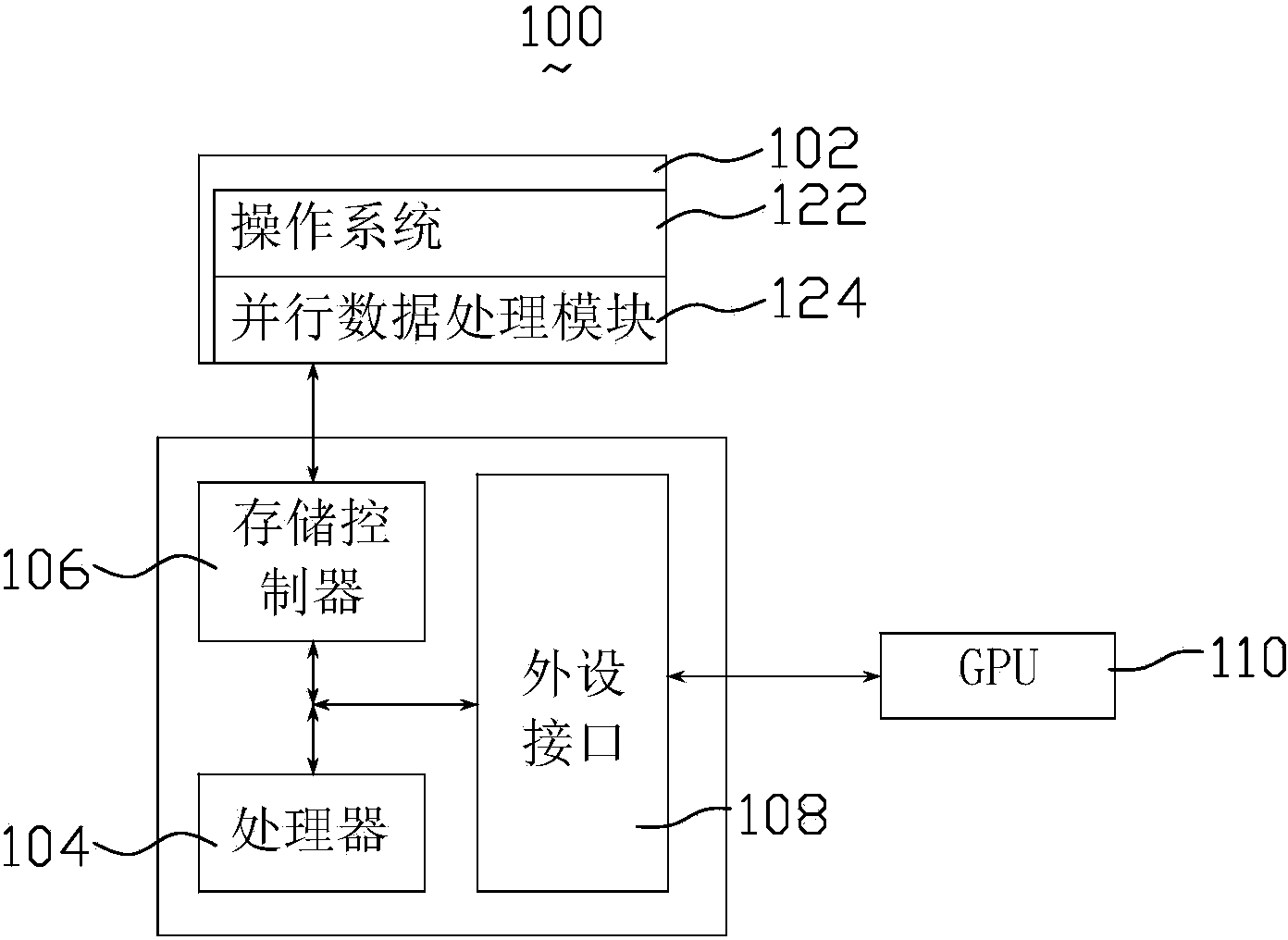
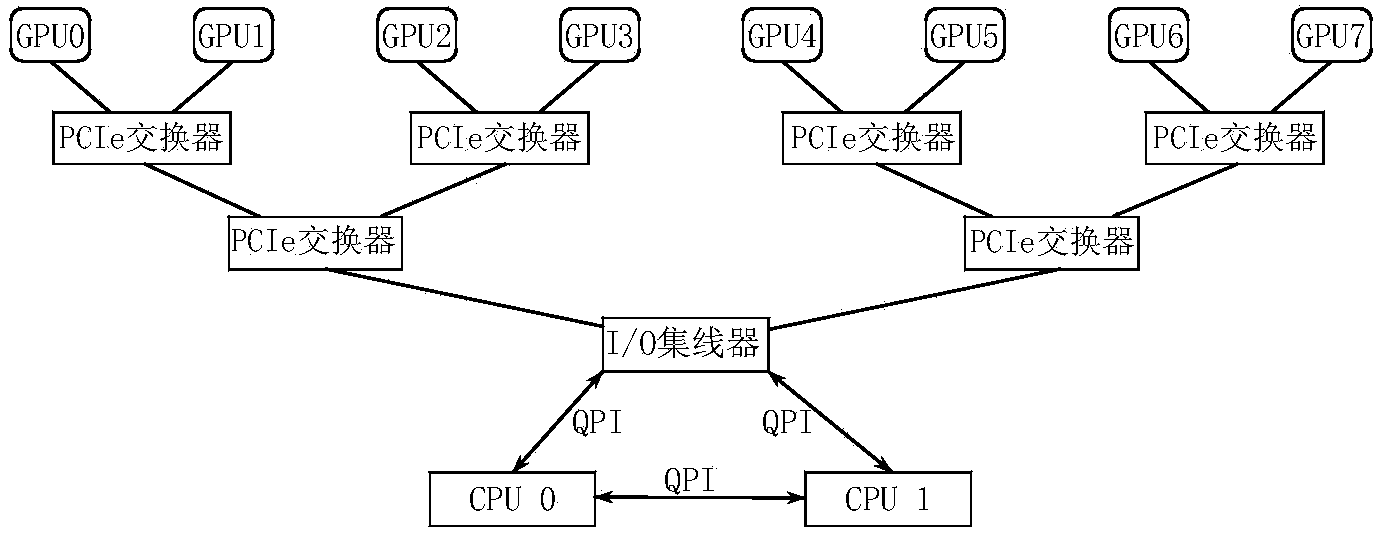
Patents
Literature
1118 results about "Video memory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
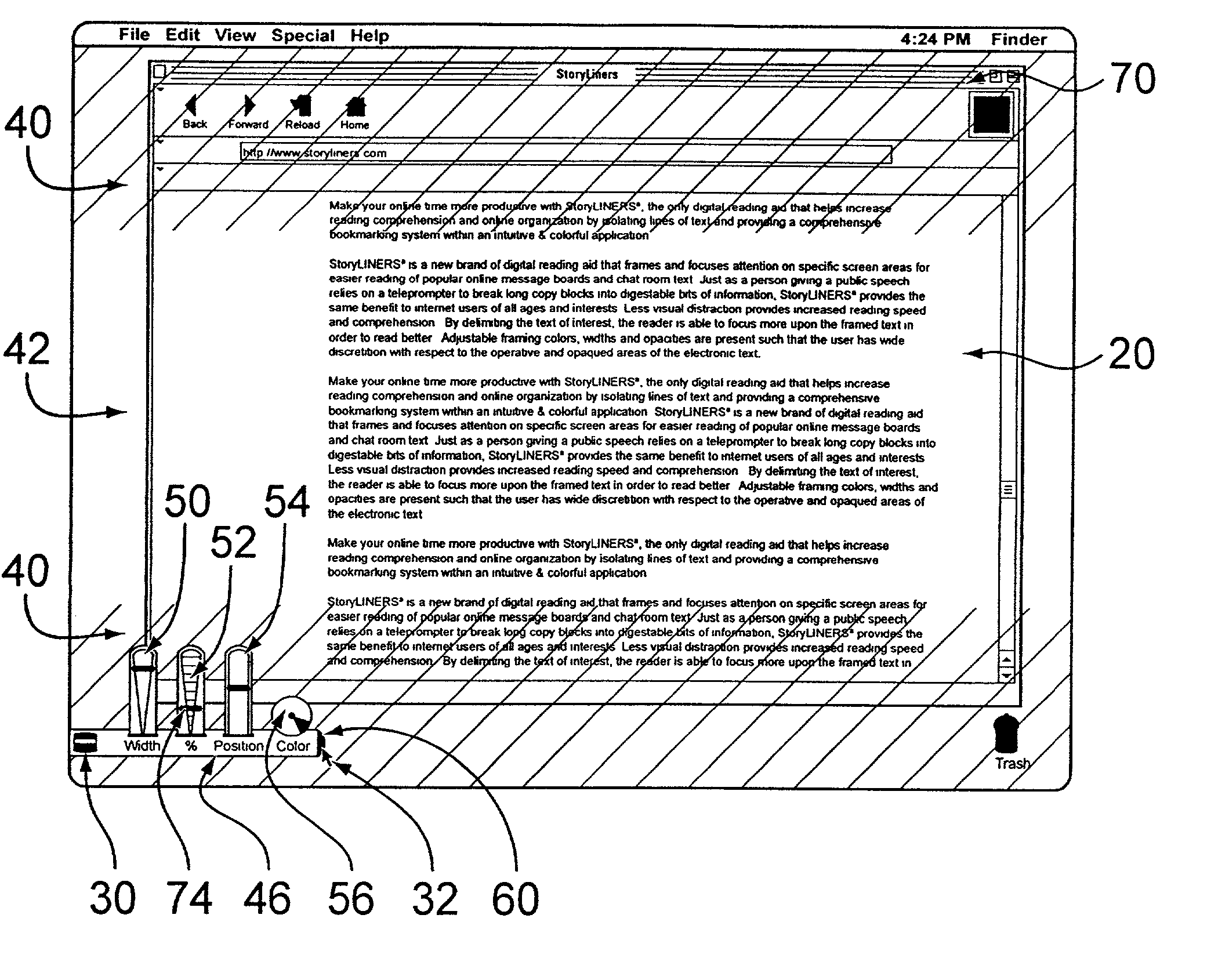
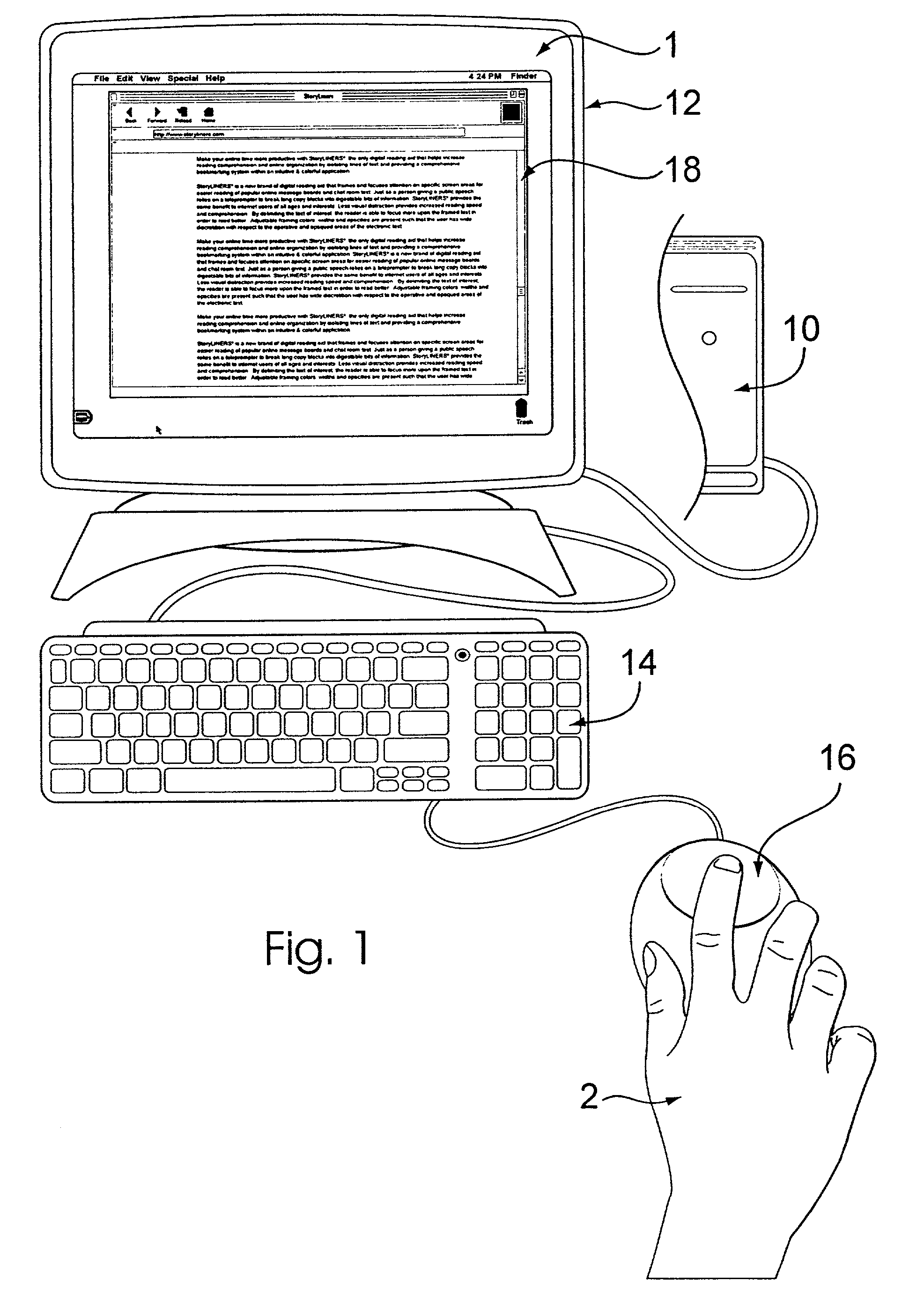
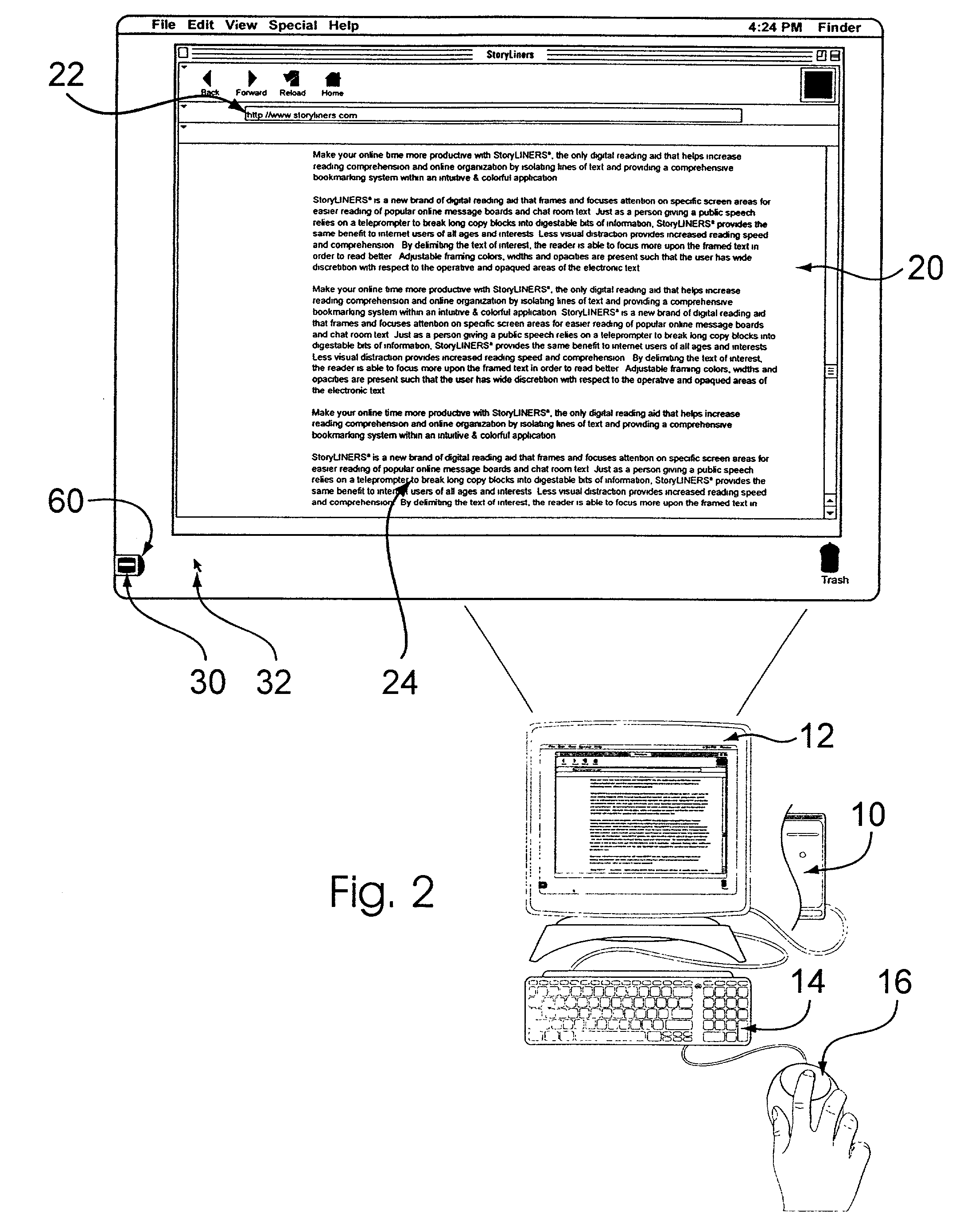
Reading aid for electronic text and displays
InactiveUS20020167534A1Easy to readReadily more readableCathode-ray tube indicatorsSpecial data processing applicationsVideo memoryVisibility
A reading aid for electronic text serves to frame specific and generally desired portions of text or other displayed information for easier reading and attention-focusing purposes. In conjunction with video memory or other video signal transmission elements, an overlay generator serves to bias a portion of the video signal for a computer display. The bias is such that the framed portion of the display is made distinct from the framing portion which generally maintains its visibility and / or legibility despite opacity. In this way, the framed portion is not subject to over-isolation. While the user may scroll the opaqued portion into the framed portion of the display, the framing portion is generally visible but held in contrast or distinction to the framed portion. Adjustments may be made to the framed and framing areas, and additional features are provided.
Owner:BURKE GARRETT
Sequential and video access for non-volatile memory arrays
An array of non-volatile memory cells arranged in logical columns and logical rows, and associated circuitry to enable reading or writing one or more memory cells on a row in parallel. In some embodiments, the array of memory cells may include a phase change material. In some embodiments, the circuitry may include a write driver, a read driver, a sense amplifier, and circuitry to isolate the memory cells from the sense amplifier with extended refresh. In some embodiments, the circuitry may further include shift registers and one or more arithmetic logic units to provide a video memory.
Owner:OVONYX MEMORY TECH LLC
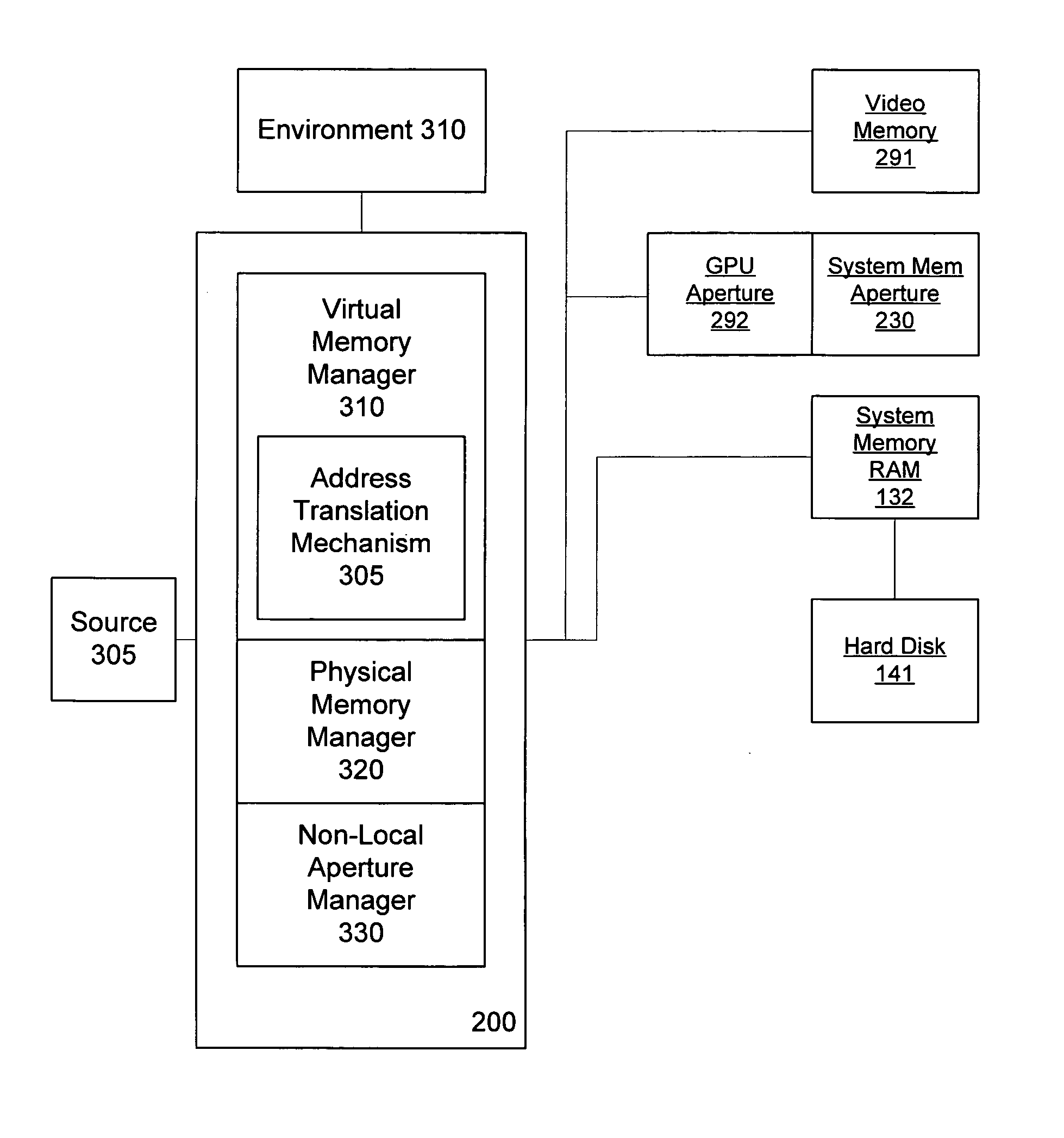
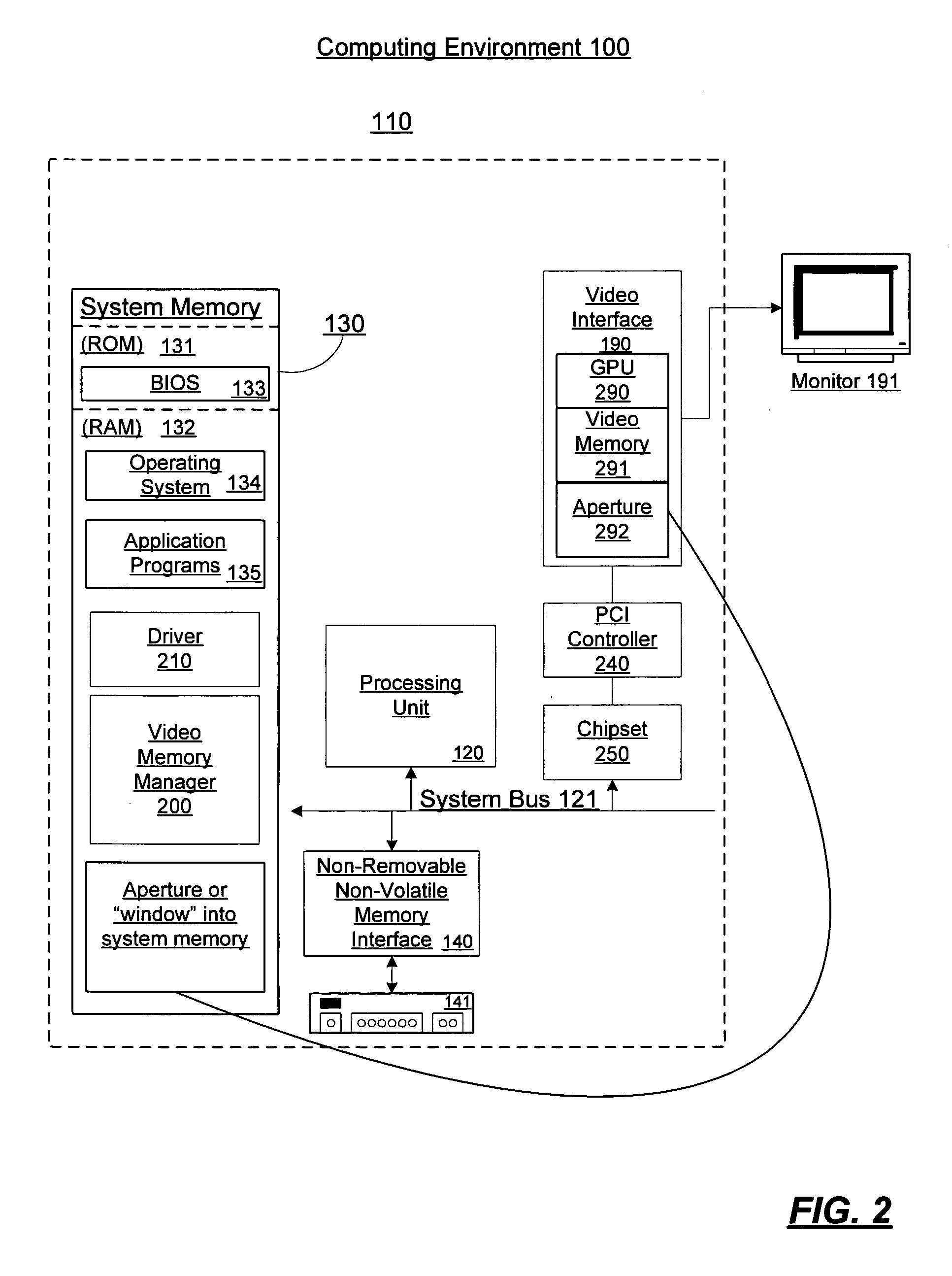
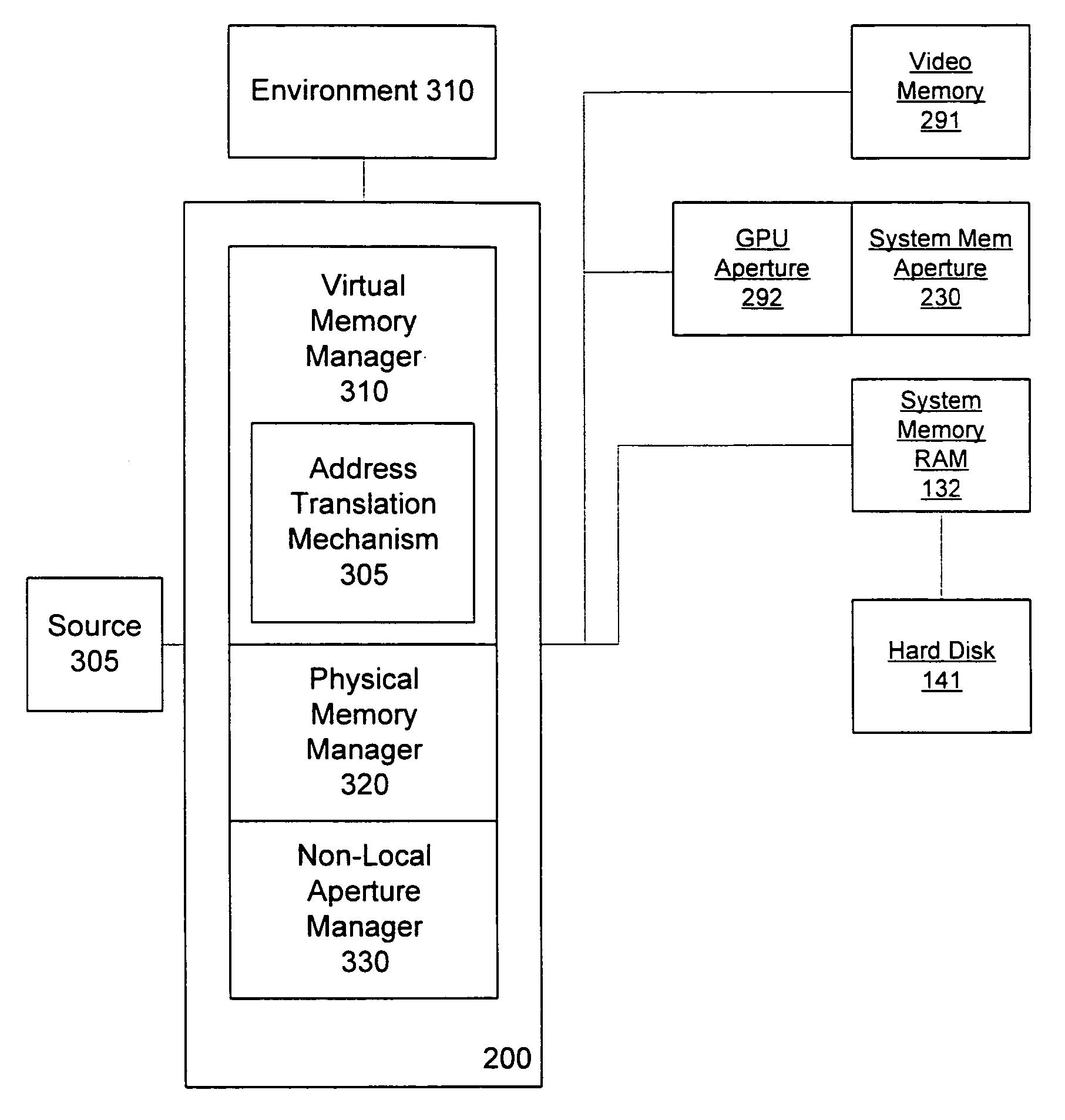
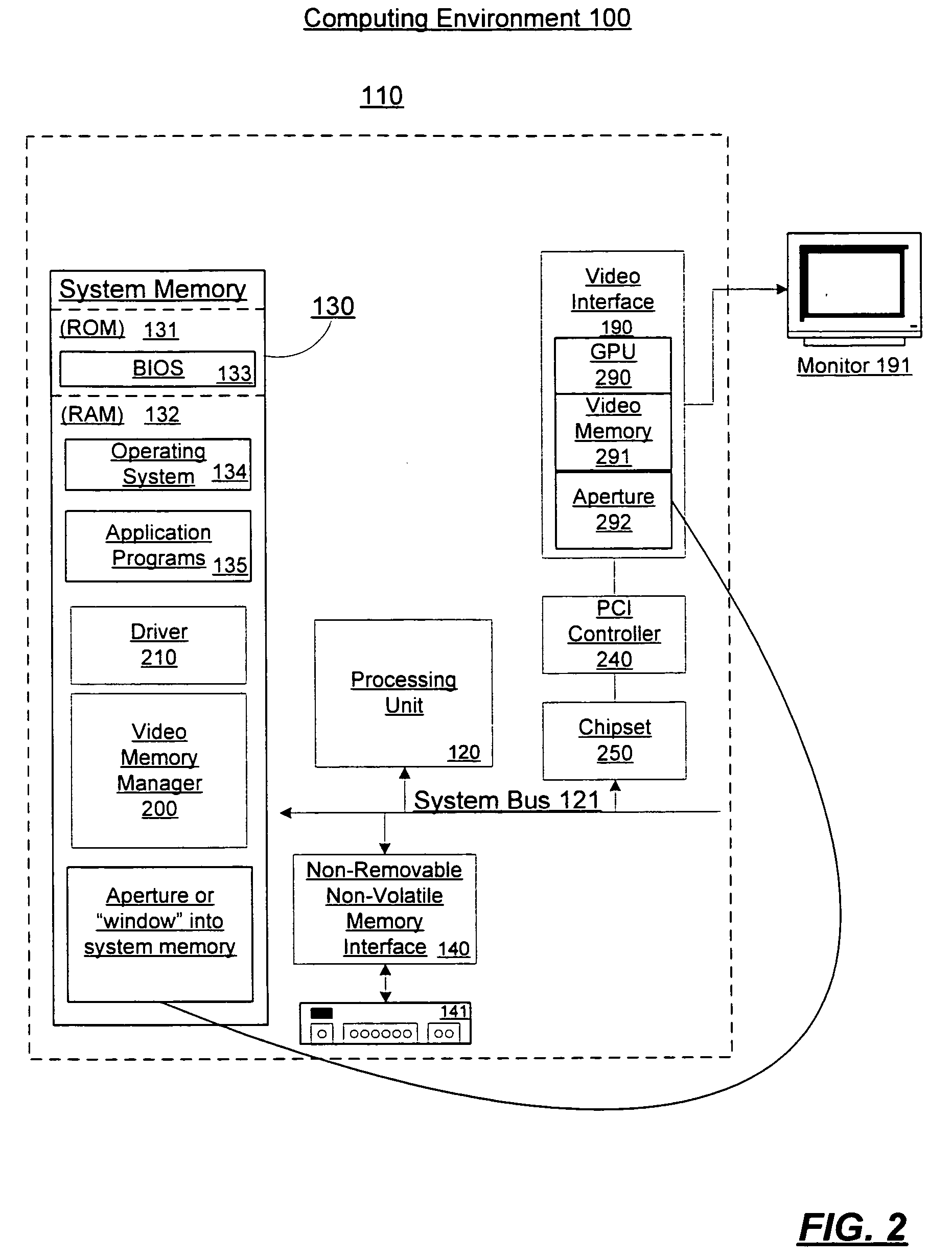
Video memory management
A video memory manager manages and virtualizes memory so that an application or multiple applications can utilize both system memory and local video memory in processing graphics. The video memory manager allocates memory in either the system memory or the local video memory as appropriate. The video memory manager may also manage the system memory accessible to the graphics processing unit via an aperture of the graphics processing unit. The video memory manager may evict memory from the local video memory as appropriate, thereby freeing a portion of local video memory use by other applications. In this manner, a graphics processing unit and its local video memory may be more readily shared by multiple applications.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Automated multimedia data processing network
InactiveUS7010508B1Reduce processing timeReduce amount of paperwork and processing timeFinanceVideo memoryApplication software
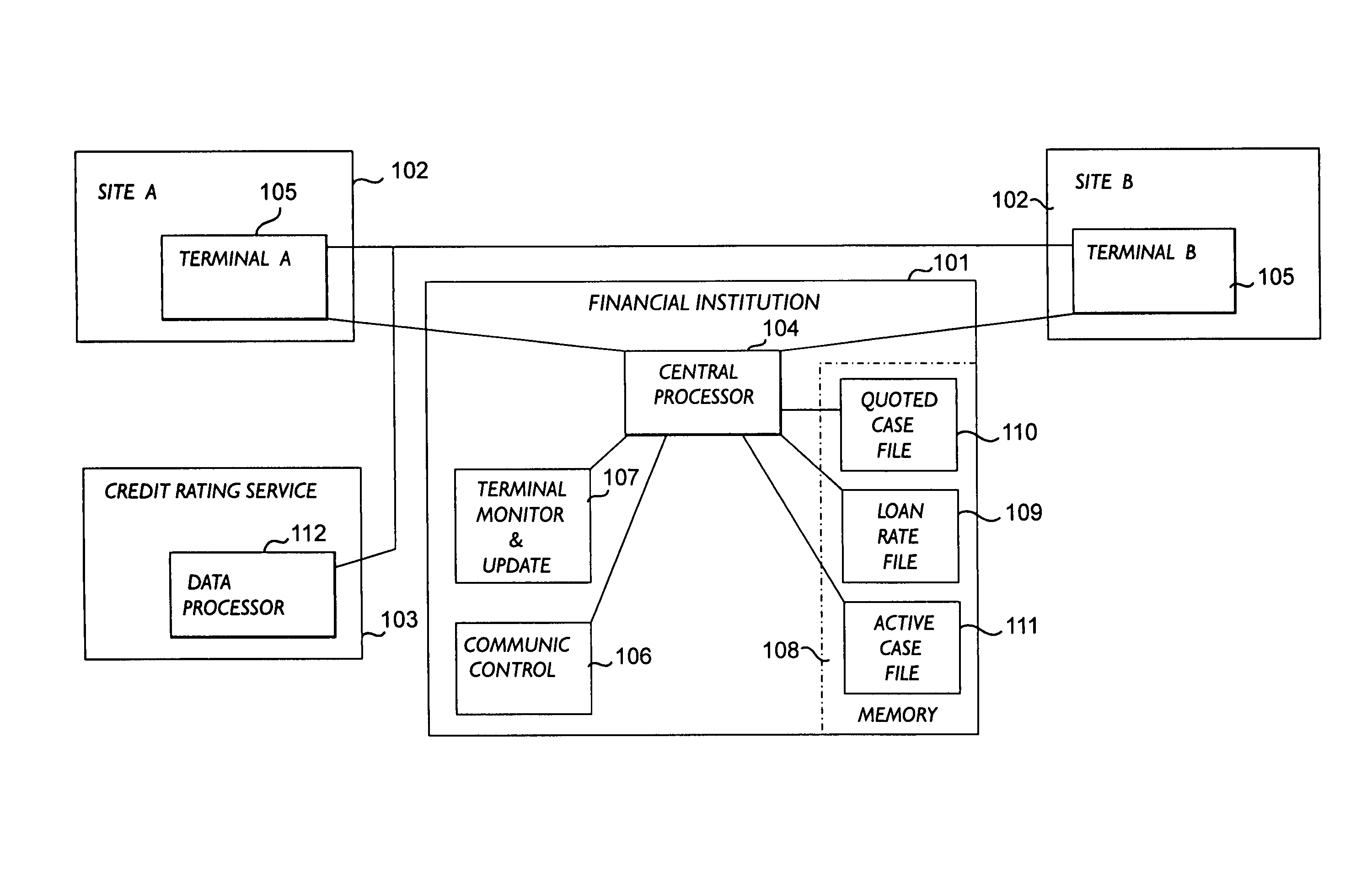
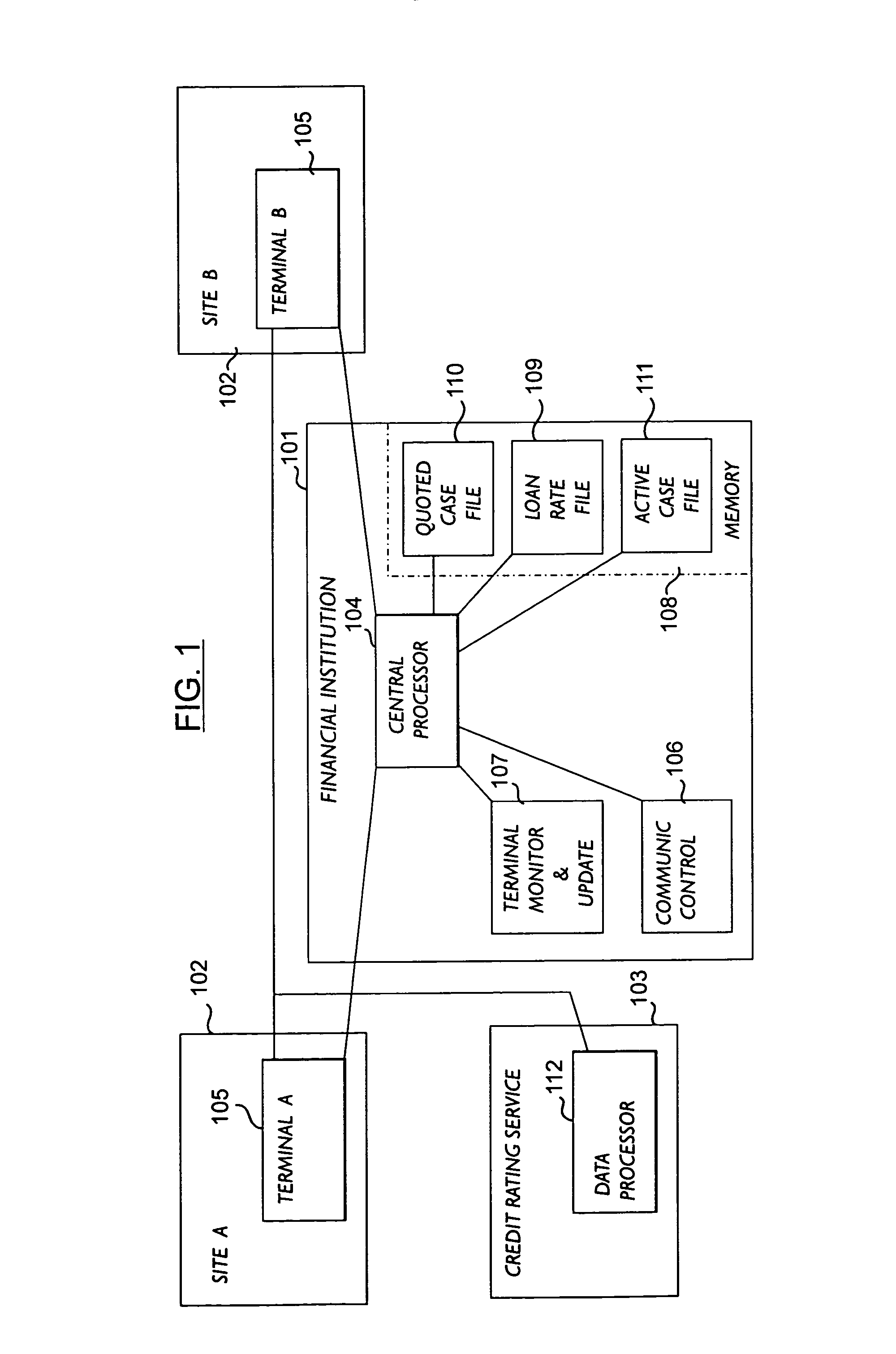
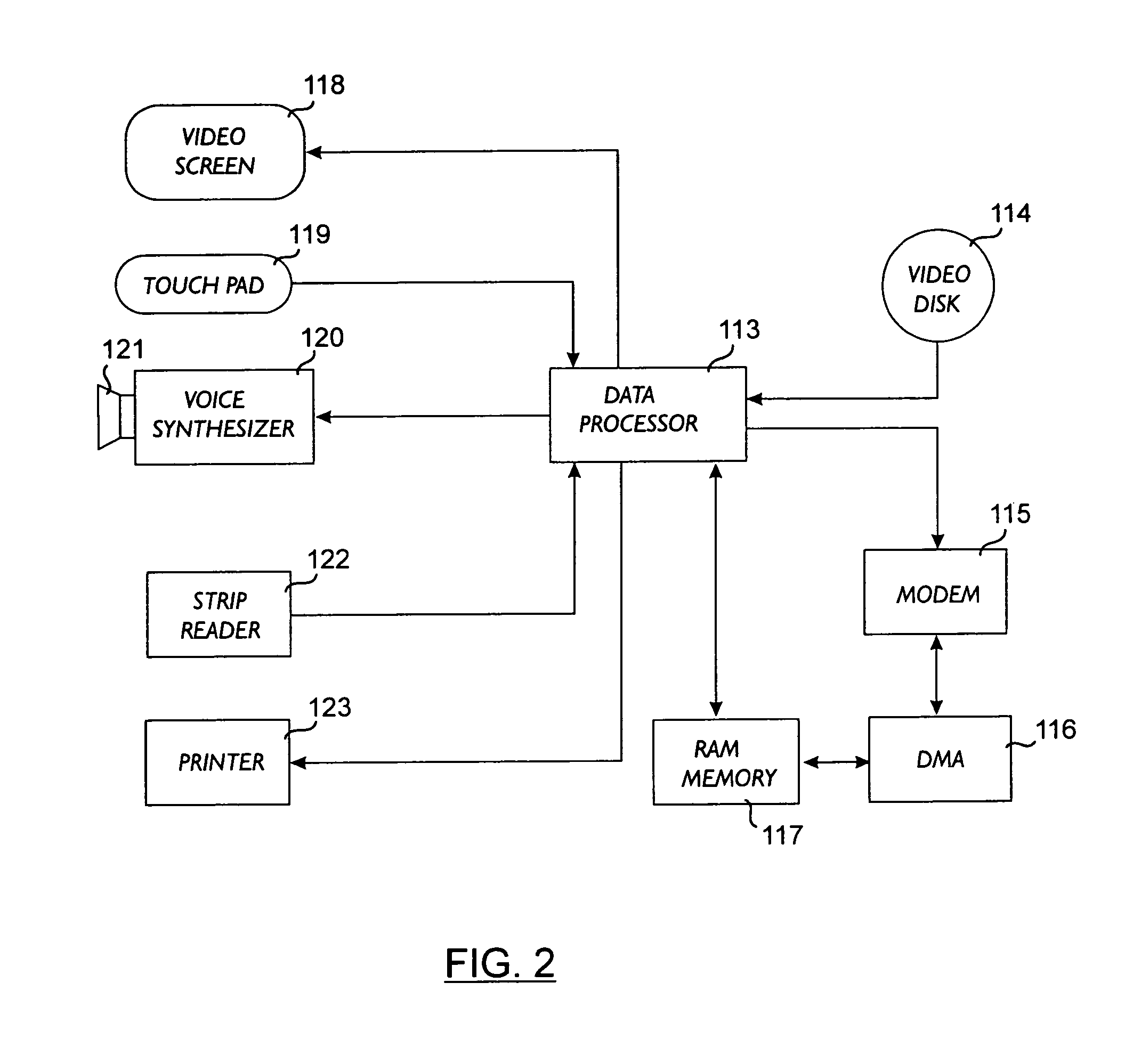
A system for filing applications with an institution from a plurality of remote sites, and for automatically processing said applications in response to each applicant's credit rating obtained from a credit reporting service comprising a series of self-service terminals remotely linked via a telephone line to a first computer at the institution and to a second computer at the credit reporting service headquarters. Each remote terminal comprises a video screen and a video memory which holds image-and-sound-generating information arranged to simulate the aspect and speech of an application loan officer on the video screen. The simulated loan officer is used to acquire loan request data from the applicant by guiding him through an interactive sequence of inquiries and answers. The system may be utilized as a trading network whereby stations are used by sellers and buyers to place and accept offers for securities, the central installation acting as a central computerized database where all transactions are processed and the various data items stored and automatically updated.
Owner:LOCKWOOD LAWRENCE B
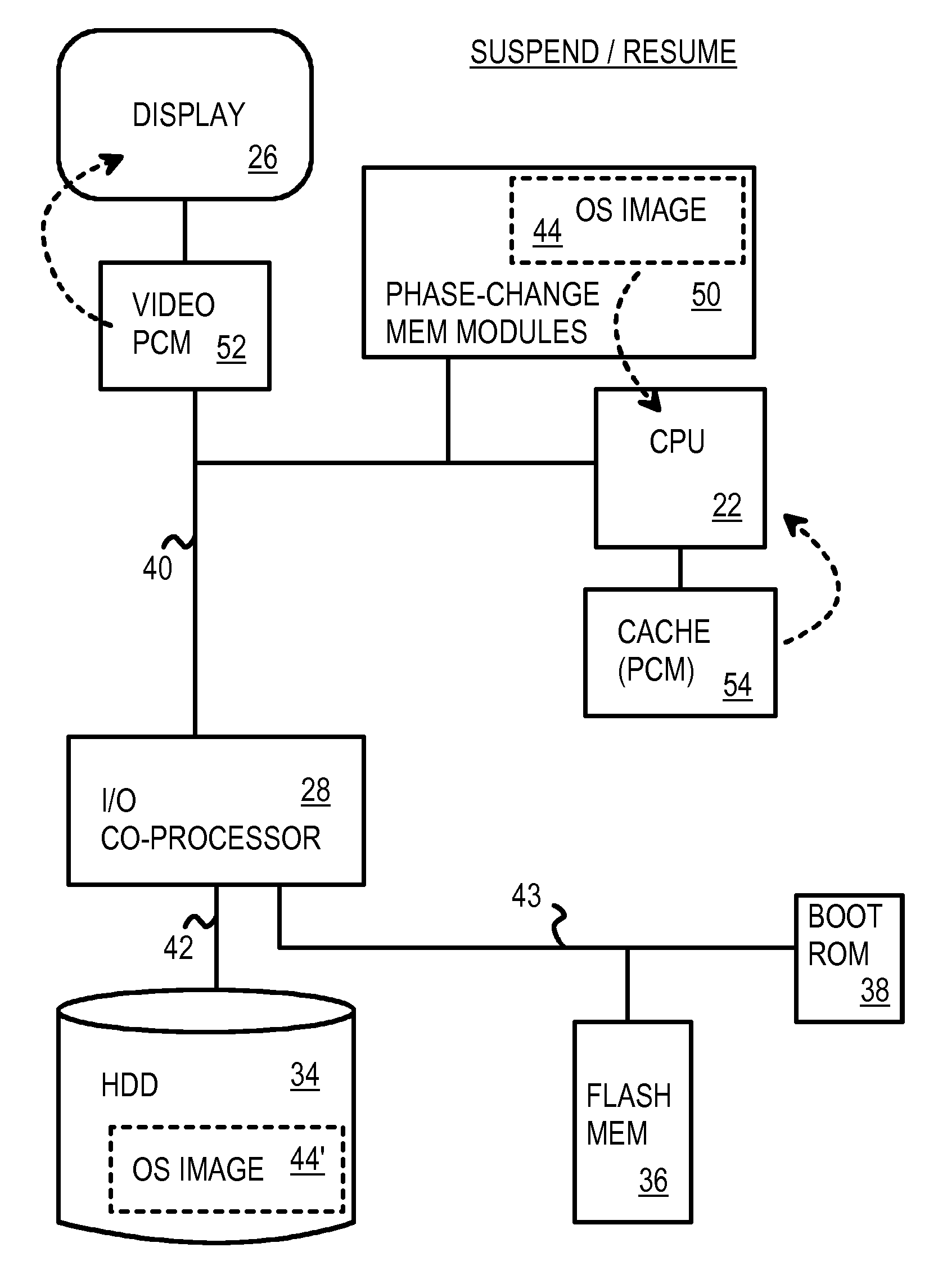
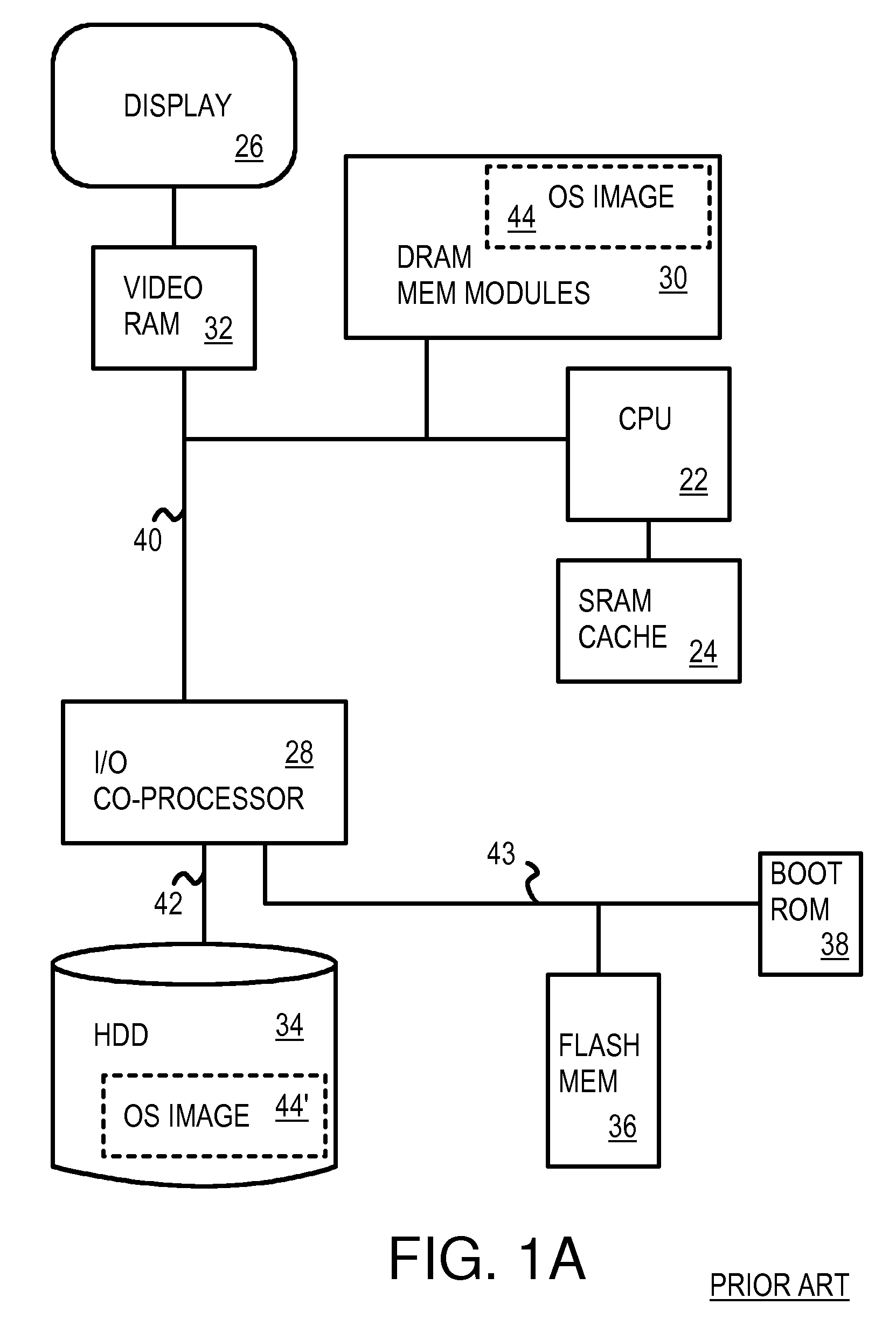
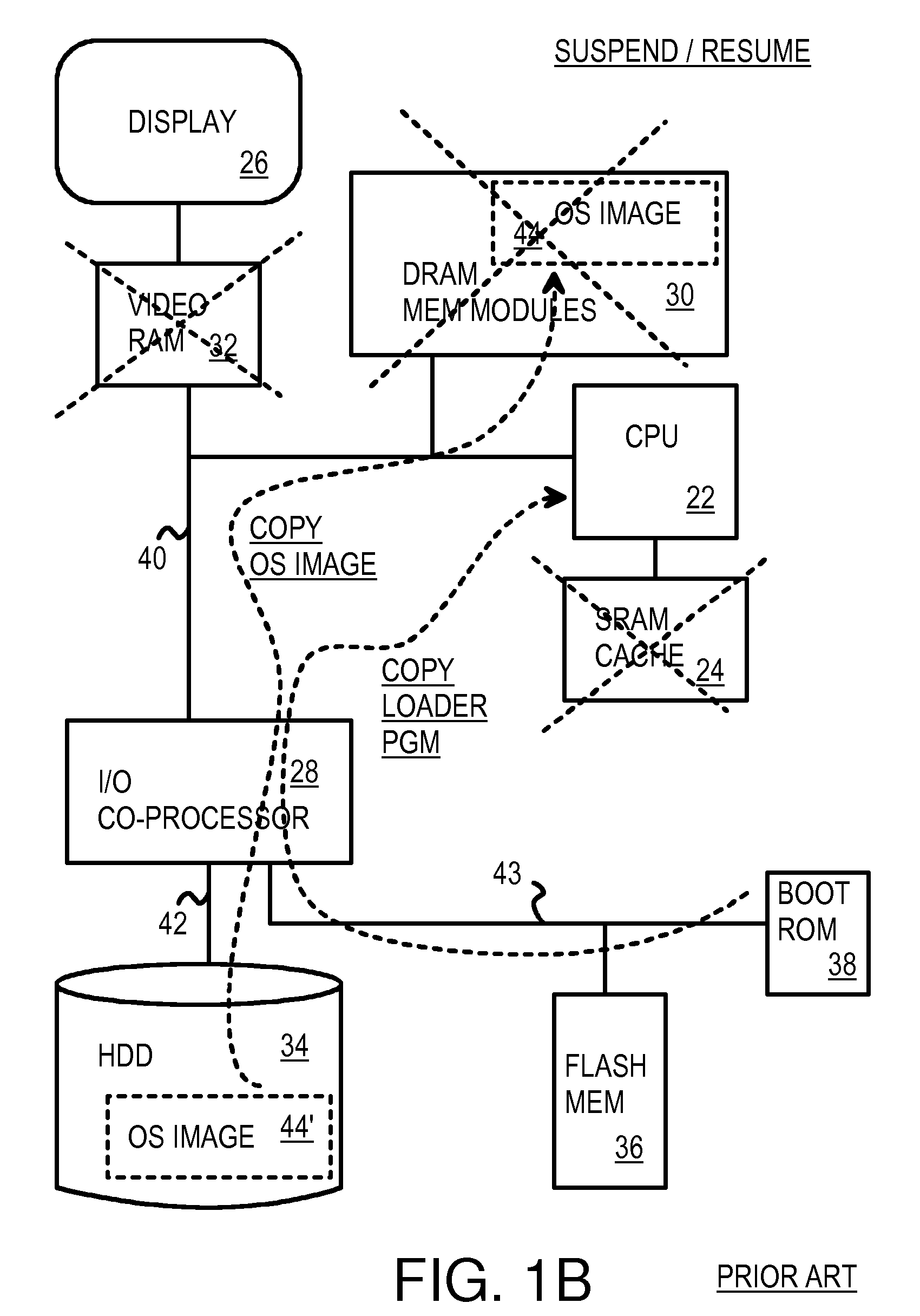
Fast Suspend-Resume of Computer Motherboard Using Phase-Change Memory
InactiveUS20080270811A1Digital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionVideo memoryVideo storage
A personal computer motherboard has a main memory of phase-change-memory (PCM) chips in PCM memory modules. An operating system (OS) image is stored in the PCM memory modules and is retained during suspend since the PCM chips are non-volatile. The microprocessor can directly read the OS image retained in the PCM memory modules without copying an OS image from a hard disk to the main memory upon resume. Therefore a boot loader program in the boot ROM does not have to be fetched to the microprocessor for suspend / resume. The video memory can also be PCM, allowing the frame buffer to be retained during suspend / resume, yet be directly addressable by the microprocessor. The display is quickly activated since the frame buffer does not have to be re-constructed after suspend / resume. PCM cells use amorphous and crystalline states of a variable resistor to store data.
Owner:SUPER TALENT ELECTRONICS
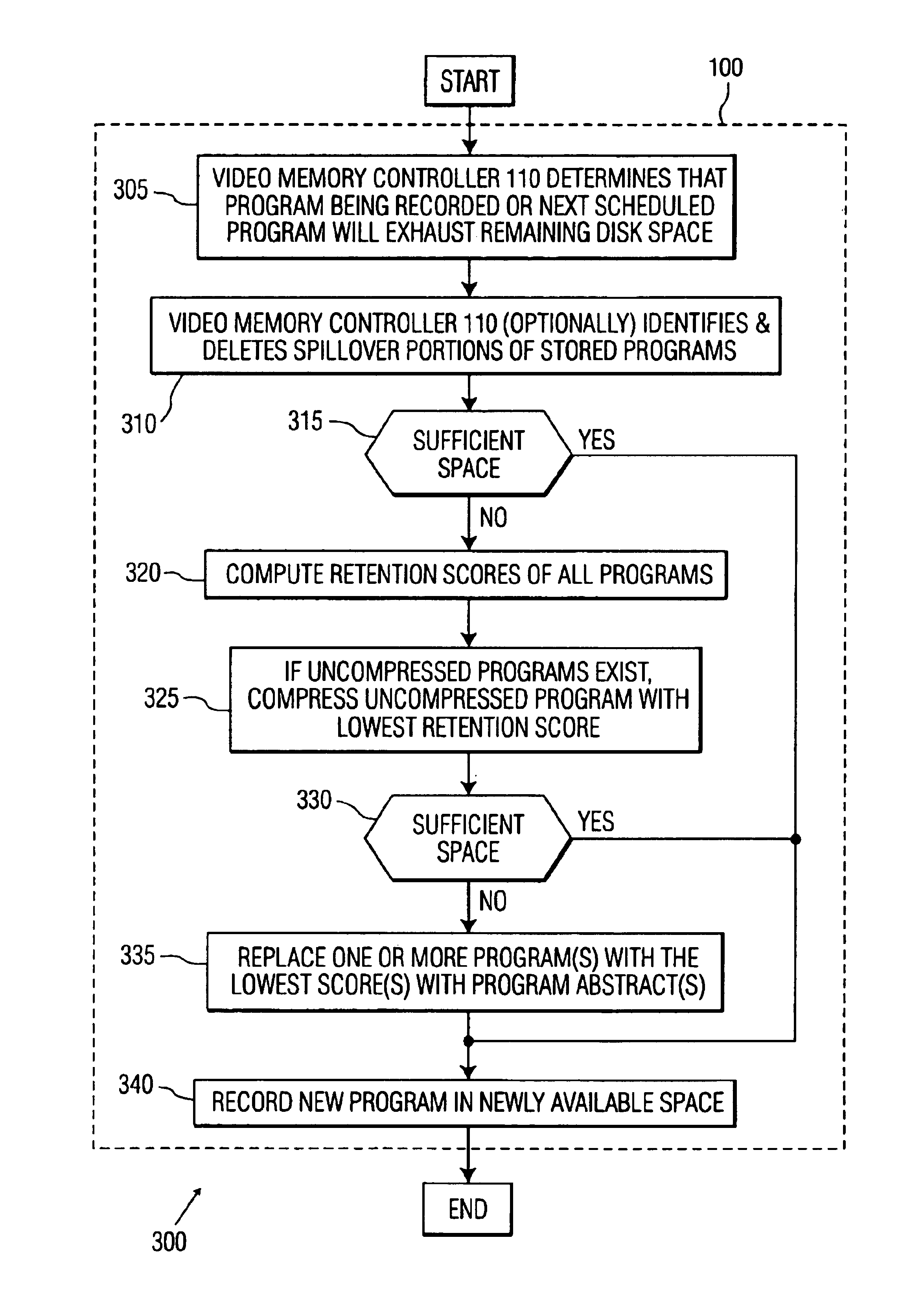
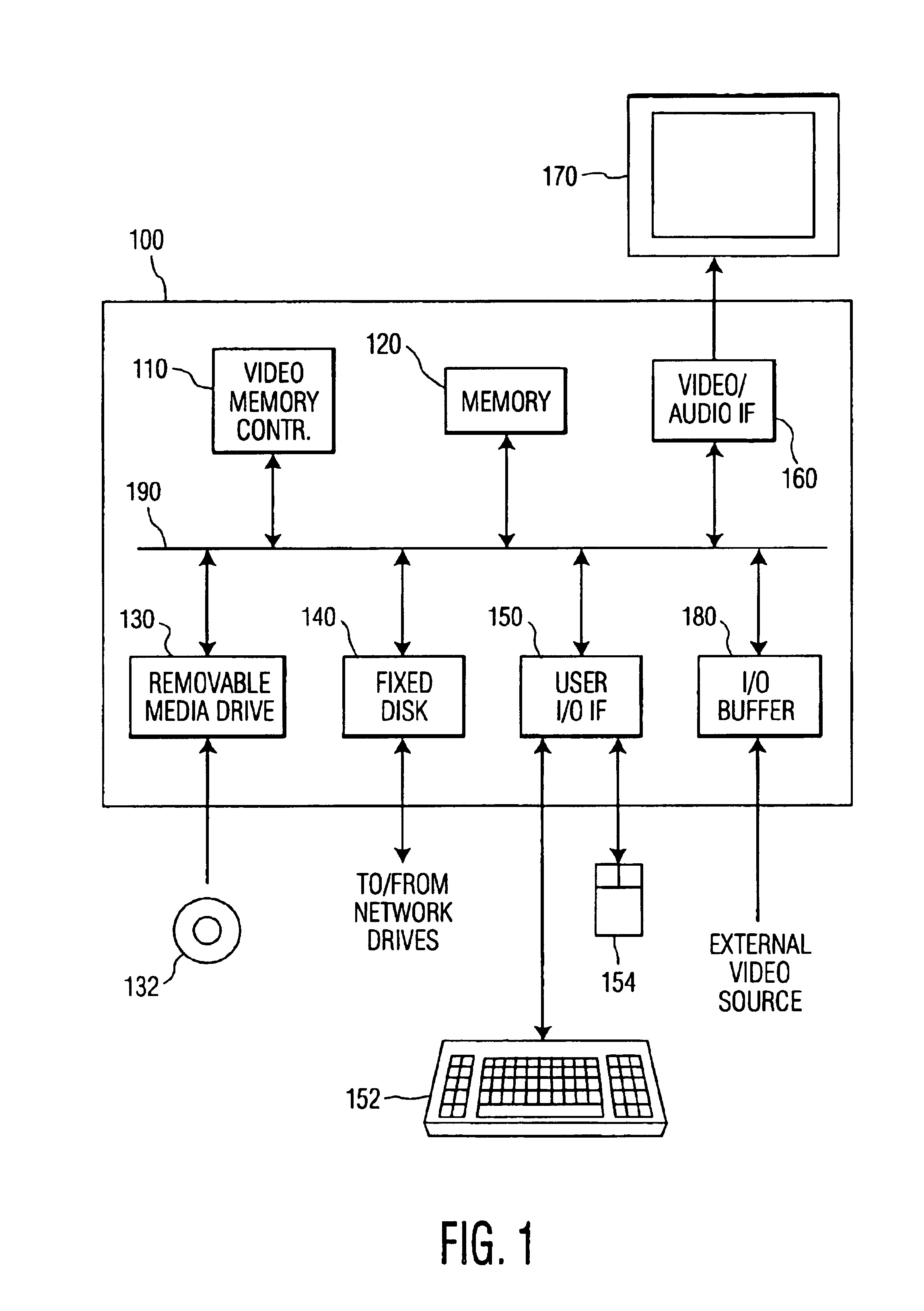
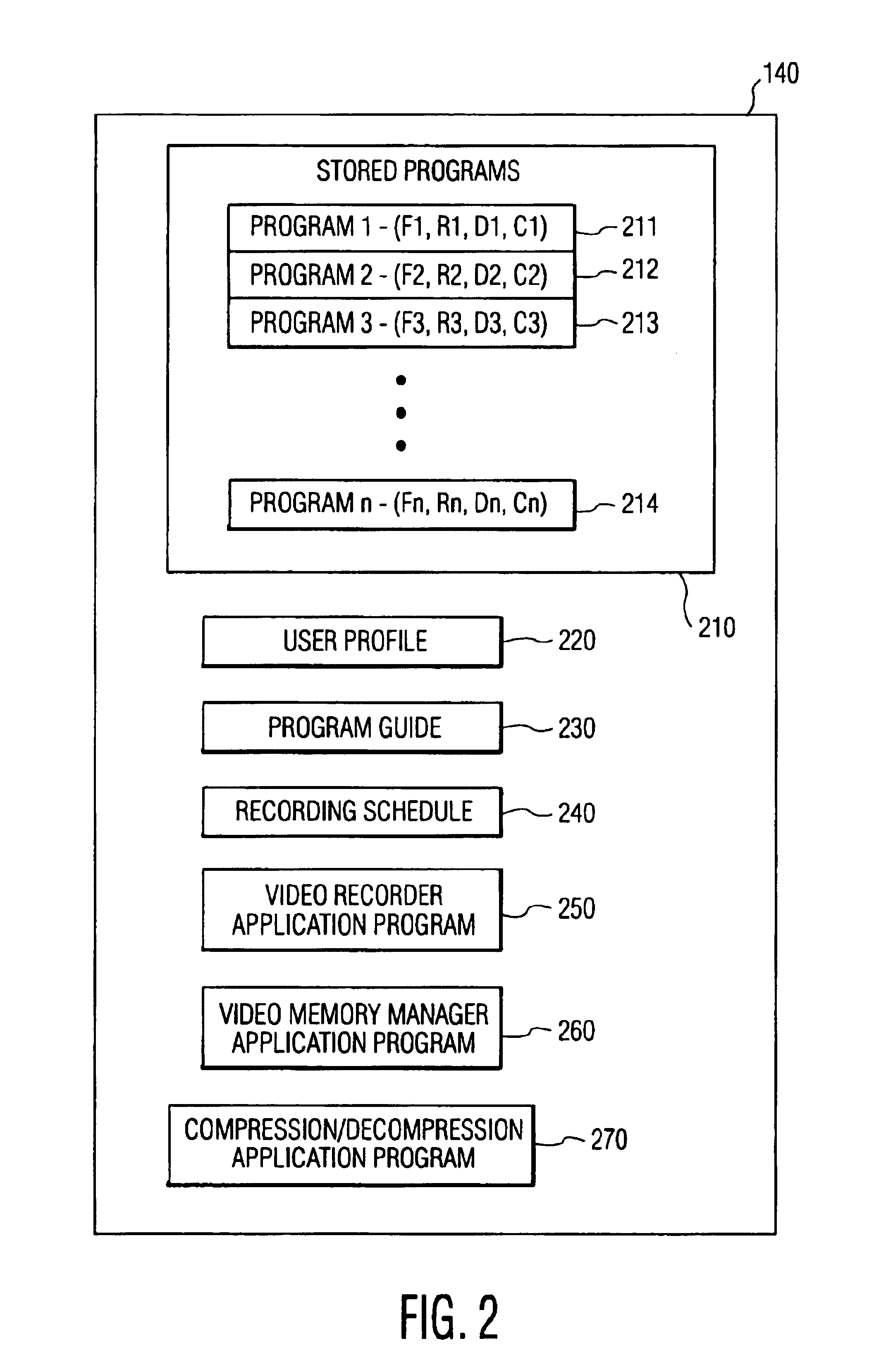
Video memory manager for use in a video recorder and method of operation
InactiveUS6920281B1FairnessTelevision system detailsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsVideo memoryVideo storage
There is disclosed a video memory manager for use in a video recording device that stores of video programs on a disk drive. The video memory manager comprises a video memory controller for detecting that the disk drive does not contain sufficient storage space to store a next-to-be-recorded program. The video memory controller, in response to the detection, determines a first retention score associated with a first video program and a second retention score associated with a second video program. The first and second retention scores indicate a desirability of retaining the first and second video programs respectively. The video memory controller deletes a least desirable one of the first and second video programs.
Owner:HEPING GROUP
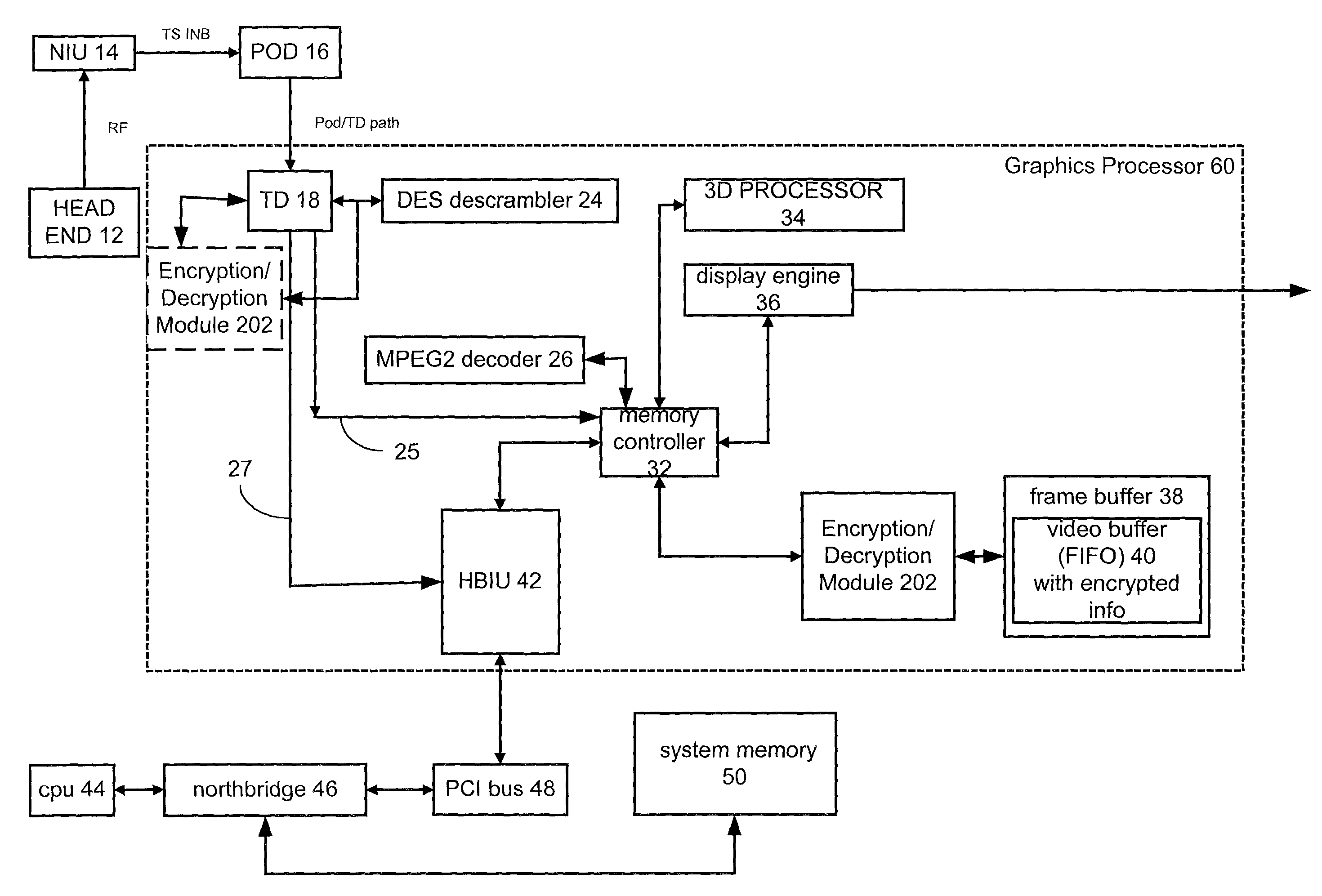
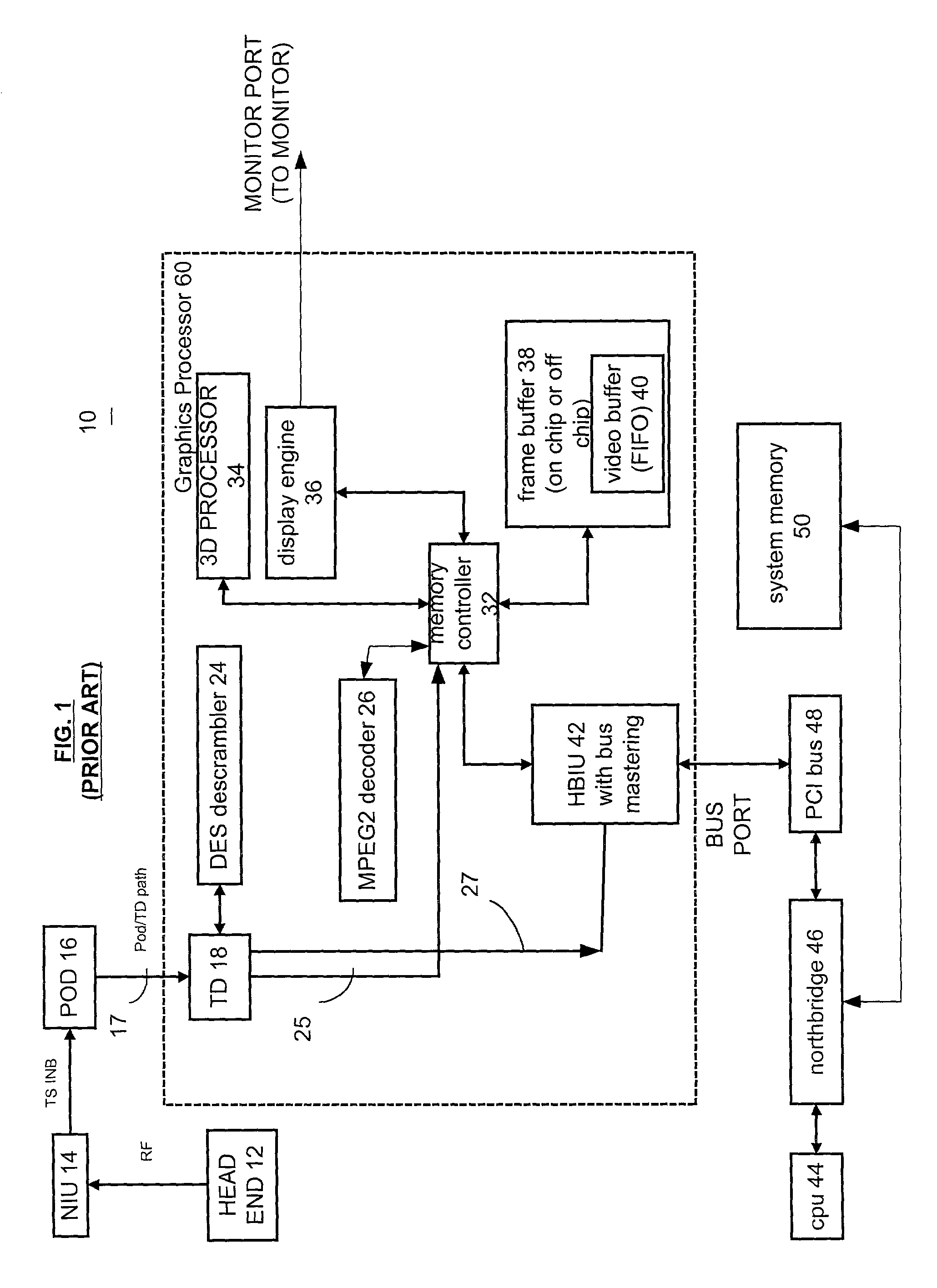
Method and apparatus for maintaining secure and nonsecure data in a shared memory system
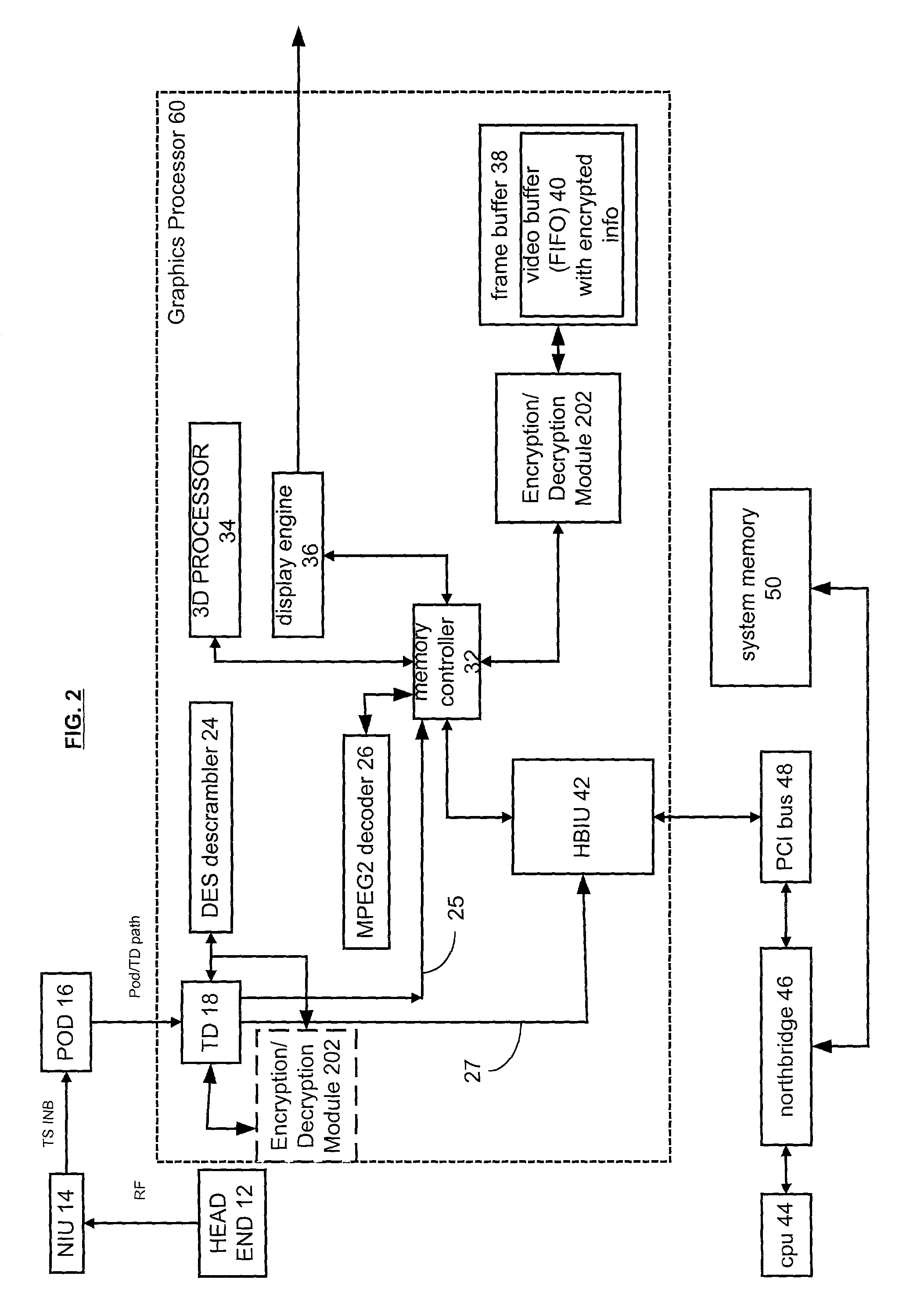
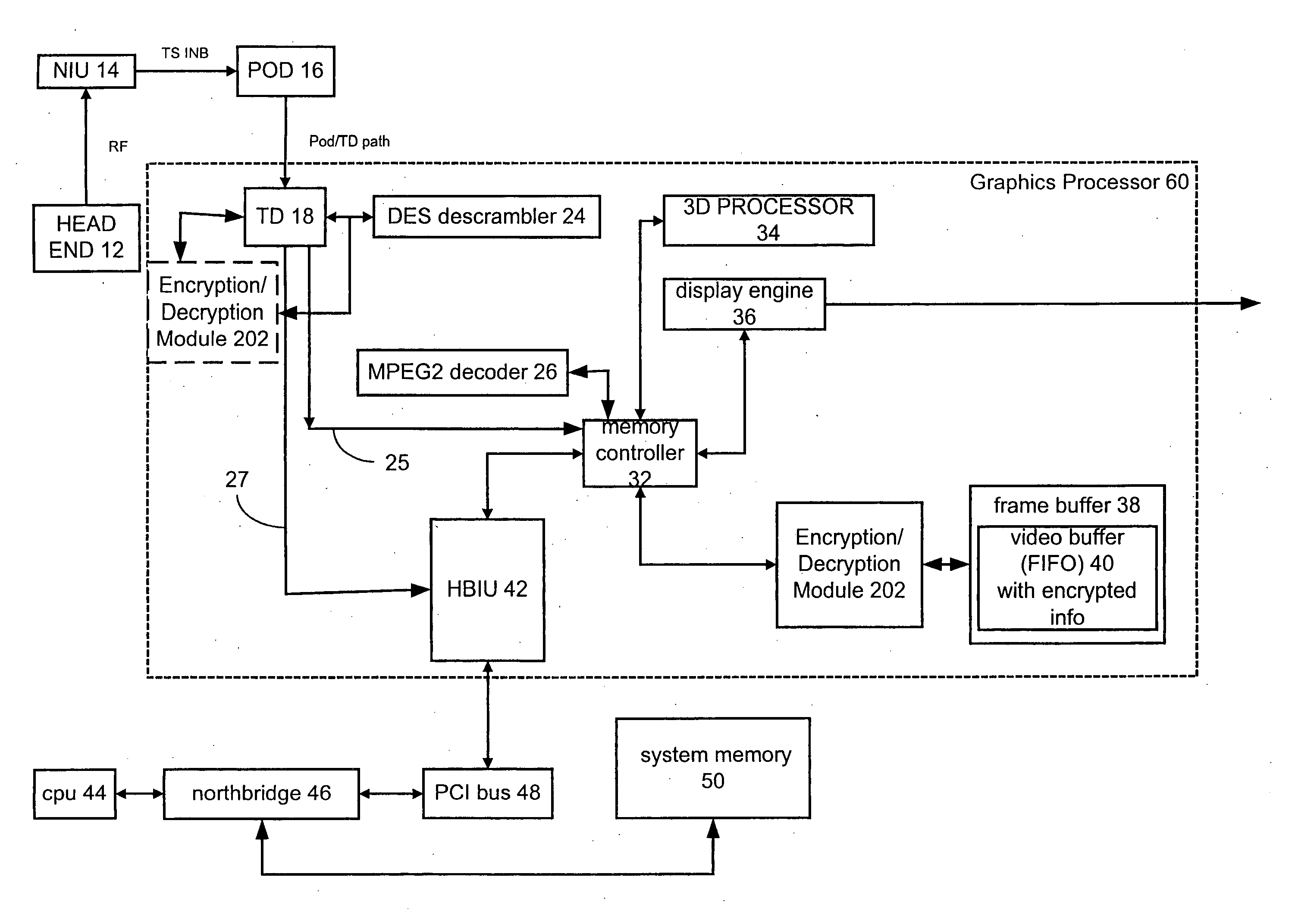
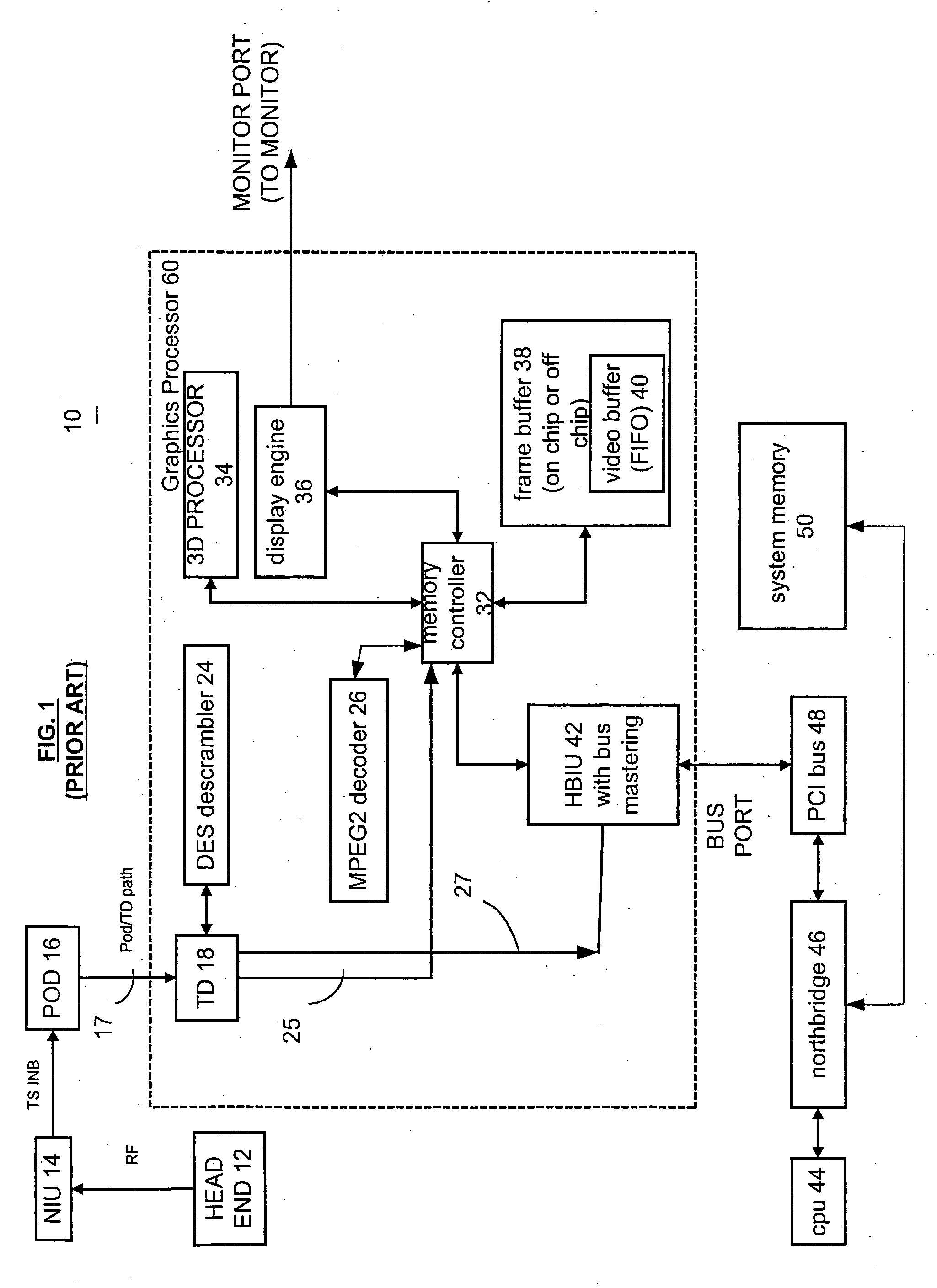
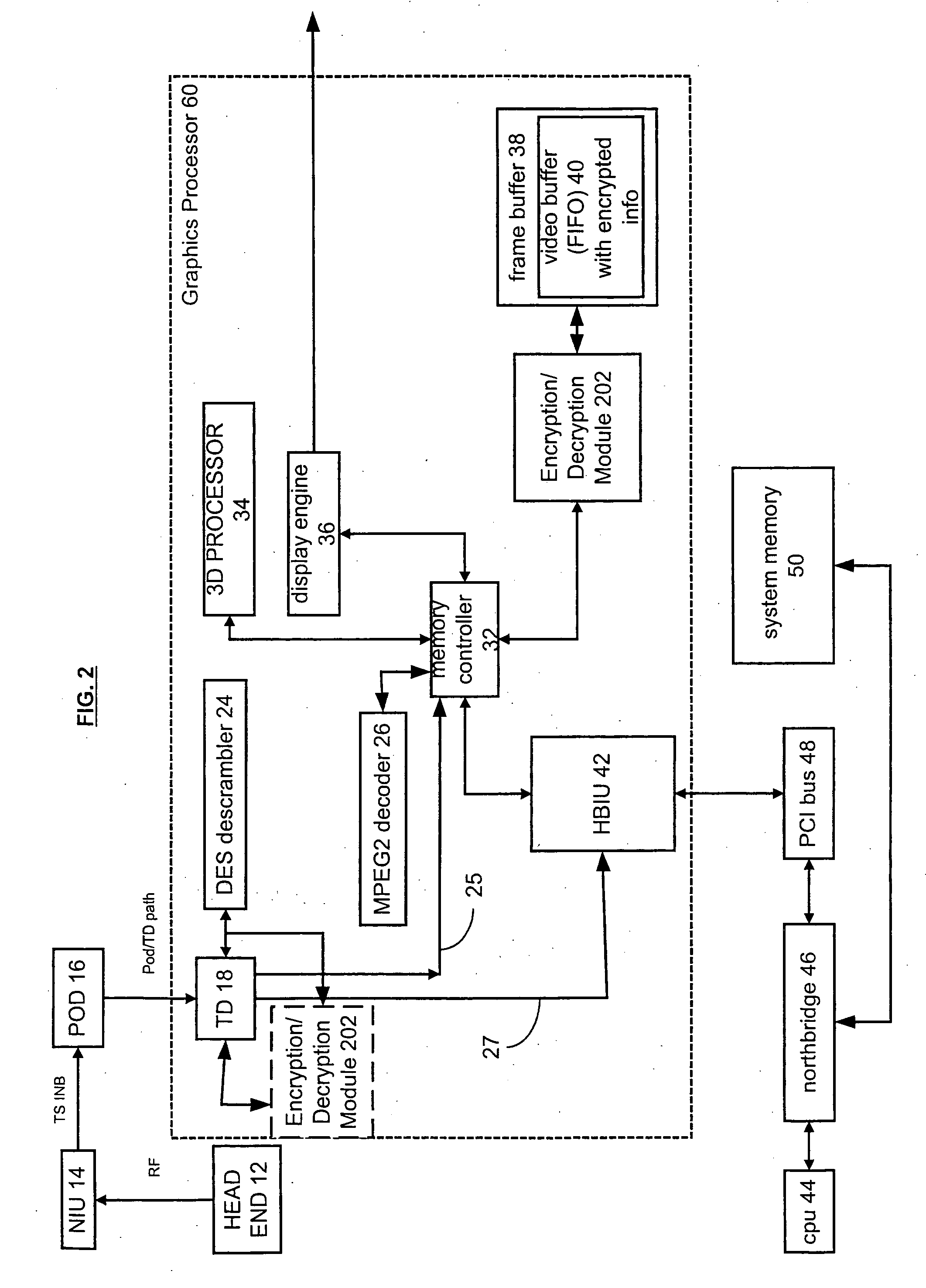
A graphics processor receives a compressed encrypted video stream. The graphics processor decrypts the compressed encrypted video stream and stores a decrypted version (i.e., a decrypted compressed video stream) in a protected portion of an on-chip or off-chip video memory. The graphics processor then permits processors and other bus masters on the graphics processor to access the on-chip video memory, but conditionally limits access to other bus masters that are located off-chip, such as a central processing unit located off-chip and coupled to the graphics processor via a bus.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
Medical apparatus and method for setting up a medical apparatus
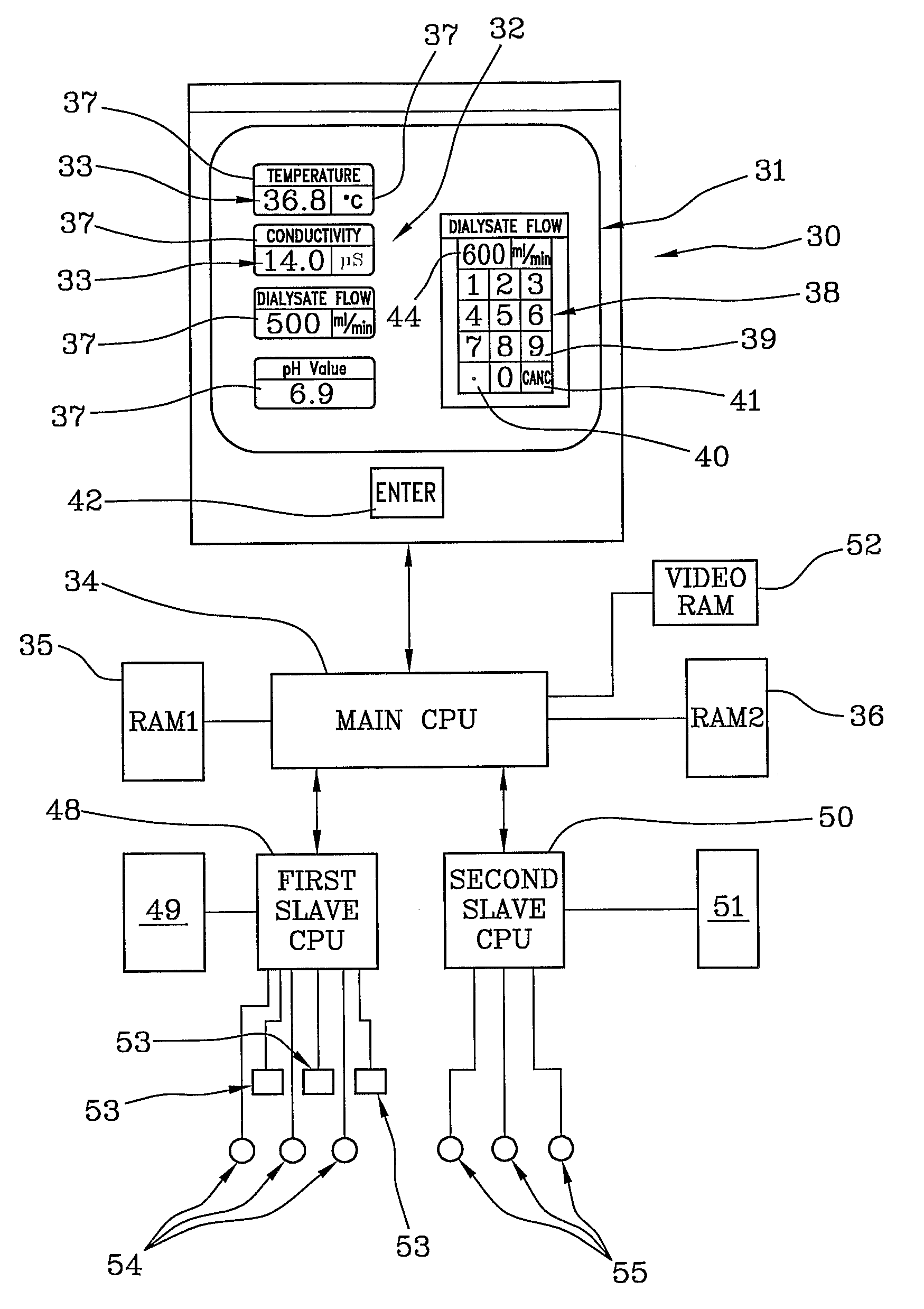
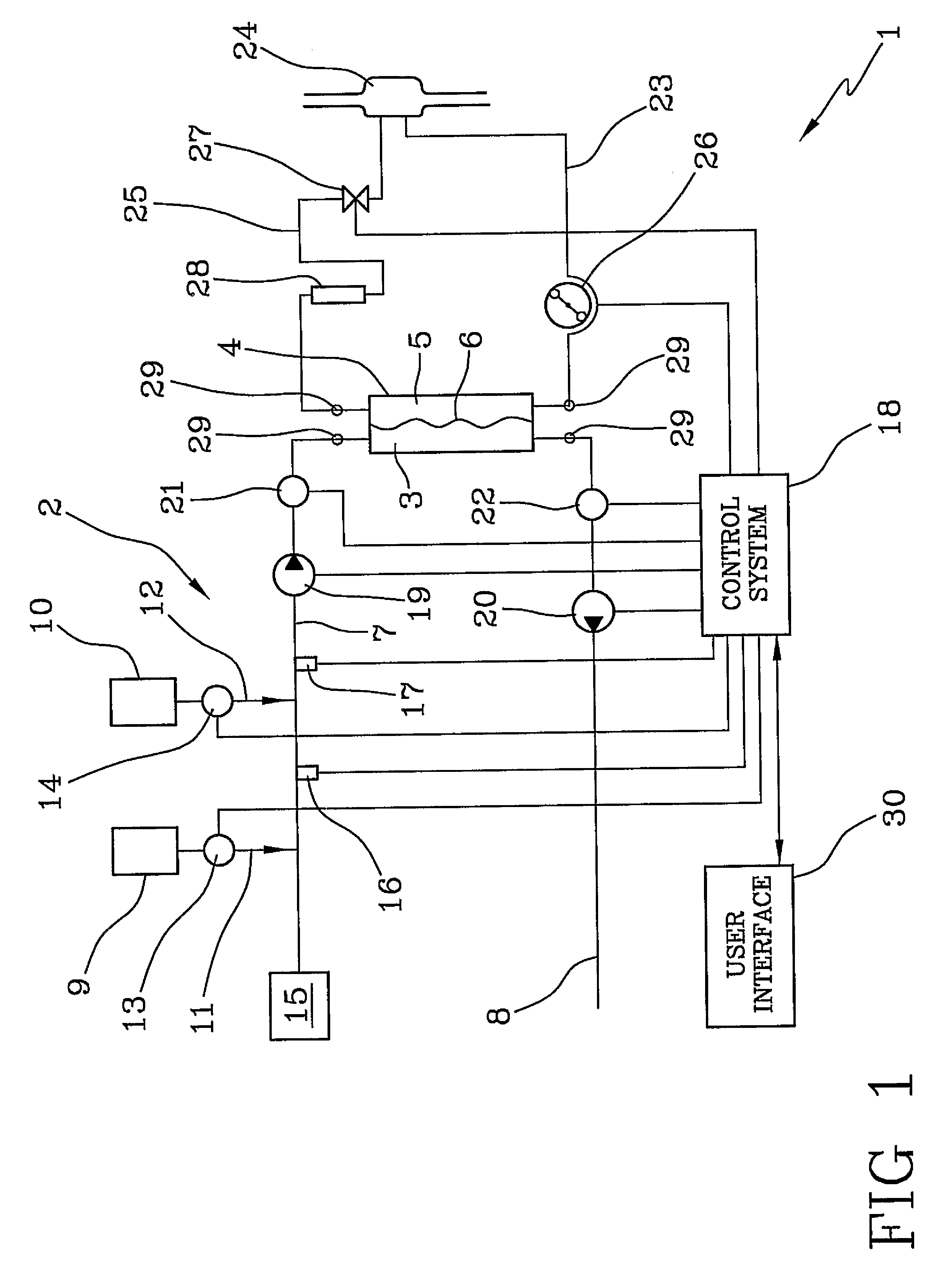
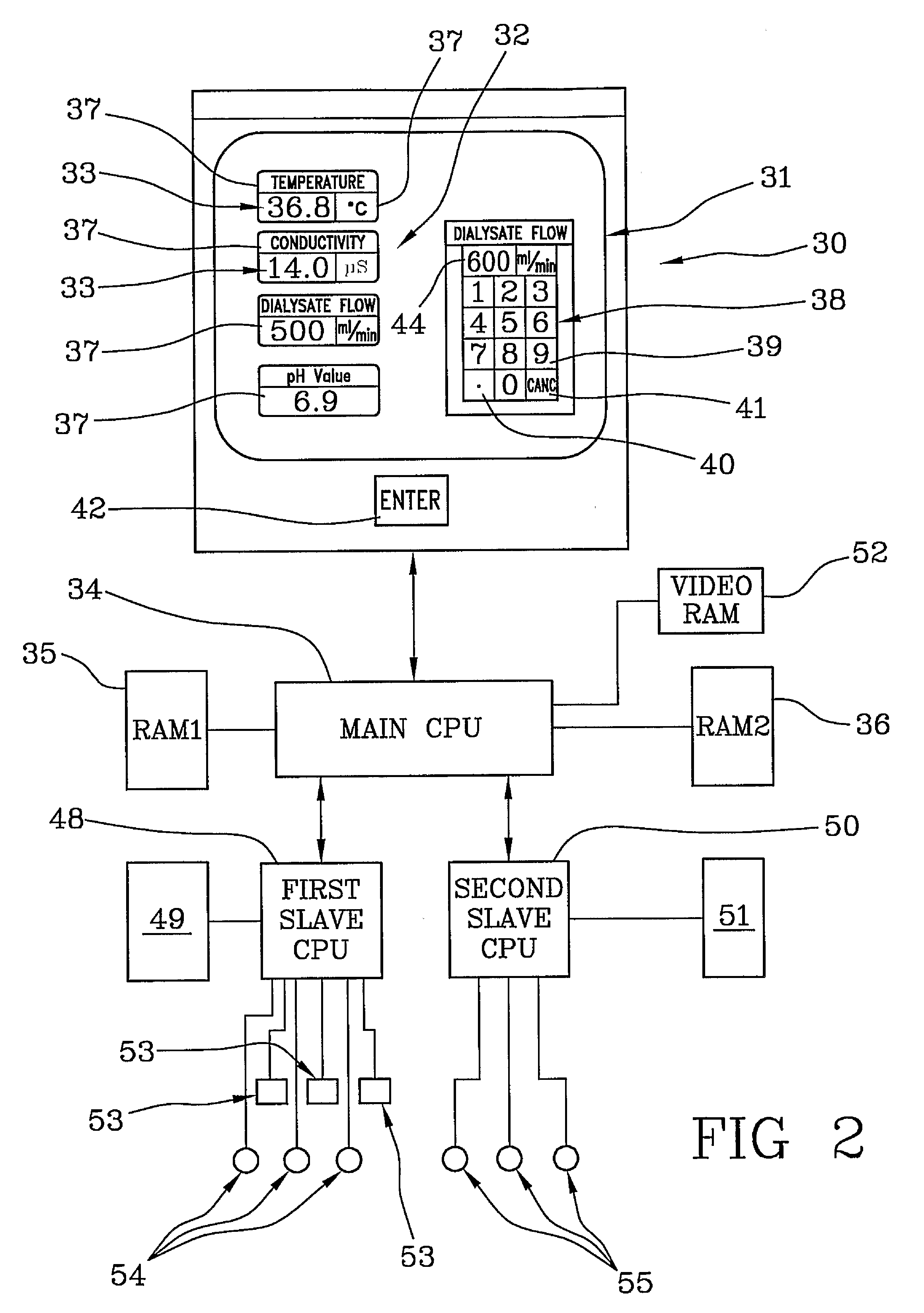
ActiveUS7922899B2Improve ease and reliabilityReduce data entryLiquid separation auxillary apparatusSolvent extractionData validationVideo memory
A medical apparatus comprises a user interface for setting parameters and includes: a screen for visualizing values of said parameters, a main control unit connected to the interface, a first memory and a video memory both connected to the main control unit for storing data corresponding to images on screen; the main control unit allows setting of a new value for a parameter, displays the new value on a screen region, stores the new value in the first memory, captures from the video memory data representative of said screen region, verifies from said representative data if the displayed value corresponds to the value in the first memory. A method for setting up a medical apparatus is also disclosed.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Three-dimensional terrain model real-time smooth drawing method with combination of GPU technology
InactiveCN105336003ATroubleshoot preprocessing issuesEliminate noise3D modellingVideo memoryEngineering
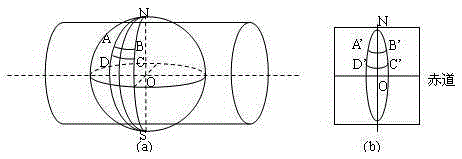
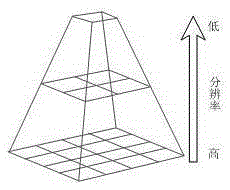
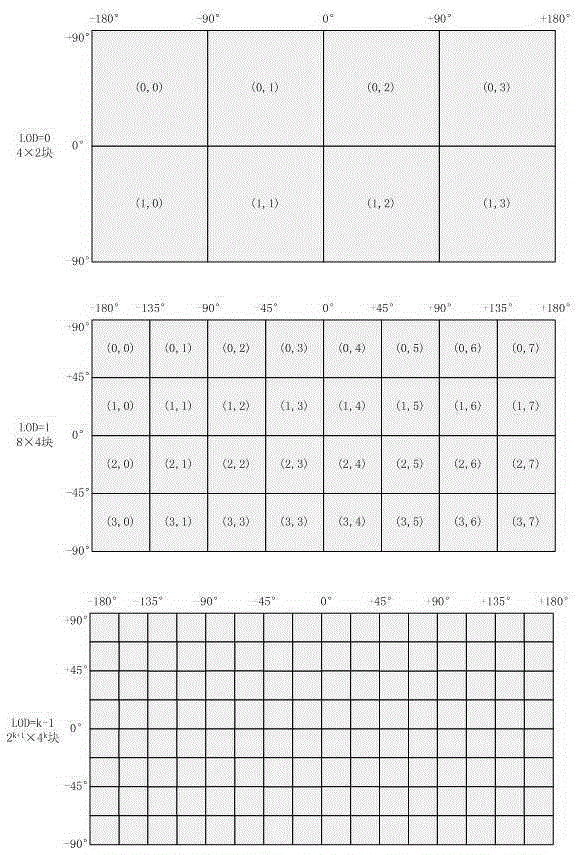
The invention provides a three-dimensional terrain model real-time smooth drawing method with combination of a GPU technology, and belongs to the technical field of image processing. The objective of the invention is to provide the three-dimensional terrain model real-time smooth drawing method with combination of the GPU technology so that cache reuse in multiple times of drawing can be realized based on the current popular programmable GPU technology with a global digital elevation model acting as a data source, and load of computation space is effectively reduced. The method comprises the steps of construction of a multi-resolution pyramid model, elimination of image noise points, filtering of images, partitioning of planar projection of the earth according to equal latitude and longitude, and construction of different hierarchical levels of pyramid layers according to a mode from the top to the bottom. Acceleration and enhancement of terrain rendering are realized based on the programmable GPU technology, i.e. all phases of a graphical drawing pipeline are controlled by using shader languages, two and textures are respectively generated by vertex information and index information of elevation data to be stored in video memory for scheduling of whole terrain drawing; and vertex interpolation and migration are performed in the geometric phase by utilizing a curved surface subdivision and fractal technology so that procedural details are generated and the phenomenon of edges and corners of the terrain mesh when resolution is insufficient can be compensated.
Owner:PLA AIR FORCE AVIATION UNIVERSITY
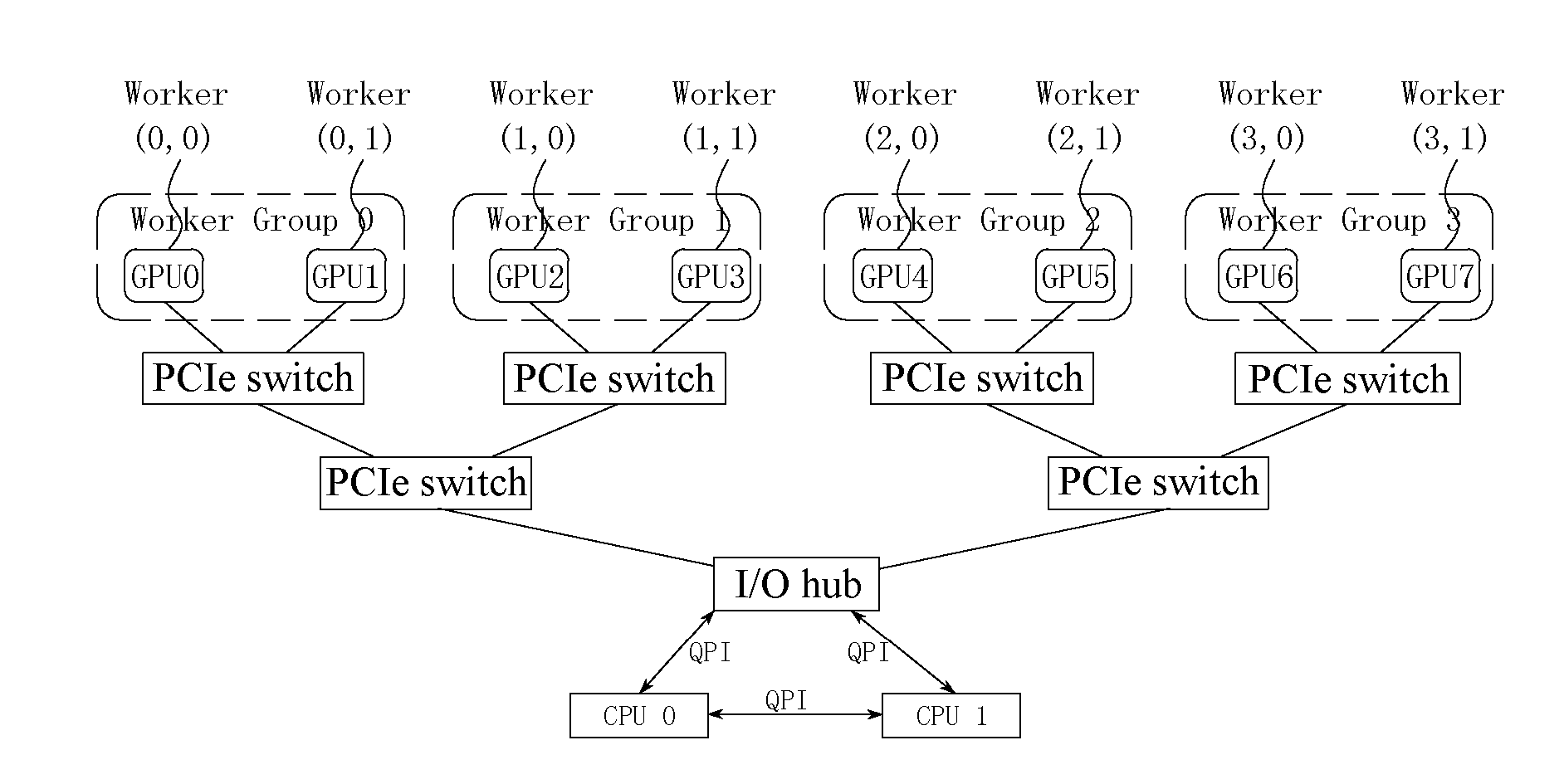
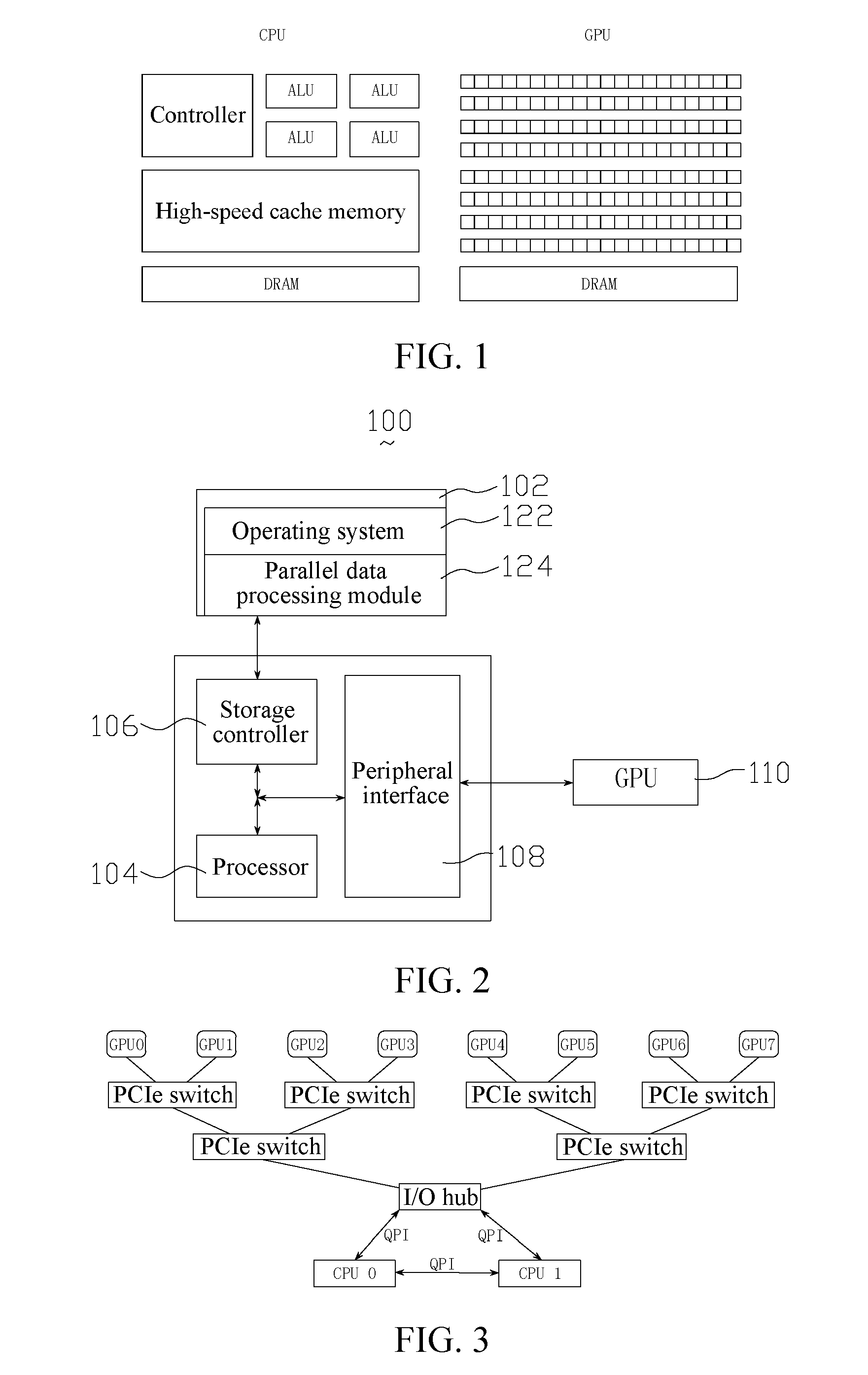
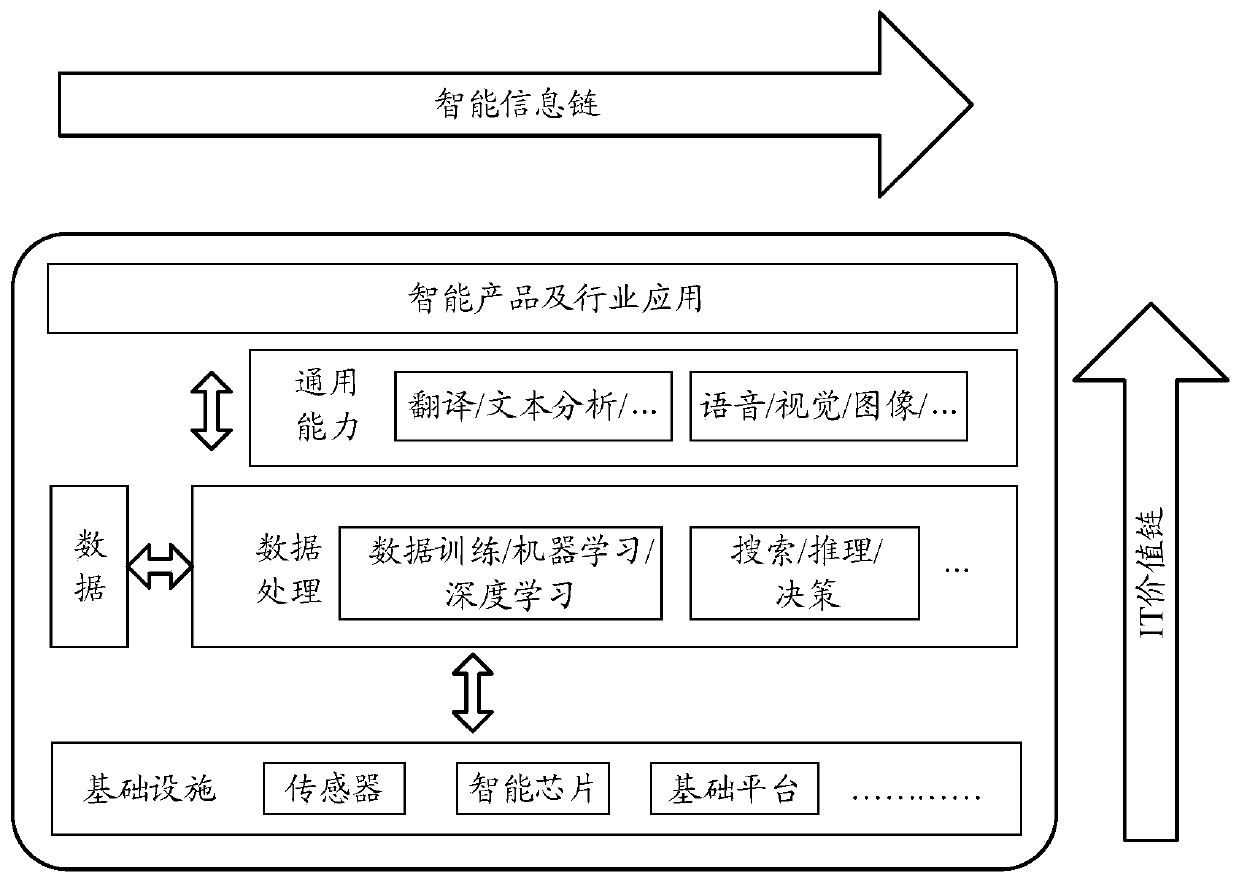
Parallel model processing method and device based on multiple graphics processing units
ActiveCN104036451AImprove processing efficiencyImprove the efficiency of storage accessProcessor architectures/configurationProgram controlGraphicsVideo memory
The invention relates to a parallel model processing method based on multiple graphics processing units (GPUs). The method includes the steps: creating multiple Workers used for respectively controlling multiple Worker Groups in a central processing unit (CPU), wherein each Worker Group comprises the GPUs; binding each Worker with one corresponding GPU; loading one Batch of training data from a nonvolatile memory into a GPU video memory corresponding to one Worker Group; transmitting data, needed by the GPUs for data processing, among the GPUs corresponding to one Worker Group in a Peer to Peer manner; controlling the GPUs to perform data processing in parallel through the Workers. By the method, efficiency of parallel data processing of the GPUs can be improved. Besides, the invention further provides a parallel data processing device.
Owner:SHENZHEN TENCENT COMP SYST CO LTD
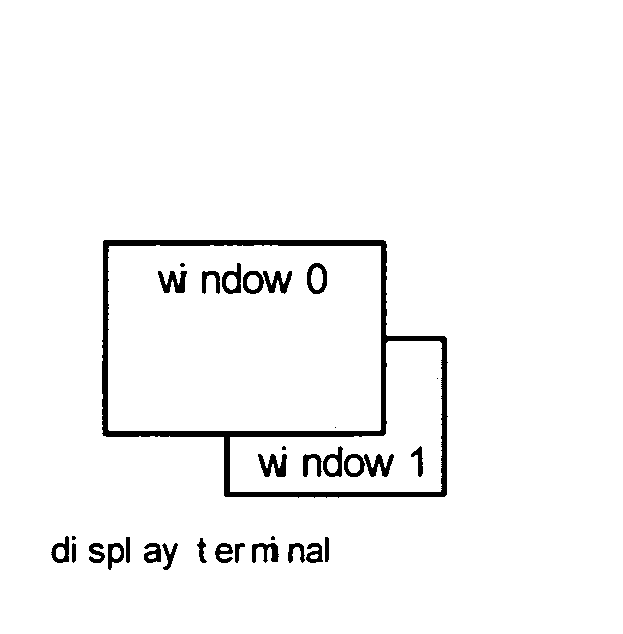
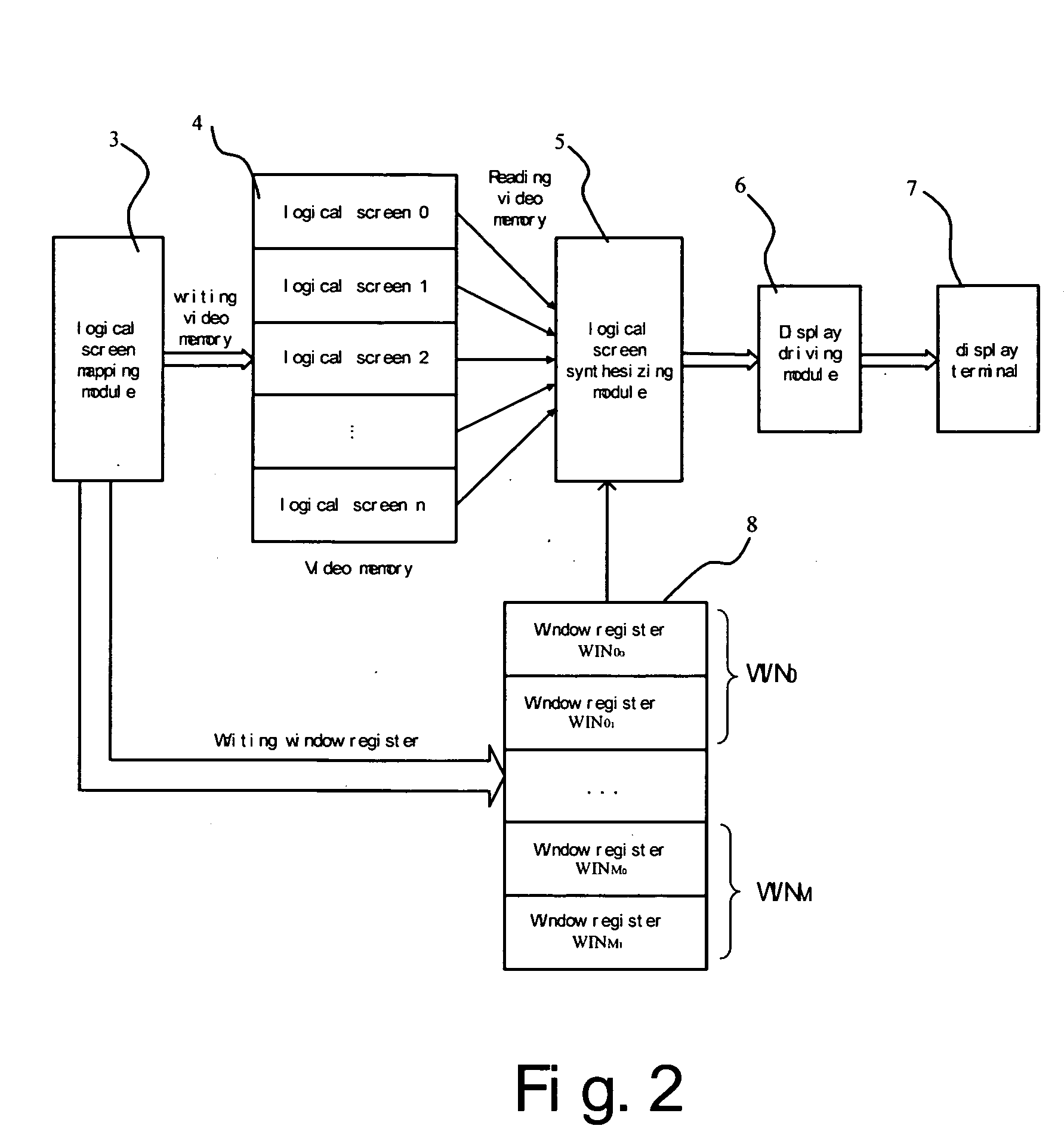
Multi-screen synthesizing display apparatus and method
ActiveUS20070216700A1Attenuation bandwidthReduce overheadCathode-ray tube indicatorsProgram controlVideo memoryVideo storage
A multi-screen synthesizing apparatus and method have been disclosed by the present invention. Display data of windows required to be displayed on the display terminal are mapped onto at least one logical screen by storing data in a video memory. Each of the windows is correlated with a set of window registers, and the location coordinates of the window and the identification of the corresponding logical screen are stored into the window register set when displaying the windows, the window register set having the highest priority level are found out, based on the location coordinates of the current scanning pixel, as the selected window register. The display data corresponding to the current pixel are read out from the logical screen corresponding to the selected window register and output to the display terminal. According to the present invention, the display data are not necessary to be written repeatedly during the switching operations of windows, thus the overhead for the CPU to process the display task can be reduced without increasing the occupied bandwidth. Thereby the display efficiency of various electronic devices having display ability can be improved and the display cost can be reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
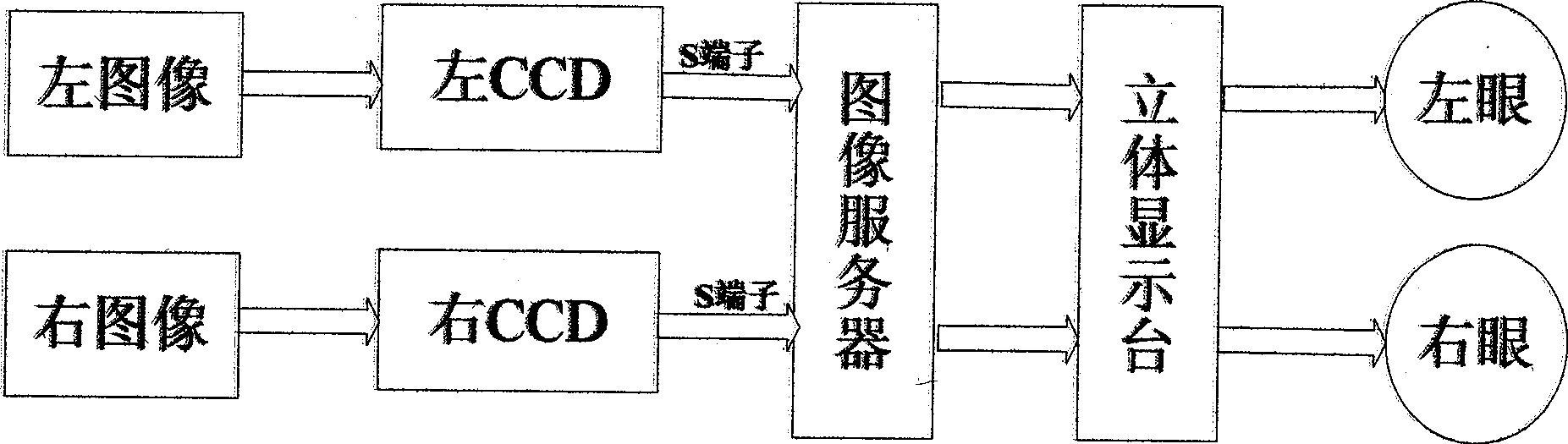
Binocular endoscope operation visual system
InactiveCN101518438AMeet the needs of 3D stereo visionStereoscopic effect is goodLaproscopesEndoscopesVideo memoryLaparoscopy
A binocular endoscope operation visual system mainly comprises a binocular endoscope, an image server and an endoscope stereo display unit. Two ways of clear abdominal cavity image video signals are obtained by the binocular endoscope, two ways of video streams enter a memory of an image processing server or a video memory by a two-way image capture card, and a left-way image and a right-way image which are processed are respectively displayed in a left displayer and a right displayer. By a flat mirror, the contents of the left displayer and the right displayer respectively enter the left eye and the right eye of an observer, thereby the stereo effect is realized. The binocular endoscope operation visual system is suitable for the circumstance of a medical surgical endoscope operation, can completely satisfy the stereoscopic vision requirement of a laparoscope operation of a minimally invasive operation robot, realizes the binocular stereoscopic vision real-time display in the laparoscope operation, has reliable performance, simple structure and high commercialization level, and adapts the germfree circumstances of the operation.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method and apparatus for maintaining secure and nonsecure data in a shared memory system
A graphics processor receives a compressed encrypted video stream. The graphics processor decrypts the compressed encrypted video stream and stores a decrypted version (i.e., a decrypted compressed video stream) in a protected portion of an on-chip or off-chip video memory. The graphics processor then permits processors and other bus masters on the graphics processor to access the on-chip video memory, but conditionally limits access to other bus masters that are located off-chip, such as a central processing unit located off-chip and coupled to the graphics processor via a bus.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
Methods and systems for cryptographically protecting secure content
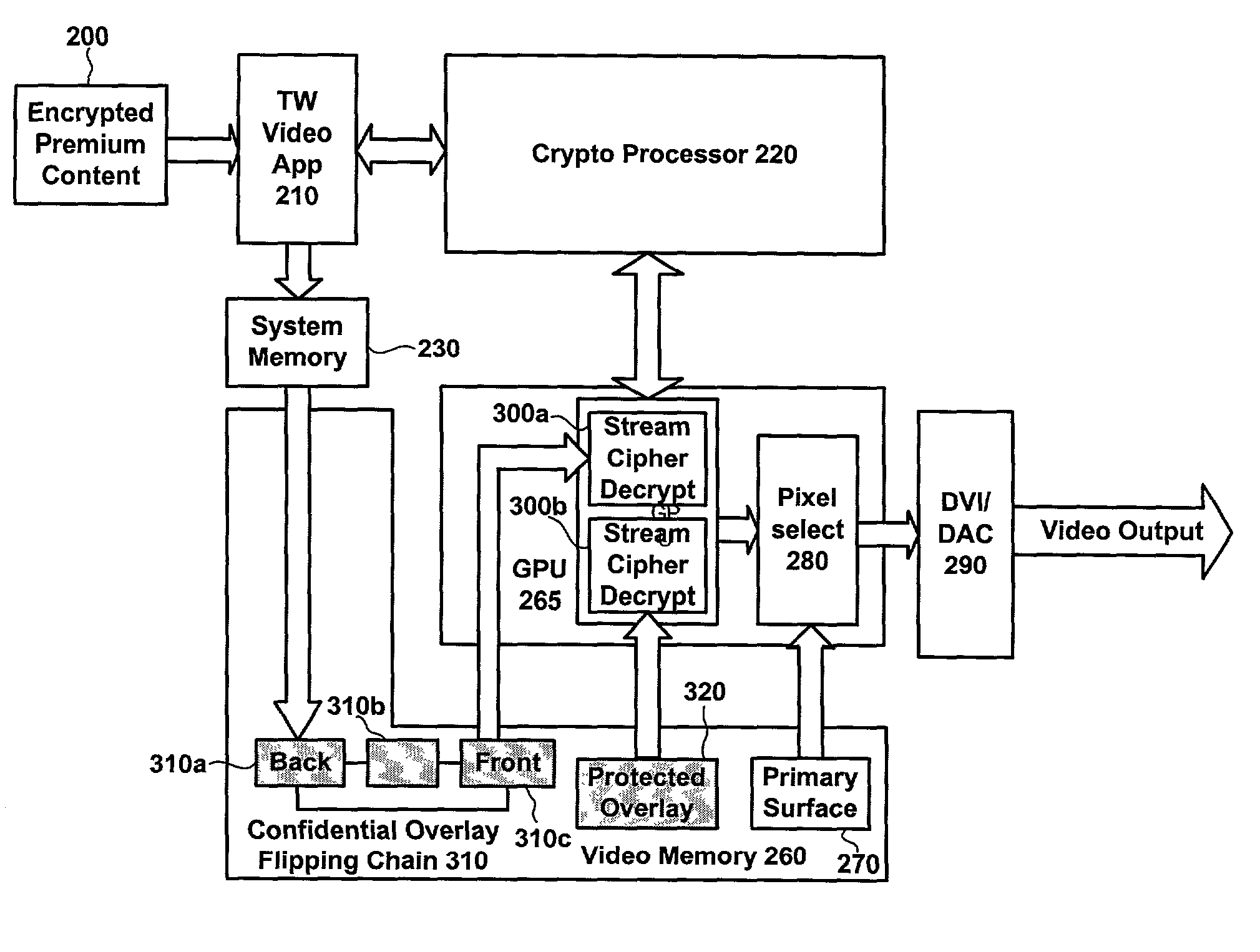
ActiveUS7203310B2Hinder availabilitySatisfy confidentialityTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionGraphicsVideo memory
Methods and systems are provided for cryptographically protecting secure content in connection with a graphics subsystem of a computing device. Techniques are implemented to encrypt the contents of video memory so that unauthorized software cannot gain meaningful access to it, thereby maintaining confidentiality. Moreover, a mechanism for tamper detection is provided so that there is awareness when data has been altered in some fashion, thereby maintaining integrity. In various embodiments, the contents of overlay surfaces and / or command buffers are encrypted, and / or the GPU is able to operate on encrypted content while preventing its availability to untrusted parties, devices or software.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
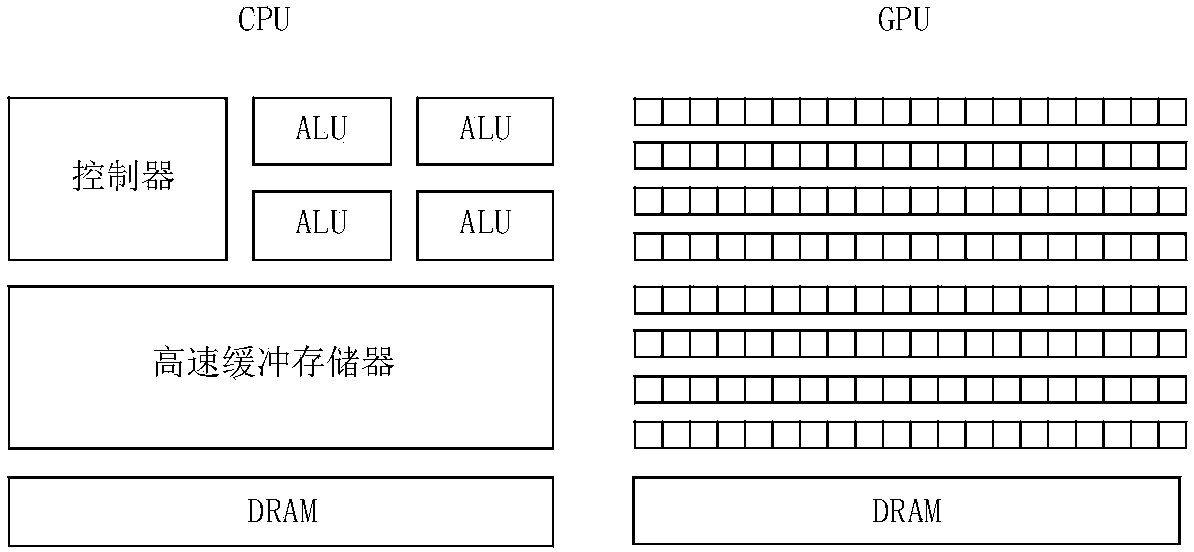
Construction method of GPU and CPU combined processor
InactiveCN101526934AWork is not tiredDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionVideo memoryOperational system
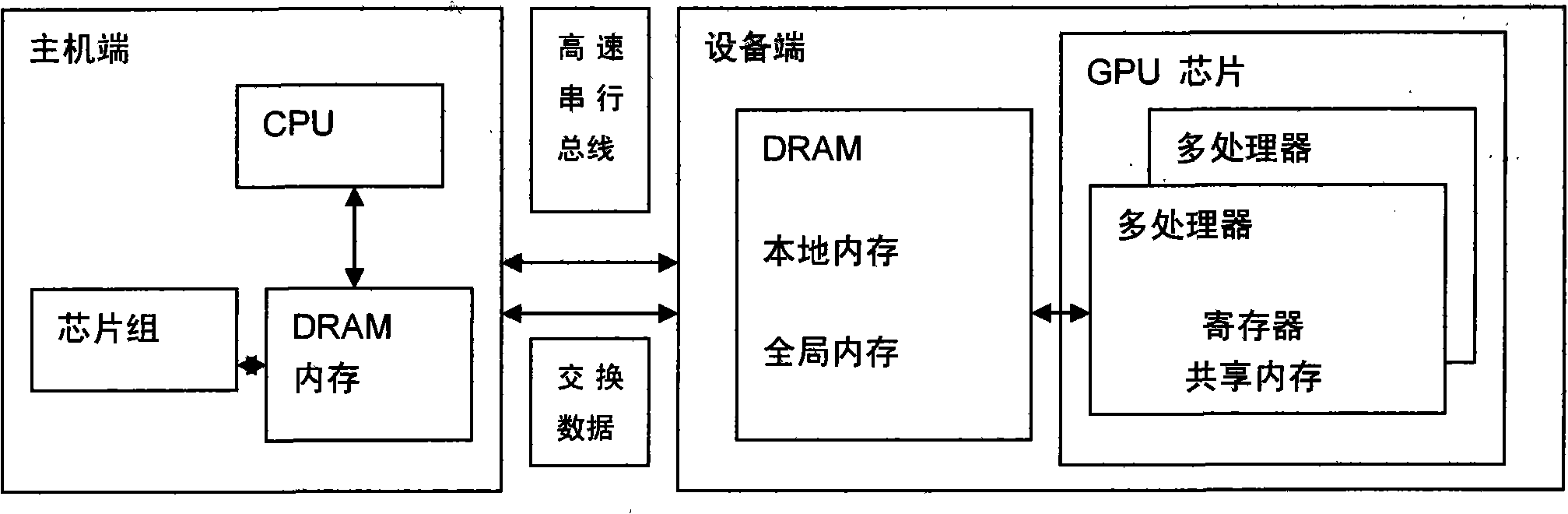
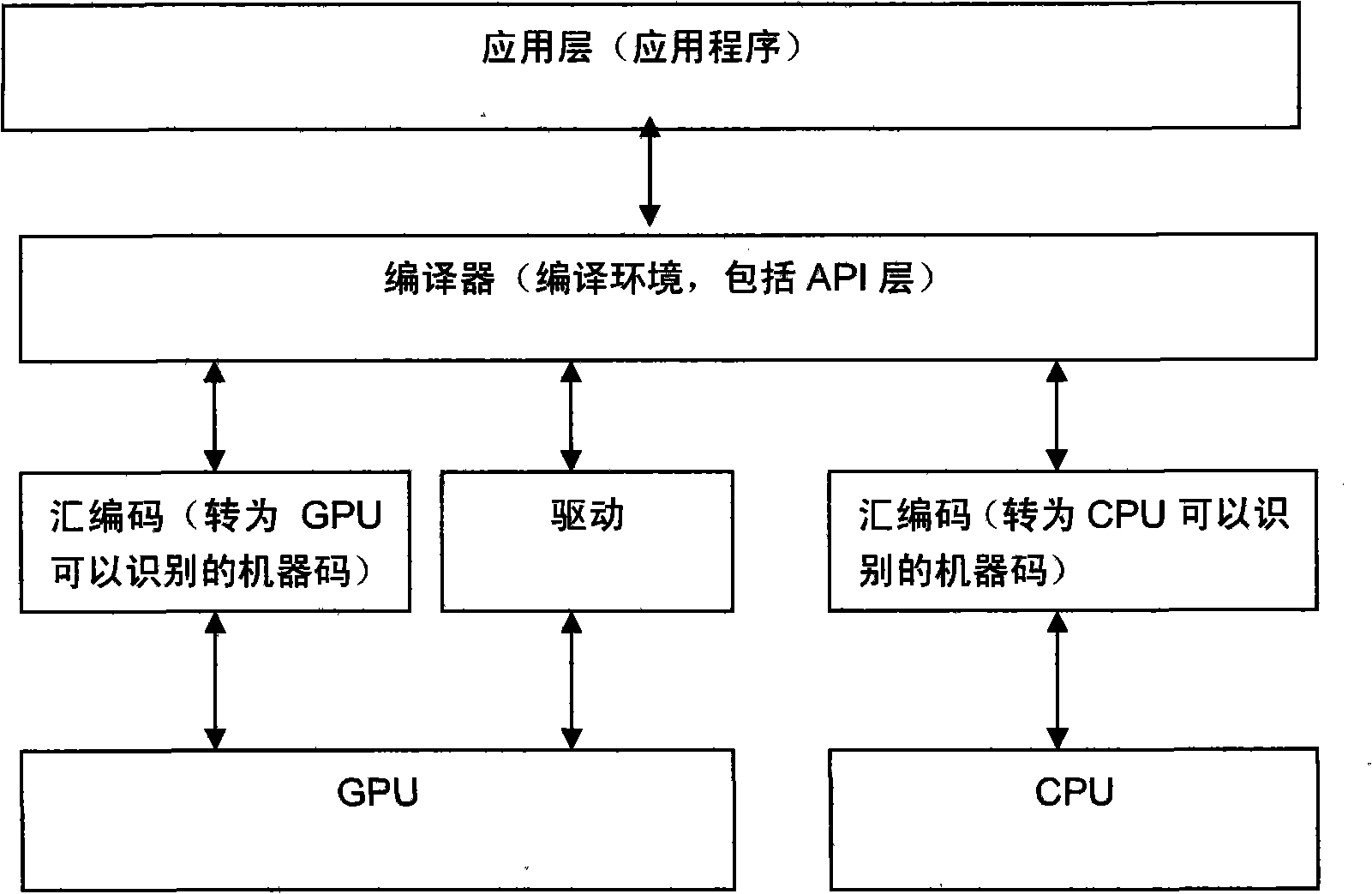
The invention provides a construction method of a GPU and CPU combined processor, which comprises the following steps: a CPU and a GPU are coupled to construct a combined processor, wherein the CPU is responsible for the general-purpose processing tasks of an operation system, system software, general-purpose application program, and the like which have complex instruction scheduling, circulation, branches and logical judgment; and the GPU is responsible for the highly-parallel calculating processing of large-scale data without logical relation; and the CPU and the GPU jointly finish the same large-scale parallel calculating application. In the GPU and CPU combined processor, a plurality of cores of CPU are communicated with each other by a memory bus and carry out calculation, and the cores of the GPU exchange data and are calculated by a uniform shared memory (a video memory on the GPU); the GPU and the CPU are connected by a high-speed serial bus and exchange calculating data by the memory of the CPU and the shared memory of the GPU; and the construction method can fully utilize the parallel processing capacity of the cores of the GPU and realize the rapid parallel calculation of enormous data volume.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
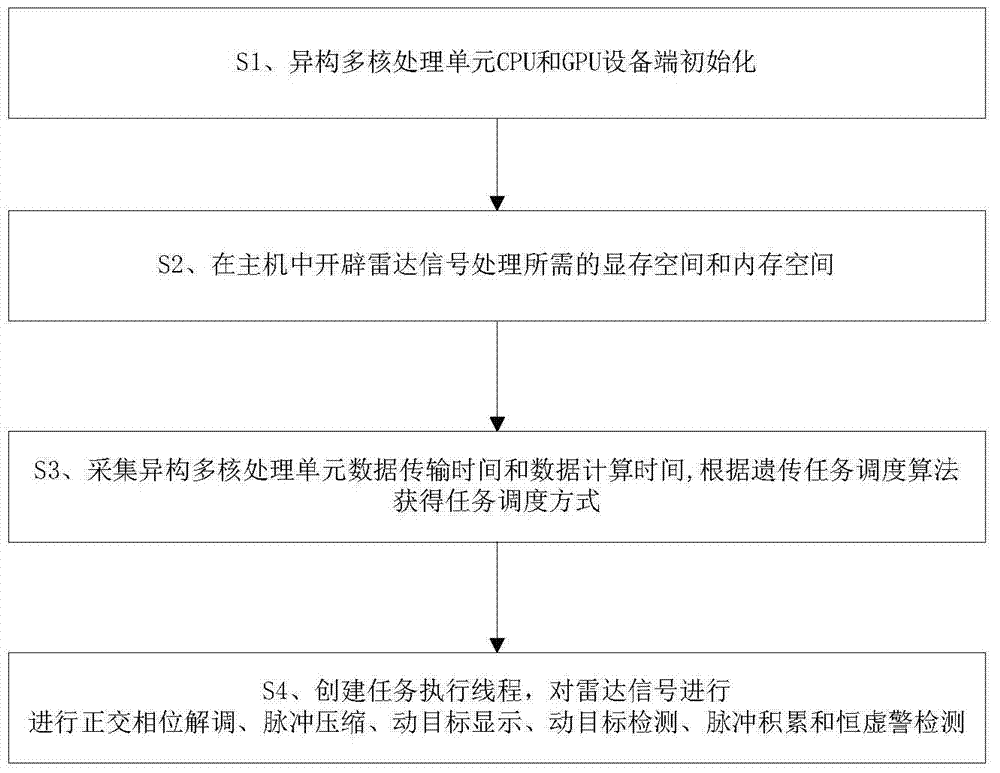
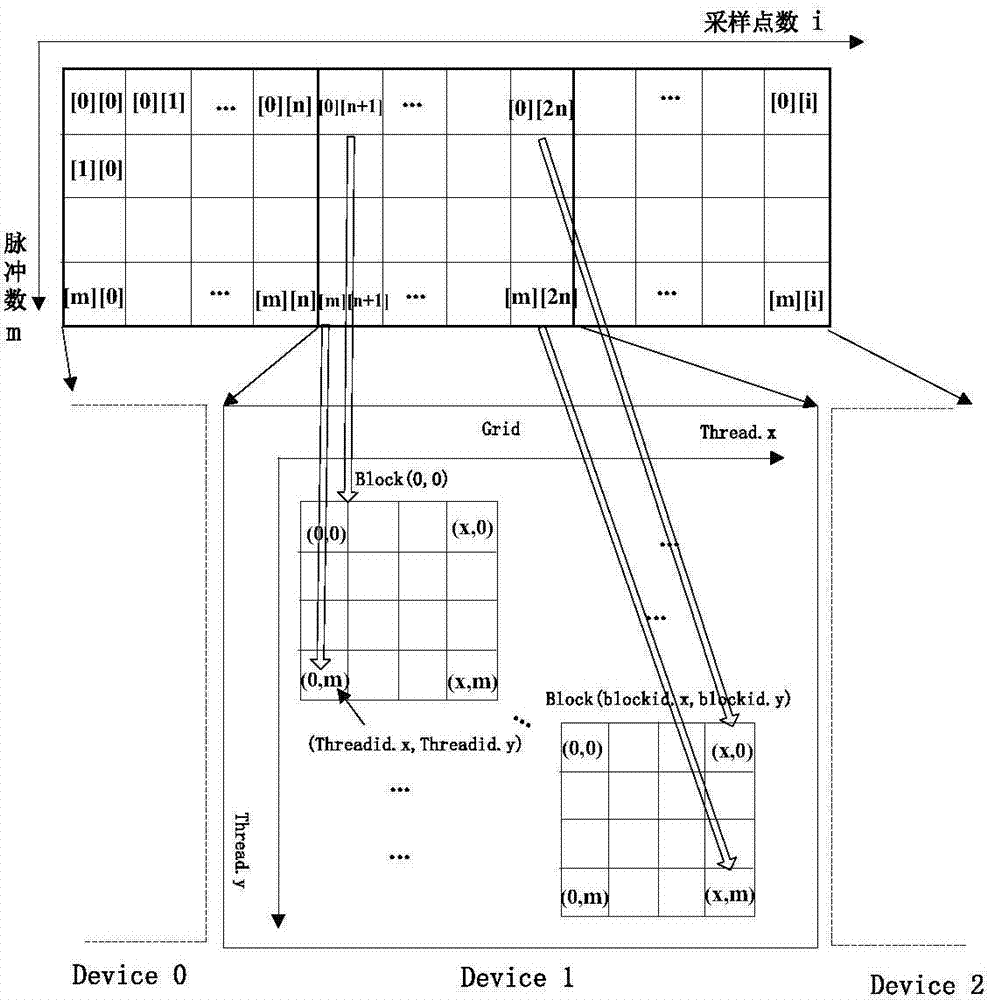
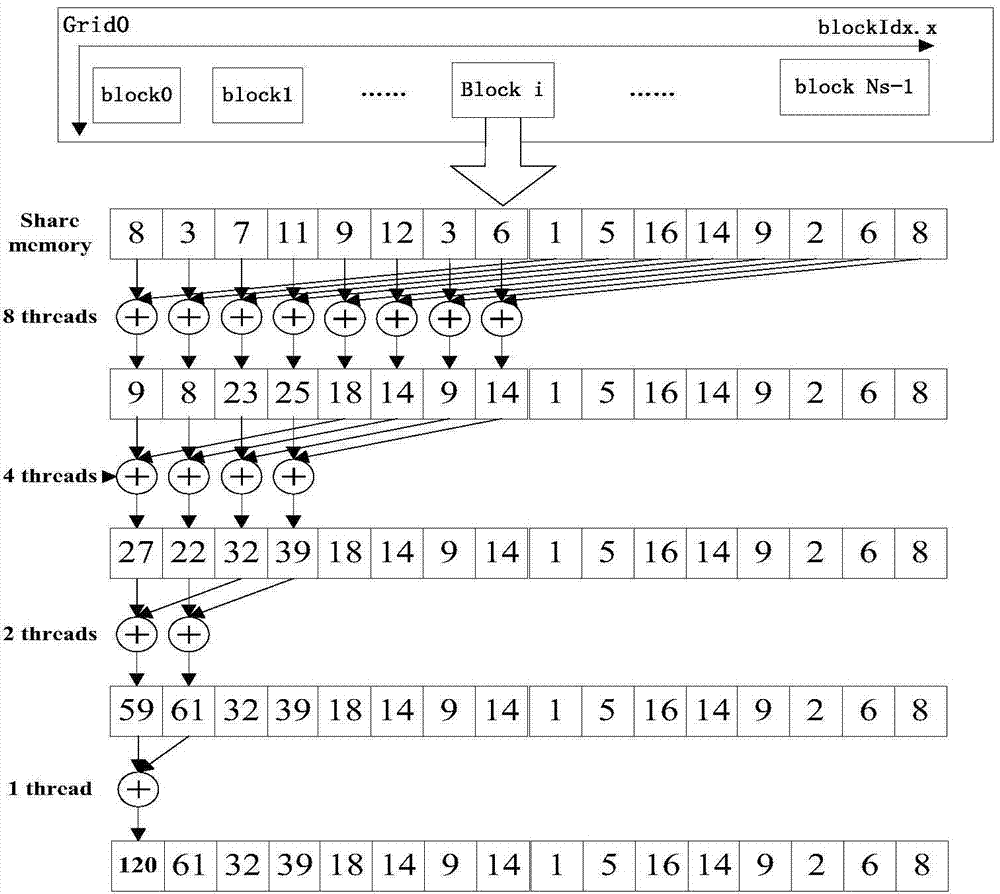
Radar signal parallel processing method and system based on heterogeneous multinucleated system
ActiveCN104849698AImprove compatibilityLow costWave based measurement systemsVideo memoryRadar signal processing
The invention discloses a radar signal parallel processing method and system based on a heterogeneous multinucleated system. The method comprises the following steps: S1, initializing equipment-end parameters, opening up a task execution thread, and dividing thread grids of data processing and the dimensions of a thread block; S2, opening up a video memory space and a memory space which are needed for the signal processing; S3, acquiring data transmission and calculating time needed by signal processing of a single time, and scheduling a genetic task scheduling algorithm to obtain a task scheduling mode; and S4, acquiring laser sampling data for storing in the memory space by means of segments according to a time sequence, sending the data to a CPU and a GPU according to the task scheduling mode, mapping sampling points to each thread and performing concurrent execution according to the thread grids and the dimensions of the thread block, and scheduling a filter coefficient to perform orthogonal phase demodulation, pulse compression, moving object display, moving object detection, pulse accumulation and constant false alarm detection on the sampling data. By applying the method and system provided by the invention, the speed of a general processor in executing the signal processing is improved, and the requirement for real-time performance of radar signal processing is met.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
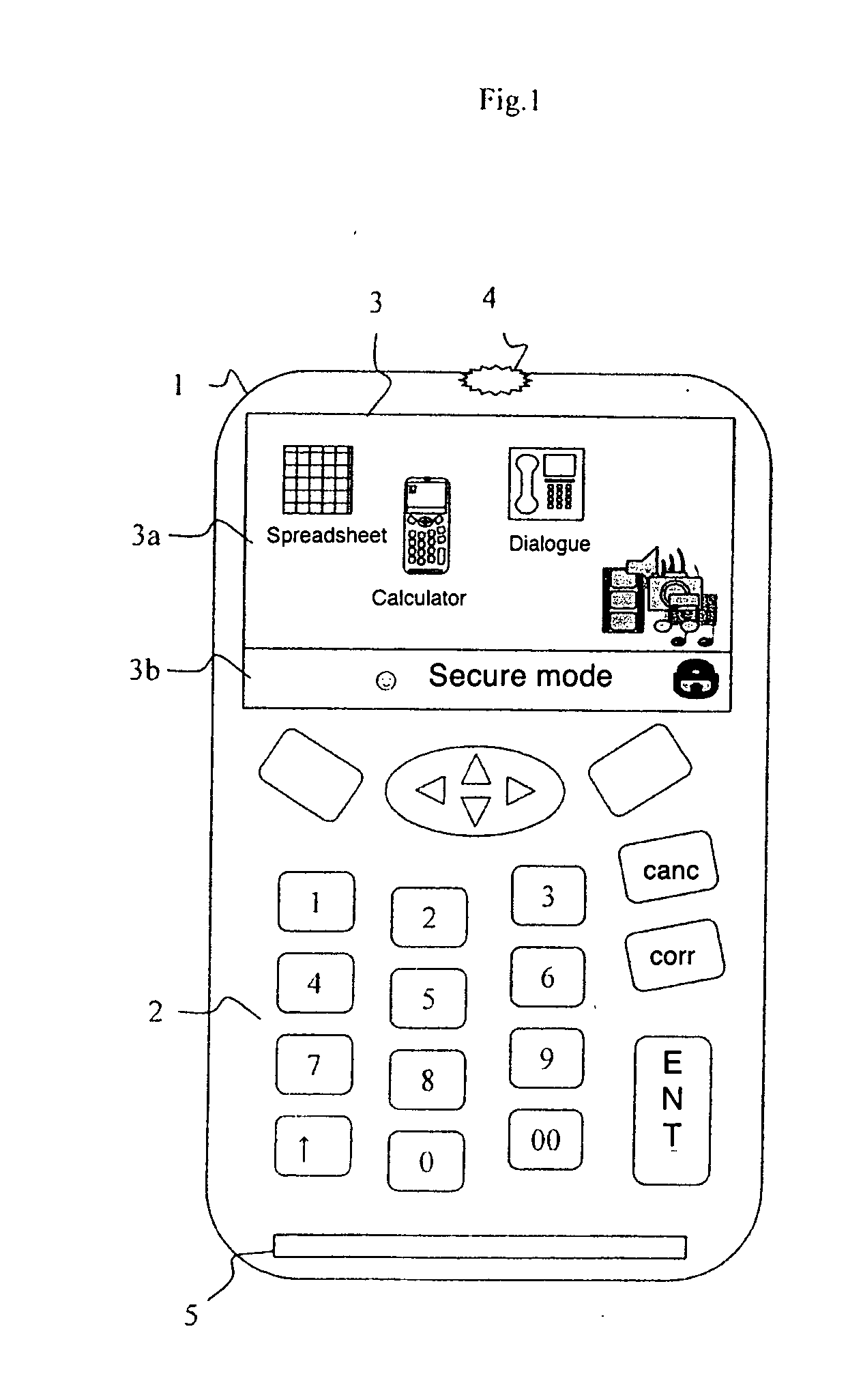
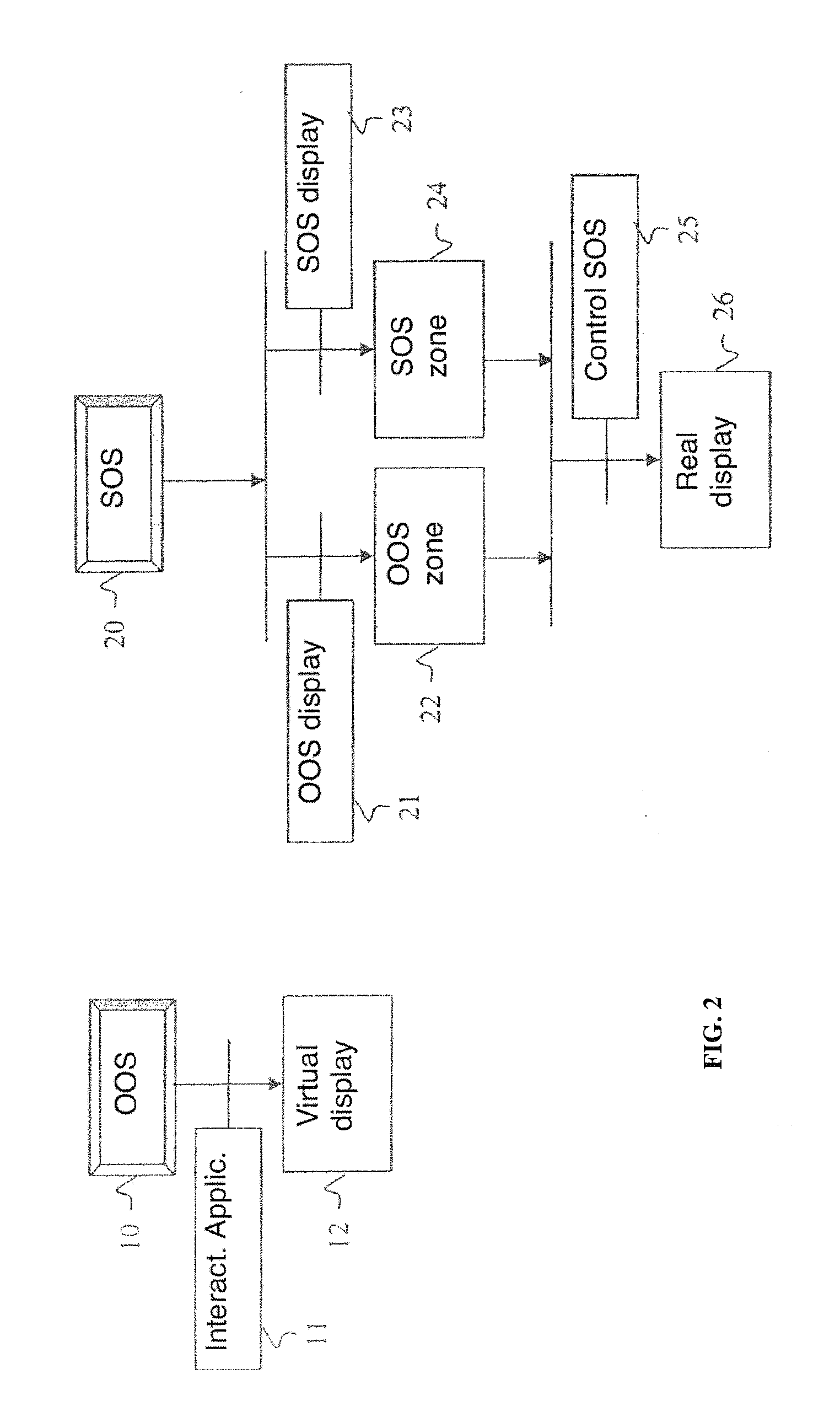
Secure display method and device
ActiveUS20080316357A1Television system detailsDigital data processing detailsVideo memoryVideo storage
A secure display device is designed to display on a screen a first set of information edited by an open operating system. A secure operating system resident in a dedicated circuit edits a second set of information. A filter allocates, independently of the open operating system, a first zone of the screen to the first set of information and a second zone of the screen to the second set of information. The zones and can have a non-zero intersection and any value. A real video memory is used for transferring the two sets of information to the screen under the sole control of the secure operating system so as to produce a secure display of the second set of information.
Owner:BANKS & ACQUIRERS INT HLDG
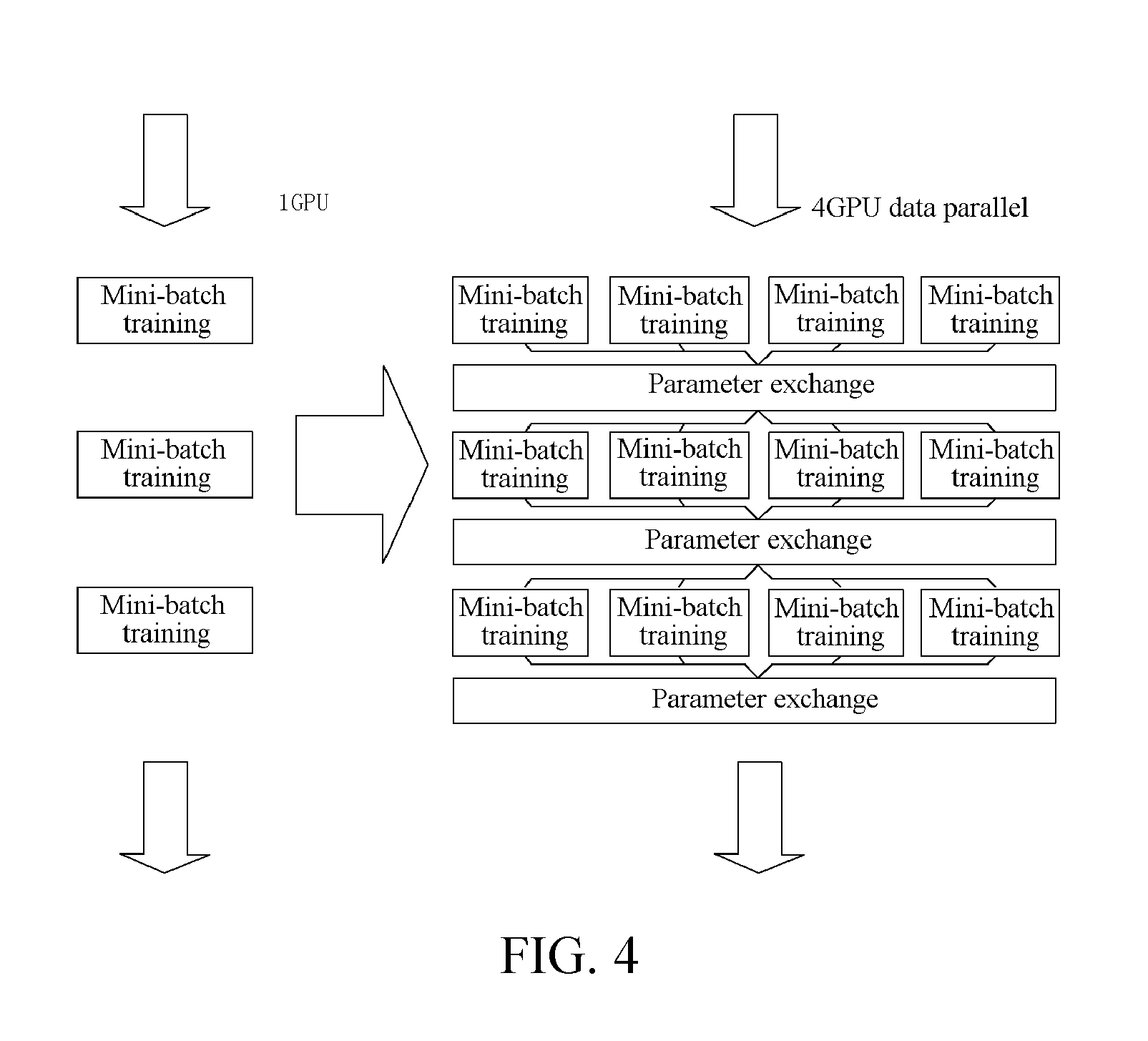
Data parallel processing method and apparatus based on multiple graphic processing units
ActiveUS20160321777A1Enhance data parallel processing efficiencyImprove Parallel Processing EfficiencyResource allocationProgram synchronisationGraphicsVideo memory
A parallel data processing method based on multiple graphic processing units (GPUs) is provided, including: creating, in a central processing unit (CPU), a plurality of worker threads for controlling a plurality of worker groups respectively, the worker groups including one or more GPUs; binding each worker thread to a corresponding GPU; loading a plurality of batches of training data from a nonvolatile memory to GPU video memories in the plurality of worker groups; and controlling the plurality of GPUs to perform data processing in parallel through the worker threads. The method can enhance efficiency of multi-GPU parallel data processing. In addition, a parallel data processing apparatus is further provided.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
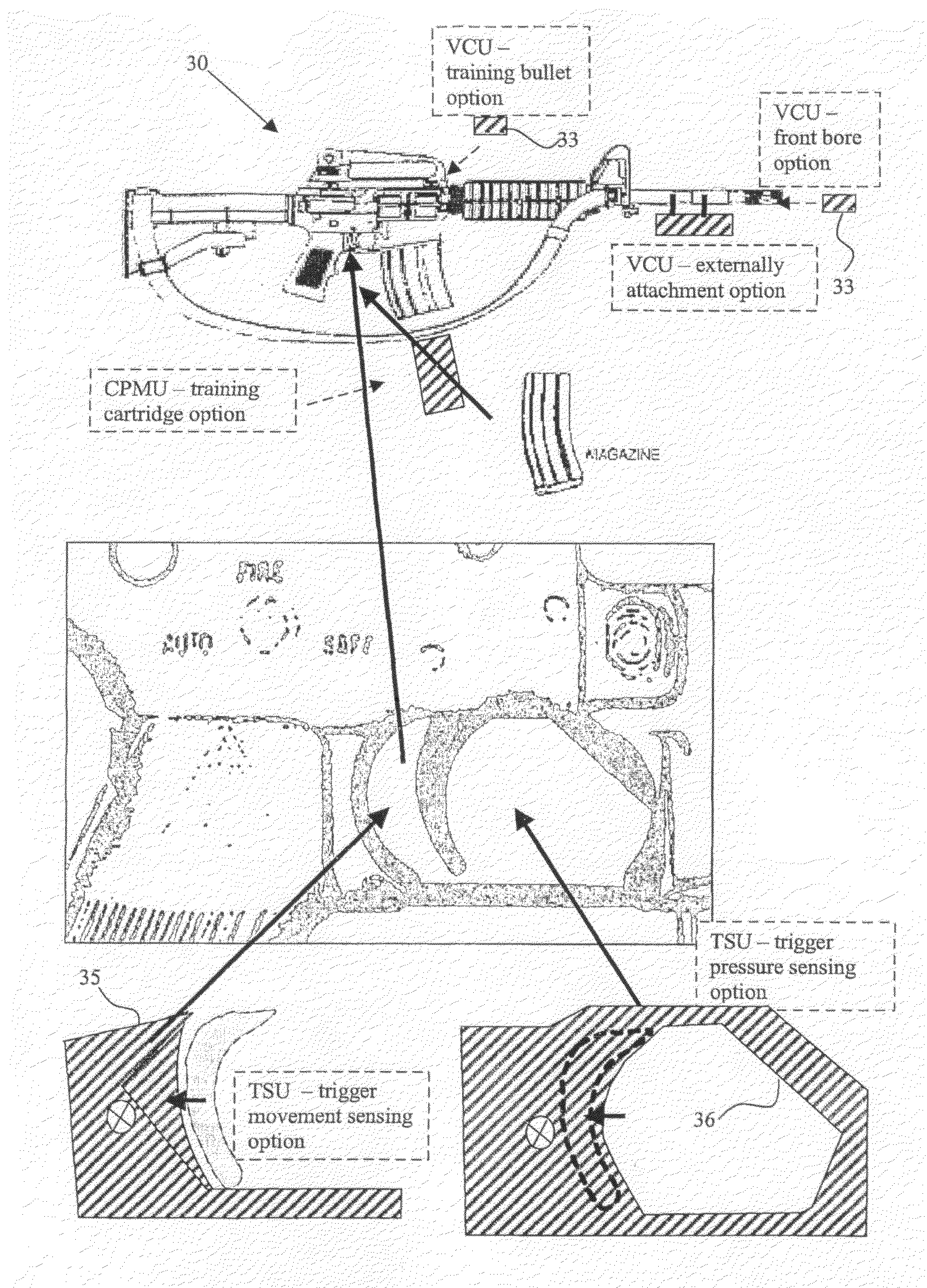
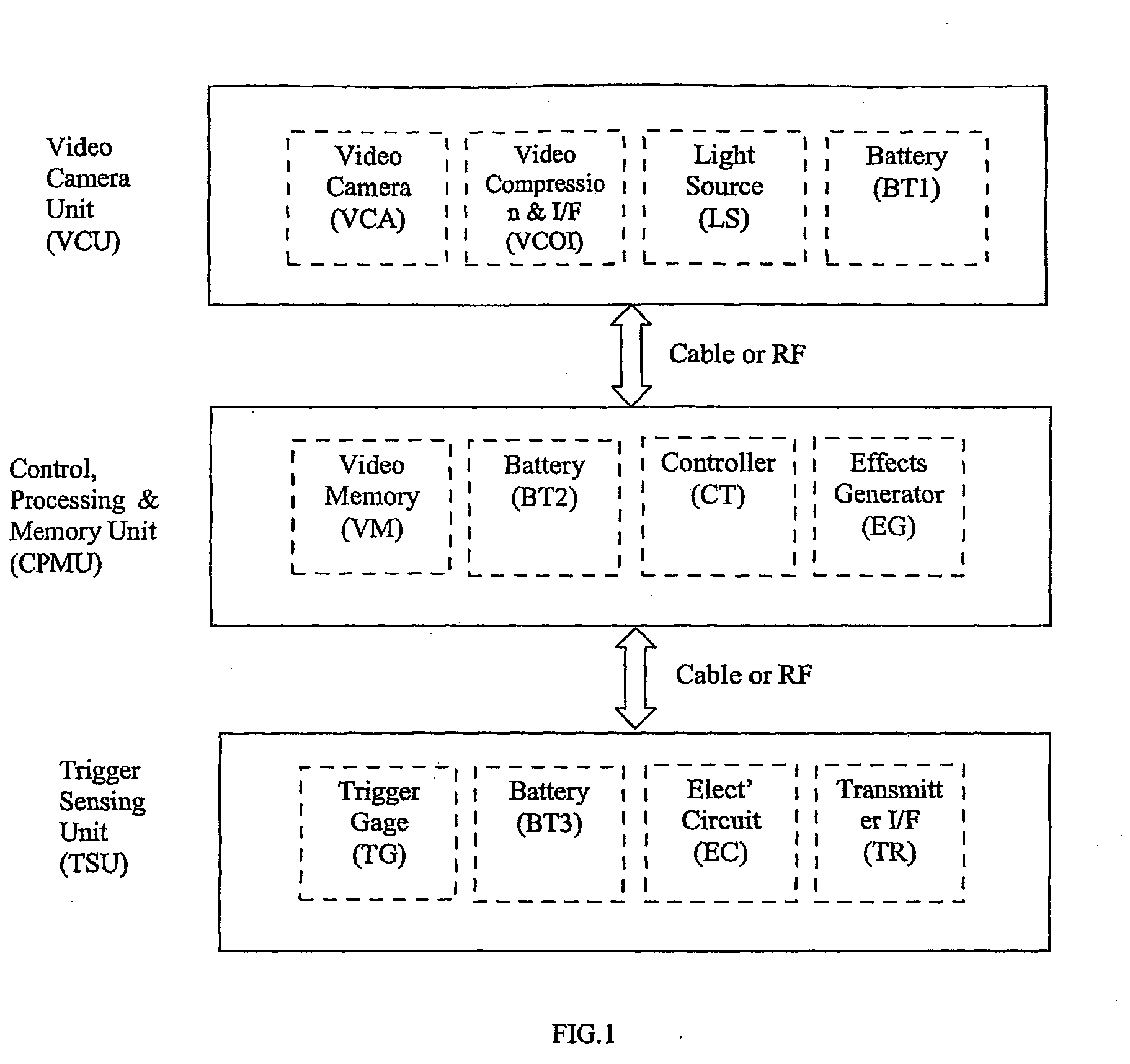
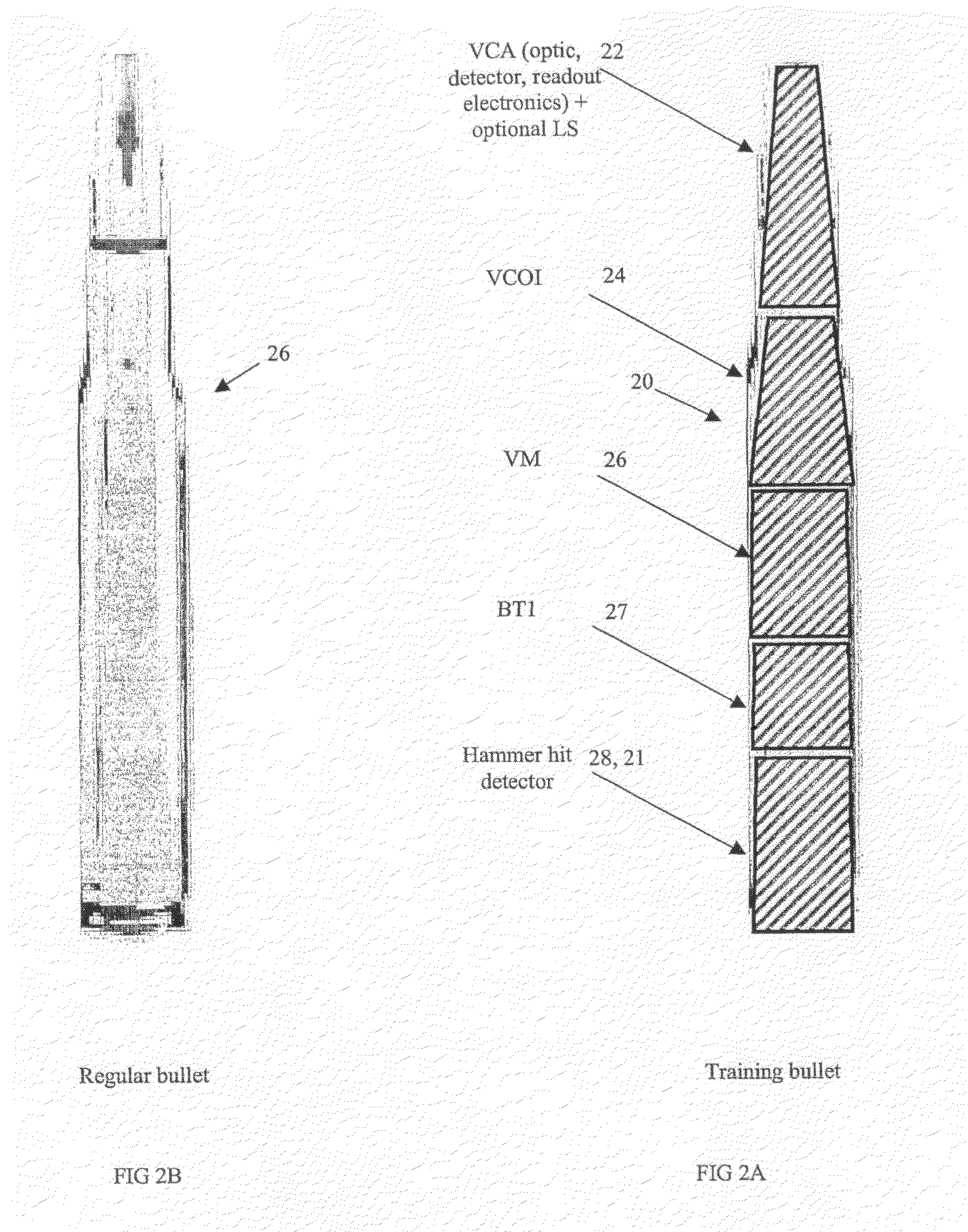
Video Capture, Recording and Scoring in Firearms and Surveillance
InactiveUS20080233543A1Easy to installLow costTraining ammunitionAiming meansVideo memoryVideo storage
A video camera and recording device integrated with a real or toy weapon to provide video recording of the assault and aiming process of the weapon holder in operational training, actual combat, hunting, sports and gaming scenarios. A video camera is boresighted with the weapon, and a video memory stores the recorded dynamic scenario, and a trigger sensor which continually senses and records the triggering actions imposed by the weapon holder. The trigger sensor is attached to the actual trigger of the weapon thus enabling normal operation of the weapon. The video camera, may be mounted internally within the bore of the weapon, such that the external form of the weapon is not altered, thus achieving closer operation to real life situations. The recorded trigger data is utilized upon playback of the recorded video, enabling quick review and scoring of the recorded aiming process for training and gaming.
Owner:ESHEL AVIV LTD
Graphics controller integrated circuit without memory interface
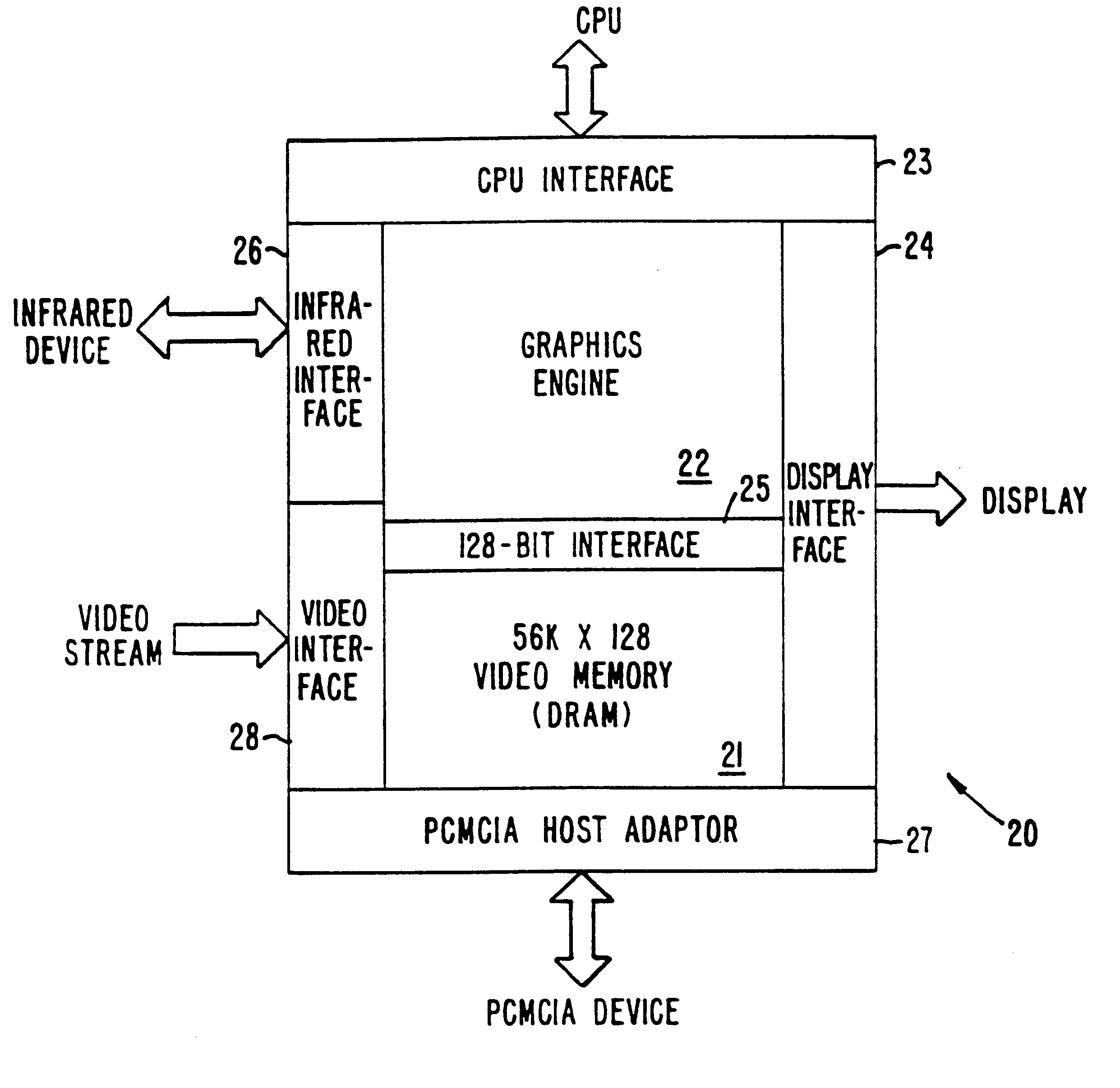
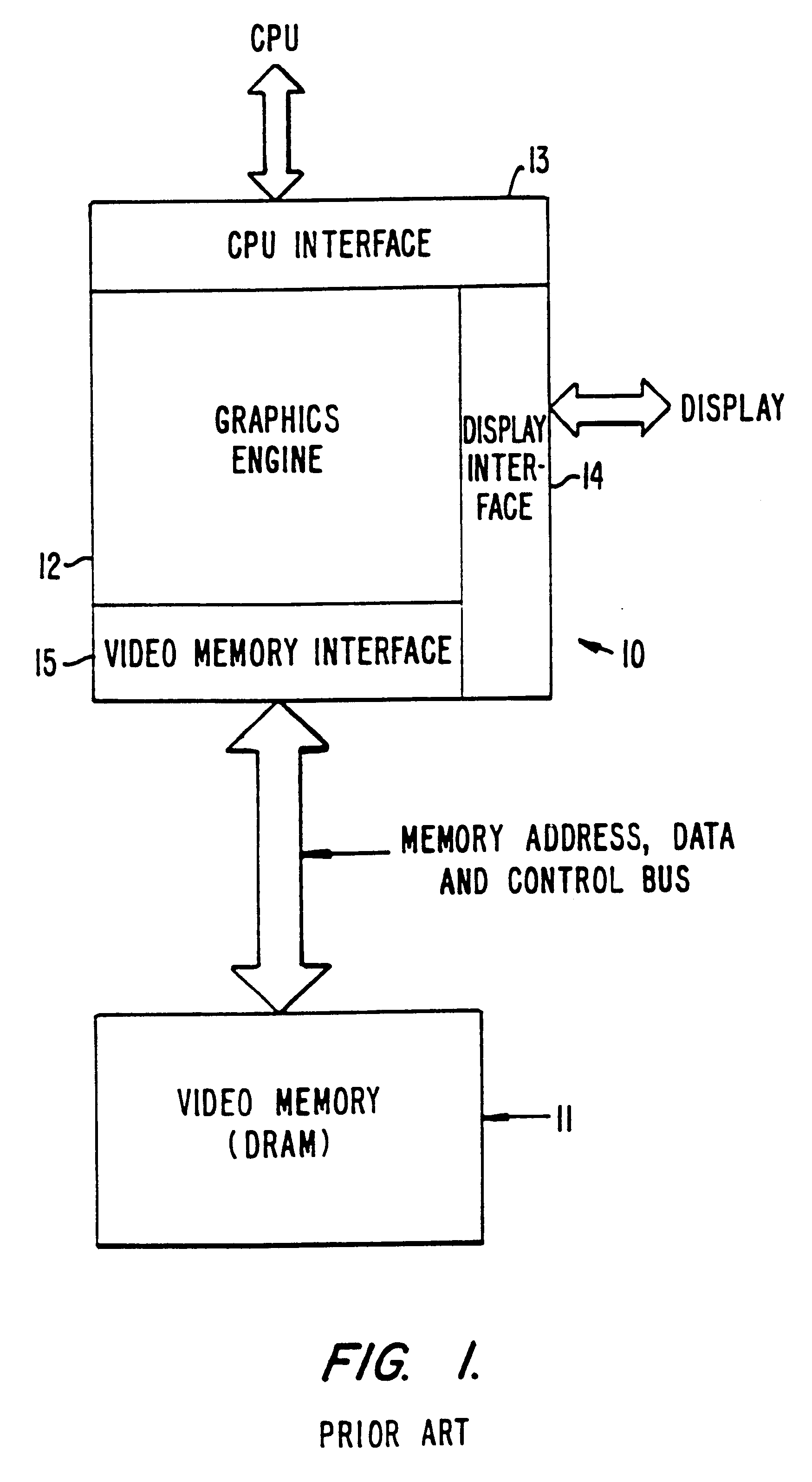
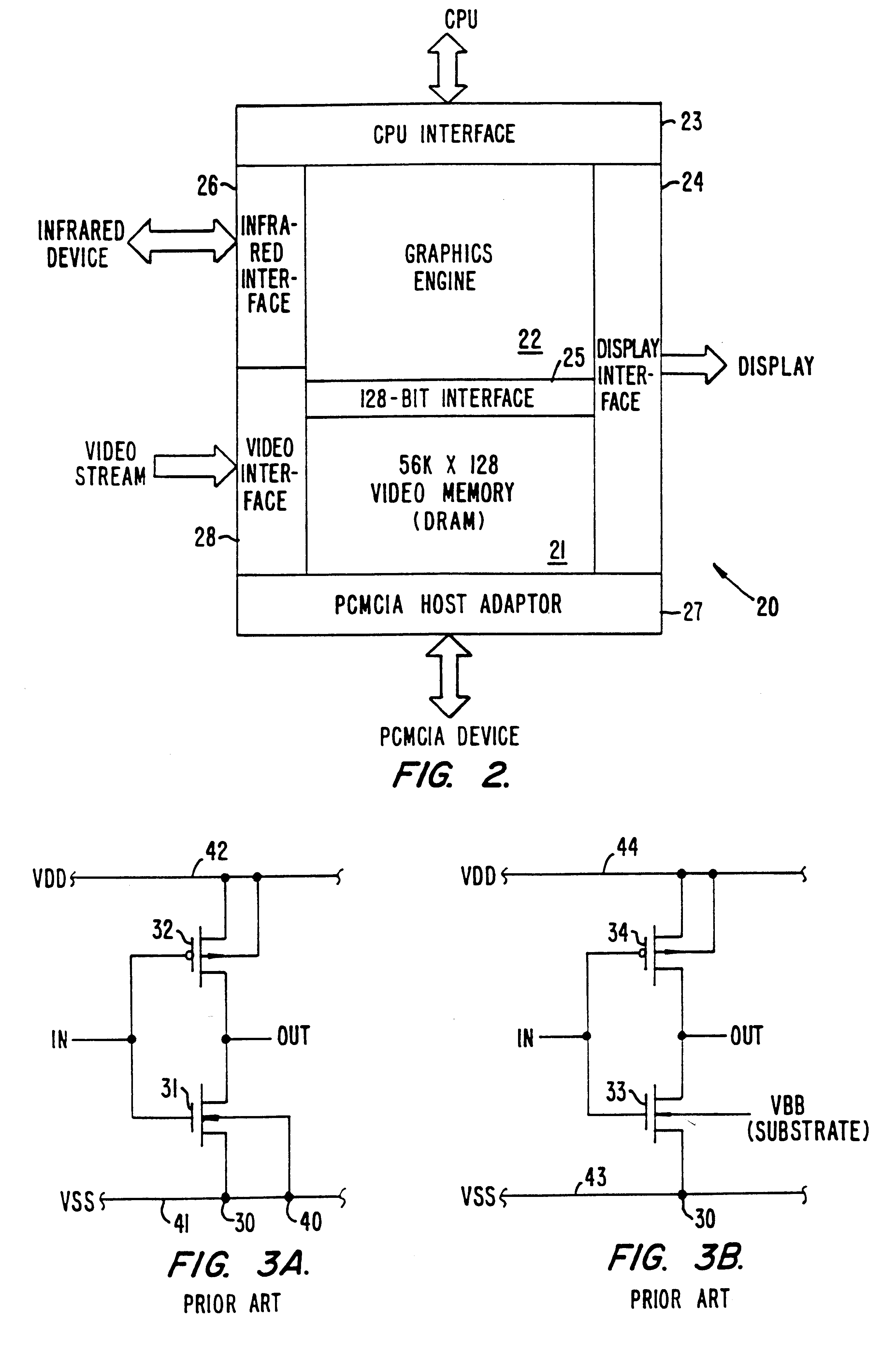
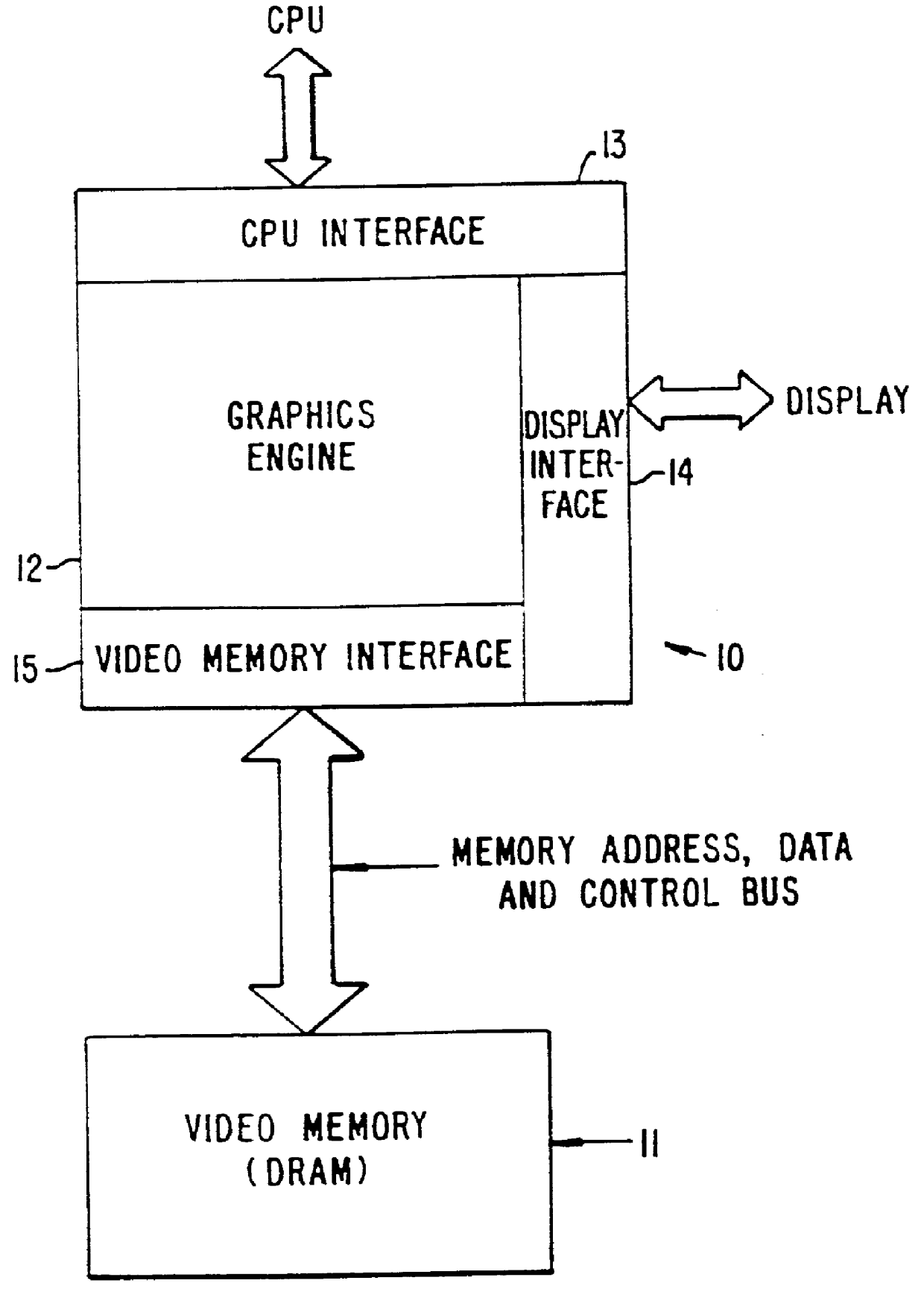
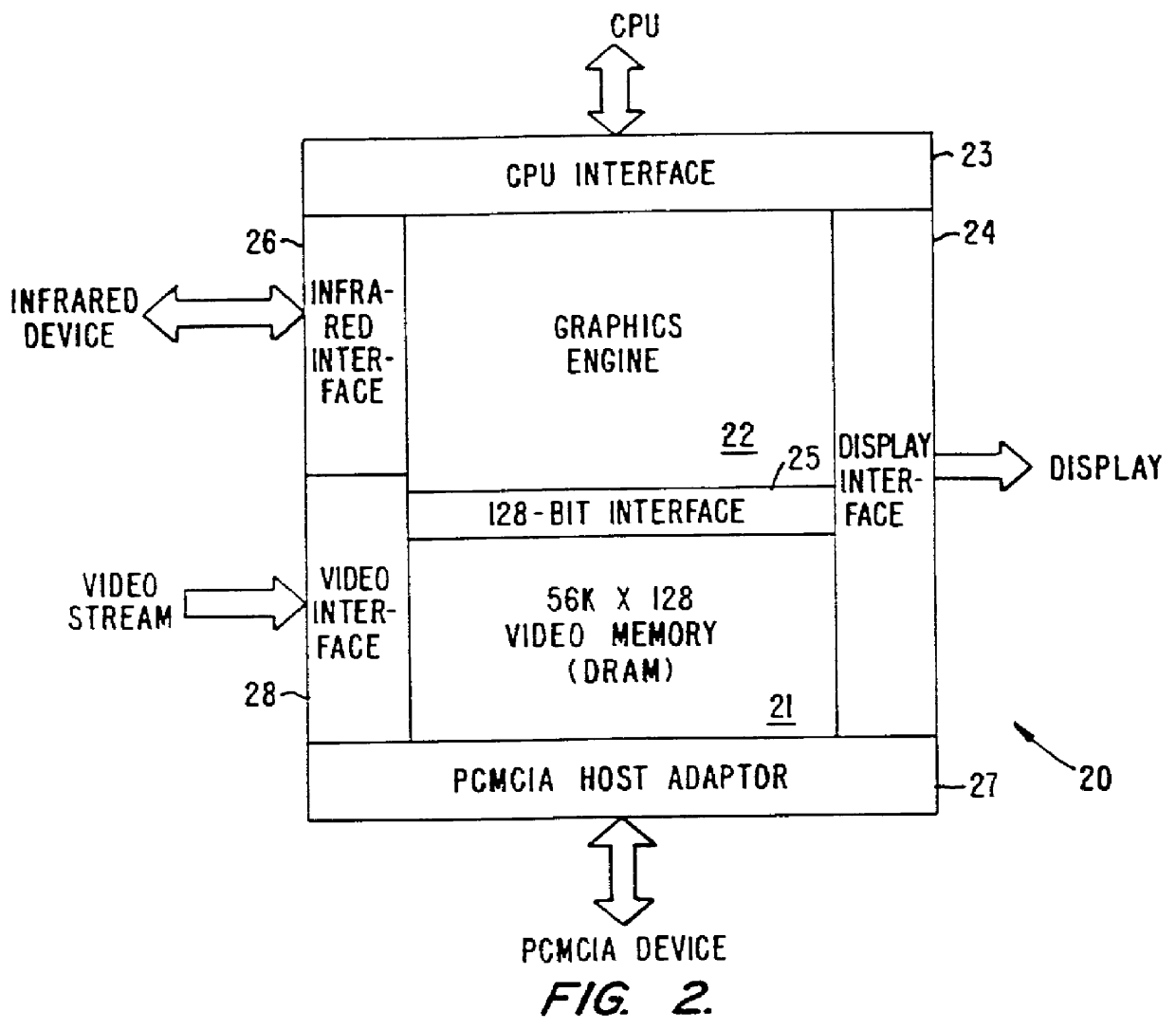
InactiveUS6356497B1Input/output to record carriersCathode-ray tube indicatorsVideo memoryInternal memory
A CMOS integrated circuit that comprises a graphics controller system that consists of a graphics engine and video memory together with some interface blocks, a PCMCIA host adapter, an infrared interface for generating video images on a LCD or CRT display unit, and a video stream interface for receiving video signals. Since the video memory is integrated on the same integrated circuit as the graphics controller, no package pins are required for the memory interface. The pins thus saved are used to provide access to an on-chip PCMCIA host adapter. The internal memory interface is 128 bits wide. Simultaneous performance improvement and power dissipation reduction is achieved because of the wide memory interface and the elimination of the large parasitic capacitances associated with a package pin connection.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
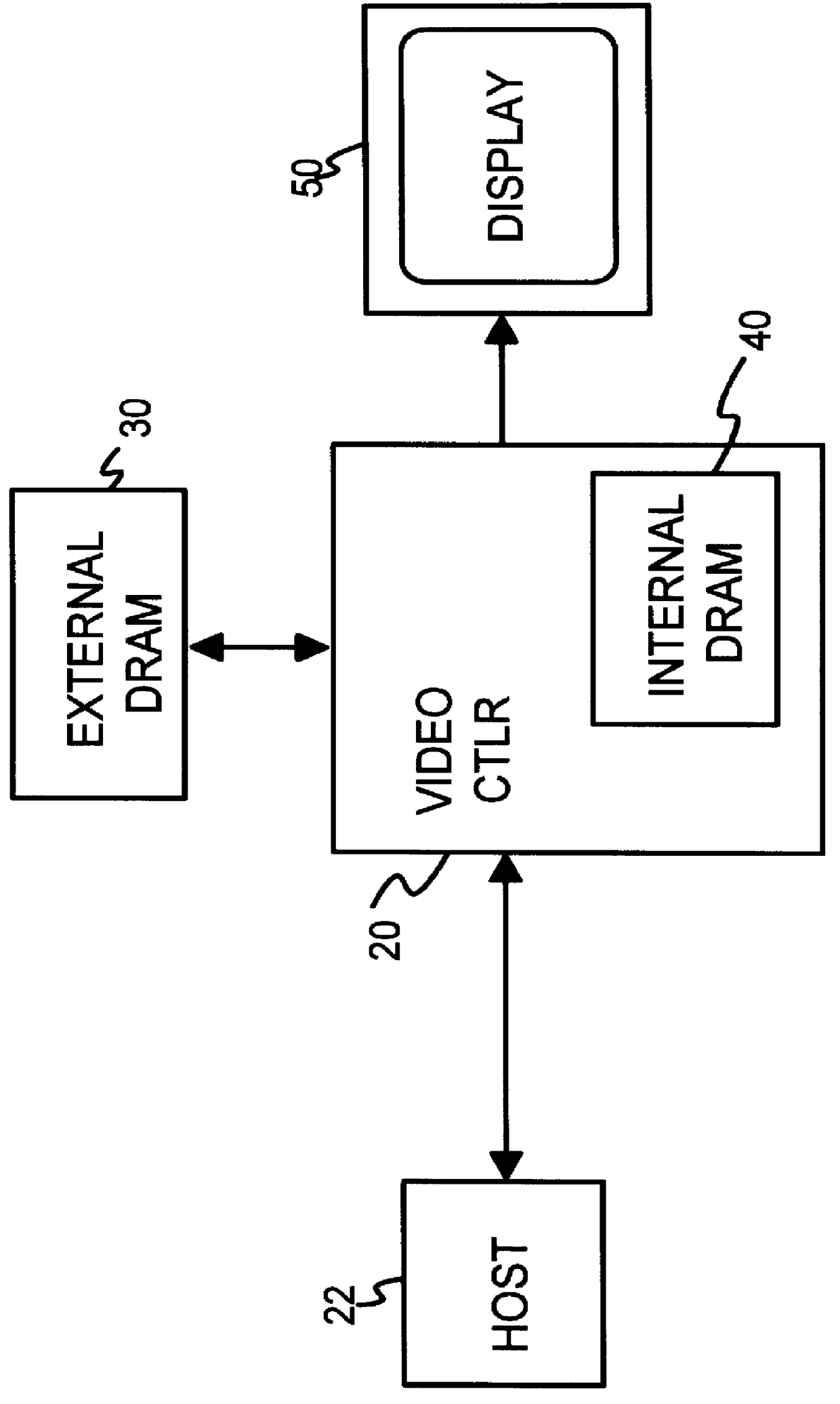
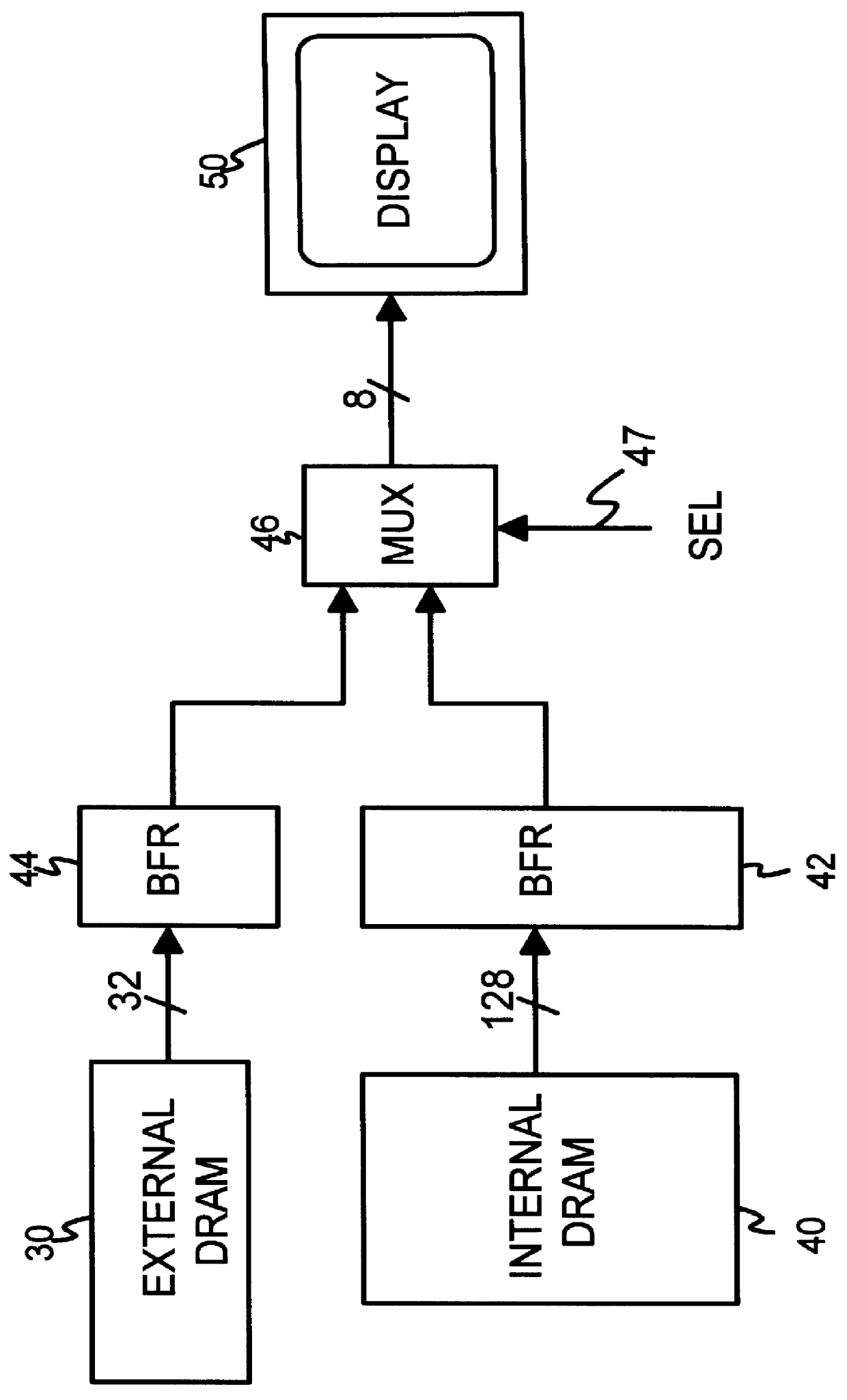
Testable interleaved dual-DRAM architecture for a video memory controller with split internal/external memory
A video sub-system features reduced power consumption by integrating a video memory onto the same chip as the video memory controller. The video memory is preferably a small DRAM sufficiently large to store all pixel data for lower resolutions, but insufficient for higher resolutions. At higher resolutions, an external DRAM supplements the internal DRAM. The amount of external DRAM needed depends upon the resolution to be supported. The internal DRAM has a wide data bus and thus high bandwidth, since no external I / O pins are needed. The external DRAM is narrow to minimize pincount and power consumption. Since the external DRAM is slower and lower in bandwidth, pixel data from both internal and external DRAMs are interleaved together for each horizontal scan line. Thus the lower bandwidth of the external DRAM is masked by the high bandwidth of the wide internal DRAM. Either the internal or the external DRAM, or both, are automatically tested with a pseudo-random number generator that writes pseudo-random numbers to the DRAM while simultaneously supplying pixel data to the graphics data path for display. A checksum of the pixel data output from the graphics data path is generated for the first screen of pixels or frame, while on the second frame the pseudo-random number generator is disabled and the DRAM supplies the same pixel data that was written to it by the pseudo-random number generator during the first frame. The checksums for the first and second frames should match if the DRAM is free of faults.
Owner:FAUST COMMUNICATIONS LLC
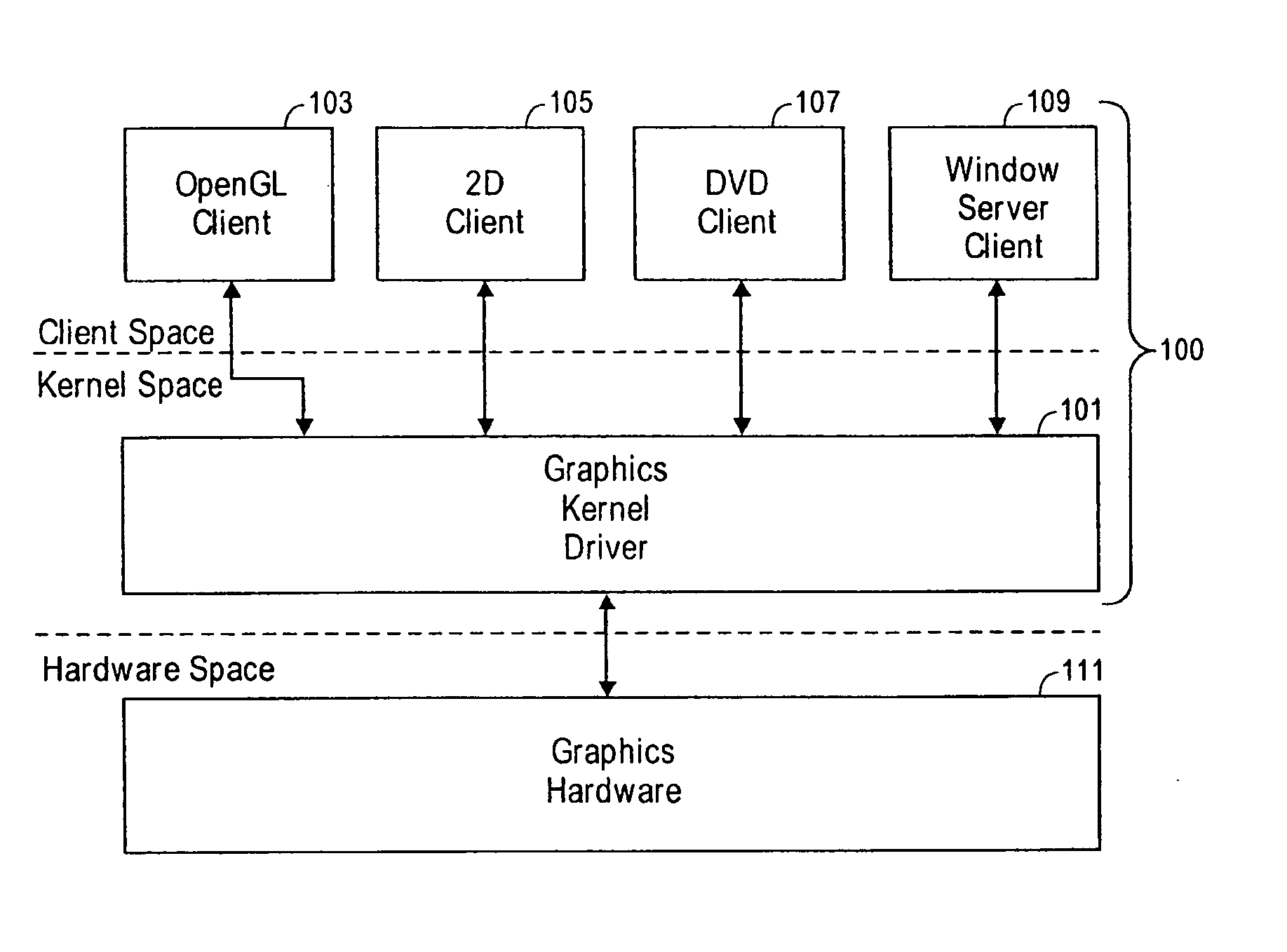
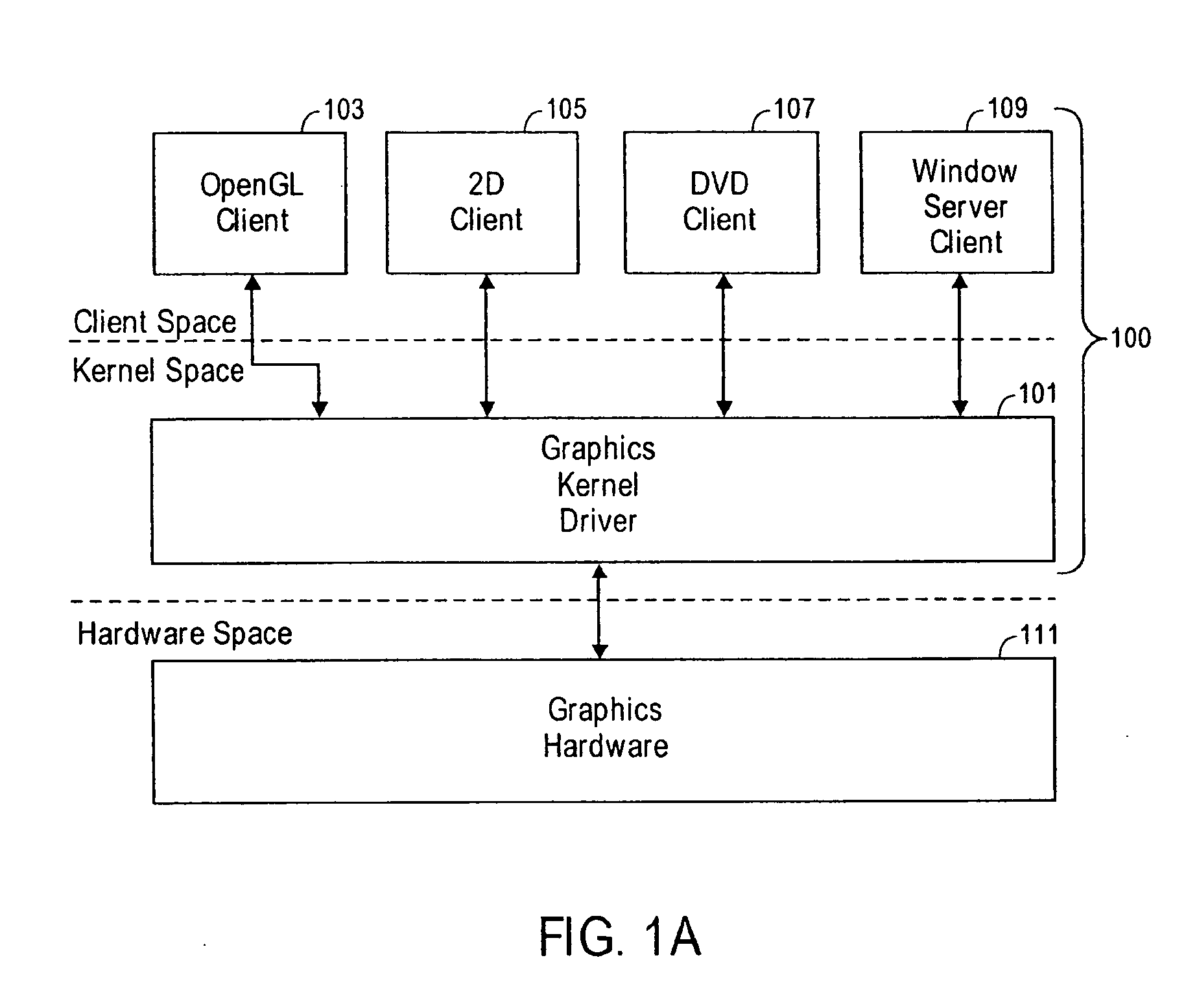
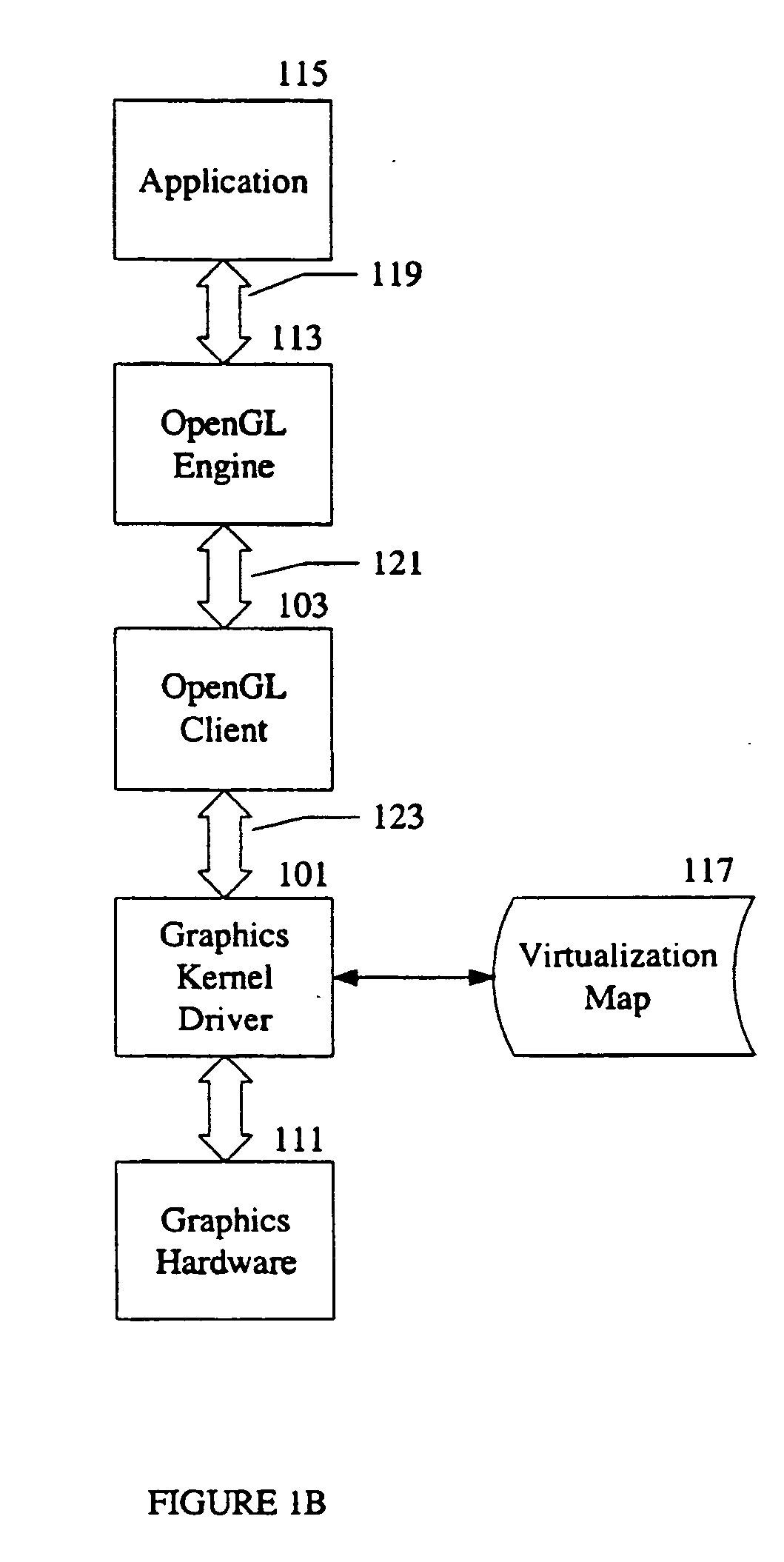
Virtualization of graphics resources and thread blocking
InactiveUS20050237330A1Clients can be simplifiedMemory adressing/allocation/relocationCathode-ray tube indicatorsVirtual memoryVirtualization
Virtualization of graphics resources and thread blocking is disclosed. In one exemplary embodiment, a system and method of a kernel in an operating system including generating a data structure having an identifier of a graphics resource assigned to a physical memory location in video memory, and blocking access to the physical memory location if a data within the physical memory location is in transition between video memory and system memory wherein a client application accesses memory in the system memory directly and accesses memory in the video memory through a virtual memory map.
Owner:APPLE INC
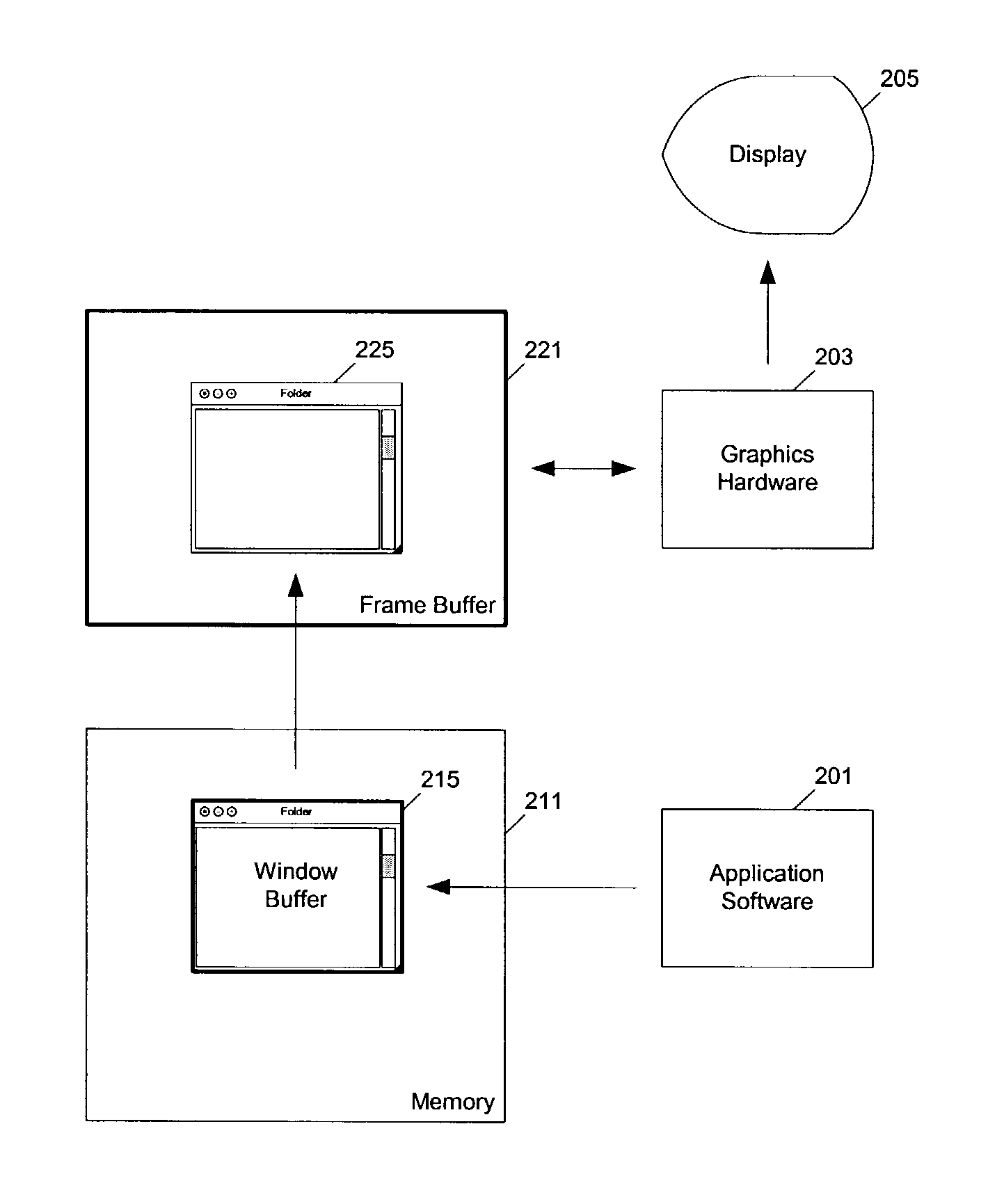
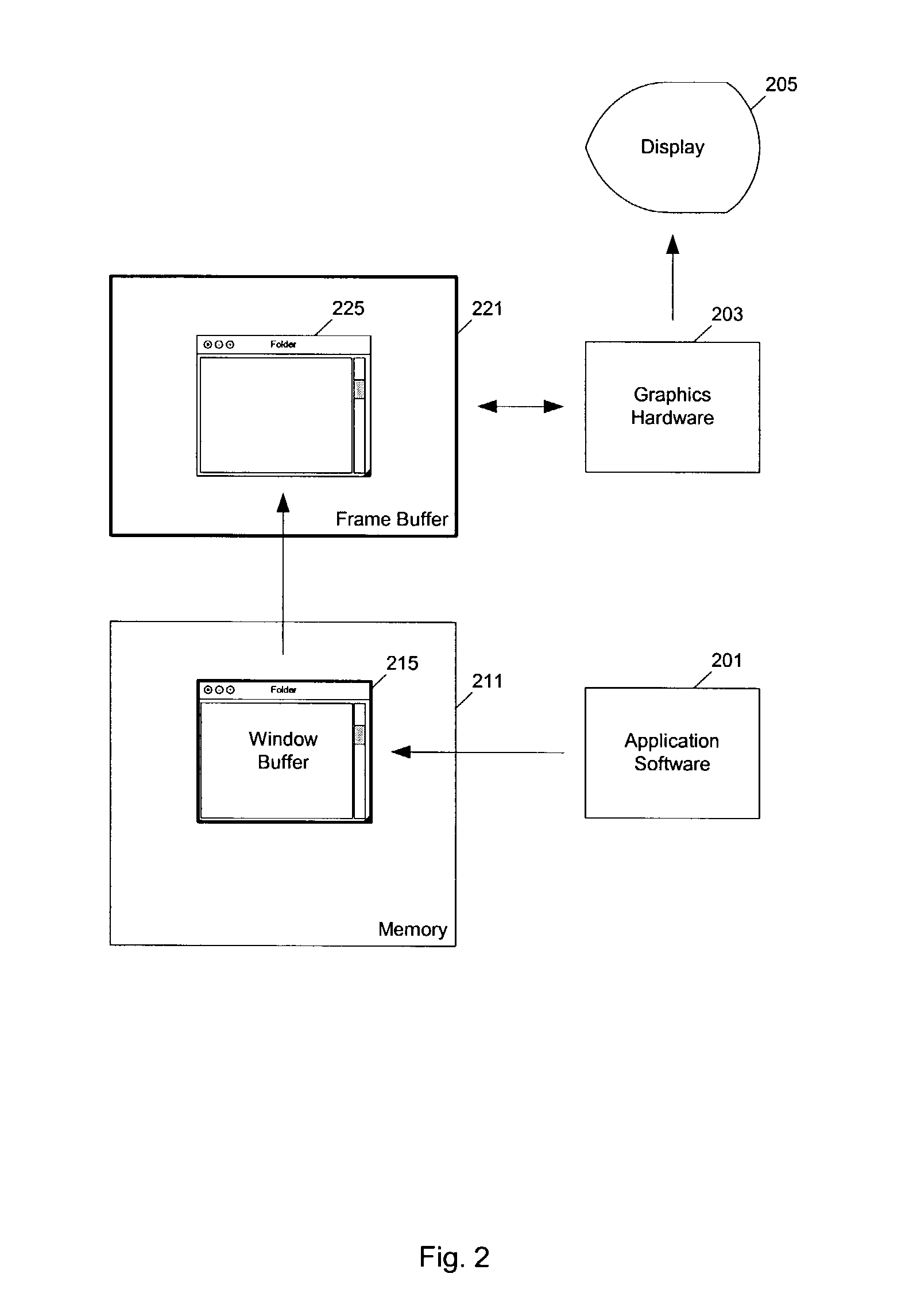
Method and apparatus to accelerate scrolling for buffered windows
ActiveUS7313764B1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingVideo storageData processing system
Methods and apparatuses to accelerate scrolling for buffered windows. In one aspect of the invention, a method to scroll a buffered window on a data processing system includes: determining a second region of a second pixel image of a window in a frame buffer, which corresponds to a first region of a first pixel image of the window buffered in a window buffer that is scrolled from a first position to a second position in the first pixel image of the window in the window buffer; and scrolling the second region in the frame buffer to synchronize the second pixel image in the frame buffer with the first pixel image in the window buffer. In one example according to this aspect, the second region in the frame buffer is scrolled using graphics hardware; the frame buffer is located inside a video memory under control of the graphics hardware.
Owner:APPLE INC
Graphics controller integrated circuit without memory interface pins and associated power dissipation
InactiveUS6041010AInput/output to record carriersCathode-ray tube indicatorsInternal memoryVideo memory
A CMOS integrated circuit that comprises a graphics controller system that consists of a graphics engine and video memory together with some interface blocks, a PCMCIA host adapter, an infrared interface for generating video images on a LCD or CRT display unit, and a video stream interface for receiving video signals. Since the video memory is integrated on the same integrated circuit as the graphics controller, no package pins are required for the memory interface. The pins thus saved are used to provide access to an on-chip PCMCIA host adapter. The internal memory interface is 128 bits wide. Simultaneous performance improvement and power dissipation reduction is achieved because of the wide memory interface and the elimination of the large parasitic capacitances associated with a package pin connection.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
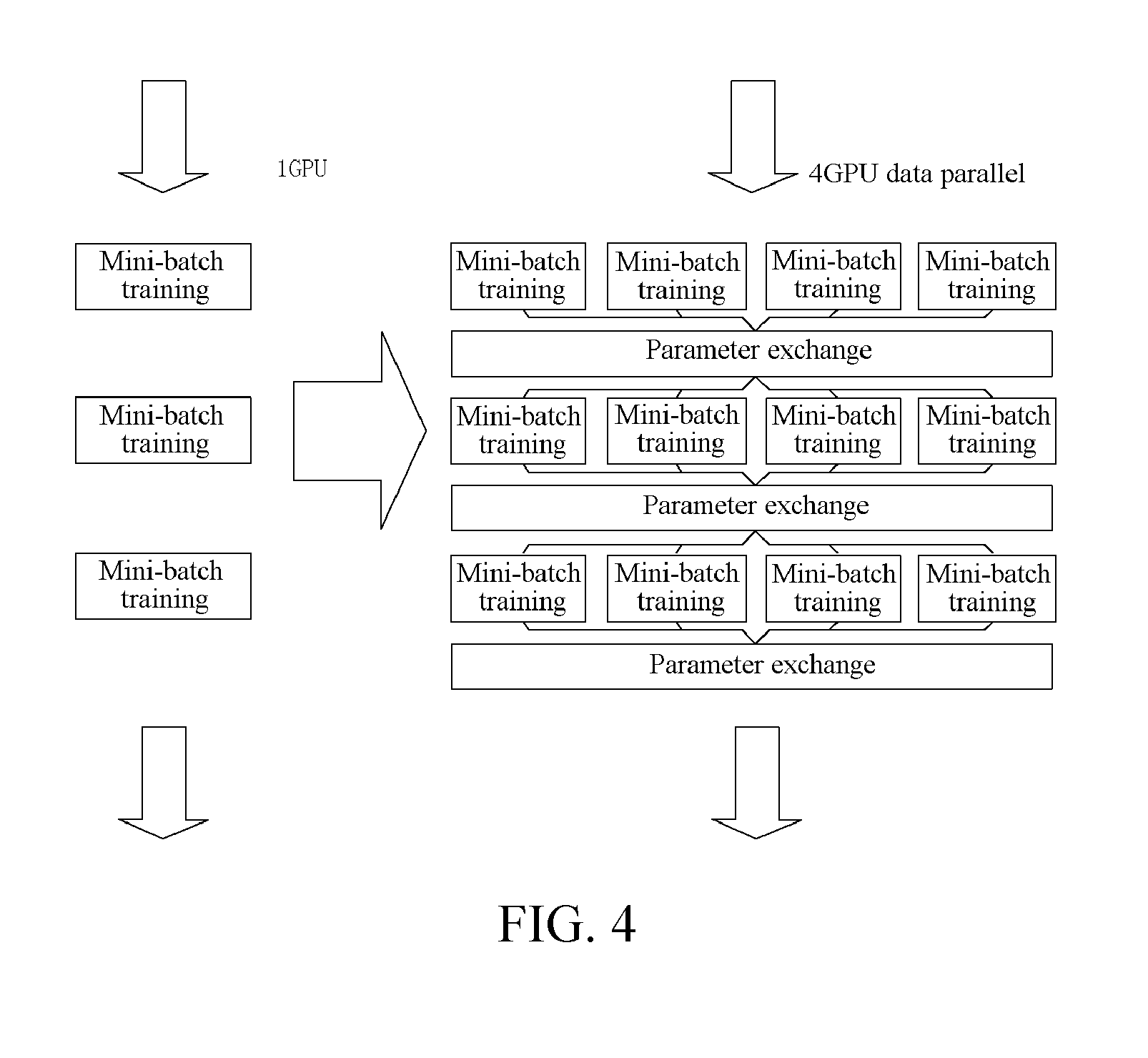
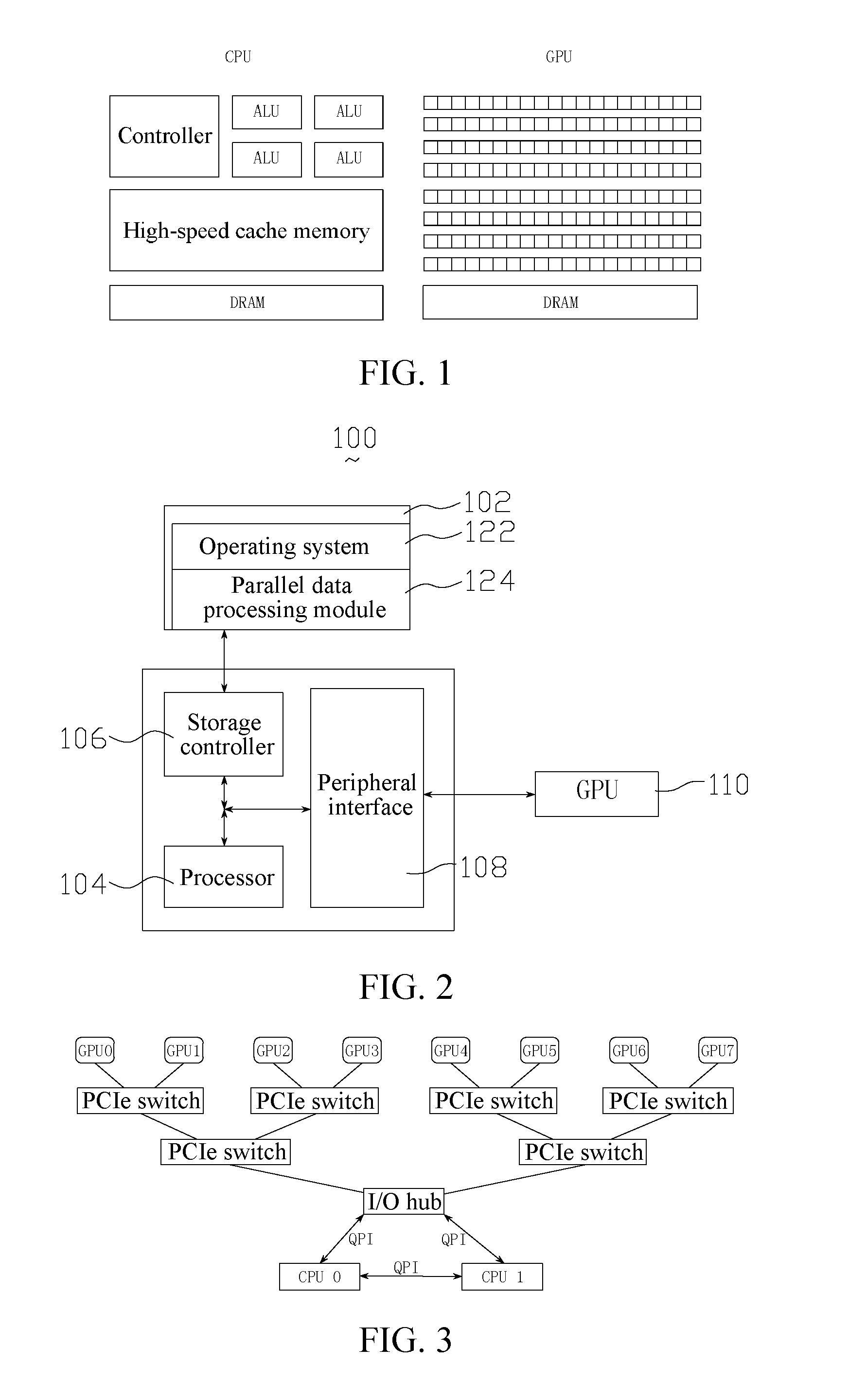
Model Parallel Processing Method and Apparatus Based on Multiple Graphic Processing Units
ActiveUS20160321776A1Improve Parallel Processing EfficiencyImprove data processing efficiencyProcessor architectures/configurationProgram controlVideo memoryGraphics
A parallel data processing method based on multiple graphic processing units (GPUs) is provided, including: creating, in a central processing unit (CPU), a plurality of worker threads for controlling a plurality of worker groups respectively, the worker groups including a plurality of GPUs; binding each worker thread to a corresponding GPU; loading one batch of training data from a nonvolatile memory to a GPU video memory corresponding to one worker group; transmitting, between a plurality of GPUs corresponding to one worker group, data required by data processing performed by the GPUs through peer to peer; and controlling the plurality of GPUs to perform data processing in parallel through the worker threads.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
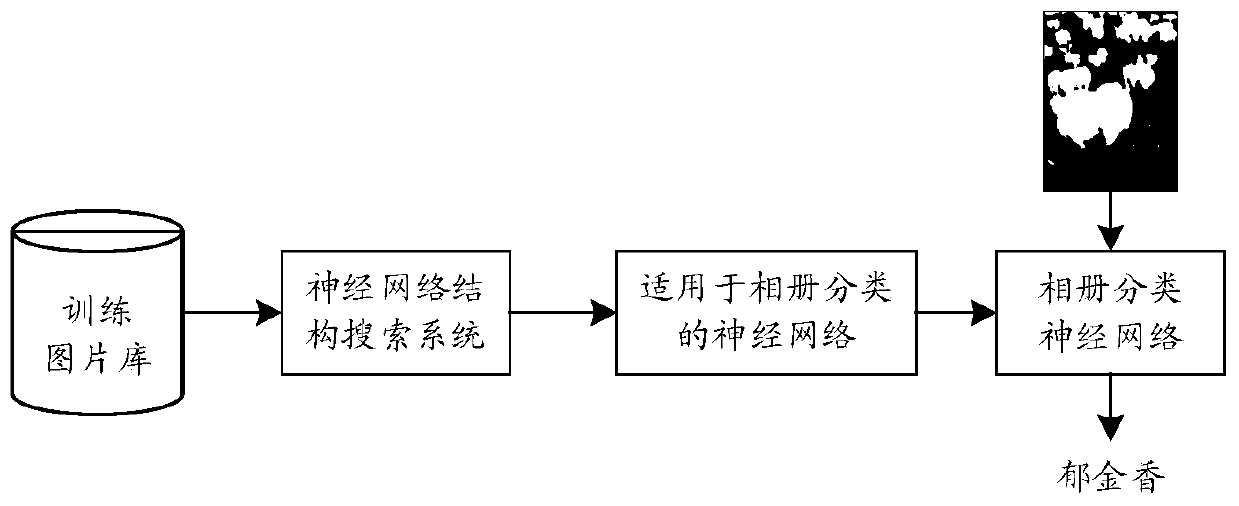
Neural network construction method and device and image processing method and device
ActiveCN110175671AIncrease the number ofBuild applicableCharacter and pattern recognitionStill image data clustering/classificationVideo memoryImaging processing
The invention discloses a neural network construction method and device and an image processing method and device in the field of computer vision in the artificial intelligence field. The neural network construction method comprises the following steps: determining a search space and a plurality of construction units; stacking the plurality of construction units to obtain a search network, with the search network being a neural network for searching a neural network structure; and optimizing a network structure of a construction unit in the search network in the search space, wherein in the optimization process, the search space is gradually reduced, the number of the construction units is gradually increased, and due to the reduction of the search space and the increase of the number of the construction units, the video memory consumption generated in the optimization process is within a preset range; and establishing the target neural network according to the optimized construction unit. Under the condition that video memory resources are certain, the neural network meeting application requirements well can be constructed.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
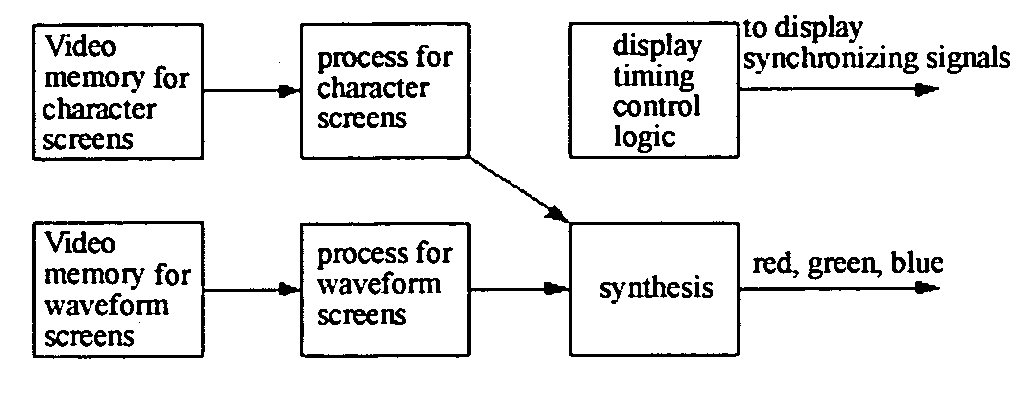
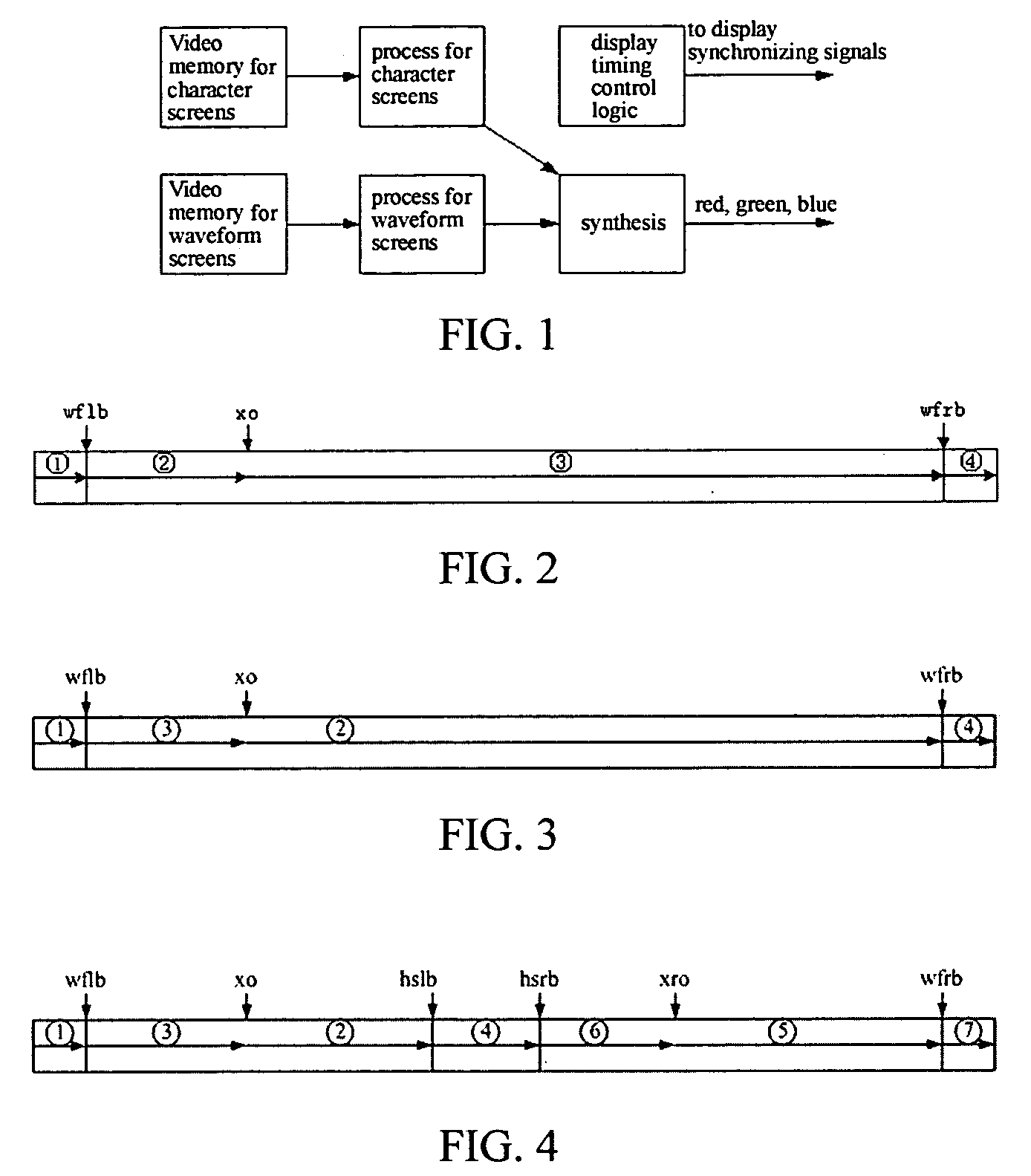
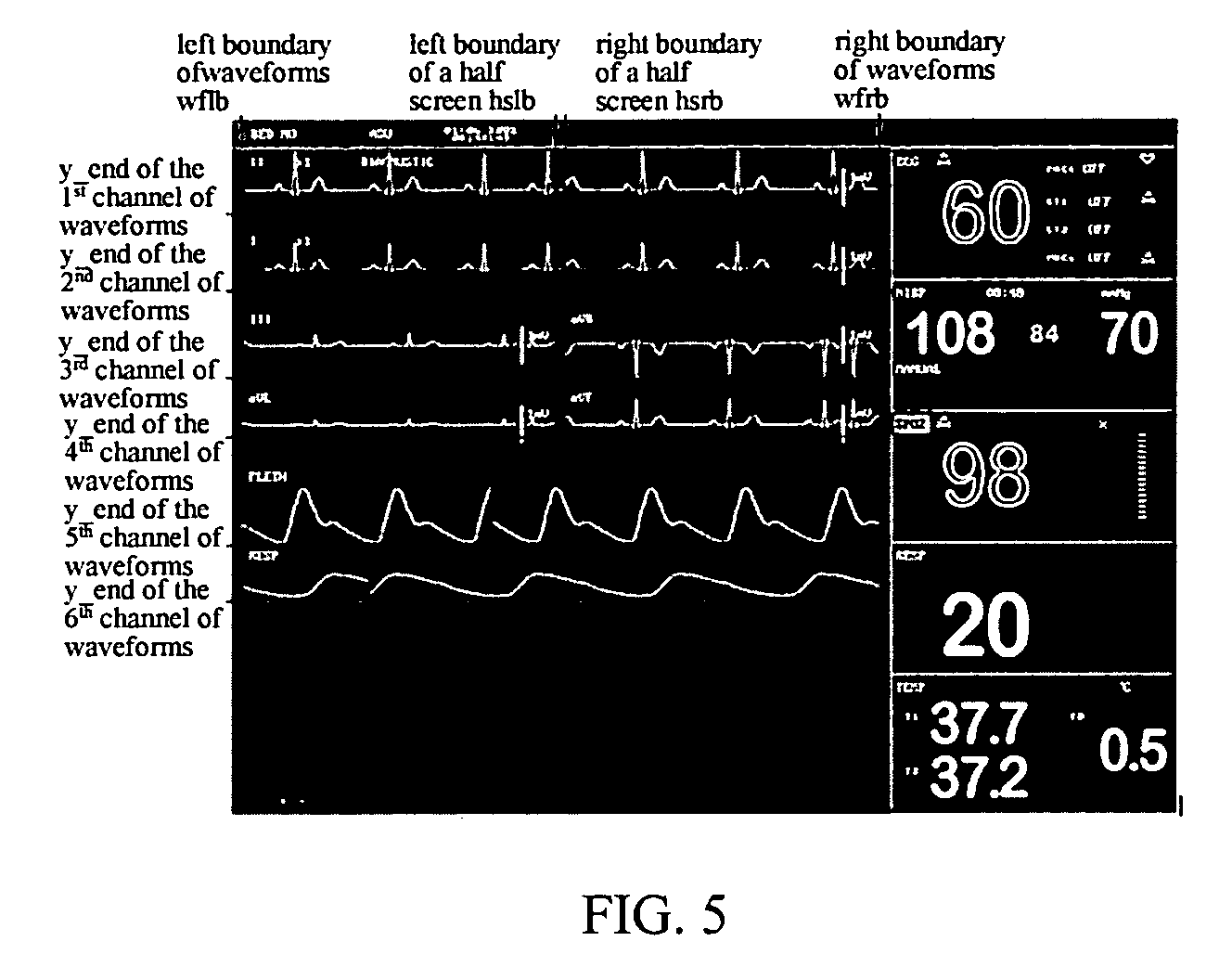
Method of displaying multi-channel waveforms
ActiveUS20060161360A1Improve efficiencyLow costDigital variable displayLocal control/monitoringExtensibilityVideo memory
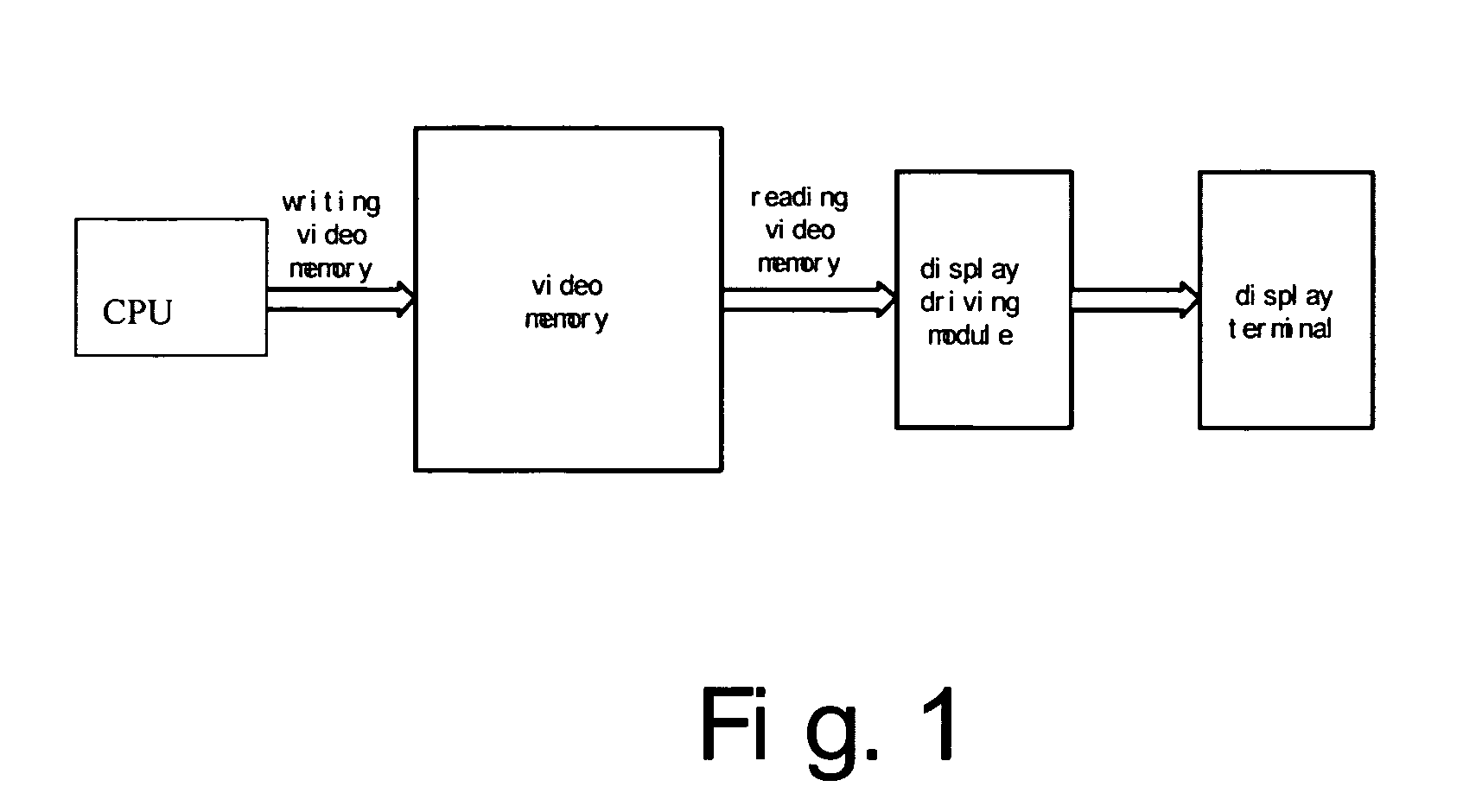
A method of displaying multi-channel waveforms, which is used for displaying multi-channel waveforms dynamically in embedded systems, the method comprising the steps of: dividing at least one waveform screen in a video memory which is mapped to a display terminal into a plurality of waveform windows, wherein boundaries of each of the windows are defined by a plurality of values set in at least a set of boundary registers; establishing a waveform parameter table in a memory of the system, which contains characteristic parameters of each waveform in each of the waveform windows; writing waveform data into a logical space in the waveform screen corresponding to a waveform by writing operations from CPU to the video memory; and on a basis of the parameters of the waveform windows in the waveform parameter table, performing a display mode defined by the parameter by means of is changing the mapping relationship between the video memory and the display terminal, before transmitting the data of each of the waveform windows read out from the video memory to the display terminal by a display drive circuit. According to the method of present invention, the inconsistency between the increase of waveforms and the resultant significant increase of logic resources and degradation of the performance of chips for display can be solved, which enables the system advantageous in high efficiency, low cost and excellent extensibility.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Video memory management
A video memory manager manages and virtualizes memory so that an application or multiple applications can utilize both system memory and local video memory in processing graphics. The video memory manager allocates memory in either the system memory or the local video memory as appropriate. The video memory manager may also manage the system memory accessible to the graphics processing unit via an aperture of the graphics processing unit. The video memory manager may evict memory from the local video memory as appropriate, thereby freeing a portion of local video memory use by other applications. In this manner, a graphics processing unit and its local video memory may be more readily shared by multiple applications.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
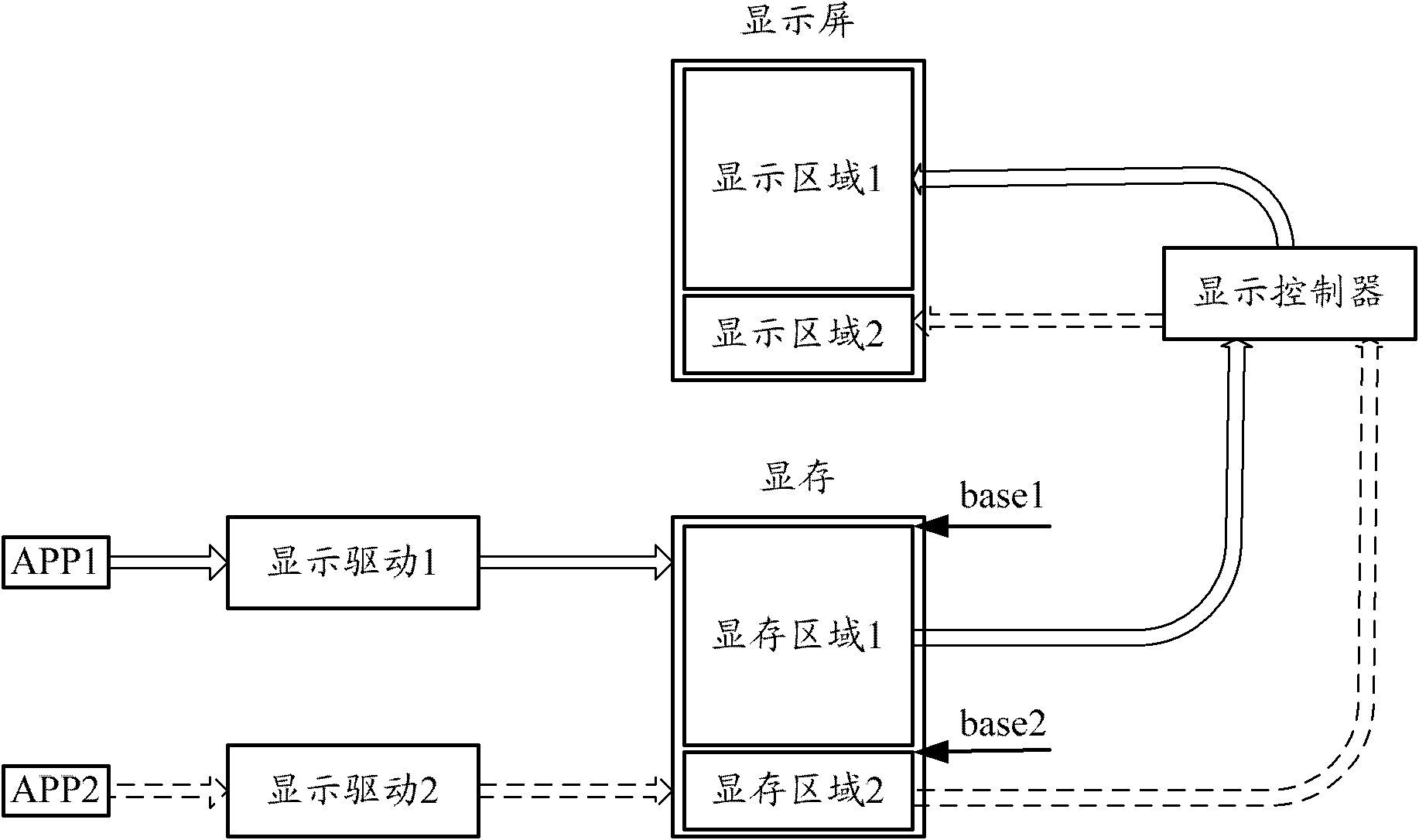
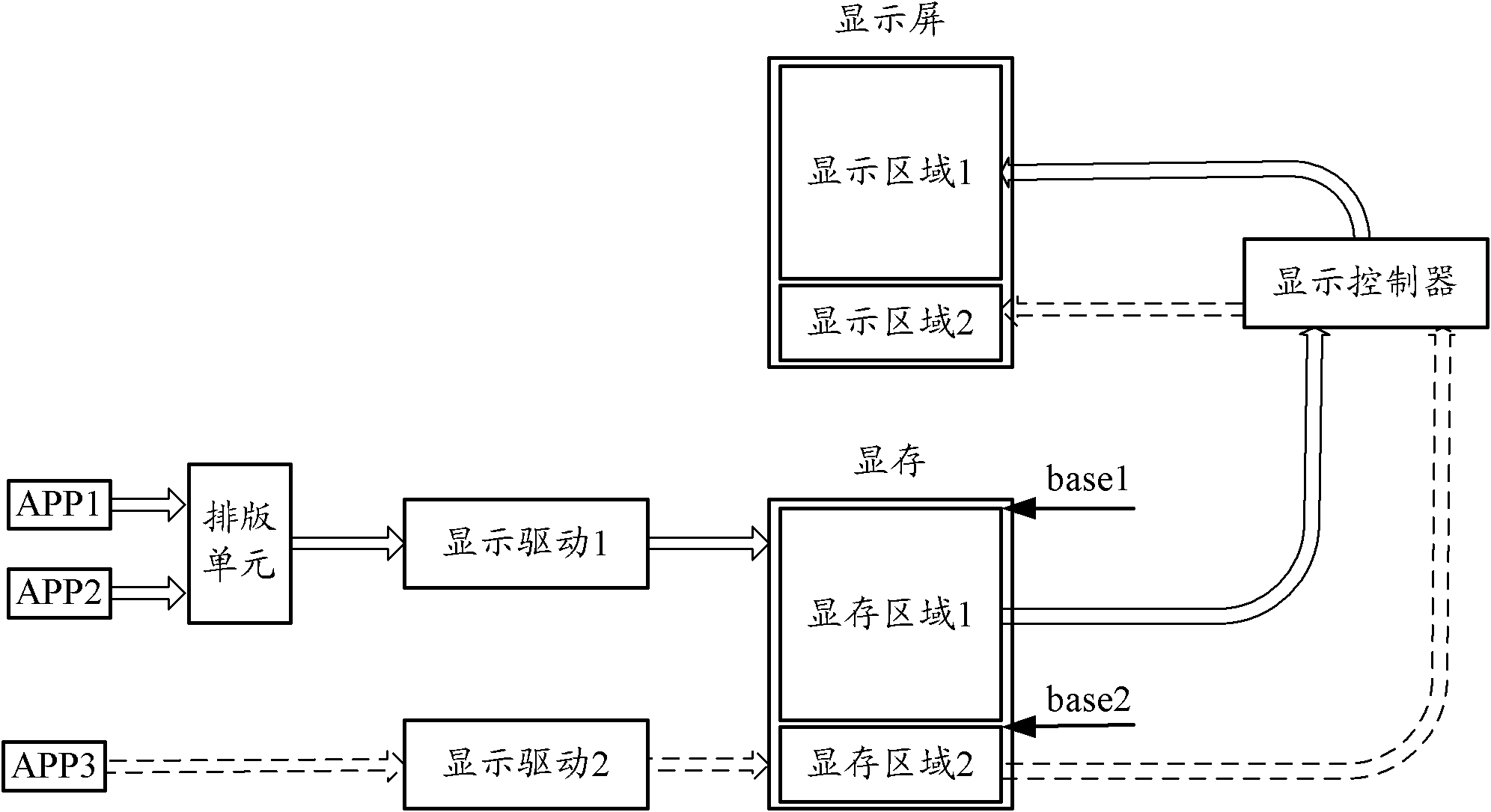
A system and method for realizing split-screen display
InactiveCN102279723AGuaranteed independenceImprove versatilityCathode-ray tube indicatorsDigital output to display deviceVideo memoryComputer engineering
The present invention provides a system and method for realizing split-screen display. The display screen is logically divided into N display areas. The system includes: a display controller, video memory and N display drivers, wherein the video memory contains N Each display driver corresponds to a display area respectively, and each display area corresponds to a display area respectively, and the N is an integer more than 2; when the display driver is called by an upper-level application program (APP), obtain the described The data of the APP is written or updated to the corresponding video memory area; the video memory area buffers the data to be displayed in the corresponding display area; the display controller reads the data of each video memory area and transmits it to the corresponding display area of each video memory area . The present invention realizes split-screen display on the same display screen, without customizing the display screen, and ensures the independence of each display area.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
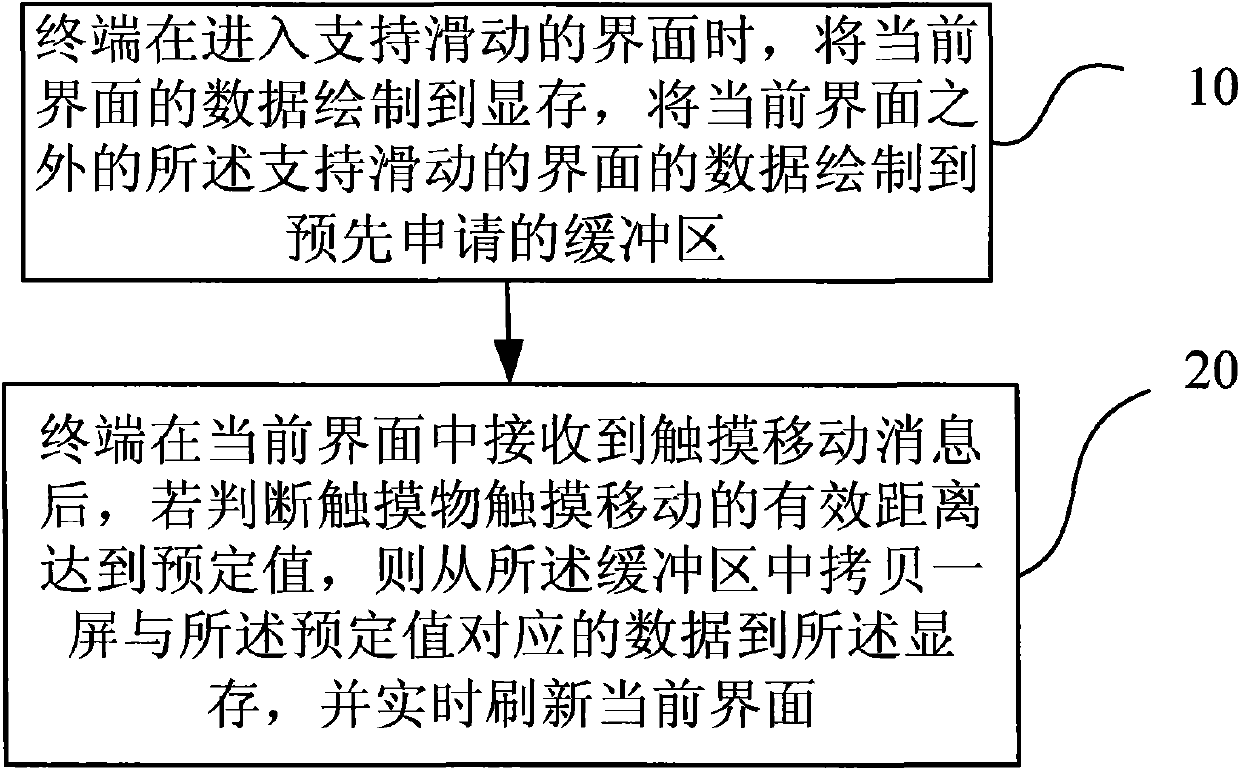
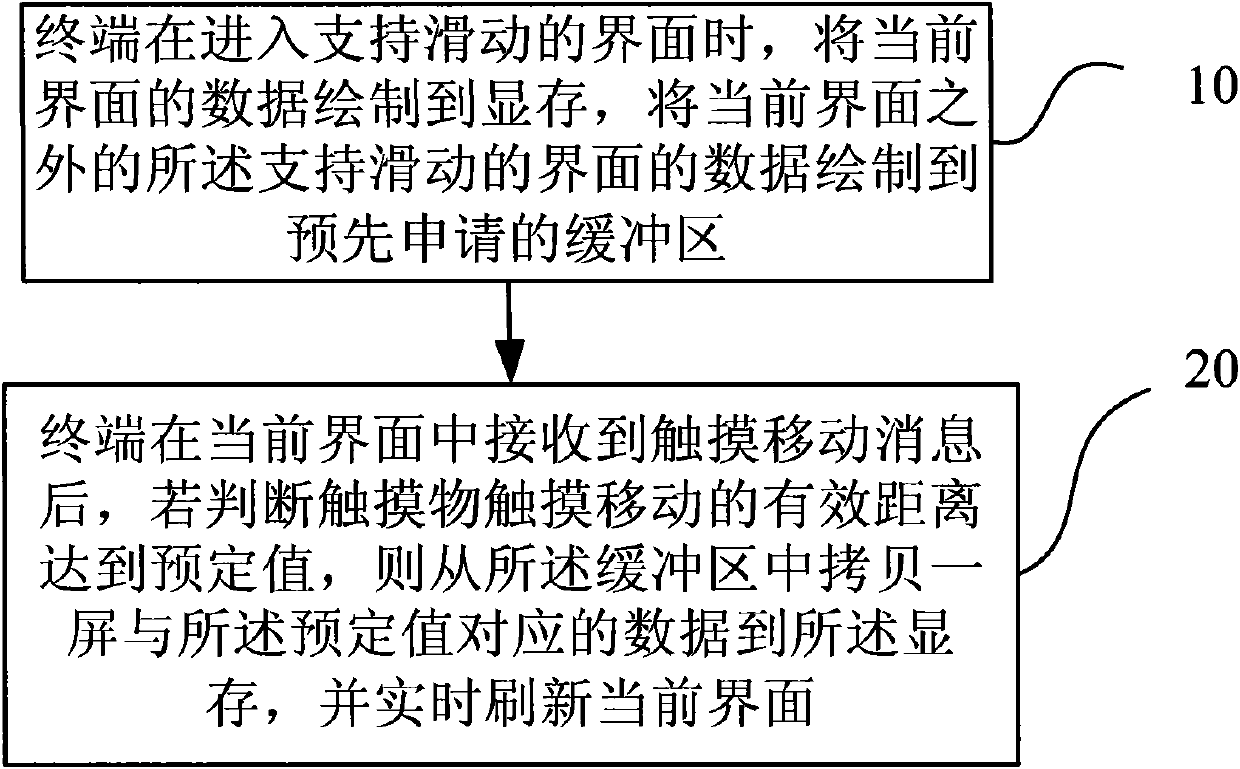
Method for sliding interface of touch screen and terminal
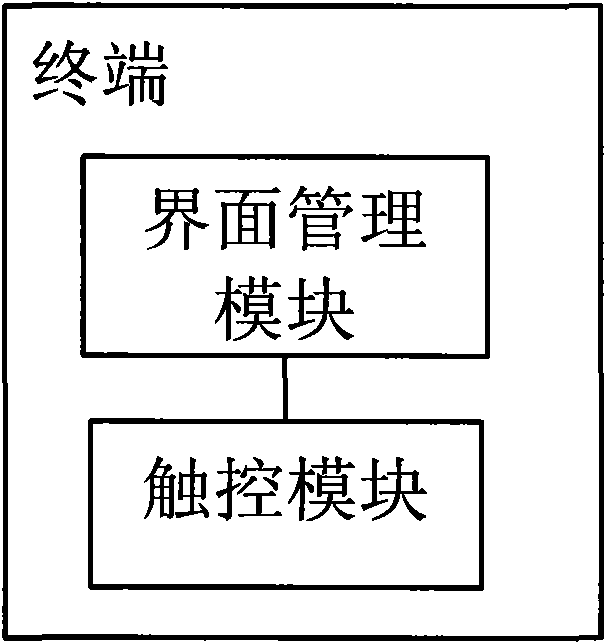
InactiveCN101950235AHigh speedImprove efficiencyInput/output processes for data processingVideo memoryTouchscreen
The invention provides a method for sliding an interface of a touch screen and a terminal. The method comprises the following steps of: when entering an interface supporting sliding, drafting the data of the current interface in a memory, and drafting the data of the interface supporting the sliding in a buffer zone applied for in advance except the data of the current interface; and after a message of touching movement in the current interface is received, if judging that the effective distance of the touching movement of a touching article reaches a preset value, copying a screen of data corresponding to the preset value from the buffer zone in the memory, and refreshing the current interface in real time. In the method, a mode of directly operating the memory to refresh the screen whenthe interface contents are updated along with the sliding is adopted, so that the sliding speed and efficiency of the interface are effectively improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com