Patents
Literature
69 results about "Biplane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A biplane is a fixed-wing aircraft with two main wings stacked one above the other. The first powered, controlled aeroplane to fly, the Wright Flyer, used a biplane wing arrangement, as did many aircraft in the early years of aviation. While a biplane wing structure has a structural advantage over a monoplane, it produces more drag than a similar unbraced or cantilever monoplane wing. Improved structural techniques, better materials and the quest for greater speed made the biplane configuration obsolete for most purposes by the late 1930s.
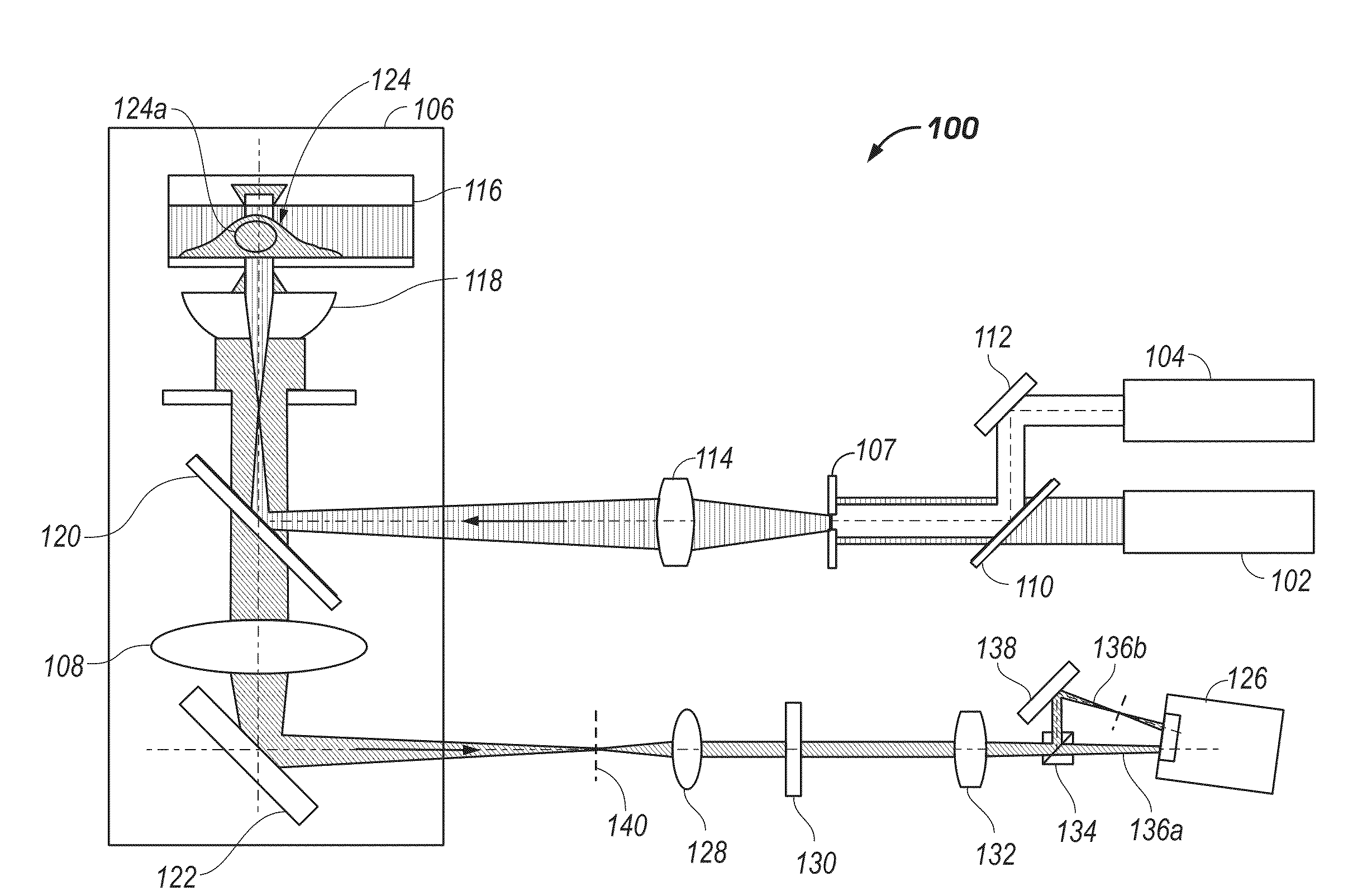
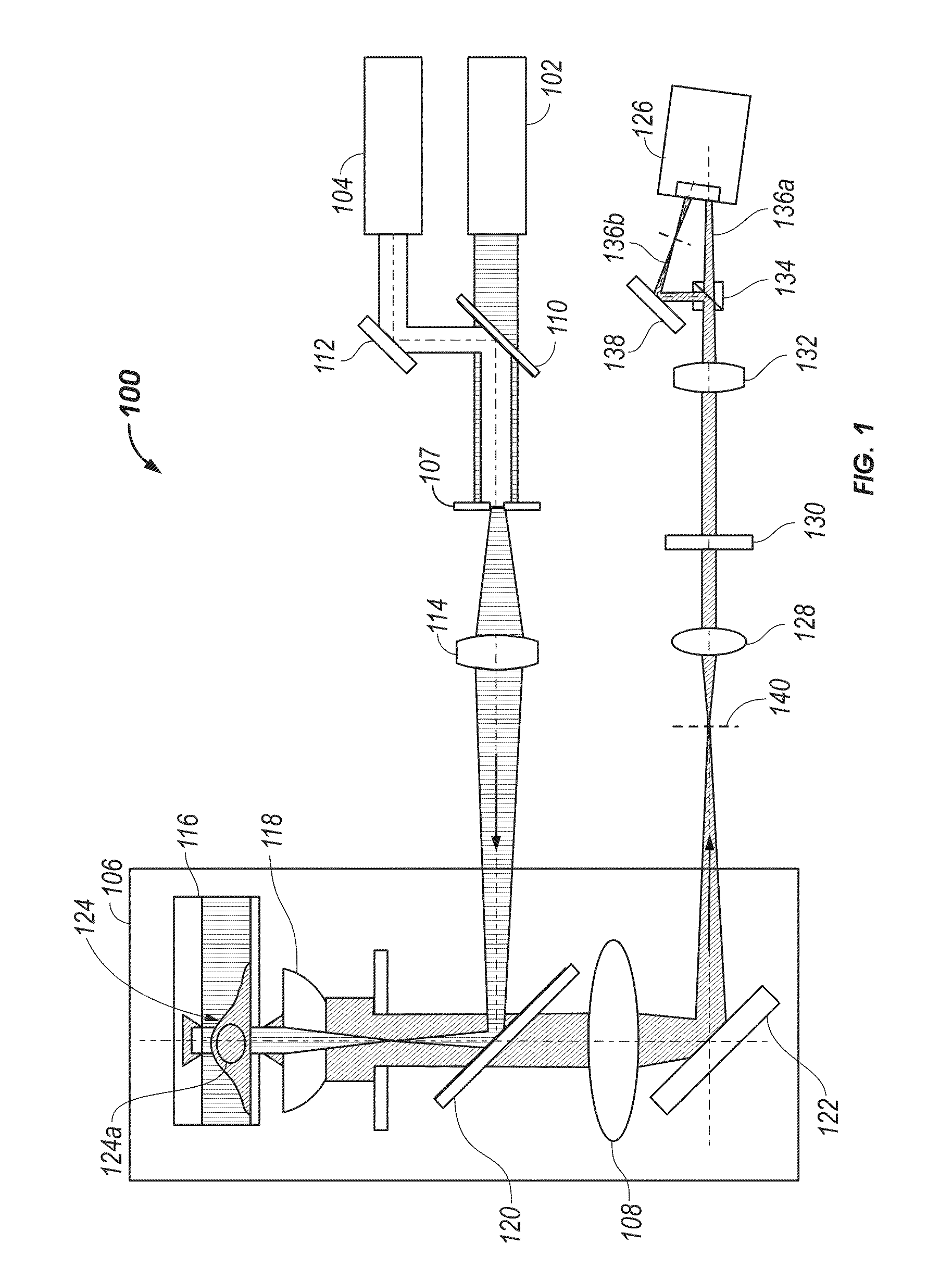
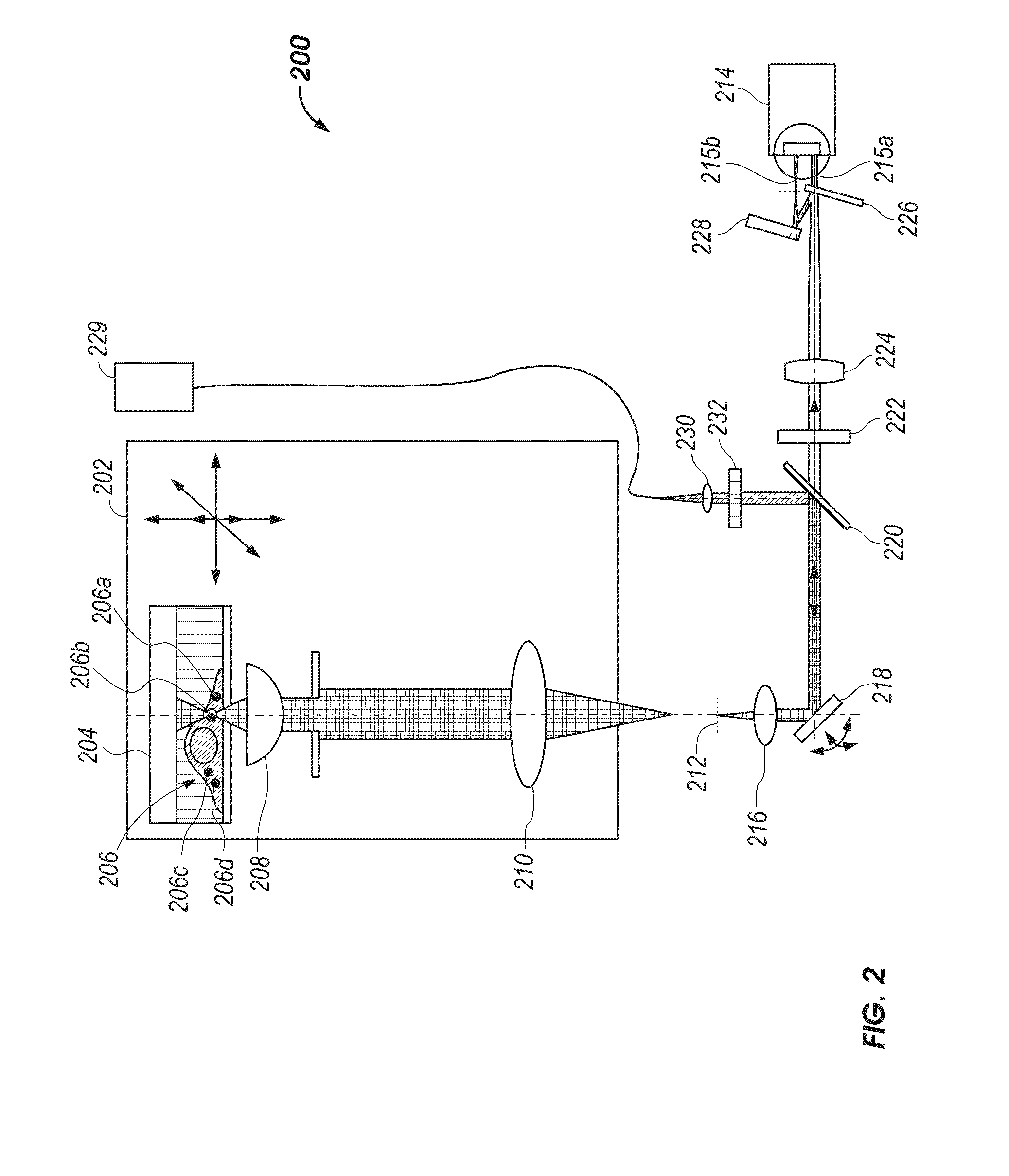
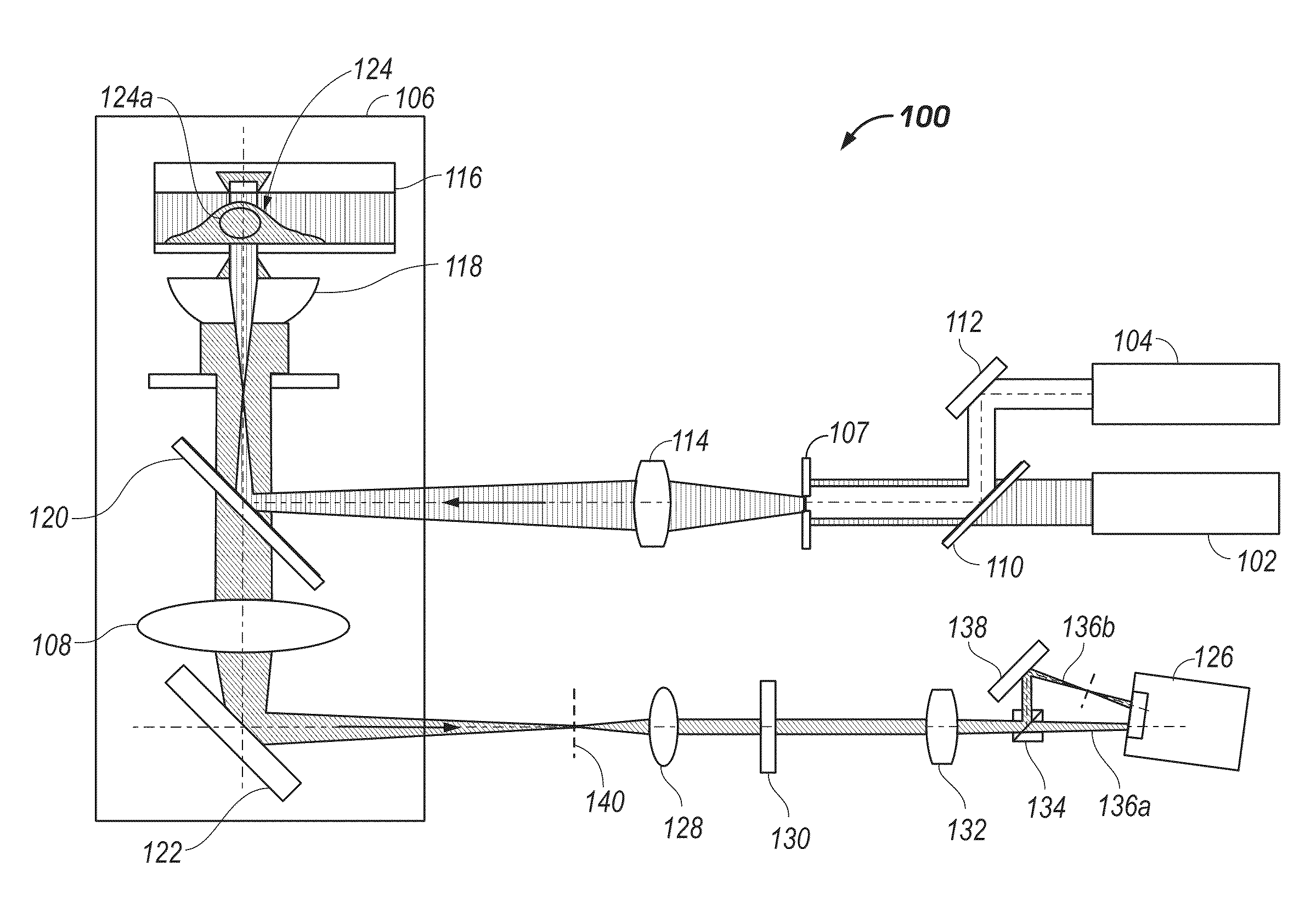
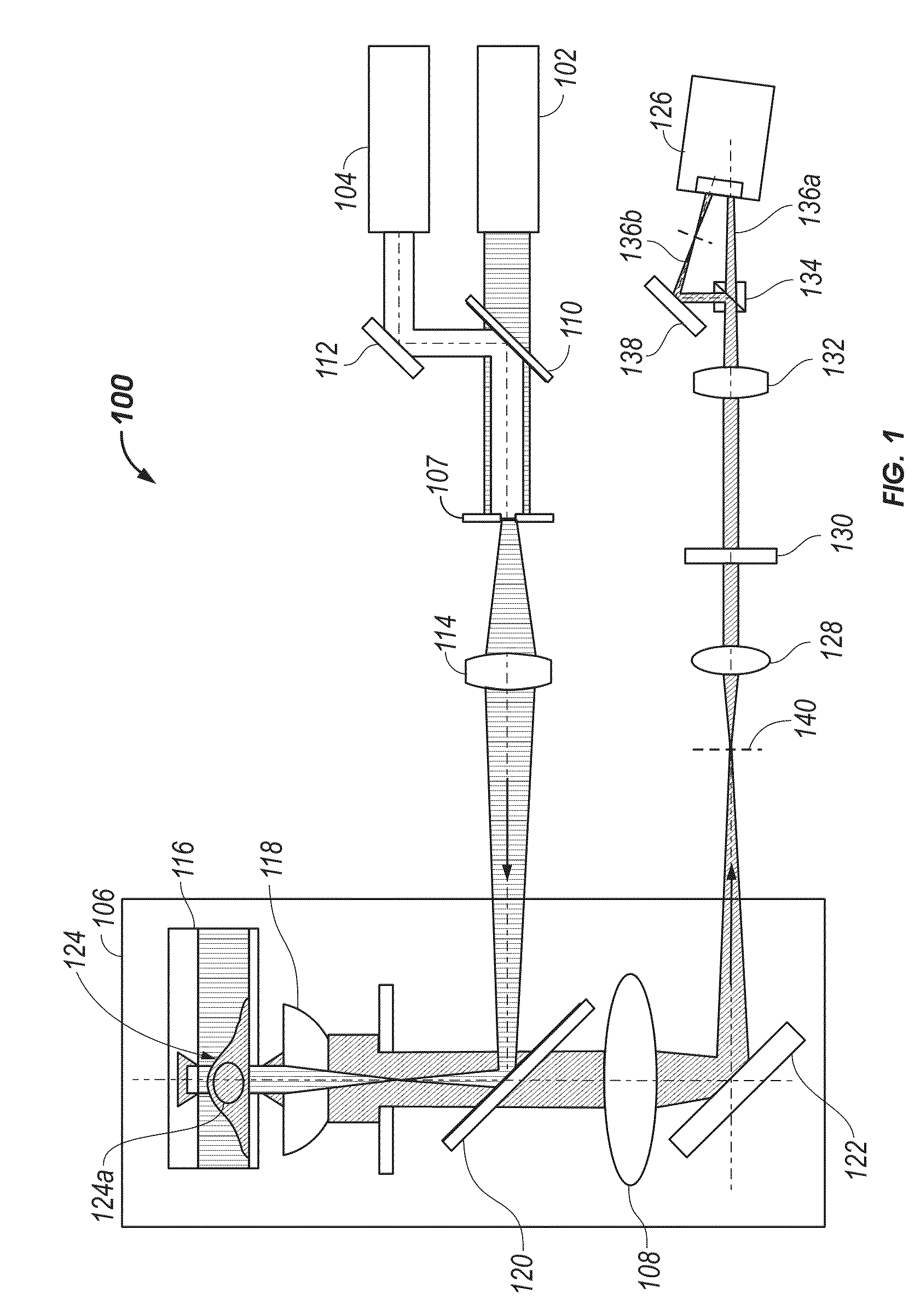
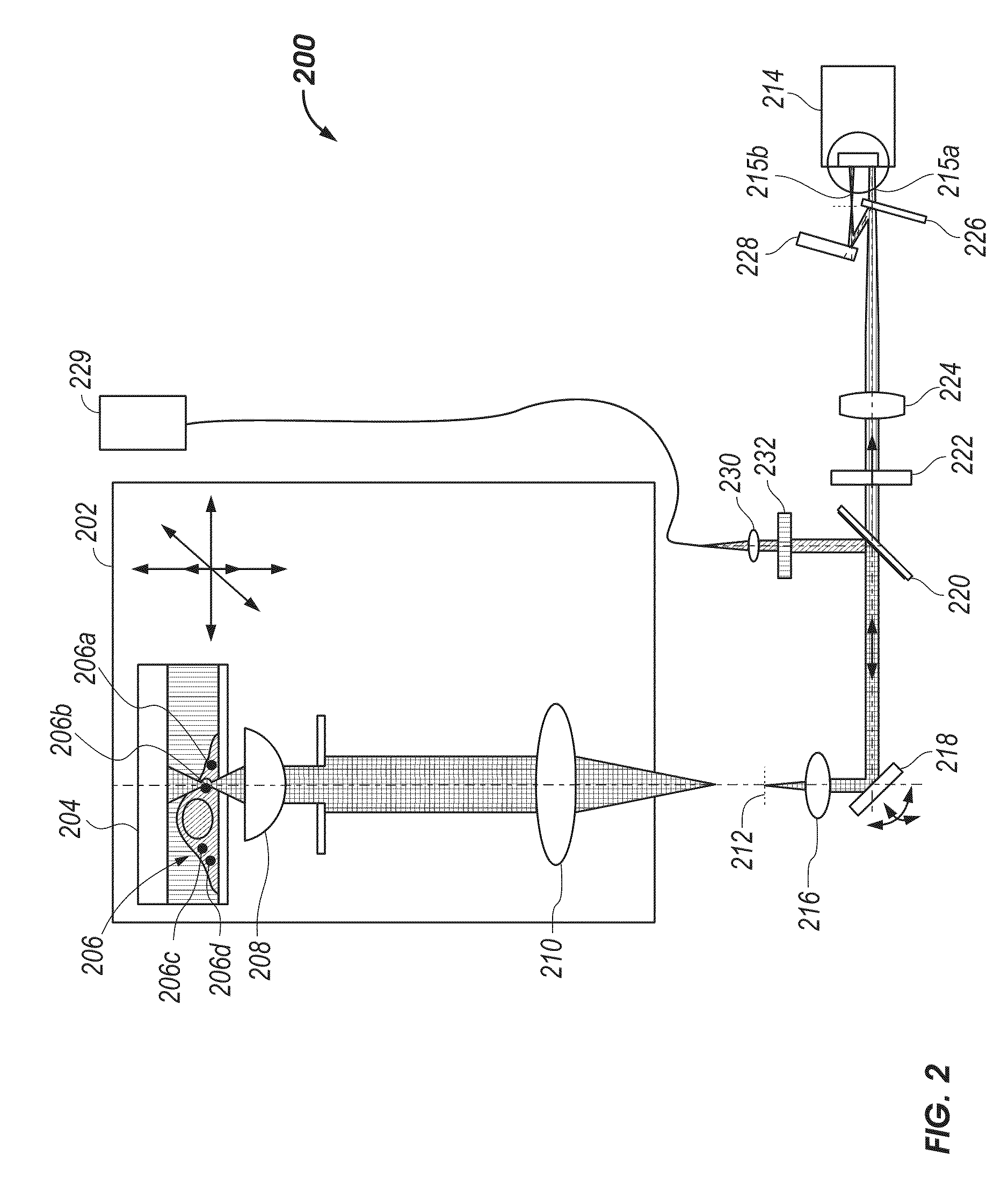
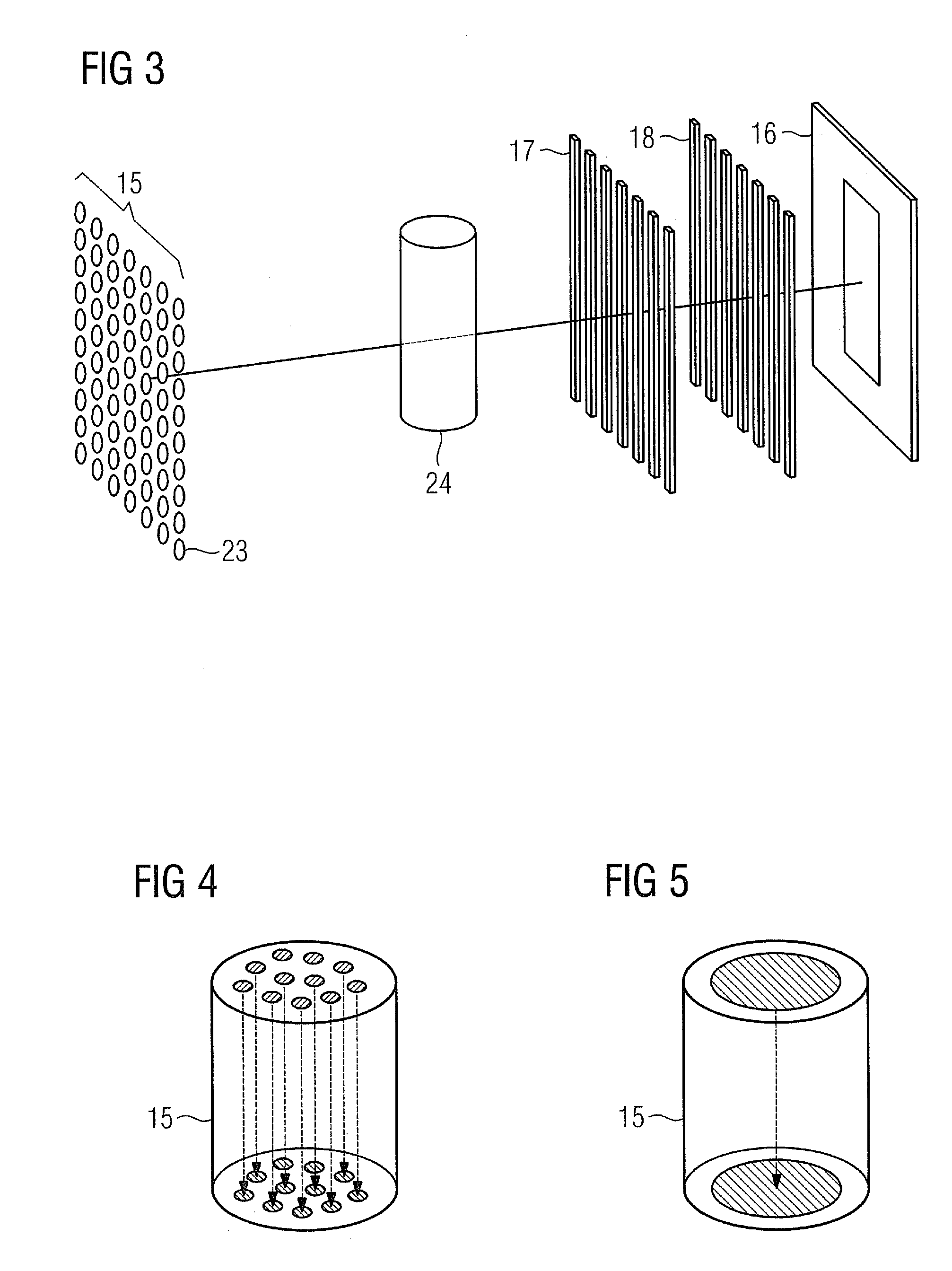
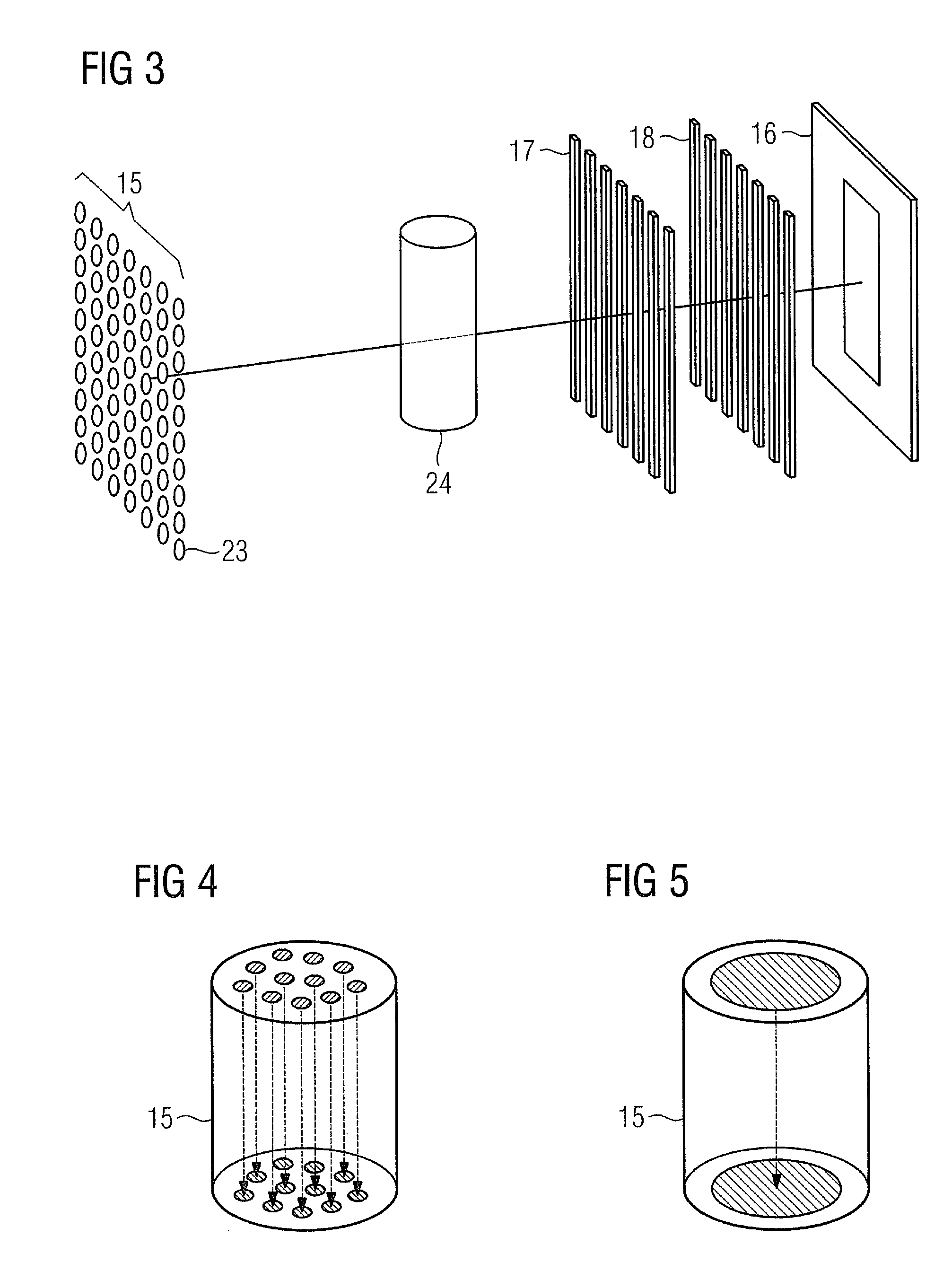
3D Biplane Microscopy
A microscopy system is configured for creating 3D images from individually localized probe molecules. The microscopy system includes a sample stage, an activation light source, a readout light source, a beam splitting device, at least one camera, and a controller. The activation light source activates probes of at least one probe subset of photo-sensitive luminescent probes, and the readout light source causes luminescence light from the activated probes. The beam splitting device splits the luminescence light into at least two paths to create at least two detection planes that correspond to the same or different number of object planes of the sample. The camera detects simultaneously the at least two detection planes, the number of object planes being represented in the camera by the same number of recorded regions of interest. The controller is programmable to combine a signal from the regions of interest into a 3D data.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MAINE +1
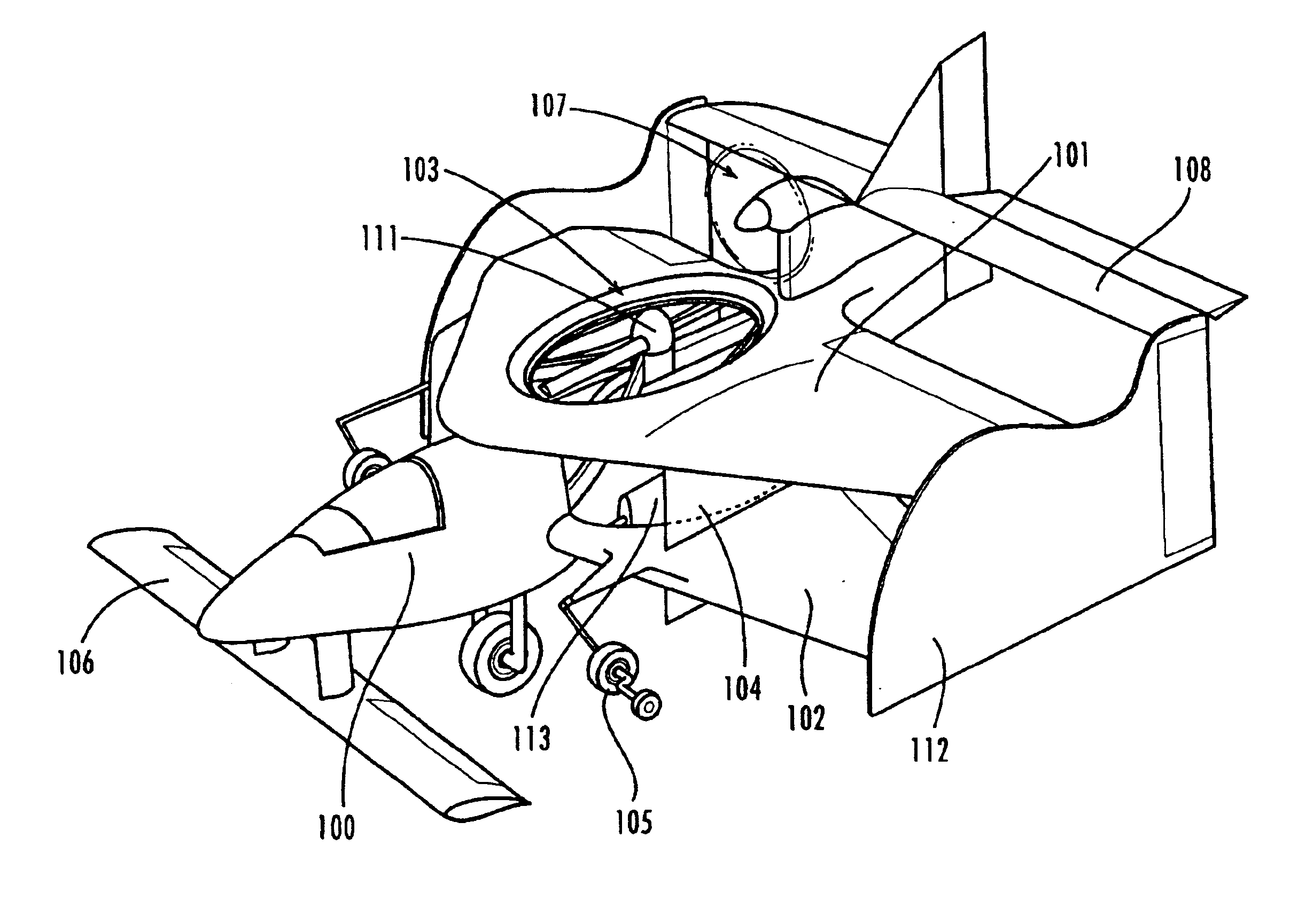
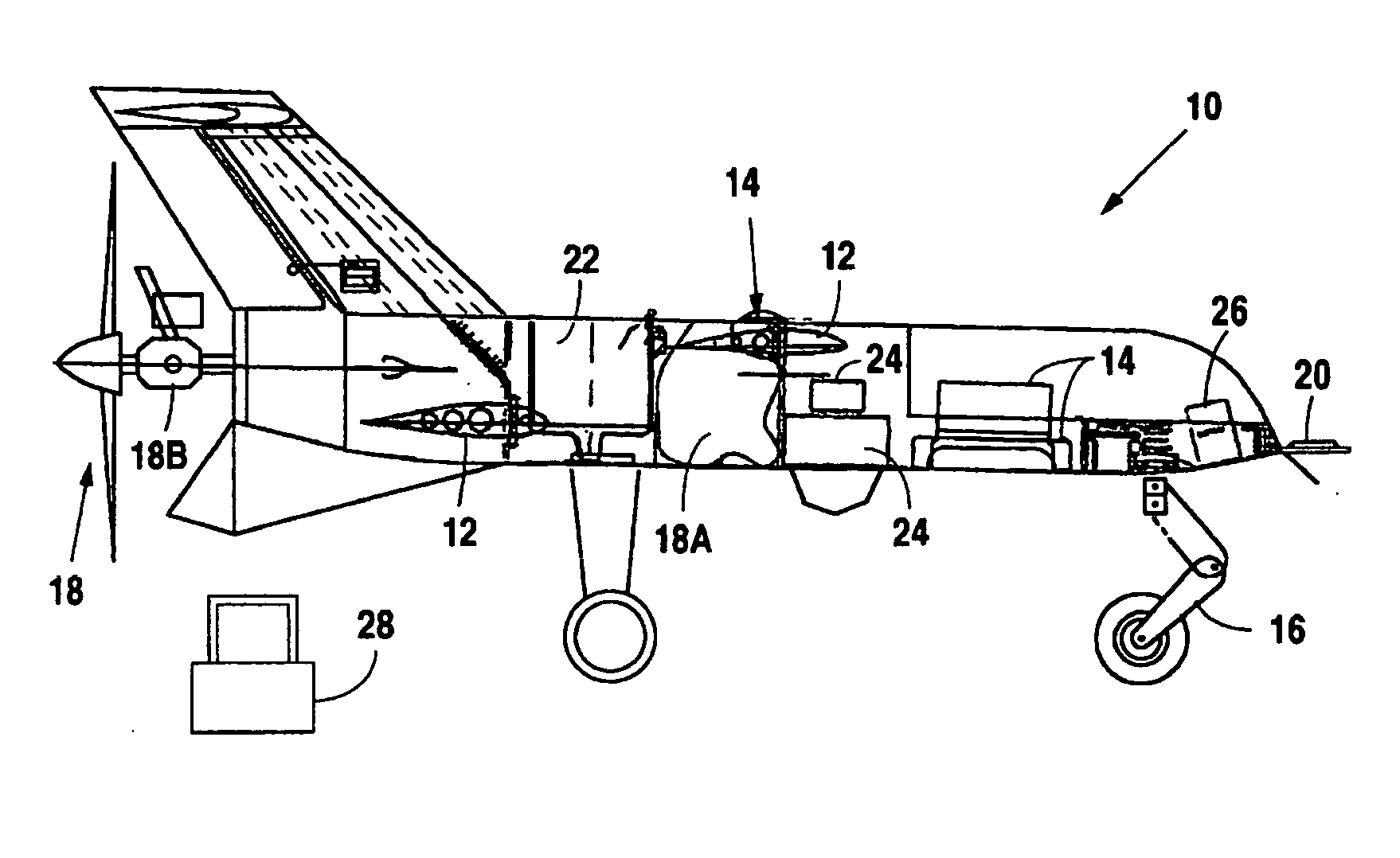
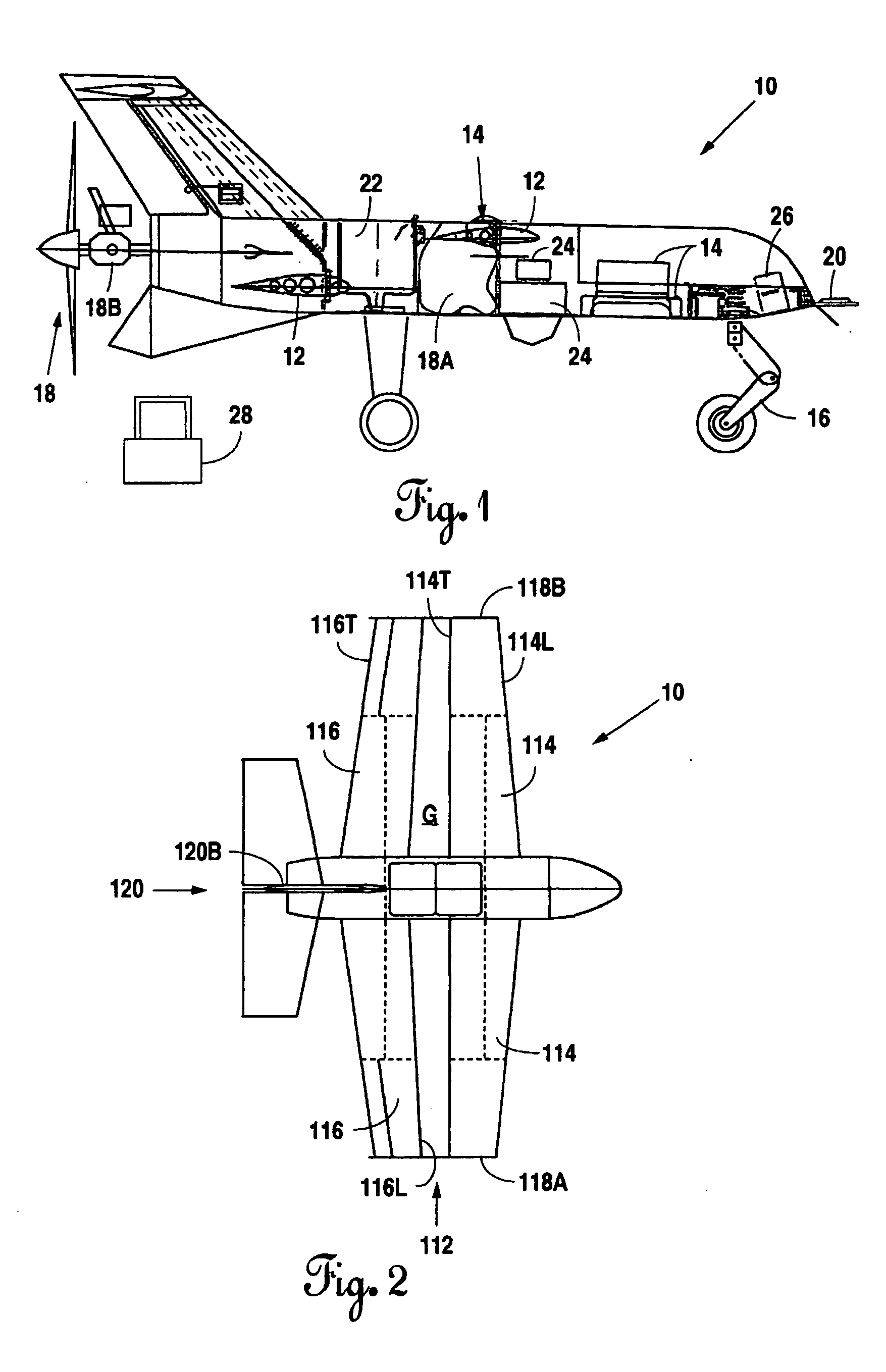
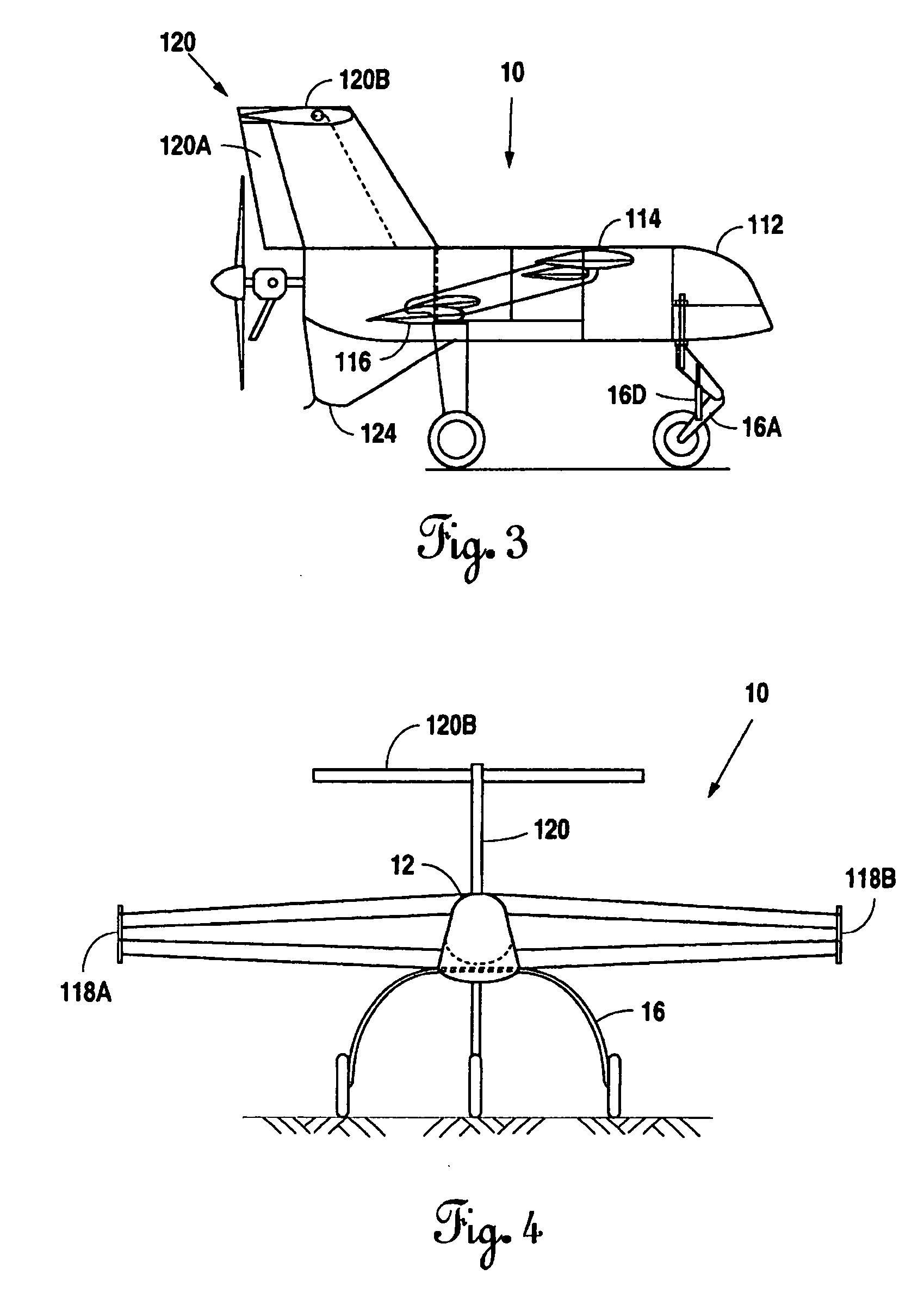
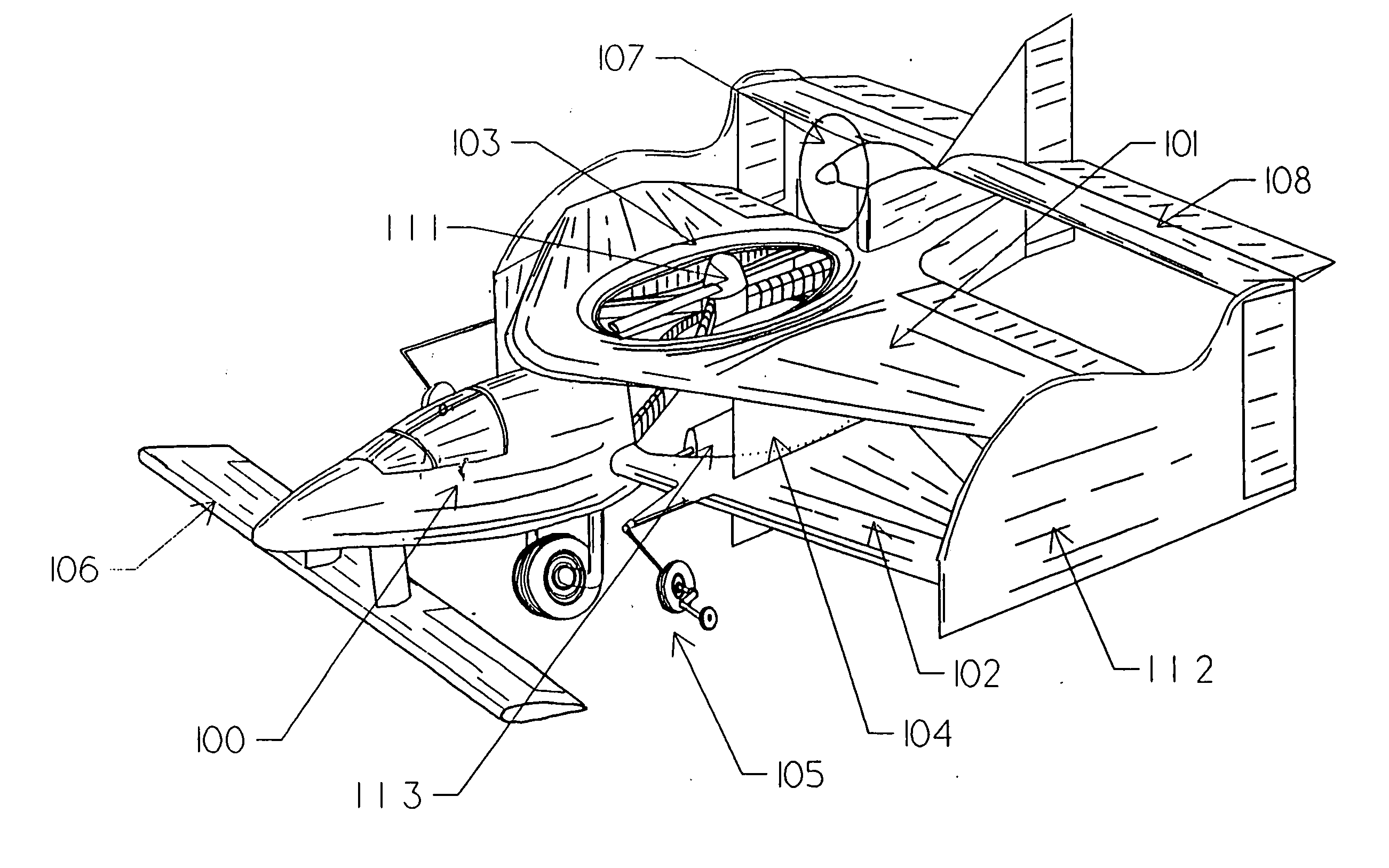
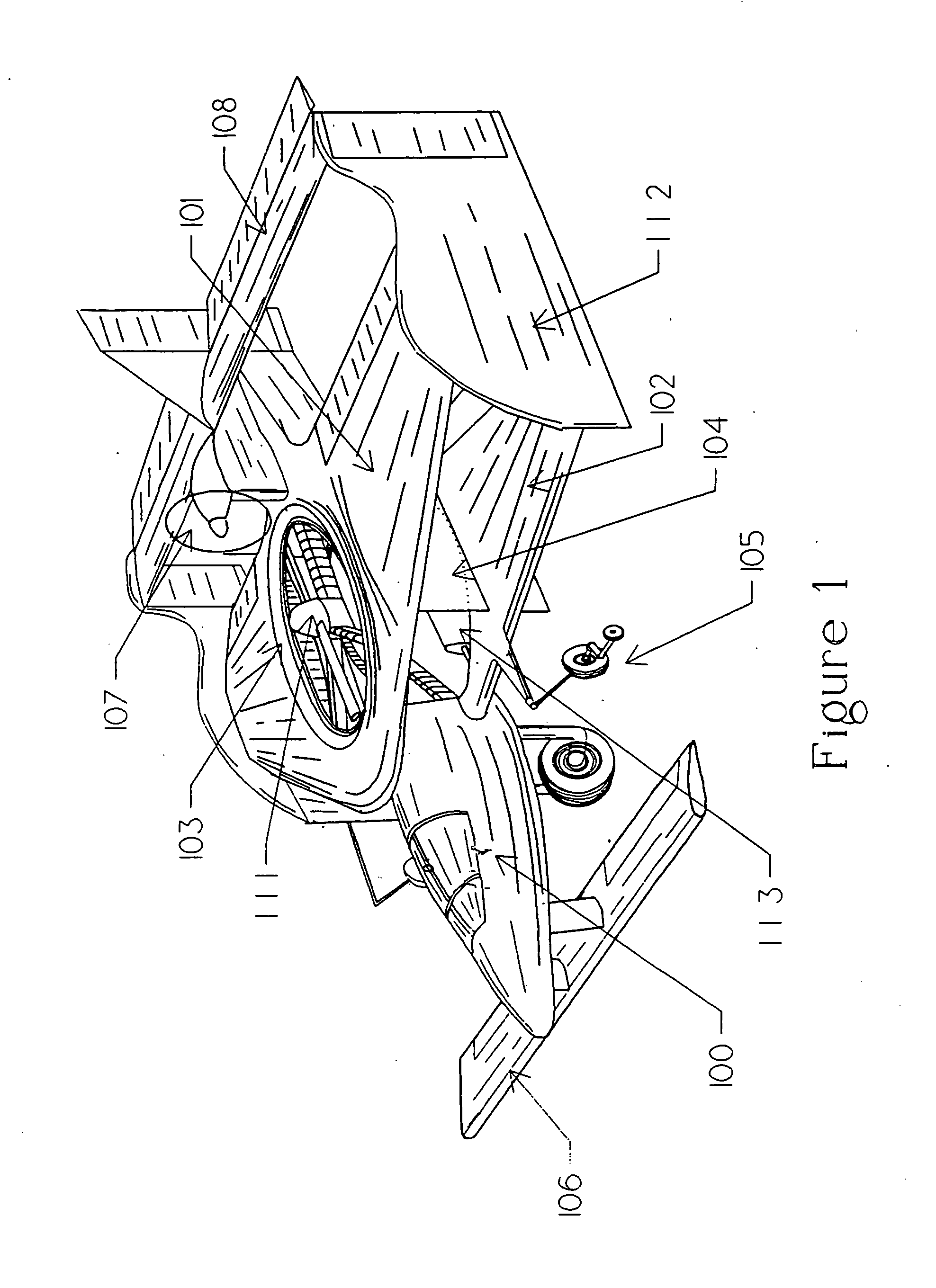
V/STOL biplane aircraft
InactiveUS6848649B2Reducing ducted fan outlet airflow velocityReduce loadAircraft navigation controlAircraft stabilisationHigh resistanceDrivetrain
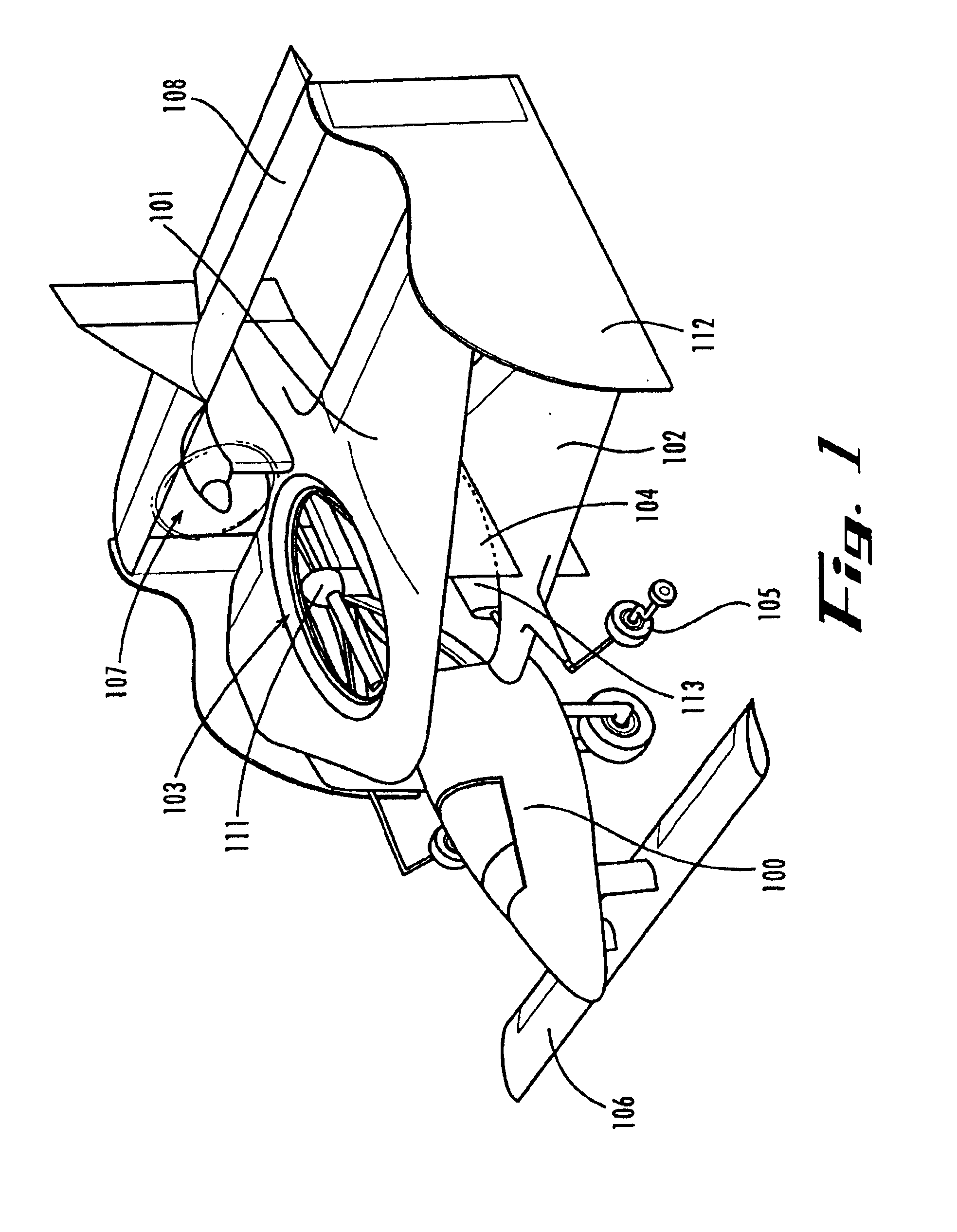
The present invention is a 2 passenger aircraft capable of vertical and conventional takeoffs and landings, called a jyrodyne. The jyrodyne comprises a central fuselage with biplane-type wings arranged in a negative stagger arrangement, a horizontal ducted fan inlet shroud located at the center of gravity in the top biplane wing, a rotor mounted in the shroud, outrigger wing support landing gear, a forward mounted canard wing and passenger compartment, a multiple vane-type air deflector system for control and stability in VTOL mode, a separate tractor propulsion system for forward flight, and a full-span T-tail. Wingtip extensions on the two main wings extend aft to attach to the T-tail. The powerplants consist of two four cylinder two-stroke reciprocating internal combustion engines. Power from the engines is distributed between the ducted fan and tractor propeller through the use of a drivetrain incorporating two pneumatic clutches, controlled by an automotive style footpedal to the left of the rudder pedals. When depressed, power is transmitted to the ducted fan for vertical lift. When released, power is transmitted to the tractor propeller for forward flight. The aircraft can also takeoff and land in the conventional manner with a much larger payload, and is easily converted to amphibious usage. Landing gear is a bicycle arrangement with outriggers. The aircraft combines twin engines, heavy-duty landing gear, controlled-collapse crashworthy seats with a low stall speed and high resistance to stalls to eliminate any region of the flight regime where an engine or drivetrain failure could cause an uncontrollable crash.
Owner:CHURCHMAN CHARLES GILPIN
3D biplane microscopy
A microscopy system is configured for creating 3D images from individually localized probe molecules. The microscopy system includes a sample stage, an activation light source, a readout light source, a beam splitting device, at least one camera, and a controller. The activation light source activates probes of at least one probe subset of photo-sensitive luminescent probes, and the readout light source causes luminescence light from the activated probes. The beam splitting device splits the luminescence light into at least two paths to create at least two detection planes that correspond to the same or different number of object planes of the sample. The camera detects simultaneously the at least two detection planes, the number of object planes being represented in the camera by the same number of recorded regions of interest. The controller is programmable to combine a signal from the regions of interest into a 3D data.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MAINE +1
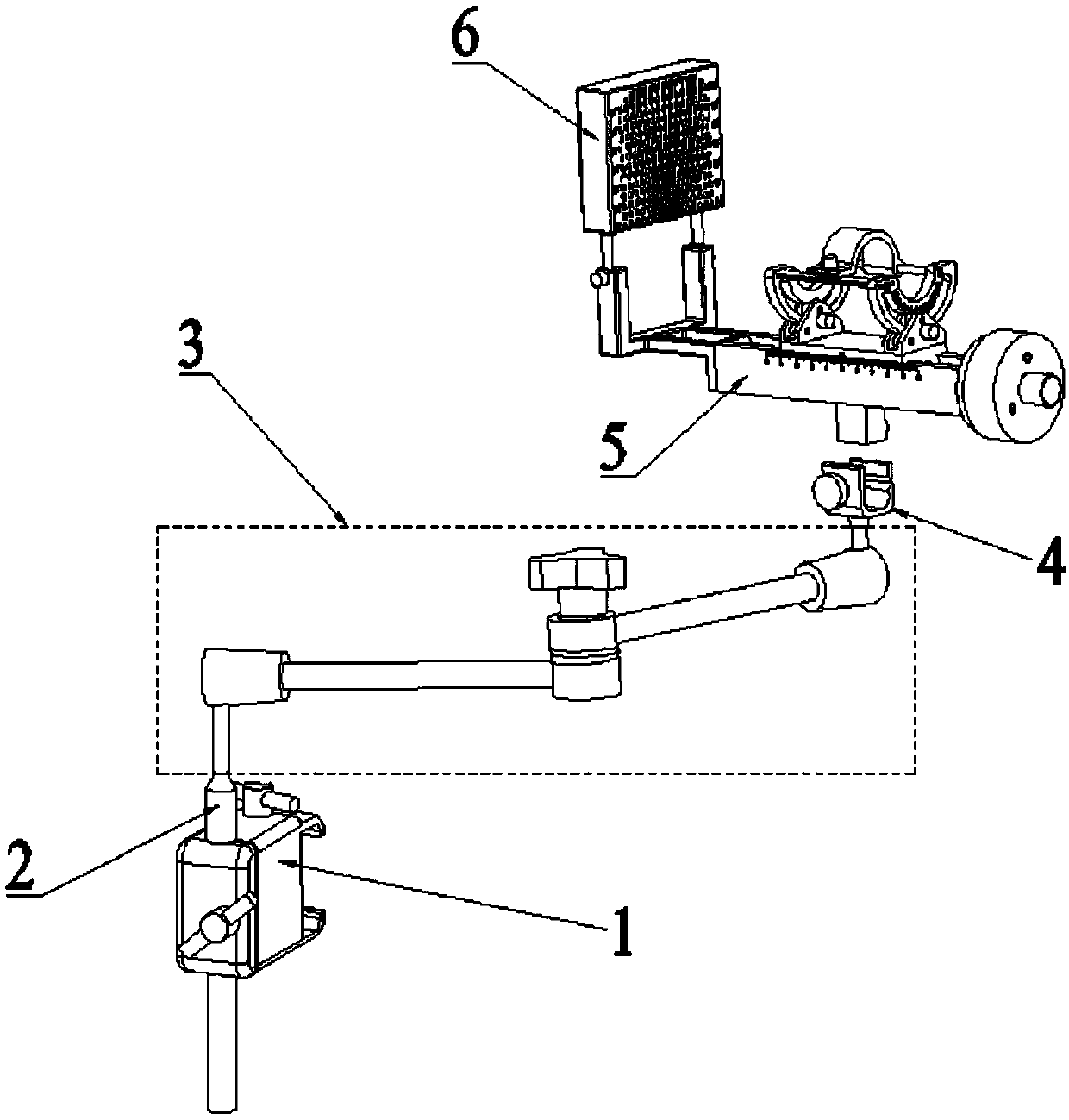
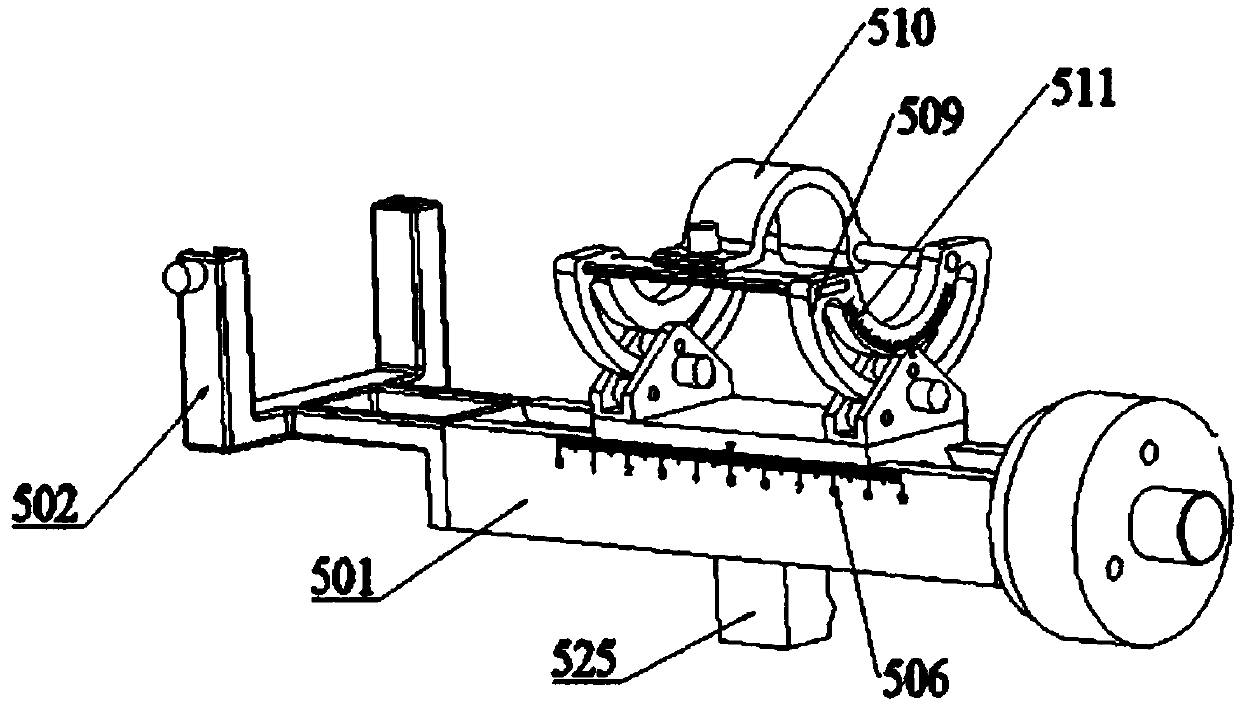
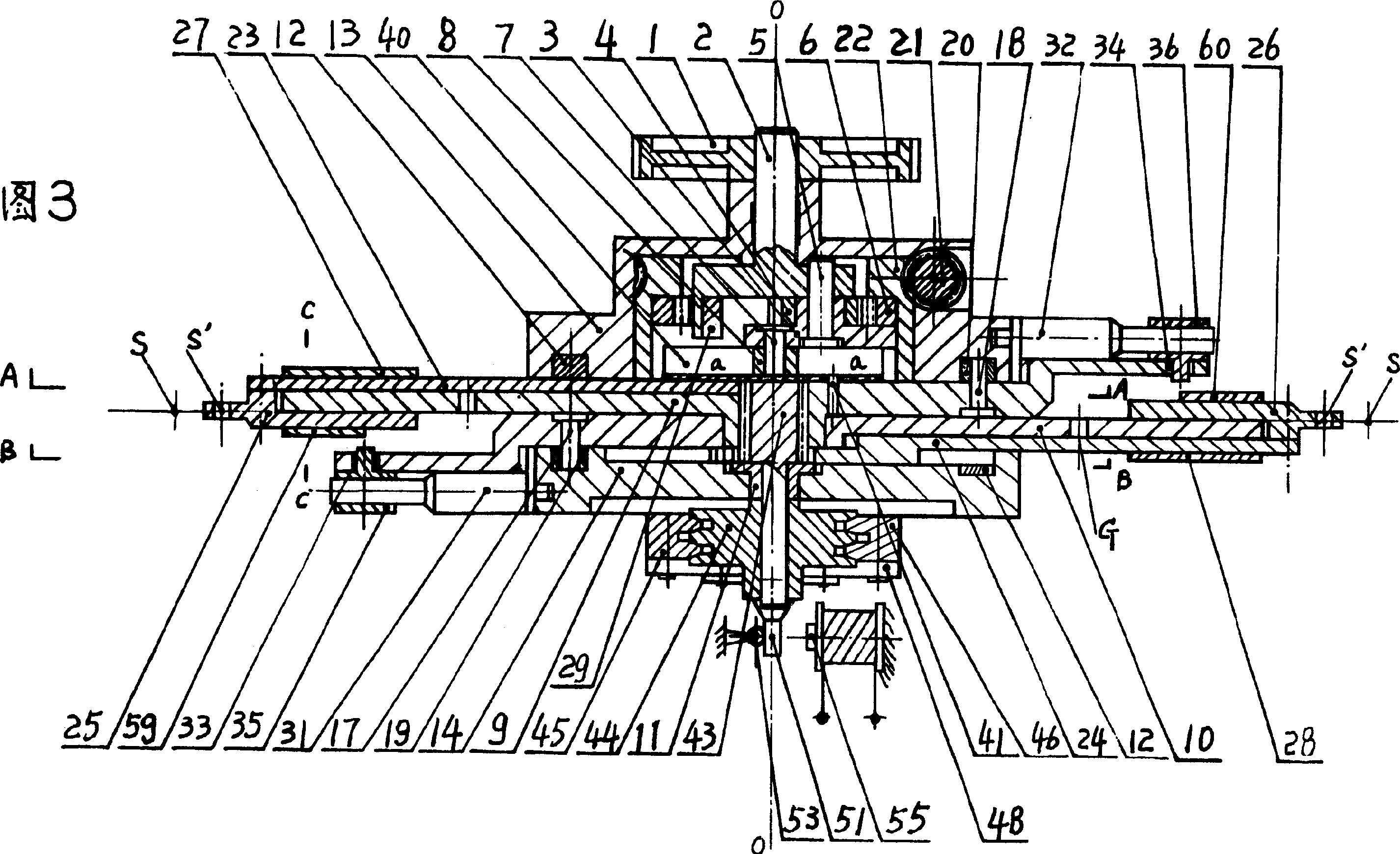
Orthopedic robot navigation device and positioning system
ActiveCN101700184APositioningHas a guiding roleProgramme-controlled manipulatorSurgical robotsEngineeringSelf positioning
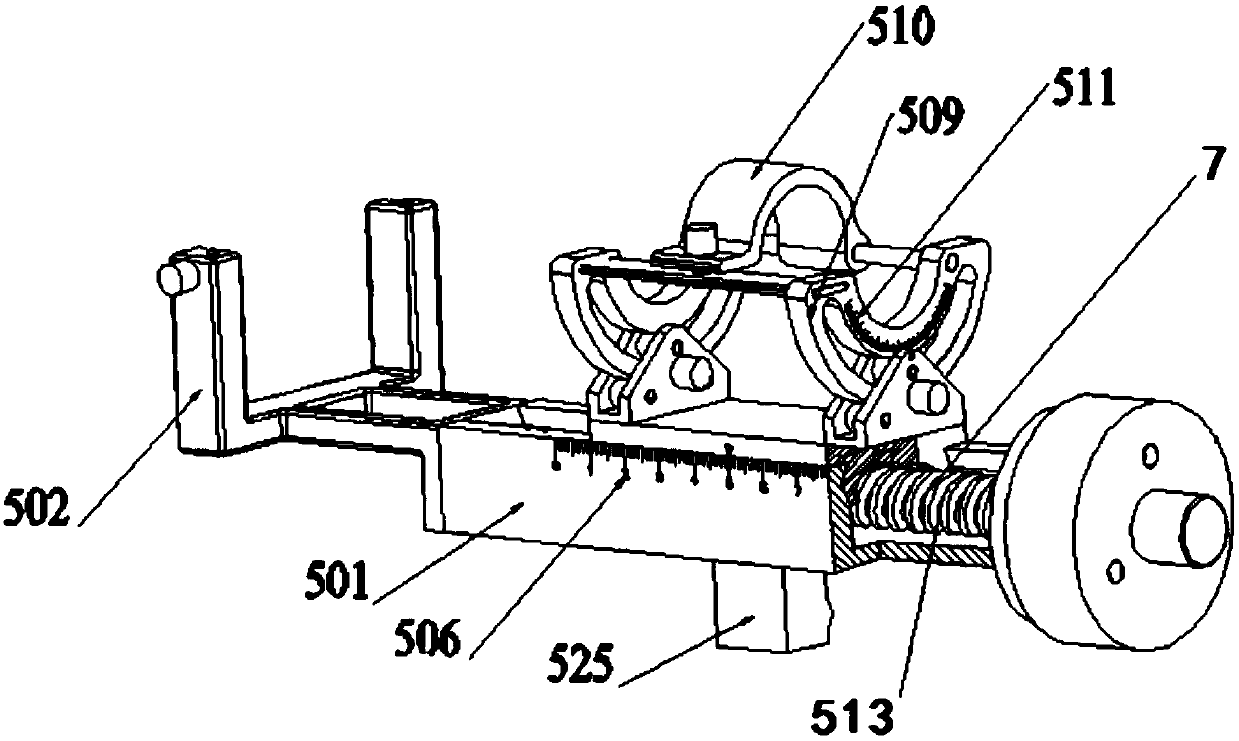
The invention relates to an orthopedic robot navigation device and a positioning system. The orthopedic robot navigation device comprises a machine seat and a four-freedom degree biplane positioning mechanism, wherein the four-freedom degree biplane positioning mechanism is arranged on the machine seat and connected with the machine seat. The four-freedom degree biplane positioning mechanism comprises a first series connection mechanical arm, a second series connection mechanical arm and a straight lever-shaped guide device, wherein the first series connection mechanical arm comprises a first horizontal motion assembly, a first vertical motion assembly and a first cardan joint which are connected in series; the second series connection mechanical arm comprises a second horizontal motion assembly, a second vertical motion assembly and a second cardan joint which are connected in series; both the first horizontal motion assembly and the second first horizontal motion assembly are connected with the machine seat; and the straight lever-shaped guide device realizes the self positioning by being clamped with the first cardan joint and the second cardan joint respectively. The device is arranged at the side surface of the wounded limb, realizes the accurate positioning by the straight lever-shaped guide device and is suitable for a bone fixing operation of any wounded limb part, thereby more favorably meeting the requirement of the operation.
Owner:BEIJING TINAVI MEDICAL TECH
Unmanned biplane for airborne reconnaissance and surveillance having staggered and gapped wings
InactiveUS20060102798A1Easy to assembleLight weightUnmanned aerial vehiclesActuated automaticallyFlight vehicleVertical stabilizer
The present invention provides an unmanned airborne reconnaissance vehicle having a fuselage, a forward wing pair and a rearward wing pair vertically separated by a gap and staggered fore and aft therebetween such that a general biplane configuration is formed. The present invention provides a pair of wing tip plates for joining the wing tips of the forward and rearward wings. The unmanned airborne reconnaissance vehicle of the present invention includes a power plant to propel the vehicle through the air and a generally T-shaped tail having a vertical stabilizer including a rudder and a full span elevator.
Owner:MISSION TECH
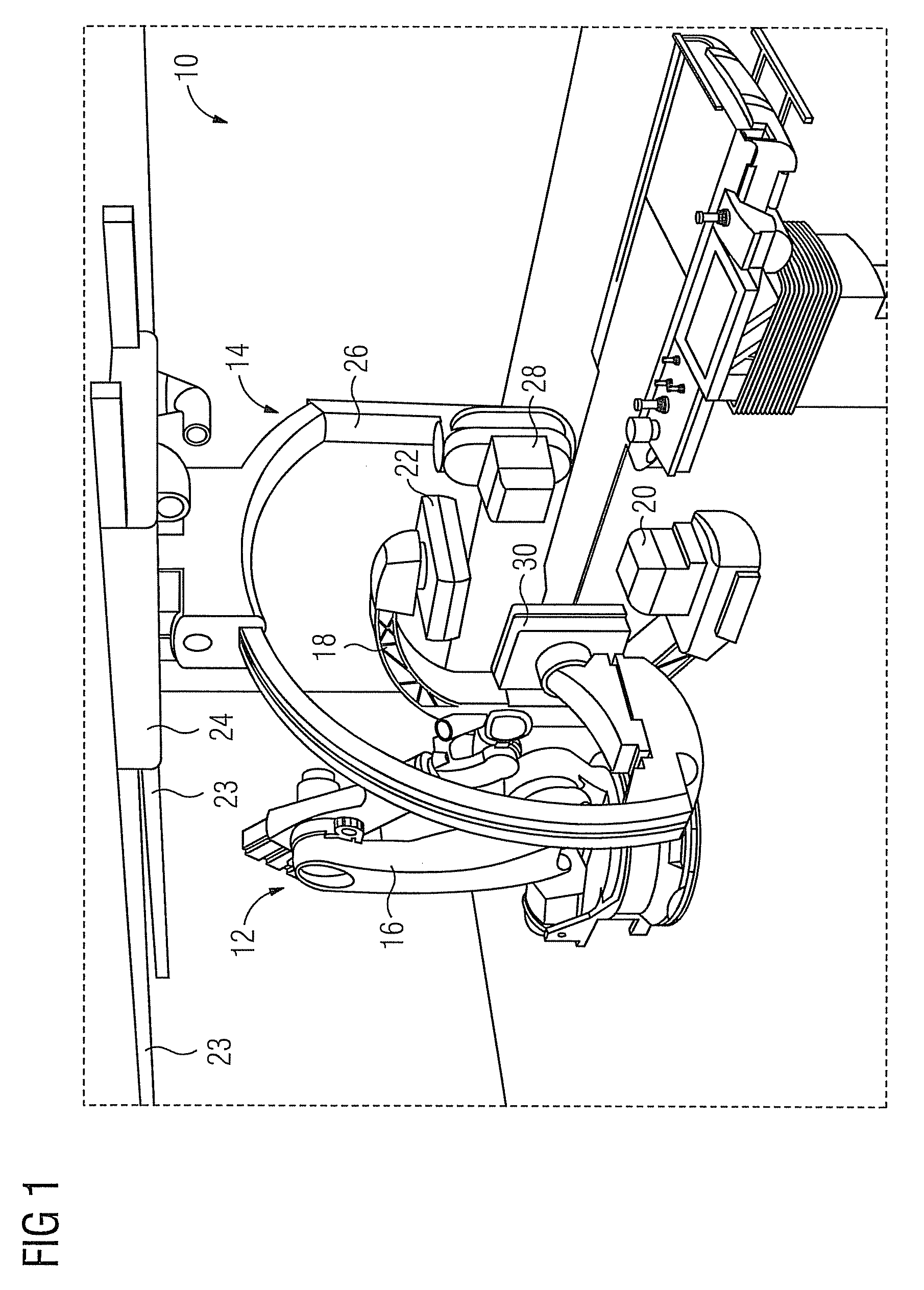
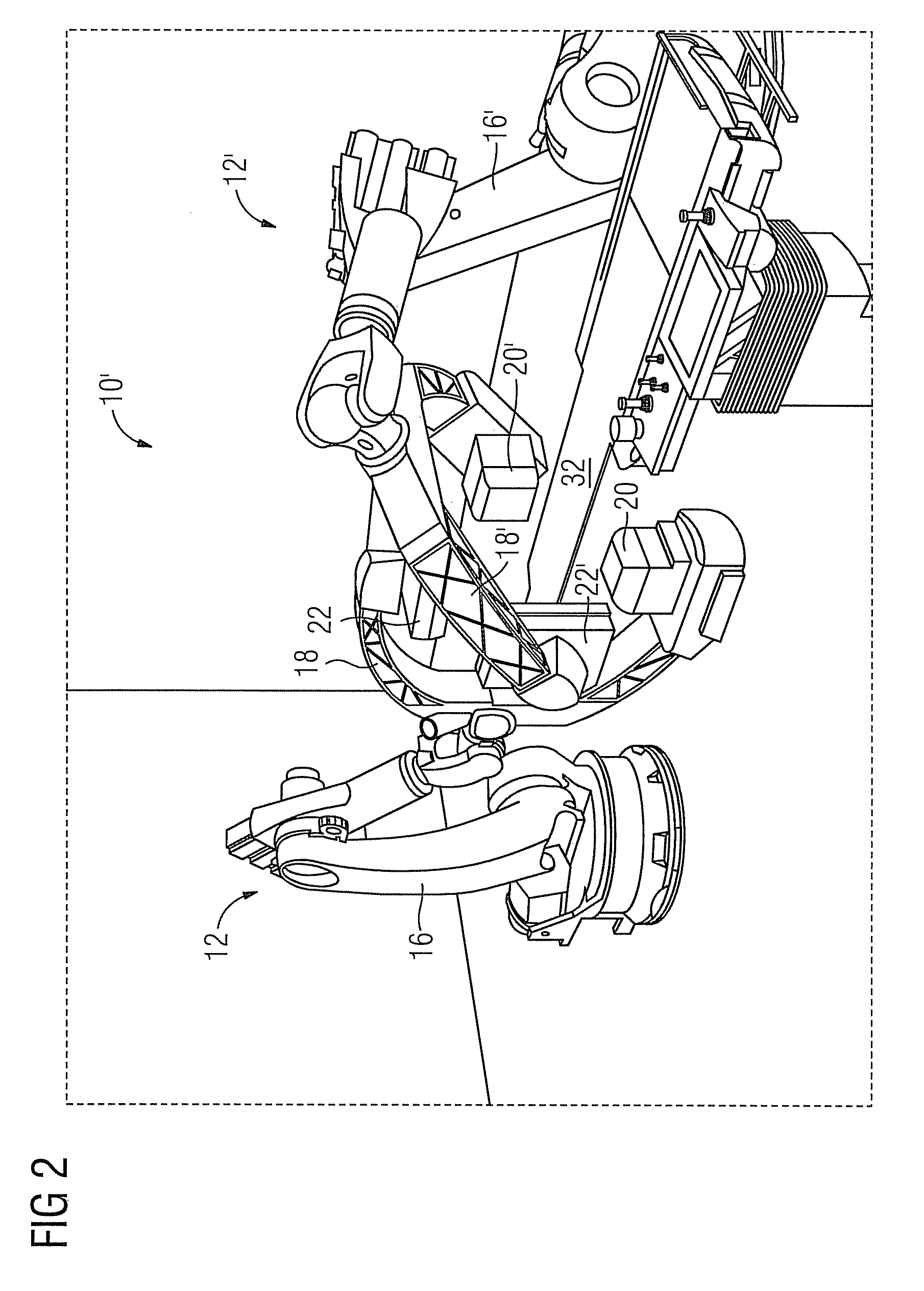
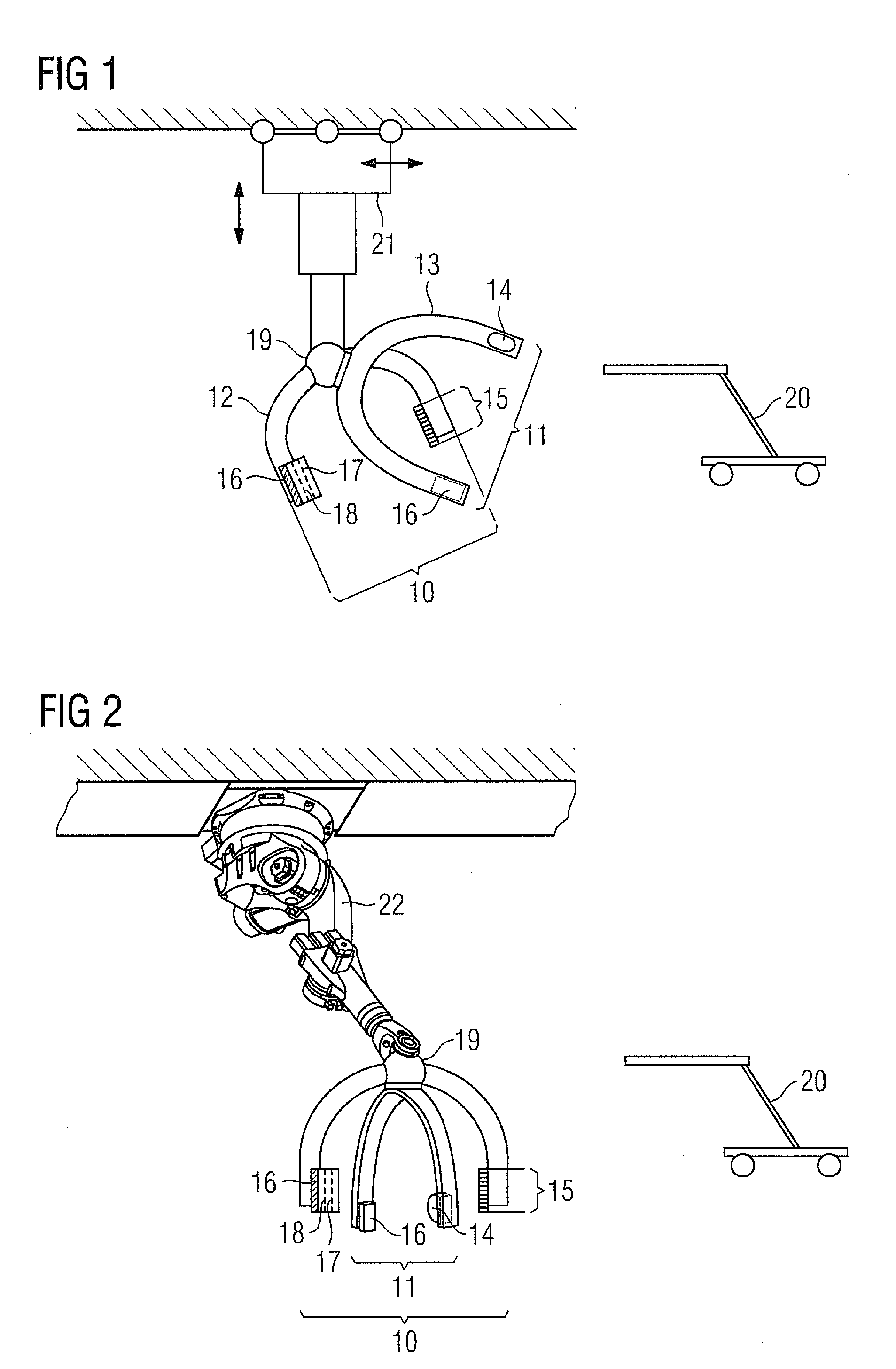
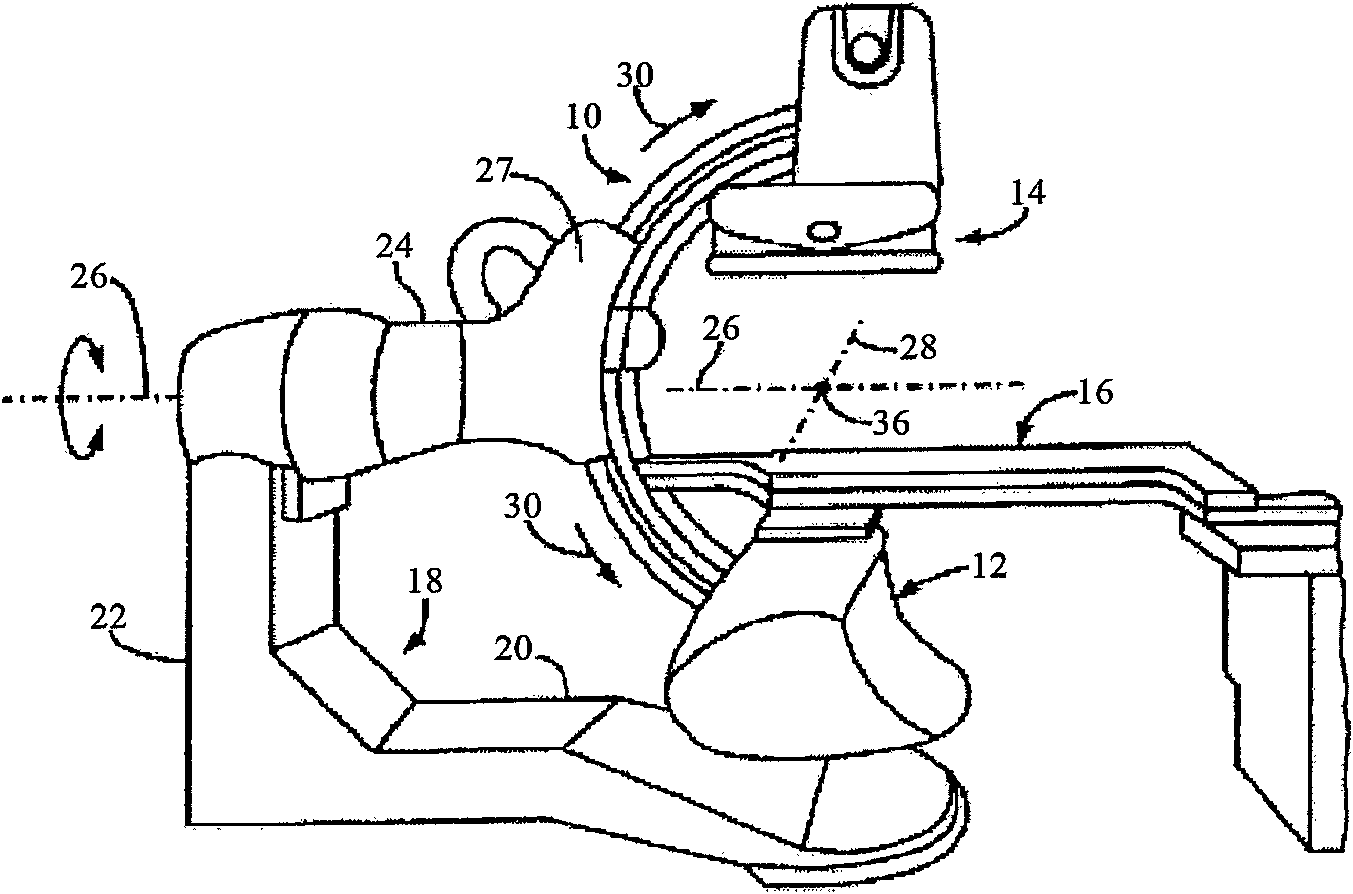
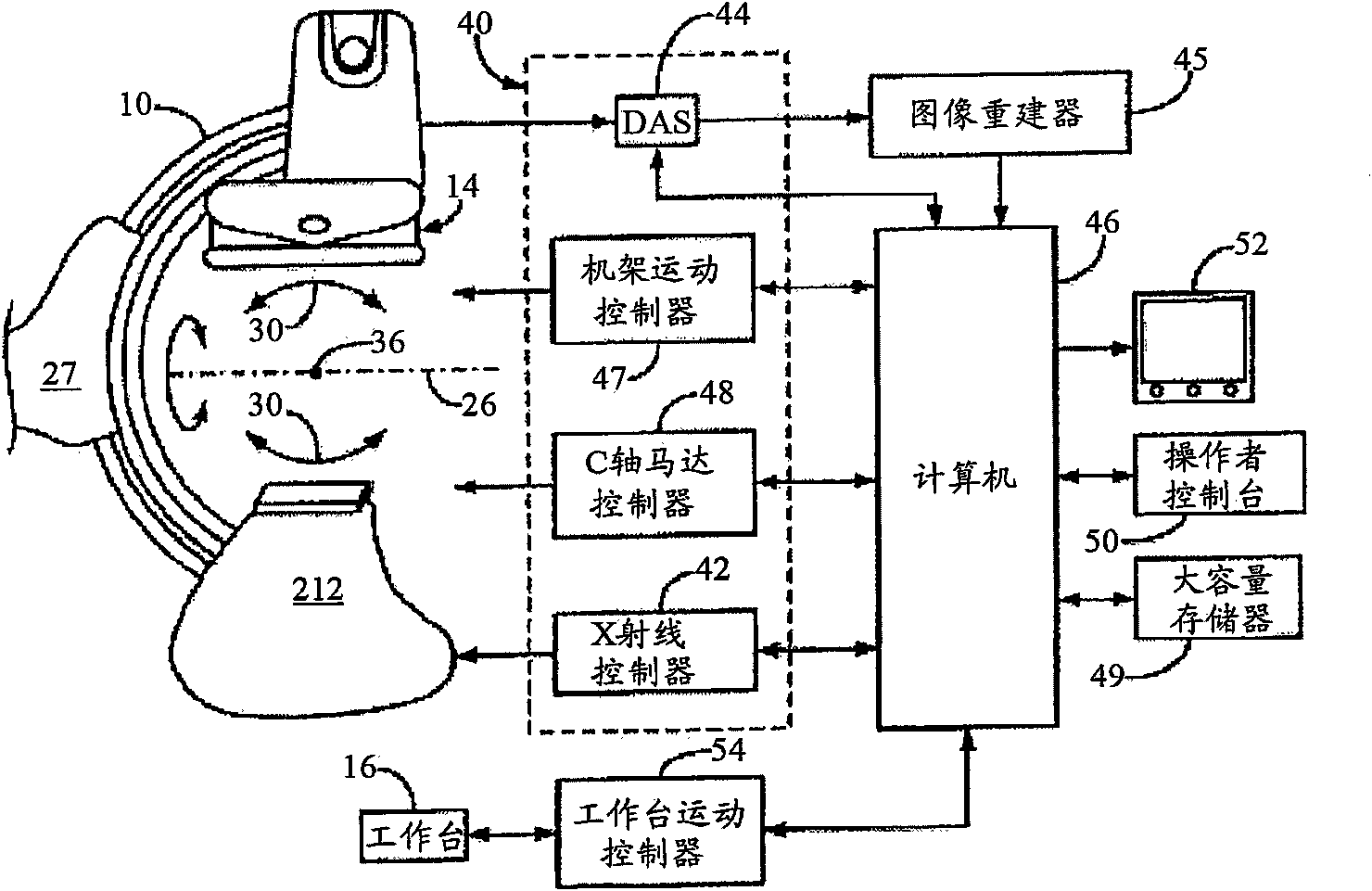
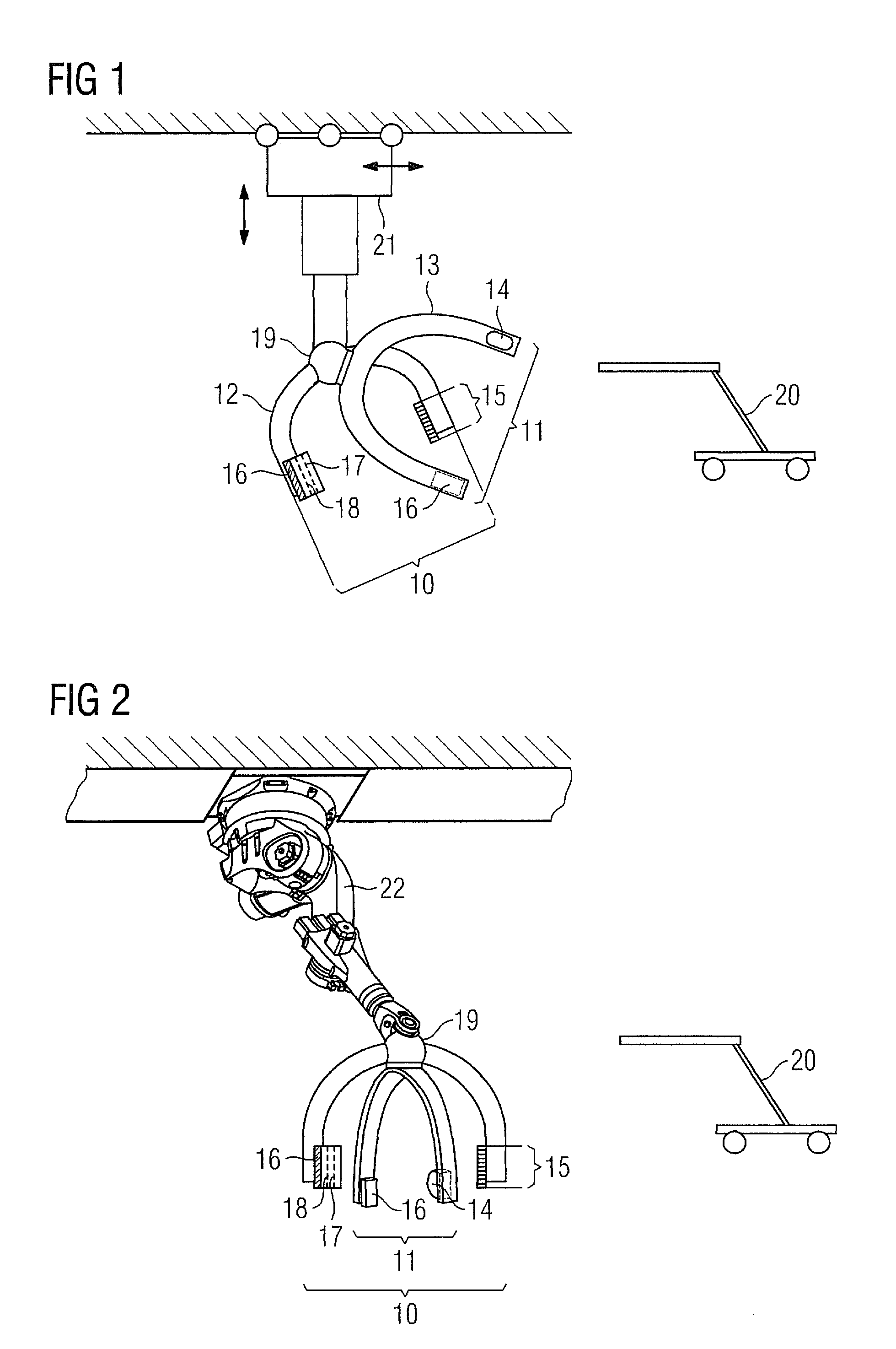
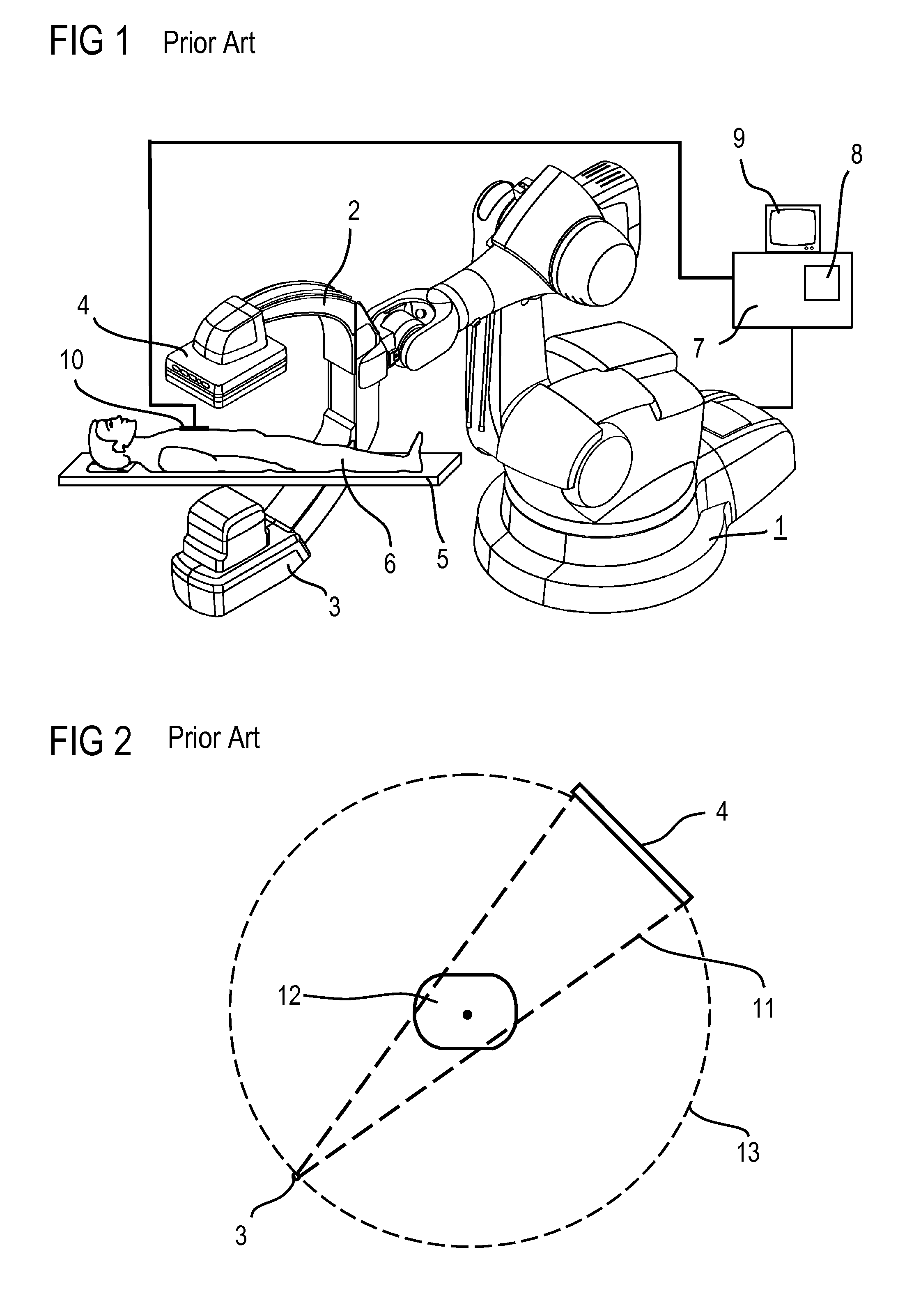
Biplane X-ray system
InactiveUS7594751B2Increase flexibilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayPhysics
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
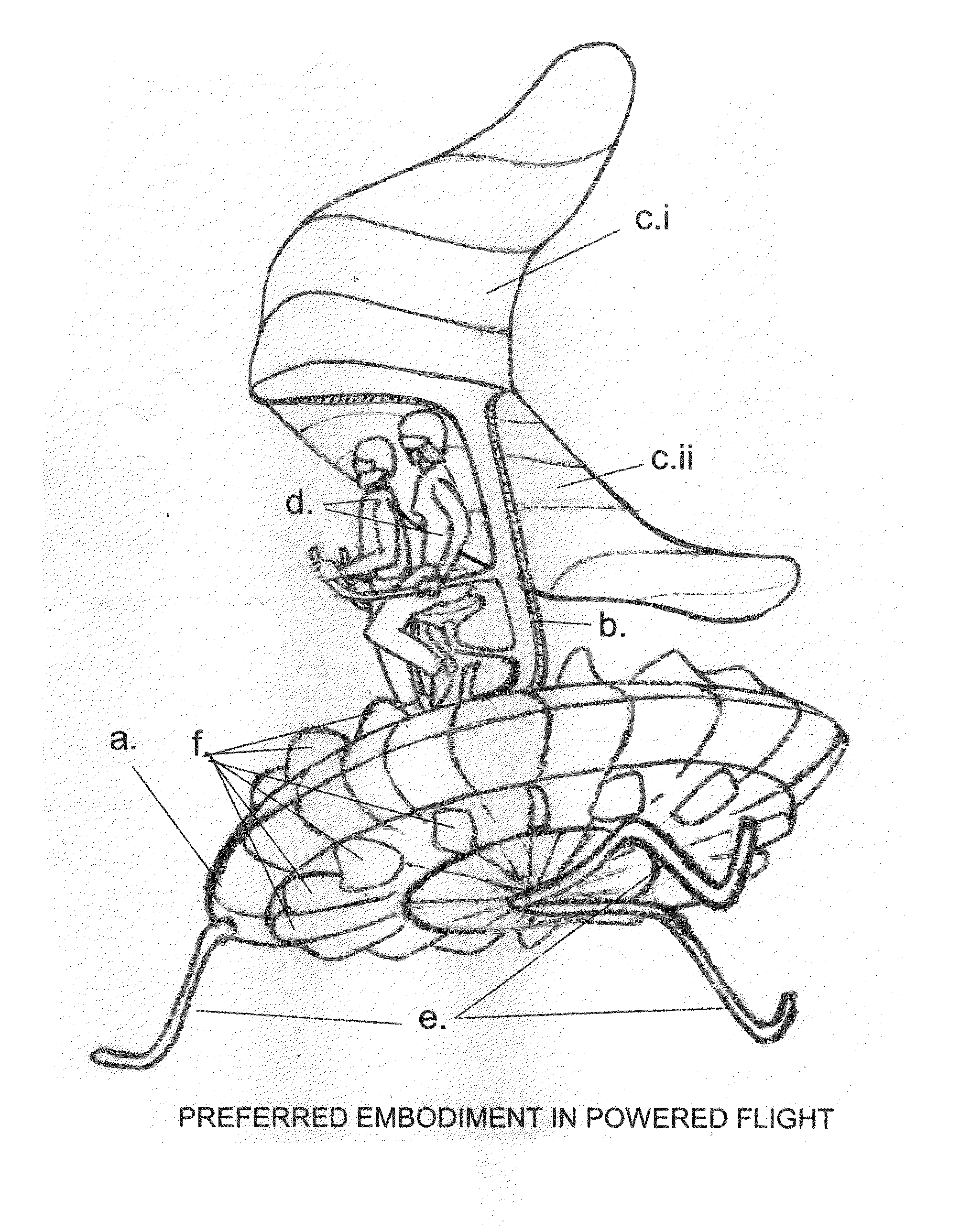
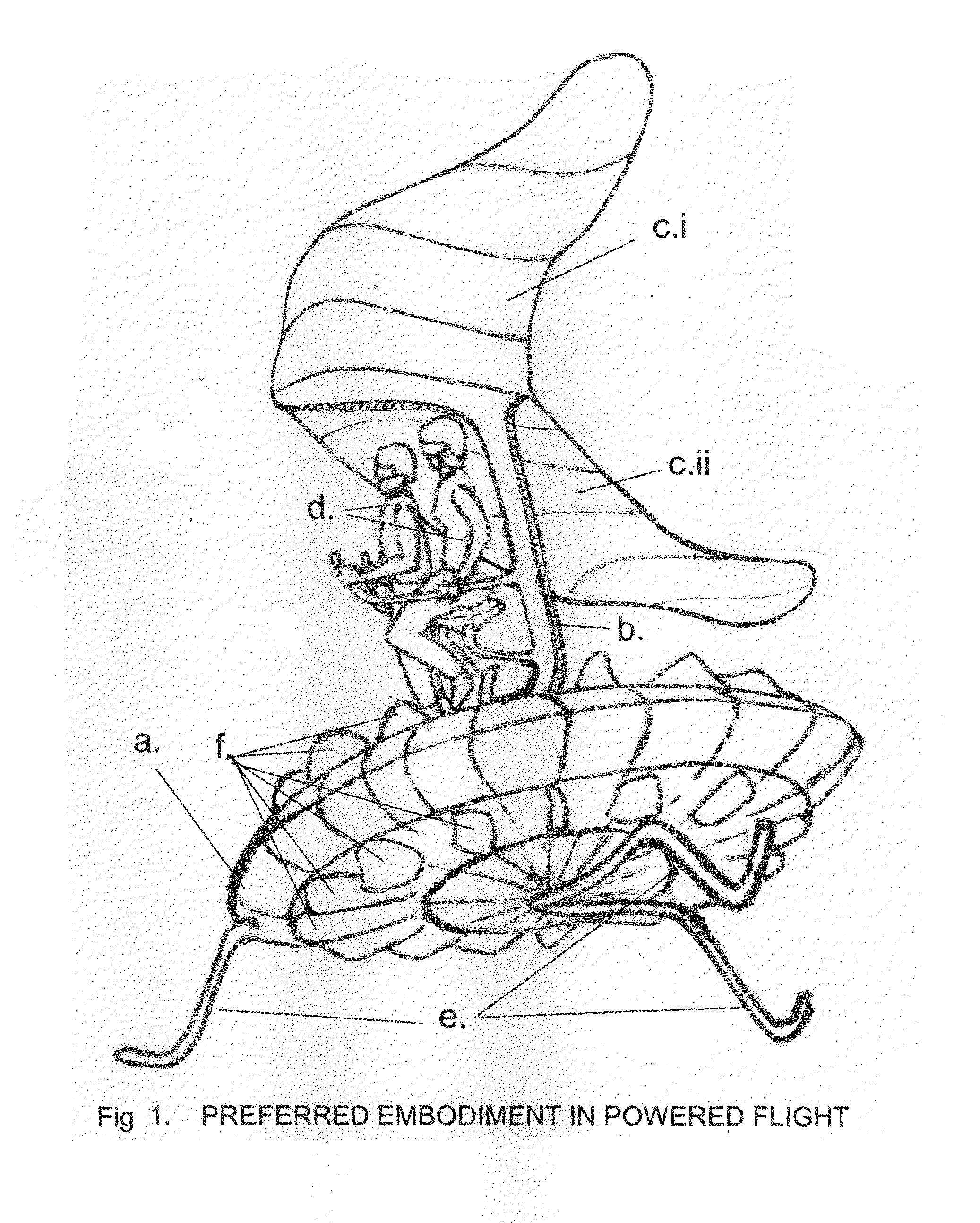
Safety flier--a parachute-glider air-vehicle with vertical take-off and landing capability
ActiveUS20110163198A1Easy to operateAvoid physical damageAircraft navigation controlPropellersRange of motionFlight vehicle
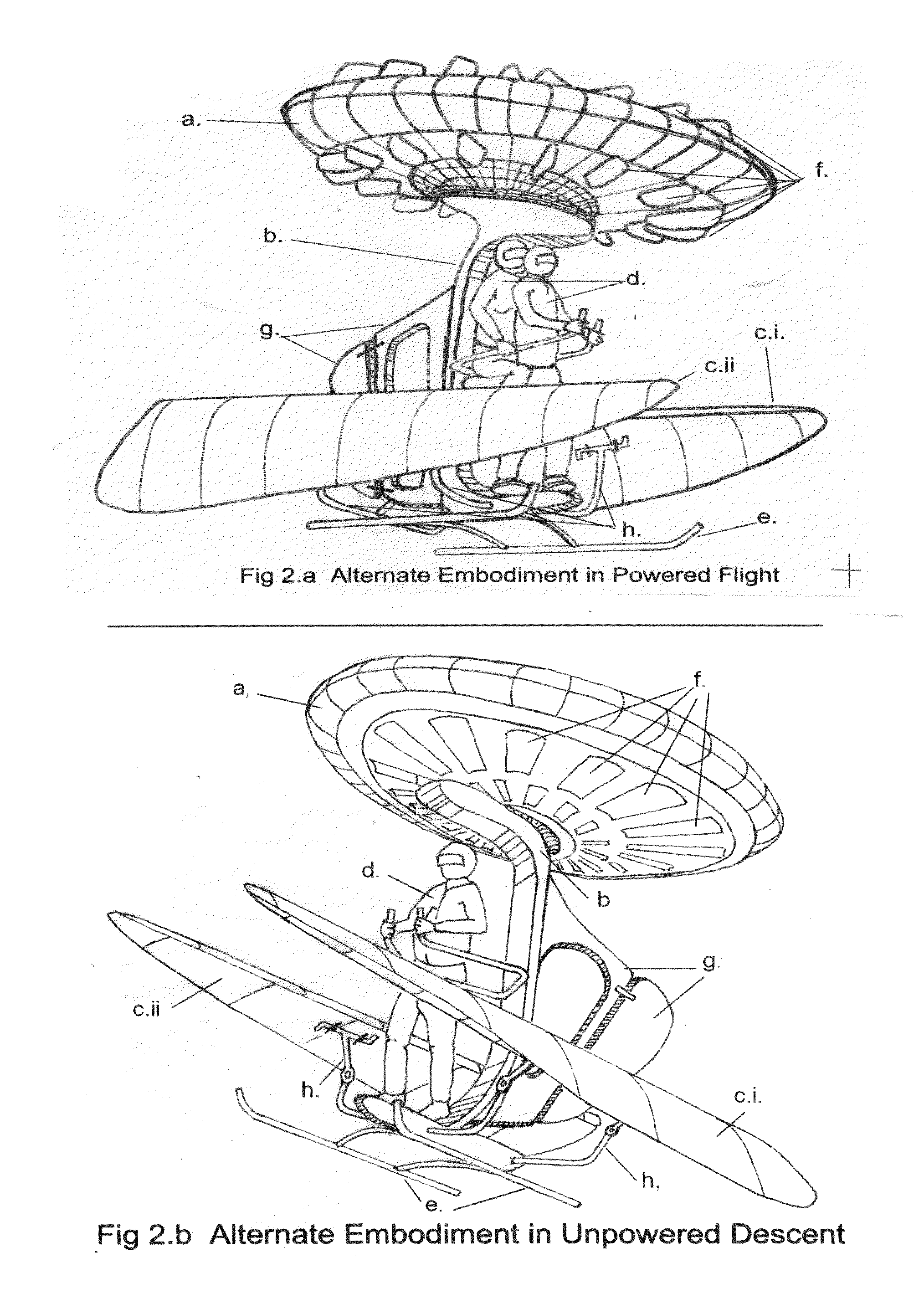
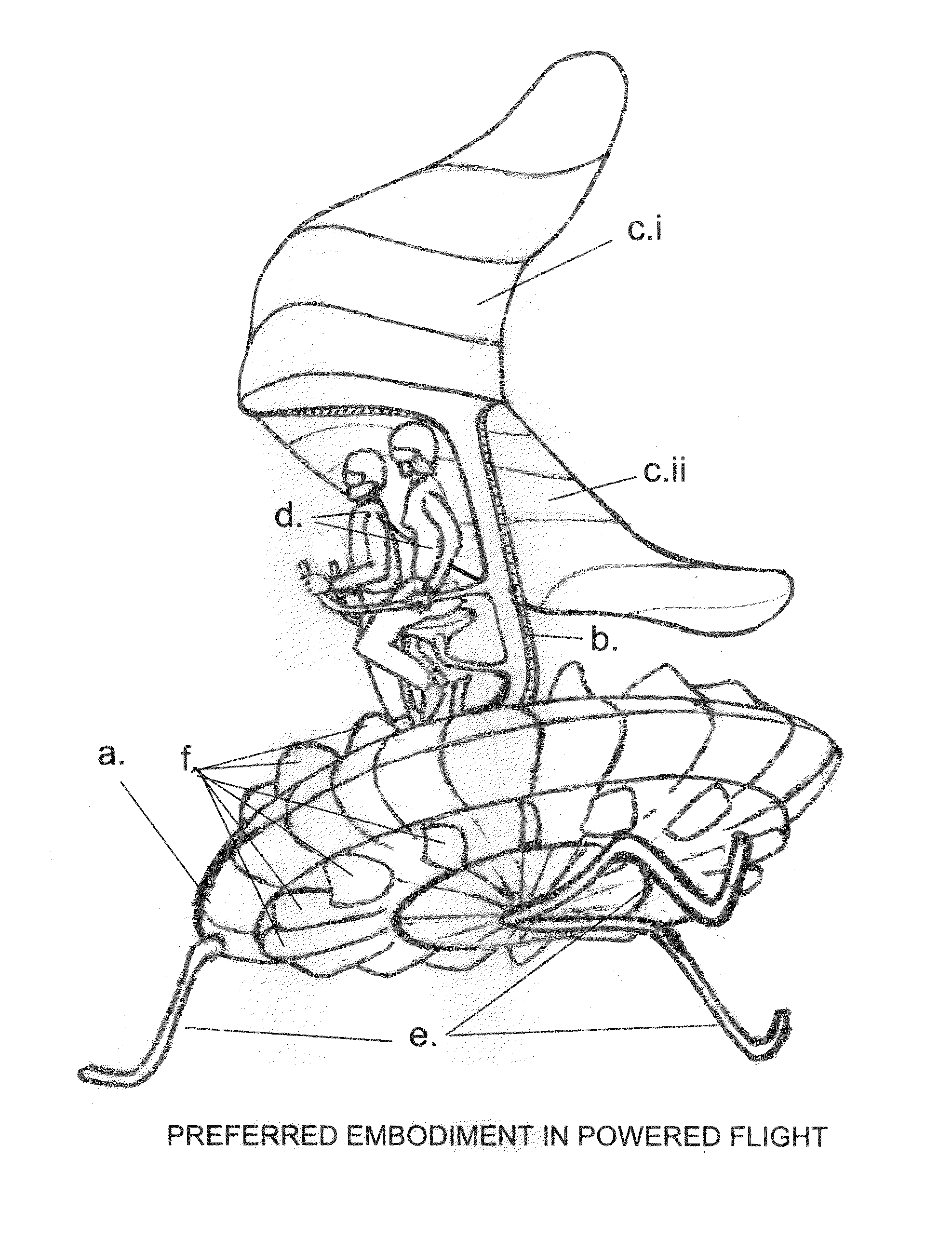
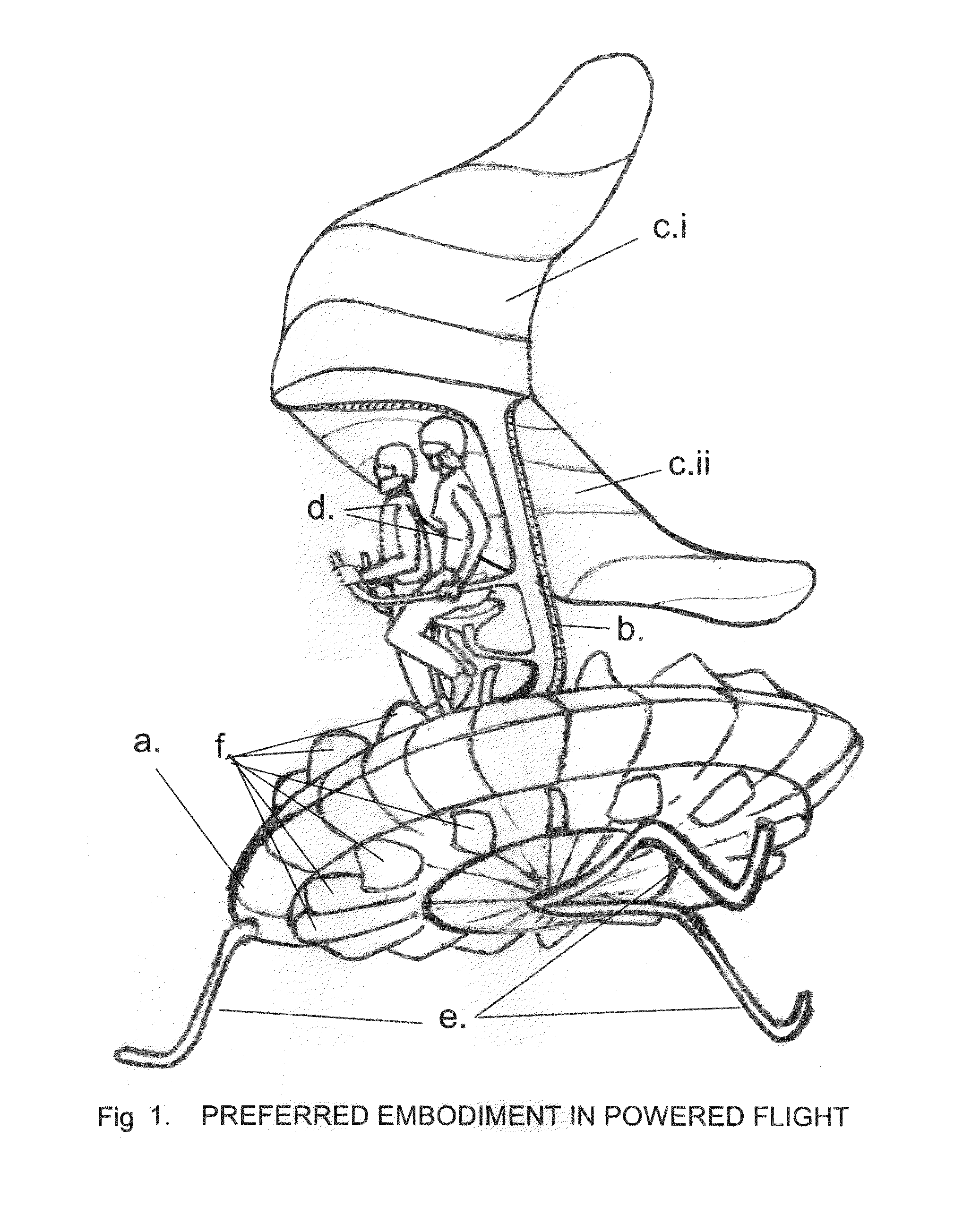
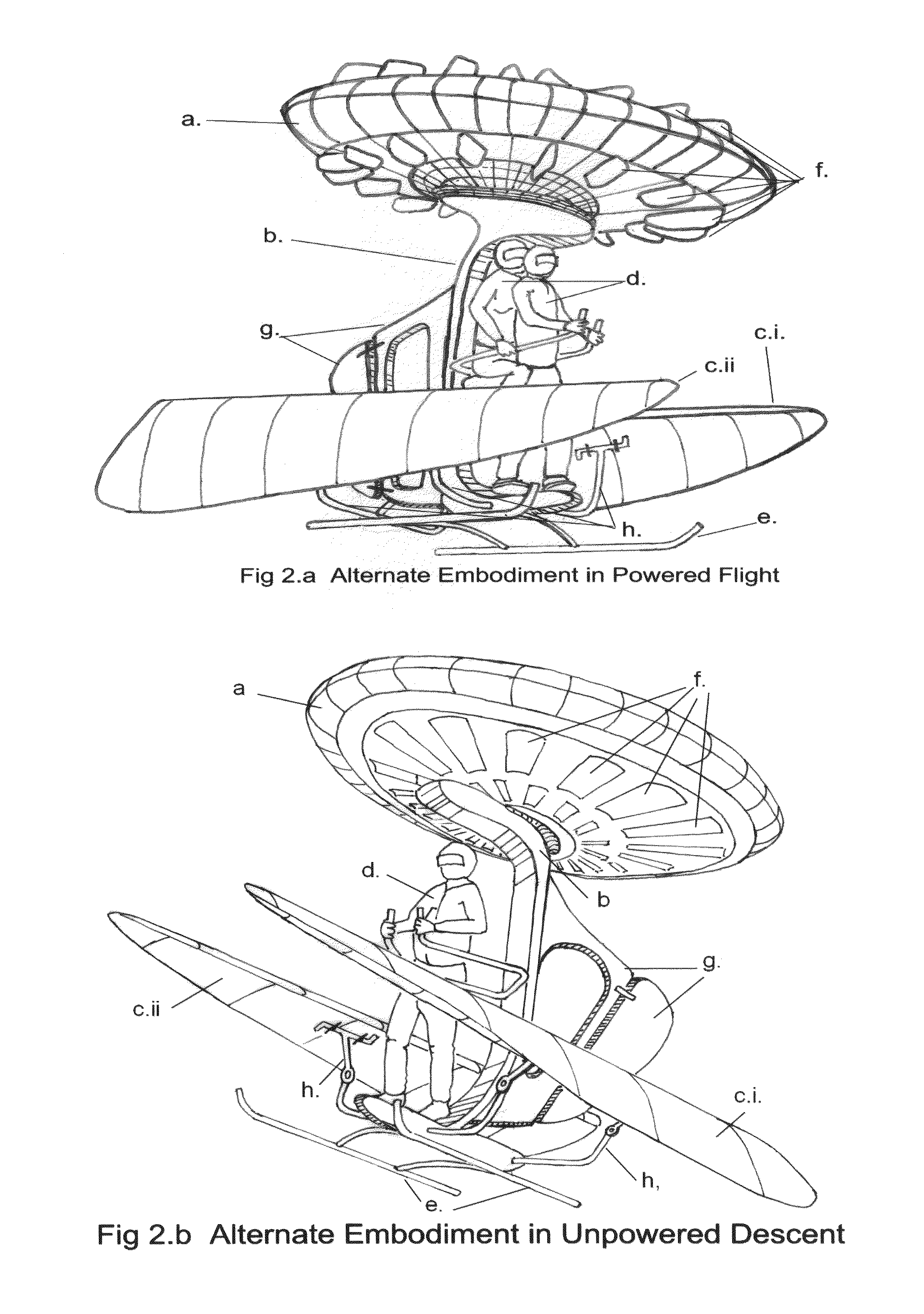
One embodiment of a Vertical Take-off and Landing (VToL) air-vehicle (FIG. 1.) having a horizontal rotor, a. providing lift and propulsion, and communicating at or near its centre to structural elements, or fuselage, b. Upon or within the fuselage structure is attached a platform, to which a payload, or occupant or pilot, d. is secured in such a manner as to permit a movement, or range-of-motion, of the payload, as a means of weight-shifting, or mass-balancing, of the vehicle for stability and control in flight. At least two planar elements, or descent-vanes, c.i & c.ii are connected to a structural element of the fuselage at a location which provides vertical and horizontal separation between the rotor and the descent-vanes, thus creating a tandem, biplane arrangement of two aerodynamically active elements which are aerodynamically balanced to provide stability and controllability in hovering flight, in forward flight, and in un-powered gliding and vertical descents. Other embodiments are described and shown.
Owner:LEAVER GLENN
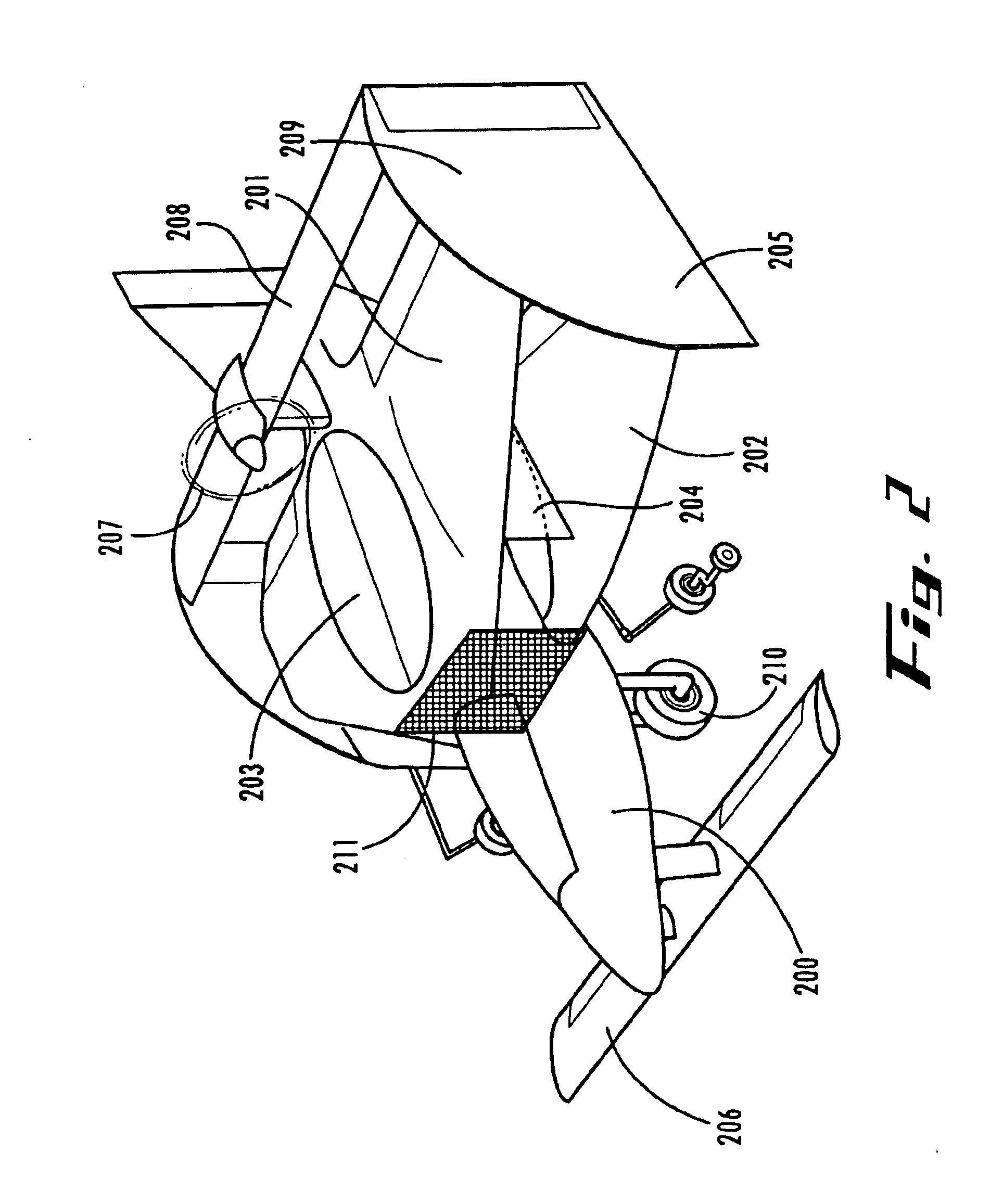
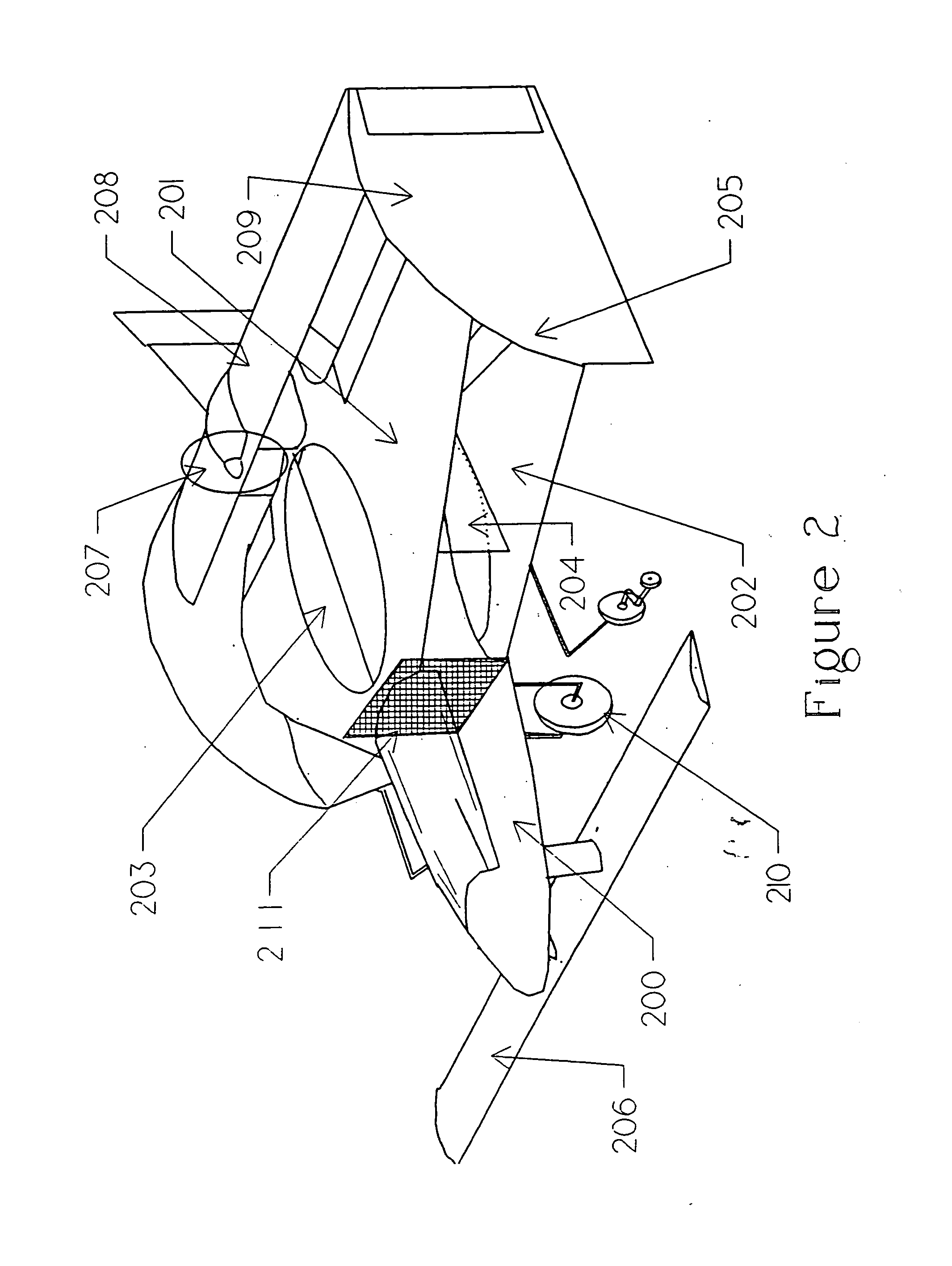
V/stol biplane
InactiveUS20050151003A1Aircraft navigation controlVertical landing/take-off aircraftsHigh resistanceDrivetrain
Owner:CHURCHMAN CHARLES GILPIN
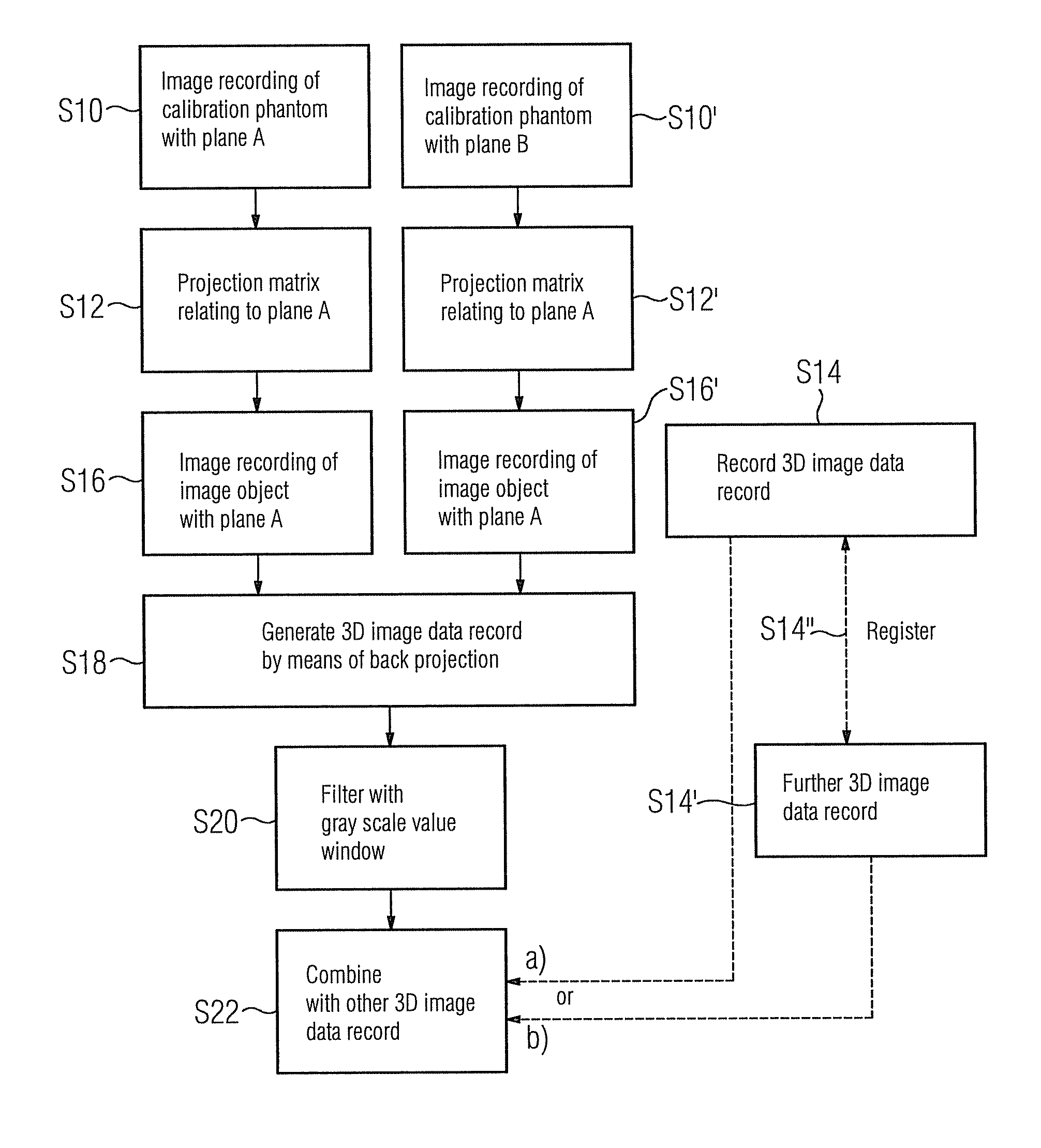
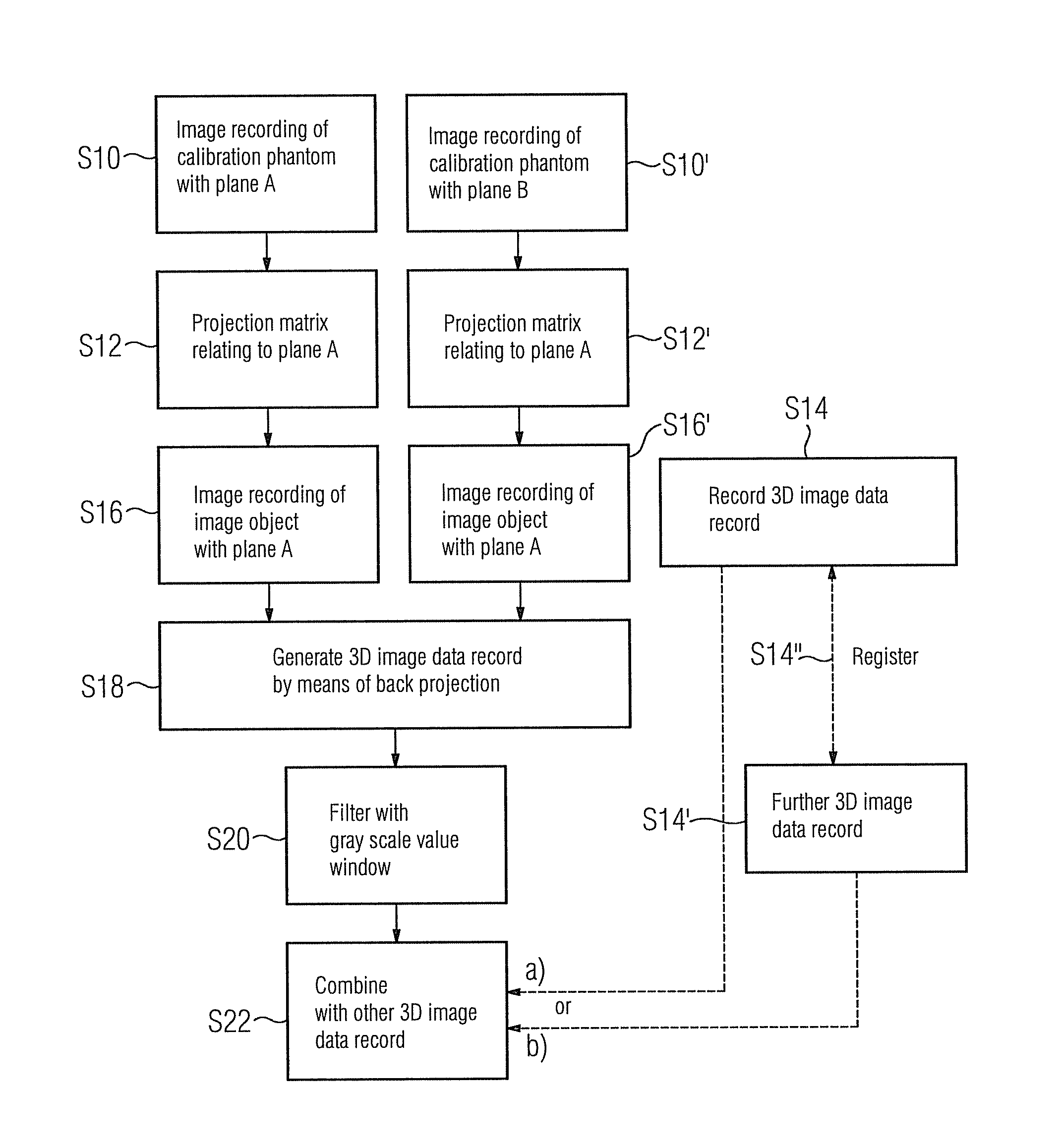
Method for providing a 3D image data record of a physiological object with a metal object therein
A method for providing a 3D image data record of a physiological object with a metal object therein is proposed. To enable an image of the metal object in the physiological object, for instance a biopsy needle in a human patient to be recorded as a 3D image in this patient, two 2D x-ray images of the patient are obtained with the needle with the aid of a biplane x-ray system, and back projection allows a 3D image data record to be generated, which is then subject to a filtering with a gray-scale value window. After filtering, information relating to the position and shape of the metal object in space is obtained. The thus obtained first 3D image data record can be combined with another 3D image data record, in particular with a 3D image data record of the patient without the metal object obtained with the same biplane x-ray system.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
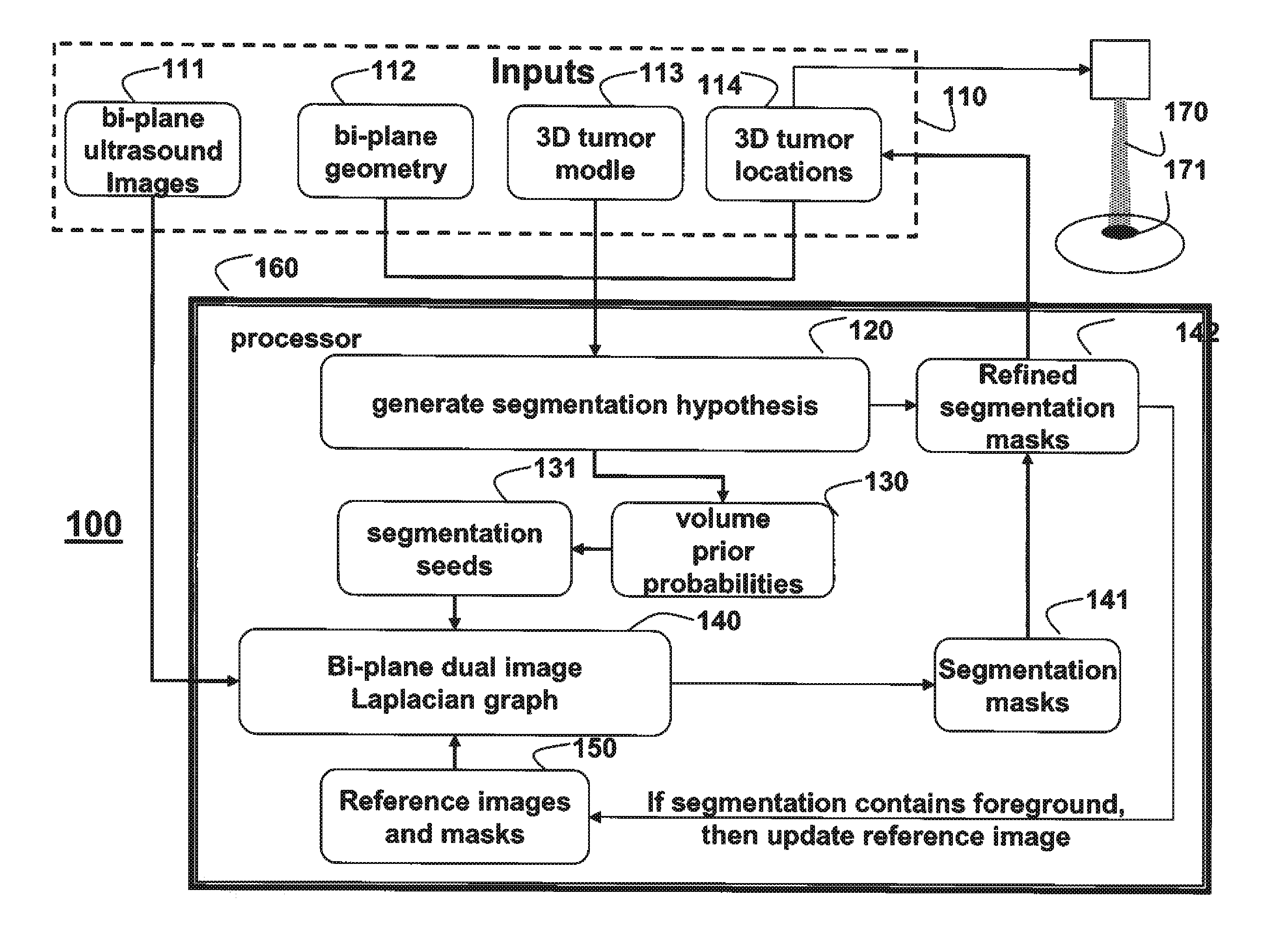
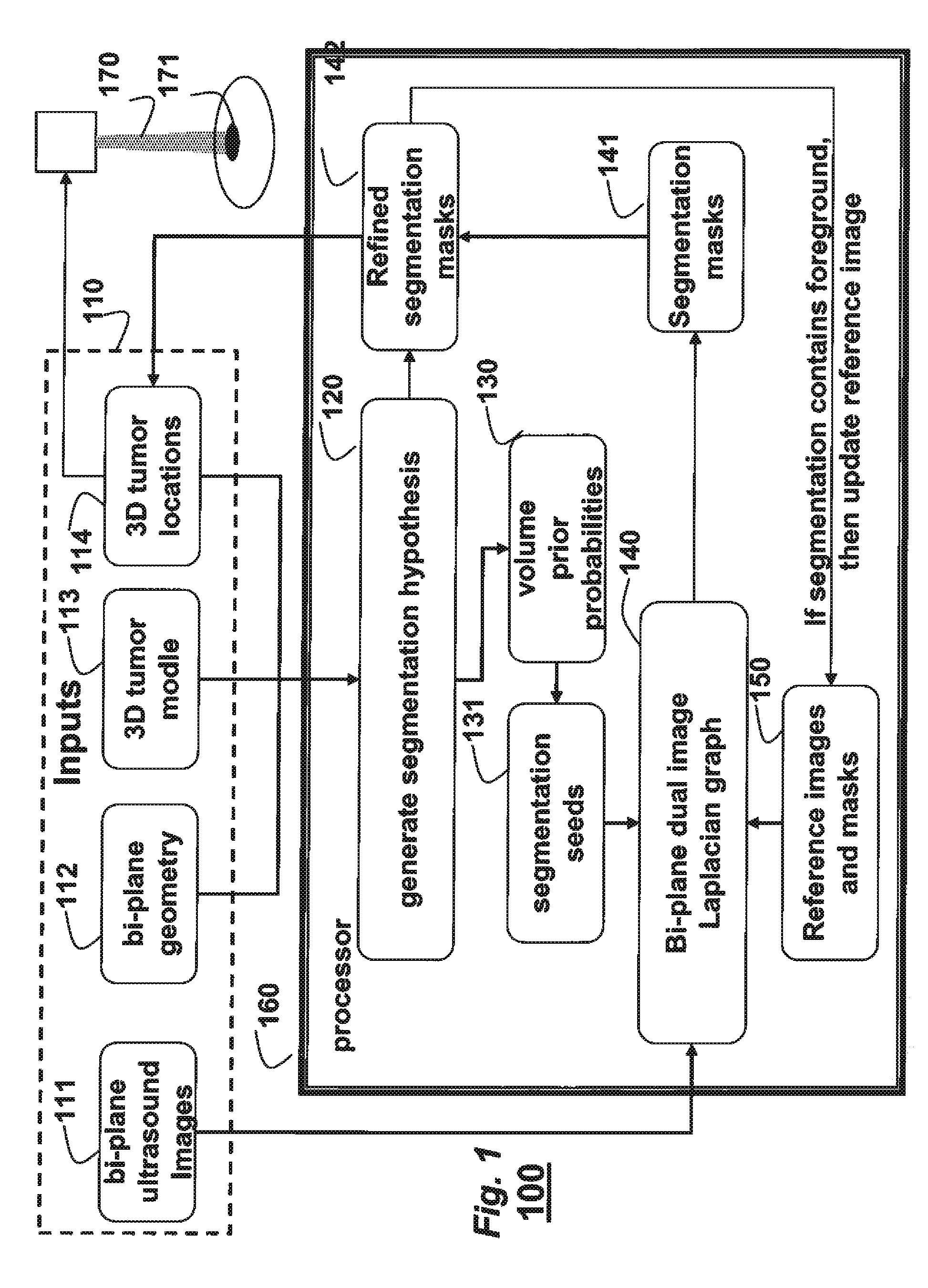
Method for Tracking Tumors in Bi-Plane Images
A tumor is tracked in sequences of biplane images by generating a set of segmentation hypotheses using a 3D model of the tumor, a biplane geometry, and a previous location of the tumor as determined from the pairs of biplane images. Volume prior probabilities are constructed based on the set of hypotheses. Seed pixels are selected using the volume prior probabilities, and a bi-plane dual image graph is constructed using intensity gradients and the seed pixels to obtaining segmentation masks corresponding to tumor boundaries using the image intensities to determine a current location of the tumor.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Safety flier—a parachute-glider air-vehicle with vertical take-off and landing capability
ActiveUS8408488B2Avoid physical damageAircraft navigation controlPropellersRange of motionFlight vehicle
Owner:LEAVER GLENN
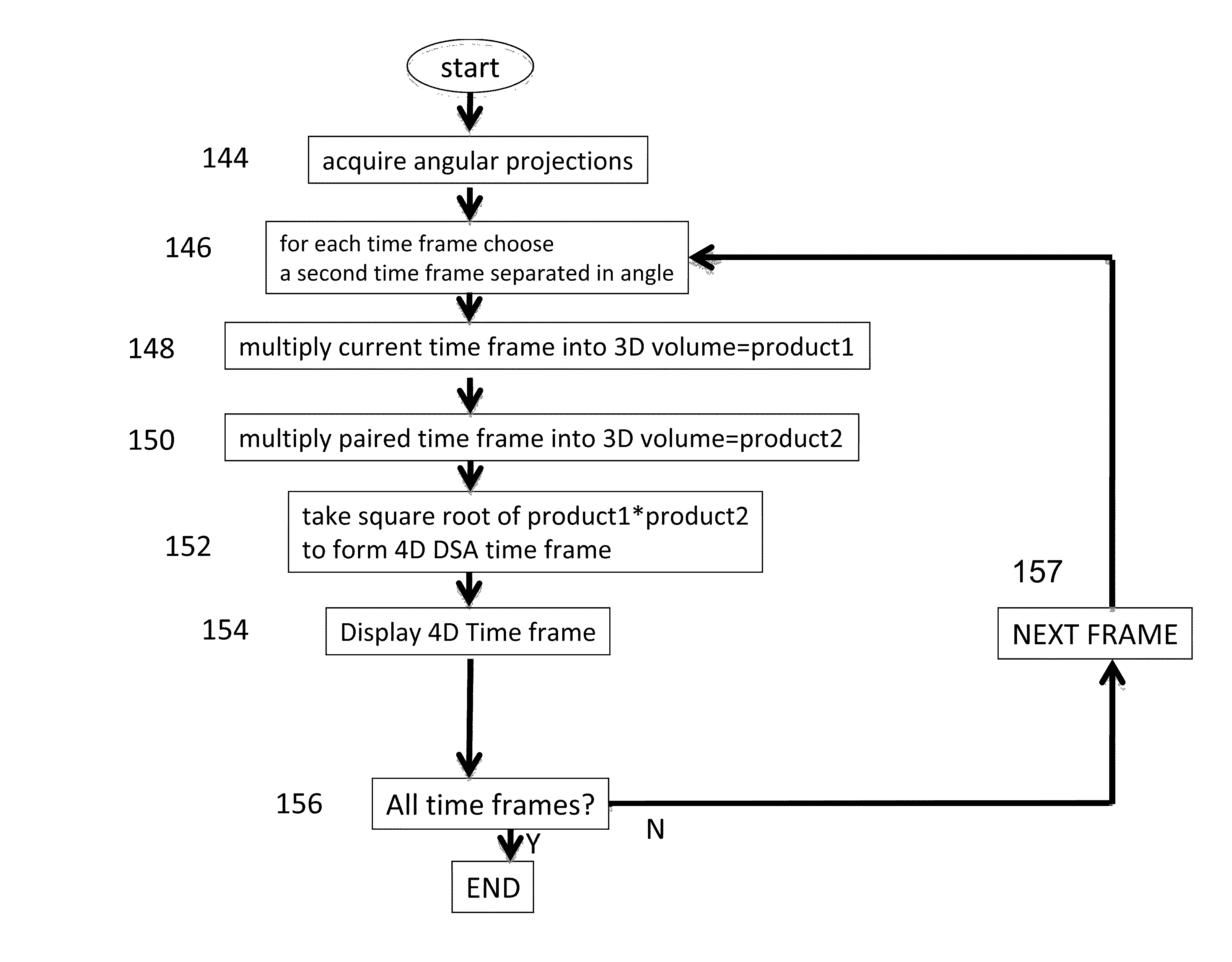
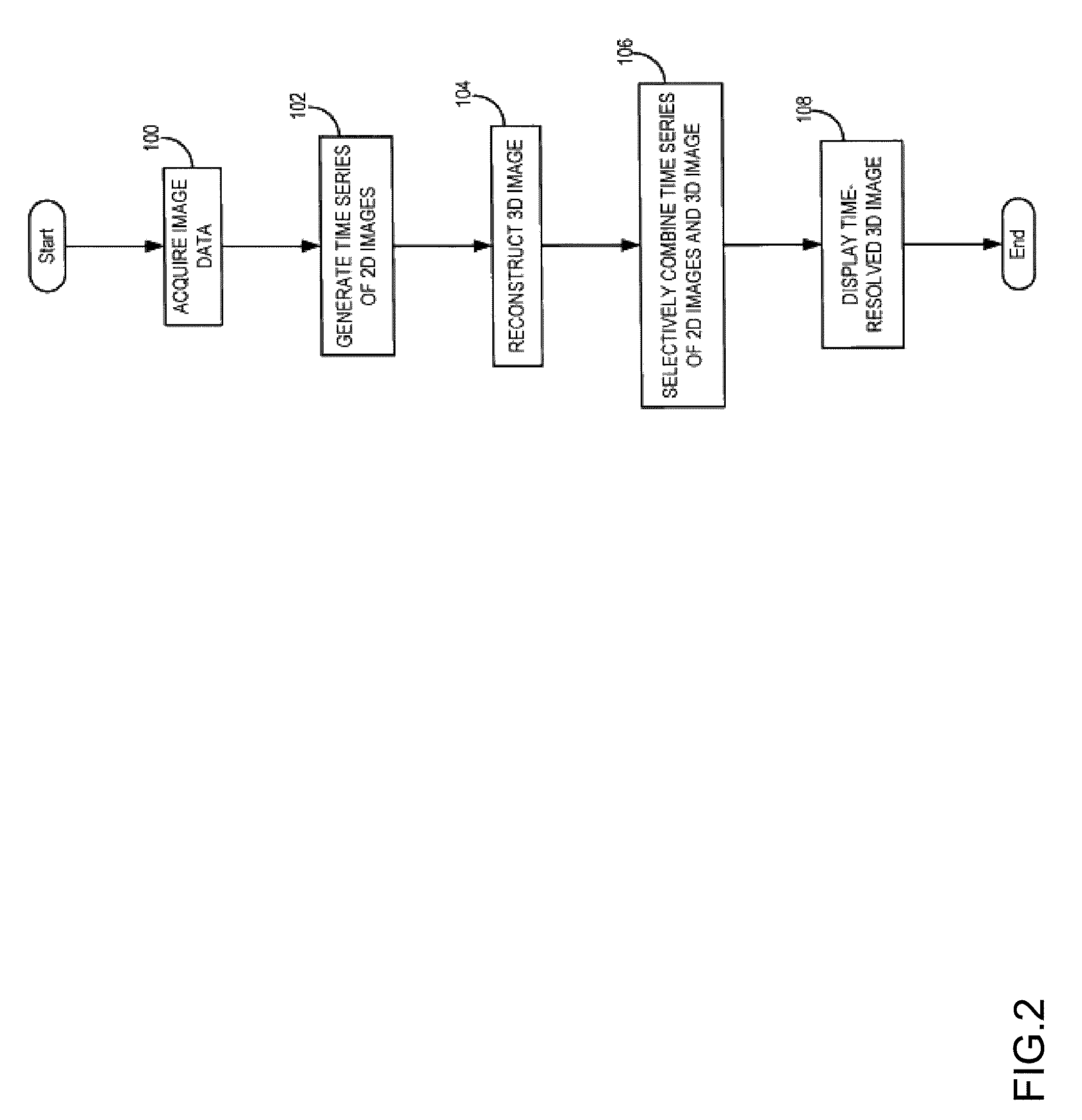
System and method for four dimensional angiography and fluoroscopy
ActiveUS8654119B2Eliminate the effects ofImprove approximationReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMultiple injectionTemporal resolution
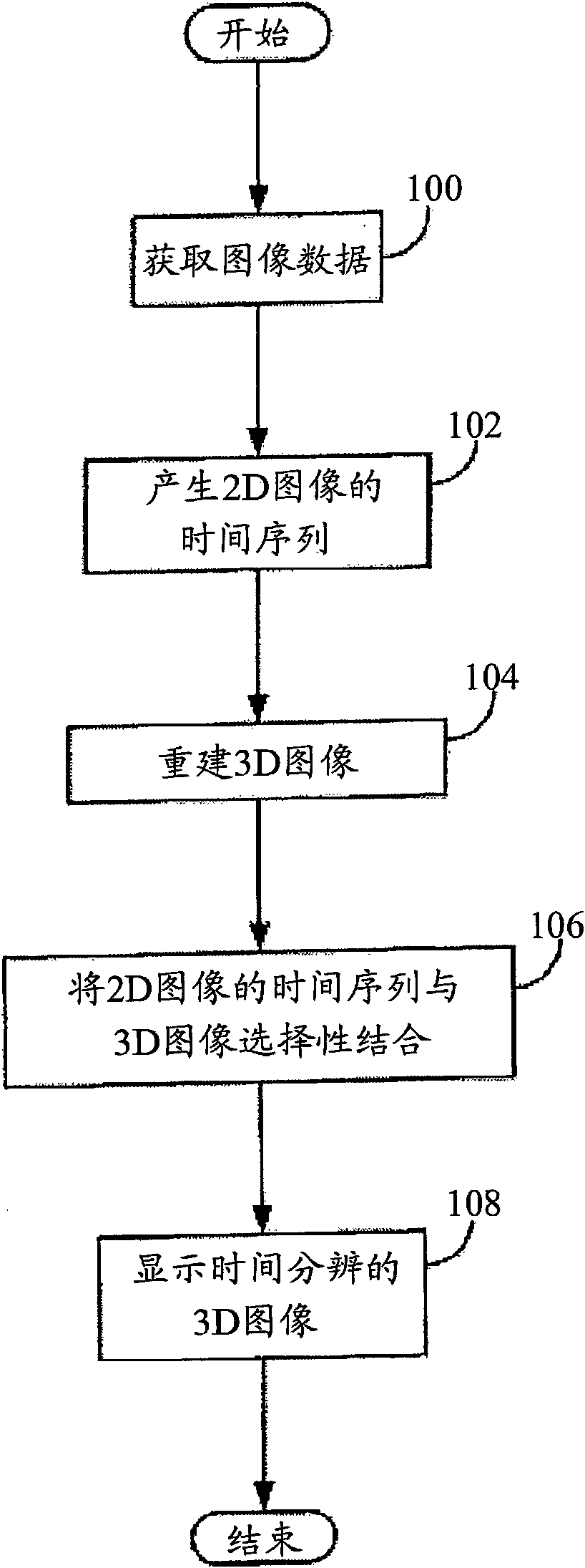
A method for generating time-resolved 3D medical images of a subject by imparting temporal information from a time-series of 2D medical images into 3D images of the subject. Generally speaking, this is achieved by acquiring image data using a medical imaging system, generating a time-series of 2D images of a ROI from at least a portion of the acquired image data, reconstructing a 3D image substantially without temporal resolution from the acquired image data, and selectively combining the time series of 2D images with the 3D image. Selective combination typically involves registering frames of the time-series of 2D images with the 3D image, projecting pixel values from the 2D image frames “into” the 3D image, and weighting the 3D image with the projected pixel values for each frame of the time-series of 2D images. This method is particularly useful for generating 4D-DSA images (that is, time-resolved 3D-DSA images) from a time-series of 2D-DSA images acquired via single plane or biplane x-ray acquisitions with 3D images acquired via a rotational DSA acquisition. 4D-DSA images can be generated either by using multiple injections or by using a single injection by combining a time-series of 2D-DSA images generated from individual projections from a rotational x-ray acquisition with a 3D image reconstructed from substantially all of the projection views acquired during the rotational x-ray acquisition. These DSA images may have a spatial resolution on the order of 5123 pixels and a temporal resolution of about 30 frames per second, which represents an increase over traditional 3D-DSA frame rates by a factor of between 150 and 600.
Owner:CMS MEDICAL +1
Biplane X-Ray Imaging System
InactiveUS20110274246A1Good and quick and simple adjustabilityImprove image qualityImaging devicesX-ray apparatusConventional X-RayX-ray
A biplane X-ray imaging system is provided. The biplane X-ray imaging system has two recording units disposed in different planes. Each of the recording units has an X-ray detector and an X-ray source. The first recording unit is a phase-contrast recording unit for phase-contrast X-ray imaging. The second recording unit is a conventional recording unit for conventional x-ray imaging.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and method for four dimensional angiography and fluoroscopy
ActiveCN102696056AReconstruction from projectionIntravenous devicesMultiple injectionTemporal resolution
A method for generating time-resolved 3D medical images of a subject by imparting temporal information from a time-series of 2D medical images into 3D images of the subject. Generally speaking, this is achieved by acquiring image data using a medical imaging system, generating a time-series of 2D images of a ROI from at least a portion of the acquired image data, reconstructing a 3D image substantially without temporal resolution from the acquired image data, and selectively combining the time series of 2D images with the 3D image. Selective combination typically involves registering frames of the time-series of 2D images with the 3D image, projecting pixel values from the 2D image frames 'into' the 3D image, and weighting the 3D image with the projected pixel values for each frame of the time-series of 2D images. This method is particularly useful for generating 4D-DSA images (that is, time-resolved 3D-DSA images) from a time-series of 2D-DSA images acquired via single plane or biplane x-ray acquisitions with 3D images acquired via a rotational DSA acquisition. 4D-DSA images can be generated either by using multiple injections or by using a single injection by combining a time-series of 2D-DSA images generated from individual projections from a rotational x-ray acquisition with a 3D image reconstructed from substantially all of the projection views acquired during the rotational x-ray acquisition. These DSA images may have a spatial resolution on the order of 5123 pixels and a temporal resolution of about 30 frames per second, which represents an increase over traditional 3D-DSA frame rates by a factor of between 150 and 600.
Owner:MISTRETTA MEDICAL +1
Orthopedic robot navigation device and positioning system
ActiveCN101700184BSolve the problem of errors caused by inaccurate positioningAvoid blocking interferenceProgramme-controlled manipulatorSurgical robotsEngineeringSelf positioning
The invention relates to an orthopedic robot navigation device and a positioning system. The orthopedic robot navigation device comprises a machine seat and a four-freedom degree biplane positioning mechanism, wherein the four-freedom degree biplane positioning mechanism is arranged on the machine seat and connected with the machine seat. The four-freedom degree biplane positioning mechanism comprises a first series connection mechanical arm, a second series connection mechanical arm and a straight lever-shaped guide device, wherein the first series connection mechanical arm comprises a firsthorizontal motion assembly, a first vertical motion assembly and a first cardan joint which are connected in series; the second series connection mechanical arm comprises a second horizontal motion assembly, a second vertical motion assembly and a second cardan joint which are connected in series; both the first horizontal motion assembly and the second first horizontal motion assembly are connected with the machine seat; and the straight lever-shaped guide device realizes the self positioning by being clamped with the first cardan joint and the second cardan joint respectively. The device isarranged at the side surface of the wounded limb, realizes the accurate positioning by the straight lever-shaped guide device and is suitable for a bone fixing operation of any wounded limb part, thereby more favorably meeting the requirement of the operation.
Owner:BEIJING TINAVI MEDICAL TECH
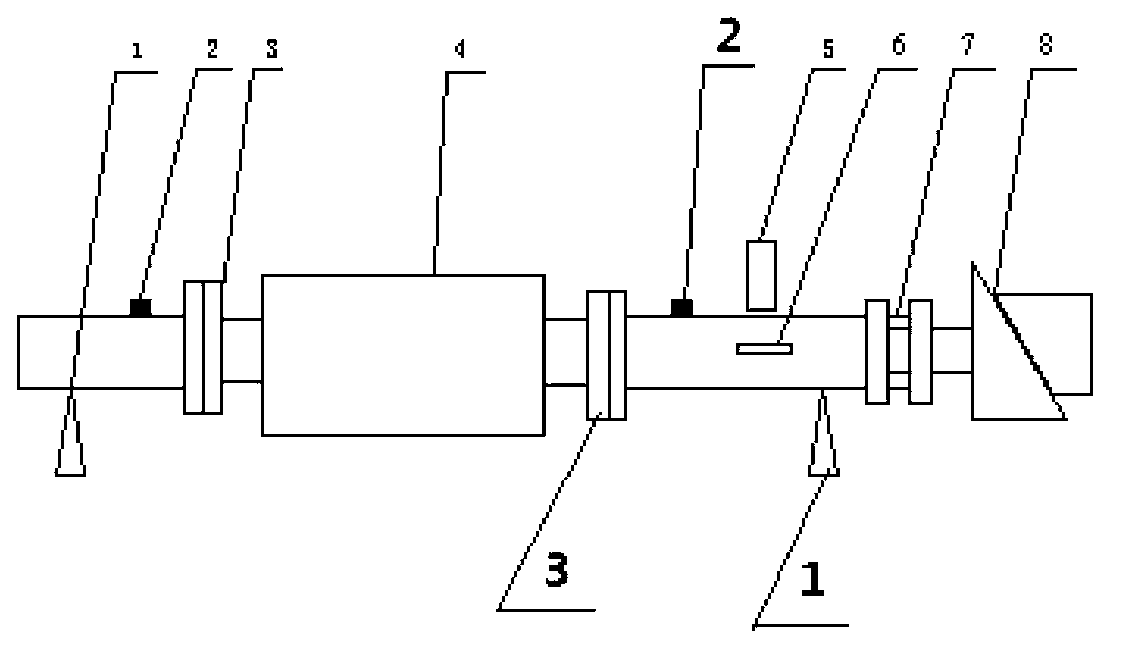
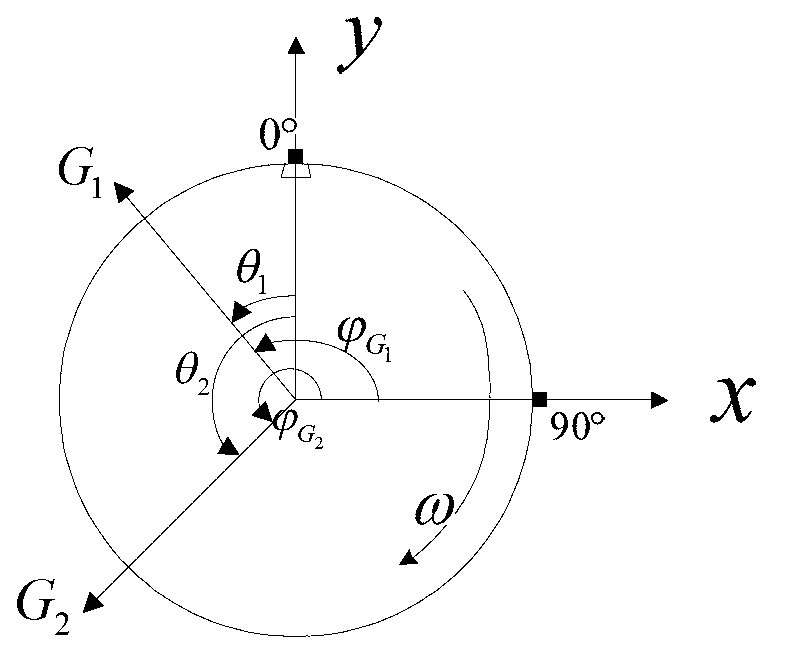
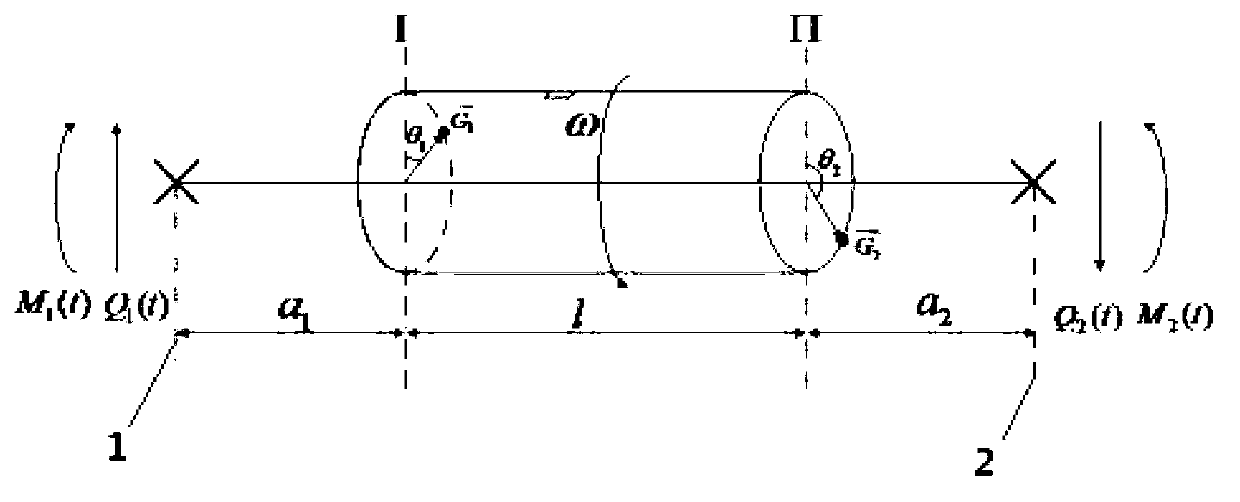
Dynamic balance method of bending moment of rotating mechanical rotor biplane
The invention discloses a dynamic balance method of the bending moment of a rotating mechanical rotor biplane. The unbalanced correction of the rotator biplane is achieved by testing the bending moment in the rotating process of the rotor. The dynamic balance method does not need to test mass, the unbalance force and corresponding angles on the rotor biplane can be directly calculated by testing the bending moment. The dynamic balance method is an on-line dynamic balance method, and has the advantages of being fast and convenient, and capable of achieving mass operation of the dynamic technique of the rotating mechanical rotor biplane. A rotor dynamic balance theory needed to be commanded is low, and the method is suitable for most technical staff.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Biplane X-ray imaging system
InactiveUS8611495B2Improve image qualityImprove visualizationImaging devicesX-ray apparatusConventional X-RayX-ray
A biplane X-ray imaging system is provided. The biplane X-ray imaging system has two recording units disposed in different planes. Each of the recording units has an X-ray detector and an X-ray source. The first recording unit is a phase-contrast recording unit for phase-contrast X-ray imaging. The second recording unit is a conventional recording unit for conventional x-ray imaging.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
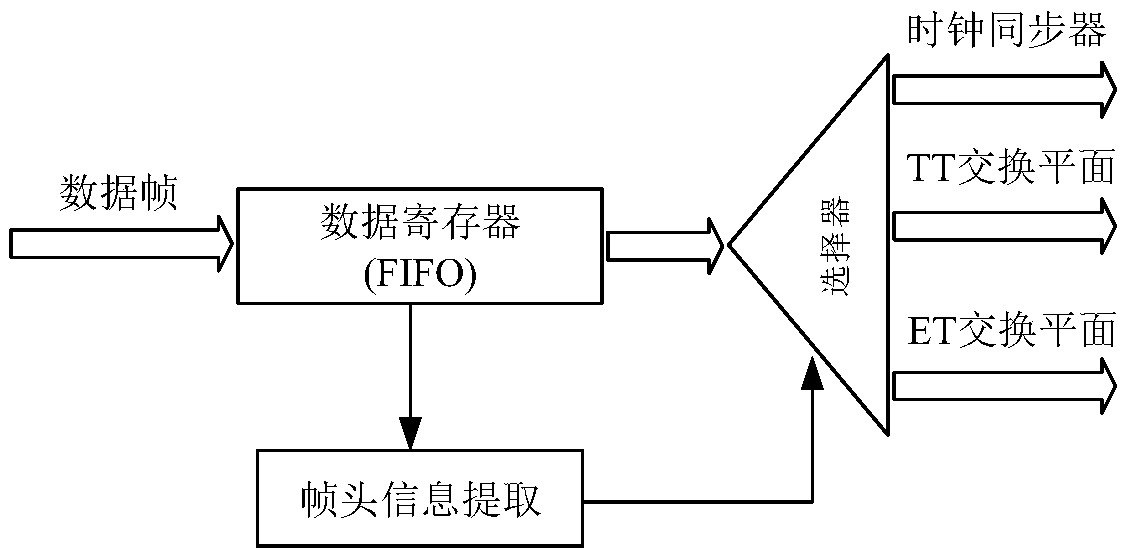
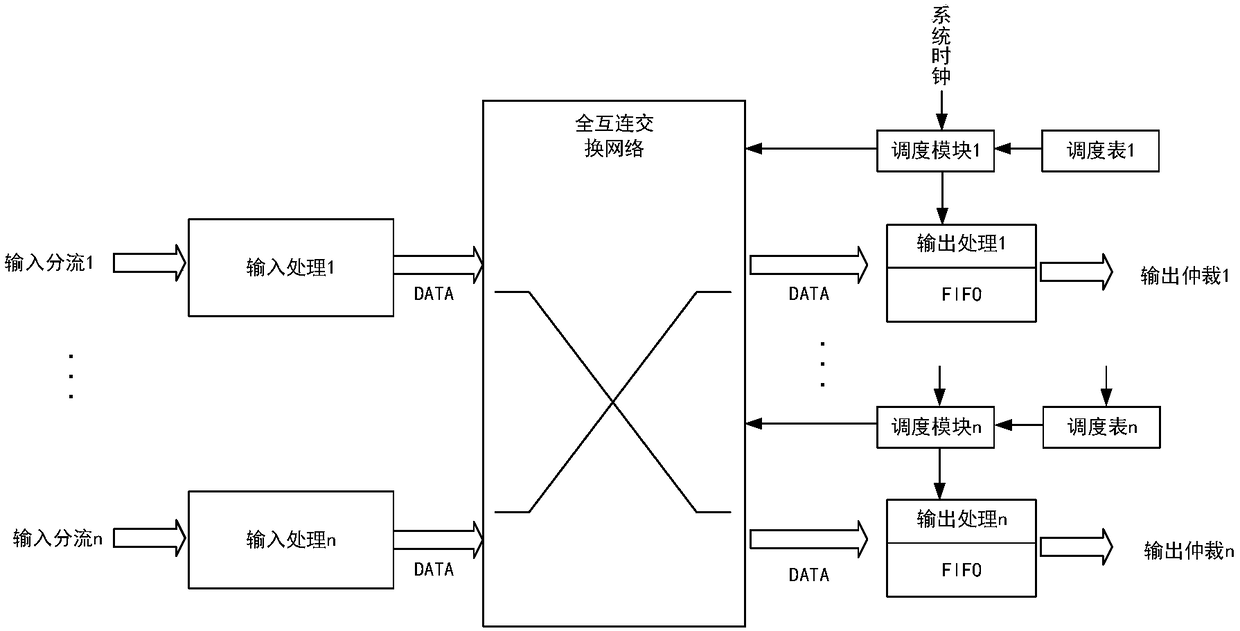
Time-triggered Ethernet switch based on biplane and packet switching method
ActiveCN108712351AReduce forwarding delayGuaranteed absolute priority forwardingTime-division multiplexData switching networksExchange networkEvent triggered
The invention discloses a time-triggered Ethernet switch based on a biplane and a packet switching method, which mainly solve the problem that the deterministic and real-time performances of the existing time-triggered Ethernet switch forwarding a time-triggered TT service are poor. The device comprises an input shunting module (1), a clock synchronizer (2), a time-triggered TT switching plane (3), an event-triggered ET switching plane (4) and an output arbitration module (5). The input shunting module is respectively connected with the clock synchronizer, the TT switching plane, and the ET switching plane, to complete switch clock synchronization and to forward the TT service frame and the ET service frame respectively; the TT switching plane and the ET switching plane are both connectedwith the output arbitration module to select a service frame which is preferentially sent and to complete sending of data. The time-triggered Ethernet switch based on a biplane and the packet switching method in the invention can ensure absolute priority forwarding of the time-triggered TT service, reduce the forwarding delay of the time-triggered TT service, and can be applied to a time-triggeredswitching network with high speed and low delay.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
High tibial biplane osteotomy navigation guide plate
PendingCN108635016AShorten recovery timeEliminate differentiation of experienceBone drill guidesPostoperative complicationTibia
An embodiment of the invention discloses a high tibial biplane osteotomy navigation guide plate. The guide plate comprises an upper split guide plate and a lower split guide plate which are fixedly connected by two connecting rods. An osteotomy guide groove is formed between the upper split guide plate and the lower split guide plate. Two non-parallel kirschner wire fixing guide holes are formed in the middles of the upper split guide plate and the lower split guide plate. Parallel guide holes are formed in the upper part of the upper split guide plate. One side of the upper split guide plateis provided with an angle guide backup plate. The upper split guide plate and the lower split guide plate are respectively provided with an upper angle positioning rod and a lower angle positioning rod in a vertical corresponding mode, and the end portions are respectively connected with an upper angle positioning guide hole and a lower angle positioning guide hole. The guide plate can not only eliminate the difference between experiences of doctors in a surgery, but also greatly reduce the operation time and the amount of bleeding during the surgery to achieve the best ideal state of osteotomy. The recovery time of a patient is greatly reduced, postoperative complications are reduced, and expenses in the recovery period are saved.
Owner:武汉嘉一三维技术应用有限公司
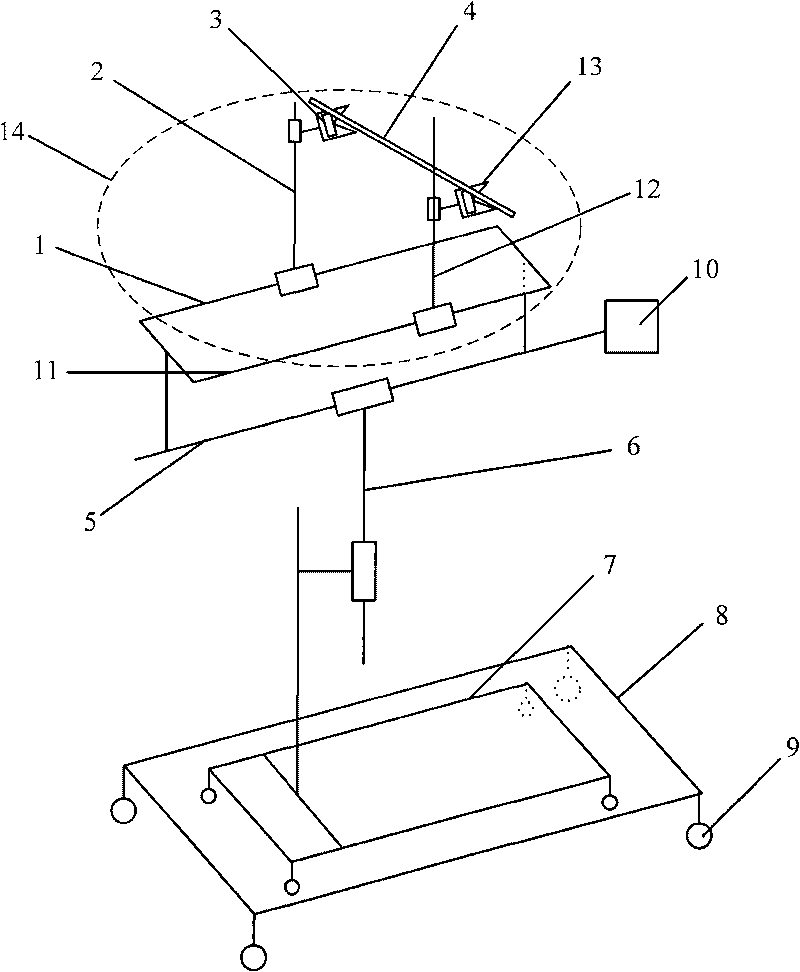
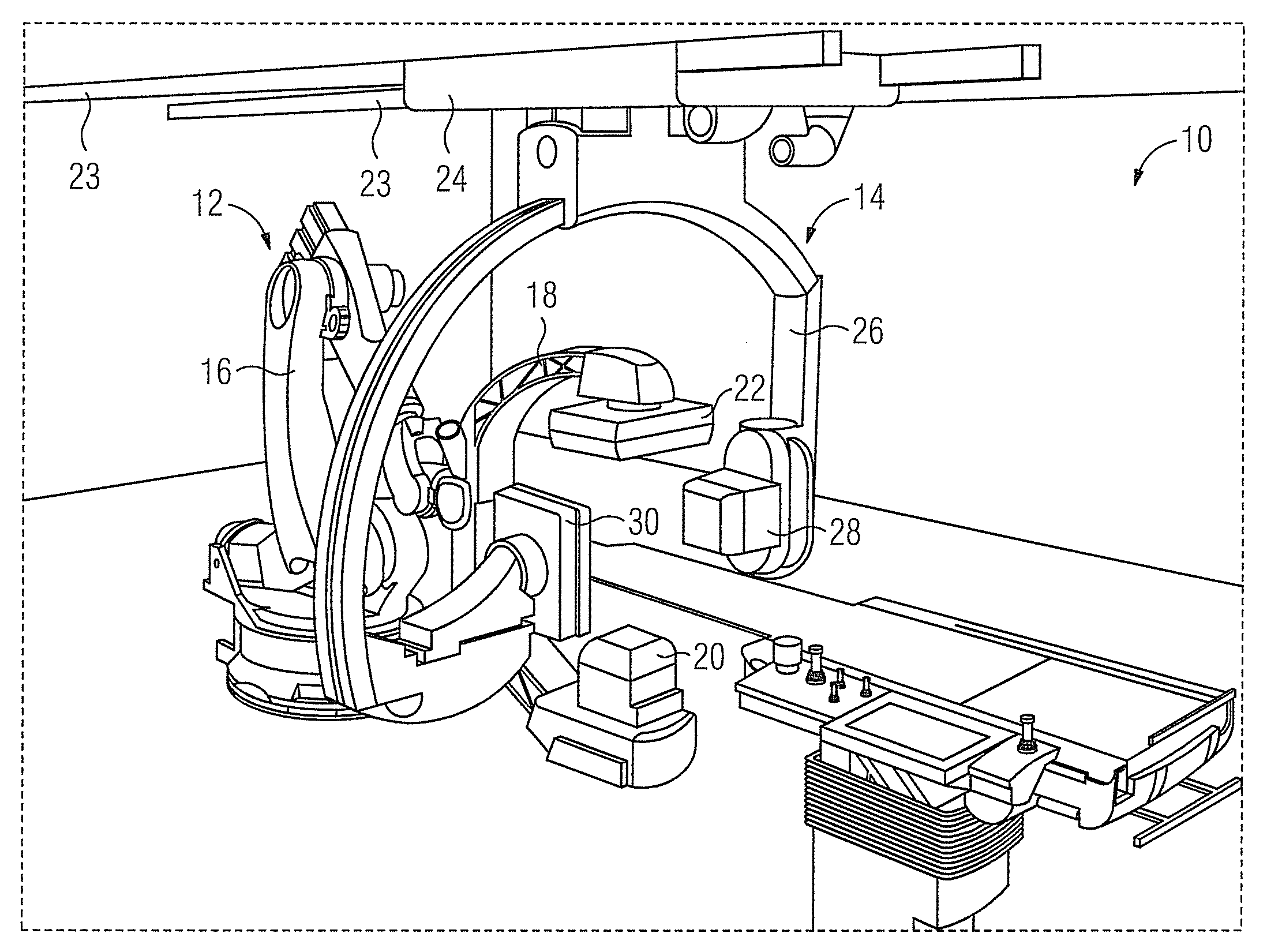
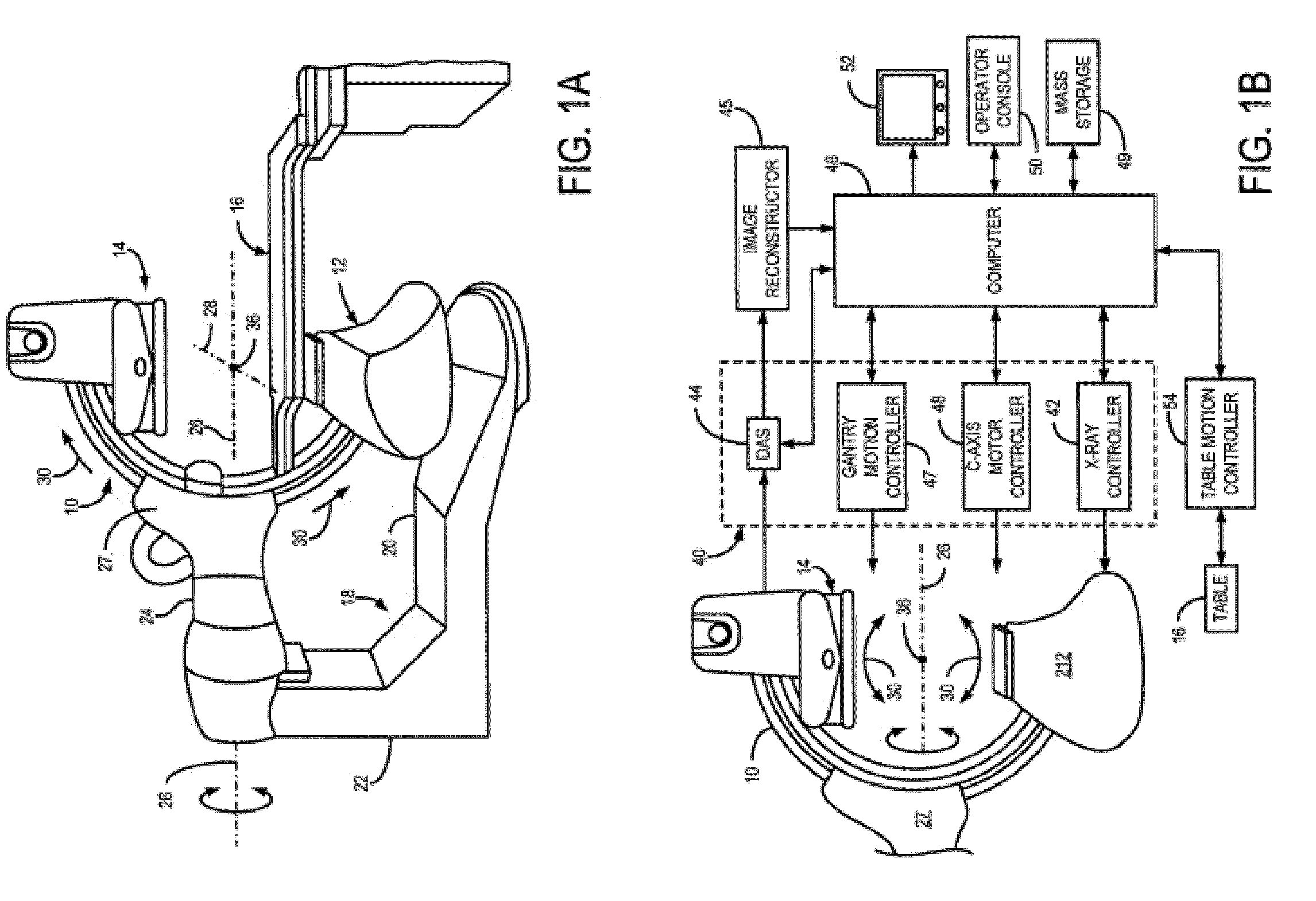
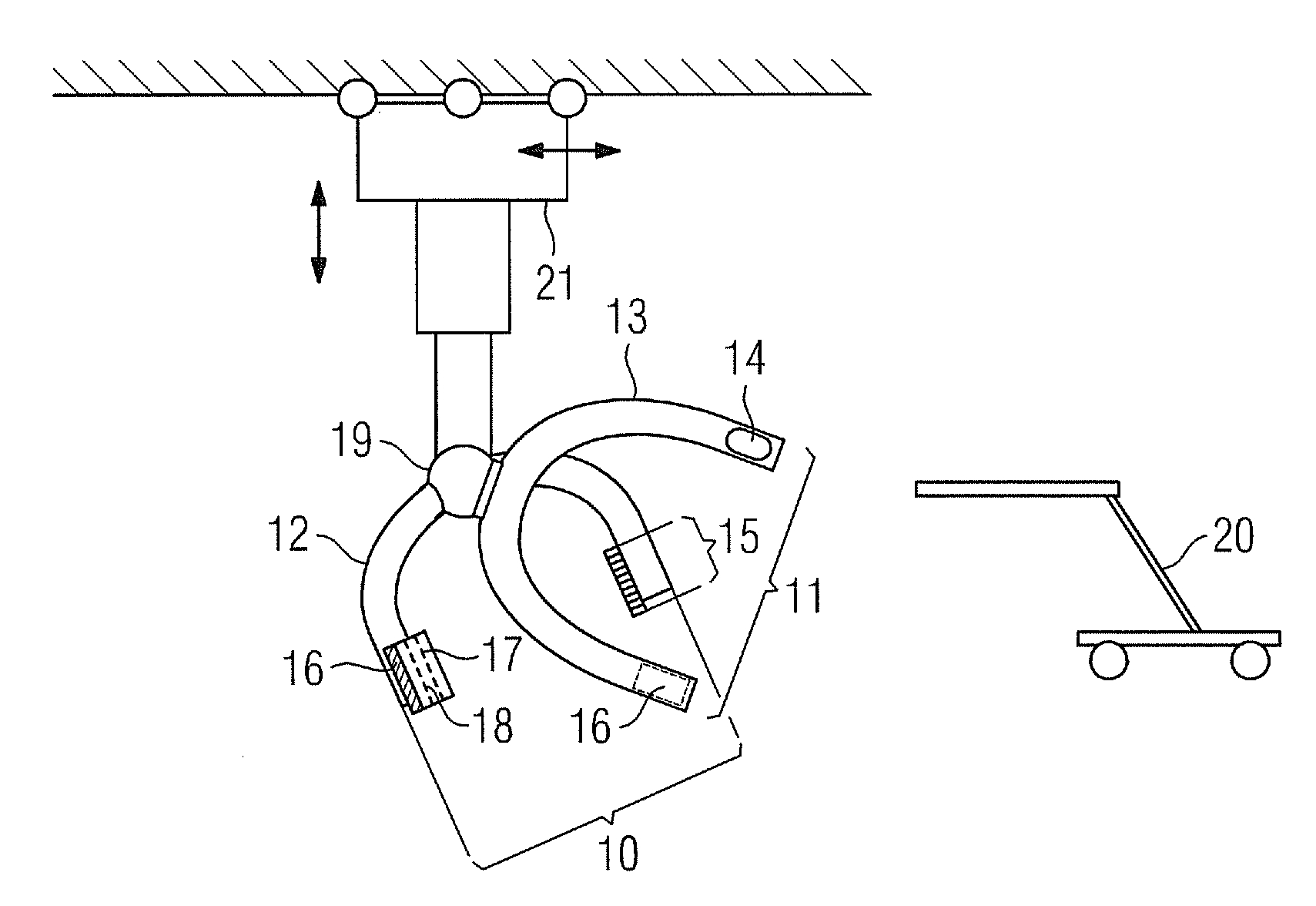
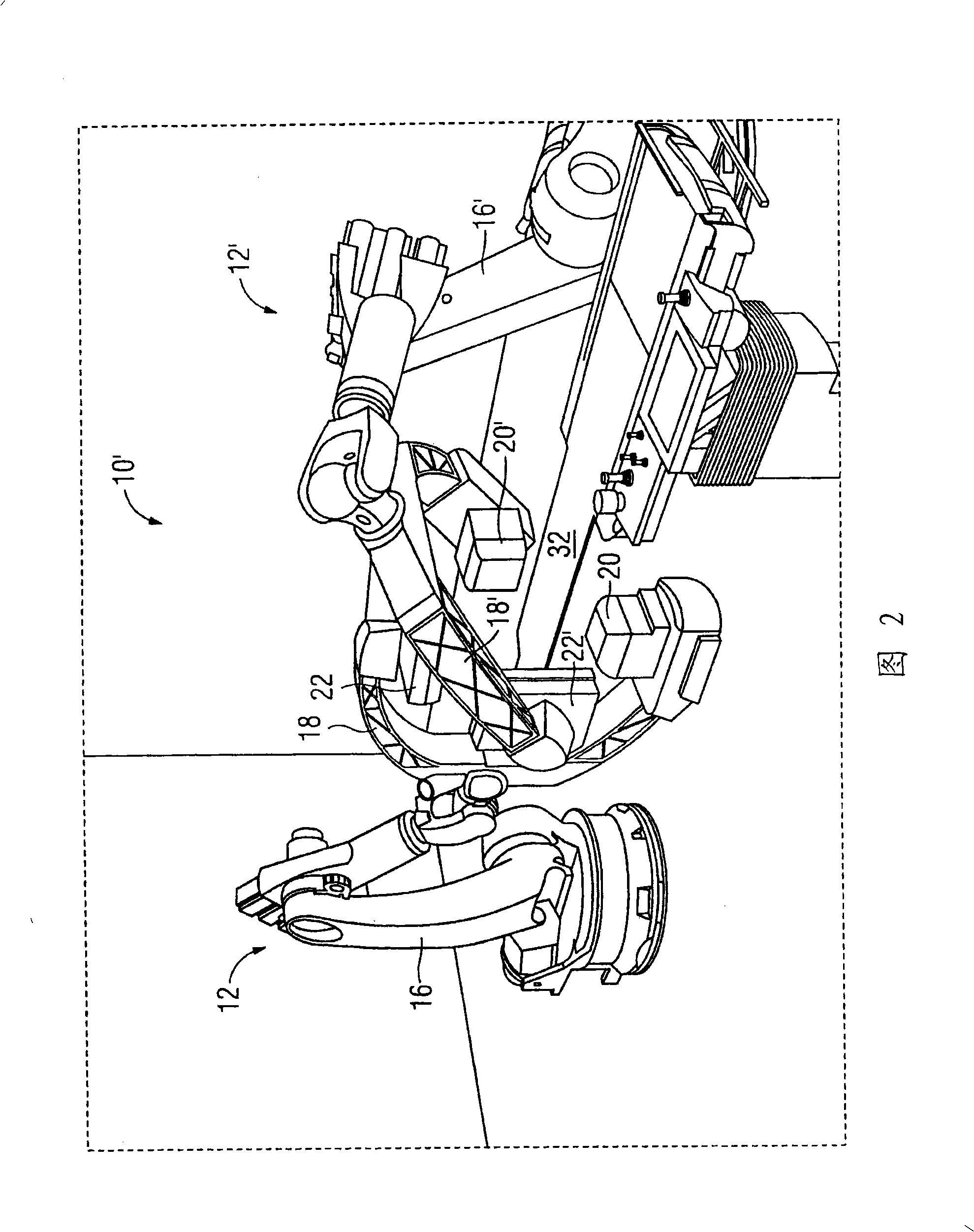
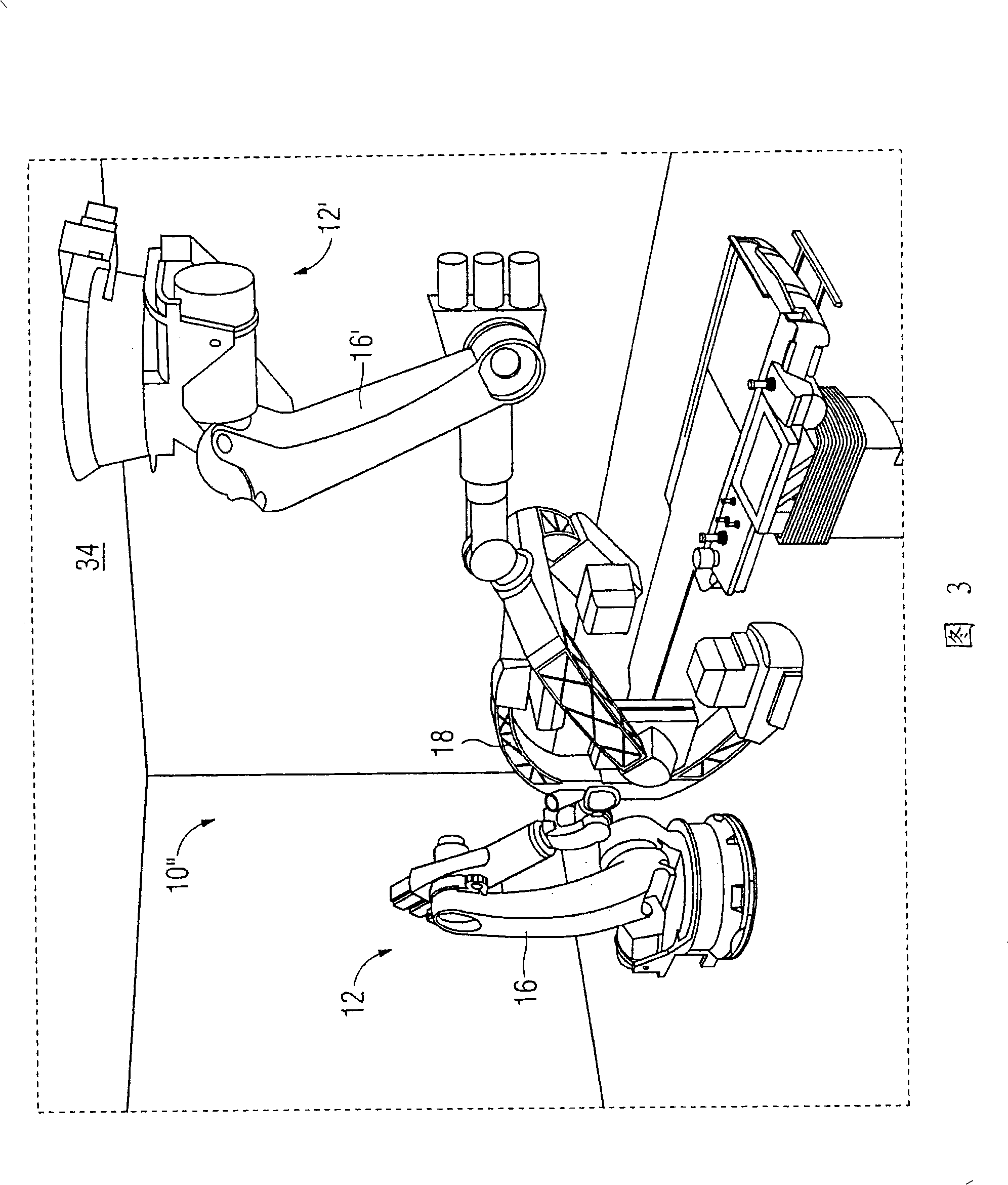
Biplane x-ray system
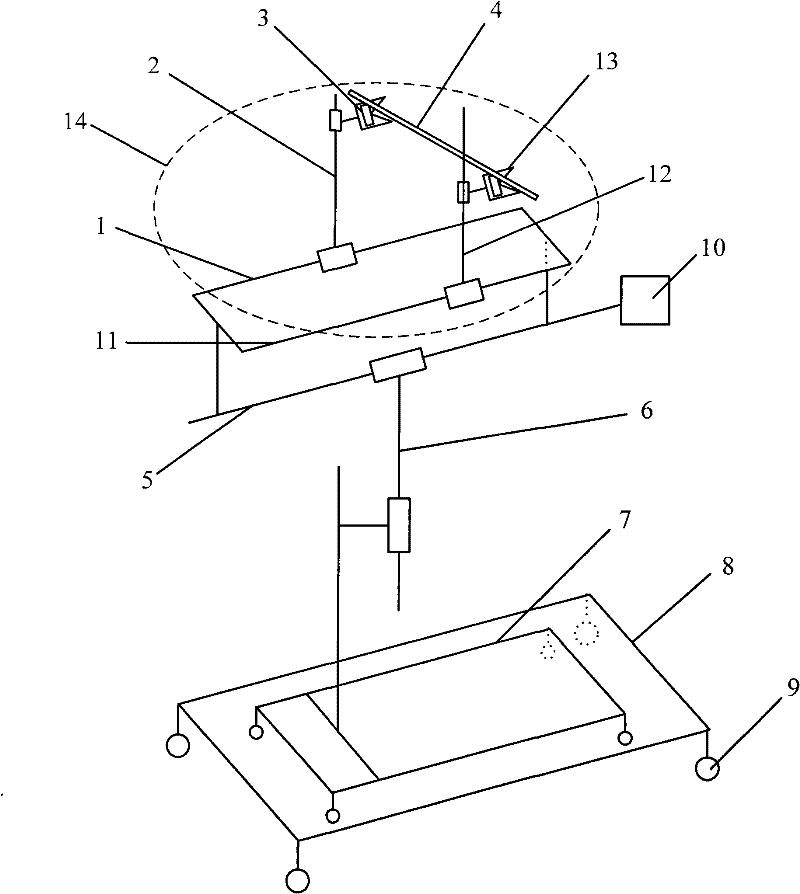
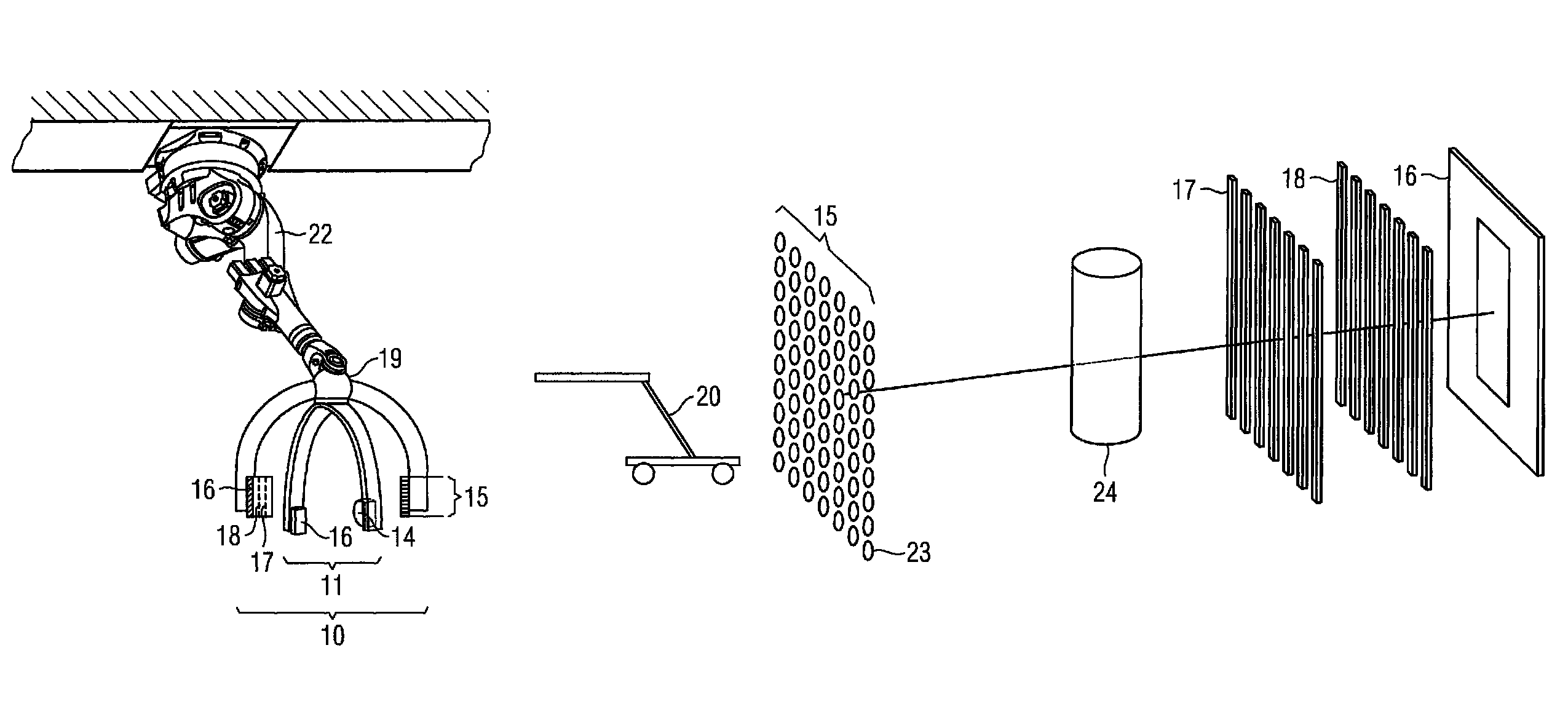
The invention discloses an X ray double surface equipment, in which, a robot (16) is adopted for moving at least one pair of X ray radioactive source (20) and X ray detector (22). The robot can be a crank arm robot (16) with a X ray C shaped arm. The X ray radioactive source (40) and the X ray detector (42) can be suspended on the roof (34) of the room by the robot arms (36, 38).
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Biplane ultrasound-guided radioactive seed implantation system for prostates
PendingCN108670375AShorten operation timeEasy to operateSurgical needlesX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapySagittal planeUniversal joint
The invention discloses a biplane ultrasound-guided radioactive seed implantation system for prostate. The system comprises a fixing seat, a supporting column, a universal joint arm, a fixing clip, astepper and an implantation template, wherein the stepper comprises a main frame, one end of the main frame is fixedly connected with a template supporting frame, and a scale ruler is arranged on theside wall of the main frame; a hollow lead screw of a coarse-fine adjustment mechanism is arranged in the main frame, and a first angle line is arranged on a rotating frame of a clamp; the template supporting frame is movably connected with the implantation template, and a second angle line and an angle value are arranged on the implantation template; the second angle line on the implantation template corresponds to the first angle line on the stepper, and the position of a puncture needle corresponding to a sagittal plane scanning image is quickly determined by adjusting the sagittal plane scanning angle of a biplane ultrasonic probe, so that operation time is shortened; coarse and fine adjustment units of the coarse-fine adjustment mechanism are coaxial, operation can be performed conveniently and quickly with only one hand during the operation, and operation efficiency is improved; the system is flexible and simple to operate, can be sterilized at high temperature, and is easy to disassemble and assemble and convenient to carry and store.
Owner:天津赛德生物制药有限公司
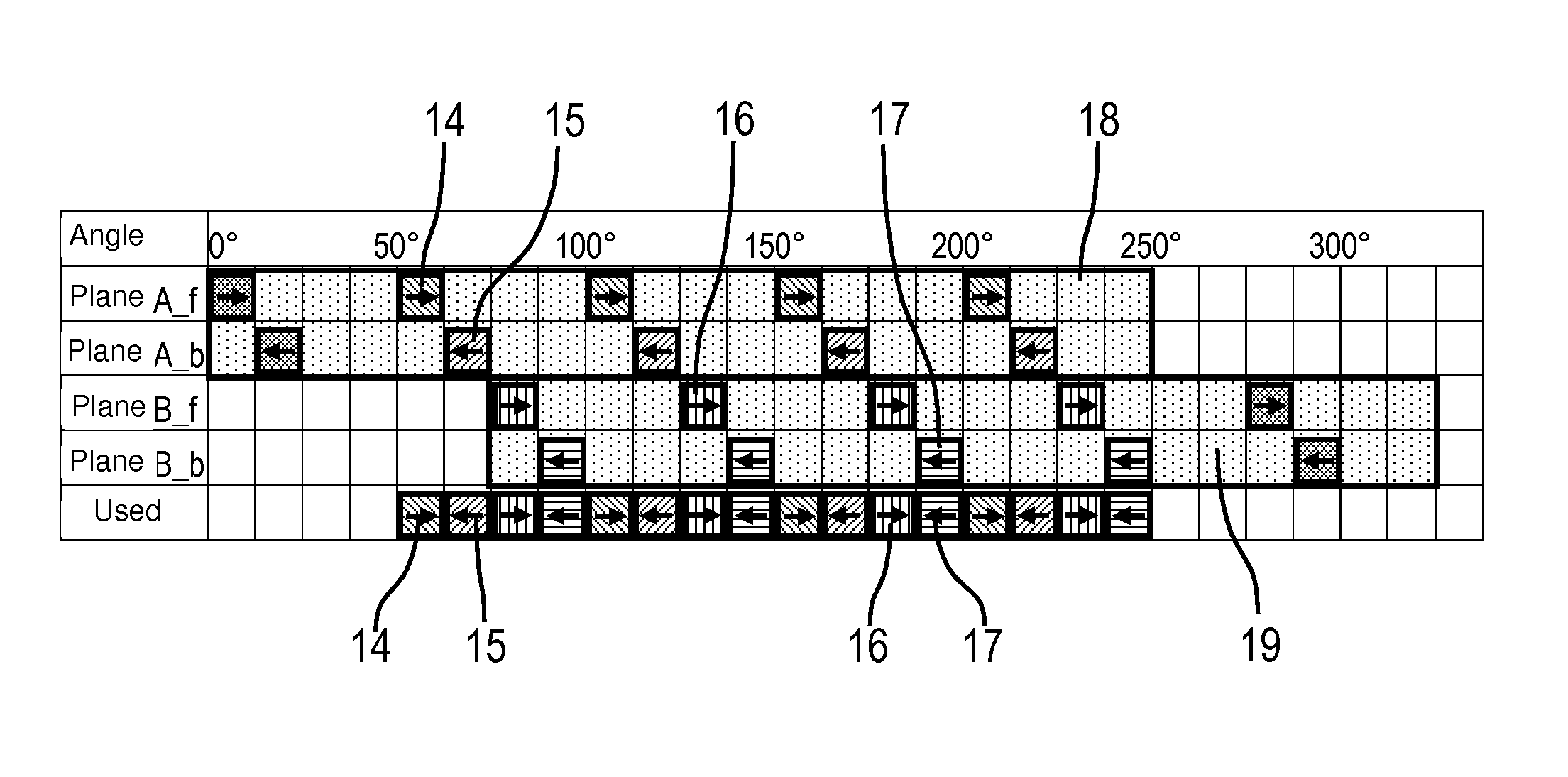
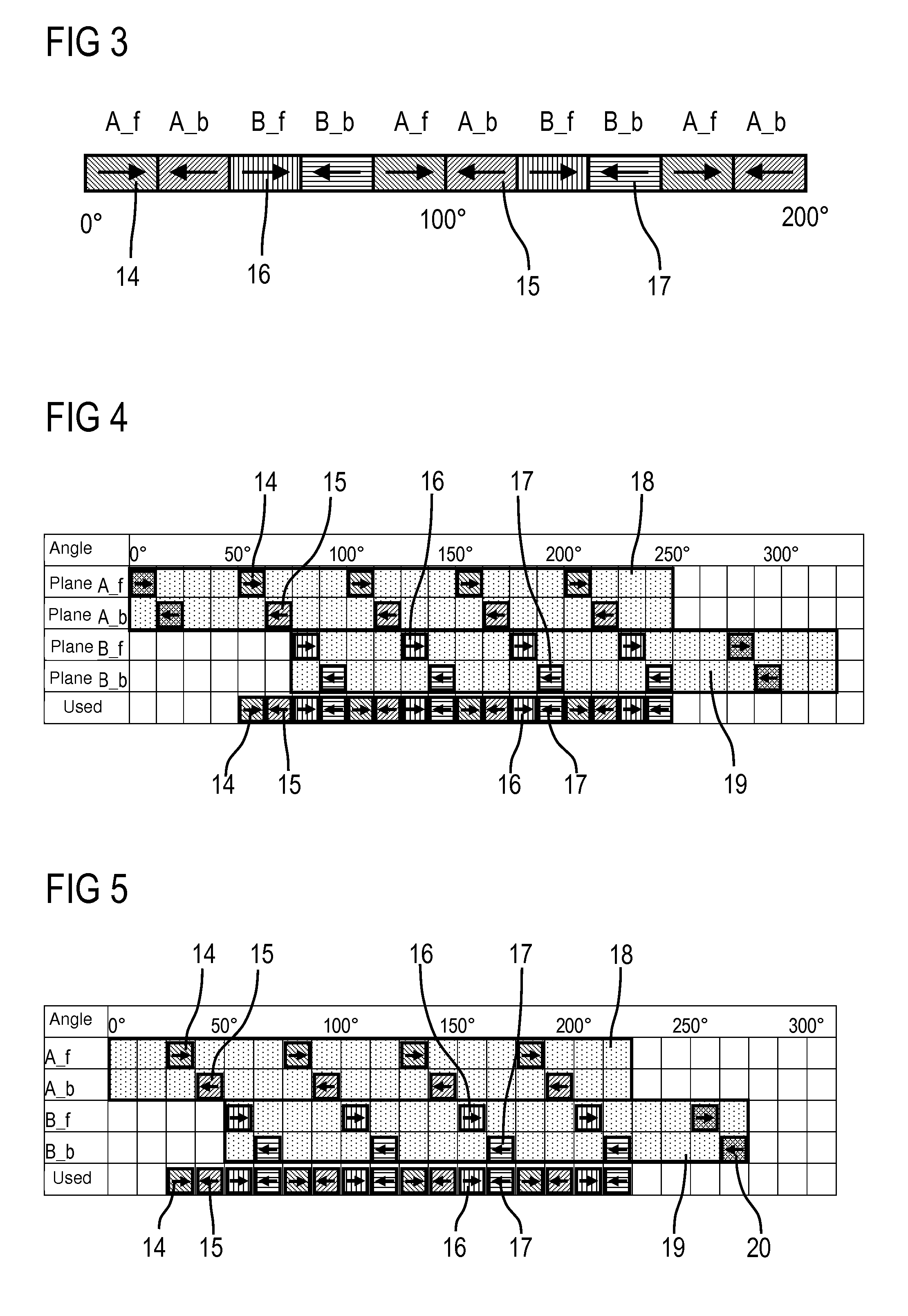
Method for 3-D data collection with a biplane C-arm system with biplane acquisition multiplexing
ActiveUS8538505B2Reduce acquisition timeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingMultiplexingCardiac phase
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Wing-changeable airplane
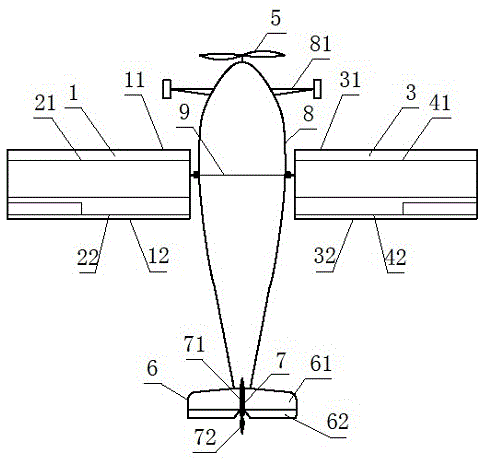
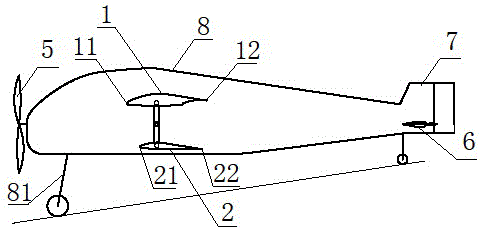
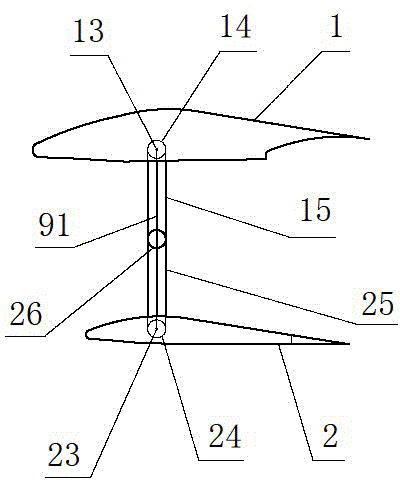
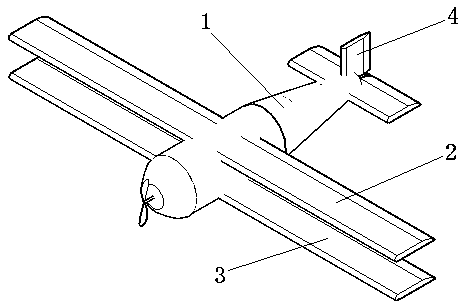
The invention relates to a wing-changeable airplane, belonging to the technical field of spacecraft instrumentation. The wing-changeable airplane comprises an upper wing, a lower wing, a tail fin, a power device, an undercarriage and an airplane body, wherein the left section of the upper wing, the left section of the lower wing and a left transmission mechanism form a left wing assembly; the right section of the upper wing, the right section of the lower wing and a right transmission mechanism form a right wing assembly; the left wing assembly and the right wing assembly are the same in structure and are symmetrically distributed at the left side and the right side of the airplane body; a middle axle rotates to drive a left rotating arm and a right rotating arm to rotate simultaneously to control the upper wing and the lower wing to be closed or opened under the control of a control system, when the upper wing and the lower wing are closed, the airplane is a monoplane; and when the upper wing and the lower wing are opened, the airplane is changed to be a biplane; the monoplane mode is suitable for cruising and has high efficiency; and the biplane mode is suitable for short-distance taking off and landing or ultra-low-speed flight. The wing-changeable airplane is suitable for low-speed flight, is suitable for being used as a training airplane, and has multiple purposes, and the cost is also saved.
Owner:TIANJIN JINHANG COMP TECH RES INST
Deformation biplane
Owner:FOSHAN SHENFENG AVIATION SCI & TECH
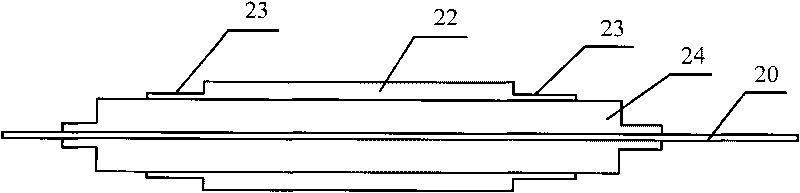
Millimeter wave one-dimensional single-pulse biplane reflecting antenna
InactiveCN104466429AImprove Radiation PerformanceReduce vertical sizeWaveguide hornsMillimetre waveCross polarization
The invention relates to a millimeter wave one-dimensional single-pulse biplane reflecting antenna. The millimeter wave one-dimensional single-pulse biplane reflecting antenna comprises a polarization grid reflecting board, a polarization twist and focusing reflecting board and a feed source, wherein the polarization twist and focusing reflecting board is located below the polarization grid reflecting board and is electrically insulated from the polarization grid reflecting board; the feed source is arranged in the center of the polarization twist and focusing reflecting board and penetrates through the polarization twist and focusing reflecting board. The millimeter wave one-dimensional single-pulse biplane reflecting antenna has the advantages that on the condition of ensuring the performance, the longitudinal dimension is effectively decreased. The feature of a low section is achieved, the purpose of reducing the overall dimension is achieved, in addition, the feed source shielding effect can be effectively avoided, the overall radiation performance of the antenna is improved, the polarization purity can be effectively improved, the cross-polarization rejection ratio can be greatly improved by adjusting the dimension of a polarization grid of an upper polarization grid layer, and therefore higher polarization purity is obtained.
Owner:北京东方安高微电子科技有限公司
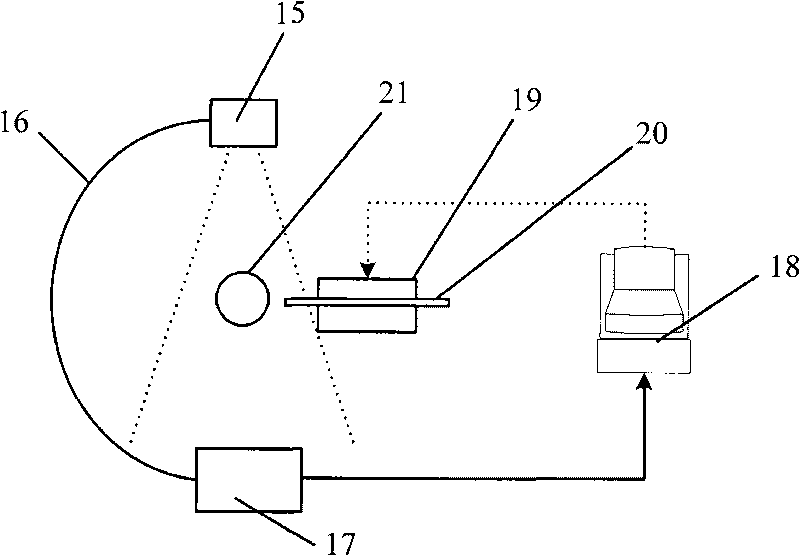
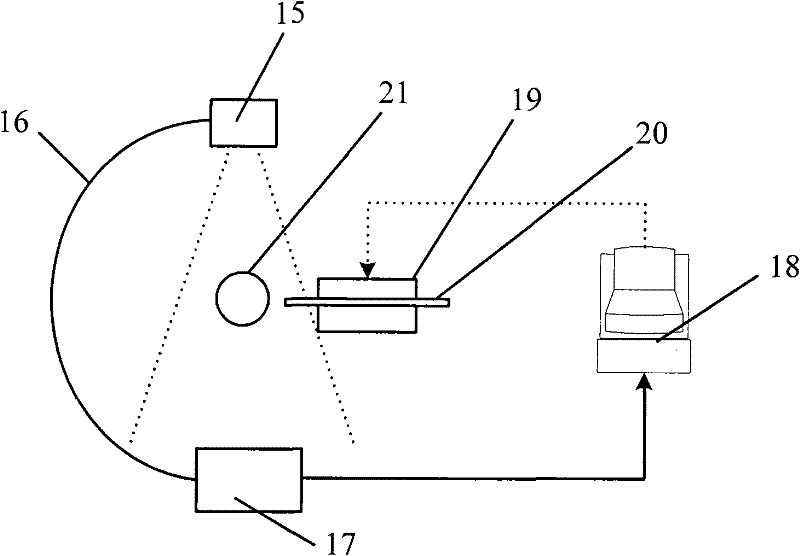
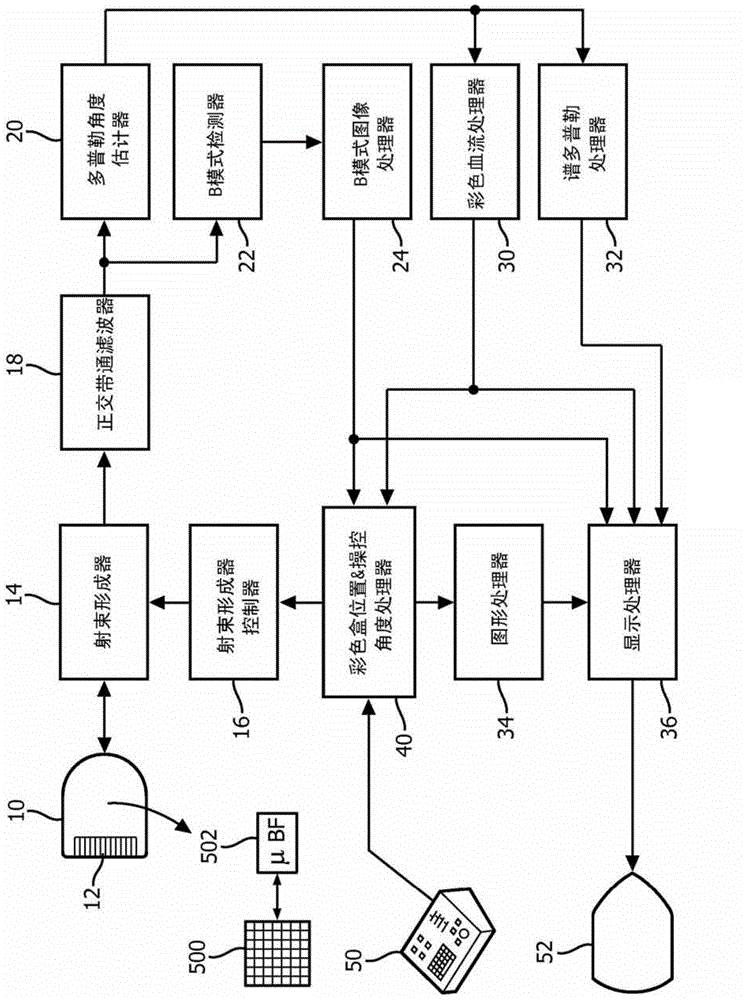
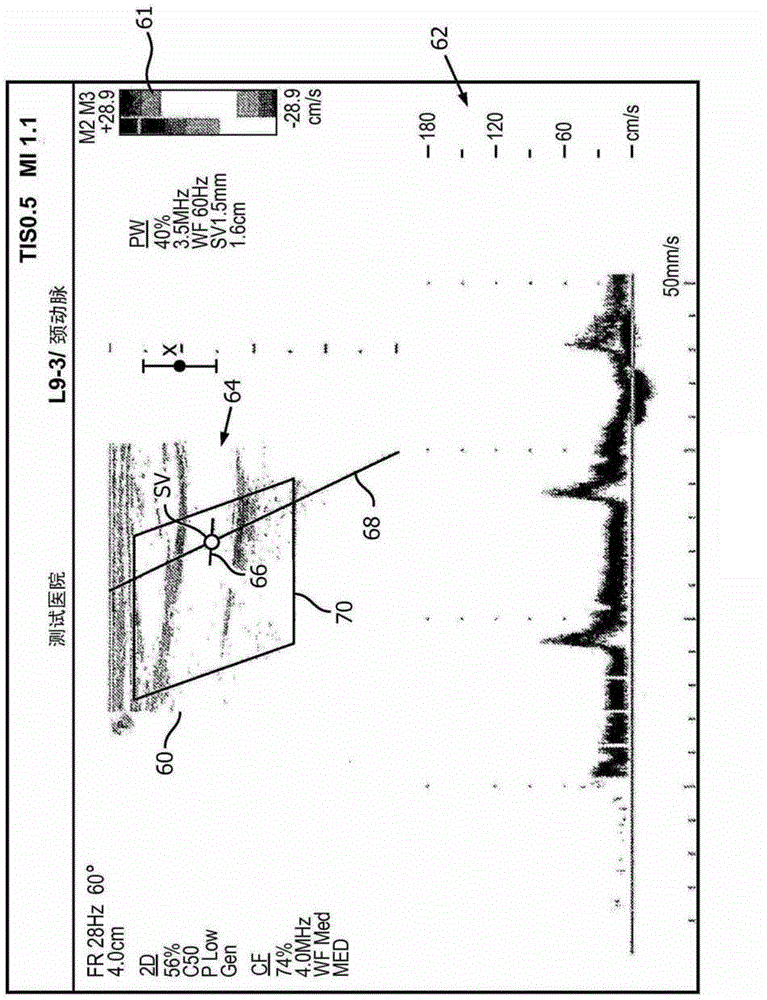
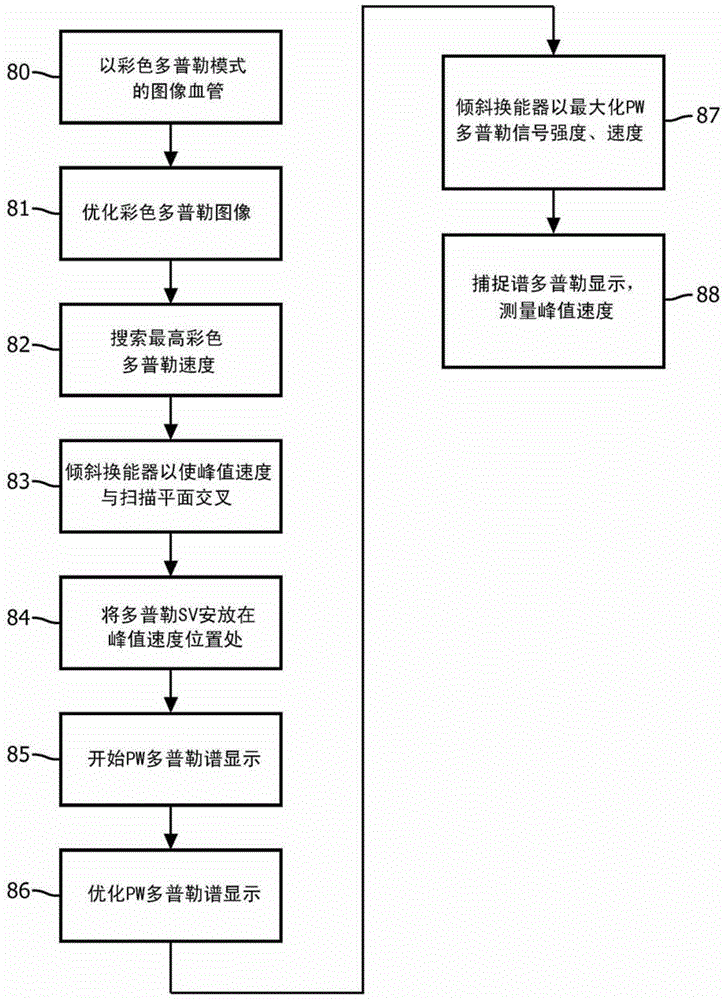
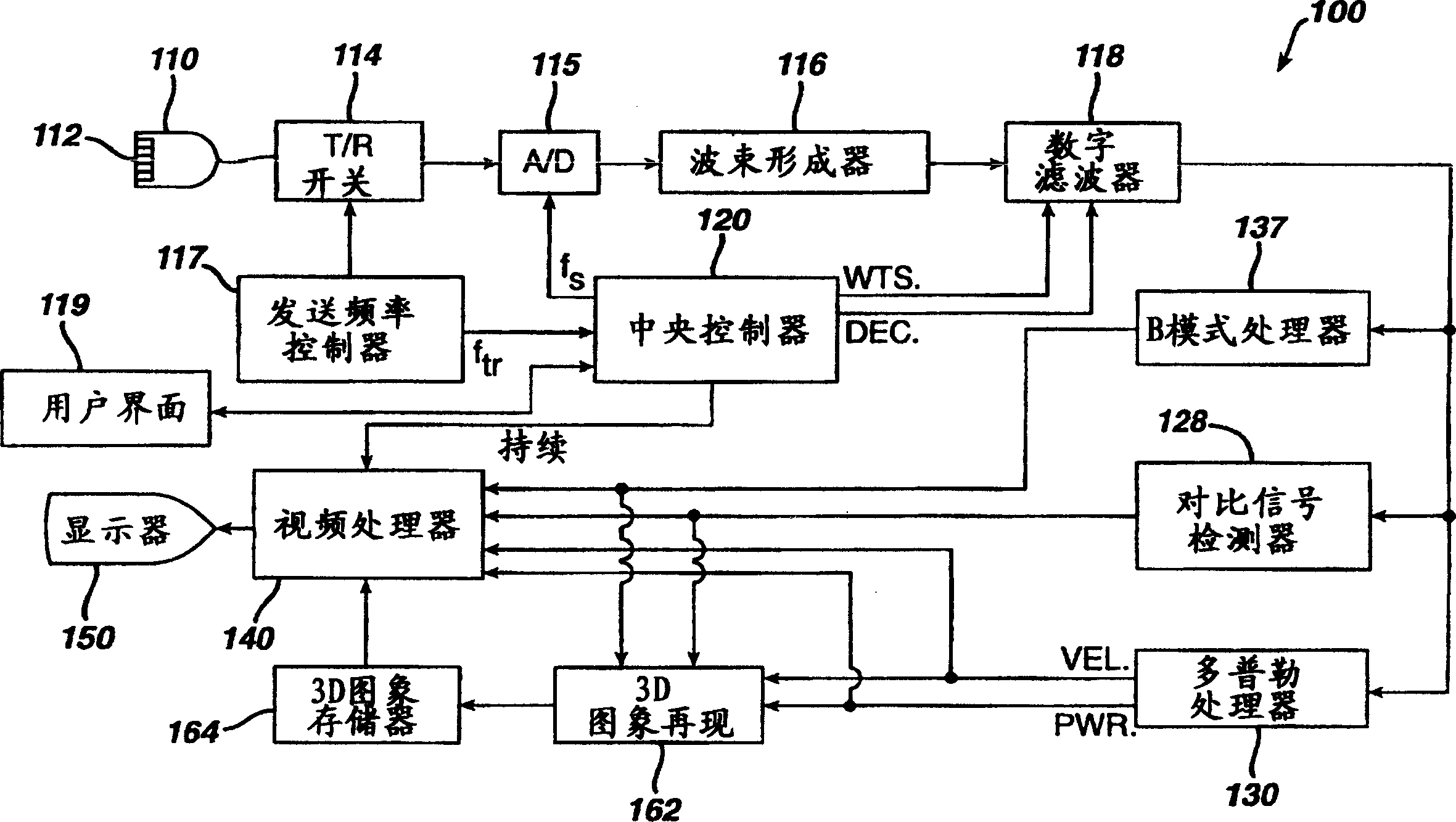
Automated biplane-pw workflow for ultrasonic stenosis assessment
An ultrasound system with a matrix array (500) probe (10) operable in the biplane mode is used to assess stenosis of a blood vessel by simultaneously displaying two color Doppler biplane images (60a, 60b) of the vessel, one a longitudinal cross-sectional view (60a) and the other a transverse cross-sectional view (60b). The two image planes intersect along a Doppler beam line (68) used for PW Doppler. A sample volume graphic (SV) is positioned over the blood vessel at the peak velocity location in one image, then positioned over the blood vessel at the peak velocity location in the other image. As the sample volume location is moved in one image, the plane and / or sample volume location of the other image is adjusted correspondingly. Spectral Doppler data (62) is then acquired and displayed from the sample volume location.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
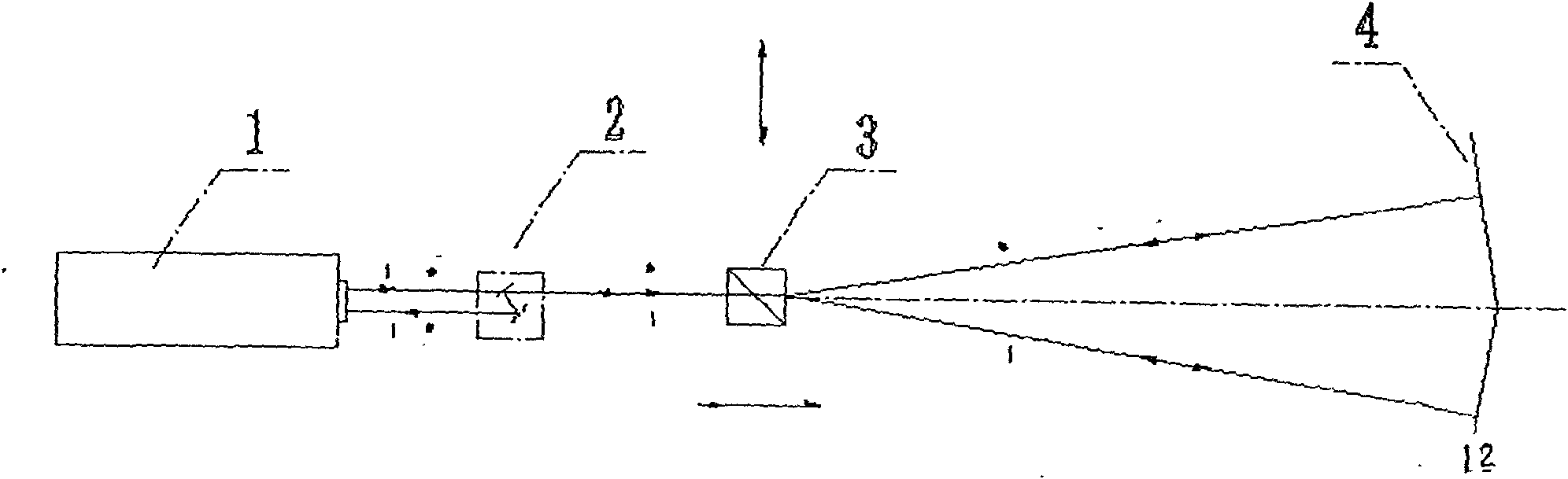
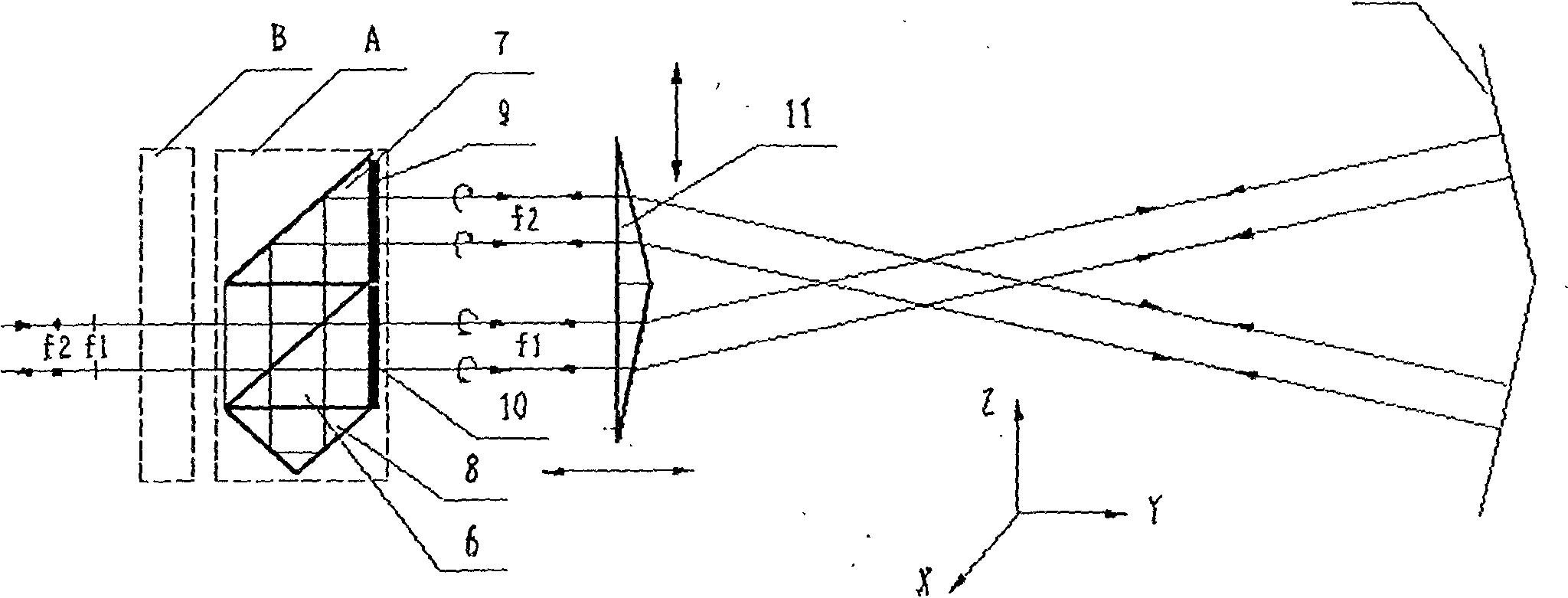
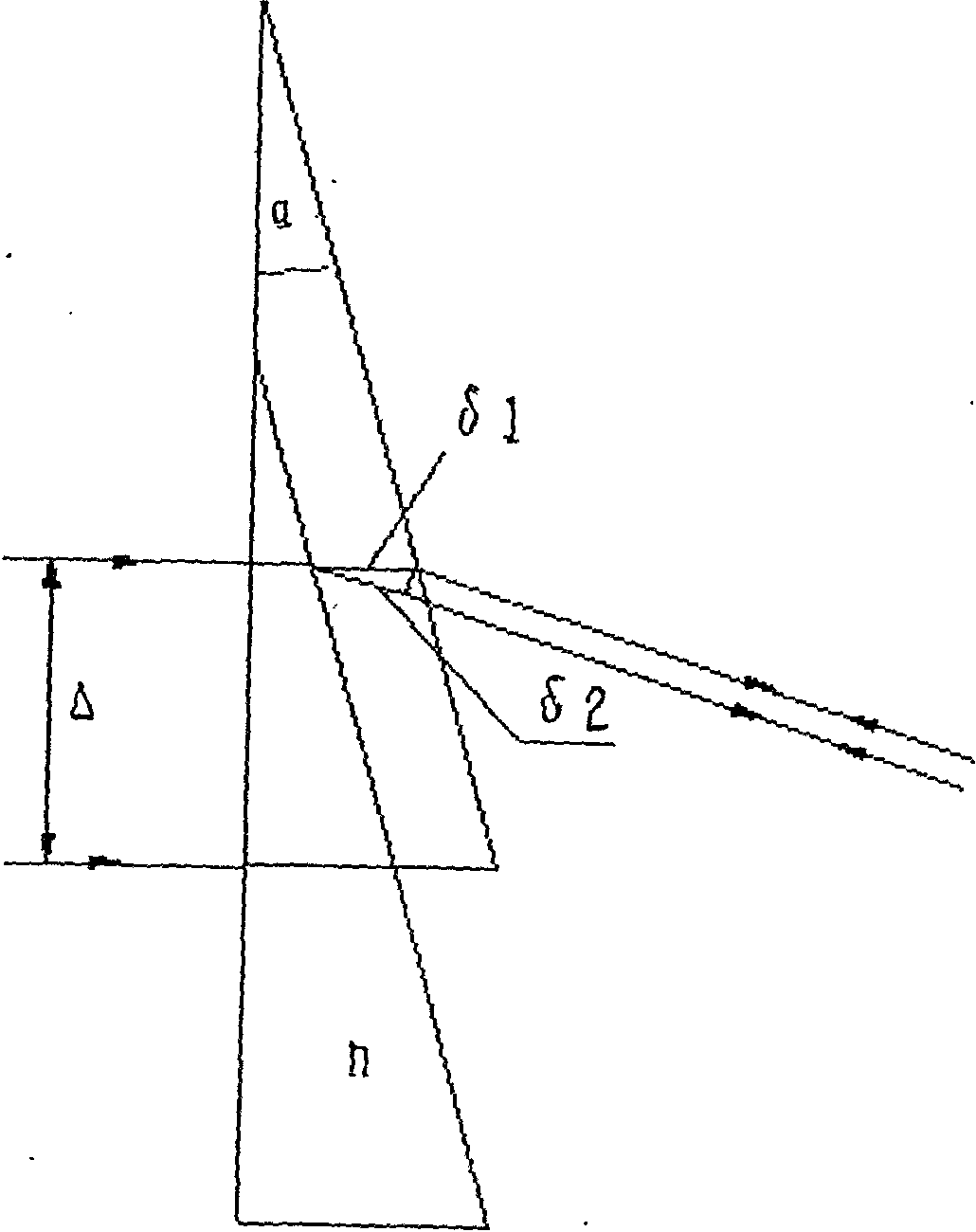
Laser straightness interferometer light path system
InactiveCN101881606AShorten the lengthHigh measurement sensitivityUsing optical meansBeam splitterPrism
The invention relates to a laser straightness interferometer light path system which solves the problem of low measuring sensitivity of the traditional straightness interferometer. The laser straightness interferometer light path system comprises a laser head (1), an assembly (A), a double optical wedge (11) and a biplane reflecting mirror (12). The assembly (A) is formed by binding a polarizing beam splitter (6), a reflecting mirror (7), a pyramid prism (8) and quarter wave plates (9) and (10) into an integer. The double optical wedge (11) is formed by binding an upper wedge and a lower wedge, and the bottom surface of the upper wedge is opposite to that of the lower wedge. f1 light and f2 light emitted by the laser head (1) respectively pass through the upper wedge and the lower wedge of the double optical wedge (11) after beam splitting by the assembly (A), vertically irradiate the two reflecting planes of the biplane reflecting mirror (12), and go back the same way. A measured object and the double optical wedge (11) move along the Y direction; when a displacement is generated in the Z direction, i.e. a straightness error exits, the f1 light and the f2 light produce opposite optical path differences, and thus, the straightness error value can be calculated out. The invention has high measuring sensitivity, compact structure, low cost and convenient assembly.
Owner:CHENGDU TOOL RES INST
Method for measuring electric parameter of gallium arsenide pseudomorphic HEMT (high electron mobility transistor) material
InactiveCN102313835ASolve the cumbersome operationLow efficiencyResistance/reactance/impedenceCurrent density measurementsSemiconductor materialsMeasurement device
The invention discloses a method for measuring an electric parameter of a gallium arsenide pseudomorphic HEMT (high electron mobility transistor) material and relates to a method for measuring the electric parameter of a semiconductor material. The method is used for measuring a carrier concentration and a mobility in the gallium arsenide pseudomorphic HEMT material by a non-contact Hall measurement method and comprises the following steps of: measuring an incident power, a reflection power and a Hall effect microwave power of the measured gallium arsenide pseudomorphic HEMT material by a microwave Hall measurement device; calculating conductance tensors of a measured sample in different magnetic fields; and calculating the carrier concentration and the mobility of the gallium arsenide pseudomorphic HEMT material. The method disclosed by the invention is nondestructive, is convenient and rapid, has high efficiency and can be used for accurately measuring the carrier concentration and the mobility in the gallium arsenide-based biplane doped pseudomorphic HEMT material. The defects that the existing measurement method is fussy to operate, has low efficiency and a certain error and cannot really and completely reflect the electrical properties of the material are overcome.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
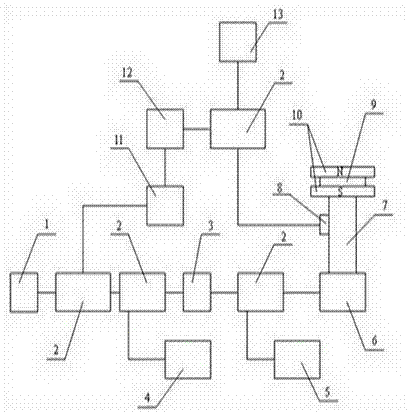
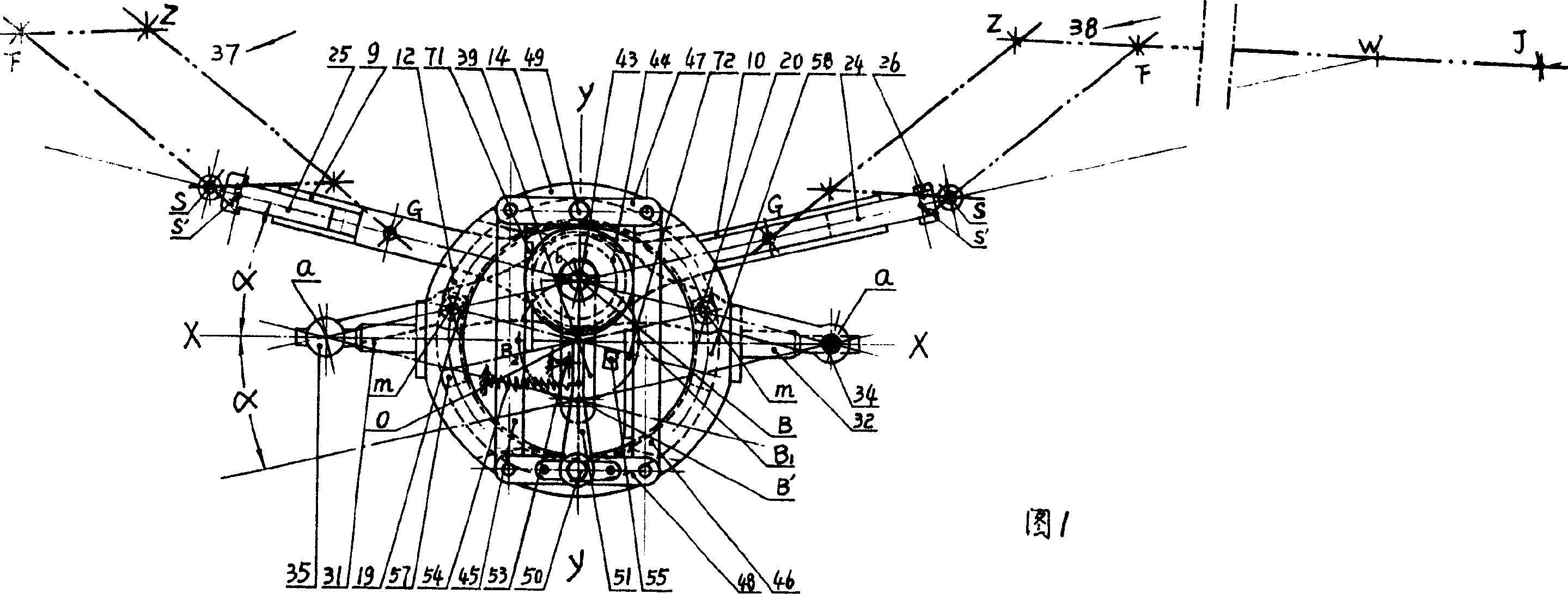
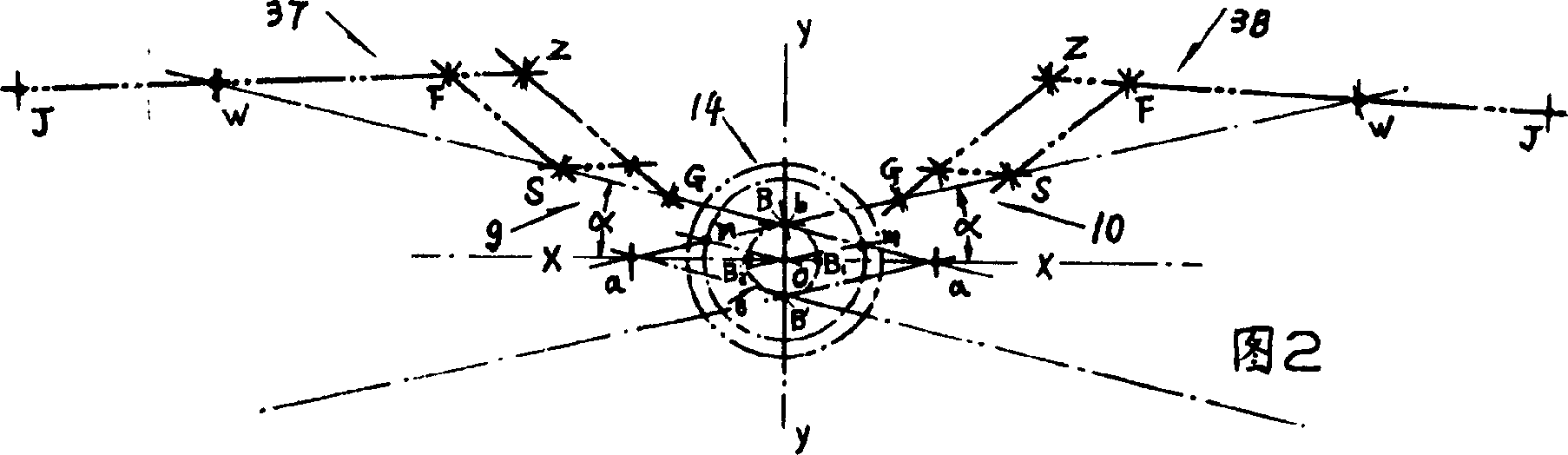
'Movable pendulum arm' and flapping-wing aircraft
InactiveCN1231391CReduce loadFlying in the sky relaxed and gracefulOrnithoptersFlapping wingFixed wing
The invention is a mechanical flapping wing flying device similar to the flying of birds and insects. The swing fulcrum a on the two driving rods is constrained on the horizontal slide rod outside the casing, the two circular trajectory points m are constrained in the inner ring groove of the casing, and the two linear trajectory points b are connected in parallel; the fixed point G on the two zoom wings is connected to the two driving rods The upper corresponding points are hinged, and the upper zoom point S of the two zoom wings is hinged with the end holes outside the staggered racks in the side slots of the two drive rods; when the drive pin is stuck, the power is input from the parallel connection to drive the wings to flutter. During the double-wing flight, the angle of the flapping wings can be changed at any time or the wings can be locked at will, and the conversion is fast and reliable. The wings can be equipped with a zoom-wing mechanism that alternately bends up and down. When the wings flap, the inertial impact at the turn-back point has double crank rollers. The mechanism absorbs and any point on the wings has alternating changes of gradual acceleration and gradual deceleration, so the flying posture is beautiful and natural. There are monoplanes and biplanes, and a variety of fixed and zooming wings. It can develop popular manned flapping-wing aircraft and unmanned flapping-wing aircraft for various purposes.
Owner:熊介良
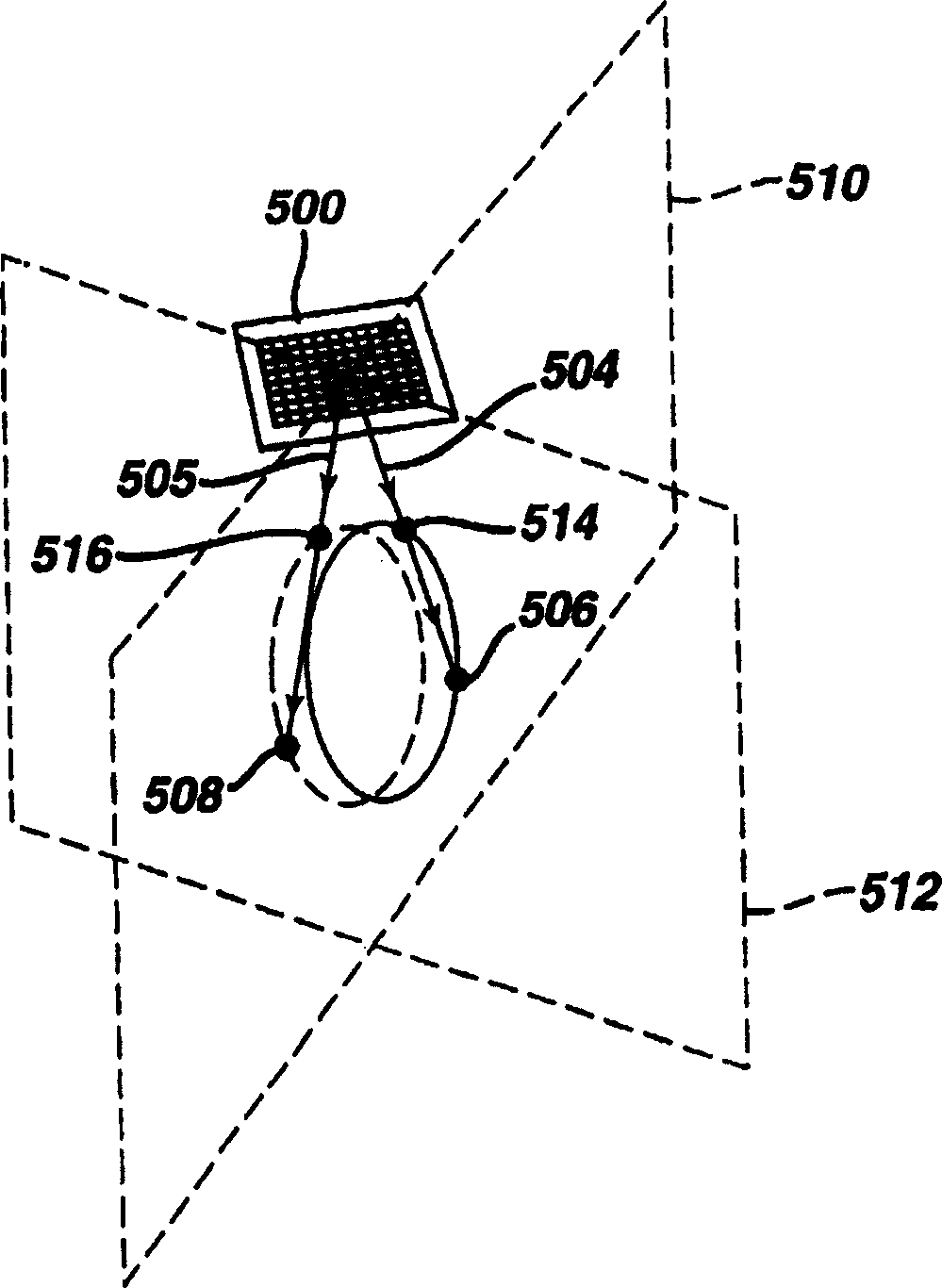
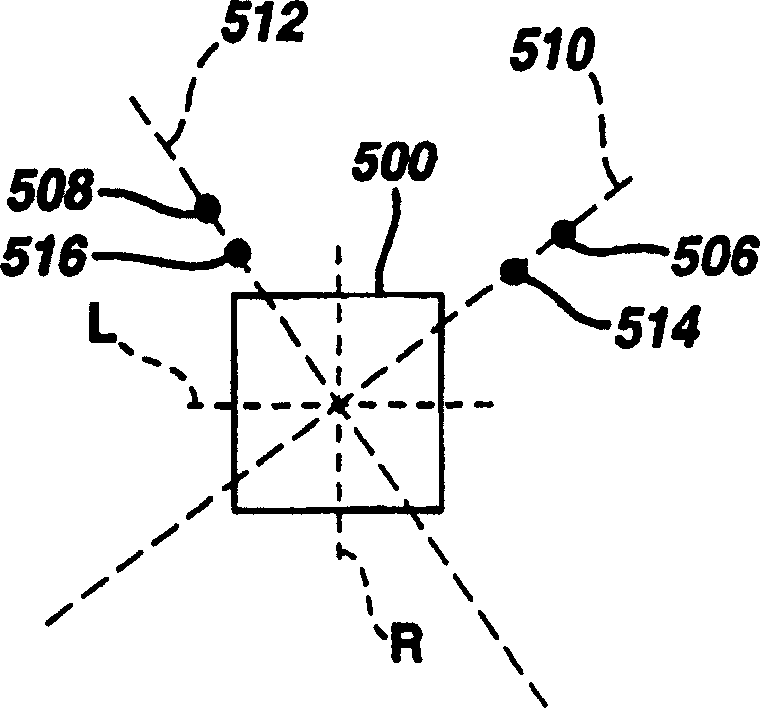
Biplane ultrasonic imaging with icon depicting the mutual plane orientation
InactiveCN1678920AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationComputer graphics (images)
An ultrasonic apparatus and method are described in which a volumetric region of the body is imaged by biplane images. One biplane image has a fixed planar orientation to the transducer, and the plane of the other biplane image can be varied in relation to the fixed reference image. In a preferred embodiment one image can be rotated relative to the other, and can be tilted relative to the other. An image orientation icon is shown on the display screen together with the two biplane images depicting the relative orientation of the two planar images.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com