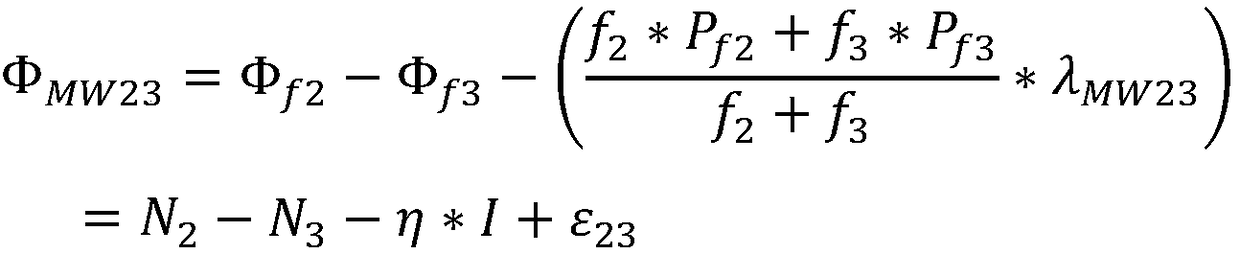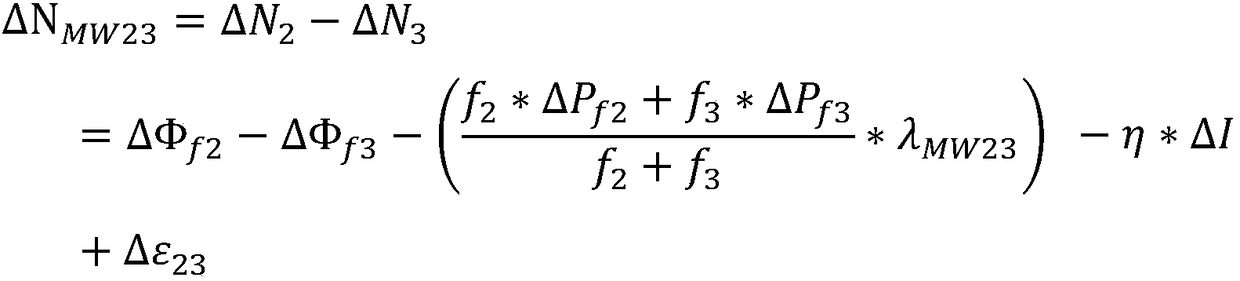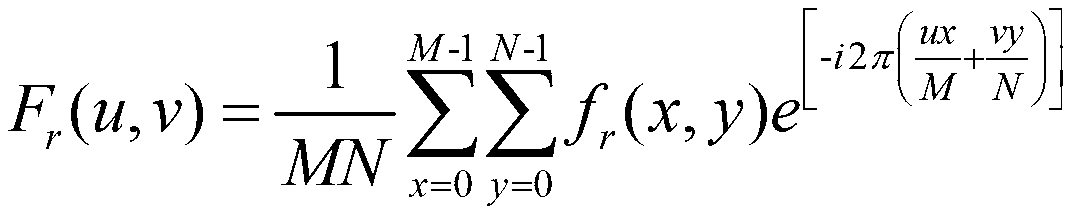Patents
Literature
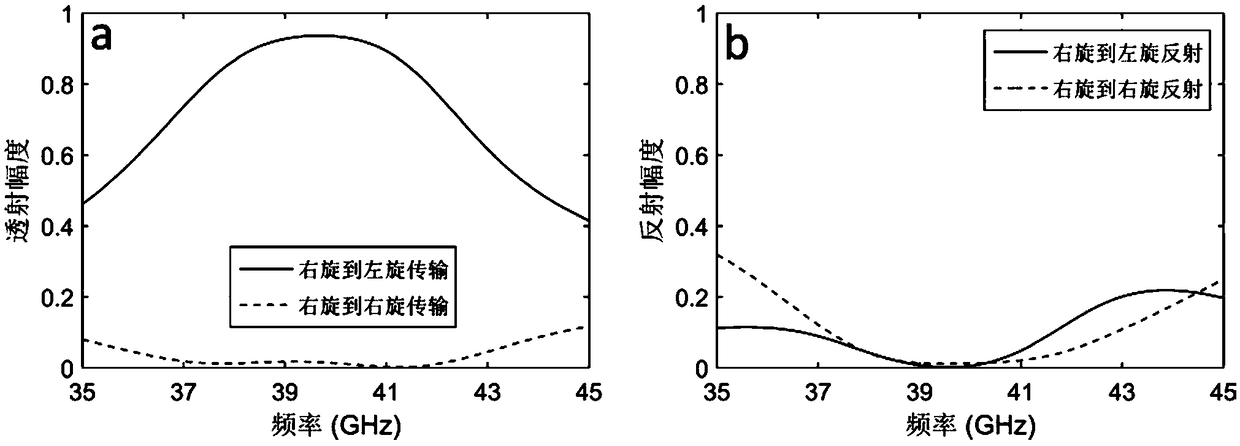
41 results about "Geometric phase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In classical and quantum mechanics, the geometric phase is a phase difference acquired over the course of a cycle, when a system is subjected to cyclic adiabatic processes, which results from the geometrical properties of the parameter space of the Hamiltonian. The phenomenon was independently discovered by S. Pancharatnam (1956) and by H. C. Longuet-Higgins (1958) and later generalized by Sir M. Berry (1984). It is also known as the Pancharatnam–Berry phase, Pancharatnam phase, or Berry phase. It can be seen in the Aharonov–Bohm effect and in the conical intersection of potential energy surfaces. In the case of the Aharonov–Bohm effect, the adiabatic parameter is the magnetic field enclosed by two interference paths, and it is cyclic in the sense that these two paths form a loop. In the case of the conical intersection, the adiabatic parameters are the molecular coordinates. Apart from quantum mechanics, it arises in a variety of other wave systems, such as classical optics. As a rule of thumb, it can occur whenever there are at least two parameters characterizing a wave in the vicinity of some sort of singularity or hole in the topology; two parameters are required because either the set of nonsingular states will not be simply connected, or there will be nonzero holonomy.
Phase arrays exploiting geometry phase and methods of creating such arrays
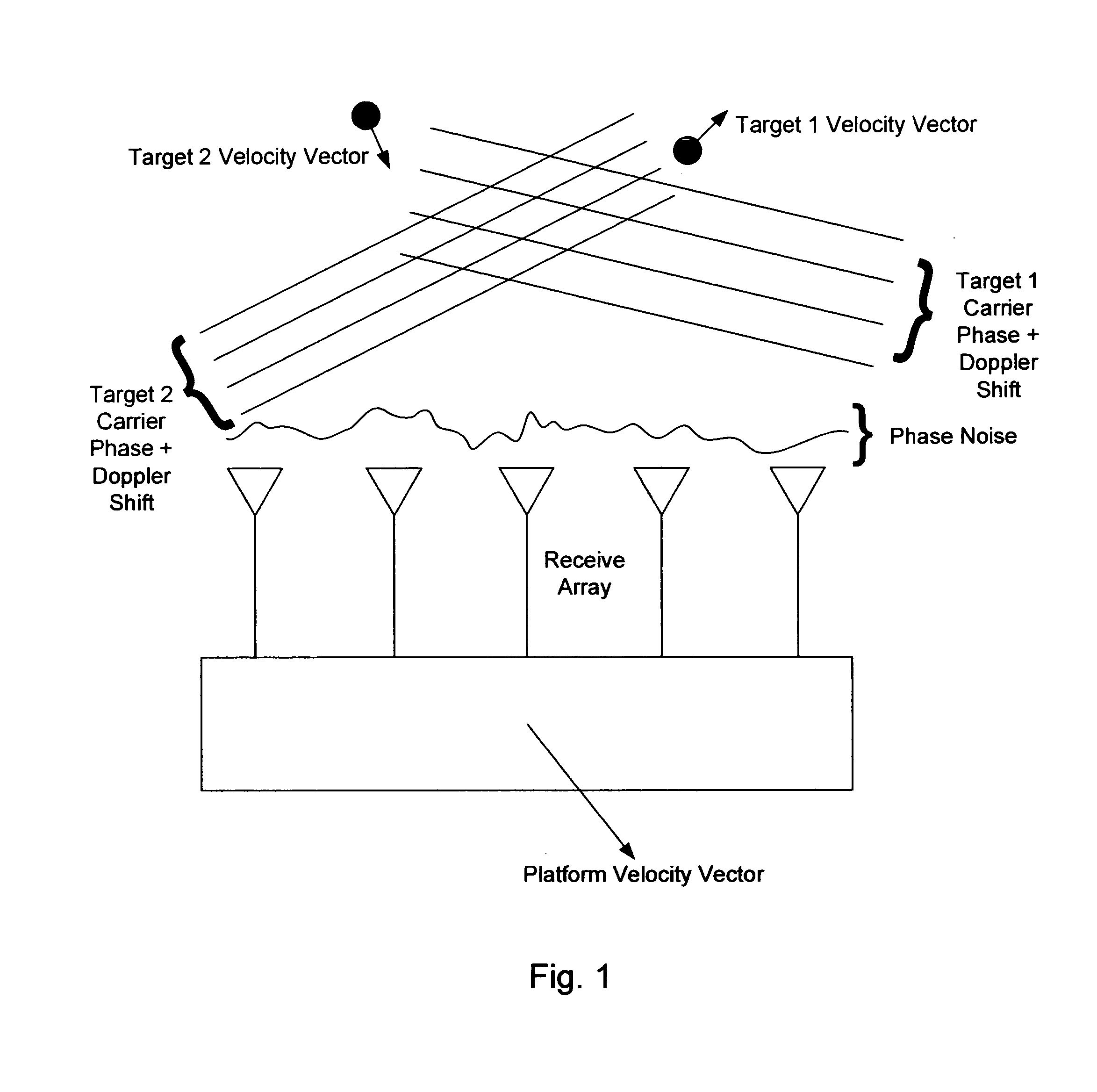
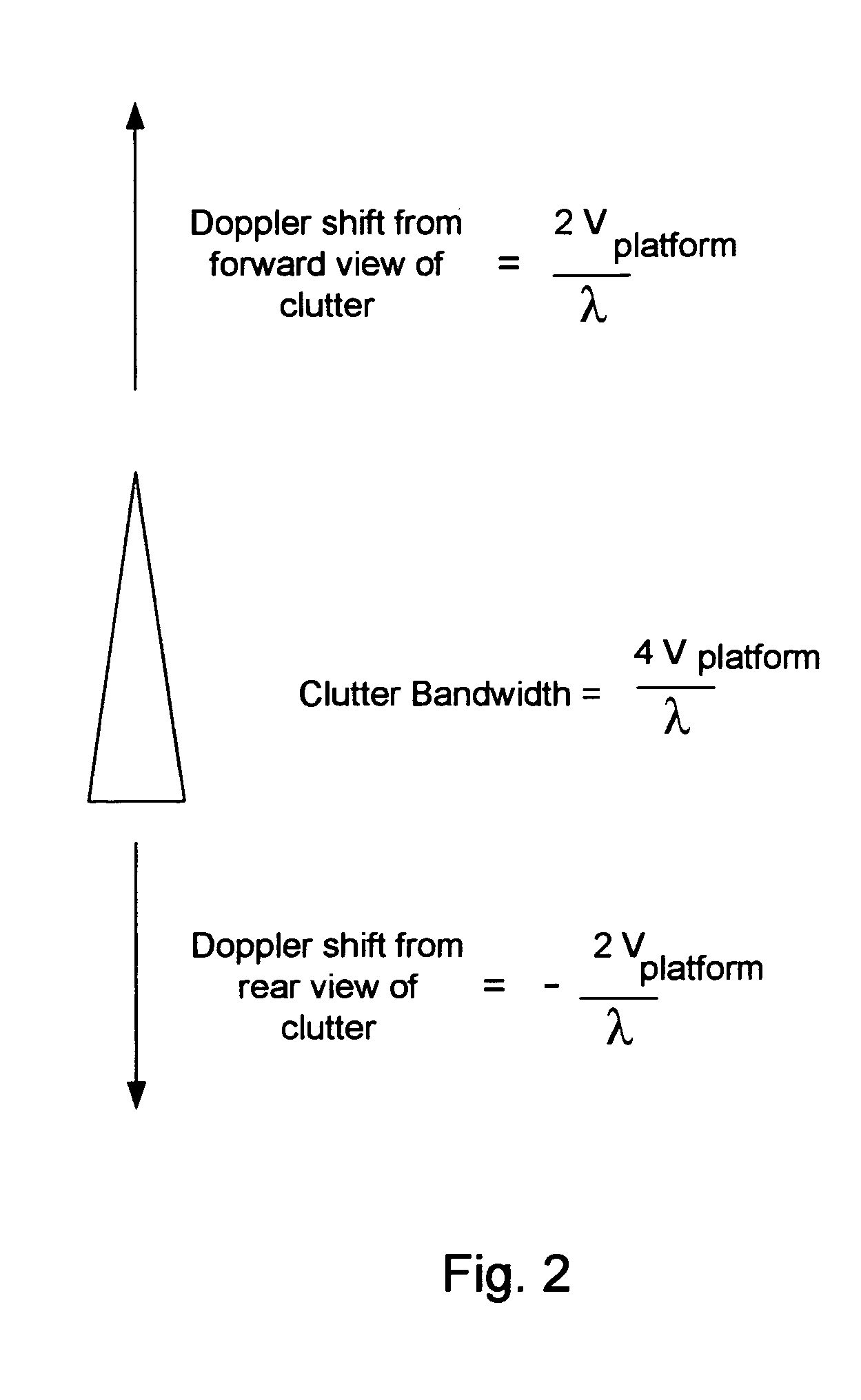
InactiveUS20070285315A1Reduce couplingMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesBeacon systemsEngineeringArray element
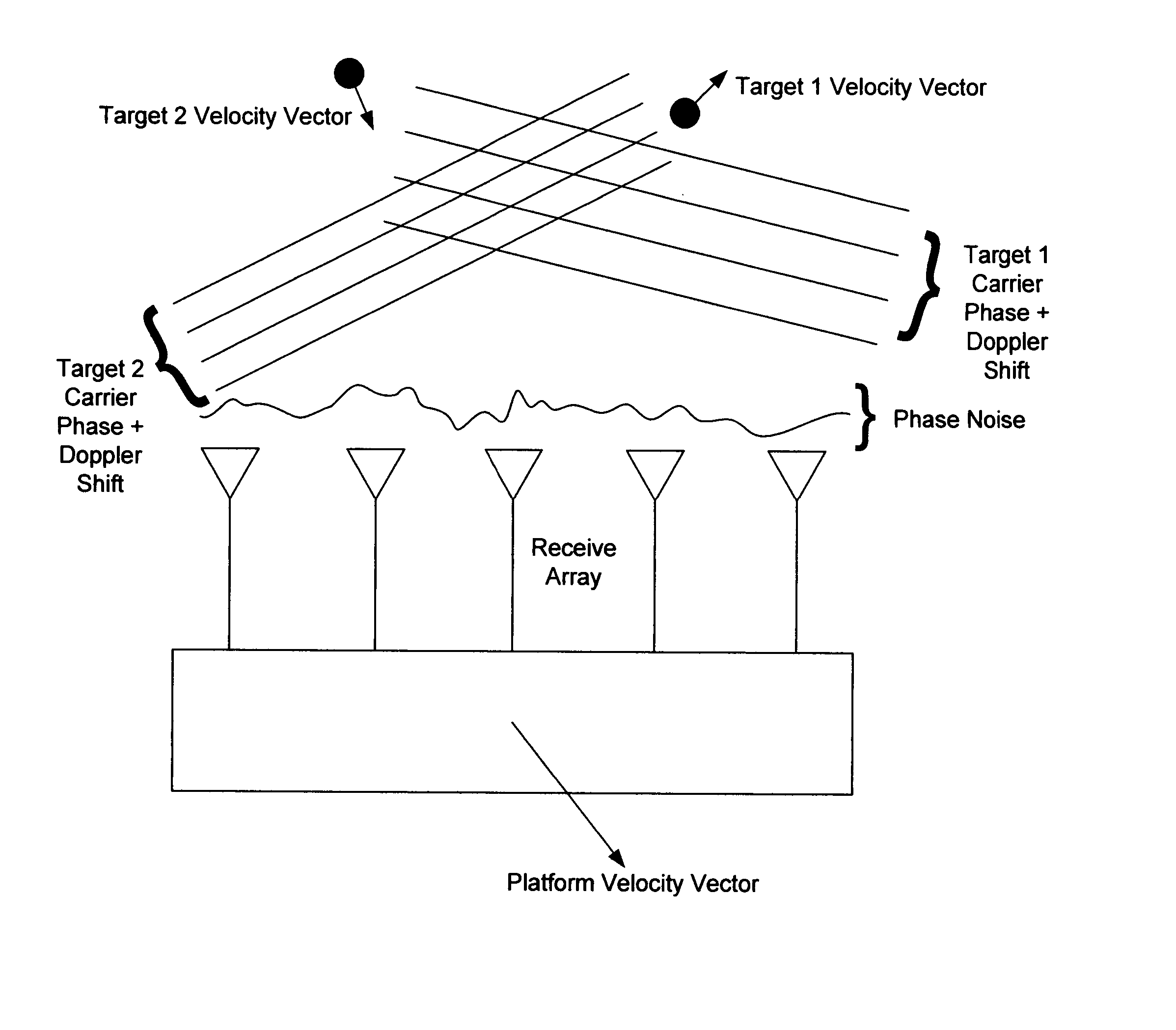
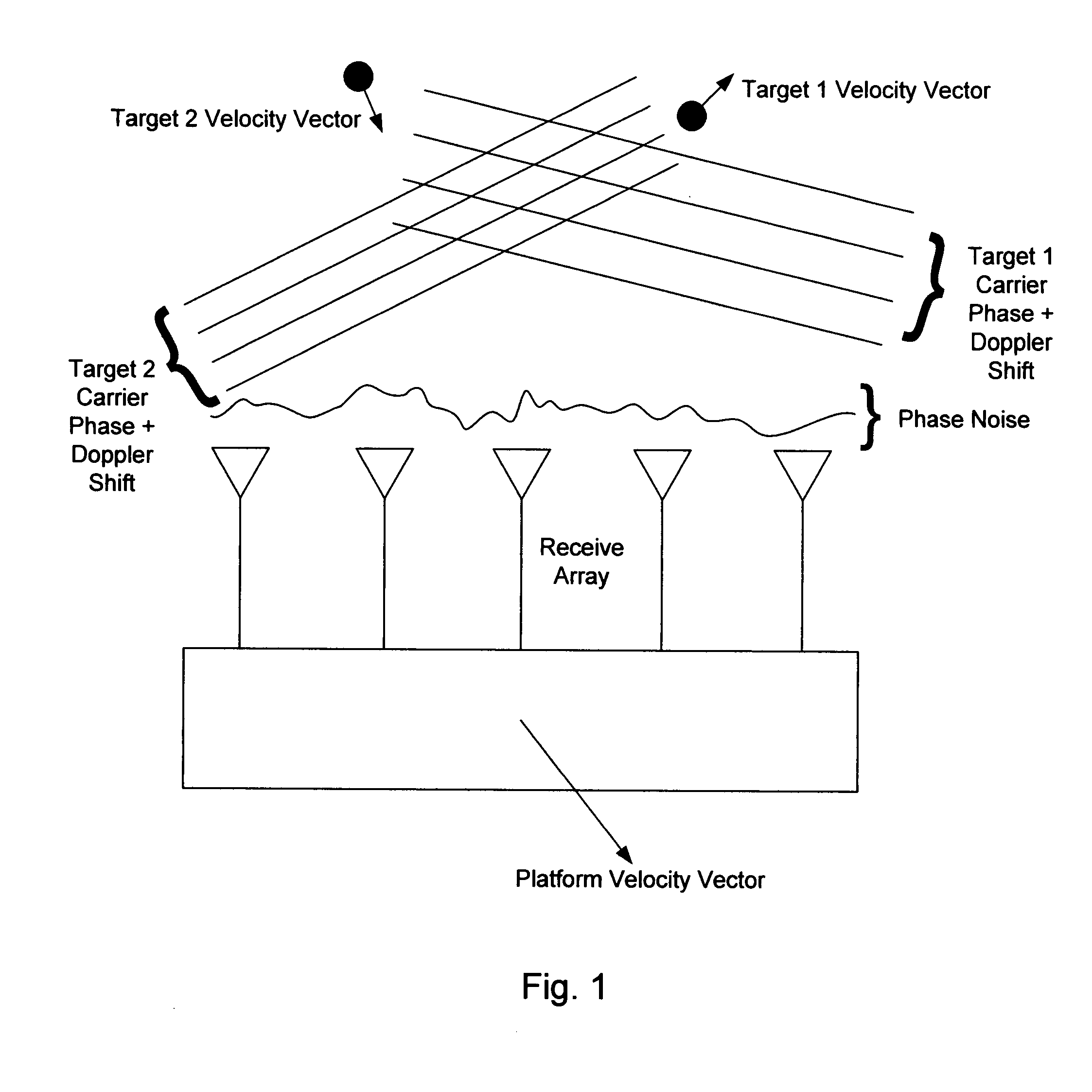
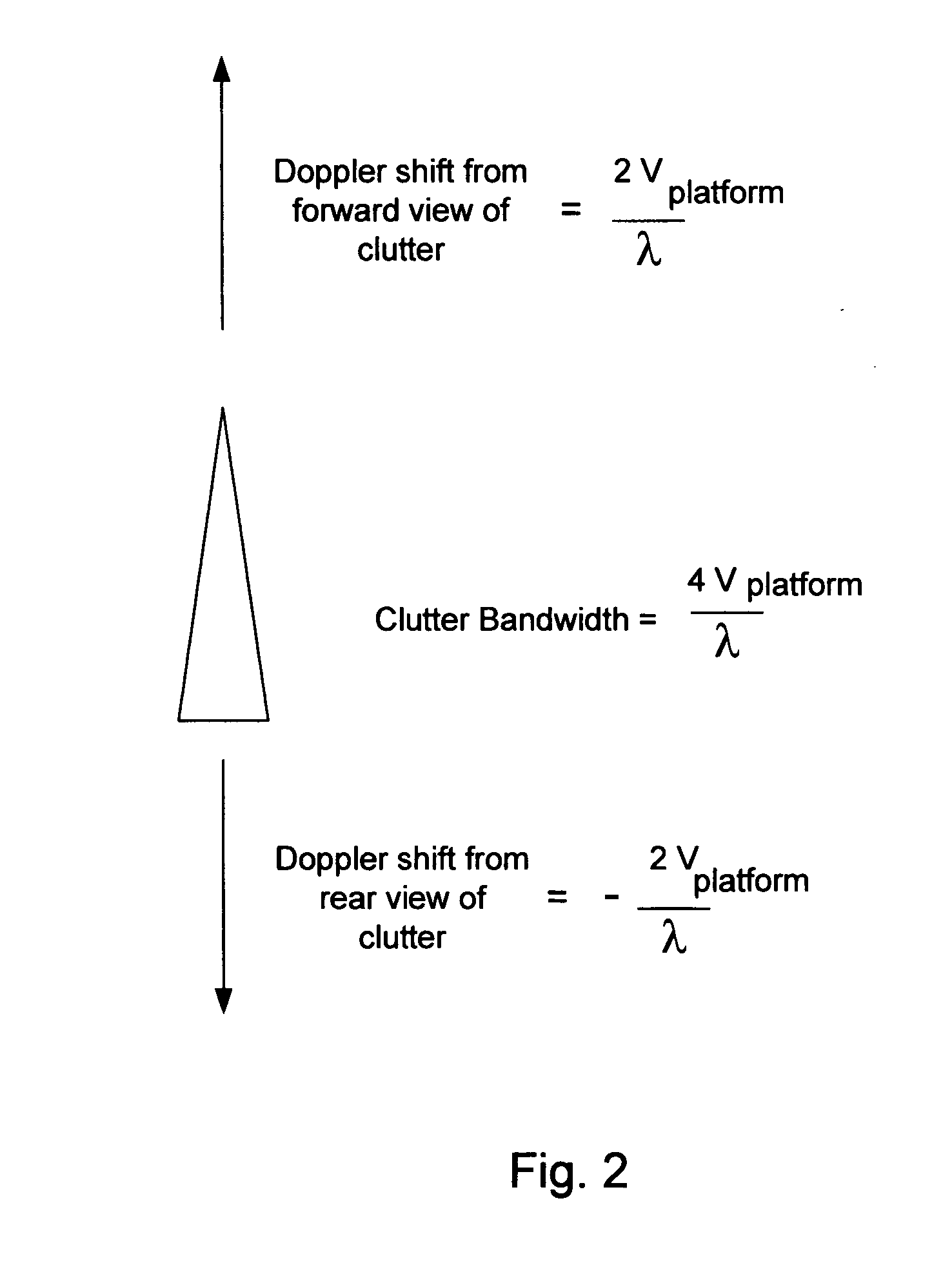
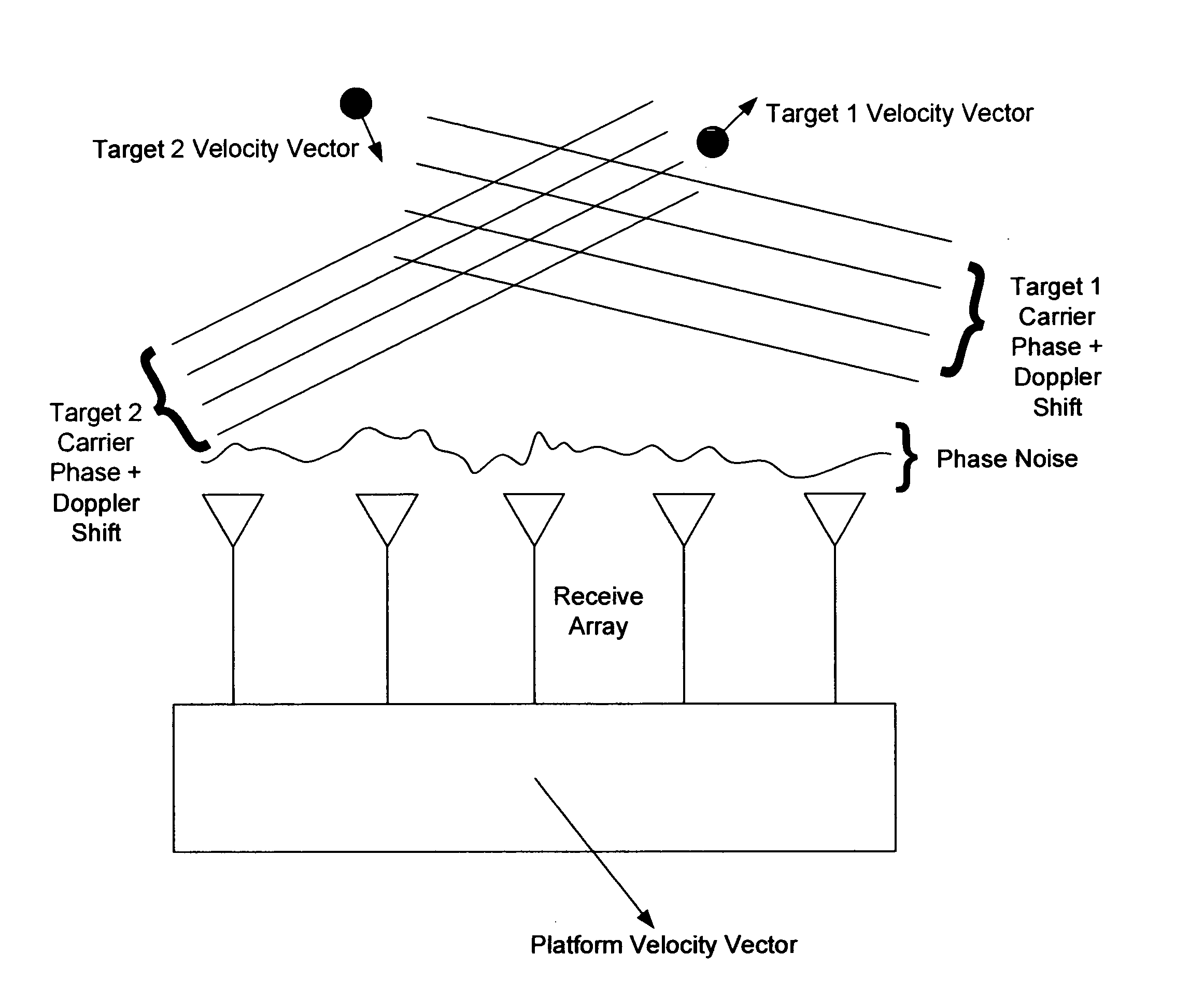
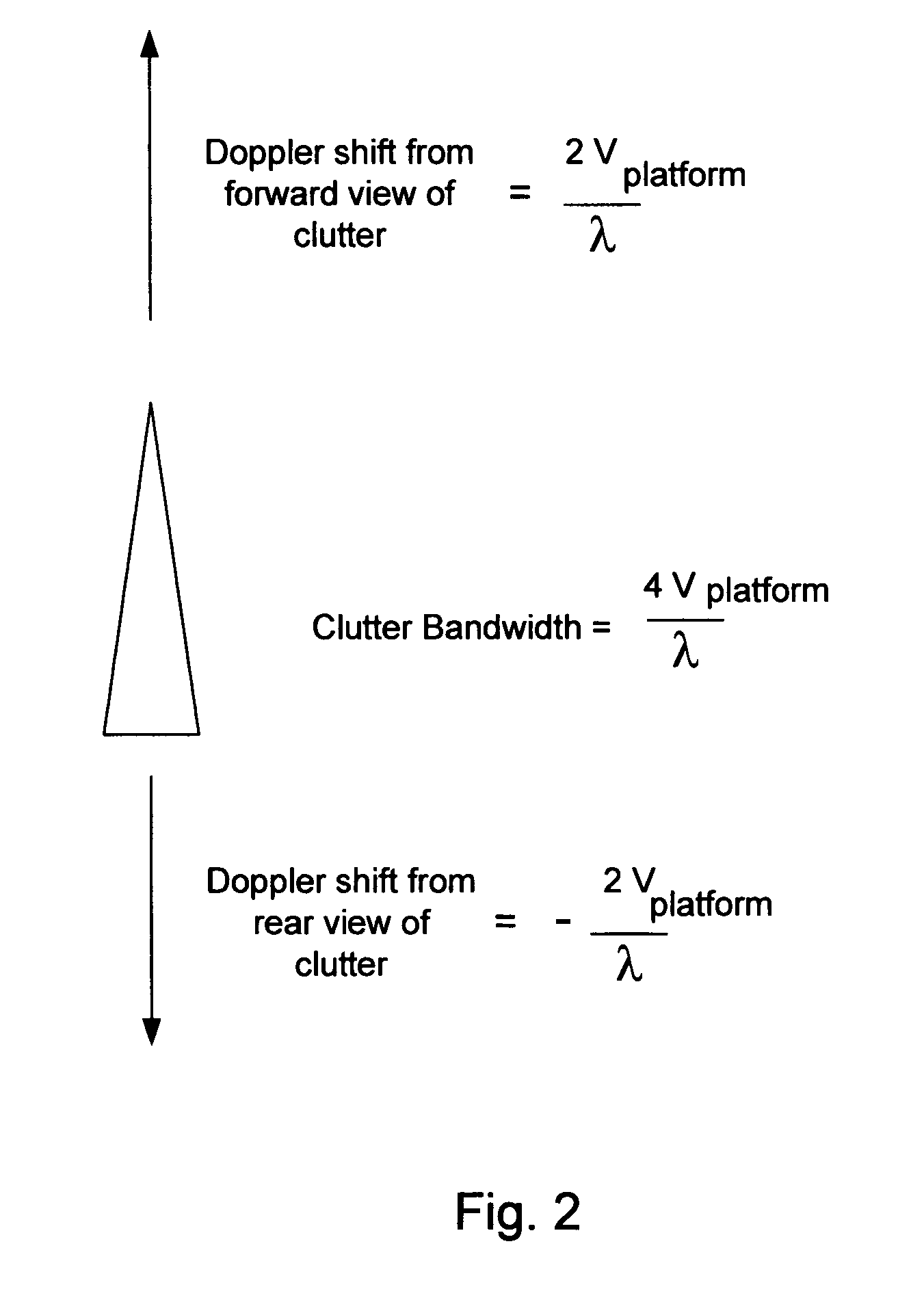
In the context of array sensors such as radar, sonar, and communications receiver arrays, the present invention exploits the geometry phase components of radiated wavefronts associated with the signals of interest in order to reduce the bandwidth requirements for DOA and beamforming processing. Additionally, geometry phase is exploited in order to effectively increase the resolution of an array without changing the size of its physical footprint or the number of array elements. Other embodiments of the invention include the use of virtual array elements for increase in effective array size.
Owner:DAVIS DENNIS WILLARD +2
Phased arrays exploiting geometry phase and methods of creating such arrays
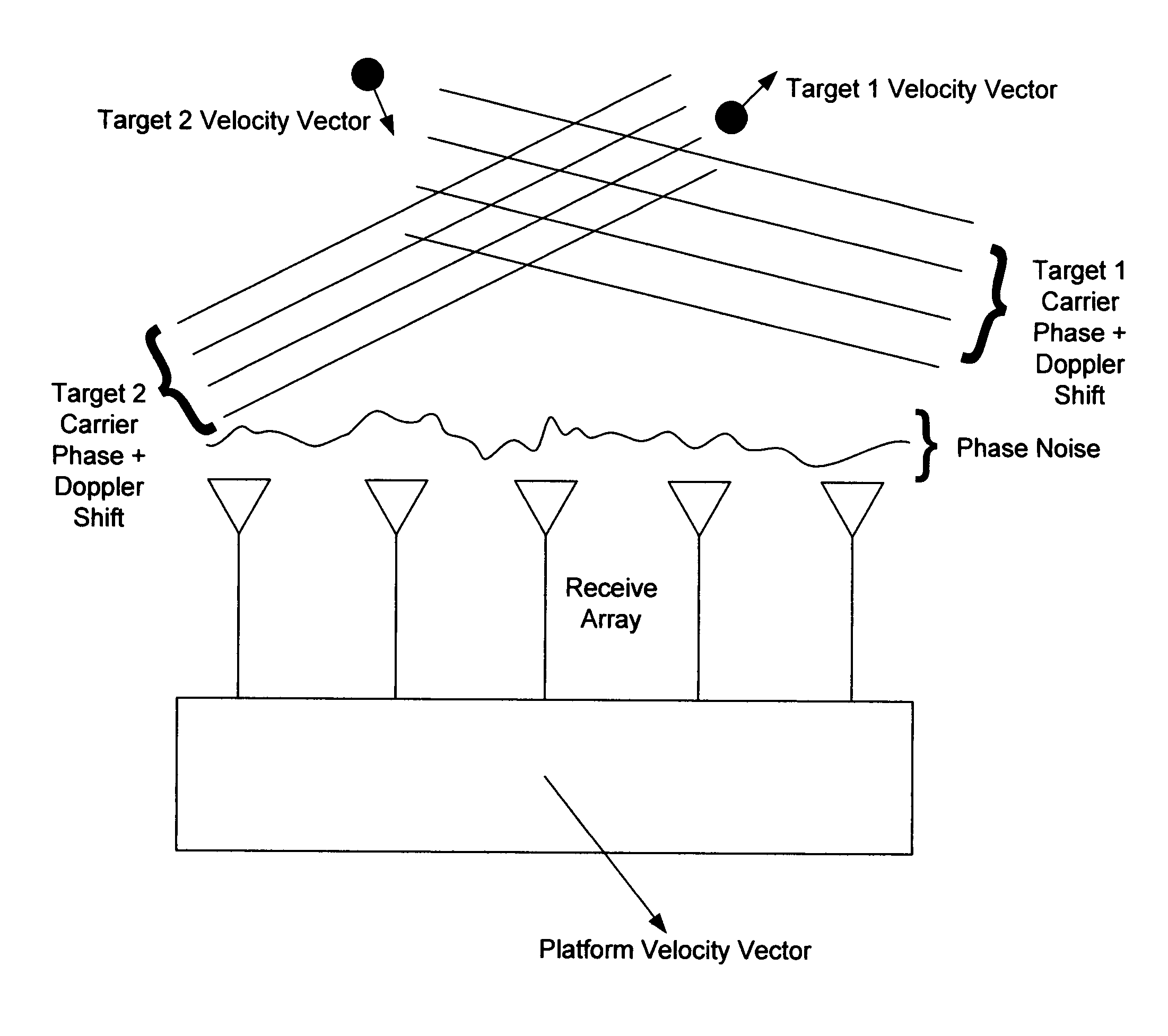
InactiveUS20050195103A1Reduce couplingMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesBeacon systemsSonarWavefront
In the context of array sensors such as radar, sonar, and communications receiver arrays, the present invention exploits the geometry phase components of radiated wavefronts associated with the signals of interest in order to reduce the bandwidth requirements for DOA and beamforming processing. Additionally, geometry phase is exploited in order to effectively increase the resolution of an array without changing the size of its physical footprint. Other embodiments of the invention include the use of virtual array elements for increase in effective array size.
Owner:DAVIS DENNIS WILLARD +2
Phase arrays exploiting geometry phase and methods of creating such arrays
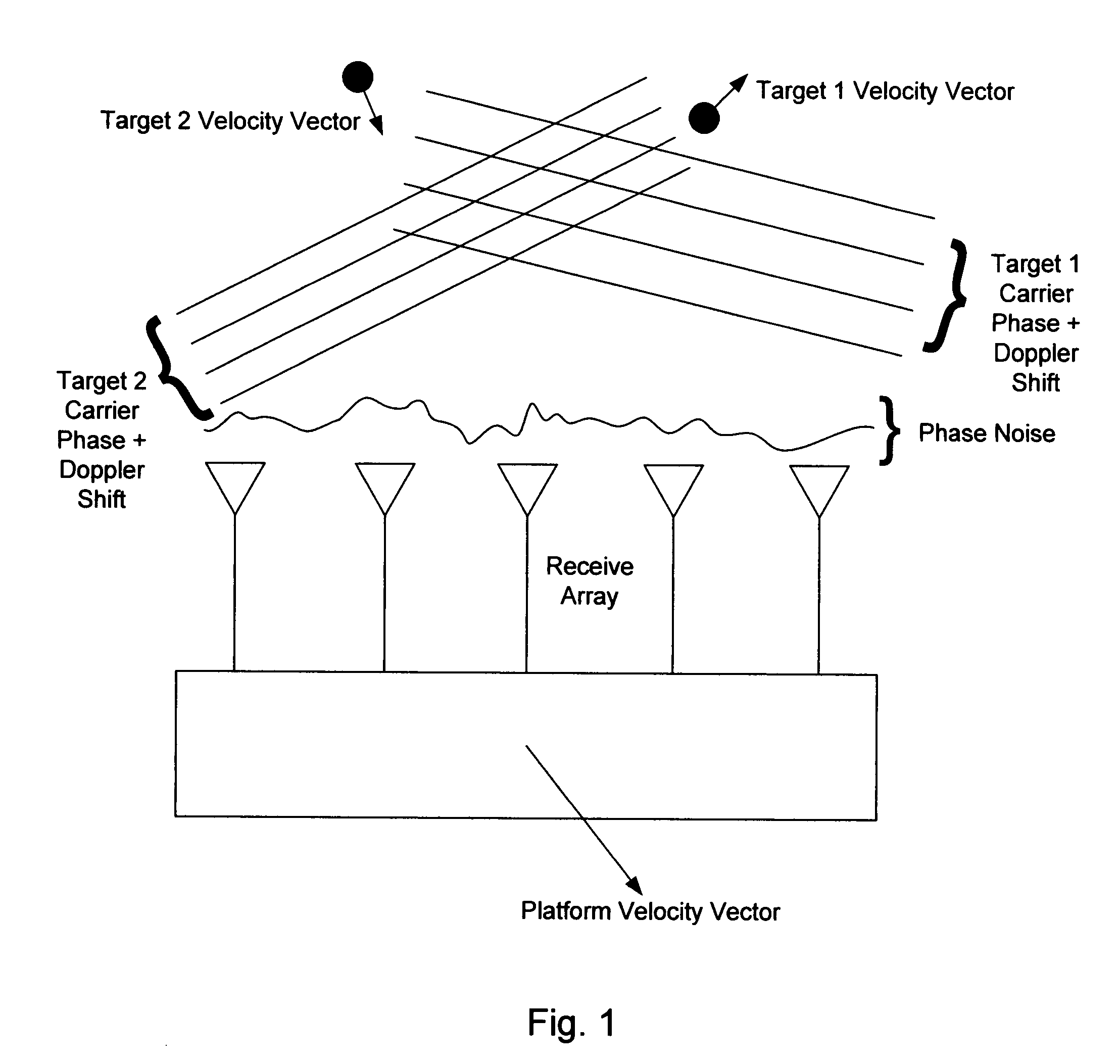
InactiveUS7714782B2Multi-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesBeacon systemsEngineeringArray element
Owner:DAVIS DENNIS WILLARD +2
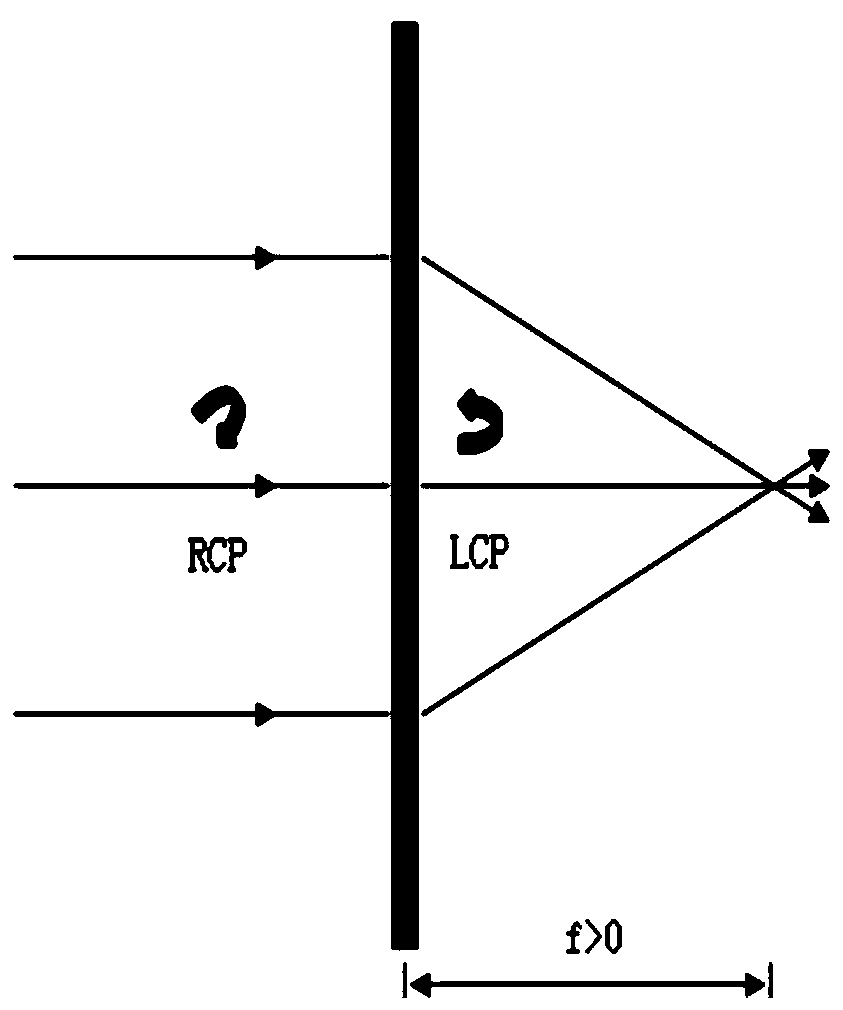
Liquid crystal geometrical phase optical elements and a system for generating and rapidly switching helical modes of an electromagnetic wave, based on these optical elements
InactiveUS8264623B2Easy to controlUniform and very small thicknessNon-linear opticsOptical radiationWavefront
Geometrical phase optical elements comprising, as a birefringent means, a liquid crystal material with a spatially inhomogeneous orientation of the molecular director in a plane orthogonal to the direction of propagation of an input radiation beam, ordered according to a predetermined geometrical pattern. Also, an optical system for generating helical modes of propagation of an optical radiation beam, including a geometrical phase optical element orientated transversely to the direction of propagation of the beam, whose optical axis is orientated according to a predetermined geometrical relation adapted to transform a circular polarized input radiation beam into a helical mode with a wavefront having a helical surface whose handedness is a function of the handedness of the input polarization, in which the switching between different orders of helicity of the radiation beam emerging from the geometrical phase optical element is carried out by switching the circular polarization state of the input radiation.
Owner:CONSIGLIO NAT DELLE RICERCHE
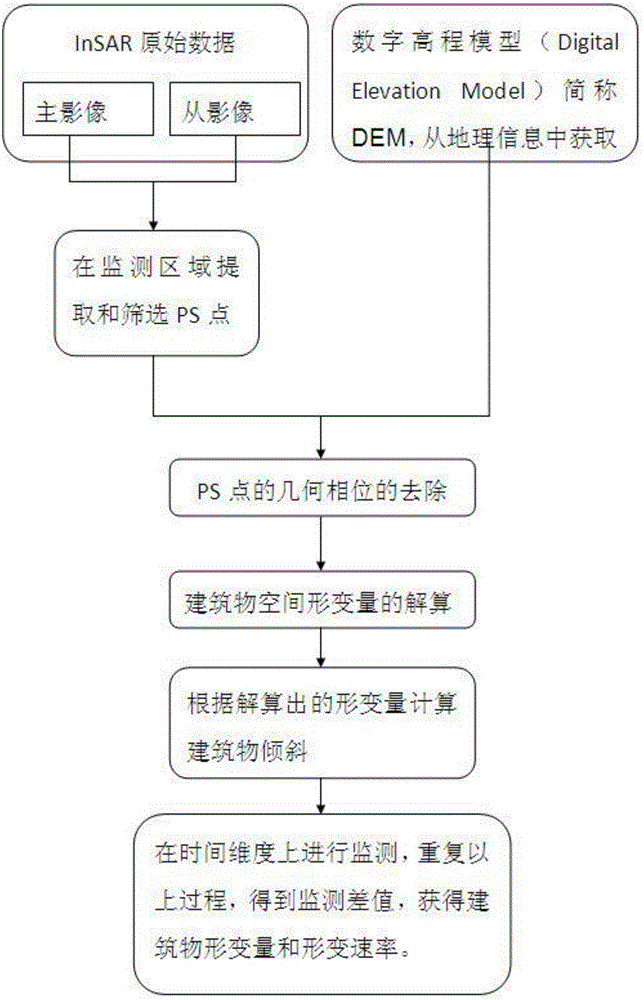
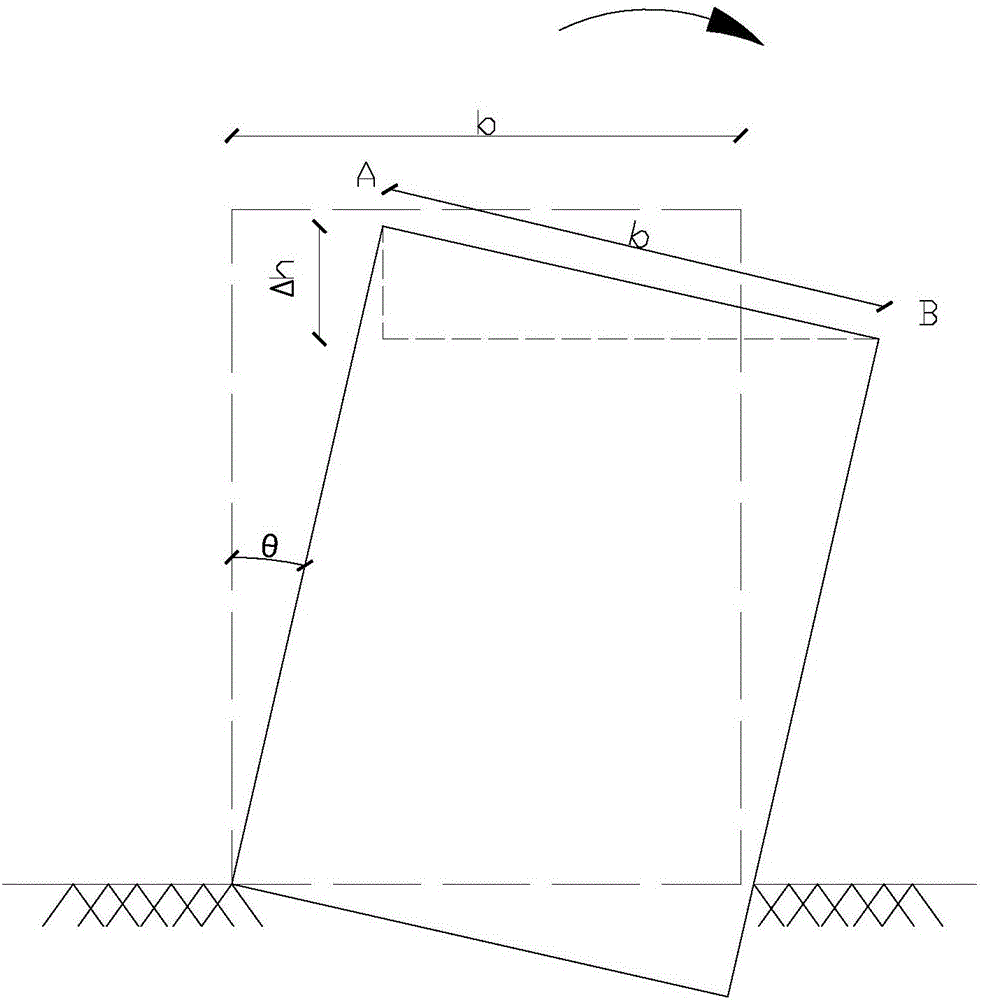
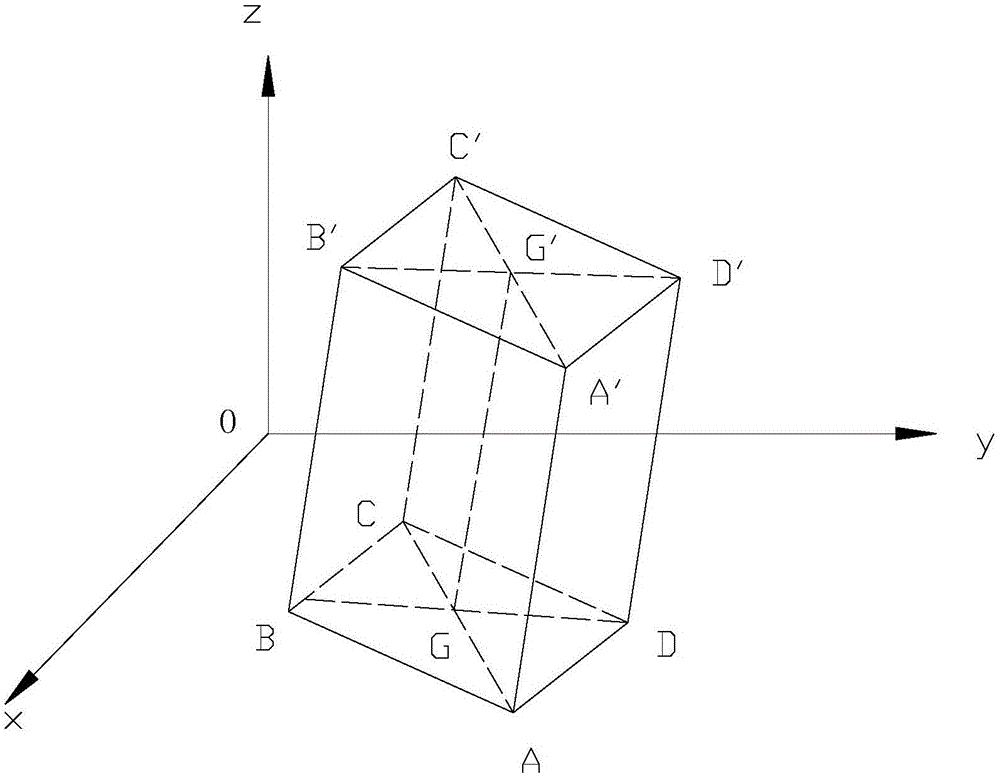
Building deformation monitoring method based on InSAR
InactiveCN106772377AAccelerated deformation warningLow costHeight/levelling measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansRadarOriginal data
The invention relates to a building deformation monitoring method based on InSAR. The method includes the following steps that S1, InSAR original data is screened; S2, PS points are extracted and screened in a monitored region; S3, geometric phase positions of the PS points are removed; S4, the space deformation quantity of a building is solved; S5, according to the solved deformation quantity, the gradient of the building is calculated; S6, monitoring is carried out on time dimension, the steps are repeated, a monitoring differential value is obtained, and the deformation quantity and deformation rate of the building are obtained. By the utilization of the InSAR technology, the deformation field of the building in the direction of a radar sight line is obtained, spatial interpolation is carried out on pixels in the deformation field in the direction of the radar sight line, wherein the coherence of the pixels is lower than an untwisting threshold value, and therefore a spatial continuous deformation field is obtained; by processing and calculating obtained data, the deformation and deformation rate of the building are obtained. The method is large in range and low in cost and easily monitors the building for a long term during monitoring of the building, and can effectively make early warning for accelerated deformation of the building.
Owner:SHENZHEN ROAD & BRIDGE CONSTR GRP
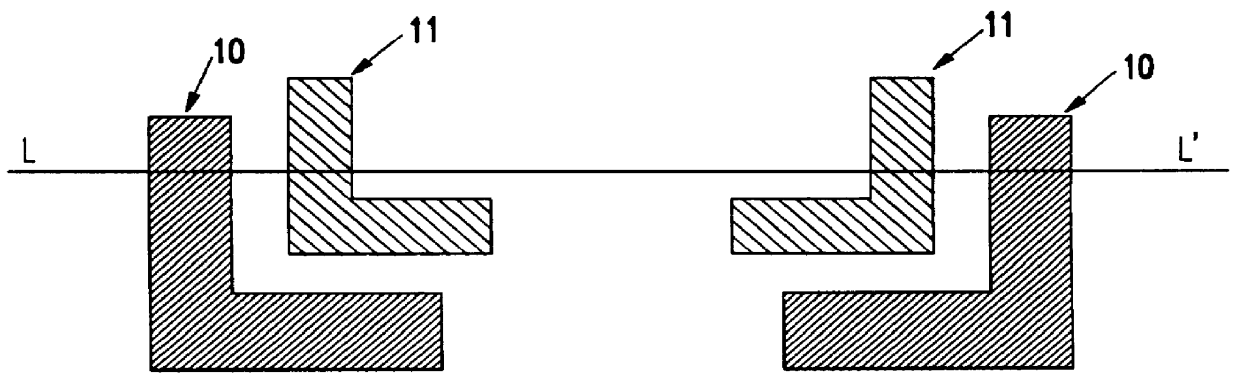
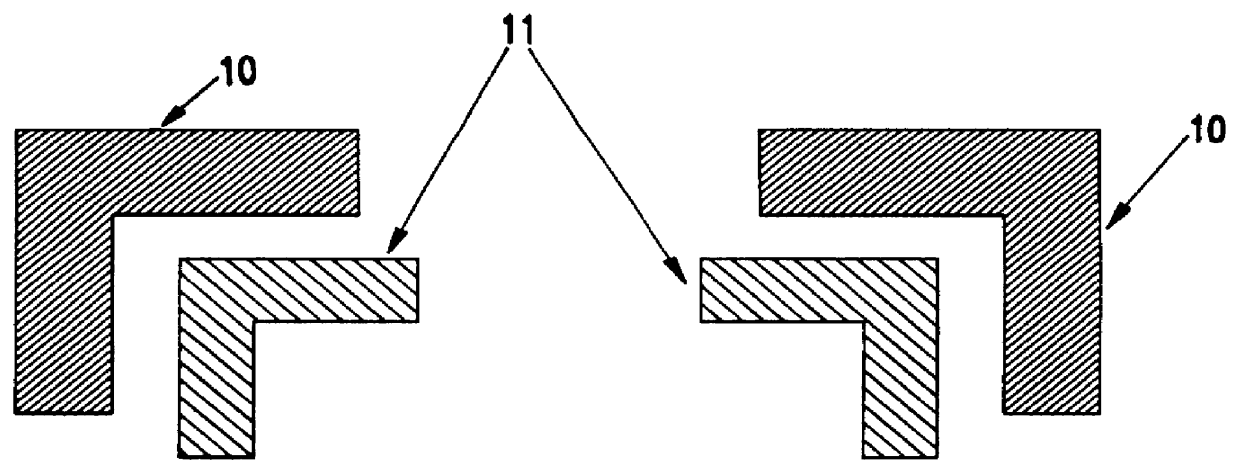
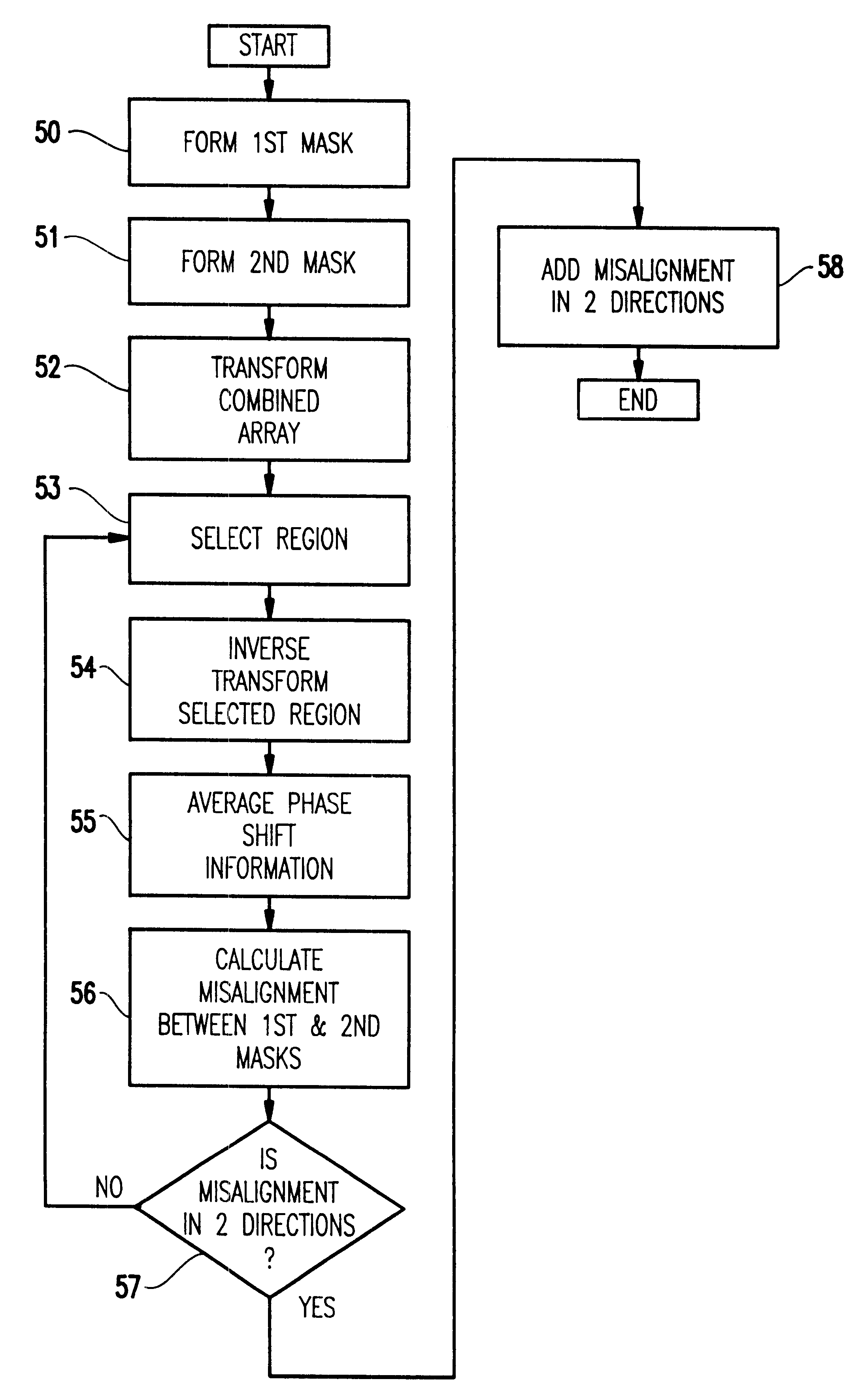
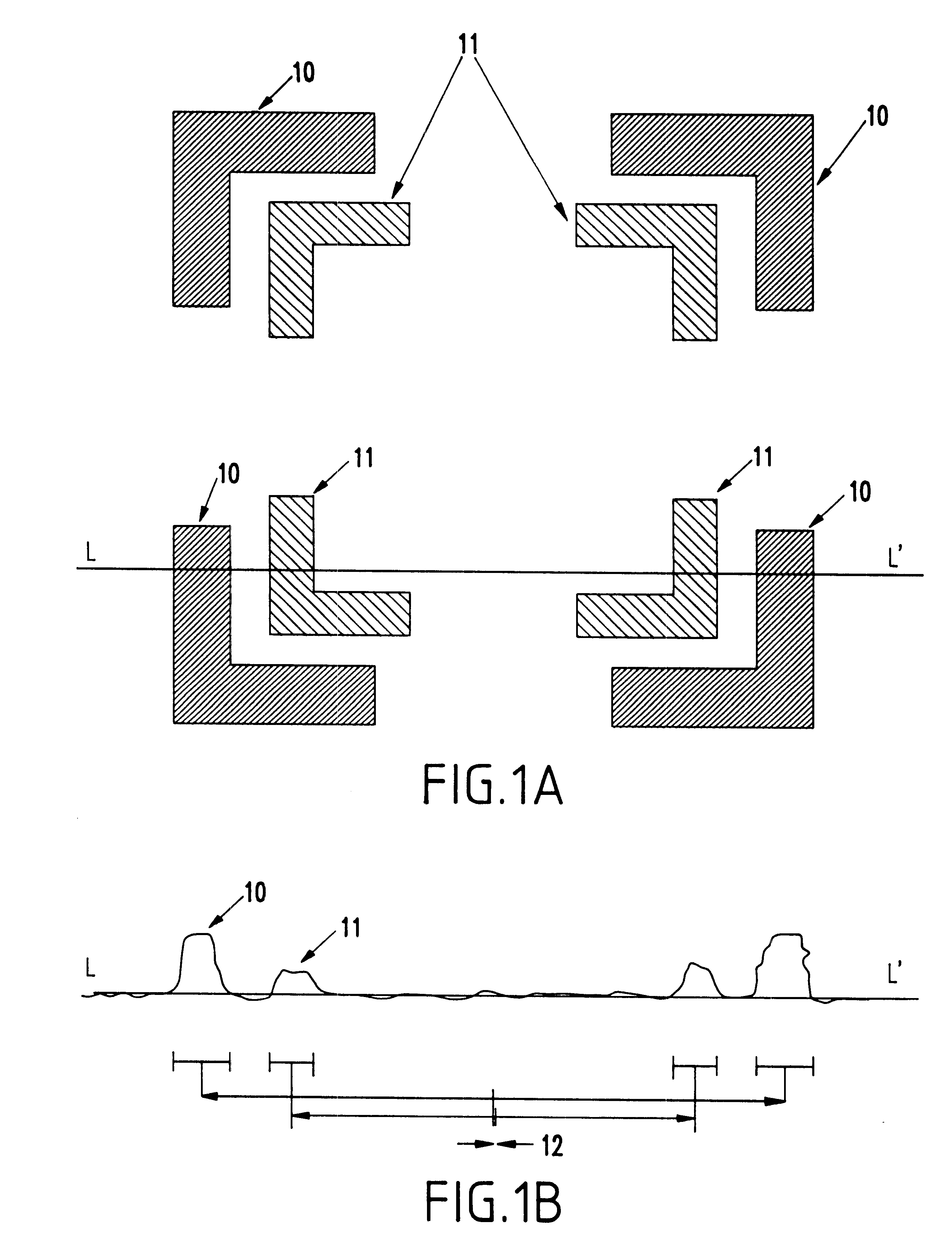
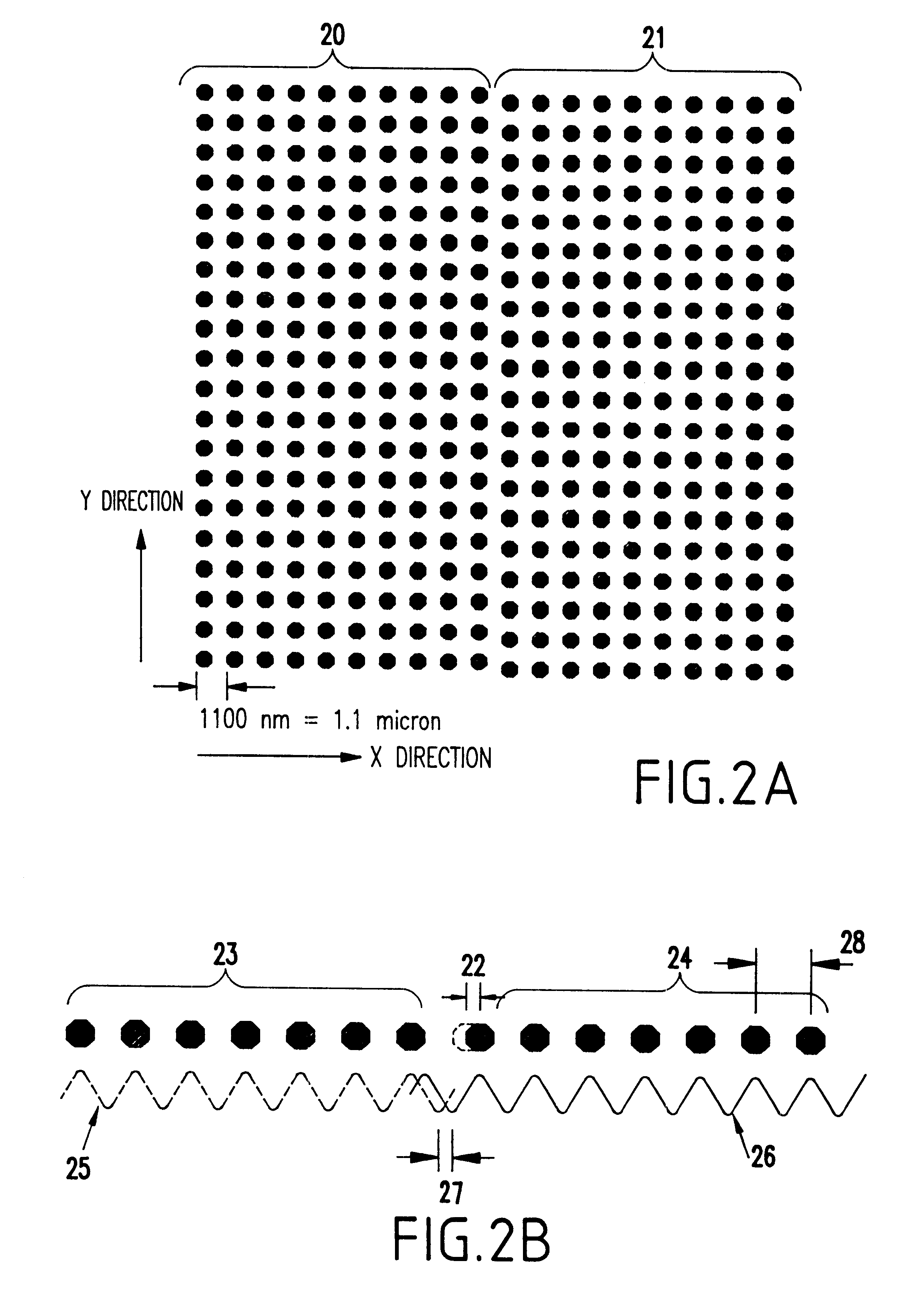
Geometric phase analysis for mask alignment
A method of measuring overlay error comprises forming a first mask having a first alignment array comprising a periodic pattern of first features having a first periodicity, forming a second mask having a second alignment array comprising a pattern of second features having the first periodicity, the first alignment array being adjacent the second alignment array, the first alignment array and the second alignment array forming a combined alignment array, transforming the combined alignment array to produce a transformed array, selecting a first region within the transformed array, inverse transforming the region to produce geometric phase shift information, averaging the phase shift information, converting the averaged phase shift information into a value for misalignment in a first direction corresponding to the first region, repeating the selecting, inverse transforming, averaging and converting using a second region within the transformed array to calculate a value for misalignment in a second direction corresponding to the second region, calculating an overlay error between the first and second mask levels by adding the components of misalignment in the first direction and second direction.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Geometric phase analysis for overlay measurement
A method of measuring overlay error comprises forming a first mask having a first alignment array comprising a periodic pattern of first features having a first periodicity, forming a second mask having a second alignment array comprising a pattern of second features having the first periodicity, the first alignment array being adjacent the second alignment array, the first alignment array and the second alignment array forming a combined alignment array, transforming the combined alignment array to produce a transformed array, selecting a first region within the transformed array, inverse transforming the region to produce geometric phase shift information, averaging the phase shift information, converting the averaged phase shift information into a value for misalignment in a first direction corresponding to the first region, repeating the selecting, inverse transforming, averaging and converting using a second region within the transformed array to calculate a value for misalignment in a second direction corresponding to the second region, calculating an overlay error between the first and second mask levels by adding the components of misalignment in the first direction and second direction.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
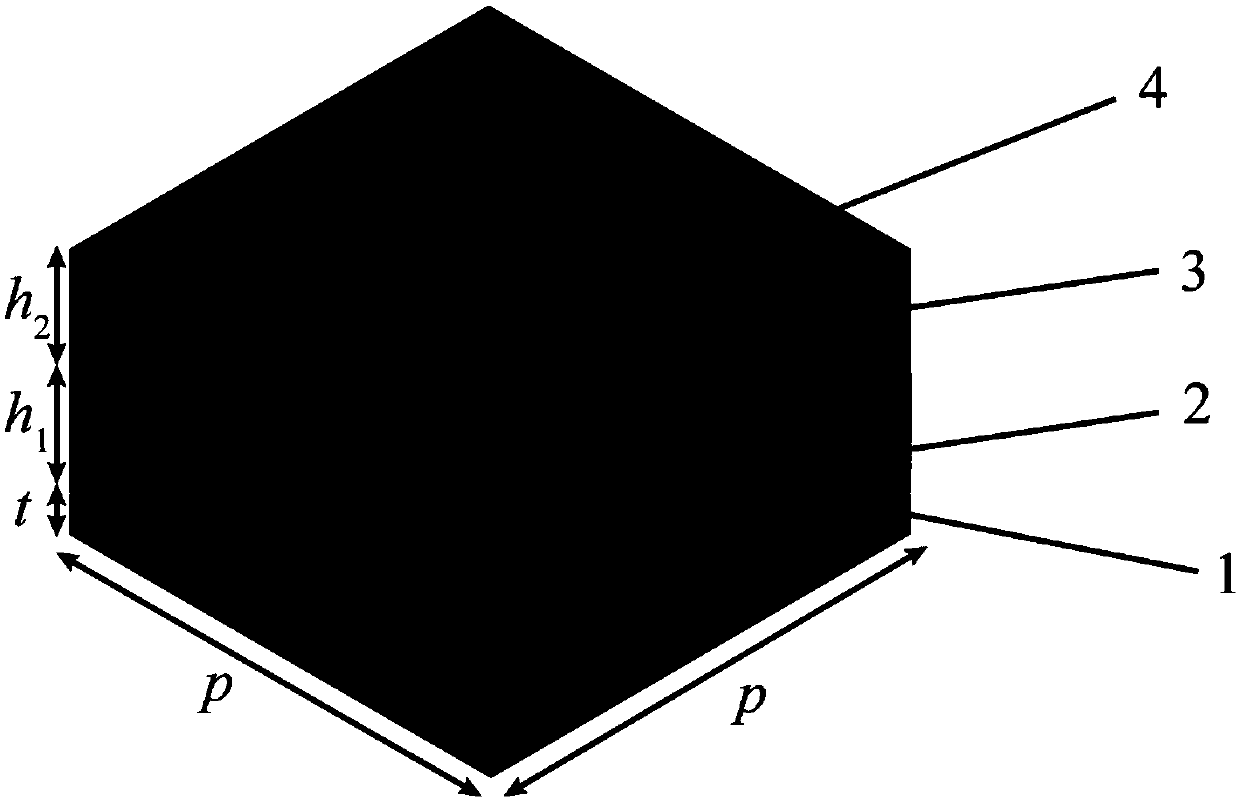
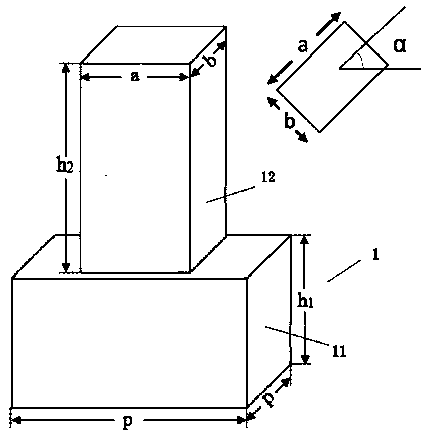
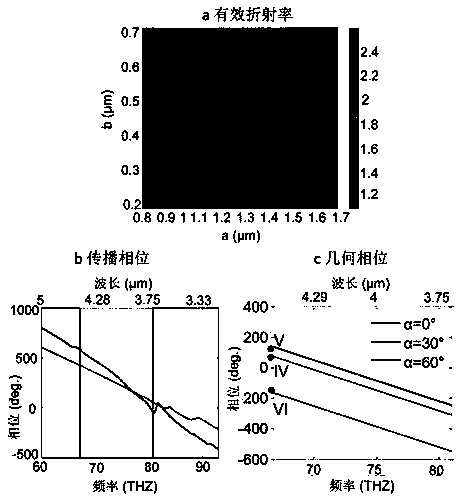
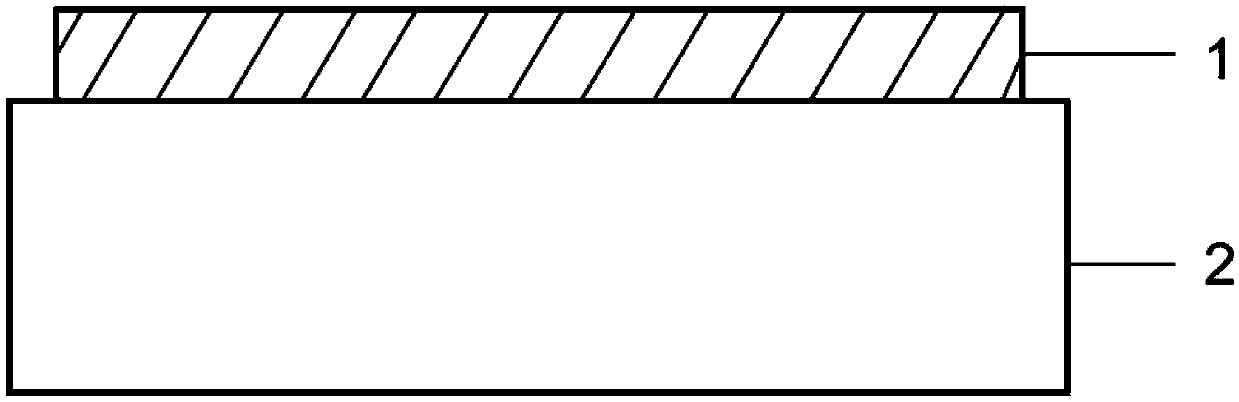
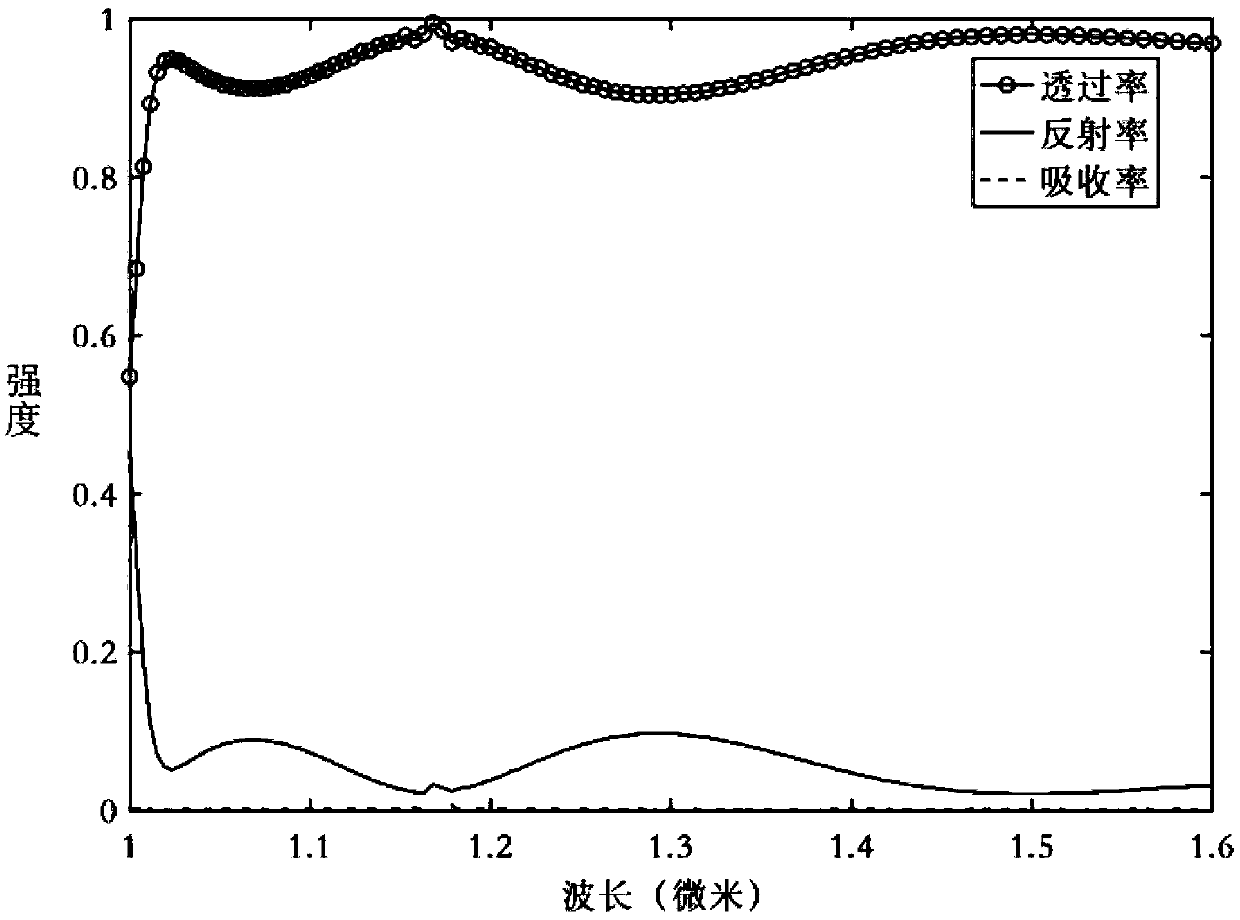
Dielectric geometric phase metasurface material with low depth-to-width ratio and structural optimization method thereof
InactiveCN108490509AGuaranteed YieldLow processing technology requirementsNon-linear opticsOptical elementsDielectricBrick
The invention discloses a dielectric geometric phase metasurface structure material with a low depth-to-width ratio and a structural optimization method thereof. The dielectric geometric phase metasurface structure material comprises a substrate, a reflecting layer on the substrate, a multi-beam interference layer on the reflecting layer and a dielectric nano brick array formed by periodically arranging a plurality of dielectric nano bricks with consistent sizes on the multi-beam interference layer, wherein the dielectric nano brick array is used for receiving perpendicularly incident circularly polarized light and adjusting the phase of the emergent light through adjusting the direction of each dielectric nano brick. The depth-to-width ratio of the dielectric geometric phase metasurface structure material is reduced to half of the depth-to-width ratio of the traditional transmission-type metasurface material, and the depth-to-width ratio is about 1.7, so that the requirements for theprocessing technology are reduced, and the finished product rate and mass production of the device are guaranteed.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
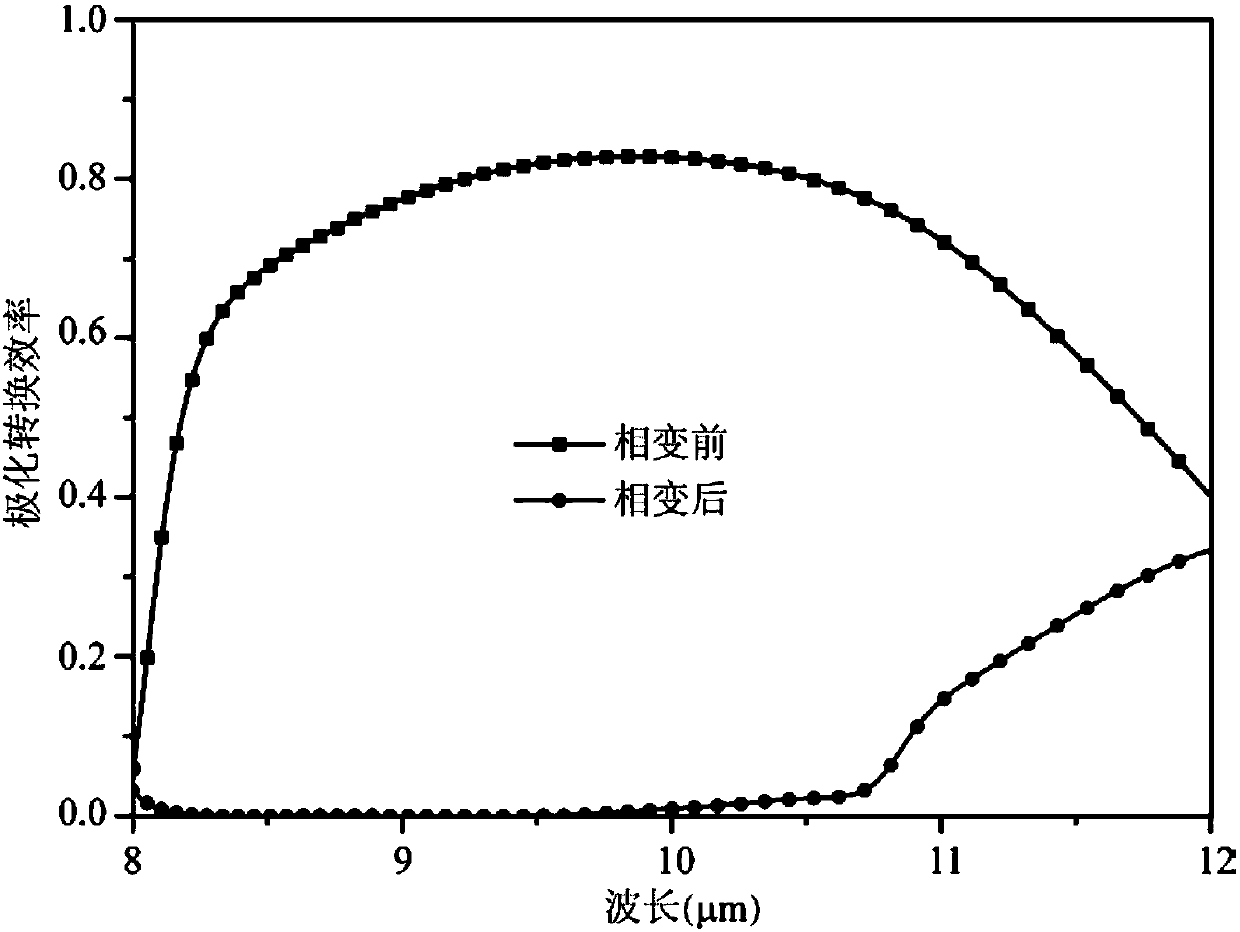
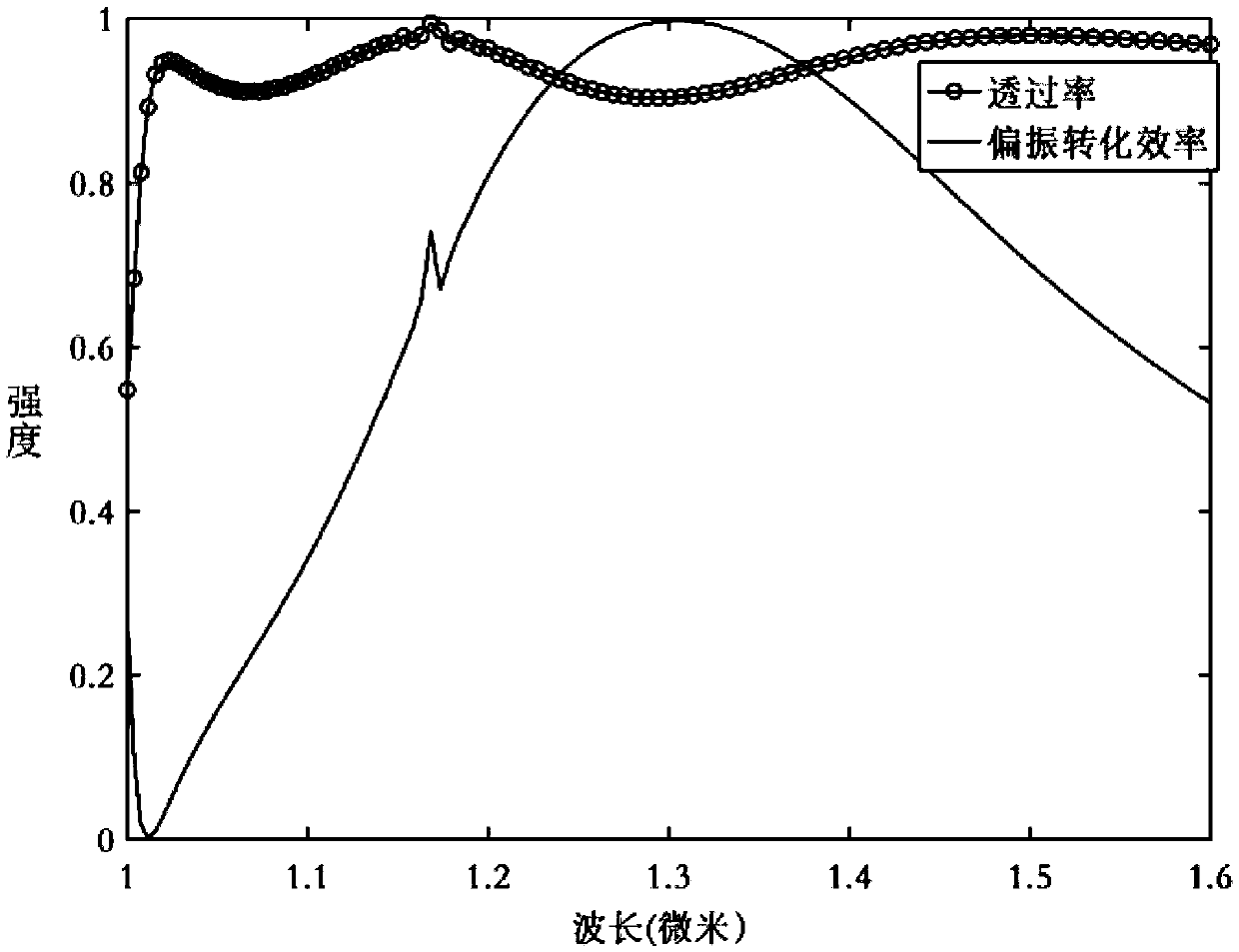
Adjustable broadband polarization conversion and dynamic geometric phase modulation device based on phase change material
ActiveCN107831607AWorking bandwidthReduce quality problemsNon-linear opticsOptical polarizationDynamic modulation
The invention provides an adjustable broadband polarization conversion and dynamic geometric phase modulation device based on phase change material, comprising a metal reflecting layer, a phase changematerial layer, a dielectric isolation layer and a super surface structural layer sequentially from bottom to top. The design of the polarization conversion and geometric phase modulation device is carried out based on the phase change material; optical material parameters of the phase change material, such as crystal state and dielectric constant, are changed by means of electric excitation, optical excitation and thermal excitation; dynamic modulation of polarization conversion is achieved within a broad band range; accordingly, designs of a novel functional device, such as adjustable beamdeflection, plate lens, and calculation of holographic and orbital angular momentums. A method of the invention may provide further improved ability of electromagnetic modulation of super surface, anda new idea and technical scheme are provided for the design of novel adjustable-function electromagnetic modulation elements.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Diamond color center gyroscope based on Aharonov-Anandan geometric phase and angular velocity measuring method
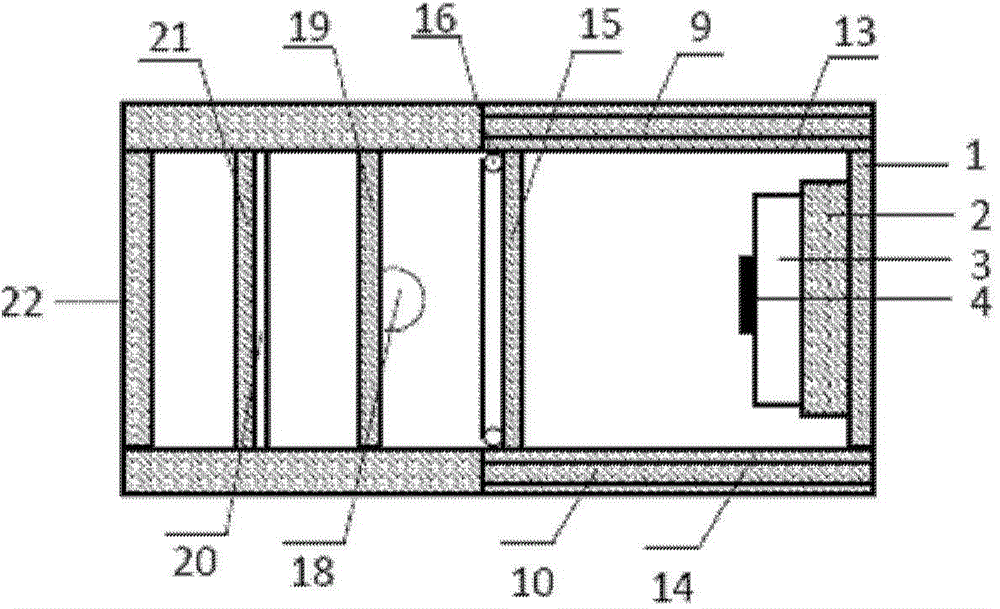
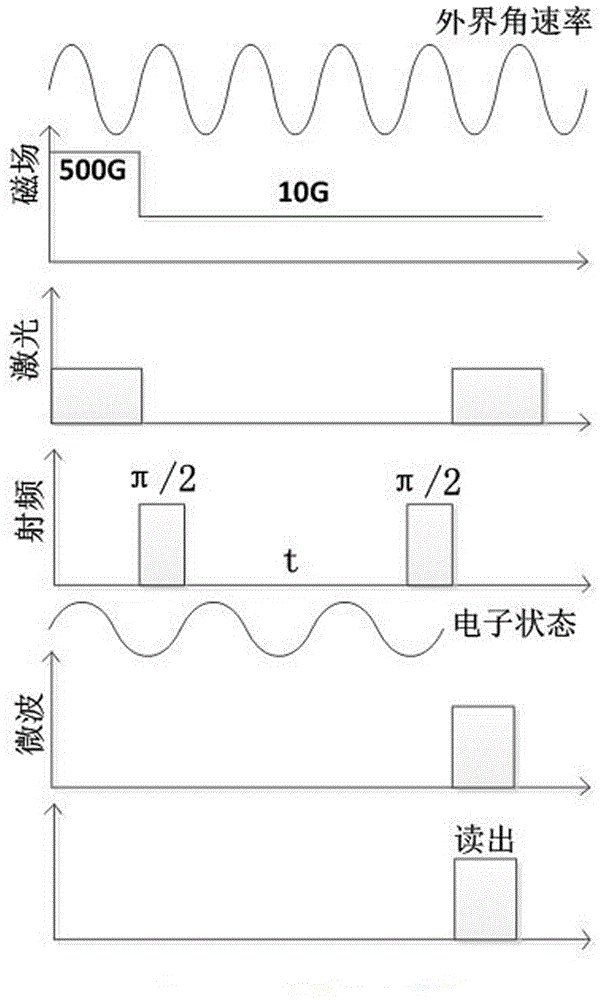
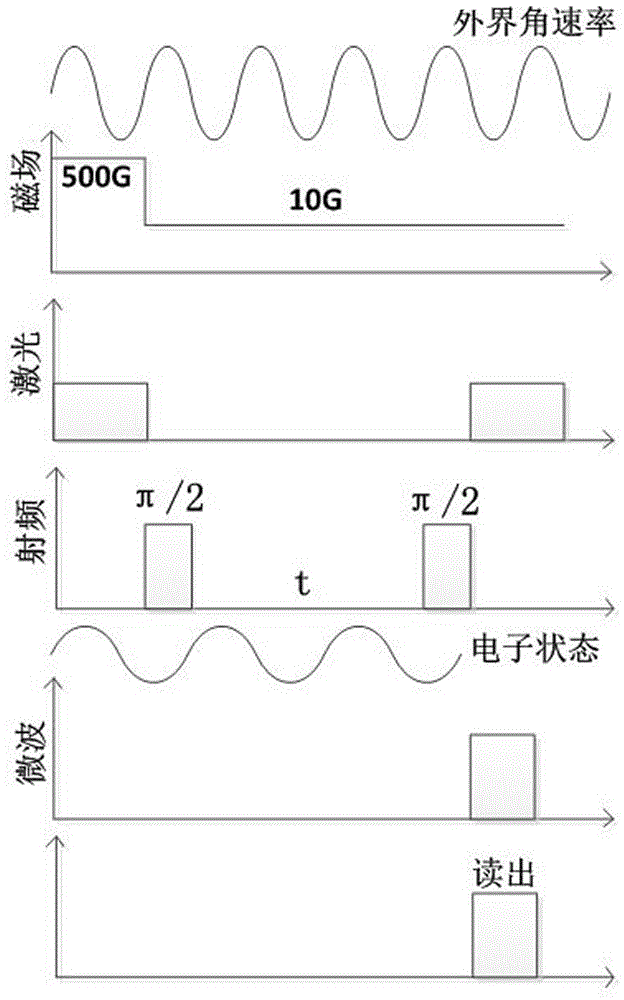
The invention discloses a diamond color center gyroscope based on Aharonov-Anandan geometric phase and an angular velocity measuring method. The gyroscope comprises a reflector, a permanent magnet, a substrate, a diamond sample, first microwave coils, second microwave coils, multiple area array CCDs, multiple filters, a third microwave coil, a first convex lens, a laser device, a polarizing sheet, a dichroscope and a second convex lens. The method for measuring angular velocity by means of the diamond color center gyroscope is further provided. The gyroscope has the advantages of being small in size, large in measuring range and the like, and therefore the gyroscope has potential application in producing ammunition.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
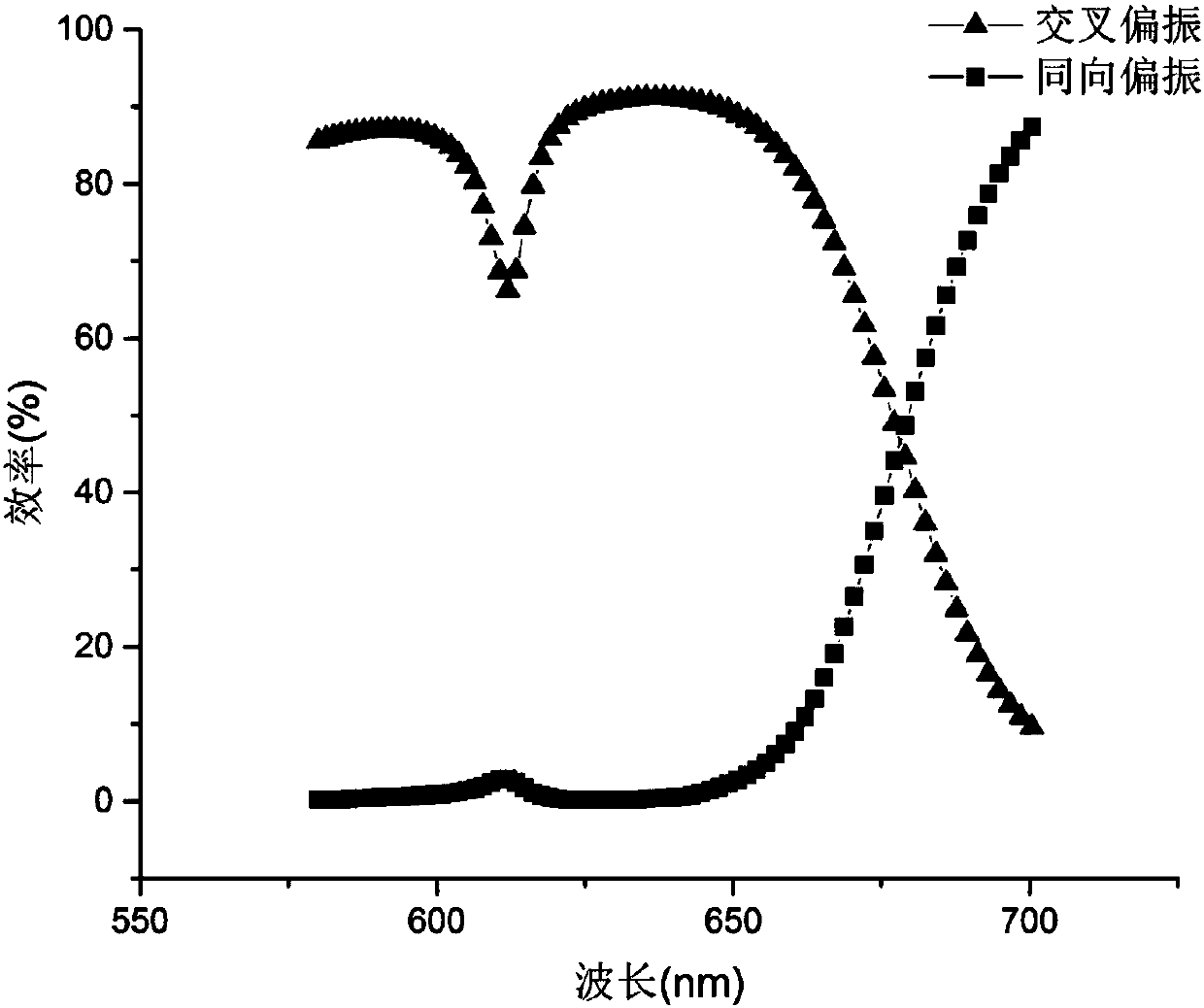
Broadband achromatic device based on medium super-surface
The invention discloses a broadband achromatic device based on a medium super-surface, relating to the field of new artificial composite material super-surfaces. The device comprises a device body, the device body comprising a dielectric rectangular block positioned on an upper layer and a substrate positioned on a lower layer. The achromatic analysis thereof comprises the steps of using a mannerof combining a geometric phase with a propagation phase to respectively control wavefront of an incident left-handed circularly polarized light and eliminate chromatic aberration; then performing sizetrimming to construct a super-surface array; and realizing analysis on the achromatic characteristic of the device body by extracting and processing right-handed circularly polarized energy of a detection surface. On one hand, the broadband achromatic device in the invention utilizes a method of combining two phases; and on the other hand, realizes achromatic in a continuous bandwidth range, thereby greatly reducing volume and cost thereof as compared with a past device.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
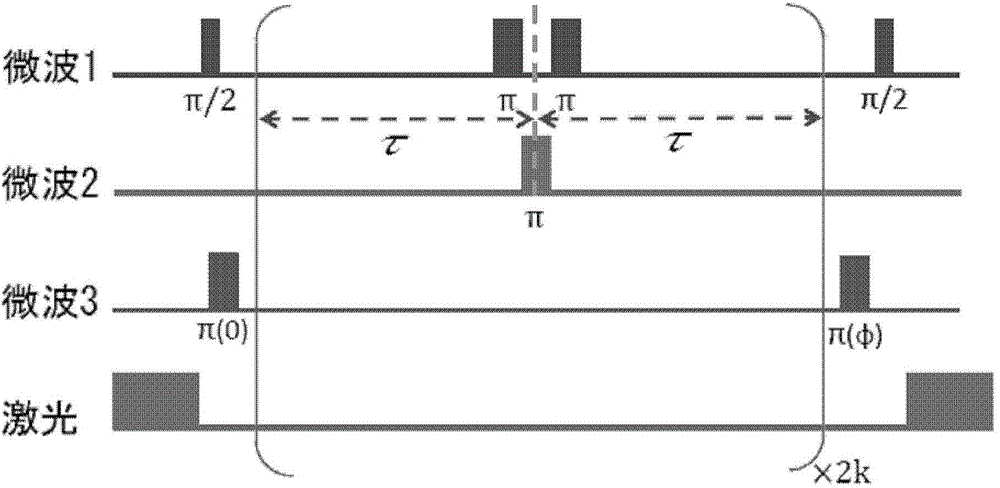
Non-commutative quantum geometric phase NV color center gyroscope
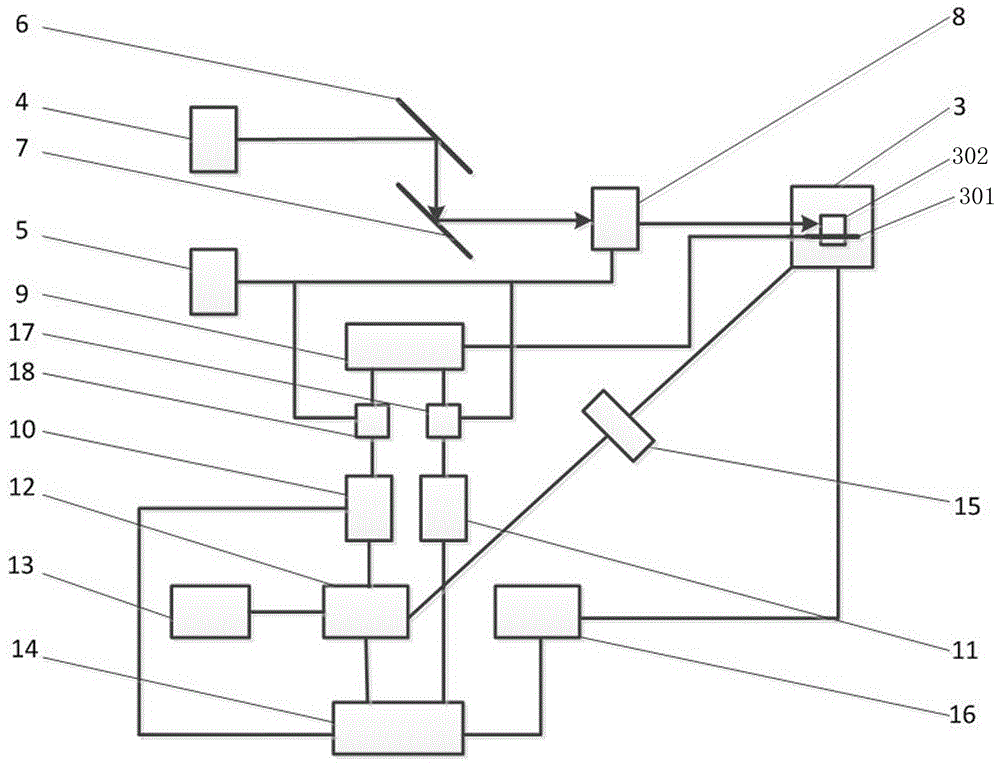
ActiveCN106441262AHigh sensitivityImprove decoherence timeTurn-sensitive devicesHigh level techniquesGyroscopeHelmholtz coil
The invention discloses a non-commutative quantum geometric phase NV color center gyroscope which comprises an angular rate sensing unit (3). The angular rate sensing unit comprises a shielding box shell (303), a laser entrance port (305) is formed in the shielding box shell, and a triaxial Helmholtz coil (307) is mounted in the shielding box shell through a coil base (308); diamond (302) with a cluster NV color center is mounted in the triaxial Helmholtz coil through a diamond support (309), a microwave-radio frequency antenna (301) is mounted on the diamond support, and photodiodes (311) are mounted at the position, around the diamond, of the diamond support. The atomic excitation, quantum manipulation and other advanced technologies are applied, the NV color center energy level is regulated and controlled under the action of laser, an applied magnetic field, microwaves and radio frequency, the frequency locking technology is utilized for detecting frequency transition, fluorescence number and layout changes are used for collecting and reading, and the high-performance non-commutative quantum geometric phase NV color center gyroscope is developed.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Reproducible lattice strain measurement method
InactiveUS20110084209A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationGamma-ray/x-ray microscopesScan lineLight beam
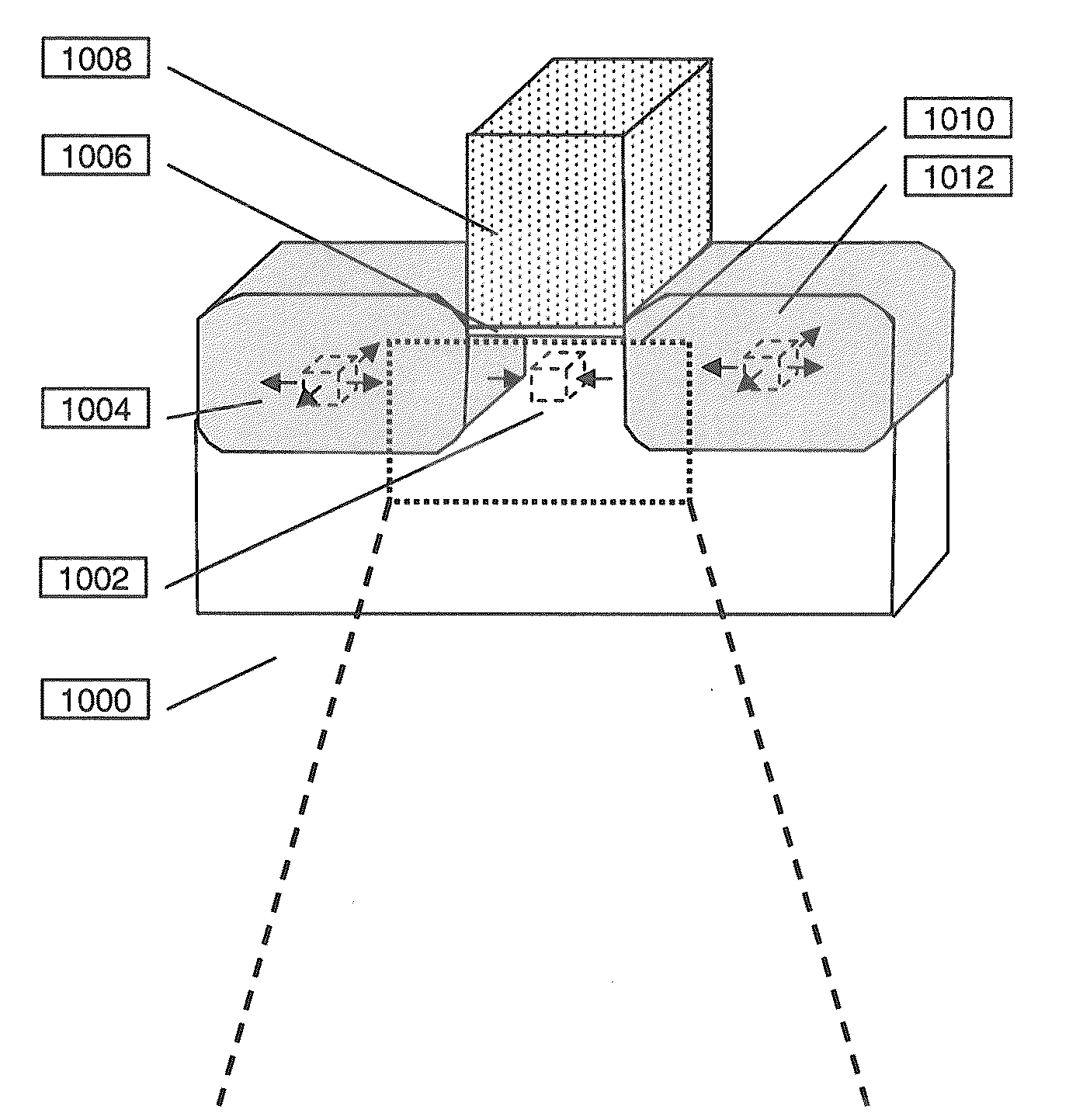
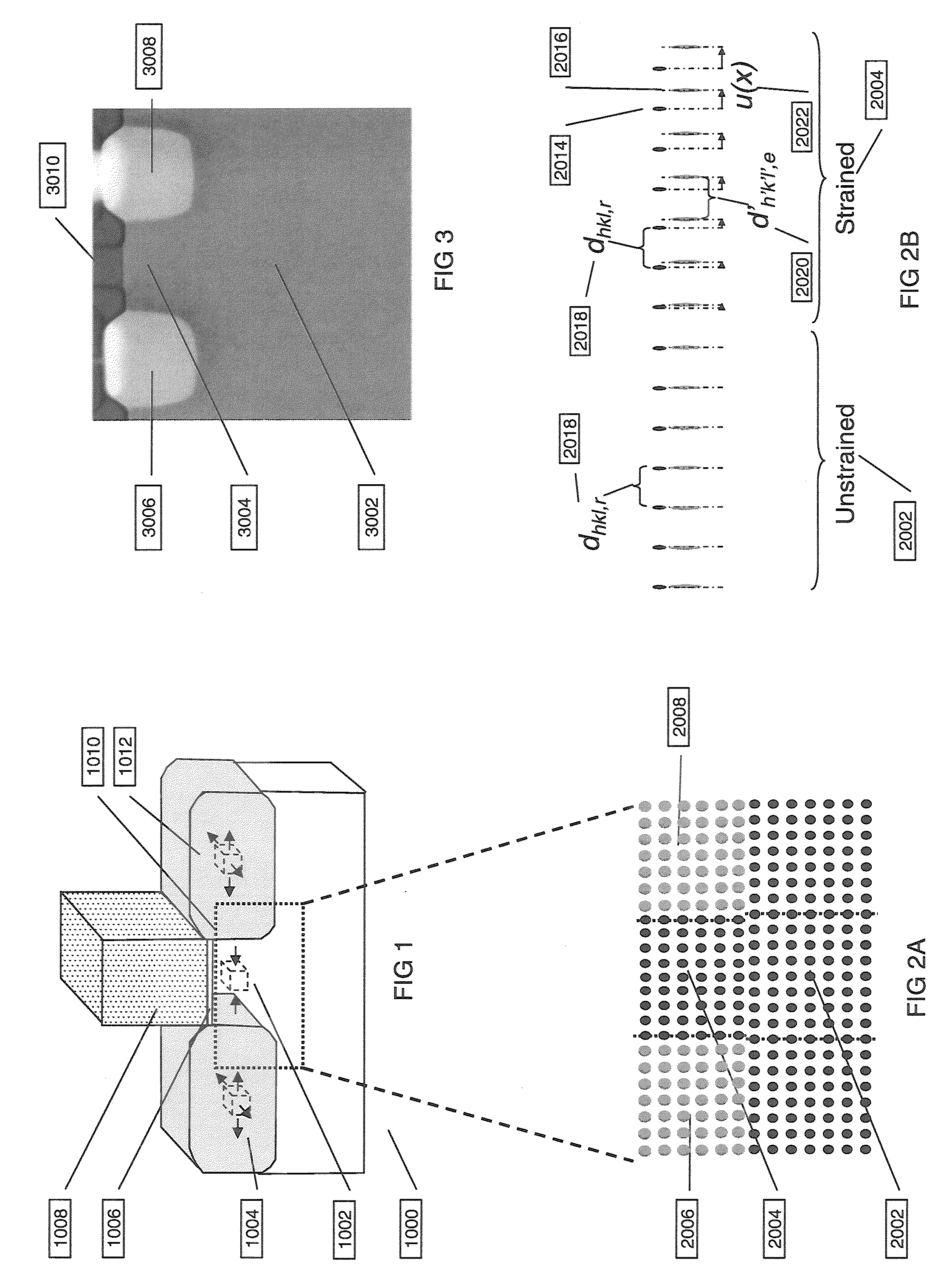
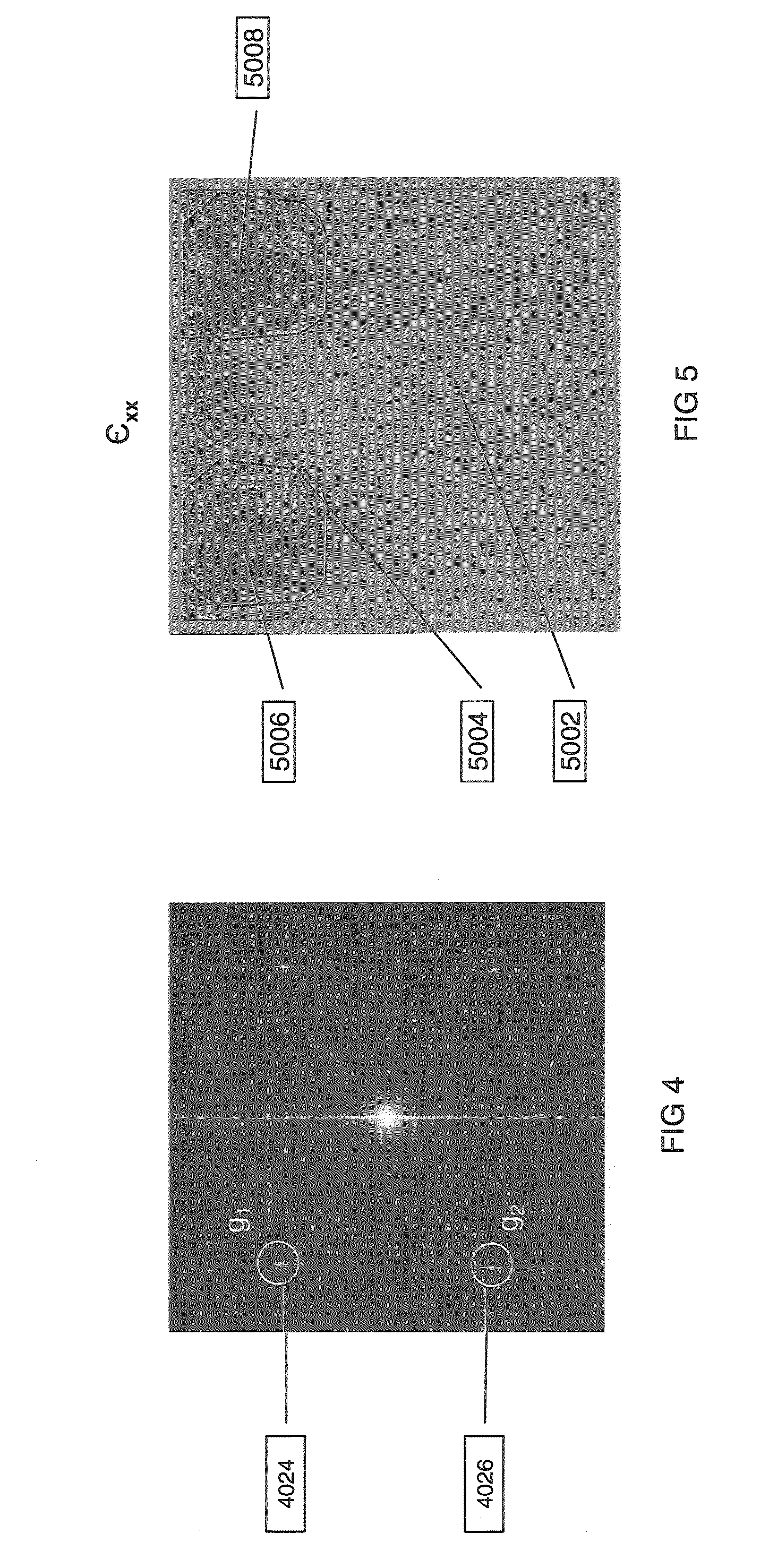
Lattice strain is reproducibly measured using geometric phase analysis (GPA) of a high angle annular dark field mode scanning transmission electron microscope (HAADF-STEM). Errors caused by beam shift (also known as fly-back error) between scan lines are eliminated.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
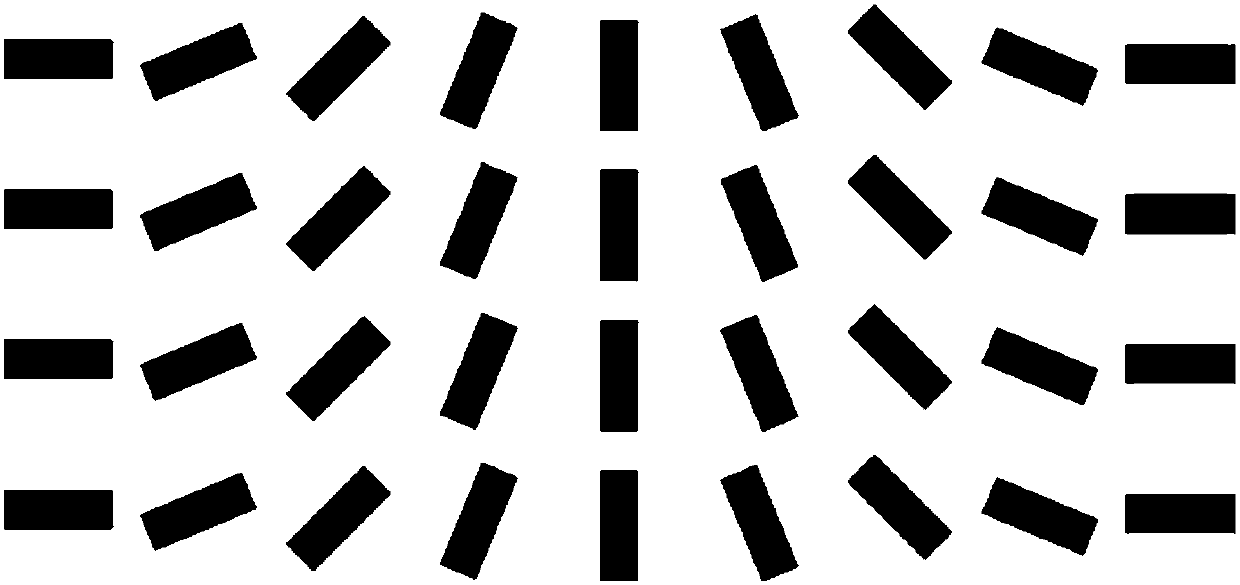
Geometric phase metasurface applied to broadband multi-mode vortex wave beam generation
The invention discloses a geometric phase metasurface applied to broadband multi-mode vortex wave beam generation. A basic unit of the metalsurface is composed of a metal rod structure, a dielectric layer and a metal backboard stacked successively from top to bottom. The unit is anisotropic via special structural design, and the reflection phase difference is 180 degree under x and y polarized electromagnetic wave irradiation. A metal rod rotates for an angle phi within the horizontal plane of the metasurface by taking the center of the metal rod itself as the origin, and circular polarized incident waves irradiated on the unit is reflected to obtain circular polarized waves with the same rotation performance plus an additional + / - 2phi geometric phase change. The units are arranged in a 2D plane according to preset phase distribution, and under irradiation of the circular polarized electromagnetic waves, the metasurface can generate four different modes of vortex wave beams in different directions. The metasurface is simple in structure, easy to process and wide in working frequency band, and can be used for information coding, and the channel capacity can be improved by mode multiplexing.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
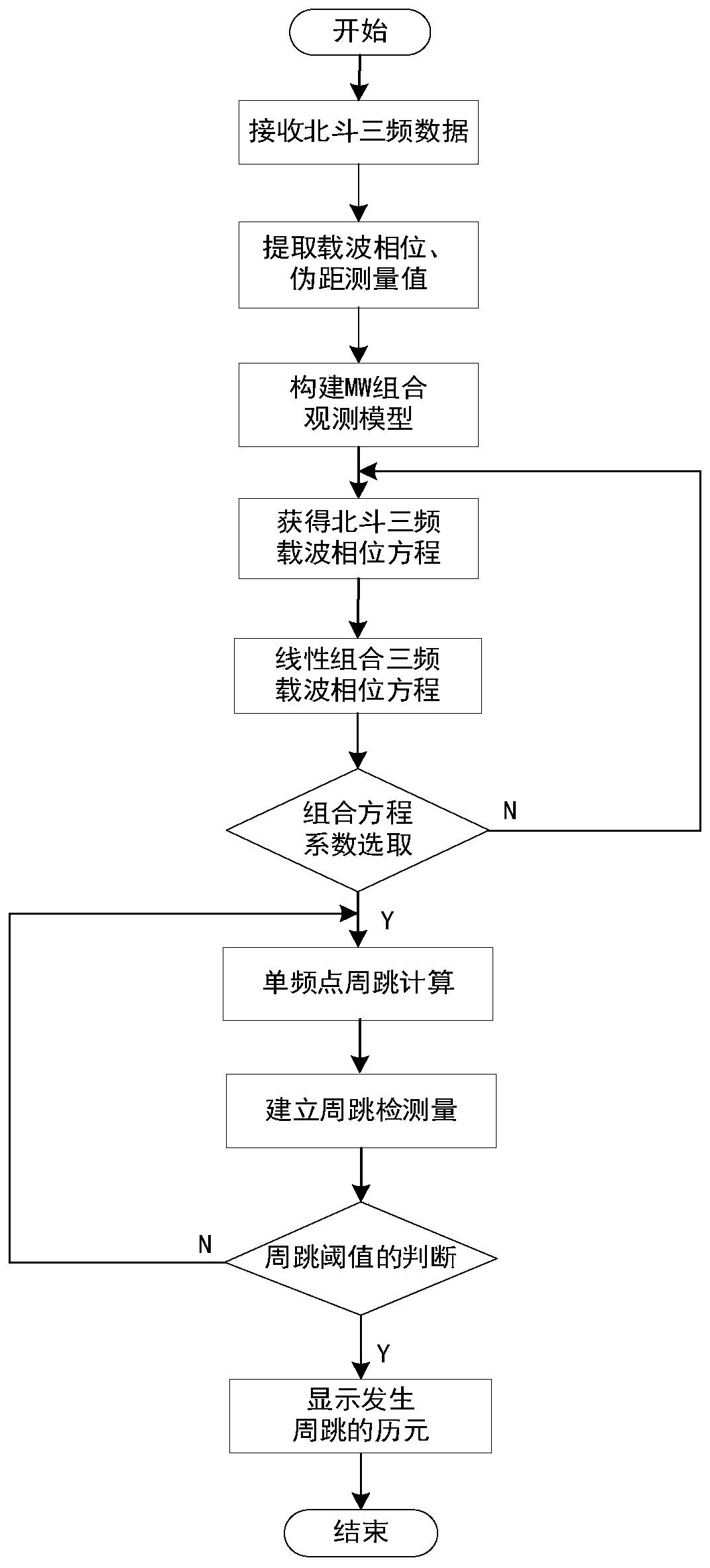
Method and apparatus for detecting Beidou triple frequency cycle slip
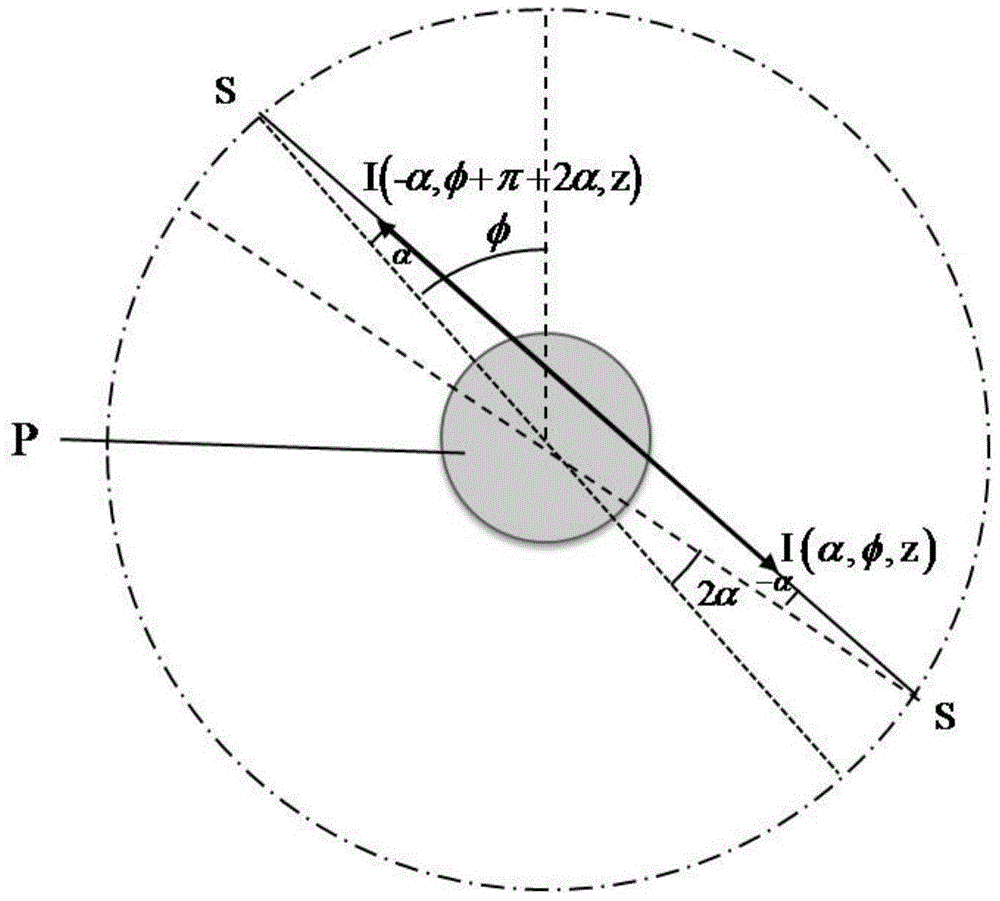
ActiveCN109358350AImprove detection accuracyReduce noiseSatellite radio beaconingAmbiguityEngineering
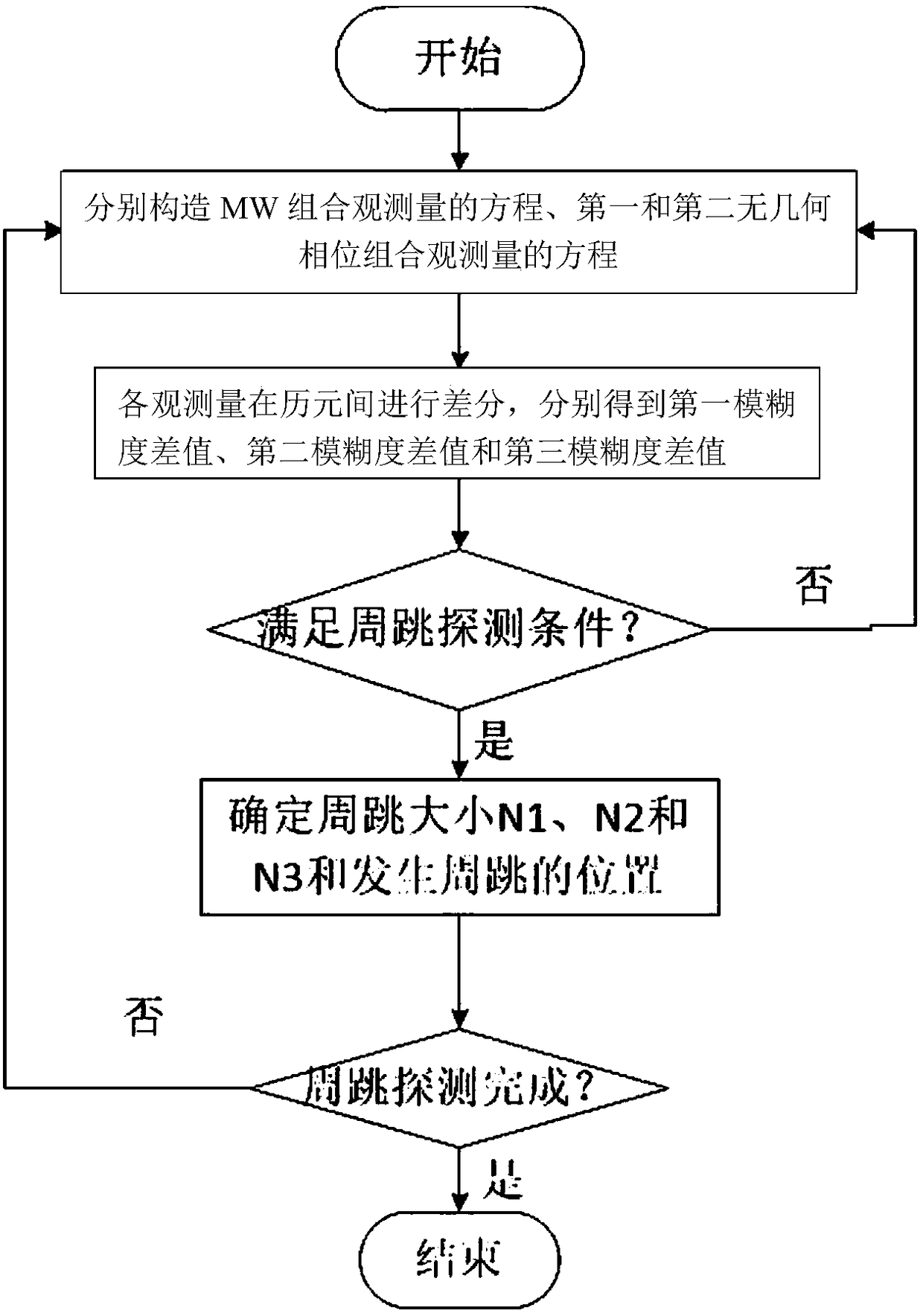
The invention relates to a method and an apparatus for detecting Beidou triple frequency cycle slip. The method comprises the steps of: establishing a MW combination observation equation using the Beidou B2 and B3 signals, and a first geometry-free phase combination observation equation and a second geometry-free phase combination observation using the Beidou B1, b2, and B3 signals; sequentially obtaining a first, a second and a third cycle slip detection amount by differentiating the ambiguity values between epochs; and determining that the cycle slip is occur when the absolute value of the first cycle detection amount is not equal to zero, the absolute value of the second cycle detection amount is greater than or equal to a first set threshold, and the absolute value of the third cycle detection amount is greater than or equal to a second set threshold. According to the method and the apparatus of the invention, the cycle slip detection is accurate, and the cycle slip of 1 week and above can be effectively detected. The method and the apparatus are suitable for real-time and dynamic cycle slip detection.
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU
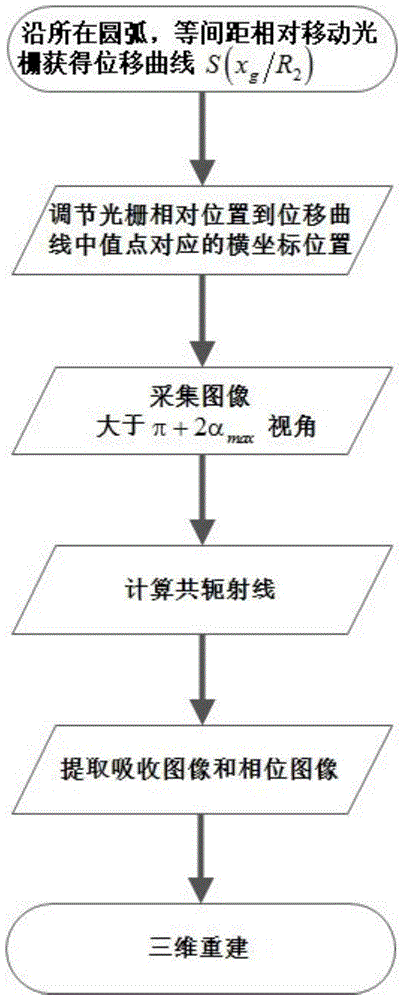
Fast fan-beam geometric phase contrast CT imaging device and method
InactiveCN105675631AExpanded imaging field of viewFast phase-contrast CT imagingMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationPhase gratingGeometric phase
The invention discloses a fast fan-beam geometric phase contrast CT imaging device and method. The phase contrast CT imaging device includes an X light source, a phase grating, a sample platform, an analysis grating and a detector. The invention adopts a cylindrical optical element, Large field of view imaging can be realized under the illumination of conventional X light sources; the invention uses cylindrical optical elements that match the geometry of light to avoid the problem of rays being blocked at large incident angles, greatly improving the imaging field of view, and at the same time combining the idea of square projection, In the traditional CT scanning mode, the phase information of the object is successfully extracted, and the fast phase contrast CT imaging is completed.
Owner:CHINA HEFEI TAIHE OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
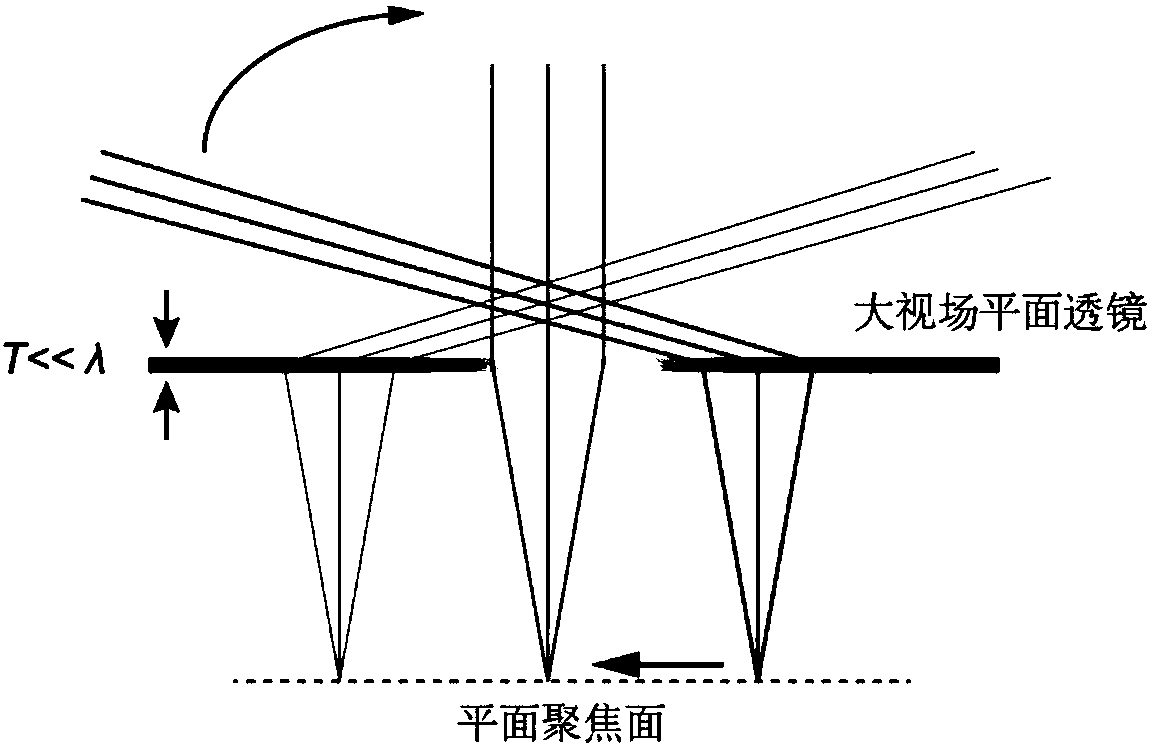
Large view field super resolution imaging device
ActiveCN106199997AEasy to manufactureEasy to implementOptical elementsElectromagnetic wave equationWavelength
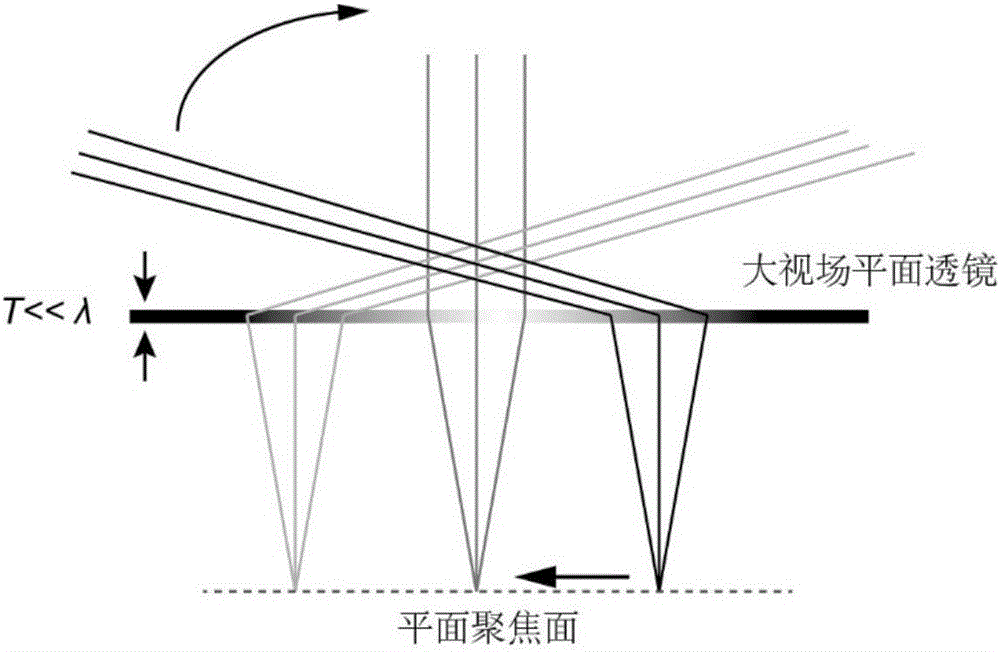
The invention discloses a large view field super resolution imaging device which comprises a base and a super-surface, wherein the base and the super-surface are successively arranged in the bottom-up sequence. The super-surface is composed of nano-unit structure arrays which are arranged in succession on an ultra-thin metal or a dielectric film. A nano-unit structure is a deep sub-wavelength structure. According to the invention, geometric phase on the nanostructure is used to control the electromagnetic wave symmetry; electromagnetic waves are converted from rotation symmetry to translational symmetry to acquire large view field perfect focusing near 180 degrees; if curved face or multi-plane combination is used, large view field imaging can be realized; the work bandwidth can cover the entire electromagnetic spectrum; the resolution is close to or even beyond the diffraction limit; and the device has a wide application prospect in the field of large view field super resolution imaging.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Near-eye display apparatus and equipment, zooming module and zooming method
PendingCN108803031AQuick responseImprove the display effectNon-linear opticsOptical elementsDisplay deviceGeometric phase
Owner:CHENGDU IDEALSEE TECH
Single-feed gain, controllable multi-shaped-beam and wideband circular polarization millimetre wave transmission array antenna
ActiveCN109462018ARealization of circularly polarized multi-shaped beamsRelative gain controlAntenna arraysRadiating elements structural formsShaped beamMillimetre wave
The invention discloses a single-feed gain, controllable multi-shaped-beam and wideband circular polarization millimetre wave transmission array antenna. The antenna comprises a circular polarizationfeed antenna (1) and a plane transmission array (2); the plane transmission array (2) is positioned at the front part of the opening of the horn mouth of the circular polarization feed antenna (1); the central axis of the circular polarization feed antenna (1) and the central axis of the plane transmission array (2) are positioned on the same central axis; the plane transmission array (2) is composed of completely same basic unit structures (3) in periodic arrangement; the central axis of the circular polarization feed antenna (1) and the central axis of the plane transmission array (2) are positioned on the same central axis; distribution of the horizontal rotation angle of each basic unit structure of the plane transmission array (2) in the plane is optimally designed; the wideband circular polarization multi-shaped-beam can be realized by utilization of the geometric phase generated by the unit; and the antenna has the wide application prospect in millimetre wave point-to-multipointcommunication and point-to-multi-area coverage aspect.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Self-interference digital holographic system
ActiveUS20190346811A1Simple componentsLow costHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic optical componentsSelf interferencePhase shifted
A self-interference digital holographic system obtains interference patterns of incident light using a simple geometric phase lens, and obtains a holographic image of a target object using the interference patterns. The self-interference digital holographic is fabricated simply in a low cost and in a miniaturized size, and the use thereof as actual products is extended to a wide range of applications. The phase of incident light is be changed by rotating a polarizer, independently of a change in the optical path. Phase-shifting effects are obtained with fewer errors in all wavelength ranges, and a more accurate holographic image is produced. A single birefringence hologram is obtained by a one-time image-capturing process by simultaneously forming interference patterns from phase-shifted linearly-polarized beams by space division, using a phase shifter on the basis of space division. Moving holographic images can be captured.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
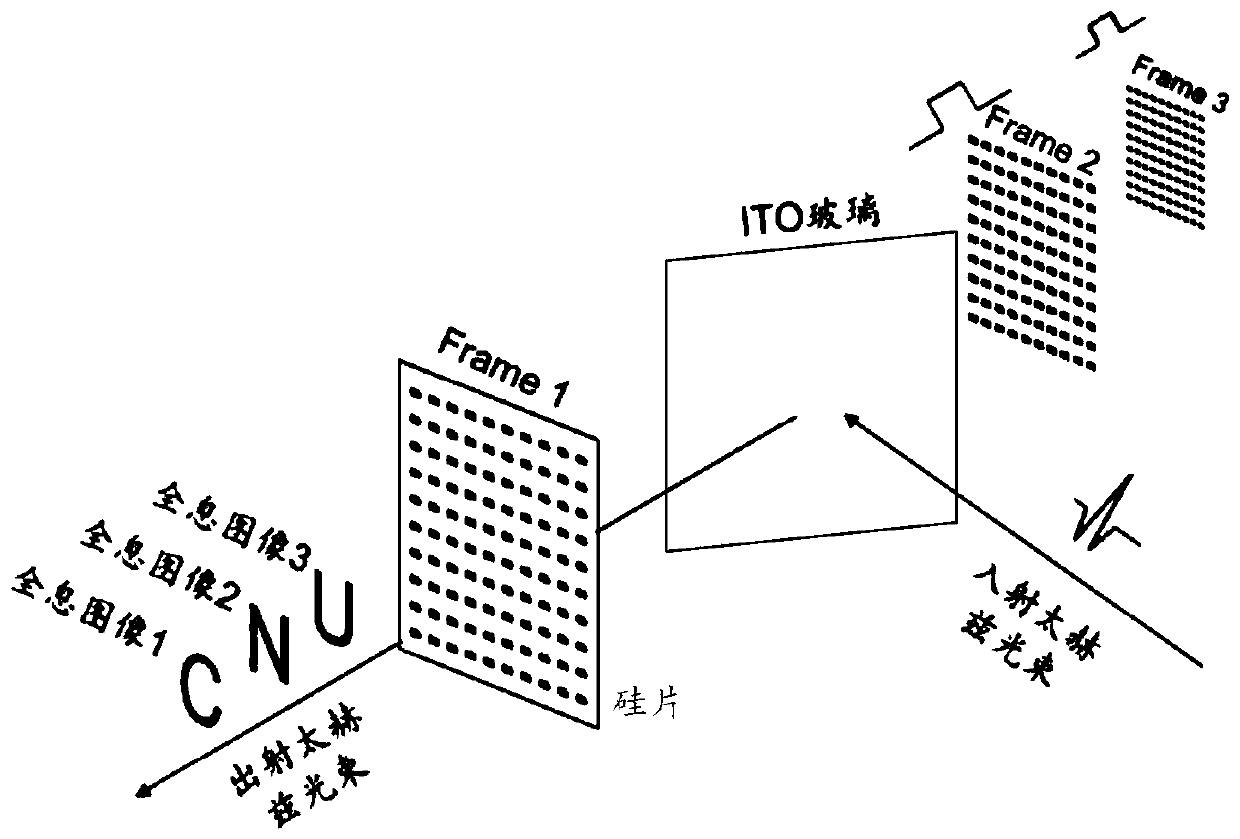
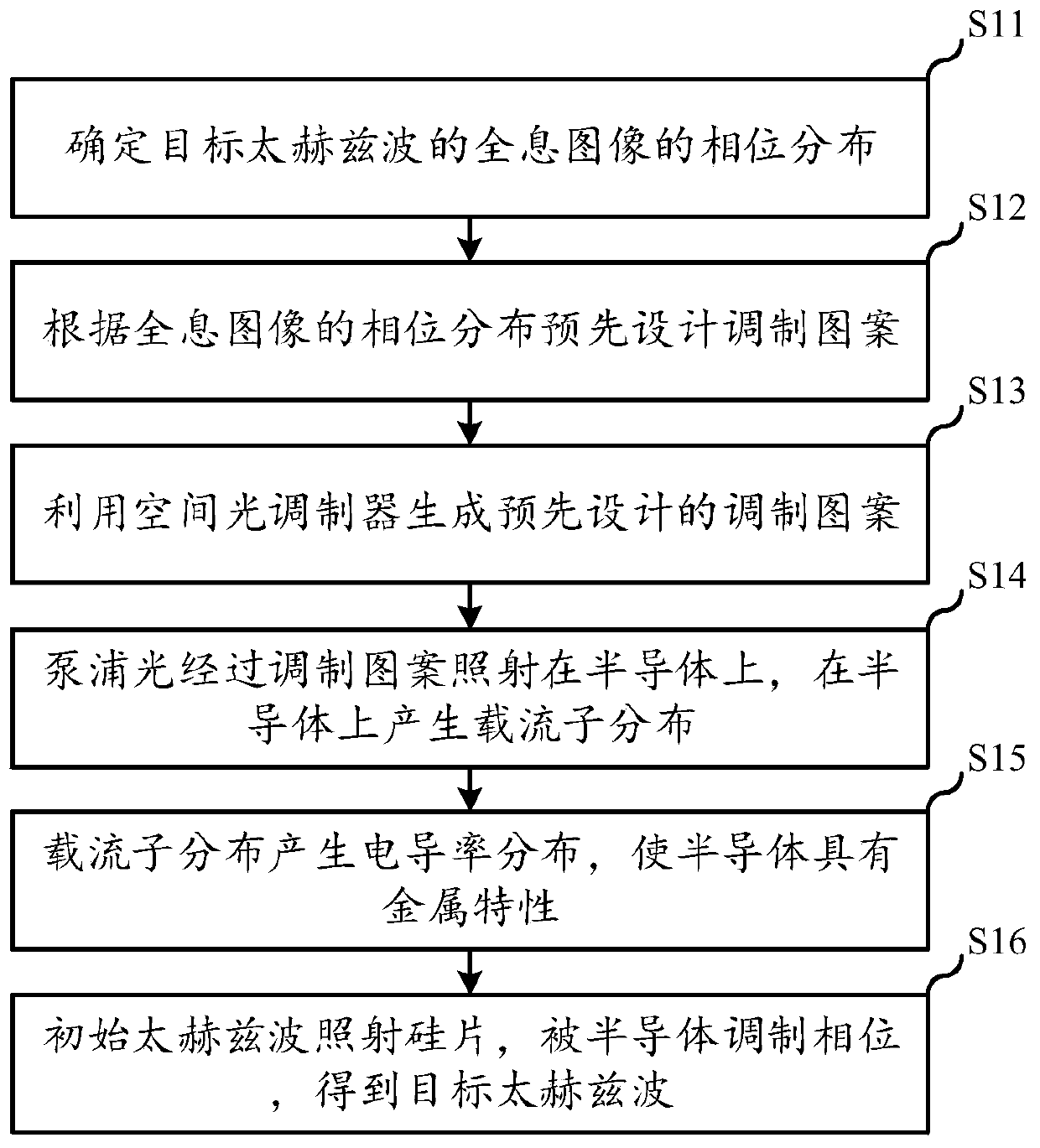
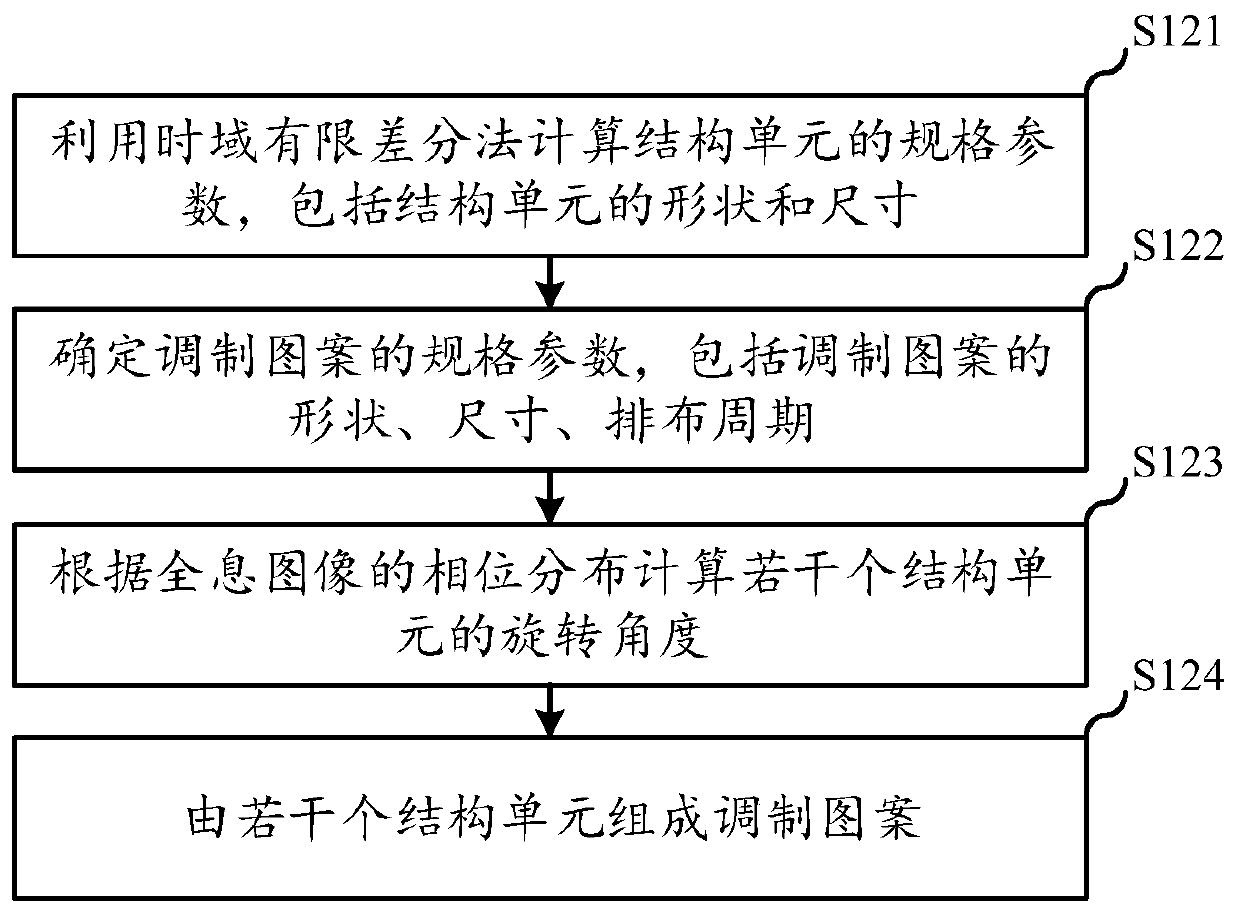
Dynamic modulation method for phase of terahertz wave
InactiveCN109884807AModulation continuousFast modulationNon-linear opticsInformation processingSpatial light modulator
An embodiment of the invention relates to the technical field of information processing, and discloses a dynamic modulation method for a phase of a terahertz wave. The method comprises the following steps that a predesigned modulation pattern is generated by utilizing a spatial light modulator; pump light is irradiated on a semiconductor through the modulation pattern, and carrier distribution isgenerated on the semiconductor; the carrier distribution generates electric conductivity distribution, so that the semiconductor has metallic properties; and an initial terahertz wave irradiates the semiconductor, and the phase is modulated by the semiconductor to obtain a target terahertz wave, wherein the modulation pattern comprises a plurality of structural units which are arranged in a discrete manner. According to the embodiment, the different modulation patterns are dynamically generated, so that a pure-phase dynamic modulation metasurface for the terahertz wave is realized, the modulation pattern adopts a geometrical phase modulation method, the modulation mode is simple, the modulation effect is stable, and continuous, fast and accurate modulation of the phase is realized while the same amplitude modulation is guaranteed.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for jointly detecting and repairing cycle slip by MW combination method and non-geometric phase method
The invention discloses a method for jointly detecting and repairing a cycle slip by an MW combination method and a non-geometric phase method. The method comprises the following steps of S1, selecting three-frequency data (B1, B2 and B3) of a Beidou navigation and positioning system to obtain a pseudo-range observation value and a carrier phase observation value; S2, constructing a three-frequency MW combined observation model, establishing a MW equation, and carrying out inter-epoch difference to obtain cycle slip detection amount delta N12 and delta N13; S3, constructing a non-geometric phase observation model; S4, selecting two groups of parameters according to a principle that an ionized layer coefficient and the observation noise of the combined observation data are relatively smallat the same time, calculating the cycle slip of the three frequency points of the two groups of the parameters according to a formula that delta N1 is equal to delta N2 that is equal to delta N3, andselecting a B combination coefficient meeting the actual situation; and S5, combining the delta N12, the delta N13 and the B combination to obtain an equation set, calculating the cycle slip on the three frequency points, and repairing the cycle slip. The method solves the defect that the non-geometric method cannot detect the non-sensitive cycle slip and the MW method cannot detect the equal cycle slip.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
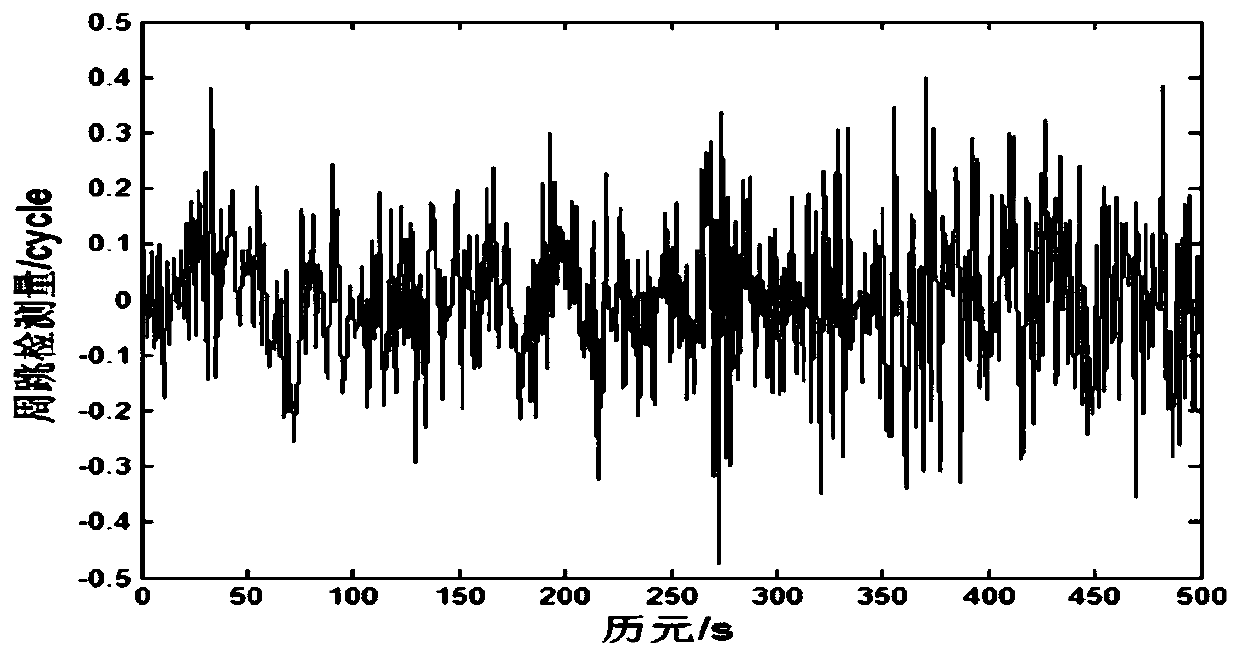
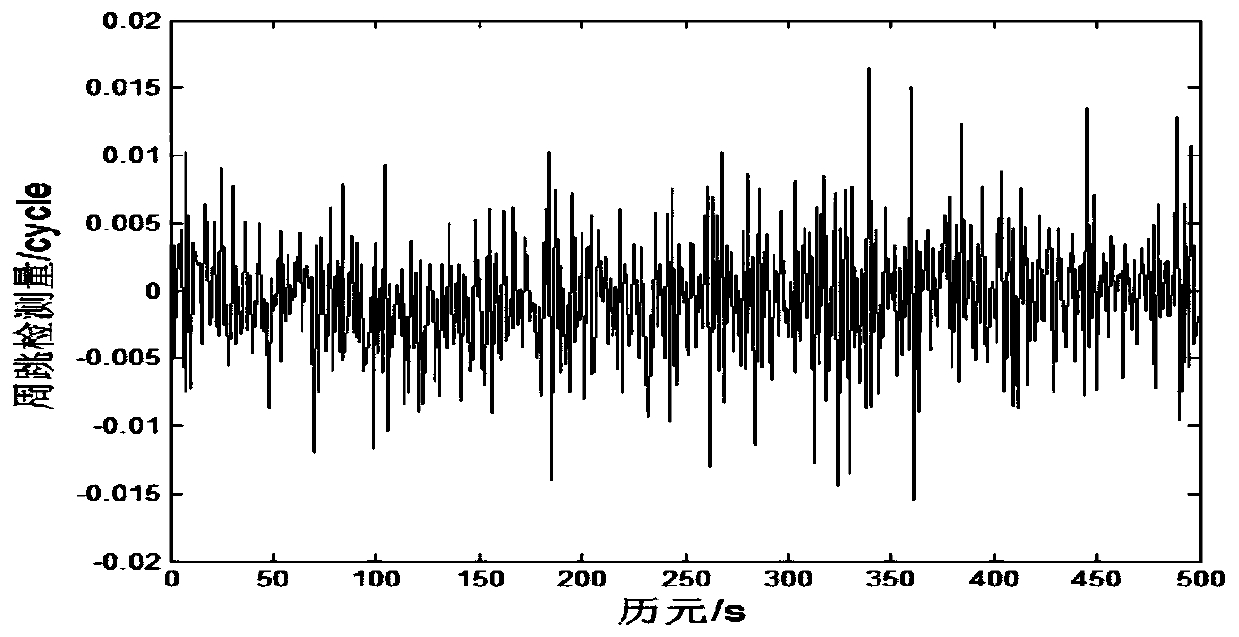
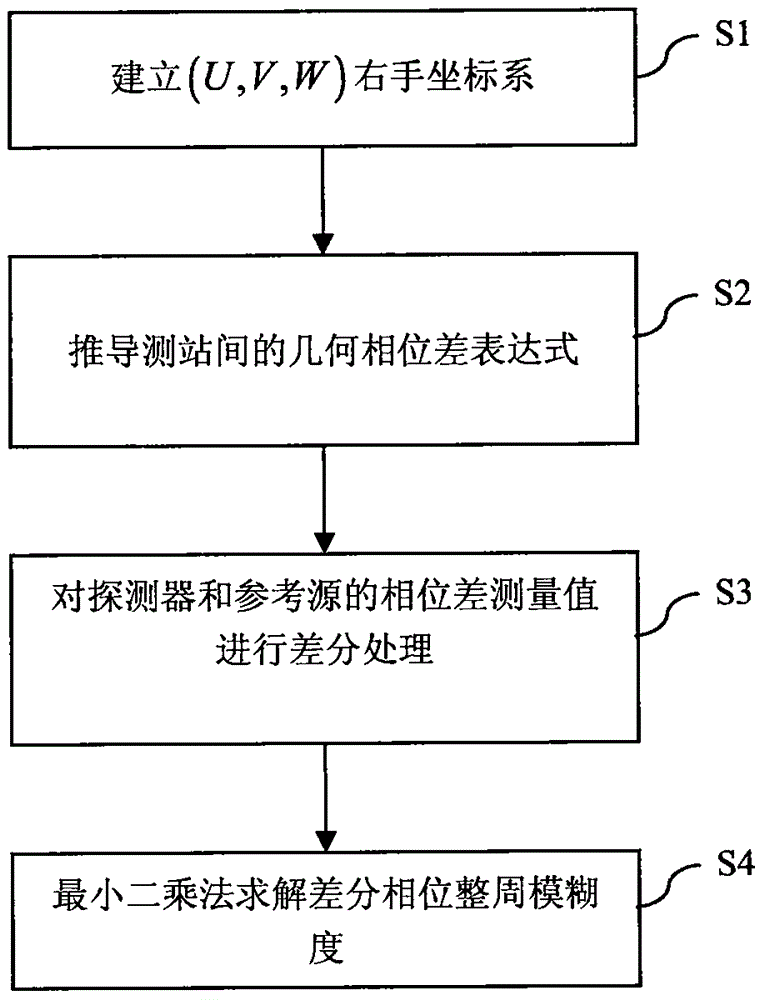
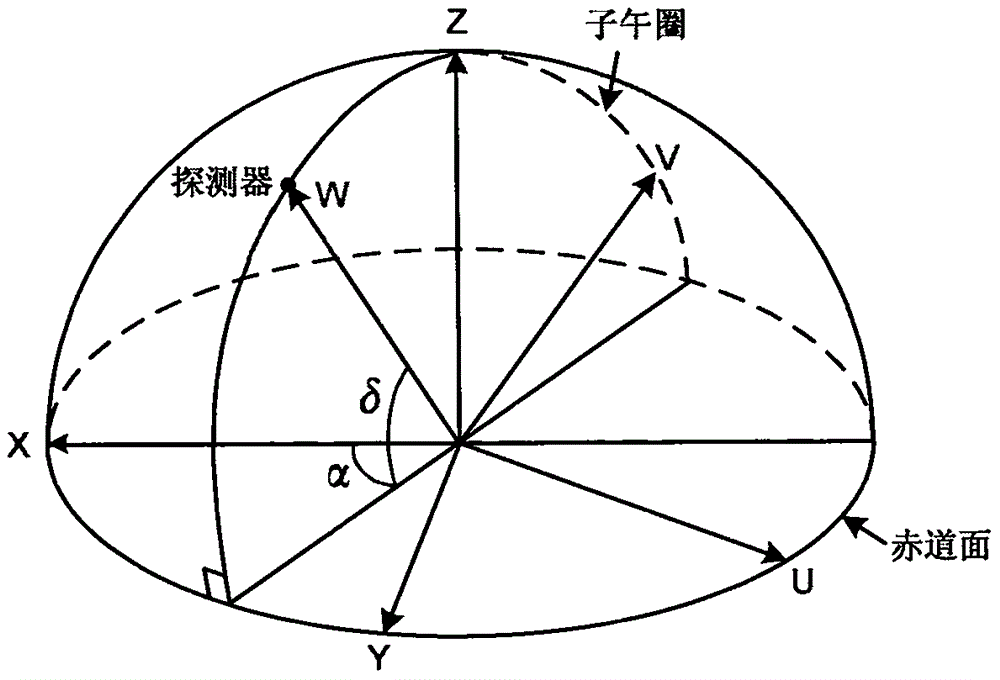
Resolution method for differential phase integer ambiguity of radio interferometry of deep space explorer
ActiveCN106840160AImprove high-precision navigation and positioning accuracyImprove precision navigation and positioning accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationDifferential phaseControl signal
The invention belongs to the field of radio interferometry of deep space explorers and discloses a resolution method for differential phase integer ambiguity of radio interferometry of a deep space explorer. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, establishing a right-hand coordinate system (U,V,W); step 2, calculating a geometric phase difference of two measuring stations; step 3, carrying out differential processing on phase difference measured value of the explorer and a reference source; step 4, solving the differential phase integer ambiguity through a least square method. By adopting the resolution method provided by the invention, the problems of resolving the differential phase integer ambiguity of the radio interferometry when the quantity of ground measuring stations is less and the deep space explore only has a conventional remote measurement or data transmission downstream measurement and control signal is solved; the high-precision navigation and positioning precision of the deep space explorer is effectively improved.
Owner:NO 63921 UNIT OF PLA
Non-linear phase gradient metasurface based on rotation crystal direction
ActiveCN108107498ASubvert cognitionPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsHigher order harmonicsUnit structure
The invention provides a non-linear phase gradient metasurface based on rotation crystal direction. The non-linear phase gradient metasurface comprises C3 and C5 sub-wavelength metal holes or slits with higher-order rotation symmetry. According to the nonlinear phase gradient metasurface, a selection rule of a conventional geometric phase metasurface unit structure is broken through, and the singular nonlinear geometric phase gradient is obtained in a linear optical system through design of the triangular, Y-shaped and pentagonal sub-wavelength metal holes or slits with multi-rotation symmetry; the phase gradient is different from the conventional nonlinear phase, the conventional nonlinear phase usually refers to the phase carried by higher-order harmonic waves (n>=2), and the generated phase gradient is from fundamental waves (n=1); and according to the non-linear phase gradient metasurface, the nonlinear phase gradient is realized in the linear metasurface, the cognition of the geometric phase in the linear metasurface for people is overthrown, and a great significance is attached to the principle and application of phase modulation in the linear optical system.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
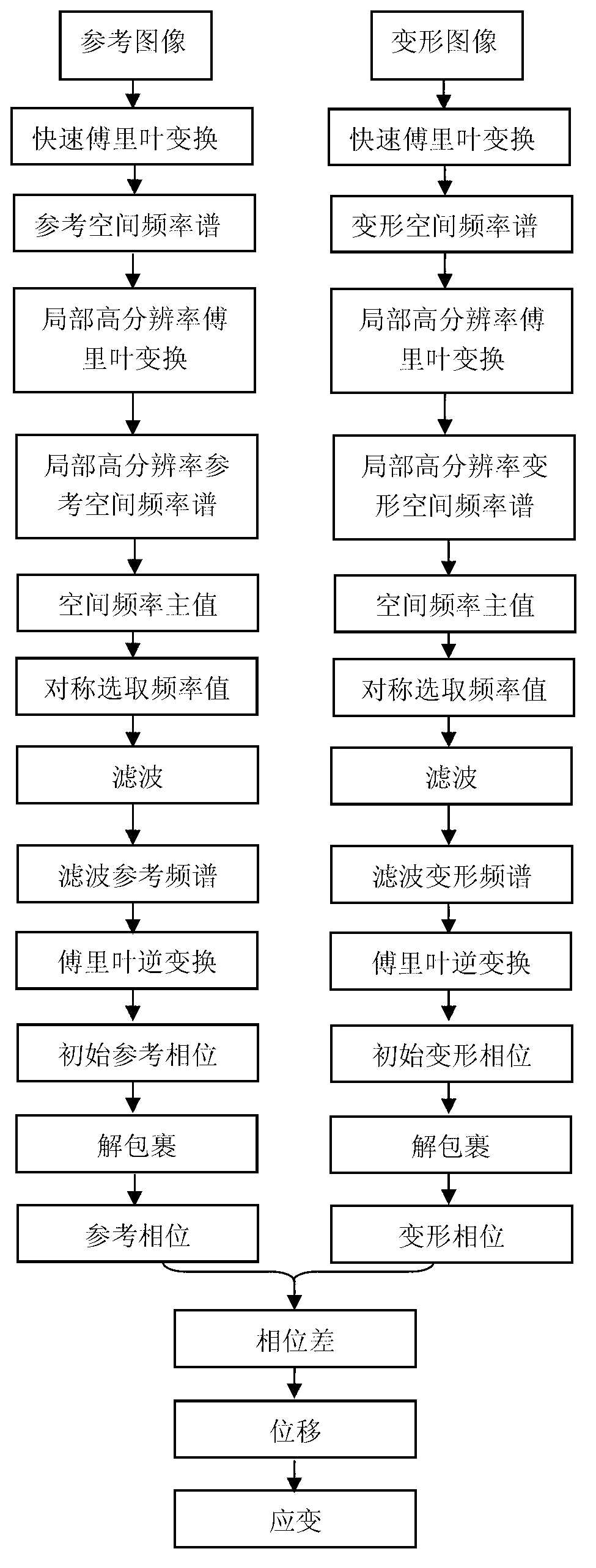
Artificial grid making geometric phase analysis method based on local high-resolution Fourier transformation
InactiveCN103218774AAccurate valueImprove calculation accuracyGeometric image transformationComplex mathematical operationsFrequency spectrumGrating
The invention provides an artificial grid making geometric phase analysis method based on local high-resolution Fourier transformation. The method comprises the following steps of firstly collecting an undeformed raster image and a deformed raster image; respectively performing fast Fourier transformation on a reference image and a deforming image; acquiring a reference spatial frequency spectrum and a deformation spatial frequency spectrum, and selecting the interval where a spatial frequency main value is positioned to perform the local high-resolution Fourier transformation to obtain a local high-resolution spatial frequency spectrum; determining the spatial frequency main value in the local high-resolution spatial frequency spectrum and taking the spatial frequency main value as a center to select a spatial frequency value; filtering on the spatial frequency spectrum formed by the selected spatial frequency value so as to obtain a filtering reference spectrum and a filtering deformation spectrum, and then performing Fourier inversion and solving a reference phase and a deformation phase; and solving a phase difference by using the reference phase and the deformation phase, and calculating displacement and strain. The displacement and strain result calculated by the method is high in precision and short in calculation time.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Vision correction device
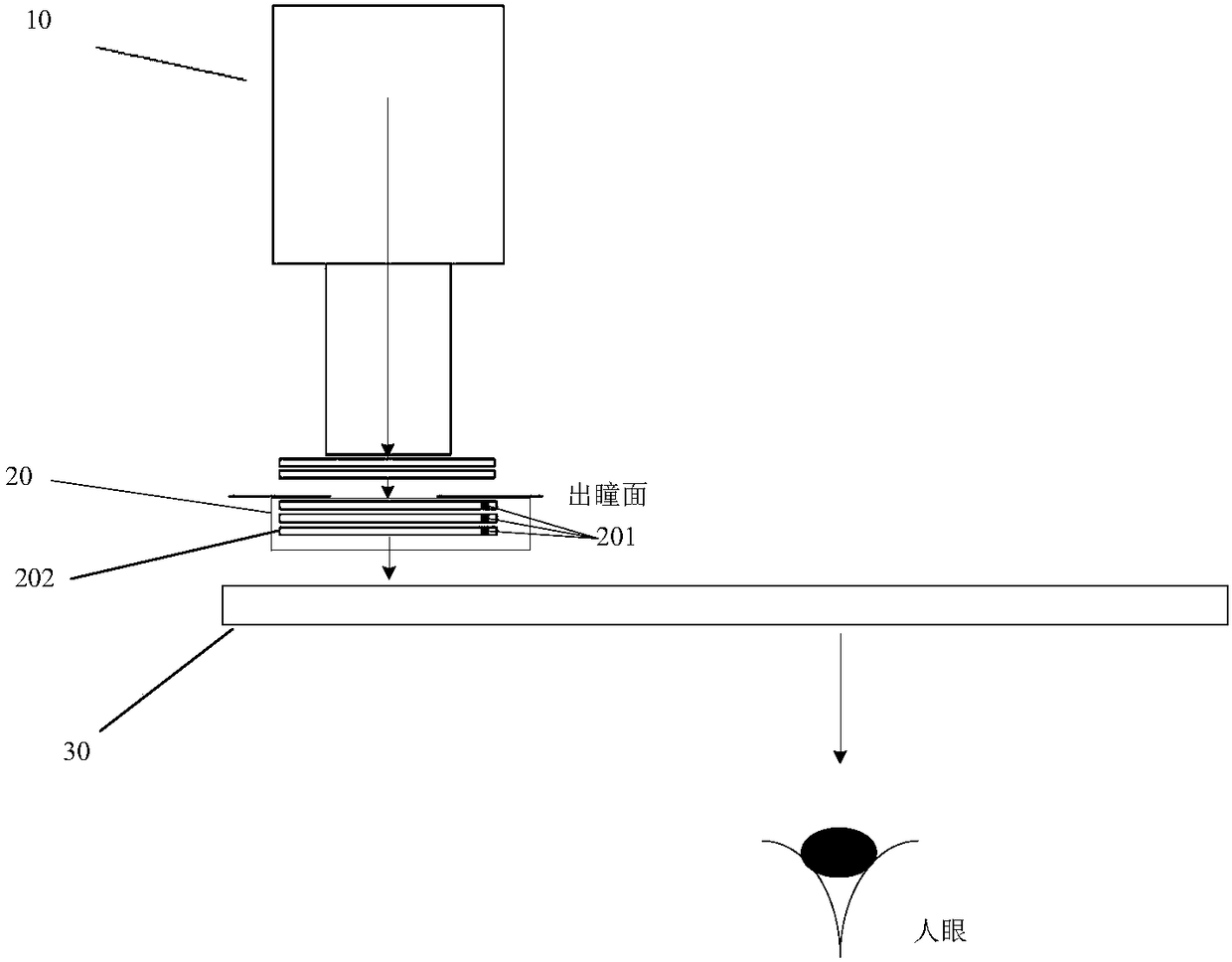
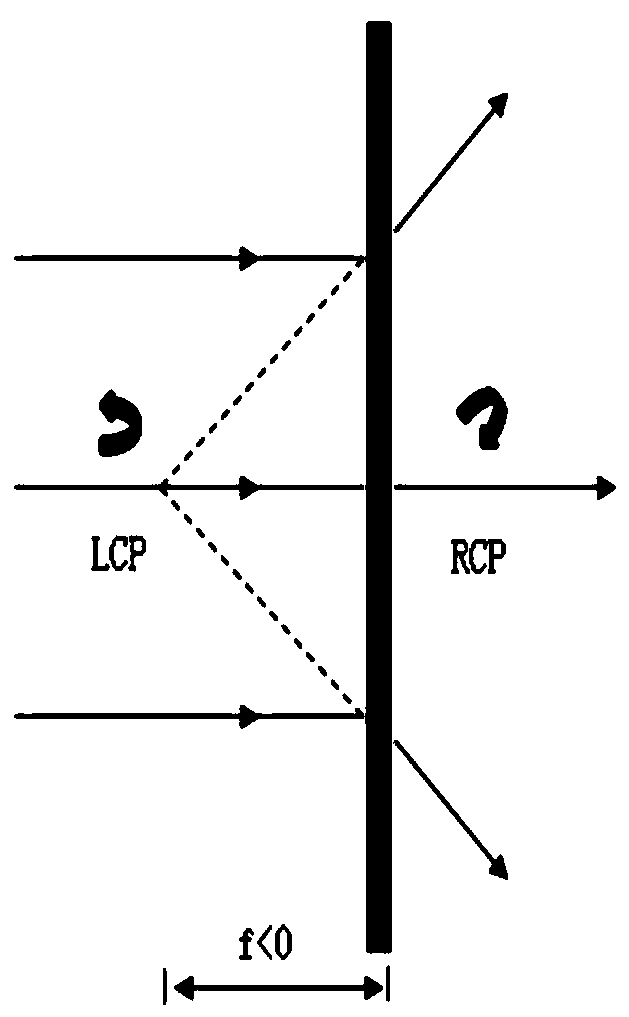
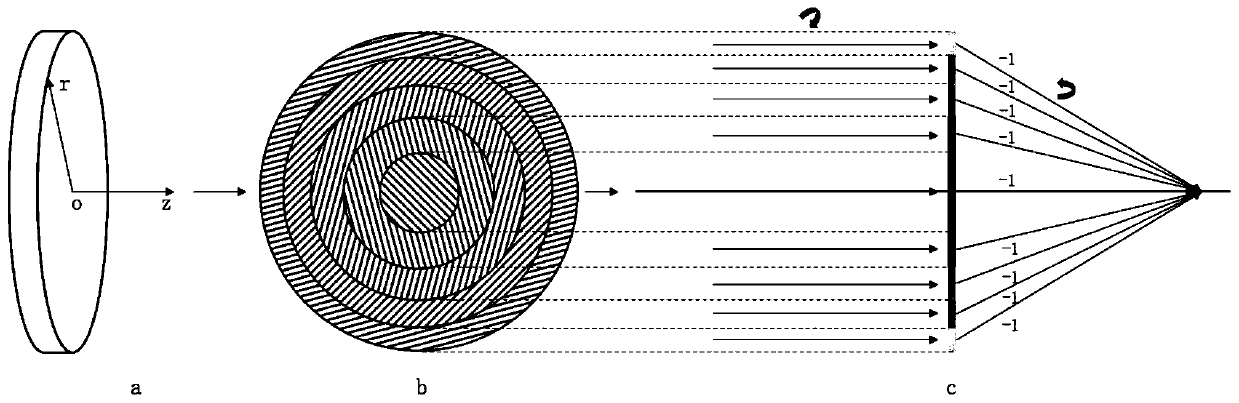
ActiveCN110361874AAvoid dependenceAchieve vision correction functionOptical partsOptical axisLight beam
The invention relates to the technical field of optics, discloses a vision correction device, and aims at solving the inherent defects of the traditional vision correction device such as thick and heavy device and aberration. The device comprises a common optical axis linear polarizer, a geometric phase lens and a 1 / 4 wave plate which is arranged between the linear polarizer and the geometric phase lens. The geometric phase lens realizes the beam diffraction and deflection by controlling the change of the long-axis direction of the birefringent material corresponding to each ring with the optical axis as the center so as to realize the convergence of the same-order diffracted beam equal to the non-zero diffracted beam by the convex lens with the real focus and / or divergence of the same-order diffracted beam equal to the non-zero diffracted beam by the concave lens with the virtual focus.
Owner:SHENZHEN LUBANG TECH CO LTD
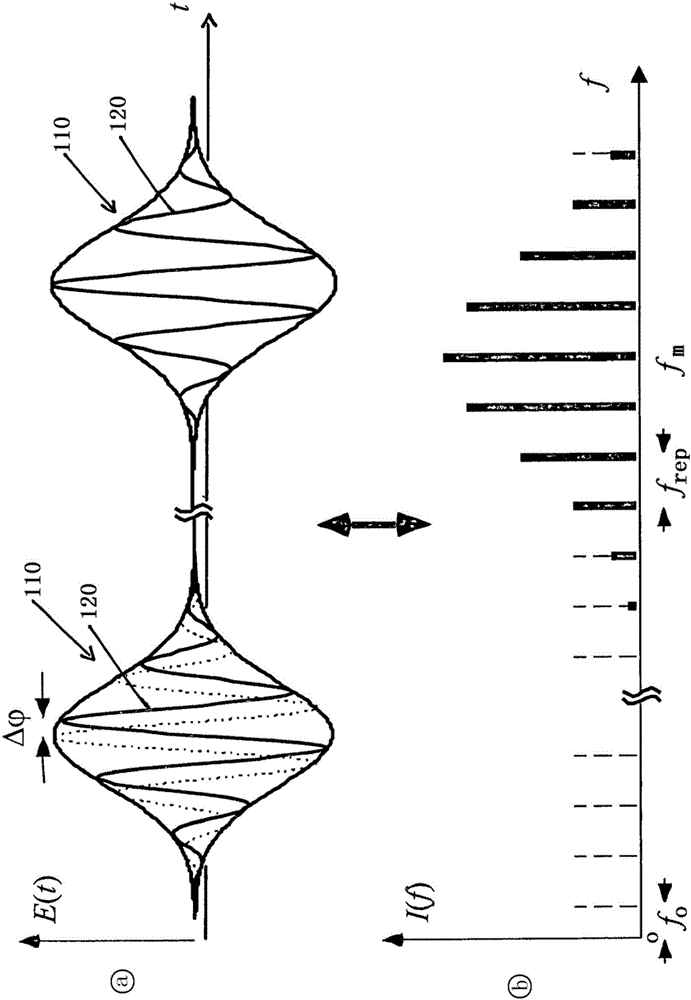
Method for operating a laser device, resonator arrangement and use of a phase shifter
The invention relates to a method for operating a laser device, comprising the steps: a) providing a laser pulse (110) in a resonator (1) so that the laser pulse (10) circulates in the resonator (1), the laser pulse (10) having a carrier wave (120); b) determining an offset frequency (f0) of the frequency comb corresponding to the laser pulse (110), the frequency comb having a plurality of laser modes (fm) at a distance (frep) from one another, the frequencies of which can be described by the formula: fm = m * frep + f0, m being a natural number; and c) varying the offset frequency (f0) by varying a geometric phase ([delta][phi]) that is impressed on the carrier wave (120) of the laser pulse (110) per resonator revolution.
Owner:MENLO SYST
Method for efficiently measuring polarization state and phase of arbitrary beam at same time and optical path
The invention relates to a method for efficiently measuring the polarization state and the phase of an arbitrary beam at the same time and an optical path. Based on the geometric phase theory, a method for simultaneously measuring the polarization state and the phase of an arbitrary beam and an optical path for realizing the method are proposed. During the measurement process, only two interferograms are acquired at the same time. By holographic numerical reconstruction of the interferograms and extraction of phase and amplitude information, the polarization and phase distribution of the measured beam can be calculated. The method can be used not only to measure the polarization state and the phase distribution of an arbitrary beam, but also to detect a polarization optical element.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Multi-channel focused vortex beam generator of all-dielectric material and preparation method
The invention discloses a multi-channel focused vortex beam generator of all-dielectric materials and a preparation method. The generator comprises a substrate and a dielectric nanopillar array. The dielectric nanopillars are arranged on the substrate in a specific manner. The multi-channel focused vortex beam generator of the all-dielectric materials adjusts a rotation angle of the nanopillar around a spindle by selecting appropriate nanopillar period and the size (length, width and height) of the nanopillar and introducing a geometric phase so as to achieve the full phase control of the wave-front phase of a transmitted beam; integrates functions of a lens and a vortex phase plate onto a dielectric nanopillar array device so as to achieve the focusing of a vortex beam and generate doughnut type energy density distribution on a set focal plane; and achieves multi-channel generation of the vortex beam on one device based on the holographic principle. The preparation method of the multi-channel focused vortex beam generator of the all-dielectric materials greatly improves the efficiency of a vortex beam generator, reduces the size of the generator, and improves the integrality of the generator.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A large field of view super-resolution imaging device
The invention discloses a large view field super resolution imaging device which comprises a base and a super-surface, wherein the base and the super-surface are successively arranged in the bottom-up sequence. The super-surface is composed of nano-unit structure arrays which are arranged in succession on an ultra-thin metal or a dielectric film. A nano-unit structure is a deep sub-wavelength structure. According to the invention, geometric phase on the nanostructure is used to control the electromagnetic wave symmetry; electromagnetic waves are converted from rotation symmetry to translational symmetry to acquire large view field perfect focusing near 180 degrees; if curved face or multi-plane combination is used, large view field imaging can be realized; the work bandwidth can cover the entire electromagnetic spectrum; the resolution is close to or even beyond the diffraction limit; and the device has a wide application prospect in the field of large view field super resolution imaging.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com