Patents
Literature
127 results about "Free field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics a free field is a field without interactions, which is described by the terms of motion and mass.
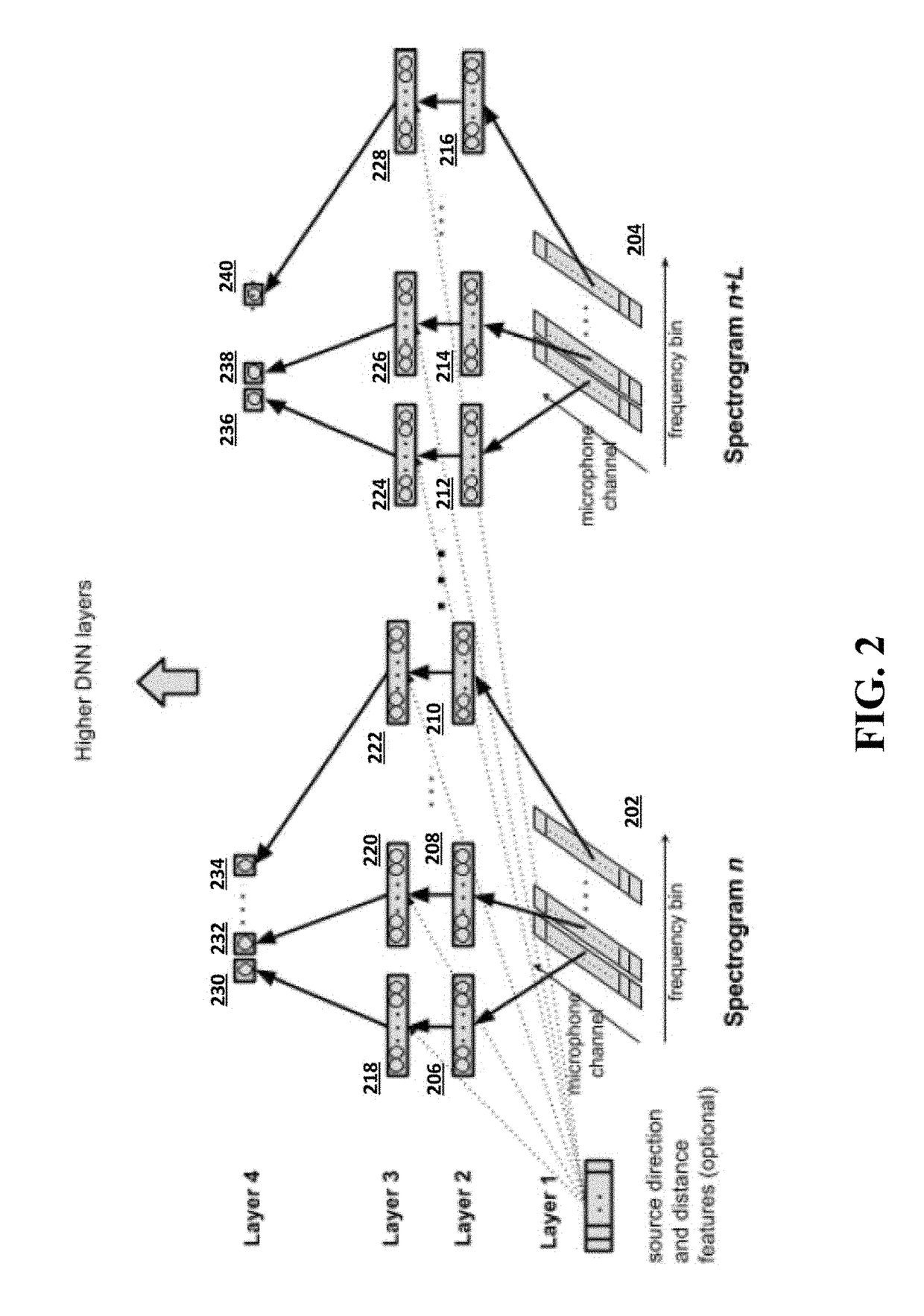
Multi-microphone neural network for sound recognition
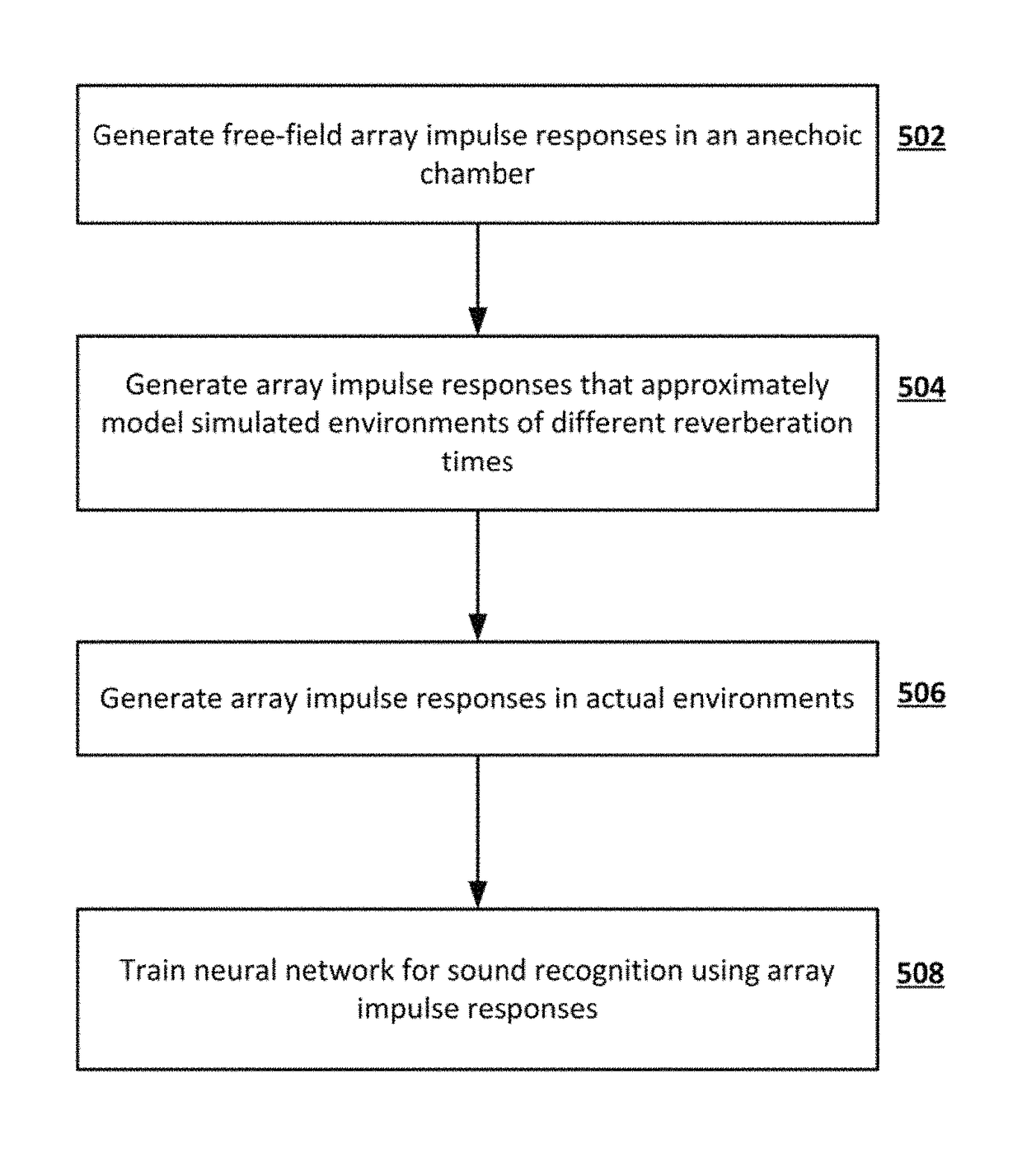
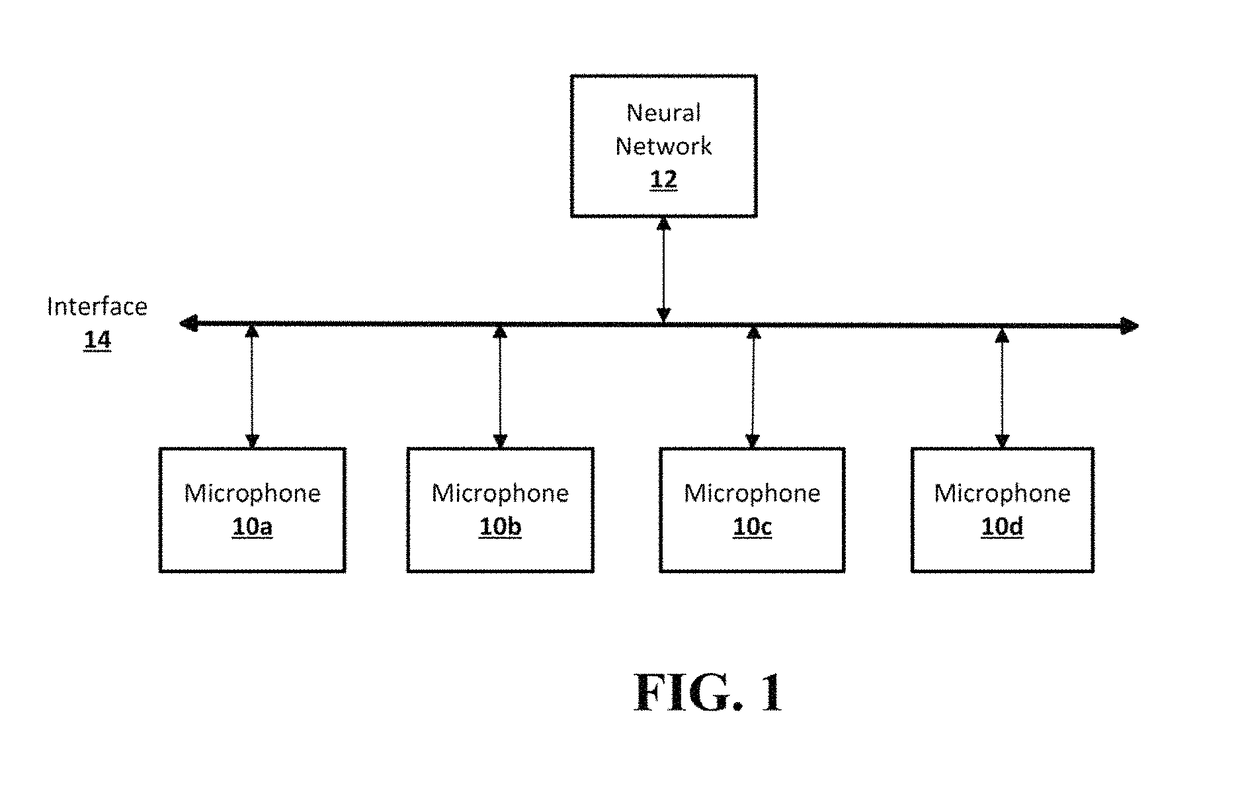
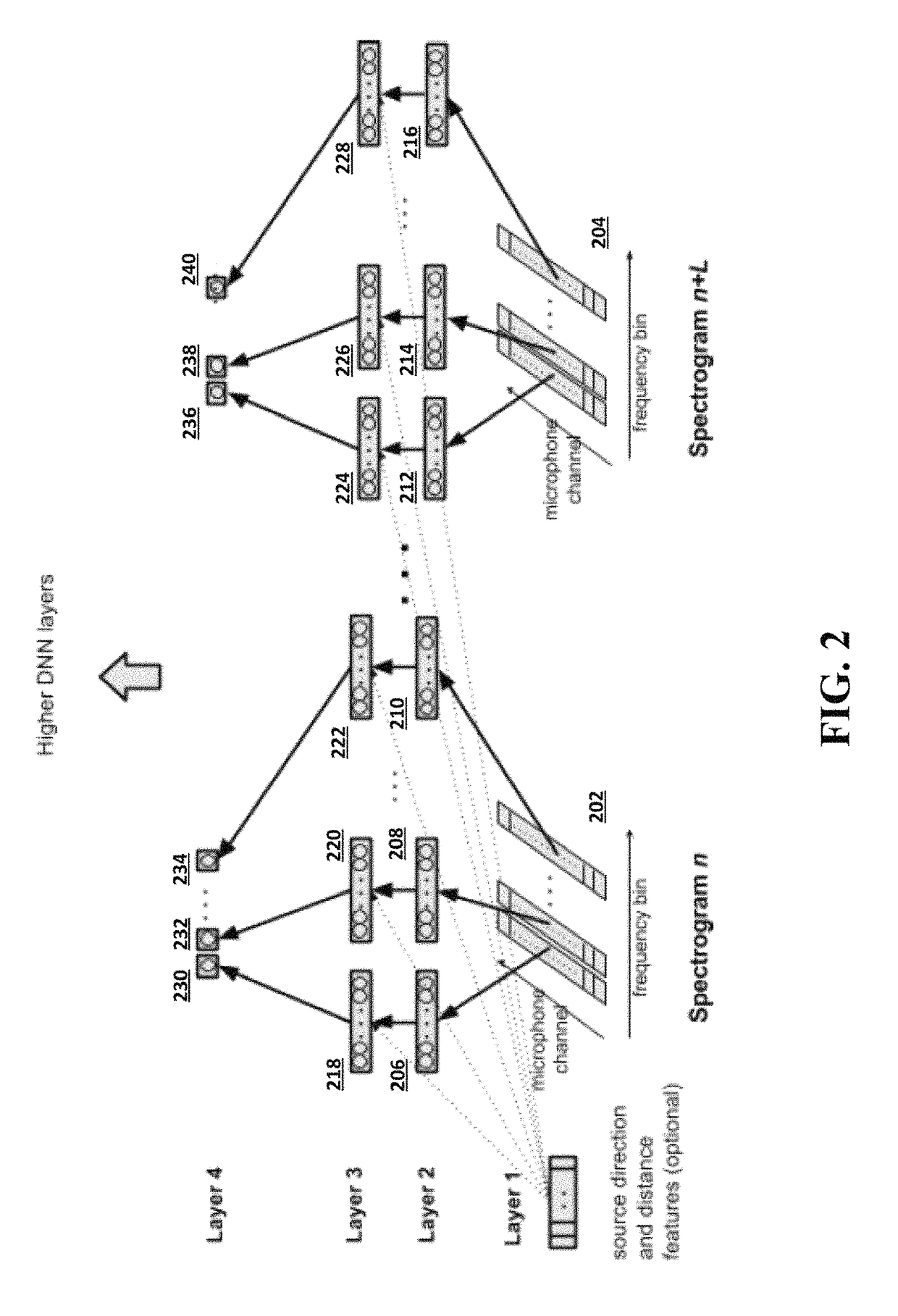
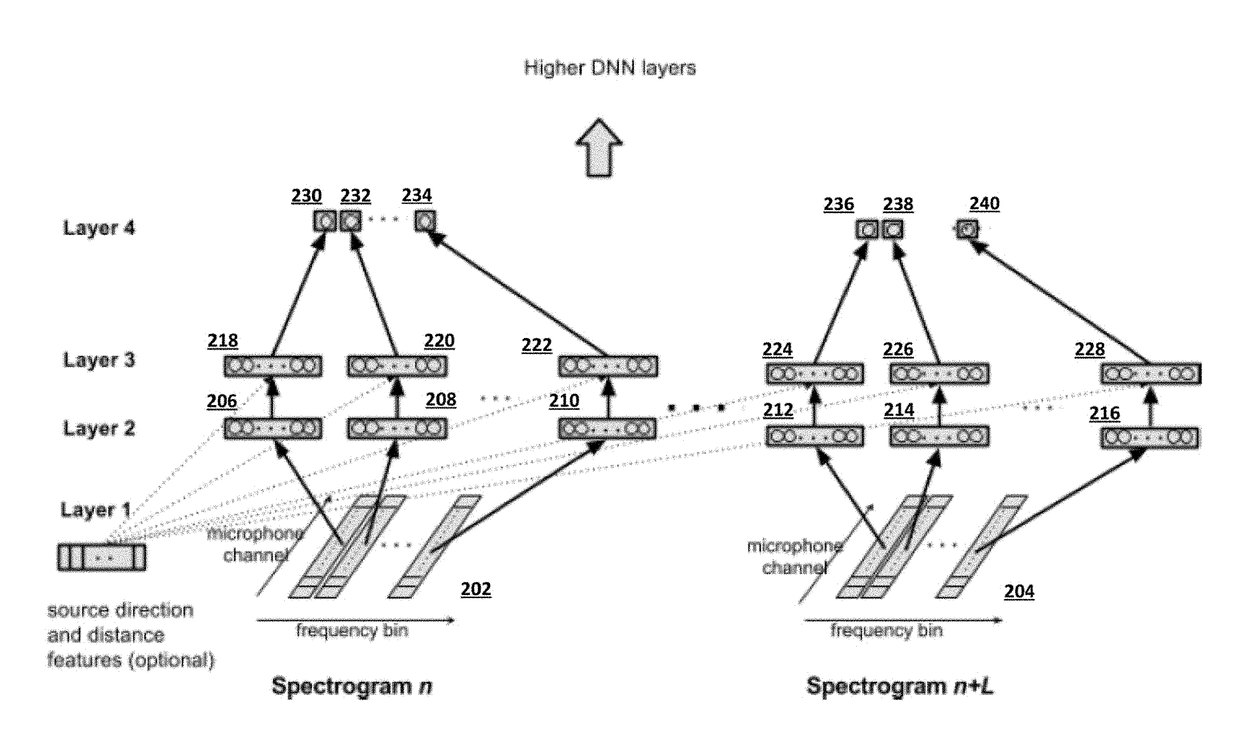
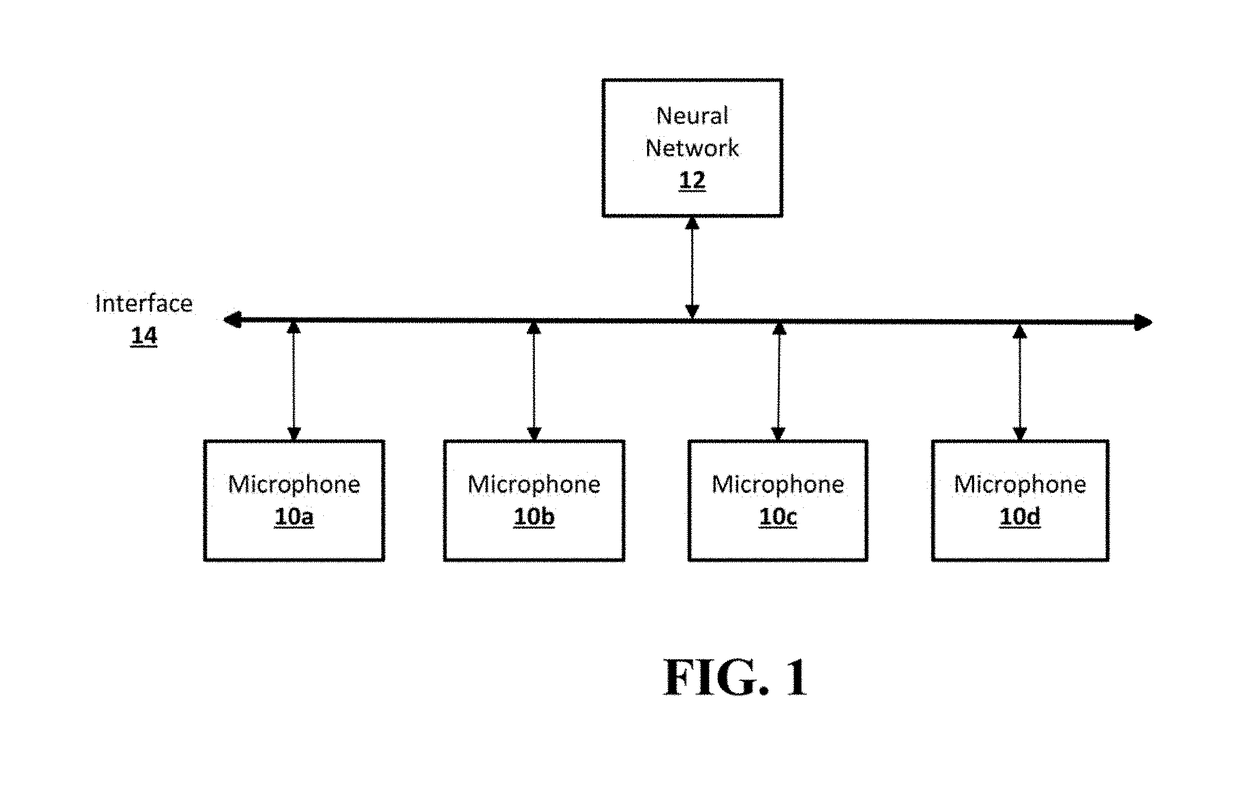
A neural network is provided for recognition and enhancement of multi-channel sound signals received by multiple microphones, which need not be aligned in a linear array in a given environment. Directions and distances of sound sources may also be detected by the neural network without the need for a beamformer connected to the microphones. The neural network may be trained by knowledge gained from free-field array impulse responses obtained in an anechoic chamber, array impulse responses that model simulated environments of different reverberation times, and array impulse responses obtained in actual environments.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Acoustic treatment performance testing
InactiveUS6155116AEliminate inconsistenciesMinimizing unwanted obstructionVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSound sourcesLength wave
A method and system for acoustic treatment performance testing in a free-field acoustic environment is provided. A sound source directs a gated acoustic pulse at an acoustic treatment. Acoustic pressures of the gated acoustic pulse and reflected energy from the acoustic treatment are measured from a location approximately in-line with the source and the acoustic treatment. This measurement location is at least one-half the wavelength of the frequency of interest away from the source and is at least a distance equal to (t*c / 2) away from the acoustic treatment where t is equal to the duration of the gated acoustic pulse and c is equal to the speed of sound in the free-field acoustic environment. The acoustic pressures of the gated acoustic pulse and reflected energy are compared as an indication of performance of the acoustic treatment at a frequency of interest.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY NAVAL RES LAB WASHINGTON
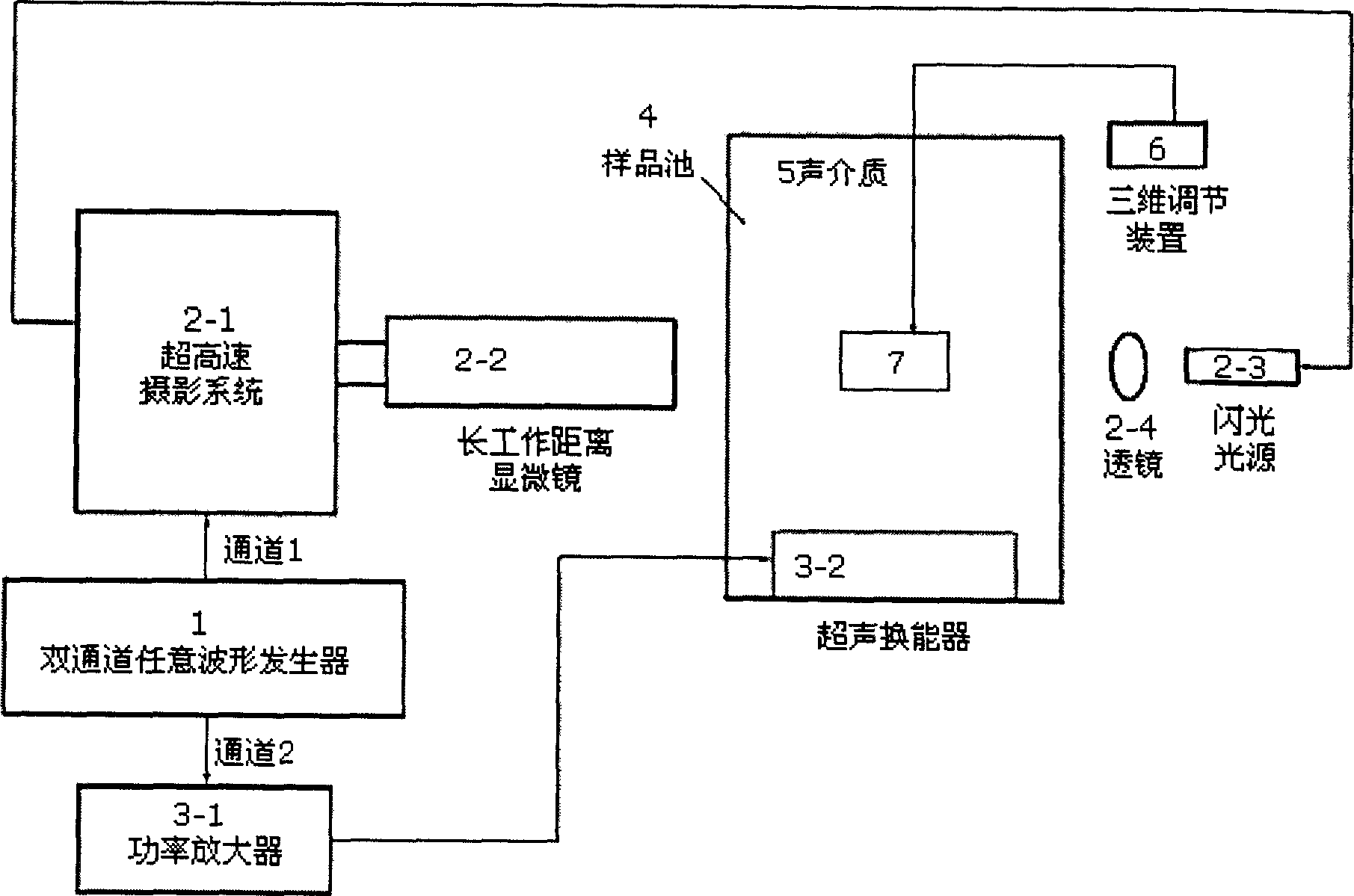
Analysis system and method of microbubble behavior in ultrasonic field based on superhigh speed photograph technology
InactiveCN1847824AObserve intuitivelyEasy to analyzeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSonificationChemical reaction
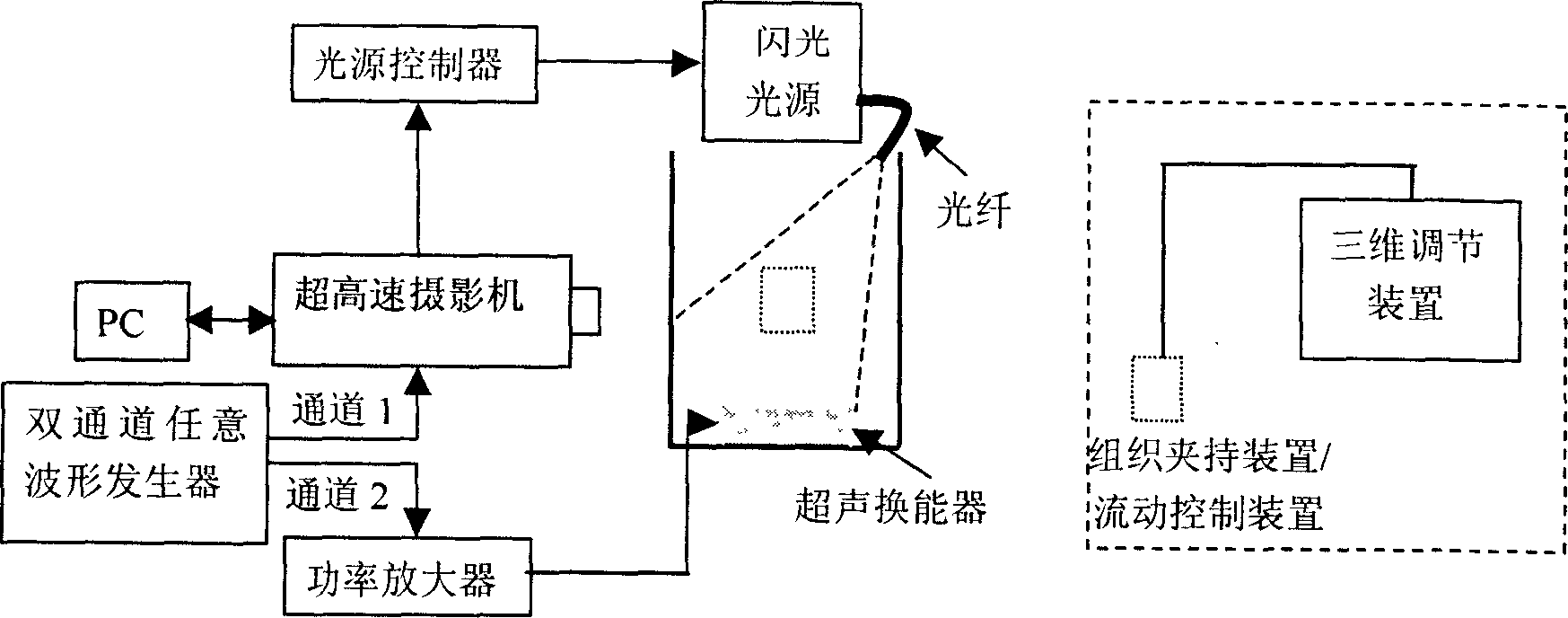
The present invention discloses analysis system and method of microbubble behavior in biomedicine ultrasonic field based on superhigh speed photograph technology. Specifically, he present invention includes proposing superhigh speed photograph system for observing the microbubbles in ultrasonic field and microscopic superhigh speed photograph system for observing single microbubble; presenting the method of analyzing the microbubble behavior in free field, near tissue and inside microtubule; and presenting the method of controlling microbubbles generation and breaking and estimating microbubble strain.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
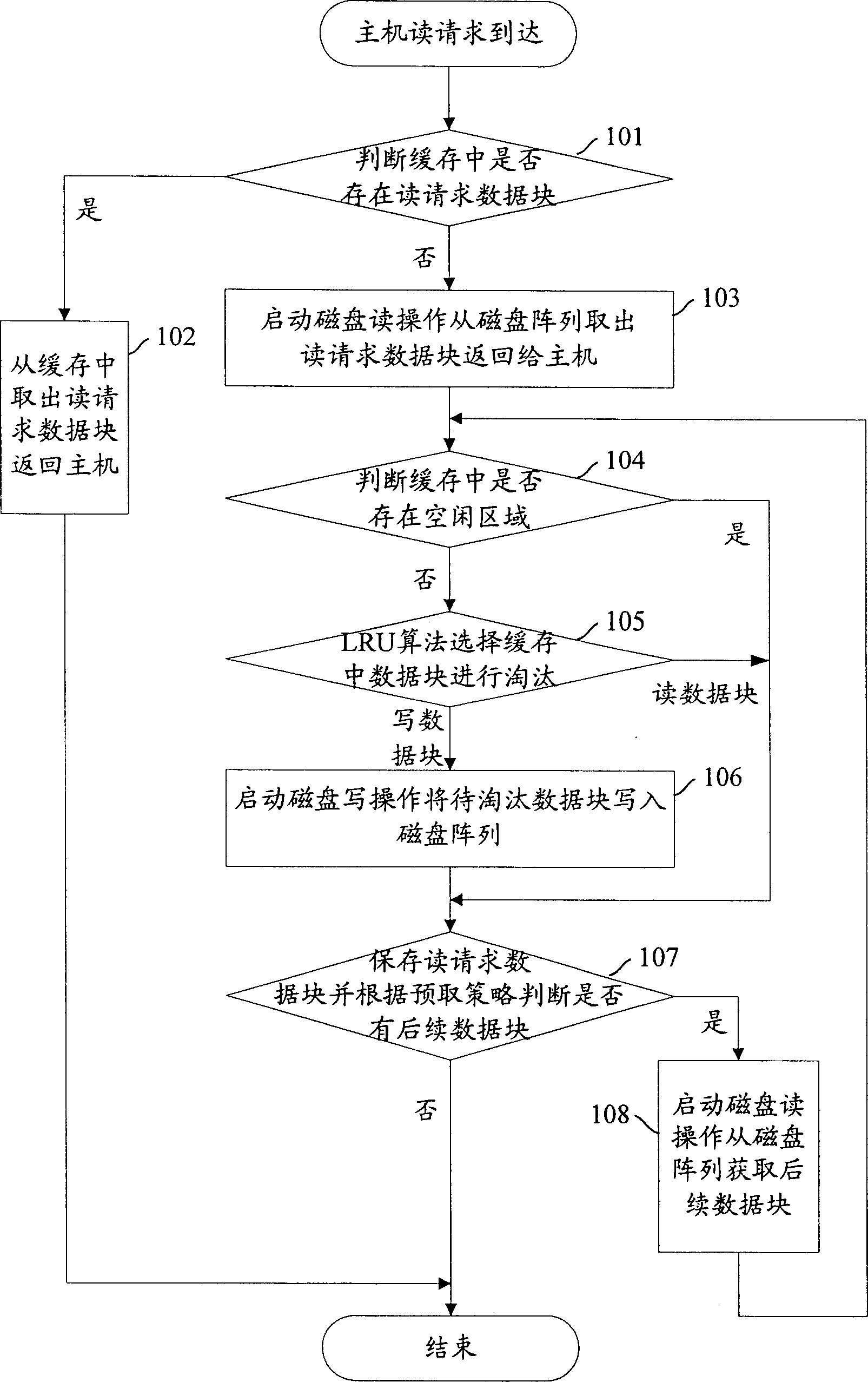
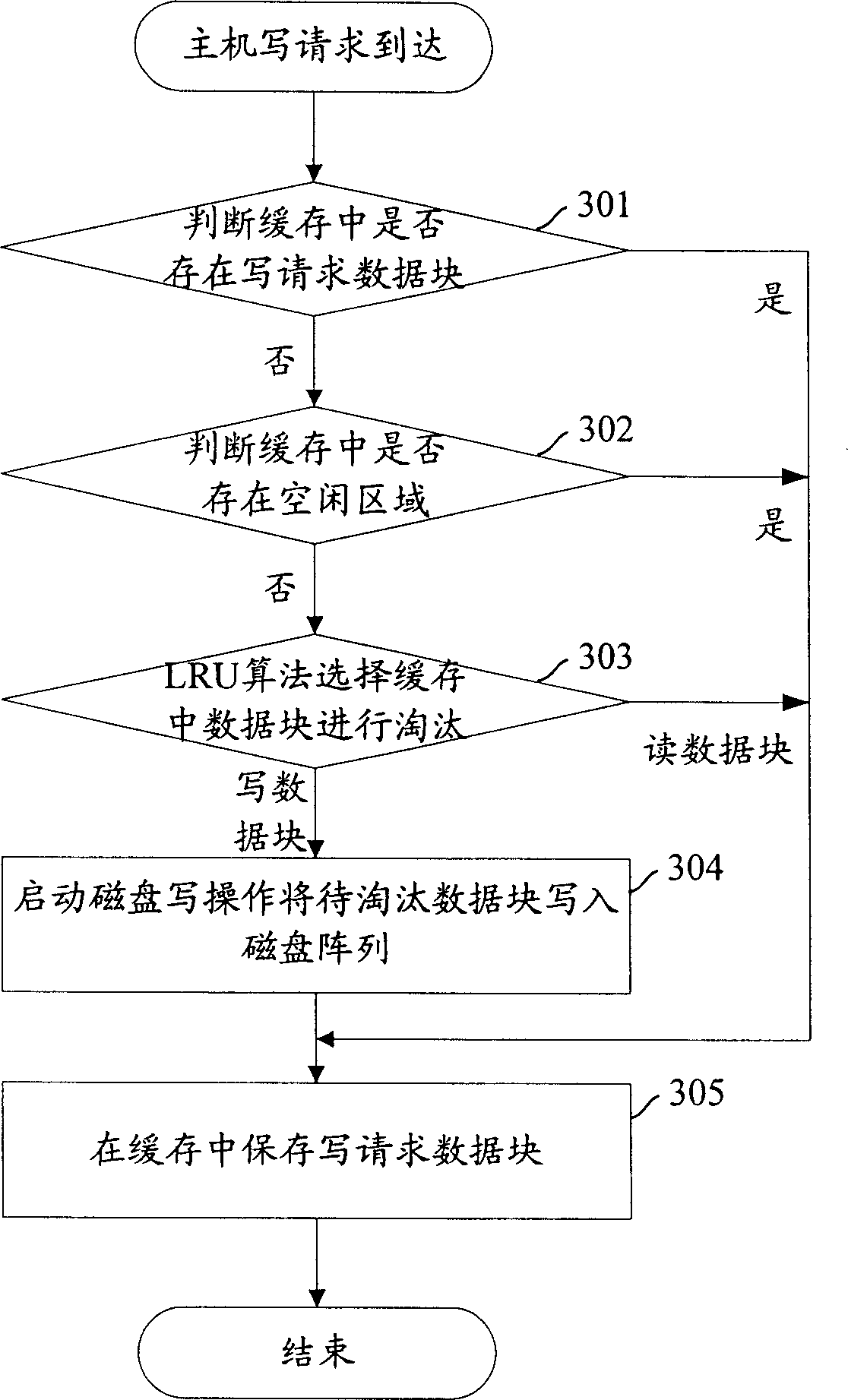
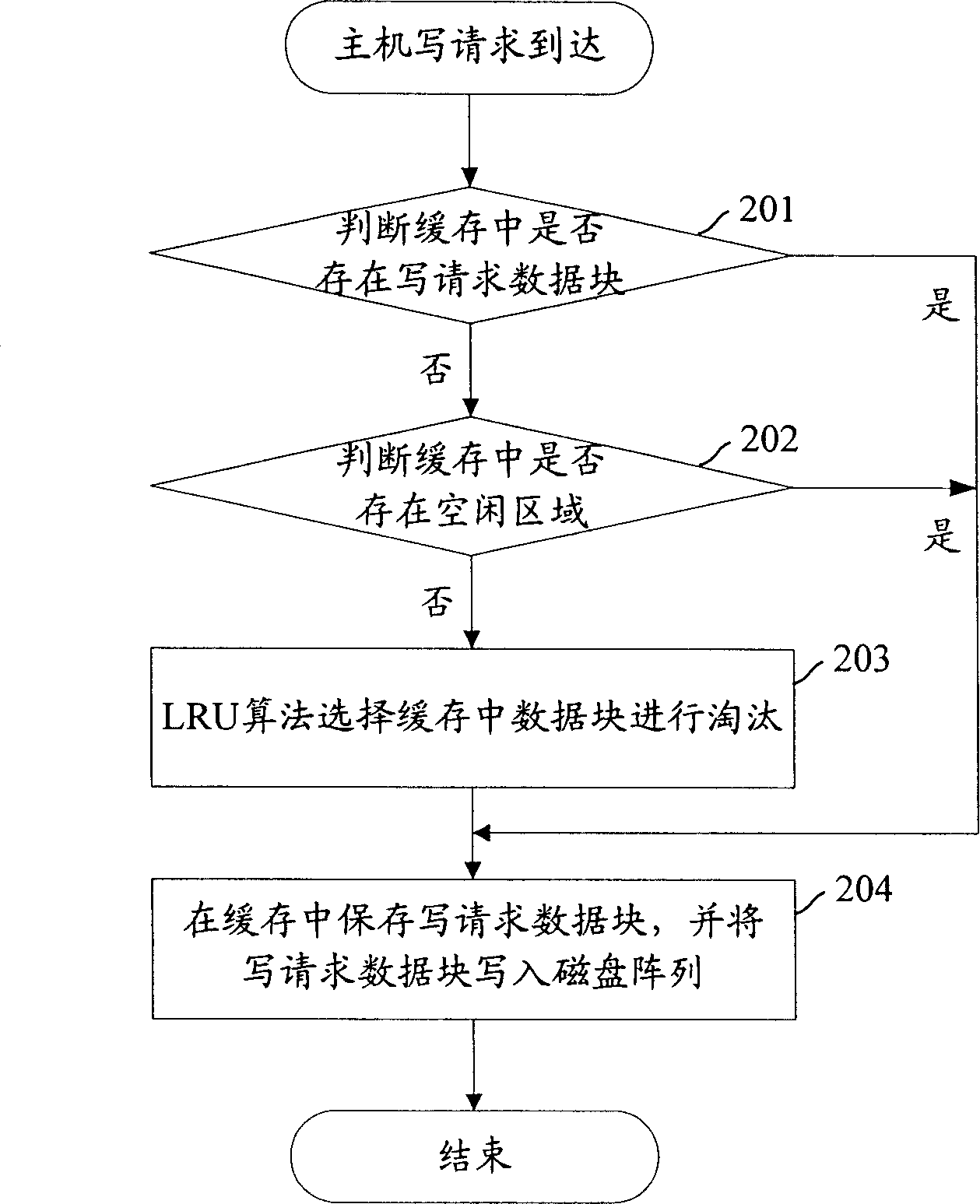
Method for managing magnetic disk array buffer storage
ActiveCN1862475AReduce mean service timeImprove performanceInput/output to record carriersMemory systemsManagement processDisk array
The present invention discloses a management method of magnetic disk array buffer memory for reading / writing request. The management process for reading request includes the following steps: when the reading request of main machine is reached, judging that the reading request data is stored in the magnetic disk array buffer memory or not, if said reading request data is stored in said magnetic disk array buffer memory, obtaining reading request data from said magnetic disk array buffer memory and returning said reading request data to main machine, otherwise, obtaining reading request data from magnetic disk, returning it to main machine and executing step b 1; b 1 includes the following contents; judging that in the magnetic disk array buffer memory a free field is existed or not, if said free field is existed, storing reading request data in said free field, otherwise, executing step C 1; step C 1 includes the following contents; selecting reading data block in magnetic disk array buffer memory, storing the reading request data in position place of selected reading data block. For writing request of main machine said invention adopts similar method to make management.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
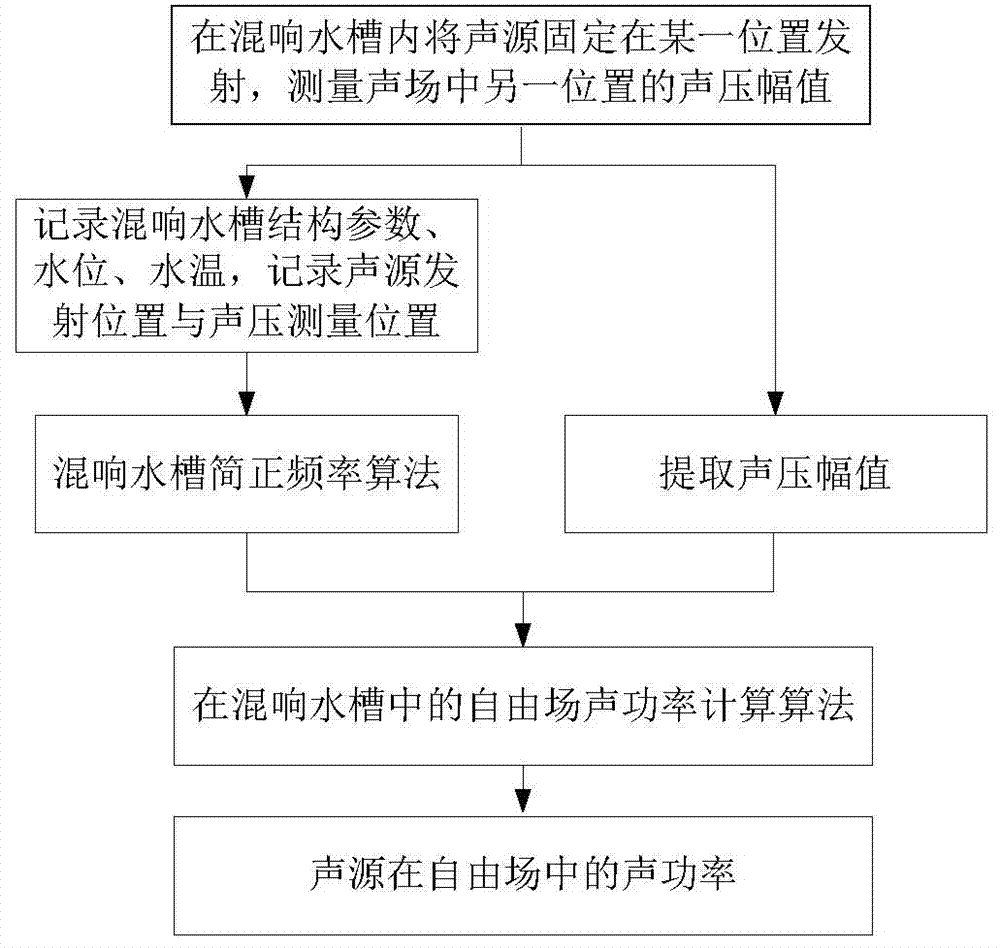
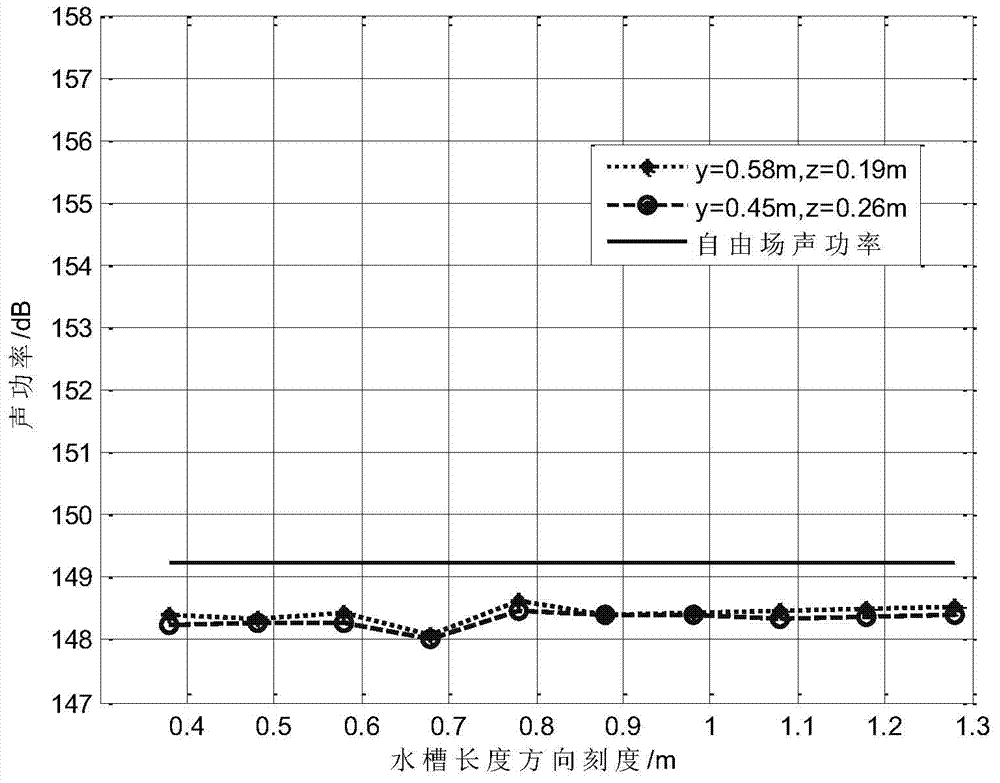
Method for measuring underwater sound source low frequency radiation sound power in rectangular reverberation water tank arranged in air
ActiveCN104501938ASimple and fast operationImprove efficiencyVibration measurement in fluidHydrophoneSound sources
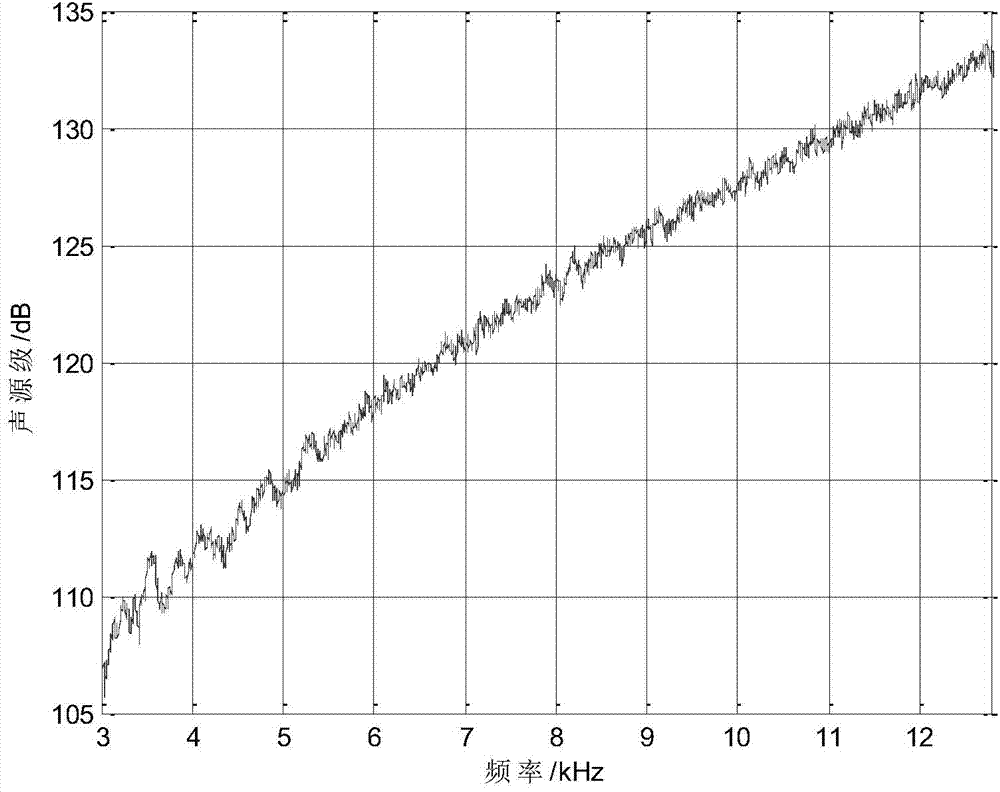
The invention relates to a method for measuring sound source radiation sound power and particularly relates to a method for measuring underwater sound source low frequency radiation sound power in a rectangular reverberation water tank arranged in the air. The method comprises steps that, a sound source is fixed at a position of a reverberation water tank for emission, and a hydrophone is fixed at another position to measure a sound pressure amplitude of the reception position; a reverberation water tank normal frequency calculation algorithm taking consideration of influence of a water tank wall structure on a sound field is employed, each-order normal frequency of the measurement water tank sound field is determined; the sound pressure amplitude measured in the step (1) and the water tank sound field normal frequency determined in the step (2) are taken as input parameters, the algorithm calculating the free field sound power in the reverberation water tank is employed, and the sound power of a to-be-measured sound source in the free field is determined. The method does not need to utilize a known sound source to carry out correction on the reverberation water tank sound field. When the sound field normal frequency in the water tank and the speed potential function are determined, influence of the water tank wall structure on the sound field is considered, so the sound field calculation result in the water tank is more accurate.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Inversion method utilizing single hydrophone to measure reverberation time of non-anechoic pool
ActiveCN104501939AEasy to measureEasy to operateReverberation timeVoltage amplitudeUltrasound attenuation
The invention relates to a reverberation time measurement method and particularly relates to an inversion method utilizing a single hydrophone to measure reverberation time of a non-anechoic pool. The method comprises steps that, a sound source level of a random non-directional sound source is measured in an anechoic pool by utilizing a calibrated hydrophone and is recorded and loaded to frequency and voltage amplitude on the sound source; the non-directional sound source and the hydrophone are put to a to-be-measured non-anechoic pool, frequency and voltage amplitude are recorded and are loaded to the non-directional sound source, the sound source and the hydrophone are simultaneously and slowly moved, and an average space sound pressure level is acquired by utilizing the hydrophone for measurement; the reverberation time of the non-anechoic pool can be acquired through inversion calculation according to the sound source level of the non-directional sound source in a free field and the measured average space sound pressure level of the sound source in the to-be-measured non-anechoic pool. The method has properties of high test efficiency and accurate result, and the average sound energy density attenuation time can be measured not on the basis of definition of the reverberation time.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
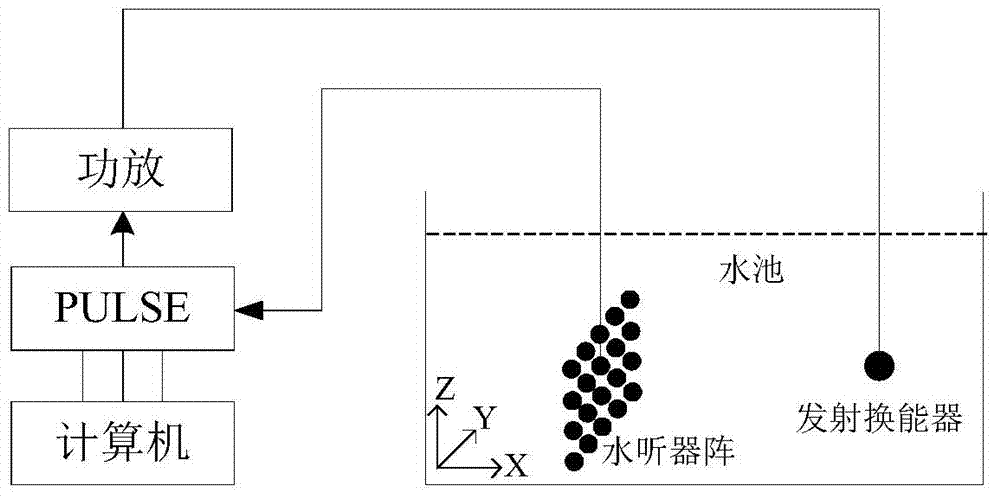
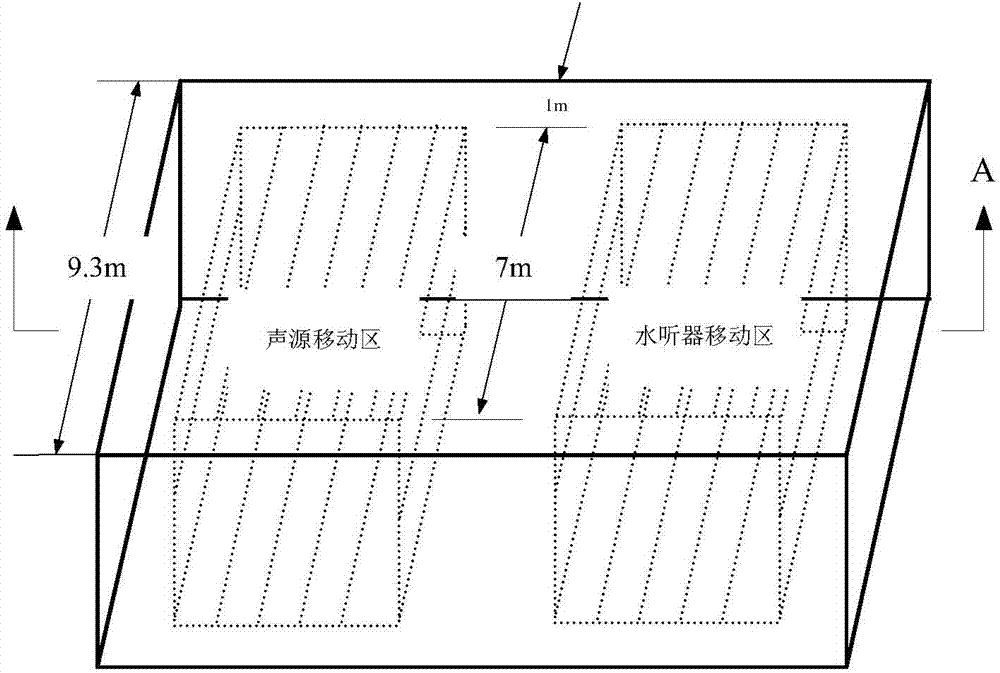
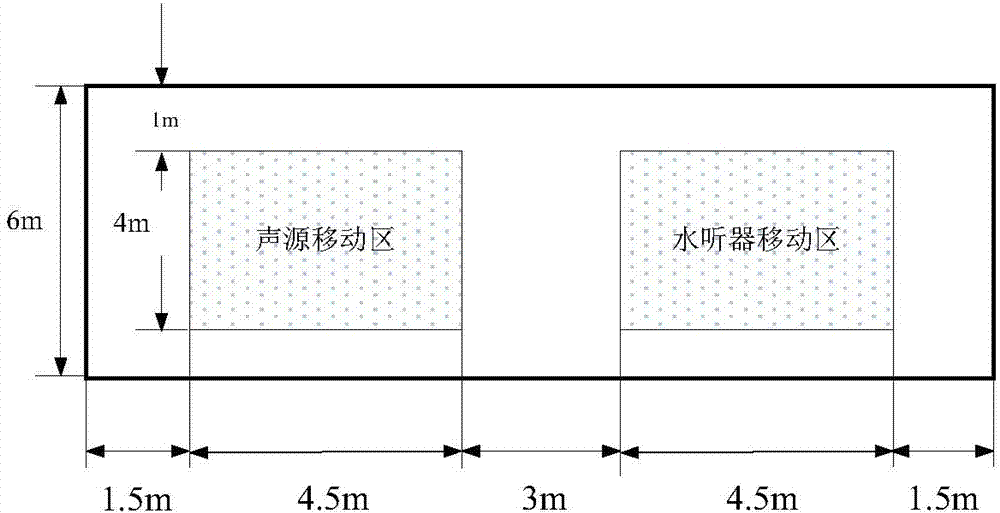
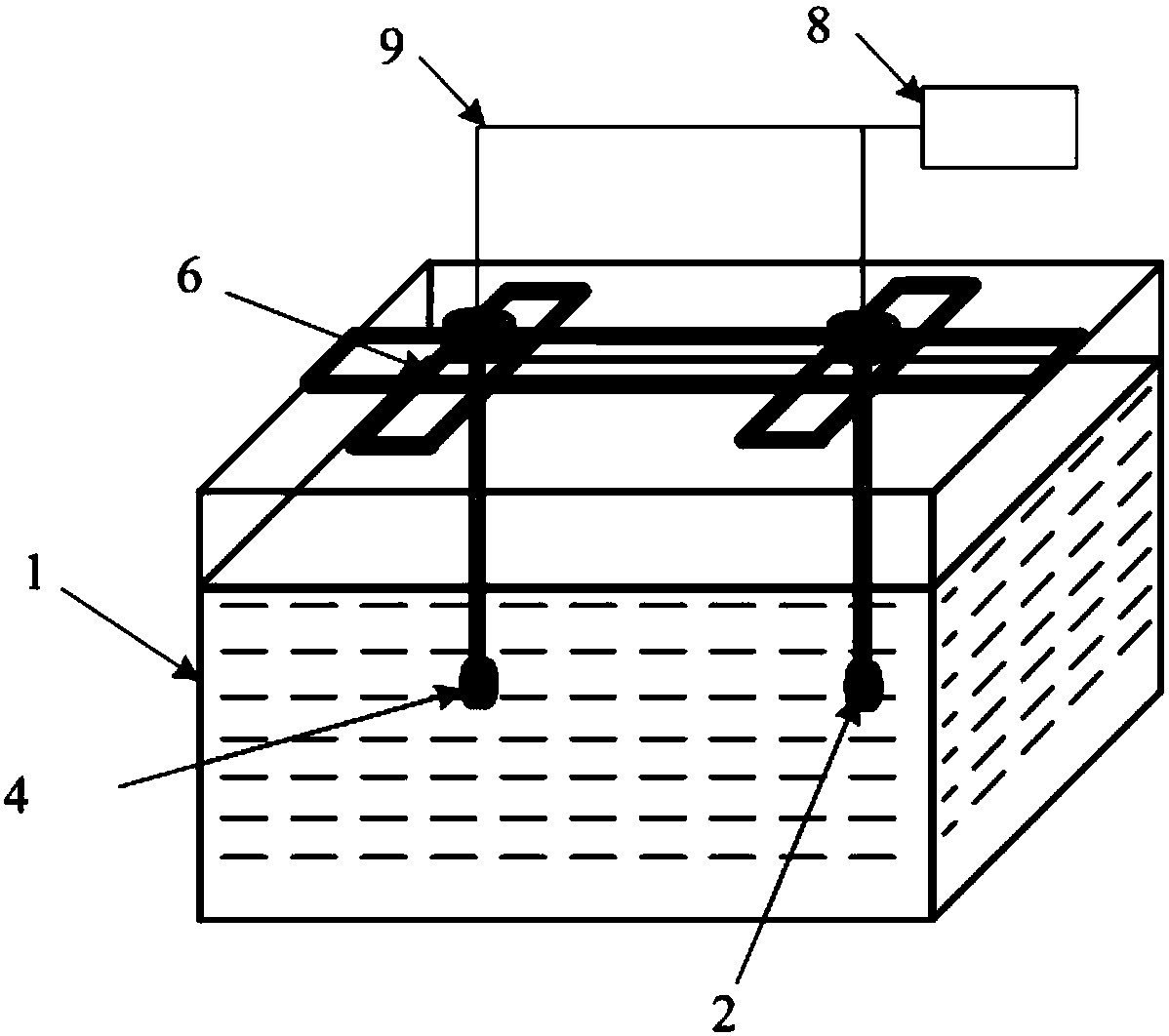
Multifunctional underwater acoustic parameter comprehensive test experimental device
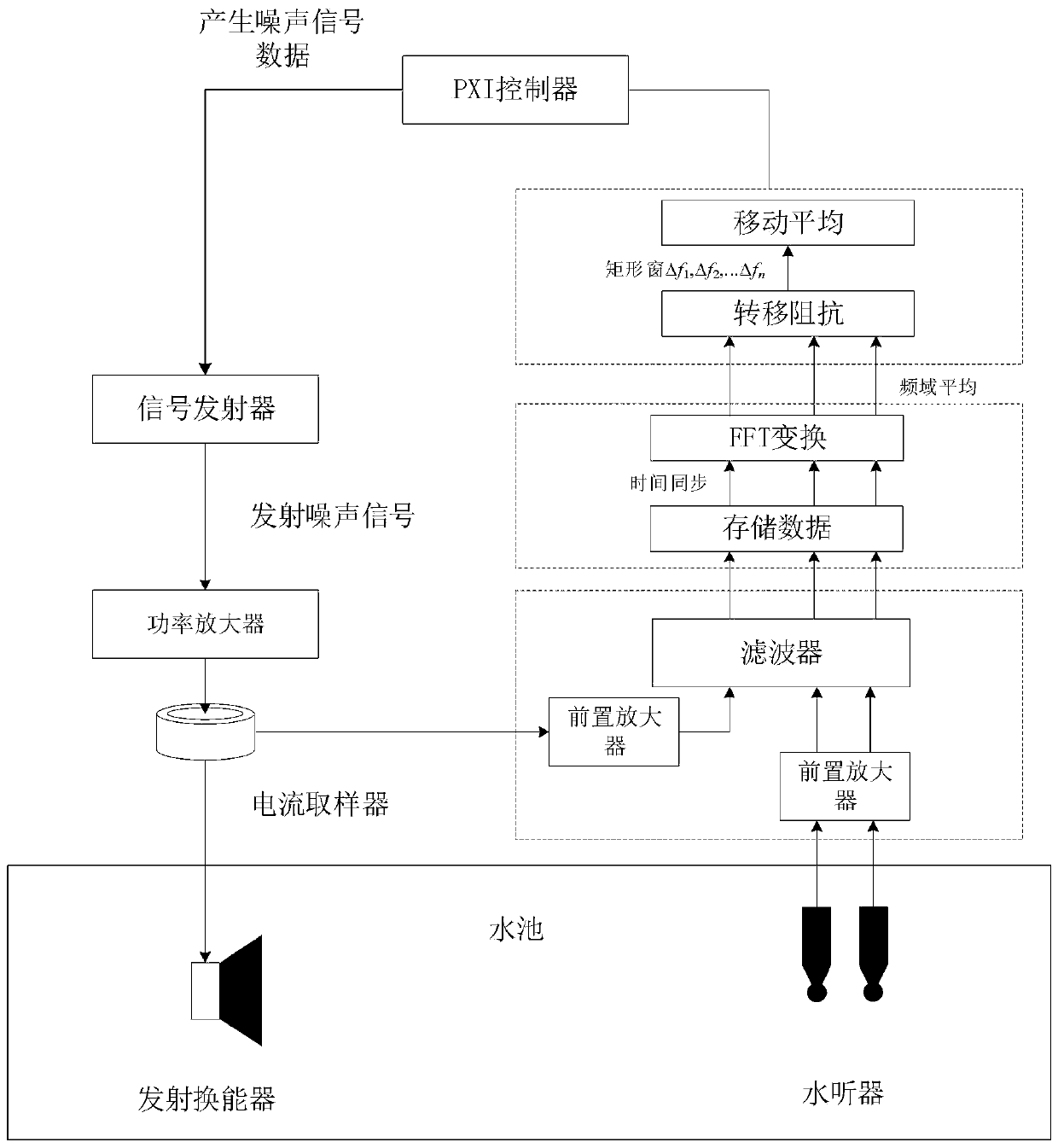
The invention discloses a multifunctional underwater acoustic parameter comprehensive test experimental device, which comprises an underwater acoustic tank, a tested transducer, a standard receiver, an auxiliary transmitting transducer, an reciprocal transducer, a rotary lifting mechanism, an electronic test equipment and a test software. The invention is a necessary experiment teaching instrumentequipment for the underwater acoustic engineering professional practice teaching courses. Various underwater sound field environments including low-frequency standing wave field, a medium-high-frequency free field, a reverberation field and the like can be simulated in a limited space in a laboratory under different frequency bands, so that underwater acoustics, underwater acoustic transducer, sonar and other professional theoretical knowledge can be verified. The invention specifically relates to a multifunctional underwater acoustic parameter comprehensive test experimental device which canrealize experiment teaching of basic parameters of underwater acoustics, underwater acoustic transducer and sonar basic parameters in a laboratory with a frequency range of 2-200 kHz.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
System and method for the calibration of a hydrophone line array
ActiveUS20160091361A1Improve accuracyImprove precisionVibration measurement in fluidSeismic signal receiversMeasurement deviceAcoustic energy
A method is disclosed for calibration of a towed line array. In a low frequency band, calibration is performed using an acoustic field observed by reference standard hydrophones. The observations form a model of a complex acoustic field throughout a space occupied by a measurement apparatus. The array sensitivities are computed by comparing output voltages of the array with the acoustic field estimated at the locations occupied by hydrophones of the array. Variations in the acoustic field that cannot be accounted for by free field propagation theory are included in the calculation of array channel sensitivities. The method extends the low frequency limit for the calibration to less than the minimum frequency at which free field propagation conditions can be approximated. Boundary reflections and spatial variations in the acoustic field are recognized. The spatial distribution of acoustic energy is used to provide low frequency calibration with improved precision.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
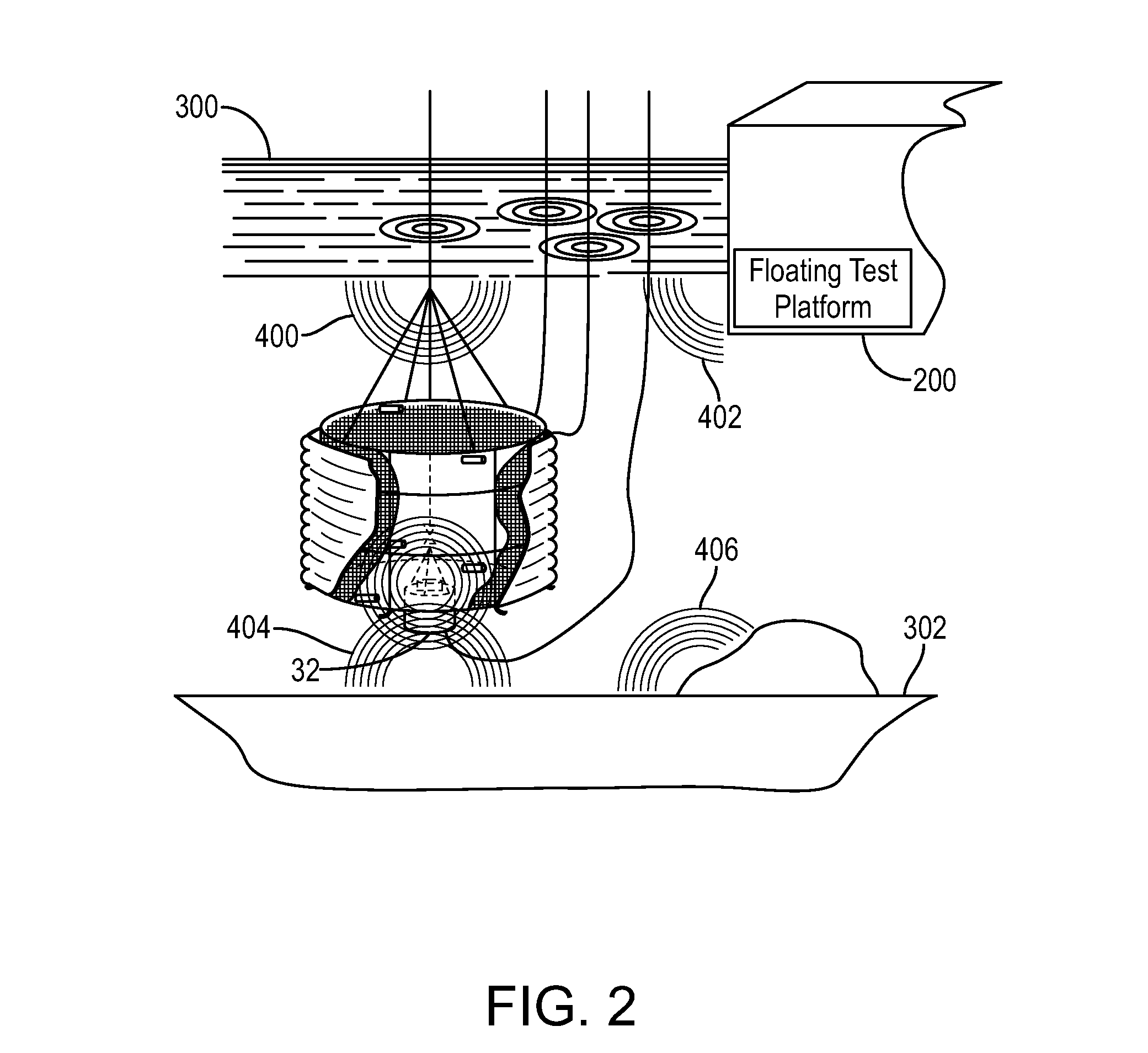
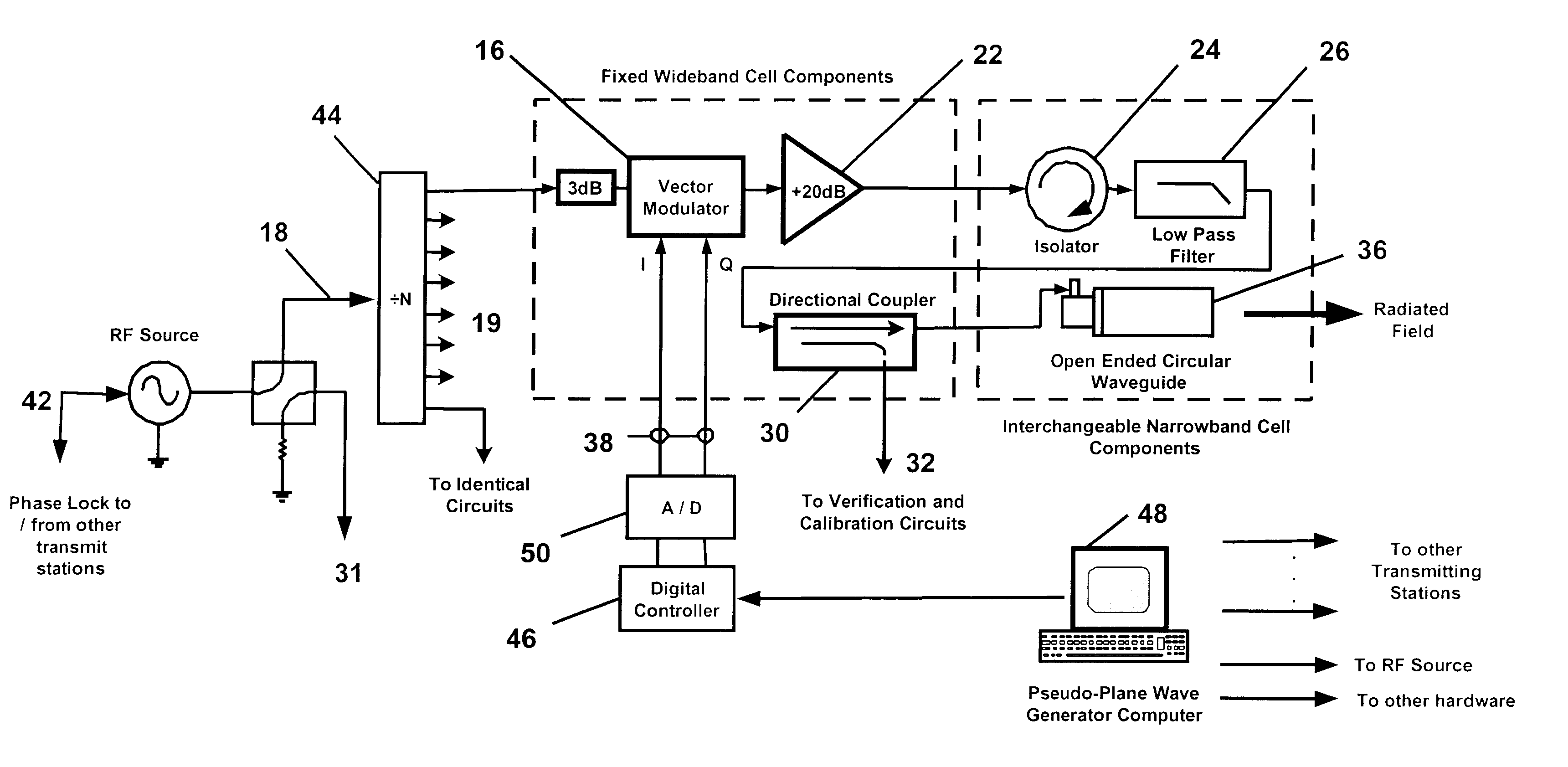
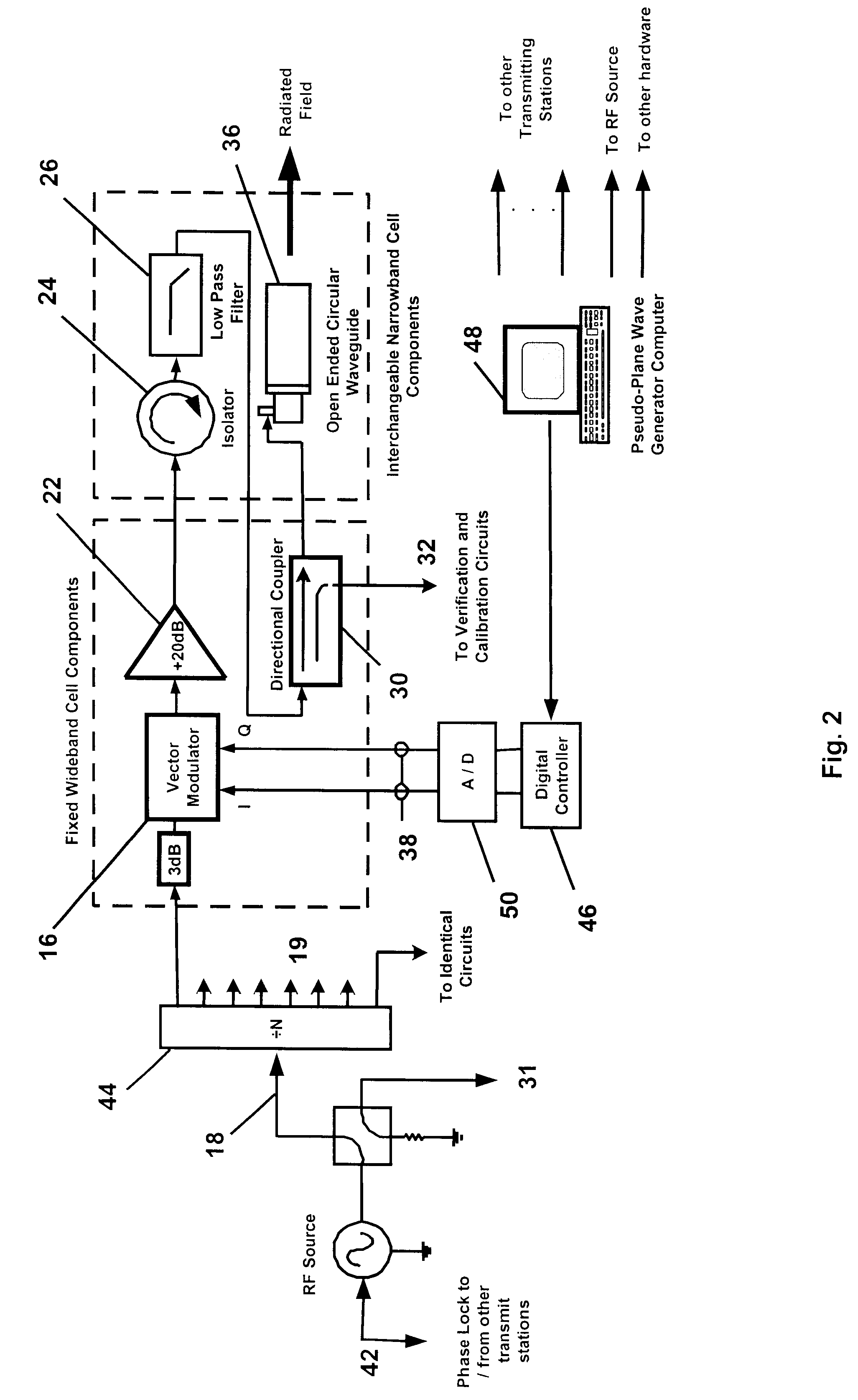
Method for creation of planar or complex wavefronts in close proximity to a transmitter array
InactiveUS6639548B2Weather/light/corrosion resistanceElectrical measurementsElectromagnetic environmentElectromagnetic radiation
An apparatus and method for generating an electromagnetic environment in which the free field, plane wave response of electronic systems of an electrically large (greater than several wavelengths in its longest dimension) object, or objects, under test can be measured in the electromagnetic radiating near field of the transmitter array apparatus. The apparatus comprises: (1) one or more transmitting station(s), each station home to an array of radiating elements; (2) a software operating system and computer that controls the electronic circuits of the apparatus and executes an optimizing algorithm based on a Genetic Algorithm to control the radiation of each transmitting station; and (3) mechanical and electrical circuits that enable the apparatus to conduct self calibration and adjustment as required. In operation, the apparatus is placed and distributed about an object under test. With input from an operator, an optimization procedure based on a Genetic Algorithm determines the magnitude and phase of each radiating element, of each transmitting station. The apparatus then creates an electromagnetic environment that couples to sensors through small apertures distributed about the object under test, and causes the electronic behavior of electronic systems of the object under test to mimic their response to a true free field, plane wave environment.
Owner:DONALD E VOSS D B A VOSS SCI
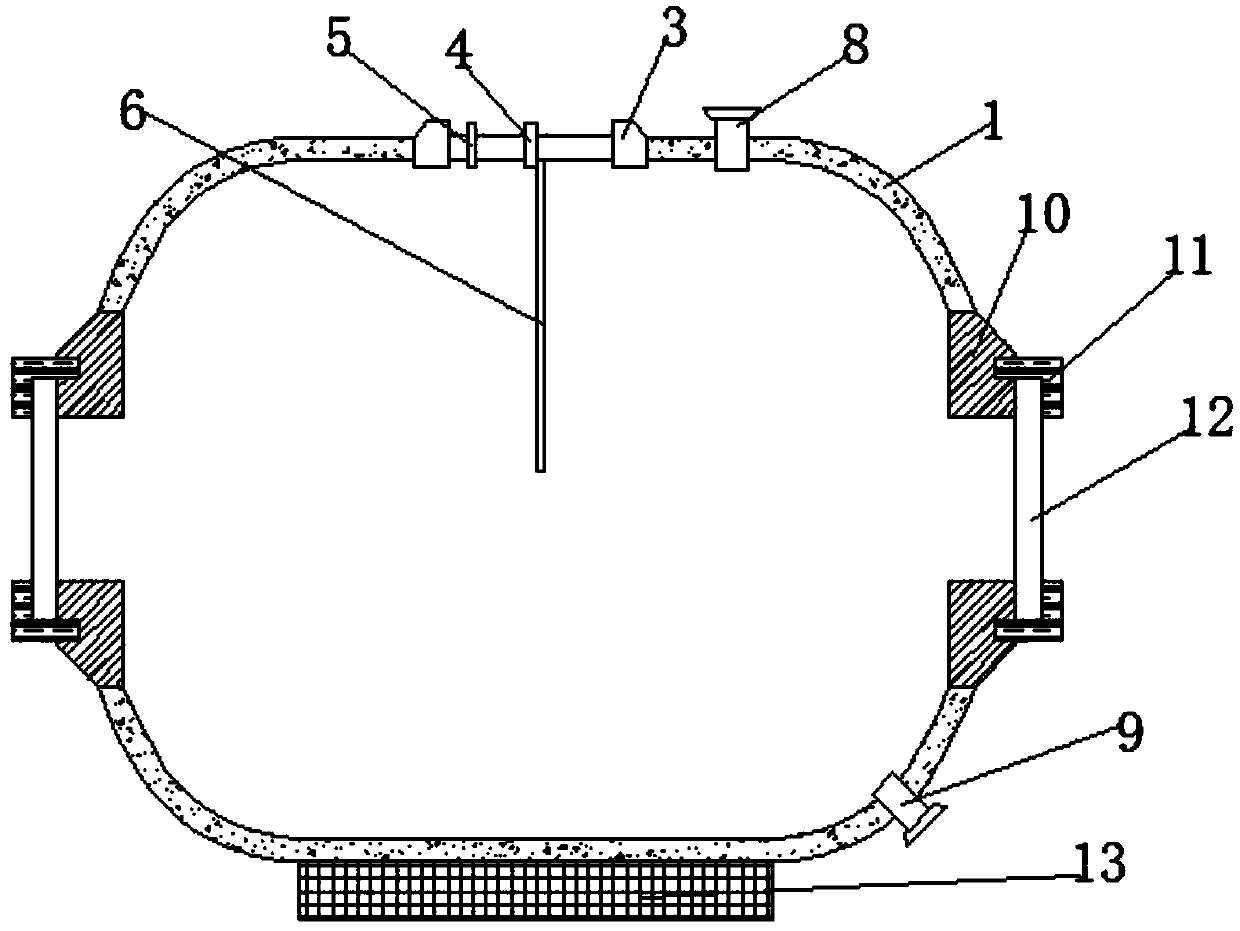
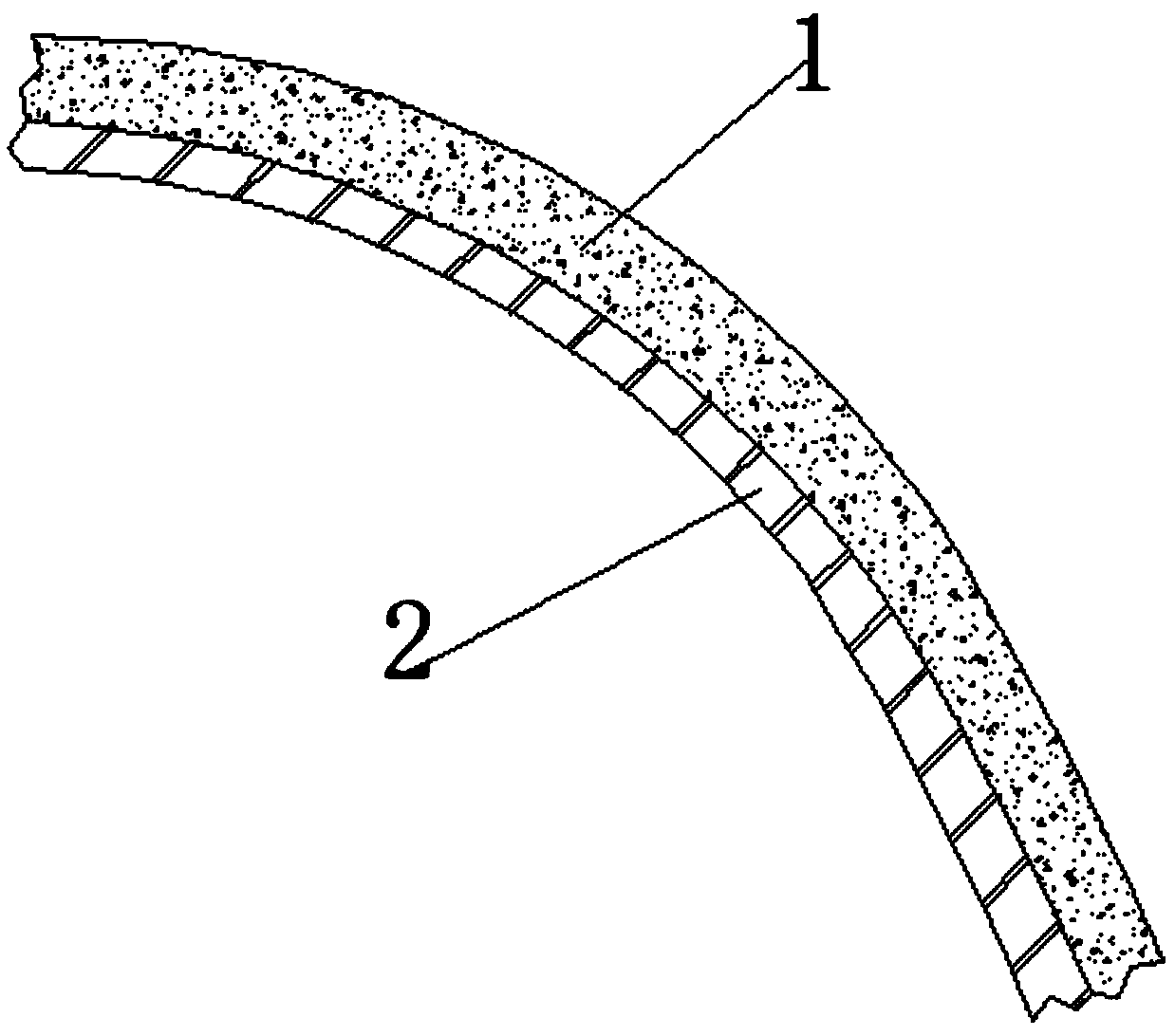
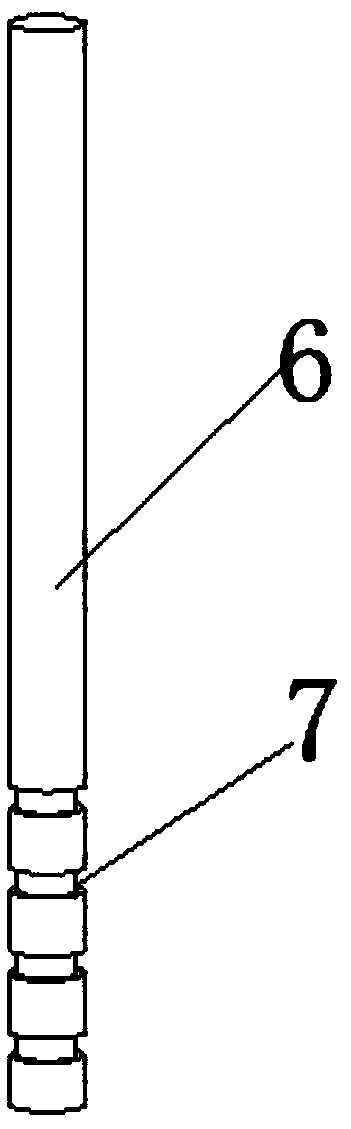
Explosion experimental device for simulating underground free field environment
InactiveCN109596666AReasonable designImprove accuracyMaterial exposibilityDetonationImpedance matching
The invention discloses an explosion experimental device for simulating an underground free field environment. The device comprises a spherical pressure container, an inner wall sprayed layer, an operation sealing head, a detonation line interface, a pressure sensor test interface, an explosive fixing rod, a fixing groove, a water inlet, a water outlet, an installation base, a flange plate, toughened glass and a base support. The explosion experimental device has the beneficial effects that the spherical pressure container is used as a main body, meeting the requirement of certain amount of explosive for many experiments; the device can be pressurized so as to simulate a certain deep water environment; a spherical tank is provided with an observation window which allows an operator to observe shapes of bubbles in the tank in experiment; the interior of the tank is treated by spraying or pasting multiple layers of material better in wave impedance matching, so as to absorb or suppress reflected impulse load to realize an underground free field environment.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
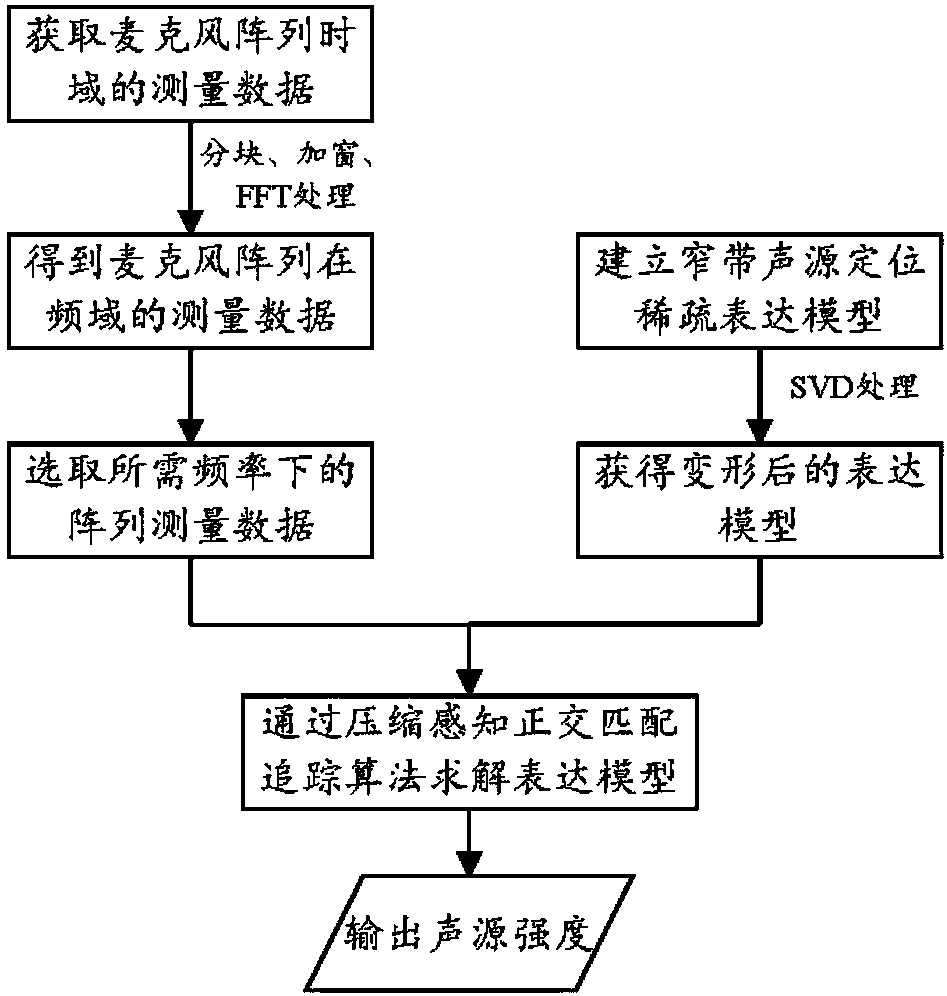
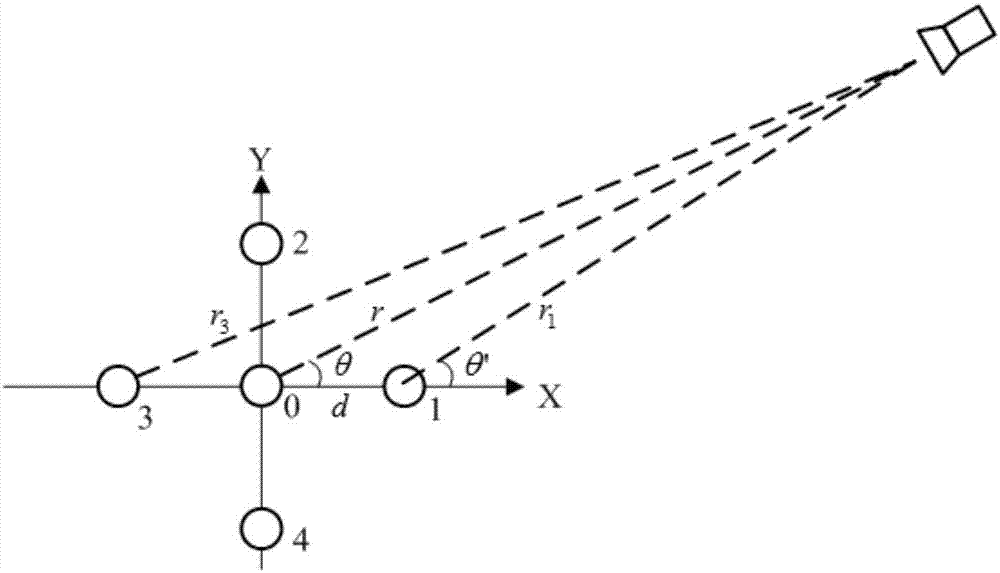
Three-dimensional sound source localization method based on compressed sensing
ActiveCN107247251AImprove noise immunityPosition fixationSound source locationSingular value decomposition
The invention discloses a three-dimensional sound source localization method based on compressed sensing, so as to solve the technical problem of poor anti-noise performance of the existing three-dimensional sound source localization method. In the technical scheme, the measurement value of sound source signals is acquired through a microphone array, a selected three-dimensional sound source area is subjected to uniform mesh generation, and each mesh node is used as a hidden sound source position; according to a Helmholtz equation of a free field Green's function, a measurement matrix between the mesh node and the microphone array is built, and a three-dimensional narrowband sound source localization sparse representation model between the measurement value of the microphone array and unknown sound source signals is acquired; through carrying out singular value decomposition on the measurement value of the microphone array in the sparse representation model, a sound source localization sparse representation model after deformation is acquired; and finally, a compressed sensing OMP (orthogonal matching pursuit) algorithm is adopted to carry out iterative solution on the representation model after deformation, the sound source strength of each mesh node in the sound source area is acquired, and the sound source is localized. The anti-noise performance of sound source localization is improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
A method for simulating progressive failure, like solid-liquid phase transformation behavior of rock and soil media
InactiveCN109284523AAccurate predictionReasonable assessment of hazardsGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationStart upNewtonian fluid
The invention relates to a rock-soil medium progressive failure, solid-like. The smooth particle dynamics (SPH) method is improved from three aspects: boundary condition, constitutive relation and artificial stress, so that the SPH can reproduce the progressive failure of rock and soil media under strong earthquake dynamic condition, solid-like-liquid phase change behavior, constructing slip-freeboundary modified by seismic wave velocity to apply seismic wave, creating free-field boundary to prevent seismic wave reflection, using particle rheology for reference, combining Drucker-Prager constitutive model and Newtonian fluid constitutive model construct a new unified constitutive model, which can describe the phase from sliding (solid-like) to flowing (liquid-like) in geotechnical media.The invention effectively reproduces the kinematic characteristics of the start-up, high-speed flow and accumulation process of the landslide, analyzes the progressive failure of the rock and soil medium and the penetration process of the sliding surface under the action of the strong earthquake, thereby accurately predicting the sliding distance, and reasonably assesses the earthquake-triggered landslide. The hazard caused by debris flow provides scientific basis for the planning and design of earthquake prevention and disaster reduction.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Photoacoustic free field detector
InactiveUS20090038375A1Enhanced signalHigh levelAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAcoustic energyAbsorbent material
The invention relates to a photoacoustic detector including an acoustically open measuring area which is not completely surrounded by a housing. The detector includes an arrangement for introducing excitation light into the measuring area, such that the excitation light can be absorbed by absorbent materials which are located in the measuring area and which are used to produce acoustic energy. The invention also relates to a detector which includes at least one acoustic sensor and an arrangement is provided in order to concentrate the acoustic energy, in order to reach a local maximum of the acoustic pressure on at least one position. The at least one sensor is arranged in the vicinity of the at least one position, whereon the local maximum of the produced acoustic pressure is present or can be produced. The invention also relates to an associated method.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Junction-free field-effect transistor and preparation method thereof
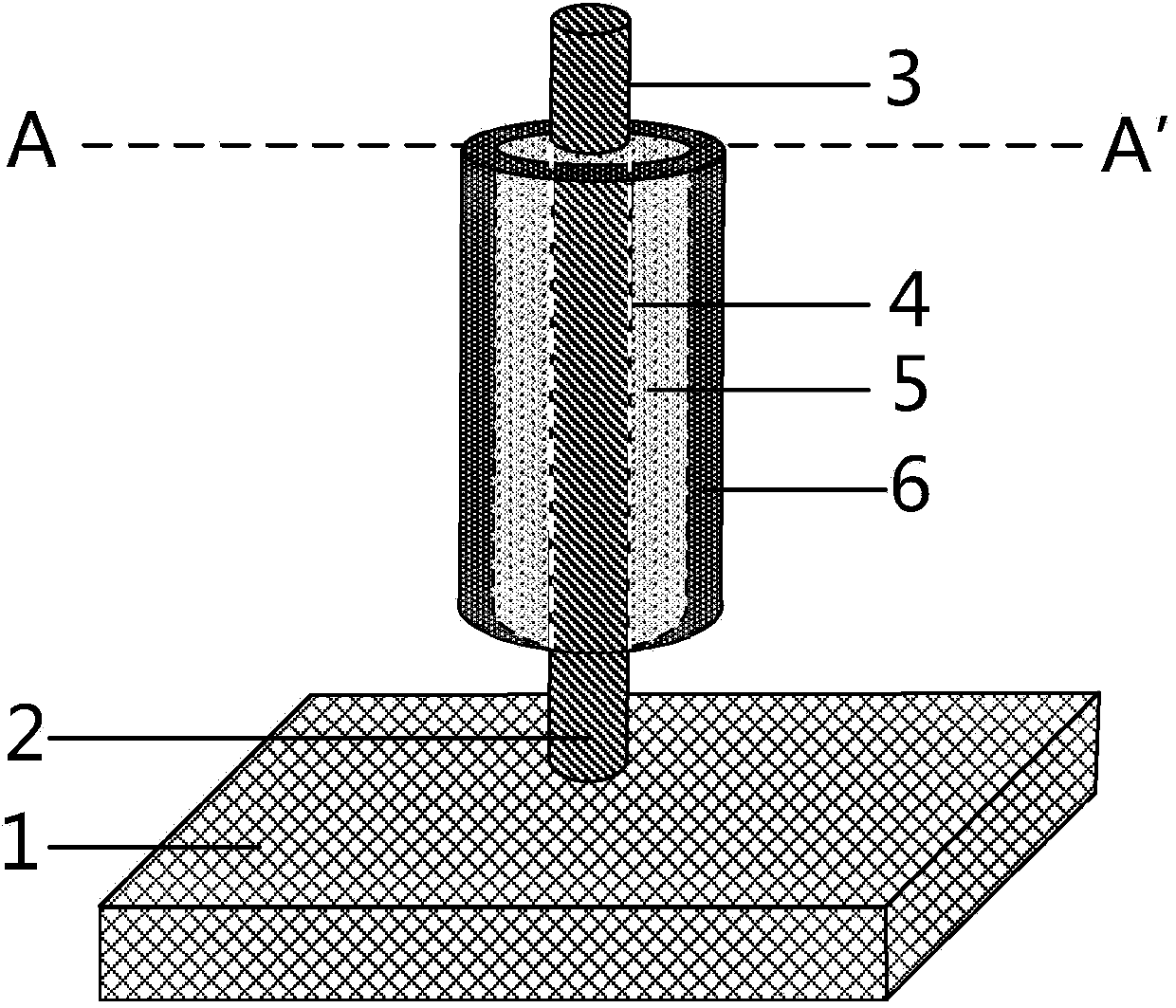
ActiveCN104201195AHighly integratedGood gating abilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricImpurity diffusion
A surrounding gate field-effect transistor combined with a vertical channel (4) and a junction-free structure comprises a surrounding semiconductor channel in the vertical direction, a surrounding gate electrode (6), a surrounding gate dielectric layer (5), a source region (2), a drain region (3) and a semiconductor substrate (1), wherein the source region (2) is located at the bottom of the vertical channel (4) and connected with the substrate (1), the drain region (3) is located at the top of the vertical channel (4), and the gate dielectric layer (5) and the gate electrode (6) surround the vertical channel (4) circularly. The impurities of the same type and concentration are doped into the source region (2), the drain region (3) and the vertical channel (4). The same impurities are doped into source and drain channels of the transistor, so that heat budget is greatly reduced, the impurity diffusion and abrupt junction forming problems are eliminated, process requirements are simplified, integration machining photo-etching ultimate limit is broken through by utilizing the vertical channel and a surrounding gate structure, and the integration degree is improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
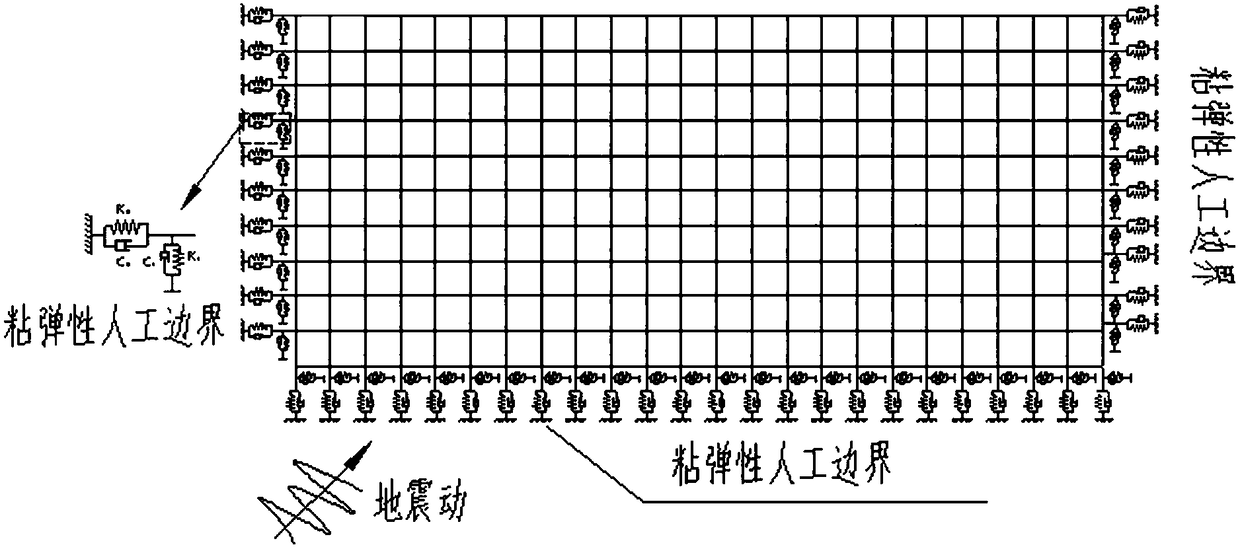
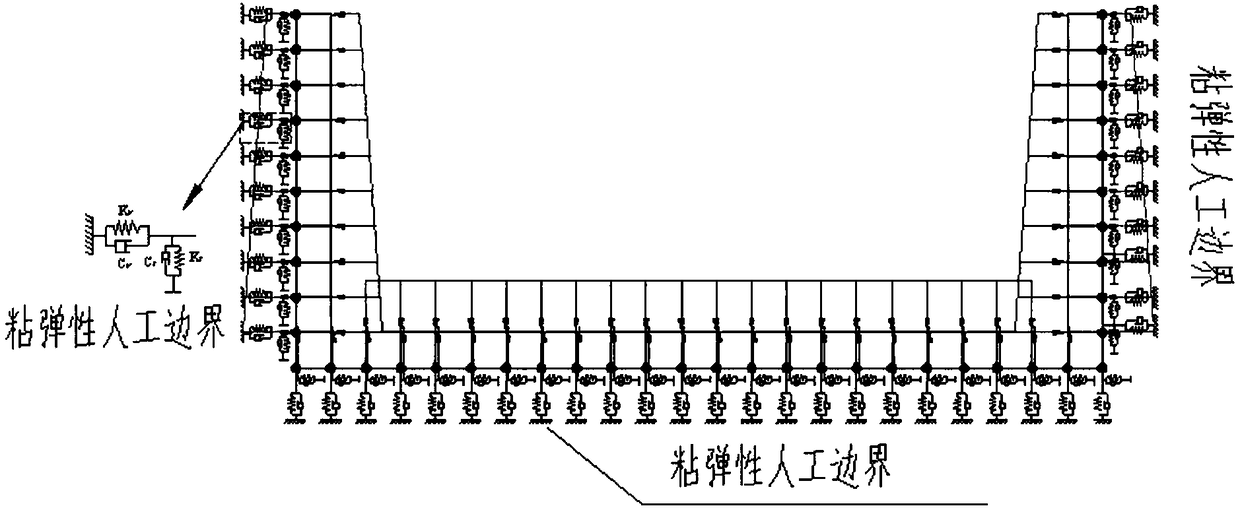
Oblique incidence fluctuation analysis method for seismic waves of horizontal layered site
ActiveCN108549104AHigh precisionImprove computing efficiencySeismic signal processingTime domainSoil science
The invention discloses an oblique incidence fluctuation analysis method for seismic waves of a horizontal layered site, and the method comprises the following steps: (1), solving a one-dimensional time domain free field of the layered site when the seismic waves are obliquely incident, considering the nonlinear characteristics of a soil body when solving the free field, and considering the soil body as a viscoelastic material; (2), carrying out the artificial boundary transformation of the free field, and considering the initial stress of the soil body during the artificial boundary transformation; (3), determining an equivalent load of the artificial boundary through a geotechnical analysis model based on an OpenSees calculation platform; (4), applying an equivalent load to the artificial boundary, and carrying out the nonlinear fluctuation analysis. The method provided by the invention enables the soil body to be taken as the viscoelastic material, gives consideration to the nonlinearity and hysteretic characteristics of the soil body under the dynamic action, is high in precision, and is high in calculation efficiency.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
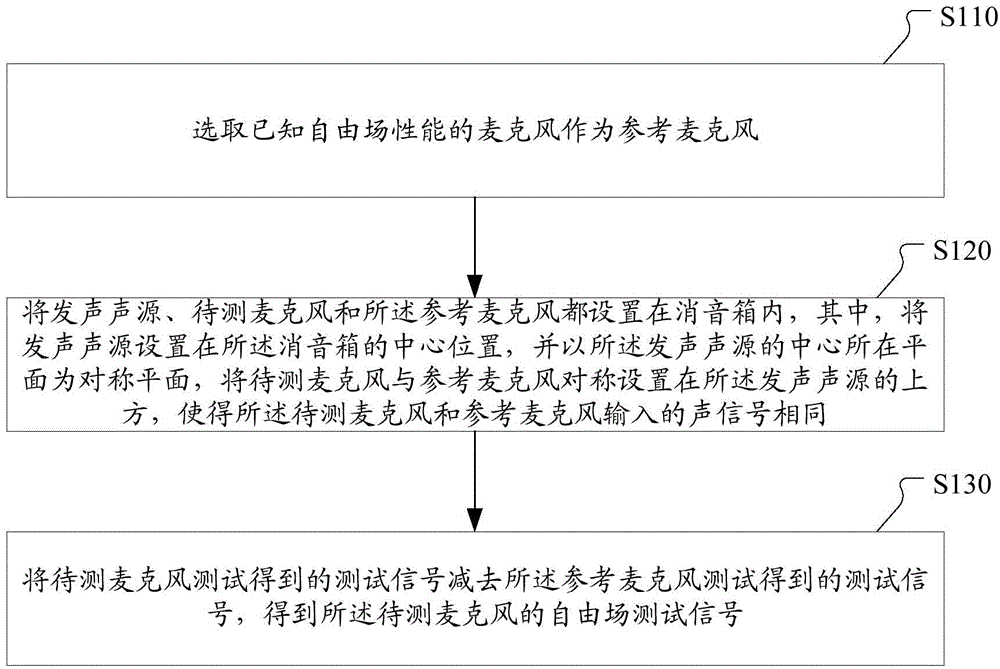
Microphone testing method and testing system
ActiveCN104640055AReduce precisionReduced precision requirementsElectrical apparatusSound sourcesEngineering
Owner:GOERTEK INC
Free field restoration method of unstable state planar sound source
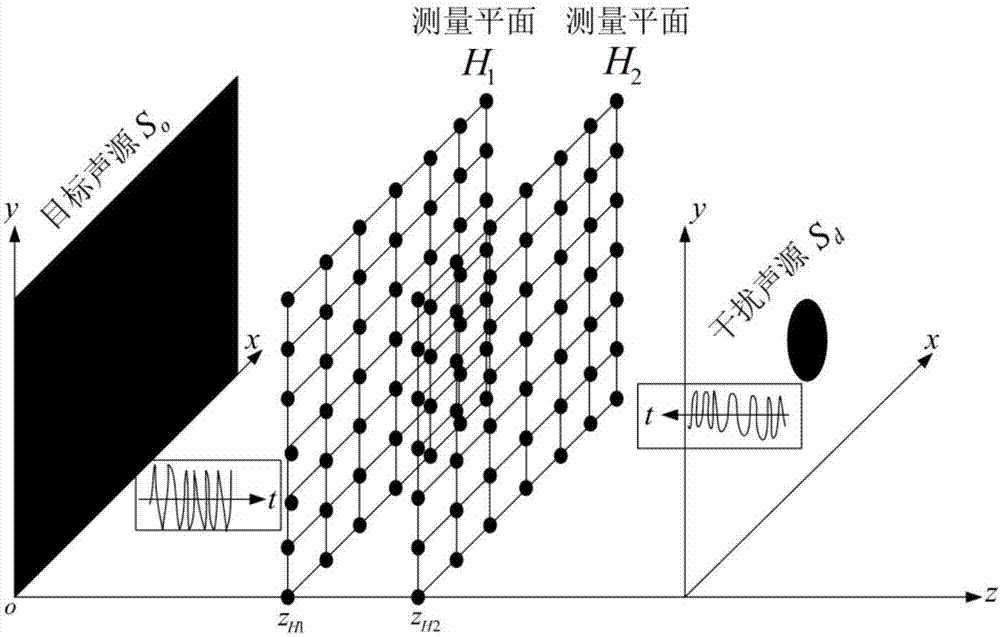
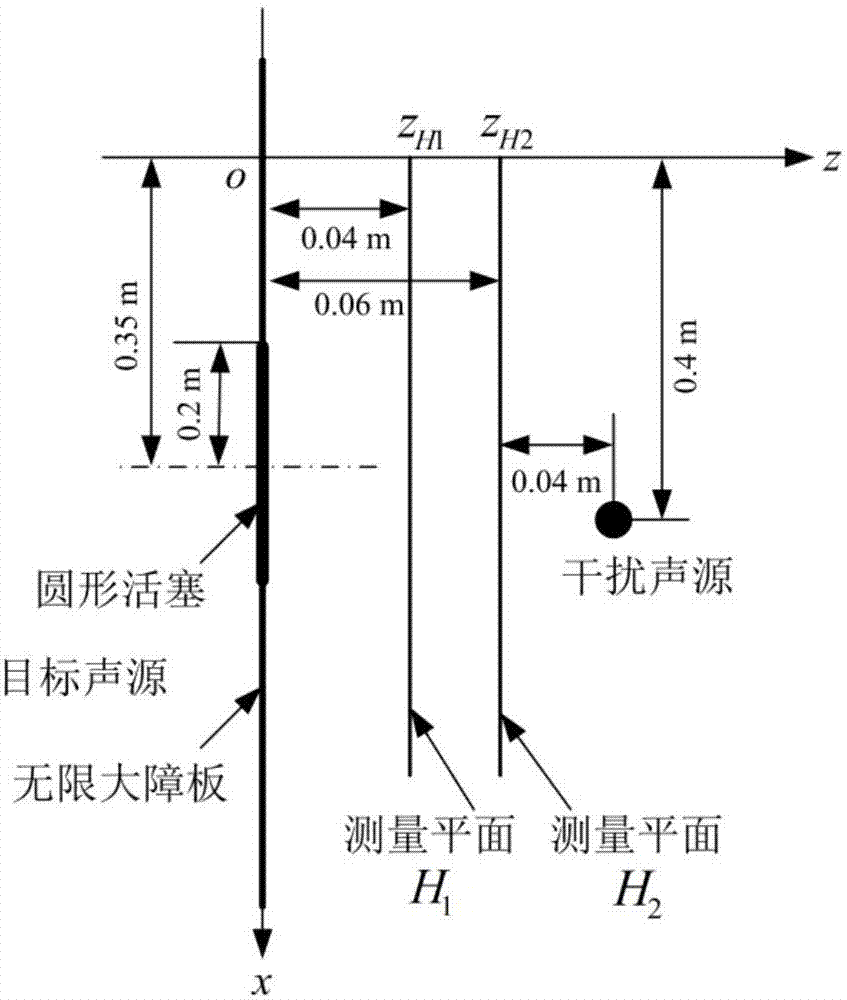
ActiveCN107478325AEliminate unsteady scattered sound fieldSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementSound sourcesSignal on
The present invention discloses a free field restoration method of an unstable state planar sound source. Time-domain sound pressure signals on two measurement planes are subjected to two-dimensional space Fourier transform to obtain sound pressure time-domain wave number spectrums at each wave number on corresponding planes; the two sound pressure time-domain wave number spectrums on the measurement planes and a time-domain pulse response function between known sound pressures are employed to separate from an unstable state outward sound field and an unstable state inward sound field; a target sound source surface reflection coefficient is taken as a boundary condition to establish a relation of the unstable state inward sound field and a scattering sound field and calculate an unstable state scattering sound field; and the unstable state scattering sound field is removed from the separated unstable state outward sound field, and the time-domain sound pressure signals radiated on the measurement planes in the target sound source free field condition is restored. The free field restoration method of the unstable state planar sound source eliminates the unstable scattering sound on the time domain and restores the time-domain sound pressure radiated on the measurement planes in the target sound source free field condition so as to provide a pre-processing means for accurate analysis of the time variation radiation features and vibration features of the target sound source in the real sound field environment.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Bounded space correction method for low-frequency super-directional multi-polar vector array
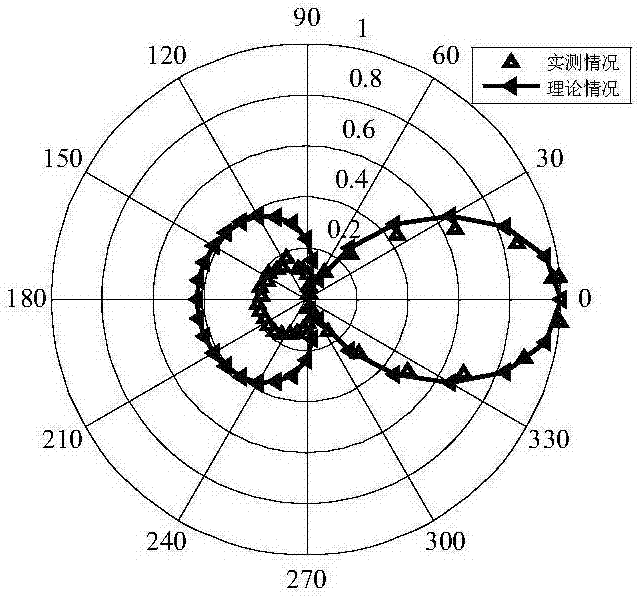
ActiveCN107037418AOvercoming the problem of large-scale free-field space required for calibrationEasy to operateWave based measurement systemsSound sourcesBound water
The present invention belongs to the field of underwater acoustic vector array calibration, and more particularly relates to a bounded space correction method for the low-frequency directional multi-polar vector array for the calibration of the super-directional multi-polar vector array within the low-frequency ranging from 20 to 1000 hz. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a super-directional multi-polar vector array including 0 to 4 matrixes; producing by a modulating signal generator a CW pulse signal to be loaded by a power amplifier into a sound source to form a testing sound field; rotating super-directional multi-polar vector array for 0 to 360 degrees; and collecting and storing the receiving signals of the 0 to 4 elements with each array element consisting of a sound pressure signal and two channels of vibration velocity communication signals, etc. The method of the invention overcomes the problem that currently, the calibration of a small-scale array needs a large-scale free field space and provides a calibration method for bounded water areas. The method has strong operability, is convenient and practical to use and can be widely used in the calibration of low-frequency super-directional vector array, making it widely used in various fields of low-frequency water sound metering.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
An accelerated processing method for a large field of view intelligent video surveillance system
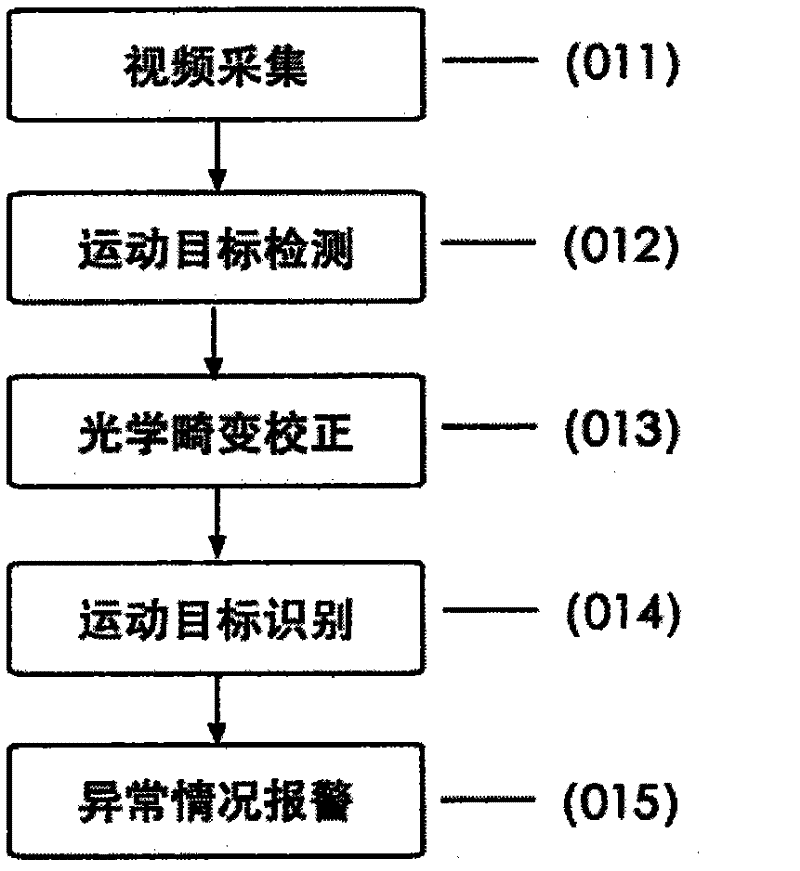
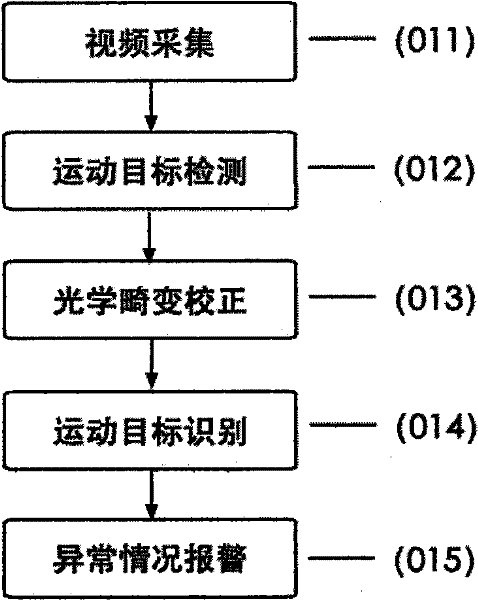
InactiveCN102291568AMeet real-time requirementsSimple methodCharacter and pattern recognitionClosed circuit television systemsImaging processingPhotodetector
The invention relates to an accelerated processing method of a large field of view intelligent video monitoring system, and belongs to the fields of computer image processing technology and photoelectric detection technology. This method uses a large field of view imaging device to collect images; uses a transmission cable to input the images into a computer in real time; performs image processing in the computer, and sends an alarm if it meets the detection requirements of the monitoring system. This method is the first to propose a distortion-free fast projection method for local viewing angles in a large field of view. Break the conventional practice of the existing intelligent video surveillance system to complete the distortion correction of the global image first, and then perform operations such as moving target detection and recognition; first complete the detection of moving targets in the global large field of view, and then only perform local Distortion correction and recognition are performed on the small viewing angle image, which reduces the amount of calculation data and reduces the time cost of image processing. On the premise of ensuring accurate recognition, it meets the requirements of real-time online processing of the monitoring system.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for calibrating sound pressure in low-frequency sound wave free field
ActiveCN102523057AInhibition effectEasy to operateSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionTransmission monitoringSignal onLow frequency band
The invention relates to a method for calibrating sound pressure in a low-frequency sound wave free field. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) arranging an emitting sensor and a receiving sensor on a calibration bracket in a finite area, wherein the emitting sensor emits a pulse signal with a certain parameter, and the receiving sensor acquires a received sound pressure signal; 2) changing an absolute position of the calibration bracket in a calibration area, retaining the emitting sensor and the receiving sensor at the original positions of the calibration bracket, keeping a relative position between the emitting sensor and the receiving sensor unchanged, and acquiring the received sound pressure signal by the receiving sensor; and 3) synchronously superposing the signals acquired twice, averaging the superposed signal, and thus obtaining a required sound pressure signal of the free field. The method has the advantages that: the method is easy and convenient to operate; influence of boundary reflection is not needed to be considered; the influence of a reflected signal on a through sound signal can be effectively suppressed at a low frequency band of the sound wave; the lower frequency limit of sound pressure calibration of the indoor free field is expanded; and the method is reliable.
Owner:THE 715TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP
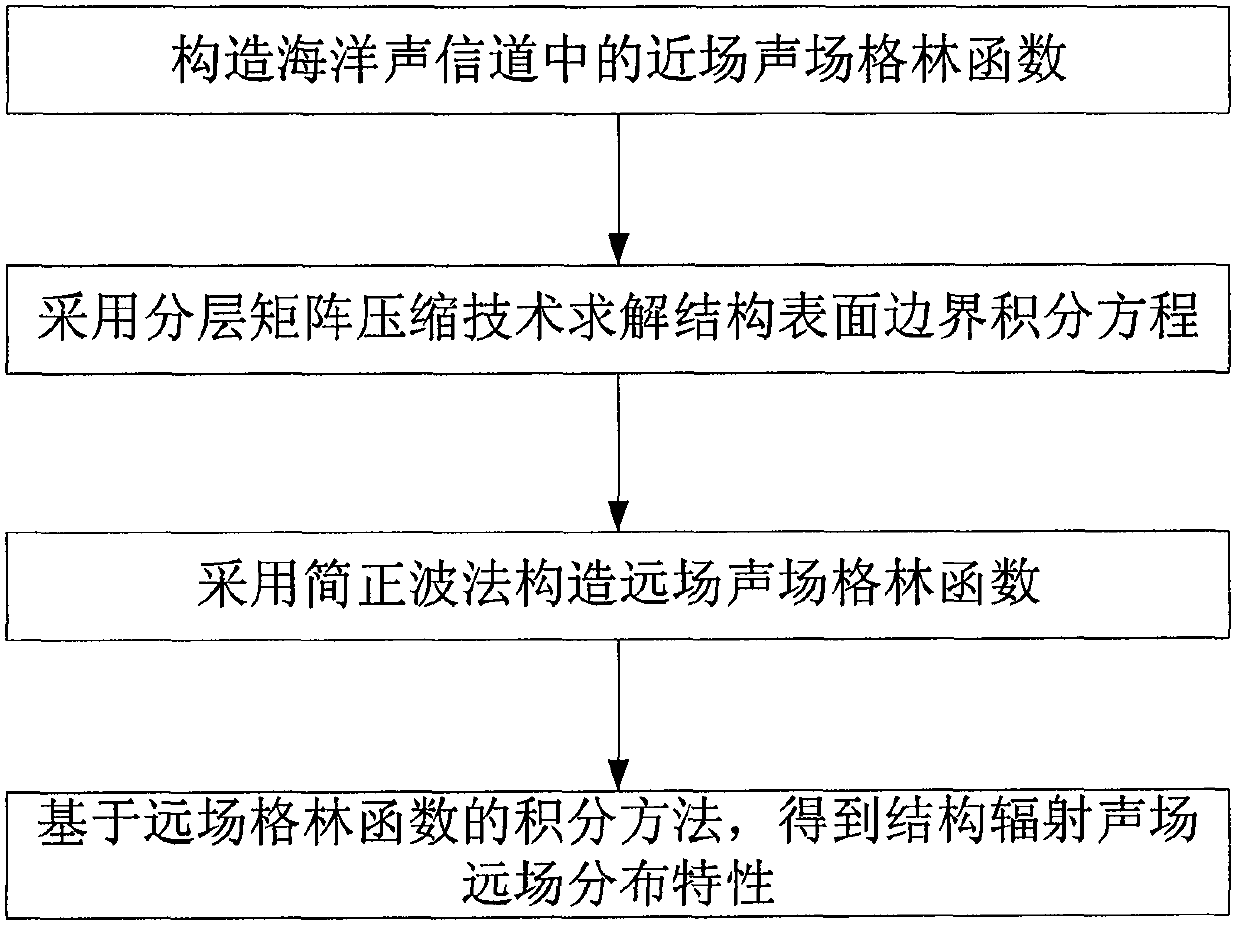
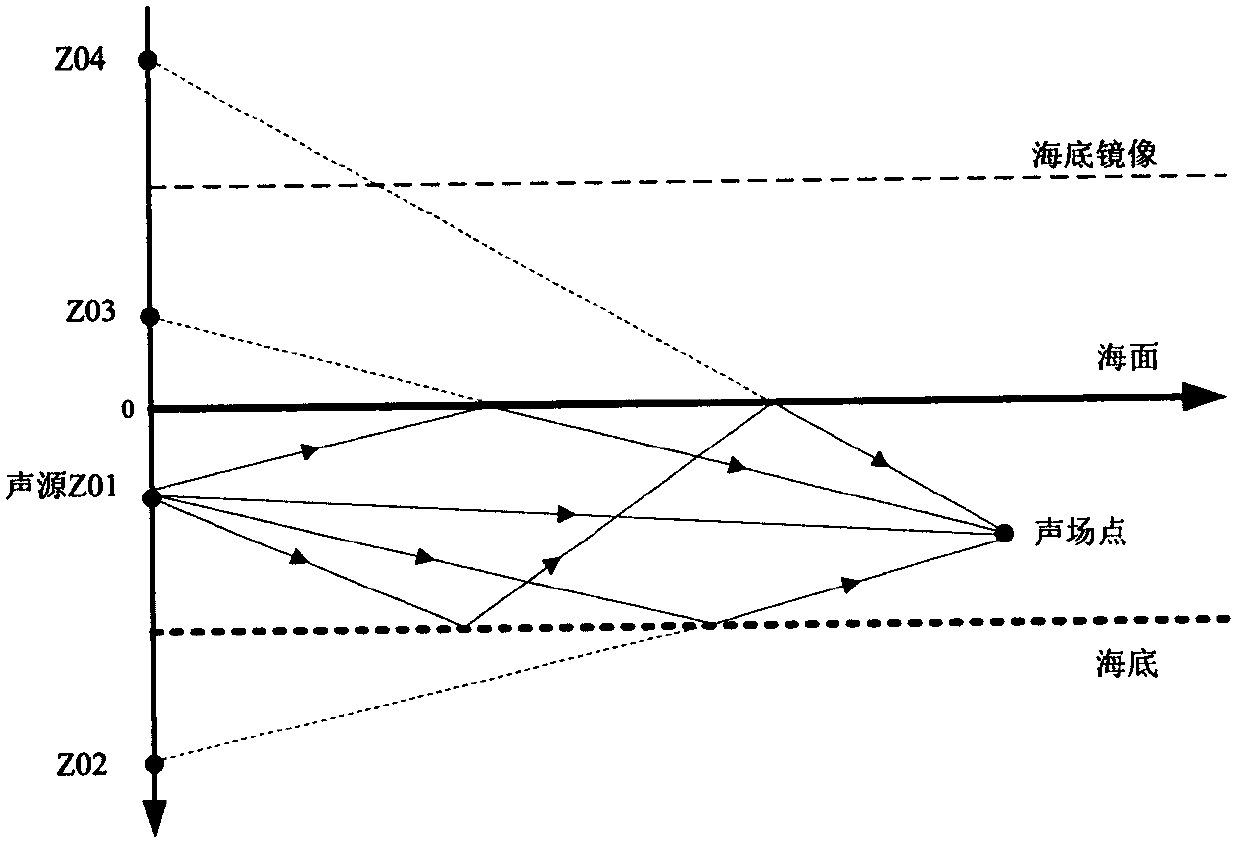
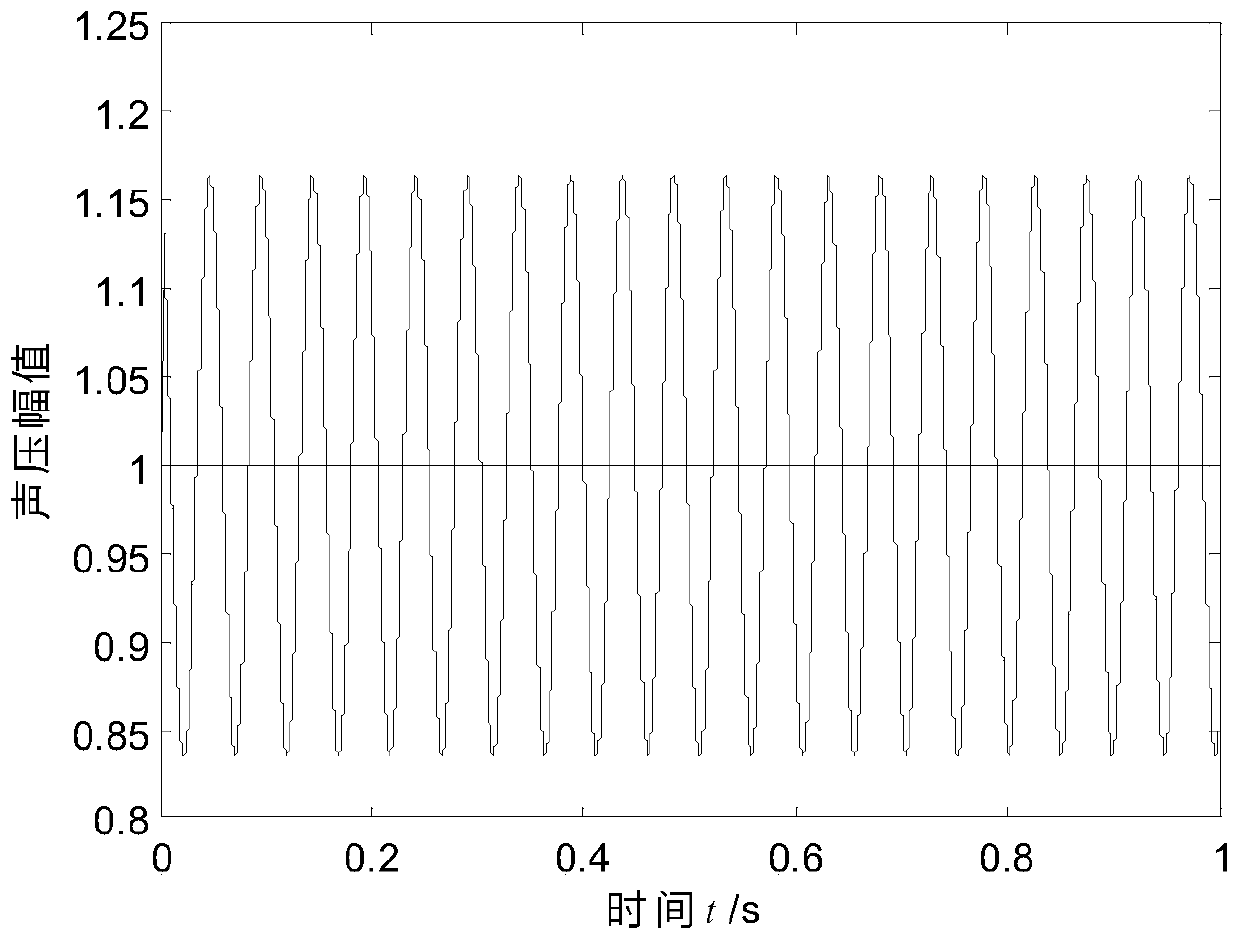
A method for calculating a complex structure radiation sound field in a marine acoustic channel
PendingCN109657257AReduce consumptionImprove adaptabilityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsOcean bottomDecomposition
The invention discloses a method for calculating a complex structure radiation sound field in a marine acoustic channel, and belongs to the technical field of acoustic numerical calculation. The limitation that a traditional boundary element method is only suitable for free field sound field calculation is broken through, and a sound field Green function in an ocean sound channel is established. Ahierarchical matrix compression technology is adopted to divide a radiation impedance matrix into a series of hierarchical matrix blocks with different sizes, and an iteration method is further utilized to solve a matrix equation. Compared with the prior art, the method has the effects and benefits that the acoustic calculation function of the traditional boundary element method is expanded frominfinite uniform media to the bounded space of the ocean channel, and the influence of sea surface, seabed boundary and sound velocity gradient distribution can be considered. And on the other hand, the radiation impedance matrix is subjected to hierarchical compression, the consumption of a computer memory is greatly reduced by utilizing the low-rank characteristic approximate decomposition of the matrix block, the influence of the diversity of a sound field Green function under the complex marine channel condition is avoided, and the algorithm adaptability is good.
Owner:中国船舶重工集团公司第七六〇研究所
Broadband calibration method for sensitivity free field of hydrophone based on pink noise
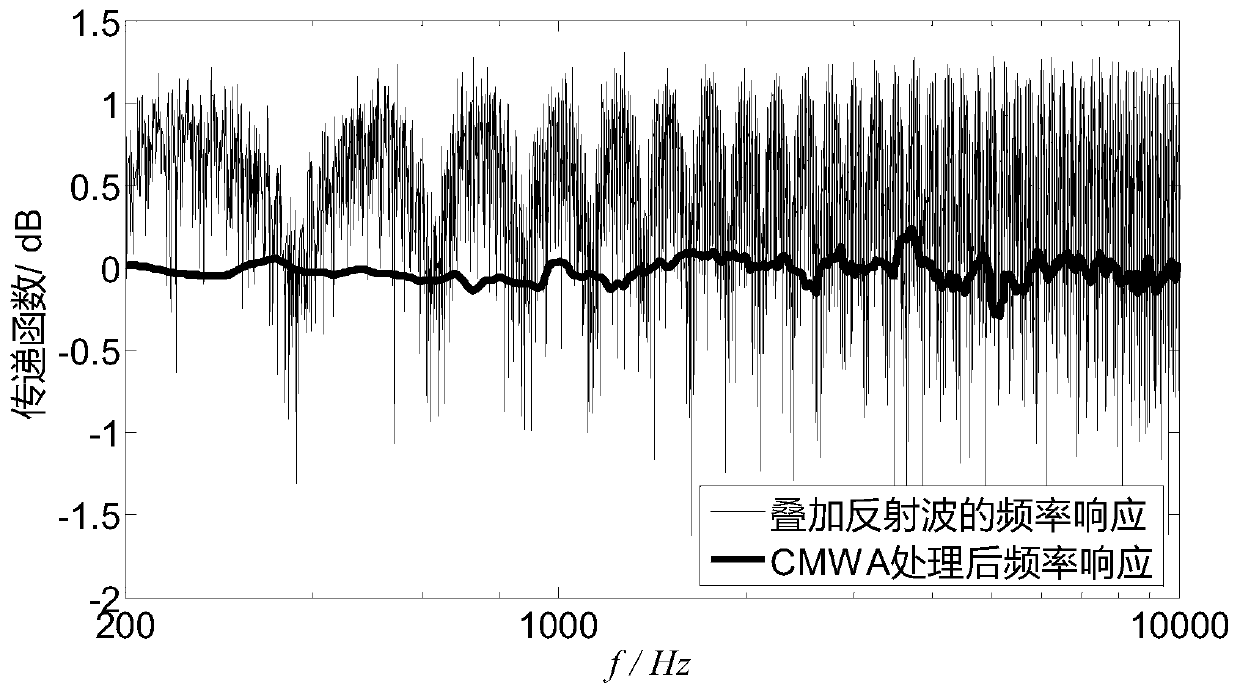
ActiveCN110186546AHigh precisionEliminates the effects of reverberation in reflected wavesWave based measurement systemsVibration measurement in fluidMoving averageControl signal
The present invention discloses a broadband calibration method for sensitivity free field of a hydrophone based on pink noise. The calibration method relates to the field of free-field underwater acoustic measurement and is mainly used for broadband measurement of hydrophone free field sensitivity. According to the method of the invention, a signal source is controlled to transmit a broadband pinknoise signal; a transmitted current signal and a received voltage signal are subjected to synchronous treatment such as interception and zero padding and FFT transformation; finally a transfer function in the frequency domain is obtained. By analyzing the direct wave and reflected wave of a tank, the transfer function is subjected to moving average with a rectangular window; the reverberation influence of the reflected wave of the tank is eliminated; a broadband transfer function of the free field between a transmitting transducer and the hydrophone is obtained; and the broadband measurementfor hydroacoustic parameters such as hydrophone sensitivity is realized. The method can be used for broadband calibration of the hydrophone in an anechoic tank, a reverberant tank, an outfield lake and sea.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Multi-microphone neural network for sound recognition
A neural network is provided for recognition and enhancement of multi-channel sound signals received by multiple microphones, which need not be aligned in a linear array in a given environment. Directions and distances of sound sources may also be detected by the neural network without the need for a beamformer connected to the microphones. The neural network may be trained by knowledge gained from free-field array impulse responses obtained in an anechoic chamber, array impulse responses that model simulated environments of different reverberation times, and array impulse responses obtained in actual environments.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Experimental and numerical combined method for high pressure pulsating bubble motion and load in water
ActiveCN108846185AImprove research technologyImprove research toolsDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsChemical industryUnderwater explosion
The invention discloses an experimental and numerical combined method for high pressure pulsating bubble movement and load in water. The method comprises the following steps of: (1), using the Rayleigh-Plesset spherical bubble theory to calibrate the free-field high-pressure pulsating bubble experiment method, and determining a bubble initial condition; (2), using the calibrated bubble experimentmethod to carry out bubble dynamics experiments under different boundary conditions; (3), using a boundary element method to calculate dynamic characteristics of aspherical bubbles on the basis of theobtained experimental result; (4), adopting an auxiliary function method to calculate the velocity field and the pressure field around the bubbles; and (5), performing post-processing on the calculation result. The invention is suitable for studying the motion and load characteristics of the bubbles near a structure and a free surface in the gravity field, has the calculation accuracy and efficiency meeting the engineering needs, and has wide application prospect in the fields of underwater explosion, cavitation, medicine, cleaning, the chemical industry and the like.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
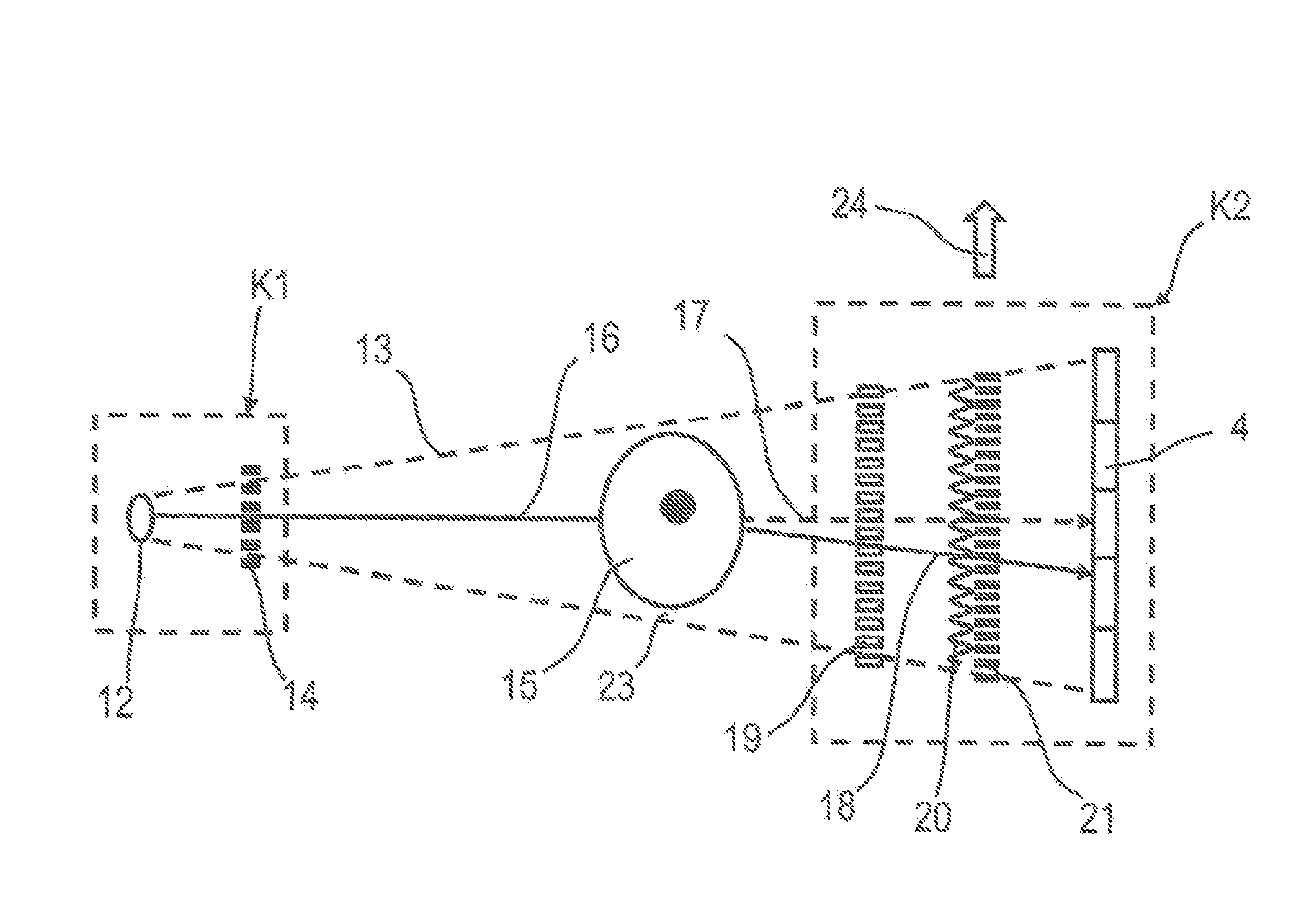
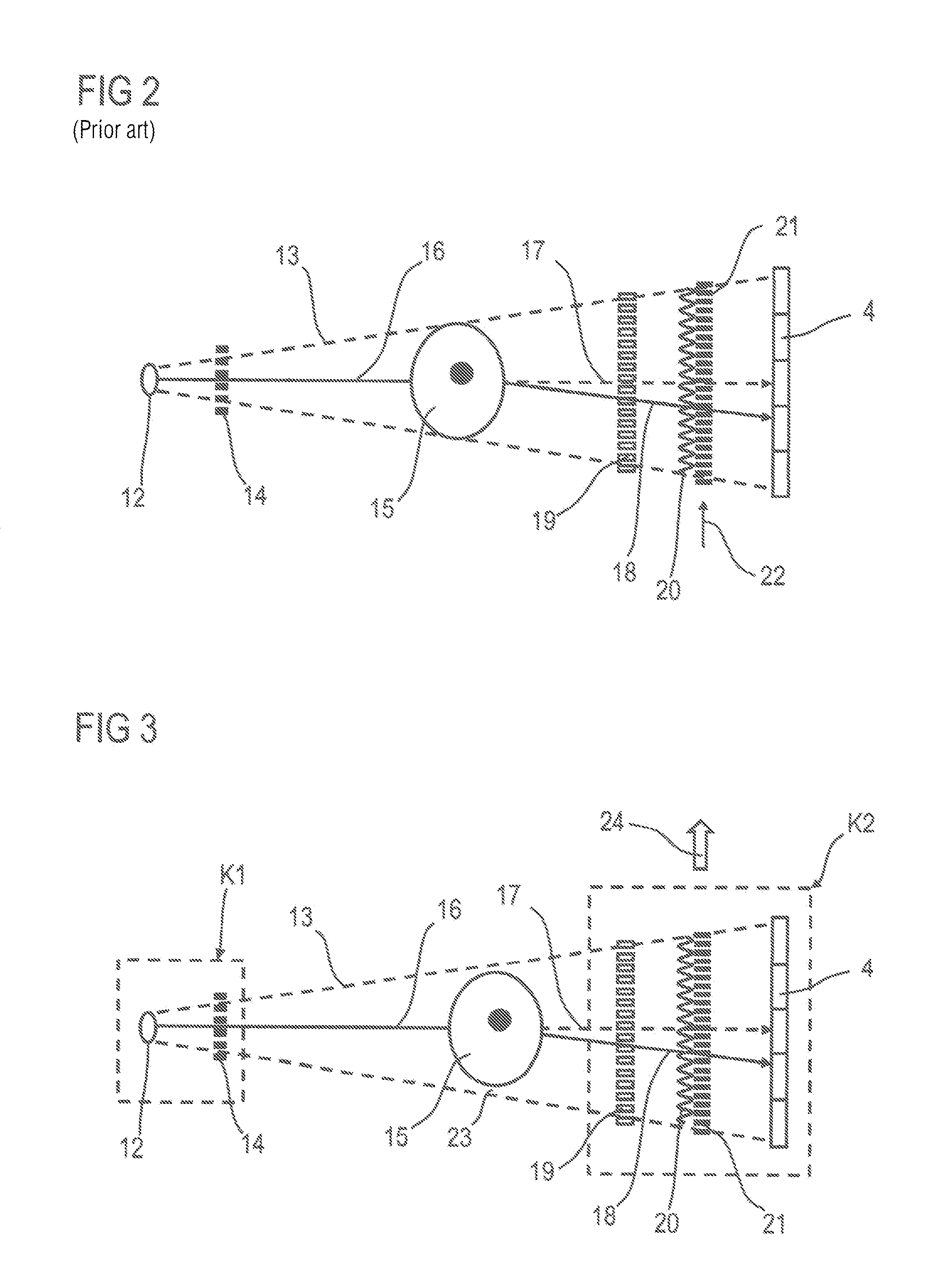
Method for examining an object using an x-ray recording system for phase contrast imaging with displacement measurement
ActiveUS20150092915A1Material analysis by transmitting radiationRadiation diagnosticsX-rayReference image
A method, for examining an object using an X-ray recording system, includes aligning the object in the X-ray beam and the X-ray recording system with one another such that regions in the X-ray beam are uncovered for measurement of a free field. During an X-ray image recording, the components are moved relative to one another with a lateral displacement. In a position of the relative lateral displacement of the components, a reference image containing free fields is recorded. The X-ray image recording is generated from partial images during the displacement and the position of the second component relative to the first component is determined for each partial recording such that the displacement distances of the displacements and the reference phases are calculated from a selected set of pixels and the measured intensity values thereof. Finally, the image information is determined from the partial images, the displacements and the reference phases.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
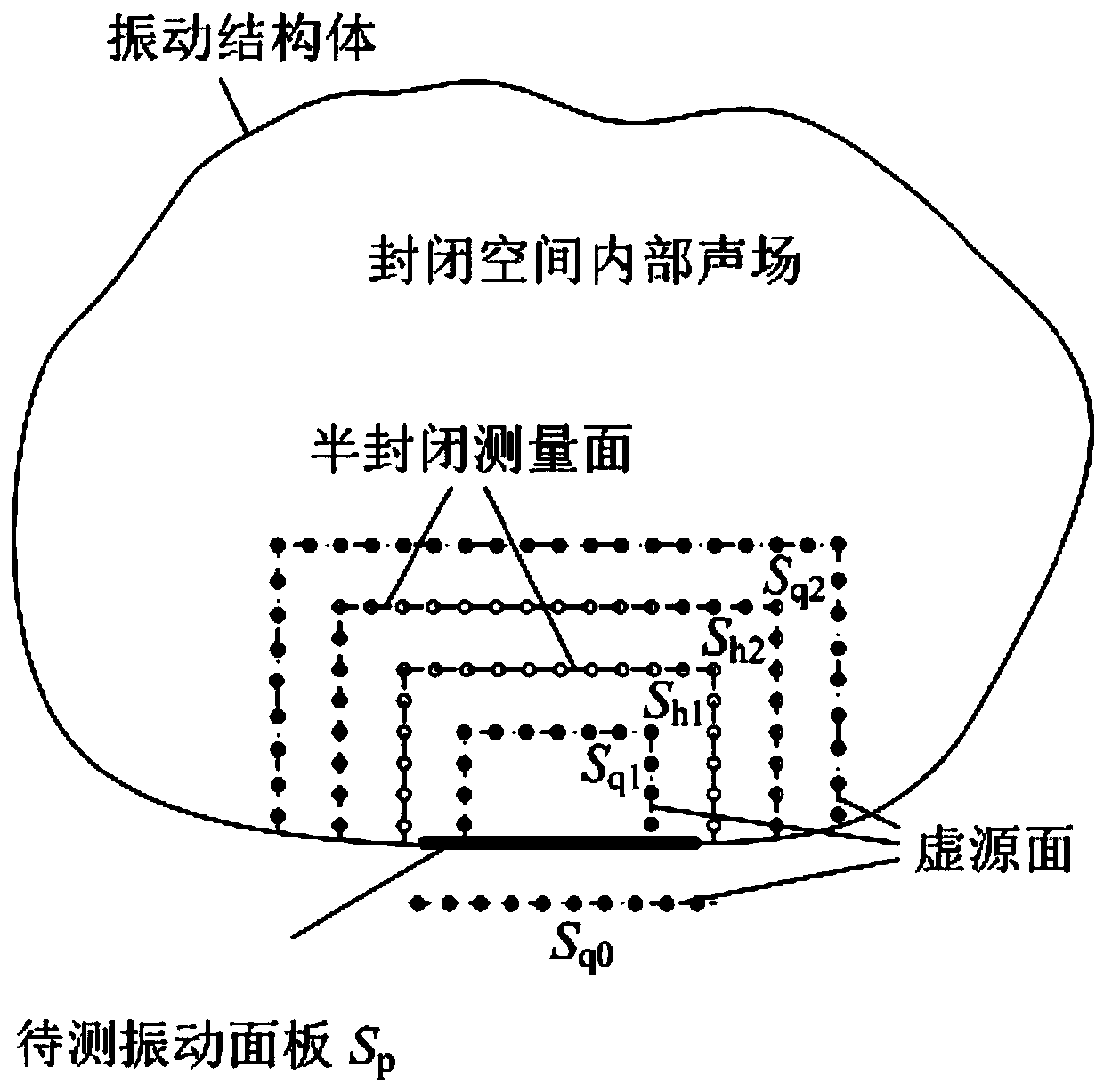
Closed space panel acoustic contribution degree identification method based on local measurement
ActiveCN111157096ASimple calculationImprove computing efficiencyVibration measurement in fluidSound pressureSound field
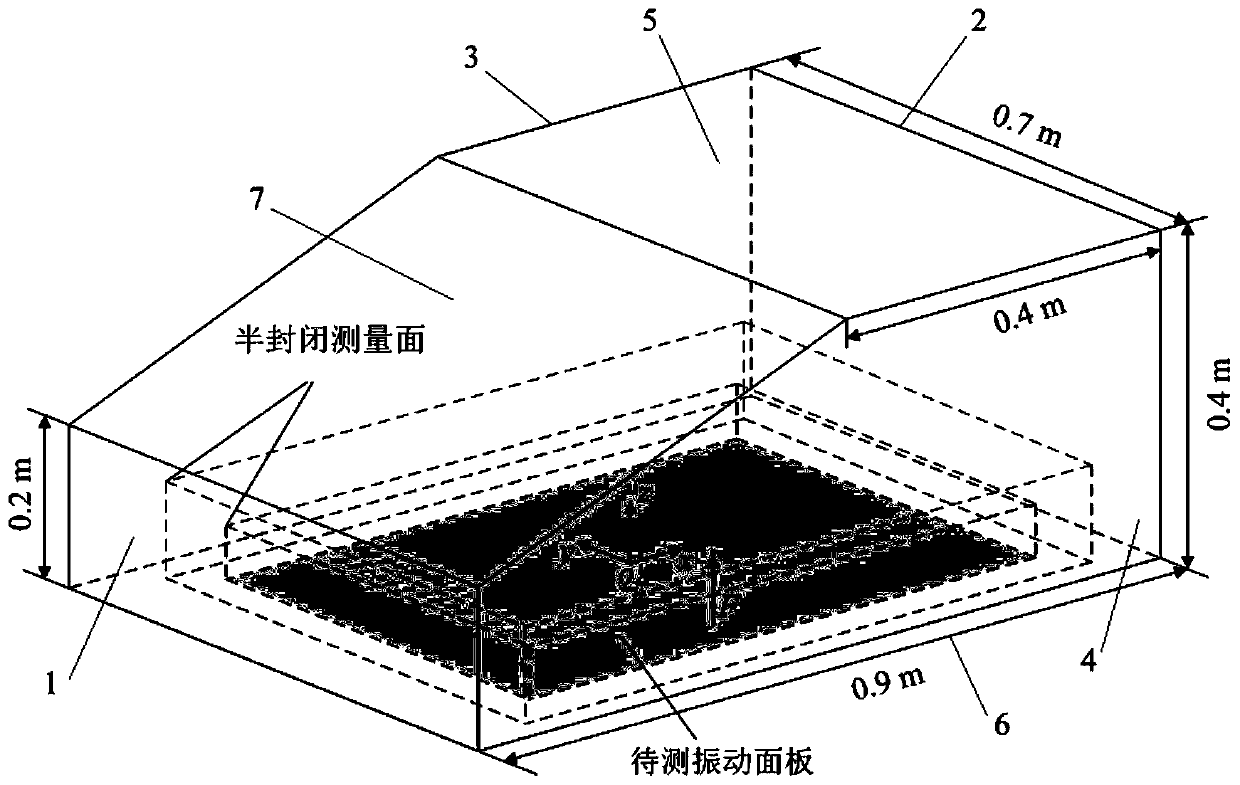
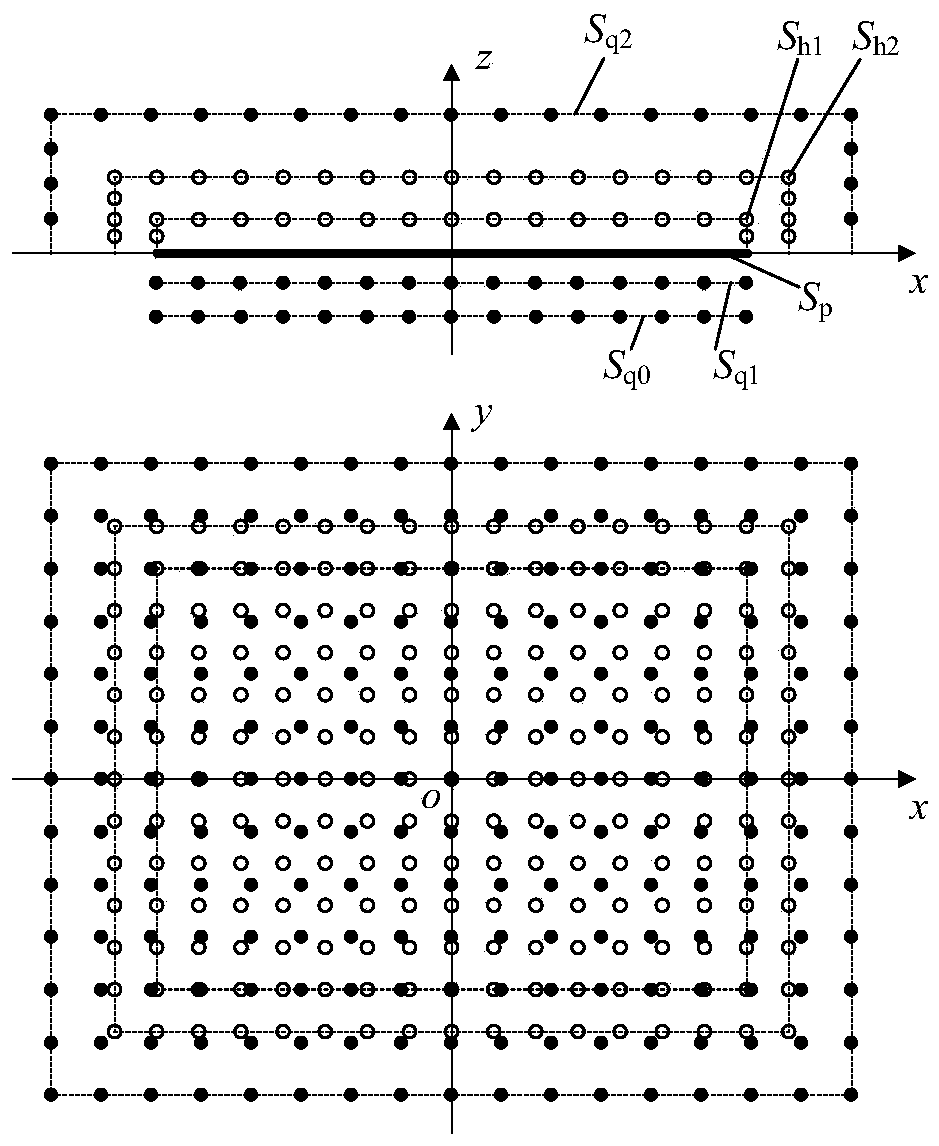
The invention discloses an enclosed space panel acoustic contribution degree identification method based on local measurement, and the method comprises the steps: setting two semi-enclosed holographicmeasurement surfaces in an enclosed space, and measuring the sound pressure values of the holographic measurement surfaces; based on an acoustic equivalent source principle, establishing an outer sound field virtual source surface and an inward sound field virtual source surface in the closed space, establishing a transfer relationship between the holographic measurement surface and the sound field virtual source surface, and calculating a source intensity column vector on the inward sound field virtual source surface; utilizing the admittance boundary condition of the surface of the to-be-measured vibration panel and the source intensity column vector on the inward sound field virtual source surface to calculate a scattering sound field generated when the inward sound field virtual source surface is incident to the surface of the to-be-measured vibration panel, and restoring the sound pressure and the normal vibration speed on the to-be-measured vibration panel under the free field condition; dividing the to-be-measured vibration panel into a plurality of discrete units, and calculating the acoustic contribution degree of the to-be-measured vibration panel to the closed sound field. According to the method, the local acoustic contribution degree of the closed space structure panel can be flexibly and quickly identified.
Owner:NANCHANG INST OF TECH
Coaxial four-reflecting optical system
InactiveCN101576648AAvoid blockingEasy to adjust and processOptical elementsOptoelectronicsOptic system
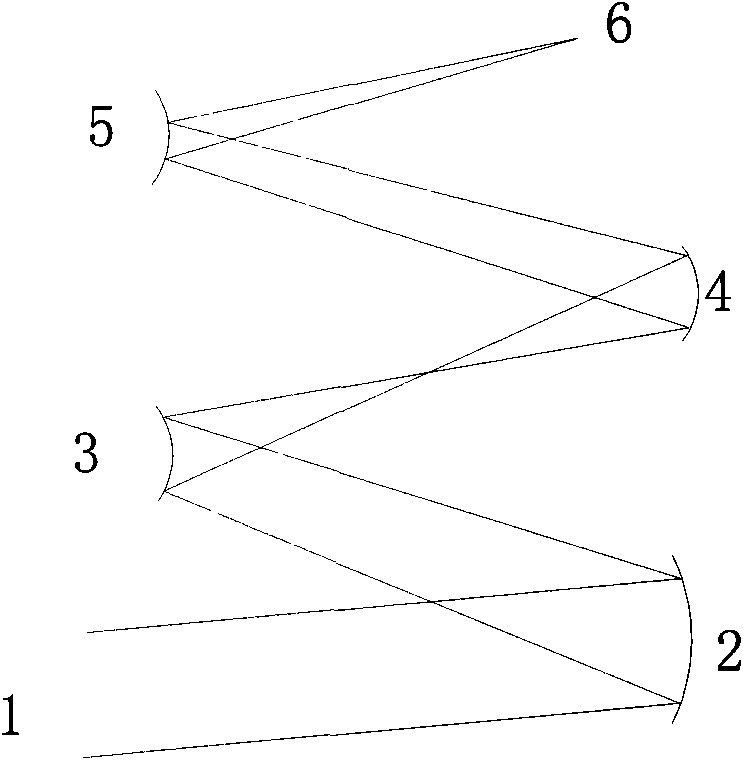
The invention relates to a coaxial four-reflecting optical system which comprises a main mirror (2), a secondary mirror (3), a third mirror (4) and a fourth mirror (5). The main mirror (2) and the third mirror (4) are arranged on the same side, and the secondary mirror (3) and the fourth mirror (5) are arranged at the other side corresponding to the main mirror (2) and the third mirror (4); the secondary mirror (3) is arranged on a reflected light path of the main mirror (2), the third mirror (4) is arranged on a reflected light path of the secondary mirror (3), and the fourth mirror (5) is arranged on a reflected light path of the third mirror (4). The coaxial four-reflecting optical system has large obstacle-free field of vision, is convenient to process, mount and adjust and is ideal to adjust the distortion.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
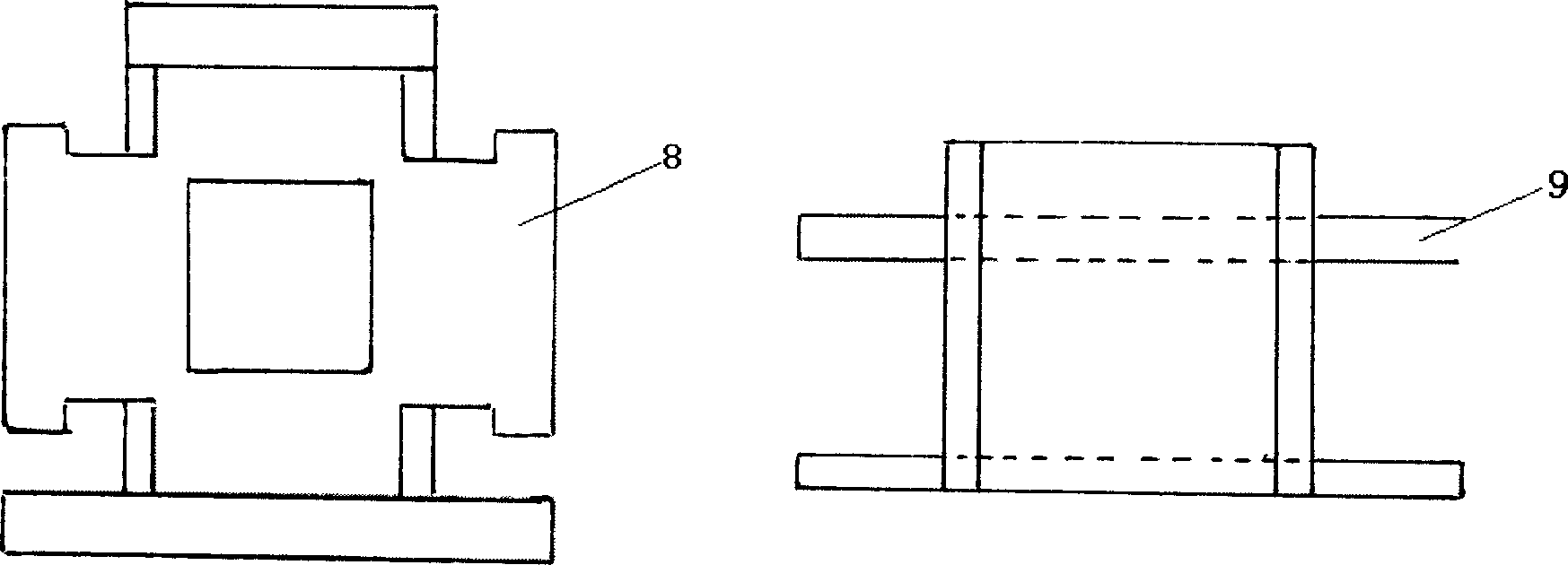
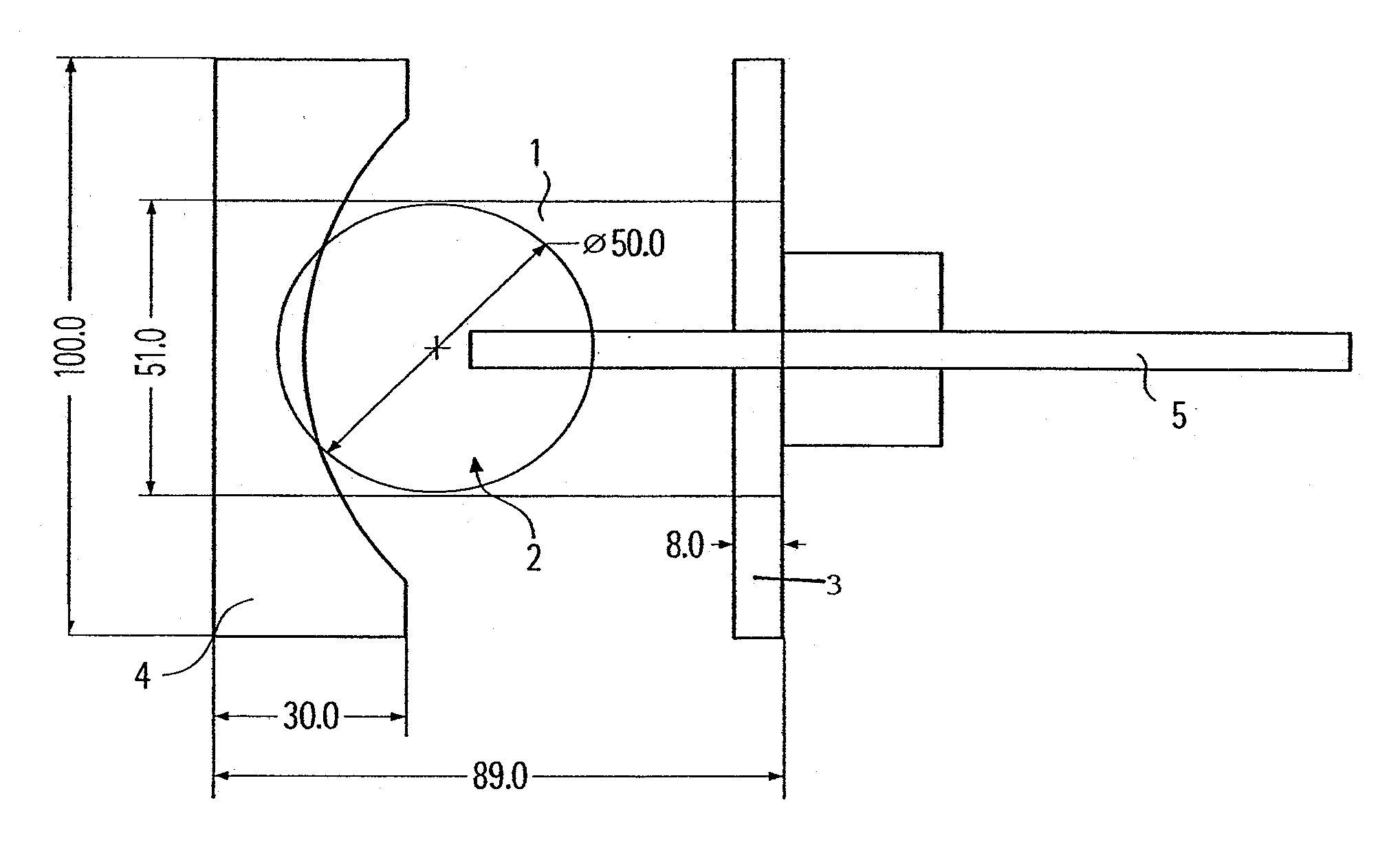
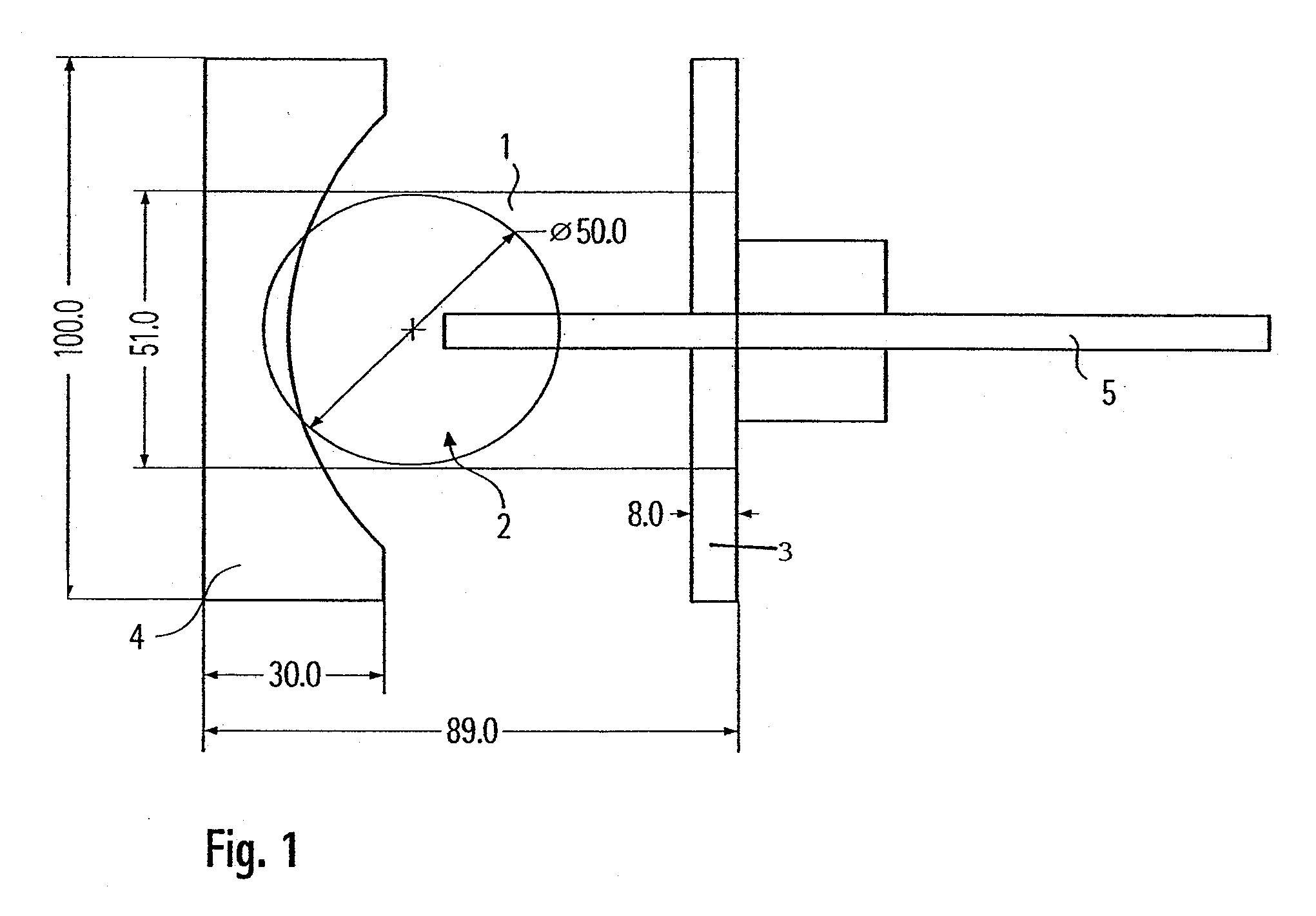
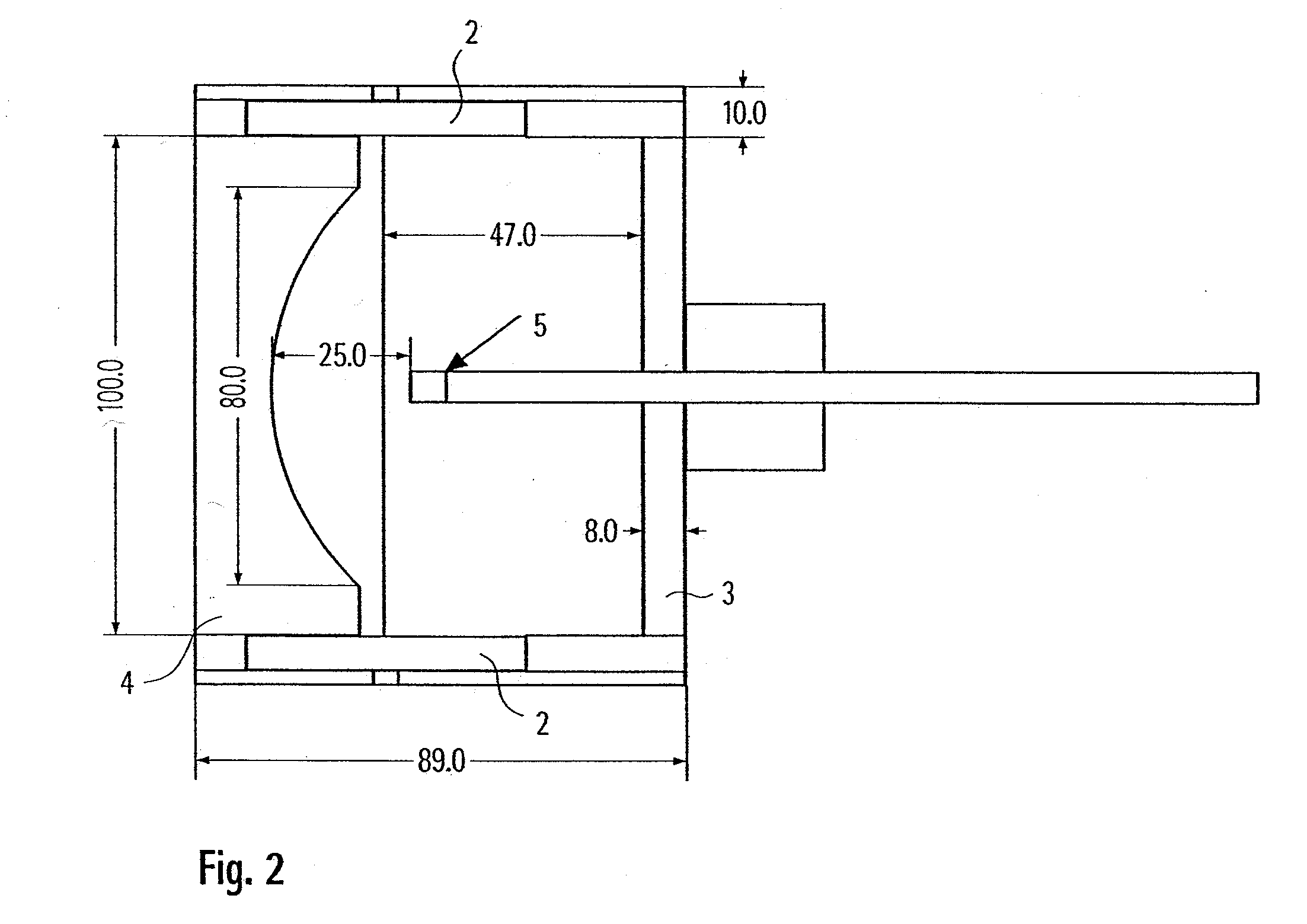
Free field pressure sensor with round cake-like integral structure
ActiveCN105784252AWith low temperature drift performanceImprove piezoelectric performance reliabilityFluid pressure measurement using piezo-electric devicesShock waveElectricity
The invention discloses a free field pressure sensor with a round cake-like integral structure, and belongs to the technical field of explosive shock wave overpressure field measurement. The sensor comprises a deflector structure, a positioning barrel, elastic elements, a core electrode, piezoelectric elements, pressure-bearing copper electrodes, an insulting positioning sleeve, a signal line, a connector and a cable connecting base. The core electrode is sleeved in a round cake-like axial through hole of the deflector structure. Two piezoelectric elements and two pressure-bearing copper electrodes are respectively arranged at two ends of the core electrode. The insulting positioning sleeve sleeves outer circumference surfaces of the core electrode, the piezoelectric elements and the pressure-bearing copper electrodes. The positioning barrel and two elastic elements are all sleeved in a gap between the insulating positioning sleeve and the round cake-like axial through hole of the deflector structure. One end of the connector is fixed in the axial through hole of a supporting rod of the deflector structure. The cable connecting base is installed in the other end of the axial through hole. Two ends of the signal line are respectively fixed in a through hole of the core electrode and on the cable connecting base. According to the invention, the free field pressure sensor with a round cake-like integral structure has the advantages that the water tightness and the impact resistance are relatively good, and the demands of an outdoor explosion test can be met.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method and device for creating a system layout of a free-field photovoltaic power plant with array solar trackers
InactiveUS20150100281A1Simple and efficient and cost-effectiveEasy to calculateGeometric CADSolar heating energySpace powerPhotovoltaic power station
Provided herein is a method and a device for creating a system layout of a photovoltaic open-space power plant, which includes power plant components, in particular solar trackers, having the following method steps: providing configuration data which specifies the photovoltaic open-space power plant and the power plant components thereof, and providing configuration rules which are preset for the photovoltaic open-space power plant, and providing configuration parameters which put the configuration rules in concrete terms; and initialising and subsequently optimising a selection of, and an allocation of location to, necessary power plant components for the system layout properties of the photovoltaic open-space power plant by the configuration data provided and the configuration rules put into concrete terms for creating the system layout of the photovoltaic open-space power plant.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Two-dimensional control and ultrasonic imaging monitoring method for flowing micro-bubbles in non-free field
ActiveCN104287776ARealize two-dimensional space manipulationHigh-resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsMicro bubbleUltrasonic imaging
The invention discloses a two-dimensional control and ultrasonic imaging monitoring method for flowing micro-bubbles in a non-free field. The two-dimensional control and ultrasonic imaging monitoring method for flowing micro-bubbles in the non-free field comprises the steps of: arranging two control ultrasonic energy converters and a pipeline in a controlled region reasonably to determine relative spatial positions of the two control ultrasonic energy converters and the pipeline; propelling a micro-bubble suspension liquid in a sound-transmitting pipe, starting up the control ultrasonic energy converters, exciting the control ultrasonic energy converters by using continuous sine electric signals, adjusting an excitation electric signal power and changing resultant force applied to a micro-bubble group in the vertical direction to control the micro-bubbles to move in the vertical direction; enabling the micro-bubbles to move in the horizontal direction by changing phase position or frequency of the excitation electric signal; placing an ultrasonic array energy converter to a position where the micro-bubble group control process can be monitored and generating a micro-bubble group wavelet conversion ultrasonic monitoring image. According to the two-dimensional control and ultrasonic imaging monitoring method for flowing micro-bubbles in the non-free field, two-dimensional control of flowing micro-bubbles in the non-free field of a single-side sound-transmitting medium under ultrasonic monitoring can be realized, and sensitivity of micro-bubble monitoring is improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com