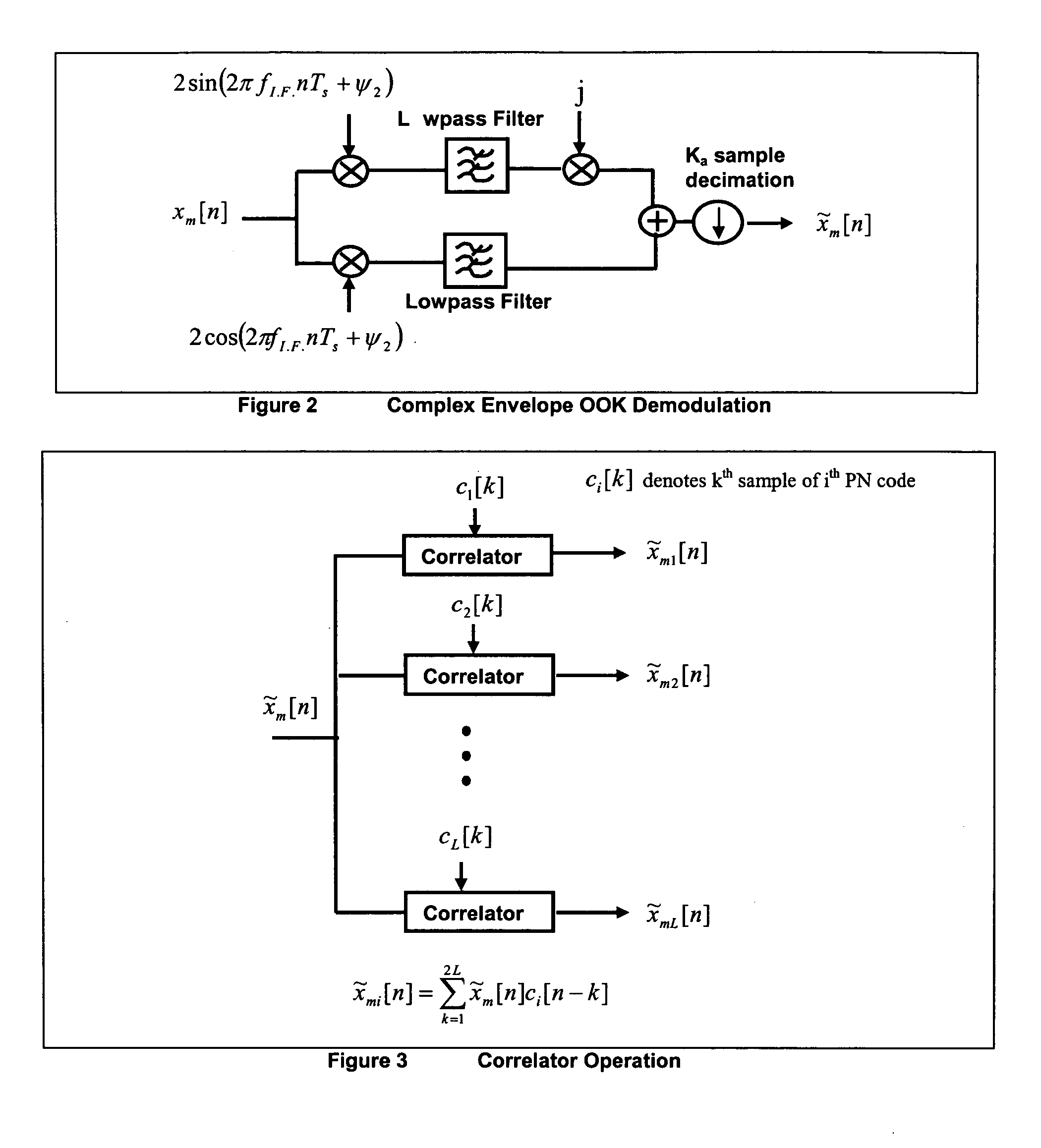
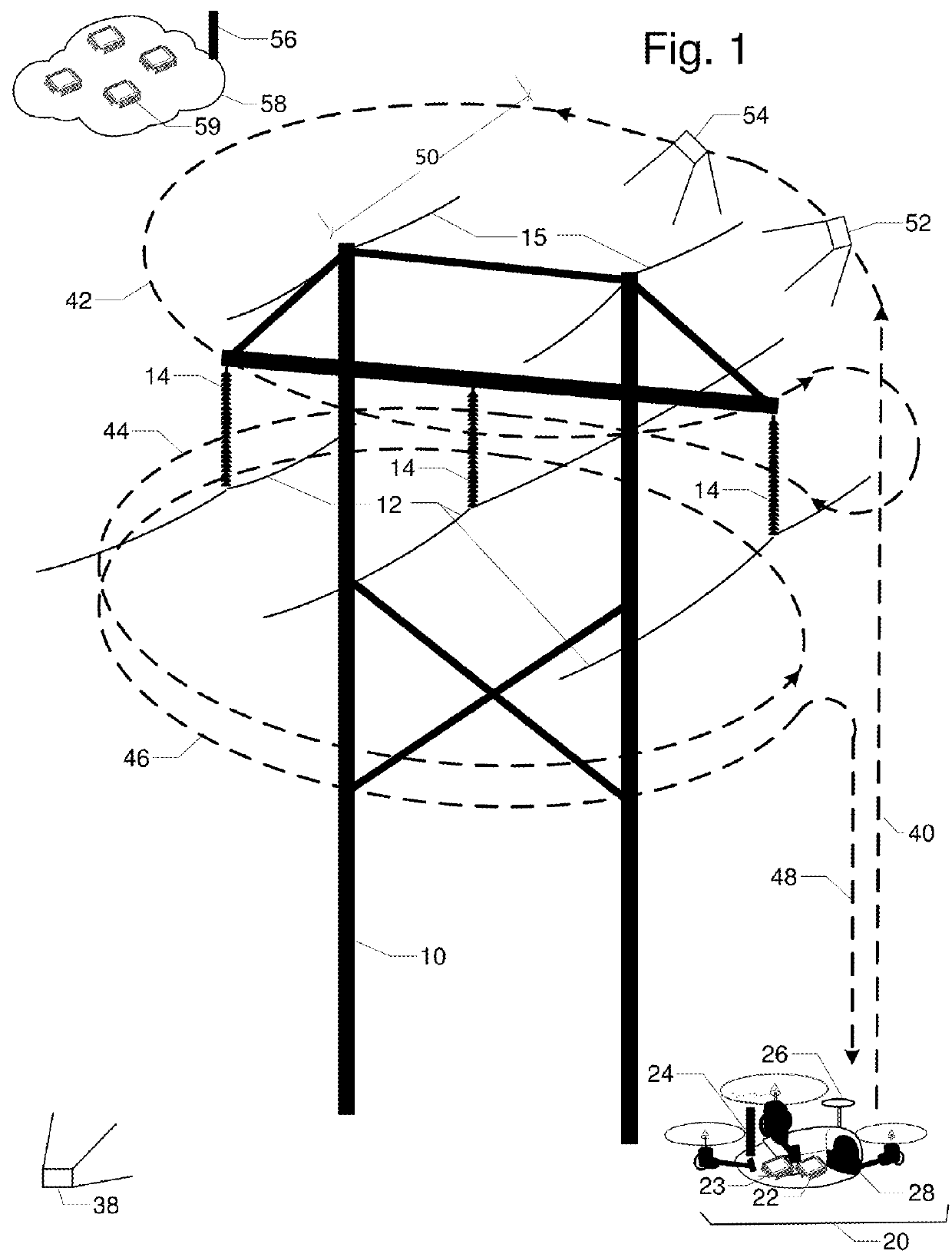
Patents
Literature
62 results about "Radiolocation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Radiolocating is the process of finding the location of something through the use of radio waves. It generally refers to passive uses, particularly radar—as well as detecting buried cables, water mains, and other public utilities. It is similar to radionavigation, but radiolocation usually refers to passively finding a distant object rather than actively one's own position. Both are types of radiodetermination. Radiolocation is also used in real-time locating systems (RTLS) for tracking valuable assets.
Short range spread-spectrum radiolocation system and method
InactiveUS6556942B1Sufficient gross rangingLow costDirection finders using radio wavesBeacon systems using radio wavesData setTriangulation
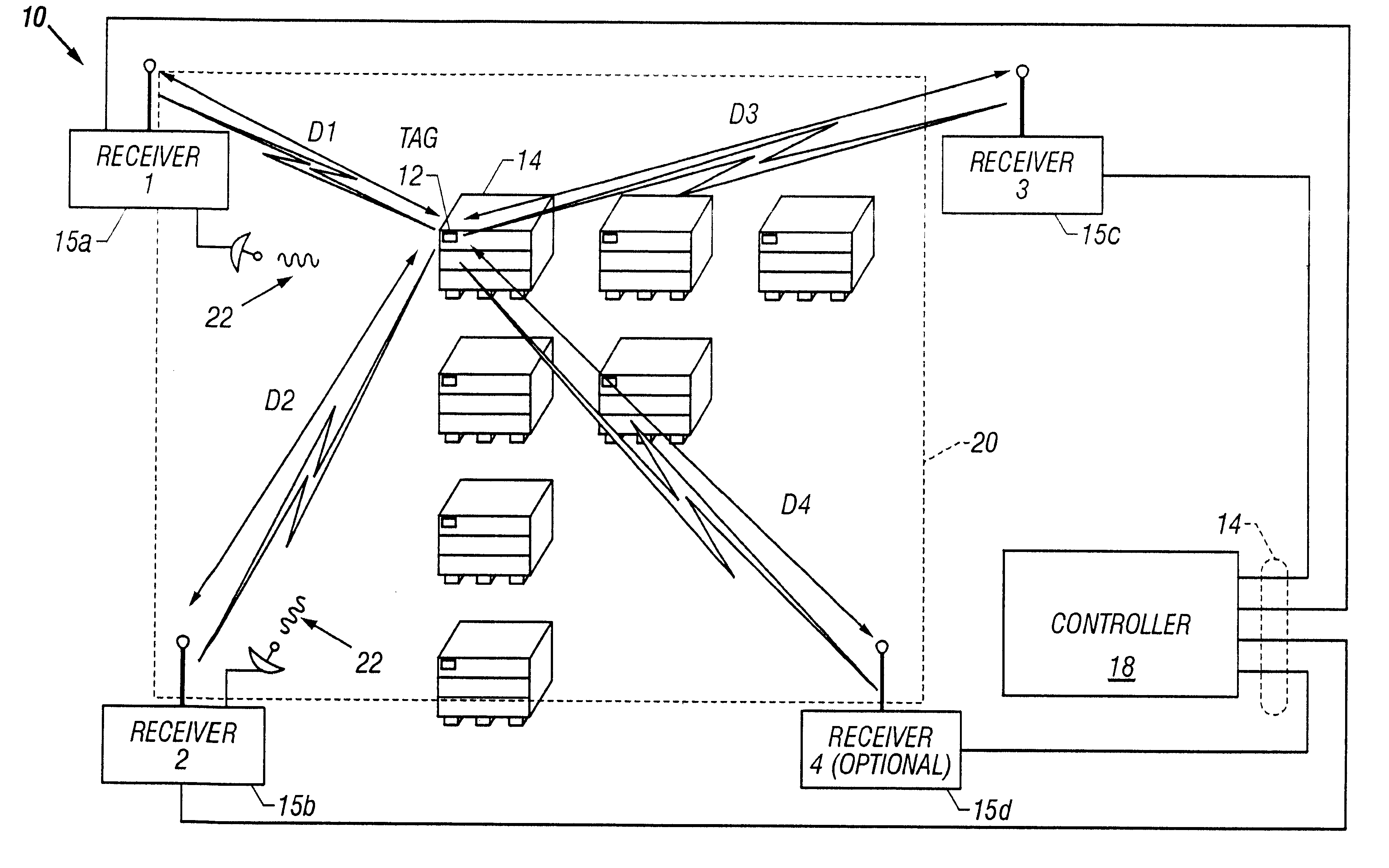
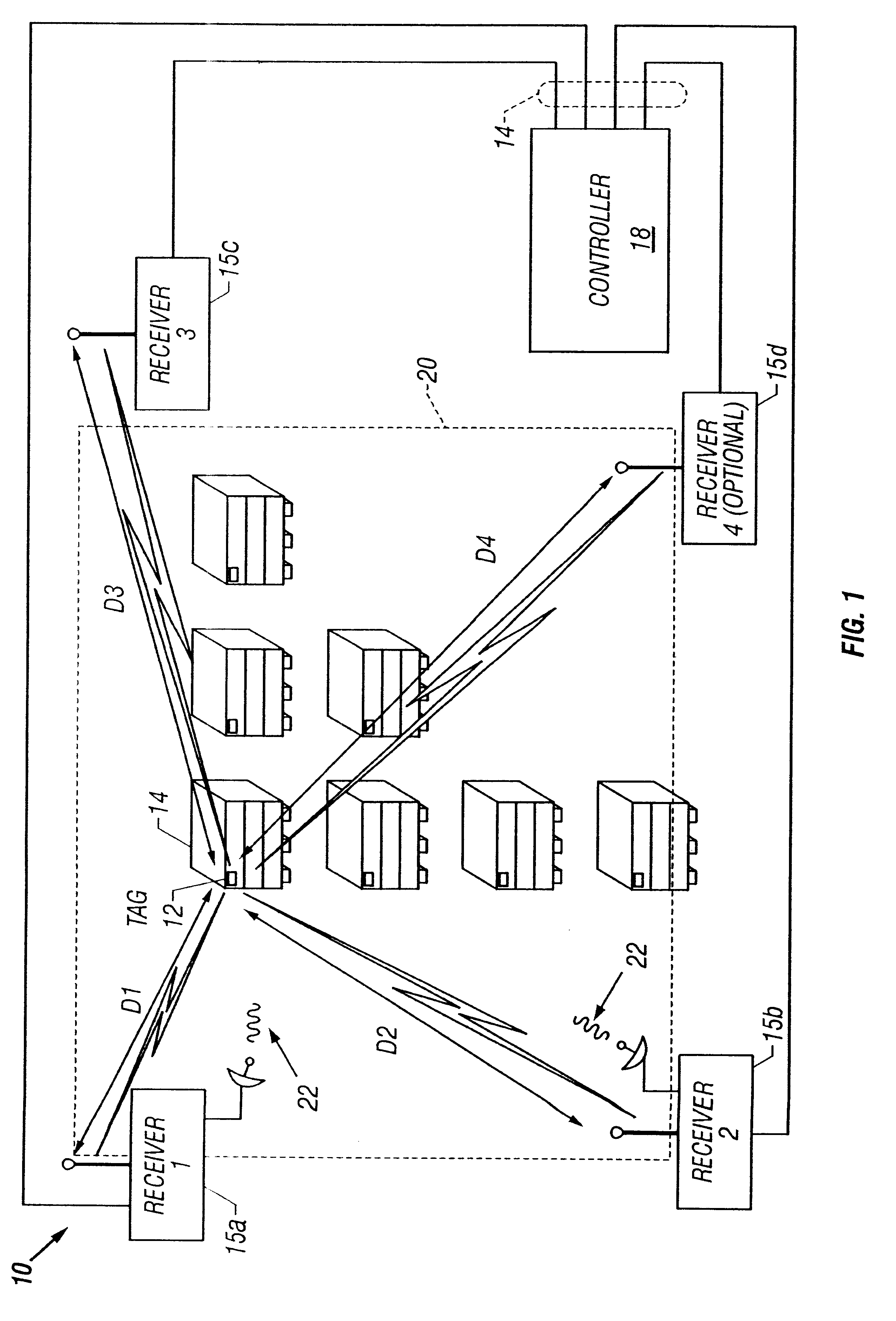
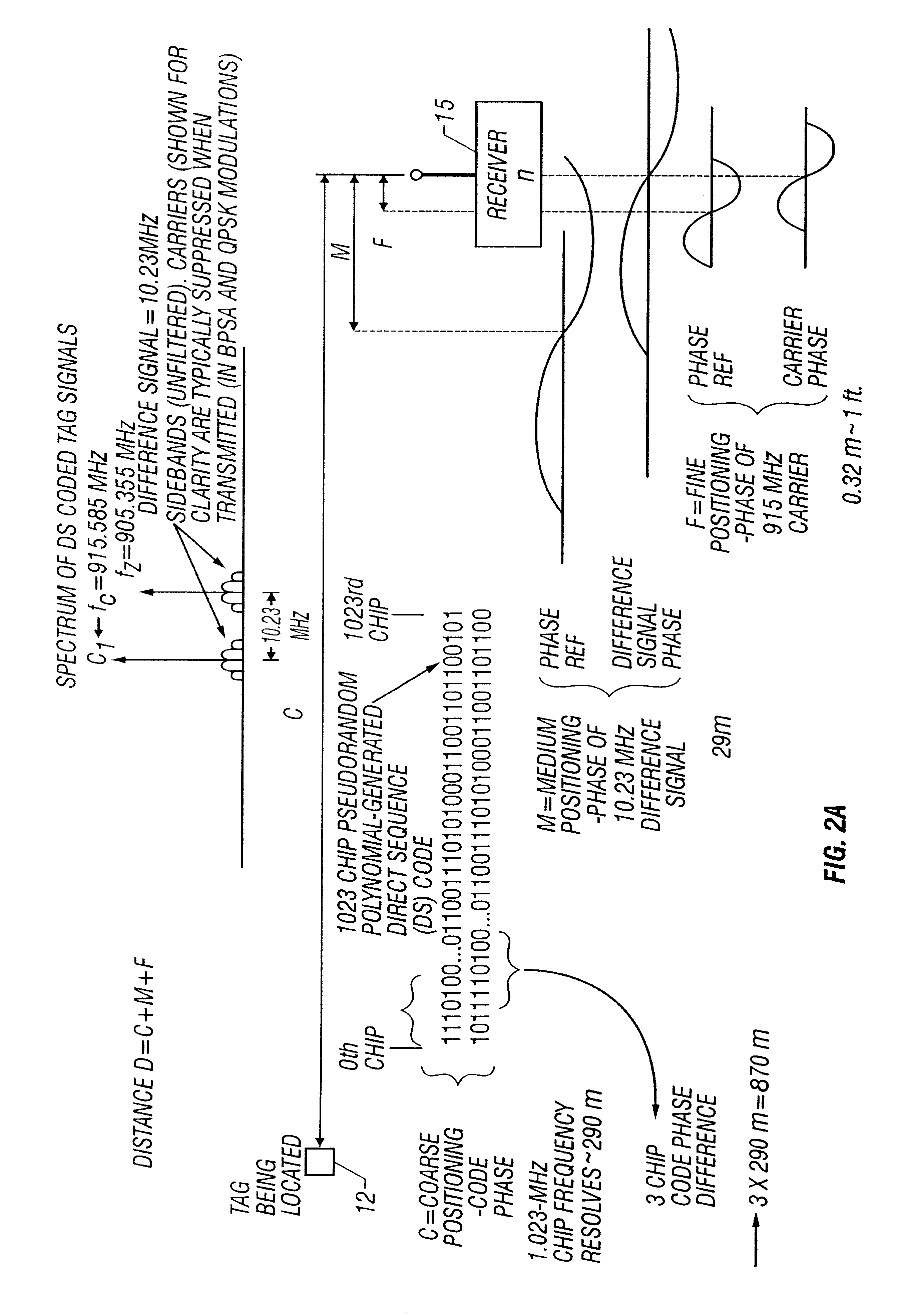
A short range radiolocation system and associated methods that allow the location of an item, such as equipment, containers, pallets, vehicles, or personnel, within a defined area. A small, battery powered, self-contained tag is provided to an item to be located. The tag includes a spread-spectrum transmitter that transmits a spread-spectrum code and identification information. A plurality of receivers positioned about the area receive signals from a transmitting tag. The position of the tag, and hence the item, is located by triangulation. The system employs three different ranging techniques for providing coarse, intermediate, and fine spatial position resolution. Coarse positioning information is provided by use of direct-sequence code phase transmitted as a spread-spectrum signal. Intermediate positioning information is provided by the use of a difference signal transmitted with the direct-sequence spread-spectrum code. Fine positioning information is provided by use of carrier phase measurements. An algorithm is employed to combine the three data sets to provide accurate location measurements.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
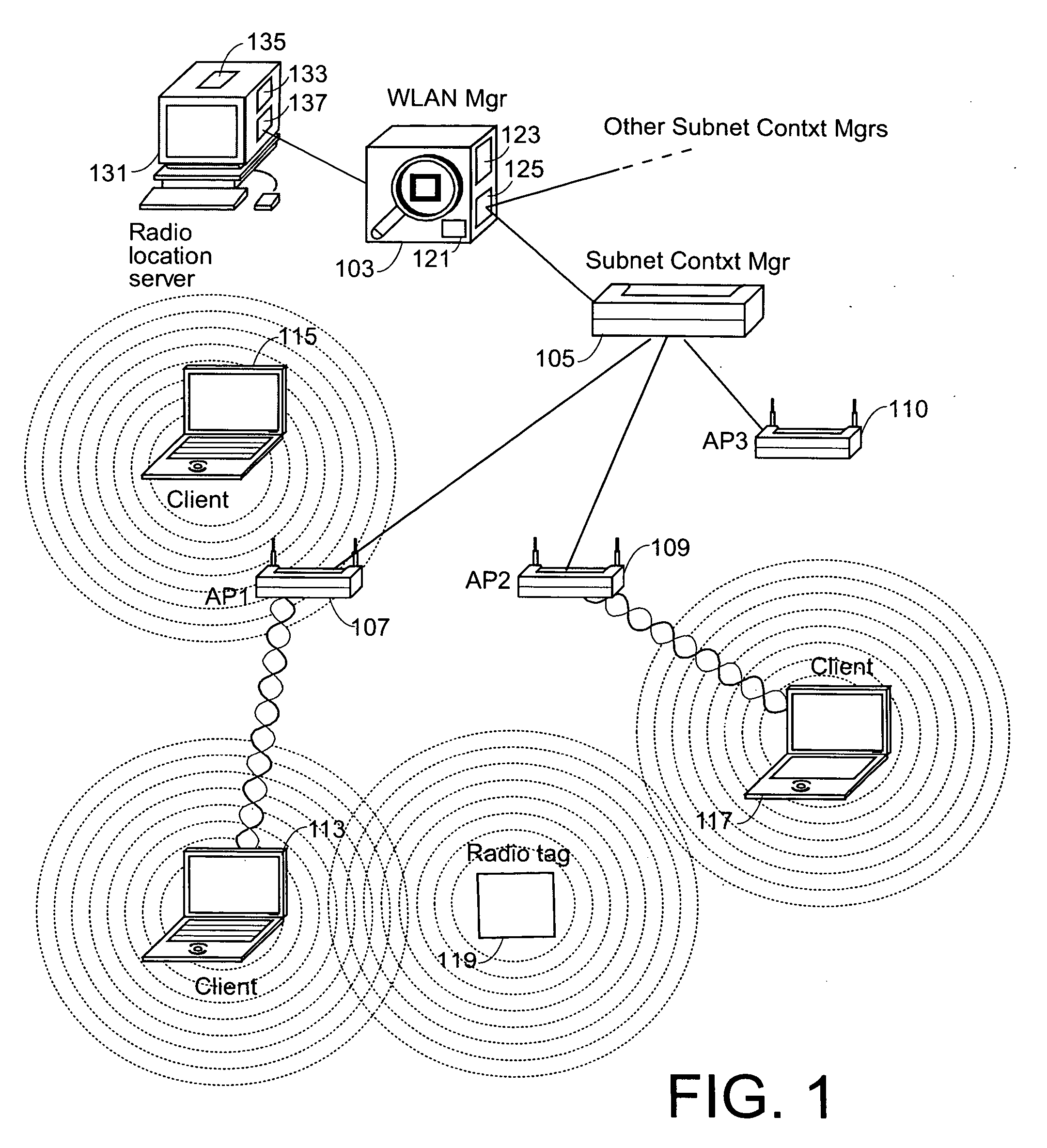
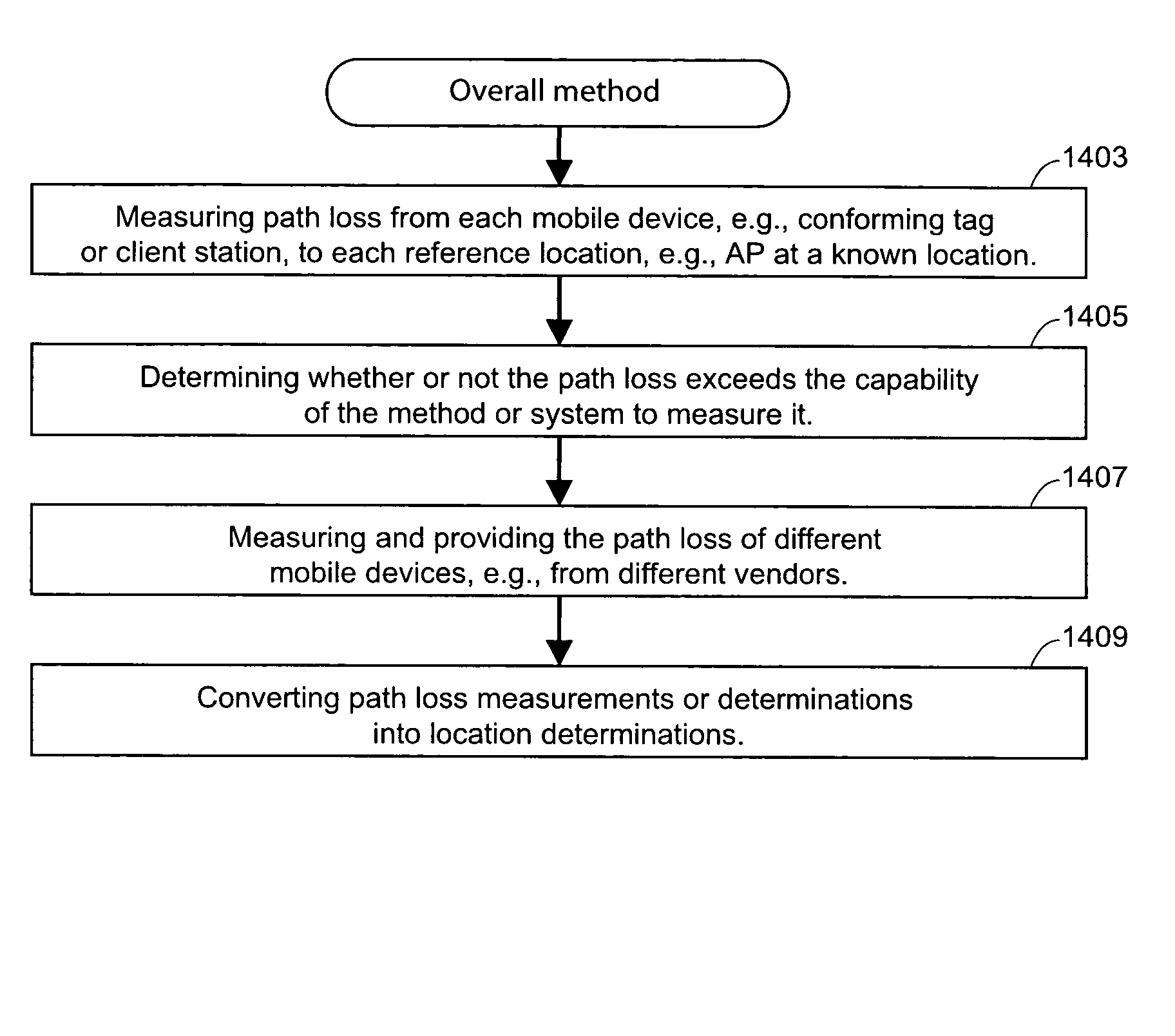
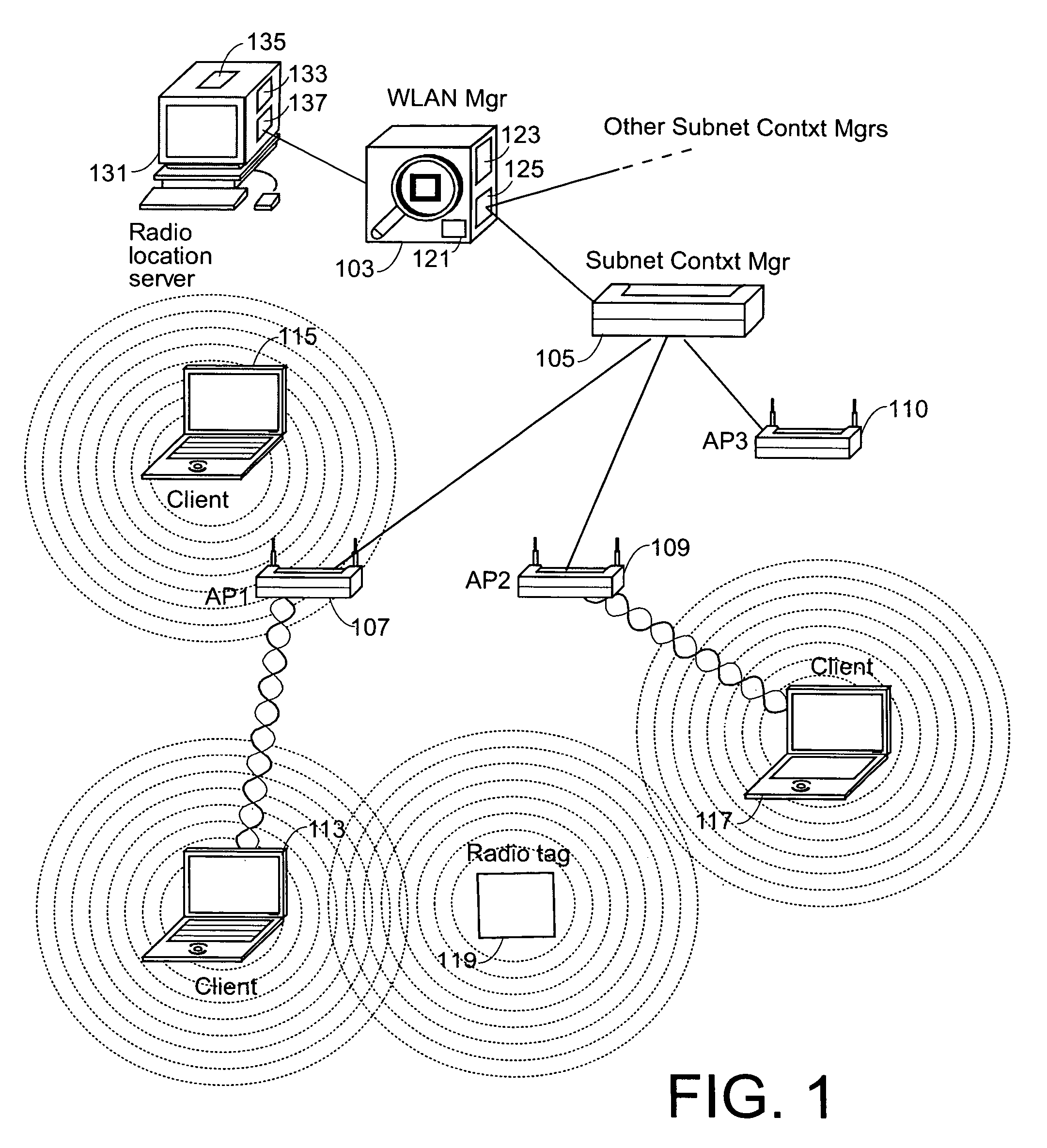
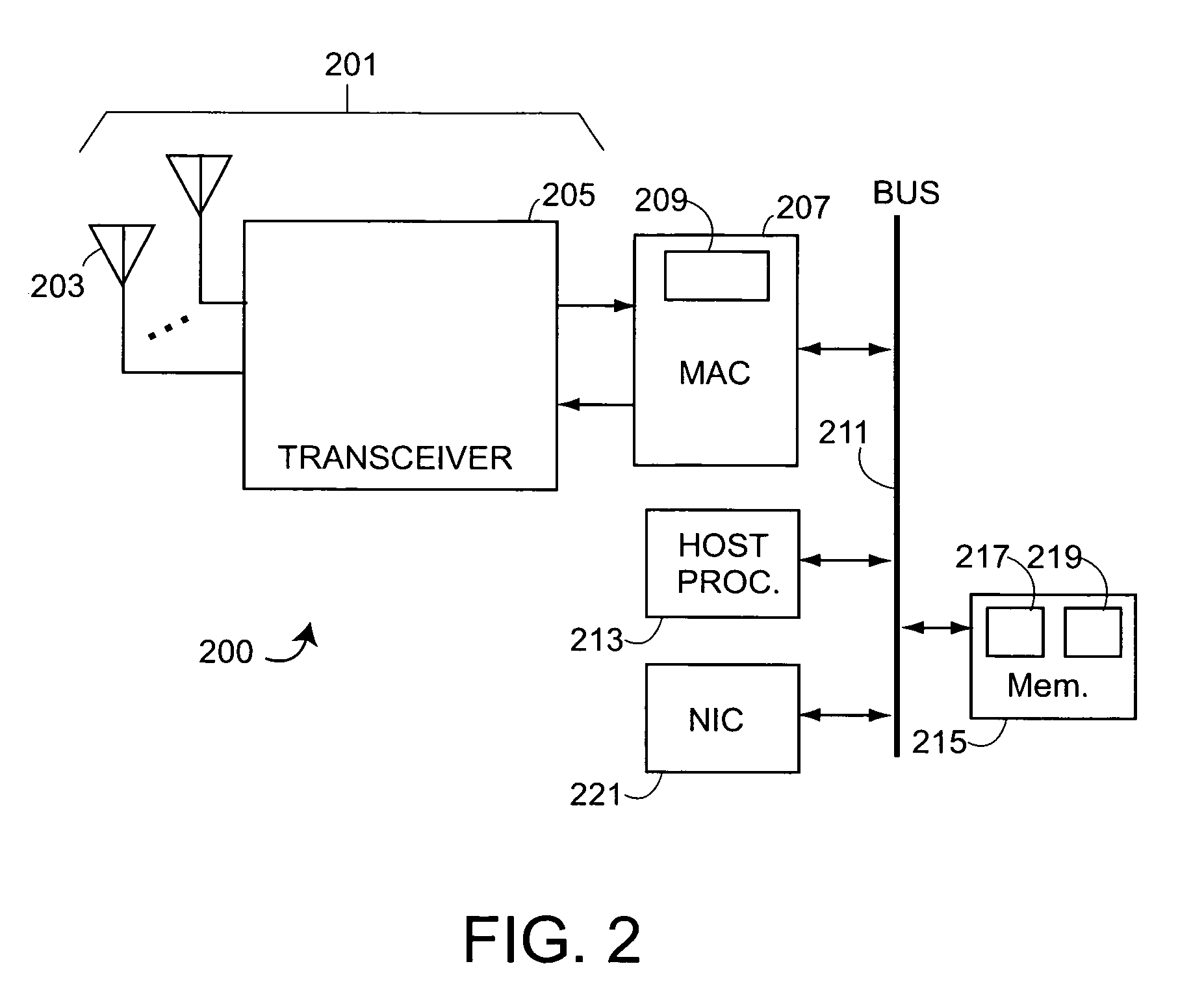
Tag location,client location, and coverage hole location in a wireless network
InactiveUS20060075131A1Reduce power consumptionEfficient methodNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionRadiolocationPublic infrastructure
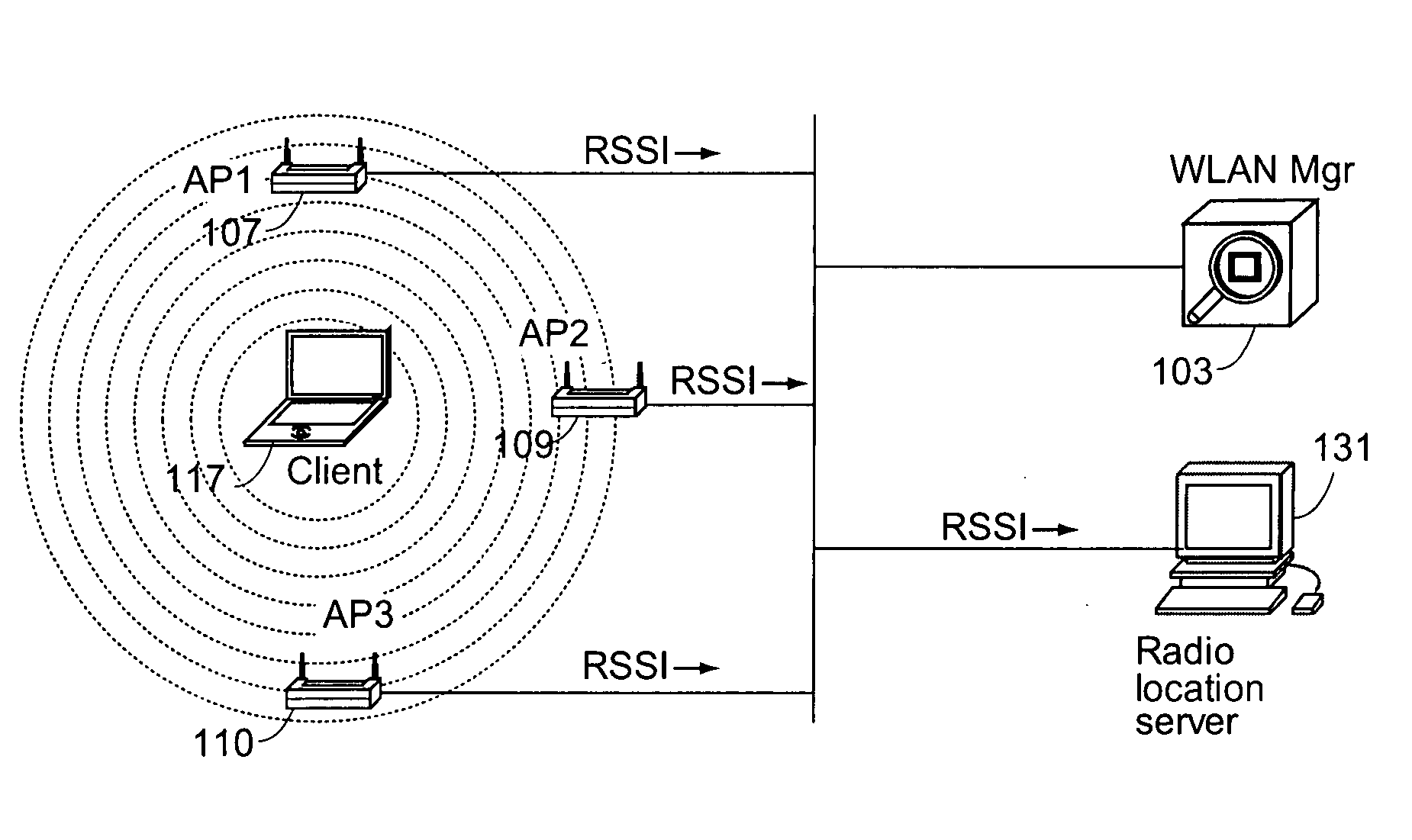
Determining the location of a radio tag or client station of a wireless network, and the location of coverage holes by receiving from a plurality of wireless stations of the wireless network path loss information of the path loss of one or more location frames received at the respective wireless stations. The location frames transmitted by the radio tag or client station having a pre-defined frame structure. The radio tags and client stations use a common infrastructure for transmitting a location frame configured for radiolocation by path loss measurement. The common infrastructure includes a pre-defined protocol common for both radio tags and client stations for transmitting information for reception by the plurality of stations of the wireless network for radiolocation. The pre-defined protocol includes using the location frame having the pre-defined frame structure.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
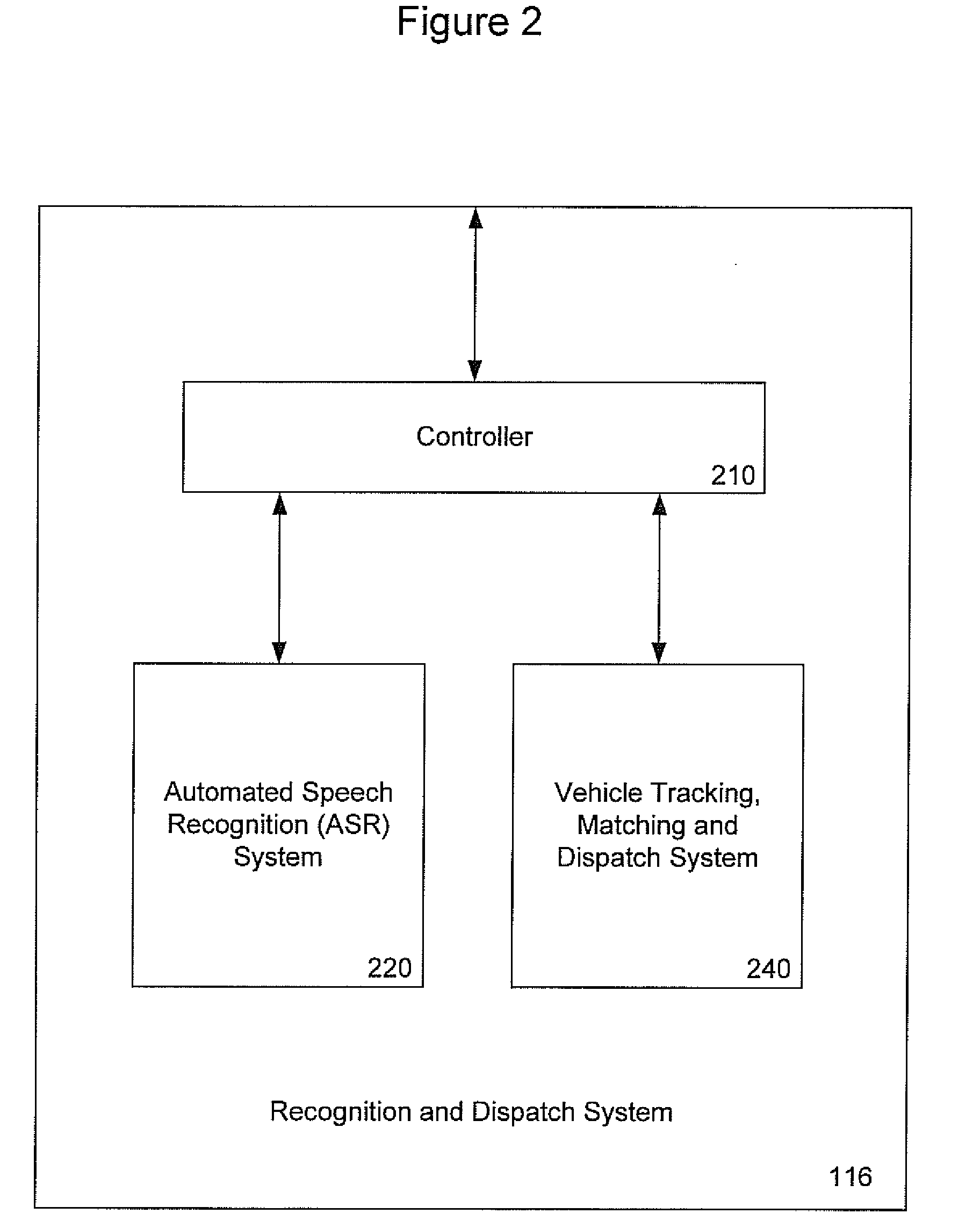
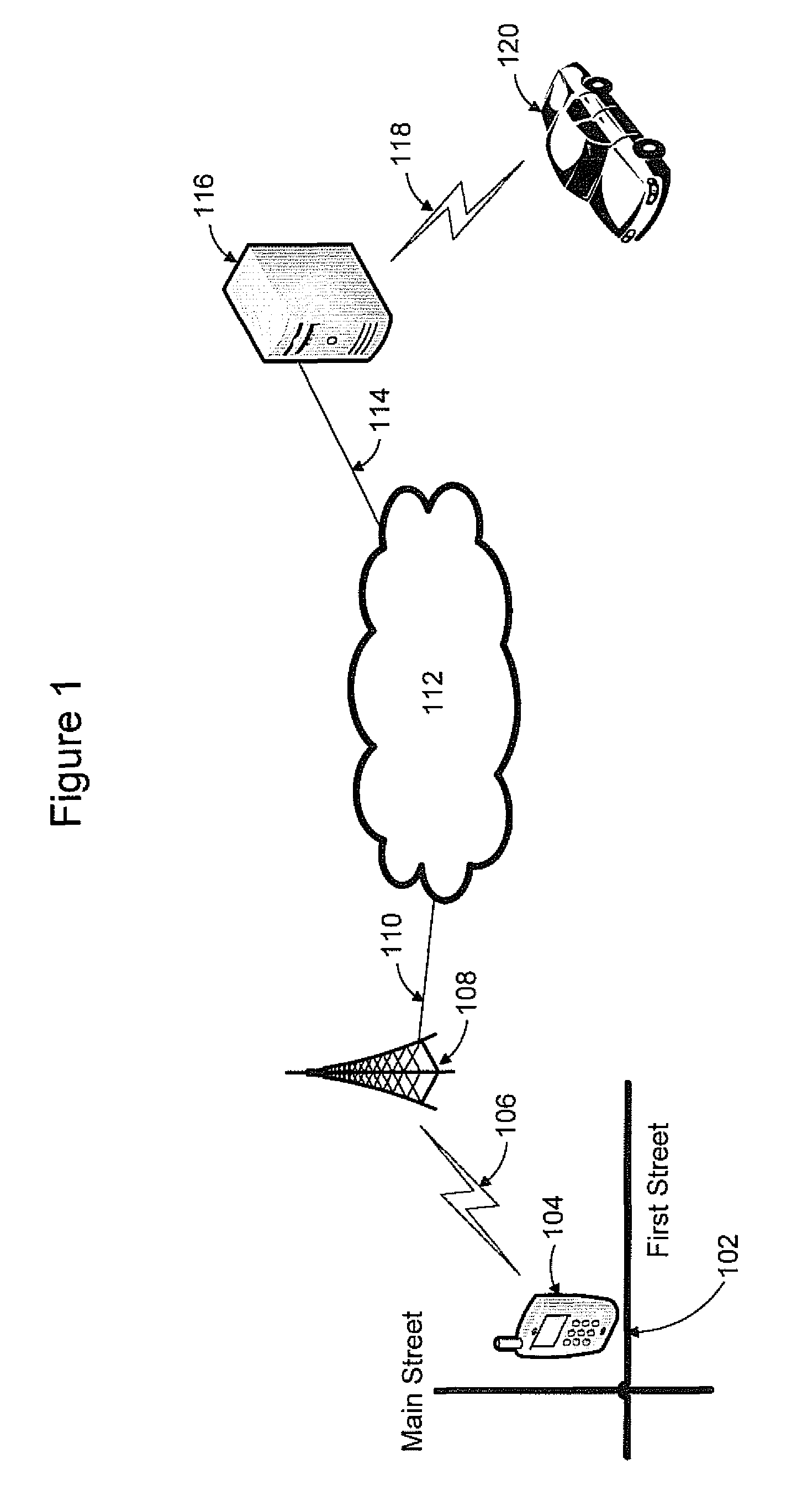
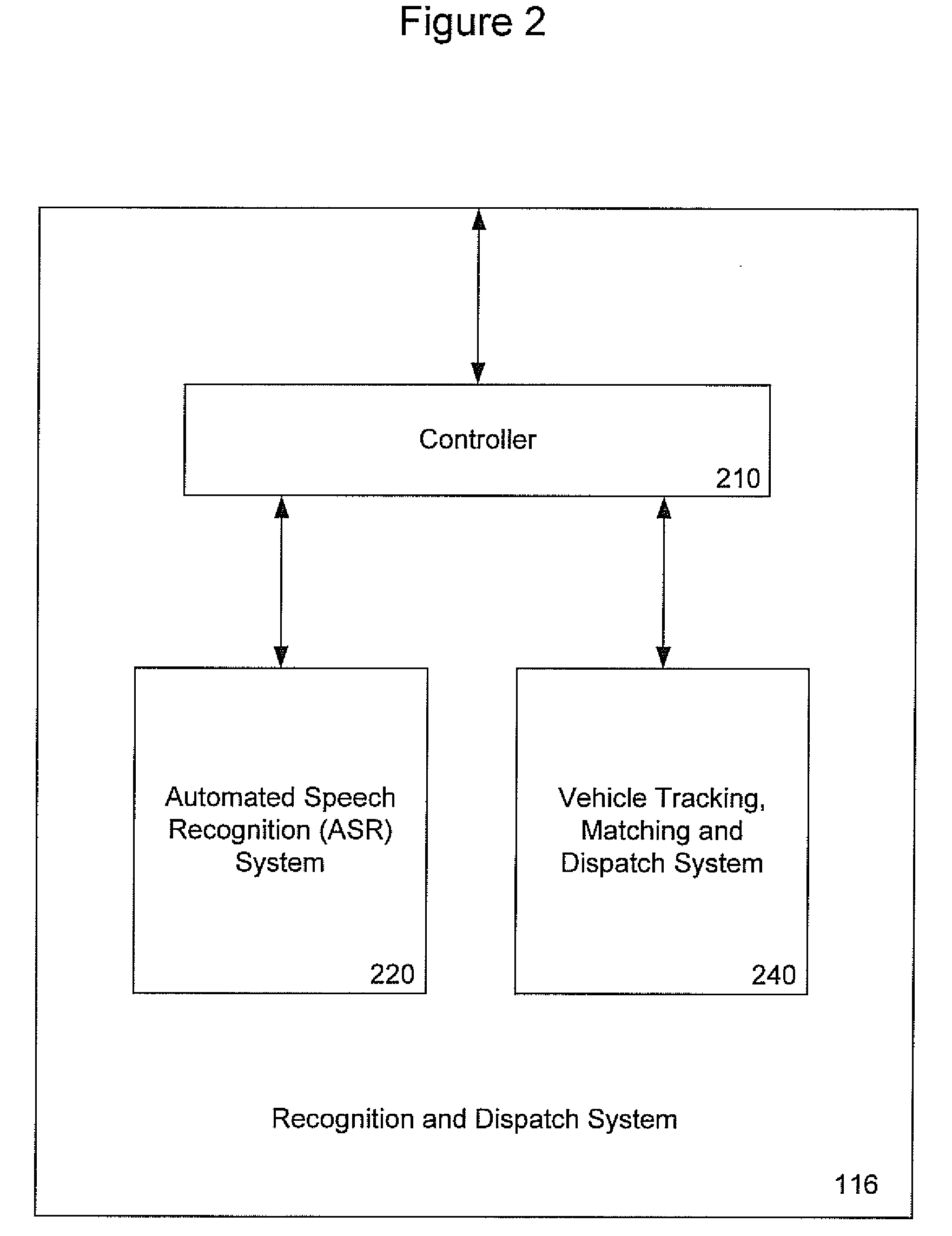
Automatic Service Vehicle Hailing and Dispatch System and Method
ActiveUS20090156241A1Removal costEliminate inconvenienceSpecial service for subscribersMessaging/mailboxes/announcementsRelevant informationRadiolocation
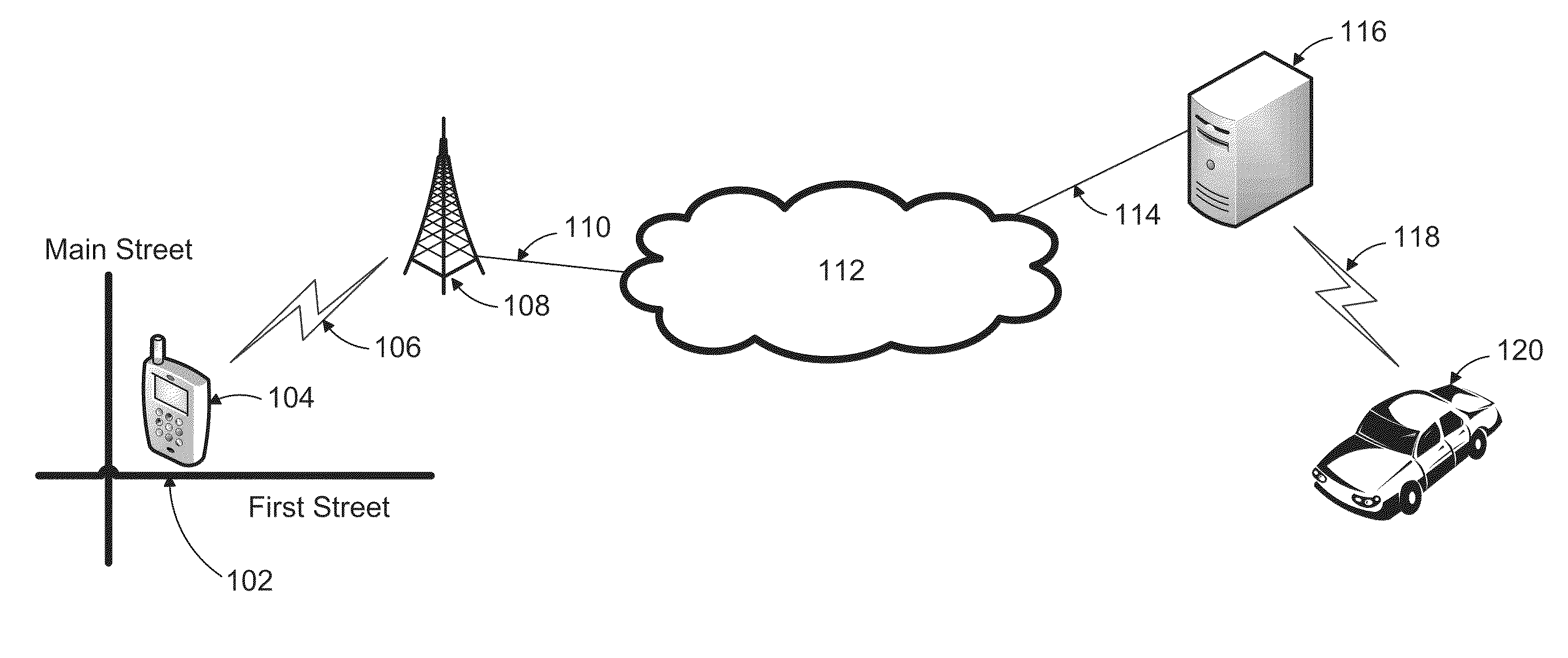
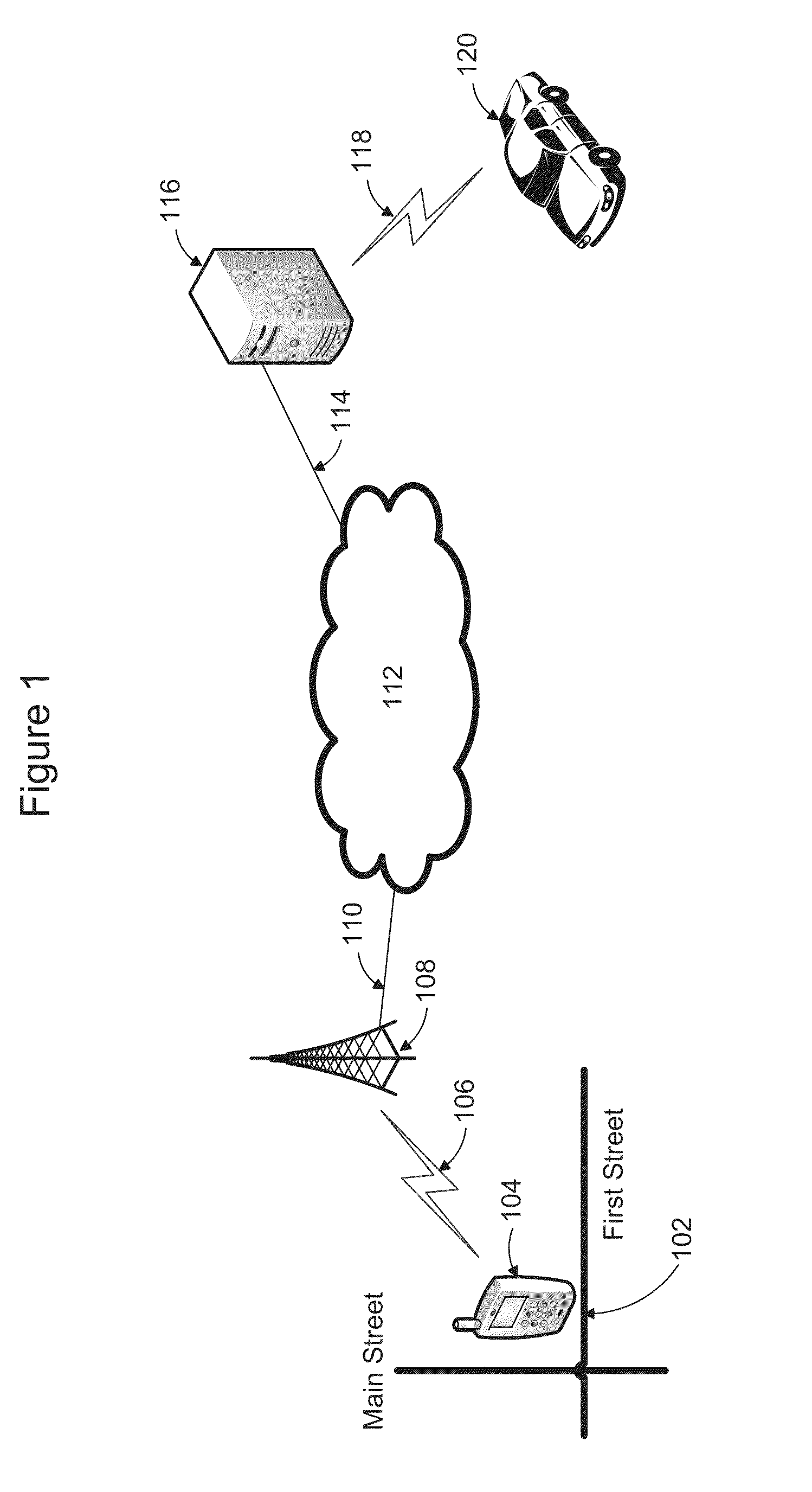
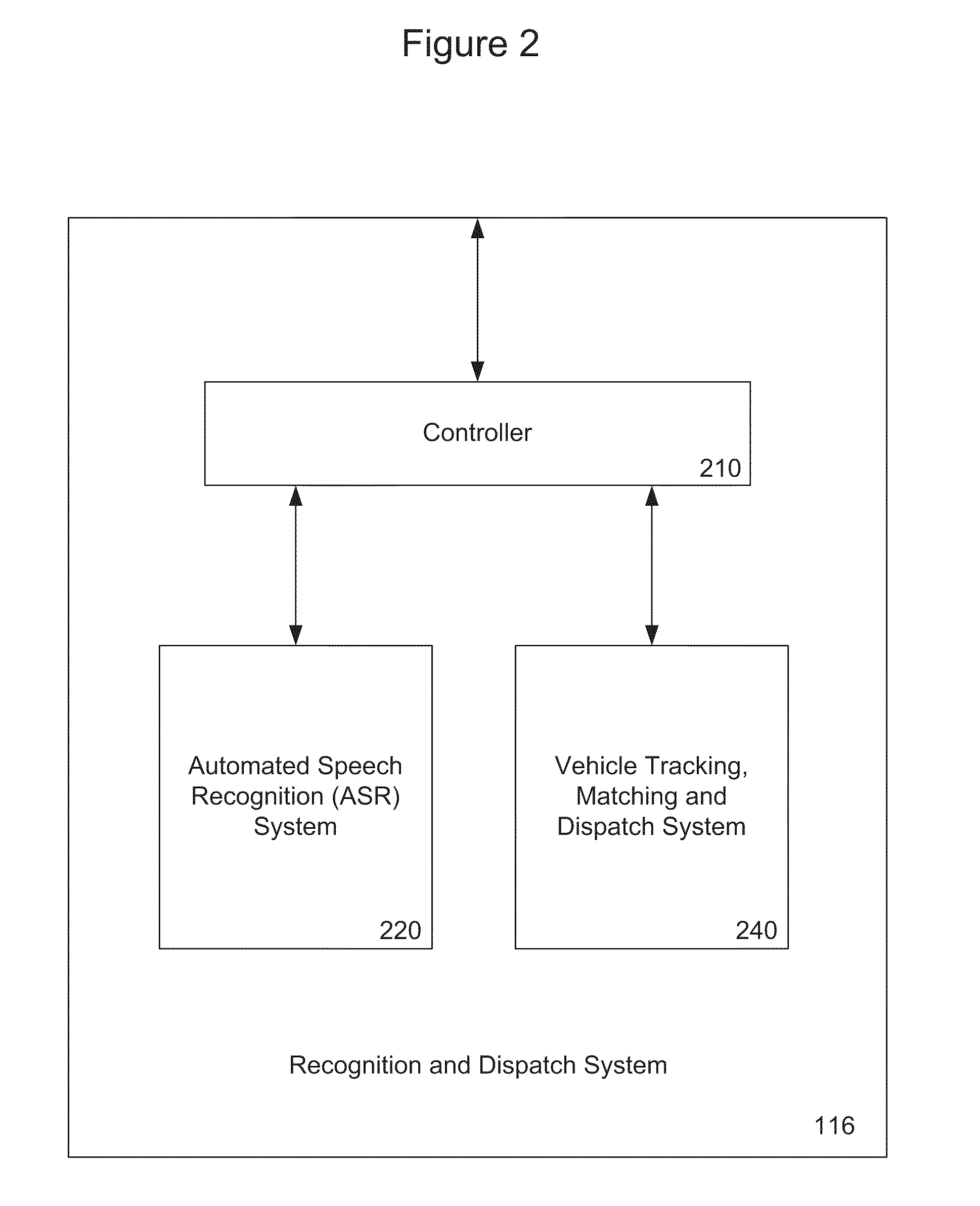
A system and method are provided for improving efficiency of operation and convenience of access to a fleet of taxis, or other service vehicles, requiring rapid, on-demand dispatch to customer-determined locations. Automatic speech recognition (ASR) and / or radiolocation technology are used to automate the entry of the customer pickup location, and optionally the dropoff location and other relevant information as well. A customer speaks the pickup location into a cellular telephone which then digitizes and transmits it as a data communication to an ASR system. The ASR system decodes the digitized utterance into a pickup location which is passed to a vehicle matching and dispatch system. The vehicle matching and dispatch system matches a taxi and dispatches it to the pickup location. In one embodiment, the identified pickup location is transmitted to the customer's cellular telephone for confirmation or correction, before dispatch of the requested taxi.
Owner:PROMPTU SYST CORP
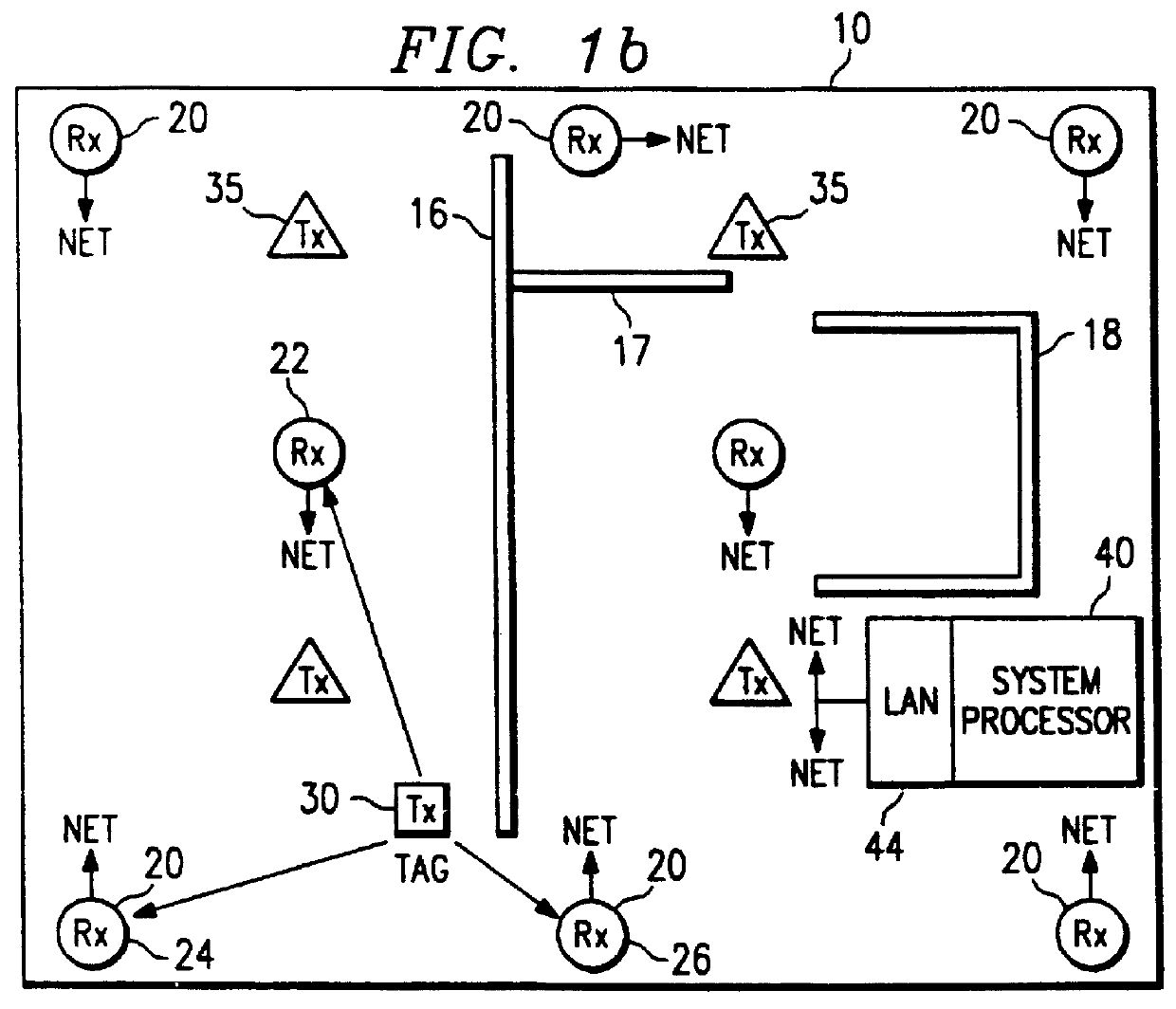
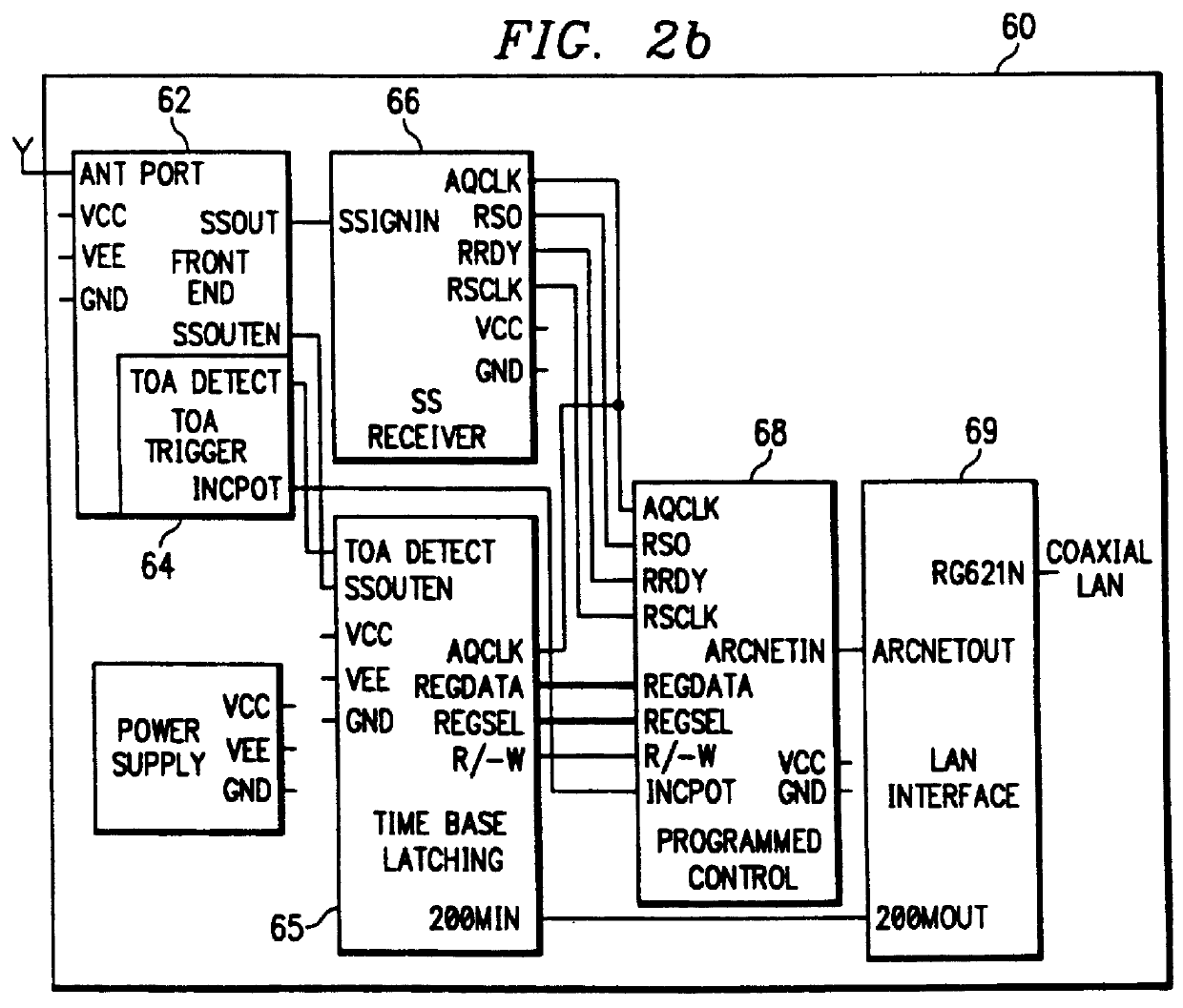
Location system adapted for use in multipath environments
InactiveUSRE36791E1Facilitates discriminationLow costDirection finders using radio wavesMemory record carrier reading problemsImage resolutionRadiolocation
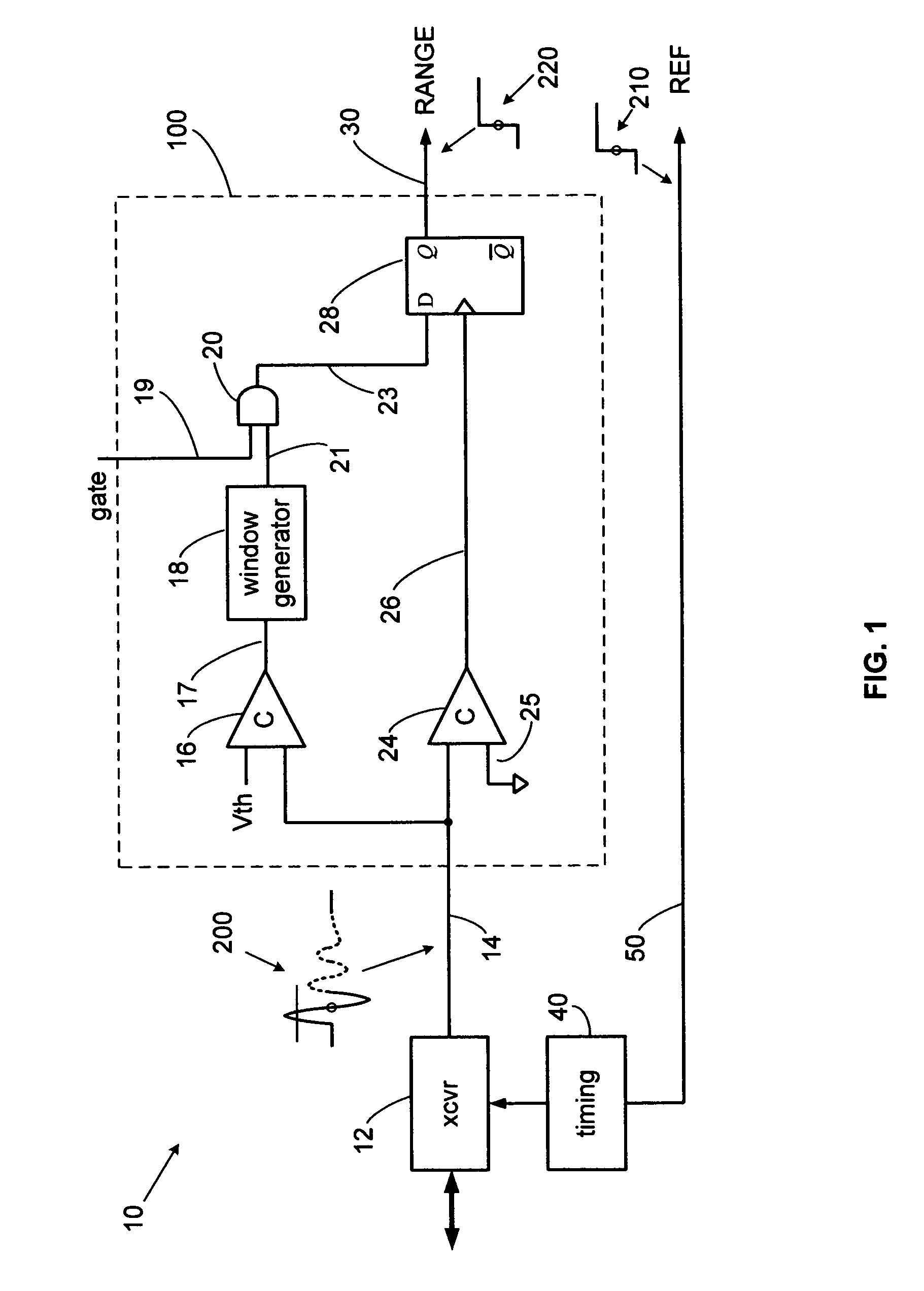
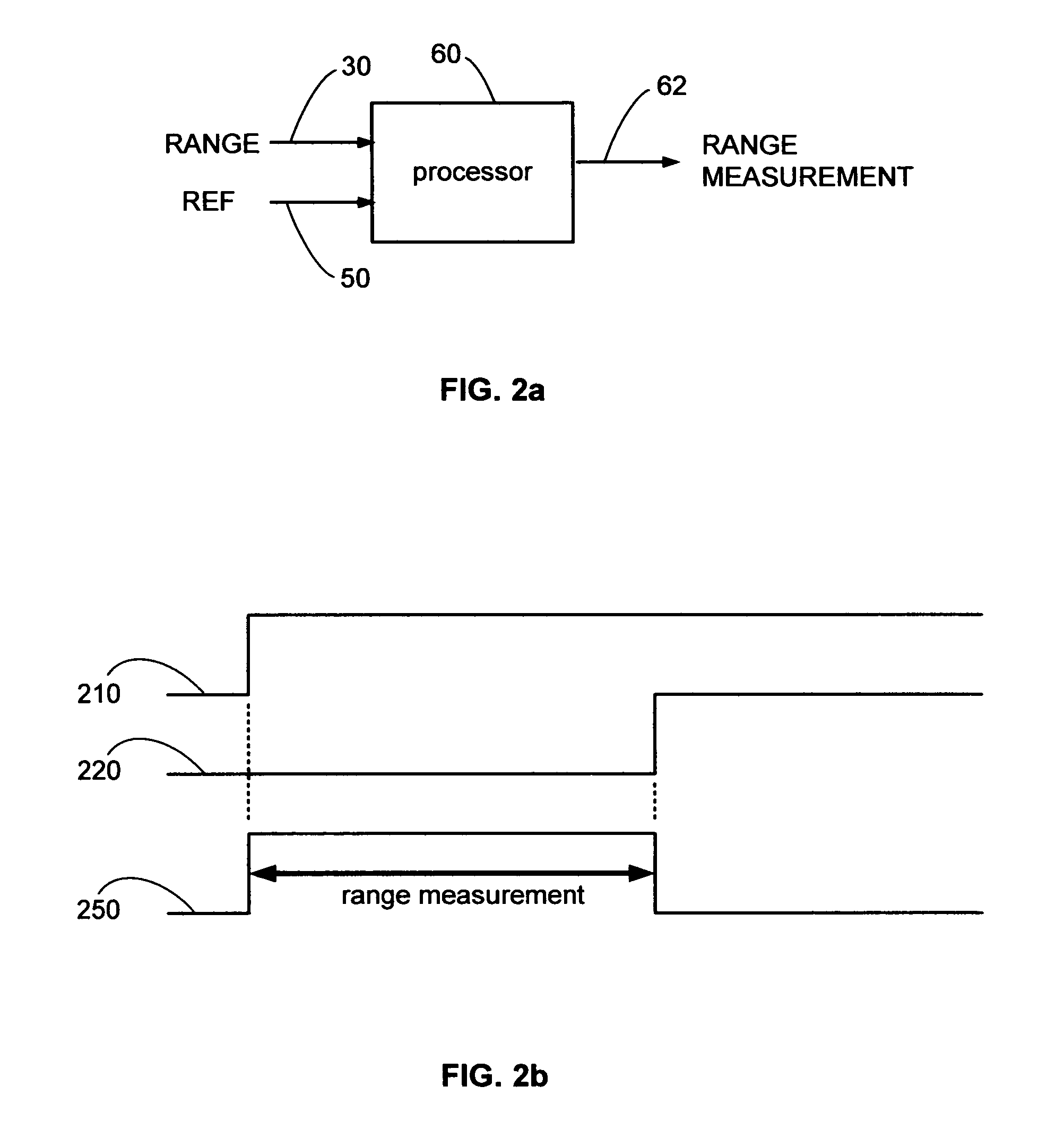
A radiolocation system for multipath environments, such as for tracking objects in a semiconductor fabrication facility (FIGS. 1a-1b), includes an array of receivers (20) distributed within the tracking area, coupled to a system processor (40) over a LAN. A TAG transmitter (30) located with each object transmits, at selected intervals, spread spectrum TAG transmissions including at least a unique TAG ID. In a high resolution embodiment, object location is accomplished by time-of-arrival (TOA) differentiation, with each receiver (FIG. 2b) including a TOA trigger circuit (64) for triggering on arrival of a TAG transmission, and a time base latching circuit (65) for latching the TOA count from an 800 MHz time base counter. In a low resolution embodiment, each receiver of the array is assigned a specific location-area, and receives TAG transmissions almost exclusively from TAGs located in that area, thereby eliminating the need for any time-of-arrival circuitry.
Owner:FRESHLOC TECH
Mobile field electrical supply, water purification system, wash system, water collection, reclamation, and telecommunication apparatus
InactiveUS20050016906A1Highly mobileHighly self-containedLiquid separation auxillary apparatusGeneral water supply conservationCollection systemDistillation
A mobile emergency response apparatus providing water collection, handling, treatment, and storage capabilities, as well as serving as mobile telecommunication system. The apparatus comprises a raw water filtration system, a sodium ion exchange system, a storage system with a plurality of tanks, a reverse osmosis system, and heating and distributions systems. The apparatus also comprises a mobile electrical power system. Optionally, the apparatus includes a desalination system, a disinfection system, a rainwater collection system, a fluid containment and recovery system, and an auxiliary fluid distribution system. The disinfection system may include a chlorination, ultraviolet light, or ozone disinfection system, and may further include a distillation system that may be conventionally powered or solar powered. Water may be distributed through a plurality of auxiliary devices. The telecommunication system includes both satellite and terrestrial transmission and receiving capability, and location identification devices such as a global positioning system and a radiolocation system.
Owner:NU ELEMENT
Automatic service vehicle hailing and dispatch system and method
ActiveUS8005488B2Special service for subscribersSpeech recognitionTelecommunicationsRelevant information
A system and method are provided for improving efficiency of operation and convenience of access to a fleet of taxis, or other service vehicles, requiring rapid, on-demand dispatch to customer-determined locations. Automatic speech recognition (ASR) and / or radiolocation technology are used to automate the entry of the customer pickup location, and optionally the dropoff location and other relevant information as well. A customer speaks the pickup location into a cellular telephone which then digitizes and transmits it as a data communication to an ASR system. The ASR system decodes the digitized utterance into a pickup location which is passed to a vehicle matching and dispatch system. The vehicle matching and dispatch system matches a taxi and dispatches it to the pickup location. In one embodiment, the identified pickup location is transmitted to the customer's cellular telephone for confirmation or correction, before dispatch of the requested taxi.
Owner:PROMPTU SYST CORP
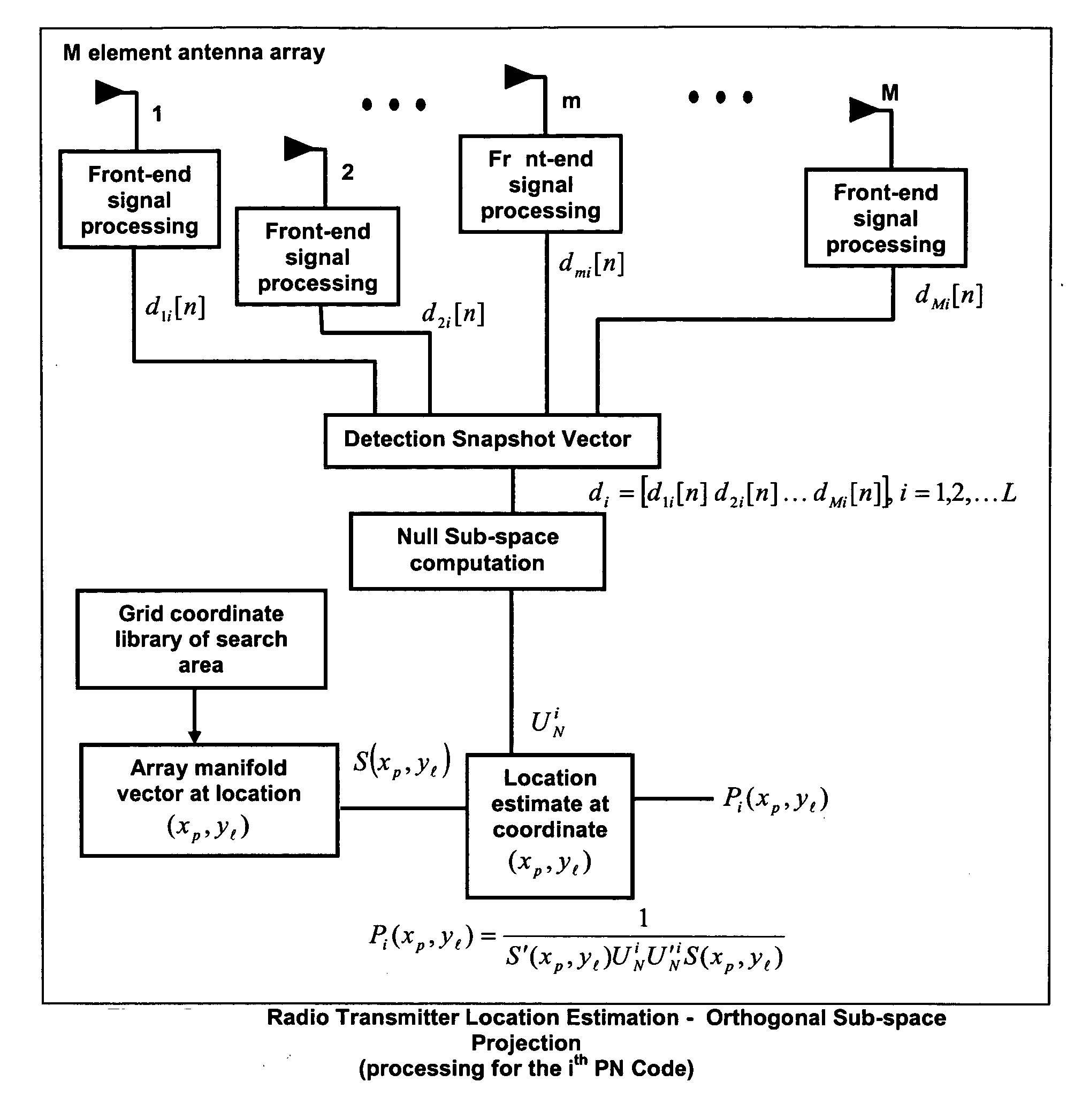
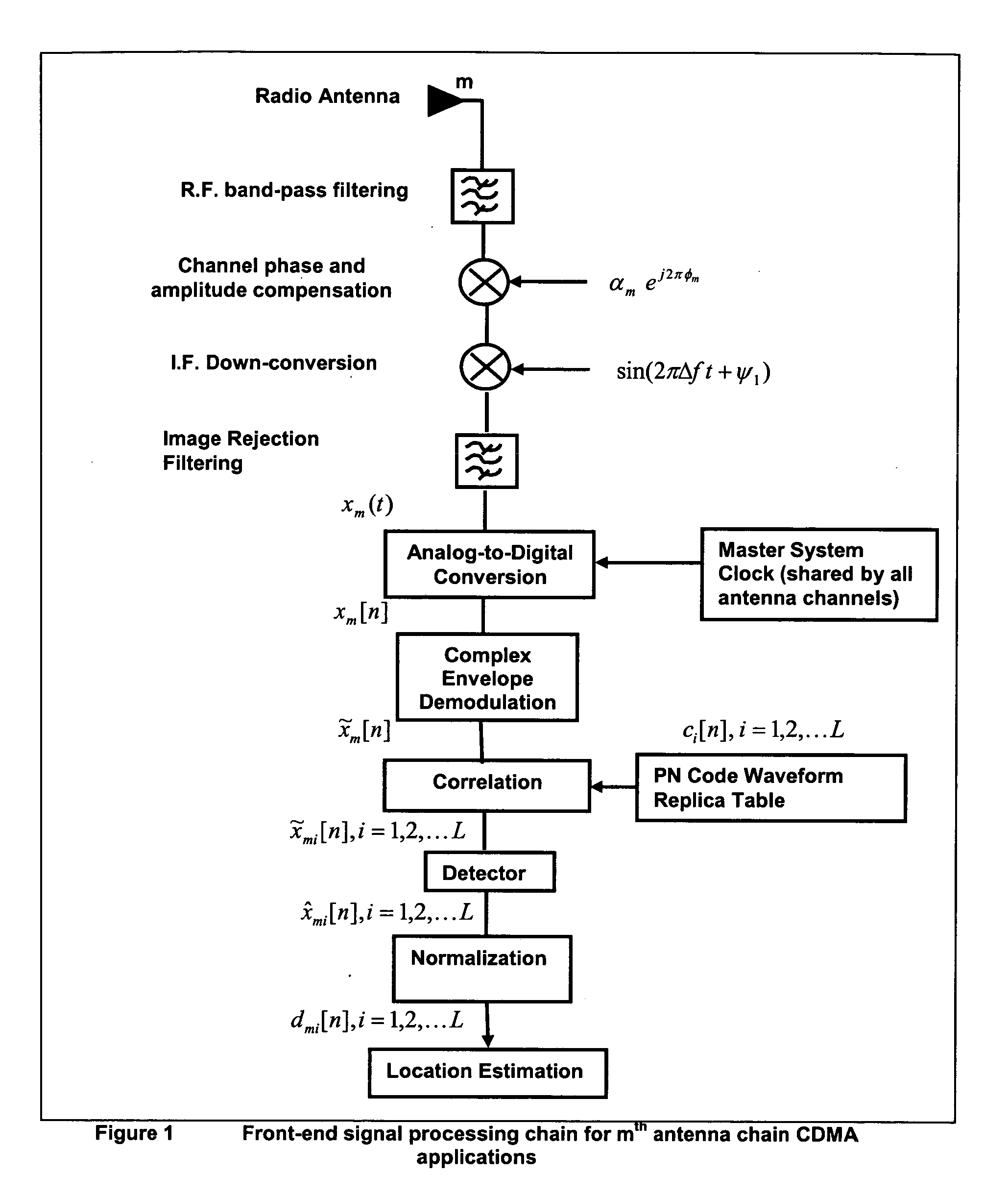
Random antenna array interferometer for radio location
InactiveUS20050007278A1Effective of noise powerReduce coherenceDirection finders using radio wavesImage resolutionCarrier signal
This invention relates to a method and system for the radio location of CDMA and non-CDMA enabled transmitters within a reception zone. The invention exploits the superposition of antenna patterns that create complex and asymmetrical interference structures at very small scales. By randomly distributing a random antenna array of M elements across a two or three-dimensional surface, fine scale interference structures on the scale of ¼ the carrier wavelength are generated. Once the minimum number of antennas are placed, additional antennas will not improve the resolution. Such interference structures when sampled at ⅛ the carrier wavelength or greater yields unique spatial patterns with respect to a given antenna array geometry and transmitter location. The invention incorporates signature recognition (matching) and orthogonal sub-space projection estimators to derive location estimates of a radio transmitter.
Owner:LOTEK WIRELESS
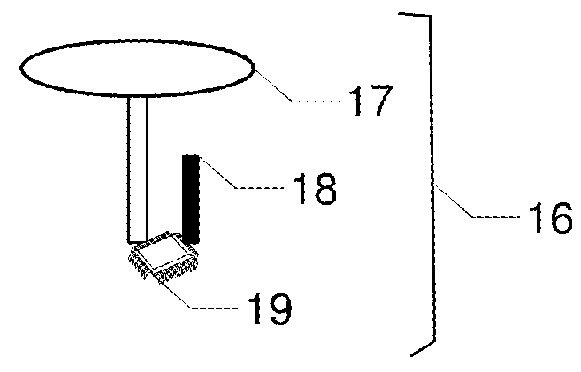
Flight Planning for Unmanned Aerial Tower Inspection with Long Baseline Positioning
ActiveUS20180095478A1Accurate calculationFull coverageSatellite radio beaconingElectromagnetic wave reradiationTransmission towerRadio equipment
FIG. 1 is a perspective view of transmission tower 10, phase conductors 12, insulators 14, and shield wires 15. They are to be inspected by unmanned aerial vehicle UAV 20 with embedded processor and memory 22, radio 24, location rover 26, and camera 28. Continuously operating reference station 16 has GNSS antenna 17, GNSS receiver 19, and radio 18. The relative location between UAV 20 and reference station 16 can be accurately calculated using location corrections sent by radio 18 to radio 24. Camera 28 on UAV 20 is first used to capture two or more orientation images 38 and 39 of tower 10; lines 12 and 15; and insulators 14 from different vantage points. Terrestrial or close-range photogrammetry techniques are used create a three dimensional model of tower 10; lines 12 and 15; and insulators 14. Based on inspection resolution and safety objectives, a standoff distance 50 is determined. Then a flight path with segments for ascent 40, one or more loops 42, 44, 46, and a descent 48 is designed to ensure full inspection coverage via inspection images like 52 and 54.
Owner:VAN CRUYNINGEN IZAK
Tag location, client location, and coverage hole location in a wireless network
InactiveUS7293088B2Reduce power consumptionEfficient methodNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionWireless mesh networkRadiolocation
Determining the location of a radio tag or client station of a wireless network, and the location of coverage holes by receiving from a plurality of wireless stations of the wireless network path loss information of the path loss of one or more location frames received at the respective wireless stations. The location frames transmitted by the radio tag or client station having a pre-defined frame structure. The radio tags and client stations use a common infrastructure for transmitting a location frame configured for radiolocation by path loss measurement. The common infrastructure includes a pre-defined protocol common for both radio tags and client stations for transmitting information for reception by the plurality of stations of the wireless network for radiolocation. The pre-defined protocol includes using the location frame having the pre-defined frame structure.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
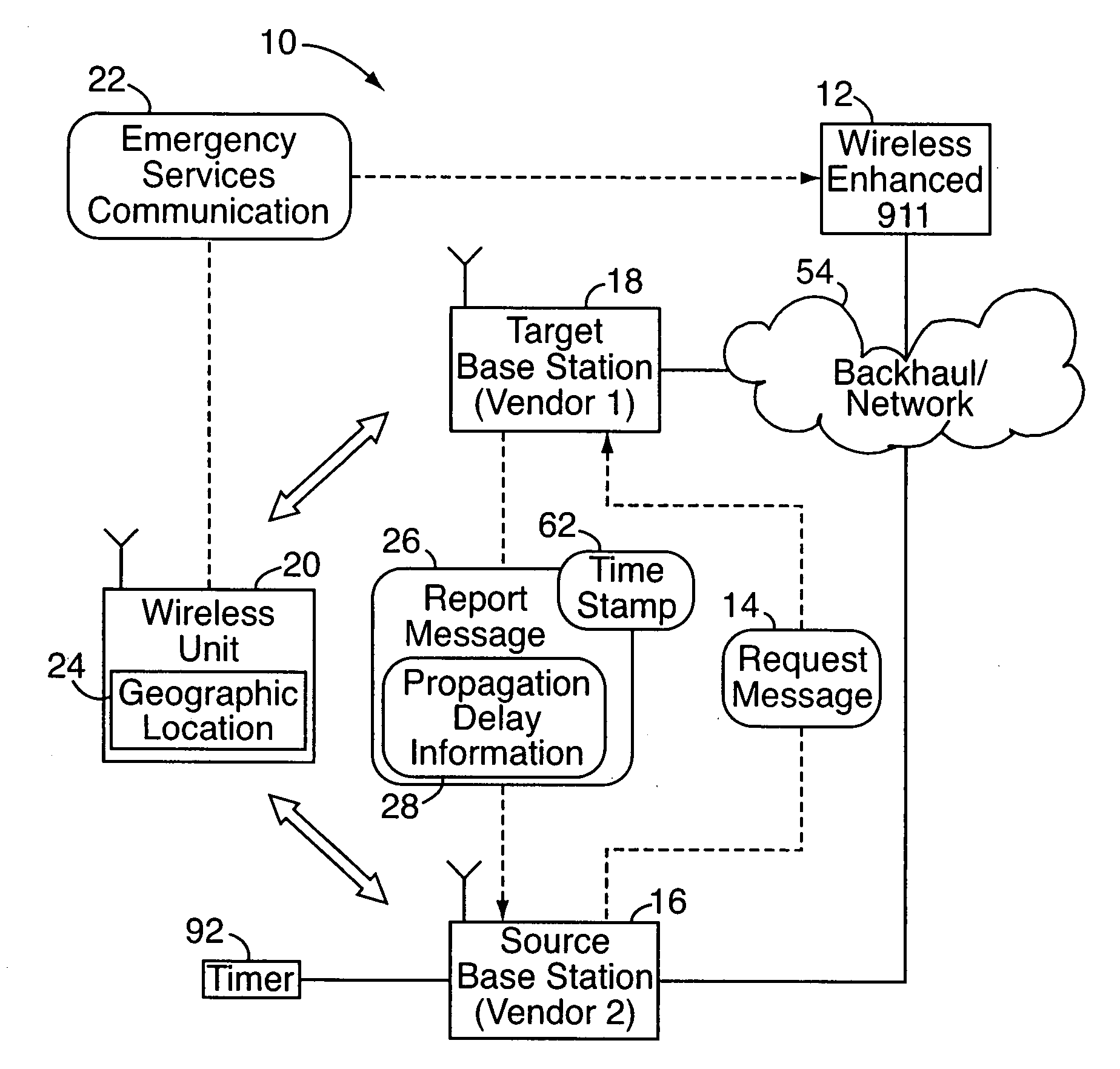
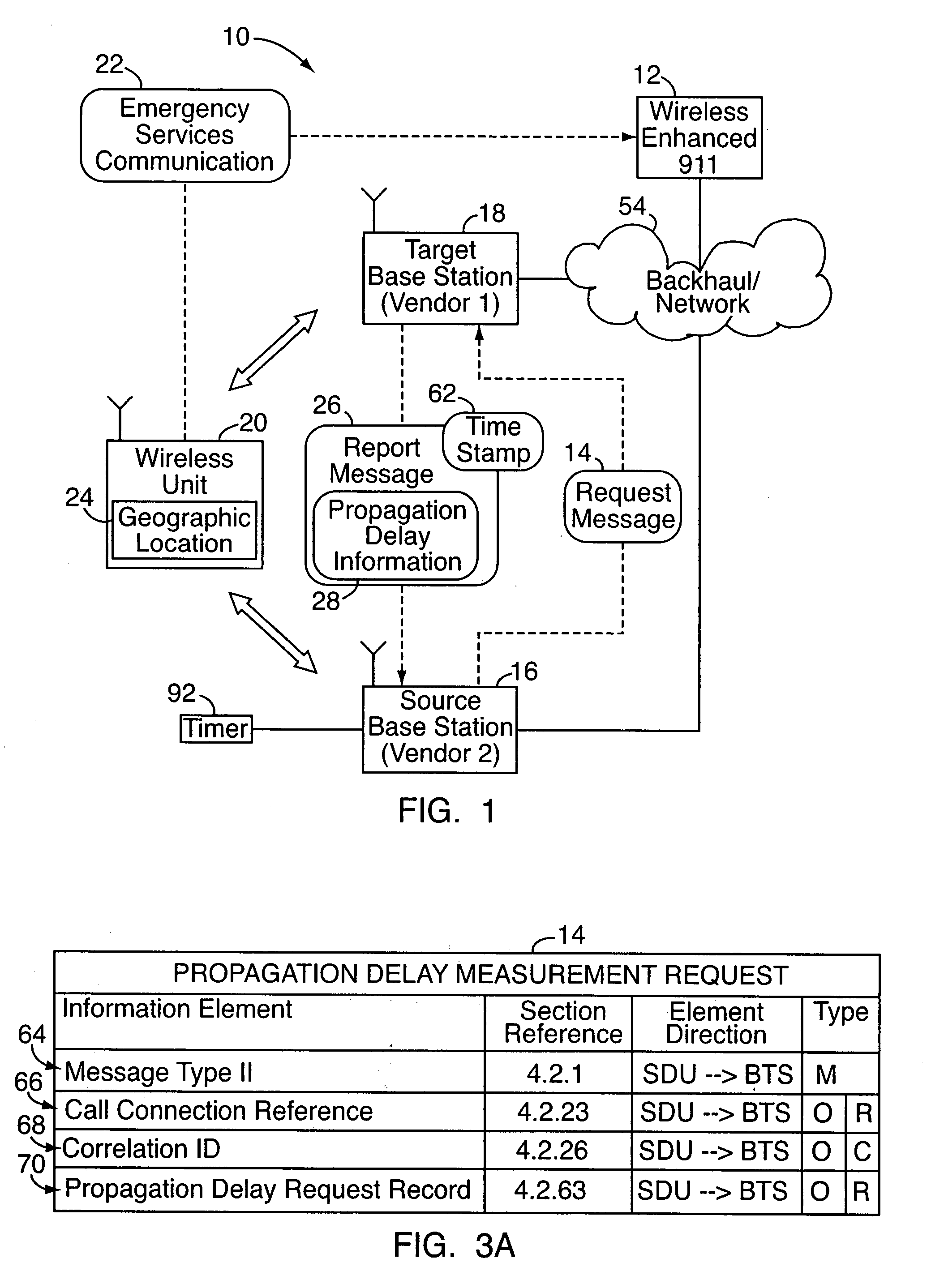
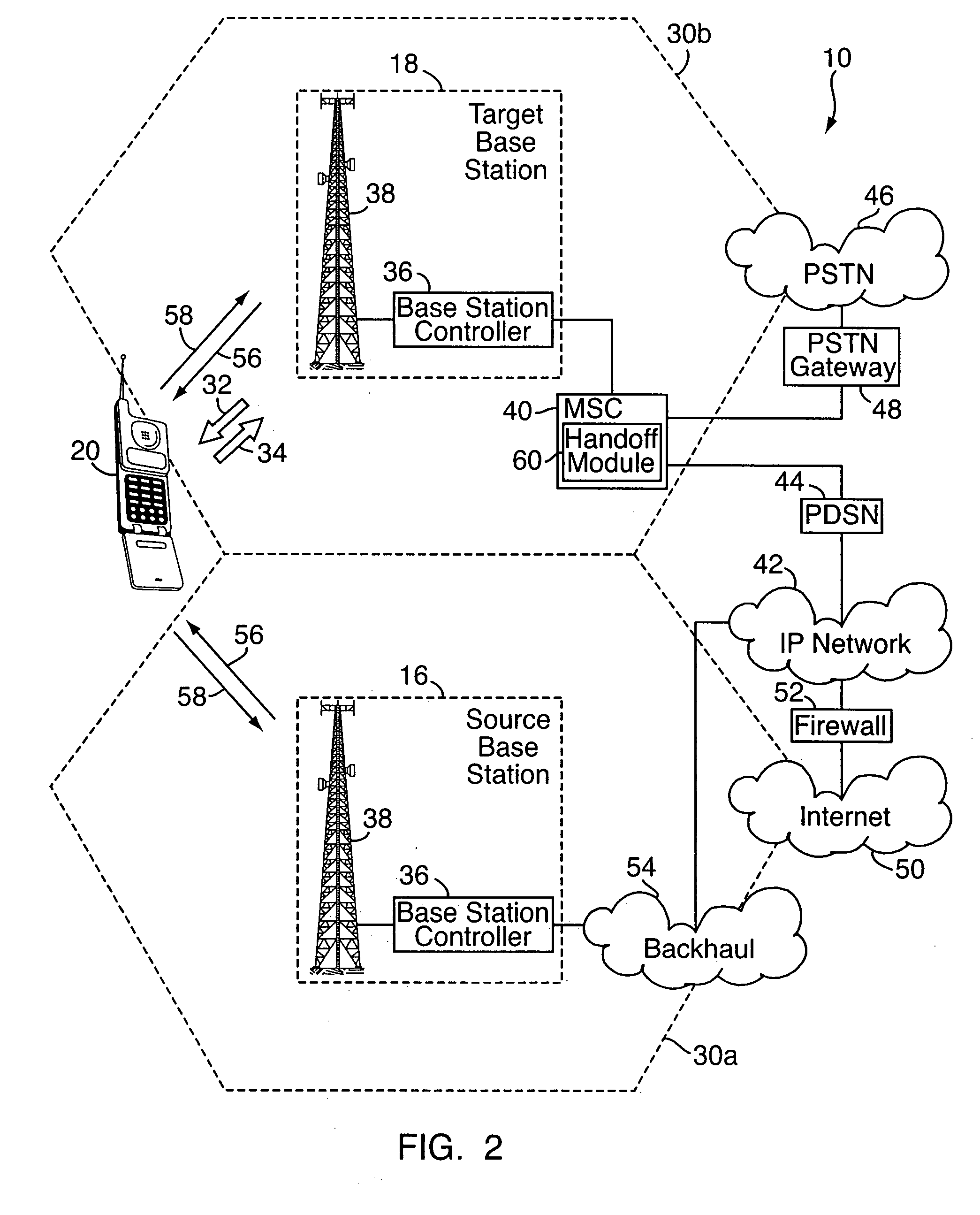
Signaling method to support geo-location emergency services
ActiveUS20080233916A1Reduce bandwidth usageTelephonic communicationTime-division multiplexPropagation delayInformation networks
In a method to support geo-location emergency services in a wireless network, a request message is transmitted from a source base station of one vendor to a target base station of another vendor. For example, the request message might be sent subsequent to a wireless unit initiating an emergency services communication, where it is desired to determine the location of the wireless unit by radiolocation, or otherwise at the network level. Upon receiving the request message, the target base station transmits a report message to the source base station, which includes a one-way transmission delay (or other propagation delay information) of the wireless unit as measured at the target base station. Communication protocols in the network are configured so that there are no automatic transmissions of propagation delay information. Instead, base stations transmit propagation delay information only upon the receipt of request messages requesting the information.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Procedure for determining the probability of finding a parking place
ActiveUS8423275B1Indication of parksing free spacesNavigation instrumentsNatural satelliteParking space
A procedure for determining the probability of finding a parking place within a certain period of time on a pre-set stretch of road of an area with a multiplicity of stretches of road. With this procedure, motion profiles are detected and statistically evaluated of users of radiolocation-aided, especially satellite-aided, navigation aids in the area. For each usera) A “parking place found” event is determined;b) The stretch of road in which the “parking place found” event occurred is detected;c) The travel time is detected which the user expended in each of the stretches of the road until the “parking place found” event occurred.From the data thus acquired for a multiplicity of users, a probability is determined of finding a parking place within the set time span on the stretch of the road.
Owner:TELENAV
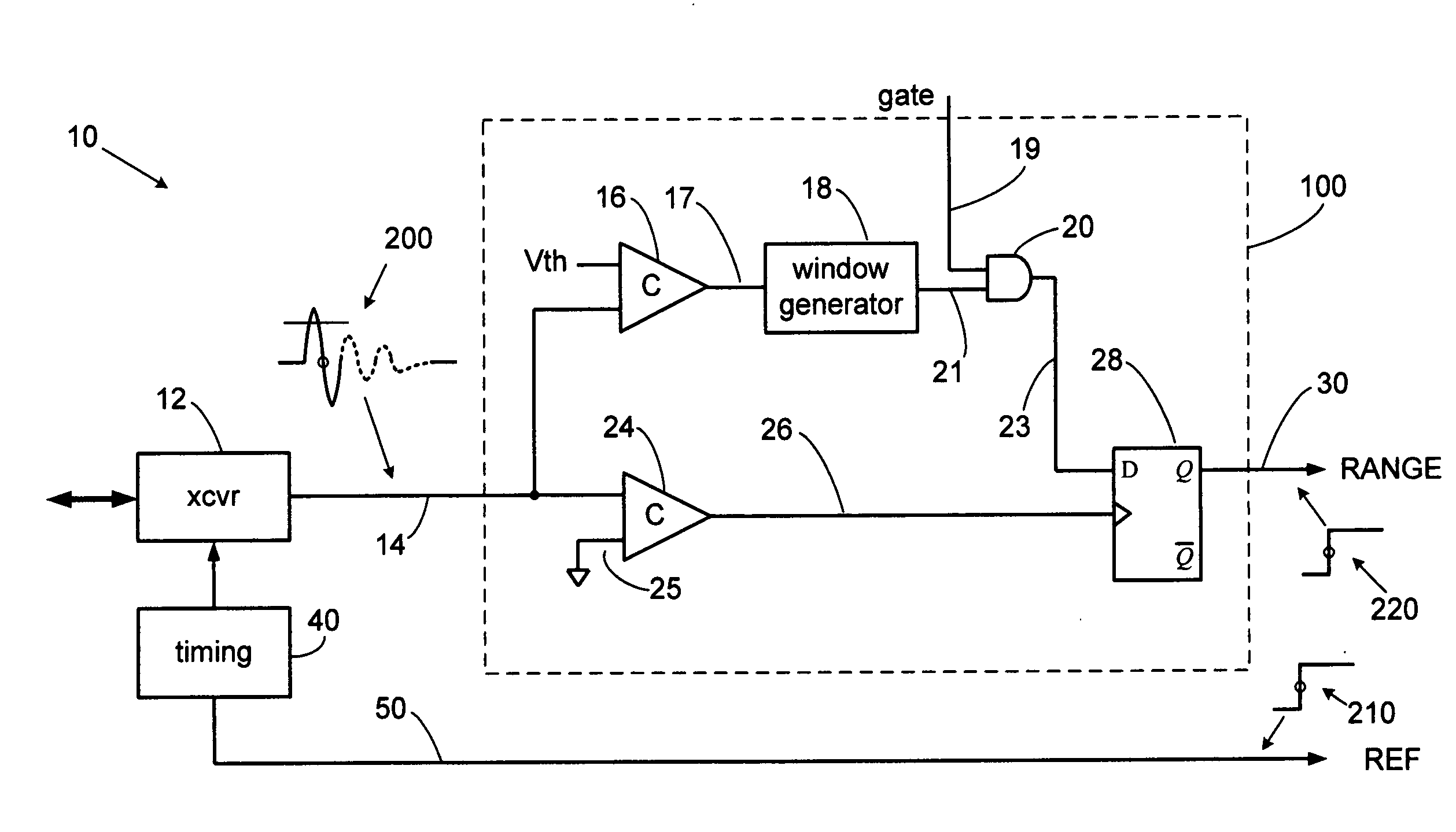
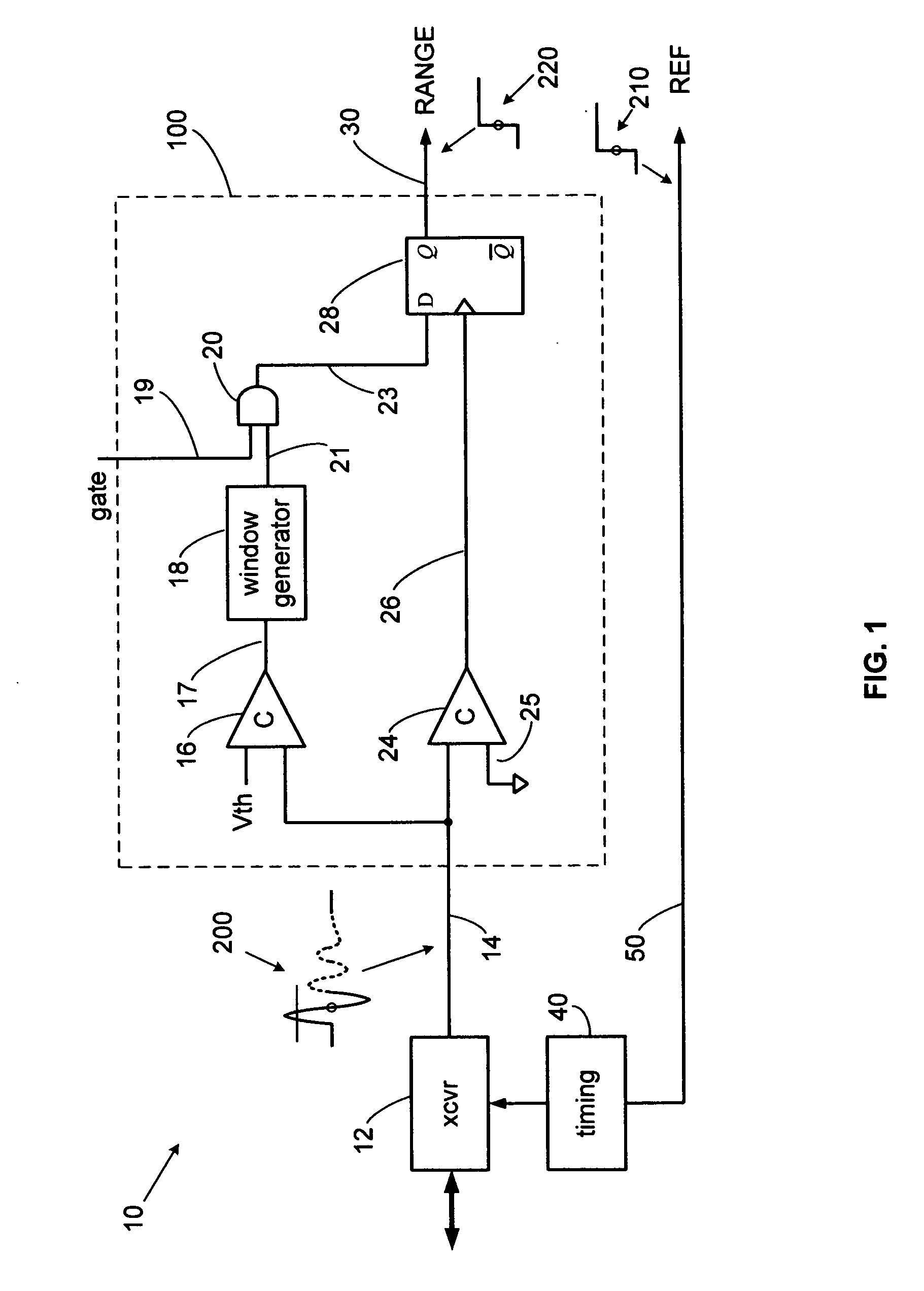
Precision pulse detection system for radar sensors
ActiveUS20080048905A1Improve accuracyGood anti-noise performanceAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsResistance/reactance/impedenceHandwritingPhase detector
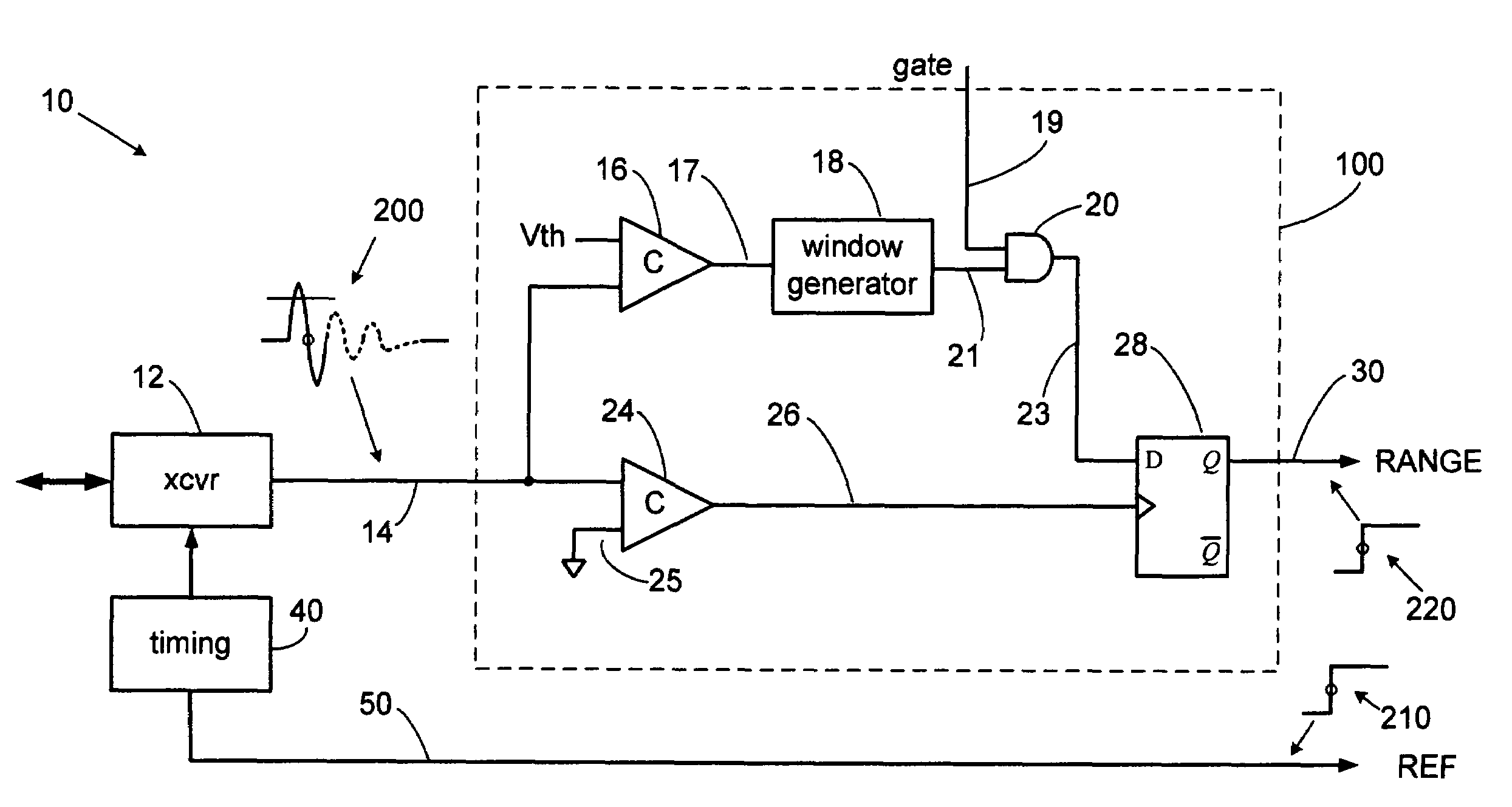
A precision pulse detection system for time-of-flight sensors detects a zero axis crossing of a pulse after it crosses above and then falls below a threshold. Transmit and receive pulses flow through a common expanded-time receiver path to precision transmit and receive pulse detectors in a differential configuration. The detectors trigger on zero axis crossings that occur immediately after pulse lobes exceed and then drop below a threshold. Range errors caused by receiver variations cancel since transmit and receive pulses are affected equally. The system exhibits range measurement accuracies on the order of 1-picosecond without calibration even when used with transmitted pulse widths on the order of 500 picoseconds. The system can provide sub-millimeter accurate TDR, laser and radar sensors for measuring tank fill levels or for precision radiolocation systems including digital handwriting capture.
Owner:MCEWAN TECH
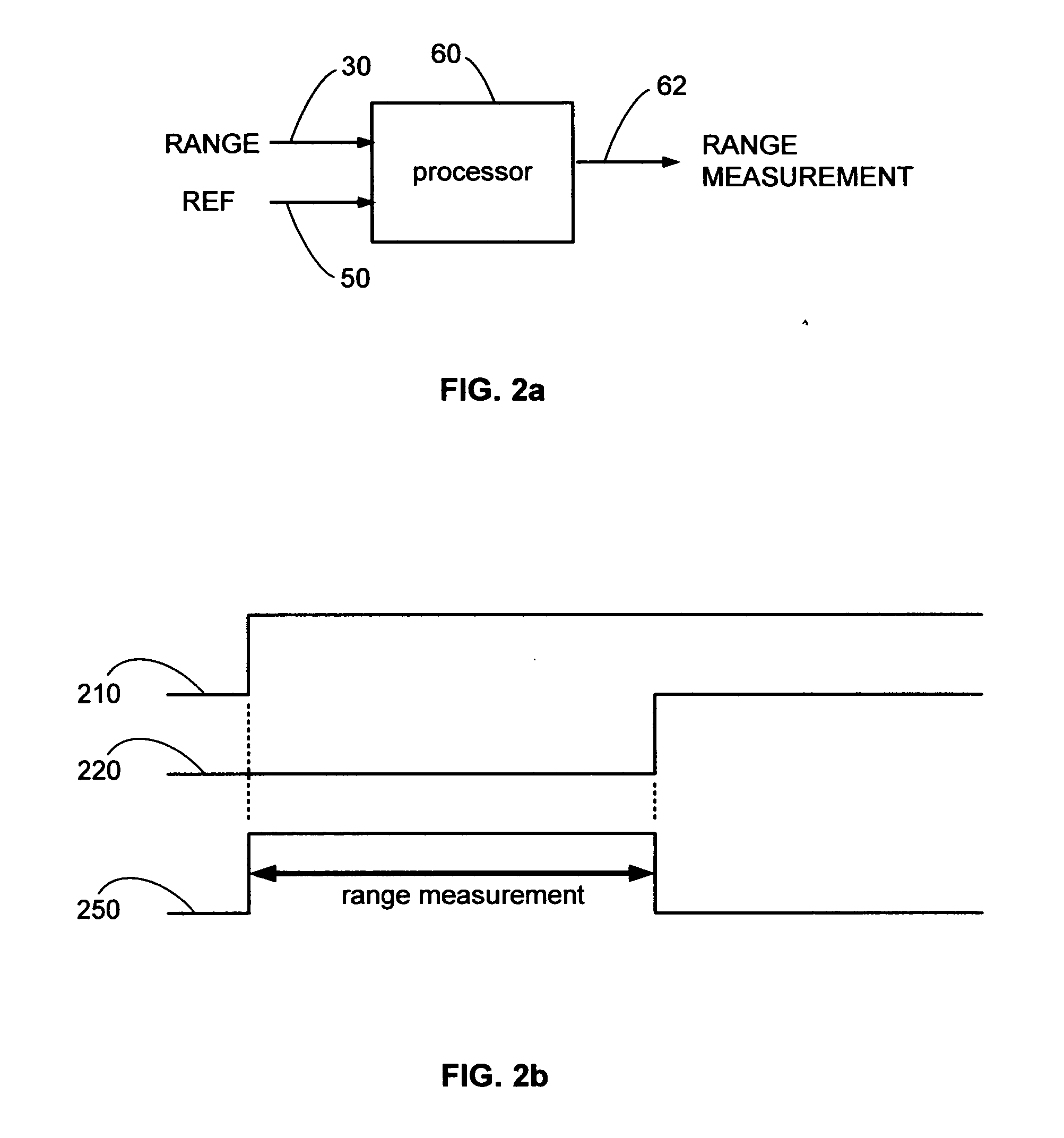
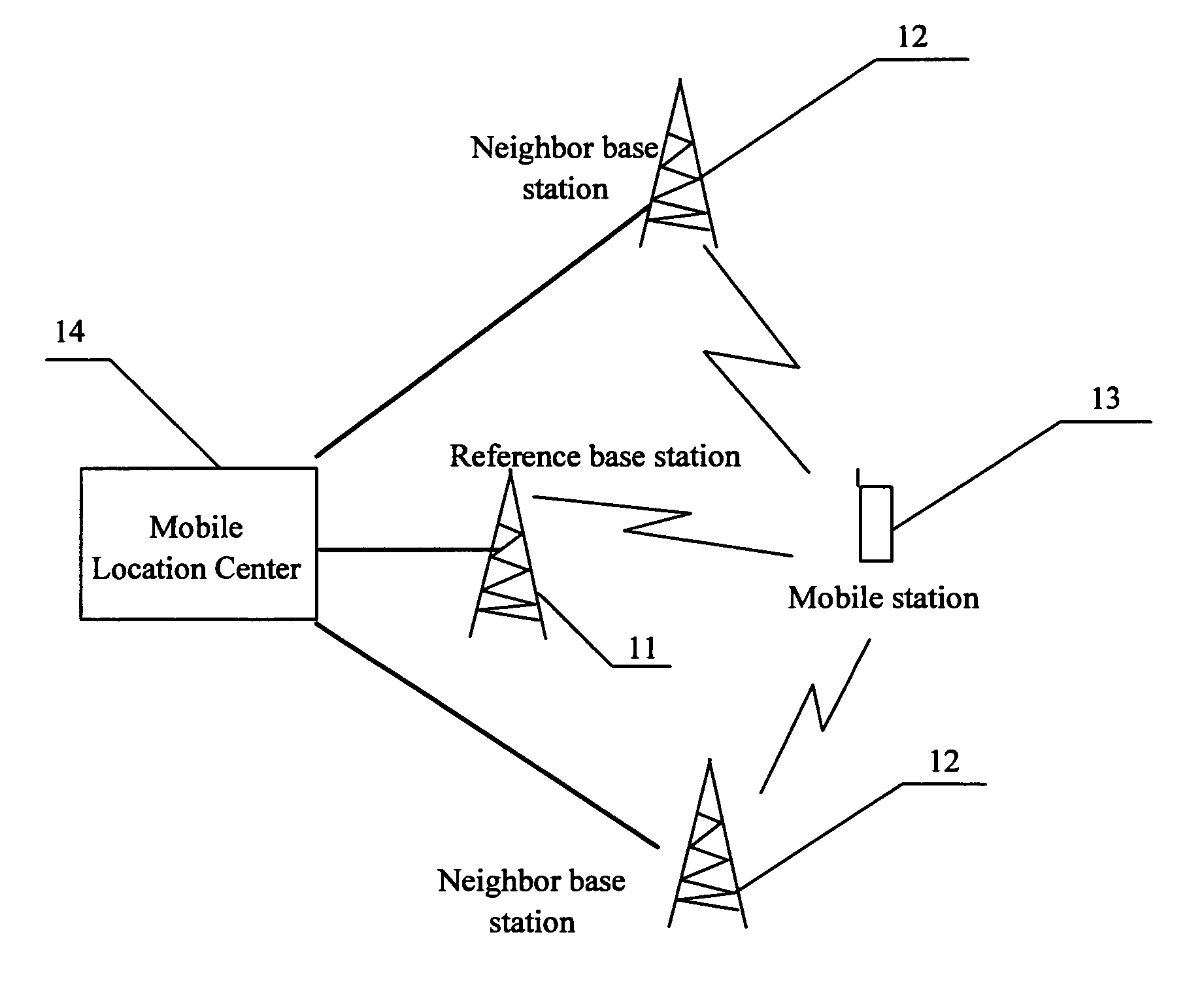
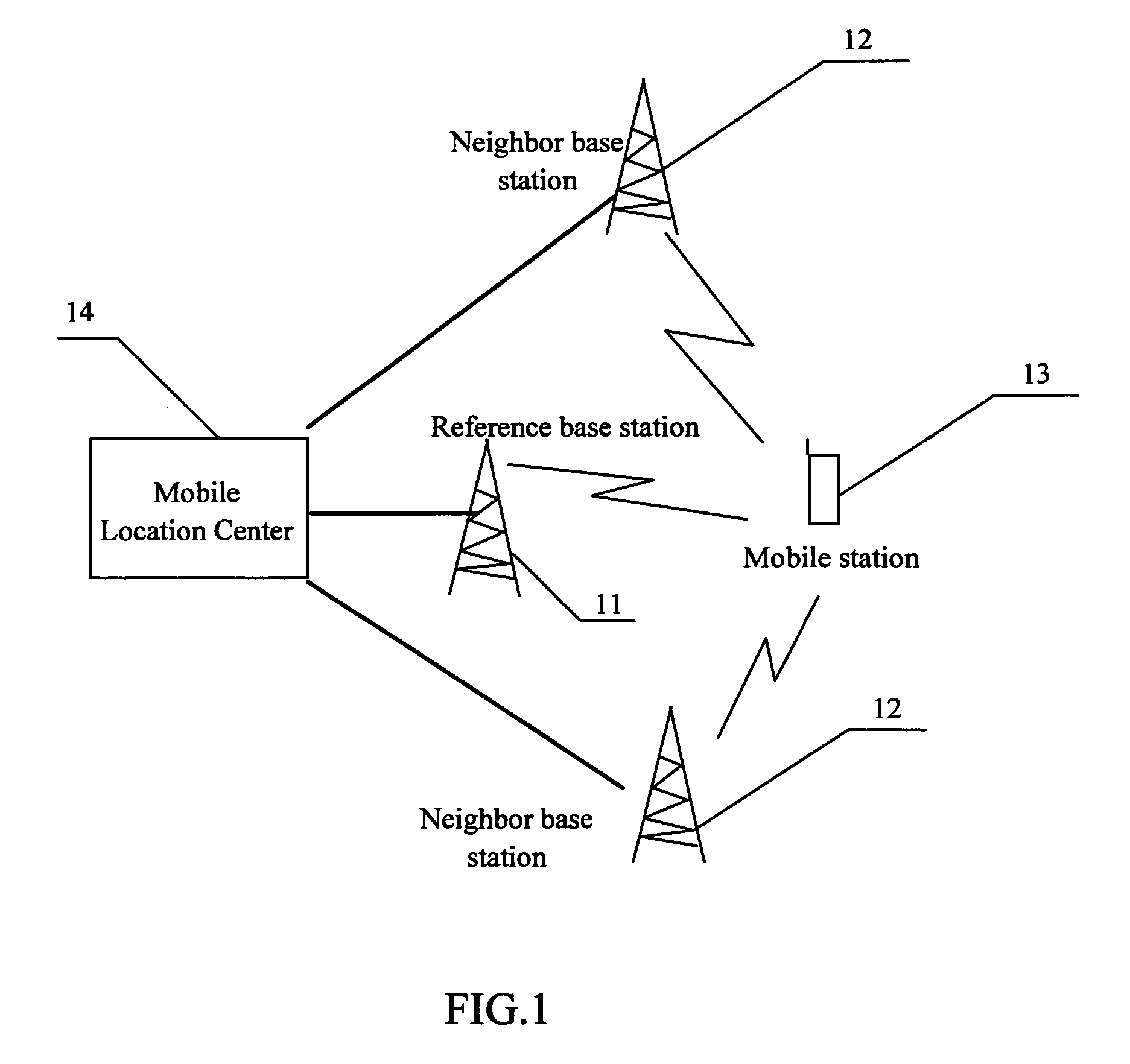
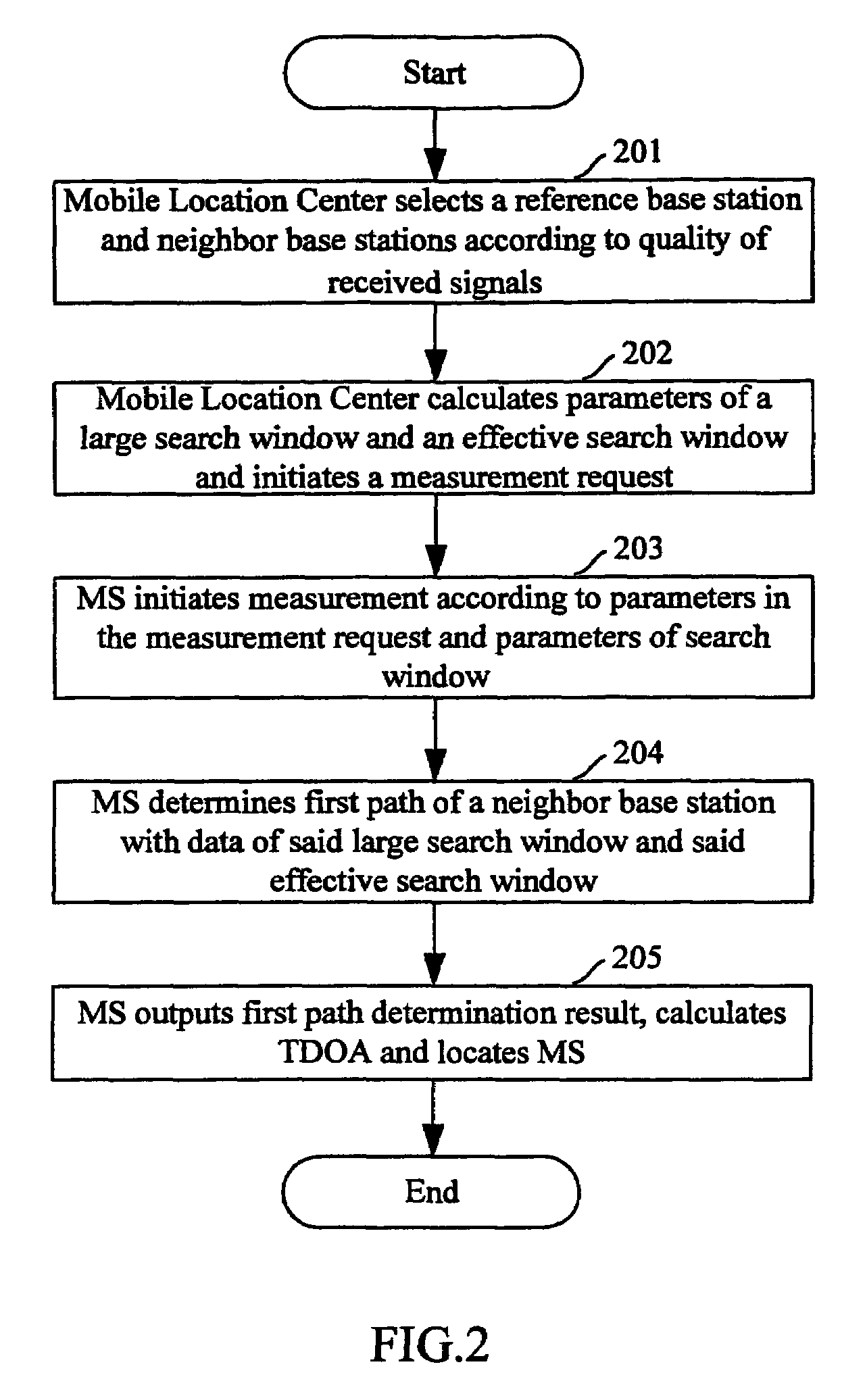
Method of locating and measuring a mobile station
InactiveUS7065369B2High measurement accuracyHigh positioning accuracyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMobile stationWireless positioning
The invention discloses a method of locating and measuring a mobile station, which relates with the radio locating technique in mobile communication field. Comparing with the conventional radio locating technique, the method improves the first path determination method of a neighbor base station downlink signal as follows: with geometrical relationship such as the distance between a MS to the reference base station and the distance between a neighbor base station to the reference base station, an effective range of the downlink signal first path of the neighbor base station can be calculated; the effective range is an effective search window that is shorter than the original large search window, and the first path determination of the neighbor base station downlink signal is made within the effective search window. The invention raises the first path determination accuracy of a neighbor base station downlink signal, so the mobile station locating accuracy is raised too.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Automatic Service Vehicle Hailing and Dispatch System and Method
ActiveUS20110320232A1Special service for subscribersSpeech recognitionRelevant informationRadiolocation
A system and method are provided for improving efficiency of operation and convenience of access to a fleet of taxis, or other service vehicles, requiring rapid, on-demand dispatch to customer-determined locations. Automatic speech recognition (ASR) and / or radiolocation technology arc used to automate the entry of the customer pickup location, and optionally the dropoff location and other relevant information as well. A customer speaks the pickup location into a cellular telephone which then digitizes and transmits it as a data communication to an ASR system. The ASR system decodes the digitized utterance into a pickup location which is passed to a vehicle matching and dispatch system. The vehicle matching and dispatch system matches a taxi and dispatches it to the pickup location. In one embodiment, the identified pickup location is transmitted to the customer's cellular telephone for confirmation or correction, before dispatch of the requested taxi.
Owner:PROMPTU SYST CORP
Precision pulse detection system for radar sensors
ActiveUS7446695B2Improve accuracyGood anti-noise performanceAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsResistance/reactance/impedenceHandwritingPhase detector
A precision pulse detection system for time-of-flight sensors detects a zero axis crossing of a pulse after it crosses above and then falls below a threshold. Transmit and receive pulses flow through a common expanded-time receiver path to precision transmit and receive pulse detectors in a differential configuration. The detectors trigger on zero axis crossings that occur immediately after pulse lobes exceed and then drop below a threshold. Range errors caused by receiver variations cancel since transmit and receive pulses are affected equally. The system exhibits range measurement accuracies on the order of 1-picosecond without calibration even when used with transmitted pulse widths on the order of 500 picoseconds. The system can provide sub-millimeter accurate TDR, laser and radar sensors for measuring tank fill levels or for precision radiolocation systems including digital handwriting capture.
Owner:MCEWAN TECH
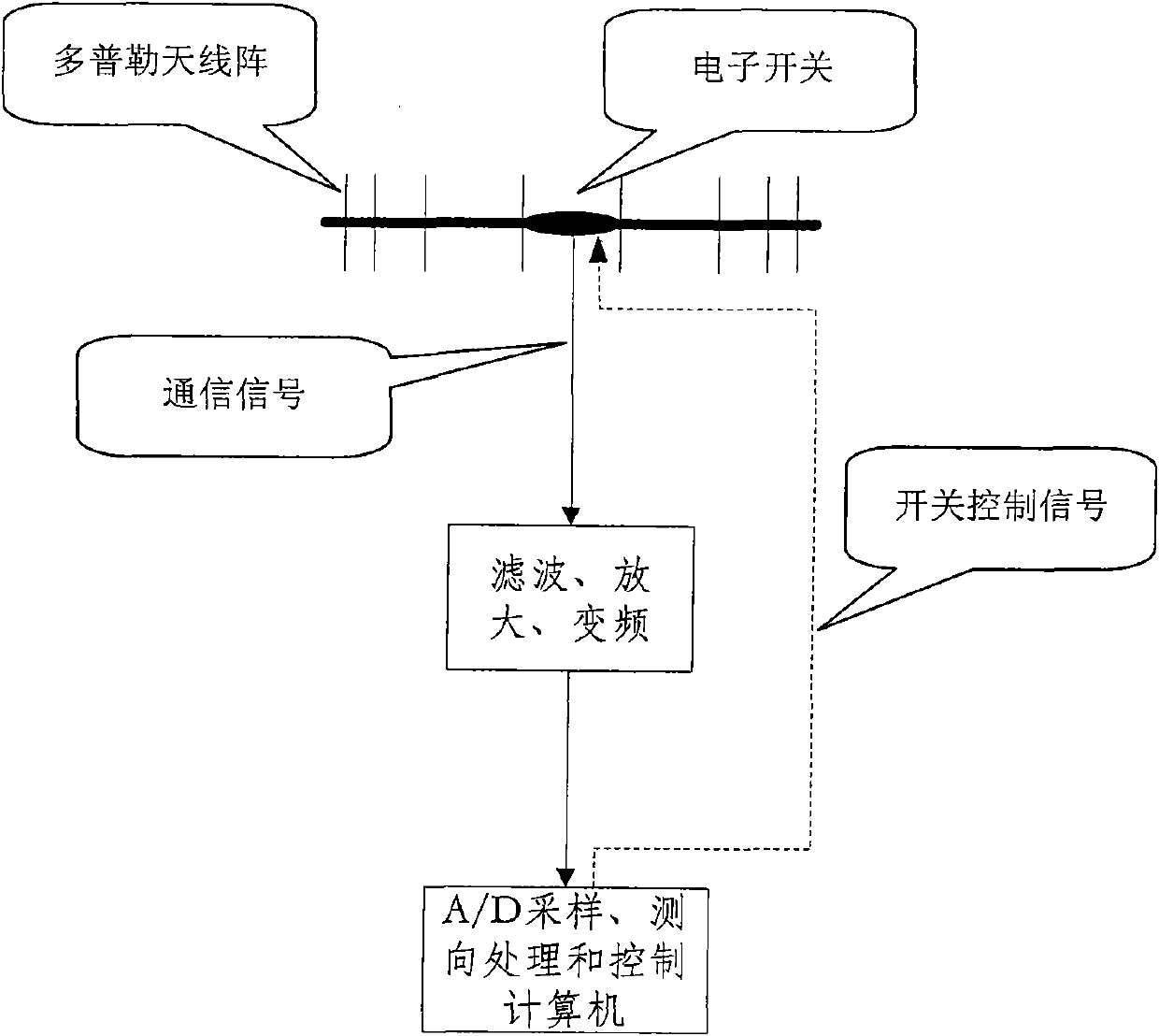
Single-channel radiolocation direction-finding system direction-finding method thereof
InactiveCN102565756AIncrease costImprove reliabilityDirection findersDigital signal processingFiltration
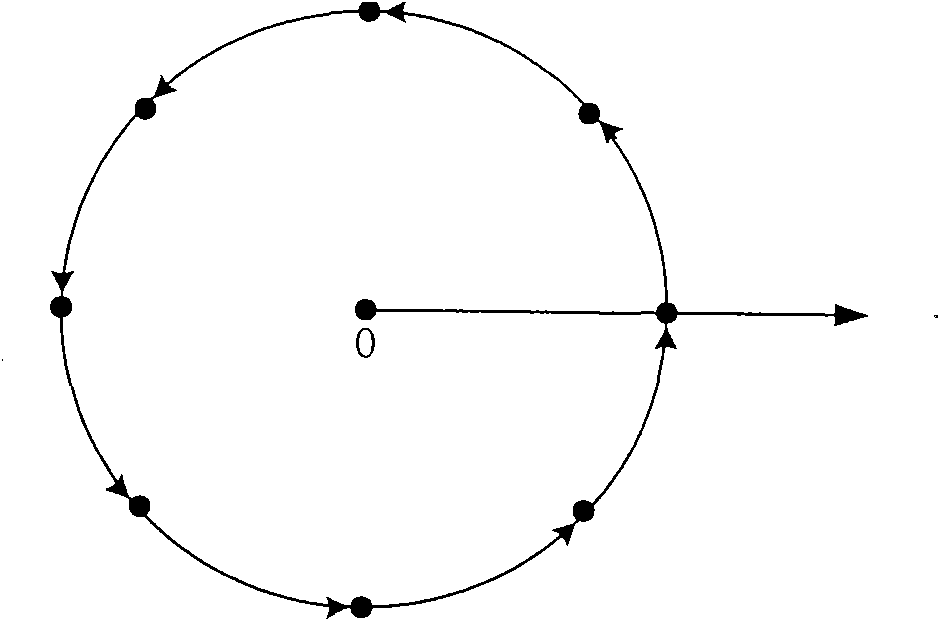
The invention relates to the field of radiolocation direction-finding systems, and aims to provide a single-channel radiolocation direction-finding system and a direction-finding method thereof to reduce cost and improve direction-finding accuracy. The single-channel radiolocation direction-finding system is characterized by comprising a direction-finding antenna array, a single-channel receiver with the functions of filtration, amplification, frequency conversion and amplitude limitation, and a direction-finding microprocessor for A / D sampling and digital signal processing, wherein the direction-finding antenna array mainly comprises N identical antenna units which are arranged on the circumference of a concentric circle, wherein N is greater than or equal to 3; and each antenna unit is connected with the single-channel receiver through a radio-frequency electronic switch. The invention utilizes a single-channel radio direction-finding technology combined with a phase interference method and a Doppler direction-finding principle, and only needs one single-channel receiver with the functions of filtration, amplification, frequency conversion and amplitude limitation, thereby reducing the complexity and the cost of equipment, improving reliability, reducing the calculated amount of back-end signal processing, and improving direction-finding accuracy.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
Electric vehicle wireless charging transmitting and receiving automatic alignment system
ActiveCN105186593AEasy to operateQuick alignmentBatteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemElectric machineryRadiolocation
The invention discloses an electric vehicle wireless charging transmitting and receiving automatic alignment system. The electric vehicle wireless charging transmitting and receiving automatic alignment system comprises a wireless receiving device and a wireless transmitting device, a communication connection being established between the wireless receiving device and the wireless transmitting device. The automatic alignment system further comprises a radio positioning device and a motor positioning driving device; the motor positioning driving device is arranged at the bottom of an electric vehicle; the wireless receiving device is arranged on the motor positioning driving device, and can move leftwards and rightwards under the driving of the motor positioning driving device; a communication connection is established between the radio positioning device and the motor positioning driving device; the radio positioning device includes a radio range-measuring circuit and a radio answering circuit; a communication connection is established between the radio range-measuring circuit and the radio answering circuit; after the radio range-measuring circuit transmits range-measuring radio signals, the radio answering circuit transmits response signals; the radio range-measuring circuit calculates position difference according to time length for receiving the response signals; and therefore, the motor positioning driving device can be controlled to move according to the position difference.
Owner:XIAMEN NEWYEA SCI & TECH
A Positioning Method of Ground Mobile Communication Network Corrected by Map Elevation
InactiveCN102300311AHigh positioning accuracySimple methodWireless communicationNatural satelliteHorizon
The invention relates to a positioning method for correcting and revising a ground mobile communication network by using a map elevation, which relates to positioning technology, and uses an electronic map marked with horizon and building elevation as the elevation constraint, and the high precision of the electronic map is decimeter or centimeter level. When using the ground mobile communication network or broadcasting network to measure the pseudo-range positioning, due to the non-line-of-sight error in the pseudo-range measurement, the current positioning accuracy is low. To improve the positioning accuracy of terrestrial mobile networks and broadcasting networks, the influence of non-line-of-sight errors must be corrected. This method utilizes the initial positioning solution and the elevation constraint to verify the accuracy of the pseudo-range measurement, judges whether the measured pseudo-range has non-line-of-sight transmission error, and corrects the pseudo-range error to improve the positioning accuracy of the mobile station. The method of the invention is simple and easy, can distinguish, estimate and eliminate non-line-of-sight propagation errors, and improves the positioning accuracy of the mobile phone to the order of meters, which has practical significance. It is suitable for radiolocation of terrestrial mobile communication network, radiolocation of terrestrial broadcasting network and radiolocation of satellite transmission network.
Owner:NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORIES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
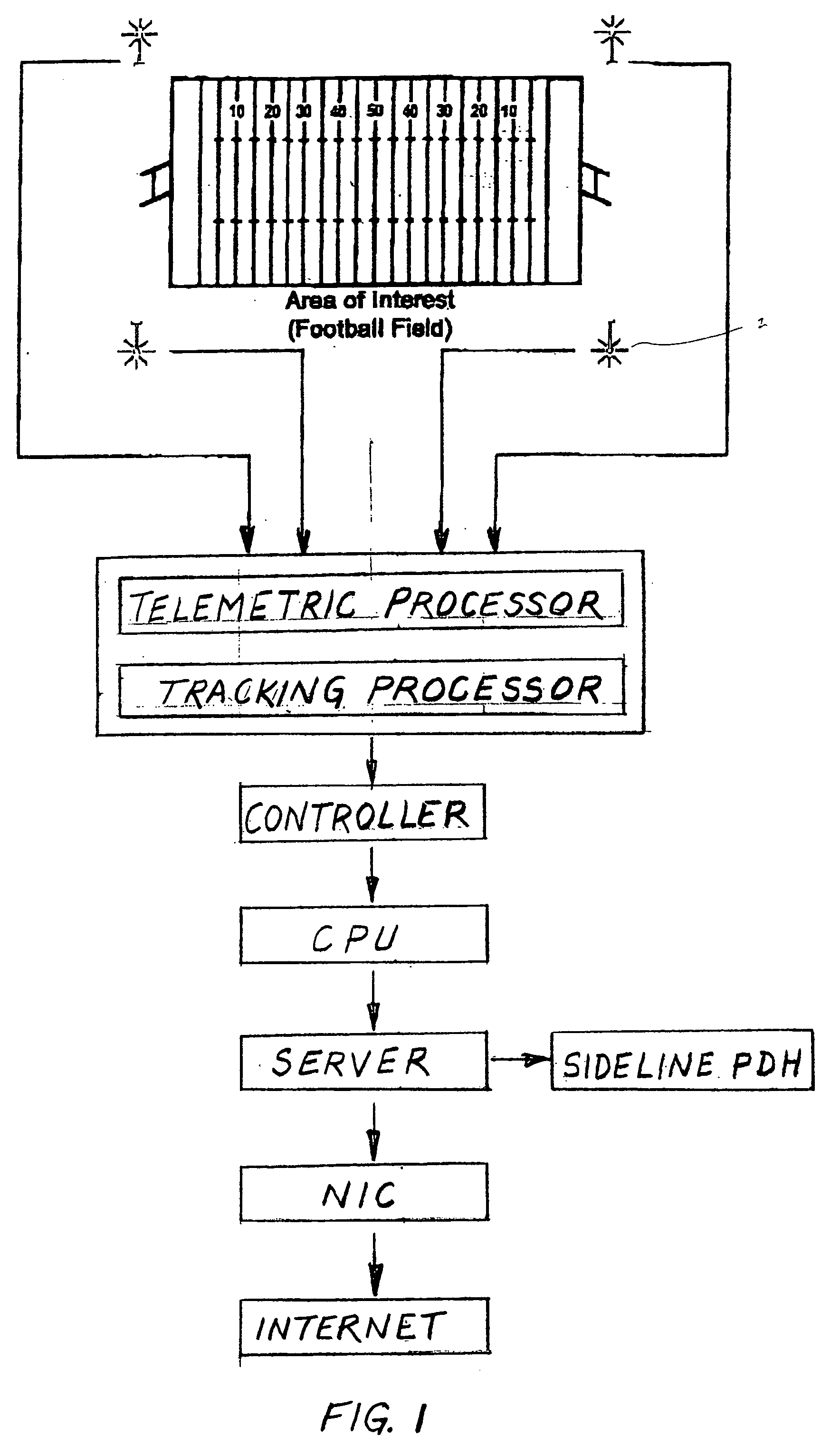
Digital integrated motion system
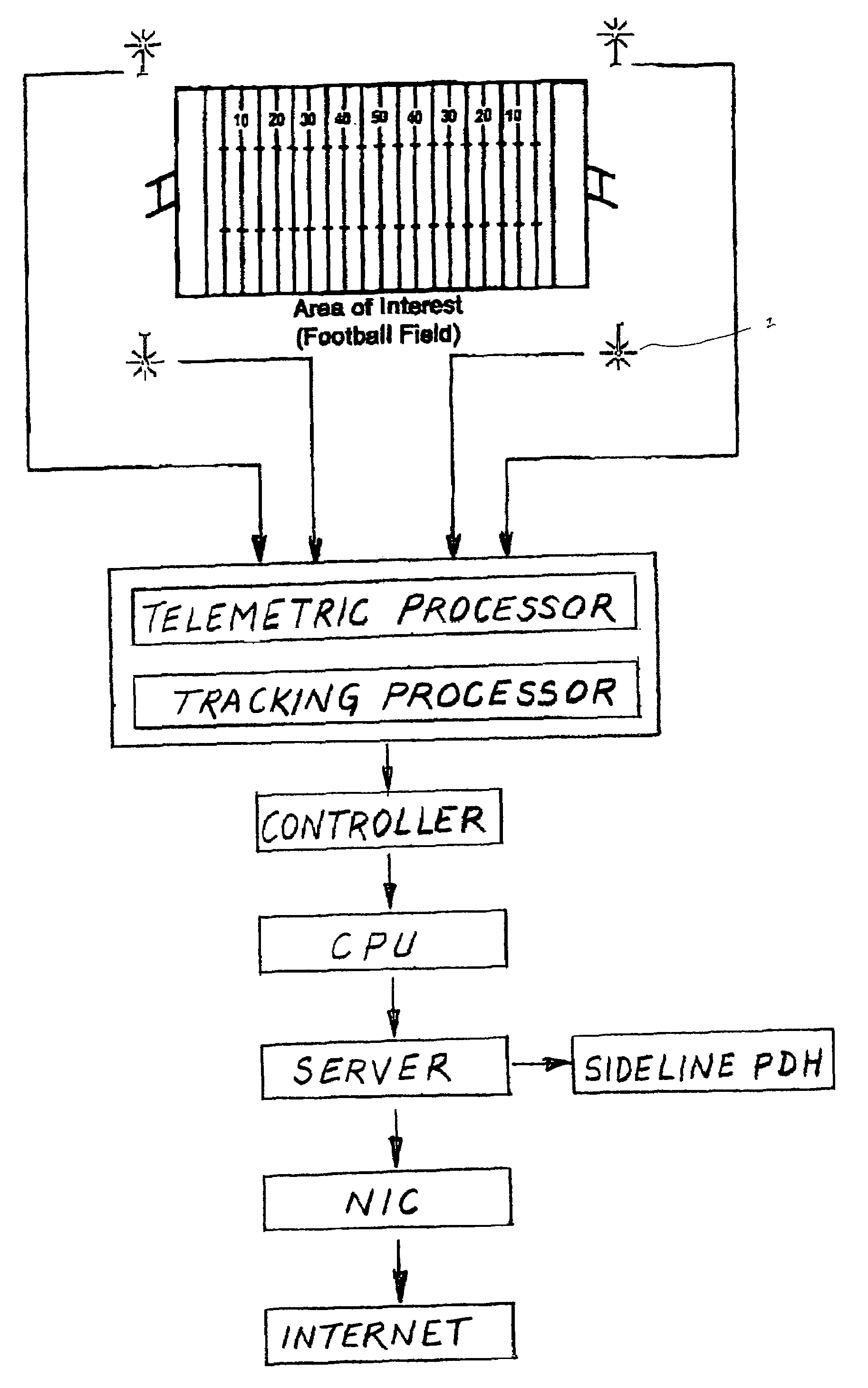
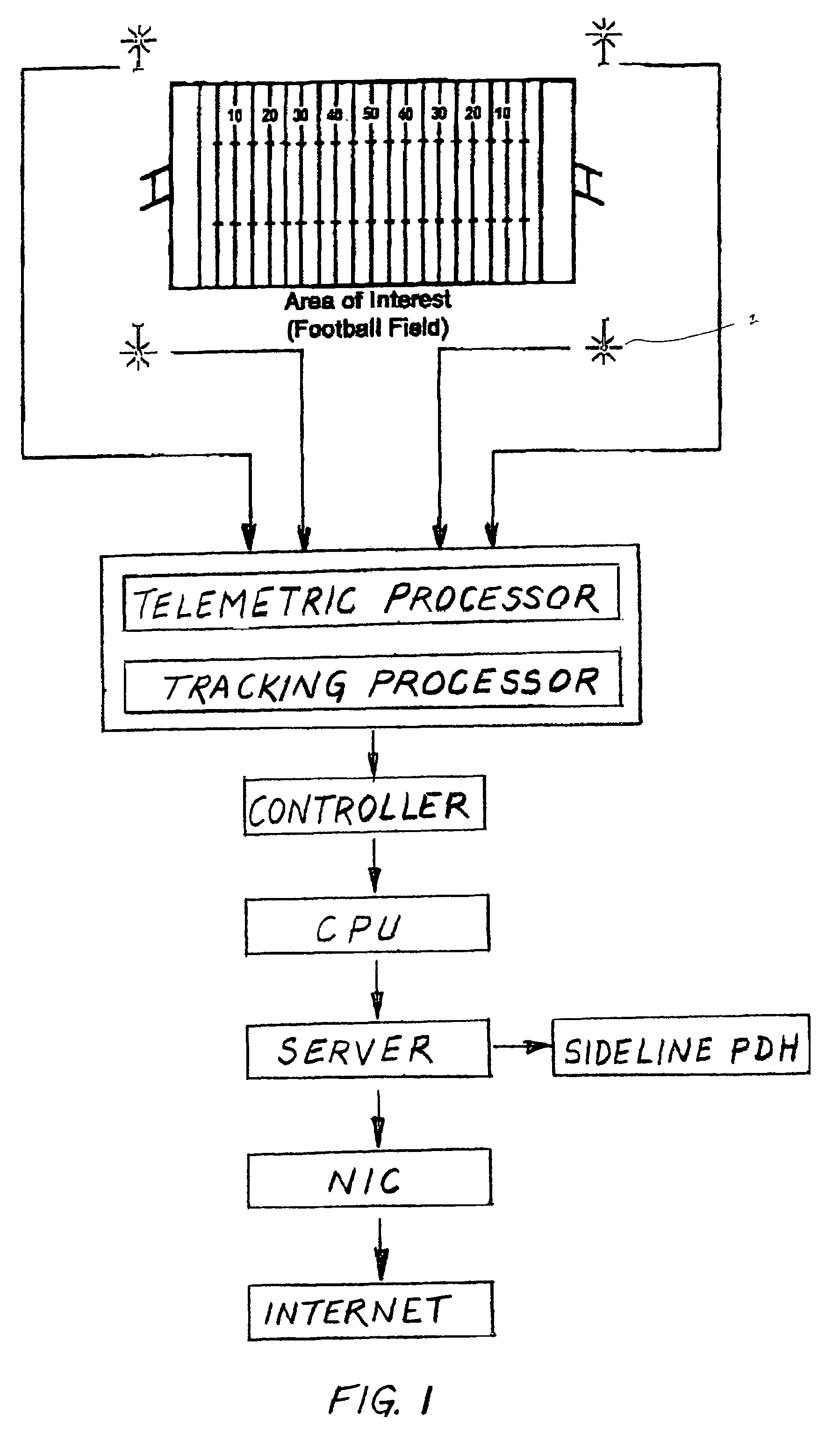
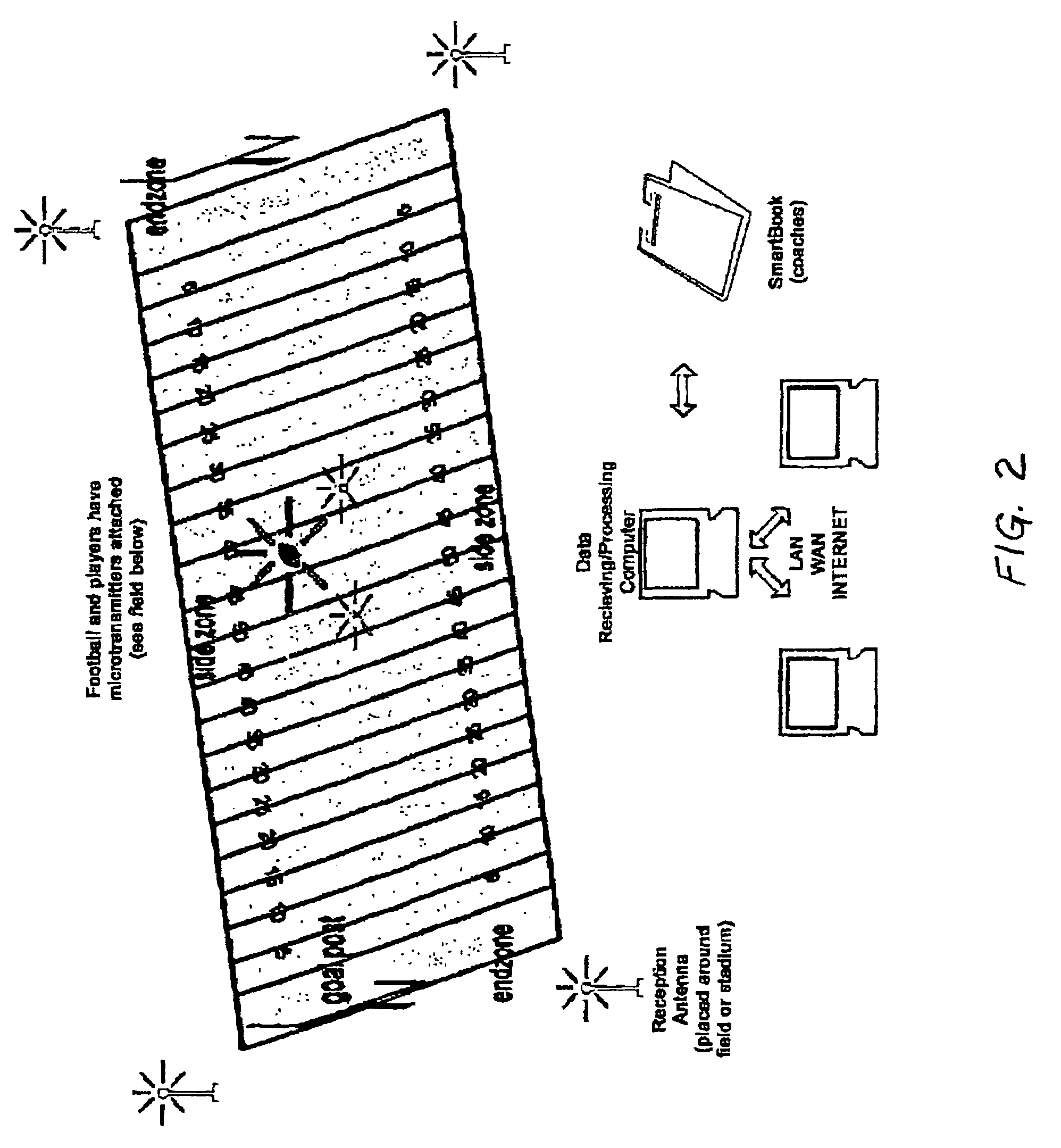
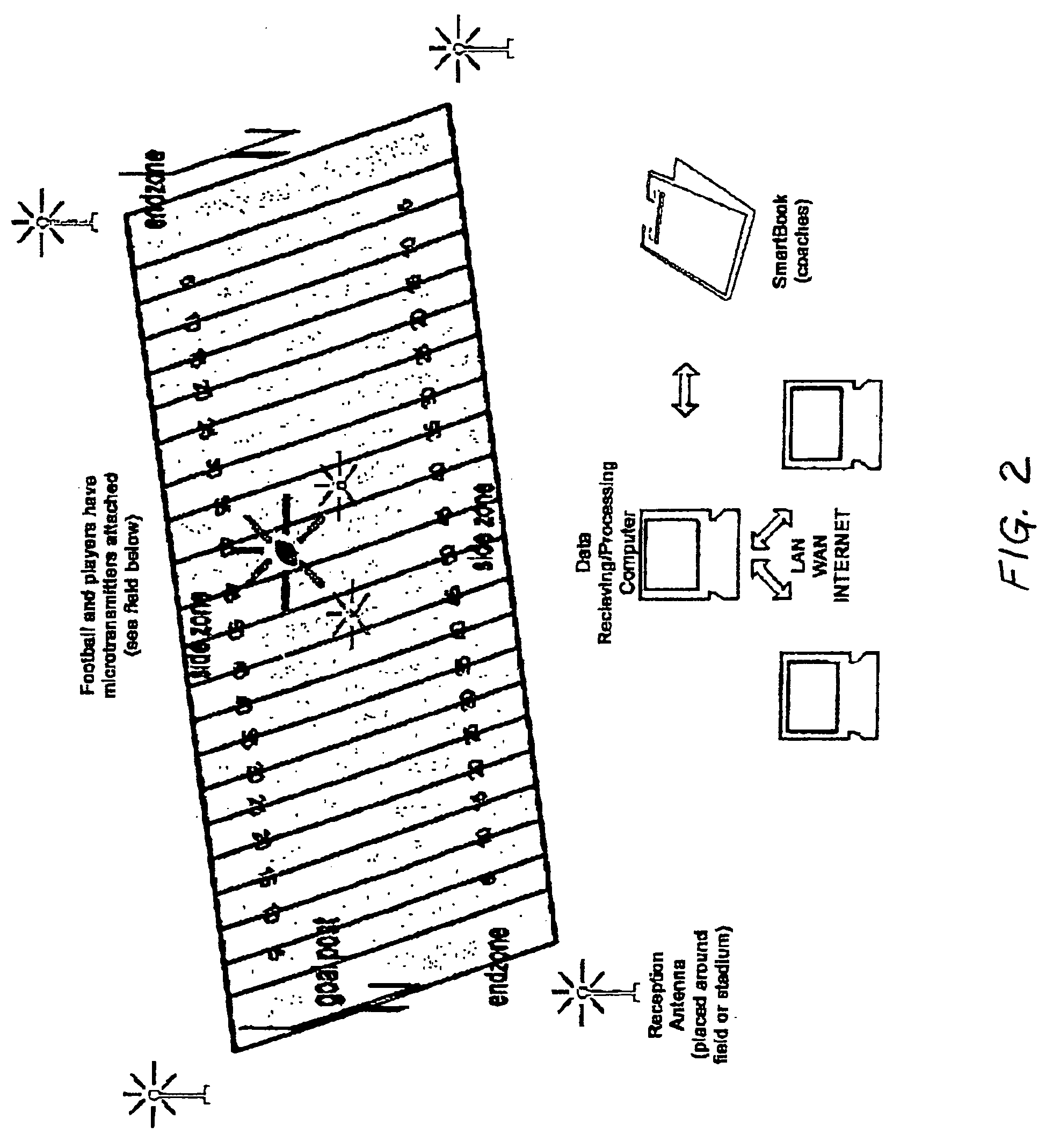
InactiveUS7339470B2Registering/indicating time of eventsAnti-collision systemsRecreationComputer graphics (images)
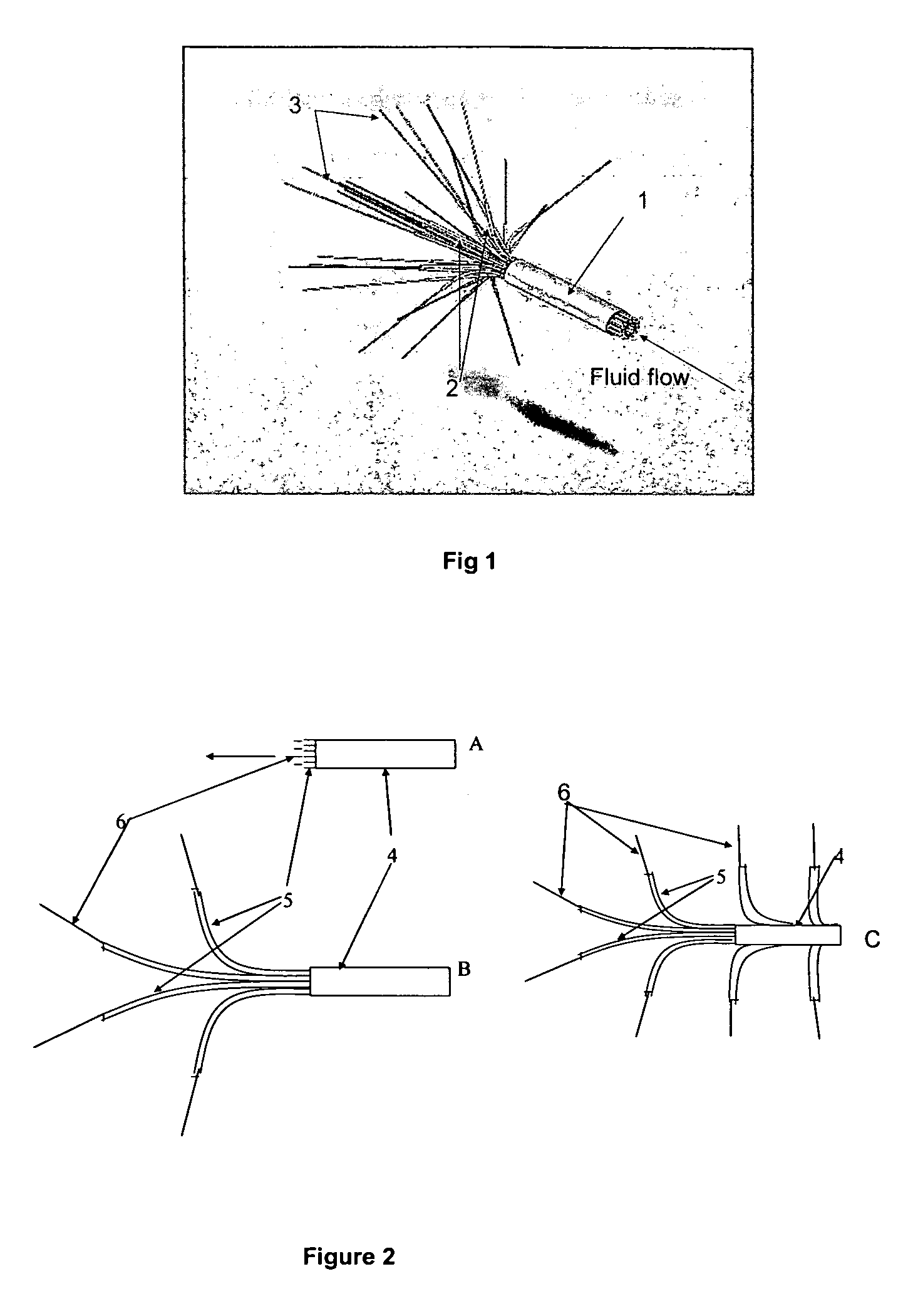
A process that records, transmits and analyzes moment-to-moment data of objects of interest at an event for the production of a digital representation of the event. This representation is the result of a short-range radiolocation system used for tracking objects. Computing systems re-create timed sequences of event and broadcasts the digital representation to both local interactive PDA's and to internet virtual casts. Four or more receivers are situated so as to cover the entire area of the event. Transmitter tags are placed on all objects (e.g., players, ball etc). The processor receives the data and compiles it for digital recreation and transmission to the aforementioned destination devices.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH INT LLC
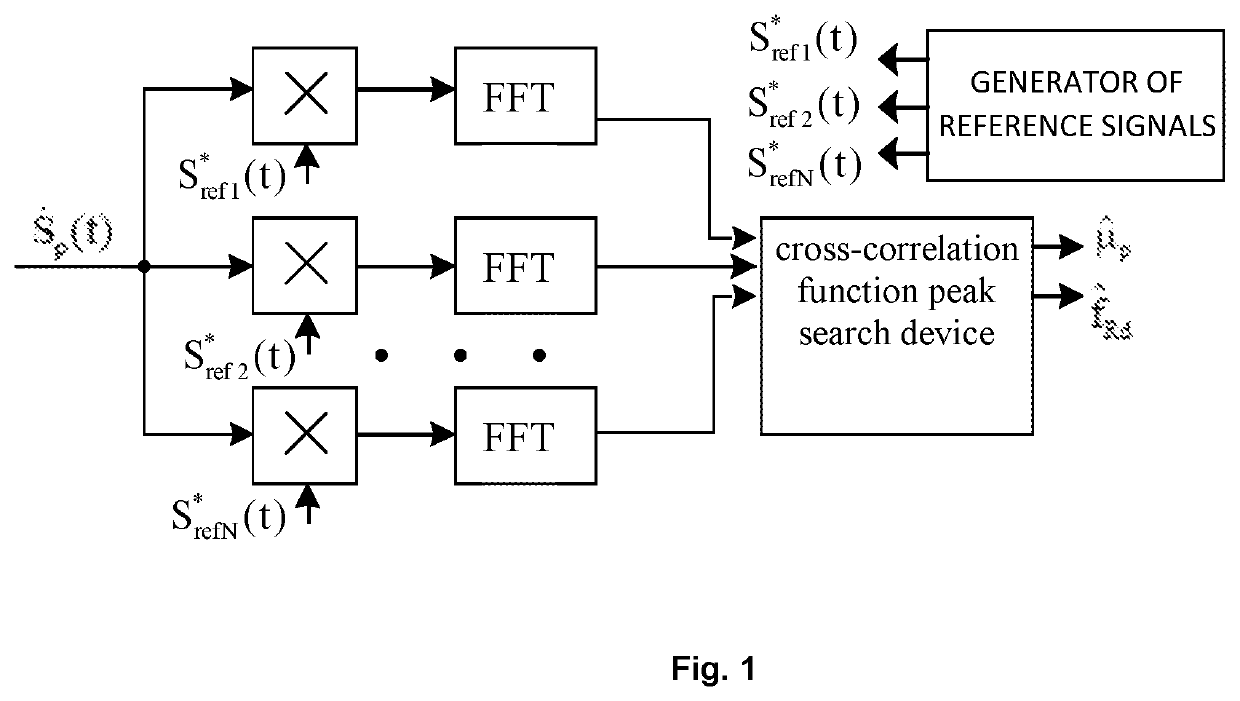
Method and device for radar determination of the coordinates and speed of objects
InactiveUS20190383930A1High measurement accuracyLower levelRadio wave reradiation/reflectionOn boardCarrier signal
The invention relates to the field of radiolocation and can be used in on-board radar stations for determining the coordinates and speed of moving and stationary objects with a high accuracy. The technical result which can be achieved is an increase in the accuracy of determining the coordinates and velocity of objects and targets having a low level of effective reflective area. The essence of the method consists in assessing the rate of change in frequency of the additional linear frequency modulation (LFM) of a signal reflected from an object and dependent on the movement of the latter, with subsequent calculation of the distance to the object taking into account the value of an initial frequency of the received LFM signal. Said technical result is achieved by the fact that the distance to the object is determined on the basis of a change in the frequency of a probing LFM signal, taking into account Doppler corrections. The method is realized with the aid of a device comprising the following, interconnected in a defined manner: M channels for emitting a continuous LFM signal at various frequencies and polarizations, N channels for receiving echo signals, an N-channel parameter assessment device, an N-channel device for generating supporting functions, a received-signal multiplier with supporting functions, a rapid Fourier transformation unit, a device for searching for the maximum of a mutual correlation function, and a sensor of the intrinsic speed of a radar-station carrier.
Owner:OBSHCHESTVO S OGRANICHENNOJ OTVETSTVENNOSTYU INNOVATSIONNYJ TSENTR SAMOTSVET
Procedure for determining the probability of finding a parking place
ActiveUS20130144826A1Instruments for road network navigationIndication of parksing free spacesNatural satelliteParking space
A procedure for determining the probability of finding a parking place within a certain period of time on a pre-set stretch of road of an area with a multiplicity of stretches of road. With this procedure, motion profiles are detected and statistically evaluated of users of radiolocation-aided, especially satellite-aided, navigation aids in the area. For each user a “parking place found” event is determined; the stretch of road in which the “parking place found” event occurred is detected; and the travel time is detected which the user expended in each of the stretches of the road until the “parking place found” event occurred. From the data thus acquired for a multiplicity of users, a probability is determined of finding a parking place within the set time span on the stretch of the road.
Owner:TELENAV GMBH
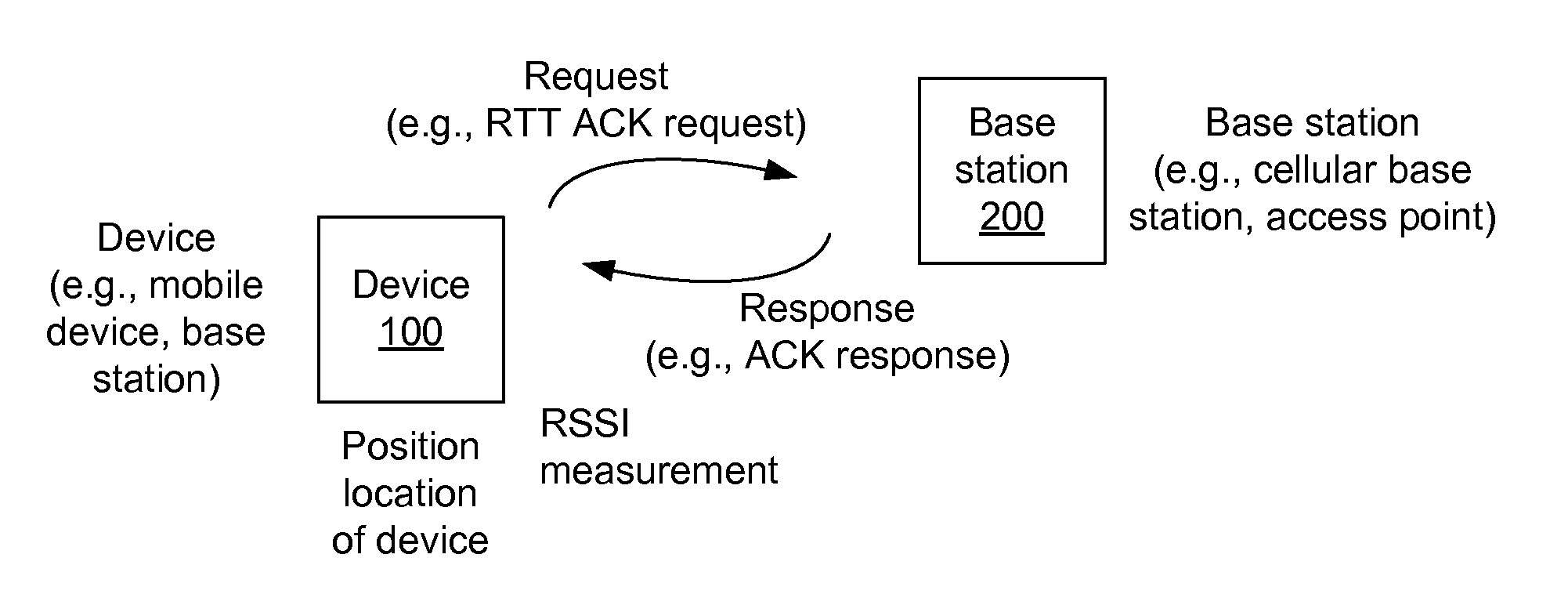
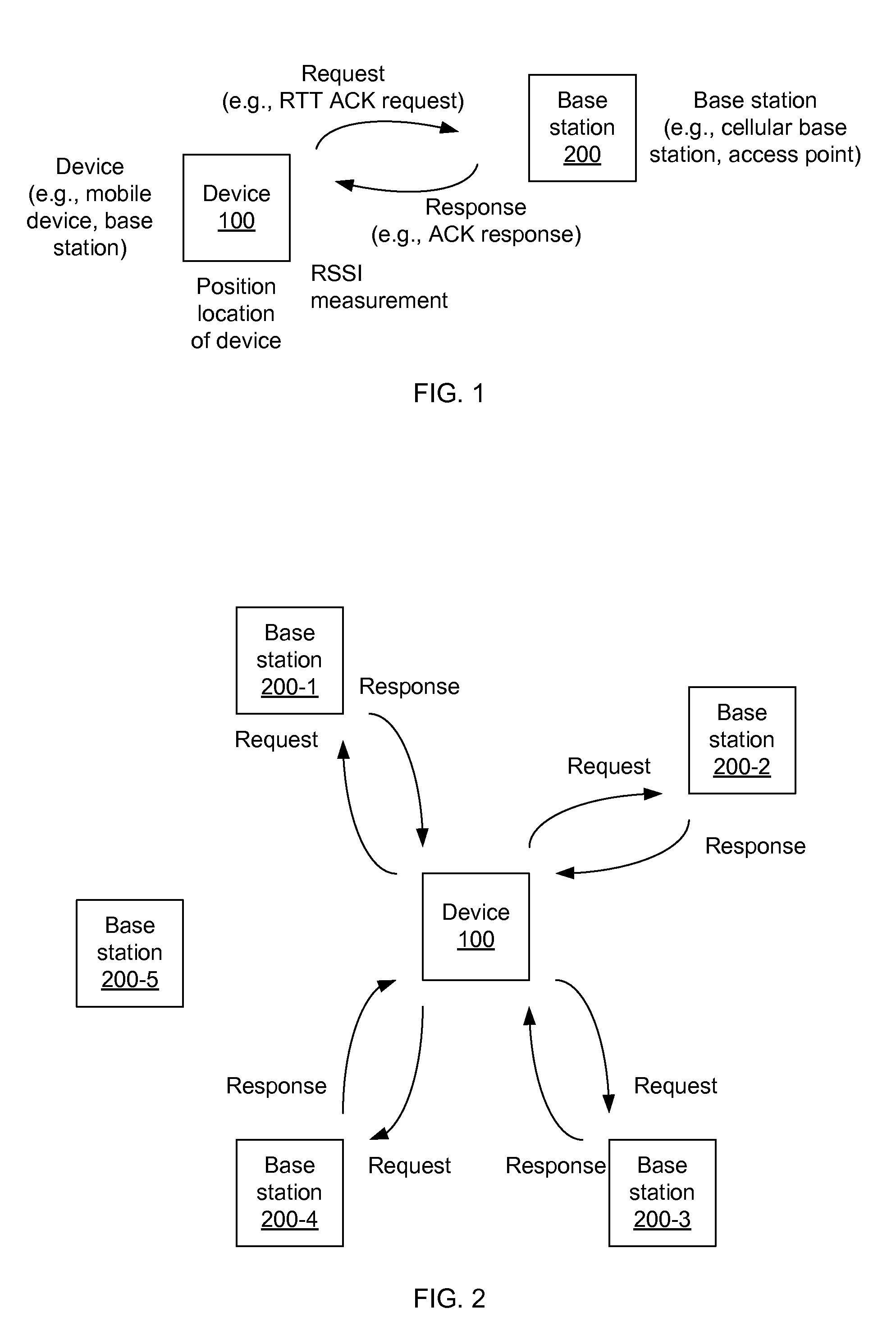
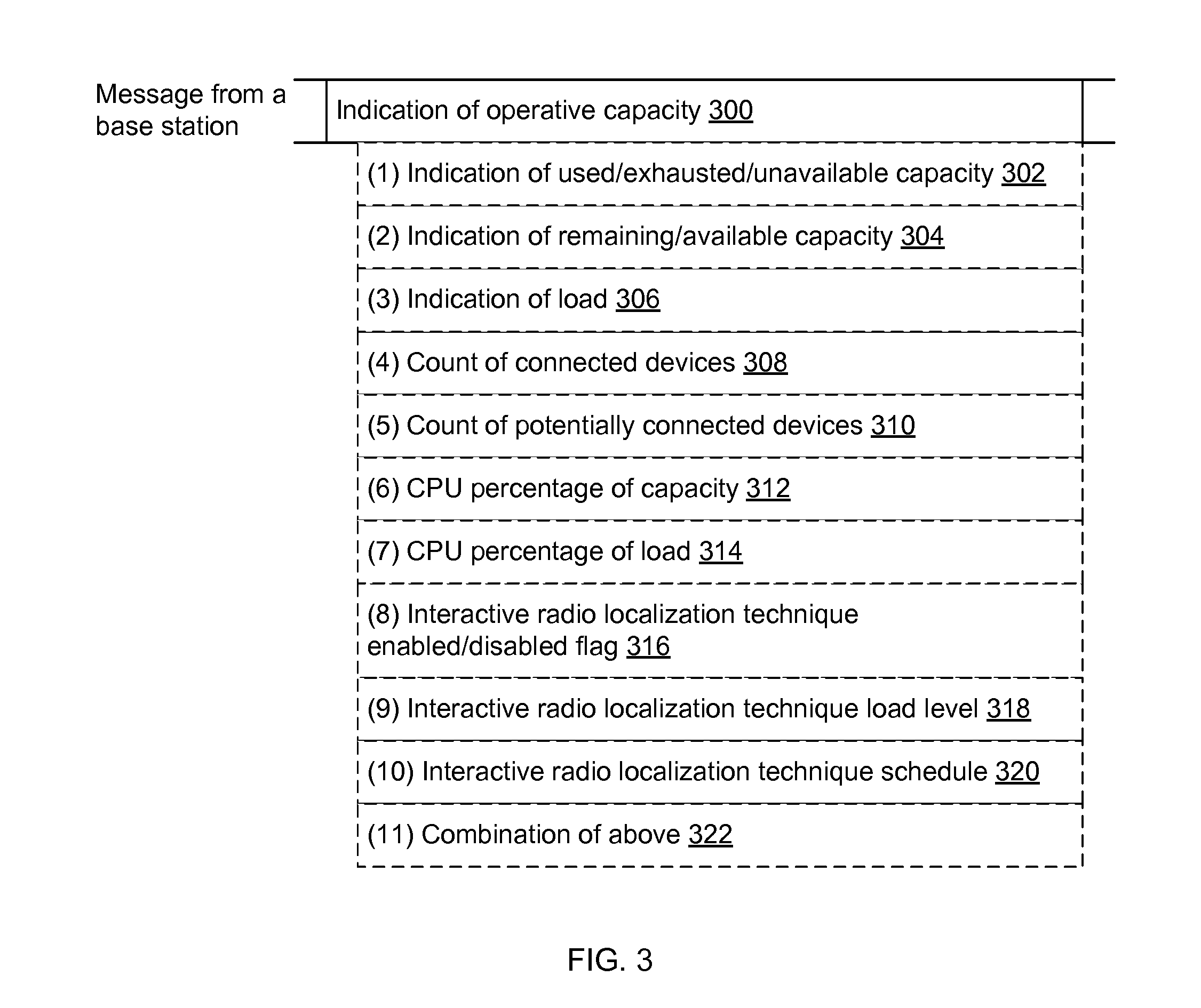
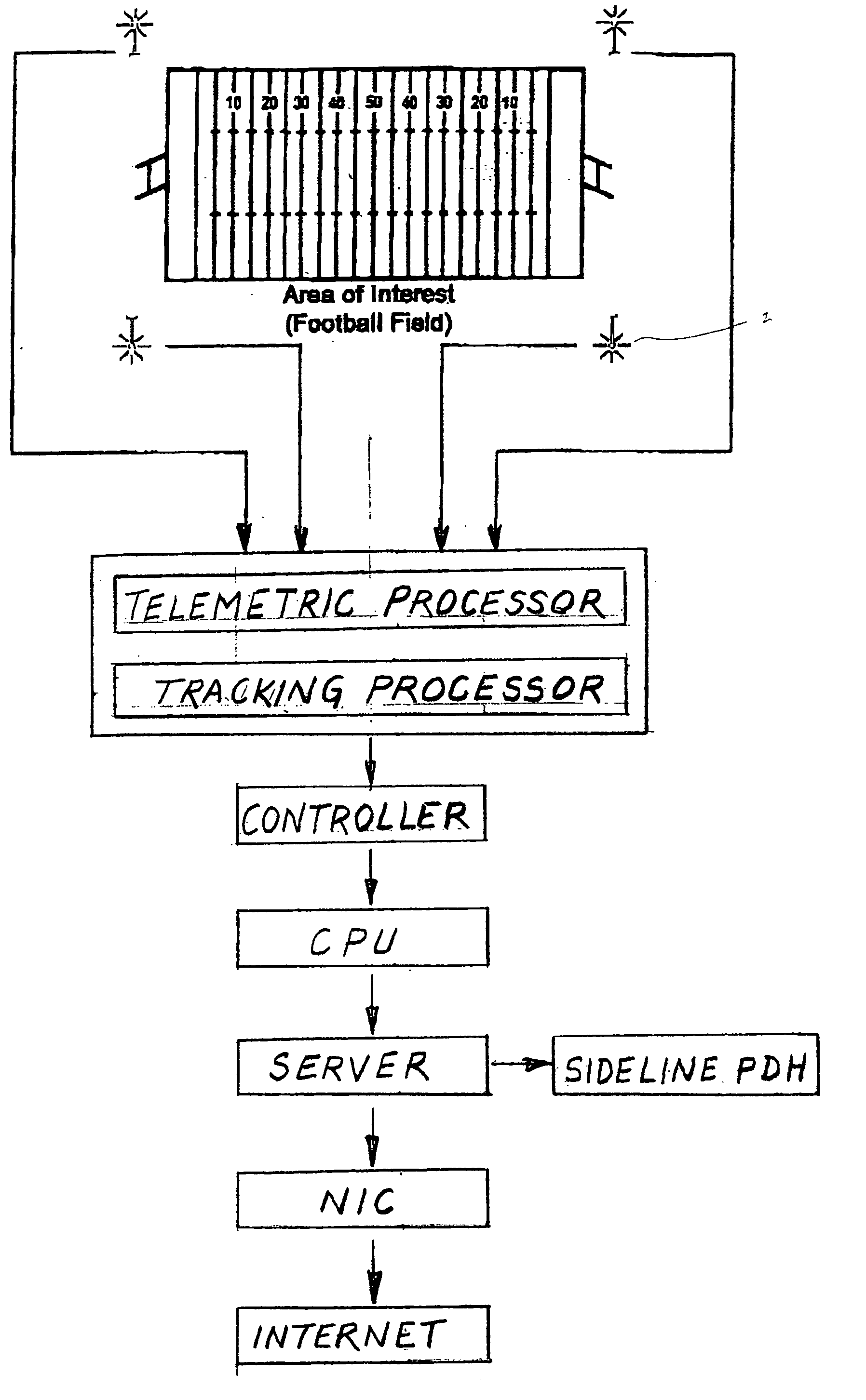
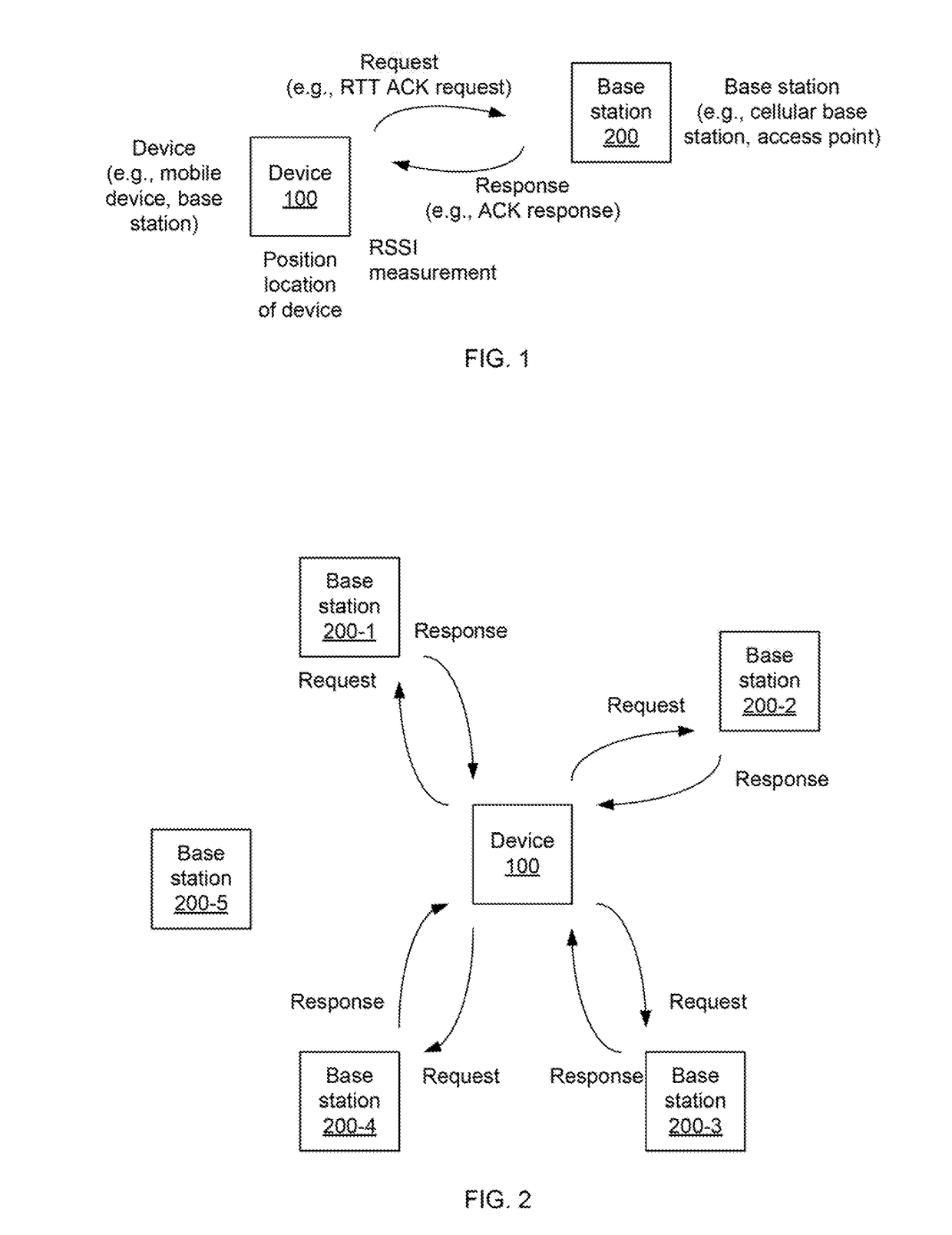
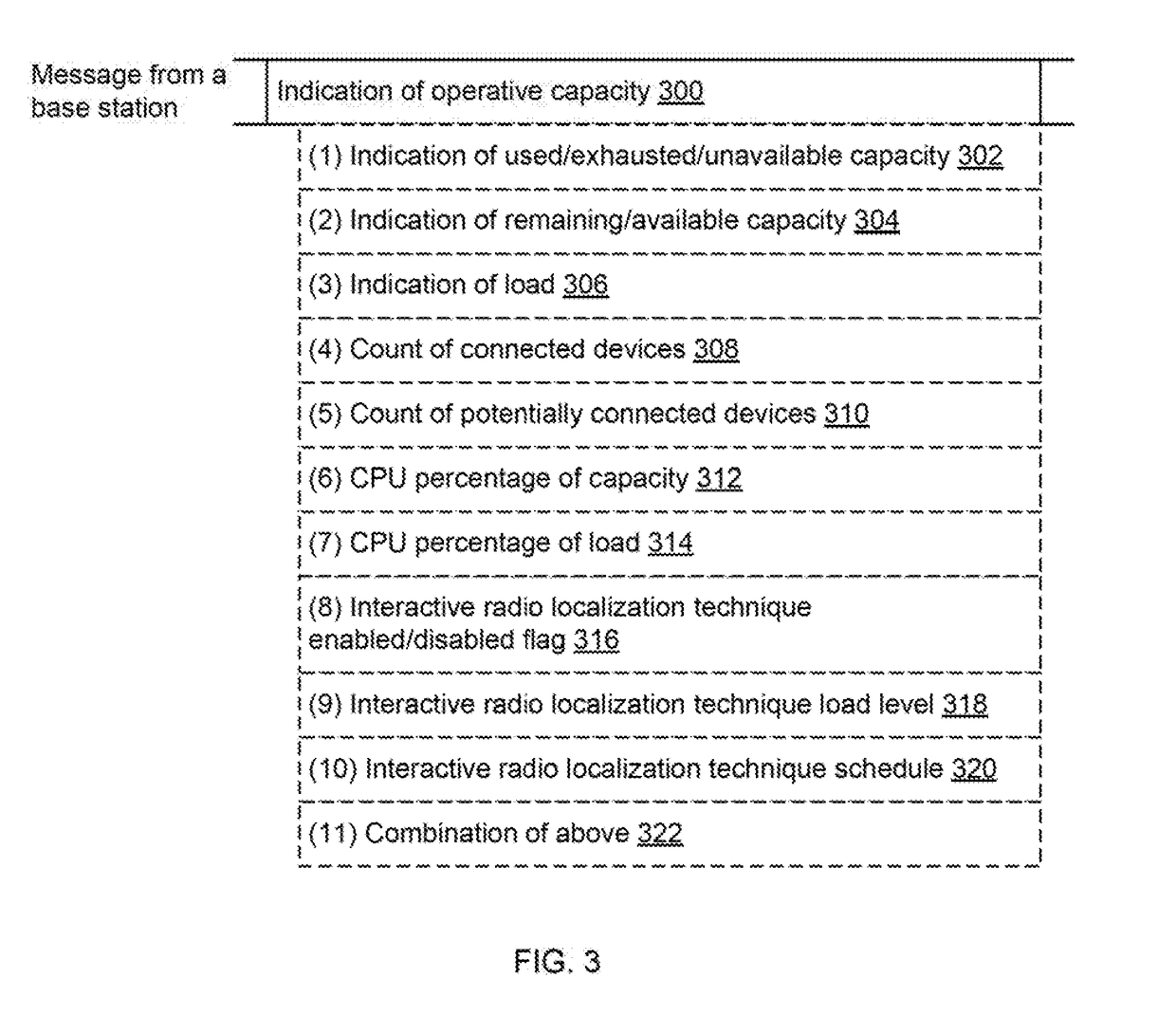
Base station selection for positioning/localization based on an indication of capacity
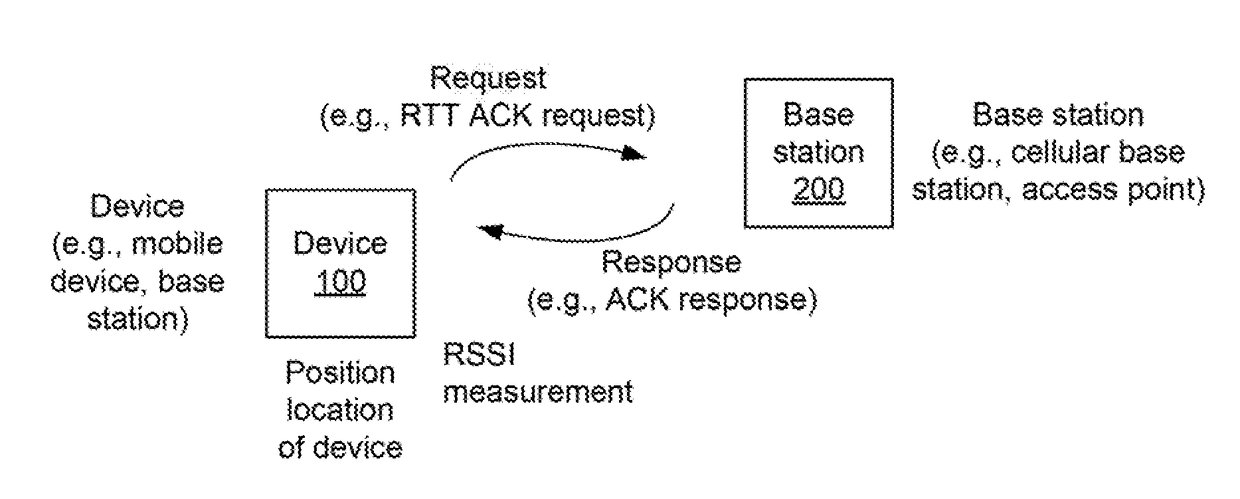
InactiveUS20160337792A1Assess restrictionPosition fixationRadiolocationElectrical and Electronics engineering
Systems, apparatus and methods for selecting a base station or a set of base stations for RTT measurements, or other interactive radio localization technique, to determine a position fix of a device are presented. The method imposes a processing load on only inactive or less active base stations. Busy or busier base stations are not used in the interactive radio localization technique. By imposing a processing load on only less active base stations, transmitting devices may be under loaded and encounter a more uniform processing delay, and thus provide a more accurate measurement resulting in a more accurate position fix.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Digital integrated motion system
InactiveUS20060224322A1Anti-collision systemsElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingThe InternetRadiolocation
A process that records, transmits and analyzes moment-to-moment data of objects of interest at an event for the production of a digital representation of the event. This representation is the result of a short-range radiolocation system used for tracking objects. Computing systems re-create timed sequences of event and broadcasts the digital representation to both local interactive PDA's and to internet virtual casts. Four or more receivers are situated so as to cover the entire area of the event. Transmitter tags are placed on all objects (e.g., players, ball etc). The processor receives the data and compiles it for digital recreation and transmission to the aforementioned destination devices.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH INT LLC
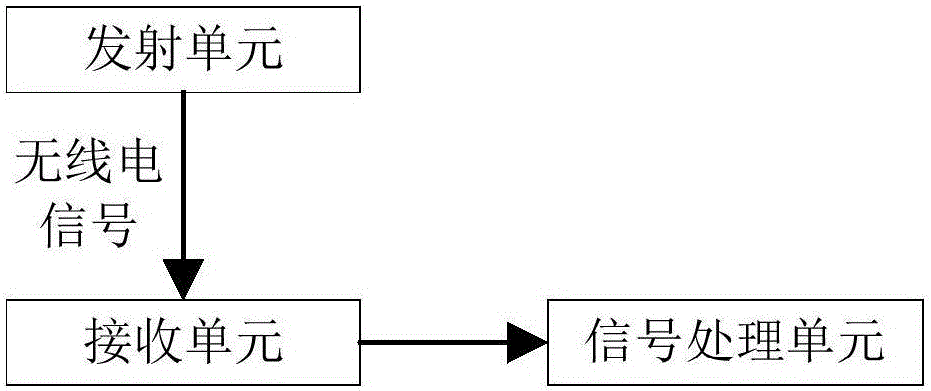
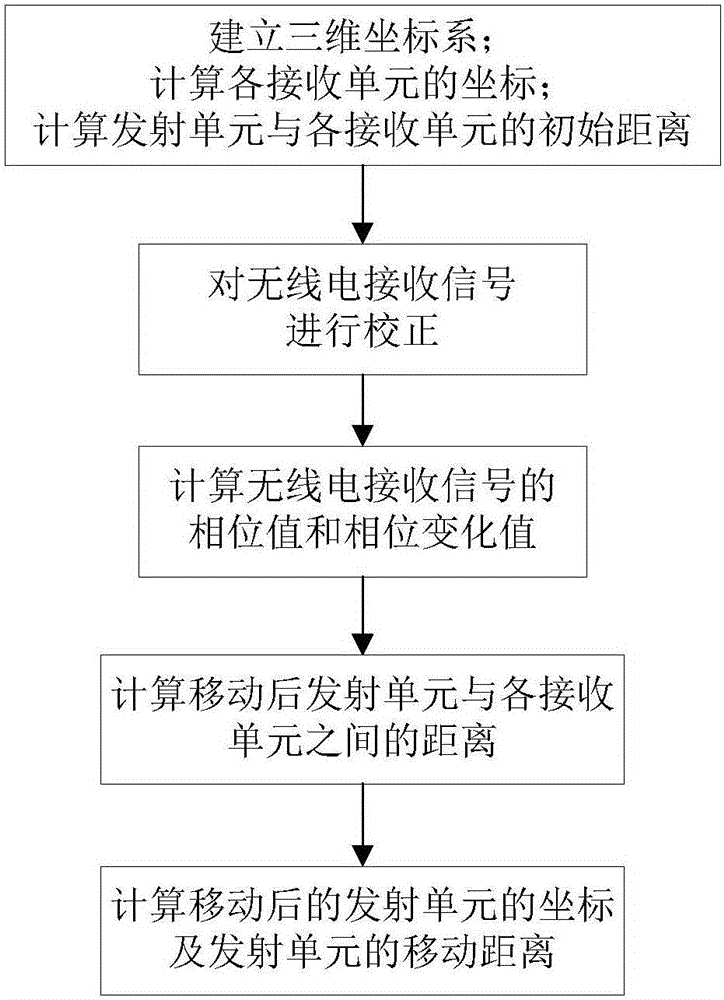
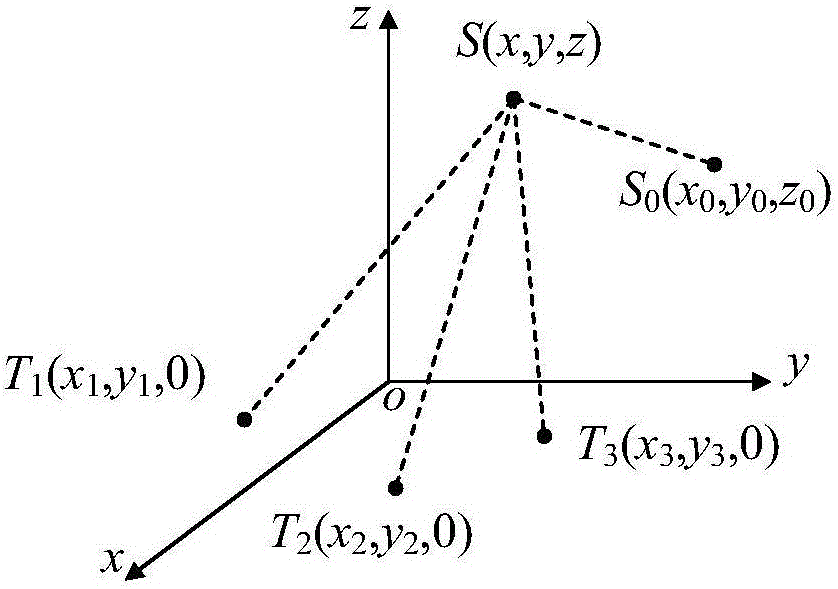
Relative position measurement method through radio positioning and measurement device thereof
ActiveCN105929364AAvoid blurRealize measurementPosition fixationGeometric relationsMeasurement device
The invention provides a relative position measurement method through radio positioning and a measurement device thereof. The measurement device comprises a transmitting unit, receiving units and a signal processing unit. Receiving signals of each receiving unit are extracted by recording the position of each receiving unit, the distance between all the receiving units and the distance between each receiving unit and the transmitting unit under the initial state so as to solve phase information. The position of the transmitting unit relative to a platform can be solved according to the space quadrilateral geometric relation of the receiving units and the transmitting unit. The phase ambiguity problem is solved, and measurement of the direction and the relative position of moving points can be realized through transmitting signals of single frequency so that the system is easy to realize, high in reliability and low in influence of external factors and can control the moving distance and the position of the moving nodes in real time and can be widely applied to the system requiring long-term monitoring and early warning.
Owner:长沙深之瞳信息科技有限公司
Aerial inventory antenna
ActiveUS20180342787A1Improve usabilityQuiet operationAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesAviationRadiolocation
The present invention teaches a frequency-scalable high-gain dual-polarization radio beam application platform for private, public, government, or military radio applications such as RFID (radio frequency identification), aerial and robotic inventory scanning, radio communications, telemetry, telecommand, aeronautical radionavigation, radiolocation, earth exploration, space research for terrestrial, air-to-ground, space-to-earth, or space-to-space uses.
Owner:ADASA
Method of automatic target angle tracking by monopulse radar under conditions of interference distorting location characteristic
InactiveUS8896483B2Improve Guidance AccuracyReduce adverse effectsRadio wave finder detailsPolarisation/directional diversityRadiolocationOptical polarization
Method of automatic target angle tracking by sum-and-difference monopulse radar covers radiolocation sphere and specifically monopulse direction finding systems. It can be used in order to increase guidance accuracy, for example, for anti aircraft missiles and of unmanned aerial vehicles to radar targets such as: radio beacons; aerial vehicles reflecting the radio signal that illuminates them; aerial vehicles and ground-based devices radiating radio signals and jamming signals. The aim of the method consists in the assurance of reliability and stability and in the enhancement of guidance accuracy of automatic target angle tracking due to elimination of automatic tracking losses and great errors arising during the influence of the signals of orthogonal polarization or polarization close to it.The proposed method provides full protection from polarization jamming for all types of monopulse radars.
Owner:MARKIN EVGENY
Joint estimation method for angle of array antenna and number of signal sources in complex noise environment
ActiveCN107966676ASolve the problem that the estimation accuracy is limited by the bandwidth formReduce computational complexityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsComputation complexityEngineering
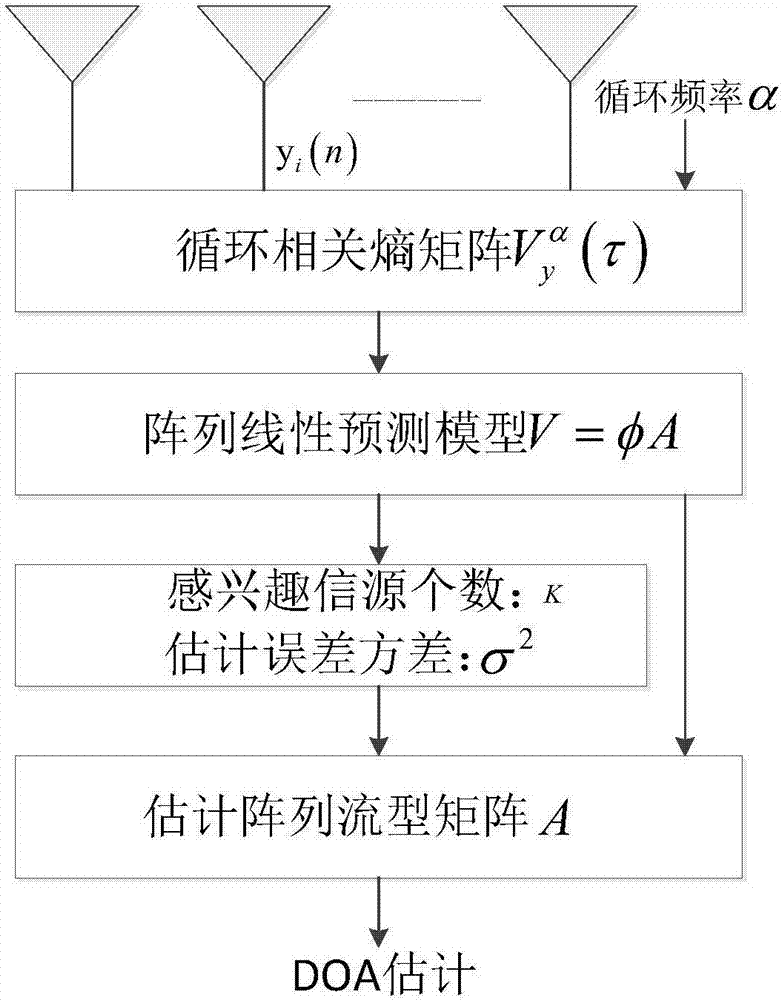
The invention relates to a joint estimation method for the angle of an array antenna and the number of signal sources in a complex noise environment, and belongs to the technical field of radio positioning. The joint estimation method comprises the steps of 1) solving a cycle correlation entropy matrix V<alpha><y>(tau) of array signals under a condition that the cycle frequency is known; 2) building a cycle correlation entropy array linear prediction model V=[Phi]A which is applicable to broadband signals and narrow-band signals; 3) estimating the number K of interested signal sources and an error variance [sigma]<2>; 4) estimating a flow pattern matrix of the array model; and 5) performing DOA estimation by using spectrum peak searching. According to the invention, a cycle correlation entropy theory is organically applied to array signal processing, correlation characteristics of the cycle correlation entropy are innovatively proposed, and the array linear prediction model is built based on the characteristics. The algorithm is put forward according to actual requirements, and has the characteristics of high anti-noise performance, low computation complexity, small number of required snapshots, high angular resolution and the like.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Multi-antenna device for the rejection of multi-paths in a satellite navigation system and associated method
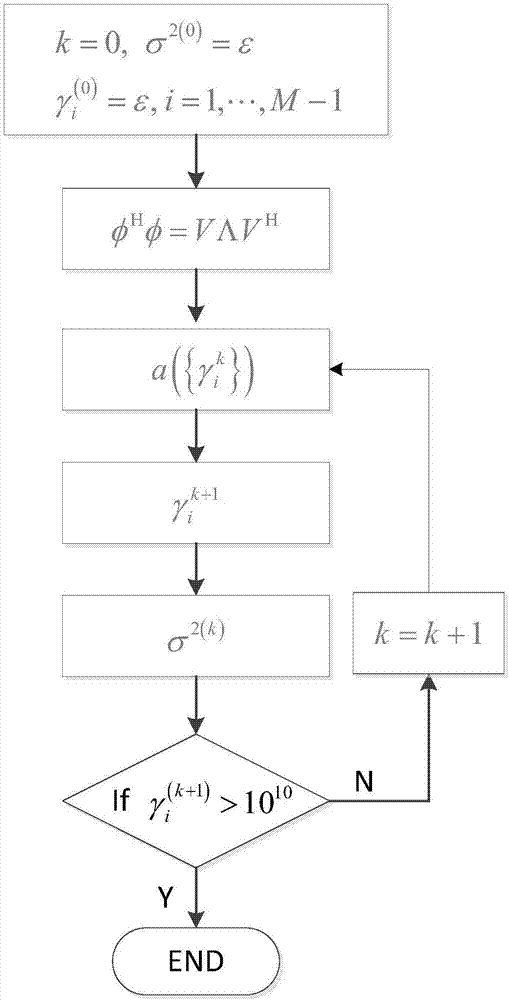
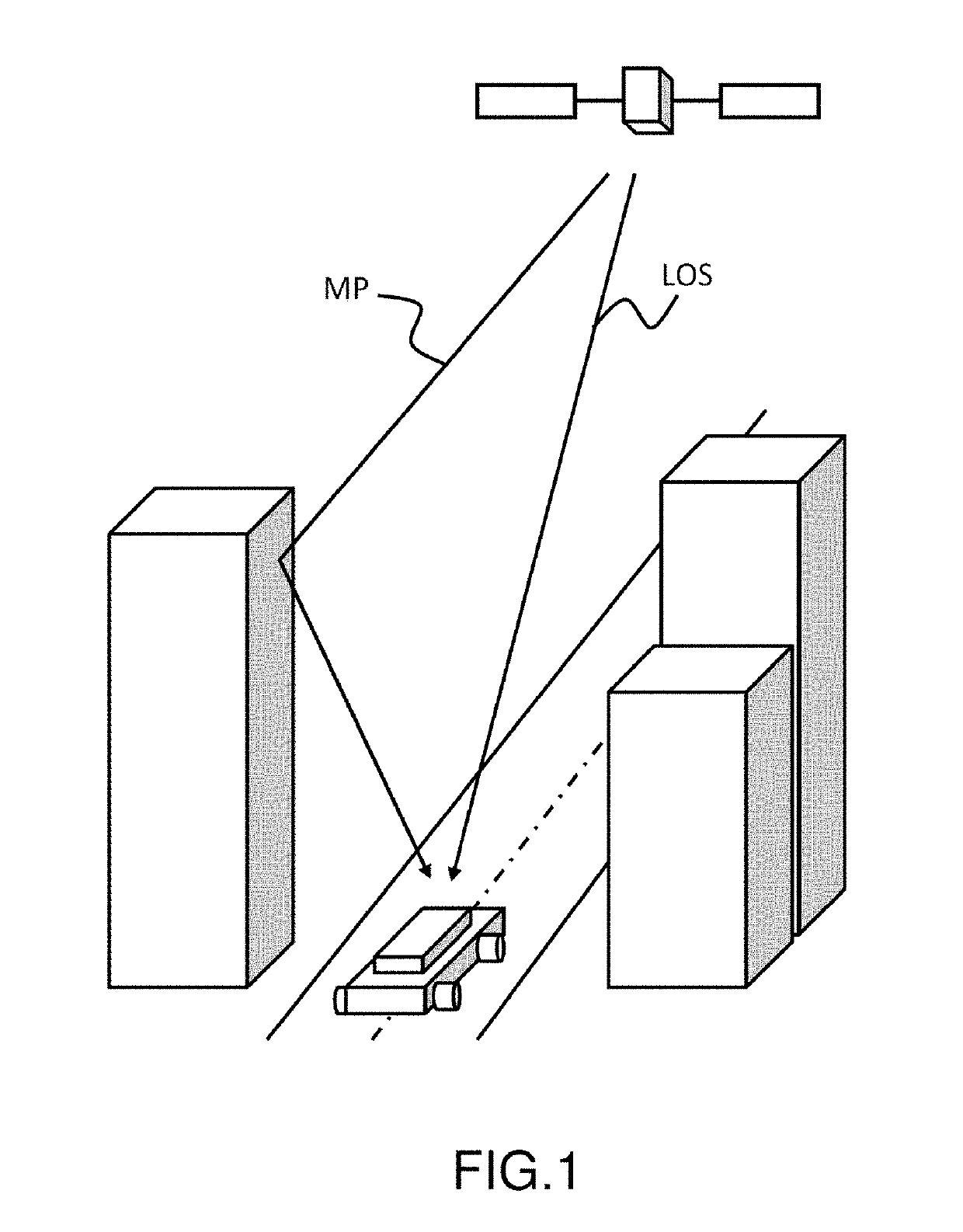
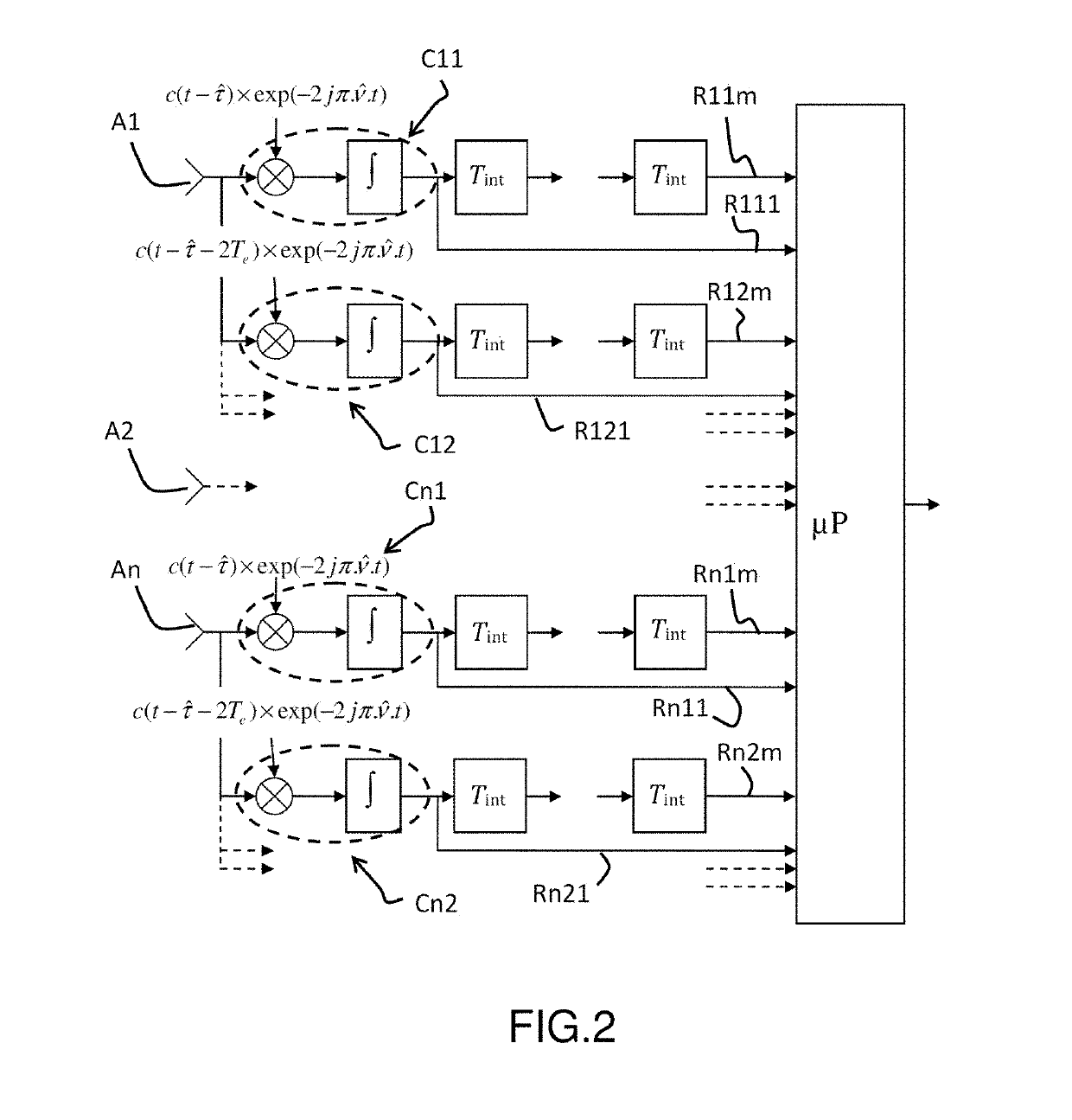
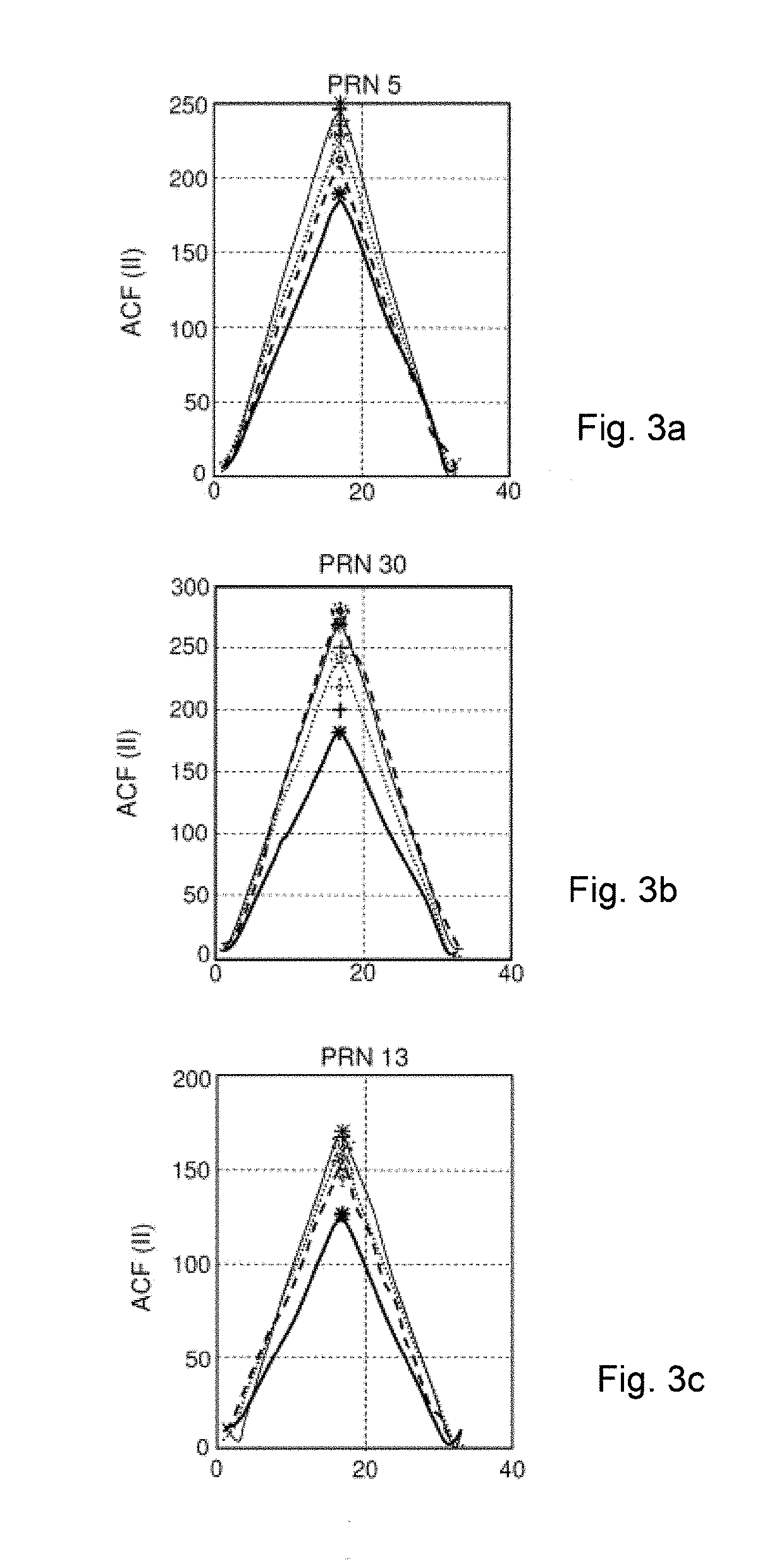
A method is provided for estimating the parameters of useful signal and multi-path signals originating from a radiolocation signal emitted by a satellite, a location device comprising at least two sensors able to receive the signal. The method comprises the steps of: correlating the signal received by the sensors with a local code by means of correlators, constructing, for each sensor, a sampled intercorrelation function intercorrelating the signal received with the local code, determining a spatio-temporal intercorrelation function on the basis of the concatenation of the intercorrelation functions obtained in the previous step for each sensor, estimating parameters representative of the useful signal and of the multi-path signals by applying a maximum likelihood algorithm, the representative parameters including at least one complex amplitude estimated independently for each sensor.
Owner:THALES SA
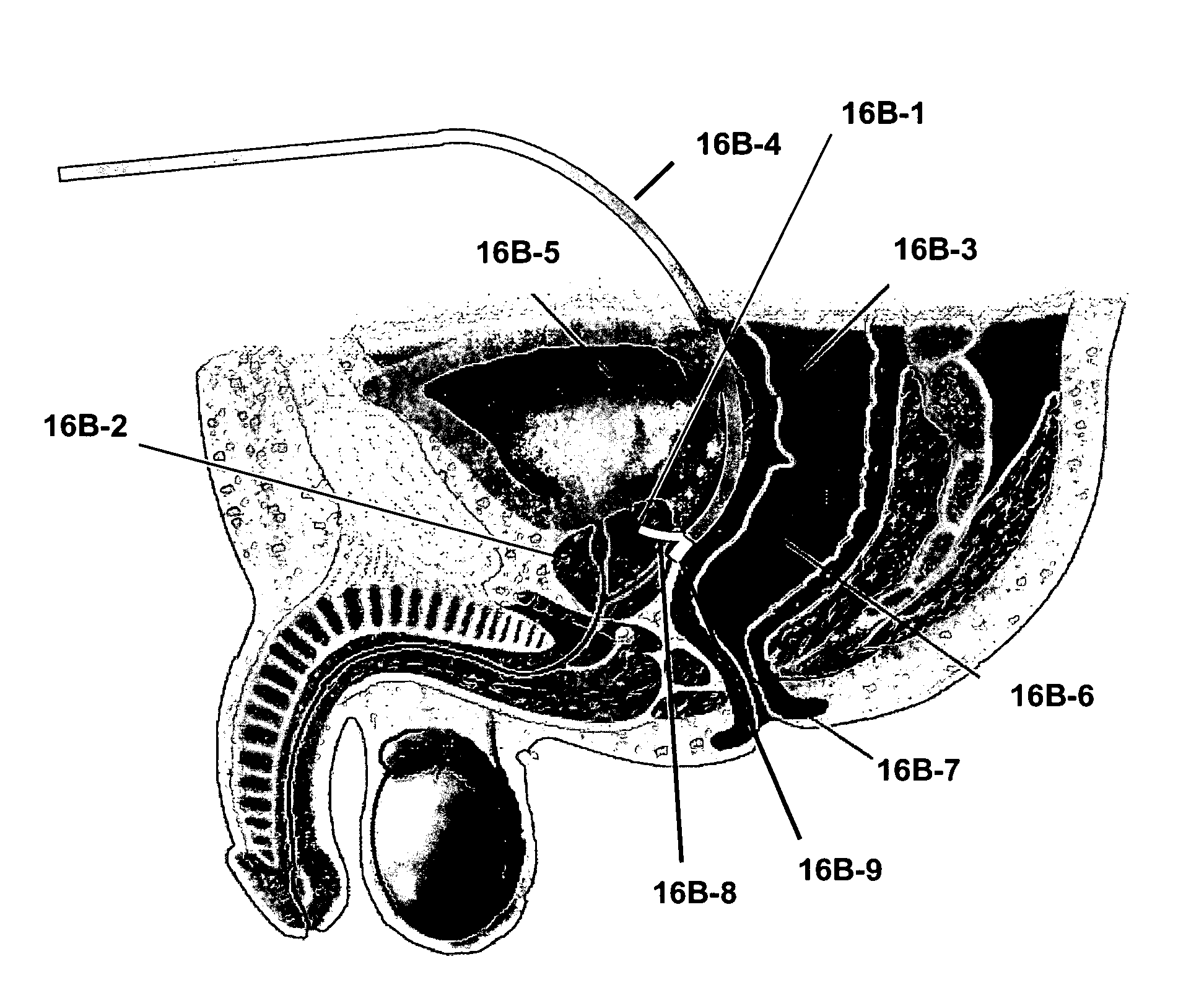
Guidance and implantation of catheters
A catheter system adapted for navigating, guiding and implanting a catheter or a plurality of catheters in a spatially-defined implantation within the tissue of a patient is provided. The system can include a tissue navigation system and a probe to inform the navigation system to guide emplacement of the catheters within a target tissue. The probe can provide images, such as fiberoptic visual images, or ultrasound images, or can provide radiolocation data, to guide the catheter emplacement. The catheters supply a pressurized liquid including a bioactive agent, such as can be used in the treatment of cancer, for example 123I- or 125I-IUDR. The system and methods provided can be used in the treatment of locally advanced tumors, such as cancers of the brain, head or neck, esophagus, prostate, ovary, liver, pancreas, bladder or rectum.
Owner:PEAK BIOSCI
Base station selection for positioning/localization based on an indication of capacity
Systems, apparatus and methods for selecting a base station or a set of base stations for RTT measurements, or other interactive radio localization technique, to determine a position fix of a device are presented. The method imposes a processing load on only inactive or less active base stations. Busy or busier base stations are not used in the interactive radio localization technique. By imposing a processing load on only less active base stations, transmitting devices may be under loaded and encounter a more uniform processing delay, and thus provide a more accurate measurement resulting in a more accurate position fix.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com