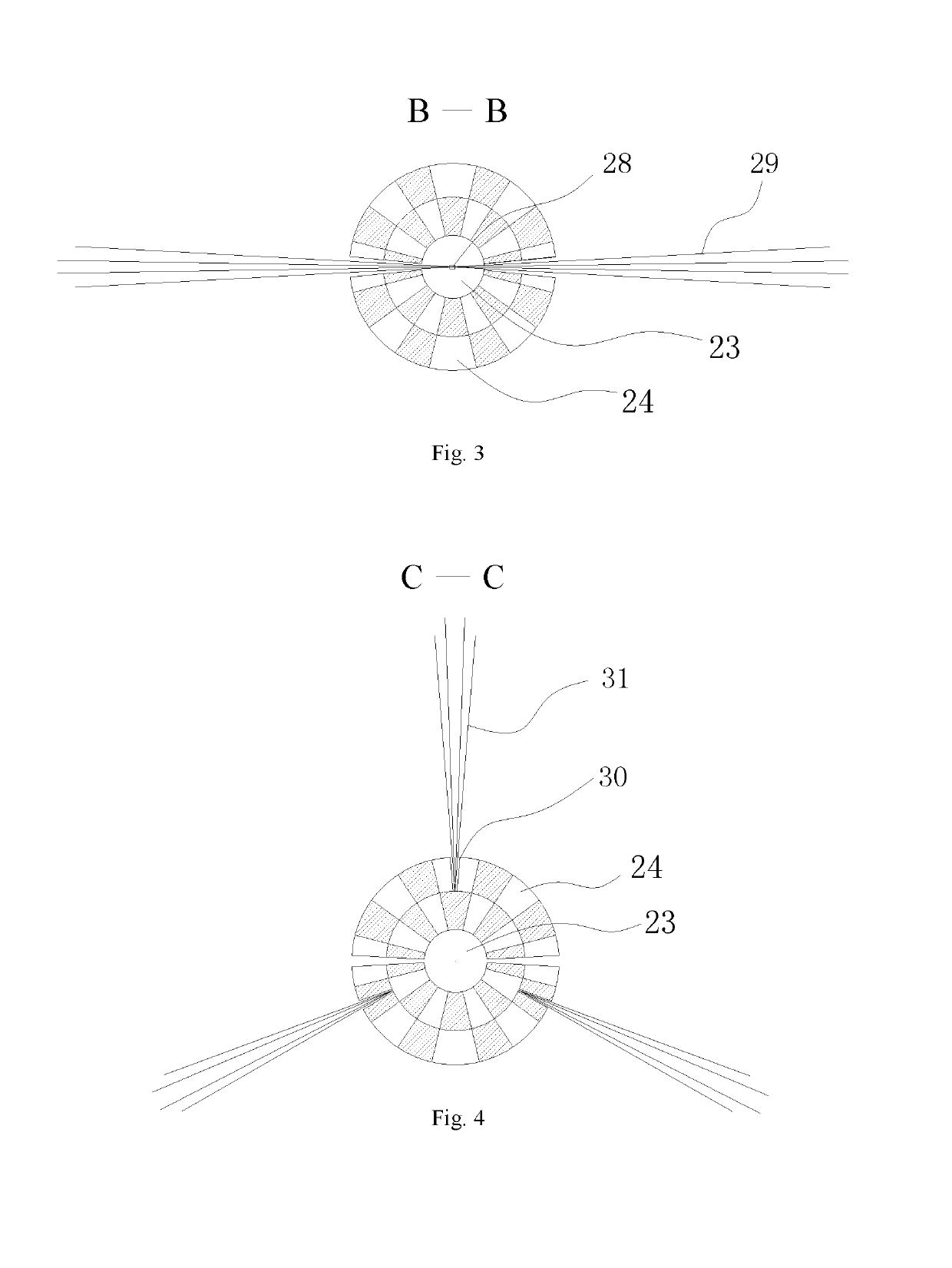
Patents
Literature
217 results about "Gps measurement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
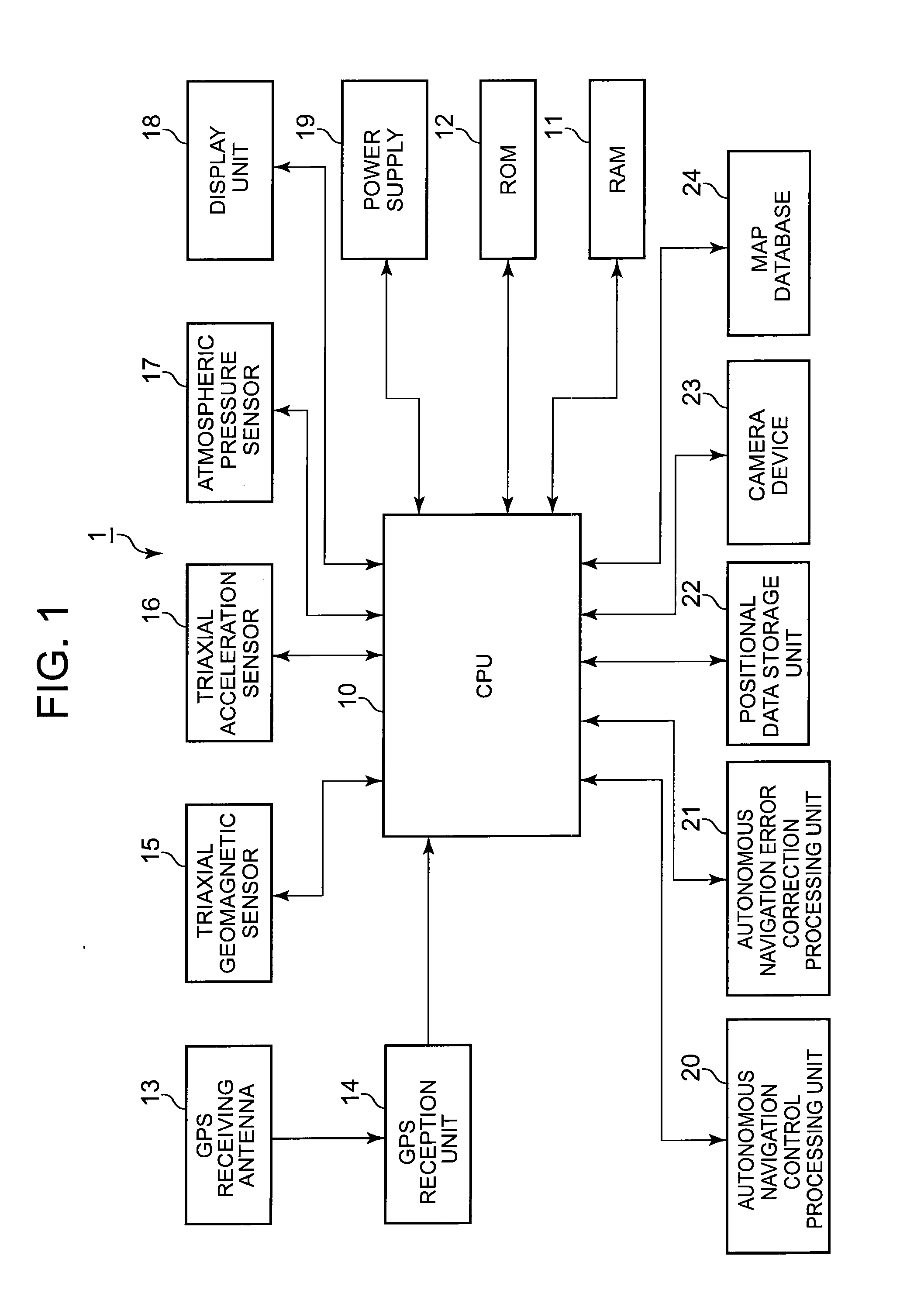
A GPS receiver measures the distance to a satellite using the travel time of radio signals. By accurately measuring the distance from 3 satellites it is possible to find your position anywhere on Earth. For GPS to work we must be able to 1) measure travel time very accurately, 2) know the exact location...
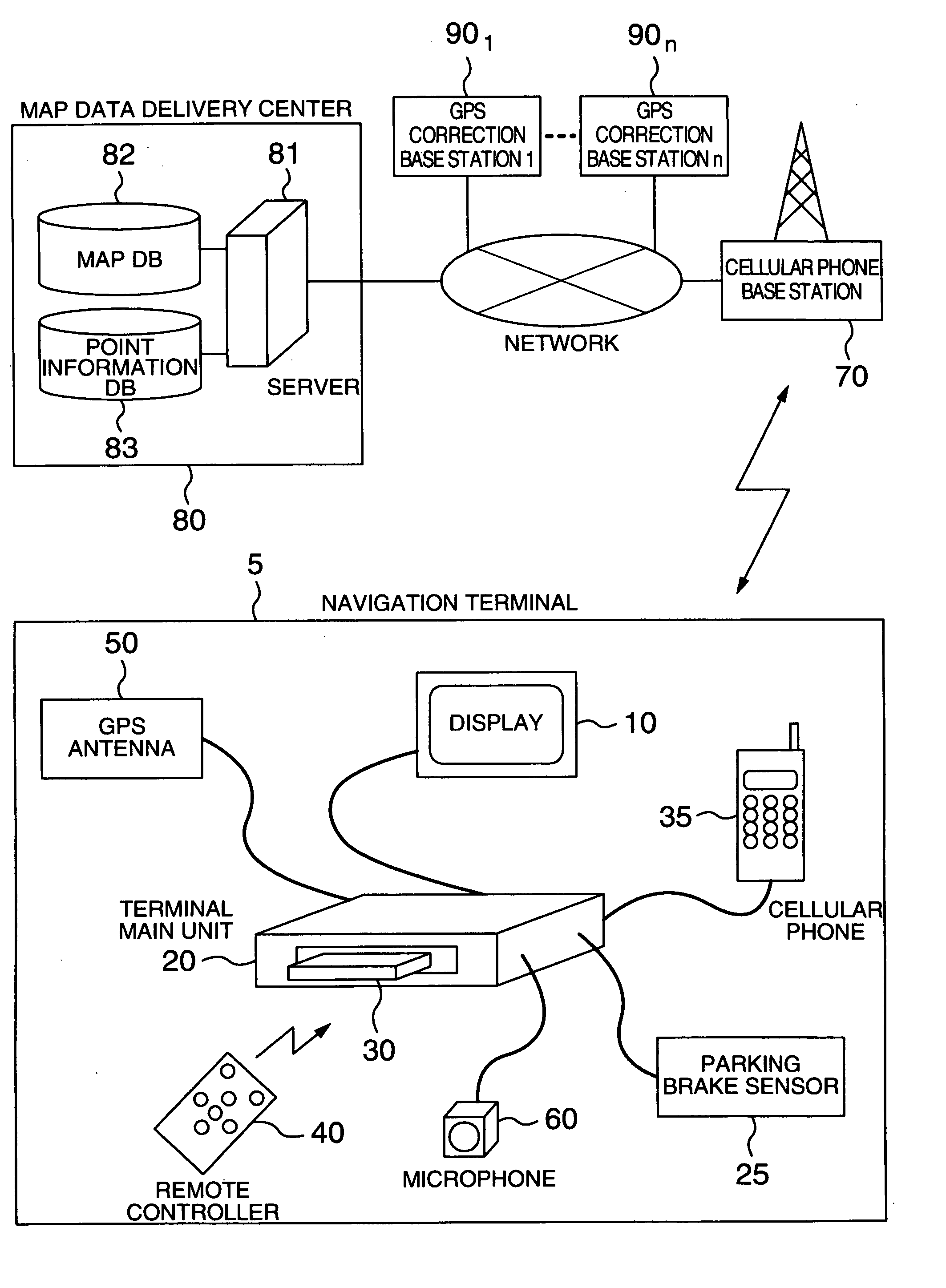
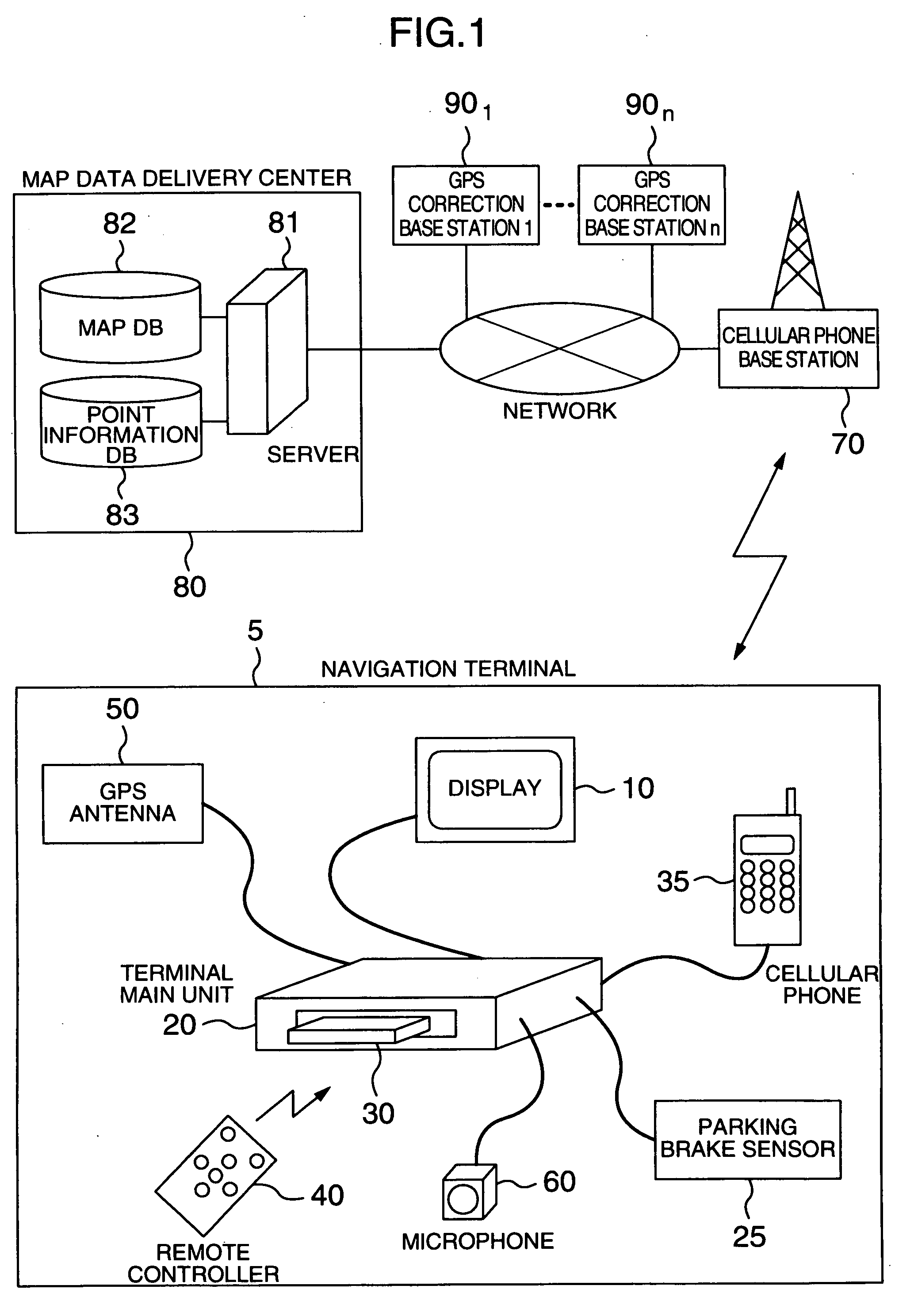
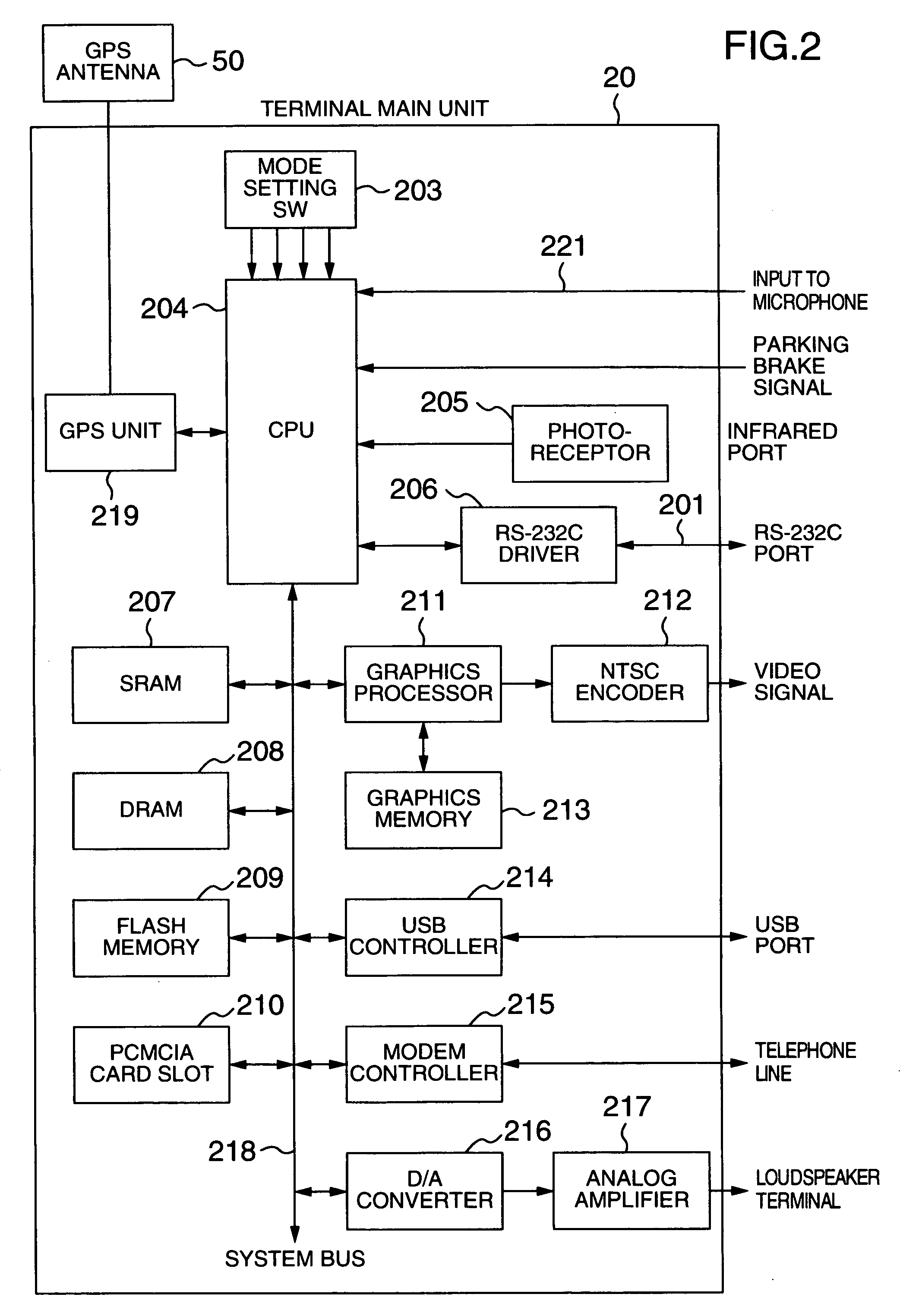
Navigation apparatus for receiving delivered information
InactiveUS20040204848A1Quick displayReduce communication data volumeInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlGps measurementComputer terminal
In a communication-type navigation system for downloading map data according to the present invention, a reduction in the amount of map information to be transferred, correction of a position measured by a GPS, and delivery of advertisements are effected. In this system, a terminal 5 stores rough map data in advance. Then, when detailed map data is required, it is downloaded from a map data delivery center to the terminal 5. Further, together with the map data, GPS correction information is delivered to the terminal 5 from the map data delivery center 80. Still further, coupon information associated with an advertisement is displayed and an electronic mail on the coupon information is issued, by the map data delivery center.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
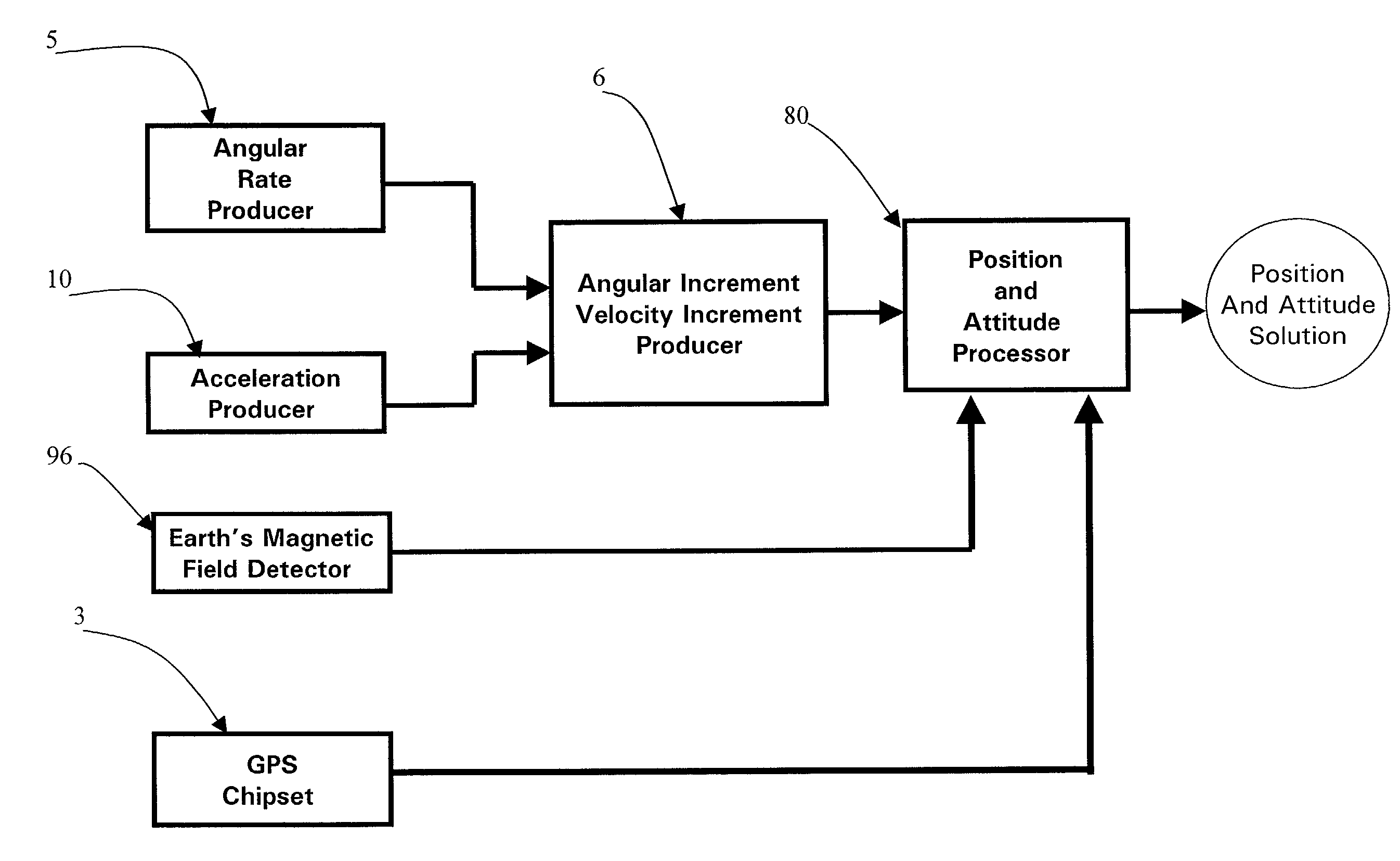
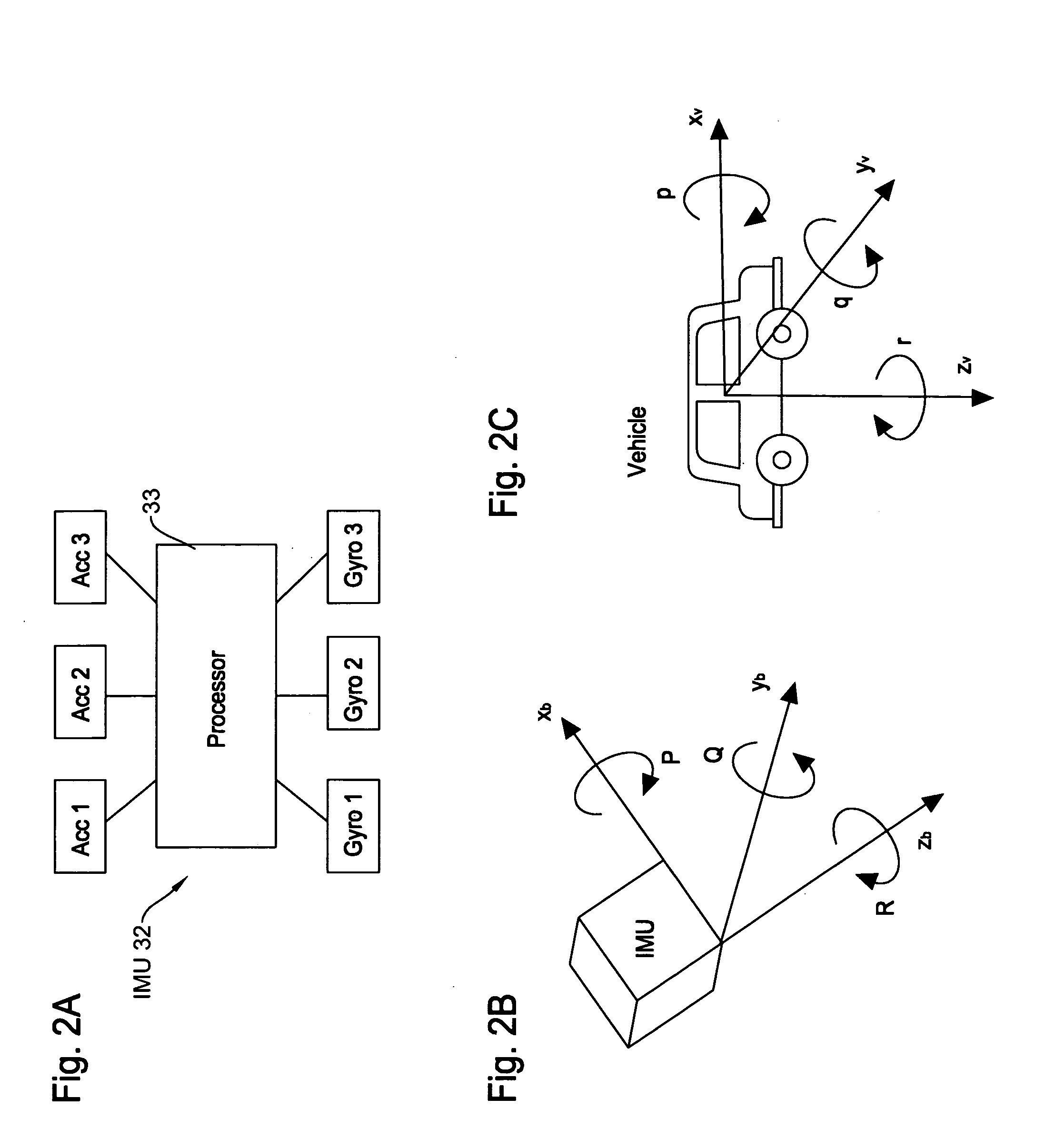
Micro integrated global positioning system/inertial measurement unit system
InactiveUS20020008661A1Precise positioningInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationCarrier signalClosed loop
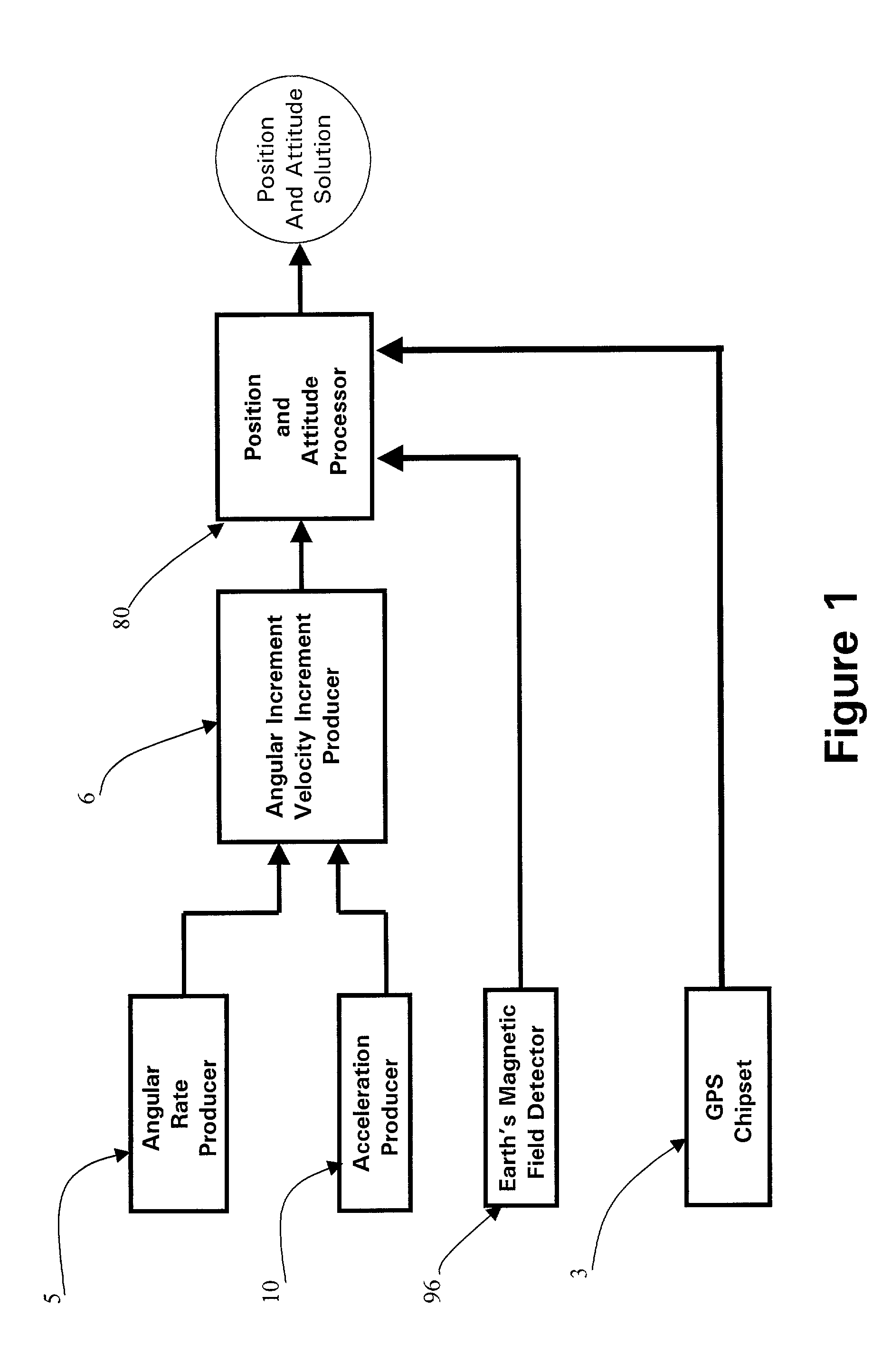
A micro integrated Global Positioning System (GPS) / Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) System, which is adapted to apply to output signals proportional to rotation and translational motion of a carrier and GPS measurements of the carrier, respectively from angular rate sensors, acceleration sensors, and GPS chipset, is employed with MEMS angular rate and acceleration sensors and GPS chipset. Compared with a conventional IMU / GPS system, the system of the present invention uses an integrated processing scheme by means of digital closed loop control of the dither driver signals for MEMS angular rate sensors, a feedforward open-loop signal processing scheme of the IMU, digital temperature control and compensation, the earth's magnetic field-based heading damping, robust error estimator, and compact sensor and circuit architecture and dramatically shrinks the size of mechanical and electronic hardware and power consumption, meanwhile, obtains highly accurate motion measurements.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
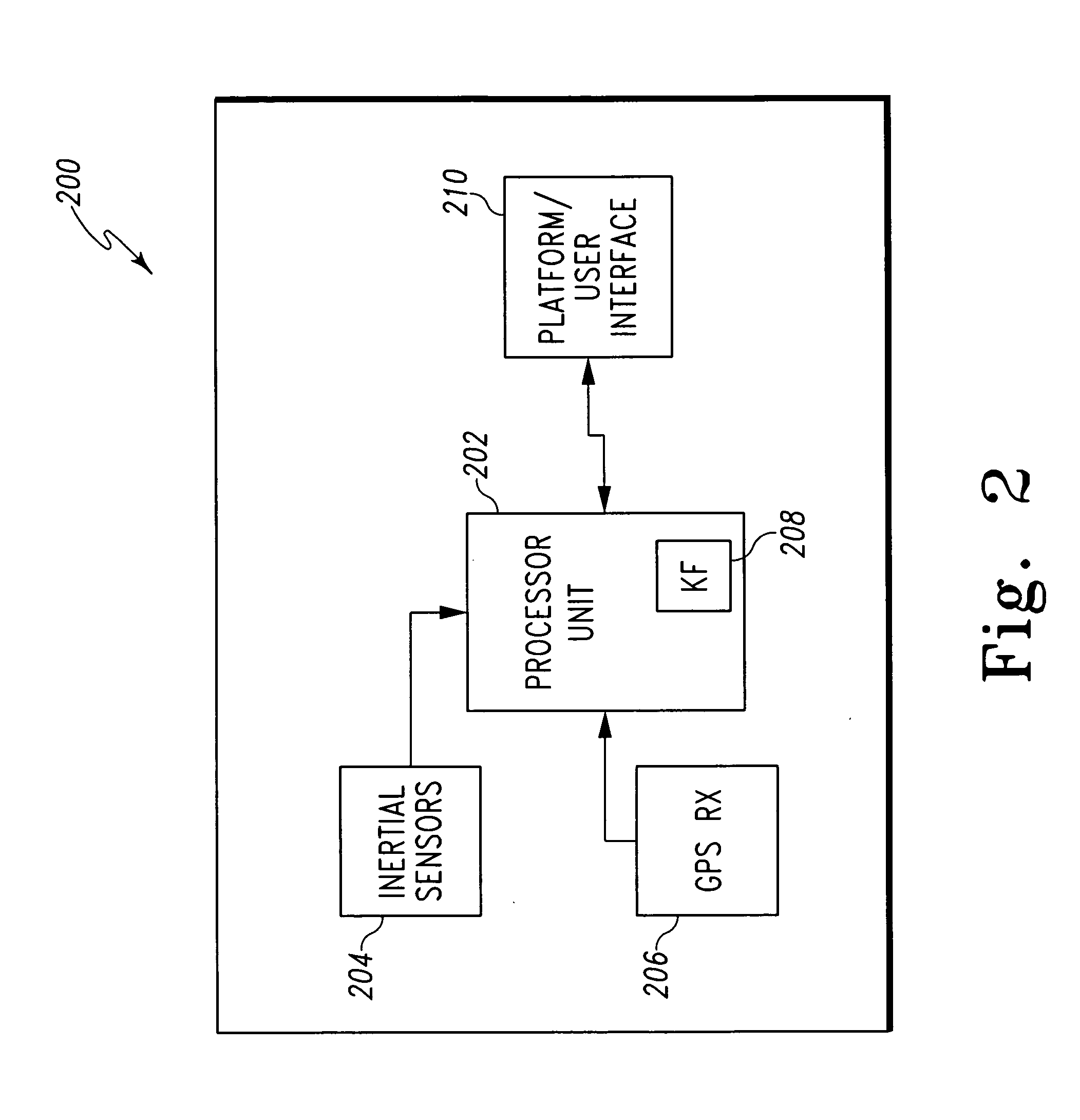
Inertial GPS navigation system with modified kalman filter
ActiveUS7193559B2Eliminate the effects ofShorten the timeAcceleration measurement using interia forcesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPhase differenceDirect observation
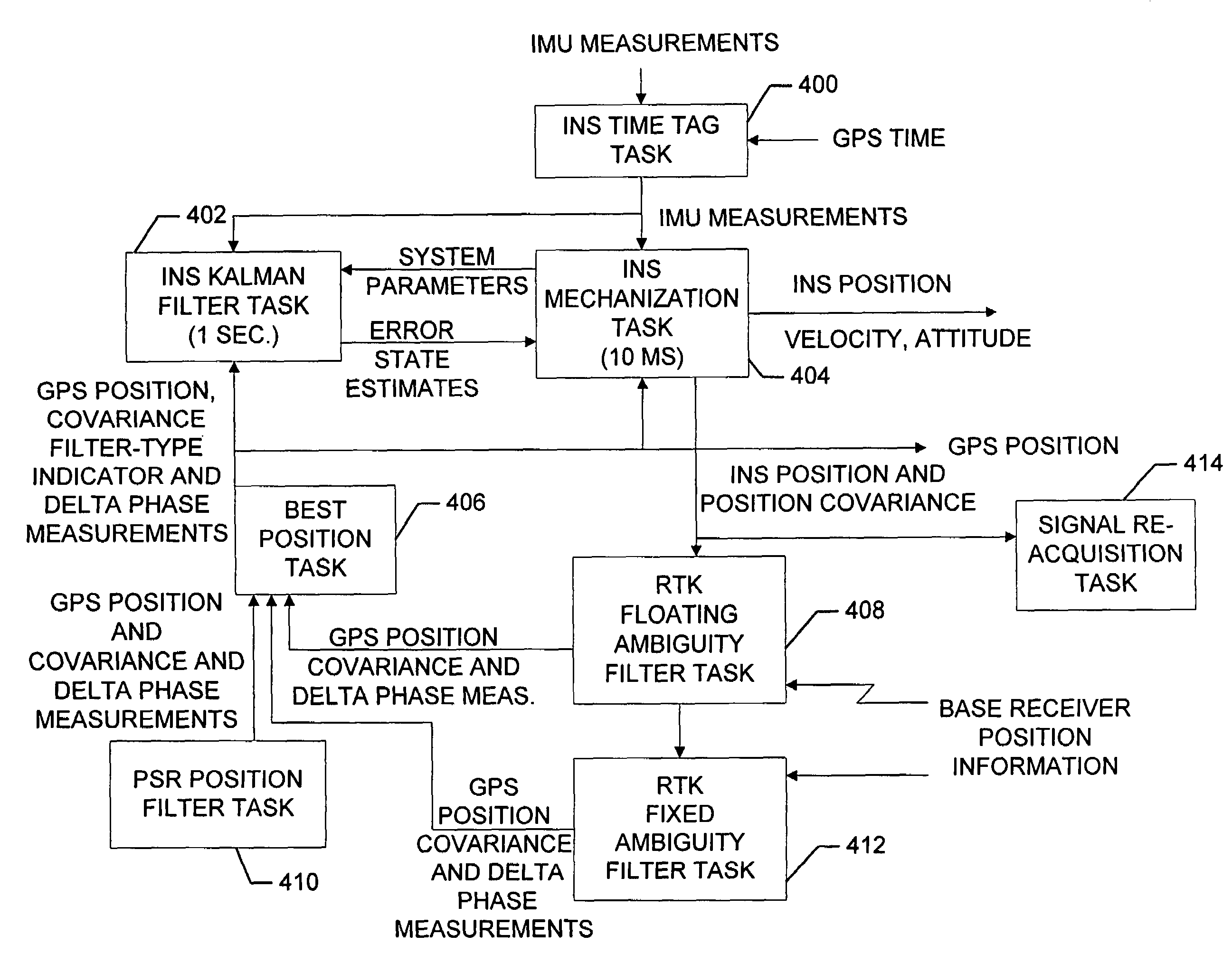
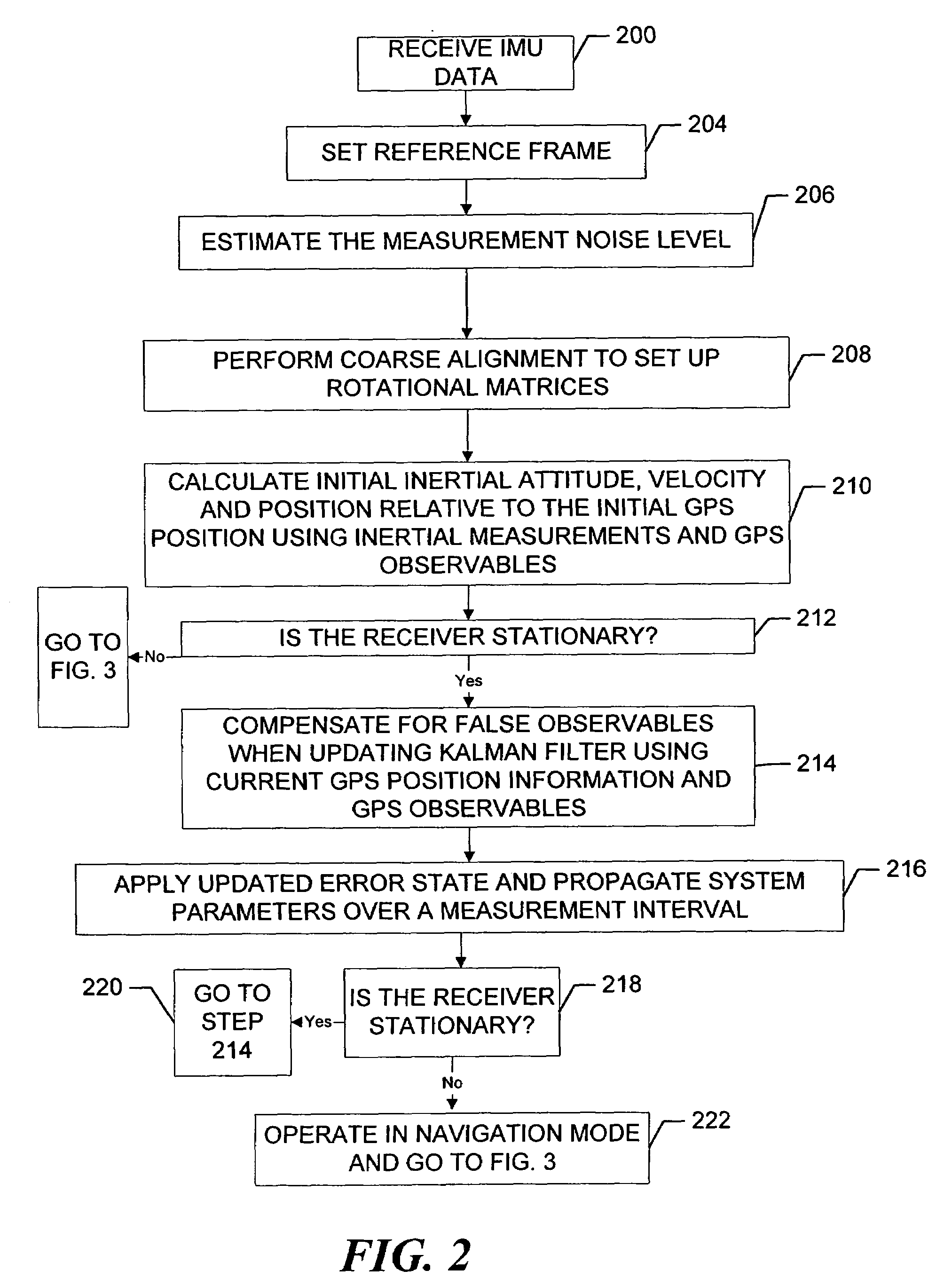
An inertial (“INS”) / GPS receiver includes an INS sub-system which incorporates, into a modified Kalman filter, GPS observables and / or other observables that span previous and current times. The INS filter utilizes the observables to update position information relating to both the current and the previous times, and to propagate the current position, velocity and attitude related information. The GPS observable may be delta phase measurements, and the other observables may be, for example, wheel pick-offs (or counts of wheel revolutions) that are used to calculate along track differences, and so forth. The inclusion of the measurements in the filter together with the current and the previous position related information essentially eliminates the effect of system dynamics from the system model. A position difference can thus be formed that is directly observable by the phase difference or along track difference measured between the previous and current time epochs. Further, the delta phase measurements can be incorporated in the INS filter without having to maintain GPS carrier ambiguity states. The INS sub-system and the GPS sub-system share GPS and INS position and covariance information. The receiver time tags the INS and any other non-GPS measurement data with GPS time, and then uses the INS and GPS filters to produce INS and GPS position information that is synchronized in time. The GPS / INS receiver utilizes GPS position and associated covariance information and the GPS and / or other observables in the updating of the INS filter. The INS filter, in turn, provides updated system error information that is used to propagate inertial current position, velocity and attitude information. Further, the receiver utilizes the inertial position, velocity and covariance information in the GPS filters to speed up GPS satellite signal re-acquisition and associated ambiguity resolution operations
Owner:NOVATEL INC
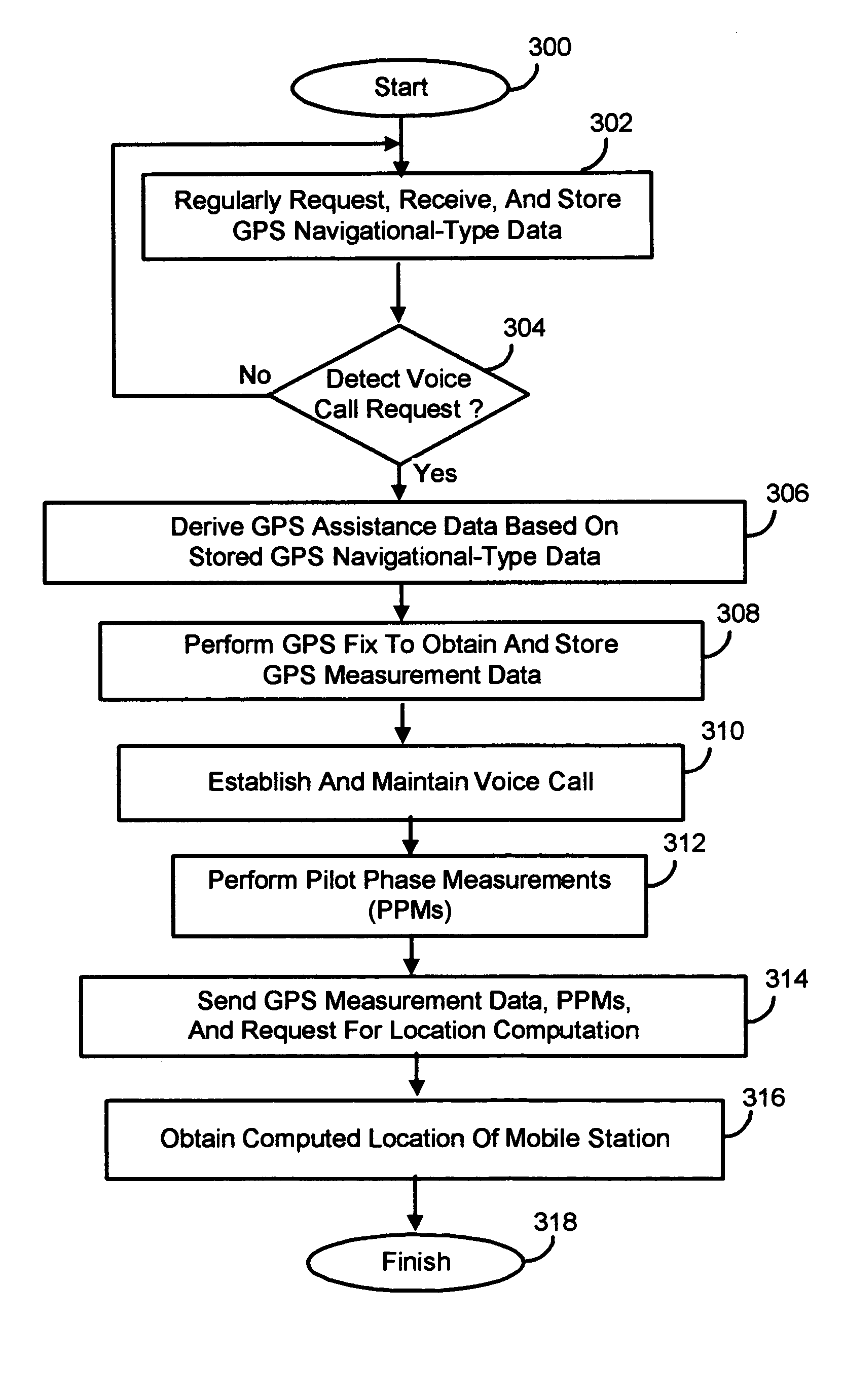
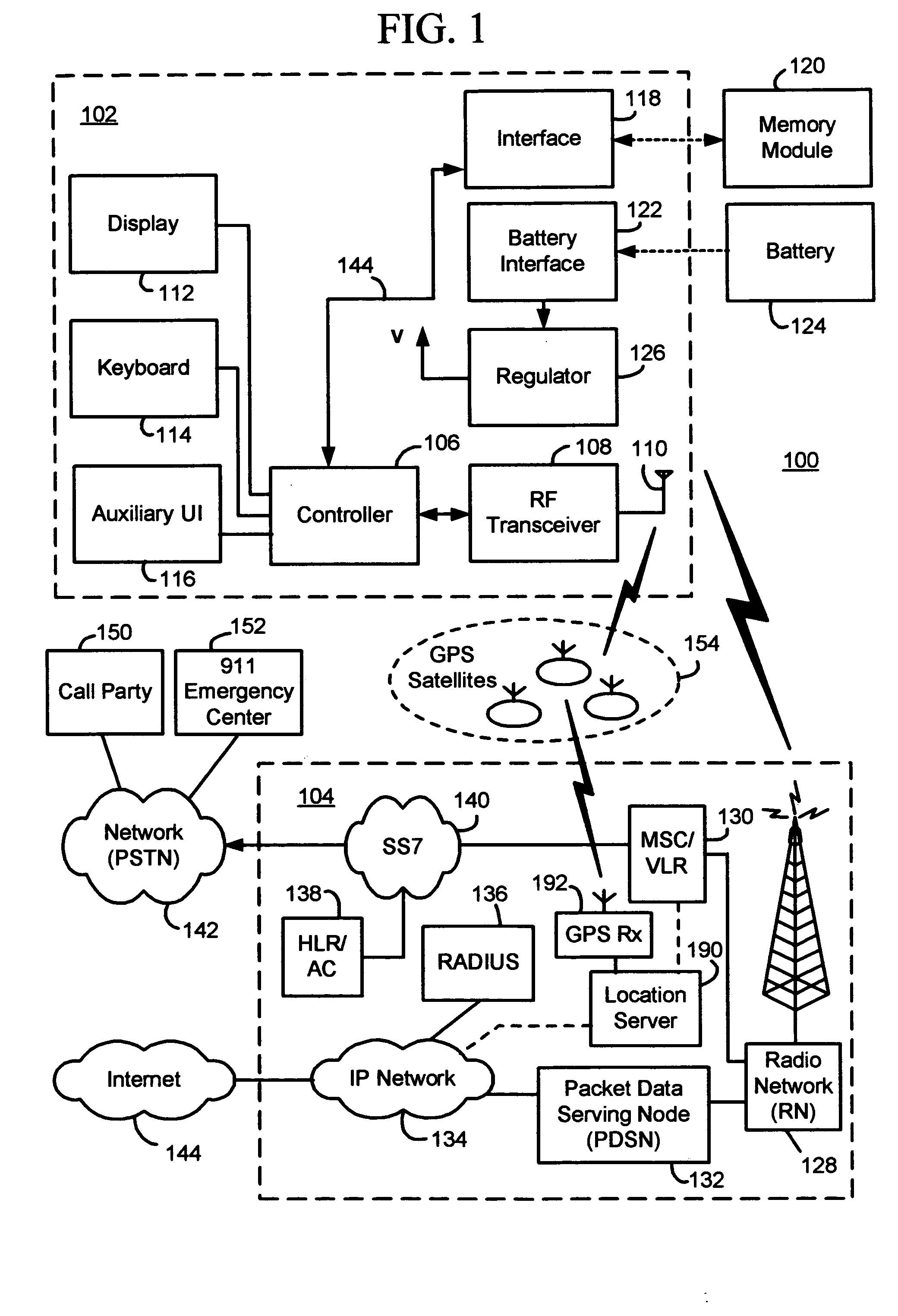
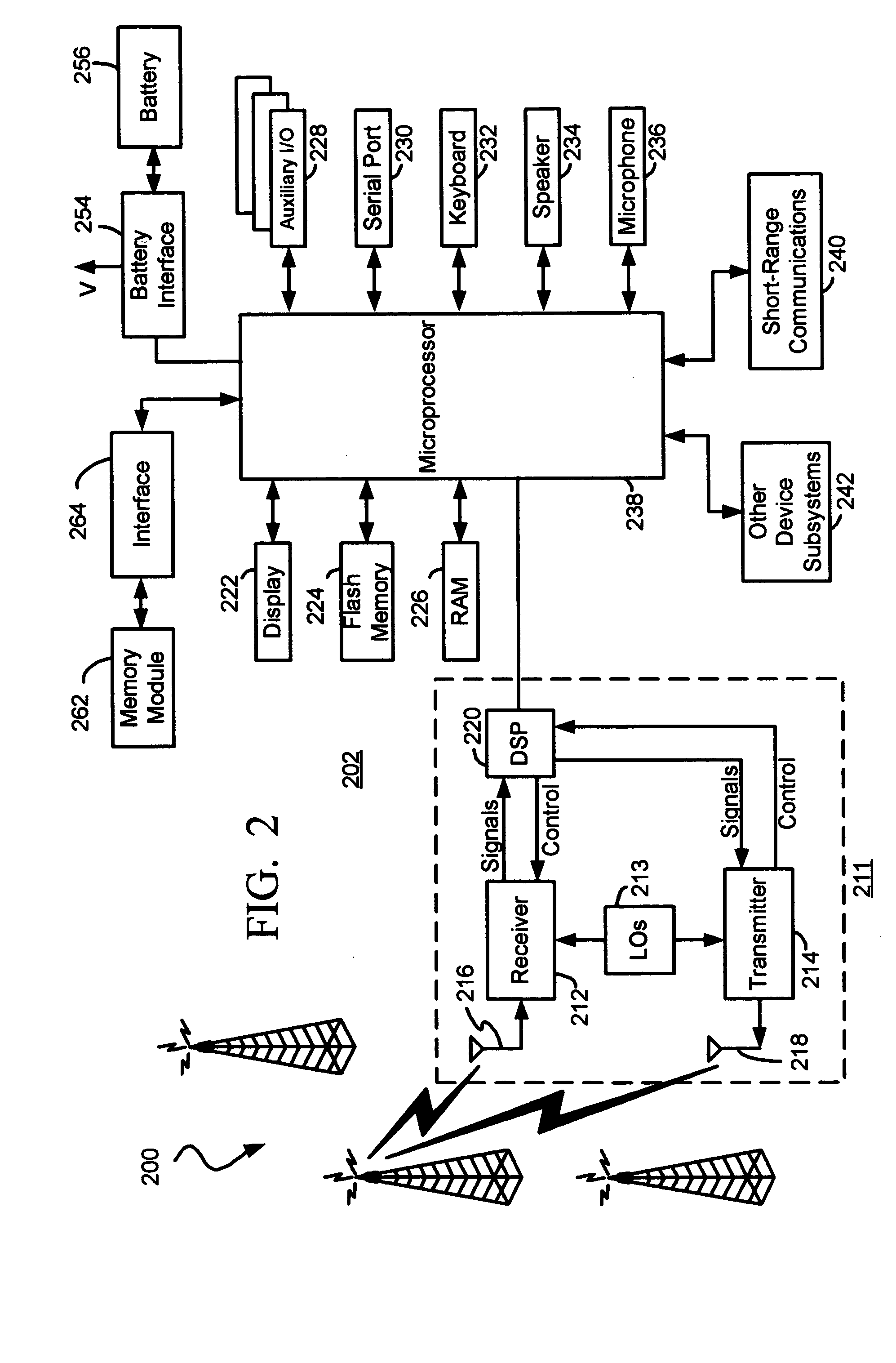
Methods and apparatus for facilitating the determination of GPS location information for a mobile station without disrupting communications of a voice call
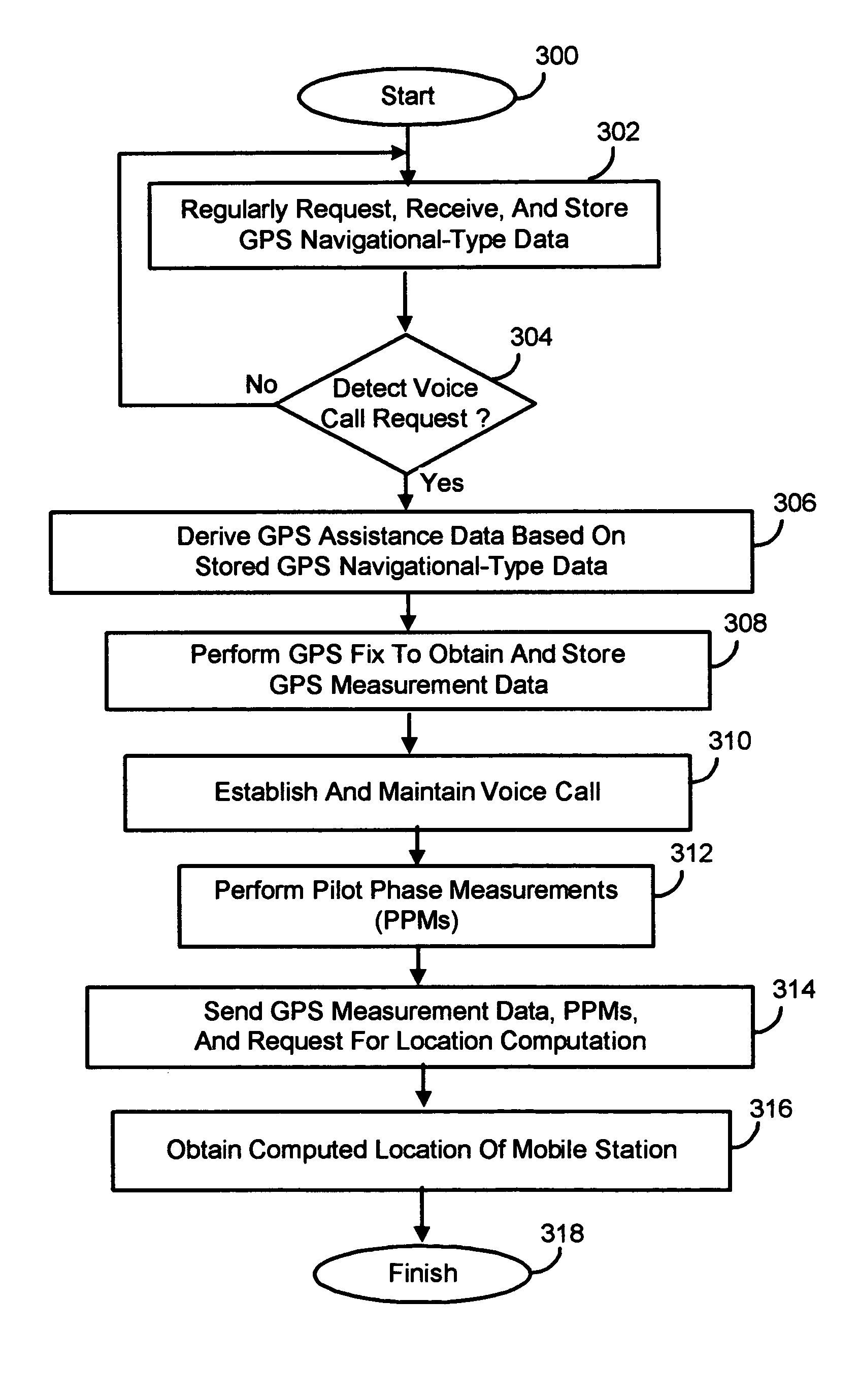
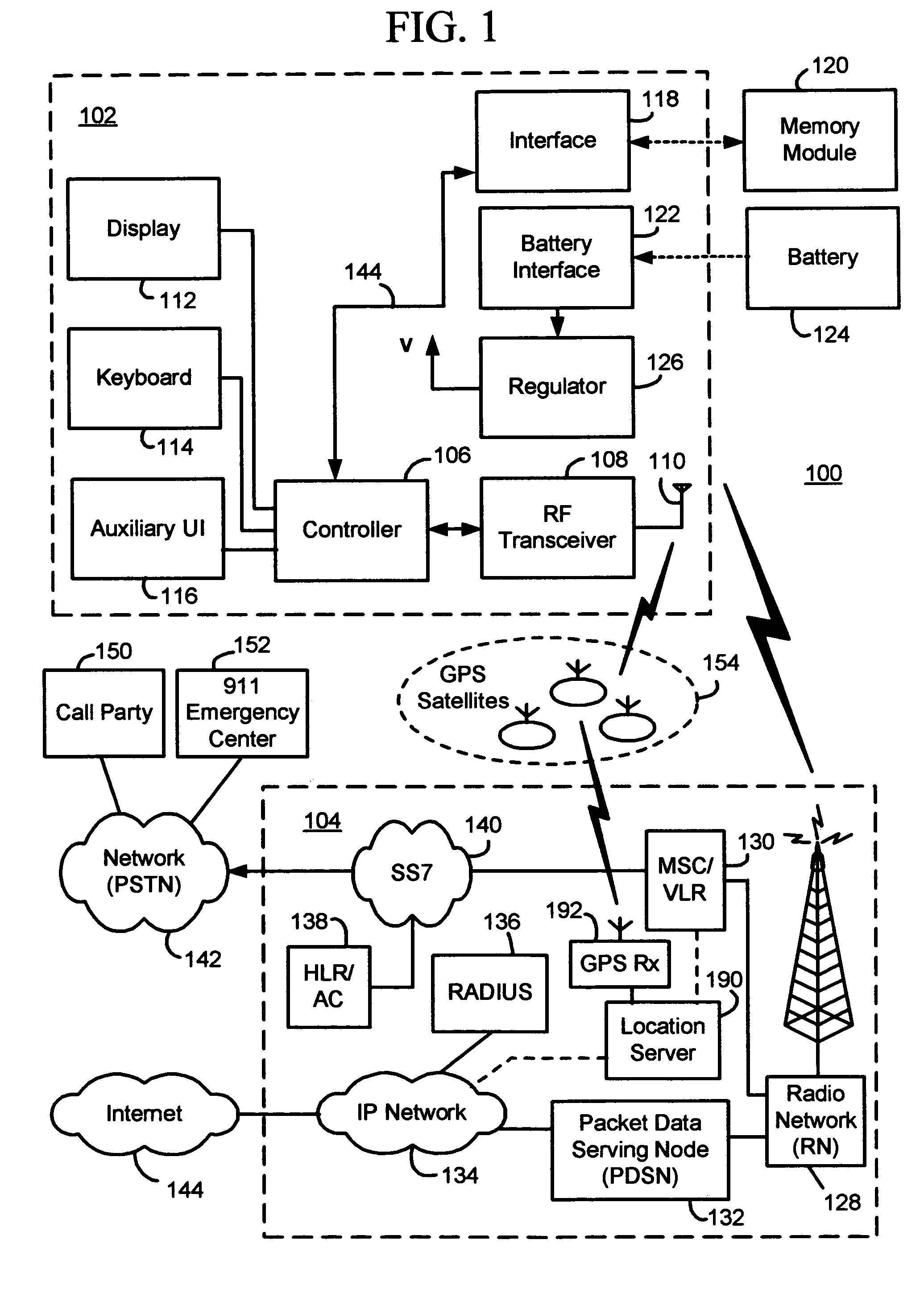
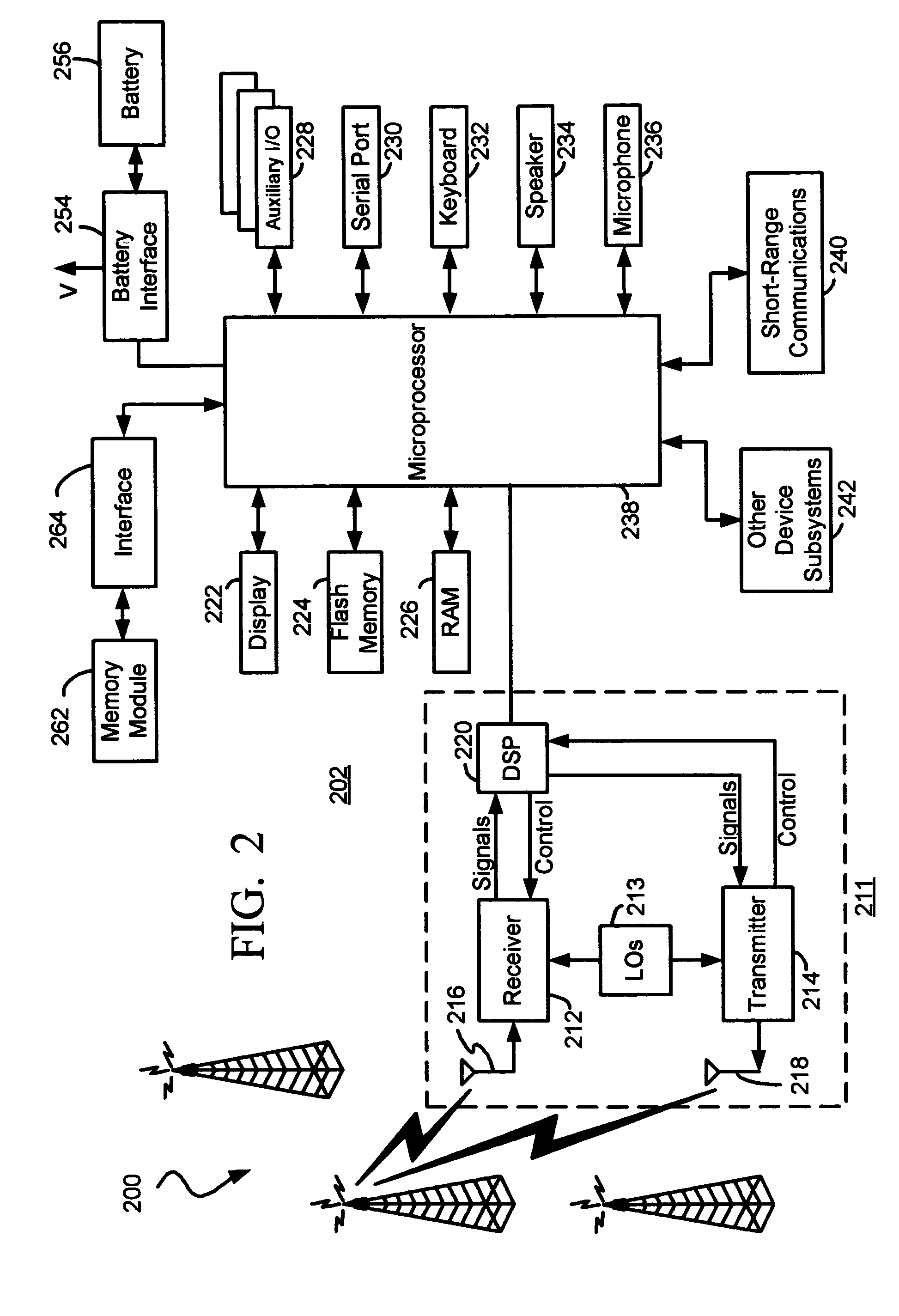
Methods and apparatus for facilitating the determination of Global Positioning System (GPS) location information for a mobile station without disrupting communications of a voice call (e.g. a 911 emergency call). In one illustrative example, the mobile station causes GPS navigational-type data to be regularly or periodically received and stored in memory prior to the voice call. At some point in time, the mobile station receives a voice call request to initiate the voice call. In response, the mobile station derives GPS assistance data based on the GPS navigational-type data. The mobile station then causes a GPS fix to be performed using the GPS assistance data, to thereby obtain GPS measurement data. Thereafter, the mobile station causes the voice call to be established and maintained through the wireless network. The GPS measurement data is transmitted to a location server for calculating the location of the mobile station.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
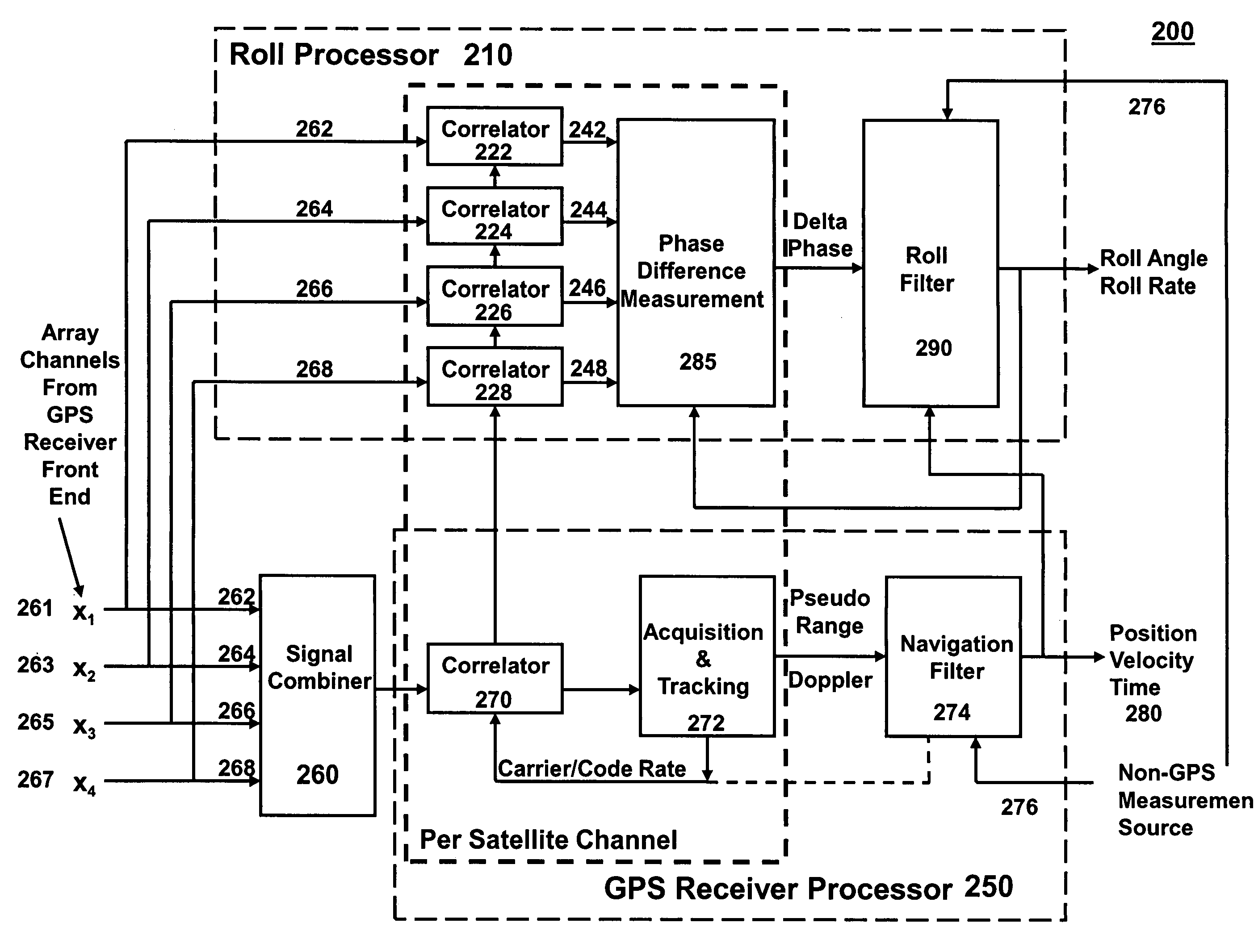
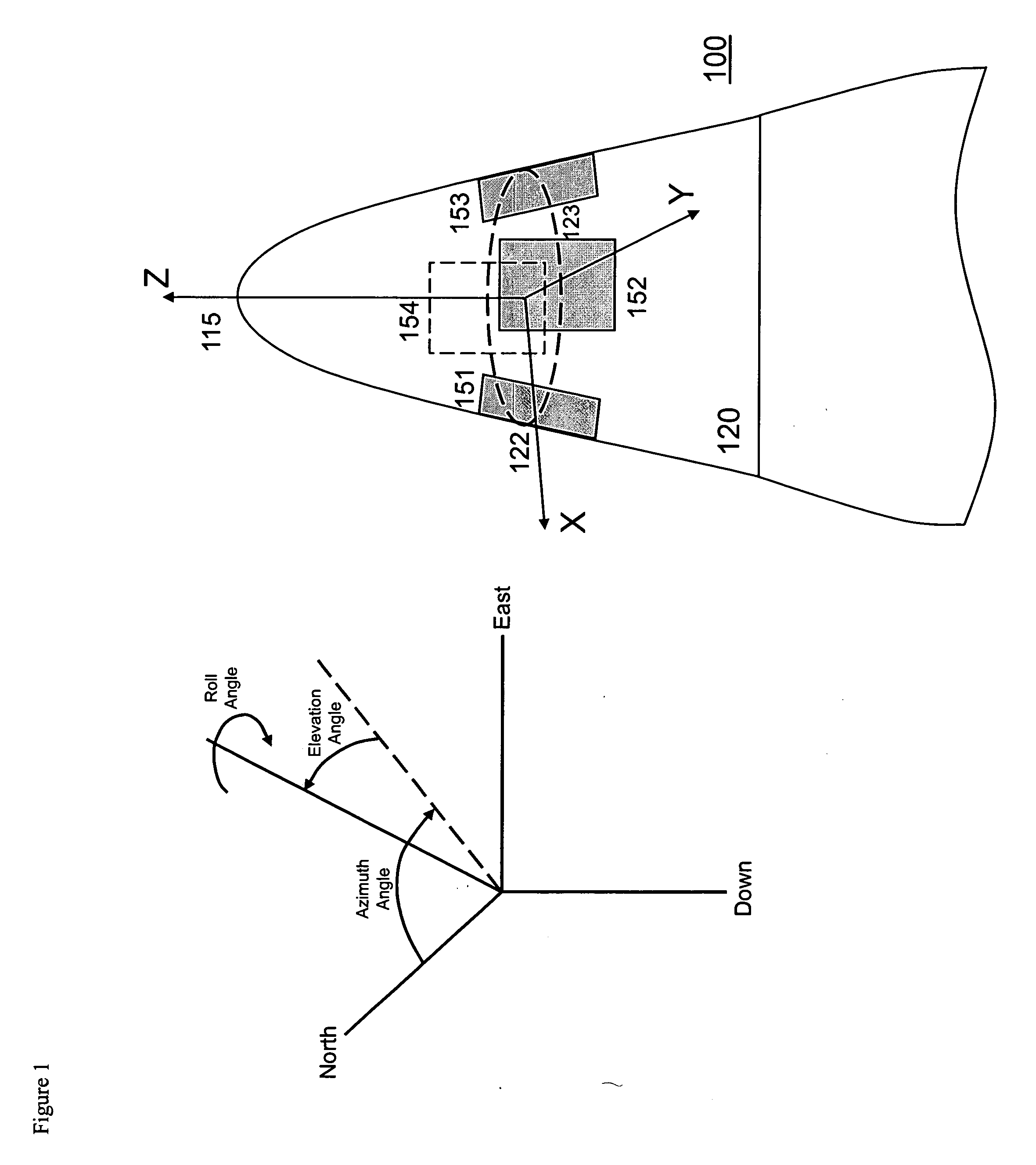
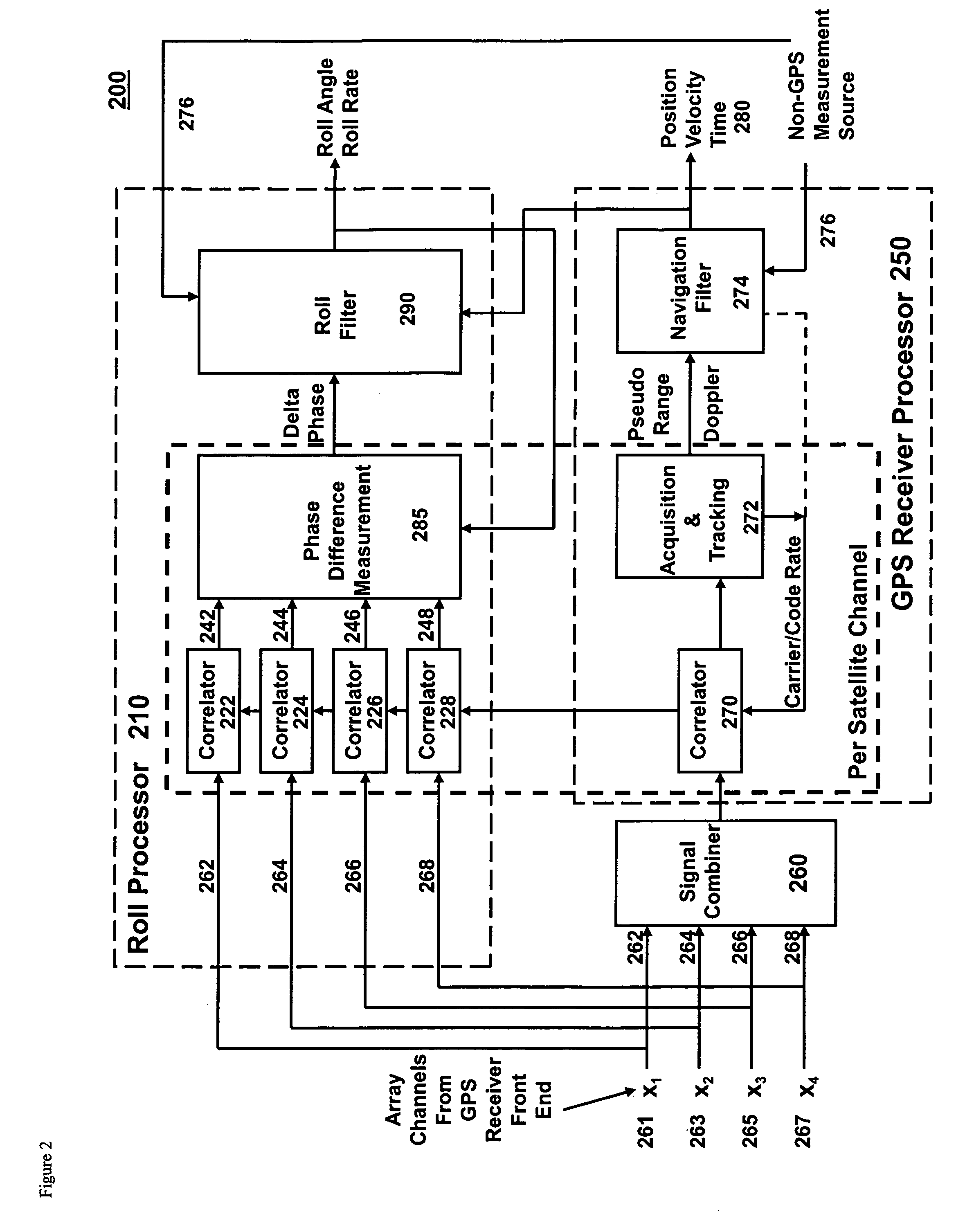
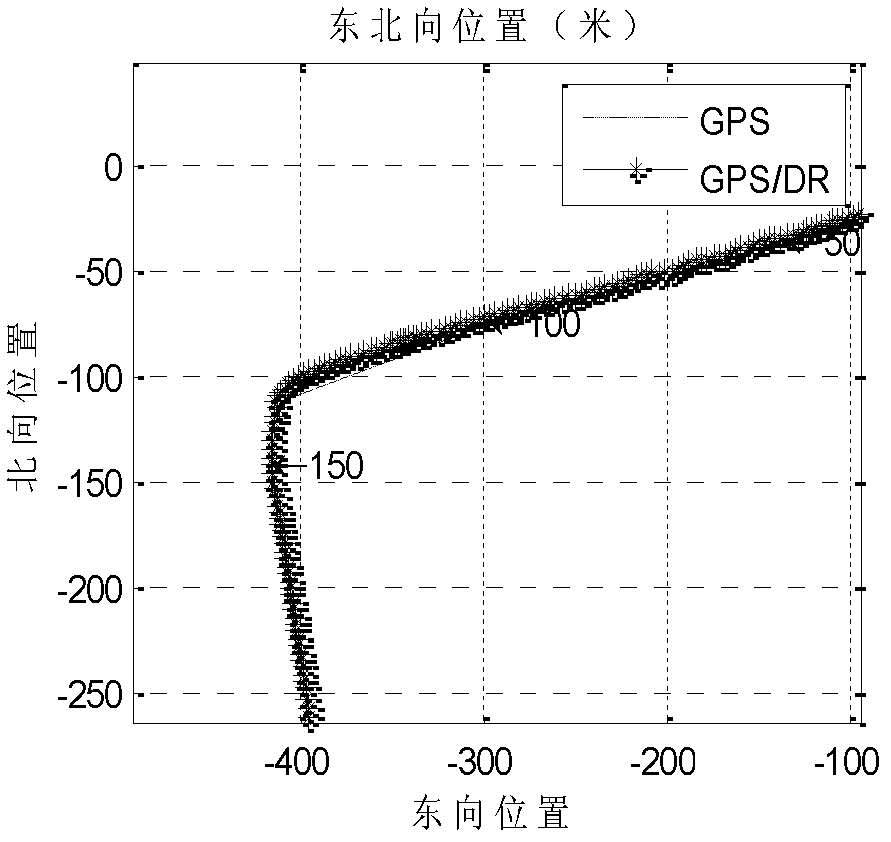
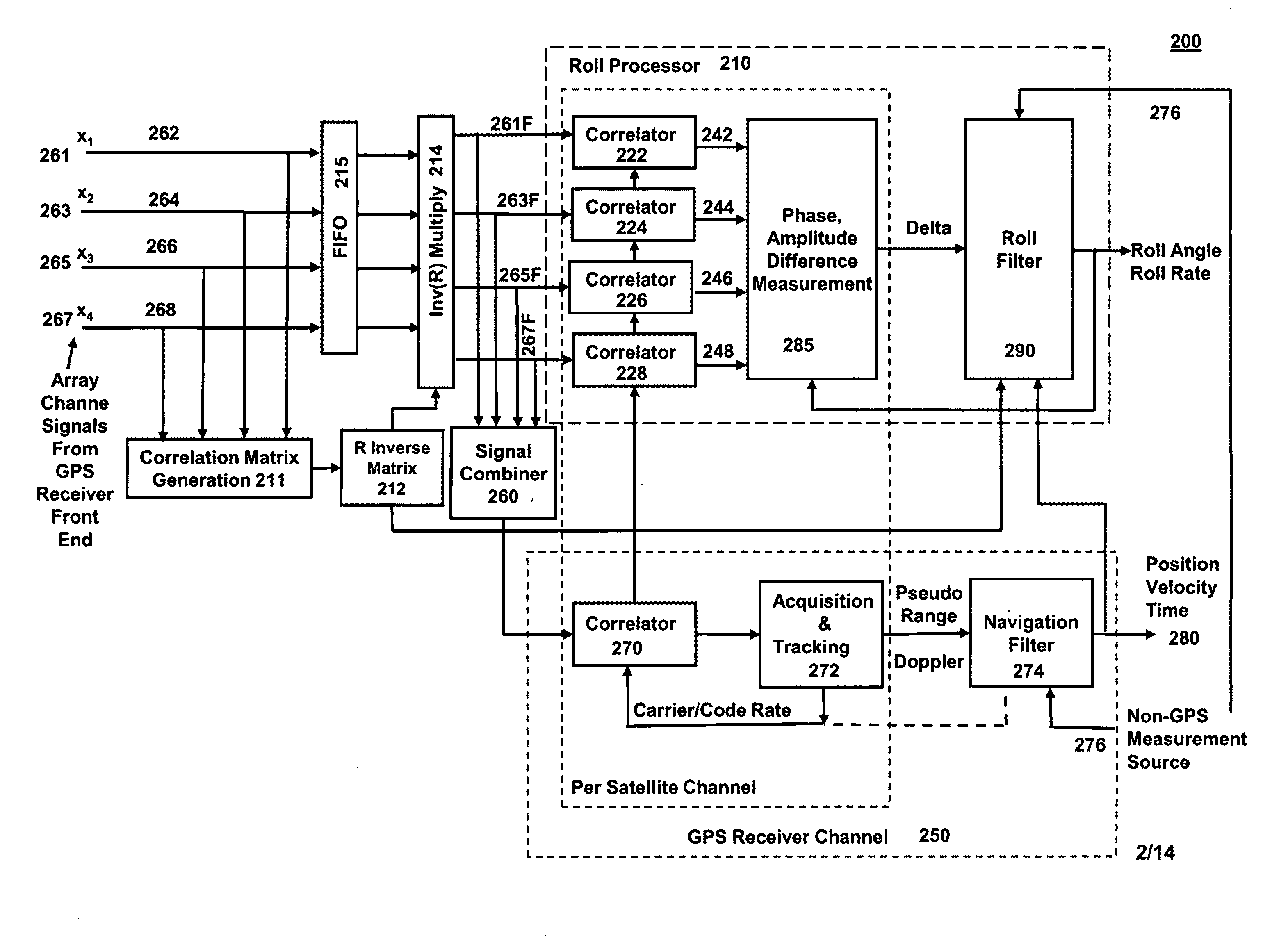
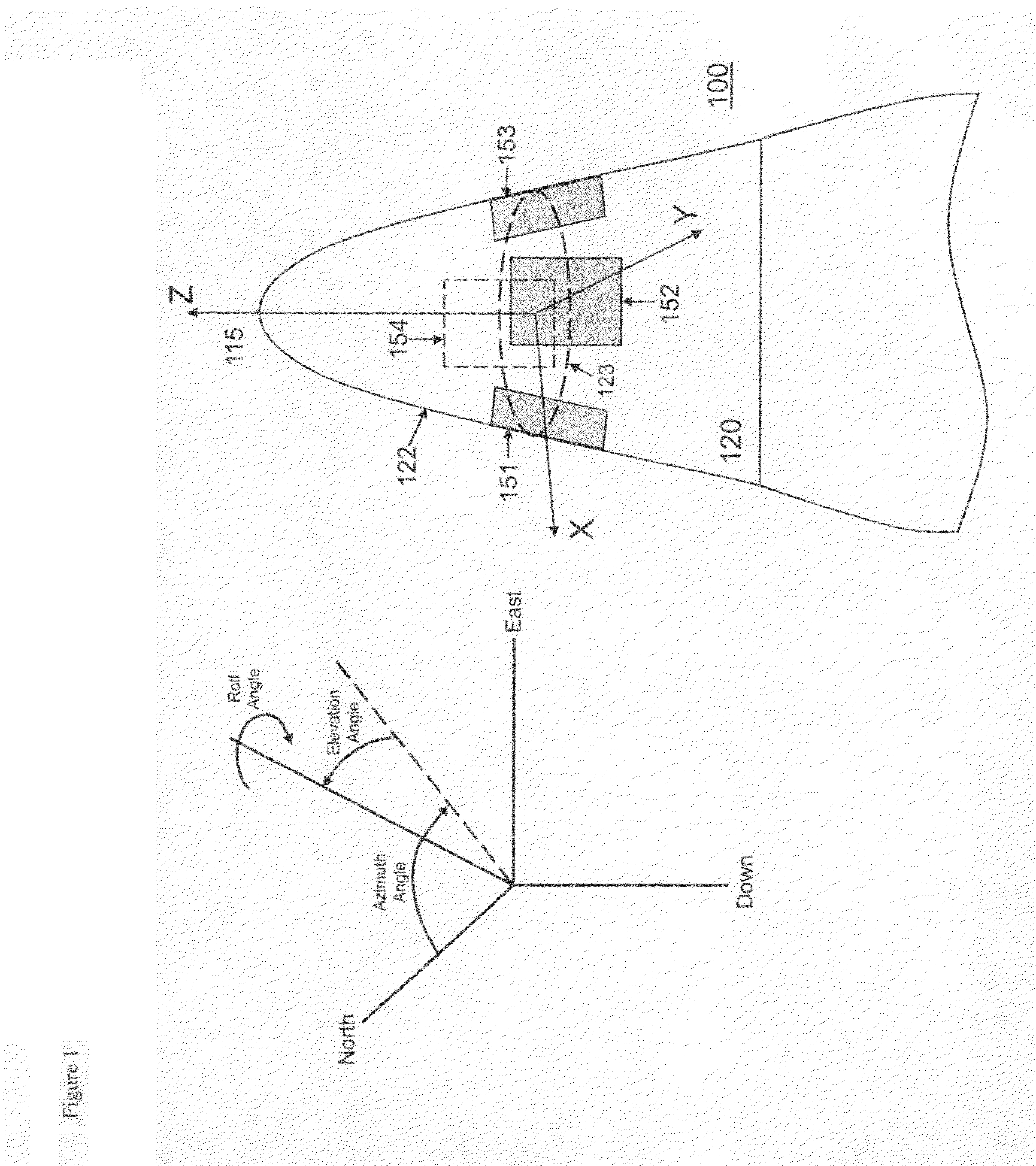
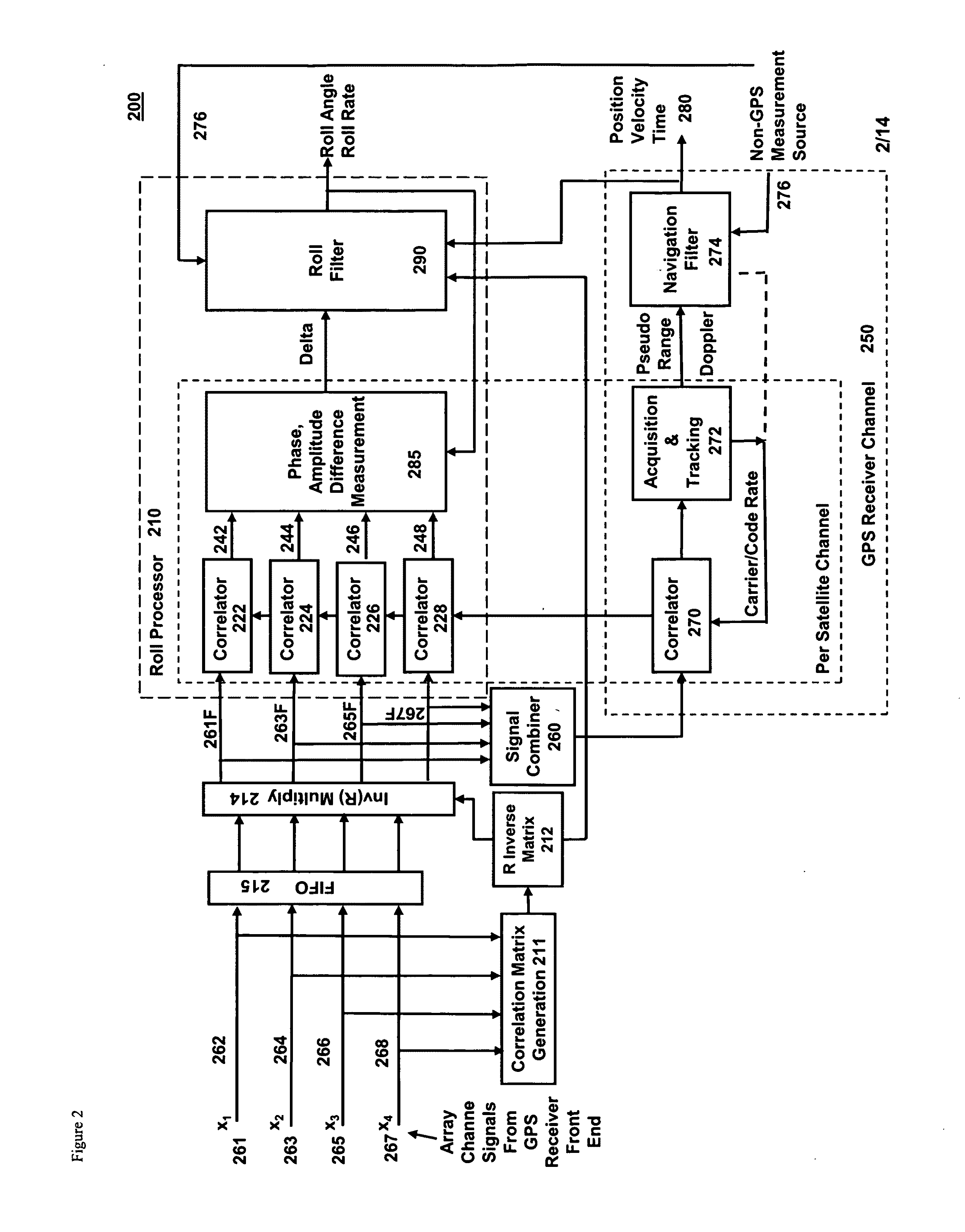
Gps-based measurement of roll rate and roll angle of spinning platforms
A system and method for determining the roll rate and roll angle of a spinning platform, using the measured phase differences between the GPS satellite signals received on two or more antennas. The measured phase differences and the navigation solution from a GPS receiver are processed in a Kalman filter to obtain the desired information. Data from non-GPS measurement sources is optionally provided to update the navigation solution. Although of wide applicability, the invention is uniquely suited to the measurement of roll rates and roll angles of fast spinning platforms with small baselines, in which the antennas are separated from each other by distances that are a fraction of the GPS signal wavelength.
Owner:MAYFLOWER COMM CO INC
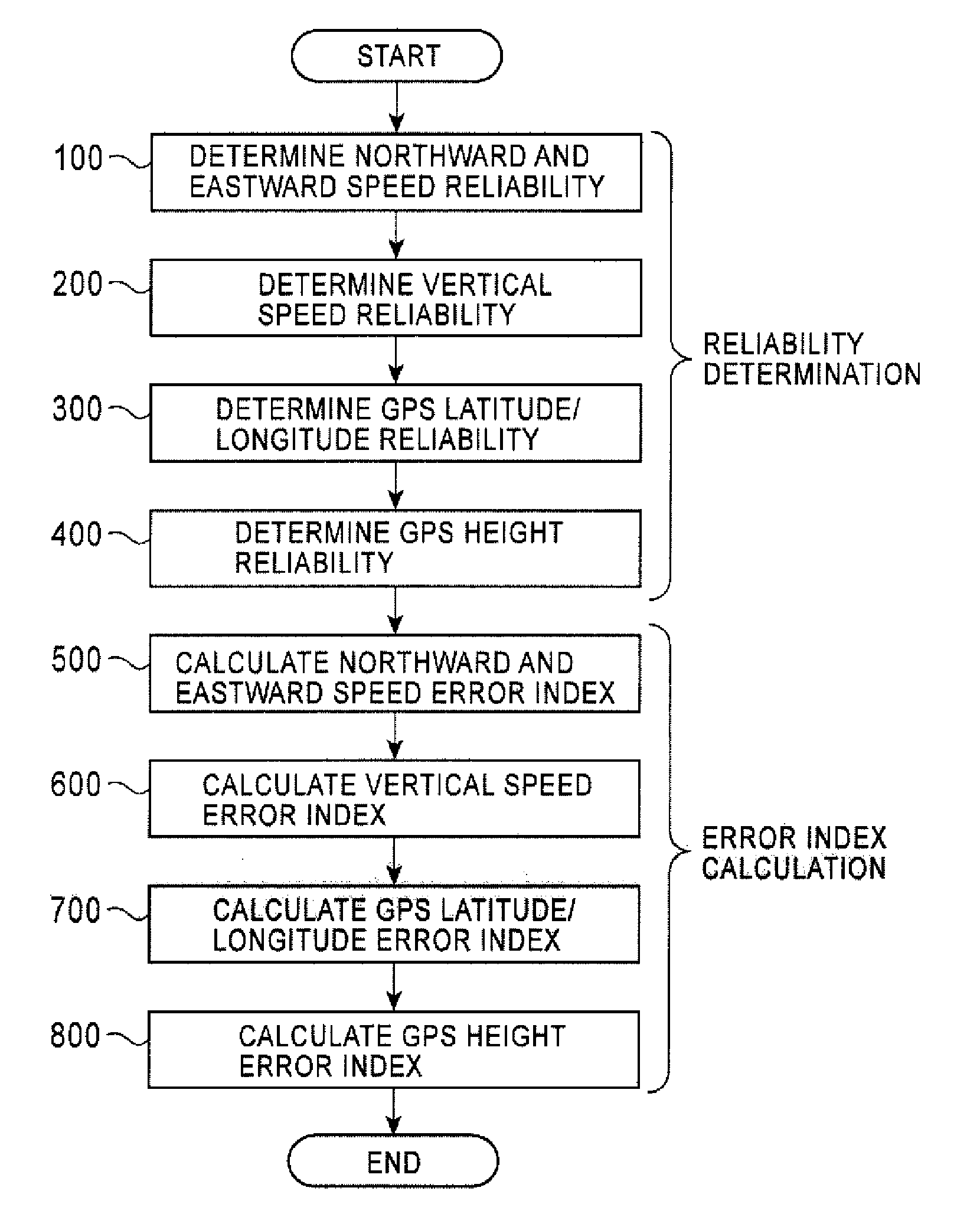
Position Sensing Device And Method
ActiveUS20090018772A1High positioning accuracyDecreasing degree of contributionRoad vehicles traffic controlPosition fixationGps measurementDependability
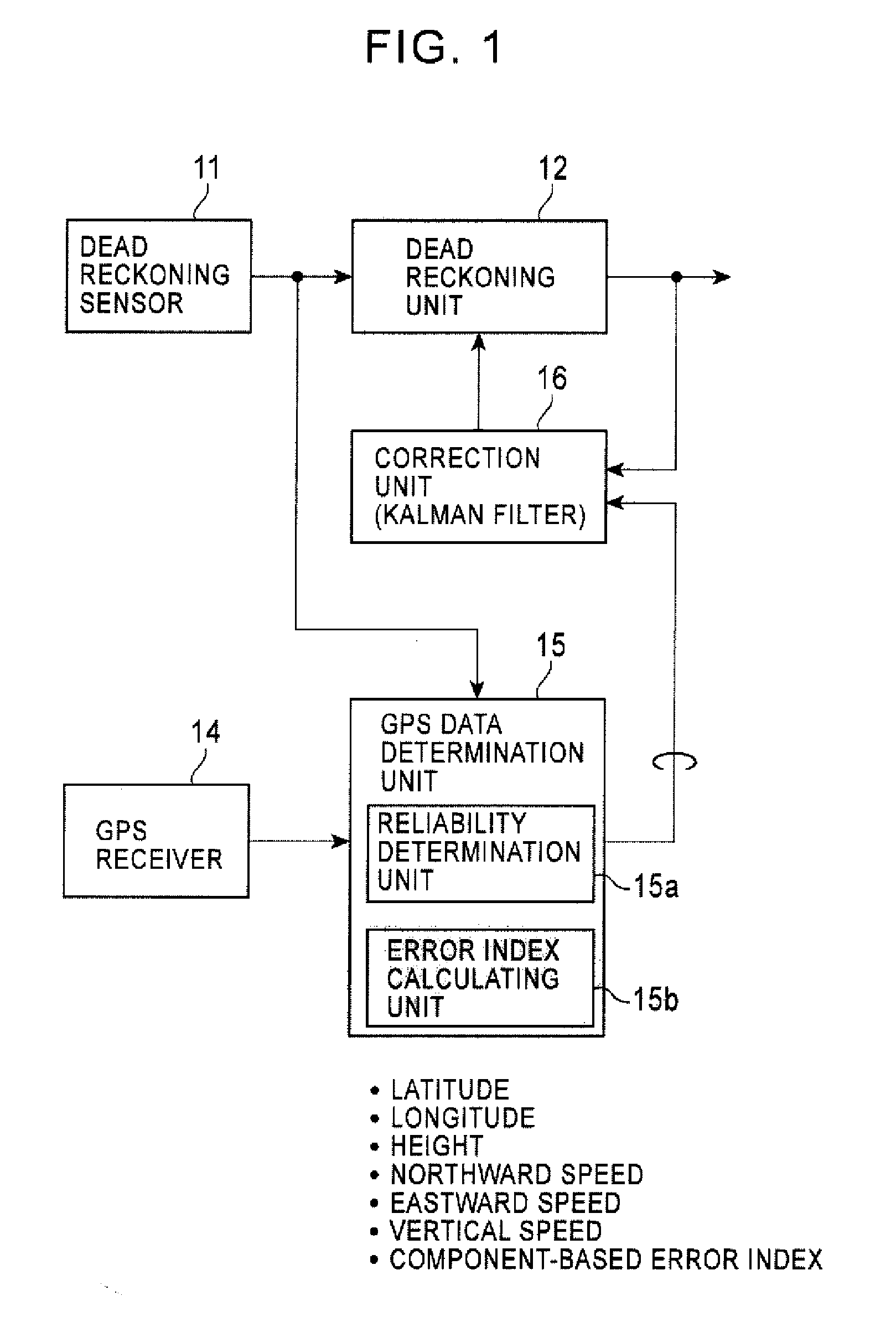
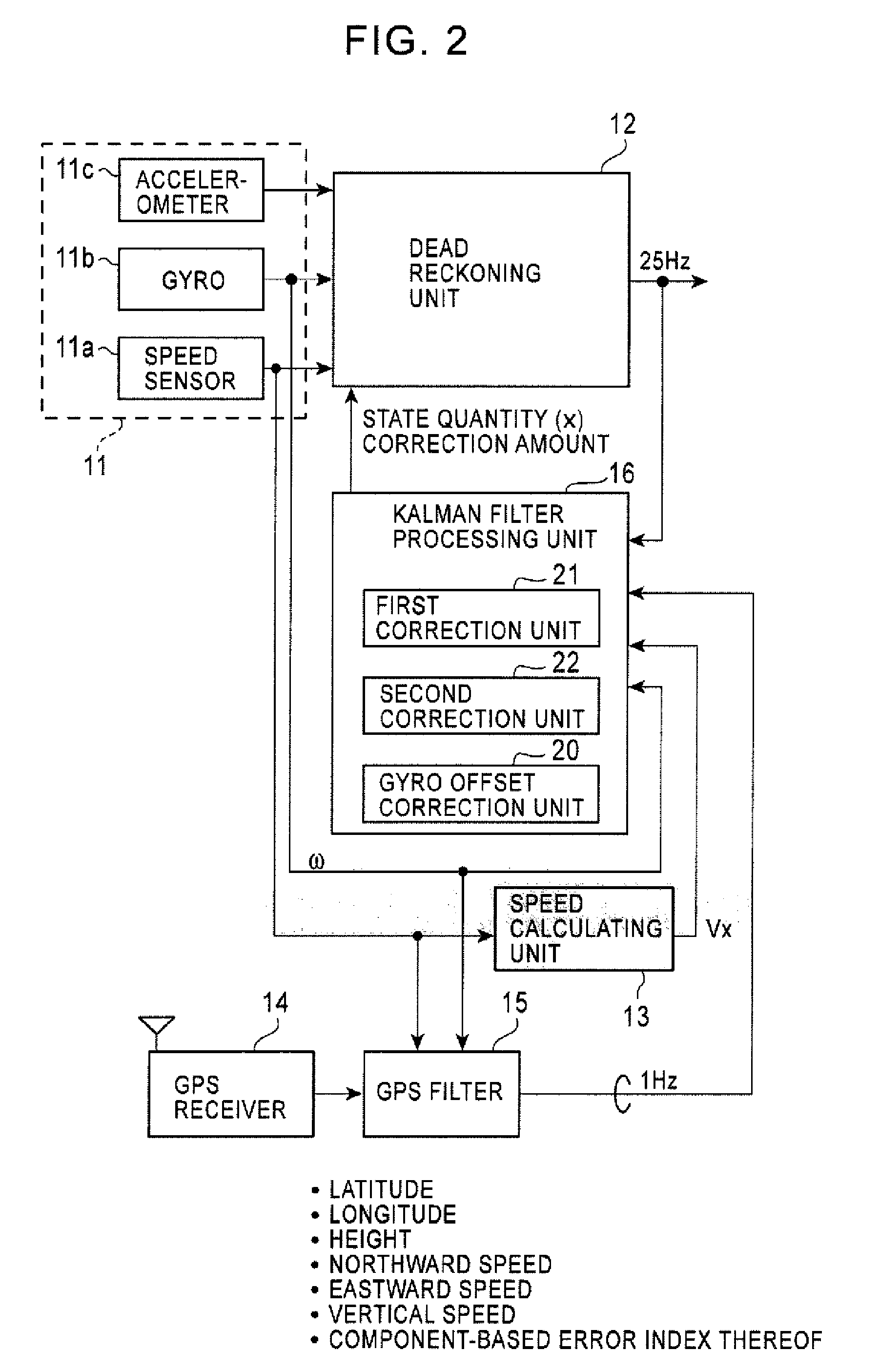
A position sensing device and method are provided for executing correction processing based on a reliability and error index of each component of GPS output data to increase positioning accuracy. Correction processing is performed to correct a position determination result obtained through dead reckoning, and a vehicle speed, a pitch angle, and a sensor mounting angle used in position determination executed through dead reckoning in a measurement period of GPS in accordance with direction-specific positional components and speed components of a vehicle, which are measured with GPS to determine a reliability of each of the direction-specific positional components and speed components of the vehicle and calculate an error index of a component determined to be a reliable component, to set the degree of contribution of a measurement component determined to be unreliable to correction processing to zero or almost zero, and to reduce the degree of contribution of a measurement component determined to be reliable to correction processing in accordance with a value of the error index.
Owner:ALPINE ELECTRONICS INC
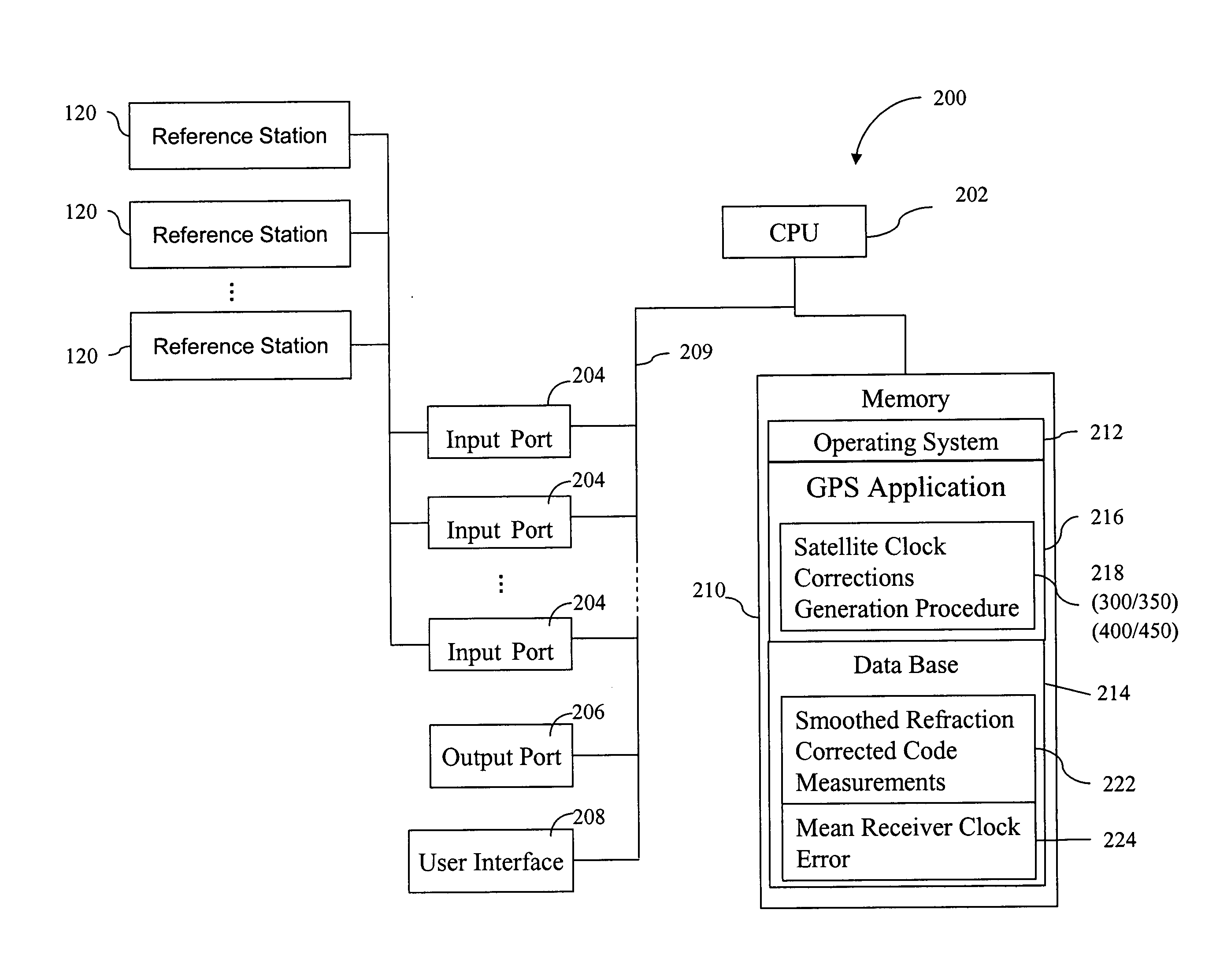
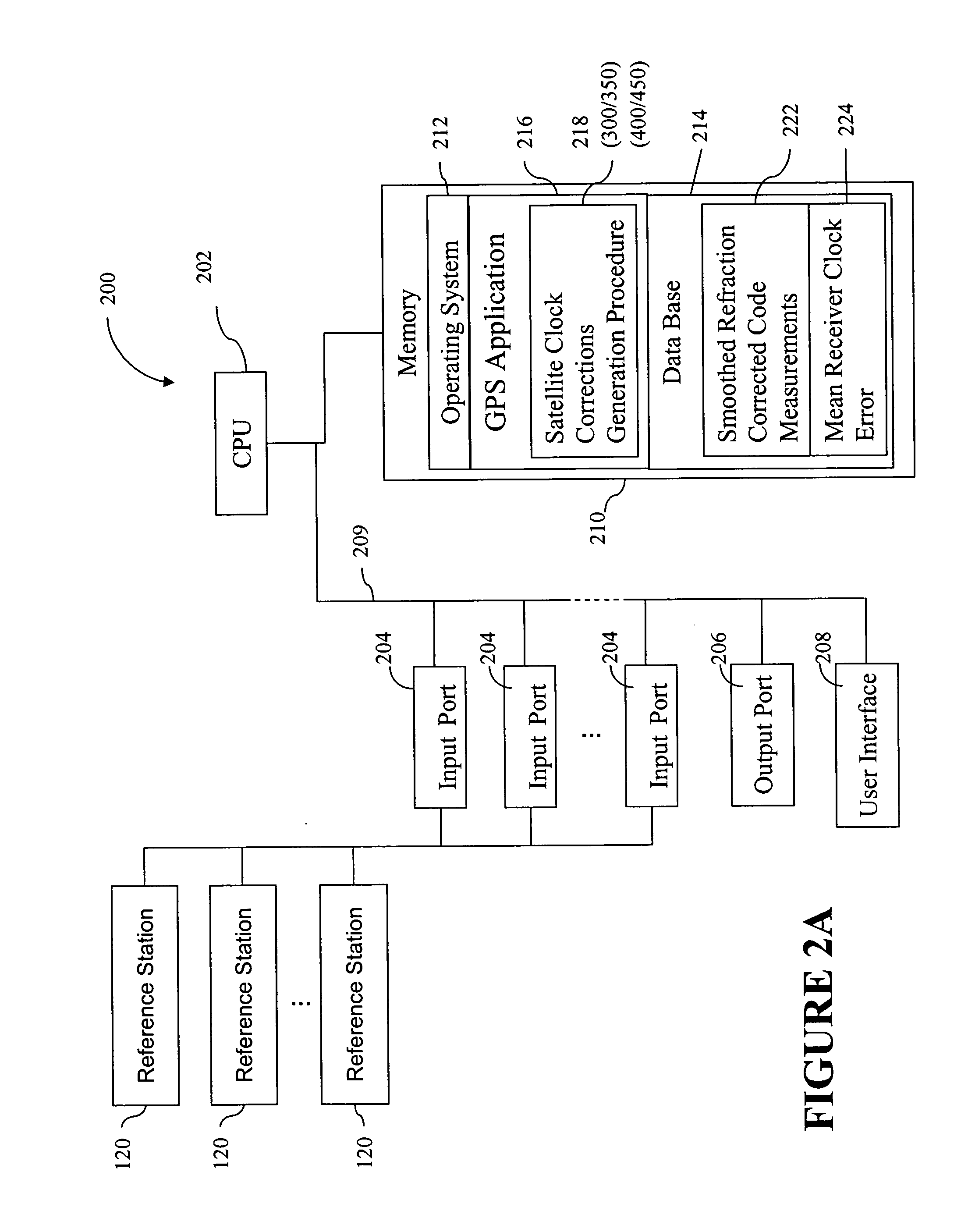
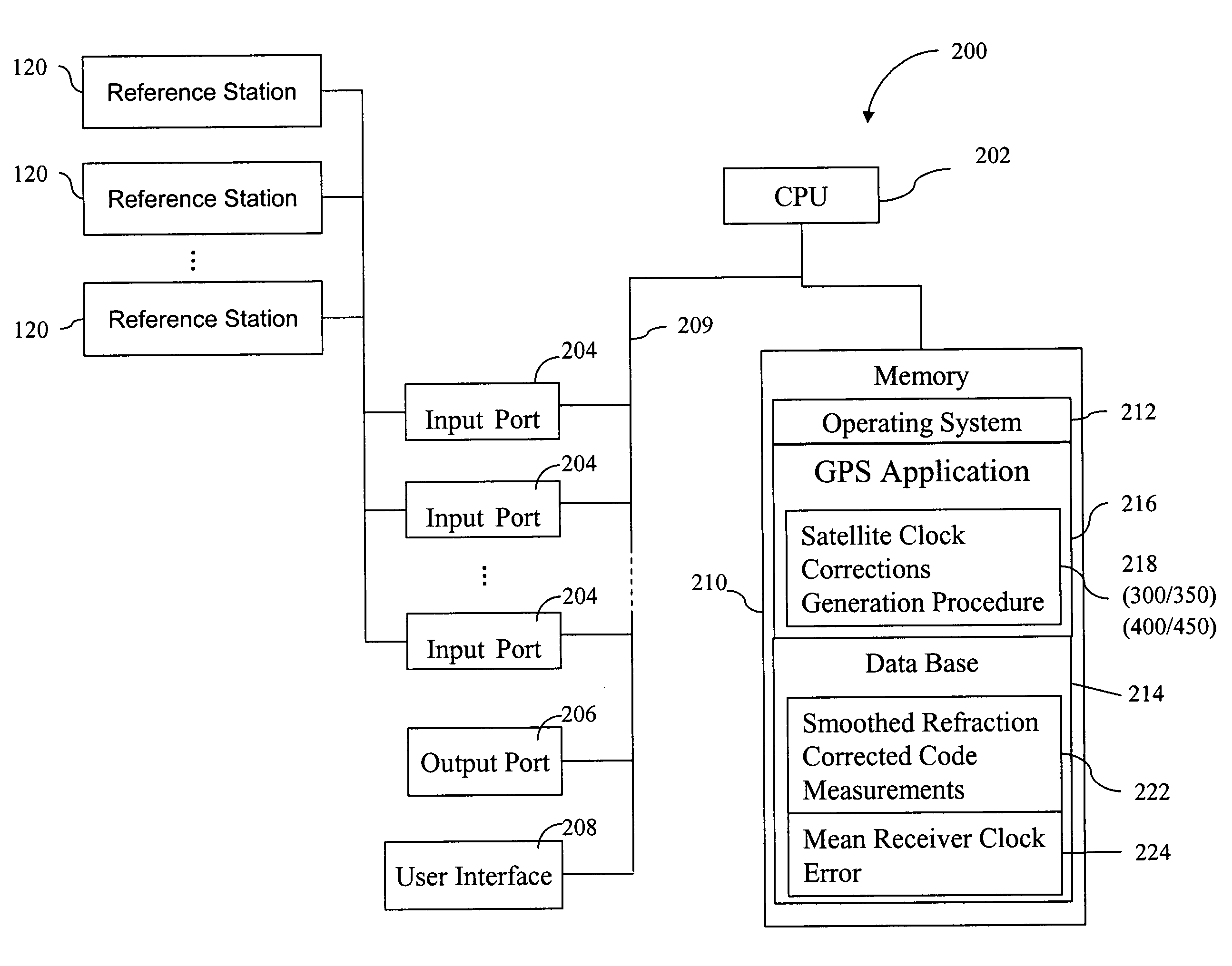
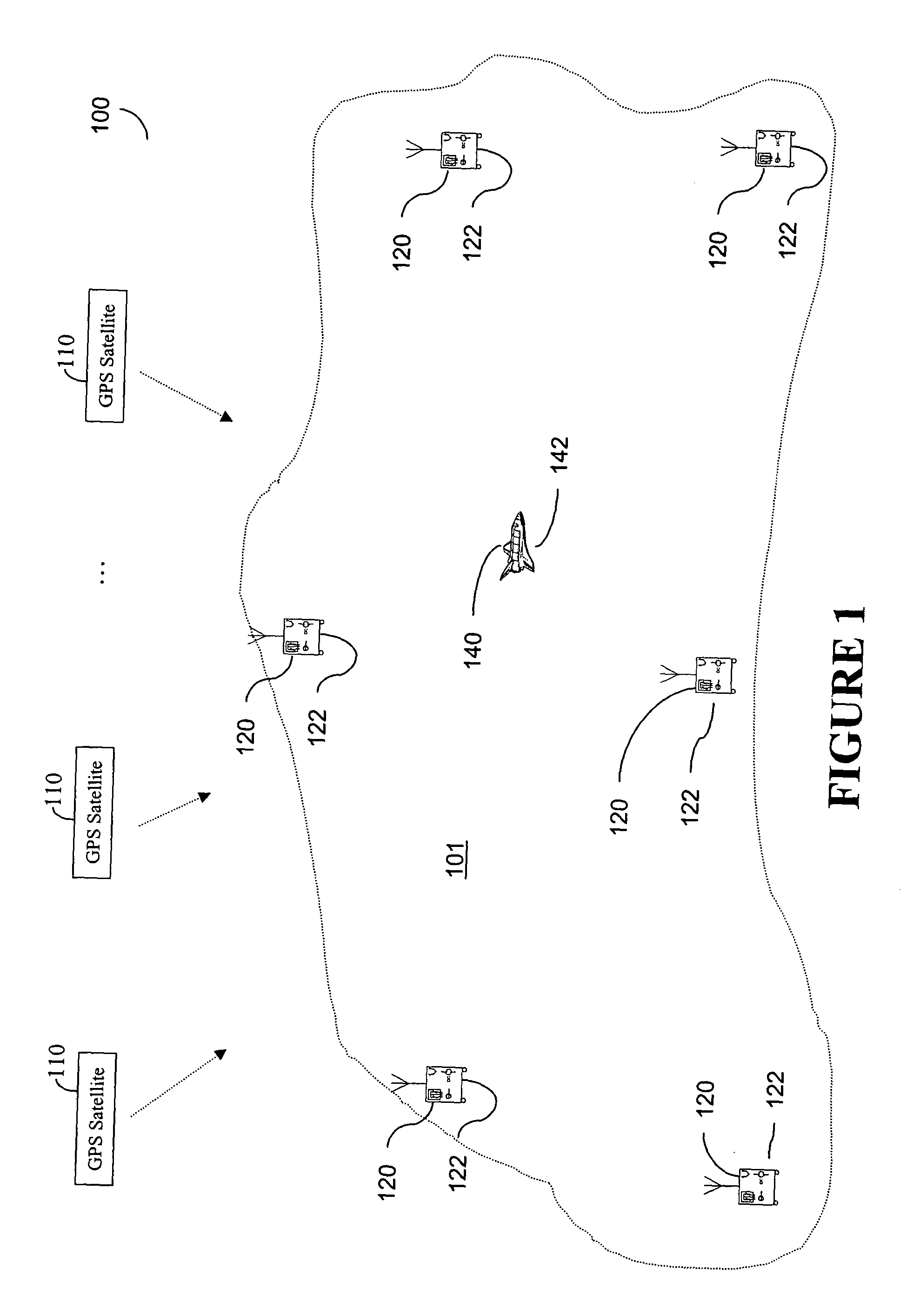
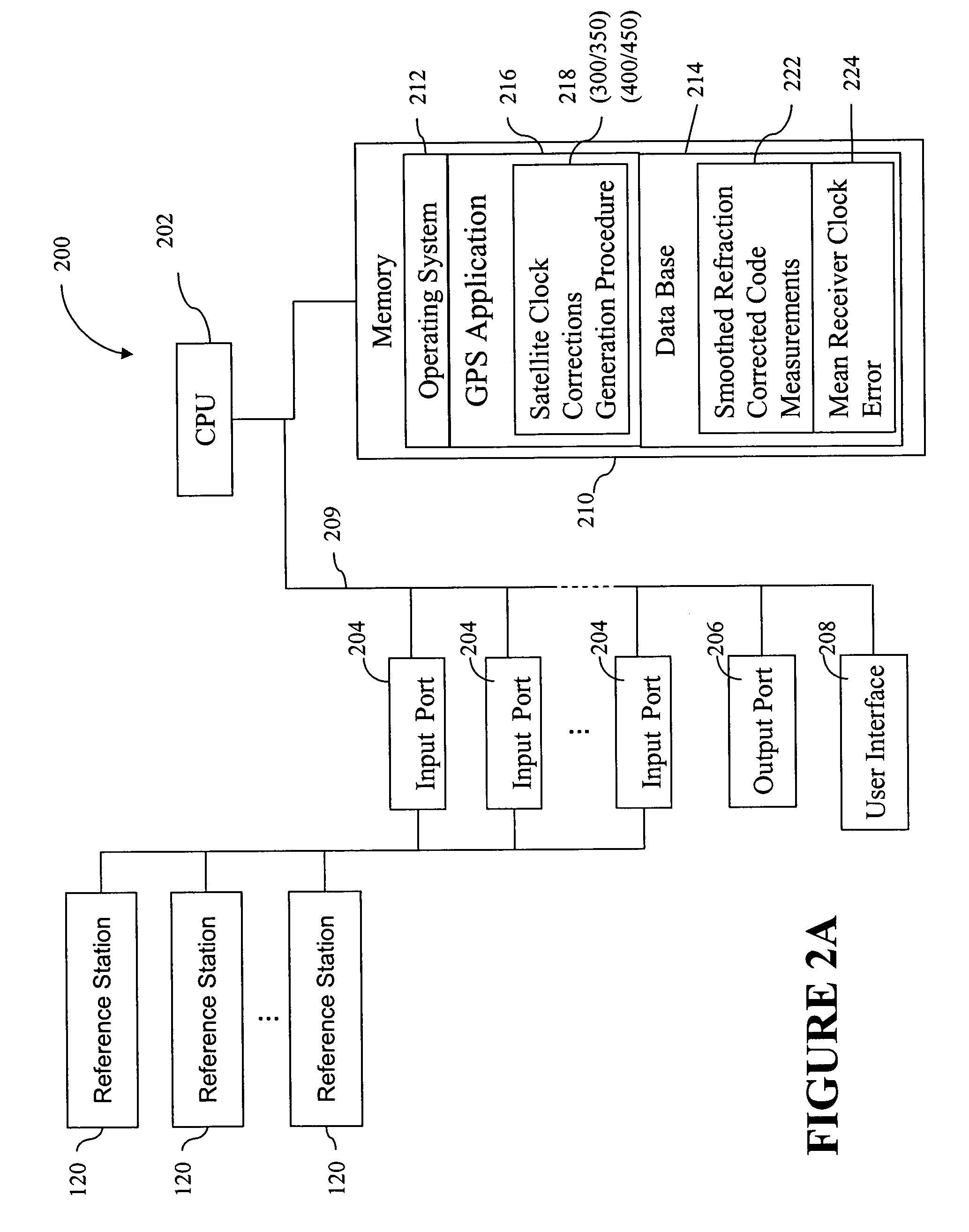
Method for generating clock corrections for a wide-area or global differential GPS system
InactiveUS20050024263A1Easy accessCancel noisePosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingDual frequencyGps measurement
A method for generating satellite clock corrections for a WADGPS network computers satellite clock corrections after removing other substantial error components. Errors caused by the ionosphere refraction effects are removed from GPS measurements taken at reference stations using dual-frequency GPS measurements. The multipath noise are removed by smoothing of GPS pseudorange code measurements with carrier-phase measurements. The tropospheric refraction effect can be largely removed by modeling, and if desired, can be improved by the use of small stochastic adjustments included in the computation of the clock correction. After removing the above error factors, satellite clock corrections are computed for individual reference stations, and an average clock correction is formed for each of a plurality of satellites by taking an average or weighted average of the satellite clock corrections over reference stations to which the satellite is visible.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Methods and apparatus for facilitating the determination of GPS location information for a mobile station without disrupting communications of a voice call
Methods and apparatus for facilitating the determination of Global Positioning System (GPS) location information for a mobile station without disrupting communications of a voice call (e.g. a 911 emergency call). In one illustrative example, the mobile station causes GPS navigational-type data to be regularly or periodically received and stored in memory prior to the voice call. At some point in time, the mobile station receives a voice call request to initiate the voice call. In response, the mobile station derives GPS assistance data based on the GPS navigational-type data. The mobile station then causes a GPS fix to be performed using the GPS assistance data, to thereby obtain GPS measurement data. Thereafter, the mobile station causes the voice call to be established and maintained through the wireless network. The GPS measurement data is transmitted to a location server for calculating the location of the mobile station.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
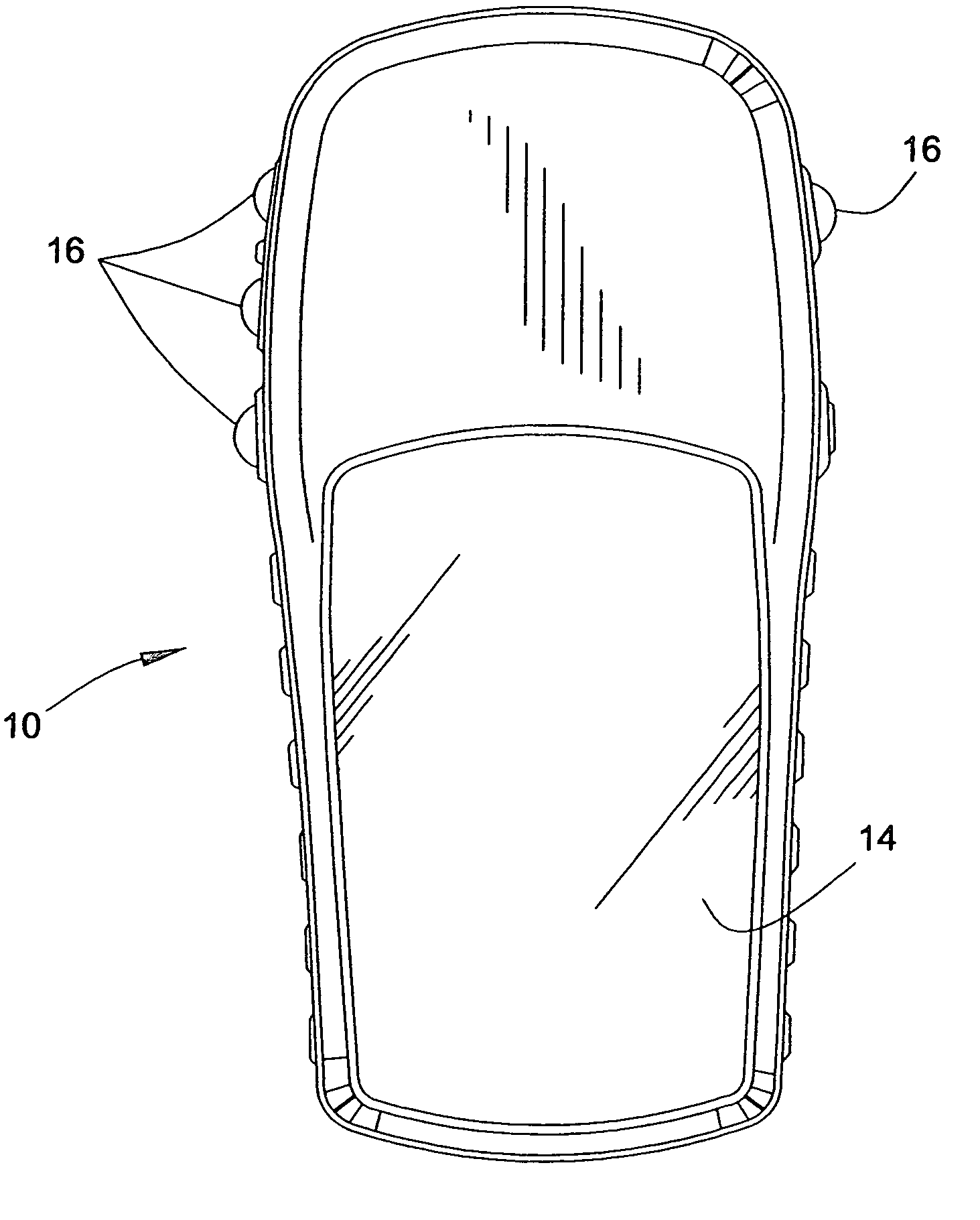
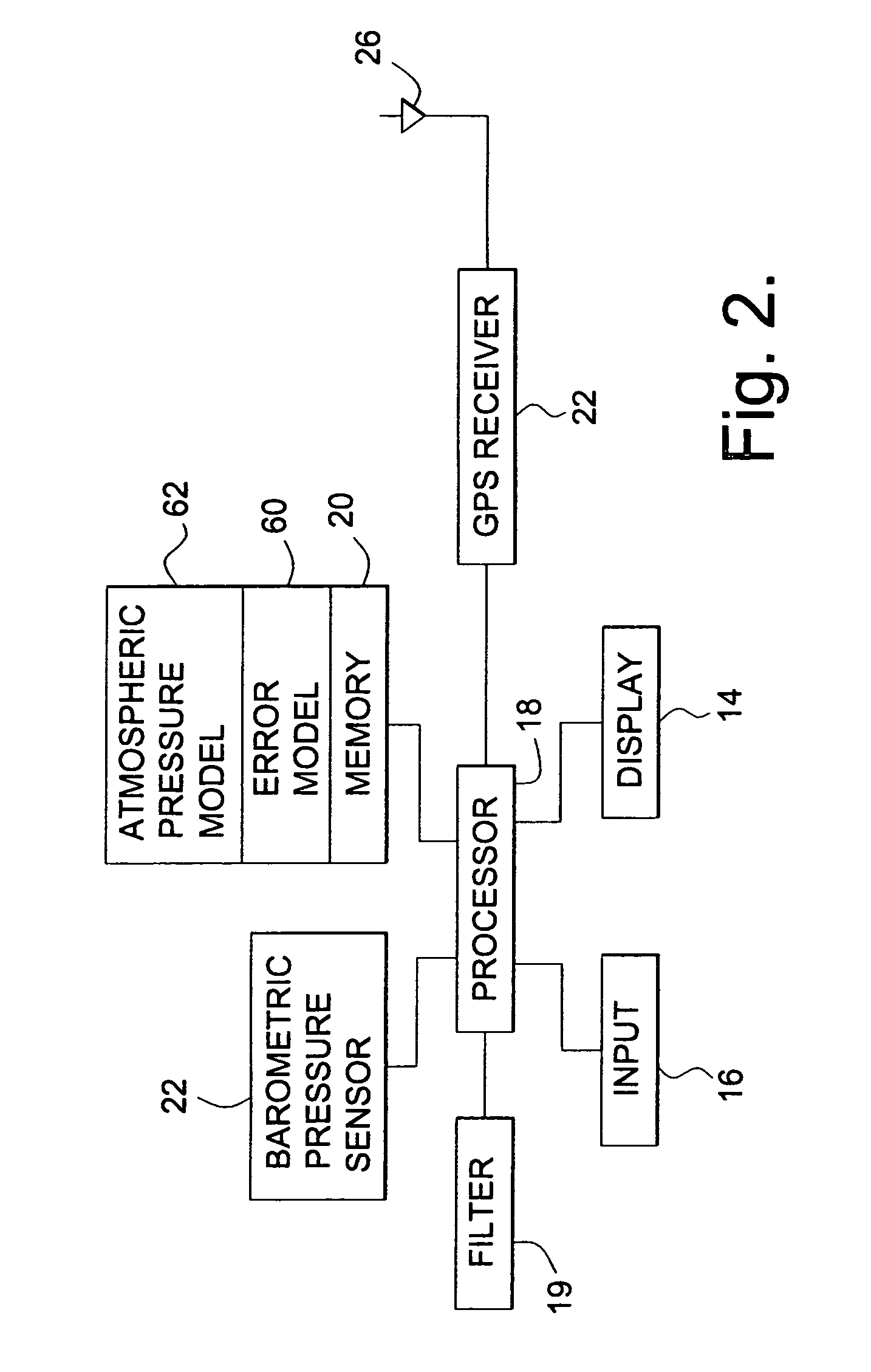
Method and apparatus for calculating altitude based on barometric and GPS measurements
A navigation device and a method of calibrating the same are provided. The device includes a barometric pressure sensor and a GPS receiver. A processor calculates barometric and GPS derived altitudes and, based on a difference therebetween, corrects barometer altitude readings that would otherwise include drift errors. The processor uses a filter, such as a state feedback loop, to determine correction factors. The state feedback loop is adjustable to operate with different time constants. An error drift model is empirically determined and used to set the time constant. The time constant may be adjusted during operation based on a relation between the barometer correction quantity and an uncertainty in the vertical component of the GPS derived altitude. The method includes updating and recalibrating an atmospheric pressure model used to derive altitudes from the output of the barometric pressure sensor.
Owner:GARMIN
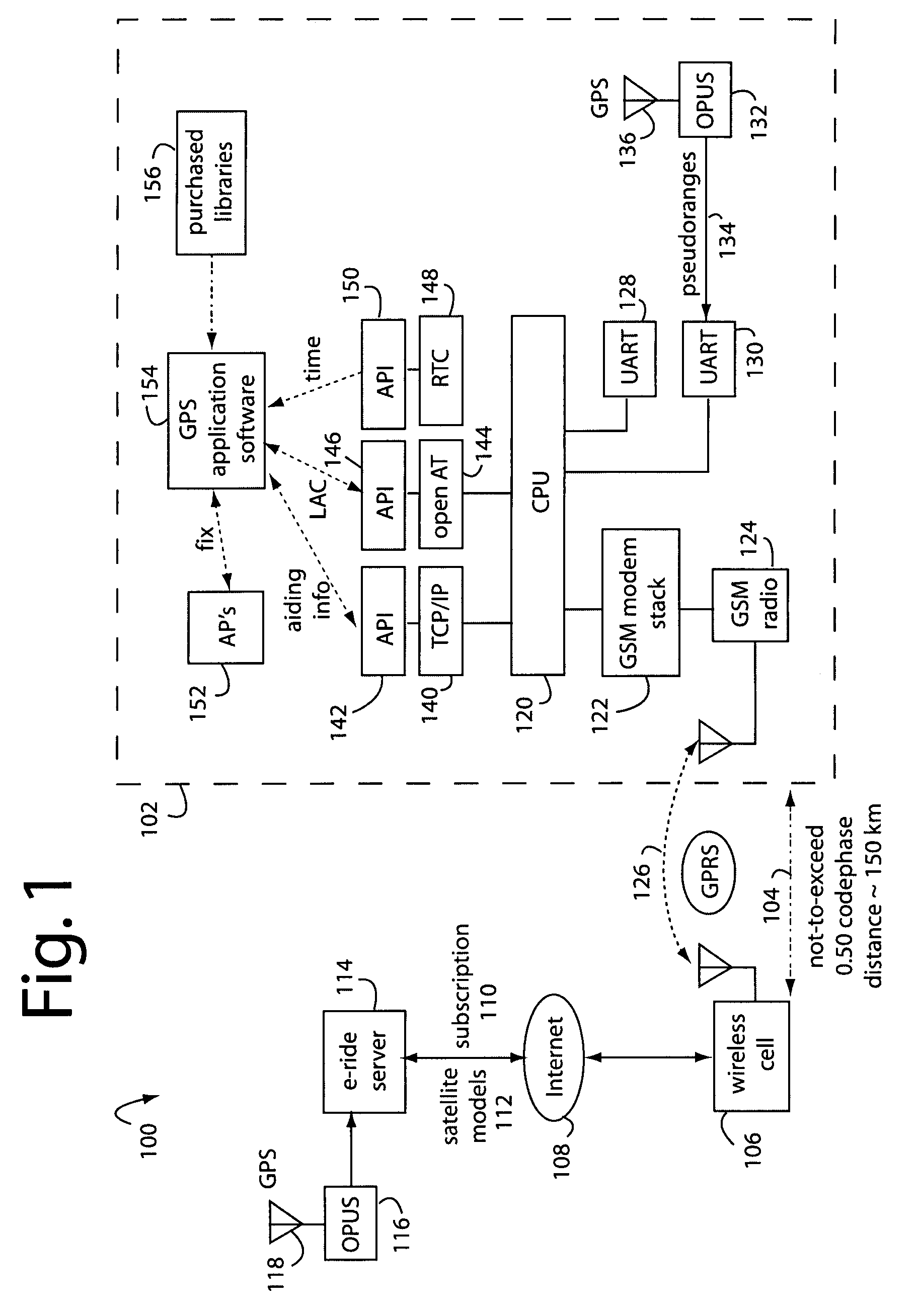
Wireless CPU GPS application
InactiveUS7463188B1Easy to migrateDirection finders using radio wavesSatellite radio beaconingSupporting systemGps measurement
A wireless handheld GPS-enabled device and supporting system comprises a wireless CPU that functions as a host processor, a GPS chipset to provide GPS measurements, and a GPS application hosted by the wireless CPU. Other applications are also hosted by the wireless CPU and are provided with position solutions from the GPS application. The GPS application calls for GPS aiding information from an Internet server via a TCP / IP socket provided by a GPRS link supported by the wireless CPU. Location area identifier (LAI) and “breadcrumb” information are provided to the GPS application so it can skip having to make a z-count determination during initialization.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
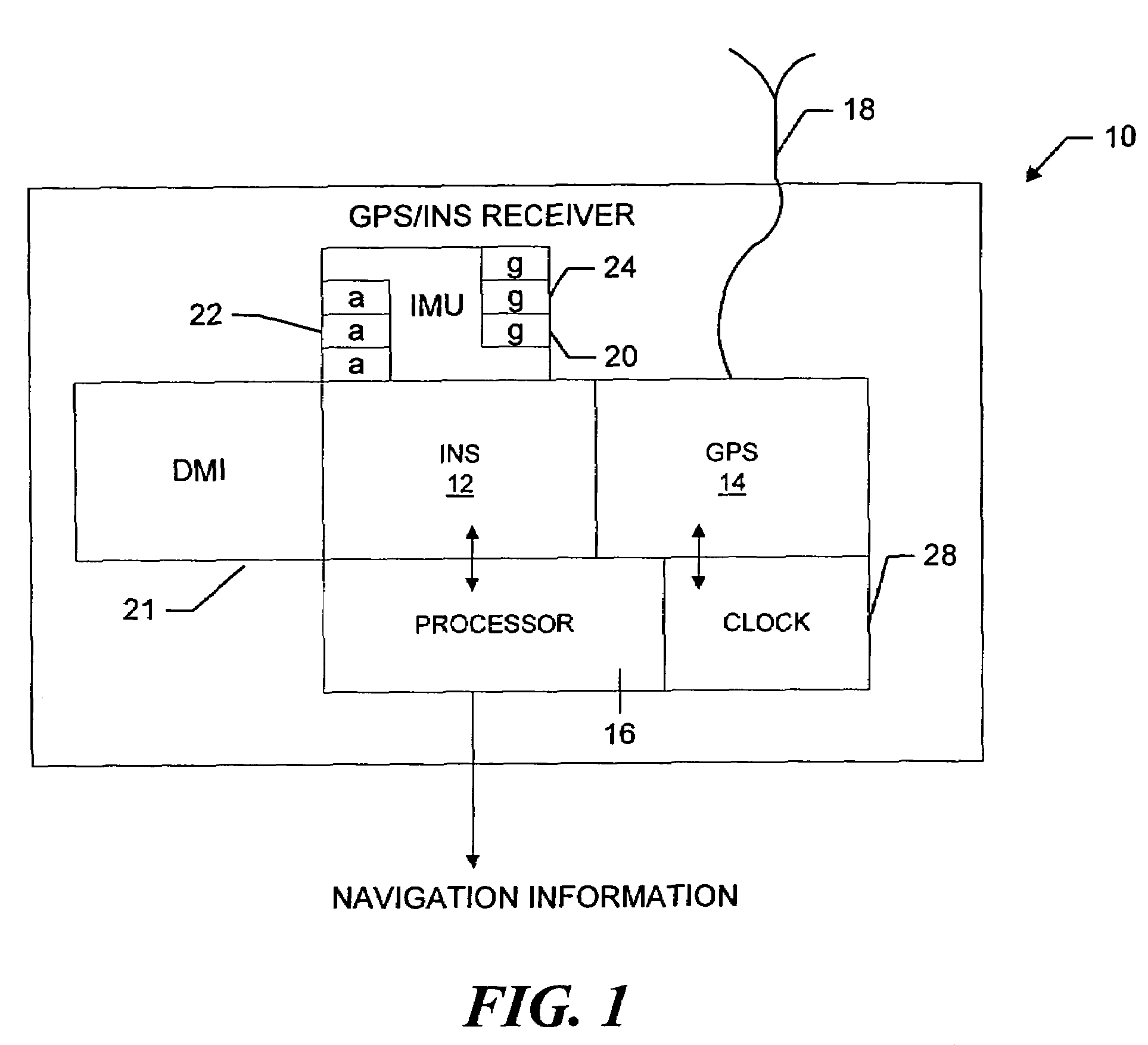
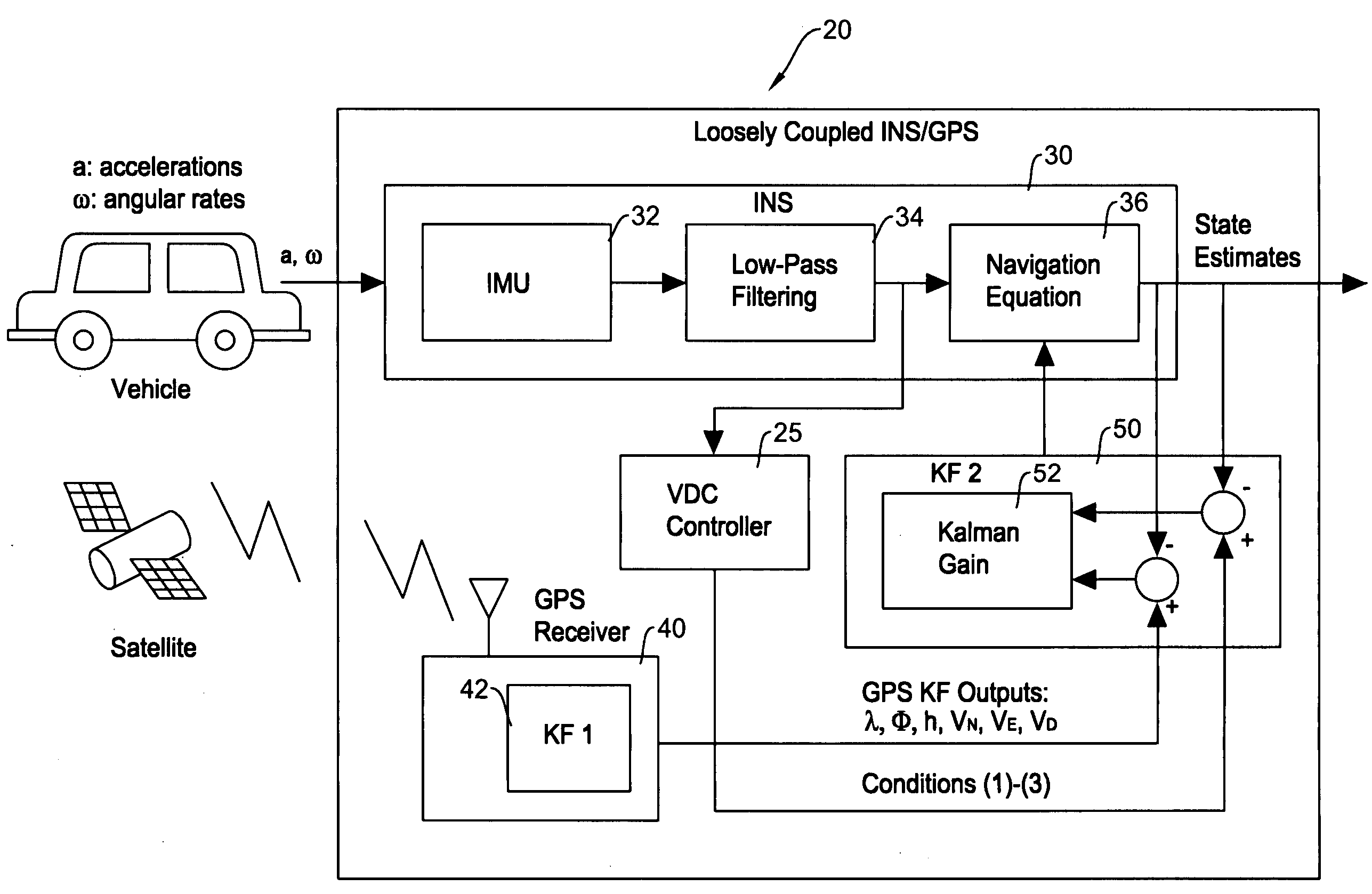
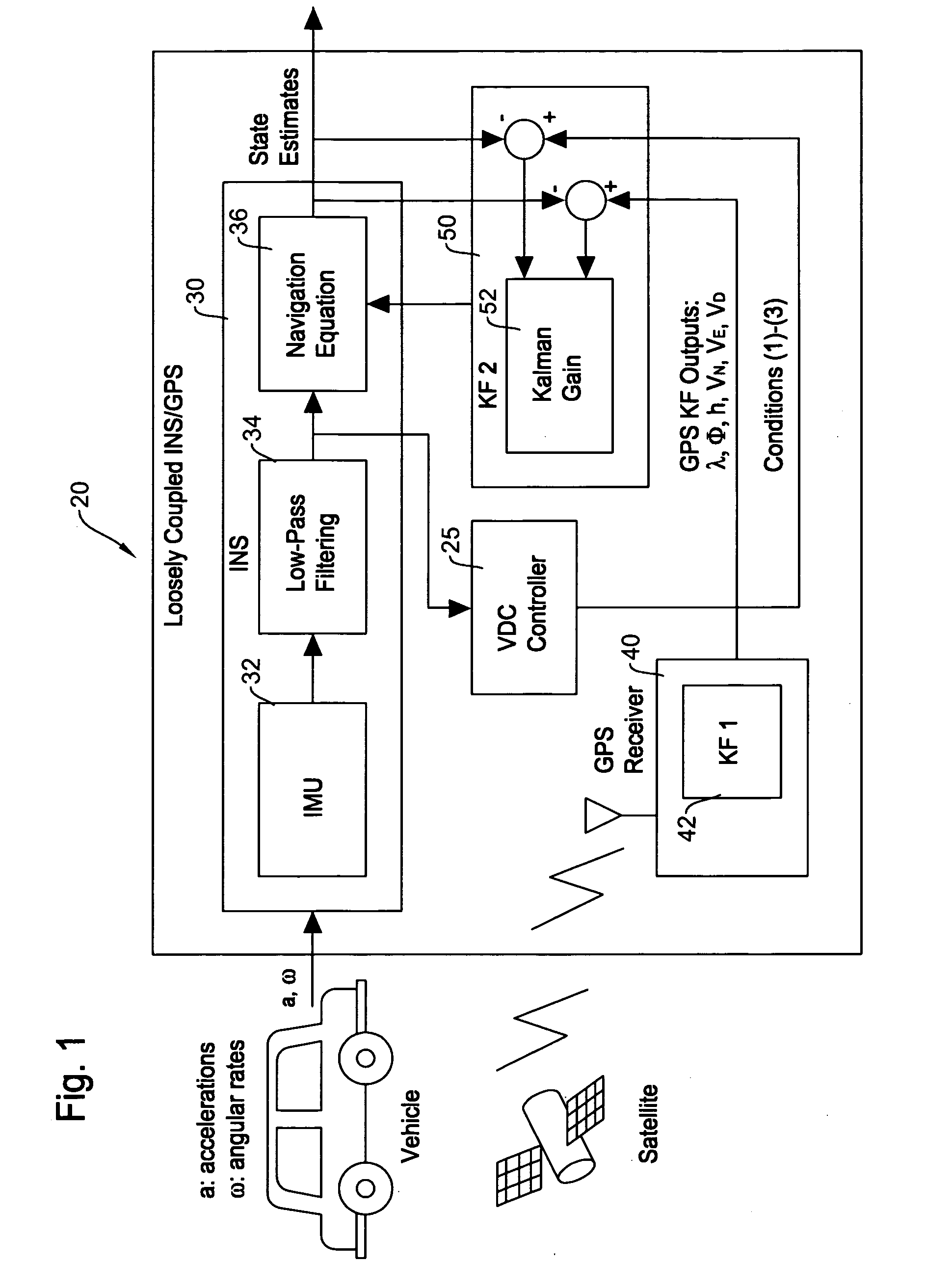
Vehicle dynamics conditioning method on MEMS based integrated INS/GPS vehicle navigation system
InactiveUS20080071476A1Low costAmount of accumulated smallPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsVehicle dynamicsEngineering
A method of compensating performance of low-cost MEMS (microelectro mechanical systems) inertial sensors in an integrated INS / GPS navigation system for automotive application is disclosed. The proposed method includes velocity and inertial sensor output conditions featured in ground vehicle dynamics. Using the conventional Kalman filter based INS / GPS system, implementation of the prescribed conditions in the present invention additionally to the GPS measurements shows accurate motion tracking even when GPS signal dropouts last for more than 2 minutes. Another aspect of the disclosure is an integrated INS / GPS navigation system which utilizes MEMS based inertial sensors for maintaining high position tracking accuracy even when a GPS signal is lost or unavailable for a long period of time by incorporating the predefined vehicle dynamics conditions when calculating optimum estimates through the Kalman filtering process.
Owner:ALPINE ELECTRONICS INC
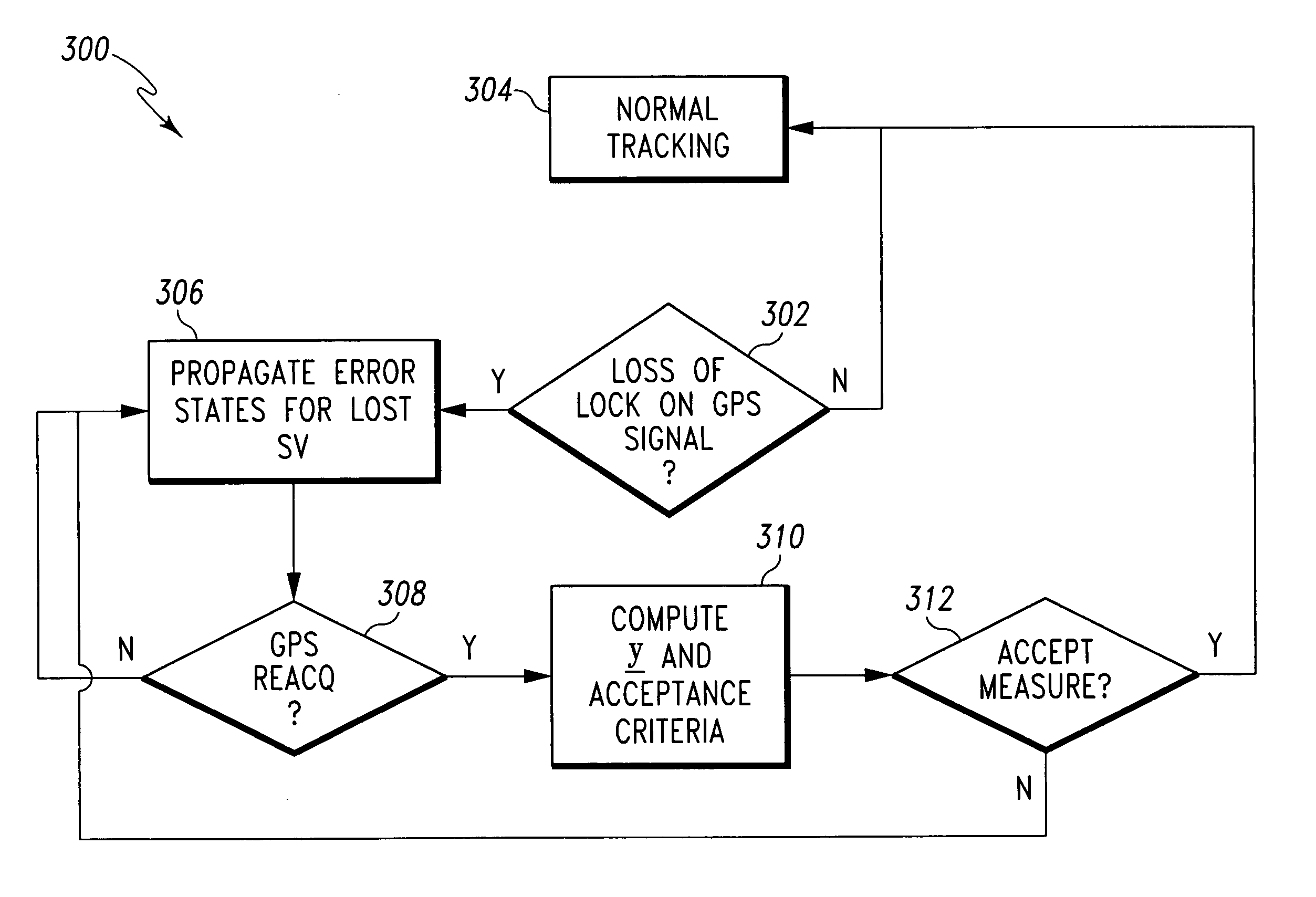
System and method for detecting false navigation signals
ActiveUS20070194984A1Improve trustPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingGps measurementKaiman filter
A system and method for detecting and excluding false GPS signals are disclosed, which predict a GPS measurement value with a high degree of confidence, compare the predicted value with measured values, and reject a false measurement based on the comparison results. As one example, a tightly coupled GPS / Inertial Navigation System (GPS / INS) is disclosed, which uses a Kalman filter for comparison of a predicted GPS measurement value with measured values (e.g., the residuals) to form the basis for the rejection of false measurements. This rejection is referred to as a chi-squared reject, and can be extended in time in order to apply the same test to a reacquired signal following the loss of an original validated GPS signal. The Kalman filter propagates the receiver's clock bias rate, and enables the system to predict the GPS measurements at the time of reacquisition. The residuals are compared to a limit defined by the uncertainties of the prediction and the measurement errors expected to be involved.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
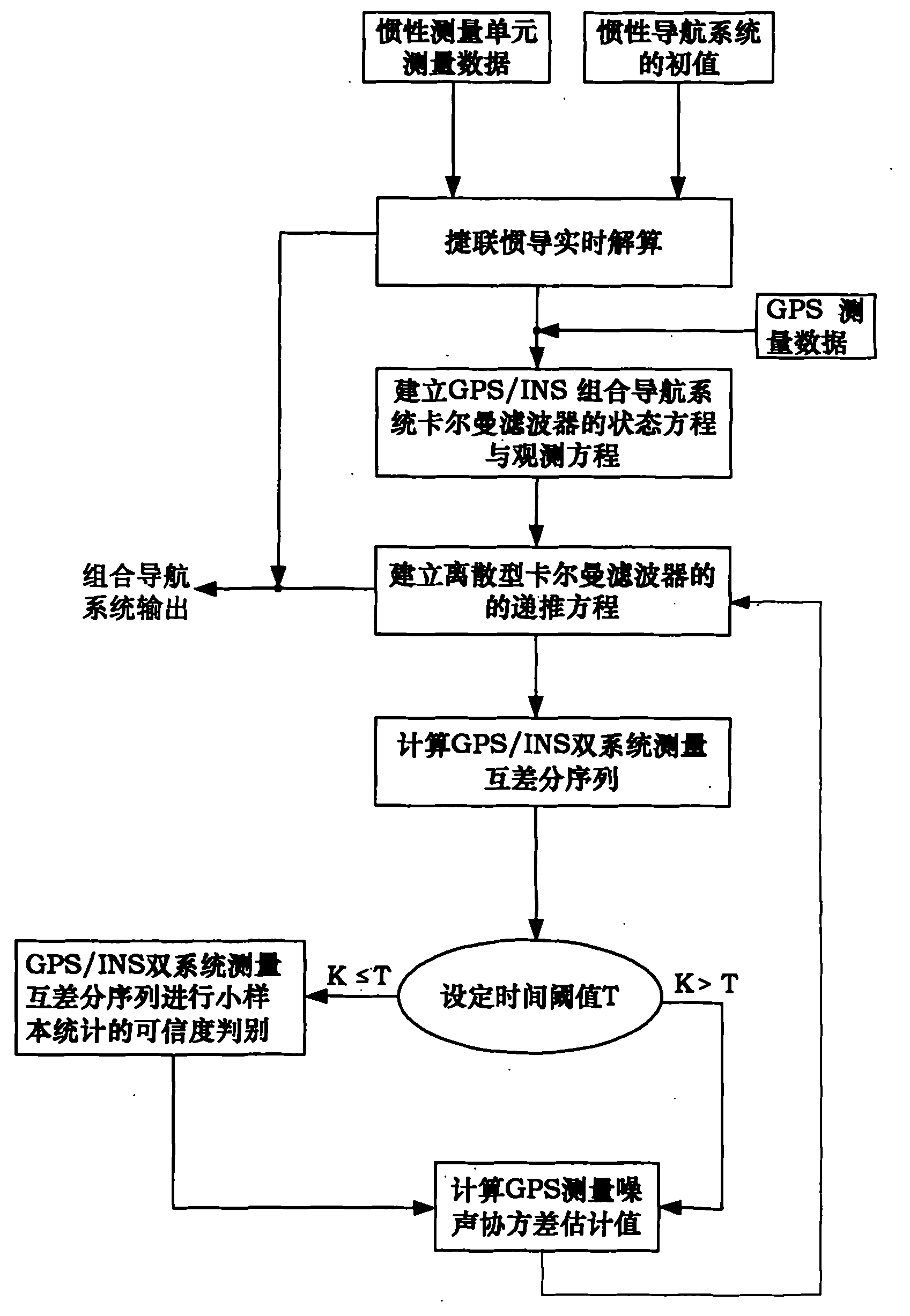
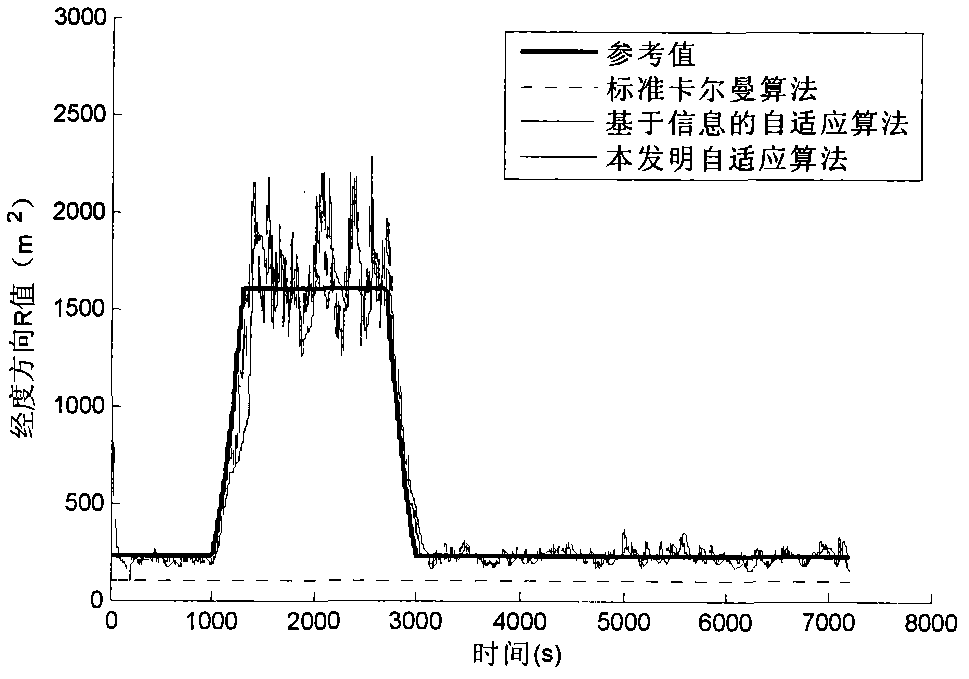
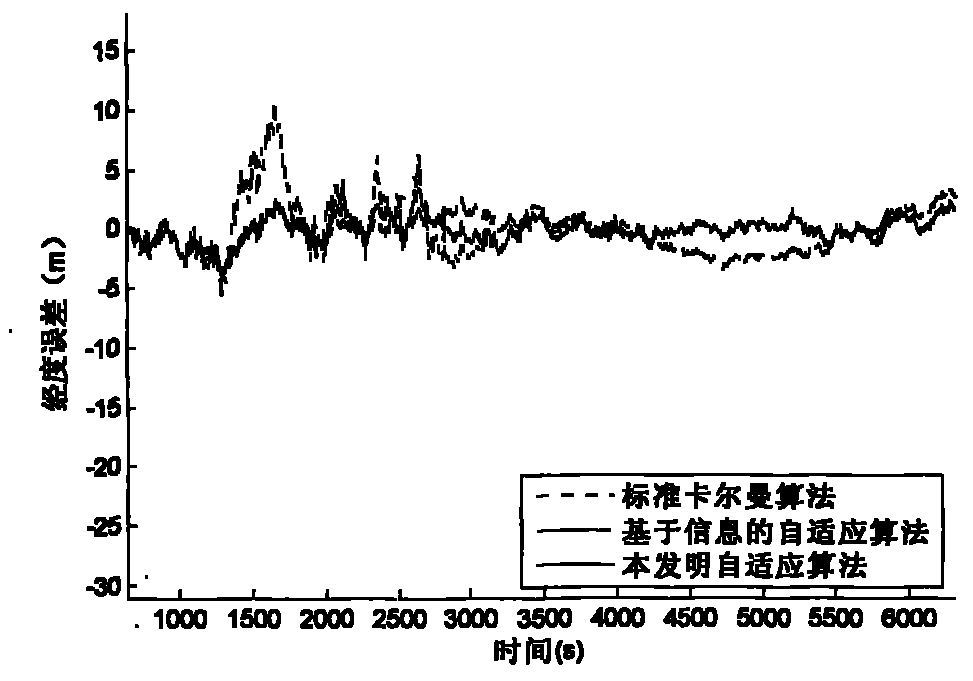
Self-adaptive filtering method based on different measuring characteristics of GPS (Global Positioning System)/INS (Inertial Navigation System) integrated navigation system
InactiveCN102096086ARealize real-time measurement statisticsImprove output accuracySatellite radio beaconingGps measurementFilter gain
The invention provides a self-adaptive filtering method based on the different measuring characteristics of a GPS (Global Positioning System) / INS (Inertial Navigation System) integrated navigation system, which comprises the following steps: using the data measured by an IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) and the initial data of an INS to carry out strapdown inertial navigation real-time computation; establishing an integrated filtering system equation of GPS / INS speed and positions; measuring a mutual difference sequence according to the GPS / INS dual systems; statistically calculating the estimated value of a GPS measuring noise covariance; and carrying out self-adaptive Kalman filtering computation. The self-adaptive filtering method provided by the invention realizes real-time tracking of GPS measuring noise and the self-adaptive adjustment of a filtering gain matrix, and enhances the positioning accuracy of the integrated navigation system.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for generating clock corrections for a wide-area or global differential GPS system
InactiveUS7117417B2Easy accessCancel noiseInstruments for road network navigationError preventionWide areaDual frequency
Owner:DEERE & CO
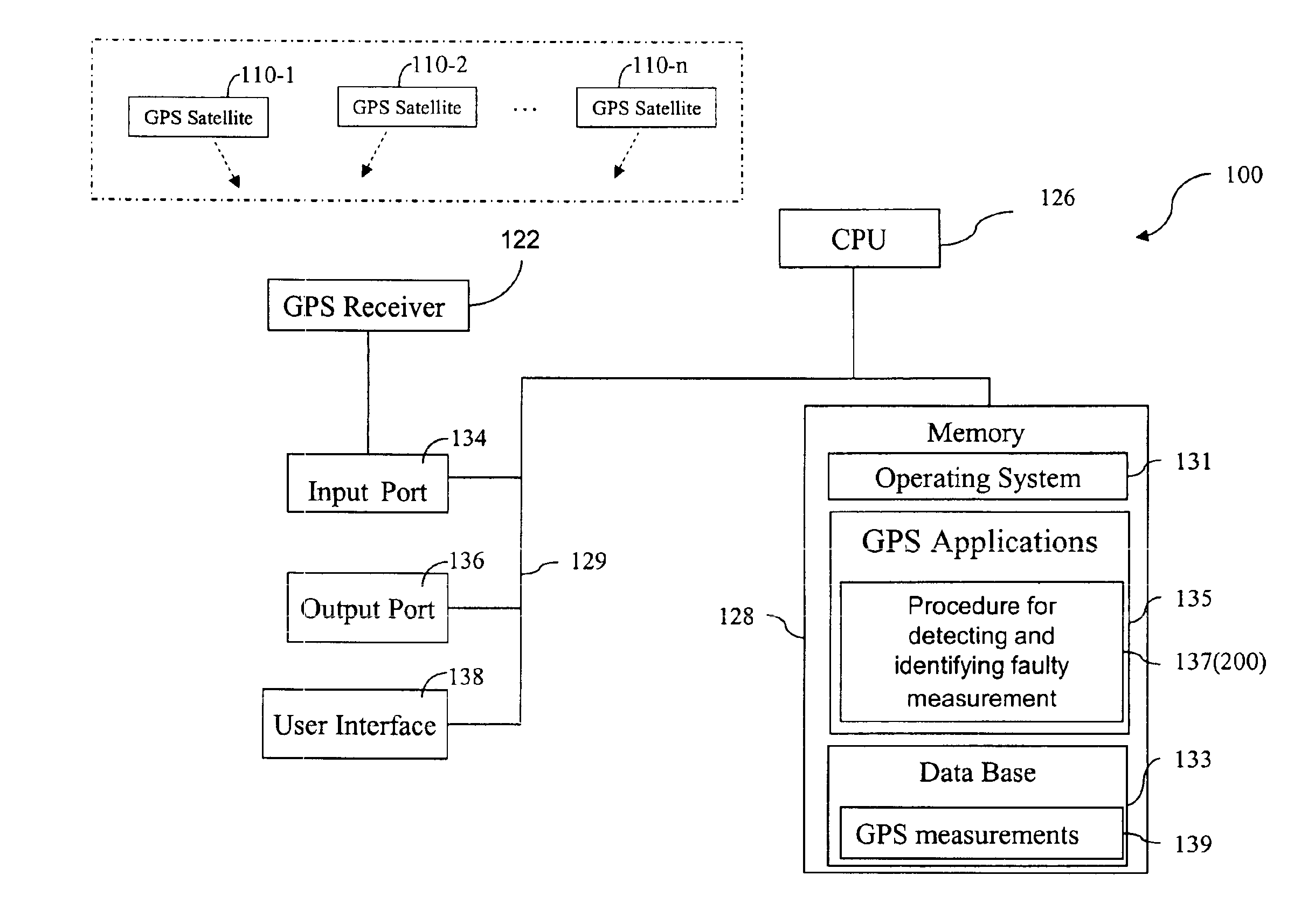
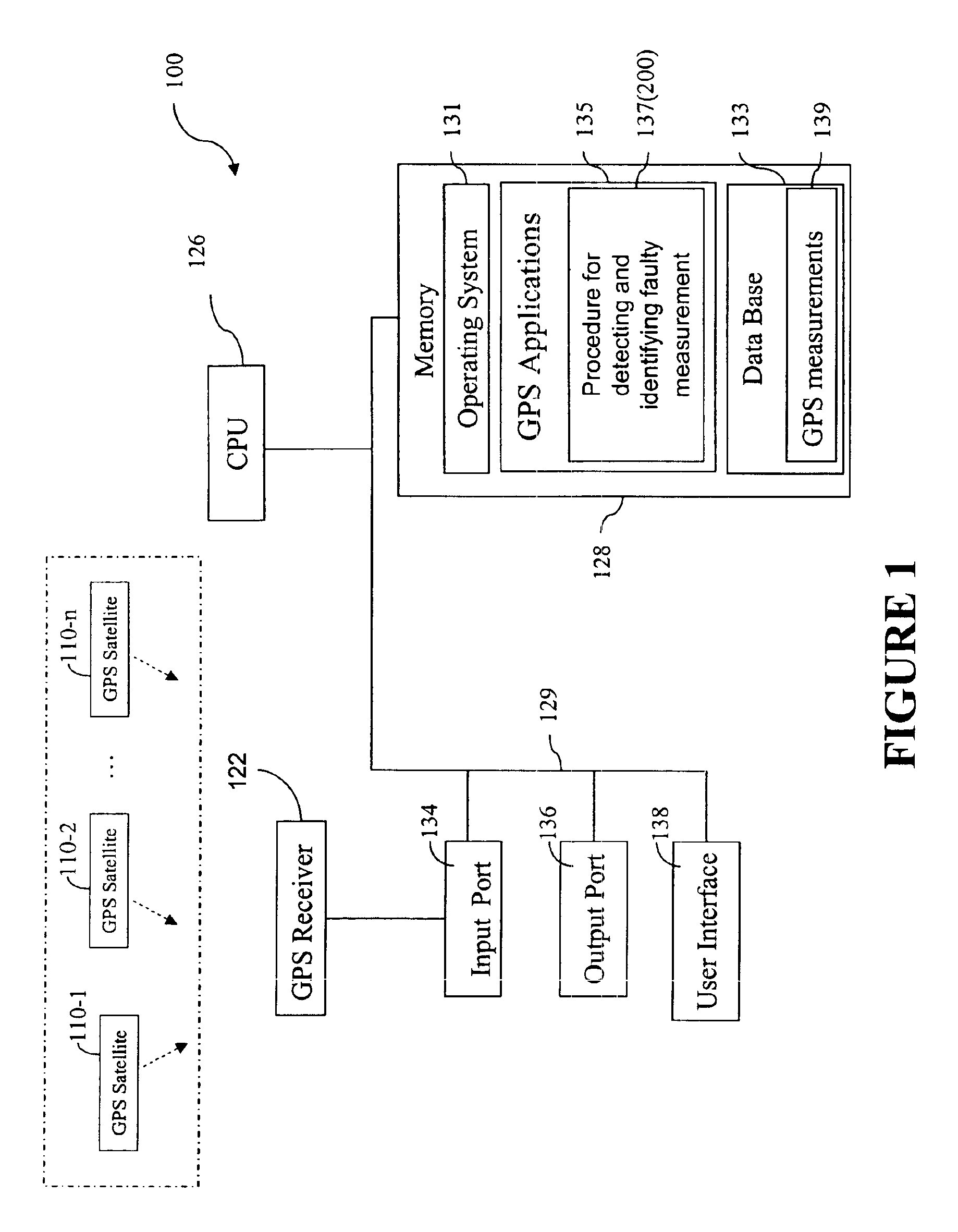
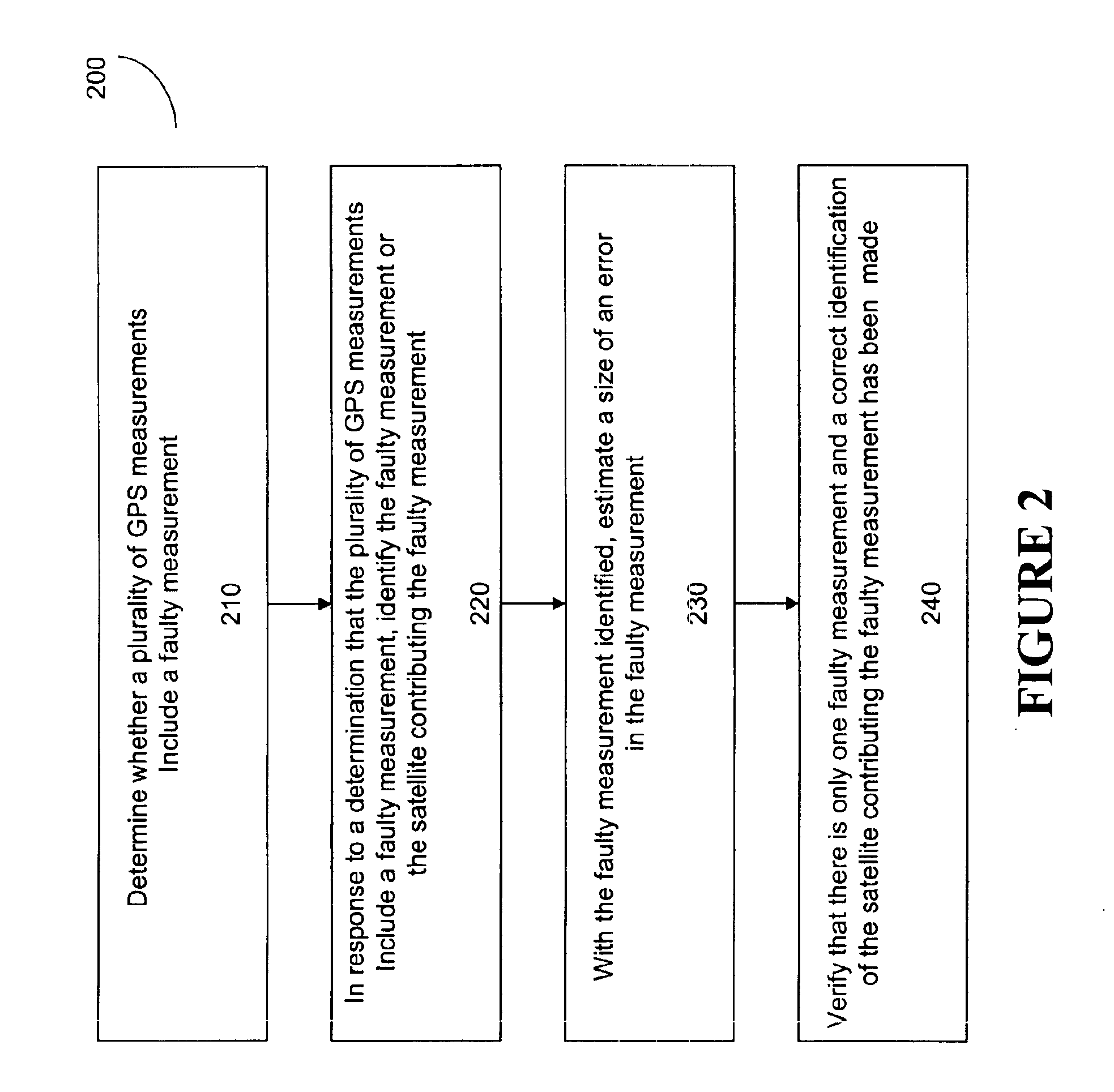
Method for receiver autonomous integrity monitoring and fault detection and elimination
A method for detecting and identifying a faulty measurement among a plurality of GPS measurements, obtained by a GPS receiver with respect to a plurality of satellites in view of the GPS receiver, determines whether the plurality of GPS measurements include a faulty measurement. In response to a determination that the plurality of GPS measurements include a faulty measurement, the method identifies a satellite contributing the faulty measurement by computing a correlation value associated with each of the plurality of satellites, and selecting a satellite associated with a highest correlation value as the satellite contributing the faulty measurement.
Owner:DEERE & CO
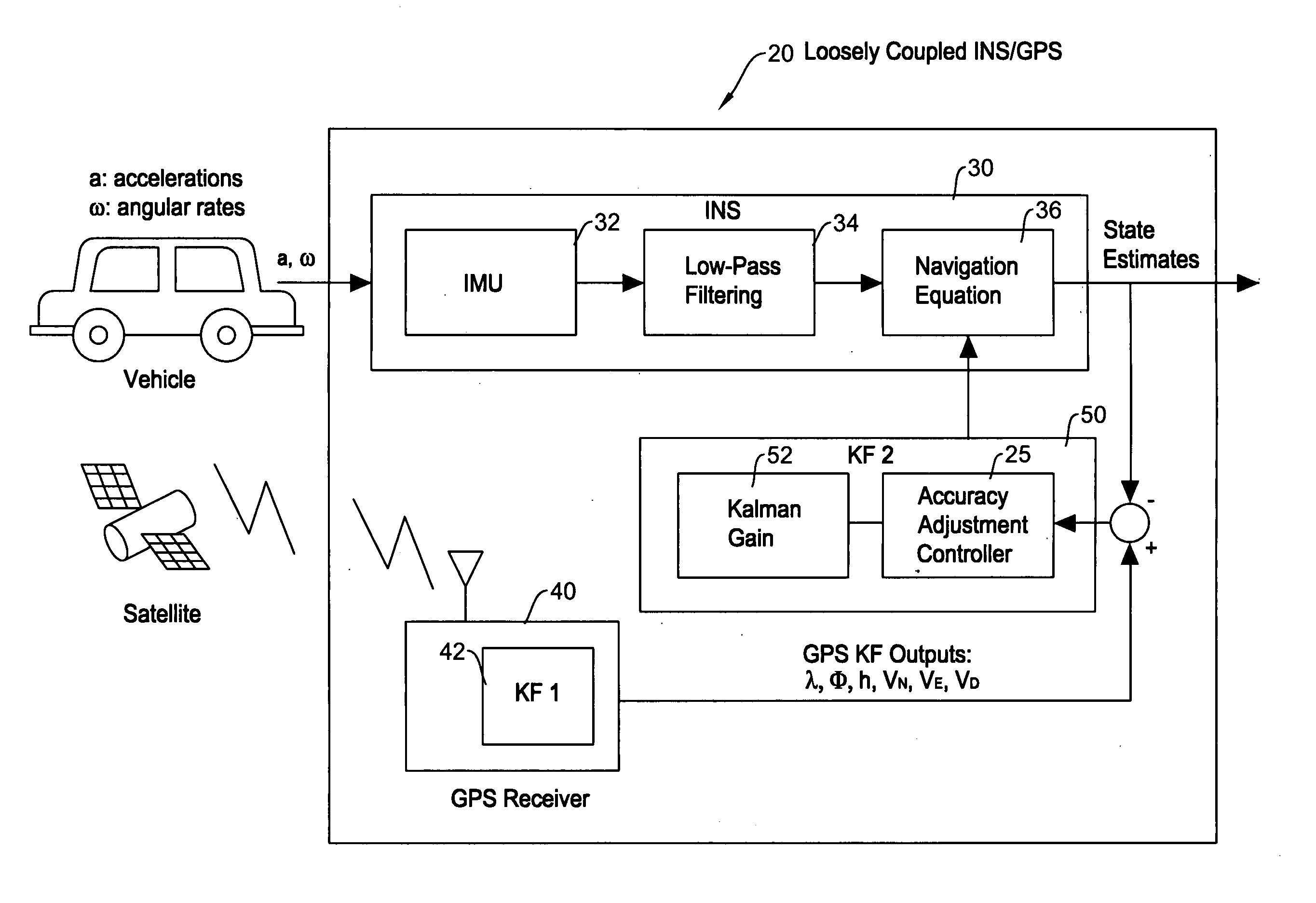
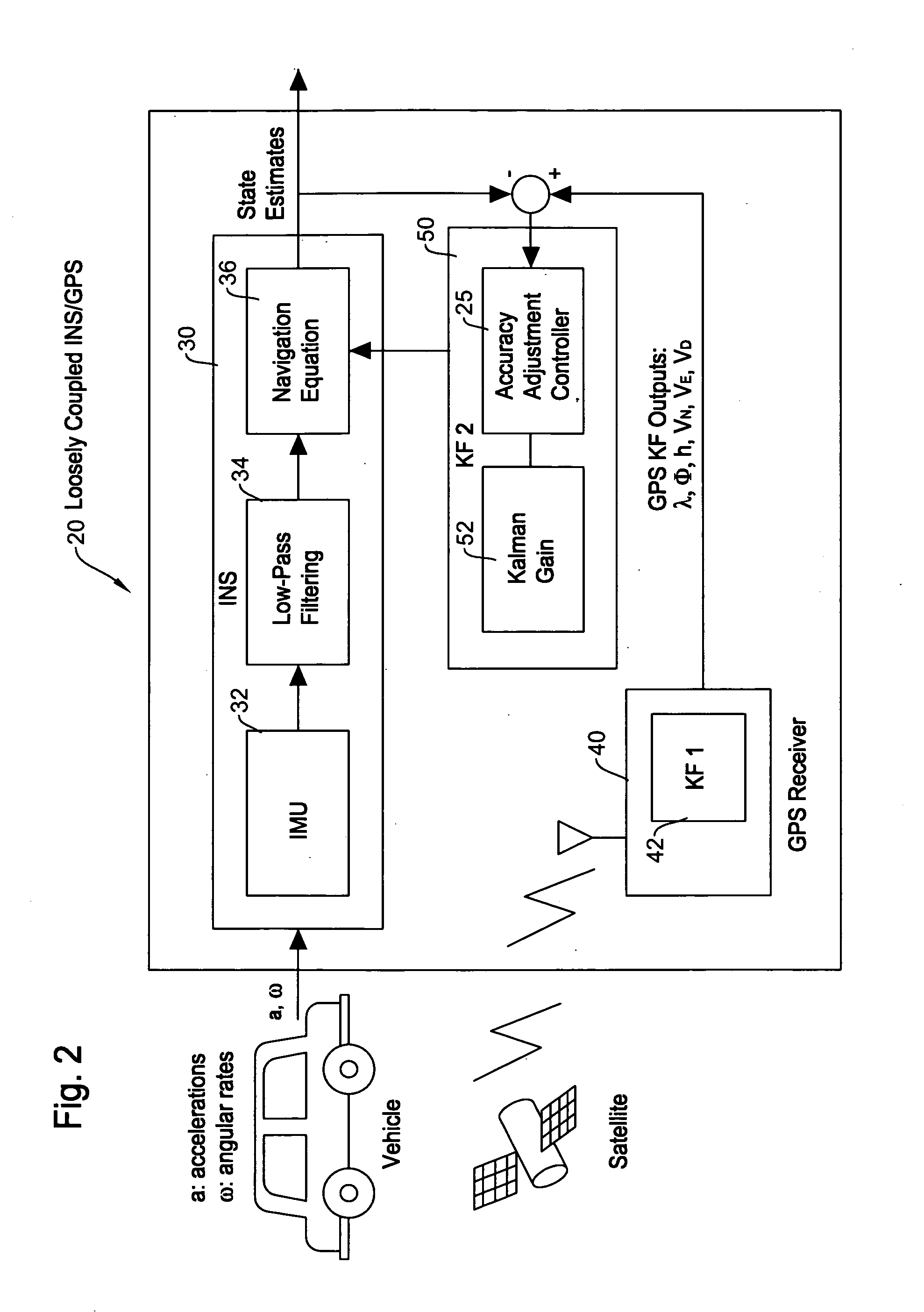
GPS accuracy adjustment to mitigate multipath problems for MEMS based integrated INS/GPS navigation systems
ActiveUS20080091351A1Level of accuracy can be always maintainedReduce decreasePosition fixationNavigation instrumentsPath lengthEngineering
A method of GPS accuracy adjustment for an integrated INS / GPS navigation system which utilizes microelectro mechanical systems (MEMS) based inertial sensors to mitigate multipath problems arising when a vehicle is in an area with many high-rise buildings is disclosed. Even when GPS measurement output values are deviated from that expected, the INS / GPS navigation system uses as many measurement outliers as possible without discarding, unless they are obvious error values. The measurement outliers occur when the integrated INS / GPS navigation system receives GPS signals which have transmitted through multipaths such as reflection by buildings, since the signal path lengths vary. Even in such a condition, rather than simply discarding such measurement outliers, the method utilizes the measurement outliers while adjusting the accuracy thereof depending on the degree of deviation. Since the integrated INS / GPS navigation system is able to utilize both the INS output and the GPS measurement, it is possible to maintain a practical level of accuracy in the position tracking when a vehicle is in an area of tall buildings.
Owner:ALPINE ELECTRONICS INC
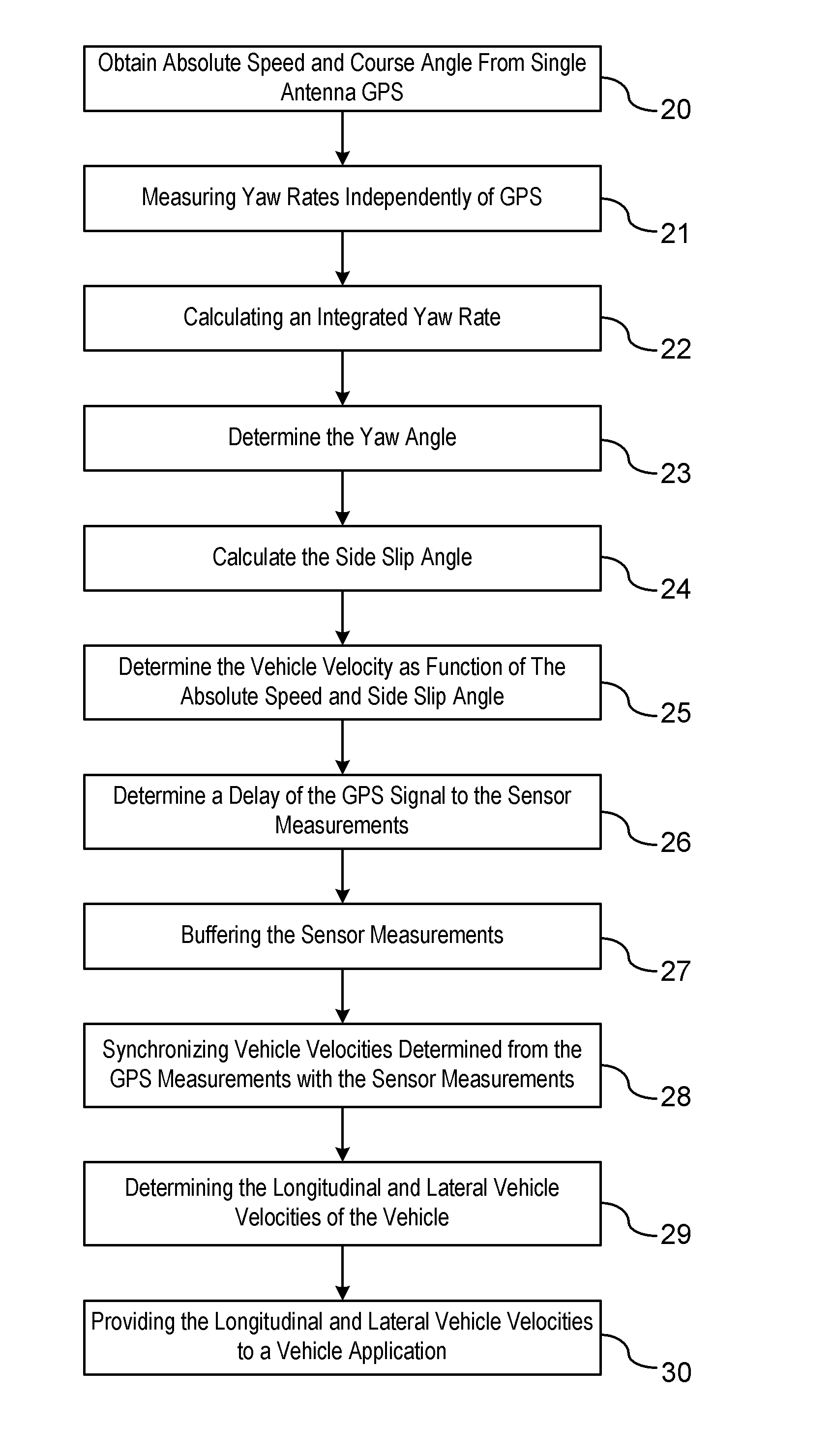
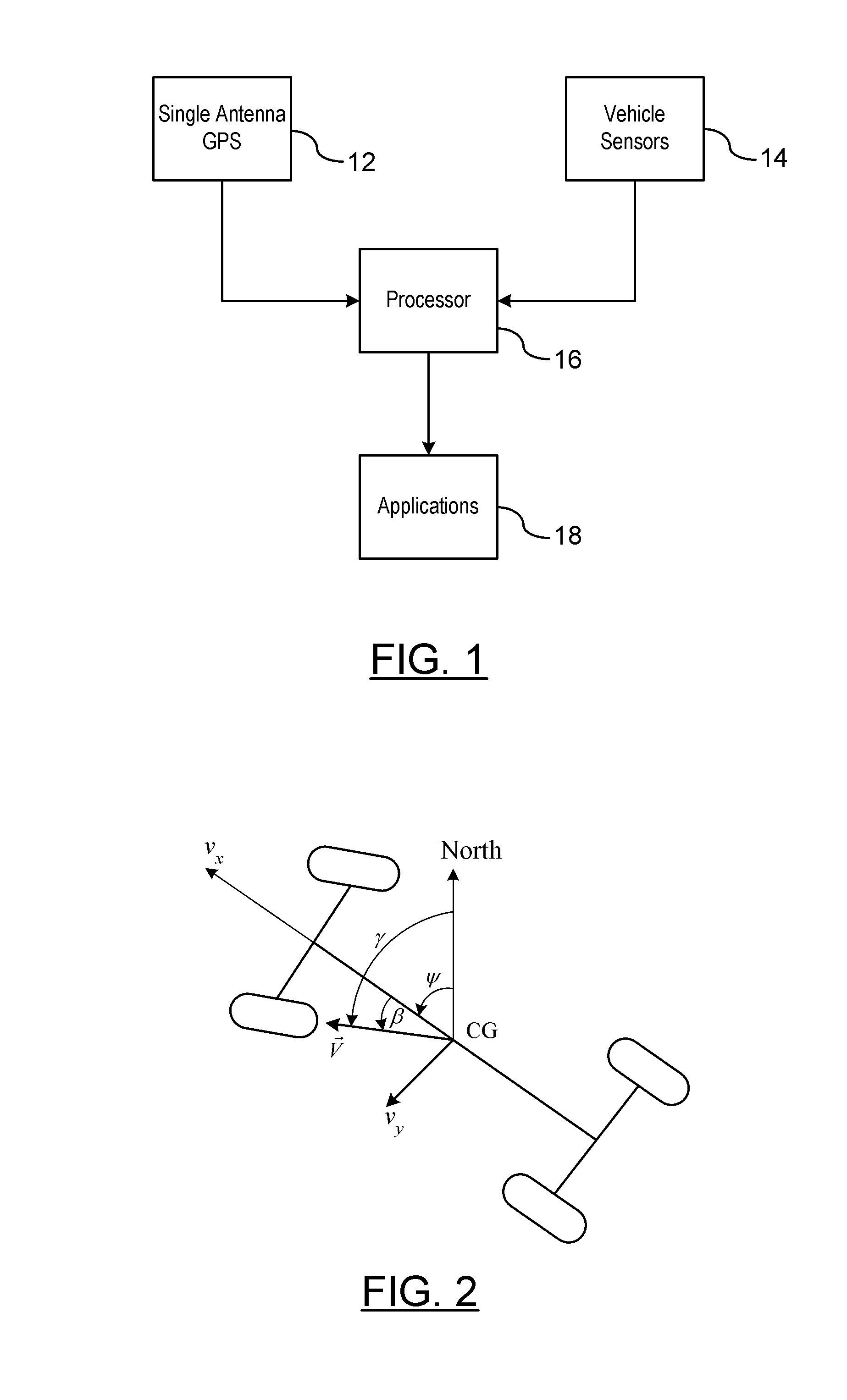
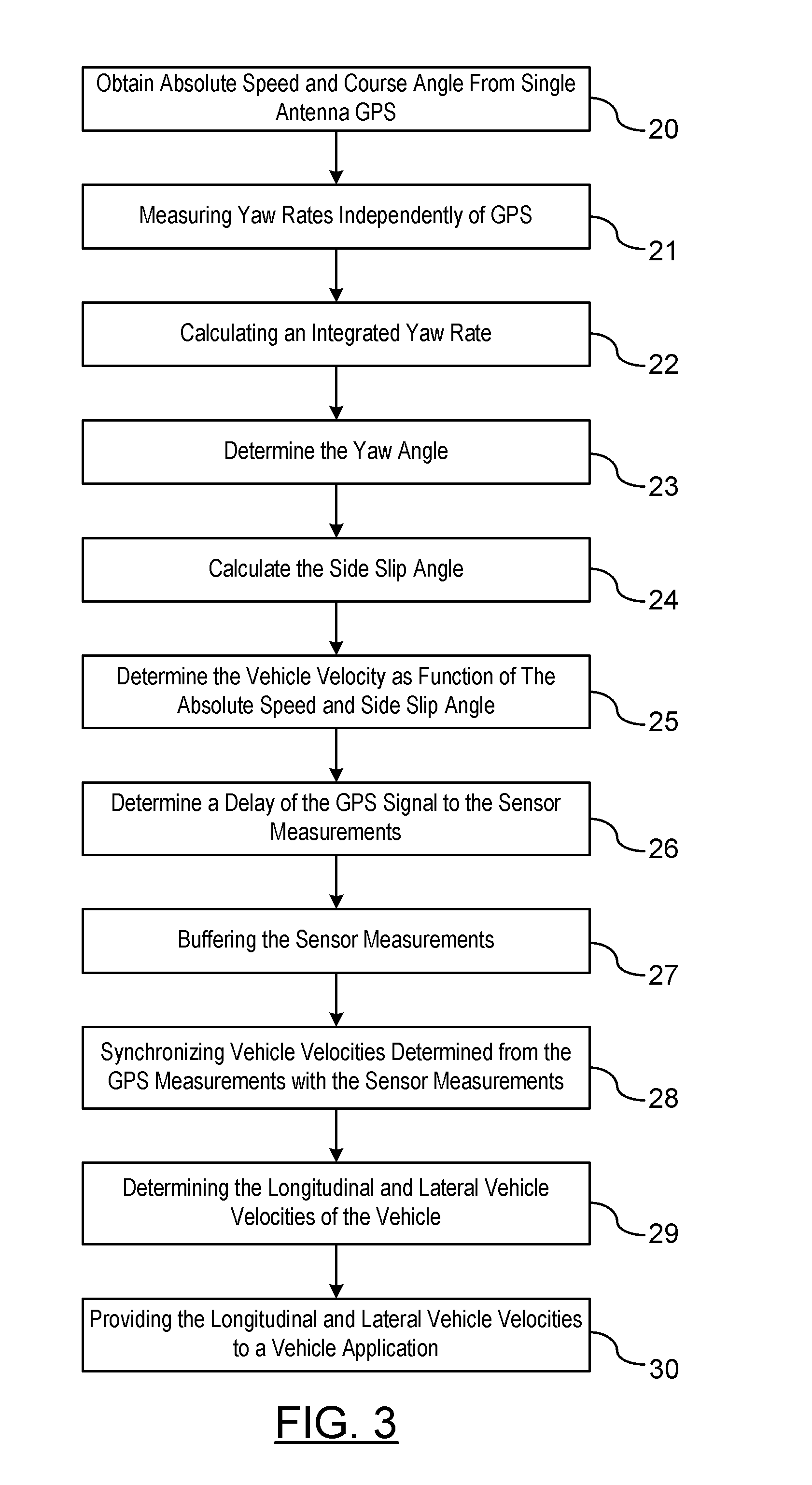
GPS-Enhanced Vehicle Velocity Estimation
ActiveUS20110112739A1Improve accuracyLow costAnalogue computers for trafficNavigation instrumentsGps measurementVehicle dynamics
A method is provided for estimating vehicle velocity for a vehicle using a single-antenna global positioning system (GPS). An absolute speed and a course angle of the vehicle is measured using the single-antenna GPS. The yaw rates of the vehicle are measured independently of the GPS. An integrated yaw rate of the vehicle is calculated as a function of the measured yaw rates over a period of time. A yaw angle is determined as a function of a reference yaw angle and the integrated yaw rate. Aside slip angle is calculated as a function of the estimated yaw angle and the course angle provided by the GPS. The vehicle velocity is determined as a function of the absolute speed and the side slip angle. The vehicle velocity is provided to a vehicle dynamic control application.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Multi-sensor combined navigation system for aviation
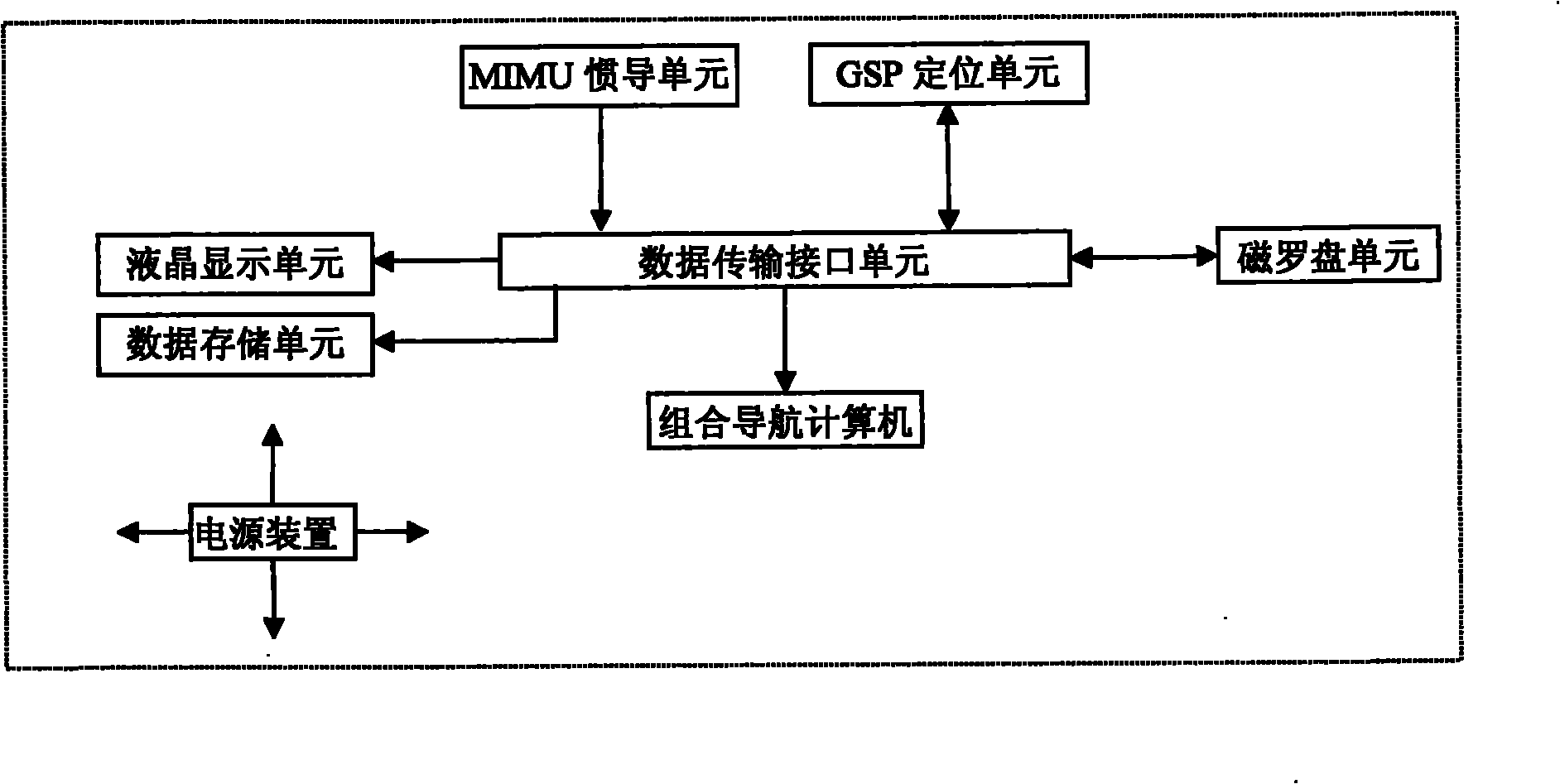
InactiveCN101865693AImprove positioning and speed accuracyLow costInstruments for comonautical navigationAviationGyroscope
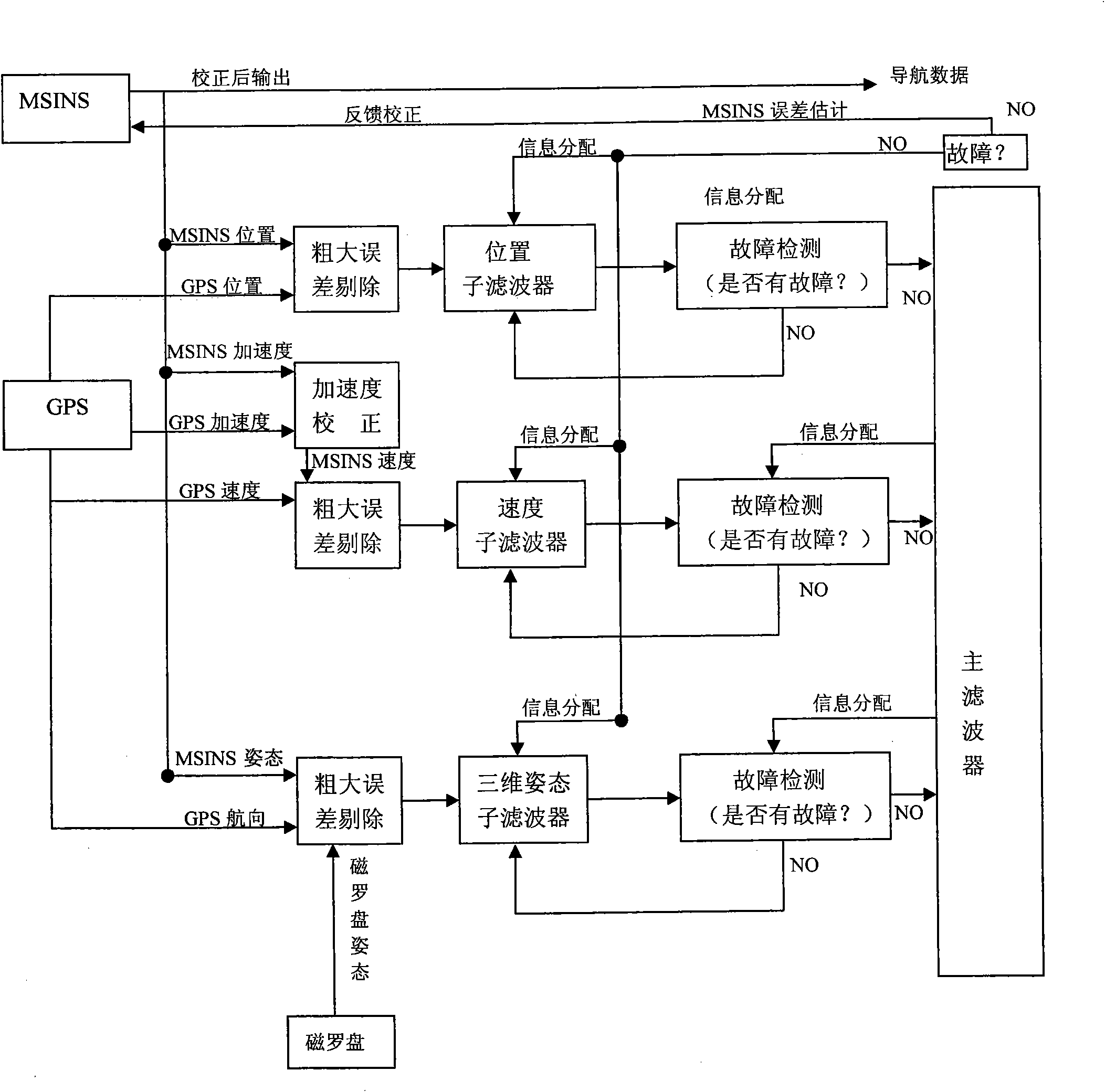
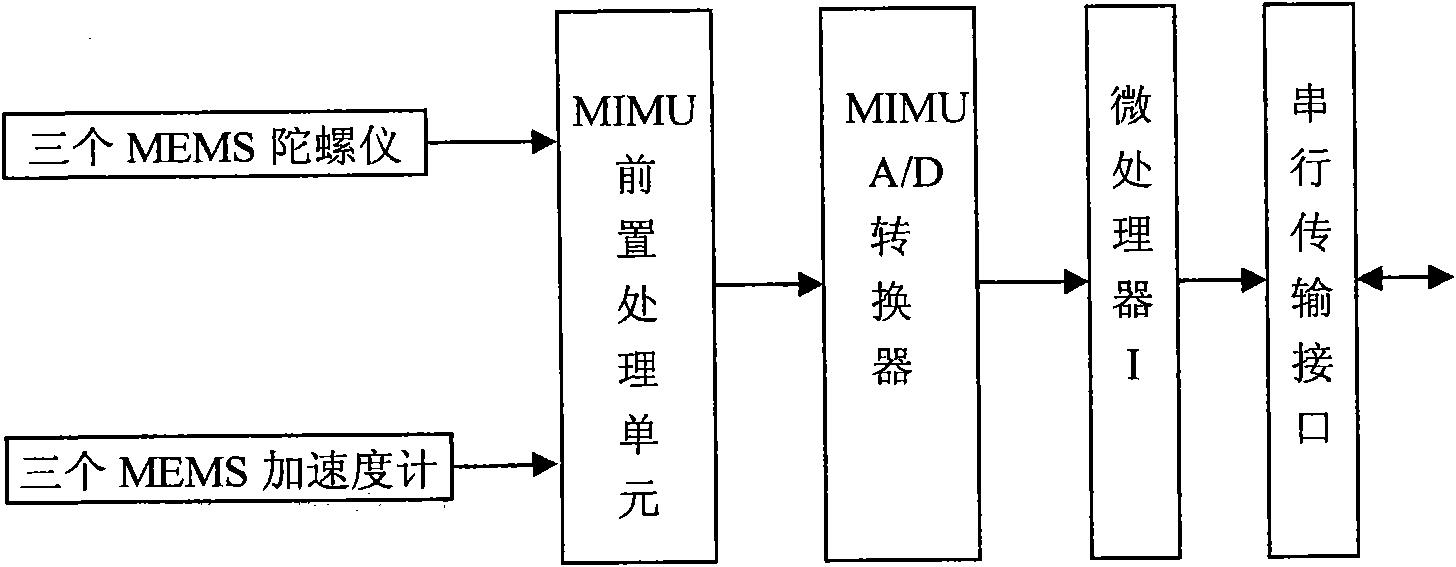
The invention relates to a multi-sensor combined navigation system for aviation, and the system comprises an MSINS unit, a GPS unit, a magnetic compass unit, a liquid crystal display unit, a data transmission interface unit, a combined navigation computer, a data storage unit and a power supply device. The MSINS unit is used for acquiring signals of an accelerometer and a gyroscope, carrying out filtration and amplification and sending the signals to a DSP for carrying out algorithm processing; a GPS module is used for outputting longitude, latitude, altitude and velocity values of X, Y and Z axes based on a geocentric coordinate system measured by the GPS; the magnetic compass unit is used for outputting three-dimensional attitude information measured by a three-axis magnetic compass; the combined navigation computer is used for receiving signals outputted by an inertial measurement unit, the GPS module and the magnetic compass, applying the federated Kalman filtering algorithm to carry out fusion treatment on data and obtaining combined navigation data; and the data storage unit is used for saving original data and result data. The system has the advantages of small volume, low cost, high reliability and high precision.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF TECH & EDUCATION TEACHER DEV CENT OF CHINA VOCATIONAL TRAINING & GUIDANCE
Accelerometer calibration method based on GPS velocity information
InactiveCN102662083ARealize dynamic calibrationHigh accuracy of measured valuesTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesGps measurementLinear motion
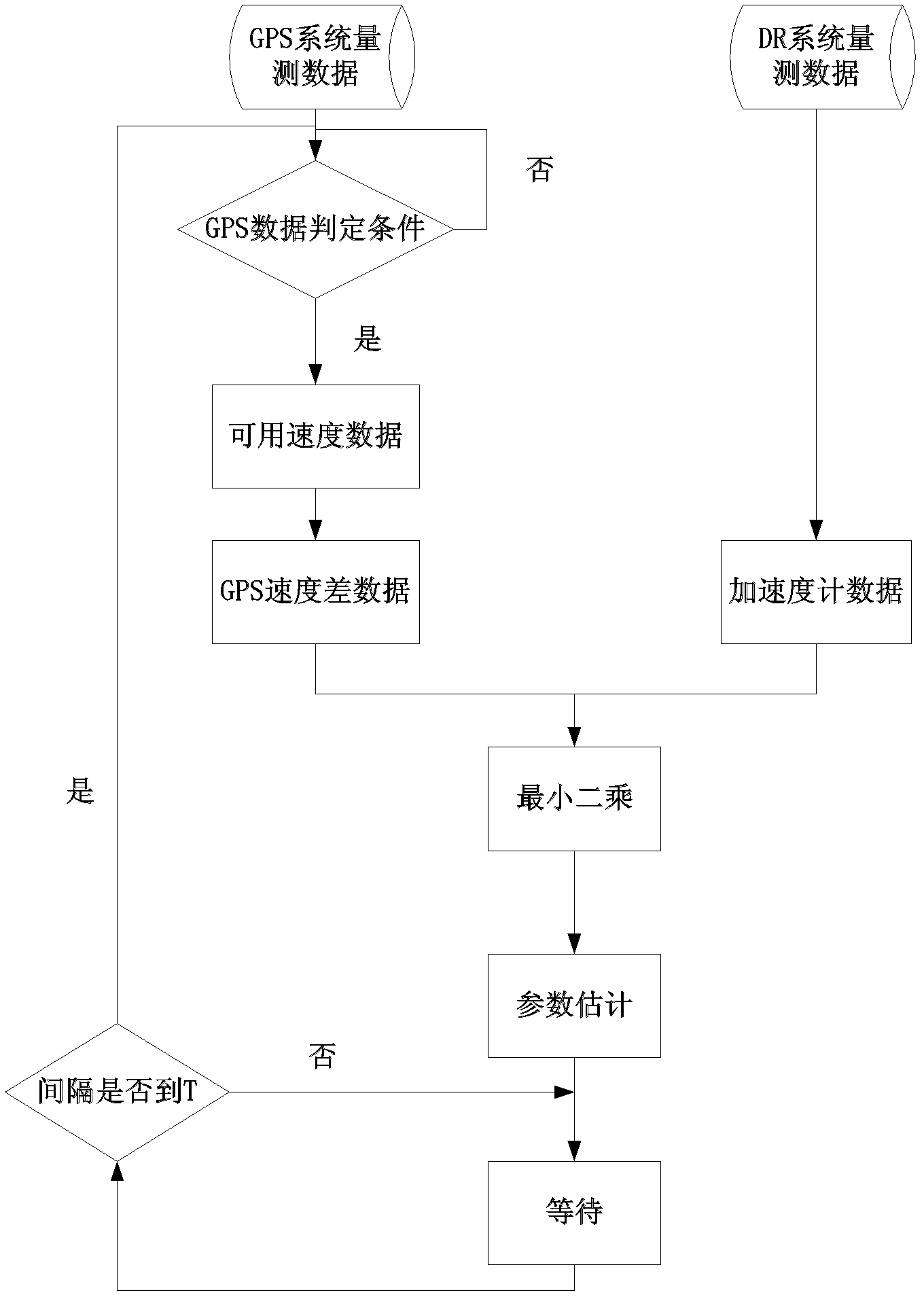
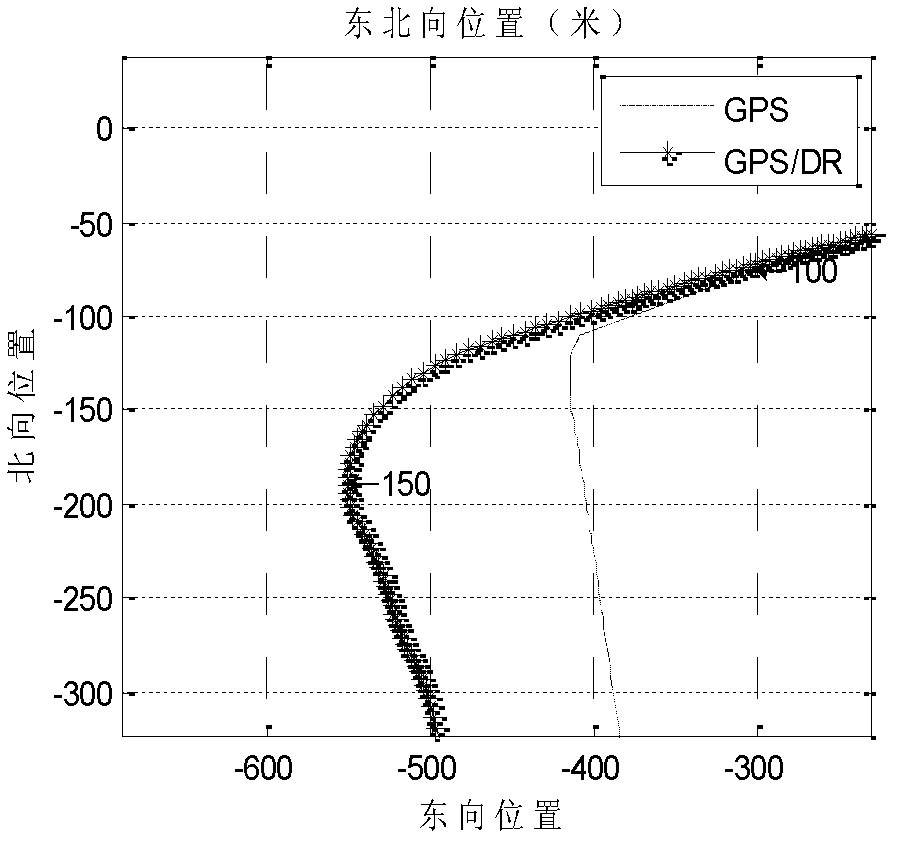
The invention, which belongs to the combined navigation technology field, discloses an accelerometer calibration method based on GPS velocity information. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, collecting measurement data of a GPS measurement system and a DR measurement system; step 2, determining usability of the GPS measurement data; step three, employing a least square method to estimate a scale factor and a zero offset error of an accelerometer; step four, comparing estimation values of the scale factor and the zero offset error of the accelerometer with estimation values of a preset accelerometer scale factor and a preset accelerometer zero offset error to determine whether updating is carried out; and step five, meeting a time interval requirement and then returning to the step two to carry out next calibration. According to the invention, a GPS characteristic that the GPS enables a measurement value precision to be high at a linear motion segment with good signal reception and high speed is utilized to realize dynamic calibration on an accelerometer, so that calibration parameter of the accelerometer can be updated regularly and an influence on the system precision by a zero offset change caused by different starting and temperature changes can be reduced. Moreover, the realization is simple, the calculation amount is small, and the result is reliable.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Antijam protected GPS-based measurement of roll rate and roll angle of spinning platforms
ActiveUS20100289687A1Low costAccurate measurementDirection controllersSatellite radio beaconingGps measurementGps receiver
A system and method for determining the roll rate and roll angle of a spinning platform in a jamming environment, by suppressing the interference signals from the received GPS signals and using the measured phase and amplitude differences between the GPS satellite signals received on two or more antennas. The measured signal differences and the navigation solution from a GPS receiver are processed in a roll filter to obtain the desired information. Data from non-GPS measurement sources is optionally provided to update the navigation solution. Although of wide applicability, the invention is uniquely suited to the measurement of roll rates and roll angles of fast spinning platforms with small baselines in the presence of jamming, and where the antennas are separated from each other by distances that are a fraction of the GPS signal wavelength.
Owner:MAYFLOWER COMM CO INC
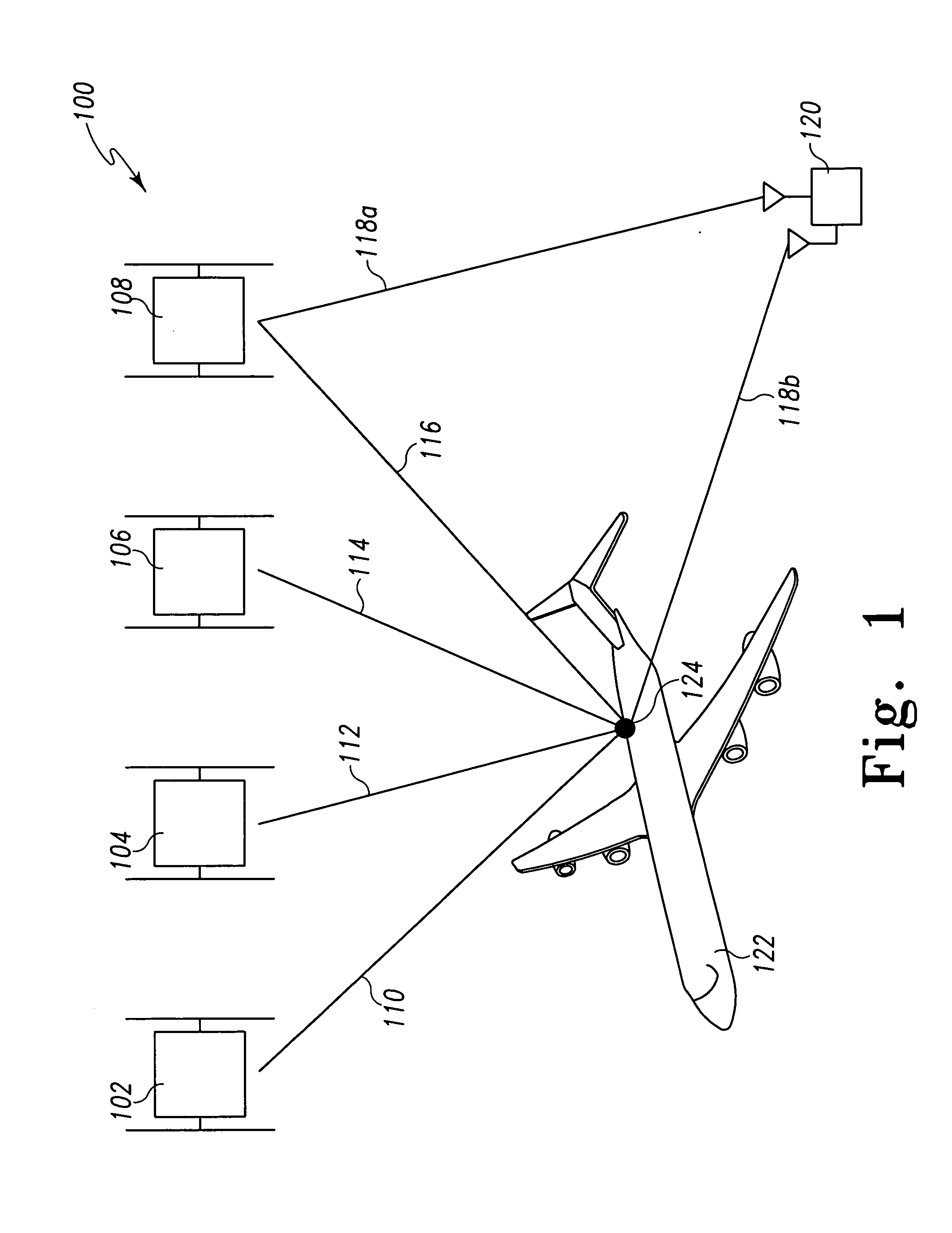
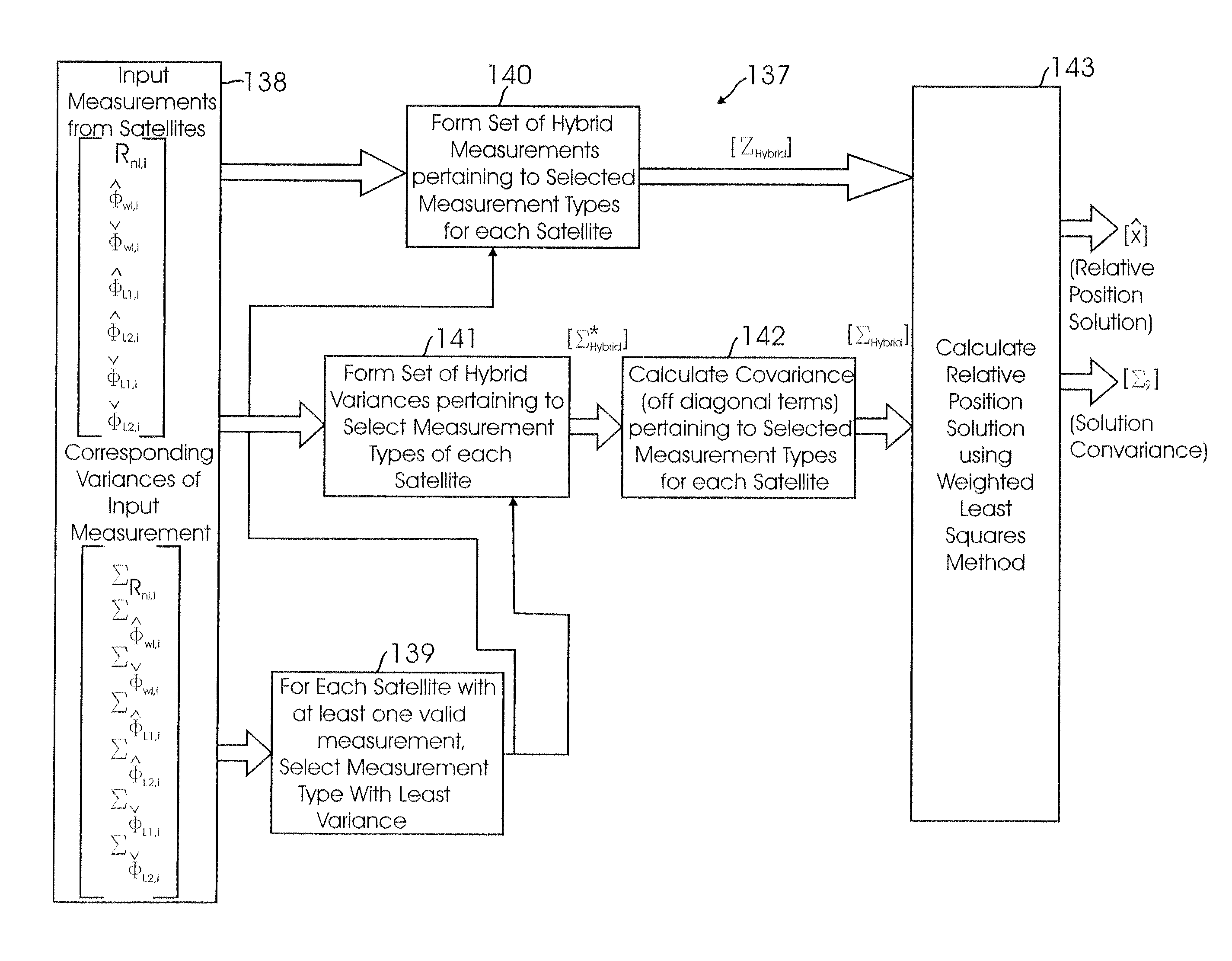
Method for fusing multiple GPS measurement types into a weighted least squares solution
ActiveUS20080036654A1Simple methodImprove accuracyPosition fixationBeacon systemsPattern recognitionGps measurement
A method of calculating position data for an airborne aircraft using a GPS-based airborne navigation system includes the processing of a position component of a relative state function by fusing a plurality of different types of measurement data available in the GPS-based system into a weighted least squares algorithm to determine an appropriate covariance matrix for the plurality of different types of measurement data.
Owner:SIERRA NEVADA CORP
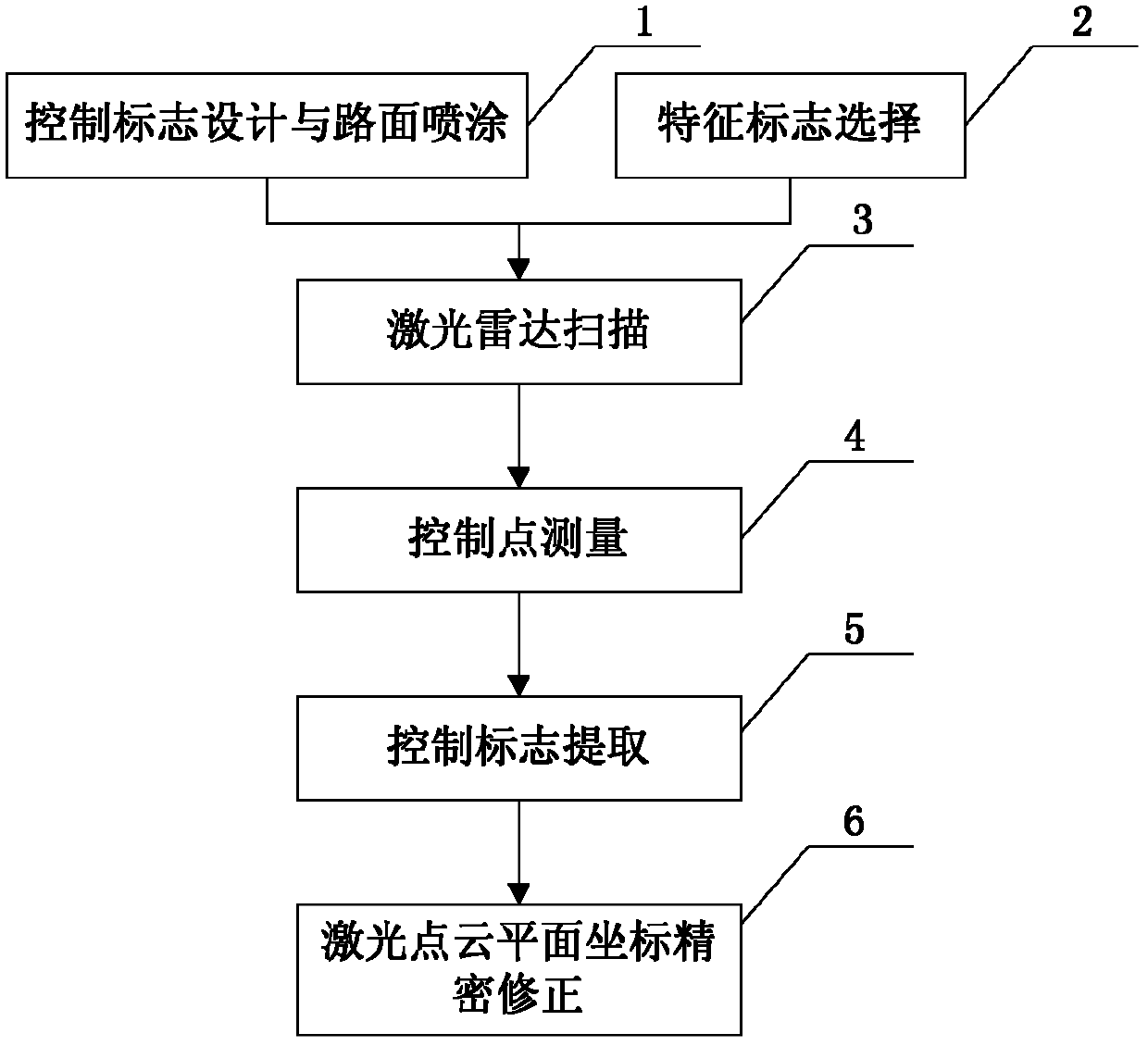
Precise plane coordinate correction method in laser radar scanning measurement
ActiveCN102518028AHigh precisionReduce intermediate errorsRoads maintainenceElectromagnetic wave reradiationGps measurementPoint cloud
The invention discloses a precise plane coordinate correction method in laser radar scanning measurement. The method comprises the following steps of: a, designing and spraying a control sign: arranging control signs along the path in a staggered form on the two sides of a highway; b, selecting a control point for the feature signs formed by two crossed straight lines along the existing road; c, laser radar scanning: determining the laser radar scanning measurement mode; d, measuring a control point, wherein the control point plane measurement adopts GPS (global position system) static positioning measurement, and a net structure is formed; e, controlling sign extraction: accurately extracting the position of the laser radar point cloud data plane of the control sign by use of the information of the laser radar point cloud data; and f, precisely correcting the laser radar point cloud plane coordinate: performing precise plane coordinate processing on the laser data according to the GPS measurement result at the control point and the laser radar point cloud extraction result of the control sign. The method has high precision, low cost and high efficiency, and is easy to implement, simple and convenient to operate and suitable for precise plane coordinate correction in the laser radar scanning measurement for road reconstruction and expansion.
Owner:CCCC SECOND HIGHWAY CONSULTANTS CO LTD
In-situ injection of soil and groundwater - high pressure rotary jet grouting in-situ remediation system and method
ActiveUS20190145190A1Efficient constructionDestroying bearing capacityDrilling rodsContaminated soil reclamationPipe waterAir compressor
Owner:BCEG ENVIRONMENTAL REMEDIATION CO LTD
Method for improving GPS integrity and detecting multipath interference using inertial navigation sensors and a network of mobile receivers
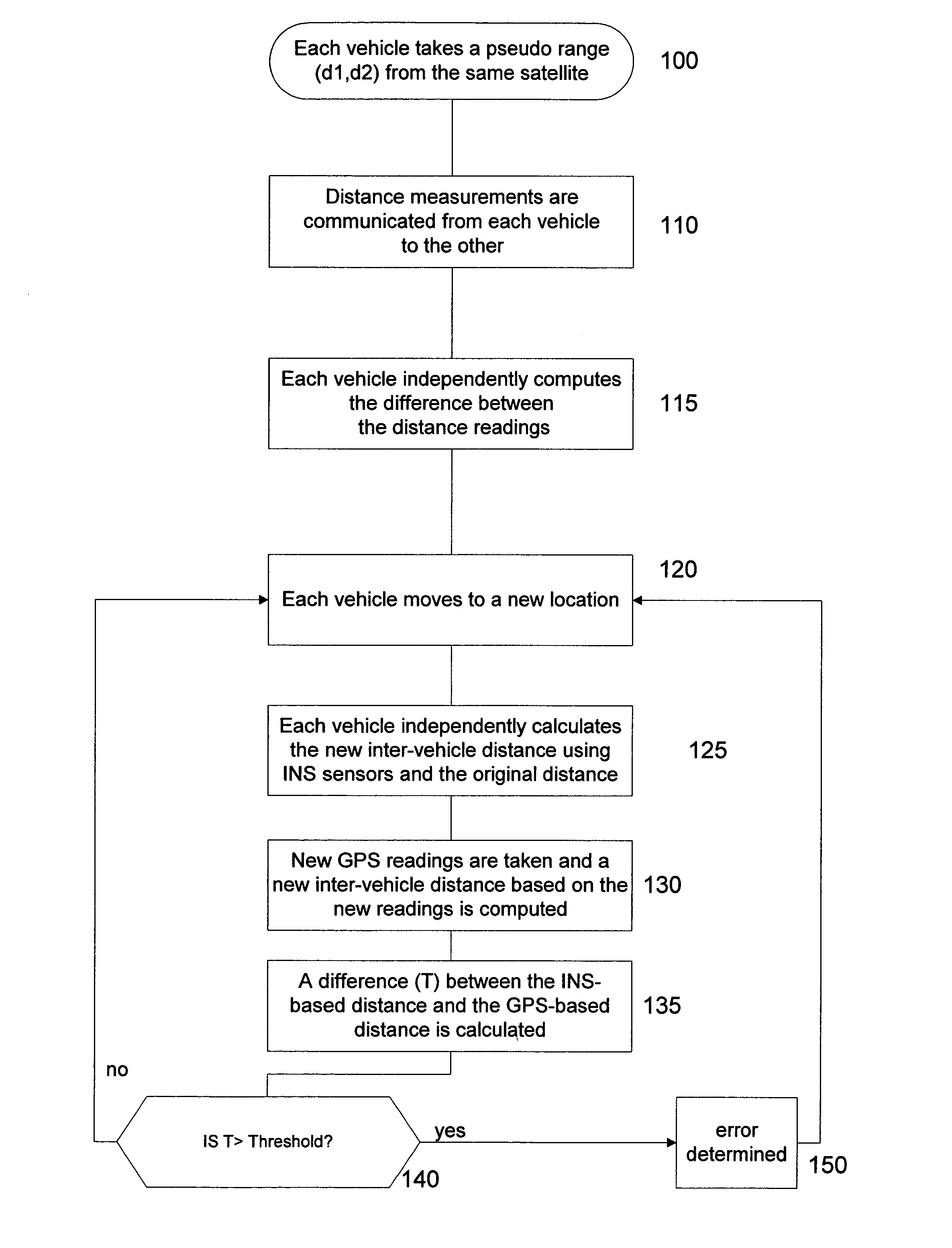
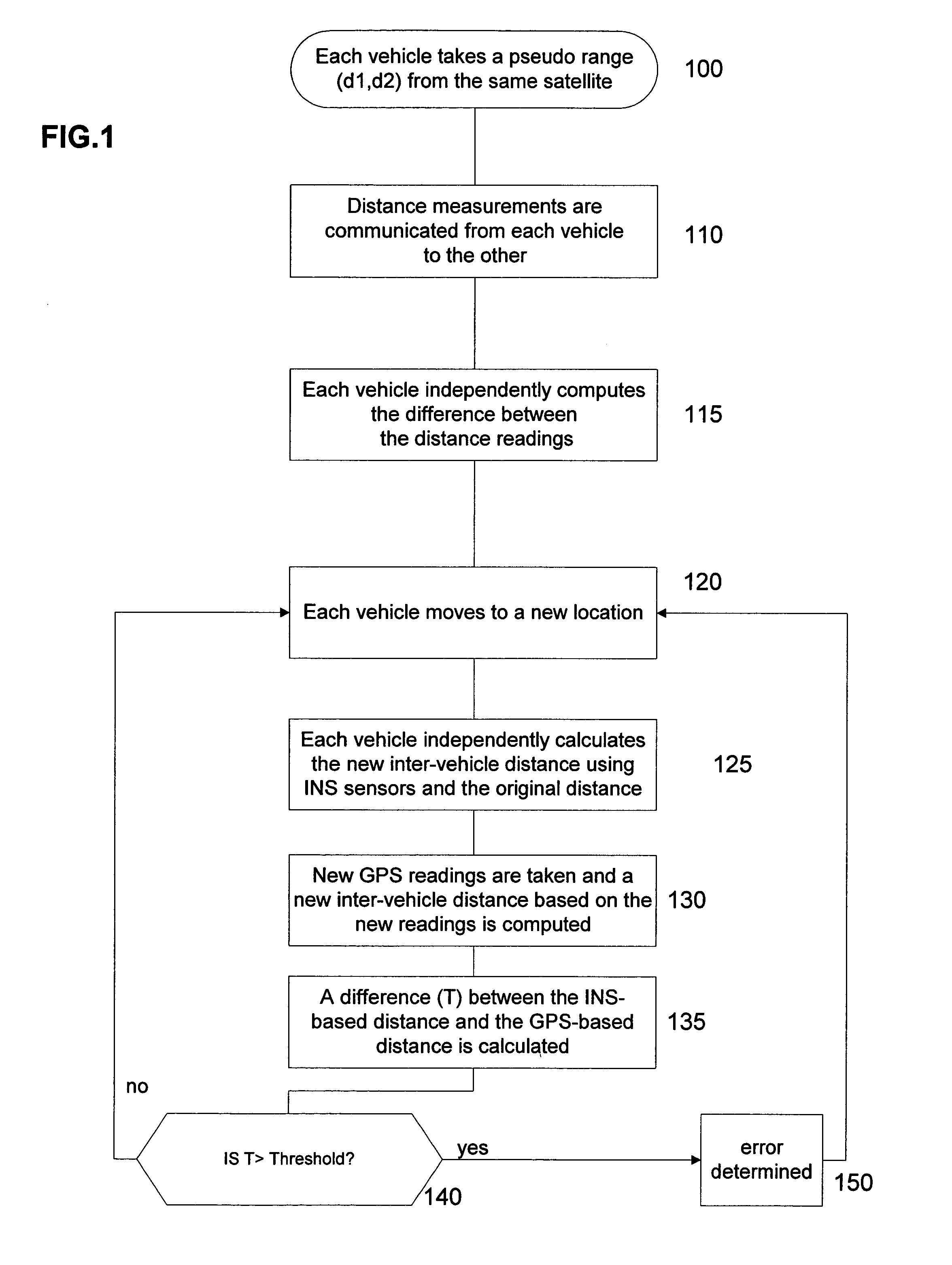
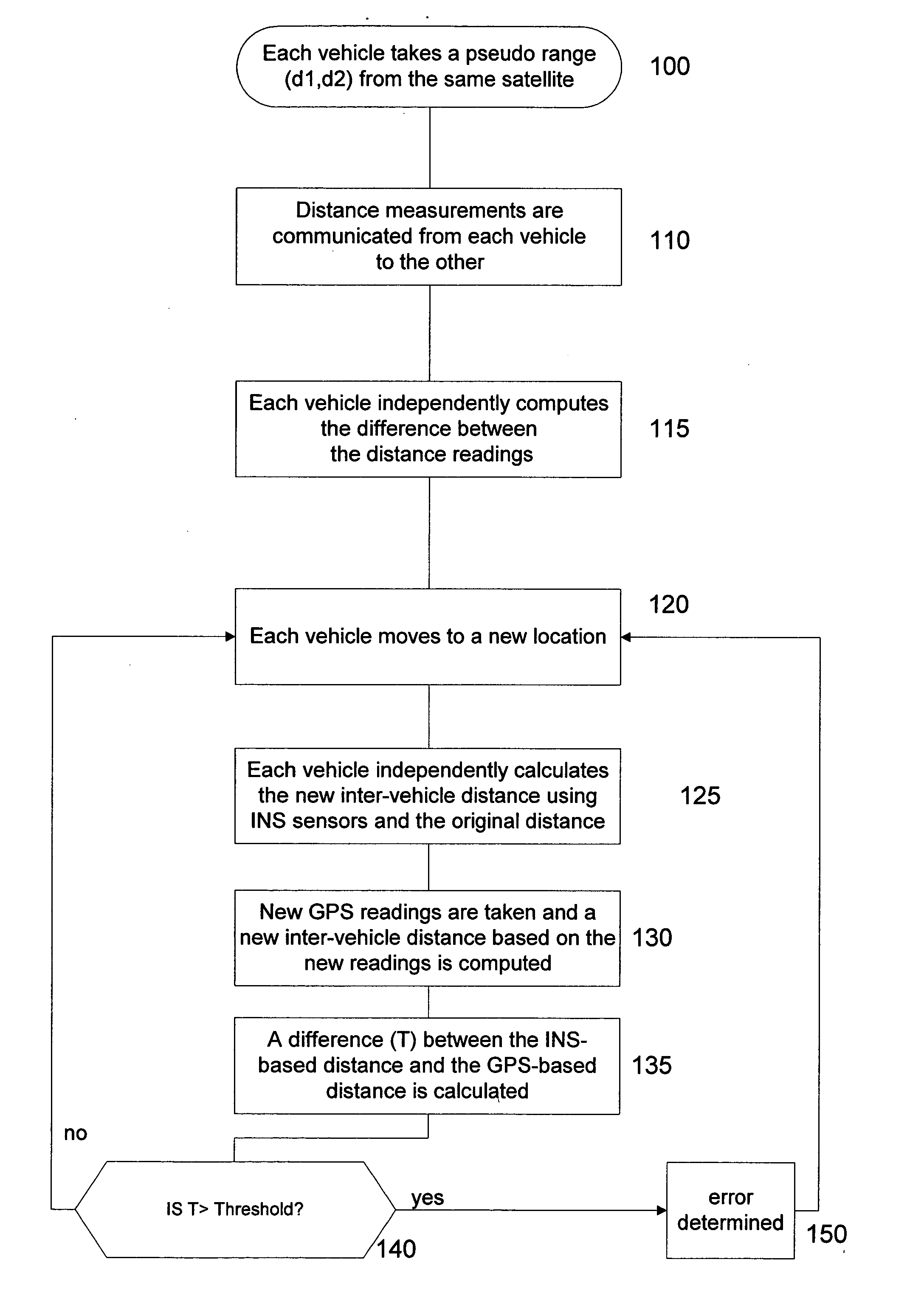
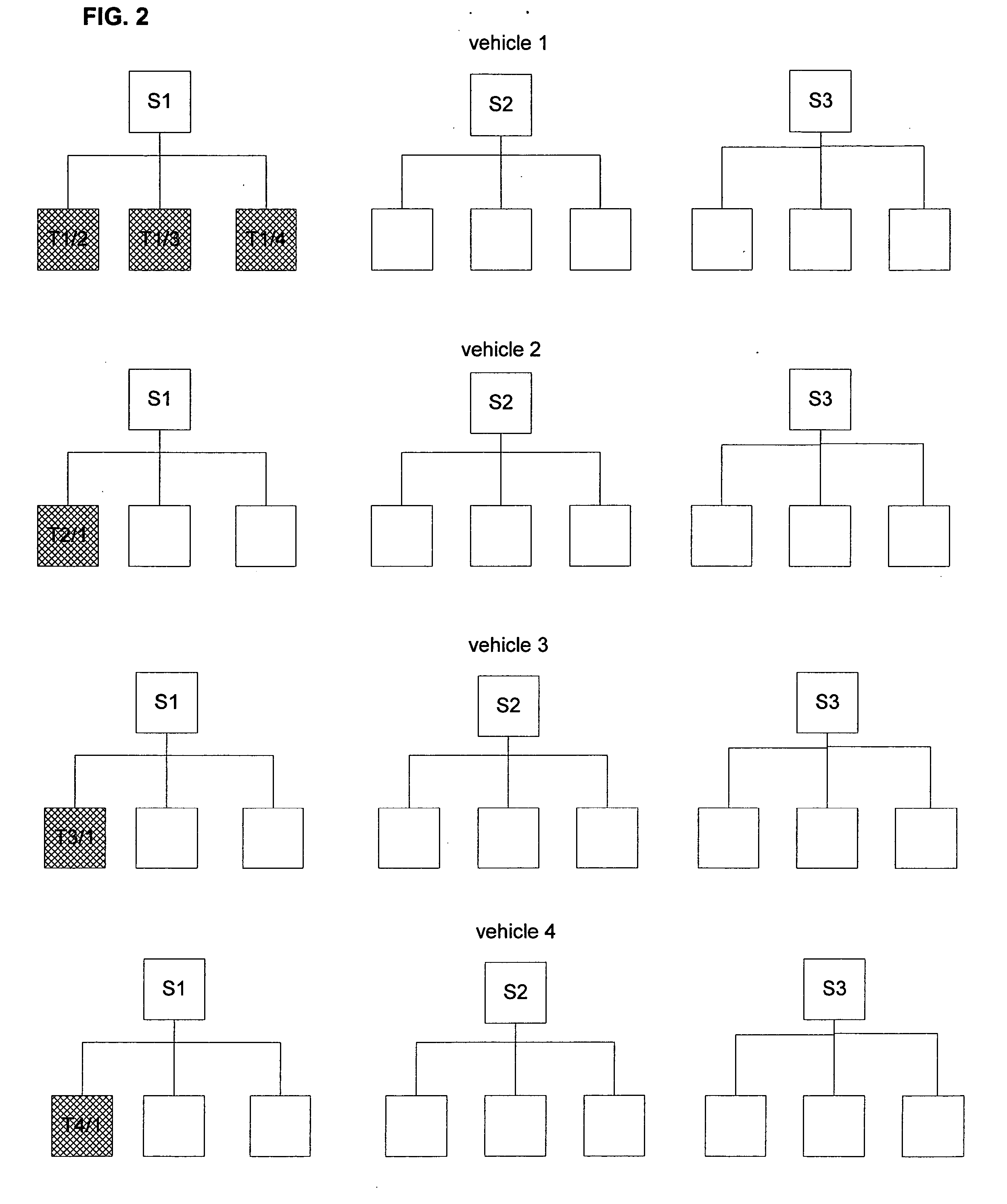
InactiveUS7110882B2Instruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsGps measurementMobile vehicle
A method for checking the integrity of GPS measurements for a moving vehicle includes determining a first inter-vehicle distance between a first vehicle and a second vehicle based on GPS measurements obtained at both vehicles, independently determining a second inter-vehicle distance based on relative motion of the first vehicle and the second vehicle obtained using INS sensors at both vehicles, and comparing the first and second inter-vehicle distances. The integrity of the GPS measurements are checked if the first and second inter-vehicle distances are nearly equivalent. Methods for error detection and for mapping GPS multipath levels at each point in a vicinity for an entire range of satellite constellations are also described.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method for improving GPS integrity and detecting multipath interference using inertial navigation sensors and a network of mobile receivers
InactiveUS20050010364A1Instruments for road network navigationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsGps measurementMultipath interference
A method for checking the integrity of GPS measurements for a moving vehicle includes determining a first inter-vehicle distance between a first vehicle and a second vehicle based on GPS measurements obtained at both vehicles, independently determining a second inter-vehicle distance based on relative motion of the first vehicle and the second vehicle obtained using INS sensors at both vehicles, and comparing the the first and second inter-vehicle distances. The integrity of the GPS measurements are checked if the first and second inter-vehicle distances are nearly equivalent. Methods for error detection and for mapping GPS multipath levels at each point in a vicinity for an entire range of satellite constellations are also described.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
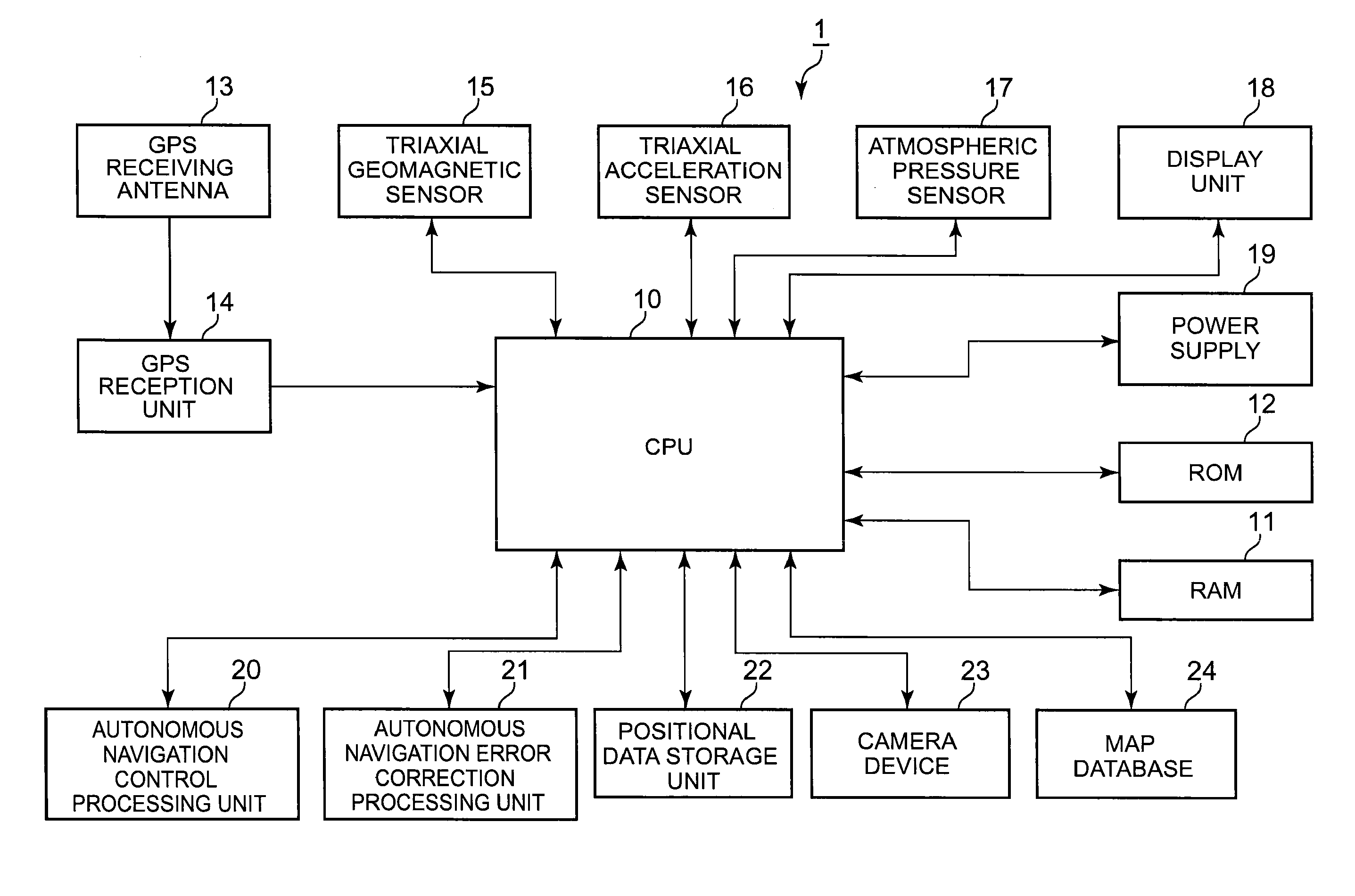
Positioning apparatus, positioning method, and storage medium for measuring position using both autonomous navigation and GPS
ActiveUS20120062414A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlGps measurementPosition control
A positioning apparatus including: a first positioning unit which intermittently receives signals from satellites and carries out a first position measurement; a second positioning unit which carries out a second position measurement by adding information of a moving direction and a moving amount to positional information of a reference position; a positioning control unit which obtains positional information corresponding to positions along a movement path by the first position measurement and the second position measurement; a reference position updating unit which updates the positional information of the reference position based on a result of the first position measurement; a distance calculating unit which calculates a distance between two positions, i.e., between the reference position and a position obtained by the second position measurement; and a positioning timing control unit which controls timing to carry out the first position measurement based on the distance.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
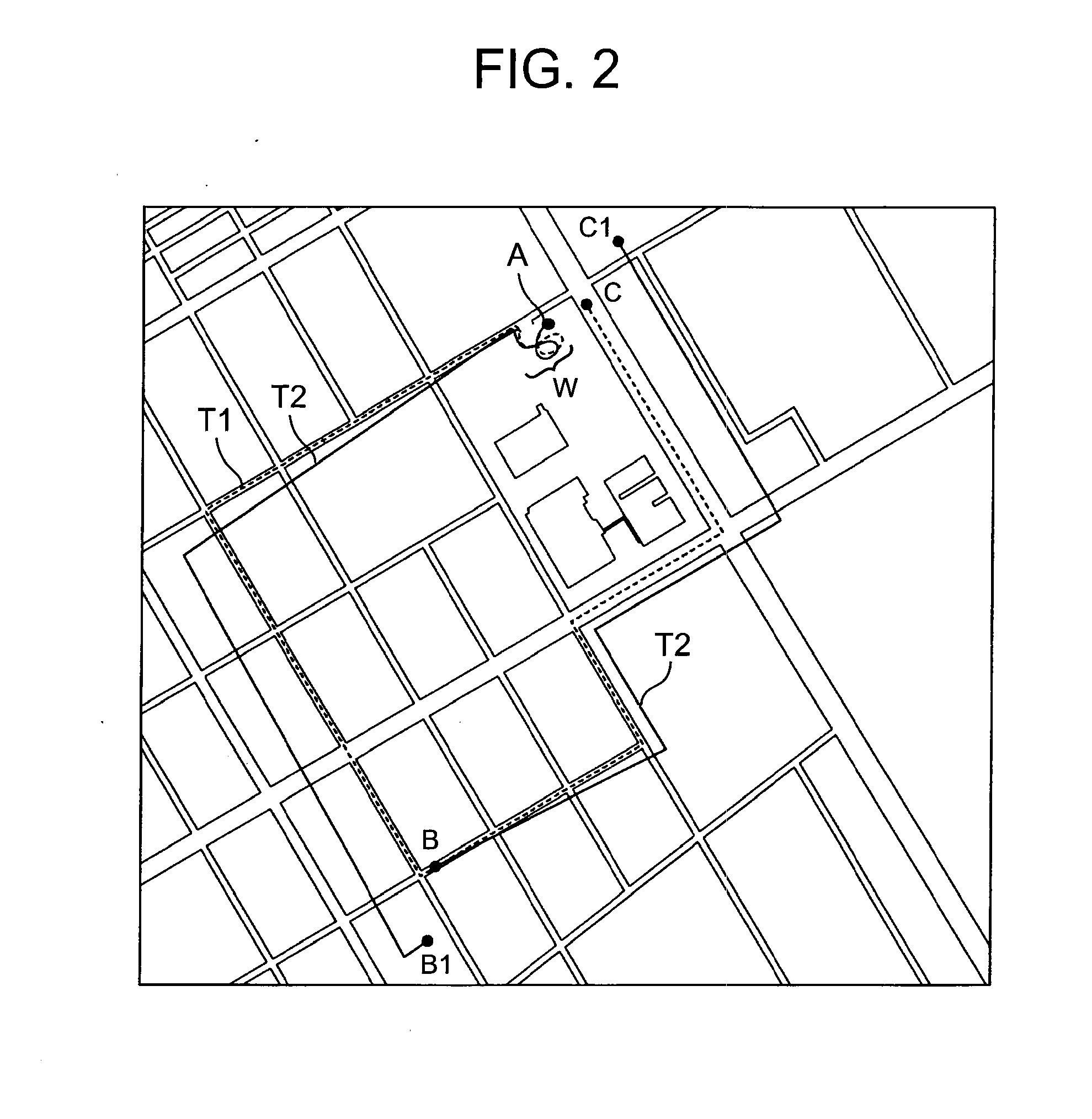
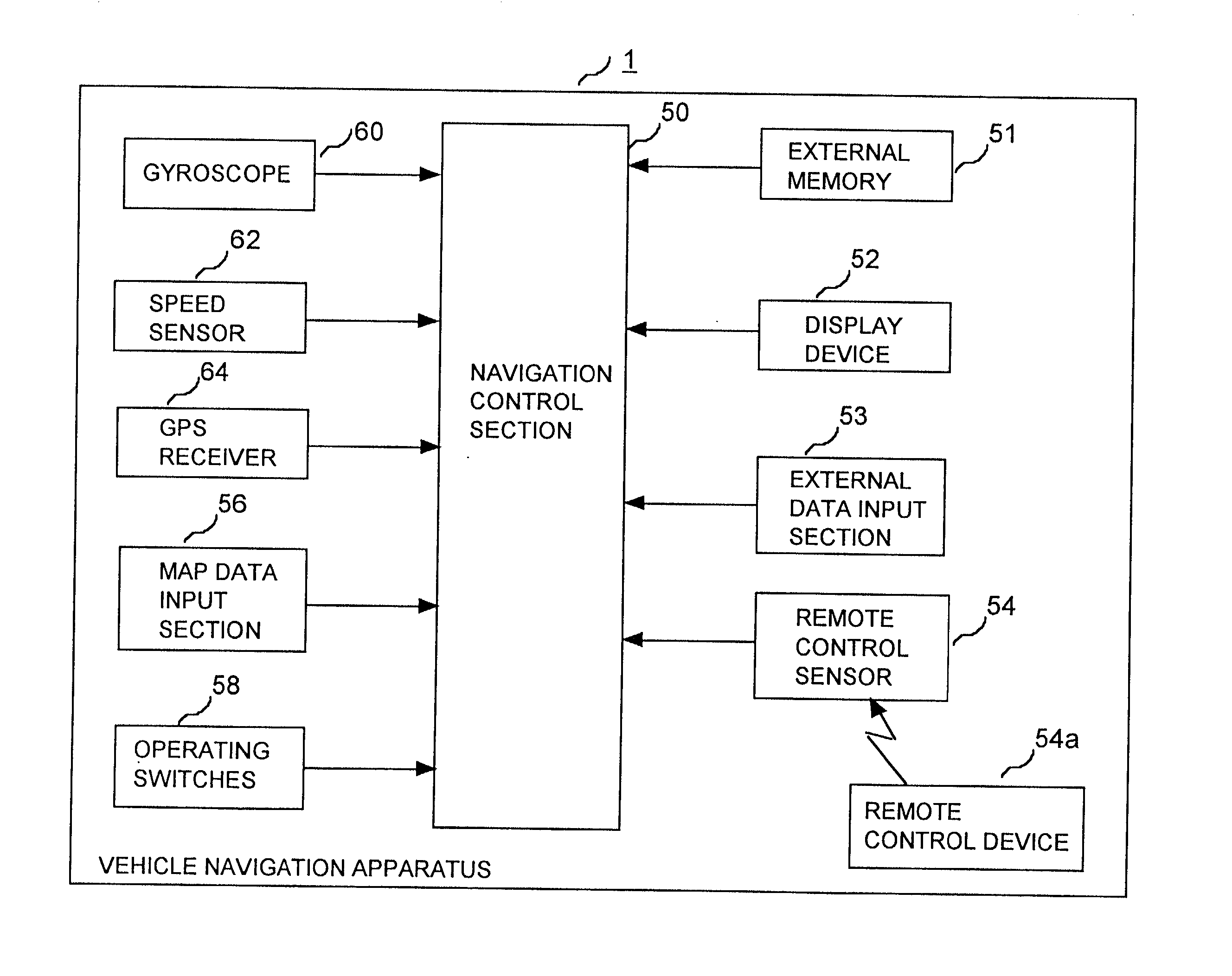
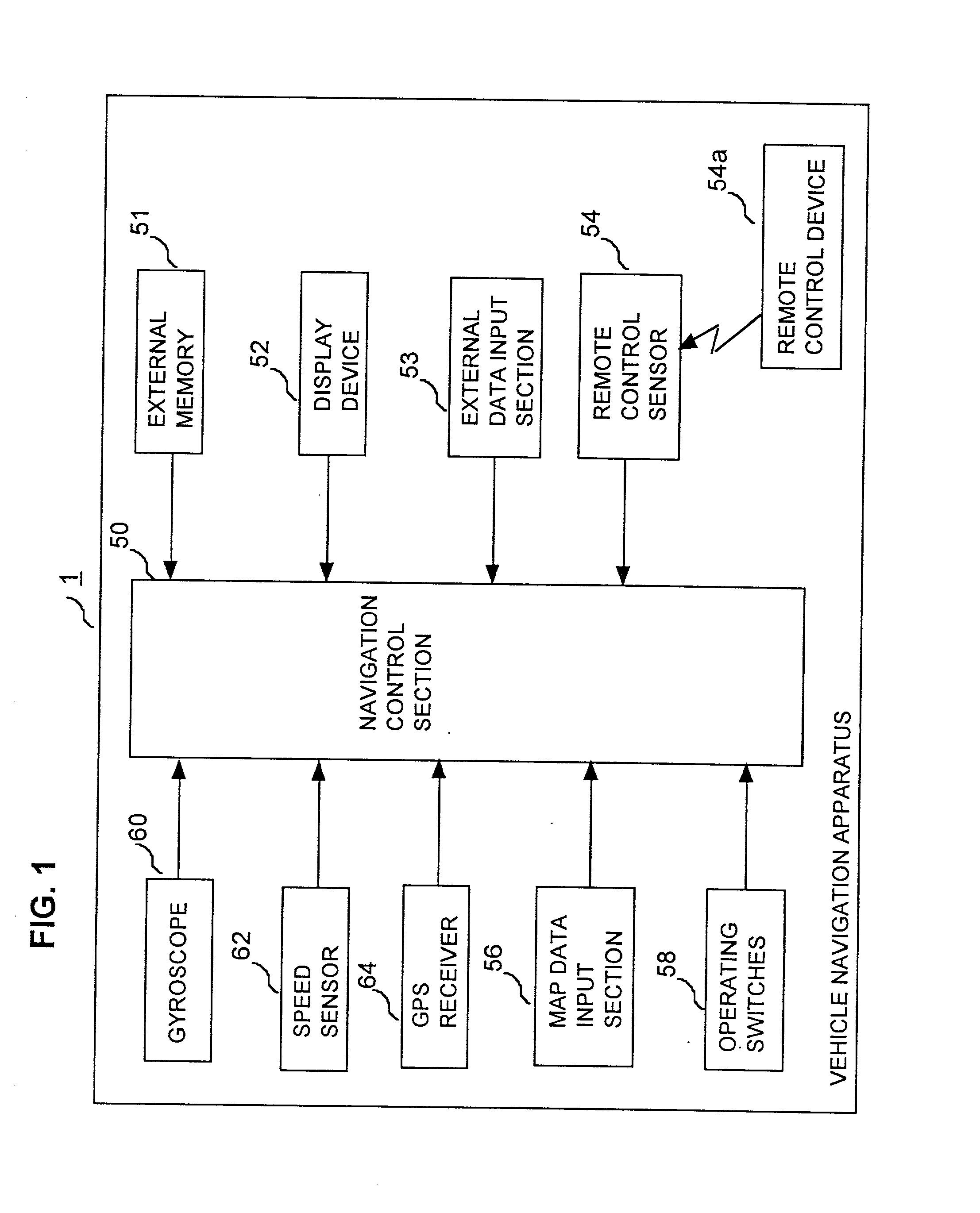
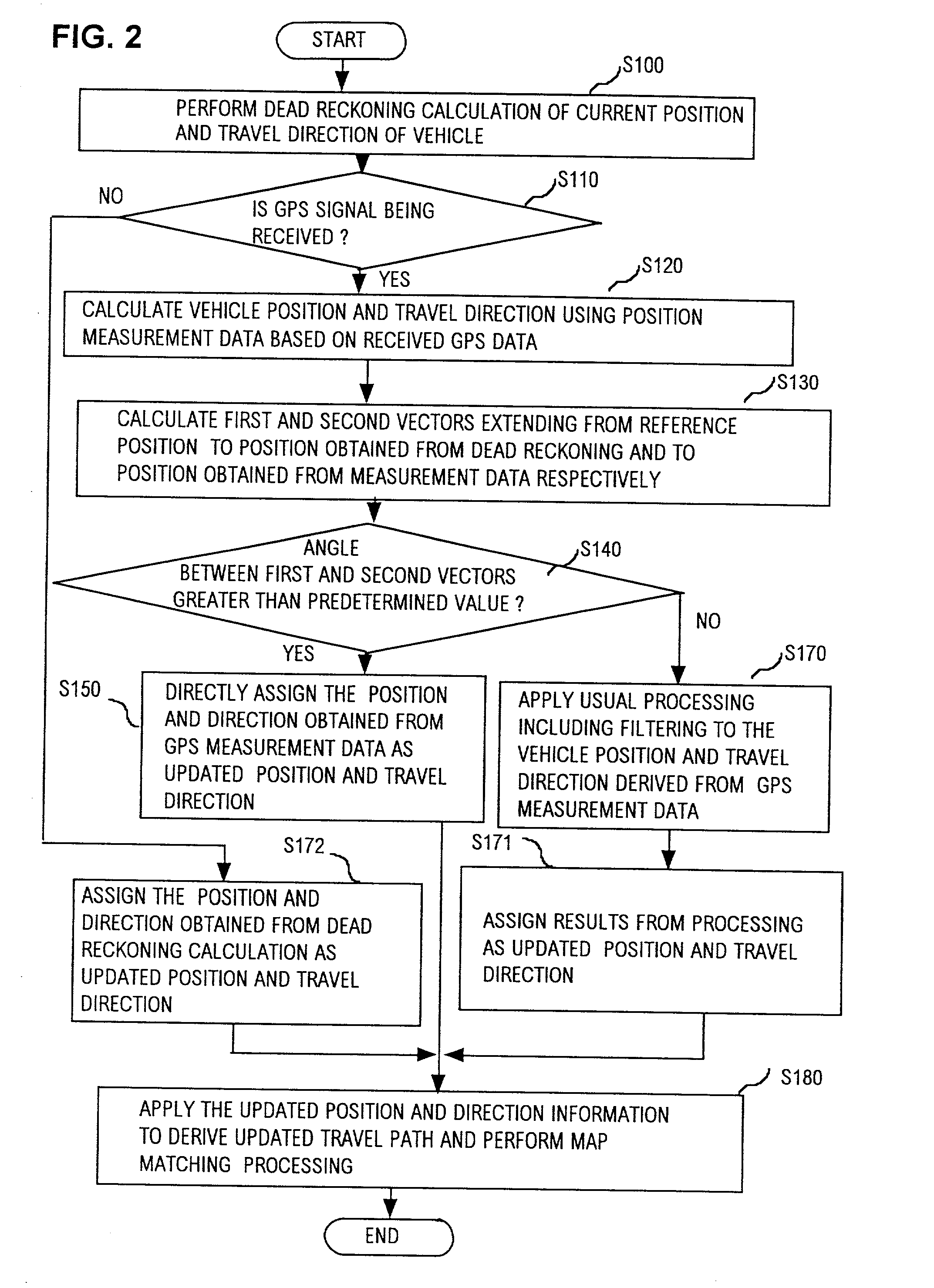
Vehicle navigation apparatus providing rapid correction for excessive error in dead reckoning estimates of vehicle travel direction by direct application of position and direction information derived from GPS position measurement data
InactiveUS20020055819A1Sufficient degree of accuracyQuick estimateInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlGps measurementError reduction
In a vehicle navigation apparatus having a control section which calculates relative vehicle positions and travel direction by dead reckoning calculations based on outputs from on-board sensors and periodically acquires GPS measurement data via a GPS receiver and applies error-reduction filter processing to these data to obtain position and travel direction information for correcting the calculated relative positions, the apparatus has a function for detecting that a travel direction obtained by dead reckoning contains an excessive error, and when that condition is detected, for directly applying an estimated vehicle position and travel direction derived directly from the GPS data, without filter processing, to correct the corresponding relative position and travel direction estimates. Rapid correction can thereby be achieved when the vehicle has been operated in a condition whereby a large amount of error has suddenly arisen in the travel direction that is estimated by the apparatus through dead reckoning calculation, e.g., after the vehicle has been rotated on a turntable with the vehicle navigation apparatus inoperative.
Owner:DENSO CORP
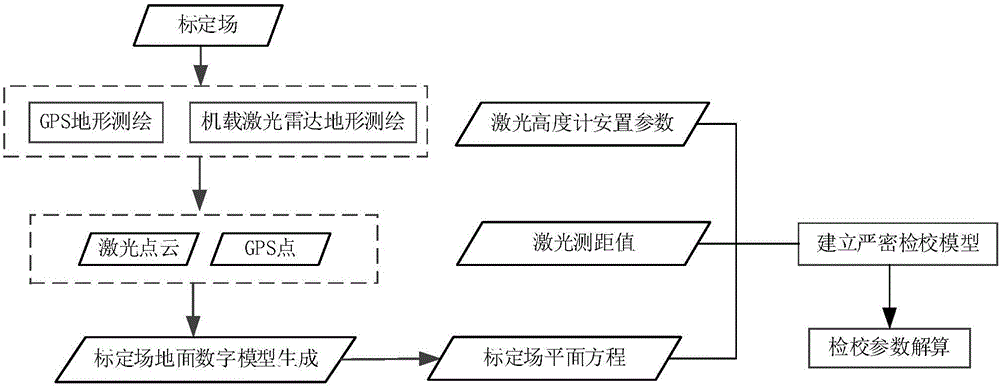
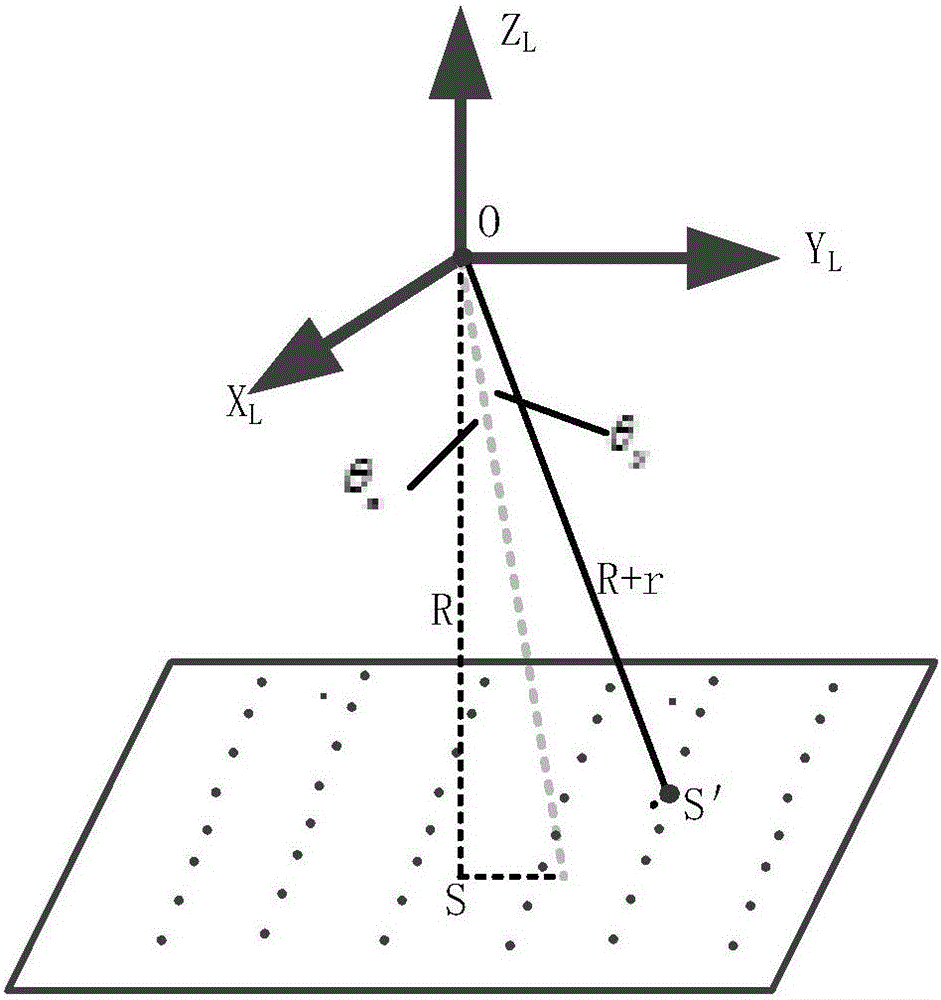
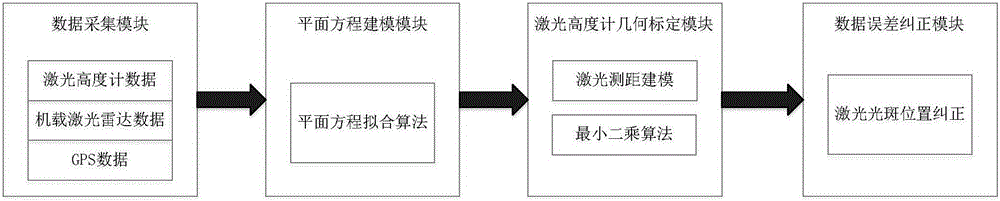
Made-in-China satellite laser altimeter on-orbit geometric calibration method and system
ActiveCN105842679ASolve installation deviationSolve the errorWave based measurement systemsTerrainOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a made-in-China satellite laser altimeter on-orbit geometric calibration method and a made-in-China satellite laser altimeter on-orbit geometric calibration system. The made-in-China satellite laser altimeter on-orbit geometric calibration method comprises the steps of: measuring terrain of a calibration field by utilizing an airborne laser radar or GPS before satellite top-crossing; fitting a surface geometry model of the calibration field by adopting laser radar point clout data or ground GPS measurement data; and placing a laser point of a satellite laser altimeter on a known plane as a constraint condition, establishing a satellite laser altimeter strict geometric calibration model, utilizing a least square principle, and solving a geometric calibration parameter of the satellite laser altimeter. The made-in-China satellite laser altimeter on-orbit geometric calibration method and the made-in-China satellite laser altimeter on-orbit geometric calibration system can effectively solve the problem that positioning precision of a laser spot is not high due to installation deviation of the satellite laser altimeter and errors of laser range finding by utilizing ground natural terrain during satellite transition, increase measuring precision of the made-in-China satellite laser altimeter, and have high applicability and practical value.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
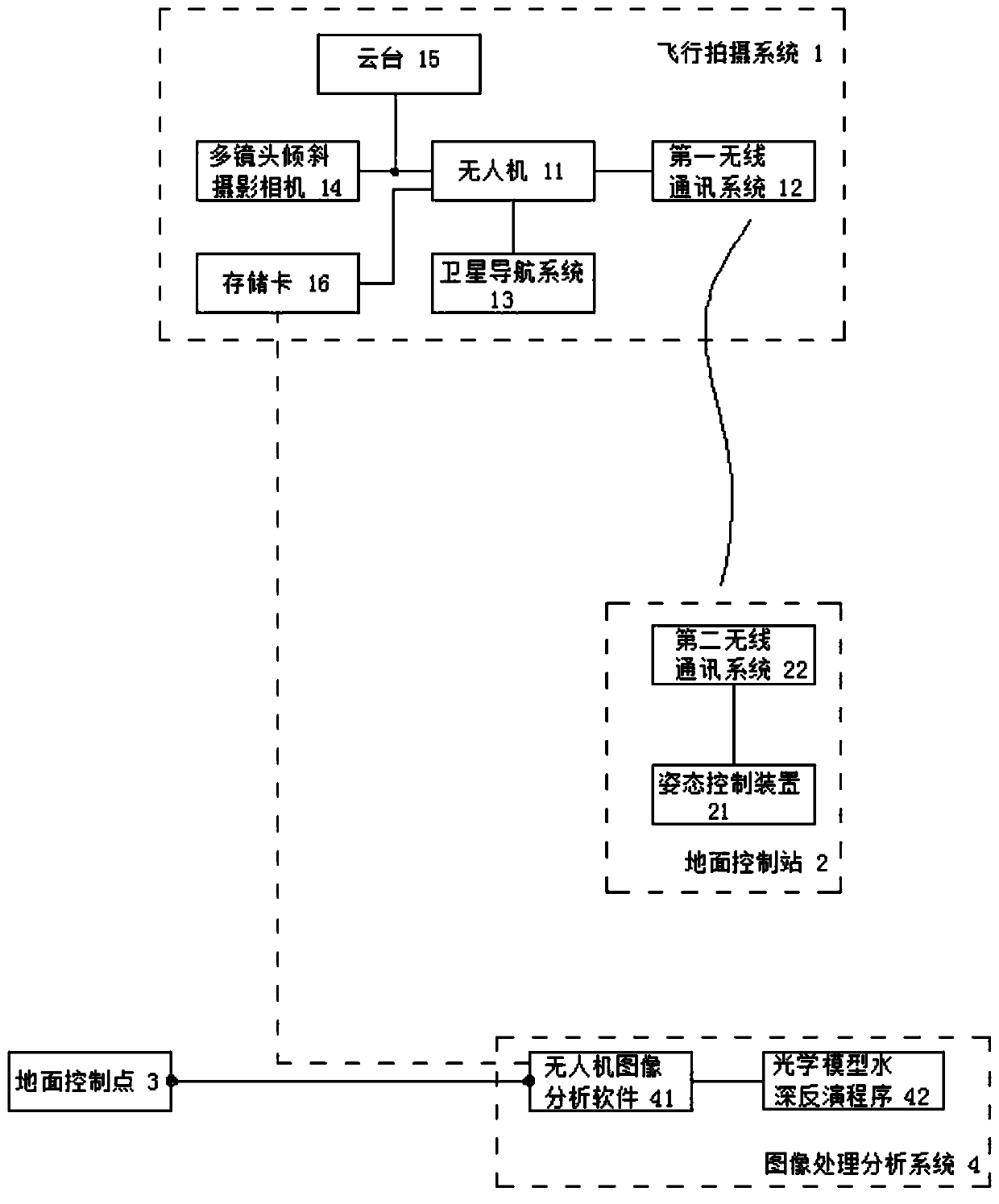
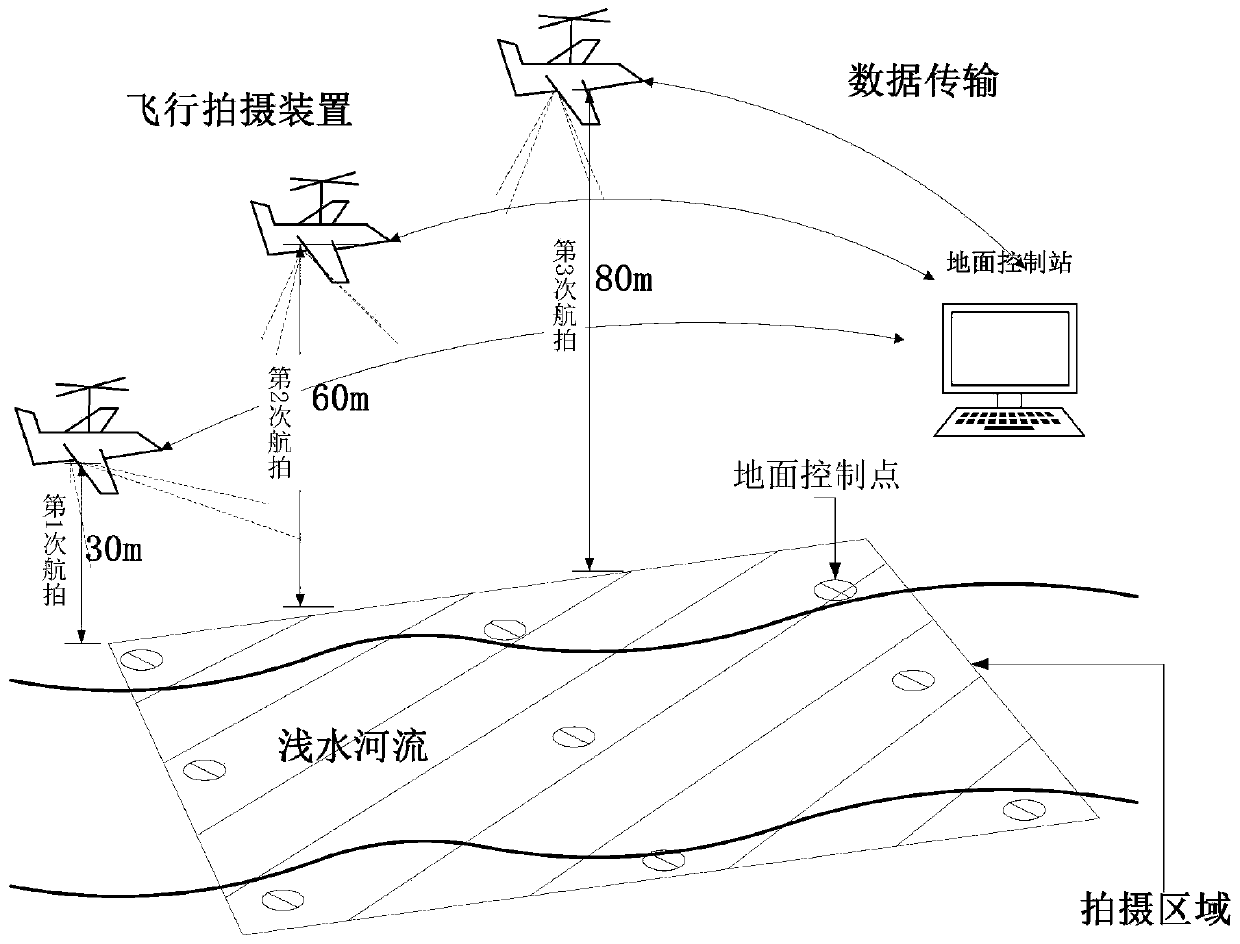
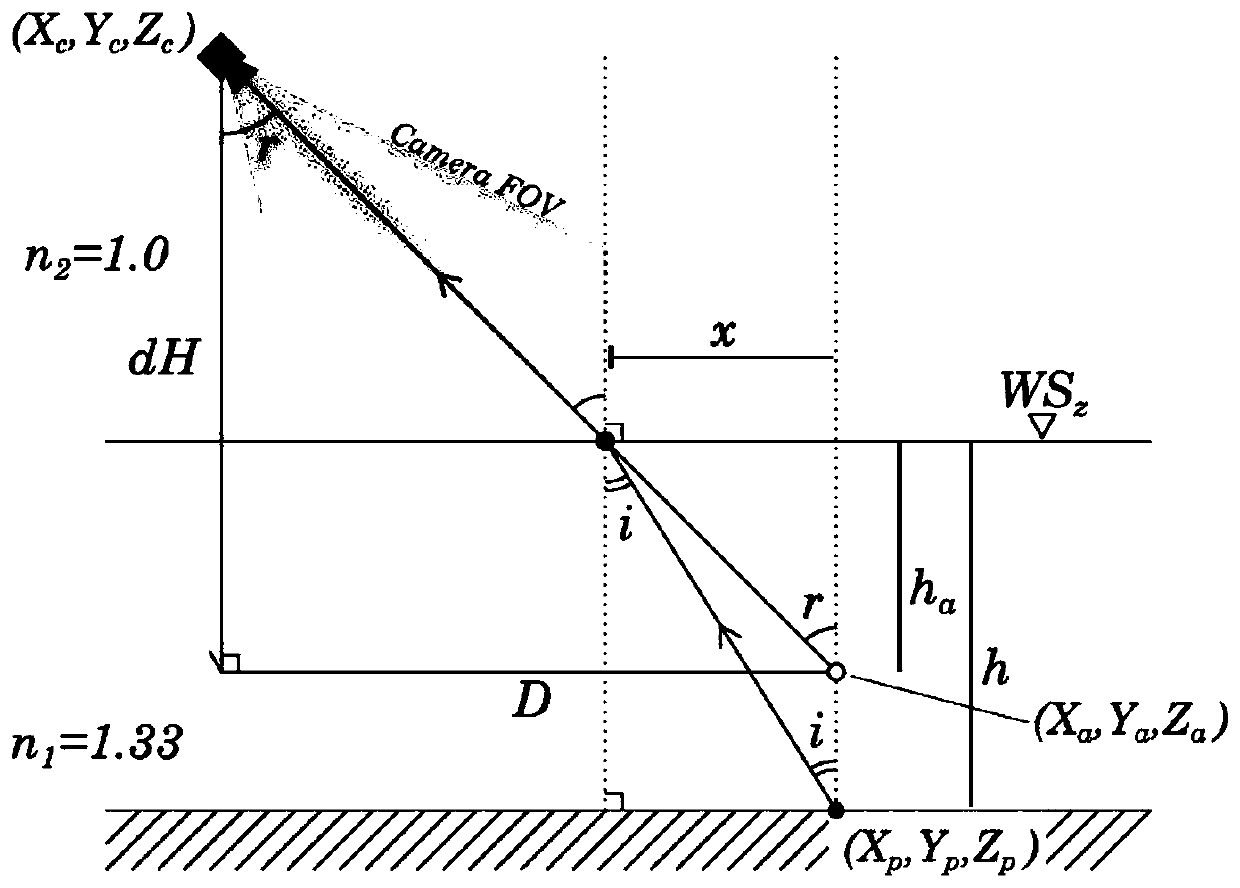
Shallow river water depth surveying and mapping method and system based on unmanned aerial vehicle multi-view shooting
ActiveCN110779498AReduce personal riskHigh measurement accuracyMeasuring open water depthWater resource assessmentTotal stationAngle of view
The present invention discloses a shallow river water depth surveying and mapping system and method based on unmanned aerial vehicle multi-view shooting. The method comprises step S1: determining a surveying time, a surveying area and surveying precision; S2: setting ground control points GCPs in the surveying area, and using a positioning instrument to perform positioning on the control points; S3: planning a flight line of an unmanned aerial vehicle, and performing aerial shooting according to the pre-determined air line; and S4: using unmanned aerial vehicle image analysis software to process an image of the multi-view shooting in step S3, surveying an orthoimage and a digital surface elevation model of the area, and applying an optical model water depth inverse program to perform refraction correction and to perform inversion to obtain a water depth value of a shallow river. Compared with conventional GPS measurement, total station measurement and echo sounding, the method is time-saving, labor-saving and cost-saving, causes no damage to a water body and a river bed, and has relative high execution efficiency; and water depth surveying and mapping is extended from point measurement to face measurement, a relatively high spatial resolution is provided, and water depth measurement precision and a spatial resolution are also improved.
Owner:INST OF GEODESY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
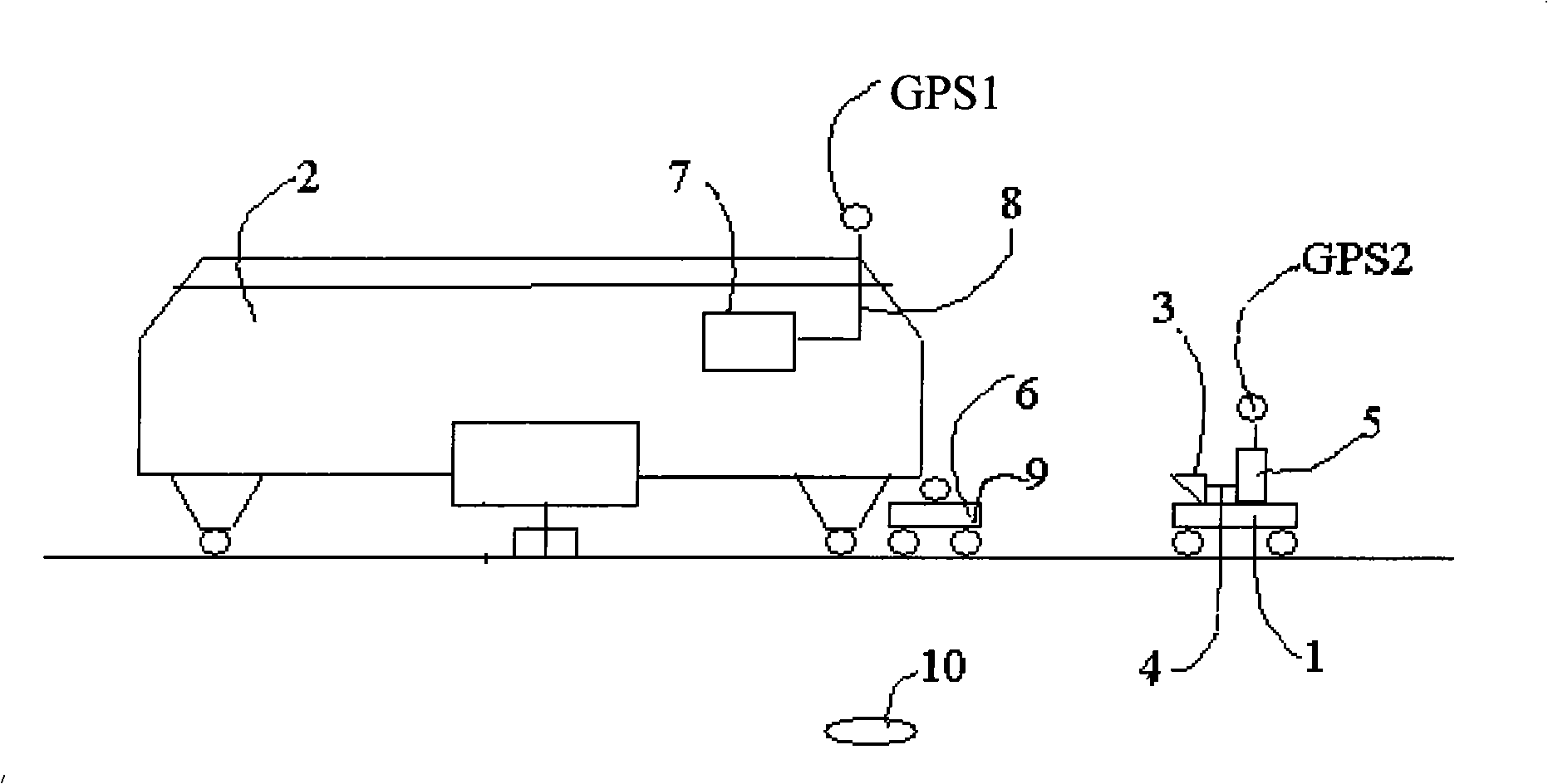
Track curve parameter measuring device and method
ActiveCN101306691AEliminate long-wave errorsBeacon systems using radio wavesSurveying instrumentsGps measurementData control
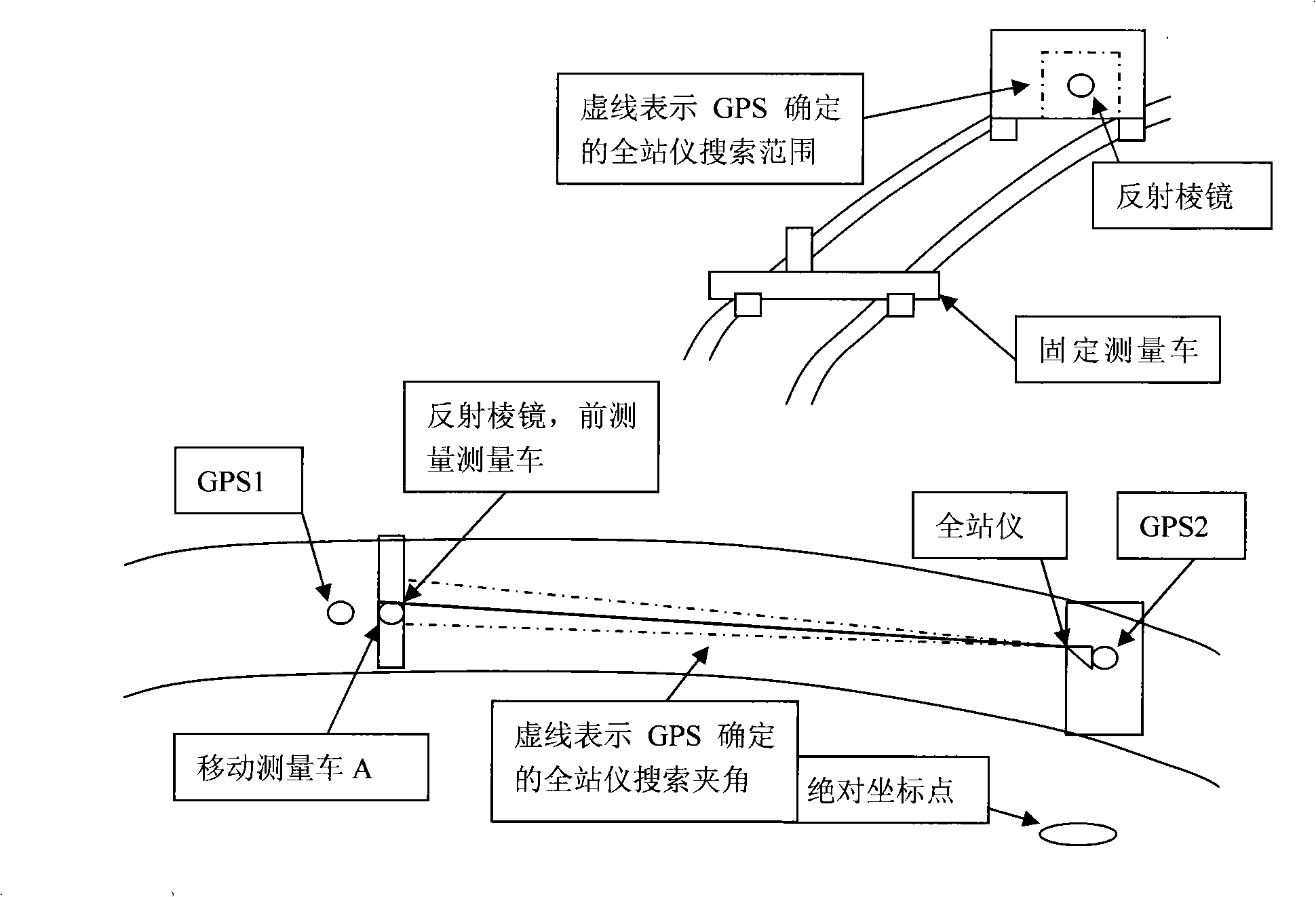
A rail curve parameter measuring device comprises a fixed measuring vehicle which is provided with an electronic total station, a vehicle mounted computer and a fixed vehicle global positioning system; a movable measuring vehicle which is provided with a front-end reflection object, a movable global positioning system, a wireless data transmission system and a tilt angle sensor; and a global positioning system base station. The method comprises the following steps: the search range of the total station to the front-end reflection object is calculated and the total station is controlled to turn to the position through the RTK-GPS measurements of geodetic coordinates of the movable measuring vehicle and the fixed measuring vehicle at the both ends of the rail section; the total station locks the front-end reflection object and measures the coordinate data thereof within the designated range, the vehicle mounted computer calculates the current rail parameters according to the coordinate and the value of the tilt angle sensor; the movable vehicle is driven to the fixed vehicle along the rail, and the vehicle mounted computer continuously calculate the rail parameters according to the new data. The rail curve parameter measuring device combines the GPS measurement and the total station optical measurement to realize the rail parameter measurement, utilizes the GPS data to control the direction orienteering of the total station, and allows the total station to carry out the precise measurement.
Owner:ZHUZHOU CSR TIMES ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com