Multi-channel focused vortex beam generator of all-dielectric material and preparation method
A technology of dielectric materials and vortex beams, applied in optics, instruments, optical components, etc., can solve problems such as difficult integration, complex optical system, and large volume
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
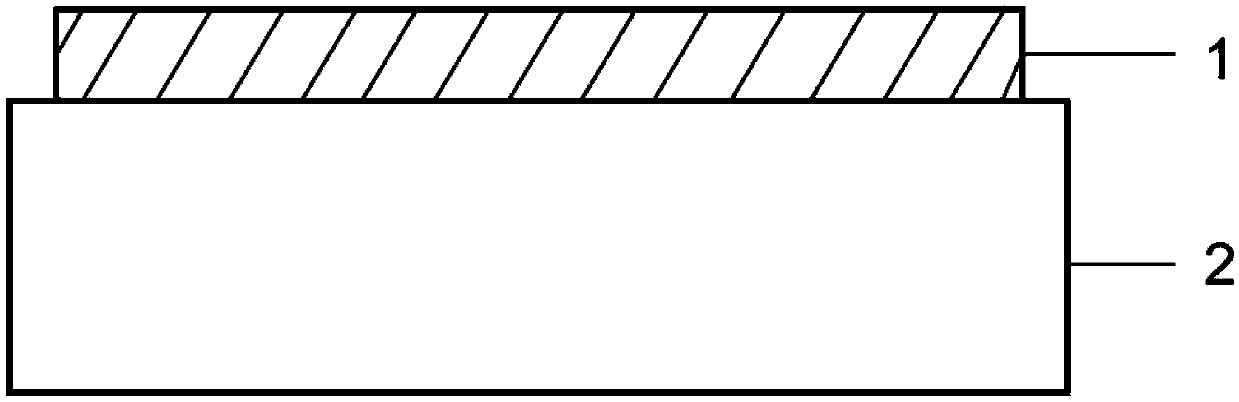
[0034] See figure 1 , a generator of multi-channel focused vortex beams based on all-dielectric materials, including a substrate 2 and a dielectric nanopillar array 1 .
[0035] ZnS nanopillar arrays grown on SiO 2 On the substrate; the height of the nanocolumn is 550nm, the length is 290nm, the width is 70nm, and the period of the nanocolumn is 320nm; in order to achieve the focus of the vortex beam and realize the multiplexing function, according to the principle of holography and the principle of equal optical path, the medium The phase difference Φ that the nanopillar array must compensate for m (x,y,0) satisfies:
[0036]
[0037]
[0038]
[0039] Where (x, y) is the central coordinate of the dielectric nanopillar on the substrate, θ is its corresponding azimuth angle, j is the imaginary unit, i represents the i-th channel, n represents the number of channels, li represents the i-th channel The topological charge number of a vortex beam. (xi,yi,fi) represen...
Embodiment 2
[0048] See figure 1 , a generator of multi-channel focused vortex beams based on all-dielectric materials, including a substrate 2 and a dielectric nanopillar array 1 .
[0049] Si nanopillar arrays grown on SiO 2 On the substrate; the height of the Si nanocolumn is 800nm, the length is 400nm, the width is 120nm, and the period of the nanocolumn is 500nm; in order to achieve the focus of the vortex beam and realize the multiplexing function, according to the principle of holography and the principle of equal optical path, the The phase difference Φ that the dielectric nanopillar array must compensate m (x,y,0) satisfies:
[0050]
[0051]
[0052]
[0053] Where (x, y) is the center coordinate of the dielectric nanopillar on the substrate, and θ is its corresponding azimuth angle. j is the imaginary unit, i represents the i-th channel, n represents the number of channels, and li represents the topological charge number of the vortex beam of the i-th channel. (xi,...
Embodiment 3
[0062] See figure 1 , a generator of multi-channel focused vortex beams based on all-dielectric materials, including a substrate 2 and a dielectric nanopillar array 1 .
[0063] The Si nanopillar array is grown on the MgF2 substrate; the height of the Si nanopillar is 1500nm, the length is 400nm, the width is 100nm, and the period of the nanopillar is 800nm; in order to achieve the focus of the vortex beam and realize the multiplexing function, according to the principle of holography and equal optical path principle, the dielectric nanopillar array must compensate for the phase difference Φ m (x,y,0) satisfies:
[0064]
[0065]
[0066]
[0067] Where (x, y) is the center coordinate of the dielectric nanopillar on the substrate, and θ is its corresponding azimuth angle. j is the imaginary unit, i represents the i-th channel, n represents the number of channels, and li represents the topological charge number of the vortex beam of the i-th channel. (xi,yi,fi) rep...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com