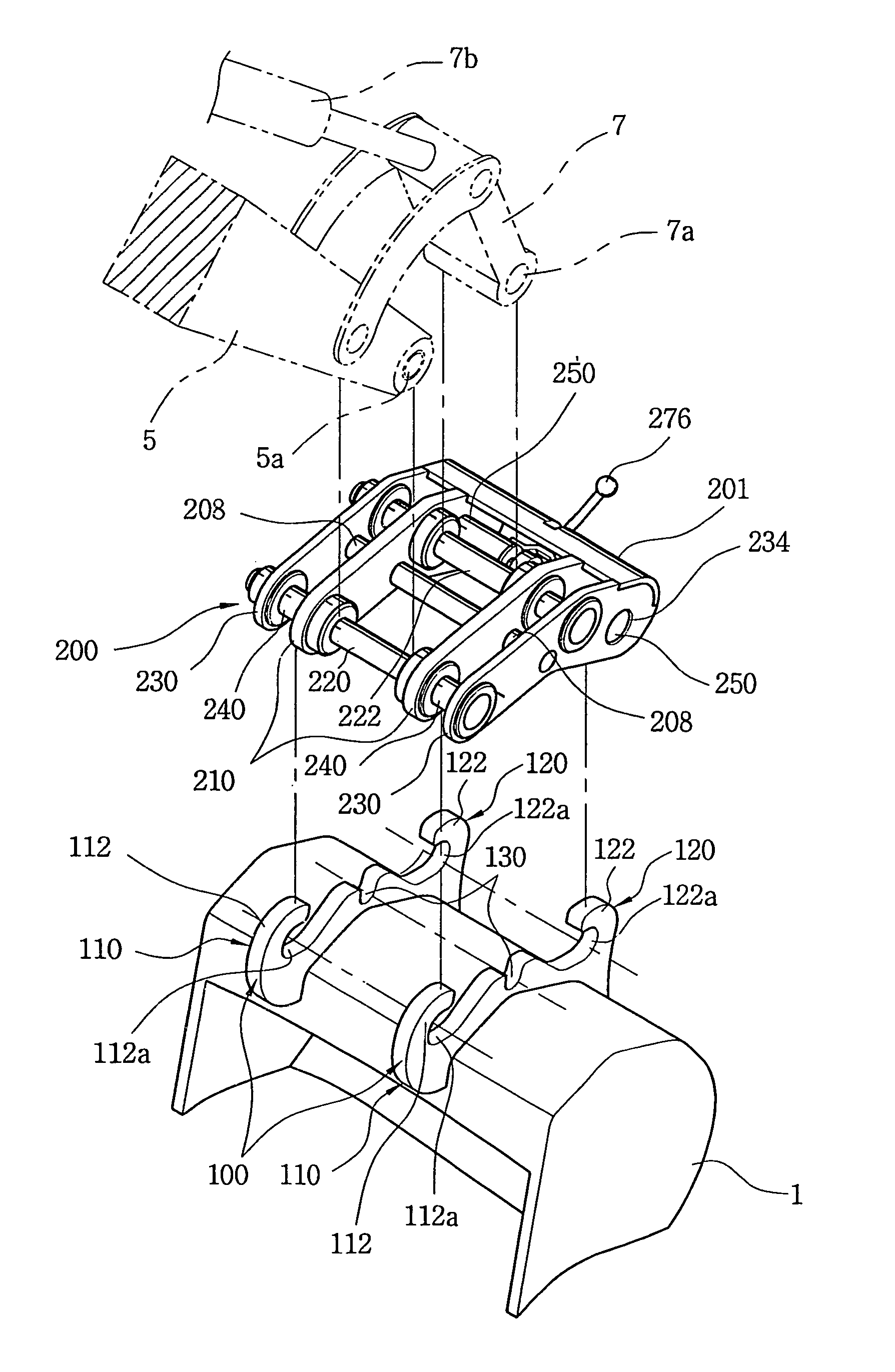
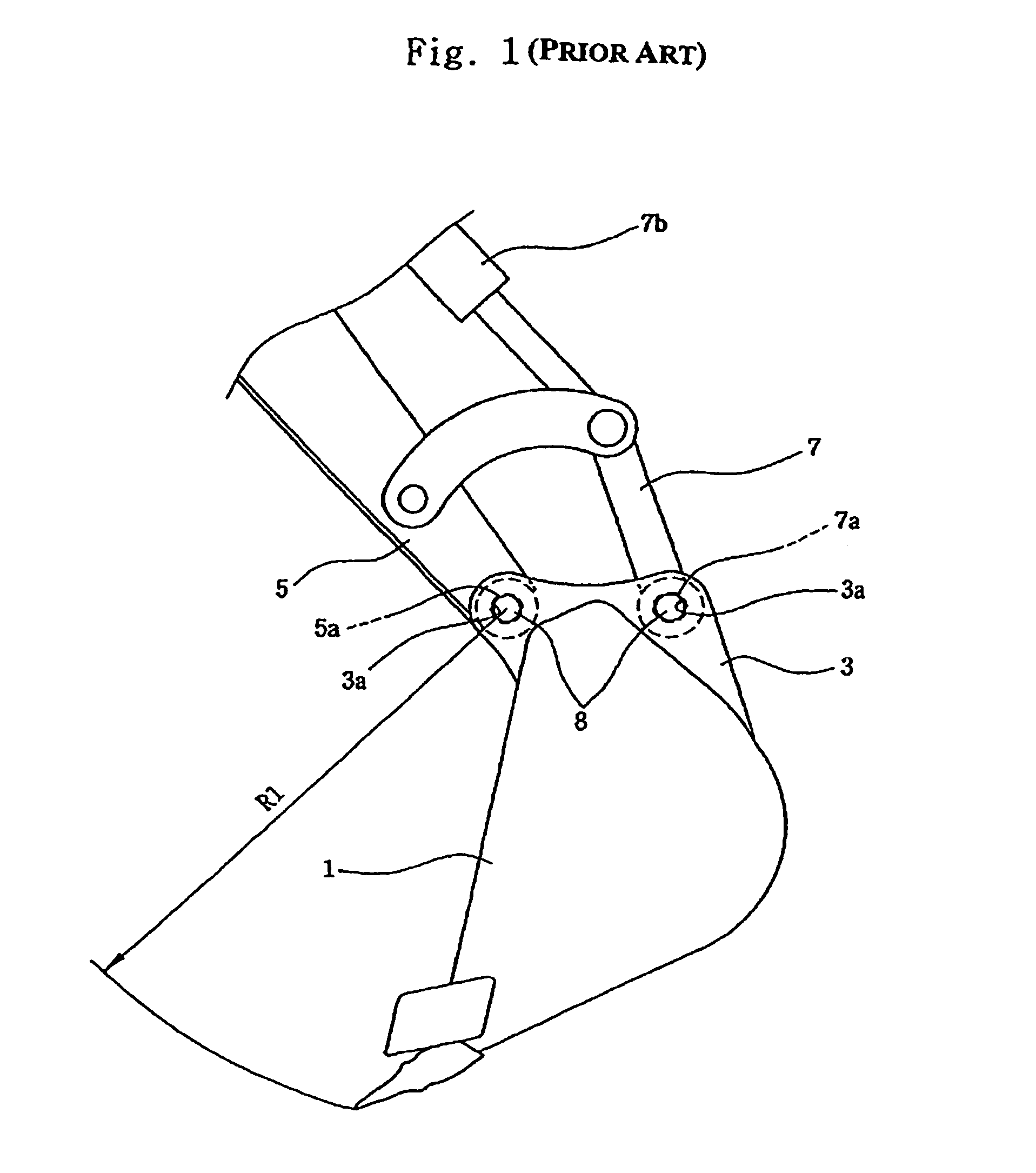
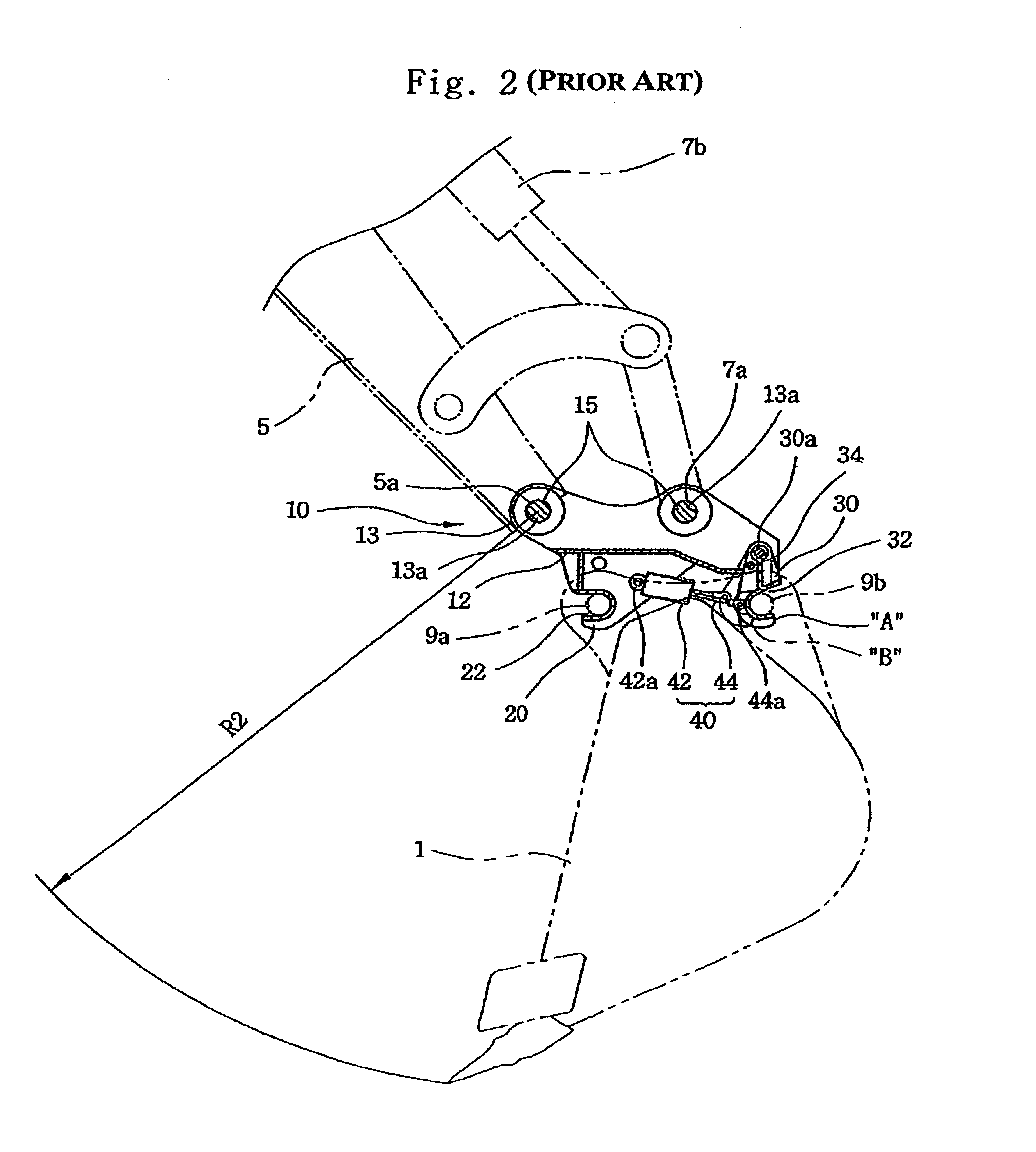
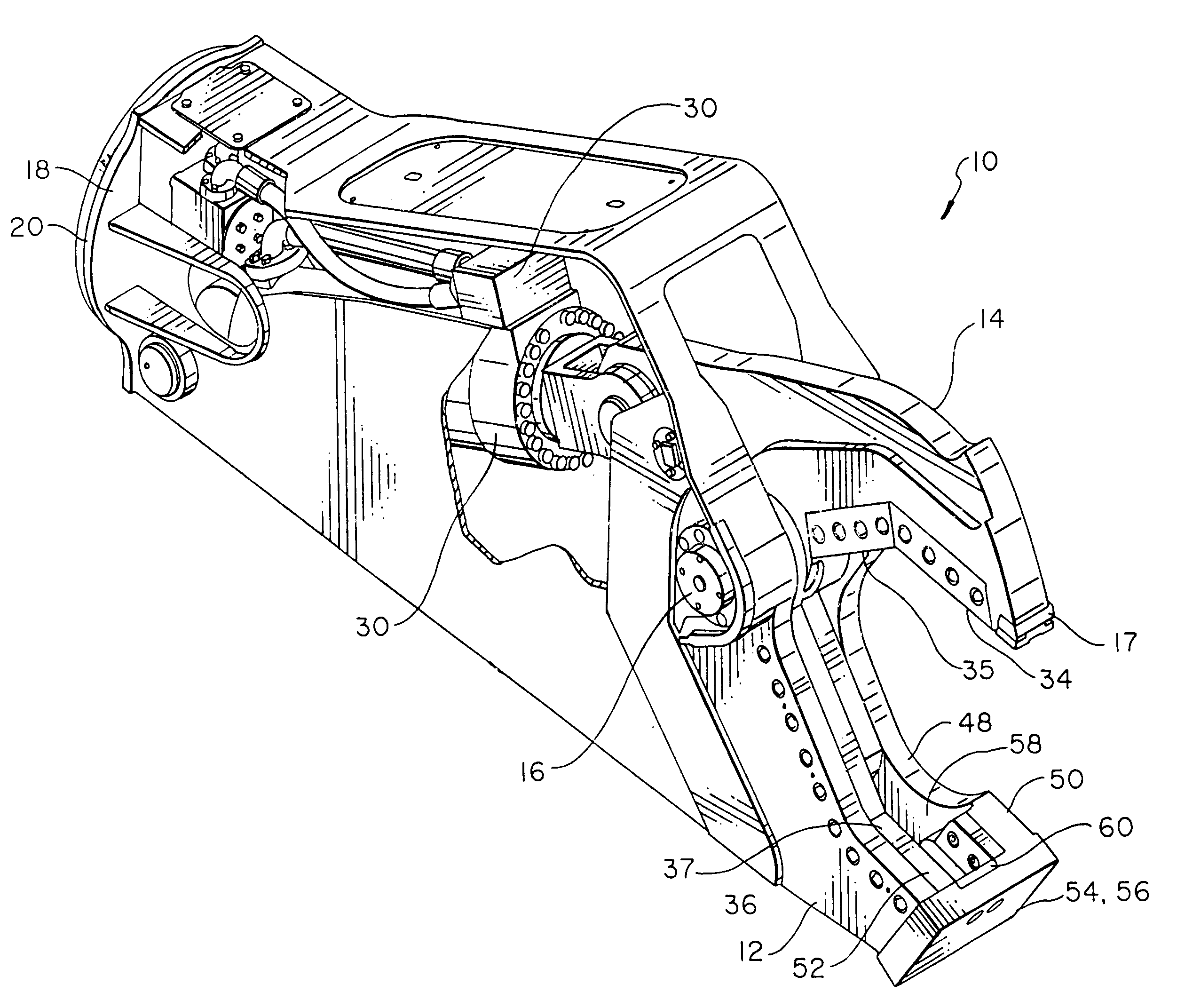
Patents
Literature
8759 results about "Excavator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
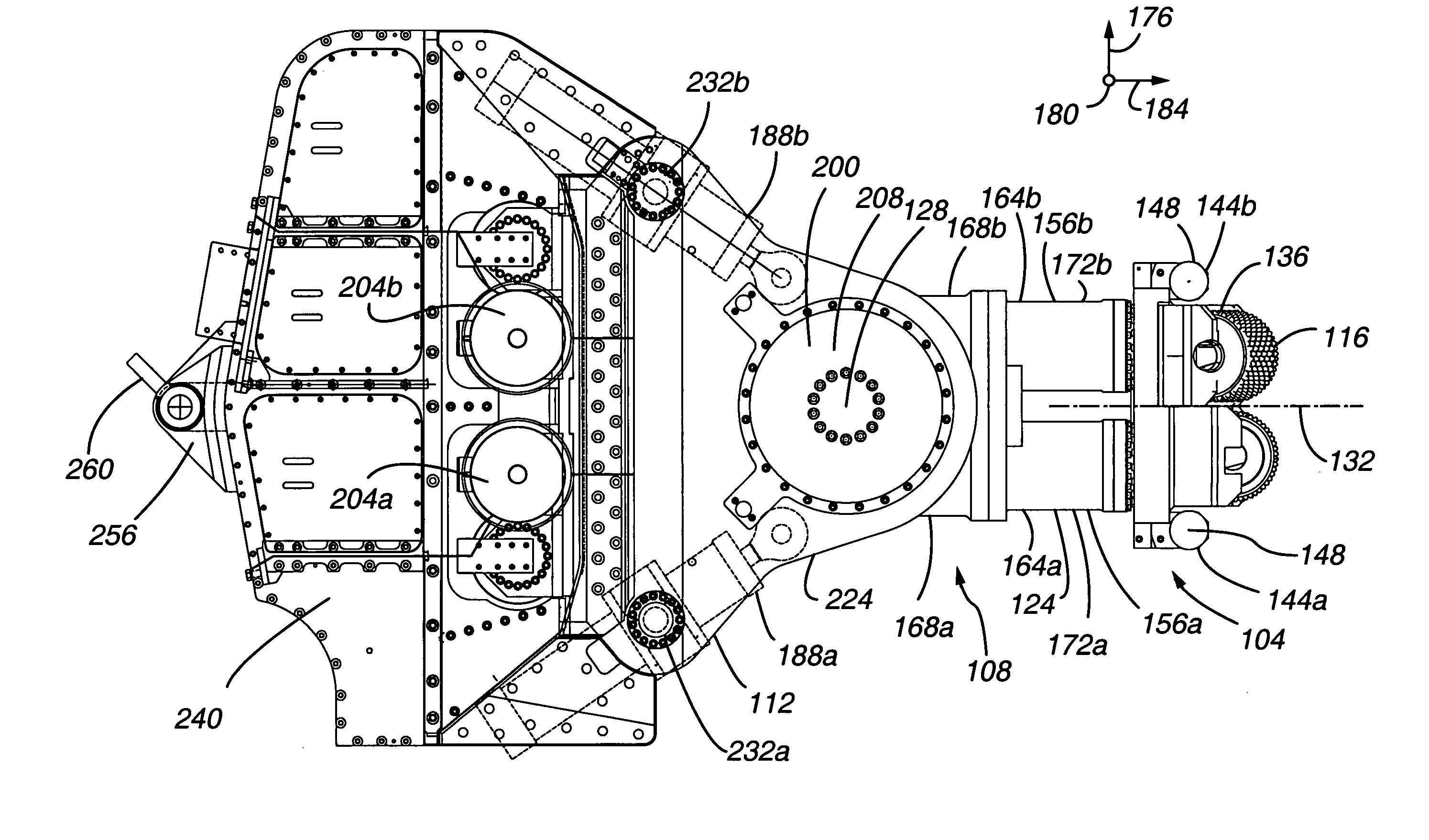
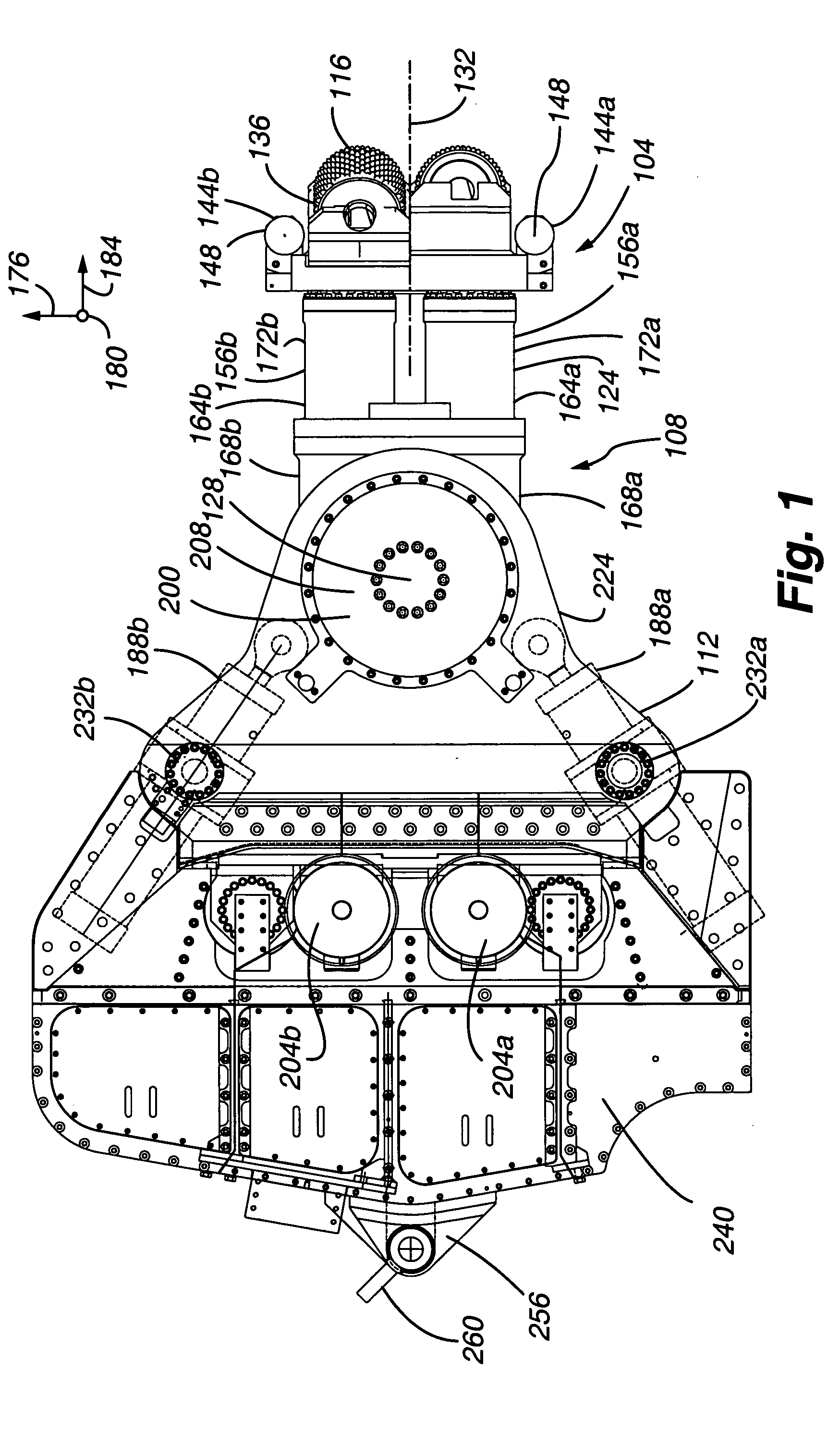
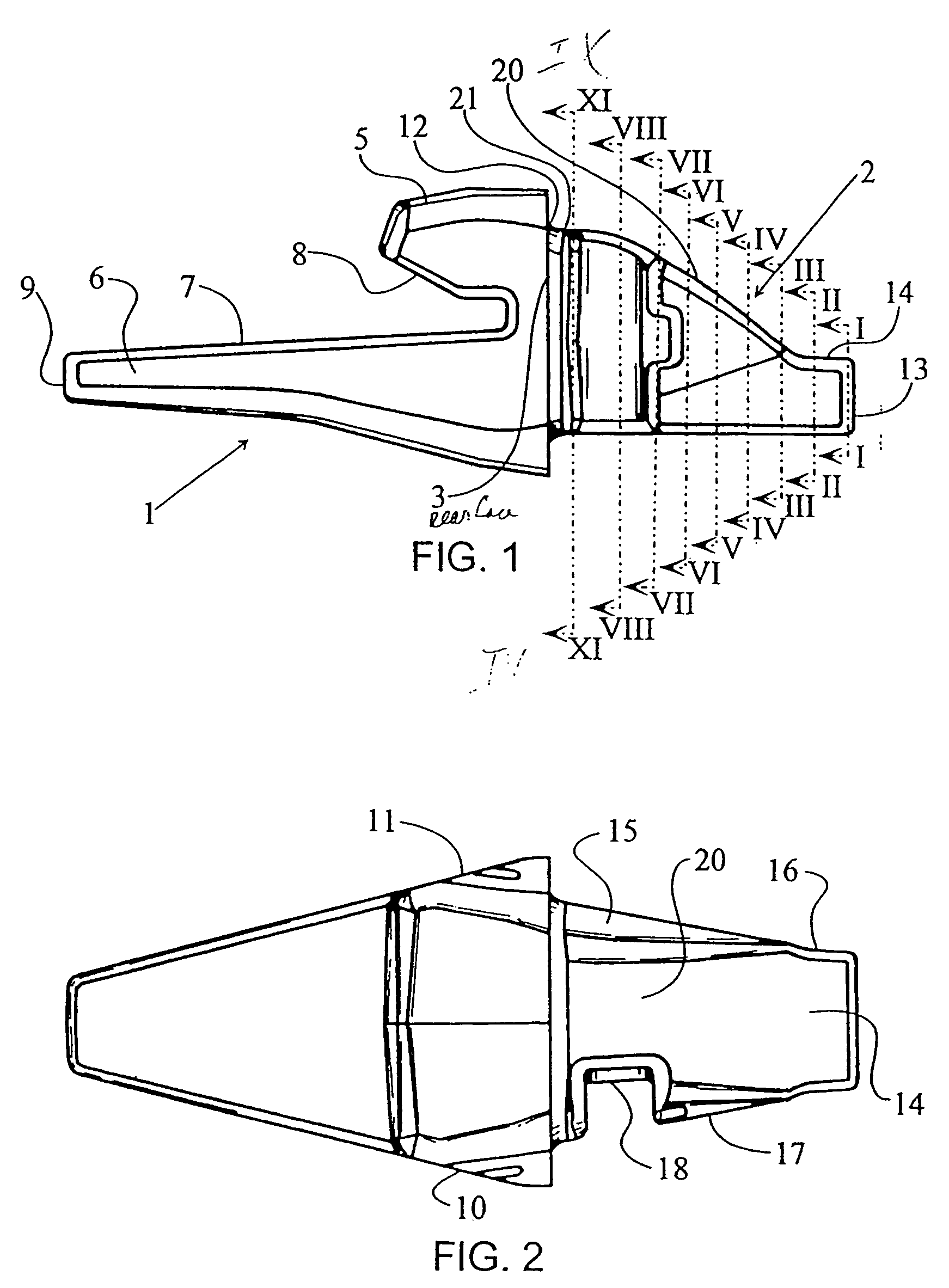
Excavators (hydraulic) are heavy construction equipment consisting of a boom, dipper (or stick), bucket and cab on a rotating platform known as the "house". The house sits atop an undercarriage with tracks or wheels. They are a natural progression from the steam shovels and often mistakenly called power shovels. All movement and functions of a hydraulic excavator are accomplished through the use of hydraulic fluid, with hydraulic cylinders and hydraulic motors. Due to the linear actuation of hydraulic cylinders, their mode of operation is fundamentally different from cable-operated excavators which use winches and steel ropes to accomplish the movements.
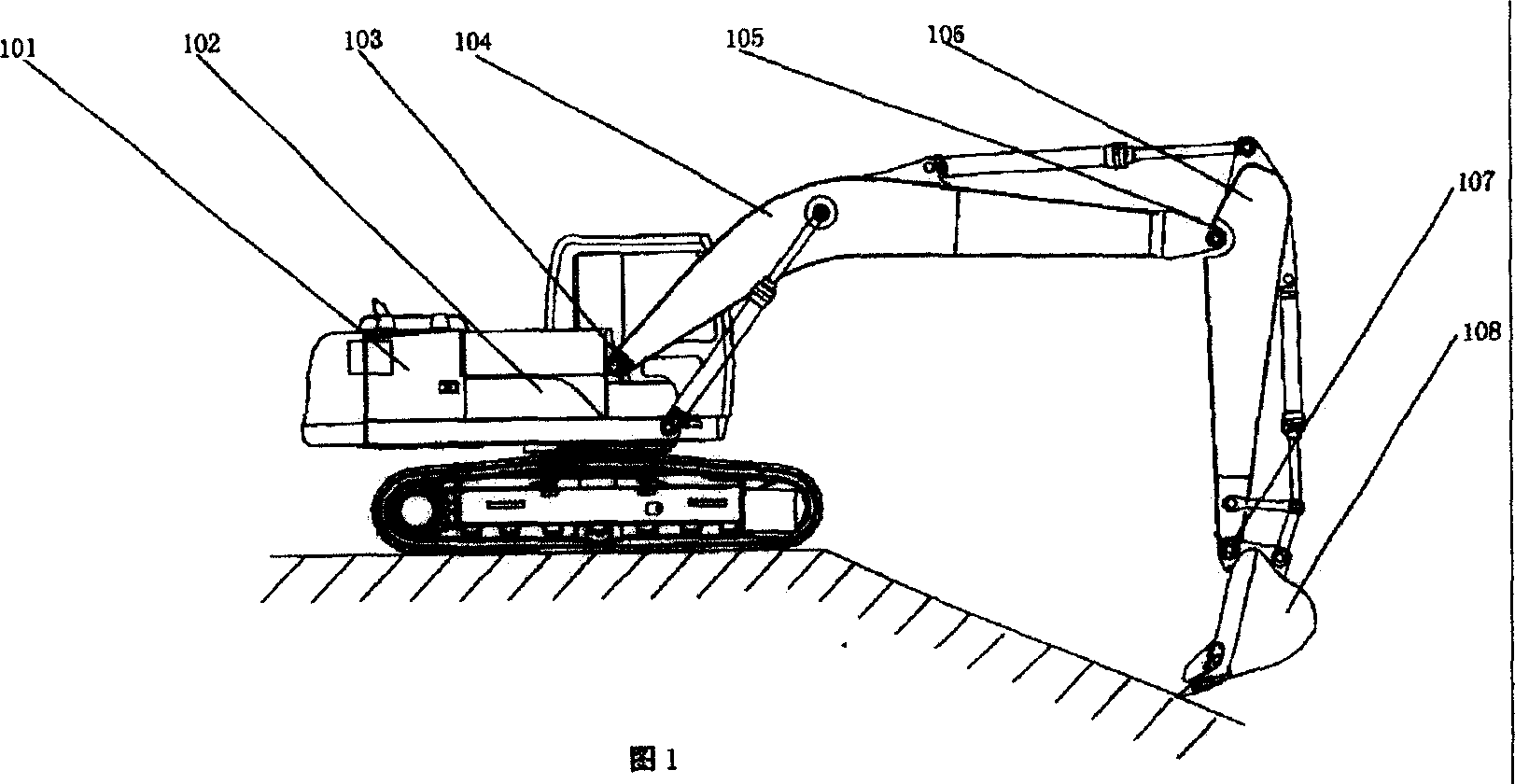
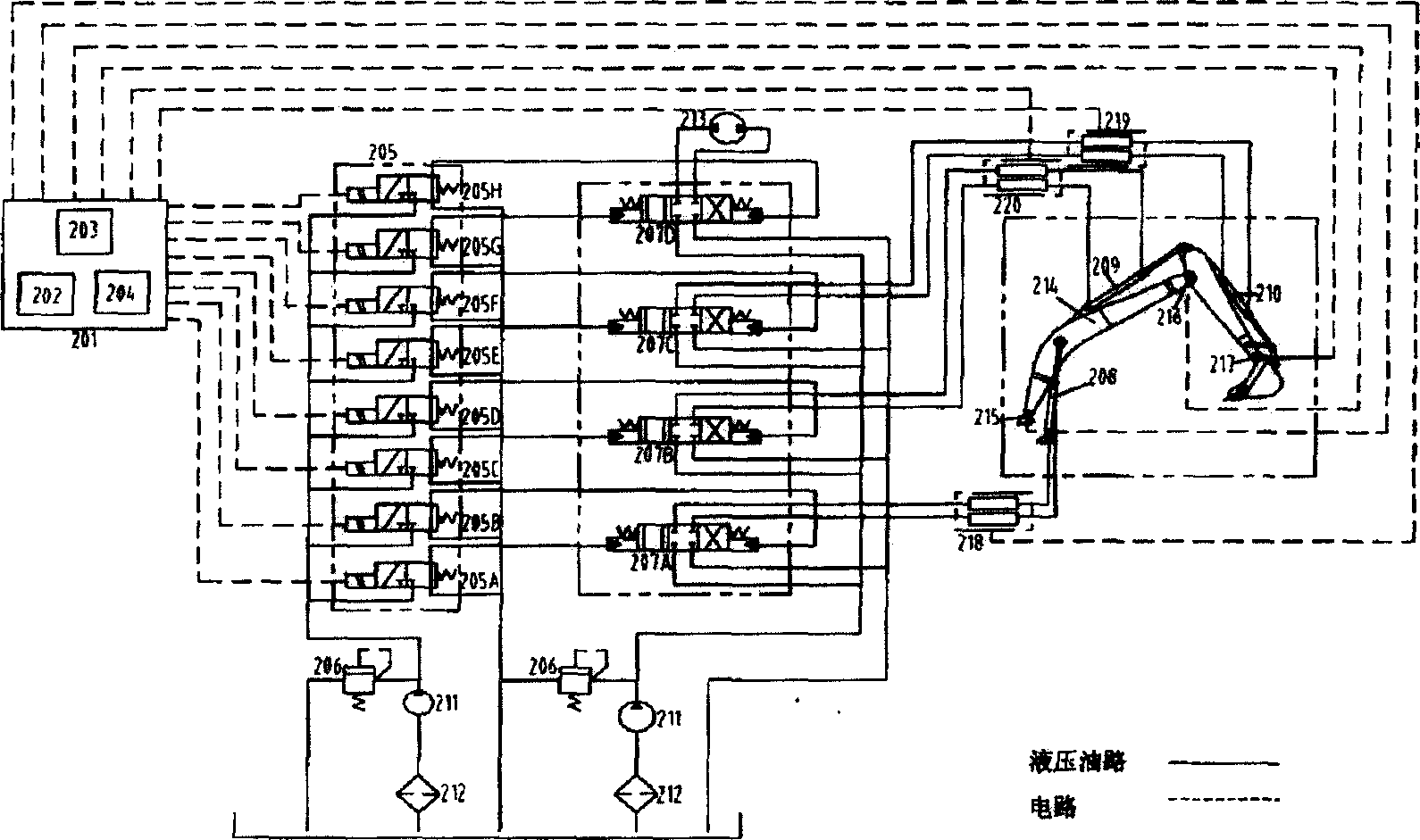
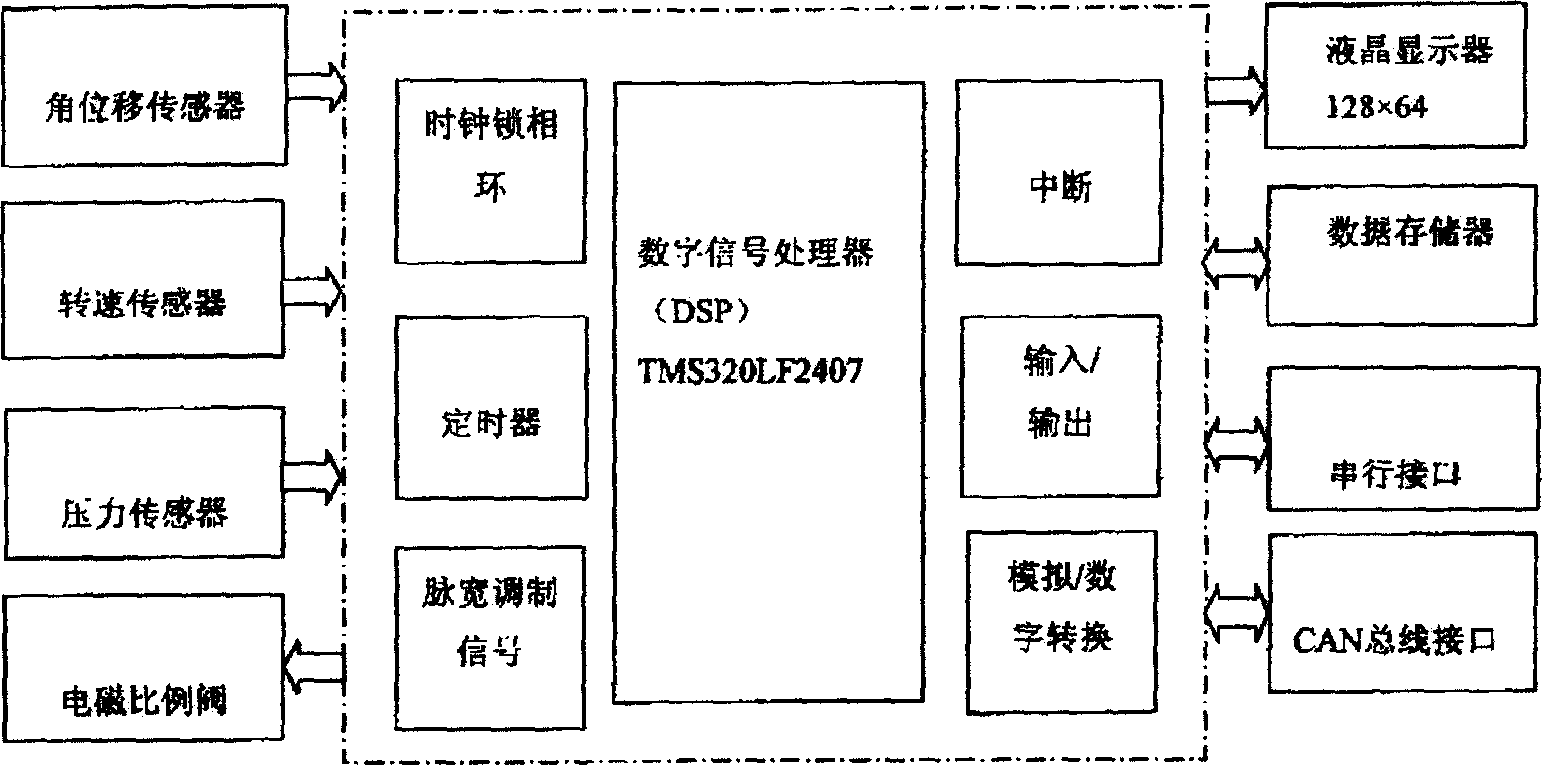
Path control system used for hydraulic digger operating device and its method
InactiveCN1651666ARealize automatic manipulationPrecise and stable positionSoil-shifting machines/dredgersPosition/direction controlHydraulic cylinderAutomatic control
The present invention relates to a track control system for hydraulic excavator working equipment and its method. Said system includes the following main components: DSP, moving arm angle detection mechanism, bucket arm angle detection mechanism, bucket angle detection mechanism, hydraulic cylinder, engine, working equipment and its driving cylinder and CAN bus. Said invention also provides the concrete steps of said control method. It can implement automatic control of hydraulic excavator working equipment, and can accurately and stably control the position and attitute of said hydraulic excavator working equipment so as to raise its working efficiency.
Owner:GUANGXI LIUGONG MASCH CO LTD
Process for the excavation of buried waste
ActiveUS7114880B2Preventing particulate emissionMachines/dredgers working methodsFouling preventionRadioactive contaminationEnvironmental engineering
Disclosed is a method of excavating large quantities of non-homogenous radioactive contaminated waste, desirably without releasing radioactive contaminated dust or exposing personnel to its hazards. The excavation of buried waste is performed in the presence of a suppression fluid that coats the waste and captures and retains particles so that they do not become airborne. Use of this suppression fluid technique allows larger mechanized excavation equipment to be used to perform the work. This keeps workers away from the waste. The waste is excavated and placed inside large steel boxes, such as a roll-off box, by the excavator. The suppression fluid covers the waste in the boxes and prevents particulate emissions from the waste.
Owner:CARTER JR ERNEST E
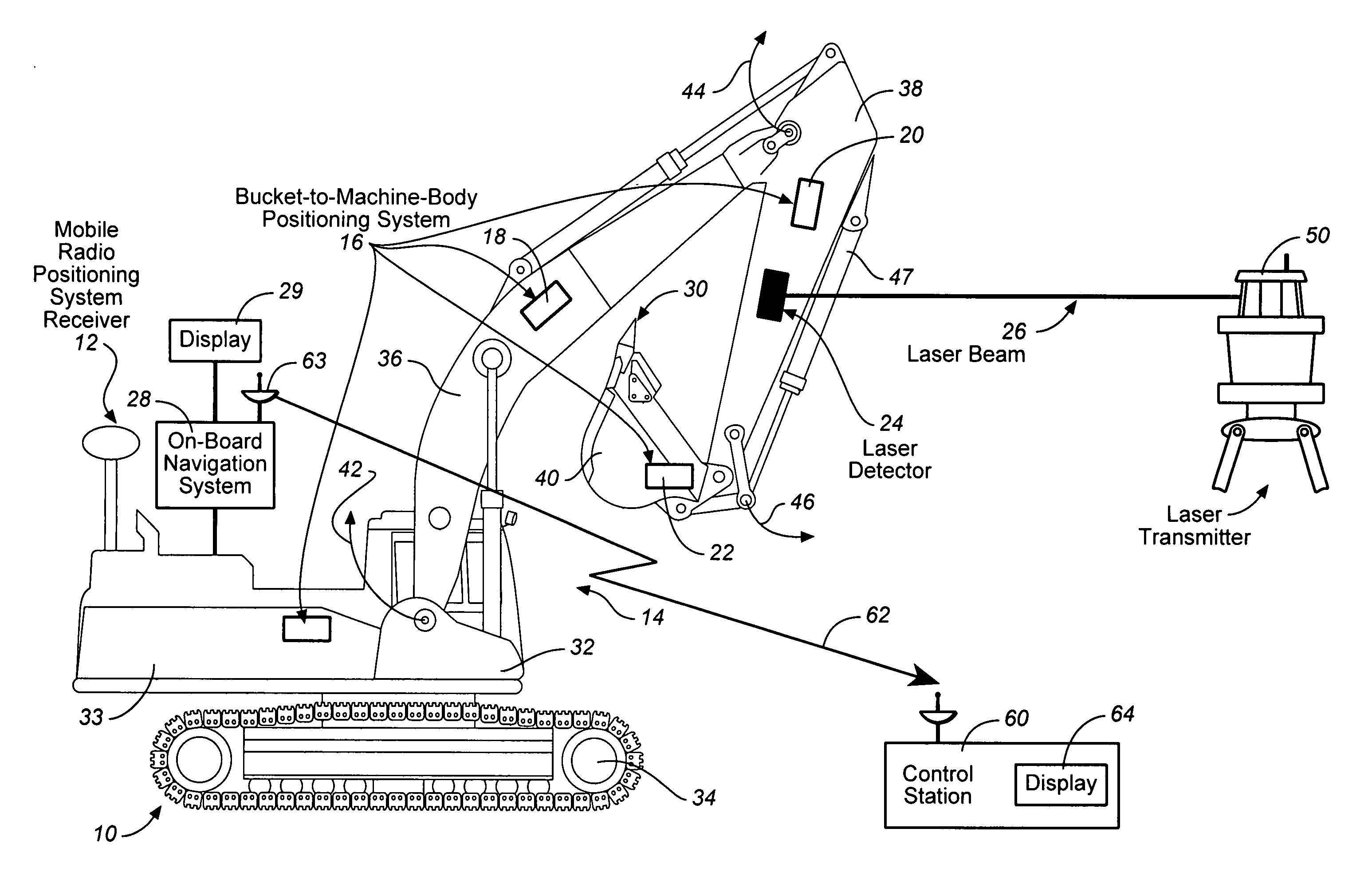
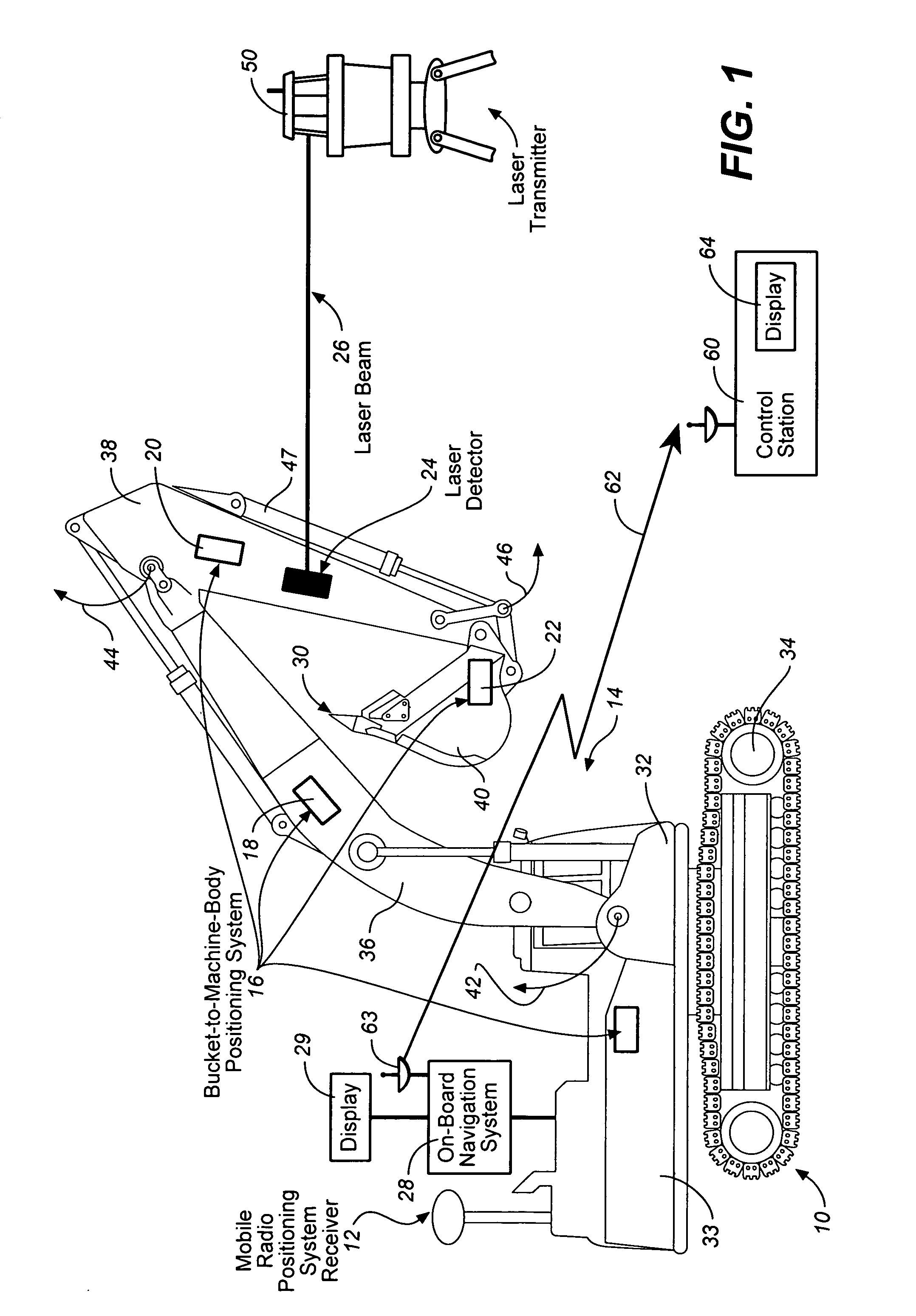
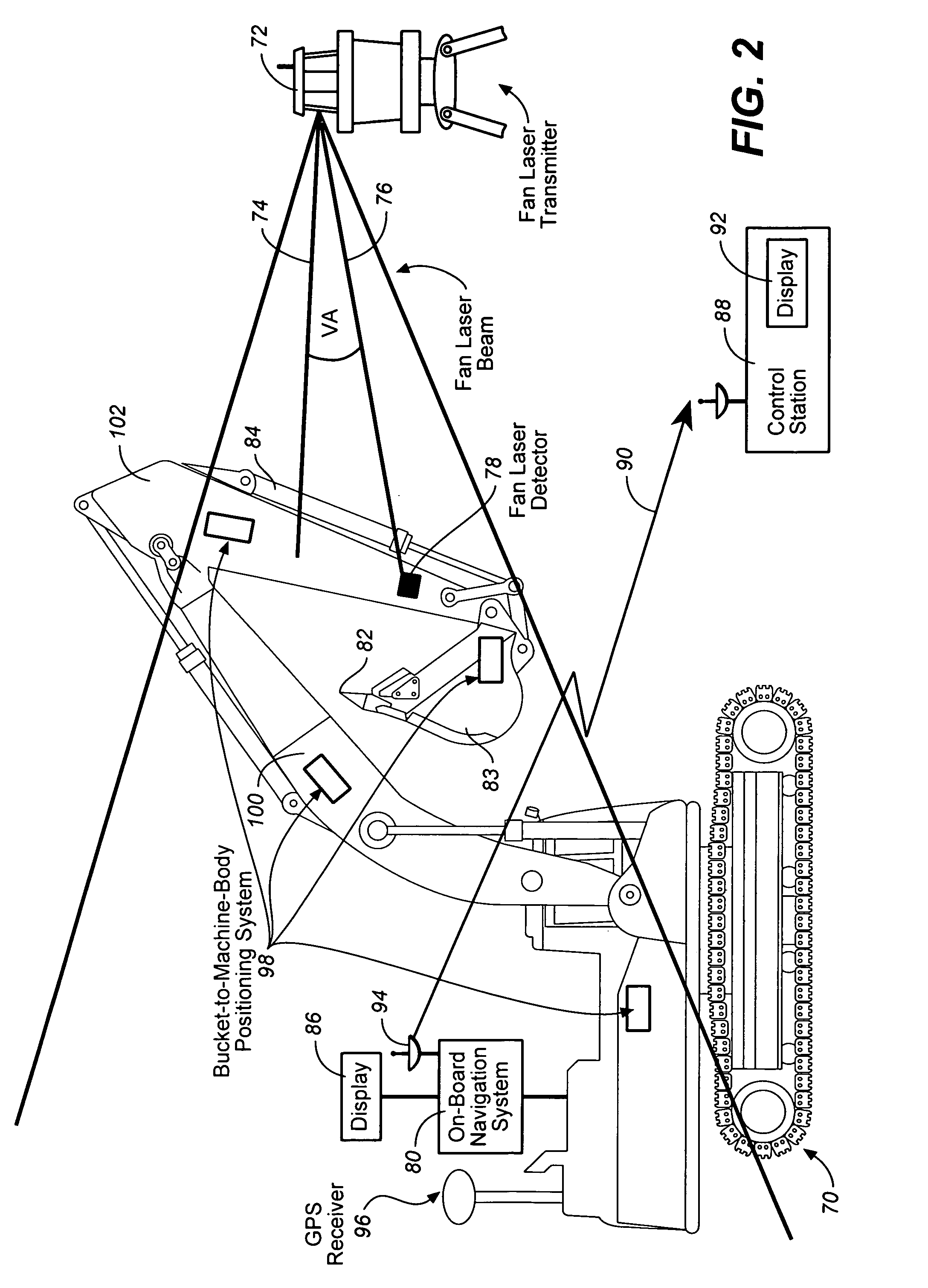
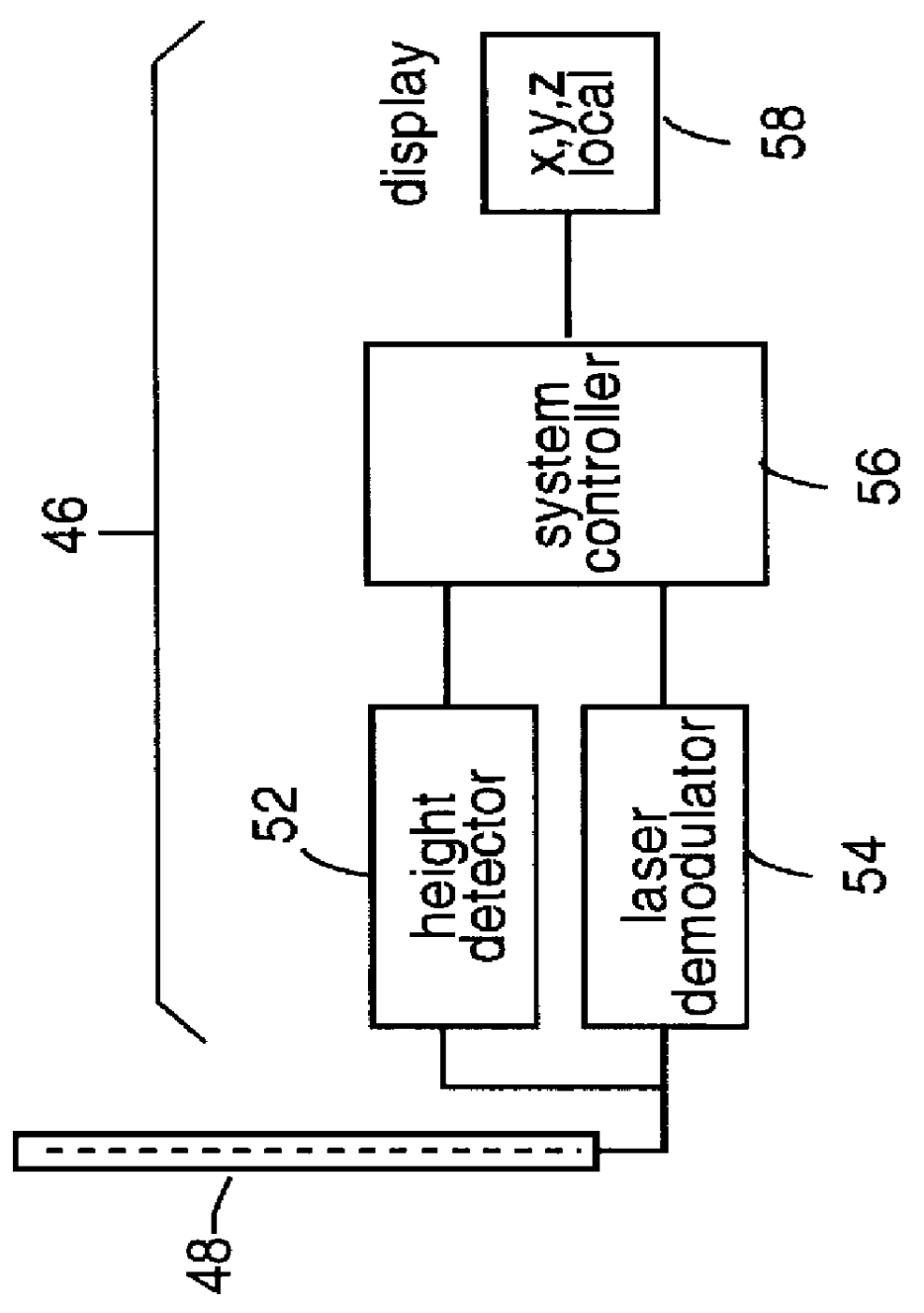
Excavator 3D integrated laser and radio positioning guidance system
InactiveUS20080047170A1Improve vertical accuracyImprove accuracyTransmission systemsBeacon systems using electromagnetic wavesGuidance systemOn board
An excavator 3D integrated laser and radio positioning guidance system (Ex_3D_ILRPGS) comprising: a mobile radio positioning system receiver configured to obtain 2D horizontal coordinates of the excavator, a bucket-to-machine-body positioning system configured to obtain coordinates of the boom, the stick and the bucket of the excavator, a laser detector configured to receive at least one laser beam and configured to provide a local vertical coordinate with a substantially high accuracy, and an on-board navigational system configured to receive and to integrate the 2D horizontal coordinates of the excavator obtained by the mobile radio positioning system receiver, the coordinates of the boom, the stick and the bucket of the excavator obtained by the bucket-to-machine-body positioning system, and the local vertical coordinate obtained by the laser detector, and configured to guide the cutting edge of the bucket of the excavator with substantially high vertical accuracy.
Owner:CATERPILLAR TRIMBLE CONTROL TECH
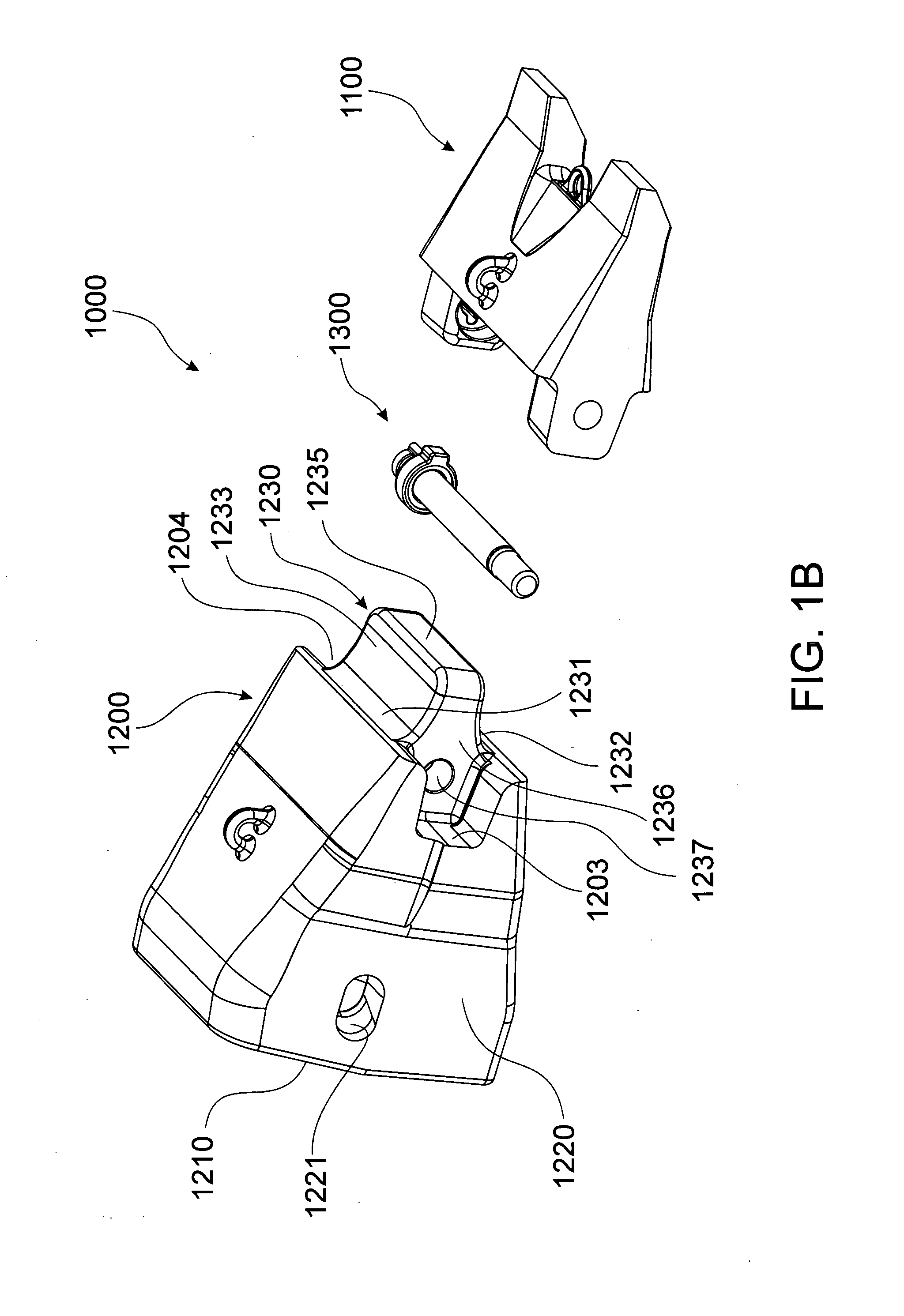
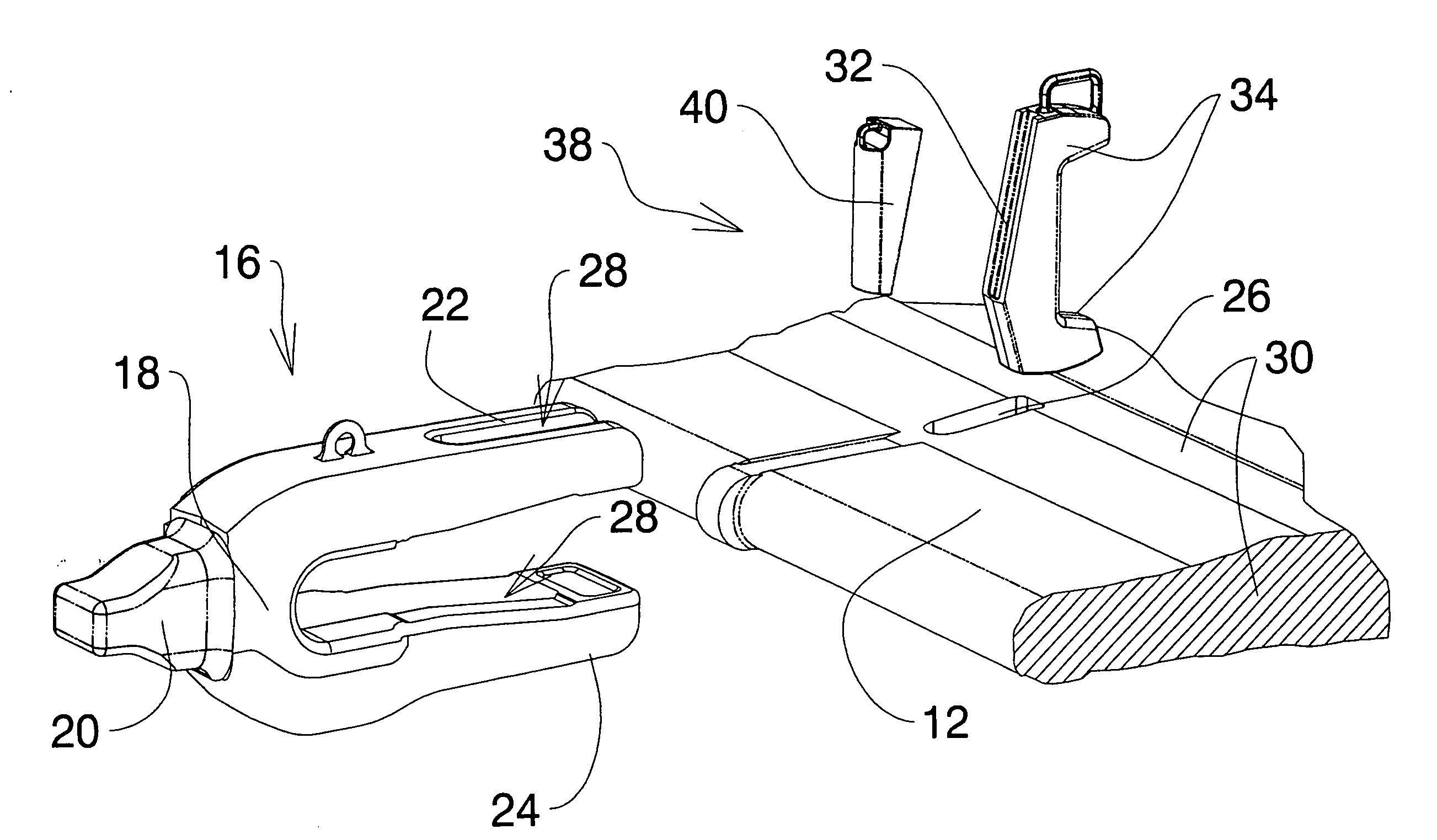
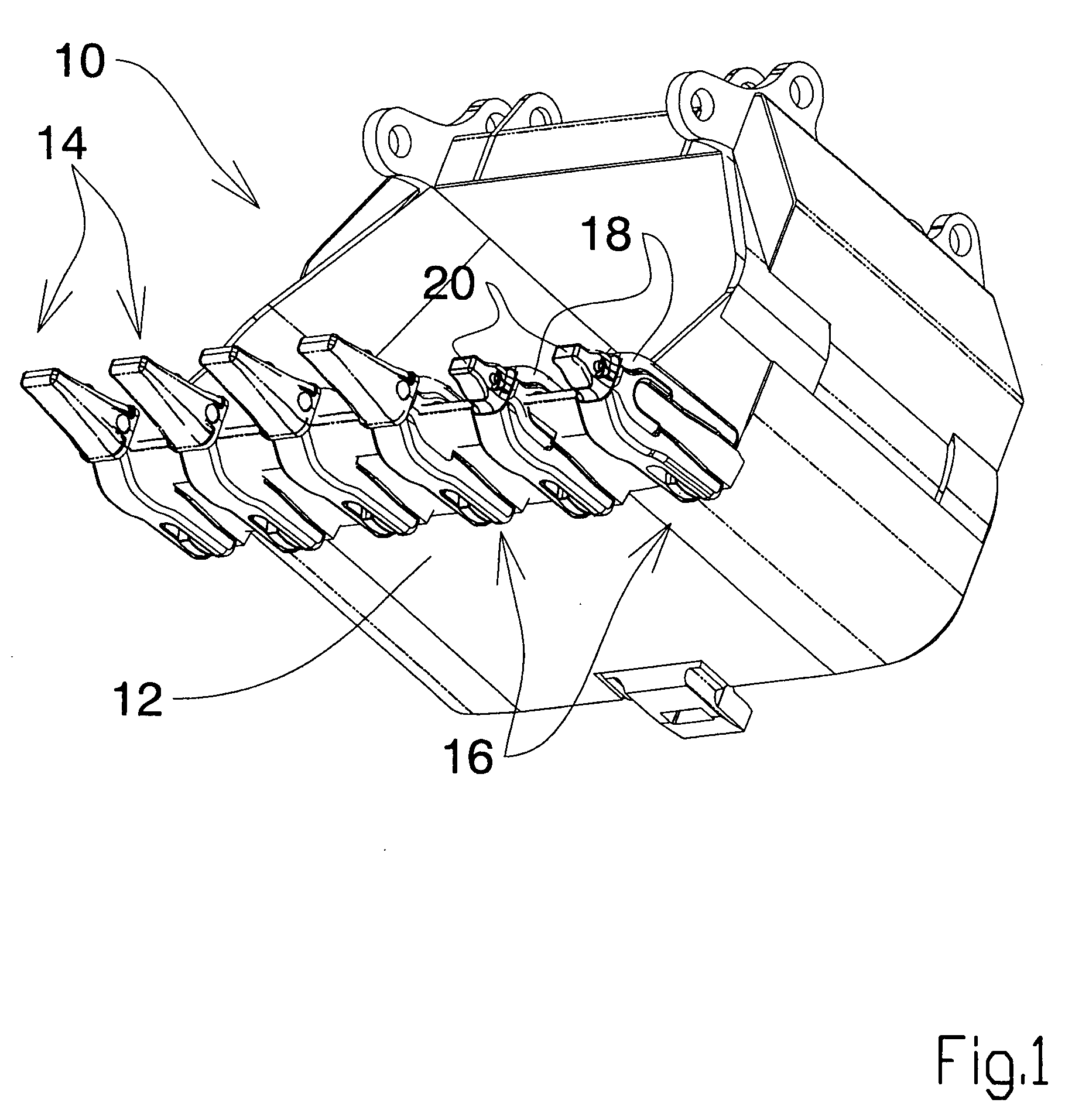
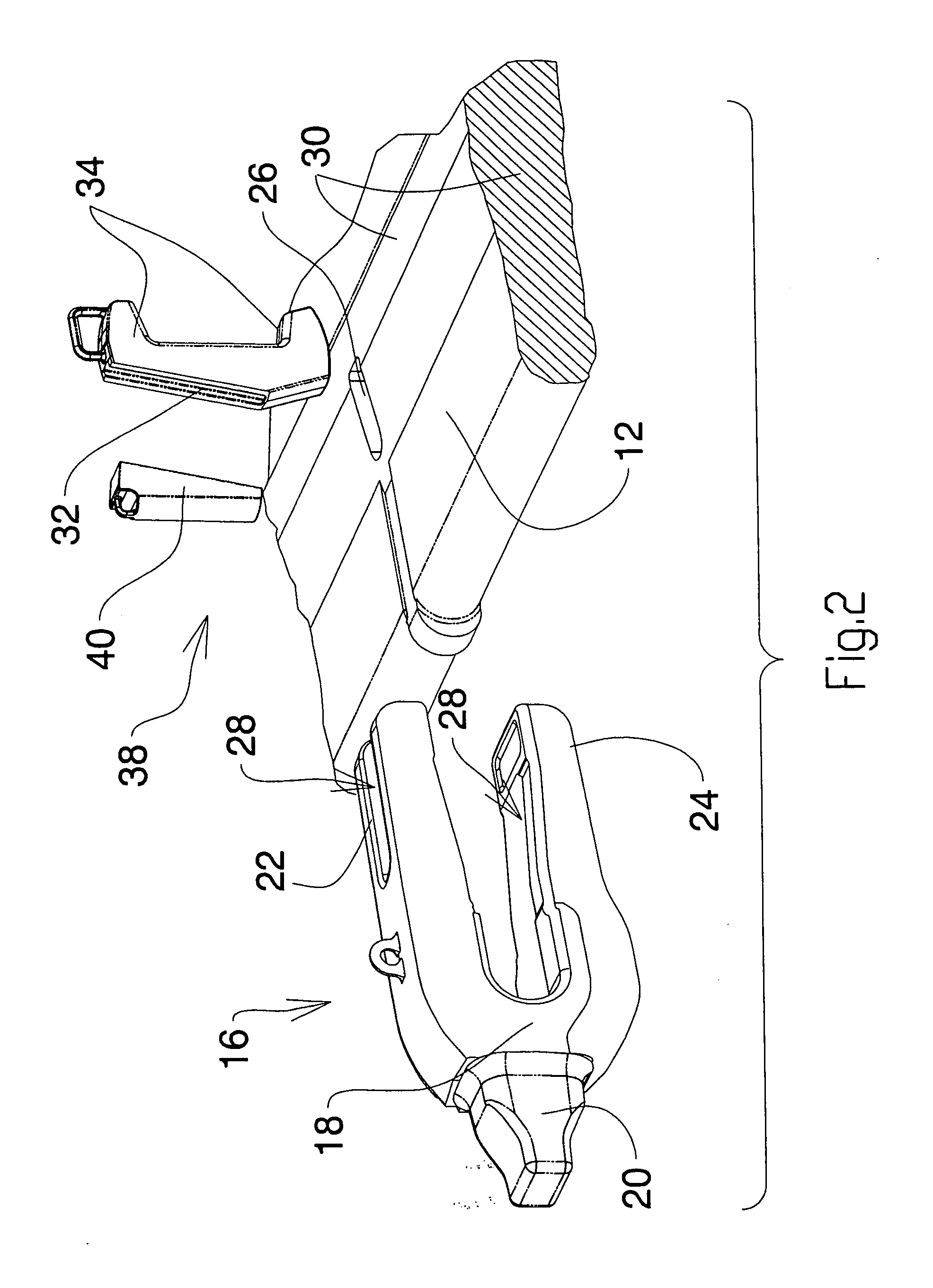
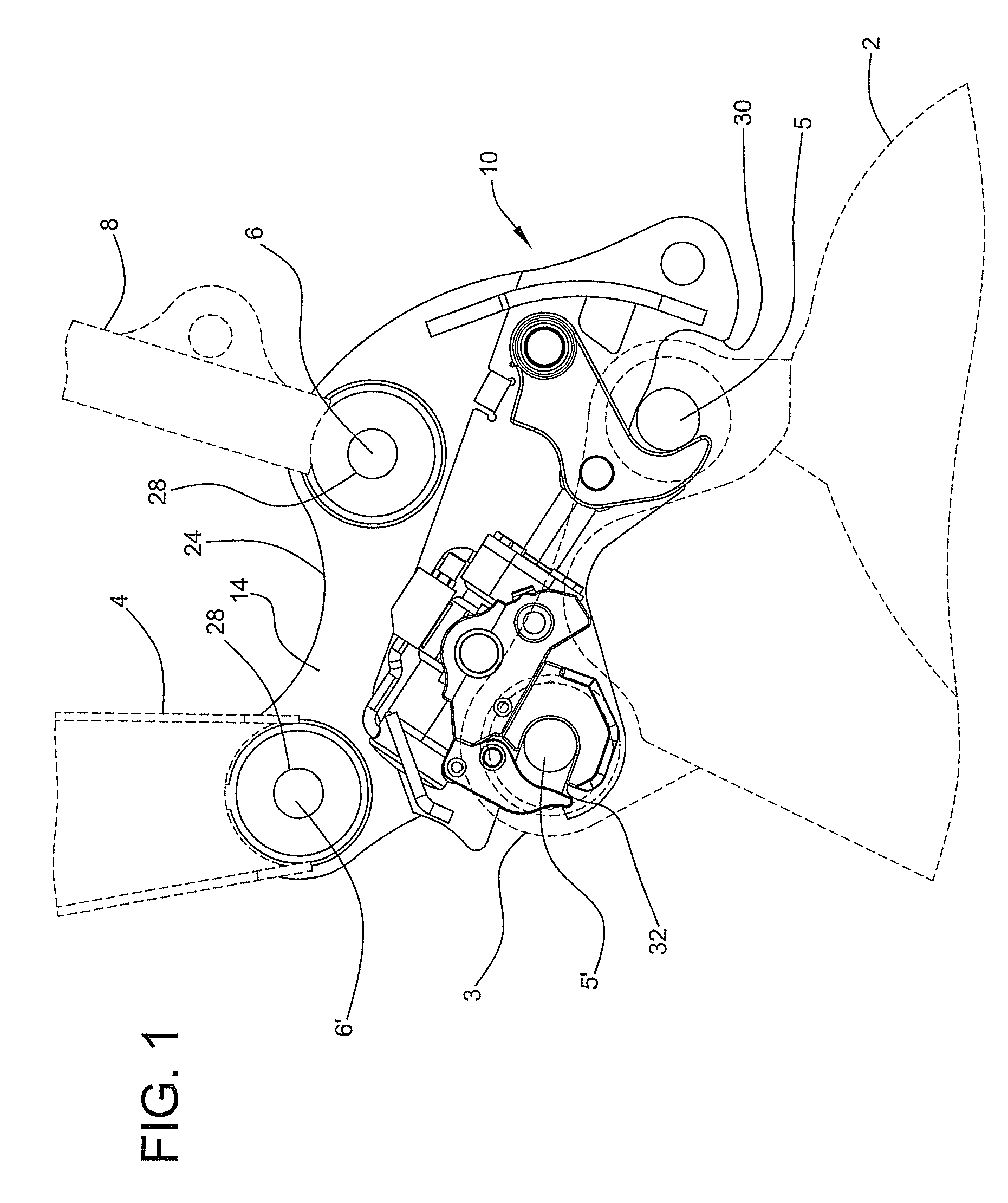
Wear Assembly and Components Thereof, Which is Intended for Machines That Are Used to Move Mateials Such as Earth and Stones
ActiveUS20080028644A1Reduce usageEasy to operateSoil-working equipmentsDragsCoupling systemExcavator
The present invention relates to a wear assembly, as well as to the different components thereof, which comprises a wear member or tooth and an adaptor member or tooth bar for wear applications in a machine for moving materials such as earth and stones.The invention contemplates a wear assembly and particularly a coupling system between the different components to one another by means of a characteristic coupling system and at least one retention system assuring the coupling and anchor between the different components, specifically between the wear member and adaptor, the latter in turn being joined to the blade of a bucket or scoop of a machine for moving materials, such as an excavator or the like.
Owner:METALOGENIA SA
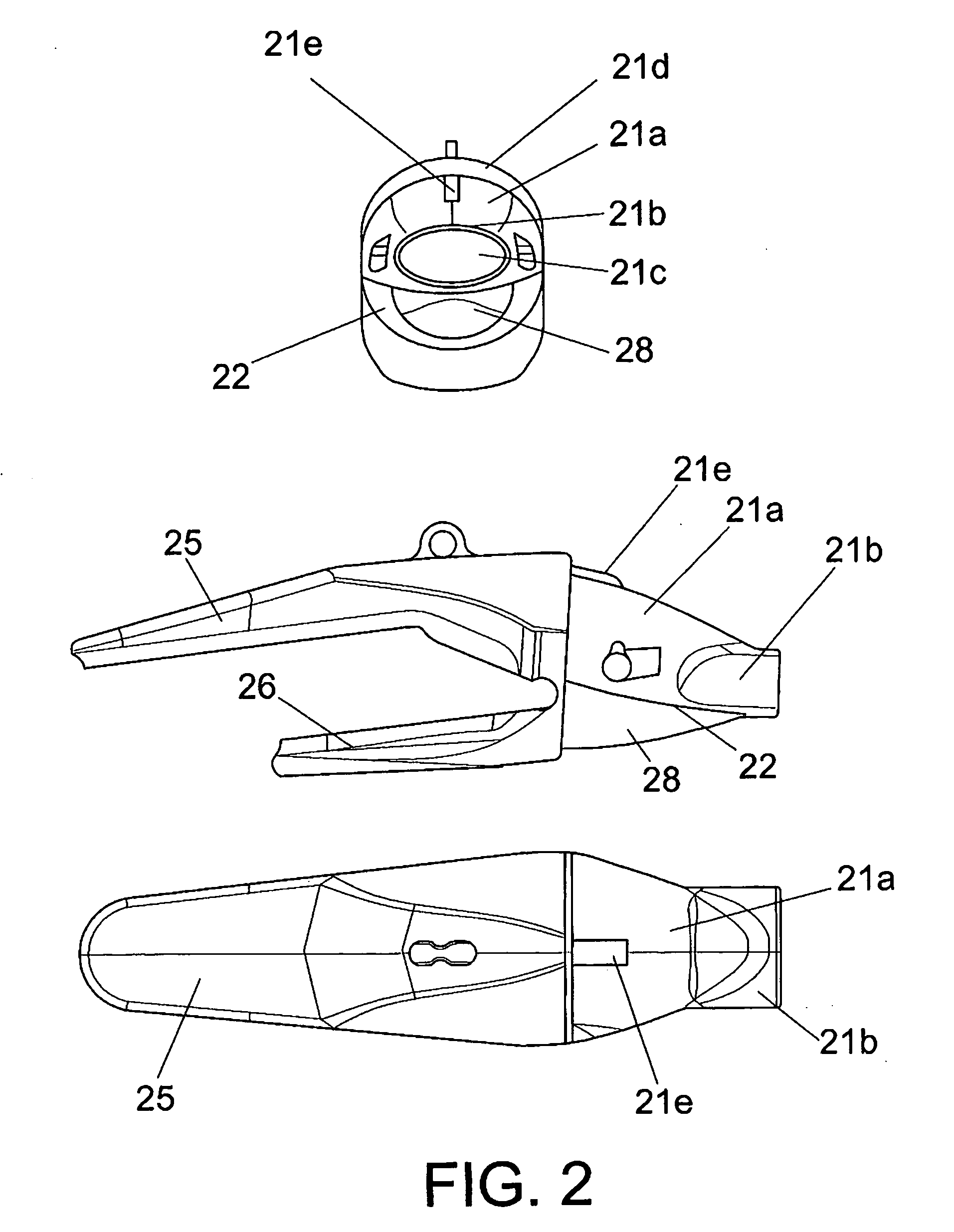
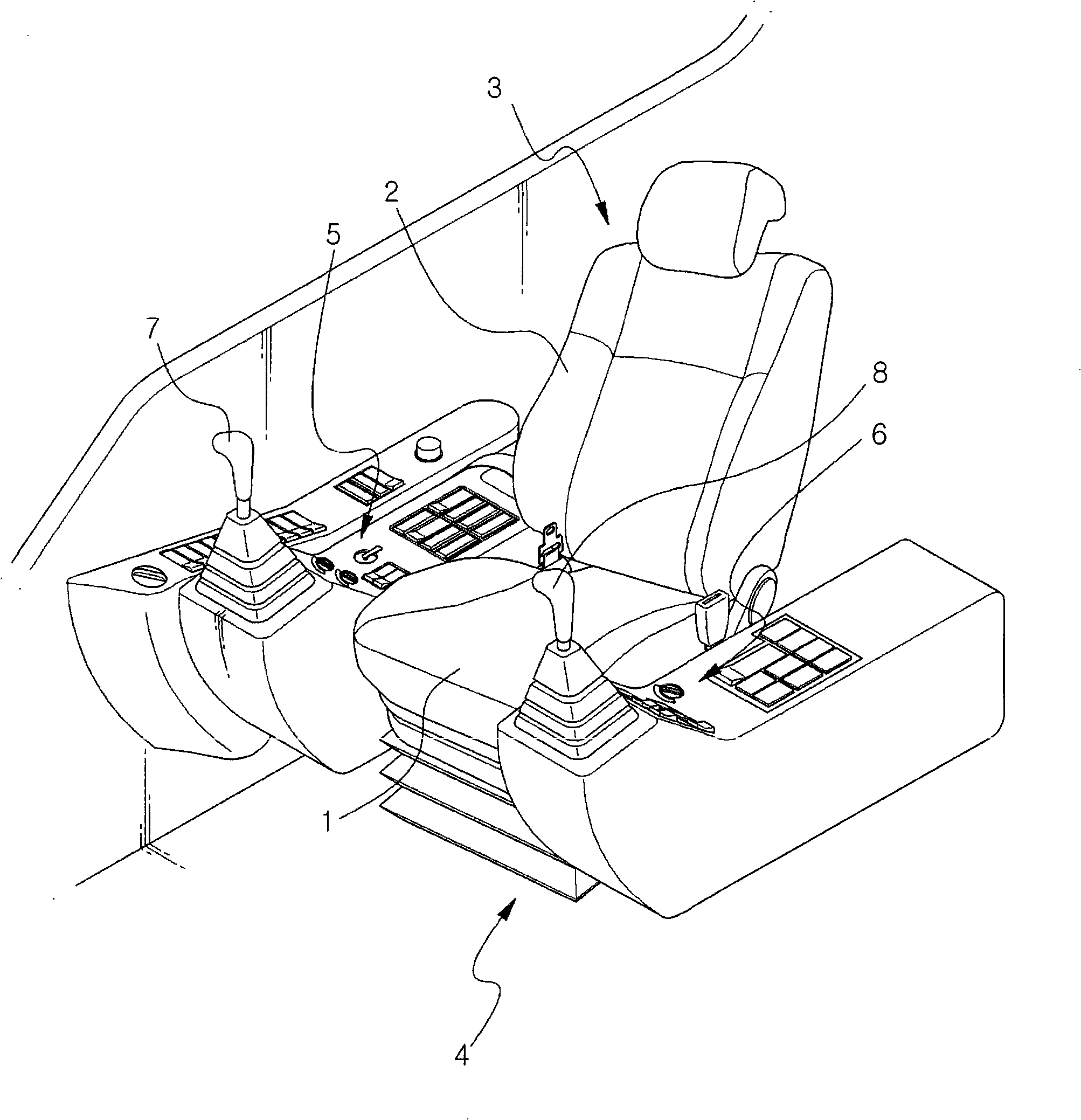
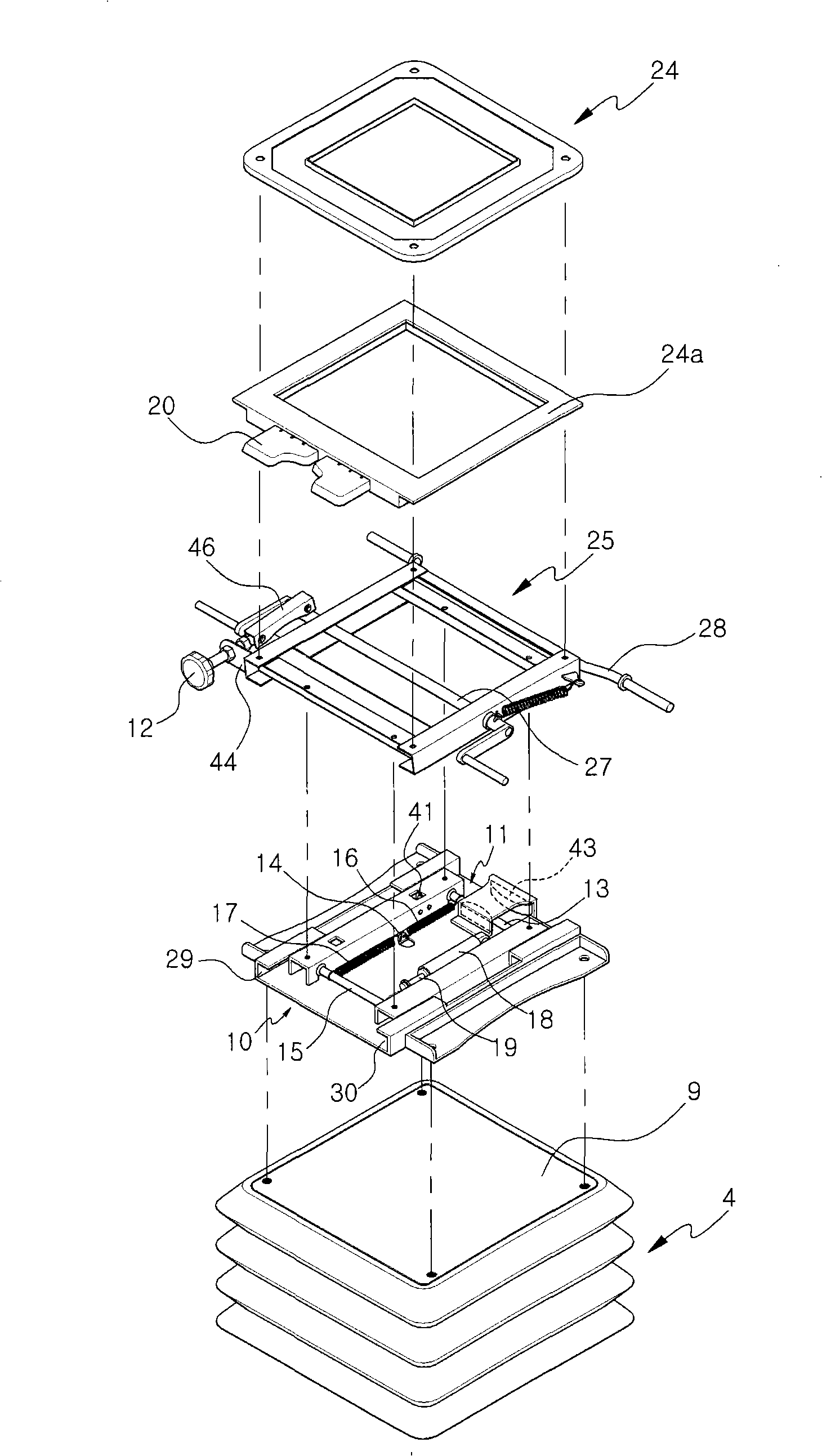
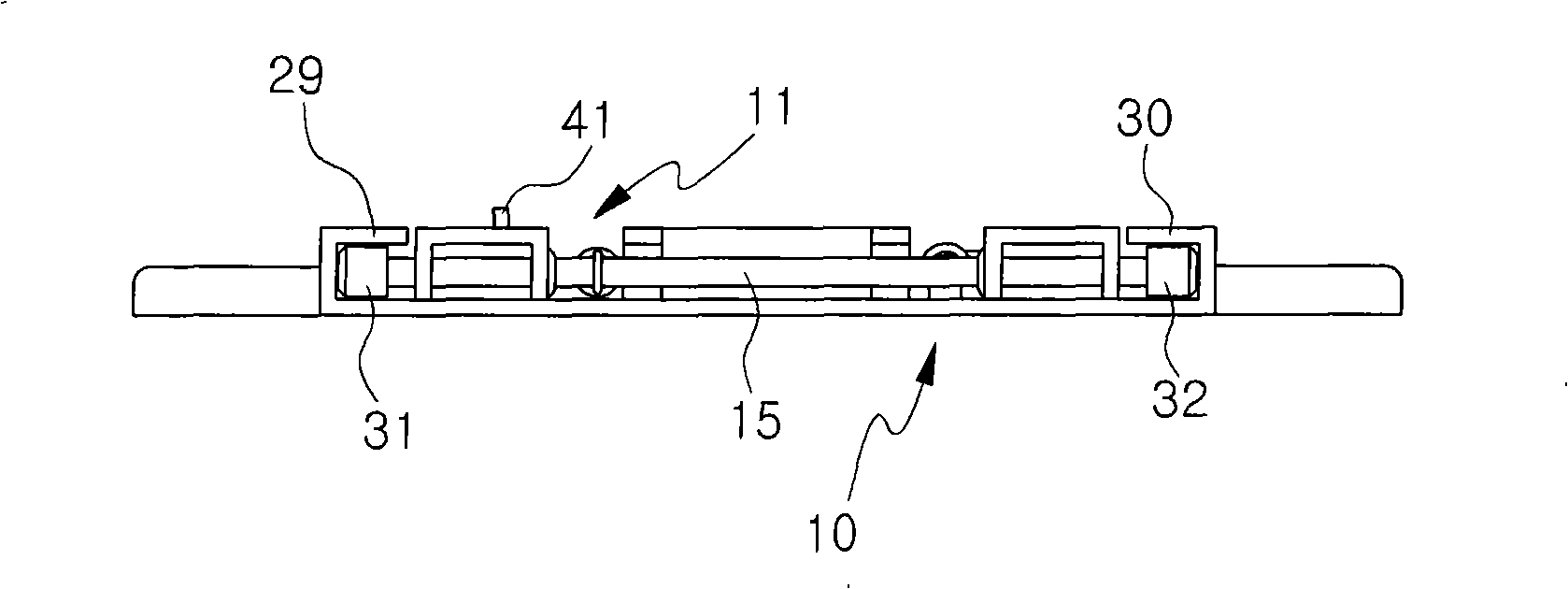
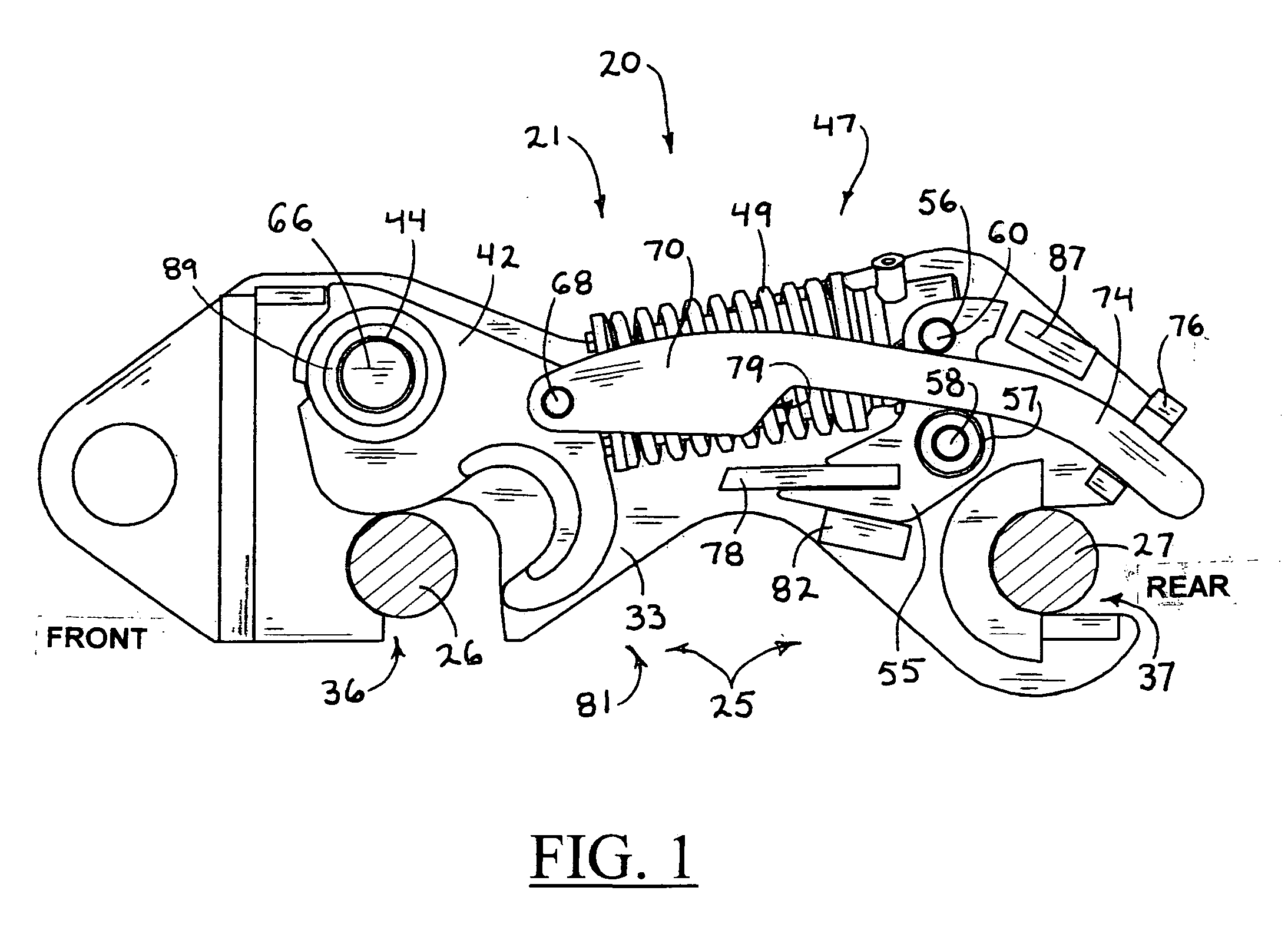
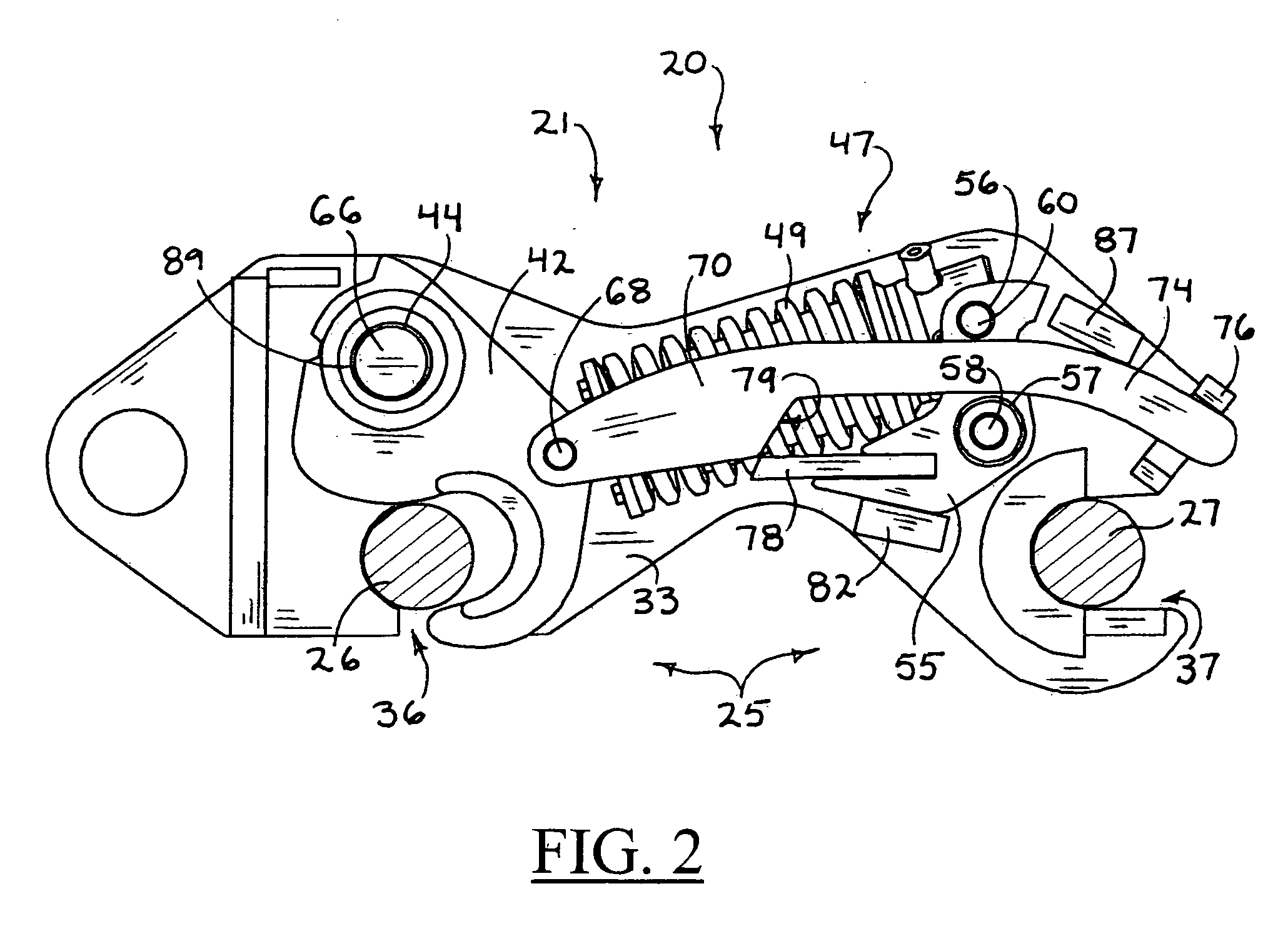
Seat for heavy equipment having buffer means in forward and backward directions
A seat for heavy equipment having a buffer means in forward and backward directions is provided, which can protect an operator by attenuating impact and vibration generated in a cab in forward and backward directions of an excavator in accordance with the driving of the buffer means in a main working mode of the excavator. The seat for heavy equipment is mounted on a suspension plate and is located between left and right console boxes.; The seat for heavy equipment includes a lower member mounted on the suspension plate; an upper member slidably mounted on the lower member in forward and backward directions of the equipment; a buffer means for attenuating impact and vibration generated in the forward and backward directions of the equipment; a tilting means including a frame, a hinge shaft, a driving shaft, and a control handle; and a locking means for locking and unlocking forward and backward movement of the upper member against the lower member when a pusher installed on one side of the frame is manipulated. In a main working mode of the equipment, a buffer function is performed through forward and backward movement of the upper member against the lower member, and when the main working mode is released, the buffer function is released.
Owner:VOLVO CONSTR EQUIP HLDG (SWEDEN) AB
Automated excavation machine
InactiveUS7695071B2Efficiently and effectively excavatingUnderground miningSlitting machinesActuatorExcavator
The present invention is directed to an excavator that is operable in manual and automatic modes and uses state machines to effect unit operations, rotationally offset swing actuators to rotate boom and cutter head, a fail safe hydraulic system to maintain gripper pressure in the event of a malfunction of the hydraulic system, differing position and pressure control functions in the hydraulic actuators, a kinematic module to effect pitch and roll adjustments, a cutting face profile generator to generate a profile of the excavation face, and an optimization module to realize a high degree of optimization of excavator operation.
Owner:MIN OF NATURAL RESOURCES CANADA
Movable arm potential energy recovery method and apparatus of hydraulic excavator
InactiveCN101435451ASmall pressure fluctuationsWorking speed adjustmentBatteries circuit arrangementsMechanical machines/dredgersRecovery methodThrottle control
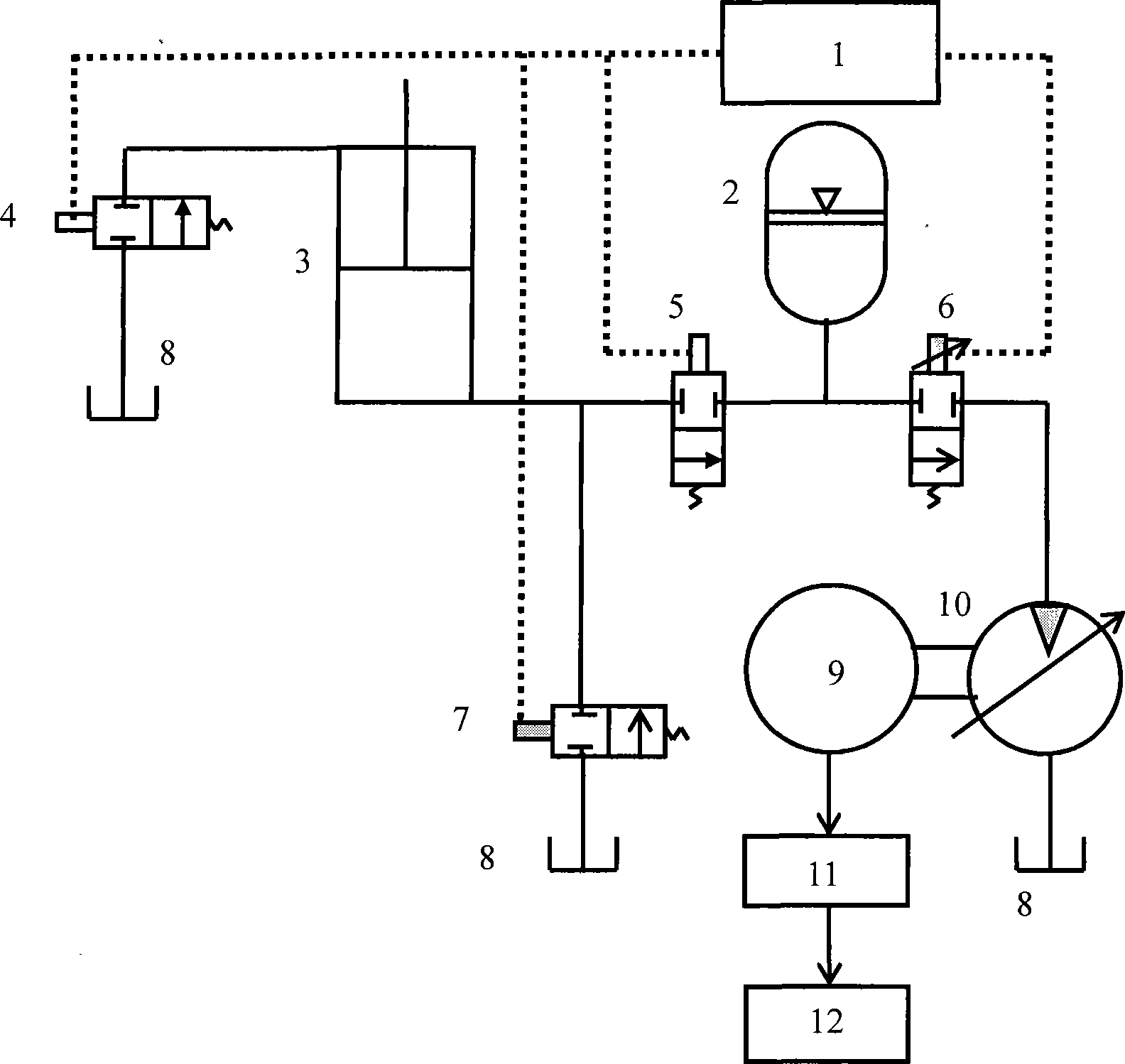
The invention discloses a method for recovering potential energy of a movable arm of a hydraulic digging machine and a device thereof. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, the potential energy is stored through an energy accumulator in the retraction process of a hydraulic cylinder; and secondly the stored energy in the energy accumulator drives a generator to generate electricity, thereby realizing the recovery of the potential energy of the movable arm of the hydraulic digging machine. A mode for storing the potential energy is to convert the potential energy into pressure energy. The energy accumulator and the generator are connected through a proportioning valve so as to control the rotational speed of the generator. The method realizes high-efficiency recovery of the potential energy of the movable arm of the hydraulic digging machine; the principle of the method is to skillfully change the working time of hydraulic oil for power generation through the function of energy storage of the energy accumulator and provide effective buffering for recovering the potential energy; in addition, through the throttling control of the proportioning valve, the method reduces pressure fluctuation of the hydraulic oil in the power generation process, realizes the adjustment of the working rotational speed of the generator, improves the working efficiency of the generator and further improves the efficiency of energy recovery.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Device for the coupling of excavator teeth
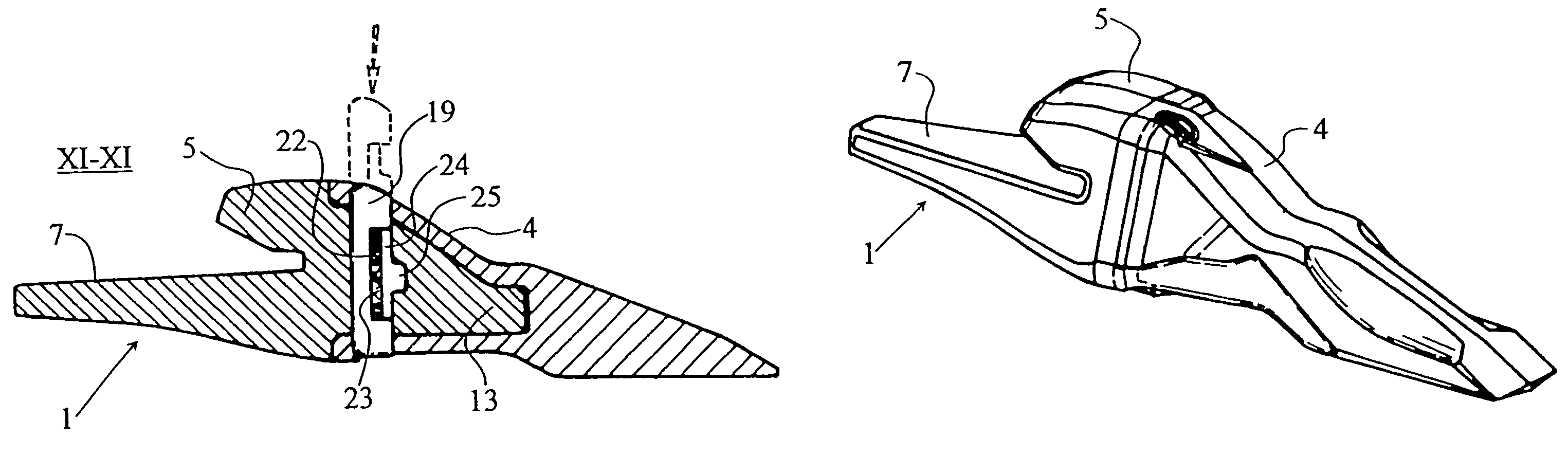
InactiveUS7168193B2Improve featuresSecure and durable couplingSoil-shifting machines/dredgersCouplingEngineering
The device is characterized in that the nose of the tooth-carrier has a general structure in which two end regions thereof, one corresponding to the area of junction of the said nose with the body of the tooth-carrier and the other to the free end of the tooth-carrier, assume in cross-section a dovetail structure, the dovetail at the first end region being inverted compared to the dovetail at the second end region, the cross-section of the end projection of the nose of the tooth-carrier being constant and the upper face of junction of the said projection with the base of the tooth-carrier assuming a curved structure with the convexity directed outwards, the lateral faces of the nose of the tooth-carrier assuming a structure of flat facets, one of them carrying in proximity to the junction with the body of the tooth-carrier a substantially vertical indentation for the coupling of the retaining cotter pin.
Owner:METALOGENIA PATENTES
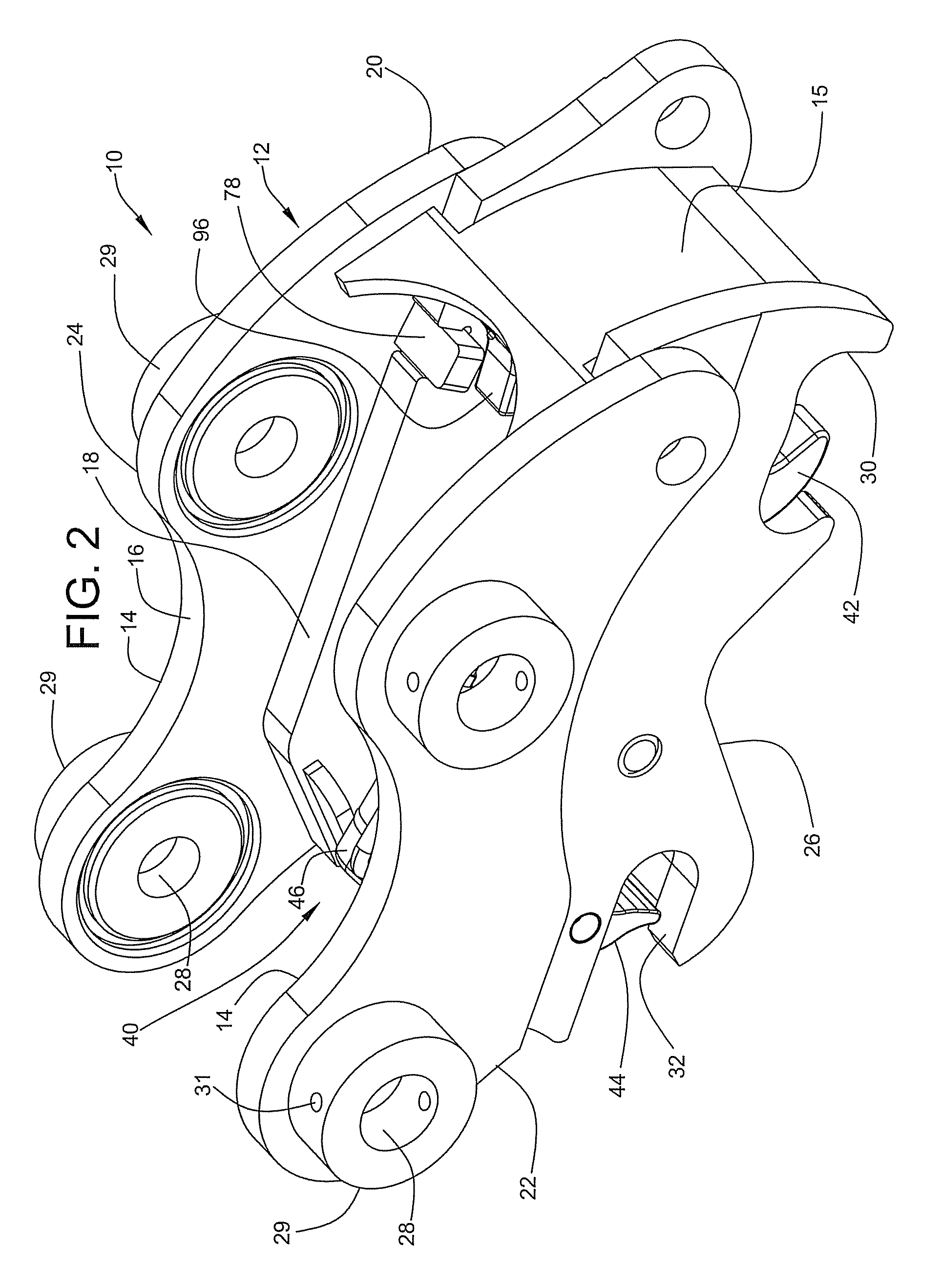
Excavator wear assembly
A wear assembly having an adaptor with a spigot portion is disclosed. The spigot portion has a transverse dimension. The wear assembly also has a wear member releasably mountable on the adaptor. The wear member has a body with a socket cavity and the socket cavity is adapted to receive the spigot portion of the adaptor. The wear member also has a pair of mounting ears extending from the body. Each of the mounting ears has a transverse dimension. The transverse dimension of each mounting ear is in the range 0.25 to 0.4 of the transverse dimension of the spigot portion.
Owner:CQMS PTY LTD
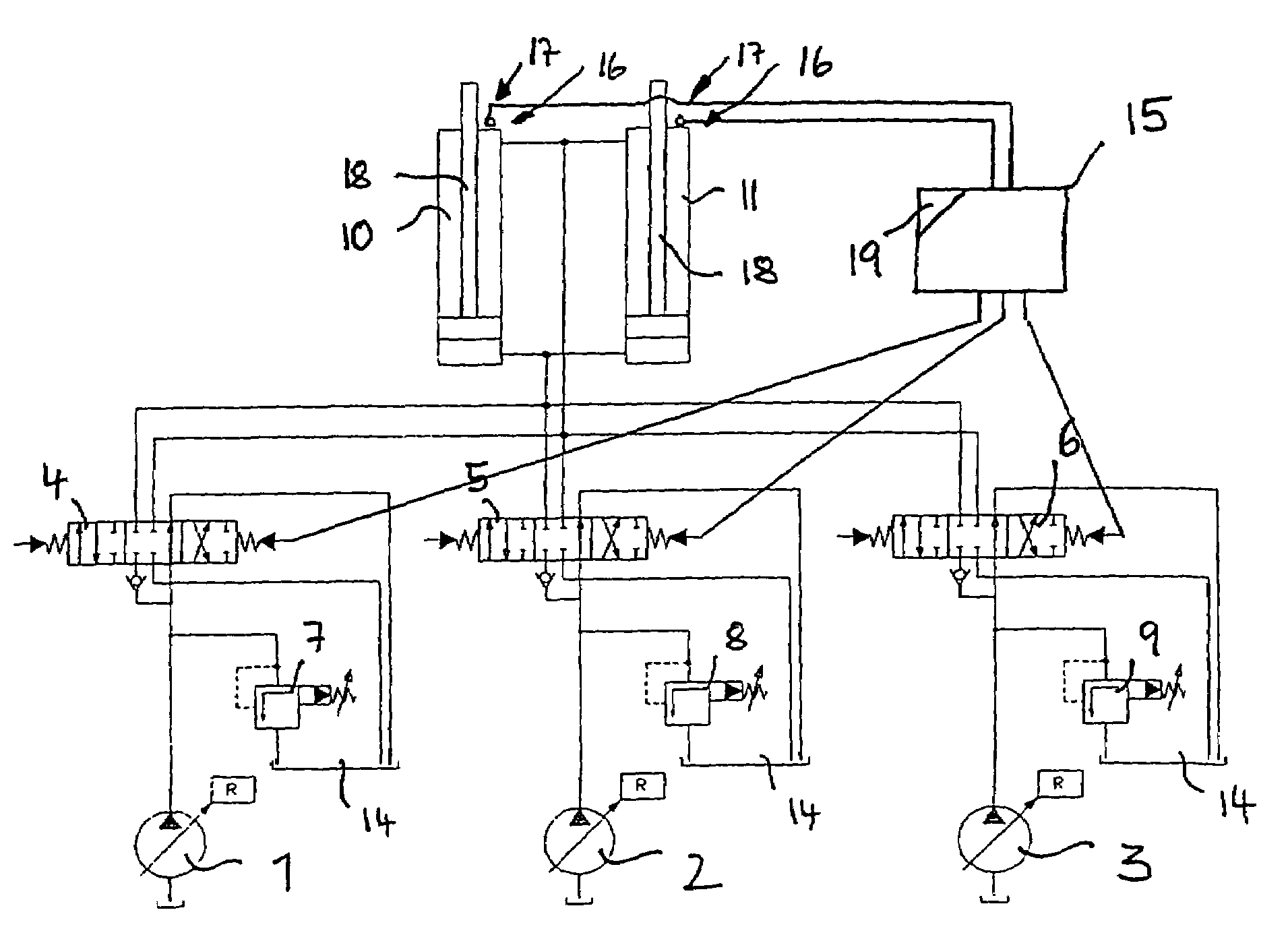
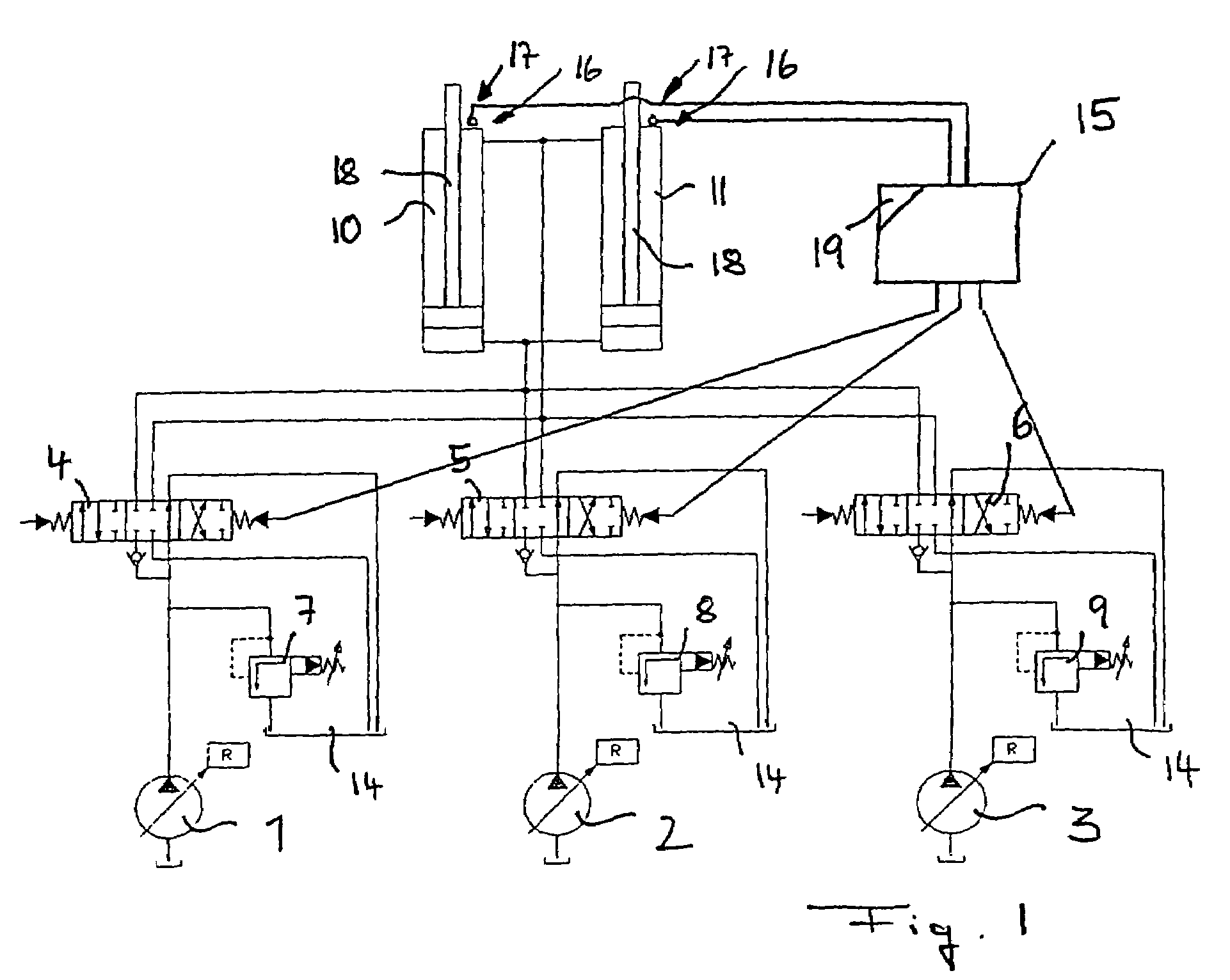
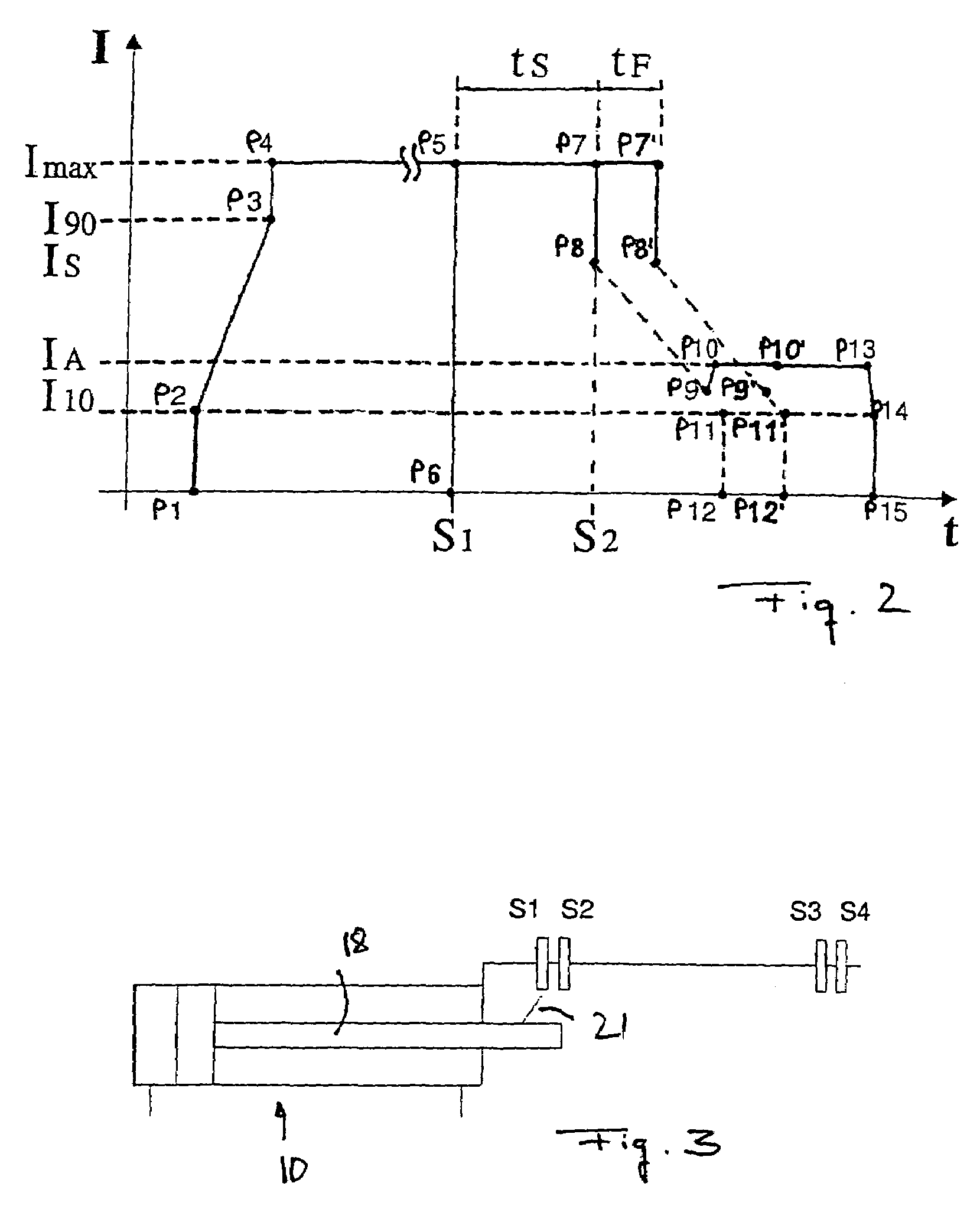
Method and device for attenuating the motion of hydraulic cylinders of mobile work machinery
InactiveUS7318292B2Good conditionServomotorsSoil-shifting machines/dredgersHydraulic cylinderEngineering
The present invention relates to a method for attenuating the motion of hydraulic cylinders of mobile work machinery, in particular of hydraulic excavators, in which prior to the hydraulic cylinder reaching one of the limits of travel, its motion speed is reduced, and the hydraulic cylinder is moved to the respective limit of travel at reduced speed; wherein for the purpose of reducing the speed, the inflow to, and / or the outflow from, the hydraulic cylinder are / is throttled by a flow control device. According to the invention, the method is characterized by, prior to the respective limit of travel being reached, the motion speed of the hydraulic cylinder is registered, and the point in time when throttling commences is changed depending on the registered motion speed. Furthermore, the present invention relates to a device for attenuating the motion of hydraulic cylinders of mobile work machinery, in particular of hydraulic excavators, a position registering device for registering a preliminary limit position of the hydraulic cylinder, a control device for throttling the inflow and / or outflow of the hydraulic cylinder, and a control device for controlling the flow control device when the preliminary limit position is reached. According the invention, the device has a speed registering device for registering the motion speed of the hydraulic cylinder when the preliminary limit position is reached, and the control device has a delay device for delaying driving the flow control device, depending on the recorded motion speed.
Owner:LIEBHERR FRANCE
Excavator wear assembly
ActiveUS20130333254A1Prevent exitIncrease radial widthSoil-shifting machines/dredgersMetal working apparatusEngineeringExcavator
A lock assembly to lock two members together, typically an excavator wear member, such as a tooth, on to an adaptor. The lock assembly has a locking pin with a flange portion and a retaining assembly that receives the locking pin. The retaining assembly includes a locking member, in the form of a locking ring, which deforms radially when a tapered portion of the locking pin is inserted into the retaining assembly. In the locked position, the locking ring engages with the flange portion of the locking pin to prevent withdrawal of the locking pin from the retaining assembly.
Owner:CQMS PTY LTD
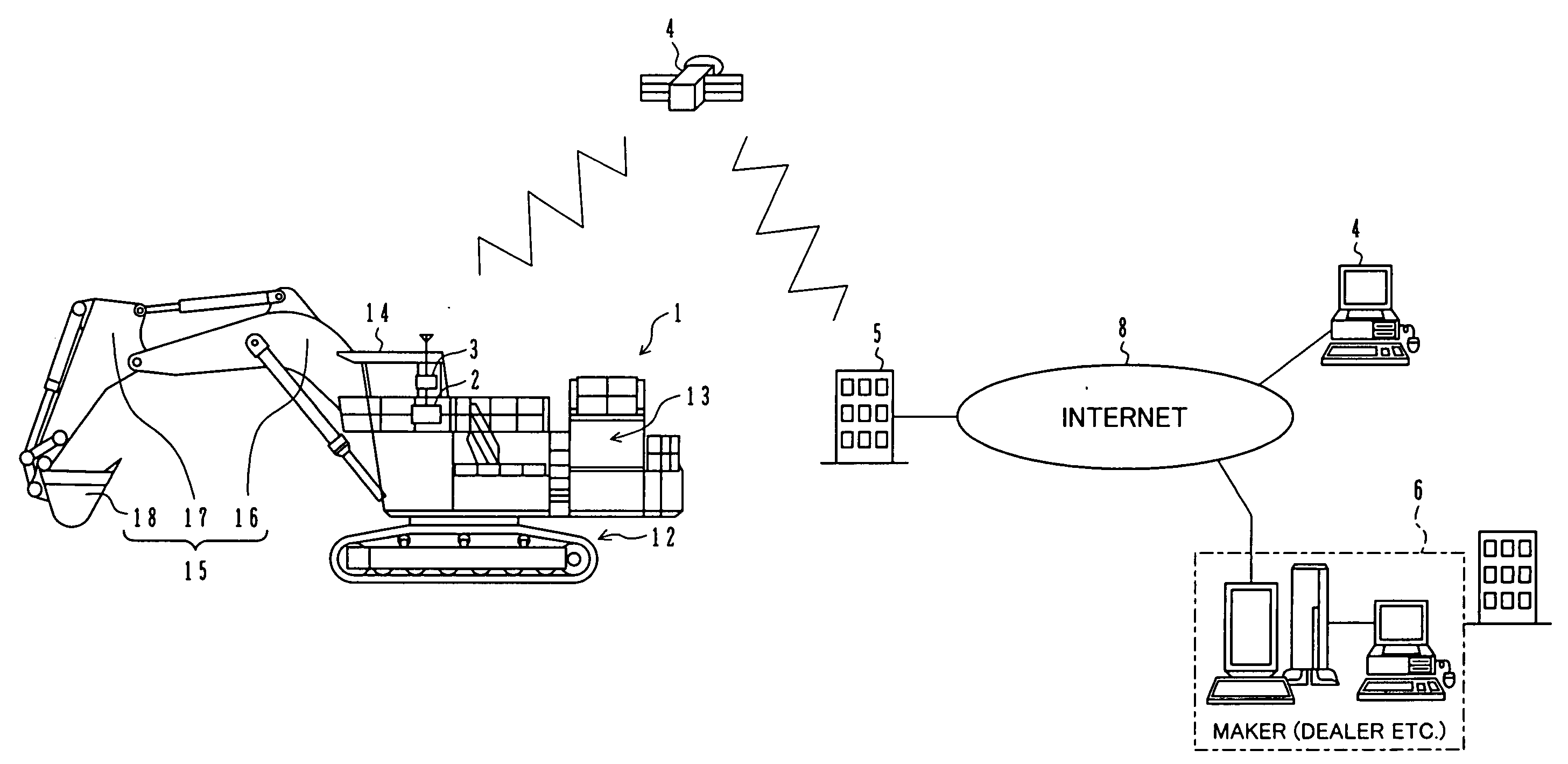
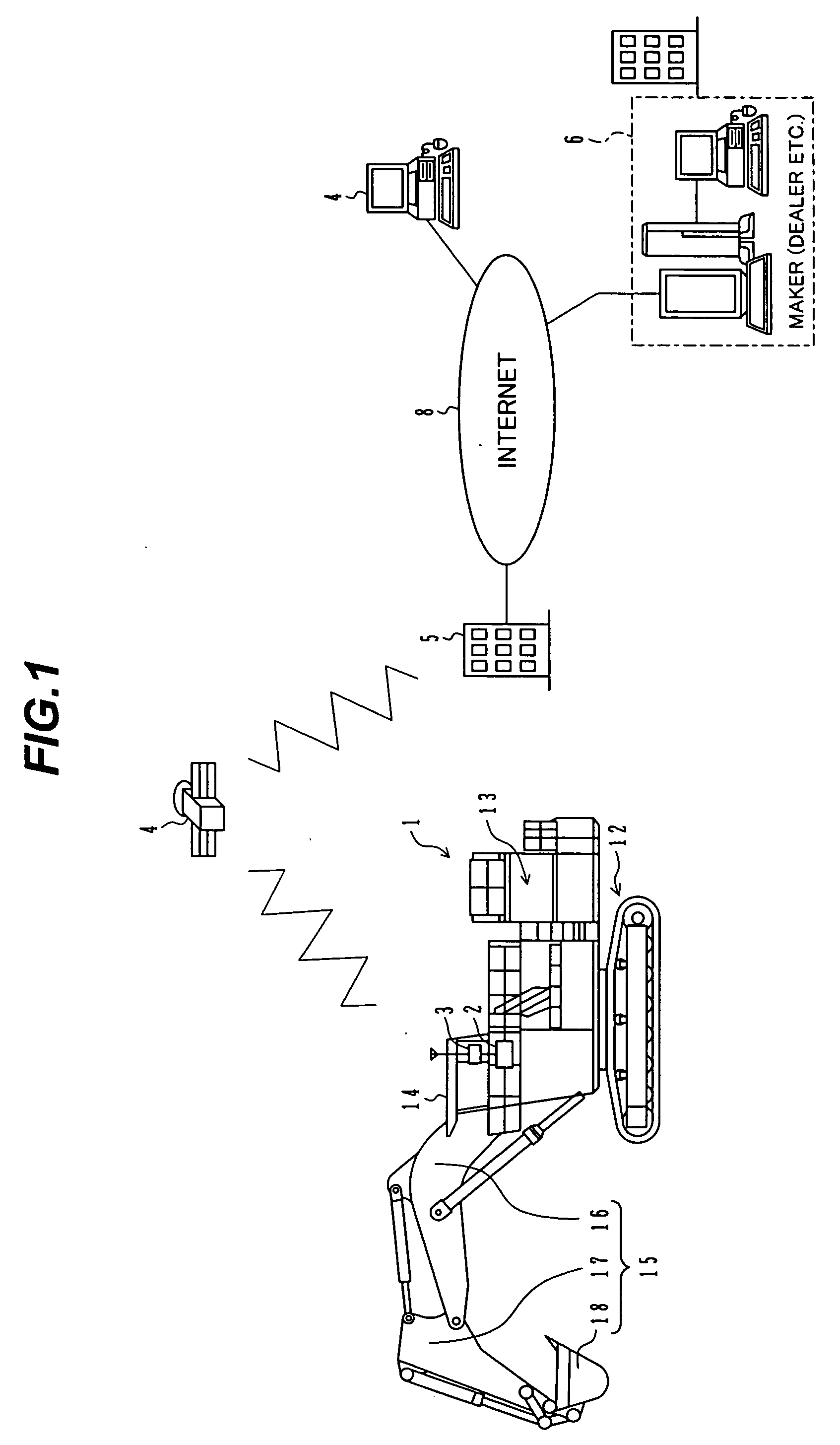
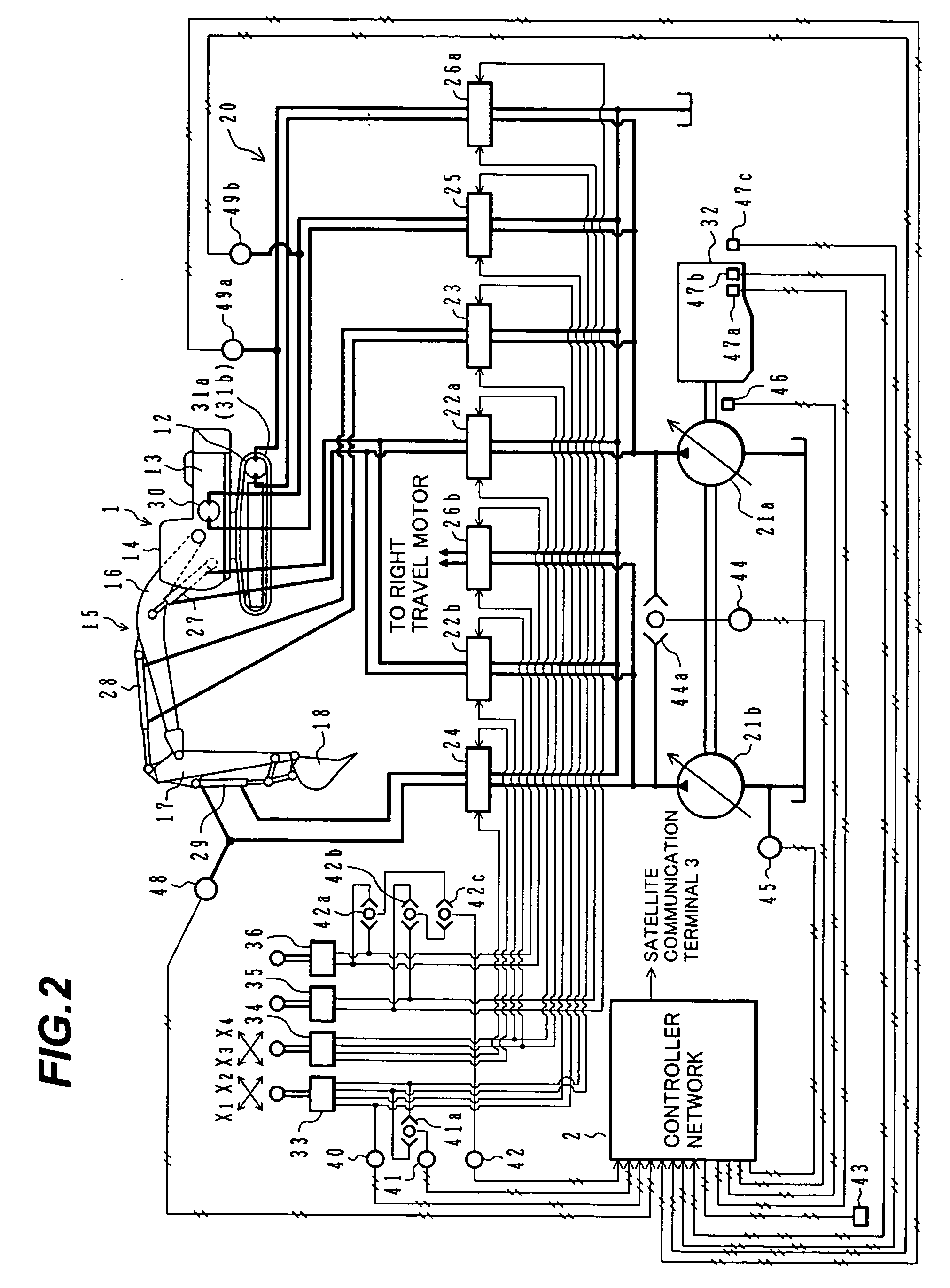
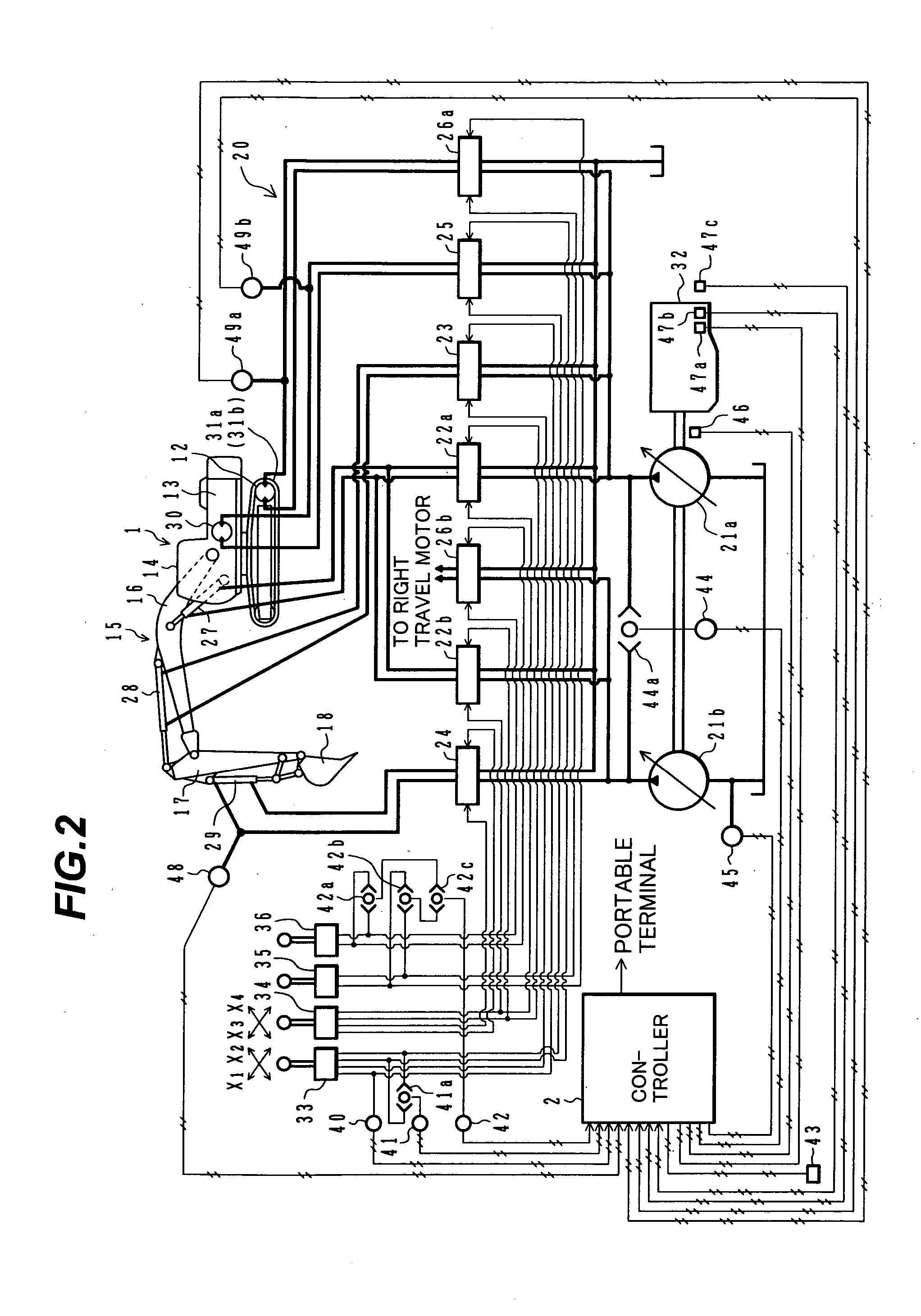
Operation information control device for construction machine and construction machine operation information control system provided with it
InactiveUS20060212203A1Drawback can be obviatedRestraining the drop in productivityVehicle testingData processing applicationsMachineOperational data store
A data recording unit 60 for managing operating situations of a hydraulic excavator 1 comprises a RAM 67 for taking in and storing plural kinds of operational information regarding the hydraulic excavator 1 as operational data, and a CPU 65 for extracting top priority operational data from among the plural kinds of operational data stored in the RAM 67, and transmitting the extracted data to the supervising side via satellite communication. Top priority data among the plural kinds of operational data of the hydraulic excavator, which may bring the hydraulic excavator into rest, can be presented to a supervisor of the hydraulic excavator, etc.
Owner:NIHON KENKI CO LTD
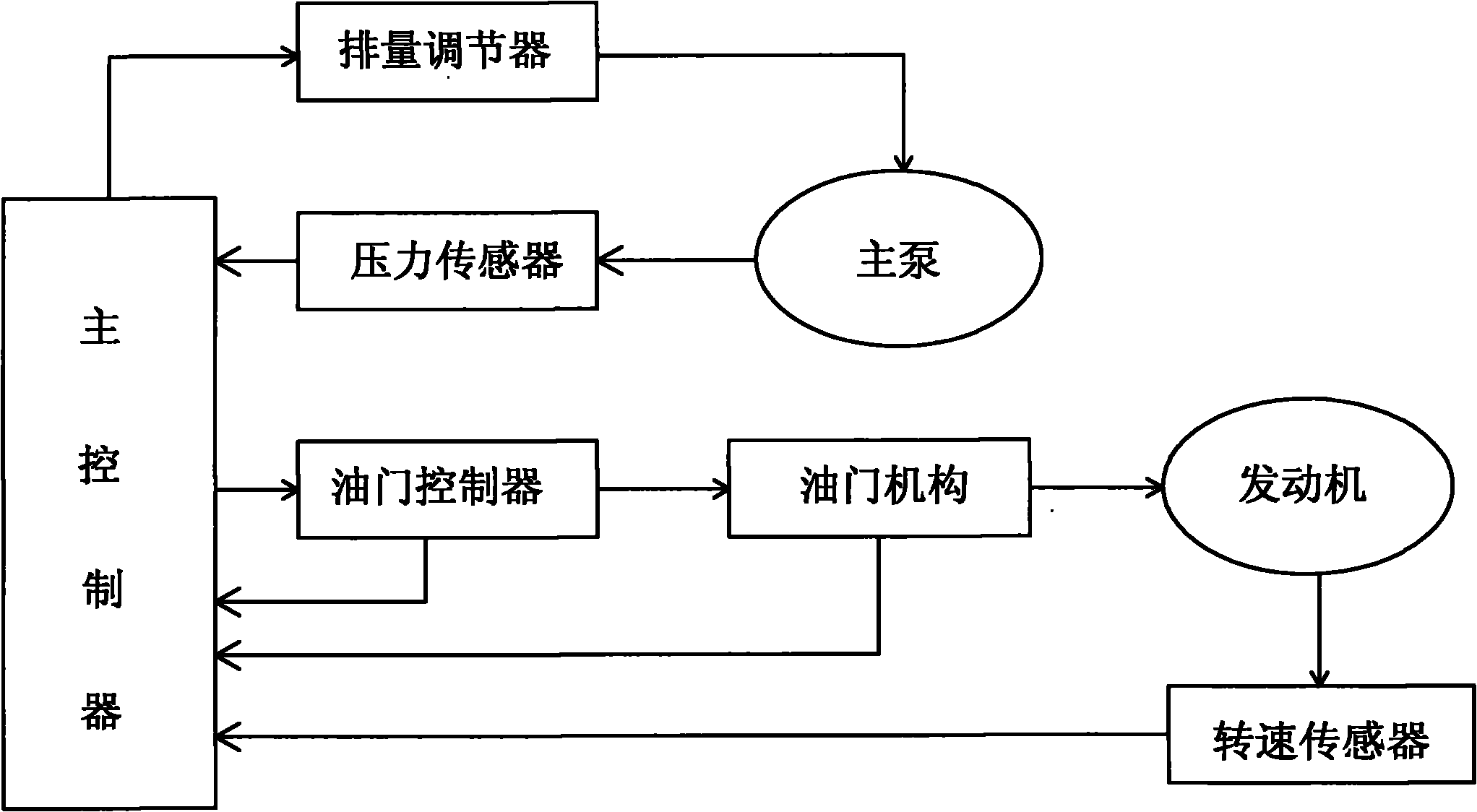
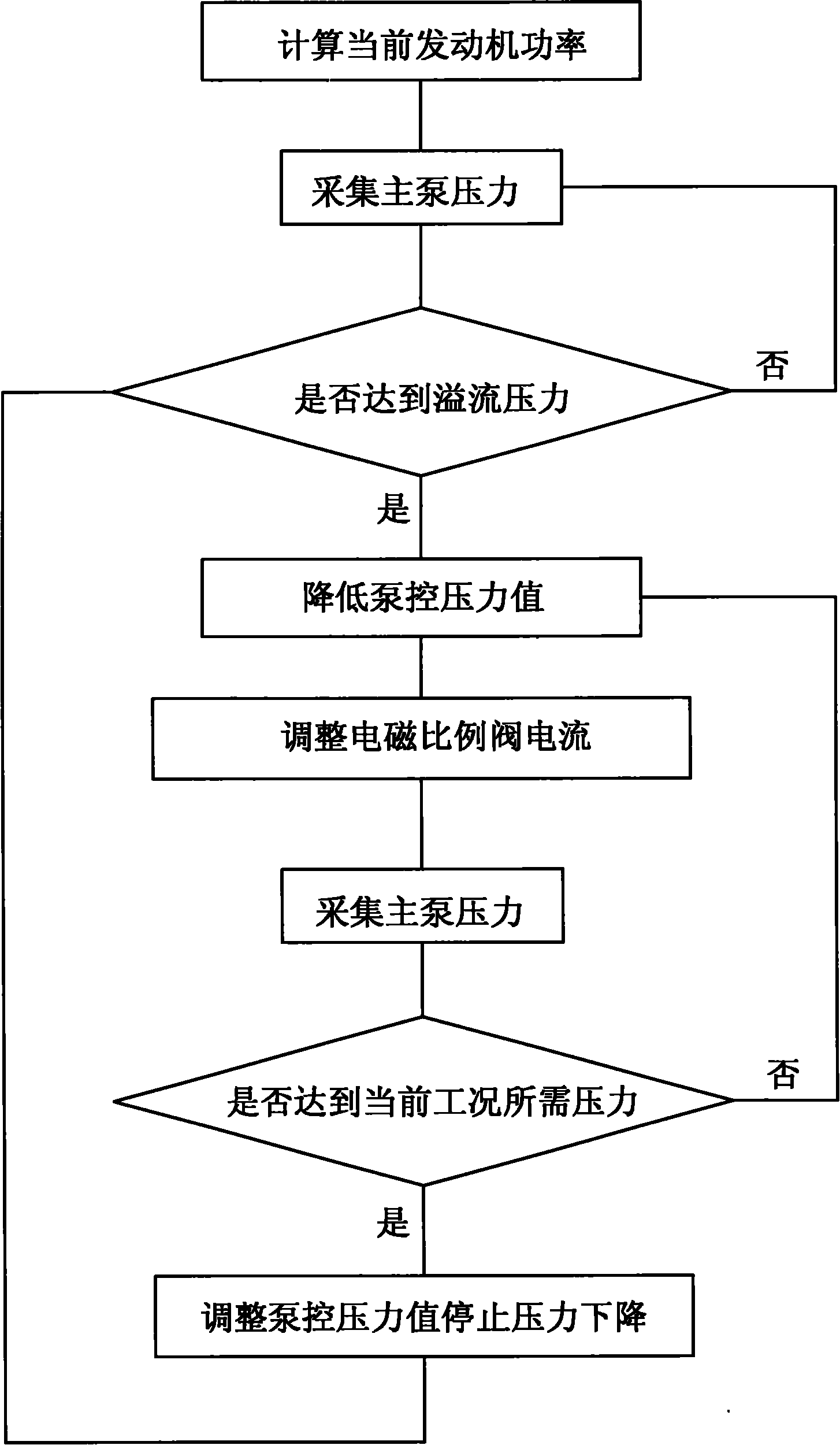
Power control system and method of excavator
InactiveCN101818508ADoes not affect powerDoes not affect response speedSoil-shifting machines/dredgersPower modeConstant power
The invention discloses a power control system of an excavator. The power control system is characterized by comprising a pressure sensor, a main pump displacement regulator, a revolution speed sensor and a loading calculation module, wherein the pressure sensor and the main pump displacement regulator are arranged on the outlet of a main pump, the revolution speed sensor is arranged on an engine, and the loading calculation module is arranged in the main controller; the pressure sensor, the revolution speed sensor and the main pump displacement regulator are respectively connected with the main controller and output engine revolution speed, throttle position and main pump displacement after being calculated by the loading calculation module to respectively control an actuating mechanism. The method is as follows: low load is a positive flow control mode; high load: a. when engine revolution speed is more than or equal to no-load speed* (1-7%), controlling by a constant power mode; and b. when the engine revolution speed is less than no-load speed* (1-7%), controlling by a limiting power mode. The invention controls by constant power comprehensive limiting power, gives consideration to the power output of a dynamic system on the premise of ensuring excavating force, dynamically adjusts the matching between the practical power of a hydraulic system and requirements, lowers power loss and reduces oil loss.
Owner:SANY HEAVY MACHINERY
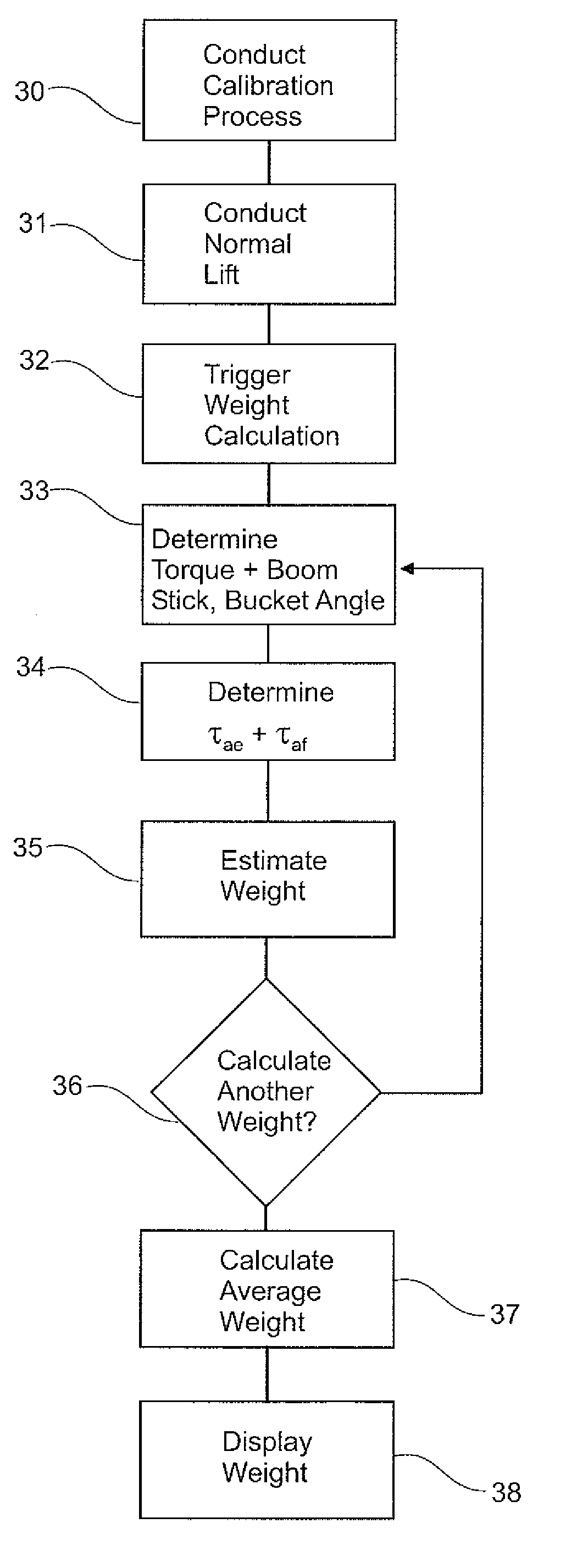
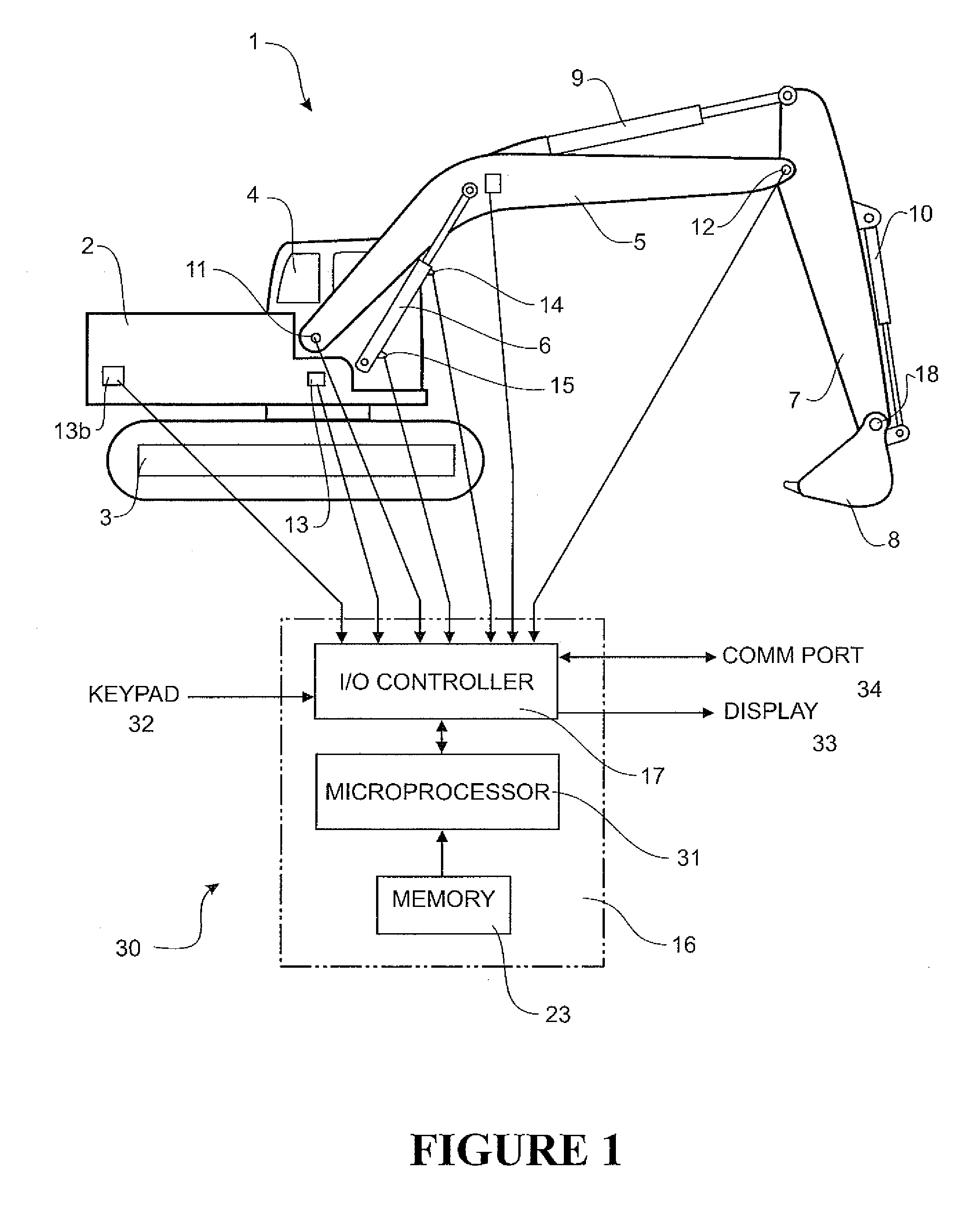
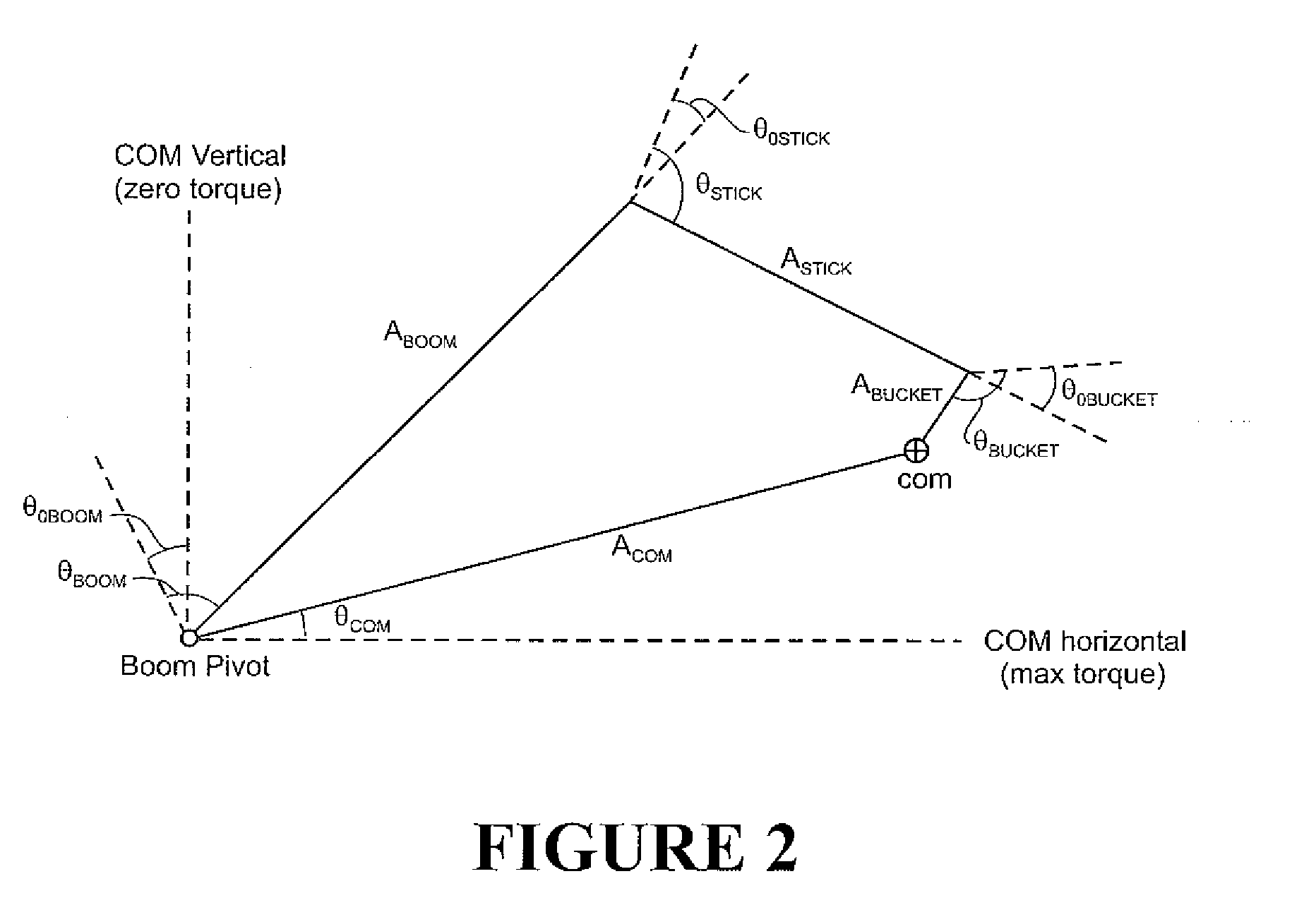
Weight Estimation for Excavator Payloads
ActiveUS20080319710A1Compensation effectDigital computer detailsSoil-shifting machines/dredgersEstimated WeightControl theory
A method for estimating weight of a payload held by load lifting machine 1, wherein the load lifting machine comprises lifting linkage with a boom 5 pivotably connected to a machine chassis 2, the method comprising calculating an estimation using the torque of the boom 5, torque of the boom during calibration lifts for first and second payloads, and dynamic torque adjustment determined for first and second payloads.
Owner:TRIMBLE INC
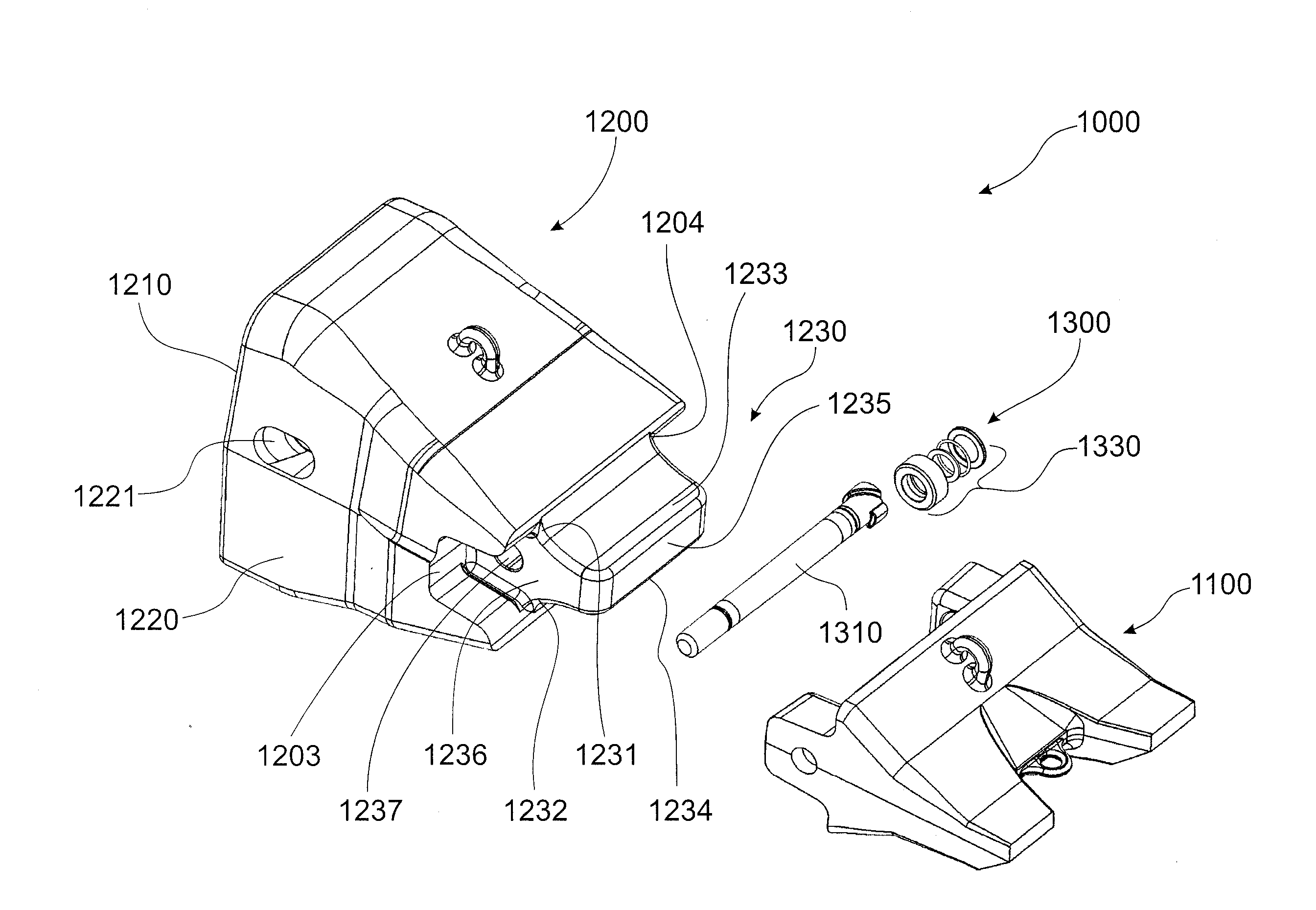
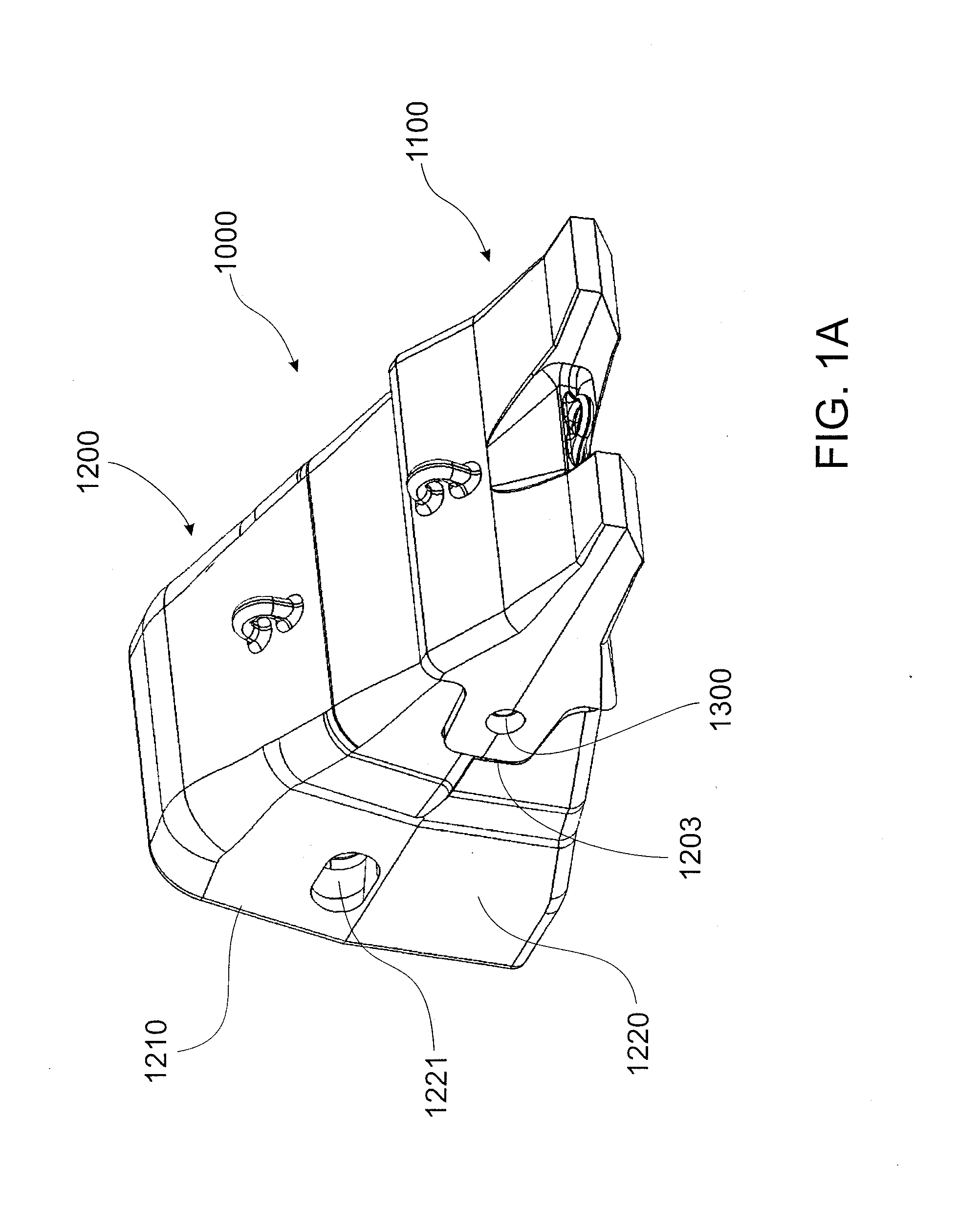
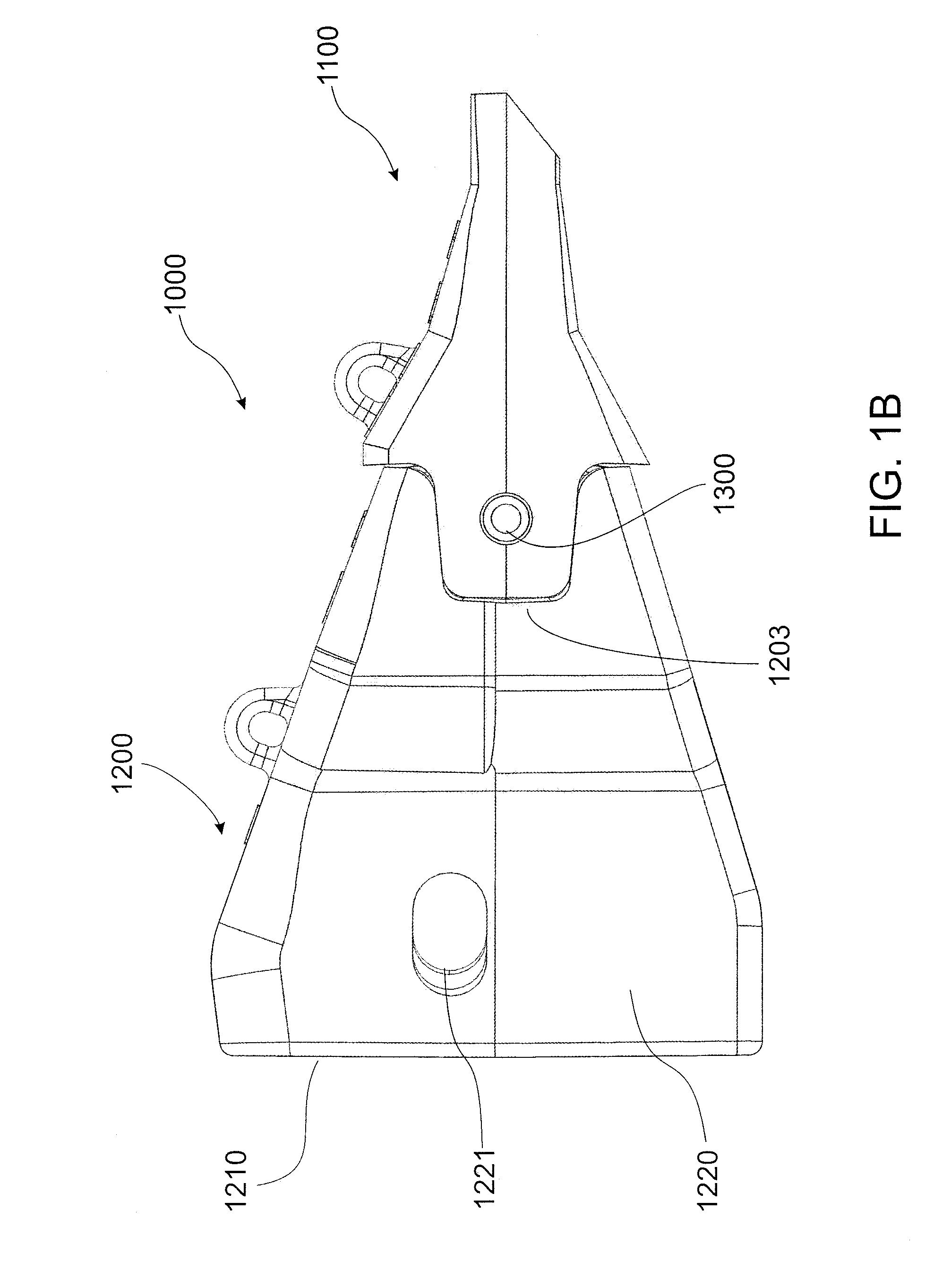
Excavator tooth retention device
A tooth retention device for attachment to an excavator bucket, which has a tooth mounting portion, a fork shaped body fitting over the edge of the bucket, a clamp passing through the body and the bucket, and a wedge holding the clamp in position, in which the wedge has a threaded rod and a threaded block on the rod. The rod is rotatable to move the block between locked and released positions.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
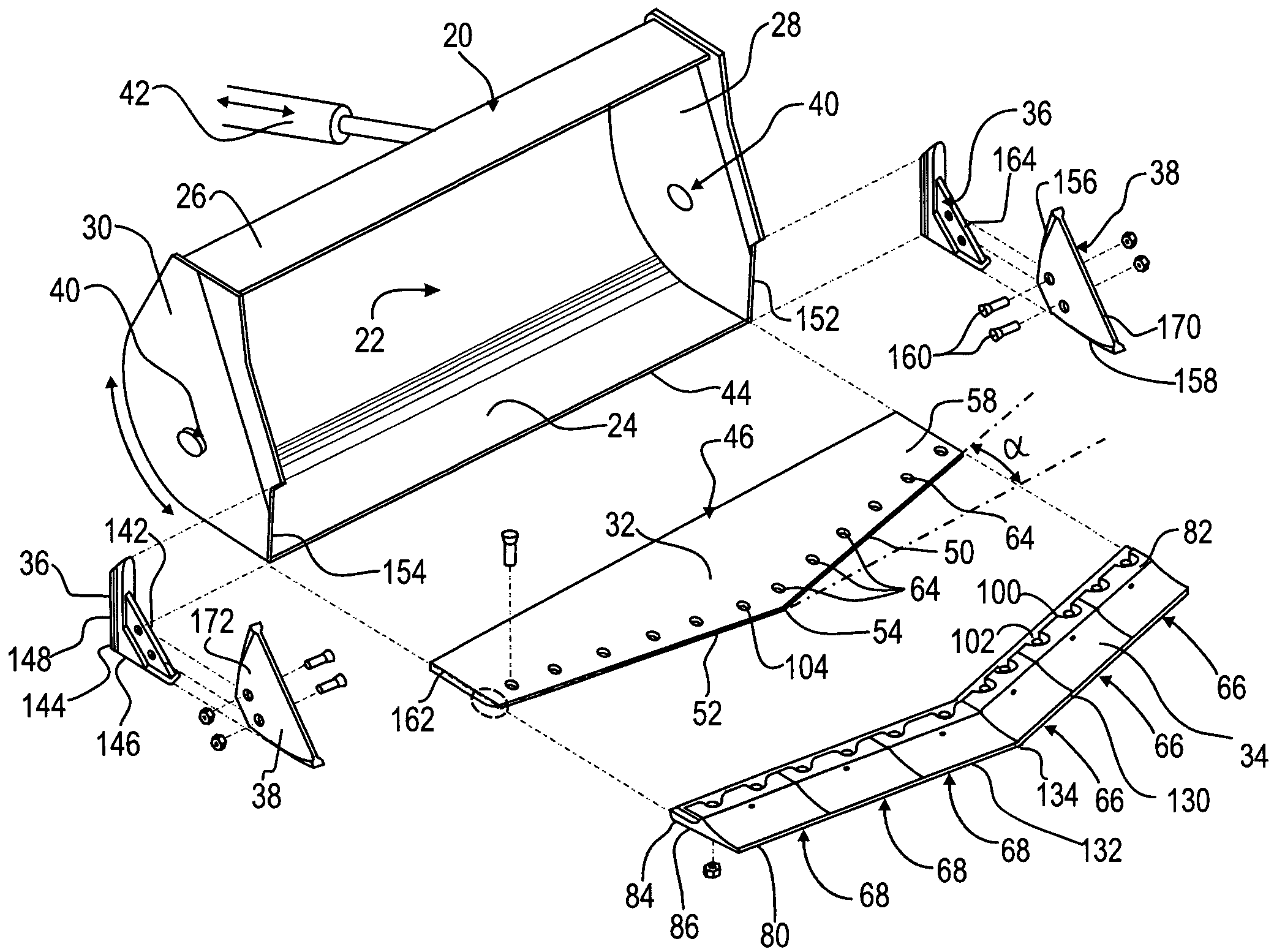
Wear plate assembly
InactiveUS7266914B2Thicker wear lip sectionEliminate and reduce movementMechanical machines/dredgersLeading edgeEdge segment
A bucket assembly is provided with a kit that includes a base plate for permanent connection to a lower part of the bucket, and sacrificial, impermanent replaceable wear edge segments for the forward lip and corner leading edges of an excavator or loader bucket. These segments form a set of “bolt on” cast wear members and wing wear segments. The base plate and wear plates are drilled and machined to accommodate the precision fitting bolting on of the replaceable lips and cast wing segments. The cast lip segments are of both left and right hand configurations and come in a variety of widths that, in combination, may tend to fit a large number of different commercially available bucket sizes. The lip top and bottom faces are shaped in a profile that may tend to result in relatively uniform wear and a reduction in friction when digging into various materials.
Owner:PENINSULA ALLOY +1
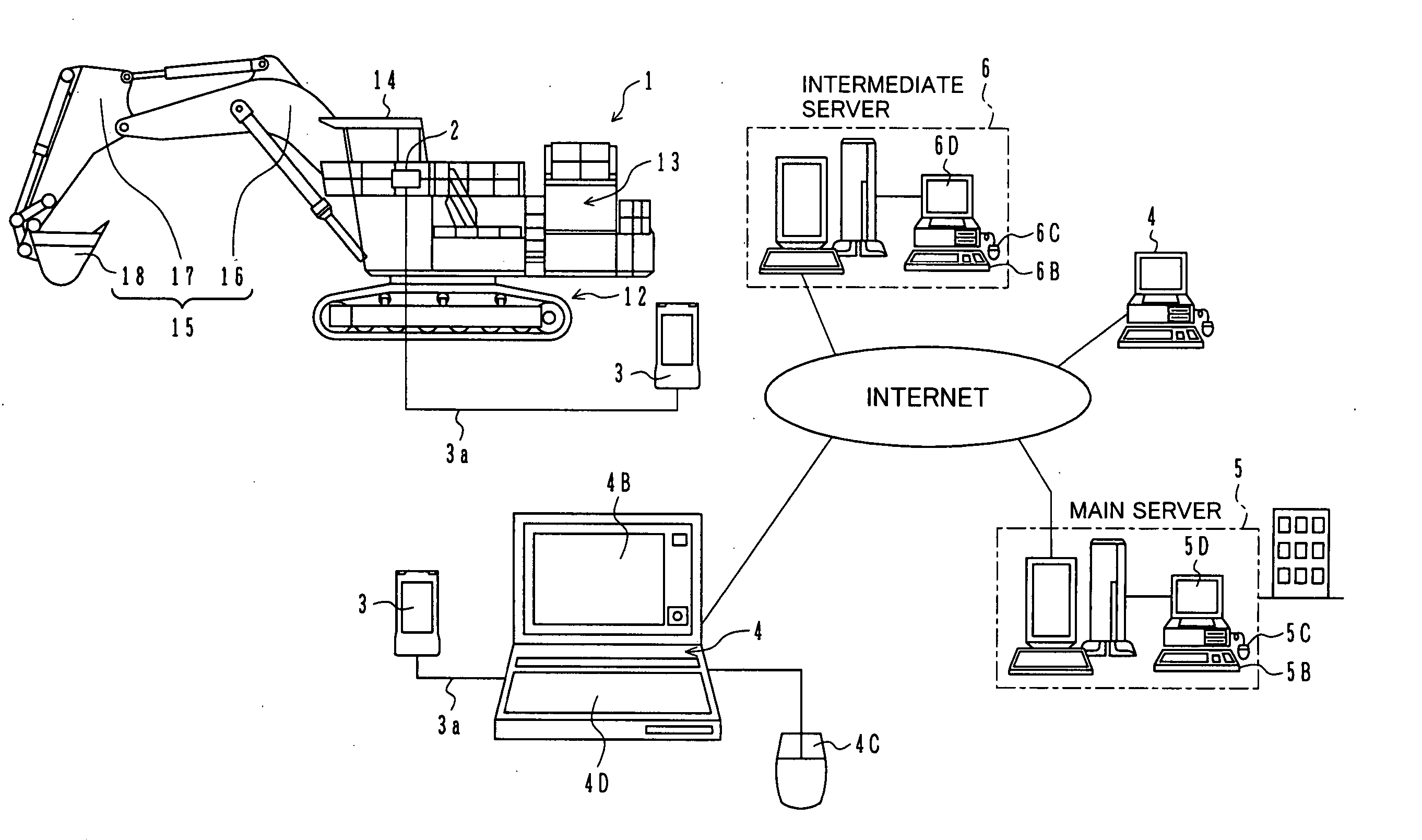
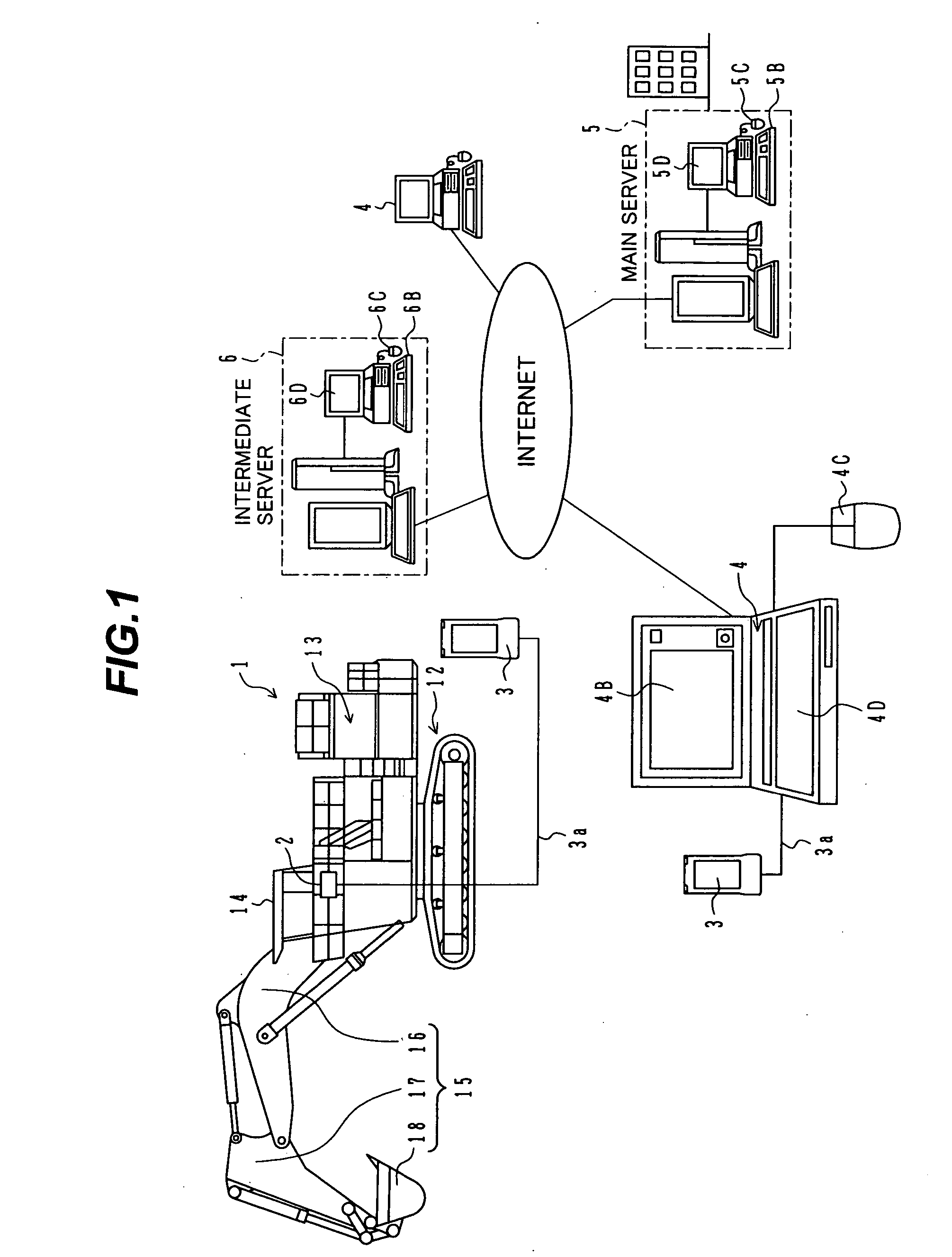
Information providing system of construction machine and information providing method of construction machine
InactiveUS20050021245A1Improve machine lifeEfficiently employedSoil-shifting machines/dredgersOffice automationComputer terminalEngineering
An information providing system for a construction machine has a plurality of information terminals (4) provided on the side of users or owners of hydraulic excavators (1), a main server (5) provided on the side of a manufacturer of the hydraulic excavators, and an intermediate server (6) provided on the side of a dealer in charge of services presented to the users or the owners. The main server (5) obtains data regarding machine operation of each hydraulic excavator (1) via information communication and stores the obtained data in a database (5A ), and outputs the obtained data regarding the machine operations of the plurality of hydraulic excavators (1), as basic information for services presented to the users or the owners, to the intermediate server (6). The intermediate server (6) outputs, to the corresponding information terminal (4), the basic information directly or after optionally selecting the basic information.
Owner:NIHON KENKI CO LTD
Anchor
An anchor for a wear assembly on an excavating bucket is disclosed. The excavator bucket lip has a base having a nose, and the wear assembly includes a wear member having a cavity in which the nose can be received, and an aperture extending between an outside surface of the wear member and the cavity, an internally toothed ring being located within the aperture; and a lock for releasably holding the wear member to the base. The lock includes an operable member and an externally toothed resilient ring, the resilient ring having a central aperture for engagement with the operable member. The operable member and resilient ring are jointly rotatable relative to the cavity and the internally toothed ring between a plurality of rotationally spaced locking positions where the lock secures the wear member to the base with varying tightness, and a release position rotationally spaced from the locking positions. The teeth of the internally toothed ring and the teeth of the resilient ring engage each other in each of the locking positions to reduce the loosening of the lock during use.
Owner:TALON ENG
Wear assembly for excavator digging edge
InactiveUS7080470B2Stable and mannerIncreased durabilityMechanical machines/dredgersMetal-working hand toolsFront edgeExcavator
Owner:ESCO GRP LLC
Quick coupler lock system
A quick coupler lock, for use as a safety to engage an attachment, such as a bucket or scoop, to a heavy equipment armature, as found in backhoes and excavators. The coupler lock prevents the unwanted release of auxiliary attachments. The coupler lock includes a coupler frame with a pin grabber, and a coupler hook rotated to engage a pin. The rotation of the coupler hook is accomplished by the extension or retraction of a coupler actuator, preferably a hydraulic cylinder held within a spring. The coupler actuator hingably connects to a pivoting lock lever. The action of the coupler actuator rotates the lock lever about the lever pin. A lock bar hingably attaches to the coupler hook and rotates with the coupler hook. The lock lever includes an arm that contacts the lock bar, to prevent movement of the coupler hook and prevent the unwanted release of the pin.
Owner:PSM
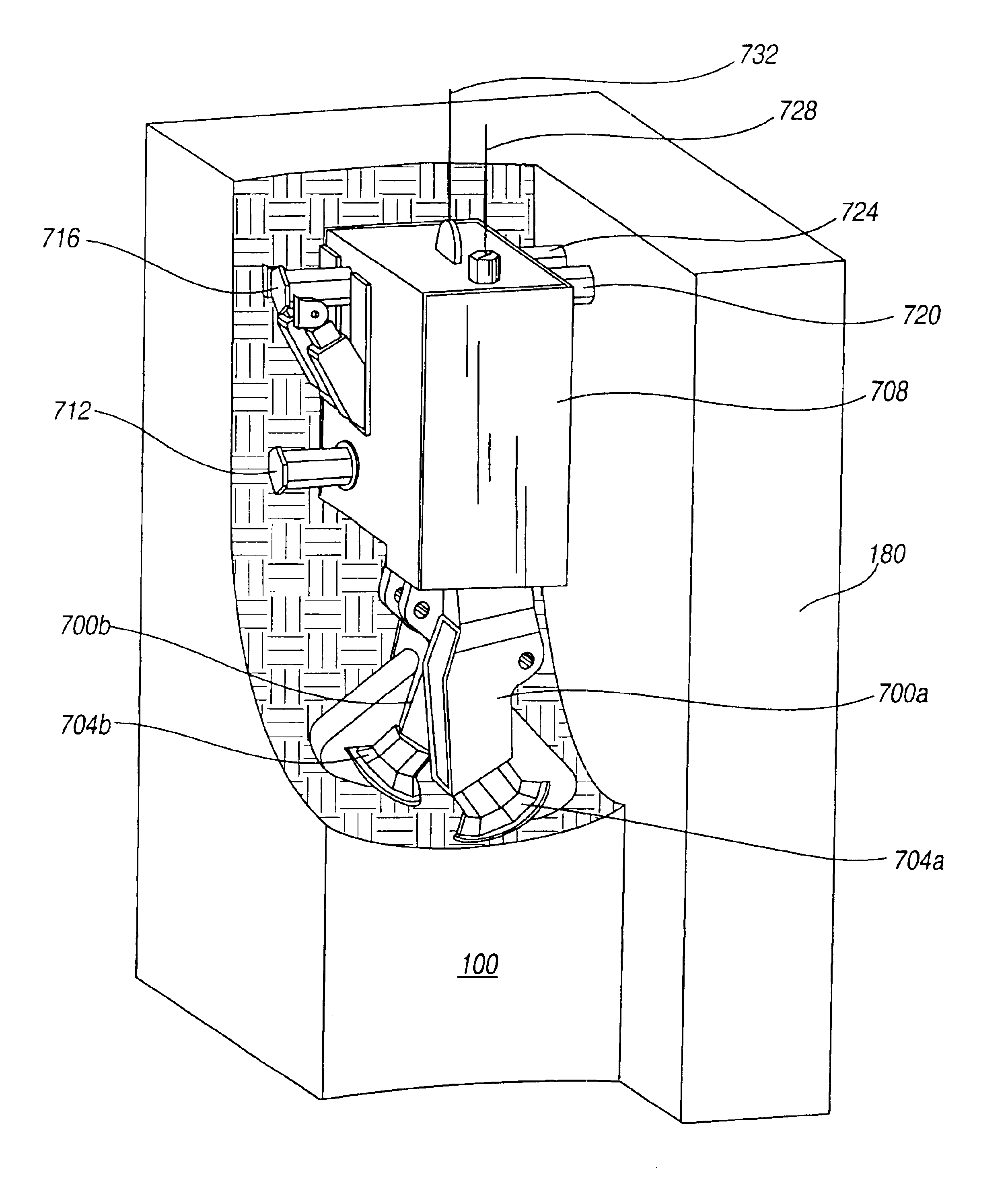
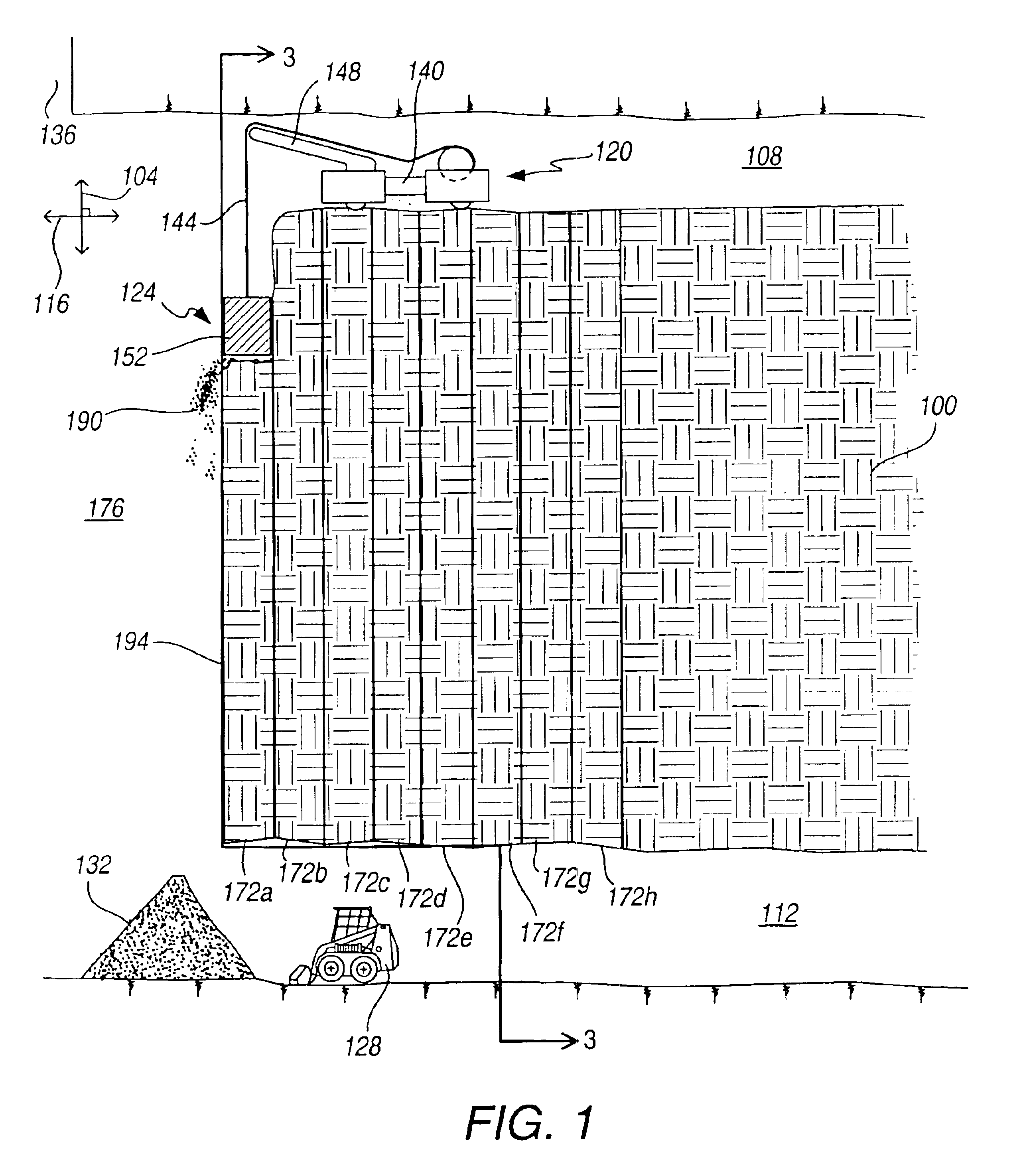
Mining method for steeply dipping ore bodies
InactiveUS6857706B2Efficiently and effectivelyAvoid a lotDisloding machinesUnderground miningEngineeringExcavator
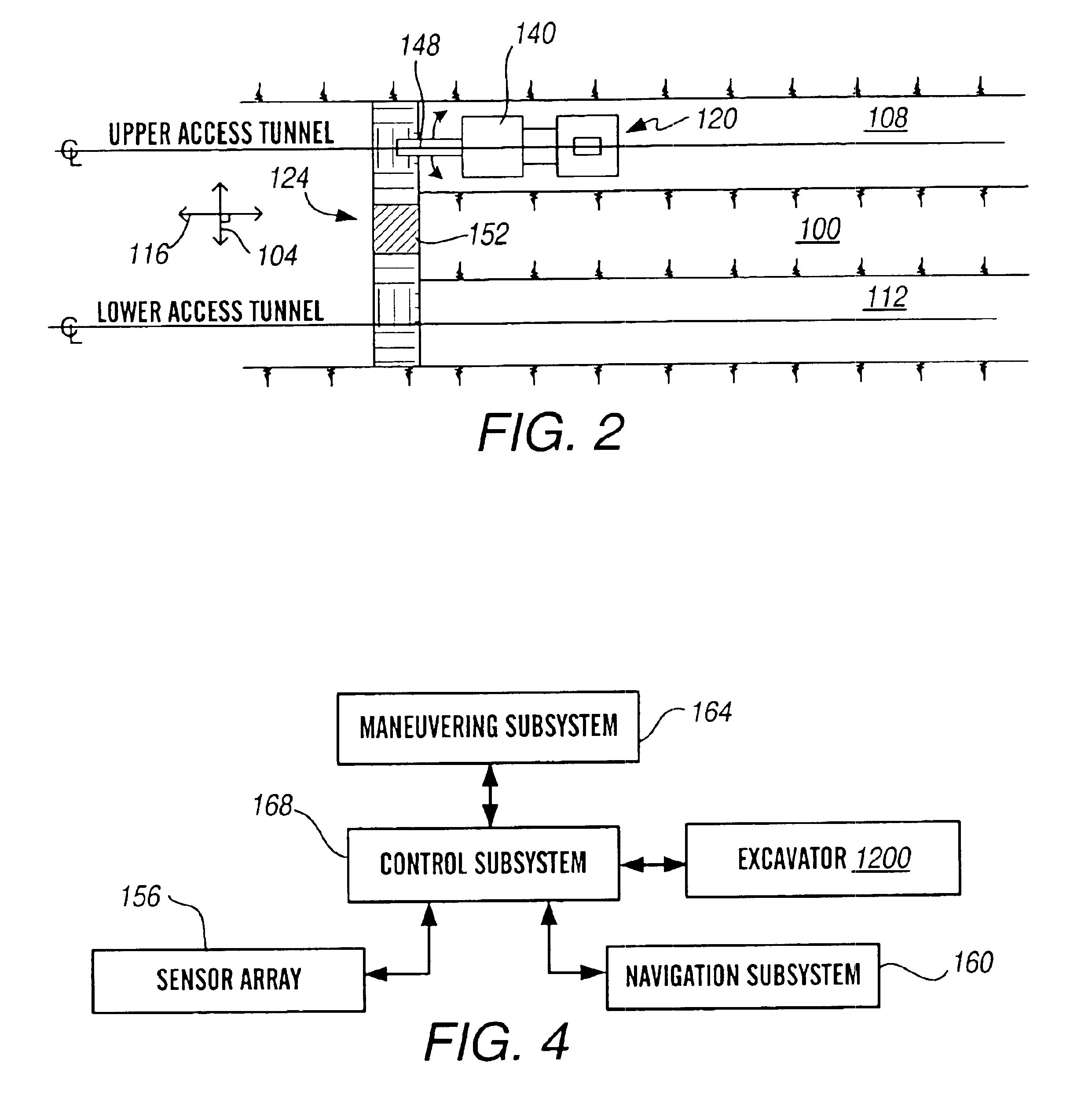
The present invention is directed to a mining method for steeply dipping orebodies. In the method, an excavator 152 is tethered to a deployment system 120 by one or more cables / umbilicals 144. The excavator 152 excavates slices 172a-h of the orebody 100 by moving generally up-dip, down-dip or a combination thereof. The excavator can be automated.
Owner:MIN OF NATURAL RESOURCES CANADA
Hybrid construction machine
ActiveCN101037869AEnsure operabilitySolve the problem of poor operabilityElectric machinesSoil-shifting machines/dredgersHydraulic pumpMotor function
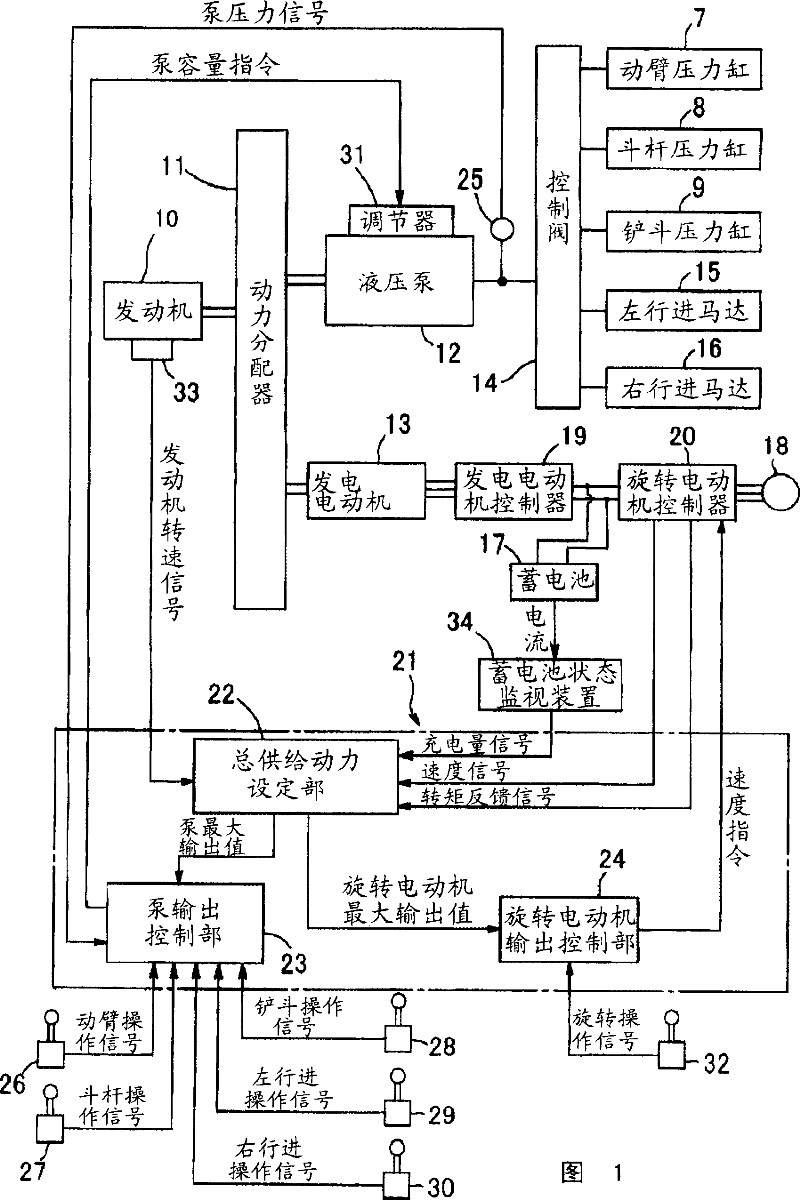
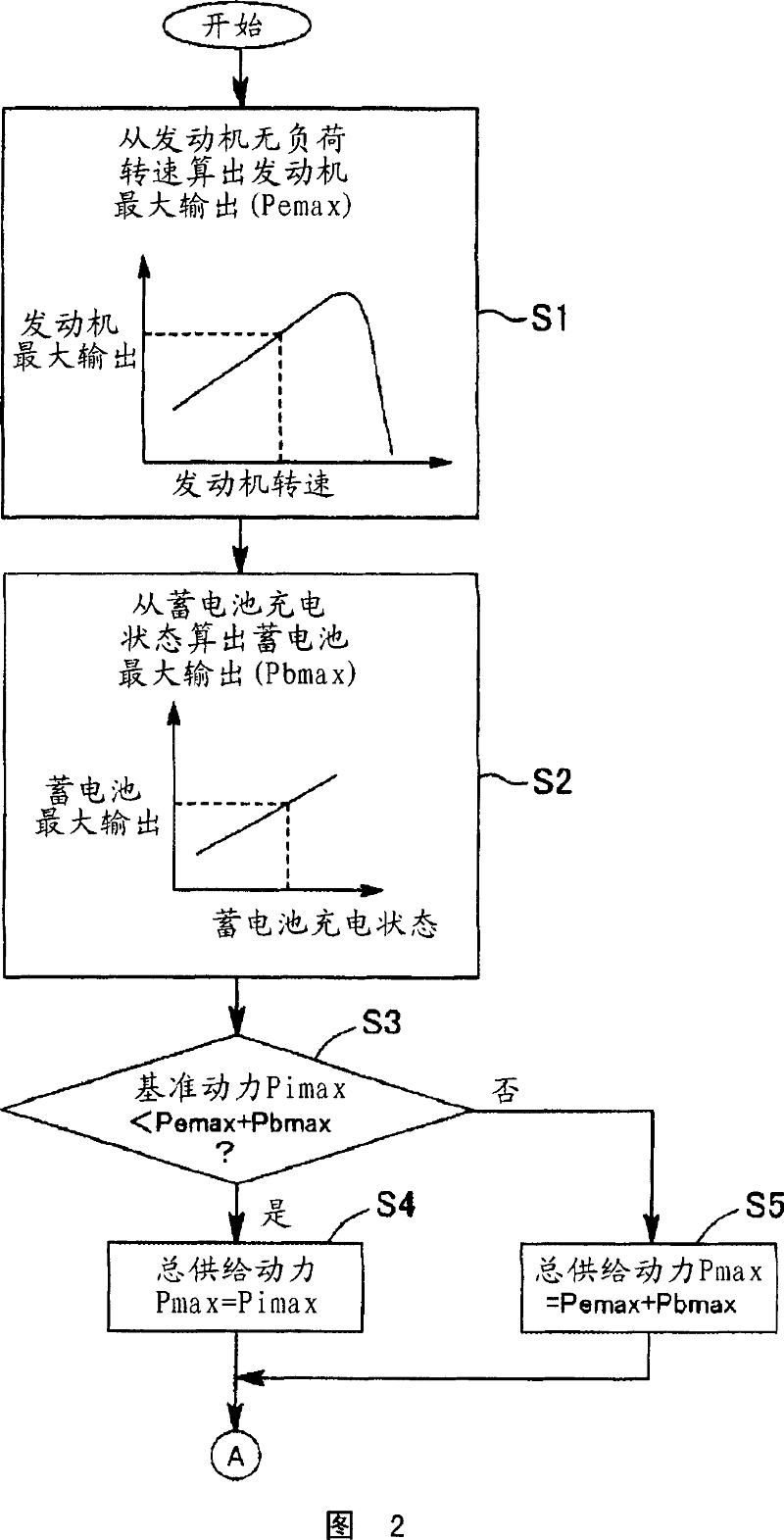
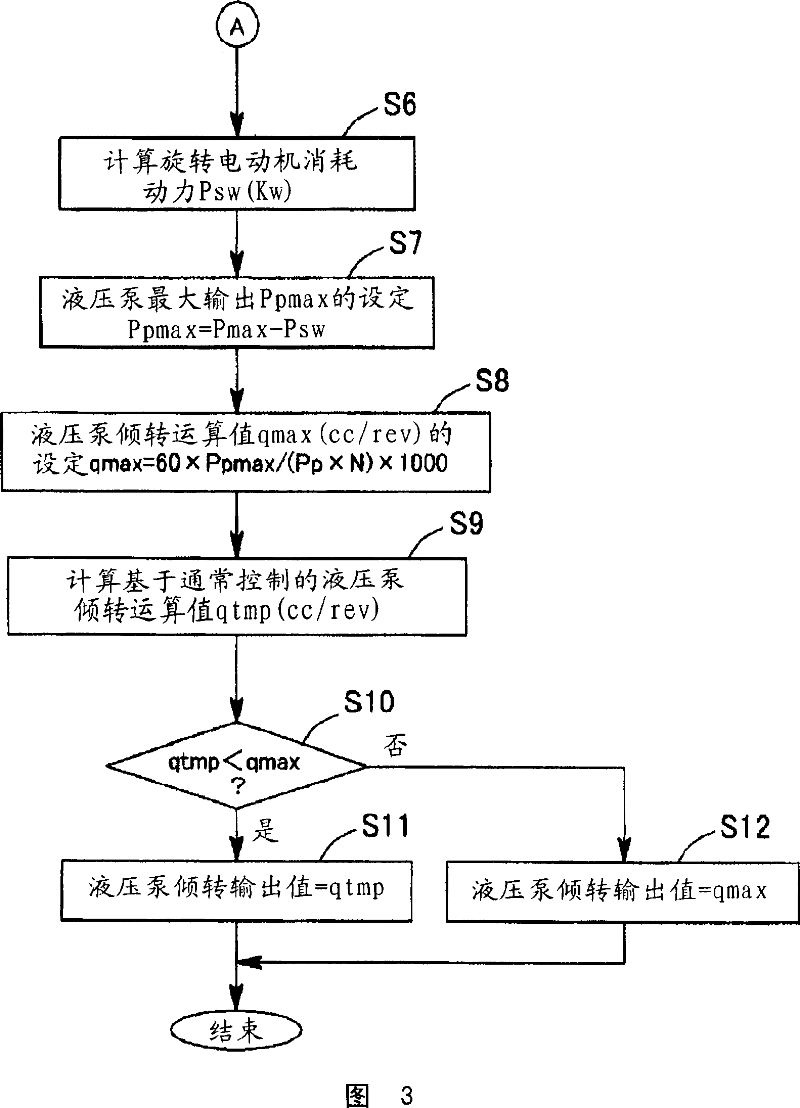
In a hybrid excavator of the invention, a hydraulic pump and a generator motor are connected in parallel to an output shaft of an engine and a rotation motor is driven by a battery. The generator motor assists the engine by performing a motor function. Power consumption of each of the hydraulic pump and the rotation motor is detected. The output of the hydraulic pump and the rotation motor is controlled such that the sum of the detected power consumption does not exceed maximum supply power set as the sum of power that can be supplied to the hydraulic pump and the rotation motor. Therefore, the equal performance and operation with the hydraulic excavator can be ensured, and the electric power storage arrangement can be protected.
Owner:KOBELCO CONSTR MASCH CO LTD
Dual Monitor Information Display System and Method for An Excavator
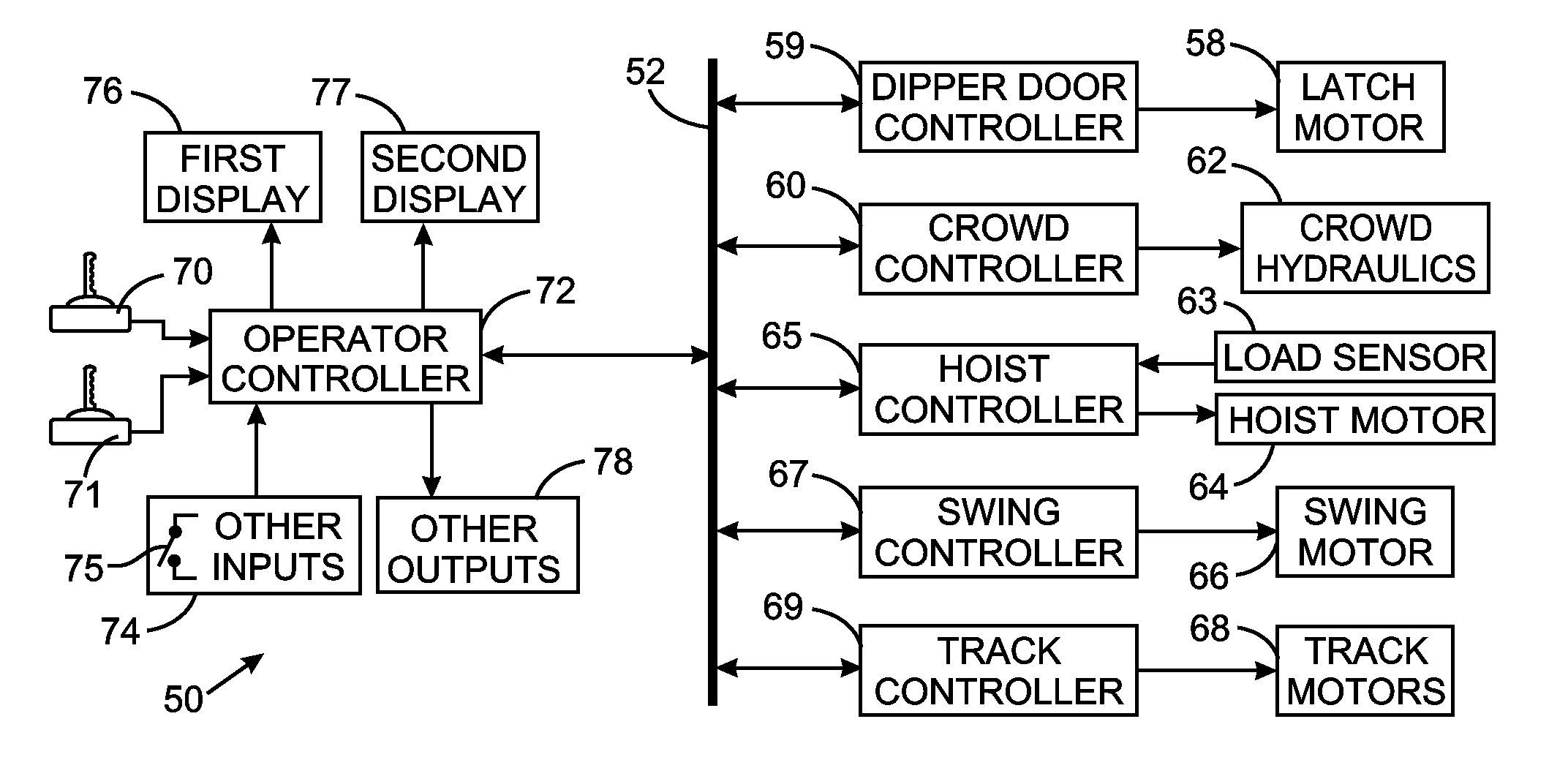
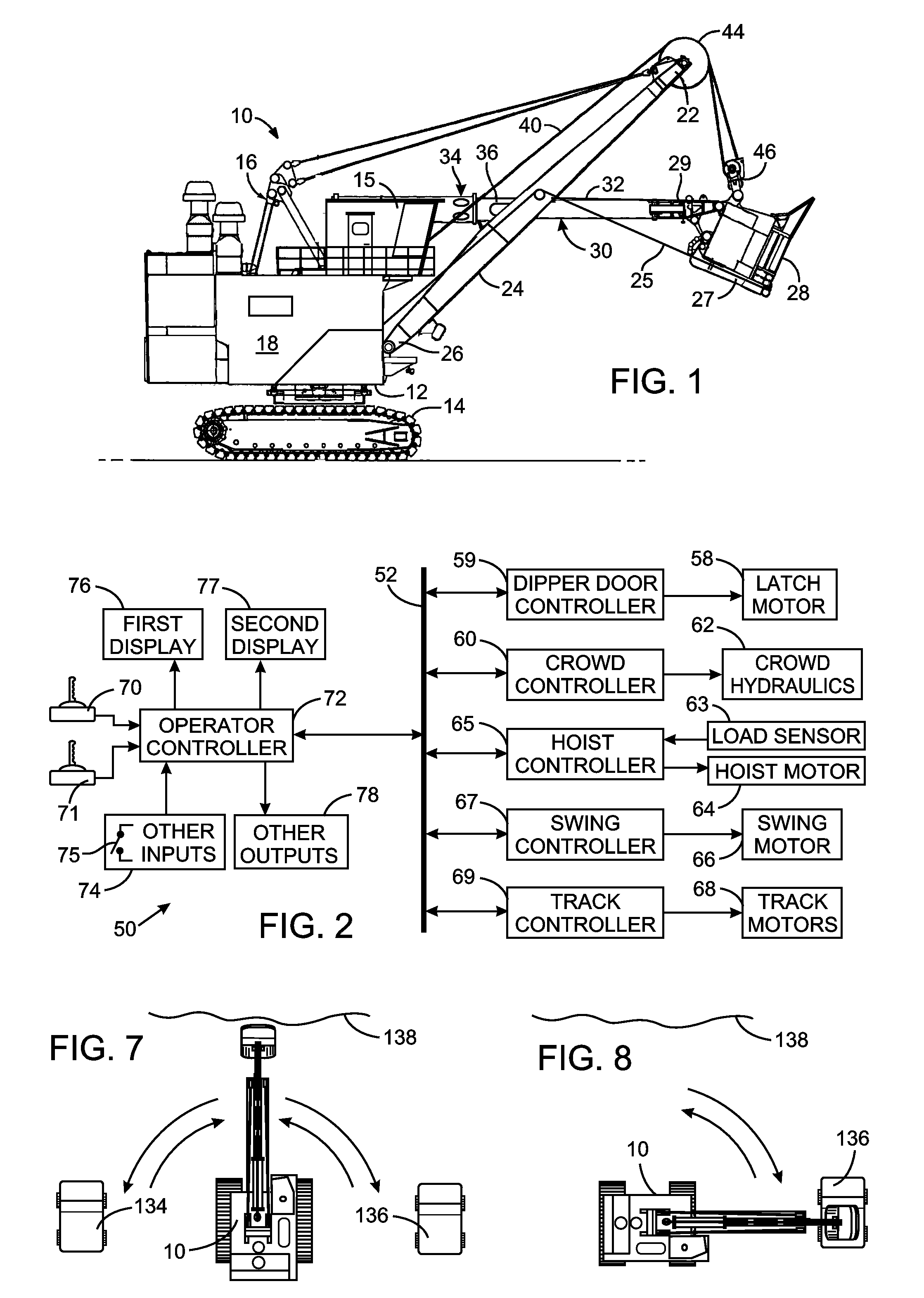
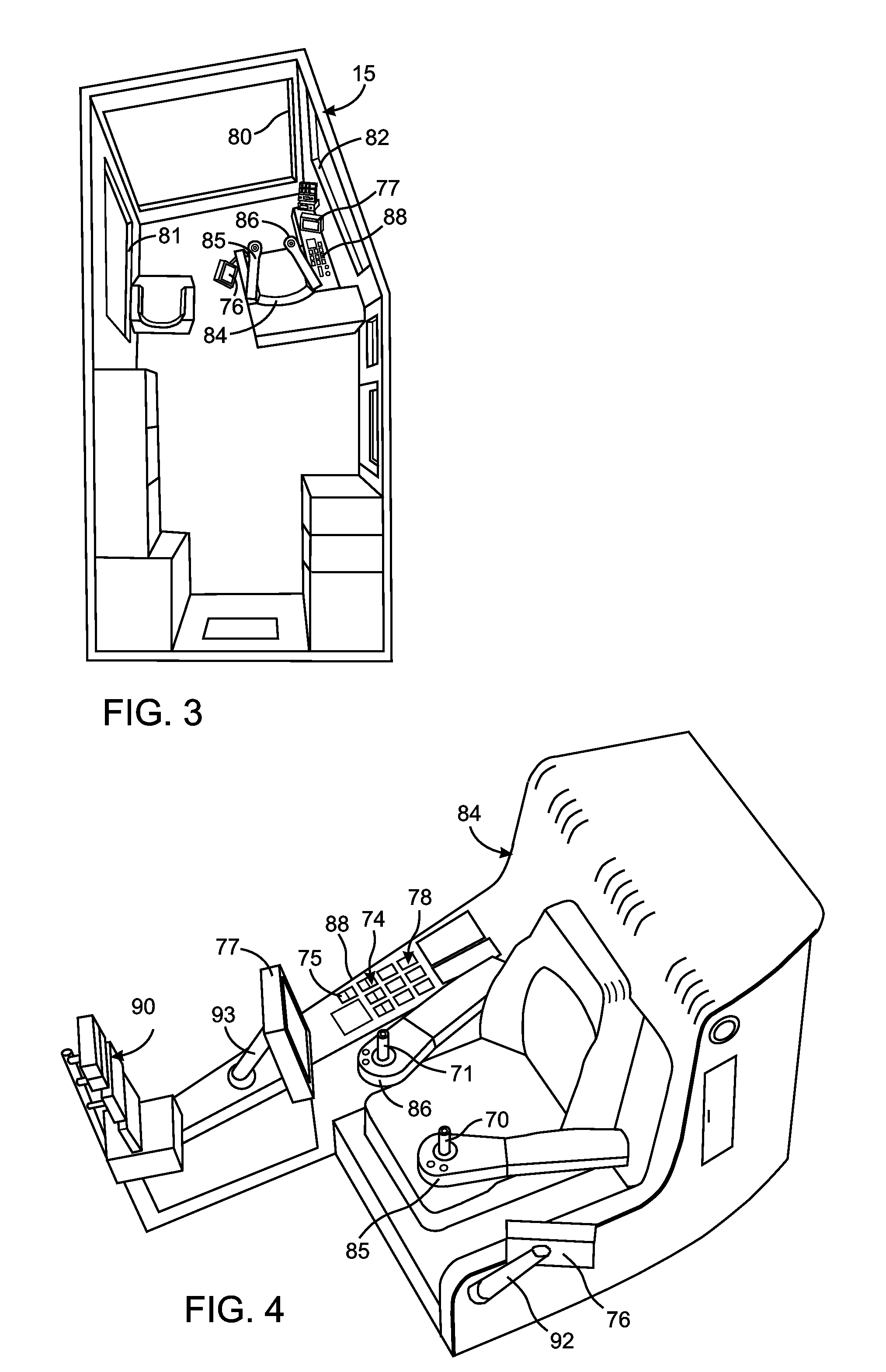
ActiveUS20110301817A1Analogue computers for trafficSignalling system detailsComputer monitorInformation display systems
The operator of a excavator sits in a seat that has a one computer monitor on the left side and another computer monitor on the right side. A control system produces first and second sets of information regarding operation of the excavator with the first set of information being particularly relevant to the digging operation. The selection of which computer monitor displays which of the first and second sets of information depends on a direction that the excavator swings between a digging site and a dumping site and that selection changes as the direction changes. This presents the first set of information on the computer monitor that is easily observable by the excavator operator during the digging operation.
Owner:CATERPILLAR GLOBAL MINING LLC
Quick coupler assembly
A quick coupler for connecting and disconnecting an implement such as a bucket to and from a machine such as an excavator. In an example, the quick coupler includes a frame having recesses configured to receive pins located on the implement. The quick coupler includes first and second securing latches that are movable between latched and unlatched positions for removably latching the pins of the implement in the recesses. A rocker assembly and a connector link are provided for moving the second latch between latched and unlatched positions.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
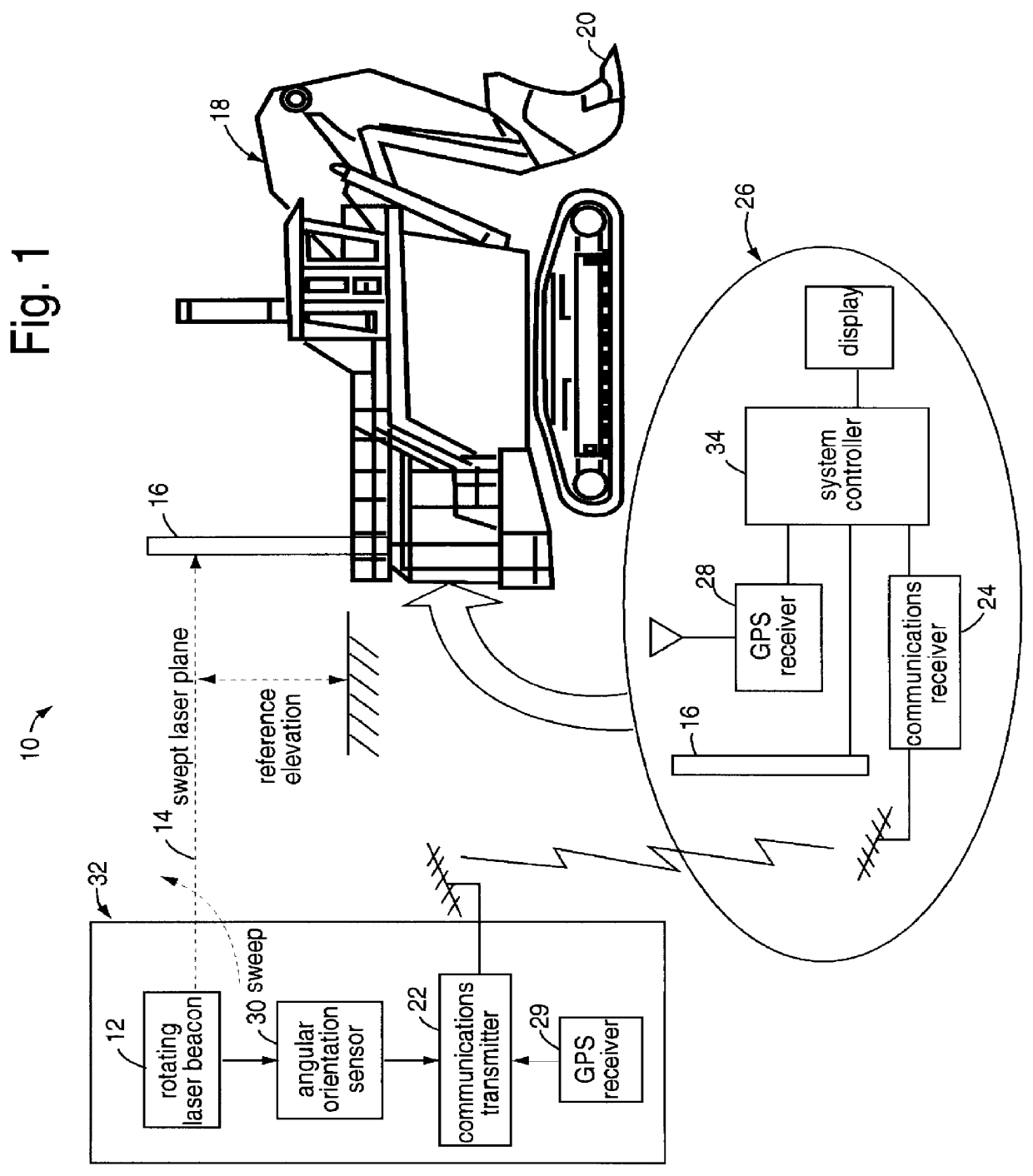
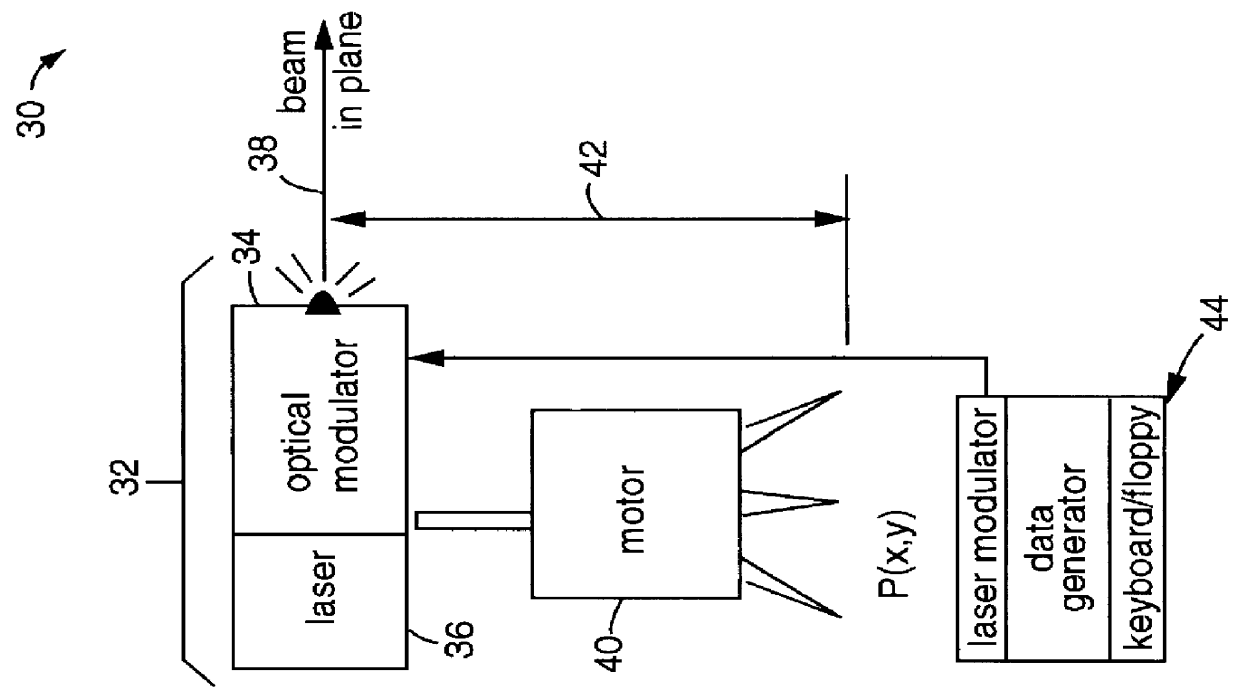
Multiple simultaneous laser-reference control system for construction equipment
A number of laser beam stations emit vertically separated parallel planes and / or ray-planes of laser light that can be discriminated by their respective plane elevations, modulation of the laser light, time synchronizing, etc. Identifying the laser plane would also imply an identification of the source laser beam station, and thus a precise indication of the elevation at the point of optical intercept. Alternatively, a single laser beam station is used that can emit several different monochromatic color planes and / or ray-planes of laser light. Monochromatic laser diodes, for example, are used for point-light sources and rotating or on-end conical mirrors are used to convert the diode laser light to the required monochromatic color planes and / or ray-planes of laser light. Receivers, generally held on masts attached to motor grader, bulldozer, loader, and excavator machines are used to sense the vertical reference position of the monochromatic color planes and / or ray-planes of laser light, relative to the earth cutting blade of the machine. Fixed-color filters, color filter wheels, and / or linear array photodetectors are used to discriminate amongst the colors and to exactly sense the plane of intersection with the machine. The results of the sensing are either displayed to an equipment operator for manual adjustment of the blade to an automatic servo control system connected to hydraulically control the blade.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
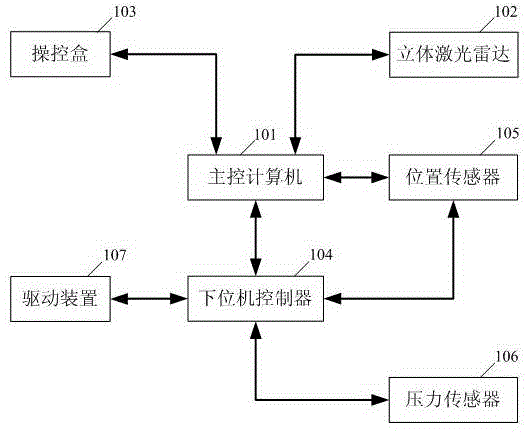
Excavating robot autonomous working control system and method
ActiveCN104476548AHigh degree of intelligenceHigh position repeatabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorSoil-shifting machines/dredgersControl systemRadar
The invention provides an excavating robot autonomous working control system and method. In the excavating robot autonomous working control system, a master control computer is connected with a three-dimensional laser radar, a control case, a position sensor and a lower computer controller; the lower computer controller is connected with a driving device, the position sensor and a pressure sensor. The excavating robot autonomous working control system and method can achieve unmanned autonomous excavation of an excavator and accordingly meet the requirements on excavation under severe environment inappropriate to human involvement. The excavating robot autonomous working control system is high in automation degree, good in man-machine interactivity, stable in operation and high in position repetition precision.
Owner:中国兵器装备集团自动化研究所有限公司
Attachment coupling device for heavy machinery
InactiveUS7014385B2Quickly and conveniently connectPreventing attachments from unwanted detaching from the heavy machineryMining devicesMechanical machines/dredgersCouplingEngineering
An attachment coupling device is designed to releasably connect a variety of attachments to an arm and a push link of heavy machinery such as hydraulic excavators. The attachment coupling device comprises a pair of mounting brackets fixedly secured to the attachment, each bracket having first and second hooks spaced apart with each other. Another major element of the coupling device is a coupler which includes, a fixed plate affixed to the arm and the push link, a pair of fixed coupling pins each protruding outwardly from the fixed plate for engagement with the first hook of each of the mounting brackets, a pair of movable coupling pins for movement between a retracted release position and an extended coupling position wherein the respective one of the movable pins comes into engagement with the second hook of each of the mounting brackets, and an actuator for causing movement of the movable coupling pins.
Owner:HANWOO TNC CORP
Heavy-duty demolition apparatus with replaceable tip and rotatable cross blade
InactiveUS6926217B1Bulky to transportEasy to replaceMechanical machines/dredgersMowersEngineeringHeavy duty
A heavy-duty demolition shear for attachment to the boom structure and hydraulic system of an excavator, has a rigid lower jaw and an upper jaw and pivot interconnecting the jaws together. The shear is attachable to the boom structure of the excavator. The upper jaw has upper shear blades, while the lower jaw has at least one lower shear blade. The lower jaw also has a rigid guide blade lying along the lower shear blade and in spaced relation therewith. The outer ends of the shear blade and guide blade are co-extensively opposed to each other so that a tie plate secures the outer ends of the lower shear blade and the guide blade together. There is an open slot between the lower shear blade and the adjacent guide blade to receive the upper shear blade and upper jaw therein. The upper jaw has a cylinder attached to the hydraulic system of the excavator for closing and opening the upper jaw relative to the lower jaw. The lower jaw and the upper jaw shear a workpiece when the upper jaw is closed upon the lower jaw. A rotatable, indexable cross blade is mounted to the tie plate substantially transverse to the lower shear blade and to the guide blade. The cross blade is seated and mounted inside the tie plate at an angle between one degree and thirty degrees, preferably about ten degrees. Thus, the cutting edge leans inwardly toward the throat of the shear, while the lower portion extends outwardly to provide upper jaw clearance within the open slot. The upper jaw includes a replaceable tip.
Owner:GENESIS ATTACHMENTS
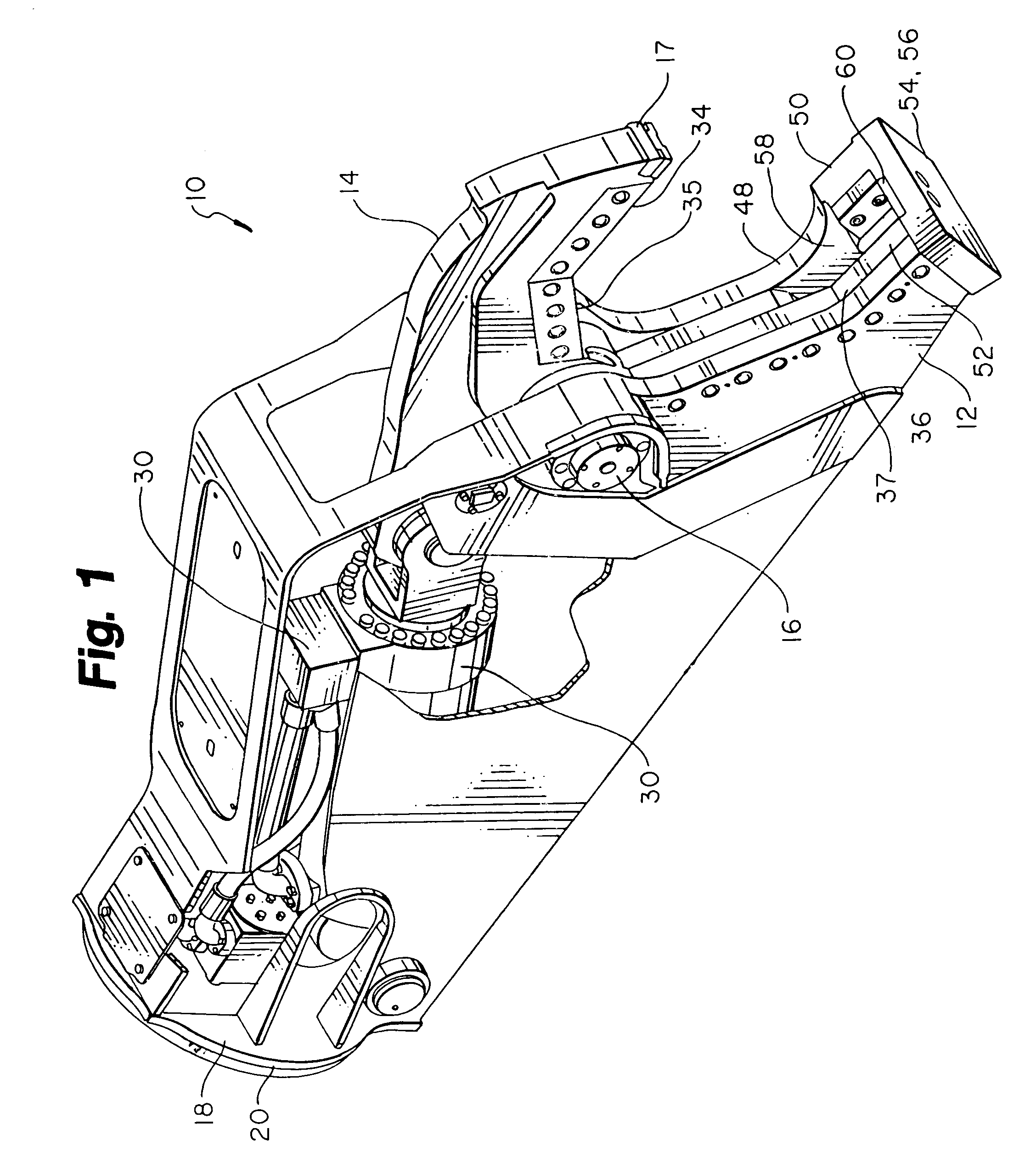
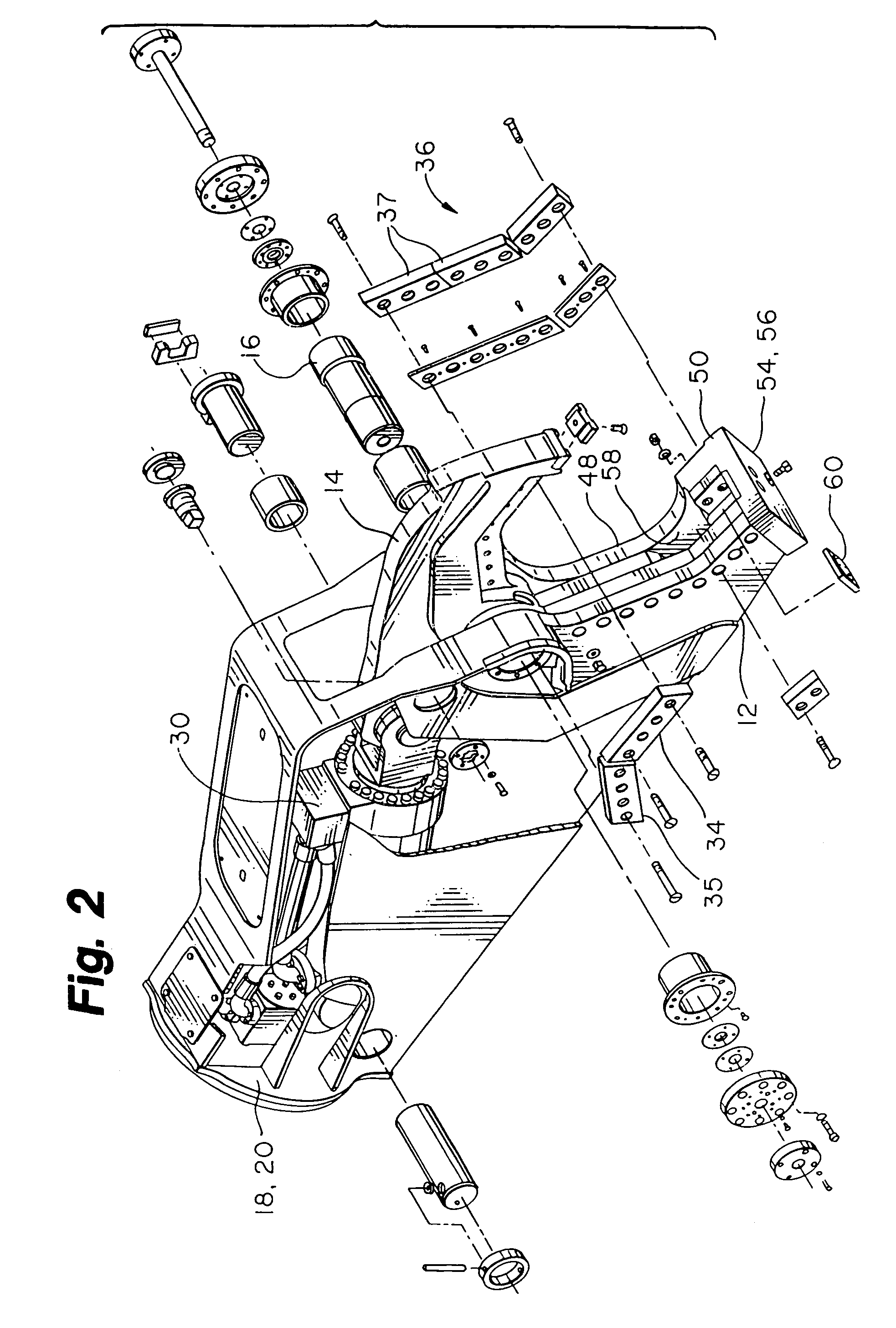
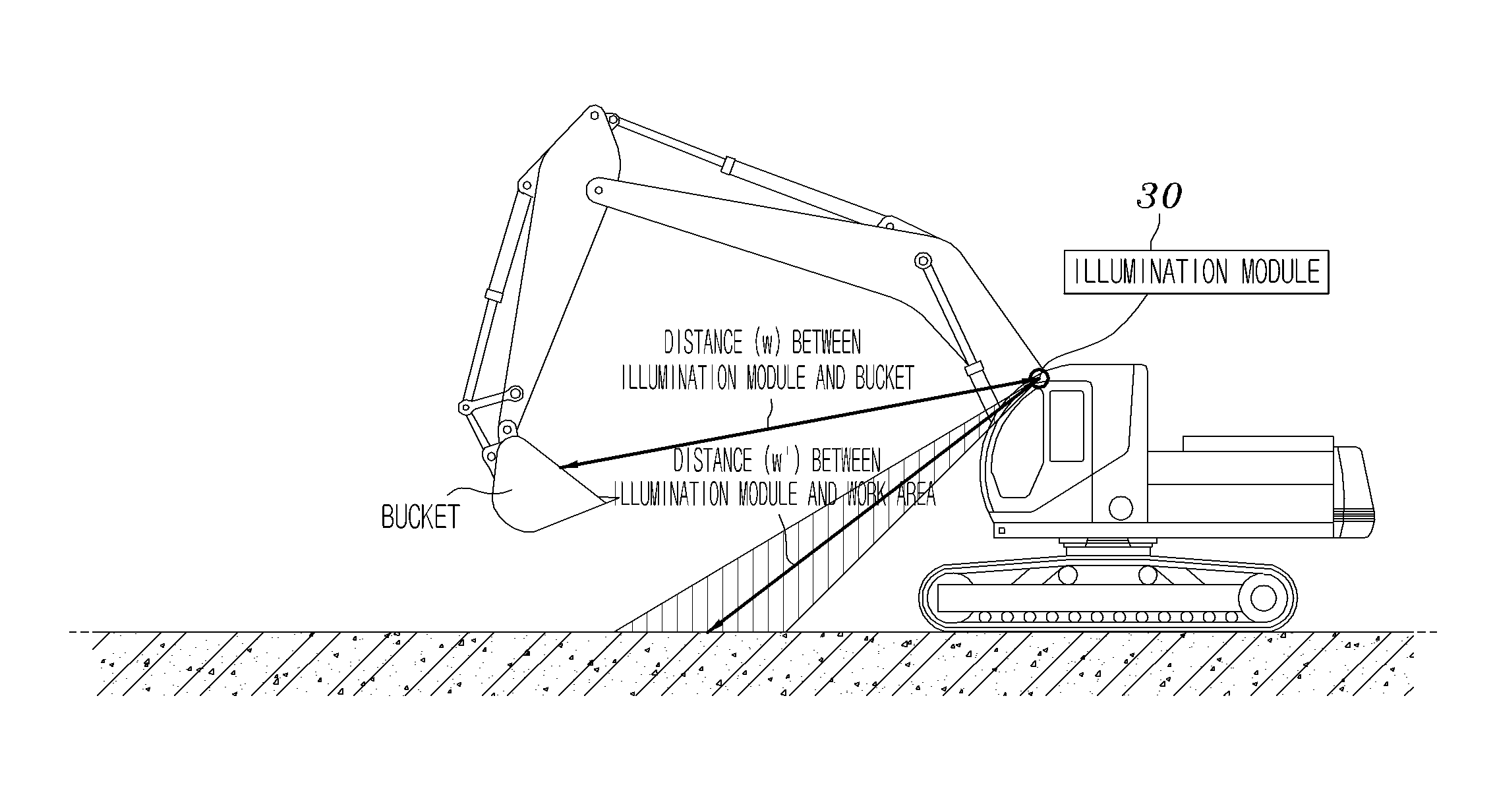
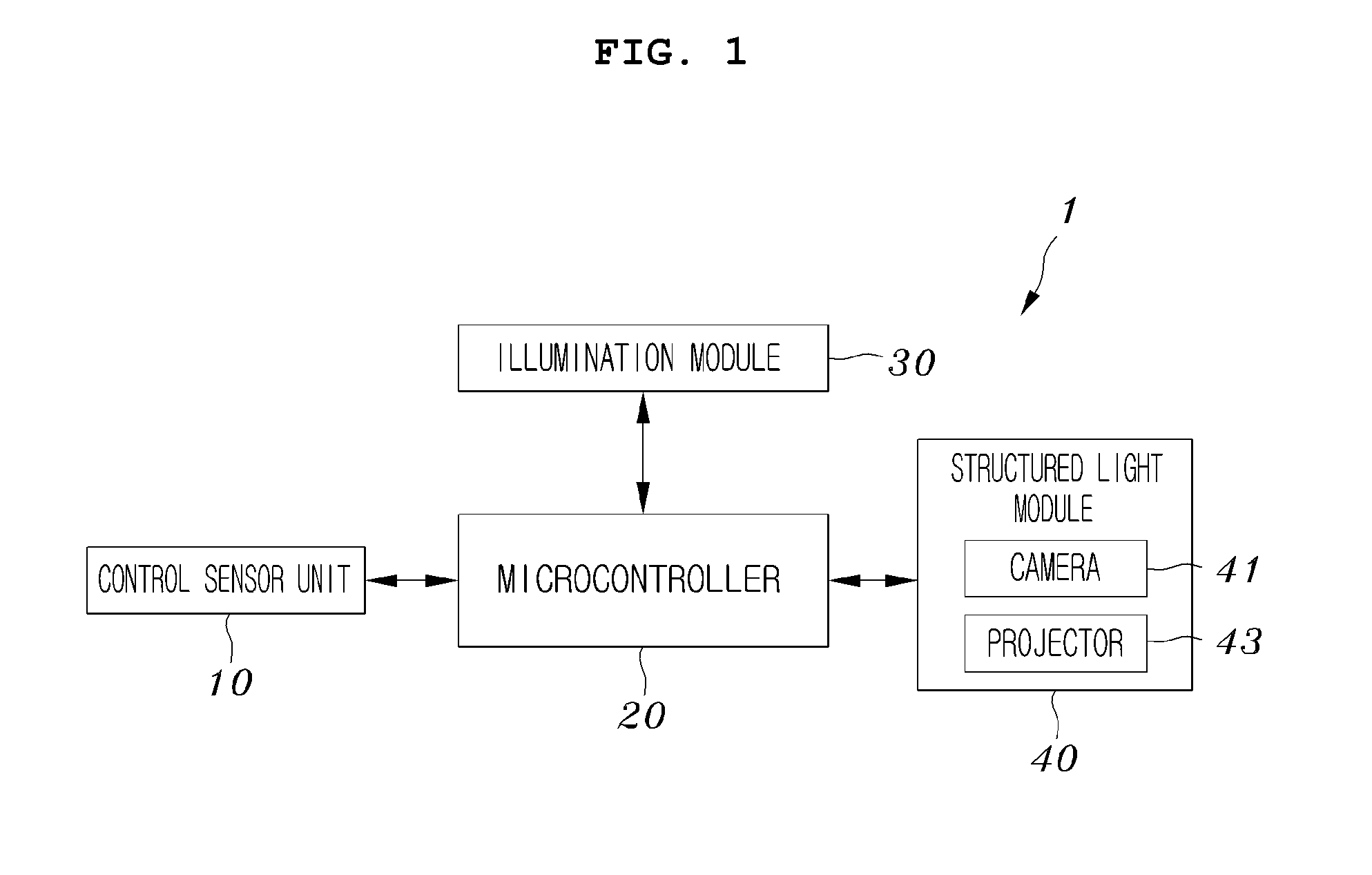
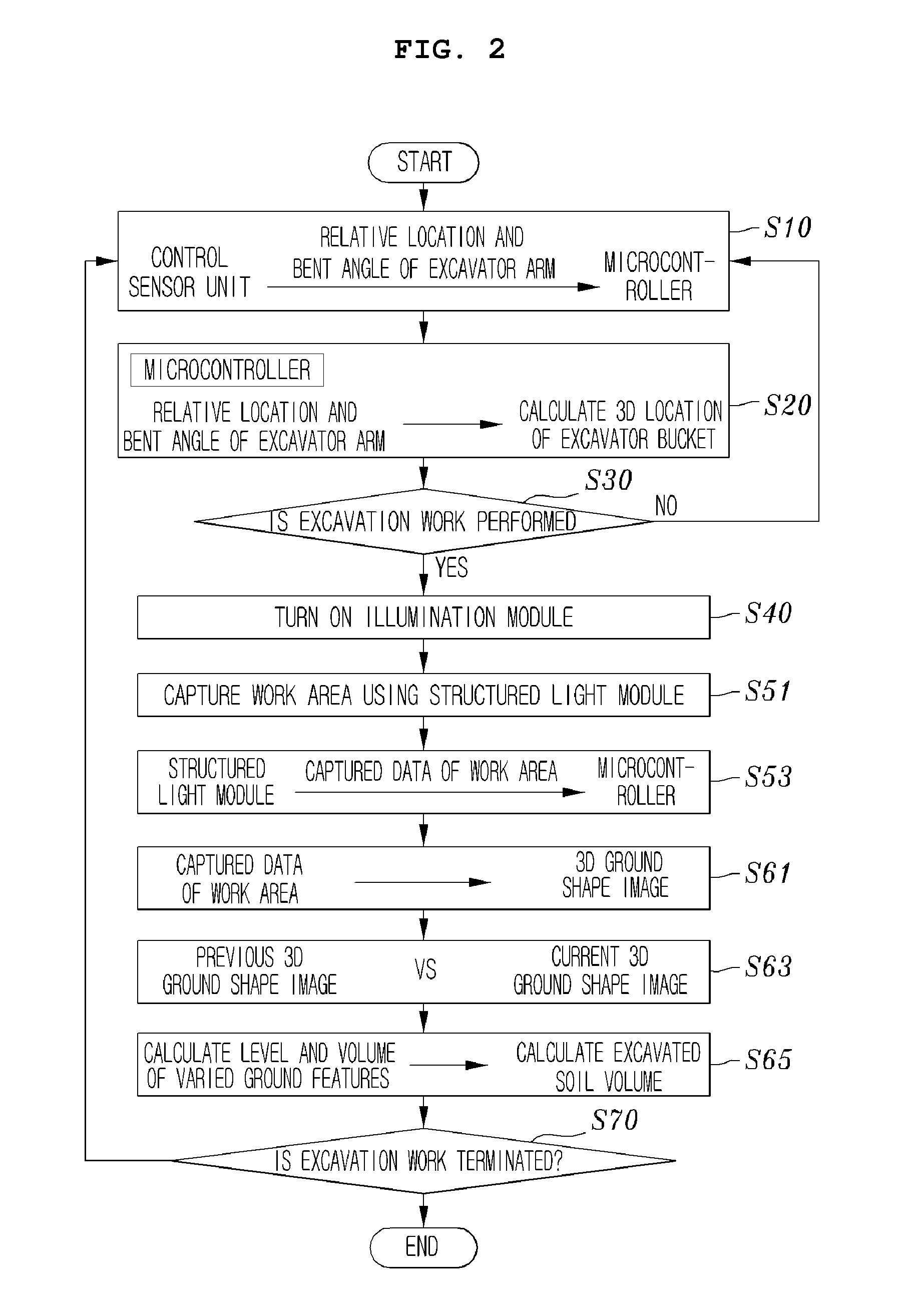
Device for computing the excavated soil volume using structured light vision system and method thereof
InactiveUS20100245542A1Accurate calculationTelevision system detailsMechanical machines/dredgersMicrocontrollerComputer module
A device for computing an excavated soil volume using structured light is disclosed. A control sensor unit is provided at the hinge points of an excavator arm, and is configured to detect and output the location and the bent angle of the excavator arm. A microcontroller is configured to output a control signal so as to capture the images of a work area of a bucket, provided at one end of the excavator arm, using the output of the control sensor unit, convert the captured images into 3-Dimensional (3D) images, and compute an excavated soil volume. An illumination module is configured to include at least one light source that is controlled by the control signal and radiates light onto the work area. A structured light module is configured to capture the work area in response to the control signal.
Owner:INHA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUNDATION
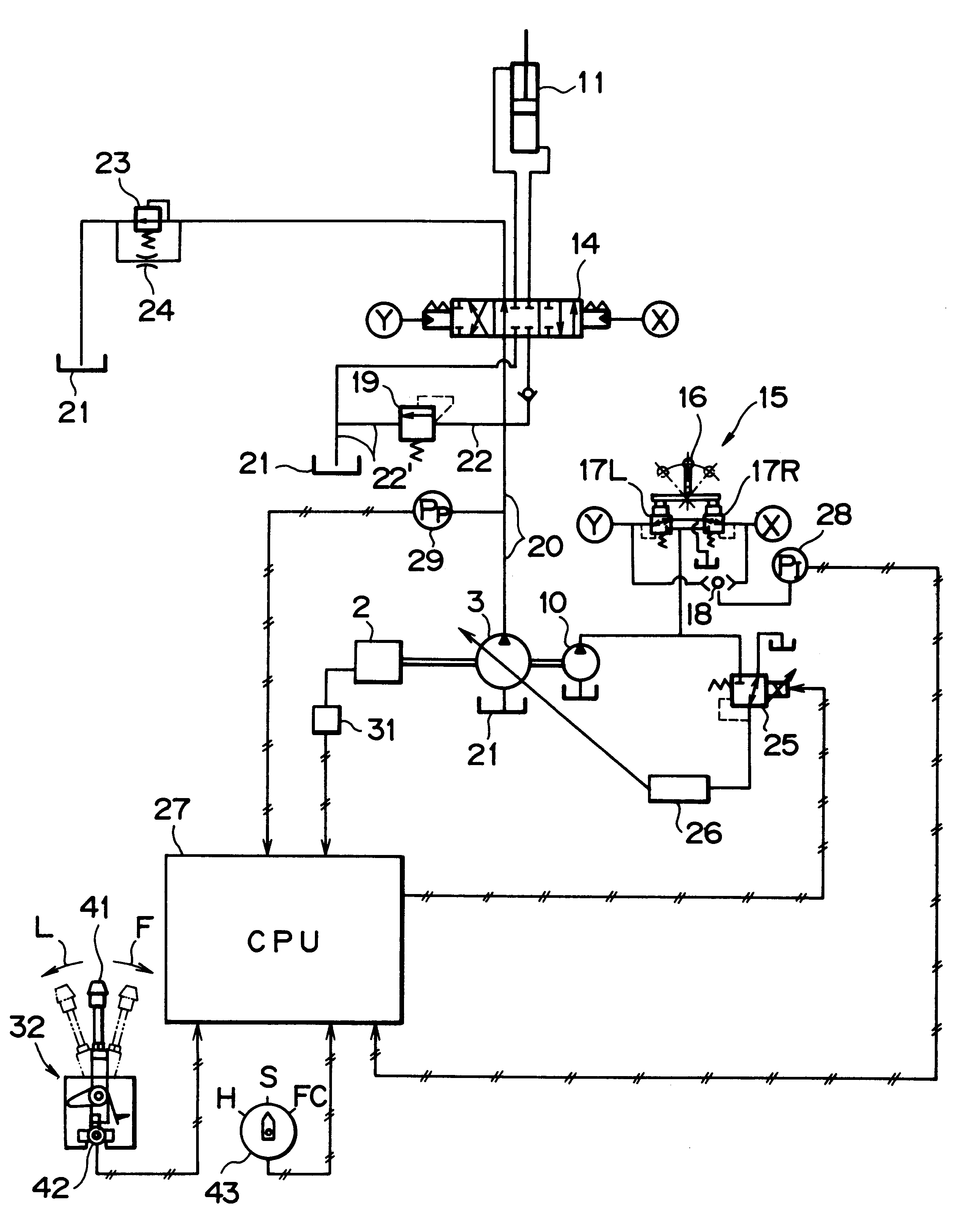
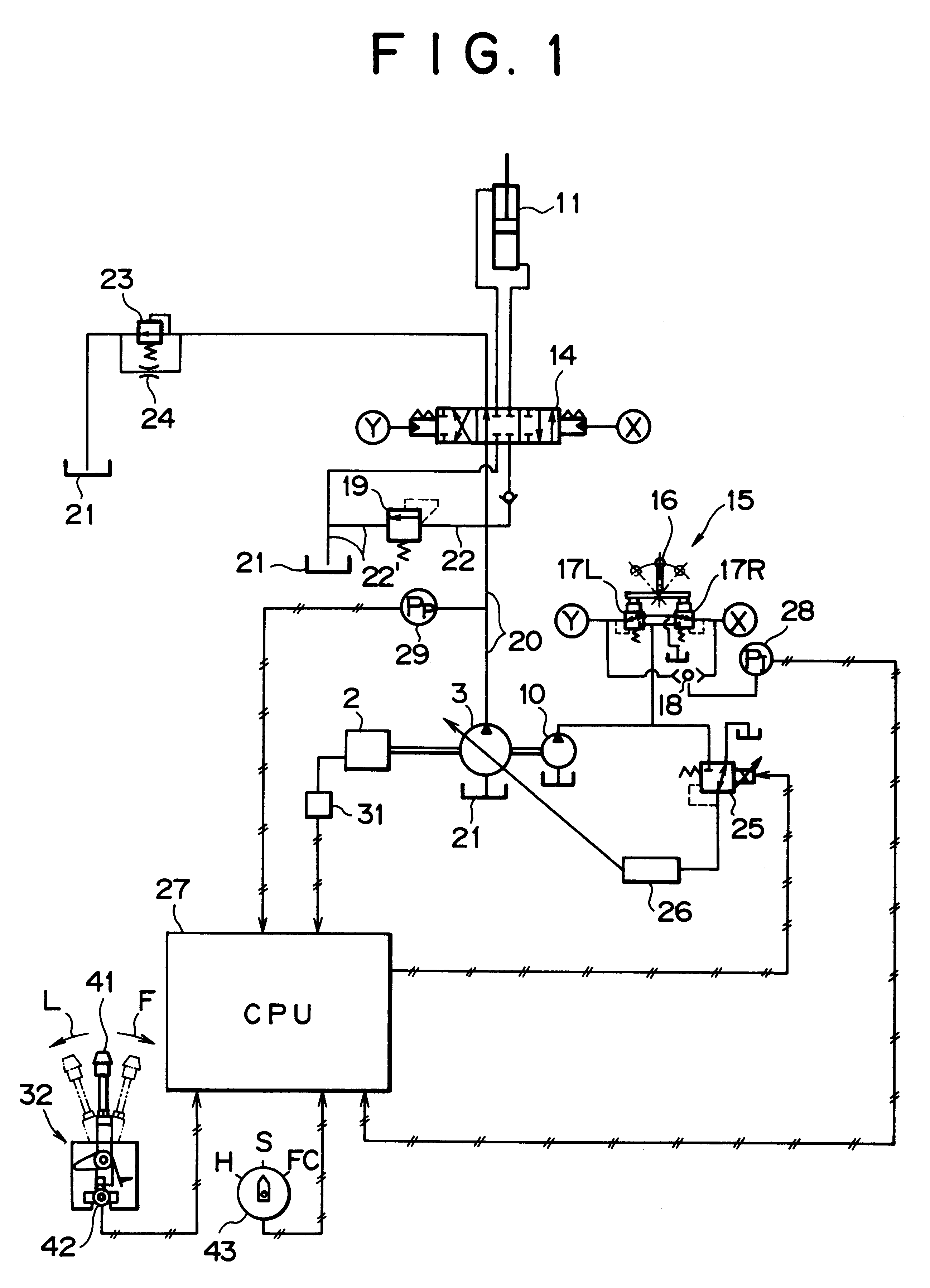
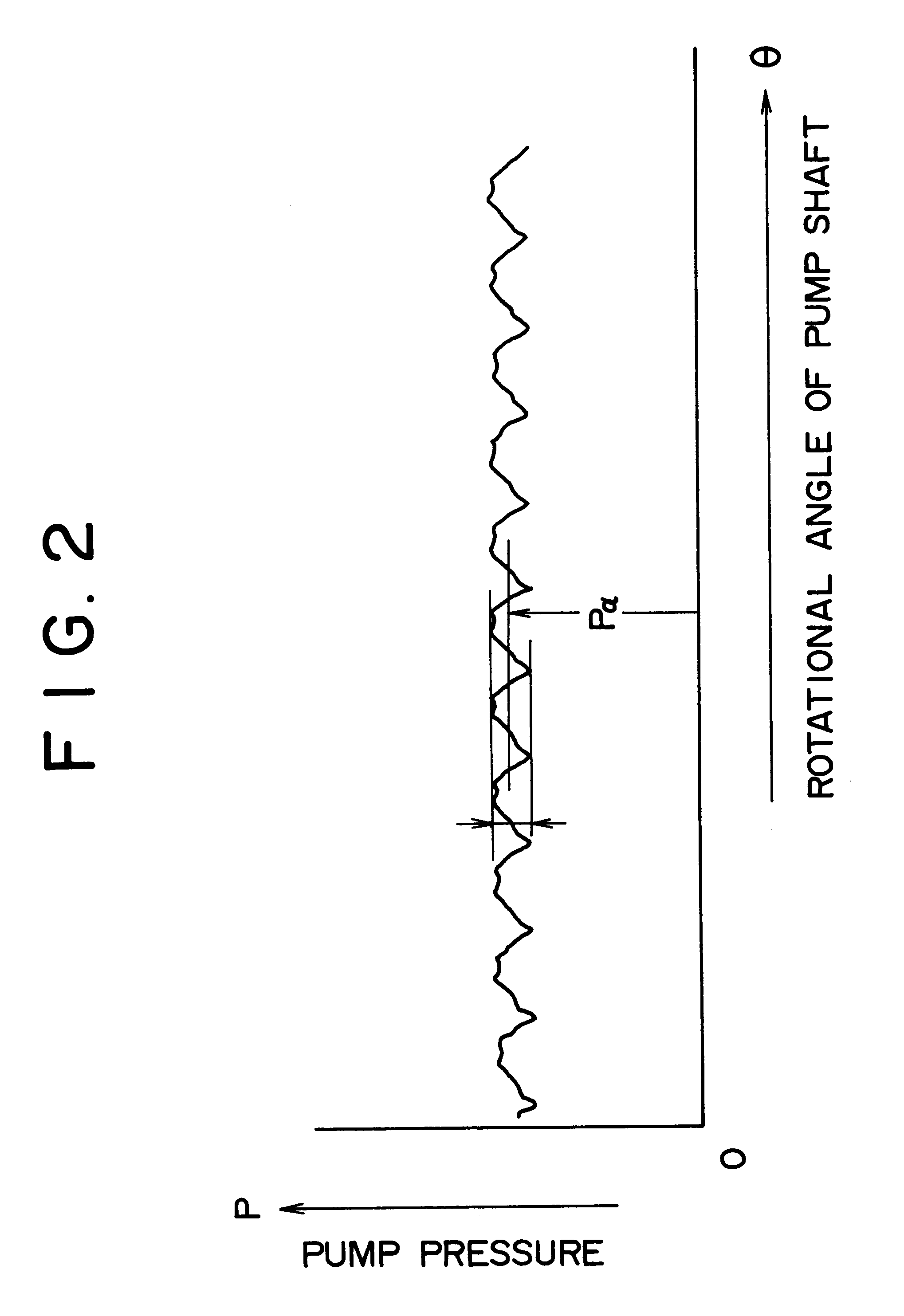
Flow rate control device in a hydraulic excavator
InactiveUS6202411B1Eliminate `` sense of incongruity ''Reduce rateFluid couplingsServomotorsHydraulic pumpActuator
A flow rate control device in a hydraulic excavator, comprising a hydraulic pump which is driven rotatively by an engine, a hydraulic actuator which is driven by a hydraulic oil discharged from the hydraulic pump, a control valve which controls the supply of the hydraulic oil to the hydraulic actuator, an operating means which operates the control valve so as to change over the valve from one position to another, a relief valve disposed in a discharge oil path extending from the hydraulic pump to limit the maximum pressure in the discharge oil path, an operational condition detecting means for detecting an operational condition of the hydraulic actuator, a pump pressure detecting means for detecting the discharge pressure of the hydraulic oil discharged from the hydraulic pump, a flow rate adjusting means for adjusting the discharge flow rate of the hydraulic oil discharged from the hydraulic pump, and a control means to which are inputted detection signals from both the operational condition detecting means and the pump pressure detecting means. When a specific operational condition of the hydraulic actuator is detected and when the said discharge pressure is held at a predetermined relief cut-off pressure or higher for a predetermined period of time, the control means makes control so that the discharge flow rate of the hydraulic oil discharged from the hydraulic pump is decreased to a relief cut-off pressure by the flow rate adjusting means. According to this construction, the relief cut-off control can be made only where required for each of various works of different conditions which the hydraulic excavator performs, such as excavating work, crushing work and land readjusting work. That is, even when the discharge pressure is held at a predetermined relief cut-off pressure or higher for a predetermined period of time, the relief cut-off control is made if the hydraulic actuator is in the specific operational condition.
Owner:KOBELCO CONSTR MASCH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com