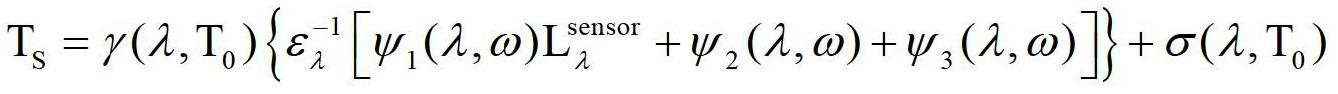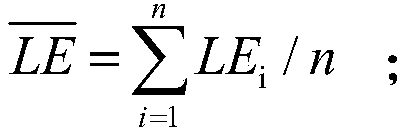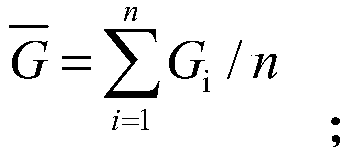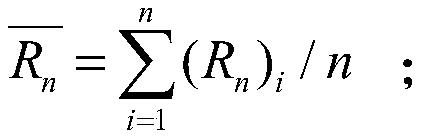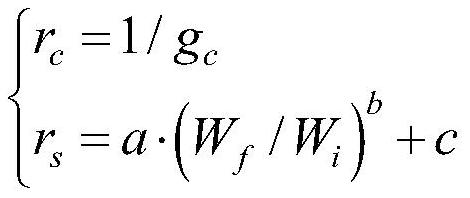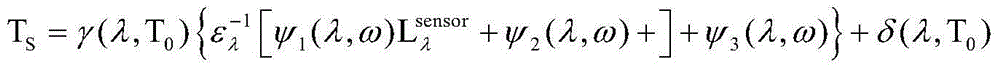Patents
Literature
31 results about "Soil heat flux" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Soil heat flux is used extensively in agrometeorological studies, as it relates to the amount of energy stored in the soil as a function of time.
Earth face evapotranspiration remote sensing inversion method and system based on MODIS data
InactiveCN103810387AAvoid the requirement for accurate atmospheric correctionReduce uncertaintyMaterial analysis by optical meansSpecial data processing applicationsData aidedObservation data
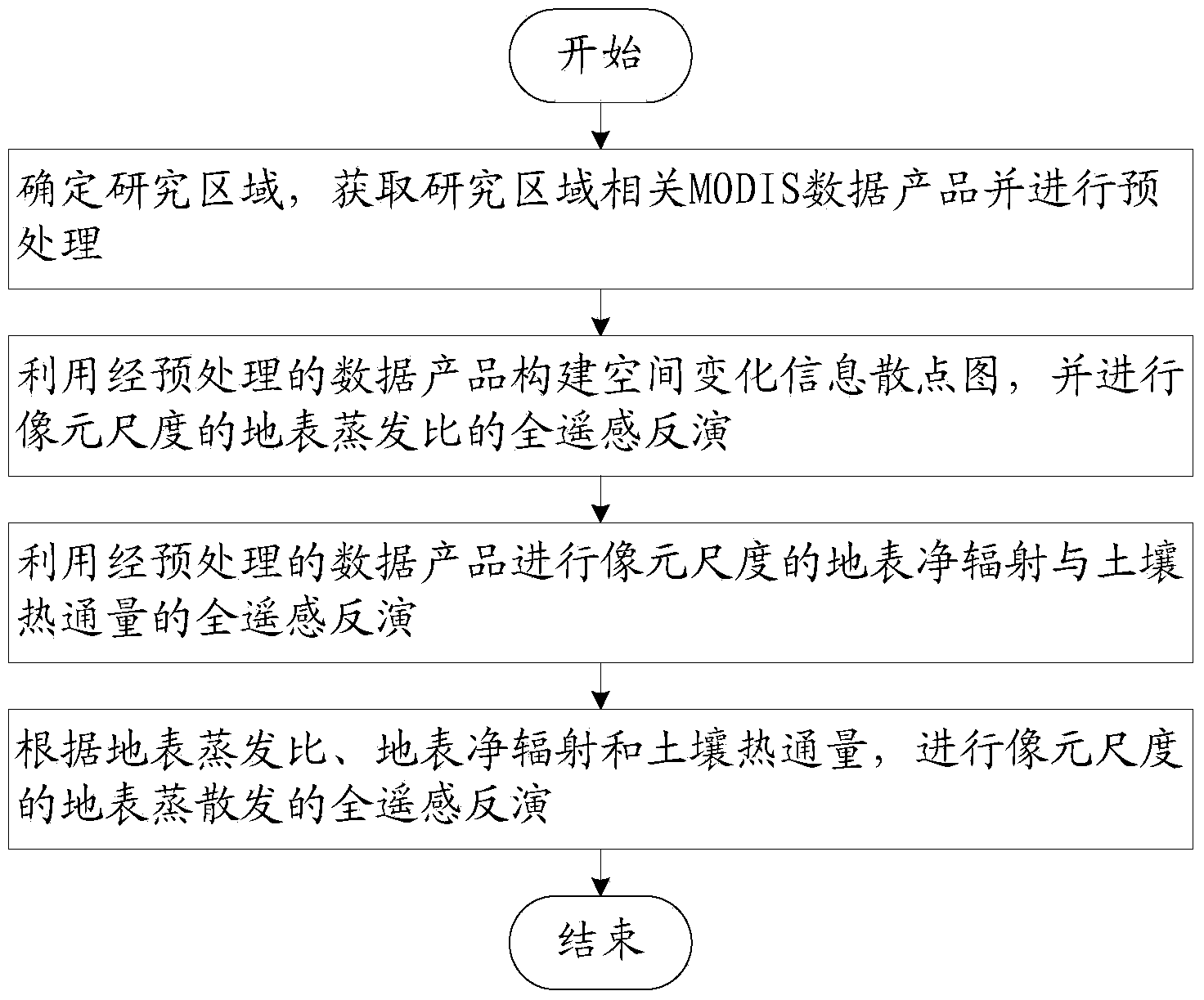
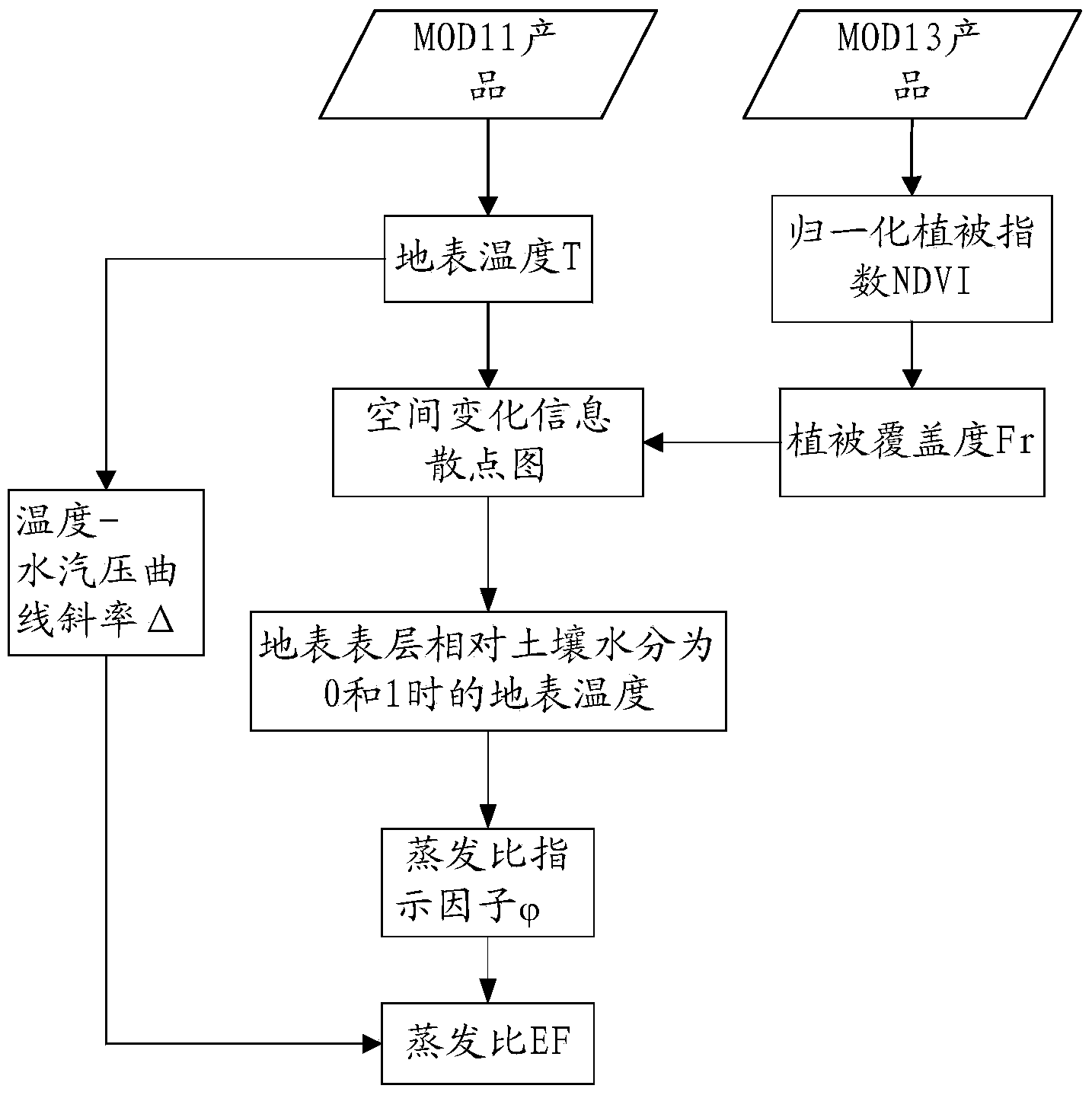
The invention relates to an earth face evapotranspiration remote sensing inversion method and system based on MODIS data. The earth face evapotranspiration remote sensing inversion method comprises the following steps that (1), a research area is confirmed, relative MODIS data porducts in the research area are achieved and pretreated; (2), a scatter diagram of space change information is built by the utilization of the pretreated MODIS data products, a remote sensing inversion of pixel sized surface evaporation ratio EF is conducted; (3), according to the relative MODIS data products, remote sensing inversions of pixel sized surface net radiation Rn and soil heat flux G are conducted; (4), according to the surface evaporation ratio EF, the surface net radiation Rn and the soil heat flux G, a remote sensing inversion of pixel sized earth face evapotranspiration LE is conducted. The earth face evapotranspiration remote sensing inversion method only needs to input the MODIS data, the problem that the current evapotranspiration remote sensing inversion usually needs more ground observation data to assist is solved, and the earth face evapotranspiration remote sensing inversion method can be used for the evapotranspiration remote sensing inversion in the area with no data or with few data.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
Remote sensing inversion method for land surface evapotranspiration of arid and semi-arid regions
InactiveCN102253184AImprove applicabilityTargeted optimizationEarth material testingSensing dataHeat flux
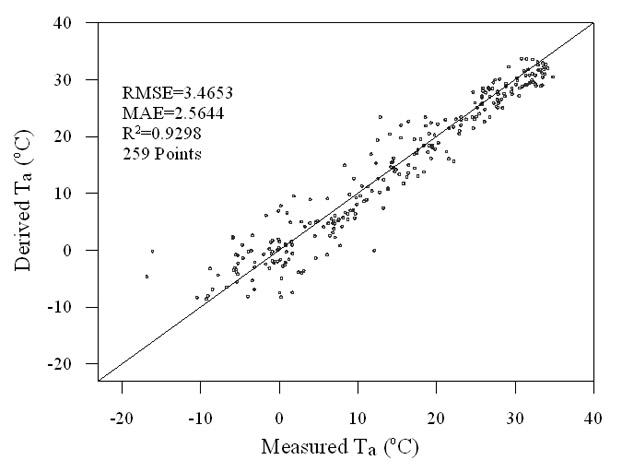
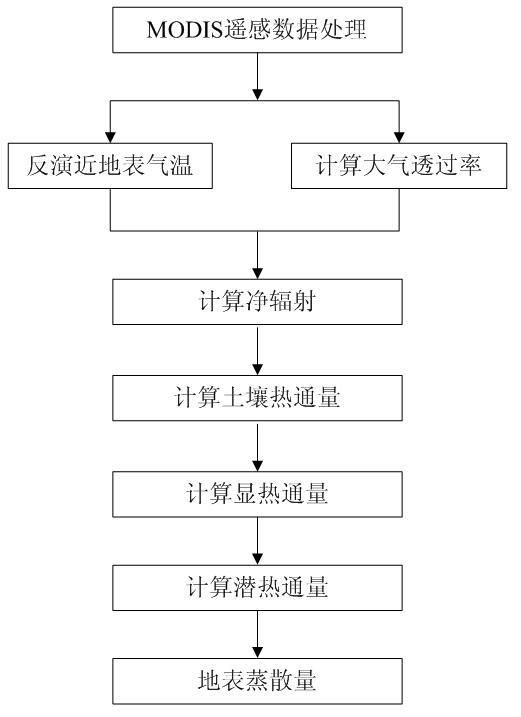
The invention discloses a remote sensing inversion method for land surface evapotranspiration of arid and semi-arid regions. The method comprises the steps of: acquiring and processing EOS / MODISE (Earth Observing System / Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) remotely sensed data; performing the inversion of near-surface temperature and computing atmospheric transmittance; obtaining a land surface latent heat flux by solving a net radiation quantity, a soil heat flux and a sensible heat flux according to a land surface energy balance equation; and figuring out land surface evapotranspiration data according to the land surface latent heat flux. According to the invention, aiming at the characteristics of rare meteorological stations in the arid region of Northwest China, a near-surface temperature inversion model and an atmospheric transmittance model both based on remotely sensed data are established, and the temperature obtained by the remote sensing inversion is used for participating in the computation instead of the observed temperatures of the stations; therefore, requirements on meteorological and other observation data are reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Surface water heat flux remote sensing inversion-based drought monitoring method and system
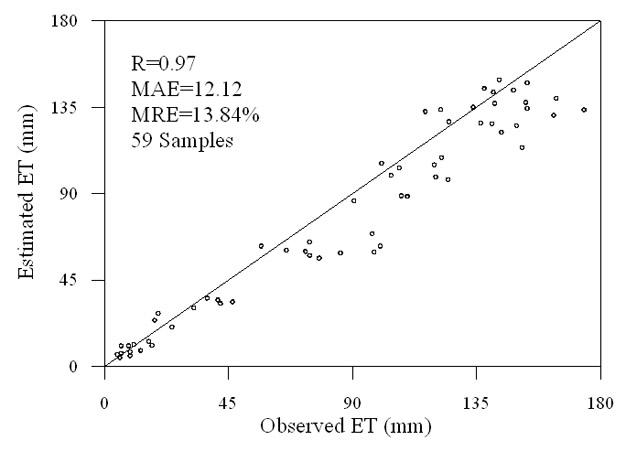
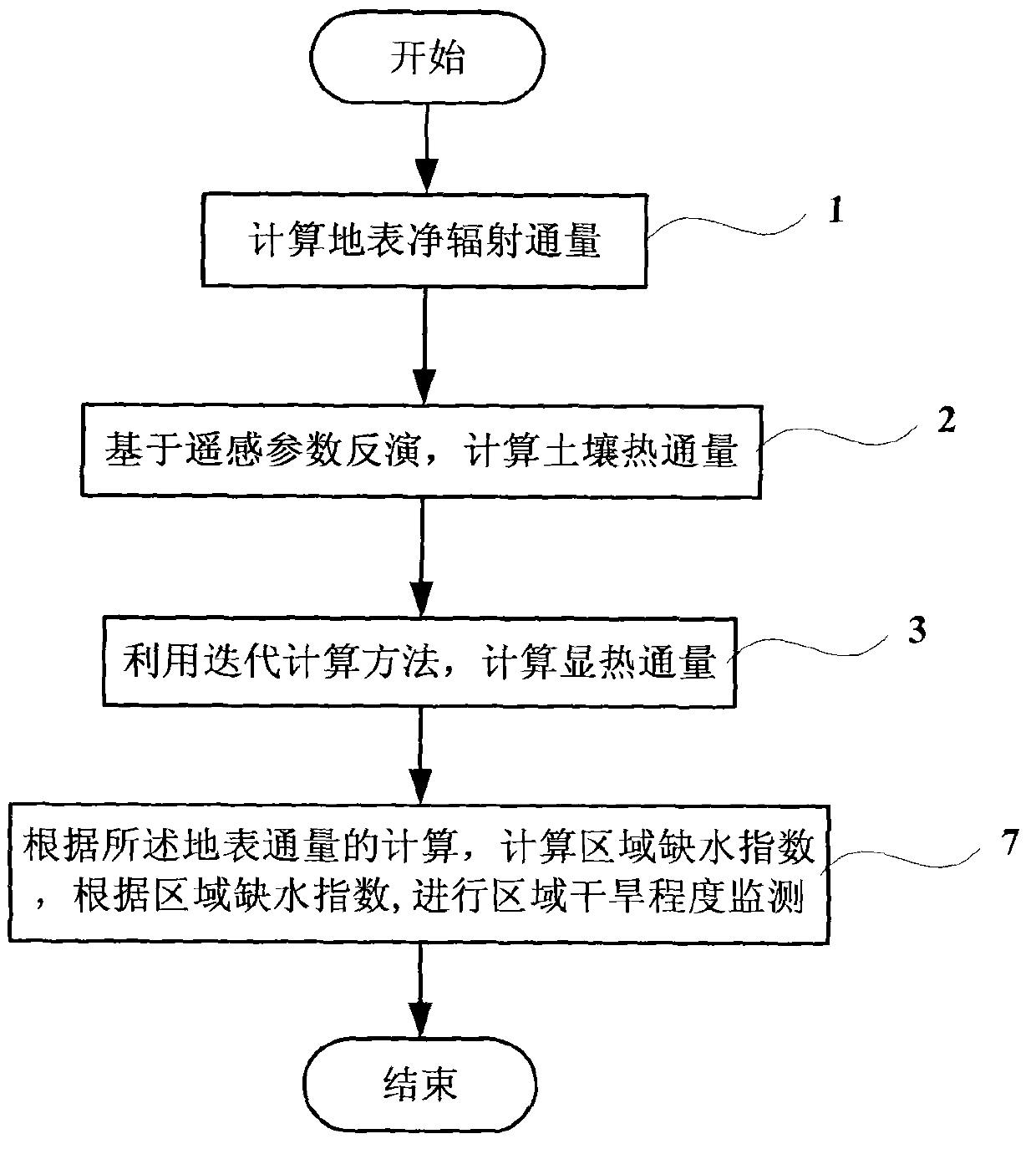
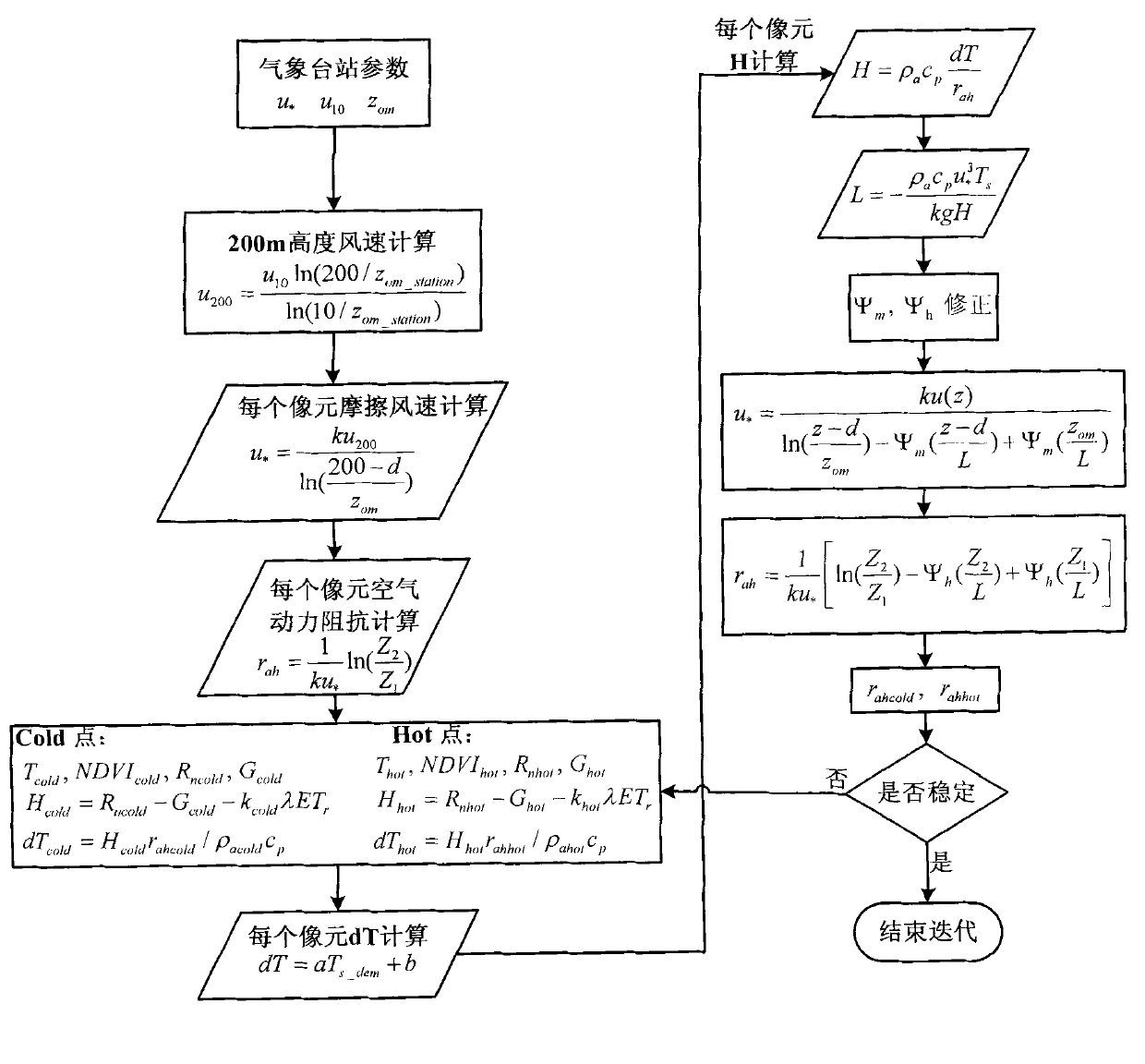
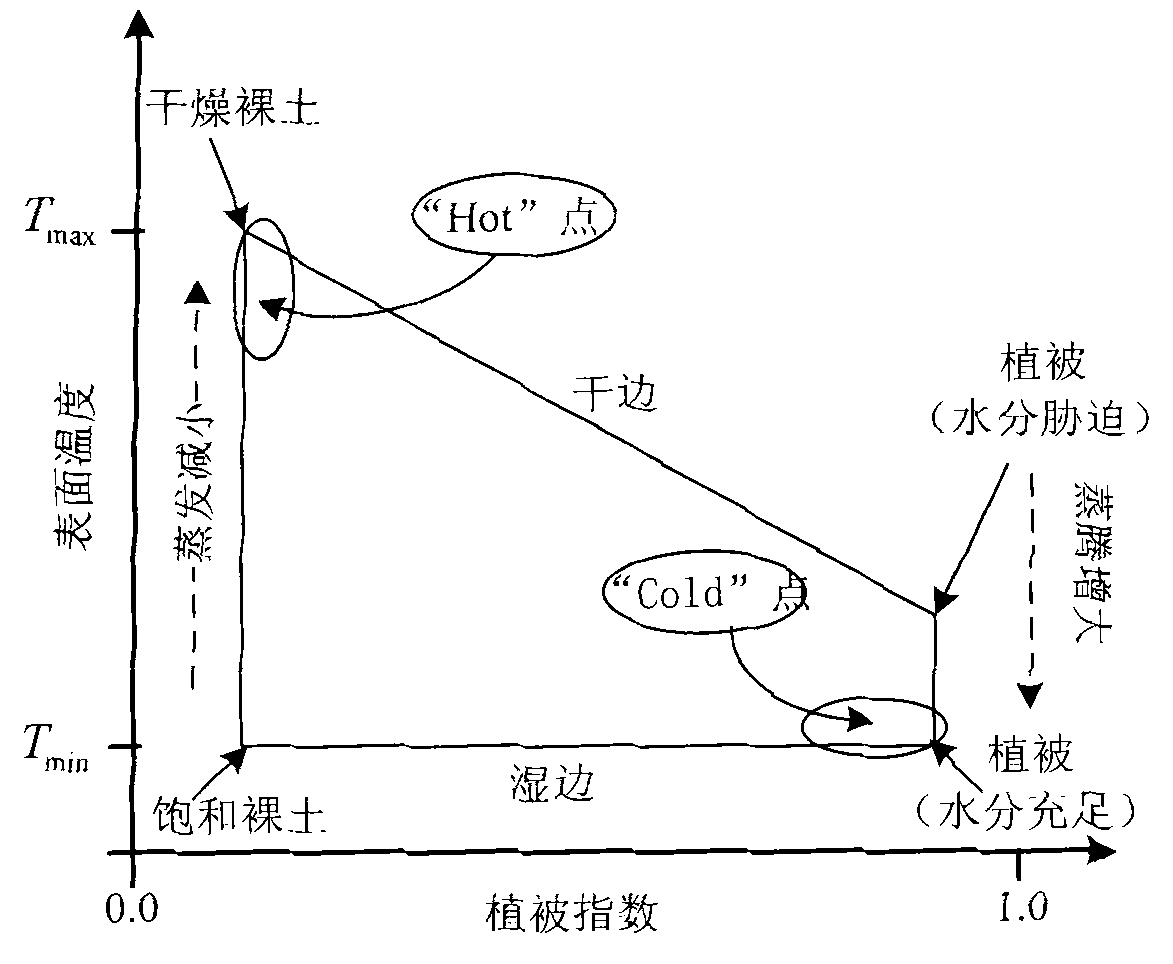
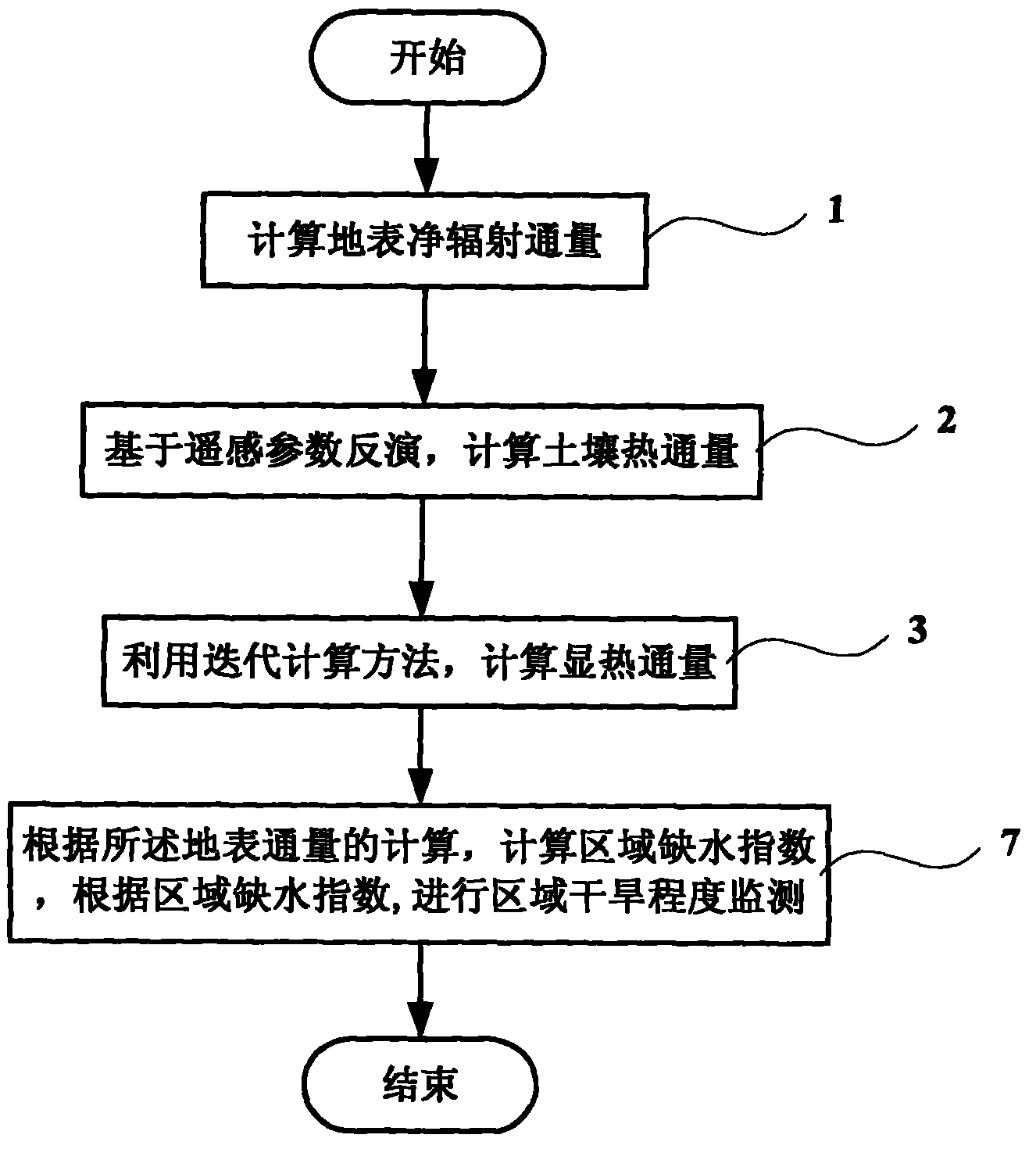
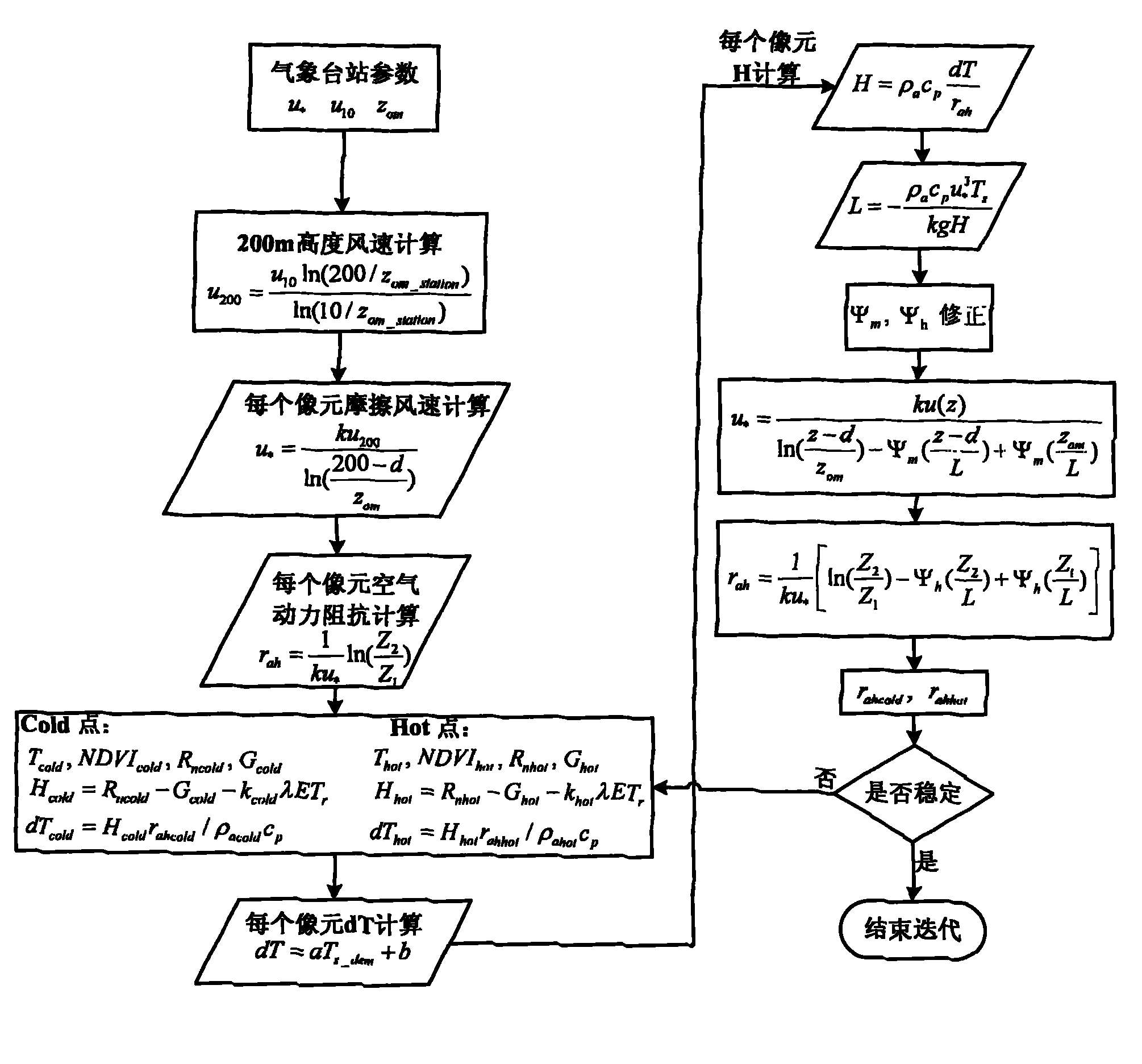
The invention discloses a surface water heat flux remote sensing inversion-based drought monitoring method and system. The method comprises the following steps of: calculating surface net radiation flux based on remote sensing parameter inversion, calculating soil heat flux by using an iterative calculation method, calculating sensible heat flux according to the calculation of the surface flux, calculating regional water shortage indexes (RWSI), and monitoring the regional drought degree.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
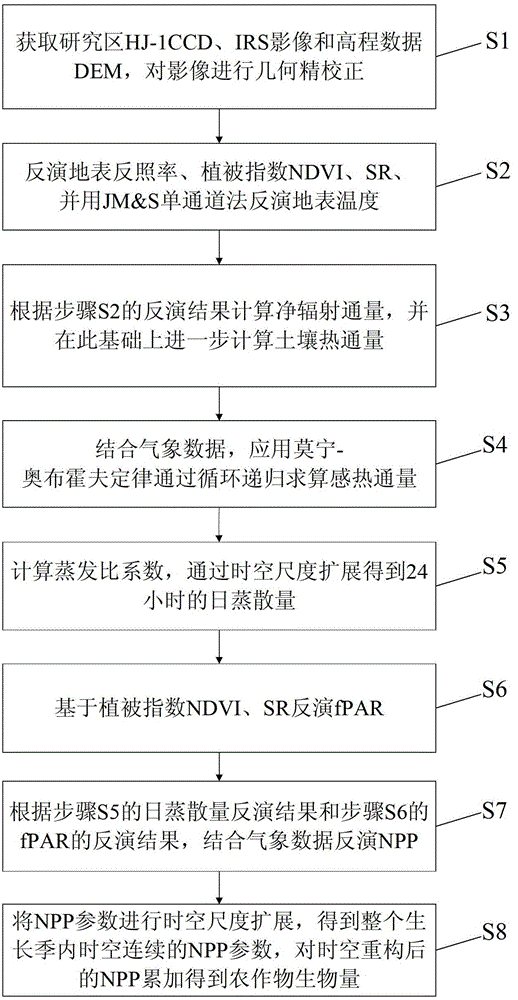
Crop biomass inversion method based on SEBAL-HJ model
ActiveCN102650587AImprove inversion accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansCyclic reductionEvaporation
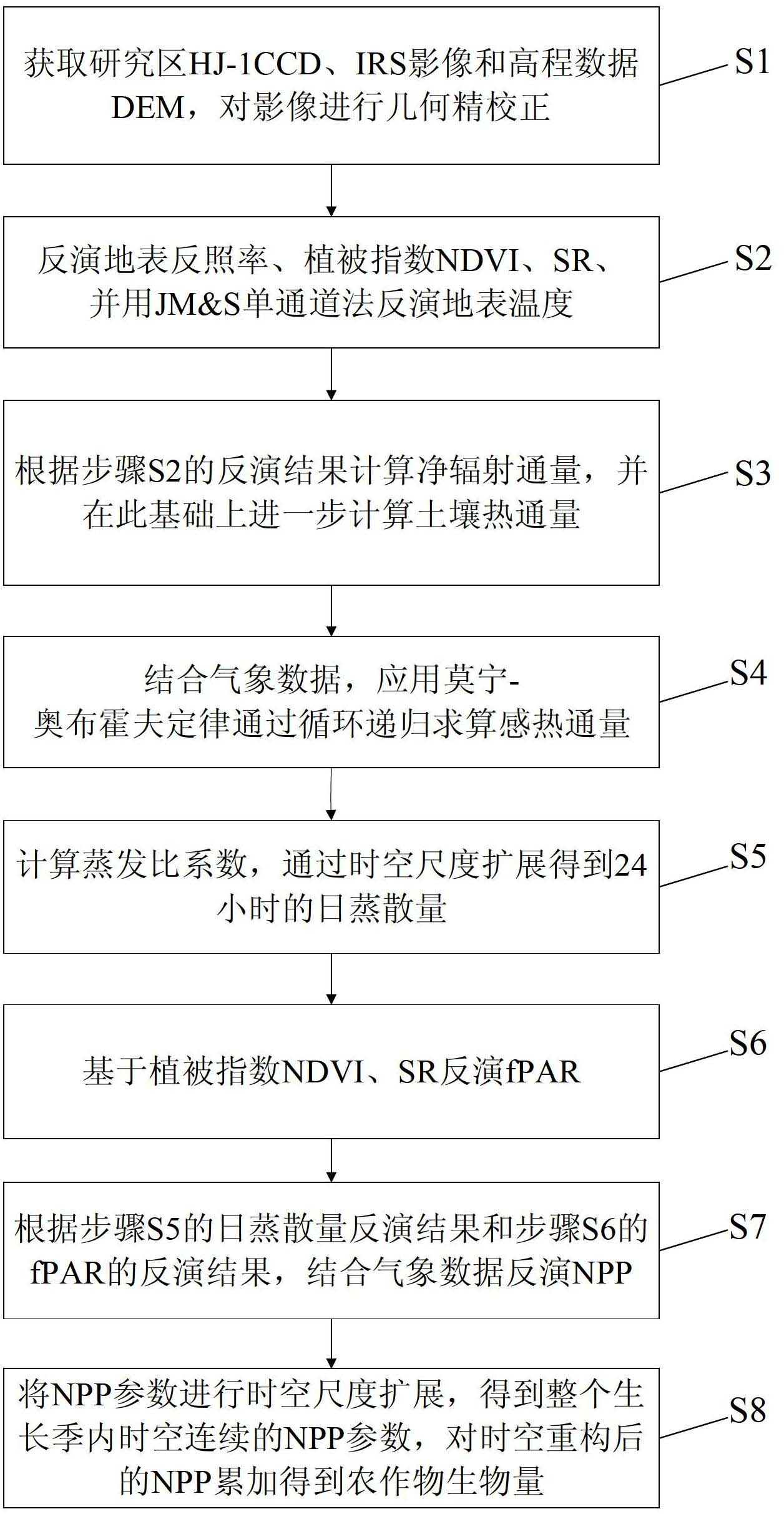
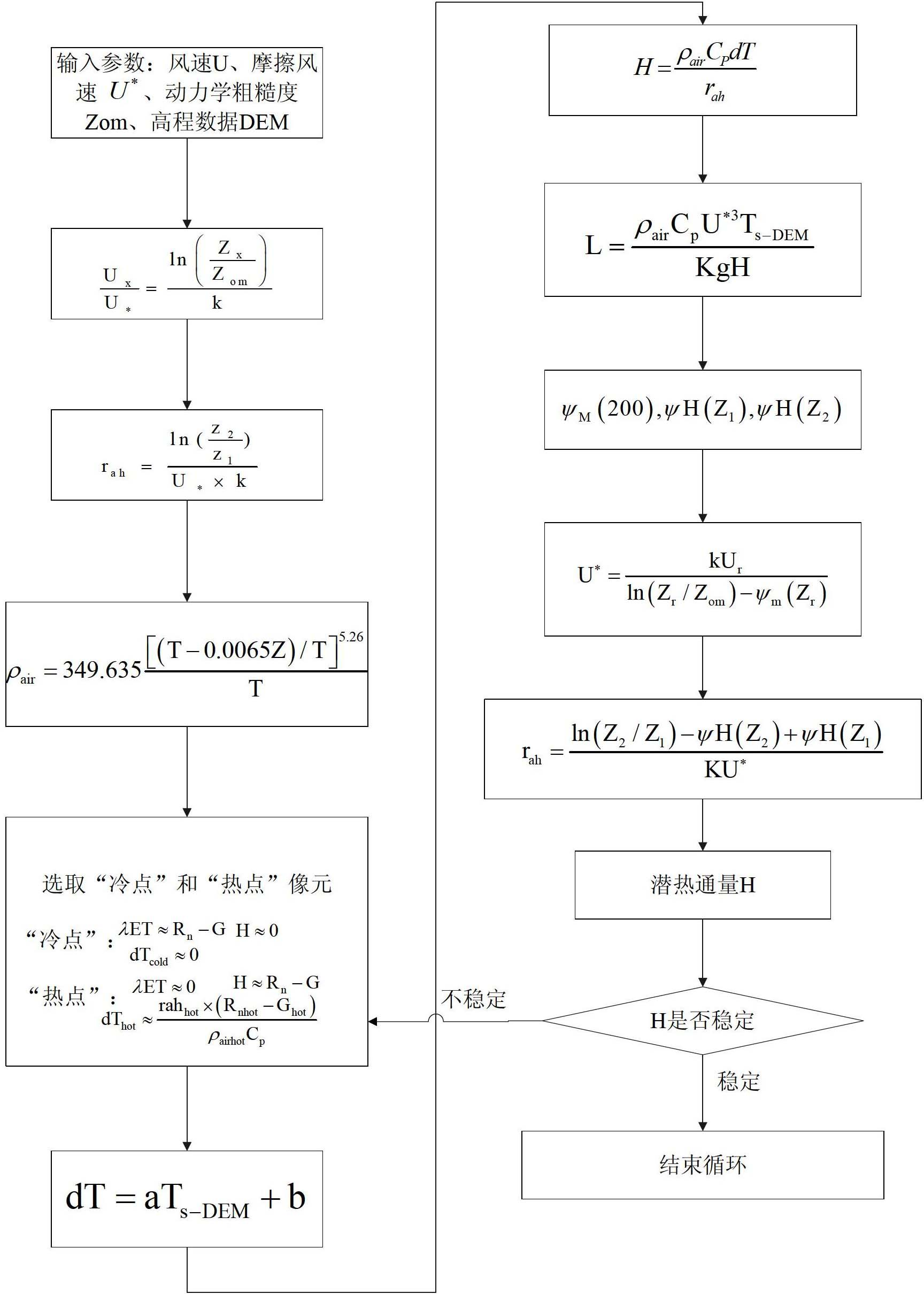
The invention discloses a crop biomass inversion method based on a SEBAL-HJ model. The crop biomass inversion method is characterized by comprising the following steps: S1, acquiring HJ-1 CCD, IRS images and elevation data DEM in a research plot, and carrying out geometric fine revision to the images; S2, inversing a land surface albedo, NDVI, SR, land surface emissivity and inversing land surface temperature; S3, calculating net radiation flux according to inversion results in the S2, and further calculating soil heat flux on the basis; S4, calculating sensible heat flux through cyclic reduction; S5, calculating the coefficient of evaporation ratio and obtaining evapotranspiration per day through space-time dimension expansion; S6, inversing fPAR on the basis of vegetative cover indexes NDVI and SR; S7, inversing NPP according to the inversion results of evapotranspiration per day in the step S5 and the inversion results of fPAR in the step S6; and S8, obtaining crop biomass through the accumulation of NPP after space-time reconstruction. According to the invention, the high-precision inversion of crop biomass is achieved, and the amount of calculation is relatively smaller.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Regional earth surface sensible heat/latent heat flux inversion method and system based on remote sensing data
InactiveCN106169014AInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsEarth surfaceNormalized Difference Vegetation Index
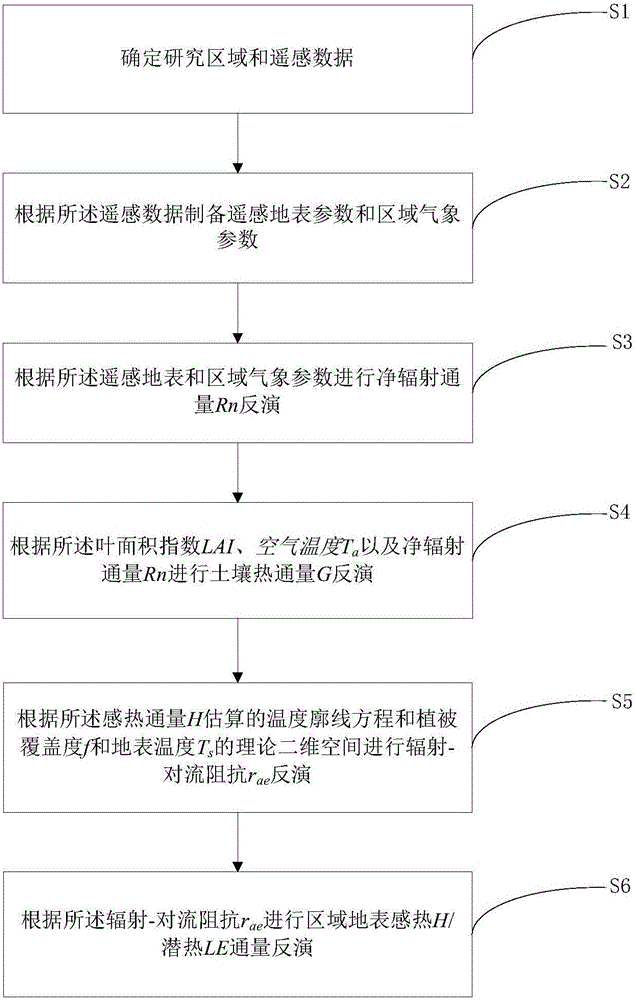
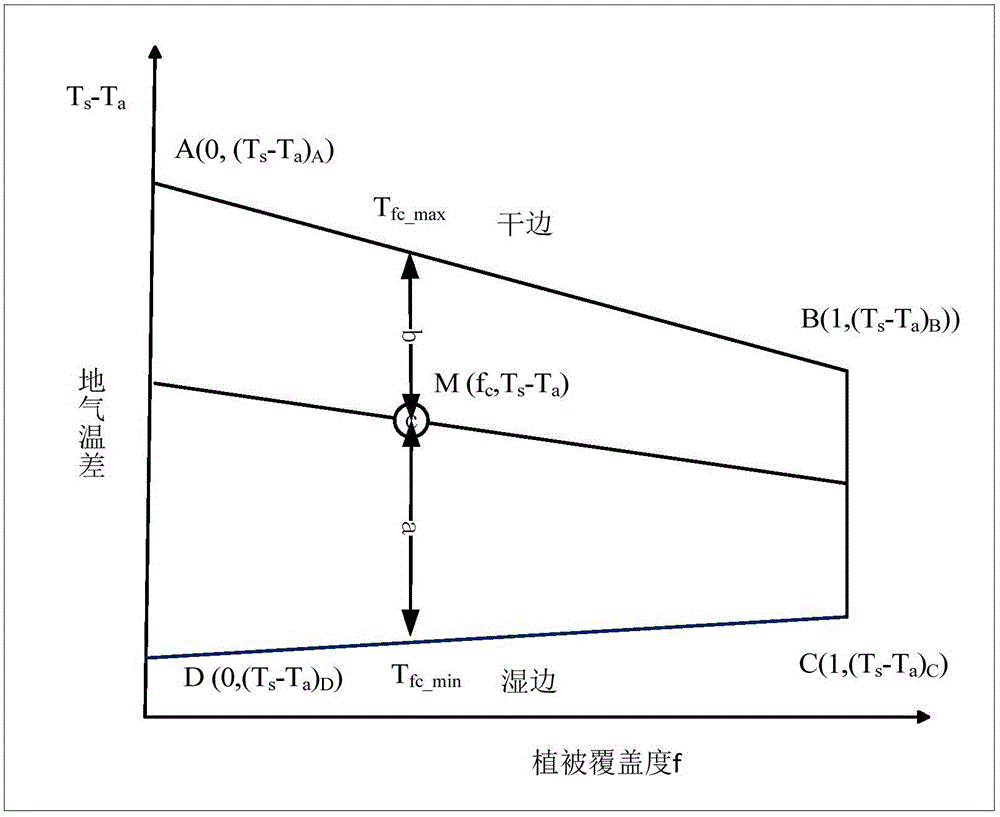
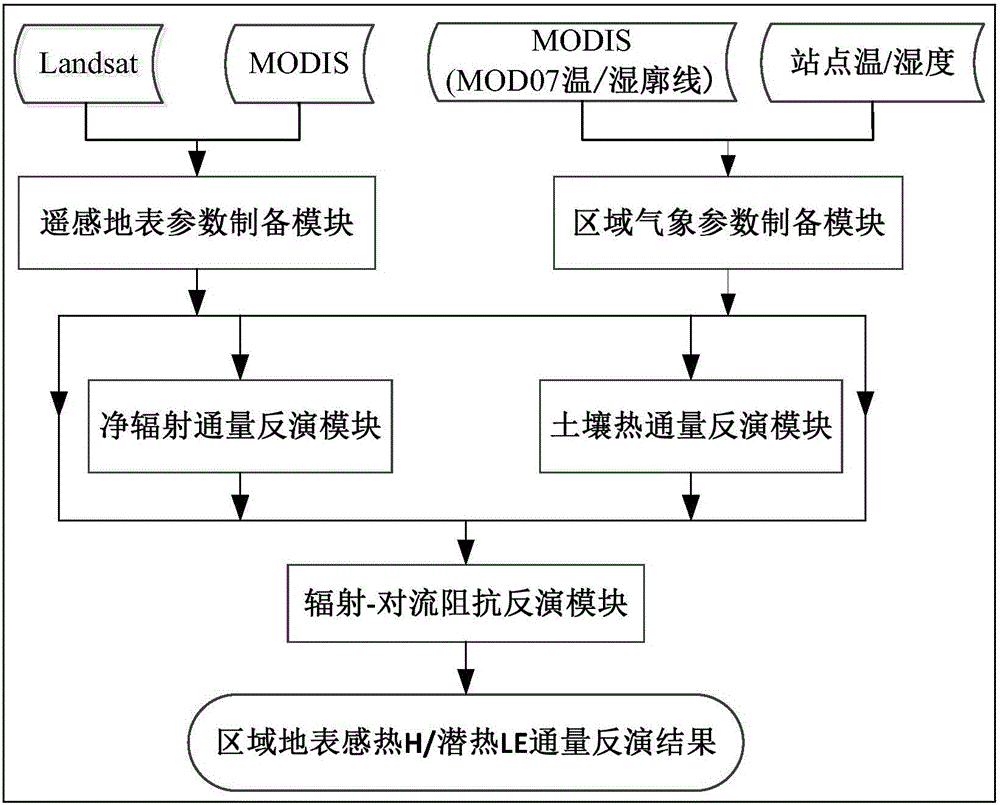
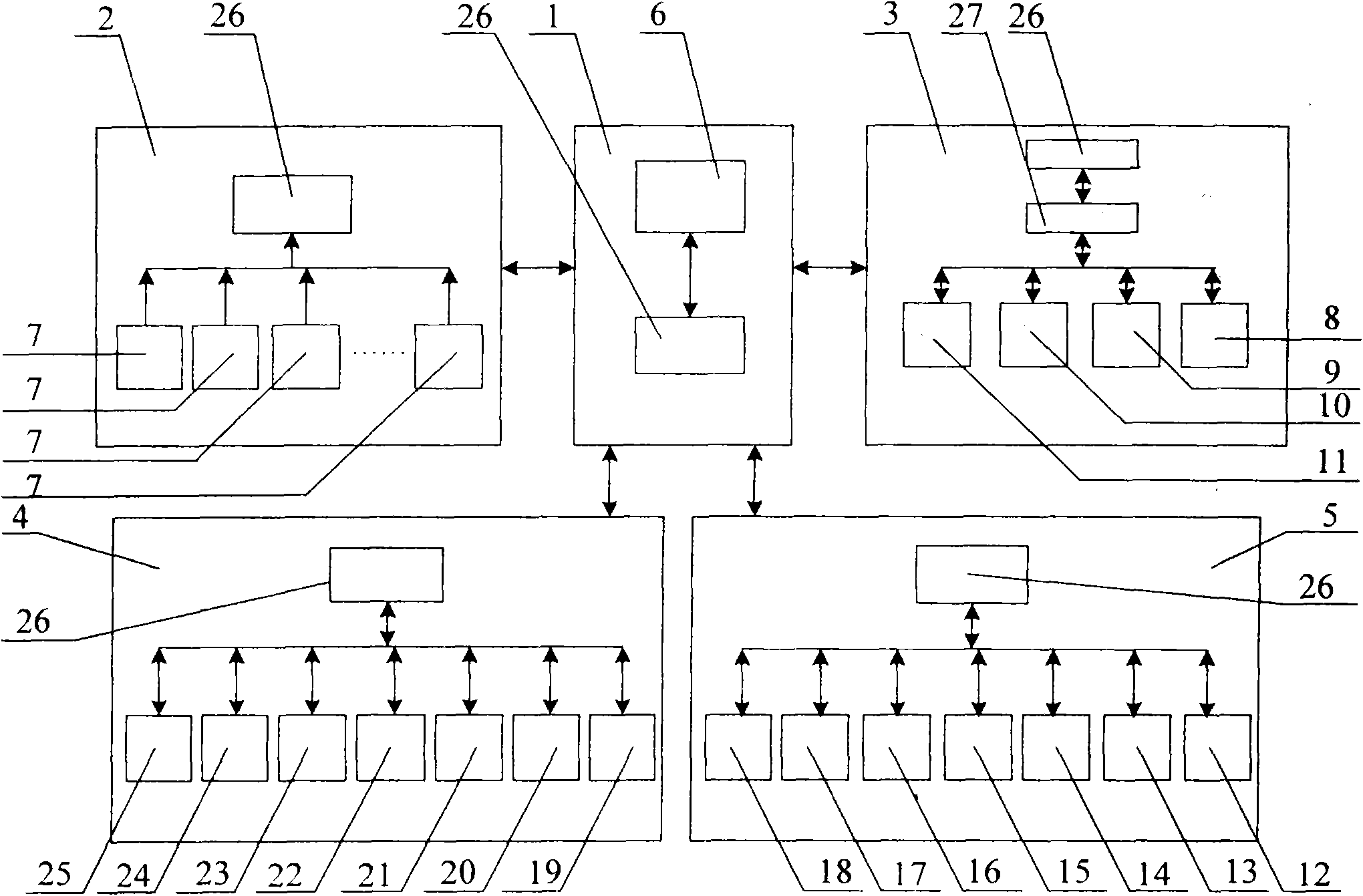
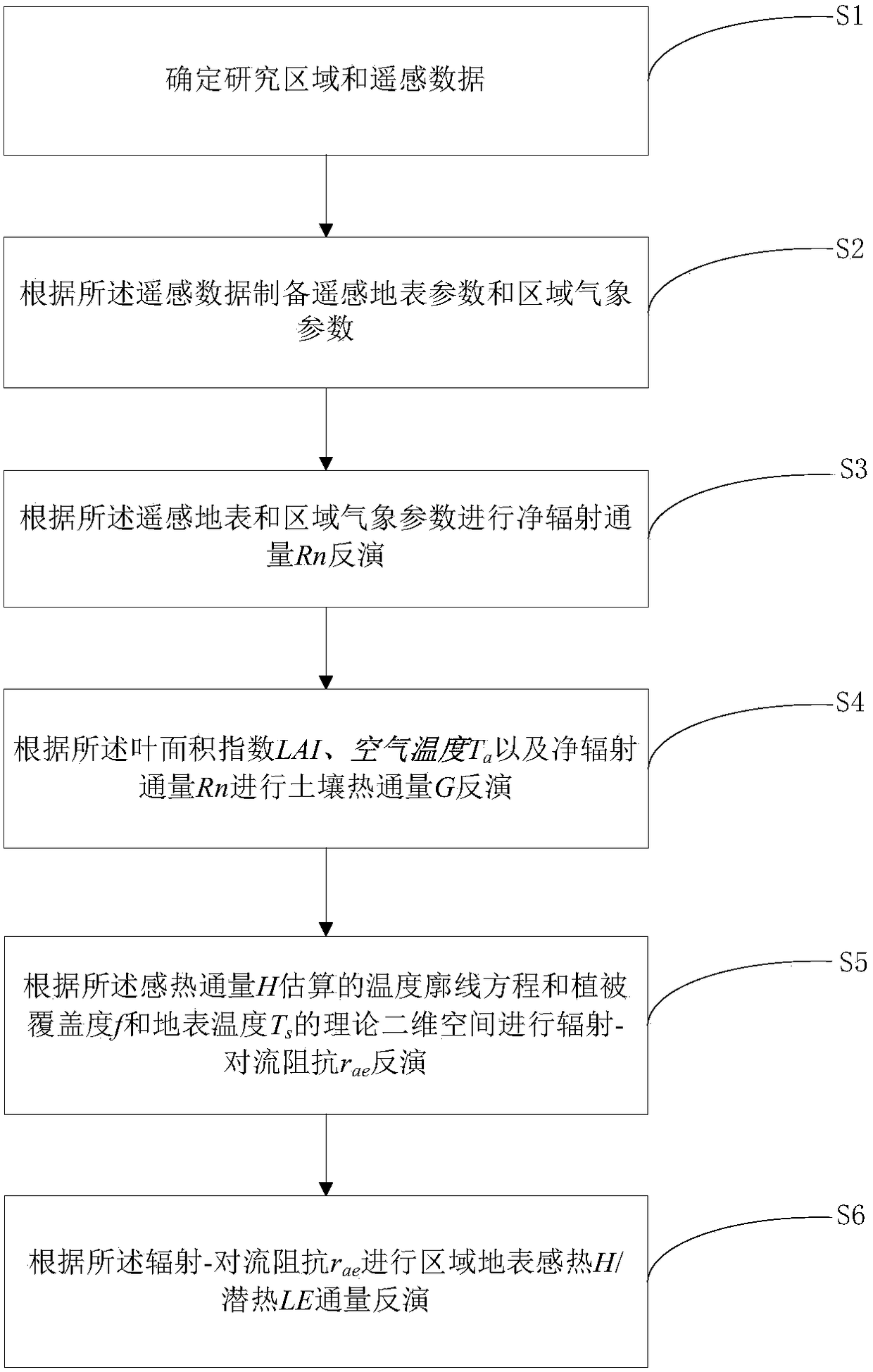
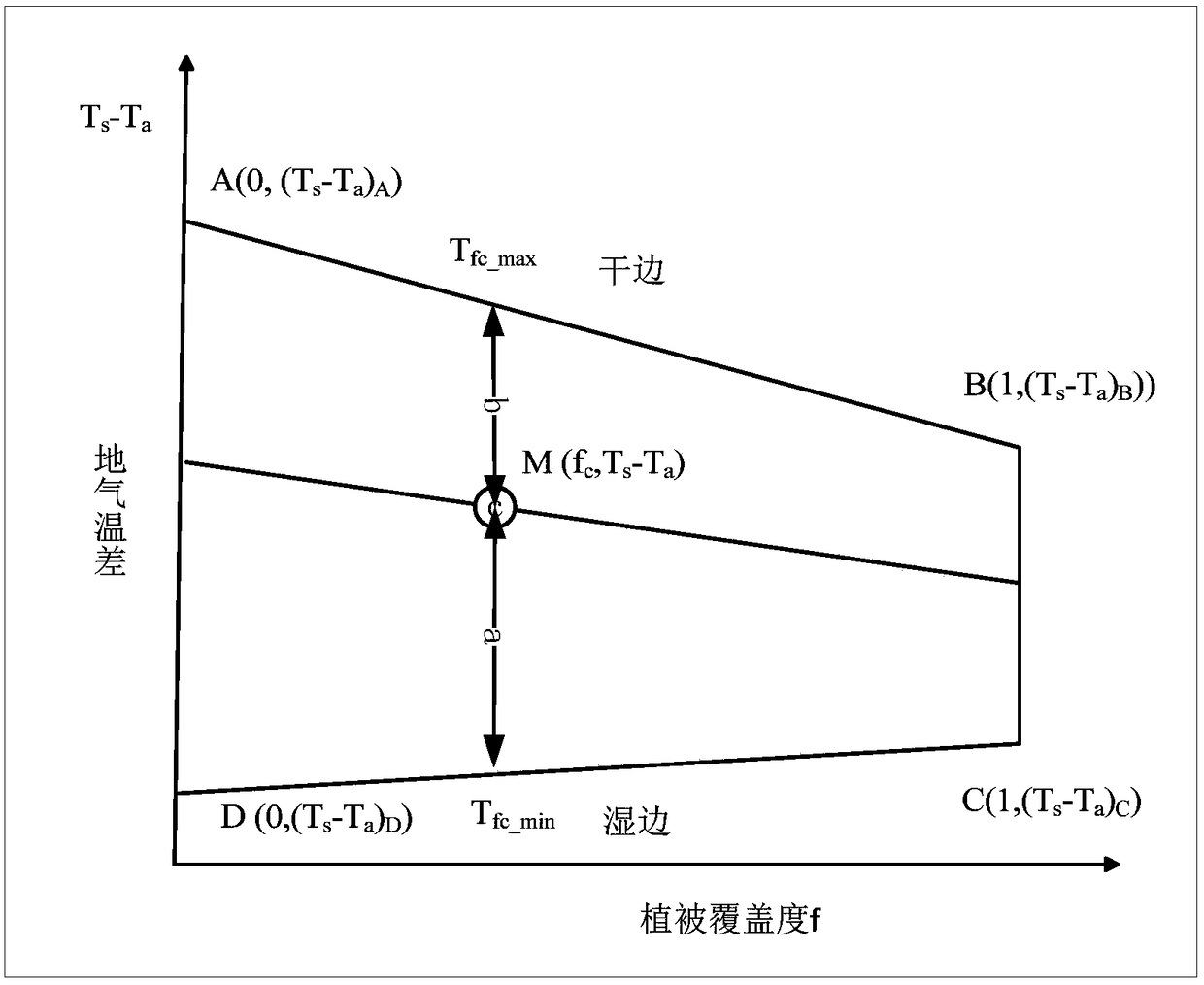
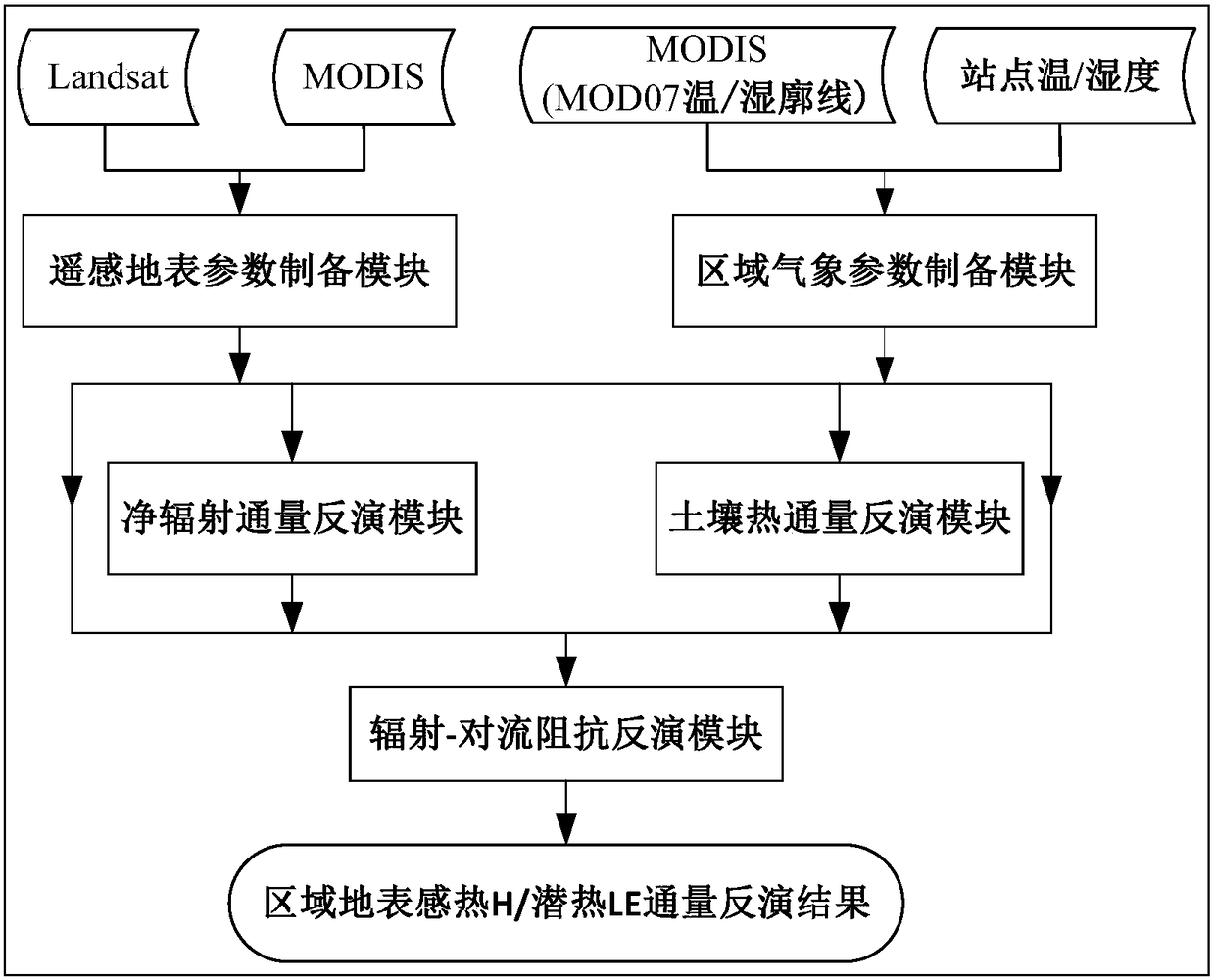
The invention discloses a regional earth surface sensible heat / latent heat flux inversion method based on remote sensing data. The method comprises the following steps that a research area and the remote sensing data are determined; remote sensing earth surface and regional meteorological parameters are prepared according to the remote sensing data, wherein the remote sensing earth surface parameters comprise a normalized difference vegetation index NDVI, vegetation coverage f, albedo, earth surface emissivity Emiss, earth surface temperature Ts and a leaf area index LAI, and the regional meteorological parameters comprise air temperature Ta and relative humidity RH; net radiation flux Rn inversion is conducted according to the remote sensing earth surface and regional meteorological parameters; soil heat flux G inversion is conducted according to the leaf area index LAI, the air temperature Ta and net radiation flux Rn; radiation-convection impedance rae inversion is conducted according to theoretical two-dimensional space of the net radiation flux Rn, soil heat flux G, the vegetation coverage f and the earth surface temperature Ts and a temperature profile equation estimated through sensible heat flux; regional earth surface sensible heat H / latent heat LE flux inversion is achieved according to radiation-convection impedance rae.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Rice field growth environment monitoring and irrigation control system
InactiveCN102141801AIncrease productionQuality improvementProgramme total factory controlHeat fluxAutomatic control
The invention discloses a rice field growth environment monitoring and irrigation control system, and belongs to an automatic control technology of agricultural engineering. The system is formed by connecting a central control unit and a rice field growth image monitoring unit, a rice grid field irrigation control unit, a rice grid field monitoring unit and a park meteorology monitoring unit by adopting Zigbee wireless communication respectively; the central control unit comprises wireless communication and an industrial control computer; the rice field growth image monitoring unit consists of wireless communication and an industrial camera; the rice grid field irrigation control unit comprises wireless communication, a controller, a flow meter, a water level meter, a water outlet valve and a water inlet valve; the rice grid field monitoring unit consists of wireless communication and sensors of water temperature, mud temperature, soil humidity, water surface evaporation, water level, soil heat flux, leaf humidity and the like; and the park meteorology monitoring unit comprises sensors of environmental temperature, humidity, dew point temperature and the like. The system has many monitoring and control projects, high automation degree, accurate and timely monitoring and control and accurate data.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG BAYI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for obtaining field evapotranspiration of field scale
ActiveCN102136035AAccurately express the continuous change of spaceReduce spatial resolutionMaterial heat developmentSpecial data processing applicationsSensing dataHeat flux
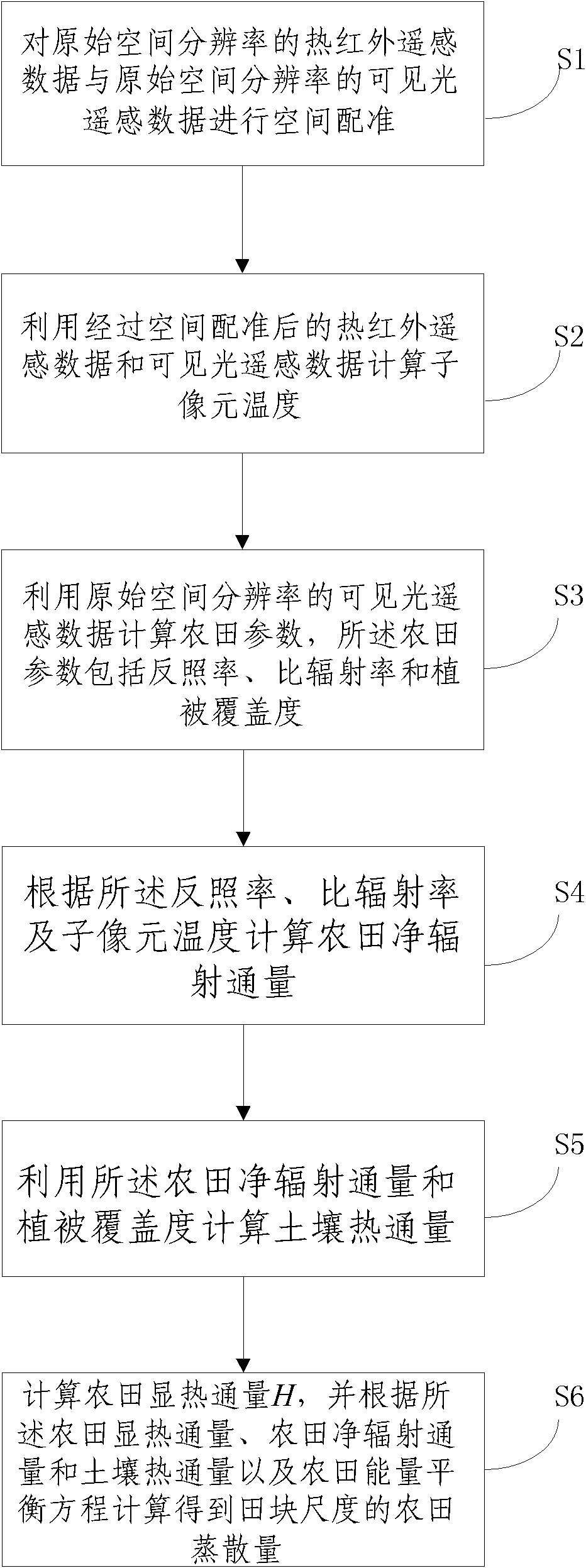
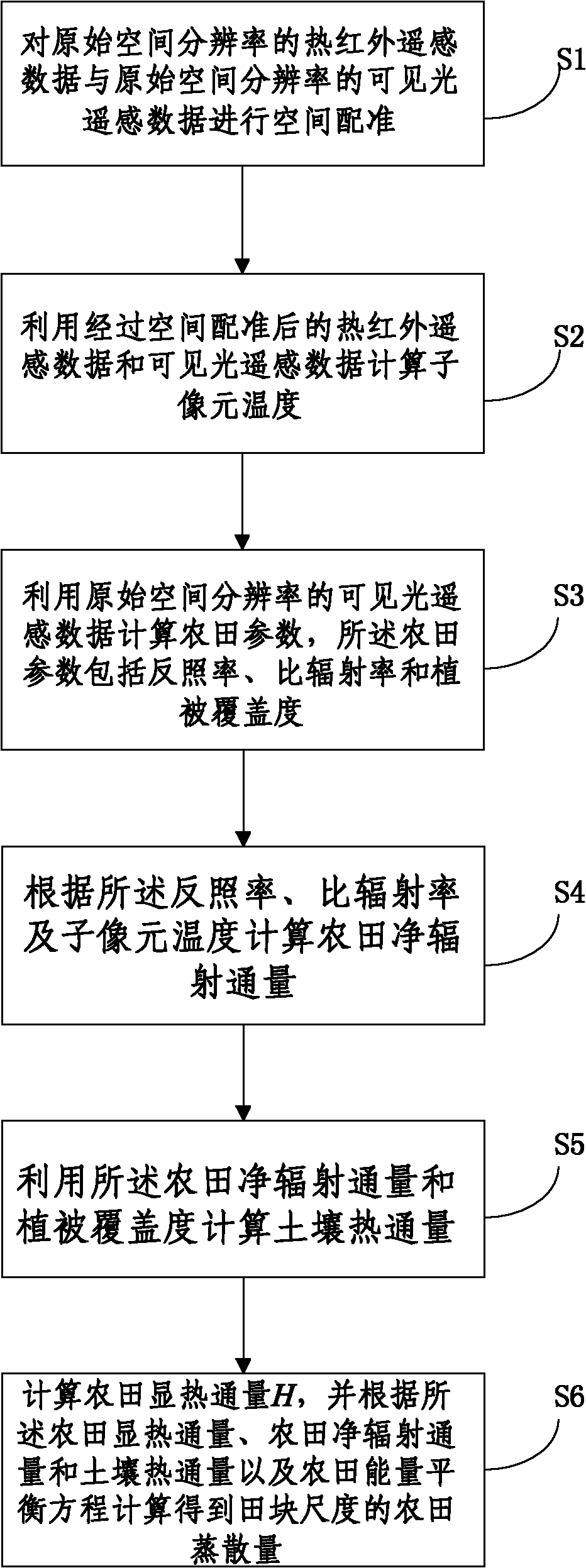
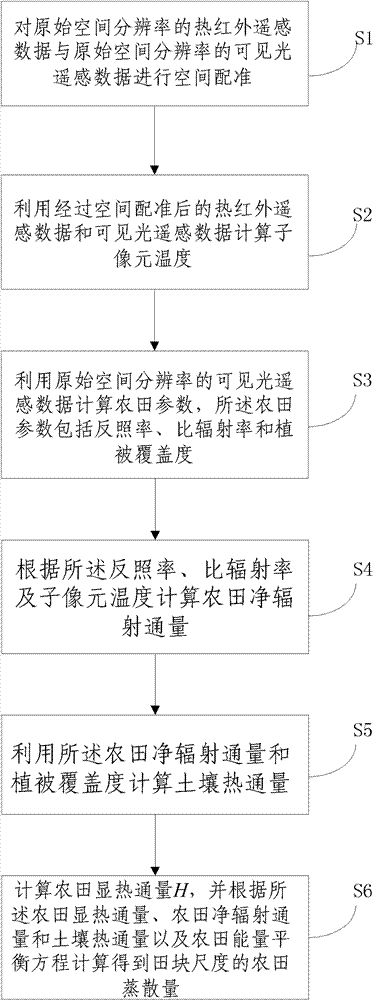
The invention discloses a method for obtaining field evapotranspiration of field scale, comprising the following steps: S1. space registration is carried out to thermal infrared remote sensing data of original spatial resolution and visible light remote sensing data of the original spatial resolution; S2. sub-pixel temperature is calculated by utilizing the thermal infrared remote sensing data and the visible light remote sensing data whichare treated with space registration; S3. field parameters including albedo, specific emittance and vegetation coverage are calculated by utilizing the visible light remote sensing data of the original spatial resolution; S4. the field net radiation flux is calculated according to the albedo, the specific emittance and the sub-pixel temperature; S5. soil heat flux is calculated by utilizing the field net radiation flux and the vegetation coverage; and S6. the field sensible heat flux H is calculated, and the field evapotranspiration of the field scale can be calculated according to the field sensible heat flux, the field net radiation flux, the soil heat flux and field energy equilibrium equation. By adopting the method in the invention, the field evapotranspiration of the field scale can be obtained.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT FOR INFORMATION TECH & AGRI
Remote remote sensing estimation method and device for changes in surface temperature days
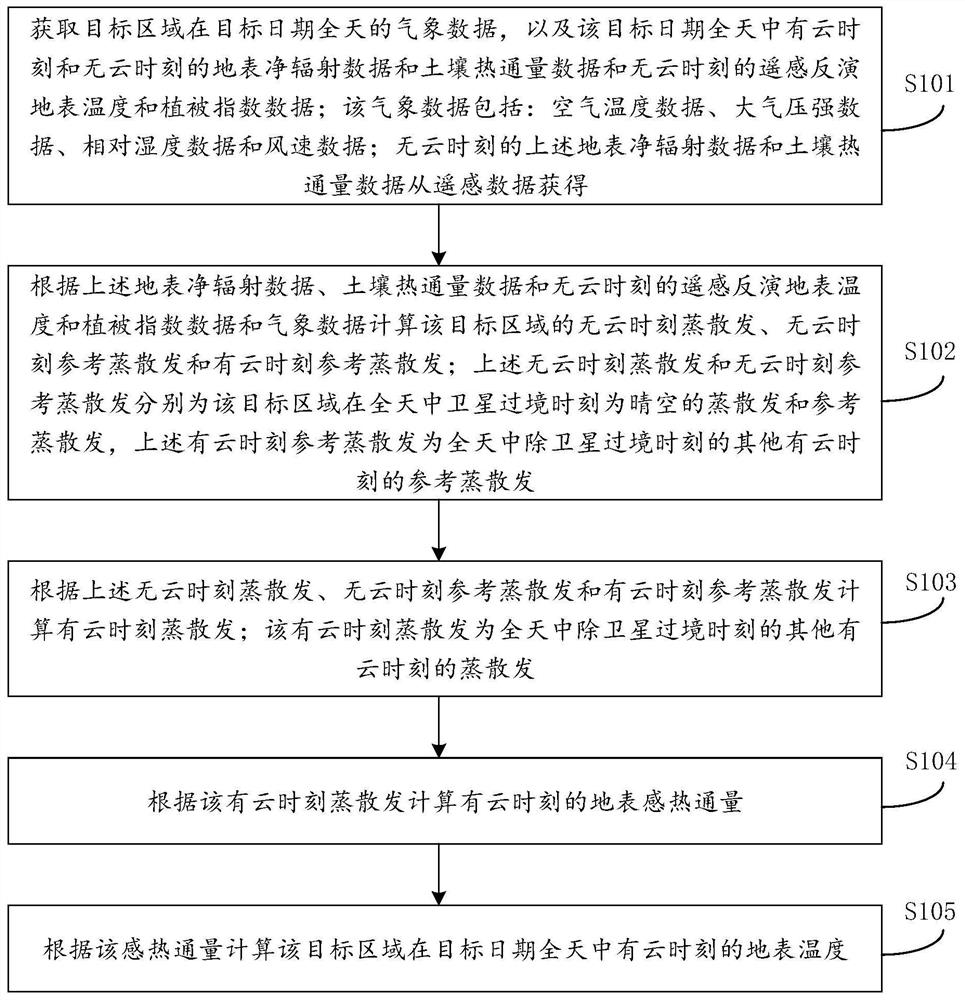
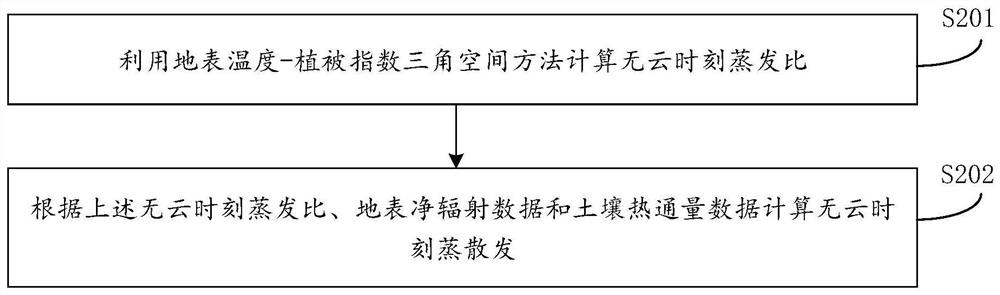
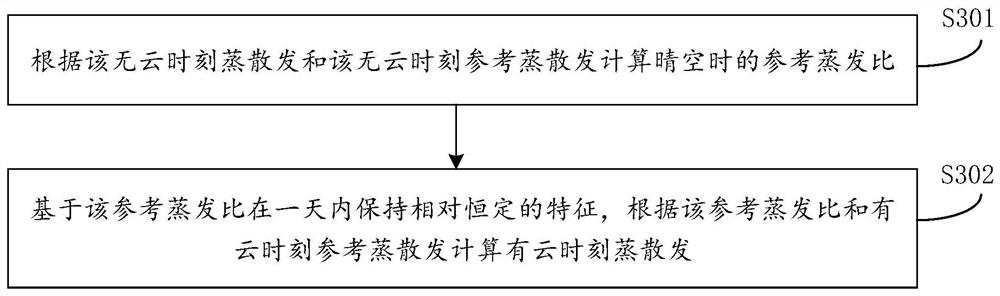
ActiveCN108829975ATroubleshoot difficult estimatesMeasurement devicesDesign optimisation/simulationVegetation IndexEstimation methods
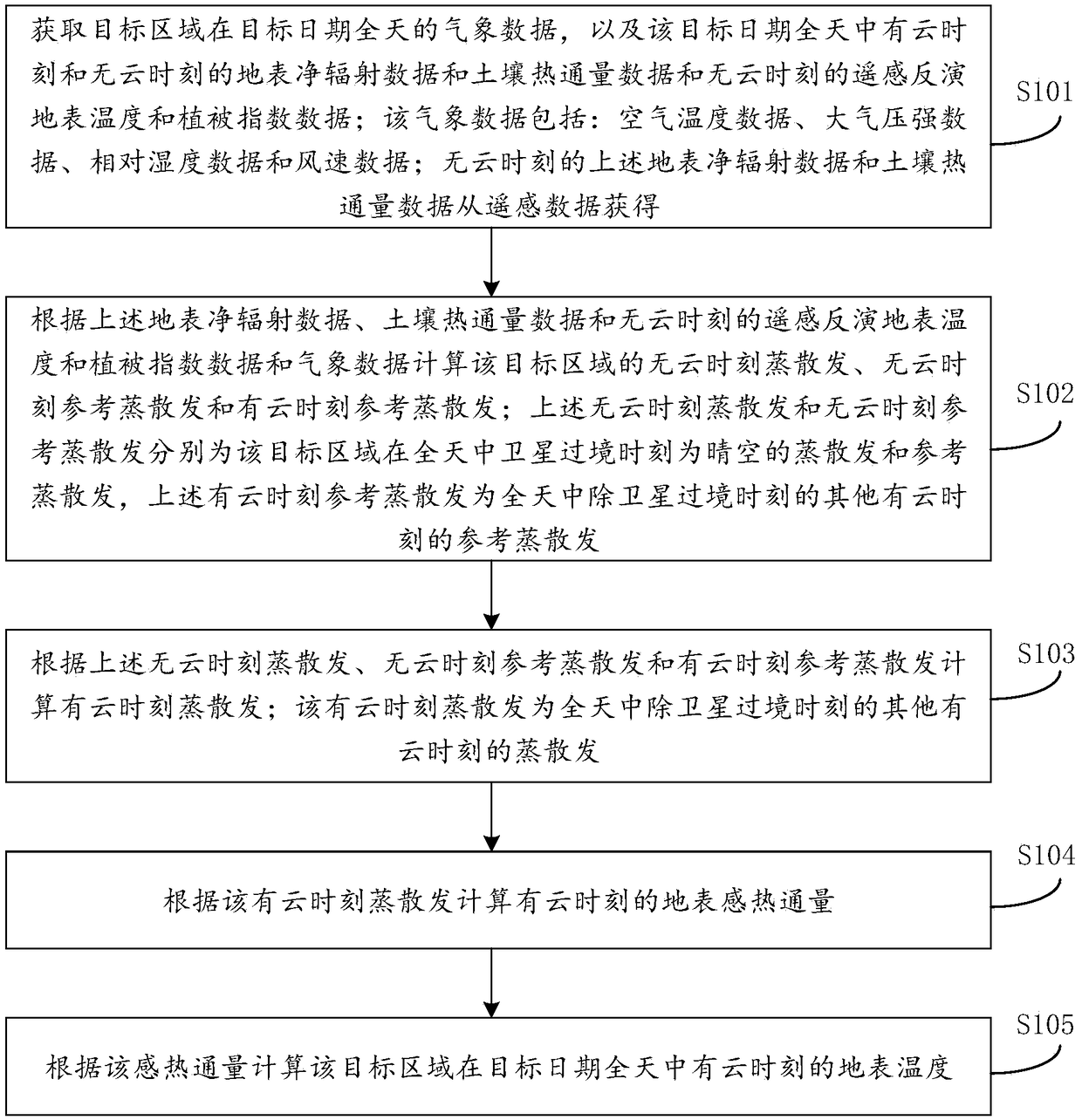
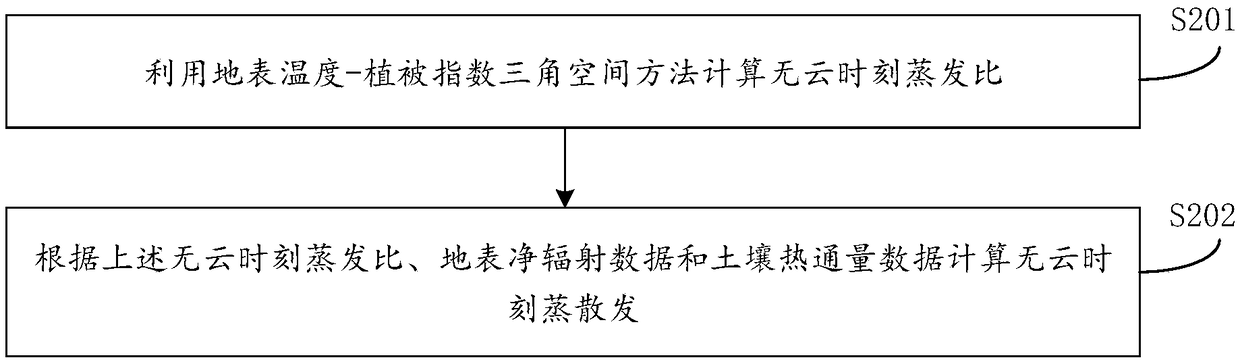
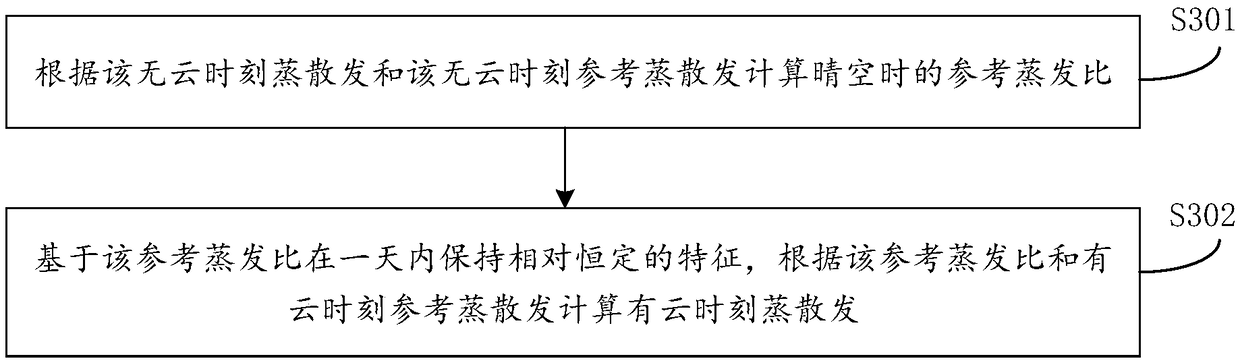
The invention provides a remote sensing estimation method and a device for changes in surface temperature days, which relates to the technical field of surface temperature remote sensing inversion. The method includes acquiring meteorological data of the target area all day on the target date, net surface radiation data and soil heat flux data with and without clouds, and remote sensing inversionof surface temperature data and vegetation index data at cloud-free time, according to the above data, the cloud-free time evapotranspiration and cloud-free time reference evapotranspiration and cloud-time reference evapotranspiration in the target area are calculated, according to the cloud-free time evapotranspiration and cloud-free time reference evapotranspiration and cloud-time reference evapotranspiration, the cloud-time evapotranspiration and the surface sensible heat flux are calculated, the surface temperature at cloud-time is calculated according to the sensible heat flux. The methodand device for remote sensing estimation method and a device for changes in surface temperature days can quickly capture the daily variation process of surface temperature under cloud conditions by remote sensing means.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS +1
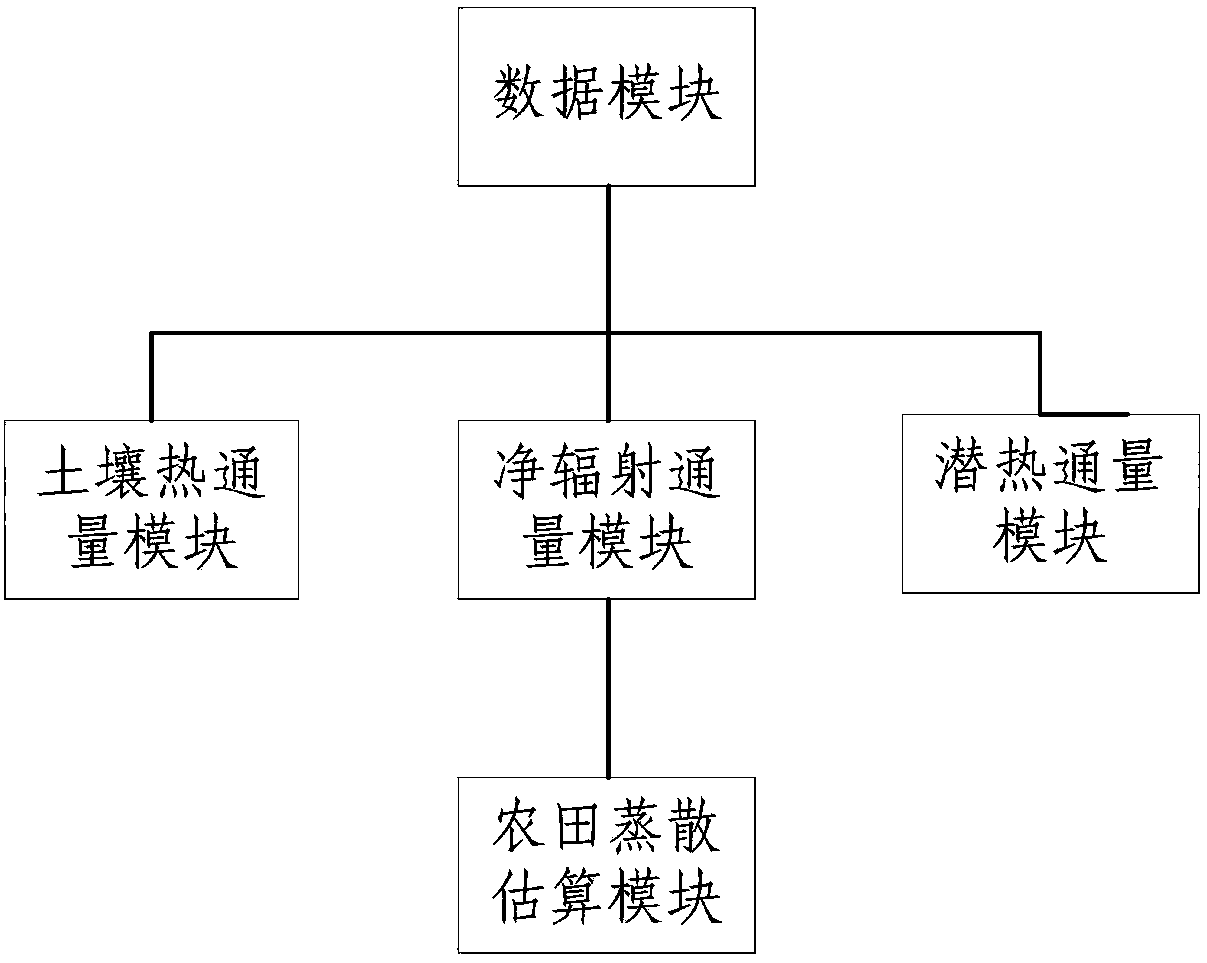
Farmland evapotranspiration estimation method and system
InactiveCN107644284AClear physical basisImprove spatial resolutionResourcesThermal infrared remote sensingEstimation methods
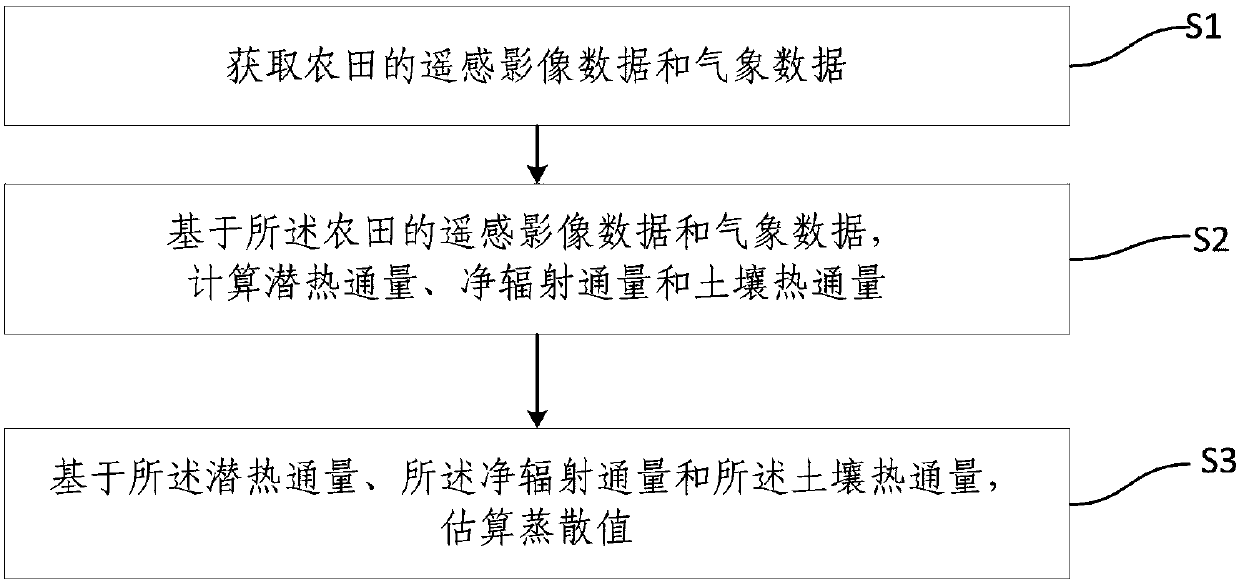
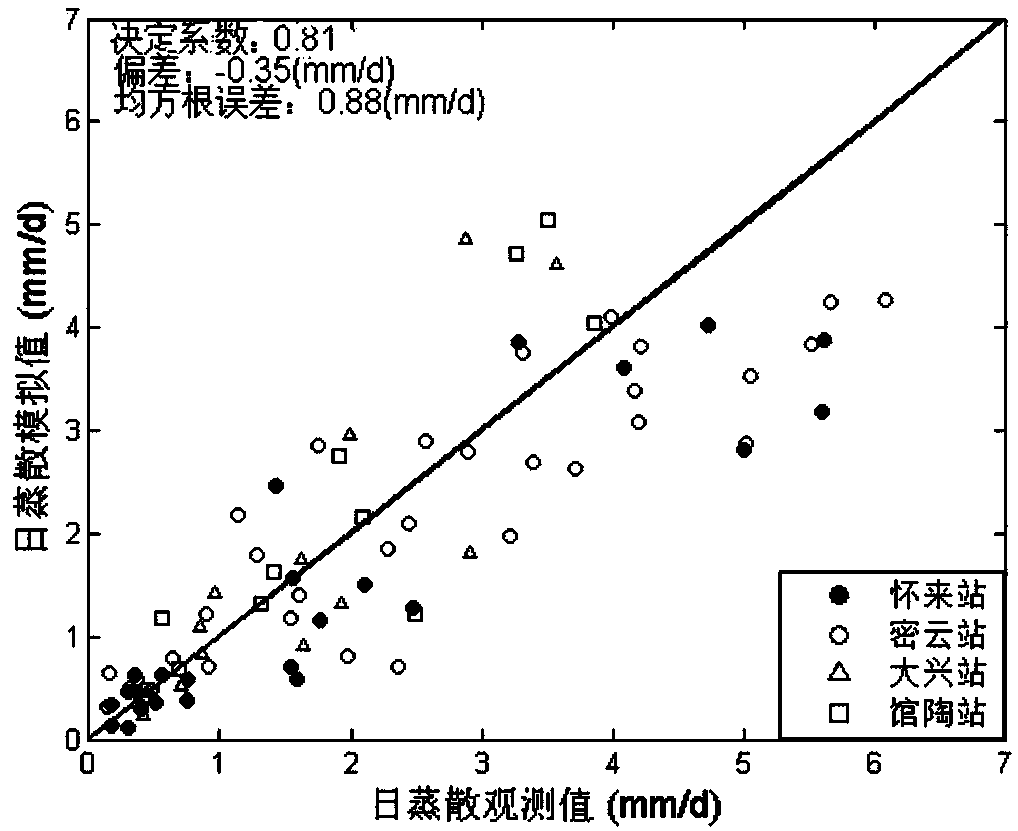
The invention provides a farmland evapotranspiration estimation method and system. The farmland evapotranspiration estimation method comprises S1, obtaining remote sensing image data and meteorological data of farmland; S2, calculating latent heat flux, net radiation flux and soil heat flux based on the remote sensing image data and the meteorological data of the farmland; and S3, estimating the evapotranspiration value based on the latent heat flux, the net radiation flux and the soil heat flux. With respect to the farmland evapotranspiration estimation method and system, by fully combining the meteorological data, optical remote sensing and thermal infrared remote sensing, the physical basis is clear, the spatial resolution is high, and the reliability of the estimation result is higher.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Precision control system for water layer of rice square field
InactiveCN103004559AEasy to controlReliable precision controlWatering devicesCultivating equipmentsAutomatic controlSoil heat flux
Owner:HEILONGJIANG BAYI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
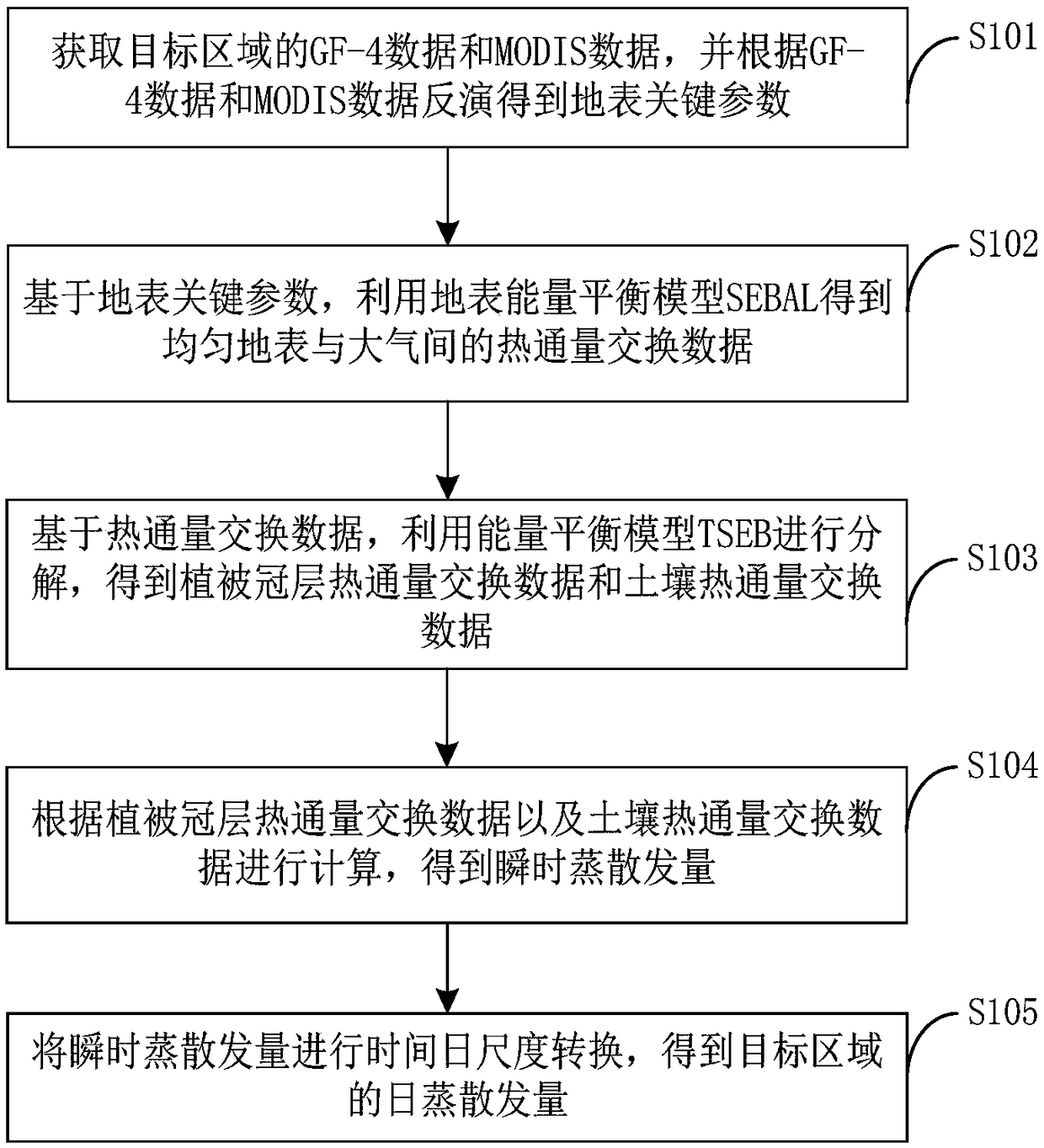
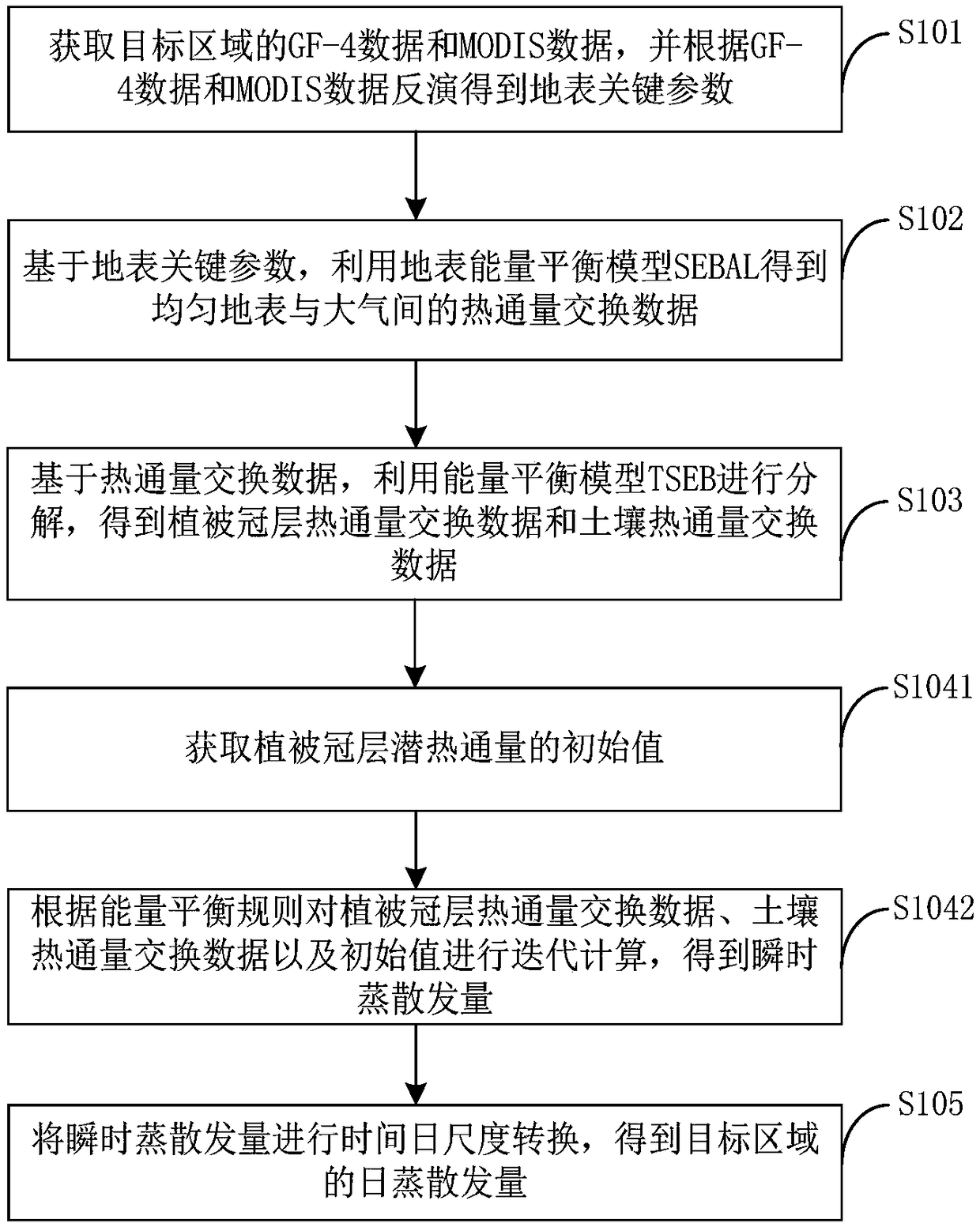
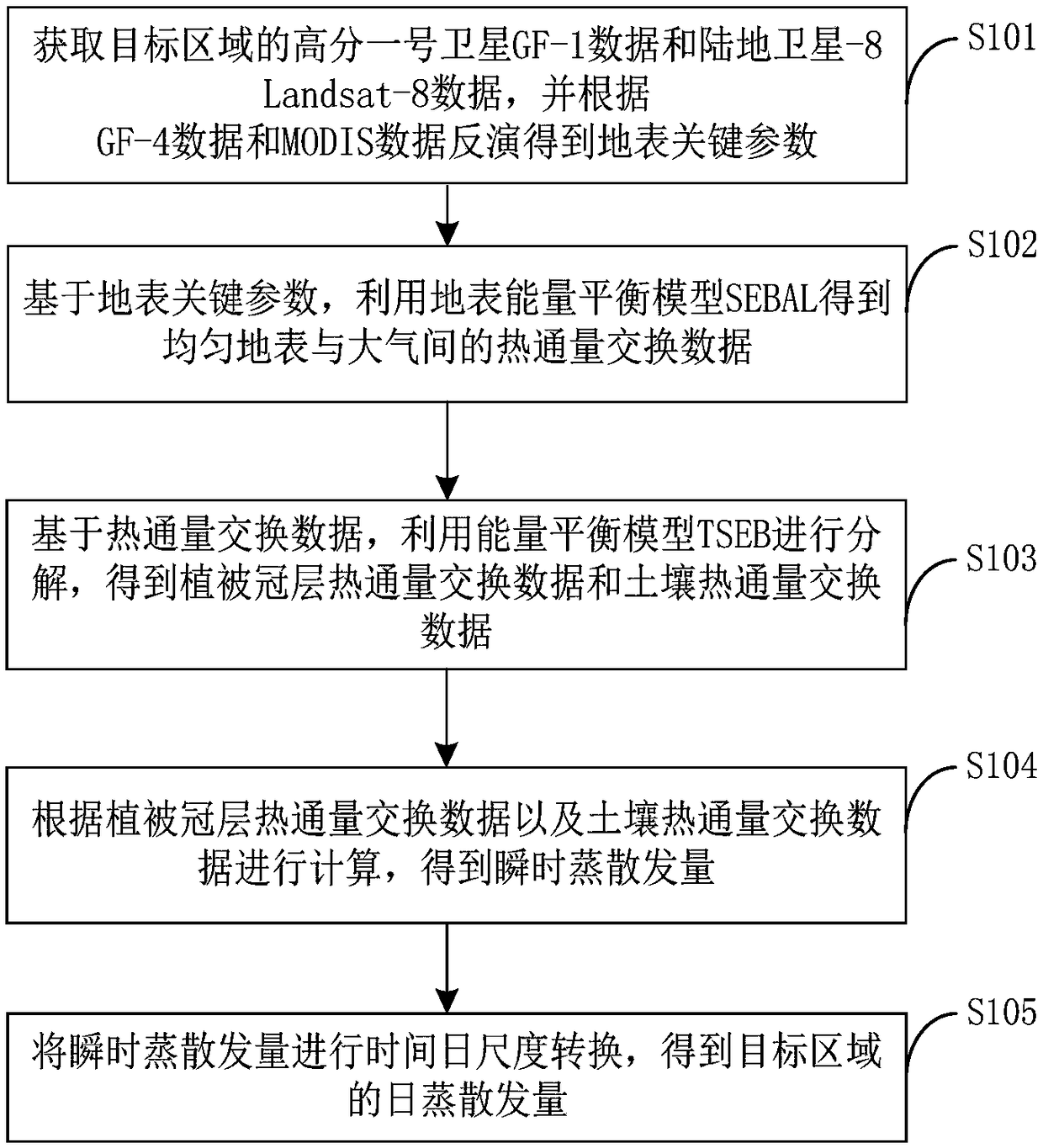
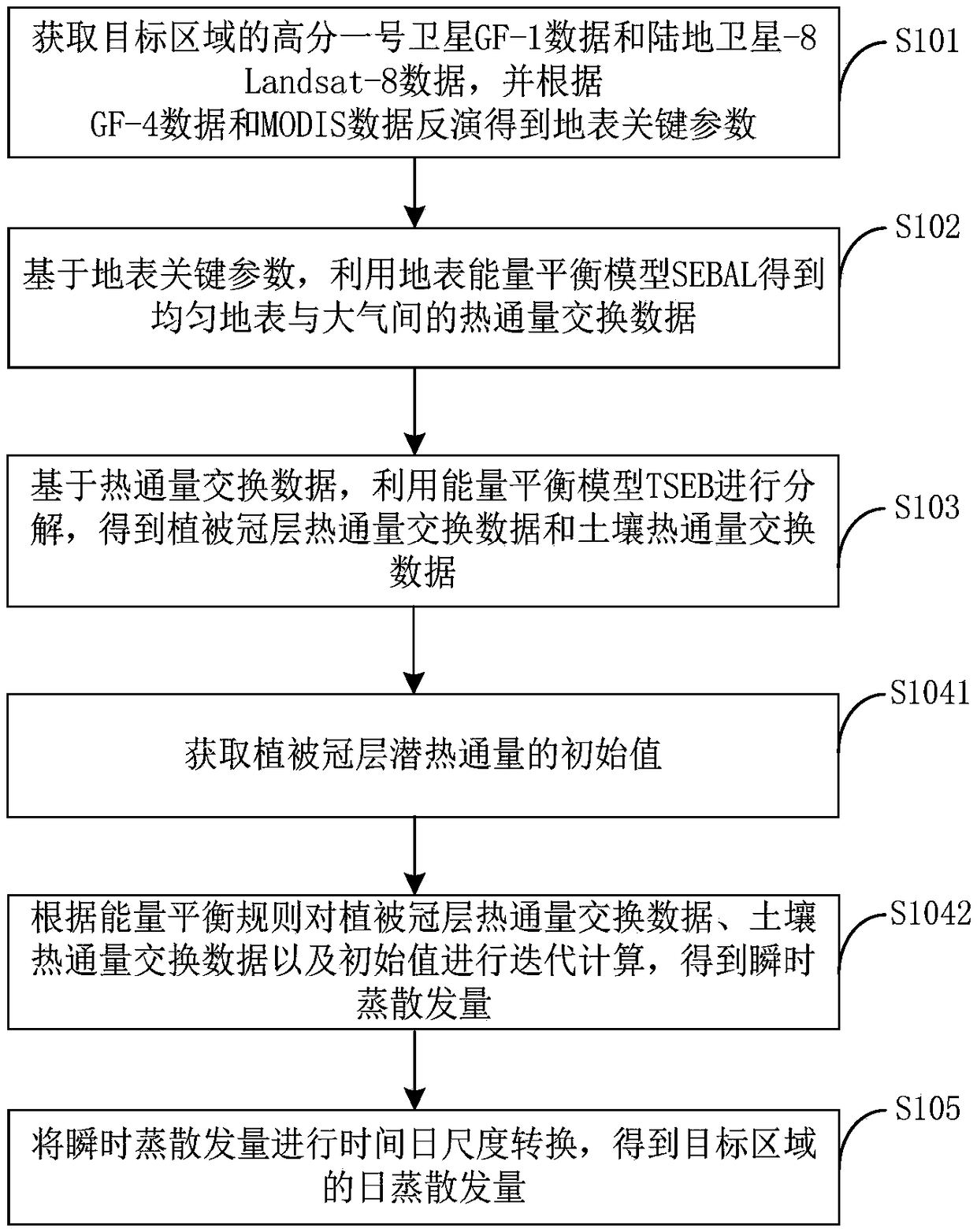
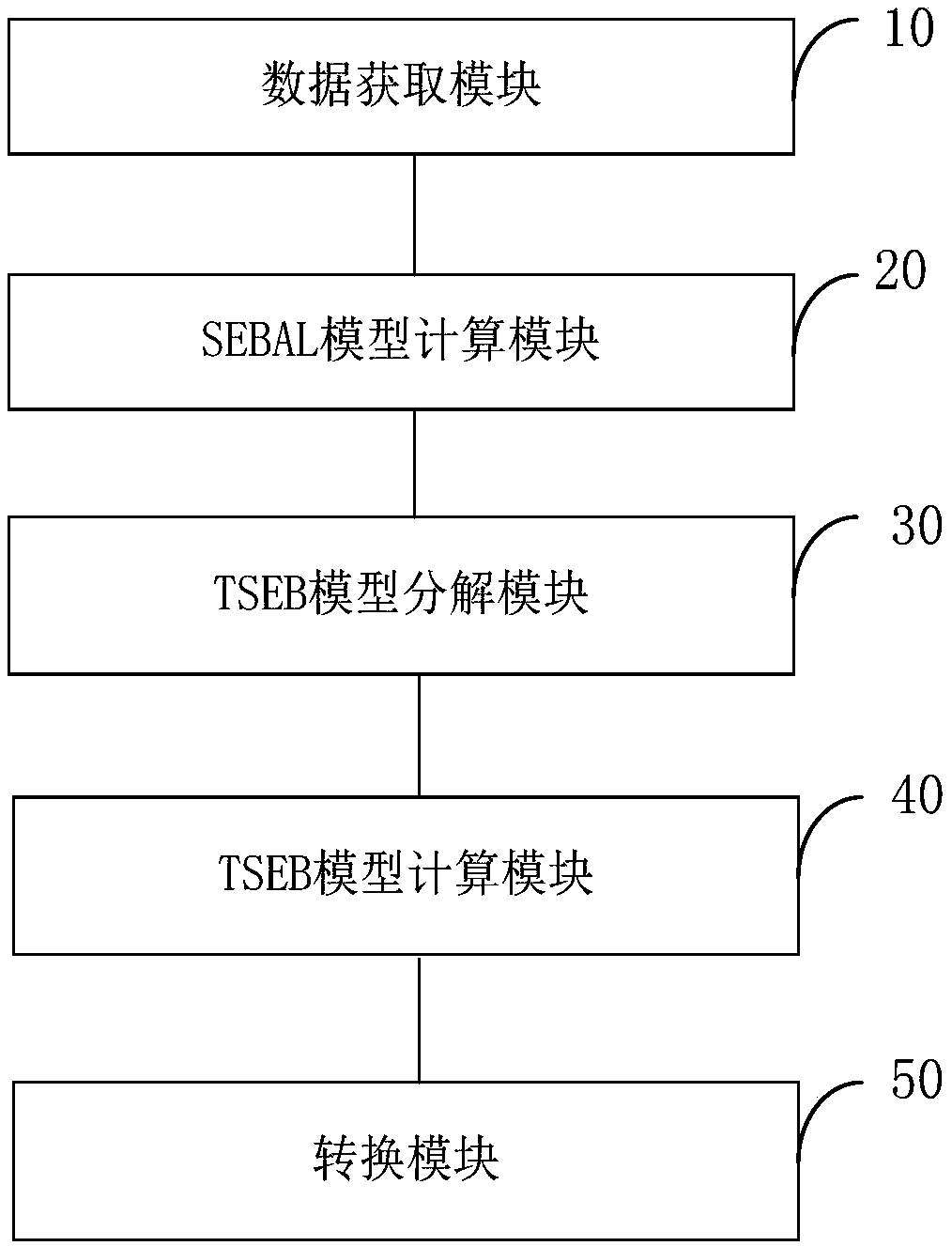
Evapotranspiration remote sensing inversion method and system based on combination of GF-4 and MODIS
InactiveCN108984867AHigh precisionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSEBALHeat flux
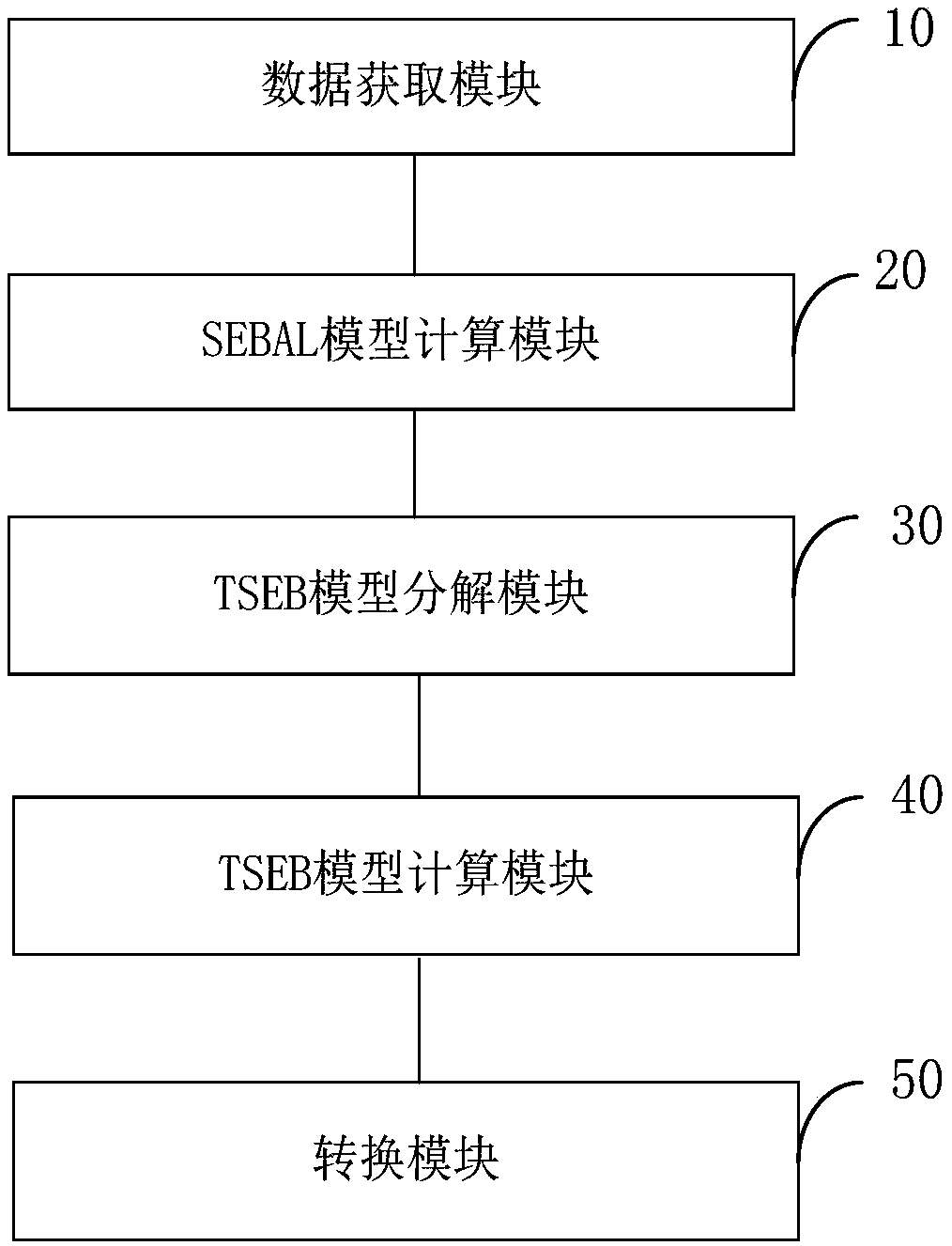
The invention provides an evapotranspiration remote sensing inversion method and system based on combination of GF-4 and MODIS. The method includes: acquiring GF-4 data and MODIS data of a target area, and obtaining surface key parameters on the basis of the GF-4 data and the MODIS data; based on the surface key parameters, obtaining the heat flux exchange data between uniform surface and atmosphere by using the surface energy balance model SEBAL; based on the heat flux exchange data, carrying put decomposition by using an energy balance model TSEB, and obtaining the heat flux exchange data ofvegetation canopy and soil; performing calculation according to the data of canopy heat flux exchange and soil heat flux exchange, and obtaining instantaneous evapotranspiration; carrying out time-daily scale conversion on the instantaneous evapotranspiration, and obtaining daily evapotranspiration in the target area. In combination with the GF-4 data and the MODIS data, the high-precision ET results can be obtained by fusing the multi-source sensor data with different spatial resolution.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
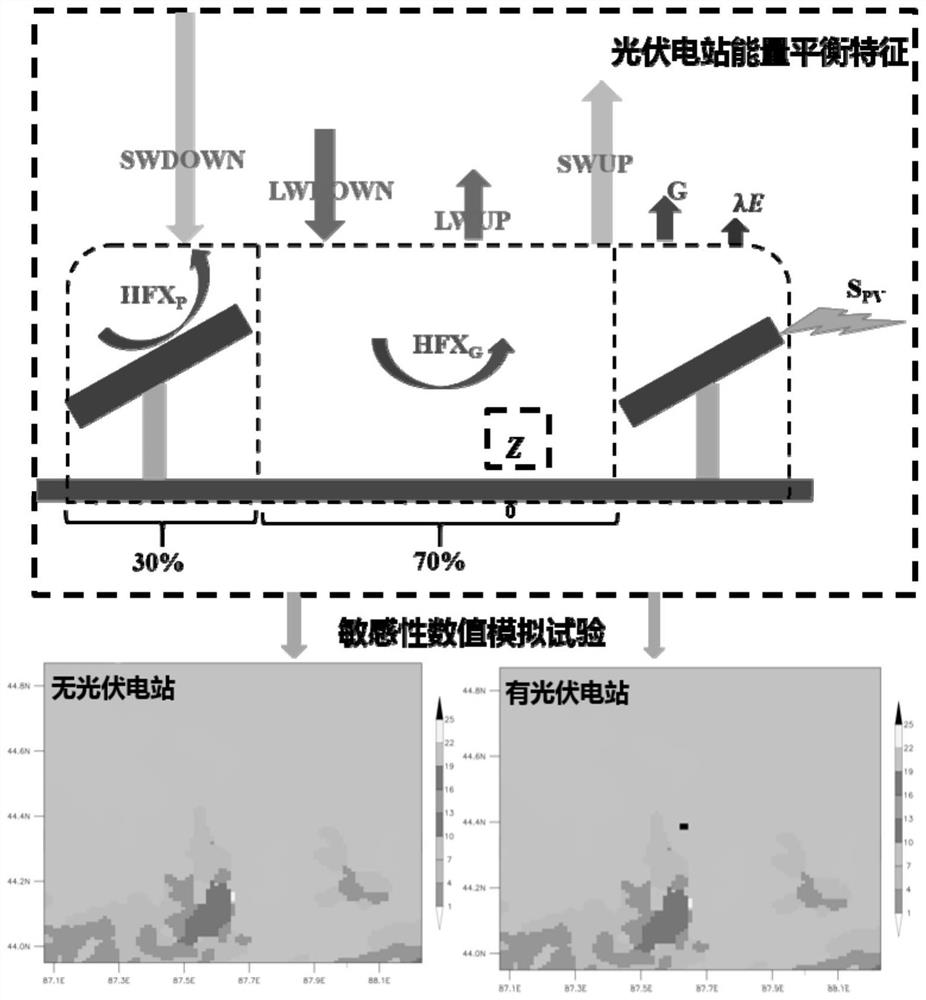
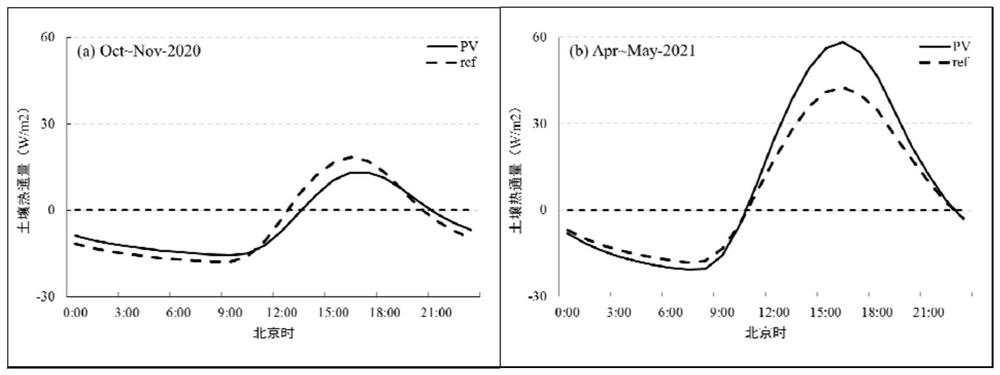
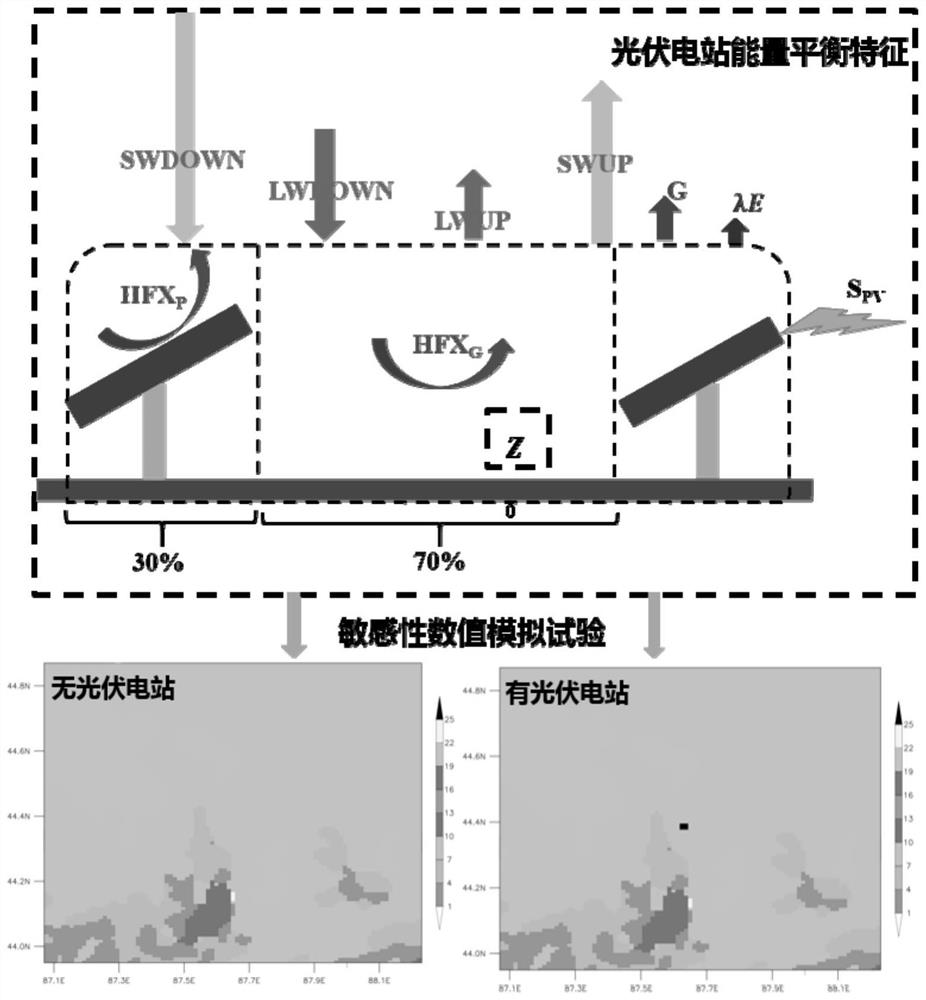
Mesoscale numerical simulation method for climate effect evaluation of onshore centralized photovoltaic power station
ActiveCN113987823ASolve the problem of objective quantitative evaluationReduce high dependencyData processing applicationsDesign optimisation/simulationHeat fluxEngineering
The invention discloses a mesoscale numerical simulation method for climate effect evaluation of an onshore centralized photovoltaic power station. The mesoscale numerical simulation method comprises the following steps of: preprocessing multisource meteorological observation data of the onshore centralized photovoltaic power station; performing surface short-wave radiation parameterization by using comprehensive albedo and photoelectric conversion efficiency; performing direct explicit numerical parameterization on heat-sensitive flux by using wind speed, air density and short-wave radiation; performing latent heat flux, soil heat flux and long-wave radiation parameterization by using a difference comparison method; carrying out parameterization on the dragging effect of a photovoltaic panel by utilizing dynamic roughness; and quantitatively evaluating the climate effect of the photovoltaic power station through a sensitivity numerical simulation test. According to the method, the objective quantitative evaluation problem of the climate influence of the large photovoltaic power station is solved; and the simulation method has relatively high universality. By adopting the method, post-evaluation can be carried out on the climate effect of the built photovoltaic power station, pre-evaluation can be carried out on the climate effect of the power station to be built, and a basis is provided for site selection and construction of a climate-friendly power station.
Owner:国家气候中心
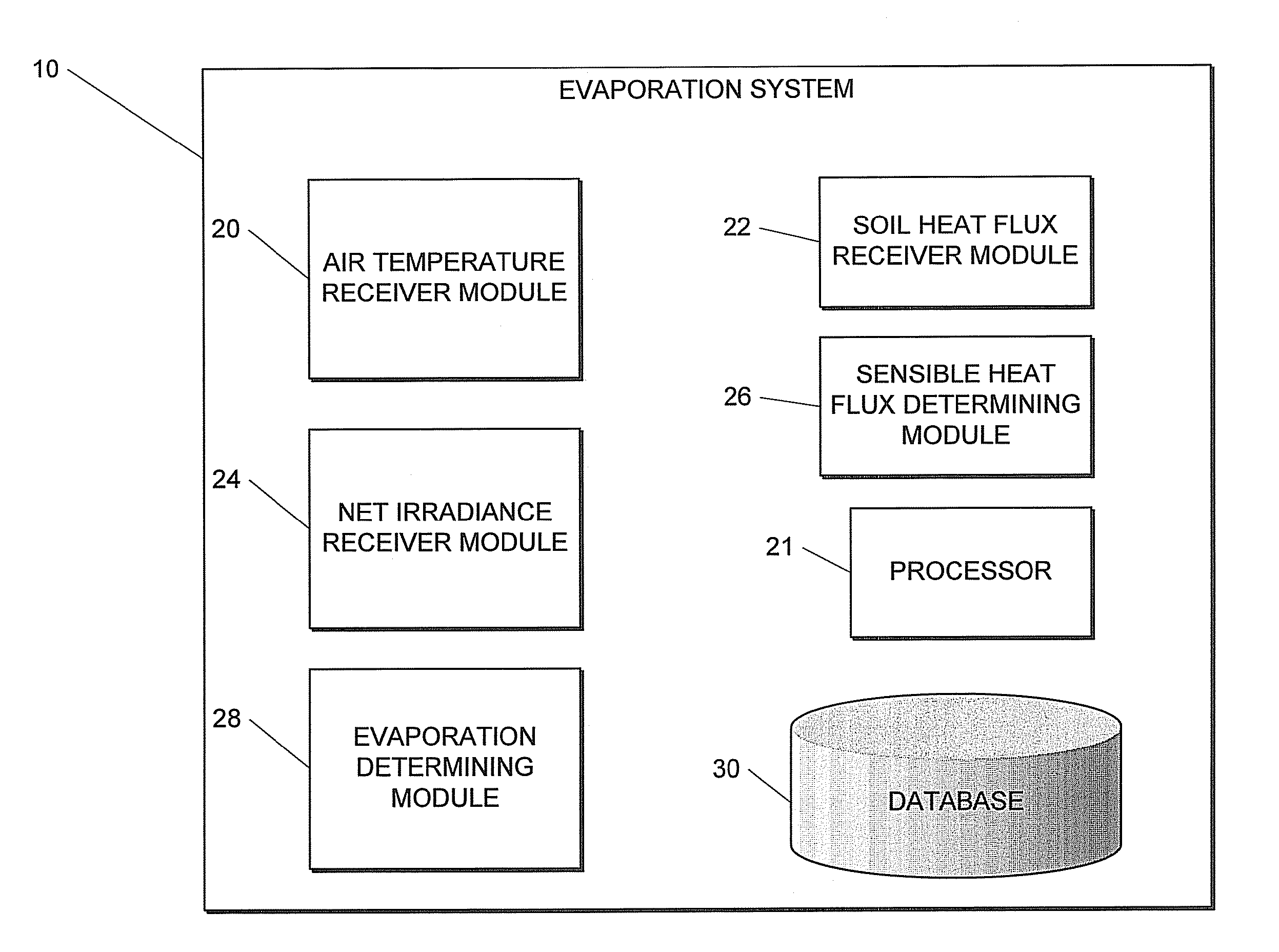
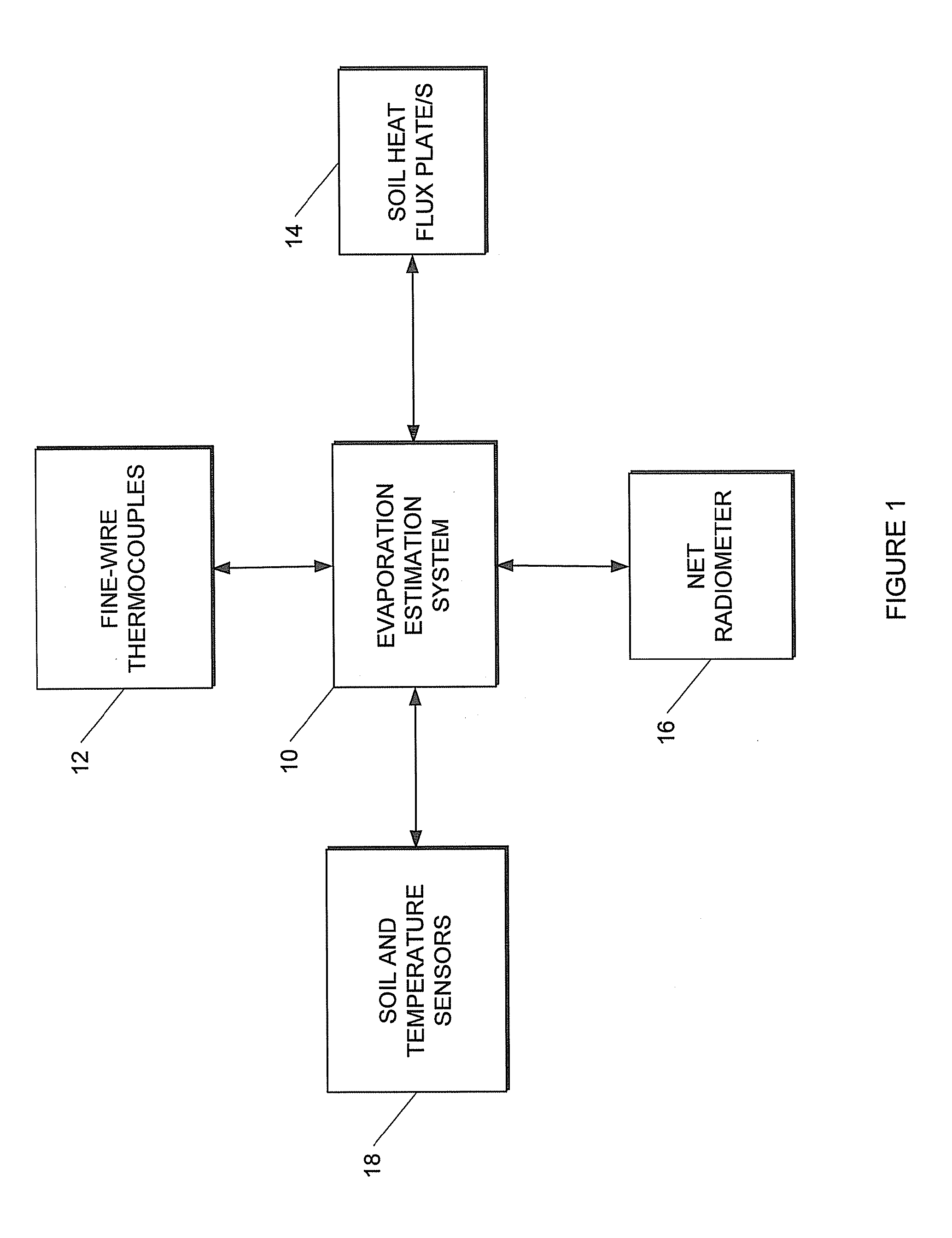
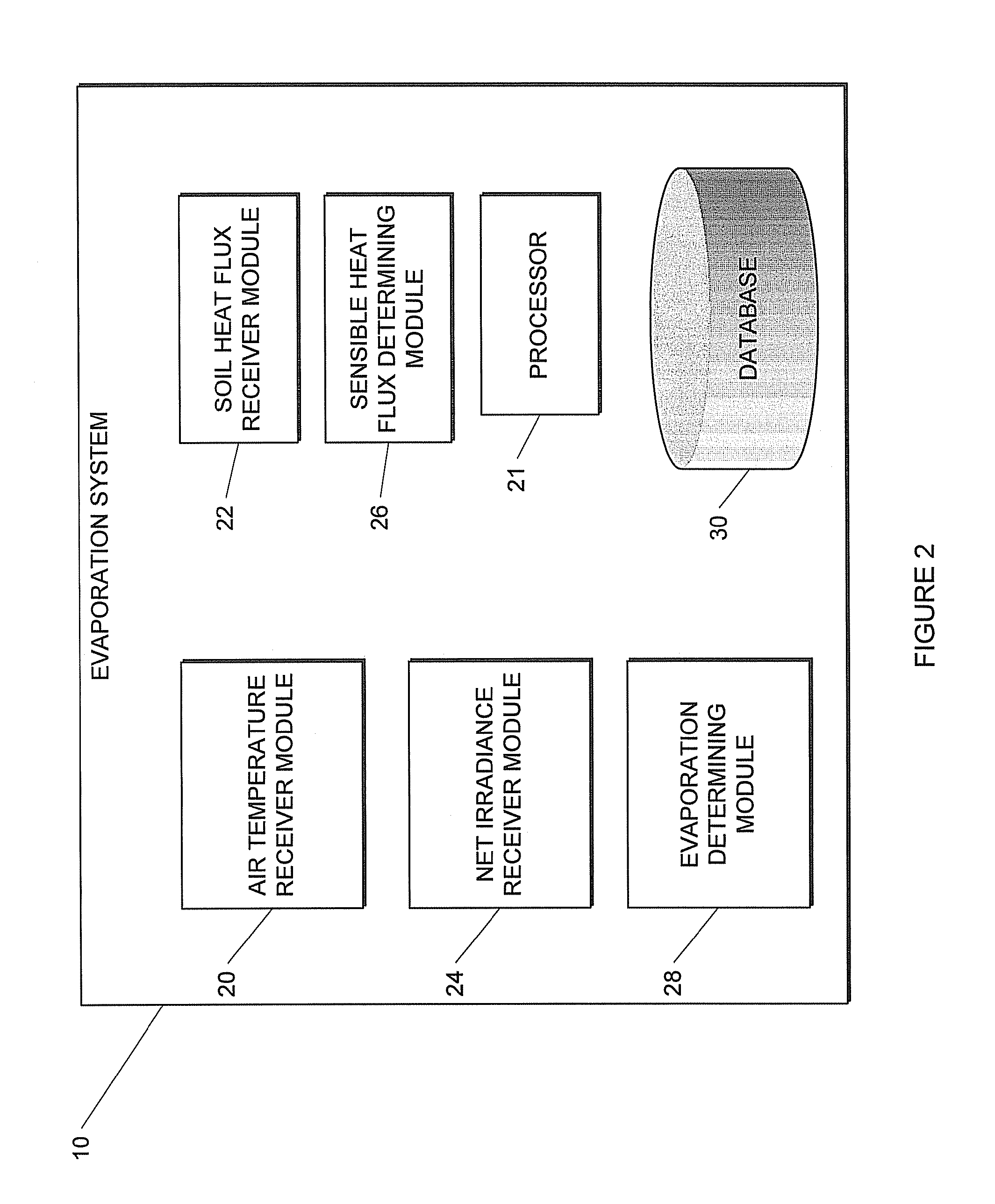
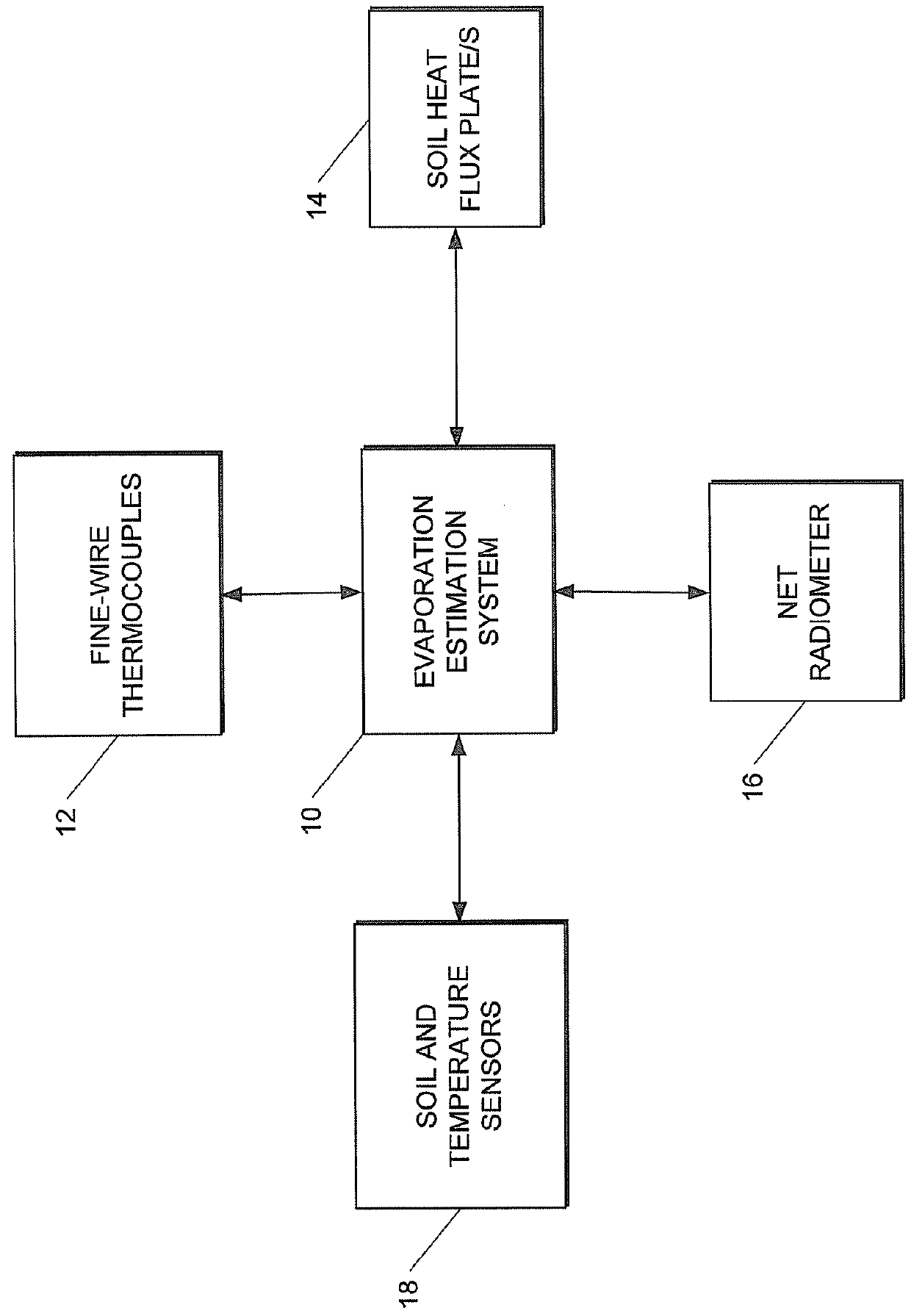
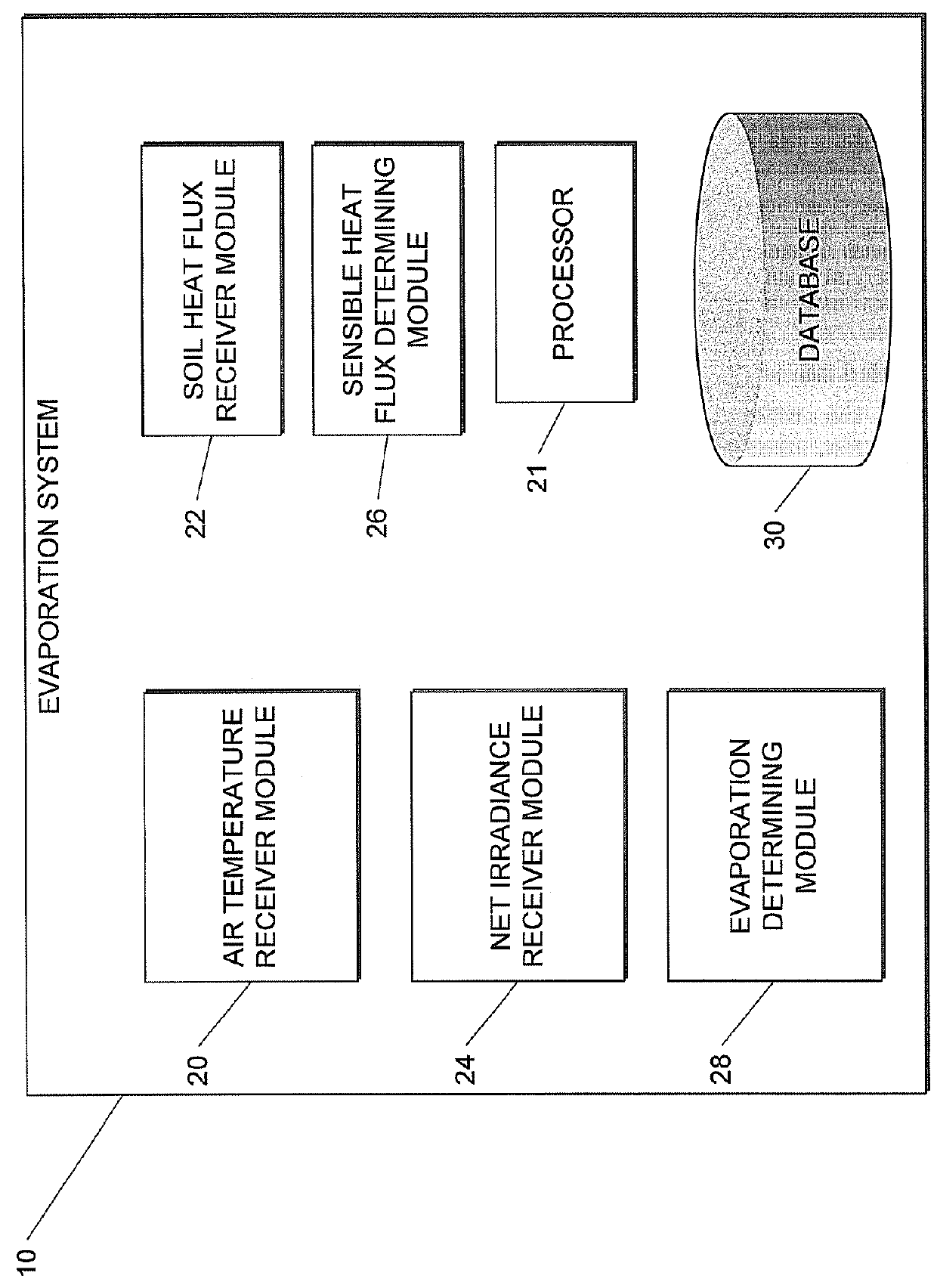
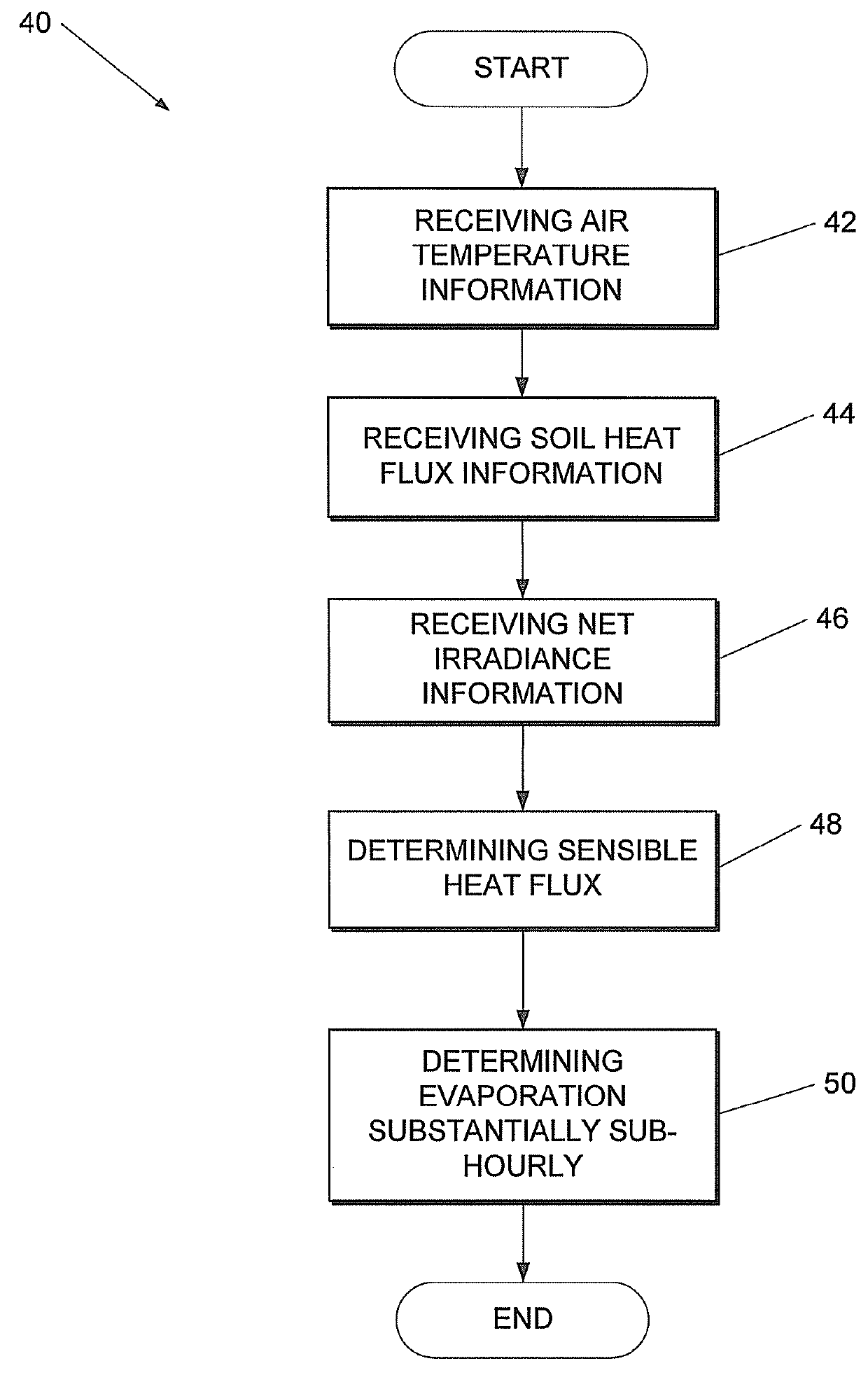
Method and system for estimating evaporation representative of an area
This invention related to a method of and a system for estimating evaporation representing an area at a particular location The method comprises receiving air temperature information, using the received air temperature information to determine at least average air temperature, standard deviation of the air temperature, and skewness of the air temperature at the particular location, receiving soil heat flux information and net irradiance information indicative of soil heat flux and net irradiance at the party location respectively, determining, sensible heat flux at the particular location by using at least the determined average air temperature, standard deviation of the air temperature, and skewness of the air temperature associated with the particular location, and determining an estimate of the evaporation at the particular location by using the determined sensible heat flux, received soil heat flux and net irradiance information.
Owner:UNIV OF KWAZULU NATAL
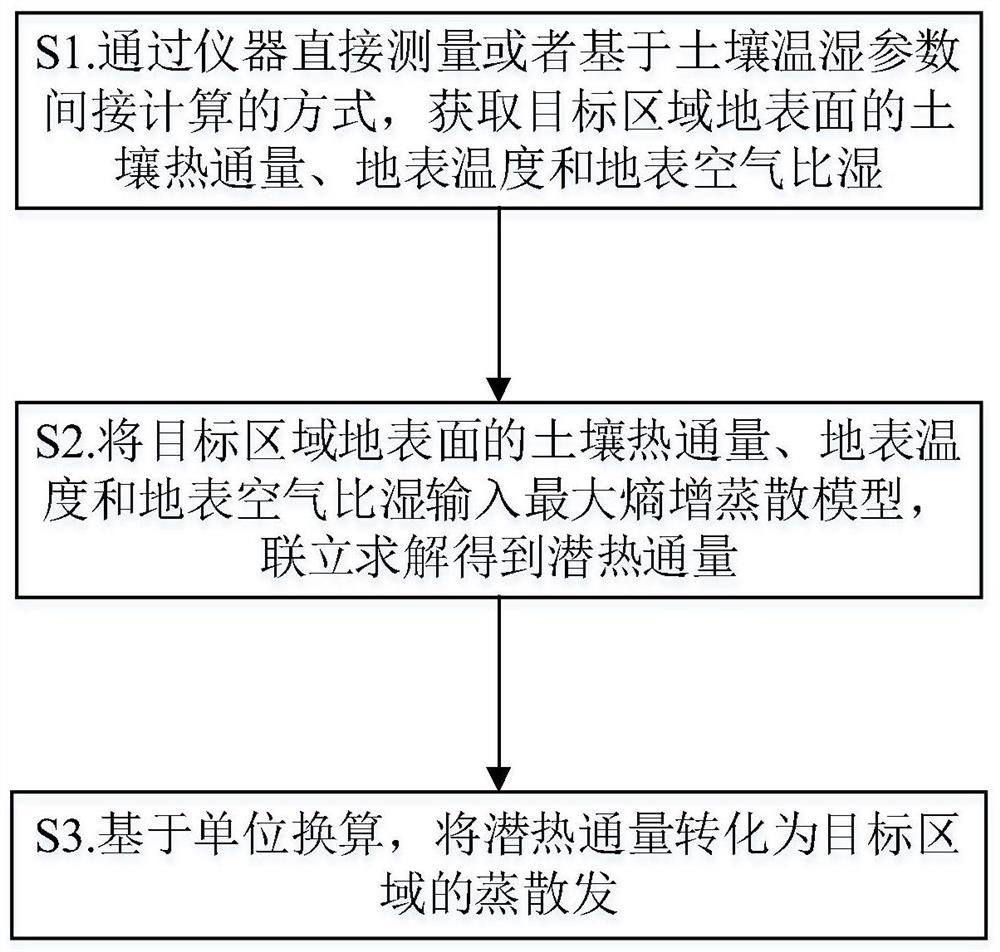
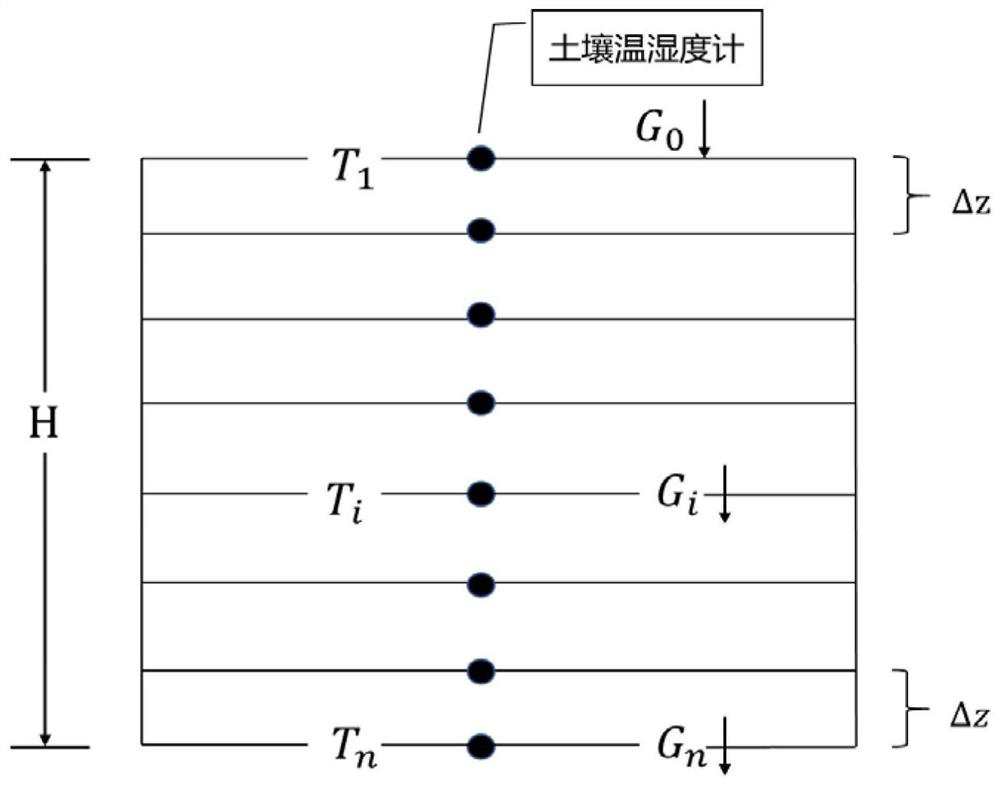
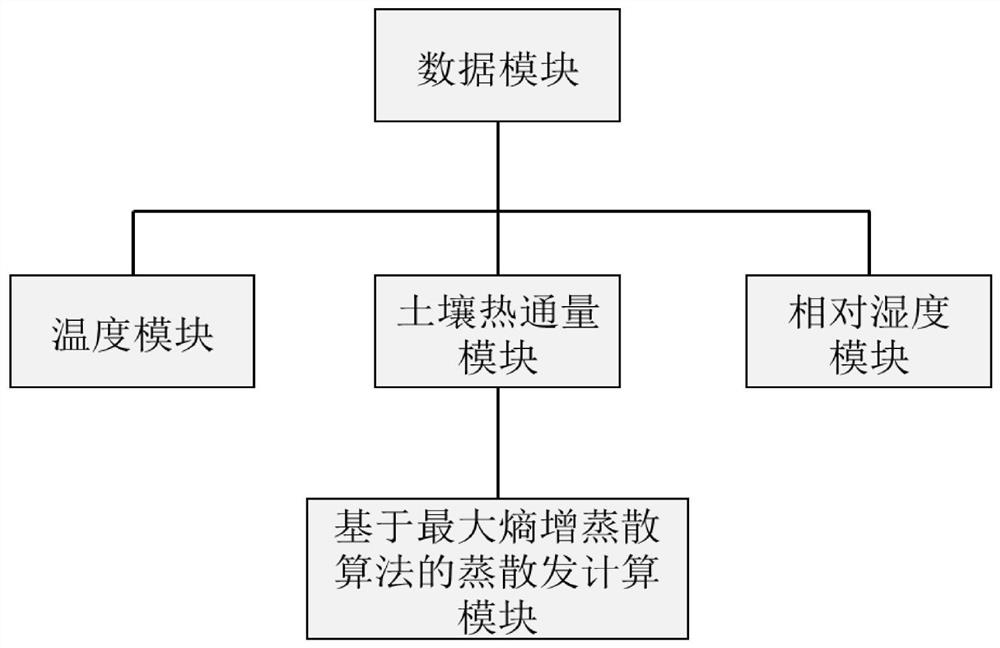
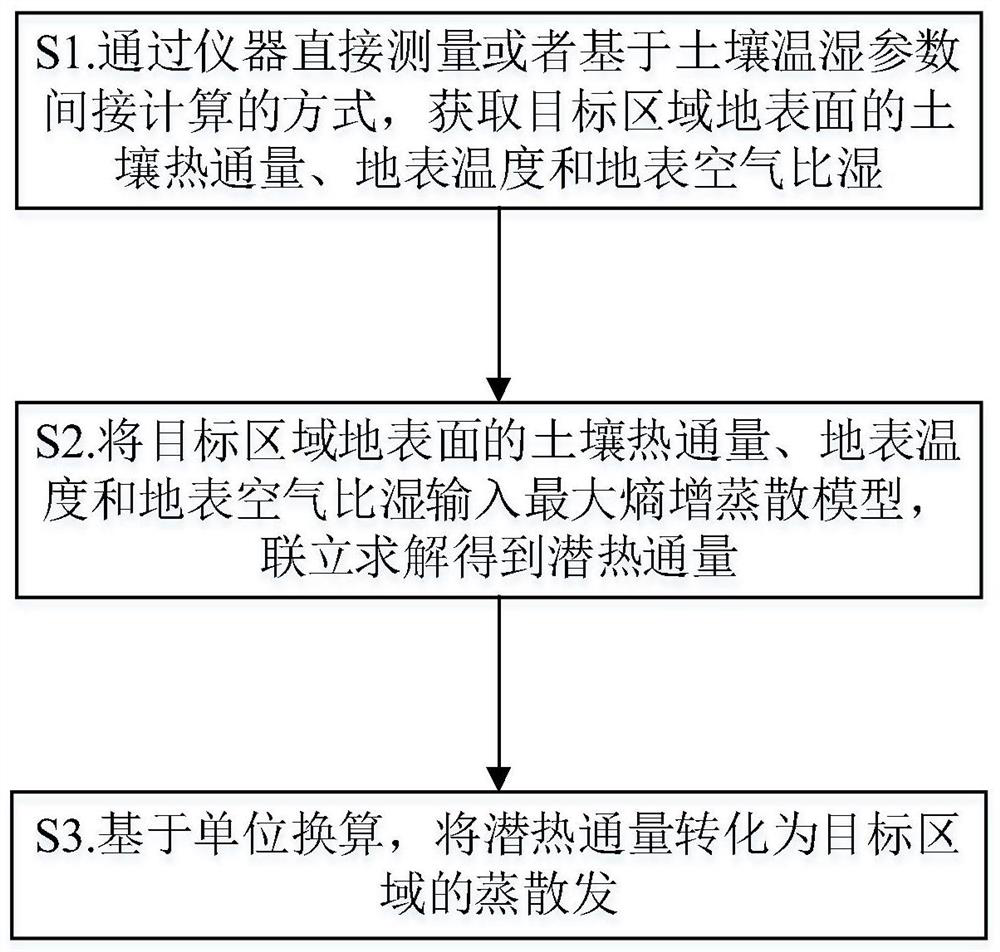
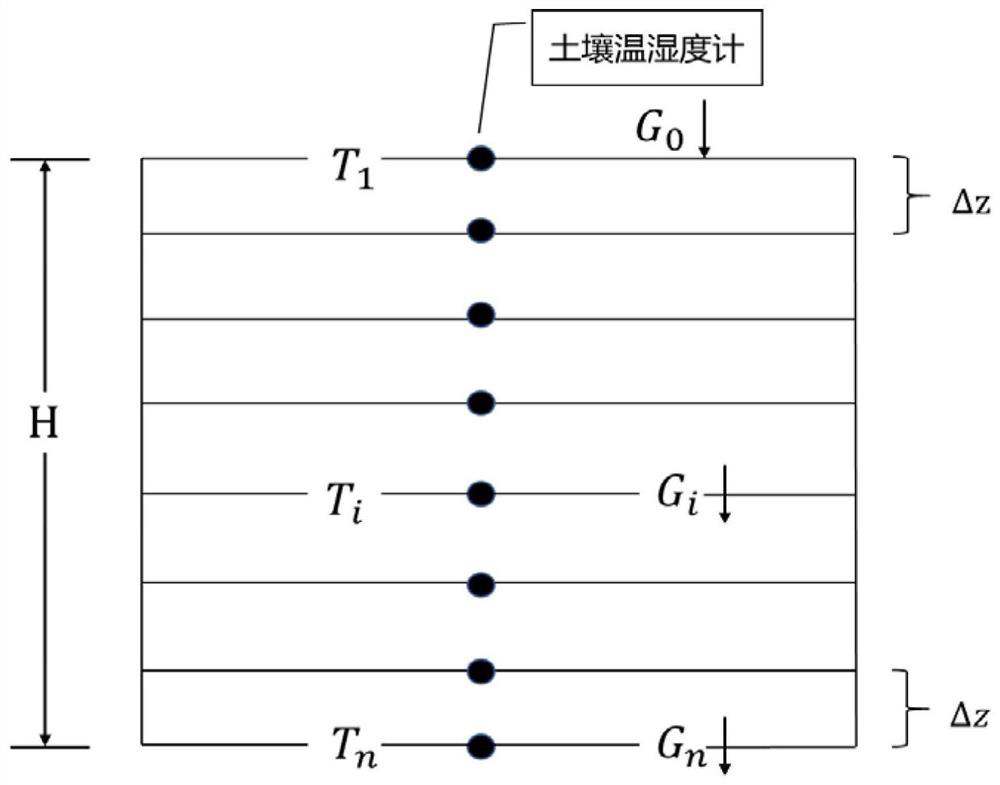
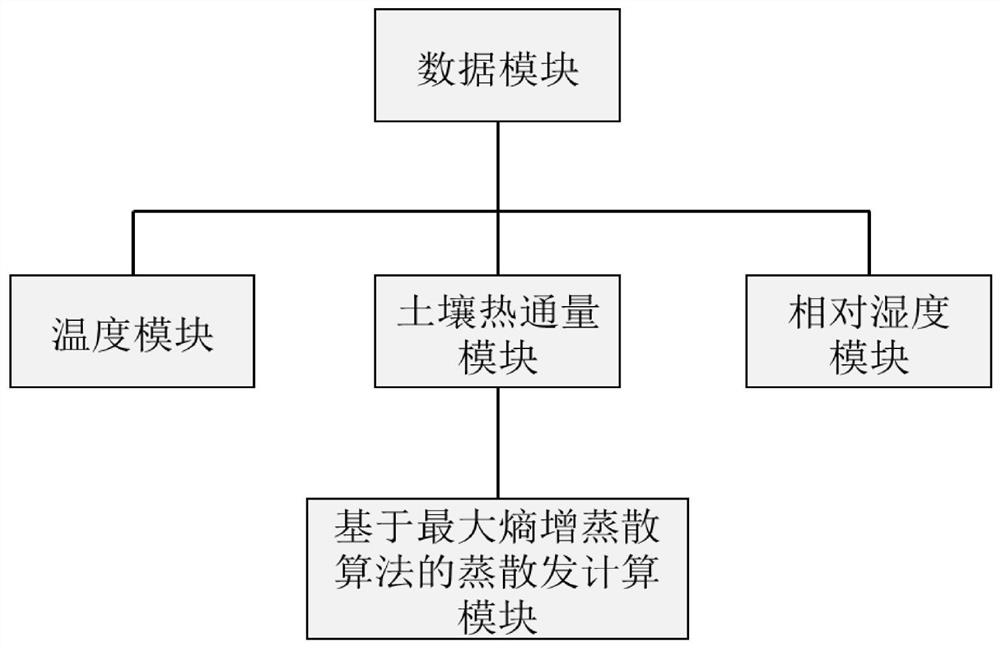
Measuring and calculating method and system for deducing evapotranspiration based on soil heat flux
ActiveCN112362693AAvoid dependenceOvercome difficultyMaterial heat developmentEarth material testingHydrometrySoil science
The invention discloses a measuring and calculating method and system for deducing evapotranspiration based on soil heat flux and belongs to the technical field of hydrological information forecasting. The method comprises the steps that: the soil heat flux, the surface temperature and the surface air specific humidity of the ground surface of a target area are obtained through direct instrument measurement or indirect calculation based on soil temperature and humidity parameters; the soil heat flux, the ground surface temperature and the ground surface air specific humidity of the ground surface of the target area areinputted into a maximum entropy increase evapotranspiration model, and simultaneous solving is performed to obtain latent heat flux; and the latent heat flux is converted into evapotranspiration of the target area based on unit conversion. According to the method, the evapotranspiration value is calculated by adopting the soil heat flux, and the obtained soil heat flux replaces a net radiation item to serve as the input of the maximum entropy increase evapotranspiration model, so that the dependence on radiation energy observation is avoided, the defects of high net radiation variable obtaining difficulty, high measurement cost, unclear error and the like are overcome, and the evapotranspiration calculation is simple, convenient and reliable.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Remote sensing inversion method and system for crop evapotranspiration based on the combination of GF-1 and Landsat-8
InactiveCN108875237AHigh precisionHigh ET resultDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsEnergy balancingHeat flux
The invention provides a remote sensing inversion method and a system for crop evapotranspiration based on the combination of GF-1 and Landsat-8. The method comprises the following steps of: obtainingthe GF-1 data and the Landsat-8 data of a target area to invert surface key parameters base on the GF-1 data and the Landsat-8 data; using the surface energy balance model SEBAL to obtain uniform heat exchange data between the surface and the atmosphere, based on the surface key parameters; using the energy balance model TSEB for decomposition to obtain vegetation canopy heat flux exchange data and soil heat flux exchange data, based on heat flux exchange data; calculating the instantaneous evapotranspiration according to the vegetation canopy heat flux exchange data and the soil heat flux exchange data; and converting the instantaneous evapotranspiration to a time-day scale to obtain a daily evapotranspiration of the target area. According to the remote sensing inversion method and the system for crop evapotranspiration based on the combination of GF-1 and Landsat-8, high-precision ET results can be inverted by combining GF-1 data with Landsat-8 data, and combining multi-source sensor data with different spatial resolutions.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
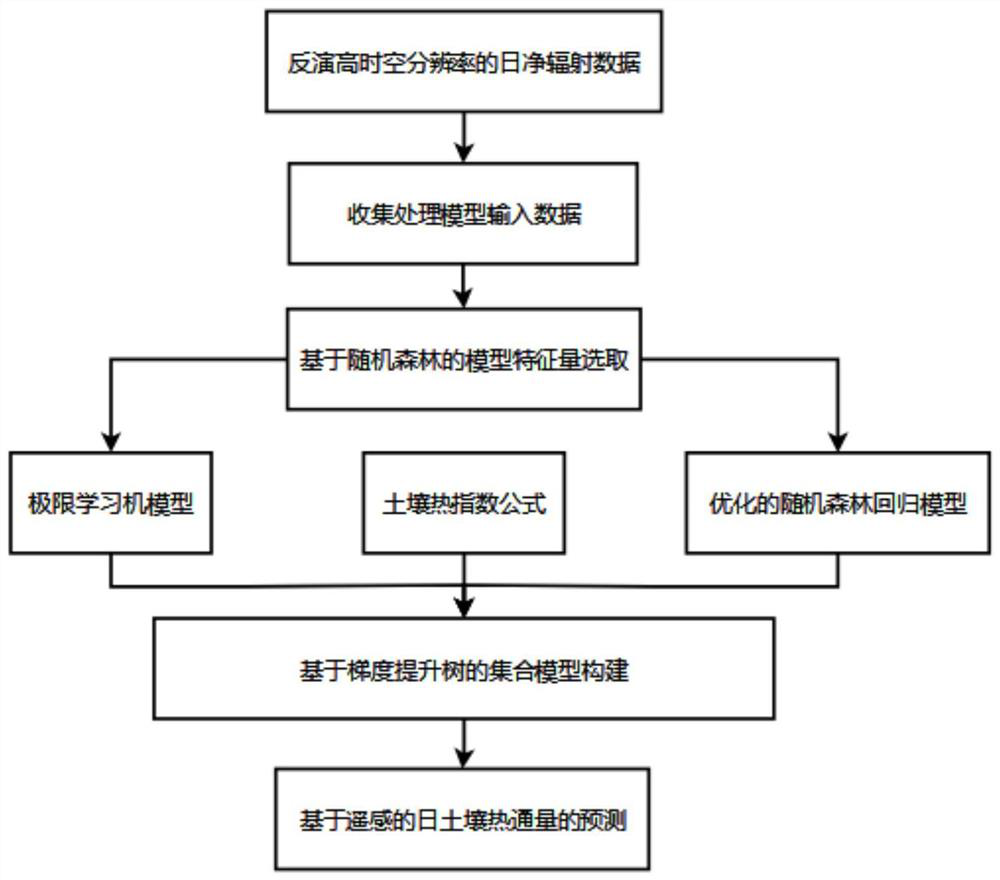
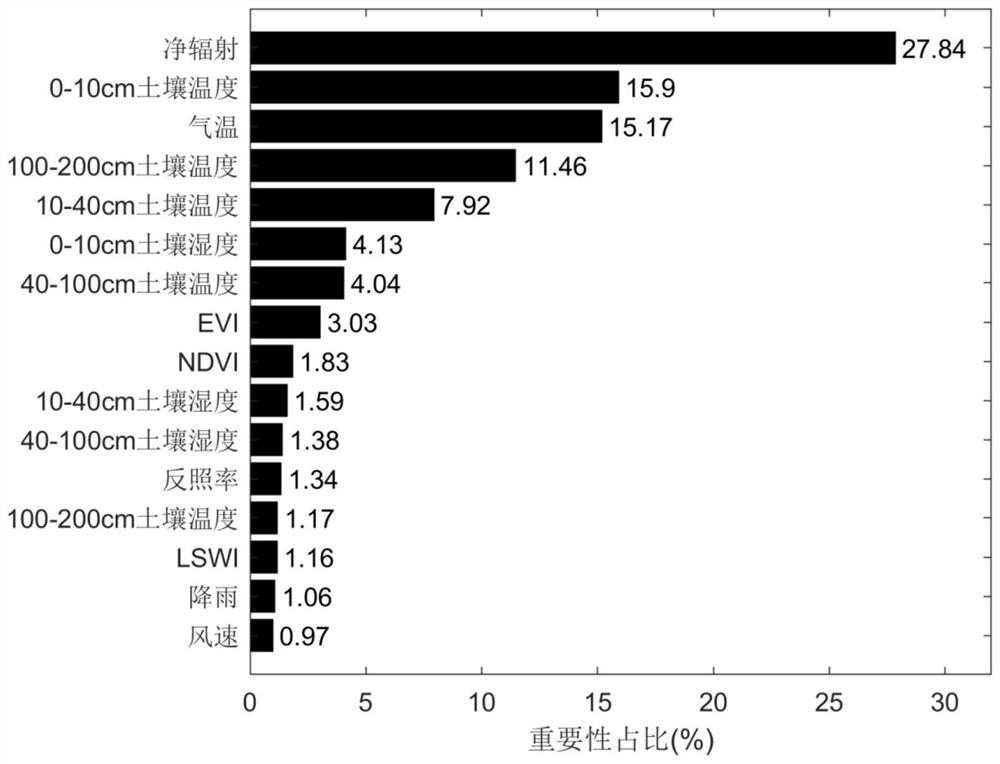
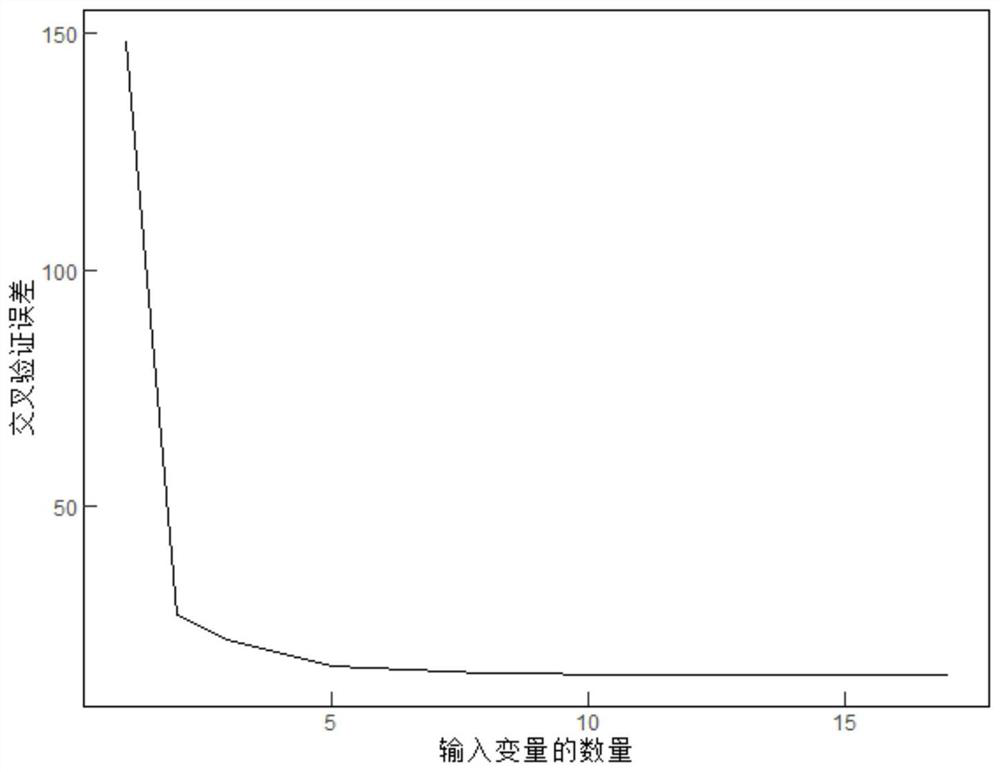
Soil heat flux prediction method based on multi-source satellite remote sensing data
ActiveCN114563353AImproving the accuracy of remote sensing simulationHigh precisionClimate change adaptationMaterial analysis by optical meansLearning machineEvapotranspiration
The invention discloses a soil heat flux prediction method based on multi-source satellite remote sensing data, and the method comprises the following steps: firstly, providing a soil heat index formula, providing reference for the evaluation of the soil heat flux of a region without data, and simulating an observation station with actual measurement data by adopting a popular machine learning method, the method comprises the following steps: respectively establishing an extreme learning machine model and a Bayesian optimized random forest regression model to estimate the soil heat flux based on a model input characteristic value screened by a random forest, and finally dynamically combining an empirical index model and a machine learning model by utilizing a GBDT gradient boosting tree method to establish an optimal soil heat flux prediction model. The method is higher in calculation precision and has practical significance. The method is superior to a traditional method for calculating the result of the soil heat flux by utilizing a formula, and the accuracy of inverting evapotranspiration by utilizing an energy conservation model is improved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
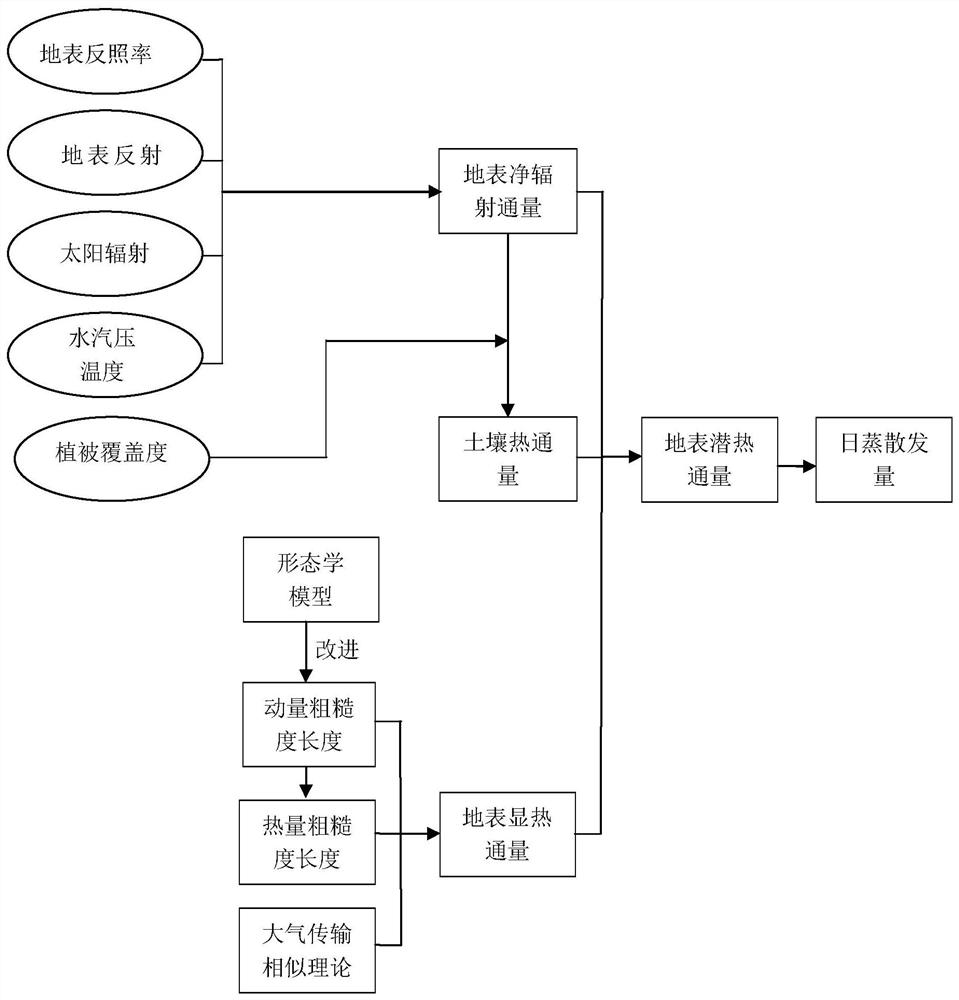
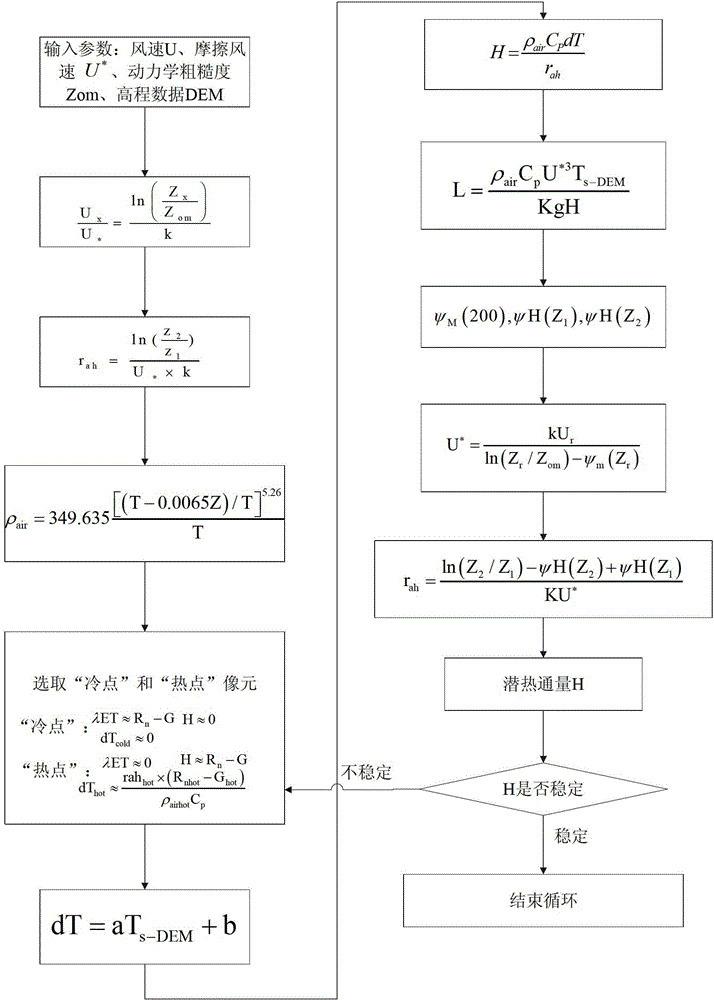
Regional evapotranspiration calculation method based on remote sensing
PendingCN112649370AAddress inherent flawsDrought Monitoring AchievedMaterial analysis by optical meansSensing dataVegetation
The invention provides a regional evapotranspiration calculation method based on remote sensing, which relates to the field of regional ecological environment evaluation, and comprises the following steps of: 1, acquiring related surface parameters by utilizing remote sensing data; 2, calculating earth surface net radiation flux Rn by utilizing the earth surface albedo alpha according to a solar radiation transmission theory; 3, calculating soil heat flux G by utilizing the earth surface net radiation flux Rn and the vegetation coverage fv; 4, calculating to obtain a momentum roughness length Z0m and a heat roughness length Z0h by utilizing a morphological model; 5, calculating sensible heat flux H by utilizing the momentum roughness length Z0m, the heat roughness length Z0h and an atmospheric transmission similarity theory; 6, calculating earth surface latent heat flux lambda E, and then calculating an evaporation ratio lambda; and 7, calculating the regional daily evapotranspiration Eday according to the evaporation ratio lambda. By means of the advantages of space continuity and time dynamic observation of the remote sensing technology, a remote sensing parameterization model of the surface momentum roughness and the zero-plane displacement height is improved based on a morphological method.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method of interpolating eddy flux observed data missing from the surface by using ALPHA invariant method
ActiveCN108984792AEffective imputationSimple methodMeasurement devicesSpecial data processing applicationsMissing dataData set
The invention belongs to the technical field of surface flux observation data processing and relates to a method of interpolating eddy flux observation data missing from the surface by using an ALPHAinvariant method. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: constructing an input data set required by the method; calculating the average latent heat flux, soil heat flux and net radiation for the target time period in which the eddy flux observation data were partially missing; based on the Priestley-Taylor equation, obtaining the average ALPHA value at the time when the corresponding time period is not missing according to the above average value; based on the characteristic of ALPHA keeping constant, taking the average ALPHA value as the ALPHA value at the time of missingdata, and interpolating the flux at the time of missing data of surface eddy flux observation according to the above equation and the equation of surface energy balance. The method is very important to estimate and validate the latent heat flux and sensible heat flux by remote sensing quickly and accurately.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS +1
Soil heat flux sensor
InactiveCN101122572AHigh sensitivityImprove stabilityMaterial thermal conductivityThermopileEnergy balanced
The invention relates to a soil thermal flux sensor for measuring soil energy balance and soil layer heat conductivity, including a body (1). An inner groove (5) for storing a thermopile (2) is arranged on the body (1). The outer lateral of the thermopile (2) is equipped with a cover plate (3). The thermopile (2) consists of two serial monomers. One end of the body (1) is equipped with a conductor (4). The body (1) is made of a material made from polytetrafluoroethylene with corrosion resistance and insect resistant performances. The thermopile arranged in the body comprises a plurality of serial monomers. The soil thermal flux sensor of the invention has the advantages of high measurement sensitivity, good stability and corrosion and insect resistance.
Owner:北京华创维想科技开发有限责任公司
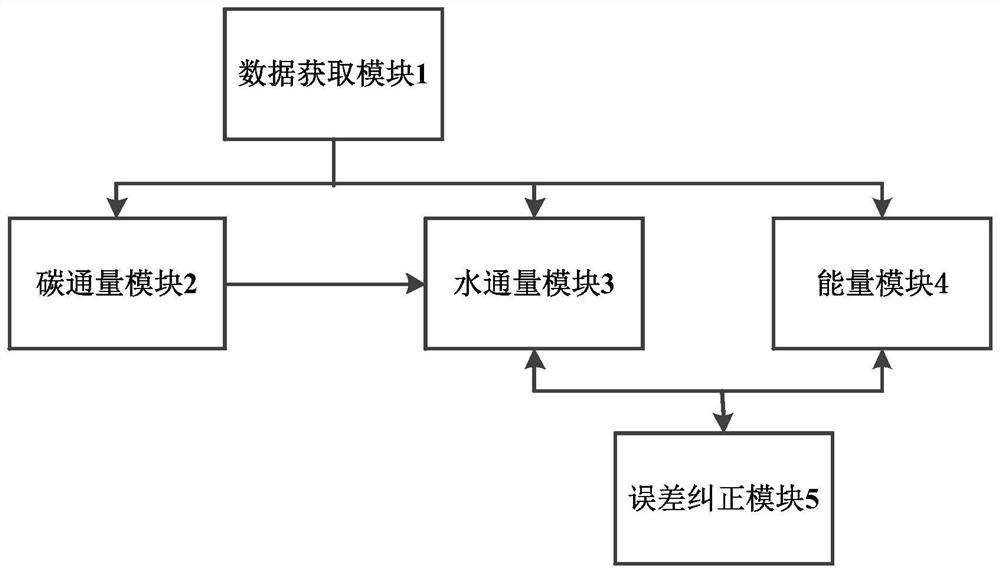
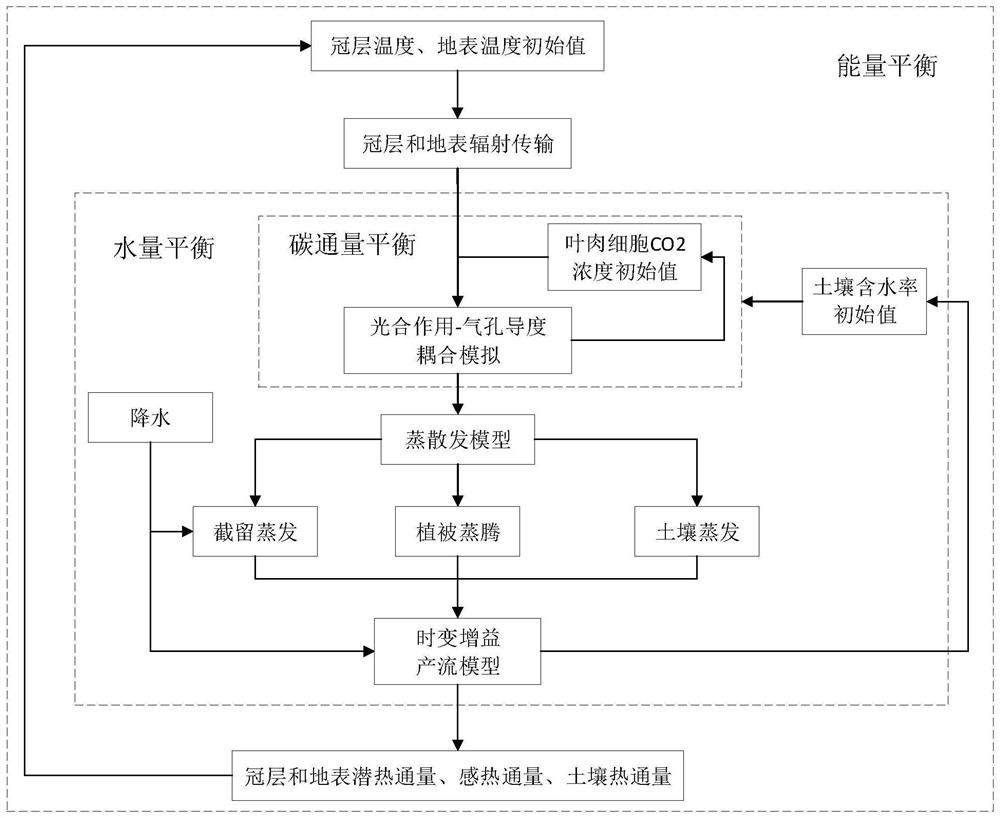
Time-varying gain model-based water, energy and carbon coupling numerical simulation method and system
ActiveCN112733385AAchieve balanceSolid physical foundationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsCarbon assimilationSoil science
The invention provides a time-varying gain model-based water, energy and carbon coupling numerical simulation method and system. The method comprises the steps of S1, receiving meteorological data and soil vegetation underlying surface type data; s2, initializing the average canopy temperature and the surface temperature in a preset first time period to obtain the net radiation flux of the canopy and the surface; s3, constructing a photosynthesis / stomatal conductance coupling model, and performing vegetation dynamic carbon assimilation simulation; s4, obtaining evapotranspiration parts based on the double-source evapotranspiration model; s5, inputting the evapotranspiration parts, intercepted precipitation and the soil moisture content in the first time period into a time-varying gain runoff production model, and iterating to obtain the soil moisture content; s6, obtaining a canopy, soil latent heat flux, a canopy, soil sensible heat flux and soil heat flux, constructing an energy balance model, and obtaining the average temperature of the canopy. According to the method, the calculation balance of water quantity, energy and carbon flux in a certain period of time can be realized, so that the calculation deviation caused by energy and material imbalance is reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Inversion method and system for regional surface sensible/latent heat flux based on remote sensing data
The invention discloses a regional earth surface sensible heat / latent heat flux inversion method based on remote sensing data. The method comprises the following steps that a research area and the remote sensing data are determined; remote sensing earth surface and regional meteorological parameters are prepared according to the remote sensing data, wherein the remote sensing earth surface parameters comprise a normalized difference vegetation index NDVI, vegetation coverage f, albedo, earth surface emissivity Emiss, earth surface temperature Ts and a leaf area index LAI, and the regional meteorological parameters comprise air temperature Ta and relative humidity RH; net radiation flux Rn inversion is conducted according to the remote sensing earth surface and regional meteorological parameters; soil heat flux G inversion is conducted according to the leaf area index LAI, the air temperature Ta and net radiation flux Rn; radiation-convection impedance rae inversion is conducted according to theoretical two-dimensional space of the net radiation flux Rn, soil heat flux G, the vegetation coverage f and the earth surface temperature Ts and a temperature profile equation estimated through sensible heat flux; regional earth surface sensible heat H / latent heat LE flux inversion is achieved according to radiation-convection impedance rae.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Method for obtaining field evapotranspiration of field scale
ActiveCN102136035BAccurately express the continuous change of spaceReduce spatial resolutionMaterial heat developmentSpecial data processing applicationsSensing dataVegetation
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT FOR INFORMATION TECH & AGRI
Surface water heat flux remote sensing inversion-based drought monitoring method and system
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
Eddy flux observation energy imbalance correction method, device and electronic equipment
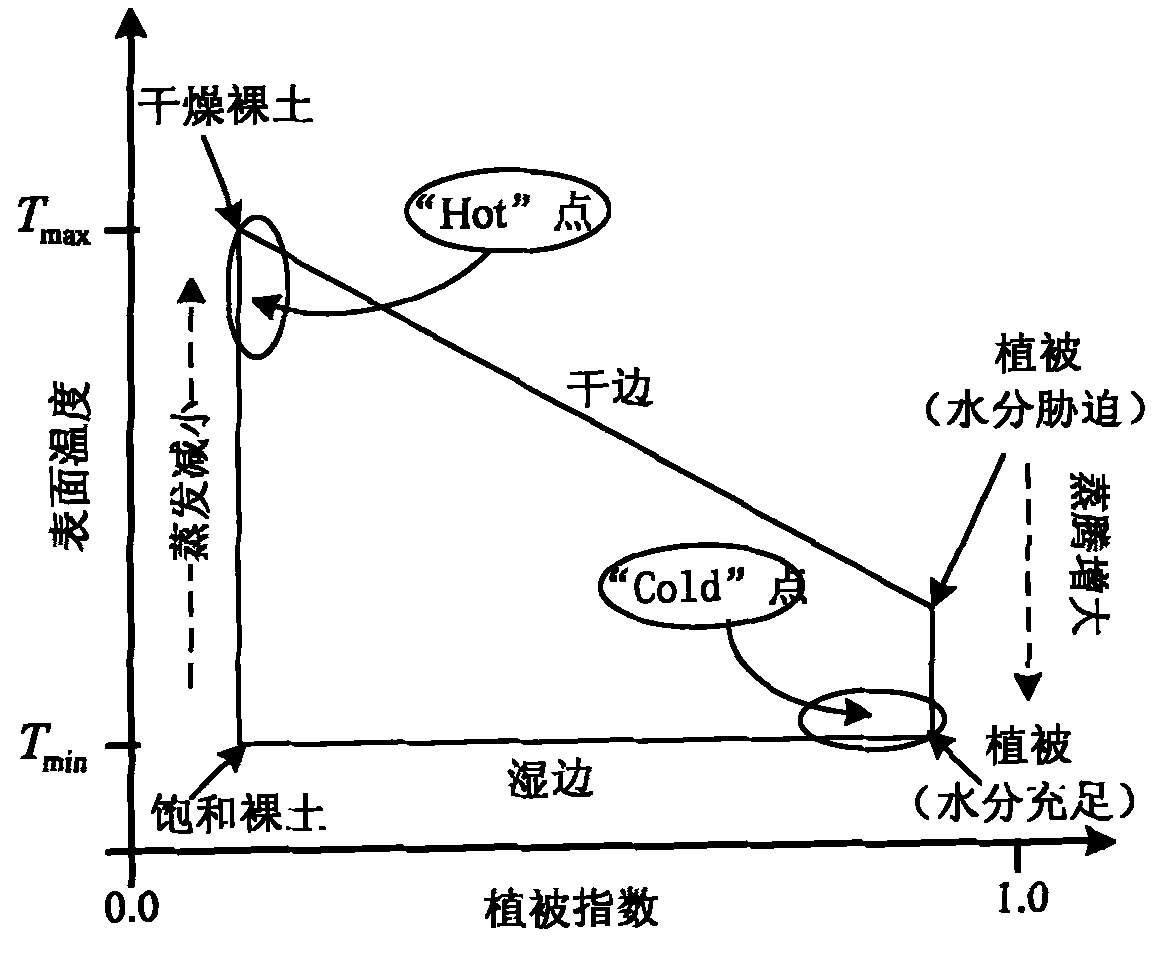
ActiveCN108983328BEffective energy imbalanceAvoid involvement in correction calculationsInstrumentsData transformationBowen ratio
The invention provides an eddy flux observation energy imbalance correction method and device, and an electronic device and relates to the meteorological monitoring technology field. By using the method, during energy imbalance correction, the flux data of a preset time scale is converted into daily-scale flux data; a Bowen ratio is used to correct the daily-scale flux data; and then, the corrected flux data of the preset time scale is obtained through the corrected daily scale data. Because a daily-scale soil heat flux is usually zero, the soil heat flux is prevented from participating in correction calculation, and a uncertainty problem generated because time or spaces between the fluxes are mismatched when energy imbalance correction is performed through directly using a Bowen ratio method in the prior art is effectively alleviated; and the effective correction of the energy imbalance phenomenon of the eddy observation flux is realized, which is beneficial to obtaining the flux dataaccording with a reality.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS +1
A method of interpolating missing eddy flux observation data on the ground using the alpha invariant method
ActiveCN108984792BAvoid missingEffective imputationDigital data information retrievalMeasurement devicesData setEarth surface
The invention belongs to the technical field of surface flux observation data processing, and relates to a method for interpolating missing eddy flux observation data on the ground using an ALPHA invariant method. The method of the present invention includes: constructing the input data set required by the method; aiming at the target time period in which the eddy flux observation data is partially missing, calculating the latent heat flux, soil heat flux and The average value of net radiation; based on the Priestley-Taylor equation, according to the above average value, the average ALPHA value of the corresponding time period without missing time is obtained; based on the characteristic that ALPHA remains constant, the average ALPHA value is used as the ALPHA value at the time of data loss, according to The above equation and the surface energy balance equation interpolate the flux at the time when the ground eddy flux observation data is missing. It is of great significance for the rapid and accurate estimation and verification of latent heat flux and sensible heat flux by means of remote sensing.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS +1
Method and system for estimating evaporation representative of an area
This invention related to a method of and a system for estimating evaporation representing an area at a particular location The method comprises receiving air temperature information, using the received air temperature information to determine at least average air temperature, standard deviation of the air temperature, and skewness of the air temperature at the particular location, receiving soil heat flux information and net irradiance information indicative of soil heat flux and net irradiance at the particular location respectively, determining, sensible heat flux at the particular location by using at least the determined average air temperature, standard deviation of the air temperature, and skewness of the air temperature associated with the particular location, and determining an estimate of the evaporation at the particular location by using the determined sensible heat flux, received soil heat flux and net irradiance information.
Owner:UNIV OF KWAZULU NATAL
Crop biomass inversion method based on SEBAL-HJ model
ActiveCN102650587BImprove inversion accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansCyclic reductionEvaporation
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Remote Sensing Estimation Method and Device for Diurnal Variation Process of Surface Temperature
ActiveCN108829975BTroubleshoot difficult estimatesMeasurement devicesDesign optimisation/simulationHeat fluxVegetation Index
The present invention provides a remote sensing estimation method and device for the intraday variation process of the surface temperature, which relates to the technical field of surface temperature remote sensing inversion. Surface net radiation data and soil heat flux data at cloudless time, remote sensing surface temperature data and vegetation index data at cloudless time; calculate evapotranspiration at cloudless time and reference evapotranspiration at cloudless time in the target area based on the above data and reference evapotranspiration at cloudy time; calculate evapotranspiration at cloudy time based on evapotranspiration at cloudless time, reference evapotranspiration at cloudless time and reference evapotranspiration at cloudy time, and calculate surface sensible heat flux at cloudy time; Sensible heat flux calculates the surface temperature at cloudy moments. The remote sensing estimation method and device for the intraday variation process of the surface temperature provided by the embodiments of the present invention can use remote sensing means to quickly obtain the intraday variation process of the surface temperature under cloudy conditions.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS +1
A Mesoscale Numerical Simulation Method for Assessment of Climate Effects of Onshore Concentrated Photovoltaic Power Stations
ActiveCN113987823BSolve the problem of objective quantitative evaluationReduce high dependencyData processing applicationsDesign optimisation/simulationHeat fluxEngineering
The invention discloses a mesoscale numerical simulation method for climate effect assessment of land centralized photovoltaic power plants, including preprocessing of multi-source meteorological observation data of land centralized photovoltaic power plants; using comprehensive albedo and photoelectric conversion efficiency to conduct surface short-wave Radiative parameterization; direct and explicit numerical parameterization of sensible heat flux using wind speed, air density, and shortwave radiation; parameterization of latent heat flux, soil heat flux, and longwave radiation using differential contrast; dynamic roughness Parameterize the drag effect of photovoltaic panels; quantitatively evaluate the climate effect of photovoltaic power plants through sensitivity numerical simulation experiments. The invention solves the problem of objective and quantitative evaluation of the climate impact of large-scale photovoltaic power plants, and the simulation method has strong universality. Using this method, it is possible to carry out post-evaluation on the climate effect of the built photovoltaic power station, and to carry out pre-evaluation on the climate effect of the proposed power station, which provides a basis for the site selection and construction of climate-friendly power stations.
Owner:国家气候中心
A method and system for calculating evapotranspiration based on soil heat flux
ActiveCN112362693BAvoid dependenceSave construction management costsMaterial heat developmentEarth material testingHydrometryEarth surface
The invention discloses a method and system for calculating evapotranspiration based on soil heat flux, and belongs to the technical field of hydrological information forecasting. Including: obtaining the soil heat flux, surface temperature and surface air specific humidity of the target area through direct measurement by instruments or indirect calculation based on soil temperature and humidity parameters; The surface air specific humidity is input into the maximum entropy-increased evapotranspiration model, and the latent heat flux is obtained by simultaneous solution; based on the unit conversion, the latent heat flux is converted into the evapotranspiration of the target area. The invention uses the soil heat flux to measure and calculate the evapotranspiration value. By obtaining the soil heat flux instead of the net radiation item as the input of the maximum entropy increase evapotranspiration model, it avoids the dependence on the observation of radiation energy, and overcomes the difficulty of obtaining the net radiation variable, which is difficult to measure. The disadvantages of high cost and unclear error make the calculation of evapotranspiration simple and reliable.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com