Method for operating a laser device, resonator arrangement and use of a phase shifter
A technology of laser device and resonator, applied in lasers, laser parts, phonon exciters, etc., can solve problems such as small offset frequency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
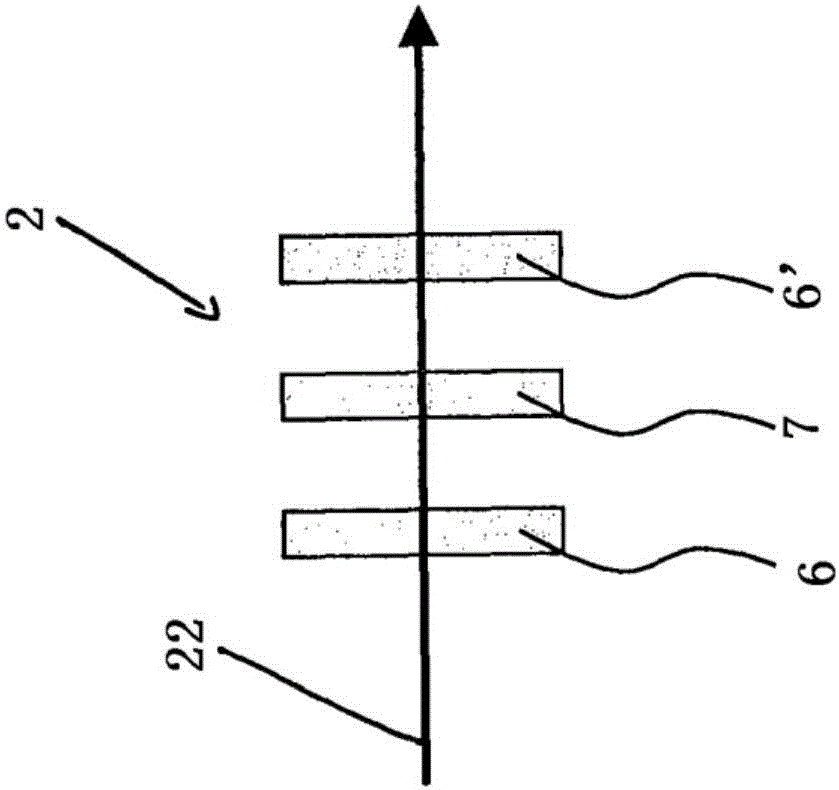
[0073] Figure 5 An inventive resonator configuration 100 utilizing the resonator 1 is shown. Figure 5 The resonators shown are ring resonators. Optionally, the resonator configuration 100 according to the present invention may also comprise linear resonators. exist Figure 6 A linear resonator is shown in .
[0074] Figure 5 The ring resonator 1 comprises a plurality of curved mirrors 3,13. Mirror 3 is an incoupling mirror configured to couple pump light P into. Mirror 3' is an outcoupling mirror for outcoupling laser light from resonator 1. The laser can be a CW laser (continuous wave) or a pulsed laser.
[0075] For some applications it is advantageous to have an active medium 24 in the resonator. The active medium 24 may be, for example, a laser active medium such as Ti:Sa crystal. Of course, other laser media are also contemplated. A deflection mirror 13 for beam guidance is provided in the resonator 1 . Thus, it may be useful to have some mirrors curved. Fo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com