Patents
Literature
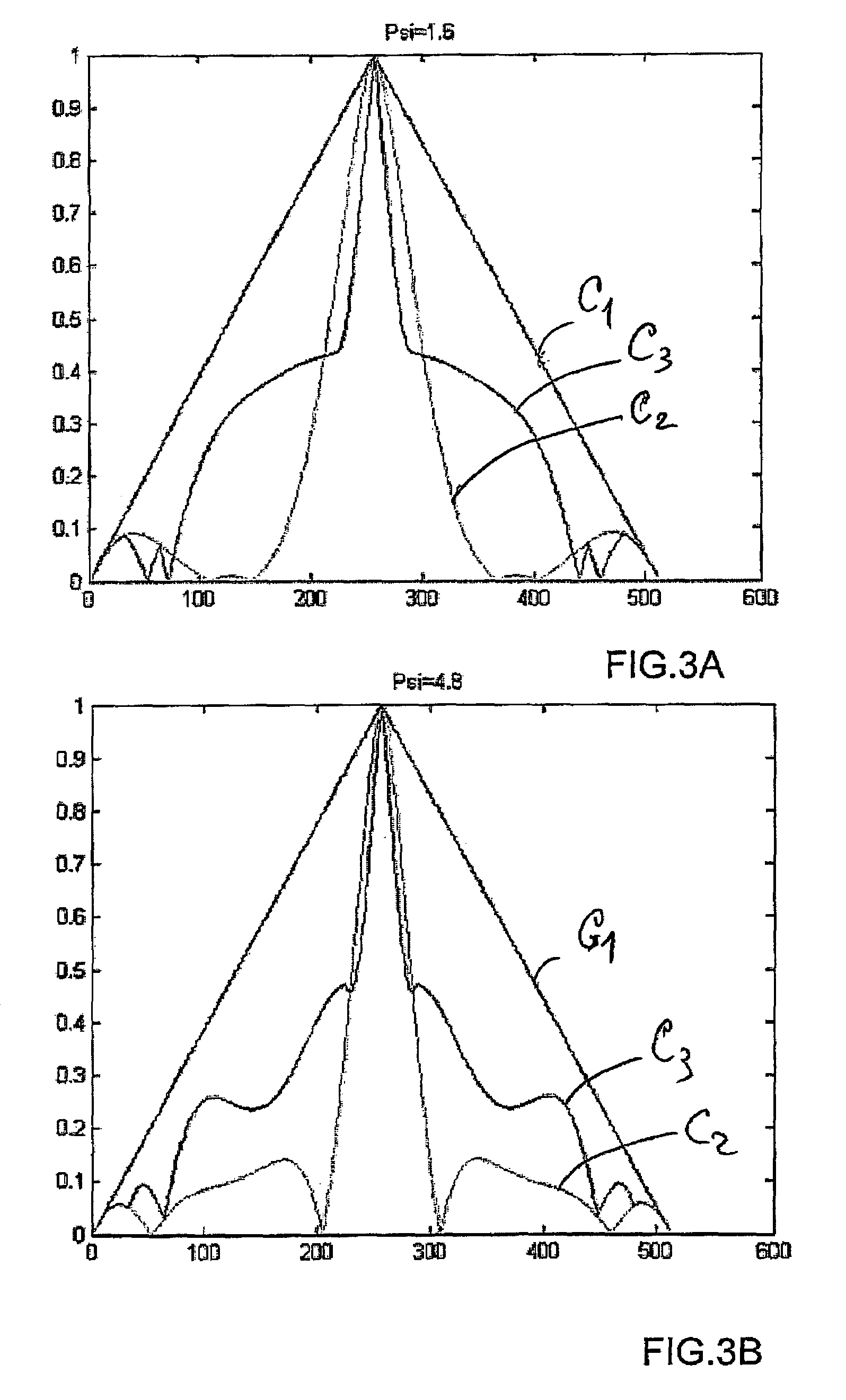
354 results about "Optical depth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, optical depth or optical thickness, is the natural logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted radiant power through a material, and spectral optical depth or spectral optical thickness is the natural logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted spectral radiant power through a material. Optical depth is dimensionless, and in particular is not a length, though it is a monotonically increasing function of optical path length, and approaches zero as the path length approaches zero. The use of the term "optical density" for optical depth is discouraged.
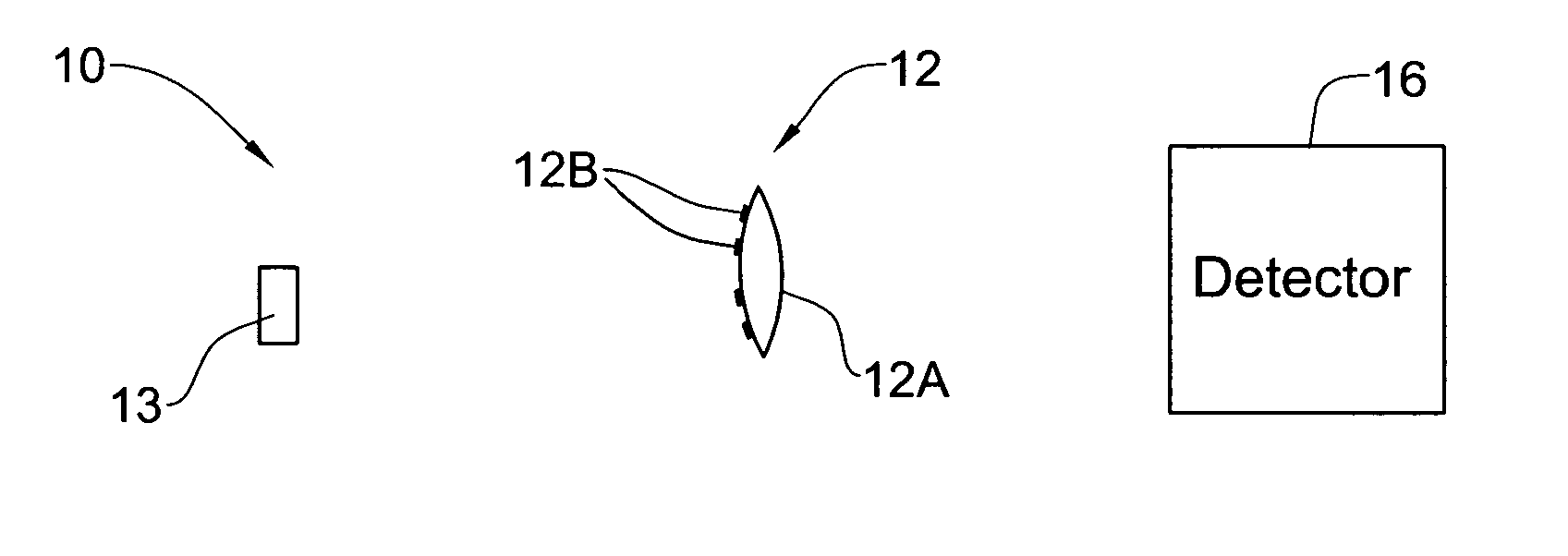
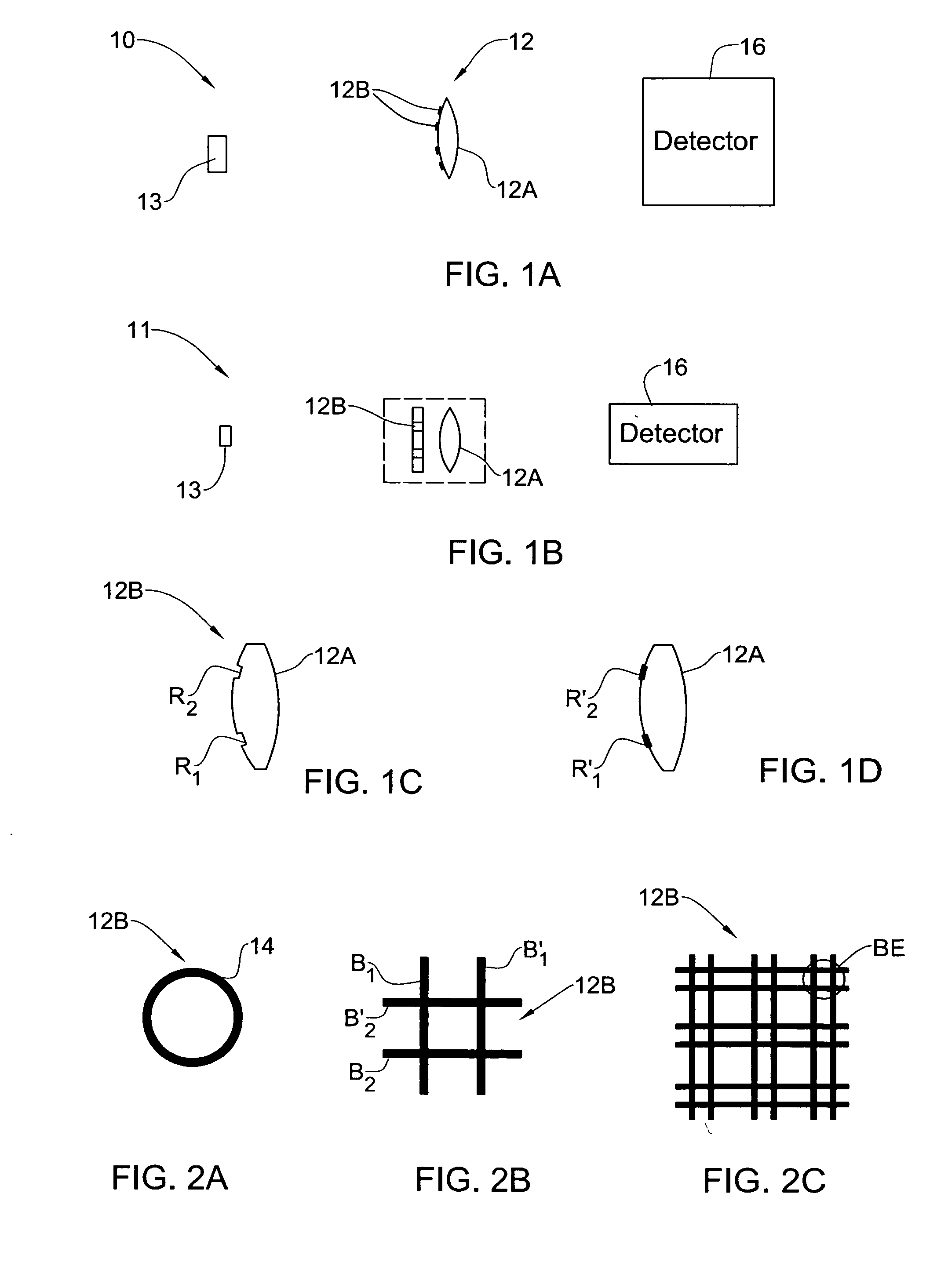
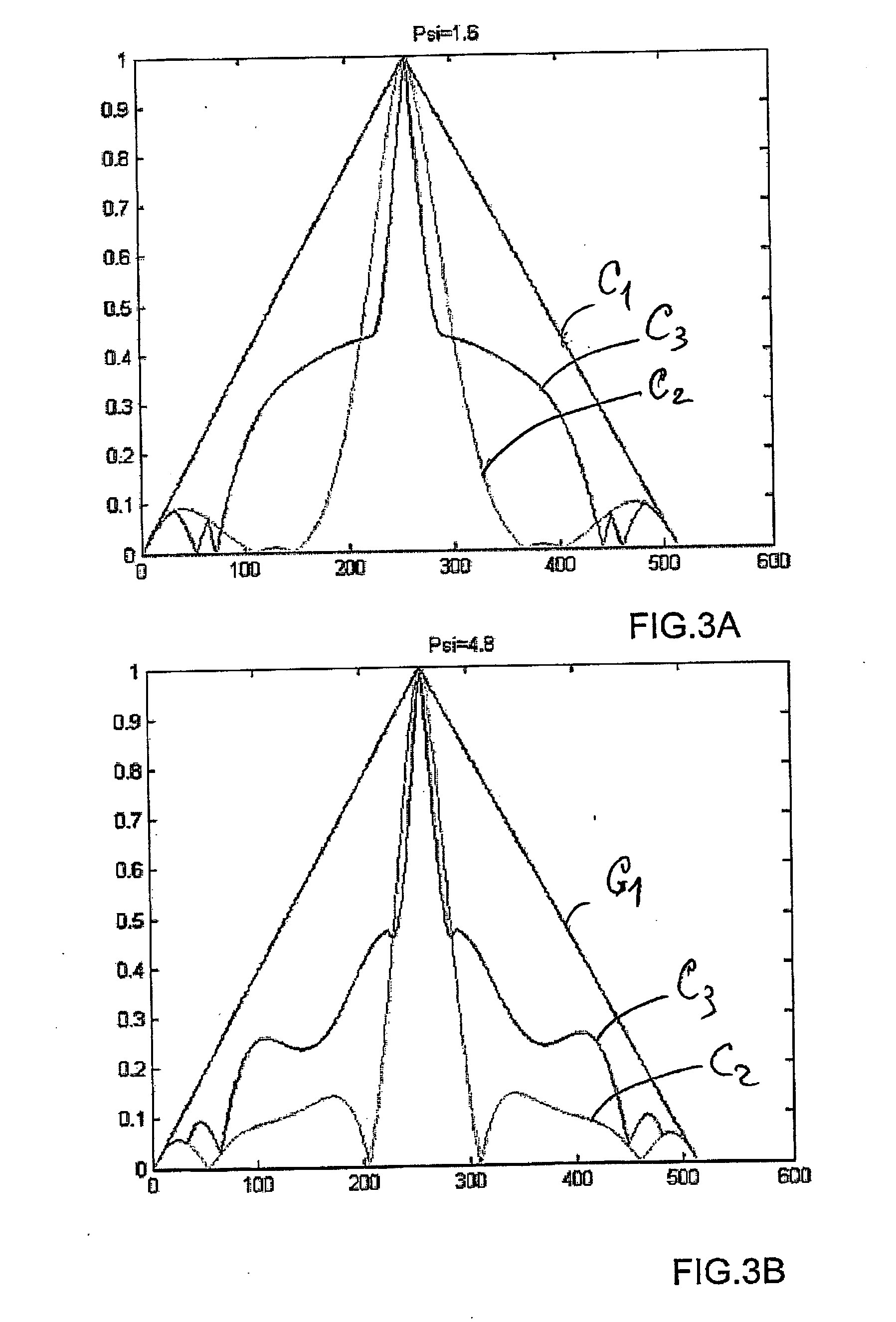
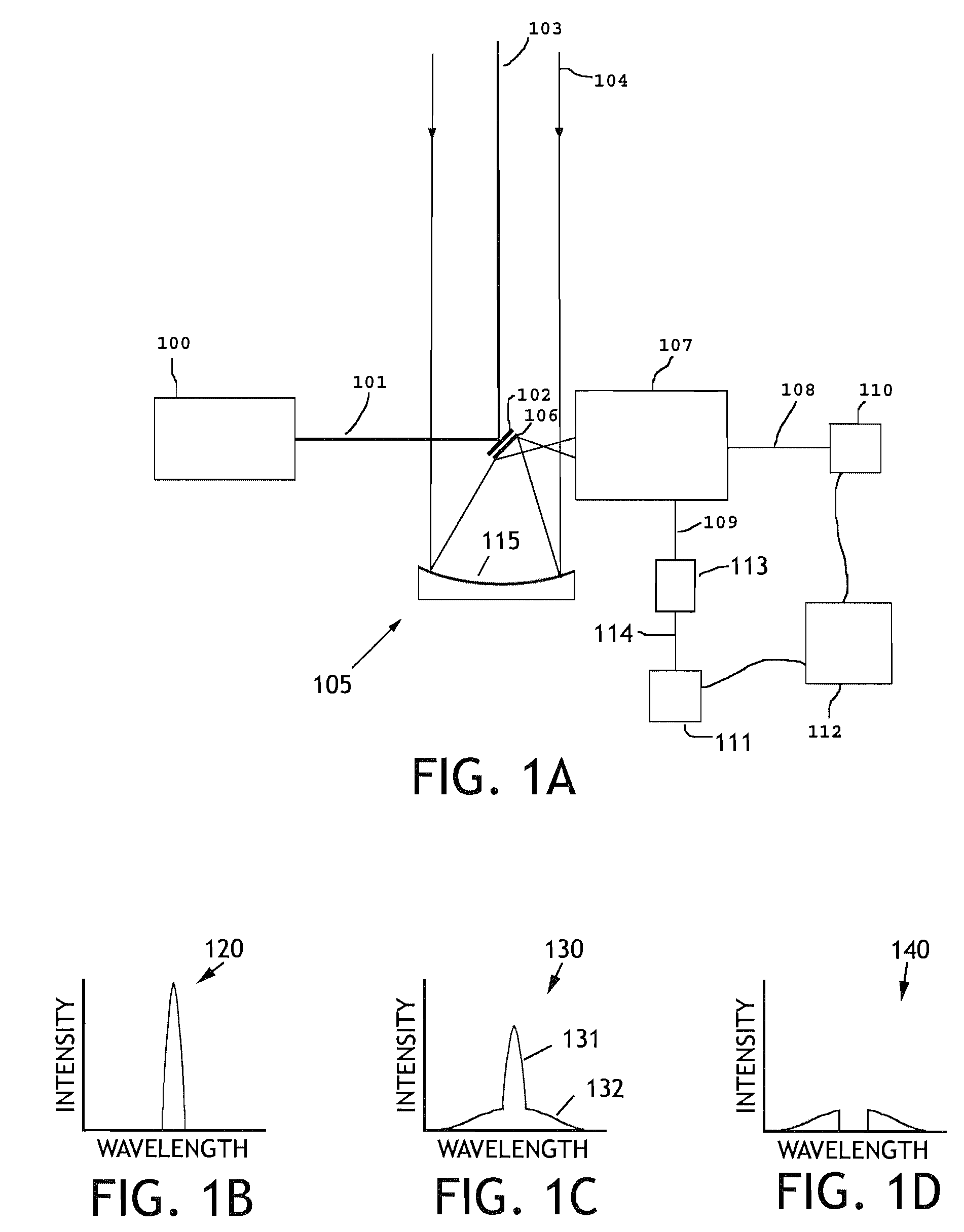
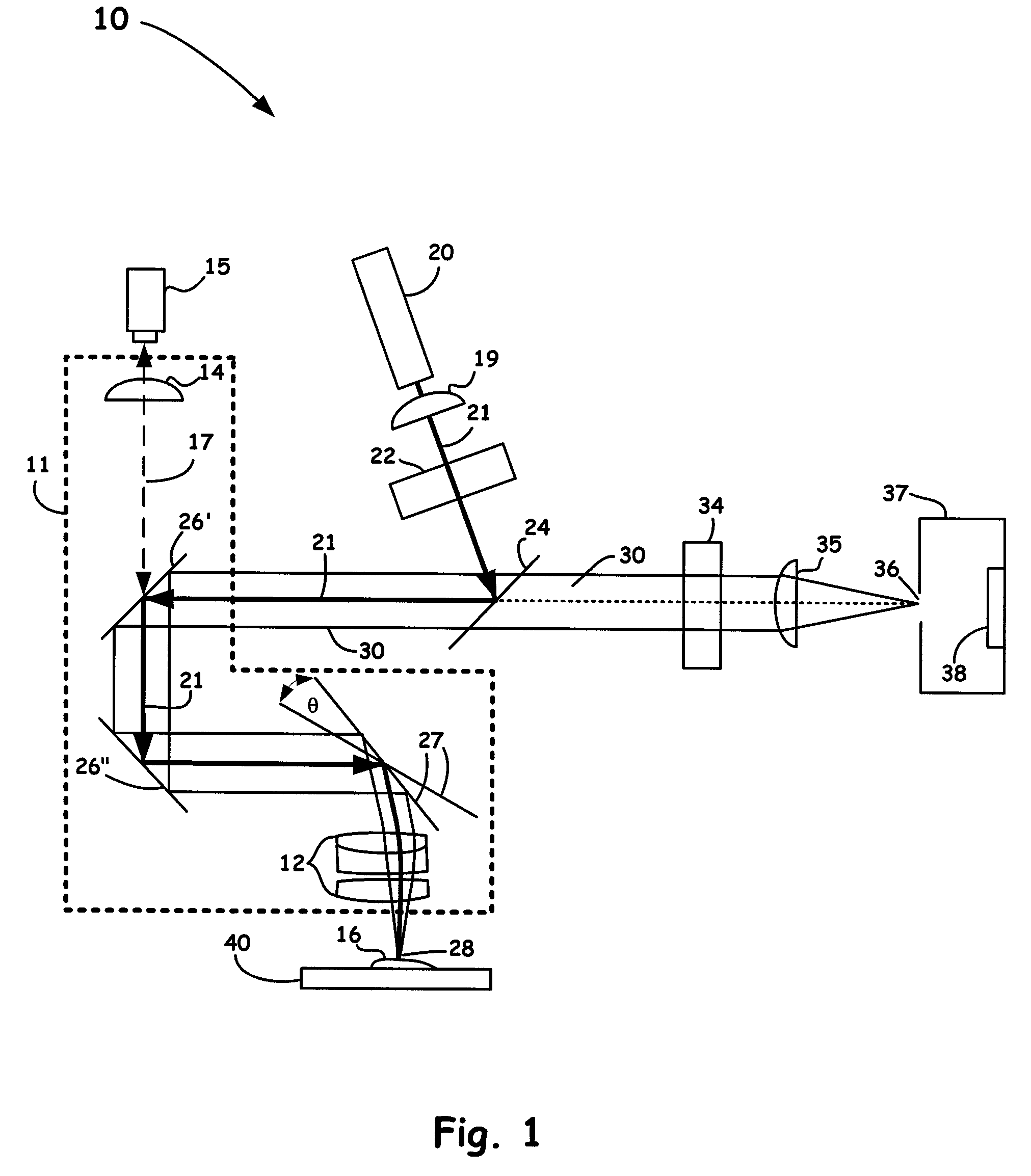
Optical method and system for extended depth of focus
ActiveUS20060034003A1Increase depth of focusEliminate needIntraocular lensOptical partsOptical propertyImaging lens
An imaging arrangement and method for extended the depth of focus are provided. The imaging arrangement comprises an imaging lens having a certain affective aperture, and an optical element associated with said imaging lens. The optical element is configured as a phase-affecting, non-diffractive optical element defining a spatially low frequency phase transition. The optical element and the imaging lens define a predetermined pattern formed by spaced-apart substantially optically transparent features of different optical properties. Position of at least one phase transition region of the optical element within the imaging lens plane is determined by at least a dimension of said affective aperture.
Owner:BRIEN HOLDEN VISION INST (AU)
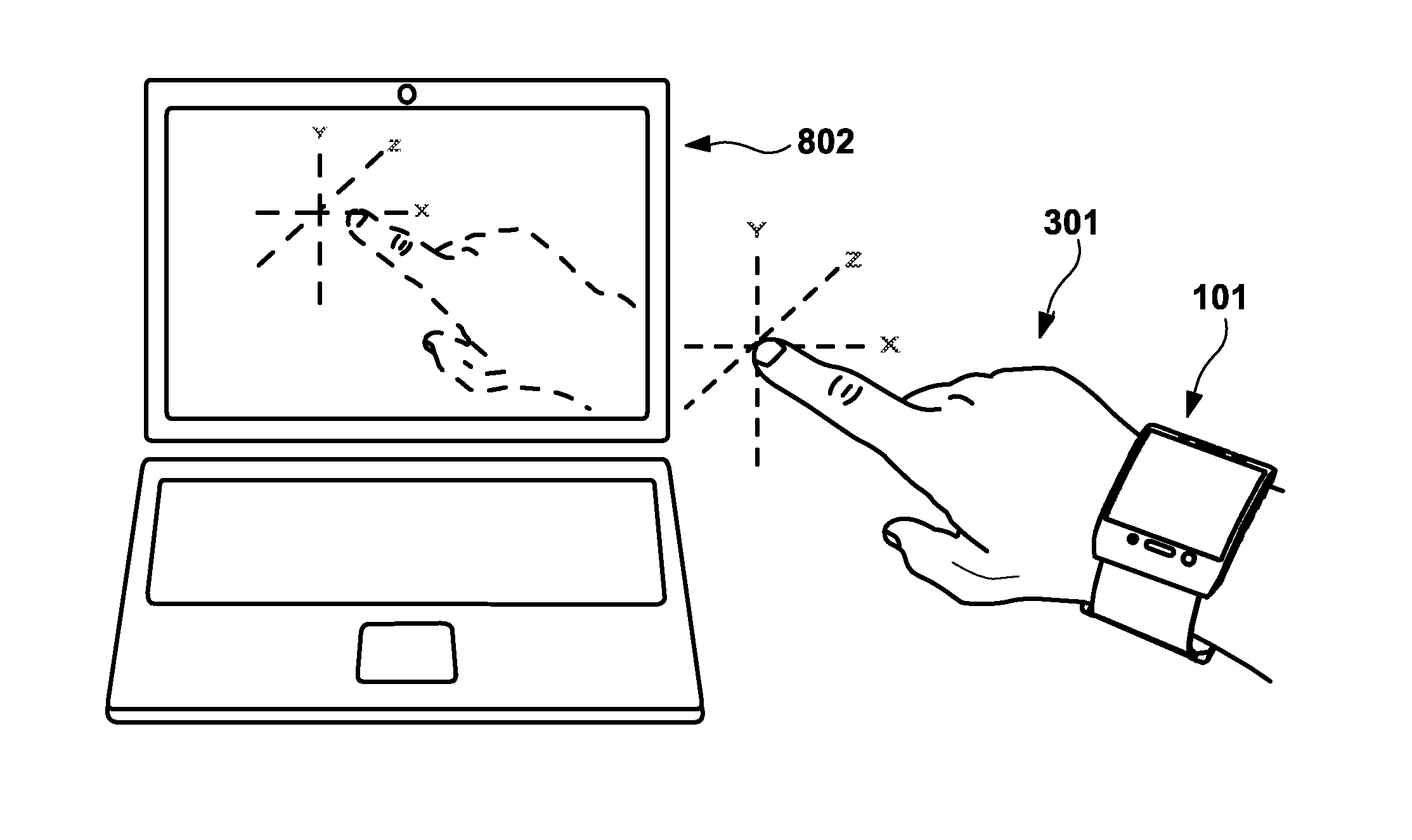
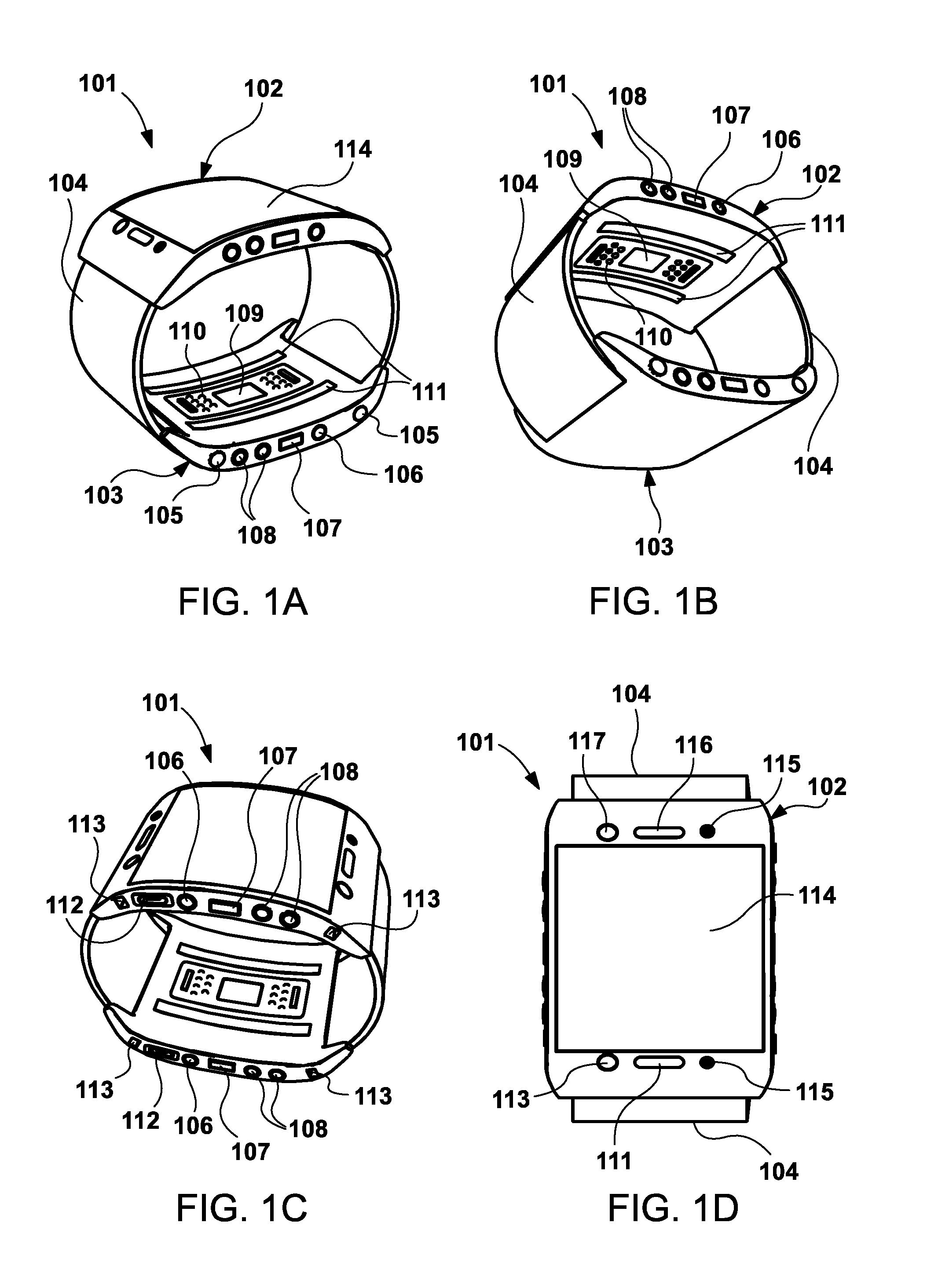
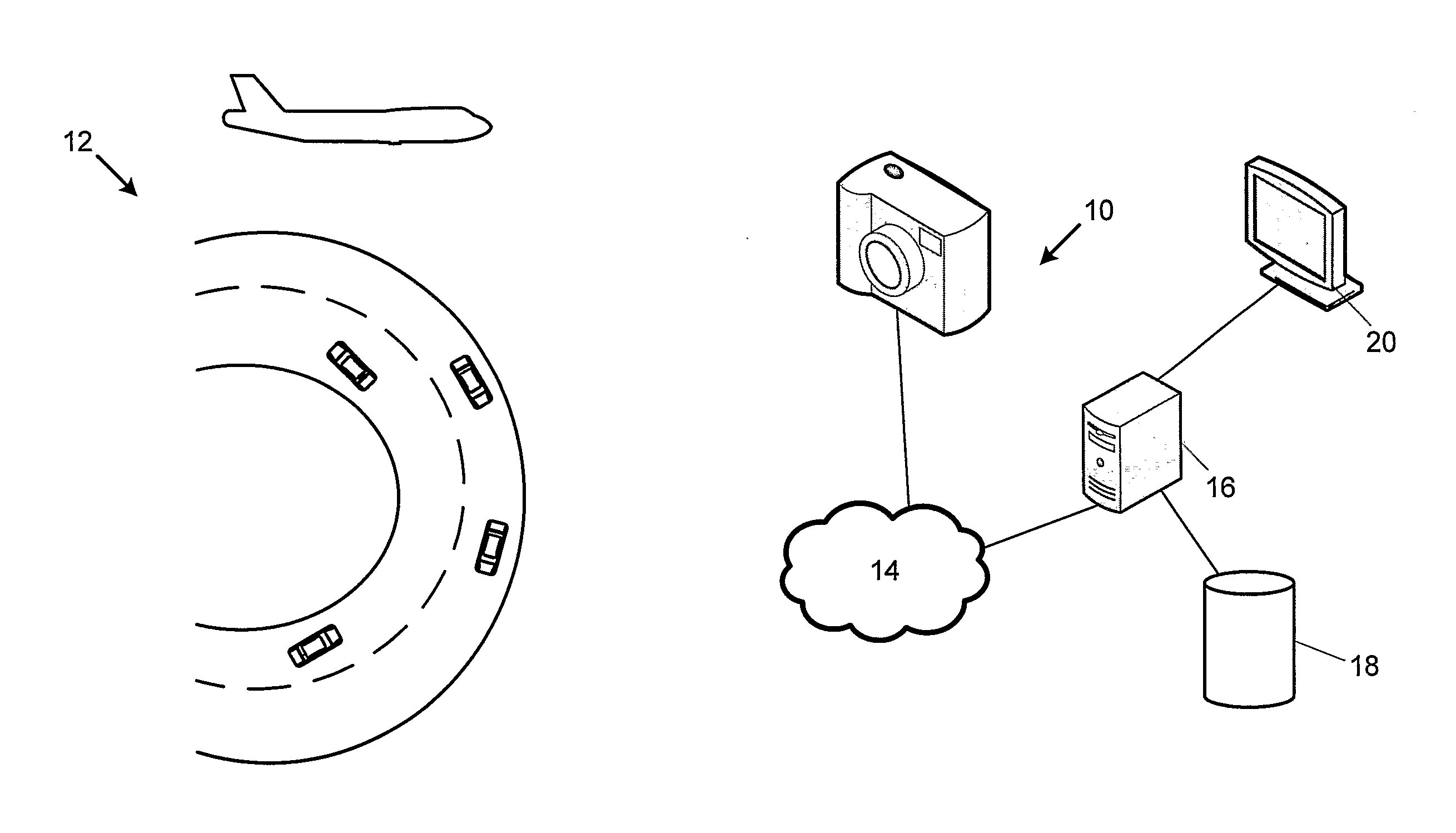
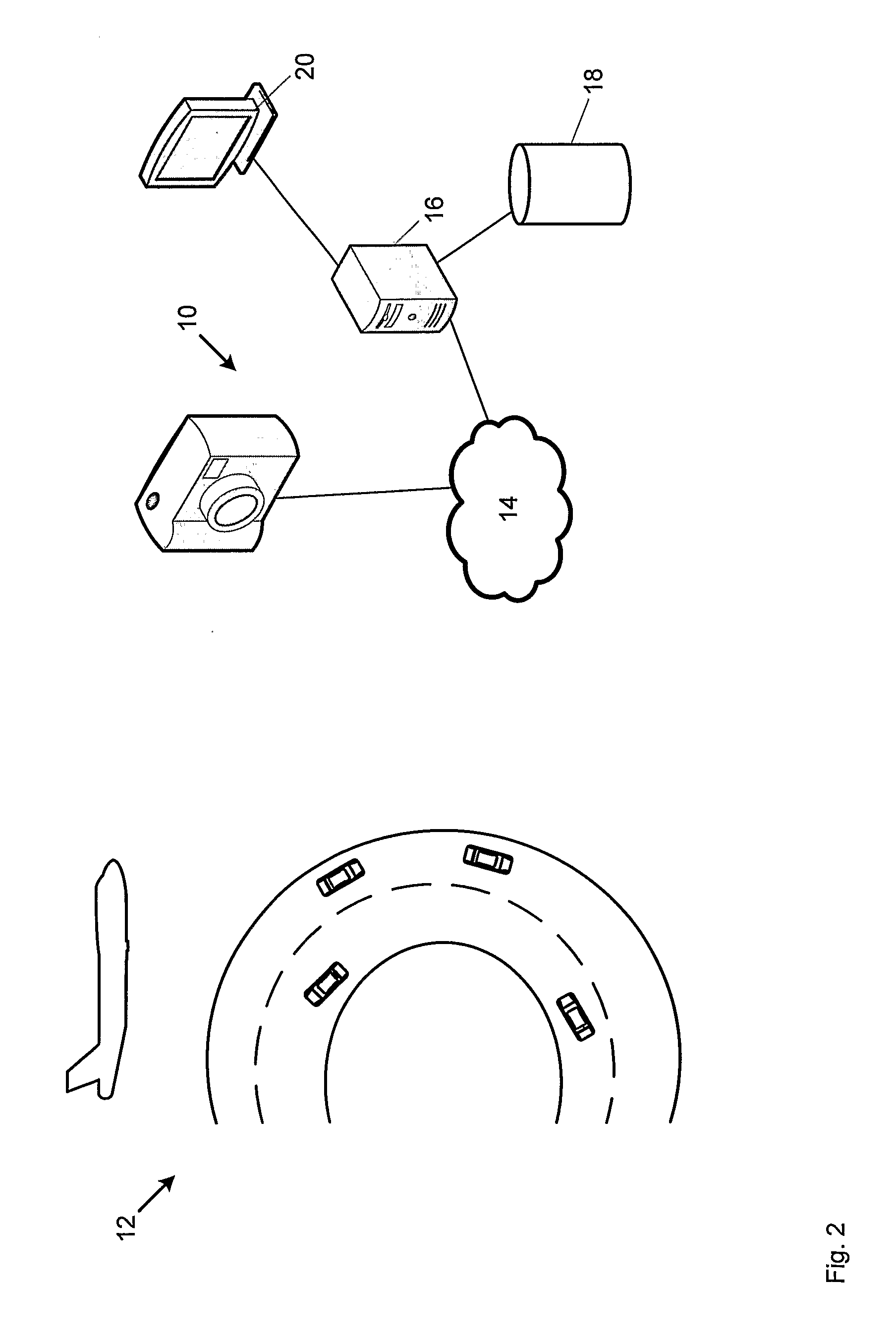
Wireless wrist computing and control device and method for 3D imaging, mapping, networking and interfacing
ActiveUS20140055352A1Simple interfaceInput/output for user-computer interactionInertial sensorsGraphicsControl system
An apparatus and method for light and optical depth mapping, 3D imaging, modeling, networking, and interfacing on an autonomous, intelligent, wearable wireless wrist computing, display and control system for onboard and remote device and graphic user interface control. Embodiments of the invention enable augmentation of people, objects, devices and spaces into a virtual environment and augmentation of virtual objects and interfaces into the physical world through its wireless multimedia streaming and multi-interface display and projection systems.
Owner:EYECAM INC
Optical method and system for extended depth of focus
ActiveUS7061693B2Increase depth of focusEliminate needIntraocular lensOptical partsOptical propertyImaging lens
An imaging arrangement and method for extended the depth of focus are provided. The imaging arrangement comprises an imaging lens having a certain affective aperture, and an optical element associated with said imaging lens. The optical element is configured as a phase-affecting, non-diffractive optical element defining a spatially low frequency phase transition. The optical element and the imaging lens define a predetermined pattern formed by spaced-apart substantially optically transparent features of different optical properties. Position of at least one phase transition region of the optical element within the imaging lens plane is determined by at least a dimension of said affective aperture.
Owner:BRIEN HOLDEN VISION INST (AU)
Optical method and system for extended depth of focus
ActiveUS7365917B2Increase depth of focusEliminate needSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensOptical propertyImaging lens
An imaging arrangement and method for extended the depth of focus are provided. The imaging arrangement comprises an imaging lens having a certain affective aperture, and an optical element associated with said imaging lens. The optical element is configured as a phase-affecting, non-diffractive optical element defining a spatially low frequency phase transition. The optical element and the imaging lens define a predetermined pattern formed by spaced-apart substantially optically transparent features of different optical properties. Position of at least one phase transition region of the optical element within the imaging lens plane is determined by at least a dimension of said affective aperture.
Owner:BRIEN HOLDEN VISION INST (AU)
Method and apparatus for high resolution coherent optical imaging
InactiveUS7242833B2Simple device designGood for high speed operationSurgeryScattering properties measurementsOptical radiationOptical depth
A method and an apparatus for examining the subsurface microstructure of a sample are provided. Radiation from a plurality of optical radiation sources travels along a first optical path. In the first optical path, a device focuses the optical radiati n from each of the optical sources into a plurality of respective focal points along the first optical path to provide substantially continuous coverage of a selected portion of the first optical path. Then, a sample on the first optical path within the selected length extending into the sample is scanned along said selected portion of the first optical path.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
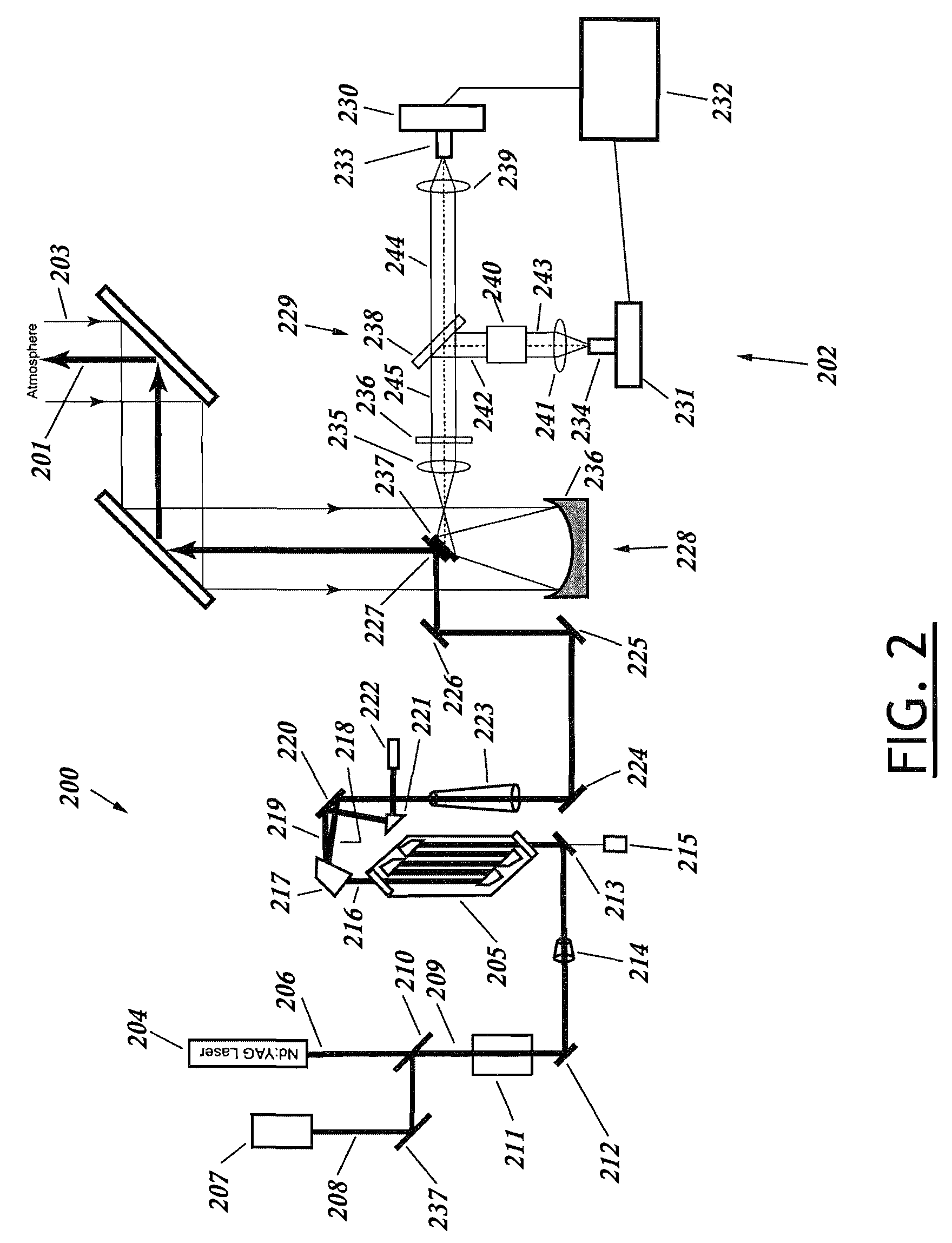
Lidar system for remote determination of calibrated, absolute aerosol backscatter coefficients
ActiveUS7656526B1Effort directedSafely and quickly and efficiently identifyRaman scatteringParticle size analysisBeam splitterAerosol backscatter
A lidar system capable of remotely identifying calibrated absolute aerosol backscatter coefficients of atmospheric aerosol particles by transmitting a beam of light and spectrally separating the intensity of Rayleigh and Mie backscattering is disclosed. The transmitter features high pulse energy to generate sufficient Rayleigh backscattering, enabling atmospheric scanning in a timely manner. The transmitter employs a seeded Nd:YAG laser and a seeded stimulated Raman scattering wavelength shifter to achieve narrow bandwidth, eye-safe laser pulses. The receiver employs a telescope, collimating lens, beam splitter, molecular absorption filter, focusing lenses, and avalanche photodiodes. Mie backscattering is blocked by the molecular absorption filter to provide a Rayleigh signal, which is used with knowledge of atmospheric density to calibrate the Mie signal. The system is intended for atmospheric research and aerosol monitoring applications where calibrated Mie scattering intensity is necessary to measure the optical depths of aerosol structures such as plumes, clouds, and layers.
Owner:UNIV FOR ATMOSPHERIC RES
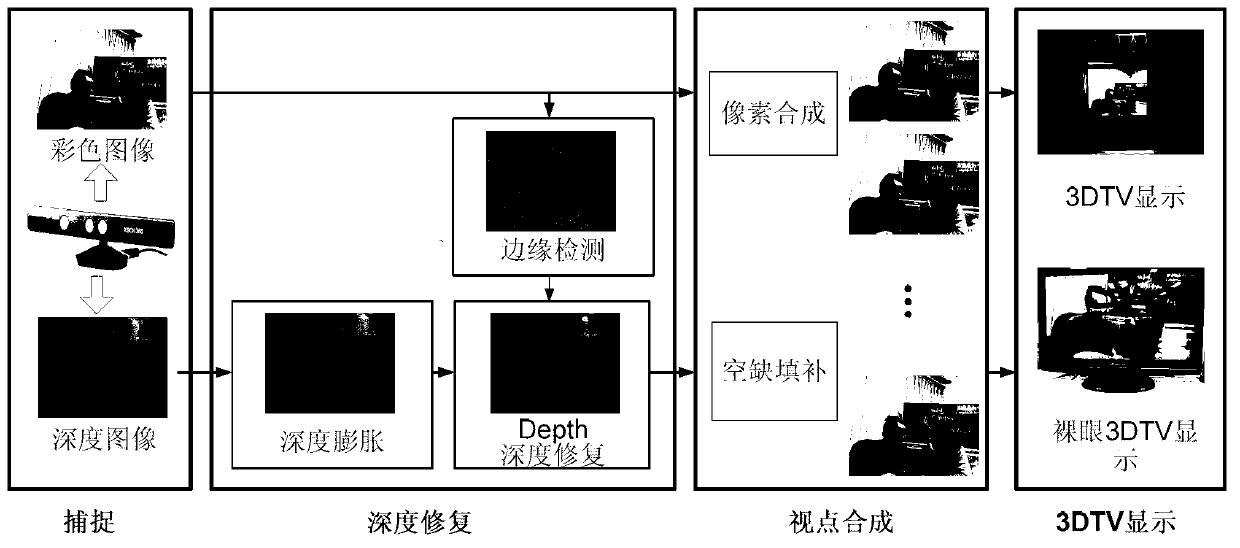
Multi-view-point computing and imaging method based on speckle-structure optical depth camera
The invention belongs to the technical field of image processing, provides a multi-view-point computing and imaging method, and aims to acquire accurate and high-precision depth information. According to the technical scheme, the multi-view-point computing and imaging method based on a speckle-structure optical depth camera comprises the following steps of: acquiring a depth map and a color map from human-machine interaction equipment Kinect of Microsoft; detecting the edge of the color map, and expanding gap information until the expanded gap covers the edge, which corresponds to the color map, near the conventional depth map; then performing double-edge filtration estimation on points on the edge of the gap according to depth information and color information; limiting the estimation process by virtue of edge information of the color map; and after the color map and the restored depth map are acquired, converting the depth map into a disparity map, and synthesizing any number of virtual viewpoint maps by a disparity map synthesis method combining a depth image and a color image. The multi-view-point computing and imaging method is mainly applied to image processing.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
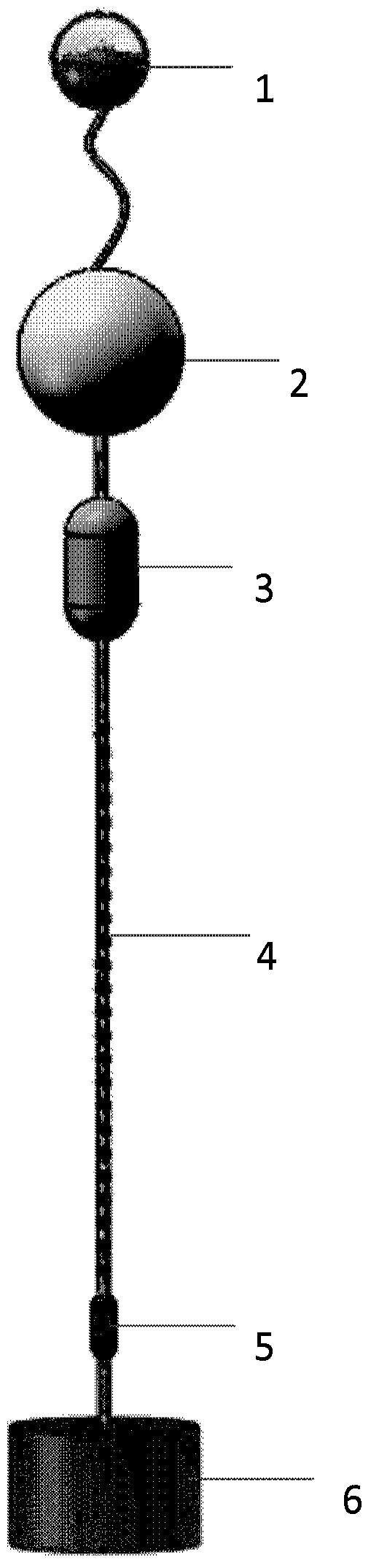
Optical fiber temperature-depth diving mark continuous measuring system
ActiveCN103759717AScientific and reasonable designHigh spatio-temporal resolutionMeasuring open water depthThermometers using physical/chemical changesSea temperatureBuoy
The invention relates to marine hydrology parameter monitoring, and particularly discloses an optical fiber temperature-depth diving mark continuous measuring system. The system comprises a communication buoy, a main floating ball, an instrument bin, a demodulating system, a temperature-depth chain, a mooring rope, an acoustical releaser and an anchoring weight, wherein the communication buoy comprises a solar cell, a big dipper communication plate card and a satellite combined antenna; the demodulating system comprises a demodulation module and a lithium battery and is arranged in the instrument bin, and the temperature-depth chain integrates a temperature sensor and a pressure sensor for measuring temperature and pressure, and the communication buoy, the main floating ball, the instrument bin, the temperature-depth chain, the releaser and the anchoring weight are successively connected through the mooring rope. The optical depth diving mark continuous measuring system provided by the invention has the advantages that the high density, real time, continuation and long-term observation of a temperature-depth vertical section from a sea surface to 500m underwater are realized, the data is exact and reliable, and the economic benefit is high; the optical fiber temperature-depth diving mark continuous measuring system is widely applied in different marine observation operations and provides a novel observation means for measuring sea temperature-depth.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
View point detecting device
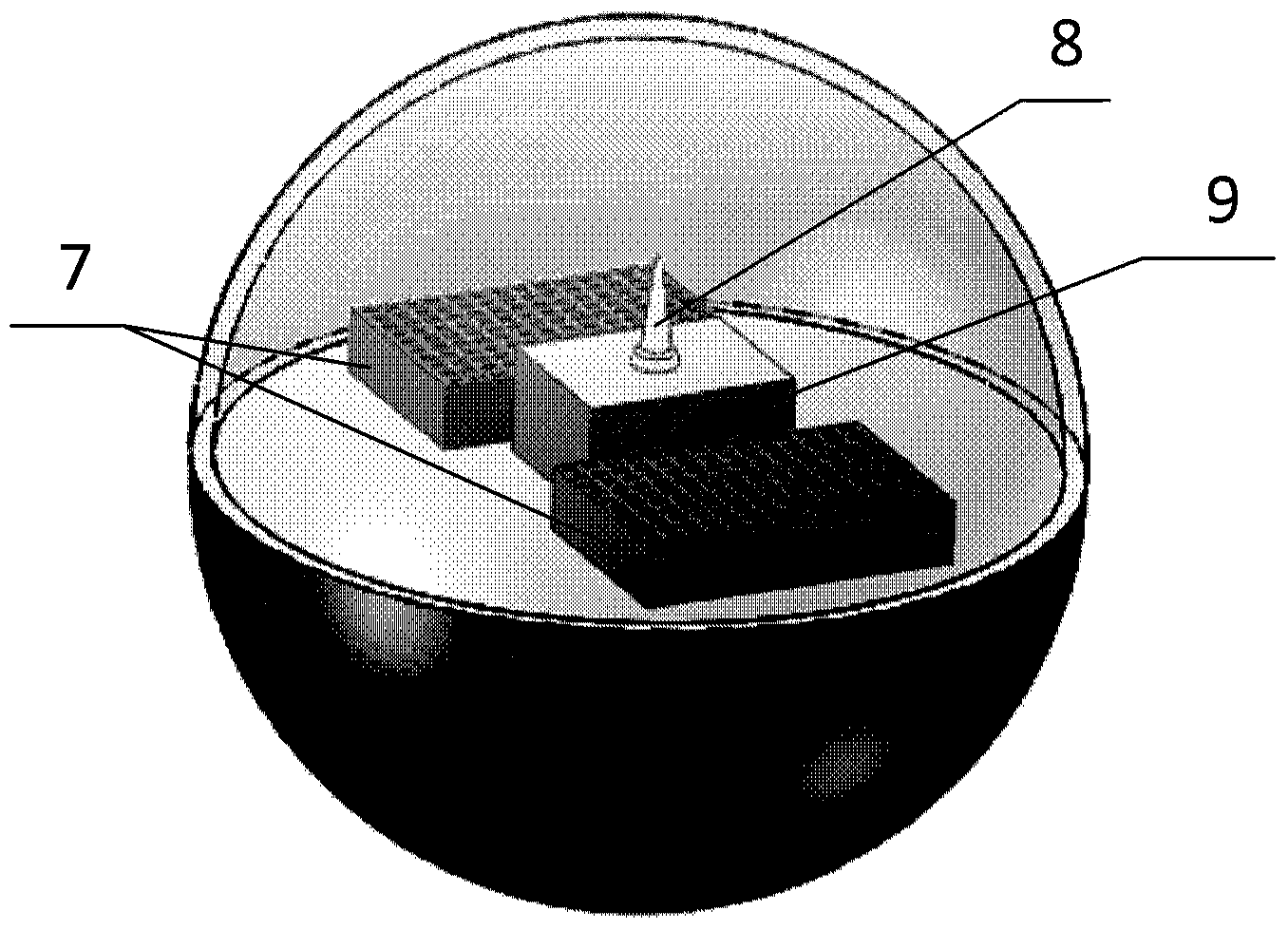
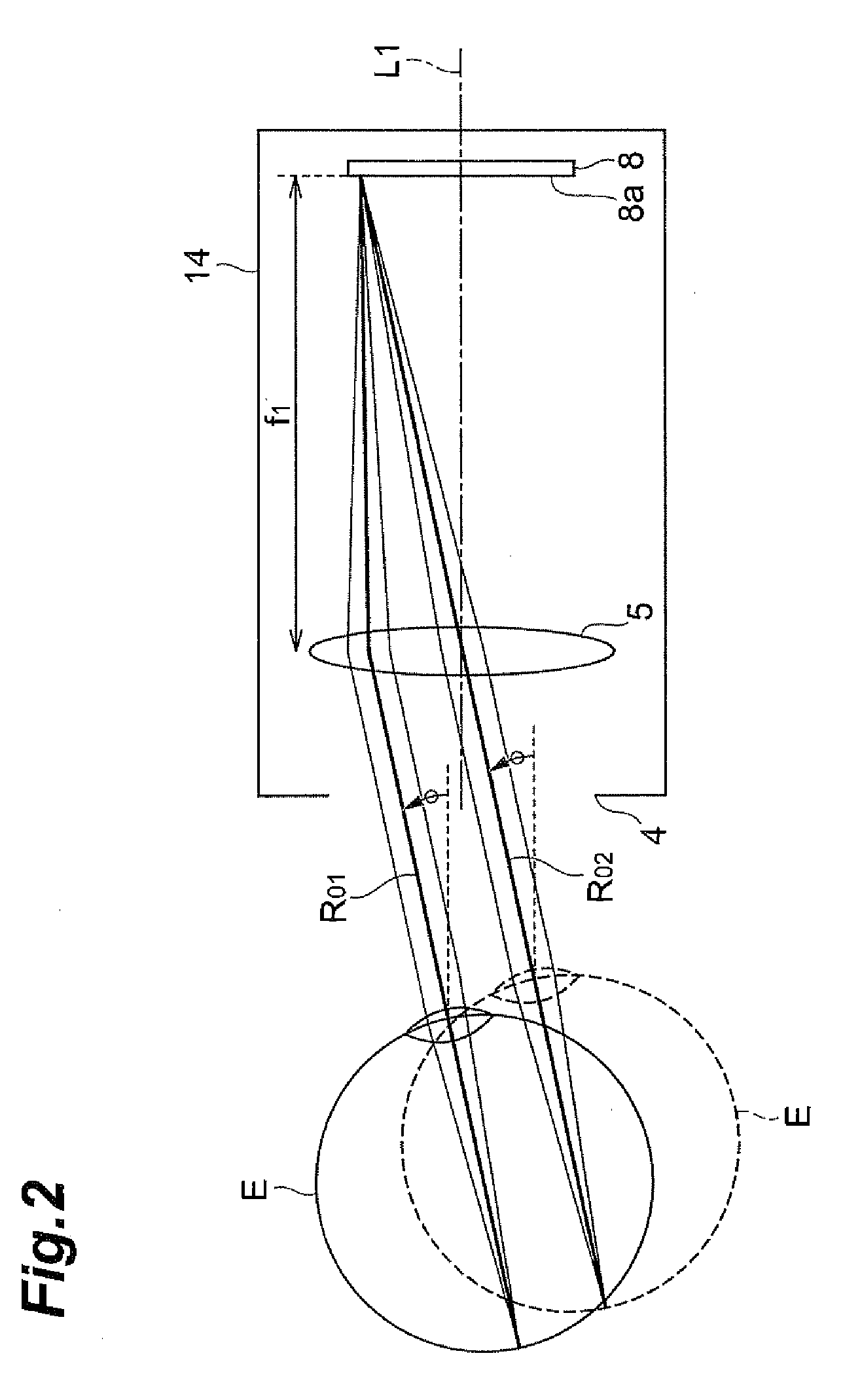
InactiveUS20090219484A1High precisionMaintain convenienceEye diagnosticsInput/output processes for data processingOptical depthComputer science
A gaze point detecting device 1 detects a gaze point of an object person by projecting a display image displayed by an LCD 8 to outside via a finder 4 and capturing an eye image of the object person by a CCD 11 in response to illumination light irradiated toward outside from the finder 4, and the device comprises an optical system 5 arranged spaced only a focal length apart from a display surface 8a on an optical path of an image displaying optical system between the LCD 8 and the finder 4; the optical system 5 being arranged on an optical path of an imaging optical system between the finder 4 and the CCD 11; a telecentric optical system including a diaphragm 9 arranged spaced only a focal length apart from the optical system 5 on the optical path; and a controller 3 that detects a position of the gaze point of the object person based on the eye image captured by the CCD 11.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP SHIZUOKA UNIV
Method and apparatus to project image on retina at various focal depths utilizing flexible substrate containing optical array
The current invention relates to the method to achieve artificial vision with using flexible substrate based light emitting arrays, or optical passage arrays, to project image upon the retina of a human eye. Further, it relates to the method to detect the real-time focal length change of the eye-lens and modify the flexible substrate curvature and distance from the eye to vary global angle configurations of light beams that go into the eye to produce images on the retina at various focus depth of the eye to achieve re-focusable artificial vision.
Owner:ZHOU YUCHEN
Scanning ir sensor for gas safety and emissions monitoring
ActiveUS20180266944A1More reliableLess expensiveMass flow measurement devicesRaman/scattering spectroscopyConfocalOptical depth
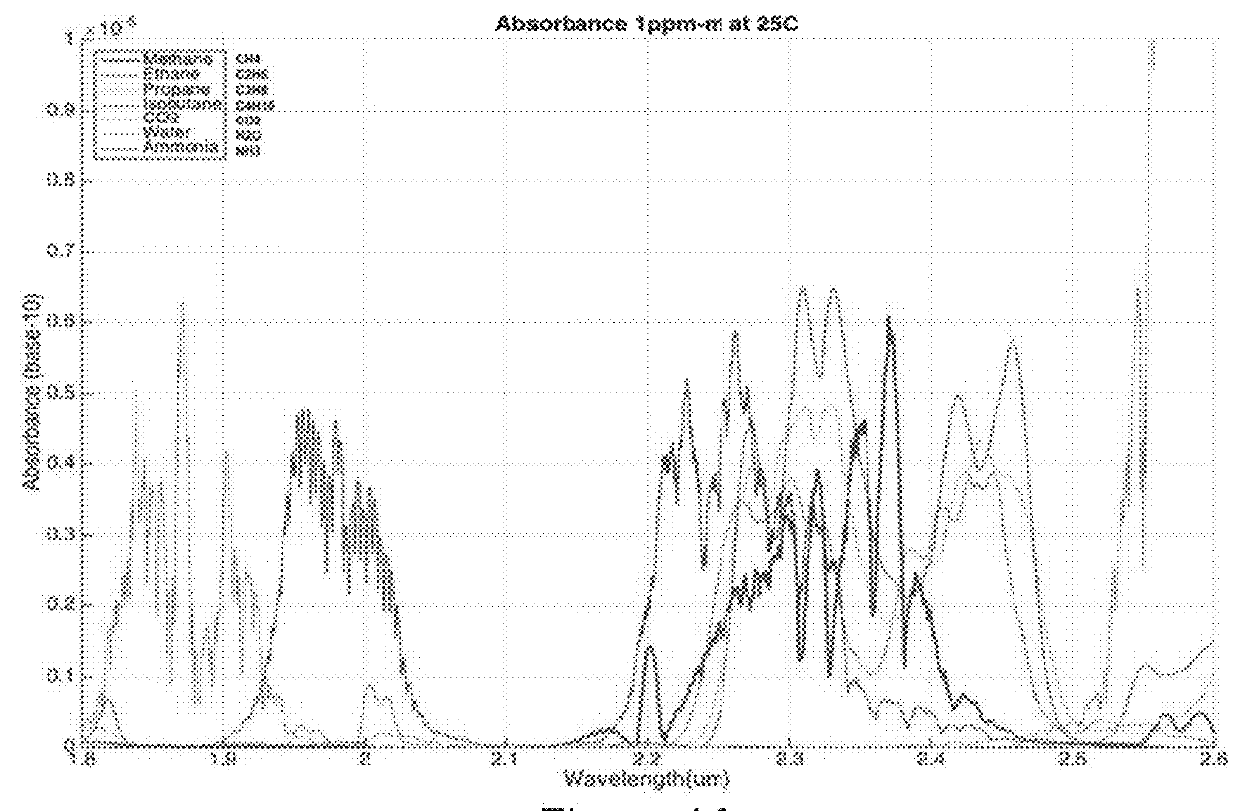
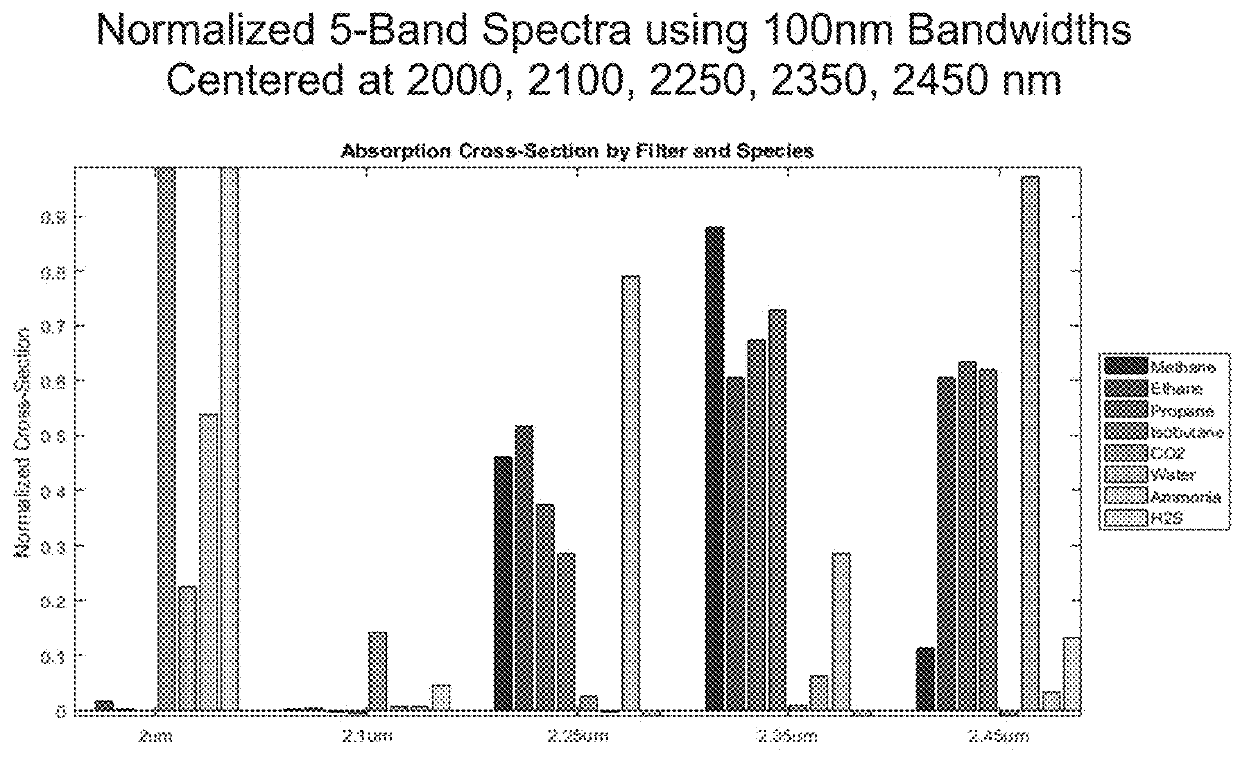
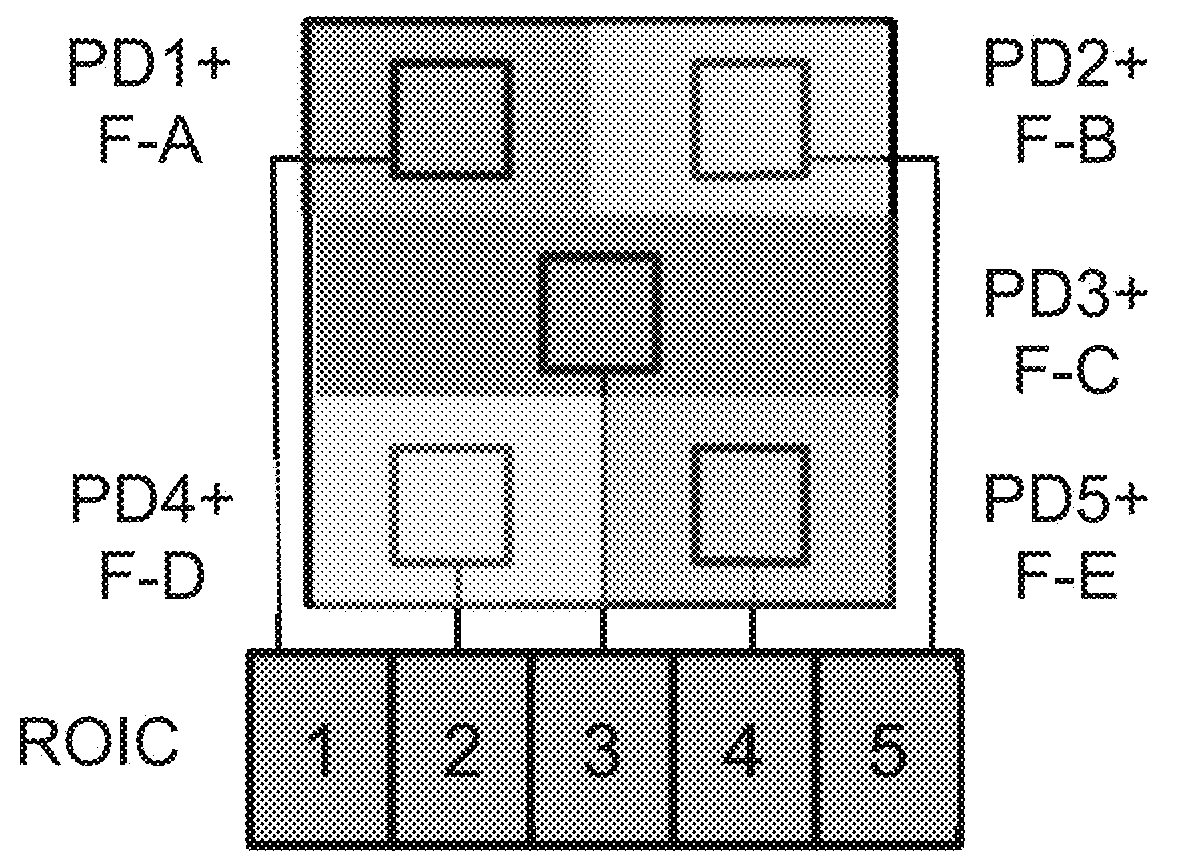
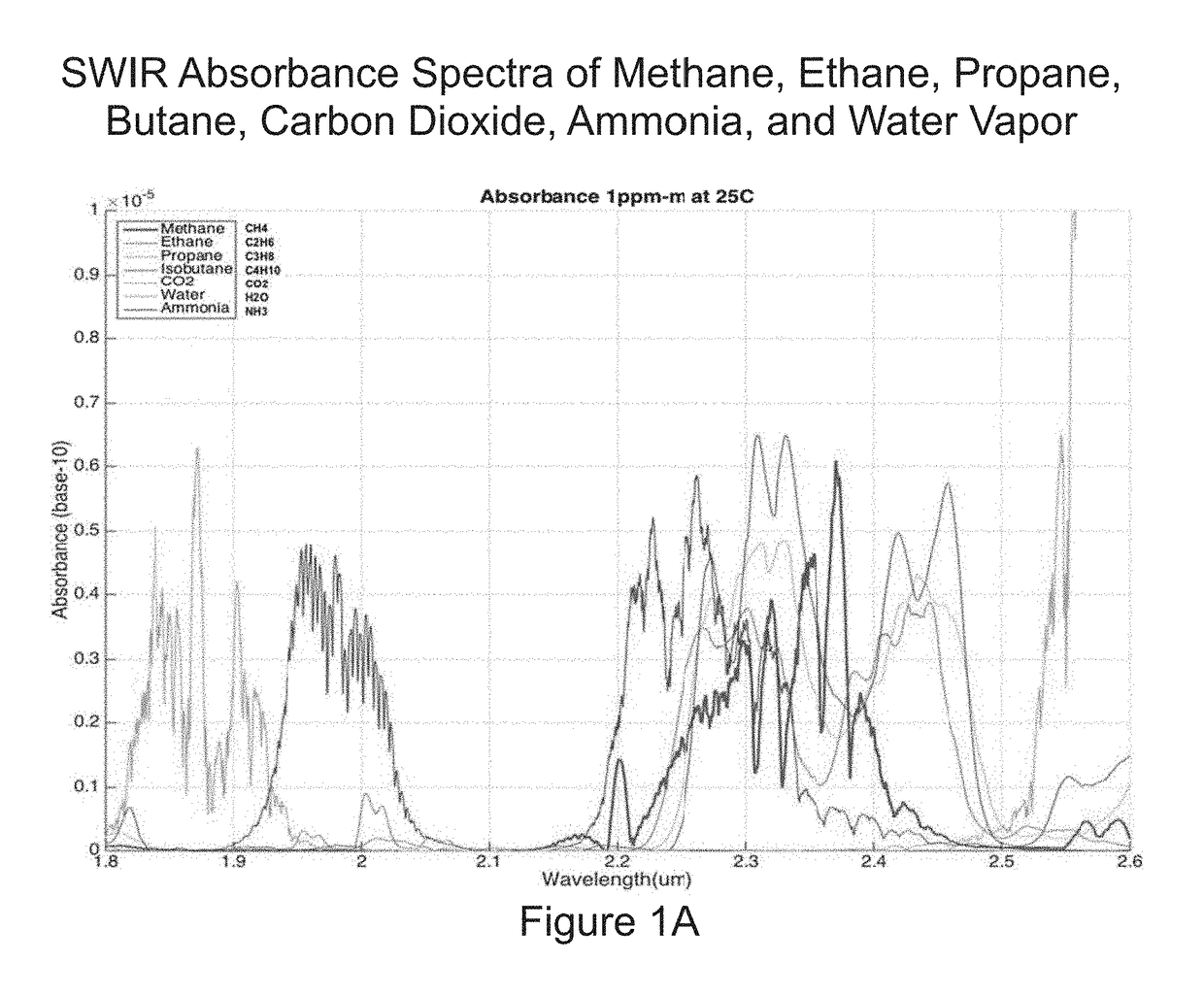
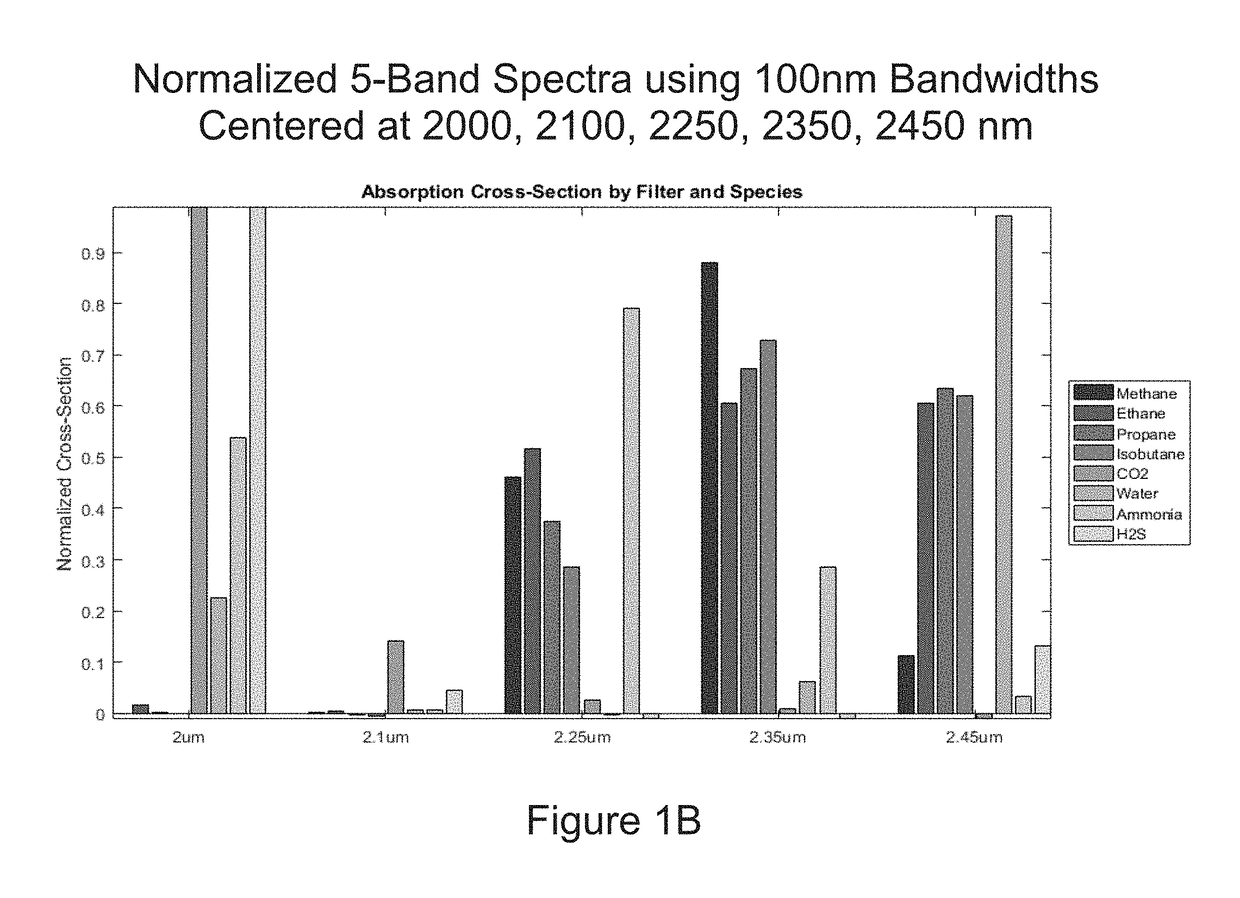
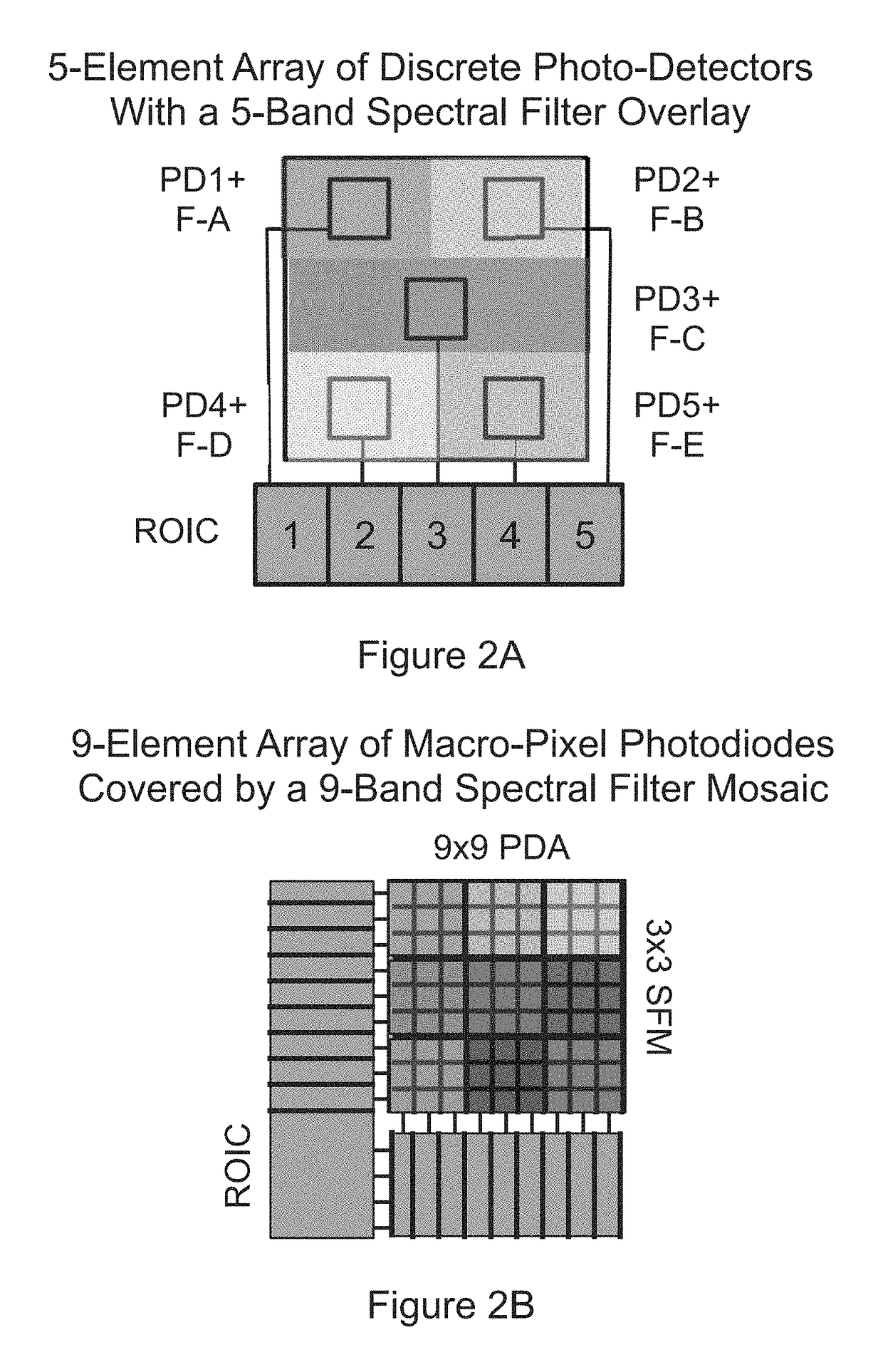
Apparatus and methods for rapidly detecting, localizing, imaging, and quantifying leaks of natural gas and other hydrocarbon and greenhouse gases. Scanning sensors, scan patterns, and data processing algorithms enable monitoring a site to rapidly detect, localize, image, and quantify amounts and rates of hydrocarbon leaks. Multispectral short-wave infrared detectors sense non-thermal infrared radiation from natural solar or artificial illumination sources by differential absorption spectroscopy. A multispectral sensor is scanned to envelop an area of interest, detect the presence and location of a leak, and raster scan the area around the leak to create an image of the leak. The resulting absorption image related to differential spectral optical depth is color mapped to render the degree of gas absorption across the scene. Analysis of this optical depth image, with factors including known inline pressures and / or surface wind speed measurements, enable estimation of the leak rate, i.e., emission mass flux of gas.
Owner:MULTISENSOR SCI INC
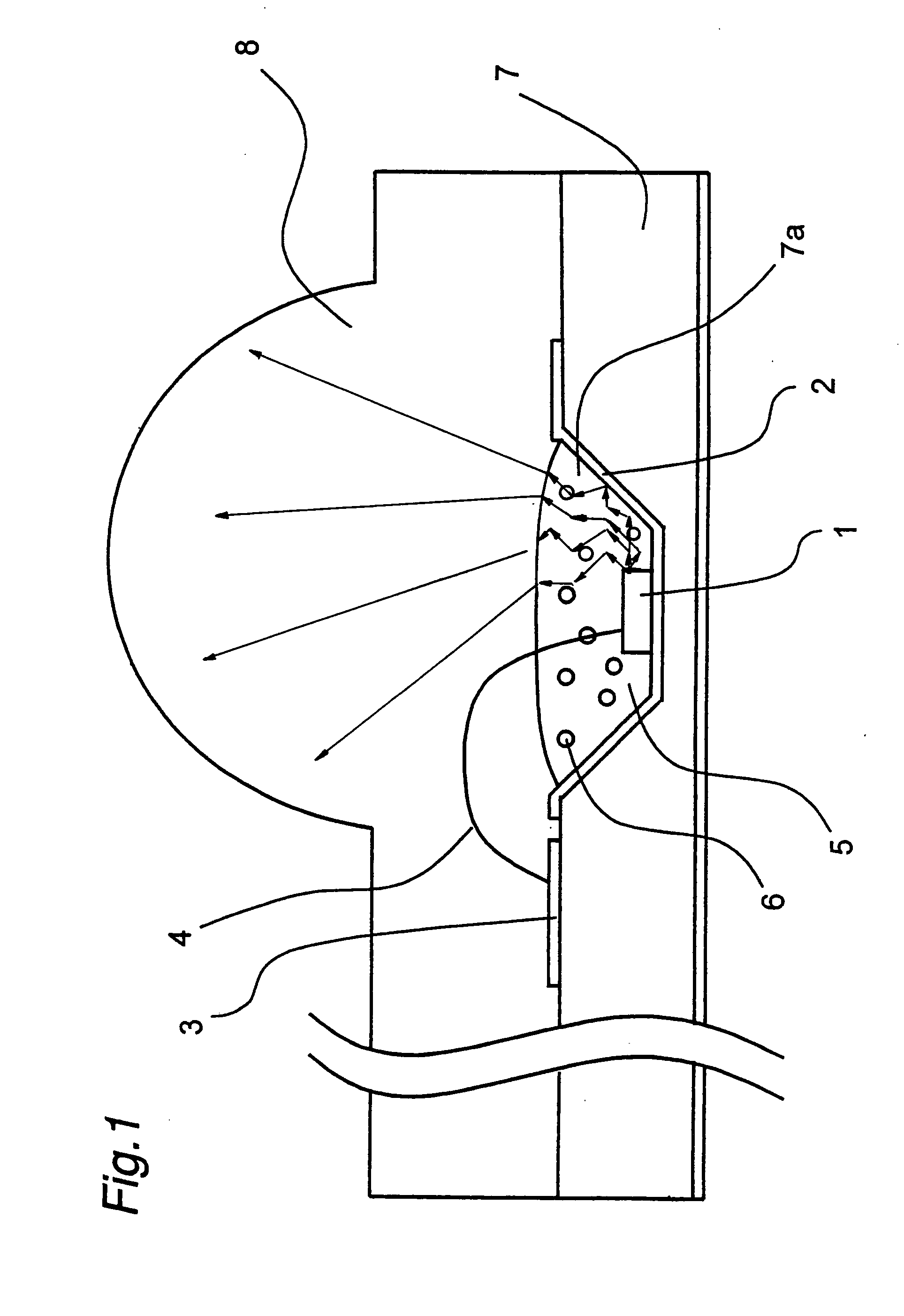
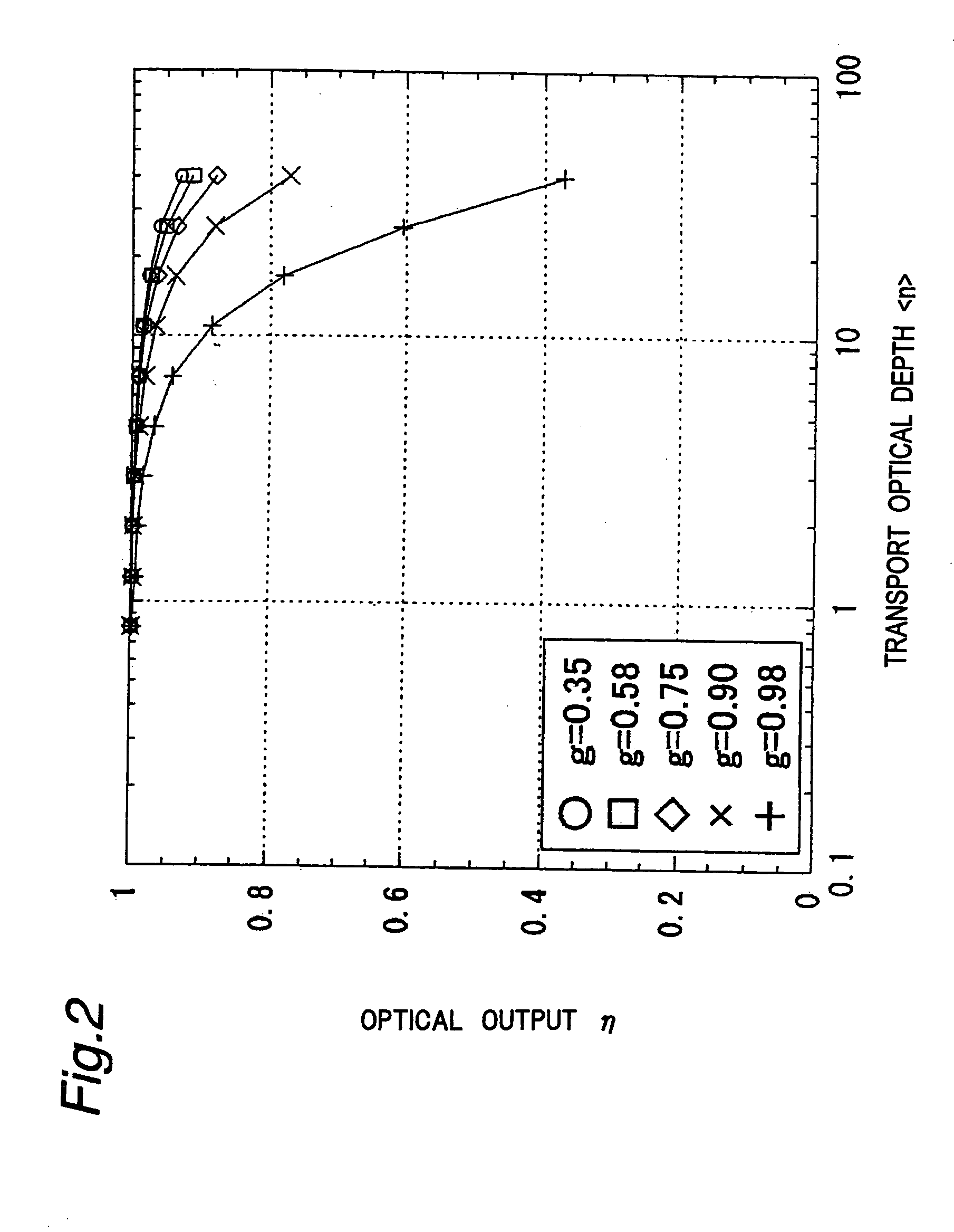
Light source apparatus and optical communication apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20050122720A1Improve communication distanceIncrease distanceSolid-state devicesFree standingOptical communicationOptical depth
A light source apparatus is provided with a light scattering region 5 containing light scattering particles 6 disposed in a part of a region extending from a semiconductor light-emitting laser chip 1 to an external space. An asymmetry factor g of the light scattering particles 6 and a transport optical depth <n> of the light scattering region 5 are set so that their product g.<n> satisfies a following condition: 2≦g·<n>≦40 The light source apparatus is of small-size and low-cost and can ensure safety of human eyes as well as obtain a high optical output.
Owner:SHARP KK
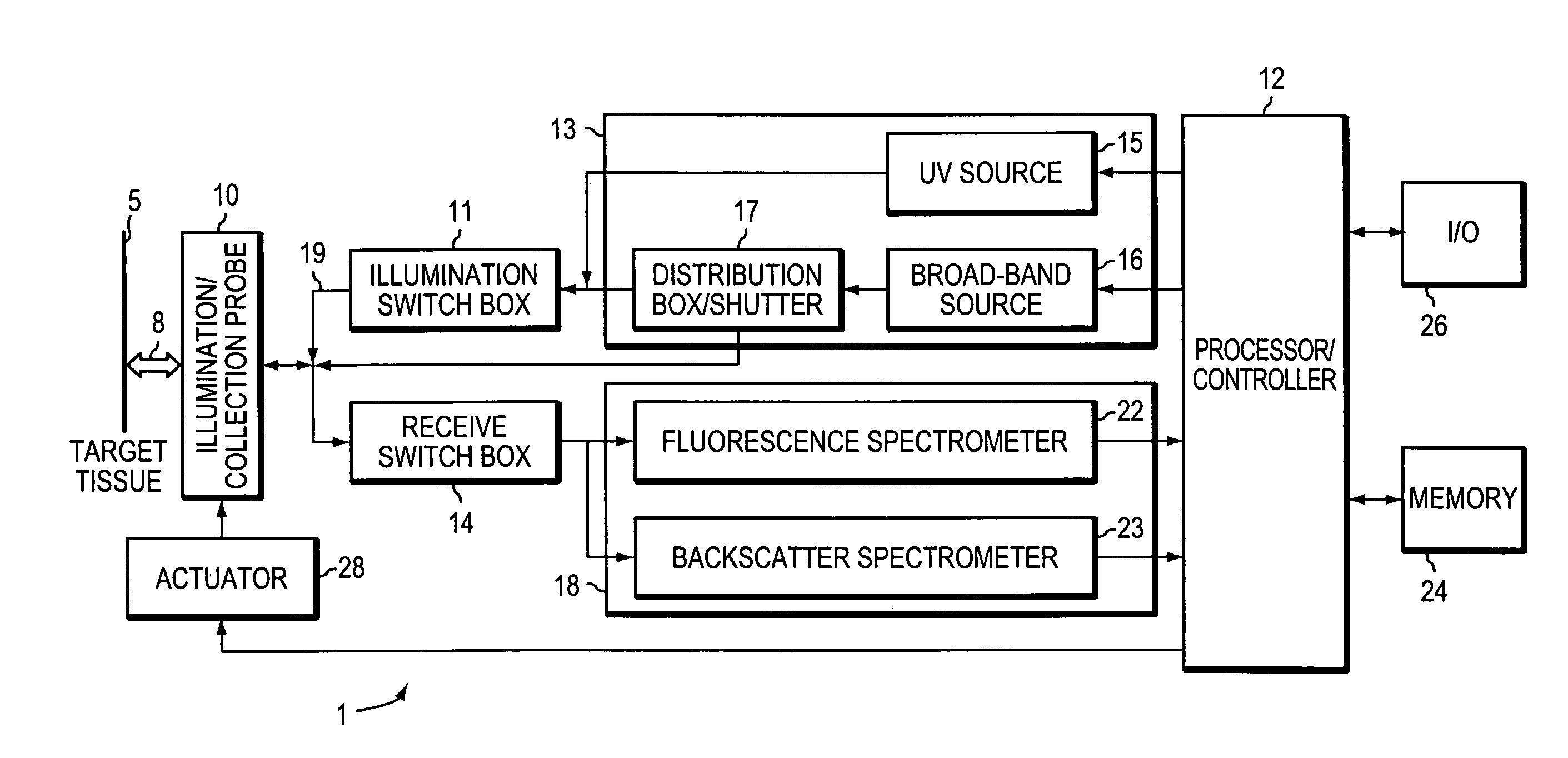
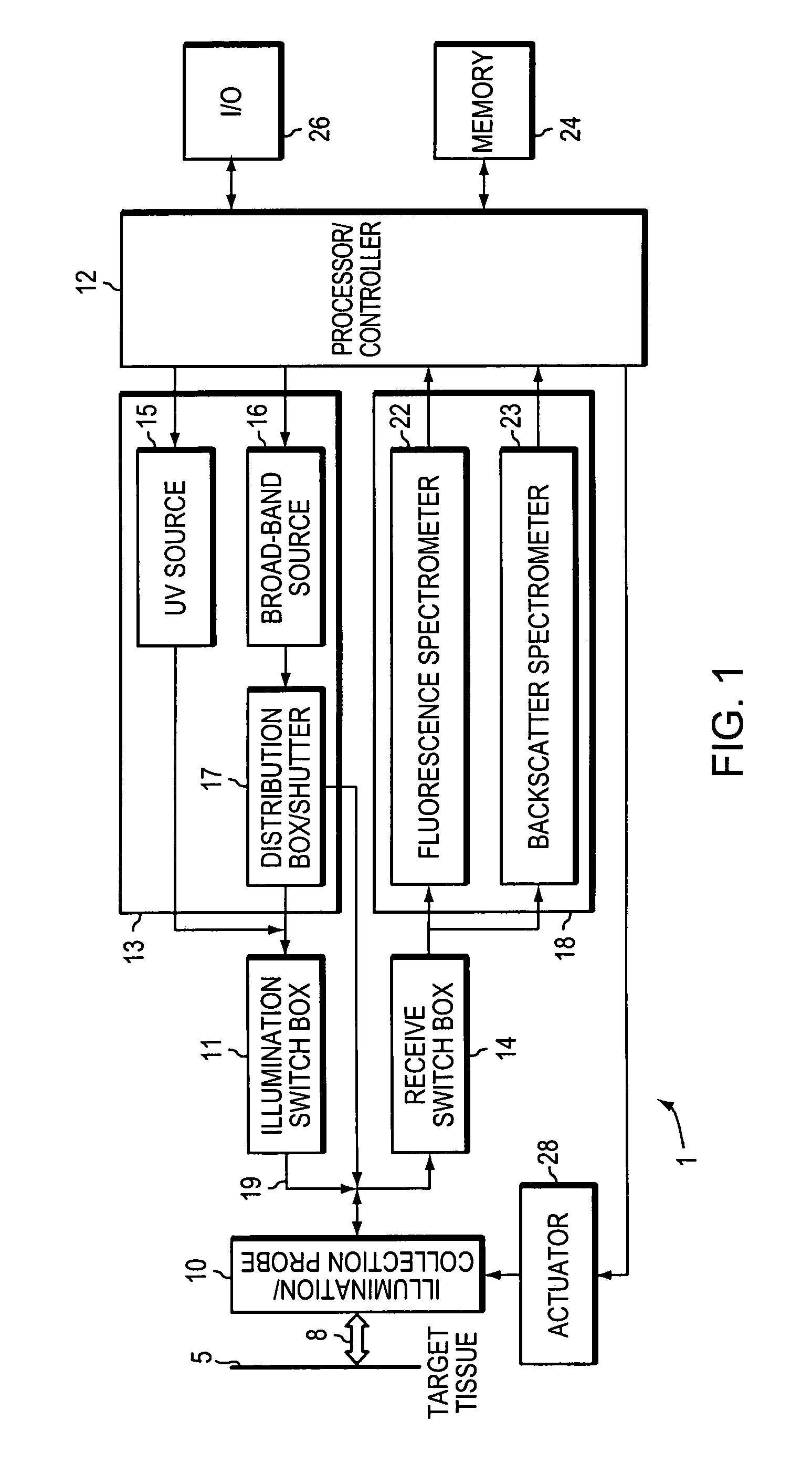
Optical methods and systems for rapid screening of the cervix
InactiveUS7127282B2Eliminate the problemDiagnostics using spectroscopySurgeryCervical tissueData set
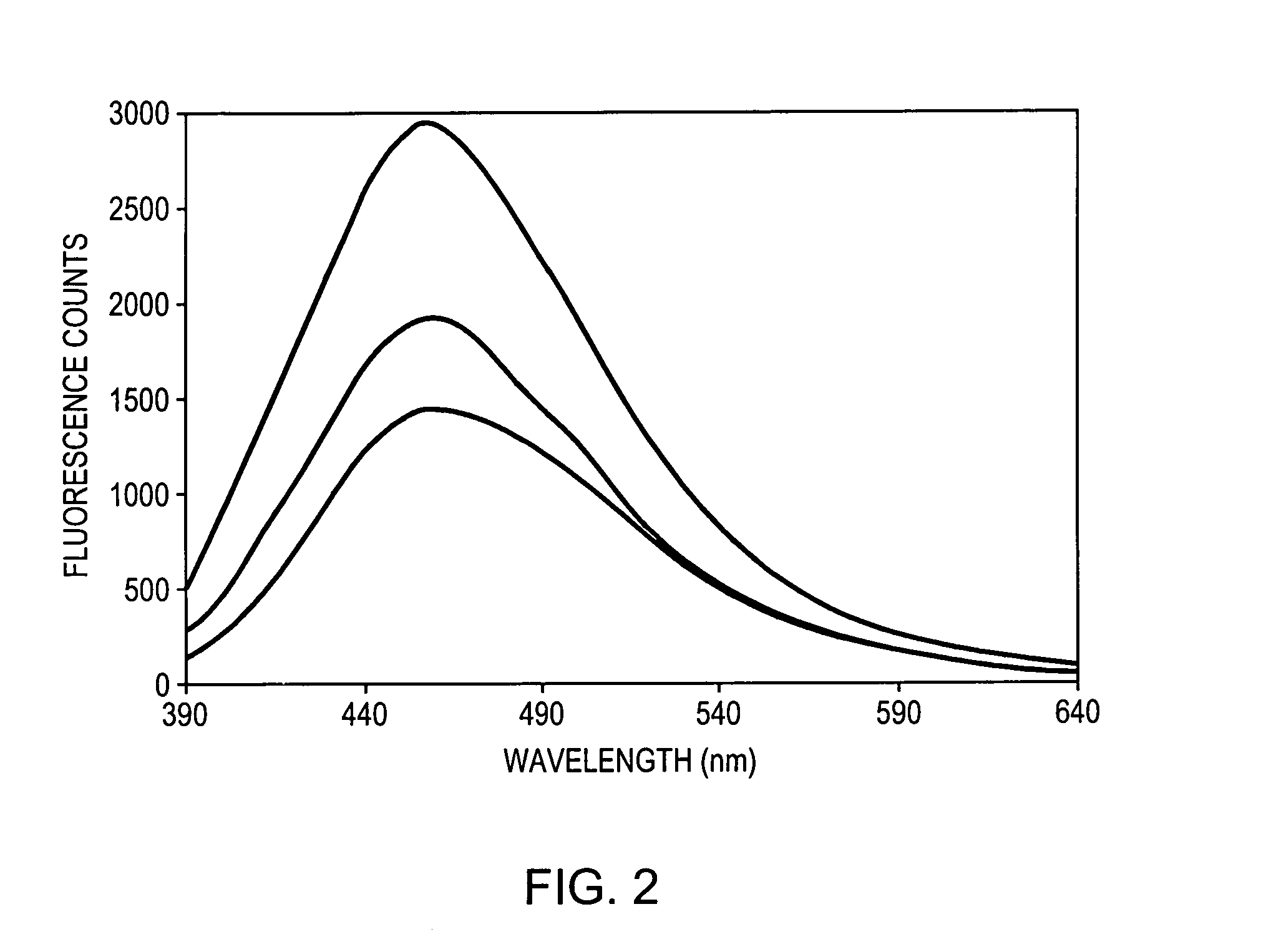
A method and a system is provided for discriminating between healthy cervical tissue and pathologic cervical tissue based on the fluorescence response of the tissue to laser excitation (LIF) and the backscatter response to illumination by white light (in the spectral range of 360 to 750 nm). Combining LIF and white light responses, as well as evaluating a spatial correlation between proximate cervical tissue sites in conjunction with a statistically significant “distance” algorithm, such as the Mahalanobis distance between data sets, can improve the discrimination between normal and abnormal tissue. The results may be displayed in the form of a map of the cervix representing the suspected pathology.
Owner:LUMA IMAGING CORP
Fluid media for bio-sensitive applications
InactiveUS20100049182A1Less sensitiveReduce riskDiagnostics using spectroscopySurgical instrument detailsFiberSpectroscopy
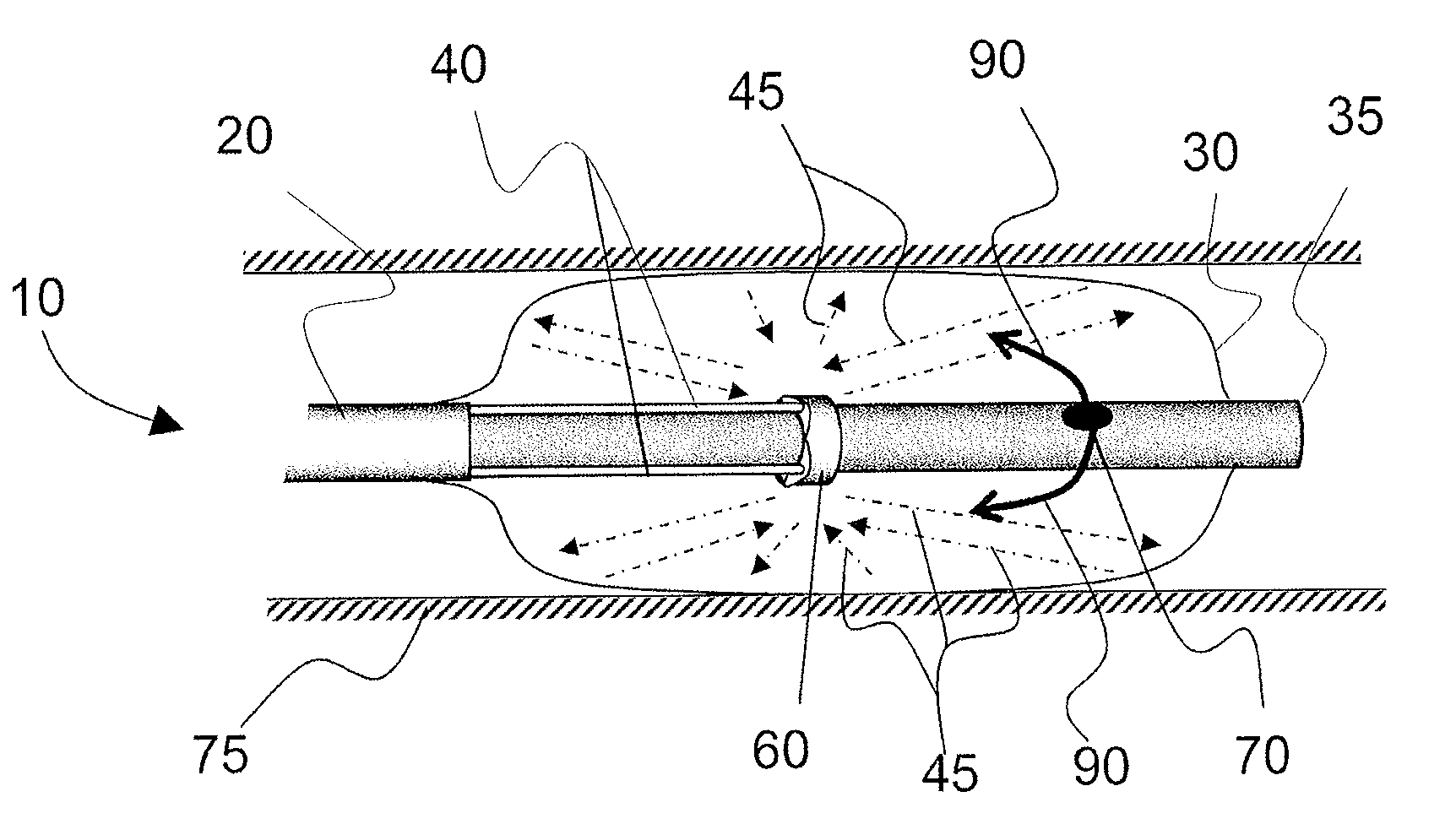
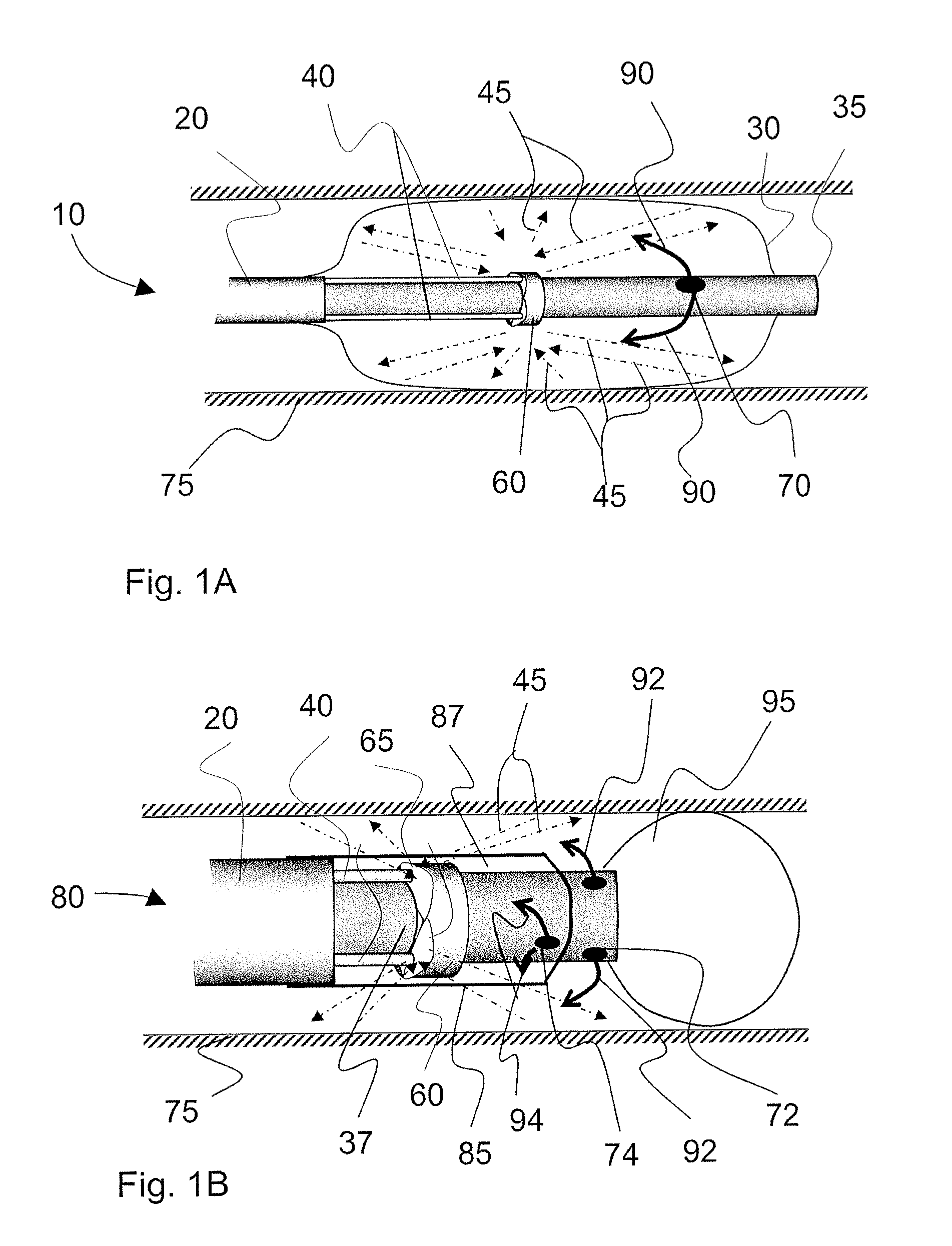
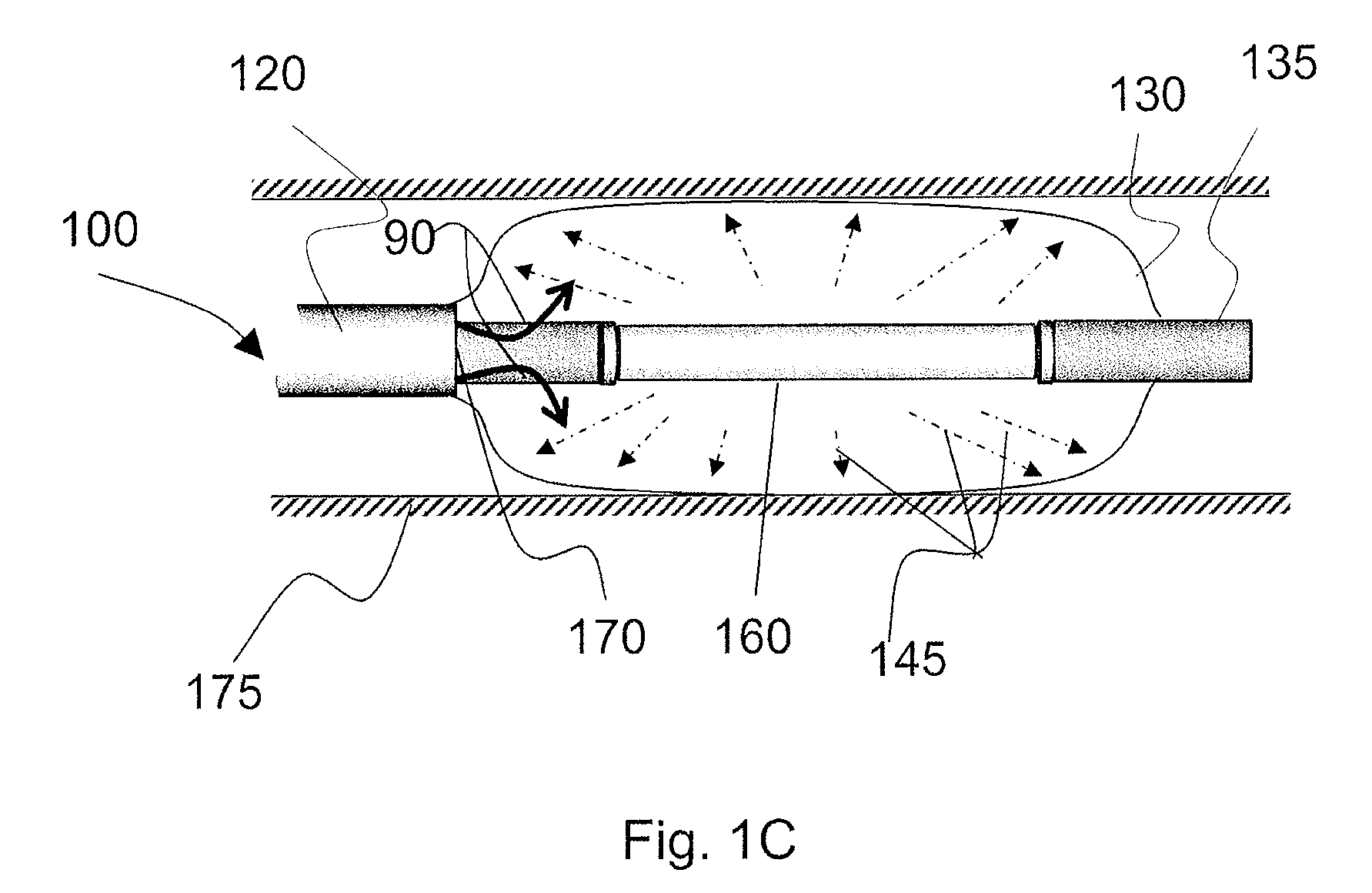
Systems, methods, and apparatus for providing a fluid and reduced-toxicity optical media with optical analysis and therapeutic energy delivery. An aspect of the invention provides an aqueous solution of increased-salinity of between about 1% and 35%. An increasing salinity in accordance with the invention provides improved transmissive efficiency at many wavelengths and less toxicity than many existing systems and methods. A catheter having integrated fibers for probing or treating internal lumens or other tissues can include a liquid-inflatable balloon or flushing mechanism using the solution for displacing blood or other obstructions in an optical path between the fiber and targeted tissue. Methods including spectroscopy can be employed with the solution for diagnosing medical conditions associated with diseased vessels or other tissues while reducing the risk of permanent damage resulting from the diagnosis. Additional applications include the deliver of therapeutic radiation externally and internally to tissues through h the solution media.
Owner:CORNOVA
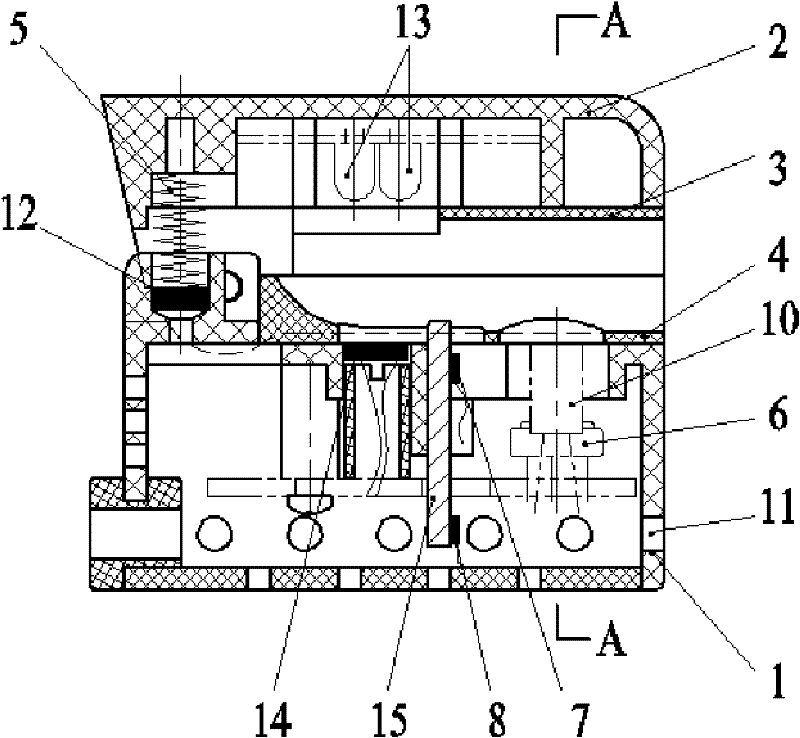
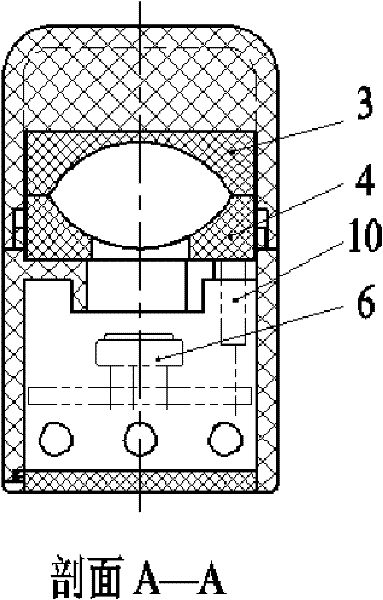
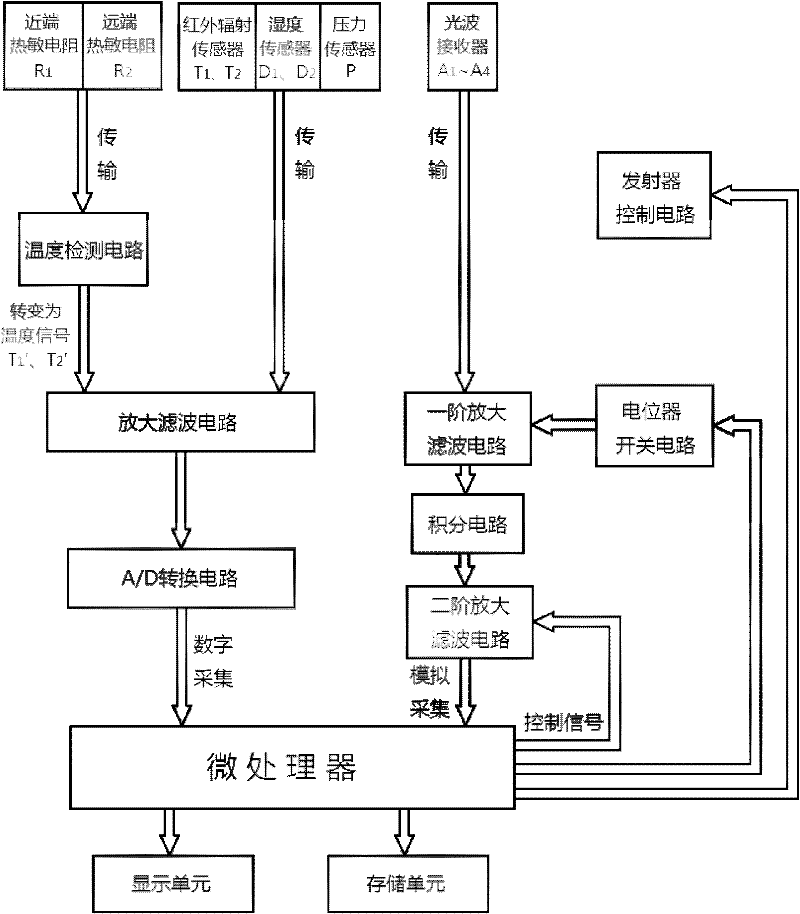
Non-invasive blood glucose detector based on metabolic heat-optical method
ActiveCN102293654AAccurate measurementIncrease profitDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBlood Glucose MeasurementRadiation sensor
The invention provides a non-invasive blood glucose detector based on a metabolic heat-optical method, and belongs to a human body blood glucose measurement device. The blood glucose detector comprises a detection probe and a data processing and displaying system, wherein the detection probe comprises a series of sensing measurement elements, such as an infrared radiation sensor, a thermistor, a humidity sensor, a light-wave receiver, a heat-conduction bar and the like, and is used for directly measuring parameters of detected positions of a human body; the data processing and displaying system comprises a microprocessor, as well as a display unit and a storage unit which are connected with the microprocessor respectively; a signal detected by the detection probe is processed by virtue of amplification filter, A / D (analog-to-digital) conversion and other modes, and then is input into the microprocessor; and the microprocessor carries out data processing according to a preset algorithm to acquire a blood glucose value detected by the detector, and displays and stores the blood glucose value. In the non-invasive blood glucose detector, a principle of combining a metabolic heat method and an optical method is adopted, so that the finally output blood glucose value has a higher reference value.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
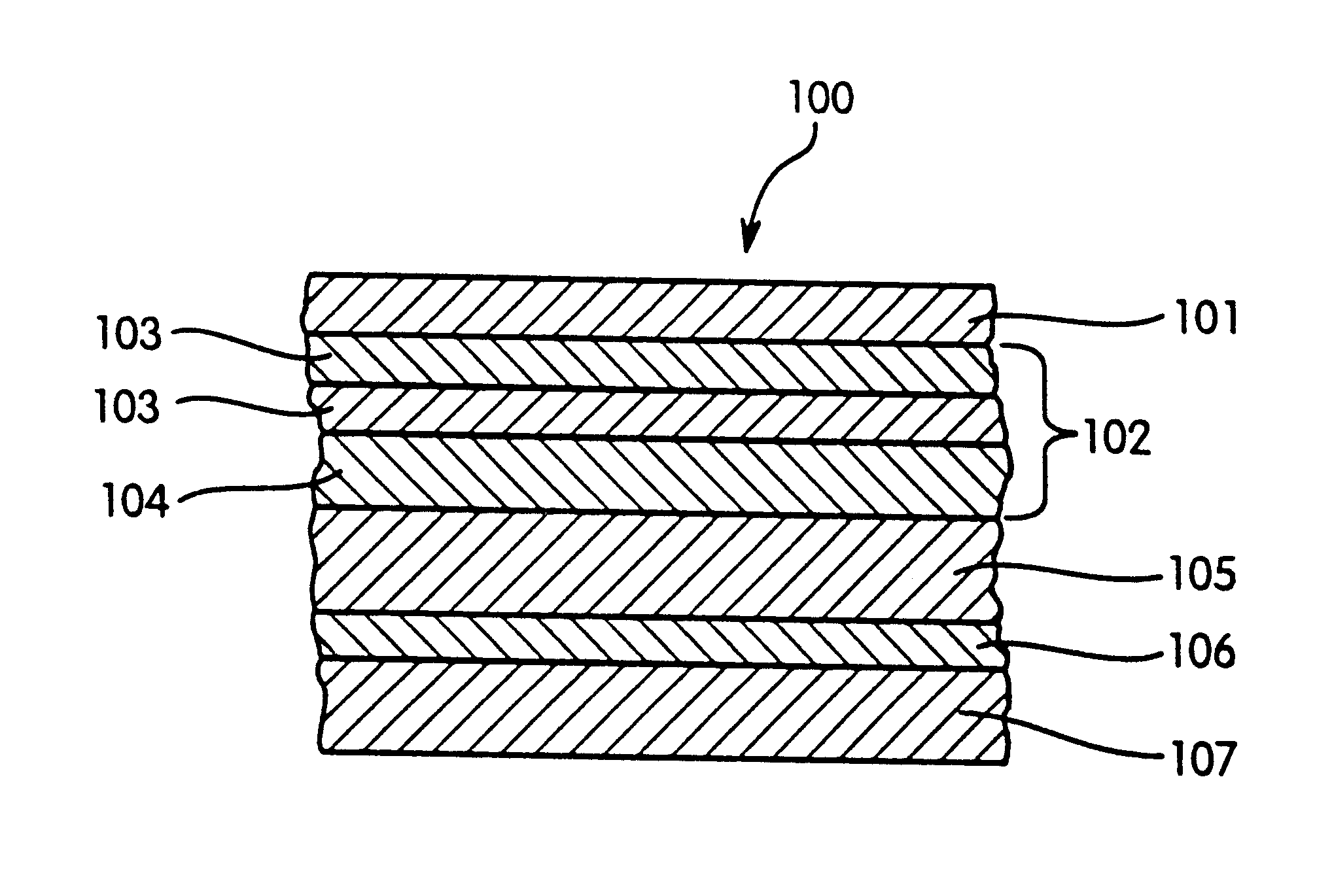
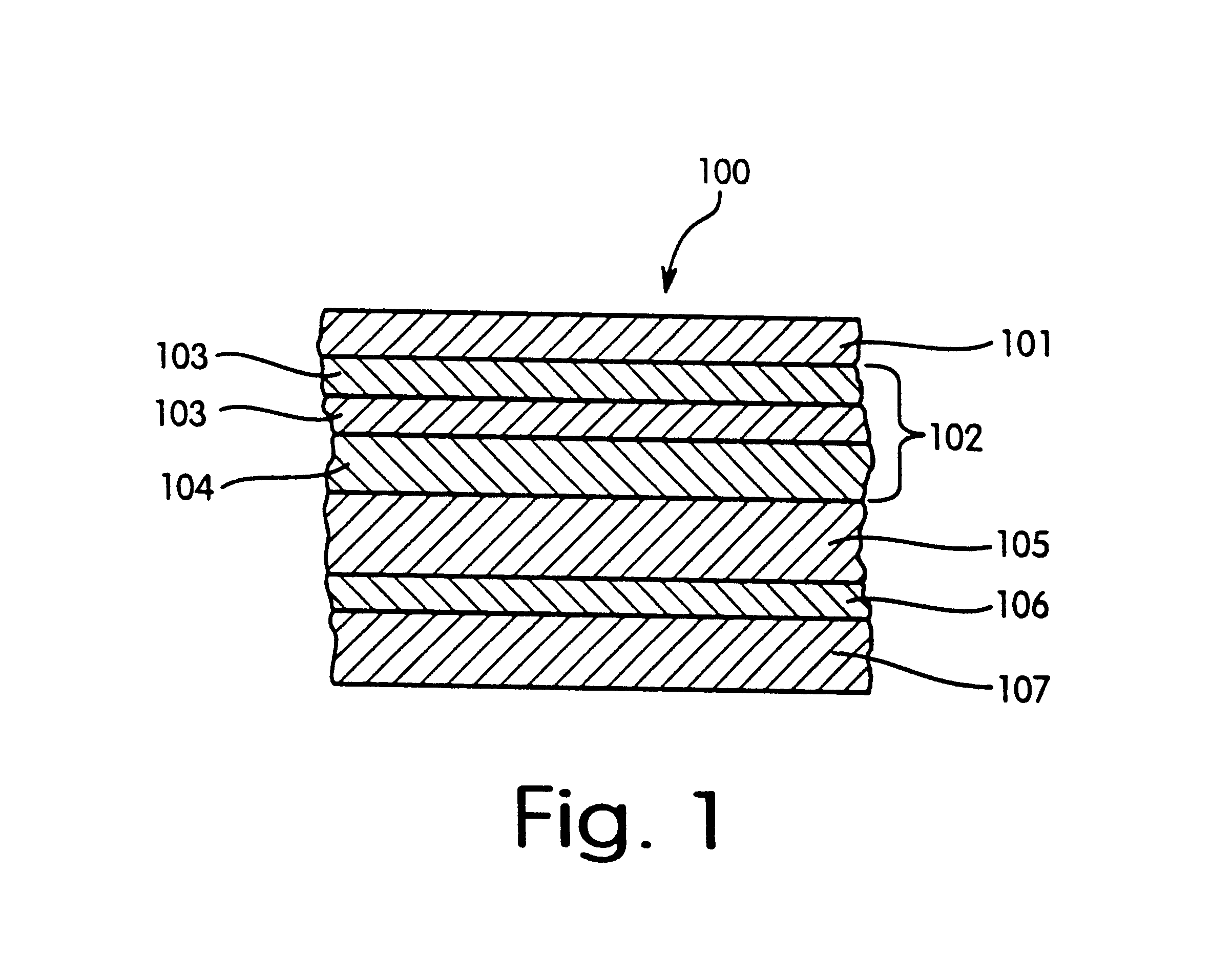
Resistant surface reflector
InactiveUS6709119B2High stability against wipingAvoid disadvantagesMirrorsMountingsSurface layerSilicon oxide
A reflector with high total reflection which is resistant to mechanical stresses. The reflector includes a reflector body and superimposed thereon (a) a functional coating such as a varnish, (b) a reflecting layer structure composed of a reflecting metallic layer and optionally arranged thereon one or several transparent ceramic layers, for example, layers having an optical depth of lambda / 2. The reflecting layer structure contains, as its surface layer, a protective layer. The protective layer is a silicon oxide of general formula SiOx, wherein x is a number from 1.1 to 2.0, or it is aluminum oxide of formula Al2O3, in a thickness of 3 nm or more. The protective layer protects the underlying layers from mechanical damages. In the DIN 58196 abrasion test the protected surface does not show any damages after 50 test cycles with 100 abrasion strokes.
Owner:CONSTELLIUM SWITZERLAND +1
Focusing leveling measuring method and device
InactiveCN101169602AImprove stabilityHigh precision measurement requirementsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOptical measurementsLaser light
The invention discloses a measuring method and device for focusing and leveling, and relates to a new method for the focusing and leveling sensor system of a wafer applicable to the projection photolithography system, and belongs to the field of optical measurement. The invention consists of three parts, namely, a light source collimating module, a focusing subsystem and a leveling subsystem. The laser of the invention emits laser light, the laser light is collimated by a single mode fiber and then passes through a drift compensation device, and then permeates a polarized optical splitter and a Lambda fourth wave plate and then shines on a measured silicon chip. The ray is led to pass through the measured silicon chip repeatedly through a planar mirror and a corner cube prism, and then is magnified in front of a position detector by a lens system, thereby obtaining the defocusing information of the silicon chip surface. The ray is rebounded along the path by a planar optical splitter, the ray permeates a lens and shines on a position-sensitive detector, thereby obtaining the two-dimensional inclination information of the silicon chip surface. The system has high resolution as well as simple structure of optical path and needs no complicated optical design.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Scanning IR sensor for gas safety and emissions monitoring
ActiveUS10190976B2More reliableLess expensiveMass flow measurement devicesRaman/scattering spectroscopyGratingSpectroscopy
Apparatus and methods for rapidly detecting, localizing, imaging, and quantifying leaks of natural gas and other hydrocarbon and greenhouse gases. Scanning sensors, scan patterns, and data processing algorithms enable monitoring a site to rapidly detect, localize, image, and quantify amounts and rates of hydrocarbon leaks. Multispectral short-wave infrared detectors sense non-thermal infrared radiation from natural solar or artificial illumination sources by differential absorption spectroscopy. A multispectral sensor is scanned to envelop an area of interest, detect the presence and location of a leak, and raster scan the area around the leak to create an image of the leak. The resulting absorption image related to differential spectral optical depth is color mapped to render the degree of gas absorption across the scene. Analysis of this optical depth image, with factors including known inline pressures and / or surface wind speed measurements, enable estimation of the leak rate, i.e., emission mass flux of gas.
Owner:MULTISENSOR SCI INC
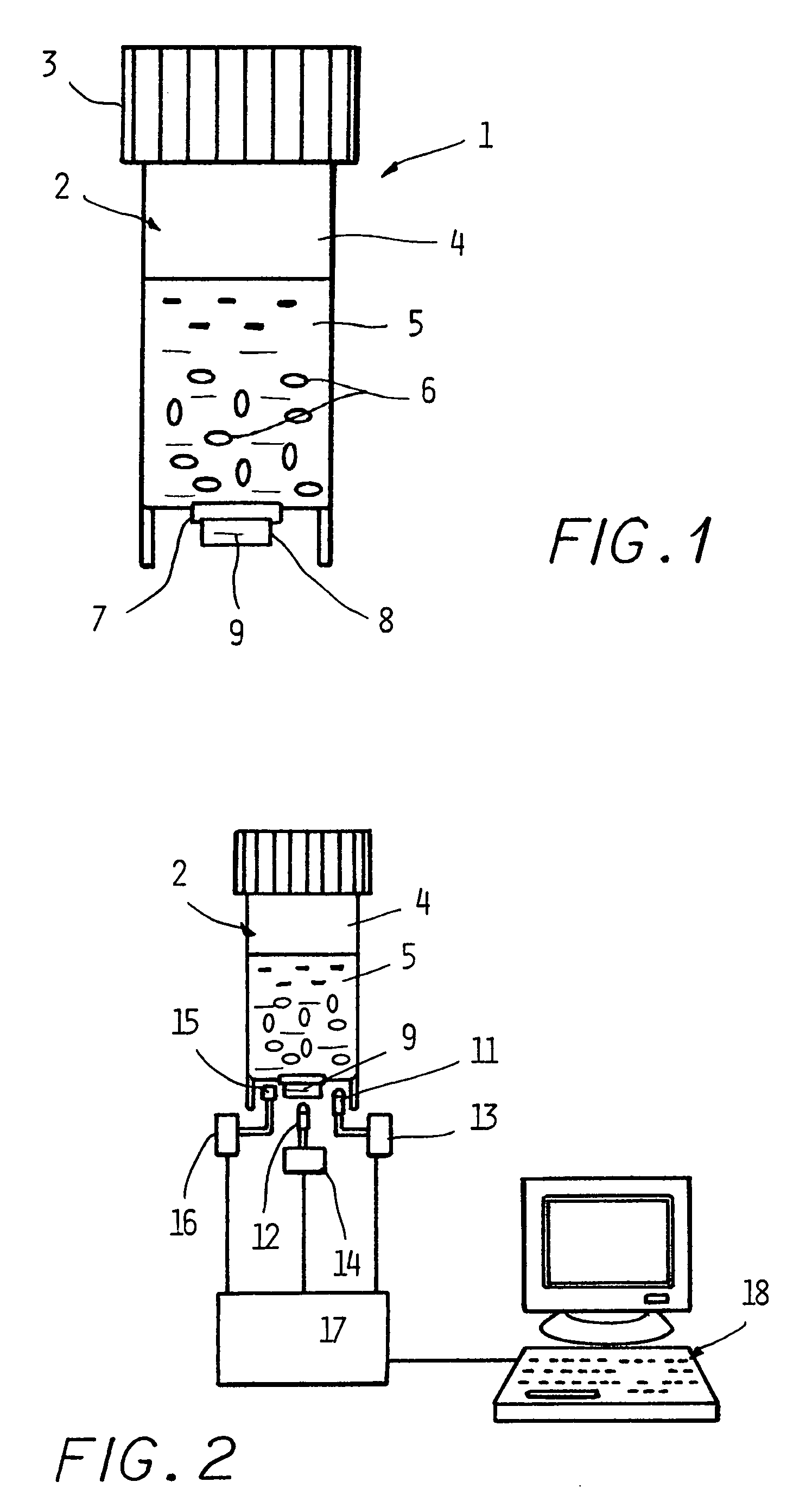
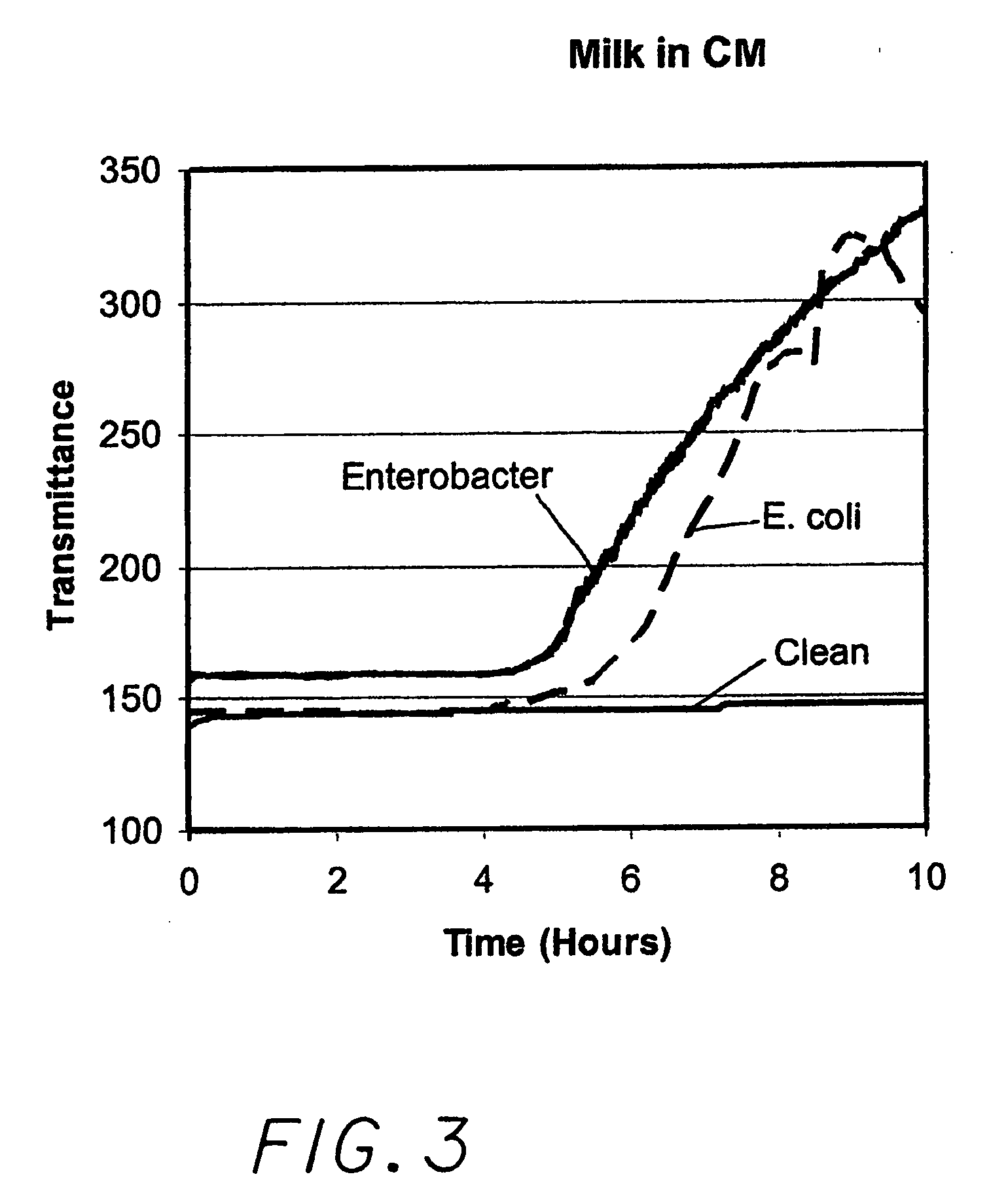
Optical Method and Device for the Detection and Enumeration of Microorganisms
ActiveUS20080176273A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOptical depthBy-product
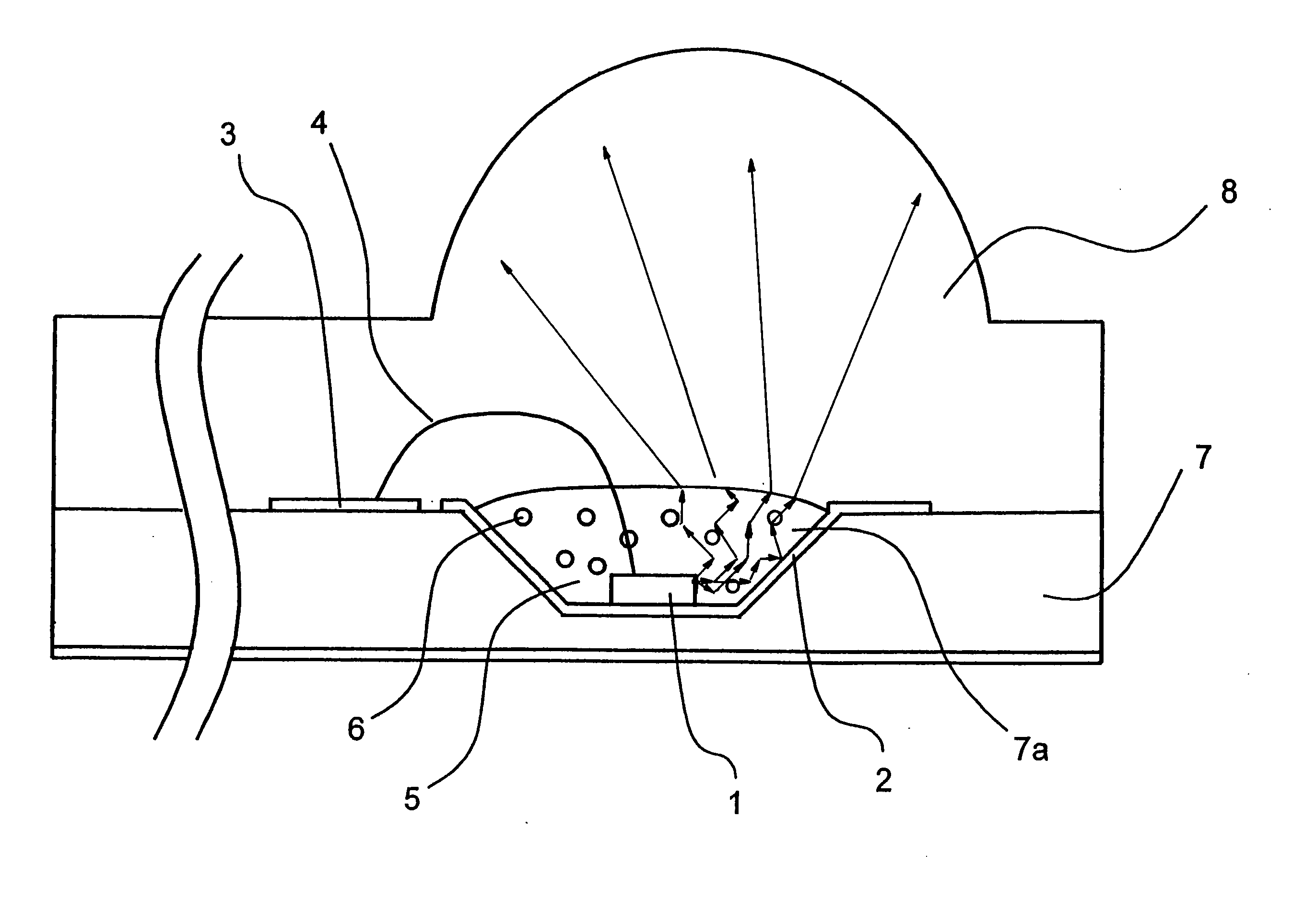
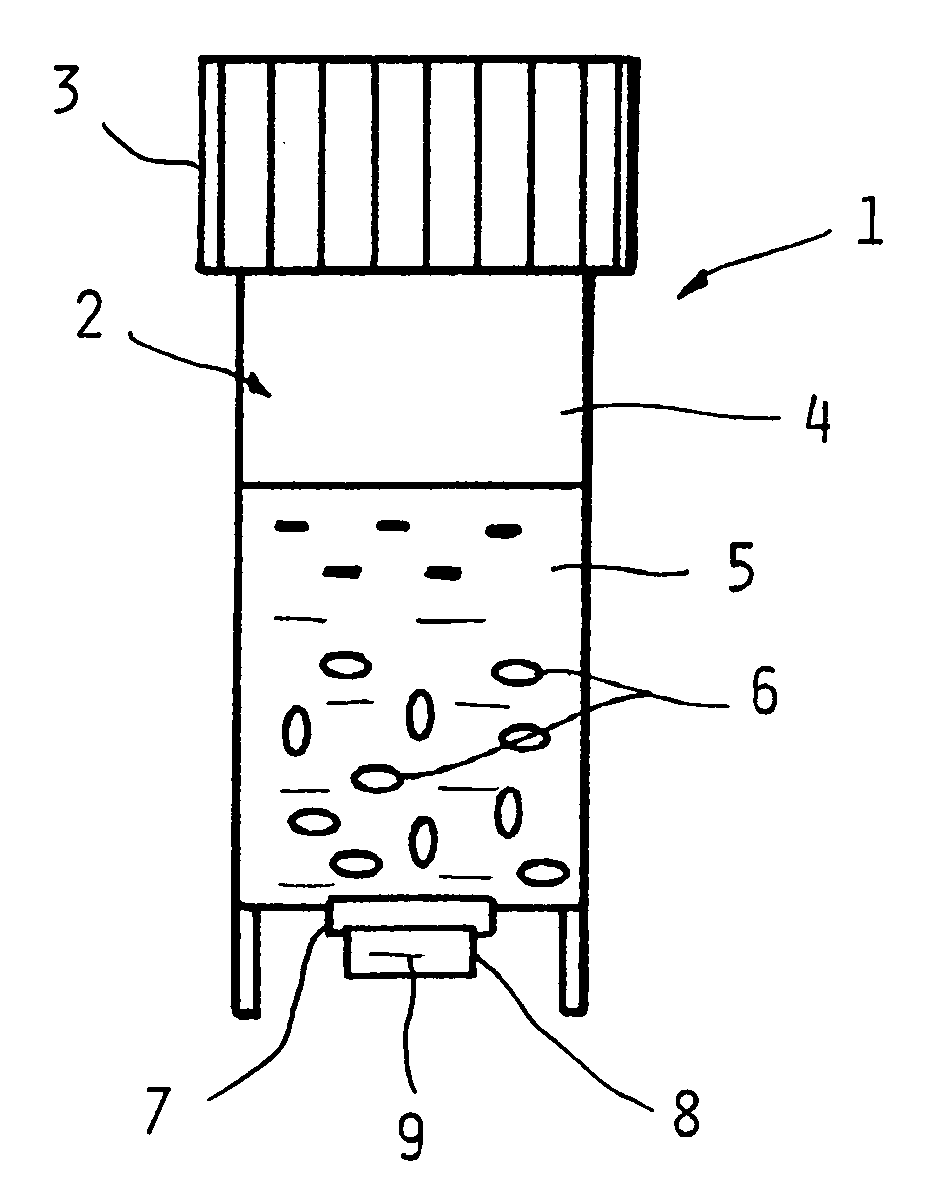
A new device and method for detecting the presence of living microorganisms in test samples are described. The device comprises a container with at least one section transparent to light, a growth zone located in said container containing a mixture of growth media capable of supporting growth of the microorganisms, and at least one indicator substrate that changes its optical properties due to growth of the microorganisms. A detection zone is located in the container adjacent to the transparent section, and a barrier layer comprising porous solid material separates the two zones, allowing diffusion of molecules and ions of metabolic by-products of the organisms, while preventing microorganisms and particulate matter of the test sample from penetrating into the detection zone.
Owner:NEOGEN CORP
Reflector with a resistant surface
A reflector with high total reflection which is resistant to mechanical stresses. The reflector comprises a reflector body and superimposed thereon (a) a functional coating such as a varnish, (b) a reflecting layer structure composed of a reflecting metallic layer and optionally arranged thereon one or several transparent ceramic layers, for example, layers having an optical depth of λ / 2. The reflecting layer structure contains, as its surface layer, a protective layer. The protective layer is a silicon oxide of general formula SiOx, wherein x is a number from 1.1 to 2.0, or it is aluminum oxide of formula Al2O3, in a thickness of 3 nm or more. The protective layer protects the underlying layers from mechanical damages. In the DIN 58196 abrasion test the protected surface does not show any damages after 50 test cycles with 100 abrasion strokes.
Owner:ALANOD ALUMINUM VEREDLUNG +1
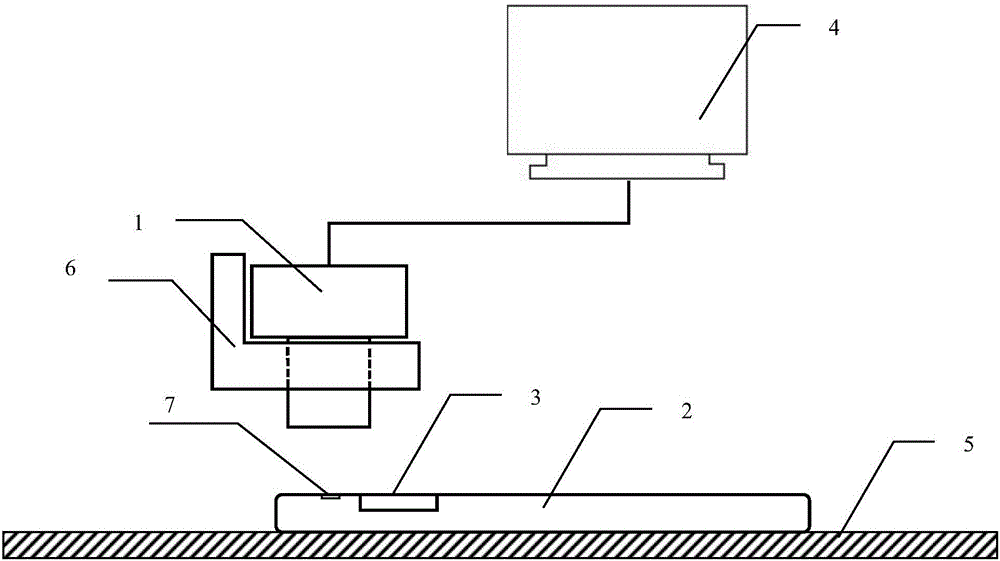
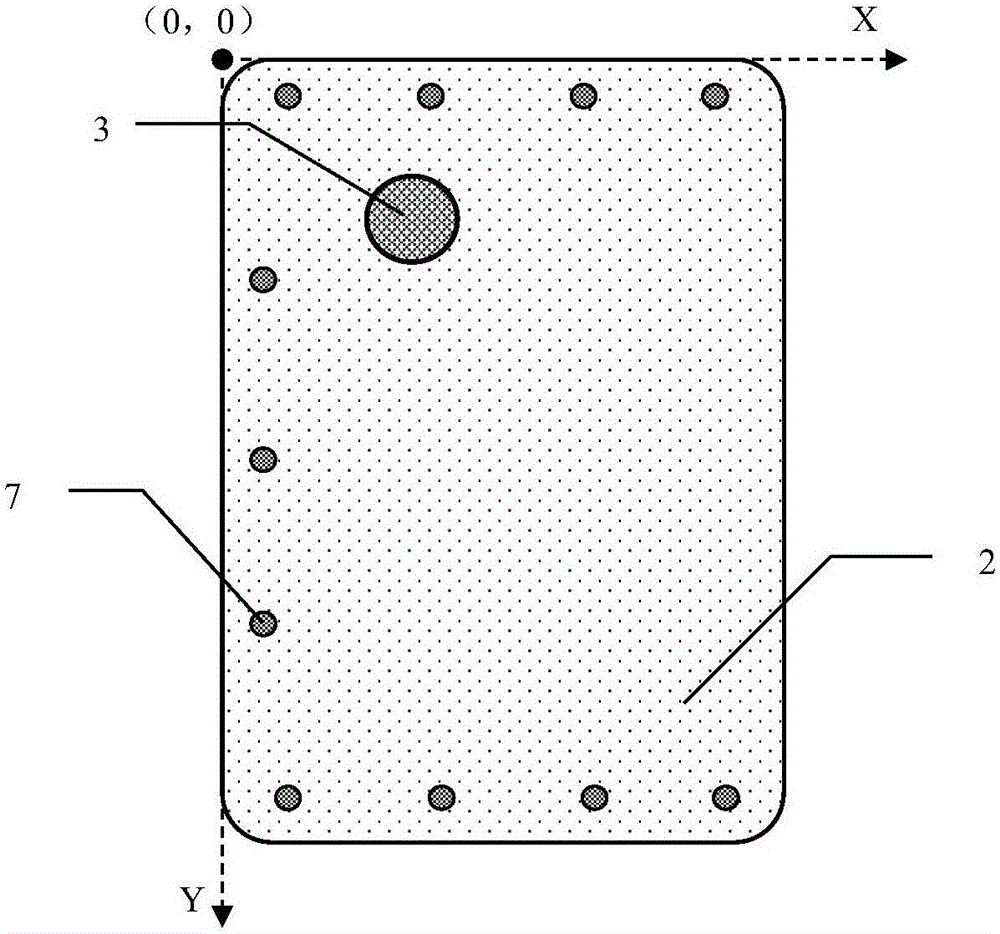
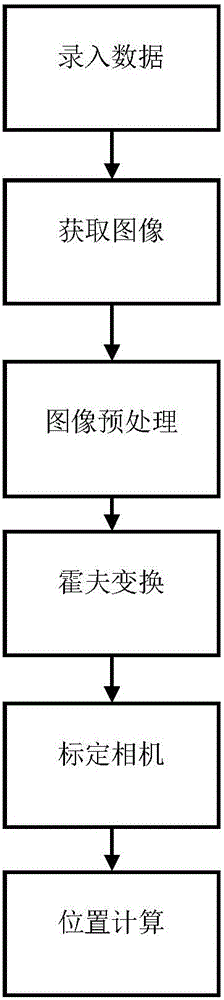
Machine vision positioning method for automatic screw assembling
ActiveCN106251354AOutstanding FeaturesHighlight significant progressImage enhancementImage analysisMachine visionOptical depth
The invention, which relates to the field of metering equipment employing an optical method as a feature, provides a machine vision positioning method for automatic screw assembling. The method comprises steps of inputting and recording data, obtaining an image, carrying out image pretreatment, carrying out Hough transform treatment, calibrating a camera, and calculating a position. According to the method, a circle in an image is searched by using the Hough transform method and the center of the circle is used as a positioning point, so that defects of high selection requirement and low precision for feature point selection according to the existing visual positioning method can be overcome; and a defect of an assembling failure caused by inaccurate product position fixation by a clamp during the automatic screw assembling process in the prior art can be overcome.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
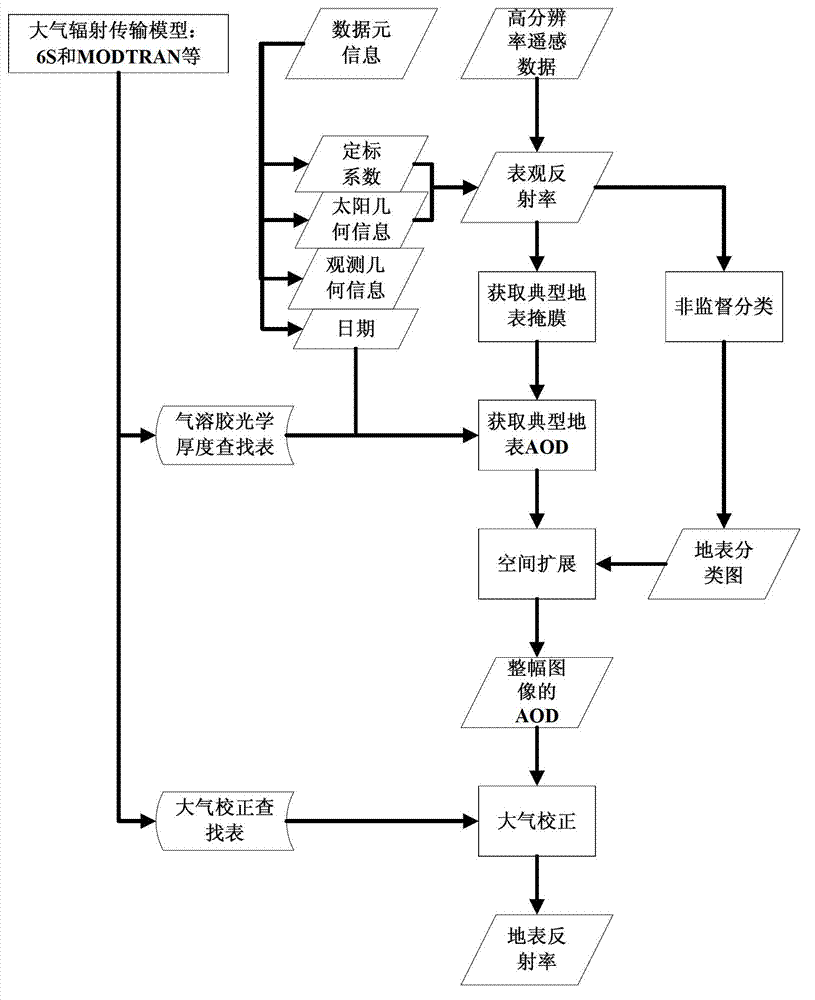
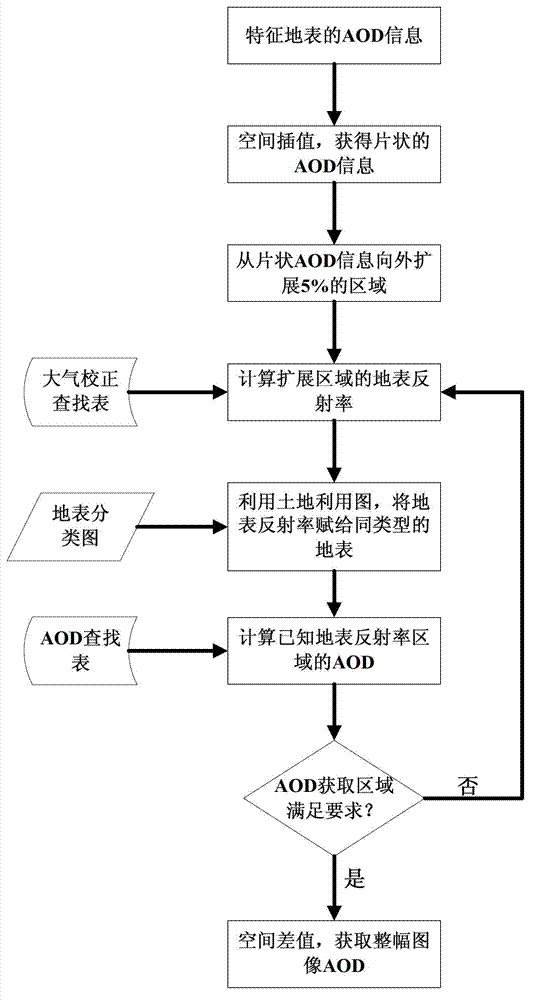
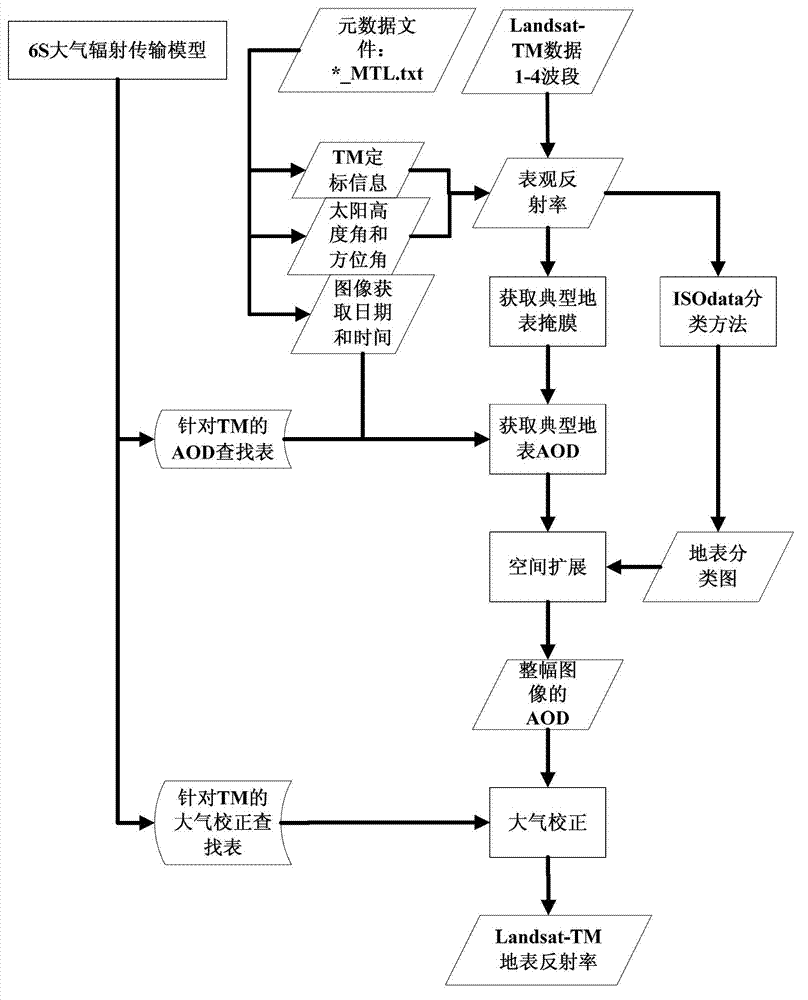
High-resolution remote sensing data atmospheric correction method
ActiveCN102955154AHigh precisionImprove usabilityWave based measurement systemsSensing dataUsability
The invention discloses a high-resolution remote sensing data atmospheric correction method comprising the following steps of: S1, obtaining related information from data element information; S2, calculating the apparent reflectance of the typical land surface; S3, obtaining a mask of the typical land surface; S4, building an AOD (Aerosol Optical Depth) inversion correction lookup table by utilizing an atmospheric radiation transmission model; S5, calculating the AOD of the typical land surface; S6, obtaining a land surface classification chart; S7, forming the AOD of an whole image through a spatial expansion method; and S8, executing atmospheric correction on the high-resolution remote sensing data according to the AOD of the whole image and the atmospheric correction lookup table to get the land surface reflectance of the high-resolution remote sensing data. In the method, the high-resolution satellite remote sensing data is used for obtaining the AOD of the whole image, the accuracy and usability of the atmospheric correction are improved, and automation of the whole flow from AOD to atmospheric correction is realized.
Owner:REMOTE SENSING APPLIED INST CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
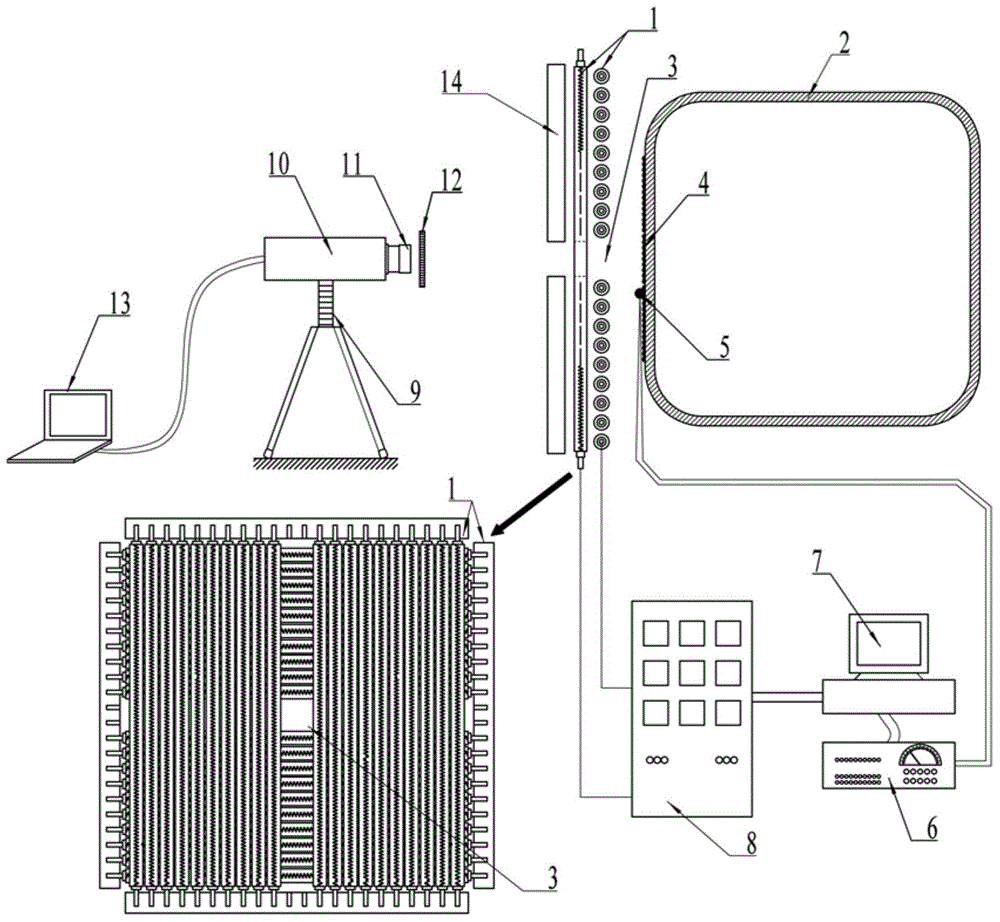
Optical method based high-speed aircraft hot surface full-field deformation measuring device
InactiveCN103558243ARealize deformation measurementGood test resultsUsing optical meansMaterial thermal analysisEngineeringRadiant heat
The invention provides an optical method based high-speed aircraft hot surface full-field deformation measuring device. The optical method based high-speed aircraft hot surface full-field deformation measuring device comprises a double-layer quartz lamp heating array, a thin-wall high-speed aircraft shell, a square transparent window, speckle particles, a thermocouple sensor, a signal amplifier, a temperature control computer, a driving power supply, a CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) camera, a lens, a narrow-band-pass optical filter and an image processing computer. In order to solve the problem of signal blockage caused by a high temperature radiant heat source between the CMOS camera and the surface of the high-speed aircraft shell, the vertical double-layer quartz lamp heating array is designed and the square transparent window with small area is formed, so that the optical camera lens can obtain images of the hot surface of the high-speed aircraft through the transparent window. The interference light ray of the quartz lamp heating array is shielded by selecting the narrow-band-pass optical filter with specific wave length, so that speckle images with high quality and no degeneration on the hot surface of the high-speed aircraft is obtained; a digital image correlation method is utilized for analyzing the speckle images under different temperatures to realize full measurement on the displacement field and the strain field of the hot surface of the high-speed aircraft in a high temperature environment.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Enhancing image data
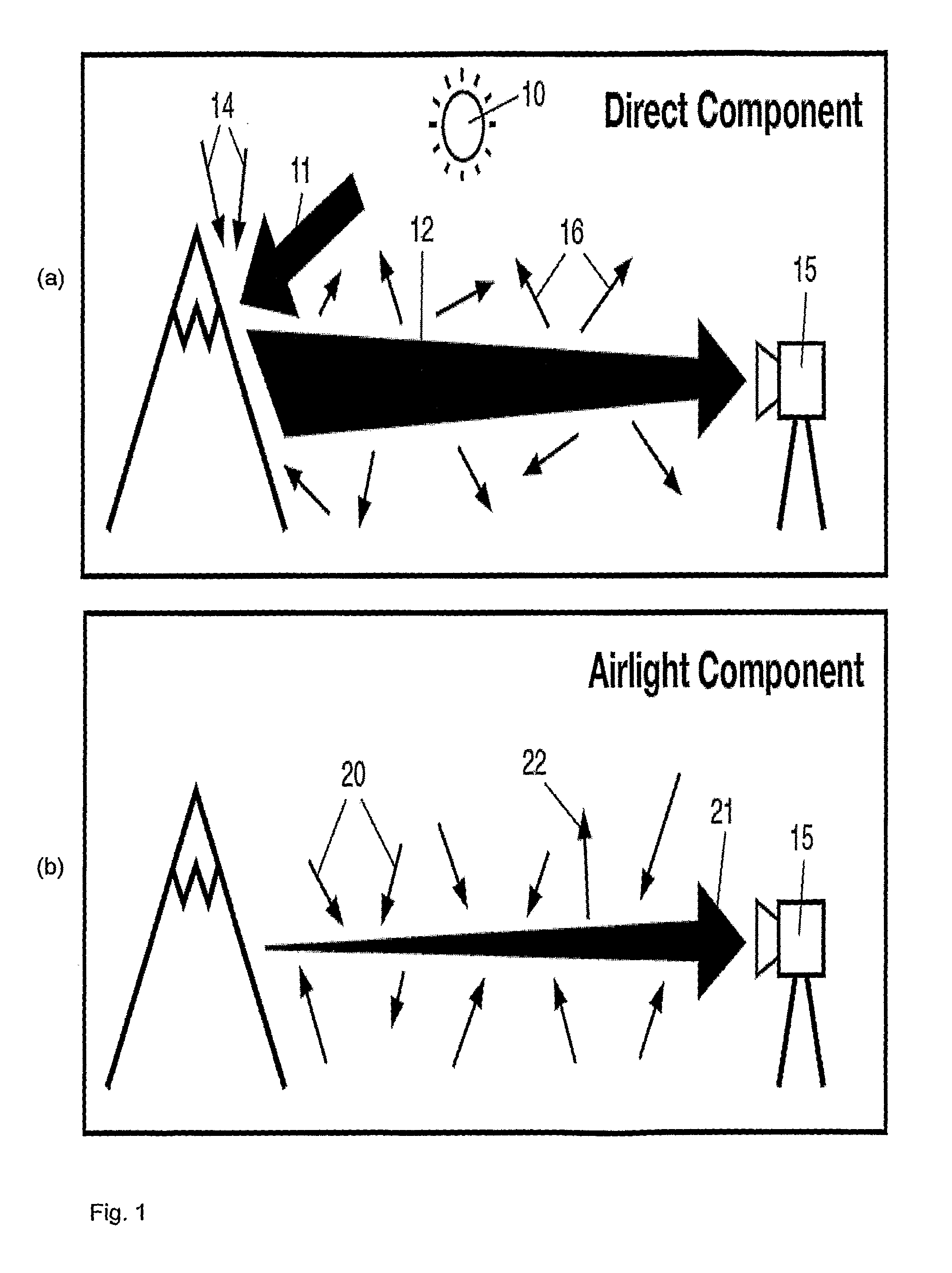
The invention concerns image processing that includes the estimation of the optical depths of points in image data in order to enhance the image data. In particular but not limited to, from the optical depth noise present in the image due to aerosol in the scene, such as fog or haze, can be reduced. The invention concerns determining.a first cost for each point independently based on a determined metric (60) and then a second cost based on an expected correlation in neighbouring points (70). The two costs are then optimized (80) to determine an estimated optical depth for each point (80) that is then used to reduce the effect of aerosol in the image (84). Applications of the invention include, but is not limited to, surveillance systems so that objects in the scene of the image can be better identified once the image data has been enhanced to reduce the estimated noise. Aspects of the invention include a method, software, computer apparatus and a field programmable gate array.
Owner:NAT ICT AUSTRALIA
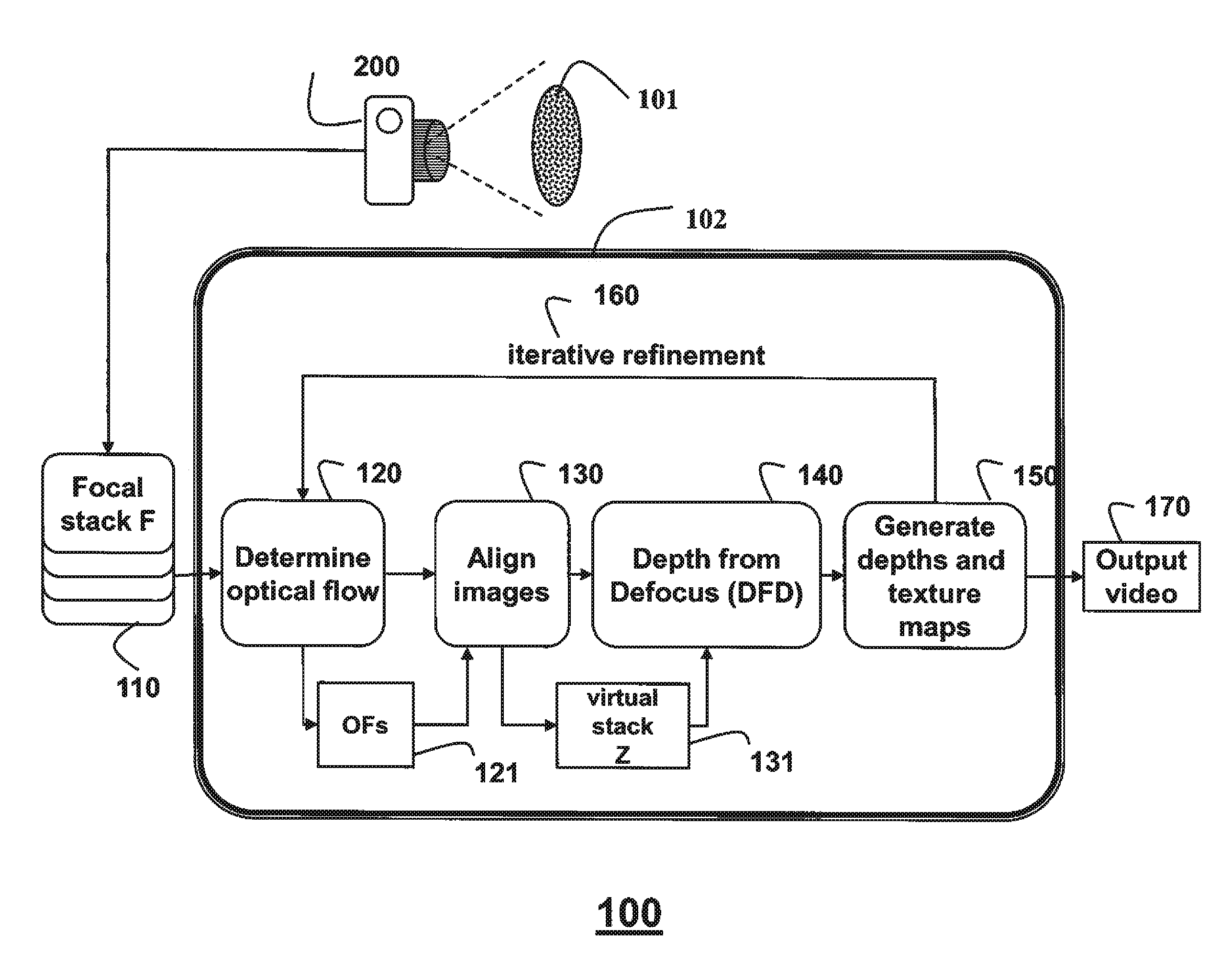
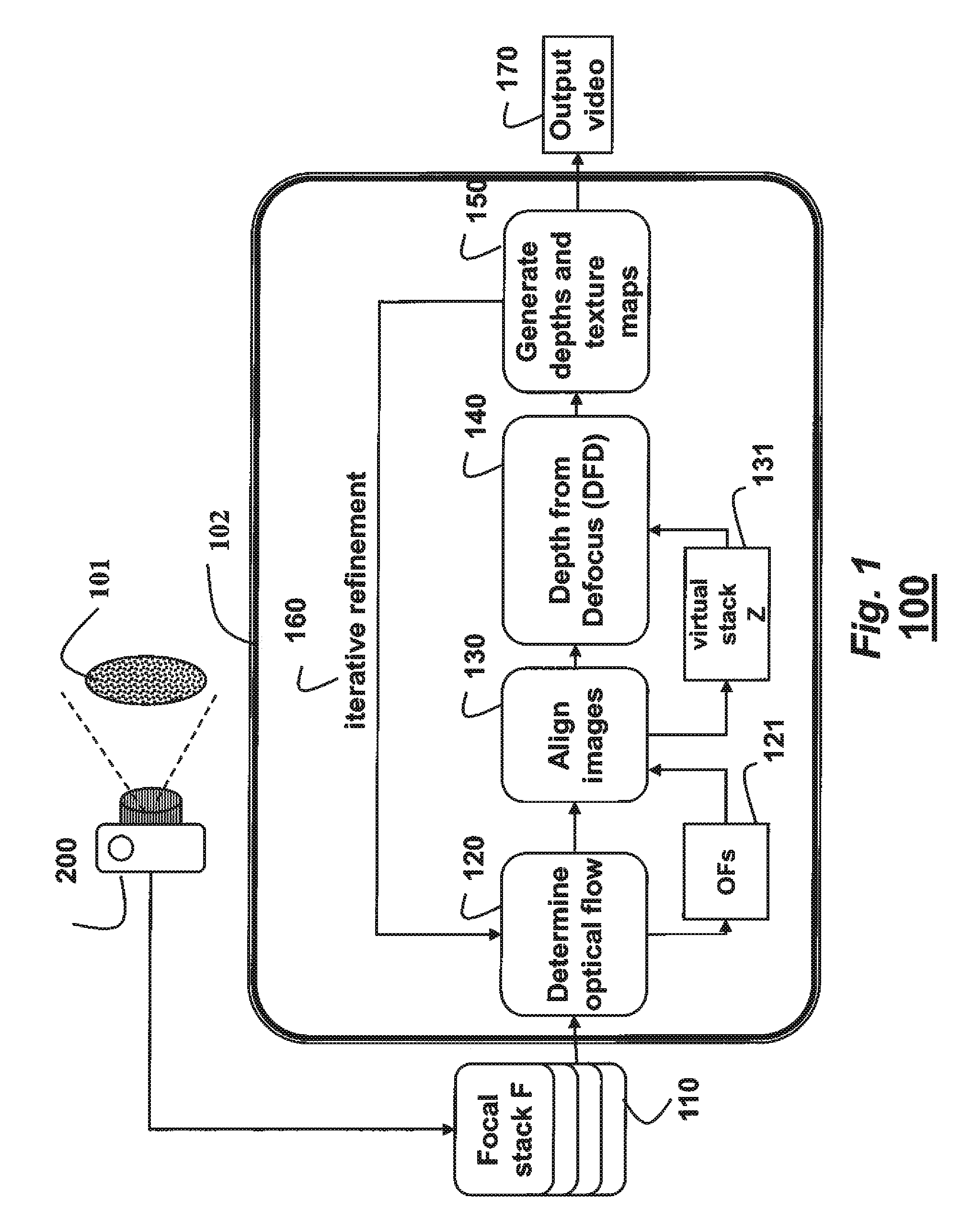
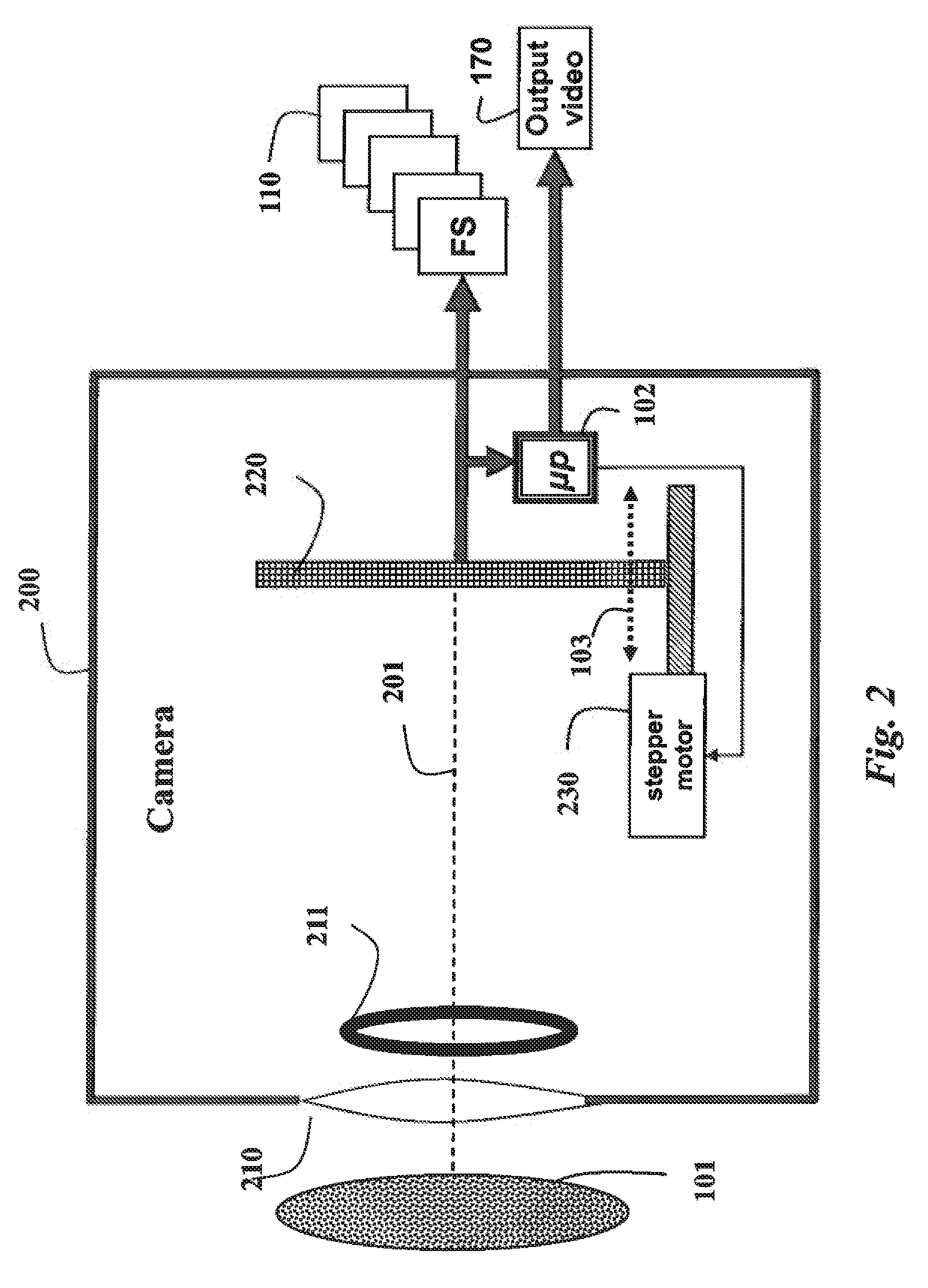
Camera and method for focus based depth reconstruction of dynamic scenes
InactiveUS8432434B2Accurate processingExtending and reducing depthTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionDepth from defocusOptical flow
A dynamic scene is reconstructed as depths and an extended depth of field video by first acquiring, with a camera including a lens and sensor, a focal stack of the dynamic scene while changing a focal depth. An optical flow between the frames of the focal stack is determined, and the frames are warped according to the optical flow to align the frames and to generate a virtual static focal stack. Finally, a depth map and a texture map for each virtual static focal stack is generated using a depth from defocus, wherein the texture map corresponds to an EDOF image.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
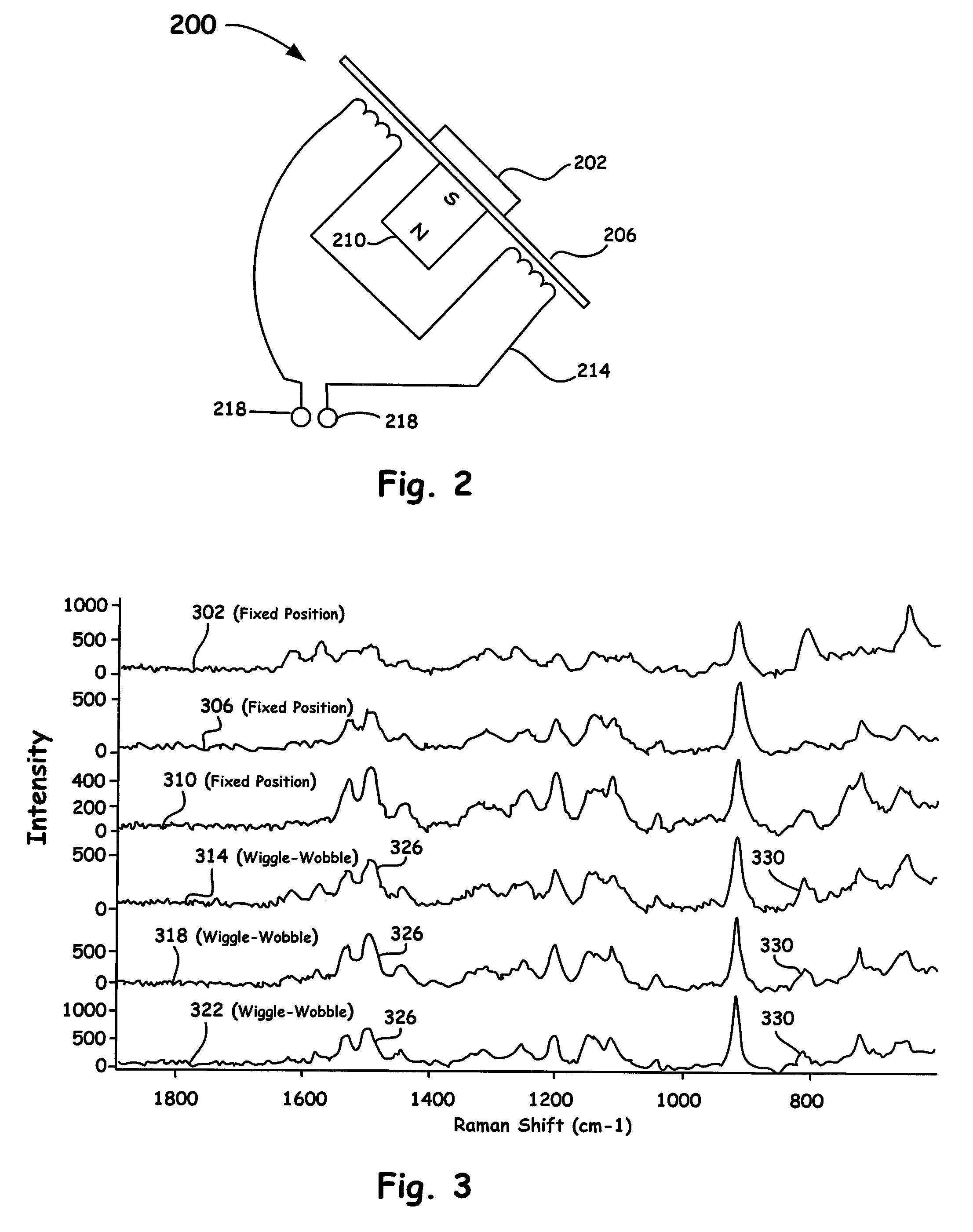
Rapid spatial averaging over an extended sample in a Raman spectrometer
ActiveUS7595873B1Rapid spatial averagingReduce sample degradationRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringSpatial averageSpectroscopie raman
An optical method and apparatus is utilized to provide rapid spatial averaging over a large sample area in a Raman spectrometer, without defocusing of the optical source or the collection optics. Spatial averaging provides a representative spectrum of a sample that is inhomogeneous, either in its composition or surface characteristics. The spatial averaging configurations and methods disclosed herein also reduce sample degradation or burning resulting from the high intensity of the directed optical source. Moreover, the dimensions of the sample area of the spatial averaging methods and configurations of the present invention are adjusted to match specific sampling requirements.
Owner:THERMO ELECTRON SCI INSTR
Optical Method and System for Extended Depth of Focus
ActiveUS20080198482A1Increase depth of focusEliminate needSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensOptical propertyImaging lens
An imaging arrangement and method for extended the depth of focus are provided. The imaging arrangement comprises an imaging lens having a certain affective aperture, and an optical element associated with said imaging lens. The optical element is configured as a phase-affecting, non-diffractive optical element defining a spatially low frequency phase transition. The optical element and the imaging lens define a predetermined pattern formed by spaced-apart substantially optically transparent features of different optical properties. Position of at least one phase transition region of the optical element within the imaging lens plane is determined by at least a dimension of said affective aperture.
Owner:BRIEN HOLDEN VISION INST (AU)
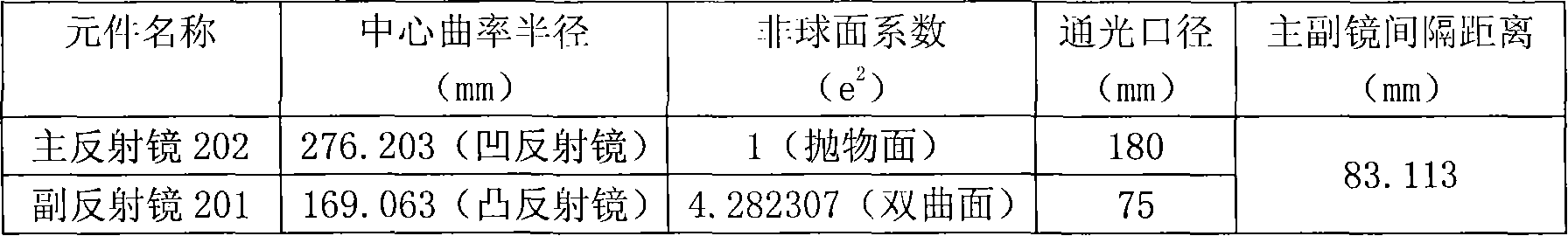
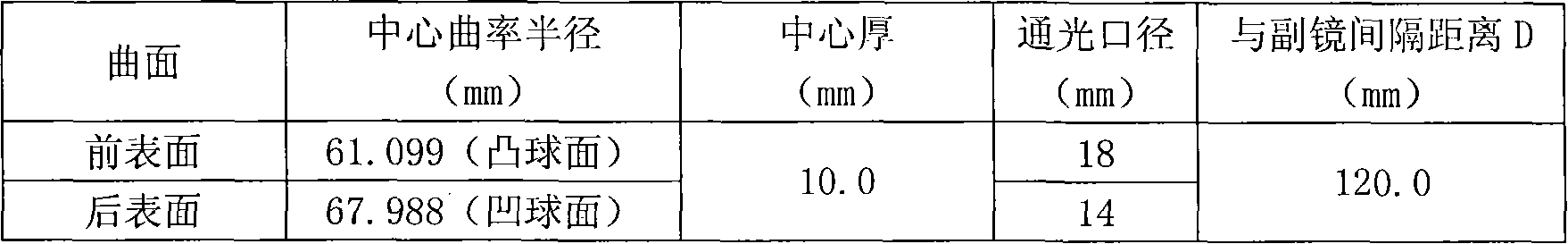
On-line verification method for processing cassegrain two-mirror optics system
The invention discloses an online test method for the processing of a Cassegrain two-reflector optical system, which is used for the online test of the processing of the non-perfect imaging Cassegrain two-reflector optical system. The optical test system consists of a standard self-collimating plane mirror, the tested Cassegrain optical system, a compensating lens and an aspheric processing surface form detection instrument. The compensating lens is arranged on the back light path of the non-perfect imaging Cassegrain two-reflector optical system to compensate the spherical aberration of the original optical system, thereby enabling the tested Cassegrain two-reflector optical system to form a perfect image on points on the axis, and meeting the processing requirements of the pair of primary and secondary reflectors.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
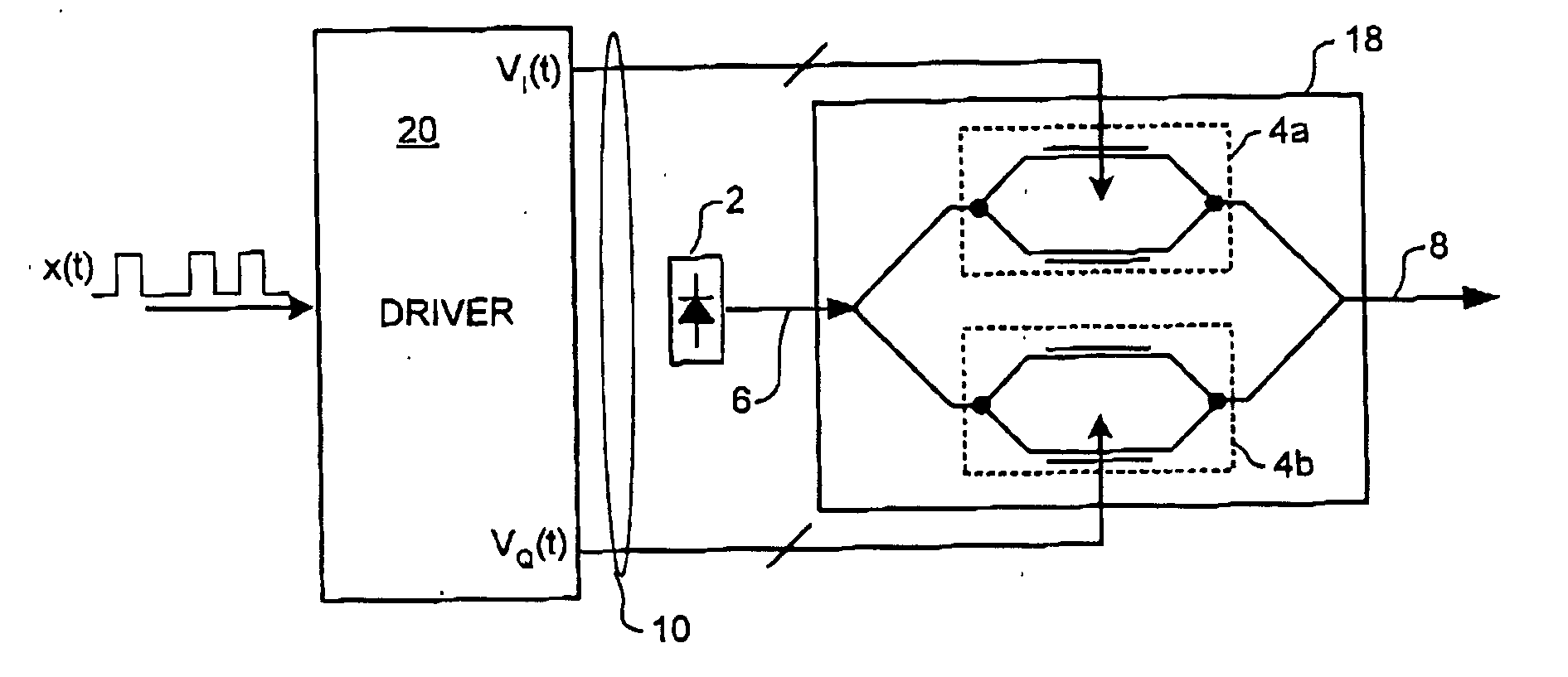
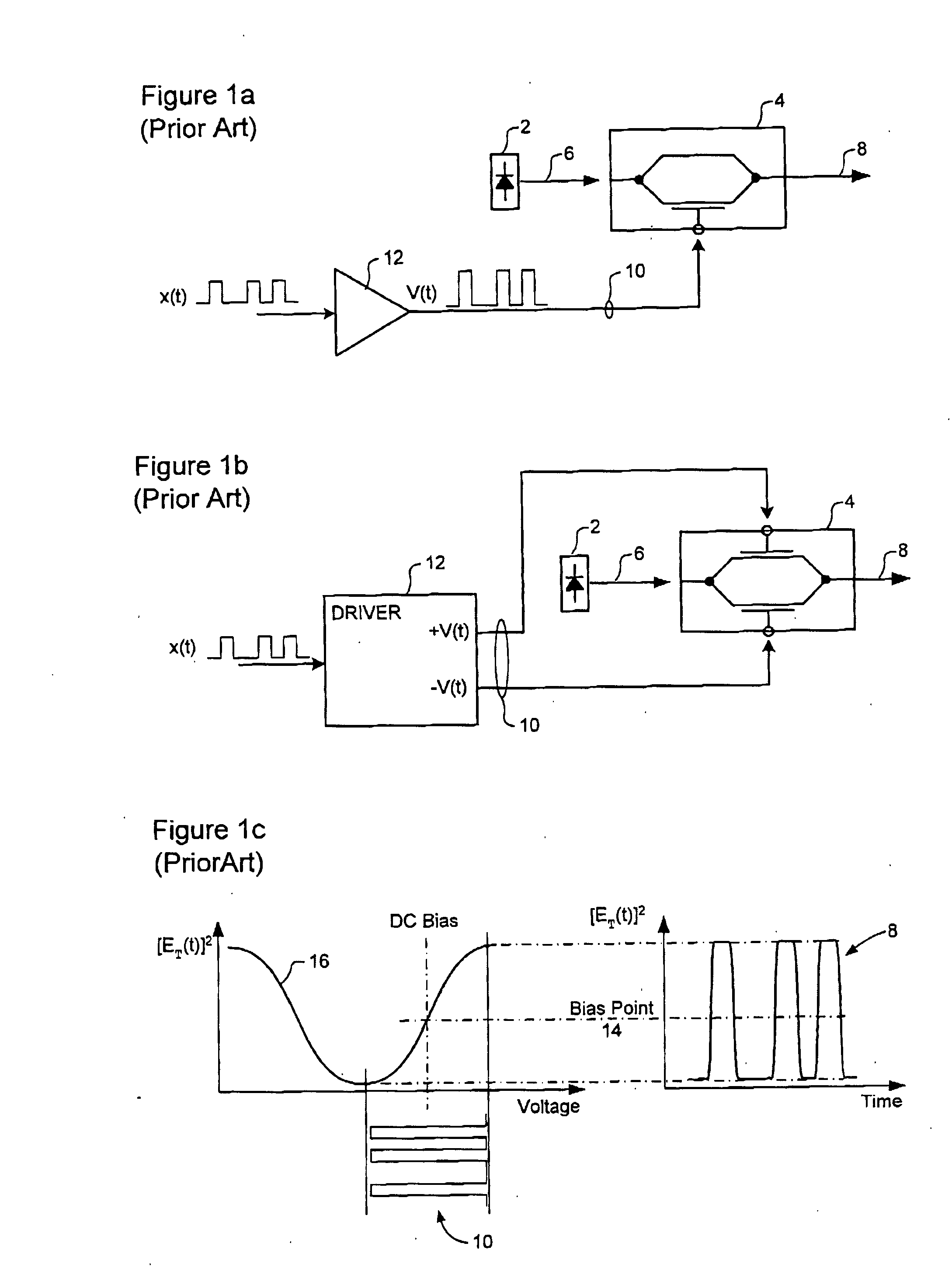
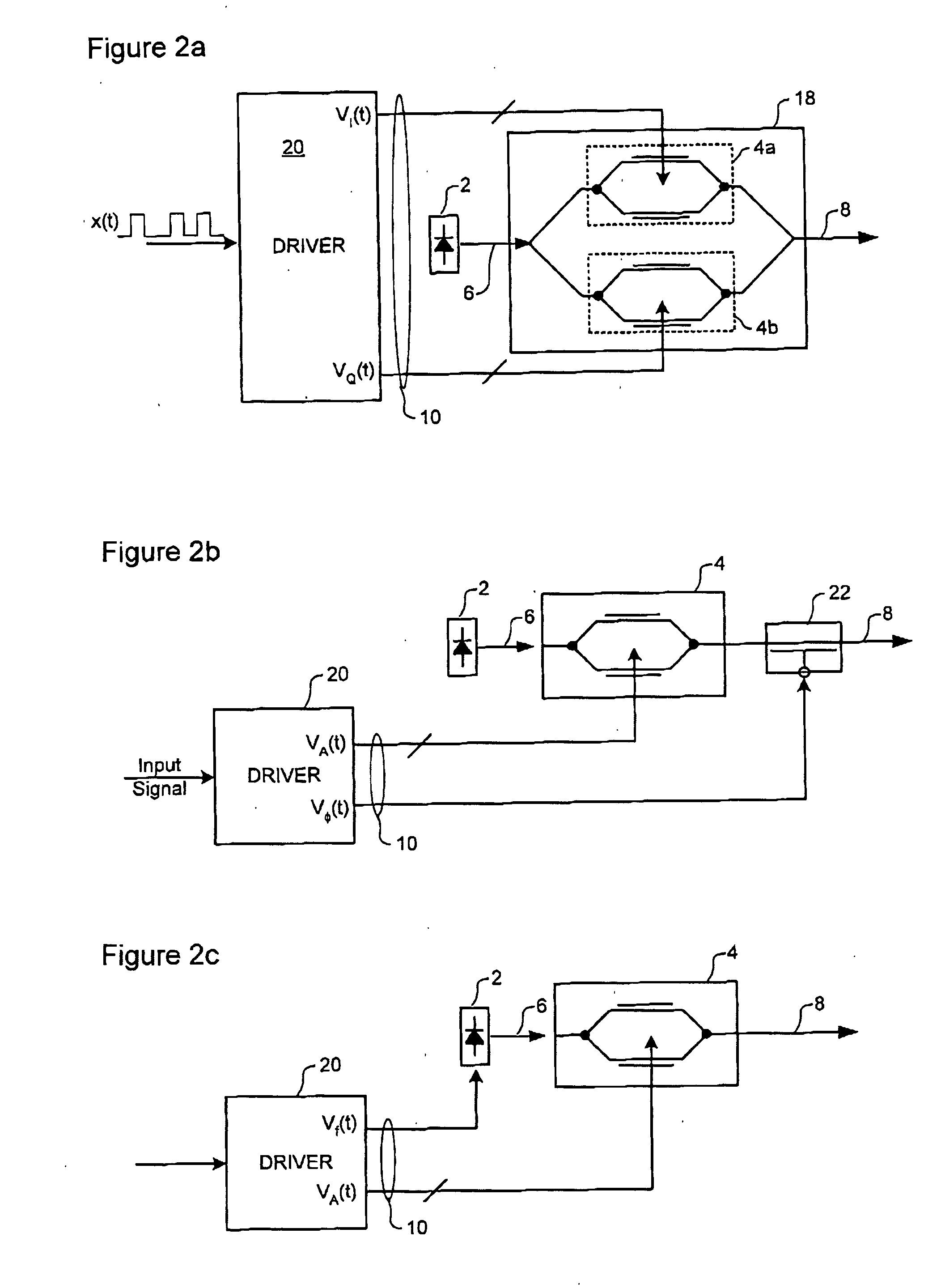
Optical E-field modulation using a Mach-Zehnder interferometer
InactiveUS20050007642A1Facilitate of impairmentLow costElectromagnetic transmissionNon-linear opticsCommunications systemCarrier signal
A method for modulating the E-field of an optical carrier signal utilizes a Mach-Zehnder modulator having a pair of independently controllable branches. A pair of independent branch drive signals VL(t) and VR(t) are derived. Each branch of the MZ modulator is driven with a respective one of the independent branch drive signals. By this means, a low cost conventional MZ modulator (interferometer) can be used to perform complex modulation of the E-field of the optical carrier. In some embodiments, this functionality is used to facilitate precompensation of optical impairments of an optical communications system.
Owner:CIENA
Optical method for detecting defect on inner wall of holes
InactiveCN101109715ARealize 3D measurementAvoid contact wearMaterial analysis by optical means3d measurementOptical depth
The invention provides a method for detecting any defect in the inner wall of a hole by an optic way, which comprises the following procedures: a light pickup picks up an image formed by laser after reflecting on the inner wall of the hole, so as to get the depth at any point on the inner wall of the hole; the light pickup picks up an image formed by an illumination light after reflecting on the inner wall of the hole, so as to get the explored image of the inner wall of the hole and get the 2D sizes of the defect; and the 3D info on the defect is obtained by combining above two dimensions. By combining laser measurement with illumination light measurement, it is not only possible to get the 2D size of the defect, but also is possible to get the depth of the defect, so as to achieve 3D measurement of the defect; the use of a non-contact measuring way avoids any contact wear between a probe and the object to be measured, and improves the inspection speed.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com