Patents
Literature
258 results about "Earth model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
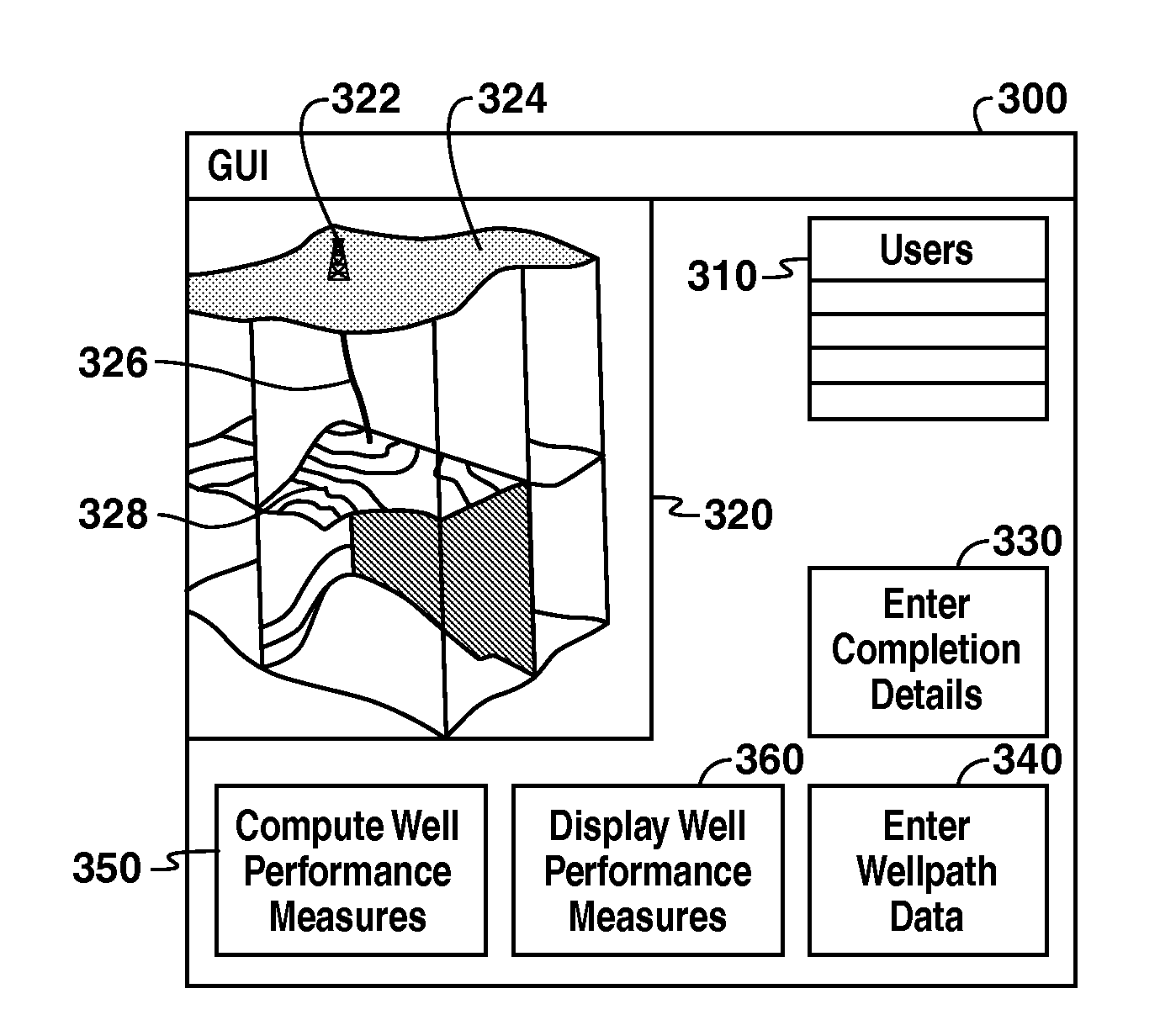
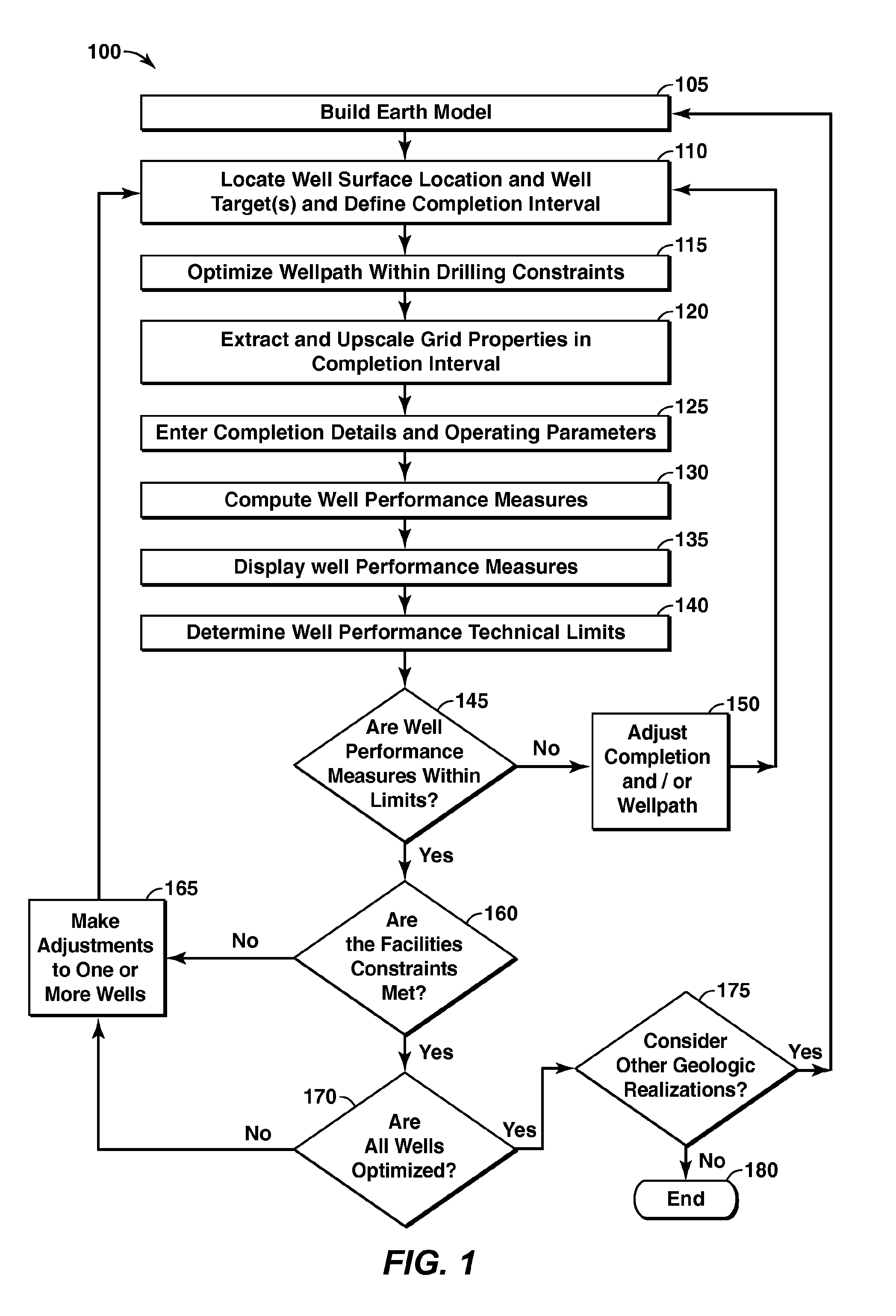
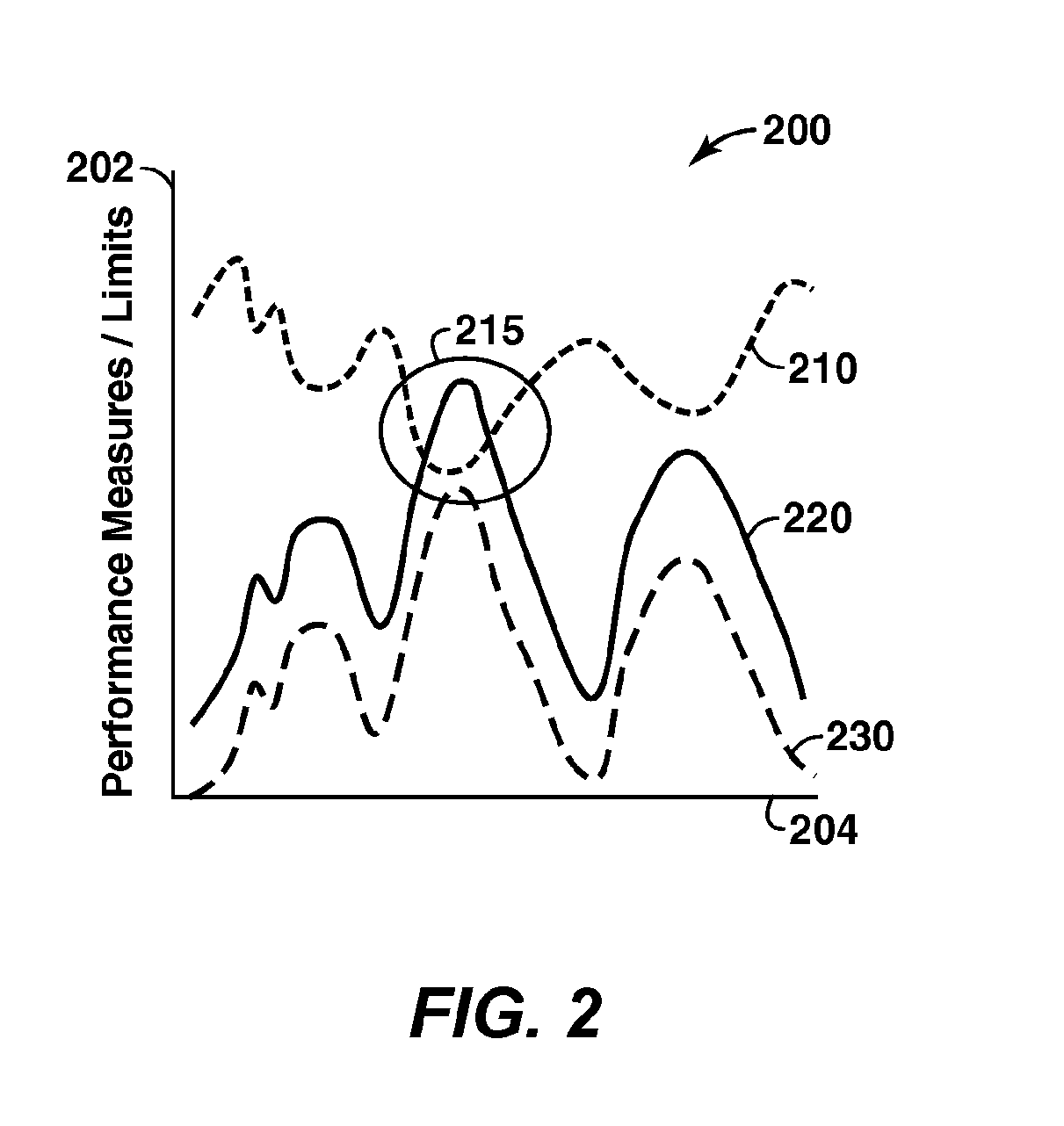
Well Performance Modeling In A Collaborative Well Planning Environment
InactiveUS20100191516A1Maximize objective functionFluid removalAnalogue processes for specific applicationsGraphicsGraphical user interface
Methods and systems are provided that may be utilized to make completion design an integral part of the well planning process by enabling the rapid evaluation of completion performance. This integration may include an earth model and may specify wellpath parameters, completion parameters, and other parameters in a simulation of operations using the earth model. The simulation generates well performance measures, which may be optimized depending on well performance technical limits. The optimization may be used to maximize an objective function. The system may include multiple users at the same or different locations (e.g. over a network) interacting through graphic user interfaces (GUI's).
Owner:BENISH TIMOTHY G +4
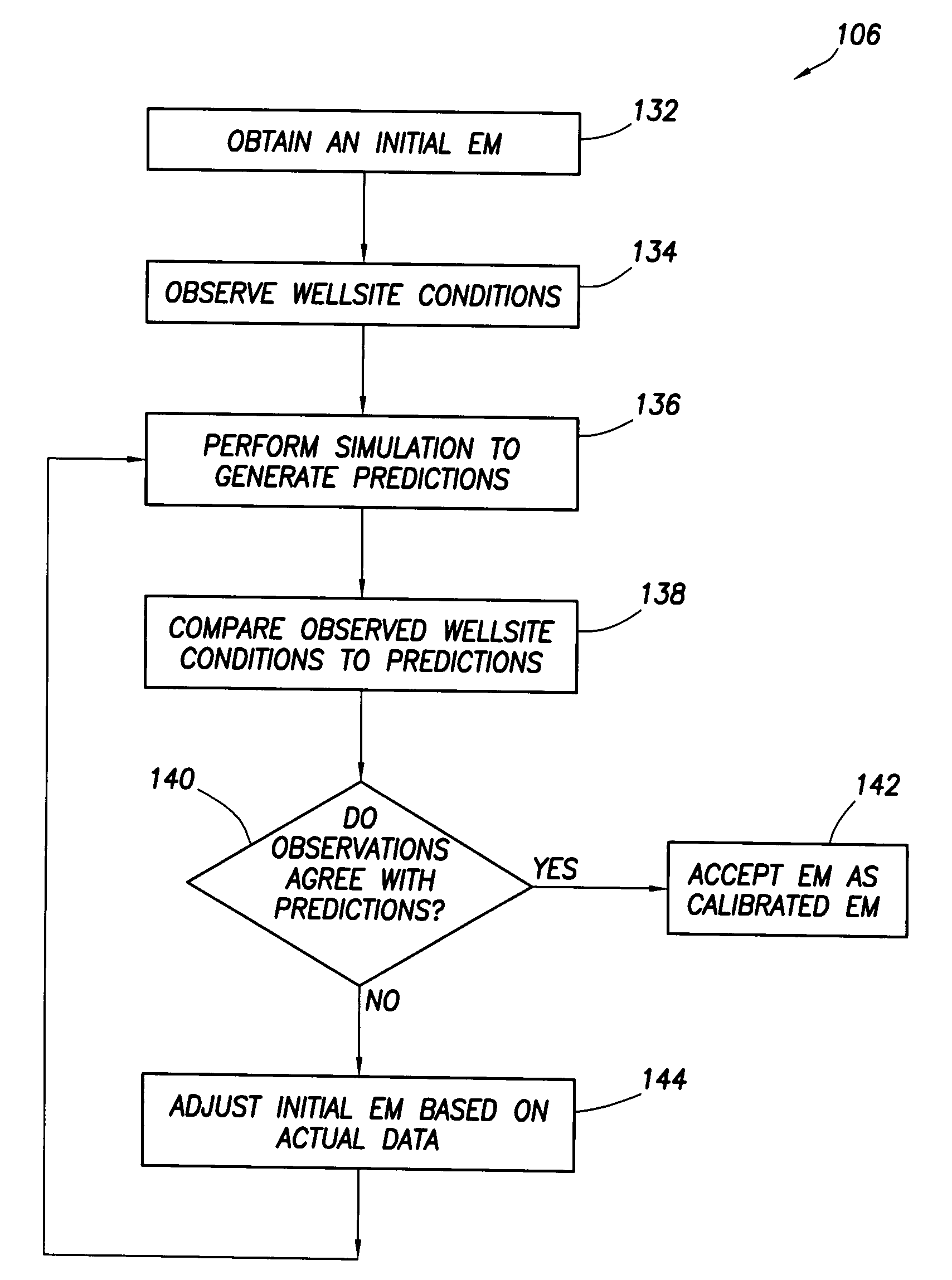
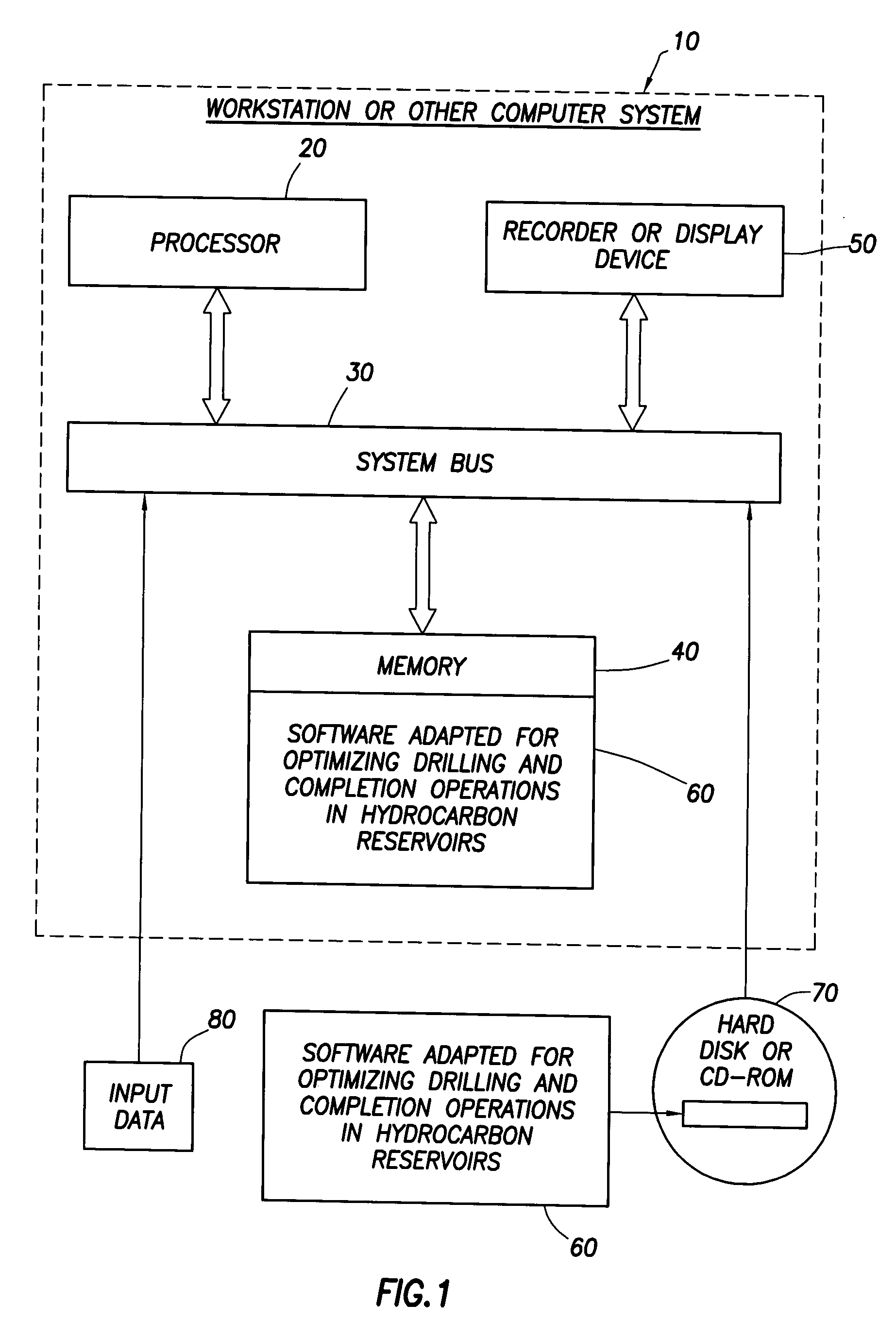
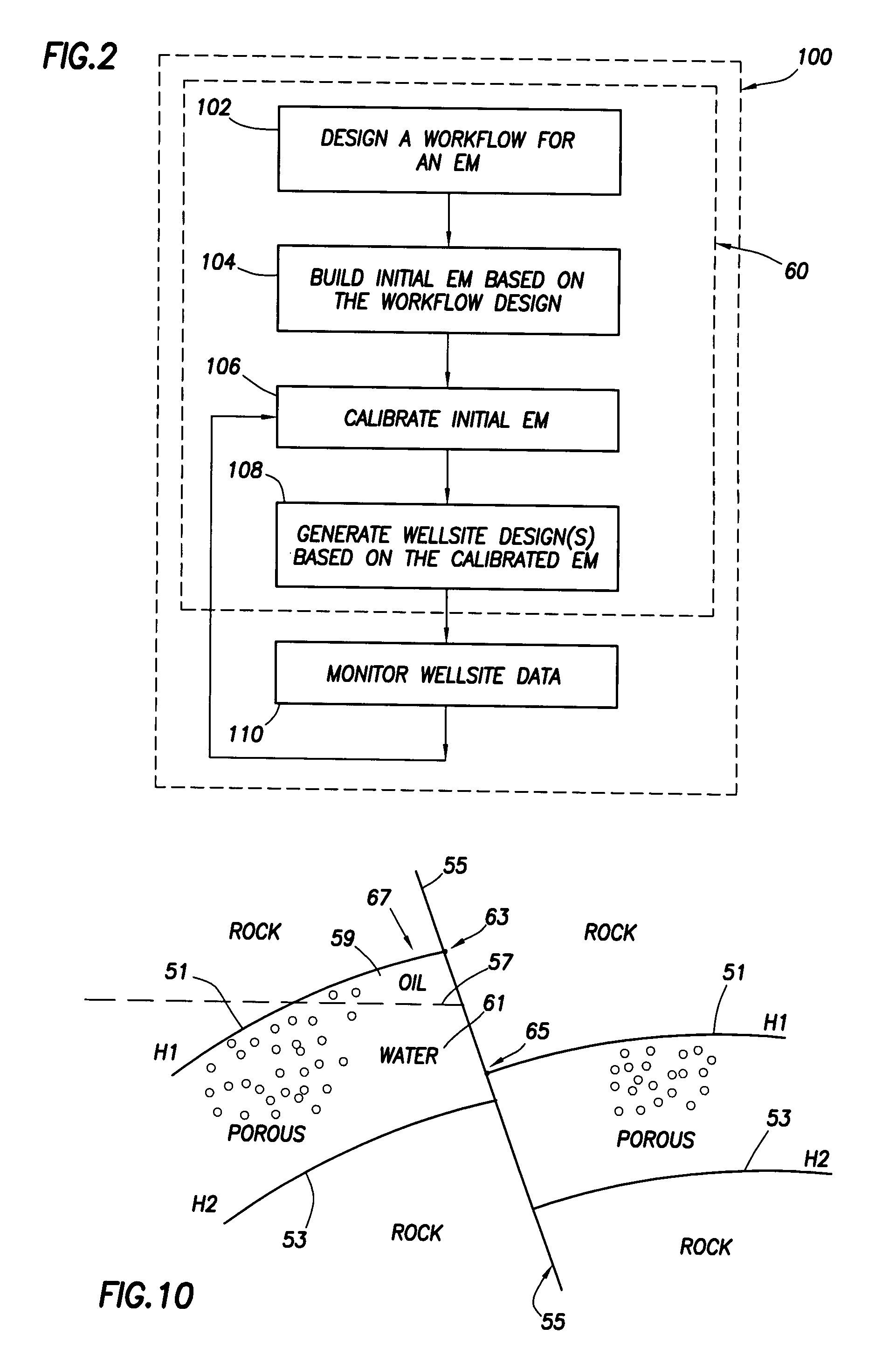
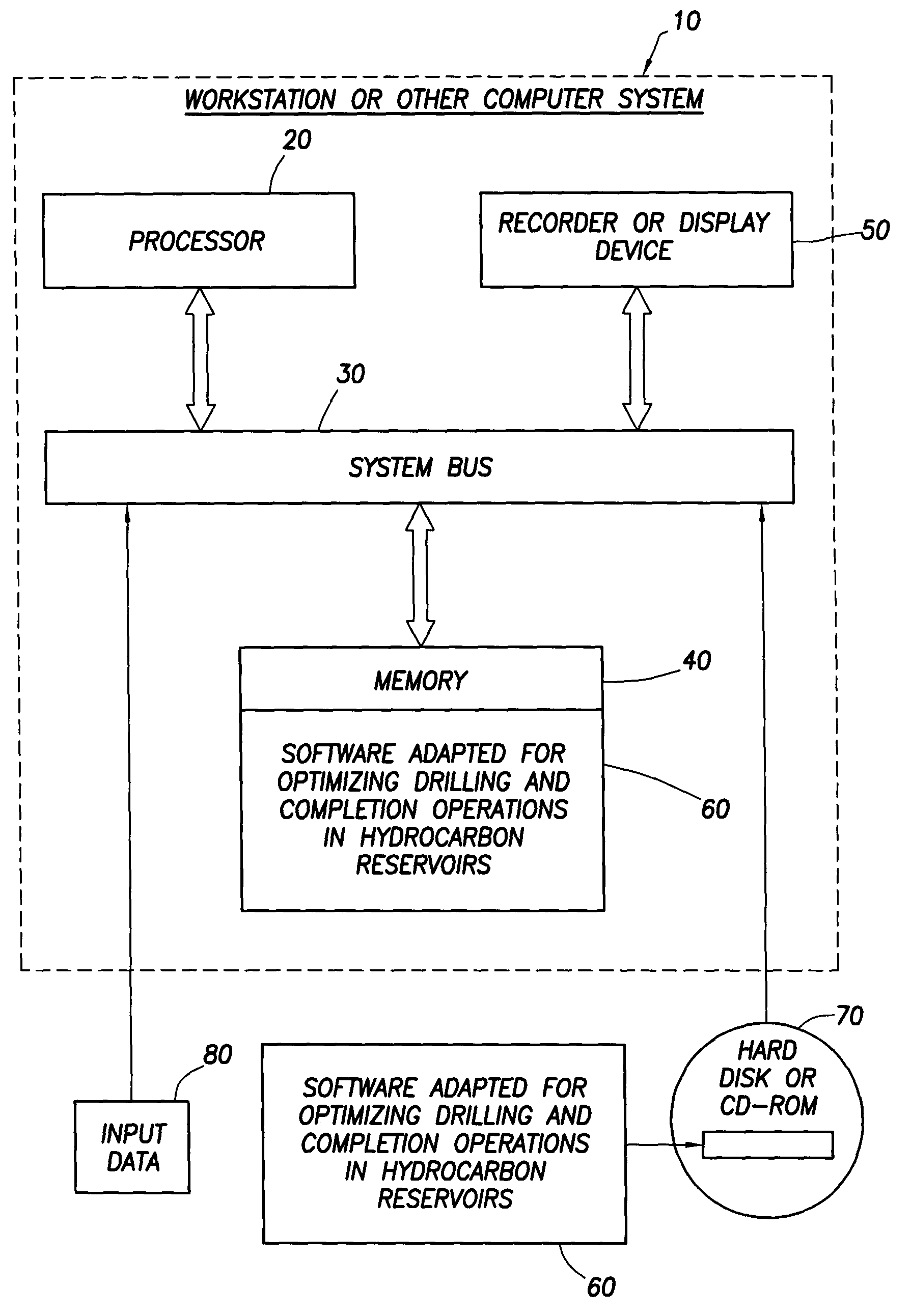
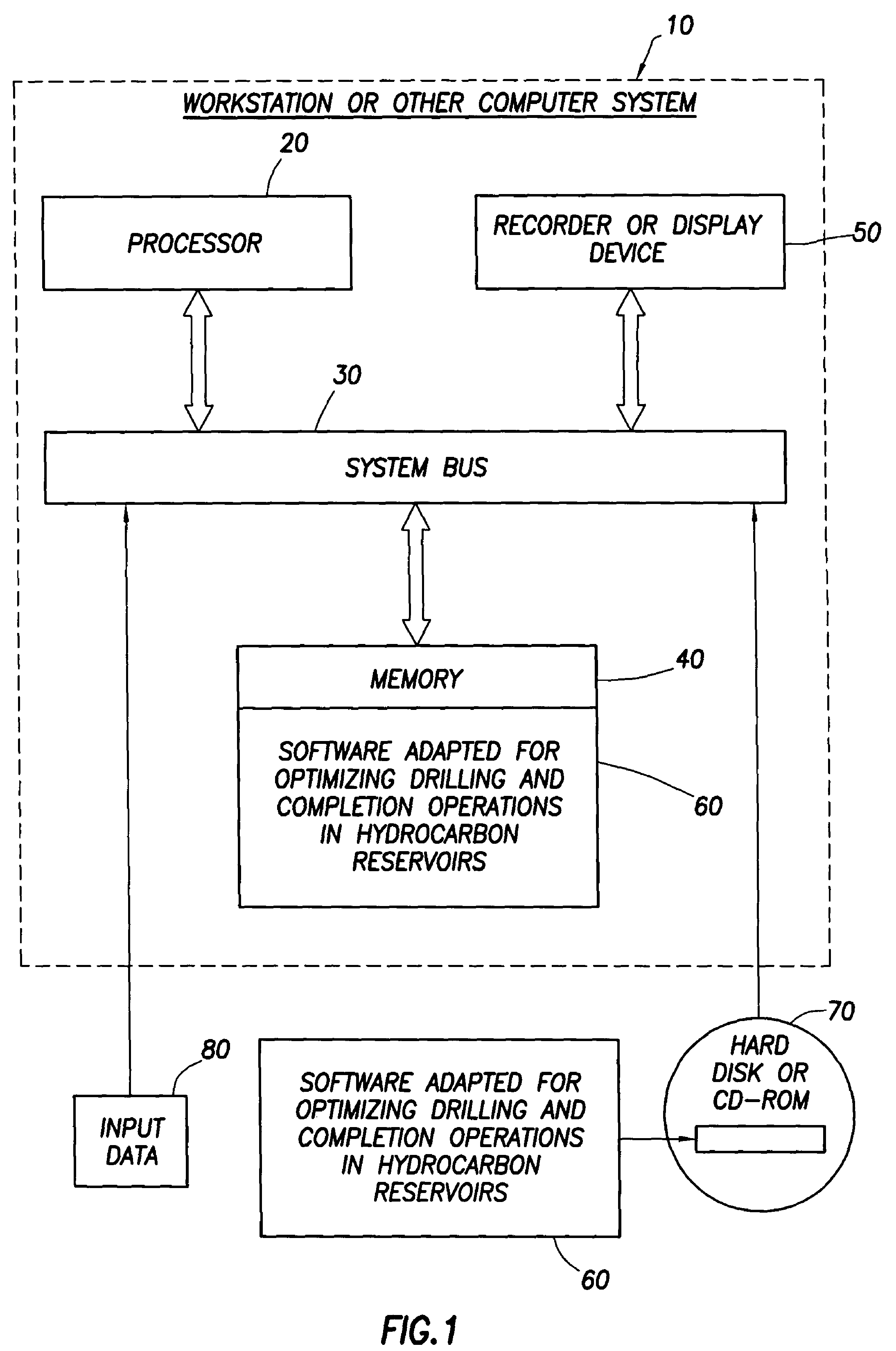
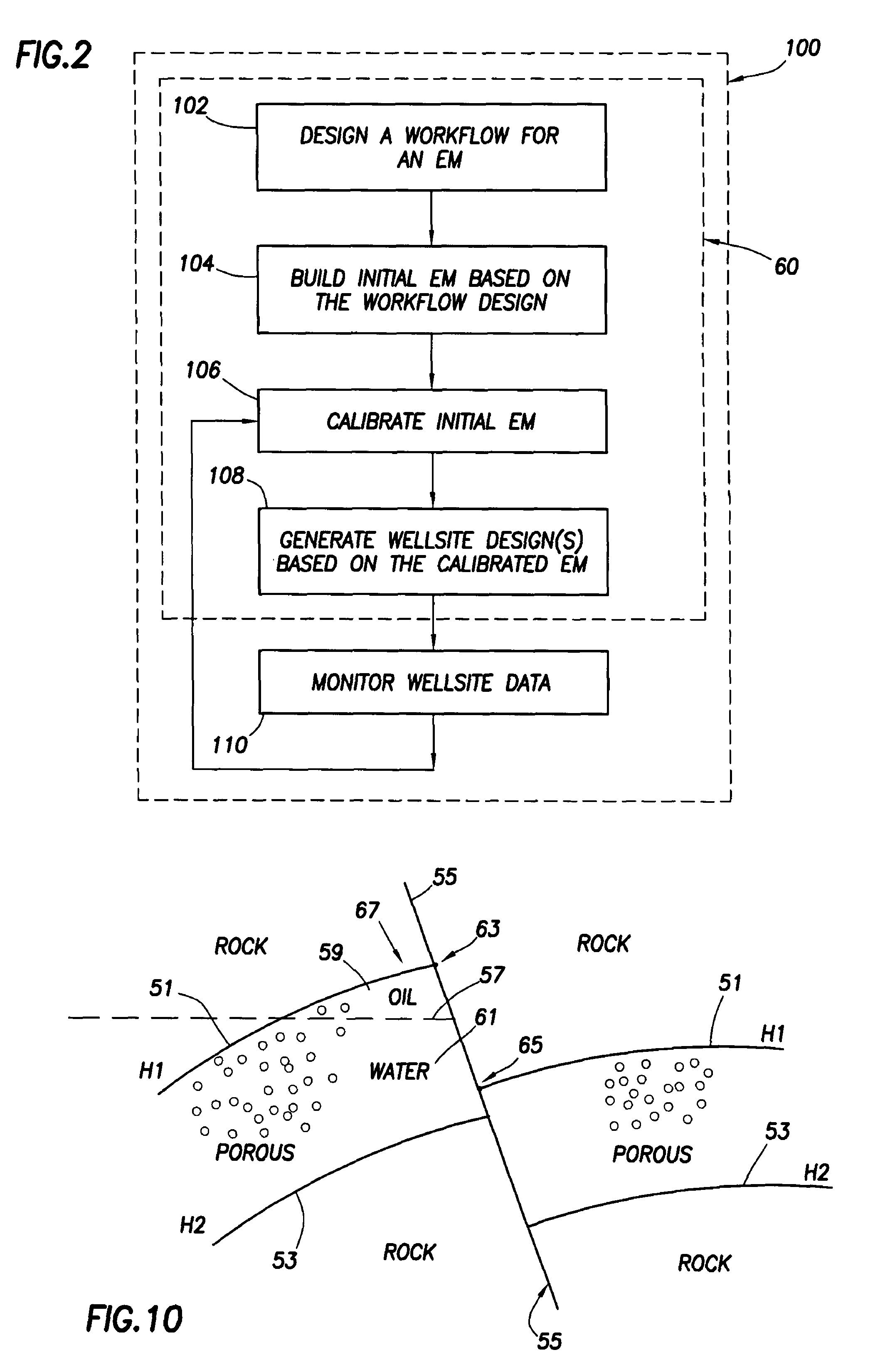
Method for designing and optimizing drilling and completion operations in hydrocarbon reservoirs
ActiveUS20070294034A1Speed maximizationMinimize damageGeometric CADElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWell drillingEarth model
A method is disclosed for generating a wellsite design, comprising: designing a workflow for an Earth Model; building an initial Earth Model based on the workflow adapted for modeling drilling and completions operations in a hydrocarbon reservoir; calibrating the initial Earth Model thereby generating a calibrated Earth Model; and generating the wellsite design using the calibrated Earth Model.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
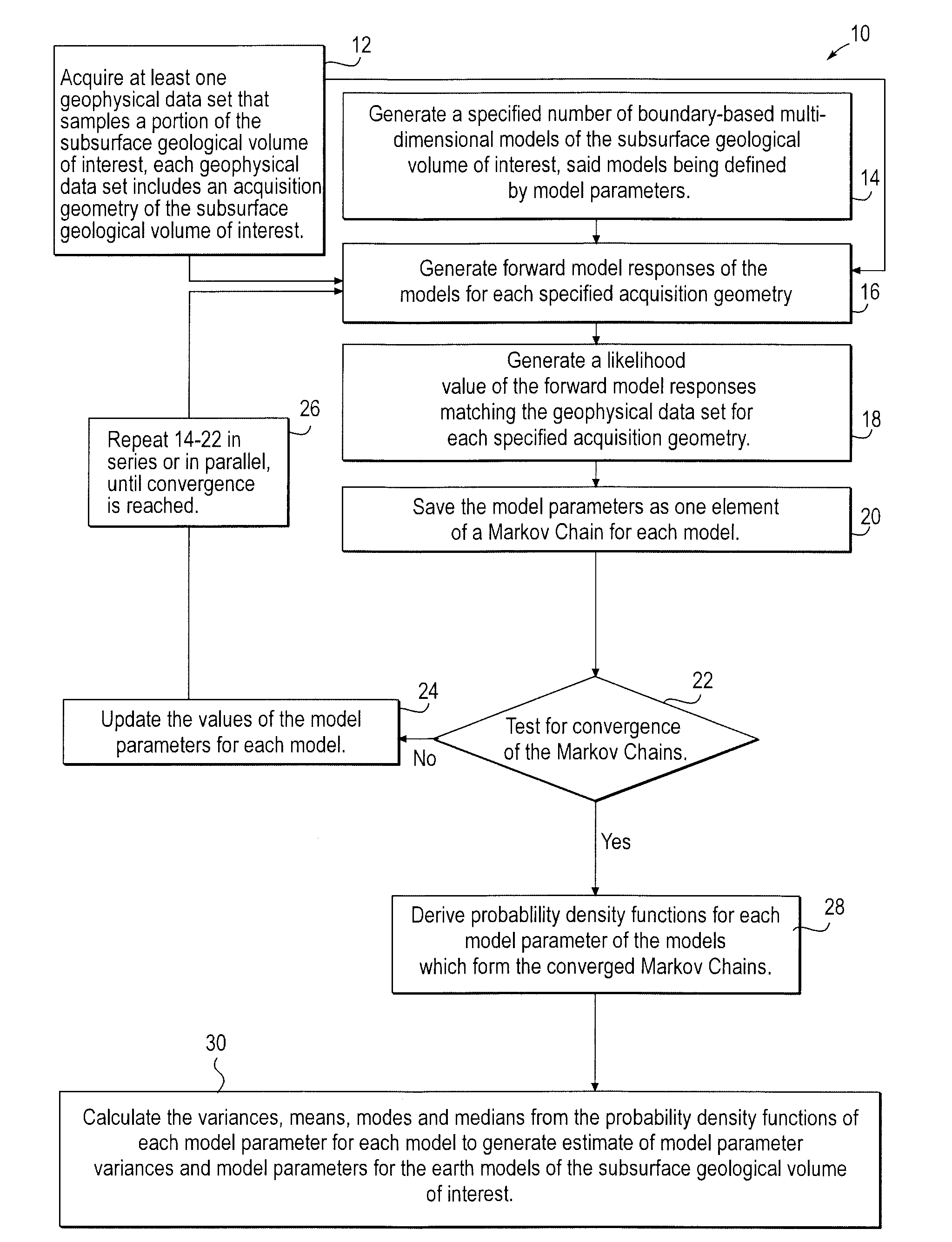
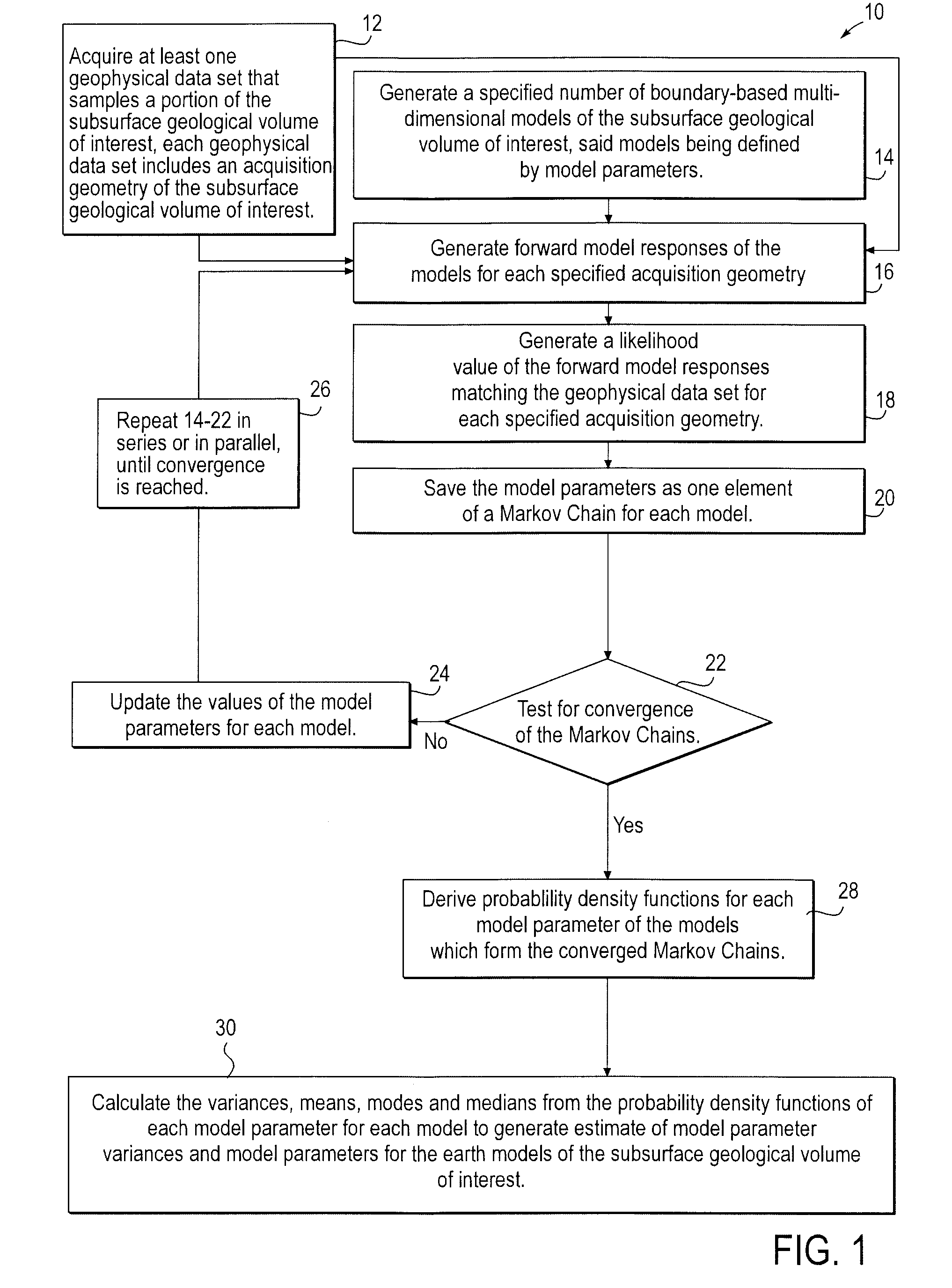
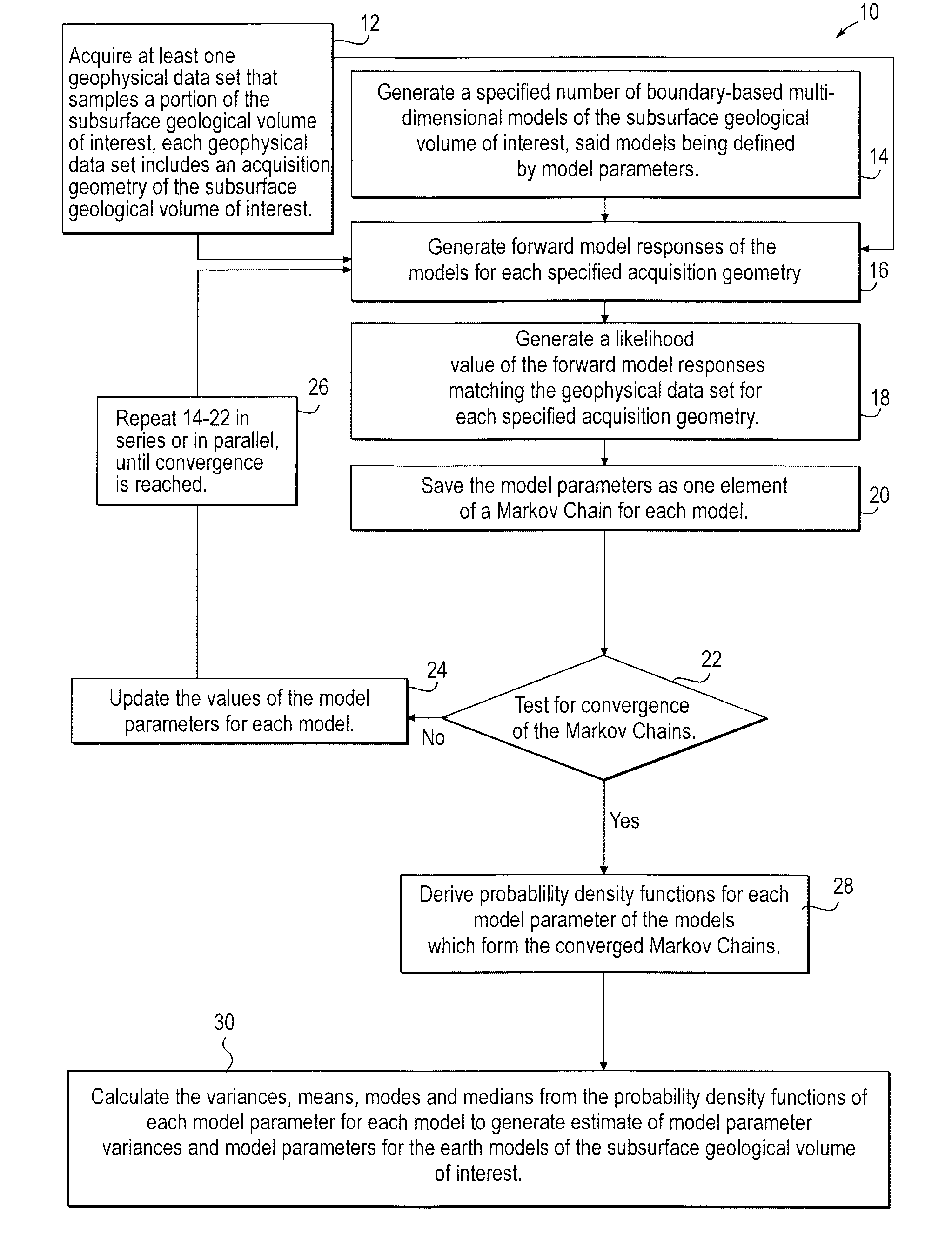
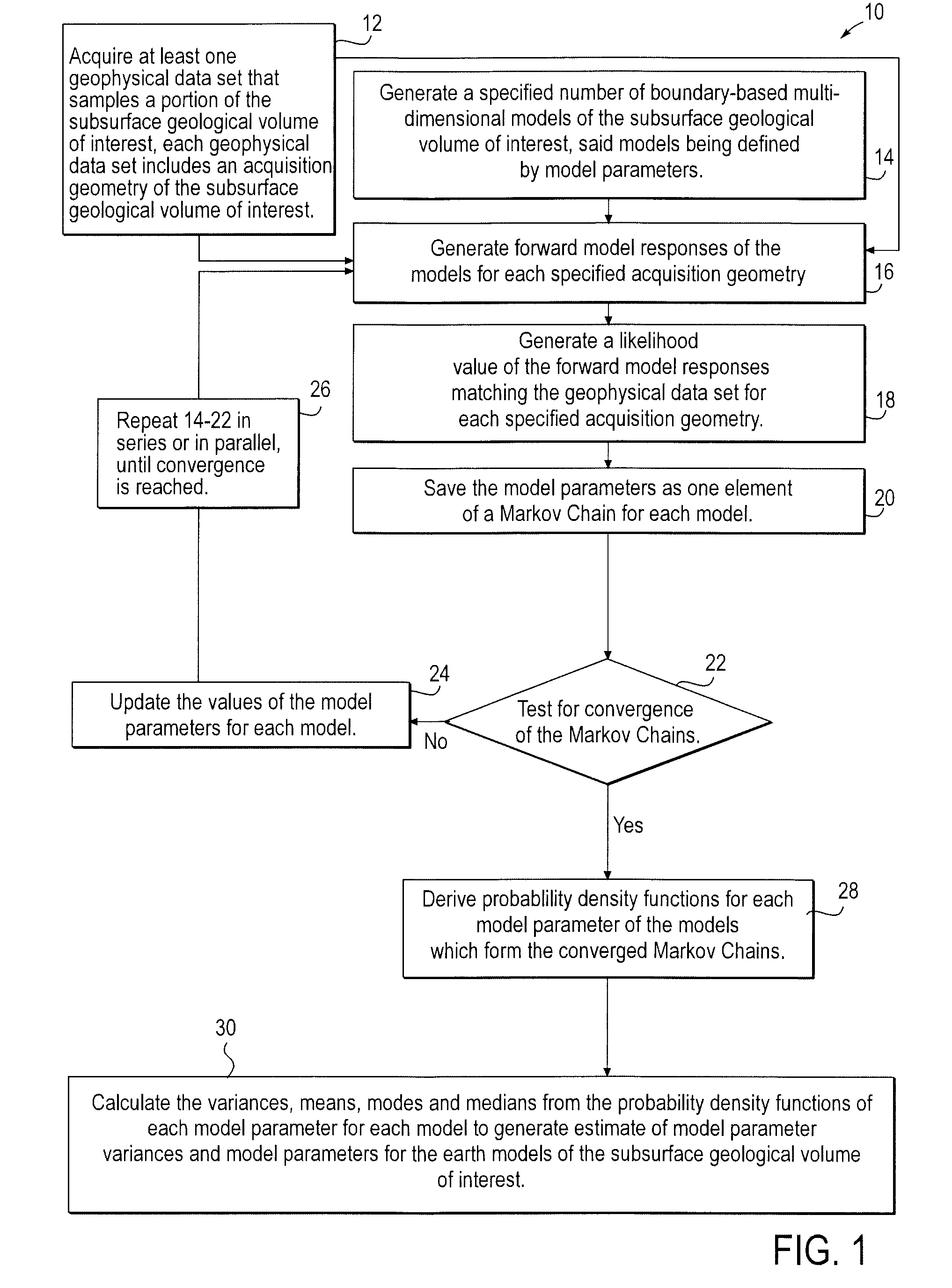
Stochastic inversion of geophysical data for estimating earth model parameters
A computer implemented stochastic inversion method for estimating model parameters of an earth model. In an embodiment, the method utilizes a sampling-based stochastic technique to determine the probability density functions (PDF) of the model parameters that define a boundary-based multi-dimensional model of the subsurface. In some embodiments a sampling technique known as Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) is utilized. MCMC techniques fall into the class of “importance sampling” techniques, in which the posterior probability distribution is sampled in proportion to the model's ability to fit or match the specified acquisition geometry. In another embodiment, the inversion includes the joint inversion of multiple geophysical data sets. Embodiments of the invention also relate to a computer system configured to perform a method for estimating model parameters for accurate interpretation of the earth's subsurface.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
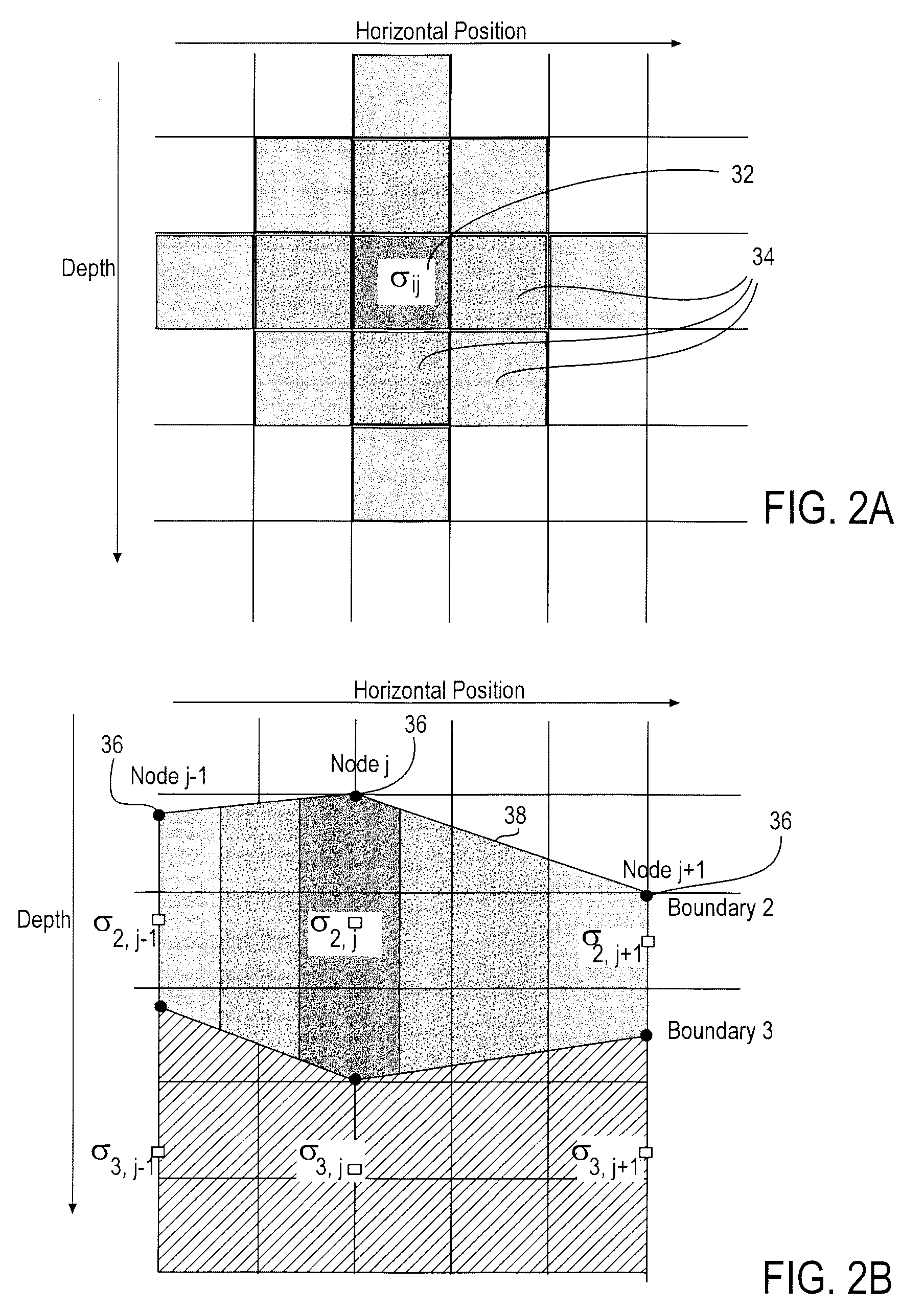
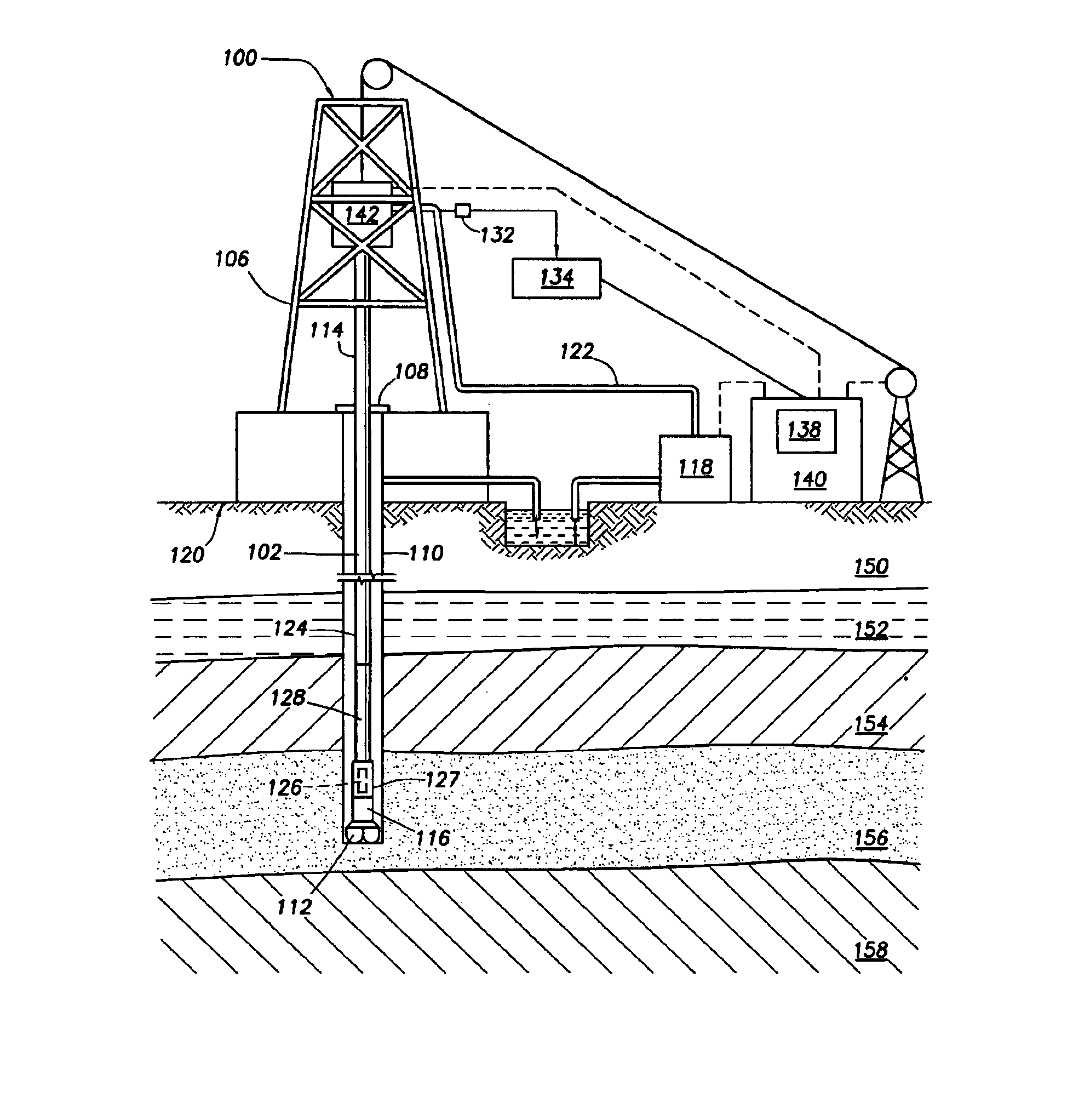
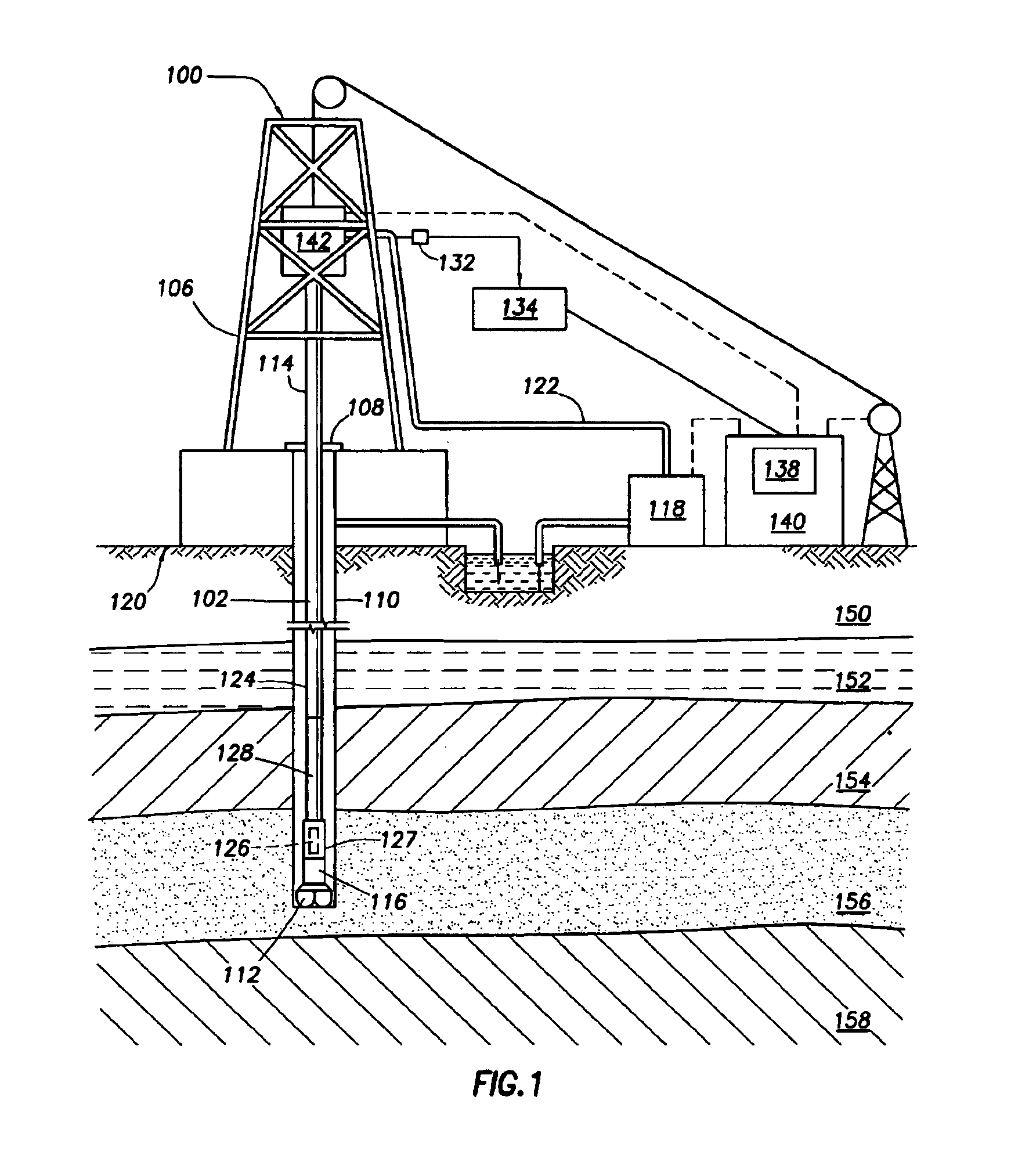
Realtime control of a drilling system using the output from combination of an earth model and a drilling process model
A system is for controlling borehole operations using a computational drilling process model representing the combined effect of downhole conditions and the operation of a drillstring. The drilling process model is continually updated with downhole measurements made during a drilling operation. From the updated drilling process model, a set of optimum drilling parameters is determined and communicated to a surface equipment control system. Further, the system allows the surface equipment control system to automatically adjust current surface equipment control settings based on the updated optimum drilling parameters. Various control scripts are generated and executed to inform the surface equipment control system based on a present drilling mode.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
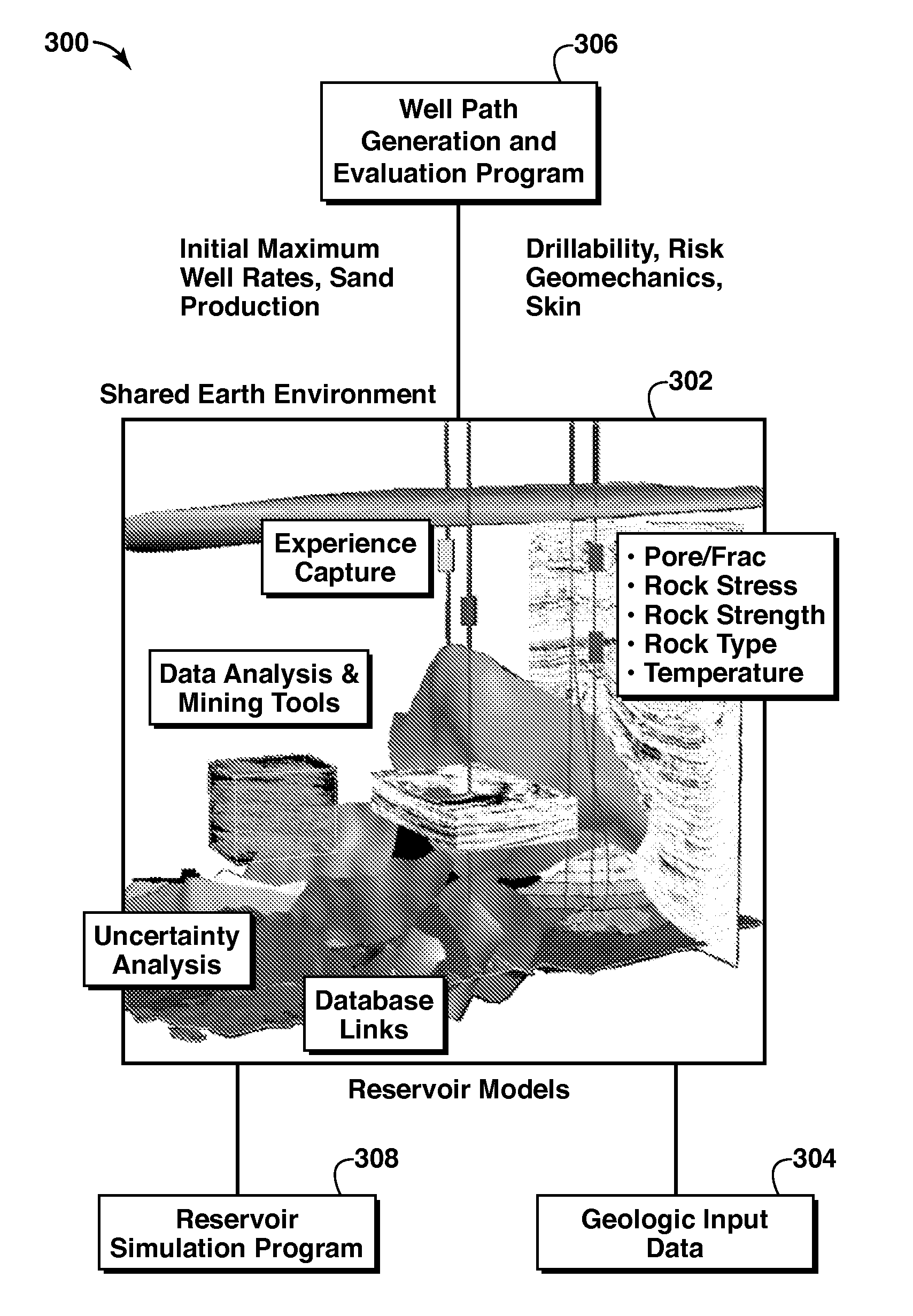
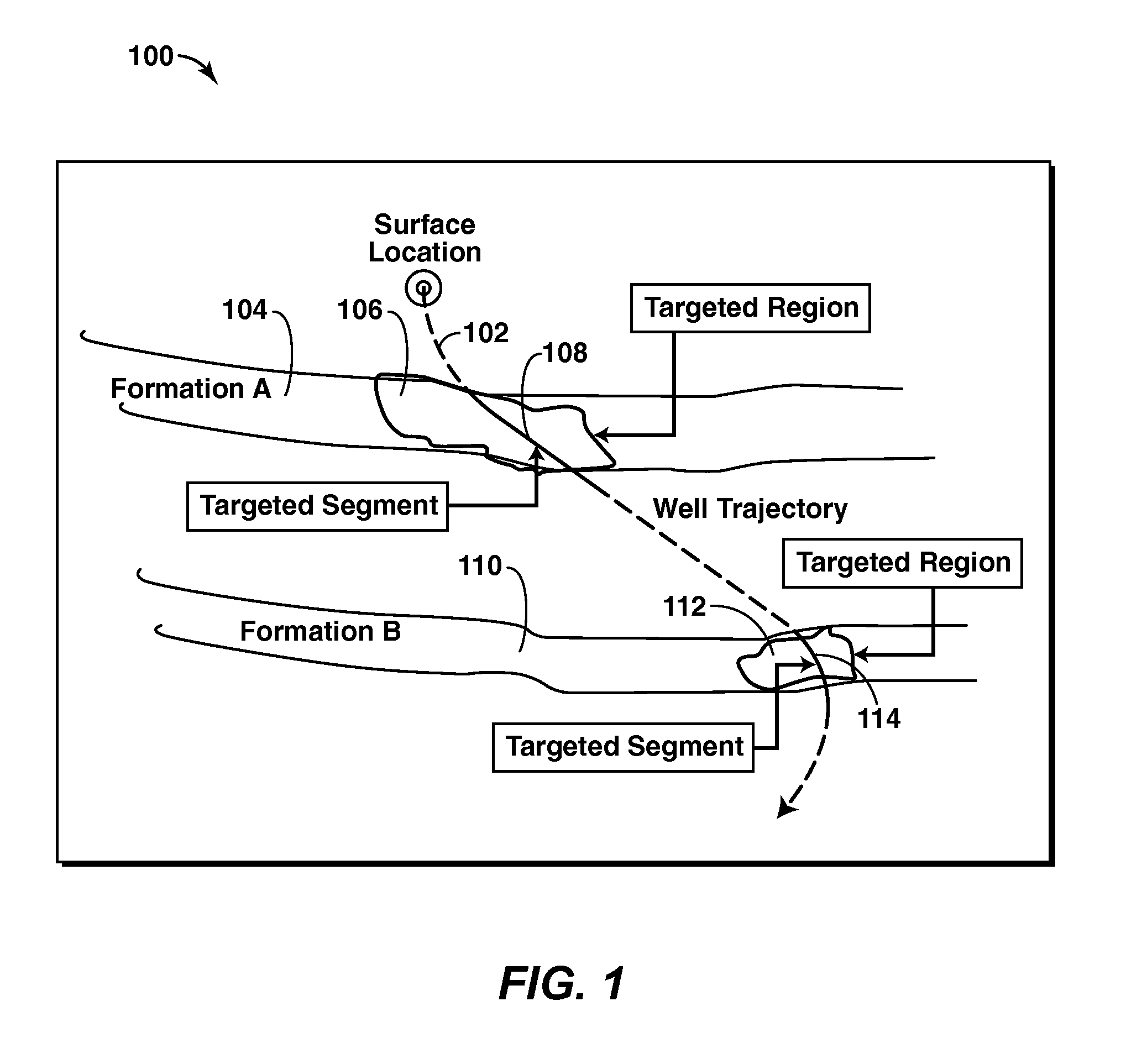
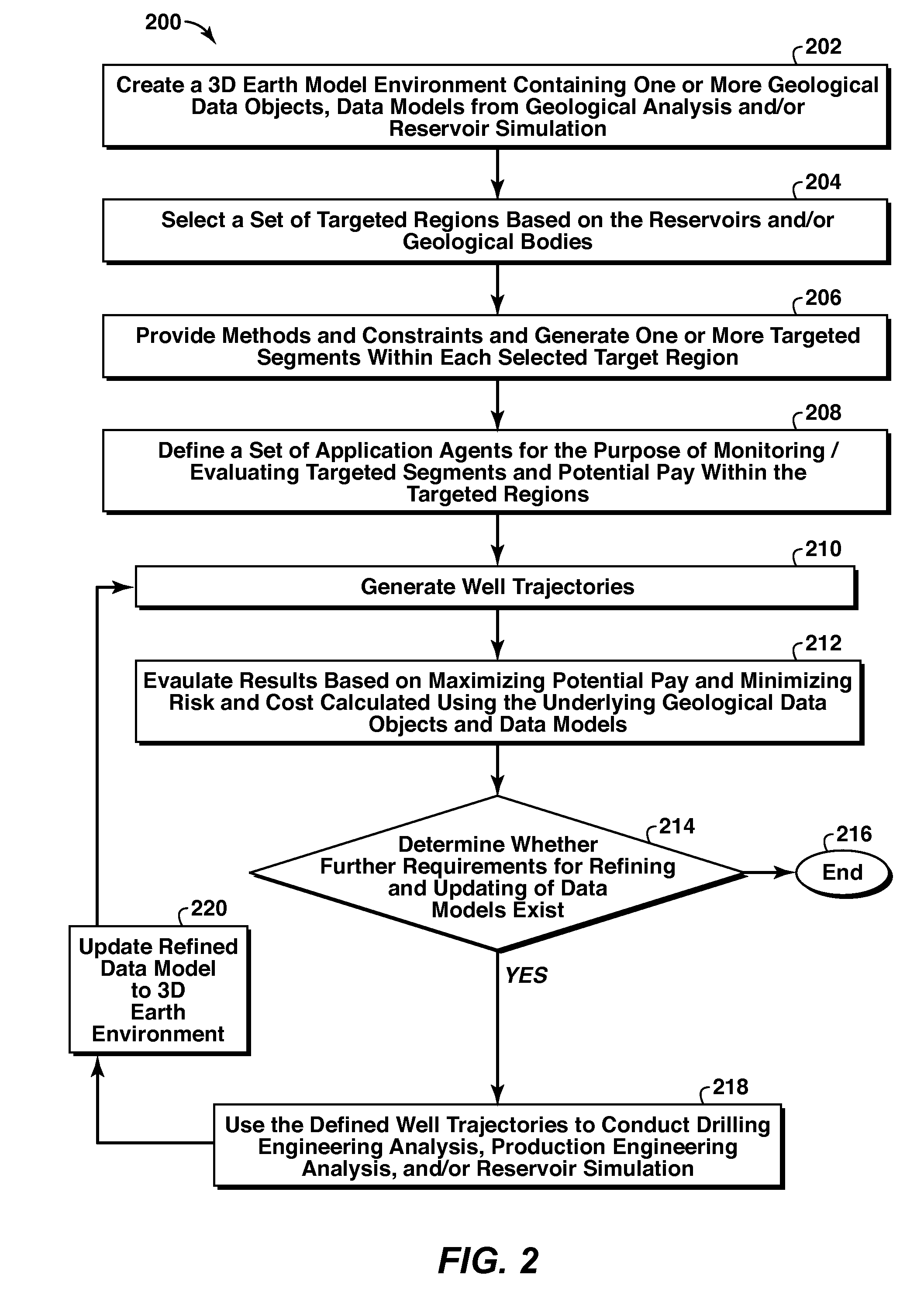
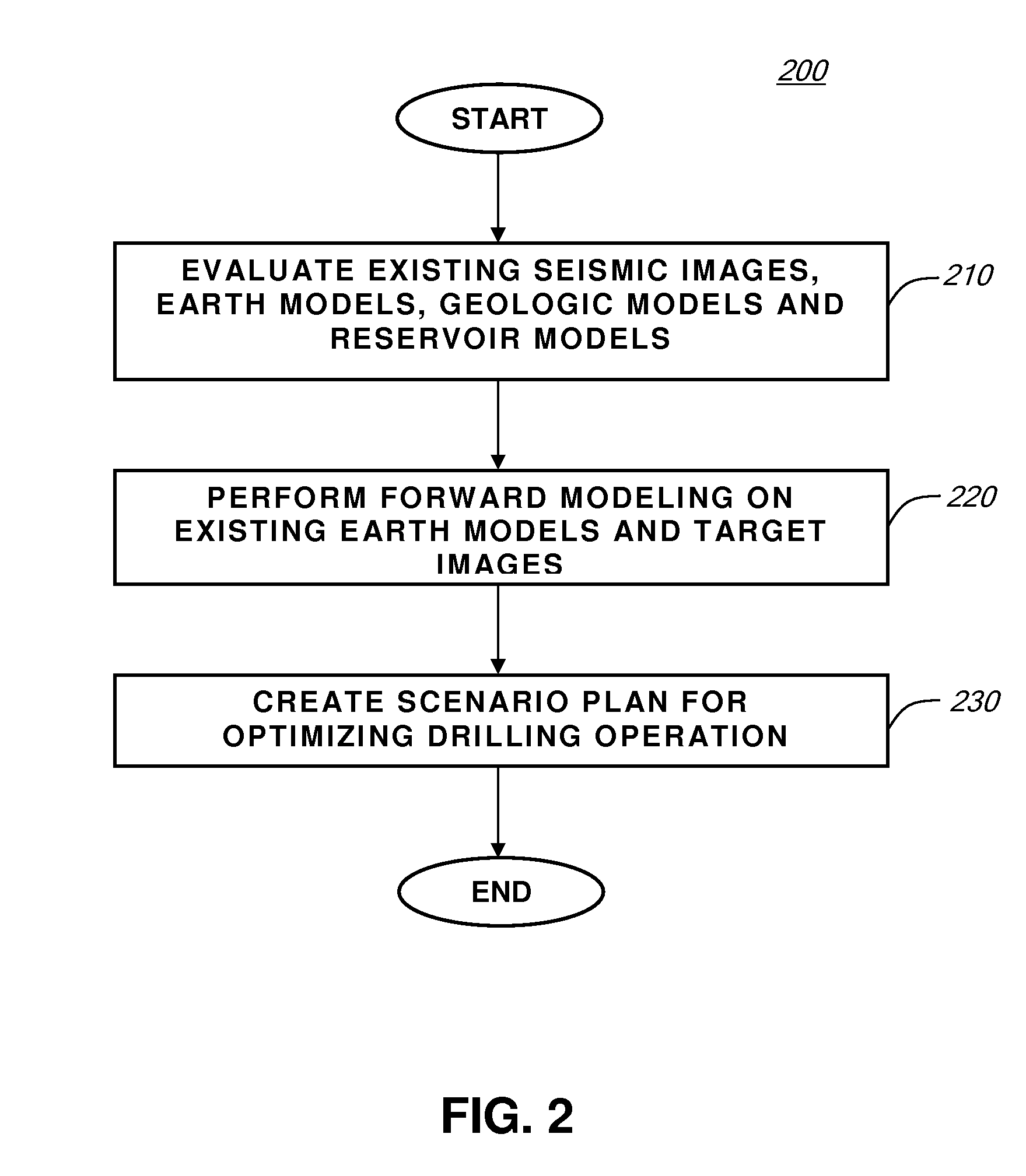
System and Method For Planning A Drilling Operation
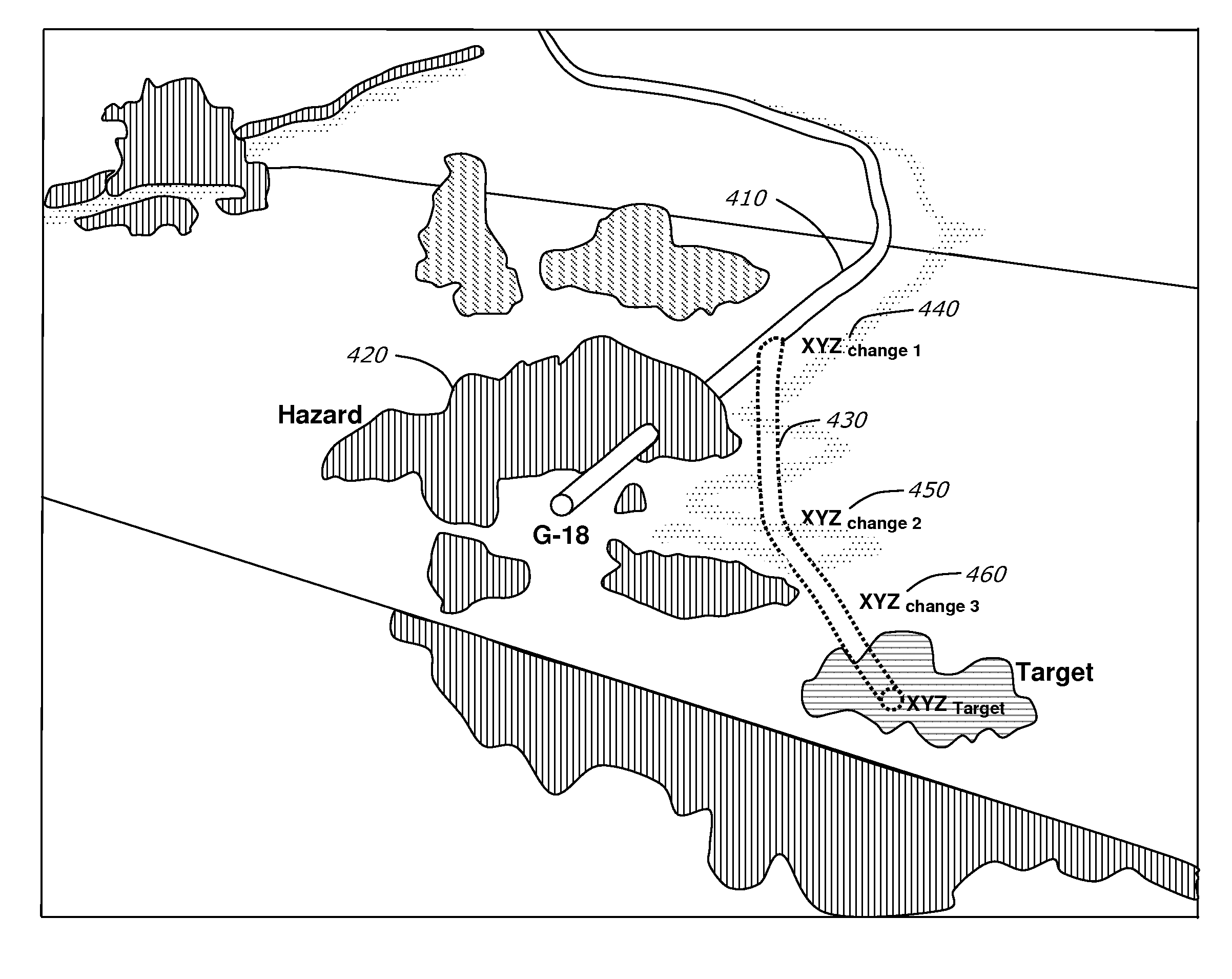
A method of planning a drilling operation IS provided that comprises selecting a set of targeted regions based on data from a three-dimensional shared earth model and generating at least one targeted segment within each one of the set of targeted regions The method further comprises defining at least one application agent for the purpose of evaluating the at least one targeted segment within each one of the set of targeted regions based on a potential payout in terms of production of hydrocarbons The exemplary method additionally comprises identifying at least one well trajectory through the at least one targeted segment within each one of the set of targeted regions And the method comprises employing the at least one application agent to evaluate well trajectories based on the potential payout in terms of at least one of production of hydrocarbons, drilling complexity, cost or stability of well planning
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
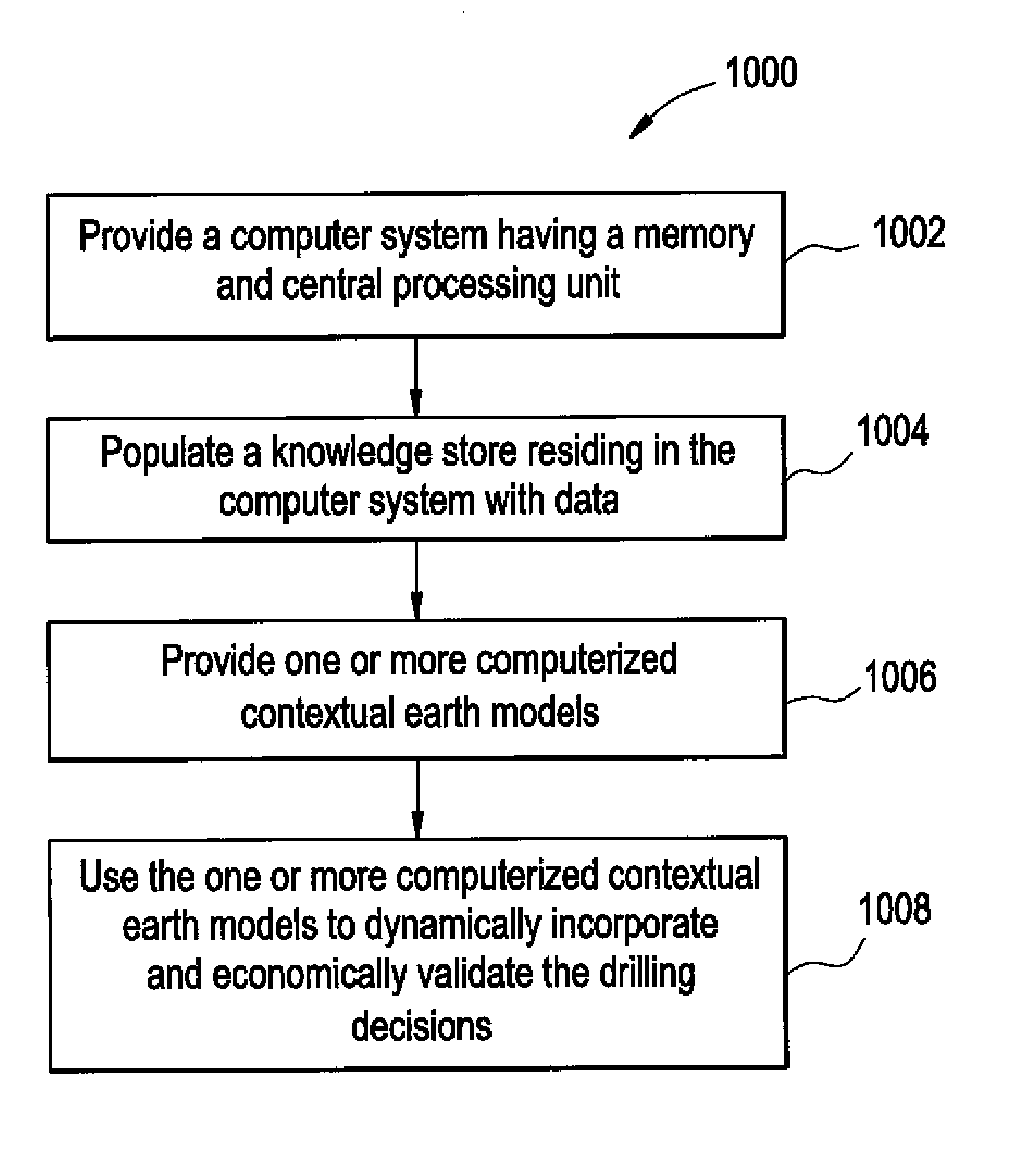
Planning and Performing Drilling Operations
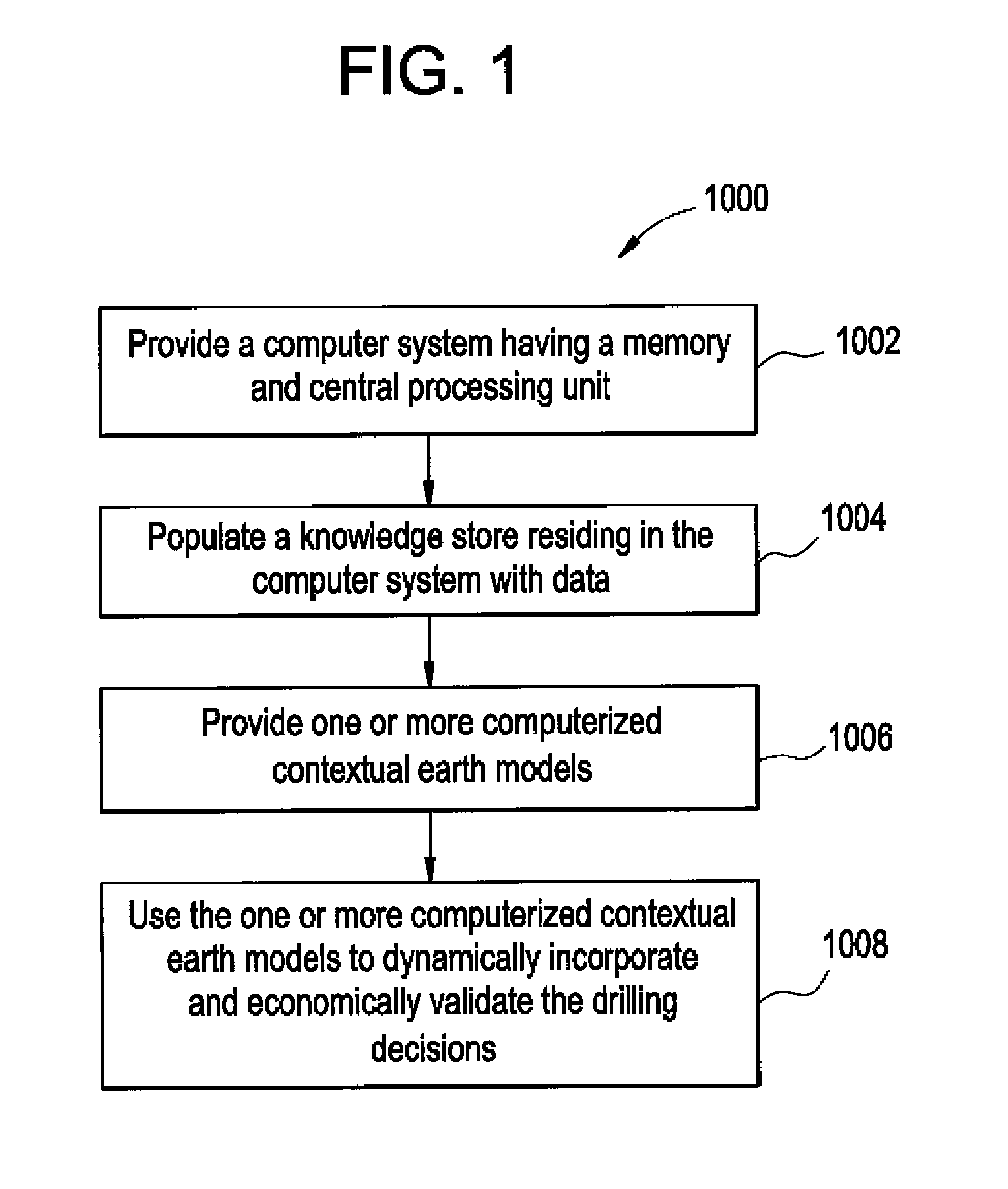
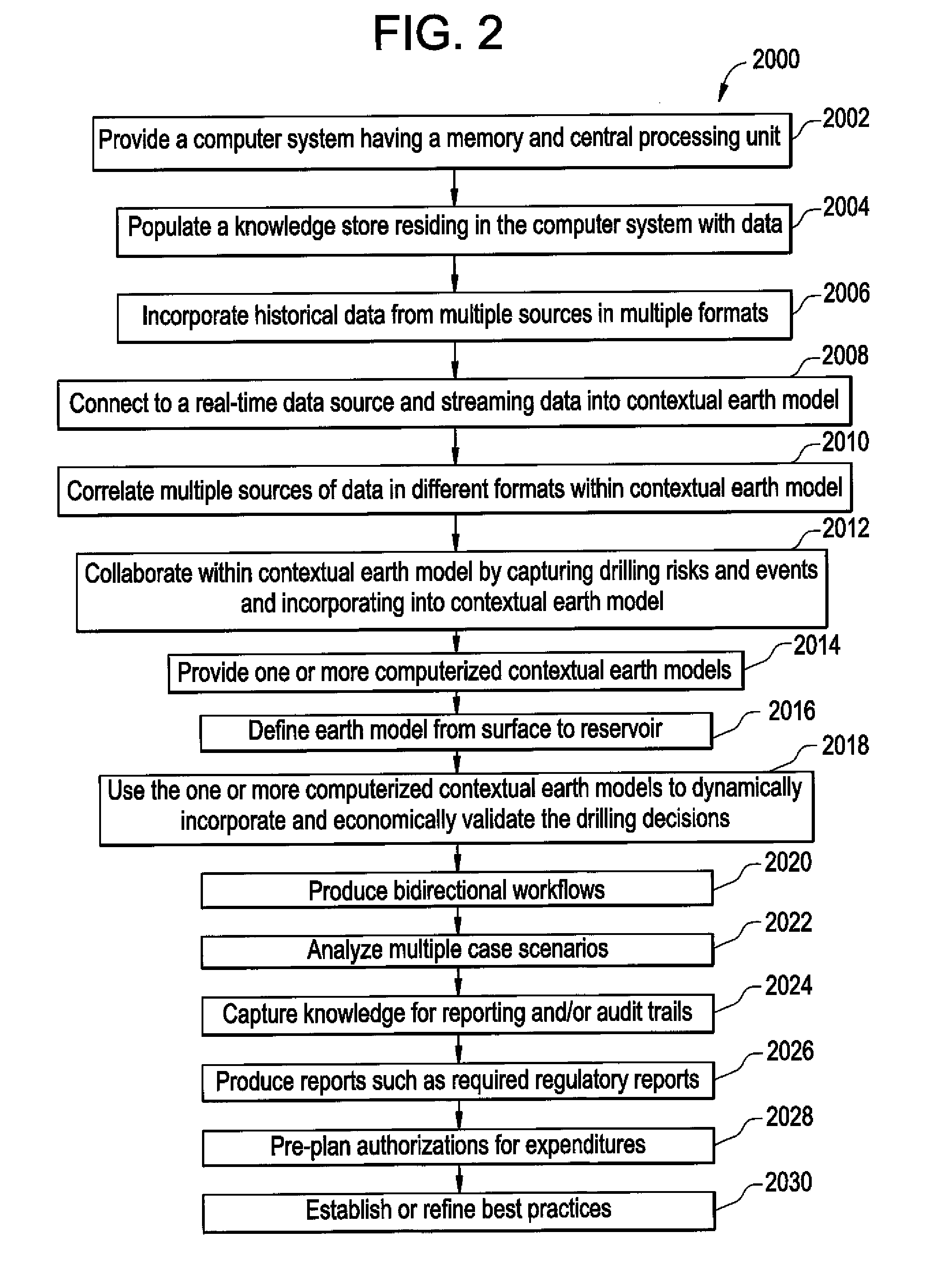
The present disclosure relates to dynamically incorporating and economically validating drilling decisions. A computer system having a memory and central processing unit is provided and a knowledge store residing in the computer system is populated with data. The data may include surface drilling parameter data, bottomhole assembly data, bit records, measurement-while-chilling data, logging-while-drilling data, drilling event data, and lessons learned data. The data may be correlated data from one or more offset wells. One or more computerized static or dynamic contextual earth models are provided and used to dynamically incorporate and economically validate the drilling decisions. The one or more earth models can be updated in real-time.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Optimizing Drilling Operations Using Petrotechnical Data
ActiveUS20090157367A1High resolutionEasy CalibrationDirectional drillingGeomodellingWell drillingEarth model
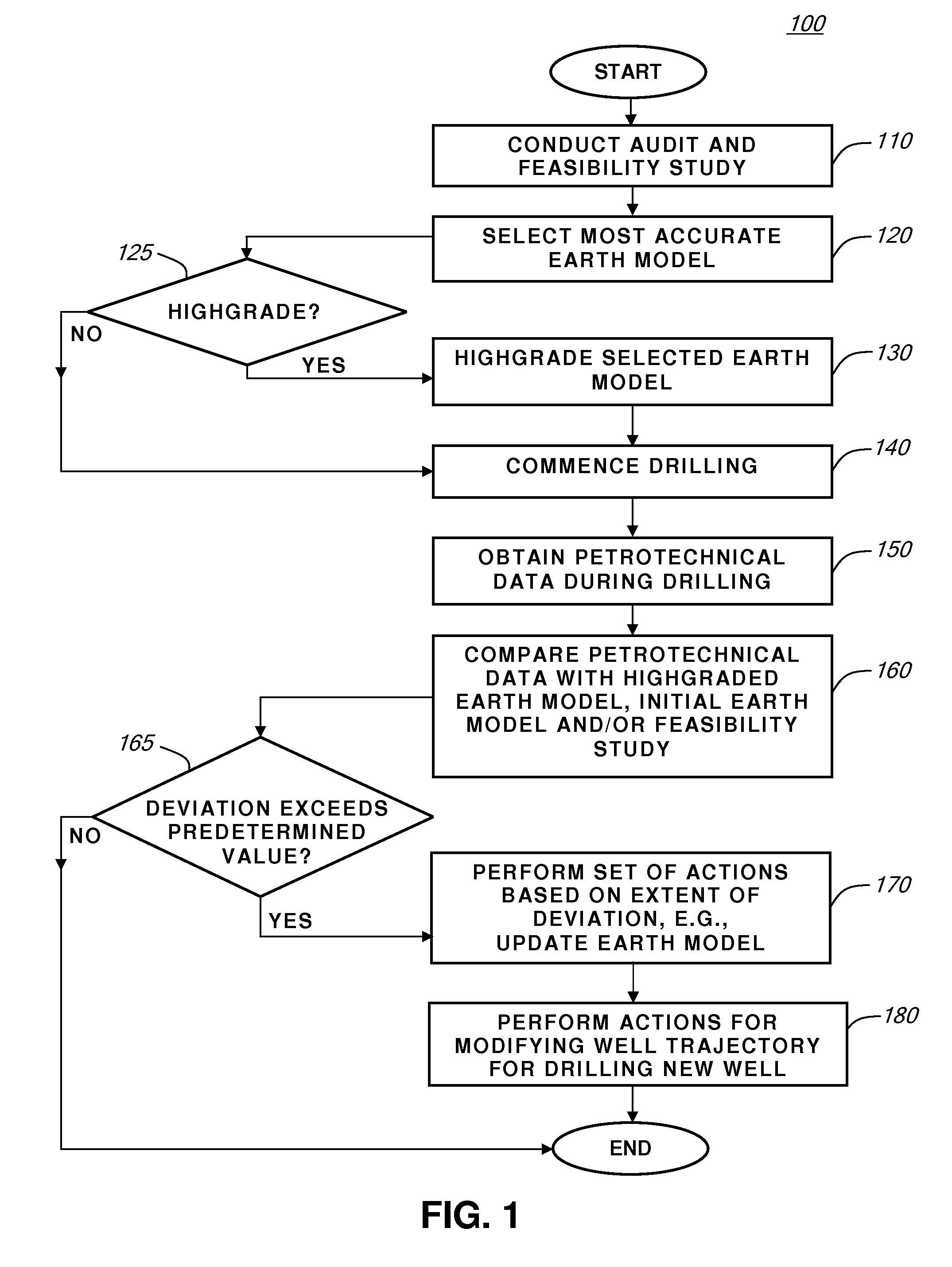
A method for optimizing drilling operations. The method includes providing an earth model of a volume having a well, obtaining petrotechnical data about the volume while drilling the well, comparing the petrotechnical data with the earth model, updating the earth model with the petrotechnical data based on the comparison, and modifying a drilling plan of the well using the updated earth model.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
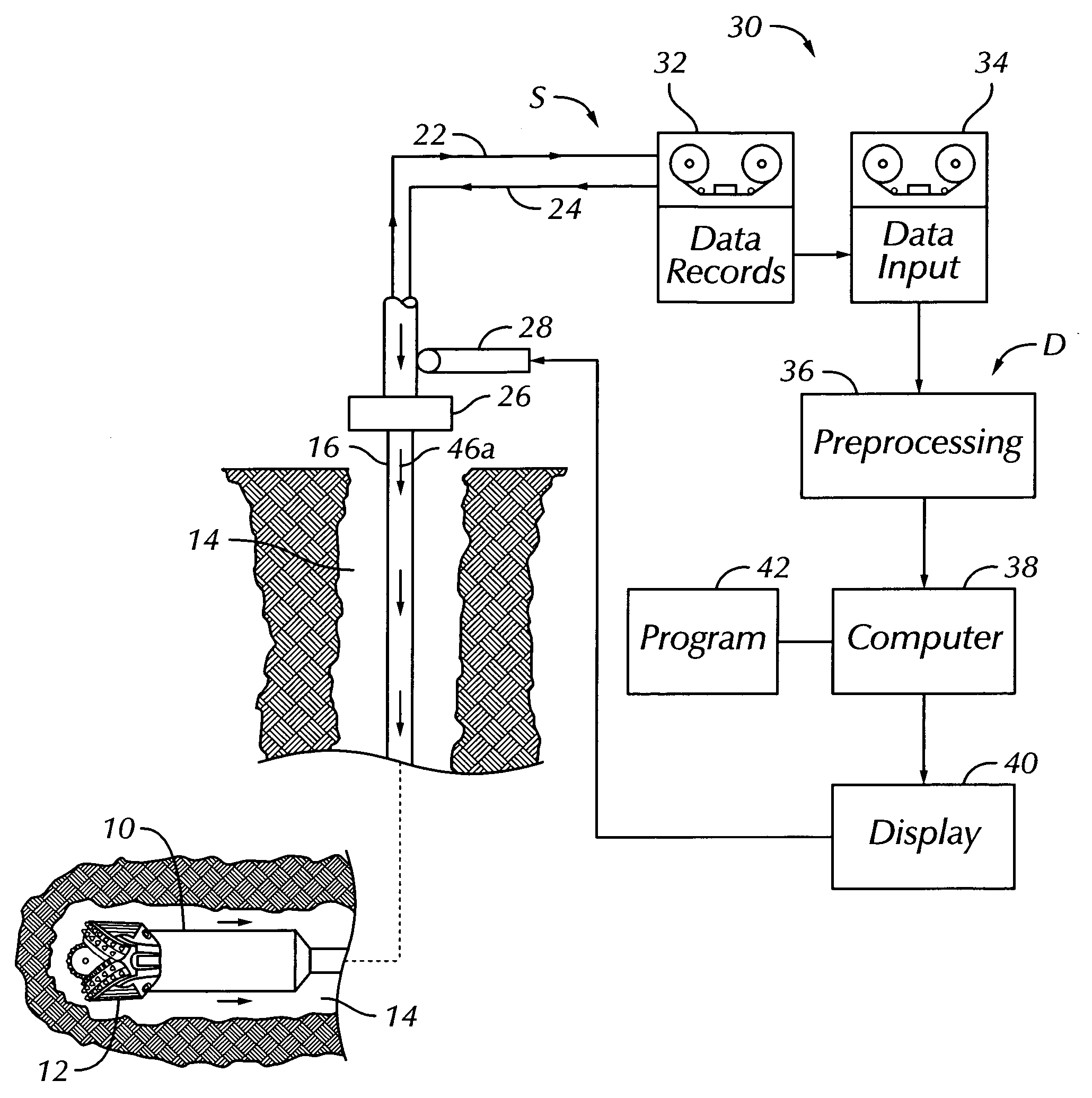
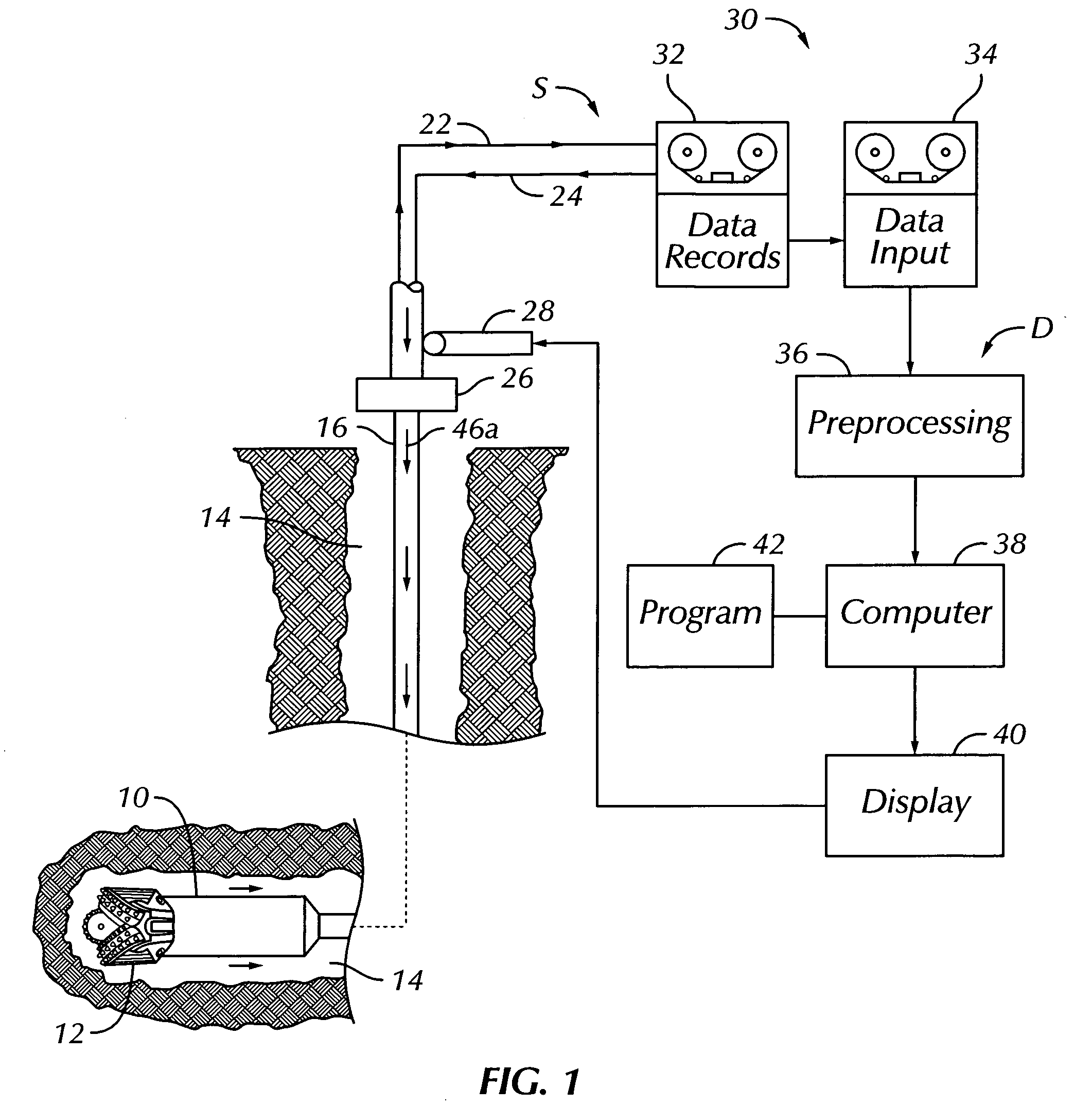
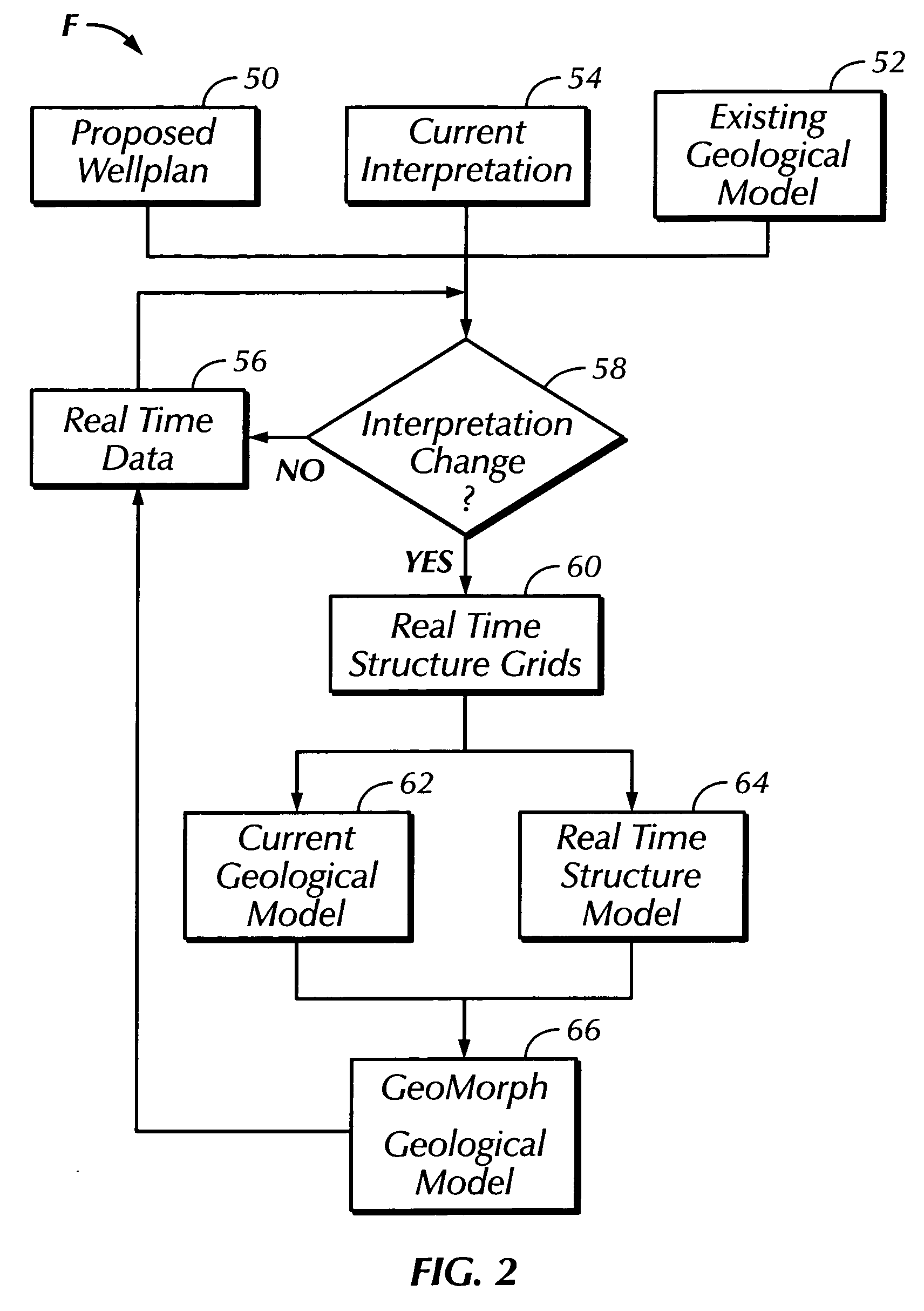
Real time earth model for collaborative geosteering
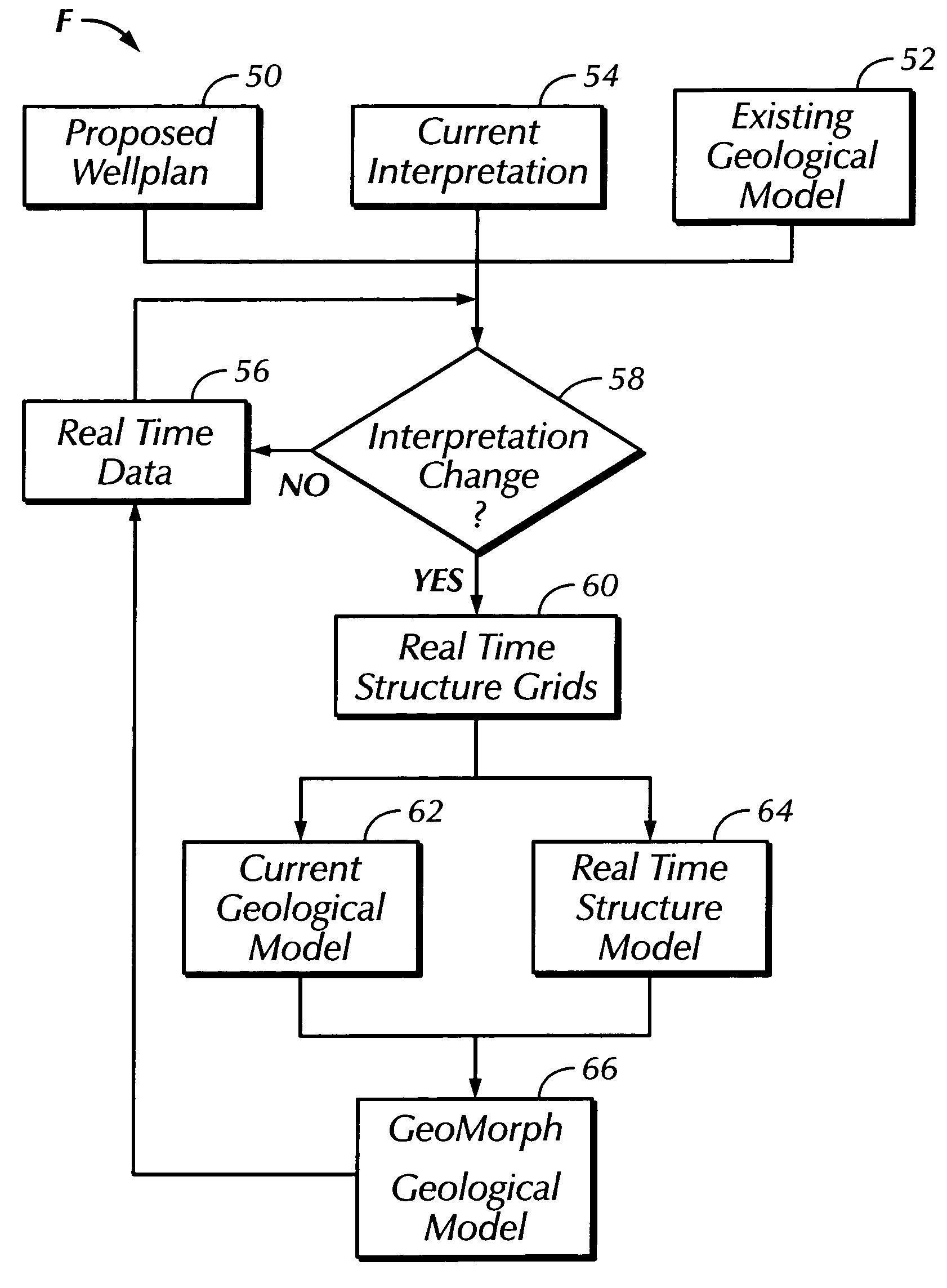
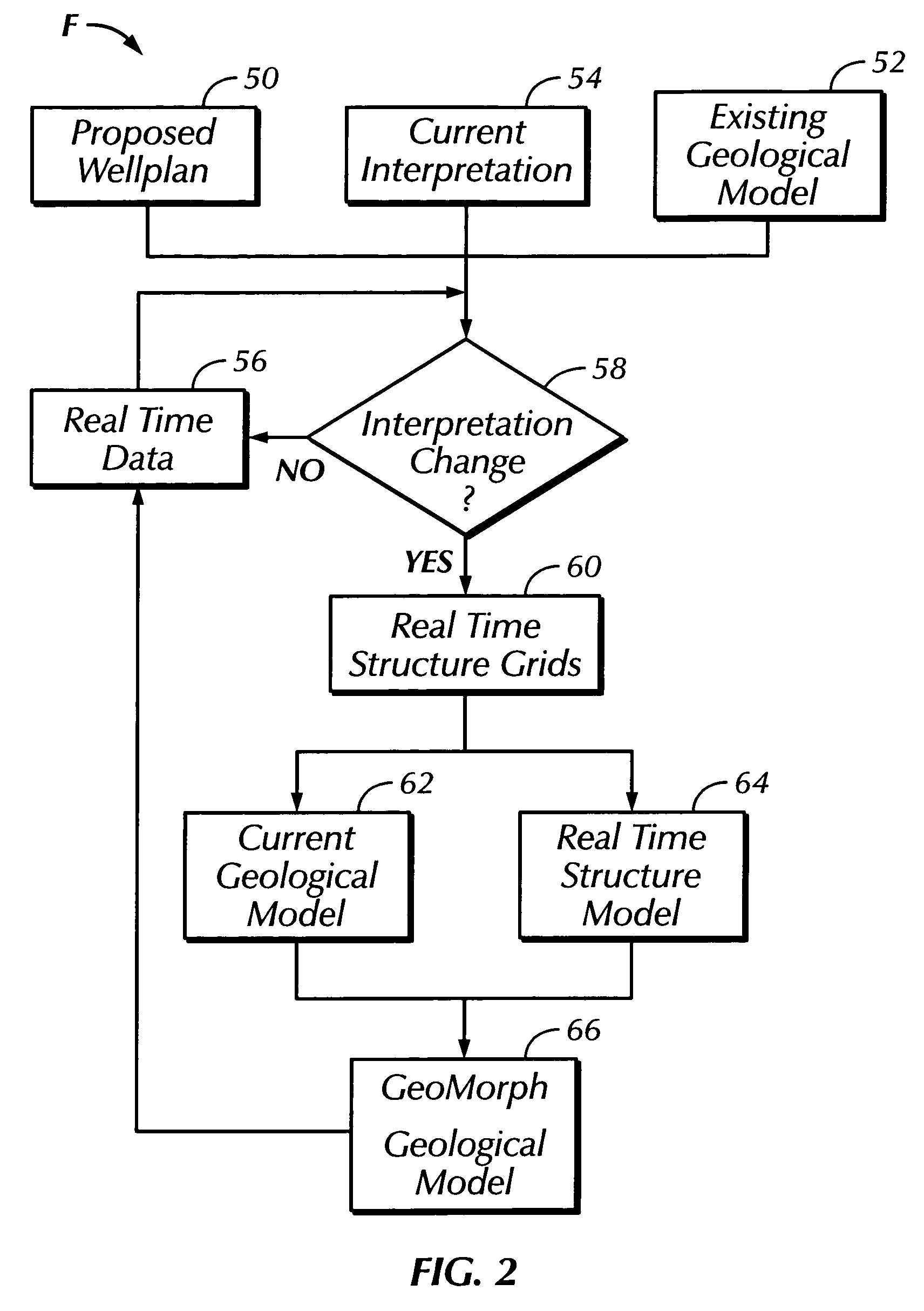
ActiveUS20050171698A1Improve drilling efficiencyImprove efficiencyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingGeosteeringWell drilling
An earth model is formed in real time during drilling of a well by incorporating up-to-the-minute knowledge derived from geology, seismic, drilling, and engineering data. The process of forming the model utilizes Logging-While-Drilling (LWD) or Measuring-While-Drilling (MWD) data directly from the drilling rig as the well is drilled. The LWD or MWD data is sent to visualization centers and compared with other data such as existing geological models, the proposed well plan and present interpretation of the subsurface stratigraphy. The results of the comparison enable experts to analyze anomalous results and update the geological model within minutes of penetration of a formation during drilling. Well drilling efficiency is improved, and an “on-the-spot” road map is provided for maximal reservoir contact and pinpoint accuracy.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
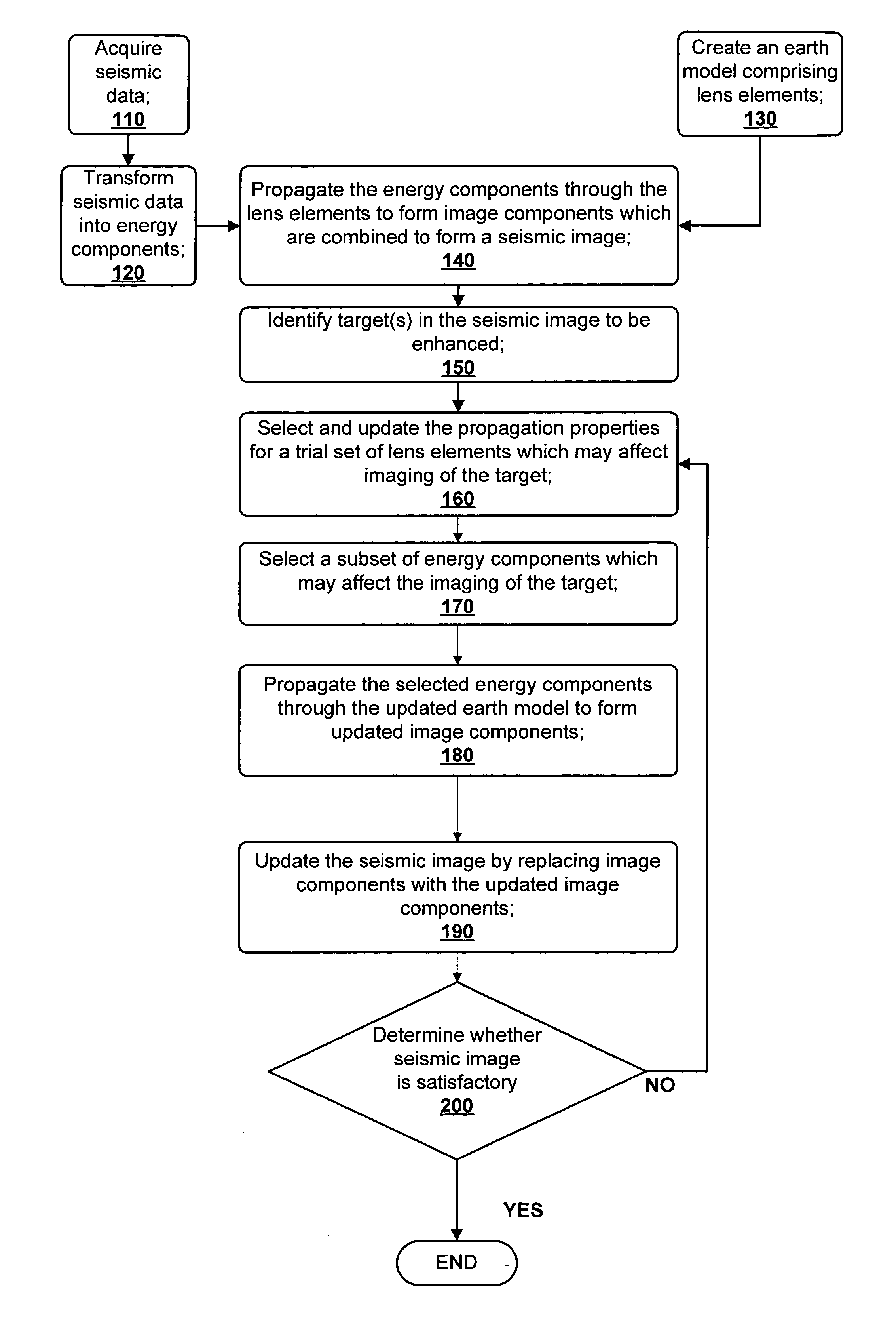
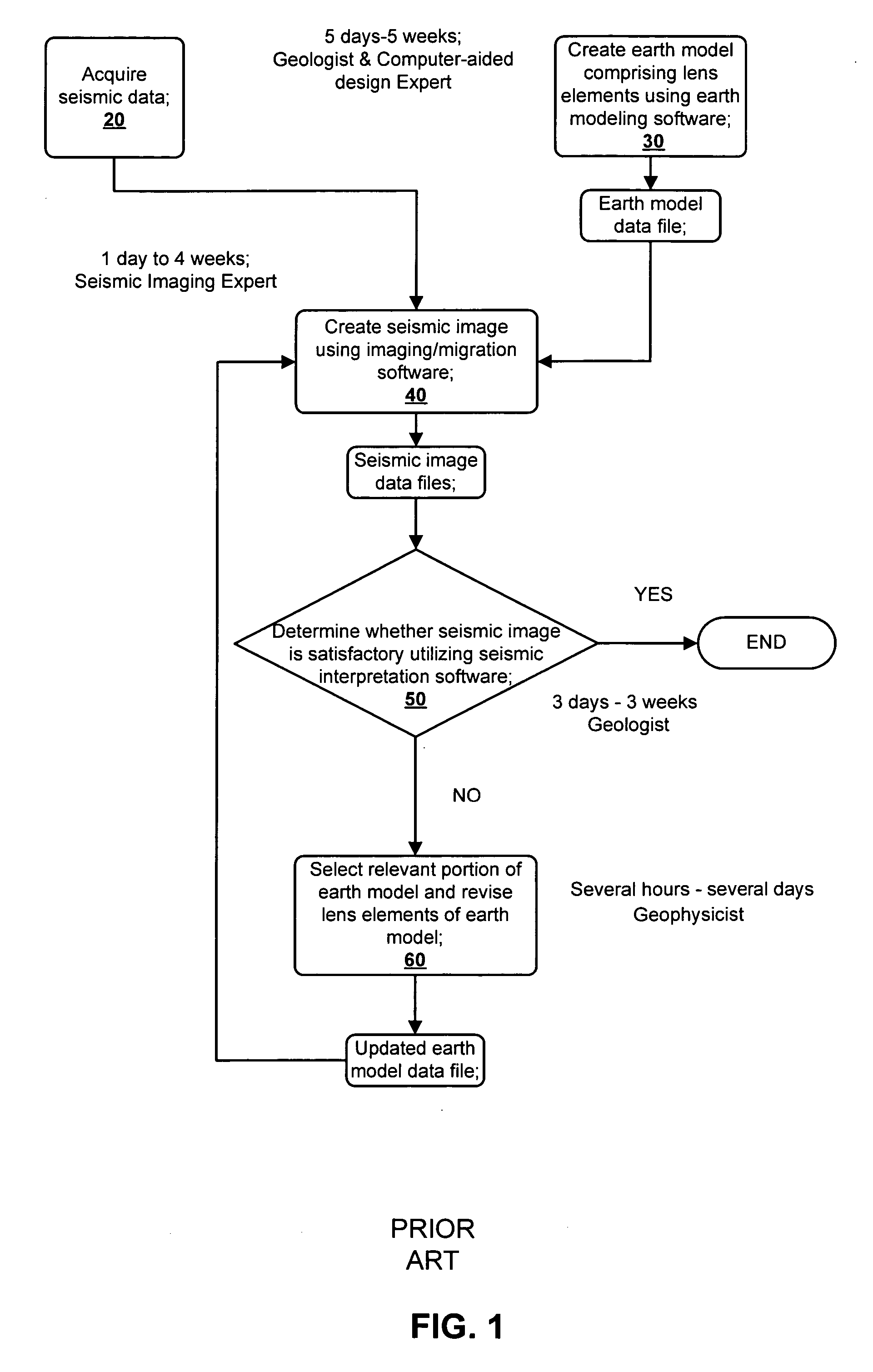
Methods for earth modeling and seismic imaging using interactive and selective updating
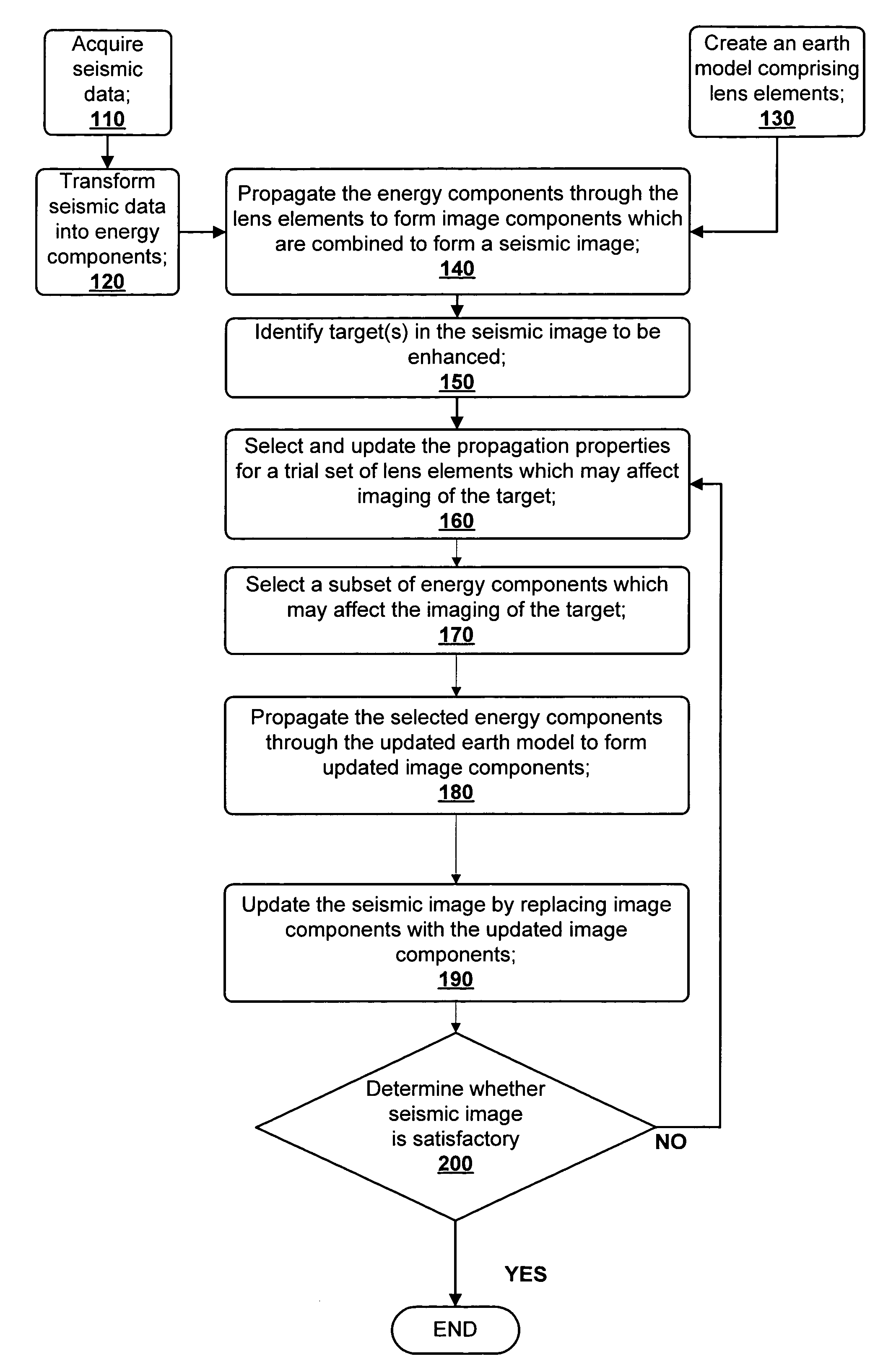
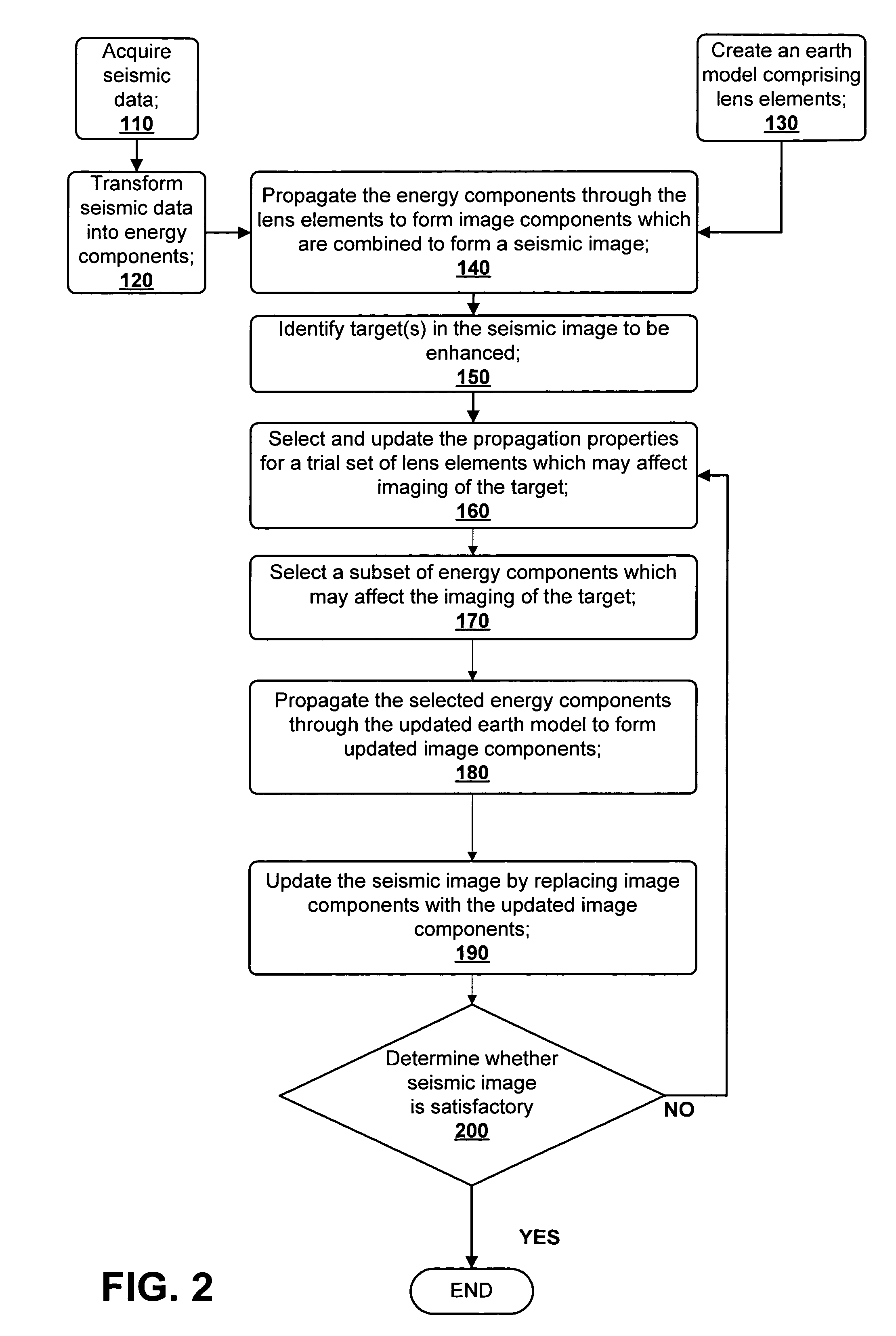
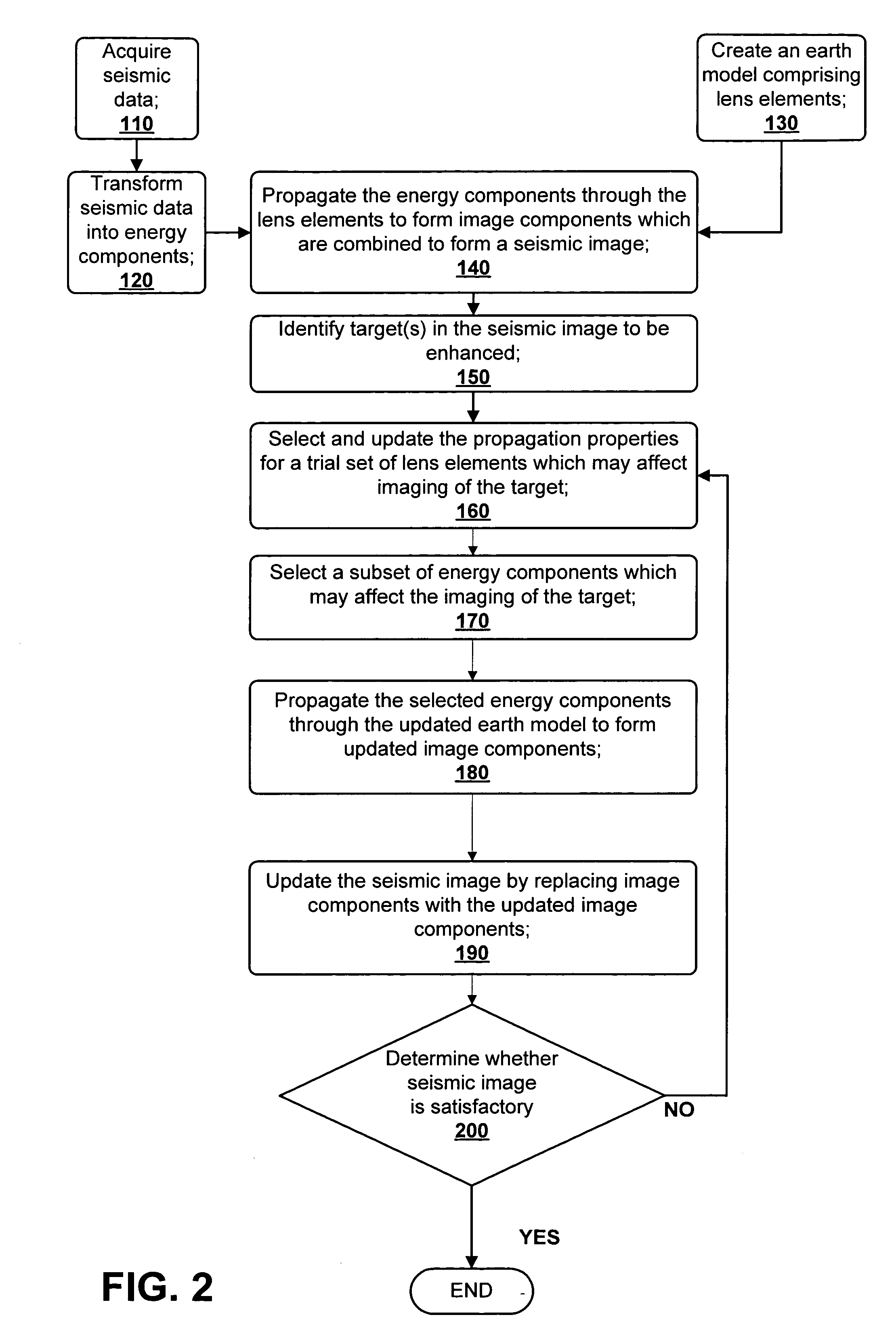
ActiveUS7480206B2Quality improvementEnhance the imageSeismic signal processingSeismic surveyGaussian beam
A method for creating an enhanced seismic image is described. Seismic data is acquired from a seismic survey conducted over a subterranean region. The seismic data is transformed into energy components, preferably Gaussian beam components. An earth model is created which is comprised of lens elements. The set of energy components is propagated or migrated through the lens elements to form image components which are combined into a seismic image. A target is identified in the seismic image for image enhancement. Ray tracing may be used to select the trial set of lens elements to be updated and to select a subset of energy components. The subset of energy components is propagated through updated earth model to form updated image components. The seismic image is updated by replacing image components with updated image components which are formed from the subset of selected energy components. This subset is ideally greatly reduced in size relative to the overall number of energy components, i.e., beam components.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
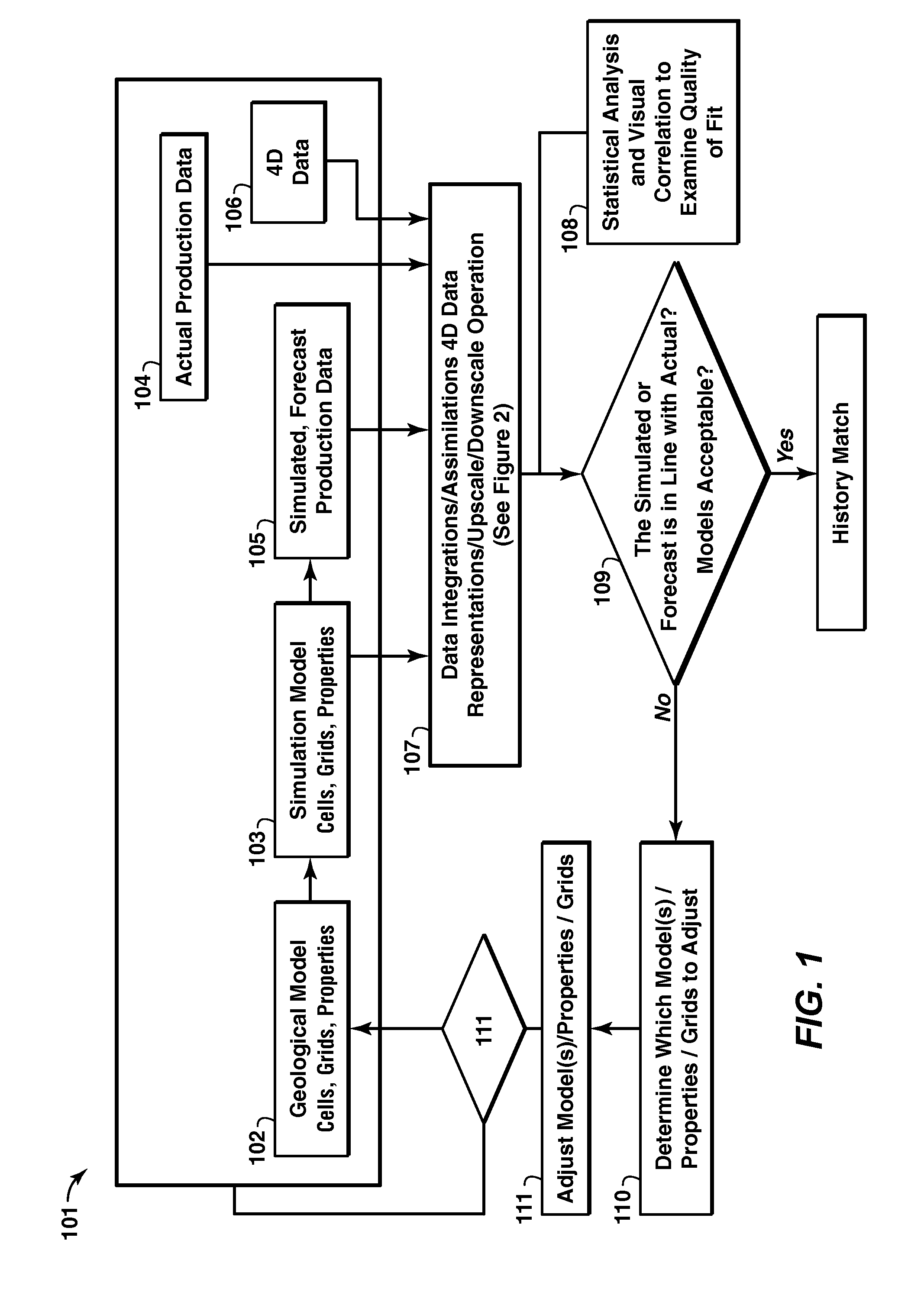
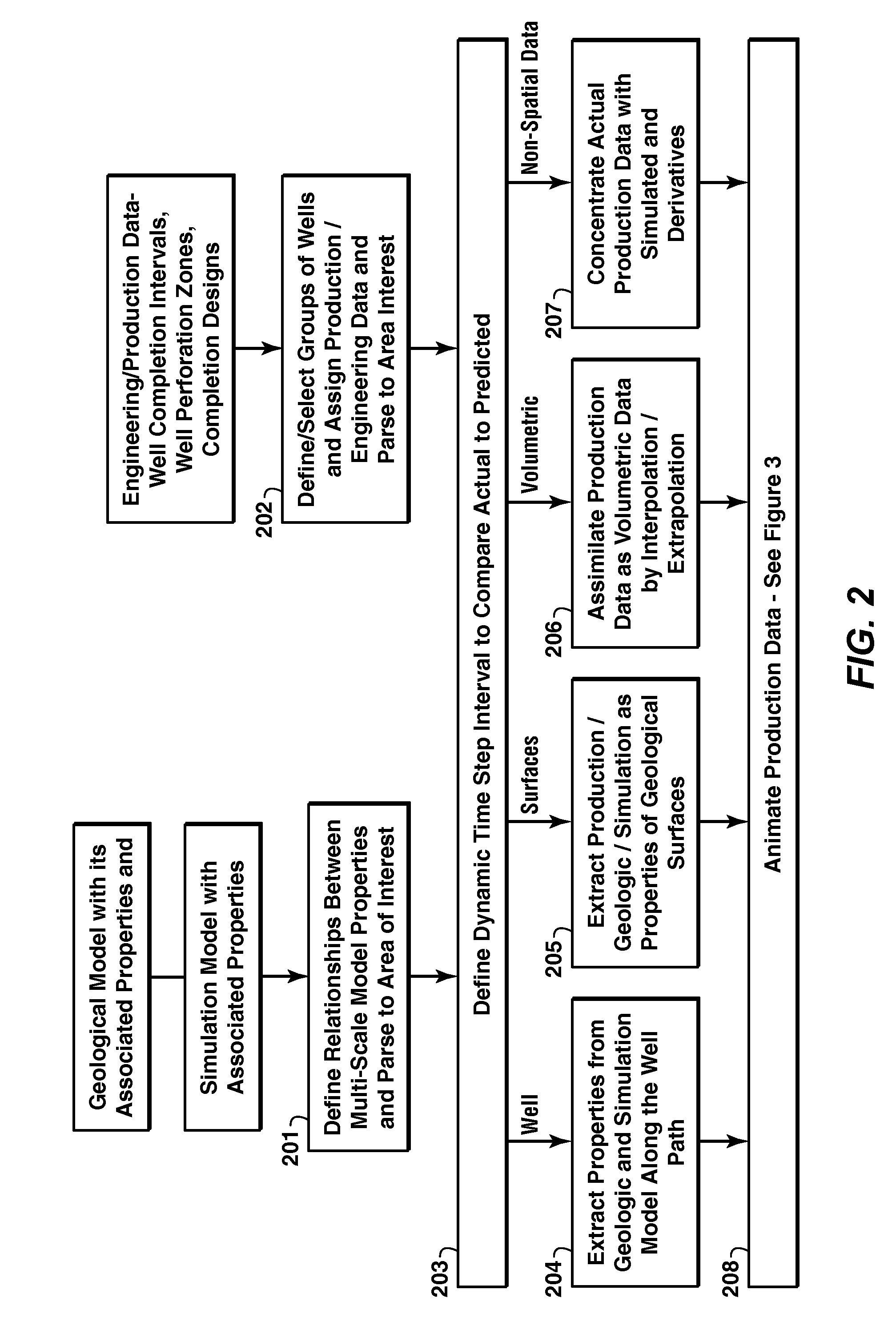
Iterative Reservoir Surveillance
Method for reservoir surveillance using a three-dimensional Earth Model (101) to improve and expedite the surveillance at all scales of investigation (field, reservoir, fault compartment, and individual well) and at all time steps (minutes, hours, days, months, years). The new method allows users to rapidly identify anomalous field and well performance (109) and provides capability to investigate root causes of the performance deviation from predicted (110). Animated co-rendered displays (107) of the earth model and actual (104) and simulated (105) production data enable the user to interactively determine model adjustments back at the basic level of the Earth Model, which are then propagated to a geologic model (102) and then to the reservoir simulator (103) to update it (111) in a physically constrained way.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Methods for earth modeling and seismic imaging using interactive and selective updating
ActiveUS20060056272A1Quality improvementEnhance the imageSeismic signal processingGaussian beamSeismic survey
A method for creating an enhanced seismic image is described. Seismic data is acquired from a seismic survey conducted over a subterranean region. The seismic data is transformed into energy components, preferably Gaussian beam components. An earth model is created which is comprised of lens elements. The set of energy components is propagated or migrated through the lens elements to form image components which are combined into a seismic image. A target is identified in the seismic image for image enhancement. Ray tracing may be used to select the trial set of lens elements to be updated and to select a subset of energy components. The subset of energy components is propagated through updated earth model to form updated image components. The seismic image is updated by replacing image components with updated image components which are formed from the subset of selected energy components. This subset is ideally greatly reduced in size relative to the overall number of energy components, i.e., beam components.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Method and apparatus for locating gas hydrate
ActiveUS20070265782A1Reduce penetrationHigh porosityElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesGas hydrate stability zoneSeismic survey
An exploration paradigm for detecting and / or characterizing gas hydrate deposits using either electromagnetic or seismic surveys, that accounts for the possibility that gas hydrate may accumulate in vertical or subvertical dikes. Geologic factors, such as the presence of the gas hydrate stability zone, indications that a prolific source of gas exists (or existed) below the gas hydrate stability zone and indications that a high flux of gas could be transported into the gas hydrate stability zone, may be considered as part of an exploration strategy. Data may be collected using seismic techniques, such as a walk-away vertical seismic profile techniques, or electromagnetic surveys that are adapted to detecting the presence of vertical or subvertical dikes. In one example, data processing and acquisition techniques may be adapted to detect hydrate dikes, and do not assume a horizontally isotropic earth model.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method for Generating a 3D Earth Model
InactiveUS20090119076A1Improved drilling processEffective predictionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyPotential wellWell drilling
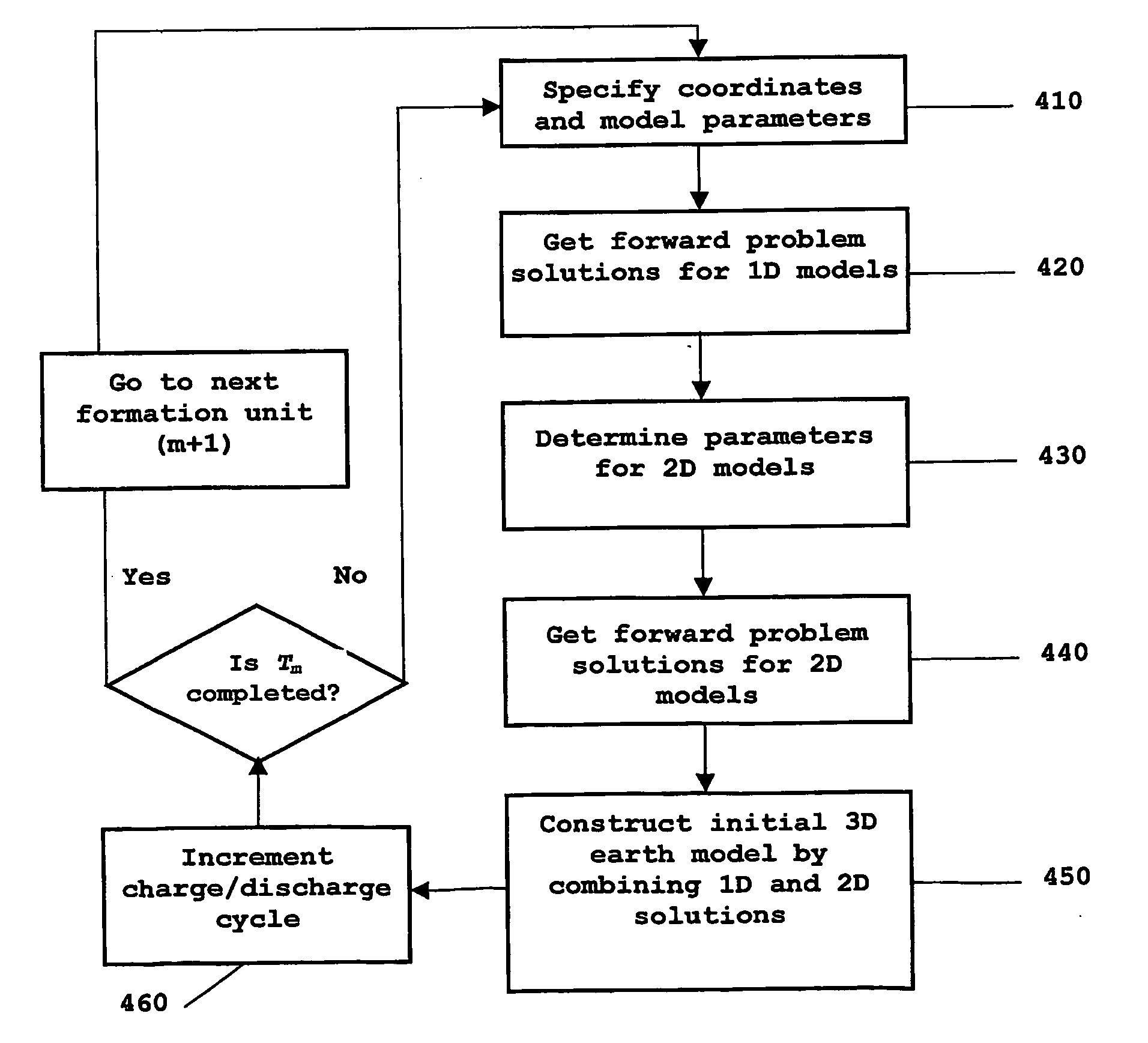
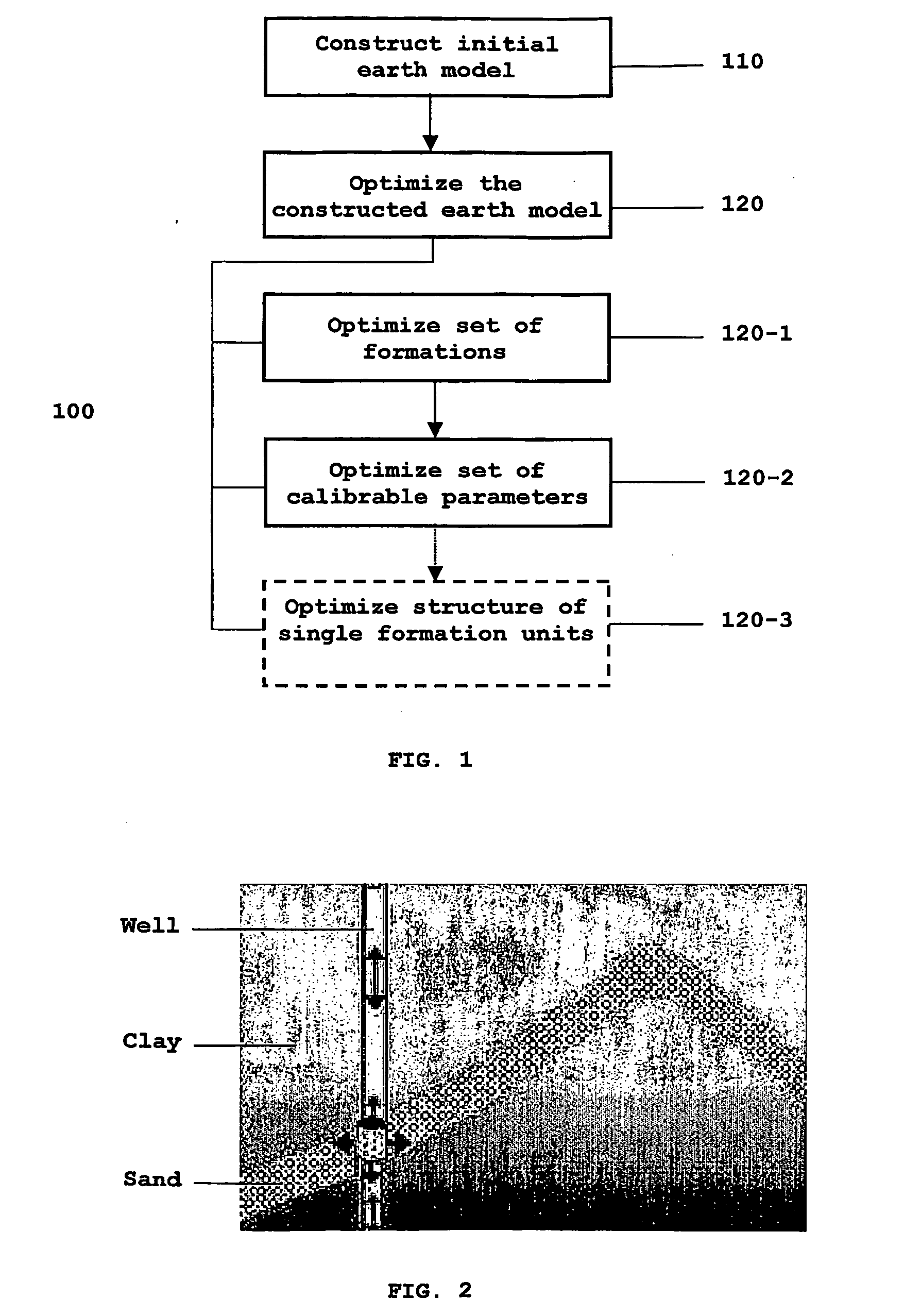
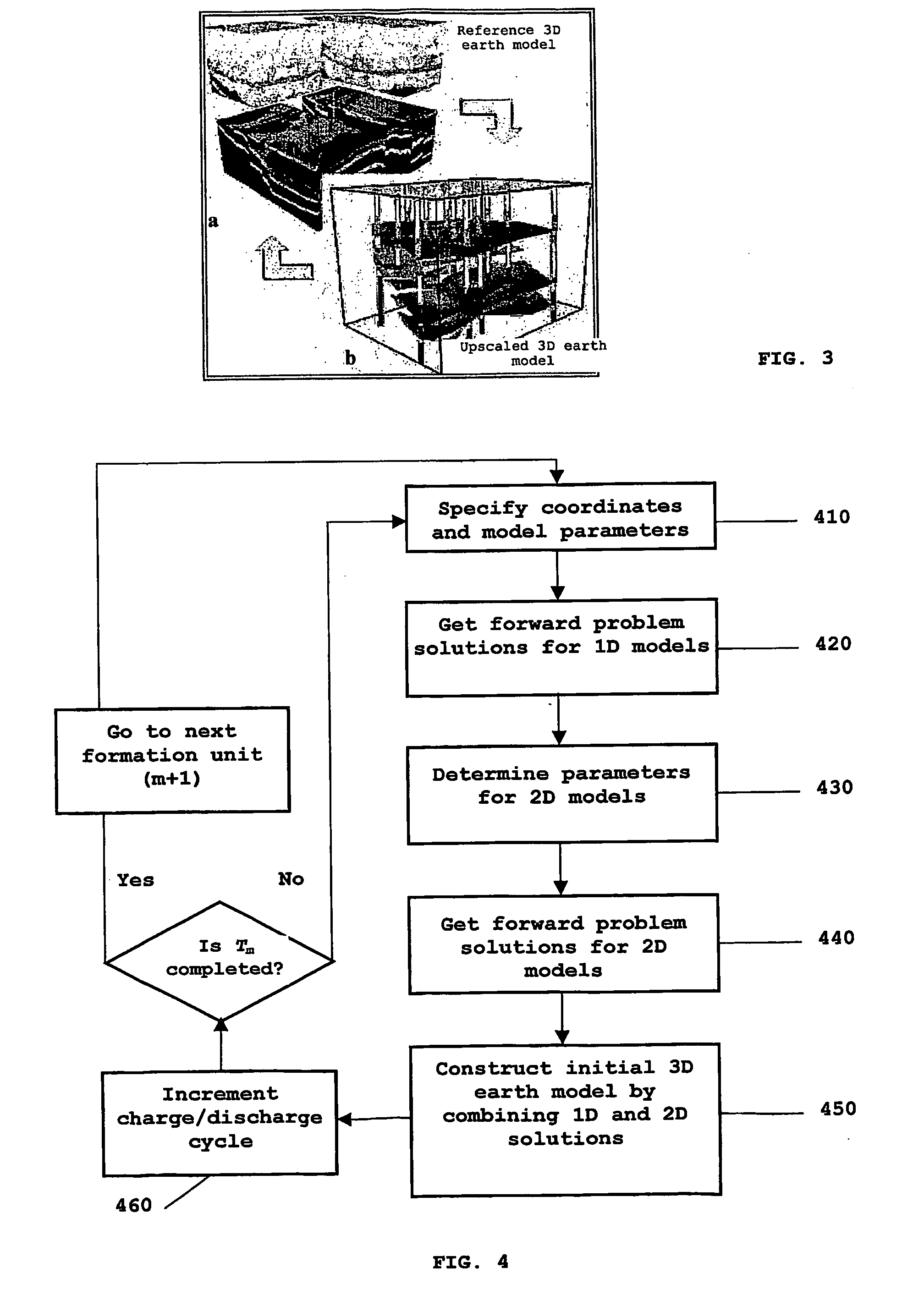
A method is provided for generating an invertible 3D hydrodynamic earth model suitable for defining target characteristics of a subsurface area formed by a plurality of formations and comprising drilling positions of potential and real wells. The method comprises constructing an initial 3D earth model by combining solutions for a set of single 1D models, each of the models corresponding to a real or potential well drilling position and covering the entire respective aggregate of formations along the wellbore, with solutions for a relevant set of 2D earth models which are constructed only for single formations, and optimizing the constructed initial 3D earth model by defining an optimal set of formations and an optimal set of calibratable model parameters. A method and system are also provided for application of the earth model construction method for predicting overpressure evolution before and during drilling. As the earth model constructed in accordance with the above method provides efficient inversion of data, in particular gathered while drilling, the prediction can be updated in real-time while drilling. The invention can ensure optimization of the drilling process and improves its safety.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method for locating walker
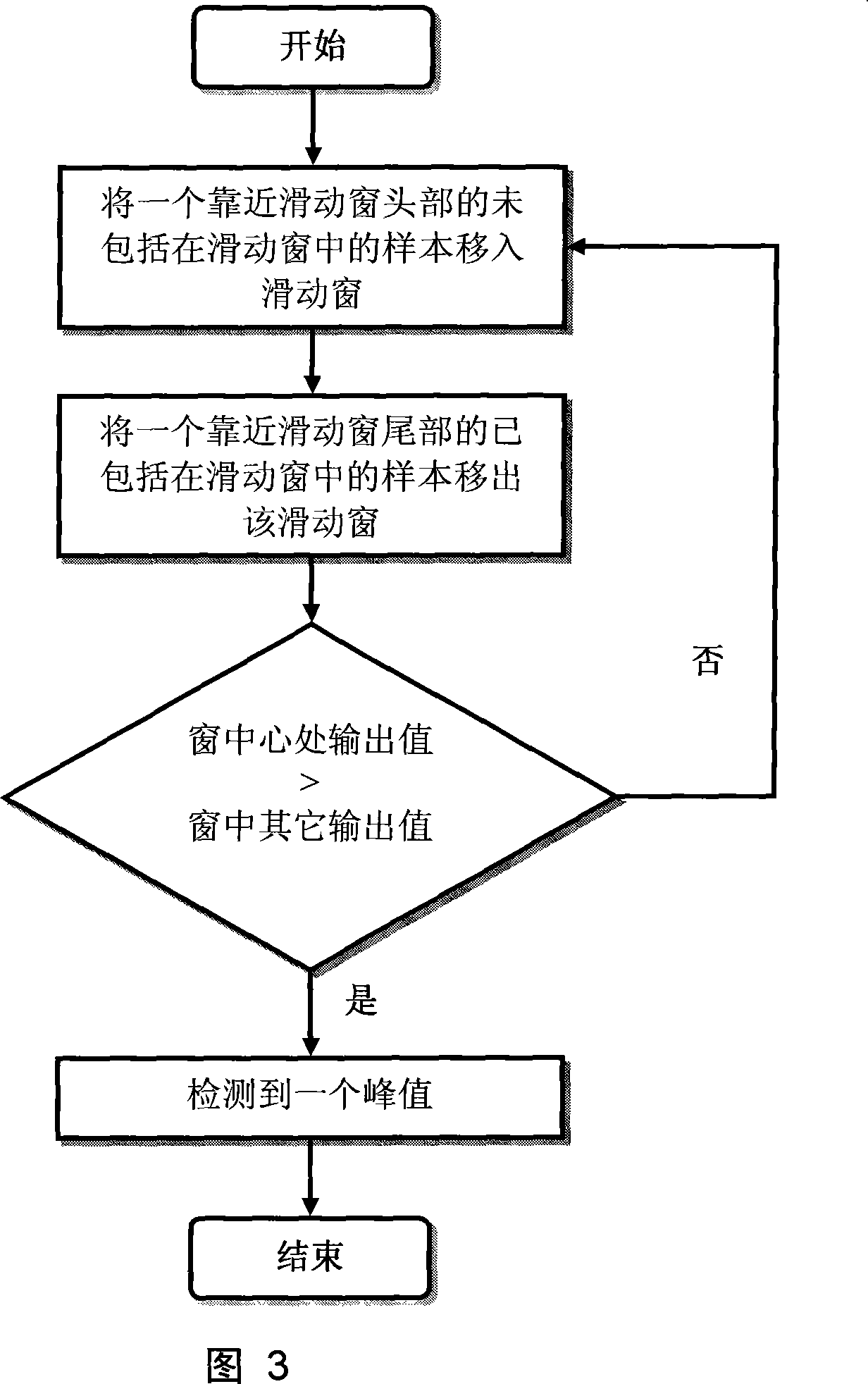
InactiveCN101226061ALow costEasy to implementNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsCompassesWalking distanceLongitude
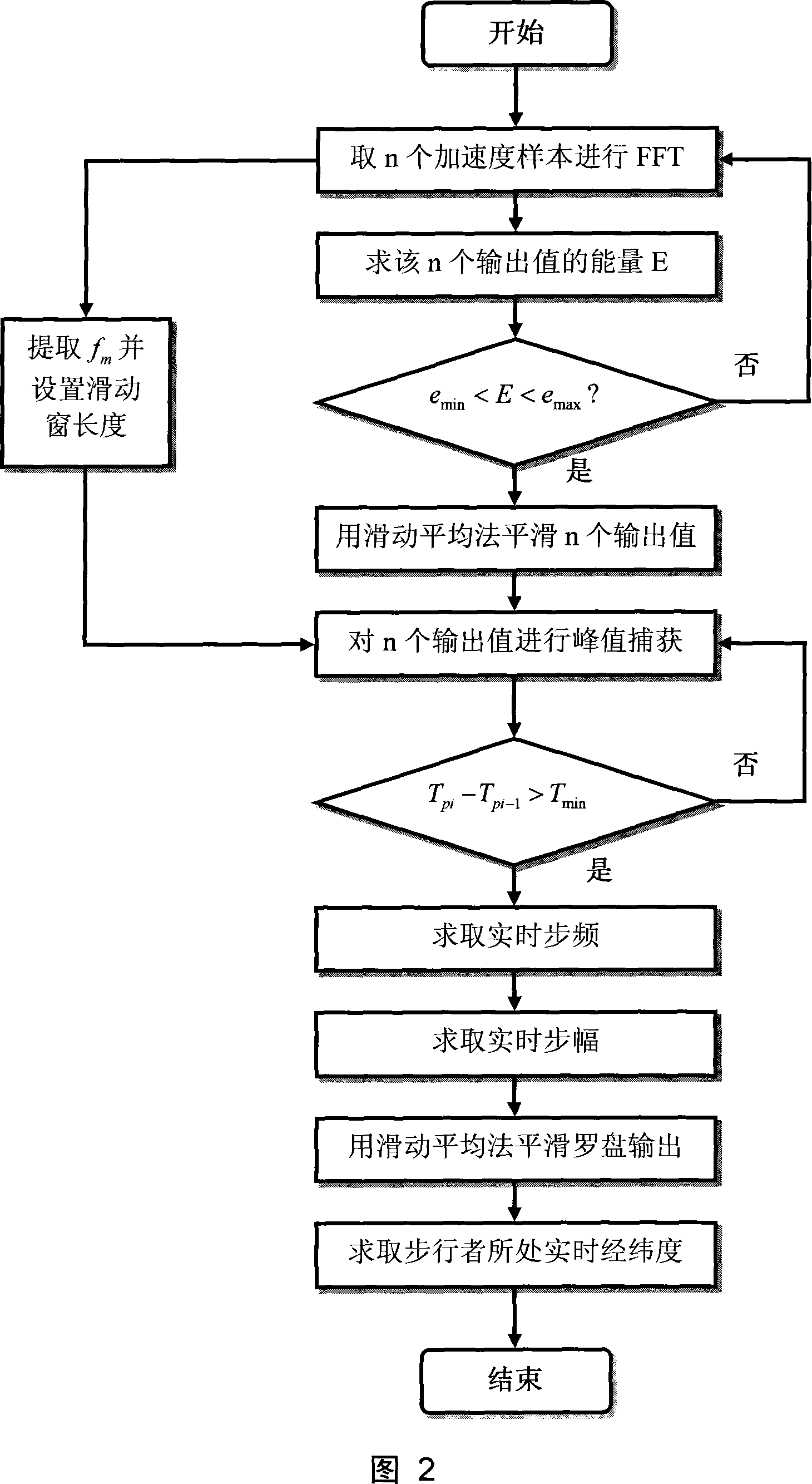
The invention relates to a positioning method suitable for walkers, belonging to the field of navigation, guidance and control areas, which comprises three parts: identify the motion state of the walker; calculate the real-time stride of the walker; work out the real-time latitude and longitude of the location of the walker by combining with course angle. The change of the location of the walker is mainly realized by the motion of two legs; walking makes body vibrate regularly; measure and analyze the features of the vibration; adopt the peak capture method aiming at the acceleration sampling to extract the real-time stride frequency of the walker; utilize the relation between the stride frequency and stride to work out the real-time stride of the walker; the real-time stride as the walking distance of the walker between the adjacent output value is combined with the course angle output by an electromagnet compass; and work out the real-time latitude and longitude of the location of the walker by utilizing the Earth model. Before estimating the stride, make a judgment that whether n acceleration output values represent the walking motion of the walker; the judgment is based on the energy of sampling acceleration. The positioning method suitable for walkers has the advantages that the positioning method can judge with high accuracy whether the walker is walking, efficiently improving the location accuracy of the walker.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Marine environment information three-dimensional visualization method
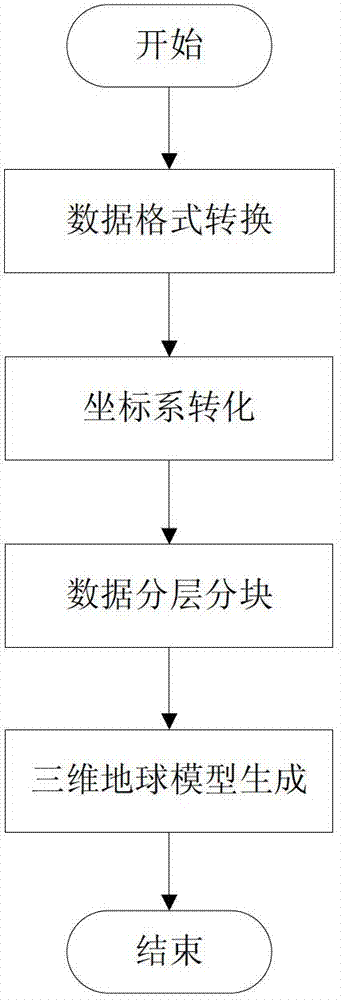
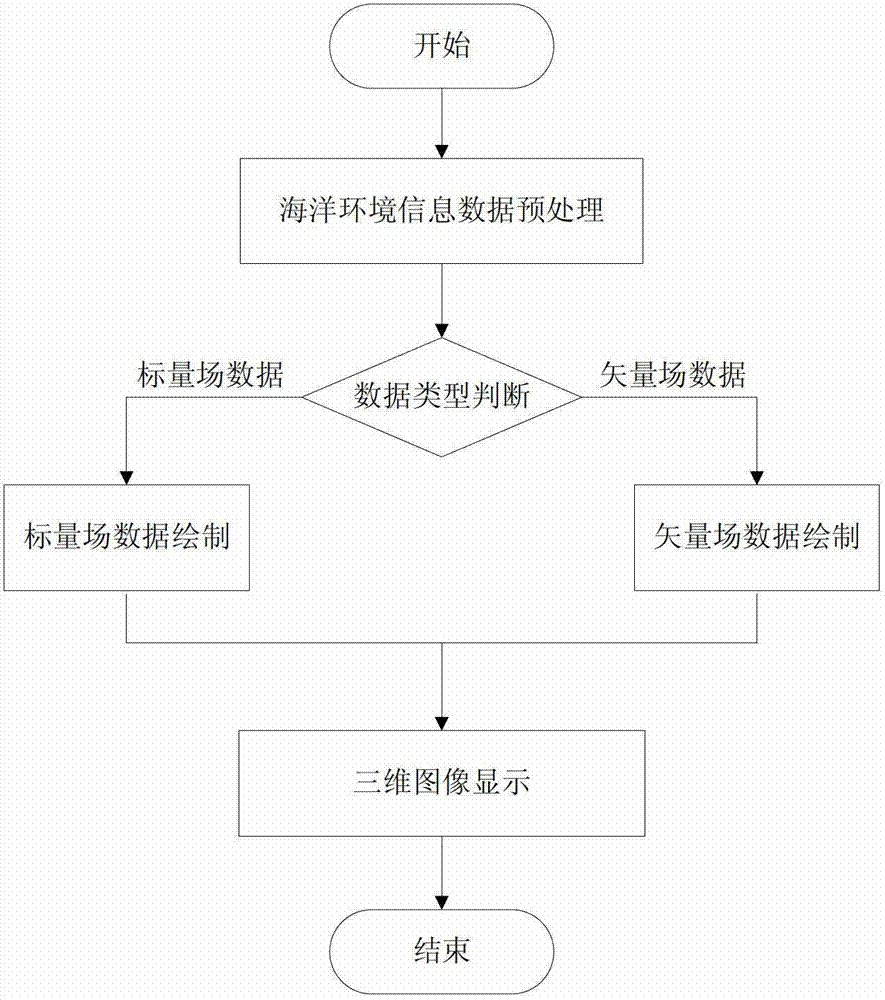
InactiveCN102831644ARealize 3D visualizationDisplay image3D-image rendering3D modellingEarth modelComputer science
The invention discloses a marine environment information three-dimensional visualization method, belonging to the field of a three-dimensional visualization technology. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, establishment of a three-dimensional earth model; step 2, three-dimensional visualization realization of marine environment information data, wherein the step 1 comprises three steps of data preprocessing, data hierarchy partitioning and three-dimensional earth model generation; and the step 2 comprises three steps of marine environment information data preprocessing, drawing of three-dimensional images and displaying of the three-dimensional images. By utilizing the visualization technology, the three-dimensional visualization of the marine environment information is realized, the three-dimensional earth model is constructed, and a micro background field is provided for the vivid and visual expression of the marine environment information; and by combining the characteristics of the marine environment information and aiming at marine environment factors of different types, different three-dimensional visualization methods are designed, thus the marine environment information is expressed more vividly and realistically, working personnel can analyze more visually, and the marine environment information can be utilized better.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method for designing and optimizing drilling and completion operations in hydrocarbon reservoirs
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
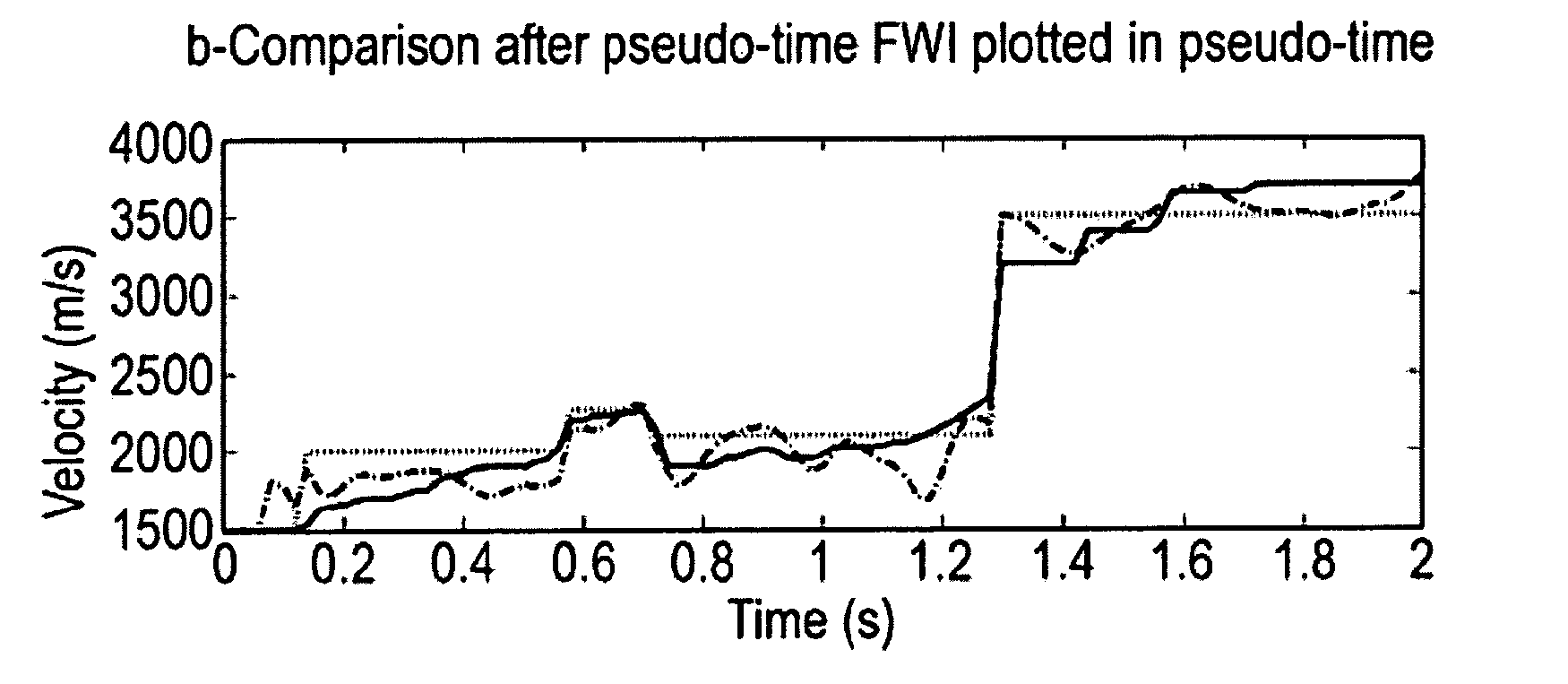
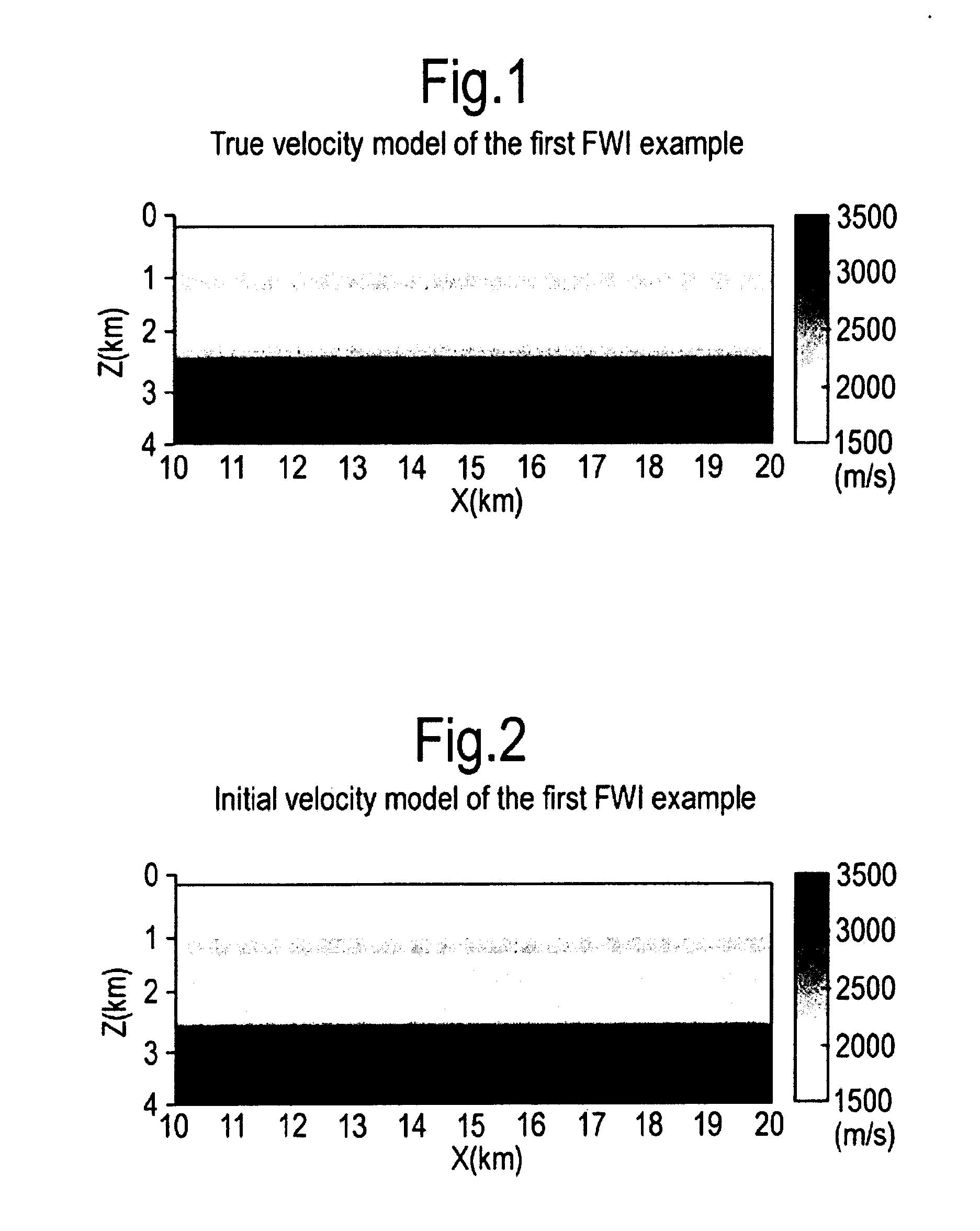
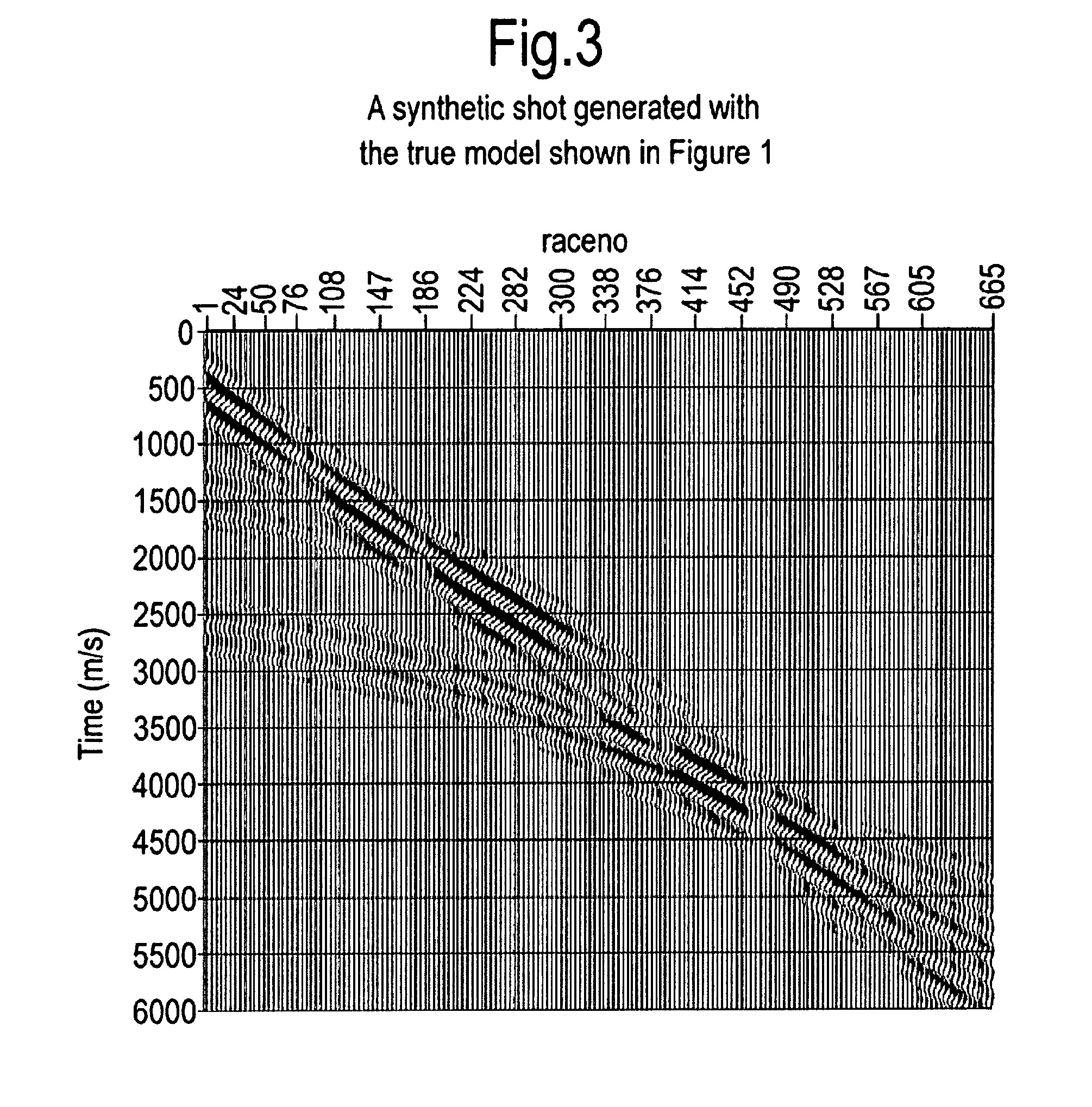
Earth model estimation through an acoustic full waveform inversion of seismic data
InactiveUS20130311151A1Optimize timingExtend depth of investigationComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationFull waveformEarth model
An improved method of estimating an earth model utilizes an acoustic Full Waveform Inversion (FWI) of seismic data in a pseudo-time coordinate system, in which the earth model m({tilde over (m)}) is parameterized with two lateral coordinates (x,y) and a vertical coordinate ({tilde over (z)}) which expresses vertical travel time of acoustic signals used to generate the seismic data.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Stochastic inversion of geophysical data for estimating earth model parameters
A computer implemented stochastic inversion method for estimating model parameters of an earth model. In an embodiment, the method utilizes a sampling-based stochastic technique to determine the probability density functions (PDF) of the model parameters that define a boundary-based multi-dimensional model of the subsurface. In some embodiments a sampling technique known as Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) is utilized. MCMC techniques fall into the class of “importance sampling” techniques, in which the posterior probability distribution is sampled in proportion to the model's ability to fit or match the specified acquisition geometry. In another embodiment, the inversion includes the joint inversion of multiple geophysical data sets. Embodiments of the invention also relate to a computer system configured to perform a method for estimating model parameters for accurate interpretation of the earth's subsurface.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
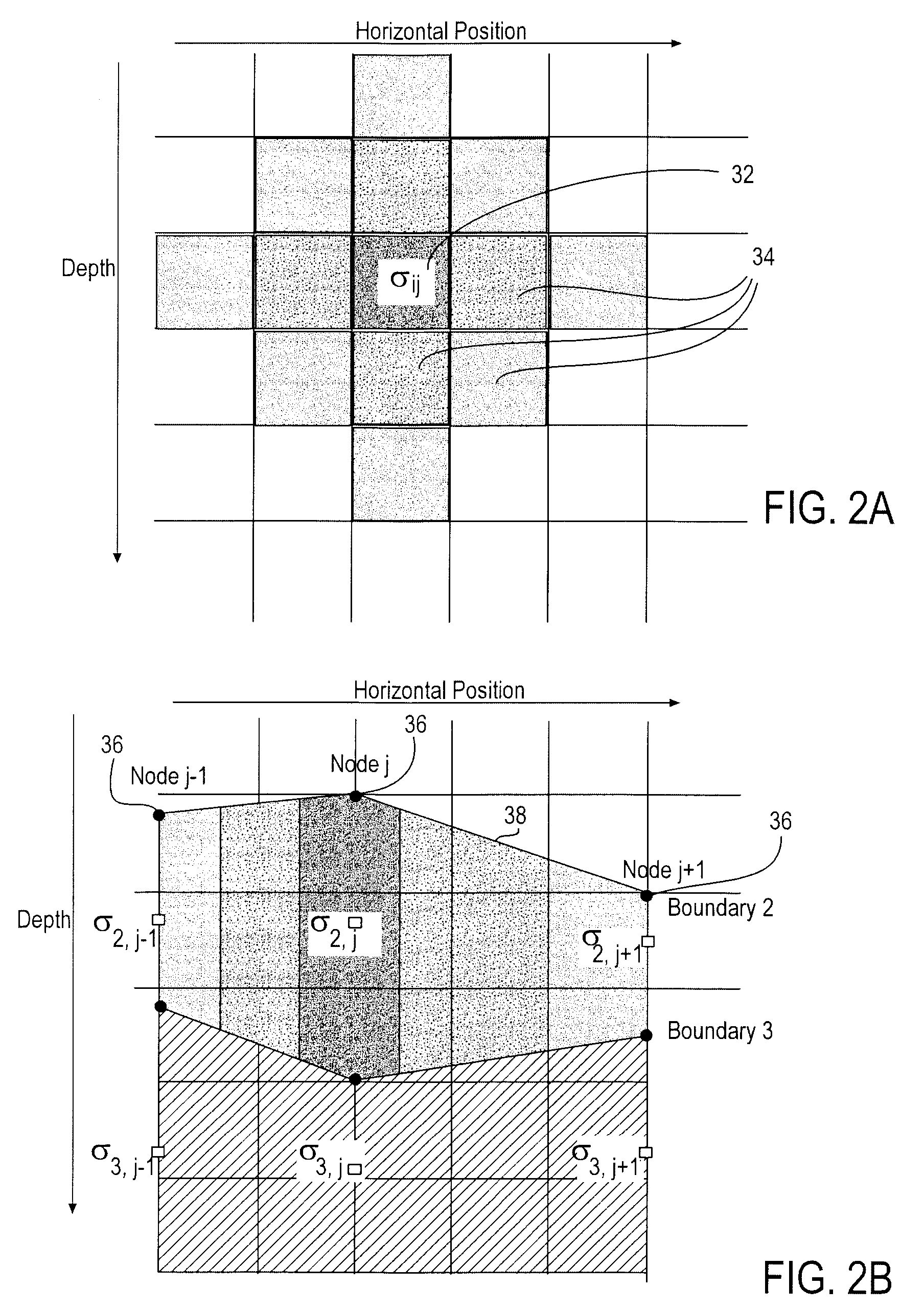
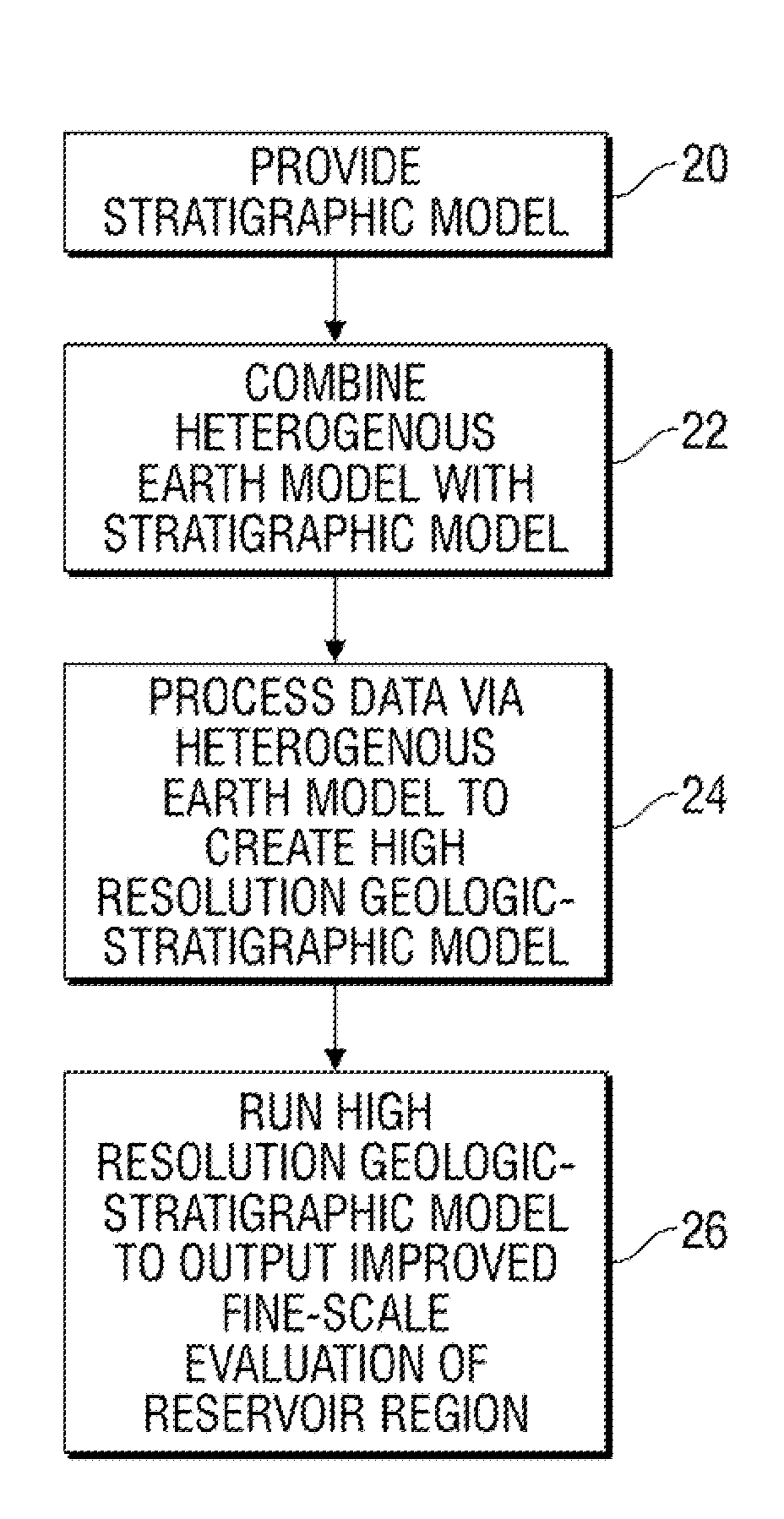
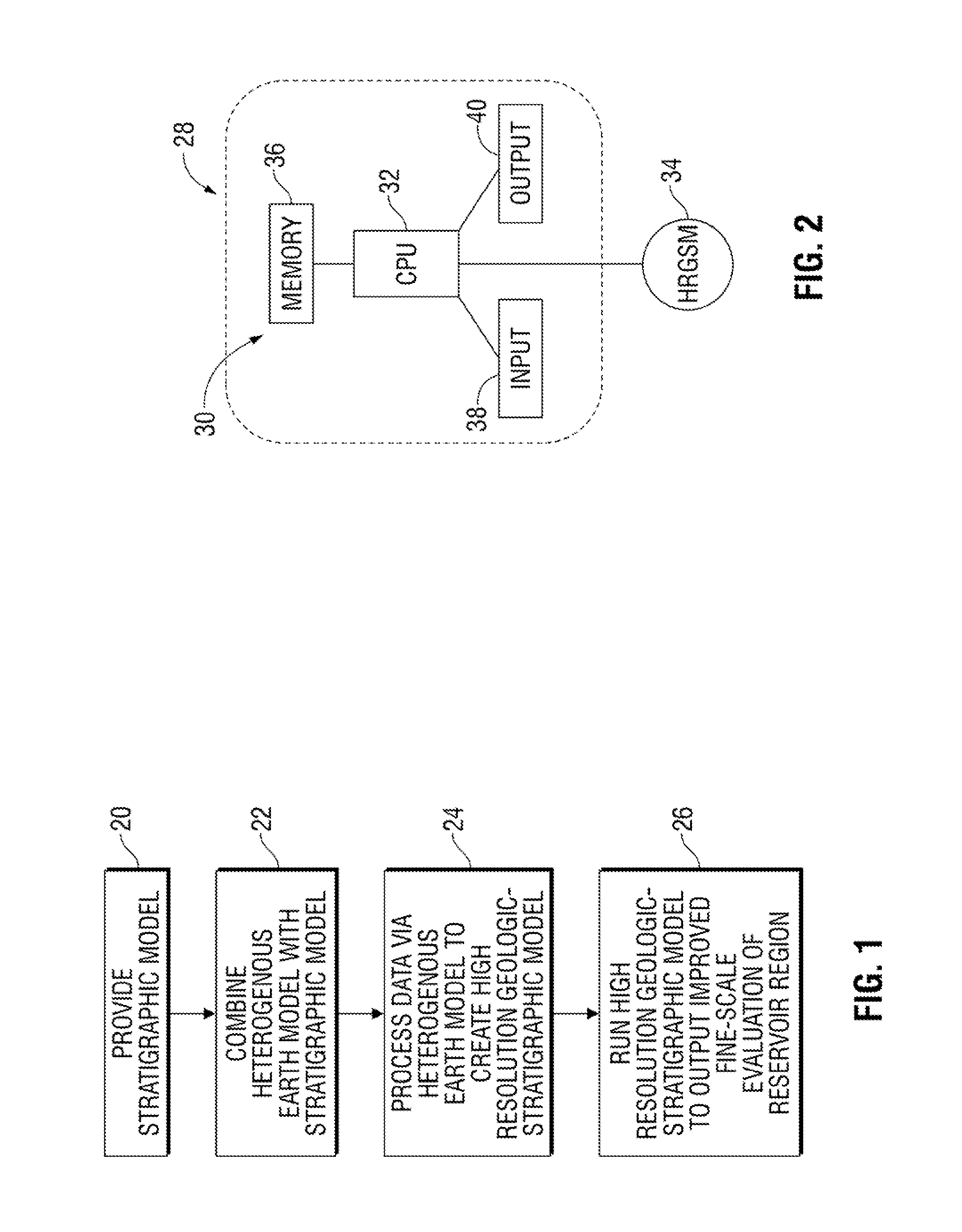
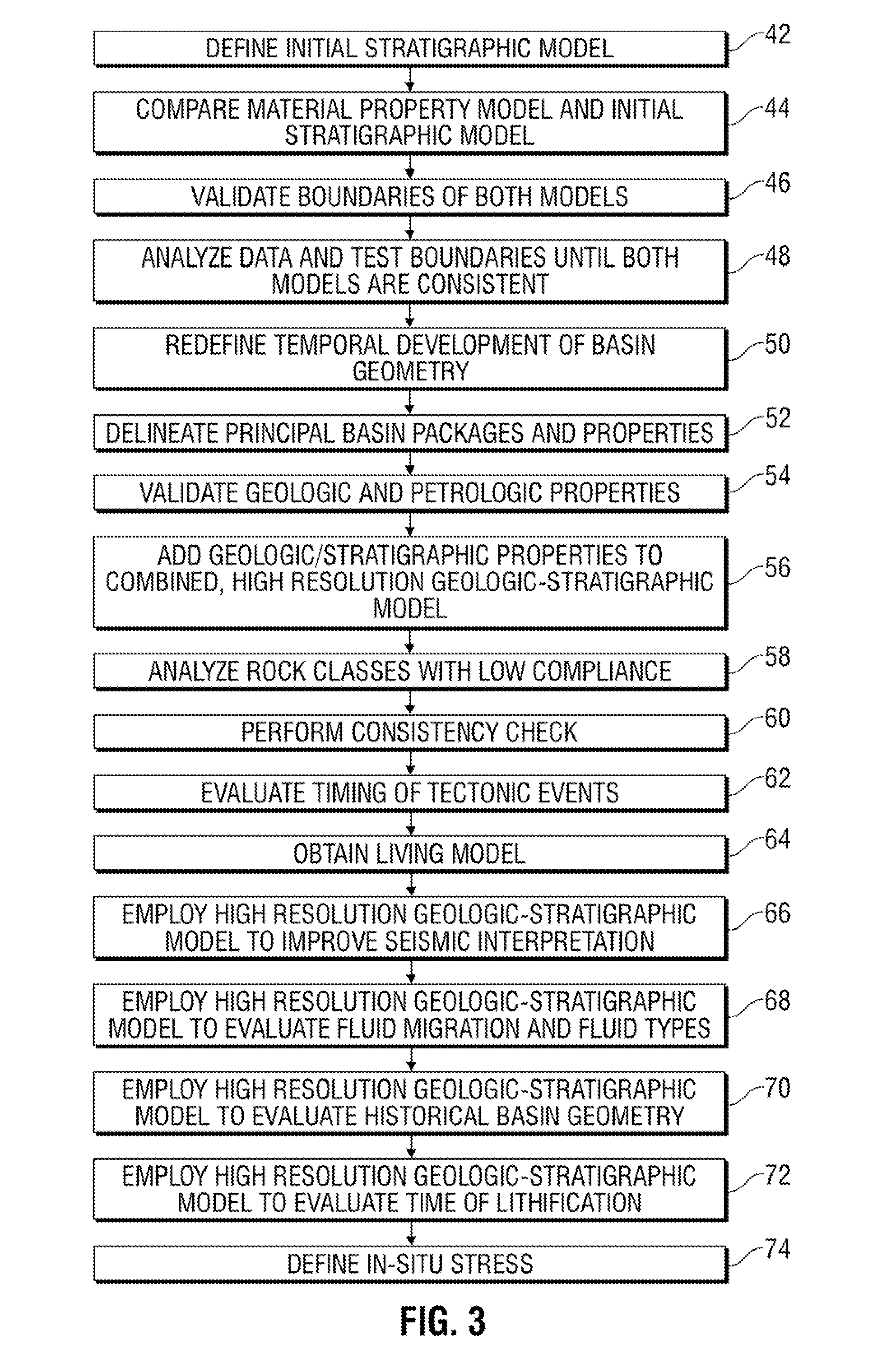
Method for modeling a reservoir basin
InactiveUS20130046524A1Simple modelHigh resolutionSeismologyAnalogue processes for specific applicationsGeomorphologyCombined use
A methodology improves the modeling of a geologic region, such as a hydrocarbon-bearing basin. The methodology comprises processing data to create a heterogeneous earth model based on a variety of data on material properties across the geologic region. The heterogeneous earth model is employed in combination with a stratigraphic model in a manner which creates a high resolution geologic-stratigraphic model. The high resolution geologic-stratigraphic model is useful for improving the analysis of hydrocarbon-bearing basins and other geologic regions.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method and system for seismic imaging and earth modeling using beam tomography
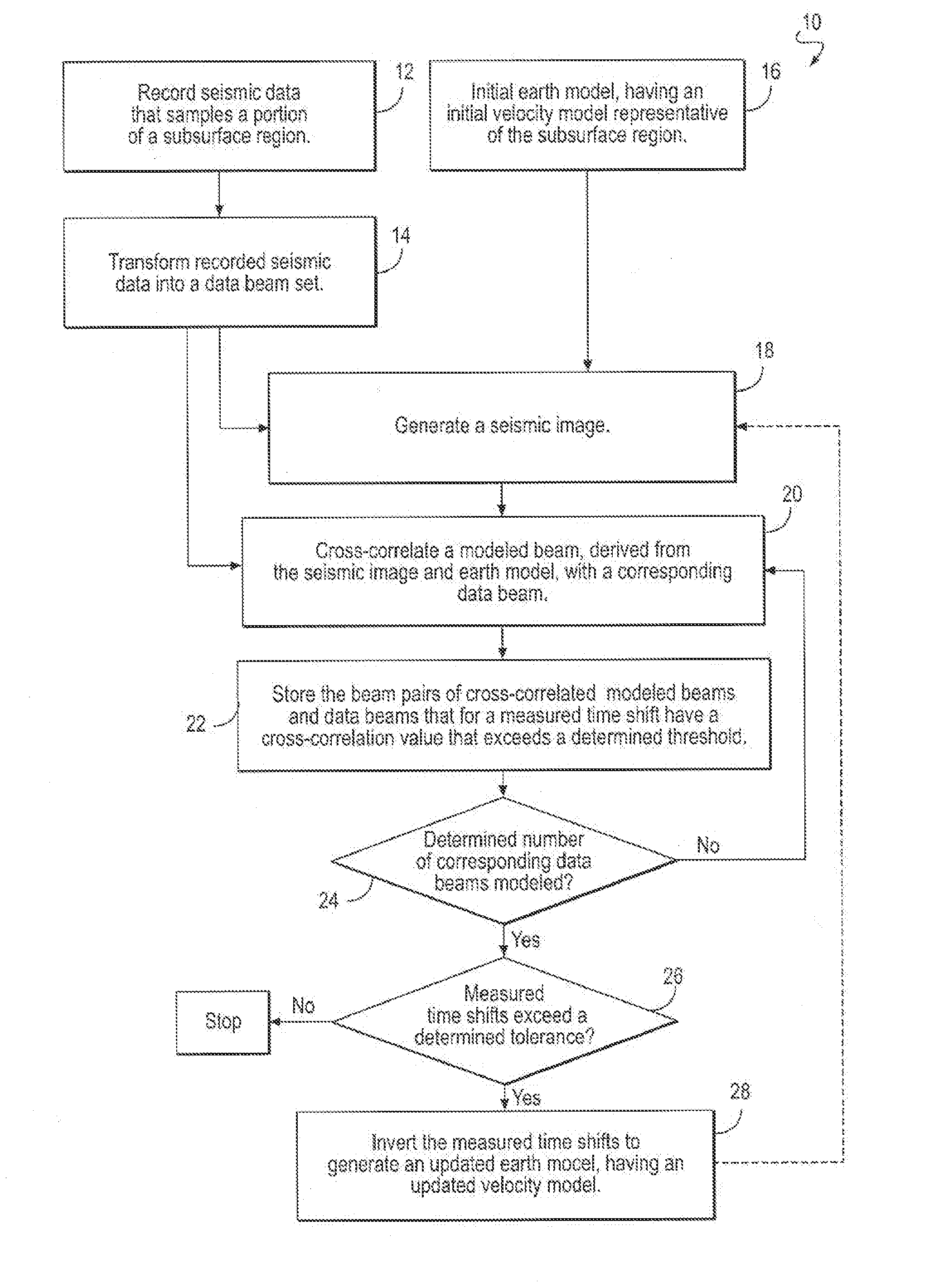
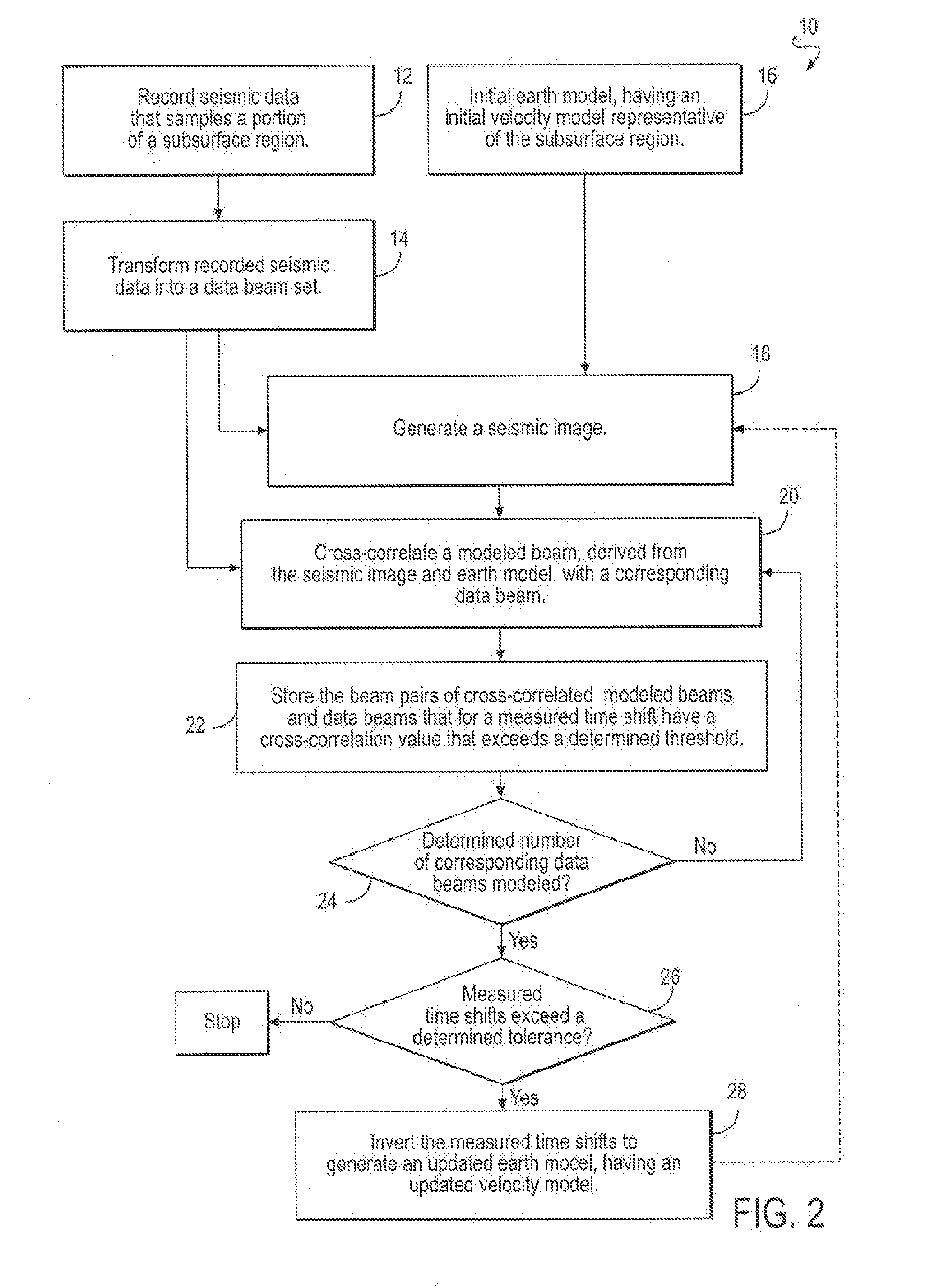
ActiveUS20110096627A1Improve earth model seismic velocityHigh speedSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsLight beamTomography
A beam tomography computer implemented method and system for generating improved seismic images and earth models without dependence on reflector structure is disclosed. Recorded seismic data is transformed into data beams which are compared to forward modeled beams using an earth model having a velocity model to compute raypaths and a seismic image to specify the reflectors. The tomographic updates to the earth model and velocity model are based on misalignments between the data beams and the same beams forward modeled from the velocity model and the seismic image. The updated earth model and seismic image better describe the true propagation of the beams through the earth.
Owner:CHEVRON CORP U S A
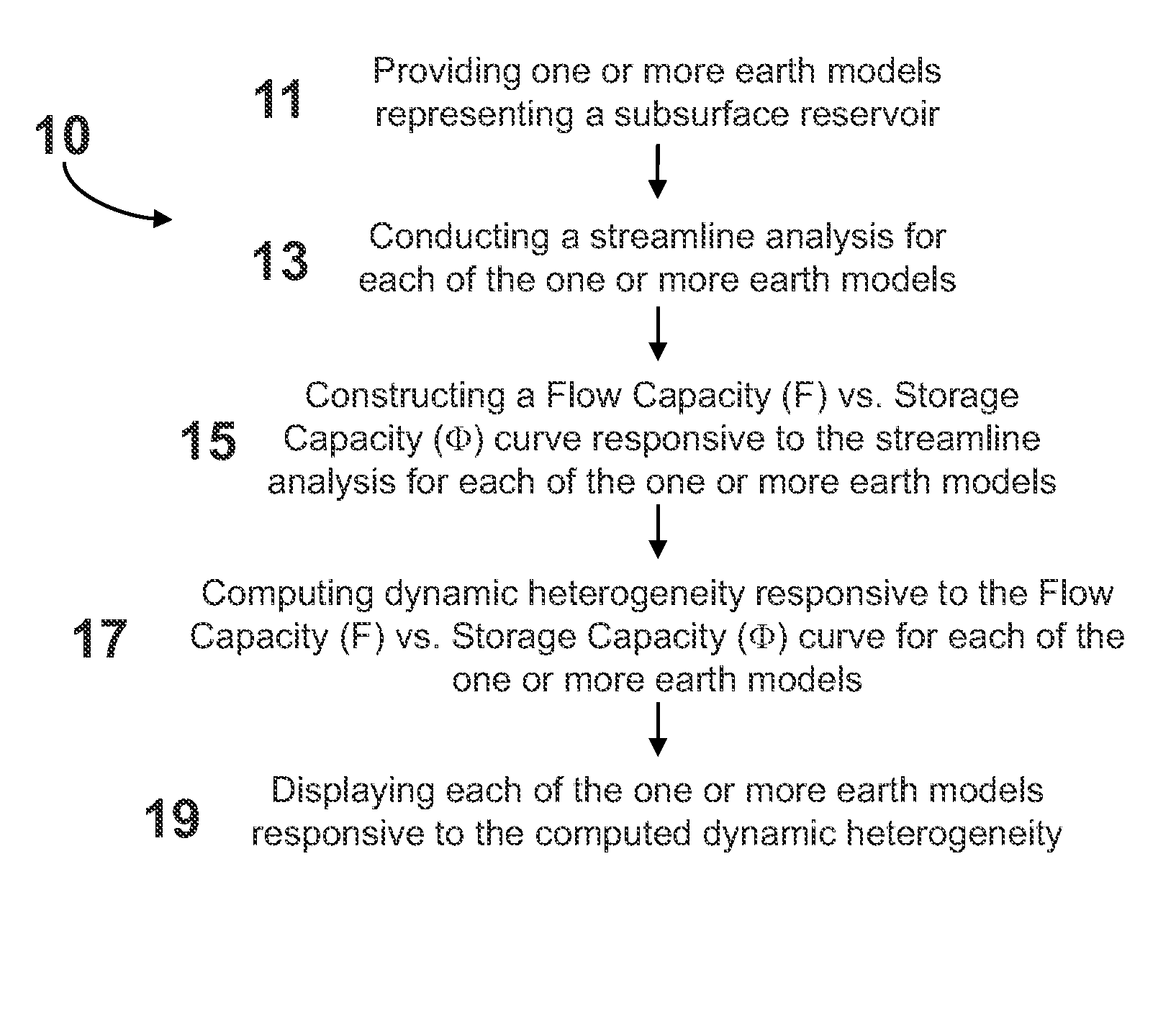
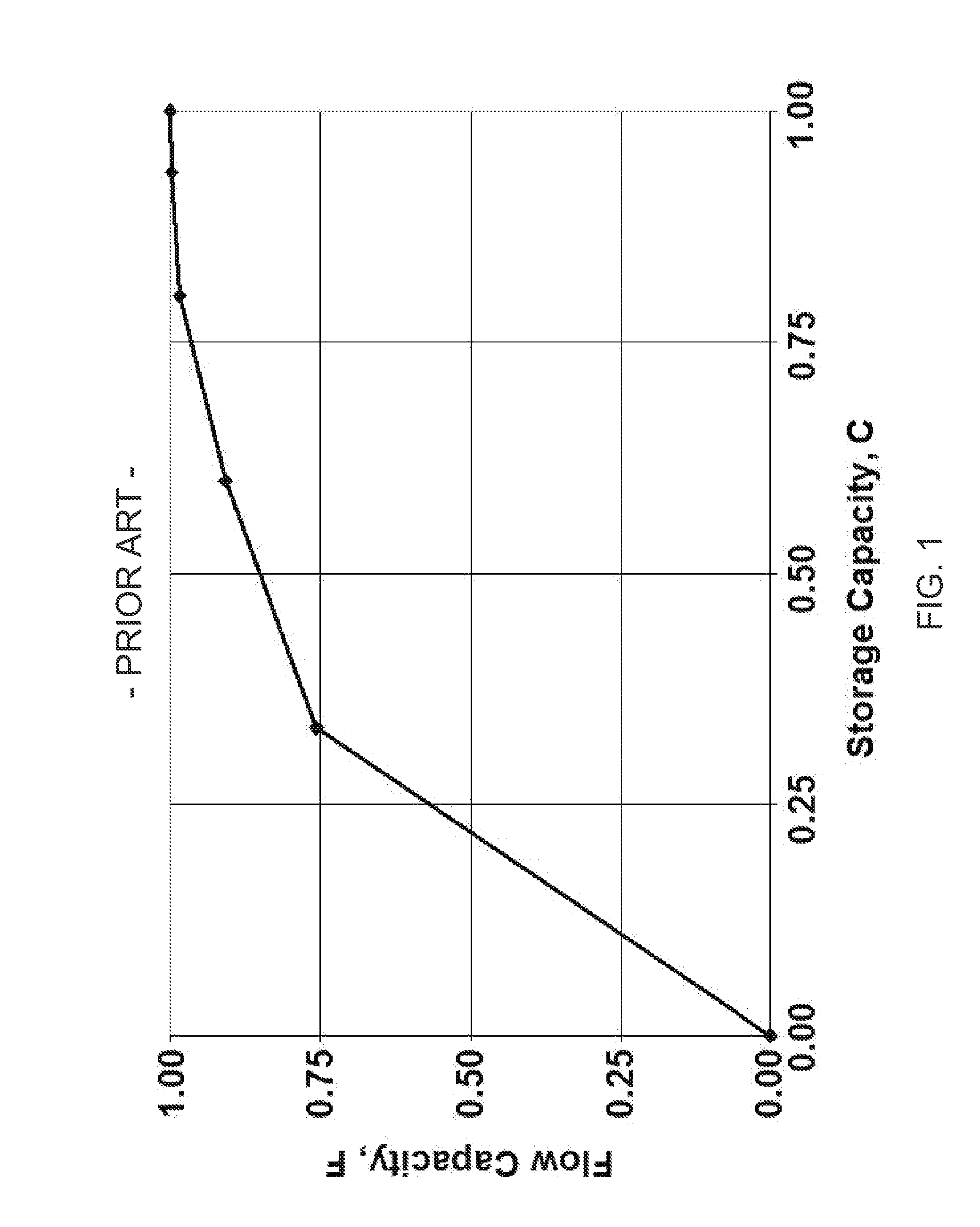
System and method for evaluating dynamic heterogeneity in earth models
A method is disclosed having application notably towards ranking earth models responsive to dynamic heterogeneity. A plurality of earth models representing a subsurface reservoir are provided. Streamline analysis for each of the plurality of earth models is conducted. Flow Capacity (F) vs. Storage Capacity (Φ) curves are constructed for each of the plurality of earth models based on the streamline analysis. Dynamic heterogeneity for each of the plurality of earth models is computed from the Flow Capacity (F) vs. Storage Capacity (Φ) curves constructed for each of the plurality of earth models. The plurality of earth models are ranked responsive to dynamic heterogeneity.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
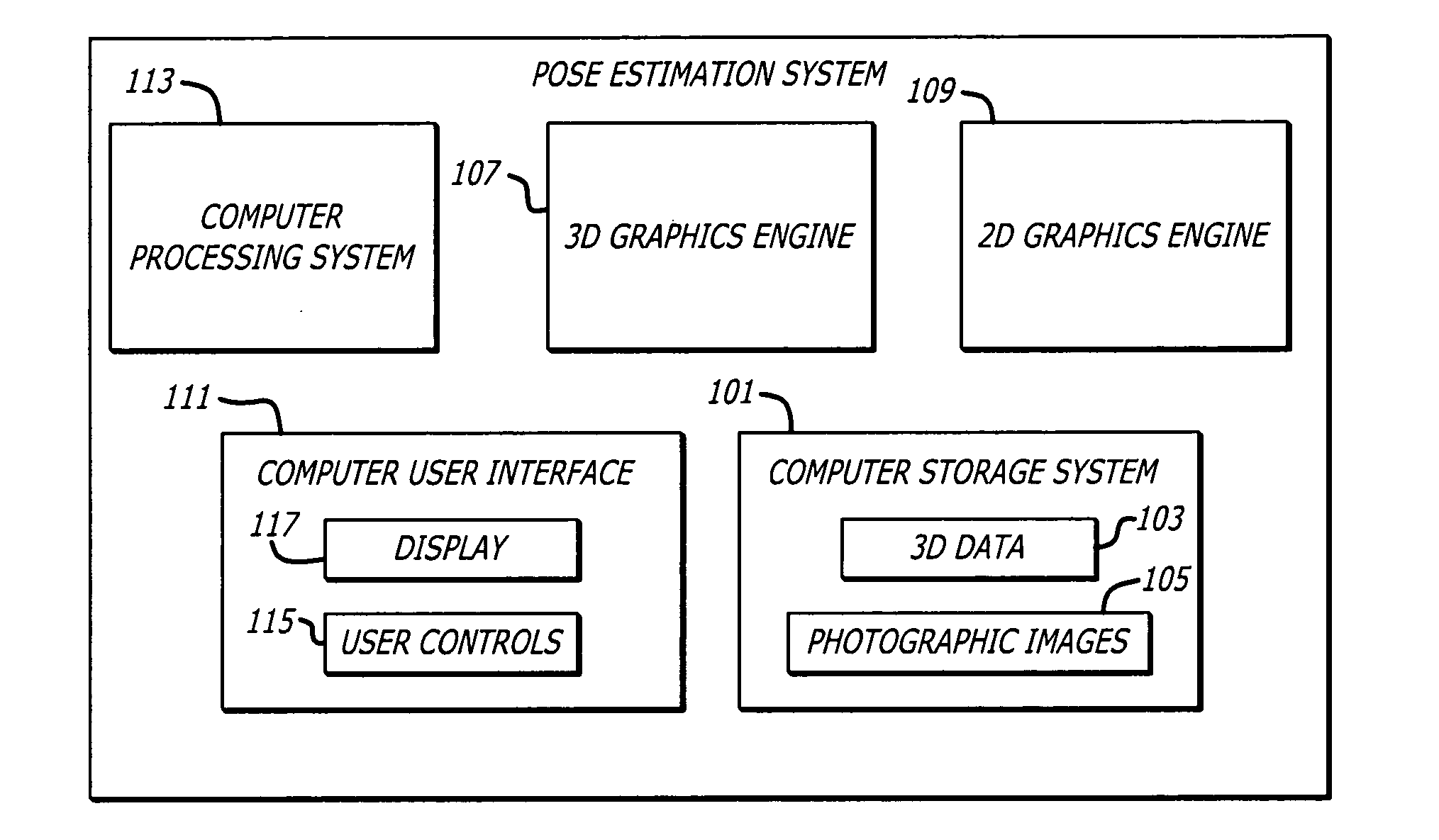
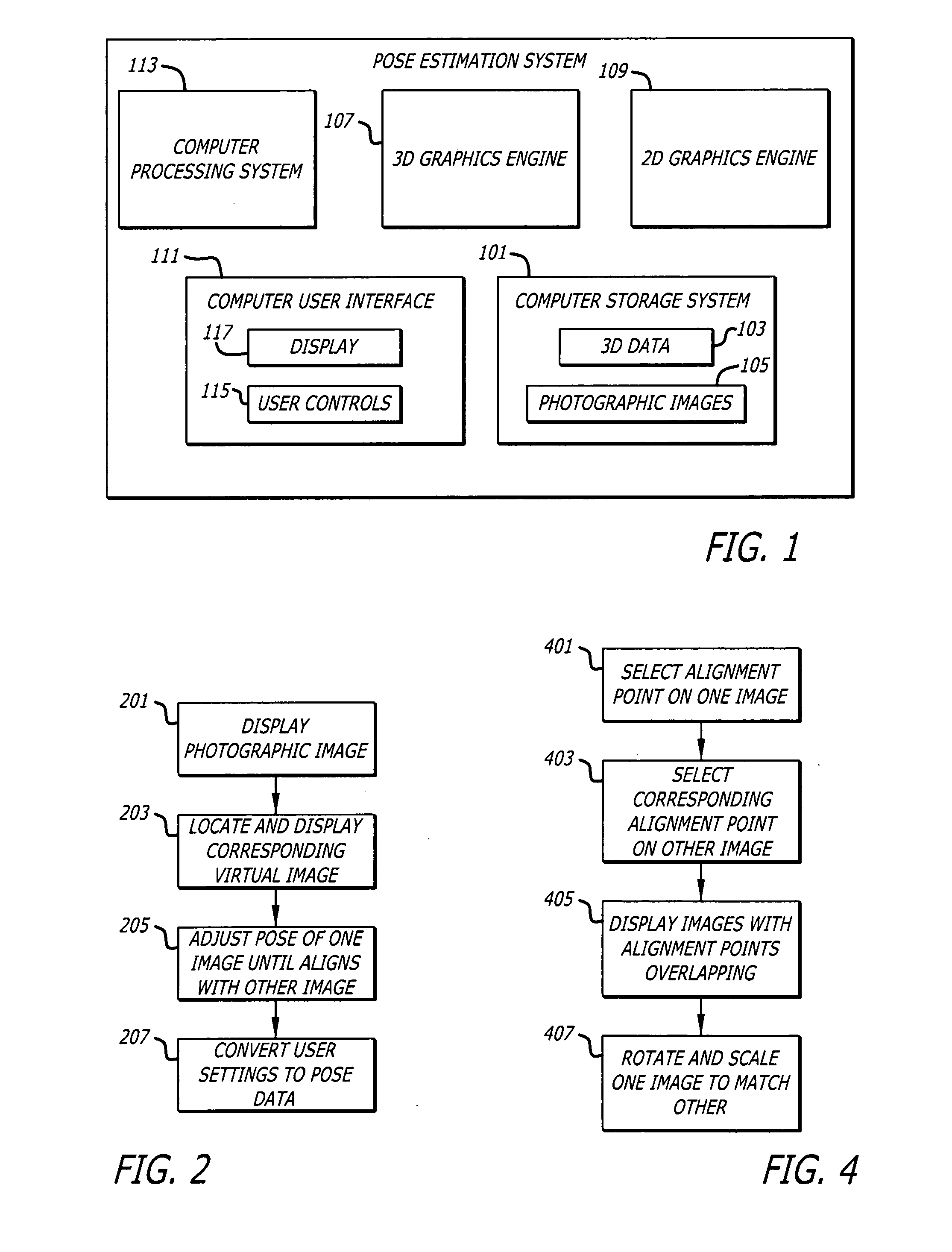
Estimating pose of photographic images in 3D earth model using human assistance
The pose of a photographic image of a portion of Earth may be estimated using human assistance. A 3D graphics engine may render a virtual image of Earth from a controllable viewpoint based on 3D data that is representative of a 3D model of at least a portion of Earth. A user may locate and display a corresponding virtual image of Earth at a viewpoint that approximately corresponds to the pose of the photographic image by manipulating user controls. The photographic image and the corresponding virtual image may be overlaid on one another so that both images can be seen at the same time. The user may adjust the pose of one of the images while overlaid on the other image by manipulating user controls so that both images appear to substantially align with one another. The settings of the user controls may be converted to pose data that is representative of the pose of the photographic image within the 3D model.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
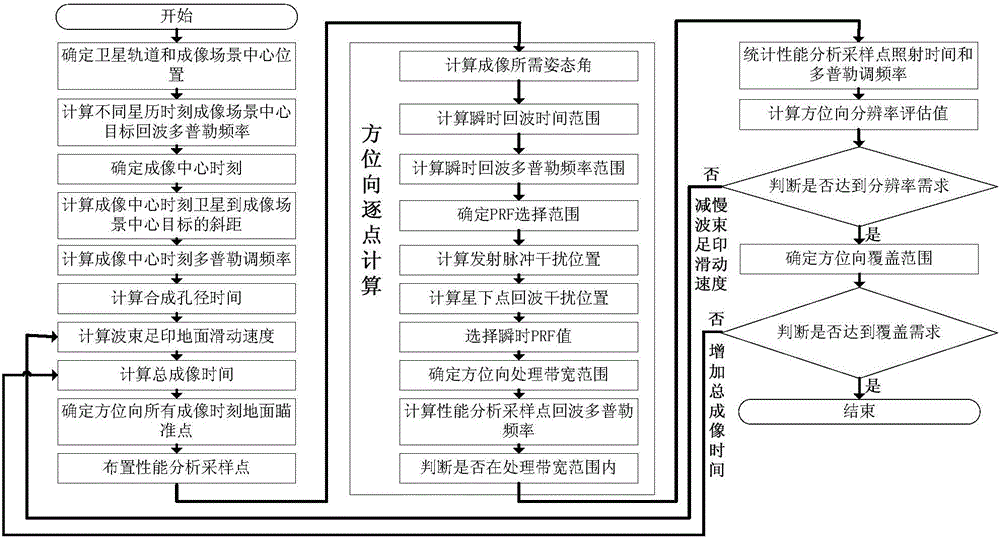
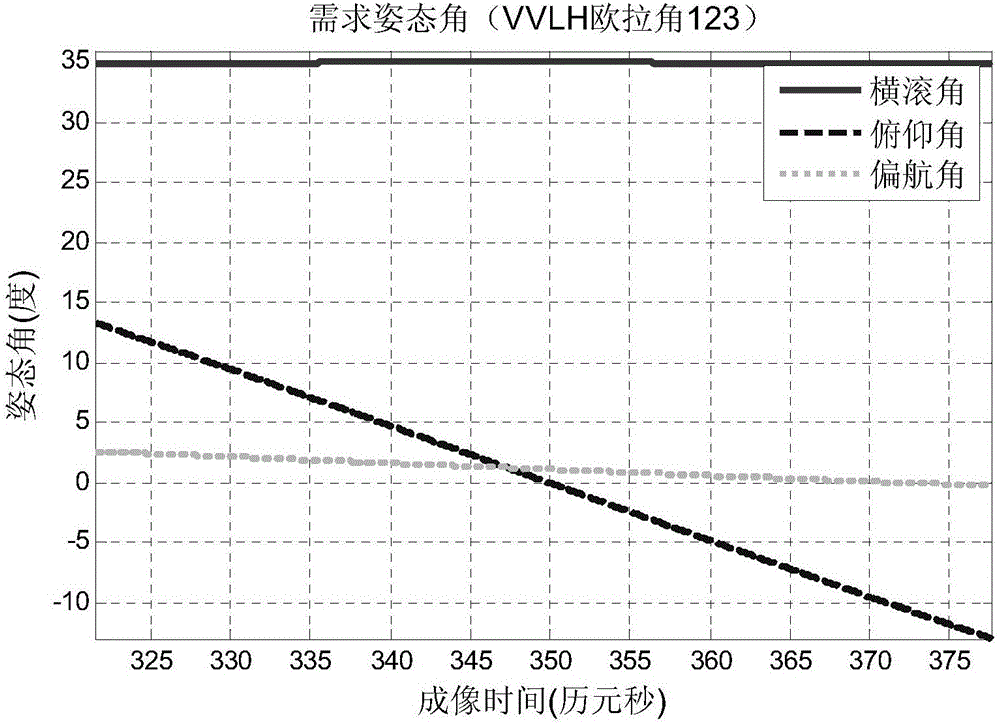
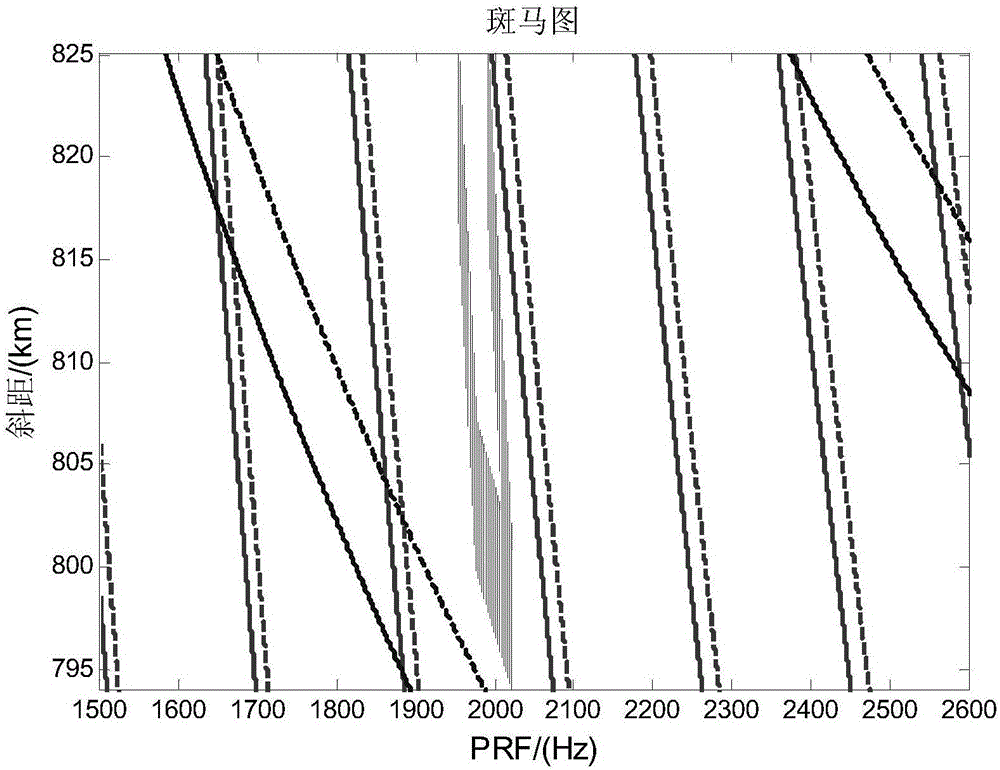
Ultrahigh-resolution agile SAR satellite sliding spotlight mode system parameter design method
ActiveCN106226768AEconomic realizationEfficient implementationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionHigh resolution imagingUltrahigh resolution
The invention relates to an ultrahigh-resolution agile SAR satellite sliding spotlight mode system parameter design method, is applicable to flexible realization of the ultrahigh-resolution imaging SAR satellite sliding spotlight mode system parameter design through whole satellite attitude, and belongs to the technical field of overall design of SAR satellites. According to the method, an accurate orbit, an earth model, system restriction factors, and imaging work characteristics of the sliding spotlight mode are fully considered, an ultrahigh-resolution agile SAR satellite sliding spotlight mode system parameter design method is provided, and an economic and high-efficiency realization method is provided for the ultrahigh-resolution satellite-borne SAR imaging; and the criterion of uniform-beam footprint ground slide speed is employed, ground aiming points of all moments within the whole imaging time are designed, parameters such as the attitude requirement and PRF at an instantaneous moment are calculated, and compared with the conventional method for calculating the parameters according to the mode far away from ground virtual aiming points, the method is higher in precision and imaging efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
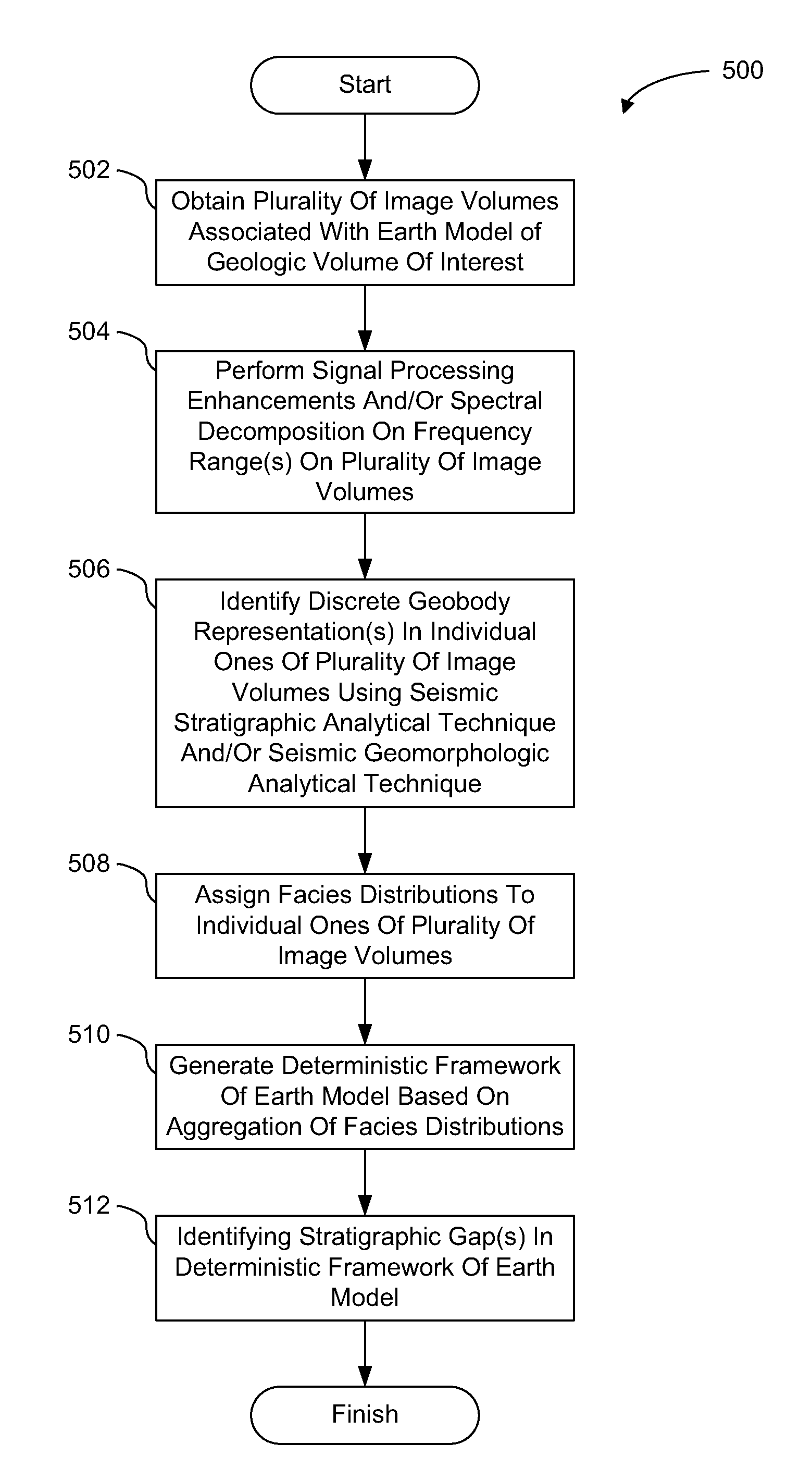
Hybrid deterministic-geostatistical earth model
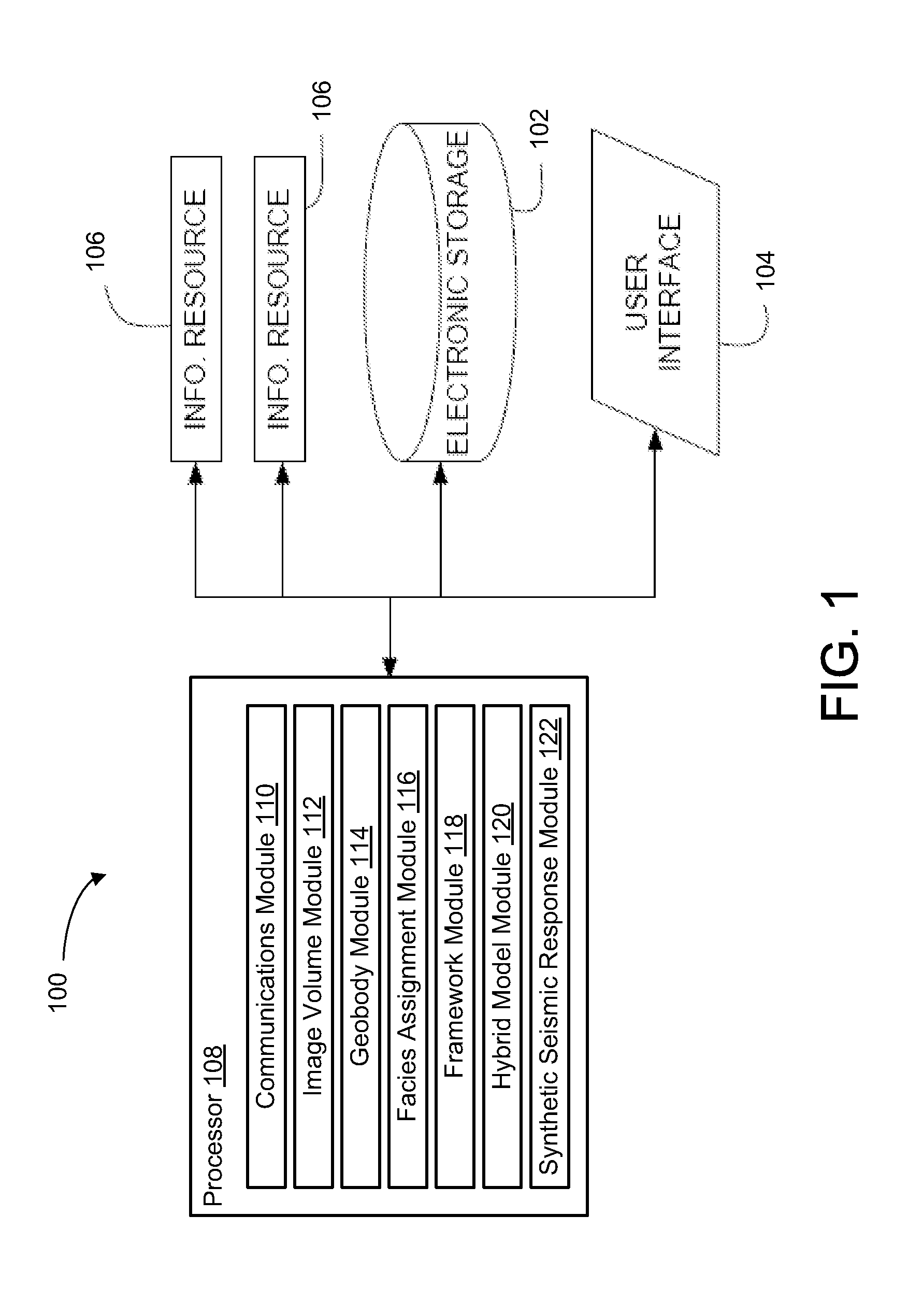
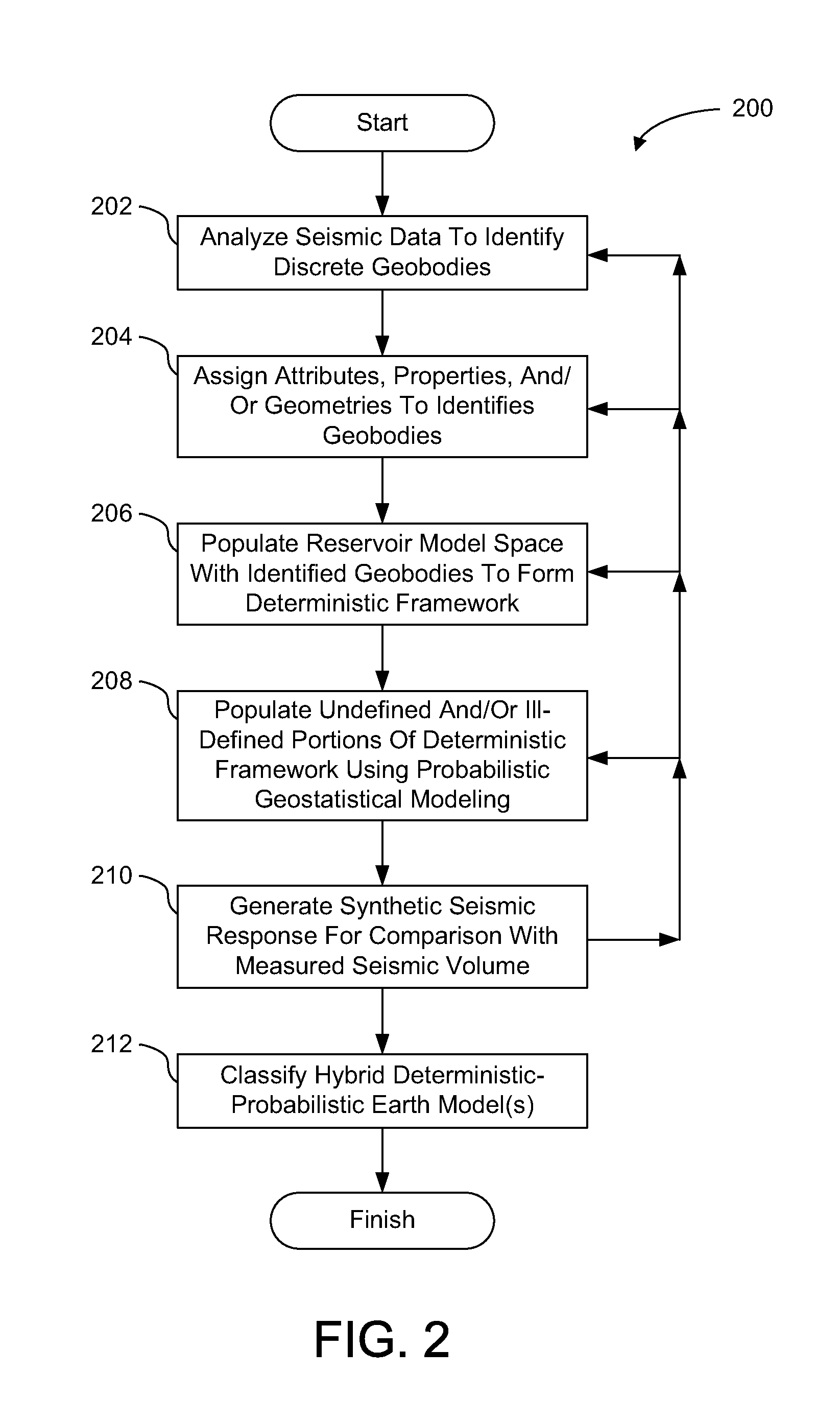
ActiveUS20130054201A1Convenient verificationGeometric CADCharacter and pattern recognitionSoil scienceEarth model
Embodiments of the present technology integrate seismic data and geologic concepts into earth model building. More specifically, exemplary embodiments provide new ways to build an earth model based on information in the seismic data and geologic concepts to use as a context to interpret the seismic data and / or to add to the earth model in regions where the seismic data is missing (e.g., either no data or no data resolvability). In some embodiments, a deterministic framework is generated for an earth models through deterministic identification of discrete geobodies. A hybrid deterministic-geostatistical earth model is generated by filling stratigraphic gaps in a deterministic framework using geostatistical information and / or seismic inversion, in accordance with some embodiments.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
System and method for attaching drilling information to three-dimensional visualizations of earth models
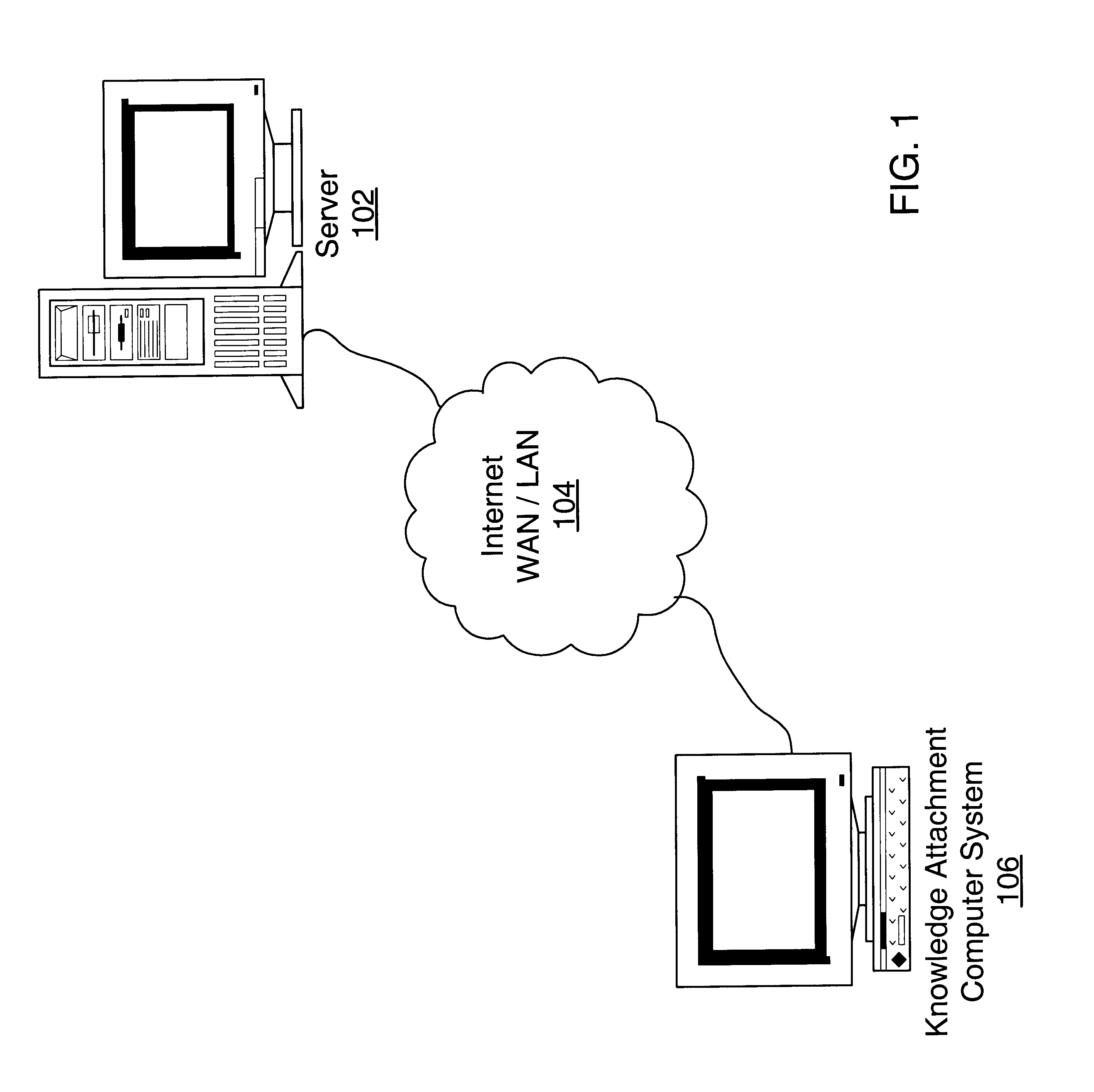
InactiveUS6801197B2Improve abilitiesProcess can be speededSeismic signal processing3D-image renderingWell drillingEarth model
A system and method for perceiving drilling learning through visualization is provided. In one embodiment using three-dimensional visualization of the earth model as a foundation, a new IT development strategy focuses on perceiving "Drilling Learning" by an intuitive method. Symbols, known as "Knowledge Attachments" are attached to each wellbore trajectory displayed in the three-dimensional environment, with each symbol indicating a specific event-such as one related to drilling operations or problems. A Knowledge Attachment system proves particularly useful to represent disparate data at once, in such a manner that the interdependencies between the earth model and drilling operational data are evident and correlated. Operational issues and lessons learned from prior wells are easily accessed and perceived in the context of the earth model. By understanding this information at the beginning of the well planning process, operational efficiencies may be improved.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS
Real time earth model for collaborative geosteering
ActiveUS7359844B2Improve efficiencyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingGeosteeringWell drilling
An earth model is formed in real time during drilling of a well by incorporating up-to-the-minute knowledge derived from geology, seismic, drilling, and engineering data. The process of forming the model utilizes Logging-While-Drilling (LWD) or Measuring-While-Drilling (MWD) data directly from the drilling rig as the well is drilled. The LWD or MWD data is sent to visualization centers and compared with other data such as existing geological models, the proposed well plan and present interpretation of the subsurface stratigraphy. The results of the comparison enable experts to analyze anomalous results and update the geological model within minutes of penetration of a formation during drilling. Well drilling efficiency is improved, and an “on-the-spot” road map is provided for maximal reservoir contact and pinpoint accuracy.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
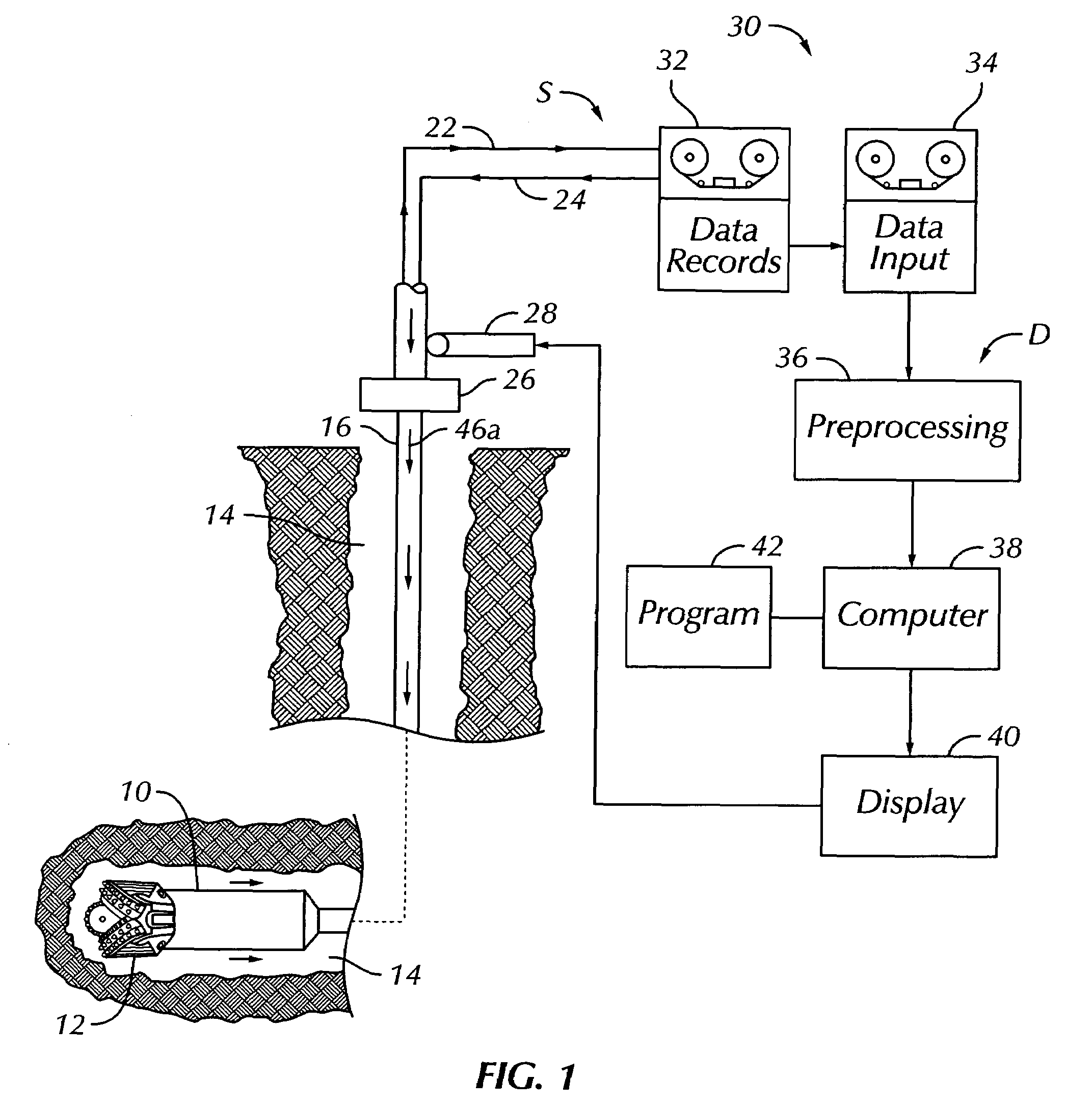
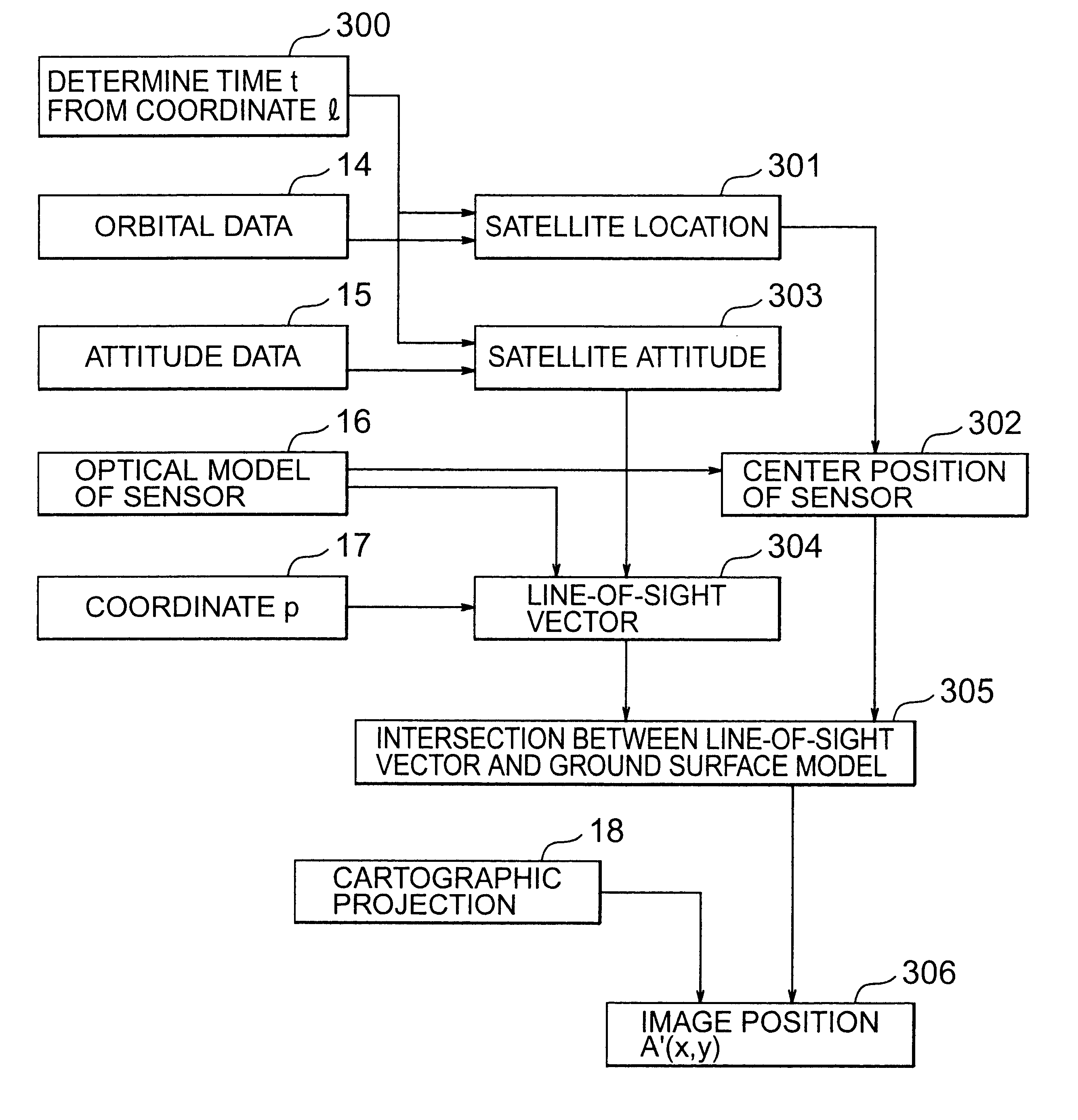
Method for orthocorrecting satellite-acquired image
InactiveUS6810153B2Improve accuracyImage enhancementGeometric image transformationImage segmentationEarth model
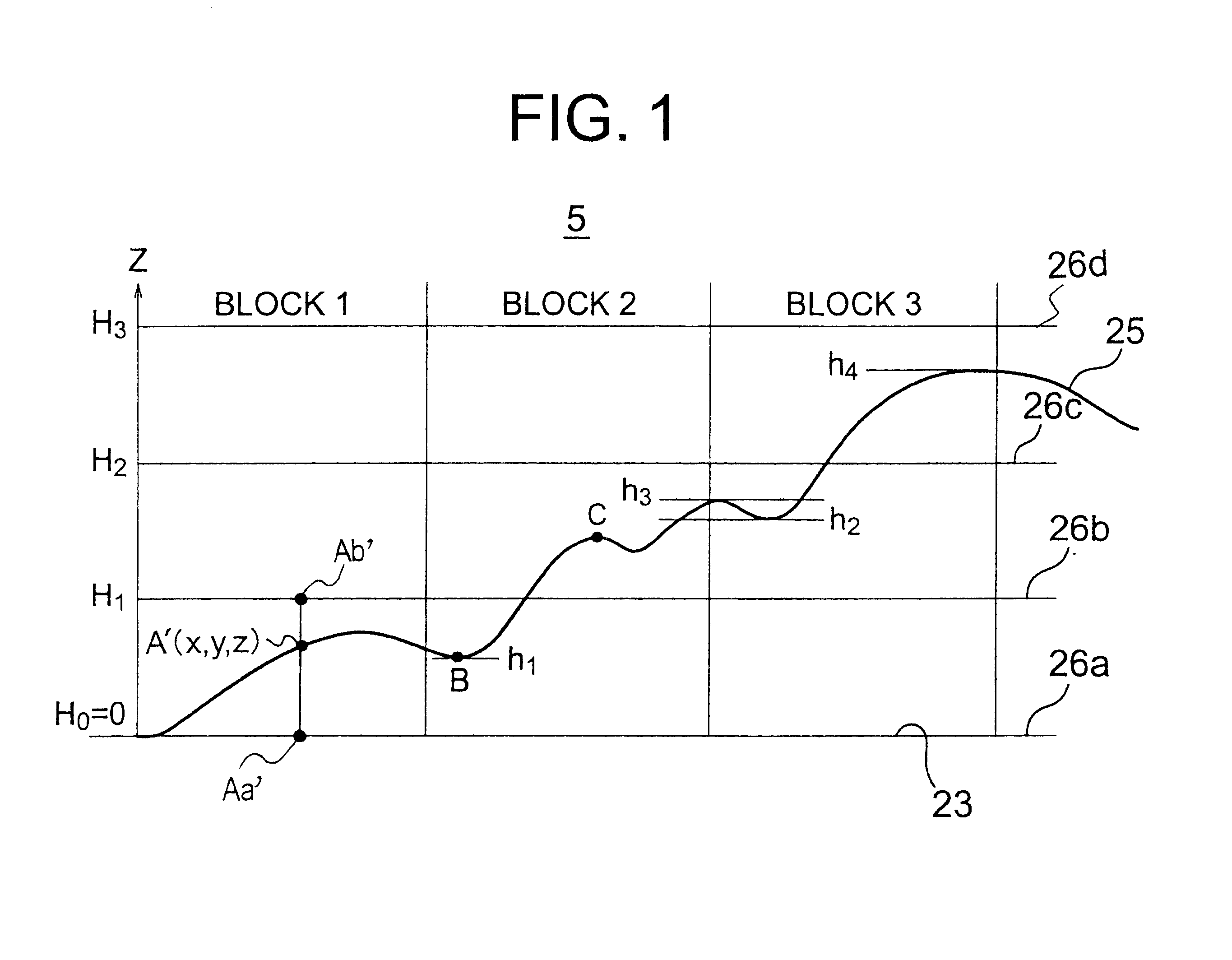
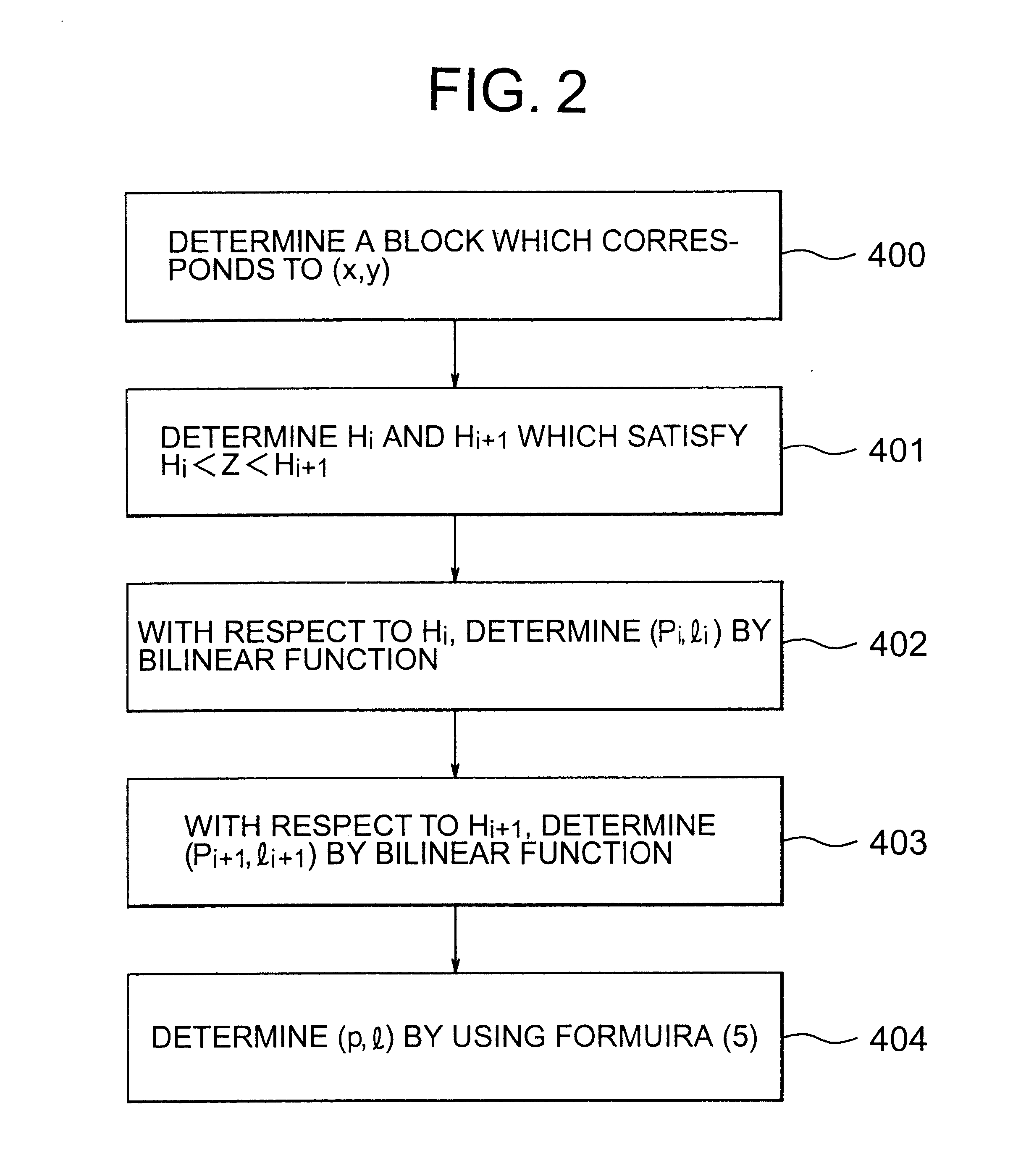
A method is provided for the orthocorrection of a satellite-acquired image. This method can be applied even if ground control points are not set. Without propagation of an error throughout the image and also without needing an excessively large amount of calculations, the method makes it possible to correct ground-relief-associated distortions caused by the relief of a ground surface. According to the method, a plurality of control planes of different elevations are set relative to a control plane of a zero elevation of a reference rotating ellipsoidal earth model. A corrected image is divided into blocks by lattices of equal intervals. With respect to each of these blocks, distortion model formulas in the form of bilinear functions are determined for the respective control planes. Concerning each pixel position in the corrected image, two pixel positions in an observed image, which correspond to the elevation value of the pixel position in the block, are calculated by using distortion model formulas for two control planes which directly sandwich the value of elevation above and below the value in the corresponding block. By the value of elevation, the two pixel positions are linearly interpolated to determine the desired pixel position in the observed image.
Owner:HITACHI SOFTWARE ENG
Efficient and accurate pseudo 2-D inversion scheme for multicomponent induction log data
InactiveUS6618676B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPermeability/surface area analysisEarth modelForward solution
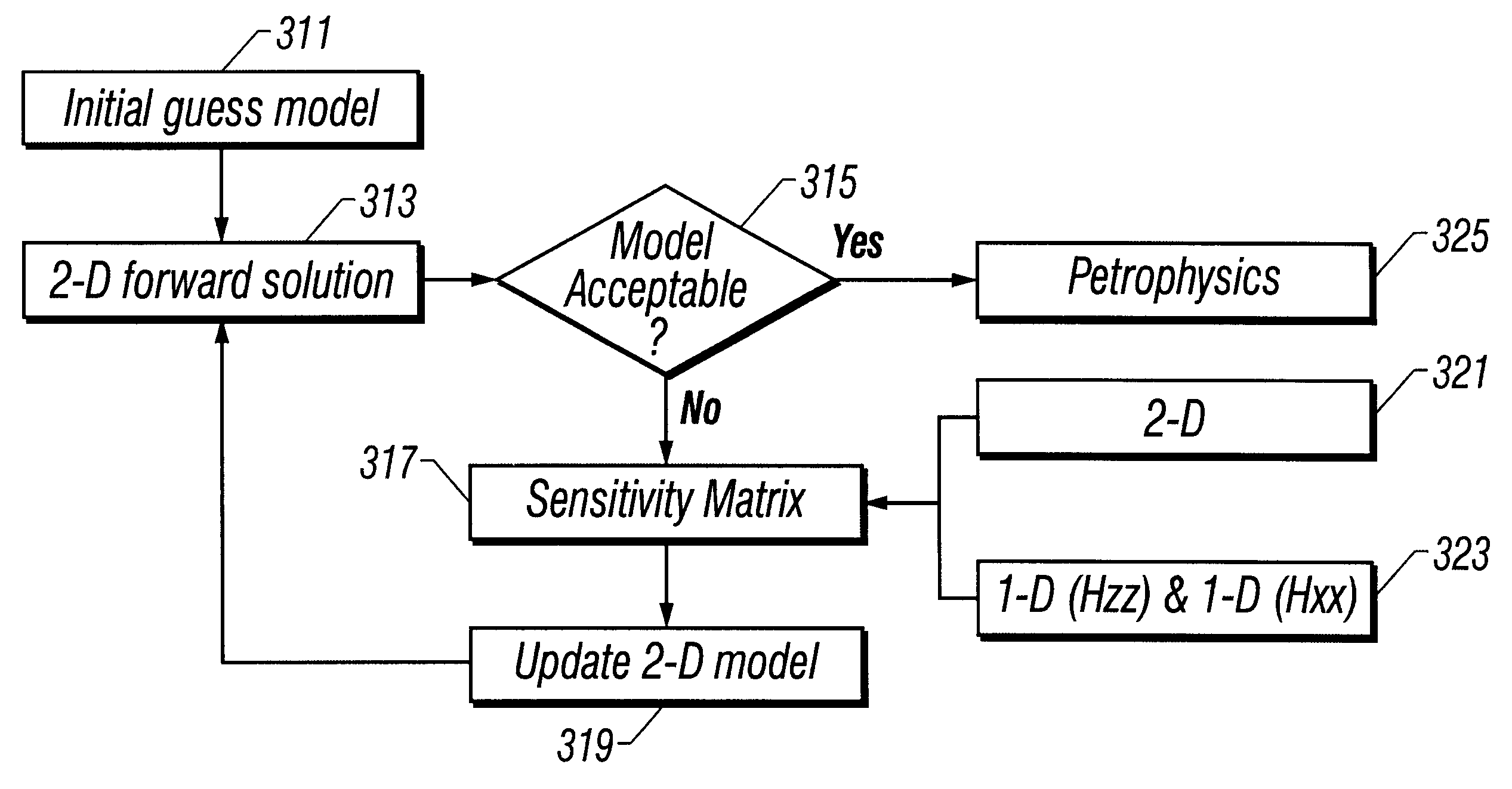
A fast, efficient and accurate pseudo 2-D inversion scheme for resistivity determination of an anisotropic formation uses data from a tool (3DEX) comprising three transmitters and three corresponding receivers sampling the formation in a plurality of spatial directions. An initial model of the formation including invasion zones is obtained using a conventional multifrequency and / or multispacing logging tool. A pseudo 2-D inversion scheme combines an accurate full 2-D forward solution of the synthetic responses of the earth model with a 1-D approximation of the sensitivity matrix of the horizontally layered anisotropic background model. The timesaving compared to a regular 2-D inversion scheme can be tremendous. The applicability of this scheme is important in cases when borehole and near-zone effects do not allow an interpretation based on 1-D inversion. A comparison of the pseudo 2-D inversion scheme versus a full 2-D inversion using a realistic synthetic example shows that the pseudo 2-D inversion scheme performs as well as the full 2-D inversion, but in a much shorter time.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
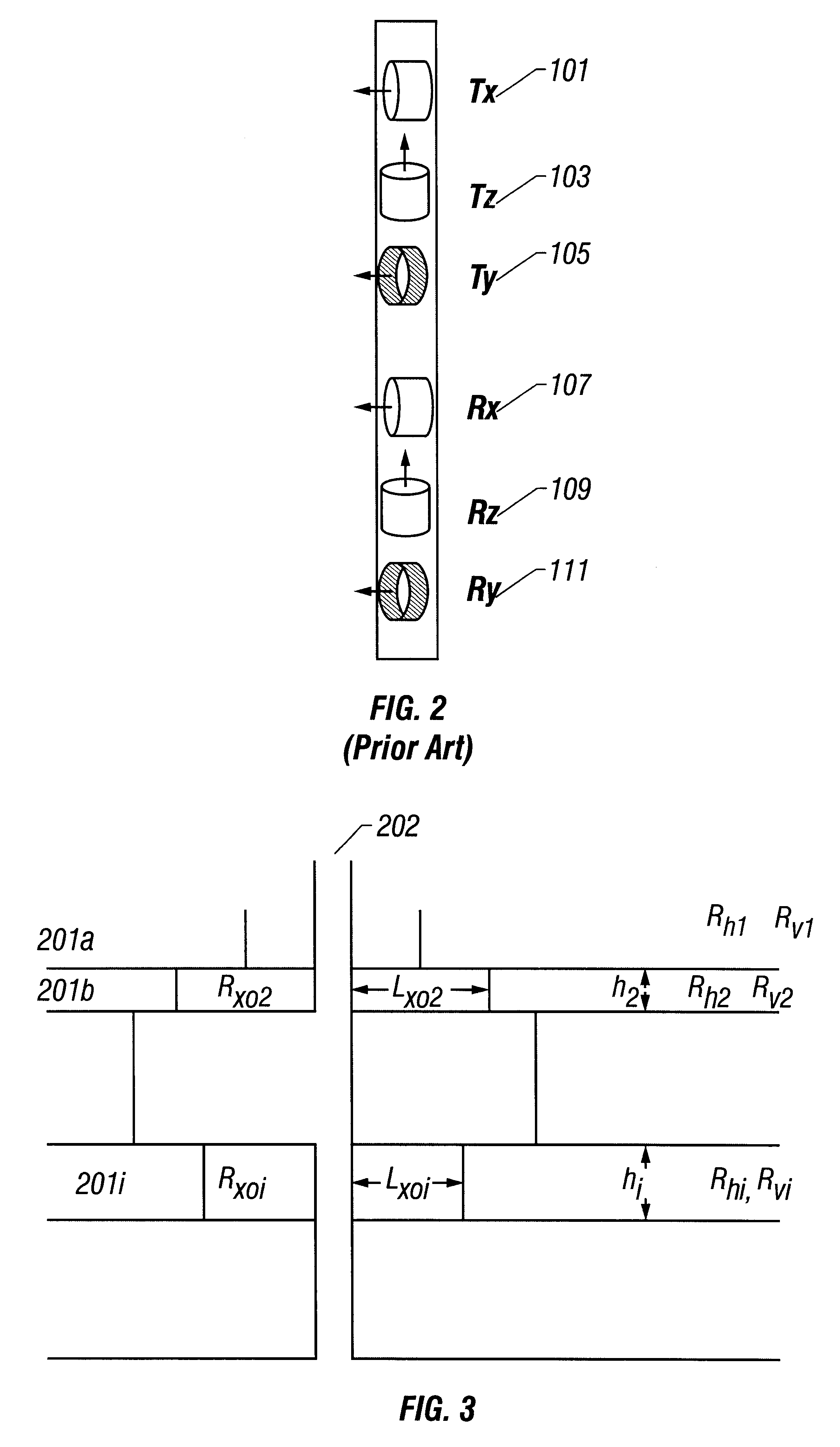
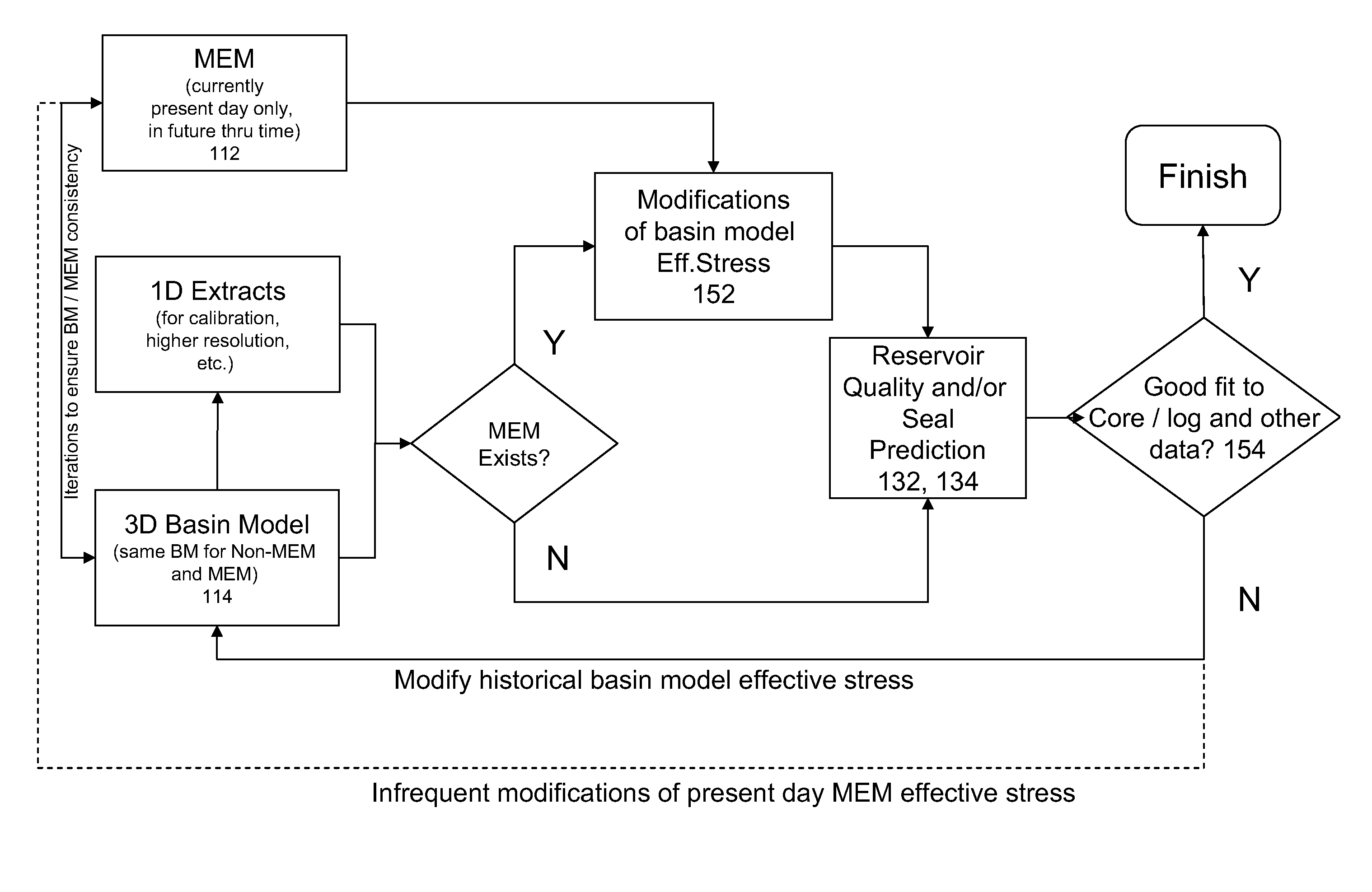
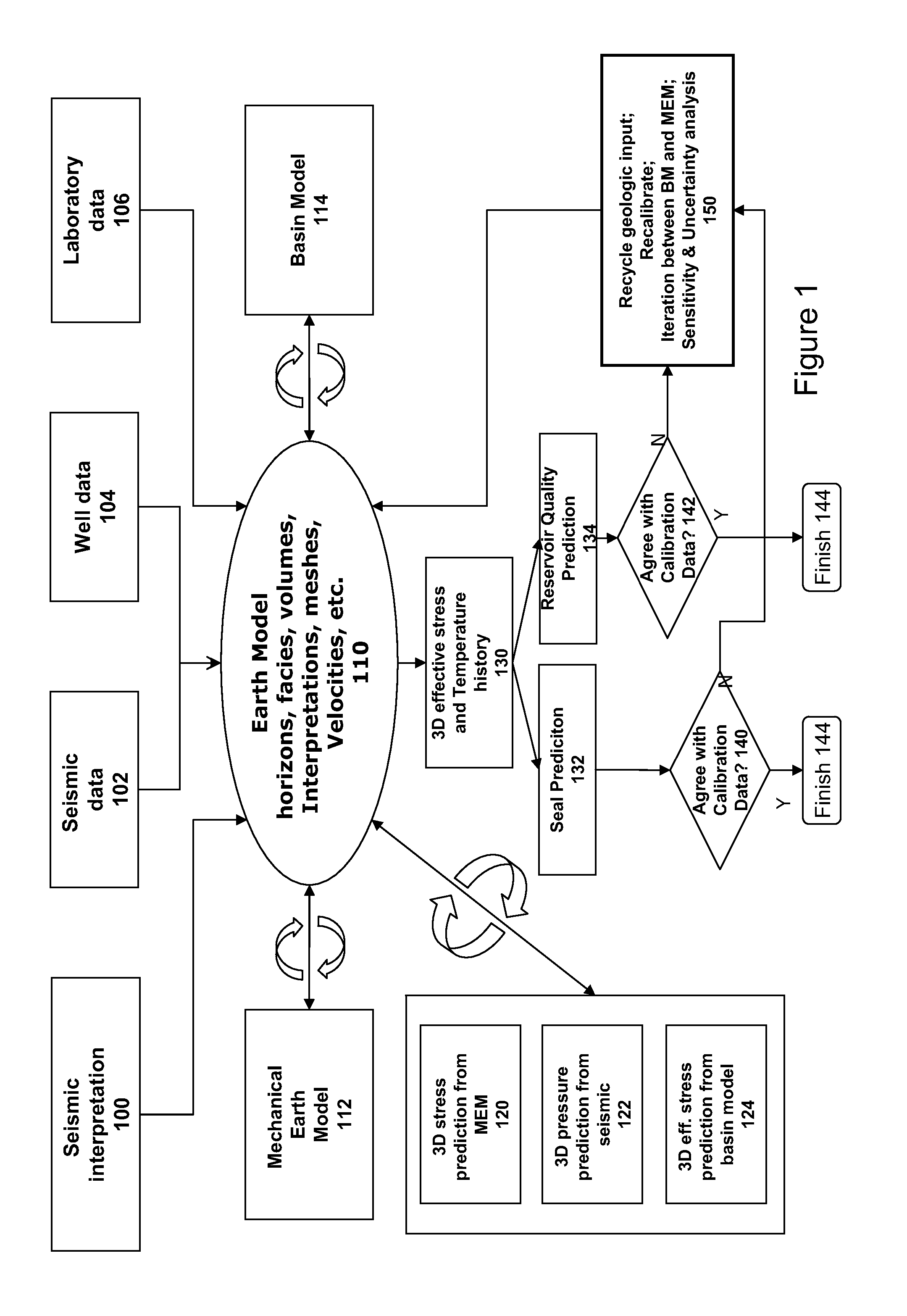
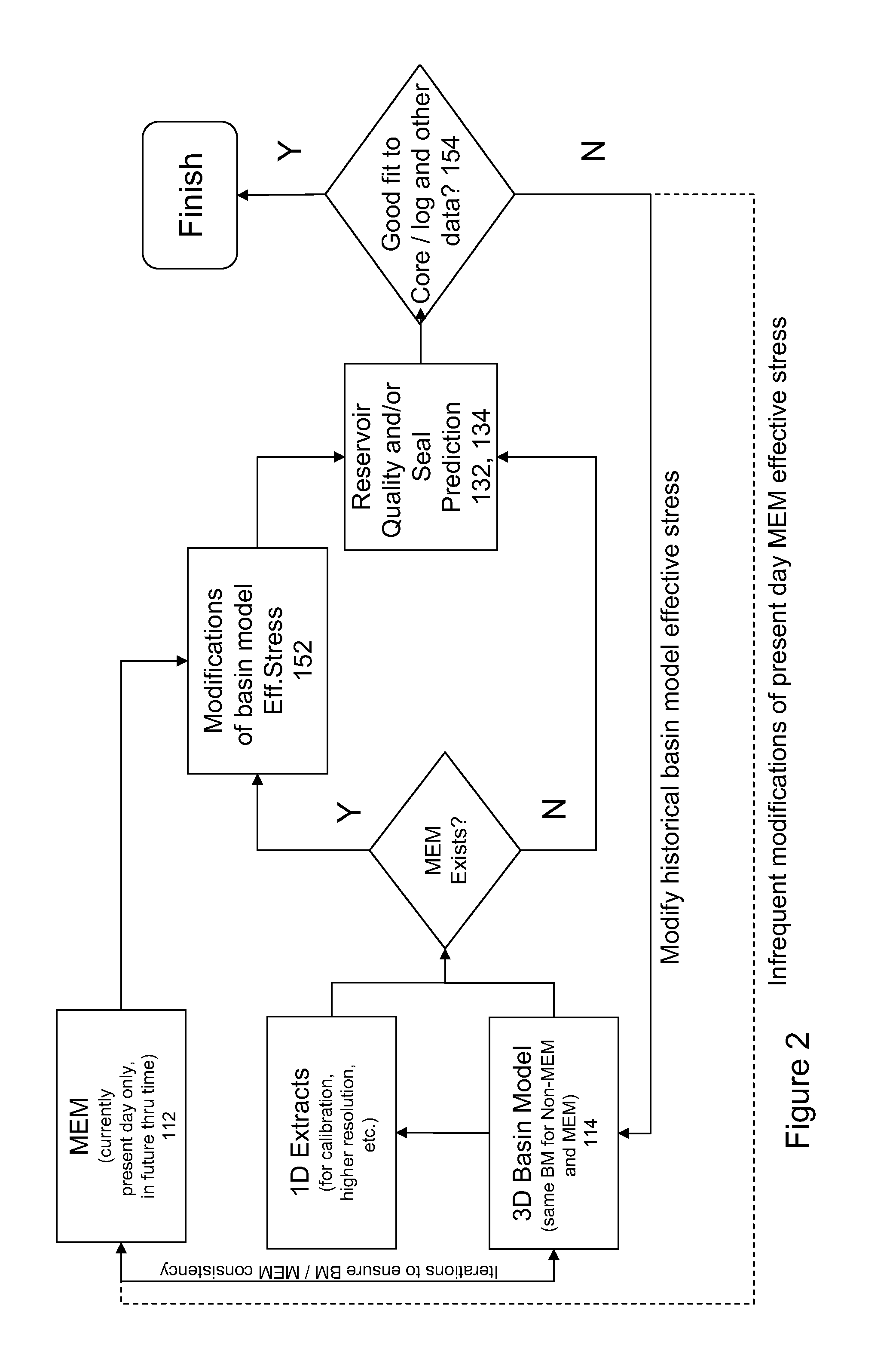
System and method for integrated reservoir and seal quality prediction
A system for and method of integrated reservoir and seal prediction is useful for evaluation of effective mean stresses affecting geologic systems through their history, and subsequently to predict reservoir and seal quality, flow and seal properties and other behaviors. Porosity and permeability as well as seal properties are modeled based on the effective mean stress. Integrated earth models are built using seismic interpretations, wells and other available data. Geo-mechanical earth models are built and stresses are computed. Basin models are built using inputs from seismic interpretation tools, wells, geochemistry, and earth and mechanical earth models. Reservoir quality and seal quality prediction is performed and the building earth models, computing stresses, building basin models and quality prediction are iterated to converge to a solution that honors well, seismic, core, geochemical and any other available calibration data.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
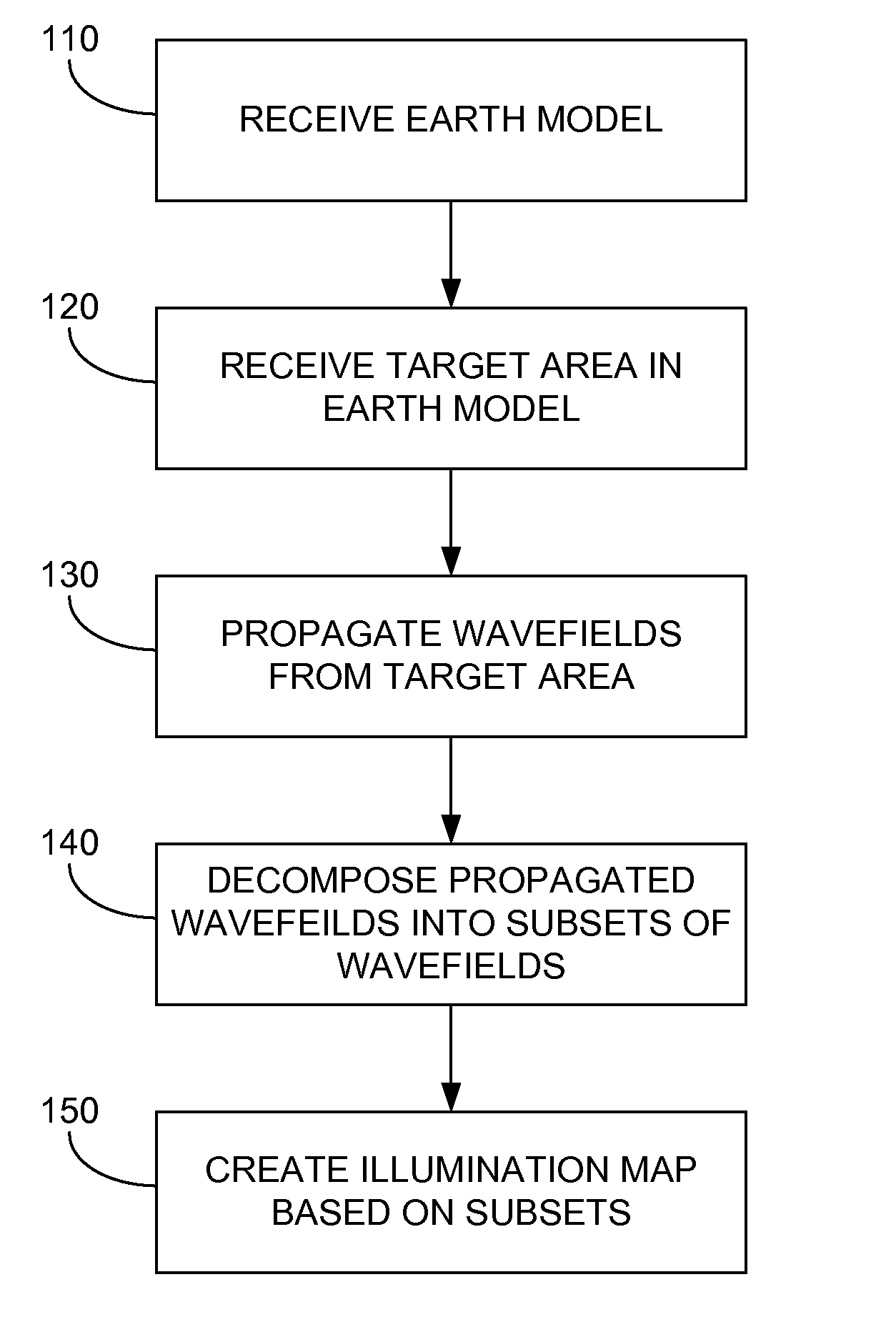
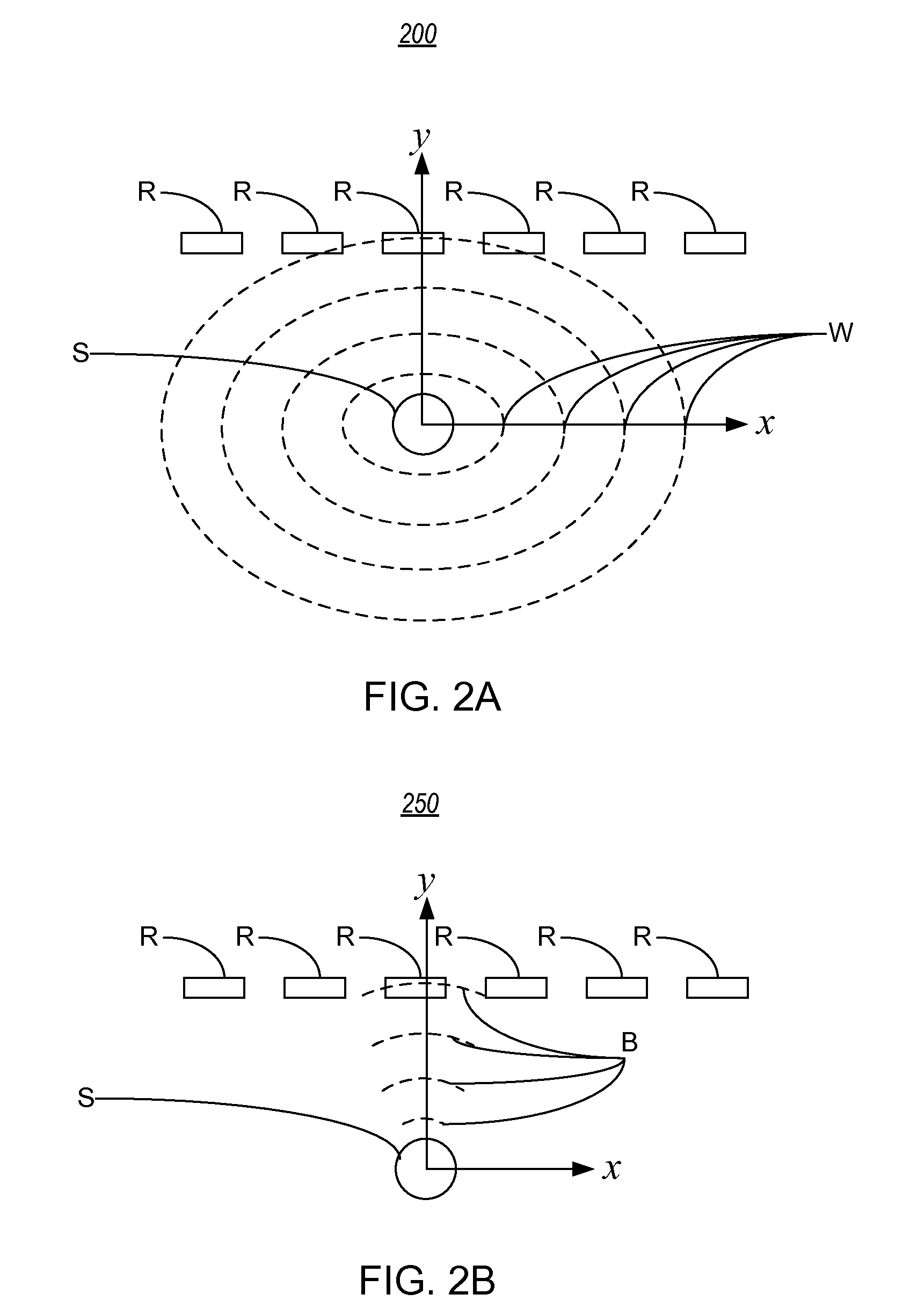
Wave equation illumination
A method for generating an illumination map. The method includes receiving an earth model that represents one or more properties of the earth. The method then includes receiving a target area in the earth model and propagating one or more wavefields from the target area to a potential seismic data acquisition region in the earth model. After propagating the wavefields, the method includes decomposing the propagated wavefields into one or more subsets of the propagated wavefields and creating the illumination map based on the subsets of the propagated wavefields. The illumination map may indicate one or more contributions of one or more synthetic source and receiver pairs for illuminating the target area in the earth model. The method may then include creating a seismic survey design based on the contributions.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com