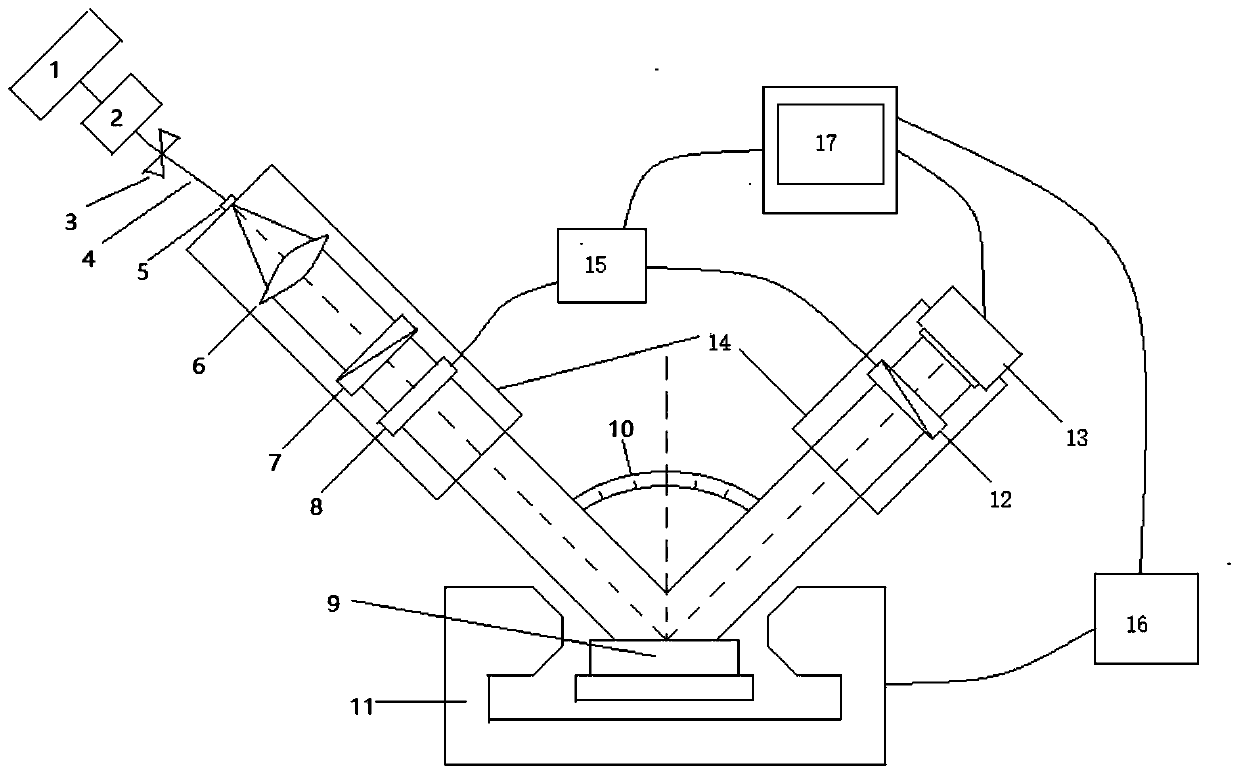
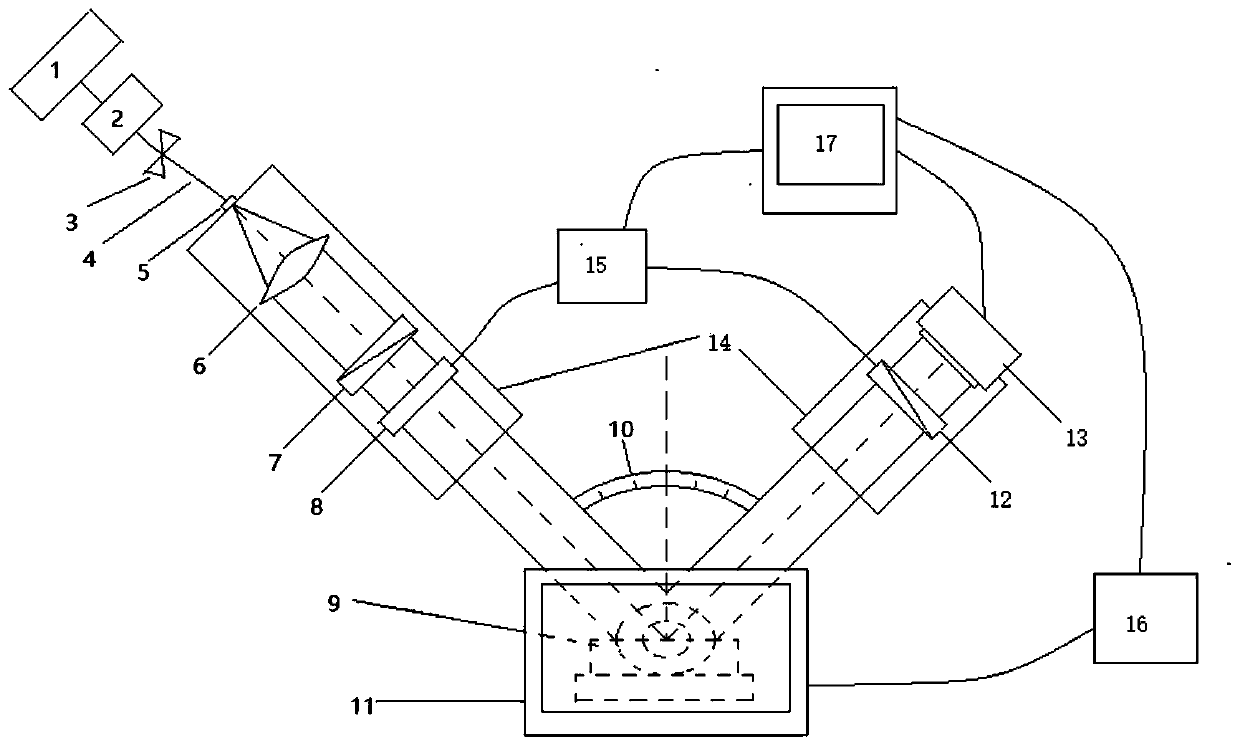
Patents
Literature
119results about How to "Fast modulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods of hyperdoping semiconductor materials and hyperdoped semiconductor materials and devices
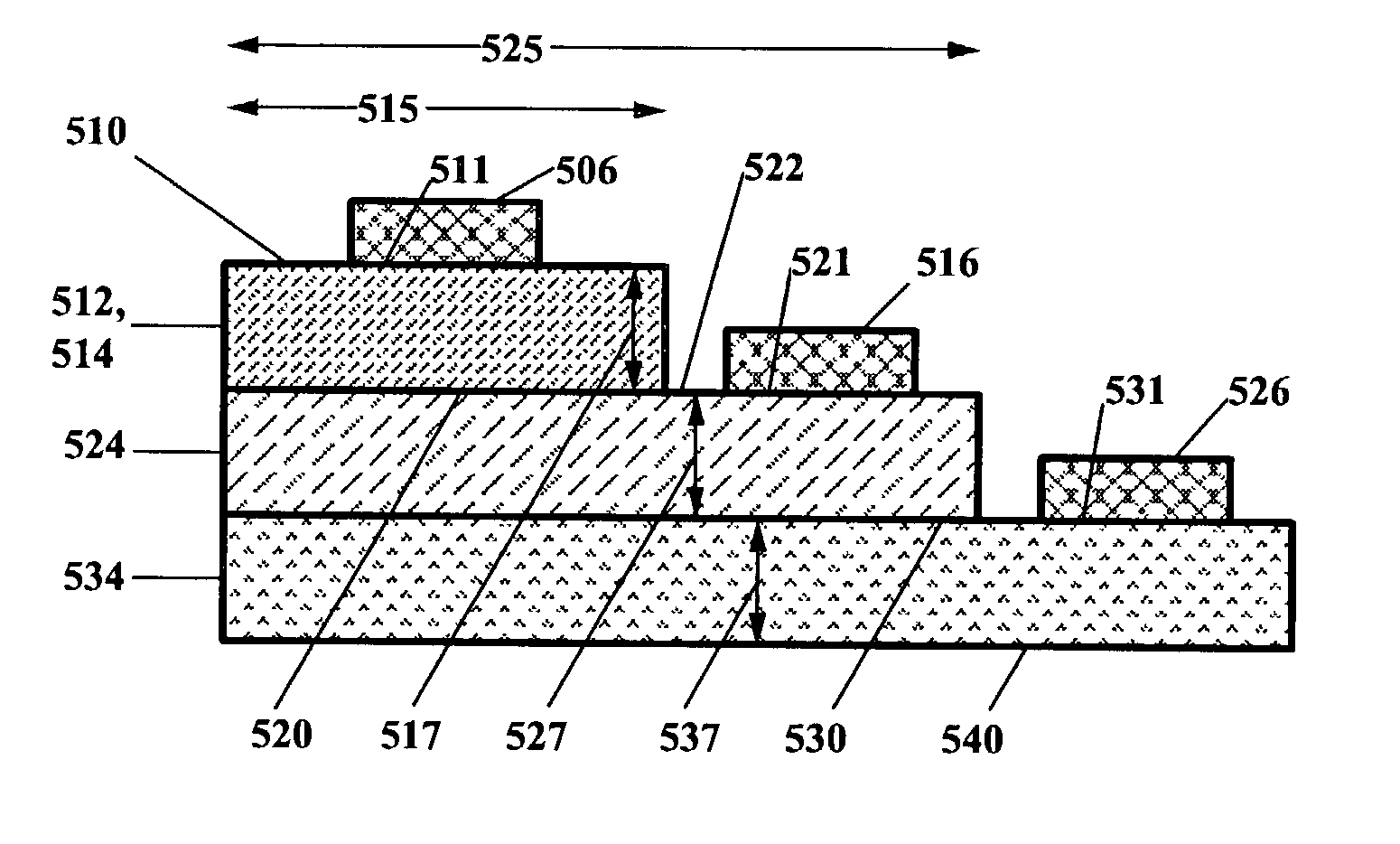
InactiveUS20030121468A1Avoiding and mitigating formationEasy to operateTransistorPolycrystalline material growthSide effectSemiconductor materials
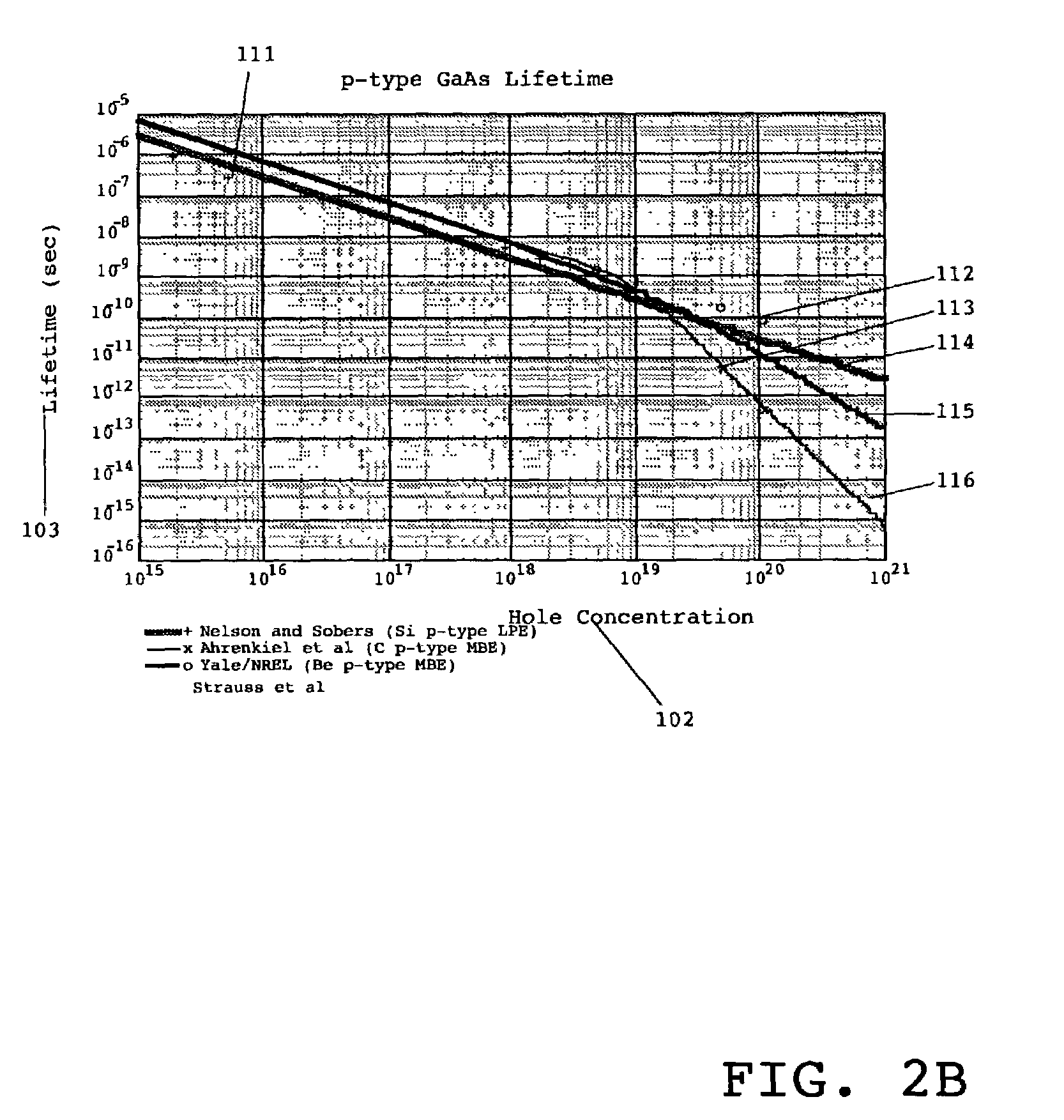
Methods are disclosed for producing highly doped semiconductor materials. Using the invention, one can achieve doping densities that exceed traditional, established carrier saturation limits without deleterious side effects. Additionally, highly doped semiconductor materials are disclosed, as well as improved electronic and optoelectronic devices / components using said materials. The innovative materials and processes enabled by the invention yield significant performance improvements and / or cost reductions for a wide variety of semiconductor-based microelectronic and optoelectronic devices / systems. Materials are grown in an anion-rich environment, which, in the preferred embodiment, are produced by moderate substrate temperatures during growth in an oxygen-poor environment. The materials exhibit fewer non-radiative recombination centers at higher doping concentrations than prior art materials, and the highly doped state of matter can exhibit a minority carrier lifetime dominated by radiative recombination at higher doping levels and higher majority carrier concentrations than achieved in prior art materials. Important applications enabled by these novel materials include high performance electronic or optoelectronic devices, which can be smaller and faster, yet still capture or emit light efficiently, and high performance electronics, such as transistors, which can be smaller and faster, yet cooler.
Owner:YALE UNIV
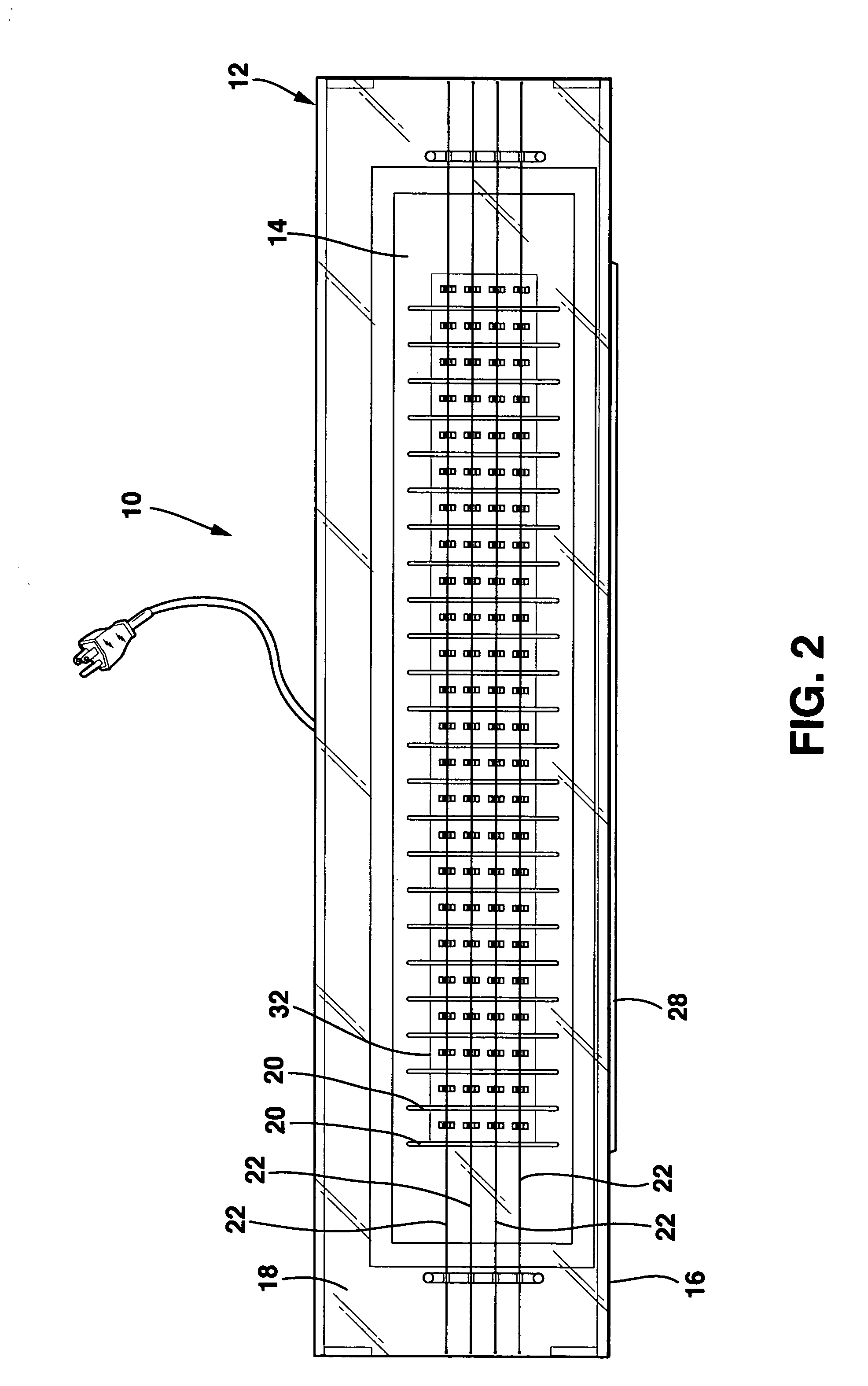
Simplified water-bag technique for magnetic susceptibility measurements on the human body and other specimens
InactiveUS7047059B2Less-expensive fabricationLess-expensive useMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesHuman bodyMagnetic susceptibility
A probe instrument using room-temperature sensor(s) that can measure variations in magnetic susceptibilities. The instrument has sufficient resolution to monitor paramagnetic materials in a human body, such as iron in a human liver, by noninvasively examining patients with iron-overload diseases. The instrument includes room temperature magnetic sensors, and detects the sample, that is, the tissue response to an alternating current field applied by an applied field coil. The applied field coil dimensions are chosen so that the applied field is optimized for maximum response from the liver while minimizing the effects due to the overlying abdominal tissue and at the same time not unduly increasing the sensitivity of the instrument to the lung. To overcome variations in the sensor output due to fluctuations in the applied field, change in the ambient temperature and mechanical relaxation of the instrument, the sensor-sample distance is modulated. The detector assembly is oscillated while the examined patient remains stationary. An improved water-bag technique is employed to eliminate background tissue response. The detector assembly forms part of a probe instrument for performing noninvasively the paramagnetic concentration of a patient.
Owner:QUANTUM MAGNETICS
Musical instrument
ActiveUS20080028920A1Quality improvementEasy to implementElectrophonic musical instrumentsMusical toneSpeech sound
A musical device is disclosed that generates note tones, influences the sound of notes that are generated independently and performs a variety of user defined or user controlled activities. These activities include but are not limited to producing musical notes, determining, influencing or changing the sound, quality, voice, volume or other characteristics of a note, activating and coordinating the replay of stored loops, recording, editing and playing user created pieces previously produced and controlling peripheral devices such as lighting. The musical device uses a combination of strings and frets to locate notes on a fingerboard that a user may activate. The notes correspond to locations on the fingerboard. As a result, the invention includes a system to generate a sound corresponding to a note selected and activated according to preselected parameters such as the voice (e.g., trumpet, violin). A user's intent to play a particular note is preferably confirmed by a system of sensors corresponding to each note position that confirms a user's intent to play a particular note. The musical device also includes one or more switches that activate functions, loops or voices corresponding to note positions on the fingerboard.
Owner:ZIVIX
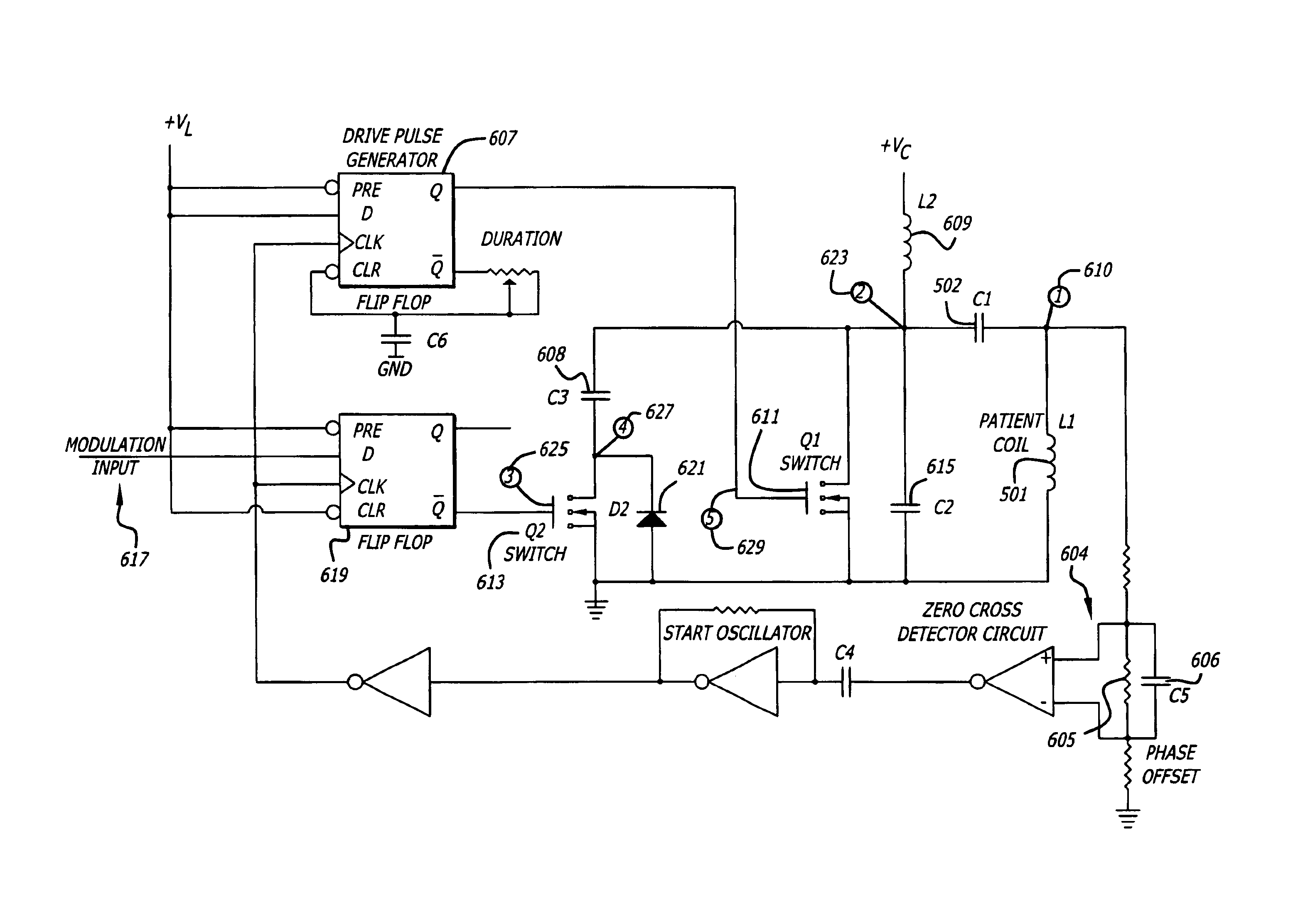
Switched reactance modulated E-class oscillator design
InactiveUS6864755B2Highly resonant operationRapid amplitude modulationMultiple input and output pulse circuitsElectrotherapyPropagation delayDetector circuits
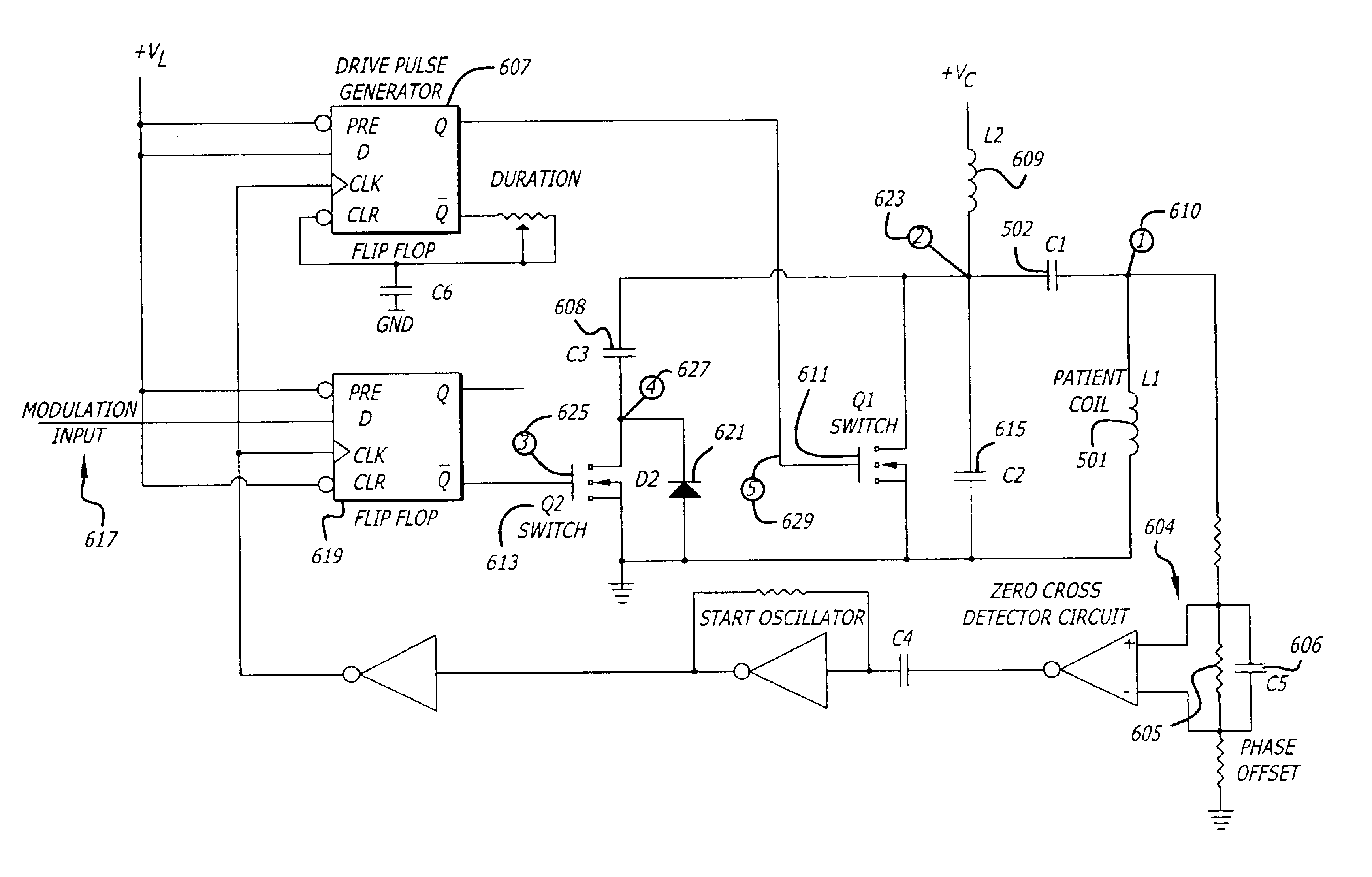
A modulated Class E transmitter is disclosed. In one embodiment of the invention, the modulated Class E oscillator achieves high coil currents (˜1A) and voltages (˜500V) with low power components by precisely timed injection of current when the oscillating current in the inductor passes through zero. A detector circuit is used to trigger the current injection at the appropriate instant regardless of changes in the resonant frequency of the system. Its phase can be adjusted to compensate for propagation delays in the drive circuitry, while amplitude modulation is accomplished by switching in additional reactive conductance to increase the current injected into the tank circuit.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN INST FOR BIOMEDICAL ENG AT THE UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Musical instrument
ActiveUS7598449B2Quality improvementEasy to implementElectrophonic musical instrumentsMusical toneSpeech sound
A musical device is disclosed that generates note tones, influences the sound of notes that are generated independently and performs a variety of user defined or user controlled activities. These activities include but are not limited to producing musical notes, determining, influencing or changing the sound, quality, voice, volume or other characteristics of a note, activating and coordinating the replay of stored loops, recording, editing and playing user created pieces previously produced and controlling peripheral devices such as lighting. The musical device uses a combination of strings and frets to locate notes on a fingerboard that a user may activate. The notes correspond to locations on the fingerboard. As a result, the invention includes a system to generate a sound corresponding to a note selected and activated according to preselected parameters such as the voice (e.g., trumpet, violin). A user's intent to play a particular note is preferably confirmed by a system of sensors corresponding to each note position that confirms a user's intent to play a particular note. The musical device also includes one or more switches that activate functions, loops or voices corresponding to note positions on the fingerboard.
Owner:ZIVIX
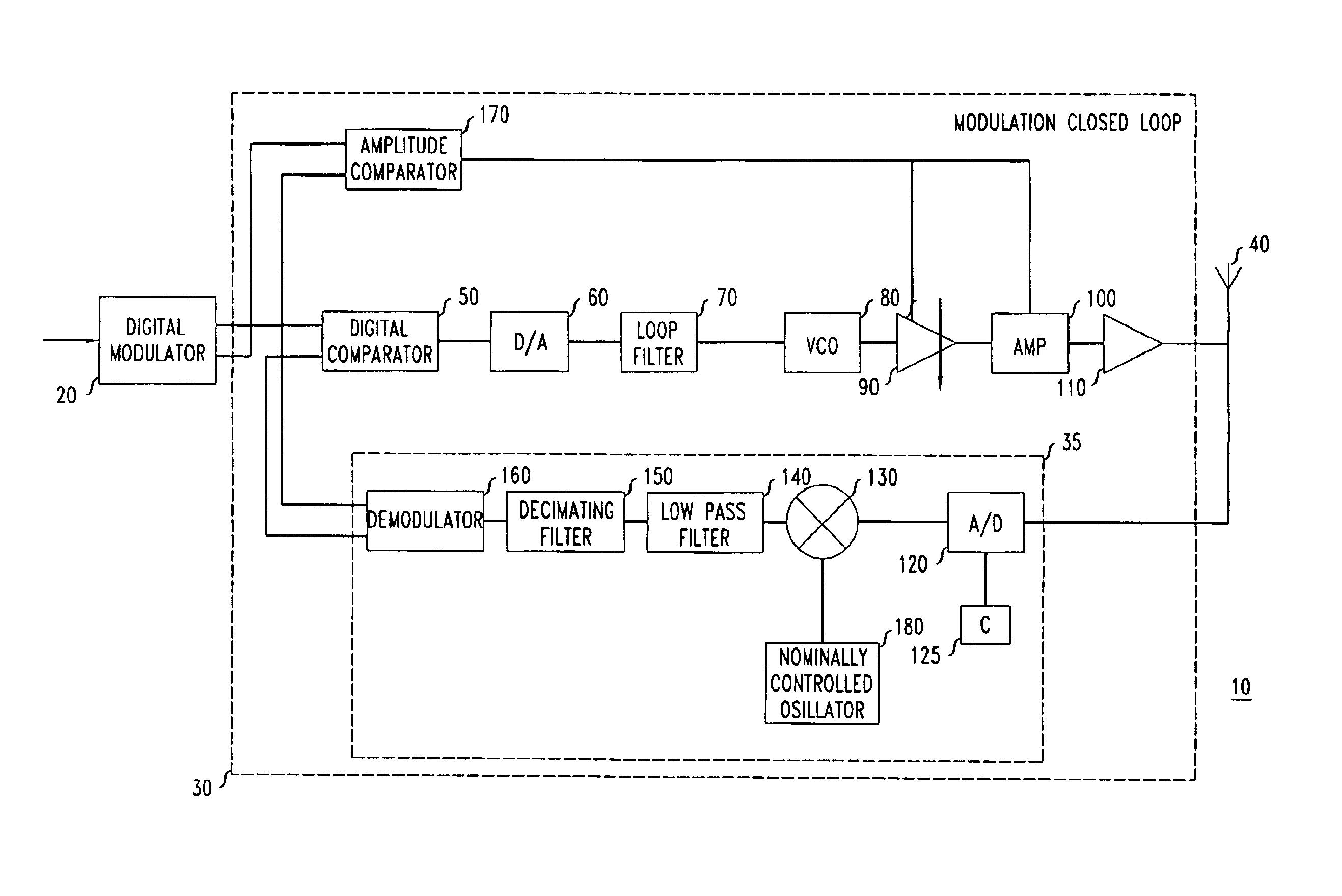
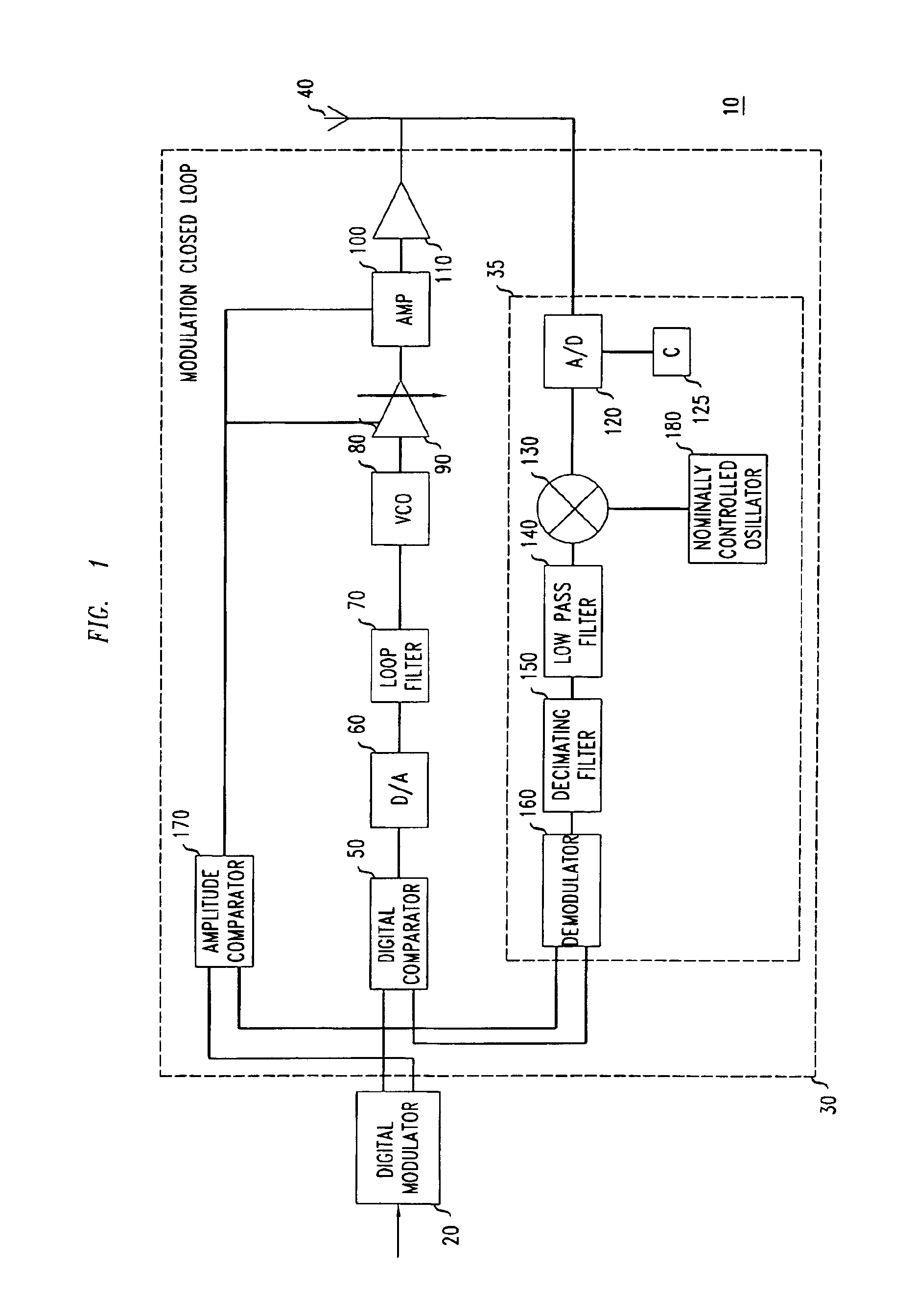
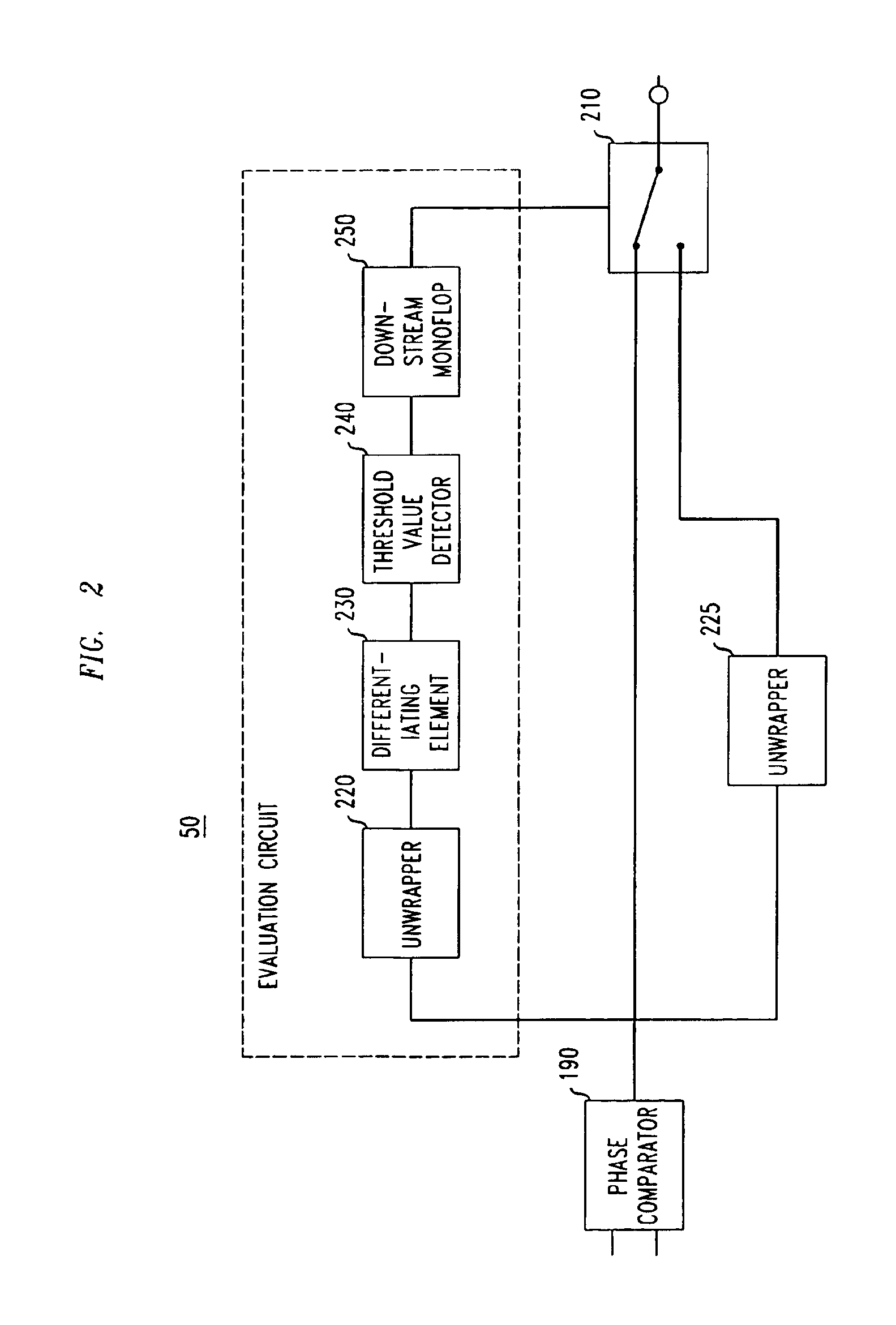
Transmitter device having a modulation closed loop
InactiveUS6898257B2Rapid locking-in characteristicFast signal transmissionResonant long antennasAngle modulation detailsClosed loopMobile radio
The invention relates, inter alia, to a transmitter device, in particular for a base transceiver station in a mobile radio system, which has a digital modulator for making available a signal containing a phase information, and a modulation closed loop having a digital phase comparator operating at baseband whose first input is connected to the output of the digital modulator. In addition, a controllable oscillator is provided for generating an RF transmission signal at a controllable transmission frequency, a device which is assigned to the controllable oscillator and has the purpose of converting the RF transmission signal into a baseband signal containing a phase information. The output of the converter device is connected to a second input of the digital phase comparator.A GSM transmitter which has such a modulation closed loop exhibits, in terms of its out-band noise and interference characteristics, significantly improved properties in comparison with a GSM transmitter which does not include a modulation loop.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Dispersive modulation-based non-mirror image optimal frequency domain imaging system and method
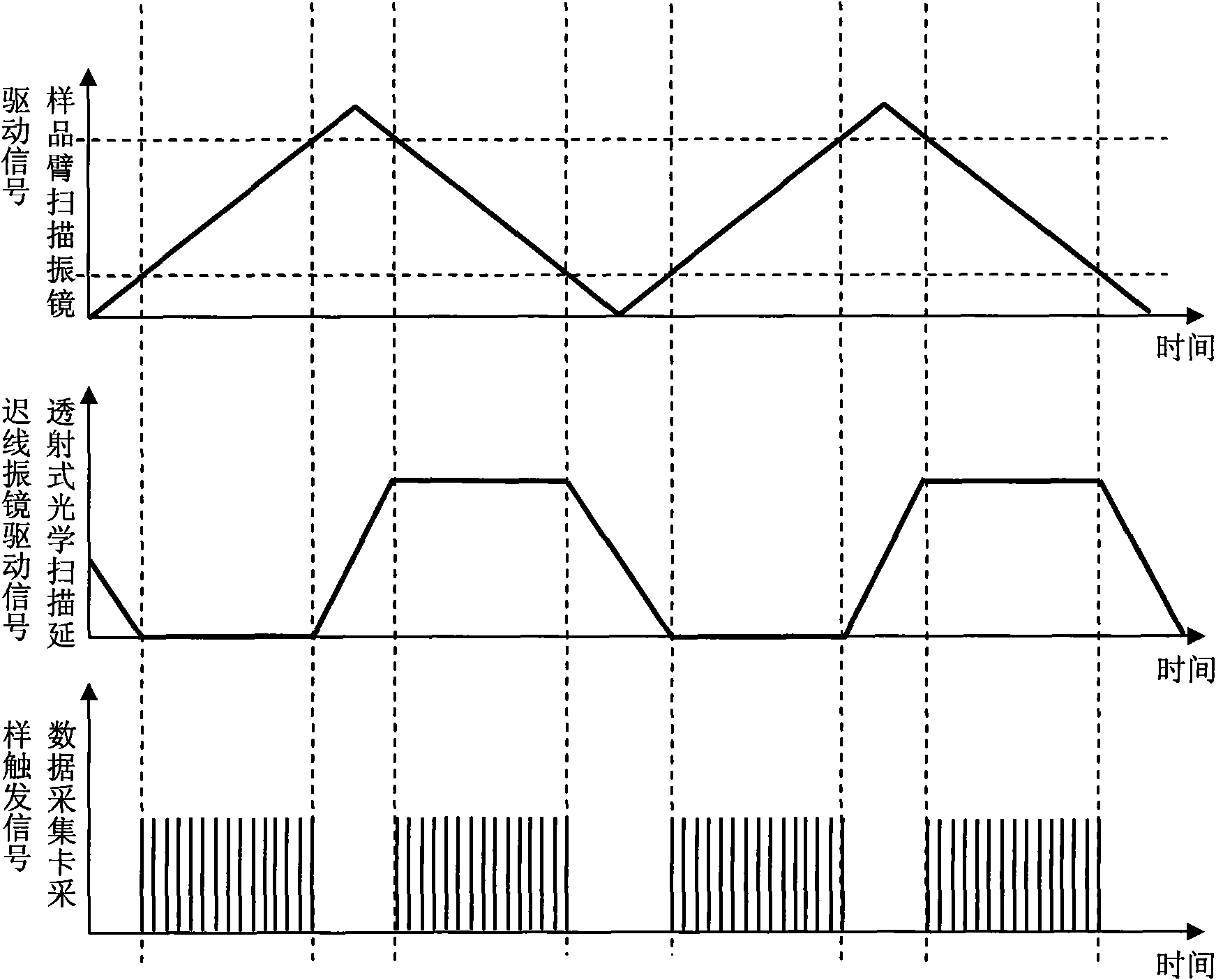
InactiveCN101803908AFast modulationSubtract the imaginary partDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFourier transform on finite groupsSample image
The invention discloses a dispersive modulation-based non-mirror image optimal frequency domain imaging system and a dispersive modulation-based non-mirror image optimal frequency domain imaging method. In the system, a transmission-type optimal scanning delay line is arranged in a reference arm for modulating dispersion so as to ensure the identity of the axial positions of a sample under different dispersion states; by changing a rotation angle of an oscillating mirror in the transmission optimal scanning delay line, the rapid modulation of dispersion is realized, and two group of interference spectrum signals of the same sample are acquired under two different dispersion states; the two group of acquired interference spectrum signals are respectively multiplied by corresponding dispersion compensation factors so as to accurately compensate the dispersion of imaginary part subjected to corresponding Fourier transform; subtraction operation is performed on the two group of interference spectrum signals subjected to dispersion compensation, then, the imaginary part of the corresponding repeated reflection signal disappears, and the real part still contains the dispersion factor; and finally, the interference spectrum signals subjected to subtraction are subjected to dispersive compensation again and then subjected to Fourier inverse transformation so as to obtain the actual reflection signal of the sample for non-mirror image reconstruction of the sample image.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Methods of hyperdoping semiconductor materials and hyperdoped semiconductor materials and devices
InactiveUS7179329B2Easy to operateIncrease computing speedTransistorPolycrystalline material growthSide effectSemiconductor materials
Methods are disclosed for producing highly doped semiconductor materials. Using the invention, one can achieve doping densities that exceed traditional, established carrier saturation limits without deleterious side effects. Additionally, highly doped semiconductor materials are disclosed, as well as improved electronic and optoelectronic devices / components using said materials. The innovative materials and processes enabled by the invention yield significant performance improvements and / or cost reductions for a wide variety of semiconductor-based microelectronic and optoelectronic devices / systems.Materials are grown in an anion-rich environment, which, in the preferred embodiment, are produced by moderate substrate temperatures during growth in an oxygen-poor environment. The materials exhibit fewer non-radiative recombination centers at higher doping concentrations than prior art materials, and the highly doped state of matter can exhibit a minority carrier lifetime dominated by radiative recombination at higher doping levels and higher majority carrier concentrations than achieved in prior art materials. Important applications enabled by these novel materials include high performance electronic or optoelectronic devices, which can be smaller and faster, yet still capture or emit light efficiently, and high performance electronics, such as transistors, which can be smaller and faster, yet cooler.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Compact laser source for active illumination for hybrid three-dimensional imagers
ActiveUS20150092258A1Improve reliabilityGood precisionLaser detailsUsing optical meansLaser sourceActive illumination
The invention generally relates to hybrid three-dimensional imagers and to a laser source for active illumination for hybrid three-dimensional imagers (i.e. 3D imagers that make combined use of different 3D imaging technologies). The invention is applicable to three-dimensional imaging systems which use a combination of different imaging techniques (hybrid technologies) to achieve a higher precision or a higher level of reliability.
Owner:IEE INT ELECTRONICS & ENG SA
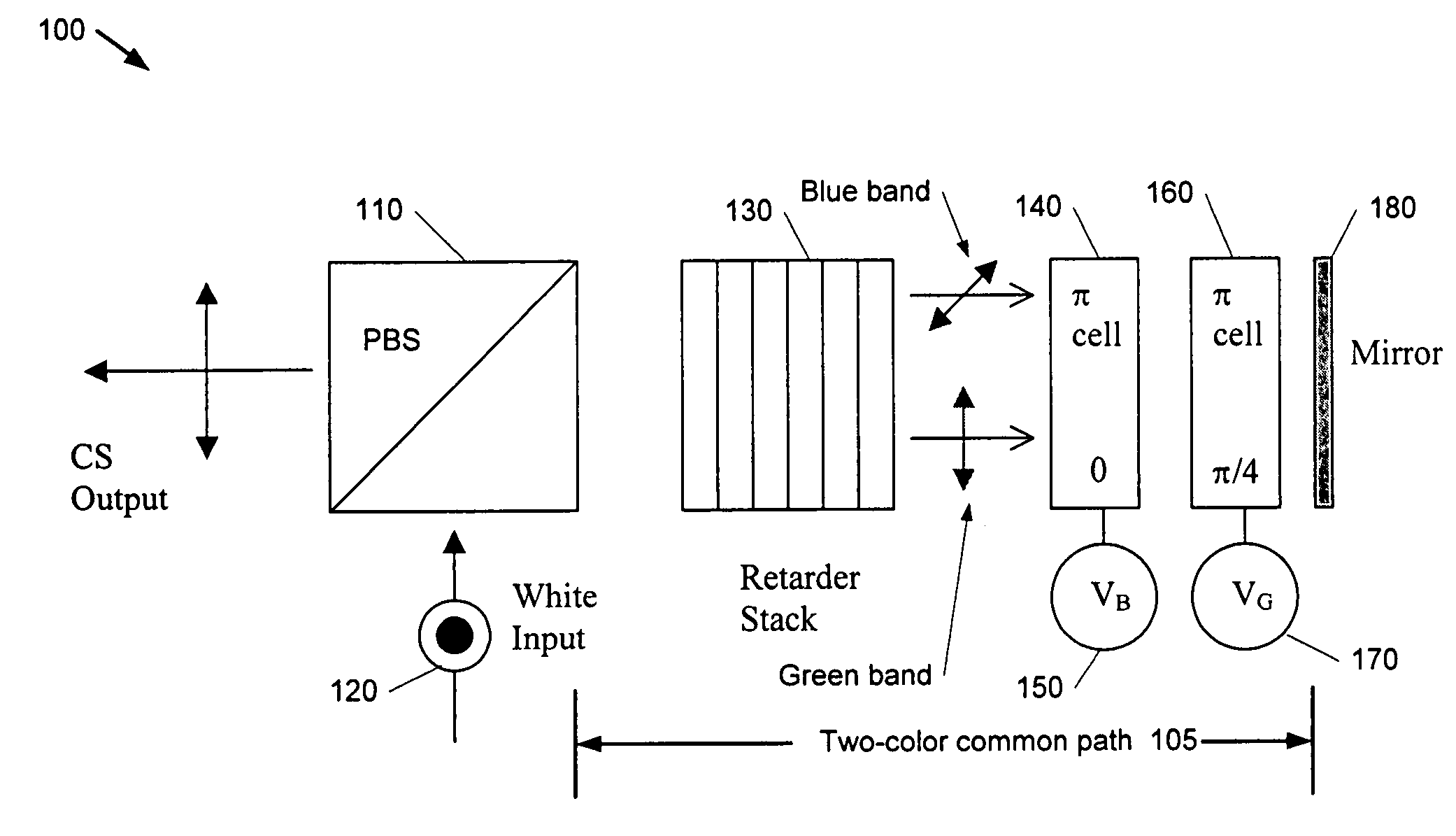
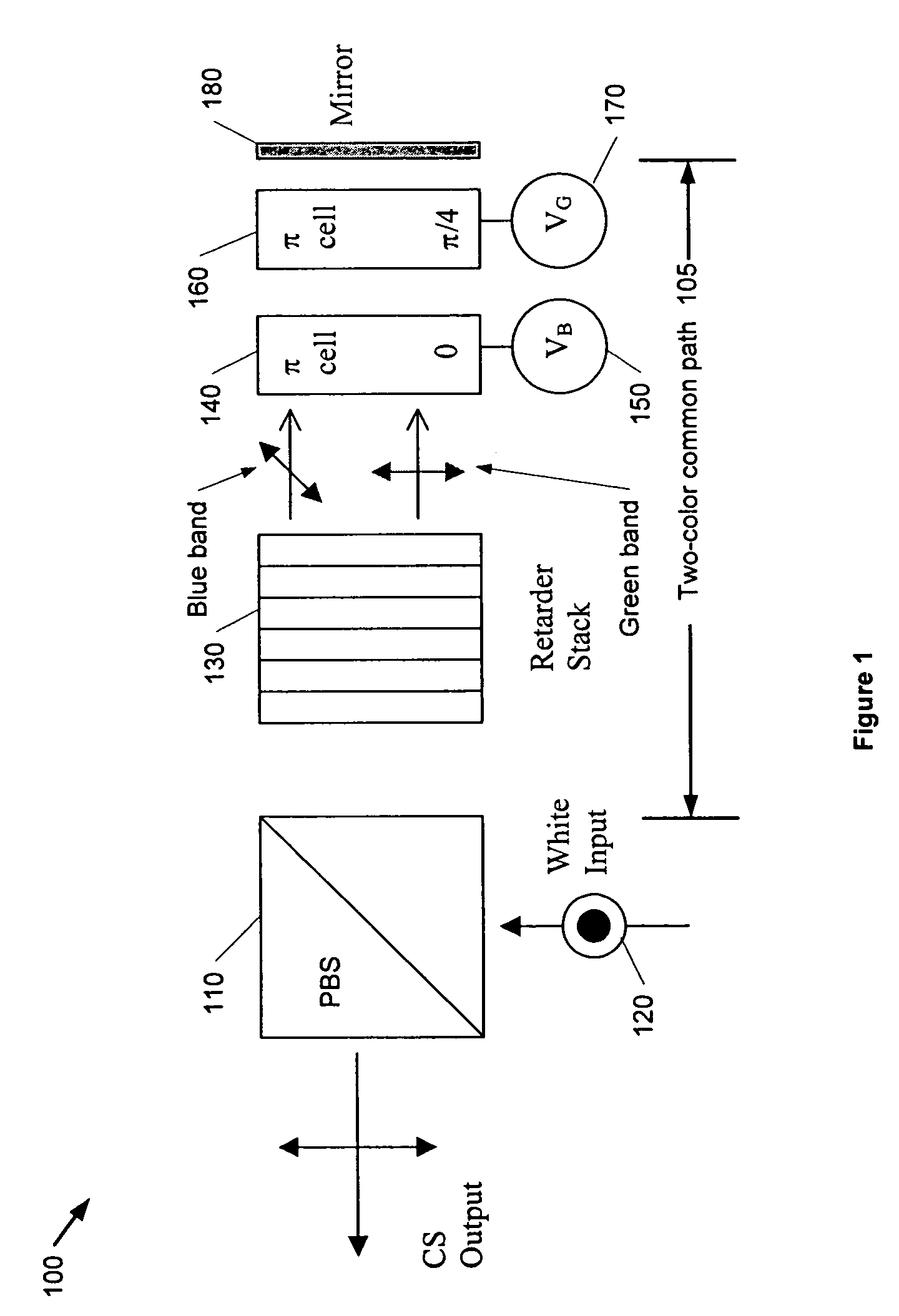
Split-path color switching system and method
InactiveUS7195356B1Improve transmittanceQuick switchProjectorsColor photographyPhysicsSingle polarization
The present application describes a retarder stack color switch using a single polarization analyzer for reflective-mode projection displays. The single polarization analyzer permits additive mode switching, which optimizes the chrominance of the additive primary outputs and the black state. Moreover, the single analyzer color switch provides a white state, which is frequently used in sequential systems. The single analyzer color switch overcomes some of the cost and manufacturing challenges associated with conventional transmissive full color switches based on retarder-stack-filters. The single analyzer color switch according to an embodiment uses a split-path so that relatively weak colors can follow a “high-efficiency” path.
Owner:REAID INC
Switched reactance modulated E-class oscillator design
InactiveUS6889087B2High operating requirementsEfficient powerElectrotherapyAmplitude modulation with voltage-dependent capacitorPropagation delayDetector circuits
A modulated Class E transmitter is disclosed. In one embodiment of the invention, the modulated Class E oscillator achieves high coil currents (˜1 A) and voltages (˜500V) with low power components by precisely timed injection of current when the oscillating current in the inductor passes through zero. A detector circuit is used to trigger the current injection at the appropriate instant regardless of changes in the resonant frequency of the system. Its phase can be adjusted to compensate for propagation delays in the drive circuitry, while amplitude modulation is accomplished by switching in additional reactive conductance to increase the current injected into the tank circuit. Frequency modulation is accomplished in an alternate embodiment.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN INST FOR BIOMEDICAL ENG AT THE UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
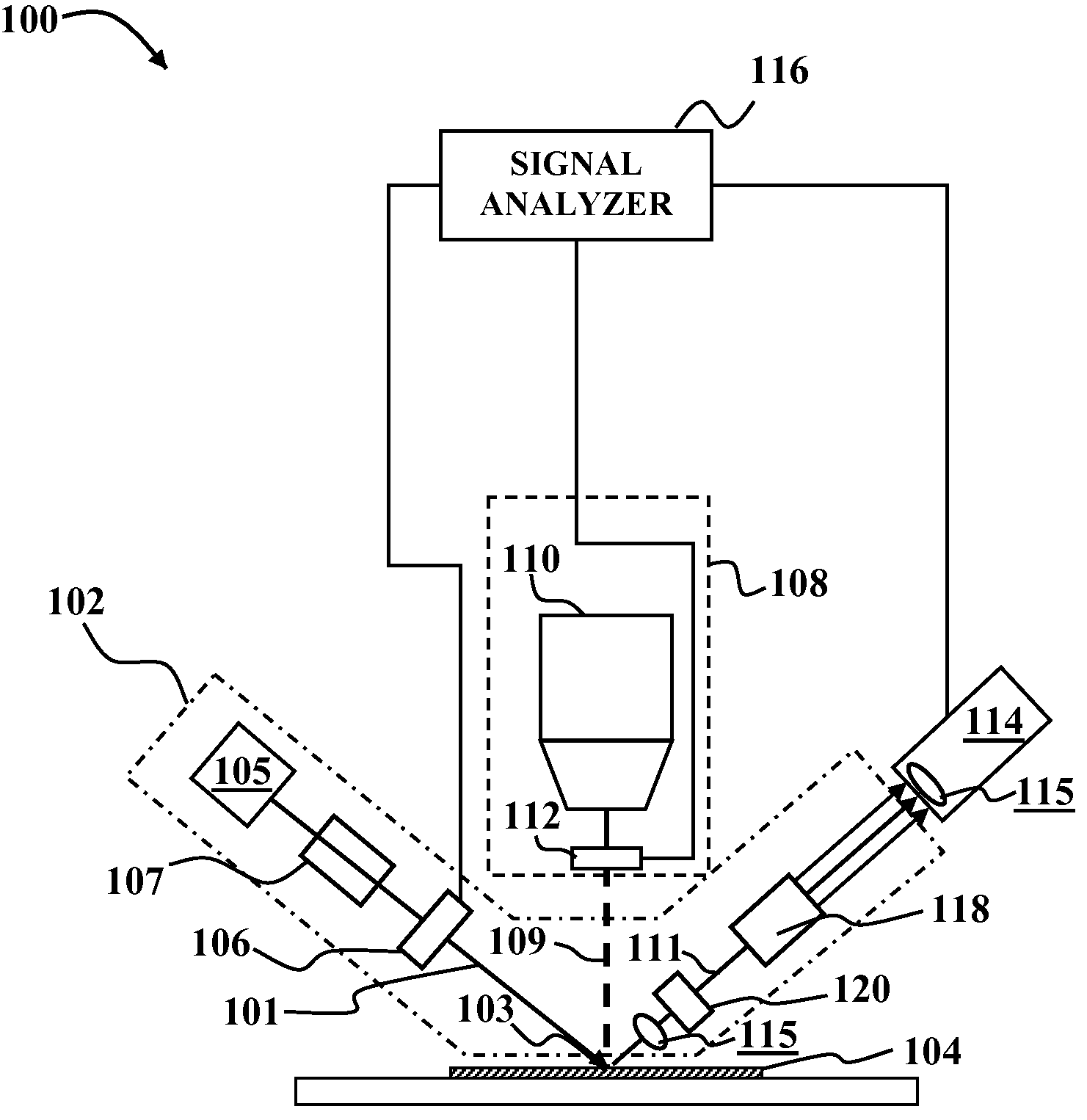
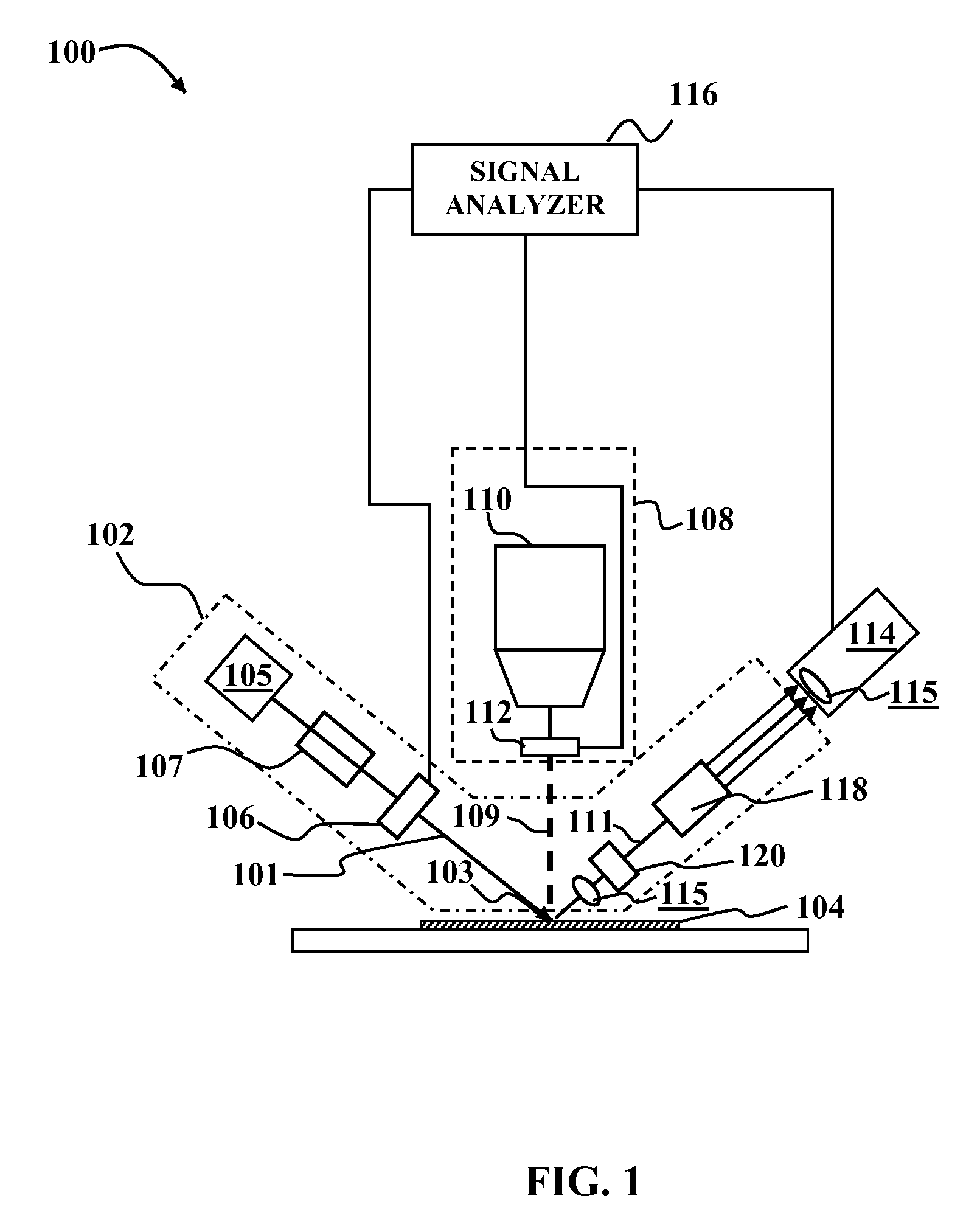
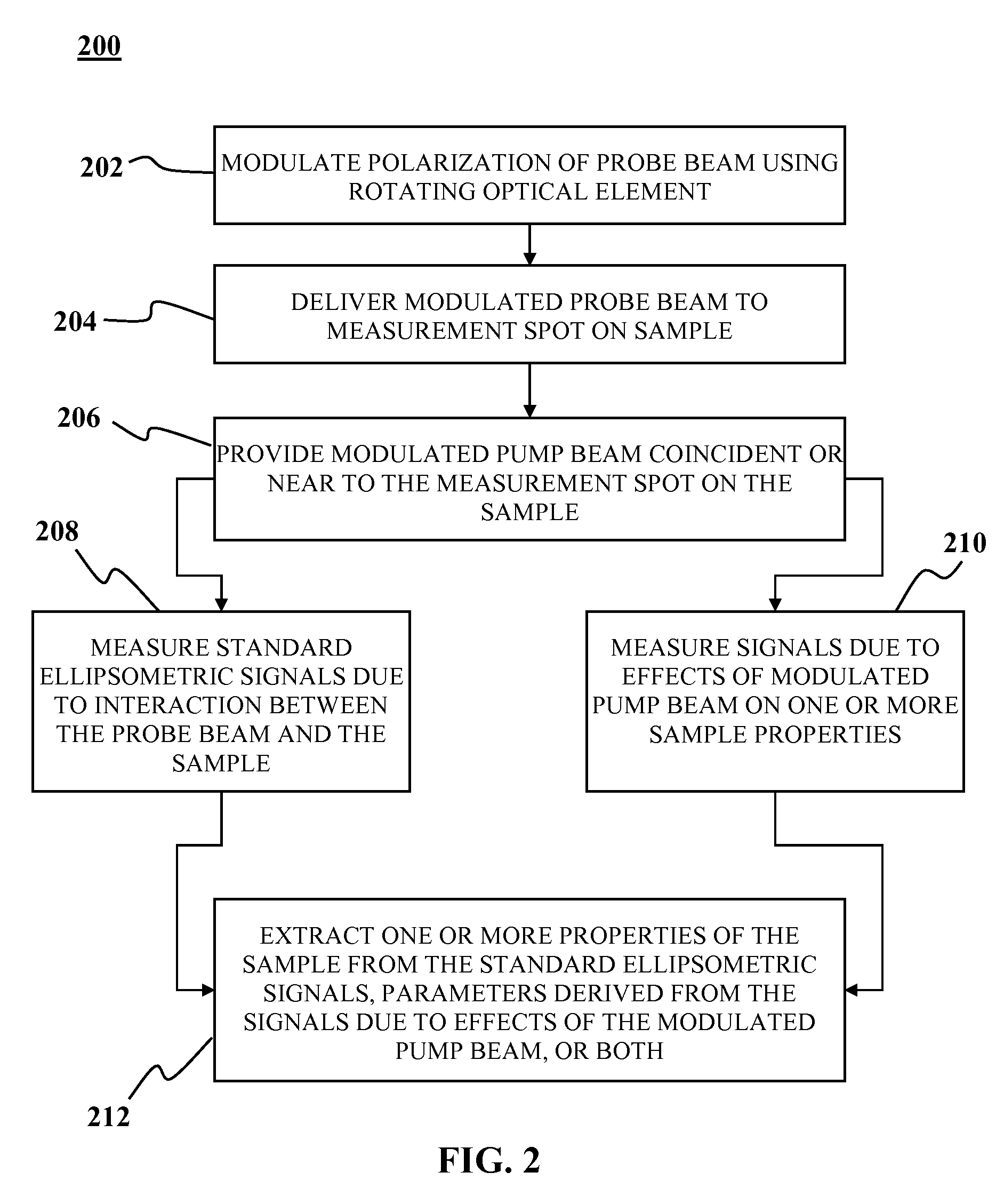
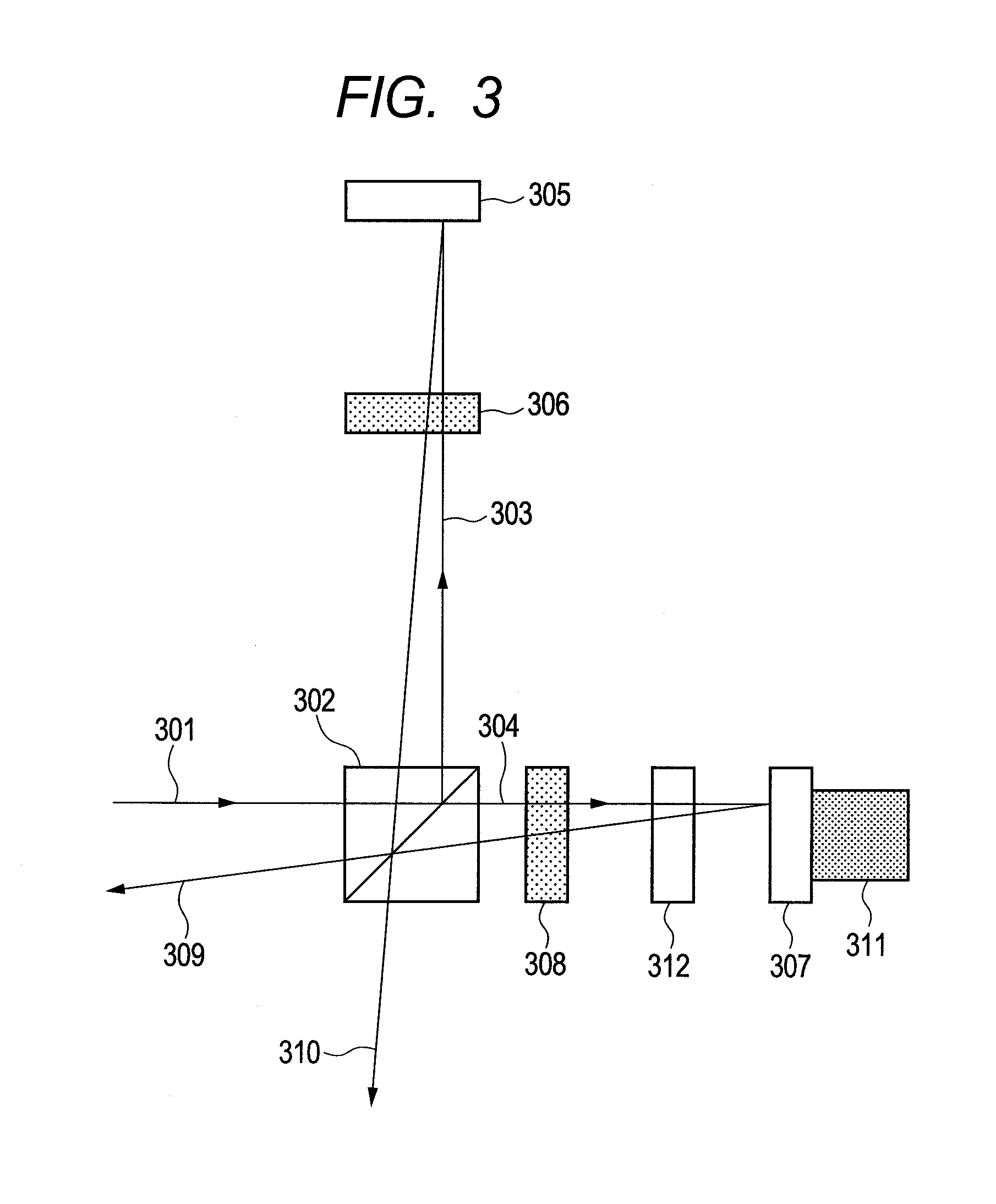
Optical measurment systems and methods
InactiveUS7847937B1High sensitivityImprove accuracyRadiation pyrometryBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsSignal analyzerLight beam
An optical measurement system includes a rotating element ellipsometer comprising a radiant source and a rotating optical element coupled to the radian source, an optical system to provide a modulated pump beam, a detection system optically coupled to the ellipsometer and a signal analyzer. The rotating element ellipsometer is configured to deliver a probe beam to a measurement spot on a sample and to measure one or more ellipsometric parameters of the sample at one or more discrete wavelengths or wavelength ranges, or a plurality of wavelengths across a wavelength range. Methods for determining sample characteristics from radiation scattered, reflected, diffracted or otherwise emitted from a sample surface using the optical measurement systems are also disclosed.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Compact laser source for active illumination for hybrid three-dimensional imagers
ActiveUS9318877B2Quick switchHigh-frequency modulationLaser detailsUsing optical meansCombined useImaging technique
The invention generally relates to hybrid three-dimensional imagers and to a laser source for active illumination for hybrid three-dimensional imagers (i.e. 3D imagers that make combined use of different 3D imaging technologies). The invention is applicable to three-dimensional imaging systems which use a combination of different imaging techniques (hybrid technologies) to achieve a higher precision or a higher level of reliability.
Owner:IEE INT ELECTRONICS & ENG SA
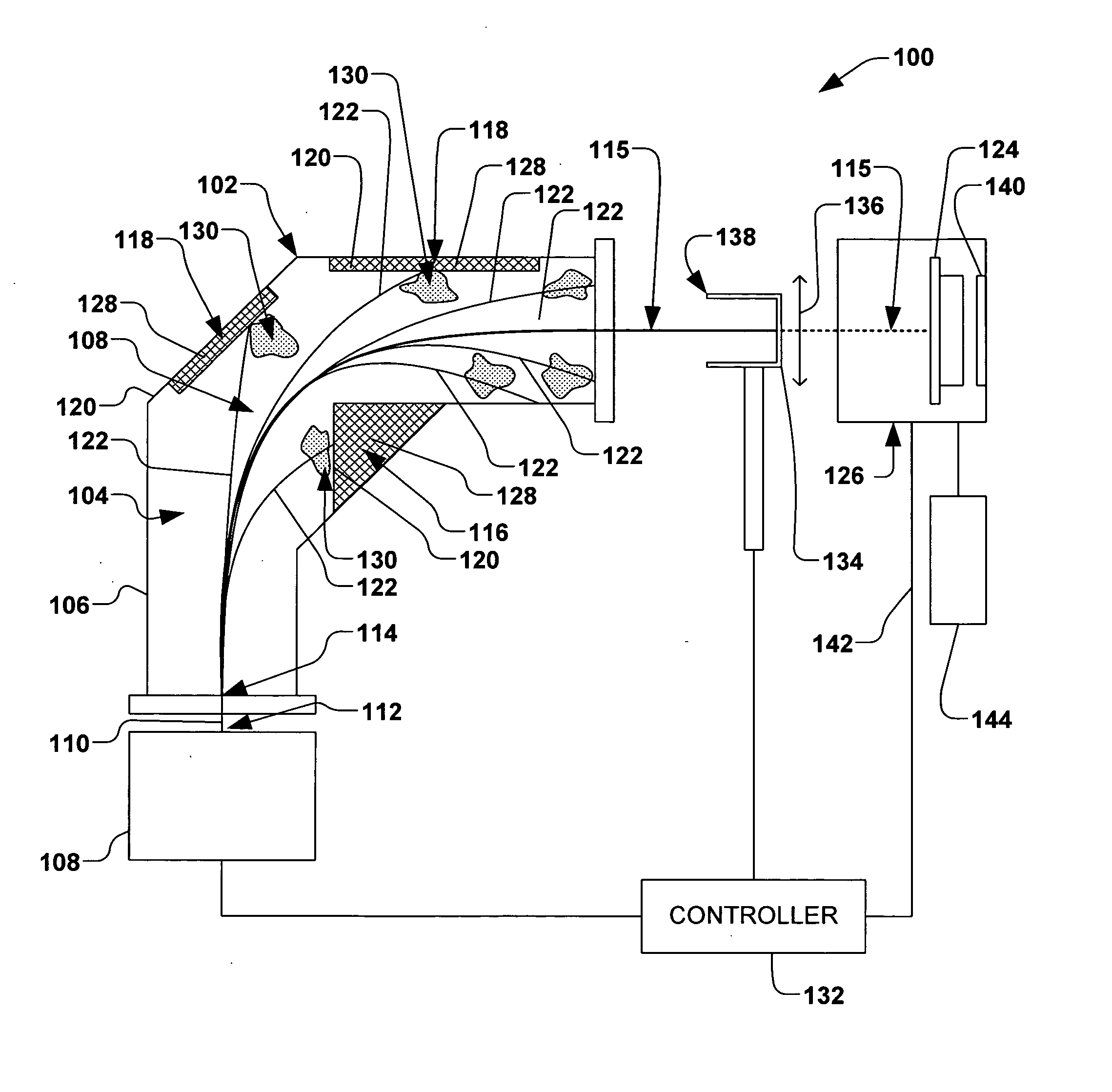
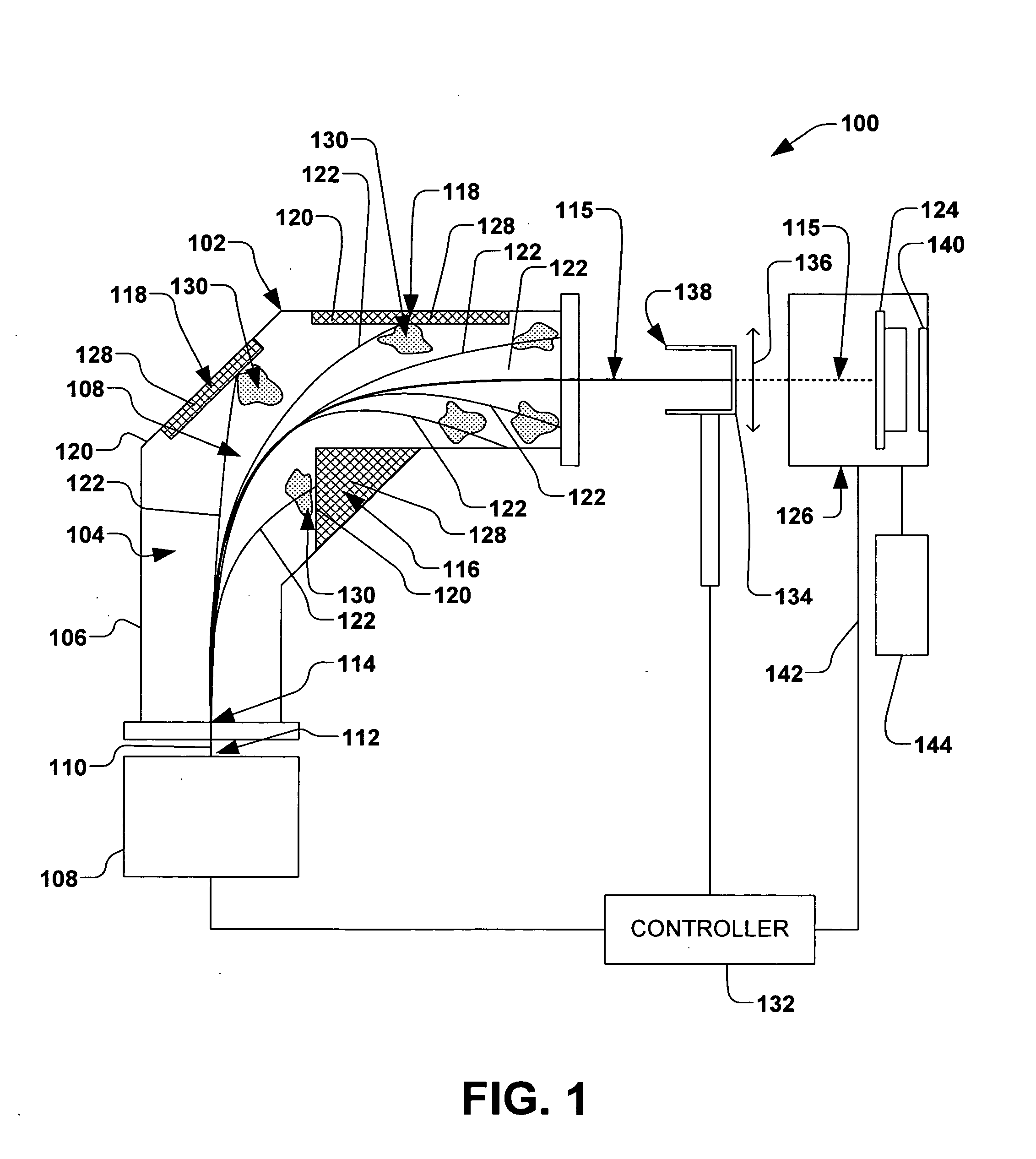
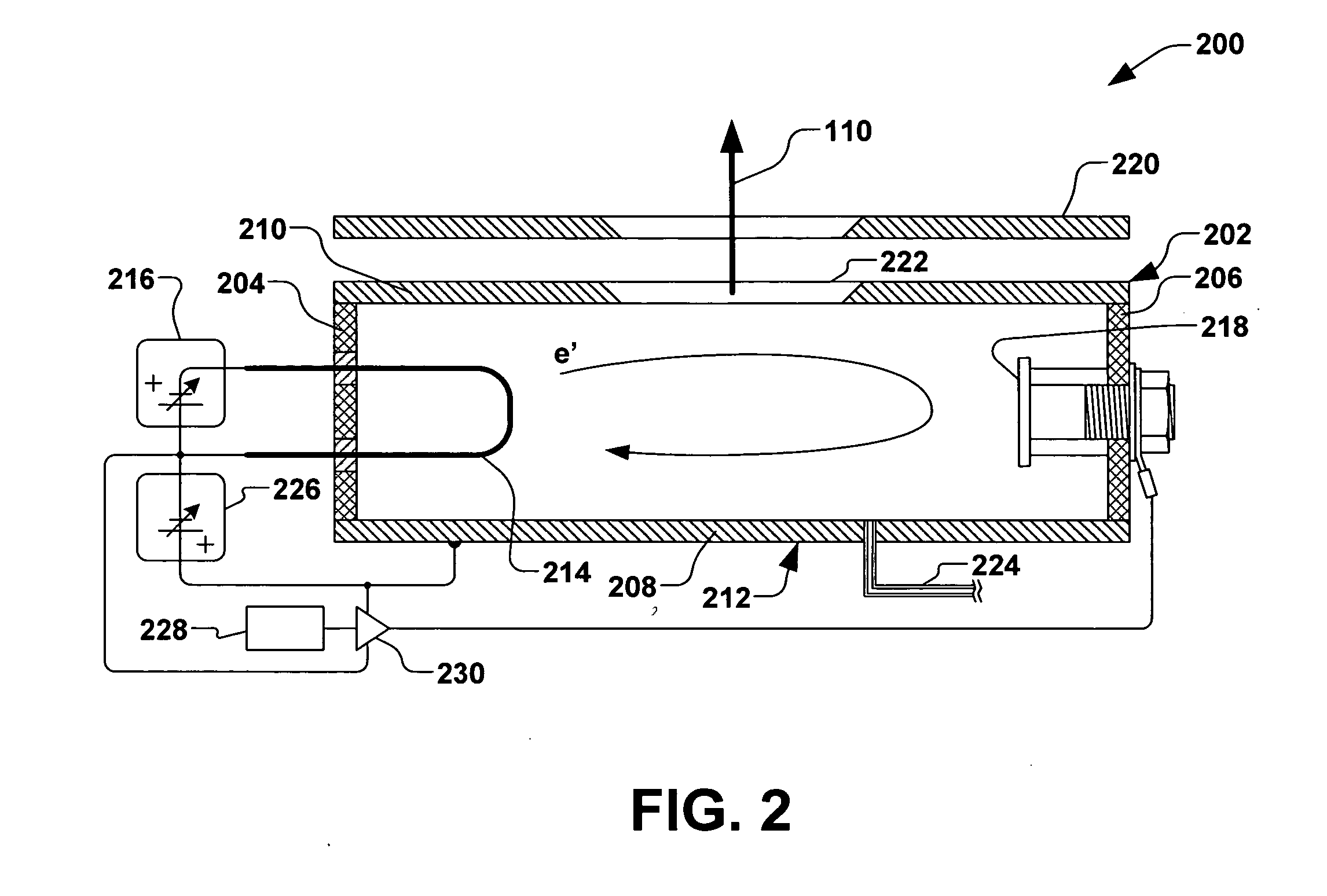
Particulate prevention in ion implantation
ActiveUS20060284116A1Reduce pollutionDeleterious effectThermometer detailsLaser detailsEngineeringParticle contamination
A system and method for mitigating contamination in an ion implantation system is provided. The system comprises an ion source, a power supply operable to supply power to a filament and mirror electrode of the ion source, a workpiece handling system, and a controller, wherein the ion source is selectively tunable via the controller to provide rapid control of a formation of an ion beam. The controller is operable to selectively rapidly control power to the ion source, therein modulating a power of the ion beam between an implantation power and a minimal power in less than approximately 20 microseconds based, at least in part, to a signal associated with a workpiece position. Control of the ion source therefore mitigates particle contamination in the ion implantation system by minimizing an amount of time at which the ion beam is at the implantation current.
Owner:AXCELIS TECHNOLOGIES
Spectrum magneto-optical ellipsometry analysis device of rotary compensator as well as application thereof
ActiveCN110333191AWide spectral rangeQuick analysisPolarisation-affecting propertiesUsing optical meansPolarizerMotor control
The invention discloses a spectrum magneto-optical ellipsometry analysis device of a rotary compensator as well as application thereof. The spectrum magneto-optical ellipsometry analysis device comprises a light source module, a light path module, a magnetic field module, a sample table, a motor control module and a detection and analysis module, the light path module comprises a collimating lens,a polarizer, a compensator and a polarization analyzer, the detection and analysis module comprises a computer and a detector, the collimating lens, the polarizer, the compensator, the sample table,the polarization analyzer and the detector are sequentially arranged along a light path direction, the polarizer and the compensator are located in an incidence light path, the polarization analyzer is located in an emergence light path, and the incidence light path and the emergence light path are located at the two sides of the sample table and respectively keep an included angle Phi with normalof the sample table. The device disclosed by the invention can represent optical and magnetic parameters of a magnetic film material under longitudinal or poloidal magneto-optical Kerr effect, can obtain thickness, optical parameters and magnetic parameters of a magnetic film sample during one test and is relatively high in automation degree.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Use of individual blade control on a propeller or rotor in axial flight for the purpose of aerodynamic braking and power response modulation
ActiveUS20180346111A1Improve aircraft flight dynamicsImproving aerodynamic brakingGas turbine type power plantsWing lift eficiencyAerodynamic dragDrive shaft
Systems and methods are contemplated for favorably improving flight dynamics of aircraft, including enhanced aerodynamic braking and improved flight maneuverability. Air braking systems selectively position a first set of blades at a negative thrust pitch to product a net negative thrust across first and second sets of blades, while balancing torque of the drive shafts to zero. First and second sets of IBC blades can be driven by the same shaft or torque-linked shafts. Flight maneuver systems operate a powerplant at a high power mode, and dissipate the energy from the high power output by positioning a first set of IBC blades at a low efficiency pitch while maintaining constant thrust. As increased or rapid flight maneuverability is required, the first set of blades is positioned toward a high efficiency pitch to instantly increase thrust to the aircraft without requiring a related increase in energy output from the powerplant.
Owner:KAREM AIRCRAFT INC
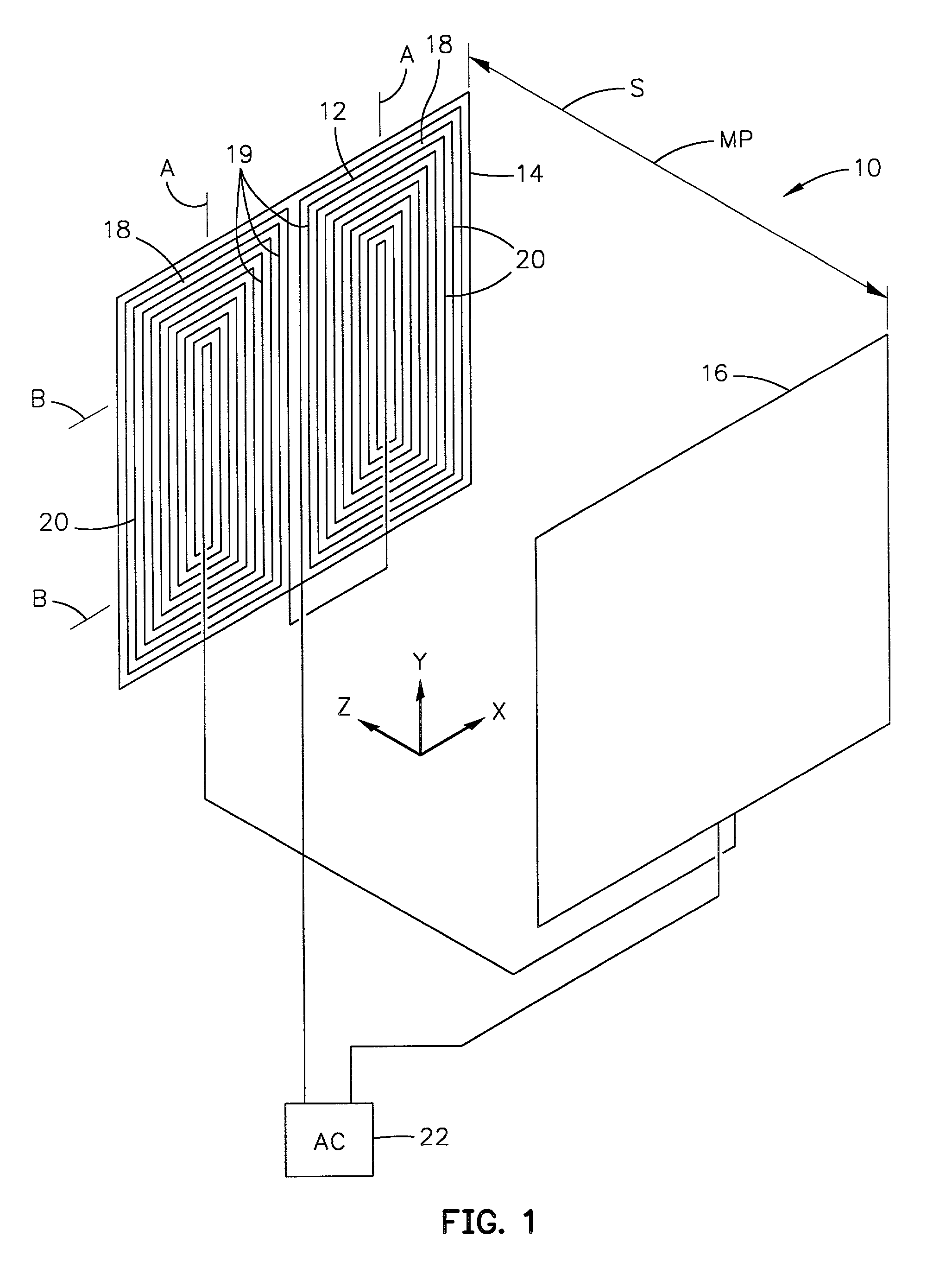
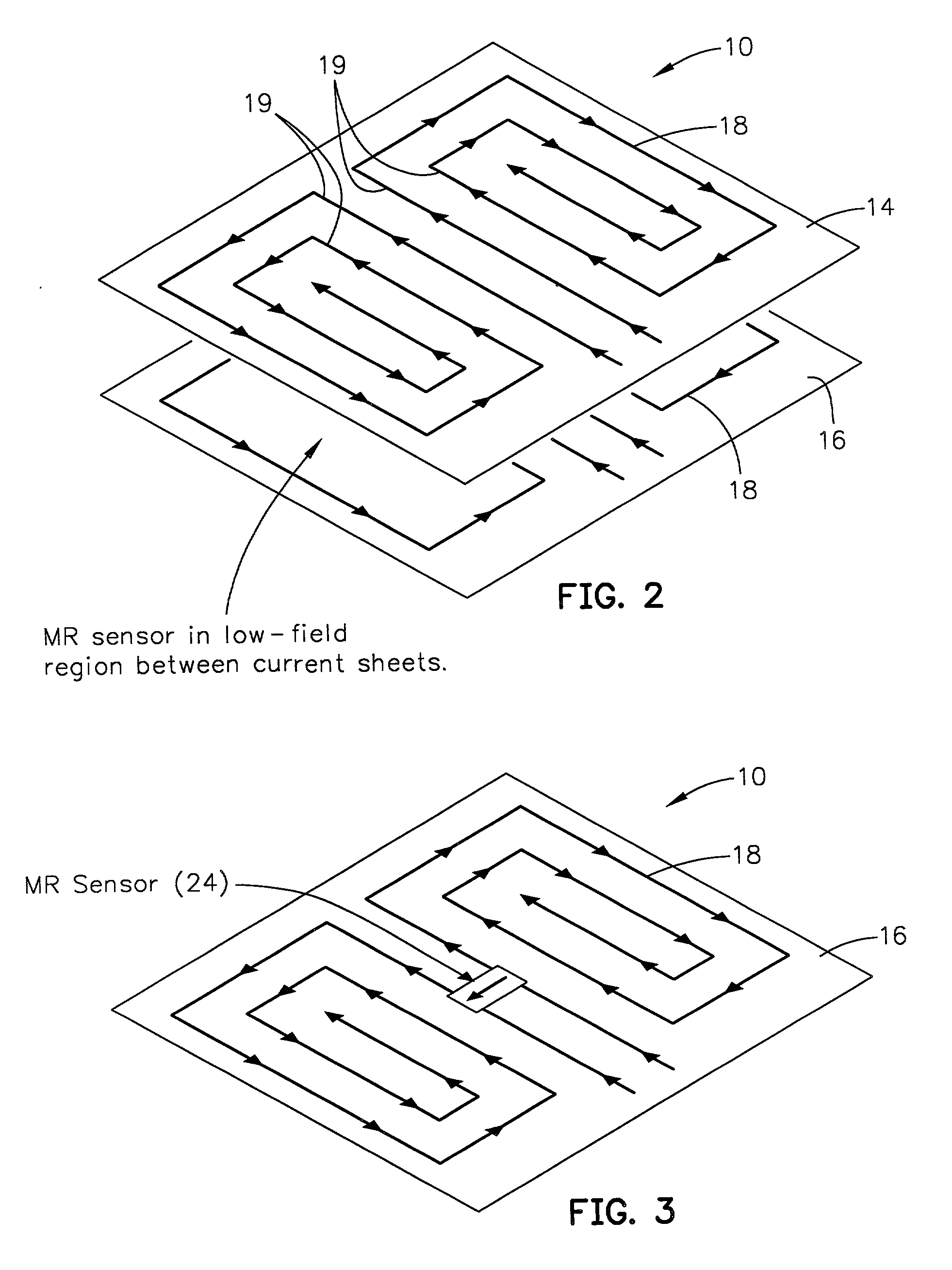
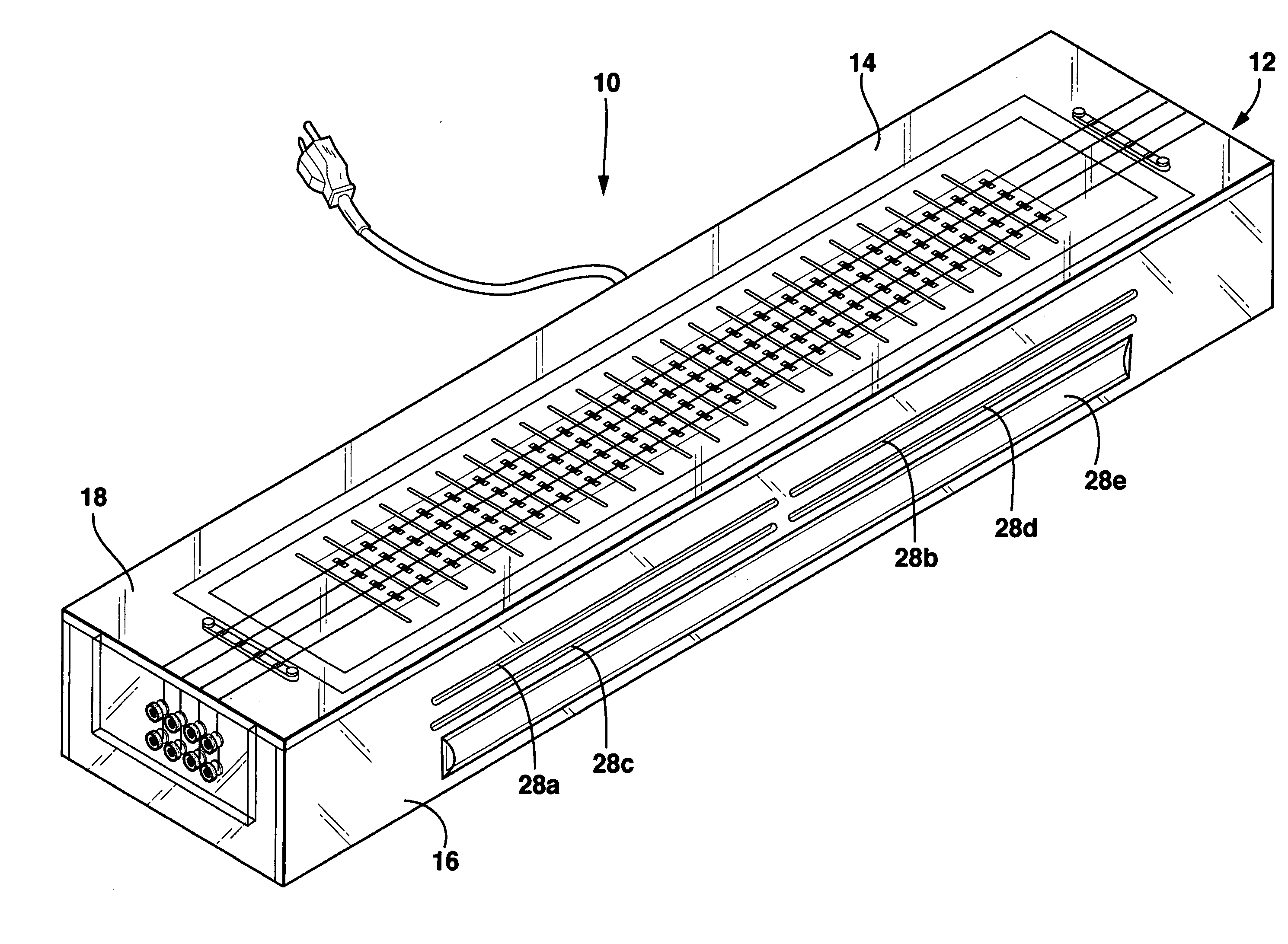
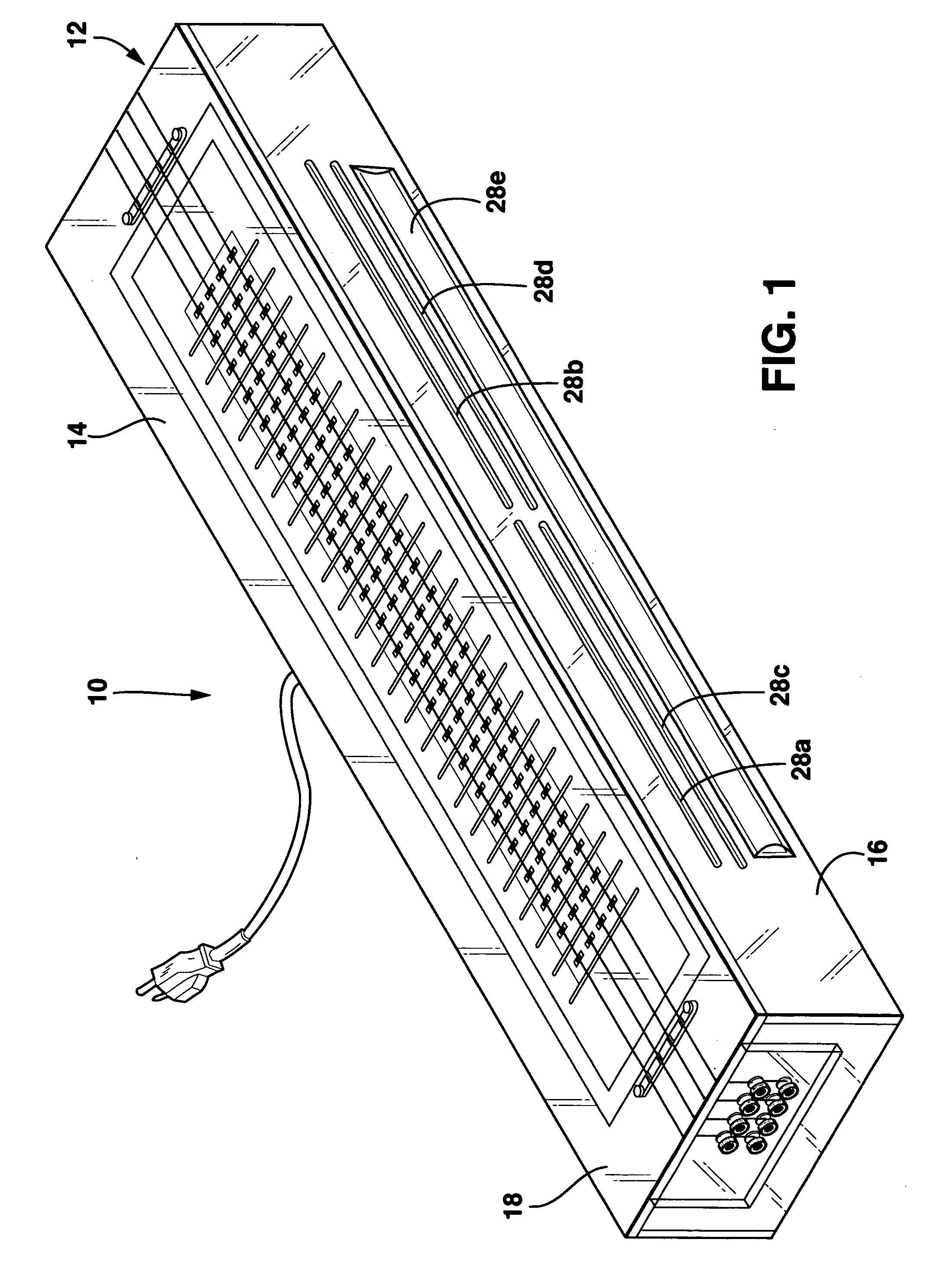
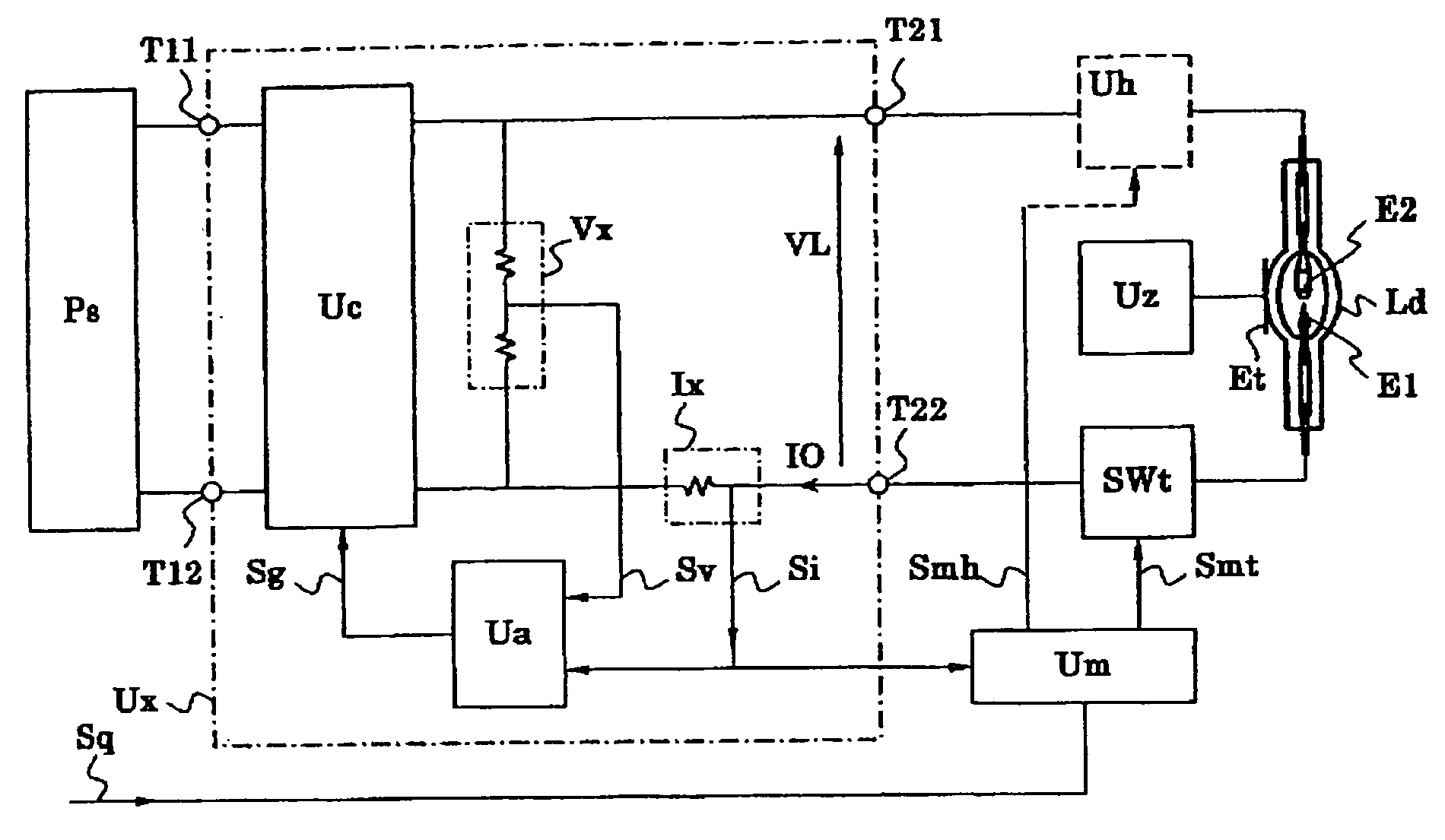
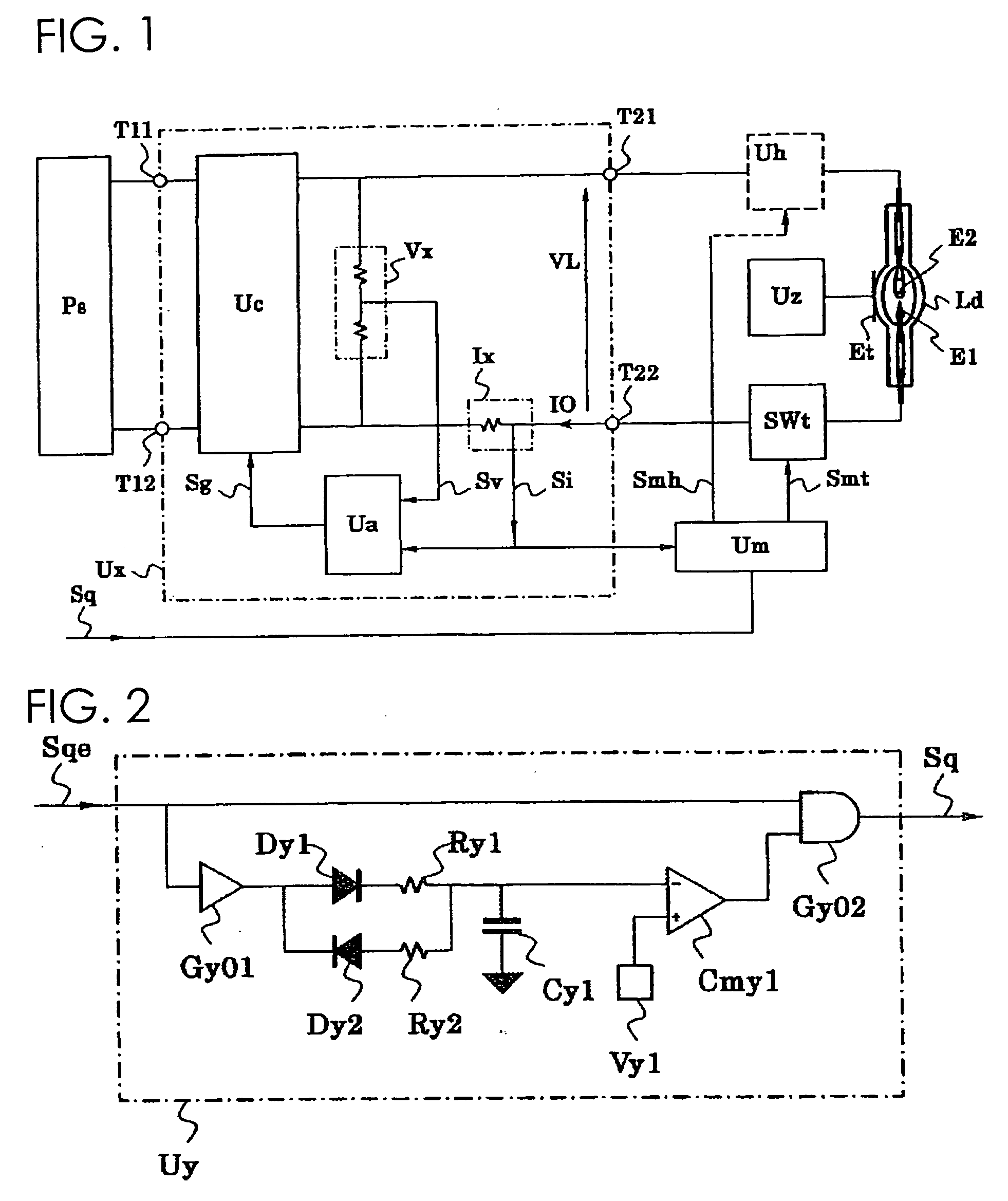
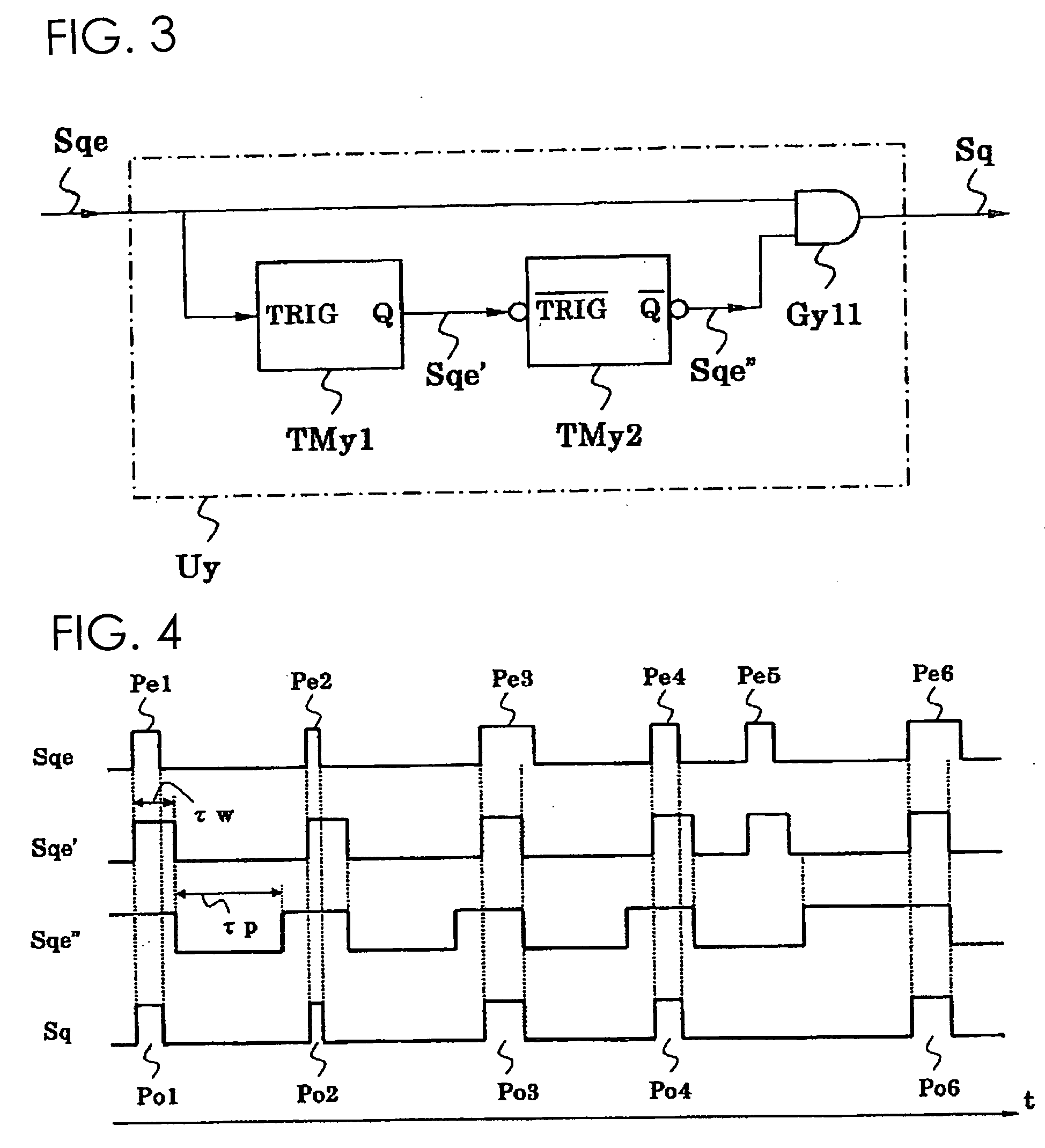
Discharge lamp lighting device
ActiveUS20060175984A1Fast modulationElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementEffect lightEngineering
The present discharge lamp lighting device is capable of rapid modulation in which a lamp current is rapidly reduced and rapidly restored. The current control circuit is provided to perform specific current control such that the brightness of a lamp is reduced by a predetermined percentage without being affected by a variation or change in lamp voltage over time, thereby reducing a lamp current.
Owner:USHIO DENKI KK
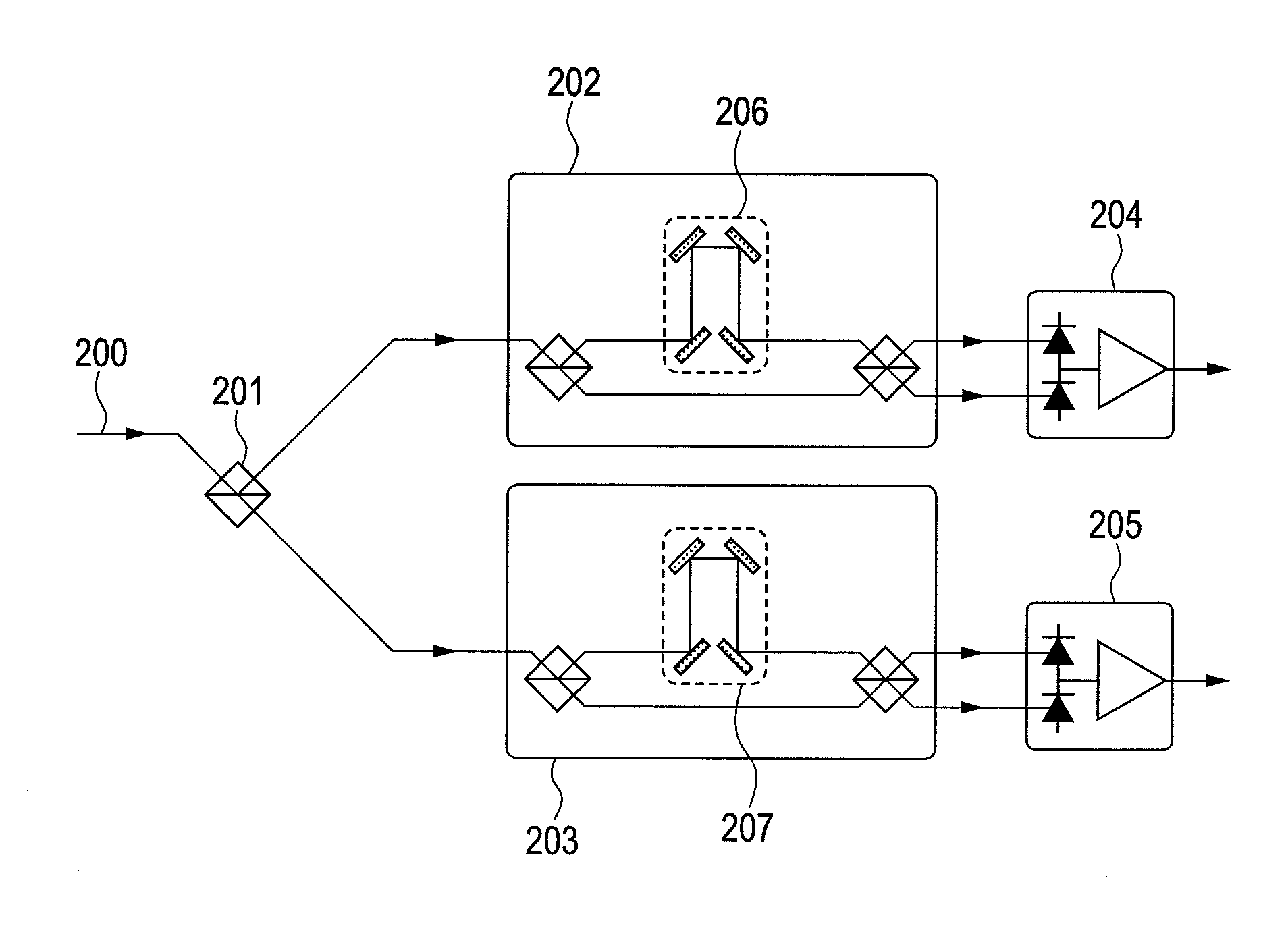
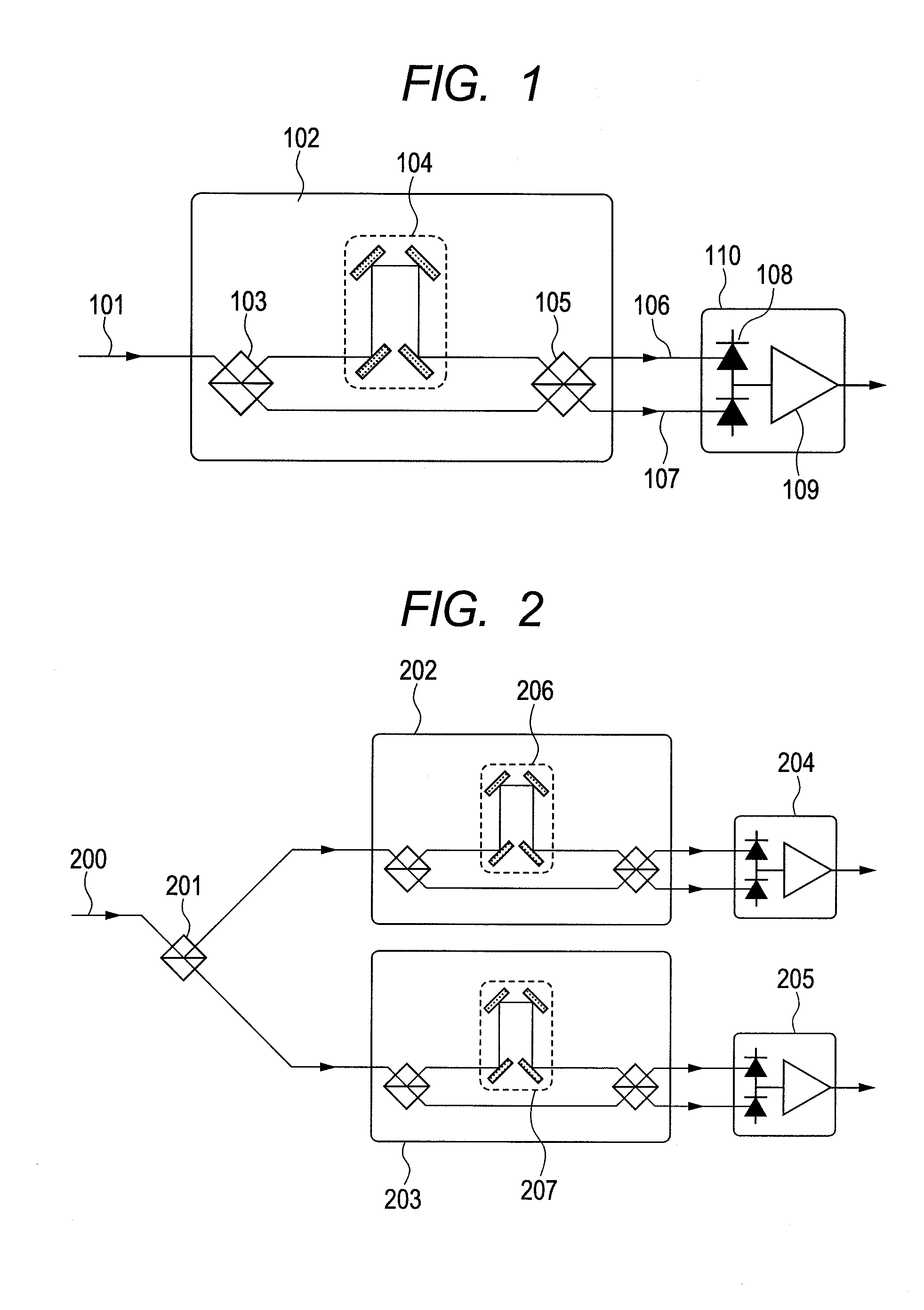
Interferometer, demodulator, and optical communication module
ActiveUS20110188850A1Minimize strokeFaster in optical phase modulation speedMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric discharge tubesPhase differencePiezoelectric actuators
When designing a demodulator for a DPSK-modulated signal, it is required that optical phase modulation is performed fast and the demodulator has a long lifetime. To achieve this object, a delay line interferometer inside the demodulator performs adjustment of phase difference between two split lights caused to interfere, using a first optical phase modulation unit such as a Piezo actuator and a second optical phase modulation unit such as a heating element that operates slower in modulation speed than the first optical phase modulation unit and is slower in deterioration speed.
Owner:LUMENTUM JAPAN INC
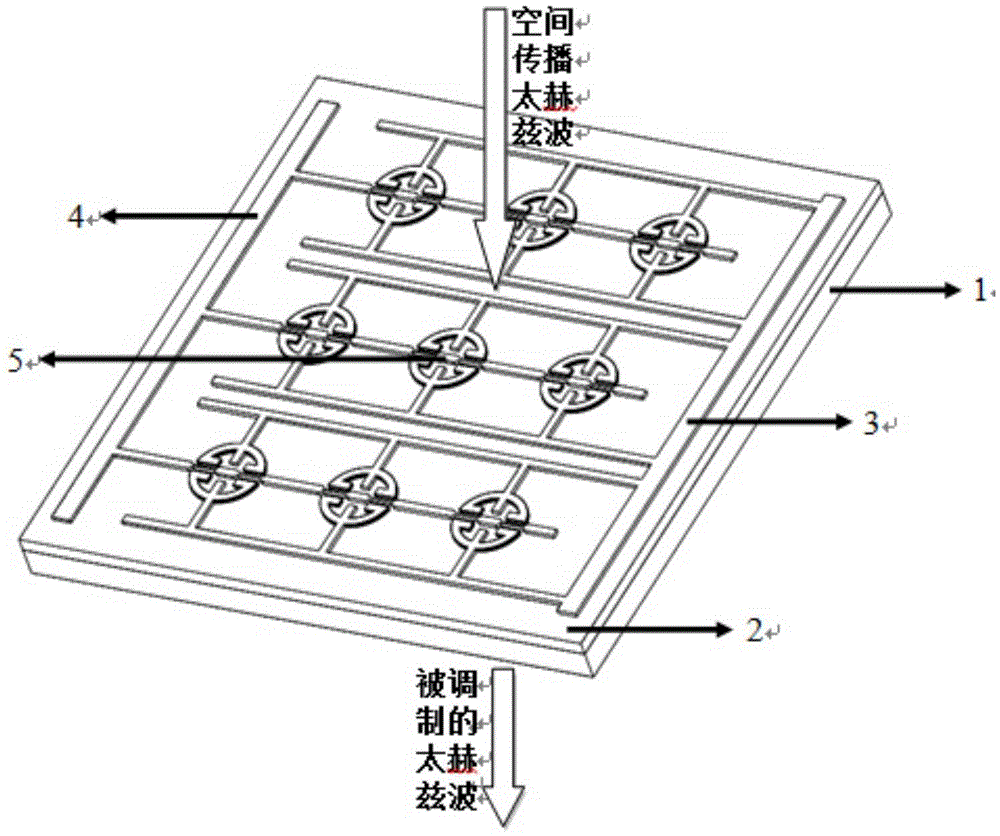
Terahertz space phase modulator based on high electron mobility transistor
ActiveCN105549228AImprove controlEnhanced resonance strengthNon-linear opticsSemiconductor materialsResonance
The invention discloses a terahertz space external phase modulator based on a high electron mobility transistor. The phase modulator combines the quick response type high electron mobility transistor with a novel artificial electromagnetic medium resonant structure, so as to be able to conduct quick phase modulation on terahertz waves transmitted in free space. The phase modulator is composed of a semiconductor material substrate, an HEMT epitaxial layer, a periodical artificial metal electromagnetic resonant structure and a muff-coupling circuit. The concentration of two-dimensional electron gas in the HEMT epitaxial layer is controlled through loaded voltage signals, so that the electromagnetic resonance mode of the artificial electromagnetic medium resonant structure is changed, and then phase modulation of terahertz waves is achieved. Over-90-degree phase modulation depth can be realized within a large bandwidth, and the maximum phase modulation depth can be about 140 degrees. Furthermore, the phase modulator is simple in structure, easy to machine, high in modulation speed, convenient to use and easy to package.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
On-chip high-speed polarization control encoder applied to distribution of quantum keys
ActiveCN107135068AFast modulationKey distribution for secure communicationBeam splitterOptical attenuator
The invention discloses a high-speed polarization control encoder on a silicon chip applied to distribution of quantum keys. The encoder comprises a polarization beam splitting rotator with an input end connected with an input waveguide; a first 1*4 beam splitter with an input end connected with a first output port of the polarization beam splitting rotator; a first phase delayer, a second phase delayer, a third phase delayer and a fourth phase delayer, wherein one end of each of the four phase delayers is connected with an output end of the 1*4 beam splitter, while the other end is connected with a first variable optical attenuator; a second 1*4 beam combiner with an input end connected with the other ends of the first variable optical attenuators behind the first 1*4 beam splitter; and a polarization beam combiner with an first input port connected with the an output end of a second 1*4 beam combiner, and an second input port connected with a second output port of the polarization beam splitting rotator via a second variable optical attenuator.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Visualizing Birefringent Structures in Samples
ActiveUS20090135422A1Increase brightnessEasy to identifyMaterial analysis by optical meansLight polarisation measurementPolarizerBroadband
Apparatus and methods are disclosed for viewing low-birefringence structures within samples directly, with the eye, in real-time. The sample is placed between an entrance polarizer and analyzer polarizer, the transmission state of one of which is changed dynamically to create a modulated view of the scene; against this background, birefringent structures are visible because of their different appearance when modulated. Modulation rates of 4 or more states per second; use of 4 or more states, or even a continuum of states, which lie substantially on a latitude line on the Poincare sphere; and orientation of the polarization components to produce a uniform background; produce a clear view that does not produce operator fatigue. Broad-band wavelength operation spanning 50 nm or more, or the whole visible range, is achieved, and it is compatible with integration into other microscopy modes such as Hoffman relief contrast.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE RES & INSTR
Real-time detecting apparatus
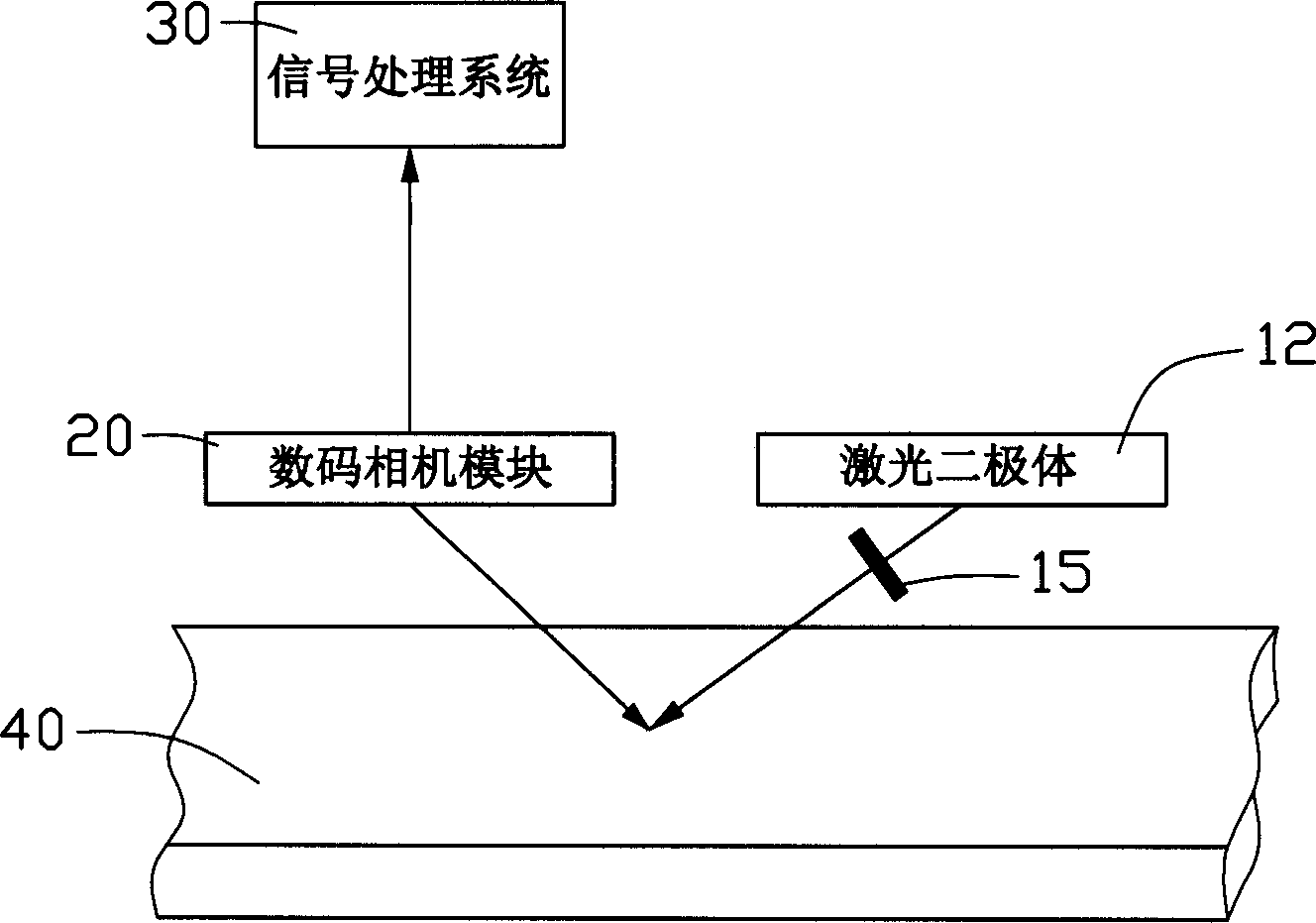
InactiveCN1707249AReduce volumeLower the altitudePolarisation-affecting propertiesCharacter and pattern recognitionLight beamLaser beams
The real-time detecting device capable of being used in the real-time detection of substrate includes one signal processing system, one laser dipole and one digital camera assembly. The laser dipole is used in emitting laser beam to irradiate the substrate; the digital camera assembly is used in taking the image of the substrate surface; the signal processing system is used in analyzing the data from the digital camera assembly to judge whether to have fault in the substrate part, and the signal processing system, the laser dipole and the digital camera assembly are connected electrically. The real-time detecting device of the present invention has small size, and convenient and accurate detection.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Direct-current drive and active temperature control system of two-stage high-frequency pulse tube refrigerator and design method thereof
InactiveCN104534719ATemperature controlEfficient conversionCompression machinesRefrigeration safety arrangementControl signalEngineering
The invention discloses a direct-current drive and active temperature control system of a two-stage high-frequency pulse tube refrigerator and a design method of the two-stage high-frequency pulse tube refrigerator. The system is composed of a first DC (direct current)-DC conversion module, a second DC-DC conversion module, a dual-channel analogue-digital signal conversion module, a two-stage weighing control module, a PID (Proportion Integration Differentiation) control module, a SPWM (Sinusoidal Pulse Width Modulation) signal modulating module, a dual-channel digital-analogue signal conversion module, a dual-channel temperature signal collecting and operation amplifying module and an H bridge power amplifying module. Cold end temperature in each stage of the two-stage refrigerator is collected and converted into appropriate voltage signals, control signals are output by treating a series of signals so that the two-stage pulse tube refrigerator can be efficiently driven by a direct current power supply, and the cold end temperature in each stage of the two-stage refrigerator is actively controlled. The two-stage high-frequency pulse tube refrigerator has a very positive connotation when being applied to spaceflight and other special fields.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Acoustooptic modulator used for femtosecond laser
The invention discloses a femtosecond pulse acousto-optic modulator, including two acousto-optic deflectors. The two acousto-optic deflector reverse placed parallel and equal sound waves frequency. The two acousto-optic deflector spaces L +- 10% L, and L value met requirement of (I). In (me), v and f respectively stands for acousto-optic deflector sonic speed and frequency, GDDm stands for the material dispersion of acousto-optic deflector, lambada stands for laser wavelength. The invention of the acousto-optic deflector on different wavelengths of laser intensity modulation, can achieve common axis modulation, also compensated acousto-optic crystal of ultra-short pulses in time and space dispersion. The invention structure is flexible and easy modulation, applied to multi-photon scanning, imaging and laser micro-processing and other fields.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Gas concentration measuring apparatus
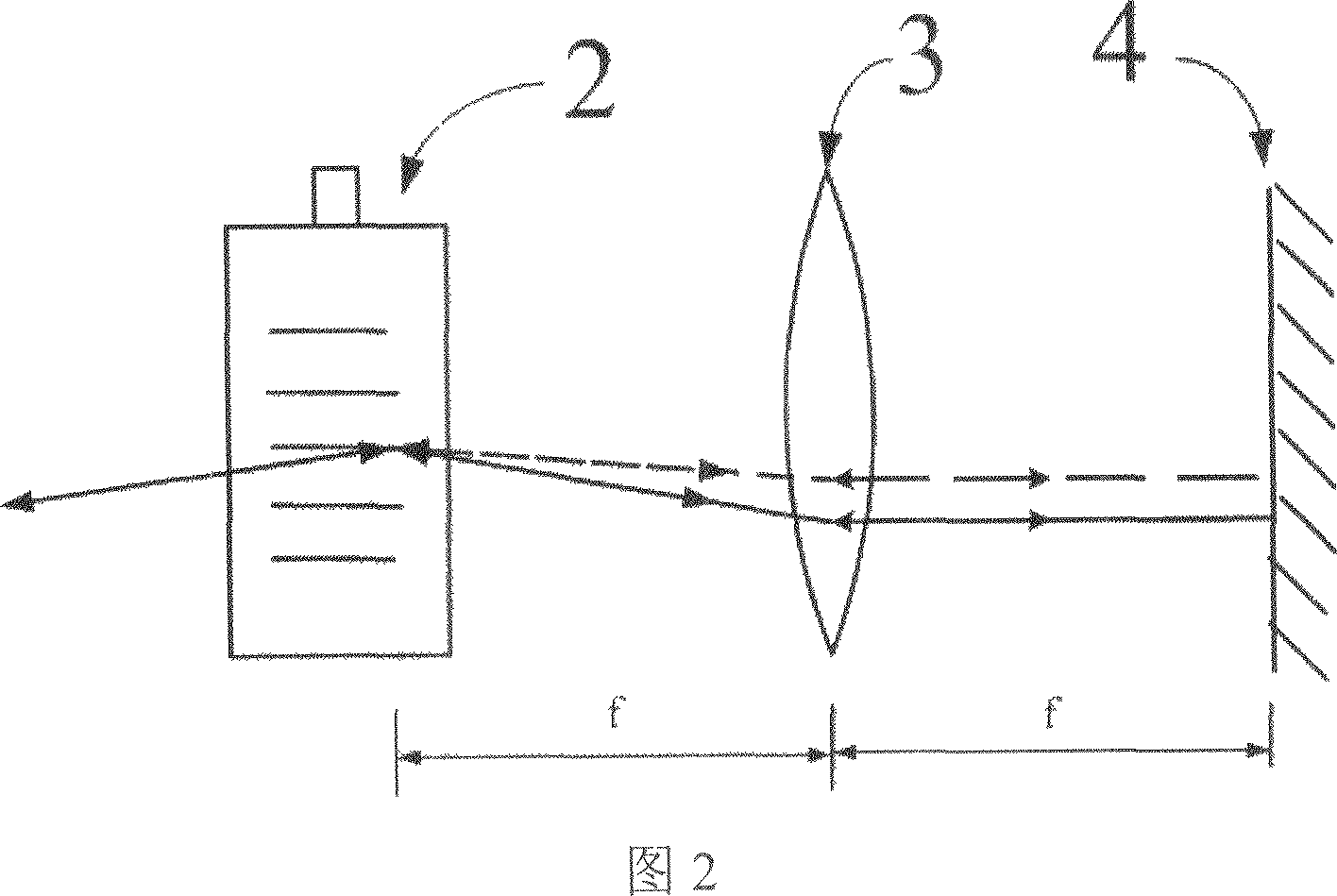
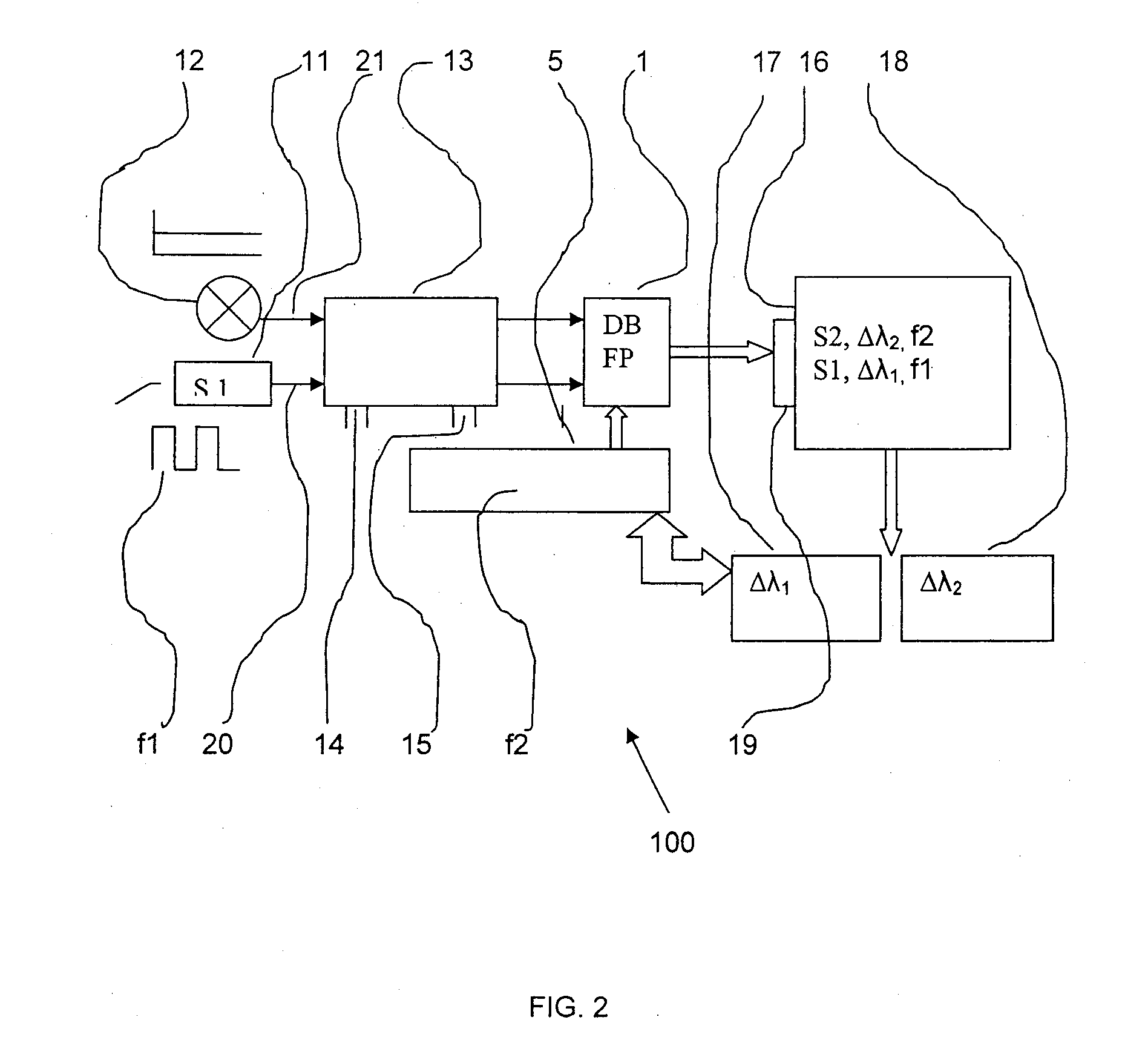
ActiveUS20080074647A1Fast modulationRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryAnesthetic gasesGas concentration
A gas concentration measuring apparatus is in miniaturized form and permits the measurement of anesthetic gas components. A variable interferometer is provided on the basis of a Fabry Perot interferometer (1) wherein the mirrors (2, 3) can be changed in spacing with respect to each other. The mirrors (2, 3) have coatings which make possible the transmission in two spectral ranges (Δλ1, Δλ2).
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
Apparatus and method for providing a user interface to an information processing system
InactiveUS20110250958A1Fast modulationCheap constructionFlexible member pumpsPump controlInformation processingOutput device
An apparatus for use as an output device of a user interface to an information processing system includes at least one device (15;20) for generating a synthetic jet flow.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Active optical device using phase change material
An active optical device is provided. The active optical device includes an optically variable layer having a refractive index which changes according to temperature; and a temperature control unit that controls a temperature of one or more regions of the optically variable layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Modulatable radiation collimator
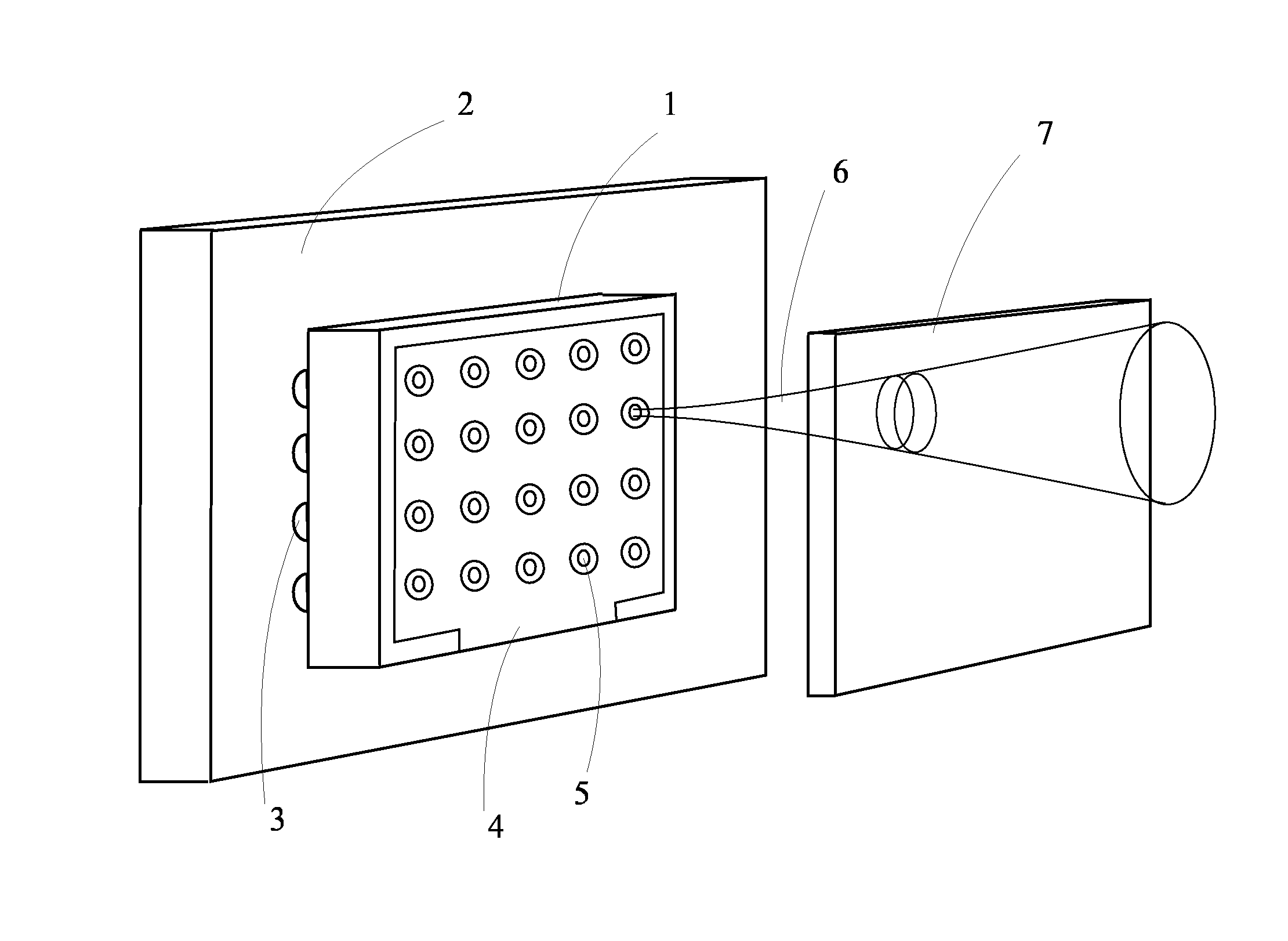
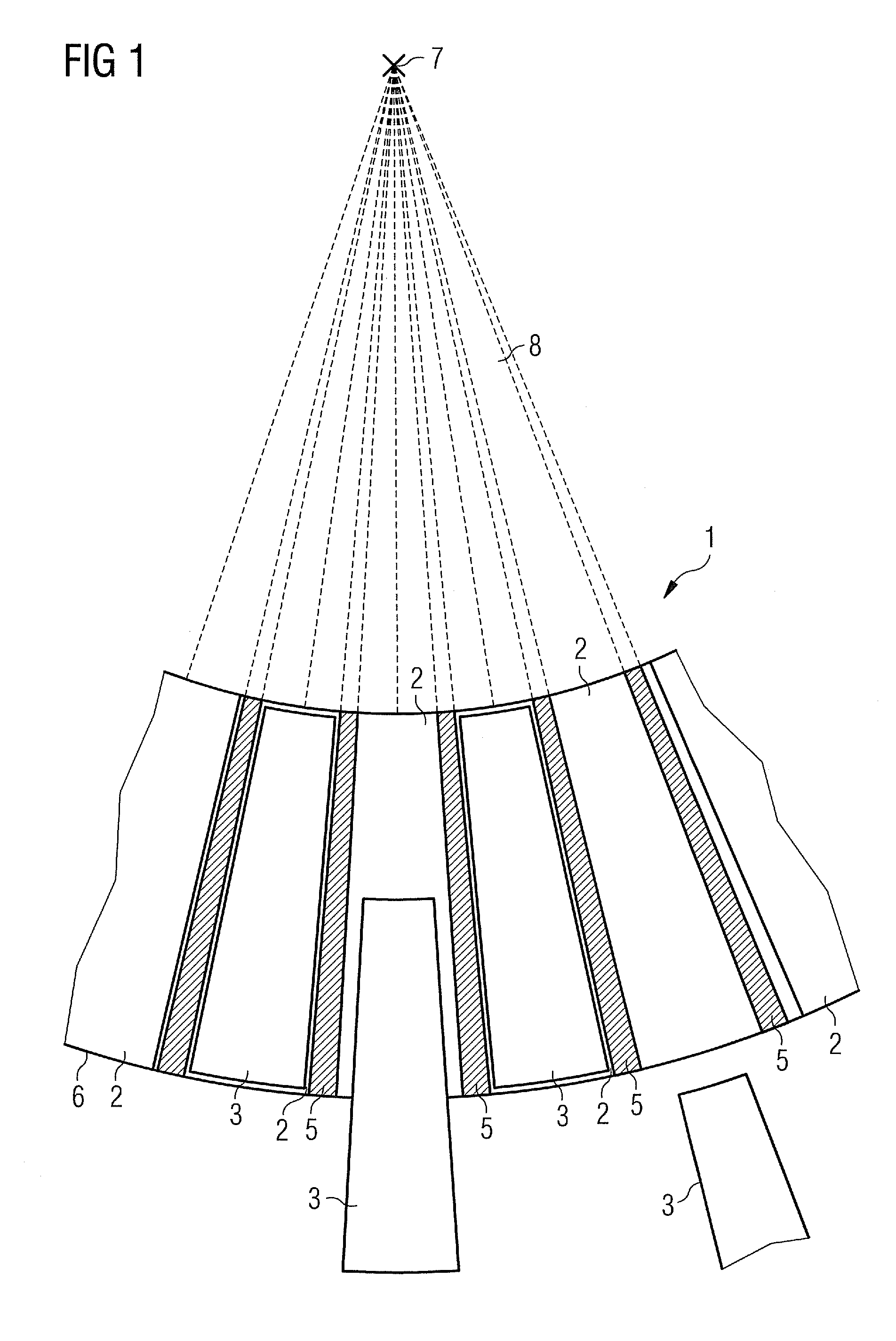
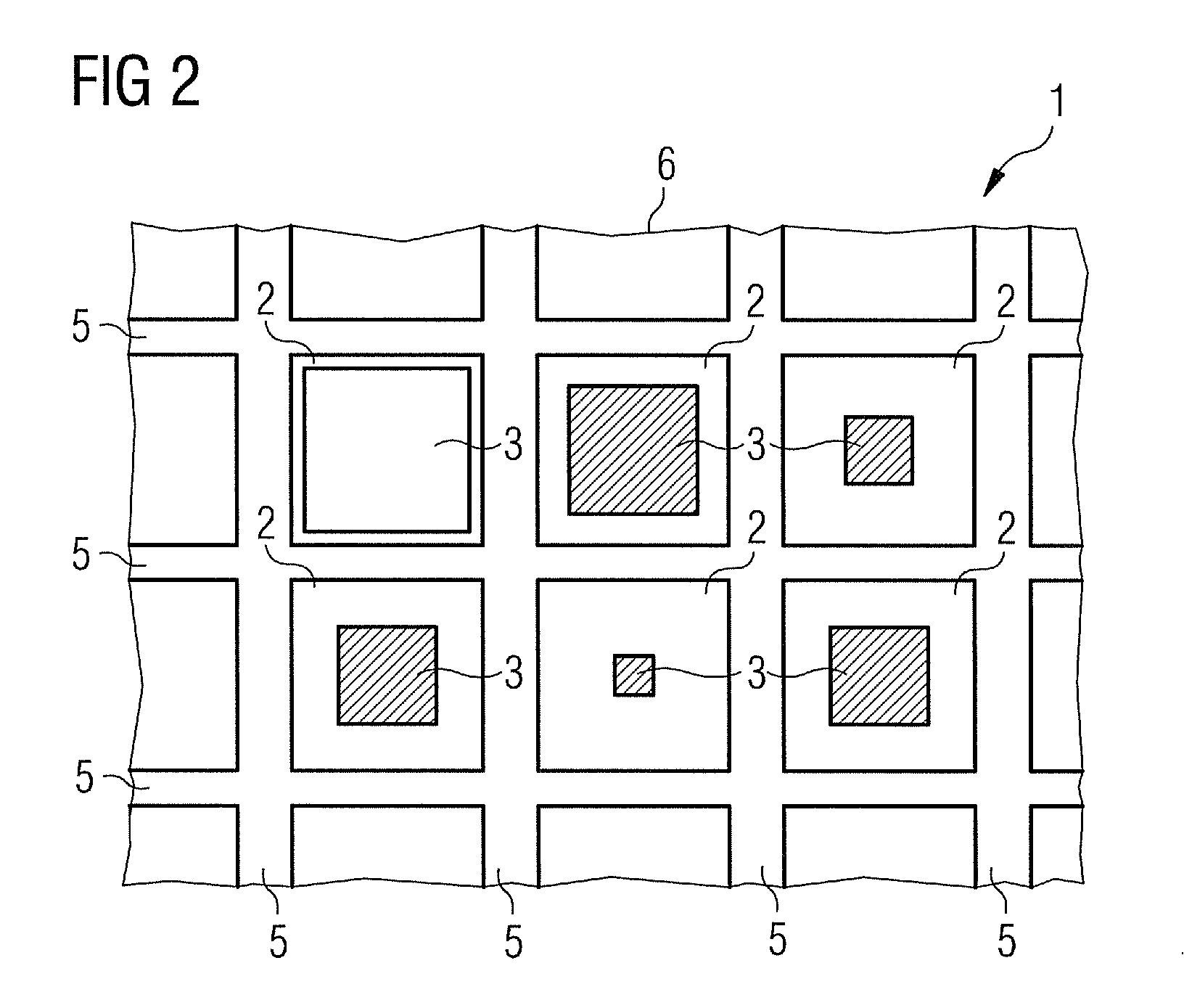
ActiveUS8094785B2High resolutionFast modulationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyX-rayHigh resolution
The invention specifies a radiation collimator, in particular an x-ray collimator, which can be arranged between a radiation source outputting radiation and an object. The radiation collimator includes absorber channels arranged adjacent to one another which form a two-dimensional collimator aperture in the form of a matrix and a first absorber element arranged in the absorber channel. The first absorber element blocks the radiation in a first position and allows the radiation at least partially through the absorber channel in at least one second position. The first absorber element is rod-shaped and can be moved in the absorber channel by a rotation about its longitudinal axis and / or by a longitudinal and / or transverse displacement from the first into the at least one second position. This is advantageous in that the two-dimensional collimator aperture can be modulated easily, rapidly and with high resolution.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Control method and device of two-way electromagnetic force control valve for common rail flow control
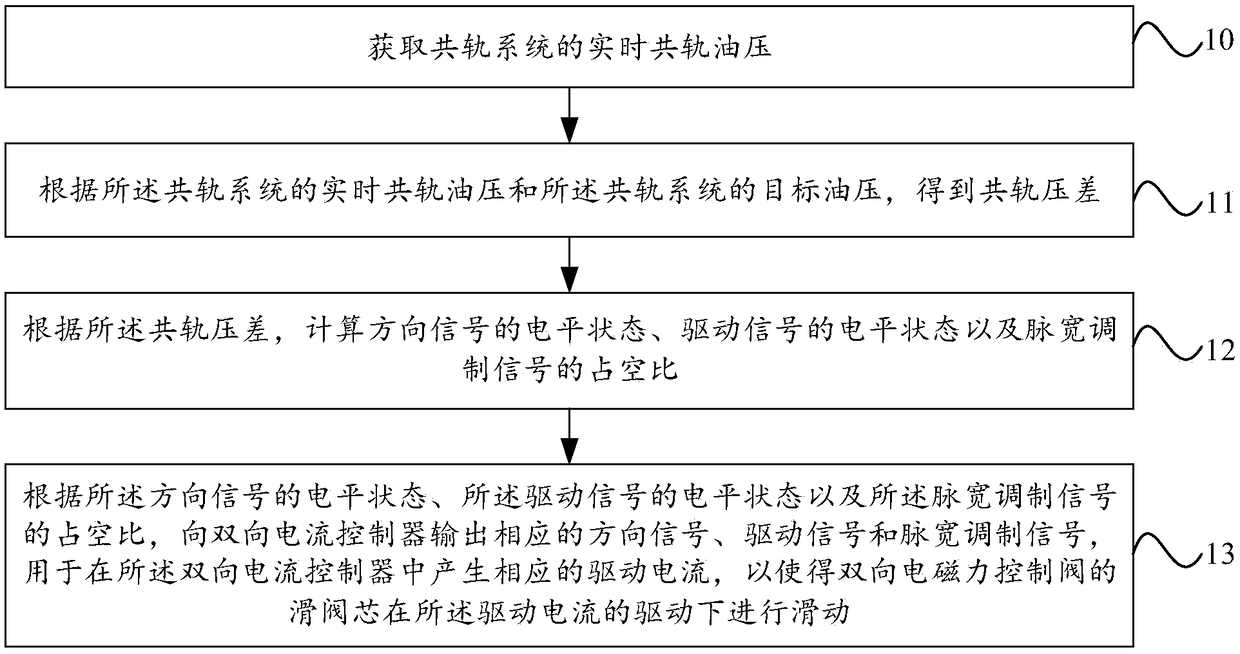
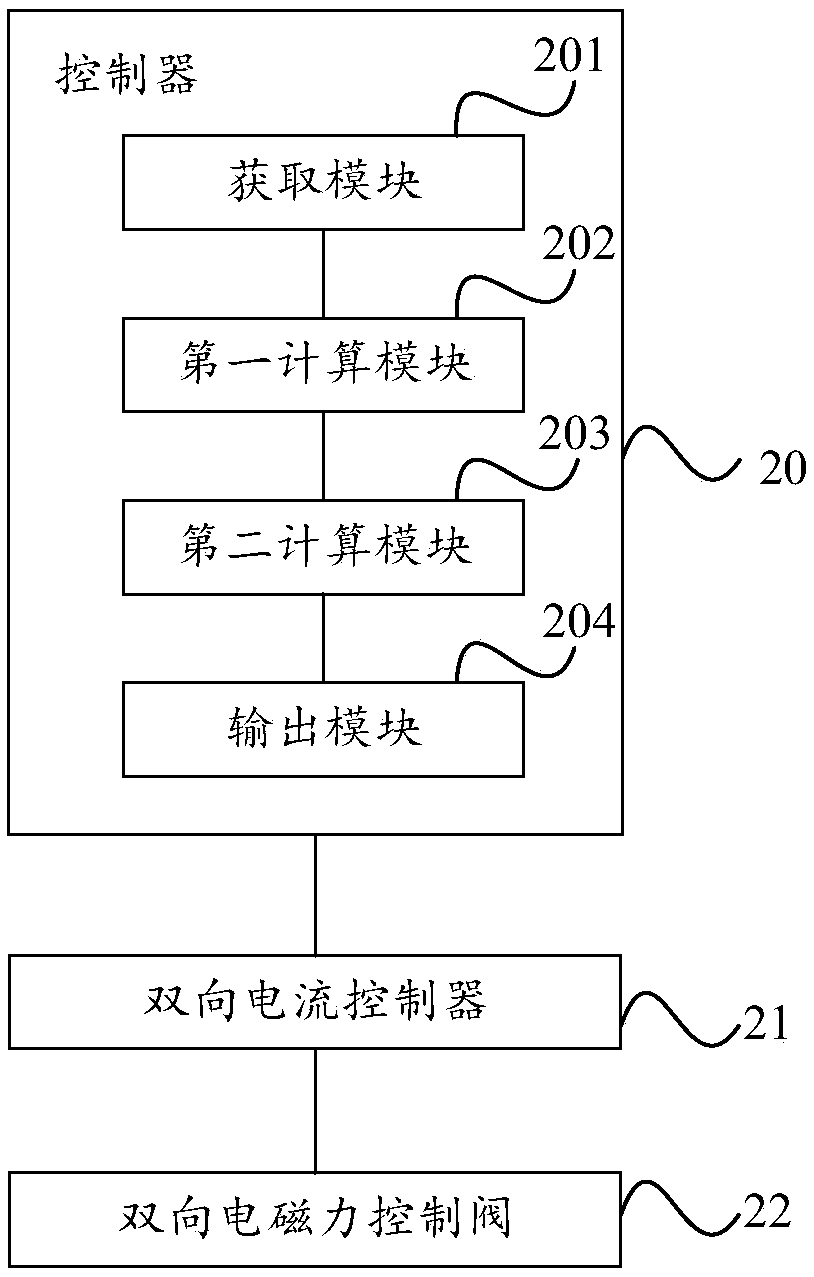
InactiveCN108286476AGood pressure regulation effectFast displacementElectrical controlFuel injection apparatusDriving currentPower flow
The embodiment of the invention provides a control method and device of a two-way electromagnetic force control valve for common rail flow control. The method comprises the steps that real-time commonrail oil pressure of a common rail system is obtained; common rail differential pressure is obtained according to the real-time common rail oil pressure of the common rail system and target oil pressure of the common rail system; the duty ratio of a direction signal, a driving signal and a pulse width modulation signal is calculated according to the common rail differential pressure; and the corresponding direction signal, driving signal and pulse width modulation signal are output to a bidirectional current controller according to the electrical level state of the direction signal, the electrical level state of the driving signal and the duty ratio of the pulse width modulation signal, and are used for generating a corresponding driving current in the bidirectional current controller, sothat a sliding valve core of the two-way electromagnetic force control valve is driven by the driving current to slide. The control method and device of the two-way electromagnetic force control valve for the common rail flow control can achieve fast and accurate adjustment of the common rail pressure of the high pressure common rail oil supply system.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Beverage preparation robot system
InactiveCN105023359AFast modulationLow costBeverage vesselsApparatus for dispensing fluids/granular materialsRobotic systemsControl system
The invention discloses a beverage preparation robot system for preparing desired beverage through catering and baking automation technology according to the requirements of customers. The beverage preparation robot system comprises a control system provided with a power supply unit and a control chip, a money input device provided with a fake money identification unit and electrically connected with the control system, a money storage device arranged close to the money input device and electrically connected with the fake money identification unit and the control system, a beverage category selection device electrically connected with the fake money identification unit and the control system, a beverage raw material treatment device electrically connected with the beverage category selection device and the control system, a beverage waste treatment device electrically connected with the beverage raw material treatment device and the control system, and a beverage delivery device electrically connected with the control system.
Owner:曾有盛 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com