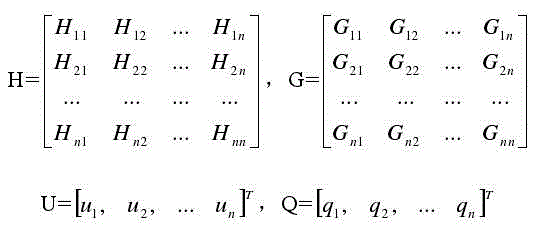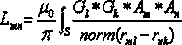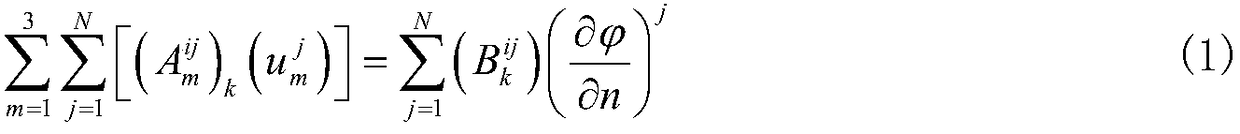Patents
Literature
135 results about "Boundary element method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The boundary element method (BEM) is a numerical computational method of solving linear partial differential equations which have been formulated as integral equations (i.e. in boundary integral form). including fluid mechanics, acoustics, electromagnetics (Method of Moments), fracture mechanics, and contact mechanics.
Numerical value simulation method of vibration and acoustic characteristics of speaker
ActiveCN102004823ASpeed up the design processOvercome the disadvantage of being limited to low frequenciesSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelGeometric modeling
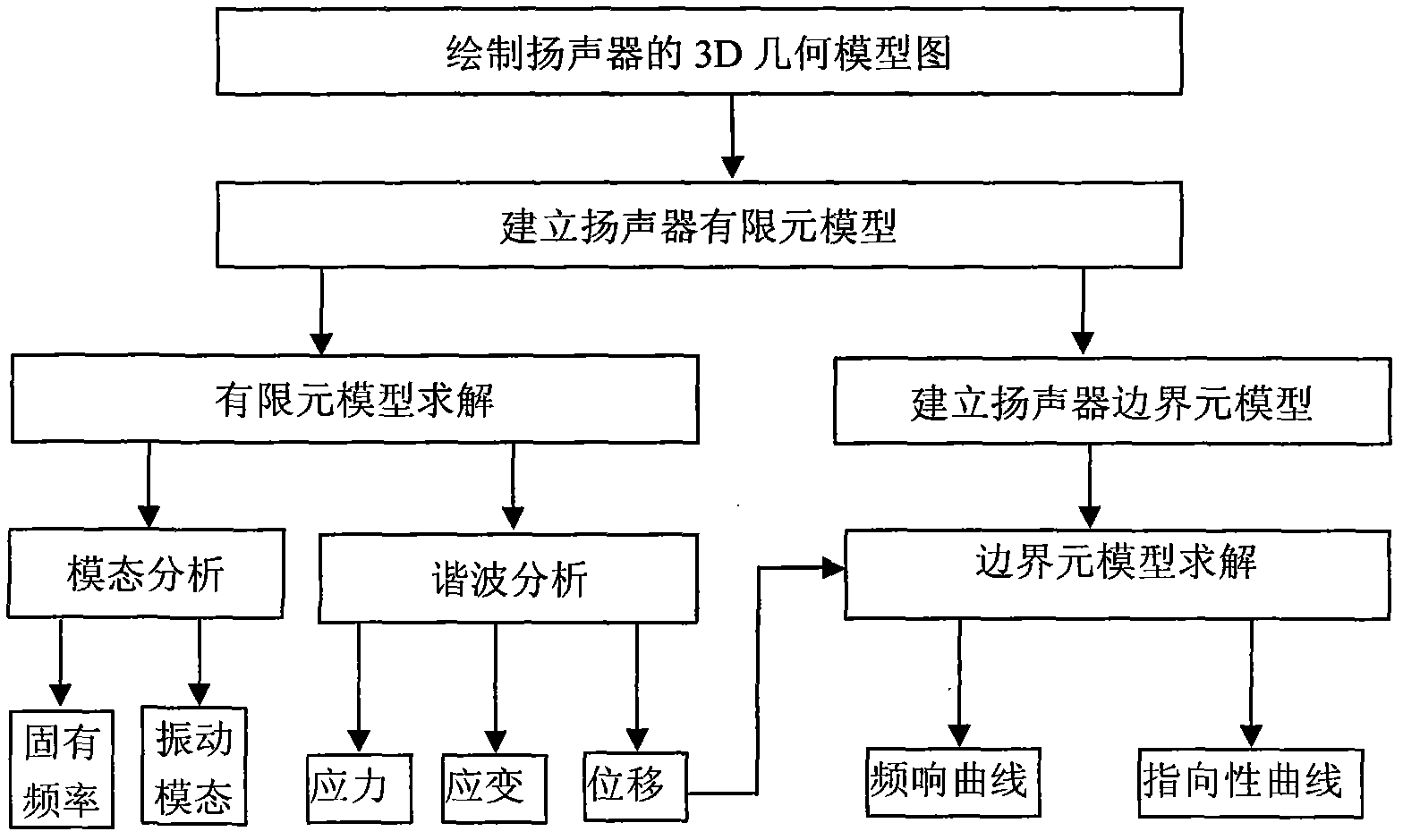
The invention provides a numerical value simulation method of the vibration and acoustic characteristics of a speaker. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, drawing a 3D (Three-Dimensional) geometric model diagram of the speaker by using 3D drawing software; then, adding the 3D geometric model diagram of the speaker to meshing software to mesh the 3D geometric model diagram into body elements, defining element types, materials and boundary conditions and applying a load to acquire a finite element model; establishing a boundary element model matched with the finite element model; and finally, solving the finite element model with a finite element solver to acquire the vibration characteristics of the speaker, and solving the boundary element model with a boundary element solver to acquire the acoustic characteristics of the speaker, wherein the vibration characteristics include the natural frequency, the vibration mode (vibration type), the displacement, the strain and the stress, and the acoustic characteristics include a frequency response curve and a directivity curve.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ELECTRO ACOUSTIC R&D CENT CAS +1
Reservoir architecture and connectivity analysis
InactiveUS20110040536A1GeomodellingComputation using non-denominational number representationBoundary element methodSeismic survey
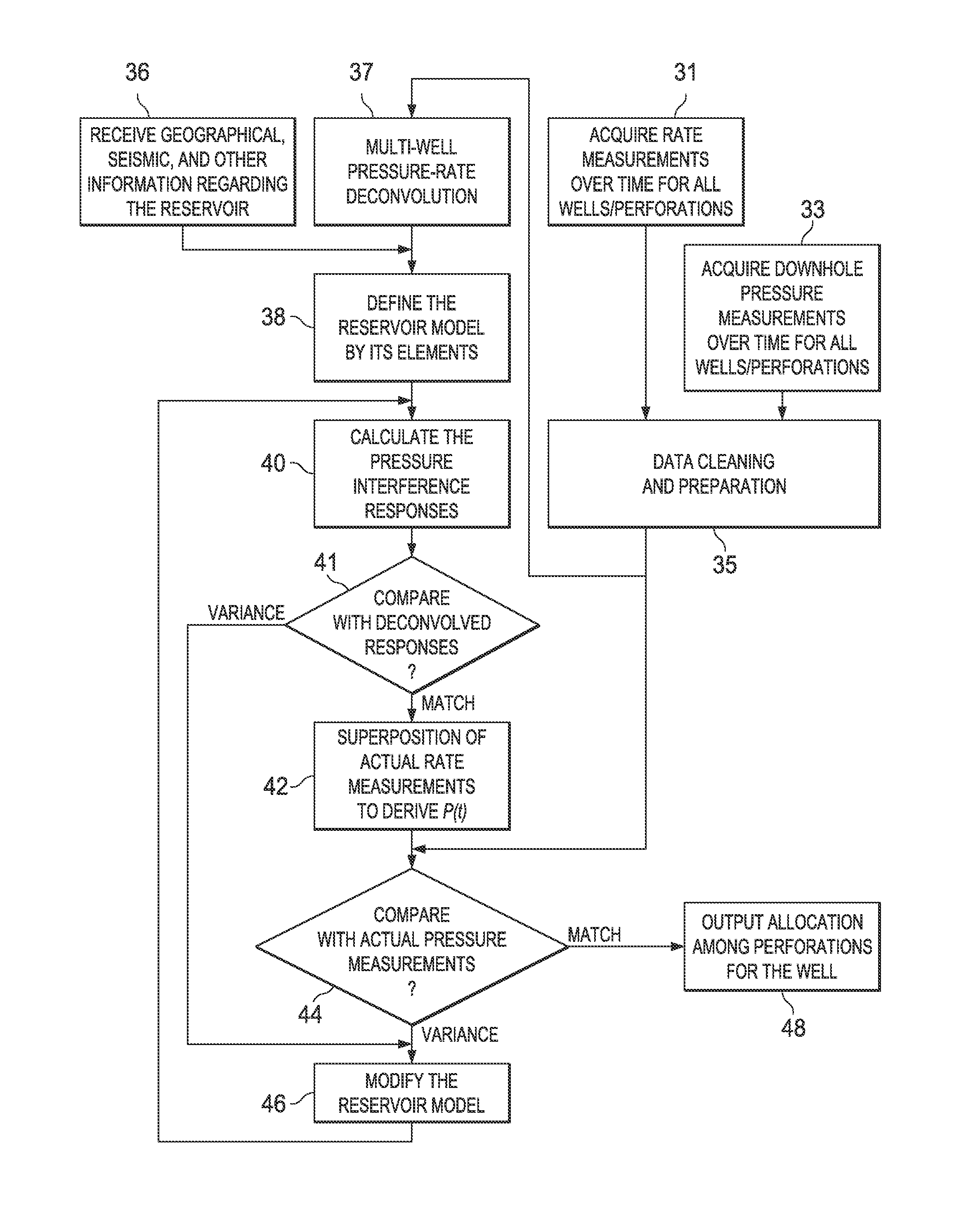
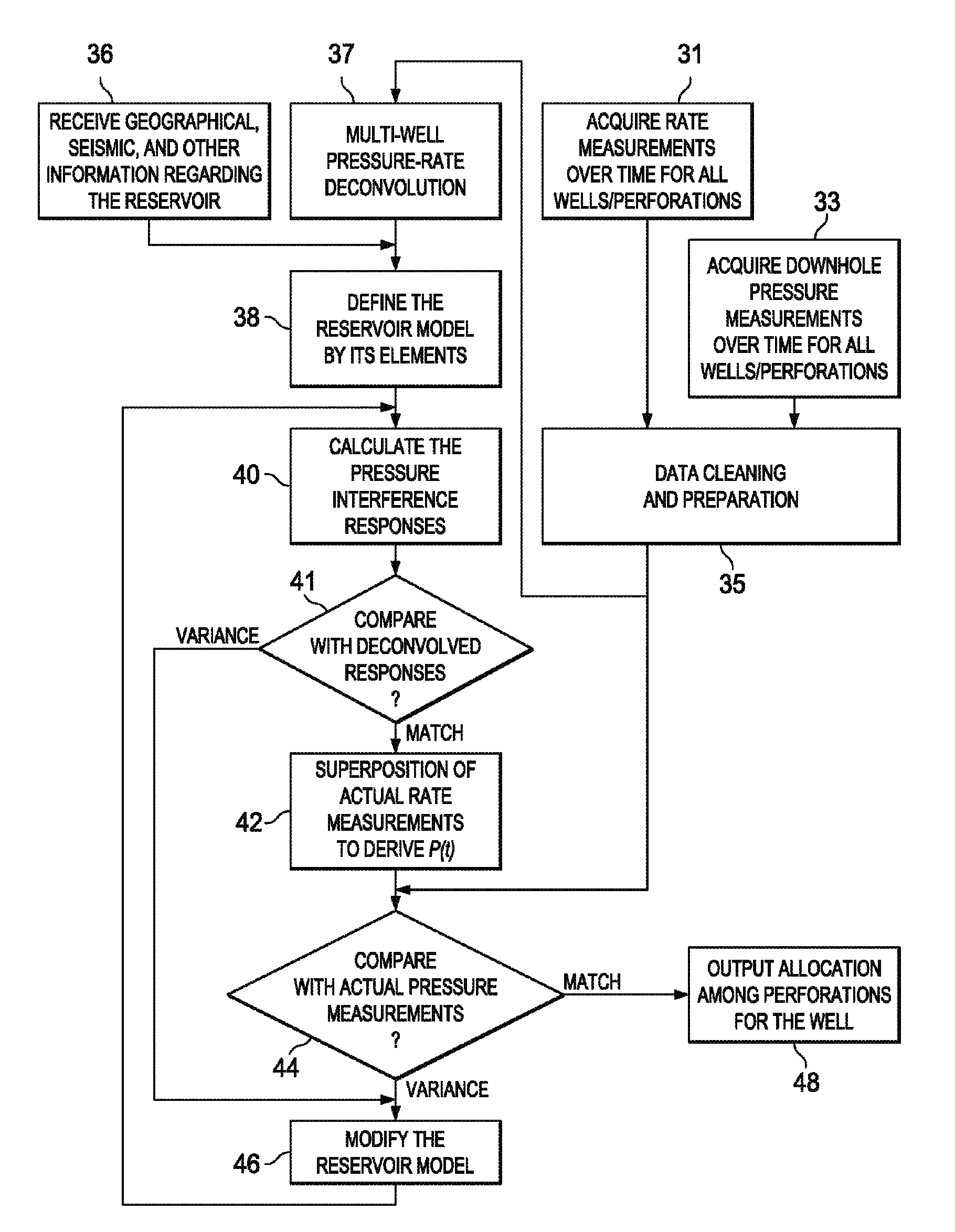
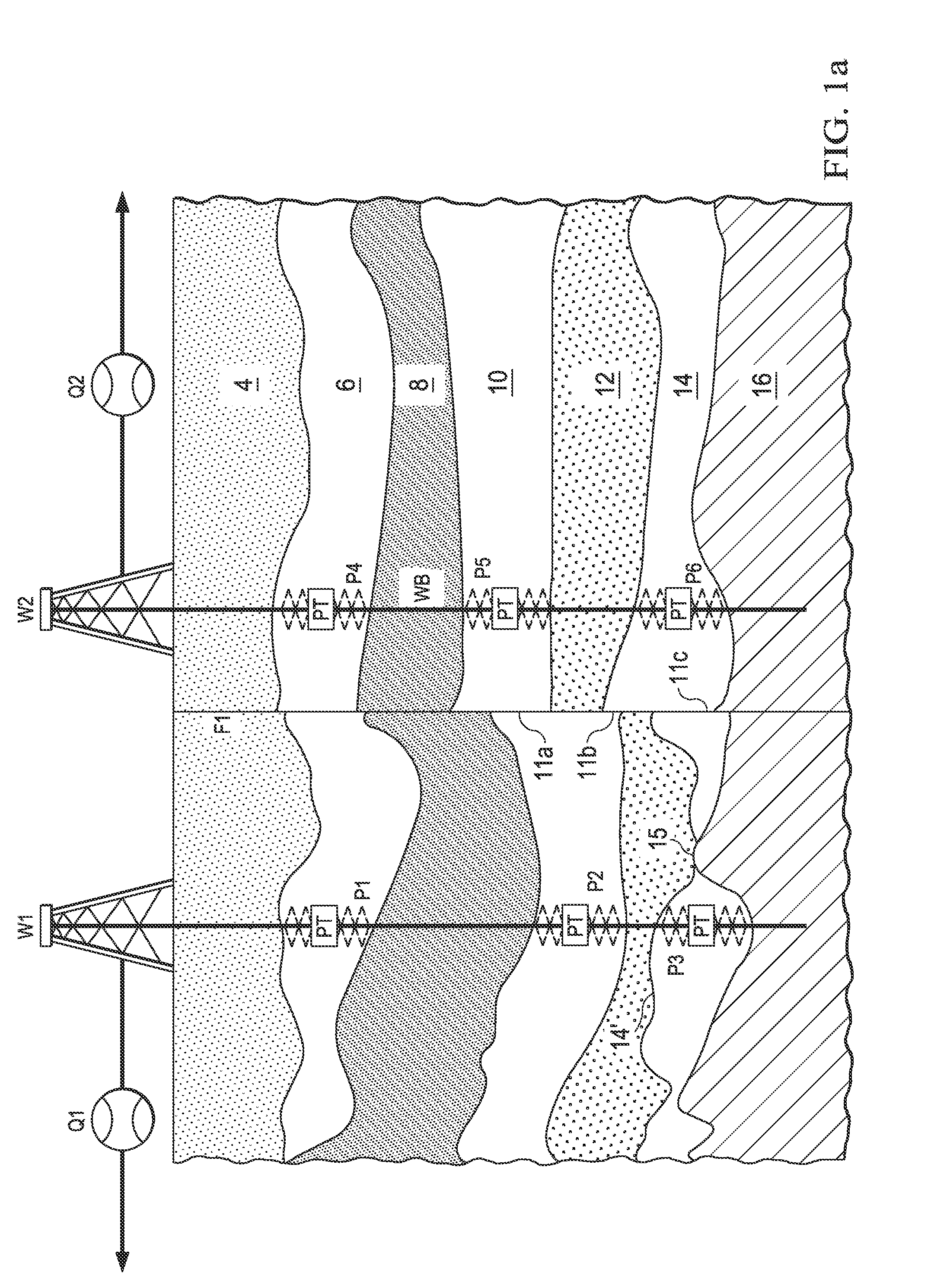
An interactive system and method of operating the system to define and evaluate a model of a hydrocarbon reservoir. The reservoir model is defined from extrinsic information such as seismic surveys, well logs, and the like, and is based on elements of formation regions, connections among the regions, wells, and perforations. A boundary-element method is used to determine pressure interference responses, corresponding to the pressure at a perforation in response to a single perforation producing fluid at a unit flow rate. These pressure interference responses are then convolved with measured well flow rates obtained during production to arrive at estimates of the wellbore pressure at one or more wells of interest. The estimated wellbore pressure can be compared with downhole pressure measurements to validate the reservoir model, or to provoke the user into modifying the model and repeating the evaluation of the model.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
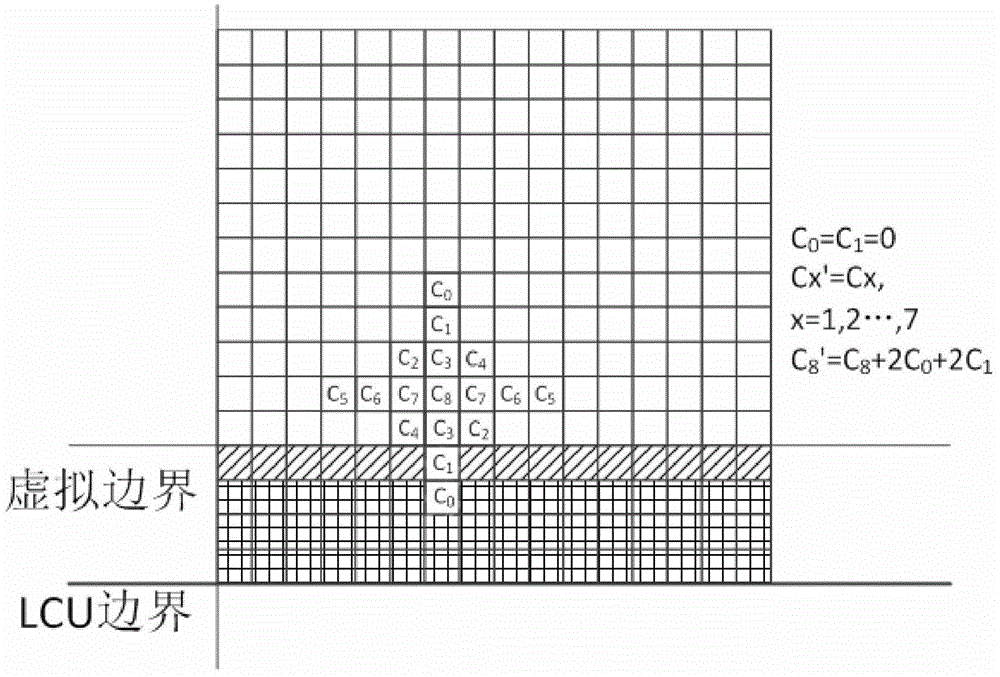
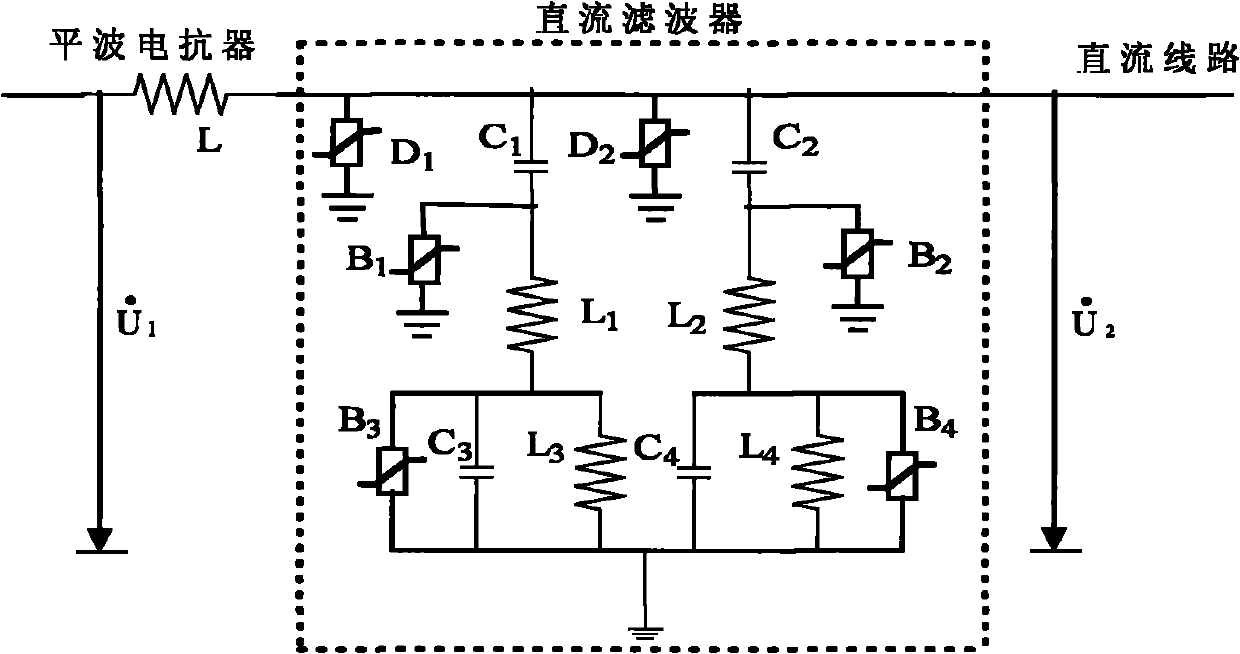
Boundary treatment method and device for adaptive loop filter
ActiveCN104702963AReduce hardware costsFacilitate parallel encoding and decodingDigital video signal modificationComputational scienceAdaptive filter
The invention discloses a boundary treatment method and device for adaptive loop filter. The method comprises the steps of determining a filter area according to an upper boundary and a lower boundary of the current maximum coding unit in a sequence; determining whether pixels at the outsides of the left boundary and the right boundary of the filter area are usable; replacing the unusable pixel samples by the closest pixel samples within the filter area during loop filter ALF process. With the adoption of the method, the problem of boundary treatment of ALF filter process can be solved, the correlation of pixels is fully utilized, the cost is tiny loss on coding performance, and the hardware cost during achieving the adaptive loop filter can be decreased.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
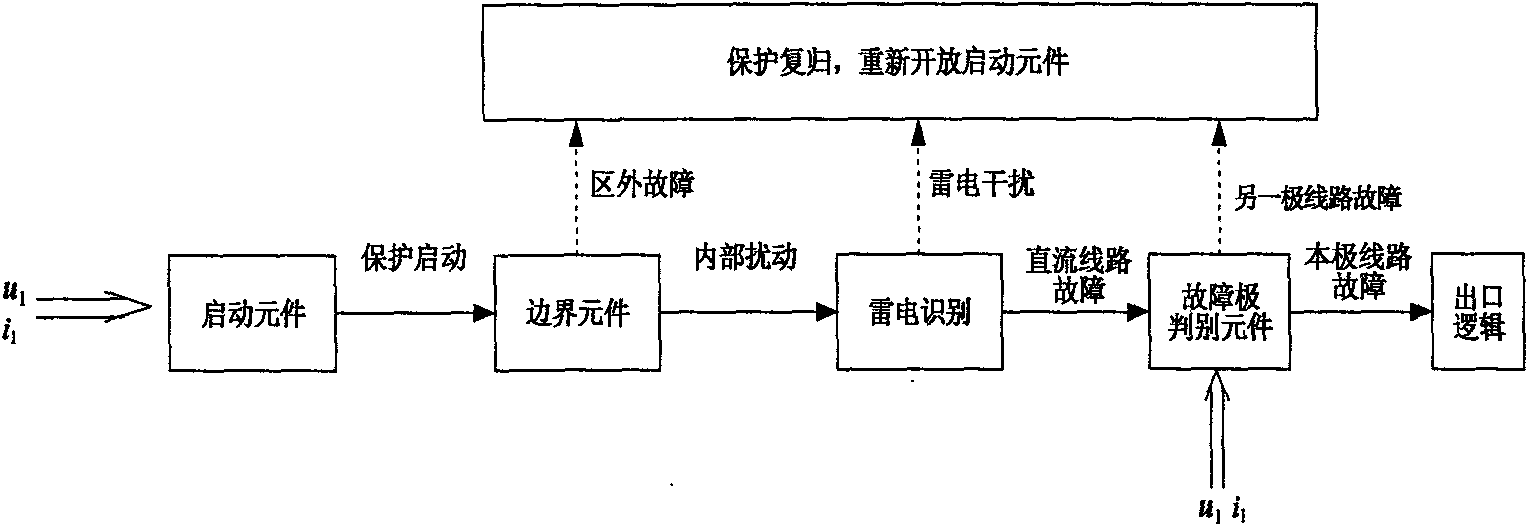
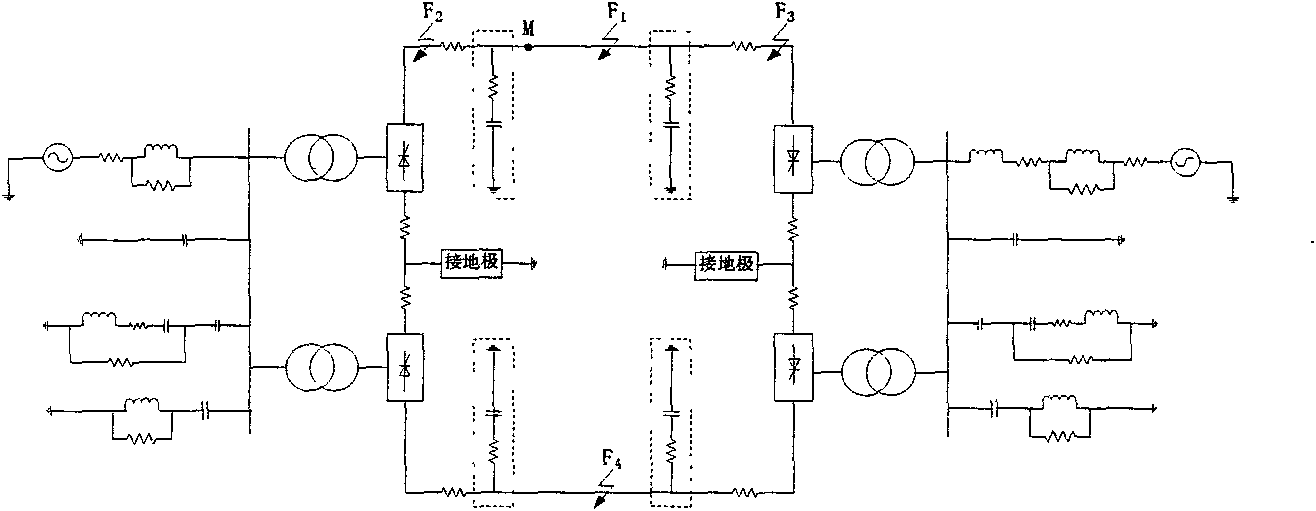
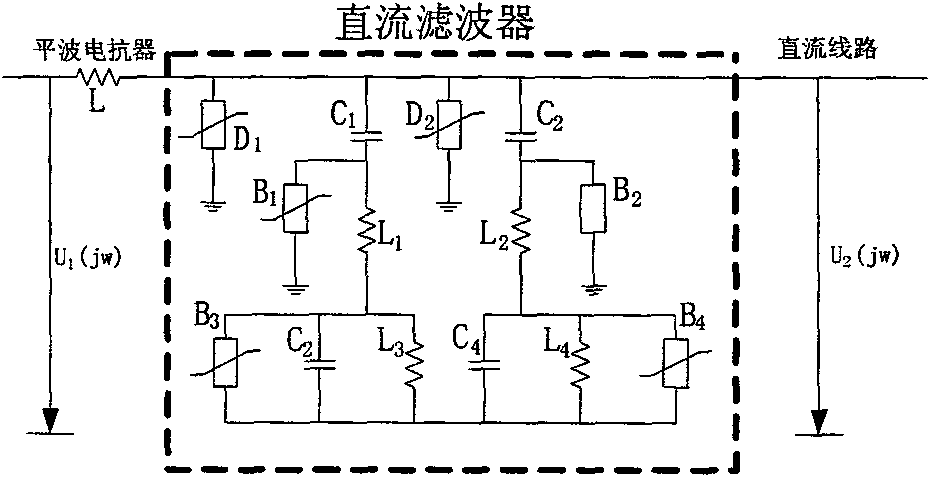
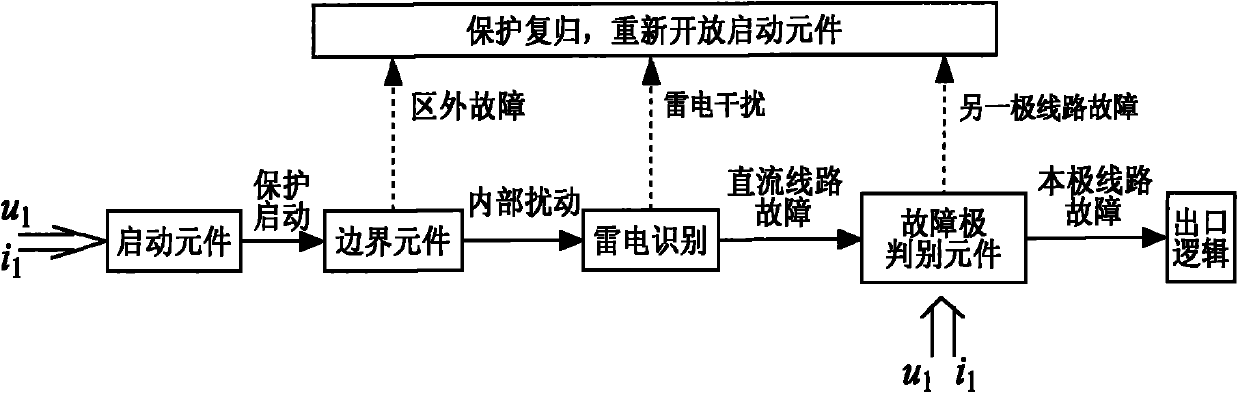
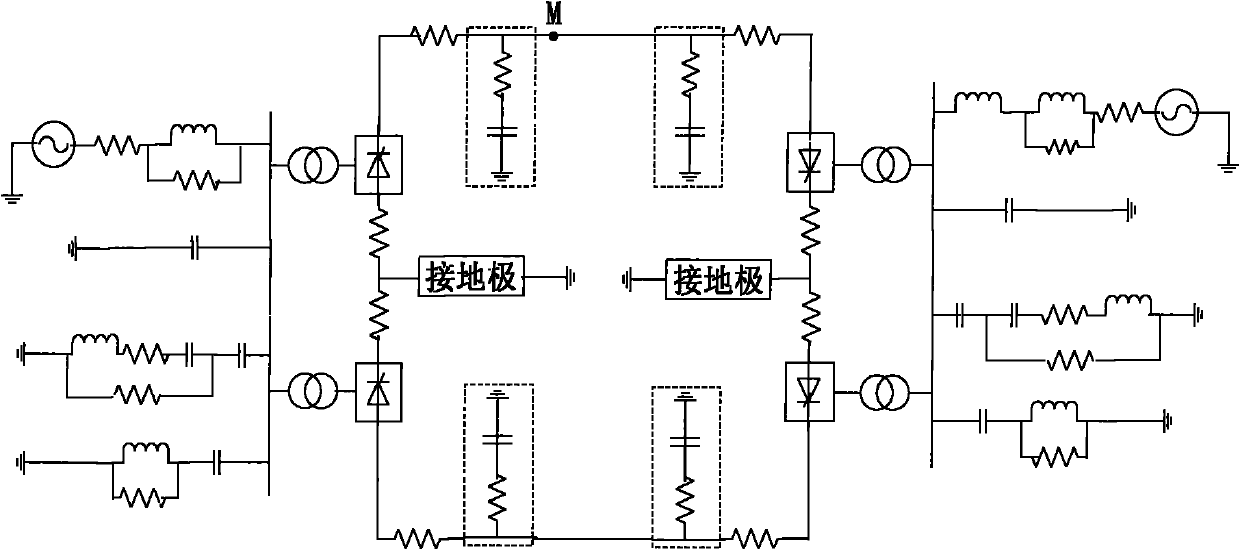
Method of boundary element utilizing polar wave S transform energy ratio to determine ultra high-voltage direct current transmission line fault
ActiveCN101860020AAvoid Transient Response ProcessesThe conclusion is accurateEmergency protective circuit arrangementsUltra high voltageDc current
The invention relates to a method of a boundary element utilizing polar wave S transform energy ratio to determine ultra high-voltage (UHV) direct current (DC) transmission line faults, belonging to the technical field of power system relay protection. The method is as follows: a starting element is started when a DC line breaks down, the polar wave voltages of the positive and negative lines are calculated according to dipolar DC voltages and DC currents measured at a protective installation part; a discrete polar wave voltage signal the sampling sequence length of which is 200 after faults is subjected to S transform, the transform result is a 101*200 time-frequency complex matrix, and mode operation is carried out on each element in the complex matrix. High-frequency component and low-frequency component of the polar wave voltage are extracted according to the obtained modular matrix, and then the ratio of the high-frequency energy to the low-frequency energy of the polar wave voltage is figured out; and whether the fault is interior or exterior is distinguished according to the value of the ratio of the high-frequency energy to the low-frequency energy. A large number of simulation results show that the invention has good effect.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
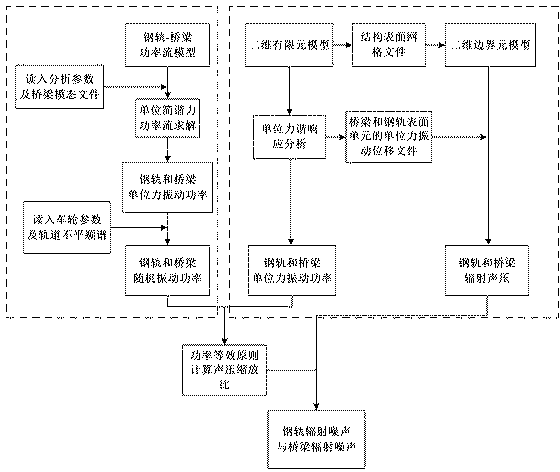
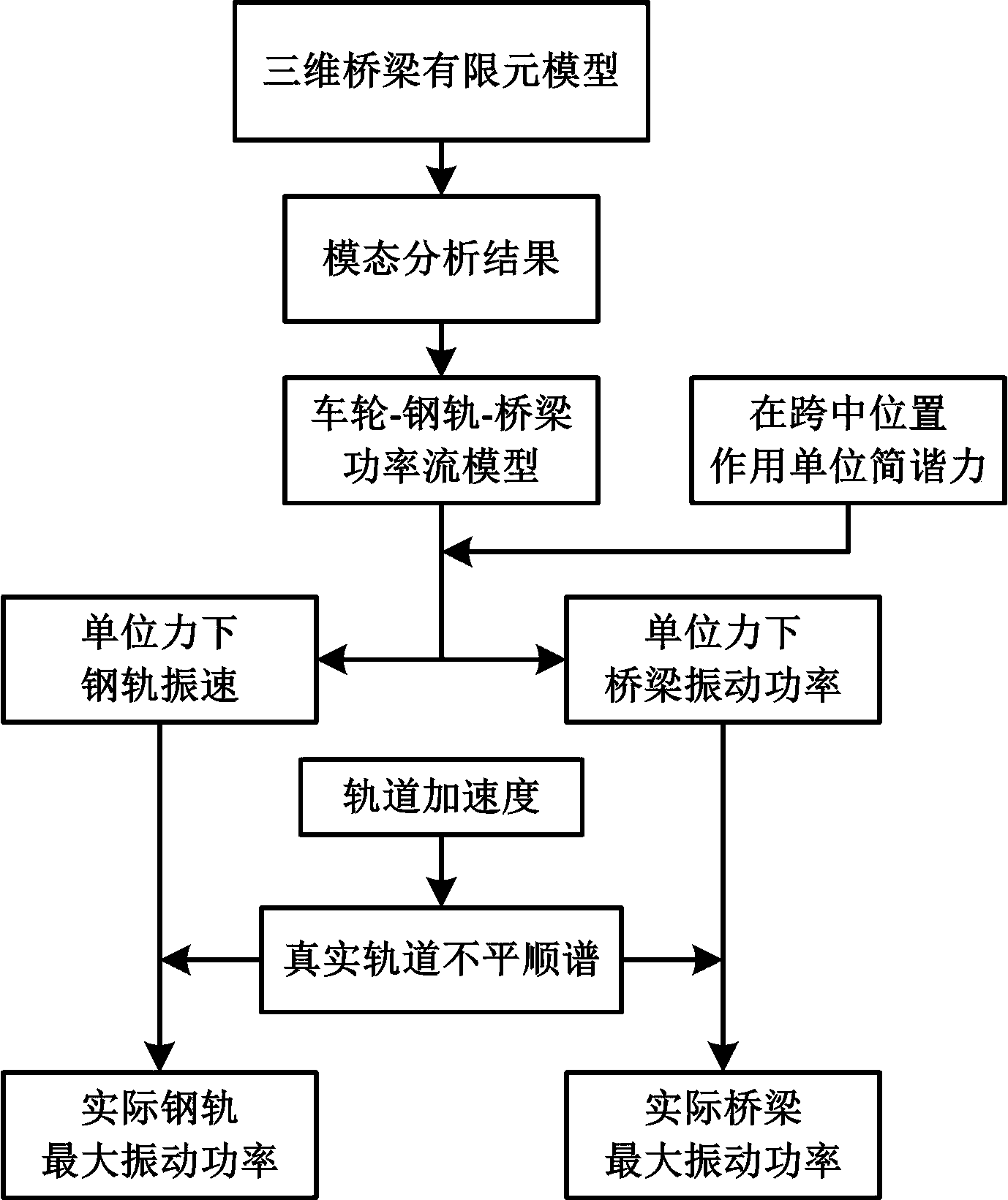
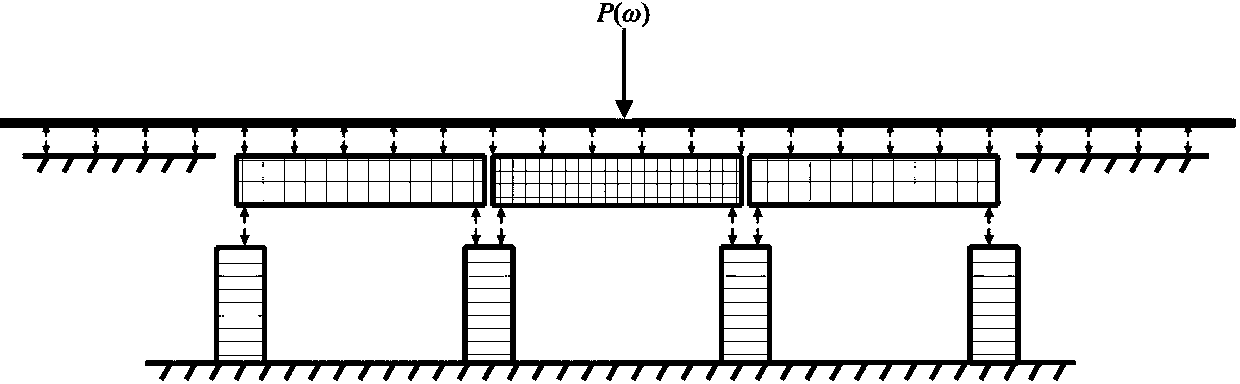
Power flow-boundary element model based elevated rail traffic vibratory-noise simulating and predicting method
InactiveCN104036087ASimulation is accurateHigh simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAuditory radiationElement model
The invention relates to a power flow-boundary element model based elevated rail traffic vibratory-noise simulating and predicting method. The power flow-boundary element model based elevated rail traffic vibratory-noise simulating and predicting method comprehensively considers bridge noise and steel-rail noise of the medium-frequency range (200-1000Hz) in elevated rail traffic, and is higher in noise prediction accuracy than that of a method only considering bridge noise or steel-rail noise. The method includes firstly establishing a rail- bridge system power flow model, calculating input power of bridges and vibration speed of steel rails when harmonic force units different in frequency act on the steel rails; secondly, calculating wheel-rail contact force spectrum under a wheel-rail-bridge coupling system through a wheel-rail combination roughness spectrum so as to obtain vibration states of the bridges and the steel rails under the action of random wheel-rail force; thirdly, respectively establishing an acoustic-radiation two-dimension finite-element-boundary element weak-coupling model for the bridges and the steel rails, and calculating vibration power and radiation sound field under the action of the harmonic force units at different frequencies; finally, acquiring practical vibration power by the power flow method and vibration power by the finite-element-boundary element model, scaling field-point sound pressure under the action of unit force to obtain the bridge noise, the steel-rail noise and the total noise thereof.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
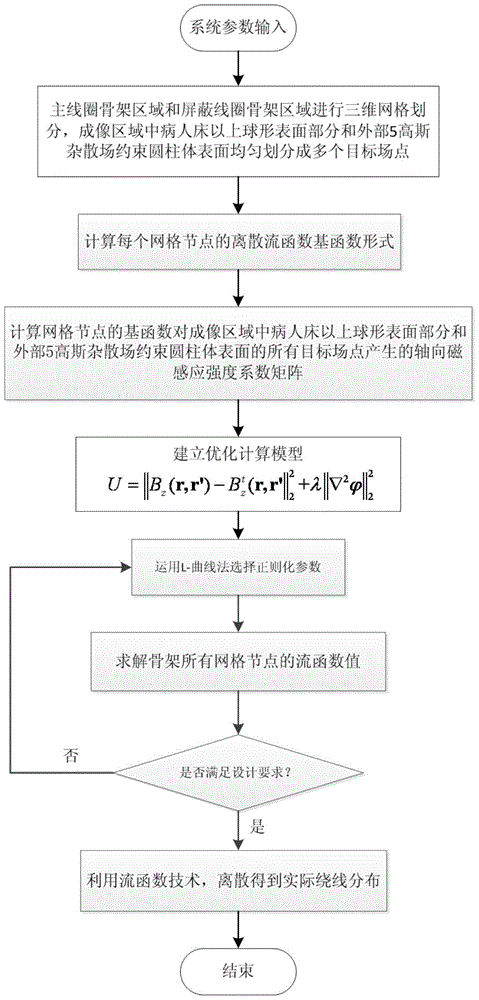
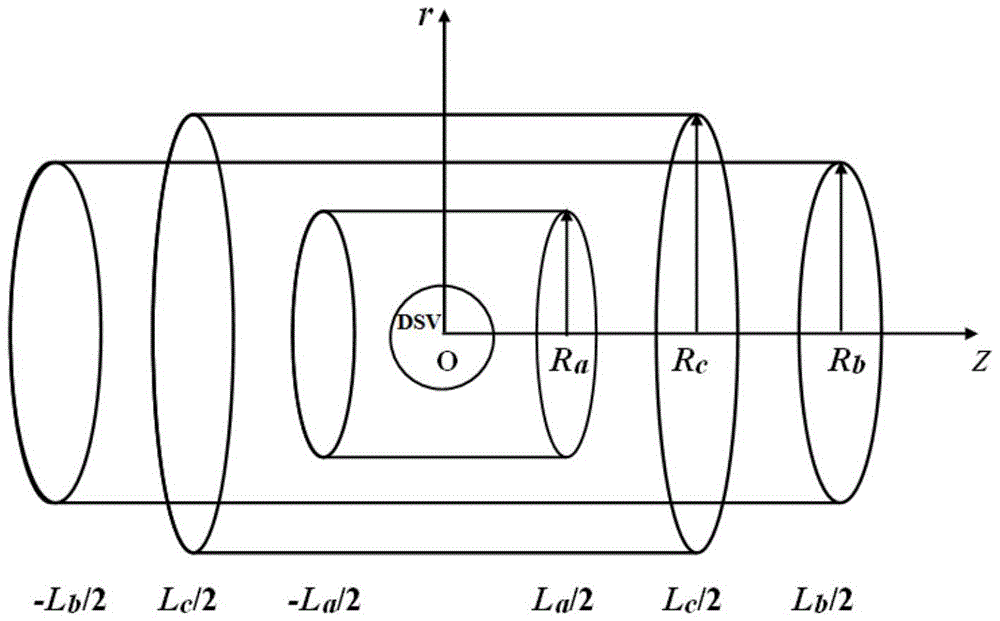
Designing method for gradient coil of self-shielding superconductive nuclear magnetic resonance imaging system
InactiveCN105718677AReduce inductanceLarge line spacingSpecial data processing applicationsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceIntensity coefficient
The invention discloses a designing method for a gradient coil of a self-shielding superconductive nuclear magnetic resonance imaging system.The designing method comprises the steps that firstly, three-dimensional continuous triangular mesh dividing is performed on a main coil framework region and a shielding coil framework region, and an axial magnetic induction intensity coefficient matrix generated by mesh nodes in the main coil framework region and the shielding coil framework region on a target field point is calculated according to a boundary elements method; secondly, an optimization calculation model is built through a regularization method, wherein the optimization calculation model comprises two parts, the first part is deviation between the axial magnetic induction intensity generated by the mesh nodes in the main coil framework region and the shielding coil framework region on a target field point and the expected target magnetic induction intensity, the second part is the quadratic sum of the flow function curvature of the mesh nodes, and flow function values of the mesh nodes in the main coil framework region and the shielding coil framework region are obtained through solution; lastly, actual winding distribution of the gradient coil is obtained through a flow function method.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Extra-high voltage direct current line boundary element method adopting polar wave wavelet energy ratio
ActiveCN102005740AAvoid Transient Response ProcessesThe conclusion is accurateEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectric power systemSample sequence
The invention provides an extra-high voltage direct current line boundary element method adopting polar wave wavelet energy ratio, belonging to the technical field of relay protection of electric power systems. The method comprises the following steps: when the direct current line has fault, computing the anode line polar wave voltage and the cathode line polar wave voltage according to the direct current voltage and direct current of the two poles measured in the relay location; selecting the discrete polar wave voltage signal with sampling sequence length of 200 after fault to undergo wavelet transform to obtain a series of high / low frequency polar wave voltage wavelet transform parameters and computing the modules of the high / low frequency polar wave voltage wavelet transform parameters; computing the ratio of high / low frequency energy of polar wave voltage after extracting the high / low frequency components of polar wave voltage according to the obtained modules; and distinguishingthe area fault from the out-area fault according to the ratio of high / low frequency energy. Lots of simulation results show the method has good effect.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
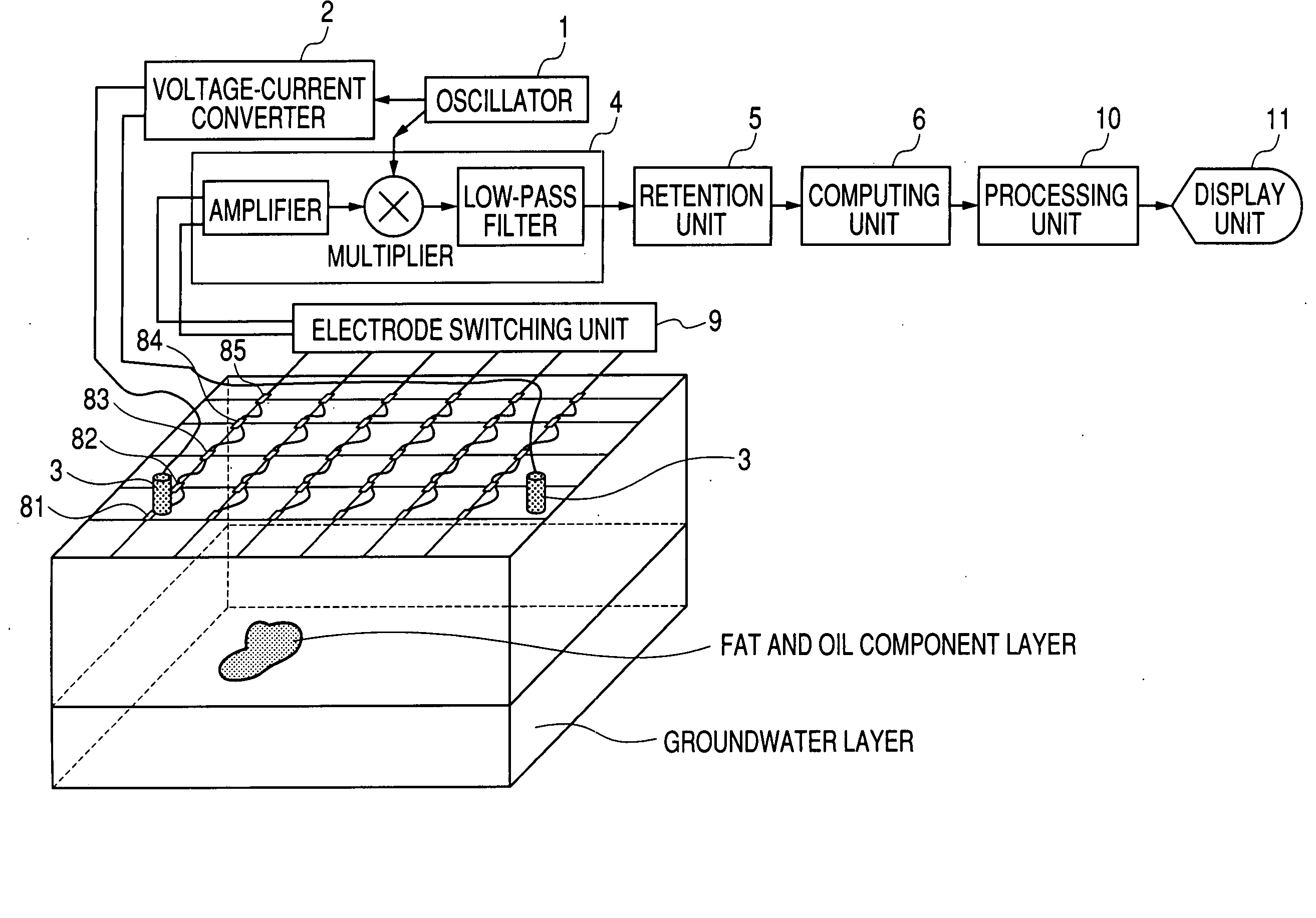
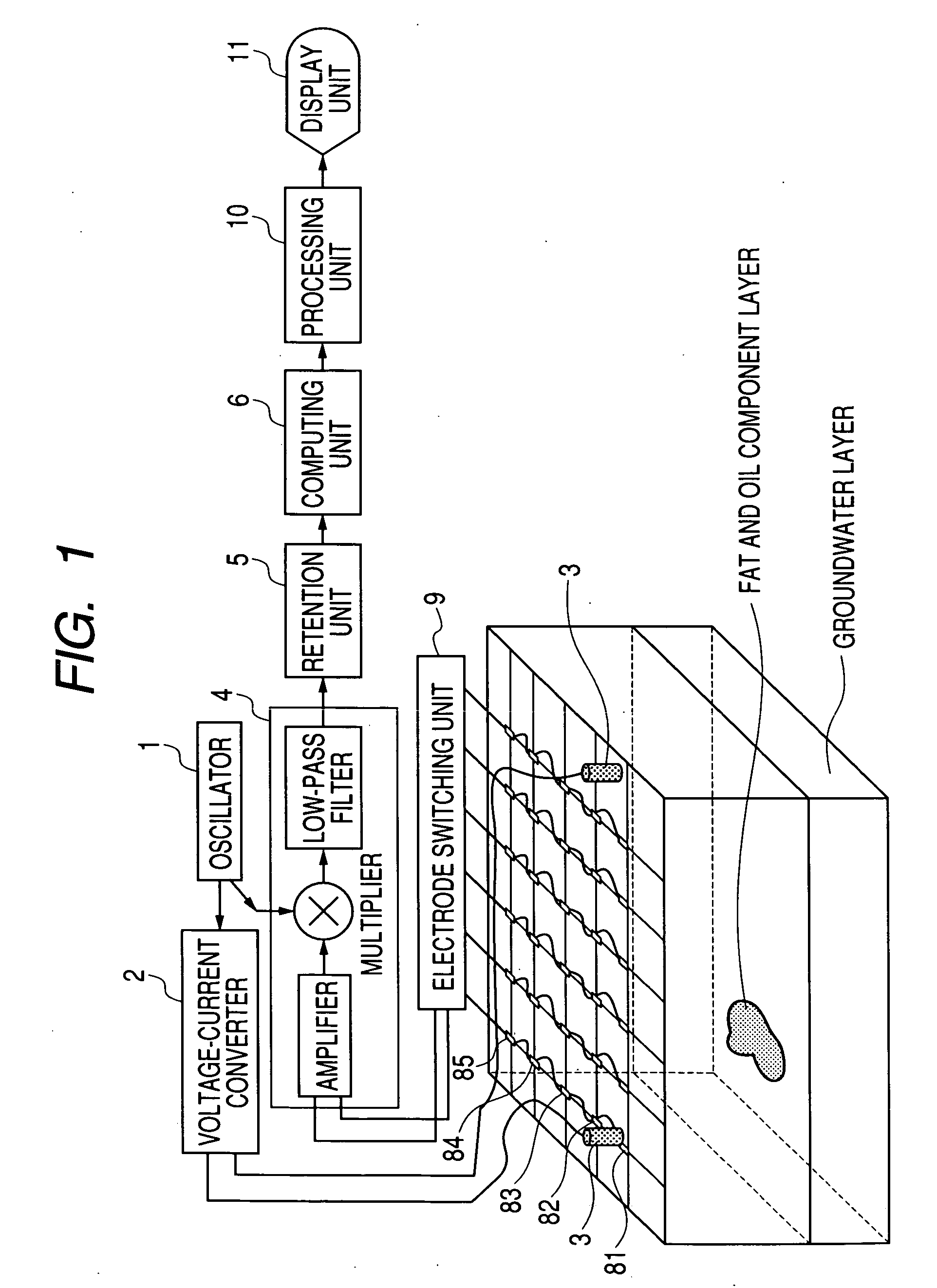
Underground exploration apparatus, system and method
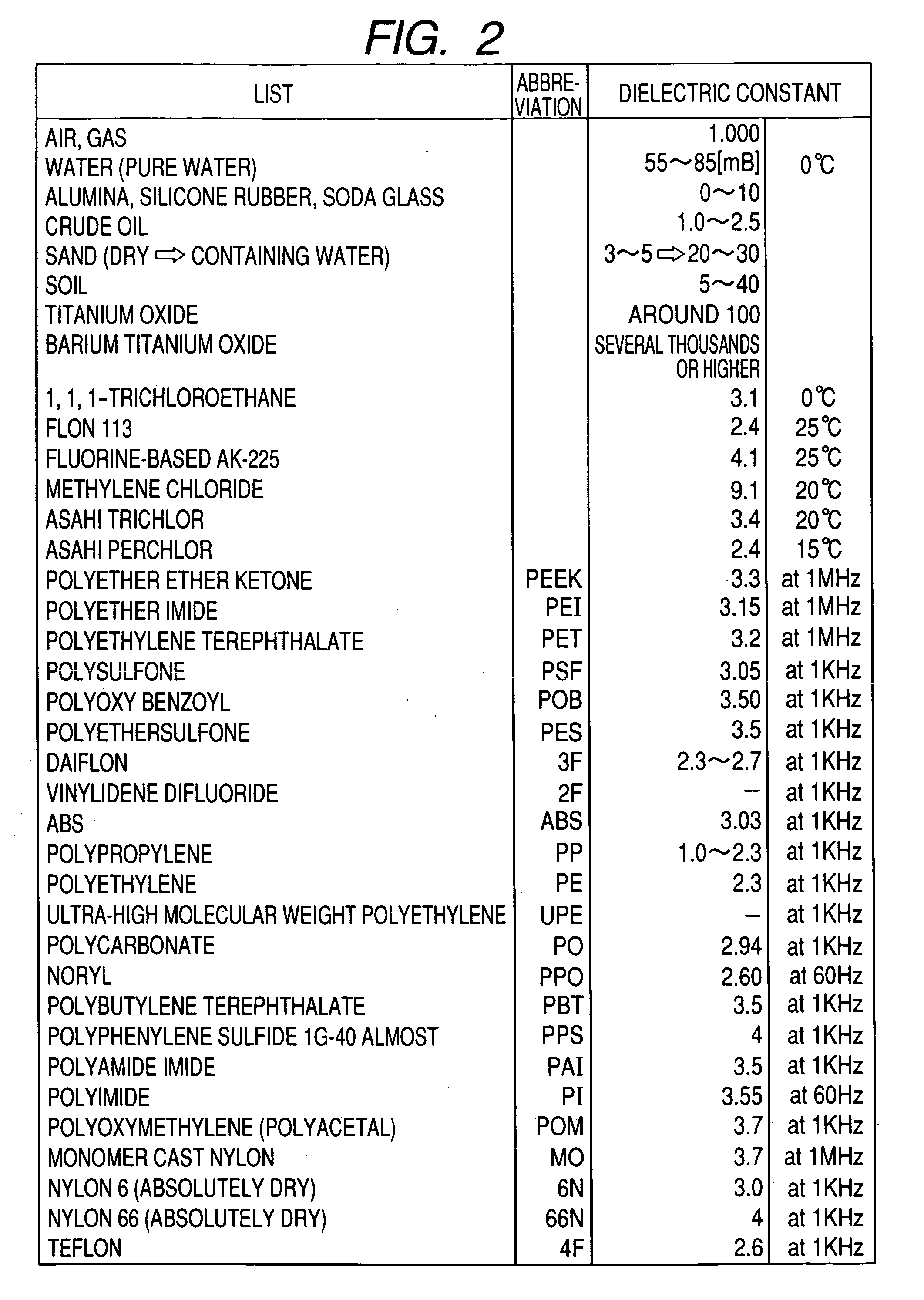
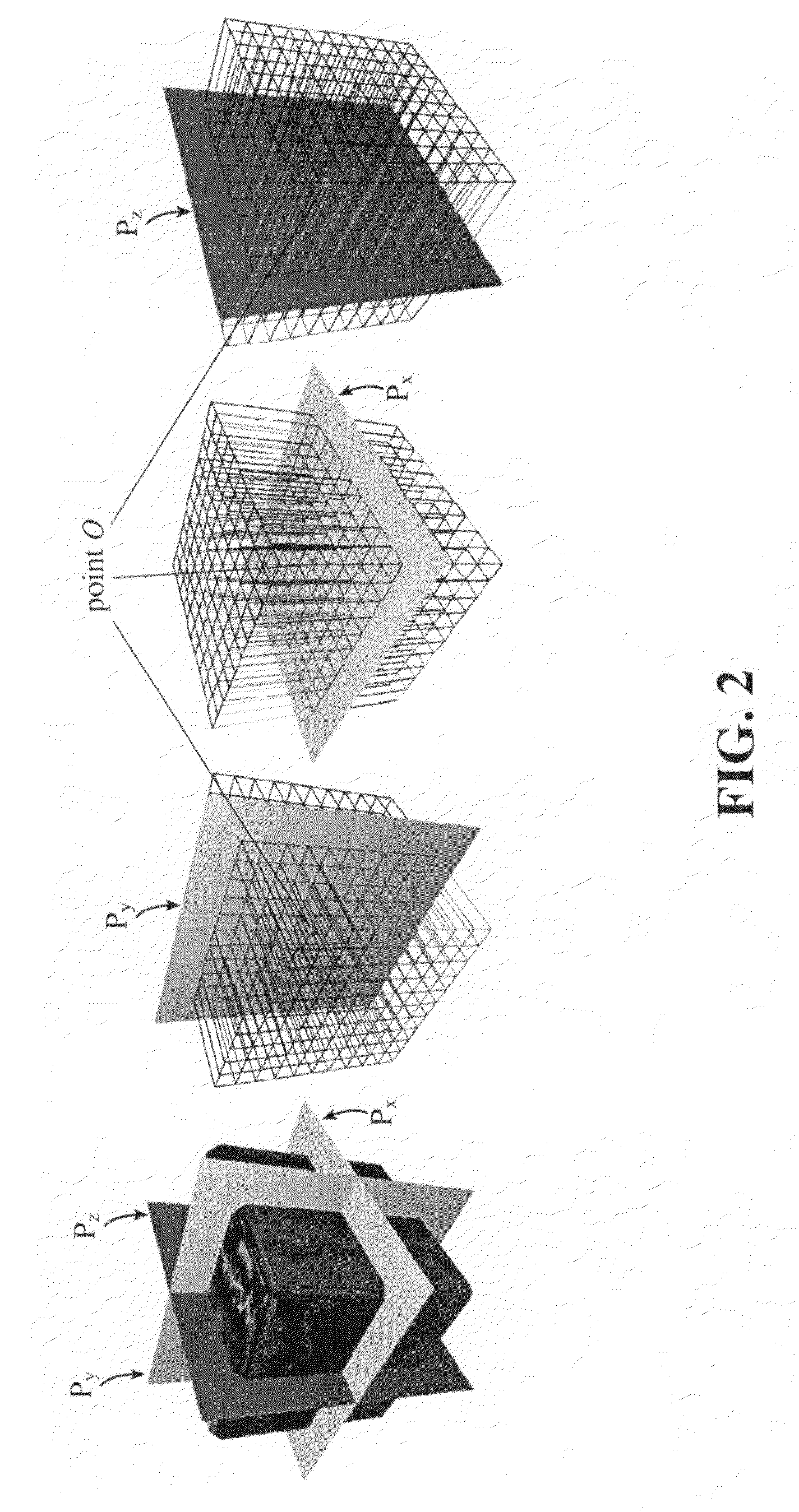
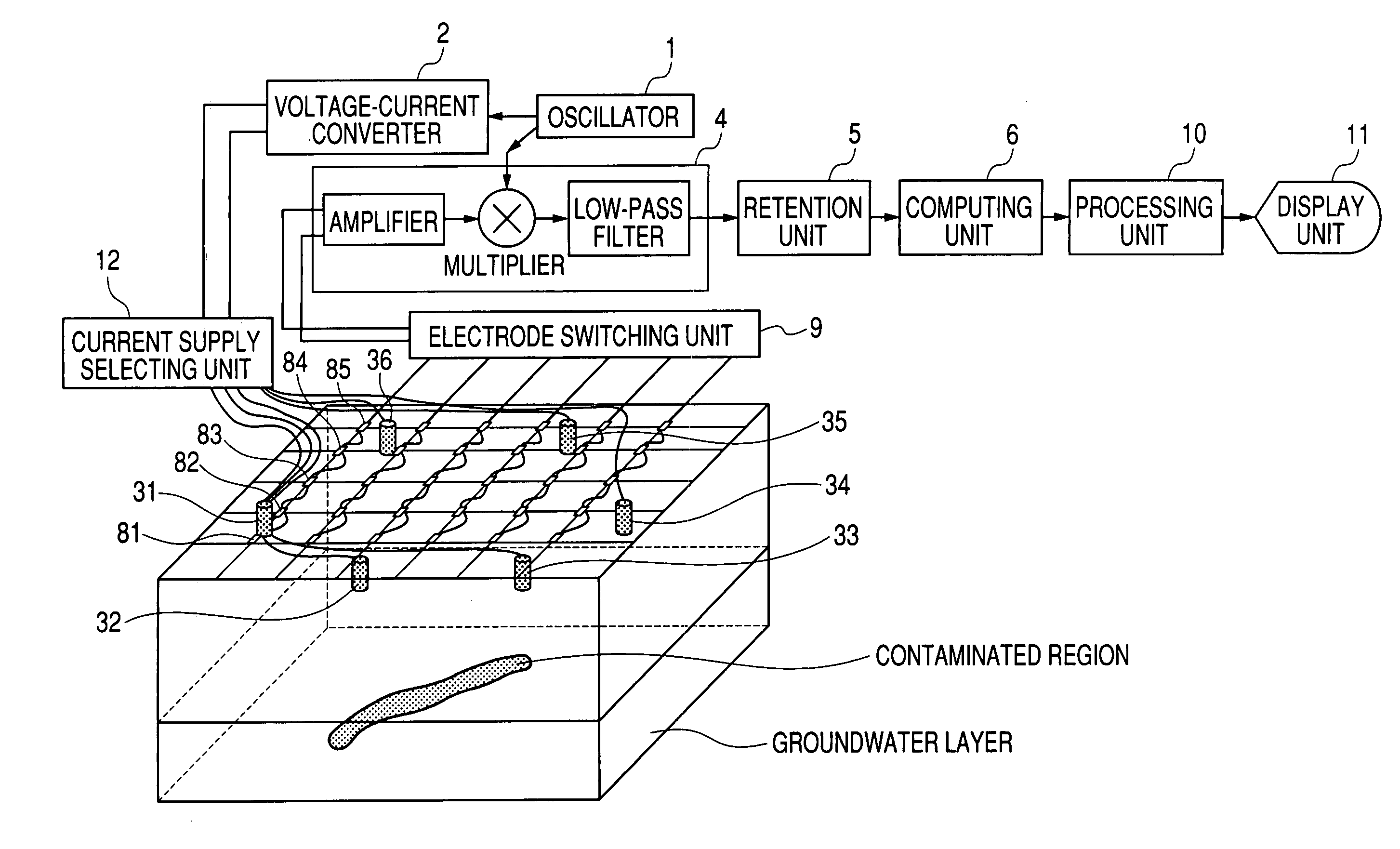
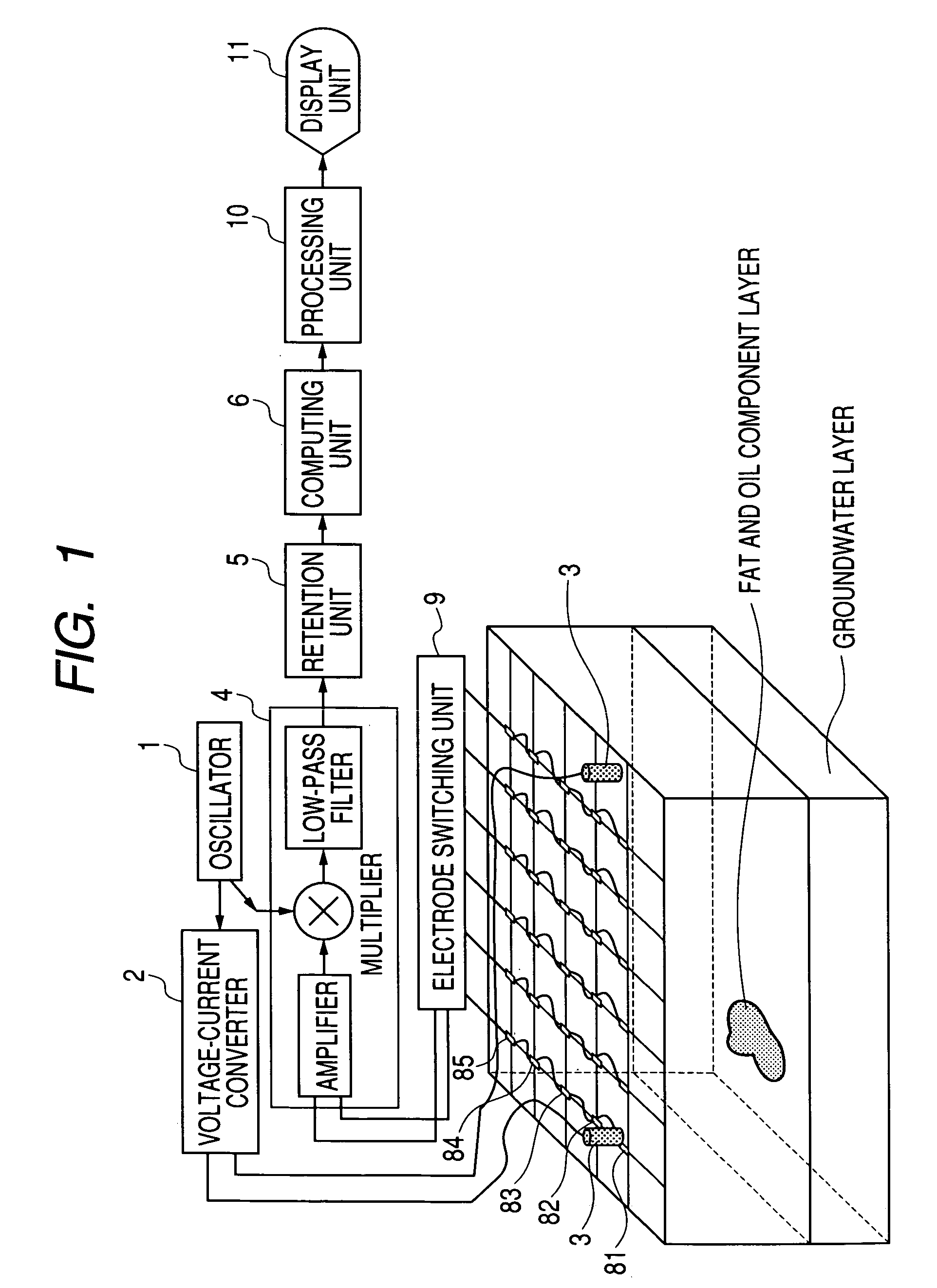
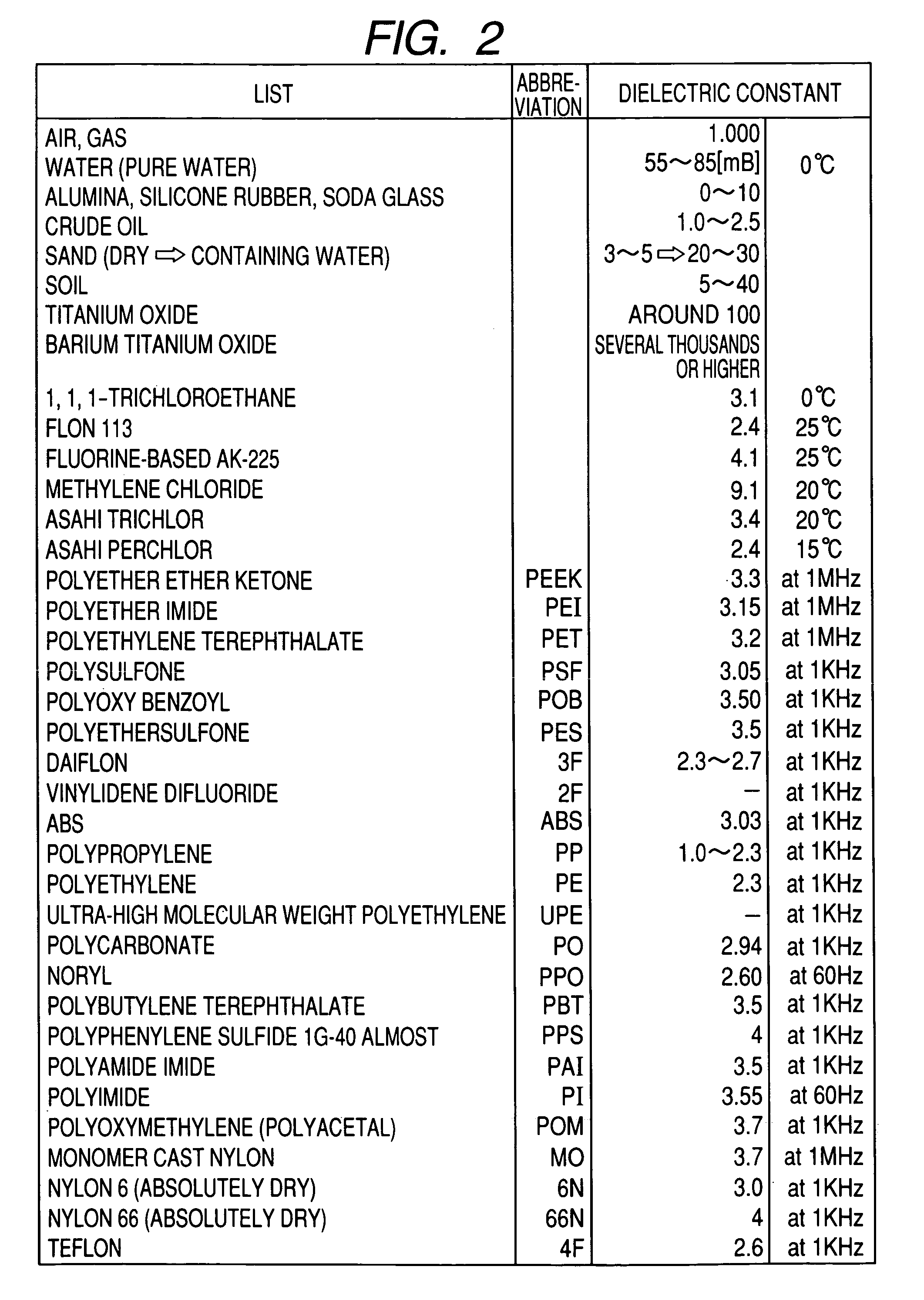
The object of the present invention is to realize a low-invasive underground exploration apparatus, system, and method which are capable of specifying the kind, three-dimensional position, and amount of a substance present in the ground. The underground exploration apparatus, system, and method includes: measuring, at multiple points, a high frequency voltage that appears upon conduction of high frequency current through the ground to obtain measurement results at two or more frequency levels; employing an ground model using the finite element method, the boundary element method, an impedance network, or the like to estimate a substance in the ground by changing unknown quantities of the ground model such as local dielectric constant and electric conductivity so as to make an error between the actual measured value and the calculated value smaller; and displaying input information of the ground model and results of the estimation processing two-dimensionally or three-dimensionally.
Owner:CANON KK
Boundary modeling method of polygonal farmland operation area
The invention discloses a boundary modeling method of a polygonal farmland operation area. The method comprises the steps that n peaks of the boundary of the polygonal farmland operation area are collected; the n peaks are put at a first quadrant of a rectangular coordinate system; the peak with the biggest X-coordinate value and the peak with the smallest X-coordinate value are determined; an upper boundary function model and a lower boundary function model are established, and boundary modeling is completed. According to the method, the boundary of the linear polygonal farmland operation area and the peaks of obstacles in the farmland operation area can be recorded and drawn precisely, so that the accurate farmland operation area is provided for an operator of an agricultural plant protection machine, and a reliable basis is provided for the path and track planning of the agricultural plan protection machine and the calculation of farmland operation area.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Long elements method for simulation of deformable objects
InactiveUS7363198B2Real timeImprove accuracyAnalogue computers for chemical processesComputation using non-denominational number representationGraphicsBoundary element method
Long Elements Method (LEM) for real time physically based dynamic simulation of deformable objects. The LEM is based on a new meshing strategy using long elements whose forms can be straight or arbitrary. The LEM implements a static solution for elastic global deformations of objects filled with fluid based on the Pascal's principle and volume conservation. The volumes are discretised in long elements, defining meshes one order of magnitude smaller than meshes based on tetrahedral or cubic elements. The LEM further combines static and dynamic approaches to simulate the same deformable medium, allowing modeling a three-dimensional internal state at any point inside the deforming medium from a reduced number of explicitly updated elements. Complex elastic and plastic deformations can be simulated in real time with less computational effort. The LEM is particularly useful in real time virtual interactions, soft tissue modeling, and graphic and haptic rendering.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Underground exploration apparatus, system and method
The object of the present invention is to realize a low-invasive underground exploration apparatus, system, and method which are capable of specifying the kind, three-dimensional position, and amount of a substance present in the ground. The underground exploration apparatus, system, and method includes: measuring, at multiple points, a high frequency voltage that appears upon conduction of high frequency current through the ground to obtain measurement results at two or more frequency levels; employing an ground model using the finite element method, the boundary element method, an impedance network, or the like to estimate a substance in the ground by changing unknown quantities of the ground model such as local dielectric constant and electric conductivity so as to make an error between the actual measured value and the calculated value smaller; and displaying input information of the ground model and results of the estimation processing two-dimensionally or three-dimensionally.
Owner:CANON KK
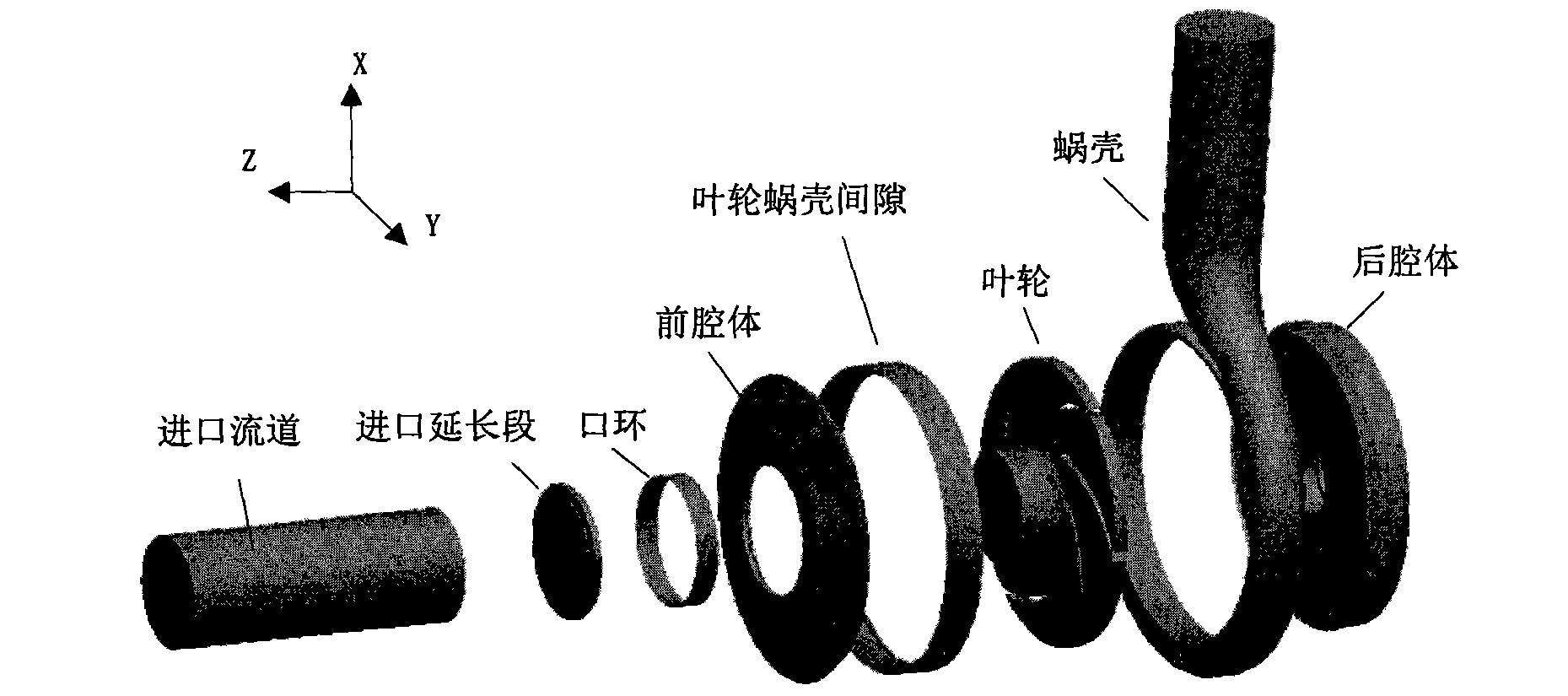
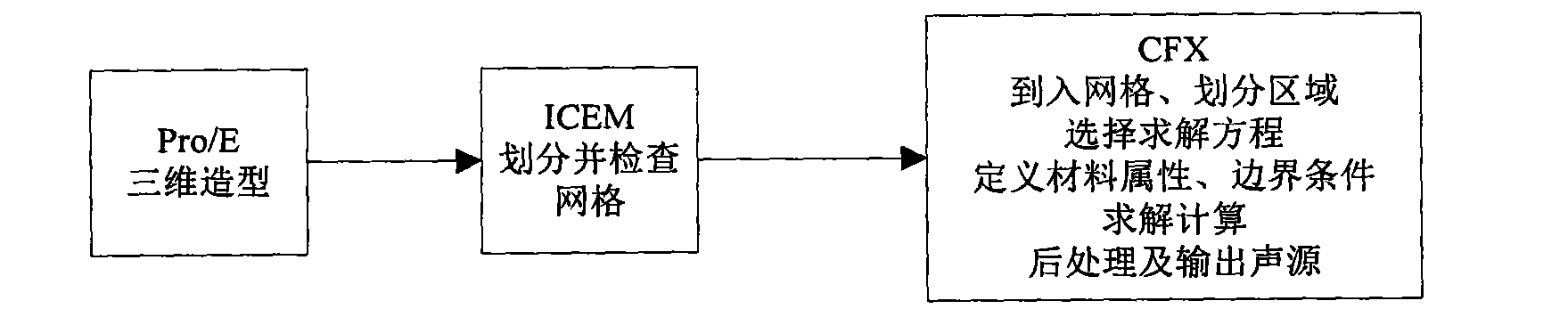
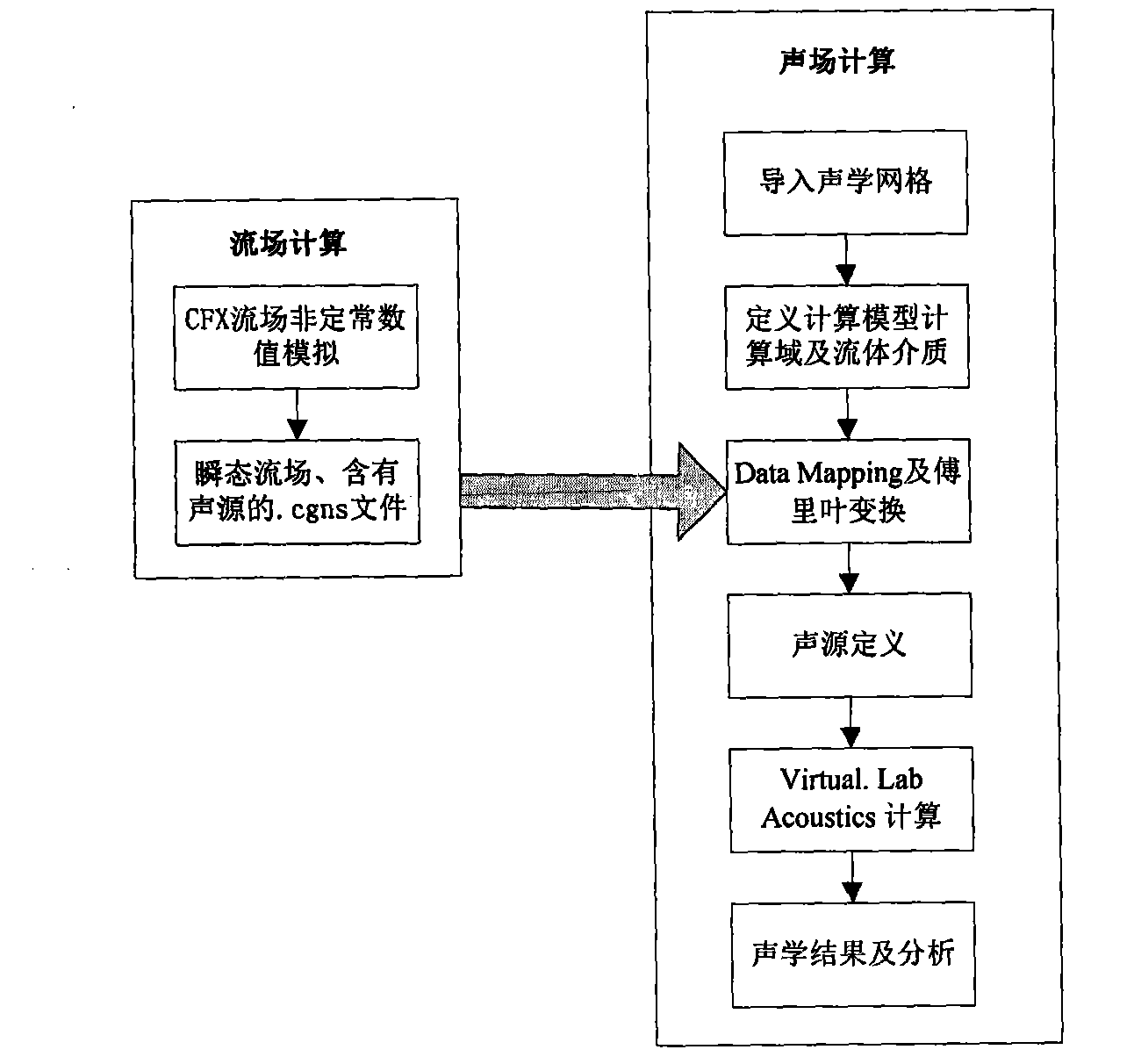
Method for predicting hydraulic noise of centrifugal pump
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
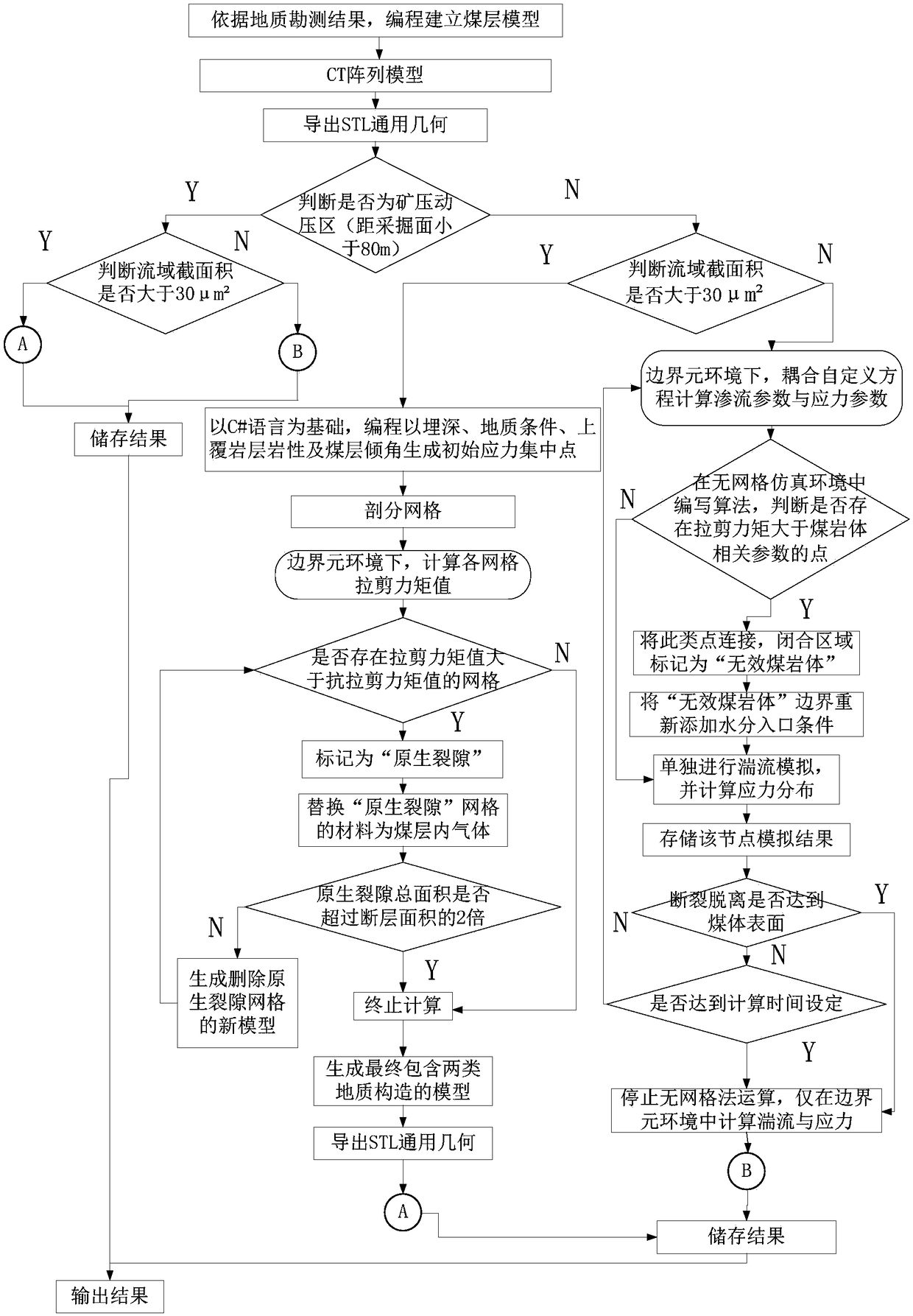
Coupling numerical simulation method of seepage-damage-stress for coal and rock mass water injection
ActiveCN109063257AEnsure safetyReduce productionUnderground miningDesign optimisation/simulationMathematical modelGeological survey
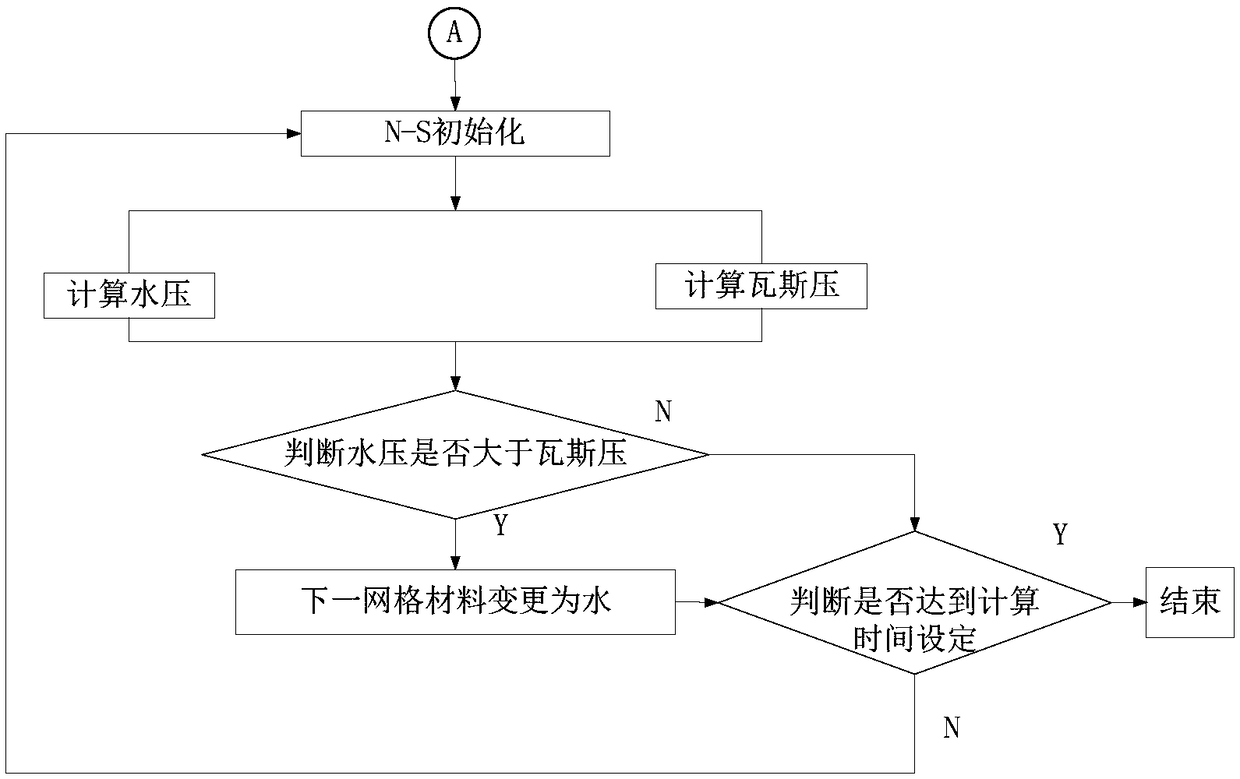
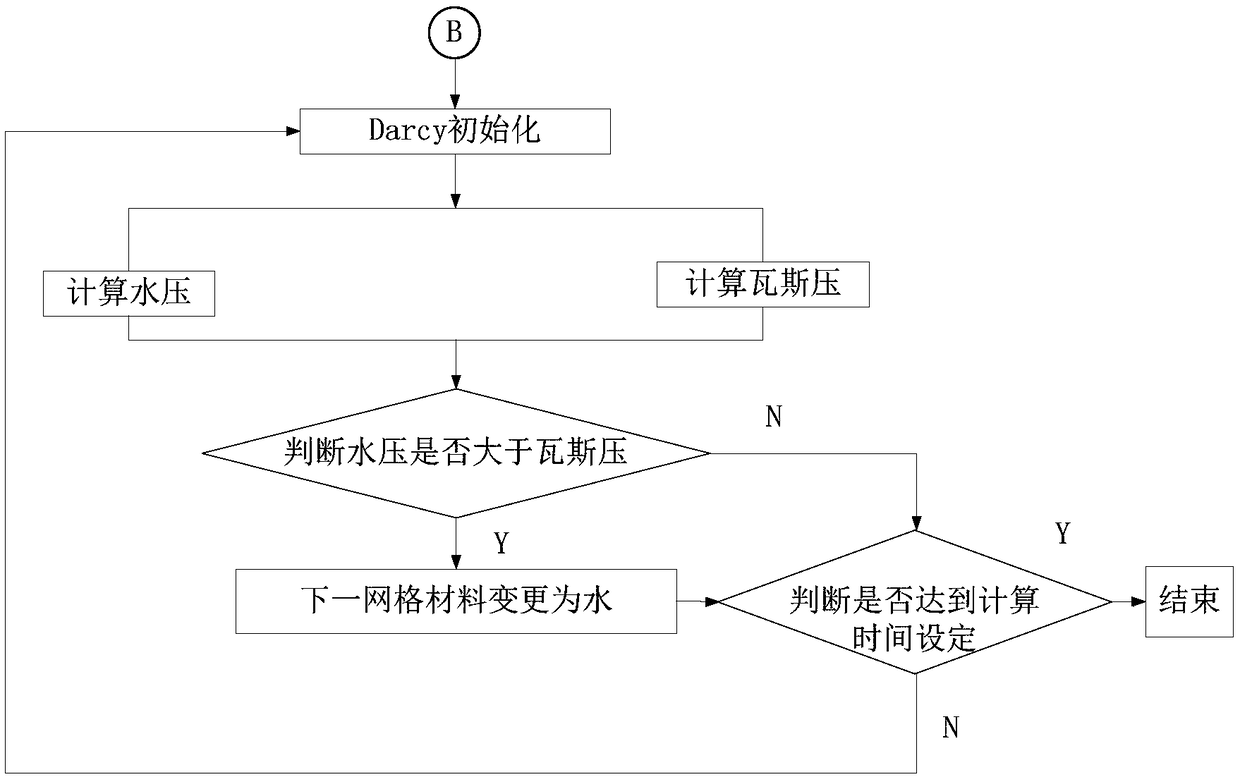
The invention discloses a water injection seepage flow in coal and rock mass zoning, damage-stress coupling numerical simulation method, according to the geological survey results, the coal seam modelis established; water injection seepage flow in coal and rock masses in non-mining affected area and mining affected area is simulated by zoning. In the non-mining influence area, the program can judge whether the coal body is deformed or even fractured under the action of water pressure stress by calculating and comparing the tensile and shear moments of each grid. At the same time, the meshlessmethod is used to simulate the fracture process of coal mass and the boundary element method is used to simulate the seepage process, which combines the advantages of the two methods on the micro-scale. In the mining-affected area, N-S equation and Darcy's law to accurately simulate the coal and rock mass water injection process in the coal and rock mass damage and moisture transport law. A soliddata basis for coal seam water injection is provided, greatly reducing the possibility of coal broken into dust particles, reducing the production of coal dust, ensuring the safety of coal seam mining.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
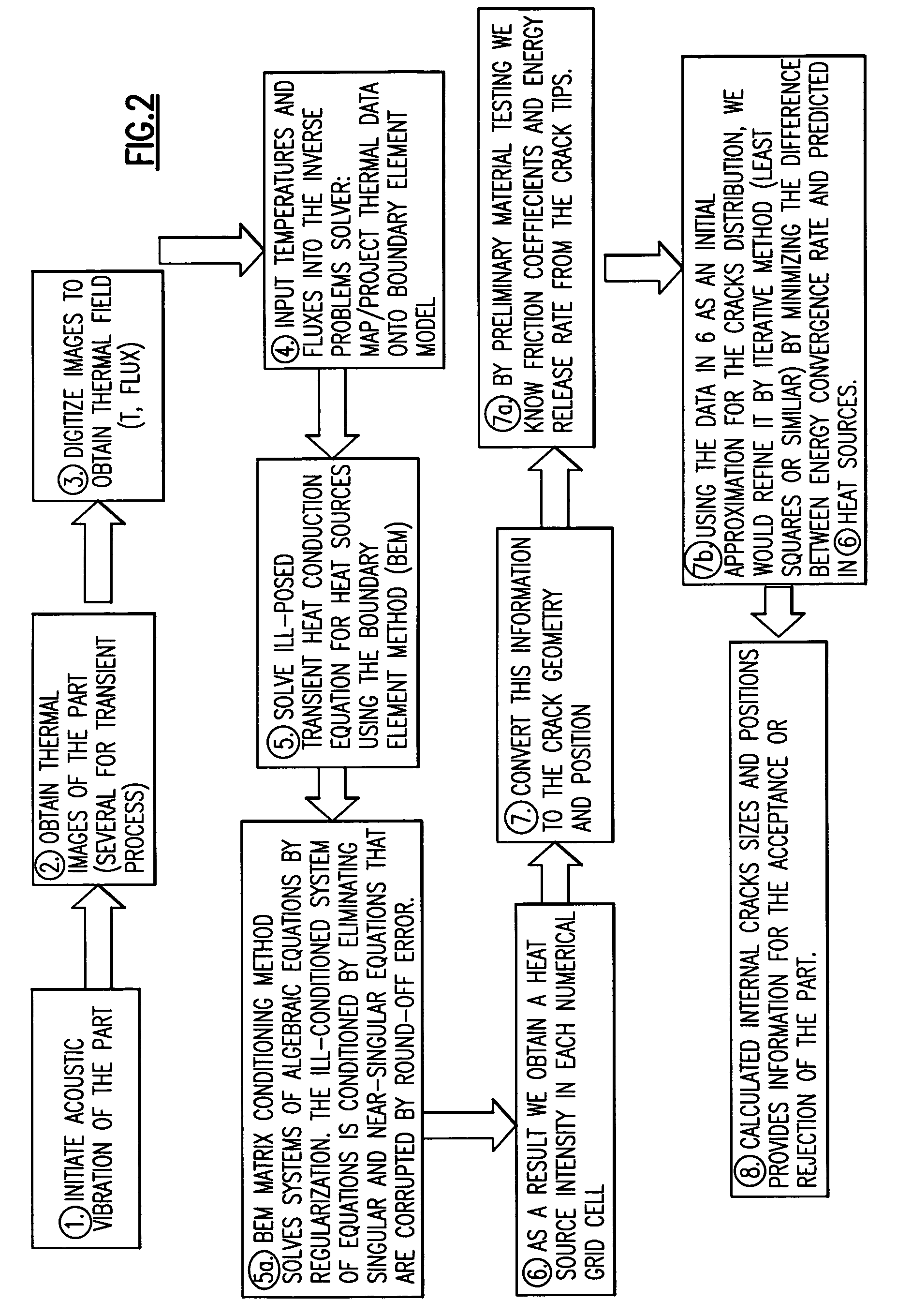
Inverse thermal acoustic imaging part inspection
ActiveUS20080053234A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by optical meansThermal energyHeat flux
A method of identifying a flaw in a part is provided that includes vibrating a part to induce heat. The heat originates in any flaws in the part. A thermal image is obtained using, for example, an infrared camera. A mathematical representation of the thermophysics, such as the heat conduction or thermal energy equations using the boundary element method or finite element method is used to identify a source and an intensity of the heat identified with the thermal image. Using the source and intensity of the heat, flaw characteristics for the part can be determined. The method is employed using an inspection system that includes a vibration device for vibrating the part. An imaging device, such as an infrared camera, measures temperature on the surface of the part. An assumption is made or additional measurements are taken to obtain values for surface flux or surface heat transfer coefficients. A processor communicates with the imaging device for receiving the surface temperature. The processor includes computer memory having part characteristics and mathematical equations. The processor uses the measured surface temperature, assumed or measured heat flux or heat transfer coefficients, part characteristics and mathematical equations to determine the flaw characteristics in the part.
Owner:RTX CORP
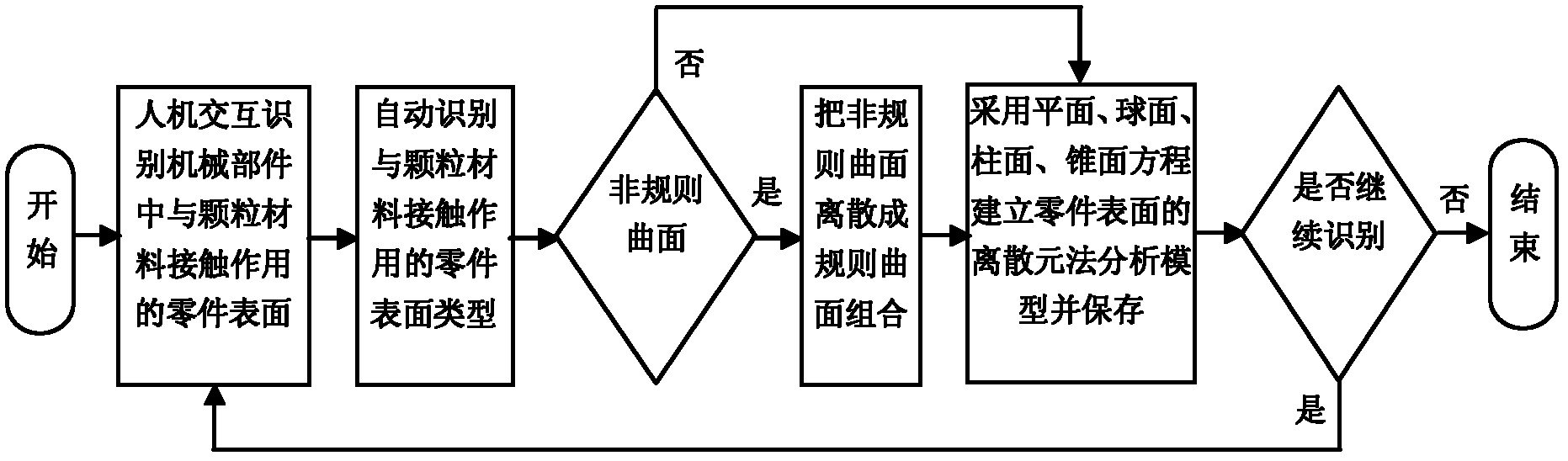
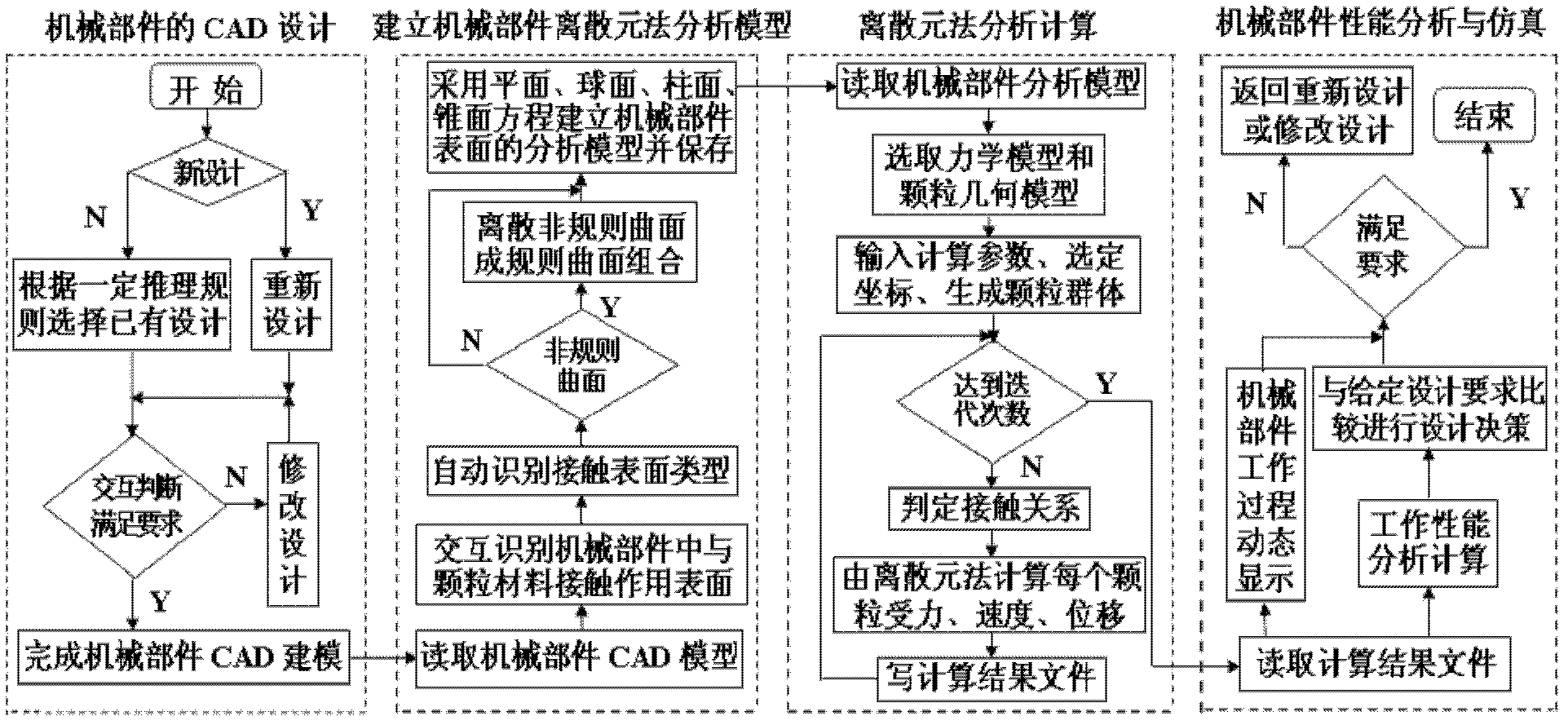
A General Method of Discrete Element Method Boundary Modeling
ActiveCN102298660AAchieve integrationImplementing Boundary Modeling MethodsSpecial data processing applicationsMotion parameterBoundary element method
The invention relates to a universal method of boundary modeling based on distinct element method, which is applicable to analyze and evaluate the service performance of a mechanical part through distinct element method. The technical solution comprises the following steps: step 1, alternately identifying a part surface for contacting particle material in the mechanical part; step 2, automatically identifying that the part surface is a regularly curved surface or an irregularly curved surface; step 3, automatically identifying the missing part of the regularly curved surface; step 4, dispersing the irregularly curved surface into combination of regularly curved surfaces; step 5, reading the parameter of the regularly curved surface; step 6, alternately adding the motion parameters and material characteristic parameters of the curved surface; step 7, storing boundary model data. By changing the CAD (Computer - Aided Design) model of the mechanical part, the performances of mechanical parts with different structures and sizes can be analyzed so as to optimize the structures and sizes of the mechanical parts, thus solving the technical problem on the optimum design of the mechanical parts and bringing about remarkable technical effects.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
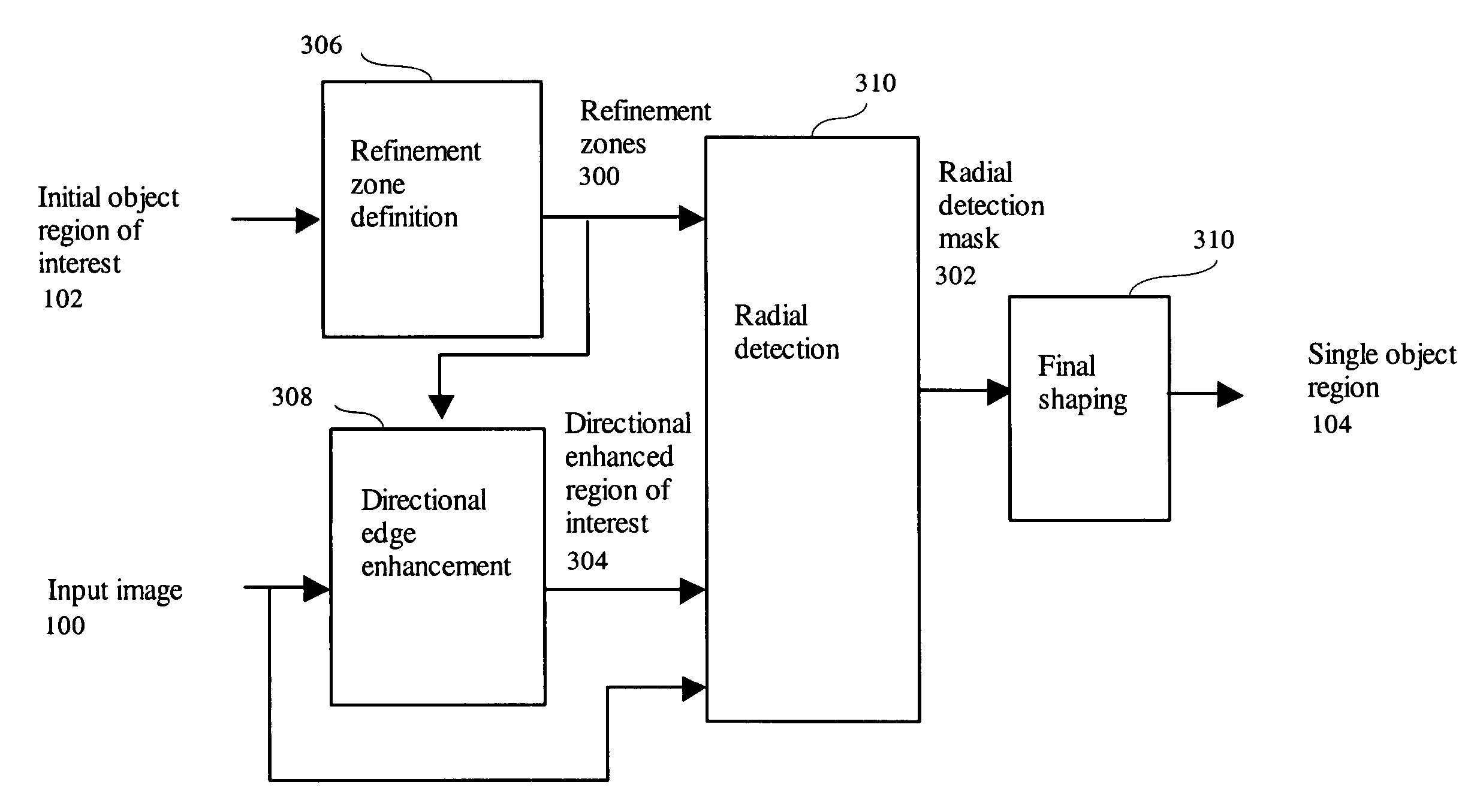
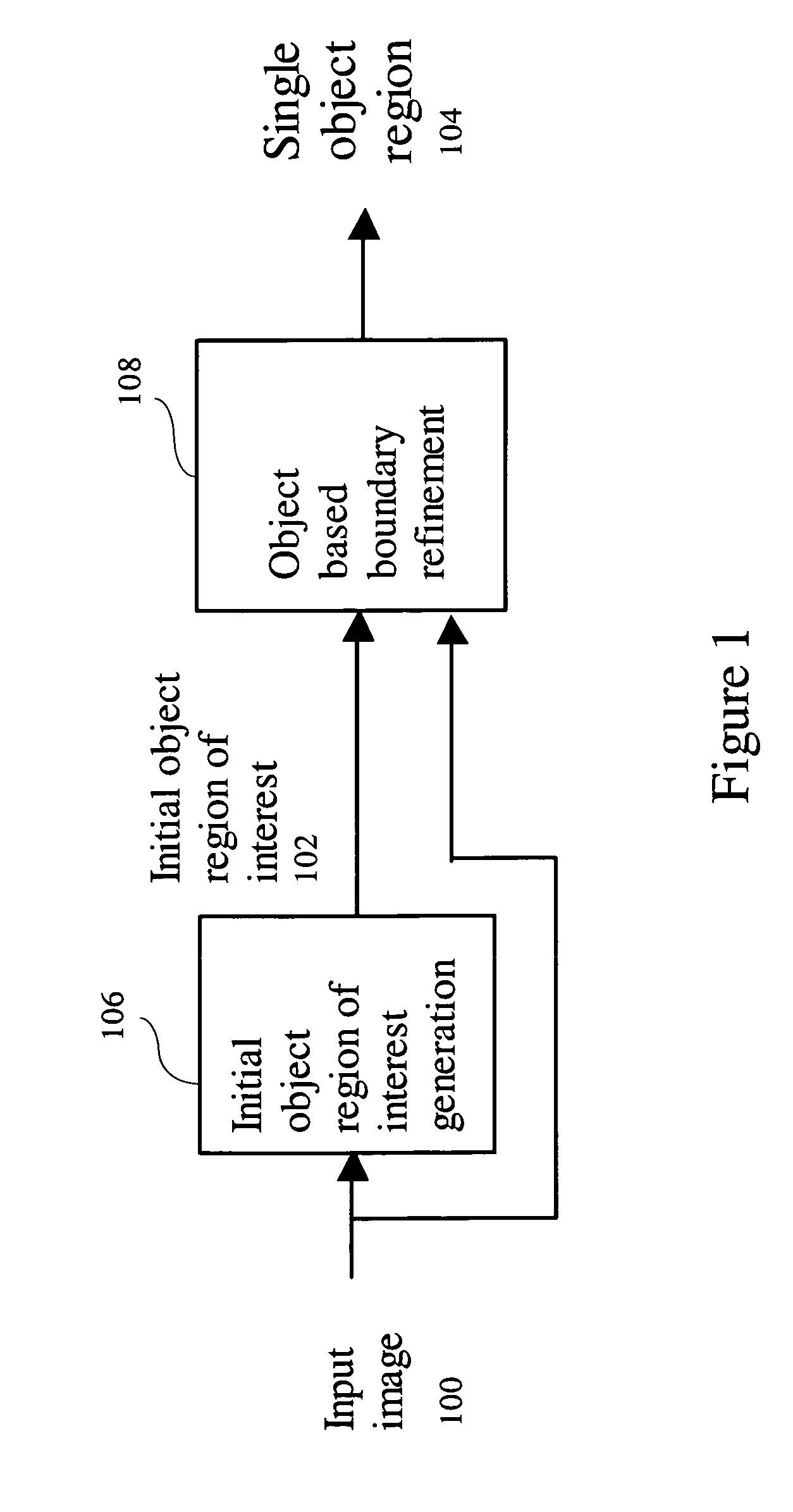
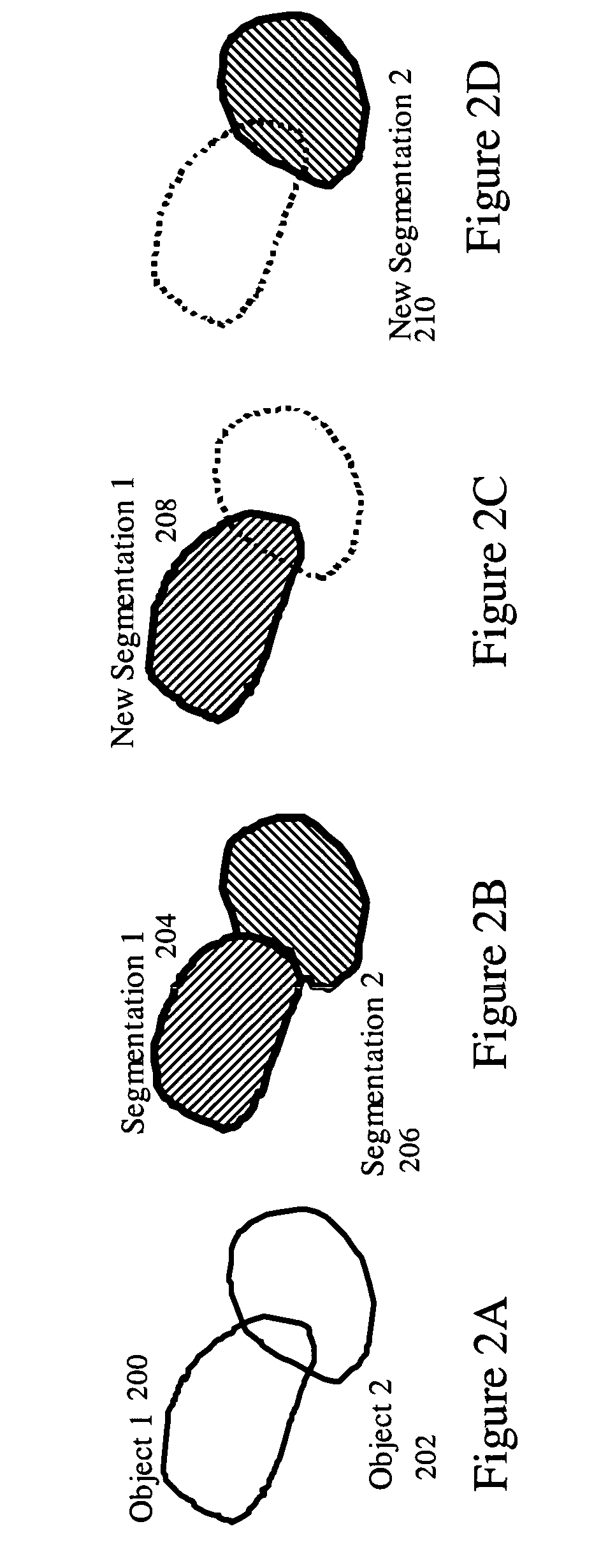
Object based boundary refinement method
An object based boundary refinement method for object segmentation in digital images receives an image and a single initial object region of interest and performs refinement zone definition using the initial object regions of interest to generate refinement zones output. A directional edge enhancement is performed using the input image and the refinement zones to generate directional enhanced region of interest output. A radial detection is performed using the input image the refinement zones and the directional enhanced region of interest to generate radial detection mask output. In addition, a final shaping is performed using the radial detection mask having single object region output.A directional edge enhancement method determining pixel specific edge contrast enhancement direction according to the object structure direction near the pixel consists receives an image and refinement zones and performs 1D horizontal distance transform and 1D vertical distance transform using the refinement zones to generate horizontal distance map and vertical distance map outputs. A neighboring direction determination is performed using the horizontal distance map and the vertical distance map to generate neighboring image output. In addition, a directional edge contrast calculation using the neighboring image and input image having directional enhanced region of interest output.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
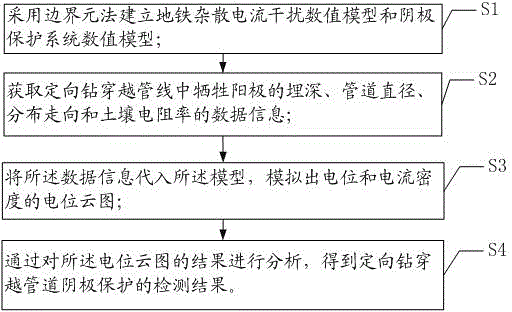
Detection method for cathode protection of directionally drilled and crossed pipeline
The invention provides a detection method for cathode protection of a directionally drilled and crossed pipeline. According to the detection method, a numerical model of a metro stray current interference and cathode protection system is established by virtue of a boundary element method, the influences of the potential and the electric current density of a magnesium positive electrode, the value of stray current and the parallel length of a metro on a crossed-section cathode protection system are simulated, and thus a preliminary scheme for improving the directionally drilled crossed-section cathode protection system can be correspondingly proposed, so that the cathode protection system of the directionally drilled and crossed pipeline is improved, a cathode protection rule is met, and the safety operation of the pipeline is effectively guaranteed.
Owner:SHENZHEN GAS CORP
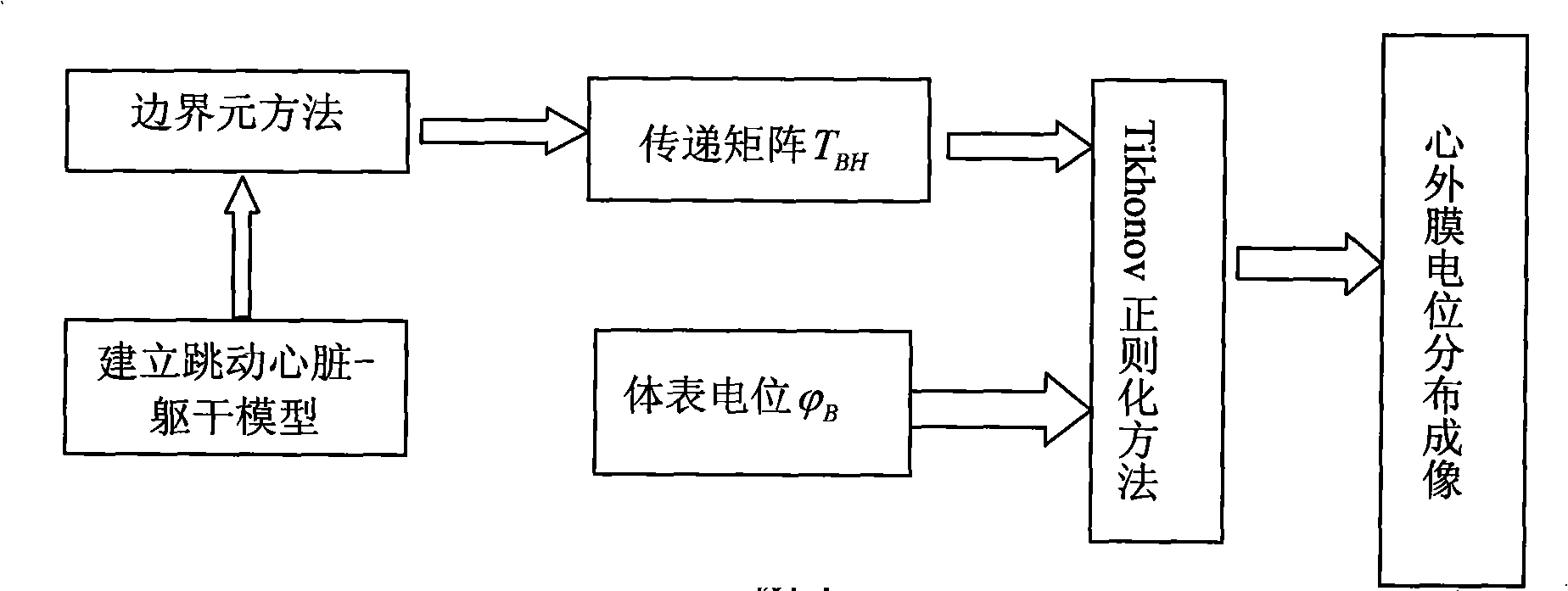
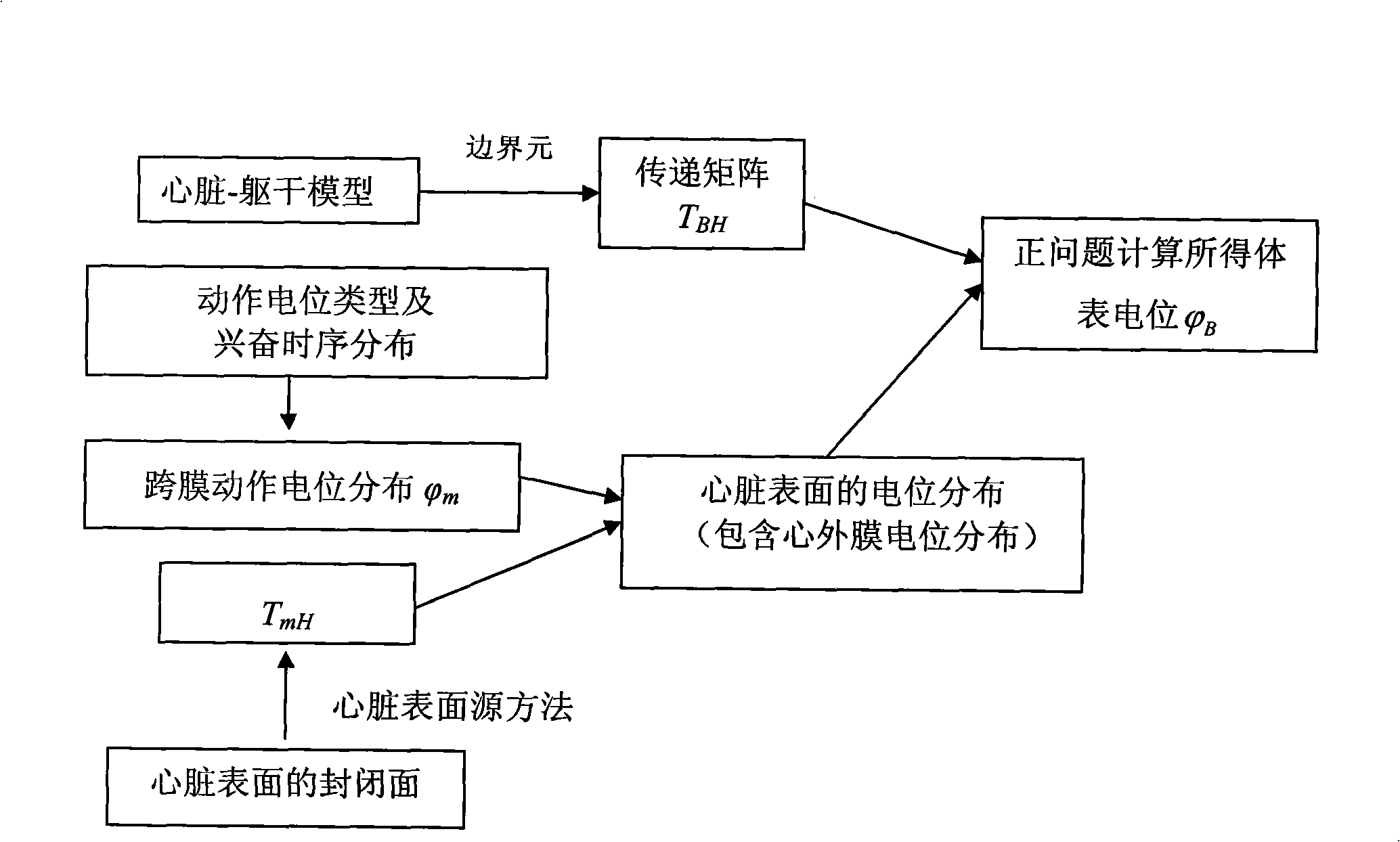
Heart electric function imaging method based on jumping heart model
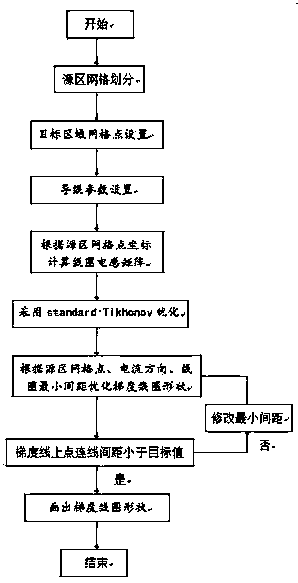
InactiveCN101283908AOvercome geometric errorsAccurate detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDiseaseElectricity
The invention discloses a heart electrical function imaging method based on beating heart model. The method comprises following steps: obtaining the position displacement change of heart based on double-ventricle electricity-coupled heart model; respectively constructing transfer matrixes TBH between epicardium and body surface potential of beating heart at different moments by adopting boundary element method; obtaining the body surface potential distribution PhiB of the body at different moments, calculating the potential distribution of the epicardium, and achieving heart electrical function imaging; and calculating the potential distribution of the epicardium by adopting normal TiKhonov regularization method. The heart electrical function imaging method based on beating heart model can effectively suppress the geometrical error caused by static heart model to obtain more accurate potential distribution imaging of the epicardium and accurately detect the electrical movement information of the heart, thus providing meaningful clinical information for the prevention and the treatment of heart diseases.
Owner:浙江华际天府智能科技有限公司
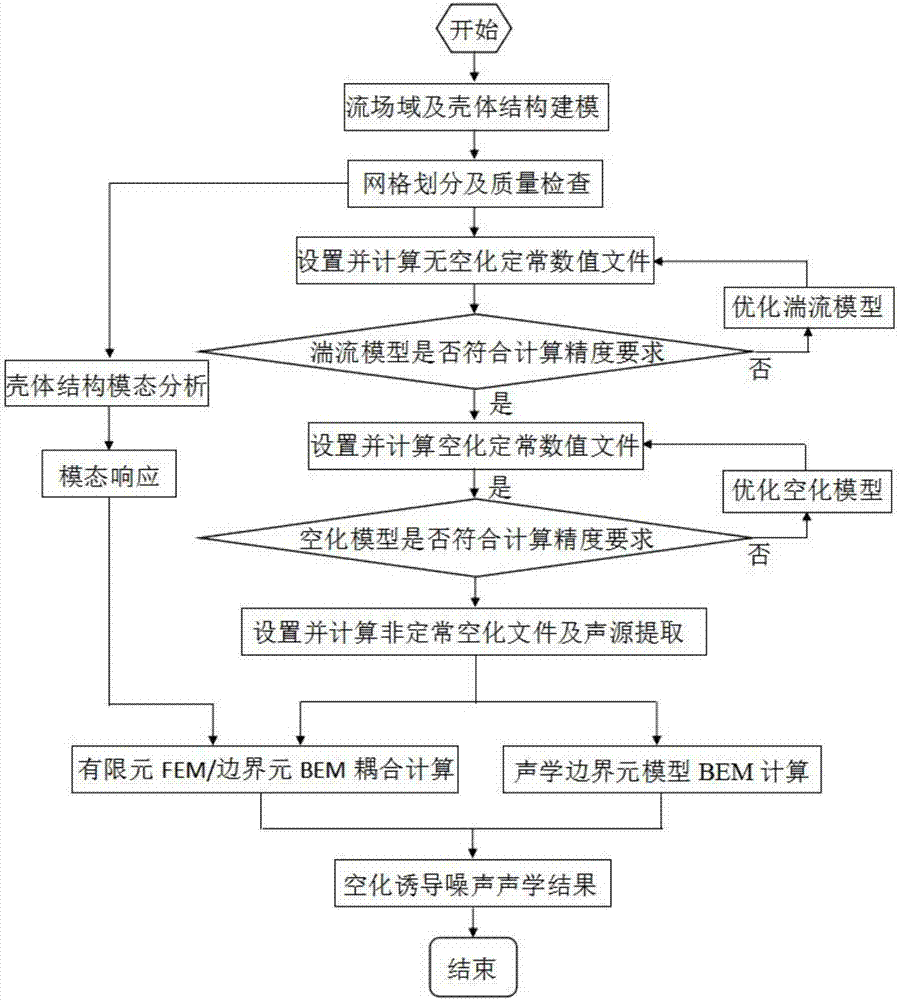
Method for forecasting cavitation induced noise values of vane pumps
InactiveCN107273570ASimulation is accurateSolving Numerical Prediction ProblemsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsCavitationEngineering
The invention provides a method for forecasting cavitation induced noise values of vane pumps, and aims at calculating inside and outside radiation noises, which undergo cavitation, of vane pumps in low-pressure or large-flow occasions. The method comprises the following steps of: modeling a flow field domain and a pump shell, carrying out mesh generation on the flow field domain and checking mesh quality, setting a pressure inlet and a speed outlet boundary condition according to specific operation parameters of a pump, setting a solver parameters, and calculating non-cavitated constant file; carrying out constant iterative calculation to obtain a cavitation numerical value result file under each cavitation number, and carrying out turbulence model verification and cavitation model verification on models; carrying out inconstant iterative calculating by taking the constant result file which is added with a cavitation model as an initial value of cavitation inconstant calculation, so as to obtain a pulse and mesh information file included under each cavitation number; and calculating a cavitation induced noise of the vane pump by applying a coupled algorithm of a sound analogy theory and a boundary element method in acoustic calculation software. The method is capable of correctly carrying out cavitation induced noise forecasting.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
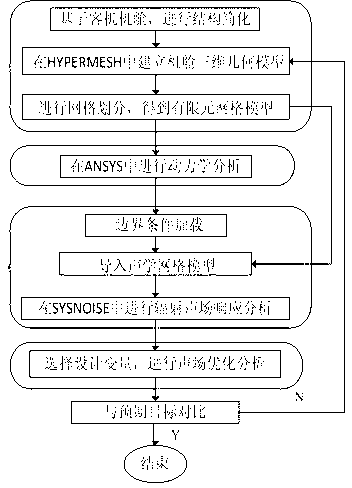
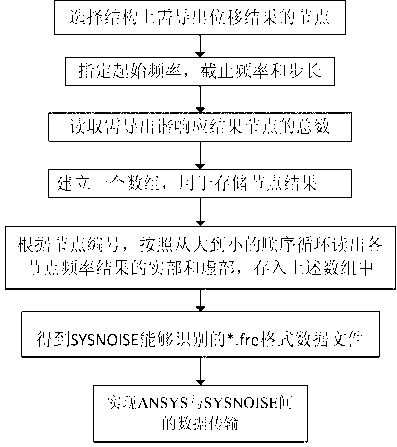
Method of acoustics simulated analysis and optimization for cabin of passenger plane
InactiveCN103258099AReduce workloadCalculation speedSpecial data processing applicationsNacelleEngineering
The invention discloses a method of acoustics simulated analysis and optimization for a cabin of a passenger plane. The method comprises the following steps that the cabin of the passenger plane is used as a prototype, a free meshing method is adopted based on HYPERMESH software, a cabin structure grid model containing seats is established, the cabin structure grid model is led into ANSYS in a *.cdb format, a Block Lanczos method is used for carrying out vibration mode analysis, a mode superposition method is used for carrying out harmonic response analysis, the vibration frequency response features of the cabin structure are obtained, a vibration frequency response feature destination file is led into SYSNOISE as an boundary incentives condition in a *.fre format which is capable of being recognized by the SYSNOISE, a direct boundary element method is used for finally obtaining sound pressure frequency response characteristics in the cabin, the cabin structure parameters are selected as design variables, and a lowest sound pressure order in the cabin is used as a design goal to carry out sound field optimization of civil aircraft cabins. According to the method of the acoustics simulated analysis and optimization for the cabin of the passenger plane, not only is the advantage that a finite element method is prone to obtaining vibration performance used, but also the advantage that the boundary element method obtains acoustic properties fast is brought in to full play, and therefore calculation speed is accelerated.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
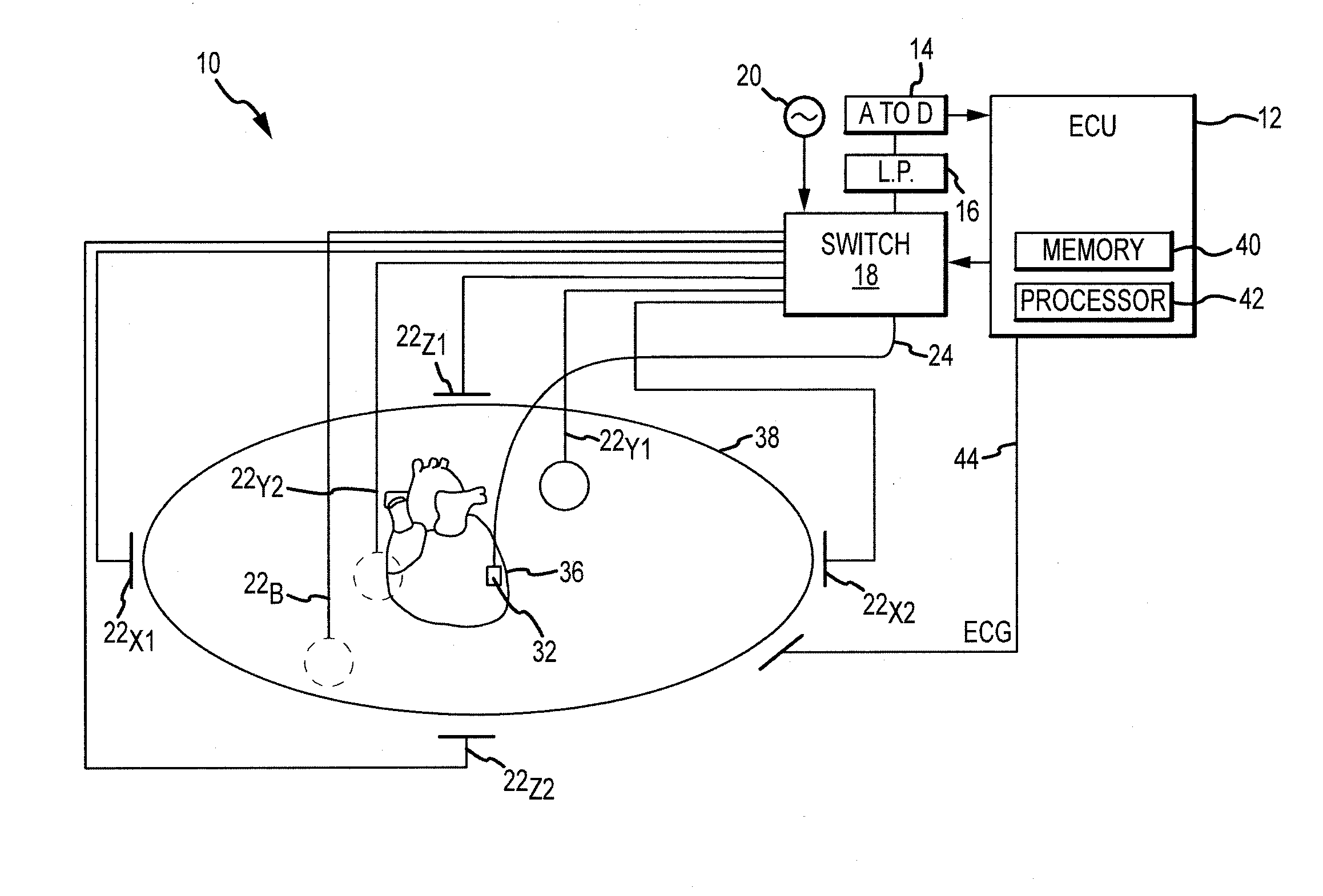
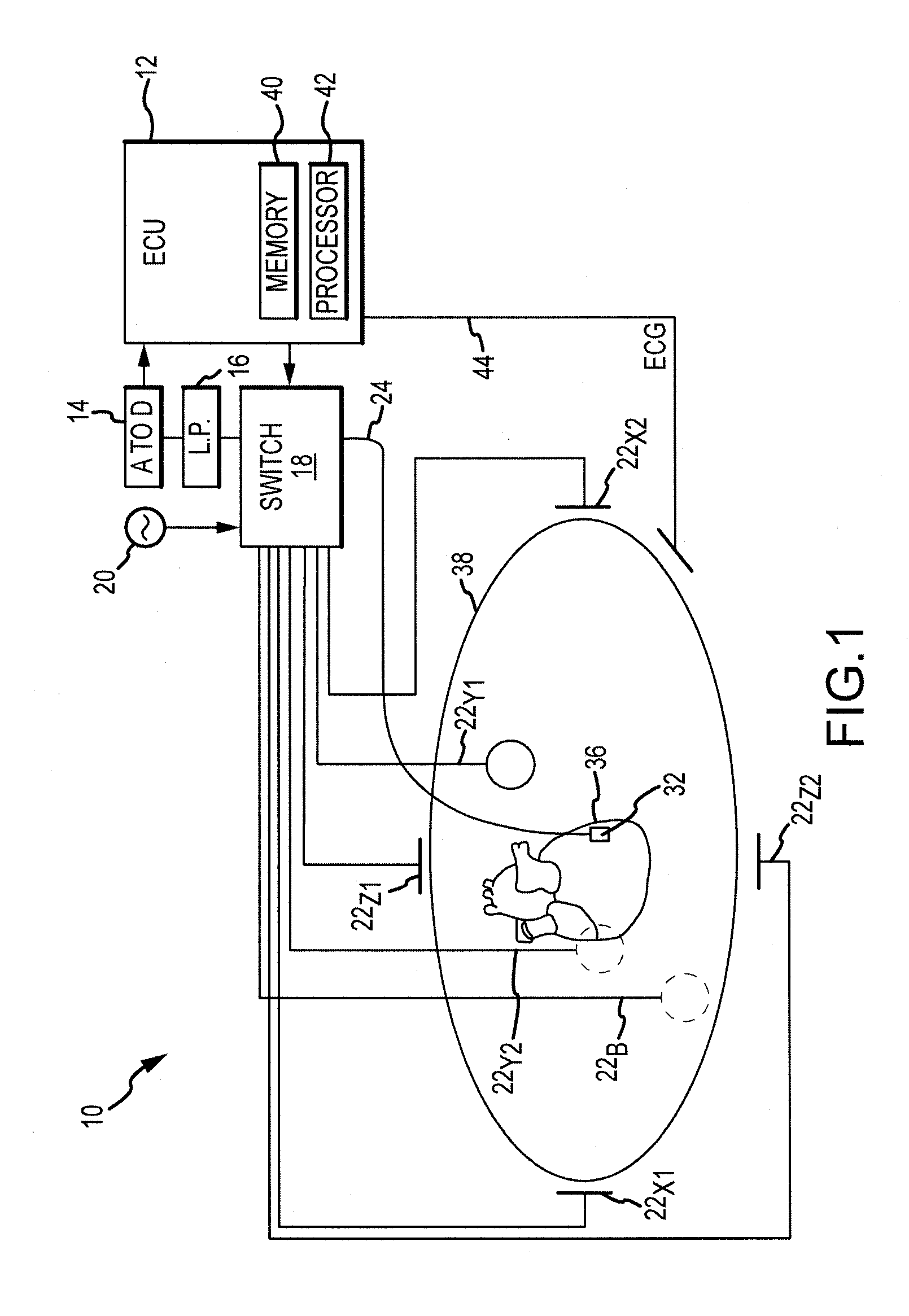
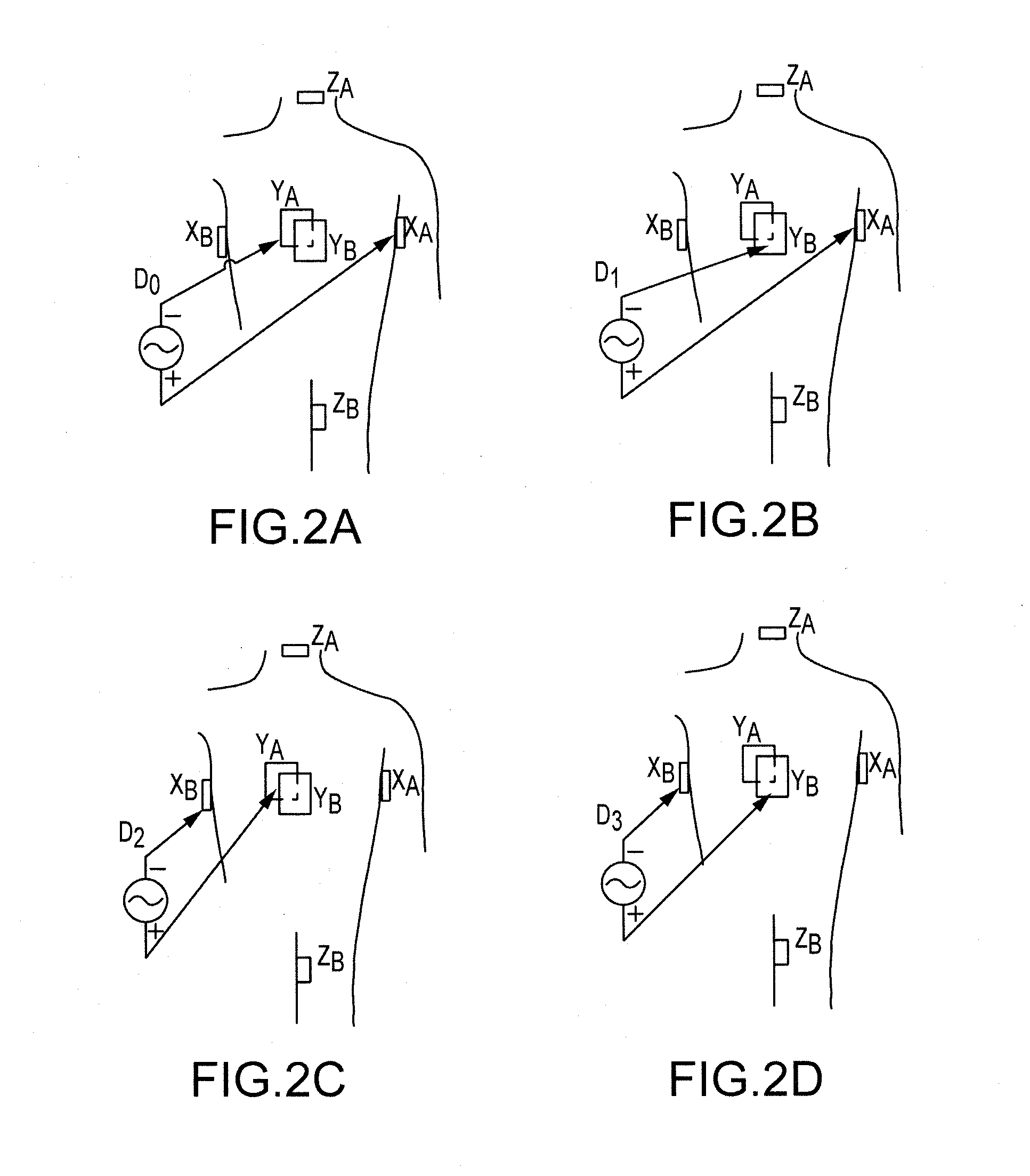
Regularization schemes for non-contact mapping with a medical device
InactiveUS20140278129A1Accurate measurementMedical simulationElectrocardiographyNon contact mappingEngineering
An embodiment of a method for solving the inverse problem of electrophysiology and determining a voltage distribution on a surface of a tissue may comprise receiving a plurality of voltages collected by a plurality of electrodes adjacent to the surface, discretizing the problem using a Finite Element Method (FEM) or a Boundary Element Method (BEM), introducing one or more regularization terms to an error minimization formulation, and solving, by a processor, the voltage distribution according to the plurality of voltages and according to the regularization terms. The regularization terms may comprise one or more of a Laplacian smoothness operator, a Tikhonov regularization matrix, a confidence matrix, and a linear operator that interpolates the plurality of electrode voltages to the tissue voltage distribution.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
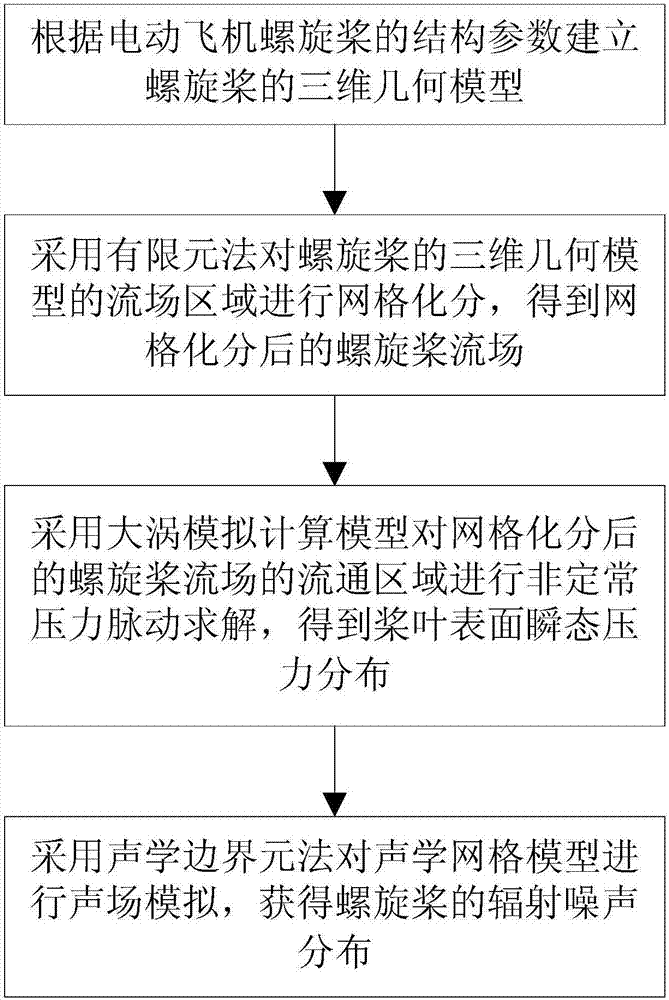
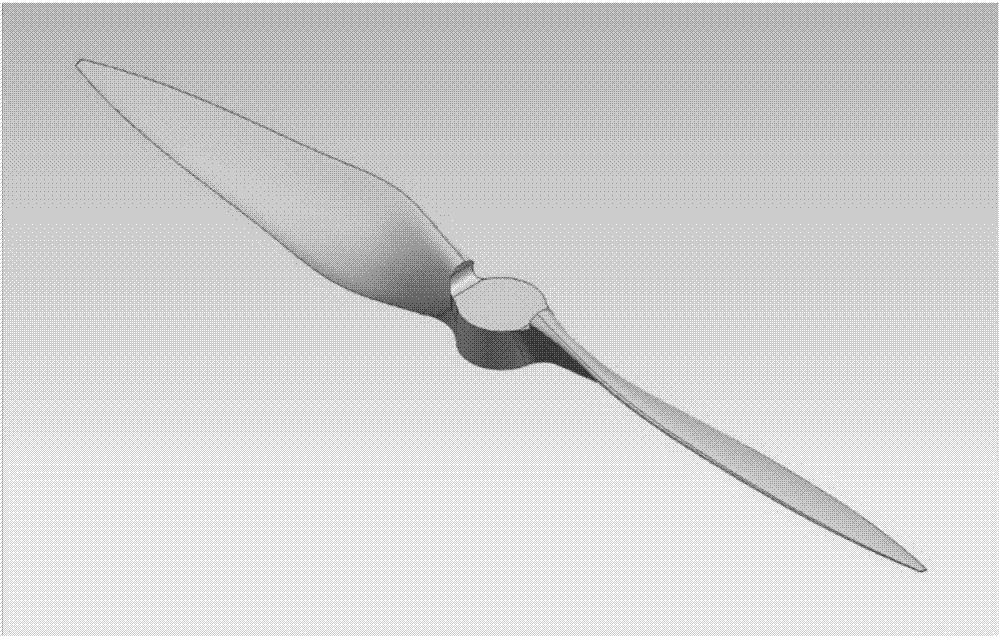
Calculation method for electric aircraft propeller noise
ActiveCN107066761ACalculations are reliableReduce noiseGeometric CADSustainable transportationElectric aircraftEngineering
The invention puts forward a calculation method for electric aircraft propeller noise. The method comprises the following steps that: according to the structure parameter of an electric aircraft propeller, establishing a three-dimensional geometric model of the propeller; adopting a finite element method to carry out mesh generation on the flow field area of the three-dimensional geometric model of the propeller to obtain a propeller flow field subjected to the mesh generation; adopting a large eddy simulation calculation model to carry out unsteady pressure pulsation solving on the circulation area of the propeller flow field subjected to the mesh generation to obtain the transient pressure distribution of a paddle surface; and adopting an acoustic boundary element method to carry out acoustic field simulation on an acoustic mesh model to obtain the radiation noise distribution of the propeller. The method comprehensively considers each influence factor of noise, and therefore, a calculation result is accurate and reliable. The method can be used for aerodynamic noise frequency domain analysis and the like, and a theoretical basis and technical guidance are provided for effectively lowering the propeller noise.
Owner:SHENYANG AEROSPACE UNIVERSITY
Design method of bi-planar shimming coil
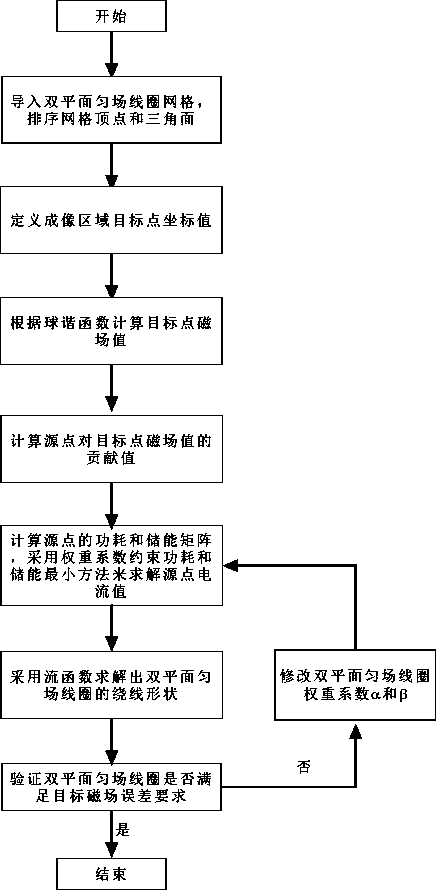
InactiveCN110568390AImprove uniformityQuality improvementMagnetic measurementsSpecial data processing applicationsImaging qualityEngineering
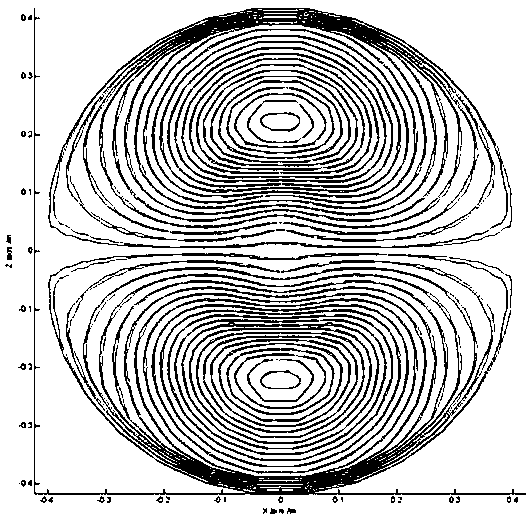
The invention discloses a design method of a bi-planar shimming coil. According to the design method, the source point grid of a biplanar shimming coil is imported; grid vertexes and triangular surfaces are sequenced; the magnetic field values of a second-order shimming coil on target points are calculated through a spherical harmonic function; MATLAB software is adopted to read each vertex and each surface of the triangular grids; the arrangement sequence of the vertexes and surfaces is optimized; the size of a wire is set according to a boundary element method; the value of the contributionof an electrified wire in a source point region to field points is calculated; the energy storage and power consumption of the bi-planar shimming coil are constrained to be minimum; current density distribution on the biplanar shimming coil is solved; and the winding shape of the bi-planar shimming coil is obtained through a stream function method. With the design method of the bi-planar shimmingcoil adopted, harmonic magnetic fields of a second order or higher orders can be eliminated, so that the uniformity of a main magnetic field is improved, and the image quality of an open type MRI system is improved.
Owner:HUIREN WANGDU MEDICAL EQUIP SCI & TECH CO LTD
Design method of biplane magnetic resonance imaging system gradient coil
InactiveCN108872896ASolve the problem of large inductanceMagnetic measurementsPower flowCoil inductance
The present invention discloses a design method of a biplane magnetic resonance imaging system gradient coil. The method comprises the steps of: performing three-dimensional continuous triangular meshdivision for a gradient coil area, according to a boundary element method, calculating a coil inductance matrix generated by the gradient coil area mesh node for a target field point, calculating thecurrent and the direction of the gradient coil plane through a coil target gradient value, an inductance constraint condition and a Tikhonov Regularization, and finally employing a stream function method to obtain actual winding distribution of the gradient coil. The design method of a biplane magnetic resonance imaging system gradient coil solves the problem that the coil inductance is large inthe gradient coil.
Owner:河北惠仁医疗设备科技有限公司
Reservoir architecture and connectivity analysis
InactiveUS8793112B2GeomodellingComputation using non-denominational number representationSeismic surveyBoundary element method
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Method for predicting acoustic radiation rule value of noise of wind turbine
ActiveCN103631994AReduce aerodynamic noiseSimple calculationForecastingSpecial data processing applicationsAuditory radiationModel method
The invention discloses a method for predicting the acoustic radiation rule value of the noise of a wind turbine. The method comprises the steps of establishing a wind turbine model, defining flow field grids, calculating a flow field based on large eddy simulation and calculating sound field distribution based on the indirect boundary element method. The method is used for predicting the acoustic radiation rule value of the noise of the wind turbine by means of flow field calculation data combined with the boundary element method, with the assistance of software, the calculating processes can be simplified greatly, the prediction process is made simple, the calculating result is accurate, the calculated amount is small, speed is high, and the method has great application value in engineering.
Owner:XINJIANG INST OF ENG
Fractal dimension-based ultrahigh voltage DC transmission line boundary element method
ActiveCN102097791AShort data lengthAccurate identificationEmergency protective circuit arrangementsHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses a fractal dimension-based ultrahigh voltage DC transmission line boundary element method. When a DC line fails, after a protective element is started, a line-mode voltage is calculated by utilizing a phase-mode transformation theory according to DC voltages of two electrodes at a protection arrangement position; and a discrete line-mode voltage signal with the sampling sequence length of 200 points is selected, and fractals are measured by adopting a box dimension method to calculate a fractal dimension D for distinguishing an internal failure from an external failure. In the method, sampling frequency is 100 KHz, a time window is 2 ms, a required data length is relatively shorter and the influence of a control system is avoided. Various failures in the full-length range of the line can be accurately identified by the method. The method ensures relatively higher resistance to transition resistance, and is not influenced by interference and highly practical.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Systems and methods of performing vibro-acoustic analysis of a structure
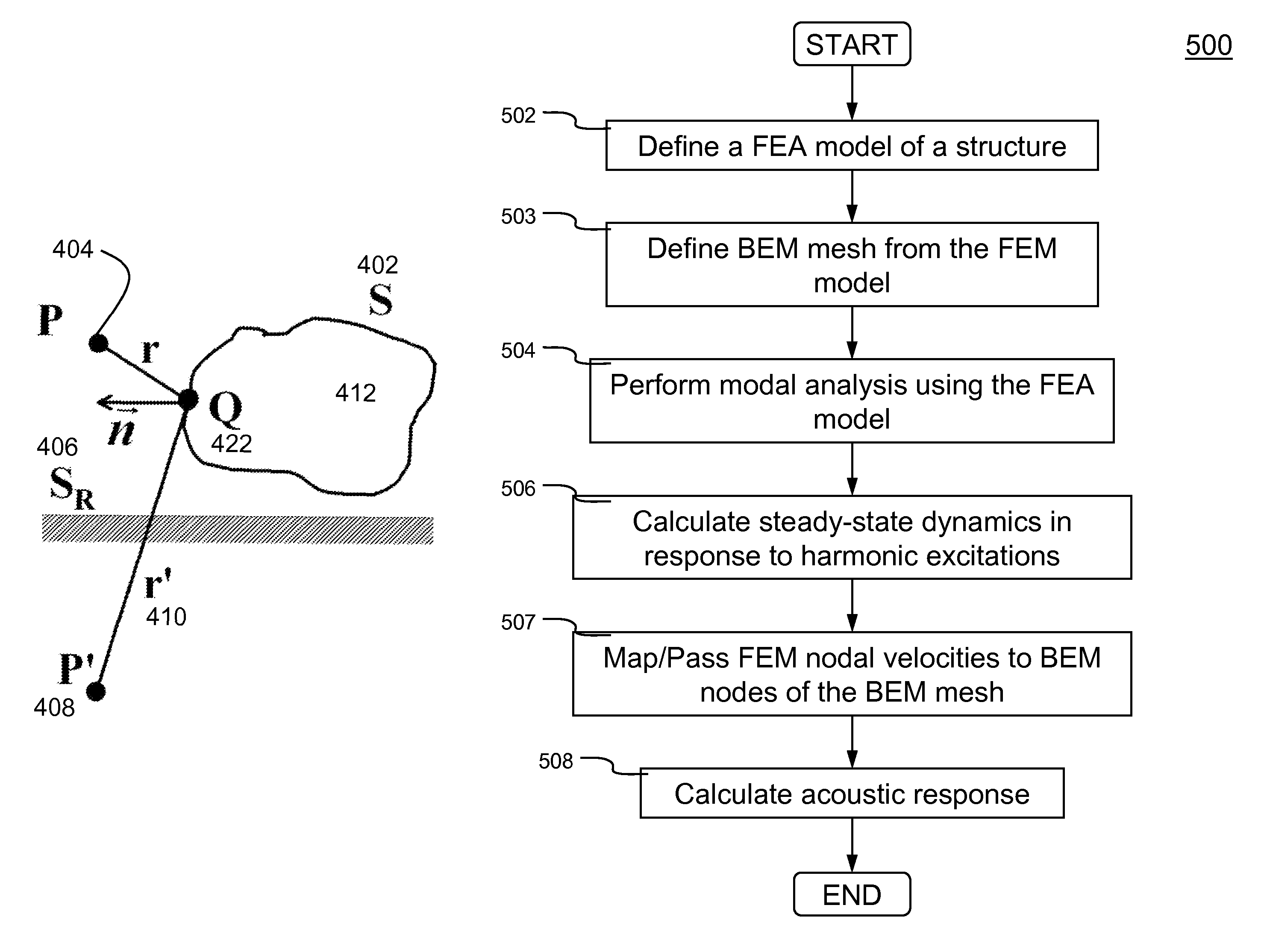
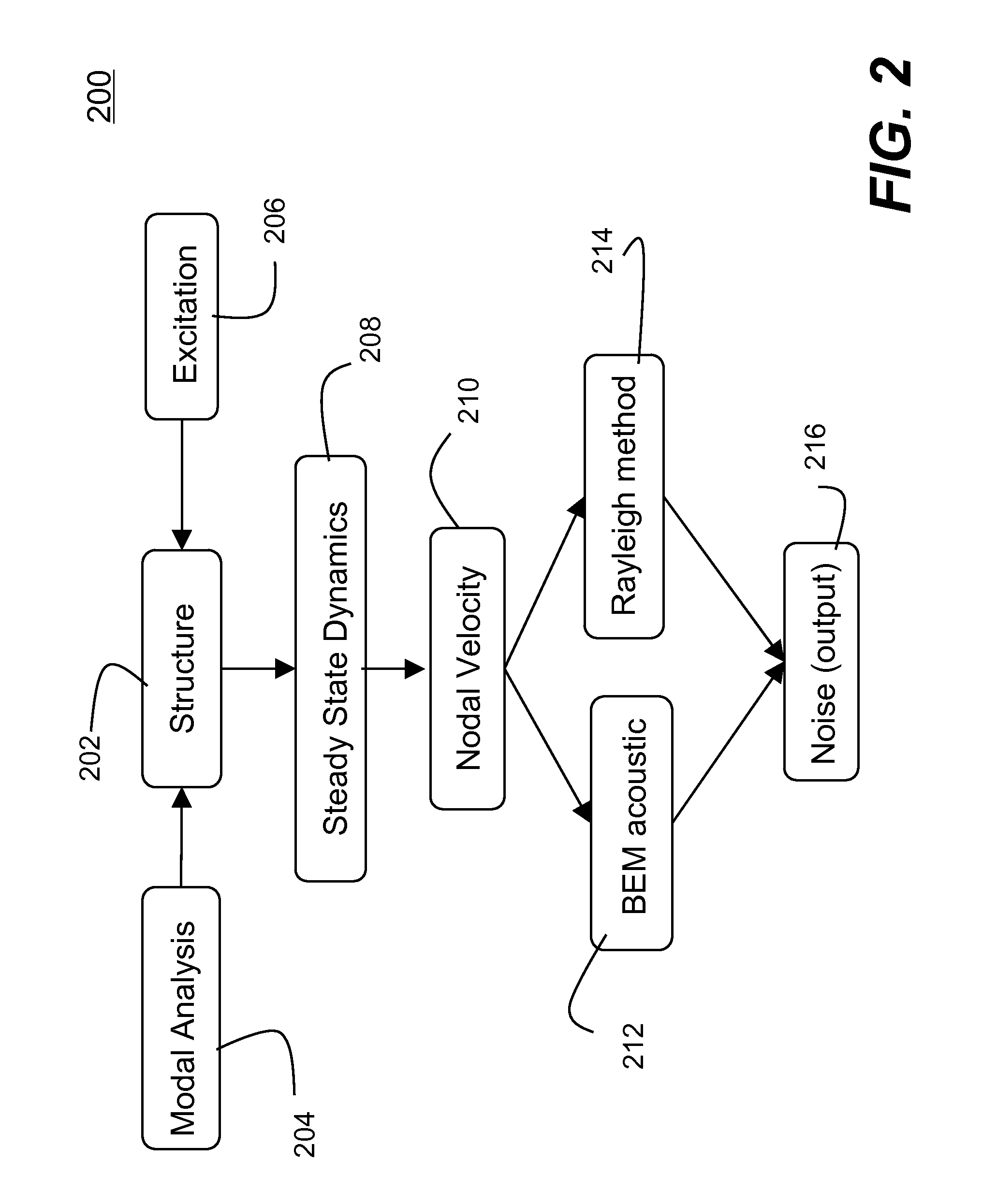
ActiveUS8306793B2Match real world resultFast convergenceFlow propertiesAnalogue computers for electric apparatusNODALElement analysis
Methods and systems for simulating acoustic field resulted from particular excitations by performing vibro-acoustic analysis of a structure are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, vibro-acoustic analysis of a structure is performed in two stages. First, steady state dynamic (SSD) responses are obtained using a finite element analysis model of a structure subject to harmonic excitations (e.g., external nodal loads, pressures, or enforced motions (e.g., ground motions), etc.). The steady state responses are the results (e.g., nodal velocities at desired locations of the structure) obtained in a finite element analysis in frequency-domain. Second, an acoustic analysis is conducted according to Helmholtz equation using the nodal velocities obtained at desired locations on the structure as a boundary condition. The acoustic analysis can be performed in a number of procedures (e.g., boundary element method, Rayleigh approximation method, etc.).
Owner:ANSYS
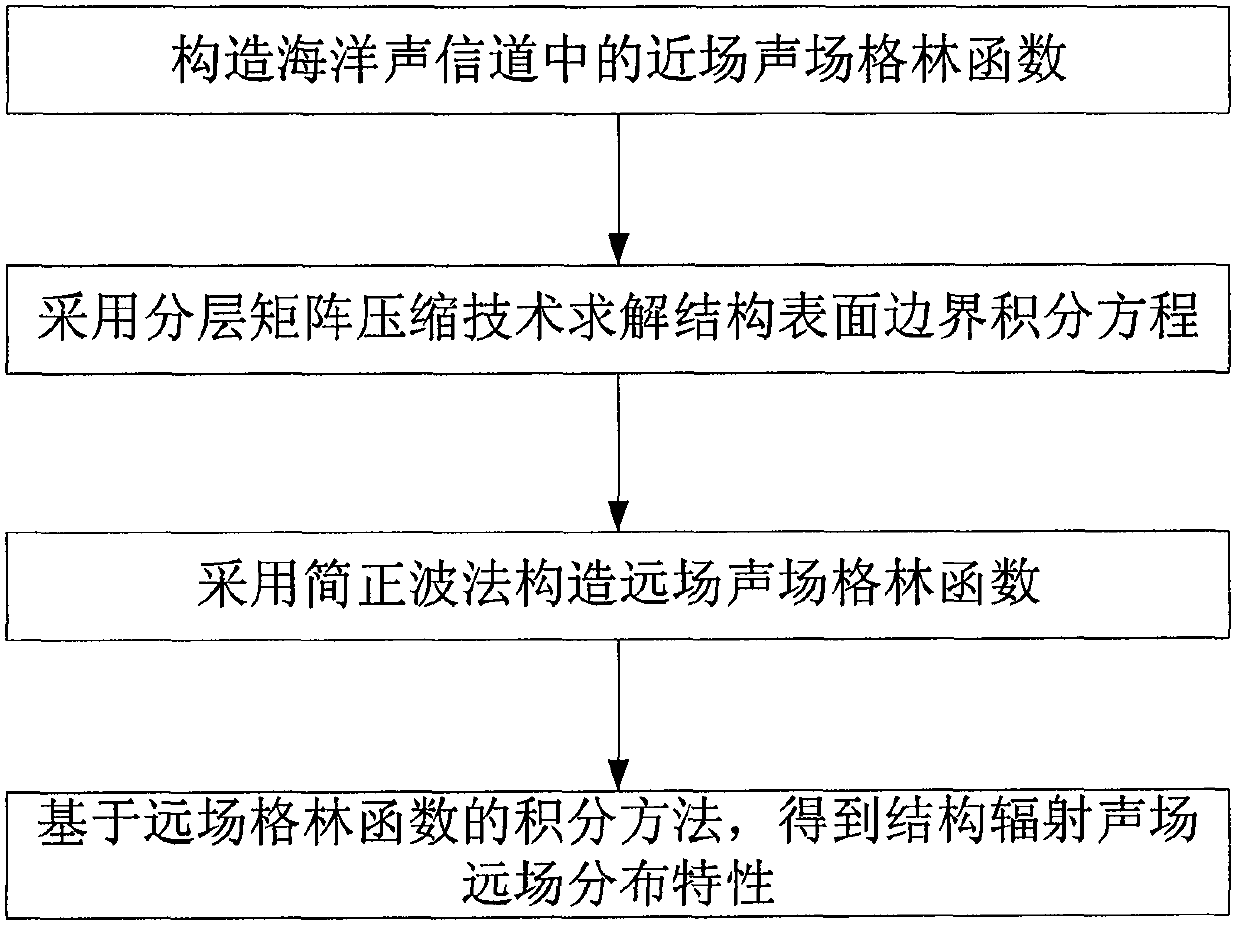
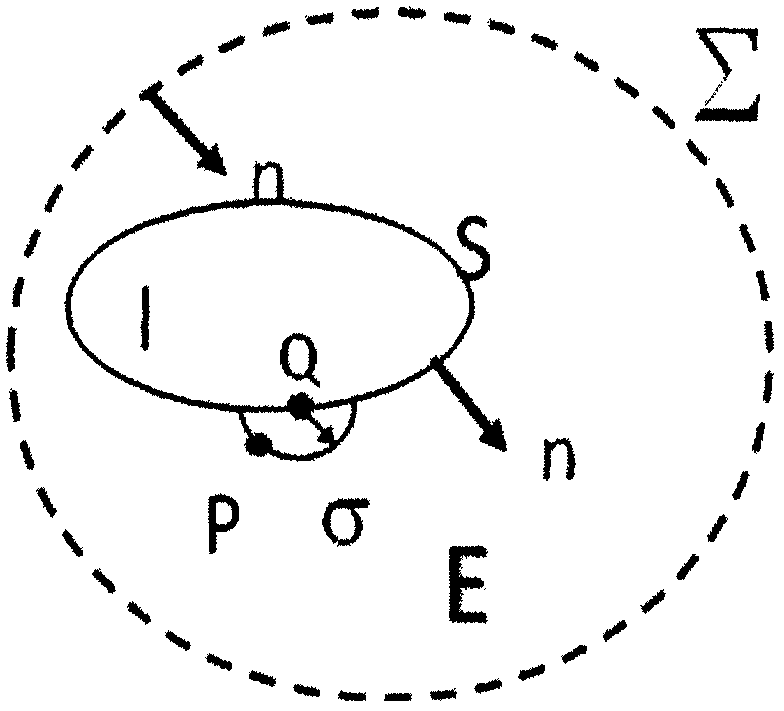
A method for calculating a complex structure radiation sound field in a marine acoustic channel
PendingCN109657257AReduce consumptionImprove adaptabilityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsOcean bottomDecomposition
The invention discloses a method for calculating a complex structure radiation sound field in a marine acoustic channel, and belongs to the technical field of acoustic numerical calculation. The limitation that a traditional boundary element method is only suitable for free field sound field calculation is broken through, and a sound field Green function in an ocean sound channel is established. Ahierarchical matrix compression technology is adopted to divide a radiation impedance matrix into a series of hierarchical matrix blocks with different sizes, and an iteration method is further utilized to solve a matrix equation. Compared with the prior art, the method has the effects and benefits that the acoustic calculation function of the traditional boundary element method is expanded frominfinite uniform media to the bounded space of the ocean channel, and the influence of sea surface, seabed boundary and sound velocity gradient distribution can be considered. And on the other hand, the radiation impedance matrix is subjected to hierarchical compression, the consumption of a computer memory is greatly reduced by utilizing the low-rank characteristic approximate decomposition of the matrix block, the influence of the diversity of a sound field Green function under the complex marine channel condition is avoided, and the algorithm adaptability is good.
Owner:中国船舶重工集团公司第七六〇研究所
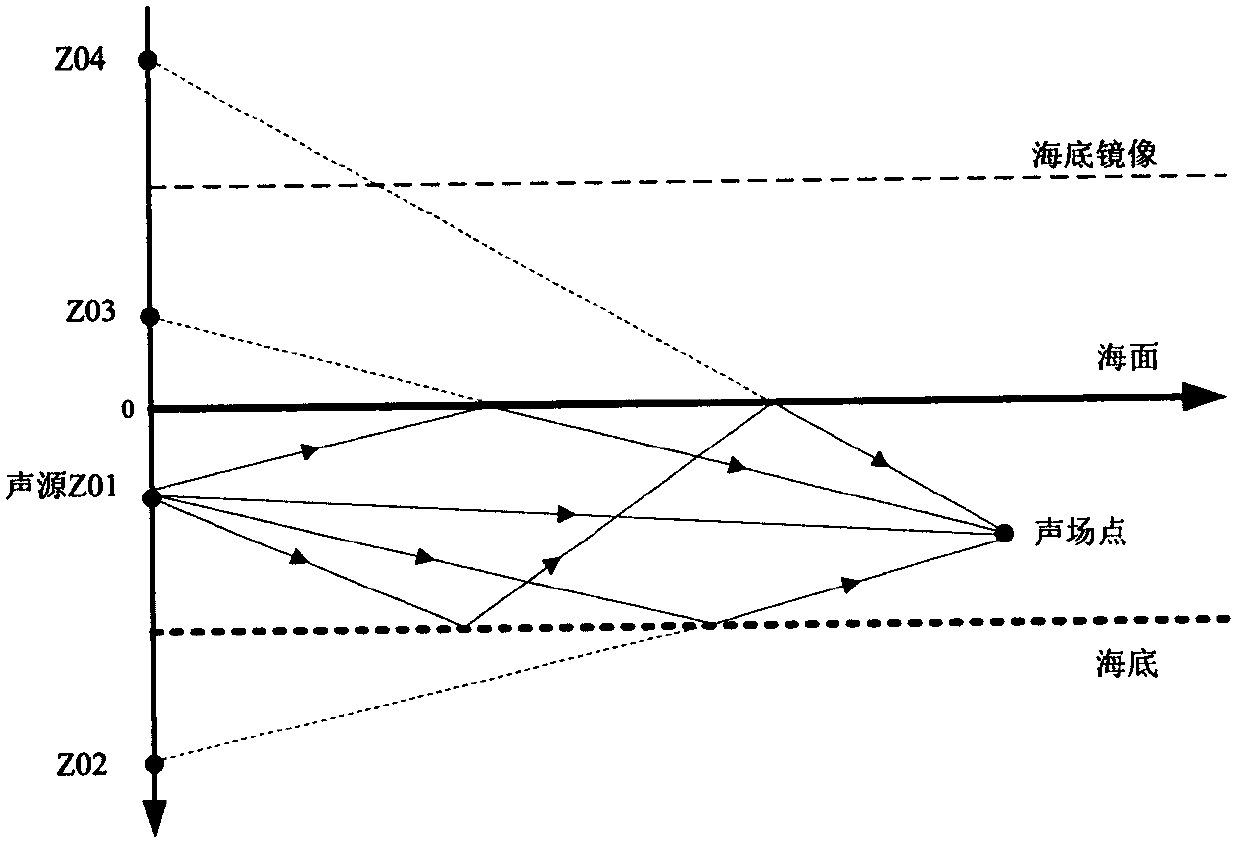
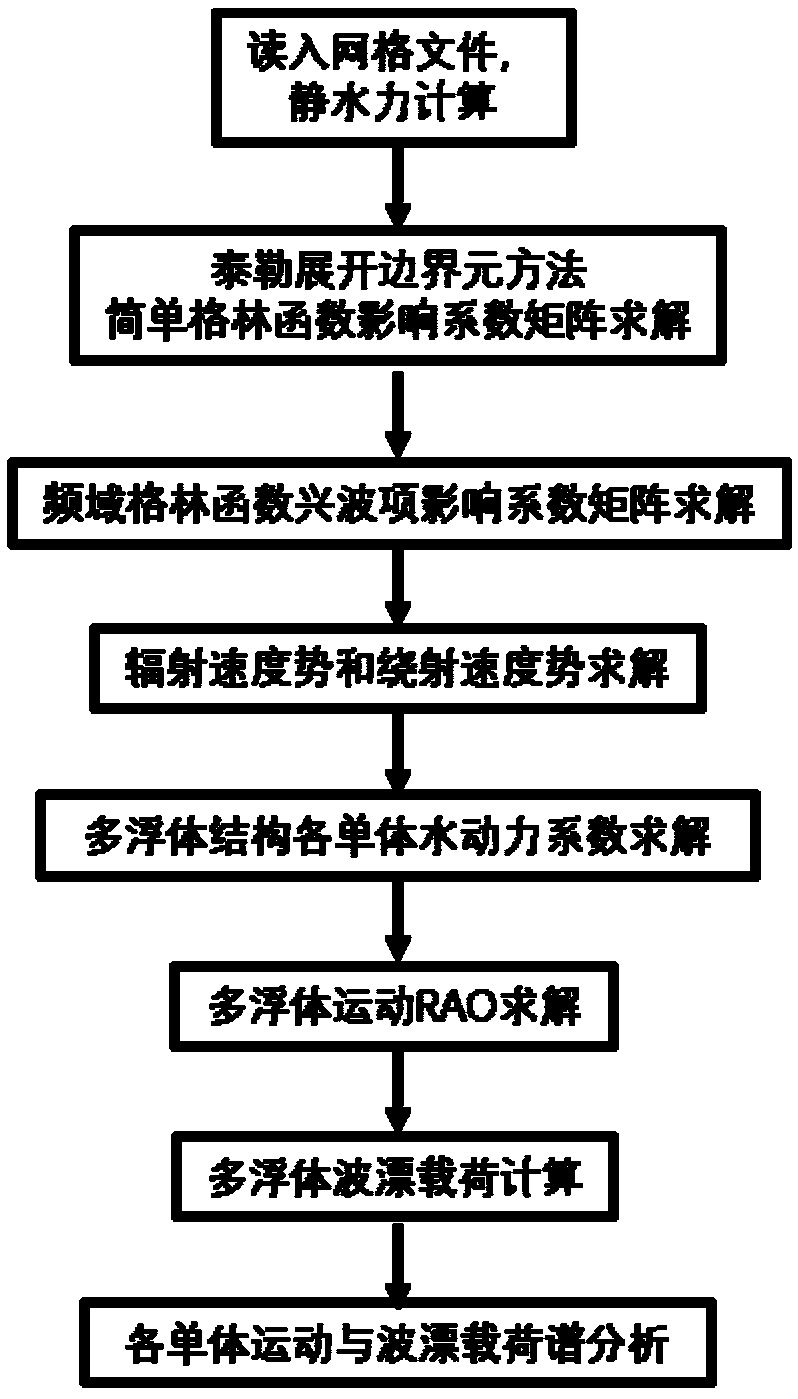
Three-dimensional frequency domain numerical method for predicting wave drift load of a multi-floating body structure
ActiveCN109344531AImprove convergence rateAccurately predict hydrodynamic coefficientsGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationBoundary element methodVelocity potential
The invention provides a three-dimensional frequency domain numerical method for predicting wave drift load of a multi-floating body structure. The method comprises the following steps: Reading the mesh file, using the mesh information to carry on the ship hydrostatic calculation; calculating The influence coefficient matrix of simple Green's function Calculating The influence coefficient matrix of complex frequency domain Green's function. Taking The Taylor expansion boundary element method solve the unit radiation velocity potential, diffraction velocity potential and their spatial derivatives. solving Hydrodynamic Coefficients of Multiple Floating Body Structures; solving multi-floating body motion equation; solving The wave forces and wave drift loads of each unit for the whole multi-floating structure. According to the response RAO of floating body motion, anyalzing and calulating the floating body motion spectrum in irregular waves. The method of the invention can accurately predict hydrodynamic coefficients, motion RAO, wave forces, wave drift loads in a six-degree-of-freedom direction of each unit of a multi-floating body structure and results of floating body motion spectrum analysis.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com