated with the one geographic coverage area. In a preferred, non-limiting application, the radio access network is shared by two operators, and the transmitted information indicates that the geographic coverage area update procedure should be performed for geographic coverage areas that are shared by the two operators and that the geographic coverage area update procedure need not be performed for geographic coverage areas that are not shared by the two operators.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
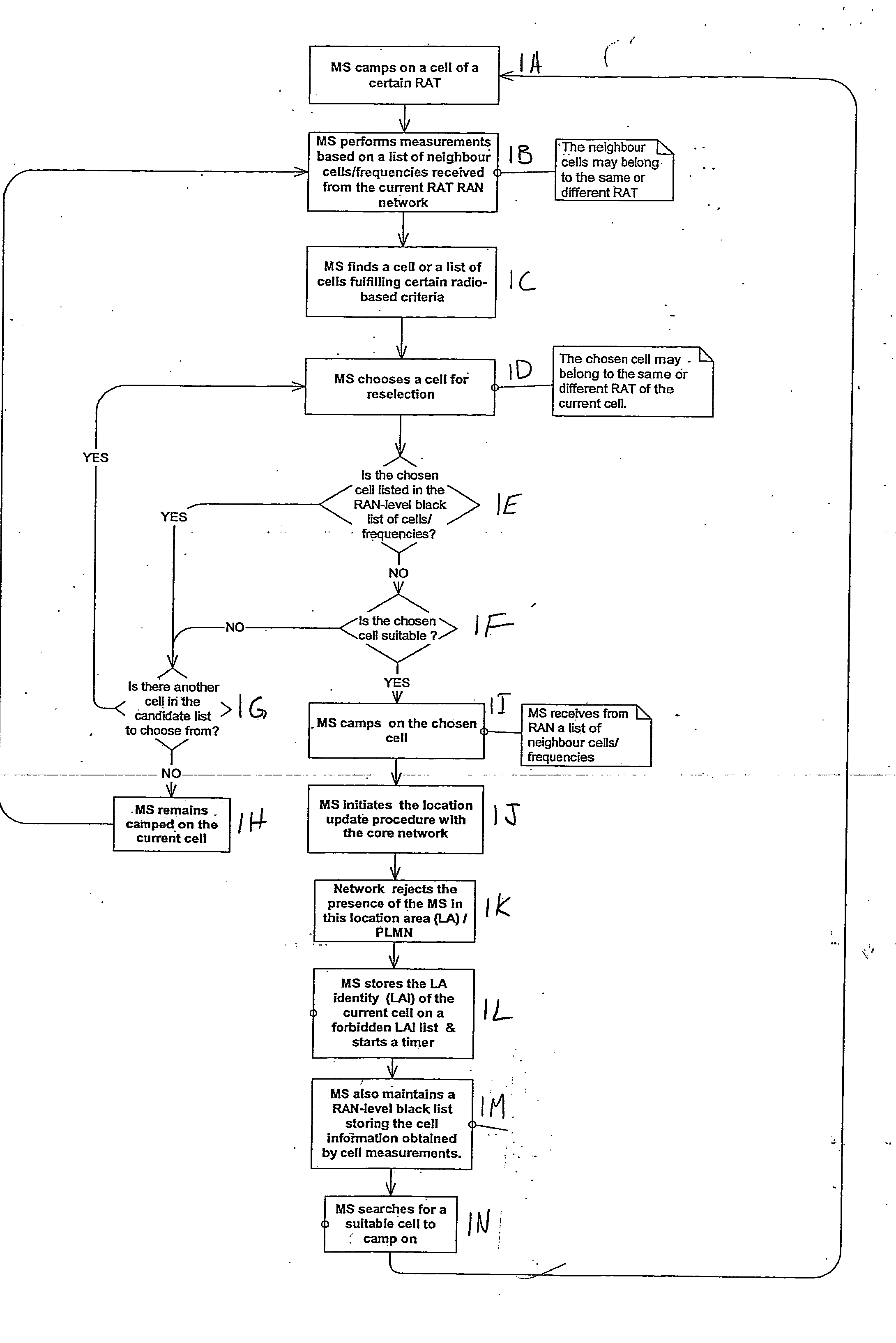
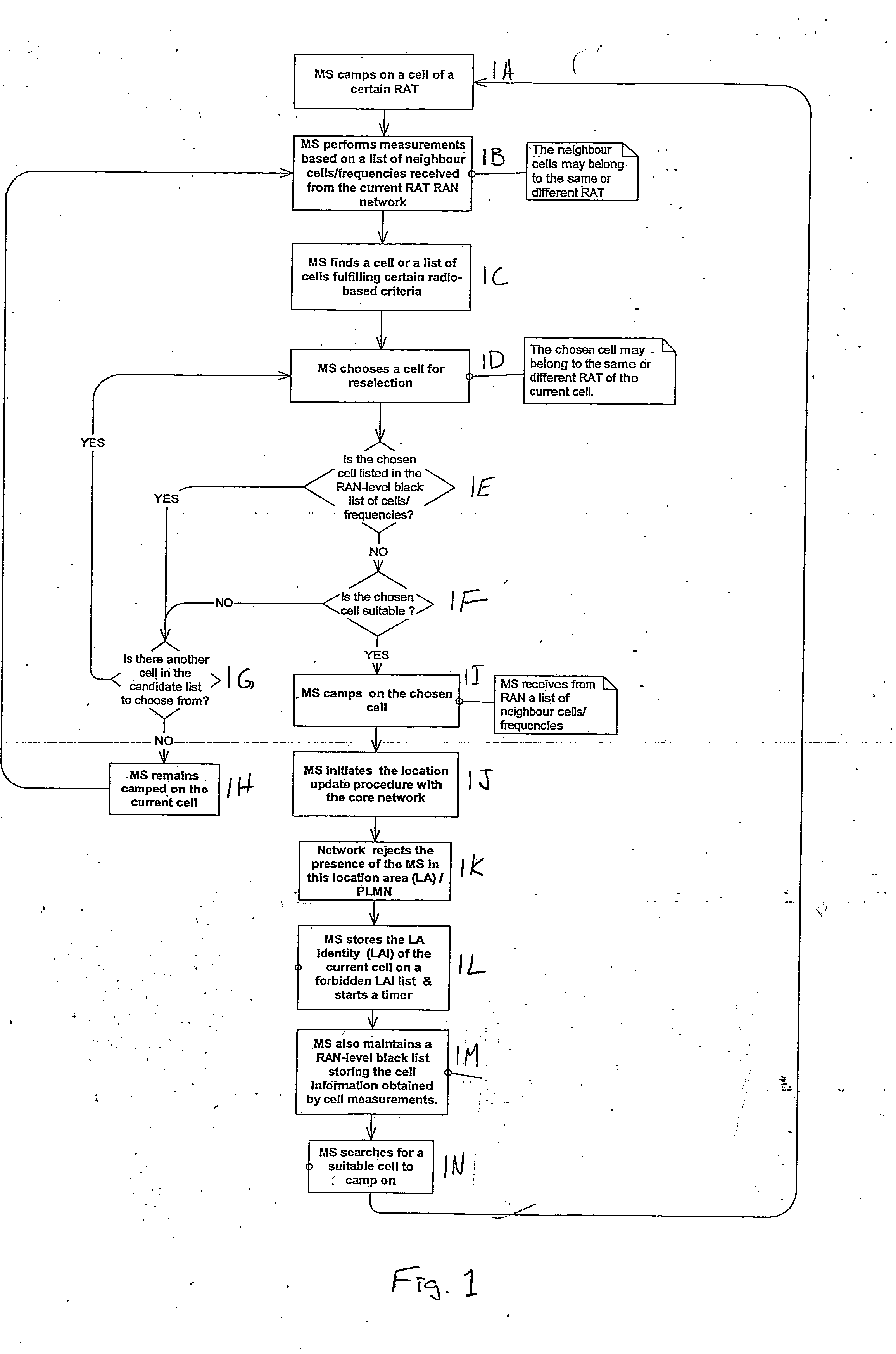
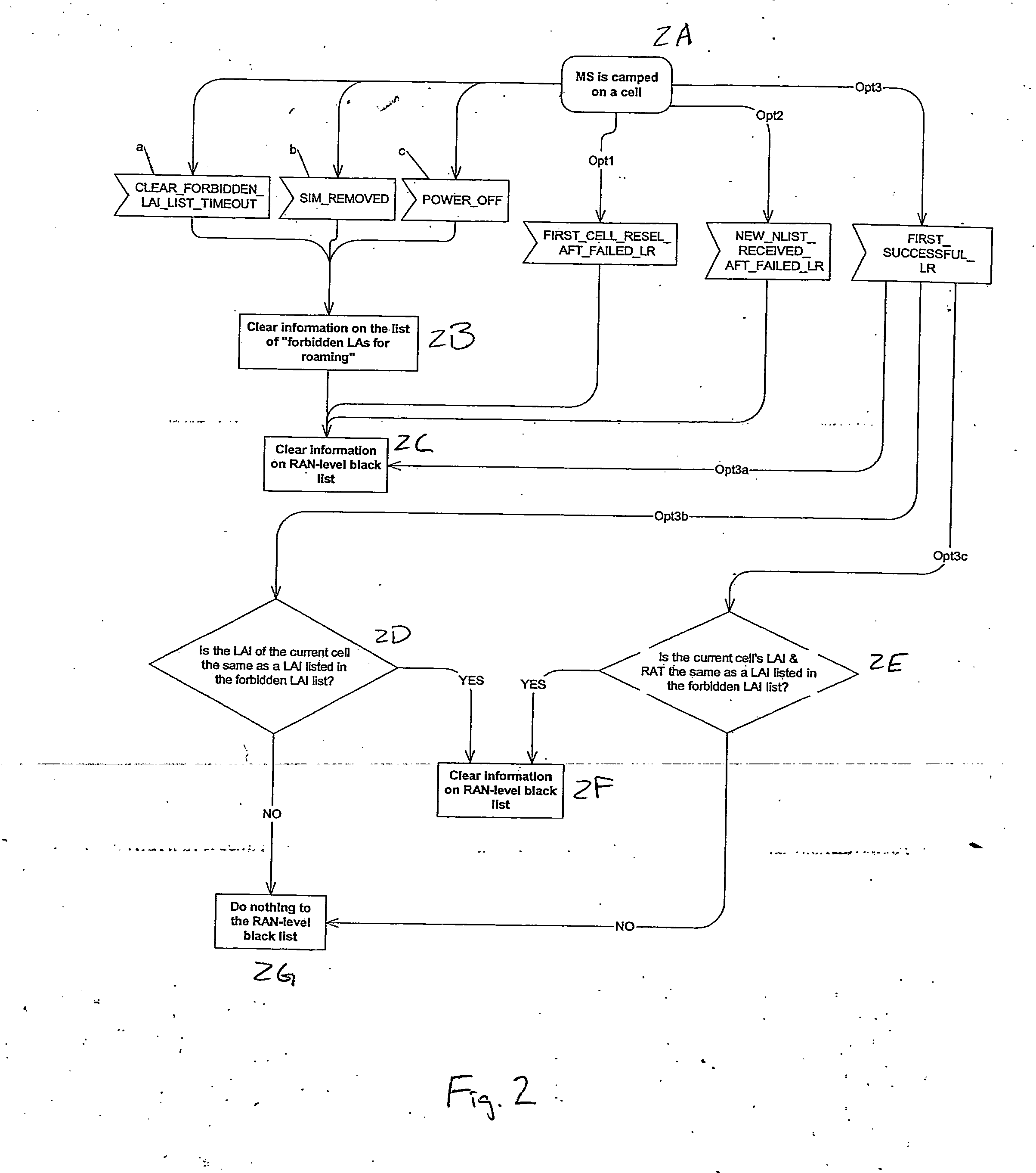
Apparatus, method and computer program product providing inclusion of local area information in broadcast messages and maintenance of radio access network black list
ActiveUS20070037577A1Avoid selectionAssess restrictionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio access networkLocation area
A method includes receiving location area-related information, associating the location area-related information with a neighbor cell information to determine if a cell belongs to a forbidden location area, and avoiding selection of the cell if the cell is determined to belong to the forbidden location area. Embodiments described include a UE, network element, computer program product, and integrated circuit.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method and apparatus for determining a geographical location of a mobile communication unit
The location of a mobile unit is determined by evaluating the instantaneous distances between an apparatus traveling above the surface of the earth and the mobile unit. The instantaneous distances are determined by measuring the travel time of a plurality of signals and calculating the distance based on the speed of the signal. One of two possible location regions is identified as the region including the location of the mobile unit by observing the motion of the mobile unit resulting from the rotation of the Earth.
Owner:SUTTON GARY
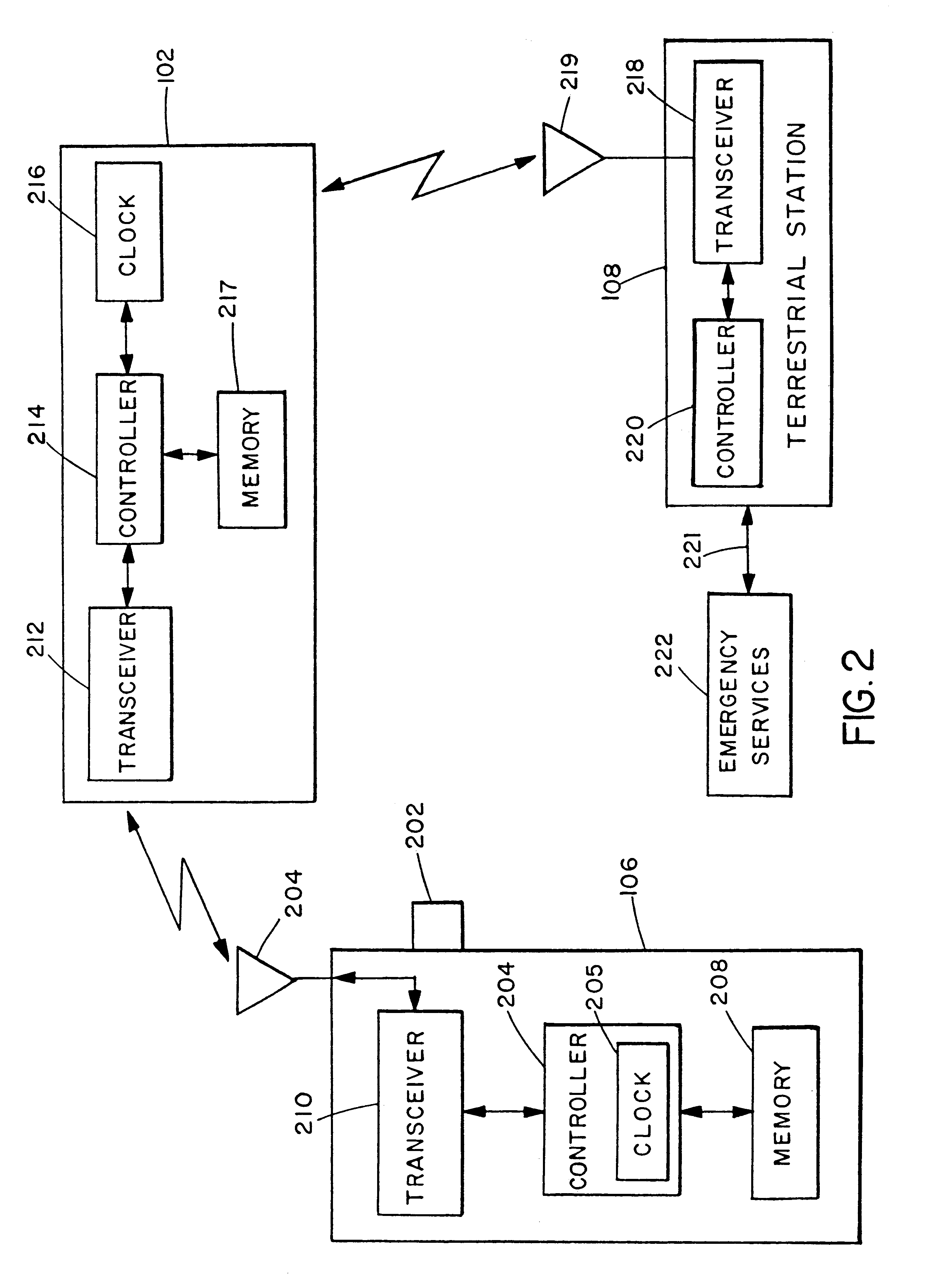
Method and system for initiating and handling an emergency call utilizing geographical zones
A method and system of making an emergency voice call is disclosed. Location data is received from a positioning device. A location area identifier is determined. The location area identifier corresponds to a geographical area encompassing a geographical location being represented by the location data. A voice call destination number is identified. The voice call destination number is associated with the location area identifier. The voice call destination number is utilized in order to communicate with a public safety answering point.
Owner:WIRELESSWERX IP LLC
System and method for population tracking, counting, and movement estimation using mobile operational data and/or geographic information in mobile network
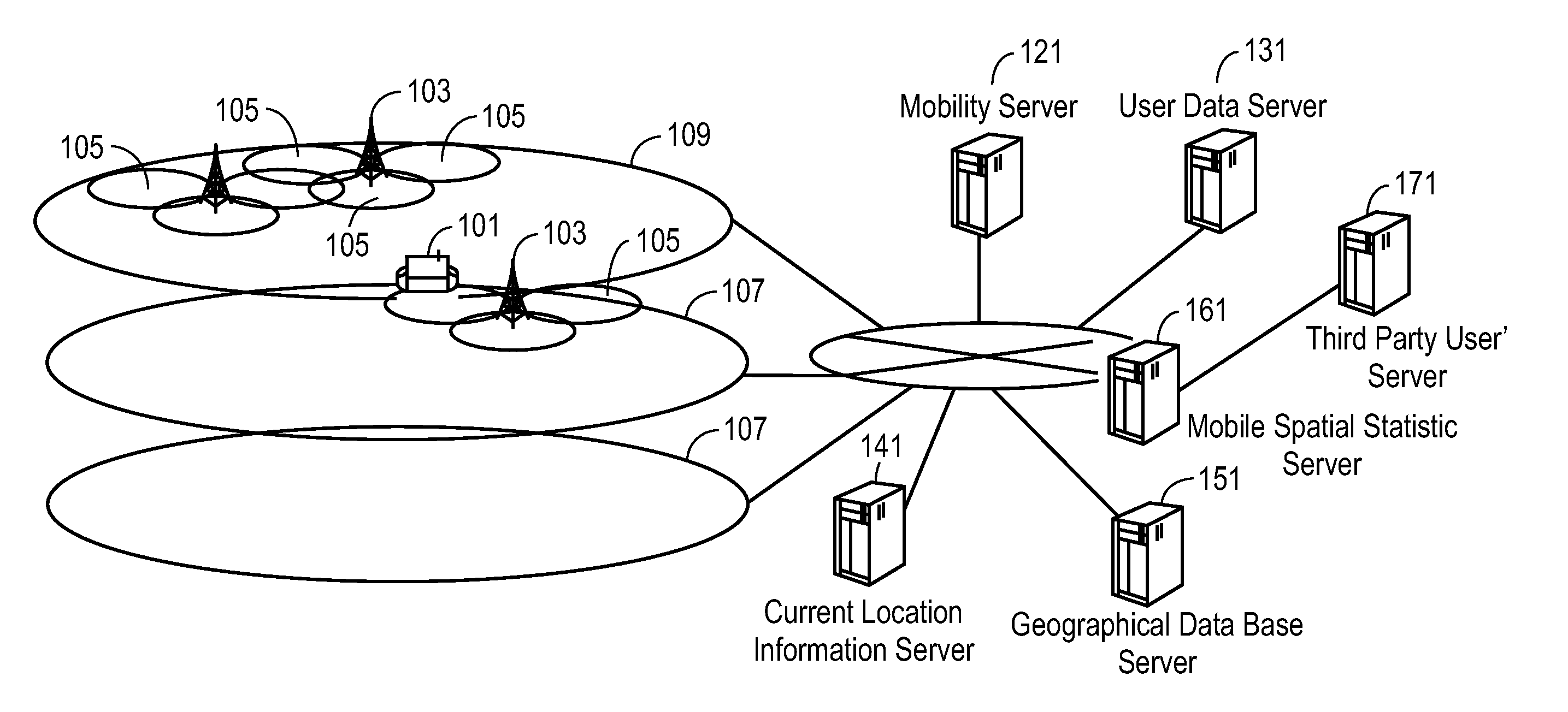
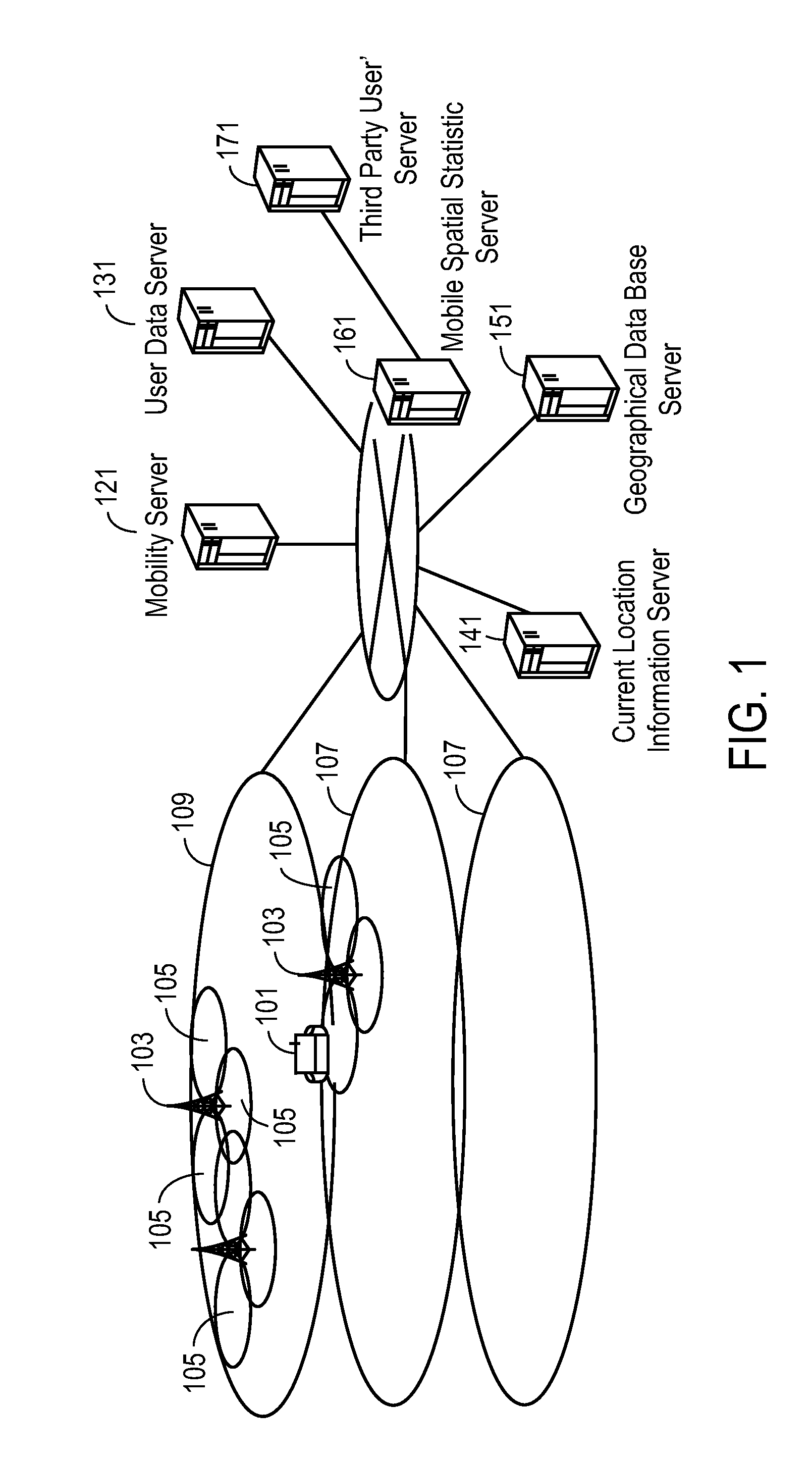
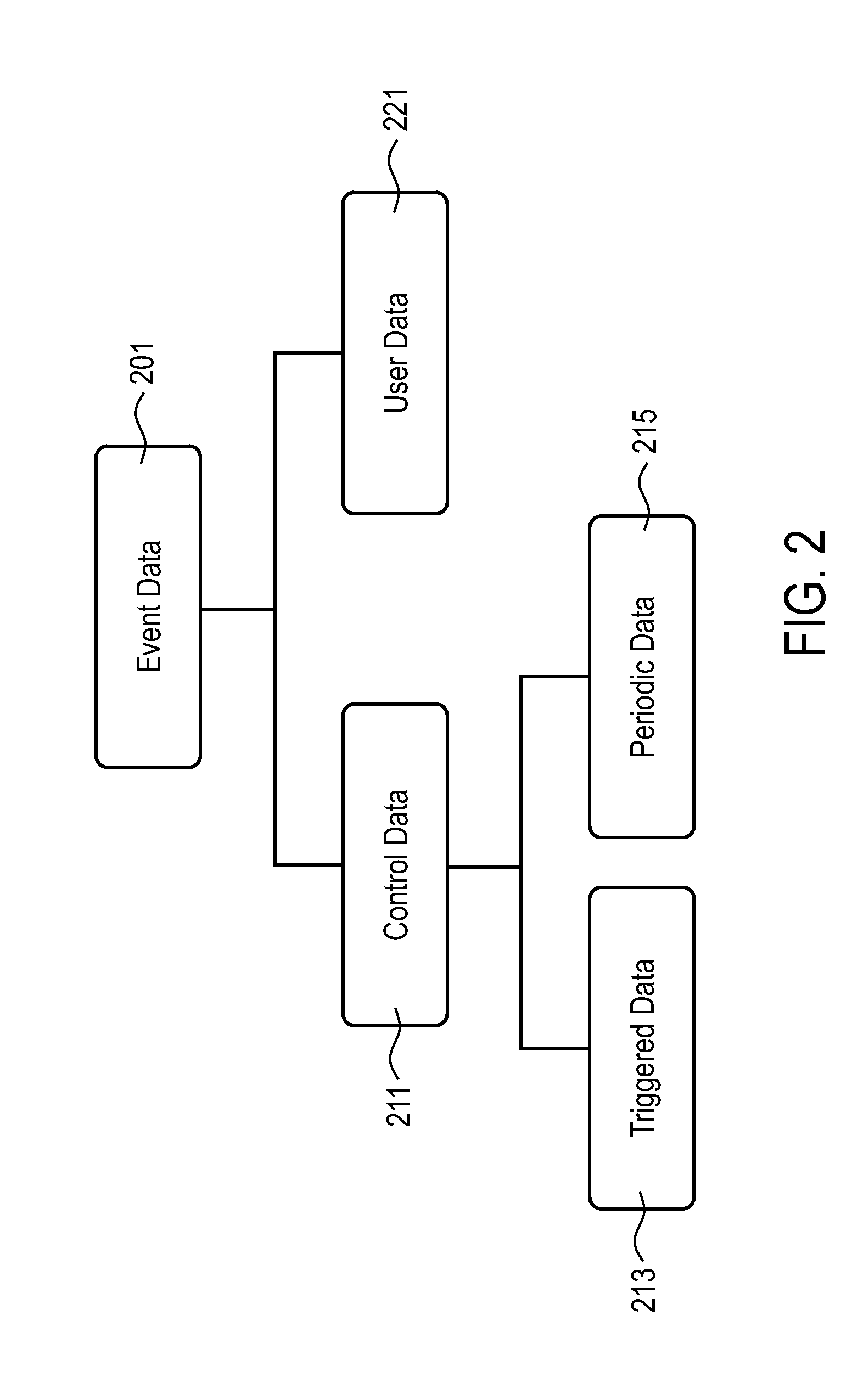
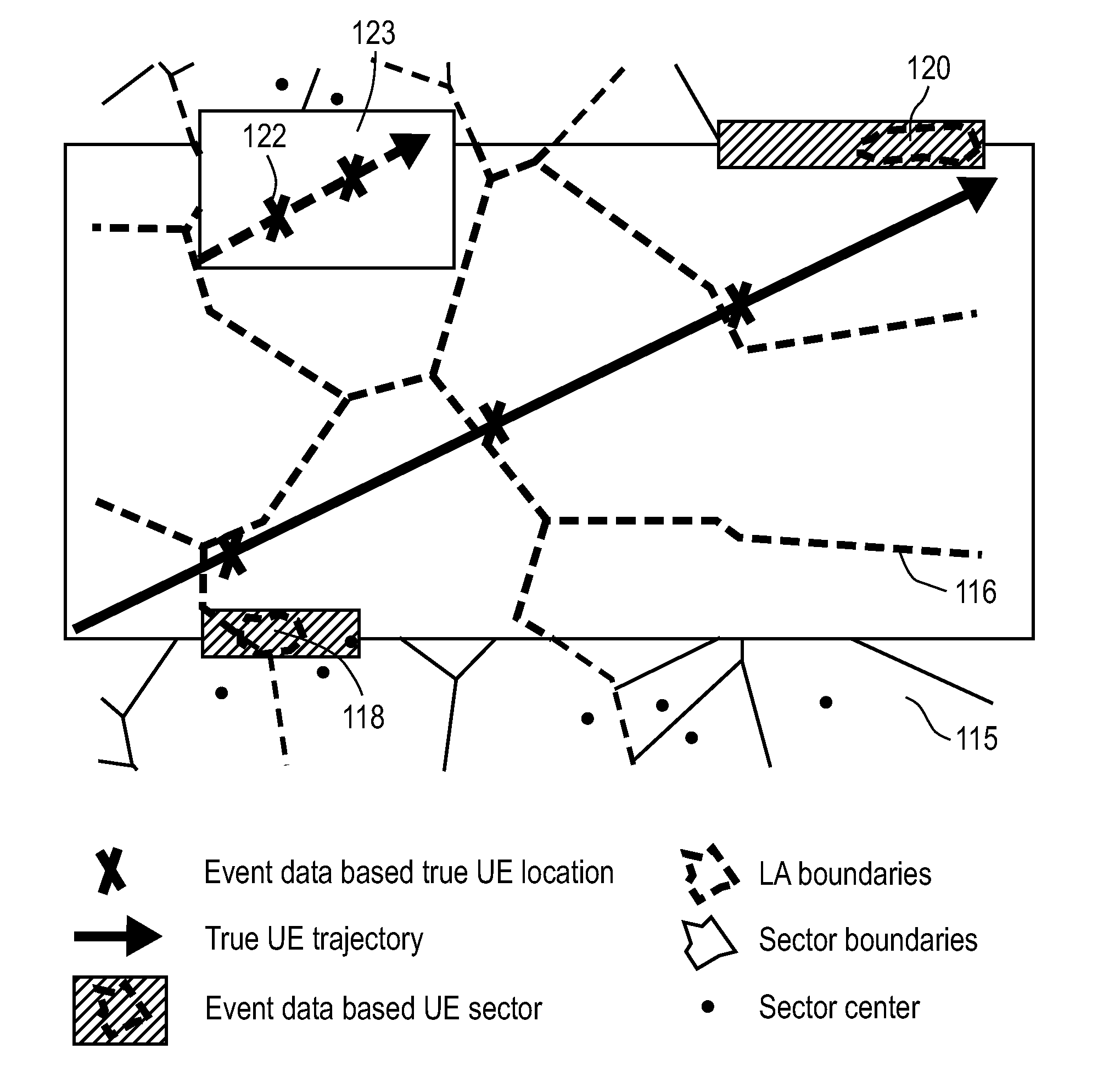
Methods and apparatuses are disclosed herein for population tracking, counting and / or movement estimation. In one embodiment, the method comprises receiving mobile phone operational data indicative of user equipment location, where the event data includes location area update messages and periodic registration messages; and performing travel estimation based on the mobile phone operation data, including performing interpolation on data associated with one or more individuals in a population to estimate intermediate positions of a trajectory of each of the one or more individuals for a specified time period based on a shortest path mesh sequence estimation algorithm.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Inter-domain coordination for mt and mo calls
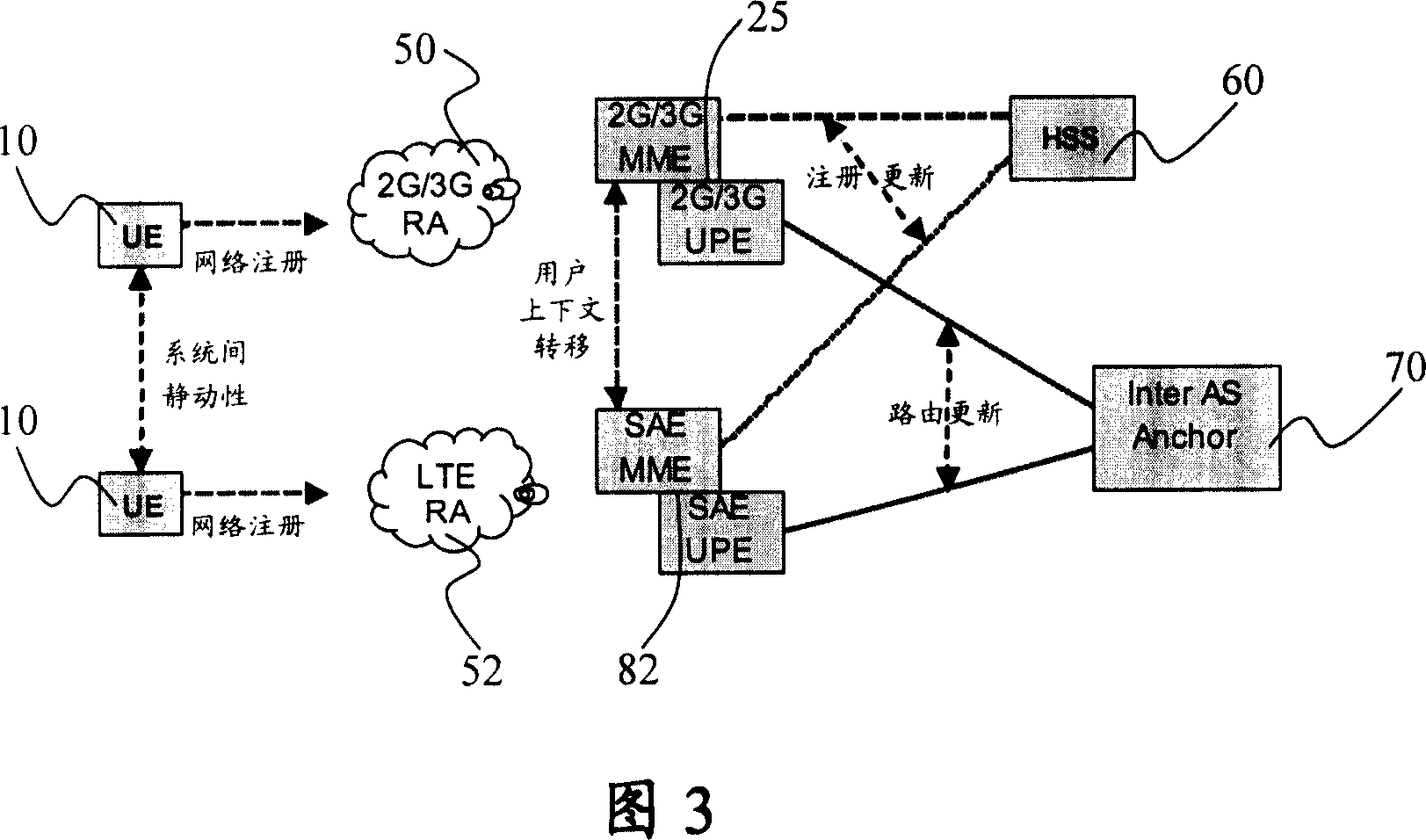
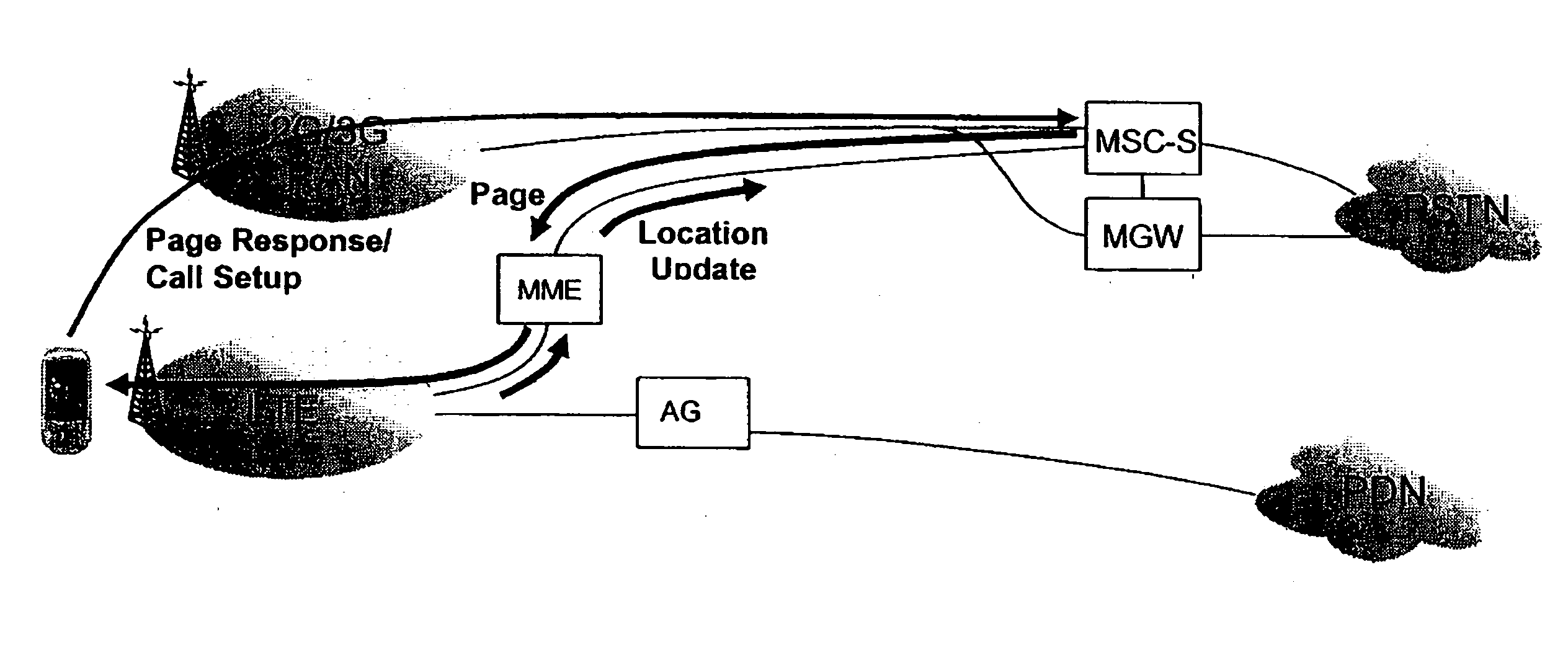
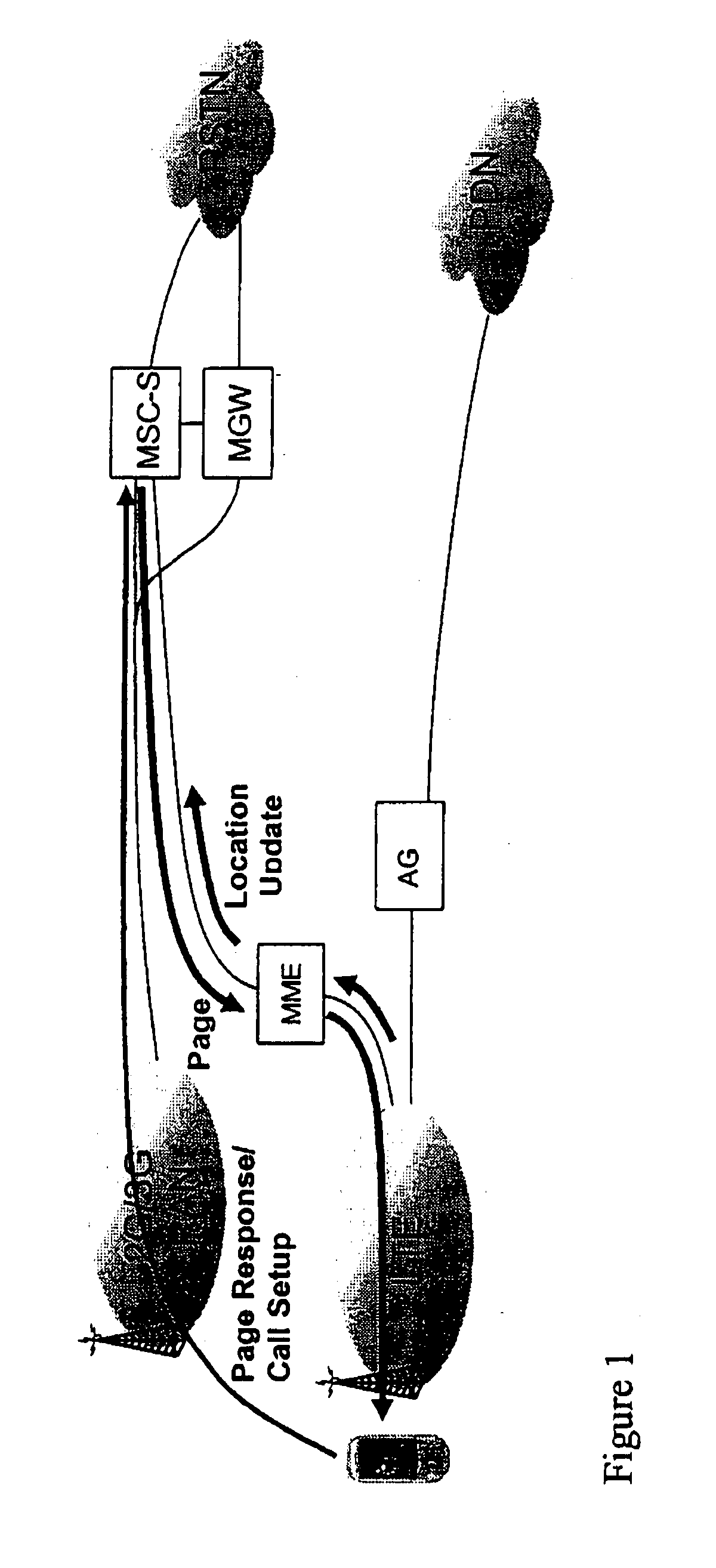
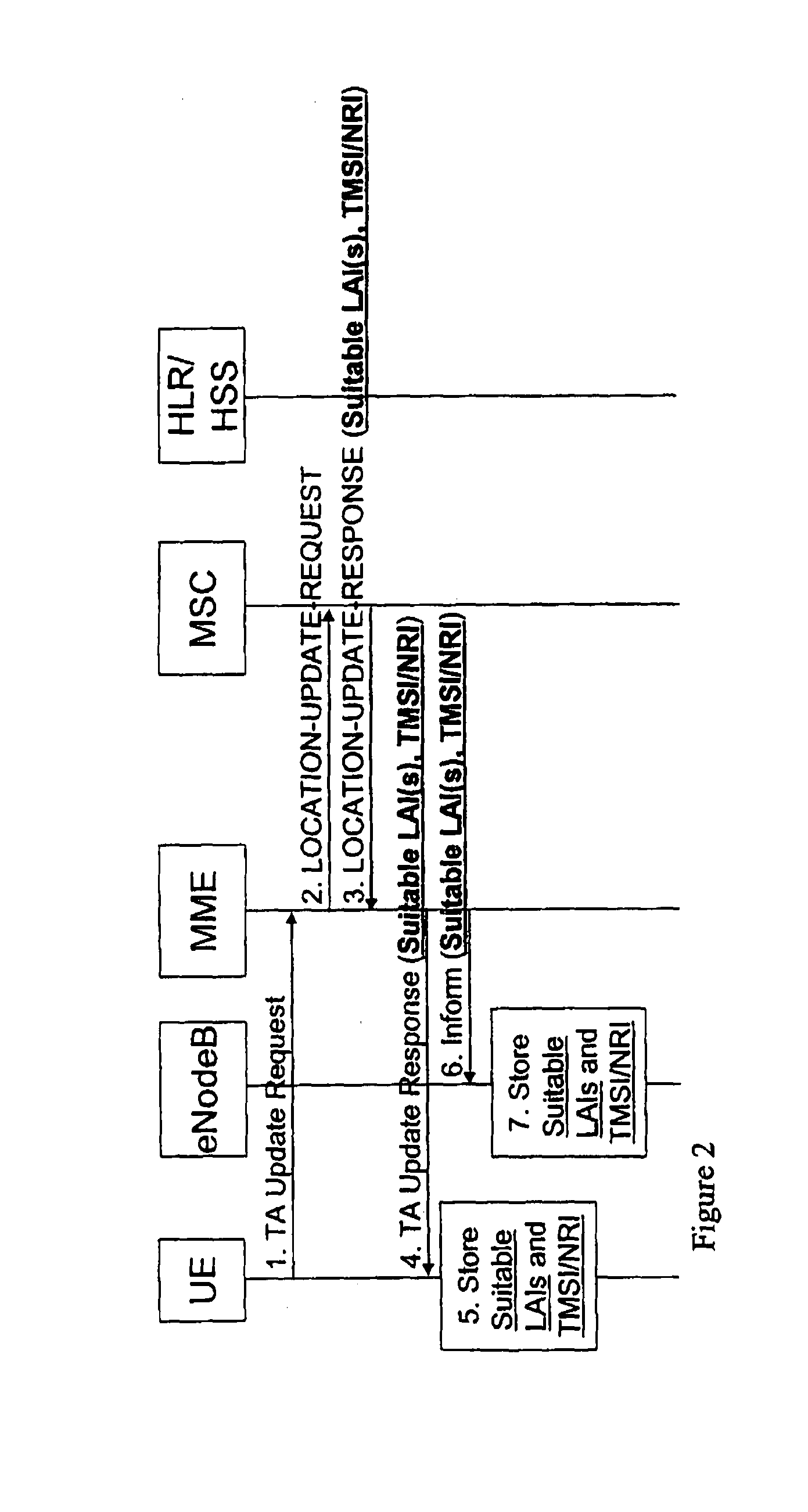
ActiveUS20100303041A1Time-division multiplexWireless commuication servicesMobility managementLocation area
A mobility management entity (MME) for setting up a call includes a first network interface which receives a tracking area update (TAU) request from a user equipment (UE). The MME includes a processing unit which translates the TAU request into a location area update (LAU) request. The MME includes a second network interface in communication with the processing unit which sends the LAU request to a mobile switching center (MSC) selected as a tracking MSC thereby establishing the MME as a network node through which the UE is paged. The second network interface receiving a LAU response from the tracking MSC that includes at least information identifying one or more suitable location area identifiers (LAI(s)) to which handover is allowed and Network Resource Identifier (NRI) information where the information indicates that the tracking MSC controls the suitable LAI(s), and the processing unit translating the LAU response into a TAU response which is sent through the first network interface to the UE. A user equipment (UE) includes a processing unit which transmits a tracking area update (TAU) request. The UE includes a network interface in communication with the processing unit which sends the TAU request to a mobility management entity (MME), and receives a TAU response having suitable location area identifiers (LAIs) and TMSI / network resource identifier (NRI). The UE includes a memory in communication with the network interface which stores the suitable LAIs and TMSI / NRI. A method for a mobility management entity (MME) for setting up a call. A method for a user equipment (UE).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Access control system, method, and arrangement in a wireless communication network
A system, method, and arrangement for controlling access to a wireless communication network. When a User Equipment (UE) is denied access to the network through a first access point, the UE stores the Location Area Identity (LAI) utilized at the first access point on a list of forbidden LAIs in the UE. If the LAI stored by the UE is utilized at another access point where the UE is allowed access, the LAI at the other access point is dynamically changed to a second LAI that is not on the UE's list of forbidden LAIs. An access point database stores a table defining which UEs are allowed to utilize each access point. The database also stores a list of rejected LAIs for each UE. A radio network controller accesses the database to determine an allowed LAI, and changes the LAI at the other access points where the UE is allowed access.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Location-based security for a portable computer
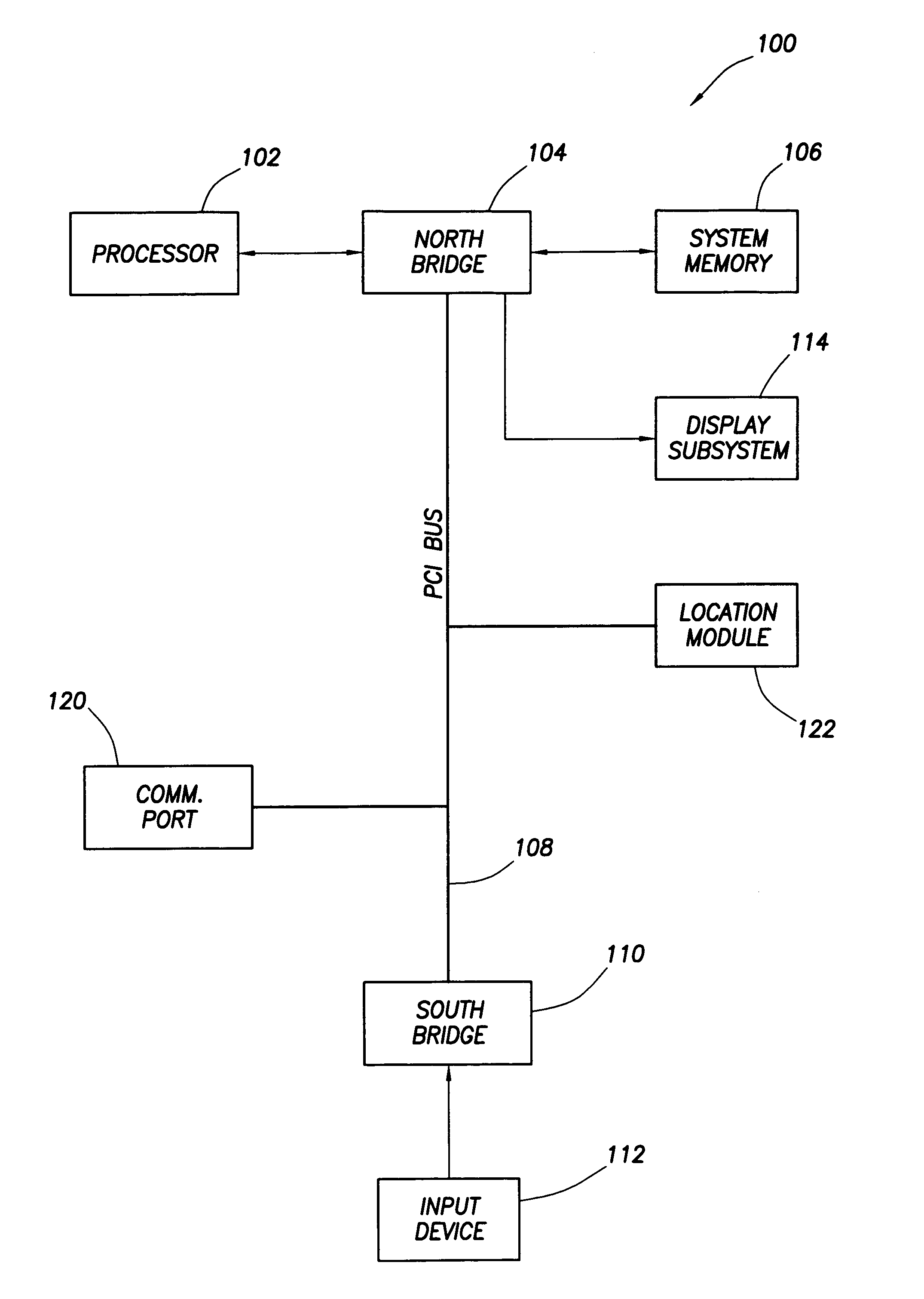
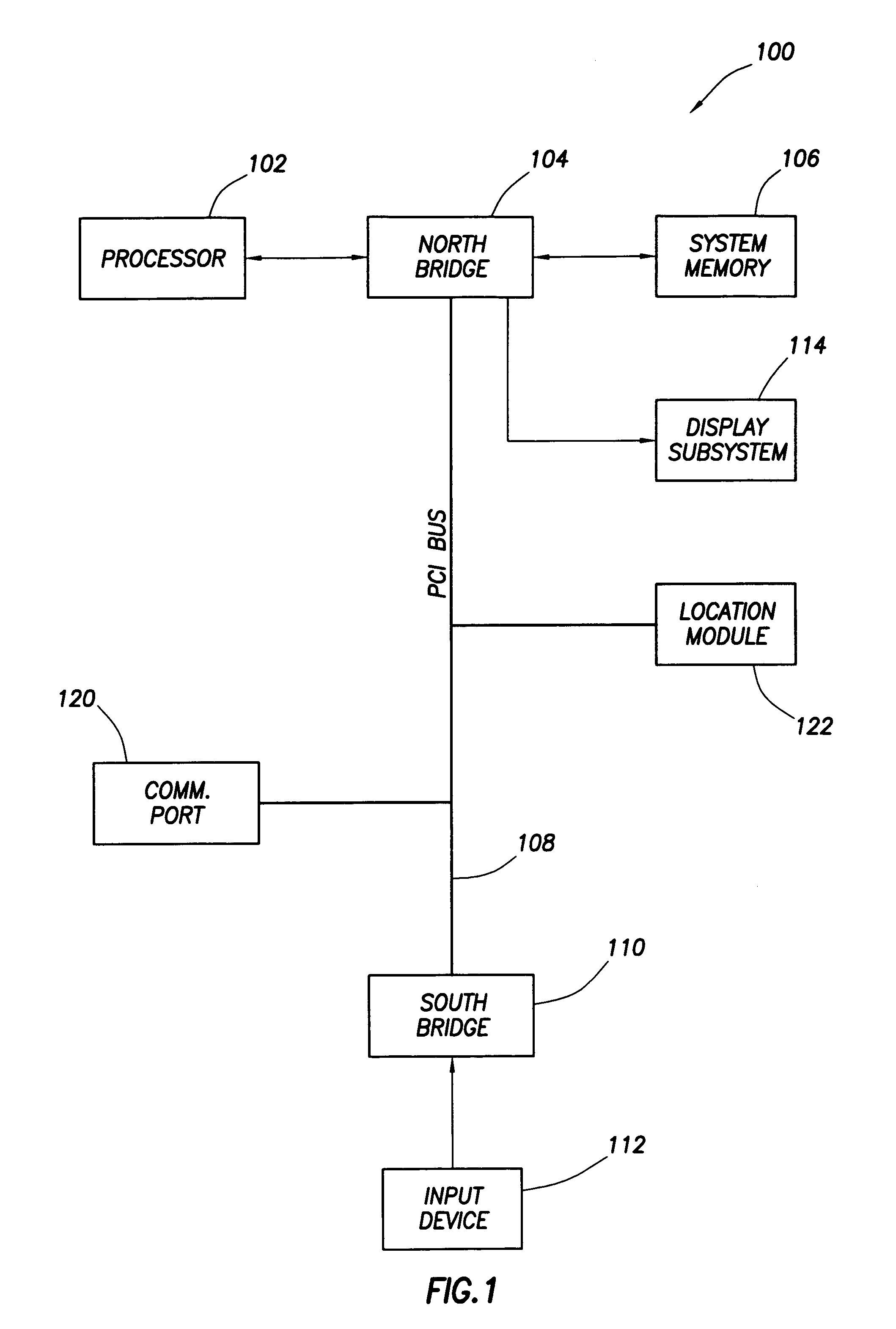
ActiveUS7051196B2Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsElectronic systemsEngineering
An electronic system embodies a security system which provides varying levels of security based on the location of the system. As such, the system includes a location module, such as a geosynchronous positioning system (“GPS”) receiver that permits the system to determine its location relative to a plurality of preset location areas. Such location areas might be programmed to include the user's office, home, predetermined location for a business trip and the like. Based on the location area in which the system is located, the system invokes a security mode associated with that particular location area. Different location areas may have different security modes.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Regulating the scope of service geographically in wireless networks based on priority
A network communication entity (e.g., an access terminal, access network and / or application server) obtains a location associated with a given access terminal that is attempting to participate in a given communication service, obtains a priority level of the given access terminal, determines a given level of service restriction for the given access terminal's participation in the given communication service based on the obtained location and the obtained priority level and restricts the given access terminal's participation in the given communication service based on the given level of service restriction. In an example, the priority levels can be established such that low-priority access terminals obtain a first level of service restriction within a defined location region, and a second level of service restriction outside of the defined location region, whereas high-priority access terminals obtain the first level of service restriction both inside and outside of the defined location region.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Location system adapted for use in multipath environments
InactiveUSRE36791E1Facilitates discriminationLow costDirection finders using radio wavesMemory record carrier reading problemsImage resolutionRadiolocation
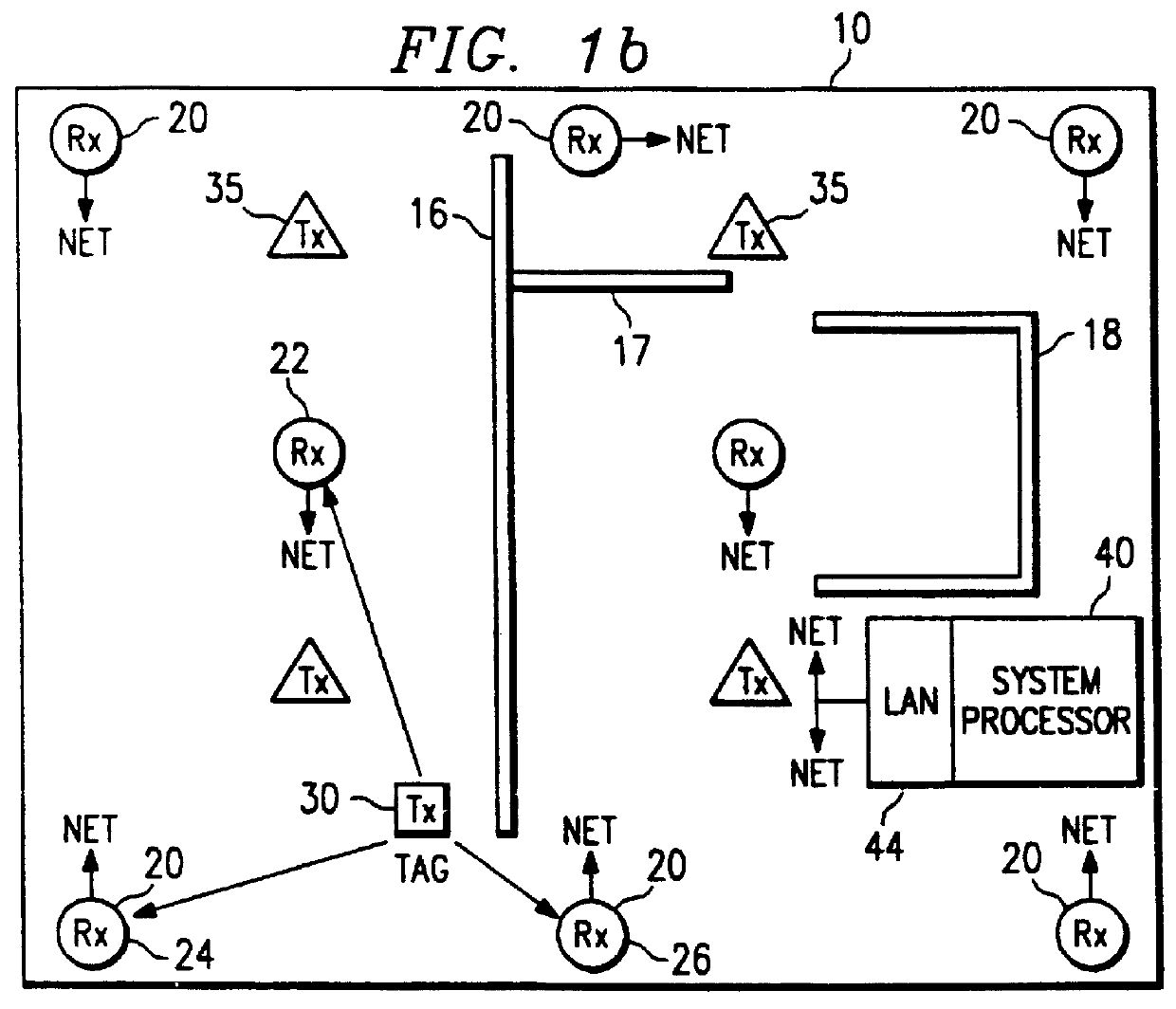
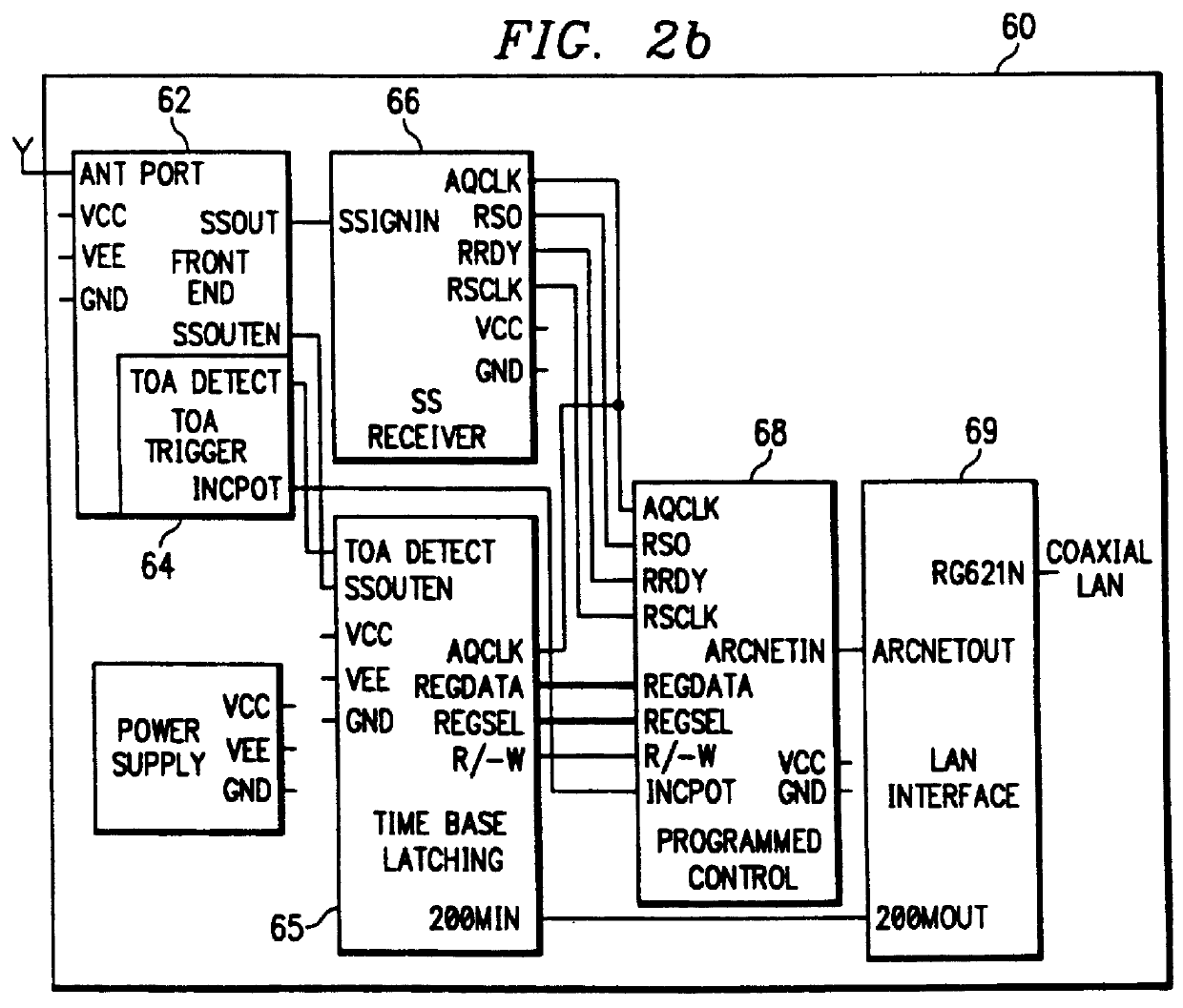
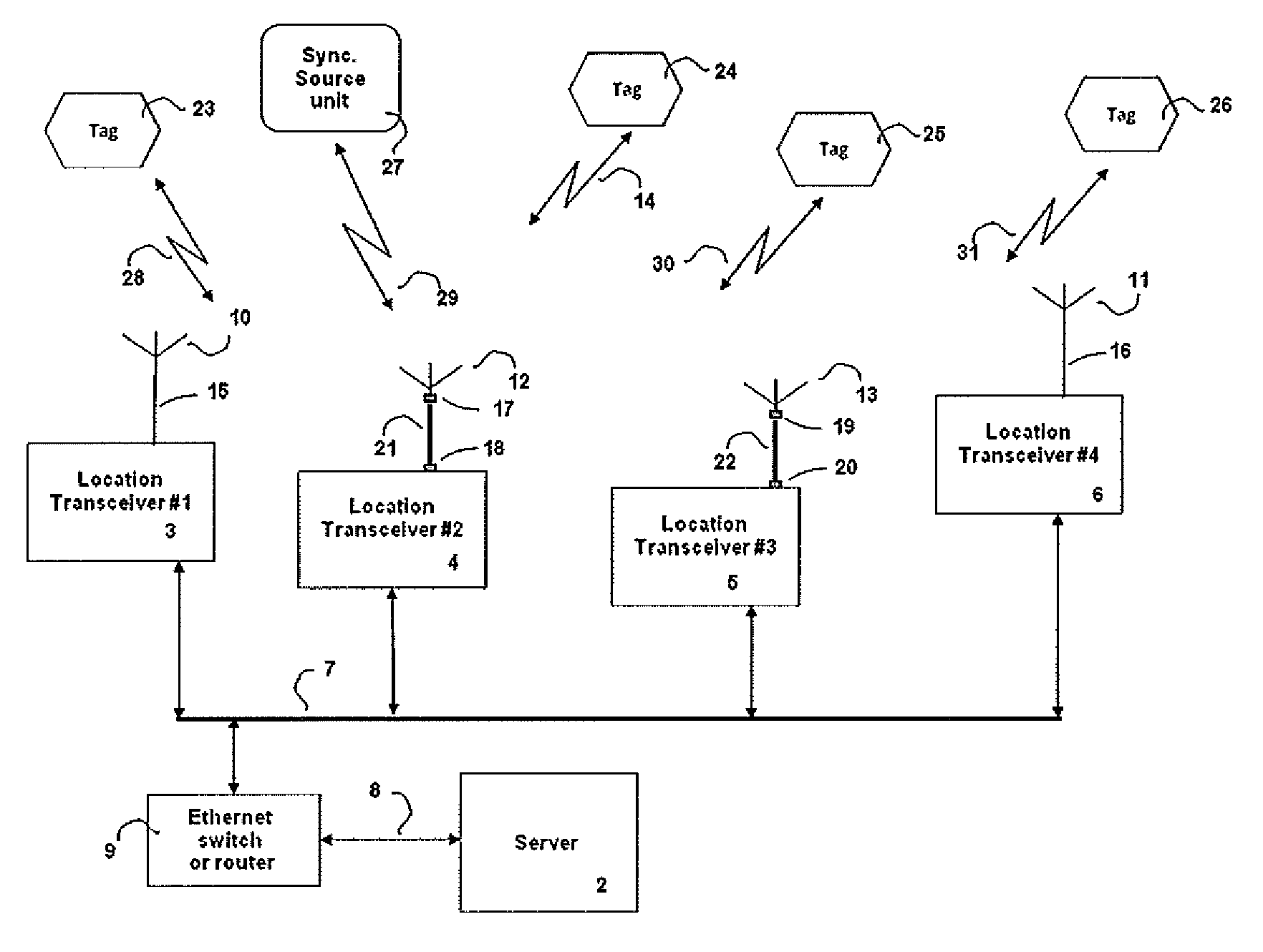
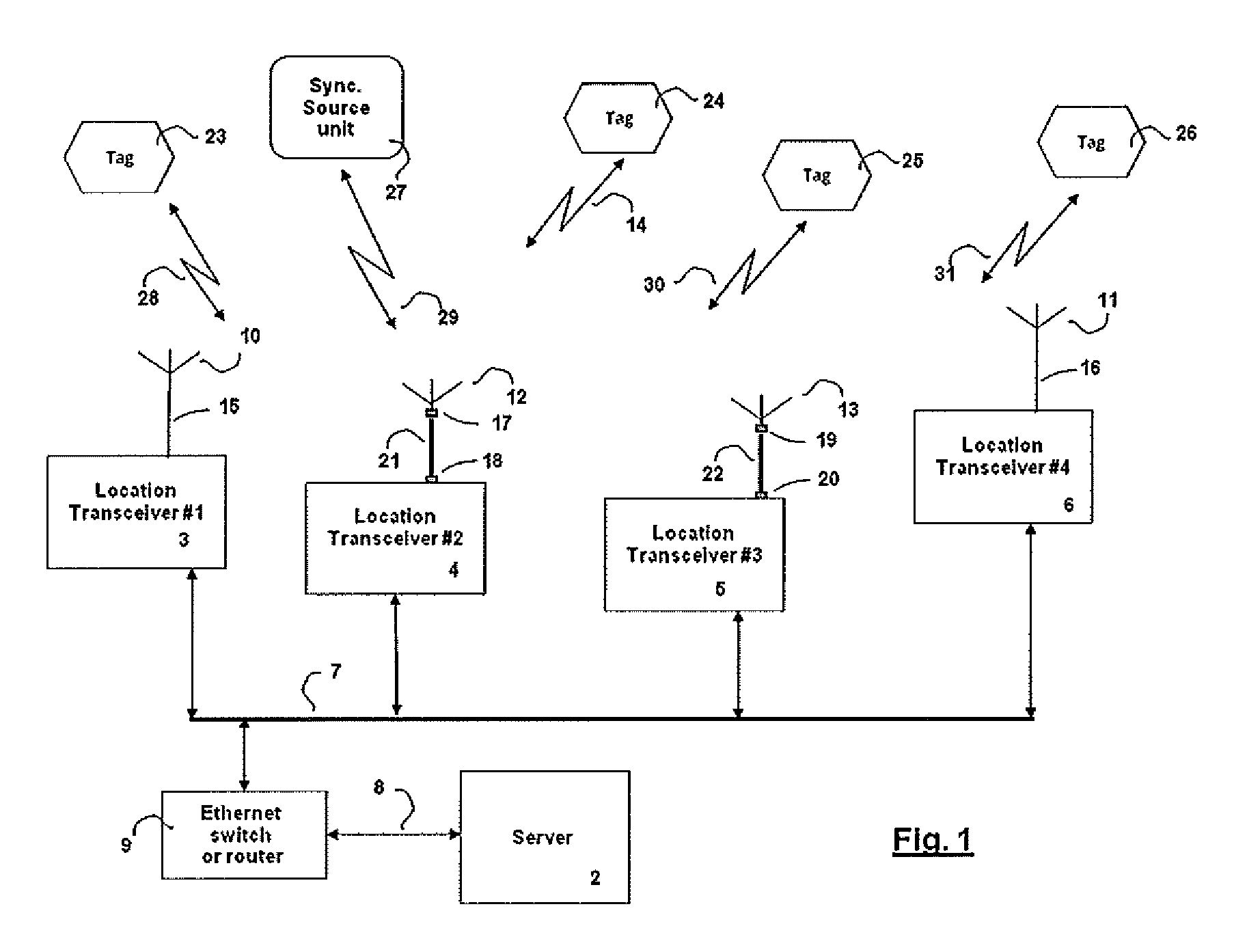
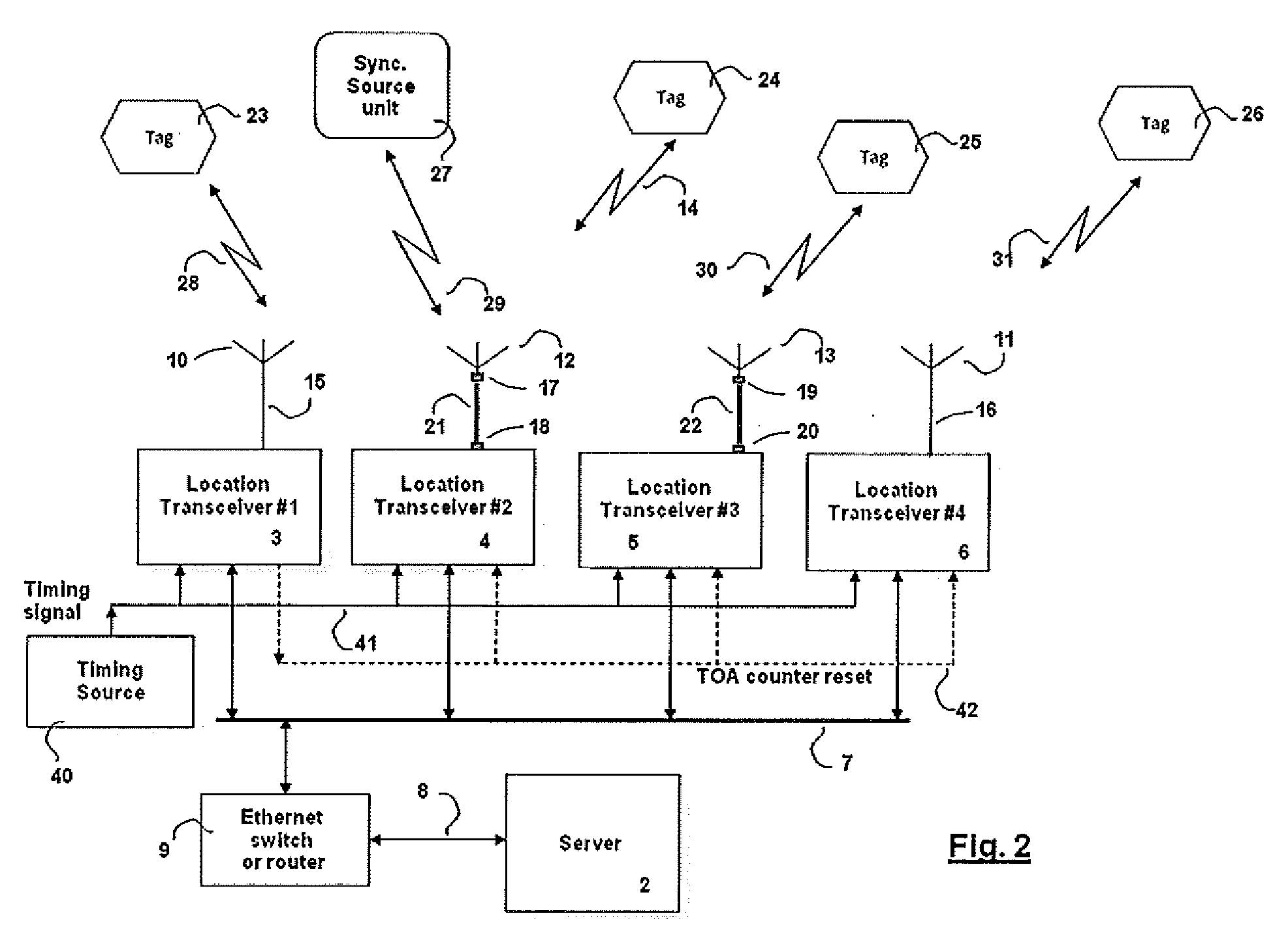
A radiolocation system for multipath environments, such as for tracking objects in a semiconductor fabrication facility (FIGS. 1a-1b), includes an array of receivers (20) distributed within the tracking area, coupled to a system processor (40) over a LAN. A TAG transmitter (30) located with each object transmits, at selected intervals, spread spectrum TAG transmissions including at least a unique TAG ID. In a high resolution embodiment, object location is accomplished by time-of-arrival (TOA) differentiation, with each receiver (FIG. 2b) including a TOA trigger circuit (64) for triggering on arrival of a TAG transmission, and a time base latching circuit (65) for latching the TOA count from an 800 MHz time base counter. In a low resolution embodiment, each receiver of the array is assigned a specific location-area, and receives TAG transmissions almost exclusively from TAGs located in that area, thereby eliminating the need for any time-of-arrival circuitry.
Owner:FRESHLOC TECH
Distributed opportunistic scheduling in IEEE 802.11 wireless location area networks (WLANs)
InactiveUS20080063106A1Maximum multi-user diversity gainMaintaining probing overheadNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexDelayed timeLocation area
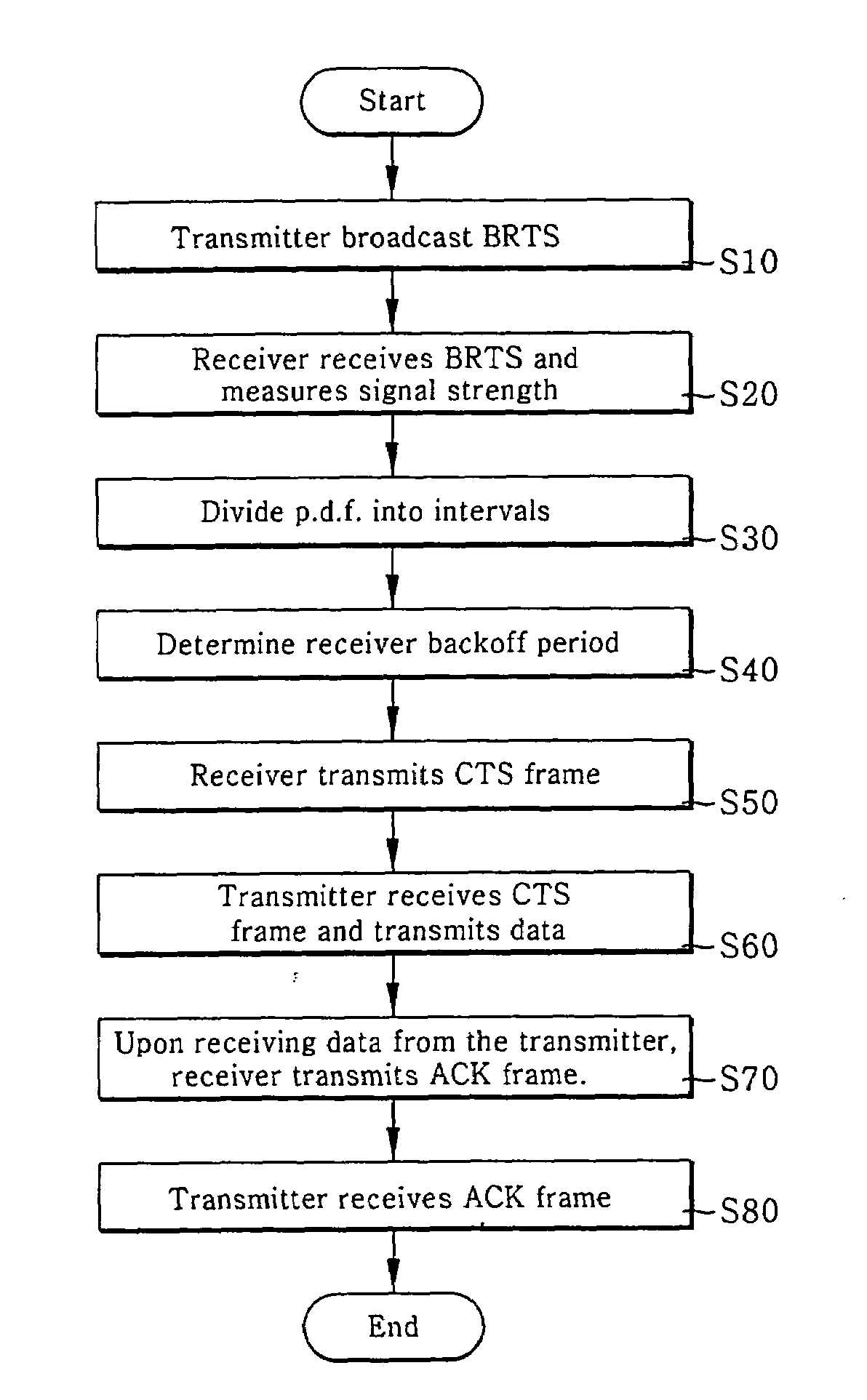
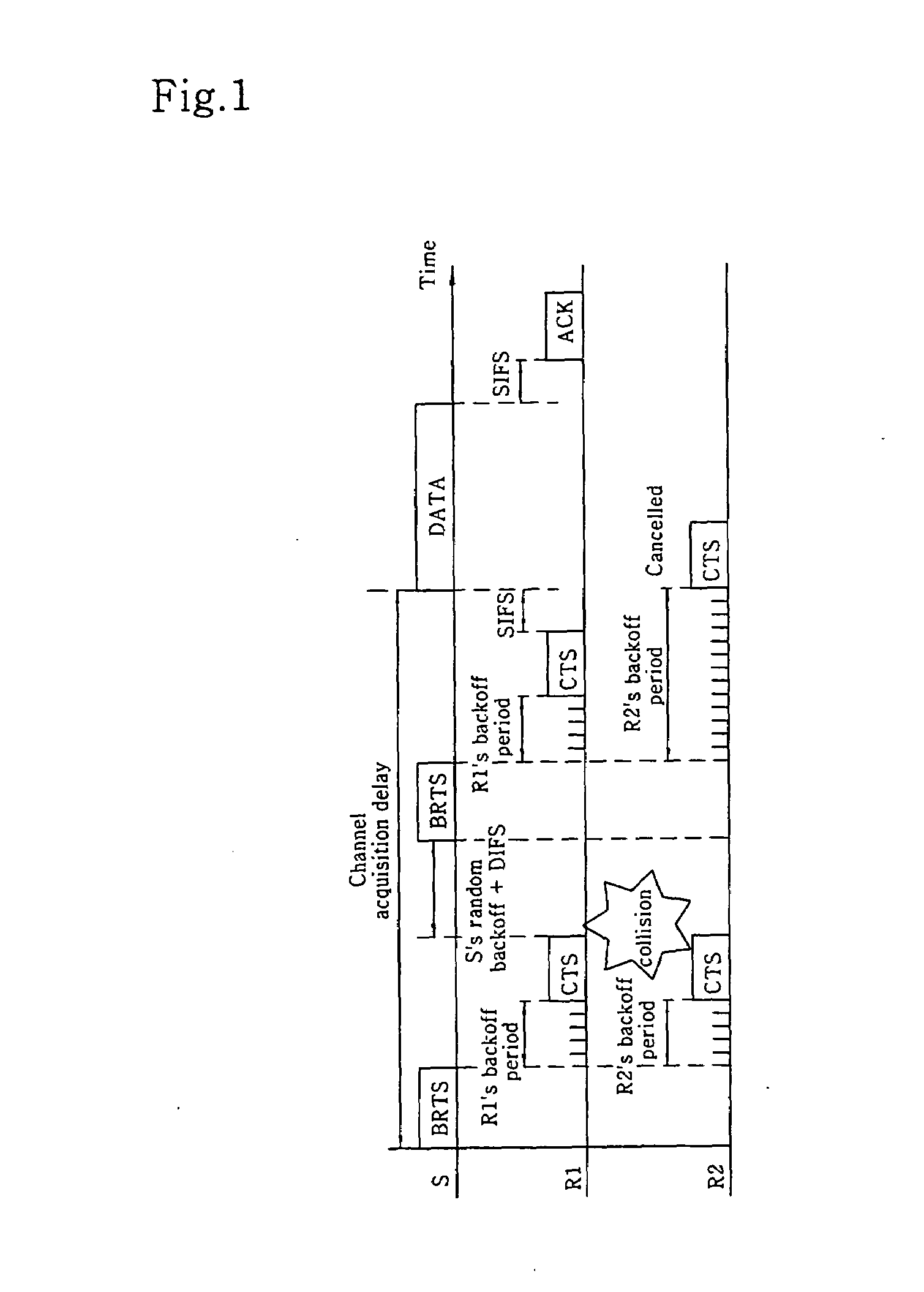
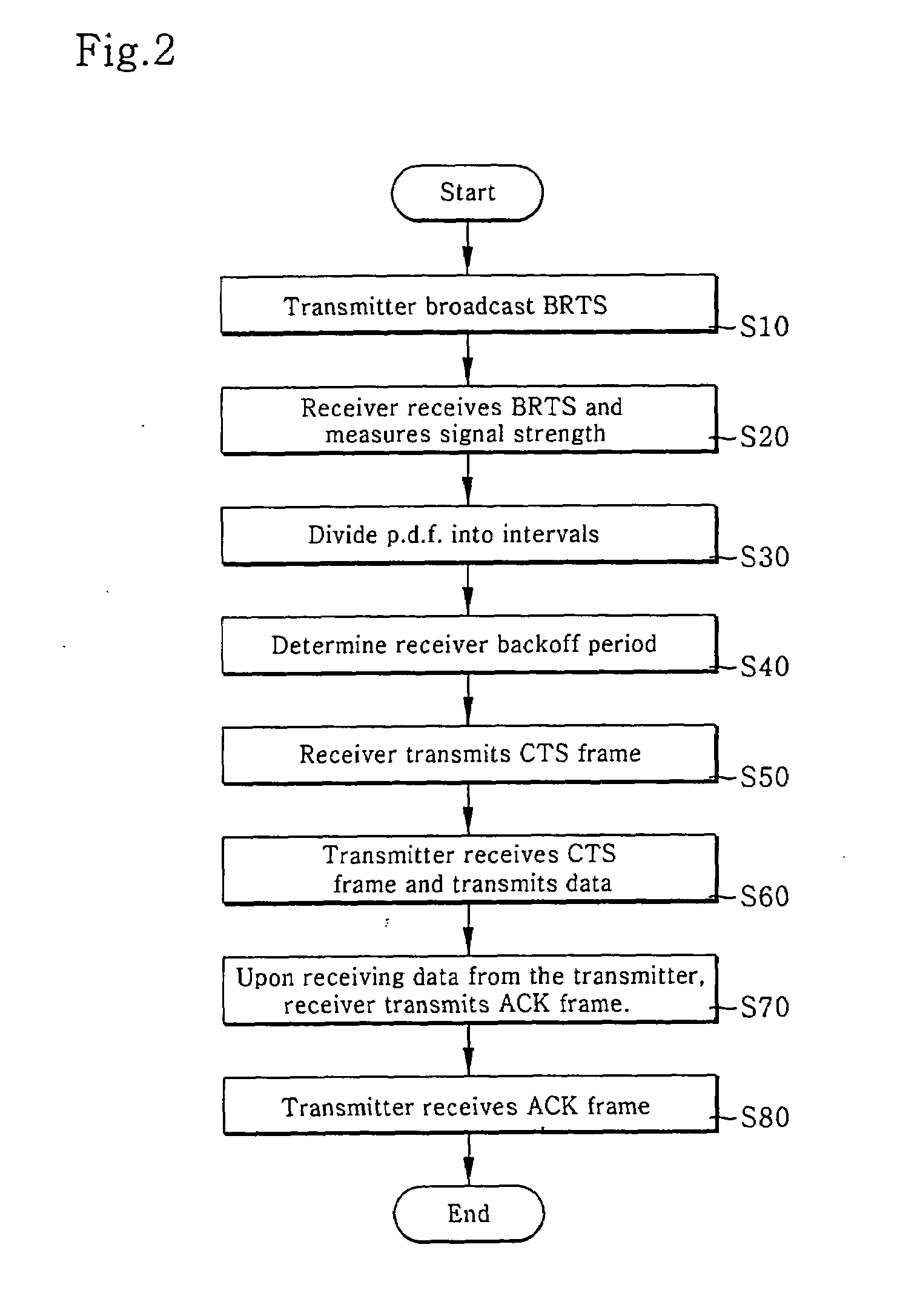
A WLAN distributed / opportunistic scheduling (WDOS) method for acquiring a multi-user diversity gain is disclosed. The WDOS method allows a transmitter (i.e., a transmission user) to observe channel conditions of receivers (i.e., reception users), and commands the transmitter to transmit packets to a specific receiver having a relative good channel condition. The WDOS method uses a modified RTS / CTS exchange method to perform the channel probing. If the transmitter broadcasts the BRTS frame, each receiver transmits a CTS frame after the lapse of its backoff period. According to the reception signal strength distribution, the backoff delay time minimizes the number of CTS collisions irrespective of the number of receivers, reduces an amount of channel probing overheads, and maximizes a multi-user diversity gain. The better the relative channel condition, the lower the backoff delay time.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Location system and method with a fiber optic link
InactiveUS20110050501A1Simple processSimplifying the fiber optic link and the transpondersPosition fixationBeacon systemsFiberTransceiver
A TDOA (time difference of arrival) location system, in which mobile wireless devices broadcast wireless signals which are received by two or more transceivers deployed in the vicinity of the mobile wireless device. Each transceiver measures the TOA (time of arrival) of the received broadcasted signal and reports the TOA to a central server. The central server then calculates the mobile device position using multi-lateration of TDOA values. The system uses fiber optic links between the antennas and the transceivers deployed in the location area to provide unique advantages that couldn't be achieved using RF coaxial cables.
Owner:AEROSCOUT
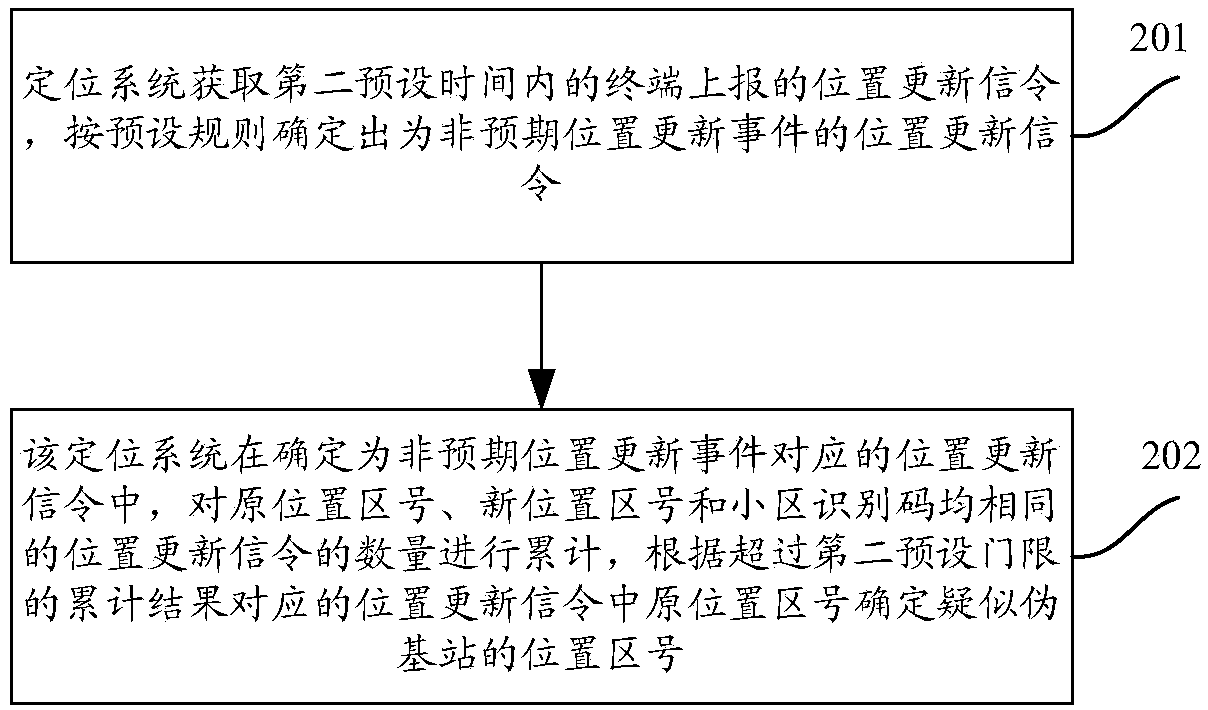
Pseudo base station positioning method
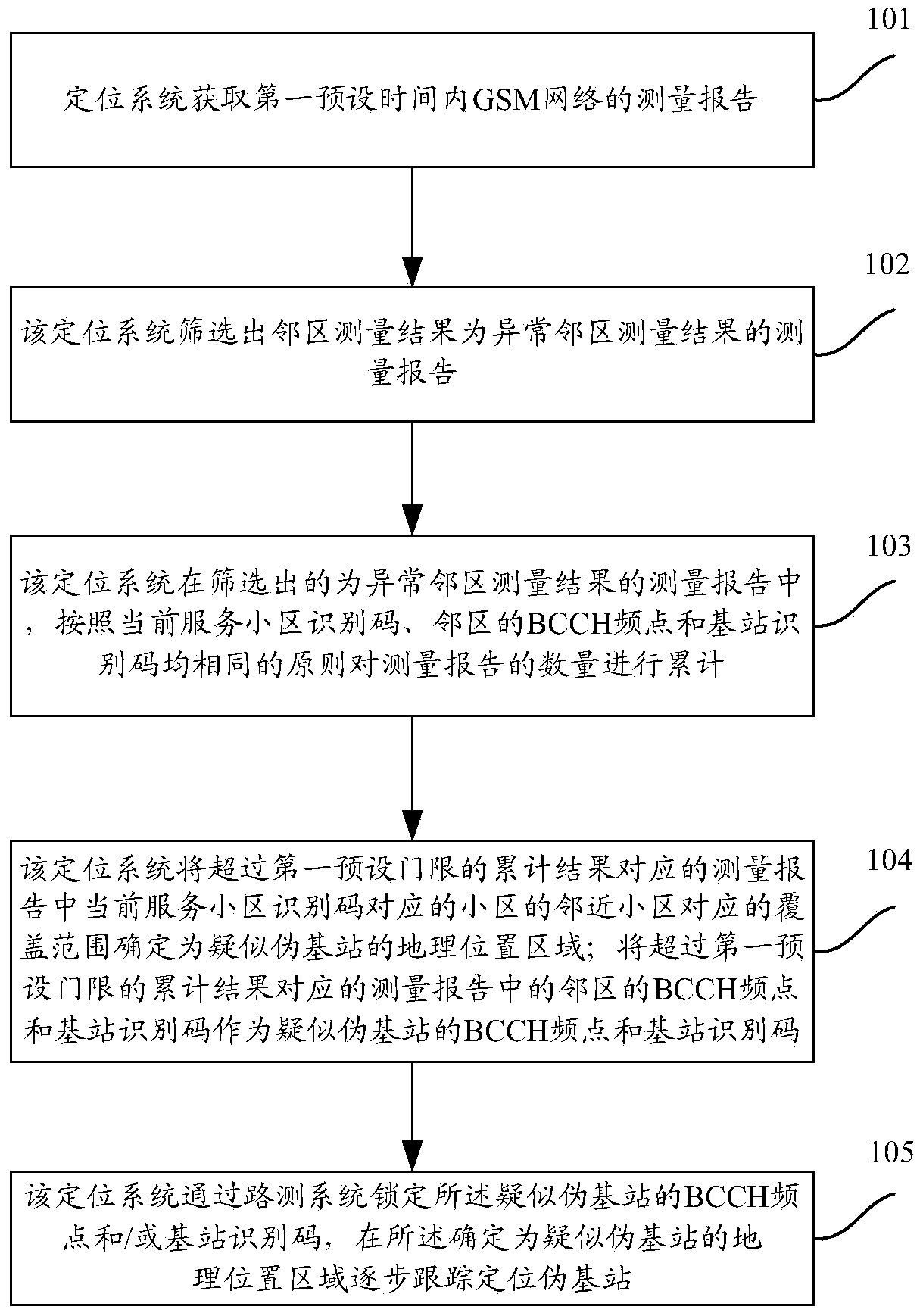
The invention discloses a pseudo base station positioning method, comprising steps of obtaining a measurement report of a GSM network in first preset time, screening out the measurement report of an adjacent area the measurement result of which is abnormal, performing analysis and statistics on the measurement reports screened out, determining geographic location areas where suspected pseudo base stations are positioned, BCCH frequency points of the suspected base pseudo base stations and identification codes of the base stations, following and positioning the pseudo base stations step by step in the determined geographic location areas where the suspected pseudo base station are positioned. The pseudo base station positioning method can position the pseudo base station quickly and accurately.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF INFORMATION & COMM
System and method for population tracking, counting, and movement estimation using mobile operational data and/or geographic information in mobile network
ActiveUS20120115475A1ResourcesWireless commuication servicesUser equipmentGeographic information system
Methods and apparatuses are disclosed herein for population tracking, counting and / or movement estimation. In one embodiment, the method comprises receiving mobile phone operational data indicative of user equipment location, where the event data includes location area update messages and periodic registration messages; and performing travel estimation based on the mobile phone operation data, including performing interpolation on data associated with one or more individuals in a population to estimate intermediate positions of a trajectory of each of the one or more individuals for a specified time period based on a shortest path mesh sequence estimation algorithm.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
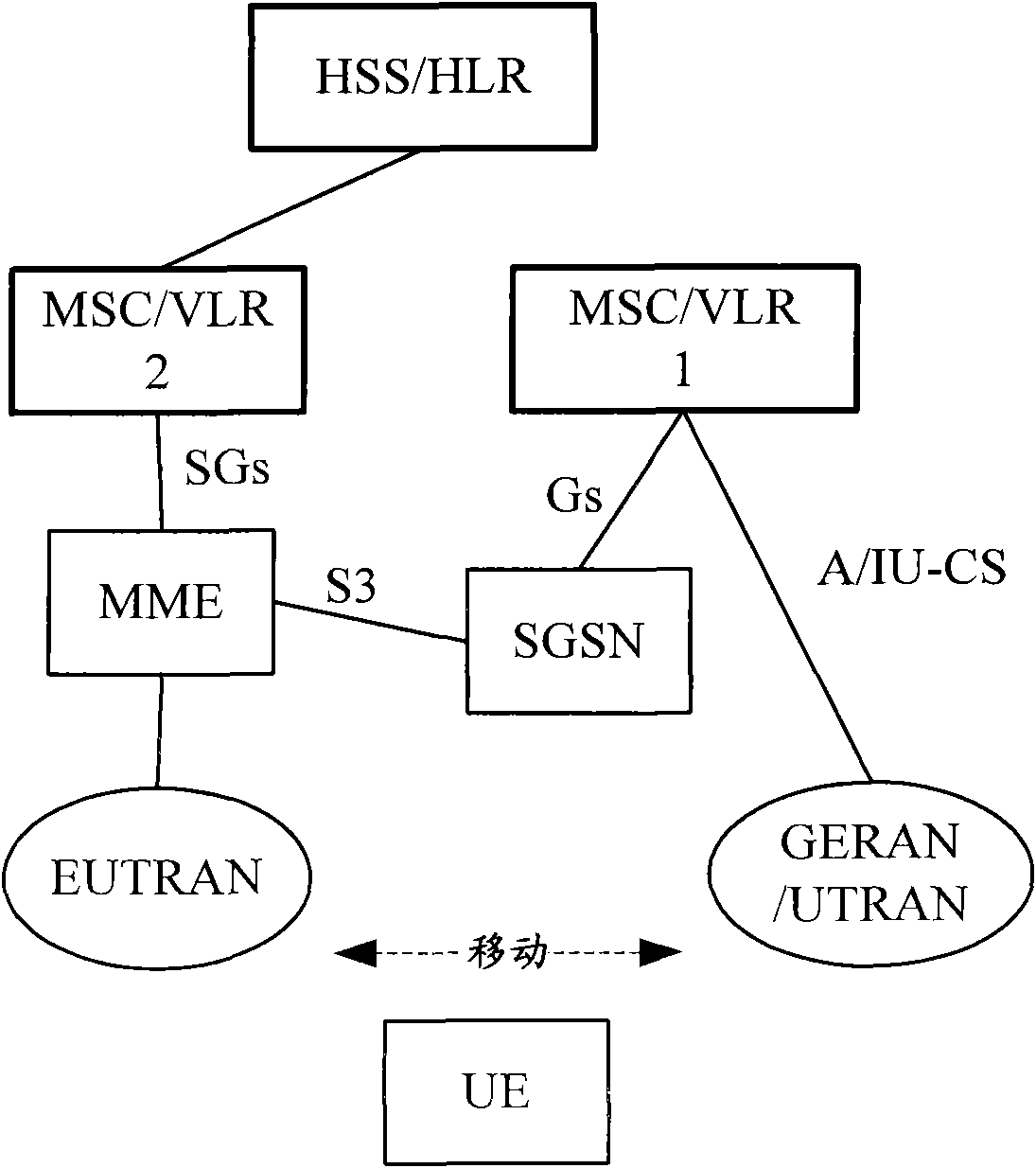
Mobile management entity operating in communications network and selection method therefor
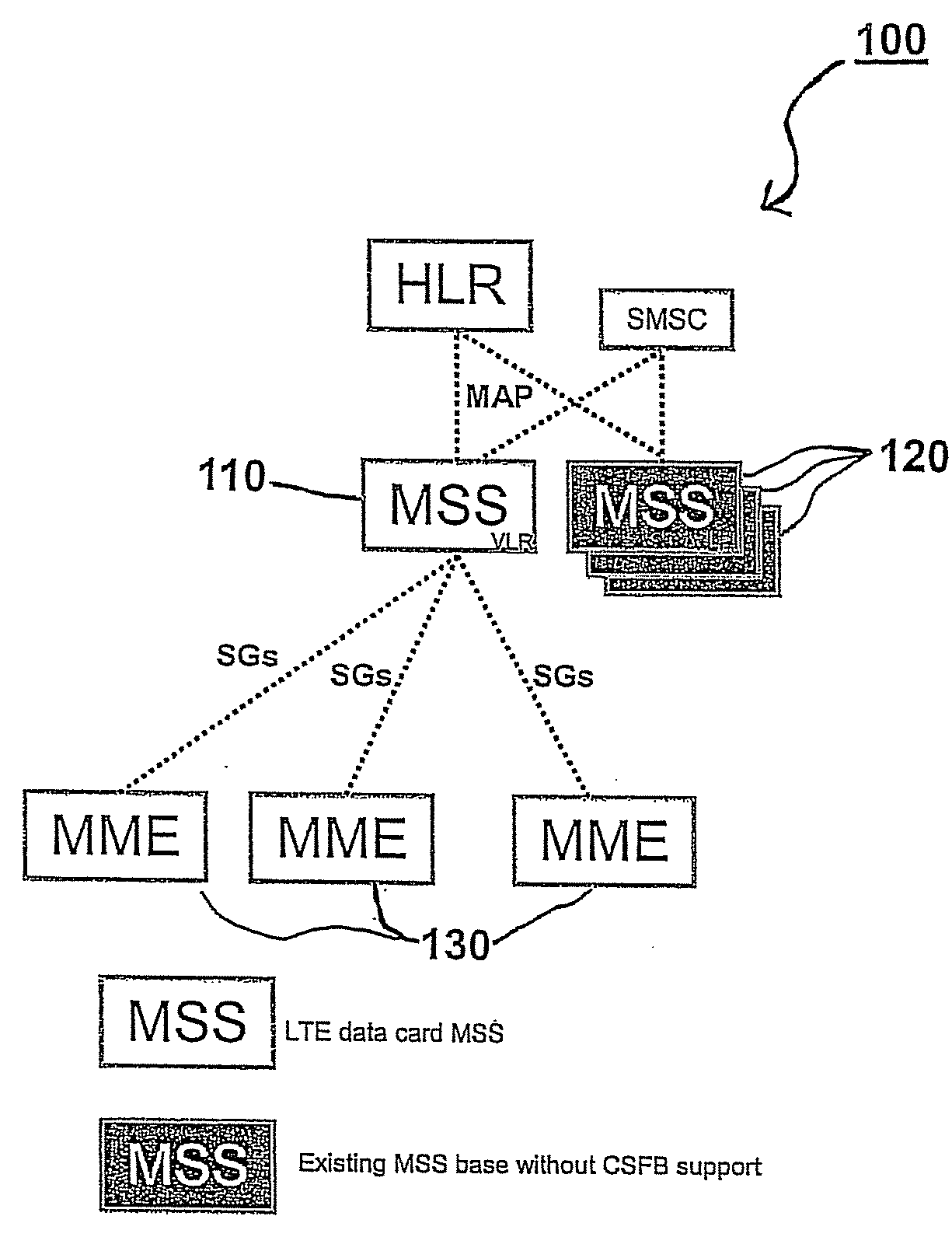
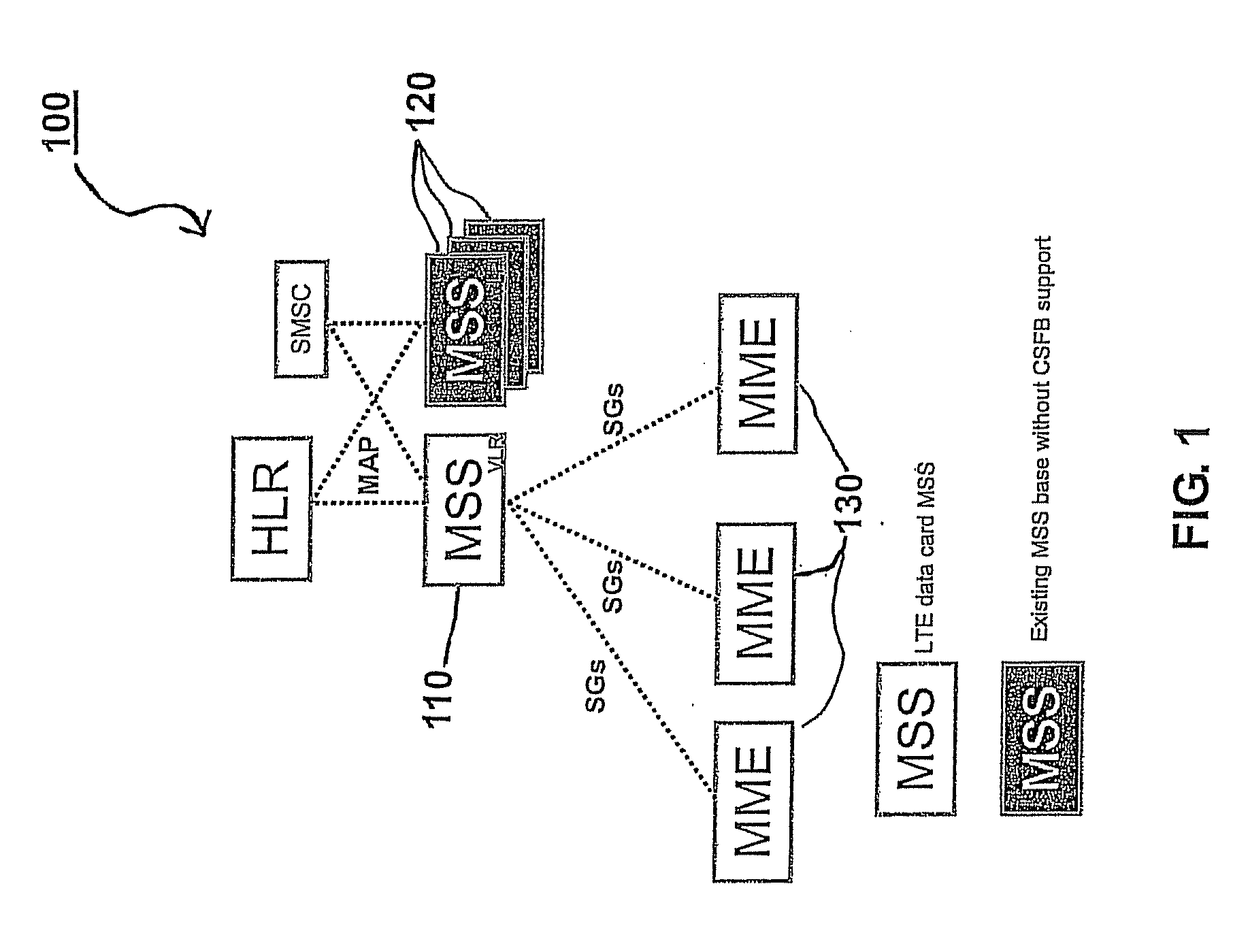
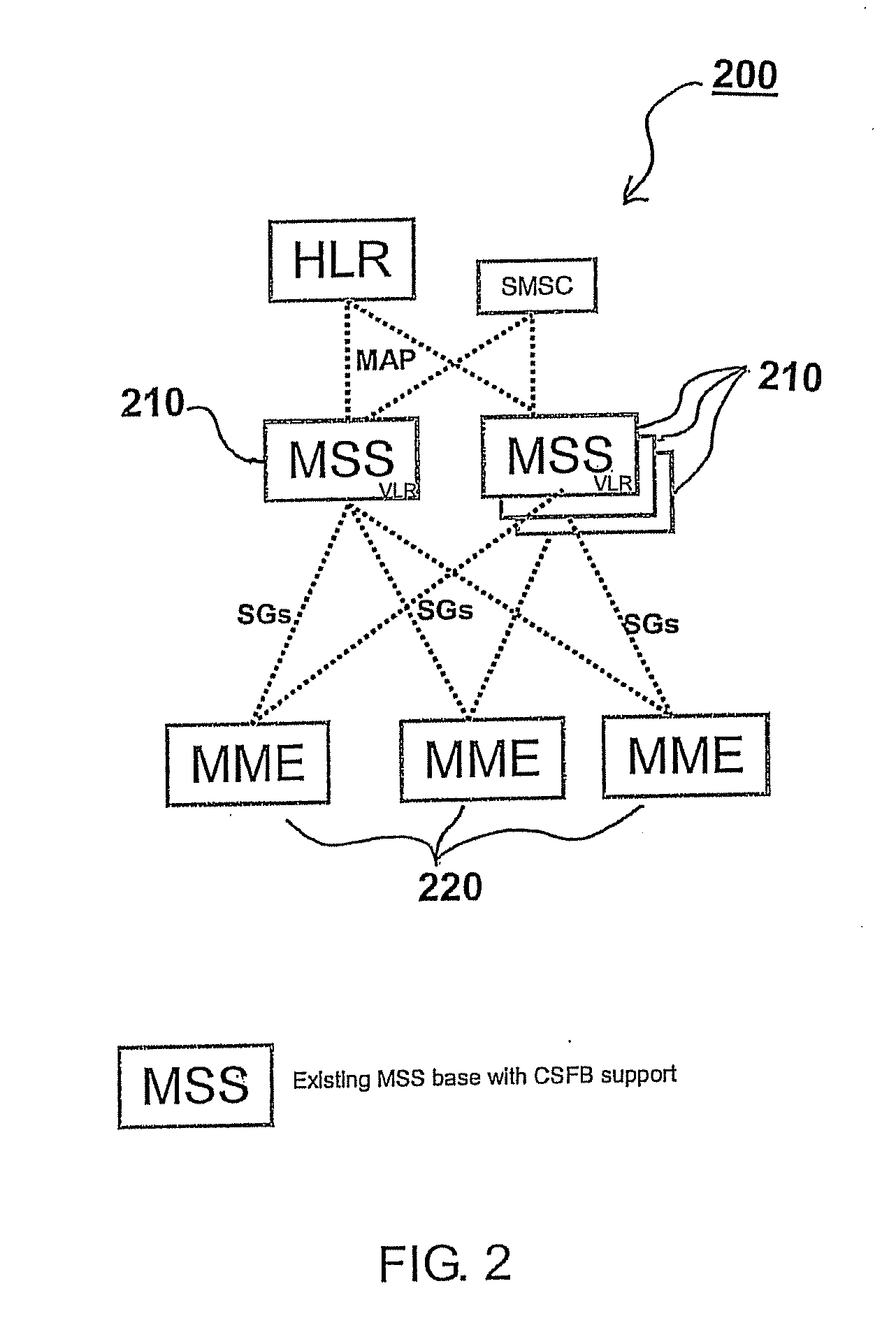
A selection method implemented as an algorithm in a mobile management entity (MME) operating in a communications network. The method includes receiving a unique identifier of a subscriber operating within the network and determining, based on the unique identifier, whether the subscriber has full circuit switching fallback (CSFB) capability or has only packet switching (PS) capability. When it is determined that the subscriber has full CSFB capability, a mobile switching center server (MSS) is selected based on original tracking area matrices and / or tracking area identity-location area identity mapping defined in the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). When it is determined that the subscriber has only PS capability, an MSS is selected from a group of MSSs having CSFB support only for short message service (SMS) delivery.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Reducing paging response time in a wireless communication system
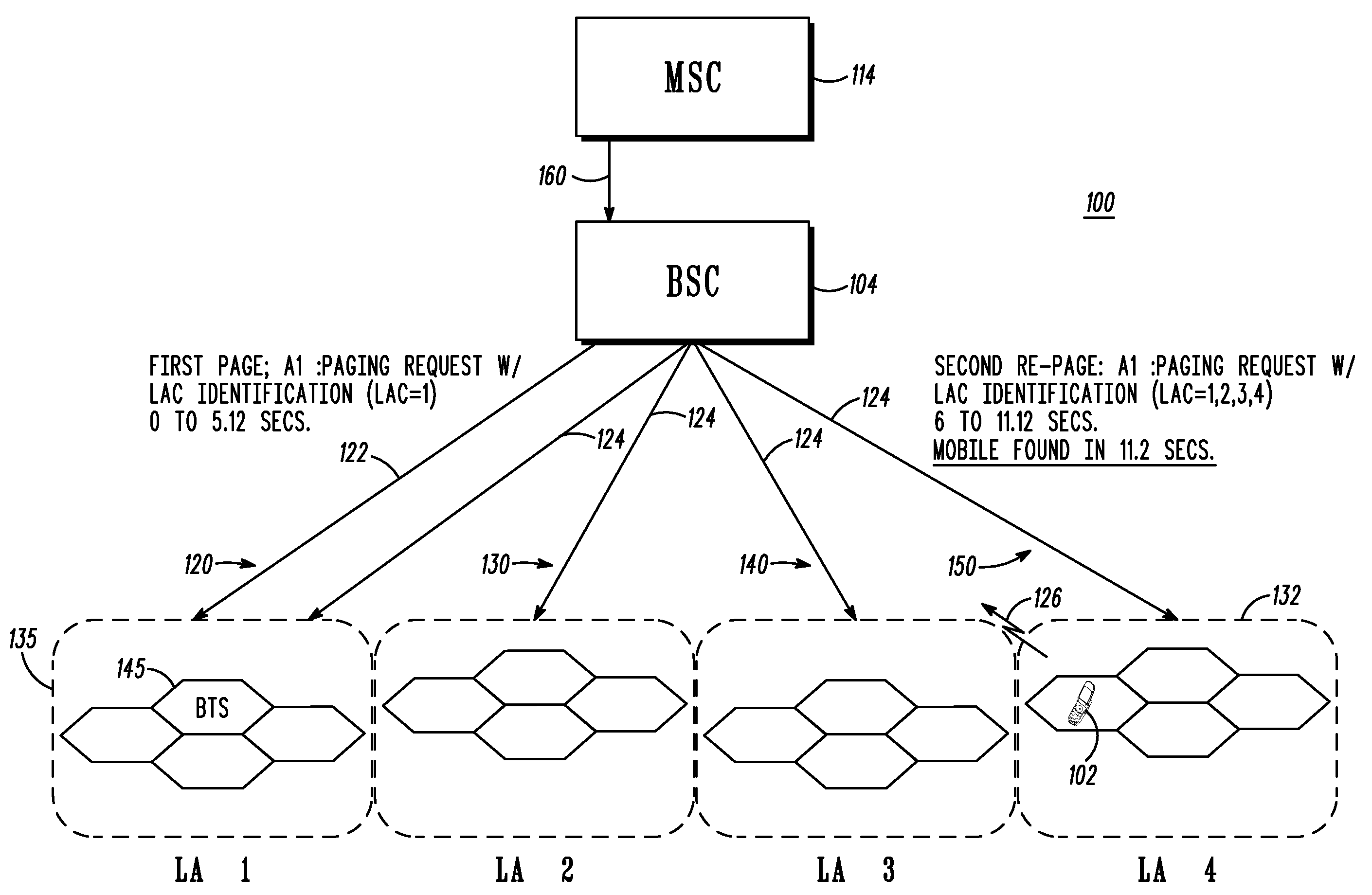
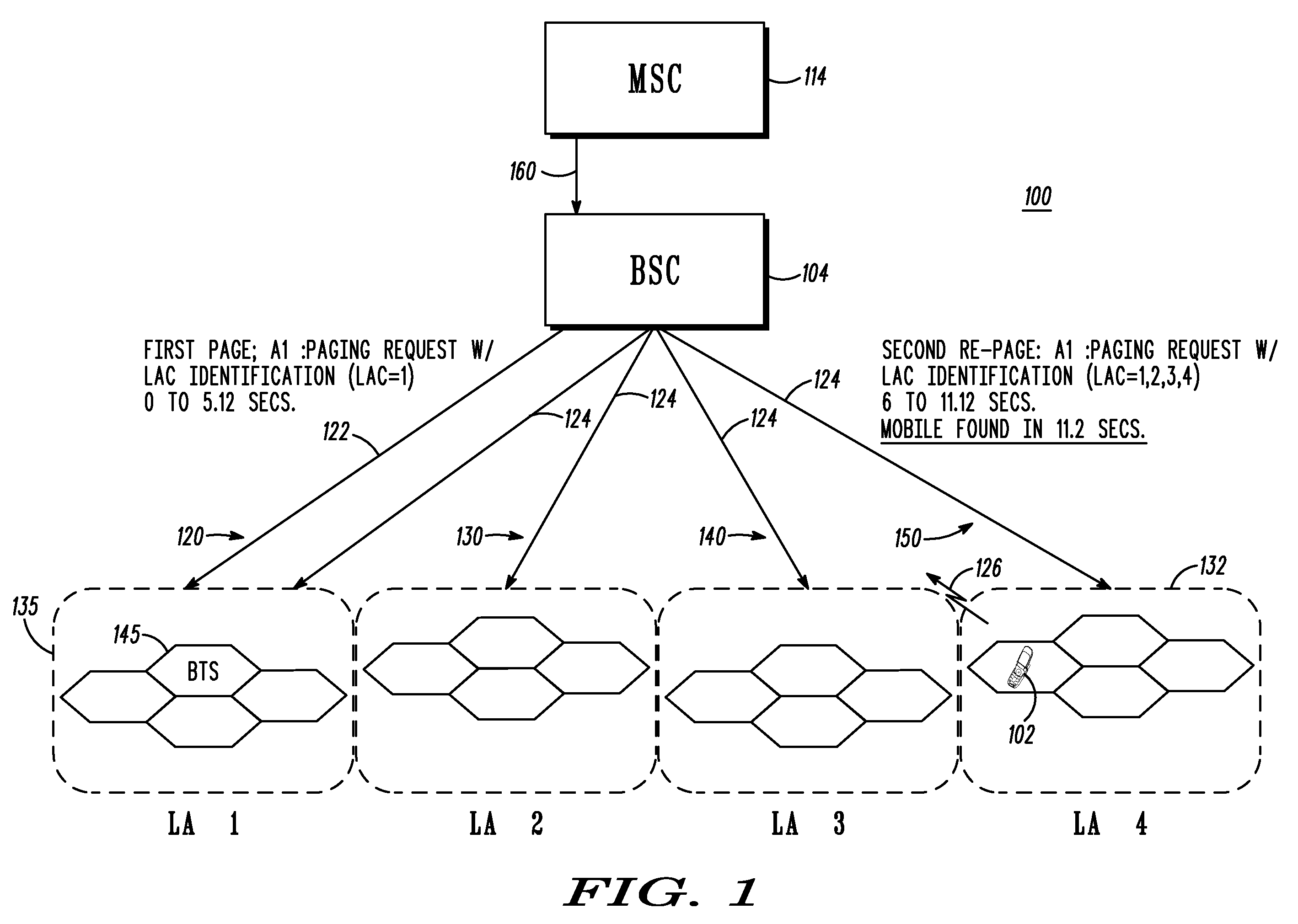
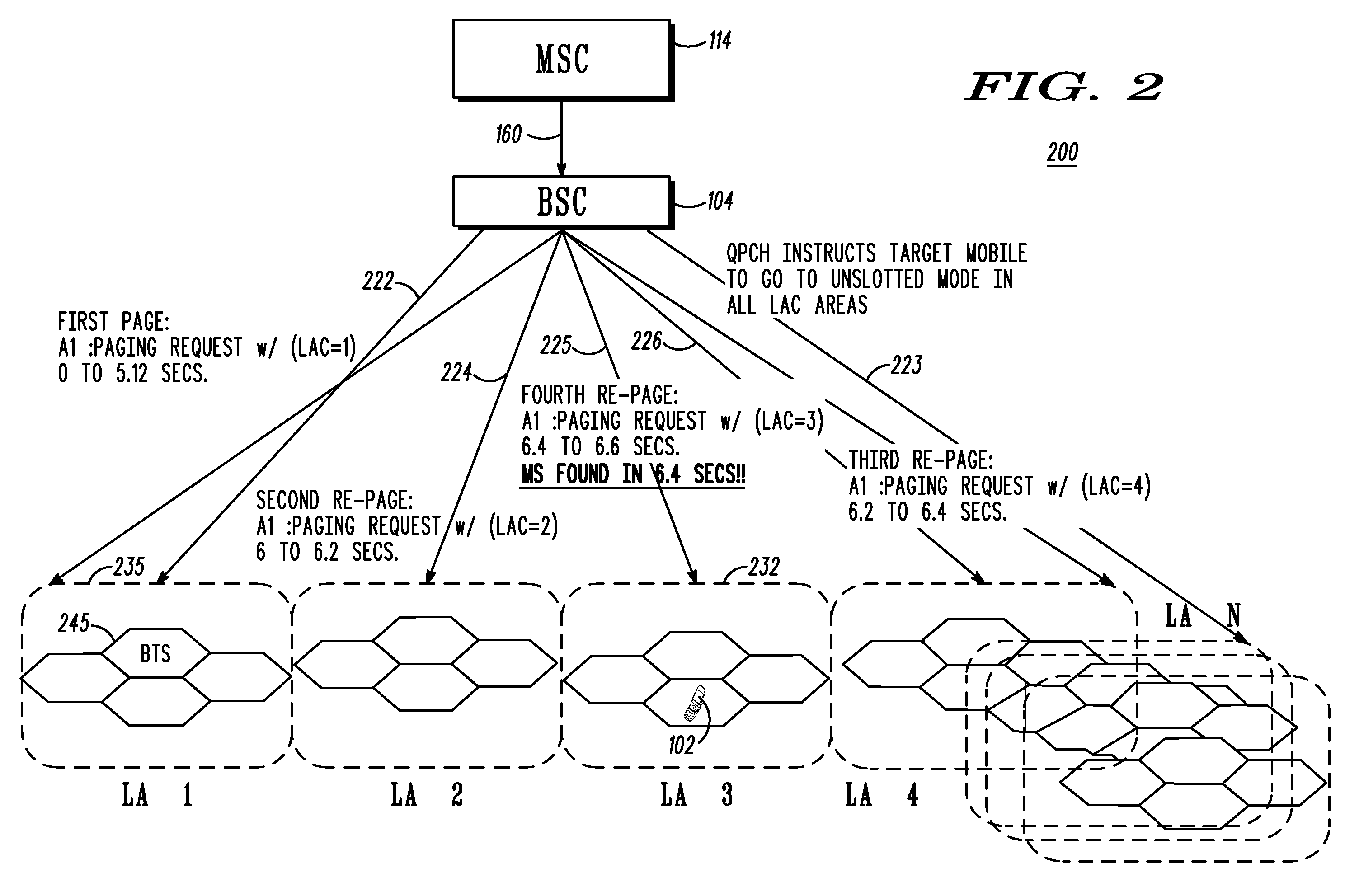
InactiveUS20080293437A1Without compromising battery lifeShort response timeRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationCommunications systemMobile station
A method and wireless communication system to reduce paging response time for a target mobile station (MS) operable using slotted and unslotted modes in multiple paging location areas of the system includes a first step 300 of receiving a paging request message for the MS. A next step 302 includes setting a paging indicator for the MS. A next step 304 includes broadcasting the paging indicator to all paging location areas of the system. A next step 306 includes operating the MS in unslotted mode upon recognition of the paging indicator. A next step 308 includes paging the MS in a last known location and failing to establish contact with the MS. A next step 310 includes re-paging the MS in selected location areas of the system based on a probability based search algorithm. A next step 312 includes operating the MS in slotted mode again upon successful call processing.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
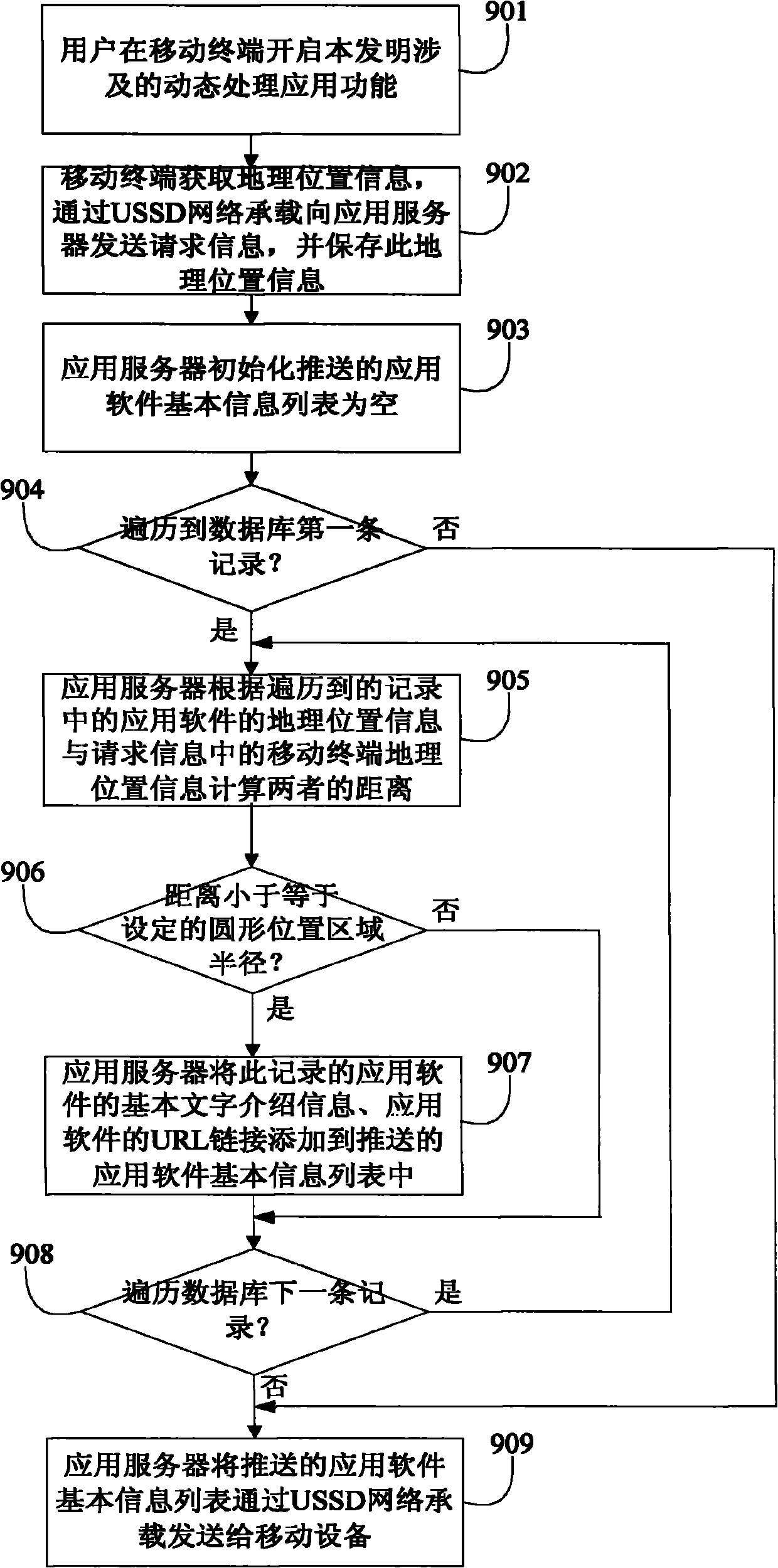
Method, mobile terminal and application server for dynamically processing application
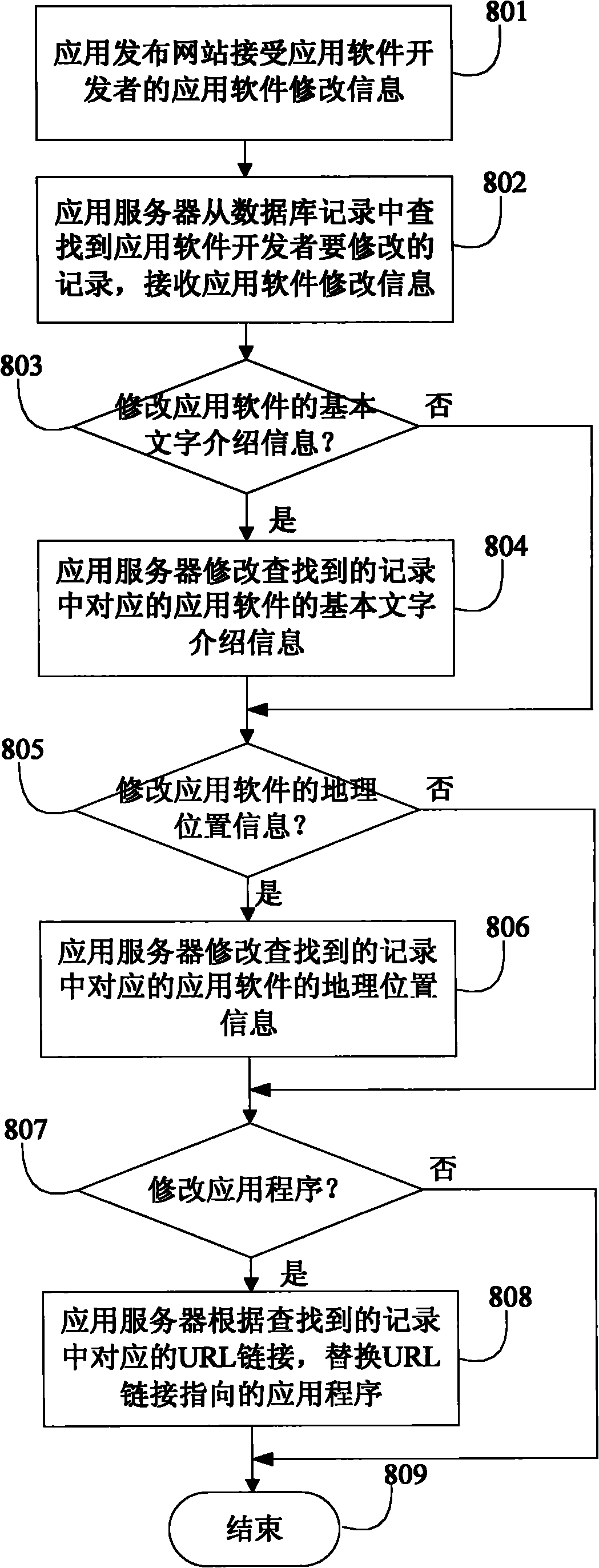
InactiveCN101951549AReduce native app installationsService provisioningTransmissionApplication serverGeolocation
The invention provides a method, a mobile terminal and an application server for dynamically processing application. The method comprises the following steps that: after receiving an instruction of a user, the mobile terminal acquires first geographical position information of the mobile terminal, sets position area information related to the first geographical position information and sends application request information to the application server, wherein the application request information carries the position area information; and after receiving the application request information, the application server matches application software in the area determined by the position area information according to the pre-stored geographical position information corresponding to application software and pushes the essential information of the matched application software to the mobile terminal. By the method, whether the application is provided for the user is automatically determined according to the geographical position of the user, so that the user can check the information in a specified area and interact with the application.
Owner:ZTE CORP
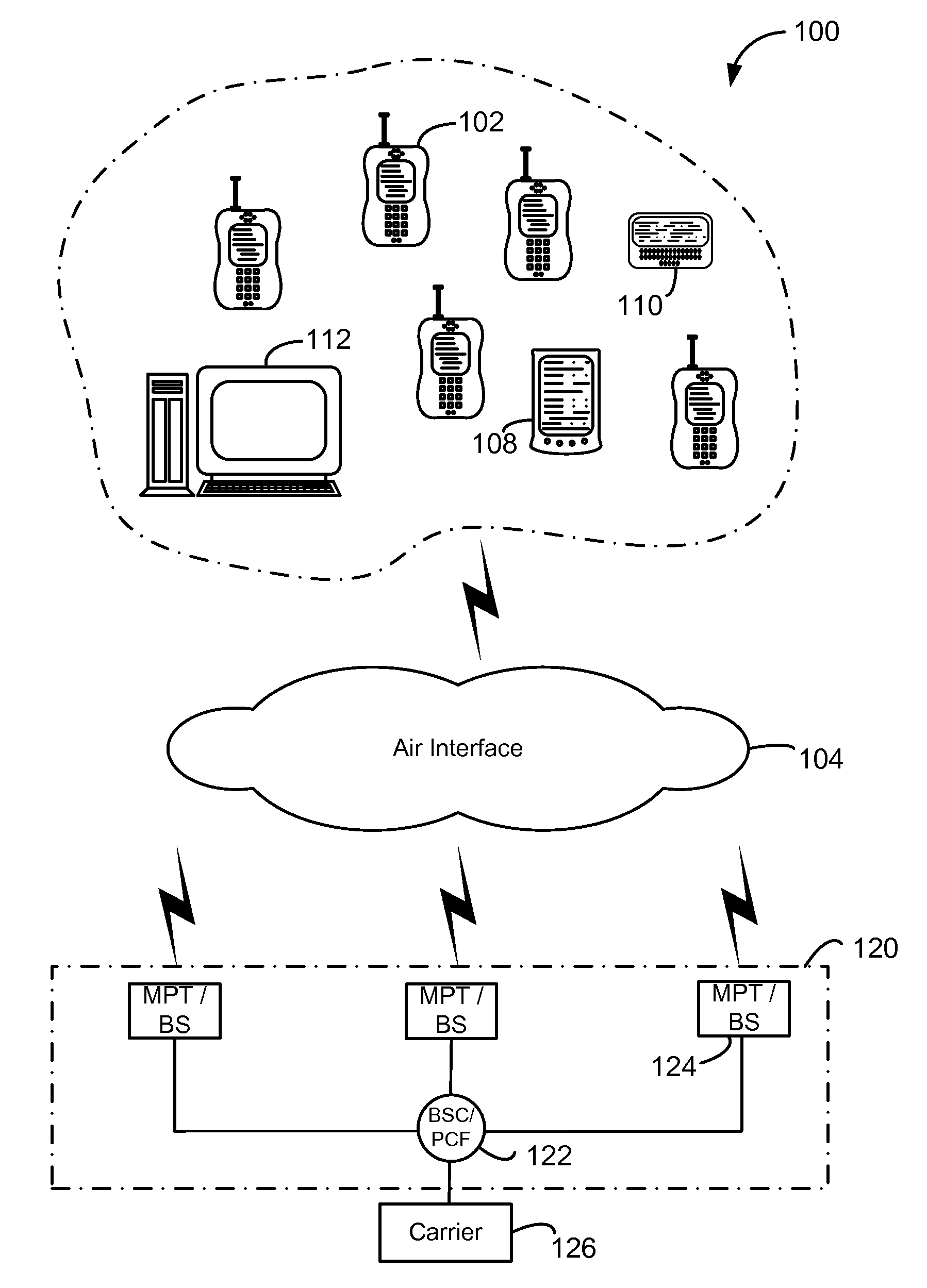
Method and system for primary paging location of mobile terminal
InactiveUS20030027572A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesTelecommunicationsProcessor register
The present invention is directed to a method and system for producing and storing "roaming" area information of a mobile terminal in a home location register or guest location register. A "roaming" area includes a group of location areas within a single service area. When a mobile terminal enters a new location area within a new roaming area or enters a new service area, the home location register (HLR) or guest location register (GLR) is updated with the roaming area information of the mobile terminal. The HLR / GLR stores this information in addition to the other information typically stored for the mobile terminal. If an MSC / VLR system restart and reload occurs or another event such that the location area information is lost, the roaming area information can be retrieved from the HLR / GLR. Likewise, if the mobile terminal does not respond to a page within the location area stored for the mobile terminal, the roaming area information can be retrieved from the MSC / VLR. Thereafter, the roaming area information can be used by the MSC / VLR to perform a primary page for a mobile terminal within the roaming area, instead of a global page within the service area, thus reducing paging congestion in the network.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Terminal state control system
InactiveUS20080188221A1More communicationEasy to distinguishAssess restrictionNetwork topologiesControl systemLocation area
When a terminal enters a cell of a personal-use base station (NBTS) arranged in a certain location area, the terminal receives a location area identifier having a number that is different from an identifier of the location area, and transmits a location updating request with the reception of the location area identifier as a trigger. On receiving the location updating request, a VLR or an NRNC having a registration table, in which the ID of the personal-use base station and the ID of a terminal allowed to use the personal-use base station are registered, judges whether the terminal issued the location updating request is the terminal allowed to use the personal-use base station by referring to the registration table. If the terminal issued the location updating request corresponds to the terminal allowed to use the personal-use base station, the terminal is placed under a status where it is capable of performing communication in the cell, and if not, the terminal is placed under a status where it is incapable of performing communication in the cell.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and system for controlling activation of ISR (Idle mode Signaling Reduction) and UE (user equipment)
InactiveCN102098655ACan't be solvedSolve the real problemNetwork data managementShort Message ServiceBiological activation
The invention discloses a method and system for controlling the activation of ISR (Idle mode Signaling Reduction) and UE (user equipment). The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out the combination of TAU (Tracking Area Update) and LAU (Location Area Update) by the UE; activating the ISR or keeping the ISR not activated under the condition of meeting preset conditions, wherein the preset conditions include: the result of the combination of TAU and LAU is as follows: only the combination of TAU and LAU of SMS (Short Message Service) over SGs (Serving Gateways) succeeds, and the UE needs to support a preset service; and the preset service comprises other CS (Circuit Switching) services except for the SMS. The invention ensures that the UE can be called when the CS services such as speech calling and the like are carried out.
Owner:ZTE CORP
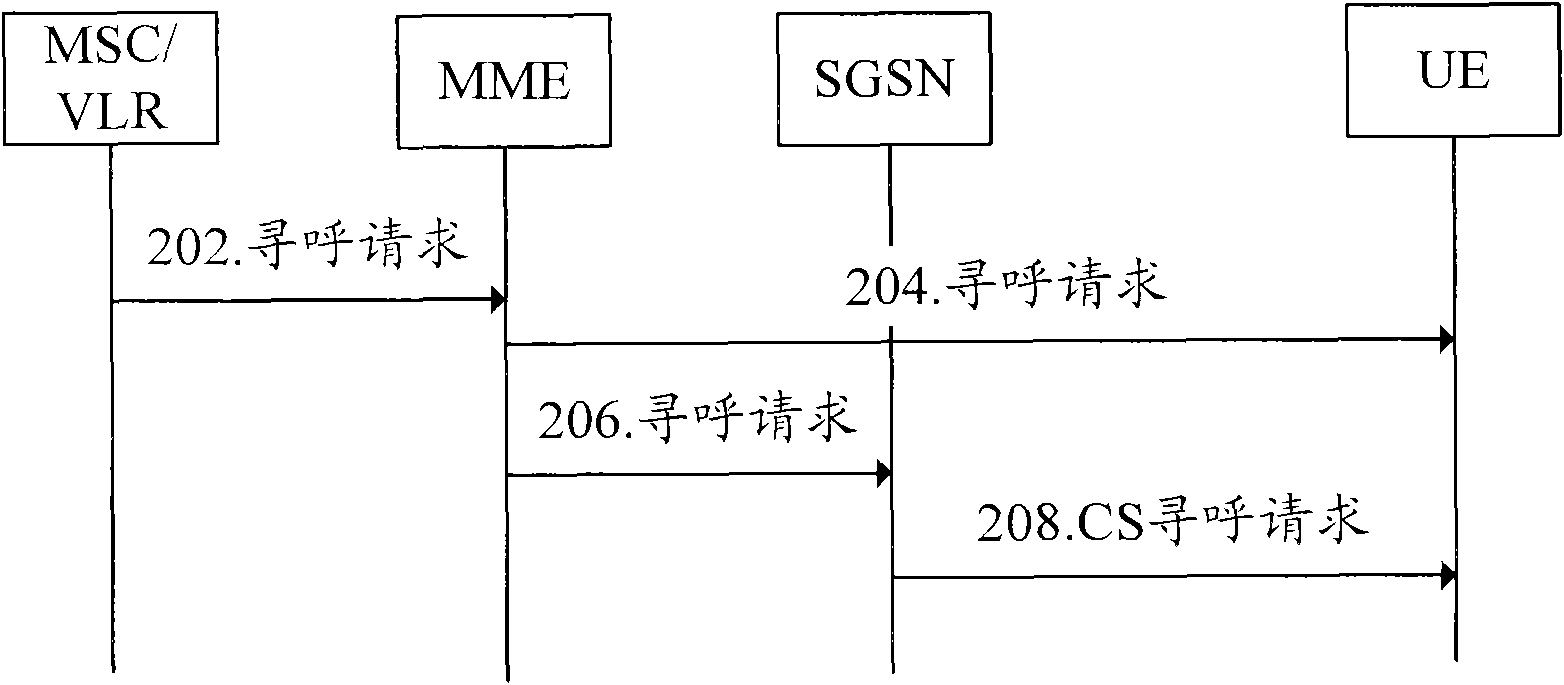
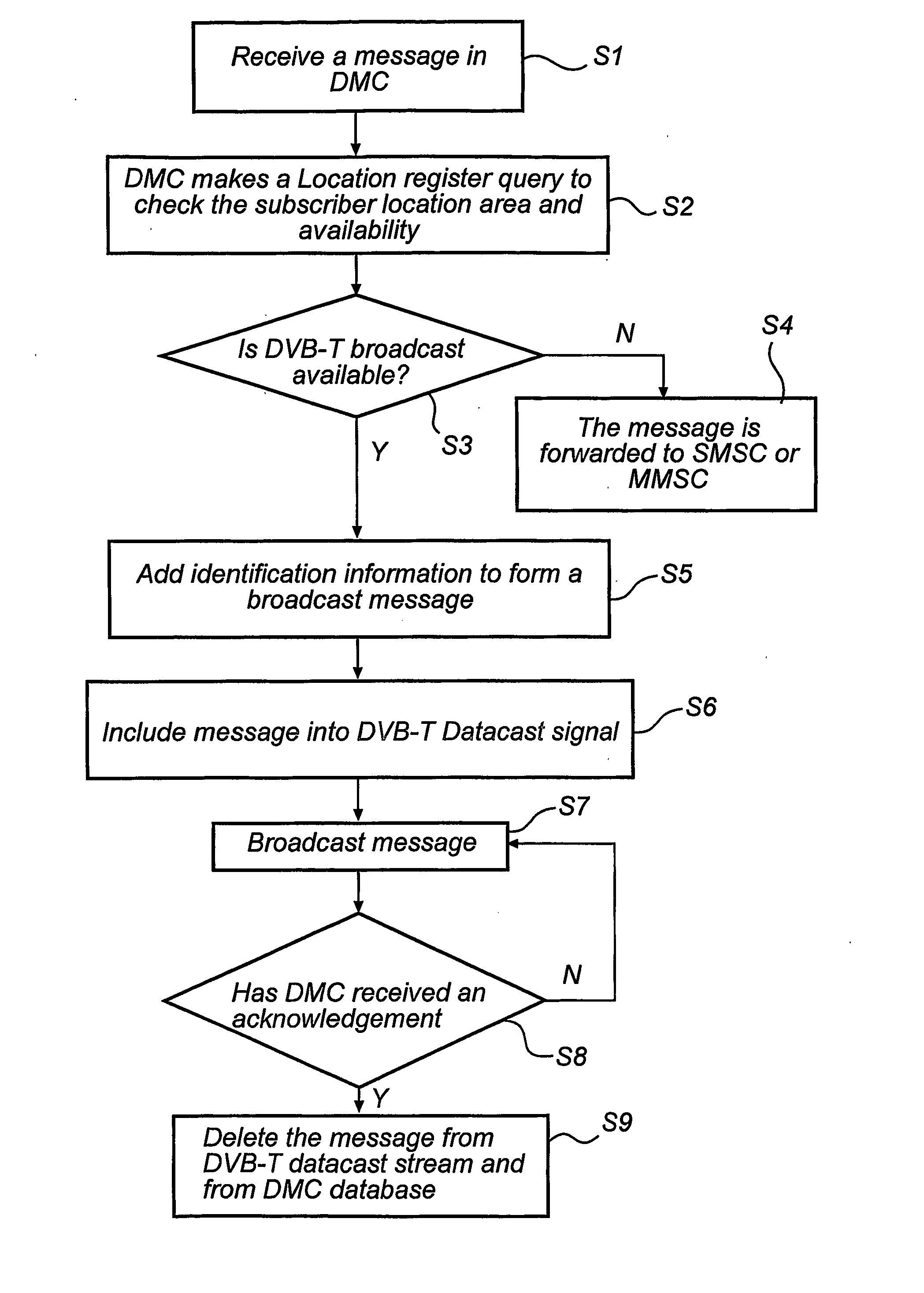
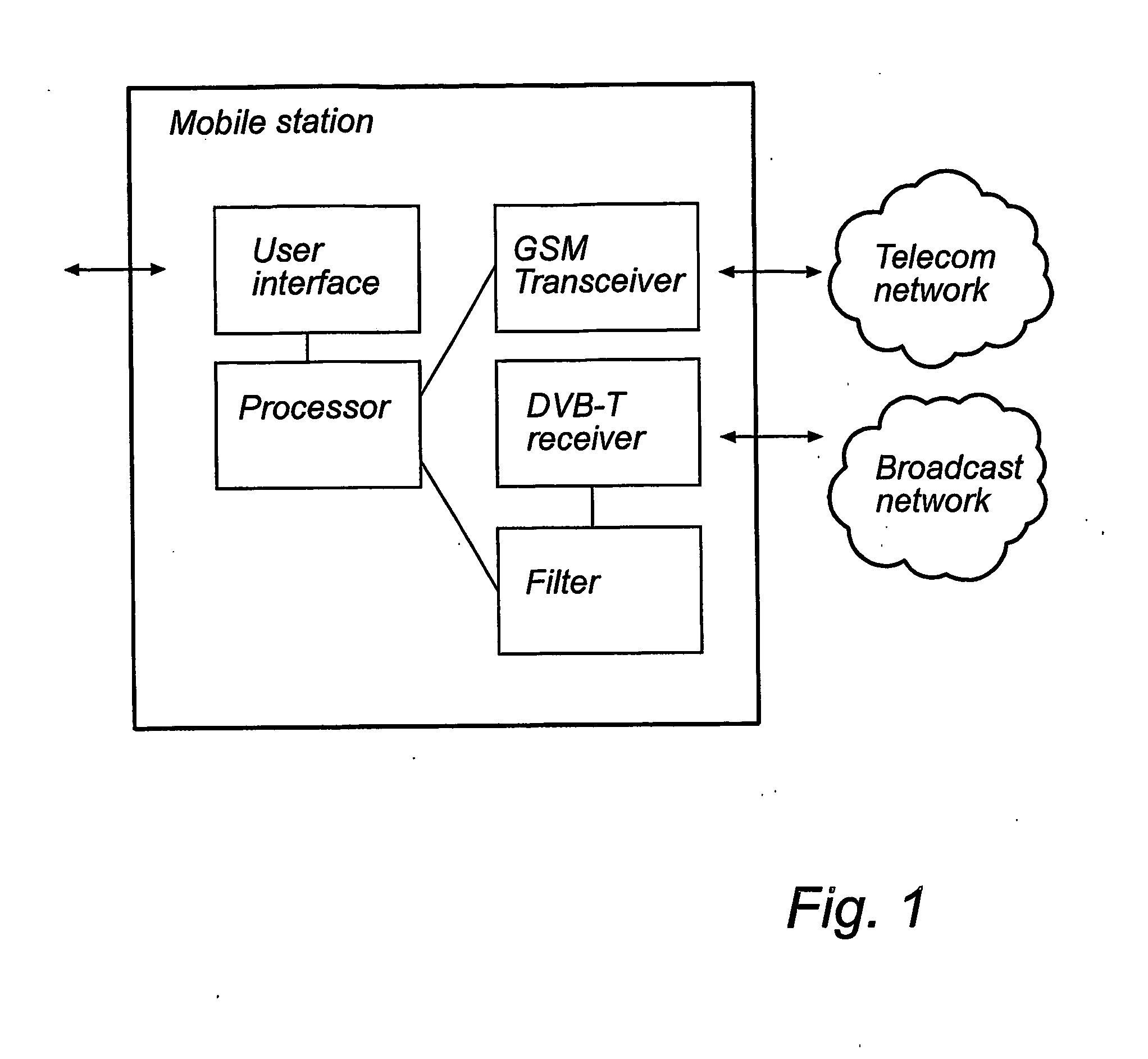
Broadcast messaging in a telecommunication network
InactiveUS20070004333A1Effective capacityUse capacityBroadcast systems characterised by addressed receiversBroadcast information monitoringTelecommunications networkMobile station
A method for transmission of a data message from a message center to a receiving mobile station in a telecommunication network is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of: Providing a data message to be forwarded to said receiving mobile station; Incorporating identification information for identification of said receiving mobile station in said data message; Storing the message in a server; Making a query to check the receiving mobile station location area and availability in the server; Broadcasting said data message in a geographical area in which said receiving mobile station is situated; and Acknowledging reception of the data message at the receiving mobile station to the message center through the telecommunication network. Further, a corresponding mobile station and telecommunications system is disclosed.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
System and Method to Determine Train Location in a Track Network
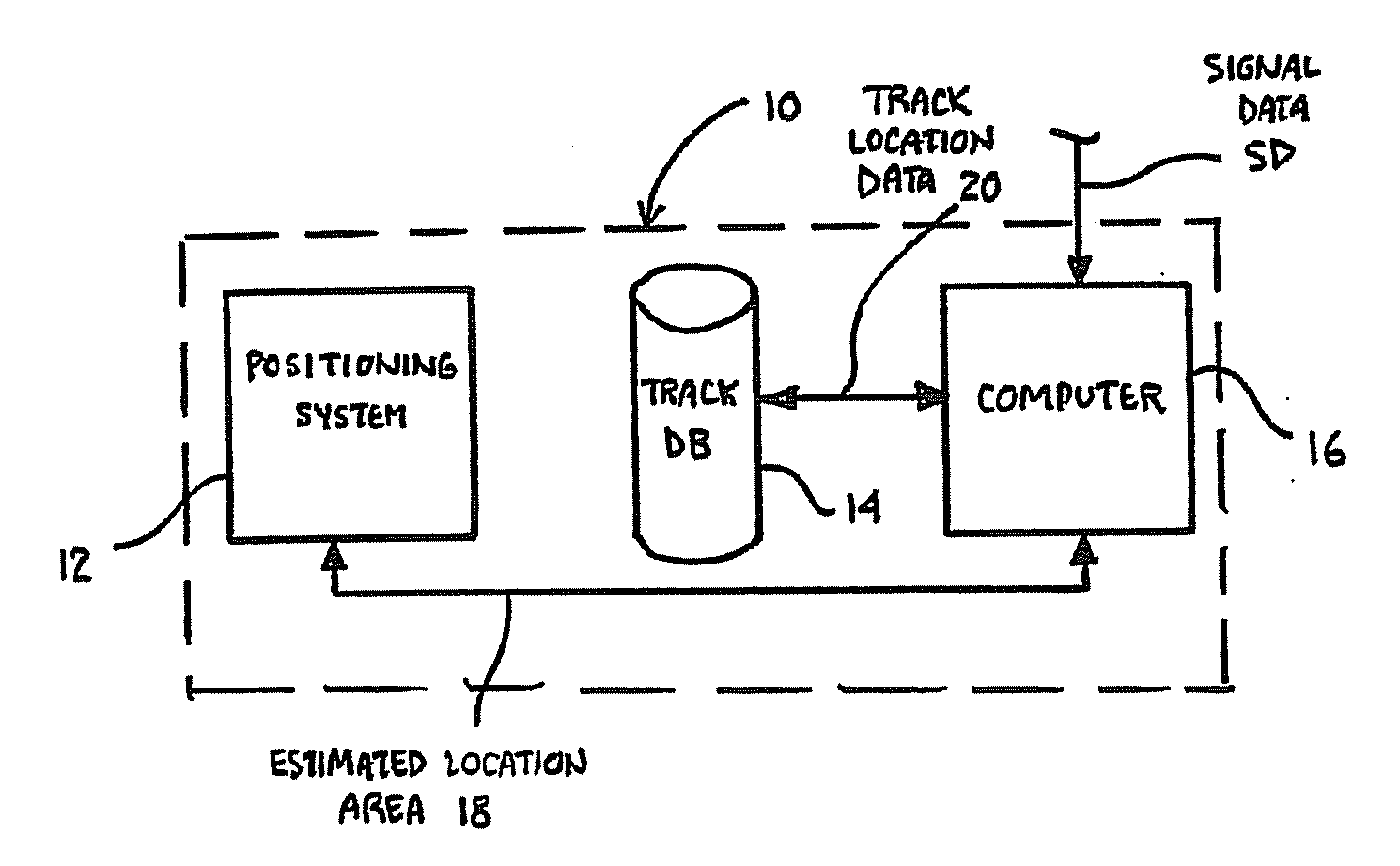
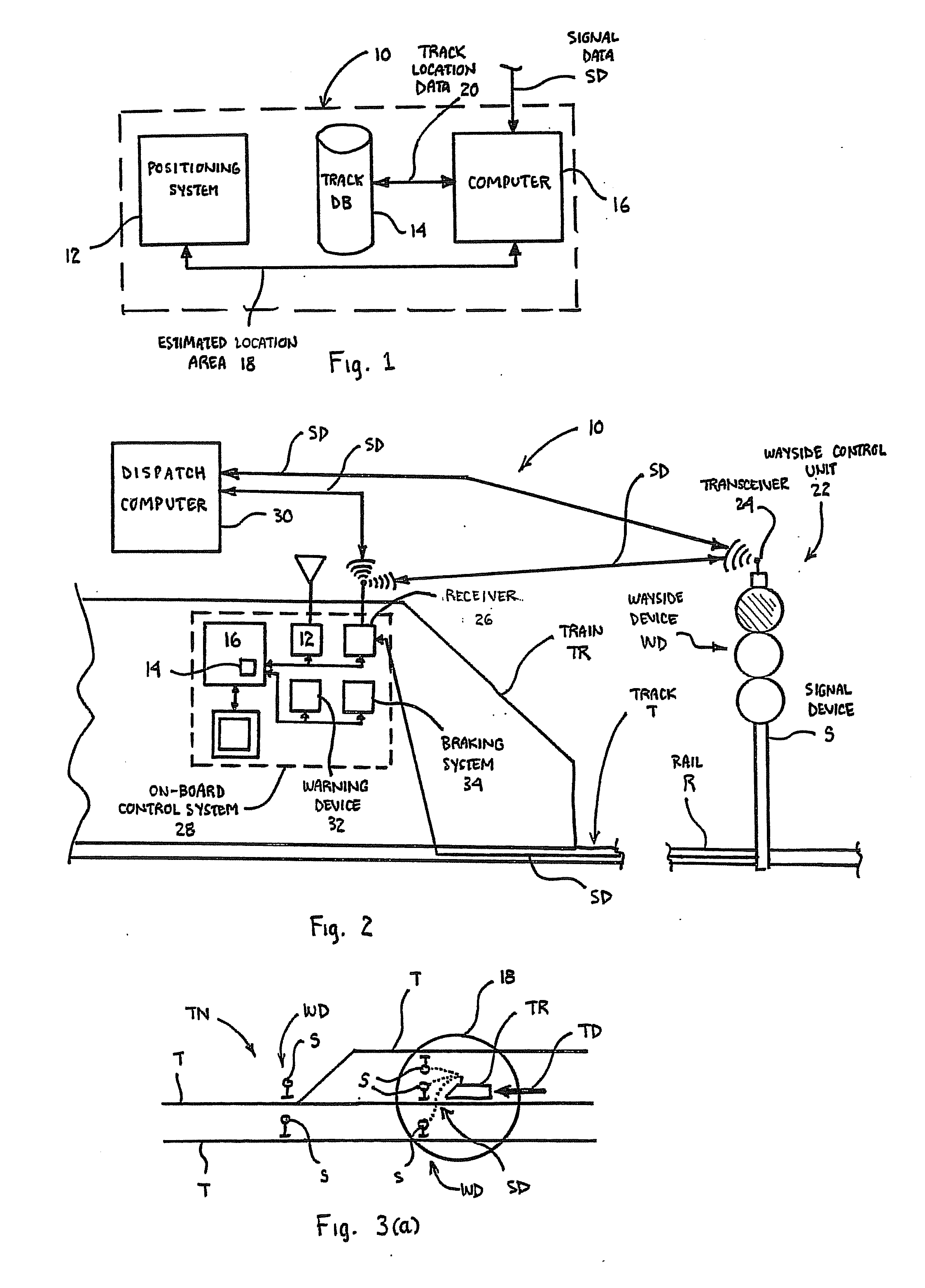
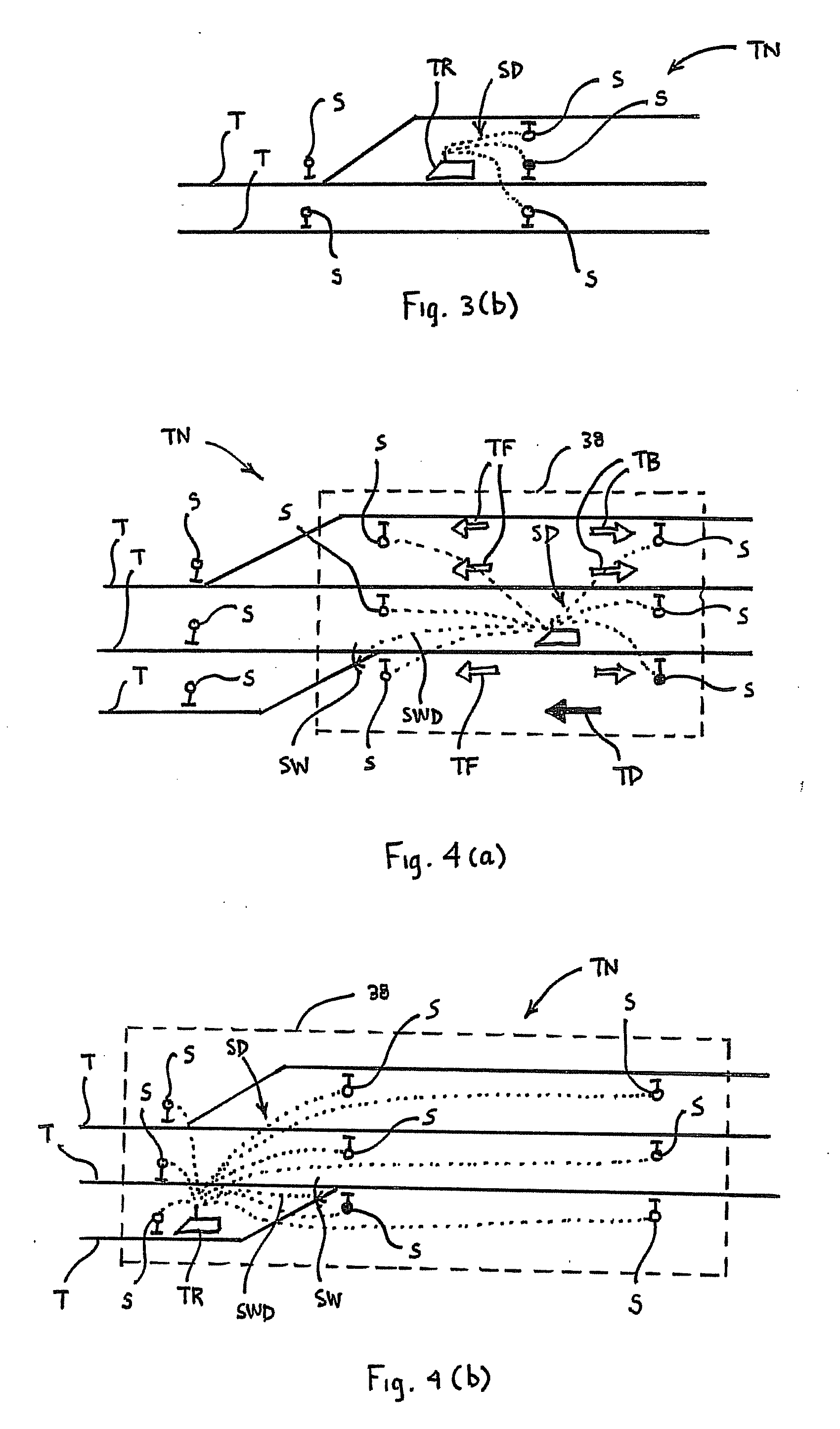
ActiveUS20090105893A1Overcome deficienciesOvercomes drawbackInstruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsEngineeringSignaling system
A system for determining a possible location of a train in a track network including interconnected tracks having wayside devices associated with these tracks. The system includes a positioning system for determining an estimated location area of a train and a track database having track location data. A computer: obtains the determined estimated location area of the train from the positioning system; identifies a plurality of tracks in the estimated location area of the train, based upon the track location data; obtains signal system data for at least one wayside device associated with at least one of the tracks identified within the estimated location area; and determines at least one possible train location on at least one of the identified tracks based at least in part upon the obtained signal system data. A method and apparatus for determining the possible location of a train is also provided.
Owner:WABTEC HLDG CORP
Scheduling location update reports of access terminals to an access network within a wireless communications system
ActiveUS20100246467A1Broadcast transmission systemsWireless commuication servicesAccess networkCommunications system
Embodiments are directed to scheduling location update reports of access terminals to an access network within a wireless communications system. The access network acquires a defined location region within a wireless communications system, and determines a location of a given access terminal within the wireless communications system. The access network selects one of a plurality of location update rules for the given access terminal based on a relationship between the defined location region and the determined location, each of the plurality of location update rules specifying different conditions for prompting location update reports from the given access terminal to the access network. The access network informs the given access terminal of the selected location update rule, and the given access terminal sends one or more location update reports to the access network in accordance with the selected location update rule.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Location area update in a communication system
InactiveUS6968196B1Increase success rateReduce in quantityRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionCommunications systemPaging
The present invention relates to a method and a controller for a radio communication system. The system comprises a plurality of location areas. The controller serves said location areas and mobile stations within said location areas. In accordance with the method a request for initiation of location area information update proceedings is received at the controller. The controller then verifies whether the mobile station is subjected to a simultaneous paging procedure. If a simultaneous paging procedure is detected, the location area information update proceedings are interrupted and an acknowledgement message is generated and transmitted, said message informing the mobile station that the location area information update proceedings are completed.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Mobile registration using a service area identifier or plurality of service area identifiers
InactiveUS20080057955A1Telephonic communicationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelecommunications networkGlobal Positioning System
A method of registering a mobile device in a mobile telecommunications network comprises the device's receiving power from a power source and transmitting a registration request signal including mobile device identification data, an associated mobile network determining a set of latitude and longitude location coordinates for the transmitting mobile device, comparing the determined set of latitude and longitude location coordinates with a table for matching the location coordinates with a service area code, determining a service area code responsive to the comparison, and storing the service area code, the mobile device identification data, the determined service area code and a location area code of the associated public mobile network for registering the mobile device in the associated mobile network. A related mobile device comprises a power source, a processor for determining whether power has been actuated, a global positioning system for determining a set of latitude and longitude location coordinates for the transmitting mobile device, the processor for comparing the determined set of latitude and longitude location coordinates with a table for matching the location coordinates with a service area code, determining a service area code responsive to the comparison and storing the service area code in memory of the mobile device.
Owner:CINGULAR WIRELESS II LLC
Method for protecting a medical device
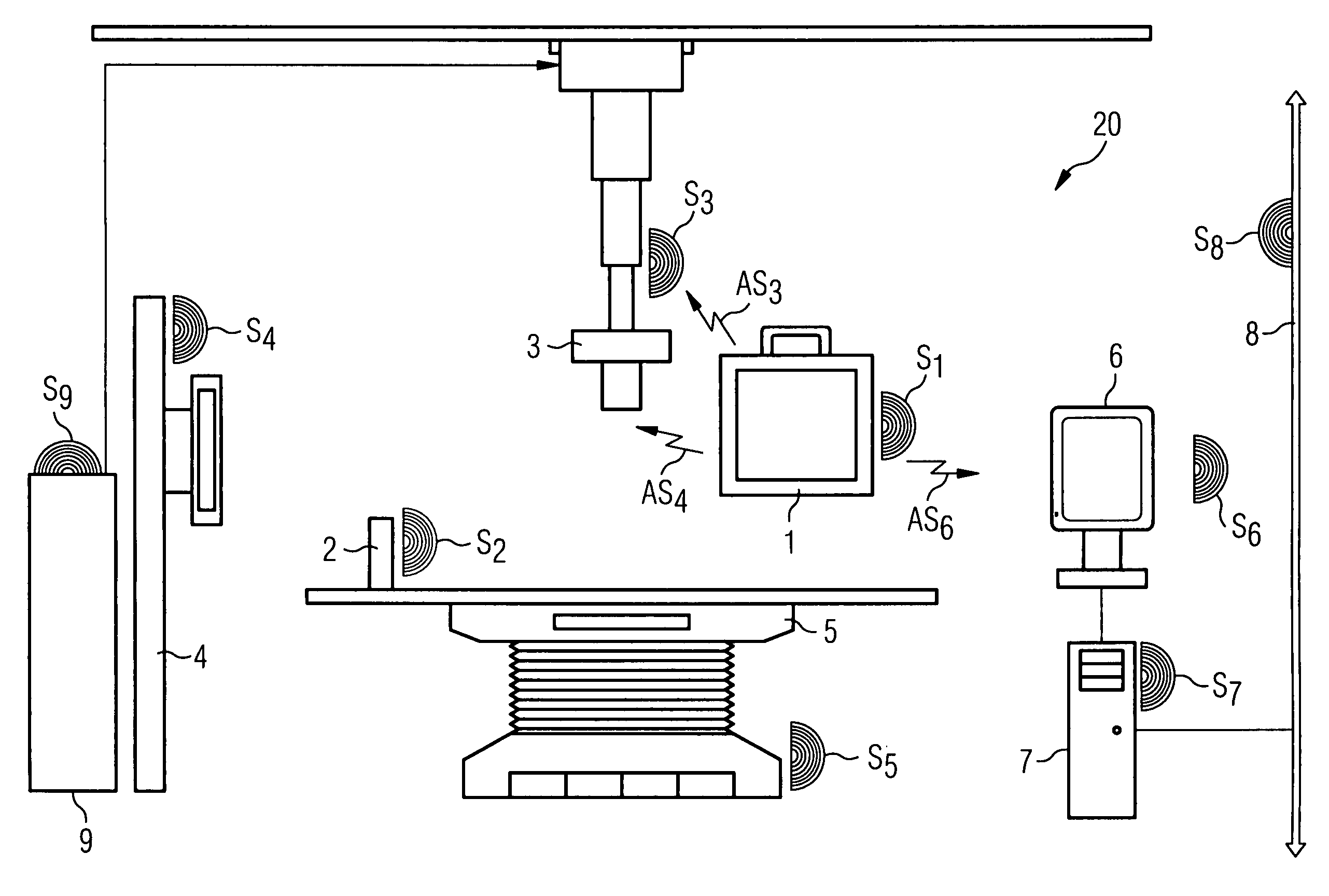
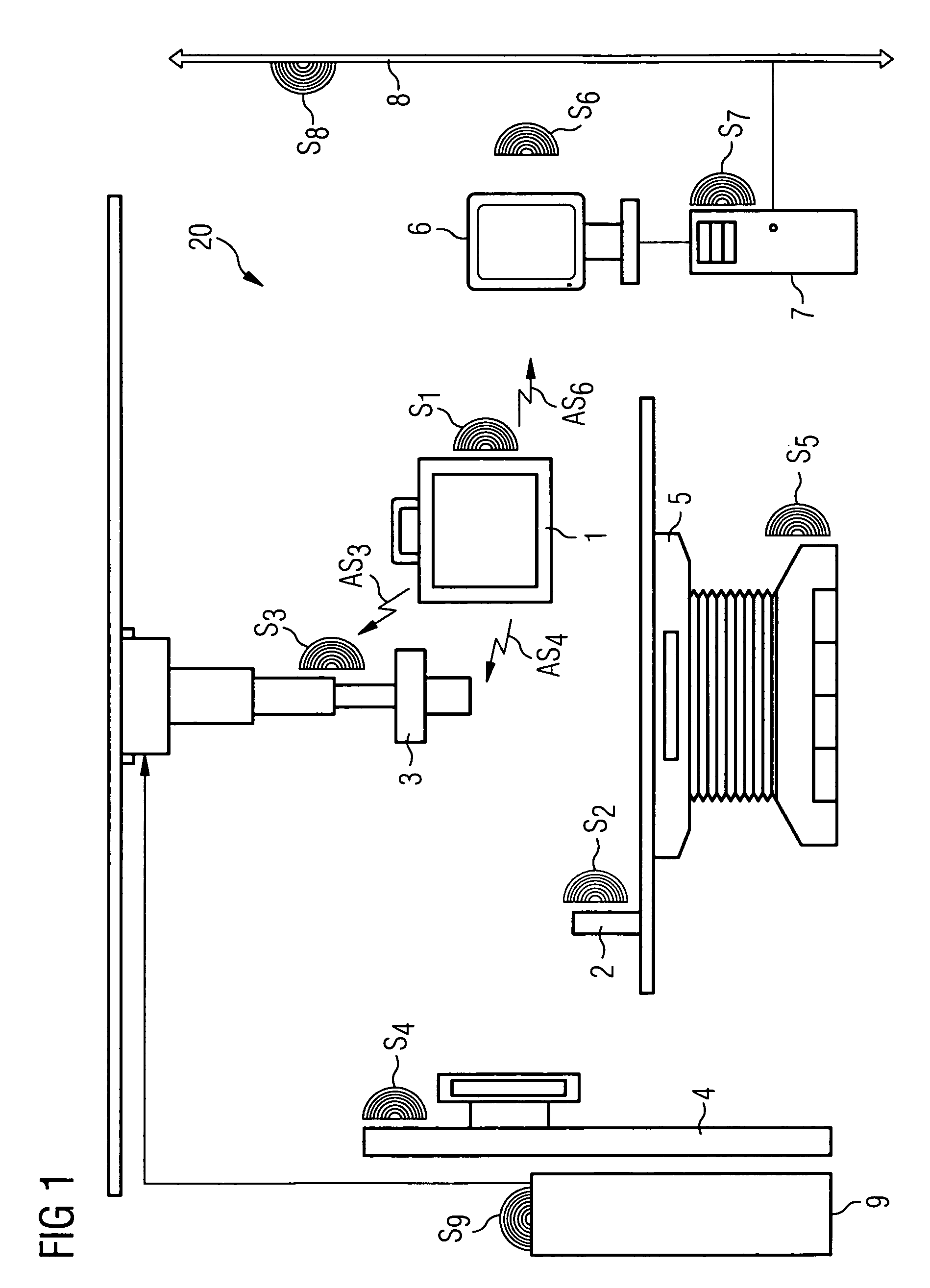
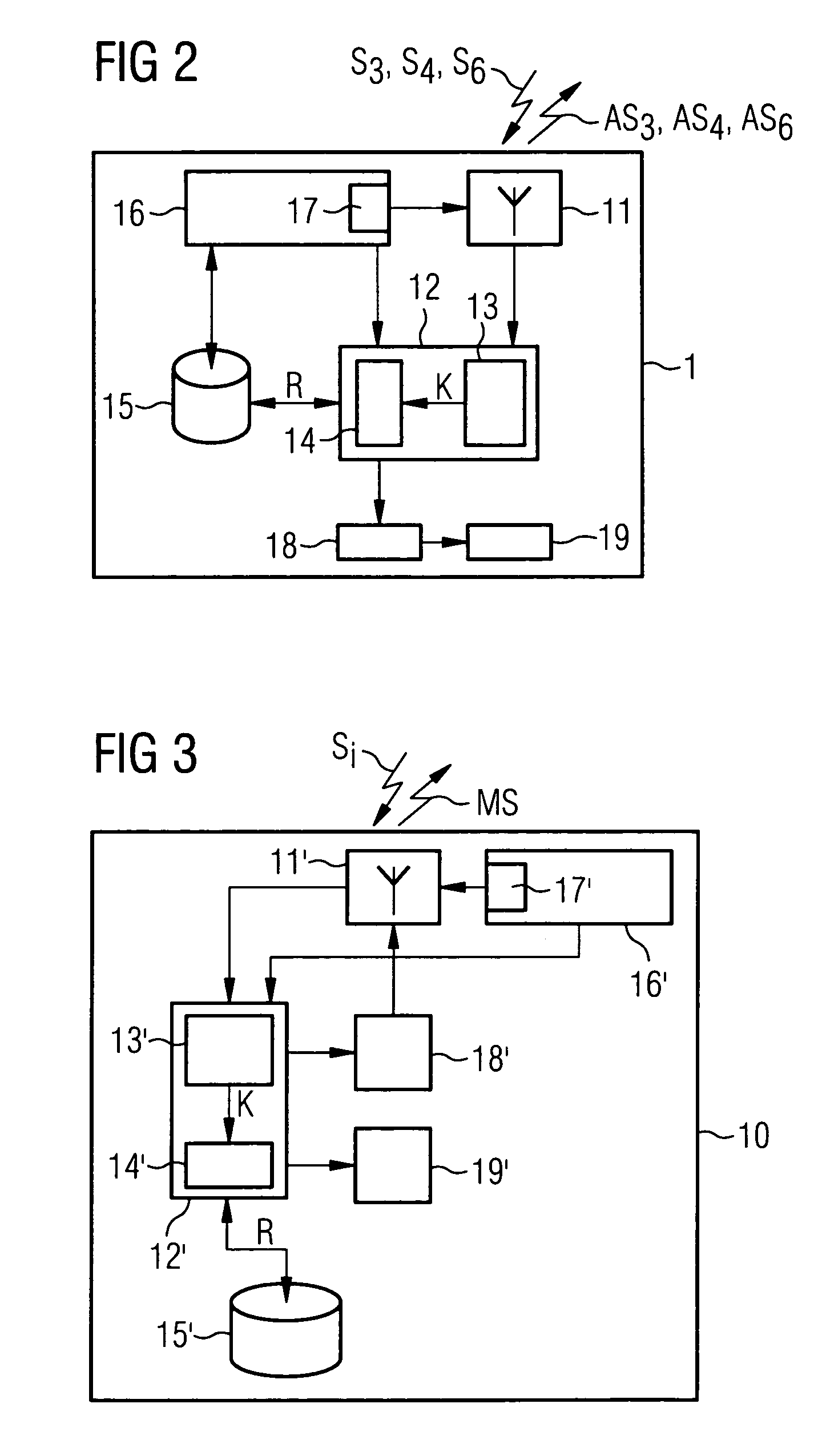
A method is disclosed for protecting a medical device against unauthorized removal from a predefined location area. To this end the device to be protected and / or at least one further device in the predefined location area transmits protection signals. The protection signals transmitted by the device to be protected and / or the protection signals received by the device to be protected are then evaluated and a specific operating state of the device to be protected is activated as a function of a result of the evaluation. A corresponding system for protecting a medical device and a medical device for use with such a protection method or system is also described.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com