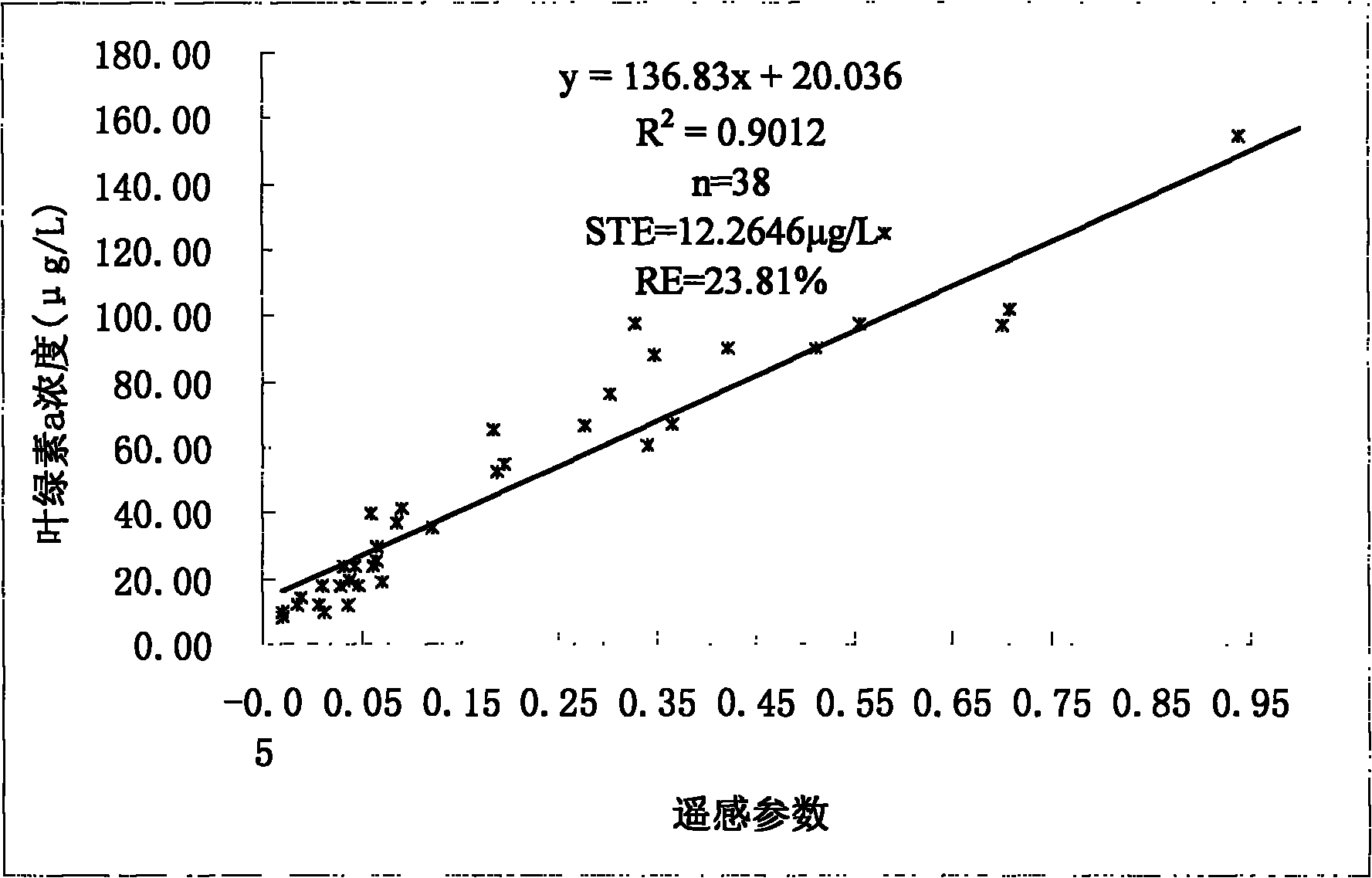
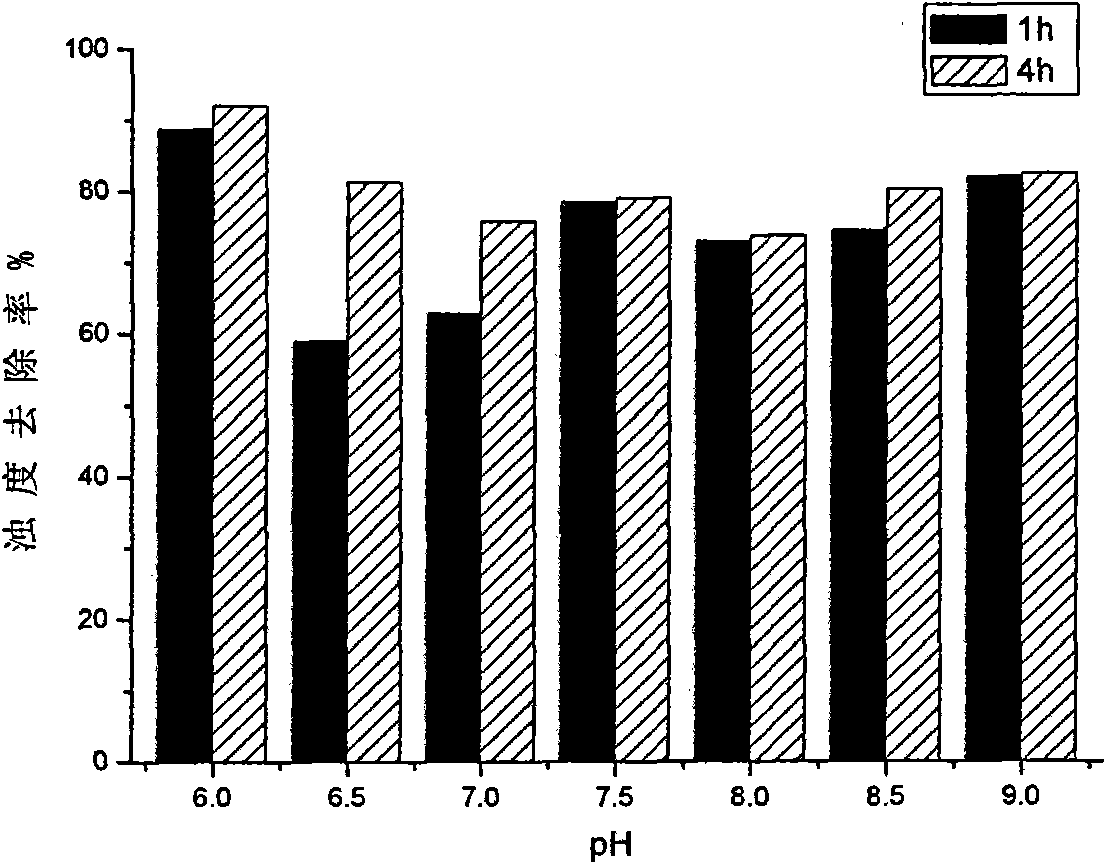
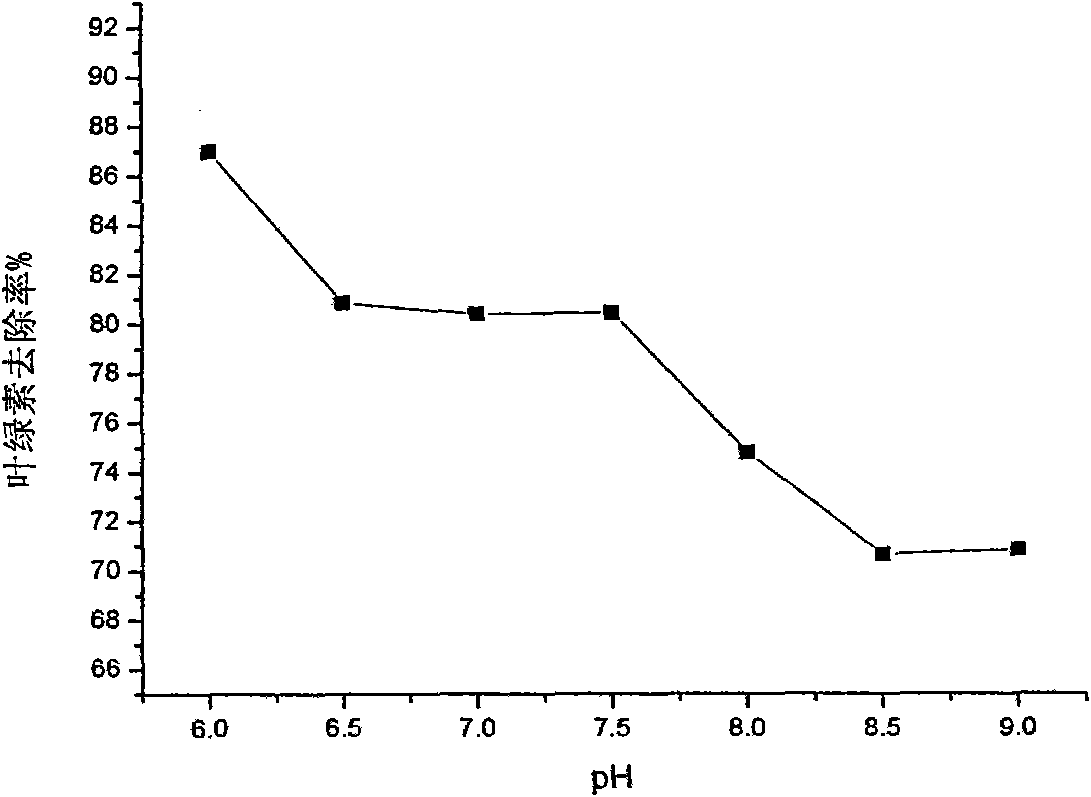
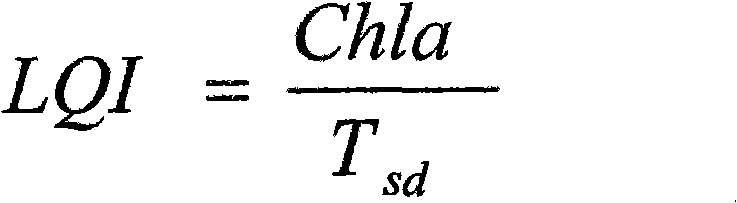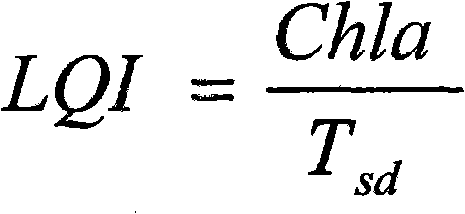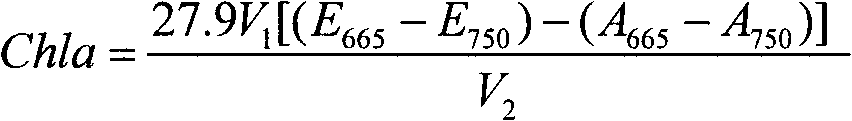Patents
Literature
322 results about "Chlorophyll a" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chlorophyll a is a specific form of chlorophyll used in oxygenic photosynthesis. It absorbs most energy from wavelengths of violet-blue and orange-red light. It also reflects green-yellow light, and as such contributes to the observed green color of most plants. This photosynthetic pigment is essential for photosynthesis in eukaryotes, cyanobacteria and prochlorophytes because of its role as primary electron donor in the electron transport chain. Chlorophyll a also transfers resonance energy in the antenna complex, ending in the reaction center where specific chlorophylls P680 and P700 are located.
Method for forecasting blue-green algae water bloom in large-scale shallow lake within 72 hours
The invention discloses a method for forecasting blue-green algae water bloom in a large-scale shallow lake within 72 hours. The method comprises the following steps of: building a content forecasting model of chlorophyll a in a water body and a probability forecasting model of water bloom generation according to an in-situ growth rate and drift rate parameters of blue-green algae; analyzing instant content of the chlorophyll a in a monitoring water area; distributing and acquiring meteorological information data in a monitoring period; inputting the built models; and outputting a predicted value of the concentration of the chlorophyll a in the monitoring water area in the next 72 hours and the water area and the probability of water bloom generation. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of strong operability, easily acquired parameters used for forecasting and high timeliness, and can be used for rapidly and accurately predicting breakout of the blue-green algae water bloom and forecasting the blue-green algae water bloom in a waterhead site and a vital landscape water area.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Method for predicting chlorophyll a concentration in water based on BP nerval net
ActiveCN101158674AReduce in quantityReduce consumptionGeneral water supply conservationTesting waterWater basedPredictive methods
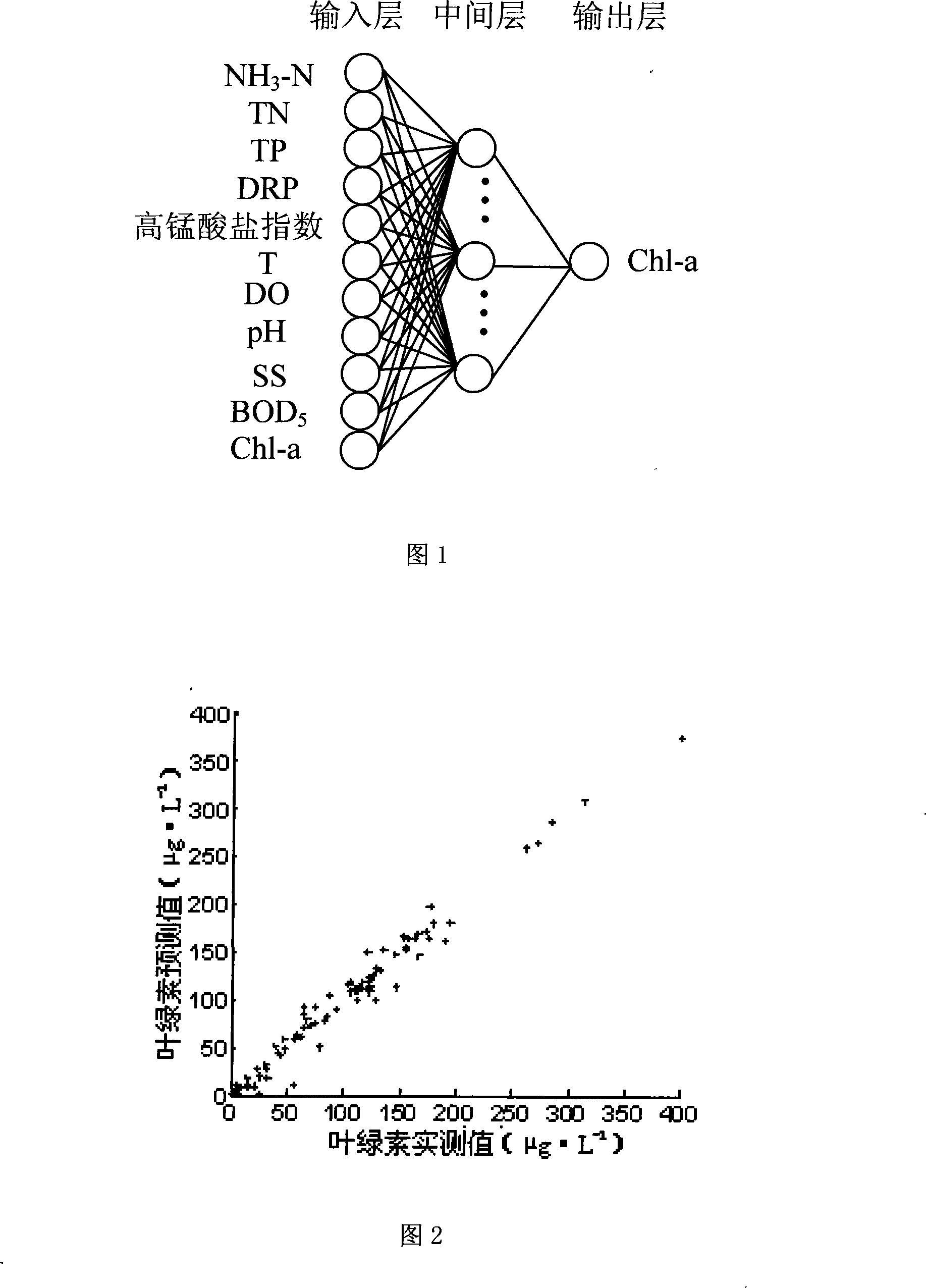
The invention relates to a density forecast method of the chlorophyll a stemmed from a water body of the BP neural network. The density forecast method comprises the following steps: (1) the chlorophyll a in the tested water body and the value of other correlative water quality index which influences the chlorophyll a are acquired as the examination data. (2) The neural network of an error back propagation is established. (3) The neural network is trained and tested. (4) The neural network which passes the test is utilized to forecast the chlorophyll a in the water body. Other water qualities which influence the chlorophyll a are: Ammonia nitrogen, total nitrogen, total phosphorus, orthophosphate, permanganate index, temperature, dissolved oxygen, pH, suspension, five-day biochemical oxygen demand. The step (1) also comprises a normalization process. The data of the chlorophyll a and other ten water quality indexes are between -1 and +1 after the data of the chlorophyll a and other ten water quality indexes are normalized. The neural network comprises an input layer, an intermediate layer and an output layer. The invention can establish a forecast model related to the chlorophyll a, just needing the experiment which has the limited times. The chlorophyll in the river can be accurately and quickly forecasted through the computer simulation experiment and the science forecast.
Owner:TIANJIN MUNICIPAL ENG DESIGN & RES INST
VCP-Based Vectors for Algal Cell Transformation
InactiveUS20090317904A1Improve efficiencyUnicellular algaeStable introduction of DNAChlorophyll aBiofuel
Provided herein are exemplary vectors for transforming algal cells. In exemplary embodiments, the vector comprises a Violaxanthin-chlorophyll a binding protein (Vcp) promoter driving expression of an antibiotic resistance gene in an algal cell. Embodiments of the invention may be used to introduce a gene (or genes) into the alga Nannochloropsis, such that the gene(s) are expressed and functional. This unprecedented ability to transform Nannochloropsis with high efficiency makes possible new developments in phycology, aquaculture and biofuels applications.
Owner:AURORA ALGAE
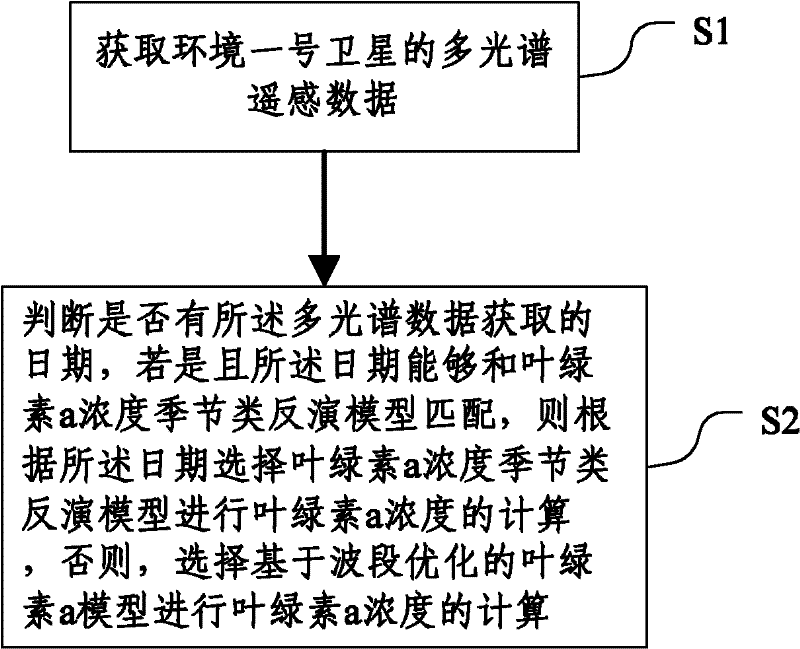
Chlorophyll a concentration inversion method and system
InactiveCN102200576AResolution timeSolve space problemsWave based measurement systemsChlorophyll aSensing data
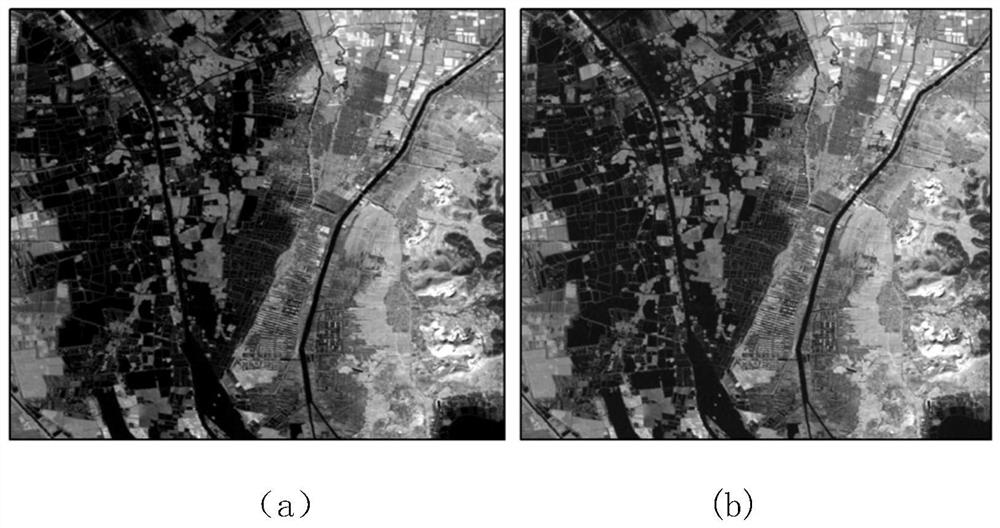
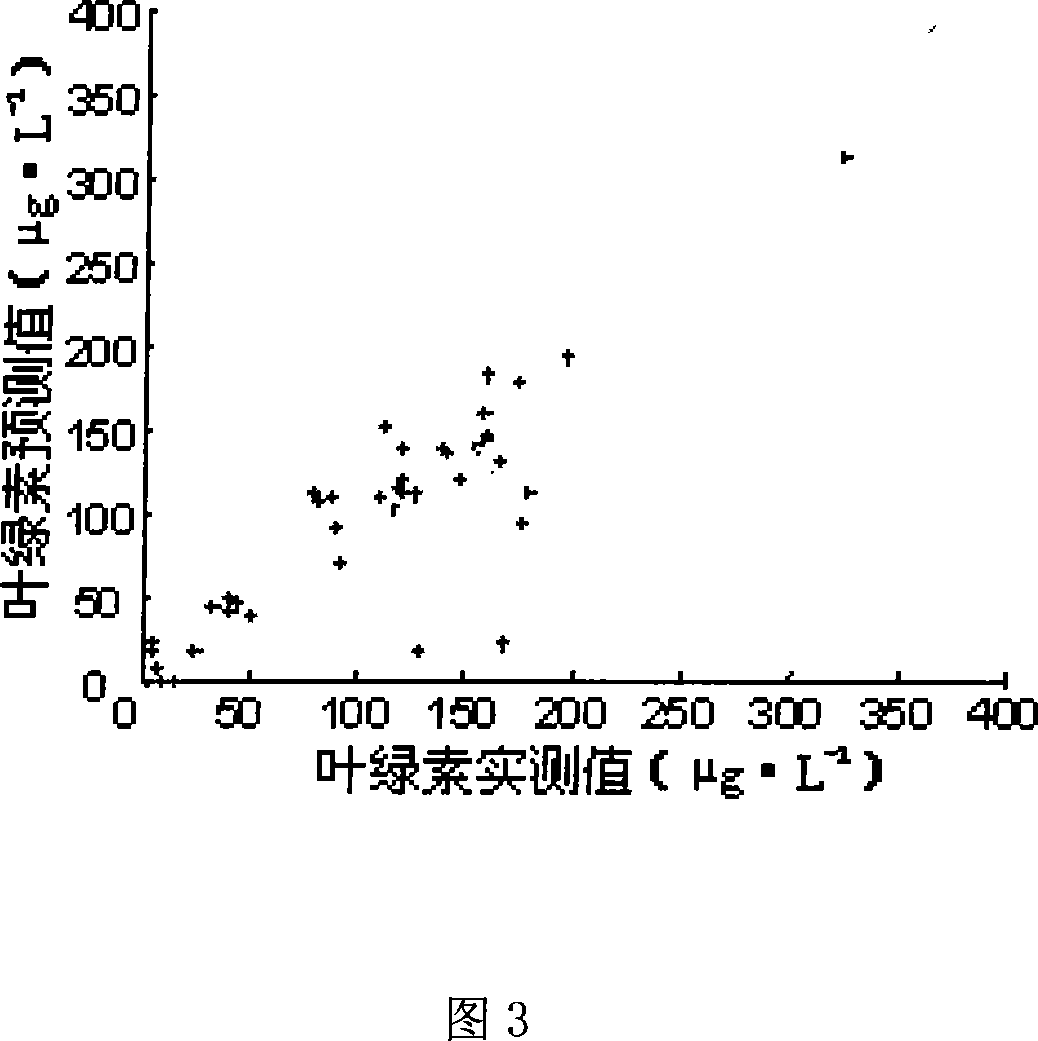
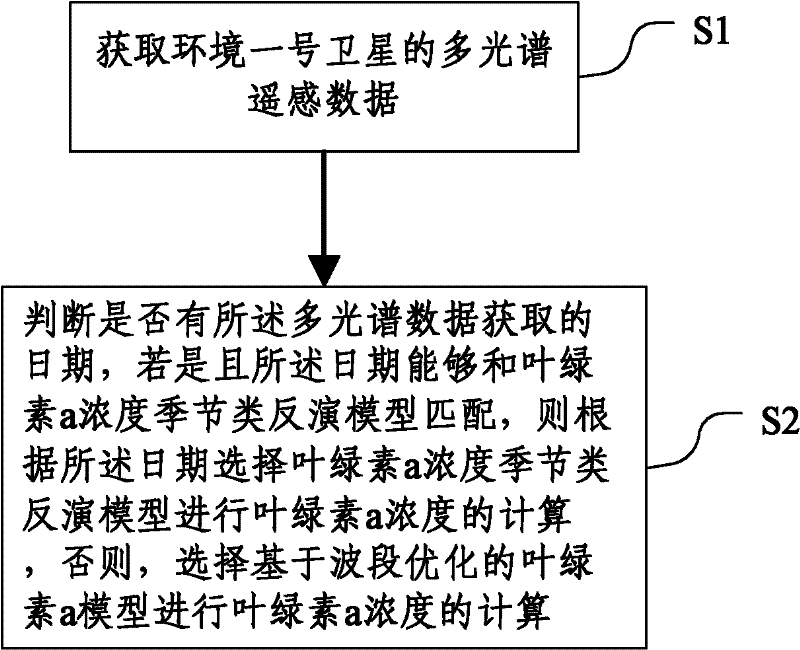
The invention discloses a chlorophyll a concentration inversion method and system. The method comprises the following steps of: S1: acquiring multispectral remote sensing data of an environment satellite No.1; S2: judging whether the date of the acquisition of the multispectral data exists or not; if the date exists and is matched with a chlorophyll a concentration seasonal inversion model, selecting a chlorophyll a concentration seasonal inversion model according to the date to calculate chlorophyll a concentration; otherwise, selecting a waveband-optimization-based chlorophyll a model to calculate the chlorophyll a concentration. Through the utilization of the multispectral and hyperspectral data of the environment satellite No.1, the problem that an inversion model is limited by time and space can be solved, and the automatic operation and service operation of a computer can be realized.
Owner:王桥
MODIS satellite high-precision monitoring method for chlorophyll-a in eutrophic lake water body
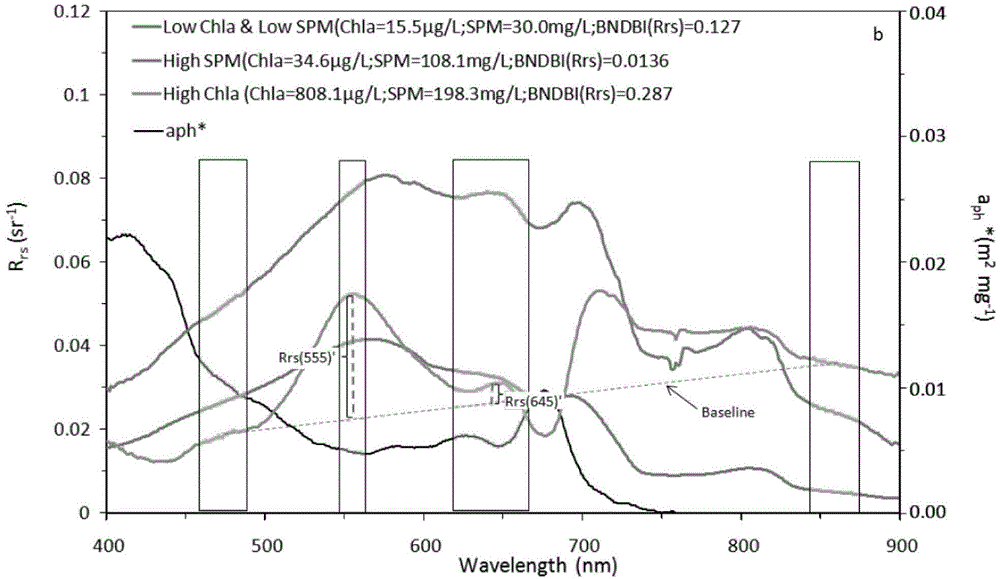
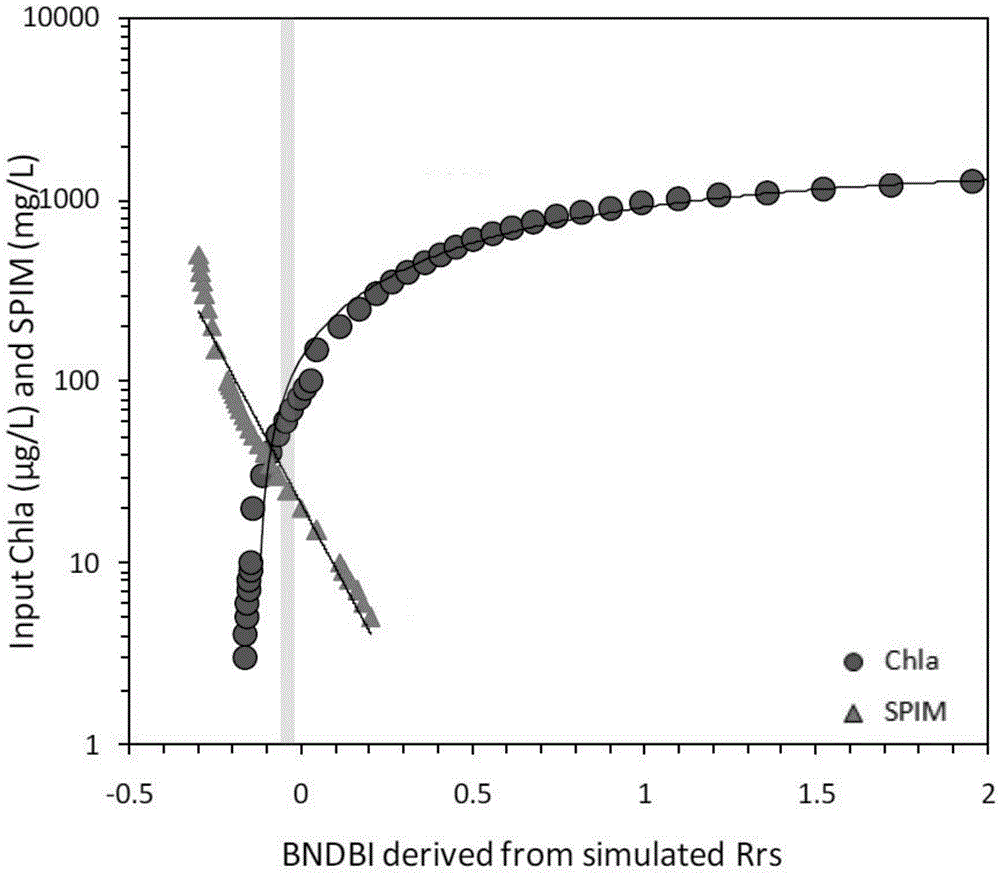
ActiveCN104820224AAchieving High-Precision EstimationReflect the space-time distributionElectromagnetic wave reradiationRayleigh scatteringEutrophication
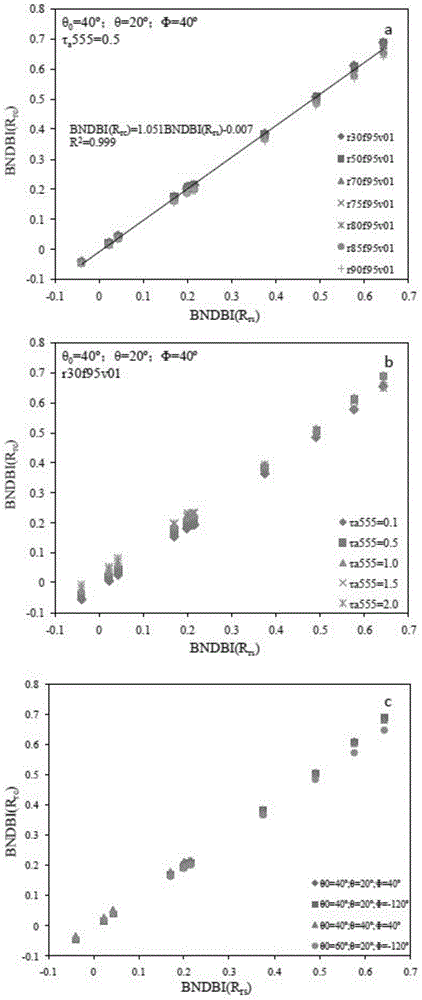
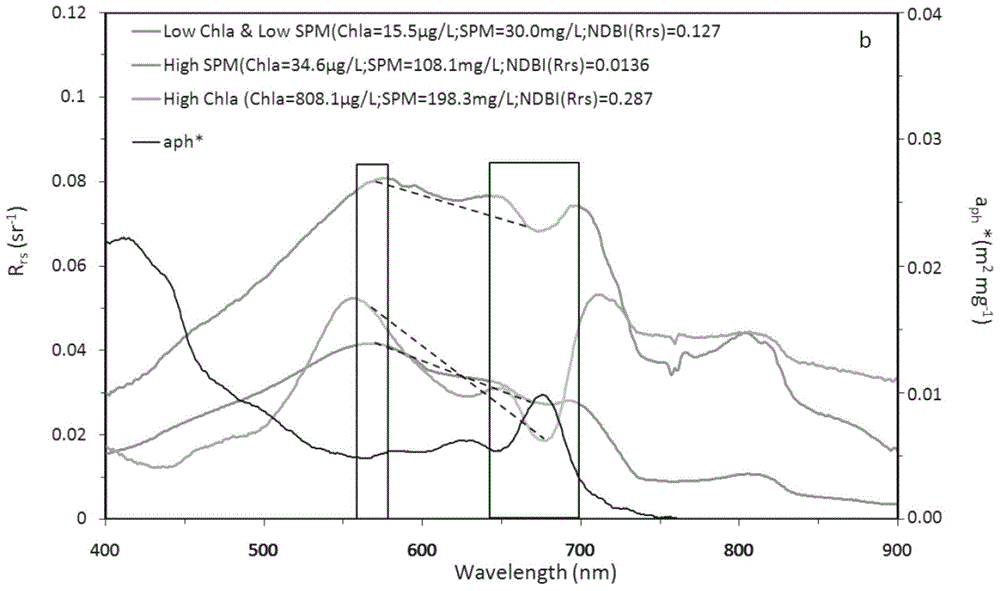
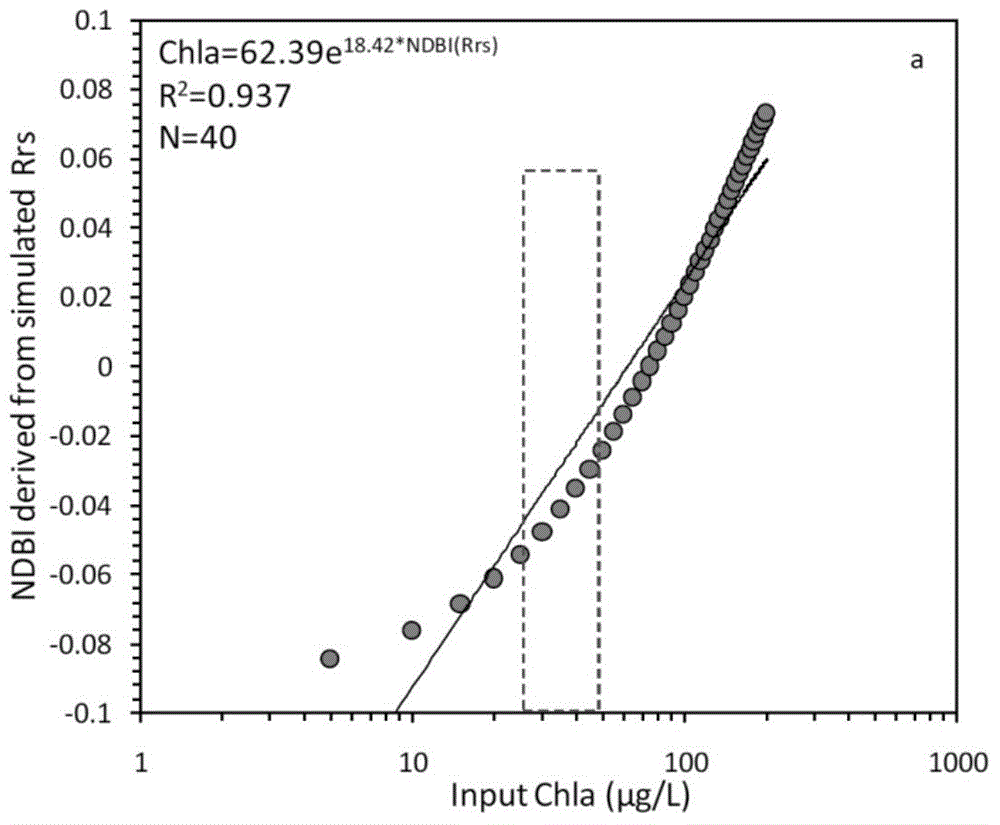
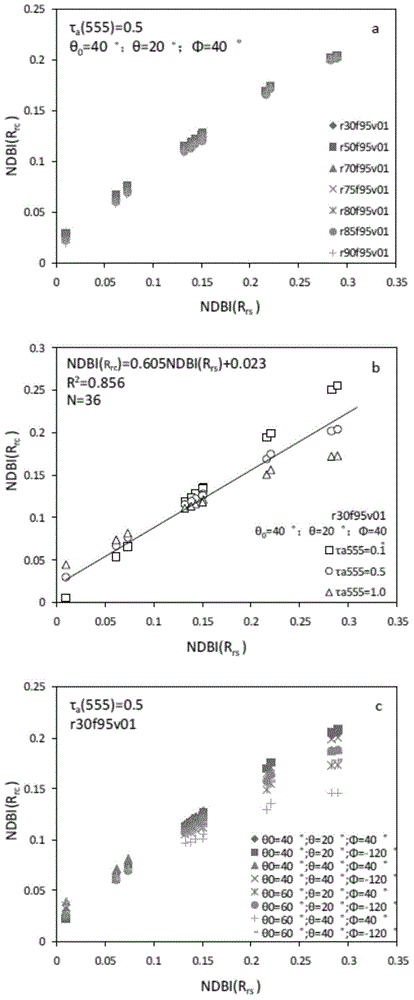
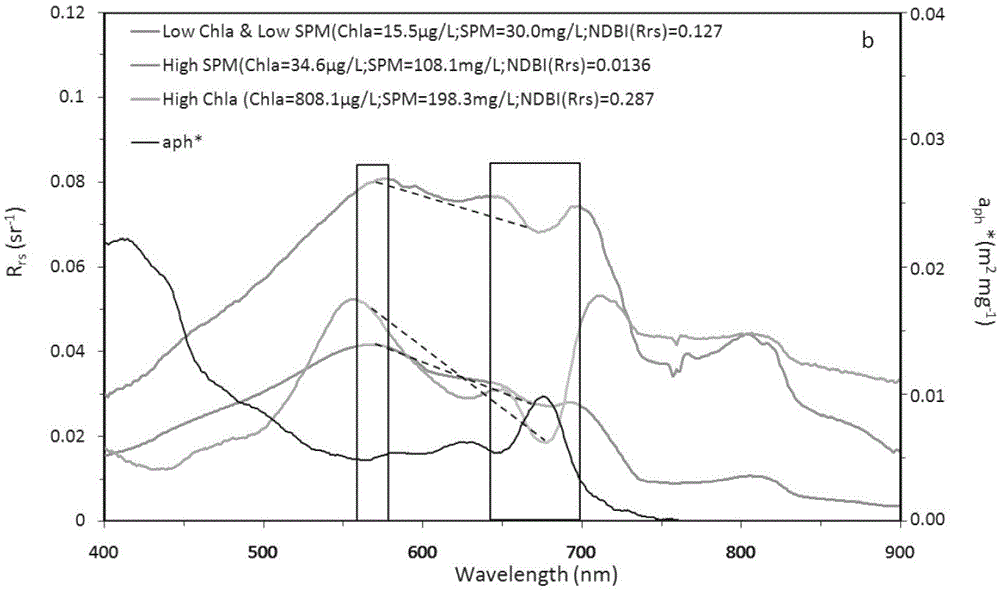
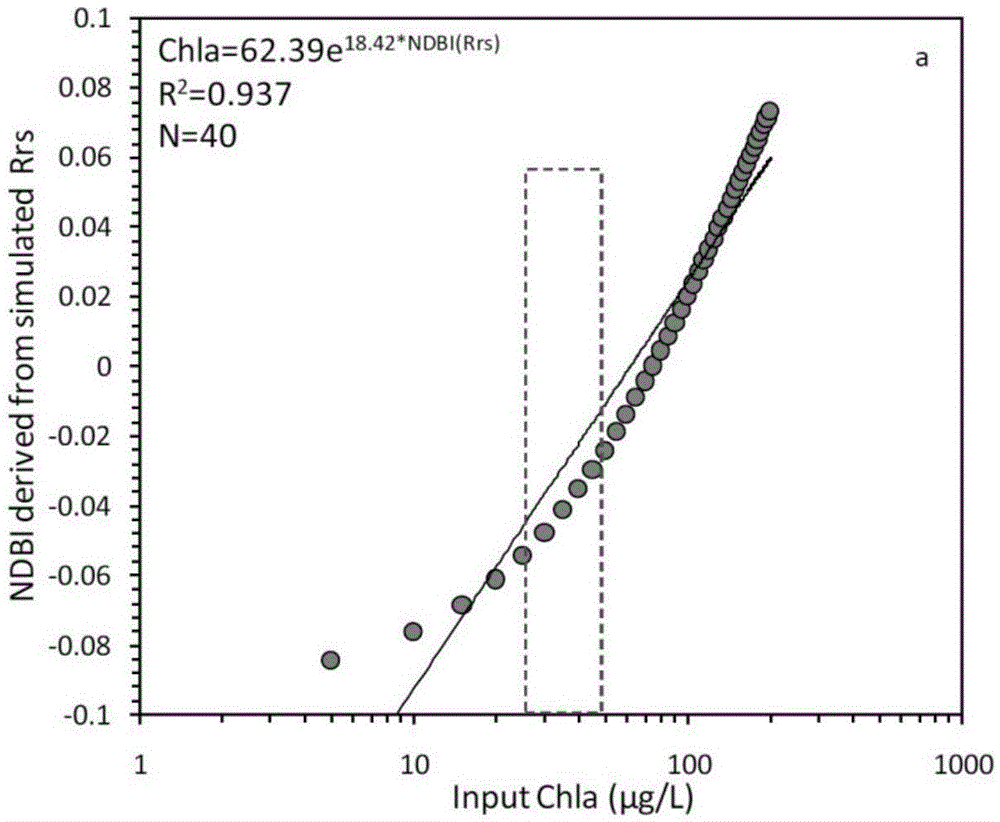
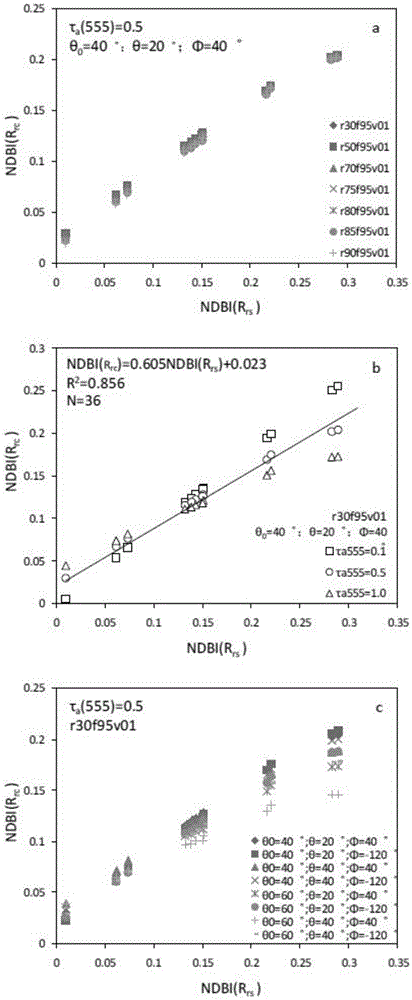
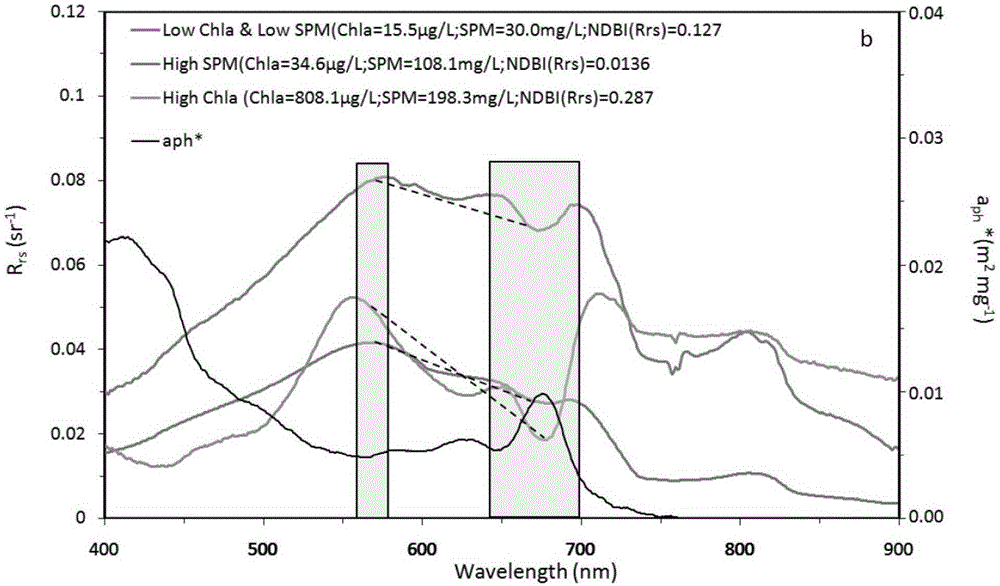
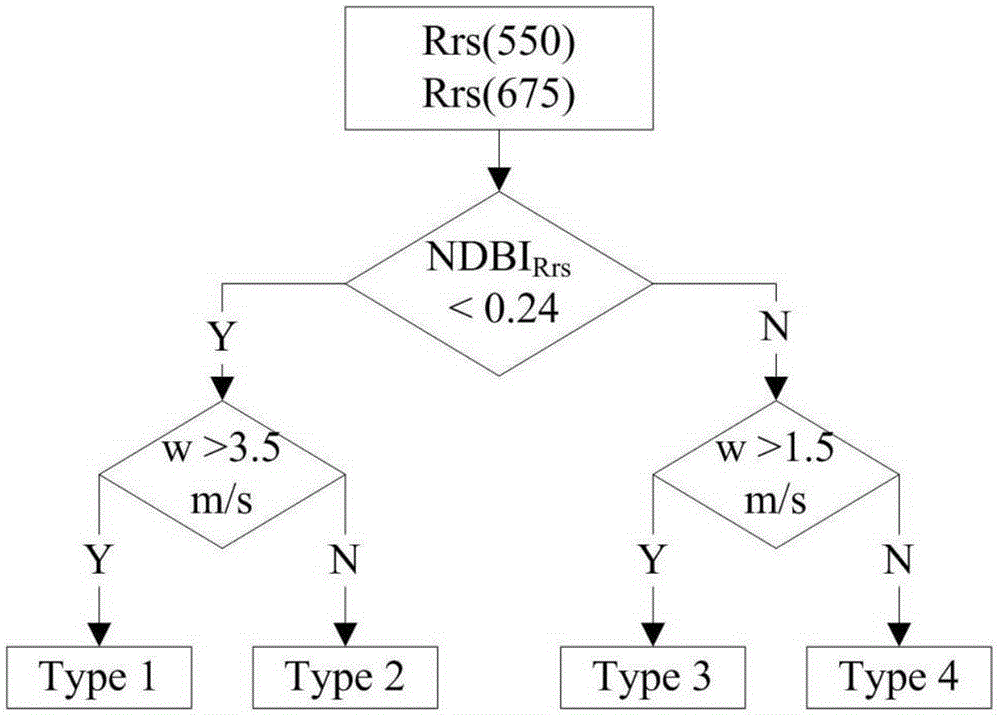
The invention provides an MODIS satellite high-precision monitoring method for chlorophyll-a in a eutrophic lake water body. The method comprises the following steps: screening a chlorophyll-a evaluation index (BNDBI) which is sensitive to the concentration change of chlorophyll-a and not affected by highly suspended matters, thin cloud and solar flares; acquiring the quantitative relationship between BNDBI and the concentration of chlorophyll-a on the basis of biological optical model simulation; acquiring a chlorophyll-a inversion algorithm based on ground measured spectrum (Rrs) and BNDBI by referring to water body spectral information and corresponding water body chlorophyll-a concentration of 2013-2014 lake field monitoring; acquiring the quantitative relationship between the ground monitoring and remote sensing reflectance ratio (Rrs) and Rrc after simulated Rayleigh scattering correction by simulating different aerosol types and thicknesses and different solar elevation angles, satellite observation angles and azimuth angles; and extending the chlorophyll-a inversion algorithm based on ground measured spectrum data to satellite image data after Rayleigh scattering correction. Based on the method, inter-annual and inter-monthly change rules and spatial distribution of chlorophyll-a in a eutrophic lake can be acquired accurately.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Analysis method of remote sensing inversion of water color parameters of inland class II water
InactiveCN105158172AHigh precisionRegionally applicableColor/spectral properties measurementsRemote sensing reflectancePhytoplankton absorption
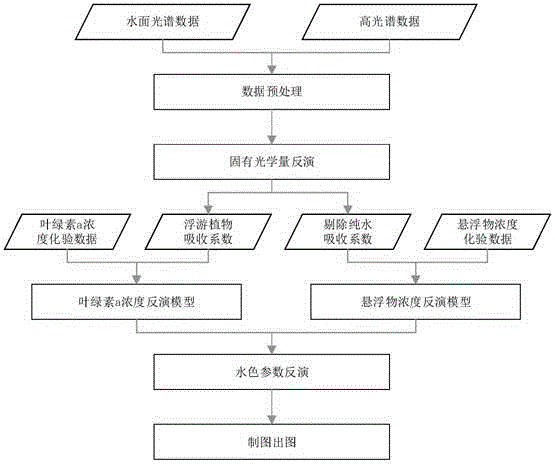
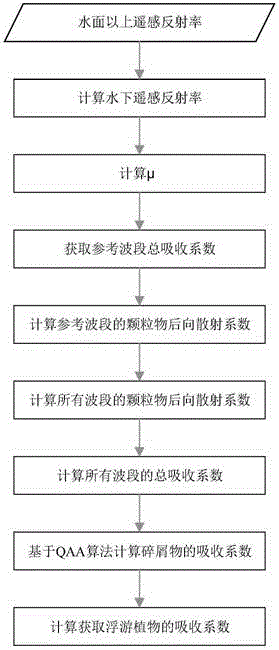
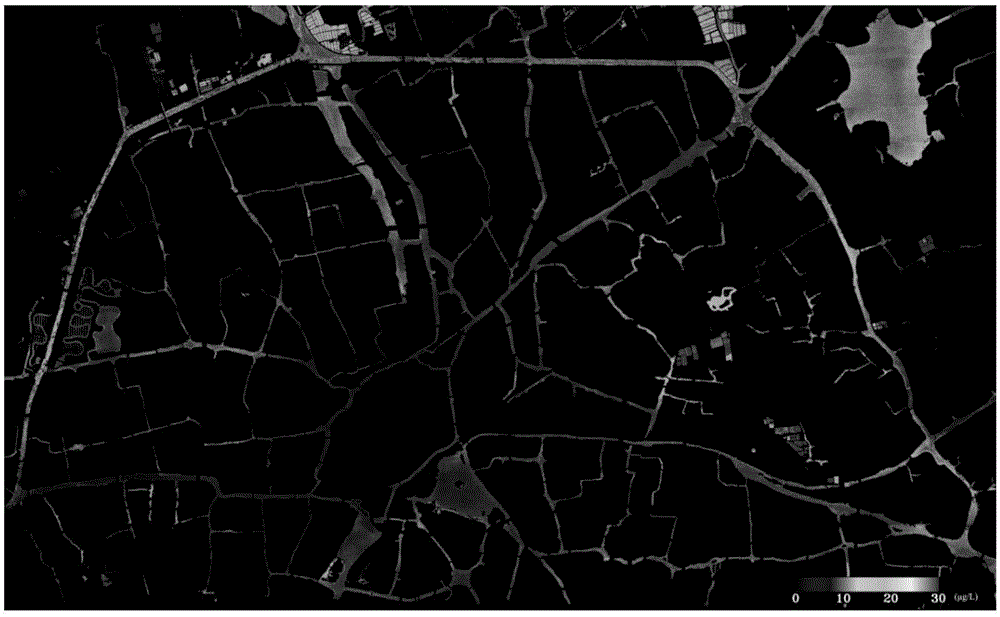
The invention discloses an analysis method of remote sensing inversion of water color parameters of inland class II water. According to the method, inherent optical quantity of the class II water is inverted with an improved QAA (quasi-analytical algorithm), and concentration inversion of the water color parameters such as chlorophyll a and suspended matters is realized based on the inverted inherent optical quantity of the class II water. The method comprises specific steps as follows: (1), data of remote sensing reflectance above the surface of the water is input, parameter inversion of the inherent optical quantity of the water is realized based on the improved QAA, and absorption coefficients and scattering coefficients of the water and absorption coefficients of phytoplankton are acquired; (2), concentration data of the chlorophyll a and concentration data of the suspended matters of the water at a sampling point are input, a chlorophyll a concentration quantitative inversion model is established according to the concentration data of chlorophyll a and the absorption coefficients of the phytoplankton, and a suspended matter concentration quantitative inversion model is established according to the concentration data of the suspended matters and the absorption coefficients of the water after removal of pure water; (3), hyperspectral data finishing atmospheric correction are input, and concentration inversion of the water color parameters of the inland class II water in a monitoring area is realized according to the step (1) and the step (2).
Owner:中国城市科学研究会
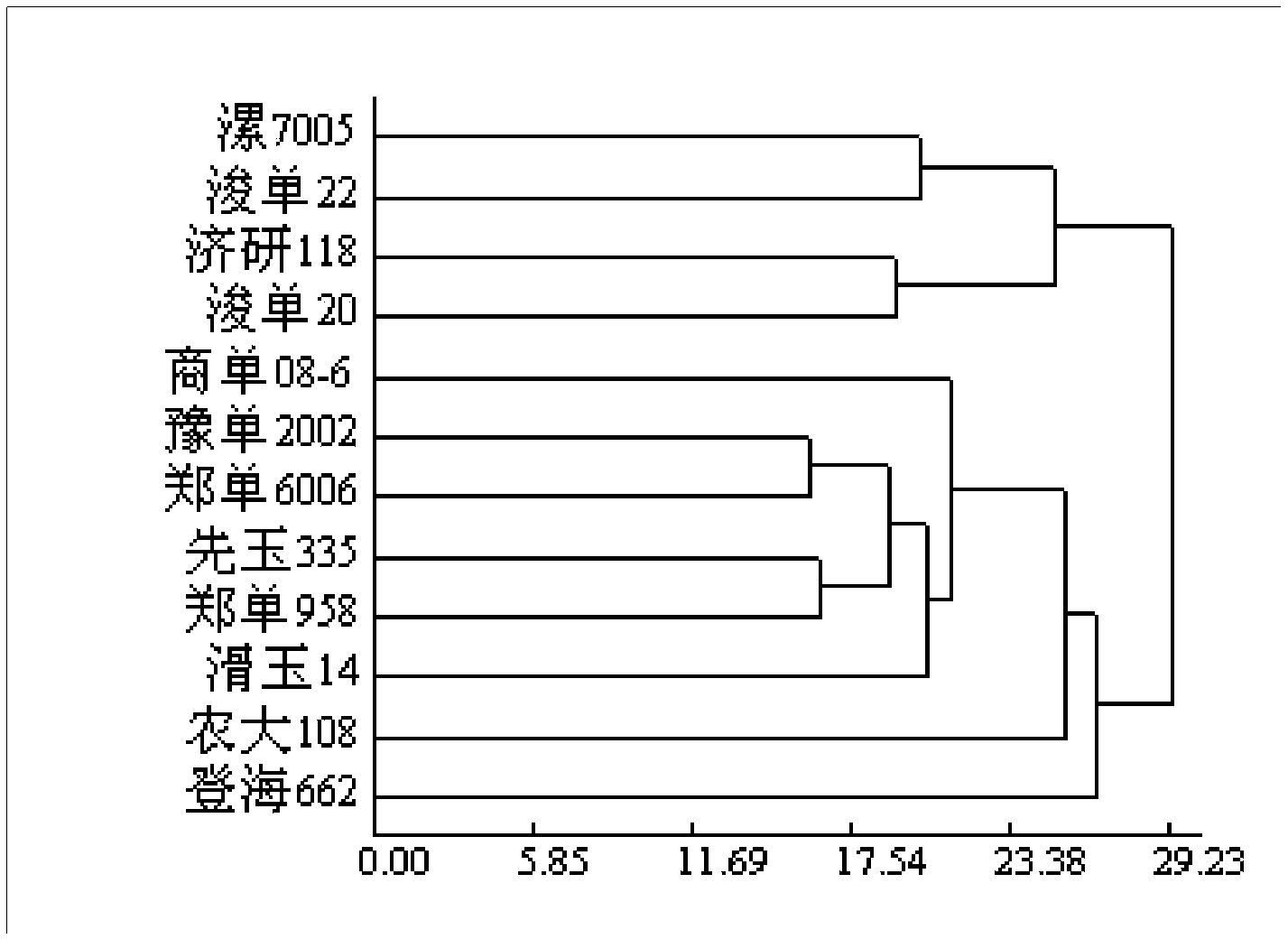
Method for evaluating flooding tolerance of maize variety
The invention discloses a method for evaluating flood tolerance of the maize variety. The method comprises the following steps of 1, after a pot is drowned, performing evaluation on four indexes, such as the color of a leaf, the form of the leaf, the color of a stem and the form of a root to preliminarily determine the flooding tolerance level; 2, performing two-sample pairing statistic analysis method on 15 shapes subjected to preliminary screening in the first step, and taking the strain height, the net photosynthetic rate, the green area, the root biomass, the root growth rate, the content of chlorophyll a, the total content of chlorophyll and an SPAD (soil and plant analyzer development) value as flood tolerance degree evaluation indexes according to the waterlogging influence degree; and 3, performing clustering analysis on the authentication indexes obtained by the second step, and classifying the varieties with different flood tolerance degrees into a flood tolerance hybrid and a non flood tolerance hybrid near to 27 according to genetic distances of all property clusters. The method for quickly and easily obtaining the flood tolerance evaluation indexes in a maize seedling stage is established according to the form change of leaves and stems above the ground as well as the physiologic and morphologic expression of plants, so that a basis is supplied to correct selection of the maize variety in an easily flooding region.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
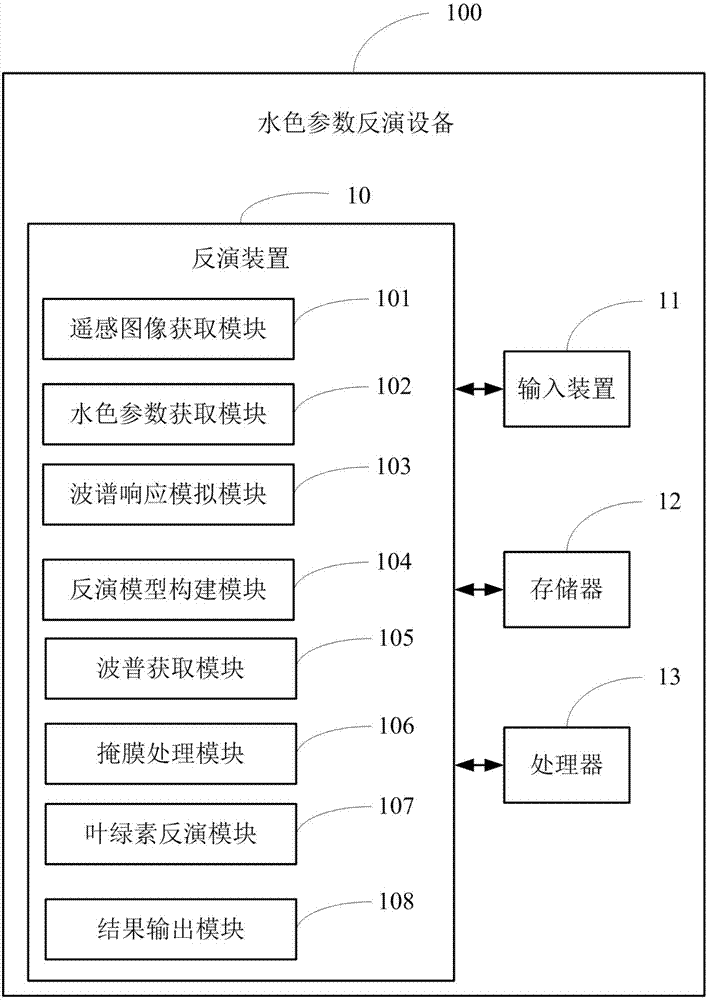
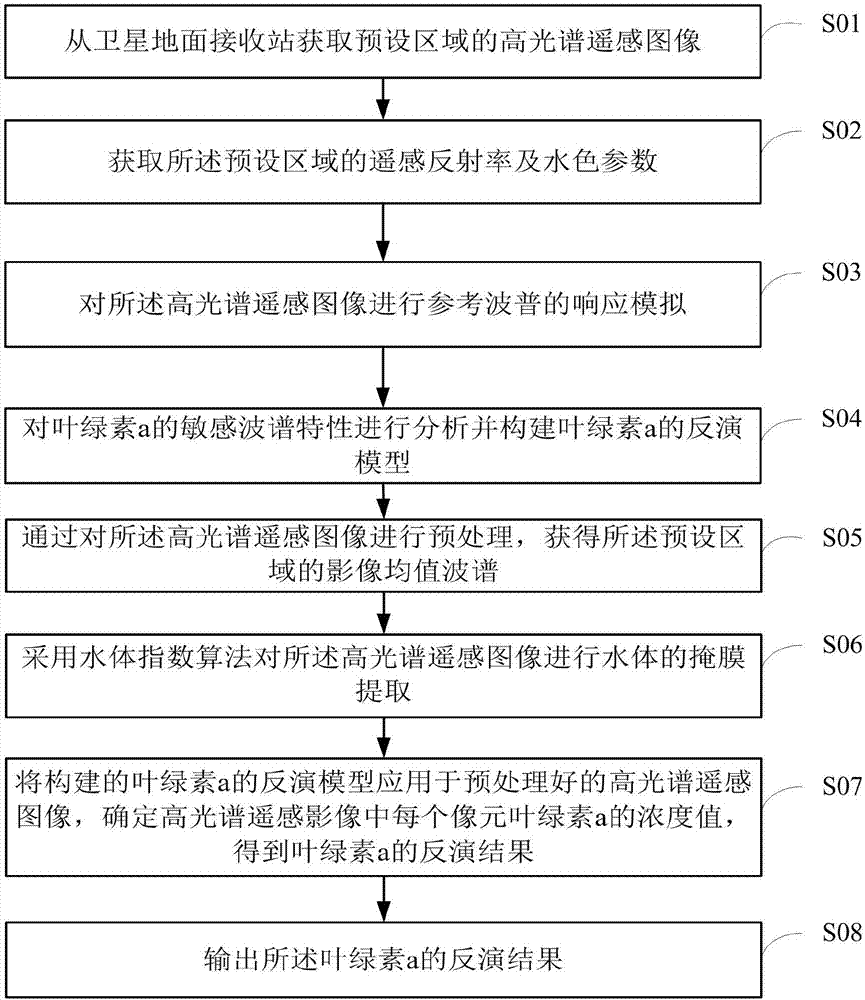
Chlorophyll remote sensing inversion device and method
InactiveCN107014763AImprove inversion accuracyScattering properties measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionChlorophyll aOptical property
The embodiment of the invention provides a chlorophyll remote sensing inversion device and a chlorophyll remote sensing inversion method. Based on sensitivity analysis of a spectral characteristic of chlorophyll a, an improved chlorophyll a inversion model is formed, and influence of complex optical property of a nearshore water body on the chlorophyll a is integrally considered; meanwhile, an HICO high spectral image is pre-processed to obtain an image mean value spectrum of an experimental sample region. The constructed chlorophyll a inversion mode is applied to the pre-processed image for chlorophyll a inversion. According to the embodiment of the invention, the inversion precision of the chlorophyll a is hugely increased.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
High-precision satellite MODIS (Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) monitoring method for chlorophyll a of eutrophic lake water body
ActiveCN104390917AAchieving High-Precision EstimationReflect the space-time distributionColor/spectral properties measurementsRayleigh scatteringEutrophication
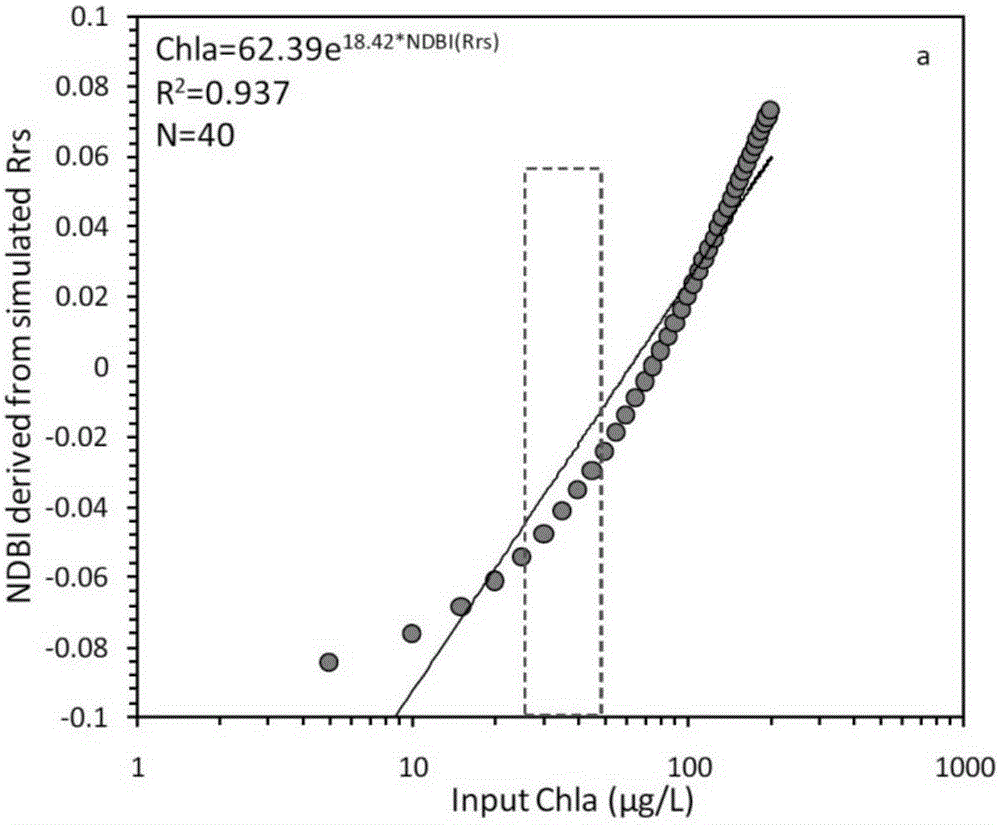
The invention provides a high-precision satellite MODIS (Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) monitoring method for chlorophyll a of a eutrophic lake water body. The method comprises the following steps: screening a chlorophyll a evaluation index (NDBI) which is sensitive to the concentration change of the chlorophyll a and is not influenced by high suspended solids; obtaining a quantitative relation between the NDBI and the concentration of the chlorophyll a on the basis of biological optical model simulation; combining spectral information of the water body and the corresponding concentration of the chlorophyll a of the water body monitored in the field in Chaohu Lake in year 2013-2014, so as to obtain a chlorophyll a inversion algorithm based on a ground measured spectrum (Rrs) and the NDBI; simulating different aerosol types and thicknesses, different solar altitudes, satellite observation angles and azimuth angles, so as to obtain a quantitative relation between the ground monitored remote sensing reflectance (Rrs) and simulated Rrc subjected to Rayleigh scattering correction; and further extending the chlorophyll a inversion algorithm based on ground measured spectral data to satellite image data subjected to the Rayleigh scattering correction. According to the method, the inter-annual and inter-monthly change rules and space distribution of the rules of the concentration of the chlorophyll a of a eutrophic lake can be accurately obtained.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Flow-cytometry-based method for rapidly measuring heterotrophic bacteria in eutrophic lake
InactiveCN103926189AShorten the timeRapid detection quantityIndividual particle analysisEutrophicationStaining
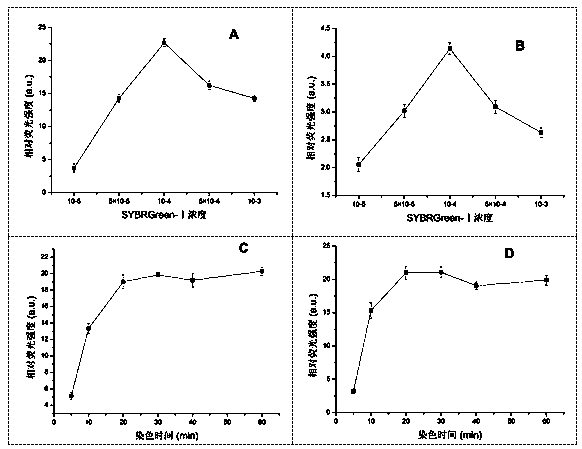
The invention aims to develop a flow-cytometry-based method for rapidly measuring heterotrophic bacteria in a eutrophic lake. The method is a flow-cytometry-based bacterium counting method. The method comprises the following steps of fixing a sample, performing ultrasonic processing, filtering, performing SYBR Green I dyeing, detecting the heterotrophic bacteria by utilizing a flow cytometer, and acquiring forward and lateral scattering light, an SYBR Green I green fluorescence signal and a chlorophyll a red fluorescence signal of autotrophic plankton, wherein the SYBR Green I green fluorescence signal is used for setting a threshold value; and eliminating the influence of the nannoplankton on bacterium detection by utilizing the forward and lateral scattering light, separating the plankton from abiological particles and cellular debris according to the intensity of the SYBR Green I green fluorescence signal, and separating the bacteria from phytoplankton according to the intensity of the chlorophyll a red fluorescence signal of the autotrophic plankton, thereby obtaining the accurate number of the heterotrophic bacteria. The method has the time-saving and labor-saving effects, the large-scale ecological survey can be developed, and the counting precision and accuracy of the bacteria are improved.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Semi-analytical method for realizing inversion of water body chlorophyll alpha concentration
The invention relates to a semi-analytical method for realizing inversion of water body chlorophyll alpha concentration, which comprises the steps of: (1) reading the data of chlorophyll alpha, water body spectroscopic data and high-spectrum remote sensing data; (2) utilizing the optical characteristics of the water body containing the chlorophyll alpha to establish semi-analytical model of the chlorophyll alpha concentration; (3) on the basis of the data in the step (1), adopting a method of enumerating by band and linear iteration, and calculating the best wave band and model parameter of the semi-analytical algorithm; and (4) on the basis of the steps (1) and (3), extracting the space distribution information of the chlorophyll alpha concentration from high-spectrum remote sensing image.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF MARINE GEOLOGY
Algae-controlling laterite compound flocculant as well as preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN101643261ASimple structureChange single force modeWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationAluminium chlorideChlorophyll a
The invention discloses an algae-controlling laterite compound flocculant as well as a preparation method and applications thereof. The method comprises the following steps: mixing 64.52-86.42% of laterite, 7.41-19.35% of polyaluminium chloride and 6.17-16.13% of ferric trichloride, and then milling to obtain the algae-controlling laterite compound flocculant. Compared with the methods by independently adding ferric trichloride or polyaluminium chloride, the algae-controlling laterite compound flocculant can obtain higher turbidity and higher chlorophyll a clearance rate, i.e. favorable effects for clearing algae and purifying water. Furthermore, with similar turbidity and chlorophyll a clearance rate, the quantities of the polyaluminium chloride and the ferric trichloride contained in thealgae-controlling laterite compound flocculant are lower than those of the polyaluminium chloride and the ferric trichloride which are independently used so as to save the cost and enhance the safetyof the flocculant in utilization. The algae-controlling laterite compound flocculant has the advantages of simple preparation procedure, moderate cost and favorable effects for clearing algae and purifying water, and is especially suitable for water bloom emergency treatment.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Four-band semi-analysis model for inverting chlorophyll a concentration in high-turbidity water body
InactiveCN102508959AImprove signal-to-noise ratioHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsParticulatesTurbidity
The invention discloses a method used for building a four-band semi-analysis model for inverting the chlorophyll a concentration in a high-turbidity water body. According to the method, a fourth band is introduced on the basis of the original three-band semi-analysis model for improvement, [Rrs-1(Lambda 4)-Rrs-1(Lambda 3)]-1 is used for replacing the Rrs(Lambda3) part in a three-band model factor and is used for reducing the backward scattering and absorption of suspension particles in the high-turbidity water body and the influence of colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM) on the remote sensing reflection rate, the chlorophyll a concentration characteristics are stressed, then, the positions of four corresponding bands are determined by a iteration method, influence factors are determined, and in addition, an inverting model is further obtained through linear regression. Compared with the three-band semi-analysis model, the model provided by the invention has the advantages that the chlorophyll a concentration in the high-turbidity water body is inverted, the influence of the suspension concentration and the CDOM is minimized, and the model precision is improved to a great degree.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method and device for classified detecting density of phytoplankton under water in site
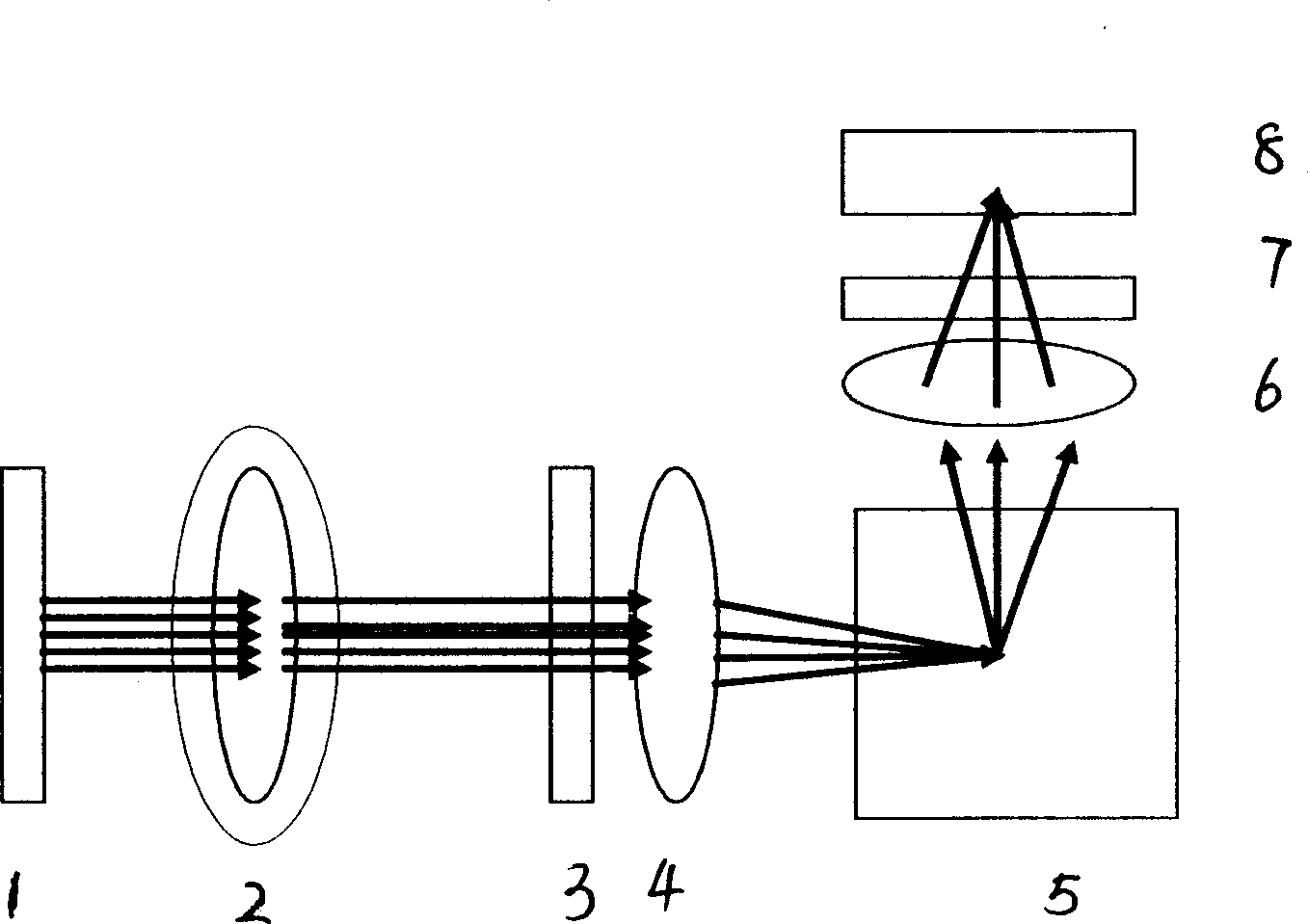
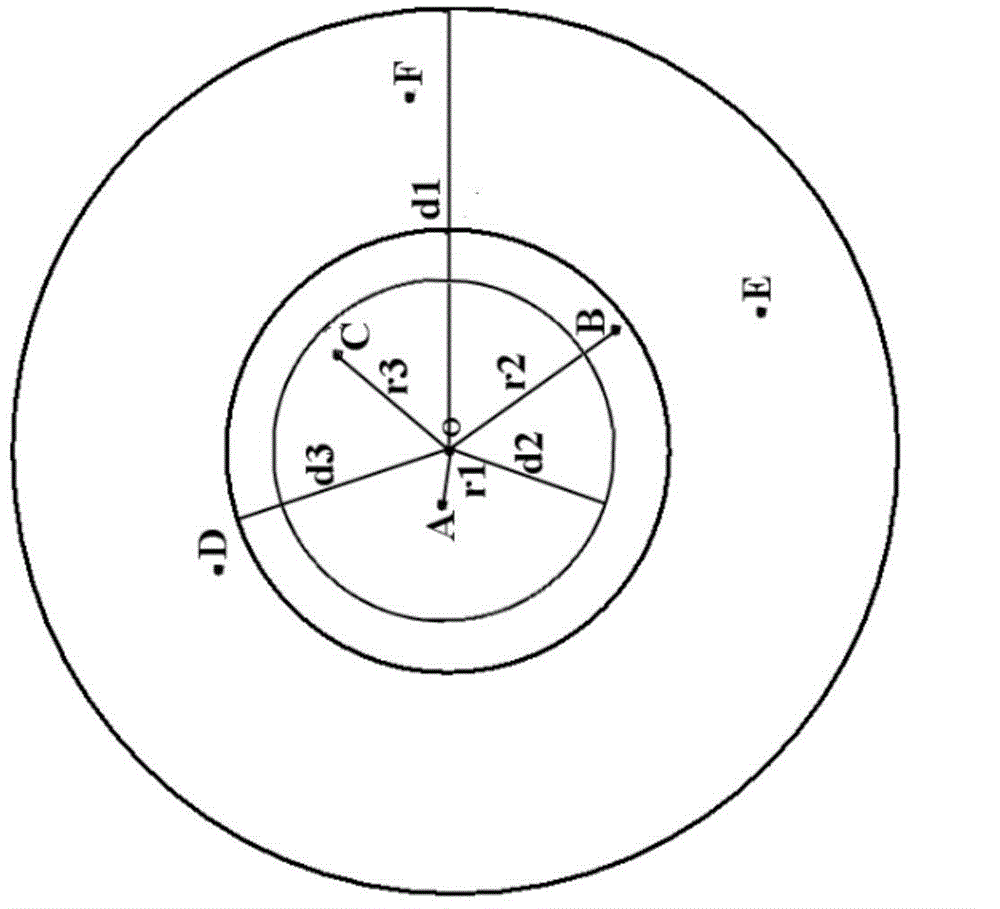
ActiveCN1916604ALow costReduce volumeColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceChlorophyll aFluorescence
A method for classifying underwater original position of polytoplankton by detecting concentration of polytoplankton includes setting a groove at one side of closed pressure box and a light shading cover at external side of said box; erecting LED array formed by parallel-arranged LED with center wavelength of 450nm, 525nm, 570nm 590nm and 620nm in light path at side surface of said groove; dividing polytoplankton to be five light spectrum set as green, blue, brown, red and mixture; measuring 685nm florescent intensity of five different exciting wavelength to calculate out chlorophyll concentration of each light spectrum according to known coefficient.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
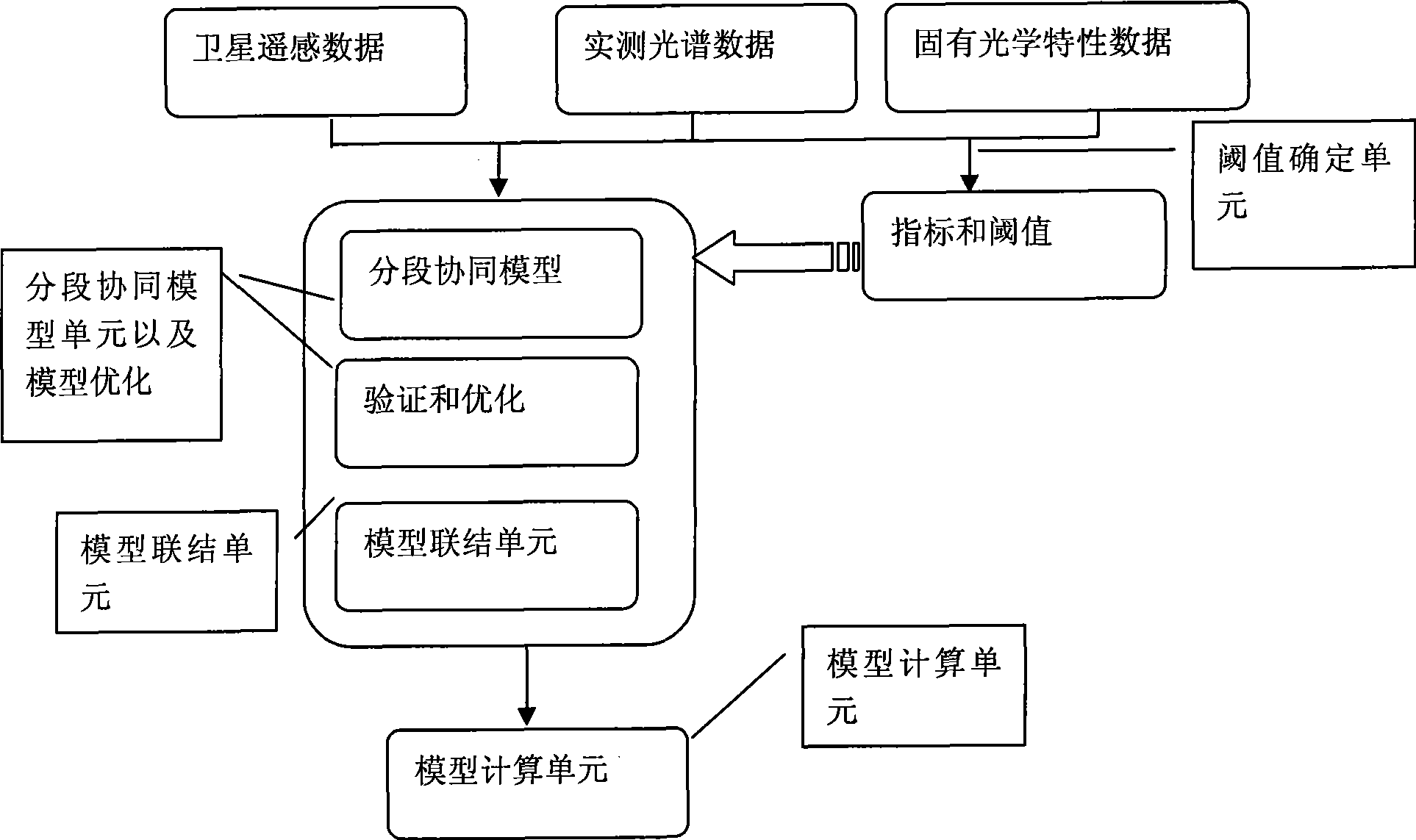
Inland water chlorophyll a concentration remote-sensing monitoring method based on segmenting cooperation model
InactiveCN101477036ADetermining Remote Sensing IndicatorsDetermine the thresholdColor/spectral properties measurementsChlorophyll aSensing data
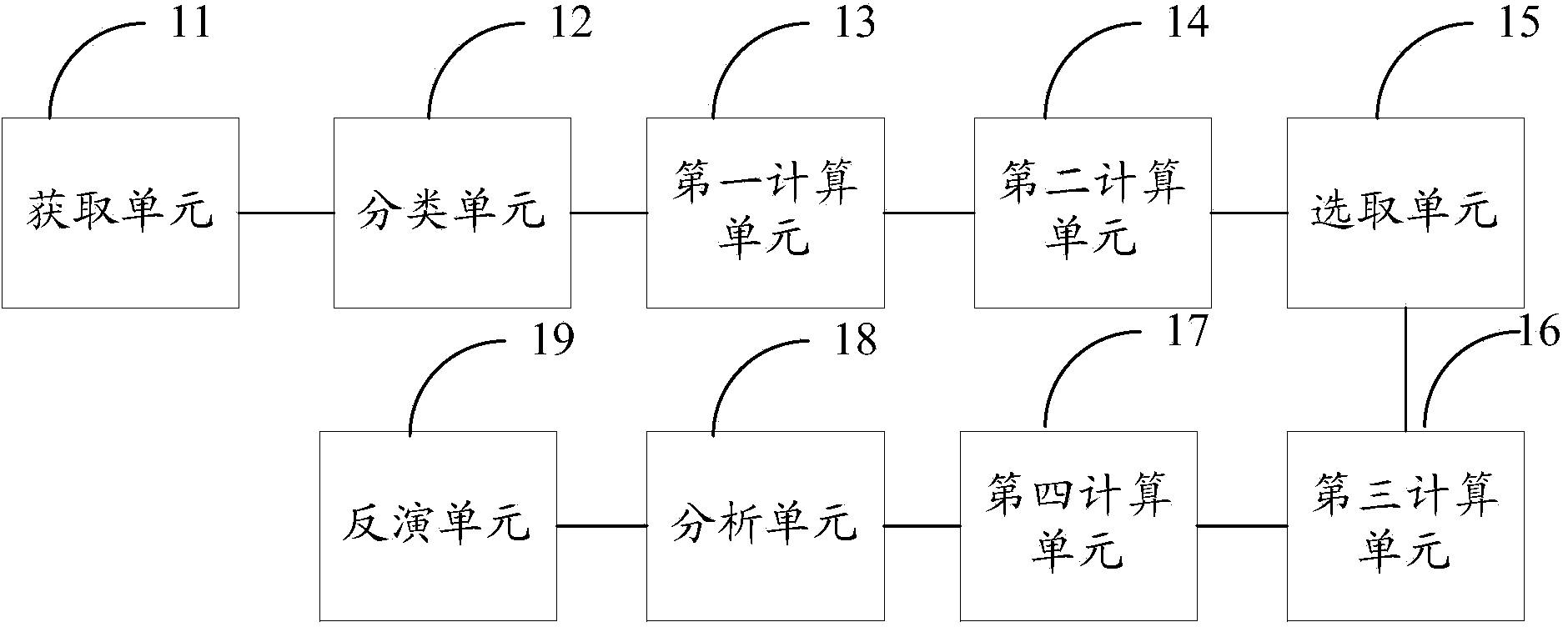
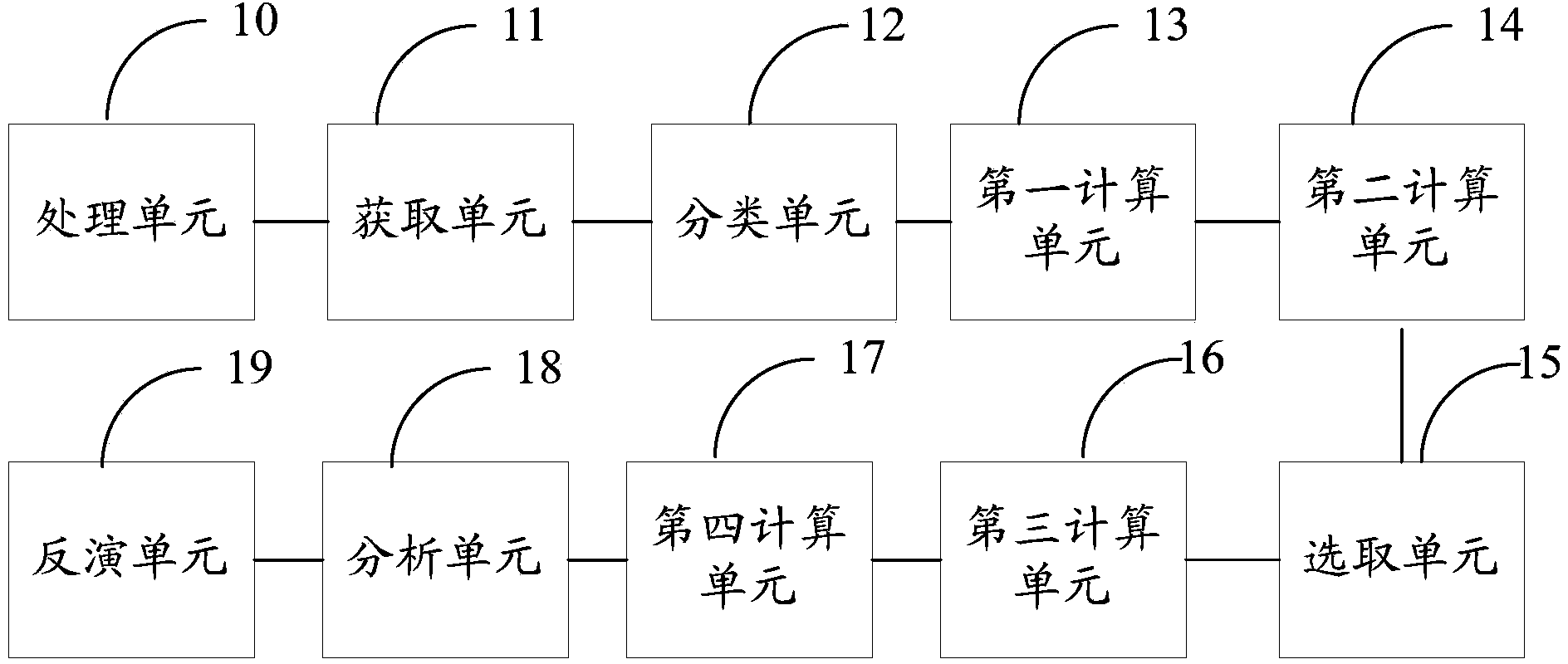
The invention provides a remote sensing monitoring method for the concentration of chlorophyll a in an inland water body based on a sectional coordination model. Aiming at the defects and disadvantages in remote sensing monitoring technology for of the concentration of the chlorophyll a, the invention provides the method which combines the advantage that an optical physical mechanism of the water body of the chlorophyll a can perform quantitative theoretical analysis and the advantages of simple calculation and high accuracy of a statistical correlation model. The method is characterized in that the method comprises four units, namely a threshold determination unit, a sectional coordination model unit, a model connection unit and a model calculation unit. The technical method jointly formed by the four units can effectively improve the inversion accuracy of remote sensing data to the chlorophyll a.
Owner:REMOTE SENSING APPLIED INST CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
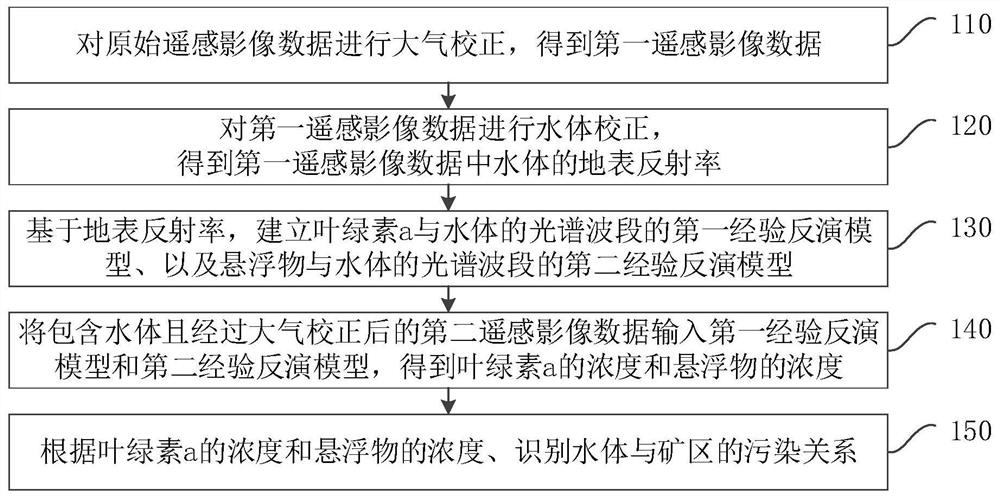
Water body pollution detection method, device and equipment and storage medium
PendingCN112014331AEliminate the effects of reflectionsEutrophication MonitoringMethods for obtaining spatial resolutionColor/spectral properties measurementsChlorophyll aSpectral bands
The embodiment of the invention discloses a water body pollution detection method, device and equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of carrying out the atmospheric correctionof original remote sensing image data, and obtaining first remote sensing image data; performing water body correction on the first remote sensing image data to obtain the surface reflectance of the water body in the first remote sensing image data; based on the surface reflectance, establishing a first empirical inversion model of the chlorophyll a and the spectral band of the water body, and a second empirical inversion model of suspended matters and the spectral band of the water body; inputting the second remote sensing image data into the first empirical inversion model and the second empirical inversion model to obtain the concentration of chlorophyll a and the concentration of the suspended matters; and identifying the pollution relationship between the water body and a mining areaaccording to the concentration of chlorophyll a and the concentration of suspended matters. Through two indexes of chlorophyll a and the suspended matter concentration, remote sensing image data are visualized, the pollution relation between the water body and the mining area can be reflected more visually, and a reference basis is provided for monitoring and treatment of water quality.
Owner:CHINA FIRST AUTOMOBILE
Diagnosis and evaluation method for water quality of eutrophic shallow lake subjected to ecological restoration
InactiveCN102053140AVisual diagnostic methodSimple diagnostic methodTesting waterChlorophyll aEutrophication
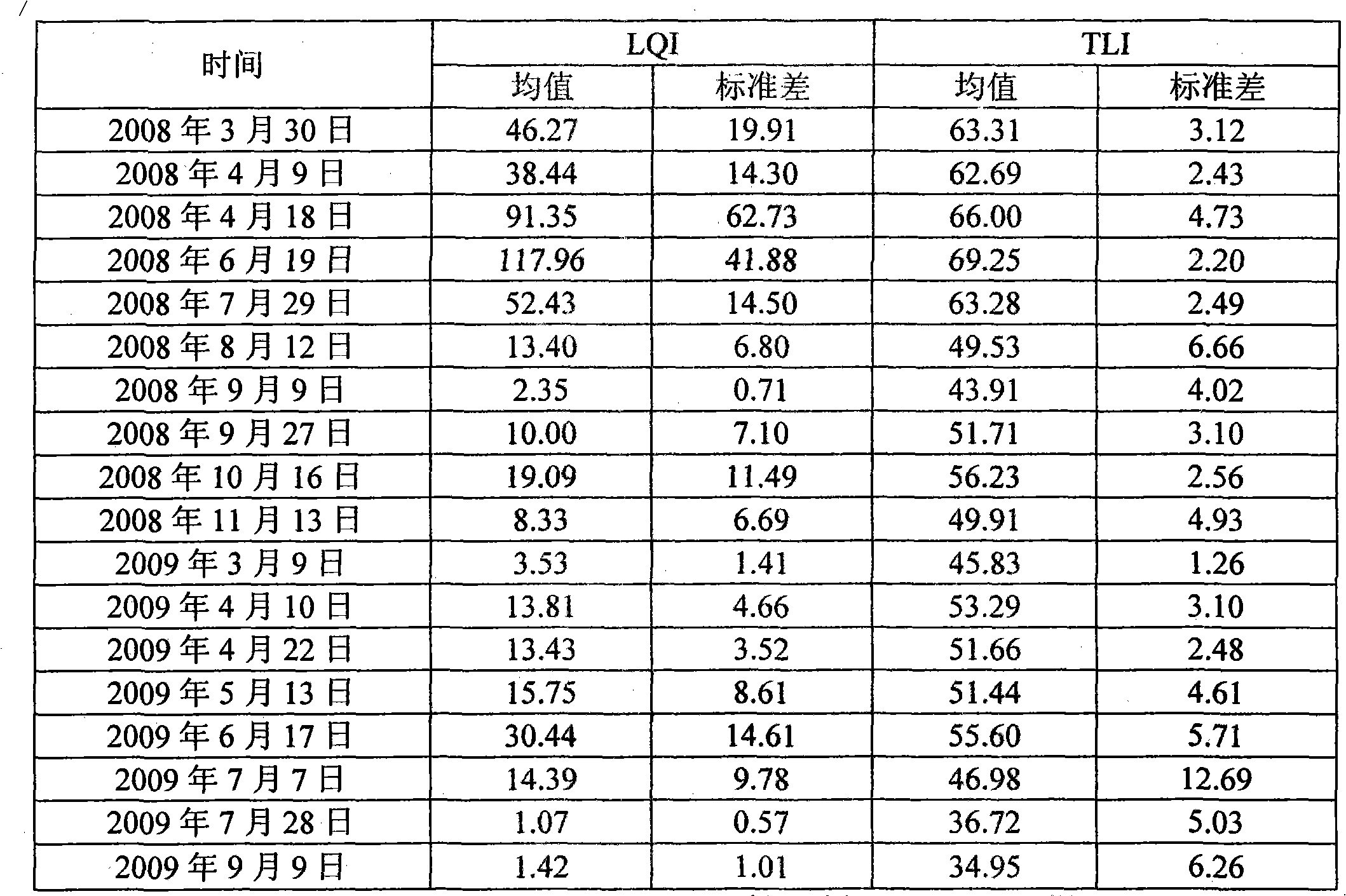
The invention provides a diagnosis and evaluation method for the water quality of an eutrophic shallow lake subjected to ecological restoration, which comprises the following steps of: selecting two factors, i.e. water transparency and chlorophyll a concentration which are important for water-quality improvement and stabilization in the ecological restoration process of the eutrophic shallow lake, comprehensively considering the interaction between the two factors, and establishing a water-quality diagnosis index-lake water quality index (LQI) of the eutrophic shallow lake subjected to the ecological restoration. The LQI can be used for quantitatively describing the conversion between the clean-water steady state and the muddy-water steady state of the eutrophic shallow lake so as to provide a visual and convenient diagnosis method for the water quality of the eutrophic shallow lake subjected to ecological restoration and also provide a scientific and reasonable reference basis for the drafting of management measures of the eutrophic shallow lake subjected to ecological restoration and the selection and the application of a subsequent ecological engineering method.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for detecting contents of chlorophyll a and carotinoid in crop laminas
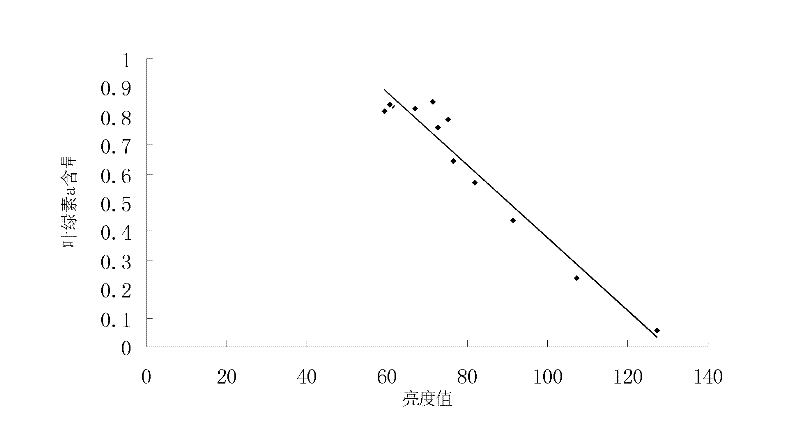
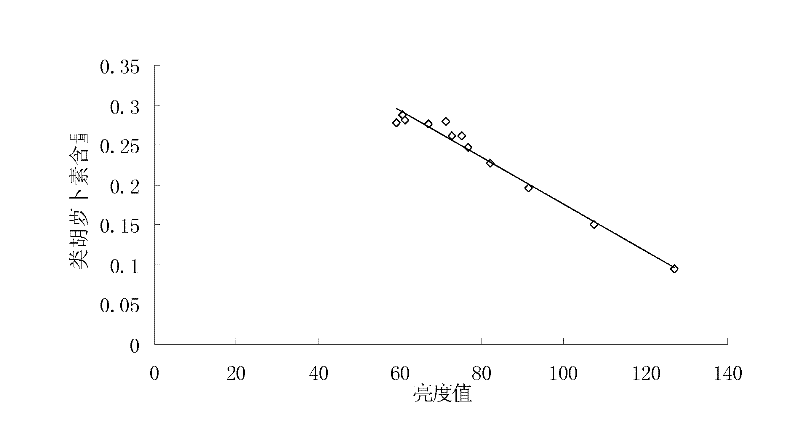
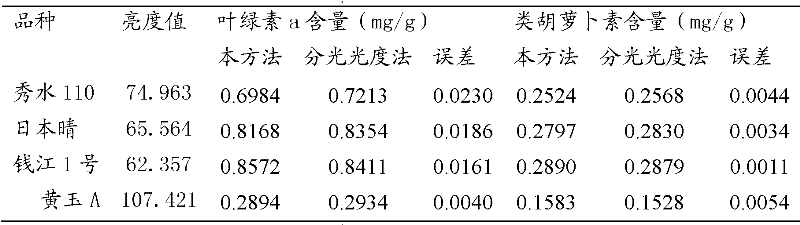
InactiveCN102519886AMeasurement results are stableSimple and fast operationColor/spectral properties measurementsFunctional relationLightness
The invention discloses a method for detecting contents of chlorophyll a and carotinoid in crop laminas. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting a set of laminas with obviously different leaf colours, obtaining an image brightness value of the set of lamina samples through scanning and image analyzing and processing, and, with the help of the contents of the chlorophyll a and the carotinoid of the set of laminas accurately measured by using a spectrophotometry, respectively establishing a functional relation between the chlorophyll a and the image brightness value of the laminas and a functional relation between the carotinoid and the image brightness value of the laminas; and then, obtaining an image brightness value of a to-be-detected lamina through scanning and image analyzing and processing, and respectively calculating the contents of the chlorophyll a and the carotinoid in the to-be-detected lamina according to the functional relations. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being simple in used equipment, simple and convenient for operation, low in cost and rapid in speed; chemical reagents and extraction are not required; detection is not influenced by time and an external environment; a measurement result is steady; and the method can be used for rapidly detecting the contents of the chlorophyll a and the carotinoid in the crop laminas anytime and anywhere.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Retrieval method and retrieval device of chlorophyll a concentration of inland case II water
ActiveCN103983584AReduce limitationsImprove smoothnessColor/spectral properties measurementsChlorophyll aRemote sensing reflectance
The invention provides a retrieval method and a retrieval device of chlorophyll a concentration of inland case II water, wherein the retrieval method of the chlorophyll a concentration of the inland case II water comprises the steps of firstly, classifying first remote sensing reflectance spectra to obtain a plurality of second remote sensing reflectance spectra taking different components as main components; calculating the weight matrixes of all the second remote sensing reflectance spectra, selecting all characteristic wave bands and calculating the chlorophyll spectral indexes; finally, carrying out weight fusion on the chlorophyll spectral indexes under all categories of all the spectra by weight to obtain weighted chlorophyll index, and fitting an inversion model to obtain the chlorophyll a concentration. Due to the method of firstly classifying and then carrying out weighted inversion, the limitation on the retrieval method caused by the area and the time can be reduced, and the smoothness and the stability of inversion results can be improved, and therefore, when the chlorophyll a concentration of a certain second remote sensing reflectance spectrum is inversed subsequently, the chlorophyll a concentration can be obtained by inversion through the inversion model corresponding to the second remote sensing reflectance spectrum, so that the universality of the method is improved.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
River water quality rapid monitoring system based on unmanned aerial vehicle hyperspectral image
InactiveCN110887792ASurface Dimension Quick MonitoringGood precisionColor/spectral properties measurementsTurbidityBiology
The invention discloses a river water quality rapid monitoring system based on an unmanned aerial vehicle hyperspectral image. The river water quality rapid monitoring system comprises an unmanned aerial vehicle hyperspectral system, a hyperspectral water quality index inversion model and a hyperspectral water pollution monitoring system. River water body hyperspectral images are obtained throughaerial photography of an unmanned aerial vehicle carrying a micro hyperspectral instrument, and are processed into water body reflectivity images through an image preprocessing system; river water samples are collected and tested to obtain river water sample water quality, and meanwhile, each pollutant concentration water sample is prepared manually in a laboratory; characteristic waveband combinations are selected as related variables for different water quality indexes, and a model for inverting the water quality according to water body spectral information is established; and the unmanned aerial vehicle water body reflectivity images are imported into the water quality inversion model, and calculating is carried out to obtain a water quality index concentration distribution diagram. Thewater quality indexes which can be monitored comprise total phosphorus, ammonia nitrogen, chlorophyll a, COD, BOD5 and turbidity, thereby helping an environmental protection department to know the overall water quality condition and pollution distribution of a river; and the water quality monitoring cost of a water area per unit area is relatively low, and the monitoring efficiency is relativelyhigh.
Owner:深圳慧格科技服务咨询有限公司
Analyzing and measuring method for chlorophyll a of phytoplankton in eutrophic water
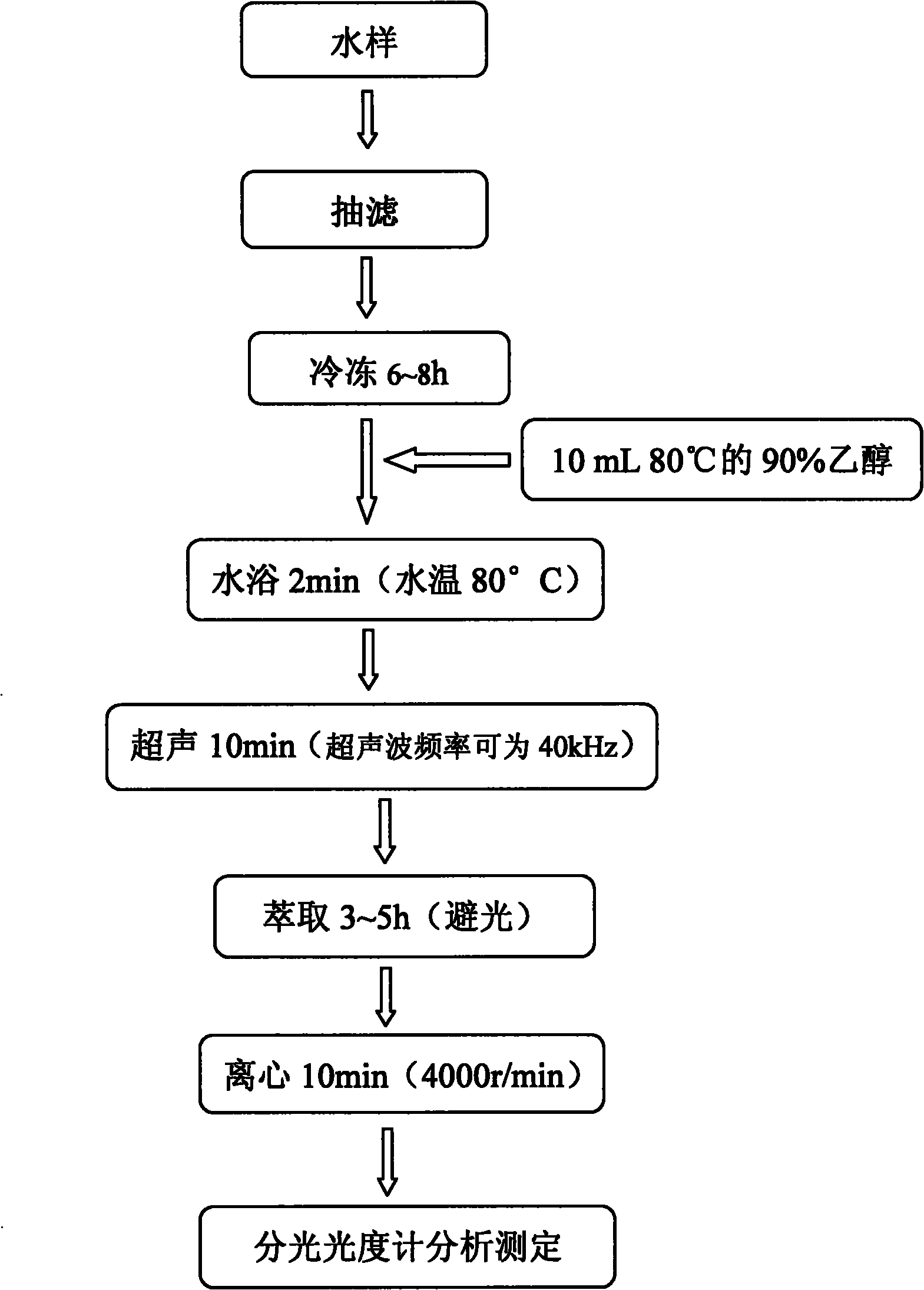
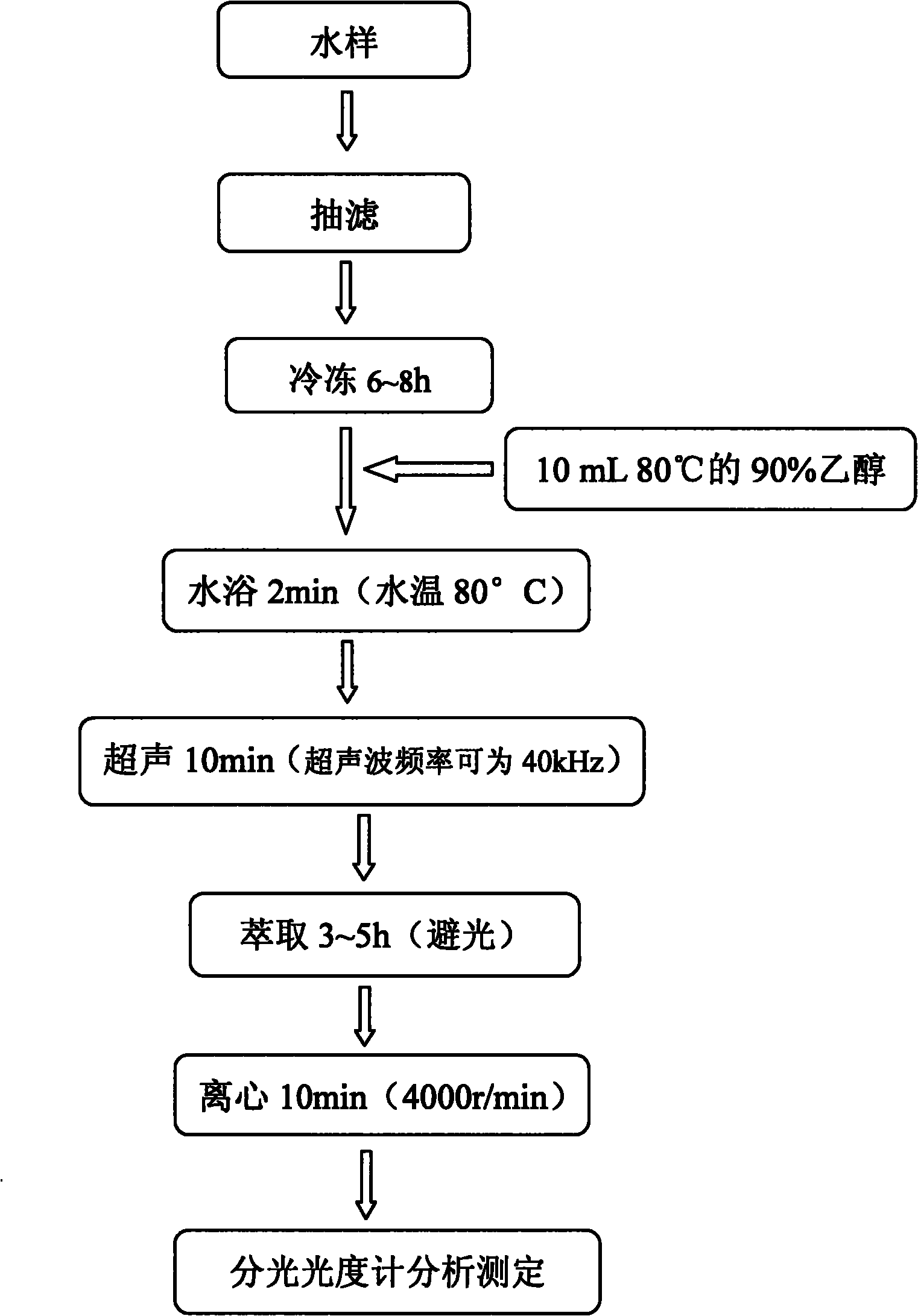
InactiveCN101858857AFully extractedComplete extraction efficiencyPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsWater bathsBathing
An analyzing and measuring method for chlorophyll a of phytoplankton in eutrophic water is a new method for extracting, analyzing and measuring the chlorophyll a of phytoplankton in eutrophic water and relates to the technical field of restoration of water environment in the environmental engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: filtering and freezing a collected water sample and then adding hot ethanol; after the water bathing and the ultrasonic treatment, extracting the water sample for a plurality of hours in dark, centrifuging the water sample, taking the supernatant and measuring the content of the chlorophyll in a water body by using the spectrophotometry. The invention has the advantages of simple and quick extraction and measurement of the sample, capability of extracting the chlorophyll in the phytoplankton to the most extent, high degree of extraction, low toxicity, good accuracy, low limit of detection and wide range of detection concentration; the problems that the traditional grinding method has high loss degree of chlorophyll and low extraction efficiency and the acetone extraction is toxic to human bodies to a certain extent are solved; and the invention is suitable for rapidly extracting and accurately measuring the chlorophyll of phytoplankton in the eutrophic water.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Hydrobiontic algae chlorophyll measuring method
InactiveCN1631117AMeasurement results are stableGood reproducibilityAlgae productsChlorophyll aCellulose acetate
The invention discloses a hydrobiontic algae chlorophyll measuring method which consists of, using spectrophotometry method to measure the algae chlorophyll content in the water, filtering subaqueous algae with cellulose acetate microporous filtering film, carrying out interception to the algae cellulose acetate through immersion with 90% ethanol, extracting the chlorophyll in algae cell into ethanol, centrifuging the tobacco extract to obtain the clarified solution, using 90% ethanol as reference, determining absorbancy of the tobacco extract at 630, 647, 664 and 750 nm with a spectrophotometer, calculating content of chlorophyll a, b, c in the water sample by utilizing the measured data.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
Eutrophic lake total algae storage remote sensing evaluation method
ActiveCN105631904AEffective assessmentImprove performanceImage enhancementImage analysisRayleigh scatteringEutrophication
The invention provides an eutrophic lake total algae storage (token state: total chlorophyll a, dimension: t) remote sensing evaluation method comprising the steps that the quantitative relation between NDBI and concentration of water surface chlorophyll a is acquired based on bio-optical model simulation and actually measured data and popularized to MODIS satellite image data through Rayleigh scattering correction; the water depth spatial distribution situation of the Chaohu Lake is determined based on the water level of the Chaohu Zhongmiao Temple and the Chaohu brake of the same day and Chaohu underwater DEM; the lake NDBI threshold is judged through screening based on actually measured profile empirical data, and the evaluation method for total storage of algae in a unit water column under the algae bloom and non-algae bloom conditions is constructed; and the evaluation method for total storage of algae in a unit image element based on MODIS satellite images is constructed. The annular and monthly change rule of eutrophic lake total algae storage and spatial distribution thereof can be accurately acquired based on the method.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Submerged macrophytes restoring process guided by water conservation fishery
InactiveCN101960951ARestrict growthImprove water qualityClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsChemical oxygen demandFood chain
The invention discloses a submerged macrophytes restoring process guided by water conservation fishery. By stocking silver carp and bighead carp and reducing COD (chemical oxygen demand), TP (total phosphor), chlorophyll and other chemical indexes of the water body, the process effectively reduces the algae biomass in the water body, improves the water body transparency, and achieves the aim of preventing algal bloom and improving the water quality, so an excellent growing condition is provided for aquatic macrophytes (in particular, the submerged macrophytes); and by adding fish and other key organisms eating attaching organisms, which is a key link in a food chain, the attaching organisms growing vigorously on the surface of the submerged macrophytes can be removed in time, and the aim of restoring the submerged macrophytes can be achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Algae bloom prediction method based on principal component analysis and BP neural network
InactiveCN110046645AEliminate short-term volatility effectsImprove training efficiencyForecastingCharacter and pattern recognitionChlorophyll aKernel principal component analysis
The invention discloses an algae bloom prediction method based on principal component analysis and a BP neural network, and belongs to the technical field of water environment management. The method comprises the steps of monitoring data randomness preprocessing; carrying out influence factor analysis based on a principal component analysis method; and constructing a prediction model by taking thechlorophyll a content and the chlorophyll a content change rate of the water body as output parameters and analyzing the prediction precision. The method is characterized in that an integral derivation data smoothing method is adopted, so that the influence of data randomness is eliminated; based on a principal component analysis method, prediction model input factors are simplified, chlorophylla content change rate is taken as an output parameter, and the defect that chlorophyll a content fluctuation interferes with a prediction result is eliminated, so that the prediction precision of thealgae bloom is effectively improved.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
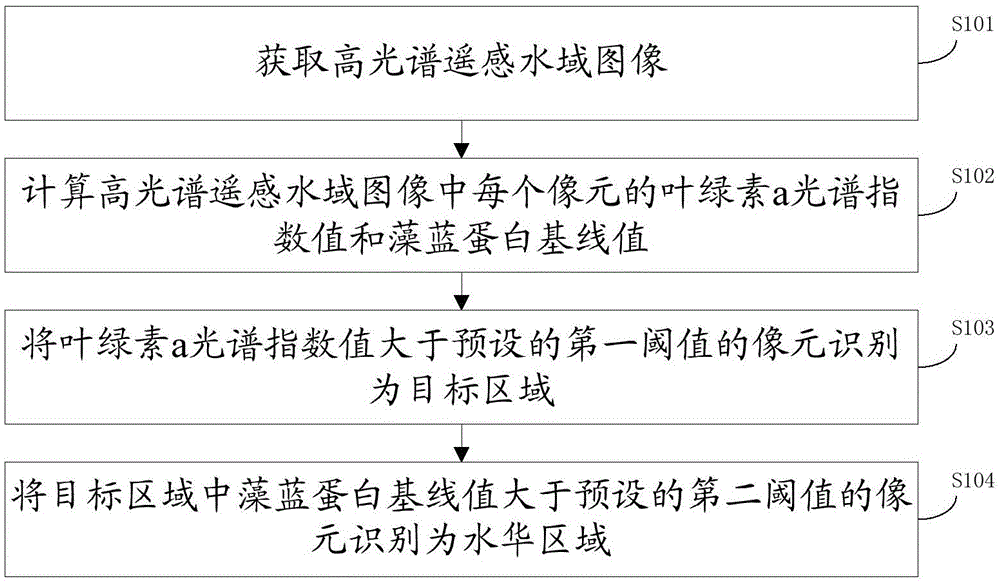
Water bloom identification method and device based on hyperspectral remote sensing image
The invention provides a water bloom identification method and device based on a hyperspectral remote sensing image, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a hyperspectral remote sensing water area image; calculating a chlorophyll a spectrum index value and phycocyanin baseline value of each pixel in the hyperspectral remote sensing water area image; recognizing pixels with the chlorophyll a spectrum index values being greater than a preset first threshold value as a target region; enabling pixels with the phycocyanin baseline values being greater than a preset second threshold value in the target region as a water bloom region. Because the chlorophyll a spectrum index value of water is remarkably less than the chlorophyll a spectrum index value of water bloom and water plants and the phycocyanin baseline value of the water plants is remarkably less than the phycocyanin baseline value of the water bloom, the method and device achieve the purpose of recognizing the water bloom region according to the characteristics of water bloom spectra.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Remote sensing estimation method for total algae stock of eutrophic lake under non-algae bloom condition
ActiveCN105203466ARealize remote sensing estimationEffective assessmentColor/spectral properties measurementsRayleigh scatteringEutrophication
The invention provides a remote sensing estimation method for the total algae stock (token: chlorophyll a gross and dimension: t) of a eutrophic lake under the non-algae-bloom condition. The method includes the steps that NDBI threshold values of the non-algae-bloom condition of the lake are screened and judged; on the basis of photobiological model simulation and measured data, the quantitative relation between NDBI and water surface chlorophyll a concentration under the non-algae-bloom condition is acquired and generalized to MODIS satellite image data corrected by rayleigh scattering; based on measured section data, a lookup table between the total biomass of an algae surface layer and the total algae stock within different water depth ranges is acquired; based on the same-day water level of the middle temple of the Chaohu Lake and the Chaohu Floodgate Station and the underwater DEM of Chaohu Lake, the water depth space distribution of the Chaohu Lake is determined; based on the total algae stock in unit pixels of an MODIS satellite image, estimation is performed. Based on the method, the inter-annual and inter-monthly change rule and space distribution of the total algae stock of the eutrophic lake under the non-algae-bloom condition can be accurately obtained.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
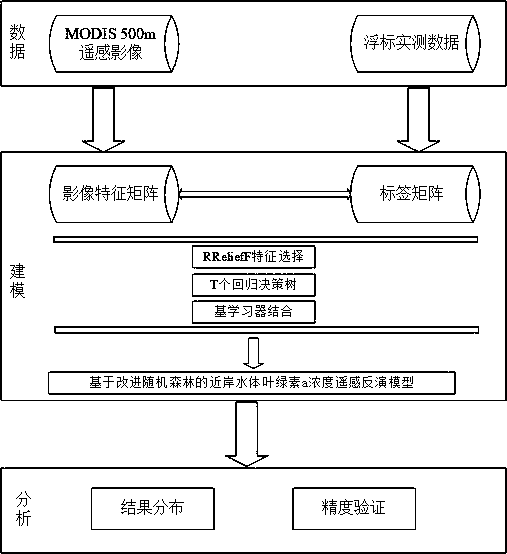
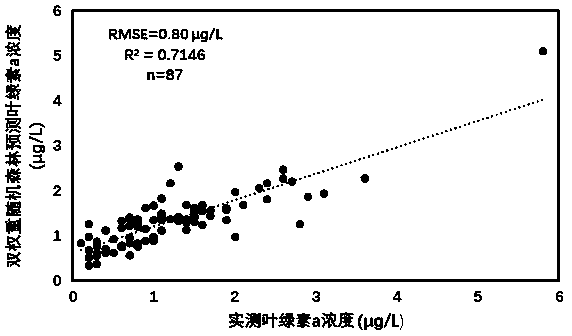
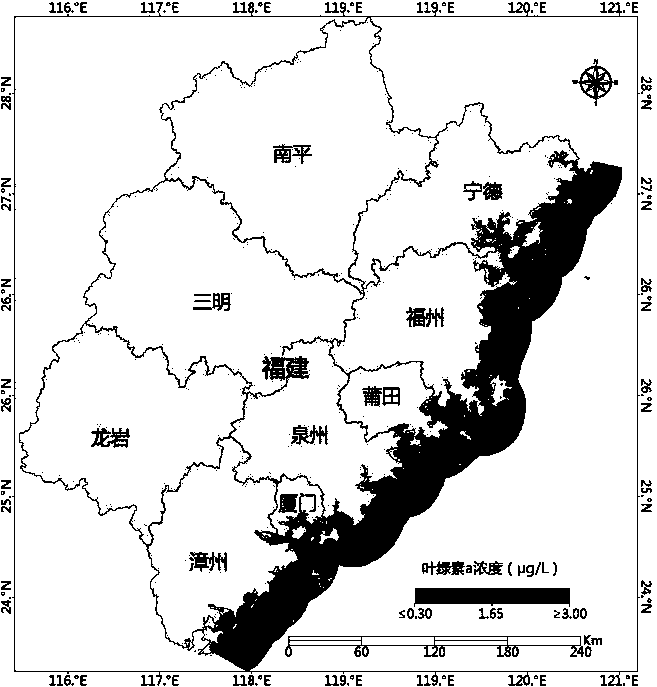
An improved random forest-based remote sensing inversion method for the concentration of chlorophyll a in an offshore water body
InactiveCN109409441AAvoid the problem of poor regression decision tree effectMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionOffshore waterBuoy
The invention relates to an offshore water chlorophyll a concentration remote sensing inversion method based on an improved random forest. remotely sensing image data by utilizing a time sequence; combining timing buoy observations, The method comprises the following steps of: establishing an intelligent remote sensing inversion model to carry out remote sensing inversion on the chlorophyll a concentration of an offshore water area by taking time continuous space sparse compensation as a modeling strategy and adopting an improved random forest-double-weight random forest method to obtain a very good inversion result, and visually and accurately displaying the spatial distribution of the chlorophyll a concentration of the offshore large range. The invention can provide a macroscopic, continuous and effective method for monitoring the concentration of chlorophyll a in the near-shore water body, can make up the deficiency of the traditional chlorophyll a concentration monitoring, and hashigher practical value.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Short-term forecasting method for eutrophication shallow lake algae source lake flooding
ActiveCN104615885AClimate change adaptationSpecial data processing applicationsEutrophicationWater quality
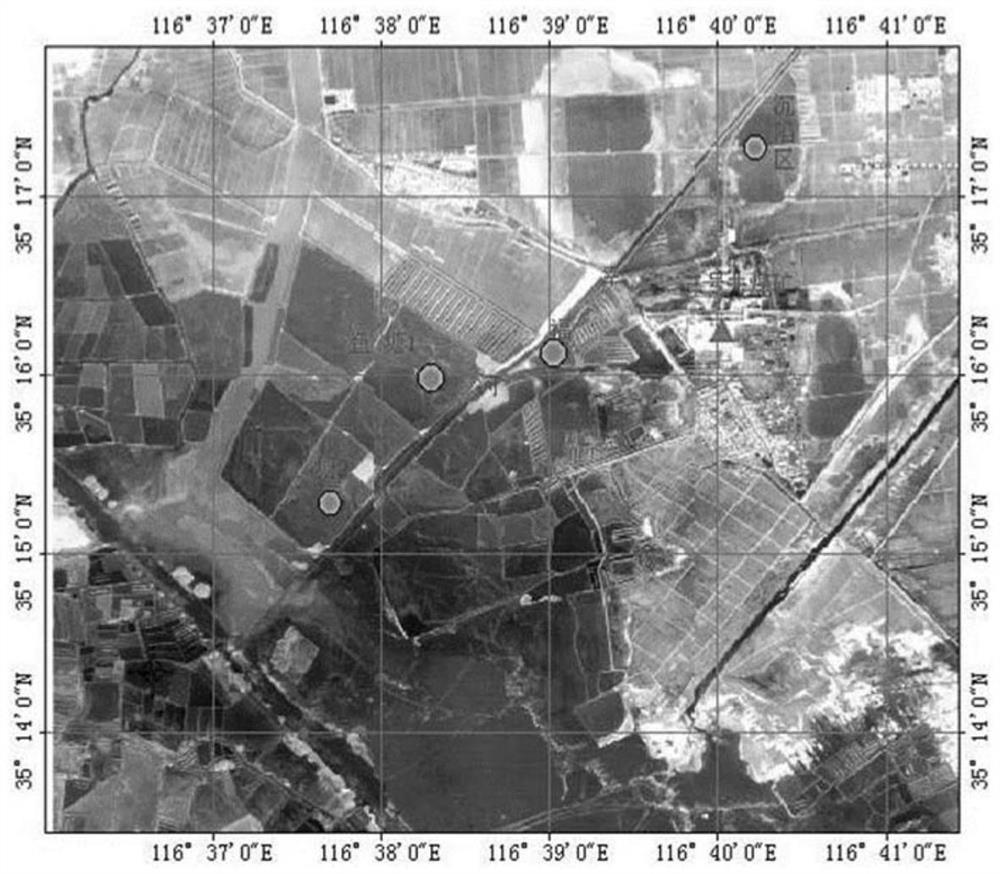
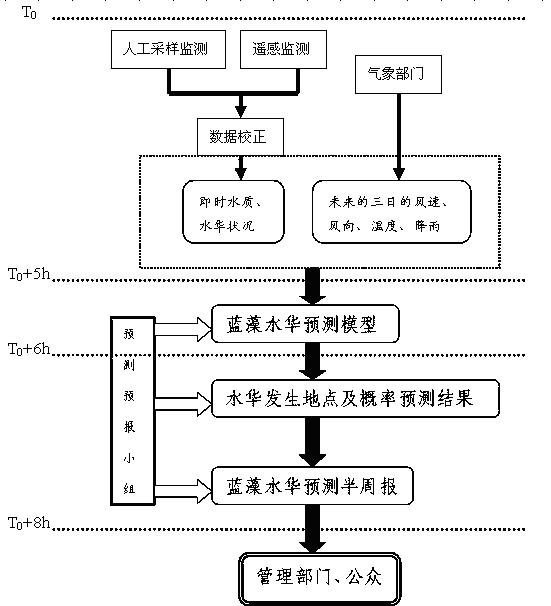
The invention provides a short-term forecasting method for eutrophication shallow lake algae source lake flooding. The method comprises the steps that a plurality of monitoring points are set in a water area where shallow lake flooding is likely to happen so as to measure meteorological parameters and water environment parameters; a space mesh dividing and interpolation algorithm is used for interpolating the water environment parameters of the monitoring points to a whole lake, and space distribution is used as the initial condition of a water quality numerical model; the wind field time and space distribution in the next three days is used as model external stress, a three-dimensional water power-water quality numerical model is driven to conduct calculation, and the time and space distribution of the shallow lake chlorophyll a and the dissolved oxygen concentration in the next three days is obtained; the time and space distribution of the chlorophyll a and the dissolved oxygen concentration is used for being combined with the meteorological parameters, so that a probability empirical formula is established, and the probability of lake flooding in the water area where the lake flooding is likely to happen in the next three days is calculated. For the water area where the lake flooding probability is large, the position and area of lake flooding are further determined.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Detection and analysis method for cell size distribution of phytoplankton
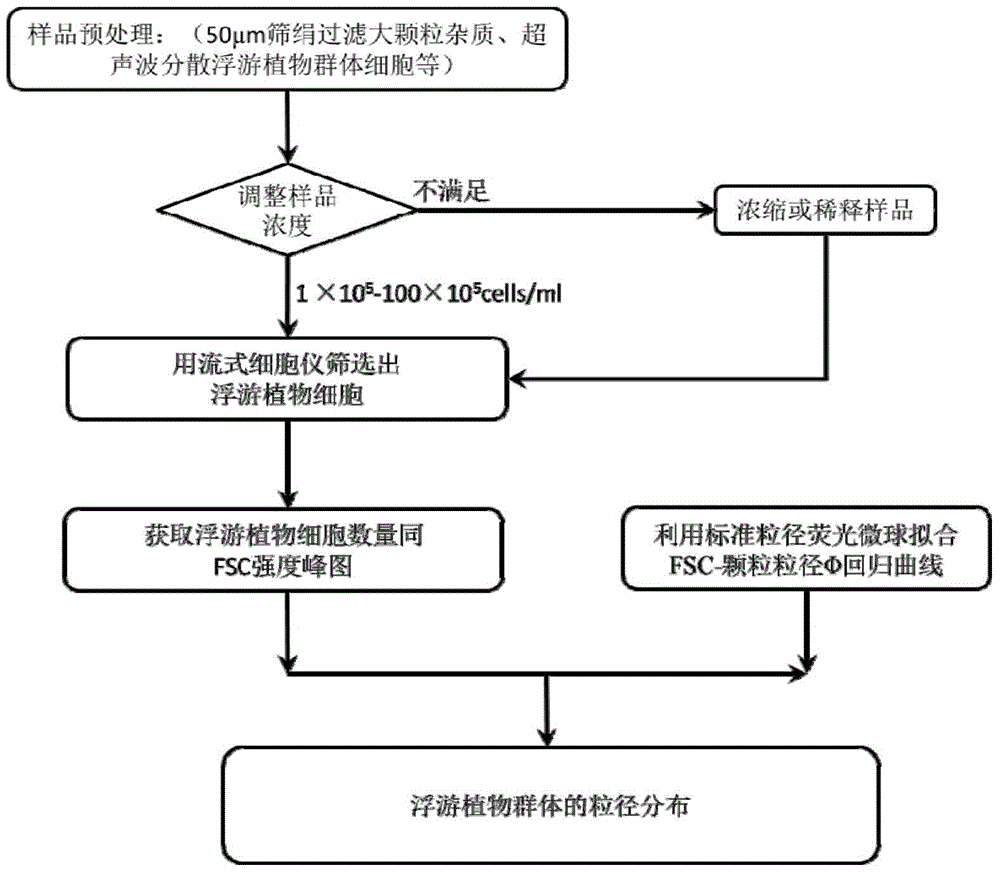
The invention discloses a method for detecting and analyzing the particle size distribution of phytoplankton cells. 1) Pretreatment is performed on samples containing phytoplankton cells, and the cell concentration is adjusted to a suitable range; 2) According to chlorophyll a autofluorescence, the phytoplankton cells were screened out by cytometer analysis; 3) Under the same test conditions, fluorescent microspheres with different particle sizes were used to fit the Φ-FSC standard curve of forward scatter signal intensity (FSC) and particle size value Φ , to obtain a fitting function that converts the FSC signal intensity into a particle size value; 4) On the basis of step 2), generate a peak diagram of the particle number distribution of the phytoplankton cells injected after screening and the FSC distribution, and on the basis of step 3), Calculate the particle size corresponding to the mean value of the cell count in the injected sample to obtain the particle size distribution of the phytoplankton cells. The invention is easy to operate, can obtain the particle size distribution of phytoplankton in a statistical sense, and can be used to carry out research on particle size composition, ecological structure and the like of phytoplankton populations.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com