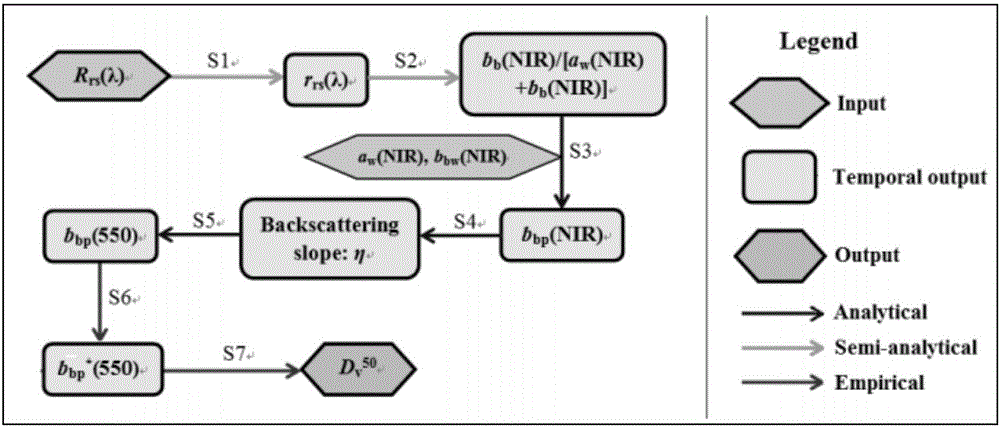
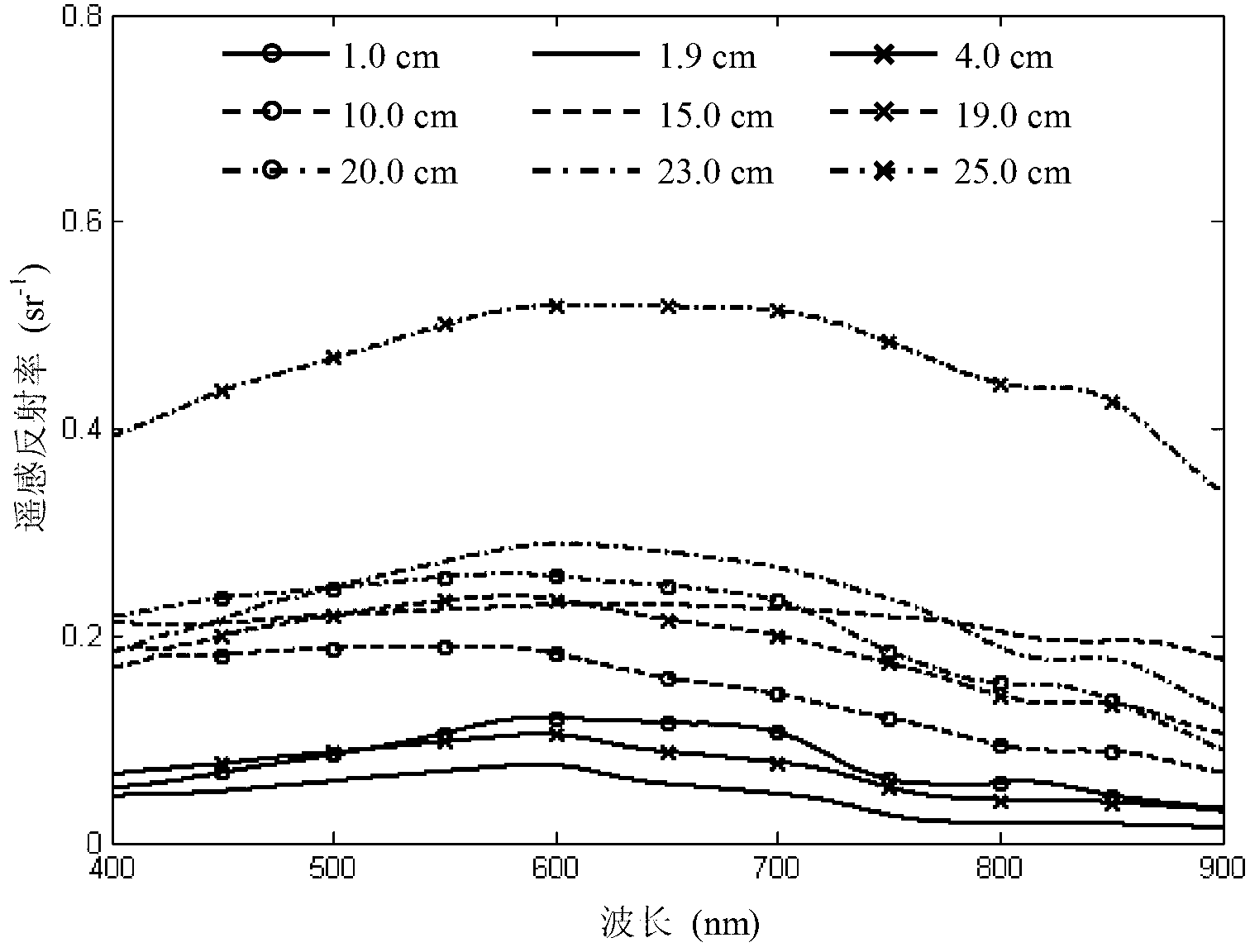
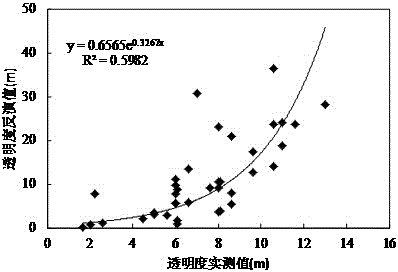
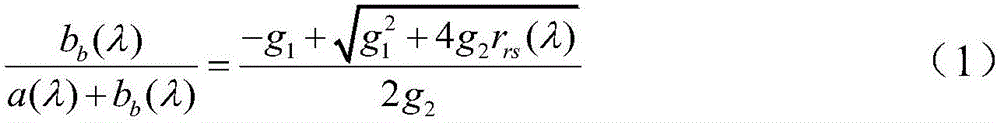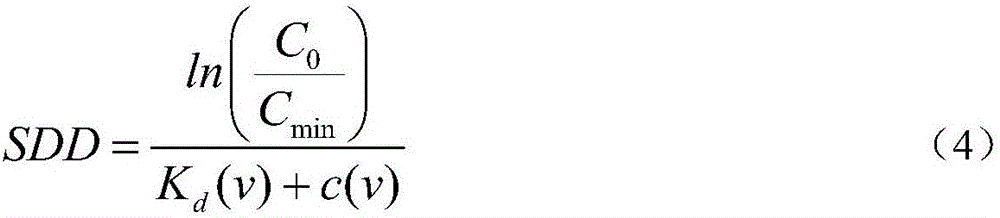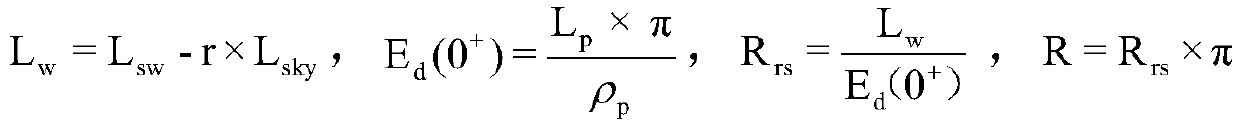Patents
Literature
133 results about "Remote sensing reflectance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
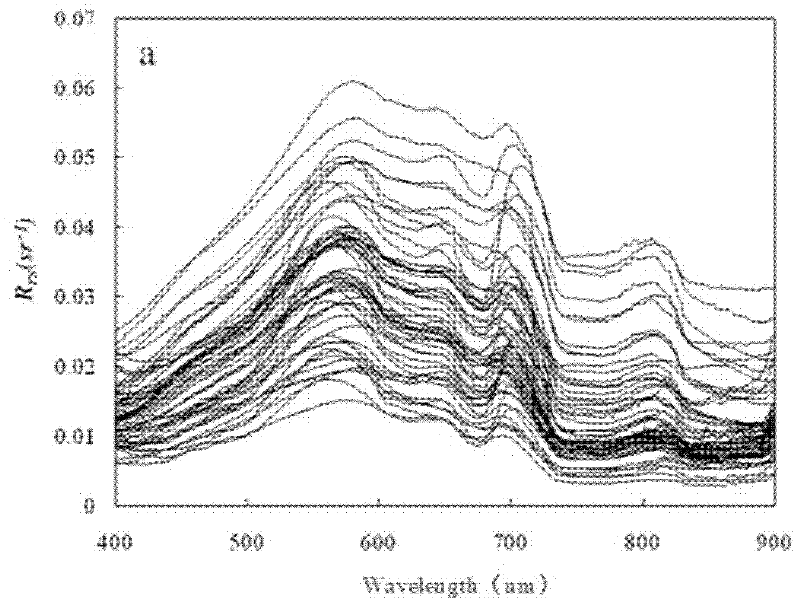
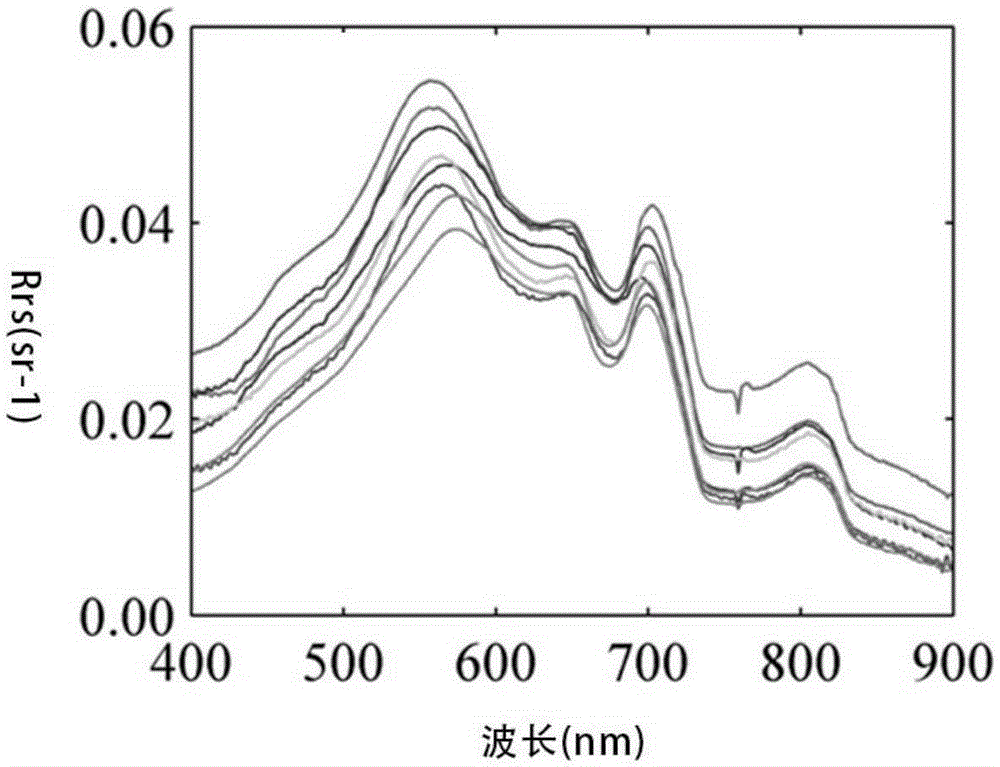
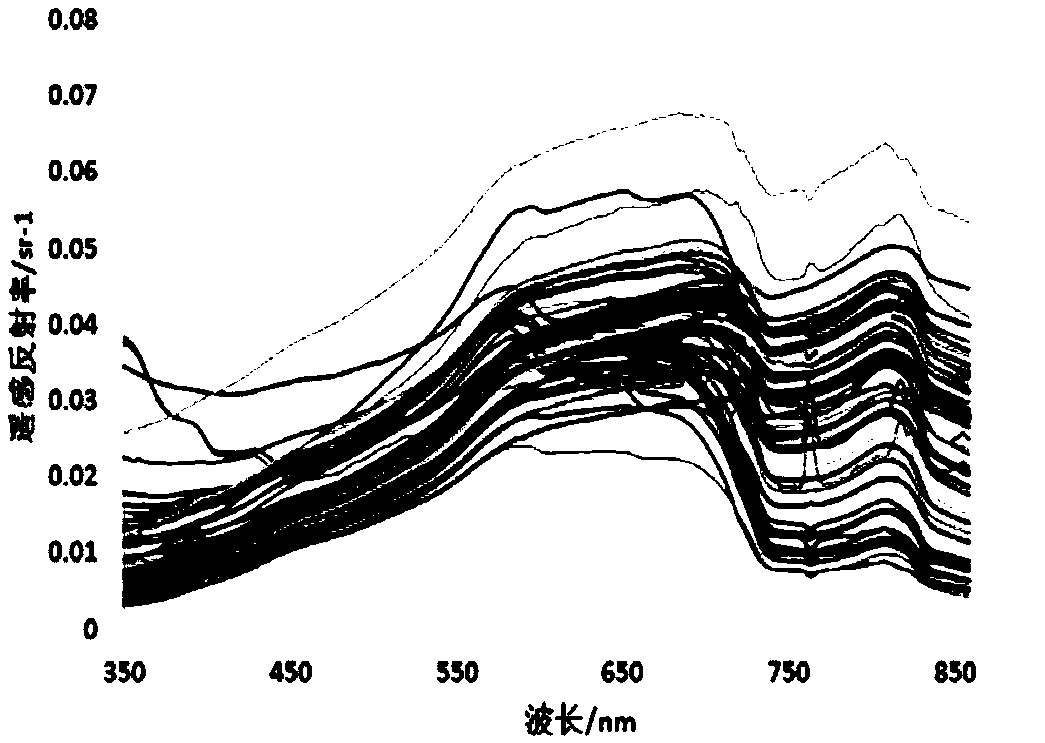
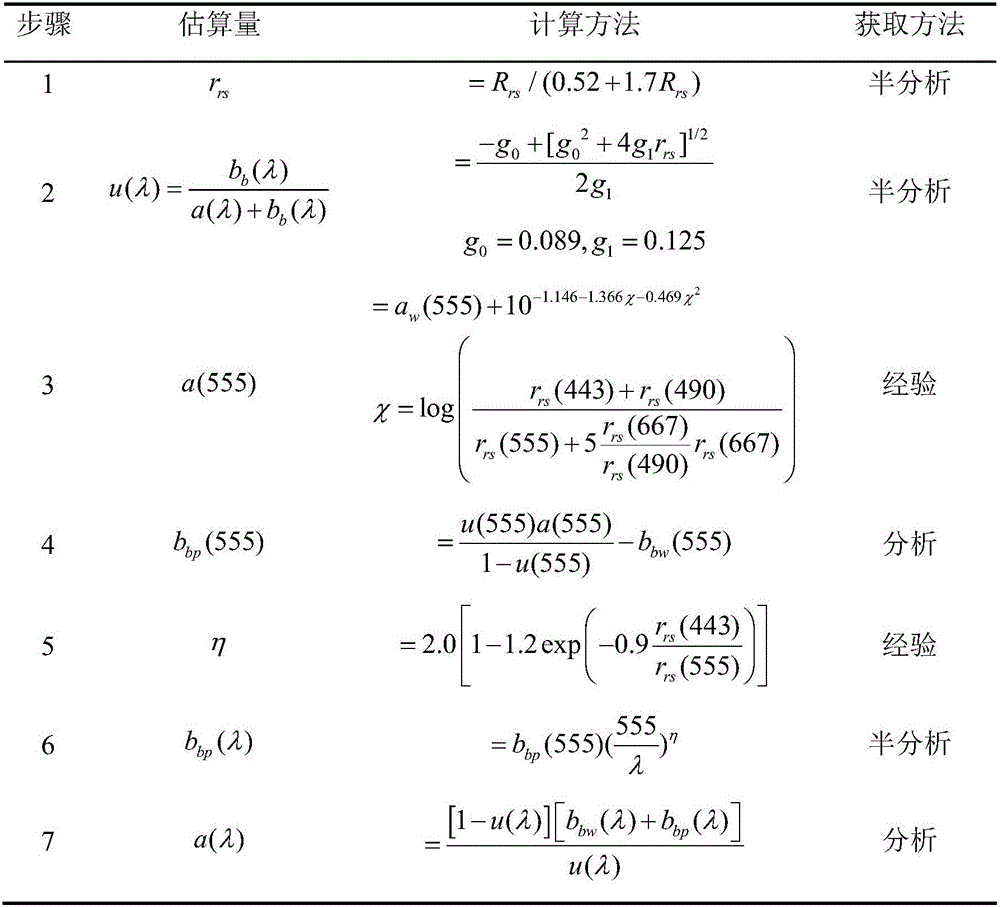
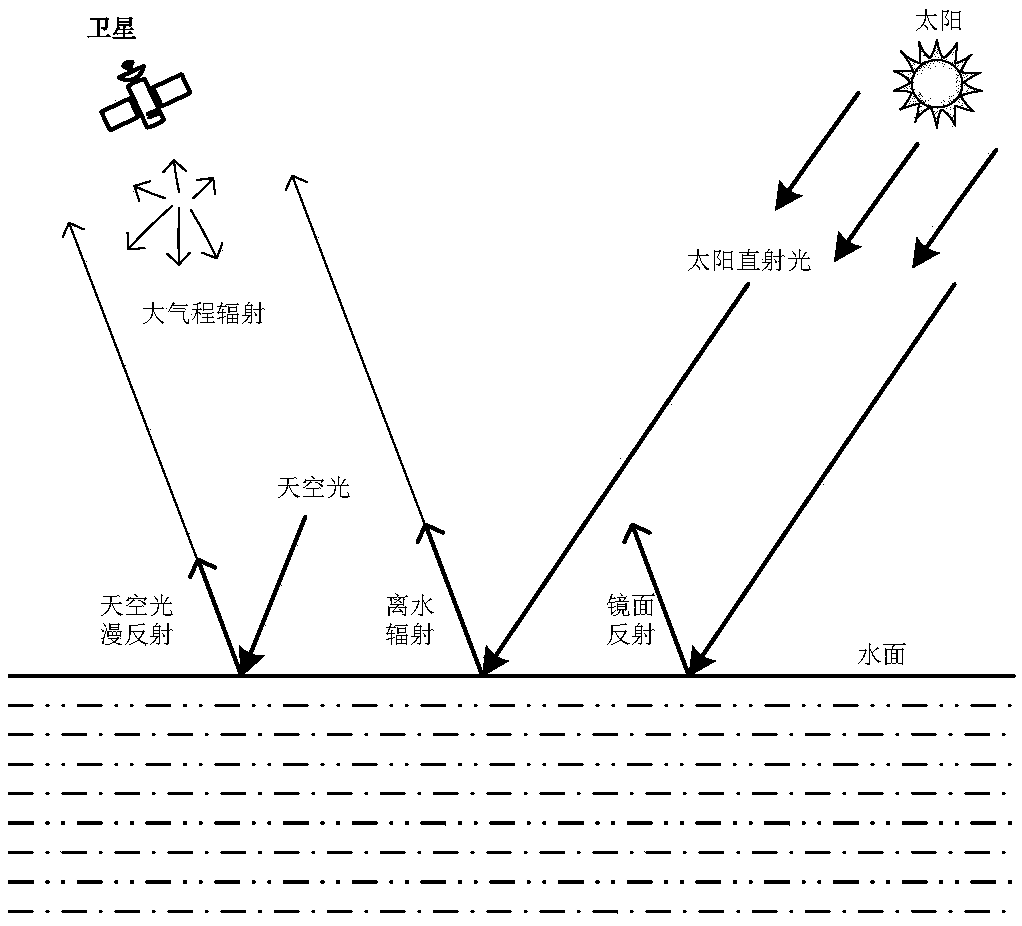
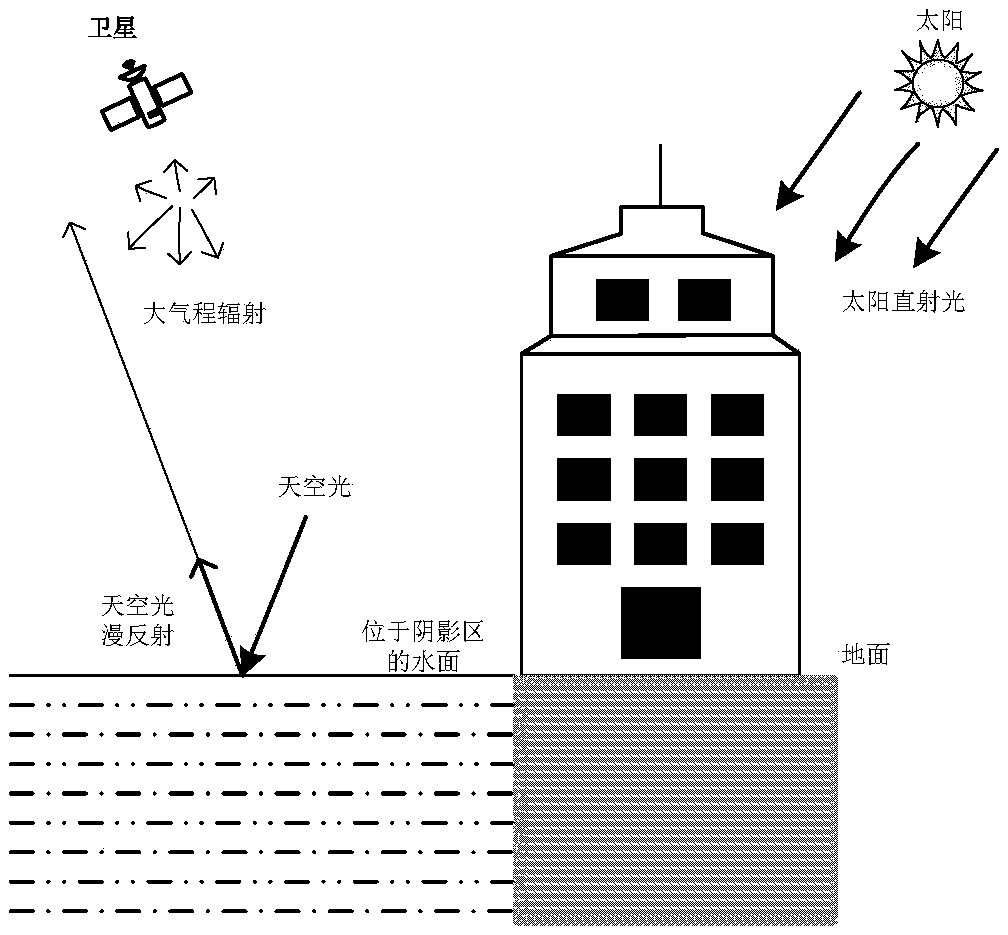
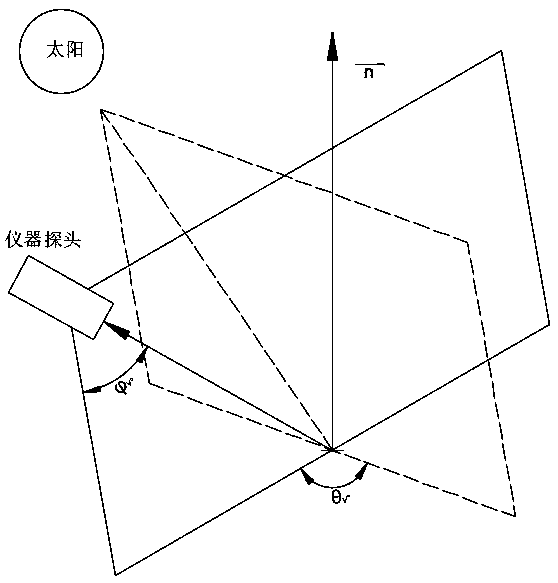
Remote sensing reflectance (Rrs) contains the spectral colour information of the water body (below the sea surface). Rrs is the ratio between water-leaving radiance (Lw, above the sea surface) and downwelling irradiance (Ed, above the sea surface).
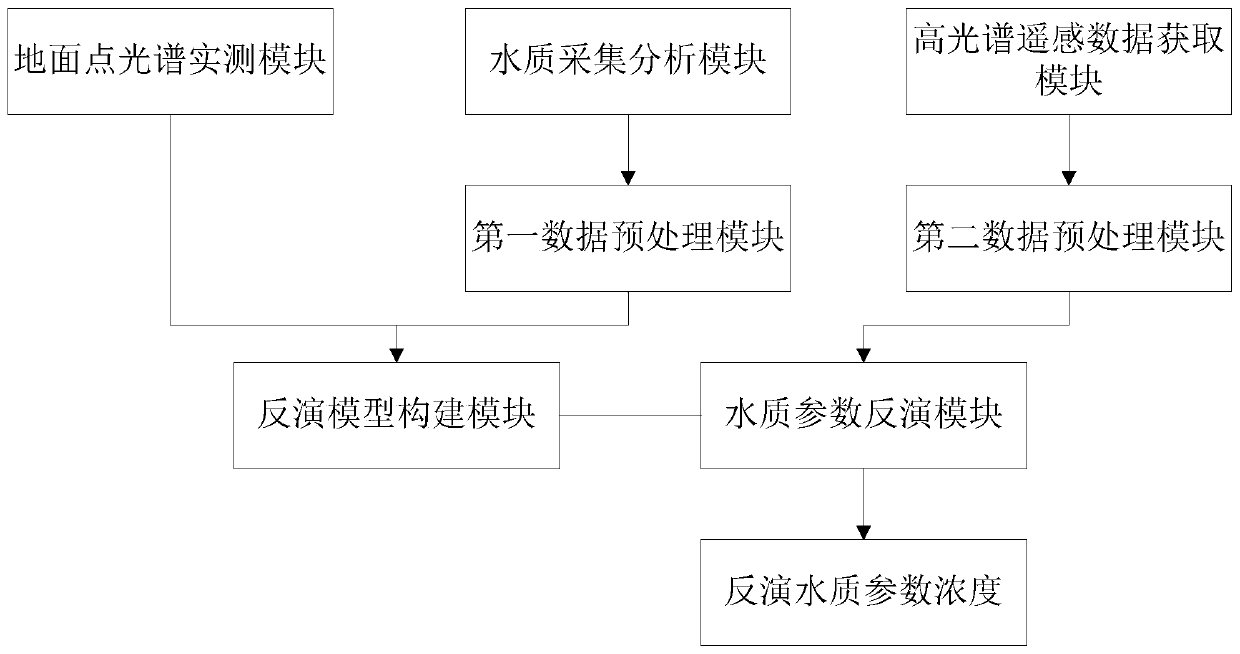
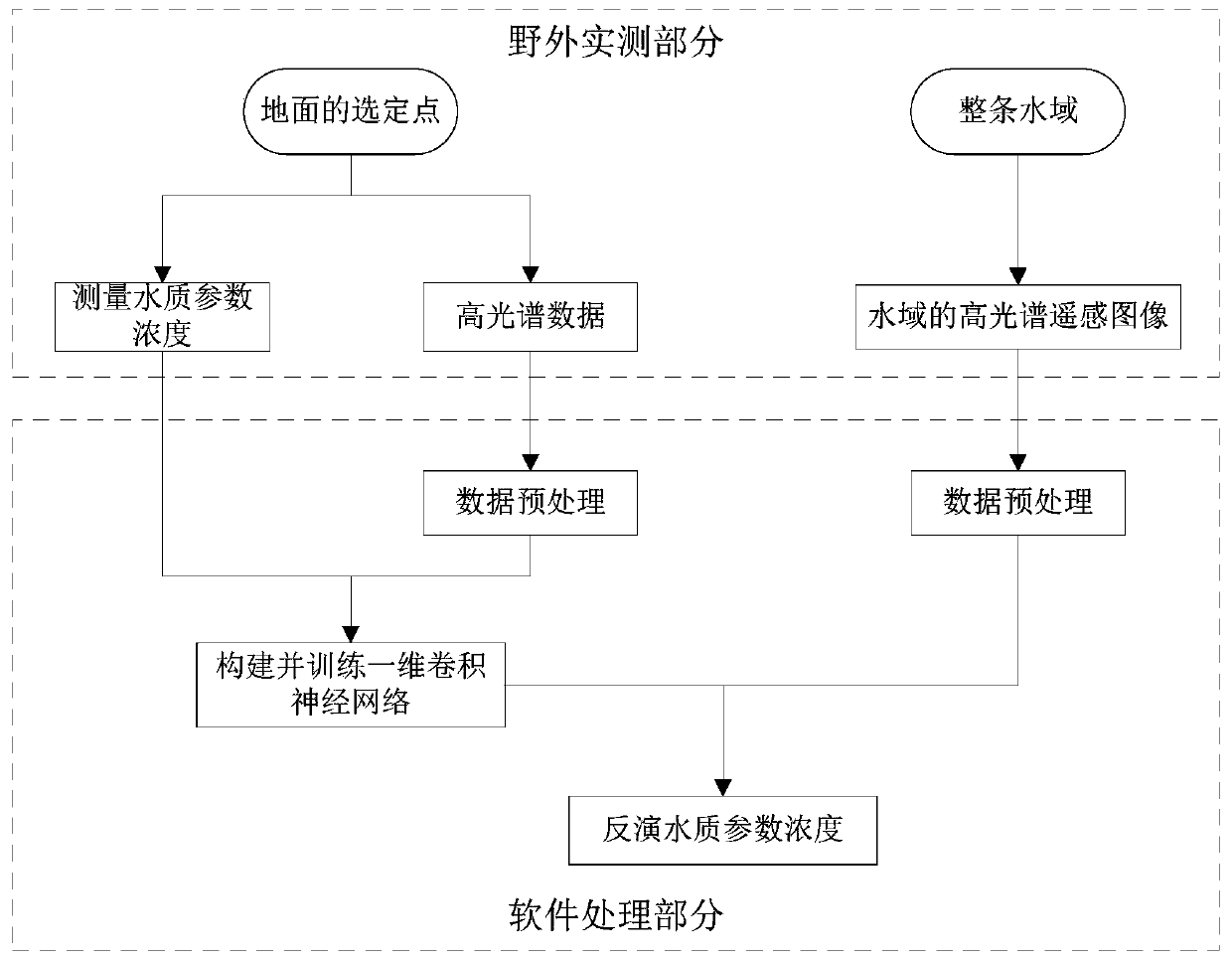
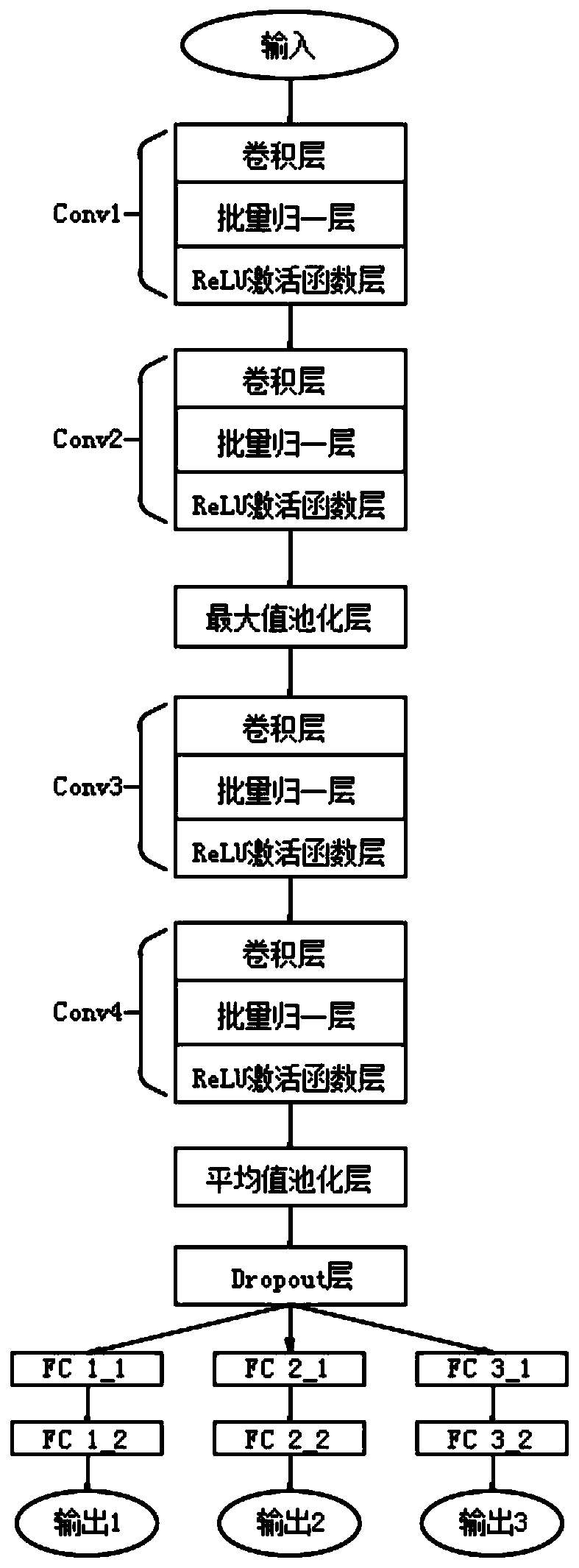
Hyperspectral water quality parameter inversion system and method based on one-dimensional convolutional neural network
InactiveCN111007021AHigh precisionLow costColor/spectral properties measurementsNeural architecturesSpectral bandsWater quality
The invention discloses a hyperspectral water quality parameter inversion system based on a one-dimensional convolutional neural network. The system is used for measuring hyperspectral data of a waterbody at a selected point through a ground point spectrum actual measurement module; a water quality acquisition and analysis module is used for acquiring a water body sample at a selected point and analyzing to obtain water quality parameter concentration; an inversion model construction module is used for training parameters of a one-dimensional convolutional neural network by taking all the spectral band information as input and taking water quality parameter concentration as output so as to fit a complex nonlinear relationship between the spectral band information and the water quality parameter concentration; a hyperspectral data acquisition module is used for acquiring a hyperspectral remote sensing image of a monitored water area and obtaining the remote sensing reflectivity of eachpoint spectral band; and a water quality parameter inversion module is used for taking the spectral band information of each point as input to obtain the water quality parameter concentration of eachpoint in the monitored water area through inversion, and meanwhile, the system does not need to add a band screening sub-module and fully utilizes all band information.
Owner:北京理工大学重庆创新中心 +1
MODIS satellite high-precision monitoring method for chlorophyll-a in eutrophic lake water body
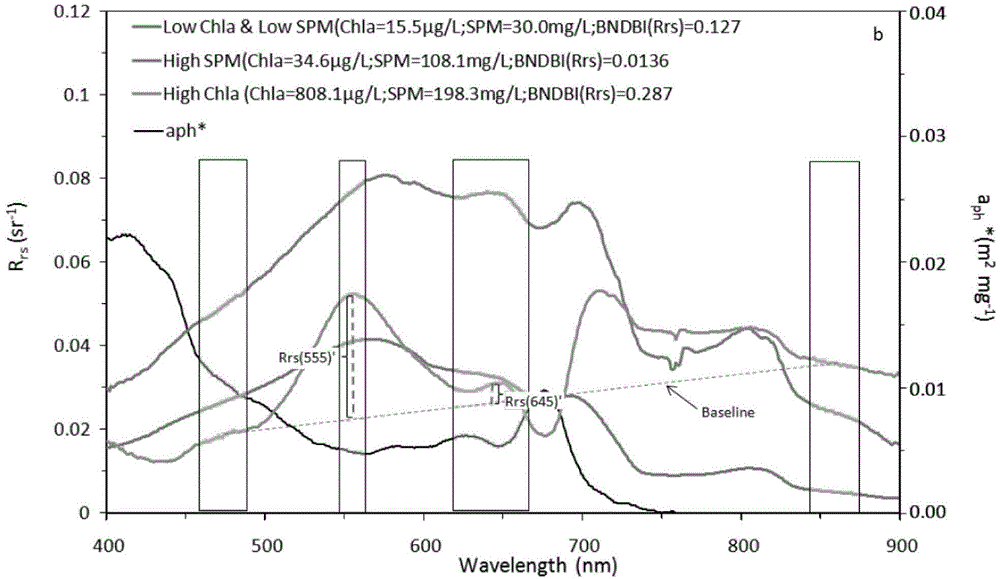
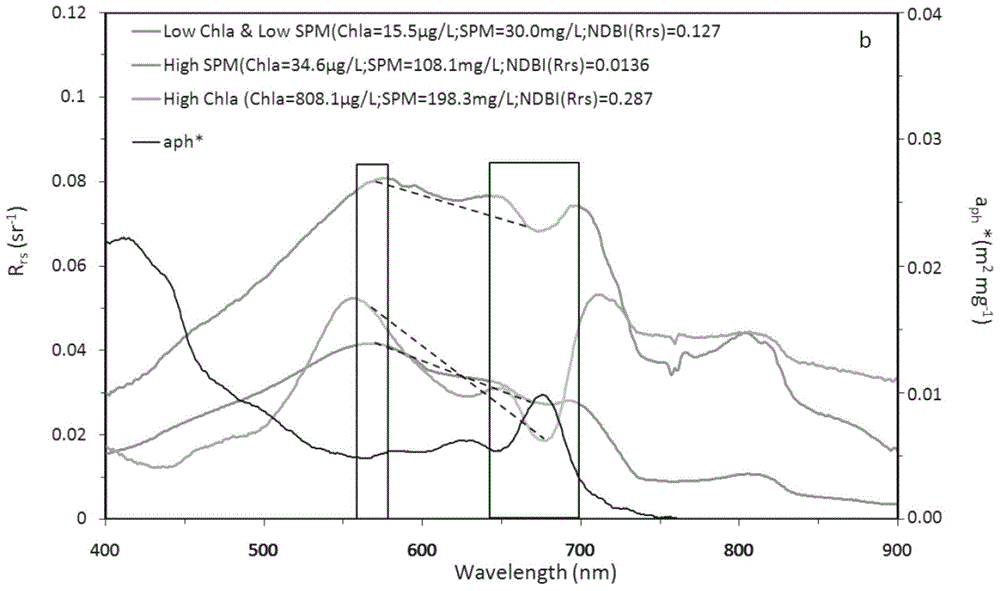
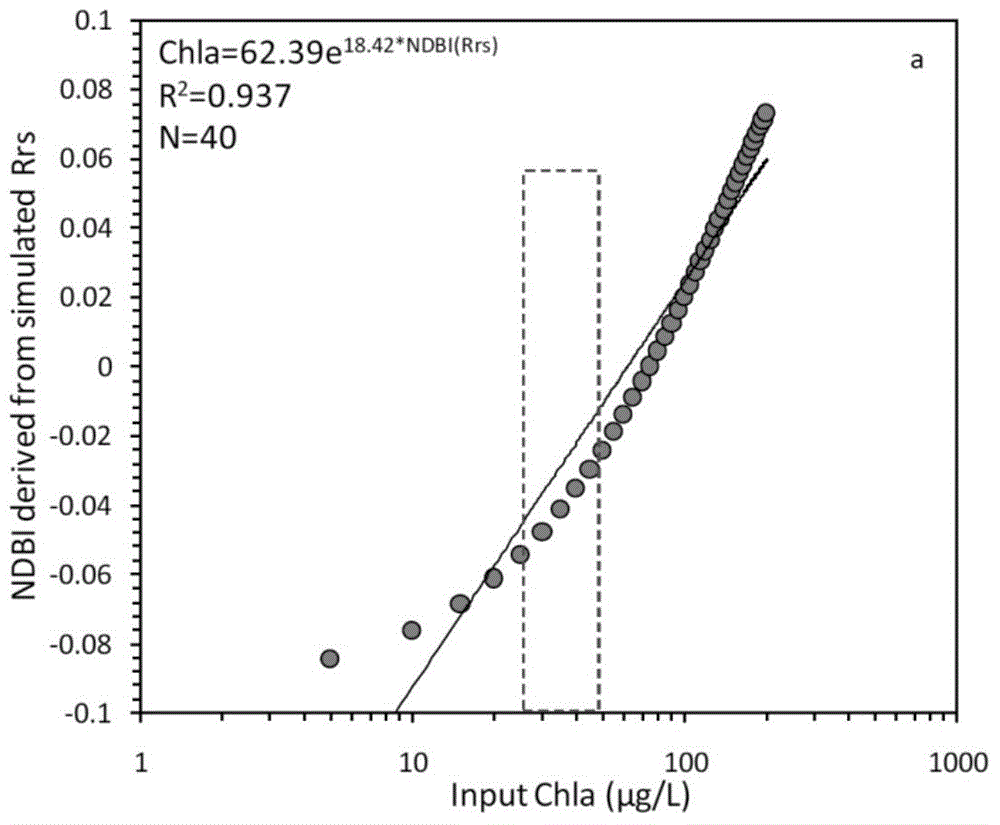
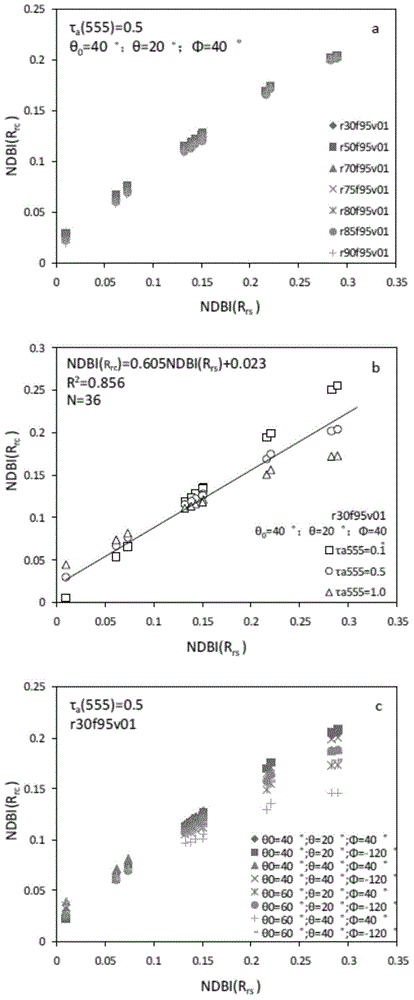
ActiveCN104820224AAchieving High-Precision EstimationReflect the space-time distributionElectromagnetic wave reradiationRayleigh scatteringEutrophication
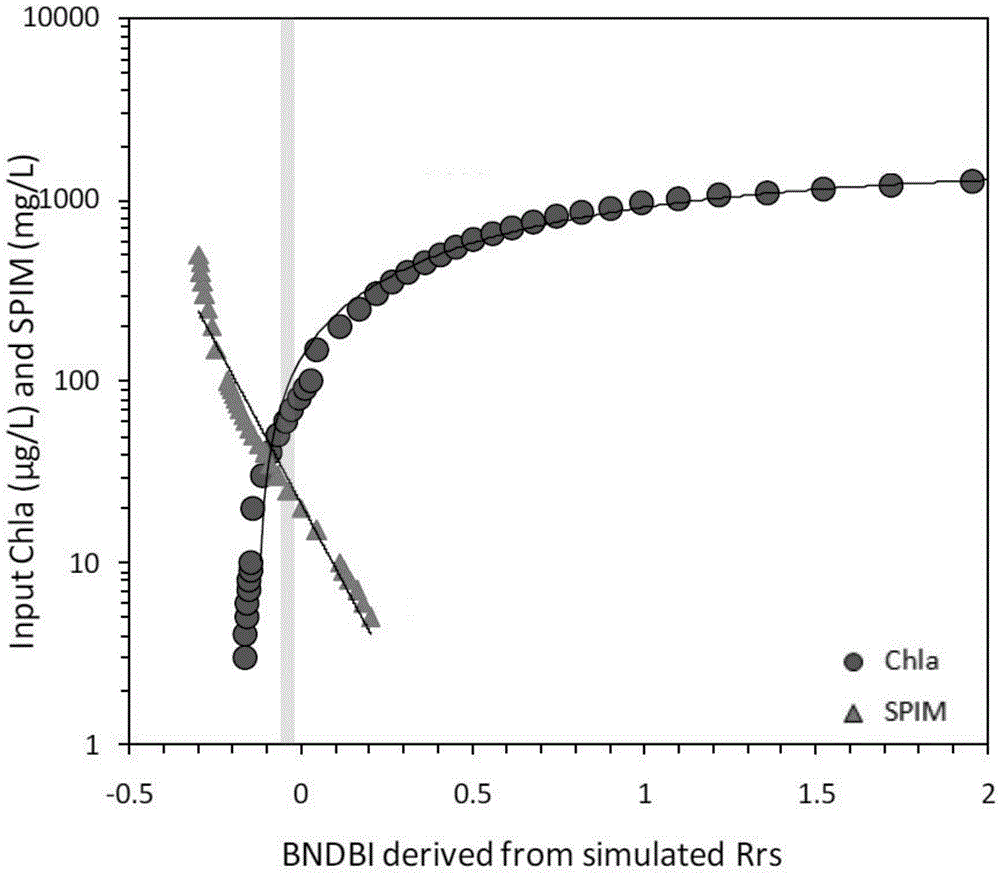
The invention provides an MODIS satellite high-precision monitoring method for chlorophyll-a in a eutrophic lake water body. The method comprises the following steps: screening a chlorophyll-a evaluation index (BNDBI) which is sensitive to the concentration change of chlorophyll-a and not affected by highly suspended matters, thin cloud and solar flares; acquiring the quantitative relationship between BNDBI and the concentration of chlorophyll-a on the basis of biological optical model simulation; acquiring a chlorophyll-a inversion algorithm based on ground measured spectrum (Rrs) and BNDBI by referring to water body spectral information and corresponding water body chlorophyll-a concentration of 2013-2014 lake field monitoring; acquiring the quantitative relationship between the ground monitoring and remote sensing reflectance ratio (Rrs) and Rrc after simulated Rayleigh scattering correction by simulating different aerosol types and thicknesses and different solar elevation angles, satellite observation angles and azimuth angles; and extending the chlorophyll-a inversion algorithm based on ground measured spectrum data to satellite image data after Rayleigh scattering correction. Based on the method, inter-annual and inter-monthly change rules and spatial distribution of chlorophyll-a in a eutrophic lake can be acquired accurately.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Analysis method of remote sensing inversion of water color parameters of inland class II water
InactiveCN105158172AHigh precisionRegionally applicableColor/spectral properties measurementsRemote sensing reflectancePhytoplankton absorption
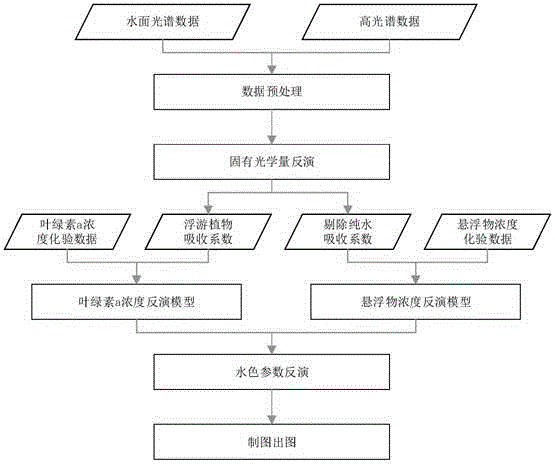
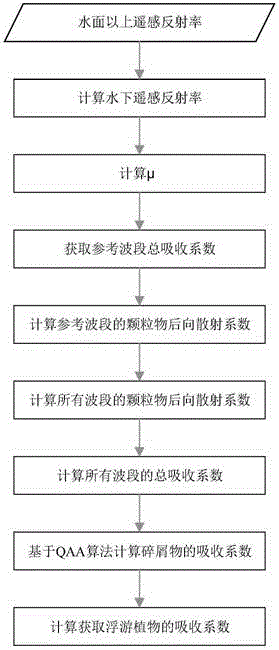
The invention discloses an analysis method of remote sensing inversion of water color parameters of inland class II water. According to the method, inherent optical quantity of the class II water is inverted with an improved QAA (quasi-analytical algorithm), and concentration inversion of the water color parameters such as chlorophyll a and suspended matters is realized based on the inverted inherent optical quantity of the class II water. The method comprises specific steps as follows: (1), data of remote sensing reflectance above the surface of the water is input, parameter inversion of the inherent optical quantity of the water is realized based on the improved QAA, and absorption coefficients and scattering coefficients of the water and absorption coefficients of phytoplankton are acquired; (2), concentration data of the chlorophyll a and concentration data of the suspended matters of the water at a sampling point are input, a chlorophyll a concentration quantitative inversion model is established according to the concentration data of chlorophyll a and the absorption coefficients of the phytoplankton, and a suspended matter concentration quantitative inversion model is established according to the concentration data of the suspended matters and the absorption coefficients of the water after removal of pure water; (3), hyperspectral data finishing atmospheric correction are input, and concentration inversion of the water color parameters of the inland class II water in a monitoring area is realized according to the step (1) and the step (2).
Owner:中国城市科学研究会
Method and device for processing remote sensing data of water environment
ActiveCN102721644AImprove processing efficiencyAvoid human interventionMaterial analysis by optical meansSensing dataWater quality
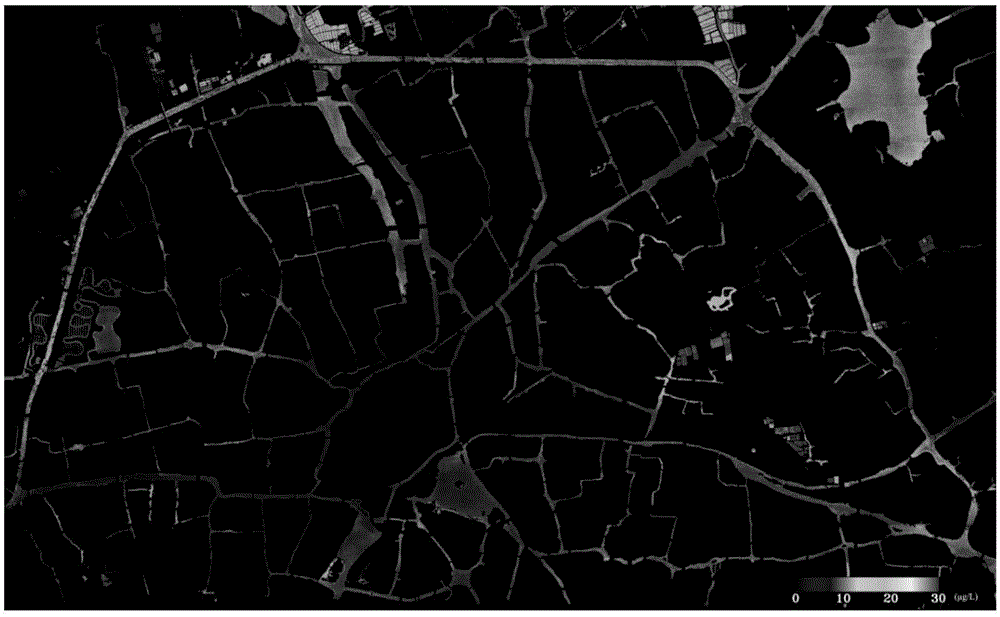
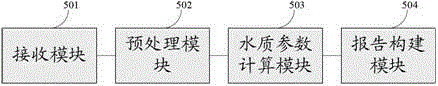
The invention provides a method and a device for processing remote sensing data of a water environment. The method comprises the following steps of: receiving the remote sensing data of the water environment in a monitored region; calculating a remote sensing reflectivity image of water according to a regional coordinate data table, a remote sensor attribute data table and a regional attribute data table which are established in advance; extracting an objective masking image of the water from the remote sensing data of the water environment; calculating a water quality parameter and concentrate image corresponding to the remote sensing data according to a water quality parameter inversion model data table, a remote sensing reflectivity image of the objective water and a water objective masking image which are established in advance; establishing a remote sensing monitoring quality report of the water environment according to a water quality parameter and concentration image; and accordingly automatically forming a water quality parameter and concentration image and a remote sensing monitoring report of the water environment. Man-made intervention is avoided, and the efficiency of processing water environment monitored data is improved.
Owner:CENT FOR EARTH OBSERVATION & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
OLCI remote sensing monitoring method for shallow lake inherent optical parameters
ActiveCN107589075AEfficient spatio-temporal distributionEfficiently reflect the spatial and temporal distributionColor/spectral properties measurementsRemote sensing reflectanceField tests
The invention provides an OLCI remote sensing monitoring method for shallow lake inherent optical parameters; the method comprises the steps: based on a quasi-analytical algorithm, assuming that 750 nm water body total absorption is equal to pure water absorption, and establishing the relationship of the water body remote sensing reflectance ratio and the total absorption coefficient, and the relationship of the water body remote sensing reflectance ratio and the backscattering coefficient; according to the characteristics of absorption coefficients of all water body components and the relationships of the absorption coefficients with remote sensing reflectance ratio spectra and the backscattering coefficient, further resolving the water body total absorption coefficient into the absorption coefficients of the water body components; combining the water body remote sensing reflectance ratio spectra and the corresponding water body component absorption coefficients measured by Chaohu lake, Taihu lake and Hongze lake field tests, establishing IOP inversion algorithms facing to different lakes with complex water body optical characteristics based on the field actually measured spectra;and extending the IOP inversion algorithm to OLCI image data corrected by 6S atmosphere, and realizing remote sensing monitoring of the water body inherent optical parameter spatial distribution of eutrophic shallow water lakes.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Lake water body blue-green algae abundance estimation method based on remote sensing
InactiveCN103760112AIncrease contentAccurate estimateColor/spectral properties measurementsRemote sensing reflectanceAtmospheric correction
The invention discloses a lake water body blue-green algae abundance estimation method based on remote sensing. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out high-spectrum remote sensing measurement on a lake water body by utilizing the concentration ratio of phycocyanin and chlorophyll to represent the blue-green algae abundance, selecting the ratio of remote sensing reflective rates of the two specific wave lengths and a function thereof as characteristics of blue-green algae, establishing an estimation model of the lake water body blue-green algae abundance, and estimating the lake water body blue-green algae abundance based on remote sensing. The method provided by the invention adopts a surface feature spectrograph or an onboard high-spectrum imager to carry out high-spectrum remote sensing on the lake water body, and the remote sensing reflective rate required for estimation can be obtained through performing radiation correction and atmospheric correction on aviation satellite high-spectrum data. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the accuracy is high, the model is simple, the remote sensing reflective rates of the two wave lengths are selected, not only can the estimation on the water body blue-green algae abundance measured by the surface feature spectrograph be realized, but also the estimation on the blue-green algae abundance by virtue of aviation high-spectrum remote-sensing images is realized.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
MODIS remote sensing monitoring method for vertical distribution pattern of eutrophic lake water algae
ActiveCN104374713AImprove practicalityInterannualColor/spectral properties measurementsRayleigh scatteringRemote sensing reflectance
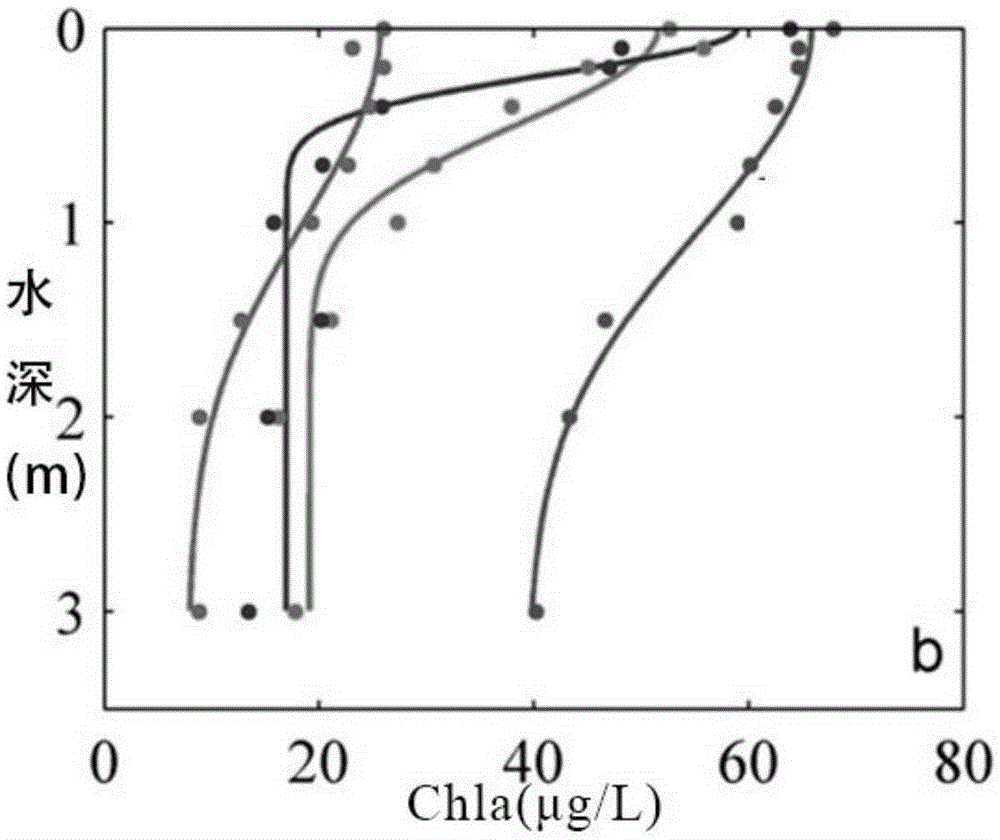
The invention provides an MODIS remote sensing monitoring method for the vertical distribution pattern of eutrophic lake water algae. The method includes: acquiring the vertical distribution pattern of the algae by means of field monitoring; on the basis of field measured water surface spectral information and environmental information, creating a ground measured spectral data (Rrs) based remote sensing monitoring method for vertical algae distribution; acquiring the quantitative relationship between ground monitoring and remote sensing reflectance Rrs and simulated Rrc after Rayleigh scattering correction by simulating different aerosol types and thicknesses and different solar altitudes, satellite observation angles and azimuthal angles; further promoting the ground measured spectral data based monitoring method for vertical algae distribution to MODIS satellite image data subjected to Rayleigh scattering correction. On the basis of the method, interannual and inter-monthly change rules and spatial distribution of the vertical distribution pattern of the eutrophic lake water algae can be acquired accurately, and scientific support is provided for scientific decision-making on water resource management and water environment protection water conservancy and environmental protection departments.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
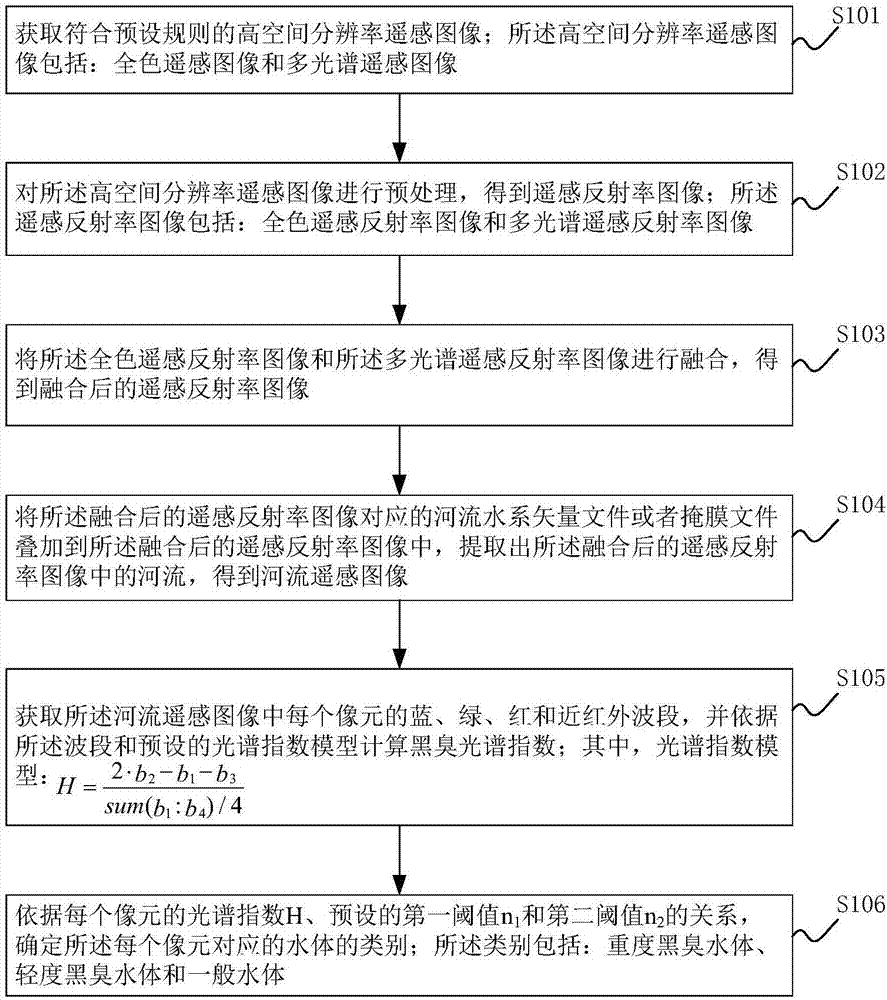
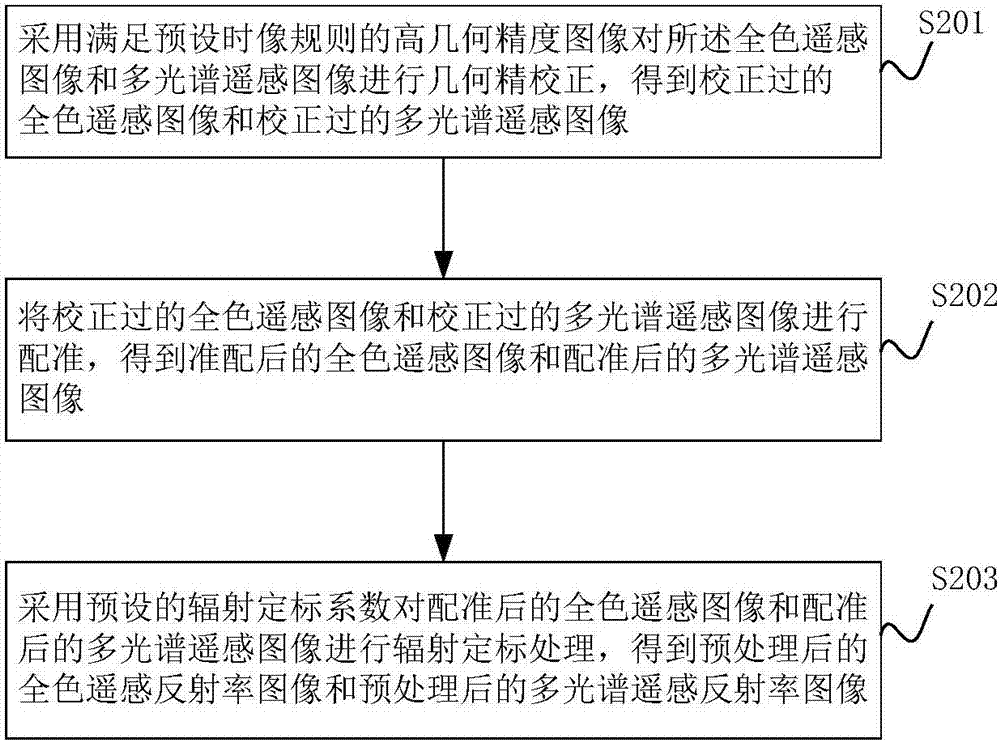
Spectral index model-based black and odorous water body identification method and system
The invention discloses a spectral index model-based black and odorous water body identification method and system. The identification method comprises the steps of processing a selected high-spatial-resolution remote sensing image, superposing a river system vector document or a mask file corresponding to the processed fused remote sensing reflectance image to the fused remote sensing reflectance image, extracting river in the fused remote sensing reflectance image to obtain a river remote sensing image; obtaining blue, green, red and near-infrared bands of each pixel in the river remote sensing image and calculating a black and odorous spectral index according to the bands and a preset spectral index model; and determining the category of the water body corresponding to each pixel according to the relationship between the spectral index of each pixel unit and preset first threshold and second threshold. By adopting the black and odorous spectral index model, the identified black and odorous spectral index of the urban river is more accurate, the categories of the water bodies of the rivers are divided into a heavy black and odorous water body, a light black and odorous water body and a general water body, and differentiation of the water bodies is more detailed.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
High-precision satellite MODIS (Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) monitoring method for chlorophyll a of eutrophic lake water body
ActiveCN104390917AAchieving High-Precision EstimationReflect the space-time distributionColor/spectral properties measurementsRayleigh scatteringEutrophication
The invention provides a high-precision satellite MODIS (Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) monitoring method for chlorophyll a of a eutrophic lake water body. The method comprises the following steps: screening a chlorophyll a evaluation index (NDBI) which is sensitive to the concentration change of the chlorophyll a and is not influenced by high suspended solids; obtaining a quantitative relation between the NDBI and the concentration of the chlorophyll a on the basis of biological optical model simulation; combining spectral information of the water body and the corresponding concentration of the chlorophyll a of the water body monitored in the field in Chaohu Lake in year 2013-2014, so as to obtain a chlorophyll a inversion algorithm based on a ground measured spectrum (Rrs) and the NDBI; simulating different aerosol types and thicknesses, different solar altitudes, satellite observation angles and azimuth angles, so as to obtain a quantitative relation between the ground monitored remote sensing reflectance (Rrs) and simulated Rrc subjected to Rayleigh scattering correction; and further extending the chlorophyll a inversion algorithm based on ground measured spectral data to satellite image data subjected to the Rayleigh scattering correction. According to the method, the inter-annual and inter-monthly change rules and space distribution of the rules of the concentration of the chlorophyll a of a eutrophic lake can be accurately obtained.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Water color exception object extraction method and system based on multi-spectral remote sensing image
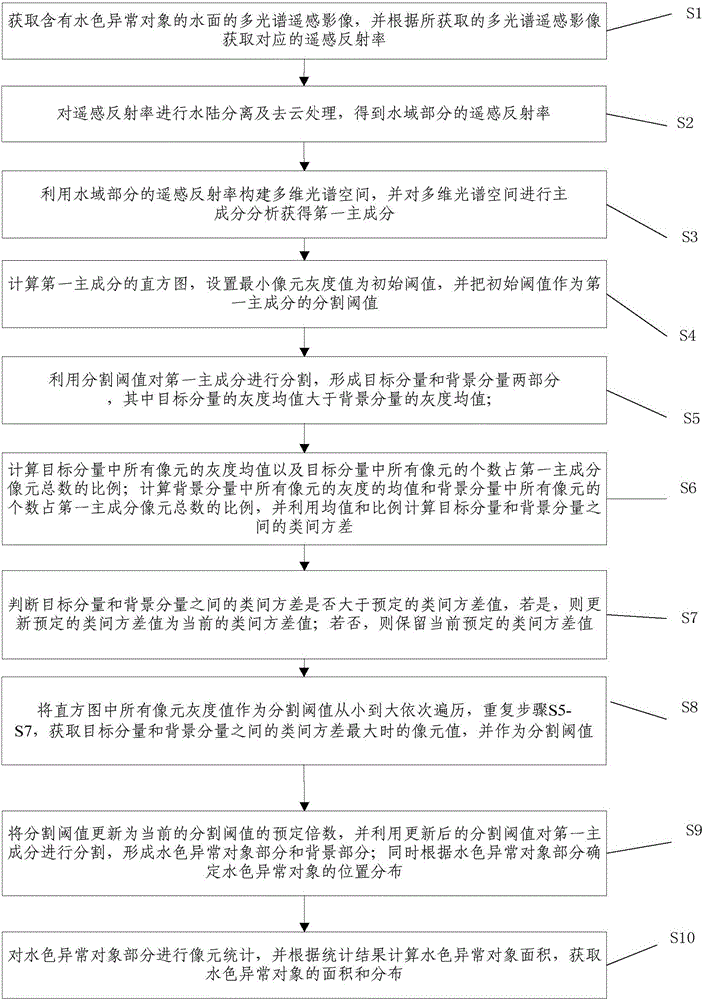
InactiveCN105761286AEasy extractionEfficient extractionImage enhancementImage analysisKernel principal component analysisPrincipal component analysis
The invention discloses a water color exception object extraction method and system based on multi-spectral remote sensing. The method comprises the steps of first acquiring the reflectance of a remote sensing image, then carrying out separation of land and water and cloud removing to obtain remote sensing reflectance of a water area portion, and conducting a principal component analysis of the multiband remote sensing reflectance to obtain a first principal component; afterwards, conducting a histogram analysis of a first principal component image, setting a threshold, segmenting the first principal component into a target component and a background component by using the threshold, segmenting the first principal component by using a threshold when the between-class variance of the target and background components is maximum and by setting the multiple, and obtaining a water color exception object portion; and conducting pixel statistics for the water color exception object portion, and obtaining the area and distribution of water color exception objects. The invention can retain the amount of multiband information to the greatest extent, thereby improving the accuracy; and meanwhile, acquires the segmenting threshold completely based on automatic calculation of a computer, thus greatly saving the information extracting time, and achieving simple and accurate extraction of distribution information of the water color exception objects.
Owner:SATELLITE ENVIRONMENT CENT MINIST OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Four-band semi-analysis model for inverting chlorophyll a concentration in high-turbidity water body
InactiveCN102508959AImprove signal-to-noise ratioHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsParticulatesTurbidity
The invention discloses a method used for building a four-band semi-analysis model for inverting the chlorophyll a concentration in a high-turbidity water body. According to the method, a fourth band is introduced on the basis of the original three-band semi-analysis model for improvement, [Rrs-1(Lambda 4)-Rrs-1(Lambda 3)]-1 is used for replacing the Rrs(Lambda3) part in a three-band model factor and is used for reducing the backward scattering and absorption of suspension particles in the high-turbidity water body and the influence of colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM) on the remote sensing reflection rate, the chlorophyll a concentration characteristics are stressed, then, the positions of four corresponding bands are determined by a iteration method, influence factors are determined, and in addition, an inverting model is further obtained through linear regression. Compared with the three-band semi-analysis model, the model provided by the invention has the advantages that the chlorophyll a concentration in the high-turbidity water body is inverted, the influence of the suspension concentration and the CDOM is minimized, and the model precision is improved to a great degree.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Quantitative remote sensing method of suspended sediment
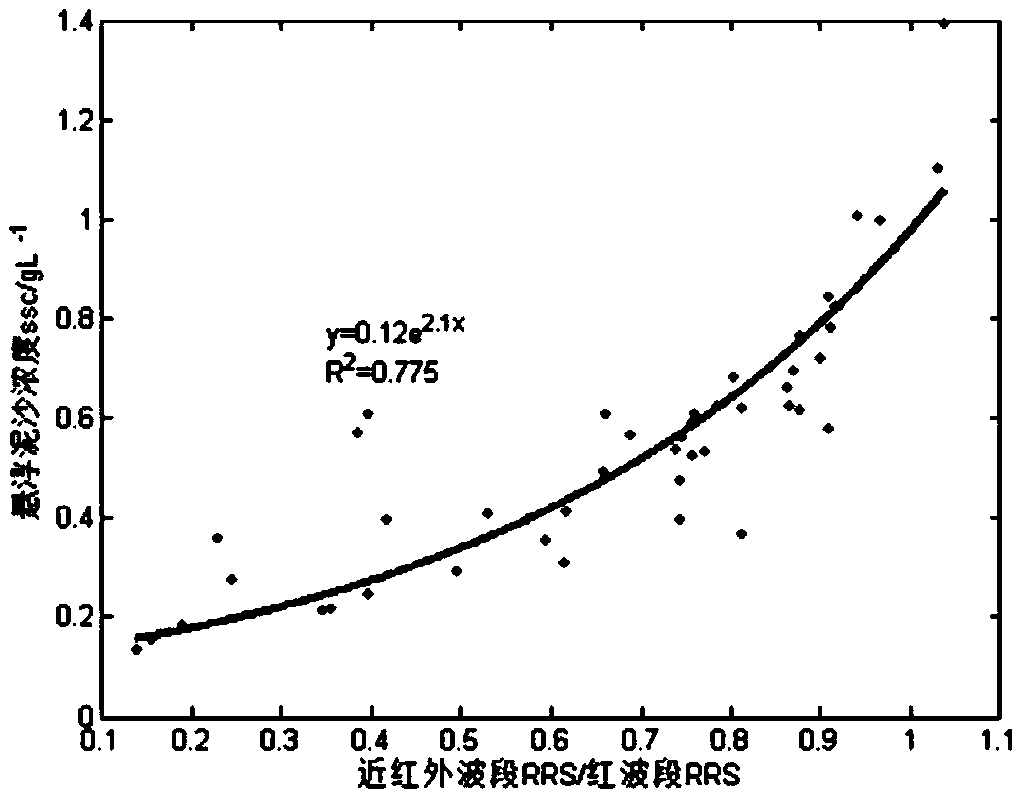
InactiveCN105300864AScientific research methodEfficient Research MethodsParticle suspension analysisModel sampleRiver mouth
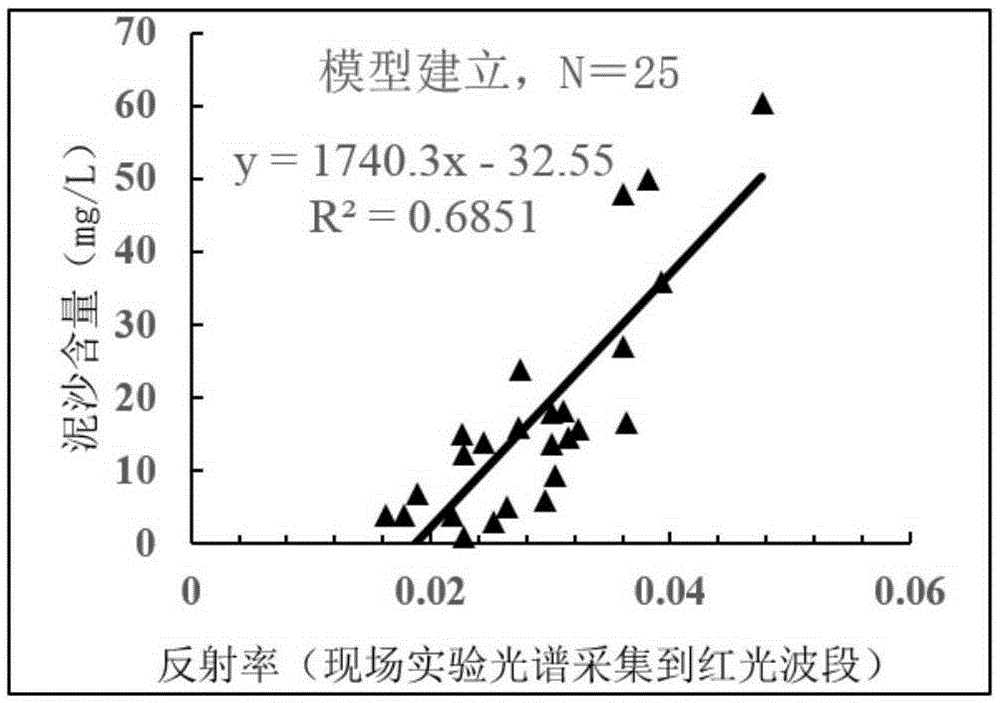
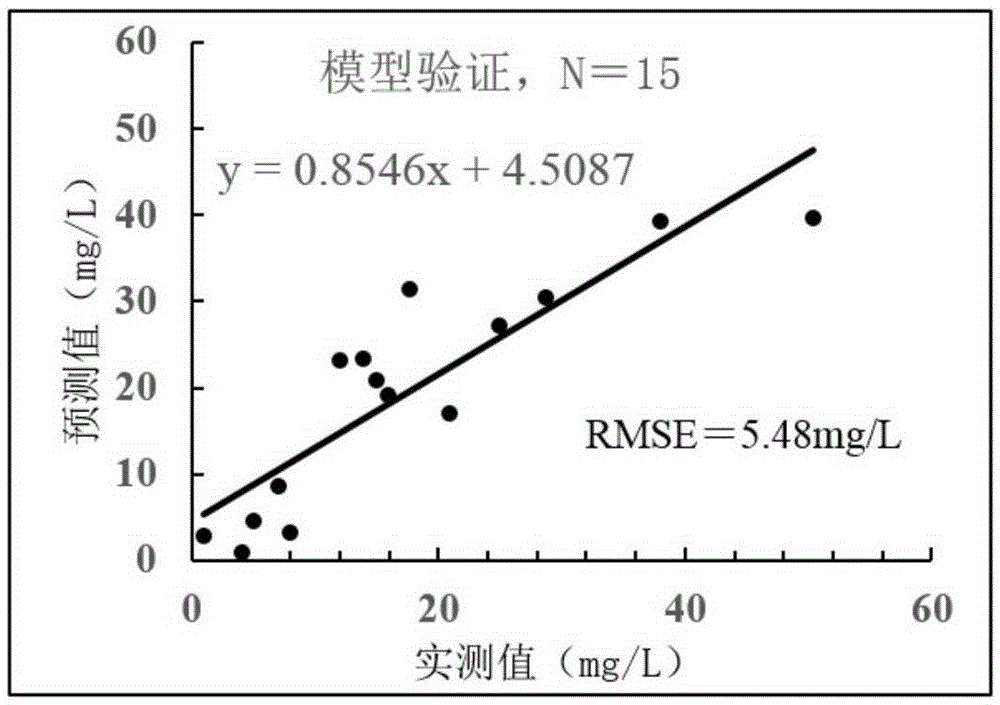
The invention discloses a quantitative remote sensing method of suspended sediment. The quantitative remote sensing method comprises the following steps: step S1, carrying out field water body spectral measurement and suspended sediment content measurement; step S2, carrying out equivalent remote sensing reflectivity calculation; step S3, randomly dividing collected water samples into a modeling sample and a verification sample; step S4, establishing a sediment remote sensing quantitative model by the modeling sample; step S5, acquiring a satellite image and pre-processing the satellite image; and step S6, carrying out inversion to obtain the content of the suspended sediment in a research region. By establishing the sediment remote sensing quantitative model, the sediment remote sensing quantitative model is applied to a satellite remote sensing image through ENVI (The Environment for Visualizing Images) software and spatial and temporal distribution of the sediment in the research region can be automatically drawn; and the method is a scientific and efficient river-mouth off-shore sediment research method.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF GEOGRAPHY GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI
MODIS remote sensing evaluation method for eutrophication lake algae gauss vertical distribution structural parameters
The invention provides a MODIS remote sensing evaluation method for eutrophication lake algae gauss vertical distribution structural parameters. Based on field actual measurement data, a function expression and remote sensing identification method for the same for alge gauss vertical distribution are determined with a combination a alge bloom identification index NDBI and synchronous external environment factor wind speed; based on Hydrolight radiation transferring simulation, ground spectrum database of different alge gauss vertical distribution can be built; by the use of a BP neural network model, a remote sensing evaluation method for the lake algae gauss vertical distribution structural parameters based on simulation data is built; with simulation of various aerosol types, thickness, various solar altitude, satellite observation angles and azimuthal angles, a quantitative relation between ground-based simulation remote sensing reflectance ratio Rrs and a simulated Rayleigh scattering corrected Rrc is acquired; the evaluation method for the algae gauss vertical distribution structural parameters based on spectrum data simulation can be promoted to MODIS satellite image data corrected by Rayleigh scattering.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Retrieval method and retrieval device of chlorophyll a concentration of inland case II water
ActiveCN103983584AReduce limitationsImprove smoothnessColor/spectral properties measurementsChlorophyll aRemote sensing reflectance
The invention provides a retrieval method and a retrieval device of chlorophyll a concentration of inland case II water, wherein the retrieval method of the chlorophyll a concentration of the inland case II water comprises the steps of firstly, classifying first remote sensing reflectance spectra to obtain a plurality of second remote sensing reflectance spectra taking different components as main components; calculating the weight matrixes of all the second remote sensing reflectance spectra, selecting all characteristic wave bands and calculating the chlorophyll spectral indexes; finally, carrying out weight fusion on the chlorophyll spectral indexes under all categories of all the spectra by weight to obtain weighted chlorophyll index, and fitting an inversion model to obtain the chlorophyll a concentration. Due to the method of firstly classifying and then carrying out weighted inversion, the limitation on the retrieval method caused by the area and the time can be reduced, and the smoothness and the stability of inversion results can be improved, and therefore, when the chlorophyll a concentration of a certain second remote sensing reflectance spectrum is inversed subsequently, the chlorophyll a concentration can be obtained by inversion through the inversion model corresponding to the second remote sensing reflectance spectrum, so that the universality of the method is improved.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Method and device for establishing water body classification model
InactiveCN107025467AImprove timelinessImprove accuracyScattering properties measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionCluster algorithmWater quality
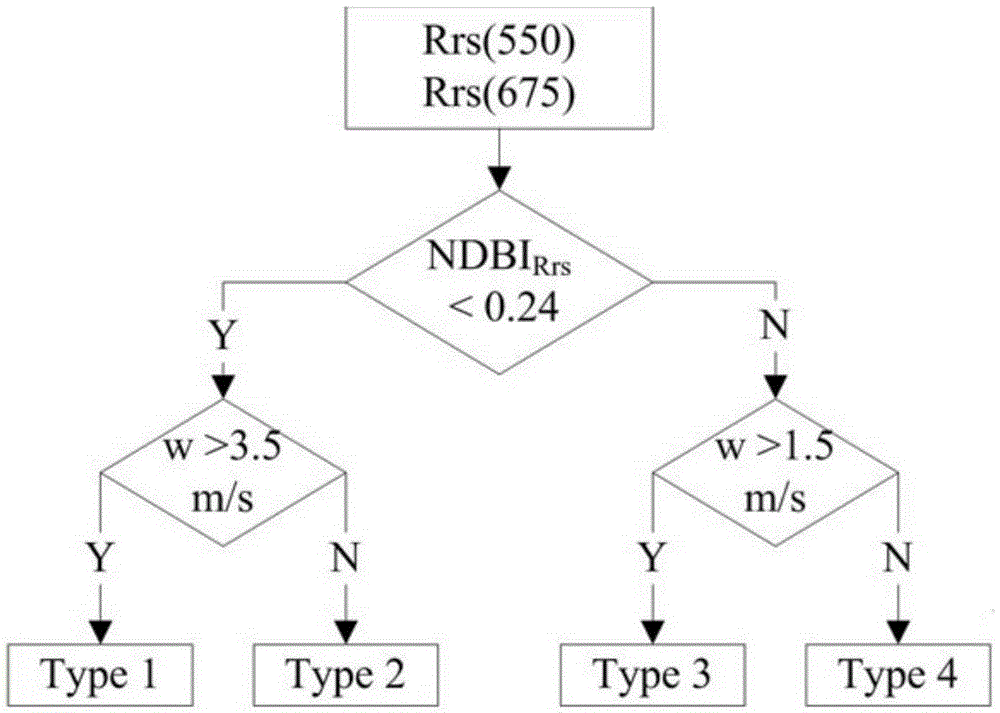
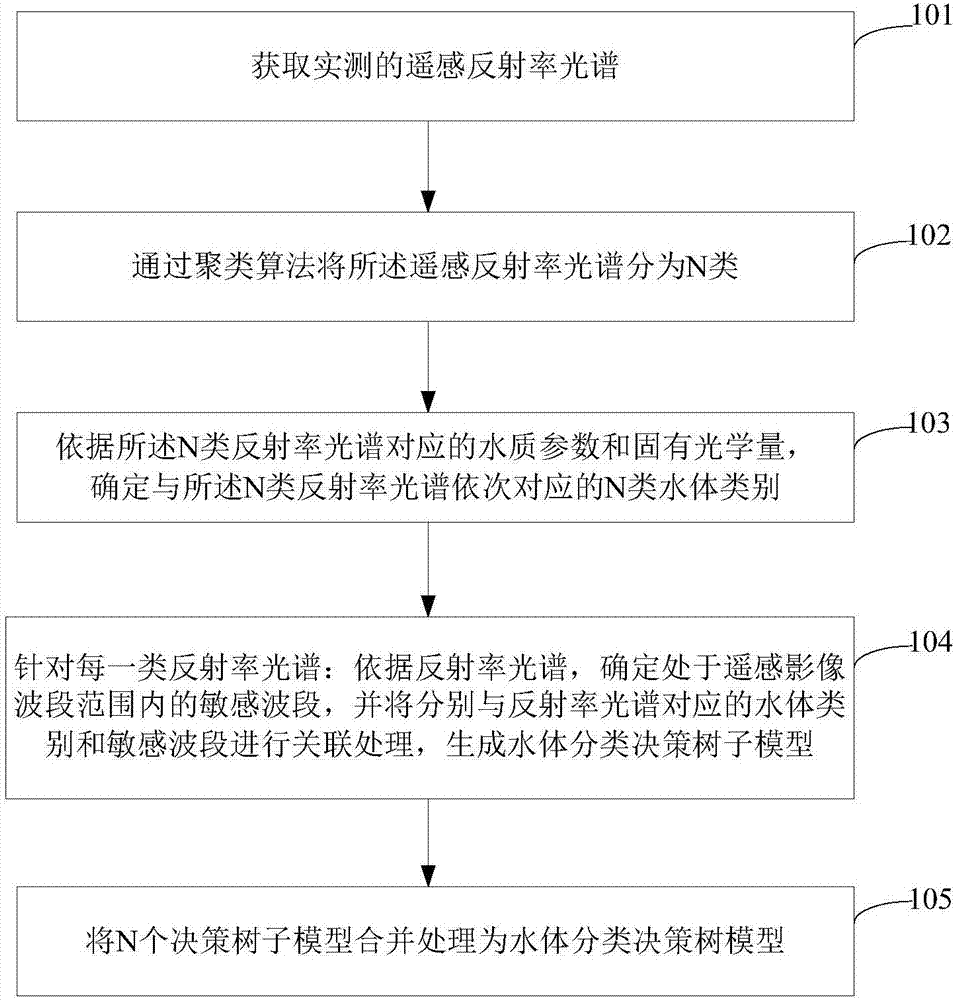
The invention discloses a method and device for establishing a water body classification model. The method for establishing the water body classification model comprises: classifying an actually measured remote sensing reflectivity spectrum into N classes by a clustering algorithm; and then determining N water body classes corresponding to N reflectivity spectrum classes in combination with a water quality parameter and an inherent optical quantity, determining a sensitive waveband in a remote sensing image waveband range for each reflectivity spectrum class, associating the water body classes corresponding to the reflectivity spectrum with the sensitive wavebands; and finally generating a water body classification decision tree model. The method and device for establishing the water body classification model can be applied to image water body classification. A user can obtain the class of the water body directly by means of the water body classification decision tree model according to the remote sensing image data of the water body, and is not required to carry out actual measurement and experiments in the field and a laboratory. The method and device are simple, convenient, and good in timeliness.
Owner:SATELLITE ENVIRONMENT CENT MINIST OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Water body water color anomaly identification method and device based on time sequence remote sensing images
ActiveCN111307727AThreshold objectiveAccurate thresholdColor/spectral properties measurementsStatistical analysisRemote sensing reflectance
The invention discloses a water body water color abnormity identification method and device based on time sequence remote sensing images, and belongs to the field of water environment pollution monitoring. The method comprises the following steps: preprocessing a multi-time-sequence remote sensing image to obtain water body remote sensing reflectivity images with different time sequences; performing spectral statistical analysis on the remote sensing reflectivity image to obtain water body pixel statistical characteristic values of different wave band long-time sequences, and establishing different wave band reference characteristic values and pixel characteristic values; making a spectral characteristic analysis on the to-be-detected remote sensing image, and creating waveband characteristic values of different wavebands; preliminarily judging whether the to-be-detected image has abnormal water color or not by comparing the wave band characteristic value of the to-be-detected image with the corresponding wave band reference characteristic value; analyzing the wave band with the abnormal water color of the to-be-detected image pixel by pixel, comparing the wave band with the pixelcharacteristic value of the corresponding wave band, obtaining the spatial distribution pixel of the abnormal water color, and obtaining the spatial distribution of the abnormal water color of the water body. According to the invention, the water color abnormity identification precision and speed of the water body are improved.
Owner:MINISTRY OF ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT CENT FOR SATELLITE APPL ON ECOLOGY ENVIRONMENT
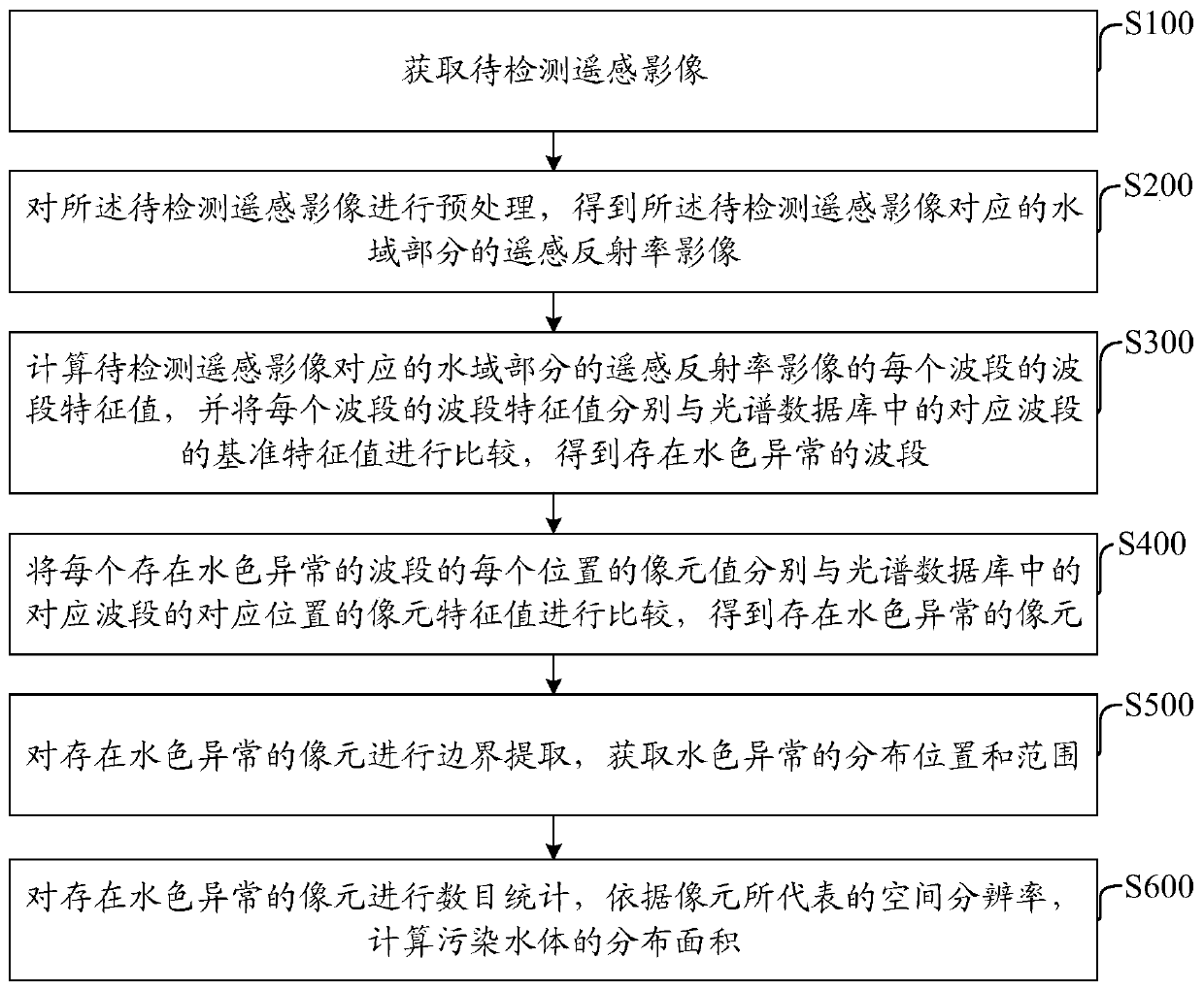
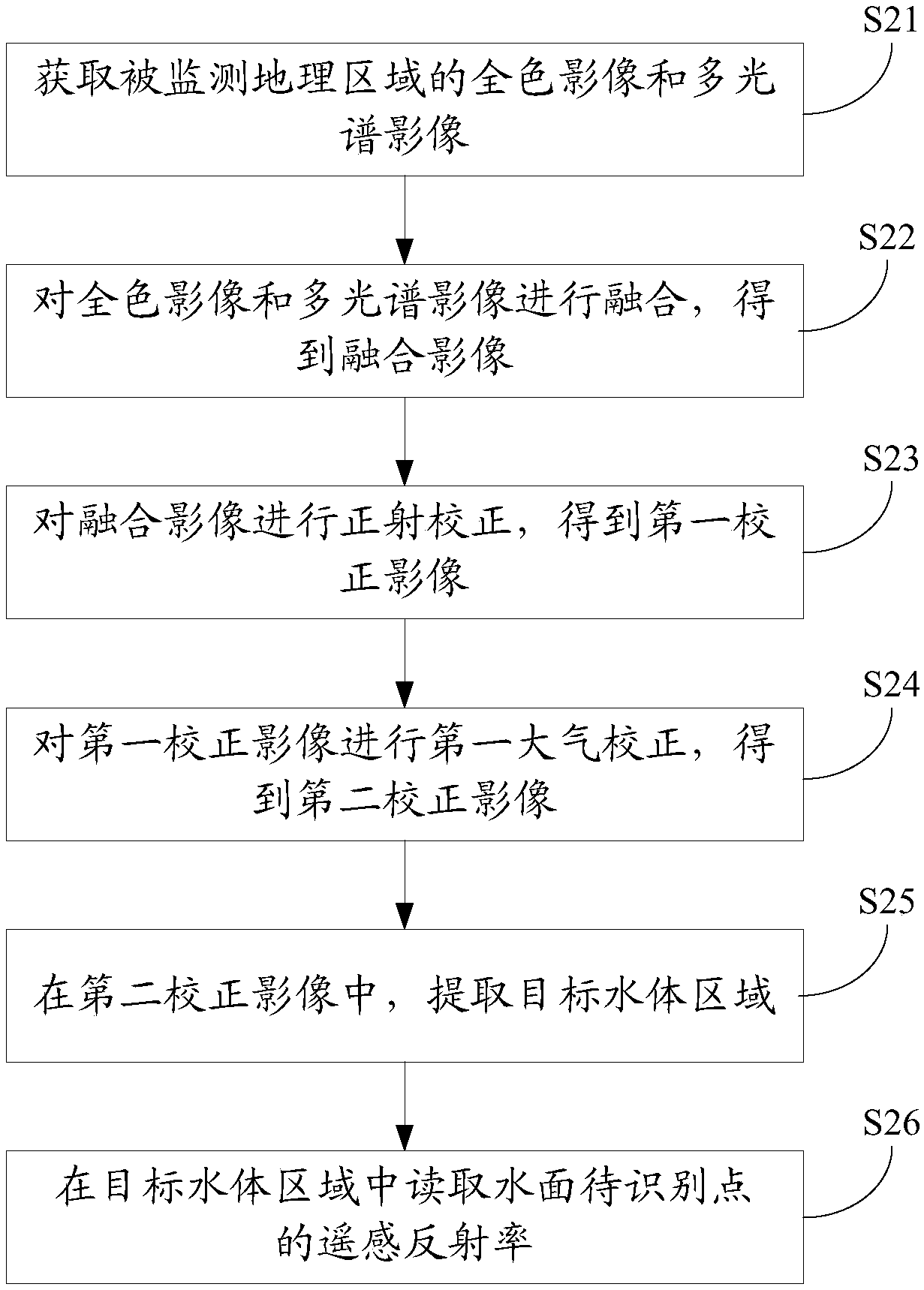
Remote sensing extraction method, remote sensing extraction device and remote sensing extraction system for polluted water body at drainage outlet
ActiveCN106950197AImprove recognition accuracyEfficient extractionScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansImage resolutionHigh spatial resolution
The invention discloses a remote sensing extraction method, a remote sensing extraction device and a remote sensing extraction system for polluted water body at drainage outlets and belongs to the field of pollution monitoring for water body. The method includes the steps of: a) on the basis of a high-spatial-resolution remote-sensing reflectance image, constructing spectral libraries of a polluted water body and a normal water body, calculating characteristic values of different wave bands in the spectral data of the polluted water body and the normal water body, and screening a characteristic wave band by comparing the characteristic values between the polluted water body and the normal water body, and respectively setting threshold values according to the characteristic value of the characteristic wave band of spectrum of the polluted water body; b) performing comparison to every pixels in the remote-sensing reflectance image waveband by waveband, if a comparison result is true, marking the pixel as a polluted water body pixel; and c) performing extraction of position information and counting of pixel number to the polluted water body pixels so as to acquire position and area of the polluted water body. The method has stronger pertinence to extraction of the polluted water body and greatly increases precision of recognizing the position and area of the polluted water body, thereby high-effectively, quickly and accurately extracting the distribution range and area of the polluted water body.
Owner:SATELLITE ENVIRONMENT CENT MINIST OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
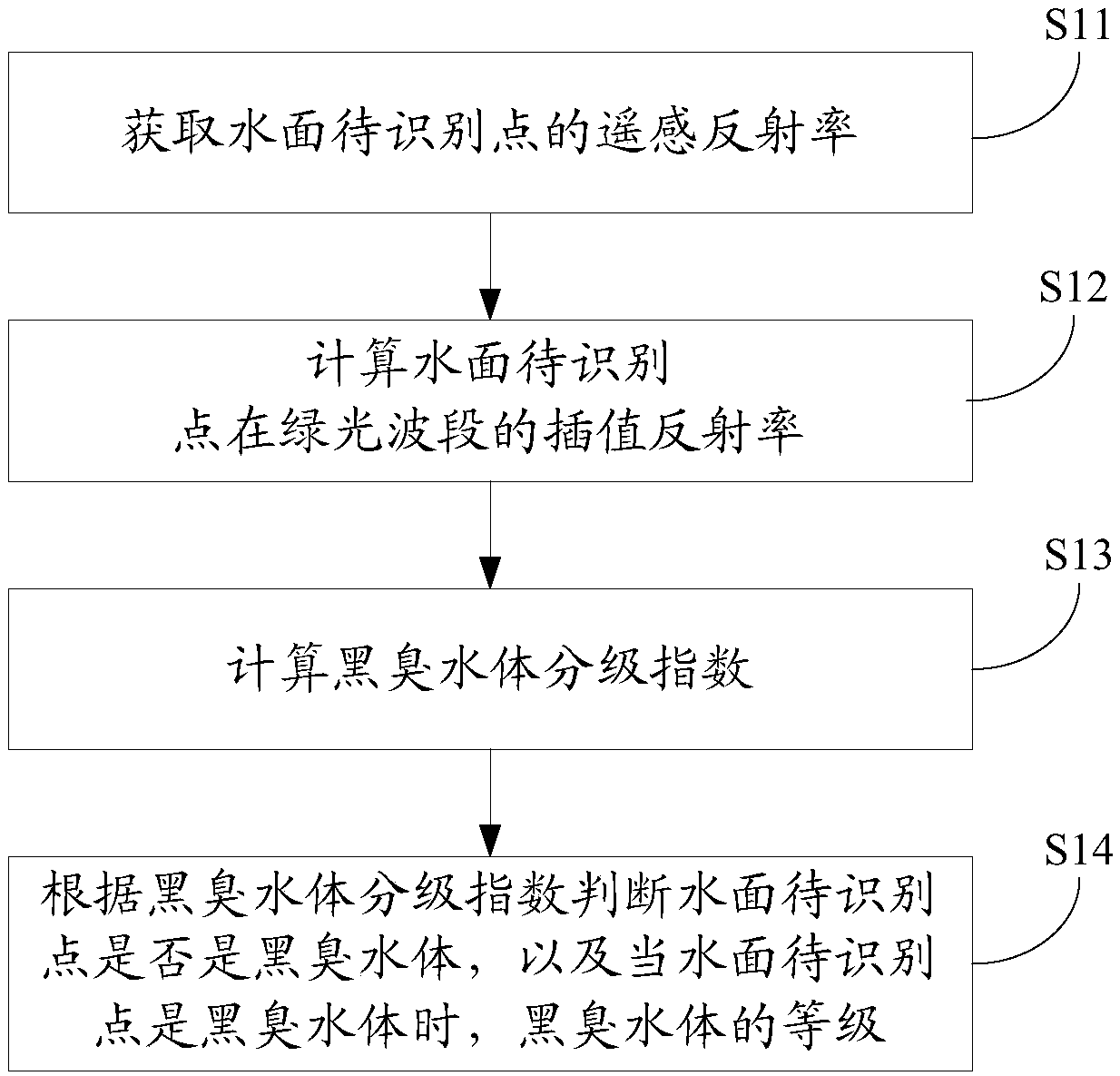
Urban black and odorous water recognition method and device
ActiveCN109374537AEfficient identificationRealize identificationColor/spectral properties measurementsRemote sensing reflectanceEnvironmental engineering
The embodiment of the invention discloses an urban black and odorous water recognition method and device. The method comprises the following steps: calculating the interpolation reflectivity of a water level to-be-recognized point in a green light wave band according to remote sensing reflectivity of a bluelight wave band and the remote sensing reflectivity of a redlight wave band of the water level to-be-recognized point; calculating the black and odorous water grading index according to the interpolation reflectivity of the green light wave band and the interpolation reflectivity of the water level to-be-recognized point as well as the remote sensing reflectivity of the redlight wave band; and judging whether the water level to-be-recognized point is urban black and odorous water or notaccording to the black and odorous water grading index and grading the urban black and odorous water when the water level to-be-recognized point is urban black and odorous water or. The method not only recognizes the urban black and odorous water effectively, but also recognizes the urban black and odorous water in a graded manner.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method of determining the volume scattering function of ocean waters in the backward direction using a satellite ocean color sensor
InactiveUS6868361B2Large scaleLarge coverageVolume/mass flow measurementAcceleration measurementOcean colorSurface ocean
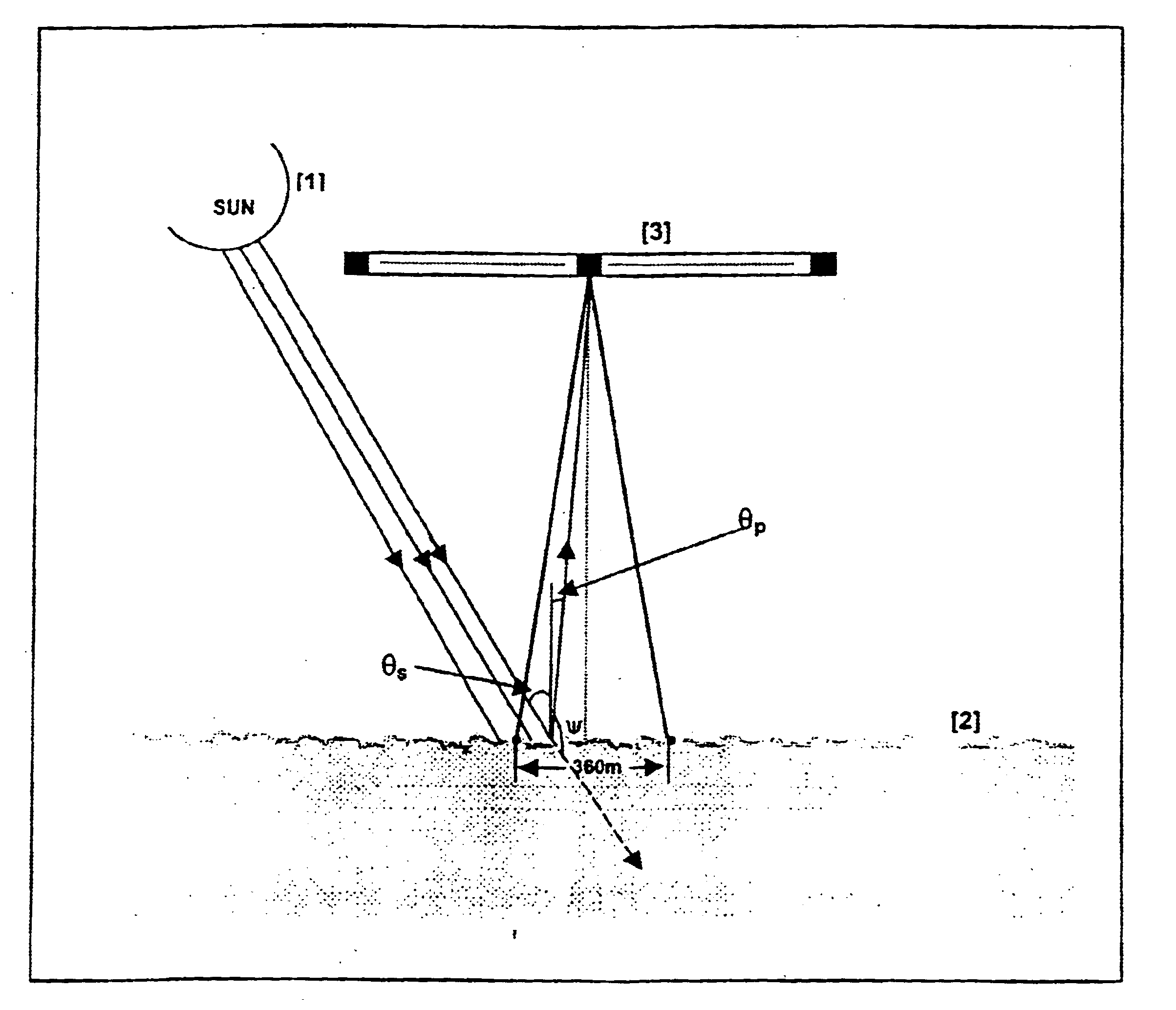
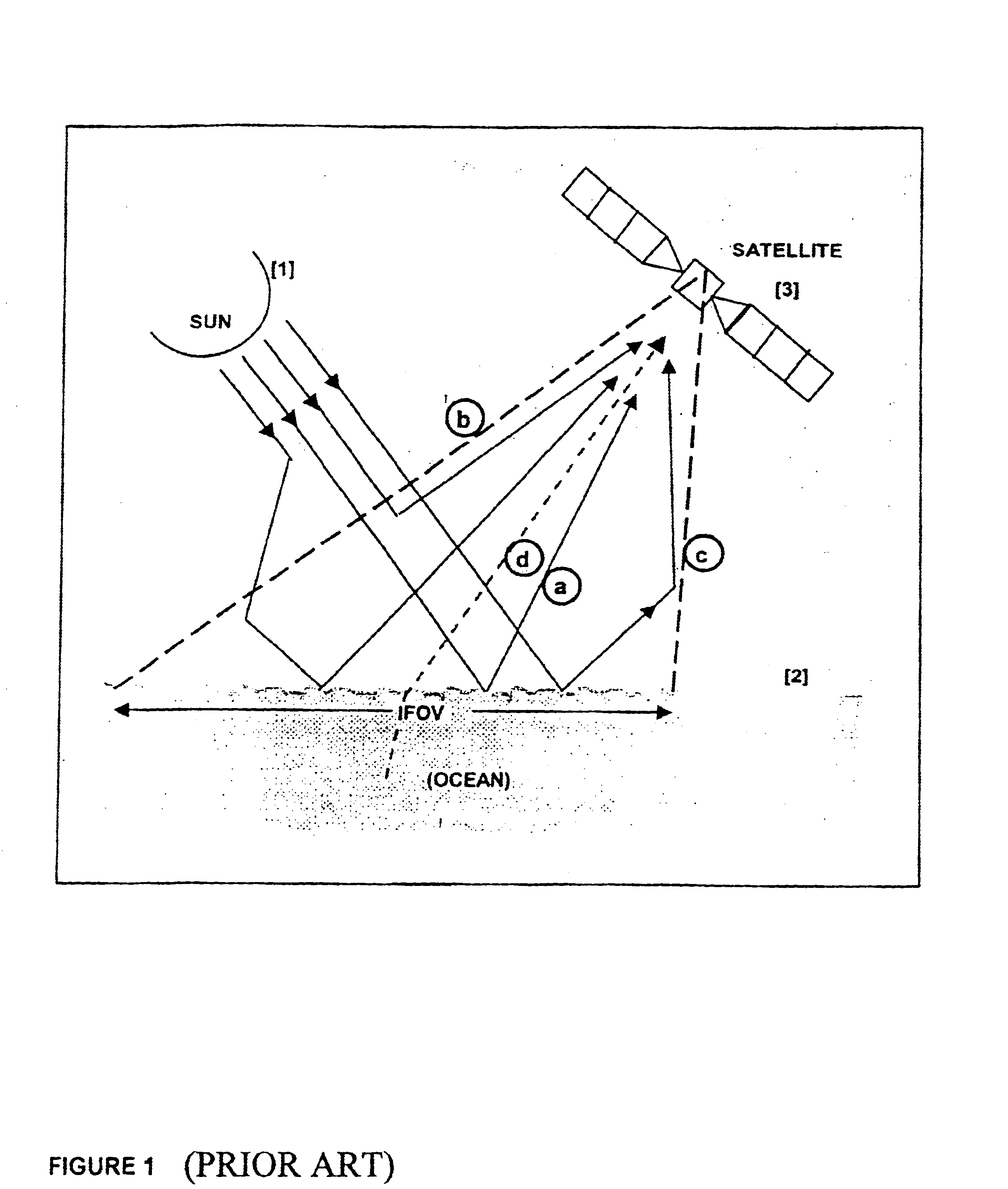
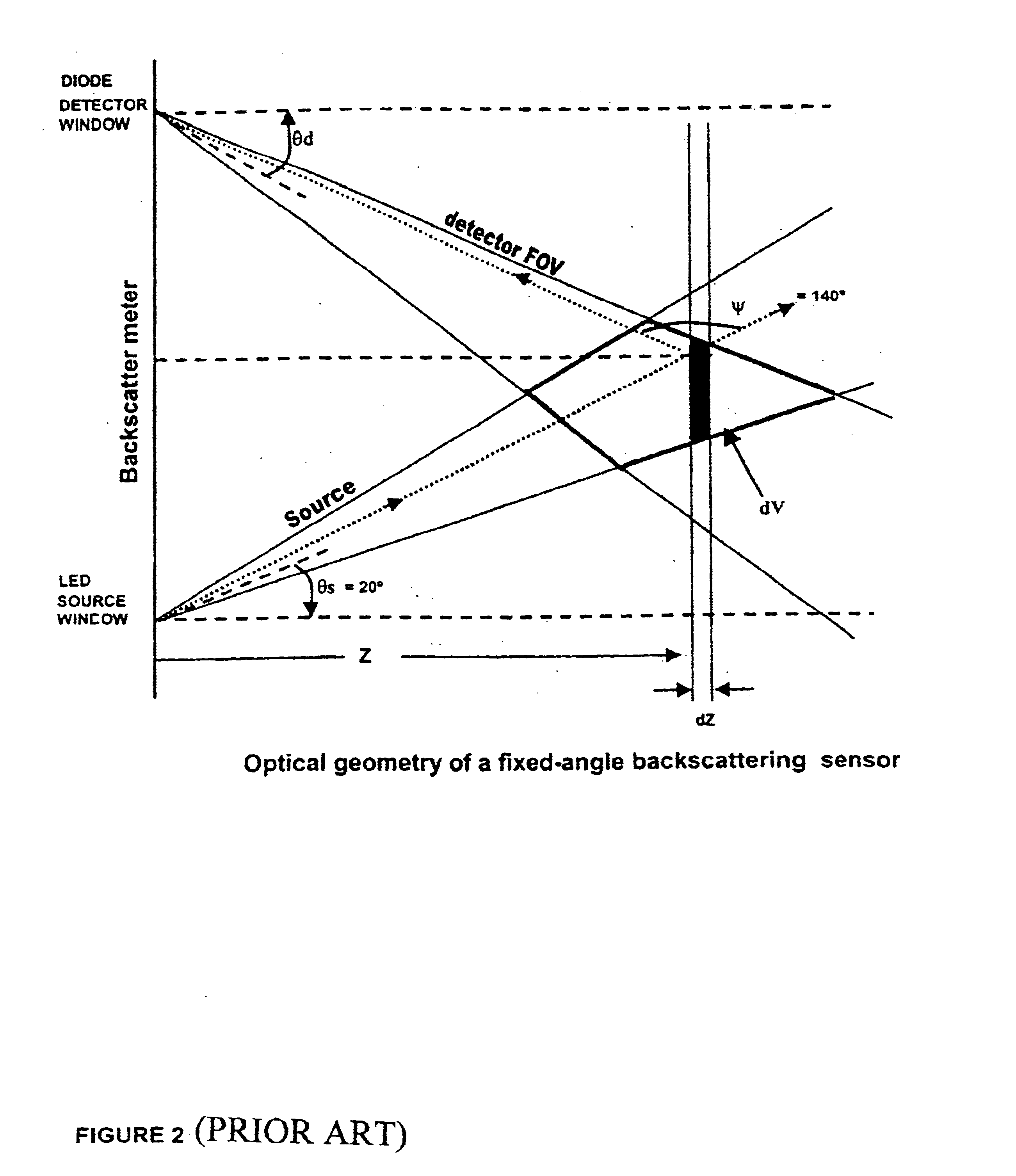
A method of determining the Volume Scattering Function of Ocean Waters in the backward direction using a Satellite Ocean Color Sensor the said method made to exploit the geometry of the sun-ocean-satellite detector to function as a backscatter system comprising of the sun [1] as a source of radiation, the ocean as the sampling volume [2], and the satellite ocean color sensor [3] as the detector of the backscattered flux from the ocean emanating from separate ocean pixels arranged on a scan line across the track of the satellite payload and arriving at corresponding pixels on the CCD array detector of the satellite sensor [3]; the output signals from each electronic pixel of the detector is shown to be related to the Volume Scattering Function at a fixed scattering angles (ψ) which bears a direct relation to the cosines of the solar incident angle (θs) and the angle (θp) of the upwelled flux at the ocean surface, the Remotely Sensed Reflectance (Rrs), and the diffuse attenuation coefficient (Kd) thereby resulting in a new product of the Volume Scattering Function at fixed backscattering angles.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
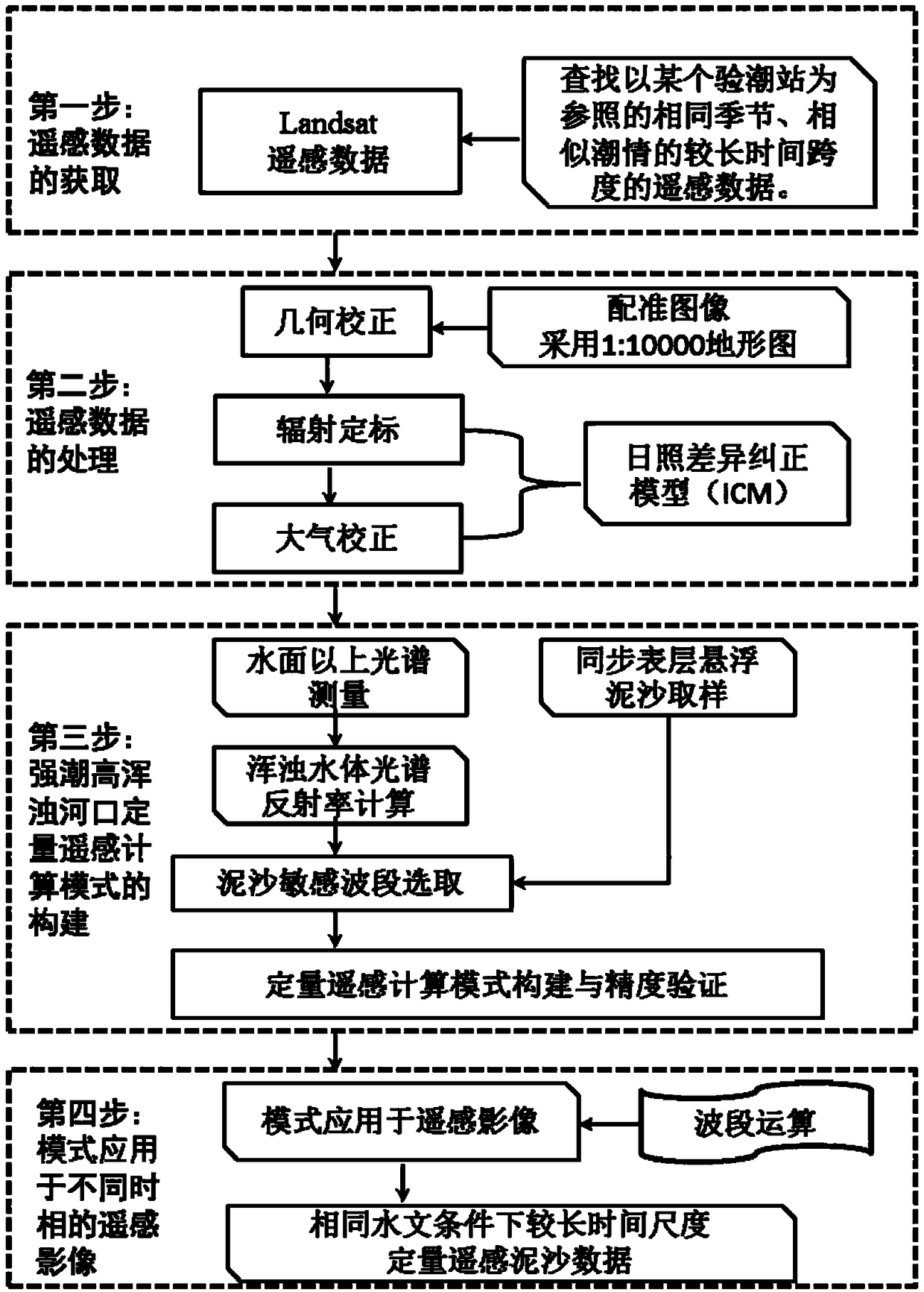
Remote-sensing calculation method of long-term variation of suspended sediments of strong-tide high-turbidity estuary
InactiveCN109283144AScattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsSpectral curveSensing data
The invention discloses a remote-sensing calculation method of long-term variation of suspended sediments of a strong-tide high-turbidity estuary. The method comprises the following steps: step S1, receiving Landsat satellite remote-sensing data in different years and the same hydrological condition; step S2, processing the remote-sensing data; step S3, carrying out spectral measurement above spring / neap-tide water surfaces, carrying out synchronous surface layer suspended-sediment sampling, obtaining remote-sensing reflectivity, analyzing wavebands where spectral curve peak values are located, selecting waveband data which are of different sensors on Landsat and correspond to reflectivity peak values, establishing a statistical regression model between surface layer suspended-sediment concentration and remote-sensing reflectivity corresponding to sensitive wavebands, and then obtaining an optimal calculation mode of quantitative remote sensing through accuracy verification calculation, wherein wavebands corresponding to the peak values are the sediment sensitive-wavebands; and step S4, applying the optimal calculation mode, which is of quantitative remote-sensing and is obtained in the step S3, to the remote-sensing data after processing in the step S2, obtaining remote-sensing data of the suspended sediments of all regions in the different years and the same hydrological condition, and carrying out analysis of long-term variation of the suspended sediments.
Owner:ZHEJIANG INST OF HYDRAULICS & ESTUARY
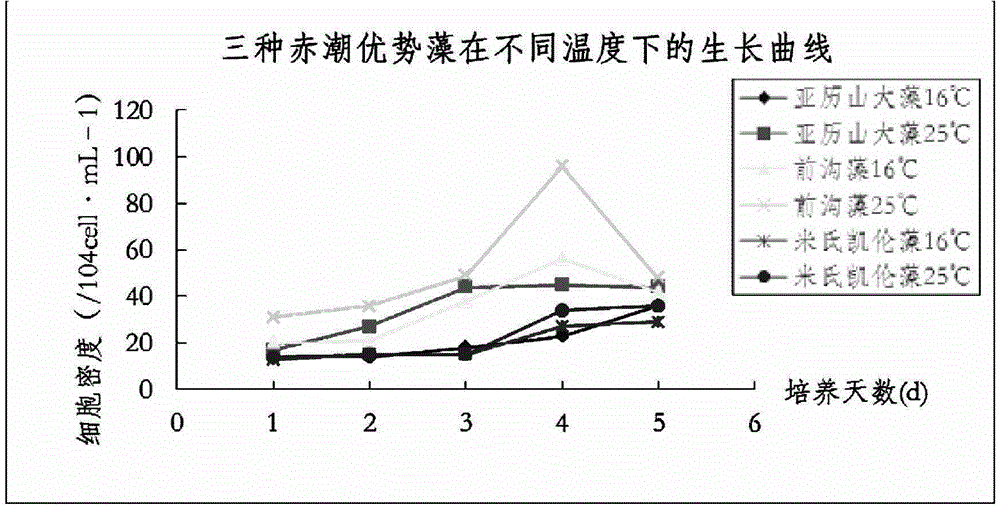
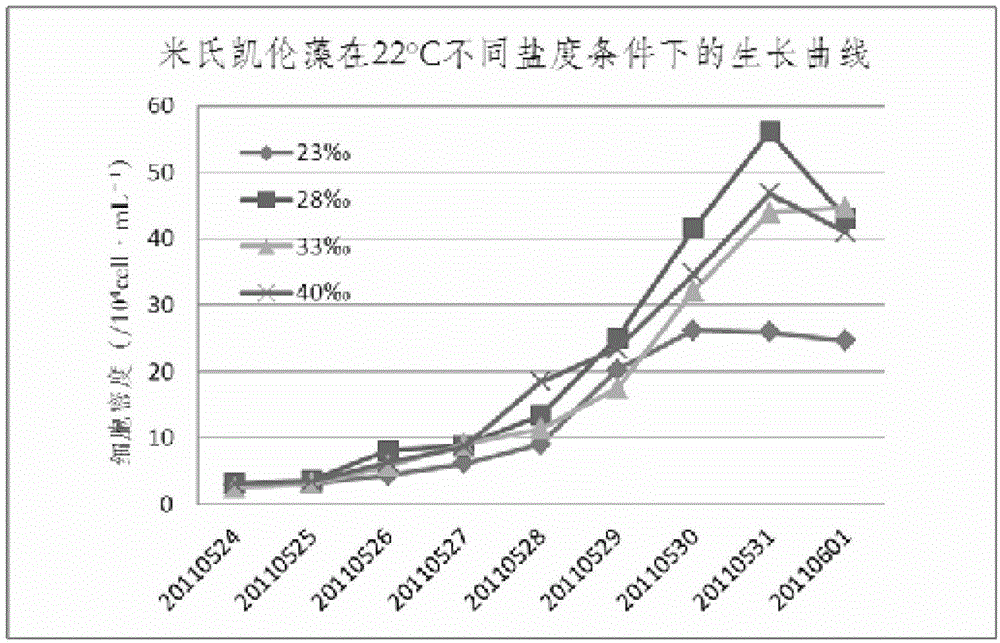
Optimal distinguishing method for red tide water body and main algae thereof
The invention relates to an optimal distinguishing method for a red tide water body and a main algae thereof, which comprises the following steps: (1) acquisition of spectroscopic data, which comprises the processes of laboratory culture of a red tide algae, measurement of the remote sensing reflectance and the post treatment of the spectroscopic data; and (2) analysis of the spectroscopic data, i.e. Carrying out comparison of spectral absorption characteristic parameters by a spectral absorption characteristic parameter extraction method through utilizing ENVI (The Environment for Visualizing Images) software, extracting wavelengths of a reflection peak and an absorption peak by a spectral differential method and carrying out comparison analysis on the water bodies before and after the red tide main algae is inoculated. According to the invention, by the spectroscopic data of different red tide main algae, which is obtained in a laboratory and the spectroscopic data flow processing, an abnormal value is removed to obtain a remote sensing spectral curve of Karenia mikimotoi, alexandrium tamarense and AmPhidinium; and the foundation is laid for the extraction of the absorption characteristic parameters and the spectral differential method.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Remote sensing retrieval method for concentration of particulate organic carbon of turbid water body
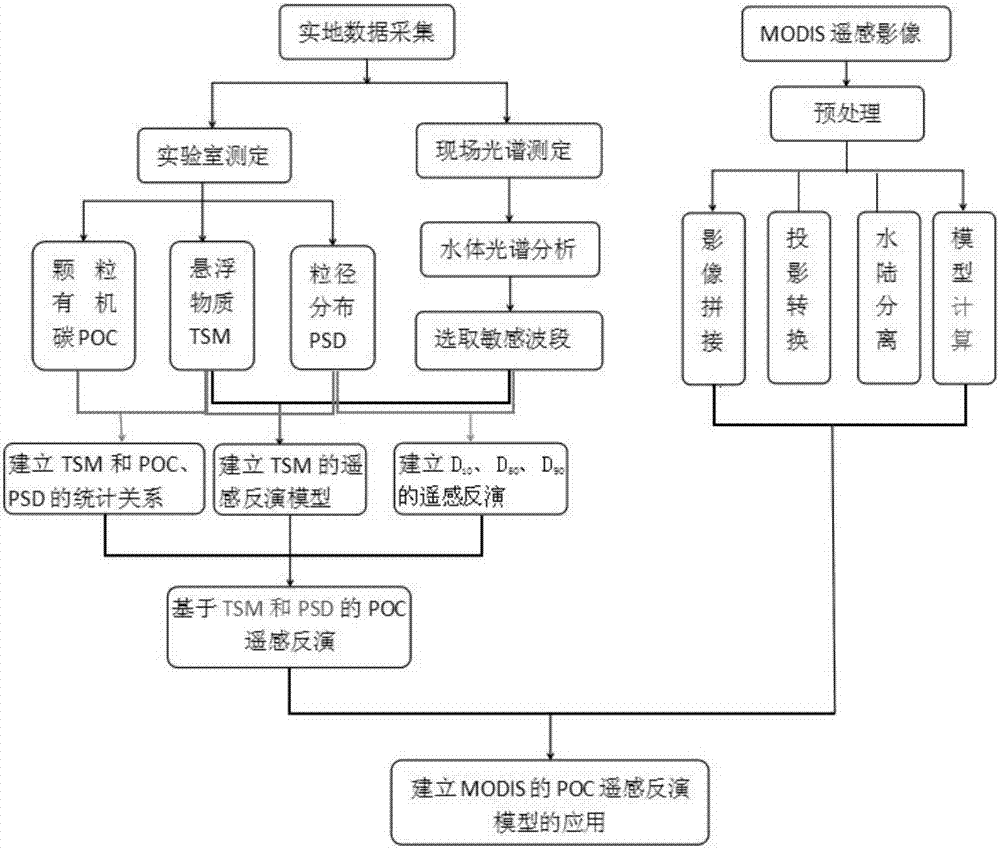
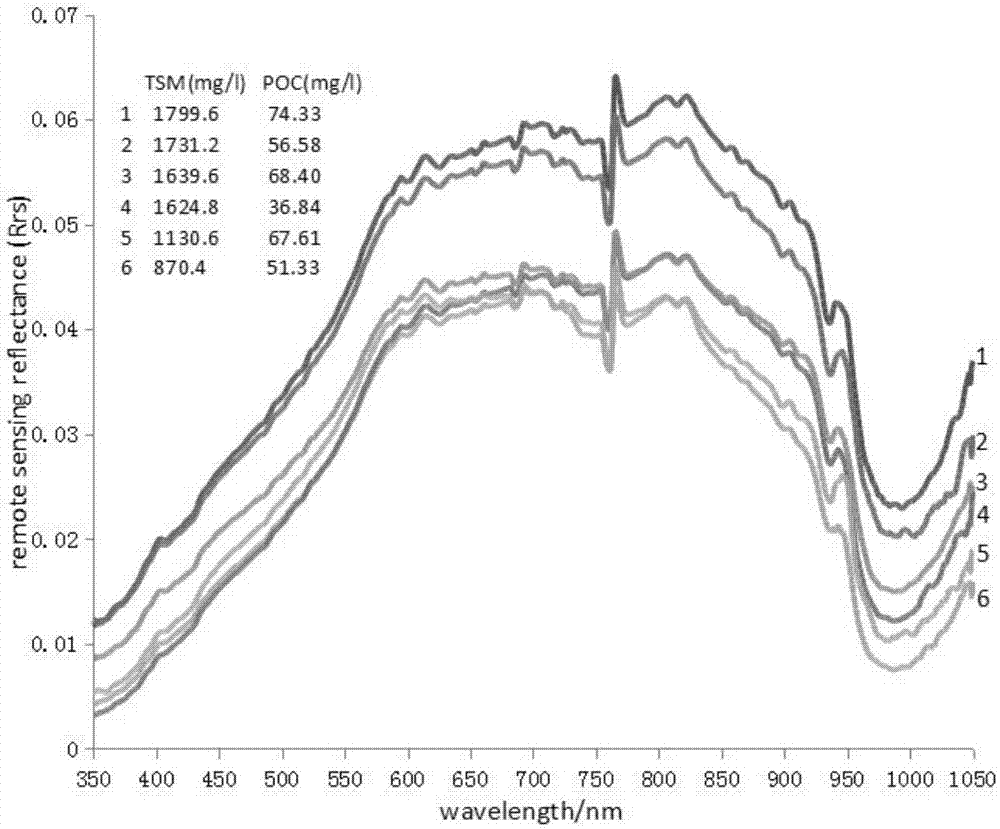
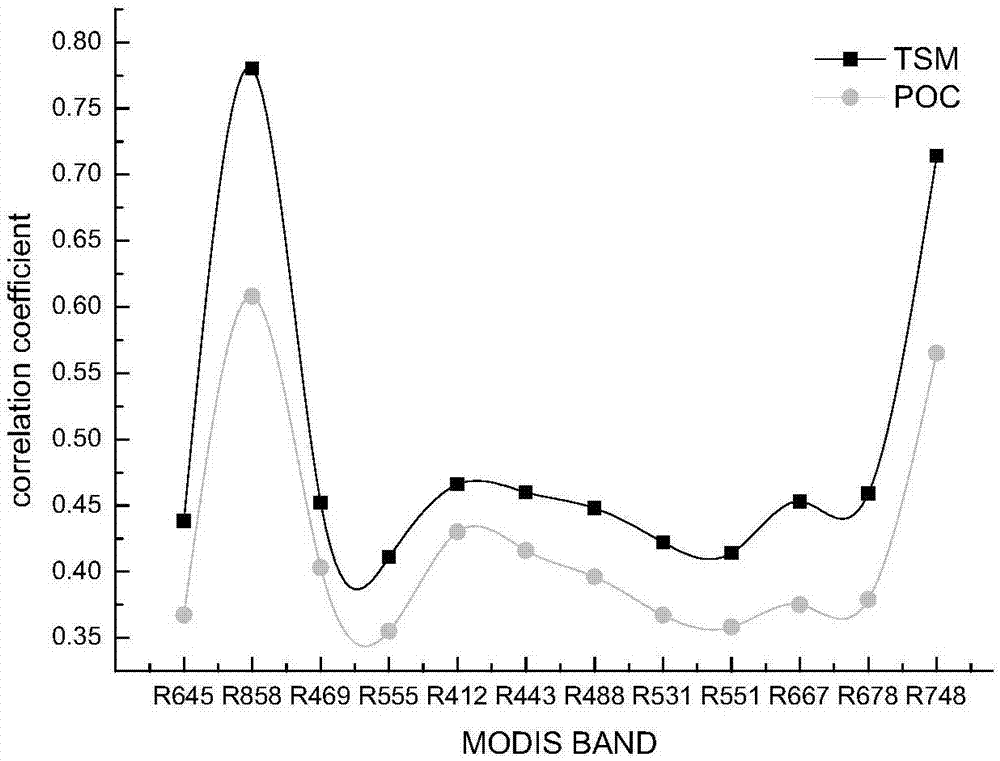
InactiveCN107064068AHigh precisionGeneral water supply conservationScattering properties measurementsSurface layerWater quality
The invention discloses a remote sensing retrieval method for a concentration of particulate organic carbon of a turbid water body, belonging to the field of remote sensing retrieval of water quality parameters. The remote sensing retrieval method comprises the following steps: acquiring the concentration of water body suspended matters on a surface layer of a research region, the concentration of particulate organic carbon (POC) and data of particle size distribution (PSD) of the suspended matters; acquiring field remote sensing reflectivity and a research region remote sensing image; and processing field remote sensing spectroscopic data so as to acquire a sensitive band of the remote sensing retrieval, establishing a statistical relation among the concentration of particulate organic carbon, the concentration of the suspended matters and the particle size distribution of particulate matters, a remote sensing retrieval model of the concentration of the suspended matters and a remote sensing retrieval model of the particle size distribution, and combining the statistical relation and the two models so as to establish a remote sensing retrieval method for particulate organic carbon based on the concentration and particle size distribution of the suspended matters. According to the remote sensing retrieval method for the concentration of particulate organic carbon of the turbid water body, the physical base of the remote sensing retrieval model can be directly reflected, and the precision of remote sensing retrieval can be improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Novel mixed method for estimating particle size of seawater suspended particulate matter by means of satellite data
InactiveCN106442233AEasy accessAccurate detection of particle size distributionParticle size analysisParticulatesSatellite data
The invention discloses a novel mixed method for estimating the particle size of seawater suspended particulate matter by means of satellite data. The method comprises the steps that seawater measured data of a seawater area to be estimated is acquired; satellite data is collected, and remote sensing reflectance data is extracted and calculated; the remote sensing reflectance of a seawater subsurface layer is calculated, and a backscattering coefficient of the suspended particulate matter is calculated by combining a total backscattering coefficient of the suspended particulate matter with a relation expression between a total absorption coefficient and the remote sensing reflectance of the seawater subsurface layer; a relation expression between the particle size of the seawater suspended particulate matter and the backscattering coefficient is derived, and a relation model between the backscattering coefficient of the seawater suspended particulate matter and the particle size of the seawater suspended particulate matter is established; an association relation process between the particle size of the seawater suspended particulate matter and the remote sensing reflectance of the seawater subsurface layer is established, and satellite-retrieved particle size distribution information of the seawater suspended particulate matter is obtained by means of monthly-composited remote sensing reflectance data. The remote sensing estimation capacity on offshore high-turbidity water body PSD distribution information can be improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Method for calculating sea ice thickness based on hyperspectral remote sensing reflectance
InactiveCN103017668ARealize computingSimple methodUsing optical meansSpectroradiometerHyperspectral image processing
The invention relates to a method for calculating sea ice thickness based on hyperspectral remote sensing reflectance. The method comprises the following steps of selecting the ratio of remote sensing reflectance of different wavelengths and functions as the characteristics of determining the sea ice thickness according to the different thicknesses of sea ice hyperspectral remote sensing reflectance; building a sea ice thickness calculation model to obtain the sea ice thickness; aiming at an aerial hyperspectral image containing sea ice, firstly, utilizing the ratio of digital quantization values of an image to identify a sea ice picture element; carrying out radiation correction and atmospheric correction on the digital quantization values of the image according to the common aerial hyperspectral image processing method to obtain the hyperspectral remote sensing reflectance of the sea ice picture element; and finally substituting into the sea ice thickness calculation model, and calculating the thickness of the sea ice picture element. The model disclosed by the invention is simple; and only remote sensing reflectance Rrs of finite wavelengths is selected. Therefore, sea ice thickness calculation of the sea ice remote sensing reflectance measured by a spectroradiometer is achieved, and calculation of the sea ice thickness by the aerial hyperspectral remote sensing image is also achieved.
Owner:THE FIRST INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY SOA +1
Method for inversely analyzing transparency of water body by virtue of inherent optical parameter
InactiveCN106053394ASolve the problem of time and space constraintsScattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsProblem of timeRemote sensing reflectance
The invention belongs to the technical field of water color remote sensing, and relates to a method for inversely analyzing the transparency of a water body by virtue of an inherent optical parameter. The method for inversely analyzing the transparency of the water body by virtue of the inherent optical parameter comprises the following steps: (1) reading data of measured transparency and data of remote sensing reflectance; (2) calculating an absorption and scattering coefficient through the remote sensing reflectance; (3) constructing an algorithm for inversely analyzing the transparency of the water body by virtue of the inherent optical parameter; (4) calculating an error between an inverse analysis value and a measured value to estimate the accuracy of the algorithm by taking the measured transparency as a true value. Compared with the prior art, the method for inversely analyzing the transparency of the water body by virtue of the inherent optical parameter has the advantages that the inherent optical parameter of the water body can be estimated according to the remote sensing reflectance to further inversely analyze the transparency of the water body, so that the problem of time-space limits of a case-two water body color constituent inverse analysis algorithm is solved, and universal applicability is achieved.
Owner:OCEANOGRAPHIC INSTR RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
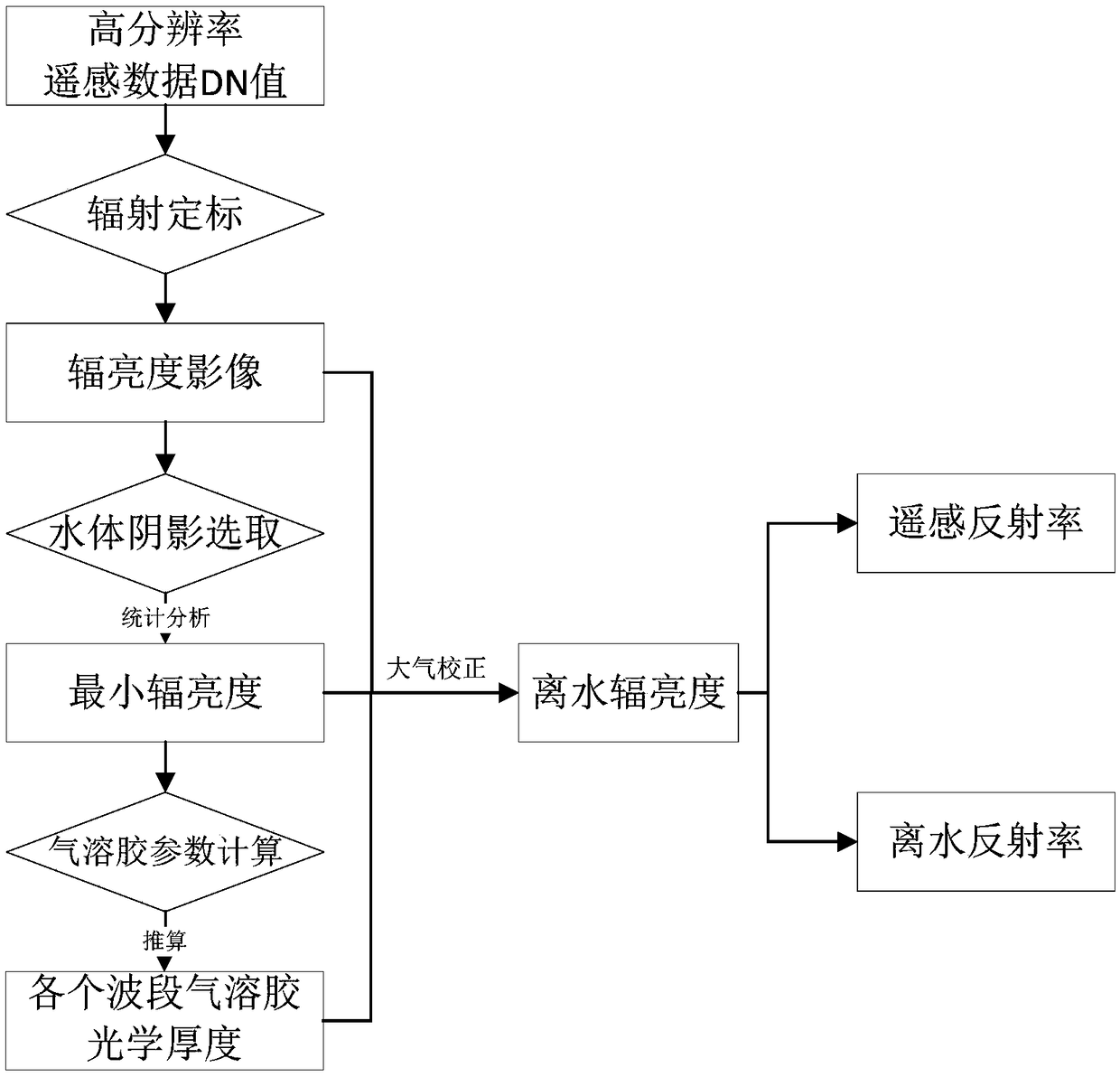
An atmospheric correction method for water body of a city river network area
ActiveCN109325973AEasy to choosePrevent overcorrectionImage analysisMaterial analysis by optical meansRiver networkTurbidity
The invention discloses an atmospheric correction method for water body of a city river network area, which comprises the following steps of preprocessing the remote sensing data to obtain a radianceimage; selecting as many water pixels located in the shaded area as possible as dark pixels, and counting the minimum values of all the selected dark pixels in each band; optimizing the aerosol turbidity coefficient and wavelength exponent to calculate the aerosol optical depth in each band; subtracting the radiance of the shadow pixel from the original radiance image, and then calculating the atmospheric upward transmittance according to the aerosol optical depth, and obtaining the water-leaving radiance of the water body; converting the radiance of water leaving to remote sensing reflectanceor water leaving reflectance, and completing the atmospheric correction of water body. The method of the invention solves the problem that it is difficult to find clear and deep water body as dark pixel in the urban river network area, and can realize atmospheric correction of type II turbidity water body in the urban river network area through common buildings and bridge shadows in the peripheryof the urban river network area.
Owner:PEARL RIVER HYDRAULIC RES INST OF PEARL RIVER WATER RESOURCES COMMISSION
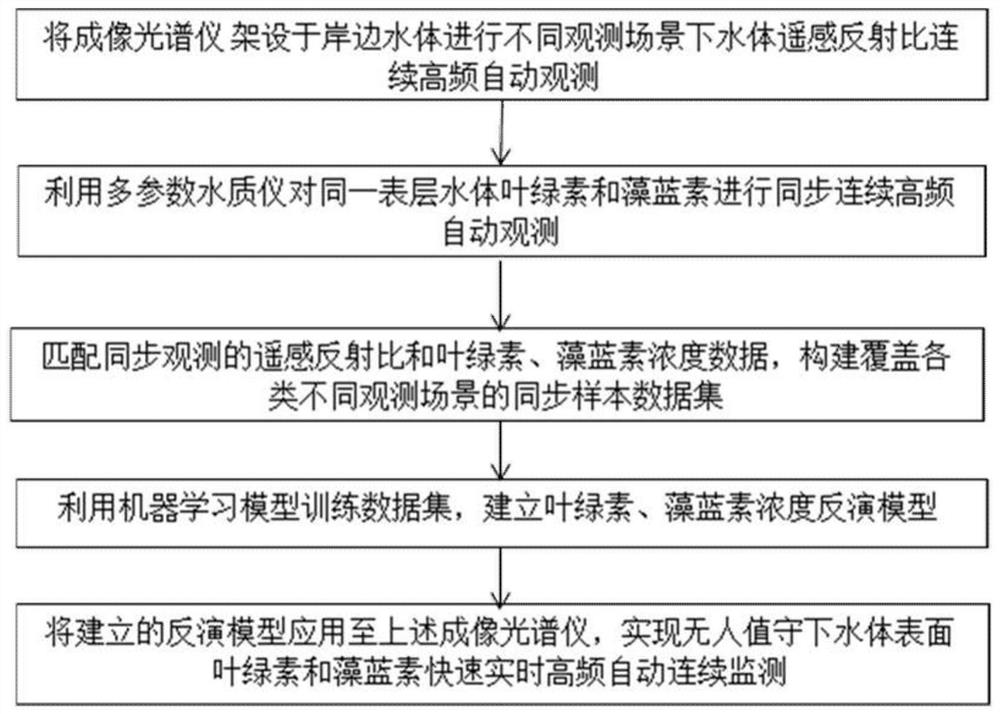
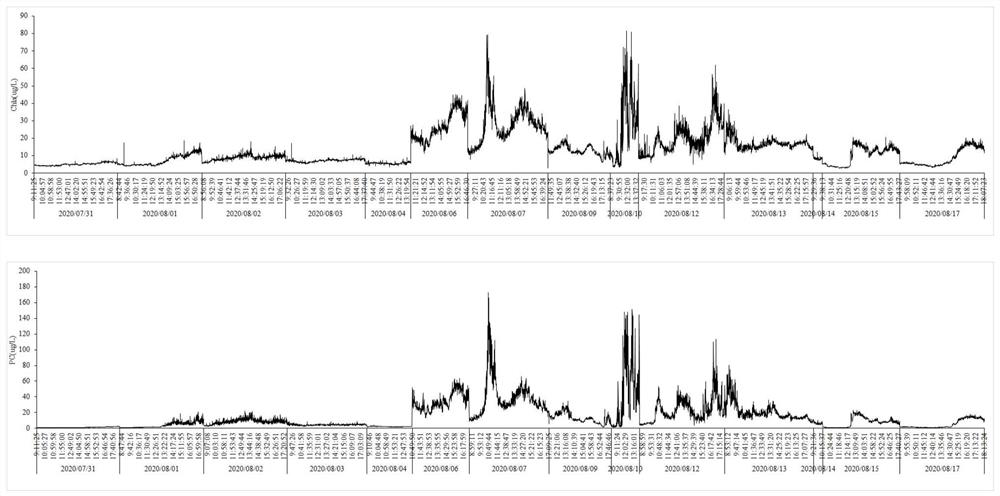
Land-based remote sensing machine learning algorithm for chlorophyll and phycocyanobilin in a water body in complex scenes
PendingCN112070234AExtended Imaging Temporal ScopeHigh resolutionMethod using image detector and image signal processingCharacter and pattern recognitionData setAlgorithm
The invention provides a land-based remote sensing machine learning algorithm for chlorophyll and phycocyanobilin in a water body in complex scenes. The algorithm comprises the steps: erecting an imaging spectrometer on a shoreside water body to carry out high-frequency automatic continuous observation on the remote sensing reflectance ratio of the water body under complex scenes of different weather conditions and water conditions; performing synchronous high-frequency automatic continuous observation on chlorophyll and phycocyanobilin on the surface layer of the same water body by using a multi-parameter water quality instrument; matching the synchronously observed remote sensing reflectance ratio and pigment concentration data, and constructing a synchronous sample data set covering different observation scenes; and establishing an inversion model by using a machine learning model and applying the inversion model to an imaging spectrometer to realize rapid real-time high-frequency automatic continuous monitoring of chlorophyll and phycocyanobilin in the water body under unattended operation. Based on shore-based remote sensing, the concentrations of chlorophyll and phycocyanobilin in the water body can be accurately and automatically inverted for the large sample data set under complex scenes of different weather conditions and water conditions, and when the algorithm is applied to an imaging spectrometer, rapid, real-time, high-frequency, automatic and continuous monitoring of chlorophyll and phycocyanobilin on the surface of the water body under unattended operation can be realized.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
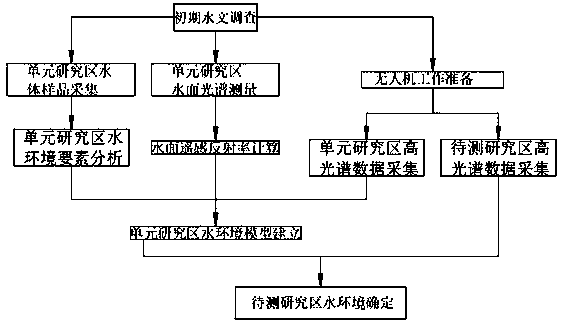
Method for inverting estuarine wetland water environment elements through hyperspectral sensor on unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveCN109738367AAvoid Difficult Collection SituationsPrecise inversionGeneral water supply conservationScattering properties measurementsContent distributionRiver mouth
The invention discloses a method for inverting estuarine wetland water environment elements through a hyperspectral sensor on an unmanned aerial vehicle, and belongs to the field of water environmentsimulation. According to the method for inverting the estuarine wetland water environment elements through the hyperspectral sensor on the unmanned aerial vehicle, the estuarine wetland water environment elements are quickly calculated out in combination with the use of the unmanned aerial vehicle through the steps of collecting a water body sample of a unit research area, calculating the remote sensing reflectance of the water surface of the unit research area, analyzing a water environment of the unit research area, making unmanned aerial vehicle work preparation, collecting hyperspectral data of the unit research area, building a water environment model of the unit research area, collecting hyperspectral data of a to-be-tested research area, determining a water environment of the to-be-tested research area, and the like; the above steps are repeated to establish multiple groups of water quality content distribution images of the estuarine wetland research areas; and the change rulesof the water quality of the estuarine wetland research areas are compared and obtained in the same direction, so that the tidal creek water quality change conditions which are quickly and dynamicallychanged can be accurately captured, and the time and labor are saved.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
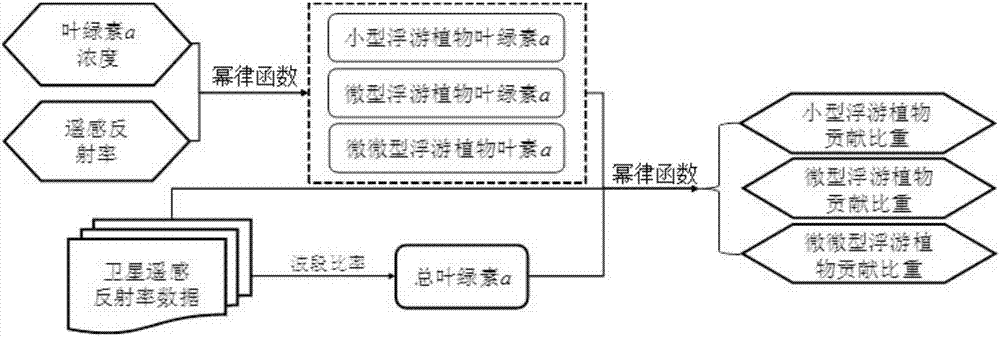
Remote sensing method for estimating particle fraction structure of offshore water body phytoplankton
The invention discloses a remote sensing method for estimating a particle fraction structure of offshore water body phytoplankton. The method comprises the steps of performing diagnostic pigment analysis (DPA) on HPLC data which are obtained through voyage, and obtaining a Chla concentration value which corresponds with each particle diameter; performing derivation based on a power exponent relation according to field measured remote sensing reflectivity data for obtaining a localized parameter; and finally applying an established model to a satellite, thereby obtaining PSC time-space distribution information which is inversed by the satellite. The remote sensing method has advantages of settling a problem of offshore water body phytoplankton particle fraction structure inversion, algorithm shortage in China, expanding application of water color remote sensing satellite data, and improving acquiring capability for an essential parameter of phytoplankton particle fraction structure.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com