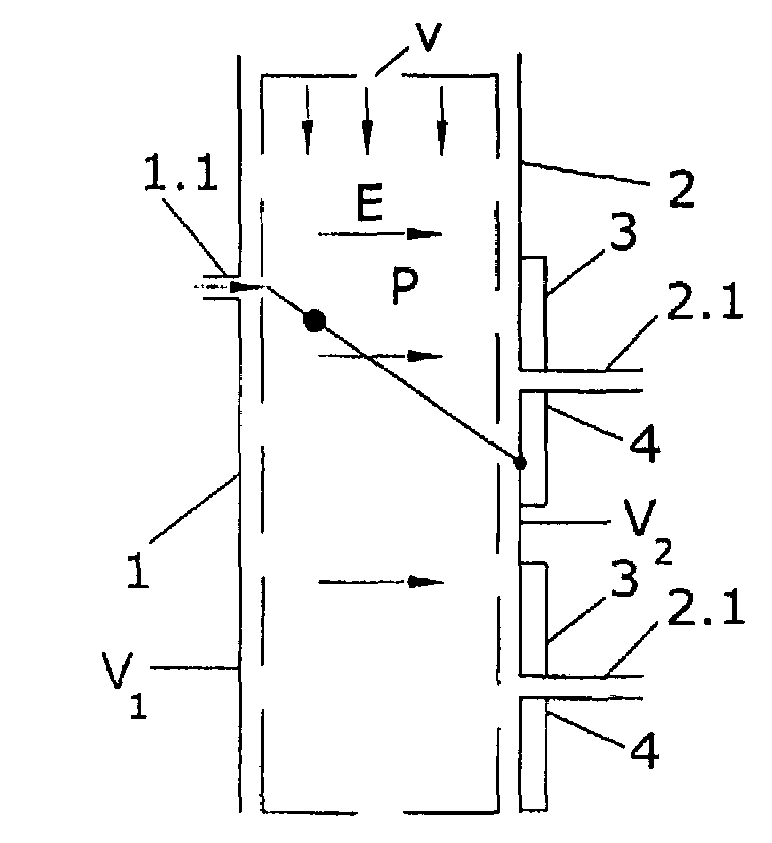
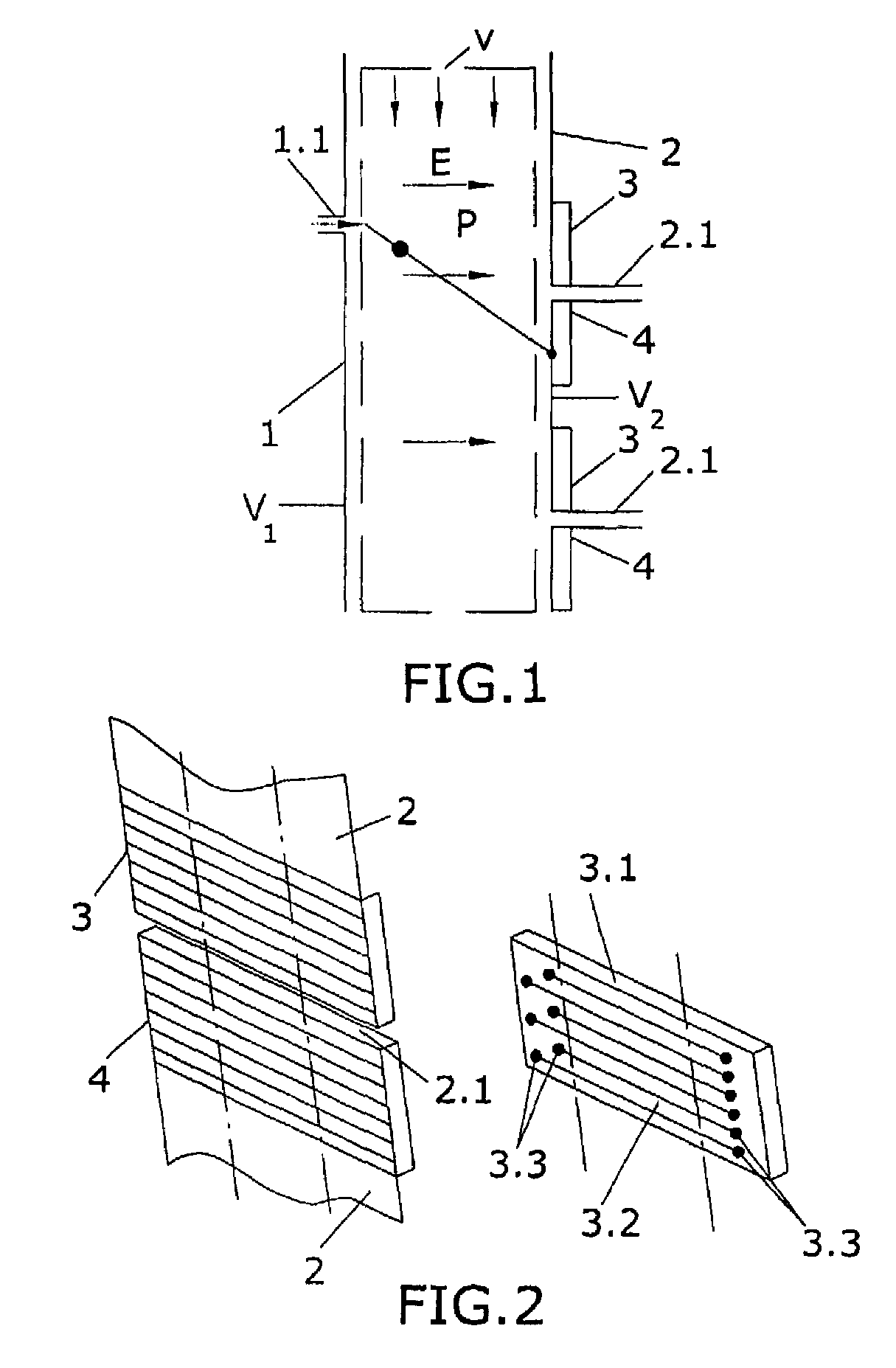
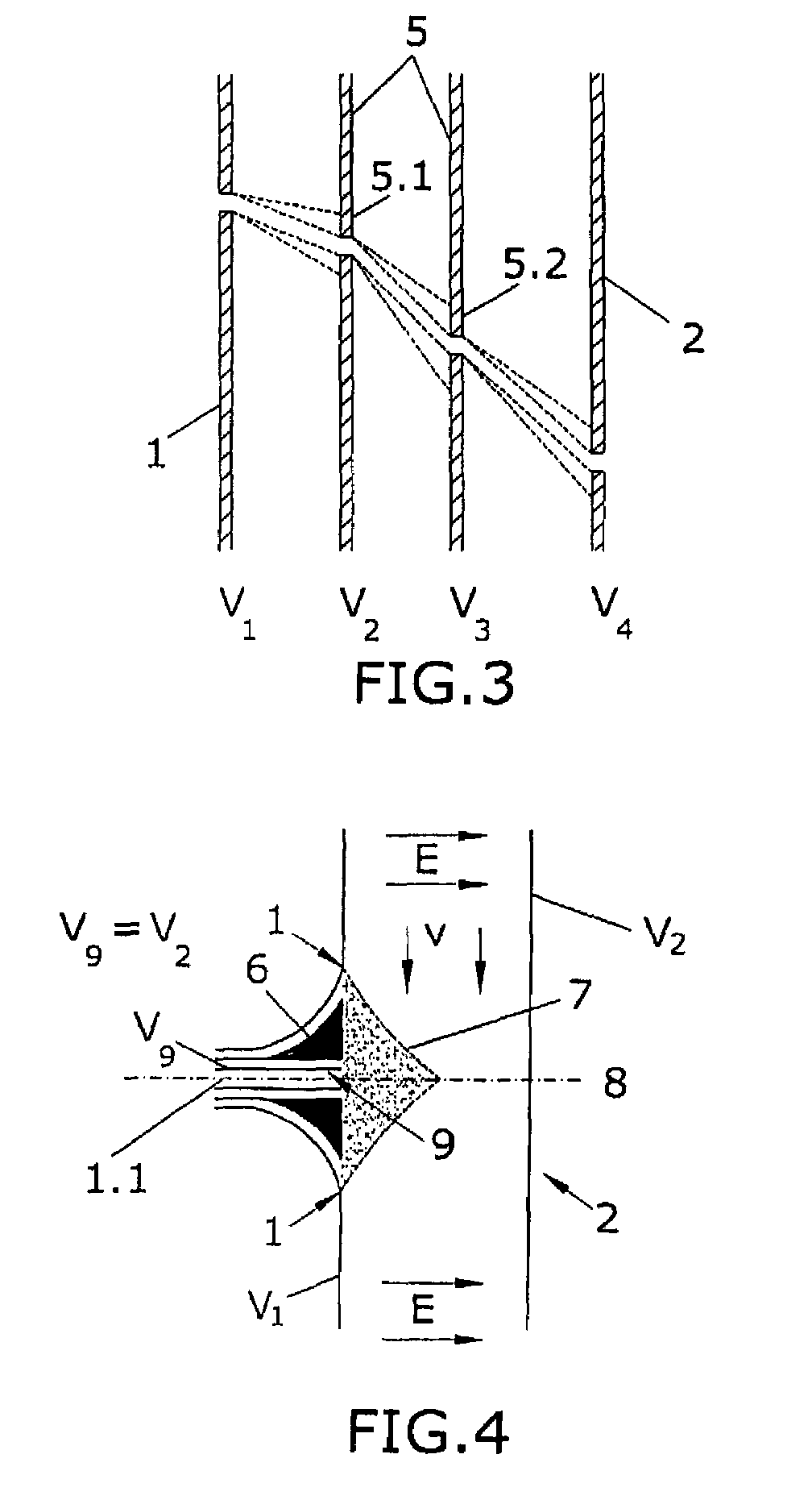
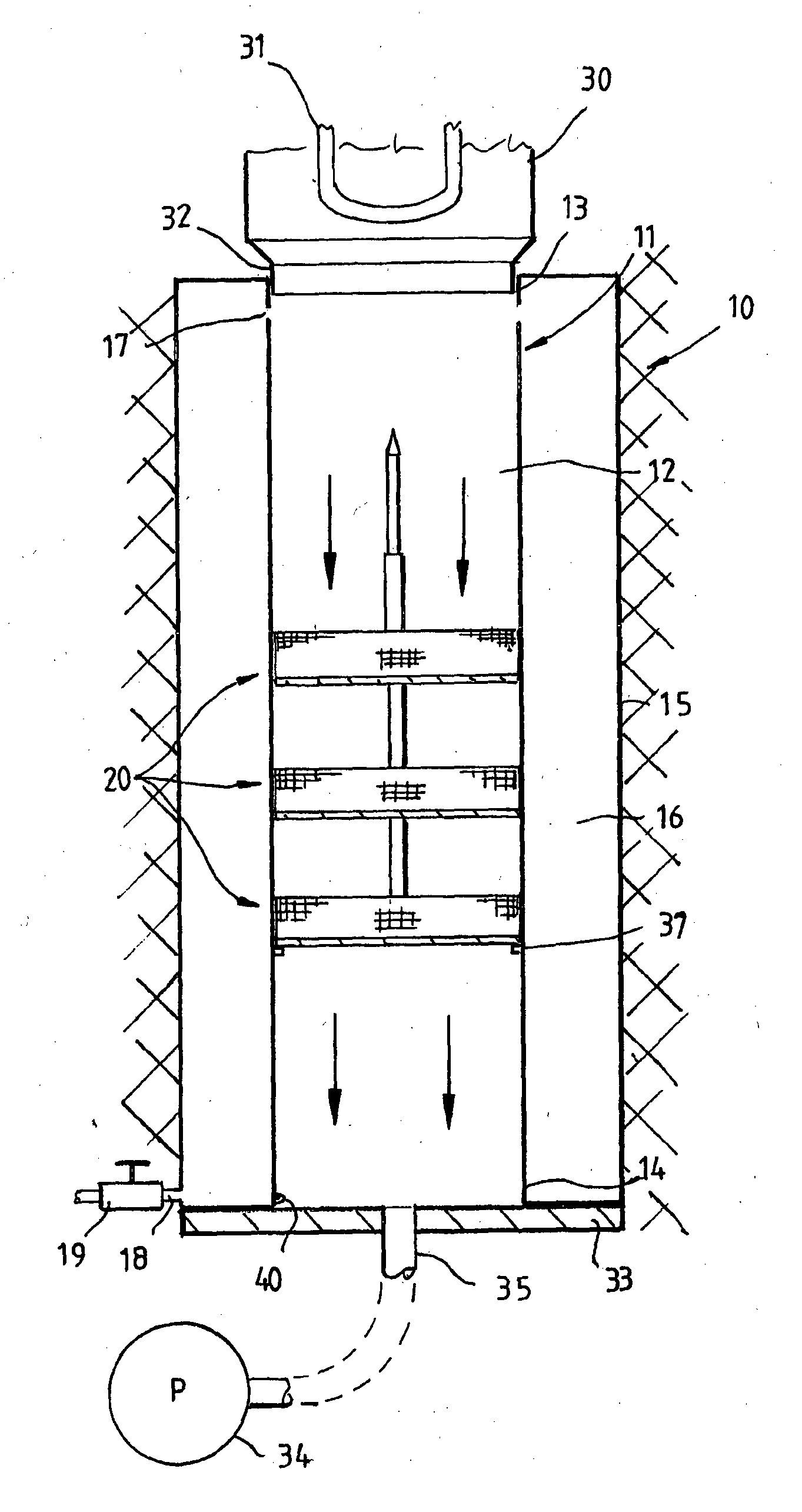
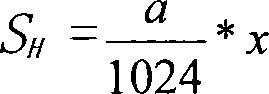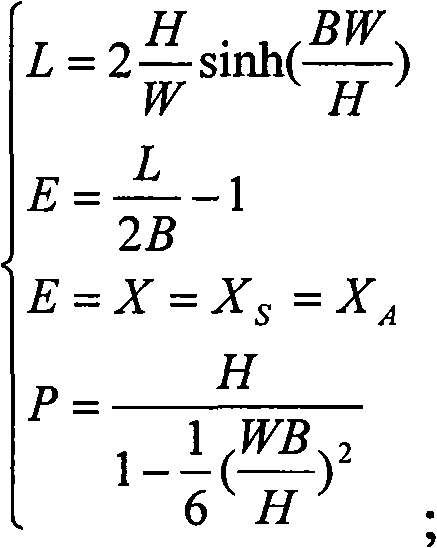Patents
Literature
224results about "Weighing apparatus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
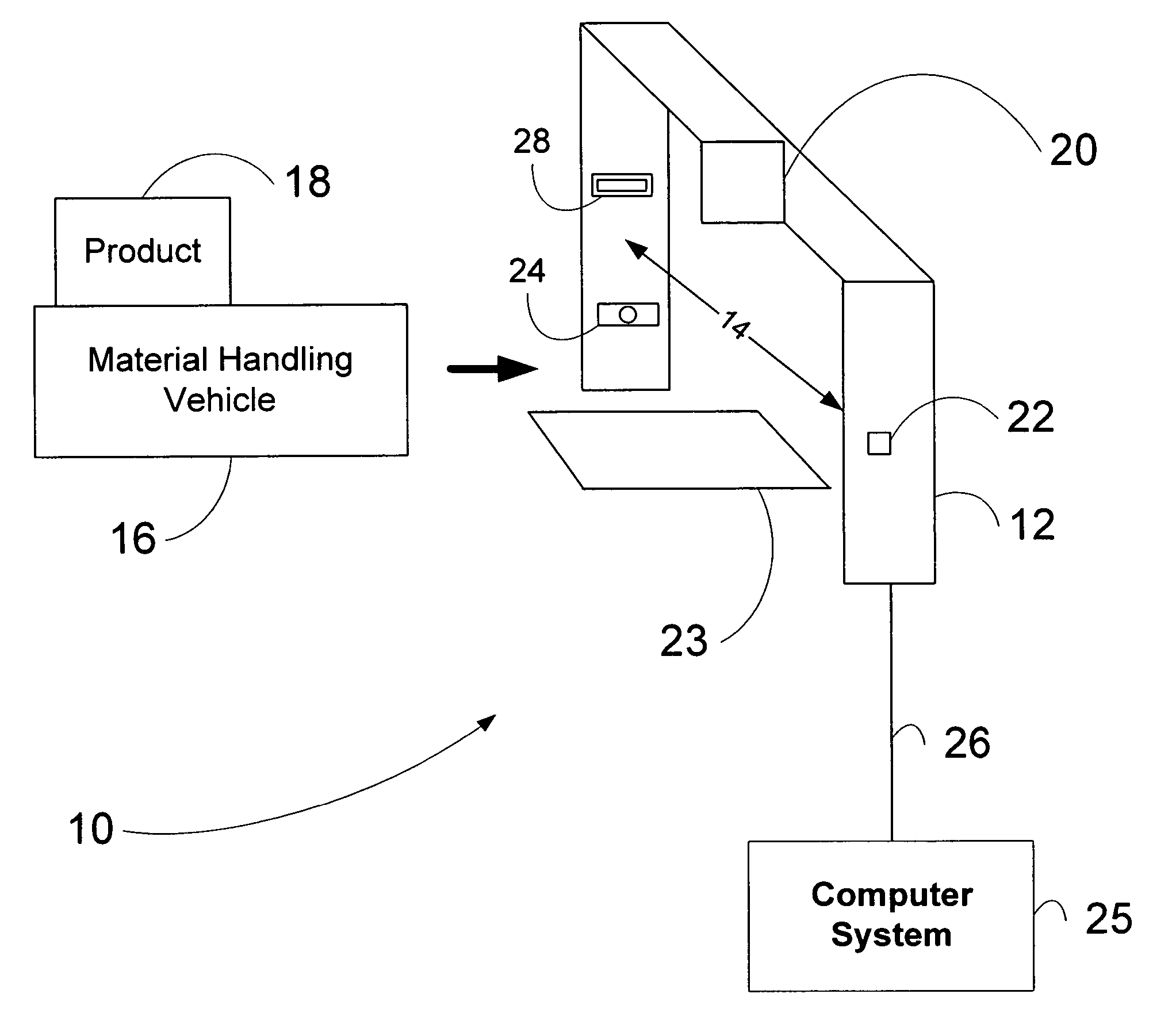
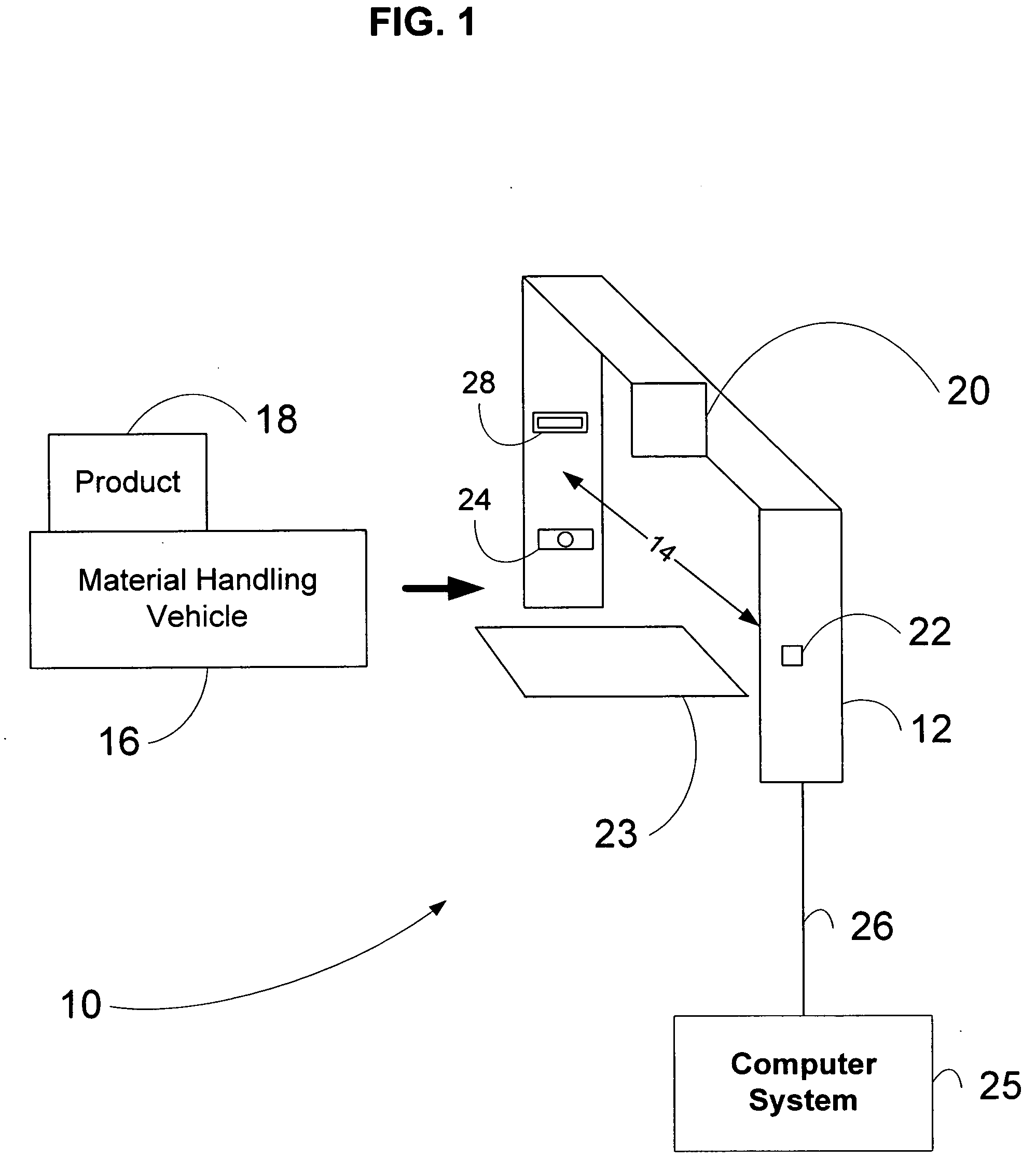
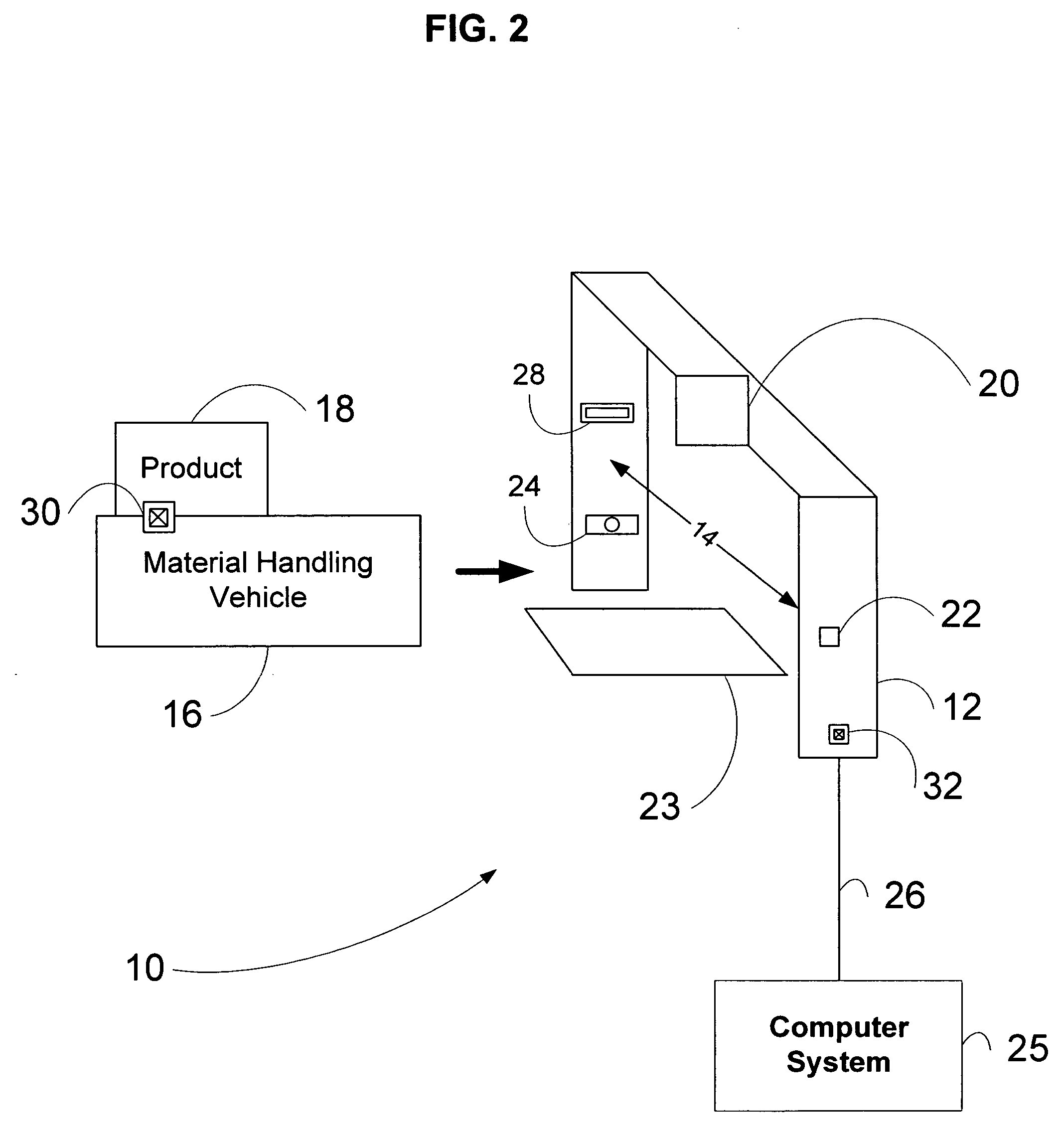
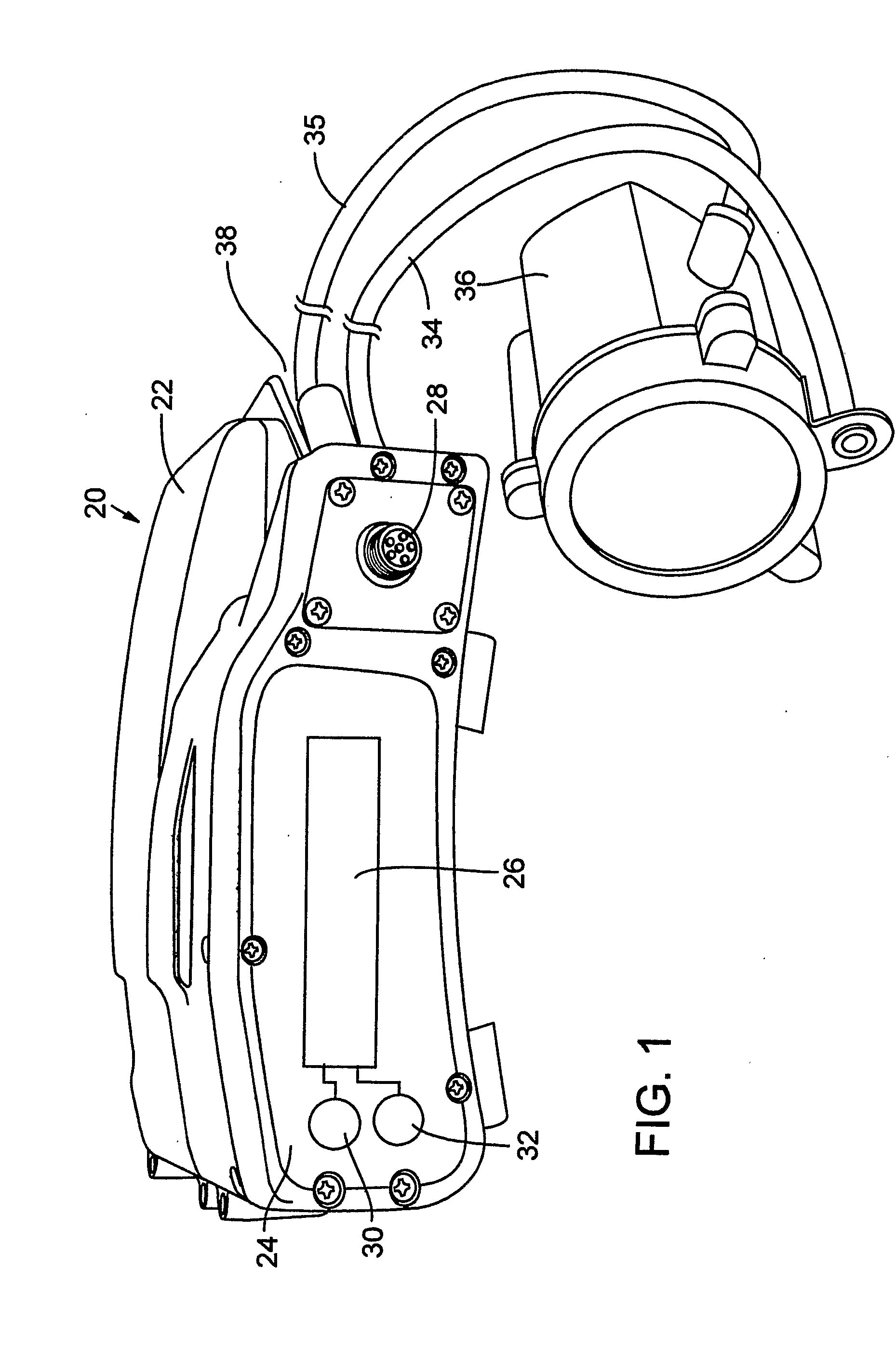
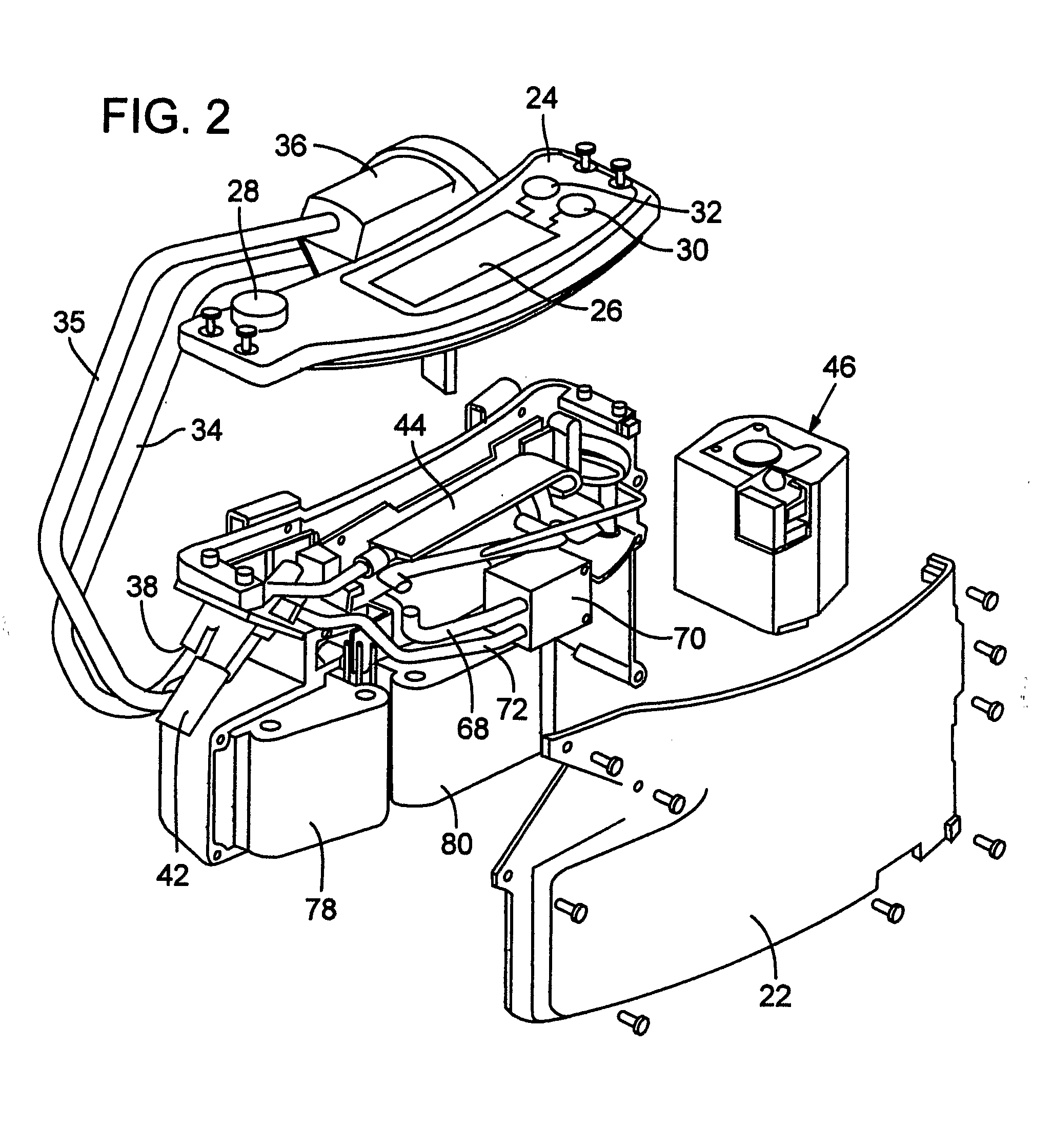
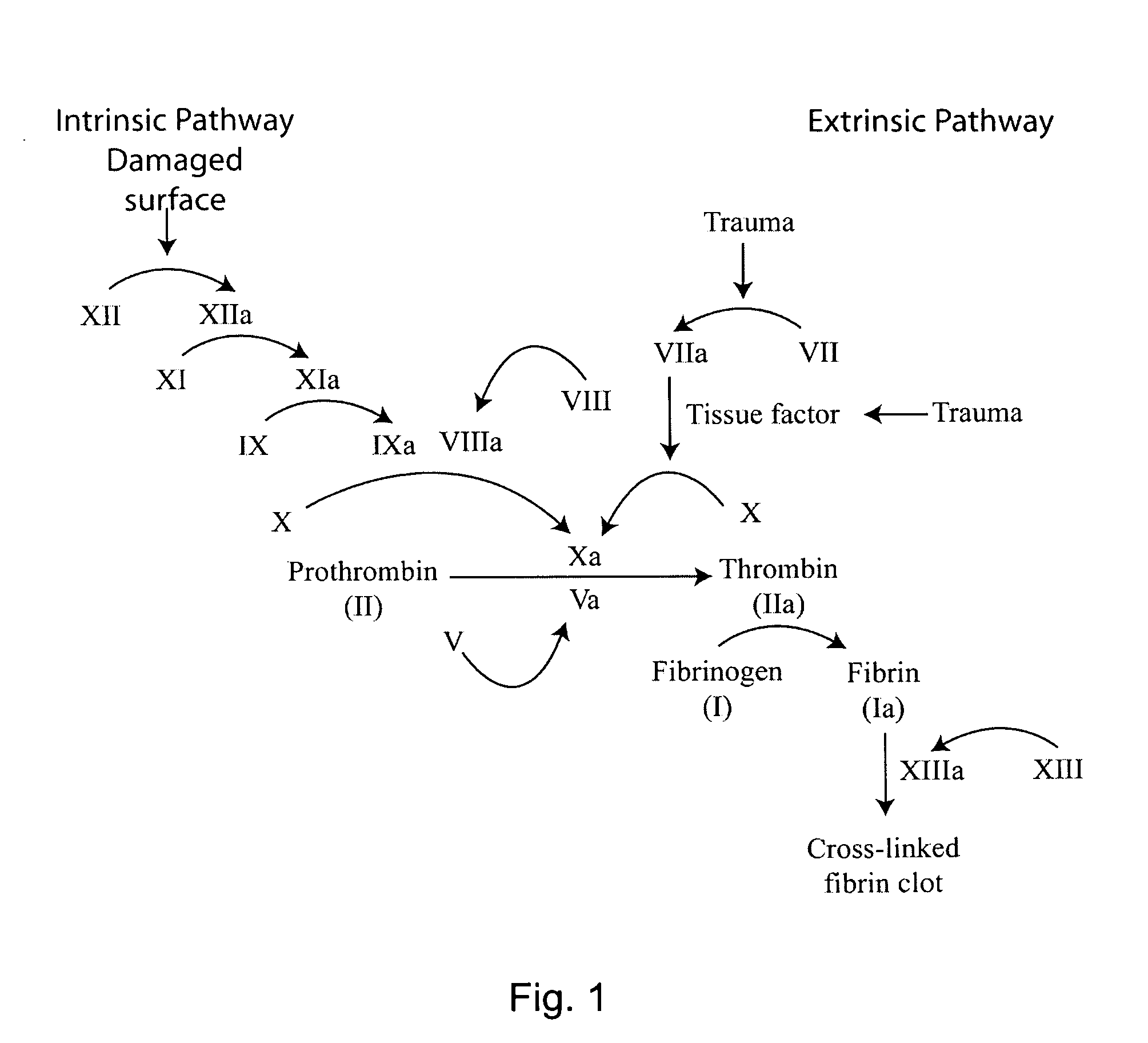
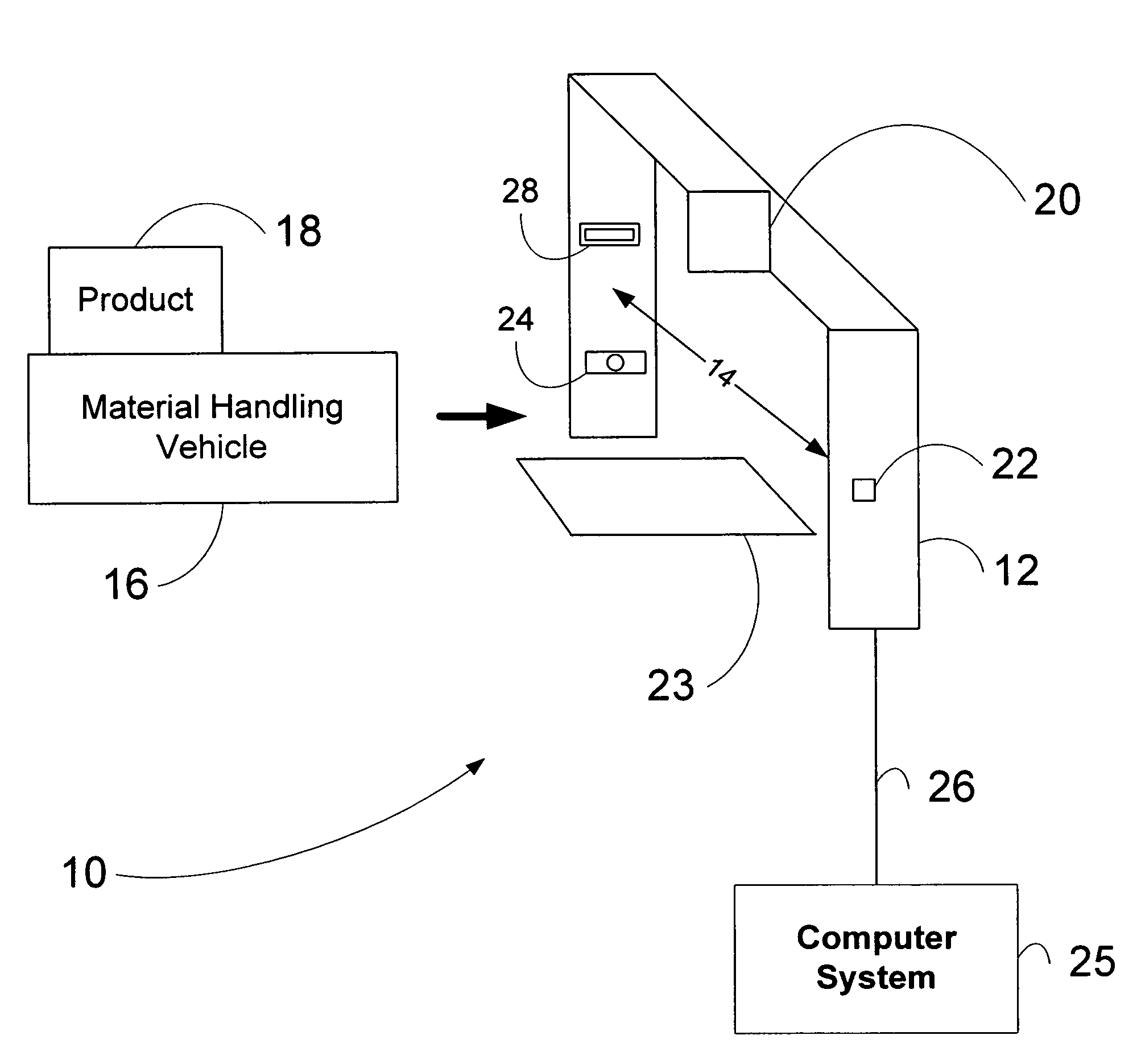
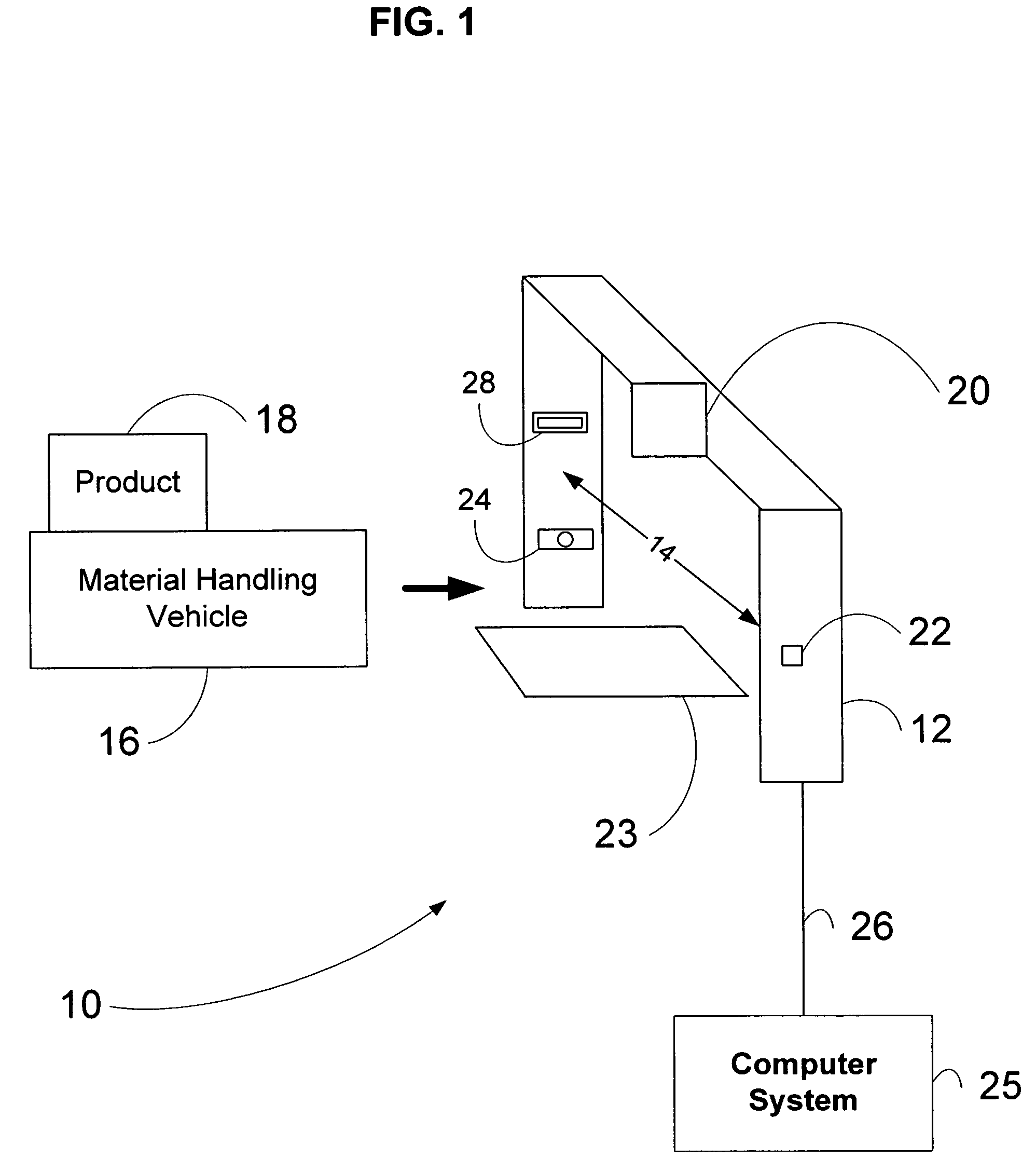
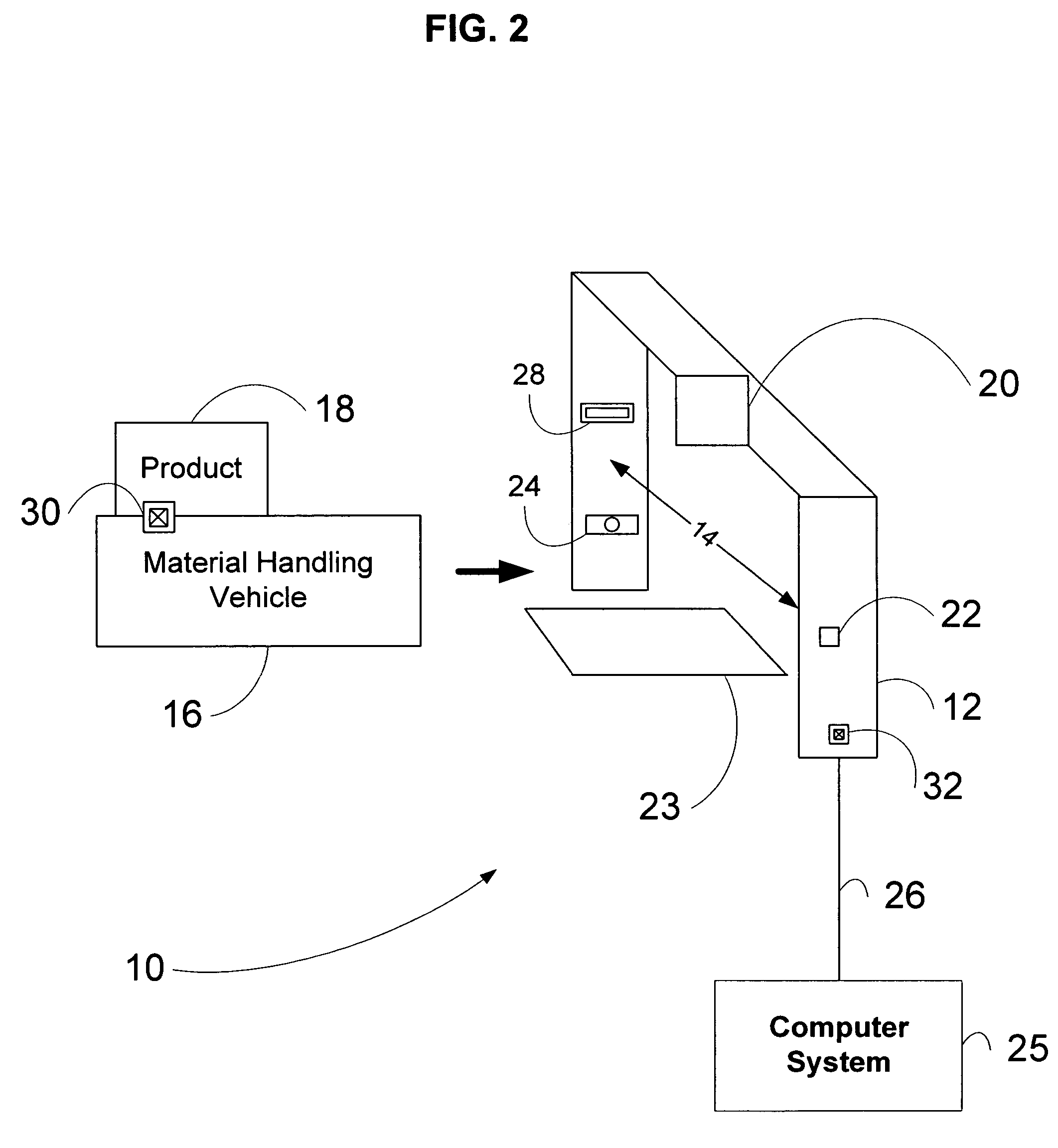
Material transport in-motion product dimensioning system and method
Methods, systems, and devices to obtain dimensions of an article or product in association with material handling vehicles are disclosed. A dimension detection device is installed in an enclosure and is used to acquire geometrical dimensions of the object in association with the vehicle. A predetermined dimension of the vehicle is subtracted from the overall detected dimension to determine the dimensions, including weight, of the product alone. One or more dimension detection devices may also be positioned on a mast or other portion of the material handling vehicle allowing the material handling vehicle to act as a mobile product dimensioning system.
Owner:RICE LAKE WEIGHING SYST
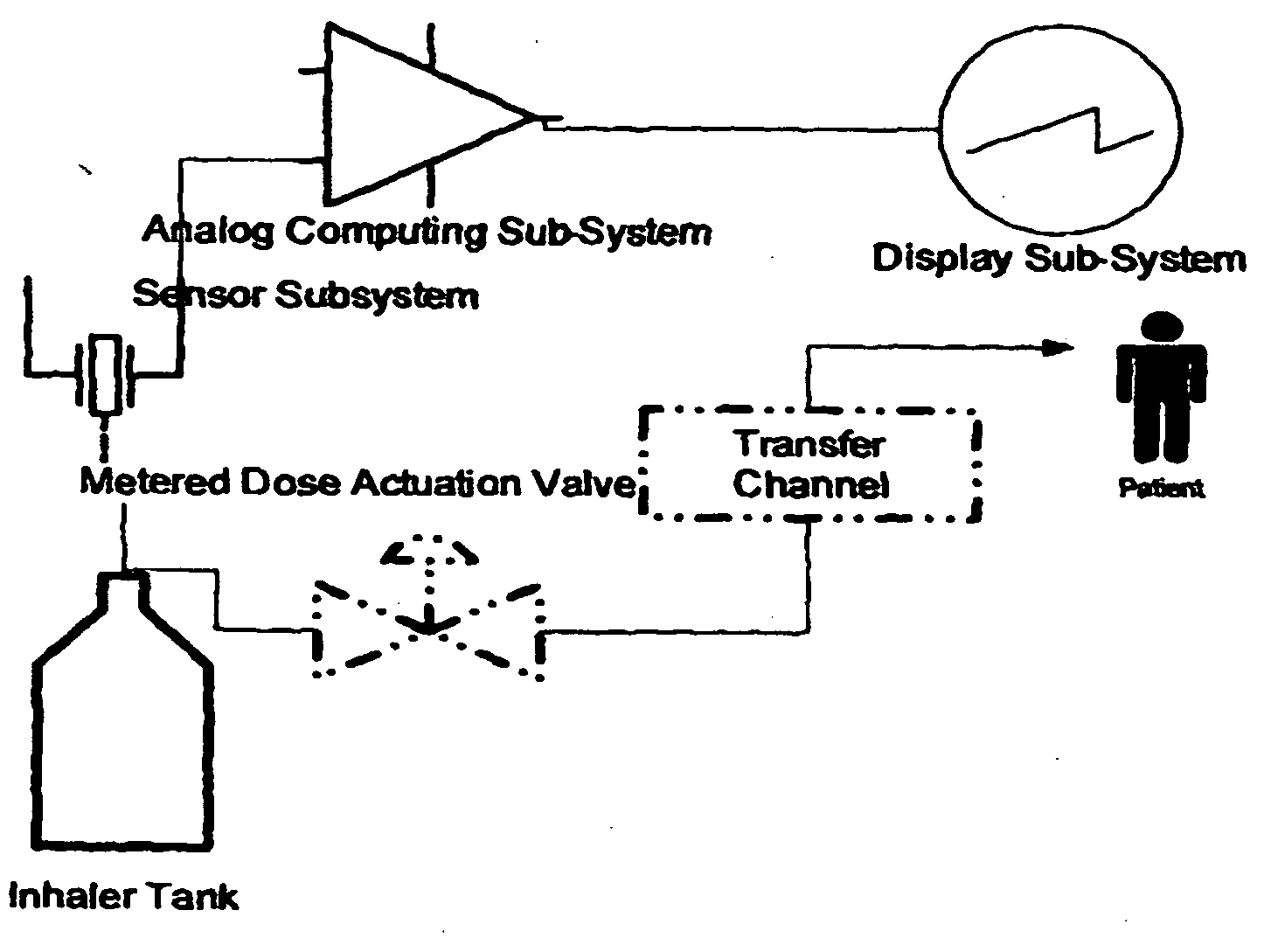
Apparatus for dispensing pressurized contents
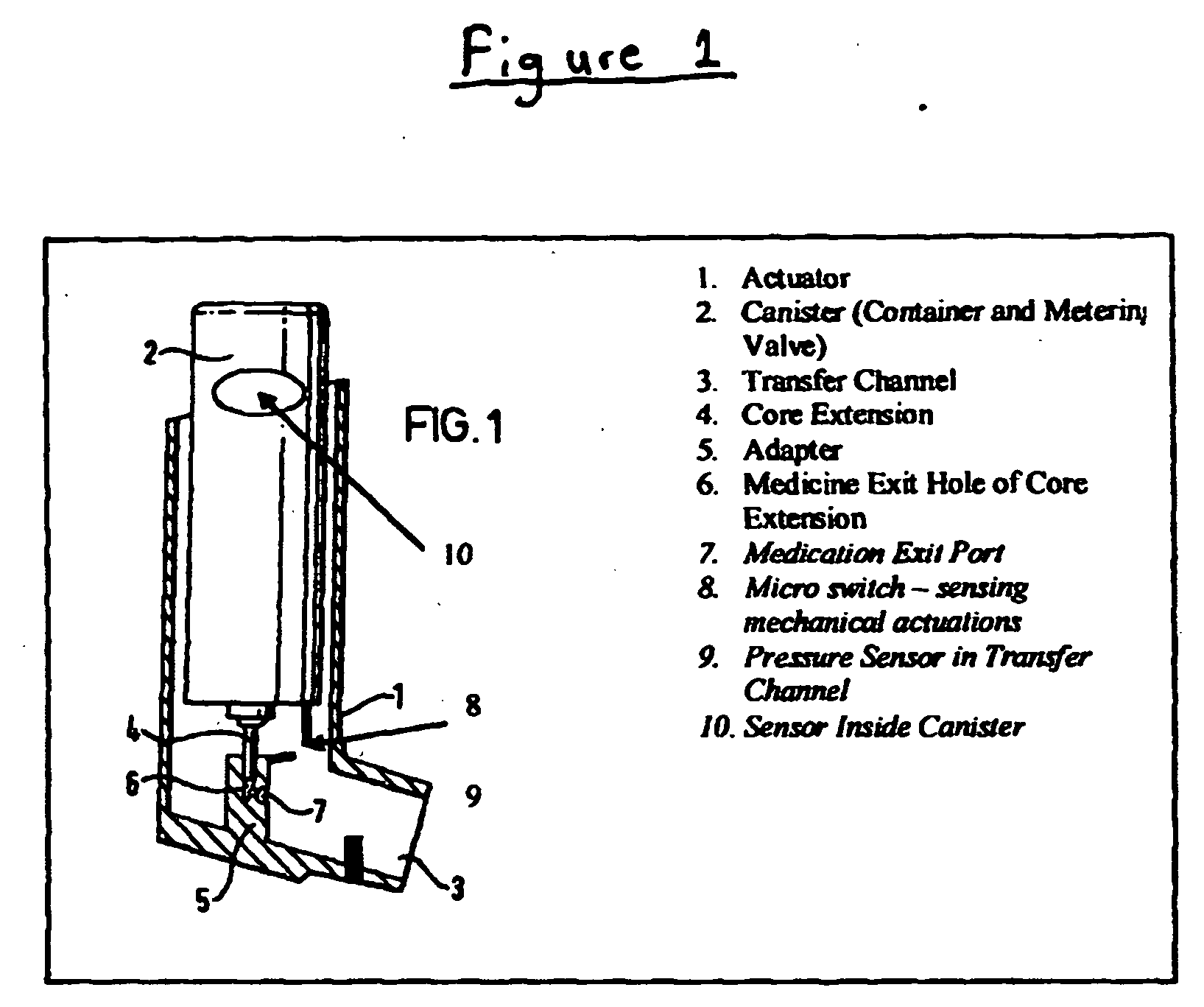
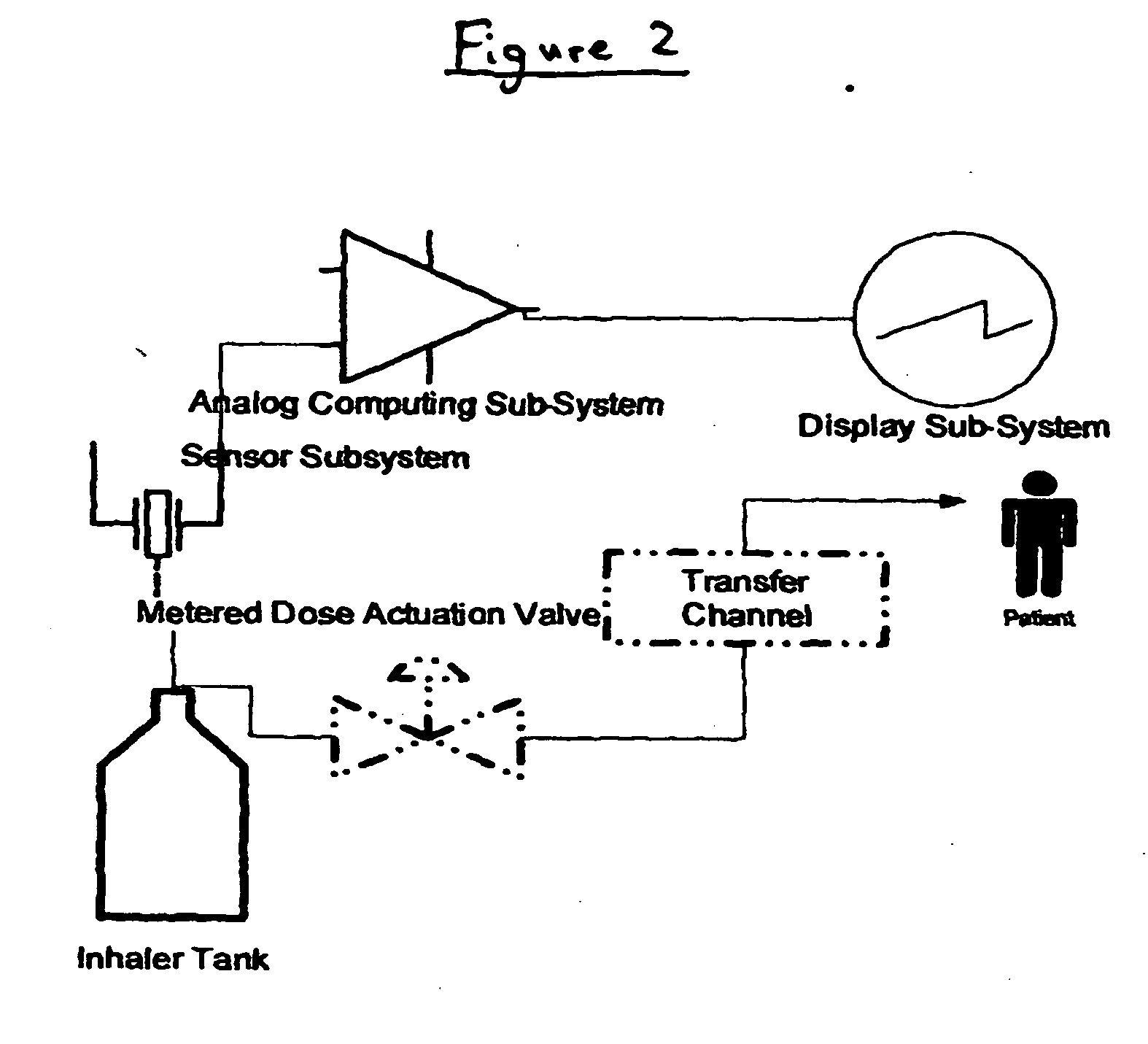
Containers for incrementally dispensing pressurized contents are described. The containers comprise a vessel suited to contain pressurized contents, a port integral with the vessel and through which pressurized contents contained in the vessel can be released from the vessel, preferably incrementally in approximately equal amounts, and a measuring device disposed in or otherwise associated with the vessel such that the quantity or amount of contents in the vessel can be measured or assessed. The measuring device senses ambient conditions in the vessel and, directly or with other components, indicates, for example, the amount of pressurized contents remaining in the vessel and displaying it to an observer. With appropriate ancillary components, the measuring device also enables the amount of contents actually released from the vessel during a particular actuation to be compared to a theoretical constant. Also, additionally, the devices of the invention may also include time logging capability (alone or in conjunction with the capability to log other data) the actuation of the dispensing valve for comparison to a prescribed method. Accordingly, devices for incrementally dispensing pressurized contents from such containers are also described. Such devices further comprise a metering value for dispensing pressurized contents from the vessel. In preferred embodiments, each actuation of the metering valve results in release of a pre-determined quantity of the vessel contents. For example, in embodiments wherein the pressurized contents comprise a therapeutic composition, the instant devices include improved Metered Dose Inhalers (MDIs) for delivery of predetermined doses of a therapeutic composition to a patient, wherein the MDIs provide for sensing of the amount, for example, of the therapeutic composition remaining in the vessel after each actuation of the metering valve.
Owner:SCHECHTER ALAN M +1
Extra high voltage transmission line online monitoring system
InactiveCN101603850AAccurately monitor working statusMaster the operationSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementCurrent/voltage measurementData informationMathematical model
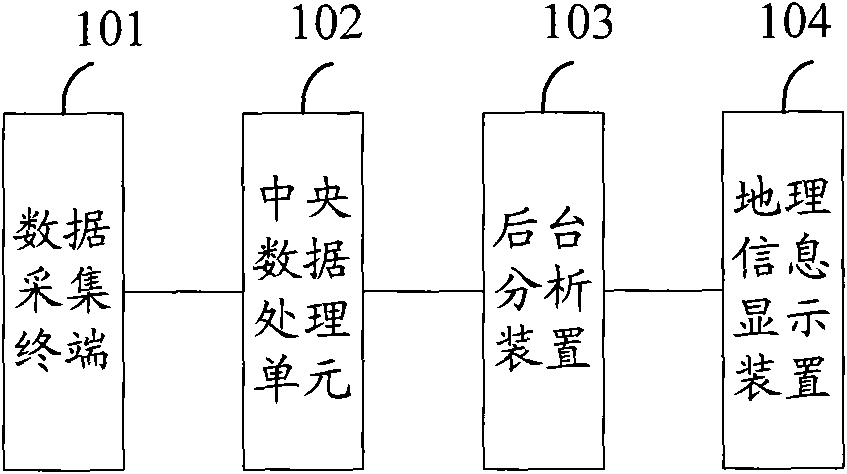
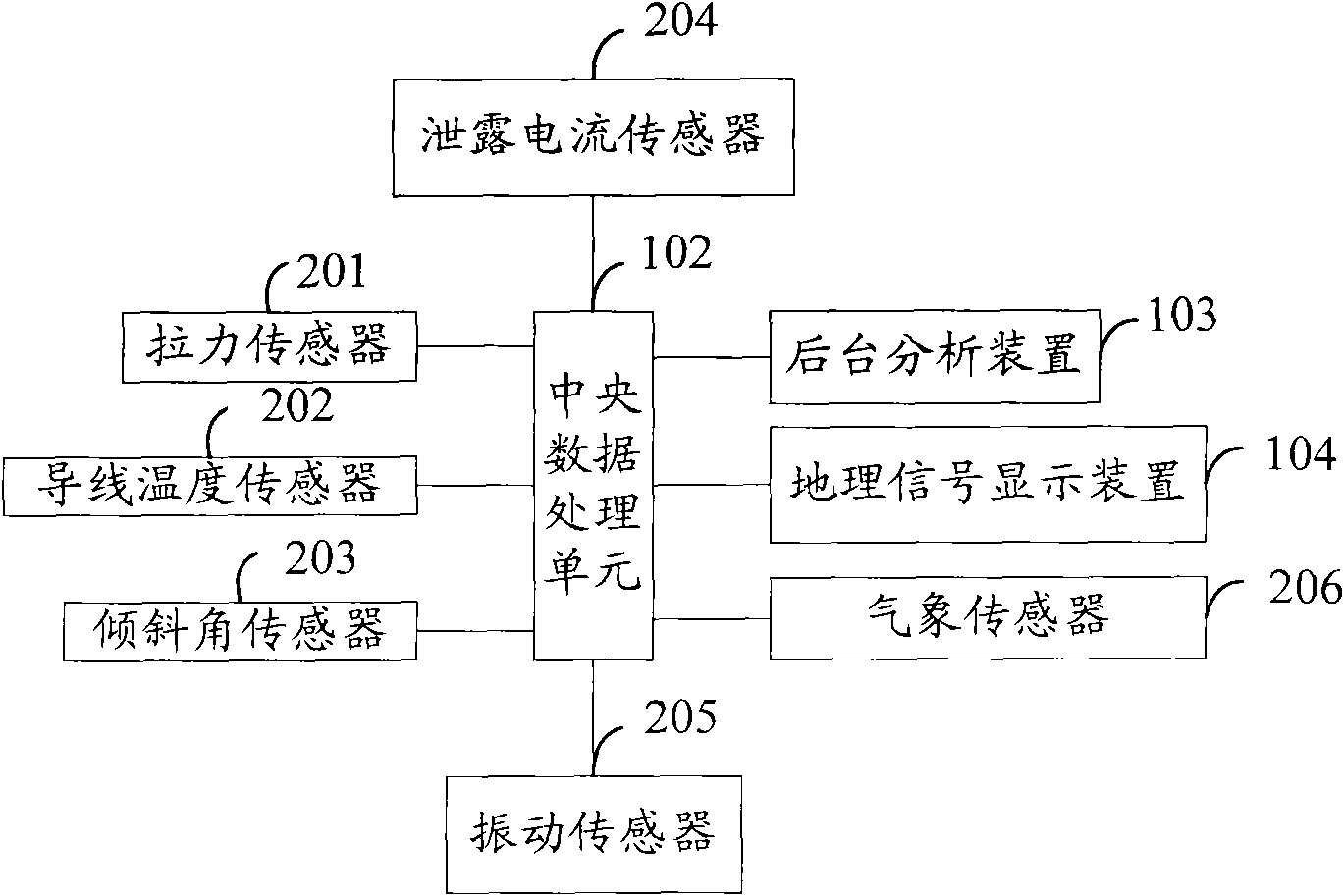
The invention provides an extra high voltage transmission line online monitoring system, comprising that a data collection terminal collects comprehensive load, temperature of a transmission line, inclination angle of a pole, inclination angle of an insulator string, leakage current of the insulator string, meteorological information, vibration of transmission line and vibration of the pole, transmits the collected signals to a central data processing unit; the central data processing unit performs anti-interference process on each signals, packs and transmits to a background analysis device through a wireless communication network, and displays data information on a GIS electronic map; the background analysis device determines whether the transmission line is abnormal or not based on each signal and combination of mathematical model, transmits alarm information in time when being abnormal. The invention performs anti-interference process on the collected data, is capable of shielding interference of extra high voltage strong electromagnetic field and accurately monitoring working conditions of extra high voltage transmission line.
Owner:CENT SOUTHERN CHINA ELECTRIC POWER DESIGN INST CHINA POWER ENG CONSULTING GROUP CORP +2
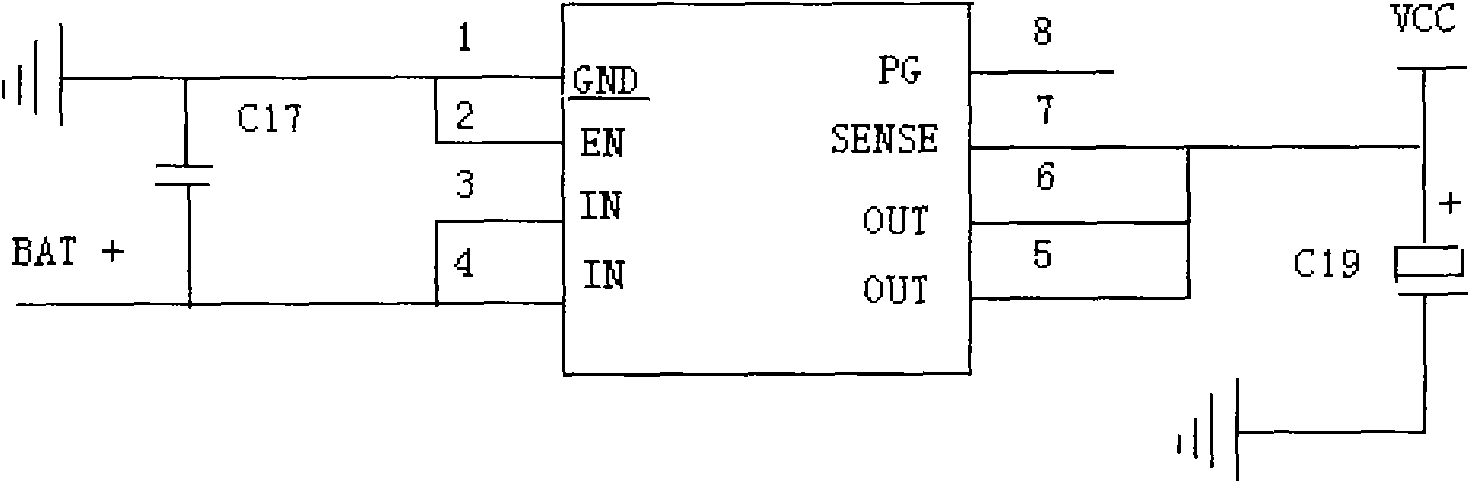
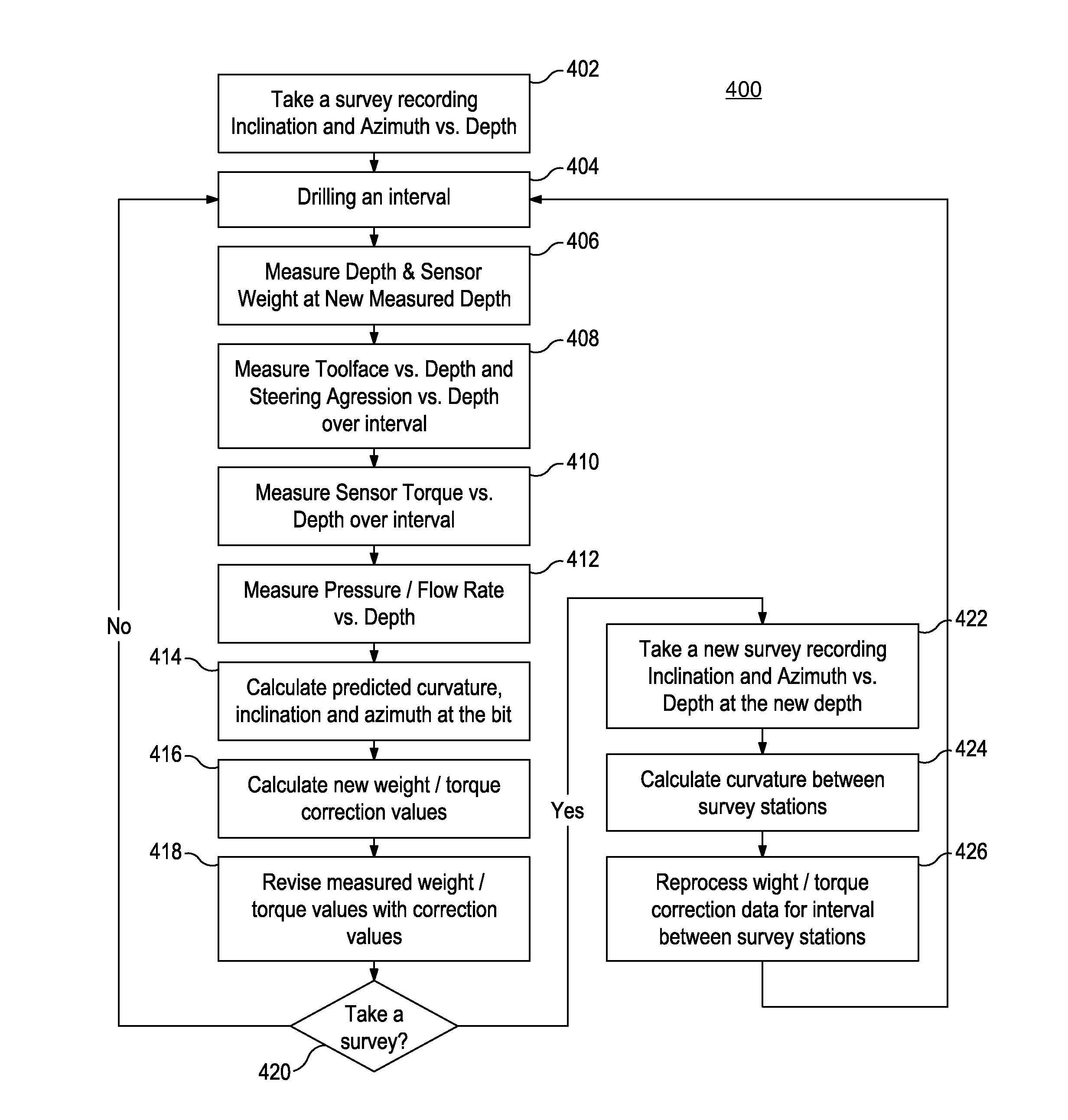
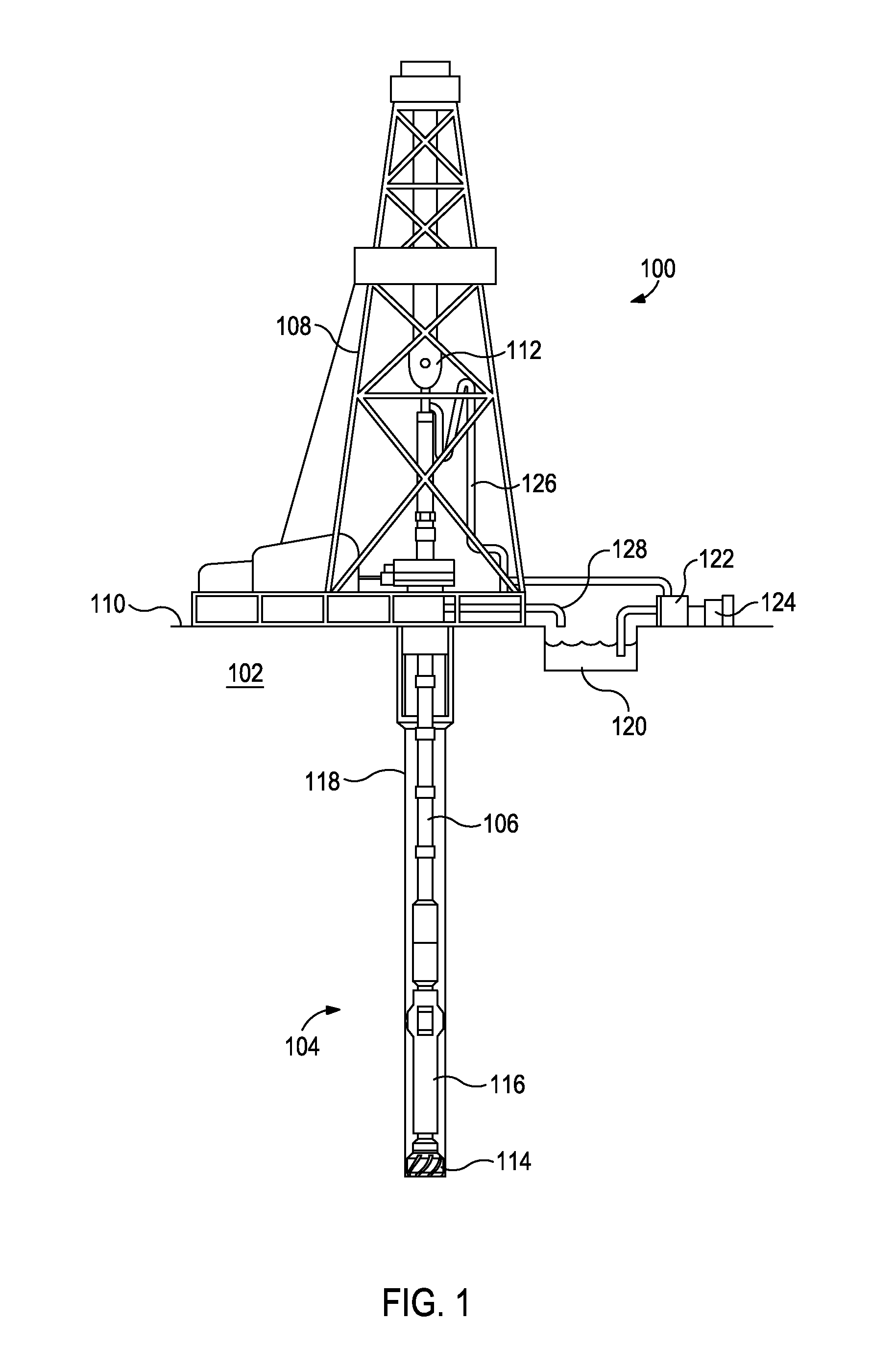
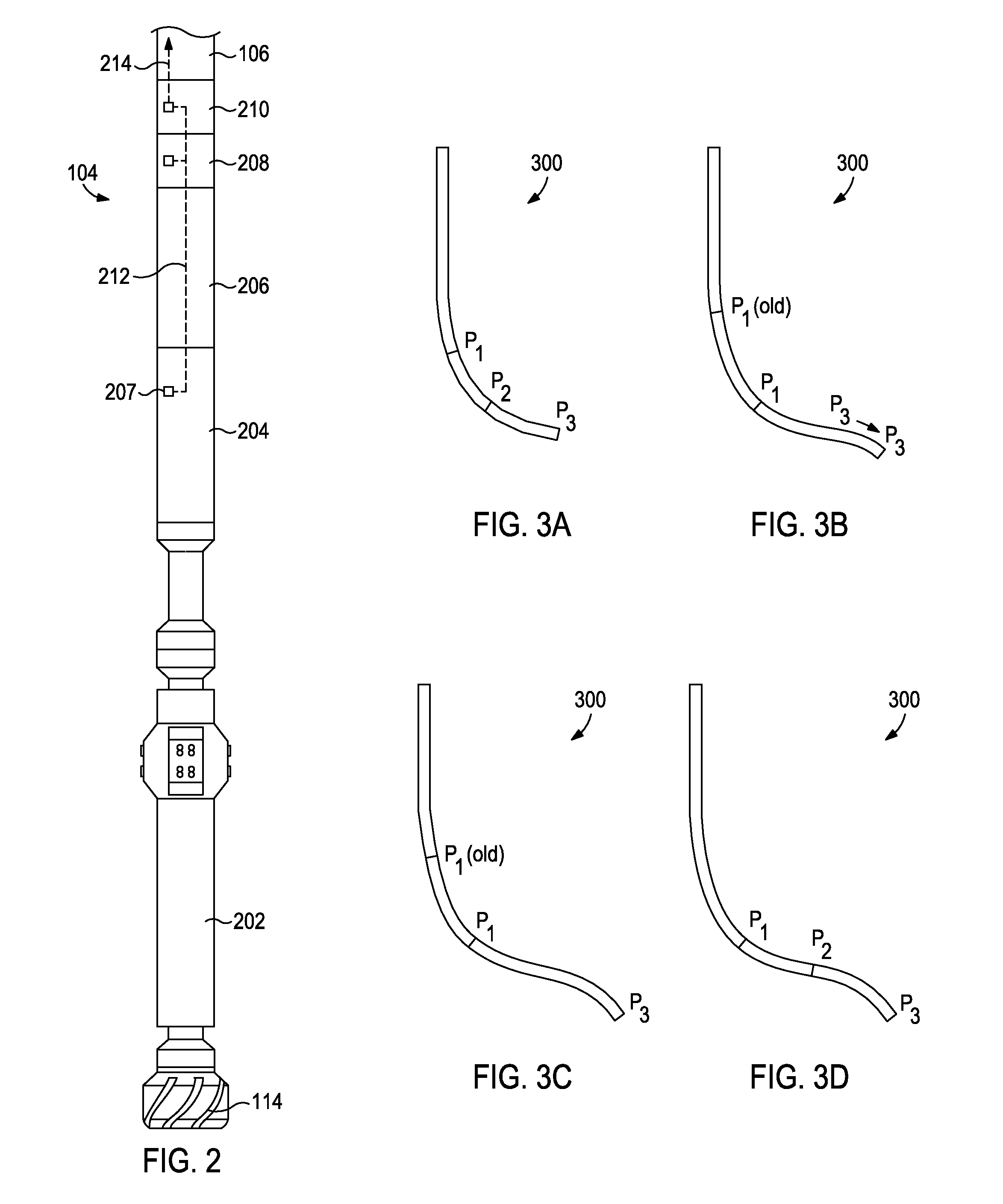
Systems and methods for automatic weight on bit sensor calibration and regulating buckling of a drillstring
ActiveUS20140231141A1Easy constructionEasy to adaptElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyEngineeringBottom hole assembly
Disclosed are systems and methods for automatic weight on bit sensor calibration and regulating buckling of a drillstring. One method includes taking a first survey recording at a first depth within a borehole, the first survey recording providing inclination and azimuth of a drillstring at the first depth, measuring a weight on a drill bit at the first depth with a sensor sub arranged on a bottom hole assembly, the bottom hole assembly forming part of the drillstring and the drill bit being disposed at an end of the drillstring, calculating a predicted borehole curvature at a second depth within the borehole, the predicted curvature including a predicted inclination and a predicted azimuth of the drillstring at the second depth, calculating a weight correction value based on the predicted hole curvature, and calibrating the sensor sub with the weight correction value.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
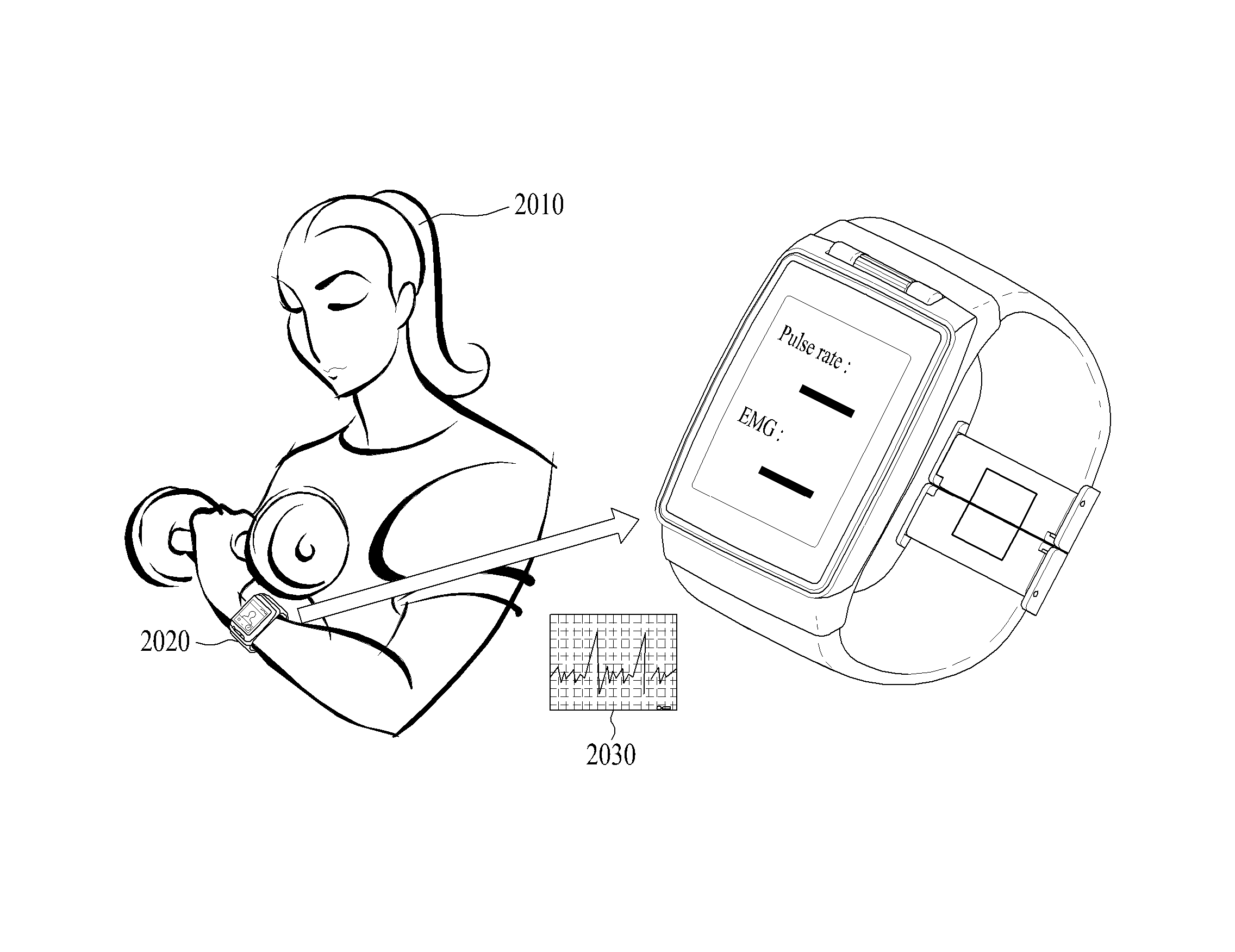
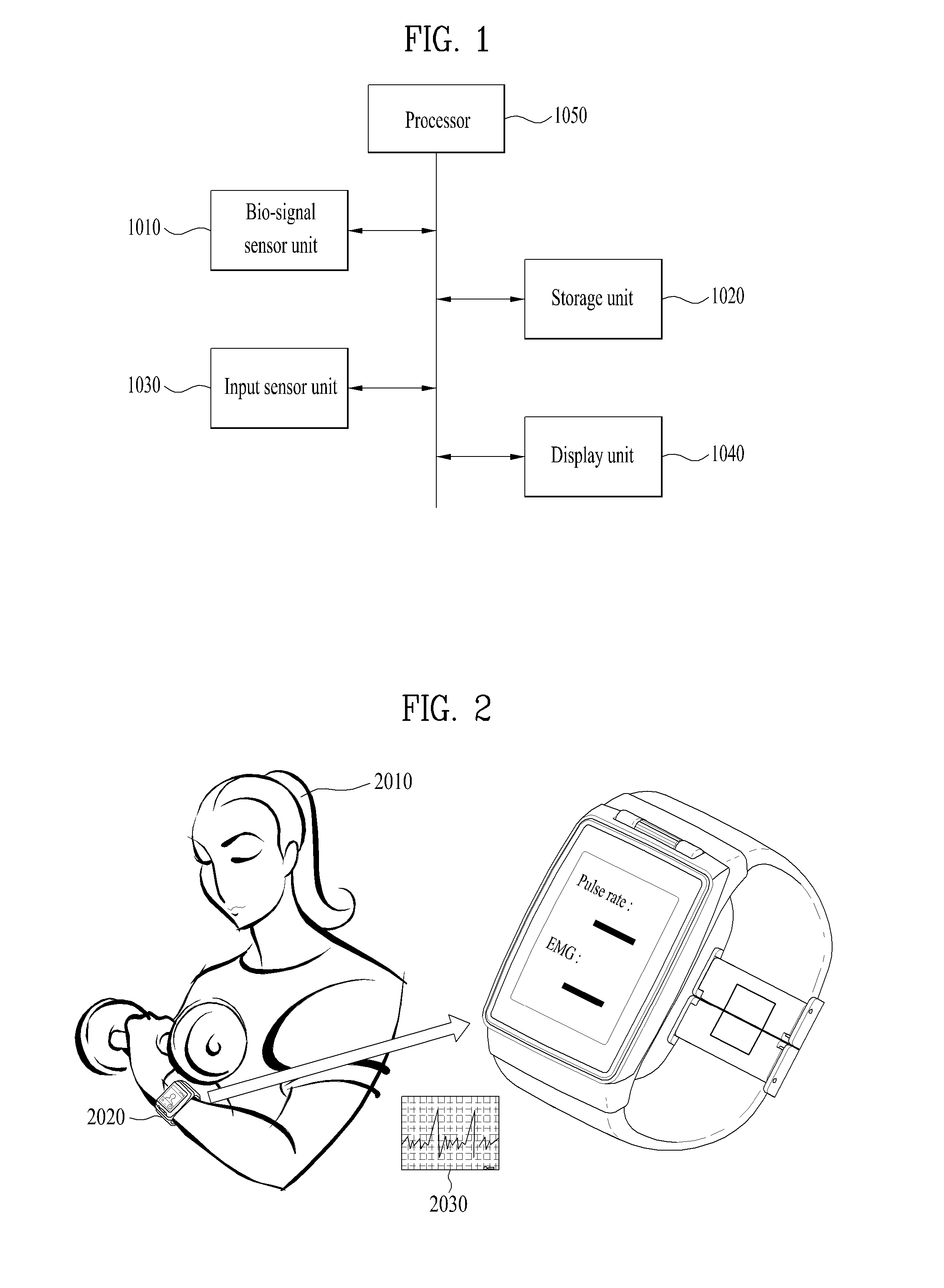
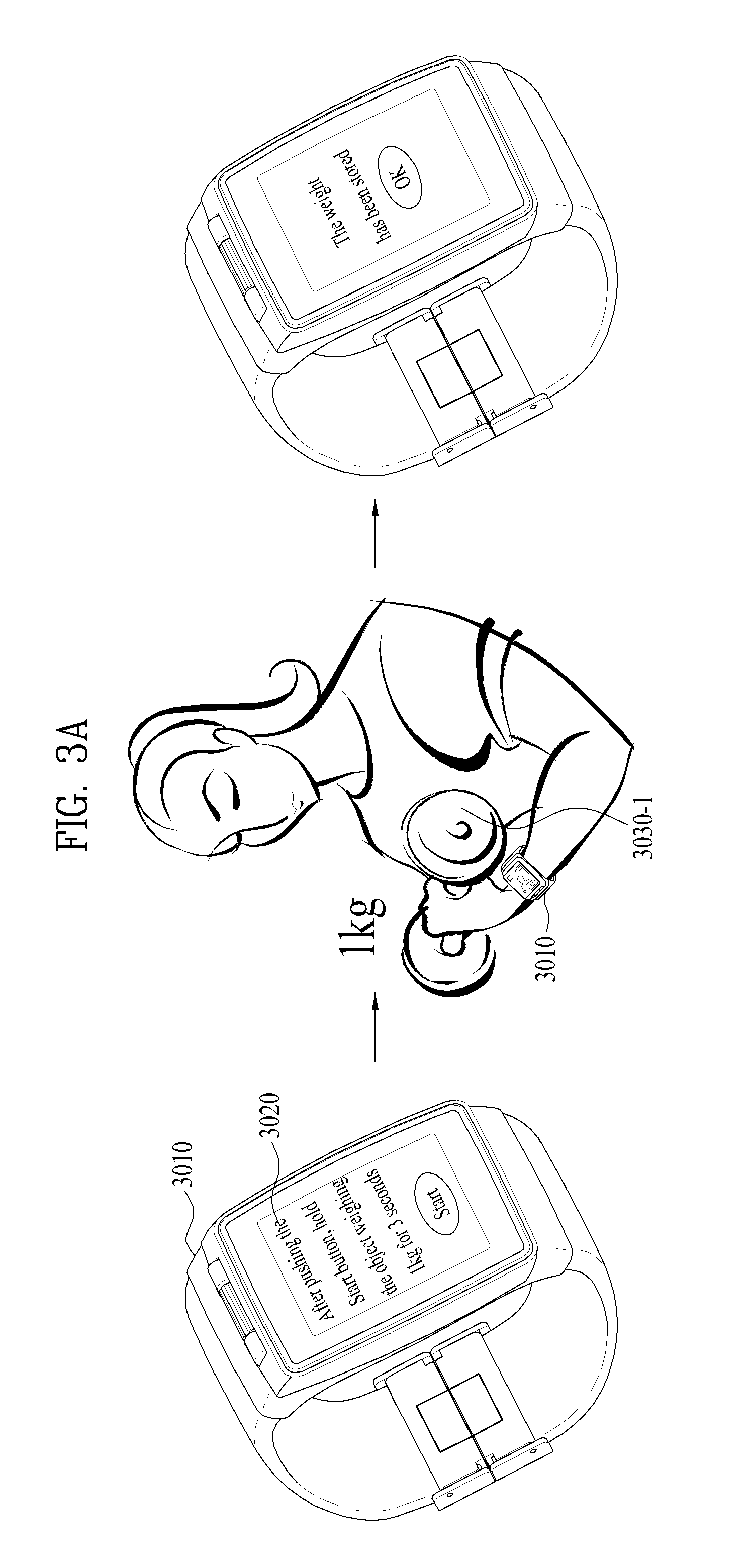
Wearable device and method for controlling the same
A wearable device and a method for controlling the same are disclosed herein. The wearable device, comprising a bio-signal sensor unit configured to sense a bio-signal; a storage unit configured to store data; and a processor configured to control the bio-signal sensor unit and the storage unit, wherein the processor is further configured to: generate first reference data including a weight of a first reference object and a first bio-signal being generated by holding the first reference object when the first bio-signal is detected, generate measurement data including a second bio-signal being generated by holding a measurement object, when the second bio-signal is detected, and obtain a weight of the measurement object by comparing the measurement data with the first reference data.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method for monitoring pig growth using binocular vision technology
ActiveCN101144705ACause stressEasy to operateClosed circuit television systemsUsing optical meansBody imagesVisual perception
The invention relates to a method for monitoring pig growth by utilizing a binocular vision technology, and the method comprises the following procedures that: a system is established and calibrated; a pig body image is obtained; the pig body image is transferred; the pig body image is processed; the height of the pig body and the area of the pig body back are measured; and the weight of the pig body is pre-estimated. The growth of the pig is monitored though the method of the invention, the stress to the growth of the pig can not be caused, the operation is easy, the labor strength is reduced, the efficiency is high, the real time is good, the realization of the automation and the network transfer are beneficial, and the remote monitoring can be realized.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Monitor and methods for characterizing airborne particulates
InactiveUS20090081804A1Minimizes effortMinimize timeChemical analysis using combustionMaterial heat developmentParticulatesAnalyte
A dust monitor is disclosed that is suitably deployed in dusty environments and capable of providing near real-time indications of exposure to airborne particulates. The monitor includes a filter and filter assembly made of materials that do not interfere with subsequent instrumental (such as spectrometric) analysis for detecting and / or quantitating an analyte. In some disclosed embodiments, the filter is made of nylon or other material that is readily subjected to thermal destruction prior to spectrometric analysis. The dust monitor also includes a humidity correction feature that permits the filter to be made of ashable organic materials even if those materials are not highly hydrophobic. Transport devices are provided for shipment of the filter and / or filter assembly to an analytical laboratory which prevent loss of particulate matter and which facilitate an accurate analysis procedure.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
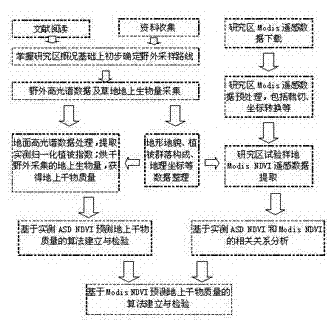
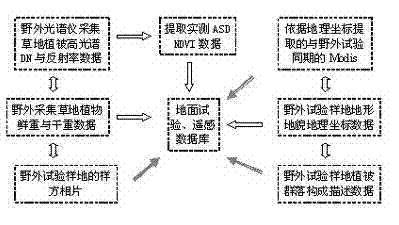
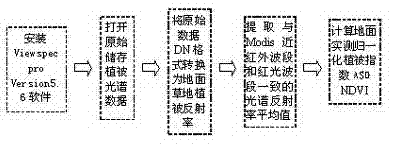
Grassland dry matter mass remote sensing estimating method
ActiveCN102393238APromote healthy and sustainable developmentMaintain ecological balanceWeighing apparatusData acquisitionRemote sensing application
The invention discloses a grassland dry matter mass remote sensing estimating method, which belongs to the field of remote sensing application. The method comprises the following steps of: collecting and processing field test data; downloading and processing Modis (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) satellite data; analyzing and modeling the data and detecting the accuracy and the like. The method for establishing a ground spectrum model for predicating ground dry matter mass and correcting a Modis spectrum model through ground hyperspectral experiments is different from the method for directly predicating biomass liveweight by using NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) data of the Modis remote sensing satellite in other like researches so that the grassland dry matter mass remote sensing estimating method is helpful for improving the predicating accuracy, is beneficial for scientific management and reasonable utilization of the grassland resources and has important practical significance in correct evaluation of the real productivity of the grassland and the sustainable use of the grass resources.
Owner:高吉喜
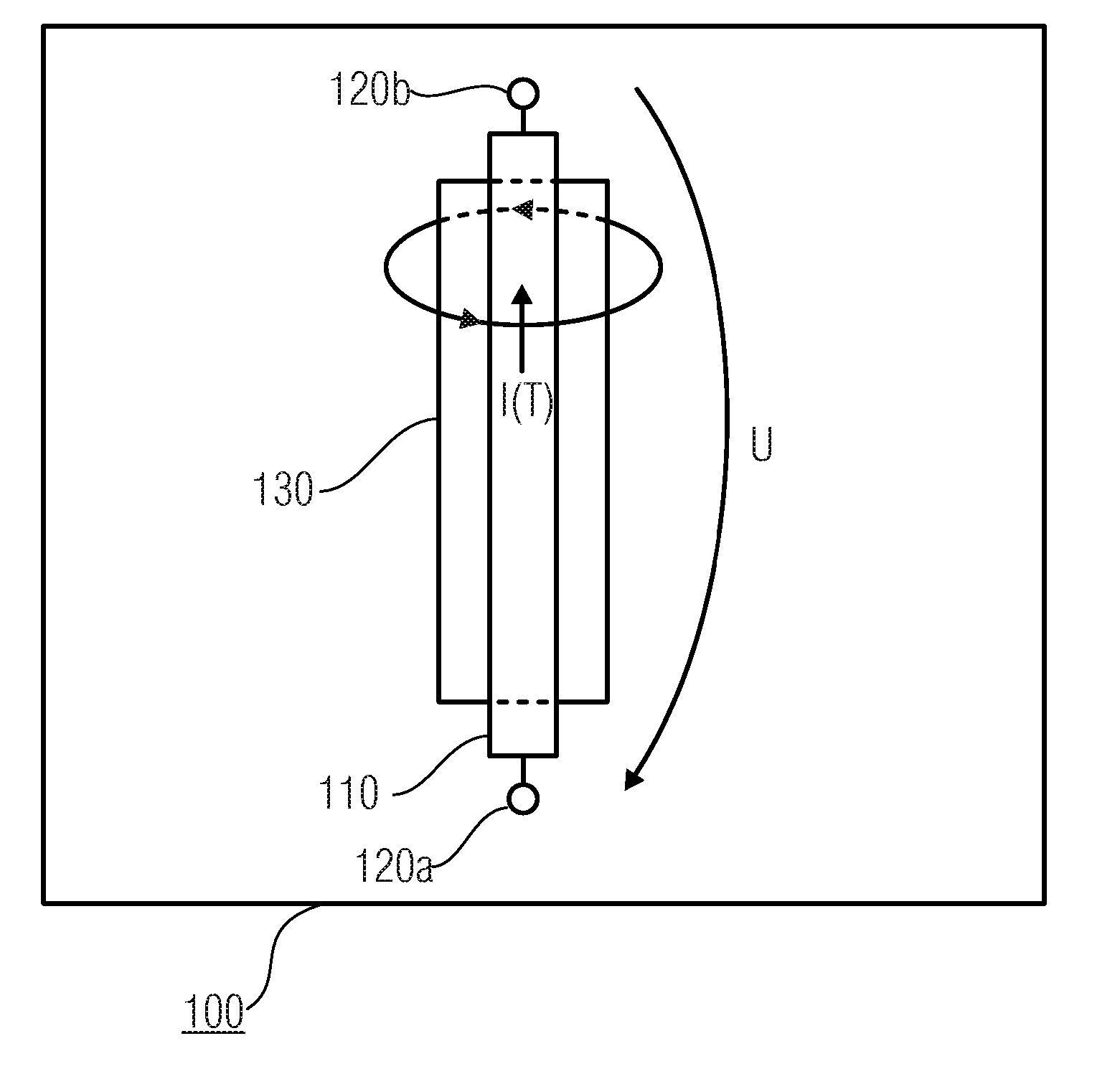
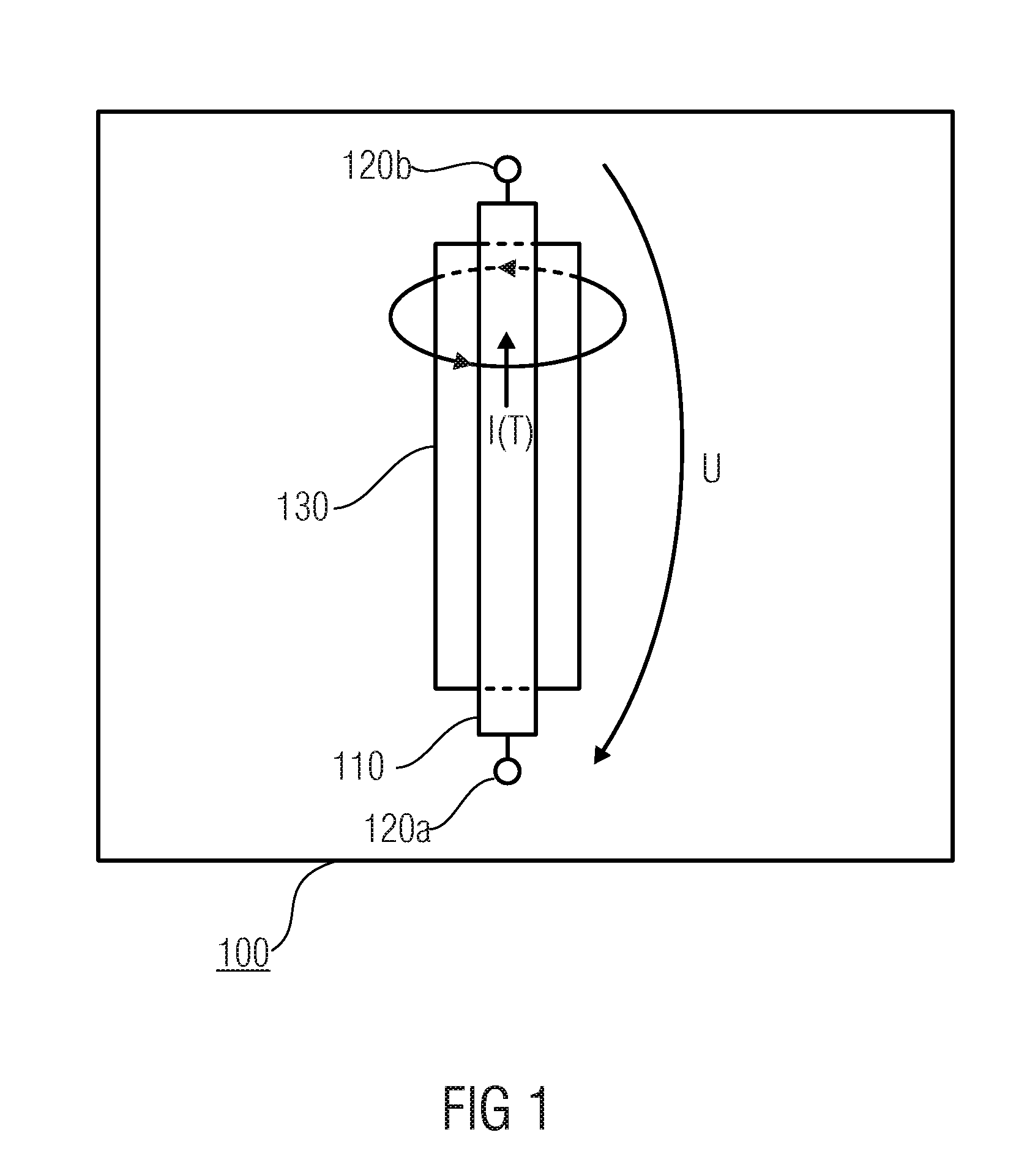
Concept for Detecting a Change of a Physical Quantity by Means of a Conductor Structure
InactiveUS20080084205A1Temperature measurement in motorsNanomagnetismElectrical conductorMagnetic reluctance
An apparatus for detecting a change of a physical quantity by means of a conductor structure having a processor for applying a defined supply signal to the conductor structure so as to effect a current flow through the conductor structure, the current flow being changeable by the physical quantity, and a detector for detecting a magnetic field caused by the current flow through the conductor structure by means of a magnetoresistive element allocated to the conductor structure, a change of the physical quantity being associated with a change of the detected magnetic field.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
High-temperature high-pressure multifunctional core sulfur deposition test device and method
InactiveCN102053055ARealize real-time online measurementRealize visual displayClosed circuit television systemsPermeability/surface area analysisData processing systemData acquisition
The invention discloses high-temperature high-pressure multifunctional core sulfur deposition test device and method. The sulfur deposition test device comprises a displacement system, a formation condition analog system, a data acquisition system and a data processing system. The sulfur deposition test method comprises the following steps of: constructing a test environment, measuring the sulfur element deposition on line, observing the sulfur element deposition process on line, and testing the change of permeability of a rock sample before and after sulfur deposition and the like. The invention has the beneficial effects of realizing the visual display of a true core sulfur deposition process, the real-time online measurement of the sulfur deposition and dynamic calculation of core permeability change caused by sulfur deposition and accurately and dynamically evaluating the damage severity of permeability of a reservoir stratum, caused by sulfur deposition in real time, and has the advantages of high degree of automation, good safety, high accuracy, high temperature and high pressure resistance, strong corrosion resistance and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Insolation sensor for solar light intensity
InactiveUS20110308318A1Photometry using reference valueMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSolar lightElectric power system
An insolation sensor is disclosed and is used to determine a solar light intensity as a basis for evaluating electric power generated by solar modules exposed to the solar light intensity. The insolation sensor includes an outer surface including a light entrance window, and at least one photo sensor configured to measure the solar light intensity. The at least one photo sensor is arranged behind the light entrance window. The insolation sensor further includes a detector device configured to detect precipitation and / or a resulting deposit on the surface which both affects the insolation sensor and the solar modules.
Owner:SMA SOLAR TECH AG
External volume insensitive flow verification
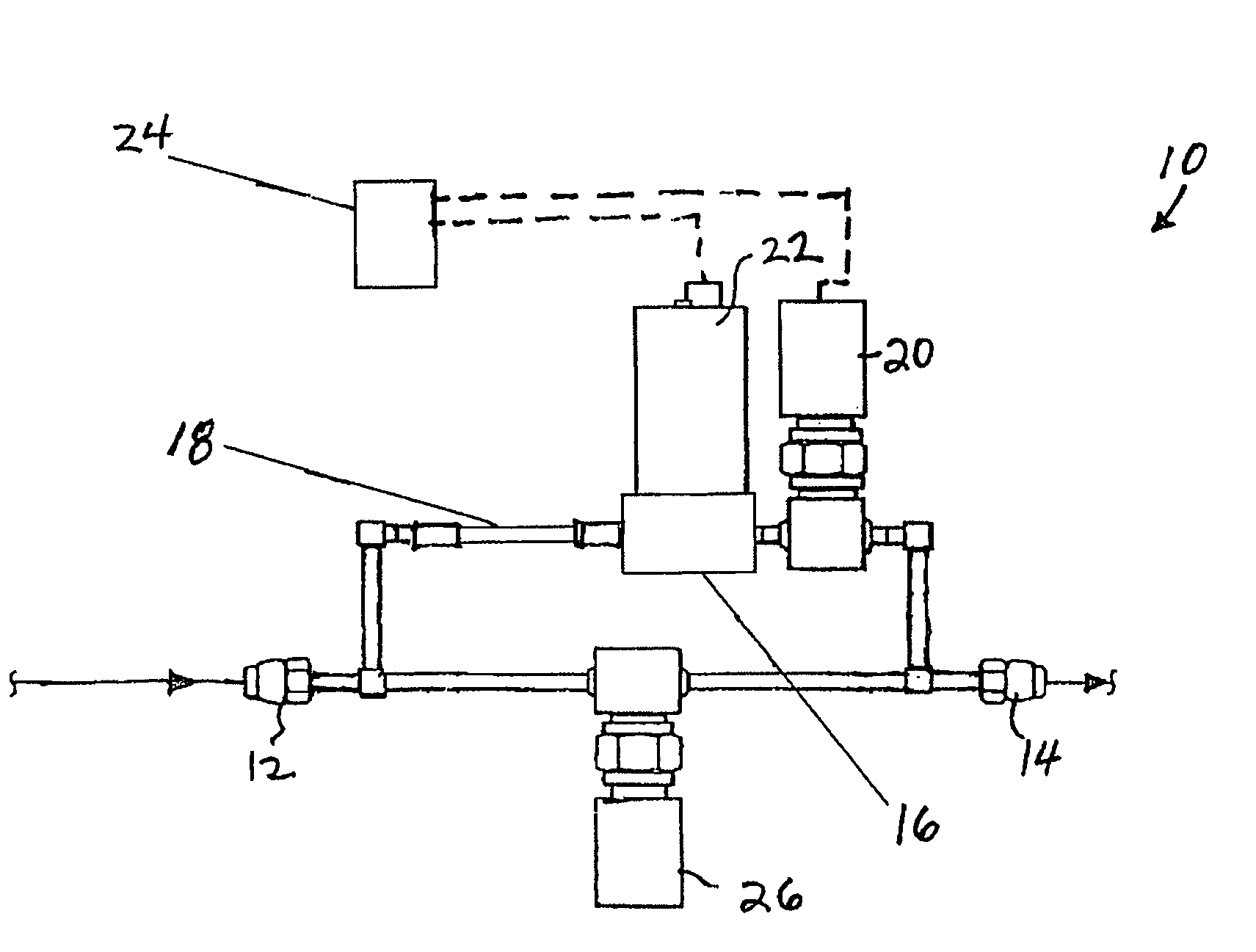
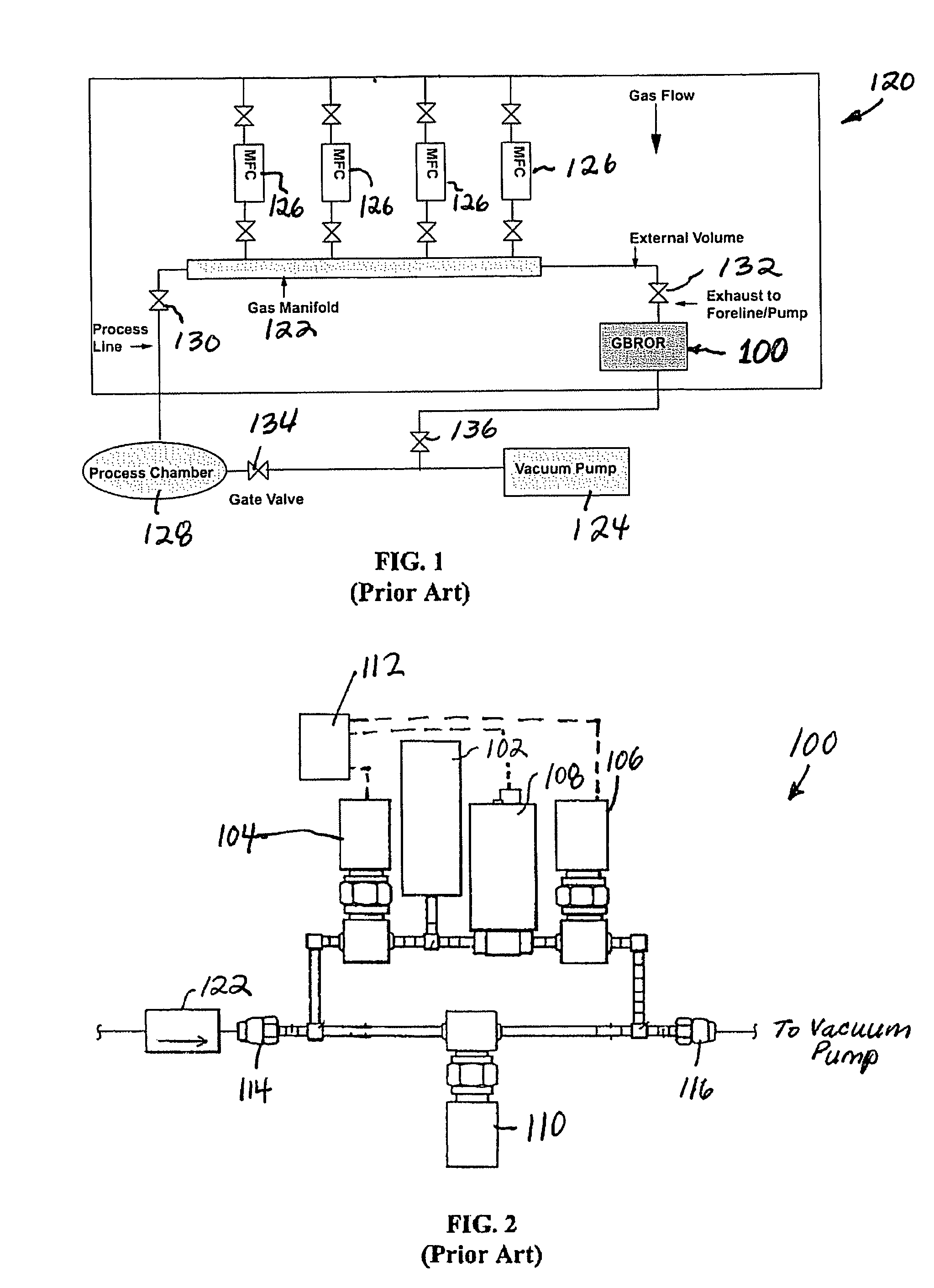
ActiveUS7174263B2Small sizeAccurate and fast measurementVehicle testingTesting/calibration apparatusControl flowMarine engineering
A flow verifier for in-situ verification of a device under test (DUT), including an inlet connectable to a DUT, an outlet connectable to a vacuum pump for drawing gas through the DUT and the flow verifier, a vessel having a predetermined volume, diffusive media connecting the inlet to the vessel, an outlet valve connecting the vessel to the outlet for controlling flow from the vessel to the outlet, at least one temperature sensor operatively connected to the vessel for providing temperature measurements from within the vessel, and a pressure transducer operatively connected to the vessel for providing pressure measurements from within the vessel.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
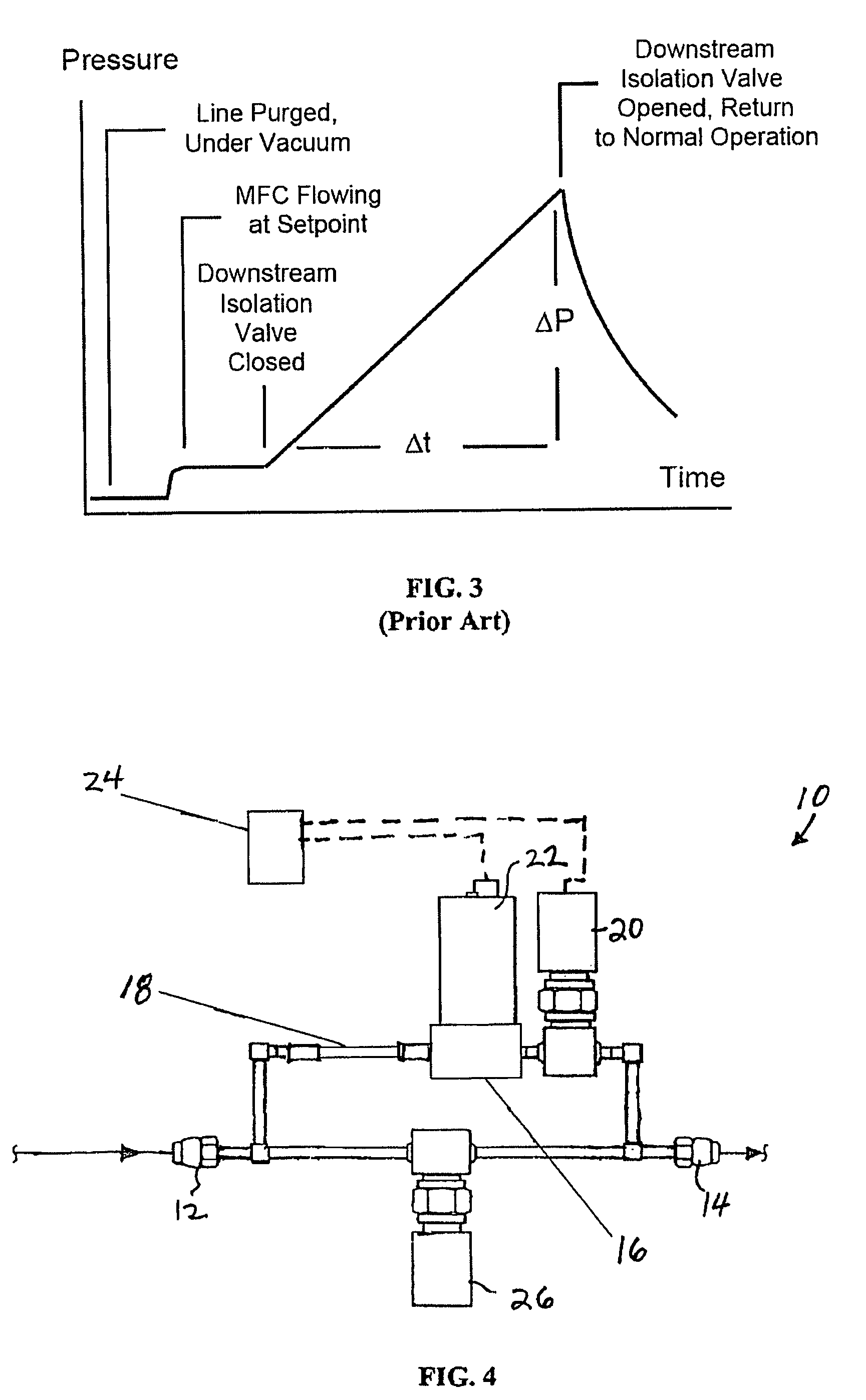
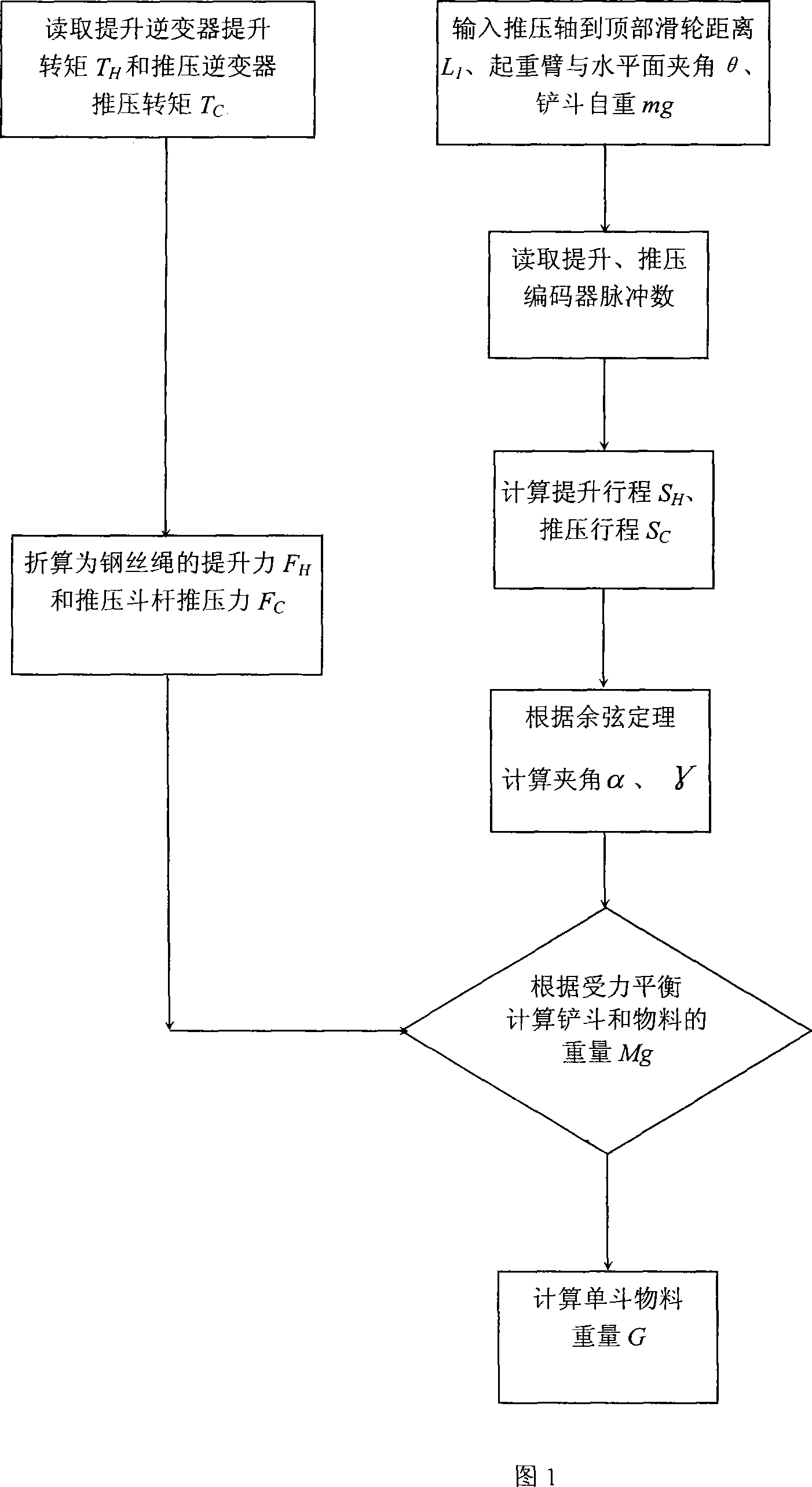
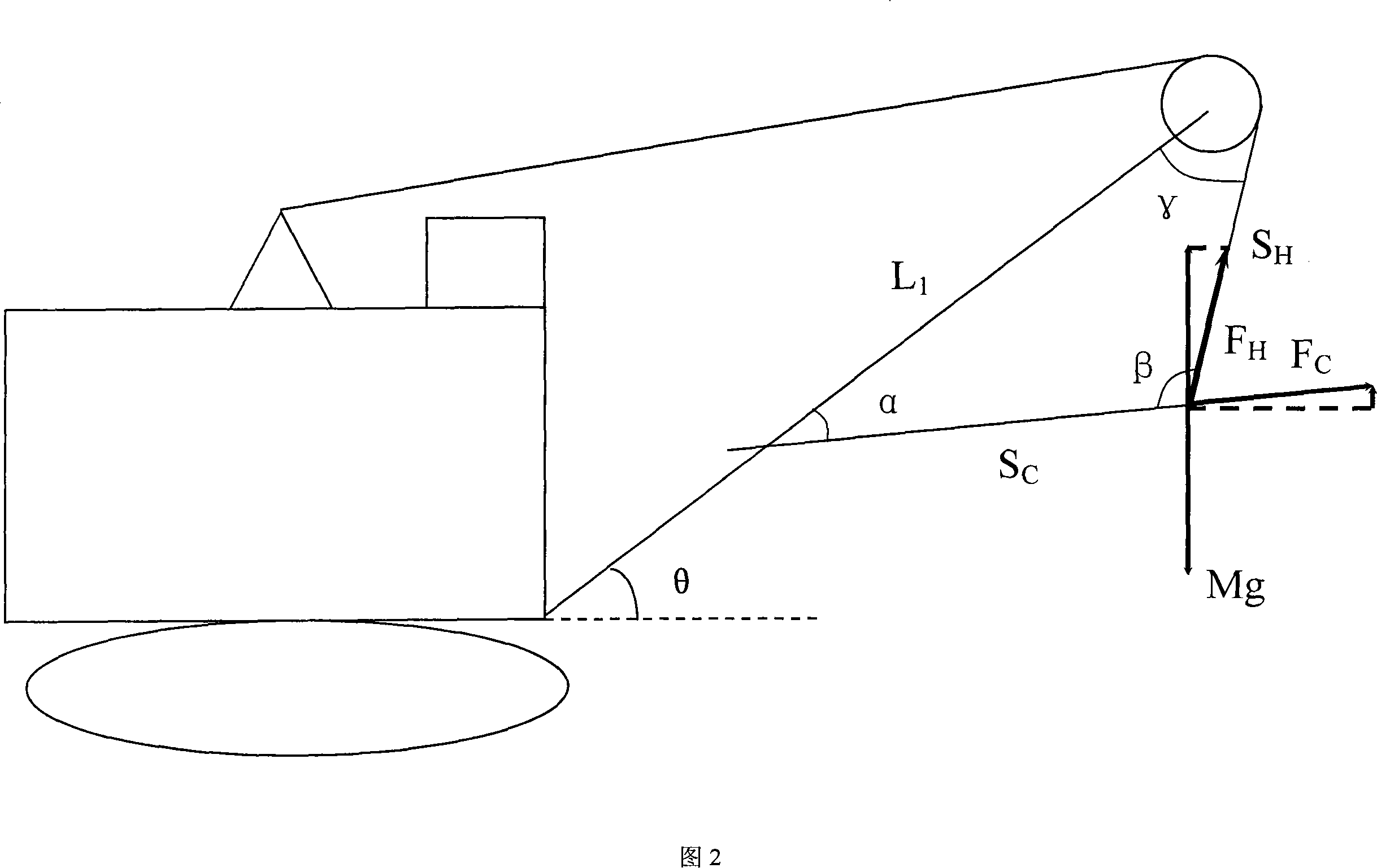
Excavator bucket material weighing method
InactiveCN101187582AAccurate measurementReduce investmentSoil-shifting machines/dredgersWeighing apparatusProgrammable logic controllerDrive motor
The invention relates to a method for weighting shovel material of an excavator, which belongs to a weighting method for weighting shovel material of a large-scale excavator. The invention mainly solves the technical difficulty that current excavators can not weight shovel material and count excavating yield. The technical proposal is that the weighting method of shovel material of a excavator comprises following steps, first, inputting L1, theta value and mg in a programmable logic controller (PLC), second, reading a pulse number x of a lifting encoder, a pulse number y of a driving encoder, a lifting motor torque TH of a lifting inverter and a driving motor torque TC of a pushing inverter through the PLC, third, calculating a lifting stroke and a pushing stroke, fourth, calculating an angle alpha and an angle gamma, fifth, calculating lifting power which is converted to an armored rope and pushing power which is converted to a pushing rod, sixth, calculating the weight of shovel and material, seventh, obtaining the weight of the material through reducing self-weight of the shovel from the weight of the shovel and the material.
Owner:TAIYUAN HEAVY IND
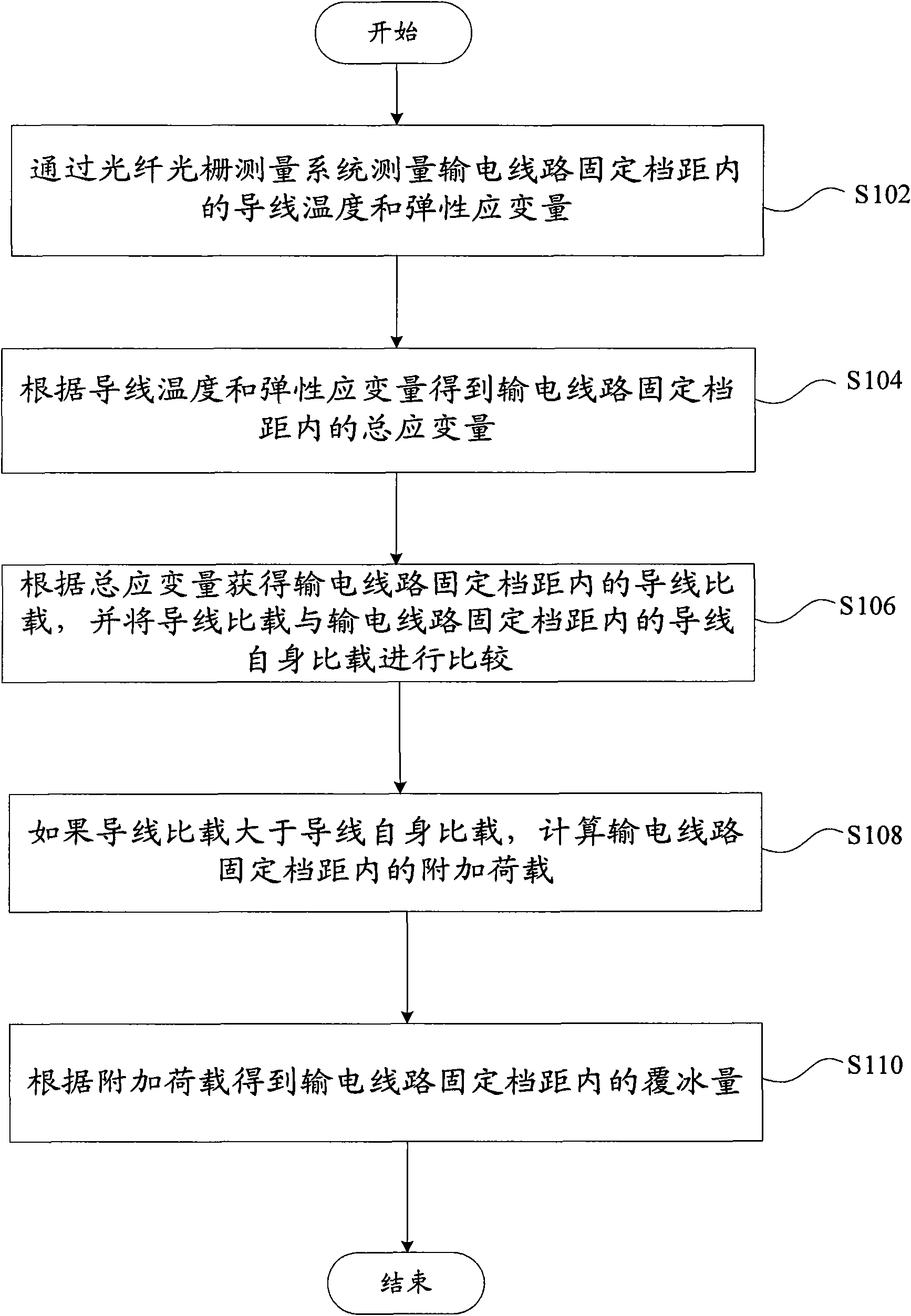
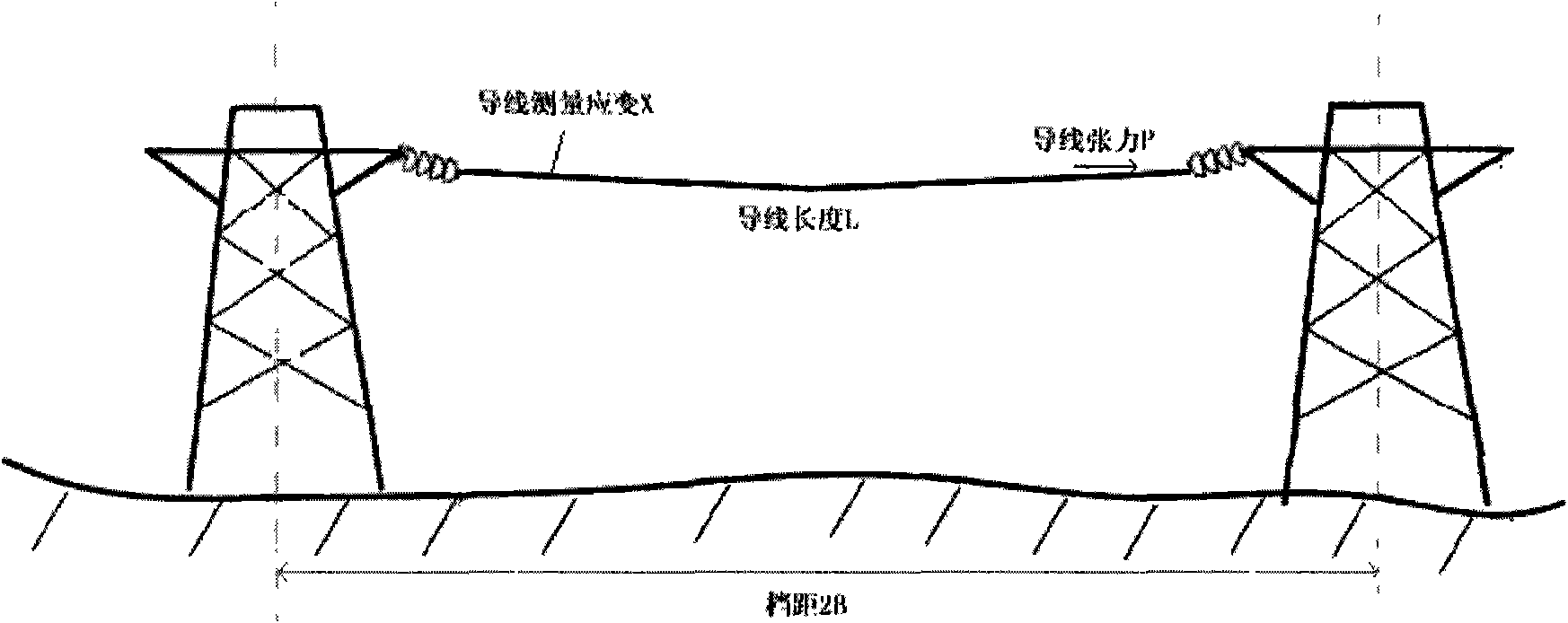
Calculating method of ice concentration of transmission line
InactiveCN101620000AThe calculation result is accurateHigh precisionIndication of weather conditions using multiple variablesThermometers using physical/chemical changesFiberGrating
The invention provides a computing method of ice concentration of a transmission line. The method comprises the following steps: the wire temperature and the elastic dependent variable in the fixed span of the transmission line are measured through a fiber grating measuring system; the total dependent variable in the fixed span of the transmission line is obtained according to the wire temperature and the elastic dependent variable; the wire specific load in the fixed span of the transmission line is obtained according to the total dependent variable and the wire specific load is compared with the wire self specific load in the fixed span of the transmission line; if the wire specific load is higher than the wire self specific load, the additional load in the fixed span of the transmission line is calculated; and the ice concentration in the fixed span of the transmission line is obtained according to the additional load. The invention overcomes the problem of higher measuring result error caused by lower measuring accuracy and poorer anti-electromagnetic interference capability due to the adoption of an electric parameter measuring method for measuring stress, temperature and inclination angle in the prior art.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Piezoelectric coagulation sensors
ActiveUS20110203367A1Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesFlow propertiesPiezoelectric actuatorsTransducer
This invention provides methods and devices to measure physical characteristics of sample fluids. Samples are introduced into a sample chamber in contact with a mechanically oscillating working member. The vibrations are received by a piezoelectric sensor transducer and correlated to a sample characteristic, such as viscosity or density. The devices include a sample chamber in contact with one or more working members actuated by a piezoelectric actuator and / or monitored by a piezoelectric sensor.
Owner:MICROPOINT BIOTECHNOLOGIES CO LTD
Material transport in-motion product dimensioning system and method
Methods, systems, and devices to obtain dimensions of an article or product in association with material handling vehicles are disclosed. A dimension detection device is installed in an enclosure and is used to acquire geometrical dimensions of the object in association with the vehicle. A predetermined dimension of the vehicle is subtracted from the overall detected dimension to determine the dimensions, including weight, of the product alone. One or more dimension detection devices may also be positioned on a mast or other portion of the material handling vehicle allowing the material handling vehicle to act as a mobile product dimensioning system.
Owner:RICE LAKE WEIGHING SYST
Wide range, very high resolution differential mobility analyzer (DMA)
InactiveUS20070044580A1Improved adjustment and precisionHigh resolutionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIsotope separationImage resolutionComputational physics
The resolution of a differential mobility analyzer (DMA) and the range of valid mobility values for the charged particles that it can detect are increased. The DMA makes use of a flat configuration and a purely two-dimensional operating model in which shims are used for improved adjustment and precision of the parallel faces that make up the analysis area. The analyzer uses a closed and pressurized aerodynamic tunnel to establish a cross flow with a very high Reynolds number.
Owner:RAMEM
Self-powered, piezo-surface acoustic wave apparatus and method
ActiveUS20110241839A1Impedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesEngineeringSurface acoustic wave
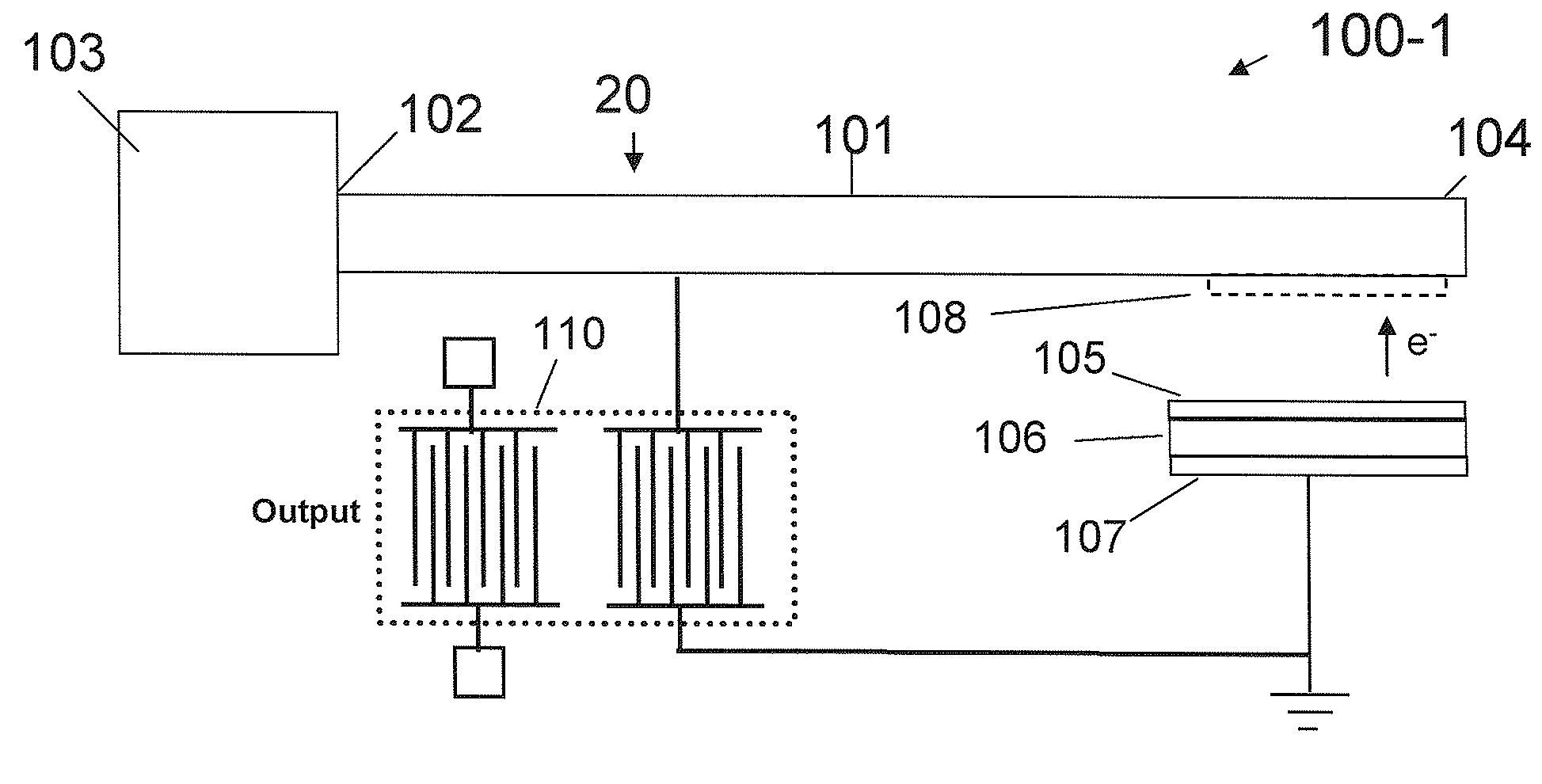
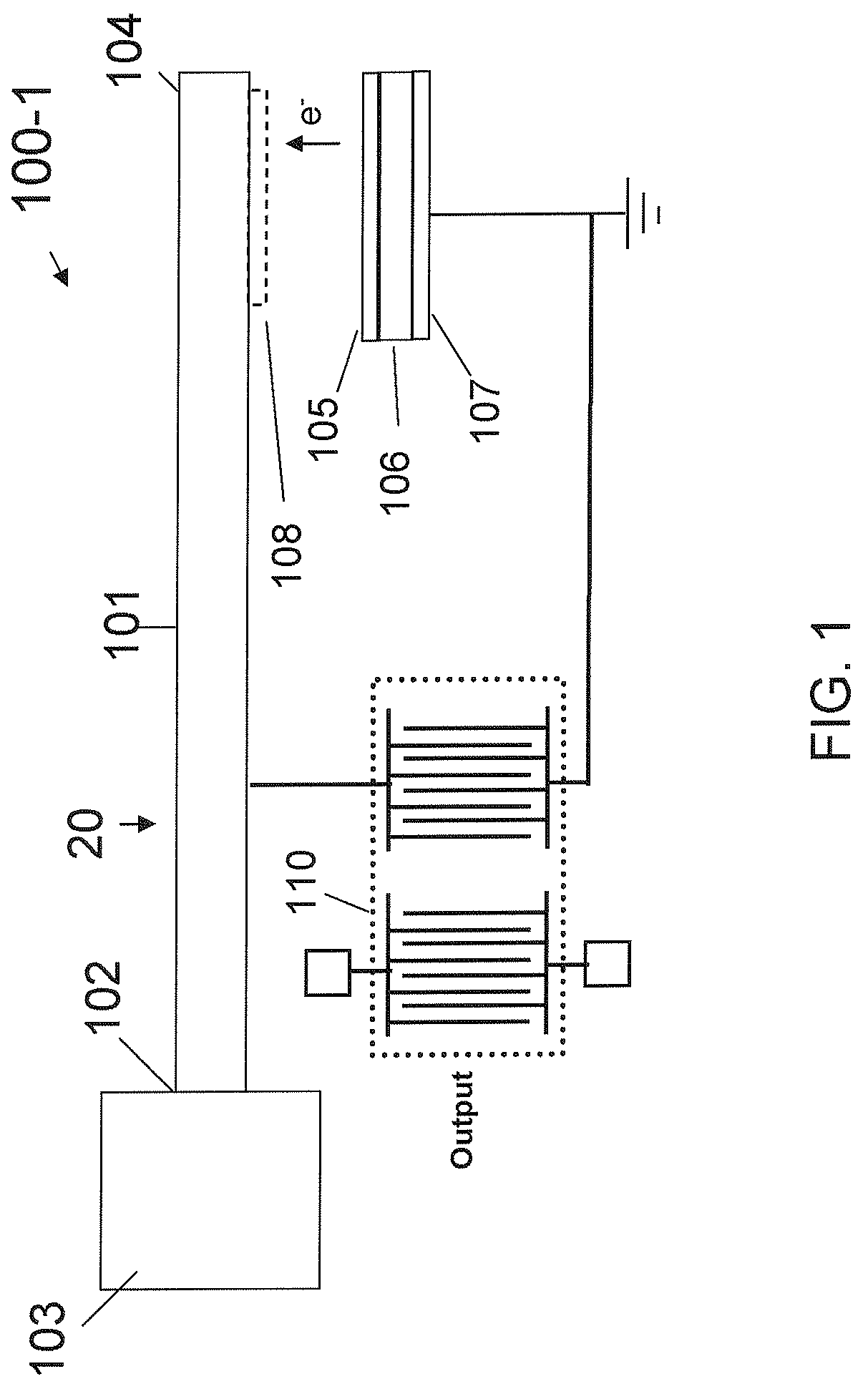
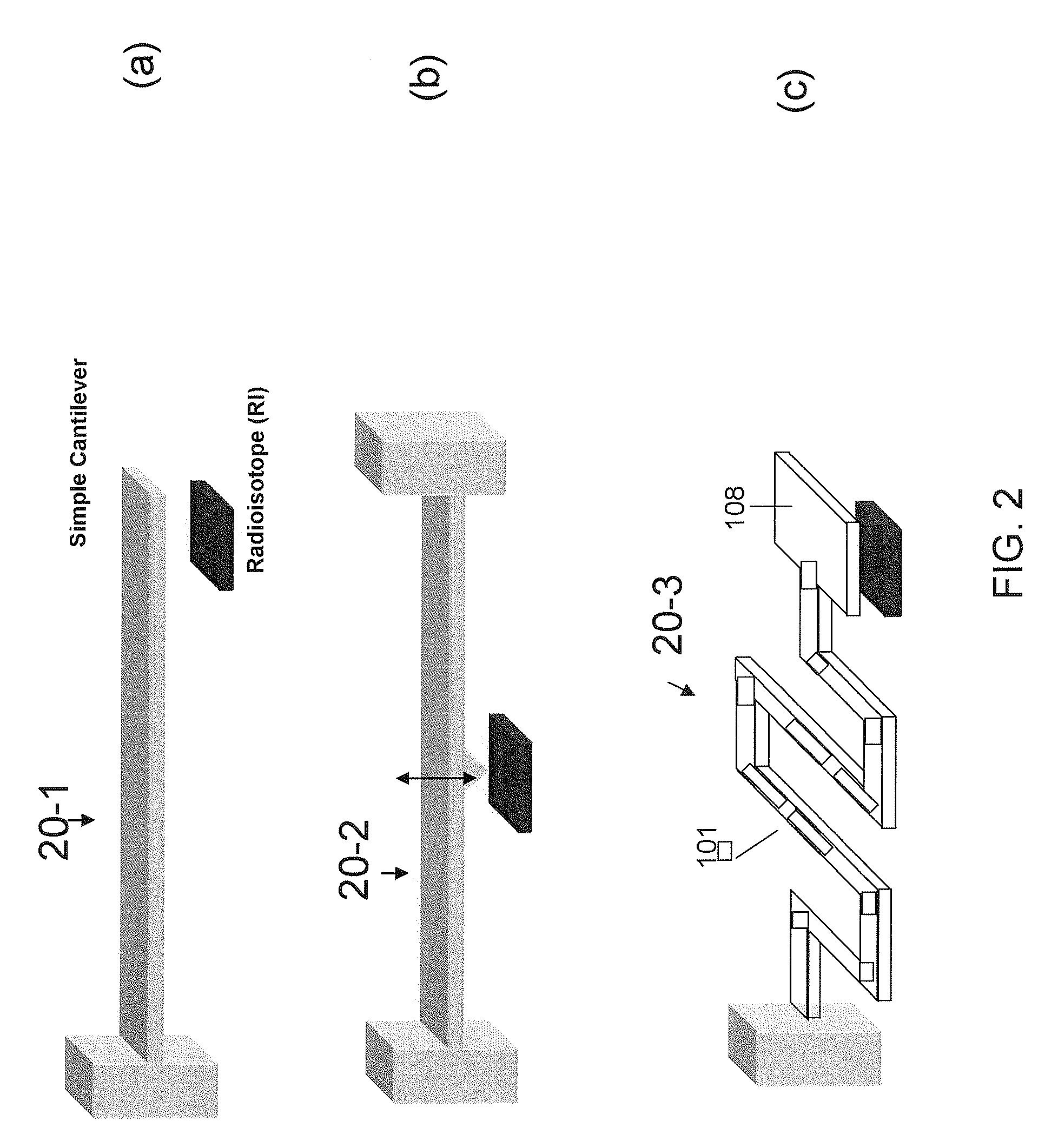
An autonomous, self-powered device includes a radioisotope-powered current impulse generator including a spring assembly comprising a cantilever, and a piezoelectric-surface acoustic wave (P-SAW) structure connected in parallel to the current impulse generator. Positive charges are accumulated on an electrically isolated 63Ni thin film due to the continuous emission of β-particles (electrons), which are collected on the cantilever. The accumulated charge eventually pulls the cantilever into the radioisotope thin-film until electrical discharge occurs. The electrical discharge generates a transient magnetic and electrical field that can excite the RF modes of a cavity in which the electrical discharge occurs. A piezoelectric-SAW resonator is connected to the discharge assembly to control the RF frequency output. A method for generating a tuned RF signal includes inputting an energy pulse to a P-SAW resonator, exciting the resonant frequency thereof, and outputting an RF signal having a frequency tuned to the resonator frequency.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Method and system for measuring ice thickness on overheaded power transmission line
InactiveCN1844849AMeasurement results in timeSynchronization of measurement resultsWeighing apparatusPull forceTransmission line
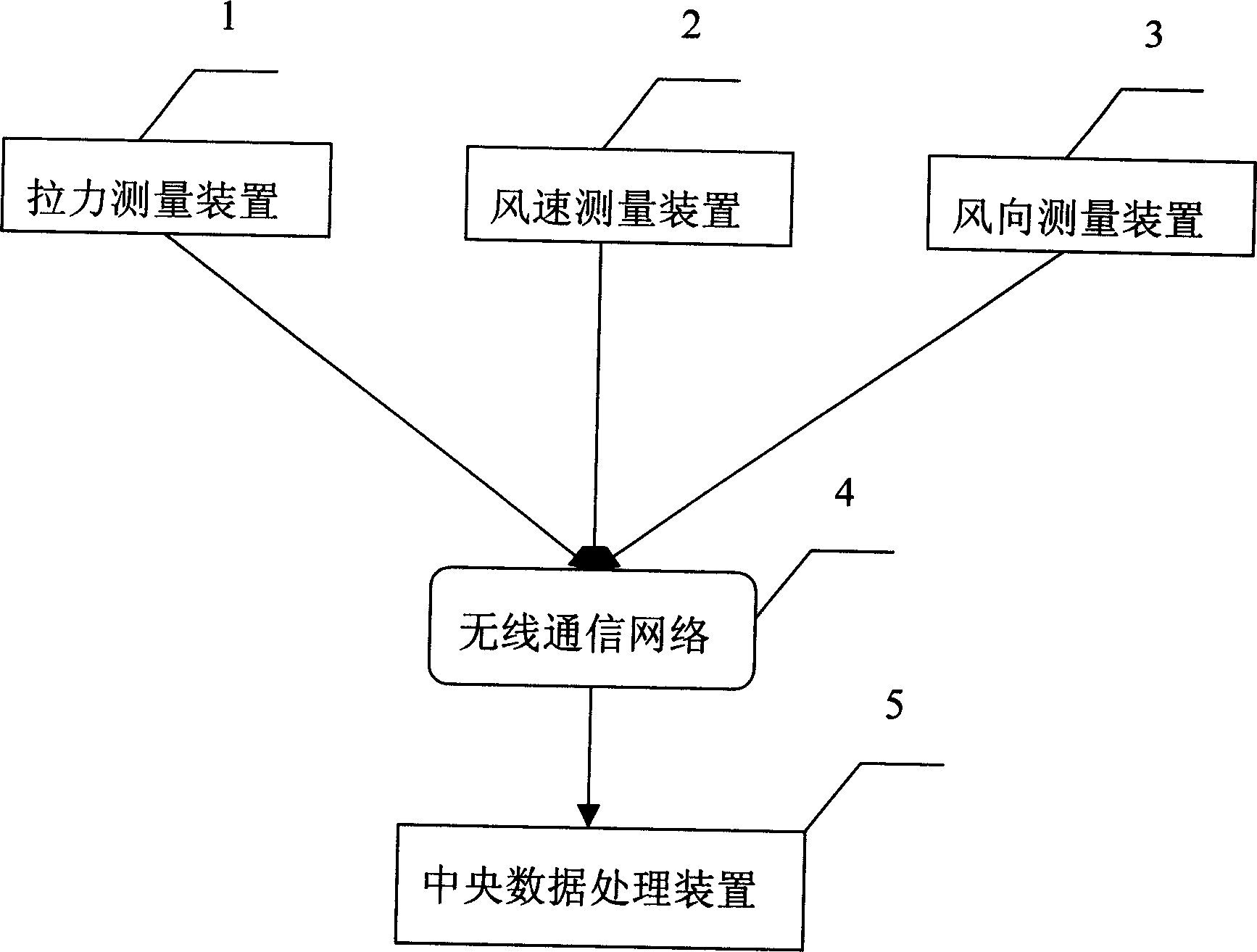
The invention relates to a method for measuring the ice thickness of span wire and earth cord, and relative system. Said method comprises: 1, collecting the drawing forces on the connecting elements of insulator or the insulated sequence and the wind speed and direction on the iron tower; 2, according to the collected data and the parameters of the wire and earth cord in different sections and integrations to attain the wind pressure on the wire and earth cord; 3, according to the wind pressure and collected drawing force, via stat calculating the ice thickness and weight of wire and earth cord. The invention can measure the ice thickness and weight of wire and earth cord.
Owner:XIAN TIANLAN ELECTRIC TECH
Wide range, very high resolution differential mobility analyzer (DMA)
InactiveUS7521673B2Improved adjustment and precisionHigh resolutionSamplingMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansImage resolutionComputational physics
The resolution of a differential mobility analyzer (DMA) and the range of valid mobility values for the charged particles that it can detect are increased. The DMA makes use of a flat configuration and a purely two-dimensional operating model in which shims are used for improved adjustment and precision of the parallel faces that make up the analysis area. The analyzer uses a closed and pressurized aerodynamic tunnel to establish a cross flow with a very high Reynolds number.
Owner:RAMEM
Method of and apparatus for determining the carbon content of soils
ActiveUS20150247787A1Lose weightInhibit gas flowWeighing by removing componentChemical analysis using combustionSoil scienceOrganic matter
Owner:YEOMANS ALLAN JAMES
Sensor apparatus and image forming apparatus incorporating same
ActiveUS20150062582A1Polarisation-affecting propertiesTransmissivity measurementsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A sensor apparatus includes an irradiation system with a light source configured to emit linearly polarized light of a first polarization direction onto a sheet-like object, in a direction oblique to a direction orthogonal to a surface of the object, a first photodetector arranged on an optical path of light that is emitted from the irradiation system and then is reflected at the object by regular reflection, a first optical element, arranged on an optical path of light reflected by diffuse reflection from an incidence plane of the object, configured to transmit linearly polarized light of a second polarization direction that is orthogonal to the first polarization direction, a second photodetector configured to receive light that has passed through the first optical element, and a detection unit configured to detect at least one of basis weight and thickness of the object.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method for creation of planar or complex wavefronts in close proximity to a transmitter array
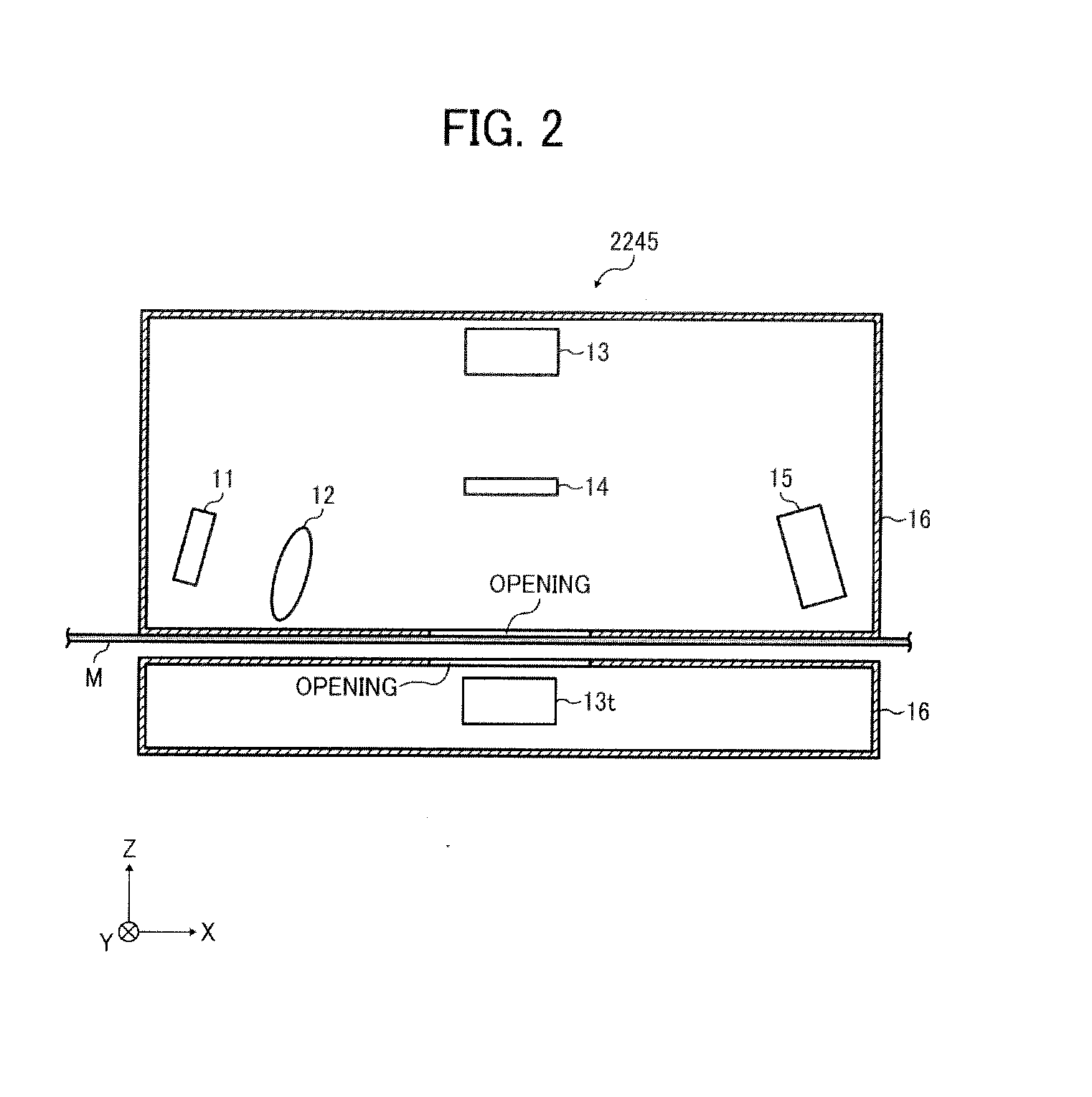
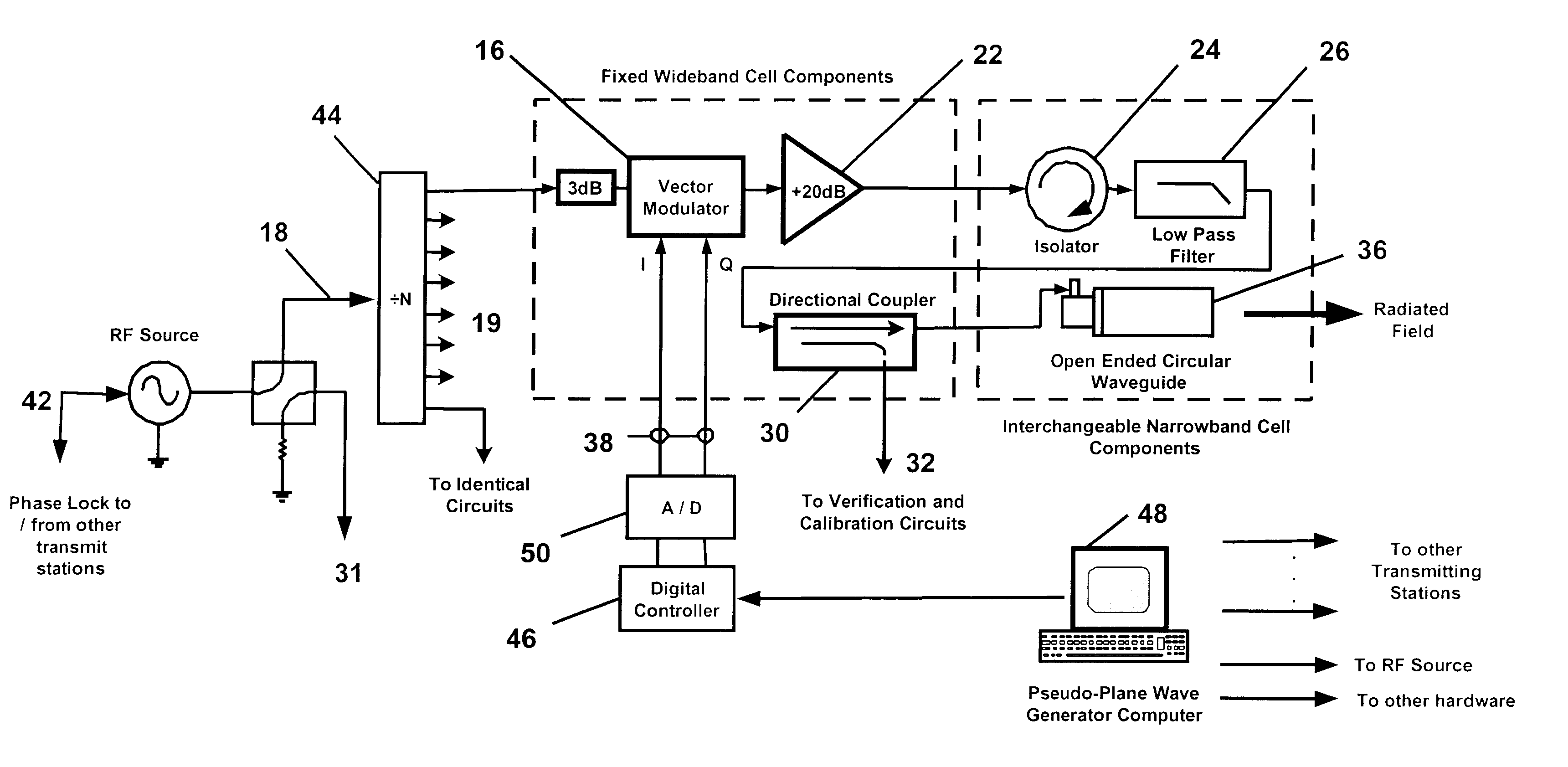
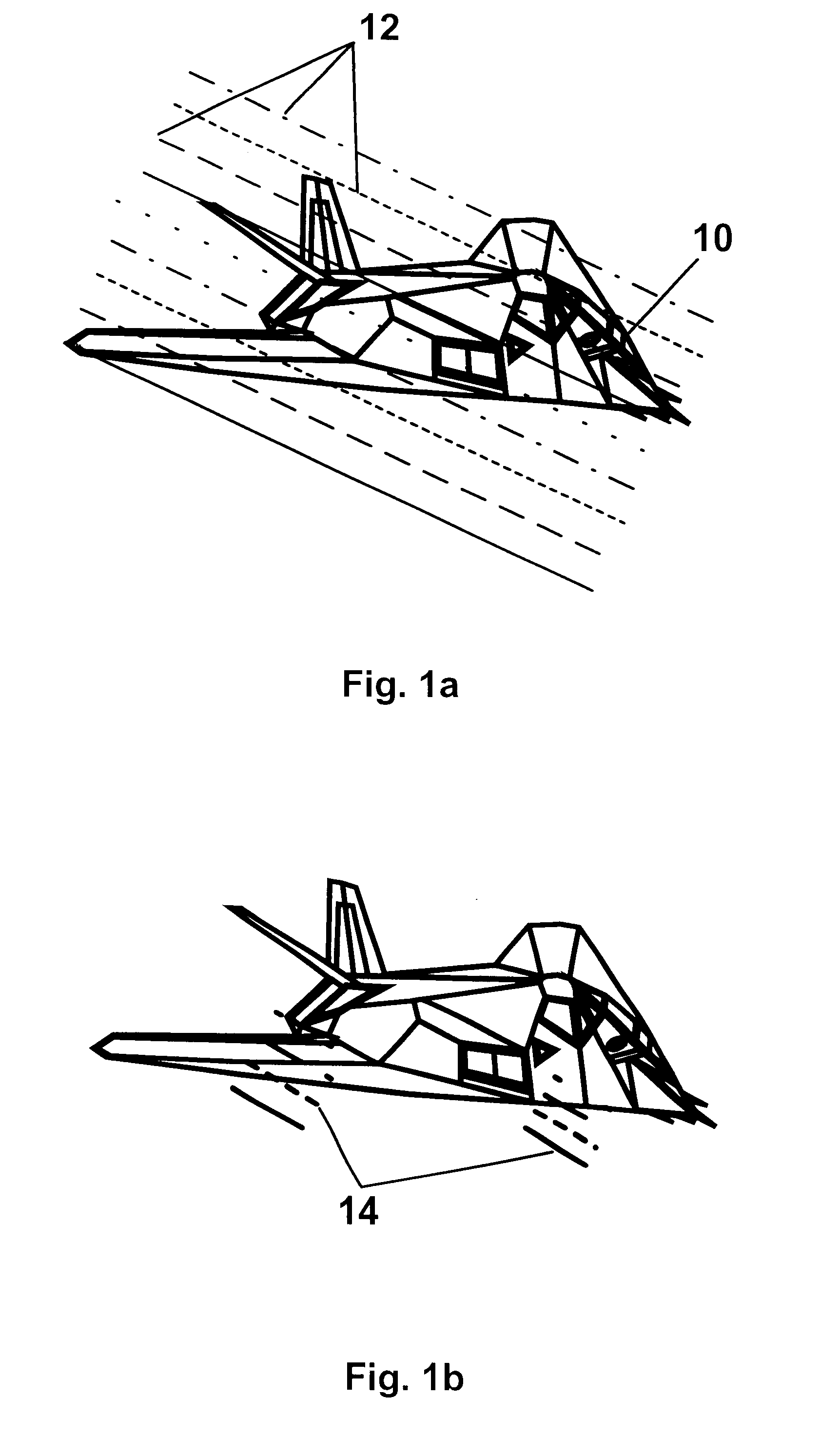
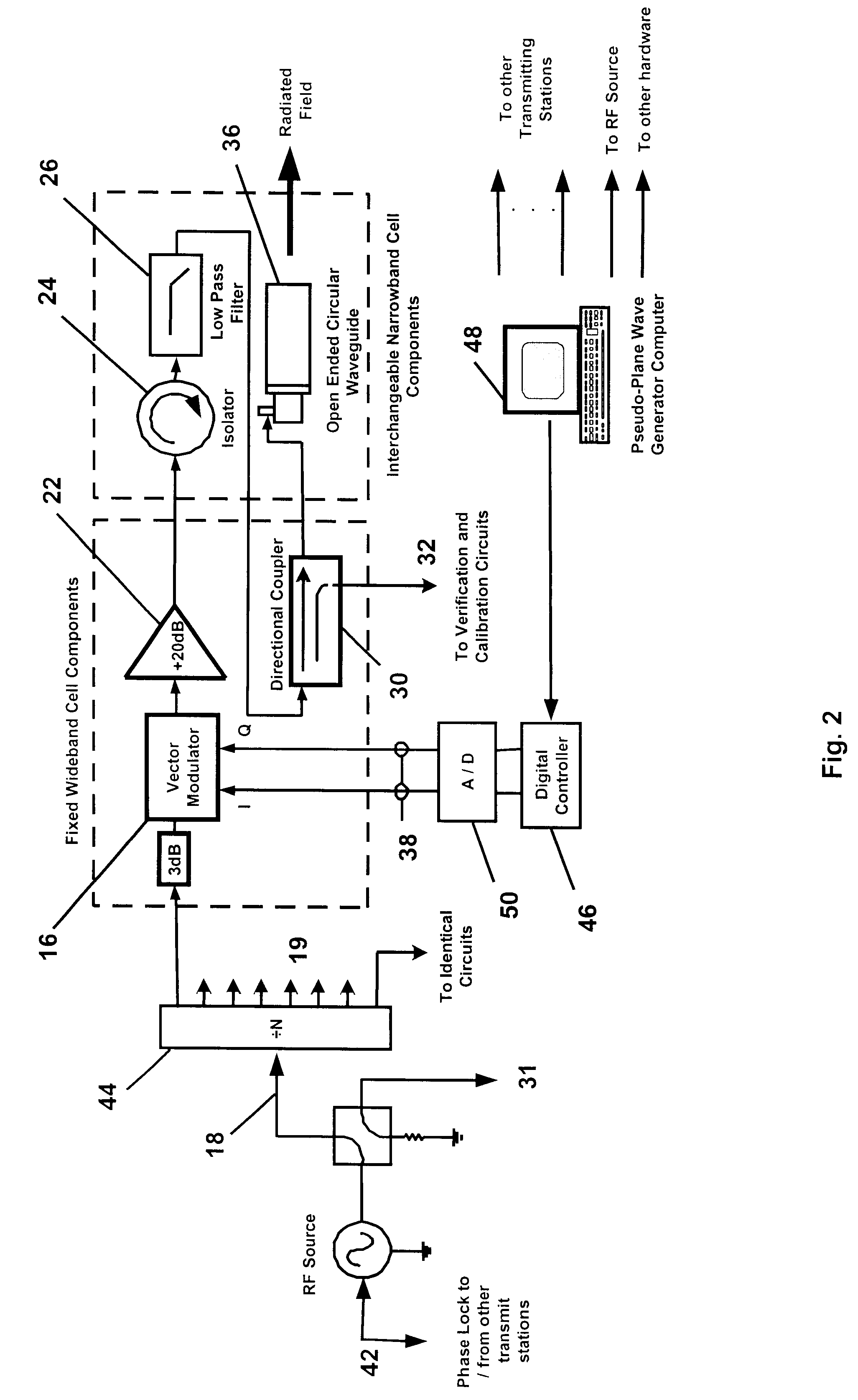
InactiveUS6639548B2Weather/light/corrosion resistanceElectrical measurementsElectromagnetic environmentElectromagnetic radiation
An apparatus and method for generating an electromagnetic environment in which the free field, plane wave response of electronic systems of an electrically large (greater than several wavelengths in its longest dimension) object, or objects, under test can be measured in the electromagnetic radiating near field of the transmitter array apparatus. The apparatus comprises: (1) one or more transmitting station(s), each station home to an array of radiating elements; (2) a software operating system and computer that controls the electronic circuits of the apparatus and executes an optimizing algorithm based on a Genetic Algorithm to control the radiation of each transmitting station; and (3) mechanical and electrical circuits that enable the apparatus to conduct self calibration and adjustment as required. In operation, the apparatus is placed and distributed about an object under test. With input from an operator, an optimization procedure based on a Genetic Algorithm determines the magnitude and phase of each radiating element, of each transmitting station. The apparatus then creates an electromagnetic environment that couples to sensors through small apertures distributed about the object under test, and causes the electronic behavior of electronic systems of the object under test to mimic their response to a true free field, plane wave environment.
Owner:DONALD E VOSS D B A VOSS SCI
Device and method for detecting the mass and the moisture content for spinning preparation machines
InactiveUS6837122B2Fine time resolutionReliable measurementSafety devices for fibre treatmentResistance/reactance/impedenceEngineeringMoisture
The device for measuring the mass and / or the moisture of a material running through a spinning preparation machine is distinguished in that it has a microwave resonator (15, 18) and associated adapted measurement electronics. The method for measuring the mass and / or the moisture of a material running through a spinning preparation machine is distinguished in that the measurement is carried out with the aid of microwaves.
Owner:TEWS ELEKTRONIK GMBH & CO KG
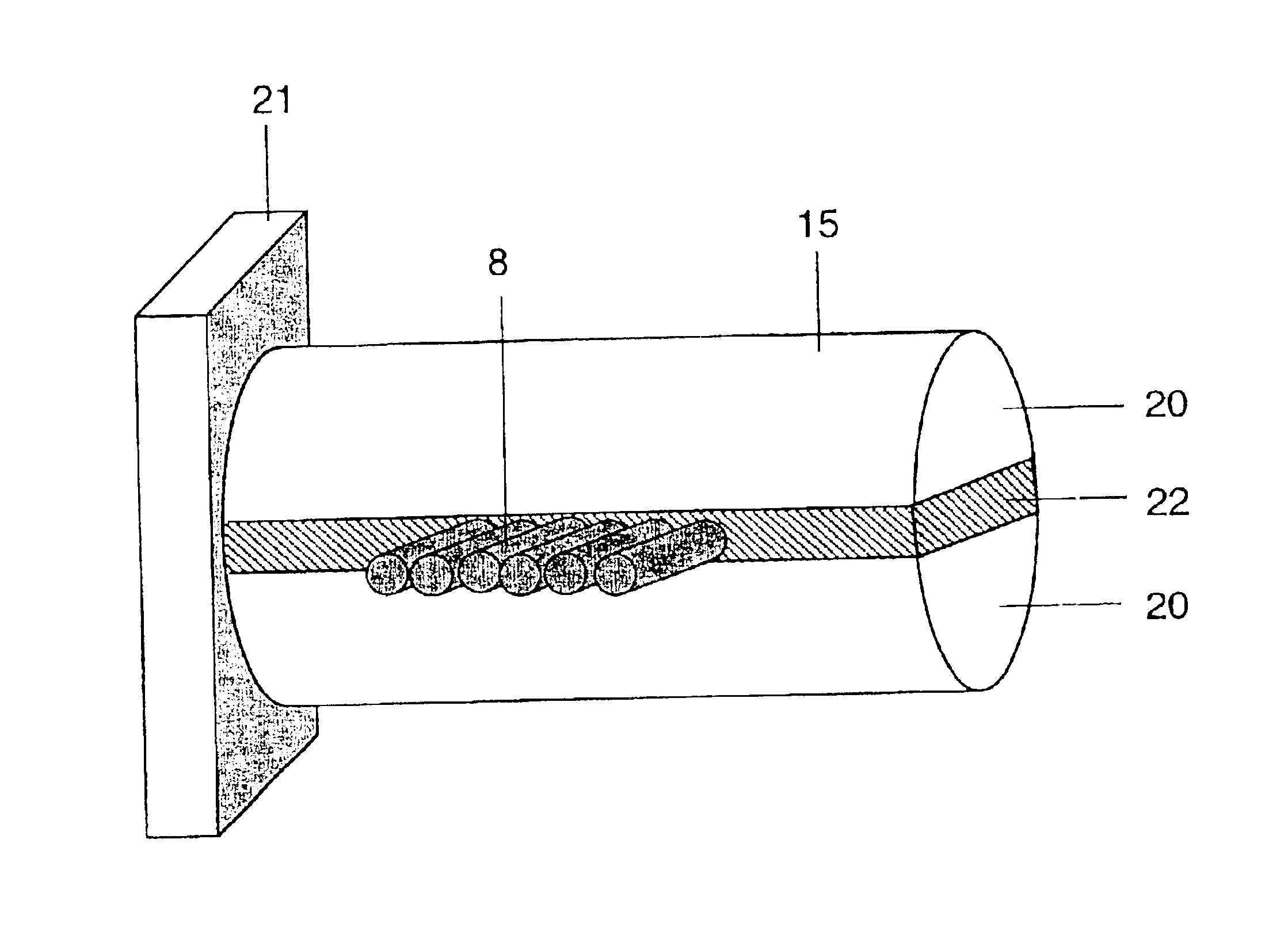
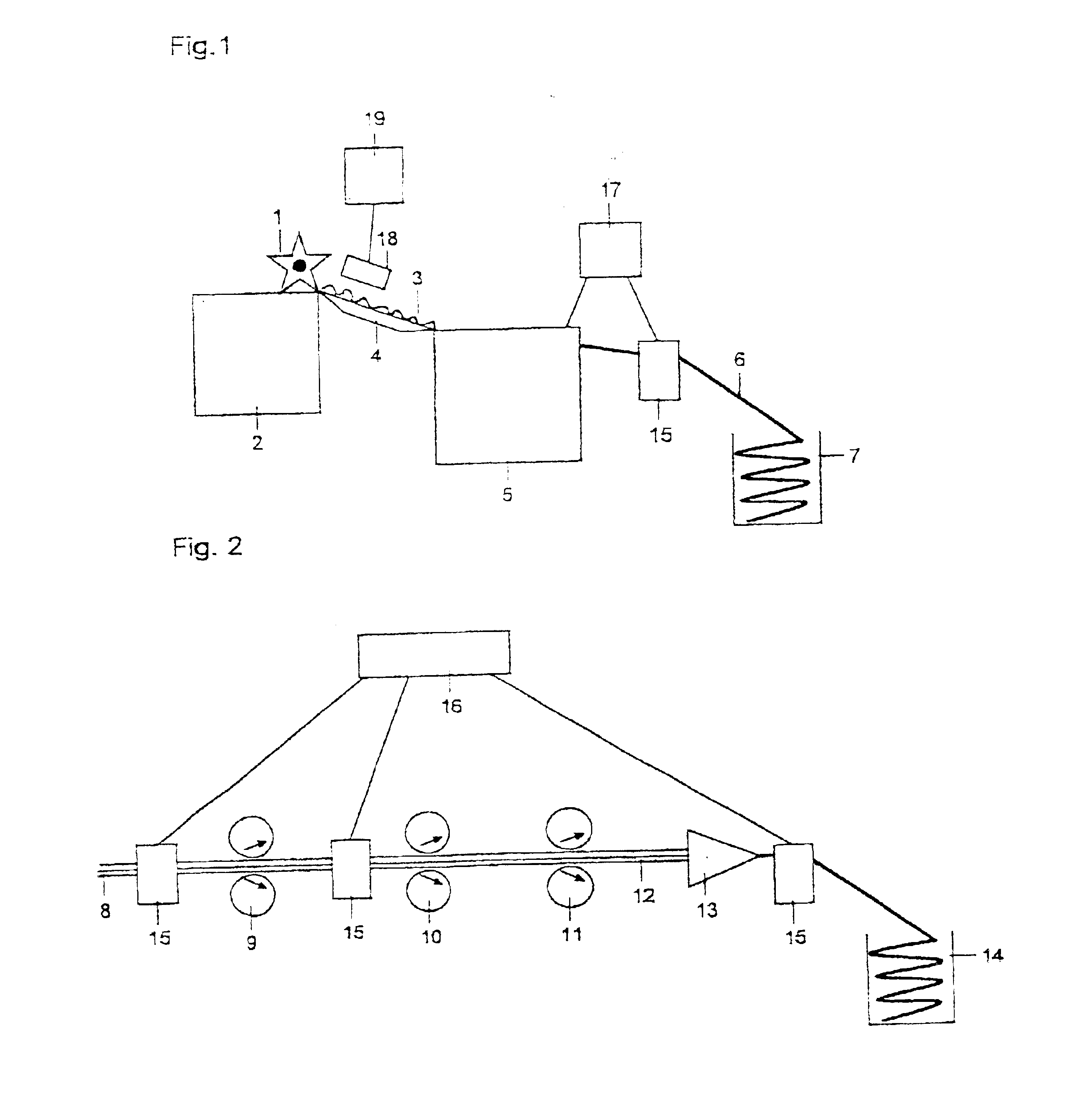
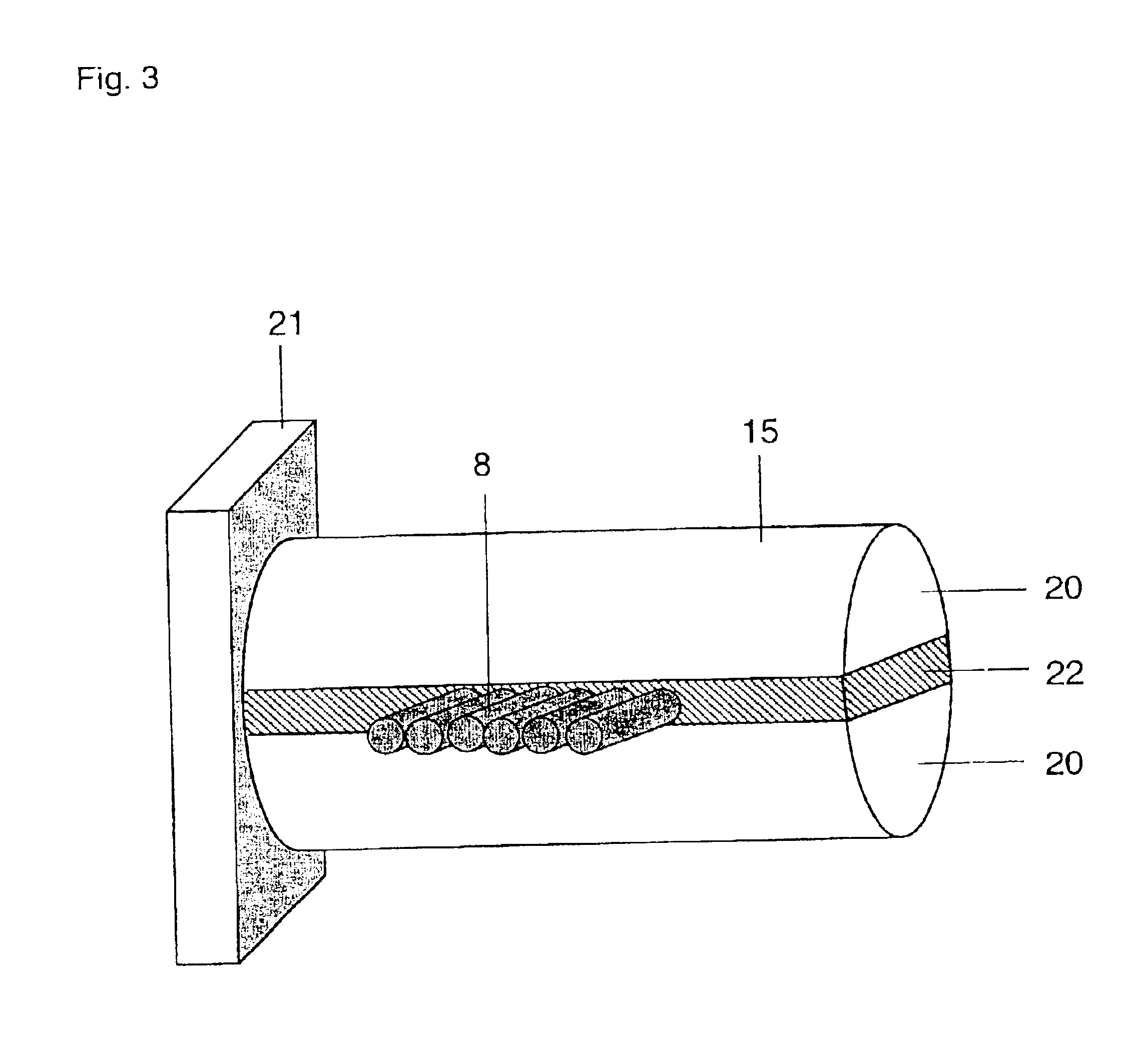
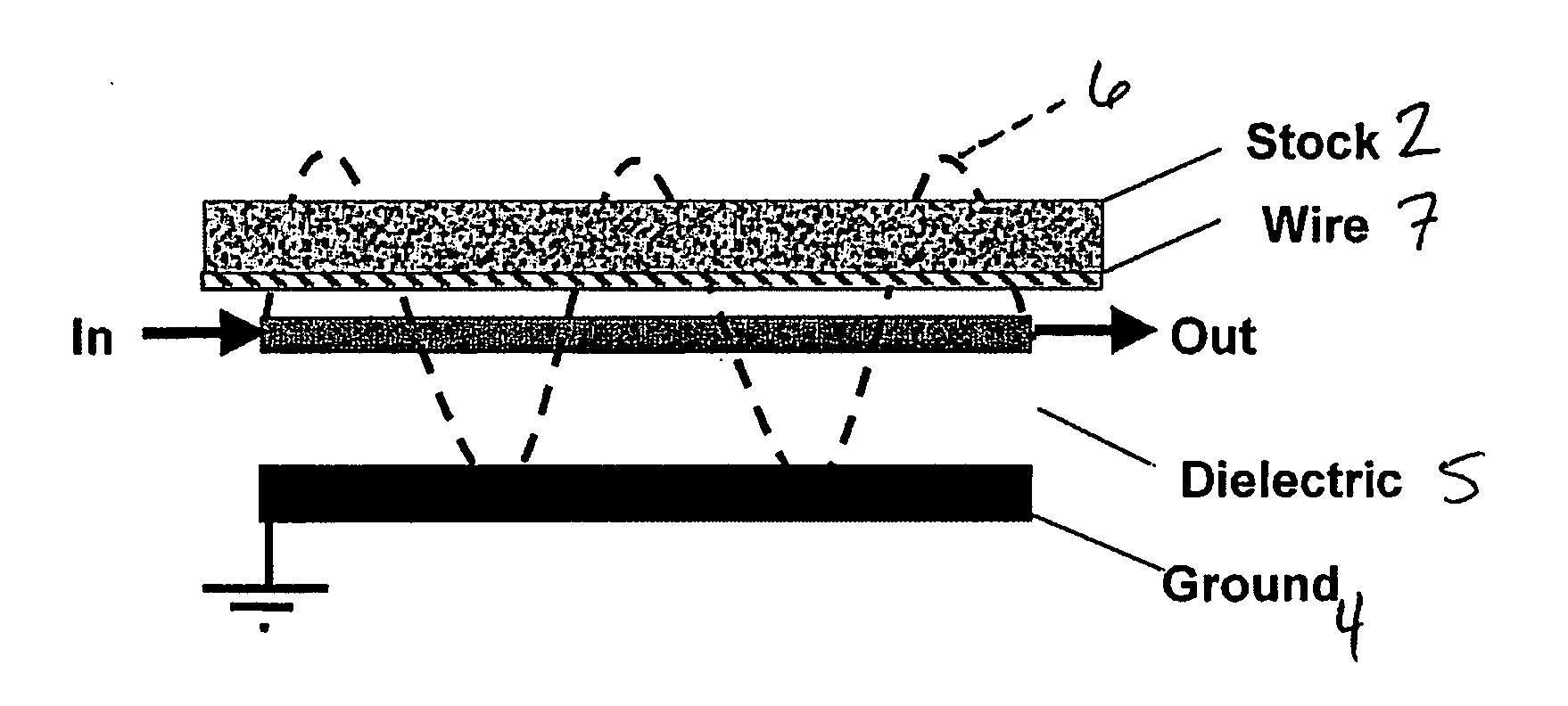
Microwave water weight sensor and process
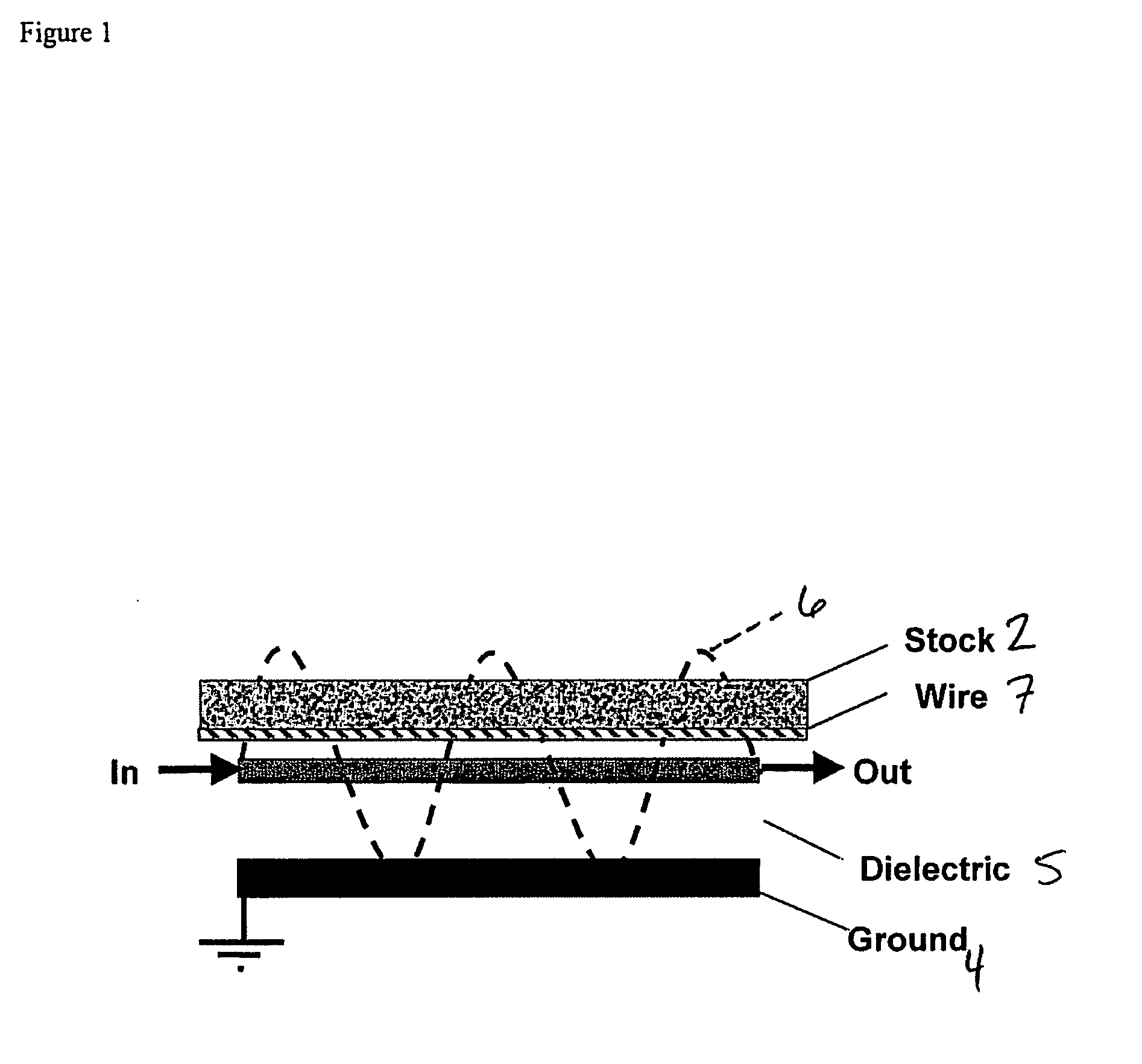
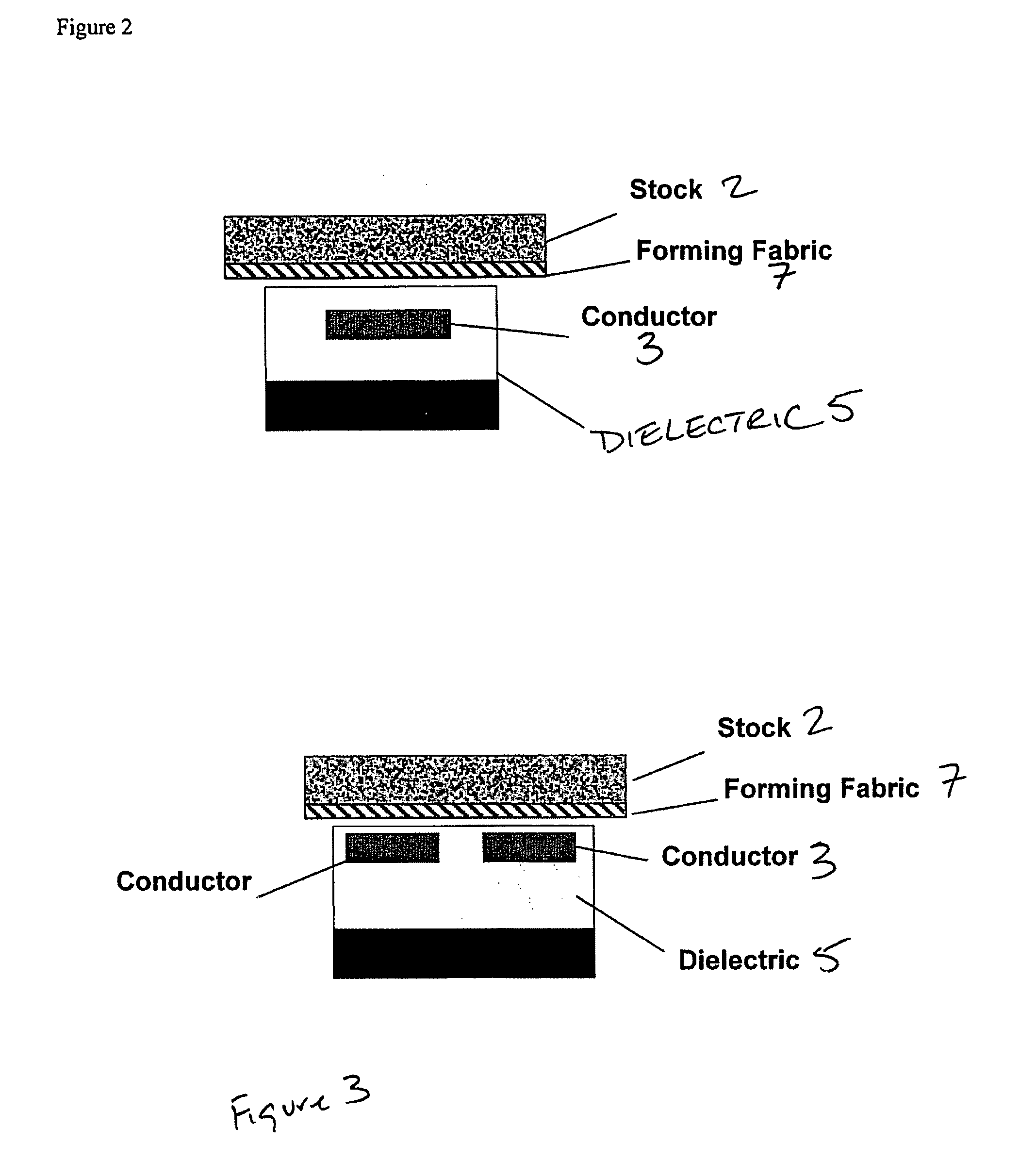
ActiveUS20060028213A1Low dielectric constantCost effectiveResistance/reactance/impedenceMoisture content investigation using microwavesElectromagnetic field couplingMicrowave signals
Sensor and process for measuring mass of water on a sheet forming fabric. The sensor includes a microwave element positionable to couple an electromagnetic field into a stock layer to be measured, and a microwave signal generator coupled to the microwave element to generate, in the microwave element, a microwave signal having a frequency lower than a relaxation frequency of water. The instant abstract is neither intended to define the invention disclosed in this specification nor intended to limit the scope of the invention in any way.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
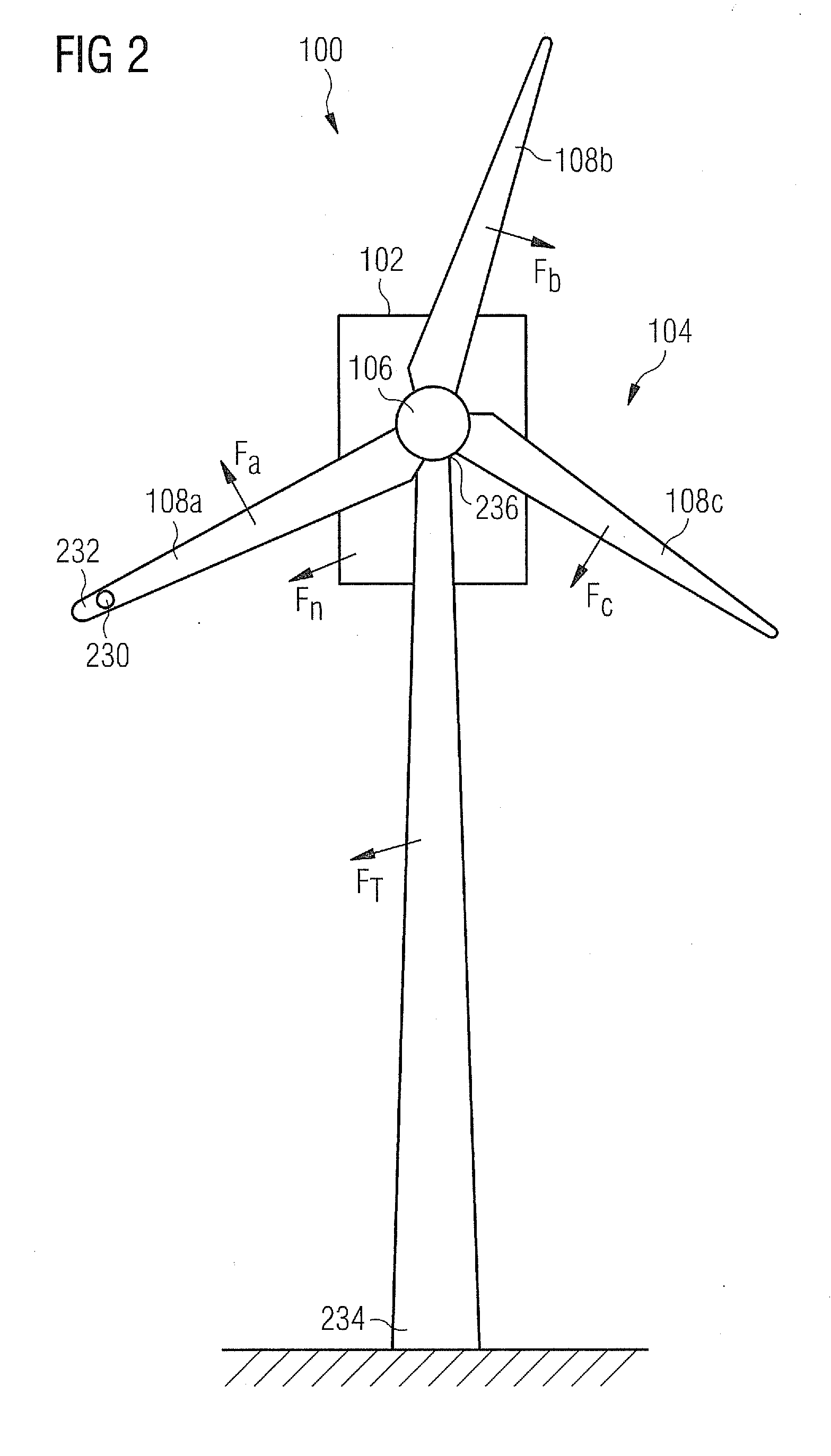
Method of and device for determining a mass condition of a rotor of a wind turbine, and method of operating a wind turbine
InactiveUS20120076651A1Accurate and easy and reliable methodPropellersWind motor controlMomentumEngineering
A method of determining a mass condition of a rotor of a wind turbine is disclosed. The method includes initiating a change of a quantity value of a quantity acting on the rotor, measuring a change of another quantity value of another quantity representative of a momentum of the rotor during a time interval, and determining the mass condition of the rotor based on the determined change of the another quantity value in relation with the initiated change of the quantity value.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method for promoting paeonia suffruticosa seedling growth and application thereof
InactiveCN104206417ABreak dormancyShorten the flowering processBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPaeonia suffruticosaActive agent
The invention relates to a method for promoting paeonia suffruticosa seedling growth and application thereof. Specifically, the invention provides a paeonia suffruticosa seedling treatment fluid, which comprises: a paeonia suffruticosa seedling growth active agent (gibberellin and / or 6-benzyladenine) and a surfactant, and also can include an agronomically acceptable soluble calcium salt. The growth active agent can break epicotyl dormancy of paeonia suffruticosa seeds, improve the germination rate / germination potential of paeonia suffruticosa seeds, accelerate the paeonia suffruticosa seed growth process, and promote seedling emergency or flowering of paeonia suffruticosa seed seedlings / tissue culture seedlings. The surfactant can make active substances fully enter cells. And the soluble calcium salt is closely related to multiple physiological functions of cells.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Washing machine and control method thereof
Disclosed herein are a washing machine that detects the weight of laundry based on the displacement of a rotary tub and a control method thereof. The washing machine includes a rotary tub displaced according to the weight of laundry, at least one sensor module to detect the displacement of the rotary tub, and a controller to calculate the weight of the laundry according to the displacement of the rotary tub. The weight of the laundry is sensed according to the displacement of the rotary tub in which the laundry is directly placed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
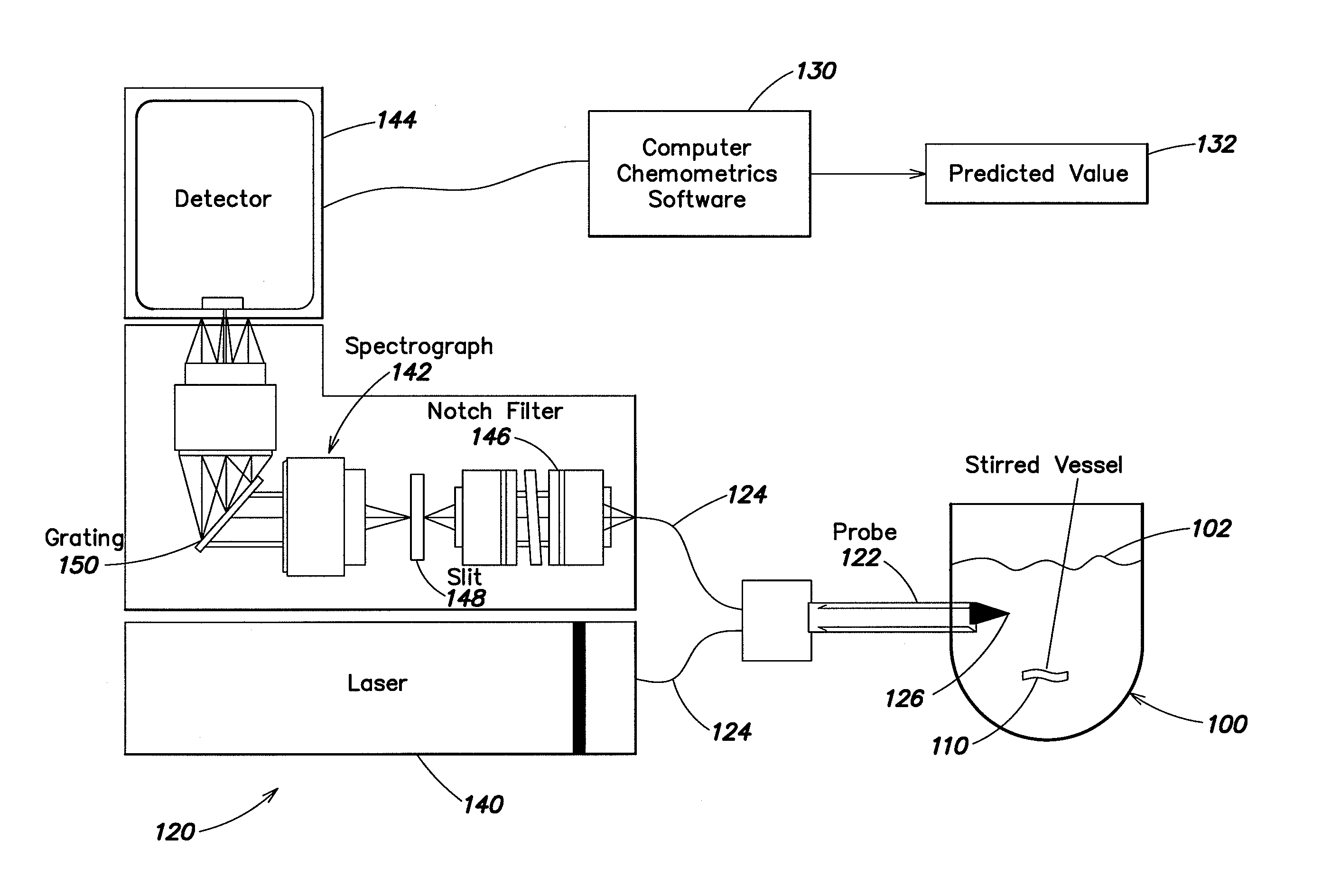
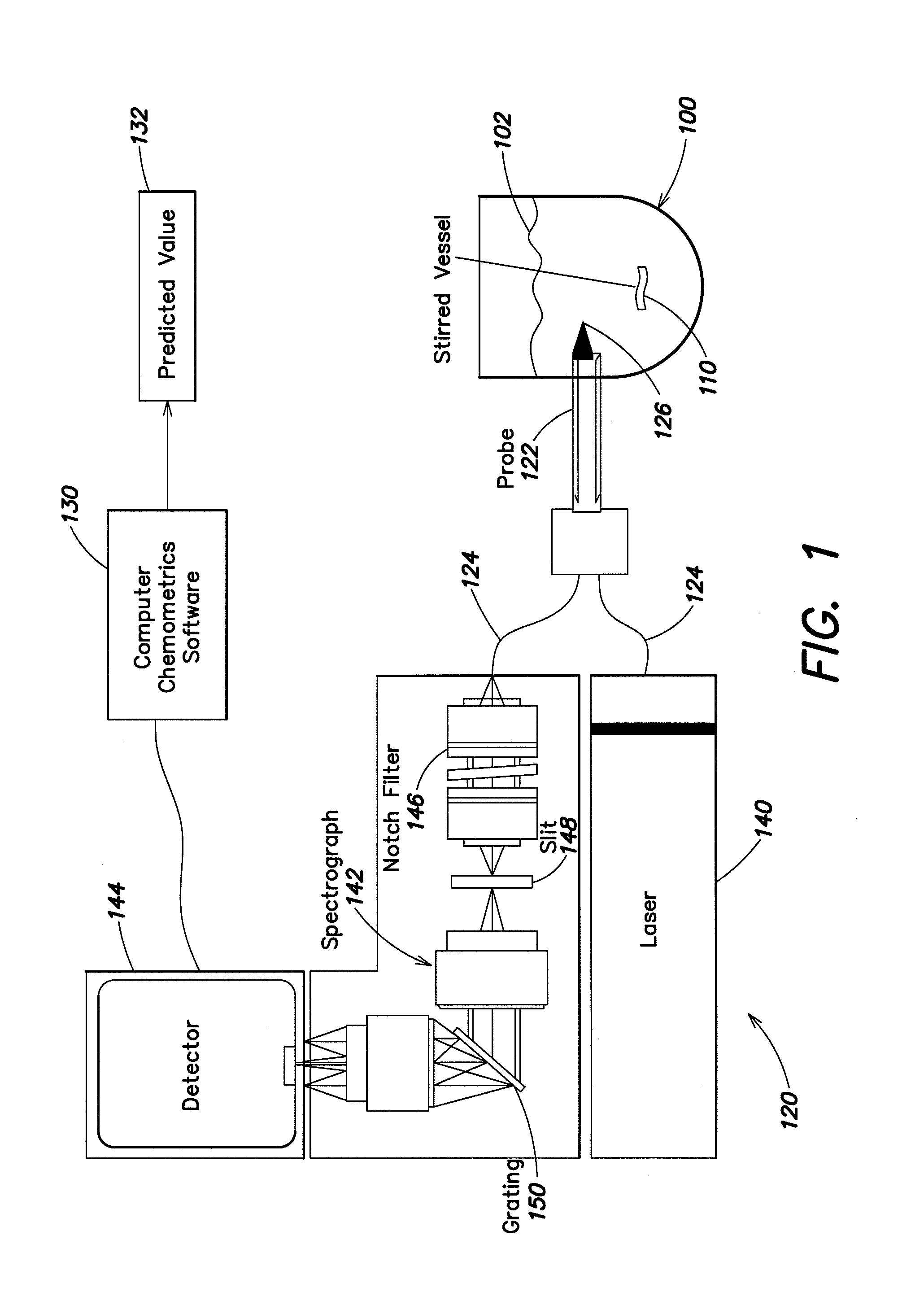
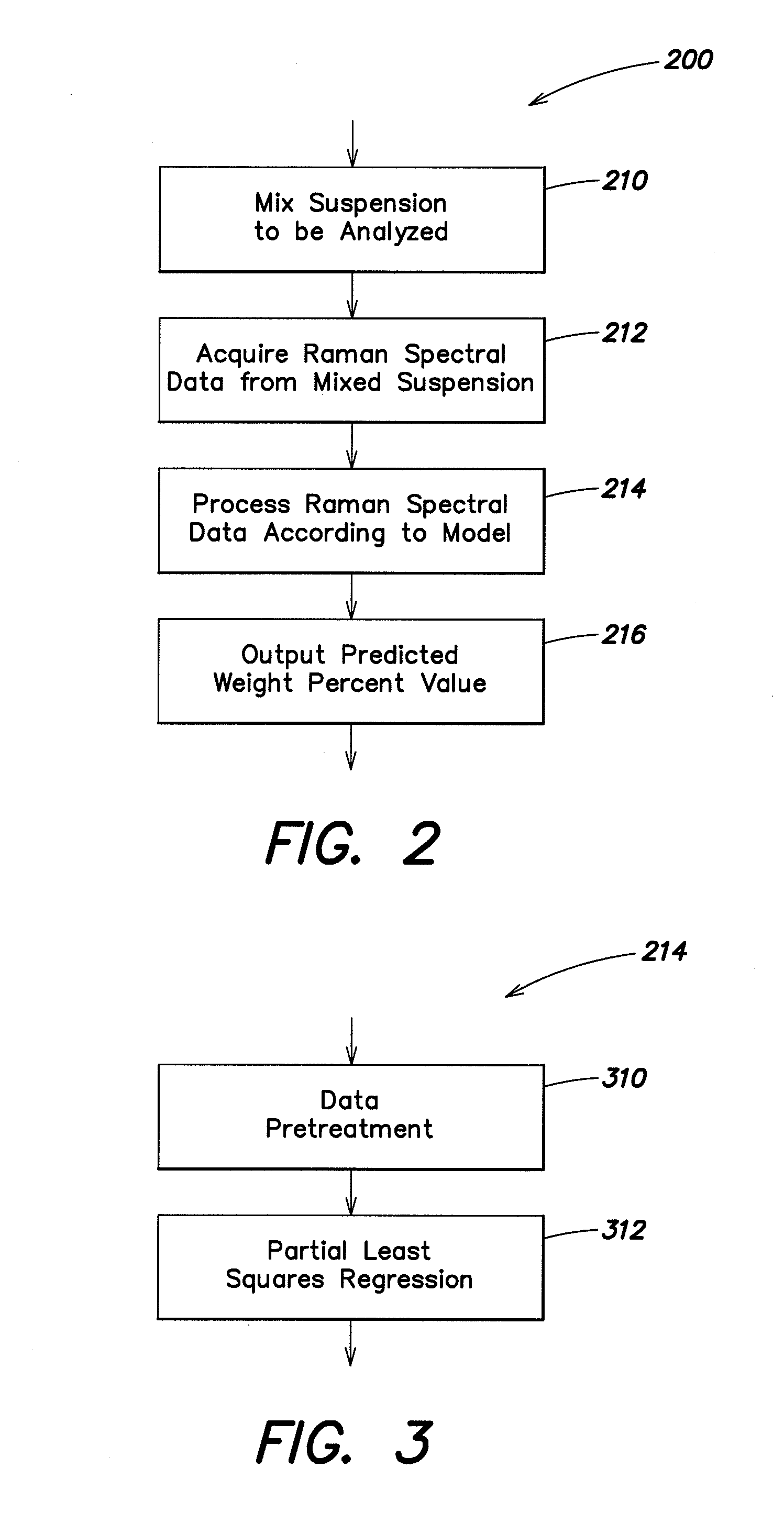
Determining percent solids in suspension using raman spectroscopy
Methods and apparatus are provided for determining weight percent of solids in a suspension using Raman spectroscopy. The methods can be utilized to acquire Raman spectral data from the suspension and to determine weight percent of solids in a process being carried out, for example, in a vessel, without the need to remove samples for analysis. The weight percent of the solids can be determined with a desired accuracy in a relatively short time, typically 10 minutes or less. The acquired Raman spectral data may be processed by chemometric software using, for example, a Partial Least Squares algorithm and data pretreatment to provide a predicted value of weight percent solids. In some embodiments, the invention is used to determine the weight percent of microparticles of a diketopiperazine in an aqueous solution.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Method for detecting scale cinder accumulation amount in boiler bent pipe
The invention discloses a method for detecting scale cinder accumulation amount in a boiler bent pipe, comprising the following steps: (1) selecting a sample on site; (2) simulating the site, adding scale cinder in one end of a test cylinder; (3) magnetizing; (4) measuring the strength value of a remanence magnetic field; (5) progressively increasing the scale cinder; (6) repeating steps (3) and (4); (7) repeating steps (5) and (6); (8) building a graph of relation; (9) detecting on site, and magnetizing; (10) measuring the strength value B of the remanence magnetic field; and (11) using the graph of relation to compare with a tested bent pipe, and finding the scale cinder accumulation amount in the detected boiler bent pipe. When being used for detection, the method can carry out nondestructive inspection to the scale cinder in a service boiler bent pipe without special treatment and has the characteristic of high sensitivity and is simple, safe and reliable.
Owner:STATE GRID HUNAN ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD ELECTRIC POWER SCI RES INST +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com