Flow-cytometry-based method for rapidly measuring heterotrophic bacteria in eutrophic lake
A flow cytometry and rapid measurement technology, which is applied in the field of rapid detection of heterotrophic bacteria in large shallow lakes, can solve the problems of interference in the measurement process, long counting time, and large differences in results, and achieve accurate quantification, high precision, and high accuracy. short time effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] The following examples further illustrate the present invention, but are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention. Unless otherwise specified, the technical means used in the embodiments are conventional means well known to those skilled in the art.
[0049] Example 1 Enumeration of Total Heterotrophic Bacteria in Large Shallow Water Eutrophic Lake Taihu
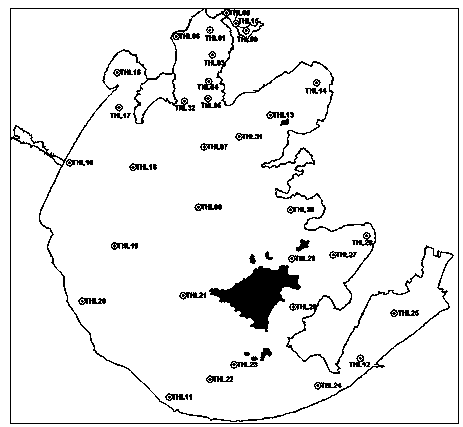
[0050] In February, May, August and November 2013, water sampling devices were used to collect surface water samples from each point in Taihu Lake, a total of 123 samples (such as Figure 3A ), collected into a pre-sterilized EP tube, added a fixative paraformaldehyde with a final concentration of 1%, and transported back to the laboratory in a refrigerated incubator.
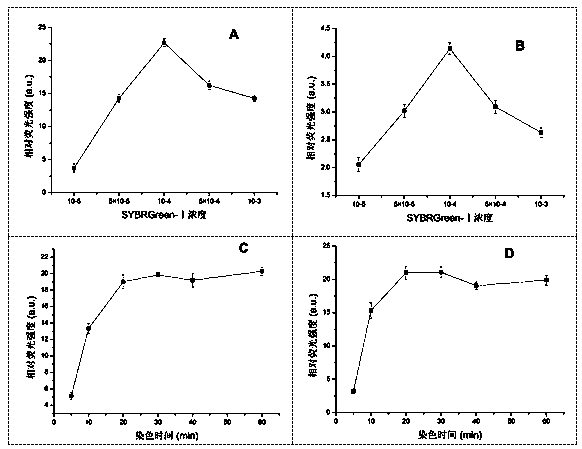
[0051] Take at least 500ul sample, dilute it 1:10 with sterile water, and mix well.
[0052] Take a 5ml sample and use an ultrasonic cleaner (power 25W) for 5 minutes of ultrasonic action to break up the bacteria that are agglomerat...
Embodiment 2
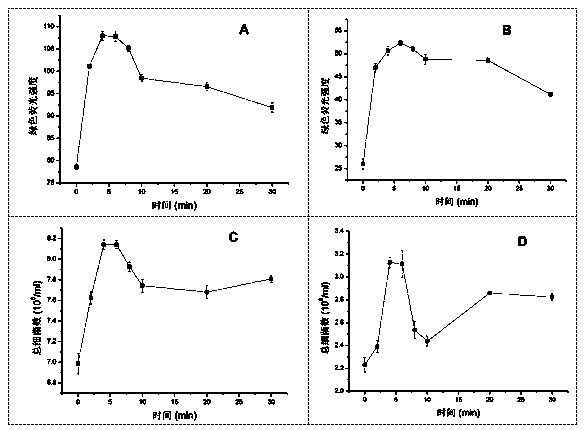
[0061] Compared with Example 1, the difference is only: in the present embodiment, in step 1, the fixative formaldehyde of final concentration 1.5% is added in the sample to be tested; in step 2, ultrasonic treatment condition Es=P*t / V, The ultrasonic power P is 50W, the ultrasonic time t is 10min, the sample volume V is 20ml, and the Es is 1500KJ / L. Step 3: Stand in the dark for 15 minutes to color the DNA.
Embodiment 3
[0063] Compared with Example 1, the difference is only that: in this example, in step 1, the curing agent glutaraldehyde with a final concentration of 0.5% is added to the sample to be tested; in step 2, the ultrasonic treatment condition Es=P*t / V, wherein the ultrasonic power P is 100W, the ultrasonic time t is 2min, the sample volume V is 8ml, and Es is 1500KJ / L. In step 3, stand in the dark for 30 minutes to color the DNA.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com